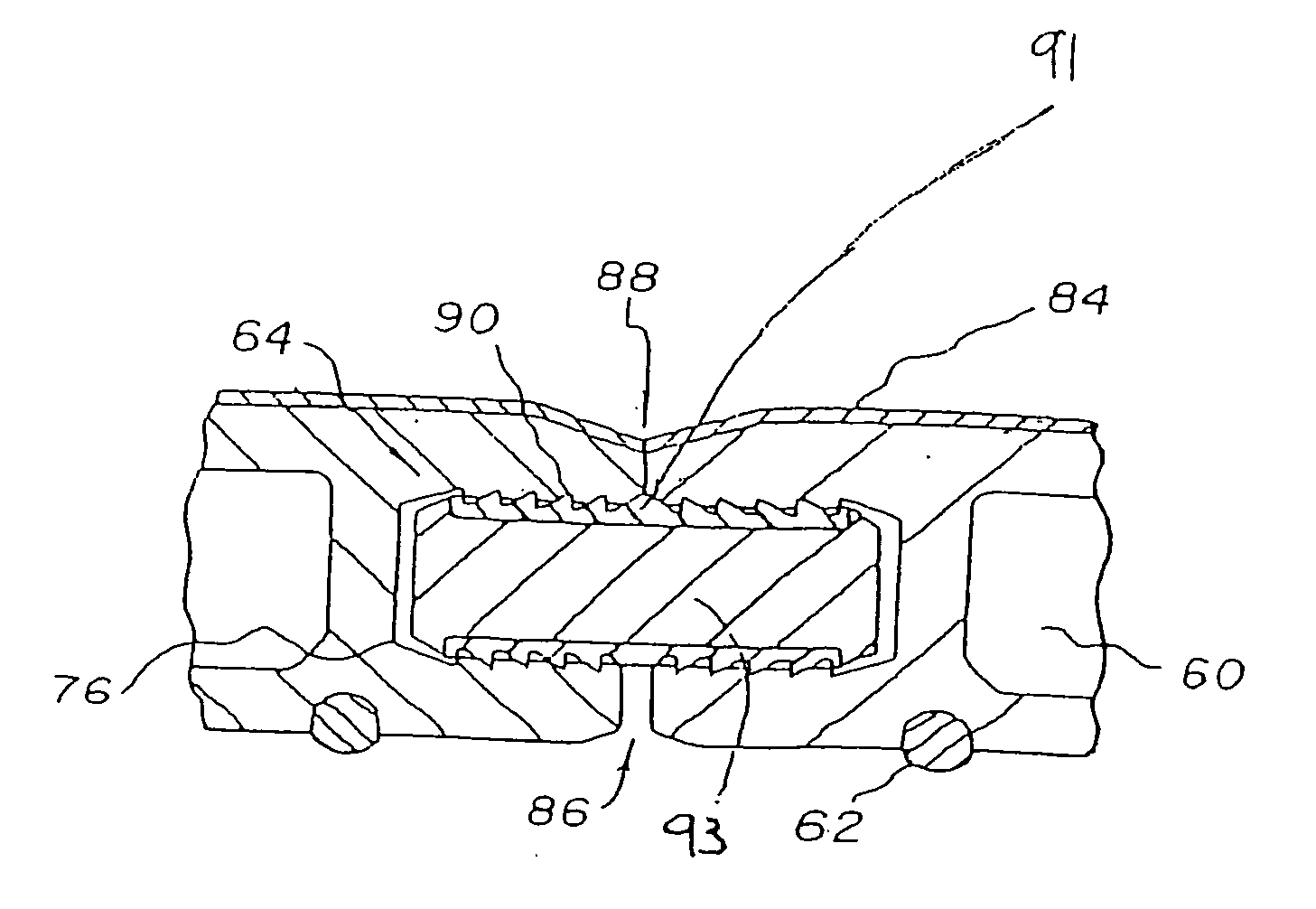
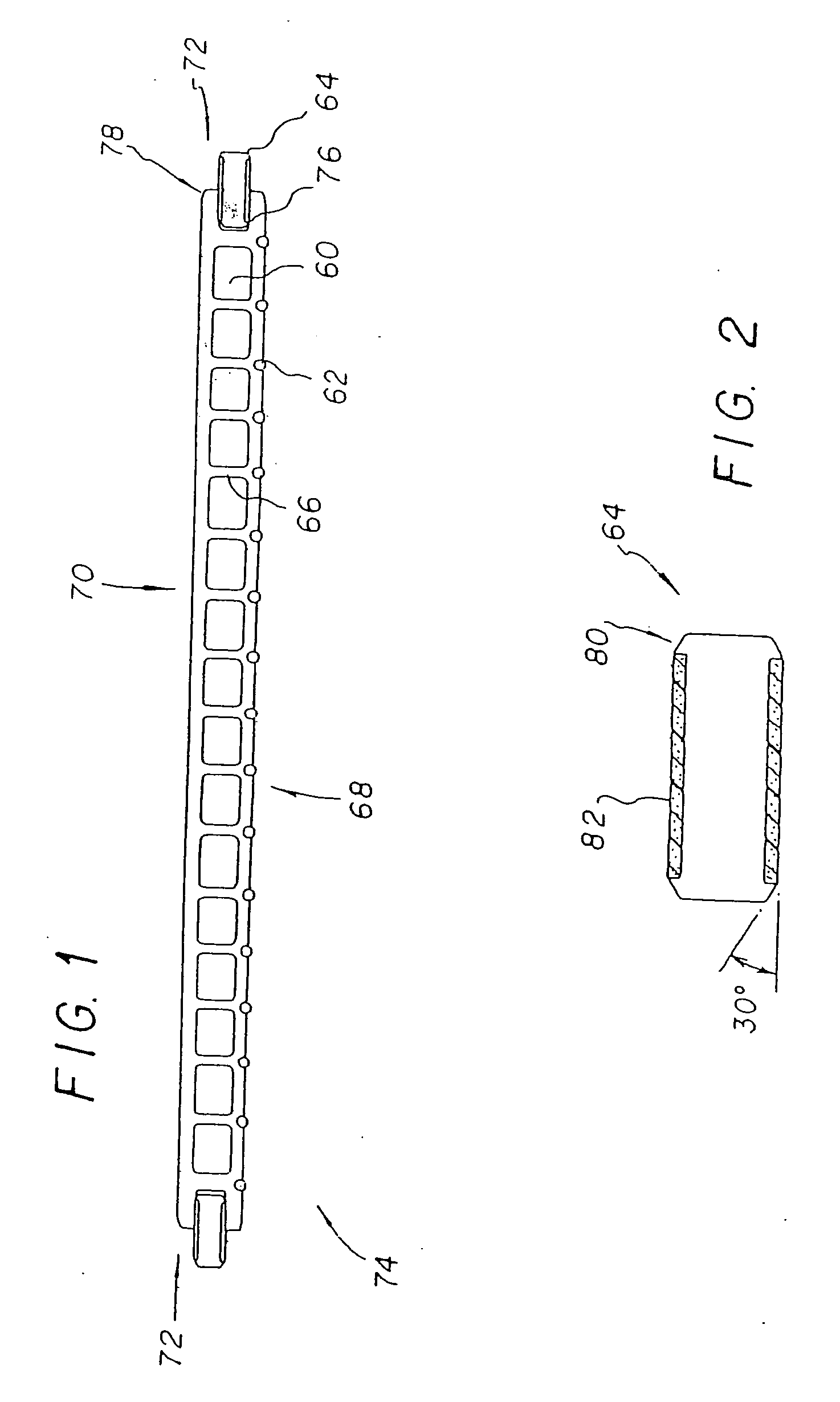
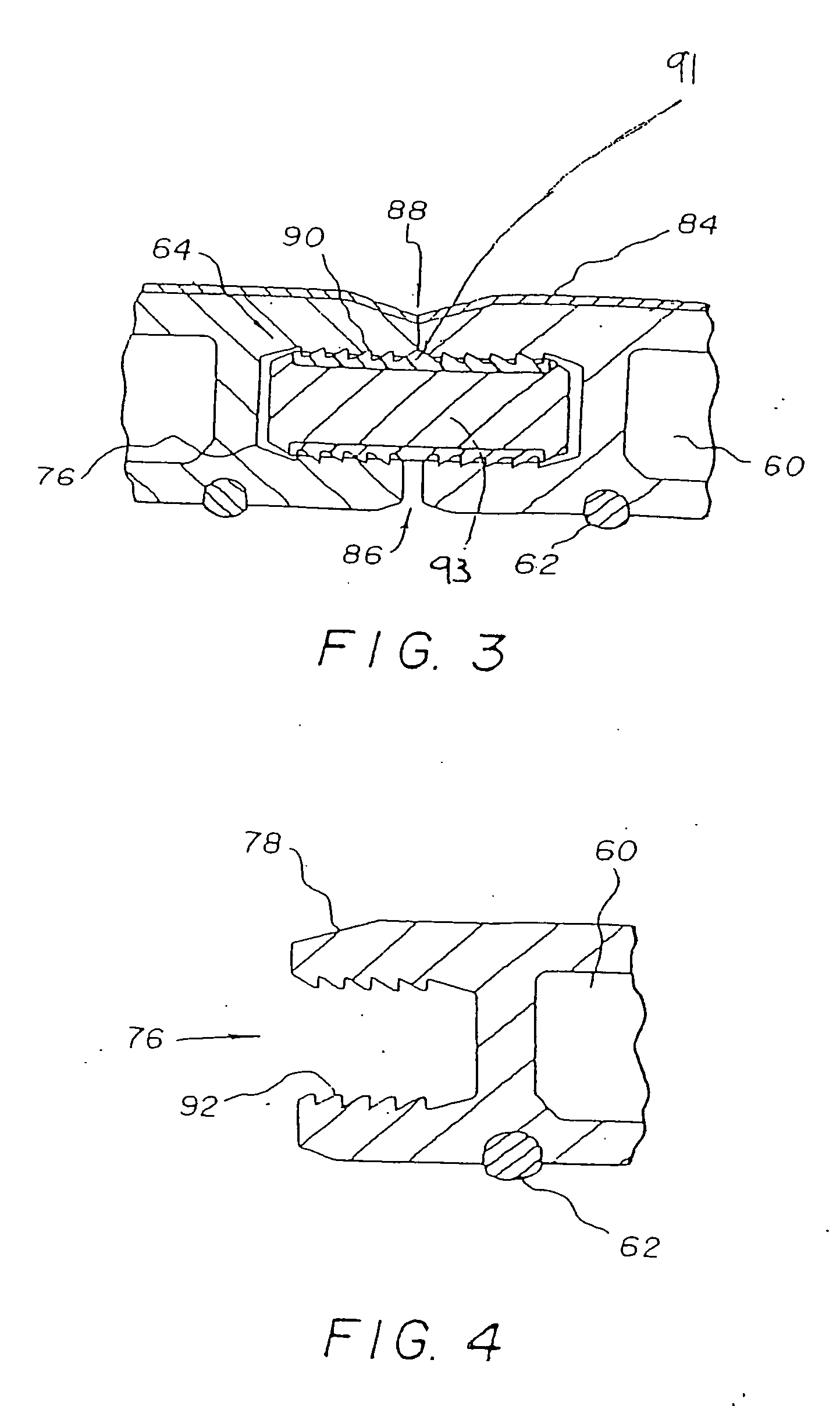
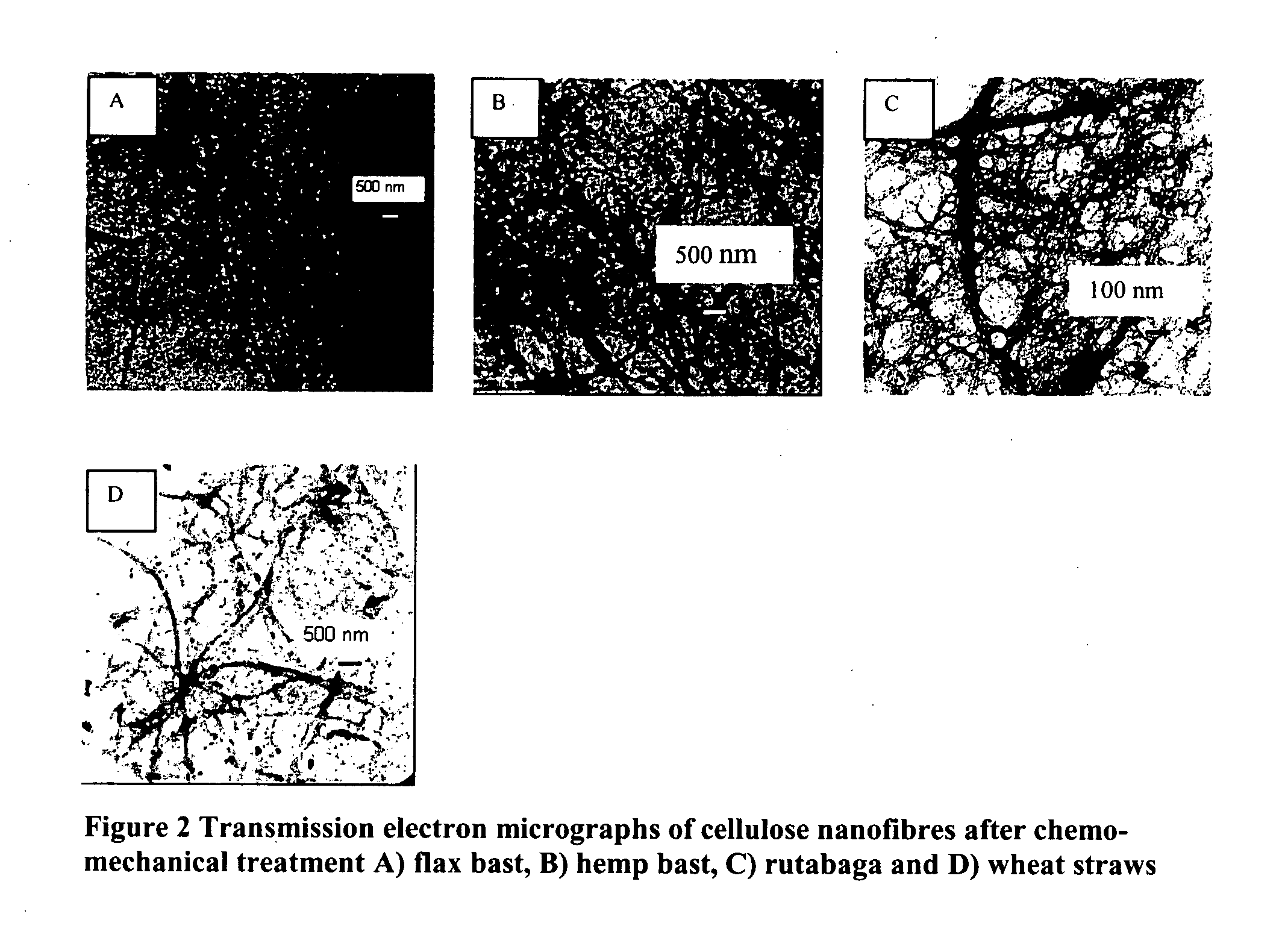
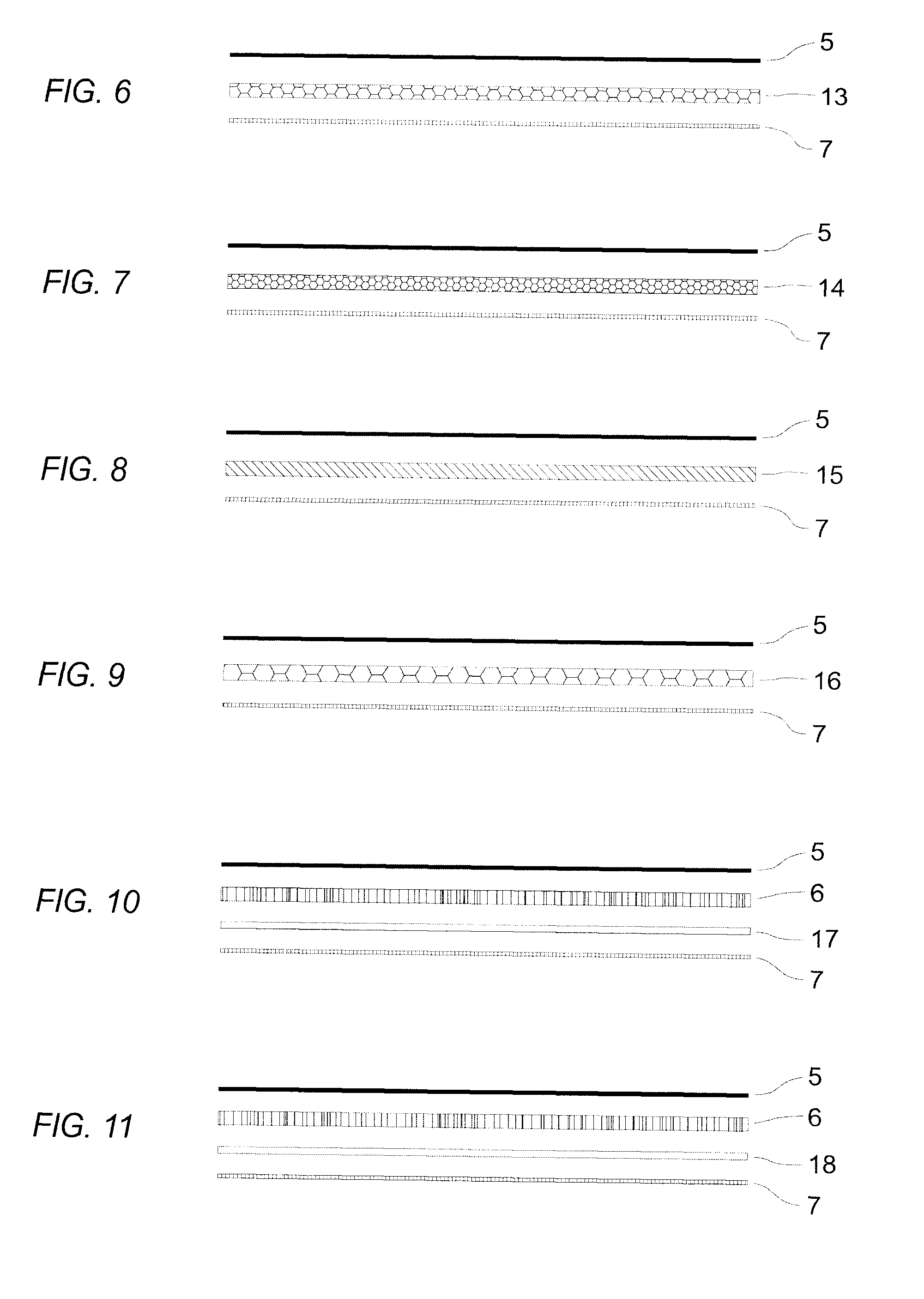
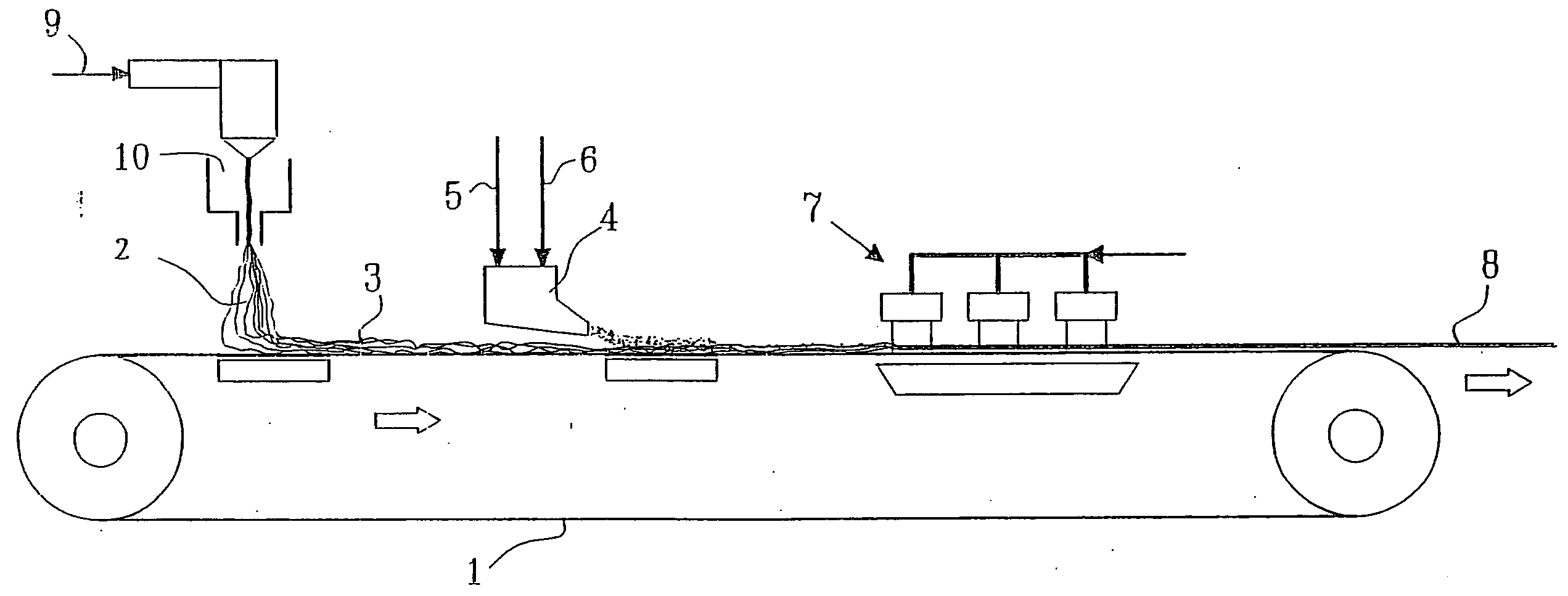
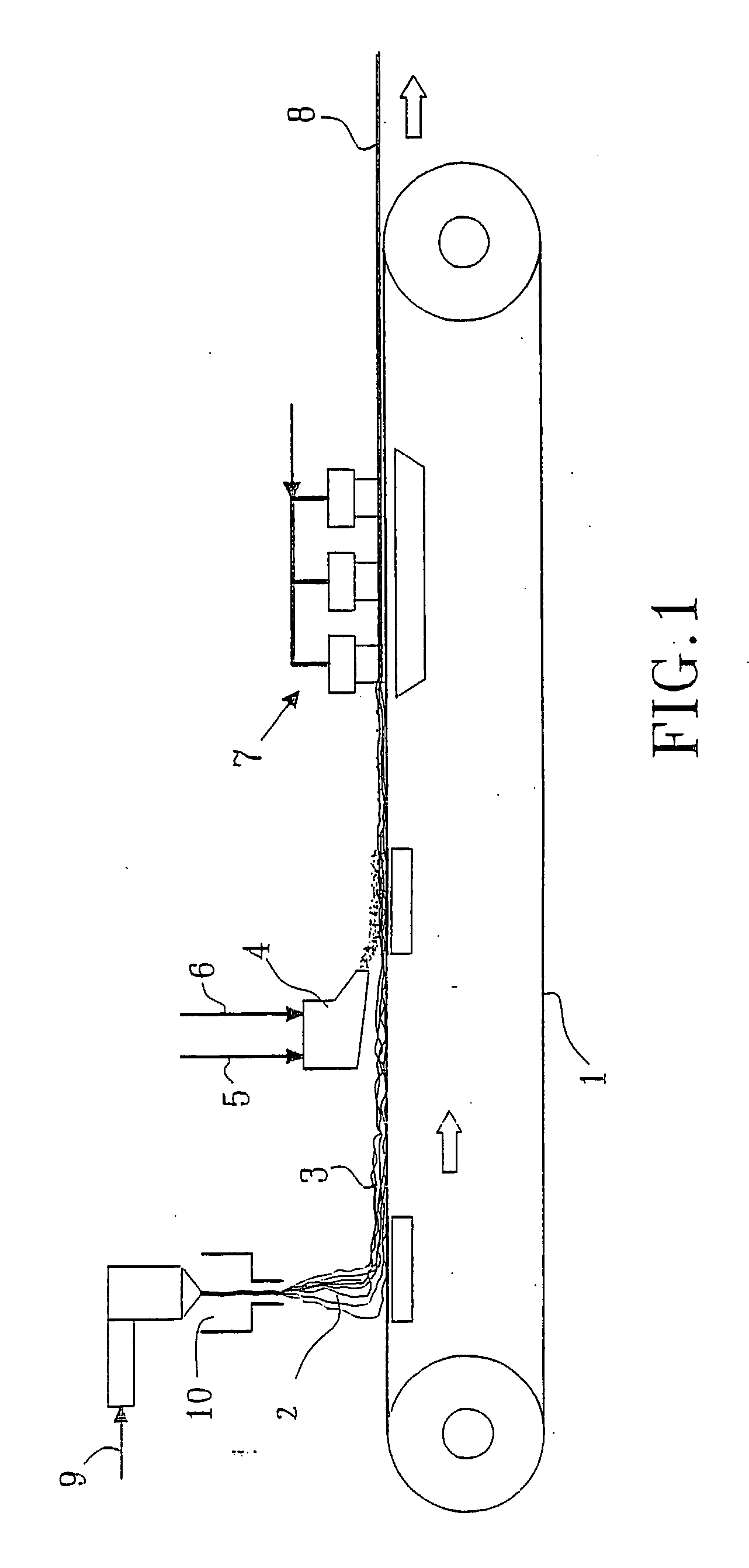
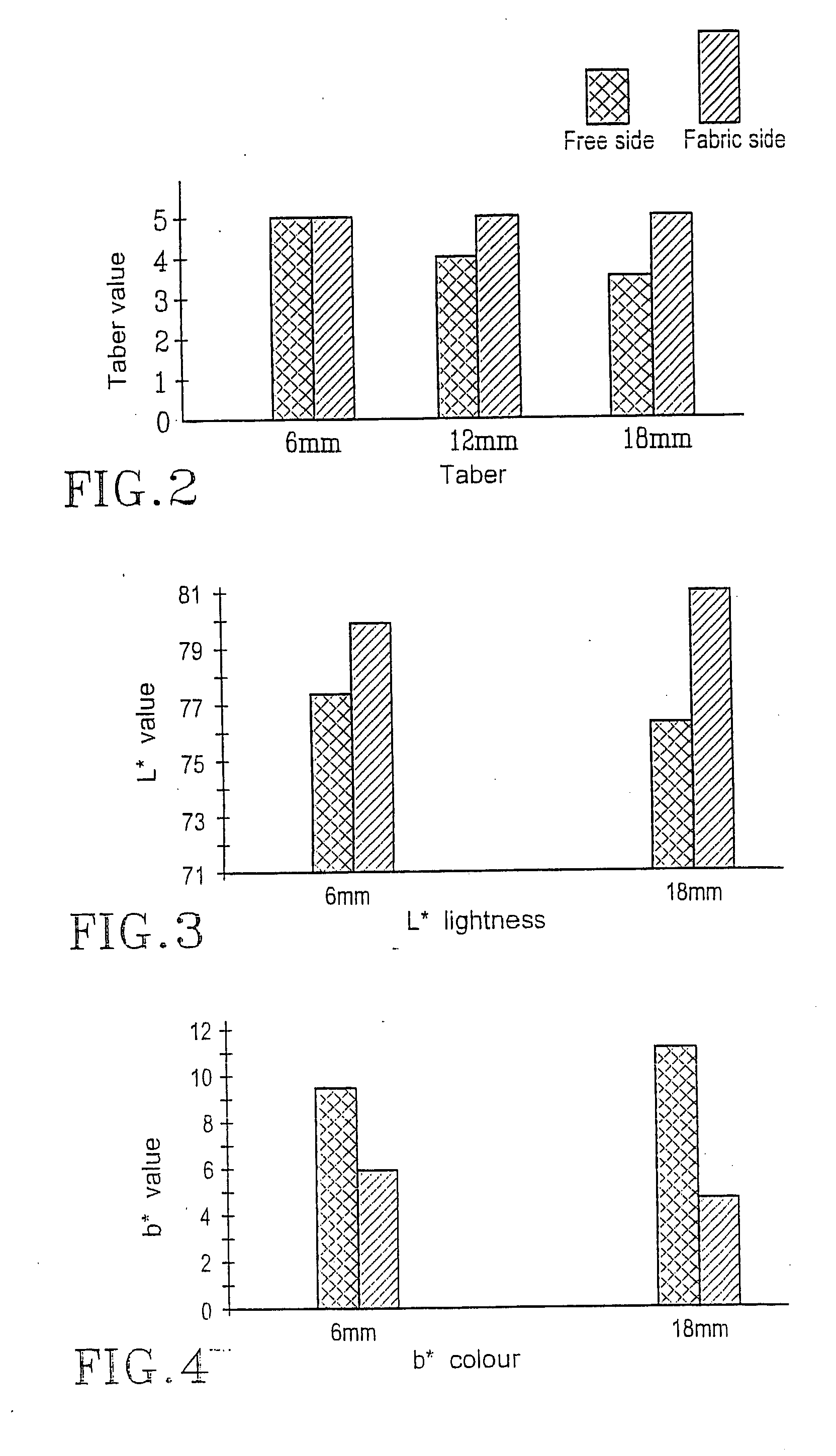
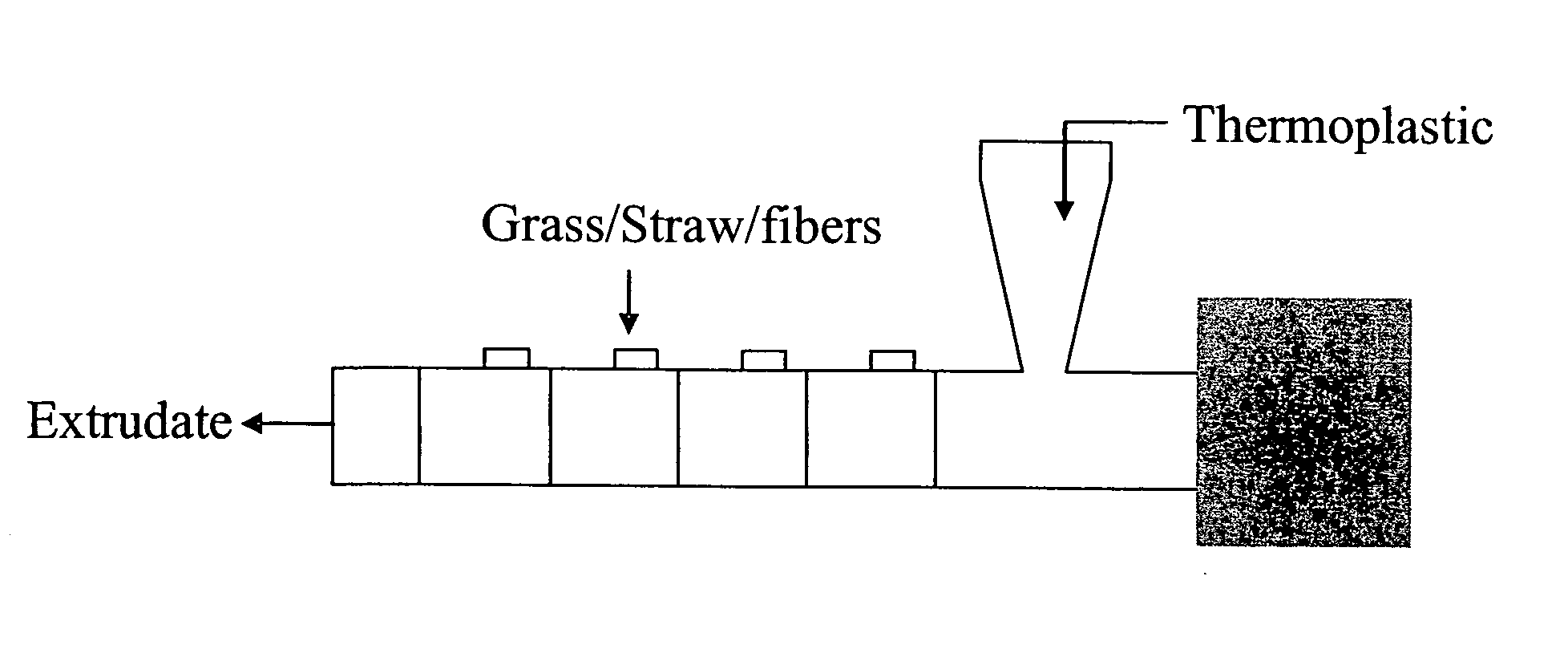
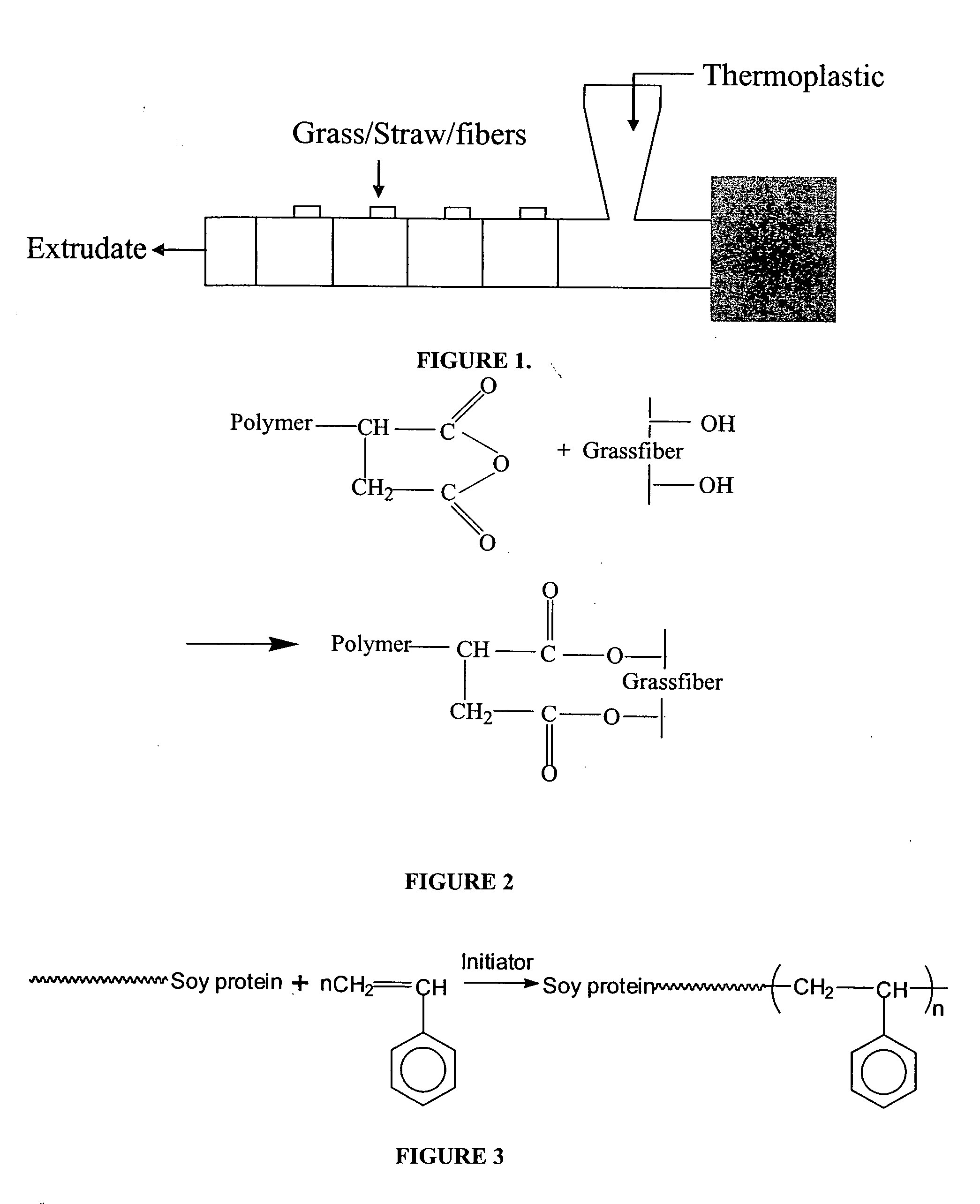
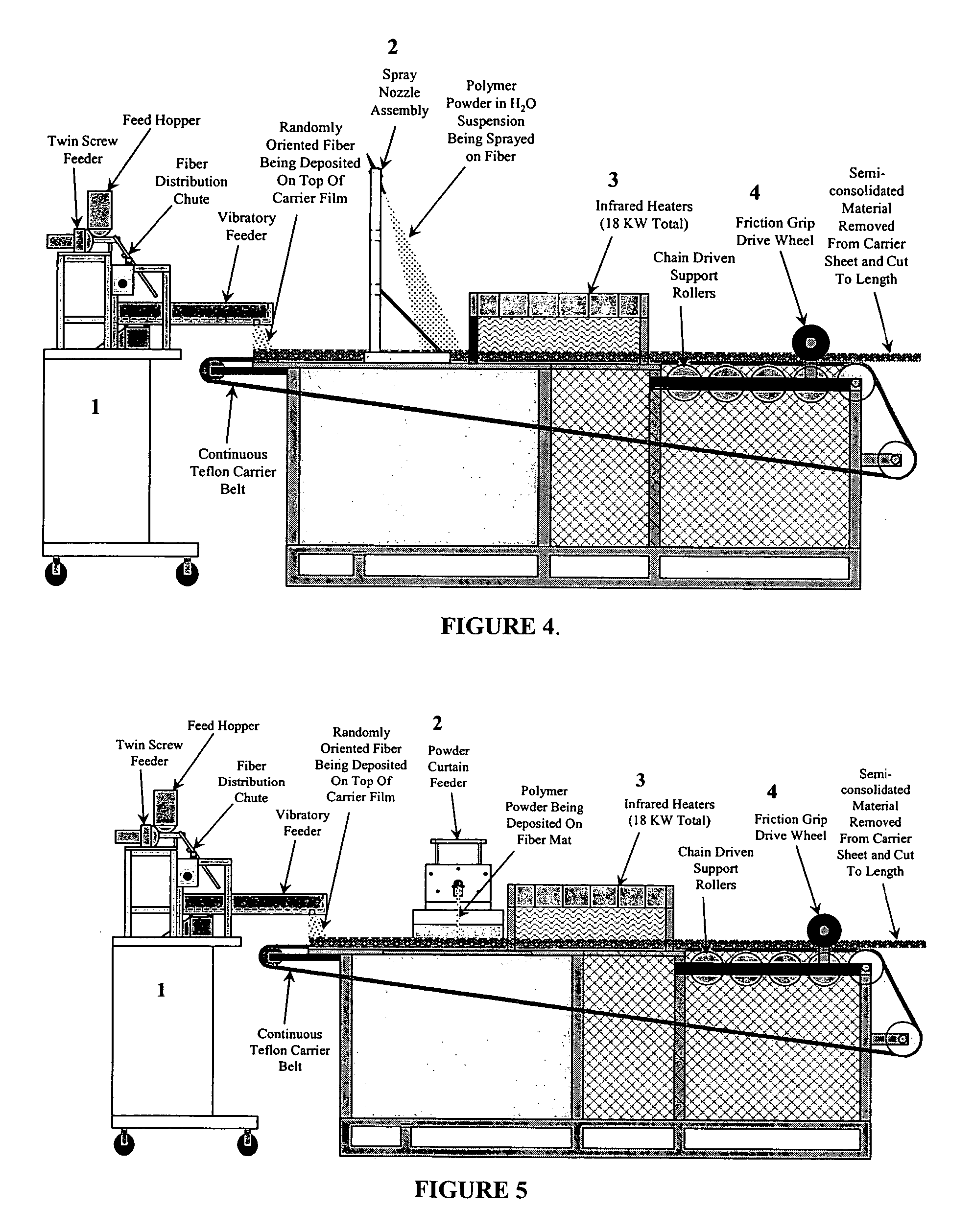
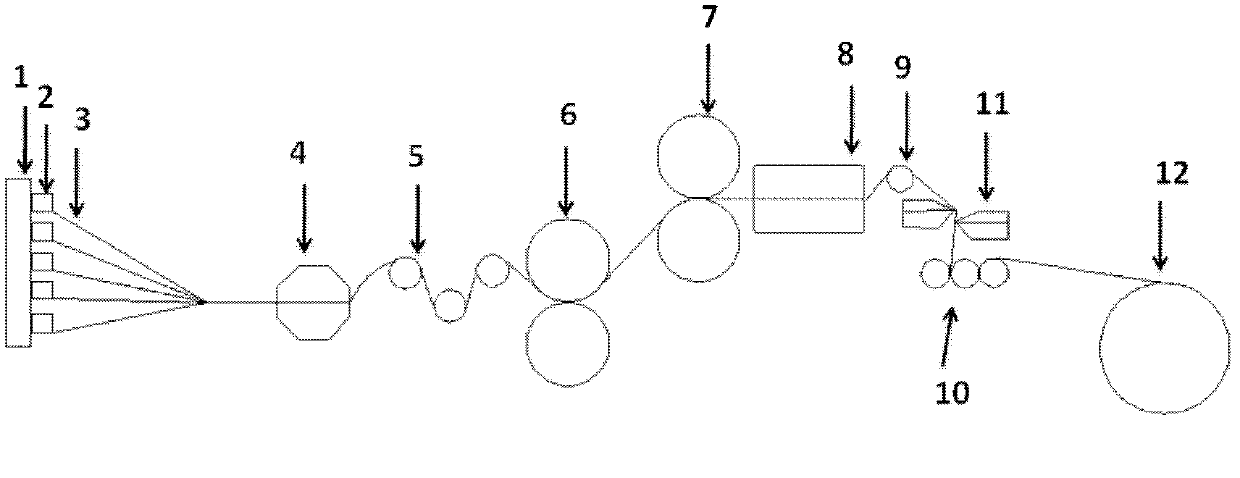
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3307 results about "Natural fiber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Natural fibers or natural fibres (see spelling differences) are fibers that are produced by plants, animals, and geological processes. They can be used as a component of composite materials, where the orientation of fibers impacts the properties. Natural fibers can also be matted into sheets to make paper or felt.
Thermoplastic starch compositions incorporating a particulate filler component
InactiveUS6231970B1Reduce molecular weightAvoid hydrolysisProtein adhesivesPaper coatingParticulatesCross-link
Thermoplastic starch compositions that include a particulate filler, e.g. an inorganic filler component, and optional fibrous component The compositions include a thermoplastic phase comprising a thermoplastic starch melt that contains, at a minimum, starch blended with an appropriate plasticizing agent under conditions in order for the starch to form a thermoplastic melt. The thermoplastic phase may also include one or more additional thermoplastic polymers and other optional reactants, liquids or cross-linking agents to improve the water-resistance, strength, and / or other mechanical properties of the thermoplastic melt, particularly upon solidification. The inorganic filler component may affect the mechanical properties but will mainly be added to reduce the cost of the thermoplastic starch compositions by displacing a significant portion of the more expensive starch or starch / polymer melt. Fibers may optionally be included in order to improve the mechanical properties of the thermoplastic starch compositions. The thermoplastic starch compositions may be shaped into a wide variety of useful articles, such as sheets, films, containers, and packaging materials. Because the thermoplastic starch compositions will typically include a thermoplastic phase that is biodegradable, and because the other components will either constitute a naturally occurring mineral and optionally a natural fiber, the overall composition will typically be more environmentally friendly compared to conventional thermoplastic materials.
Owner:BIO TEC BIOLOGISCHE NATURVERPACKUNGEN
Flooring products and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20060032175A1Improve moisture resistanceStrutsSynthetic resin layered productsThick plateNatural fiber
A plank is described wherein the plank comprises a core, and optionally, a print layer, and optionally an overlay. The core includes from about 30 wt % to about 95 wt % at least one polymeric material, by weight of the core, and from about 5 wt % to about 70 wt % of least one natural fiber or flour, by weight of the core, wherein the core includes a top surface and a bottom surface, and opposing sides, wherein said plank is substantially moisture resistant, having a swelling property of from about 0.5% to about 5% by NALFA Thickness Test Section 3.2 LF 01-2003 standard, and wherein said plank includes a bow of from about 0.5% to about 4%. In addition, a method of making the plank is further described.
Owner:MANNINGTON MILLS
Manufacturing process of cellulose nanofibers from renewable feed stocks
InactiveUS20080146701A1High aspect ratioRaise the potentialMaterial nanotechnologyFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpCelluloseNatural fiber
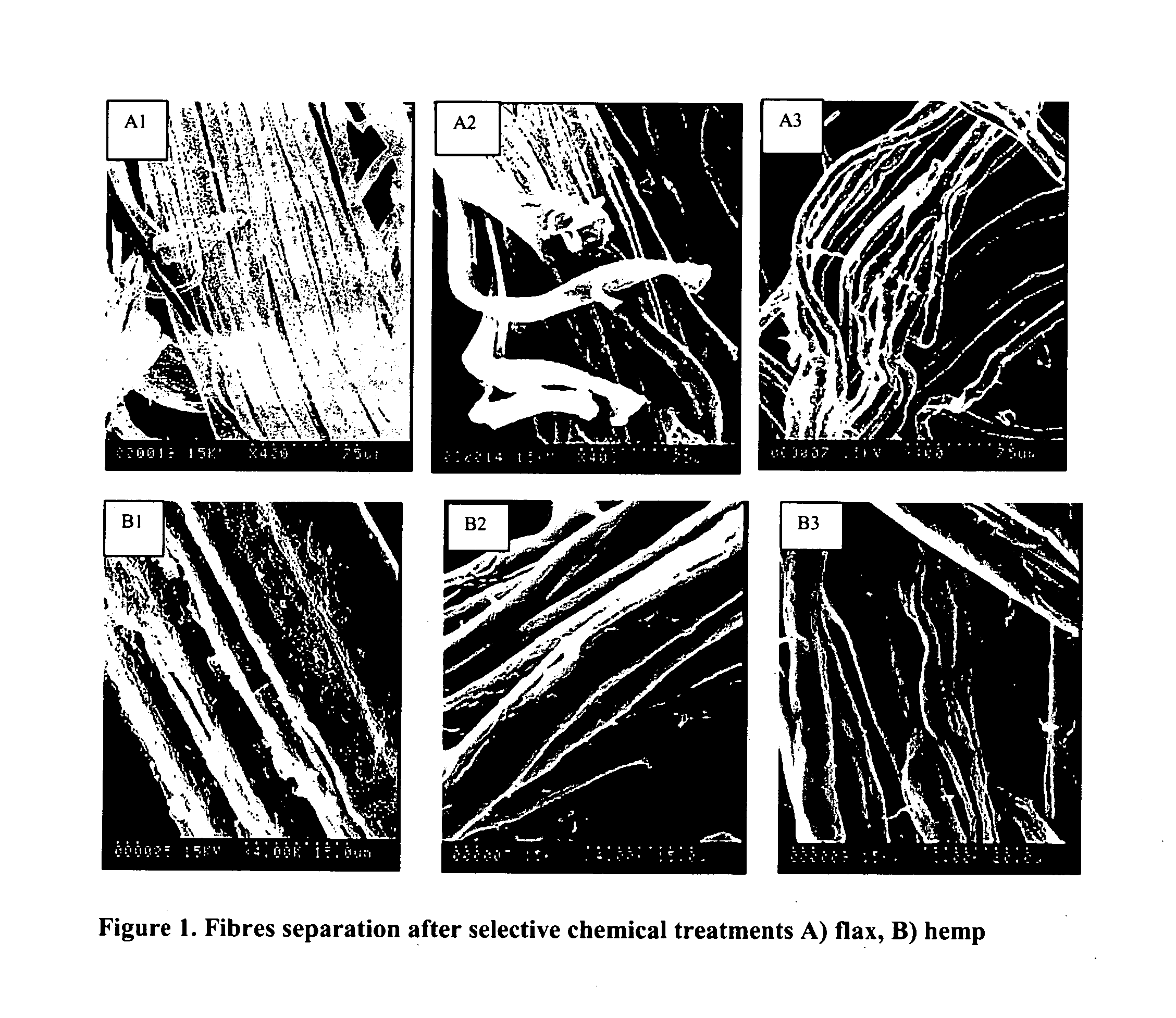
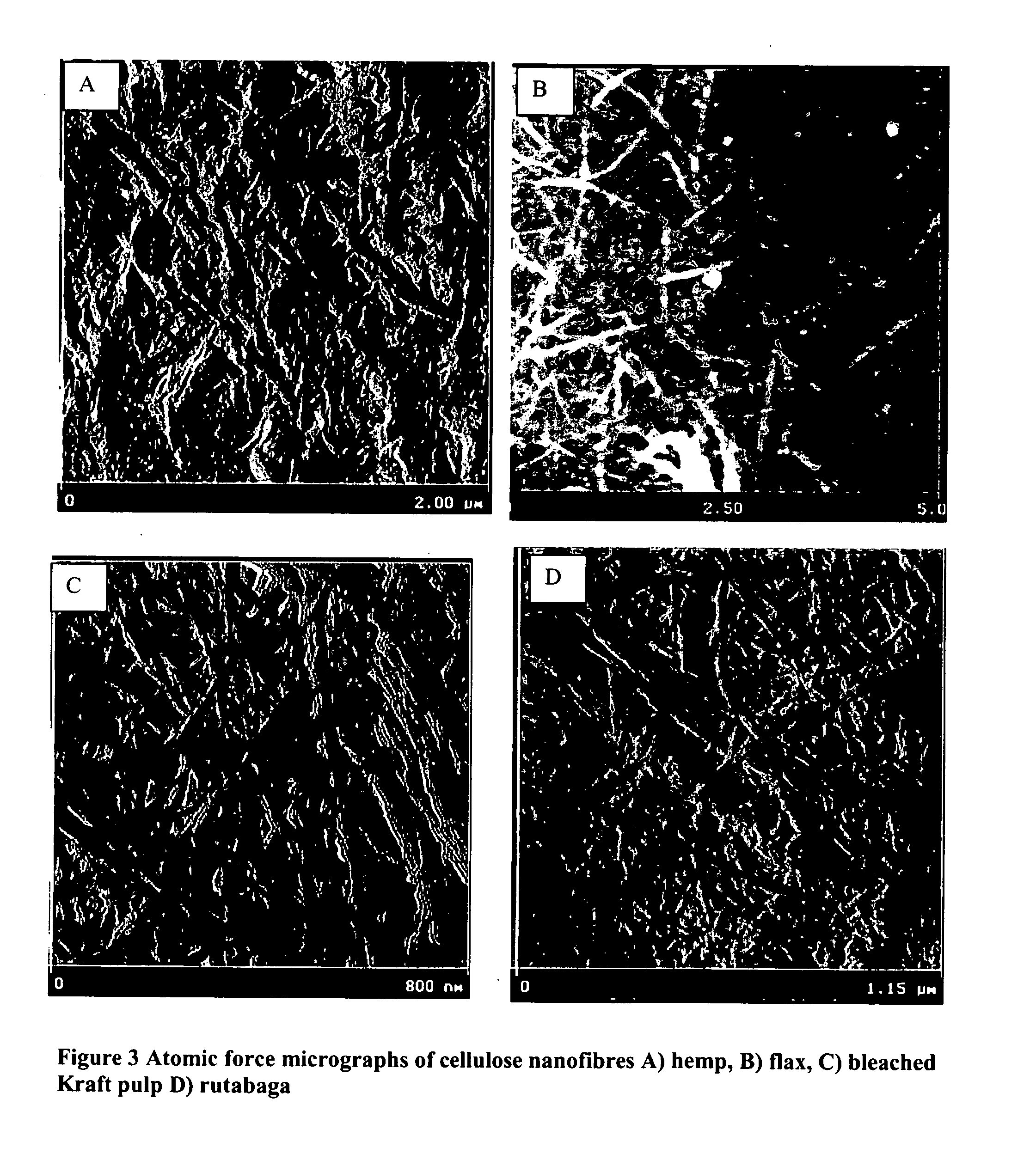
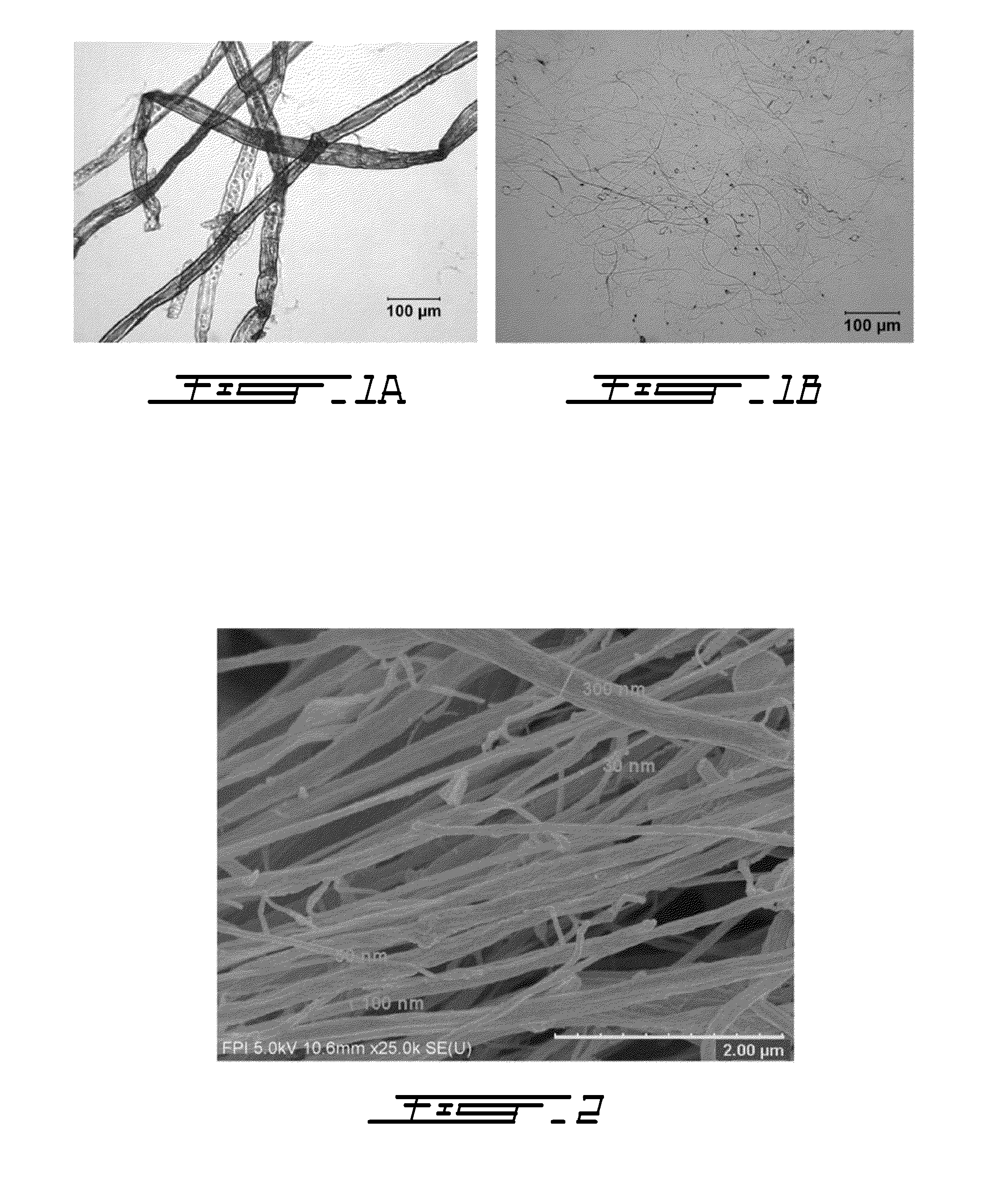
Cellulose nanofibers have been processed from renewable feedstock in particularly from natural fibers, root crops and agro fibers, wherein the pulp was hydrolysed at a moderate temperature of 50 to 90 degree C., one extraction was performed using dilute acid and one extraction using alkali of concentration less than 10%; and residue was cryocrushed using liquid nitrogen, followed by individualization of the cellulose nanofibers using mechanical shear force. The nanofibers manufactured with this technique have diameters in the range of 20-60 nm and much higher aspect ratios than long fibers. Due to its lightweight and high strength its potential applications will be in aerospace industry and due to their biodegradable potential with tremendous stiffness and strength, they find application in the medical field such as blood bags, cardiac devices, valves as a reinforcing biomaterial.
Owner:SAIN MOHINI M +1
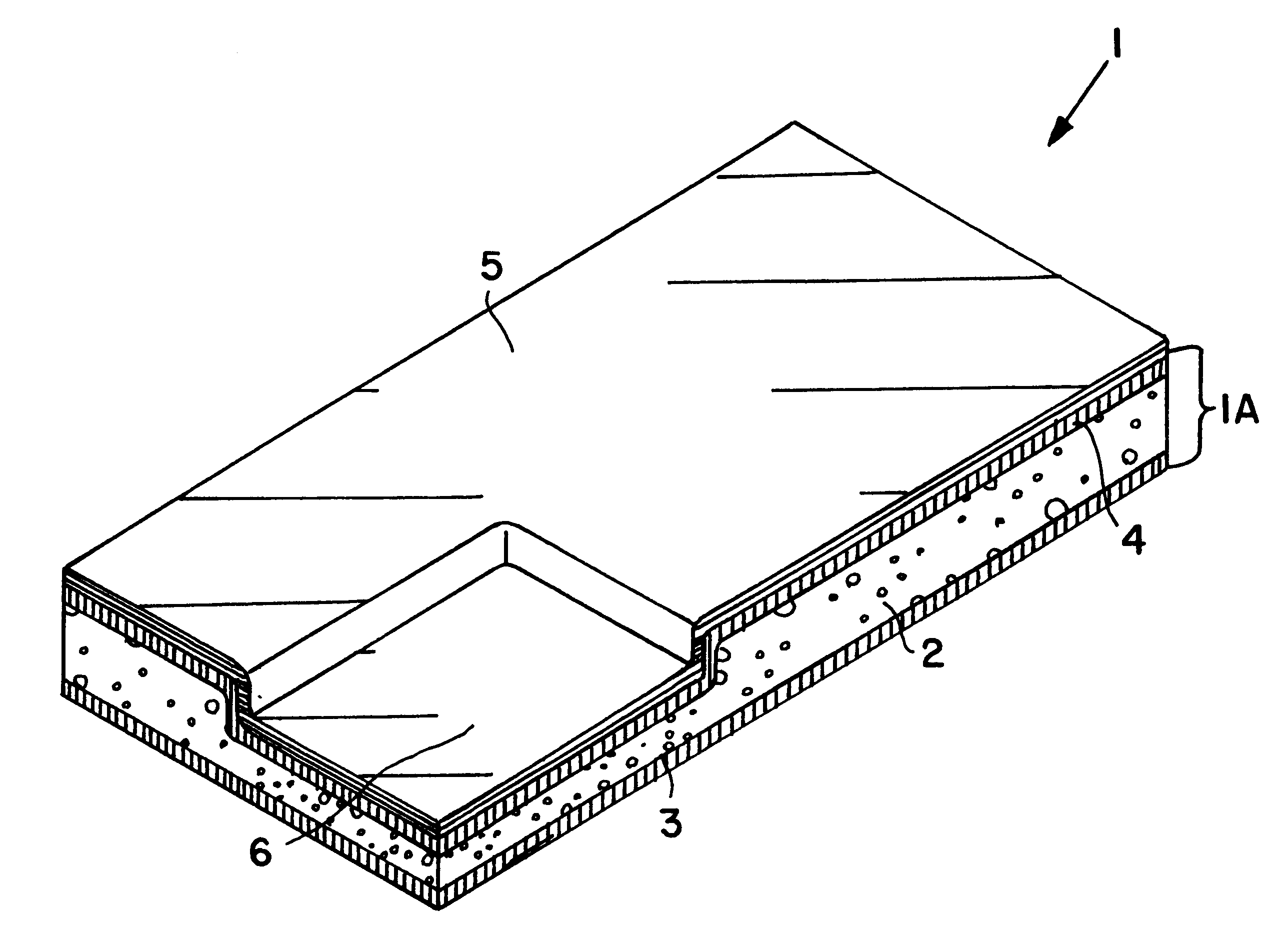
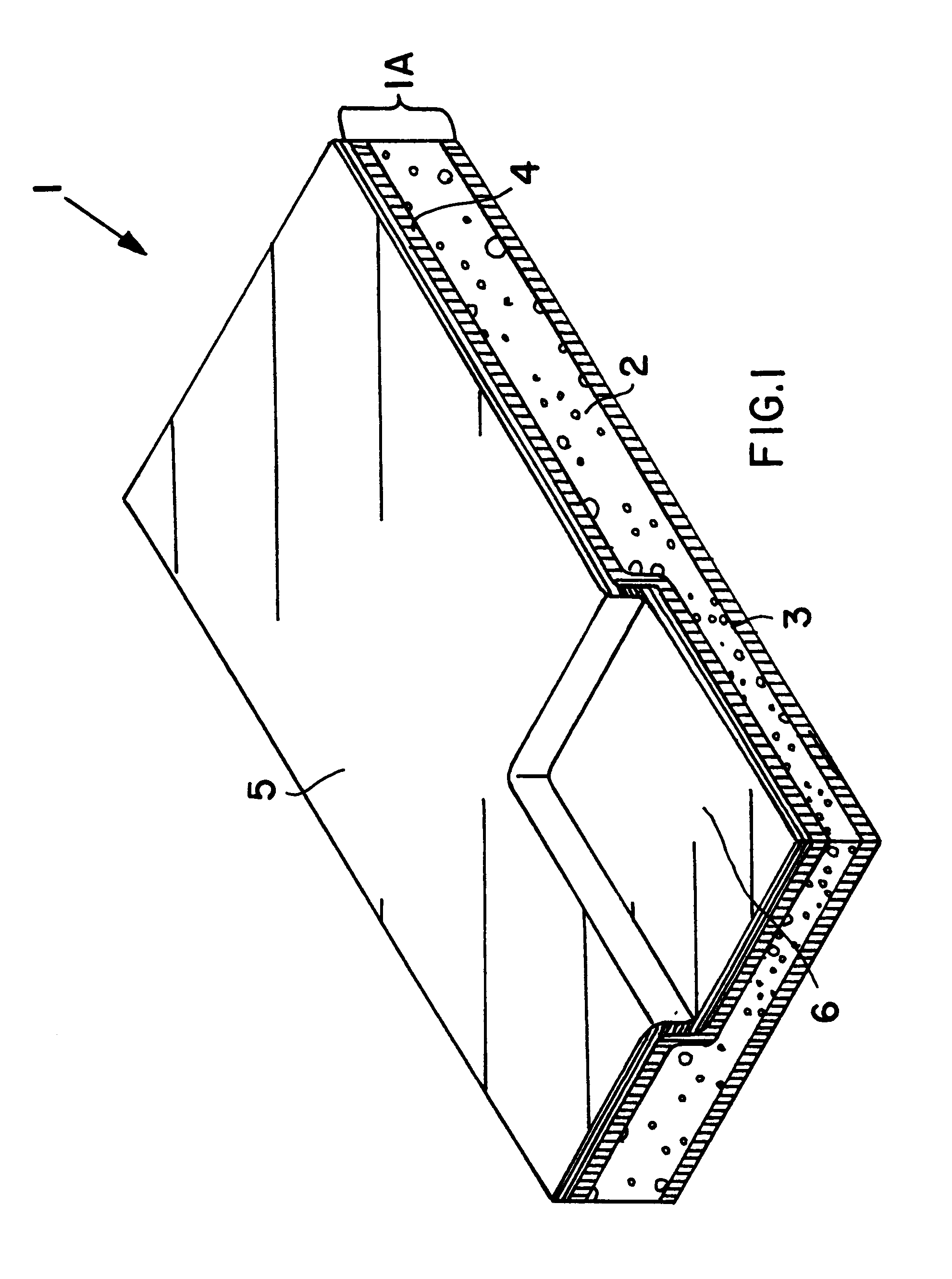
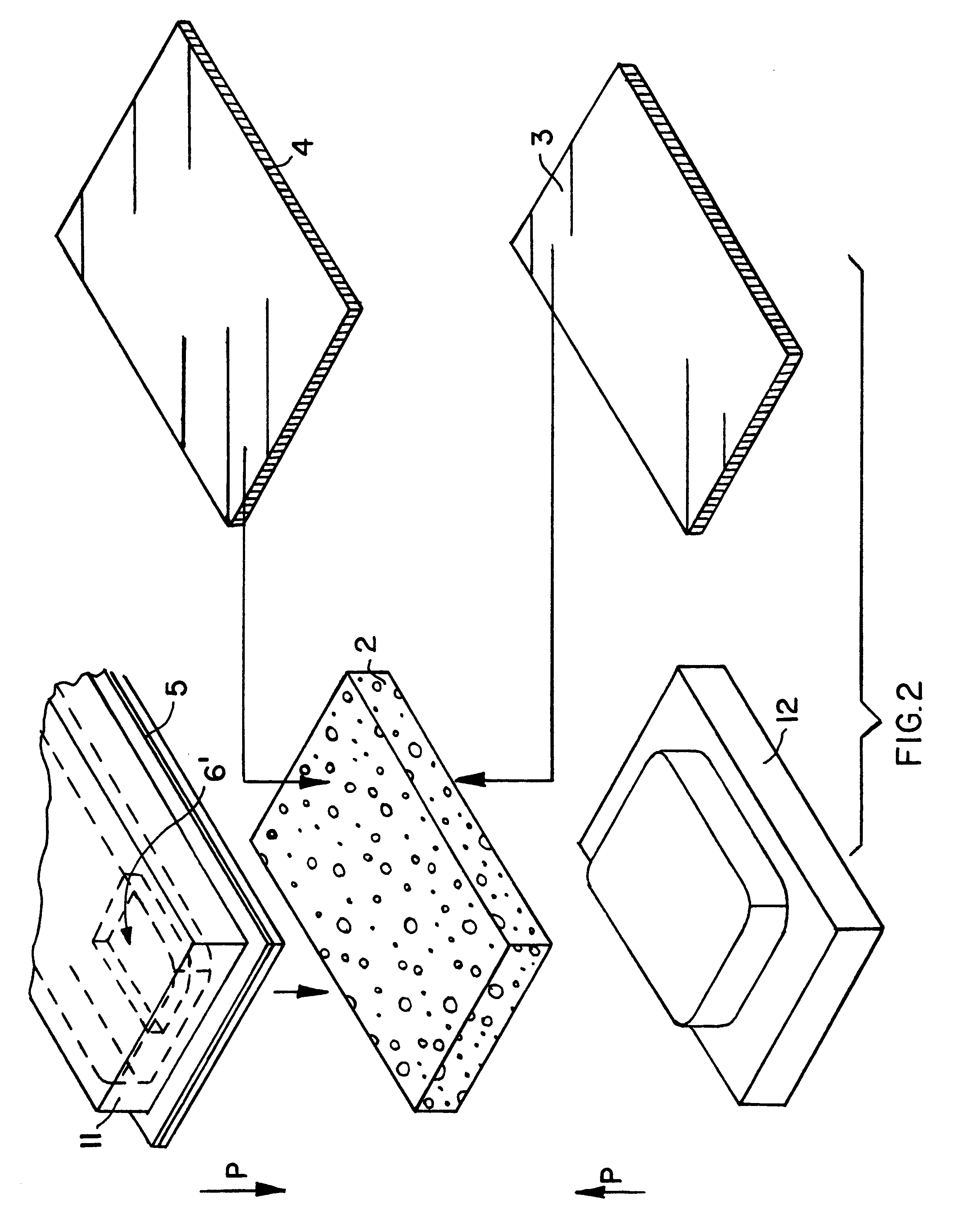
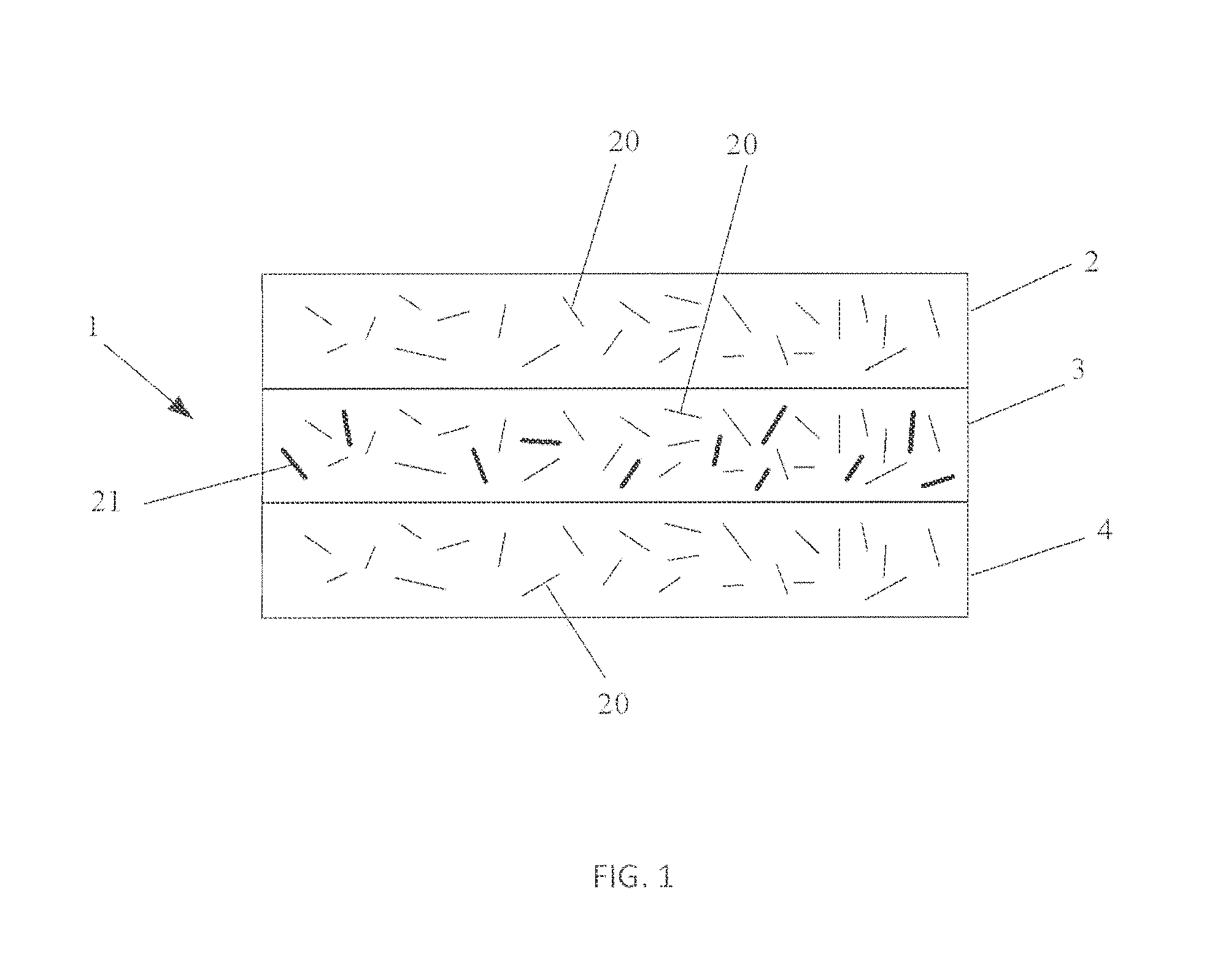
Composite structural panel with thermoplastic foam core and natural fibers, and method and apparatus for producing the same
InactiveUS6287678B1Easy to recycleEasily thermo-processedAdhesive processesLamination ancillary operationsComposite constructionShell molding
A composite structural panel includes a cover sheet laminated onto a three-layered substrate including a thermoplastic foam core sandwiched between two composite outer layers. Each composite outer layer includes natural fibers embedded in a thermoplastic matrix. The thermoplastic material of all layers is preferably polypropylene, and the core consists of an expanded cellular polypropylene rigid foam. In a method for forming the composite structural panel, a first preheated outer layer is laminated and molded onto the foam core in a first molding step, and then the second preheated outer layer and the cover sheet are laminated and molded onto the foam core in a second molding step, with a cooling-down time allowed between the two molding steps. In this manner, each preheated outer layer provides enough heat to thermally fuse the outer layer onto the foam core, without overheating the foam core to the point of softening or melting the foam core. The low density foam core provides a spacing distance between the strong composite outer layers, and therefore the finished composite structural panel has a high strength and rigidity, and a high strength-to-weight ratio. The structural panel can be molded into any desired three-dimensional contoured configuration during the molding process.
Owner:HERBERT OLBRICH
Cellulose nanofilaments and method to produce same
ActiveUS20110277947A1Improve strength propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyNatural cellulose pulp/paperPolymer sciencePaperboard
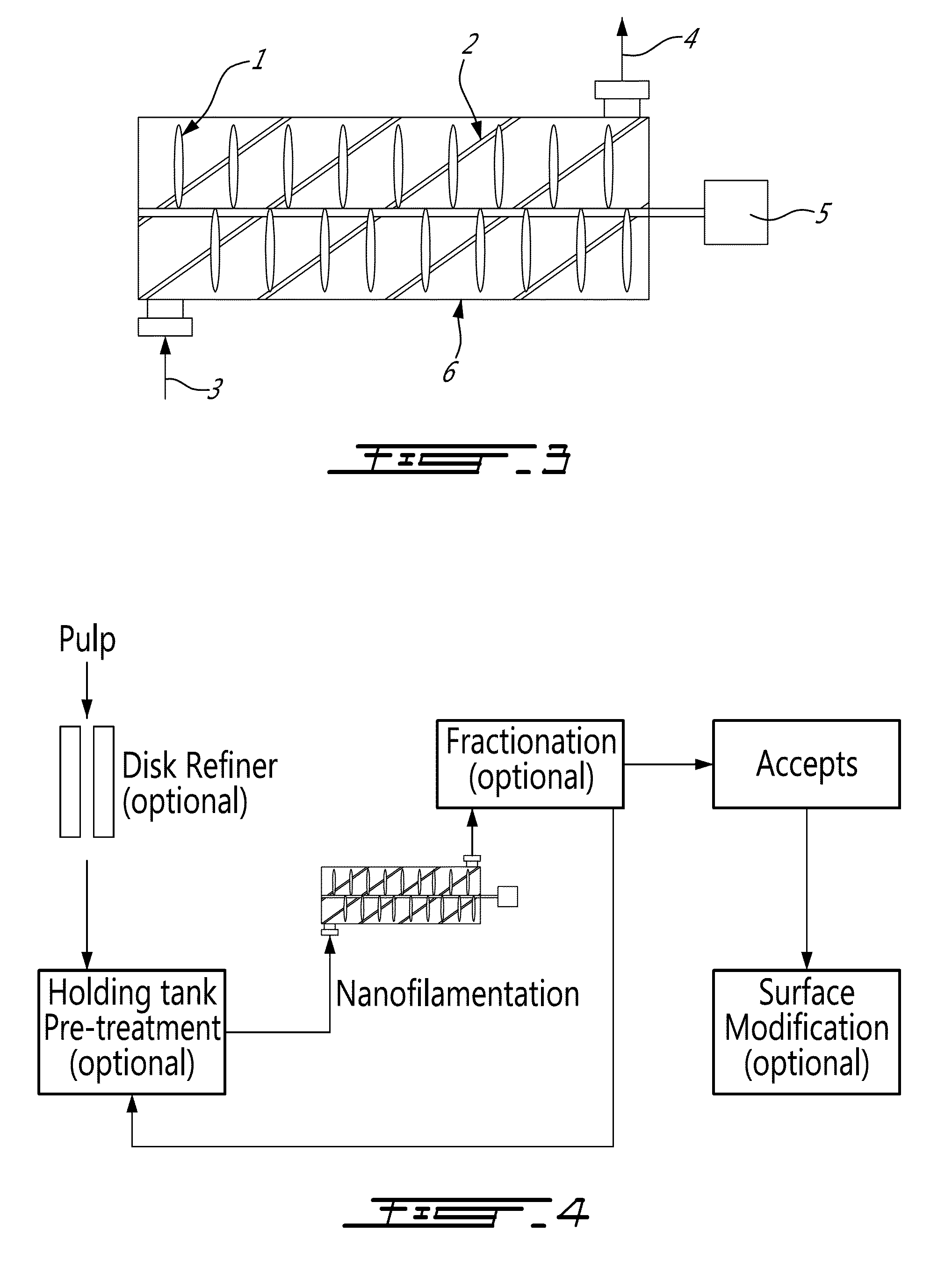
Cellulose nanofilaments from cellulose fibers, a method and a device to produce them are disclosed. The nanofilaments are fine filaments with widths in the sub-micron range and lengths up to a couple of millimeters. These nanofilaments are made from natural fibers from wood and other plants. The surface of the nanofilaments can be modified to carry anionic, cationic, polar, hydrophobic or other functional groups. Addition of these nanofilaments to papermaking furnishes substantially improves the wet-web strength and dry sheet strength much better than existing natural and synthetic polymers. The cellulose nanofilaments produced by the present invention are excellent additives for reinforcement of paper and paperboard products and composite materials, and can be used to produce superabsorbent materials.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
Flame resistant fabrics and garments made from same
InactiveUS20080057807A1Inexpensive and comfortable to wearerCotton-low durability-isWarp knittingAnimal housingPolymer scienceNatural fiber
Unique blends of fibers that incorporate synthetic cellulosic fibers to render fabrics made with such blends more durable than fabrics made with natural cellulosic fibers such as cotton. While more durable than cotton, the synthetic cellulosic fibers used in the blends are still inexpensive and comfortable to the wearer. Thus, the benefits of cotton (affordability and comfort) are still attained while a drawback of cotton—low durability—is avoided. In one embodiment, the fiber blend includes FR modacrylic fibers and synthetic cellulosic fibers, preferably, but not necessarily non-FR lyocell fibers such as TENCEL™ and TENCEL A100™. Other fibers may be added to the blend, including, but not limited to, additional types of inherently FR fibers, anti-static fibers, anti-microbial fibers, stretch fibers, and / or high tenacity fibers. The fiber blends disclosed herein may be used to form various types of FR fabrics. Desired colors may be imparted in a variety of ways and with a variety of dyes to the fabrics disclosed herein. Fabrics having the fibers blends disclosed herein can be used to construct the entirety of, or various portions of, a variety of protective garments for protecting the wearer against electrical arc flash and flames, including, but not limited to, coveralls, jumpsuits, shirts, jackets, vests, and trousers.
Owner:SOUTHERN MILLS
Vehicle interior trim panel with a soft-touch foam layer, and a method and apparatus for making the same
InactiveUS6136415ALow densityFlexible of partLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsDashboardPolyolefin
An interior trim component such as a vehicle dashboard includes a substantially rigid and form-stable substrate of polypropylene and natural fibers, a supporting halo skeleton and other frame components heat fused onto the backside of the substrate, and a polyolefin foam layer as well as a decorative polyolefin cover film laminated onto the front side of the substrate. The foam layer has an increased thickness and a decreased foam density at sharply contoured or curved areas of the trim component, in comparison to the flat surfacial areas. As a result, the trim component has a desirable soft-touch characteristic and impact absorbing properties at all areas including protruding curves and edges. A method for forming such a trim component involves steps of pre-molding the foam layer and cover film by vacuum thermoforming, pre-molding the substrate by vacuum thermoforming, and then heat laminating the pre-heated, pre-molded substrate onto the pre-molded foam layer and cover film. The sharply curved or contoured areas of the component are provided with a greater tolerance spacing between the substrate and the cover film, which are held to the respective mold contours by vacuum. Under the effect of heat and the applied vacuum, the foam layer expands to have a greater thickness and a lower density in these sharply contoured areas.
Owner:HERBERT OLBRICH
Resilient flooring compositions
InactiveUS20120276348A1Improve wear resistanceReduce the possibilityCovering/liningsSpecial ornamental structuresWood veneerNatural fiber
Resilient flooring materials made from impregnated papers or foils and core materials are provided. As well, the methods for producing such products are provided. In particular, panels, with a layered structure, created by forming an assembly which consists of laminating a heat-activated resin impregnated decorative layer with printed graphics or a wood veneer decorative layer, a core material made up of one or more heat-activated resin-impregnated papers or other materials including linoleum, natural or synthetic rubber, cork, flexible natural fiber composites or other core materials, and a heat-activated resin impregnated paper backing layer. The heat-activated resin also acts to waterproof each of the layers and abrasion particles may be incorporated to improve wear properties. The panels may also be formed into three-dimensional products.
Owner:CLAUSI ROBERT N +1
Composite material for automobile interior part and production method thereof
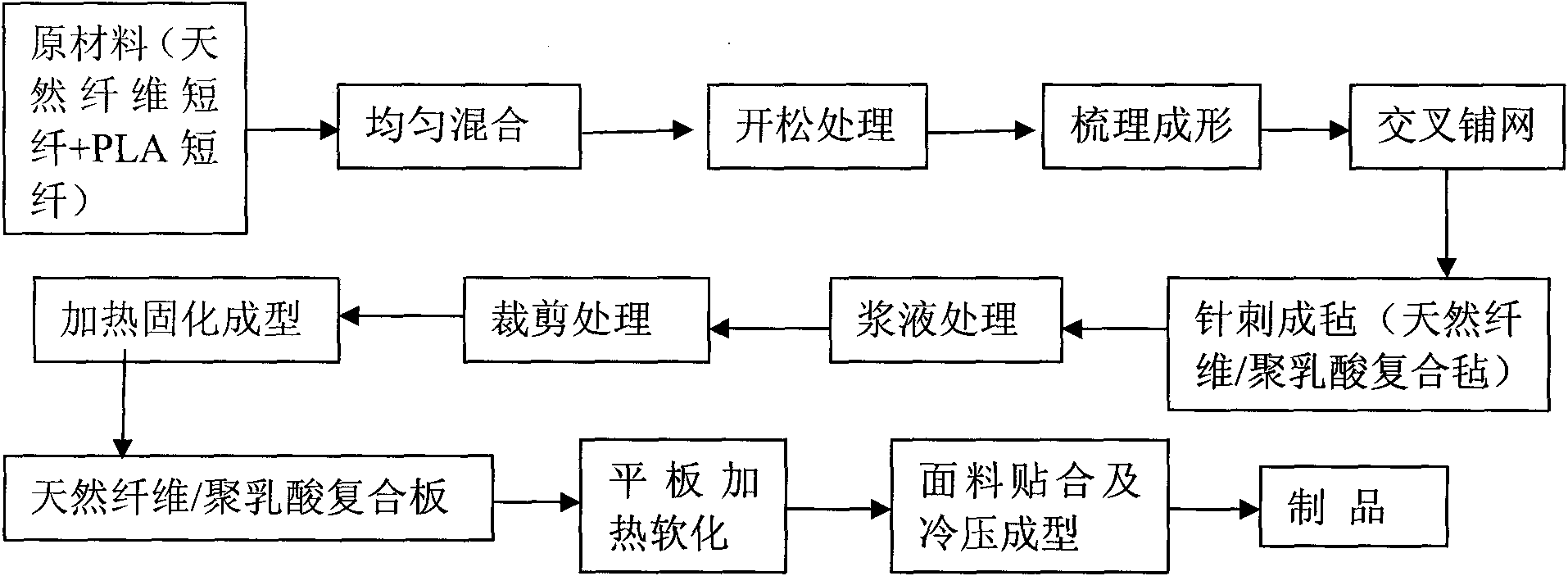
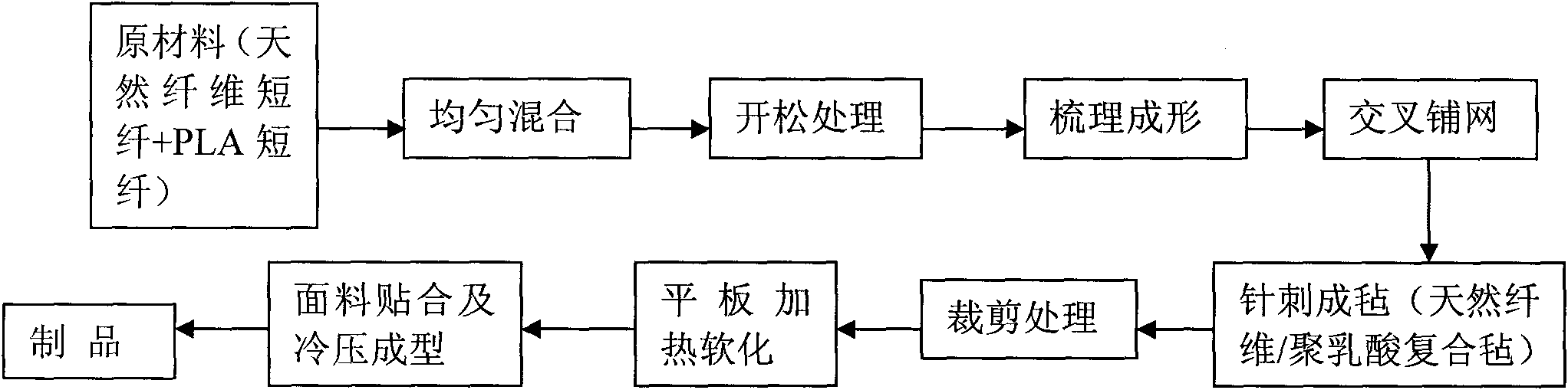
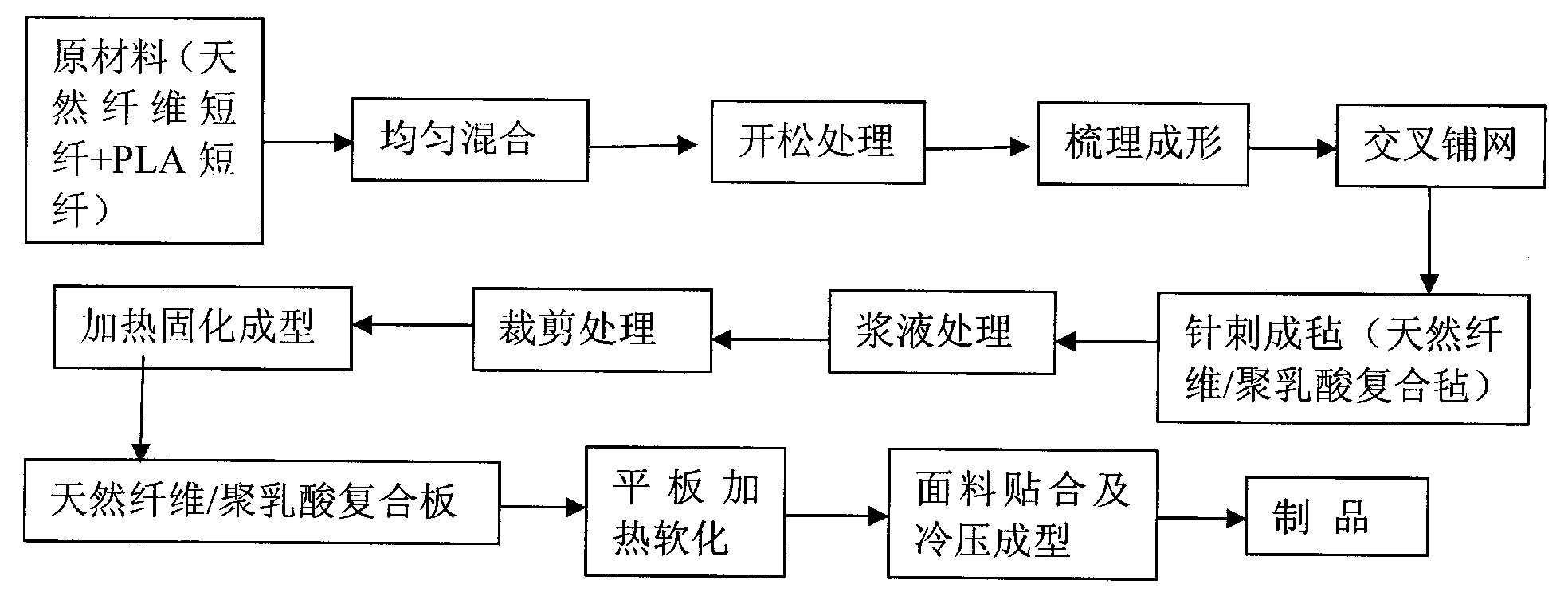
ActiveCN101812773ANo pollution in the processReduce lossVehicle componentsNon-woven fabricsMetallurgySlurry
The invention discloses a formula of a composite material for an automobile interior part. The formula consists of the following materials in percentage by weight: 40 to 60 percent of polylactic acid fiber and 40 to 60 percent of natural fiber. The production method of the invention comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing the raw materials; putting the mixture into an opener for opening, combing and shaping the obtained product, feeding the product into a lapping machine for cross lapping and feeding the cross-lapped product into a needling machine for needling to form a felt; immersing the fiber felt into a processing slurry; drying the immersed coiled material through hot blast and cutting the dried material into pieces of required size; placing the cut material into a mould for curing and shaping by heating; demoulding the material to form a composite plate; and softening the composite plate by flat panel heating, covering the plate with a surface decorative layer and performing cold molding on the plate through a product mould to manufacture the finished product finally; or softening the cut fiber felt by the flat panel heating directly, covering the plate with the surface decorative layer and performing the cold molding to manufacture the finished product finally. The composite material for the automobile interior part of the invention has the advantages of no toxicity, no pollution, simple processing technique, small energy consumption and high environment protection performance.
Owner:CHERY COMML VEHICLE ANHUI
Flame retardant microcapsule and application thereof
ActiveCN101885859AImprove flame retardant performanceHigh mechanical strengthThin material handlingMicroballoon preparationCellulosePolymer science
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
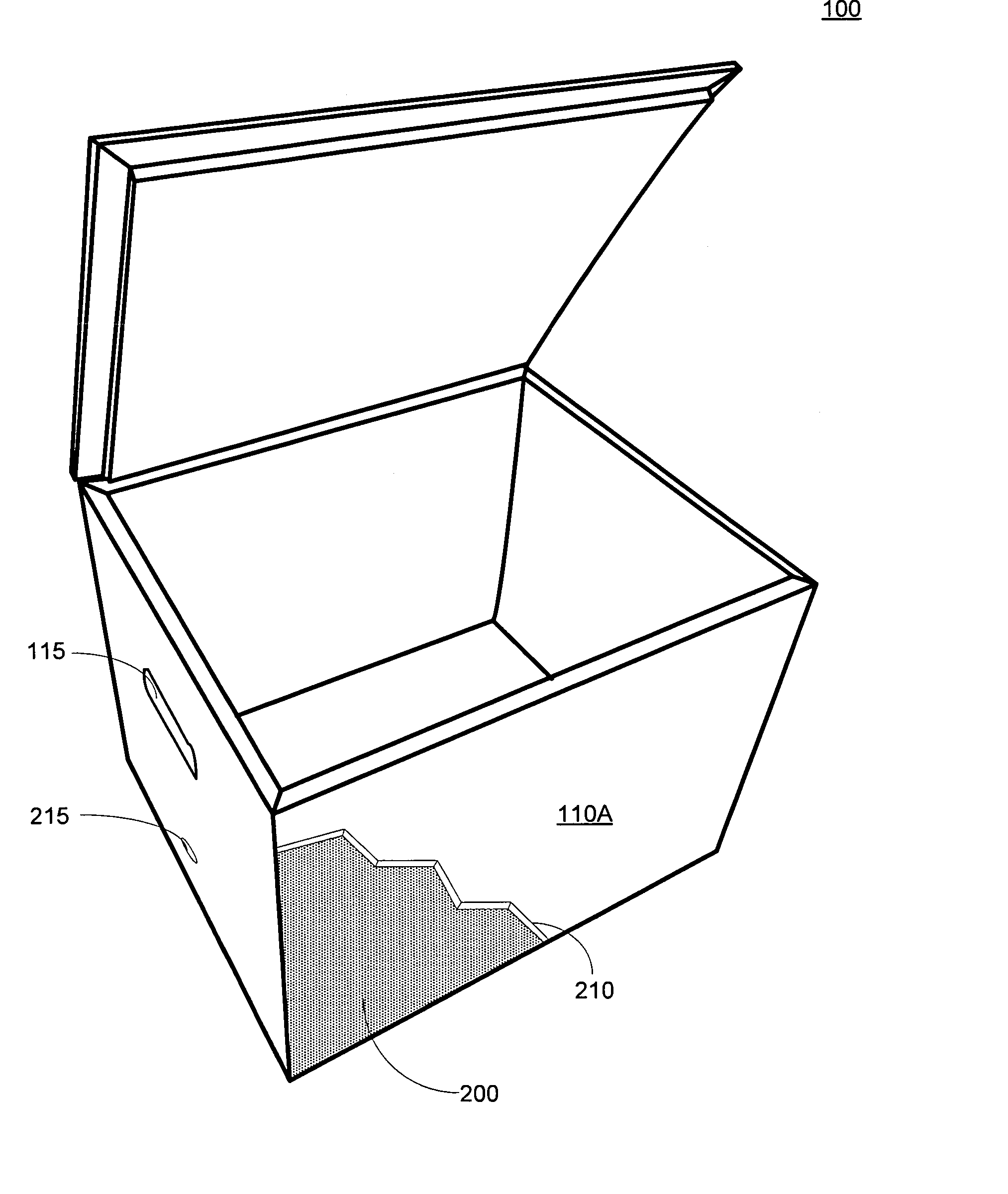
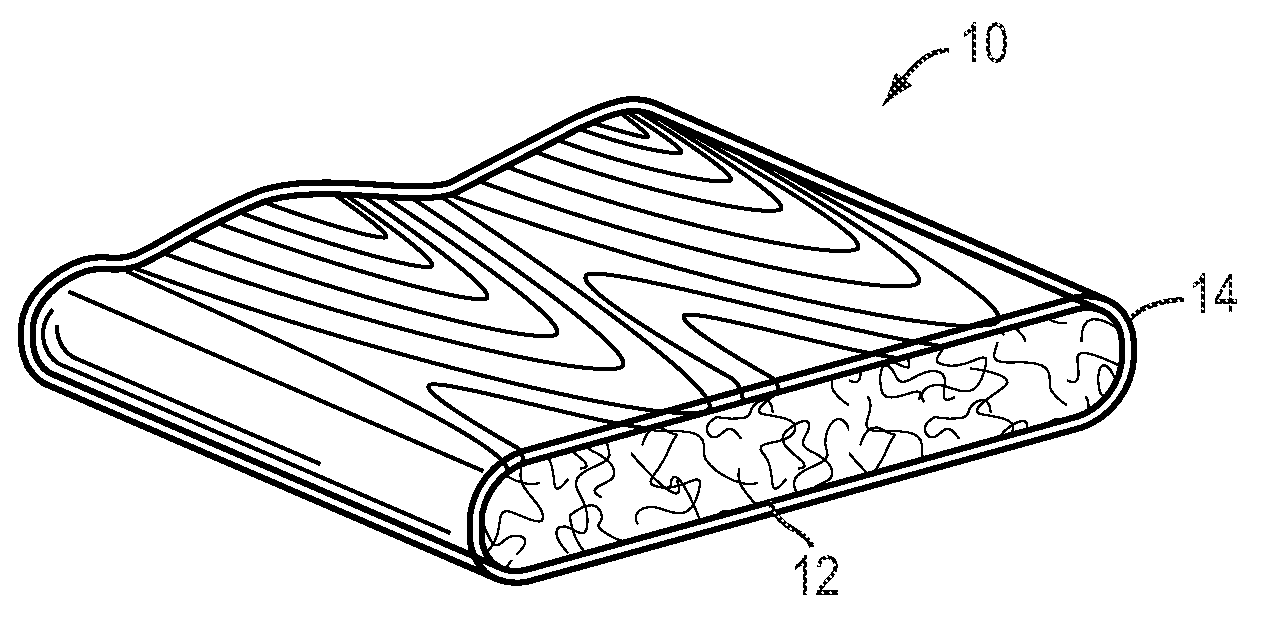
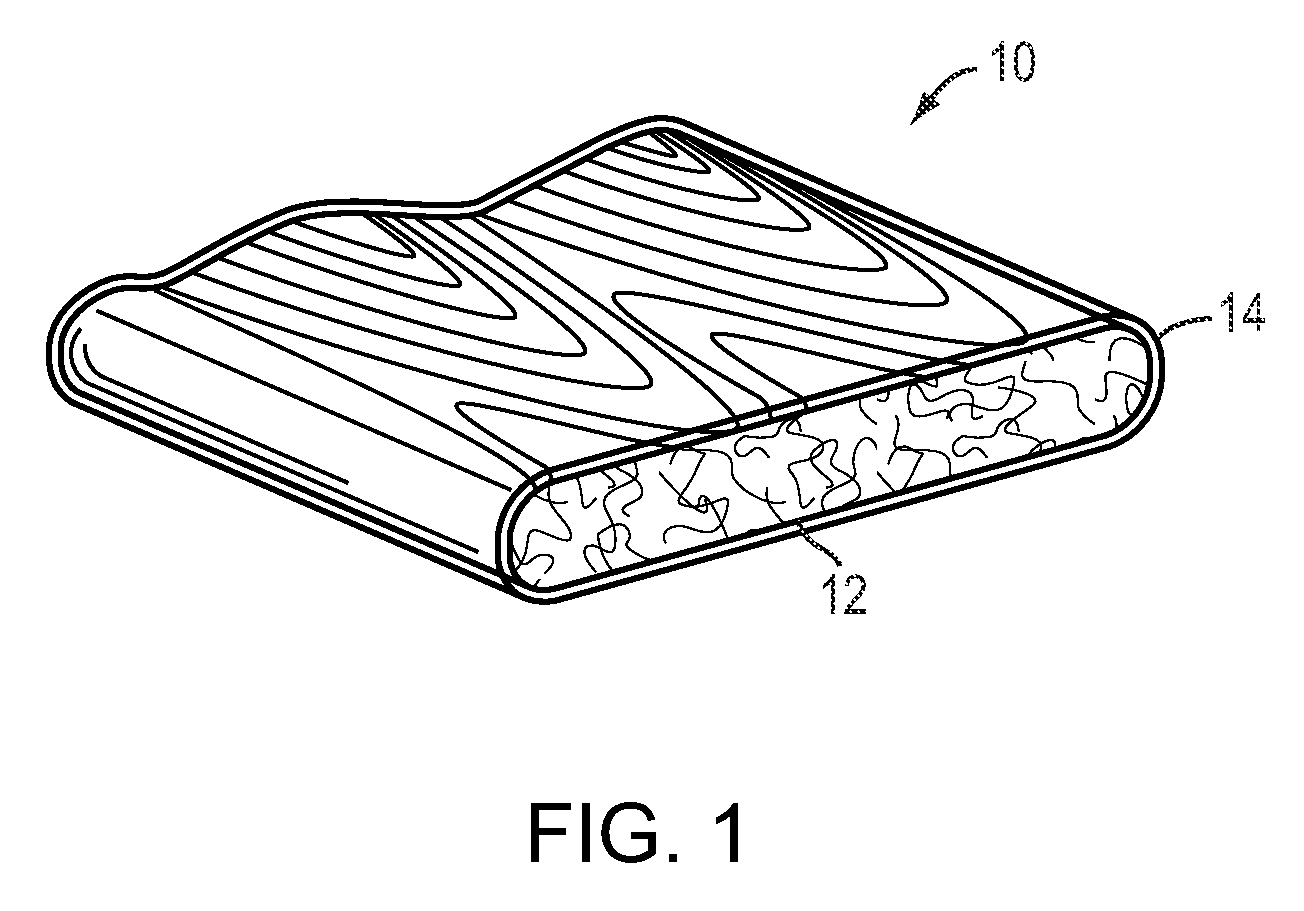
Cellulose based recyclable container
ActiveUS8365943B2Easy constructionEasy maintenanceDomestic cooling apparatusBio-packagingCelluloseNatural fiber
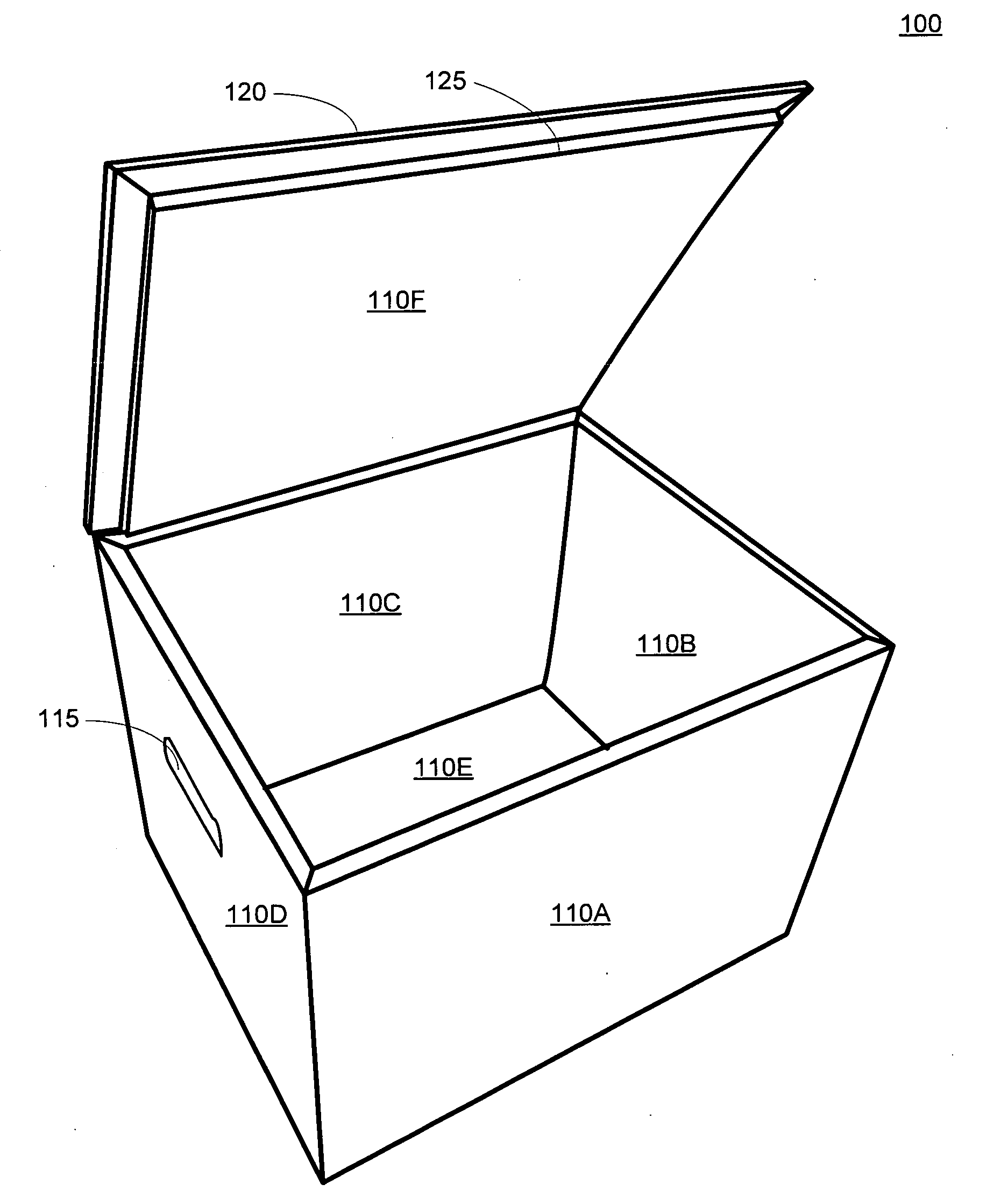
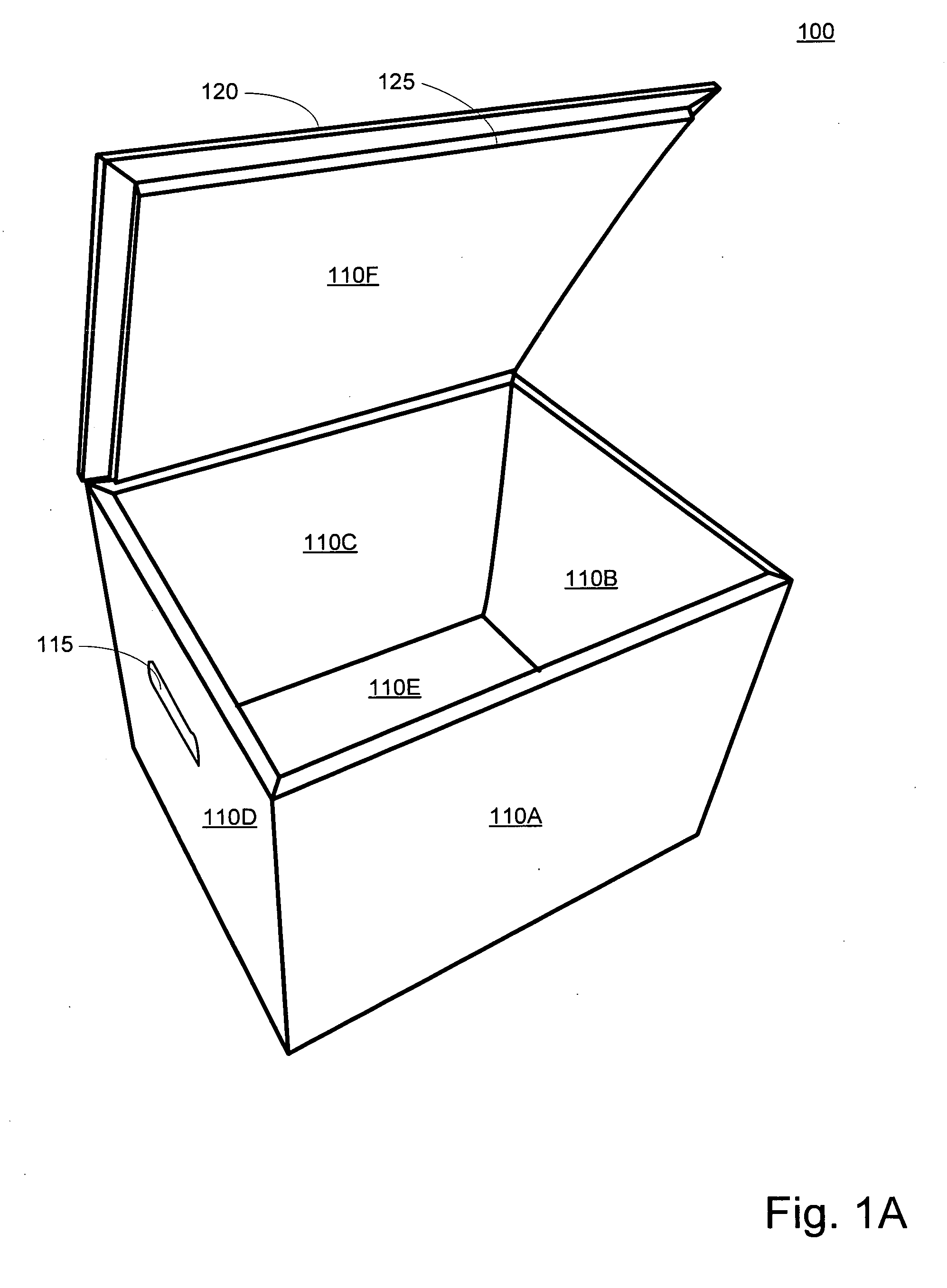
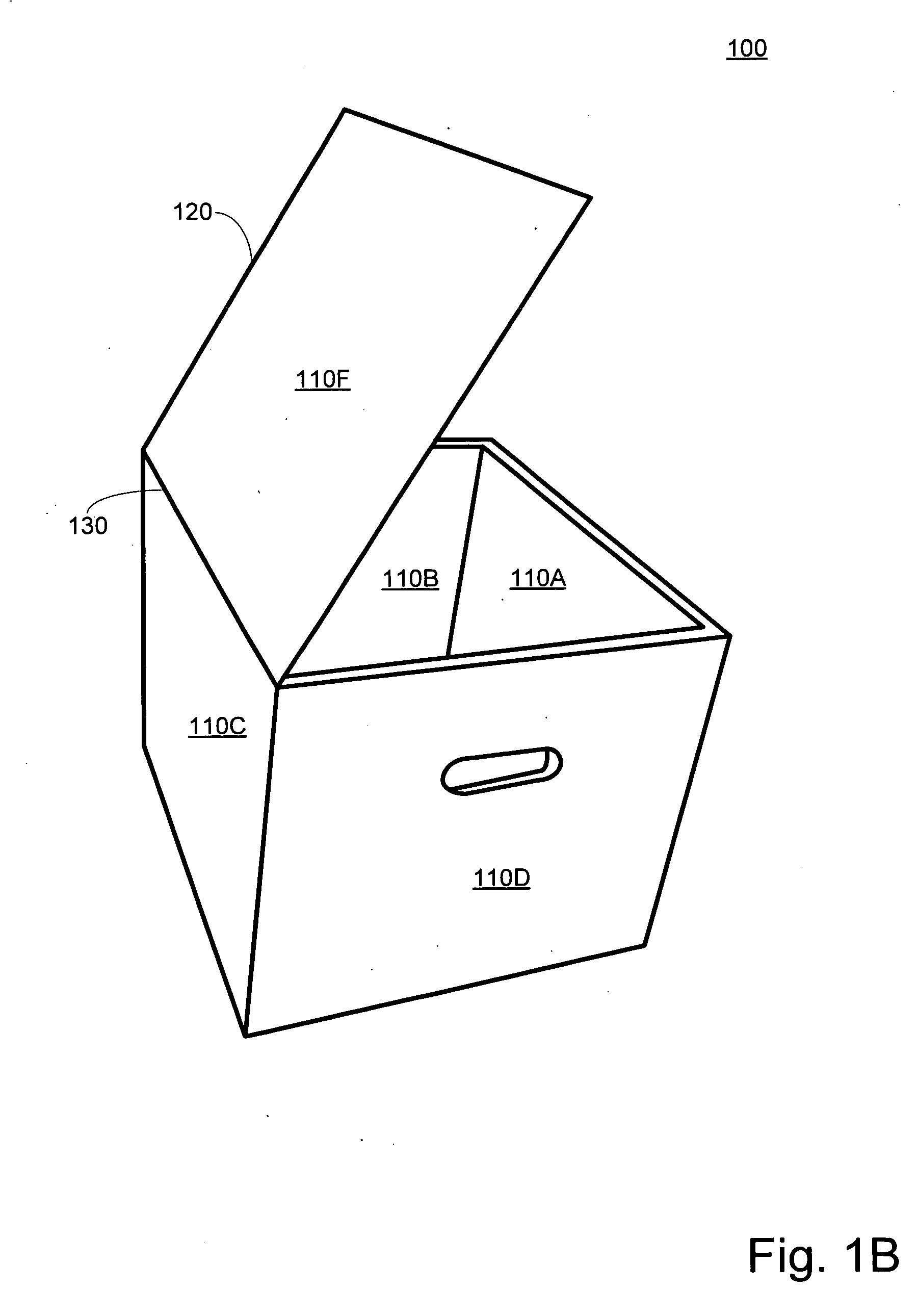
Disclosed is a portable cooler device comprised of recyclable materials. Some embodiments of the device comprise components constructed entirely of, or substantially of, cellulose. Other embodiments may be comprised of recyclable materials not classified as cellulose such as, but not limited to, cotton, bamboo, hemp, or other natural fibers. The specific percentages of recycled and / or recyclable content are not limiting factors for the invention; however, most embodiments have consistent materials of construction such that the entire device may be recycled in a single recycling process without the need for deconstruction. Further, if not recycled, embodiments are operable to biodegrade within a reasonable amount of time when exposed to the elements in a landfill. Typical embodiments are comprised of an inner shell, an outer shell having an integrally hinged lid, and pressed cellulose insulating boards sandwiched between the shells.
Owner:RECYCOOL
Wood-Plastic Composites Utilizing Ionomer Capstocks and Methods of Manufacture
An extruded composite adapted for use as a building material includes a core having a base polymer and a natural fiber in a substantially homogeneous mixture and an ionomer capstock. To improve adherence of the ionomer to a base polymer, the ionomer can be mixed with a similar or substantially similar base polymer prior to coextrusion with the core. Additionally, various additives may be mixed with the capstock material to improve visual aesthetics of the product and performance of the building material, especially over time.
Owner:FIBER COMPOSITES
Nano silver bacterial fibre and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101942759AEvenly distributedImprove antibacterial propertiesVegetal fibresNatural fiberAntibacterial property
The invention discloses a nano silver bacterial fibre preparation method comprising: adding fibre into AgNO3 solution, and adsorbing the mixture; and carrying out reduction reaction on the adsorbed fibre to obtain the nano silver bacterial fibre. The invention has simple production step, and the obtained product has the advantages of even silver nanoparticle distribution and long-lasting fibre antibacterial property and can be washed several times. The invention is suitable for natural fibre and synthetic fibre and can be used for health-care underwear, medicinal gauze, clothes, decorative textiles and the like.
Owner:金湖县农副产品营销协会
Fiber-reinforced thermoplastic matrices
The invention relates to thermoplastic matrices reinforced with a mixture of natural and synthetic fibers.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Cellulose based recyclable container
ActiveUS20100258574A1Easy constructionEasy maintenanceDomestic cooling apparatusBio-packagingCelluloseLitter
Disclosed is a portable cooler device comprised of recyclable materials. Some embodiments of the device comprise components constructed entirely of, or substantially of, cellulose. Other embodiments may be comprised of recyclable materials not classified as cellulose such as, but not limited to, cotton, bamboo, hemp, or other natural fibers. The specific percentages of recycled and / or recyclable content are not limiting factors for the invention; however, most embodiments have consistent materials of construction such that the entire device may be recycled in a single recycling process without the need for deconstruction. Further, if not recycled, embodiments are operable to biodegrade within a reasonable amount of time when exposed to the elements in a landfill. Typical embodiments are comprised of an inner shell, an outer shell having an integrally hinged lid, and pressed cellulose insulating boards sandwiched between the shells.
Owner:RECYCOOL
Composite structures
InactiveUS6872674B2Intended for useSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsCellulose fiberNatural fiber
The present invention is a non-woven web or composite structure comprising (a) from about 50 to about 90 weight percent of a natural cellulose fiber; (b) from about 10 to about 50 weight percent of a binder fiber component; (c) from 0 to about 20 weight percent of a filler; and (d) from 0 to about 8 weight percent of a dye or pigment.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
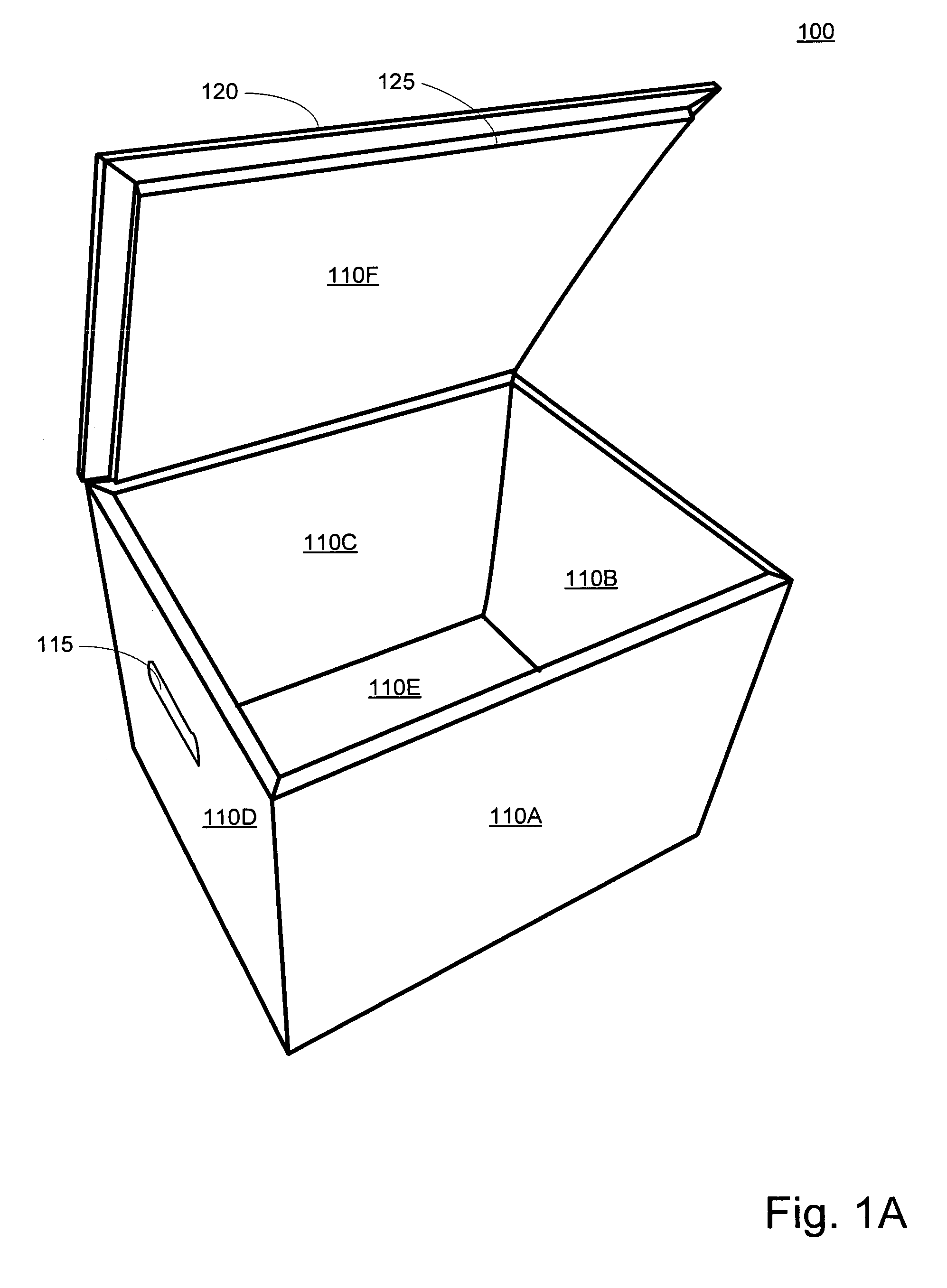
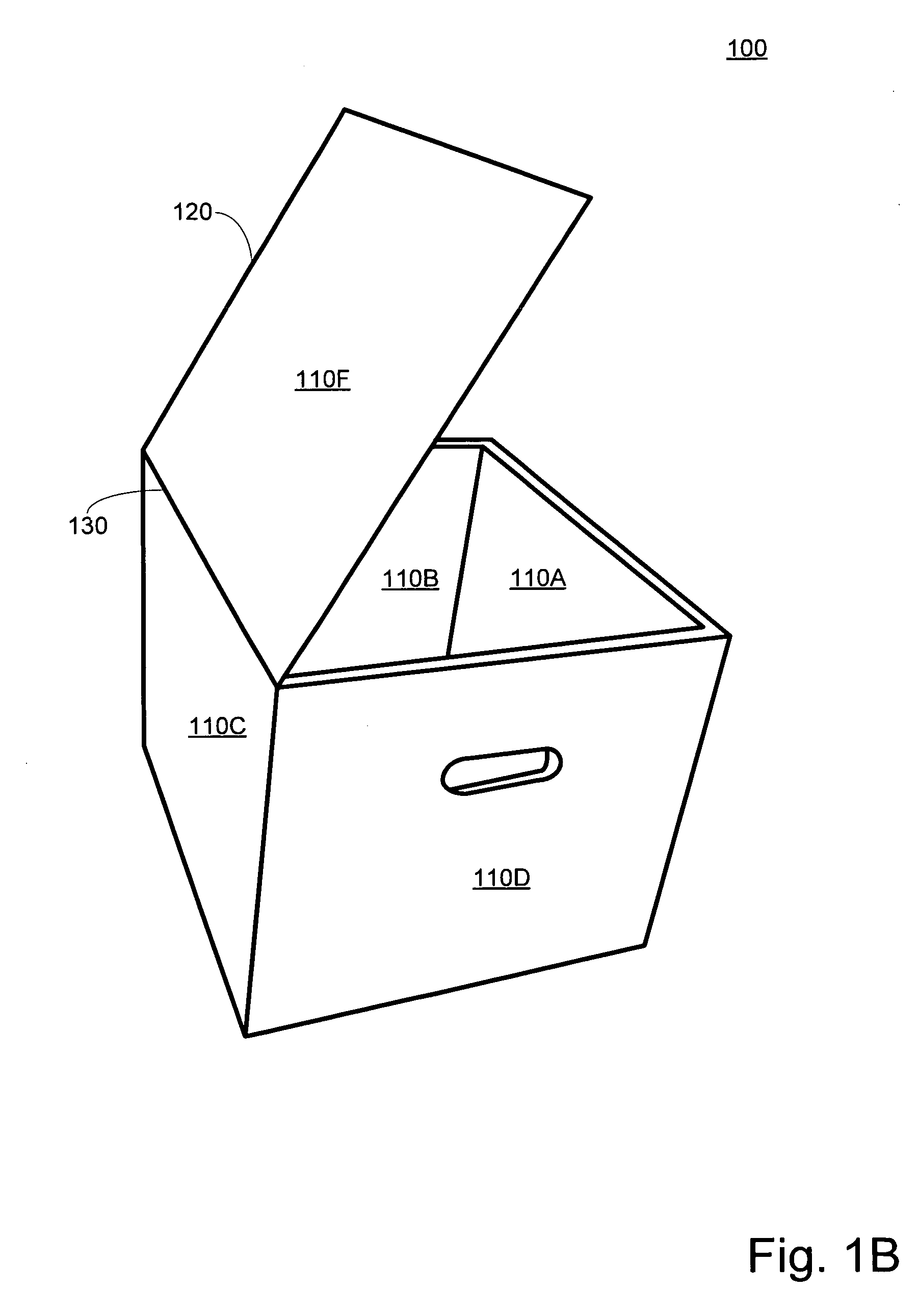
Insulated container
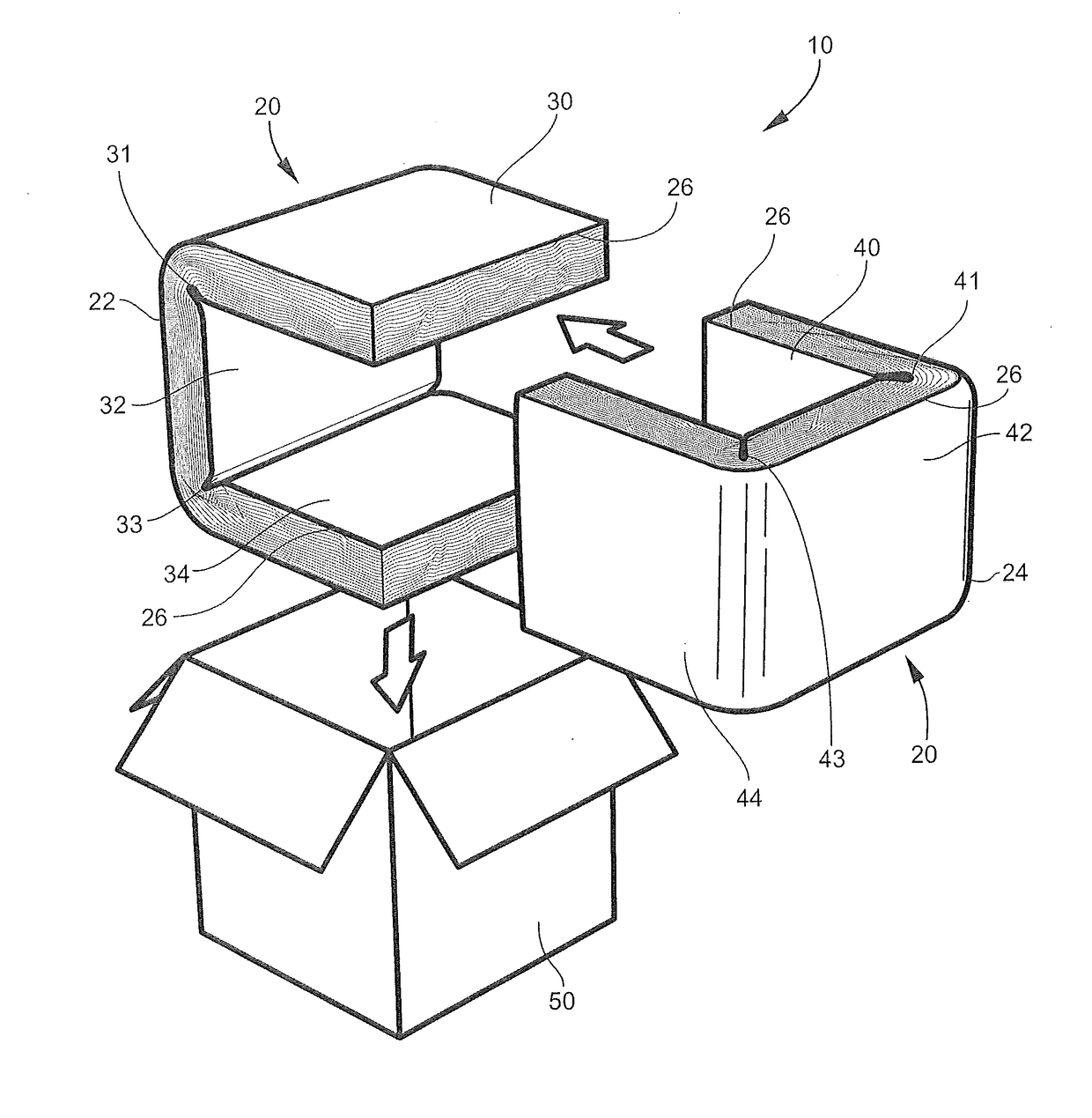
ActiveUS20170334622A1Efficient and economically manufacturedMinimize negative impactWrappersBoxes/cartons making machineryInsulation layerIsolation layer
An insulated container may include a rigid container surrounding an insulation layer formed from a post-industrial, pre-consumer card waste. The insulation layer may be characterized by a lack of any wrapping material. The insulation layer may be manufactured using a variety of converting processes including, carding, airlay, and needle punch to form a non-woven material for providing consistent density throughout the insulation layer. The insulation layer may include a natural fiber lamination layer on an outer surface of the insulation layer. The insulation layer may be biodegradable in an anaerobic environment.
Owner:AIRLITE PLASTICS
Wood-Plastic Composites Using Recycled Carpet Waste and Systems and Methods of Manufacturing
InactiveUS20080128933A1Reduce material costsPlastic recyclingBuilding constructionsFoaming agentVolumetric Mass Density
An extruded composite utilized as a building material includes a base polymer, unseparated processed recycled carpet waste, and a filler material, which may be a wood filler or other natural fiber. The recycled carpet waste may be used to decrease the amount of both base polymer and wood filler to achieve an equivalent product at lower cost. The extruded composite may also utilize chemical foaming agents to reduce density. Both foamed and non-foamed composites may be capstocked.
Owner:MATERIAL INNOVATIONS LLC
Hydroentangled nonwoven material
ActiveUS20050112980A1Improved textile feelingReduced twosidednessWoven fabricsWood layered productsPolyesterPolymer science
An improved hydroentangled well integrated composite nonwoven material, including a mixture of continuous filaments, synthetic staple fibres, and natural fibres which has a reduced twosidedness and an improved textile feeling. The synthetic staple fibres should have a length of 3 to 7 mm, and preferably there should be no thermal bondings between the filaments. The method of producing such a nonwoven material is also disclosed. The nonwoven includes a mixture of 10-50 w-% continuous filaments preferably chosen from polypropylene, polyesters and polylactides, 5-50 w-% synthetic staple fibres chosen from polyethylene, polypropylene, polyesters, polyamides, polylactides, rayon, and lyocell, and 20-85 w-% natural fibres, preferably pulp.
Owner:ESSITY HYGIENE & HEALTH AB
Composite roofing panel
InactiveUS20020040557A1Easy to installBetter imitate natural productsRoof covering using tiles/slatesNatural patternsAsphalt shingleNatural fiber
The present invention provides a composite panel for use in construction, and particularly for shingling, which comprises natural fiber and a polymer. Due to its composition and layout the construction panel provides all of the advantages of natural materials and high end roofing materials, particularly an attractive appearance, while at the same time allowing for ease of installation, little or no maintenance requirements, and providing superior impact and fire resistance when compared to other roofing materials. The construction panels can also be installed using conventional equipment and methods similar to the installation of 3-tab asphalt shingles with little or no learning curve.
Owner:COMPOSITECH
Composite thermoplastic sheets including natural fibers
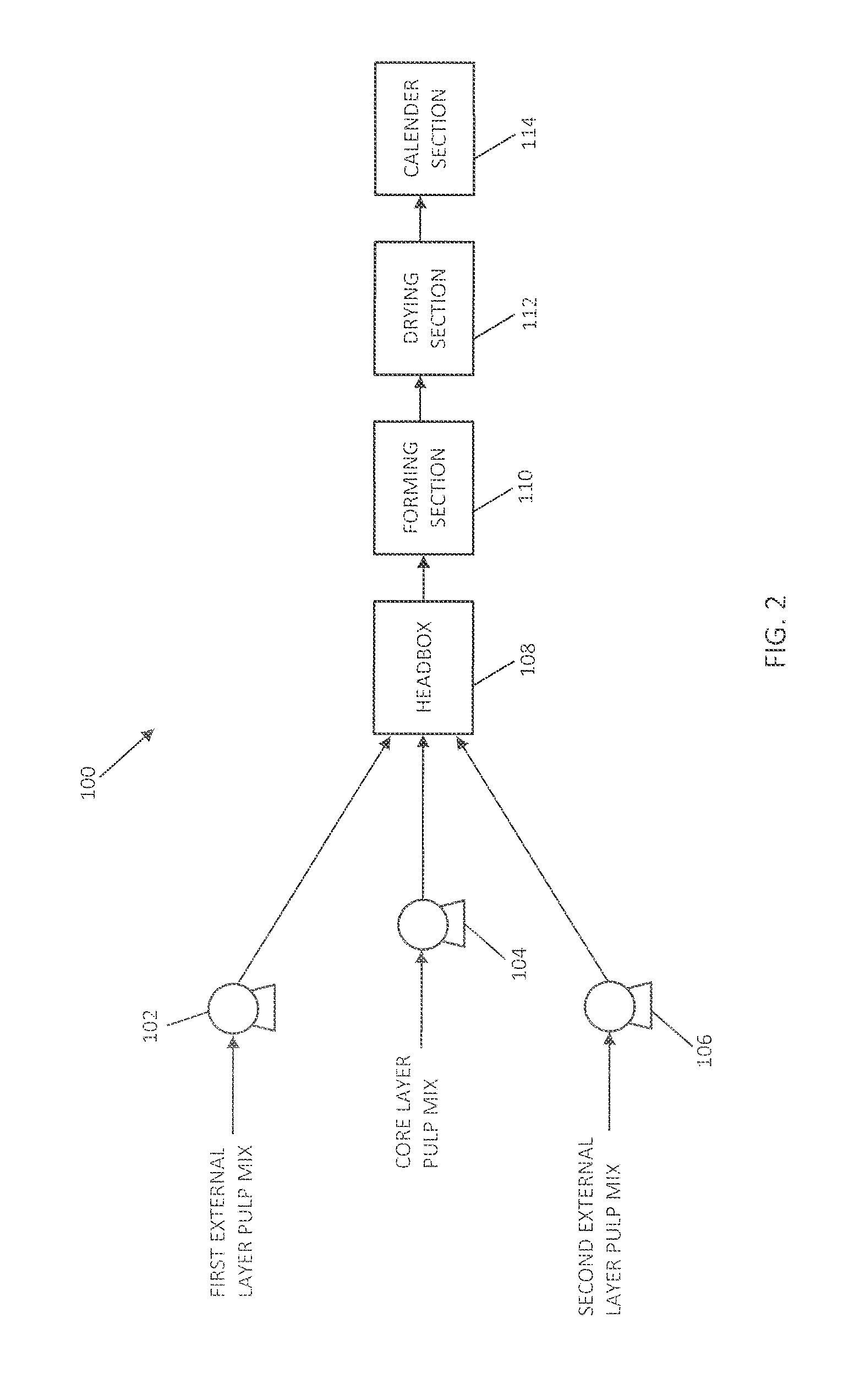
A composite sheet material includes, in an exemplary embodiment a porous core that includes at least one thermoplastic material and from about 20 weight percent to about 80 weight percent of natural fibers based on a total weight of the porous core. The natural fibers include at least one of kenaf fibers, jute fibers, flax fibers, hemp fibers, cellulosic fibers, sisal fibers, and coir fibers.
Owner:HANWA AZDEL INC
Flushable wipe and method of forming the same
ActiveUS20150330029A1Without losing its functional strength propertiesNatural cellulose pulp/paperMechanical working/deformationEngineeringLength weight
A multi-ply flushable wipe includes a ply having first and second exterior layers and a middle layer disposed therebetween. Each of the exterior layers includes at least 50% by weight natural fibers. When foam-formed, the middle layer includes at least 25% by weight natural fibers. In embodiments, the middle layer may include at least 75% by weight natural fibers. The middle layer also includes synthetic fibers that have a length within the range of 1 mm and 20 mm. The wipe may have a length weight weighted average fiber length of less than 4 mm and a wet CD strength of greater than 20 N / m. Each ply of the wipe may be formed by wetlaying the first and second exterior layers and a foam formed middle layer to form a web, imprinting the web with a structured fabric, and drying the web. The plies are then attached using a binder.
Owner:FIRST QUALITY TISSUE
Method for preparing functional material of regenerated cellulose
This invention publishes a preparation method for functionalized regenerated cellulose materials. Natural cellulose raw materials are dried and mixed with cellulose solvents, and the mixture is heated and stirred or mechanically kneaded until complete dissolution of cellulose. Functionalized fillers are added into the consequent homogeneous and transparent cellulose solution and stirred. The consequent solution is defoamed in vacuum, regenerated in coagulation bath, washed with water and dried or spun so as to obtain functionalized regenerated cellulose materials.
Owner:山东中科恒联生物基材料有限公司
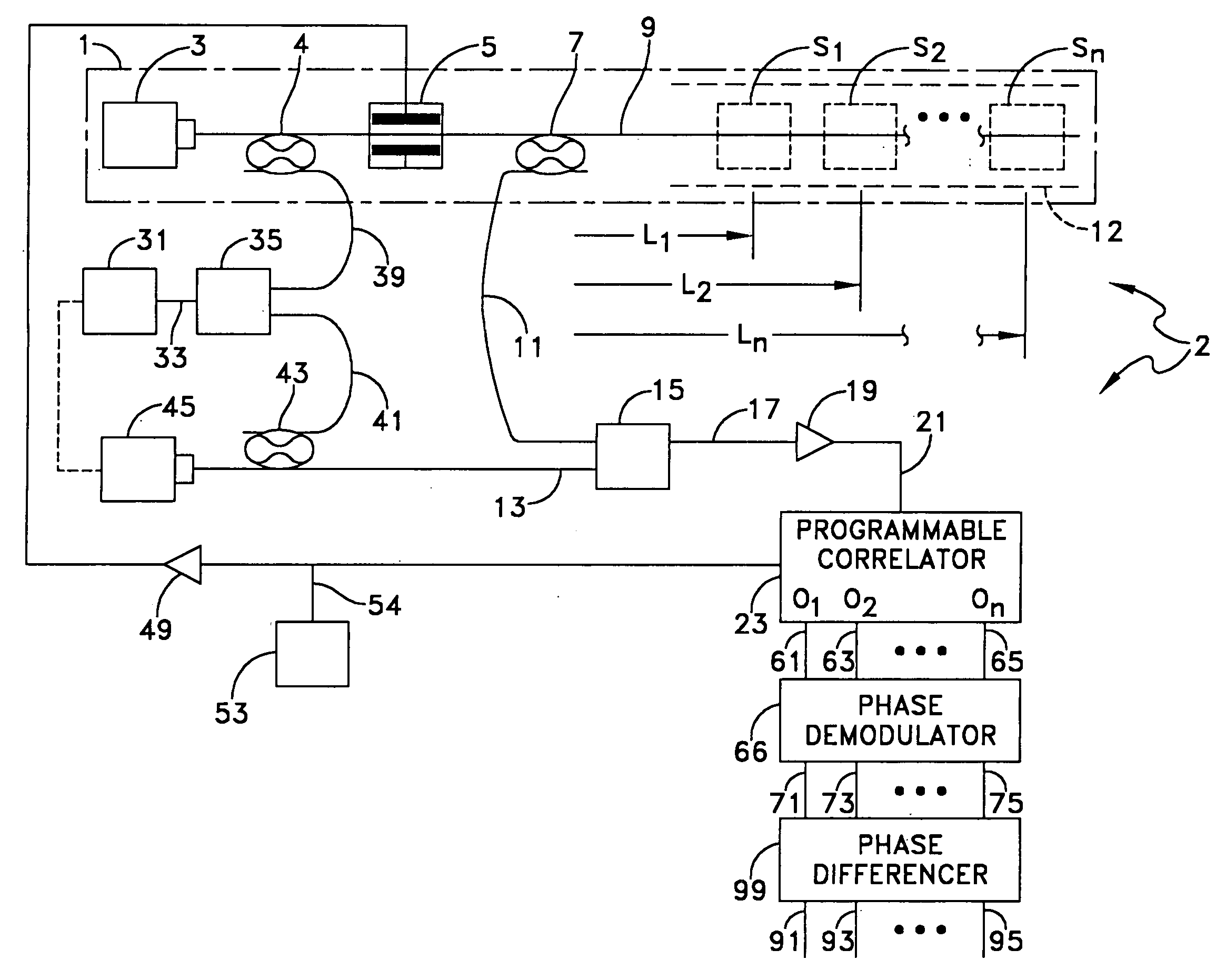
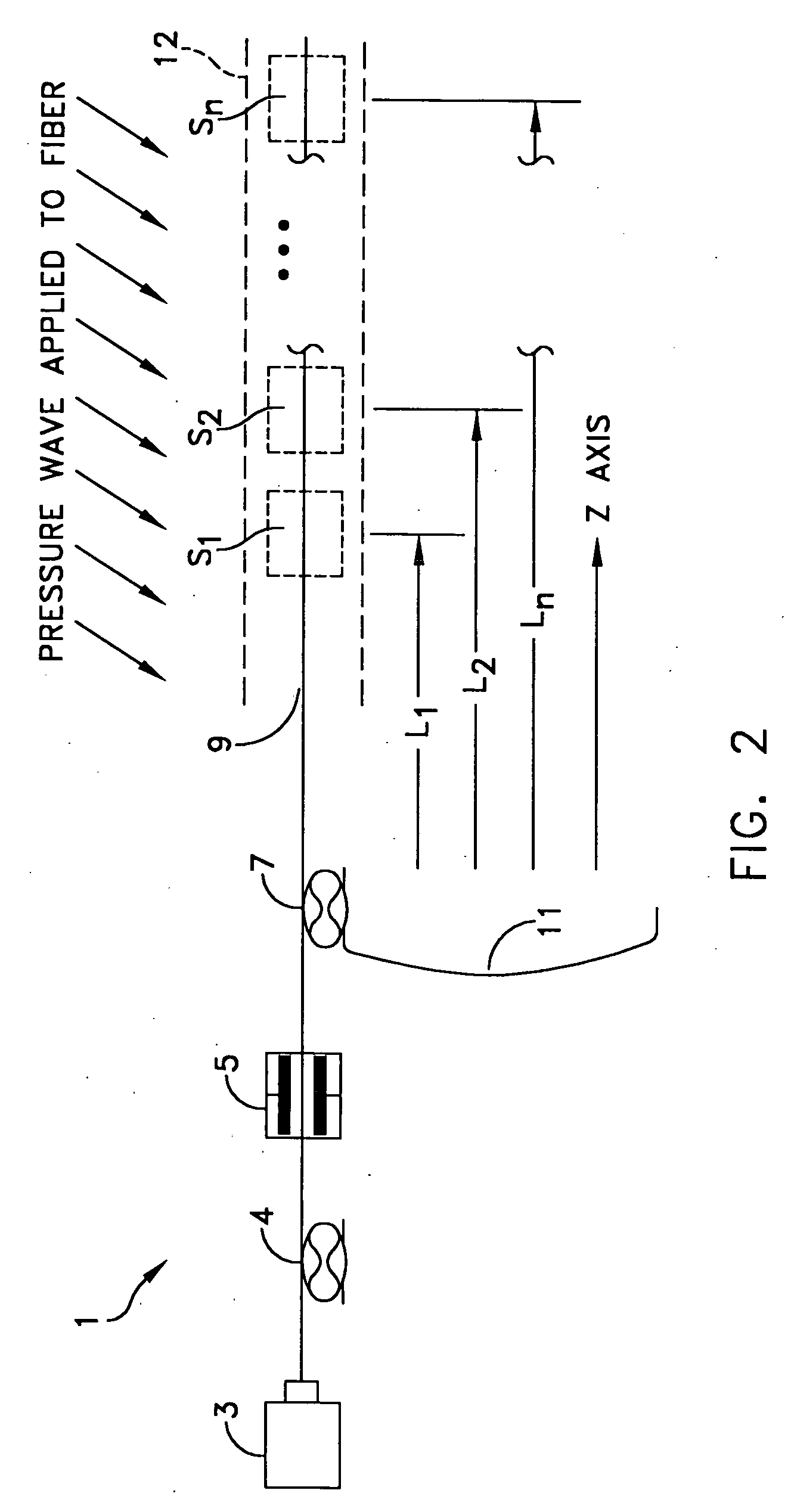
Natural fiber span reflectometer providing a virtual phase signal sensing array capability
ActiveUS20060028636A1Low costMaterial analysis by optical meansBurglar alarmRayleigh scatteringFrequency spectrum
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
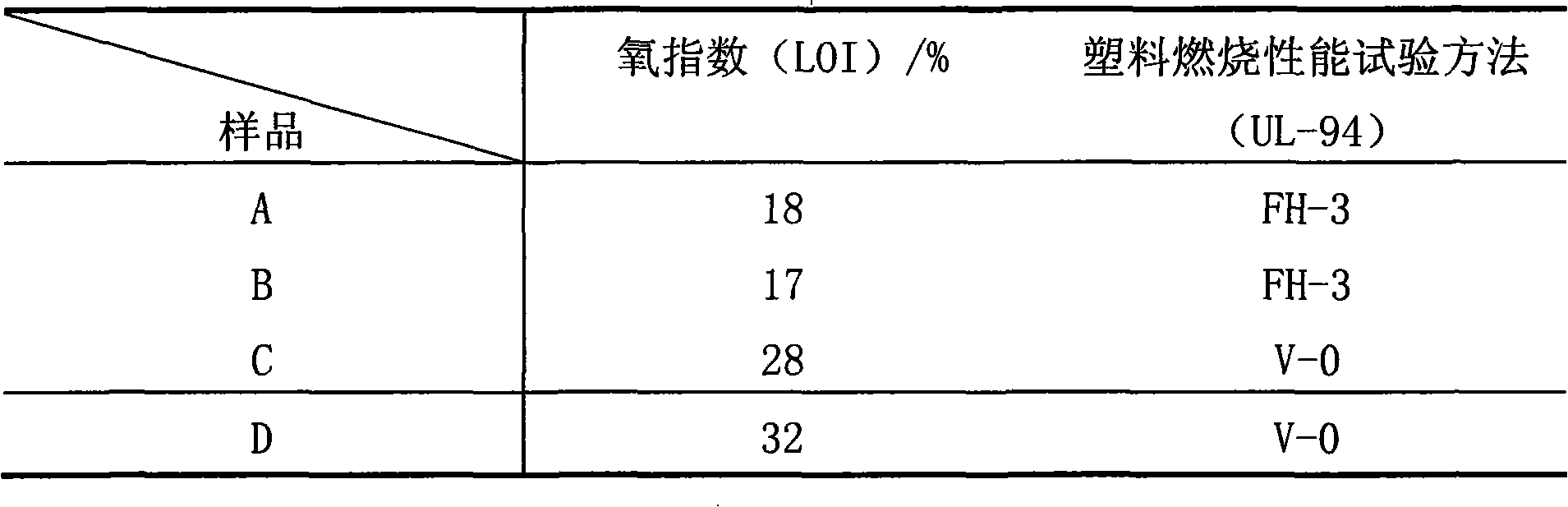
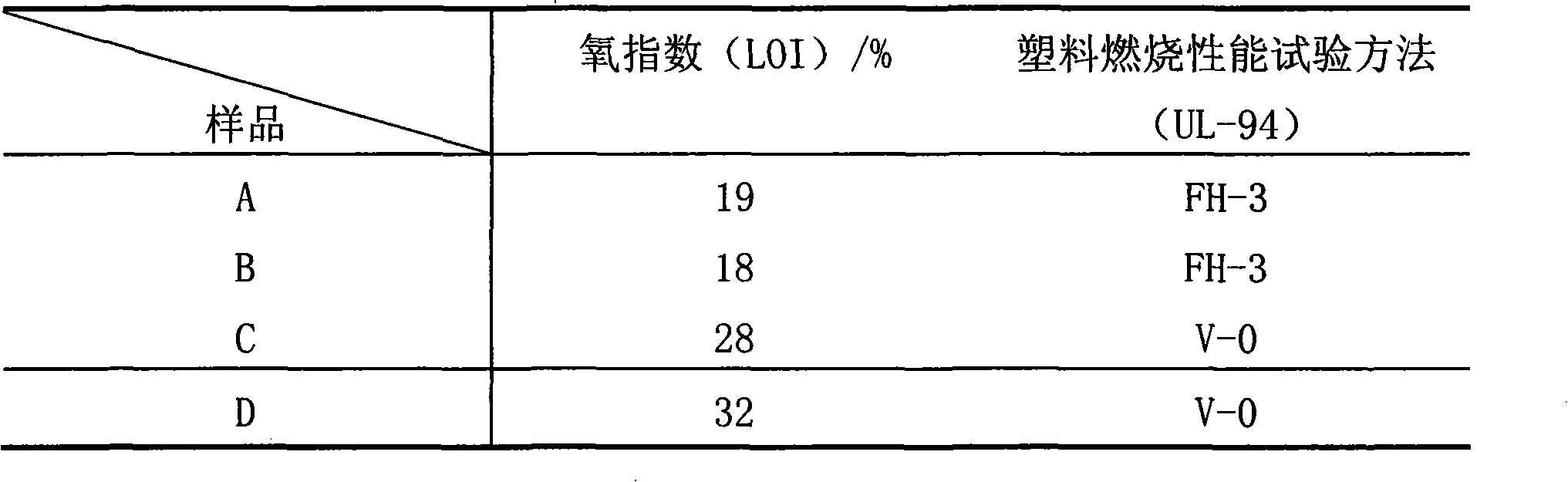
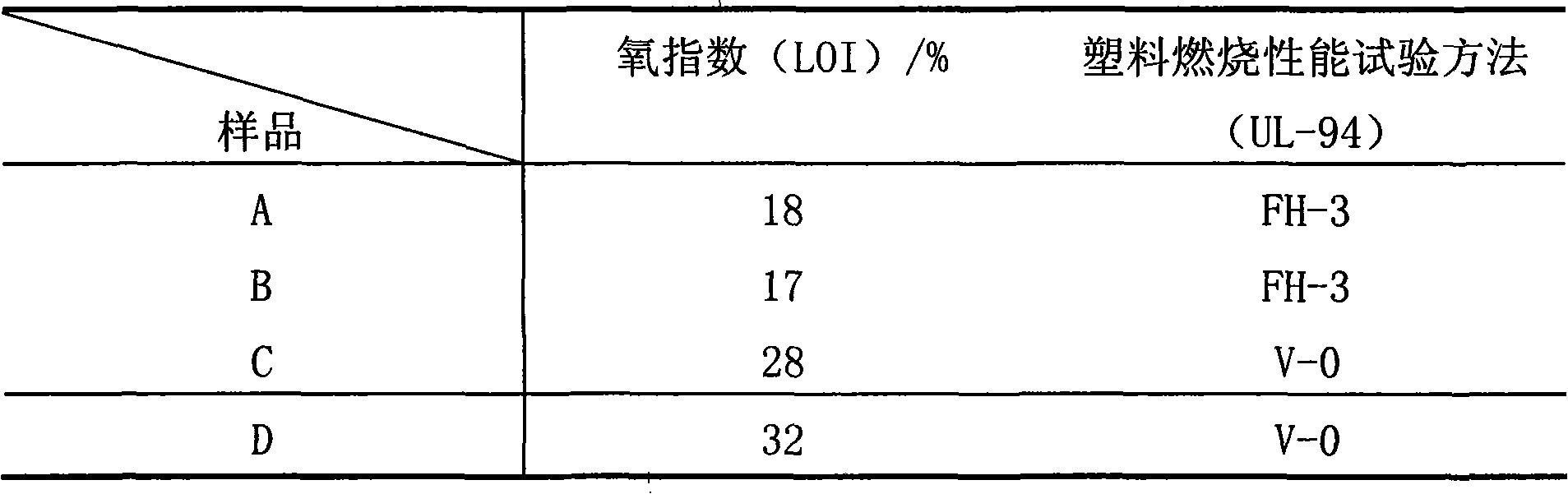
Natural fiber reinforcement halogen-free flame retardant polypropylene composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101418099AImprove flame retardant performanceImprove mechanical propertiesGlass fiberHeat deflection temperature
The invention provides a natural fiber reinforced halogen-free flame-retardant polypropylene composite material, which is characterized by consisting of the following raw materials in weight portion: 82.5 to 12 portions of polypropylene, 0.3 to 2 portions of heat stabilizer, 0.2 to 1 portion of processing assistant, 1 to 10 portions of toughening agent, 10 to 40 portions of flame retardant, 1 to 5 portions of compatilizer, and 5 to 30 portions of natural fiber. The invention also provides a method for preparing the material. The composite material has the advantages that the composite material has excellent flame-retardant effect and excellent comprehensive mechanical property; the flame-retardant property of the composite material can reach 1.6mm V0; the tensile strength is more than or equal to 60MPa; the bending modulus is more than or equal to 4,000MPa; the gap impact strength is more than or equal to 10KJ / m<2>; the shrinkage ratio is between 4 and 6 per thousand; the heat distortion temperature is more than or equal to 140 DEG C; and the composite material is a novel environment-friendly material, and has no safety and health problems of glass fibers.
Owner:SHANGHAI KINGFA SCI & TECH +1
Hydroentangled nonwoven material
An improved hydroentangled well integrated composite nonwoven material, including a mixture of continuous filaments, synthetic staple fibers, and natural fibers which has a reduced twosidedness and an improved textile feeling. The synthetic staple fibers should have a length of 3 to 7 mm, and preferably there should be no thermal bondings between the filaments. The method of producing such a nonwoven material is also disclosed. The nonwoven includes a mixture of 10-50 w-% continuous filaments preferably chosen from polypropylene, polyesters and polylactides, 5-50 w-% synthetic staple fibers chosen from polyethylene, polypropylene, polyesters, polyamides, polylactides, rayon, and lyocell, and 20-85 w-% natural fibers, preferably pulp.
Owner:ESSITY HYGIENE & HEALTH AB
Cellulosic biomass soy flour based biocomposites and process for manufacturing thereof
A process for the manufacture of natural fiber and polymer composites is described. Thermoplastically processed plasticized soy flour based plastics are used with thermoplastic polymers. Polymers of soy flour and an in situ polymerized polyvinyl polymer which links proteins and carbohydrates in the flour to form the polymer are used. The composites are useful in engineering materials.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Resin composite material and its preparation method and use
The invention belongs to the technical field of polymers and discloses a resin composite material and its preparation method and use. The resin composite material comprises: by weight, 70 to 100 parts of one or more thermoplastic resins, 0 to 5 parts of one or more anti-oxidants, 0 to 5 parts of one or more fire retardants, 0 to 10 parts of one or more compatibilizers, 0 to 3 parts of one or more weather-resistant agents, 0 to 5 parts of one or more release agents and 0 to 2 parts of one or more assistants. The preparation method of the resin composite material comprises the following steps of fully mixing the raw materials in an intermediate-speed mixer according to the ratio for 3 to 7min, adding the mixture into an extruder, and carrying out extrusion cutting to obtain the resin composite material. A method for preparing a natural fiber / resin composite material prepreg tape from the resin composite material comprises the following steps of preparing natural fibers into a cord fabric, carrying out drawing, compaction and heating drying dehydration, carrying out pre-dipping of the resin composite material at a laminating extruder, carrying out gum dipping, carrying out cooling and carrying out wrapping-up. The prepreg tape obtained by the method has low porosity and high mechanical strength.
Owner:SHANGHAI GENIUS ADVANCED MATERIAL (GRP) CO LTD
Natural fiber welding
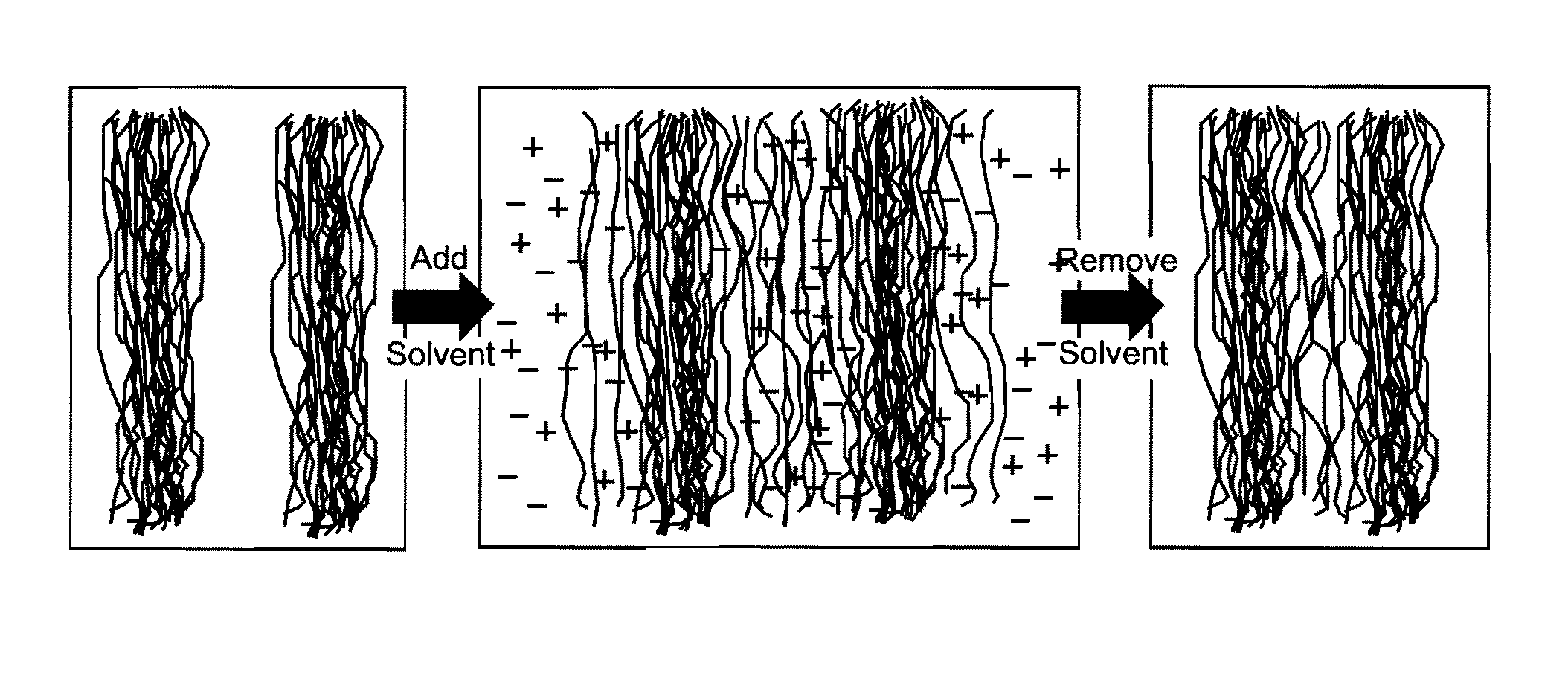
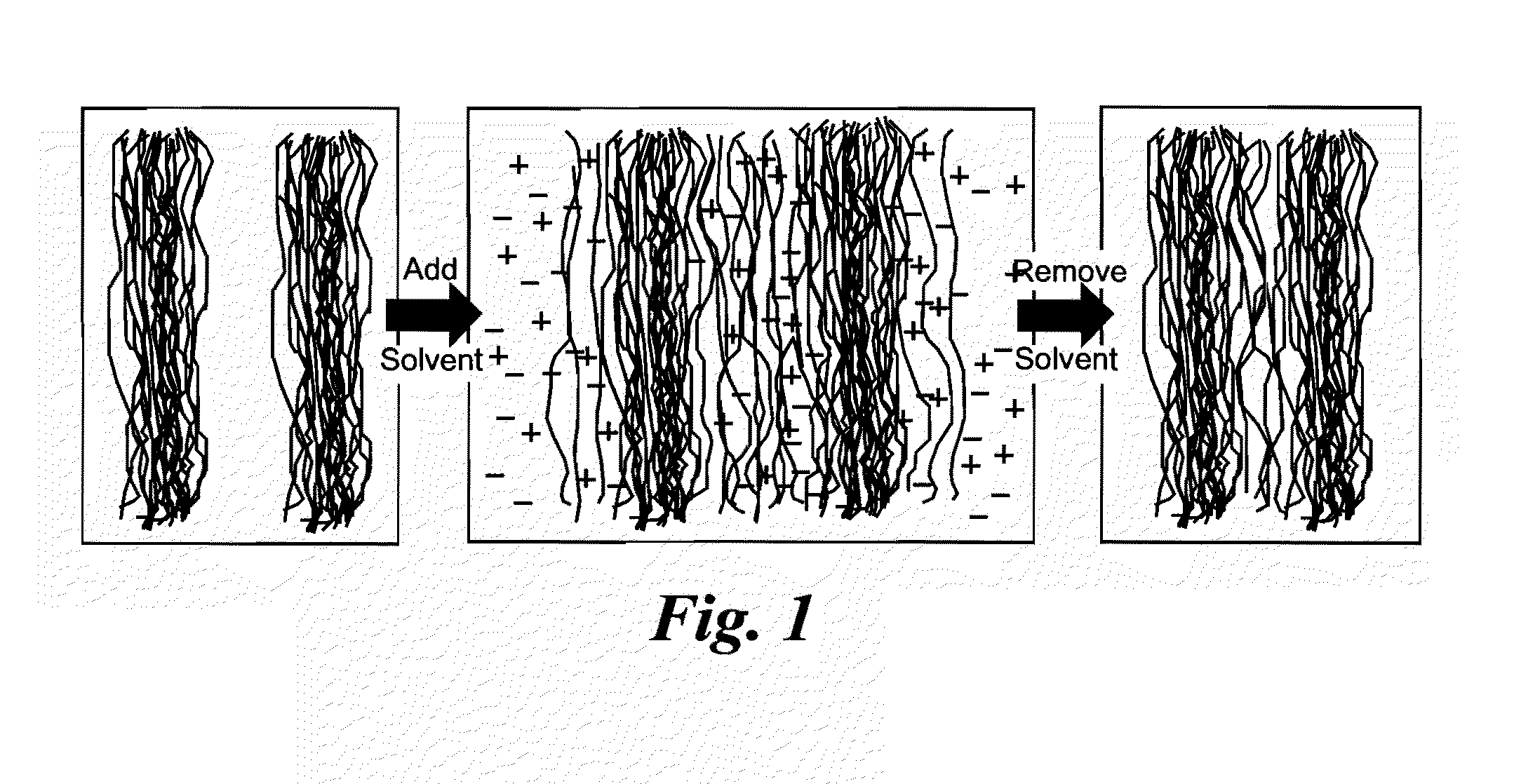
ActiveUS8202379B1Increase material densitySmall surface areaAdhesive processesLaminationPolymer scienceMixed materials
Natural fiber welding is a process by which individual fibers are swollen by an appropriate ionic liquid-based solvent system to form a congealed network. Manipulated fibrous materials may be either composed of natural polymers such as cellulose, hemicellulose, silk, et cetera, or synthetic polymers, or mixed materials. The process is principally controlled by the composition of the solvent system which includes an ionic liquid solvent plus additives such as water, methanol, et cetera. Other conditions such as the amount and placement of solvent, as well as time, temperature, and pressure control the extent to which neighboring fibers are fused. Only the material at the outer surface of fibers need be sufficiently mobile to merge with that of neighboring fibers. Material in the fiber core may be left in the native state by controlling process variables. Fibers form a congealed network upon removal of the ionic liquid-based solvent.
Owner:US SEC THE AIR FORCE THE
Wet method transfer printing method for natural fiber and polyamide fibre
InactiveCN101105006AHigh color yieldReduce consumptionTransfer printing processDyeing processPolyamidePrinting ink
The invention provides a wet-method transfer printing process of natural fiber and nylon, which mainly comprises the following steps: (1) selecting acidic printing ink or active printing ink; (2) printing: printing the surface of PET or BOPP film with the selected printing ink to obtain a transfer printed film; (3) transfer printing: treating natural fiber and nylon with a soaking liquid, subjecting the transfer printed film and printed fabric simultaneously to the compression by a rolling machine; and (4) oven-drying: oven-drying the fabric after the transfer printing is completed and baking to allow color fixation. The invention has the advantages of high transfer printing rate, high color yield of fabric, bright color, good color fastness, less pollution, reduced water consumption, simple process, high production efficiency, low cost, and success in non-paper transfer printing.
Owner:常州涵源新印花有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com