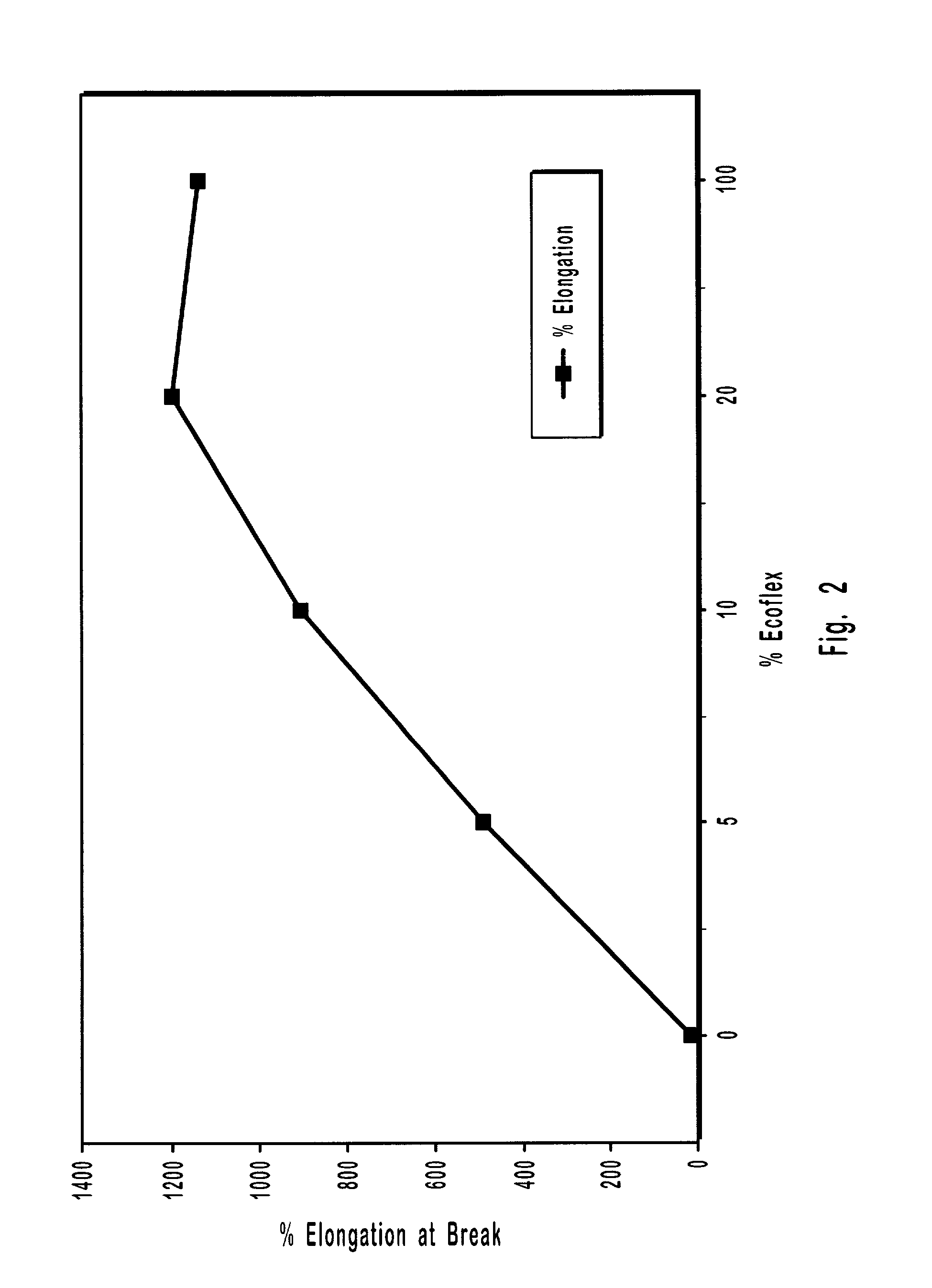
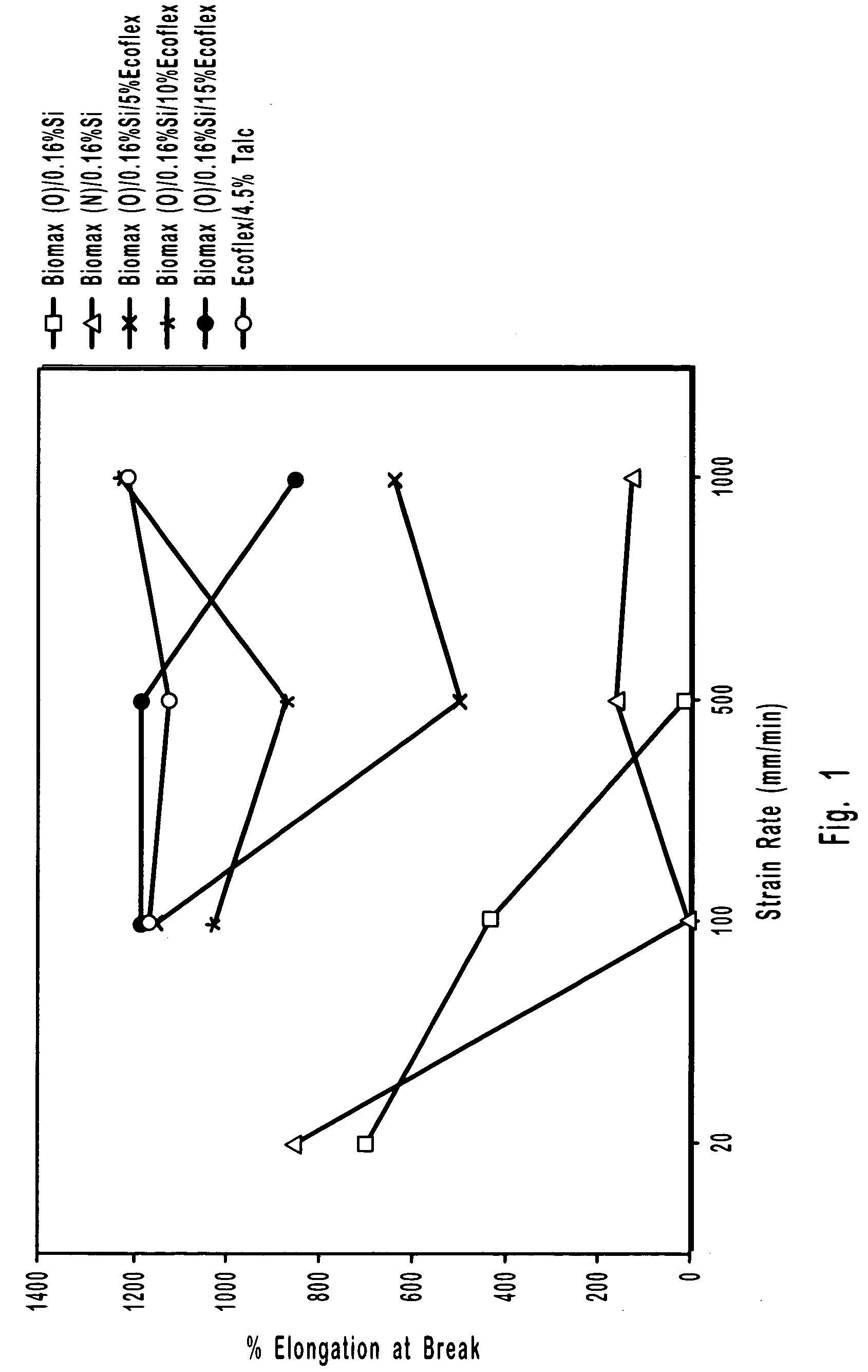
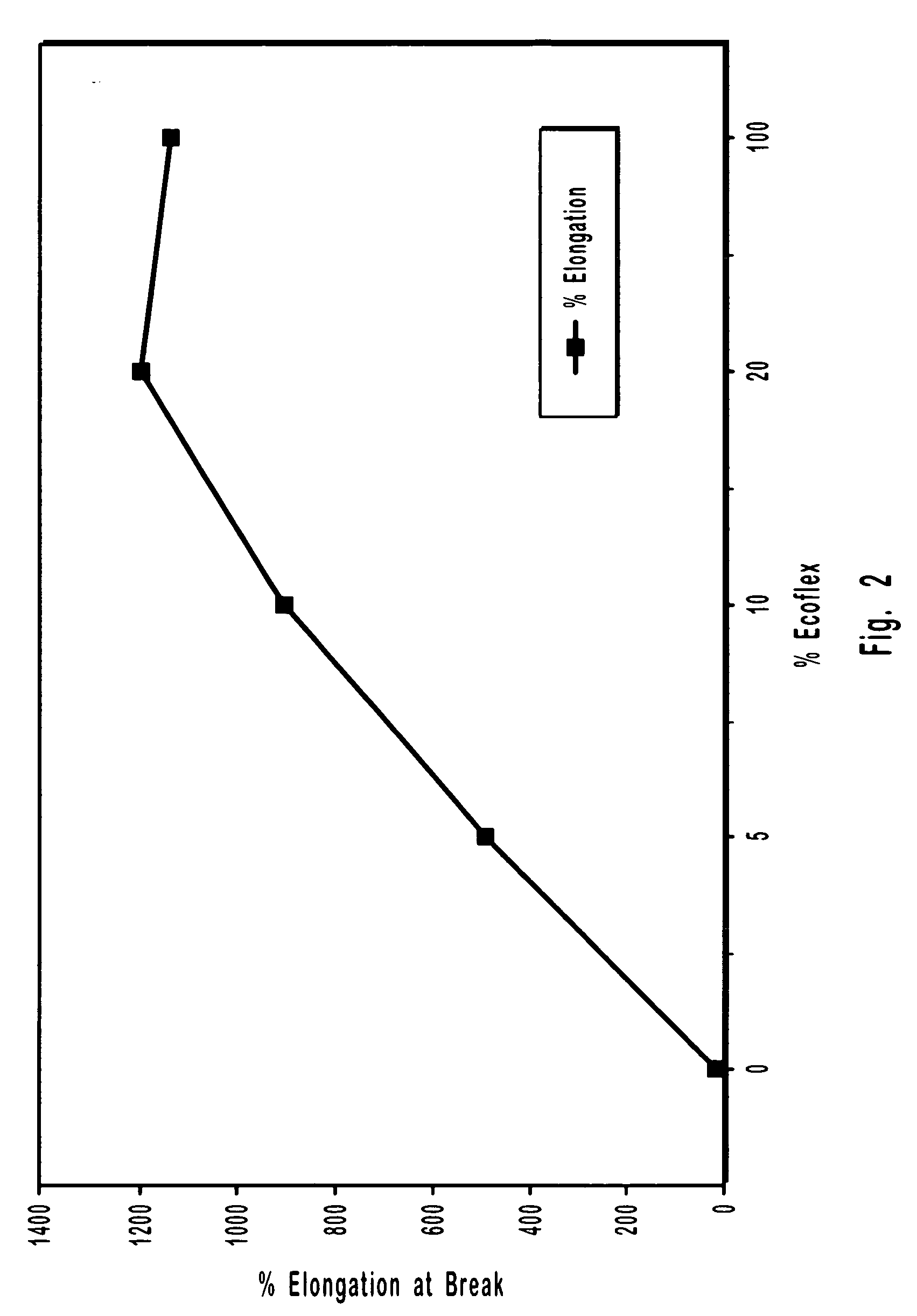
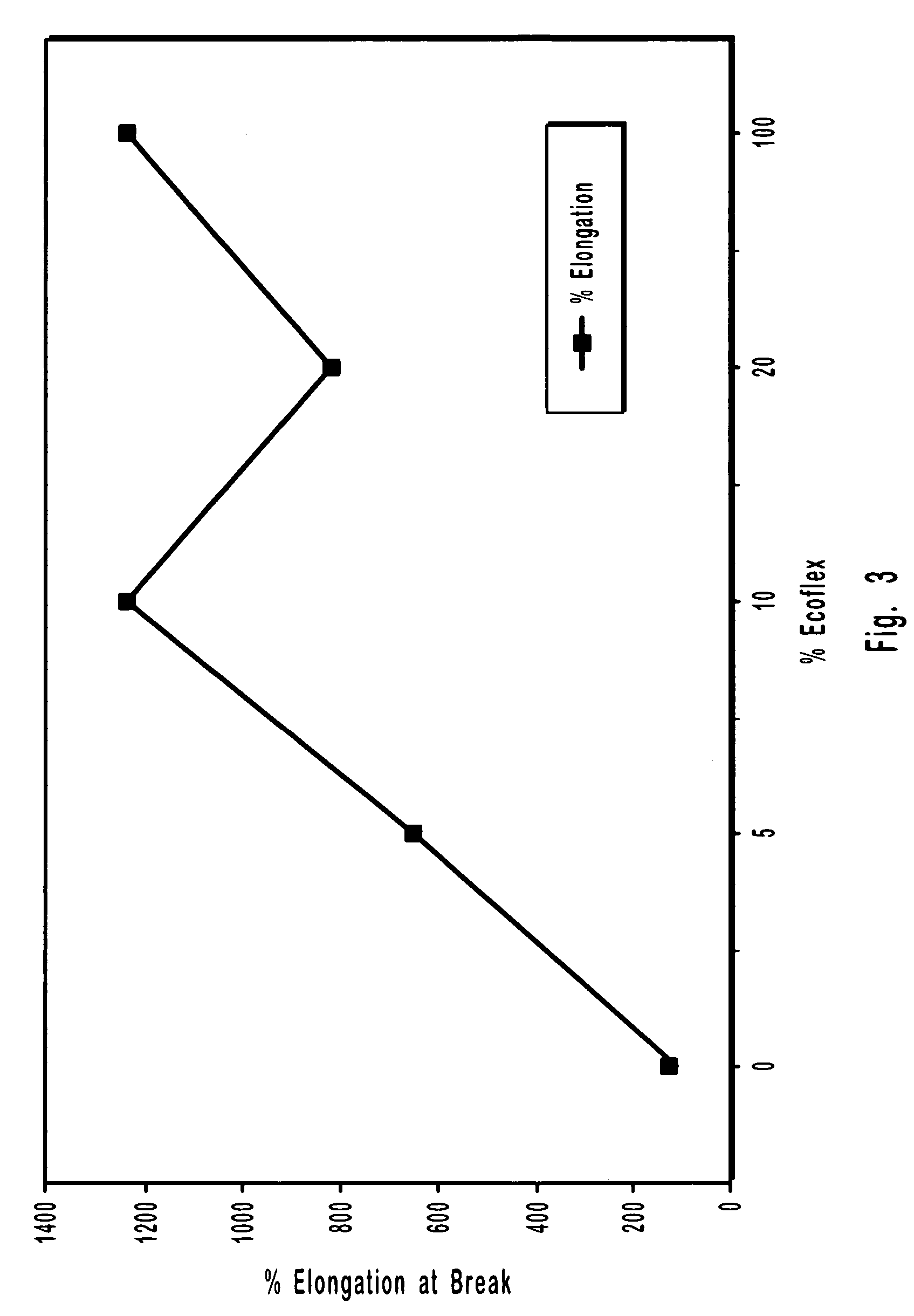
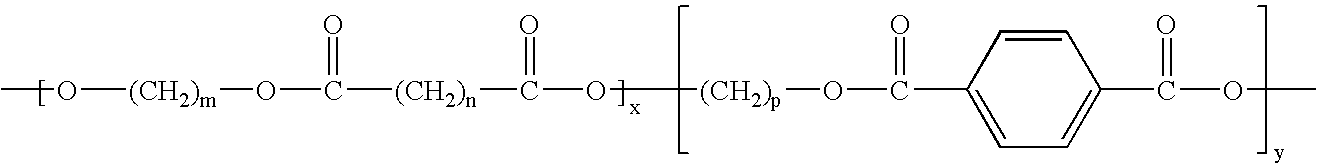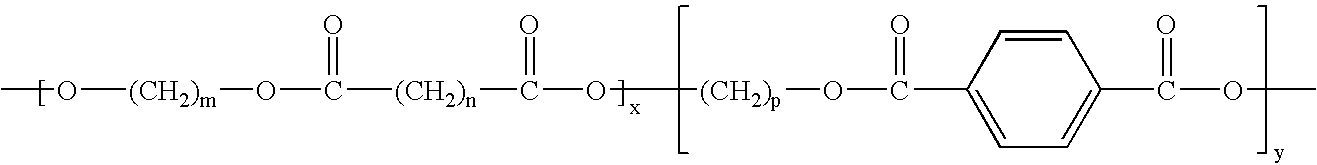Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1521 results about "Natural polymers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polymers are widely found in nature. The human body contains many natural polymers, such as proteins and nucleic acids. Cellulose, another natural polymer, is the main structural component of plants.
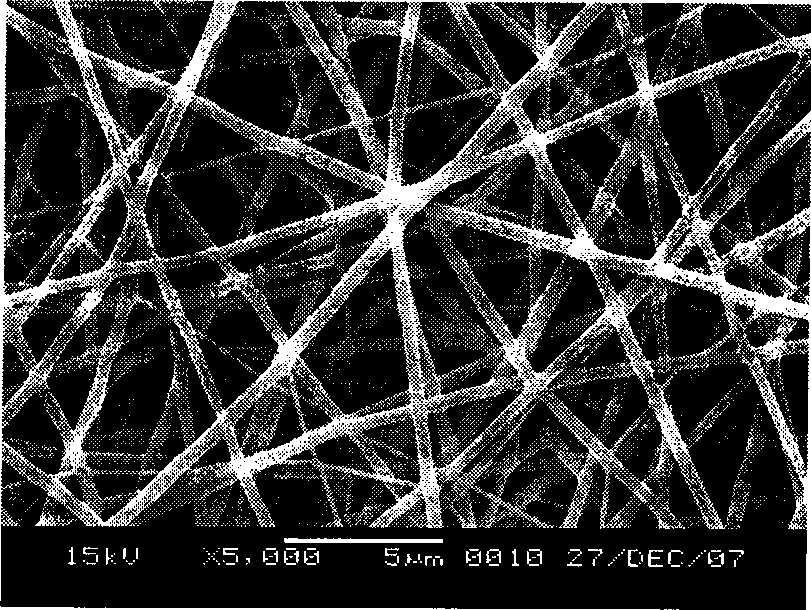
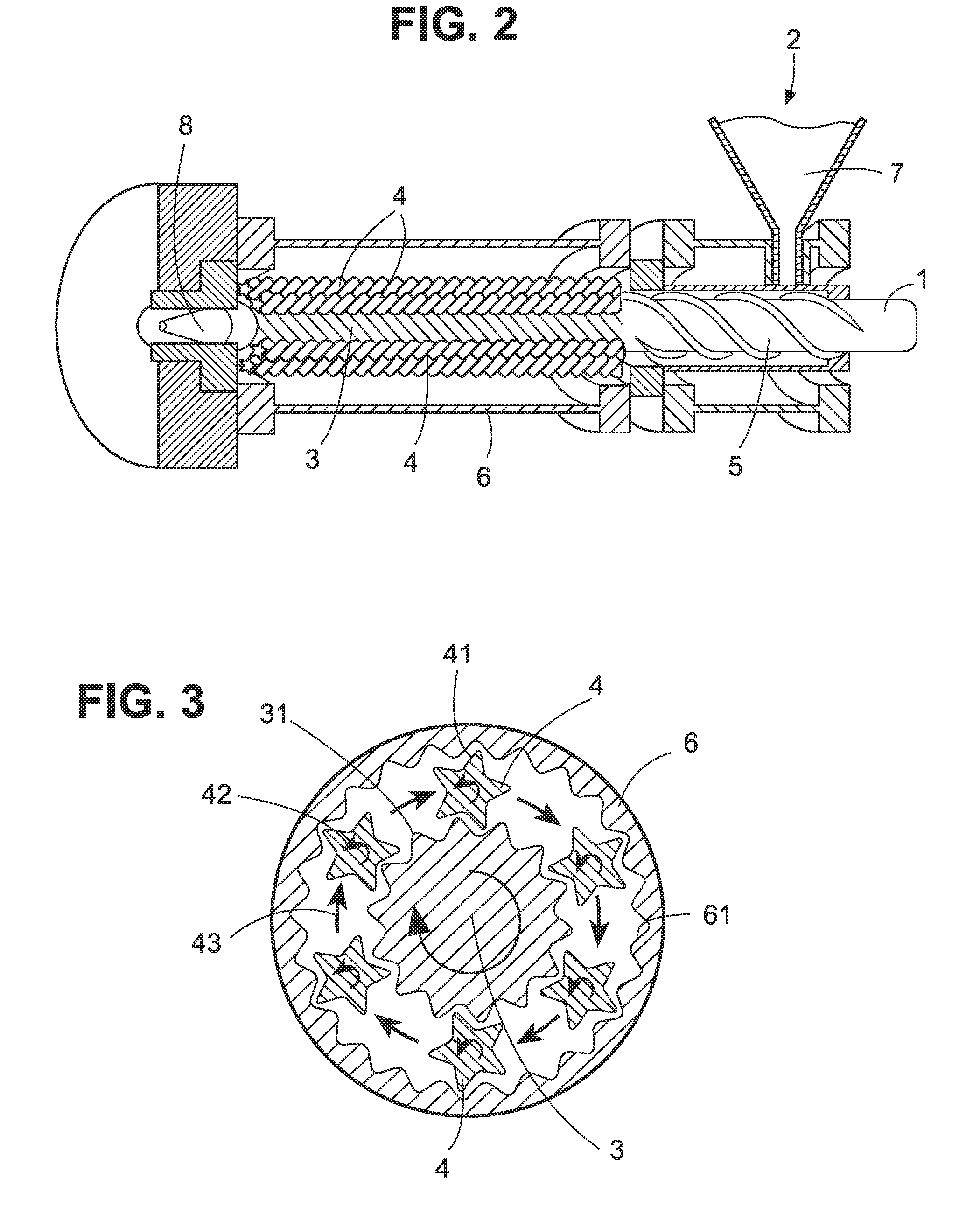
Porous polymeric matrices made of natural polymers and synthetic polymers and optionally at least one cation and methods of making
A porous polymeric matrix containing at least one natural polymer and at least one synthetic polymer and optionally at least one cation. Furthermore, a method of making a porous polymeric matrix involving mixing at least one natural polymer and inorganic salts with a solution comprising at least one solvent and at least one synthetic polymer to form a slurry, casting the slurry in a mold and removing the solvent to form solid matrices, immersing the solid matrices in deionized water to allow natural polymer cross-linking and pore creation to occur simultaneously, and drying the matrices to create a porous polymeric matrix; wherein the matrix contains a cation. Also, a method of making a porous polymeric matrix, involving mixing at least one natural polymer in an aqueous solvent and mixing at least one synthetic polymer in an organic solvent, combining the mixtures and casting in a mold, and separately removing said aqueous solvent and said organic solvent to form a porous polymeric matrix; wherein the porous polymeric matrix does not contain a cation.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Abuse-proofed dosage form
ActiveUS8114383B2Pulverisation of the dosage form is considerably more difficultComplicating or preventing the subsequent abuseOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryBreaking strengthPhysiology
The present invention relates to an abuse-proofed, thermoformed dosage form containing, in addition to one or more active ingredients with abuse potential optionally together with physiologically acceptable auxiliary substances, at least one synthetic or natural polymer with a breaking strength of at least 500 N and to a process for the production thereof.
Owner:GRUNENTHAL GMBH
Abuse-proofed dosage form
InactiveUS20070048228A1Pulverization of the dosage form is considerably more difficultComplicating or preventing the subsequent abuseBiocidePill deliveryBreaking strengthUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to a dosage form that is thermoformed without discoloration and is safeguarded from abuse, comprising at least one synthetic or natural polymer having a breaking strength of at least 500 N in addition to one or more active substances that could be subject to abuse. The invention also relates to a corresponding method for producing said dosage form.
Owner:GRUNENTHAL GMBH
Crush resistant delayed-release dosage forms
InactiveUS20060193914A1Reduce releaseAvoid overdoseSenses disorderNervous disorderDelayed Release Dosage FormWax
The invention relates to a dosage form comprising a physiologically effective amount of a physiologically active substance (A), a synthetic, semi-synthetic or natural polymer (C), optionally one or more physiologically acceptable auxiliary substances (B) and optionally a synthetic, semi-synthetic or natural wax (D), wherein the dosage form exhibits a resistance to crushing of at least 400 N and wherein under physiological conditions the release of the physiologically active substances (A) from the dosage form is at least partially delayed.
Owner:GRUNENTHAL GMBH
Process for the production of an abuse-proofed dosage form
InactiveUS20090005408A1Pulverisation of the dosage form is considerably more difficultComplicating or preventing the subsequent abuseBiocideNervous disorderBreaking strengthMedicine
The present invention relates to a process for the production of abuse-proofed, thermoformed dosage forms containing, apart from one or more active ingredients with potential for abuse and optionally physiologically acceptable auxiliary substances, at least one synthetic or natural polymer with a breaking strength of at least 500 N.
Owner:GRUNENTHAL GMBH
Process for the production of an abuse-proofed solid dosage form
ActiveUS8114384B2Intense negative effectConsiderably complicatedNervous disorderPill deliveryBreaking strengthMedicine
The present invention relates to a process for the production of an abuse-proofed solid dosage form containing at least one active ingredient with potential for abuse and a synthetic or natural polymer with a breaking strength of =500 N, characterized in that a corresponding mixture is processed by melt extrusion with the assistance of a planetary-gear extruder.
Owner:GRUNENTHAL GMBH
Dosage Form with Impeded Abuse
InactiveUS20090004267A1Prevent crushingPrevent the subsequent abuseOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryWaxBreaking strength
A multiparticulate dosage form formulated to make misuse more difficult containing least one active substance with potential for misuse (A), at least one synthetic or natural polymer (C), optionally at least one natural, semi-synthetic or synthetic wax (D), at least one disintegrant (E) and optionally one or more additional physiologically compatible excipients (B), wherein the individual particles of the dosage form display a breaking strength of at least 500 N and a release of active substance of at least 75% after 45 minutes measured according to Ph.Eur. in the paddle mixer with sinker in 600 ml of aqueous buffer solution with a pH value of 1.2 at 37° C. and 75 rpm.
Owner:GRUNENTHAL GMBH
Composite dressings for the treatment of wounds
Non-occlusive composite wound dressings that comprises a material polymer wound-healing layer comprised of isolated polymer fibers, and a synthetic polymer foam layer having at least one surface physically adhered to the natural layer by the physical interlocking of the polymer fibers with the surface. Also, a process for the preparation of a non-occlusive composite wound dressing comprising contacting a synthetic polymer foam porous surface with a solution and / or suspension of natural polymer fibers in a medium, and removing the medium from the fibers under conditions that result in the fibers penetrating into pores of the surface and that form a dried composite of the polymer foam adhered physically to a layer comprising natural polymer fiber.
Owner:SYNTACOLL
Nano-silver antibacterial hydrogel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102698313AAvoid Residual ToxicityAct as a sterilizerSurgeryAbsorbent padsEscherichia coliPorosity
The invention discloses nano-silver antibacterial hydrogel and a preparation method thereof, wherein the antibacterial hydrogel does not contain a chemical cross-linking agent, a cross-linking sensitizing agent and a cross-linking initiator; the porosity is above 90%; the cross-linking degree is above 50%; by weight, the nano-silver antibacterial hydrogel comprises 3-20% of natural polymer or a derivative thereof, 0-20% of synthetic polymer and 0..005-0.2% of nano-silver; and the nano-silver antibacterial hydrogel is prepared by blending the natural polymer or the derivative thereof, the synthetic polymer, a compound containing silver ions and water and then adopting a radiation cross-linking method. The nano-silver antibacterial hydrogel disclosed by the utility model has good biocompatibility and uniform nano-silver distribution and slow-release capability and is capable of effectively inhibiting bacteria, such as escherichia coli.
Owner:北京同威典石技术有限公司
Biodegradable polymer blends for use in making films, sheets and other articles of manufacture
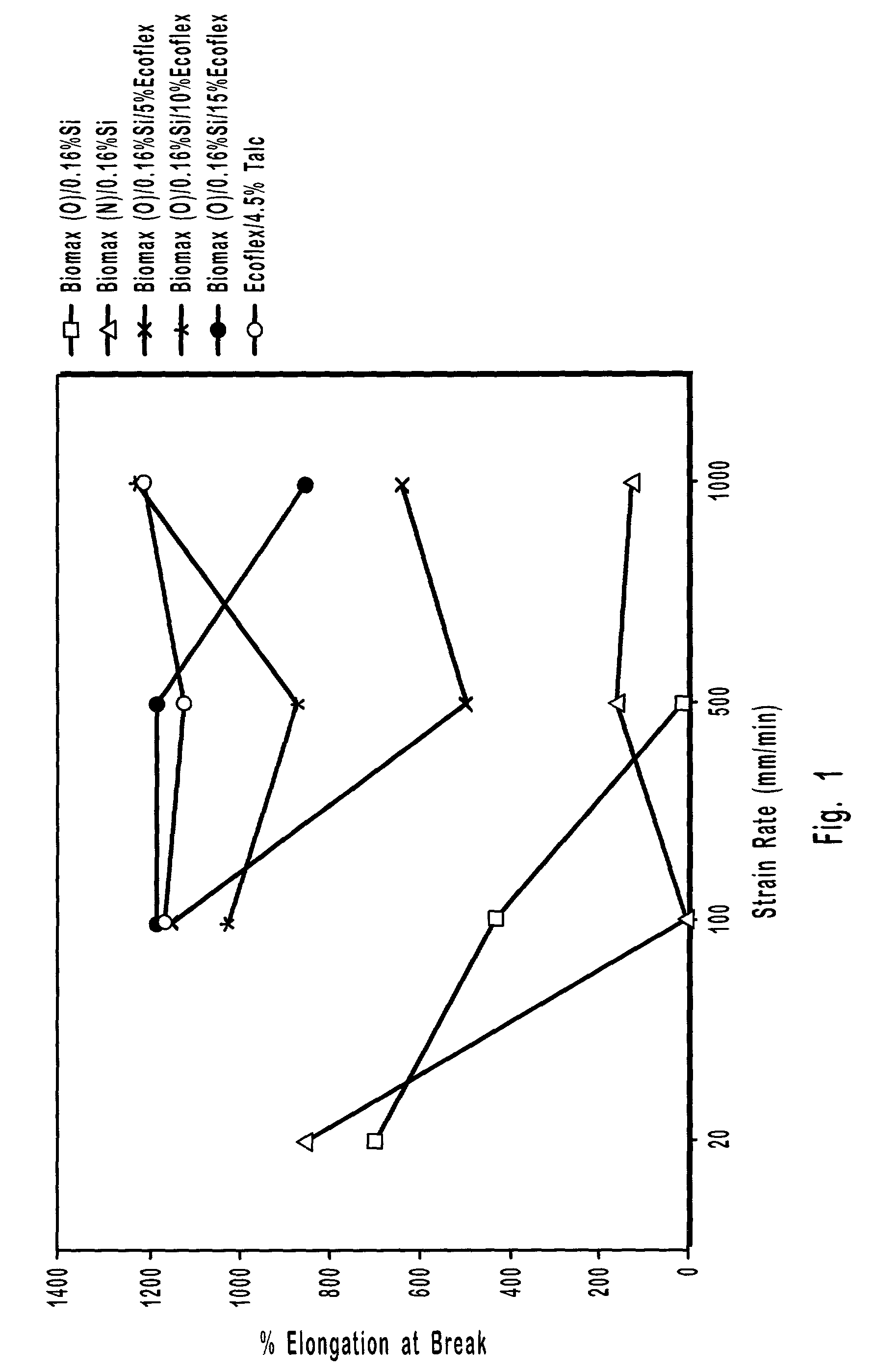
InactiveUS7214414B2Increase stiffnessIncrease flexibilitySynthetic resin layered productsEmulsion paintsPolyesterThermoplastic
Owner:BIO TEC BIOLOGISCHE NATURVERPACKUNGEN
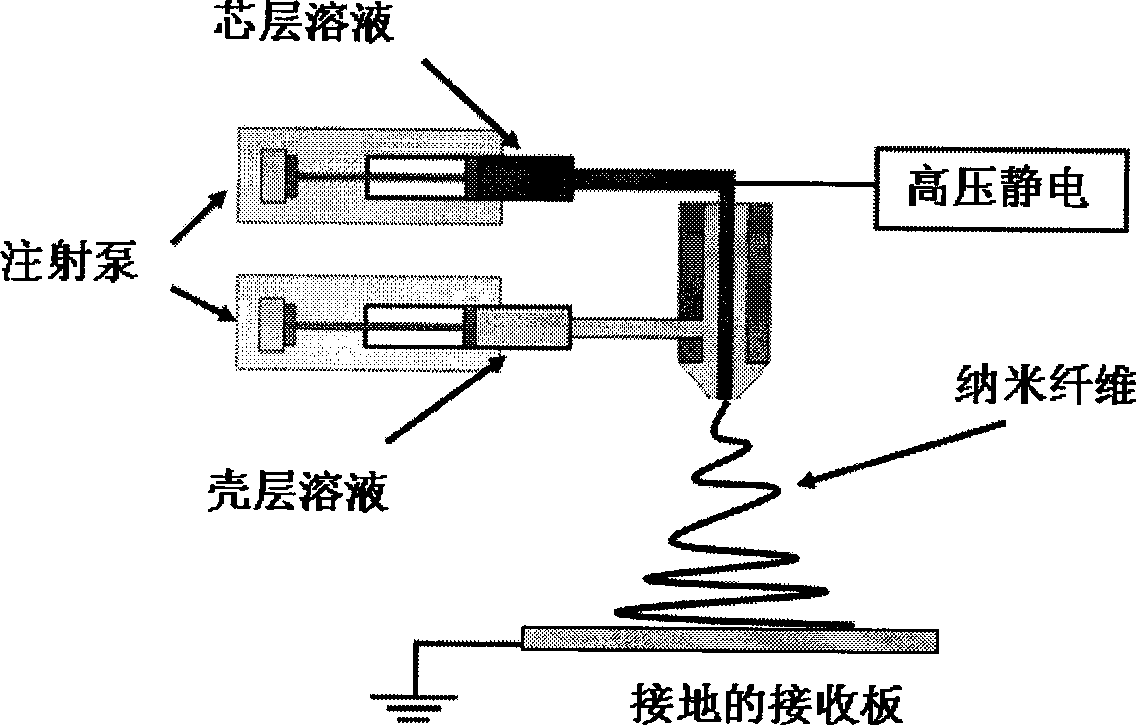
Method for producing shell-core structure medicament nano-fibre with coaxial electrostatic spinning technology
InactiveCN101509153AFix monotonic release behaviorMeet needsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismFilament/thread formingFiberDissolution
The invention relates to a method for preparing shell-core structured medicament nano fiber by coaxial electrostatic spinning technology, comprising: (1) dissolving high molecular polymer and medicament in mass proportion of 60-99.9:0.1-40 in organic solvent with high volatility, and stirring until complete dissolution to obtain shell solution; (2) dissolving one or more than one of natural polymer, medicament, and bioactive factor in the solvent, or dissolving the same in super pure water under aseptic condition to obtain core solution; and (3) carrying out coaxial electrostatic spinning, setting the spinning voltage at 15-25kv, the reception distance at 8-20cm, the spinning pushing speed at 0.1-1.5mL / h, and the spinning nozzle as 0.9mm, to obtain the shell-core structured medicament nano fiber. The preparation method is simple in operation, mild in reaction condition, low in cost and favorable for economic benefit; in preparing the shell-core structured medicament nano fiber, two or more than two medicaments can be simultaneously loaded and released, thus meeting requirements of tissue regeneration or patients.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Crush resistant delayed-release dosage forms
The invention relates to a dosage form comprising a physiologically effective amount of a physiologically active substance (A), a synthetic, semi-synthetic or natural polymer (C), optionally one or more physiologically acceptable auxiliary substances (B) and optionally a synthetic, semi-synthetic or natural wax (D), wherein the dosage form exhibits a resistance to crushing of at least 400 N and wherein under physiological conditions the release of the physiologically active substance (A) from the dosage form is at least partially delayed.
Owner:GRUNENTHAL GMBH
Composite natural polymer gel material
ActiveCN105837861ALarge specific surface areaImprove mechanical propertiesAerogel preparationColloidal chemistry detailsNon solventWater based
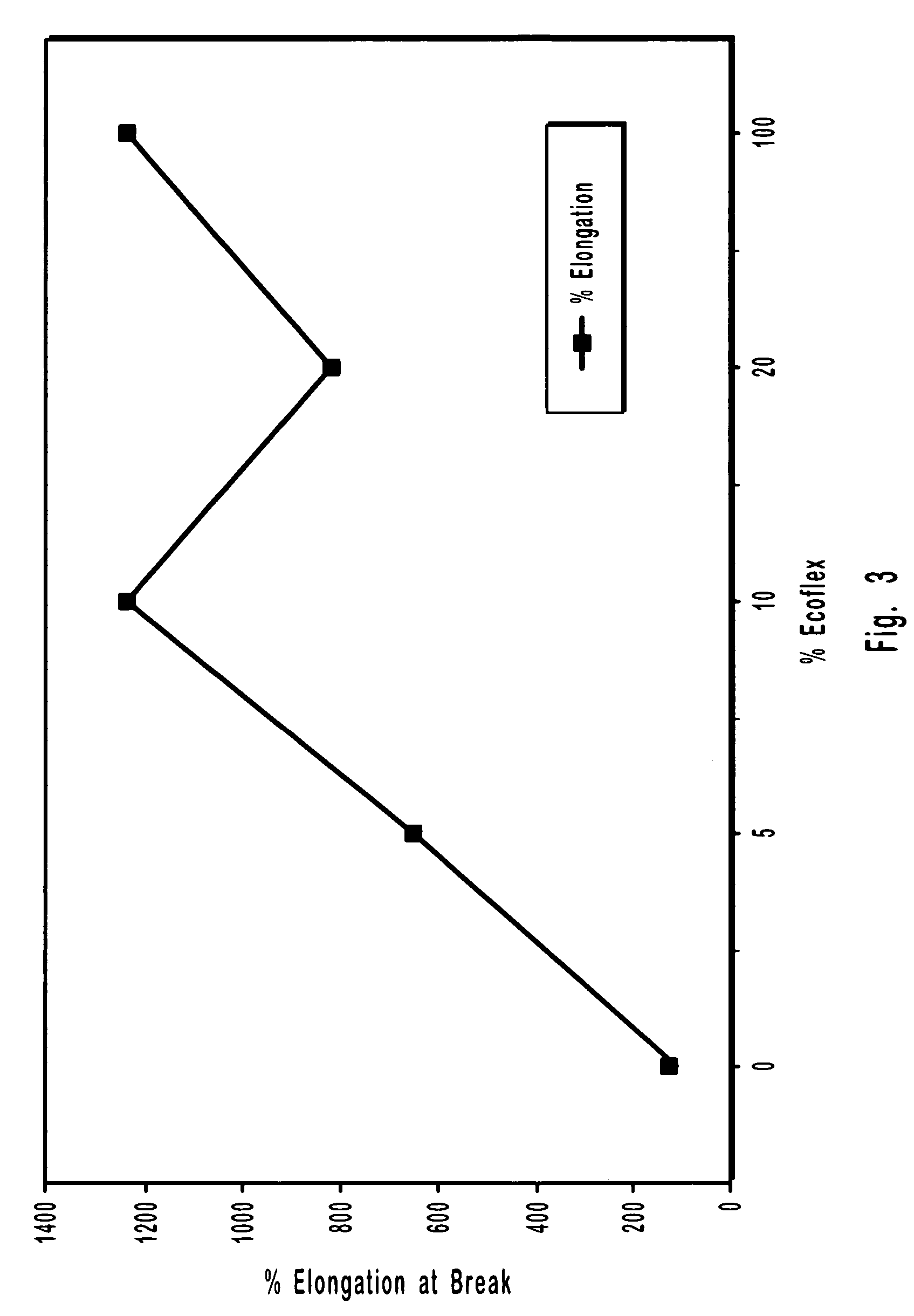
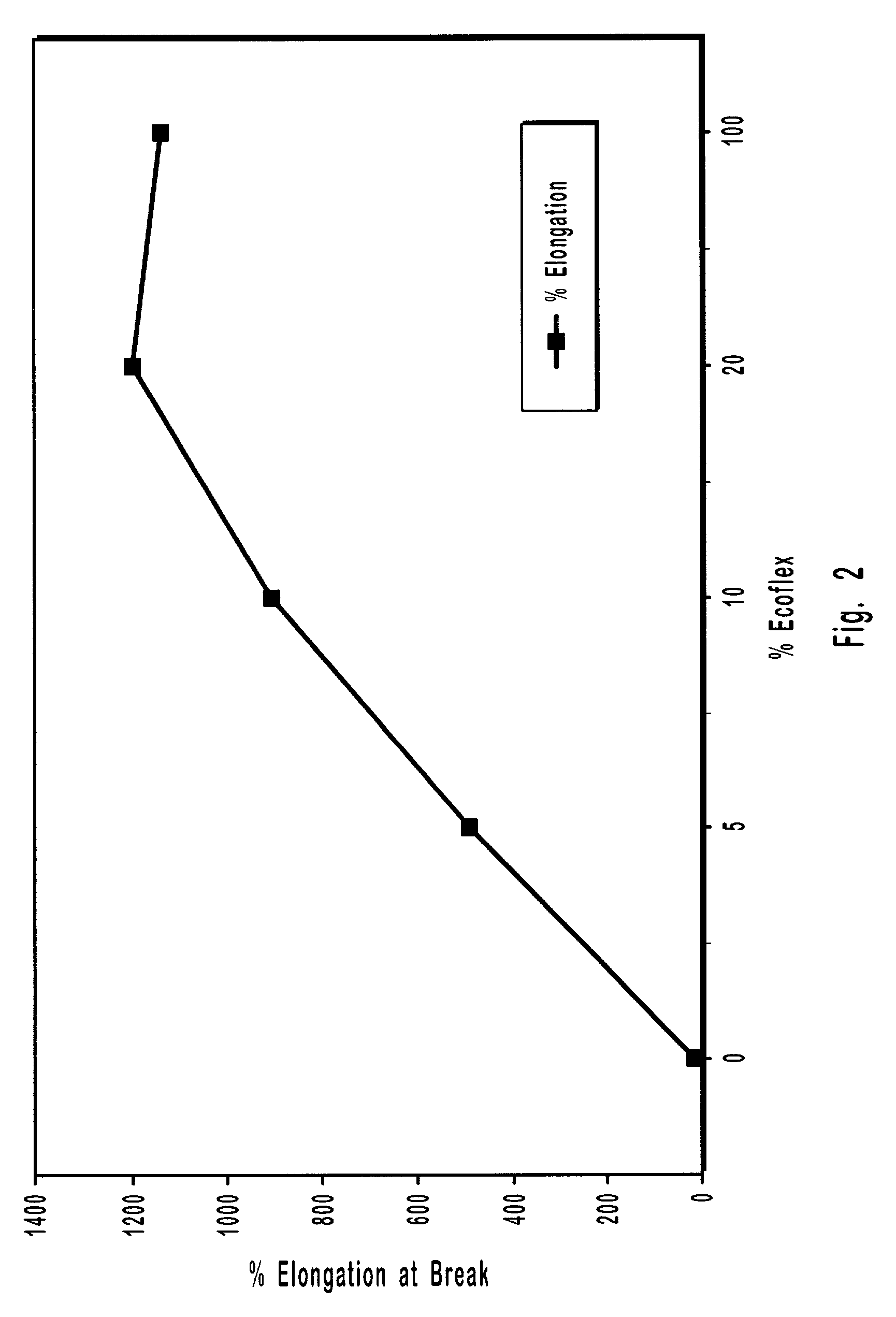
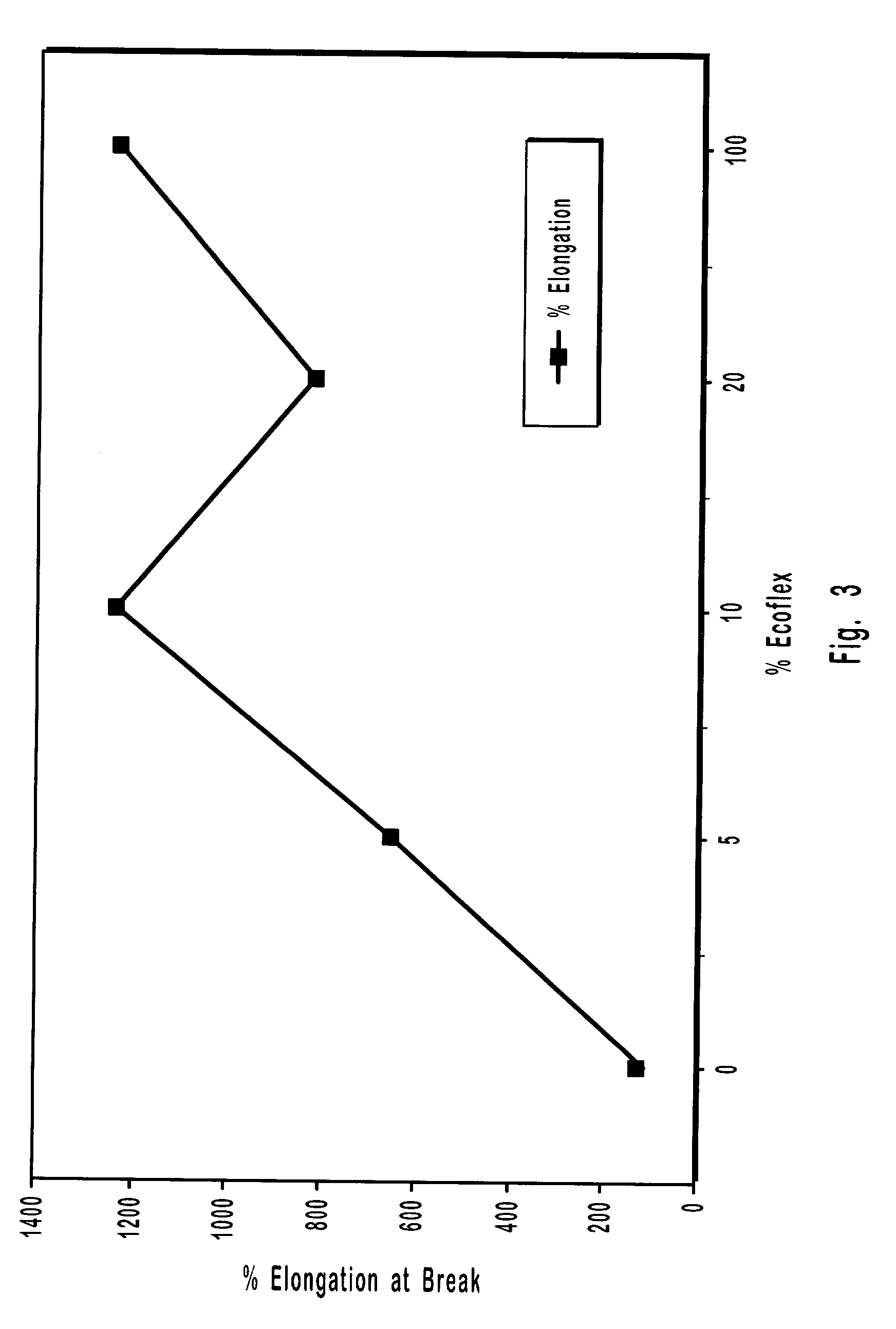
The invention discloses a composite natural polymer gel material with a cross-linking agent. The material comprises hydrogel, organogel, aerogel and bioplastics and mainly overcomes the problem of low mechanical strength of conventional natural polymer gel materials. According to the invention, a certain amount of the cross-linking agent is added into a natural polymer water-based solution or dispersion liquid, then stirring is carried out, the obtained mixture is placed in a non-solvent for physical cross-linking, and then washing is carried out so as to obtain composite natural polymer hydrogel; water in the composite natural polymer hydrogel is replaced with an organic solution so as to prepare composite natural polymer organogel; the composite natural polymer hydrogel or organogel is dried so as to prepare composite natural polymer aerogel; the composite natural polymer aerogel is subjected to hydrophobic treatment so as to obtain hydrophobic aerogel; the composite natural polymer aerogel is subjected to heat treatment so as to obtain carbon aerogel; and one or more selected from the above-mentioned gel materials are subjected to high-temperature pressing so as to prepare composite natural polymer bioplastics. The composite natural polymer gel material prepared in the invention has the advantages of excellent mechanical properties, a high specific surface area, high elongation at break, etc., and can be easily processed into molded products of a plurality of forms.
Owner:浙江绍兴万德福生物技术有限公司 +1
Preparation method of core-shell structured synthetic polymer-natural polymer composite fiber
InactiveCN102817105ASimple and fast operationMild reaction conditionsConjugated cellulose/protein artificial filamentsFilament/thread formingFiberPolymer science
The invention discloses a preparation method of a core-shell structured synthetic polymer-natural polymer composite fiber, and the method comprises the steps of: (1) selecting one or several of synthetic polymers to dissolve in a solvent, and conducting stirring until complete dissolution; (2) selecting a natural polymer to dissolve in a solvent, or adding a spinning assistant, and carrying out stirring until complete dissolution; and (3) taking the solution prepared in step (1) as an outer tube spinning solution, adopting the solution prepared in step (2) as an inner tube spinning solution, injecting them into the inner tube and the outer tube of a coaxial spinneret, and performing coaxial electrospinning at room temperature. The core-shell structured nano-fiber prepared by the invention selects the synthetic polymer as the shell layer, and can inhibit water molecules from penetrating the natural polymer as the core layer. The natural polymer as the core layer can more effectively encapsulate active substances to avoid inactivation of the active substances in the presence of an organic solvent, so that the core-shell structured composite fiber can play a good drug sustained release role in the drug carrier field, and an integral activity can be maintained.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Biodegradable films and sheets suitable for use as coatings, wraps and packaging materials
InactiveUS7297394B2Increase stiffnessIncrease flexibilitySynthetic resin layered productsPaper coatingThermoplasticPolyester
Biodegradable polymer blends suitable for laminate coatings, wraps and other packaging materials are manufactured from at least one “hard” biopolymer and at least one “soft” biopolymer. “Hard” biopolymers tend to be more brittle and rigid and typically have a glass transition temperature greater than about 10° C. “Soft” biopolymers tend to be more flexible and pliable and typically have a glass transition temperature less than about 0° C. While hard and soft polymers each possess certain intrinsic benefits, certain blends of hard and soft polymers have been discovered which possess synergistic properties superior to those of either hard or soft polymers by themselves. Biodegradable polymers include polyesters, polyesteramides, polyesterurethanes, thermoplastic starch, and other natural polymers. The polymer blends may optionally include an inorganic filler. Films and sheets made from the polymer blends may be textured so as to increase the bulk hand feel. Wraps will typically be manufactured to have good “dead-fold” properties so as to remain in a wrapped position and not spring back to an “unwrapped” form.
Owner:BIO TEC BIOLOGISCHE NATURVERPACKUNGEN
Crush resistan delayed-release dosage form
The invention relates to a dosage form comprising a physiologically effective amount of a physiologically active substance (A), a synthetic, semi-synthetic or natural polymer (C), optionally one or more physiologically acceptable auxiliary substances (B) and optionally a synthetic, semi-synthetic or natural wax (D), wherein the dosage form exhibits a resistance to crushing of at least 400 N and wherein under physiological conditions the release of the physiologically active substances (A) from the dosage form is at least partially delayed.
Owner:GRUNENTHAL GMBH
Blumea oil microcapsule textile composite finishing agent and use thereof
InactiveCN101591859AStir wellSmall particle sizeFibre treatmentMicroballoon preparationCross-linkChemical Linkage
The invention discloses a blumea oil microcapsule textile composite finishing agent and use thereof. Gelatin or acacia of natural polymers is used the main ingredient of a wall material, the blumea oil serving as a Chinese medicinal material is used as a core material, and complex coacervation is adopted to prepare an blumea oil microcapsule aqueous emulsion; a shrink-resistance crosslinker and a catalyst are added to be combined with the blumea oil microcapsule aqueous emulsion into a multifunctional blumea oil microcapsule textile composite finishing agent; researches on the use of blumea oil microcapsules in textile finishing are carried out; and a novel cross linked graft method is used to perform the microcapsule finishing of textiles to form chemical bonds between the microcapsules and the textiles though the shrink-resistance crosslinker and free formaldehyde molecules in 2D resin further participate in a cross-linking and curing reaction as a microcapsule curing agent, so the textiles achieve a long lasting antibacterial and health-care function, a shrink-resistance function and low formaldehyde release content performance.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Biodegradable Packaging Film
InactiveUS20090324917A1Conductive materialSynthetic resin layered productsWater vaporMechanical property
A biodegradable packaging film is provided. The film is formed from a blend that contains a thermoplastic starch and polylactic acid. Starch is a relatively inexpensive natural polymer that is also renewable and biodegradable. Polylactic acid is likewise an inexpensive synthetic polymer that is biodegradable and renewable, yet also capable of providing increased tensile strength to the film. Although providing a good combination of biodegradability / renewability and increased tensile strength, the polylactic acid is also relatively rigid and can result in films having a relatively high stiffness (e.g., high modulus of elasticity) and low ductility. While more ductile than polylactic acid, the thermoplastic starch is often difficult to melt process in film forming processes and very sensitive to moisture and water vapor, reducing its ability to be used as a stand alone packaging film. In an effort to counteract the effect of such polymers, an aliphatic-aromatic copolyester is also employed in the blend of the present invention. While such copolyesters are biodegradable, they also possess the melt properties and ductility that lend them well to the formation of films. Although the combination of these polymers may achieve a good balance between biodegradability / renewability, high tensile strength, and good ductility (e.g., high peak elongation), it is still often difficult to achieve a precise set of mechanical properties as desired for packaging films. In this regard, the blend also contains a filler. Due to its rigid nature, the amount of the filler may be readily adjusted to fine tune the blend to the desired degree of ductility (e.g., peak elongation) and stiffness (e.g., modulus of elasticity).
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Preparation method and application of polycaprolactone/natural polymer composite porous scaffold
InactiveCN102277737AImprove hydrophilicityEasy to spreadLayered productsFibre typesFiberPolymer science
Preparation method and application of polycaprolactone / natural polymer composite porous scaffold, method: including preparation of polycaprolactone electrospun nanofiber membrane; (1) placing polycaprolactone electrospun nanofiber membrane in alkaline solution reaction, soaking and rinsing in deionized water; (2) putting the fiber membrane obtained in (1) into DMTMM or natural polymer solution of DTMMM to react, immersing and rinsing in deionized water, and then immersing in natural polymer for room temperature reaction, to remove Ionized water soaking and rinsing; (3) Evenly coating and casting the mixed solution of natural polymer materials on the fiber membrane obtained in (2), freeze-drying, and extracting the solvent; (4) Applying the double-layer scaffold obtained in (3) After soaking in the cross-linking room temperature reaction, soaking in deionized water, rinsing, and freeze-drying. The porous scaffold prepared by the invention is stable, has suitable pore diameter, good biocompatibility and fast degradation rate, and can be used for skin and clinical tissue and organ defect repair, reconstruction or wound dressing.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Natural fiber welding
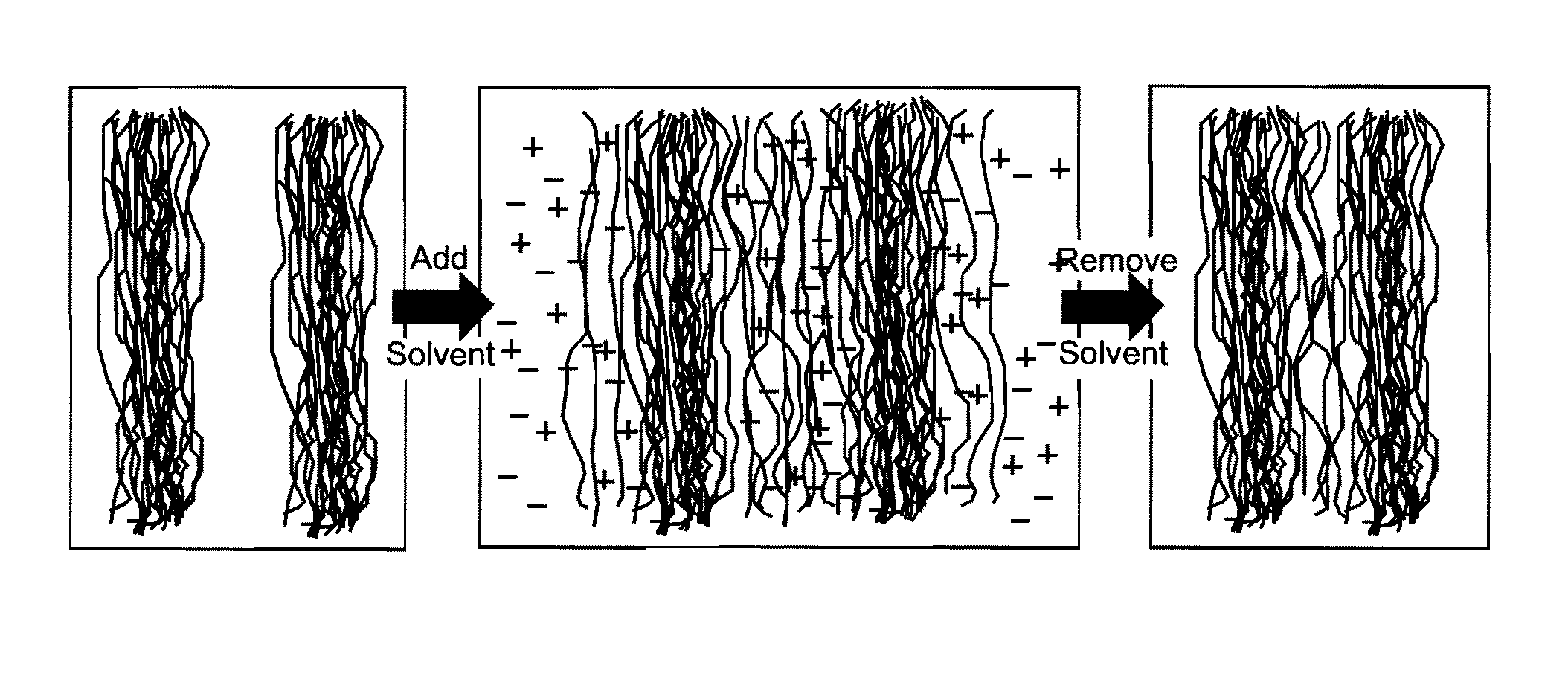
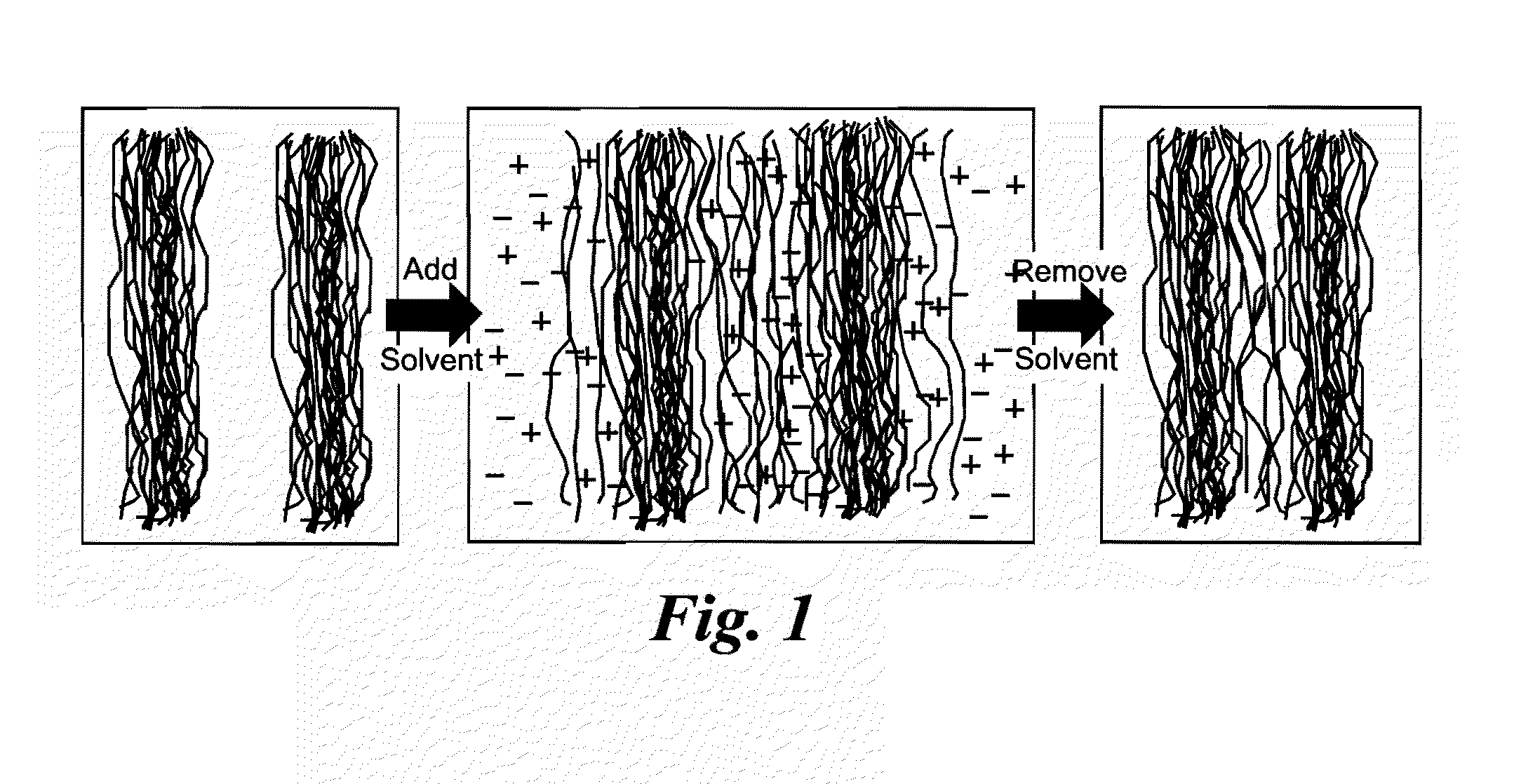
ActiveUS8202379B1Increase material densitySmall surface areaAdhesive processesLaminationPolymer scienceMixed materials
Natural fiber welding is a process by which individual fibers are swollen by an appropriate ionic liquid-based solvent system to form a congealed network. Manipulated fibrous materials may be either composed of natural polymers such as cellulose, hemicellulose, silk, et cetera, or synthetic polymers, or mixed materials. The process is principally controlled by the composition of the solvent system which includes an ionic liquid solvent plus additives such as water, methanol, et cetera. Other conditions such as the amount and placement of solvent, as well as time, temperature, and pressure control the extent to which neighboring fibers are fused. Only the material at the outer surface of fibers need be sufficiently mobile to merge with that of neighboring fibers. Material in the fiber core may be left in the native state by controlling process variables. Fibers form a congealed network upon removal of the ionic liquid-based solvent.
Owner:US SEC THE AIR FORCE THE
Biodegradable films and sheets suitable for use as coatings, wraps and packaging materials
InactiveUS20030166748A1Readily accept and retain printImprove propertiesSynthetic resin layered productsPaper coatingPolyesterThermoplastic
Biodegradable polymer blends suitable for laminate coatings, wraps and other packaging materials are manufactured from at least one "hard" biopolymer and at least one "soft" biopolymer. "Hard" biopolymers tend to be more brittle and rigid and typically have a glass transition temperature greater than about 10° C. "Soft" biopolymers tend to be more flexible and pliable and typically have a glass transition temperature less than about 0° C. While hard and soft polymers each possess certain intrinsic benefits, certain blends of hard and soft polymers have been discovered which possess synergistic properties superior to those of either hard or soft polymers by themselves. Biodegradable polymers include polyesters, polyesteramides, polyesterurethanes, thermoplastic starch, and other natural polymers. The polymer blends may optionally include an inorganic filler. Films and sheets made from the polymer blends may be textured so as to increase the bulk hand feel. Wraps will typically be manufactured to have good "dead-fold" properties so as to remain in a wrapped position and not spring back to an "unwrapped" form.
Owner:BIO TEC BIOLOGISCHE NATURVERPACKUNGEN
Biodegradable polymer blends for use in making films, sheets and other articles of manufacture
InactiveUS20050182196A1Increase dead-foldImproves dead-fold propertySynthetic resin layered productsEmulsion paintsPolyesterThermoplastic
Biodegradable polymer blends suitable for laminate coatings, wraps and other packaging materials are manufactured from a blend of suitable biodegradable polymers, such as at least one “hard” biopolymer and at least one “soft” biopolymer. “Hard” biopolymers tend to be more brittle and rigid and typically have a glass transition temperature greater than about 10° C. “Soft” biopolymers tend to be more flexible and pliable and typically have a glass transition temperature less than about 0° C. While hard and soft polymers each possess certain intrinsic benefits, certain blends of hard and soft polymers have been discovered which possess synergistic properties superior to those of either hard or soft polymers by themselves. Biodegradable polymers include polyesters, polyesteramides, polyesterurethanes, thermoplastic starch, and other natural polymers. The polymer blends may optionally include an inorganic filler. Films and sheets made from the polymer blends may be textured so as to increase the bulk hand feel. Wraps will typically be manufactured to have good “dead-fold” properties so as to remain in a wrapped position and not spring back to an “unwrapped” form.
Owner:BIO TEC BIOLOGISCHE NATURVERPACKUNGEN
Evolving new molecular function
InactiveUS20050042669A1High activityOrganic chemistry methodsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiopolymerMolecular function
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Evolving new molecular function
Nature evolves biological molecules such as proteins through iterated rounds of diversification, selection, and amplification. The present invention provides methods, compositions, and systems for synthesizing, selecting, amplifying, and evolving non-natural molecules based on nucleic acid templates. The sequence of a nucleic acid template is used to direct the synthesis of non-natural molecules such as unnatural polymers and small molecules. Using this method combinatorial libraries of these molecules can be prepared and screened. Upon selection of a molecule, its encoding nucleic acid template may be amplified and / or evolved to yield the same molecule or related molecules for re-screening. The inventive methods and compositions of the present invention allow for the amplification and evolution of non-natural molecules in a manner analogous to the amplification of natural biopolymer such as polynucleotides and protein.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Nano fibrous tissue engineering blood vessel and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101214393APromote endothelializationMeet the mechanical requirementsConjugated cellulose/protein artificial filamentsBlood vesselsFiberCross-link
The invention relates to a tissue engineering material and a preparation method thereof, in particular to a nano fiber tissue engineering blood vessel and a preparation method thereof. The invention consists of a three-dimensional reticular non-woven film formed by an inner layer of nano fiber and an outer layer of nano fiber; the inner layer of the blood vessel is natural polymer, wherein, calculated by weight, 40 percent to 80 percent is fibroin, 20 percent to 50 percent is gelatine, 0 percent to 20 percent is extracellular matrix protein; while the outer layer of the blood vessel is synthetic polymer. The preparation method is that the natural polymer is dissolved in trifluroroethyl and other solution, while the synthetic polymer is dissolved in hexafluoroisopropanol and other solution, which are respectively prepared into spinning solution; the static electricity spinning technique is adopted to subsequently form the inner and the outer layers on a gather roller; cross-linked treatment is conducted after the inner and the outer layers are taken down, to prepare the nano fiber tissue engineering vessel. The inner layer can simulate the structure of the extracellular matrix, provide good environment for endothelial cells to grow, support adhesion, proliferation and differentiation of the cells, and is good for endothelization of the blood vessel; and the outer layer has good mechanical performance.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for preparing sodium alginate-chitosan nano-grade medical dressing
ActiveCN104069536AImprove antibacterial and hemostatic effectImprove breathabilityAbsorbent padsConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsCross-linkFiber
The invention relates to a method for preparing a sodium alginate-chitosan nano-grade medical dressing, and belongs to the field of natural biological polymer materials. The method comprises the following steps: dispersing sodium alginate and synthesized polymer in an ethanol solution; and preparing a chitosan solution containing a crosslinking agent to serve as a receiving liquid, wherein fibers are cross-linked by the crosslinking agent after the sodium alginate fibers are received in the chitosan solution, the electrolyte property of the chitosan is adsorbed to the surfaces of the sodium alginate fibers due to the electrostatic effect, and the prepared sodium alginate-chitosan composite nano-fibers have good air permeability and antibacterial and hemostasis effects, is advantageous to wound tissue growth and regeneration when being applied to a wound dressing, and can be used for accelerating wound healing. The method adopts a natural polymer matrix as a raw material, and the medical dressing has low cost, no toxicity and good biocompatibility.
Owner:江苏开源康达医疗器械有限公司
Phase-change energy-storage material
InactiveCN103666381AImprove cycle stabilityRaise the ratioHeat-exchange elementsFiberSodium phosphates
The invention relates to a phase-change energy-storage material which comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 75%-99% of an energy storage main body material, 0.1%-10% of a thickening agent, 0.2%-15% of a nucleating agent and 0.01%-8% of a reinforcing material, wherein the energy storage main body material comprises crystal water and salt; the thickening agent comprises one or more of an inorganic thickening agent, fibers, polyacrylates, polyurethanes and a natural polymer thickening agent; the nucleating agent comprises one or more of sodium pyrophosphate, sodium phosphate decahydrate, calcium sulfate dihydrate, potassium sulfate, potassium borate, barium hydroxide octahydrate, sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate and sodium sulfate; the reinforcing material comprises one or more of metal and metal oxide powder, carbon materials, nanoparticles and foam materials. By selecting proper materials and ratio, the supercooling degree and the phase separation phenomenon are reduced and good circulating stability is achieved; especially the reinforcing material is added into a system to form a heat-conducting network so as to improve the heat conductivity of the material by more than two times.
Owner:PIONEER ENERGY JIANGSU
Process for the production of an abuse-proofed dosage form
InactiveUS20080311197A1Intense negative effectAvoid formingBiocideNervous disorderBreaking strengthMedicine
The present invention relates to a process for the production of an abuse-proofed dosage form containing, apart from one or more active ingredients with potential for abuse and optionally physiologically acceptable auxiliary substances, at least one synthetic or natural polymer (C) with a breaking strength of at least 500 N, wherein the formulation mixture is combined with a solvent for the polymer (C) at least in quantities such that the formulation mixture is at least uniformly moistened, the at least moistened composition is optionally divided into sub-portions, dried and shaped to yield the dosage form.
Owner:GRUNENTHAL GMBH
Process for the production of an abuse-proofed solid dosage form
InactiveUS8323889B2Considerably complicatedAvoid formingBiocideNervous disorderEngineeringBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention relates to a process for the production of an abuse-proofed solid dosage form containing at least one active ingredient with potential for abuse and a synthetic or natural polymer with a breaking strength of =500 N, characterized in that a corresponding mixture is processed by melt extrusion with the assistance of a planetary-gear extruder.
Owner:GRUNENTHAL GMBH
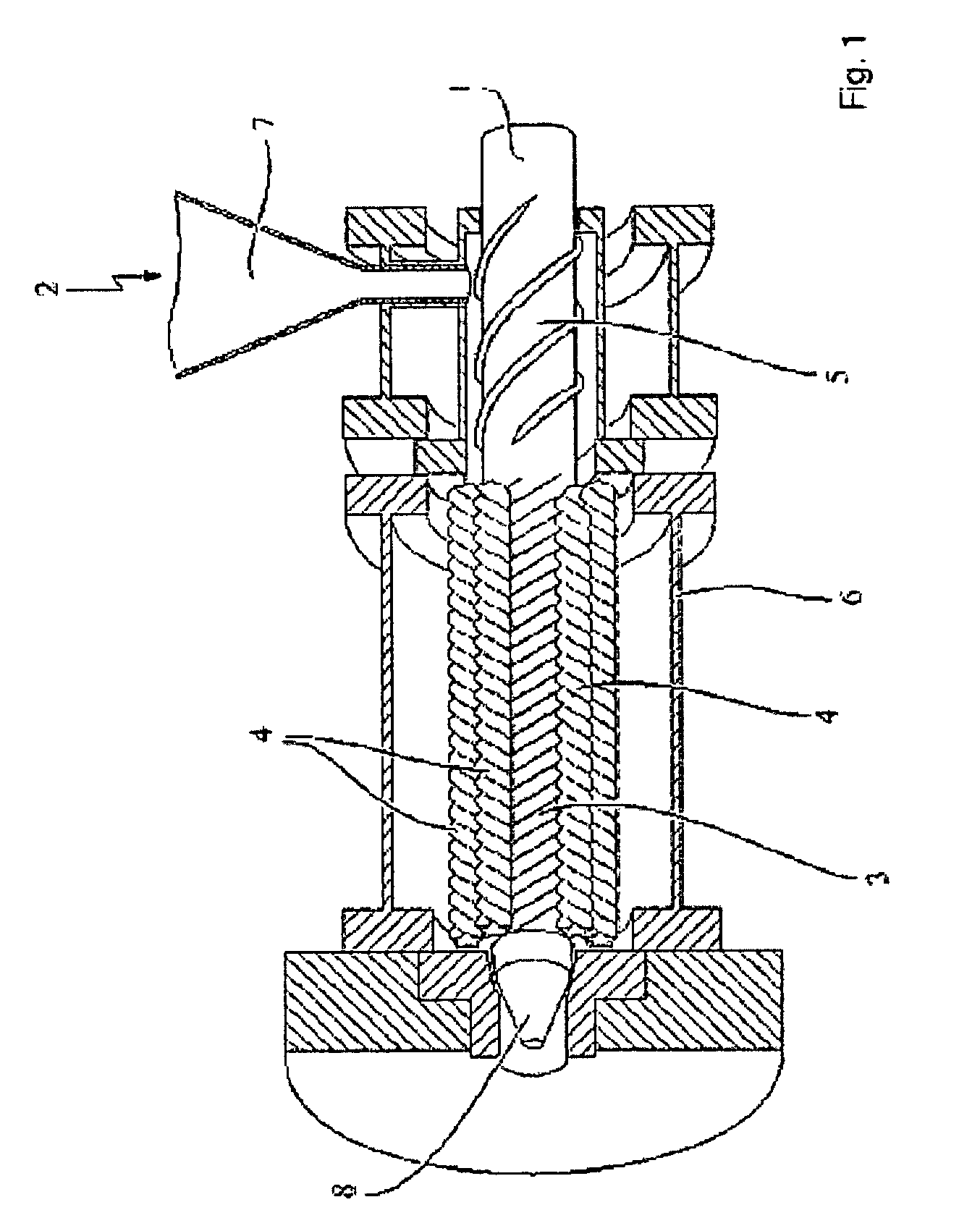
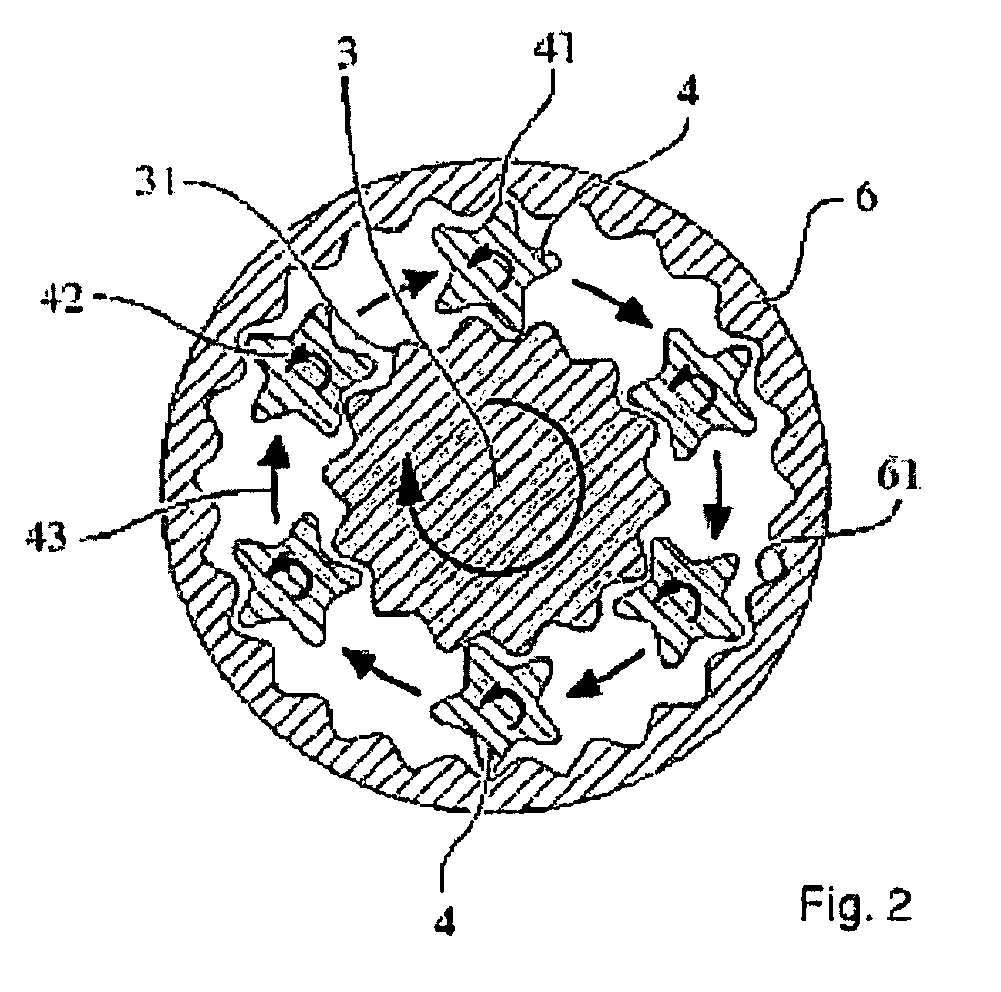
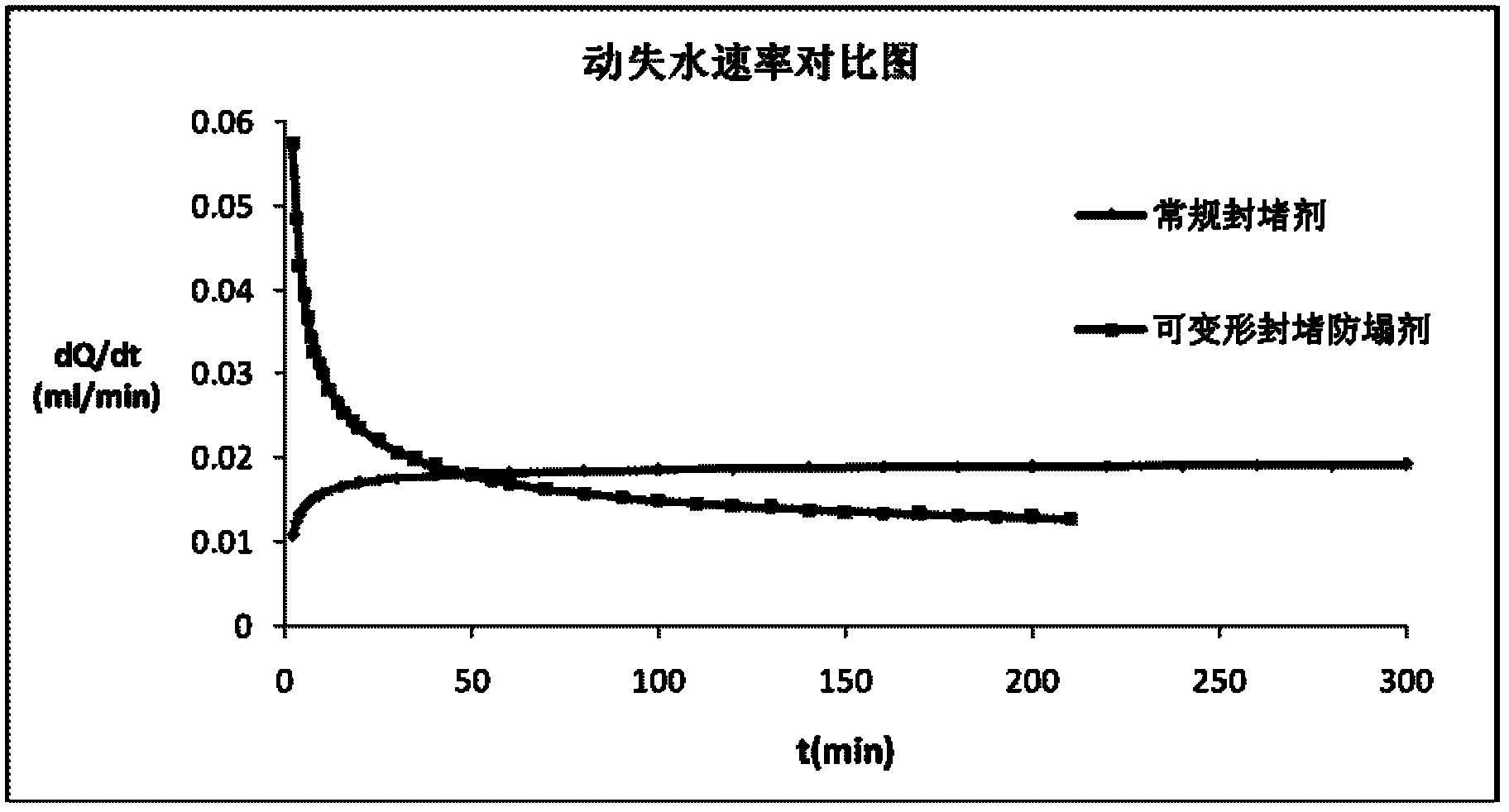
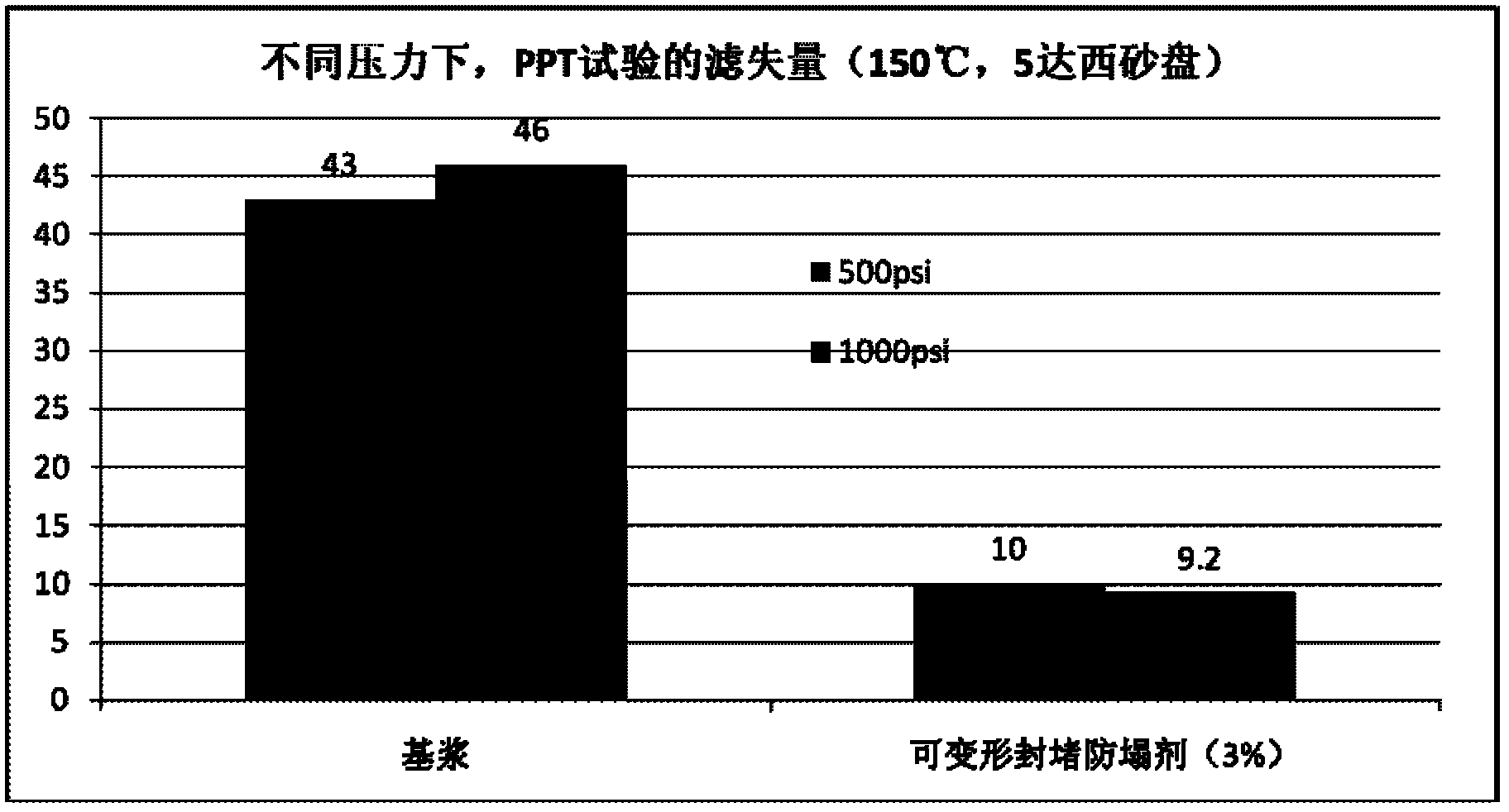
Deformable plugging and anti-sloughing agent for drilling fluid
ActiveCN102676141AImprove the blocking effectImprove compactnessDrilling compositionEngineeringNatural polymers
The invention relates to a deformable plugging and anti-sloughing agent for drilling fluid, and the deformable plugging and anti-sloughing agent comprises 10-90 parts by weight of non-deformable material, 20-80 parts by weight of nano-scale deformable redispersible polymer and 10-60 parts by weight of natural polymer modified material. The invention further relates to a preparation method of the deformable plugging and anti-sloughing agent for the drilling fluid. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing all the components according to the corresponding mixture ratio, mixing by virtue of a mixing and stirring machine for 80-120 minutes and screening by virtue of a 100-300 mesh screen, thus obtaining the deformable plugging and anti-sloughing agent.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com