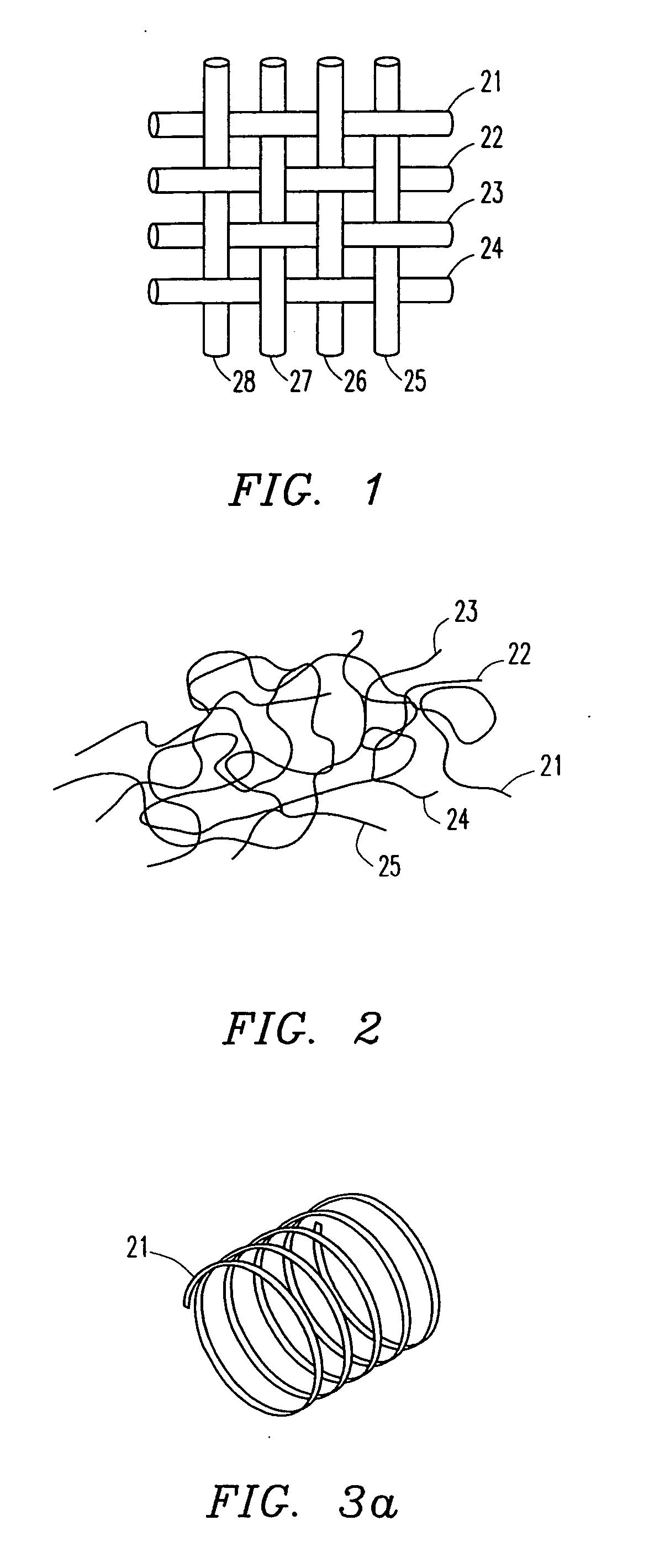
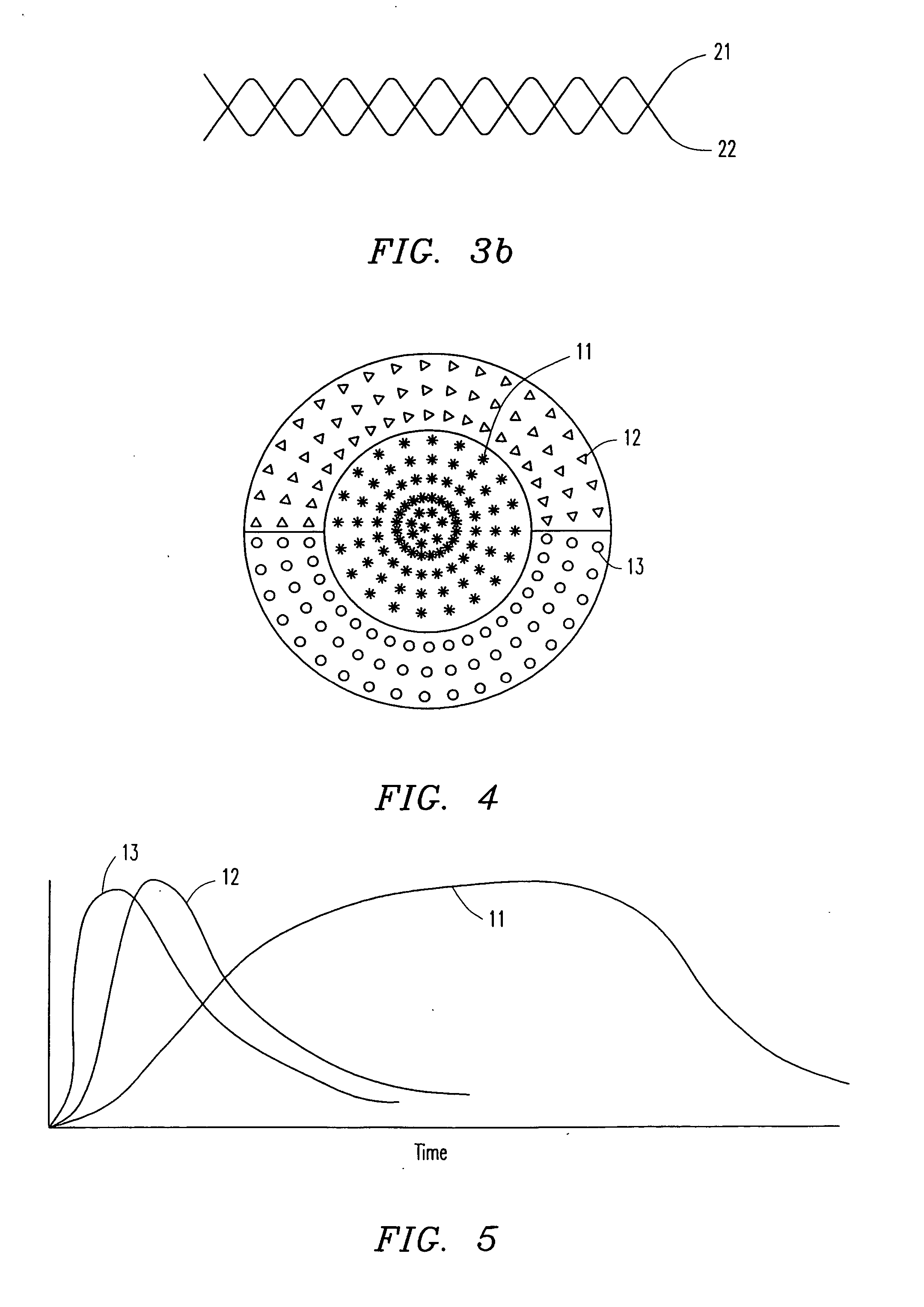
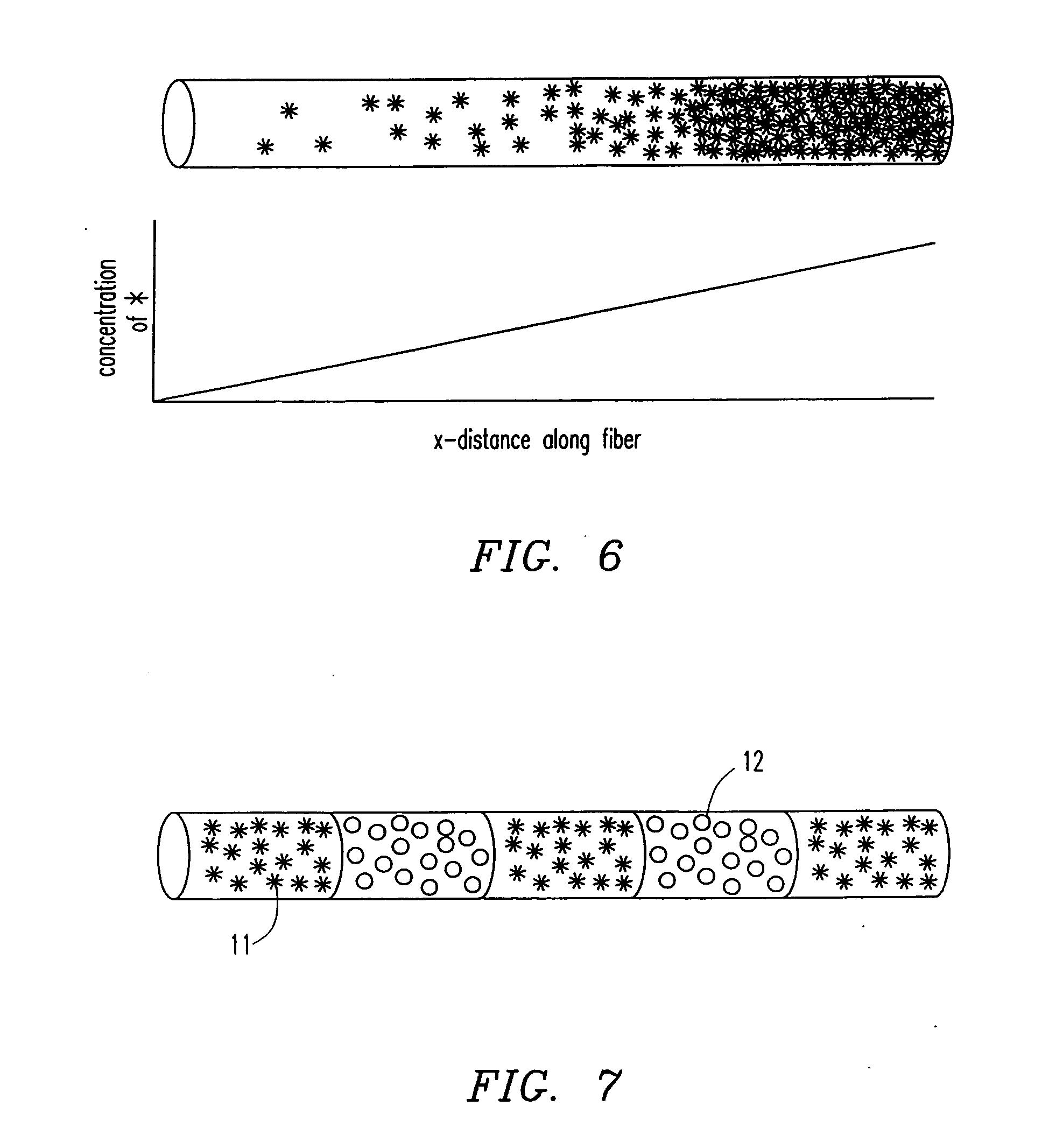
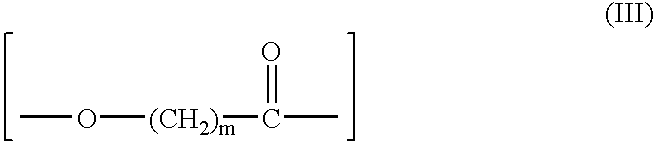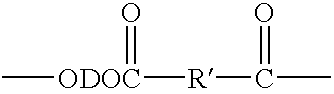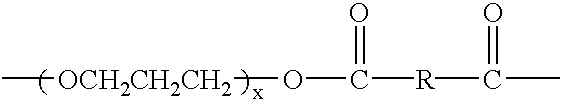Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
8447results about "Conjugated synthetic polymer artificial filaments" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
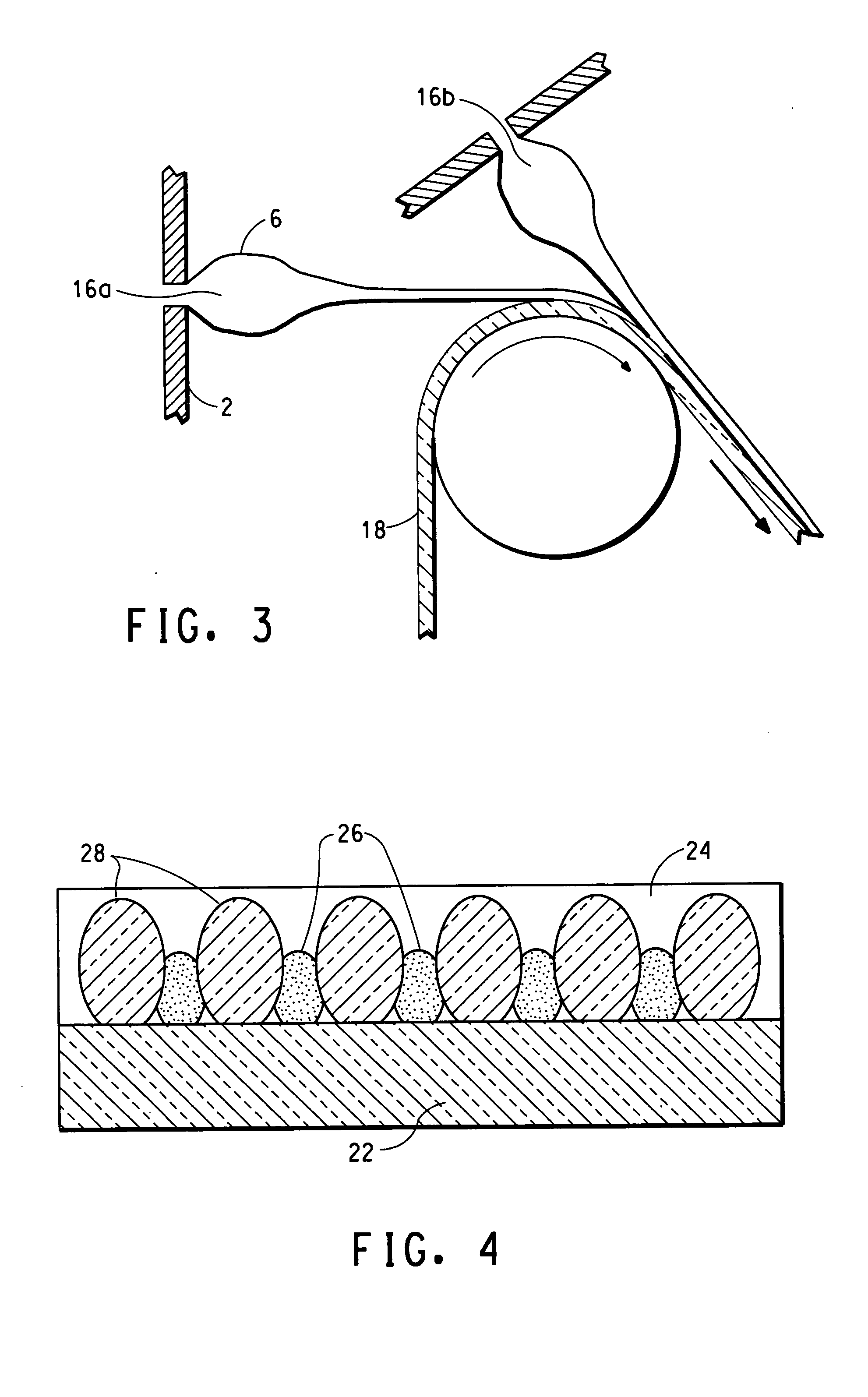
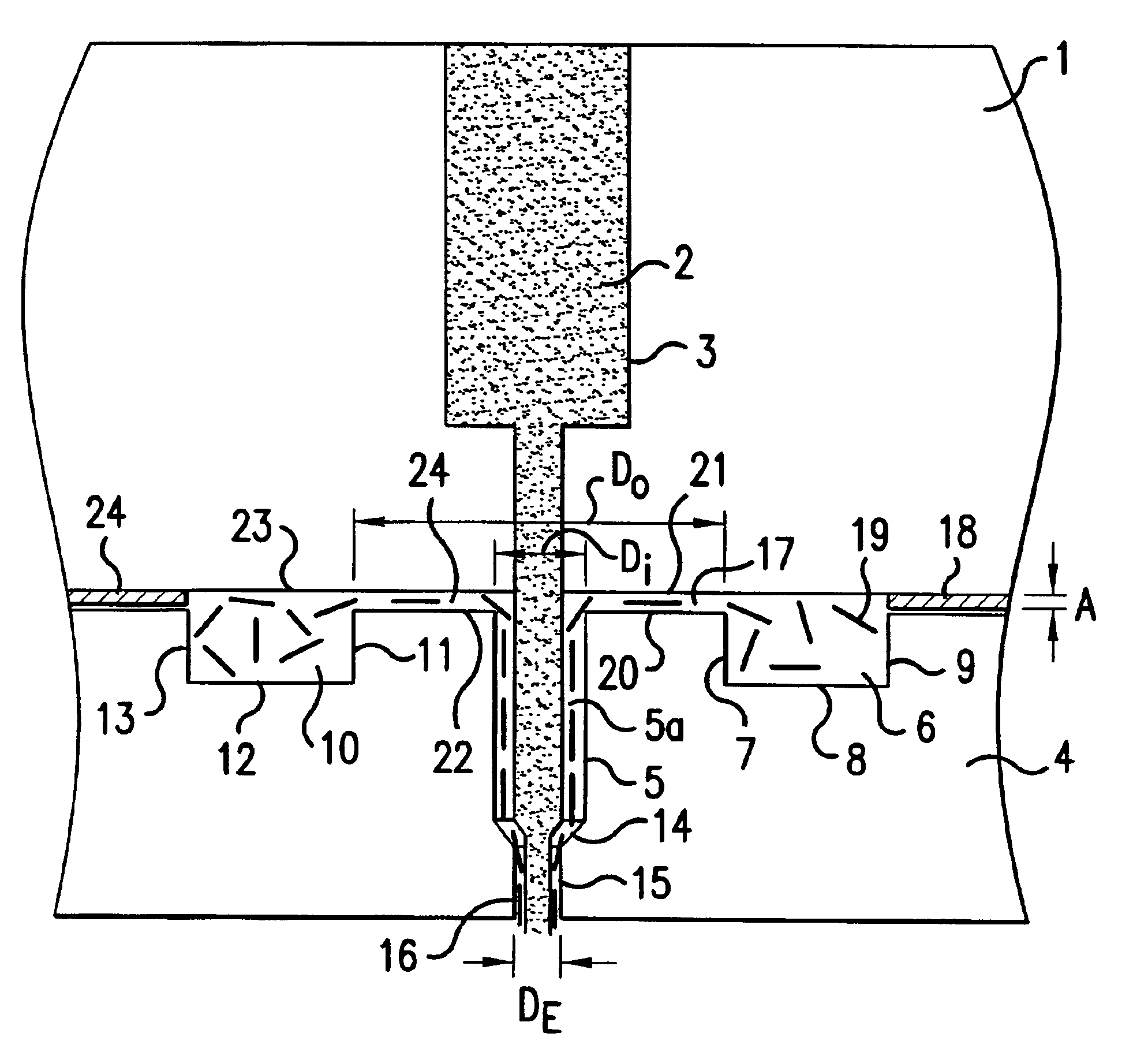
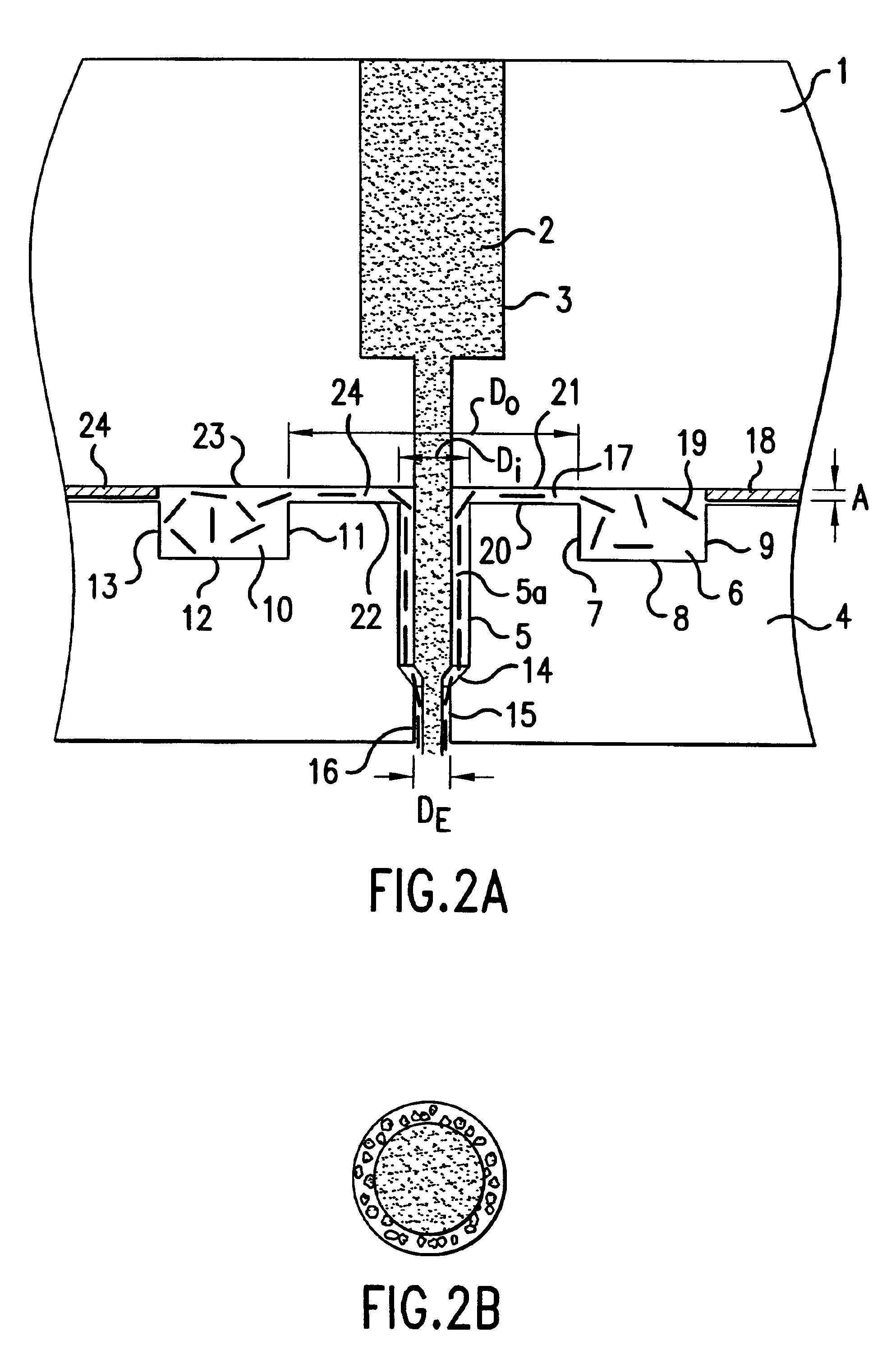
Multi-layer, elastic articles
The invention is an article comprising at least two layers, a low crystallinity layer and a high crystallinity layer. One or both layers is capable of being elongated so that a pre-stretched article is capable of being formed.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Fibers and nonwovens comprising polyethylene blends and mixtures
Polymeric blends and polymeric mixtures that incorporate a blend of a first polyethylene and a second polyethylene are described. The first and second polyethylenes have a predetermined relationship for the density and the melt index of the individual polyethylenes. Also described are fibers (including bicomponent fibers) and nonwoven materials made from the fibers where the fibers are extruded using the polymeric blends, and / or the polymeric mixtures.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
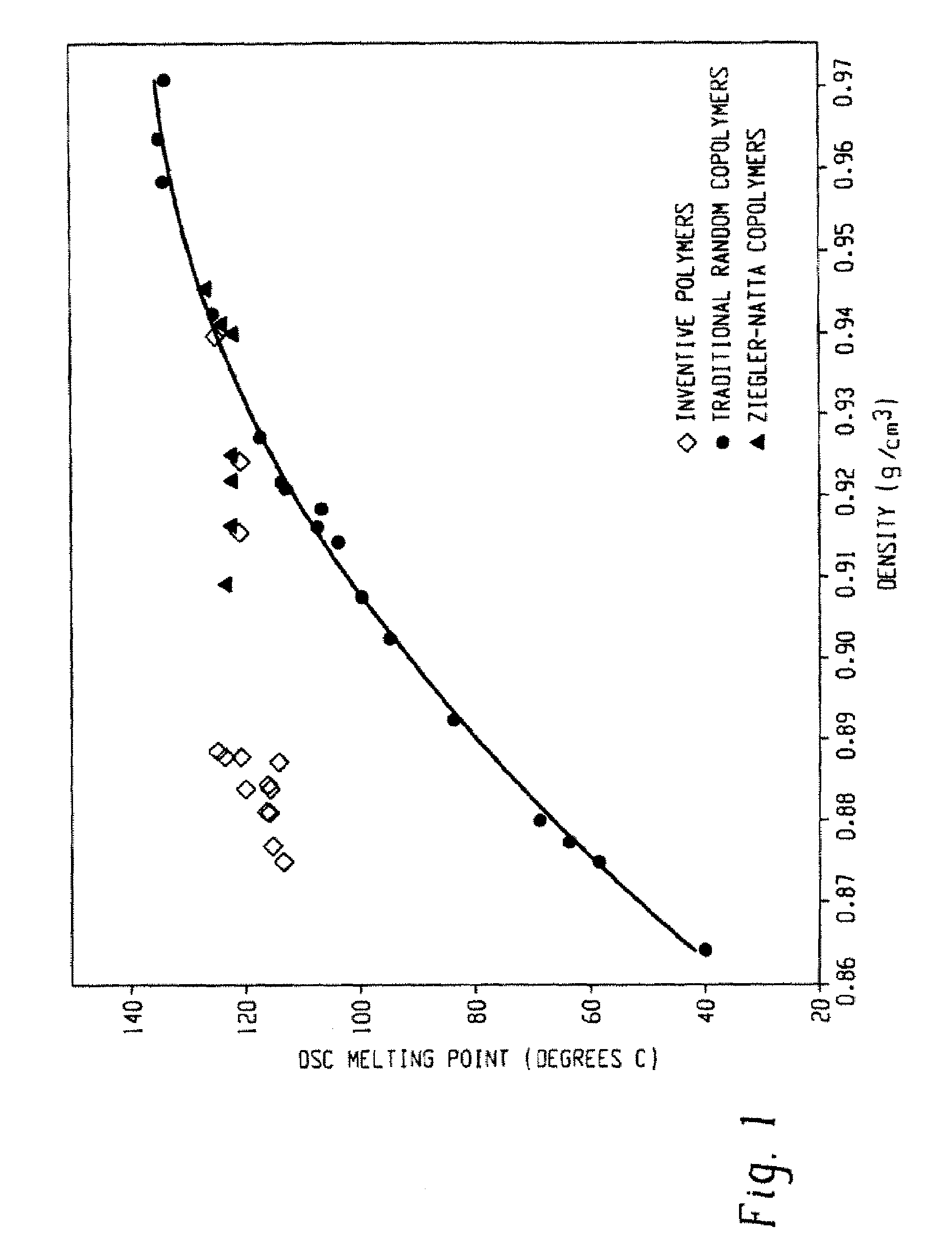
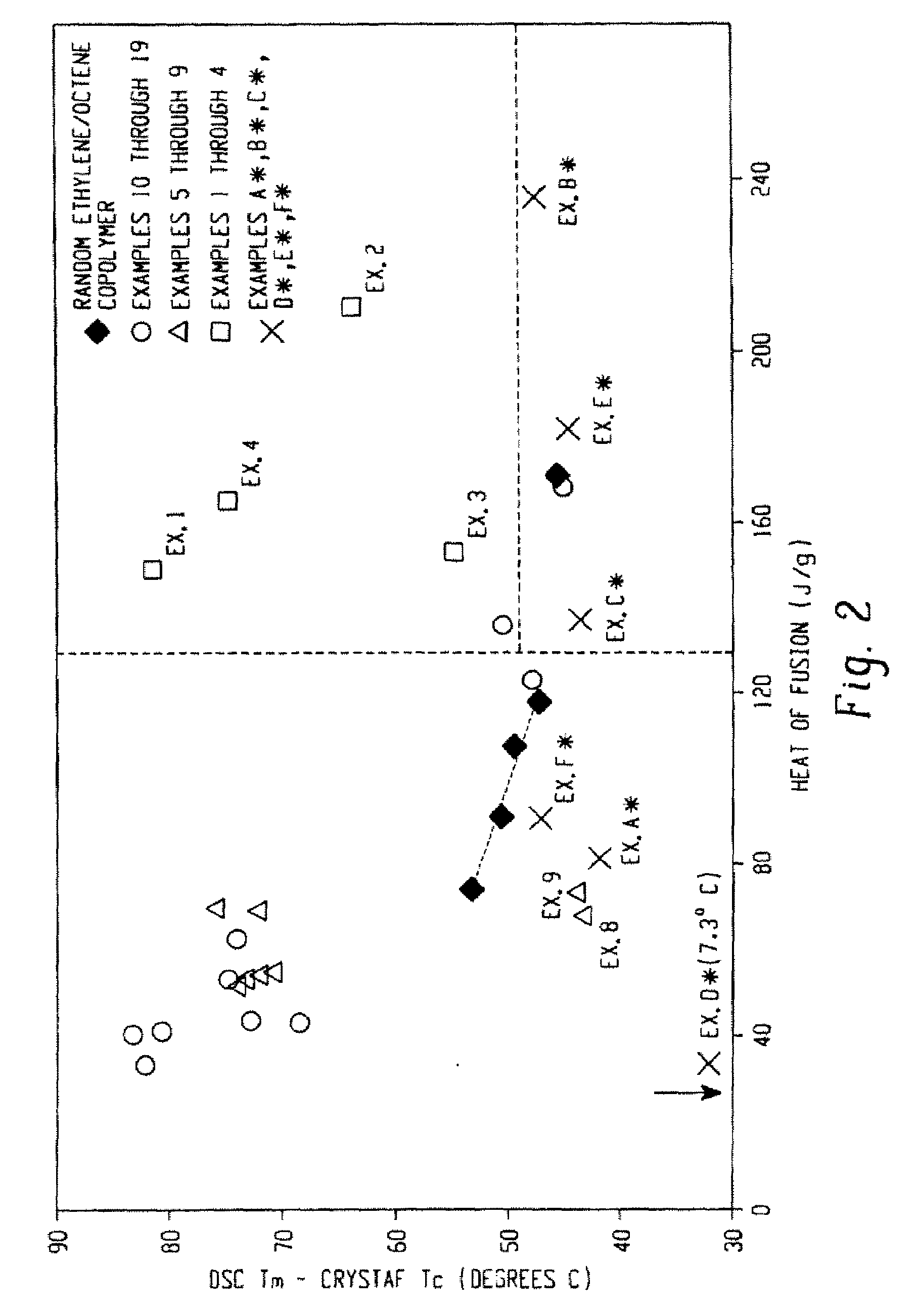
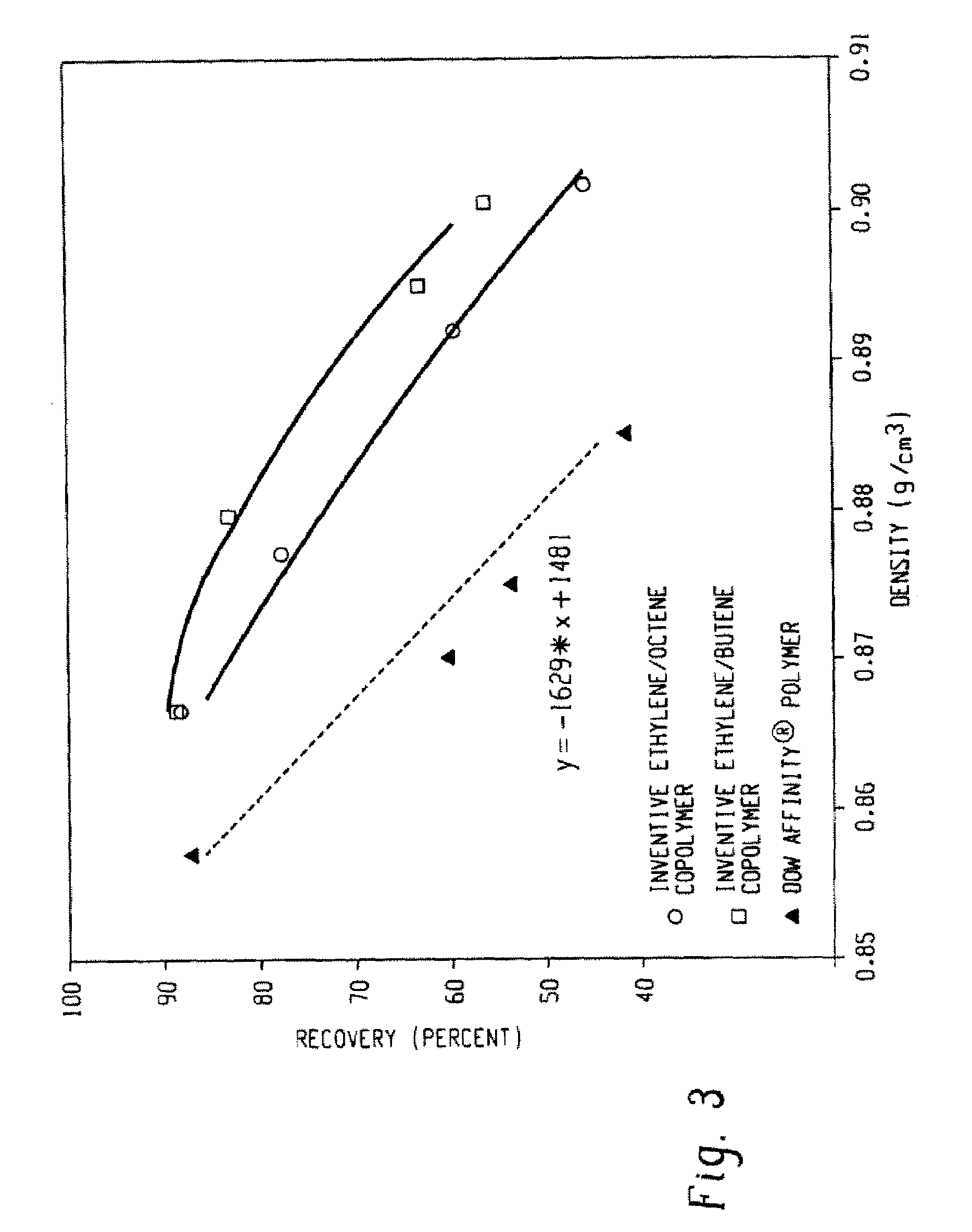
Fibers made from copolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefins
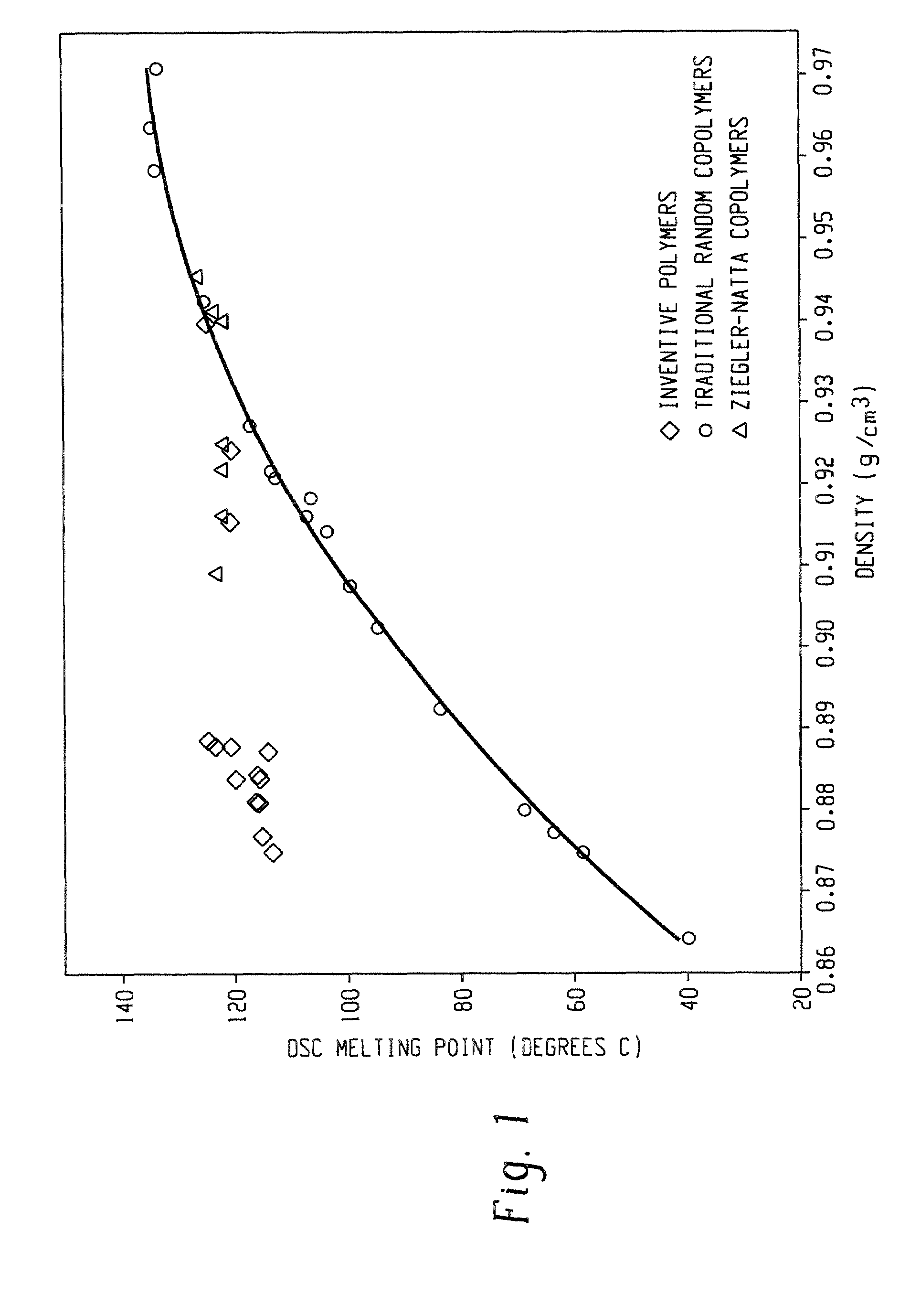
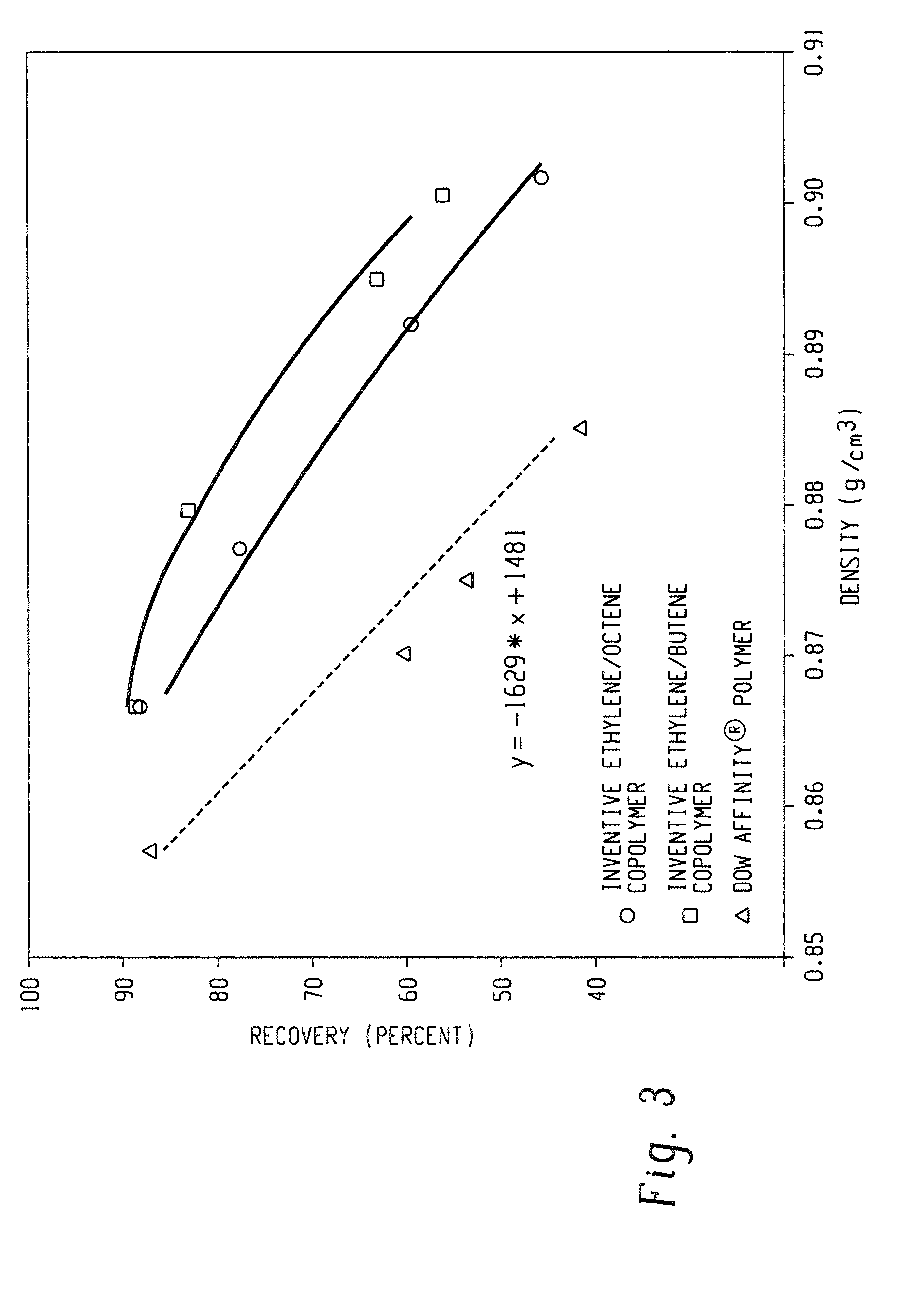
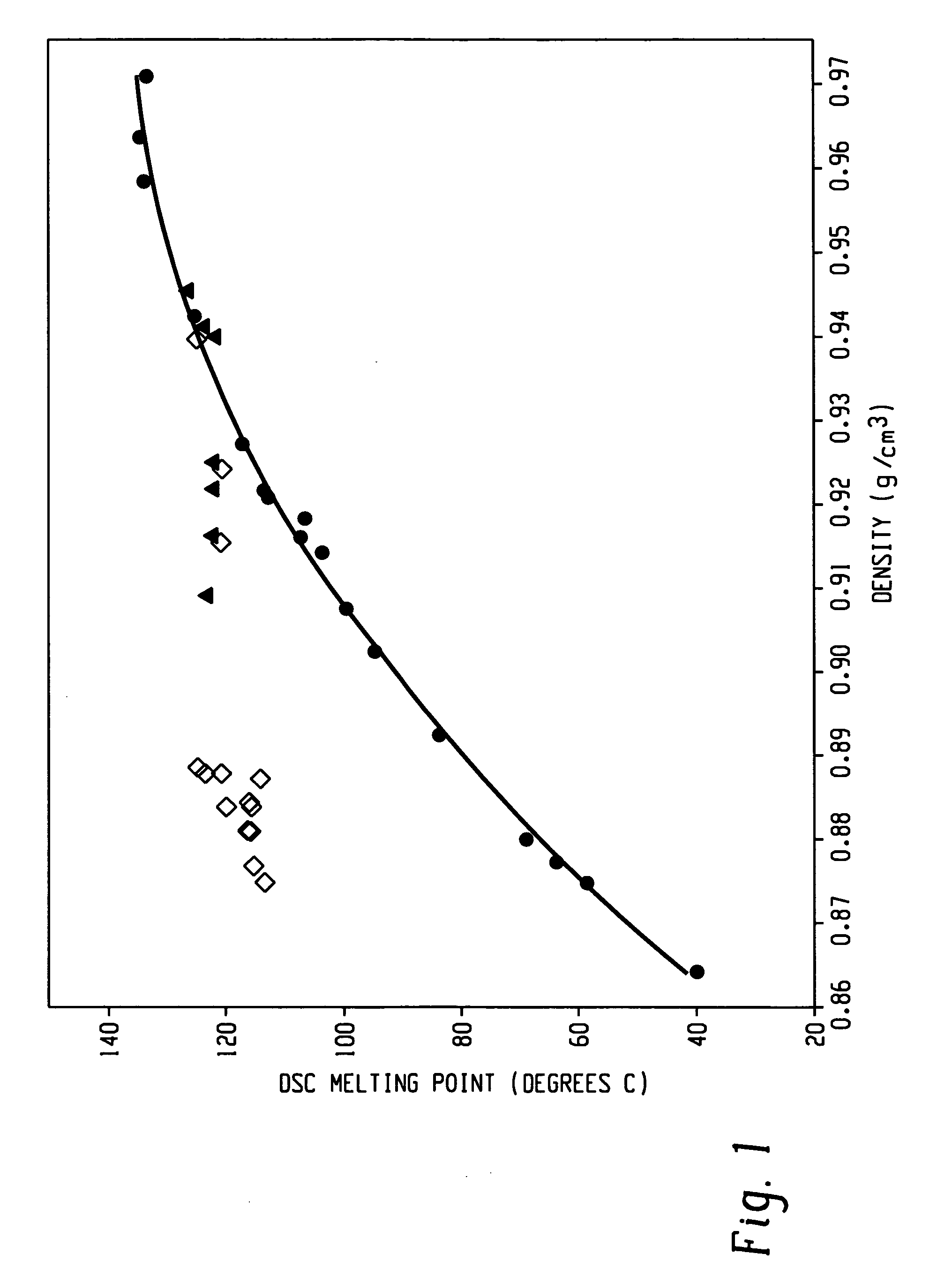
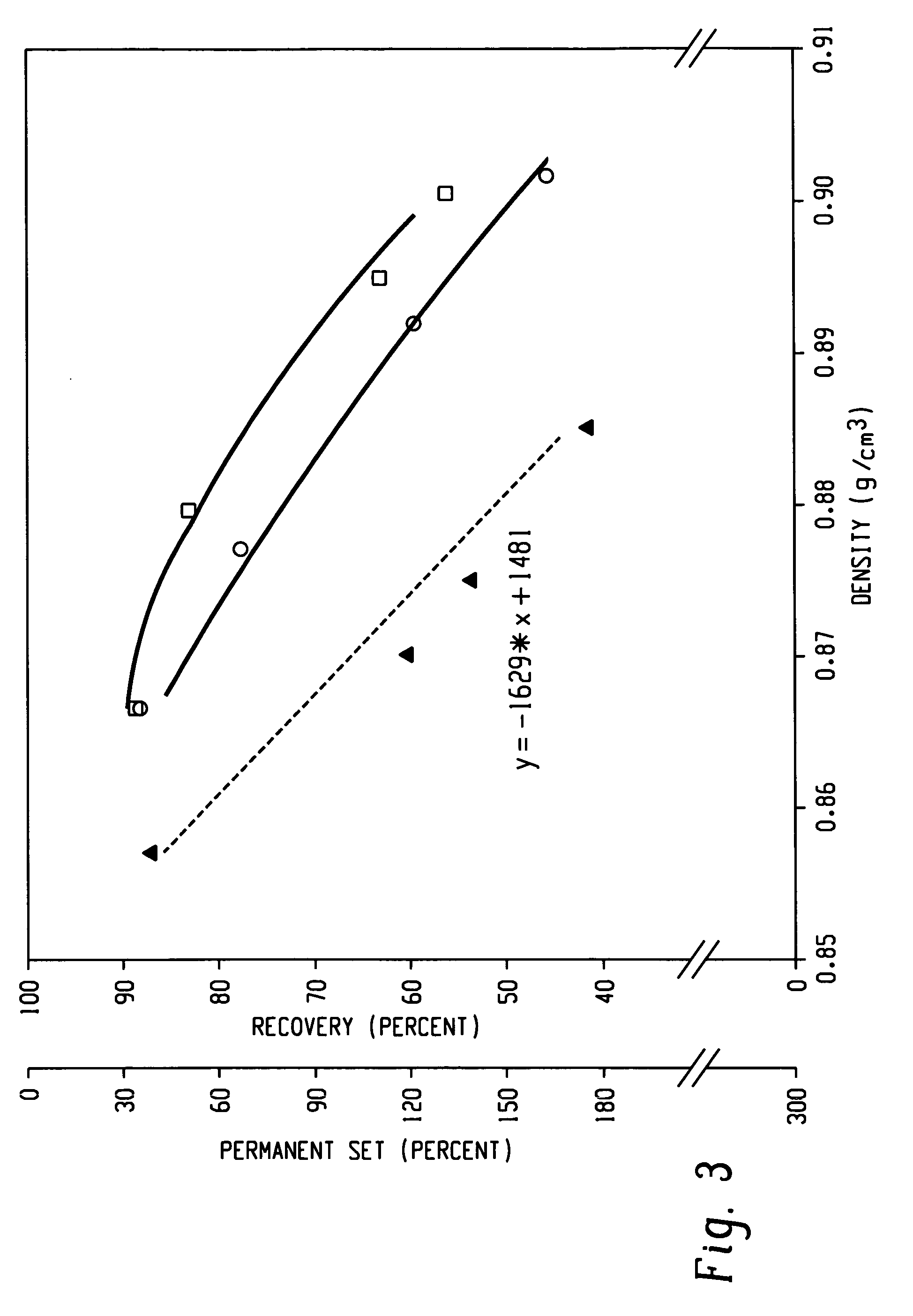
A fiber is obtainable from or comprises an ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer characterized by an elastic recovery, Re, in percent at 300 percent strain and 1 cycle and a density, d, in grams / cubic centimeter, wherein the elastic recovery and the density satisfy the following relationship: Re>1481−1629(d). Such interpolymer can also be characterized by other properties. The fibers made therefrom have a relatively high elastic recovery and a relatively low coefficient of friction. The fibers can be cross-linked, if desired. Woven or non-woven fabrics can be made from such fibers.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
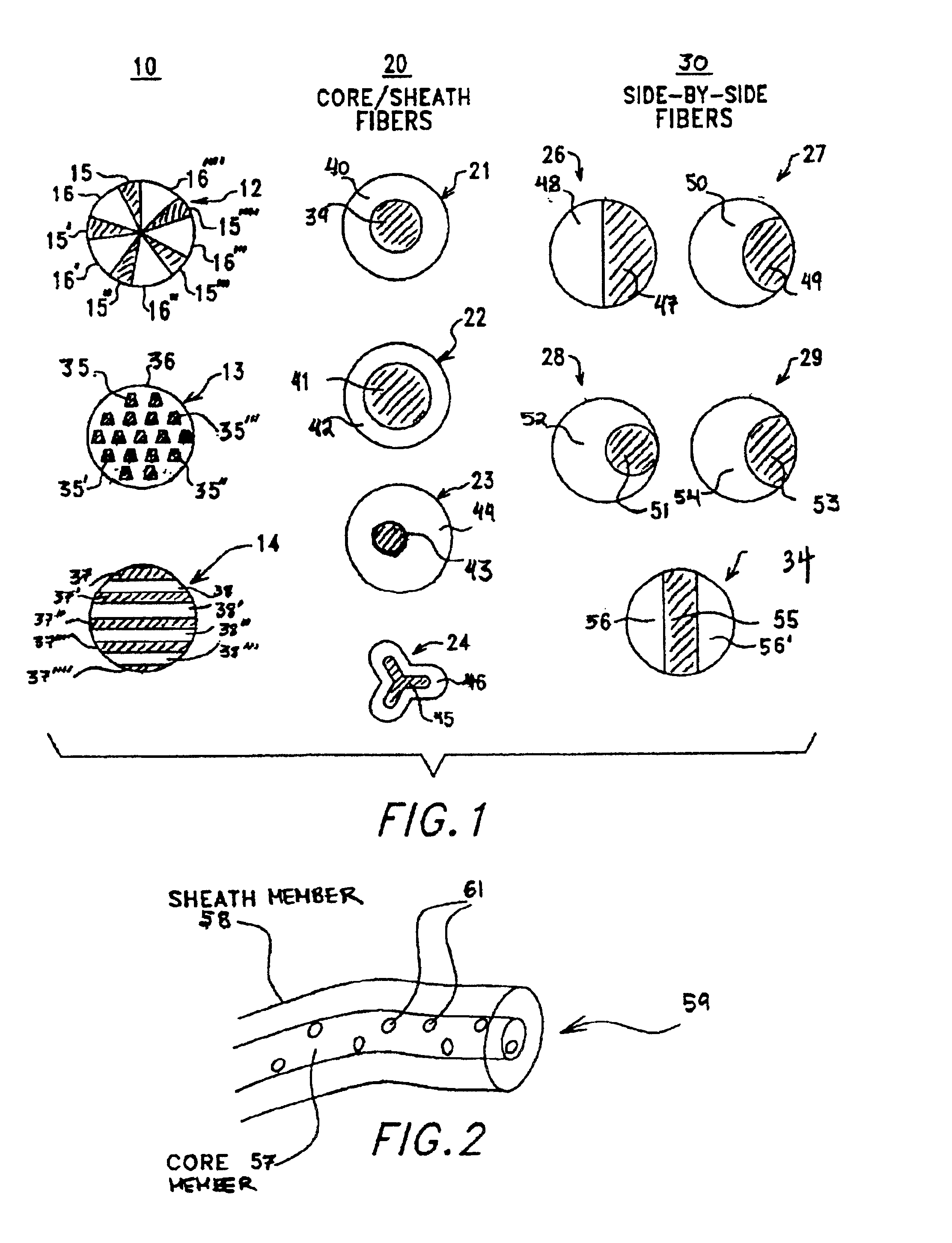
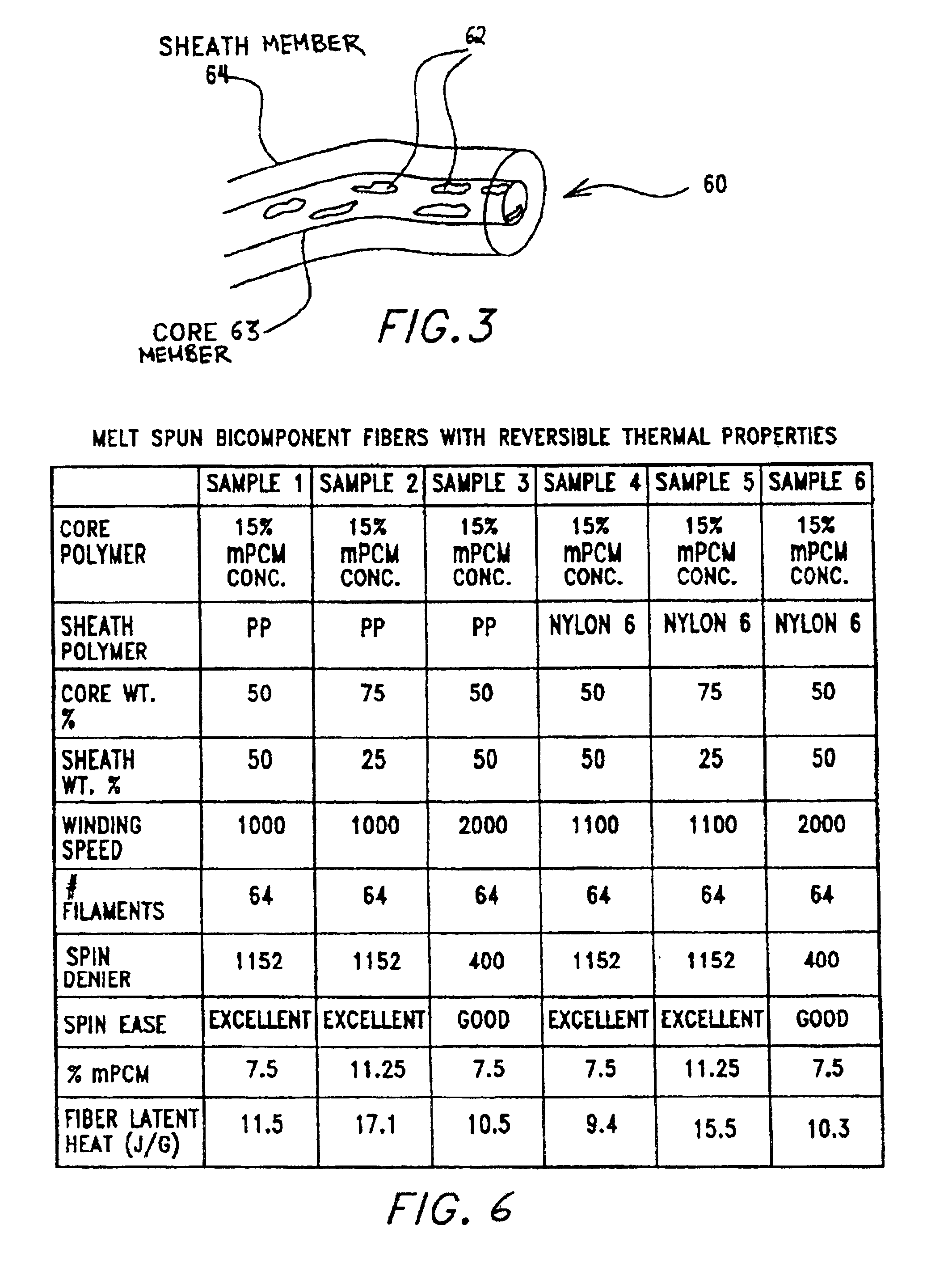
Multi-component fibers having enhanced reversible thermal properties and methods of manufacturing thereof
InactiveUS6855422B2Easy to processImprove propertiesHeat storage plantsWarp knittingMedical productPhase-change material
The invention relates to a multi-component fiber having enhanced reversible thermal properties and methods of manufacturing thereof. The multi-component fiber comprises a fiber body formed from a plurality of elongated members, at least one of the elongated members comprising a temperature regulating material dispersed therein. The temperature regulating material comprises a phase change material. The multi-component fiber may be formed via a melt spinning process or a solution spinning process and may be used or incorporated in various products where a thermal regulating property is desired. For example, the multi-component fiber may be used in textiles, apparel, footwear, medical products, containers and packagings, buildings, appliances, and other products.
Owner:HILLS CO
Nonwovens produced from multicomponent fibers
InactiveUS20080311815A1Reduce blockingReduce fusionNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperPolymer scienceSlurry
A water non-dispersible polymer microfiber is provided comprising at least one water non-dispersible polymer wherein the water non-dispersible polymer microfiber has an equivalent diameter of less than 5 microns and length of less than 25 millimeters. A process for producing water non-dispersible polymer microfibers is also provided, the process comprising: a) cutting a multicomponent fiber into cut multicomponent fibers; b) contacting a fiber-containing feedstock with water to produce a fiber mix slurry; wherein the fiber-containing feedstock comprises cut multicomponent fibers; c) heating the fiber mix slurry to produce a heated fiber mix slurry; d) optionally, mixing the fiber mix slurry in a shearing zone; e) removing at least a portion of the sulfopolyester from the multicomponent fiber to produce a slurry mixture comprising a sulfopolyester dispersion and water non-dispersible polymer microfibers; and f) separating the water non-dispersible polymer microfibers from the slurry mixture. A process for producing a nonwoven article is also provided.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Fibers comprising polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer/polylactic acid polymer or copolymer blends
InactiveUS6905987B2Improve material performancePersonal careSynthetic resin layered productsFiberPolymer chemistry
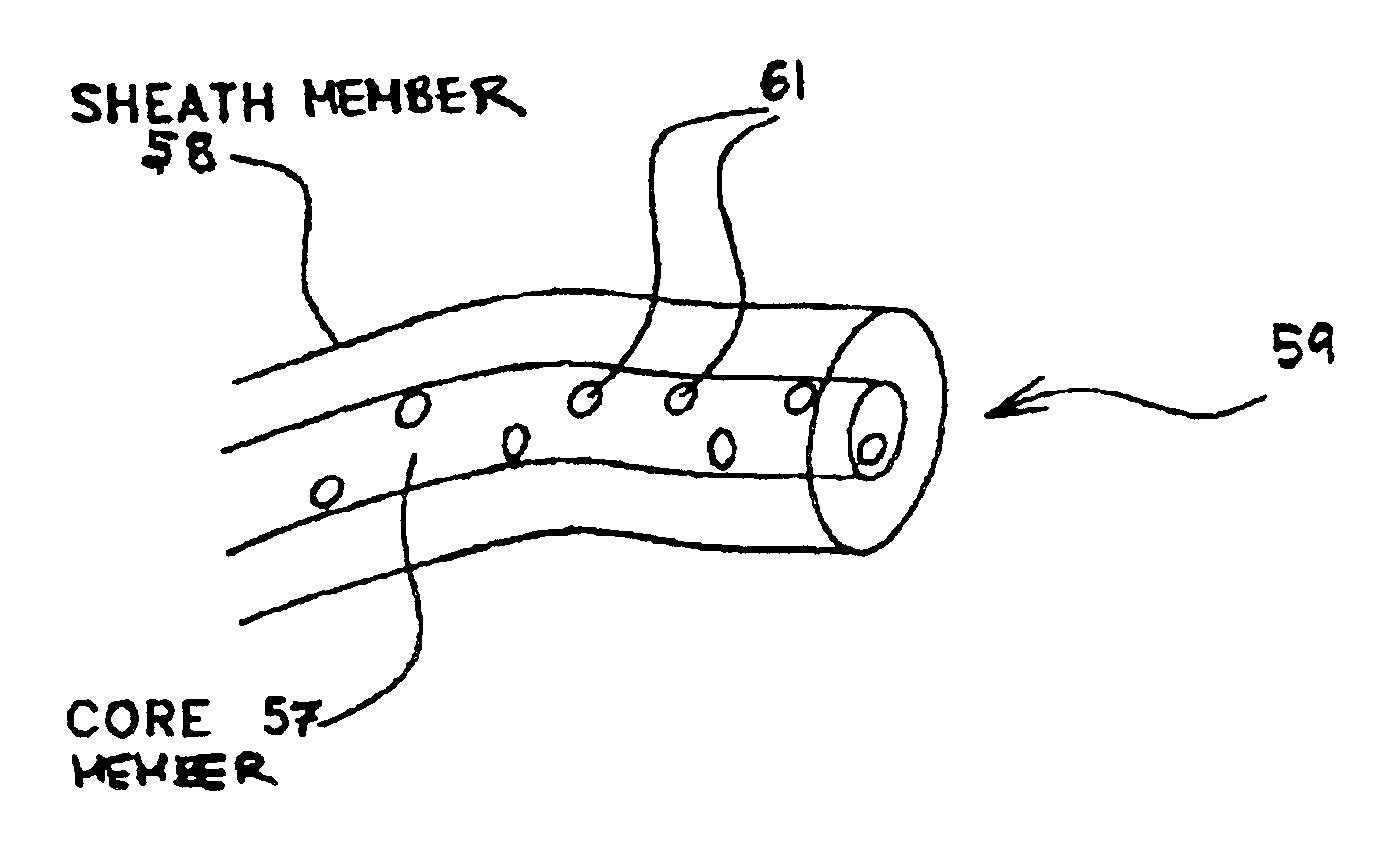
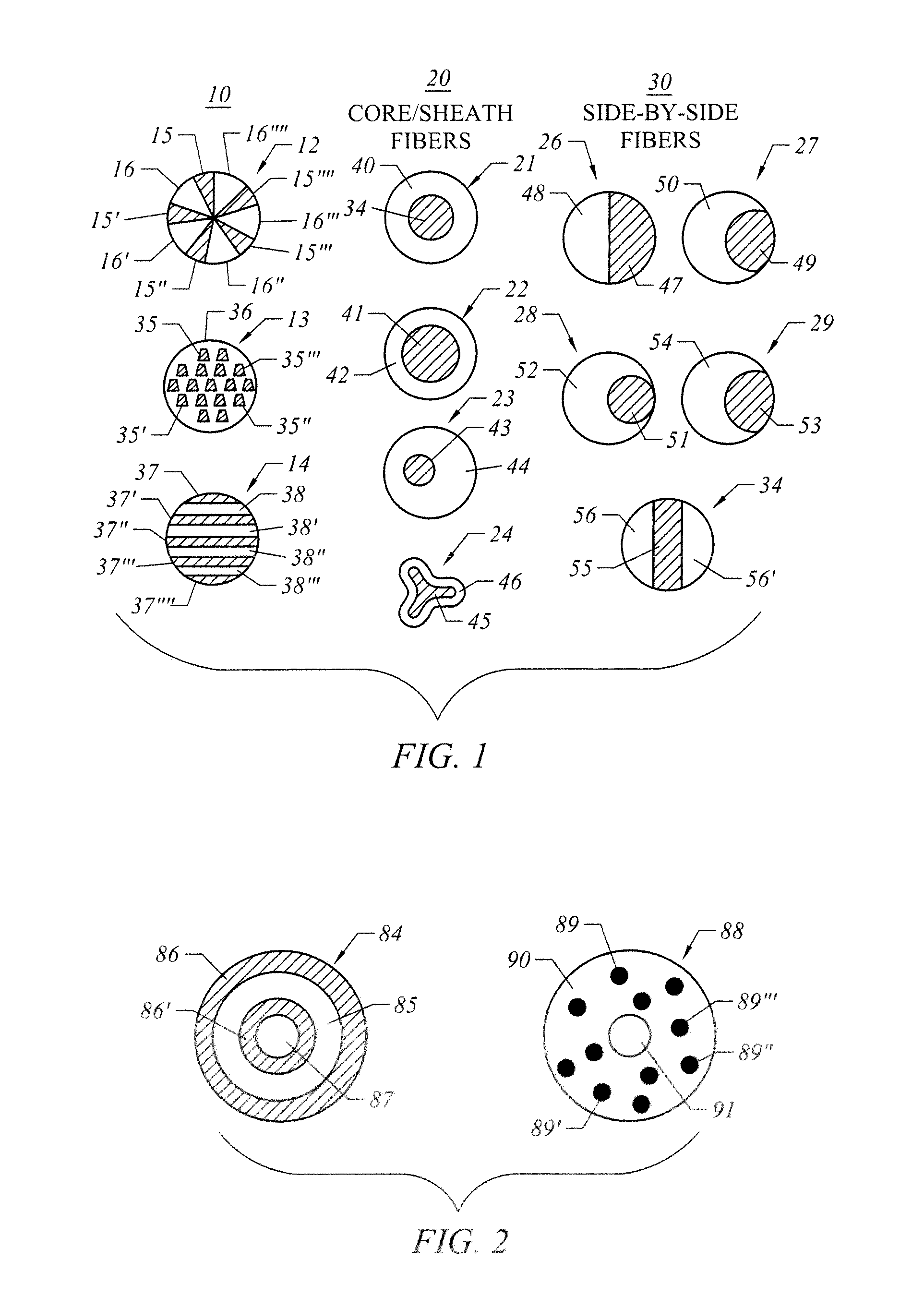
Environmentally degradable melt spun fibers comprising a polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer and a polylactic acid polymer or copolymer are disclosed. A preferred configuration of the present invention is directed to environmentally degradable fibers comprising a sheath / core structure where the core comprises a biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer and the sheath comprises a polymer or copolymer of polylactic acid. Nonwoven webs and disposable articles comprising the environmentally degradable fibers are also disclosed.
Owner:DANIMER IPCO LLC
Low emission polymer compositions
InactiveUS6331264B1Improve stabilityEmission reductionCeramic shaping apparatusMelt spinning methodsMolten stateMolten salt
The invention comprises polymer compositions containing 3-hydroxypropanoxy terminated polymer that exhibit reduced levels of degradation product emissions during processing, by contacting the polymer in the molten state with a melt stable, organic nitrogen-containing stabilizing compound, such as polyamide.
Owner:DUPONT IND BIOSCIENCES USA LLC
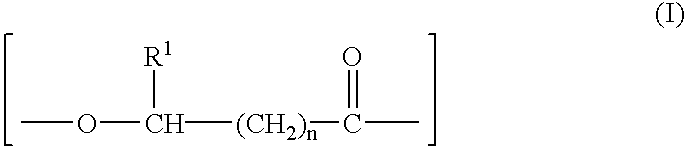
Multi-component fibers having enhanced reversible thermal properties and methods of manufacturing thereof
Multi-component fibers having enhanced reversible thermal properties and methods of manufacturing thereof are described. In one embodiment, a multi-component fiber includes a fiber body formed from a set of elongated members, and at least one of the set of elongated members includes a temperature regulating material having a latent heat of at least 40 J / g and a transition temperature in the range of 22° C. to 40° C. The temperature regulating material provides thermal regulation based on at least one of absorption and release of the latent heat at the transition temperature. The multi-component fiber can be formed via a melt spinning process or a solution spinning process and can be used or incorporated in various products where a thermal regulating property is desired. For example, the multi-component fiber can be used in textiles, apparel, footwear, medical products, containers and packagings, buildings, appliances, and other products.
Owner:HILLS CO
Soft extensible nonwoven webs containing multicomponent fibers with high melt flow rates
InactiveUS20050164587A1Improve acceleration performanceEnable formationFilament/thread formingWoven fabricsFiberPolymer science
The present invention provides nonwoven webs comprising multicomponent fibers that enable the nonwoven web to possess high extensibility. The multicomponent fibers will comprise a first component comprising a polypropylene composition having a melt flow rate of from about 100 to about 2000 grams per 10 minutes and a second component comprising a polymer composition having a melt flow rate lower than the melt flow rate of the first component. The first component comprises at least about 10% of a surface of the multicomponent fiber.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Water-dispersible and multicomponent fibers from sulfopolyesters
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Fabrication of drug loaded biodegradable polymer fibers
InactiveUS20050106211A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsFiberThree dimensional matrix
The invention provides tissue engineering compositions and methods wherein three-dimensional matrices for growing cells are prepared for in vitro and in vivo use. The matrices comprise biodegradable polymer fibers capable of the controlled delivery of therapeutic agents. The spatial and temporal distribution of released therapeutic agents is controlled by use of defined nonhomogeneous patterns of therapeutic agents in the matrices.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Recombinant expressed bioadsorbable polyhydroxyalkonate monofilament and multi-filaments self-retaining sutures
InactiveUS20090112259A1Suture equipmentsMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentMicroorganismBreaking strength
The present invention provides polymers made by genetically engineering microorganisms for making a self-retaining suture. In an embodiment of the present invention the genetically engineering microorganisms synthesize polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) polymers. In an alternate embodiment of the invention, the genetically engineering microorganisms synthesize polybetahydroxybutyrate (PHB) polymers. In an alternative embodiment of the invention, the self-retaining sutures can be made from a copolymer such as polyhydroxybutyratevalerate (PHBV), where the genetically engineering microorganisms produces PHA polymers as the monofilament base material and a different genetically engineering microorganisms produces polyhydroxybutyratevalerate (PHBV) polymers. In various embodiments of the invention, recombinant expressed self-retaining suture materials have a melting point in the range from between approximately 40° C. to approximately 180° C. In various embodiments of the invention, recombinant expressed self-retaining suture materials have extension-to-break strength of between approximately 8% and approximately 42%.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Functional fibers and fibrous materials
InactiveUS20030211799A1Synthetic resin layered productsGlass/slag layered productsFiberPolymer science
Owner:POREX CORP
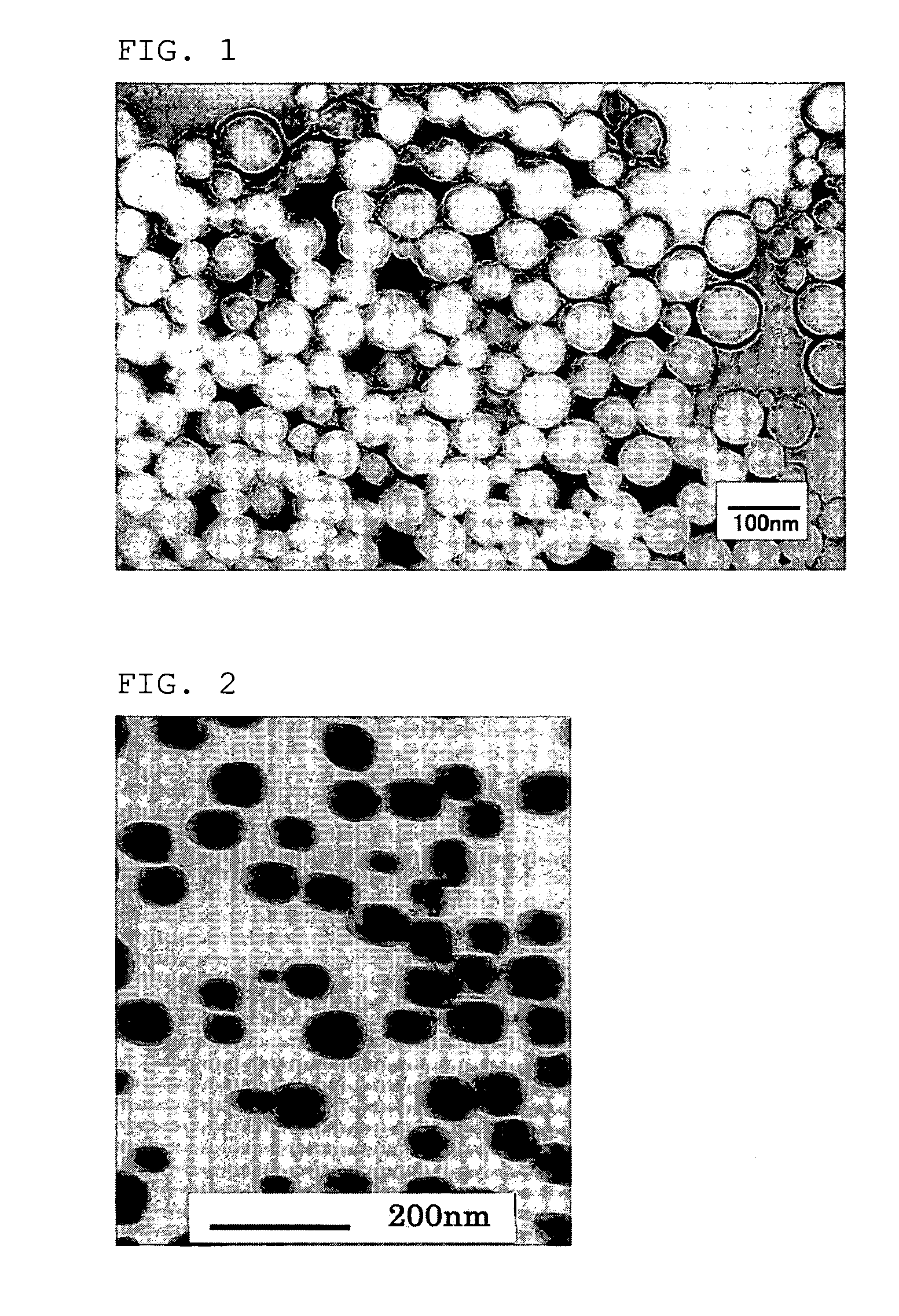
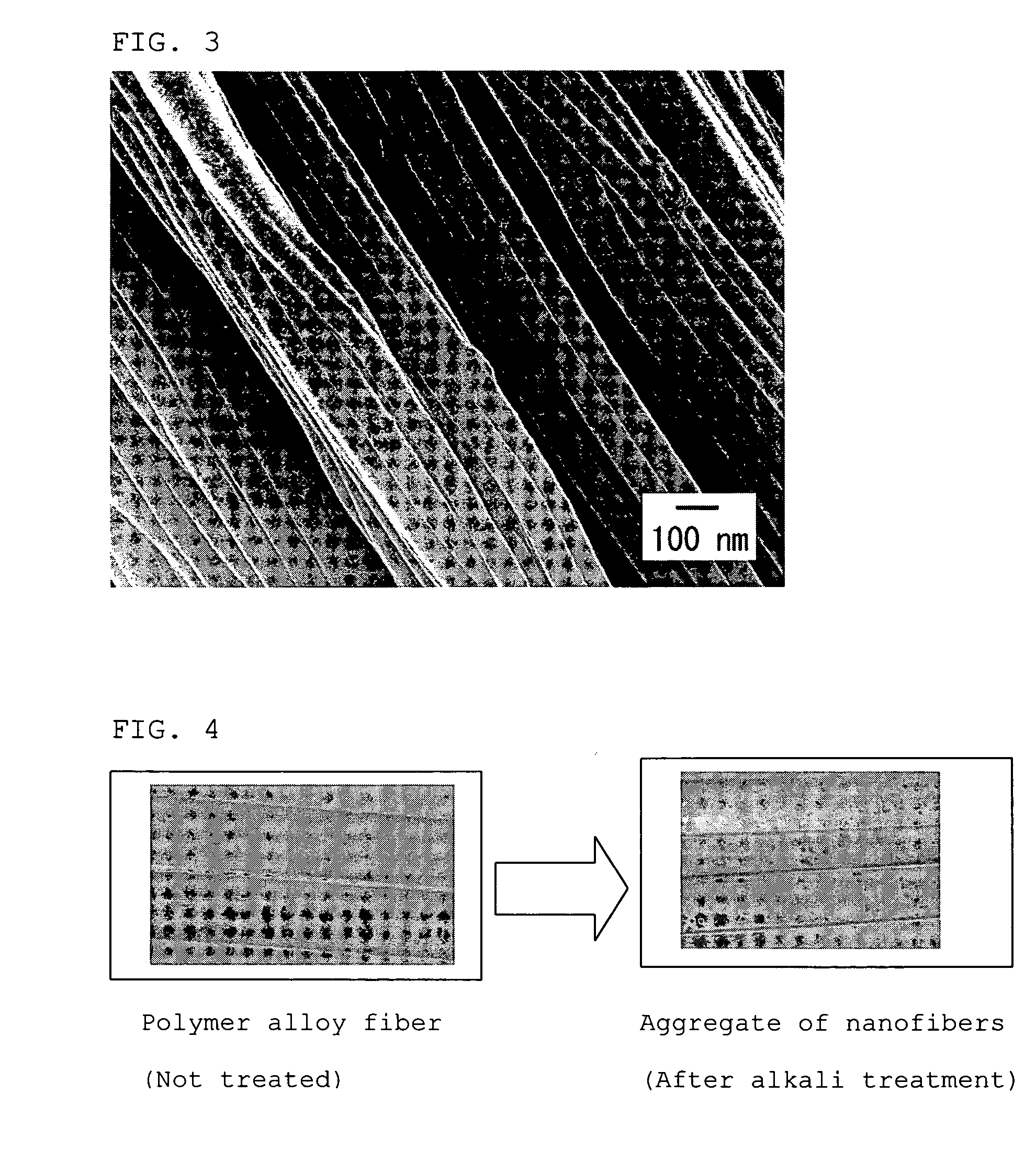
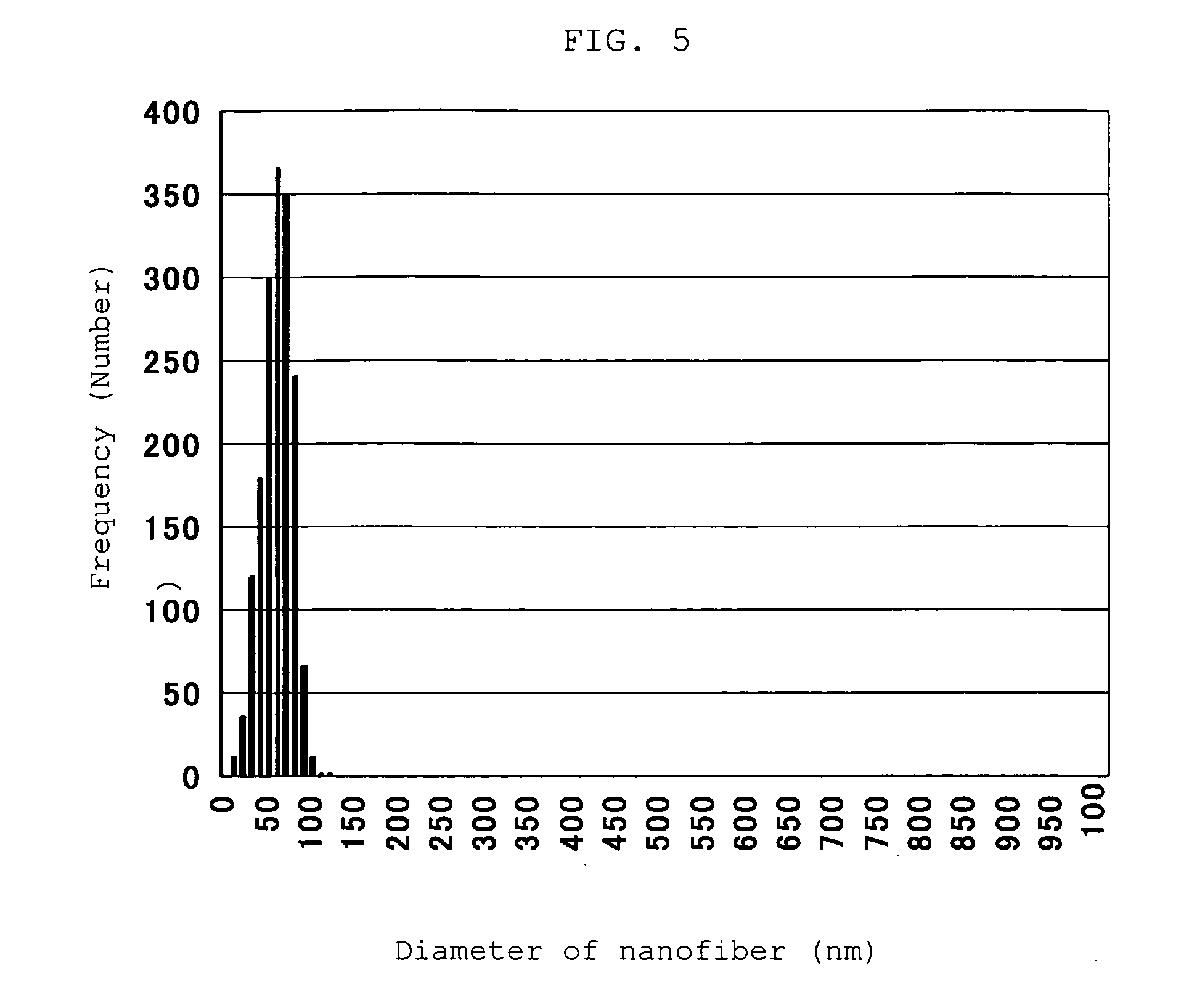
Nanofiber aggregate, polymer alloy fiber, hybrid fiber, fibrous structures, and processes for production of them
InactiveUS20060057350A1Less spreadingWide applicationSynthetic resin layered productsFilament/thread formingPolymer sciencePolymer alloy
The present invention provides an aggregate of nanofibers having less spread of single fiber fineness values that can be used in wide applications without limitation to the shape and the kind of the polymer, and a method for manufacturing the same. The present invention is an aggregate of nanofibers made of a thermoplastic polymer having single fiber fineness by number average in a range from 1×10−7 to 2×10−4 dtex and single fibers of 60% or more in fineness ratio have single fiber fineness in a range from 1×10−7 to 2×10−4 dtex.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Fabrication of drug loaded biodegradable polymer fibers
InactiveUS6858222B2Limit maximum numberOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsFiberControlled release
The invention provides tissue engineering compositions and methods wherein three-dimensional matrices for growing cells are prepared for in vitro and in vivo use. The matrices comprise biodegradable polymer fibers capable of the controlled delivery of therapeutic agents. The spatial and temporal distribution of released therapeutic agents is controlled by use of defined nonhomogeneous patterns of therapeutic agents in the matrices.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Stretchable composite sheets and processes for making
This invention relates to an improved method for preparing stretchable multiple-component bonded composite sheets which involves bonding a fibrous layer of spirally-crimpable multiple-component continuous filaments or staple fibers to one or more non-spirally-crimpable layers using an array of intermittent mechanical, chemical, or thermal bonds, and heating the bonded composite to activate the spiral crimp of the fibers in the spirally-crimpable layer. Multi-layer nonwoven fabrics prepared according to the method of the current invention have an improved combination of strength, aesthetics, stretch-recovery properties, and textile hand and drape compared to multiple-component nonwoven fabrics known in the art.
Owner:THE LYCRA CO LLC
Polymeric fibers and articles made therefrom
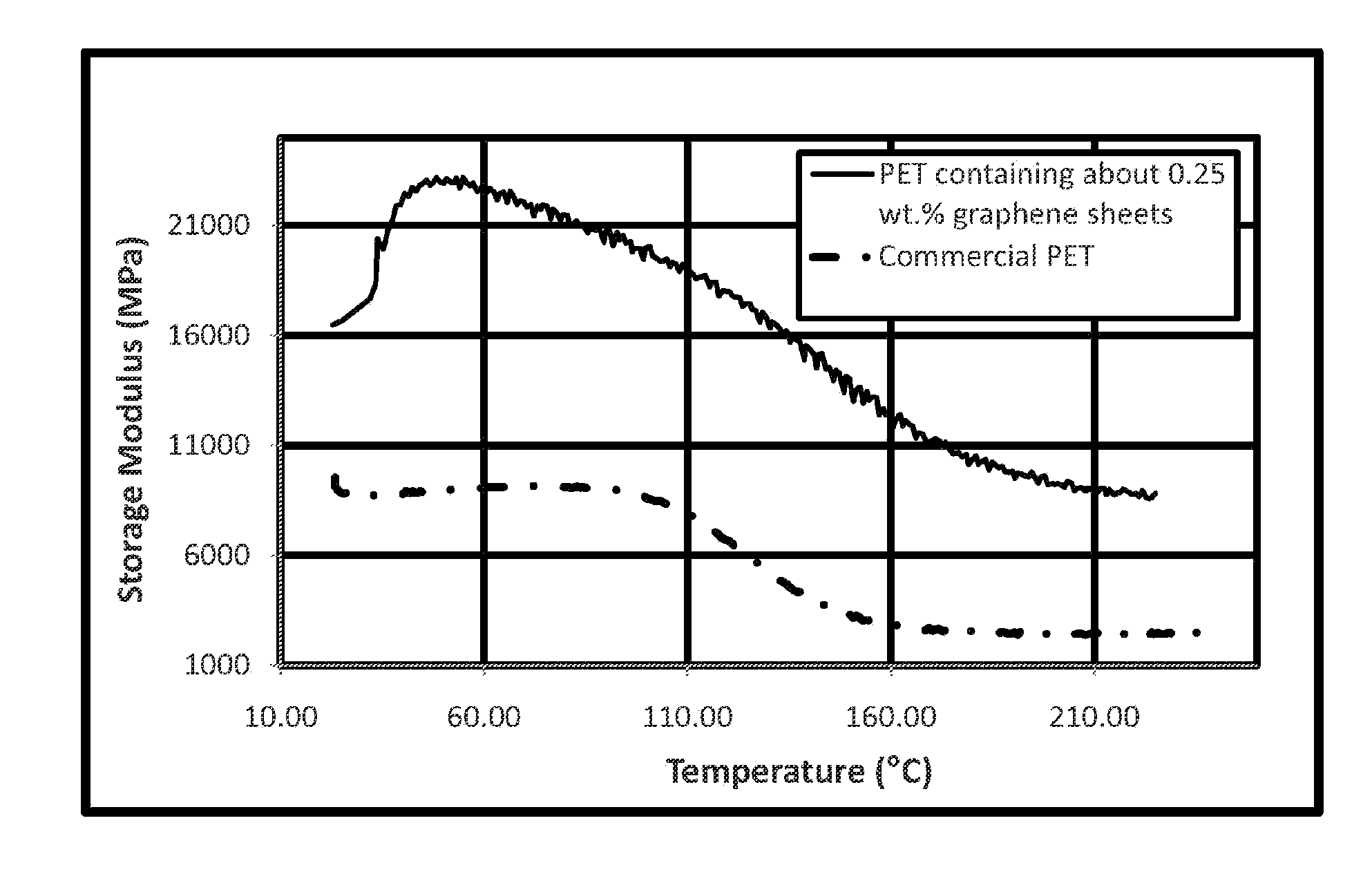
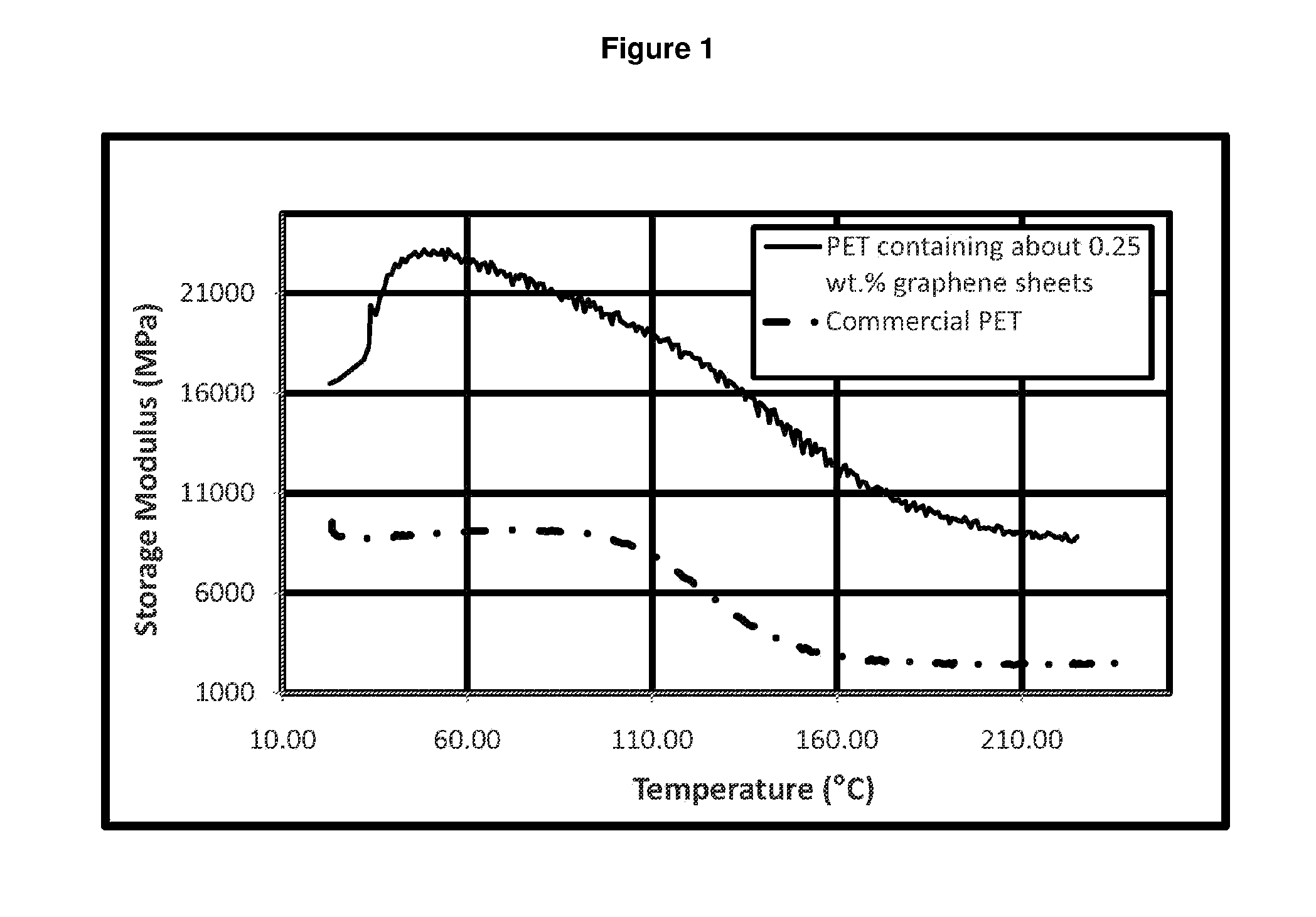
InactiveUS20120244333A1Electric discharge heatingMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentPolyesterYarn
Fibers described herein comprise a composition including a polymer and graphene sheets. The fibers can be further formed into yarns, cords, and fabrics. The fibers can be in the form of polyamide, polyester, acrylic, acetate, modacrylic, spandex, lyocell fibers, and the like. Such fibers can take on a variety of forms, including, staple fibers, spun fibers, monofilaments, multifilaments, and the like.
Owner:VORBECK MATERIALS CORP +1
Spin-printing of electronic and display components
InactiveUS20050089679A1Electrolytic capacitorsFinal product manufactureDielectricElectrical conductor
The present invention is directed to a process for printing conductors, insulators, dielectrics, phosphors, emitters, and other elements that may be for electronics and display applications. The present invention also relates to viscoelastic compositions used in this printing process. The present invention further includes devices made therefrom.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Olefin block compositions for heavy weight stretch fabrics
InactiveUS20080299857A1Improved ratio of stretch to growthHigh temperature toleranceMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentWoven fabricsSquare yardHeavy weight
Heavy weight stretch fabrics comprising ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer are described. The fabric often has a weight of at least 10 ounces per square yard measured according to ASTM 3776 and has a stretch of at least 10 percent measured according to ASTM D3107. These fabrics exhibit excellent chemical, resistance (for example chlorine or caustic resistance) and durability, that is they retain their shape and feel over repeated exposure to processing conditions, such as stone-washing, dye-stripping, PET-dyeing and the like, and industrial laundry conditions.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Taggant fibers
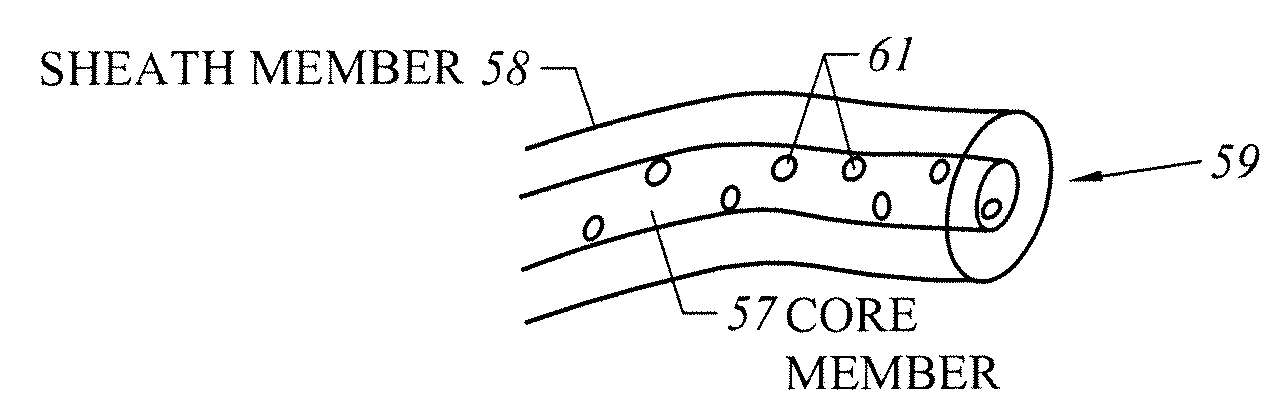
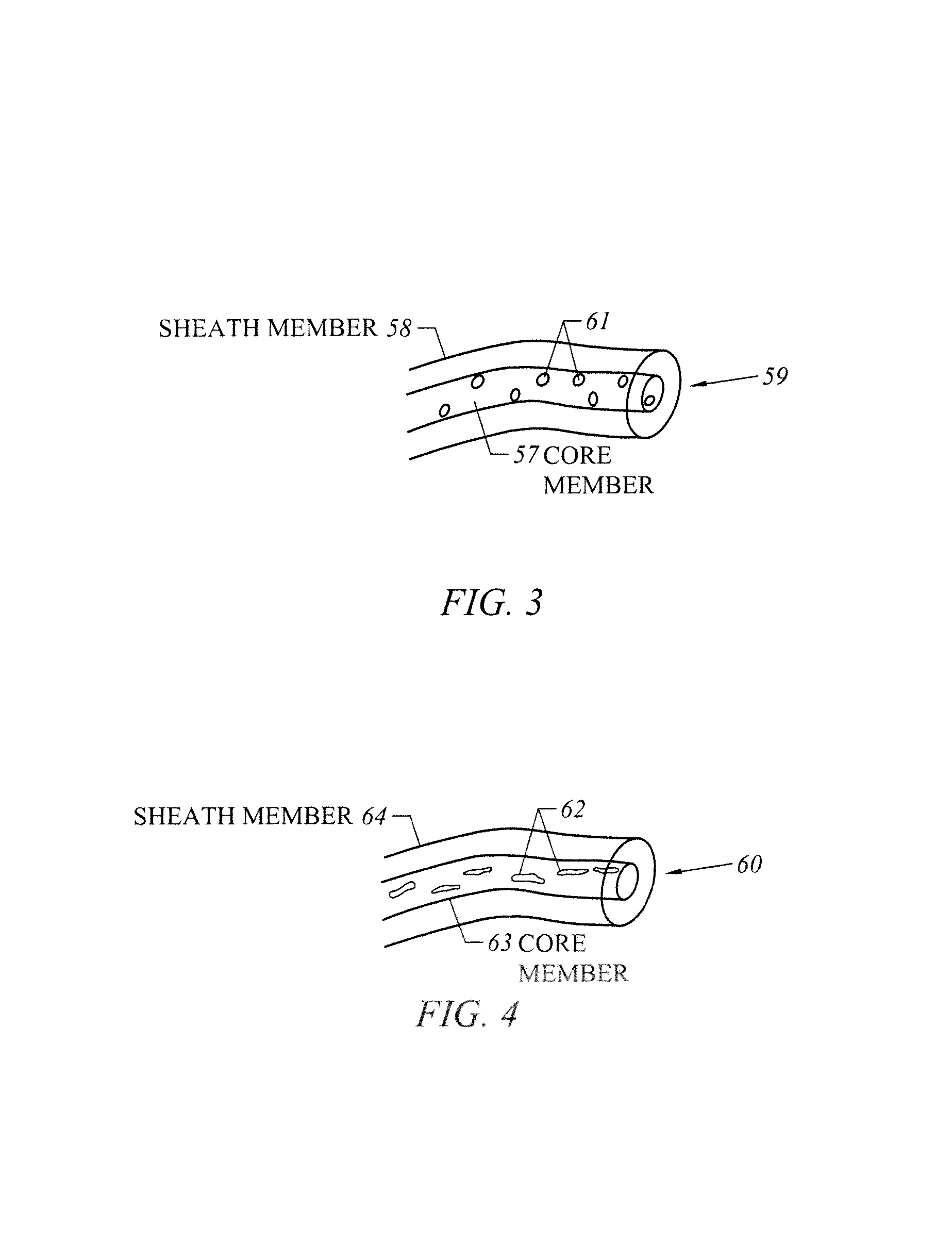
InactiveUS20050227068A1Less noticeable in useLikely to degradeMarking textilesFilament/thread formingMaterials sciencePolymer
Multicomponent fibers are provided that include a plurality of coextruded polymeric components arranged in discrete structured domains. The polymer domains have one or more identifying characteristics that can be varied to form a plurality of different identifying patterns. A plurality of islands in the sea fibers can be provided, the plurality of fibers including two or more subsets of fibers, each subset comprising a uniquely identifiable cross sectional pattern of island domains, each pattern being formed from an array comprising a predetermined number of island domains in predetermined locations within the array, wherein each pattern is determined by classifying individual island domains within the array as present or absent from the pattern. The plurality of fibers can be meltspun simultaneously to form a filament yarn or tow.
Owner:FIBER INNOVATION TECH
Composite material comprising oriented carbon nanotubes in a carbon matrix and process for preparing same
Fiber spinning of two polymer compositions wherein one of the compositions contains carbon nanotubes produces structures such as fibers, ribbons, yarns and films of carbon nanotubes. The polymers are removed and stabilization of the carbon nanotube material is achieved by post-spinning processes. The advances disclosed herein enable the carbon nanotube composites to be used in actuators, supercapacitors, friction materials and in devices for electrical energy harvesting.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Water stable fibers and articles comprising starch, and methods of making the same
Water stable fibers and articles made therefrom are formed from a thermoplastic composition comprising destructured starch, polyhydric alcohol, triglyceride, and optionally acid. Processes for making water stable compositions may comprise melt extruding a mixture of destructured starch, polyhydric alcohol, triglyceride, and optionally acid, to form an extrudate, and heating the mixture, extrudate, or both to provide a water stable article.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method of making regenerated cellulose microfibers and absorbent products incorporating same
ActiveUS20080173419A1High yieldLow costNon-fibrous pulp additionElectric discharge heatingPolymer sciencePersonal Care Product
A method of making regenerated cellulose microfibers includes forming segmented fibers with multiple longitudinally-extending segments of slightly different composition such that there is defined splittable interfaces between juxtaposed segments of the fibers which are then split into microfibers at yields of greater than 50%. Fibers so produced may be incorporated into absorbent sheet with other papermaking fibers to provide strength, softness, bulk and absorbency to tissue, towel, and personal care products.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
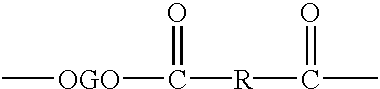
Copolyesters and fibrous materials formed therefrom
InactiveUS20020132960A1Deep dyeabilityGood printabilityMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentArtificial filaments from cellulose derivativesCelluloseFiber
This invention relates to binary blends of cellulose esters and aliphatic-aromatic copolyesters, cellulose esters and aliphatic polyesters as well as ternary blends of cellulose esters and / or aliphatic polyesters and / or aliphatic-aromatic copolyesters and / or polymeric compounds as well as fibers, nonwovens, molded objects, and films prepared therefrom.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Composite material comprising oriented carbon nanotubes in a carbon matrix and process for preparing same
Fiber spinning of two polymer compositions wherein one of the compositions contains carbon nanotubes produces structures such as fibers, ribbons, yarns and films of carbon nanotubes. The polymers are removed and stabilization of the carbon nanotube material is achieved by post-spinning processes. The advances disclosed herein enable the carbon nanotube composites to be used in actuators, supercapacitors, friction materials and in devices for electrical energy harvesting.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Preparation method of core-shell structured synthetic polymer-natural polymer composite fiber
InactiveCN102817105ASimple and fast operationMild reaction conditionsConjugated cellulose/protein artificial filamentsFilament/thread formingFiberPolymer science
The invention discloses a preparation method of a core-shell structured synthetic polymer-natural polymer composite fiber, and the method comprises the steps of: (1) selecting one or several of synthetic polymers to dissolve in a solvent, and conducting stirring until complete dissolution; (2) selecting a natural polymer to dissolve in a solvent, or adding a spinning assistant, and carrying out stirring until complete dissolution; and (3) taking the solution prepared in step (1) as an outer tube spinning solution, adopting the solution prepared in step (2) as an inner tube spinning solution, injecting them into the inner tube and the outer tube of a coaxial spinneret, and performing coaxial electrospinning at room temperature. The core-shell structured nano-fiber prepared by the invention selects the synthetic polymer as the shell layer, and can inhibit water molecules from penetrating the natural polymer as the core layer. The natural polymer as the core layer can more effectively encapsulate active substances to avoid inactivation of the active substances in the presence of an organic solvent, so that the core-shell structured composite fiber can play a good drug sustained release role in the drug carrier field, and an integral activity can be maintained.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Three-dimensional net-like structure, and method and device for producing three dimensional net-like structure
ActiveUS7625629B2Efficient use ofIncrease rangeWeft knittingSynthetic resin layered productsVolumetric Mass DensityEngineering
A method of and an apparatus for manufacturing a three-dimensional netted structure which is capable of rendering it unnecessary to carry out a finishing operation in a later stage, improving the degree of straightness of the side surfaces of the netted structure, meeting a demand for finishing the netted structure to modified shapes, and improving the durability of the netted structure. A three-dimensional netted structure (1) using thermoplastic resin as a raw material or a main raw material is characterized by a three-dimensional plate type netted structure, in which a plurality of filaments are helically and randomly entangled and partly and thermally bonded together. The density of any of at least three surfaces or four surfaces on the outer periphery of the three-dimensional netted structure is preferably relatively higher than the density of the other portion excluding these surfaces, and flaked or chipped PET bottles are used as a raw material or a main raw material for thermoplastic resin, such PET bottles being directly crushed and then melted to provide flakes, suiting to recycling promoting age, working well in waste disposal cost reduction, the uses of the three-dimensional netted structure (1) including, chiefly, shock absorbing materials, cushioning materials, and sound-absorbing materials.
Owner:C ENG CO LTD
Production of submicron diameter fibers by two-fluid electrospinning process
InactiveUS20060213829A1Conjugated cellulose/protein artificial filamentsElectro-spinningHollow fibreNanowire
Electrospinning of materials that are difficult or impossible to process into nanofibers by conventional fiber-forming techniques or by electrospinning are prepared by an electrospinning procedure which uses an electrospinnable outer “shell” fluid around an inner “core” fluid, which may or may not be electrospinnable, to form nanofibers of the inner core fluid having a core / shell morphology. The resulting shell around the nanofiber can remain in place or be removed during post-processing with the core of the fiber remaining intact. The dual-fluid electrospinning process can produce core fibers having diameters less than 100 nm, insulated nanowires, as well as tough, bio-compatible silk fibers. Alternatively, the core can be removed leaving a hollow fiber of the shell fluid.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
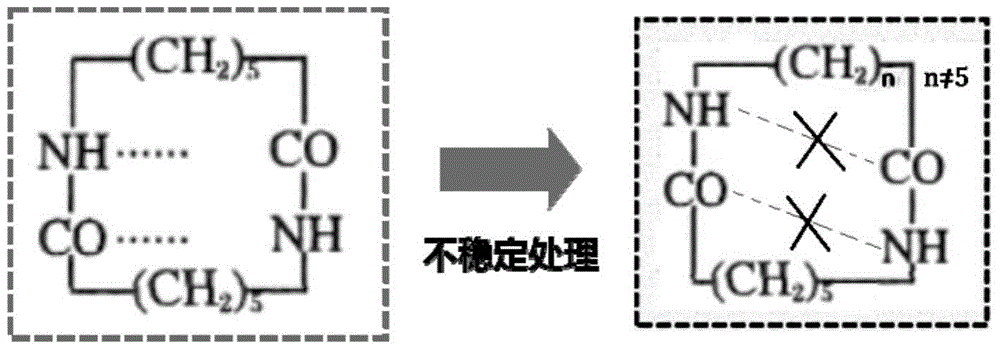
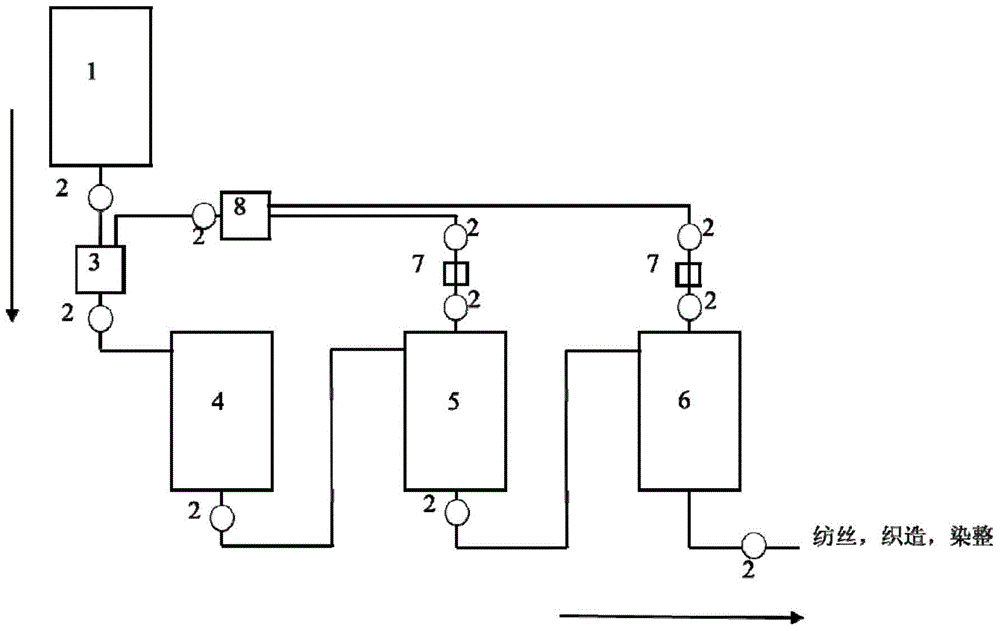
Nylon 6 polymerization method and direct spinning method of melt of polymer obtained with nylon 6 polymerization method
ActiveCN105669969AIncrease profitReduce manufacturing costFlame-proof filament manufactureHollow filament manufacturePolymer sciencePolyamide
The invention relates a nylon 6 polymerization method and a direct spinning method of a melt of a polymer obtained with the nylon 6 polymerization method. A polyamide 6 prepolymer is prepared at the low temperature, the content of oligomers in the melt is controlled in advance, polymerization is completed before a large quantity of cyclic oligomers are generated with a condensation polymerization dynamic strengthening method, a nylon 6 polymer melt with certain molecular weight is acquired, the content of extracts in the product is smaller than or equal to 1.5 wt%, and the content of cyclic dipolymers is smaller than or equal to 0.2wt%; then, direct melt spinning forming is performed after condensation polymerization dynamic strengthening ends. The process is simple, energy consumption is further reduced while the utilization rate of caprolactam is increased, the obtained melt can be directly used for melt spinning, high-capacity large-scale production is easy to realize, a modifier can be added in the polymerization process, flexible production of nylon 6 is realized, and the nylon 6 can be applied to fibers for clothes, industrial filaments, engineering plastics and other fields.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HENGYI PETROCHEMICAL RES INST CO LTD
Polyether ester elastomer comprising polytrimethylene ether ester soft segment and trimethylene ester hard segment
Owner:DUPONT IND BIOSCIENCES USA LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com