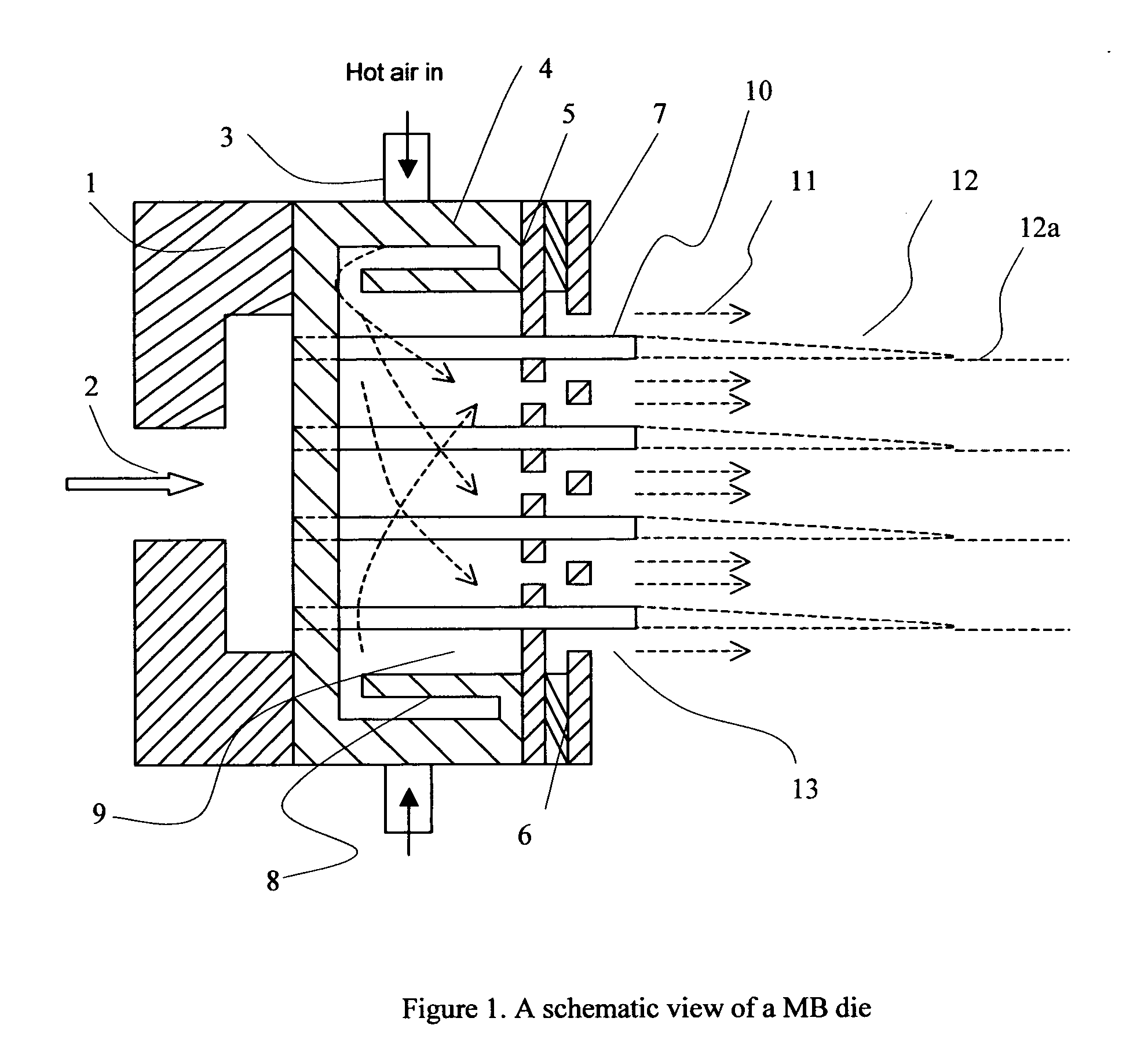
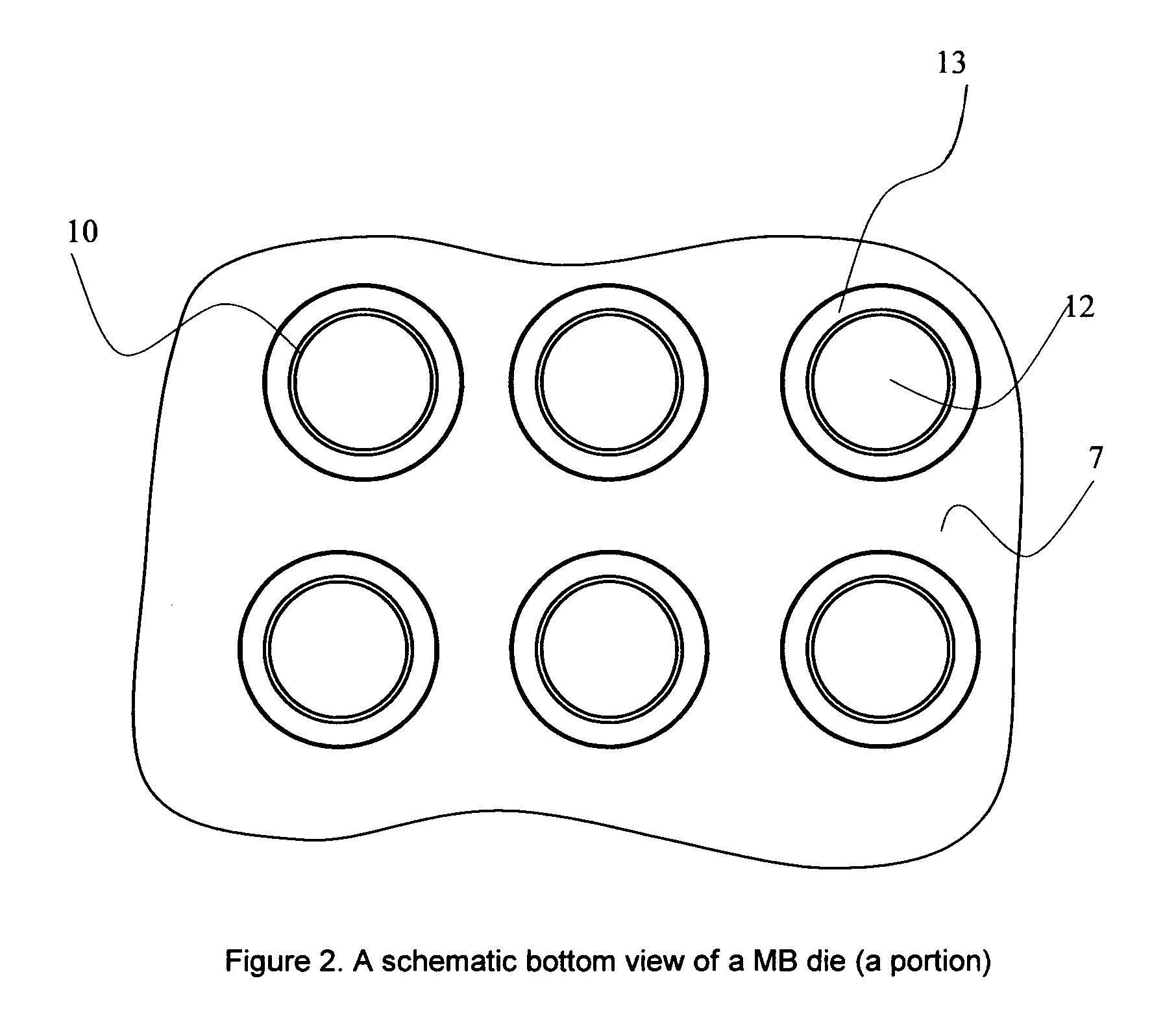
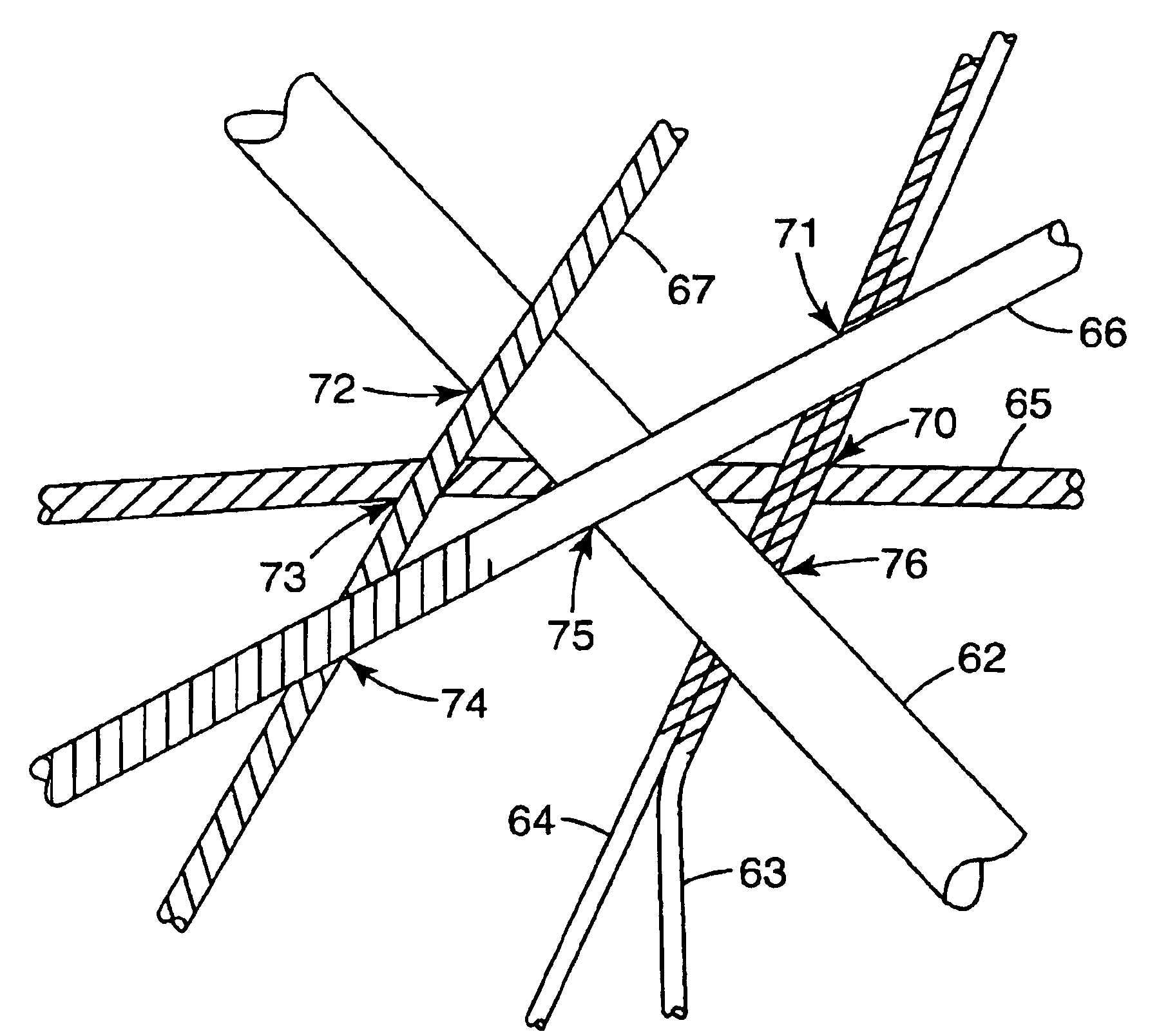
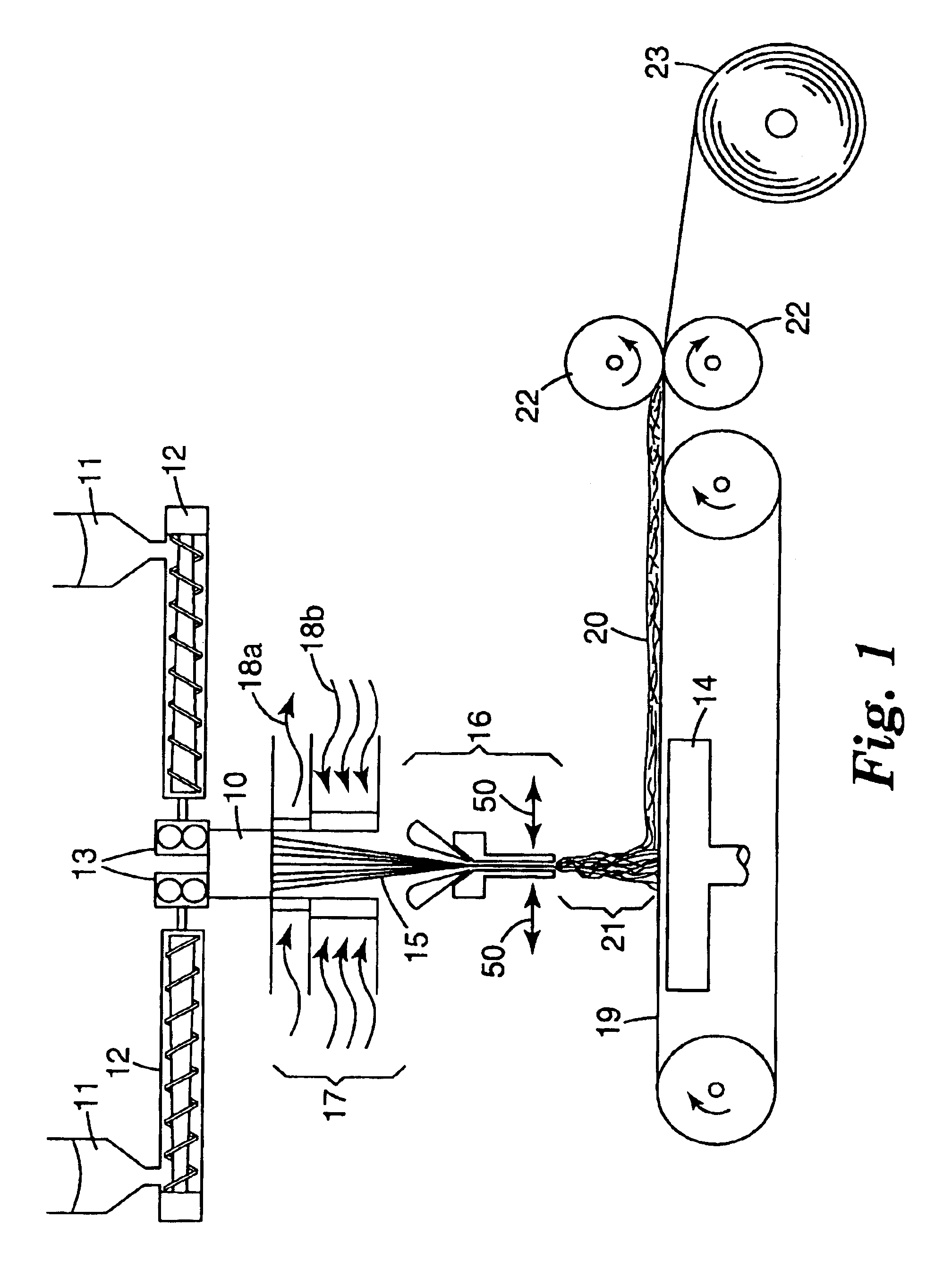
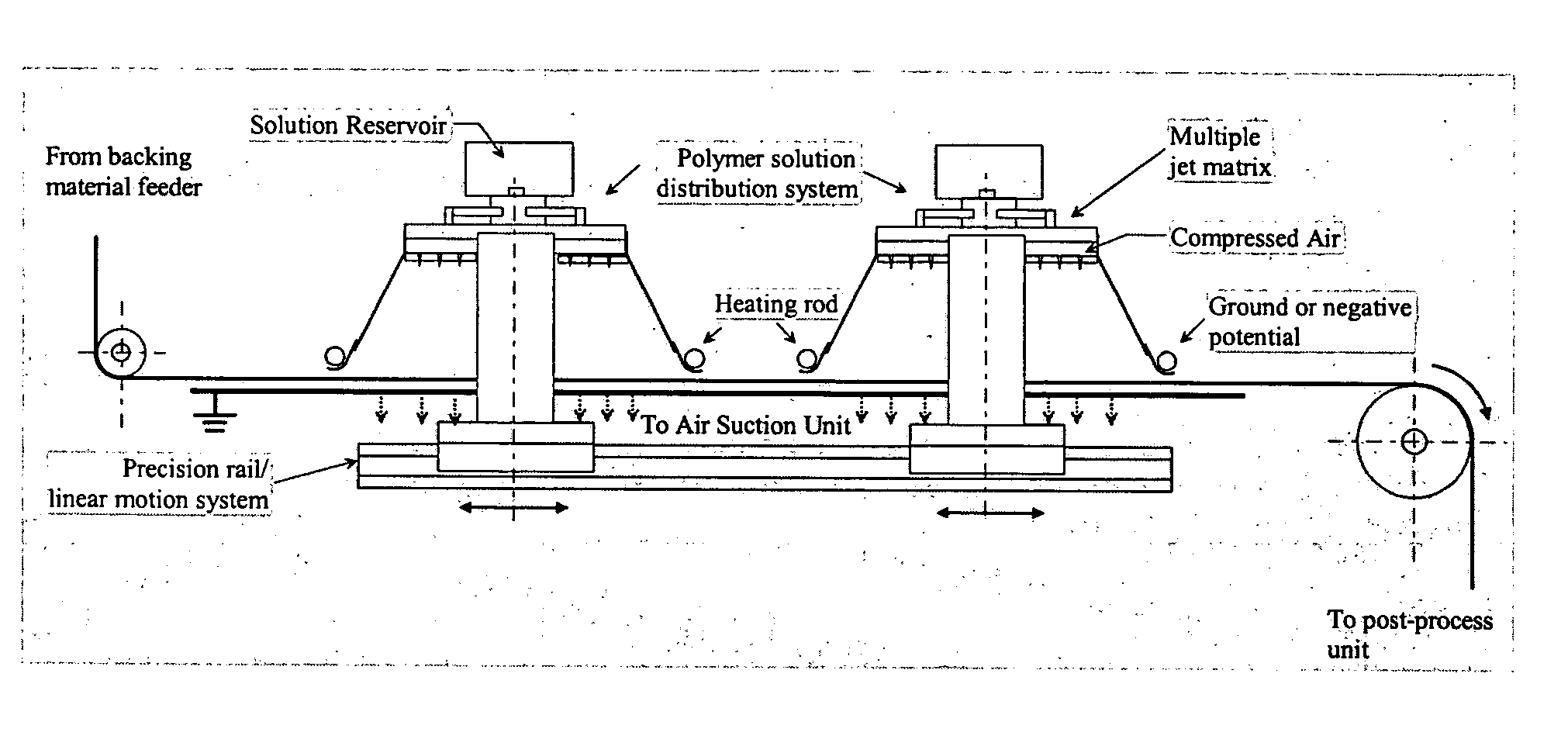
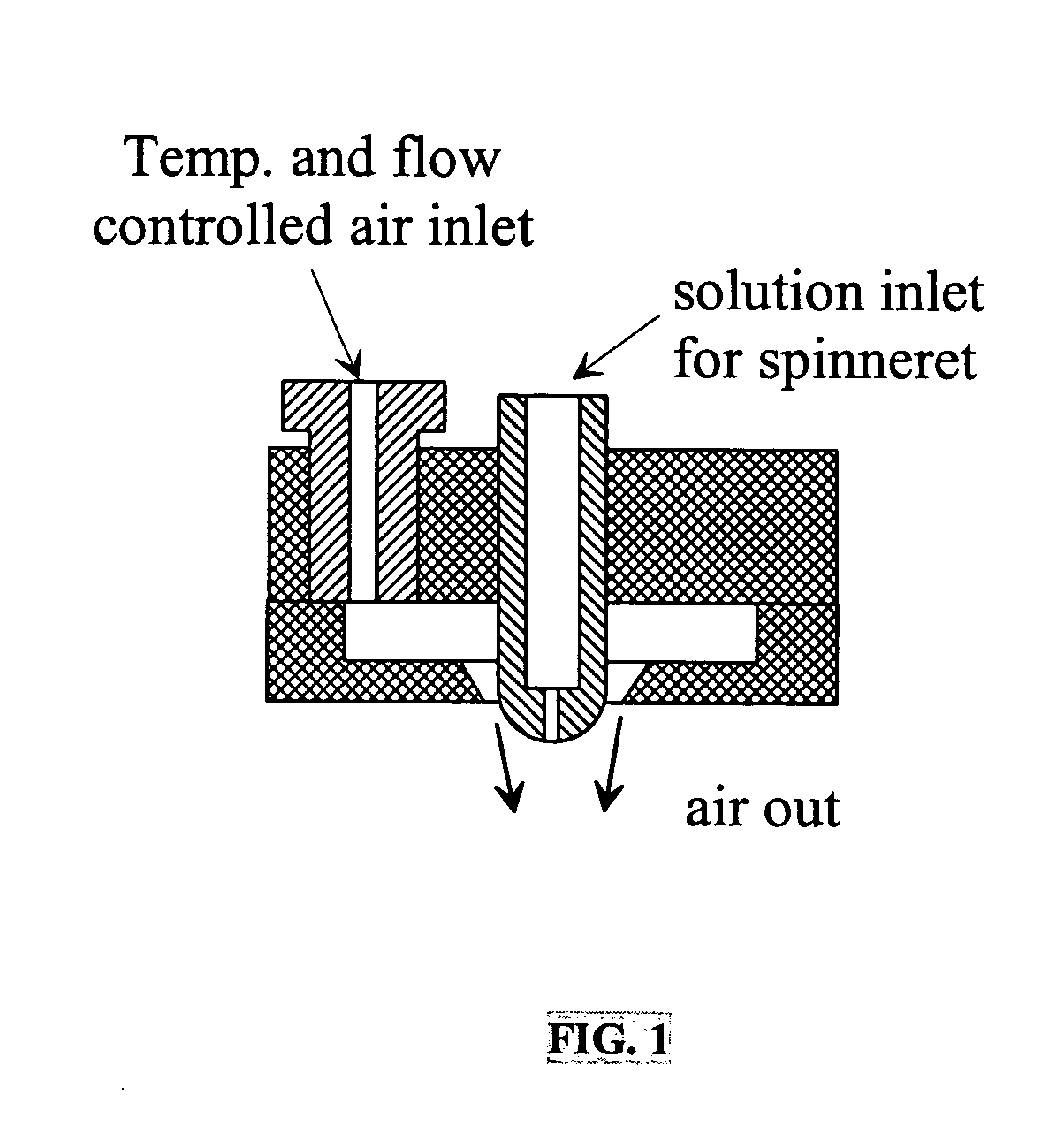
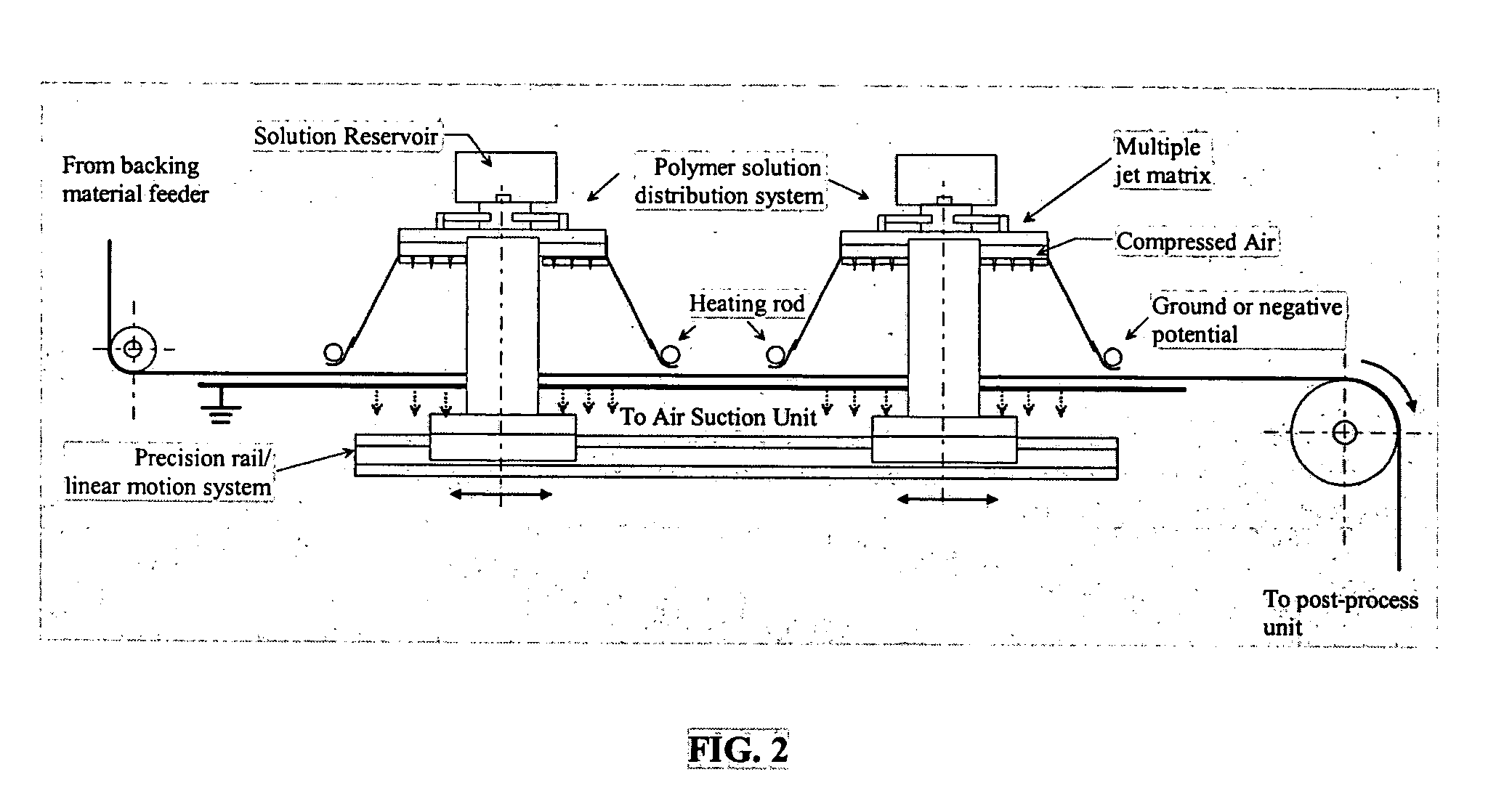
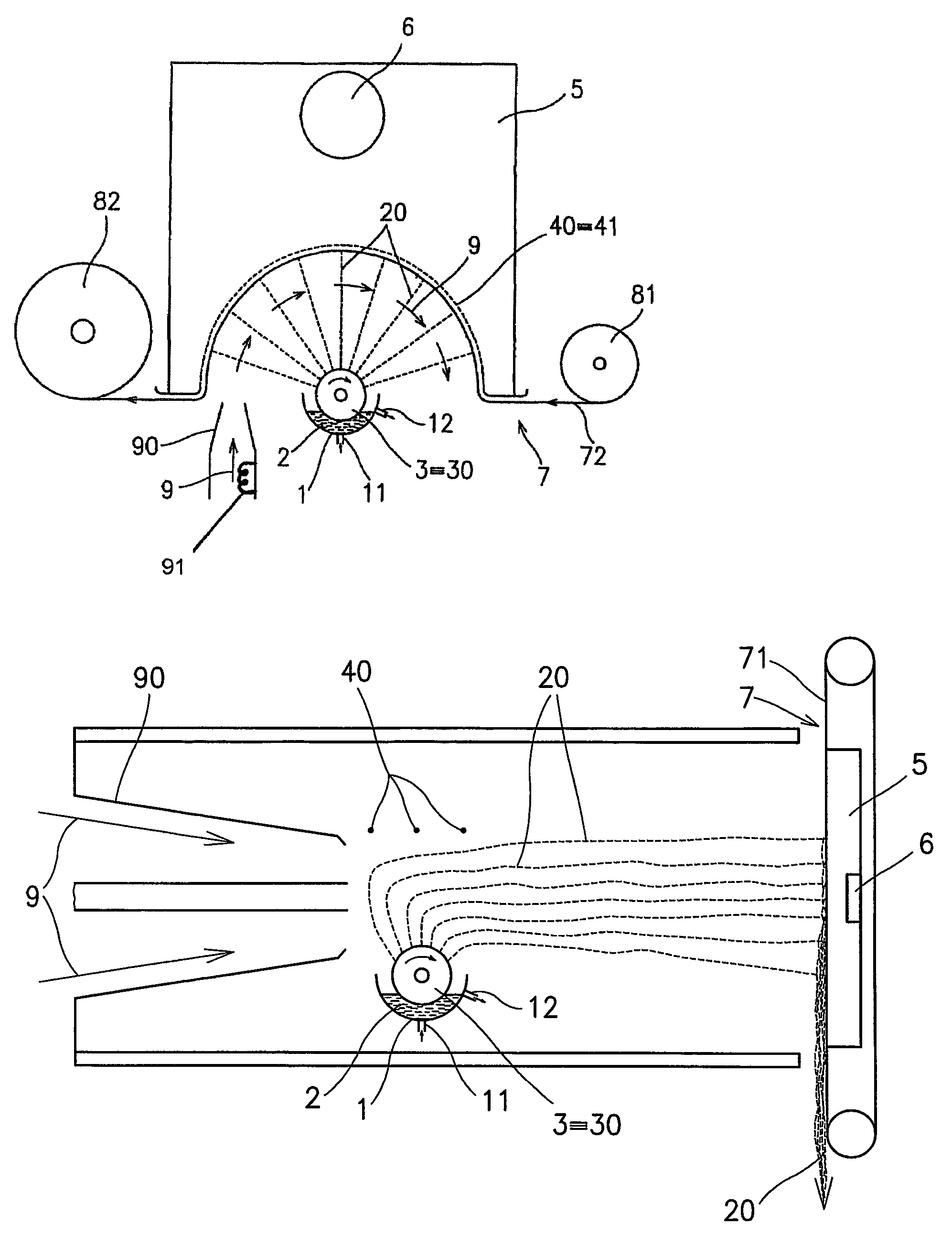
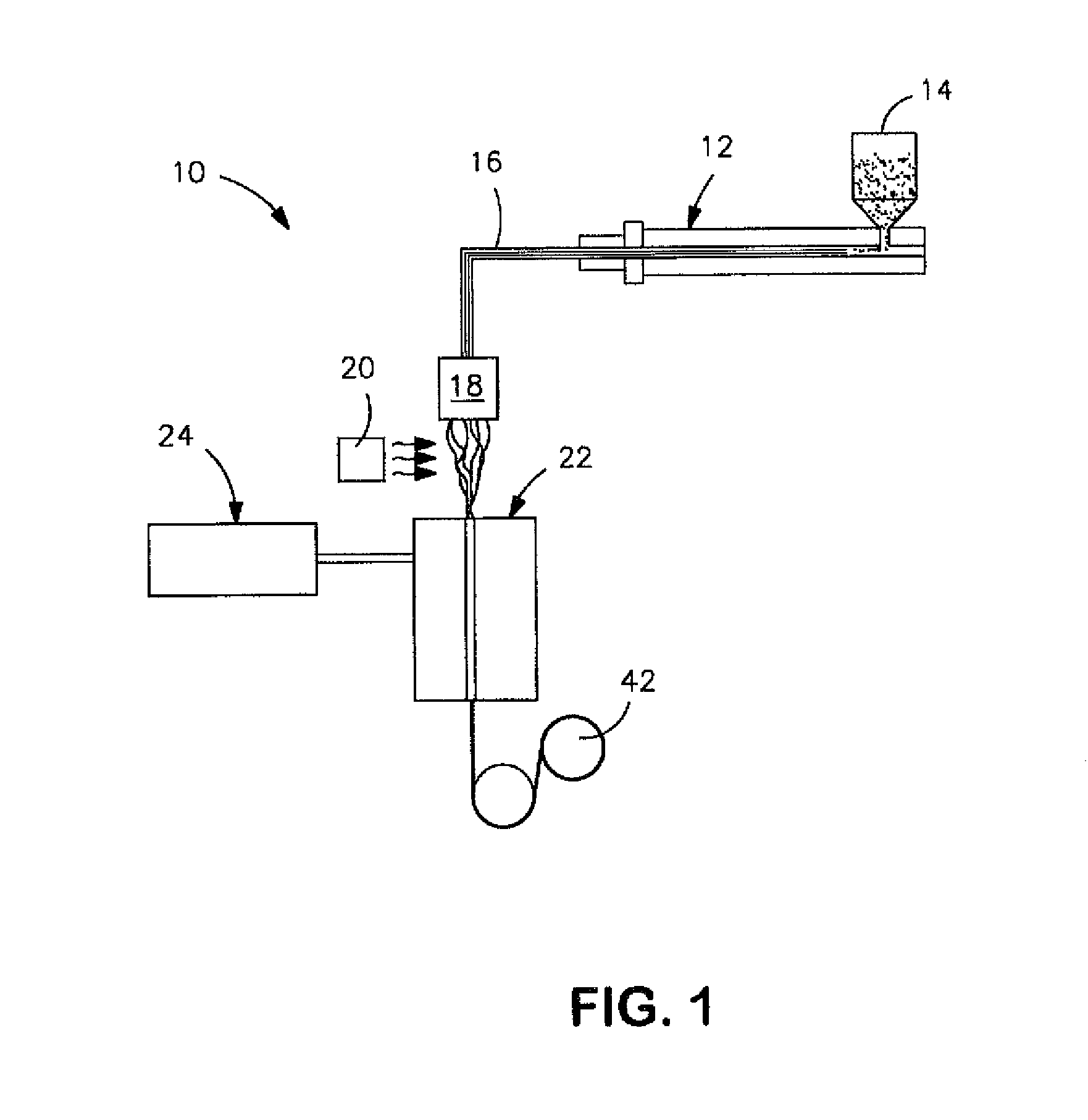
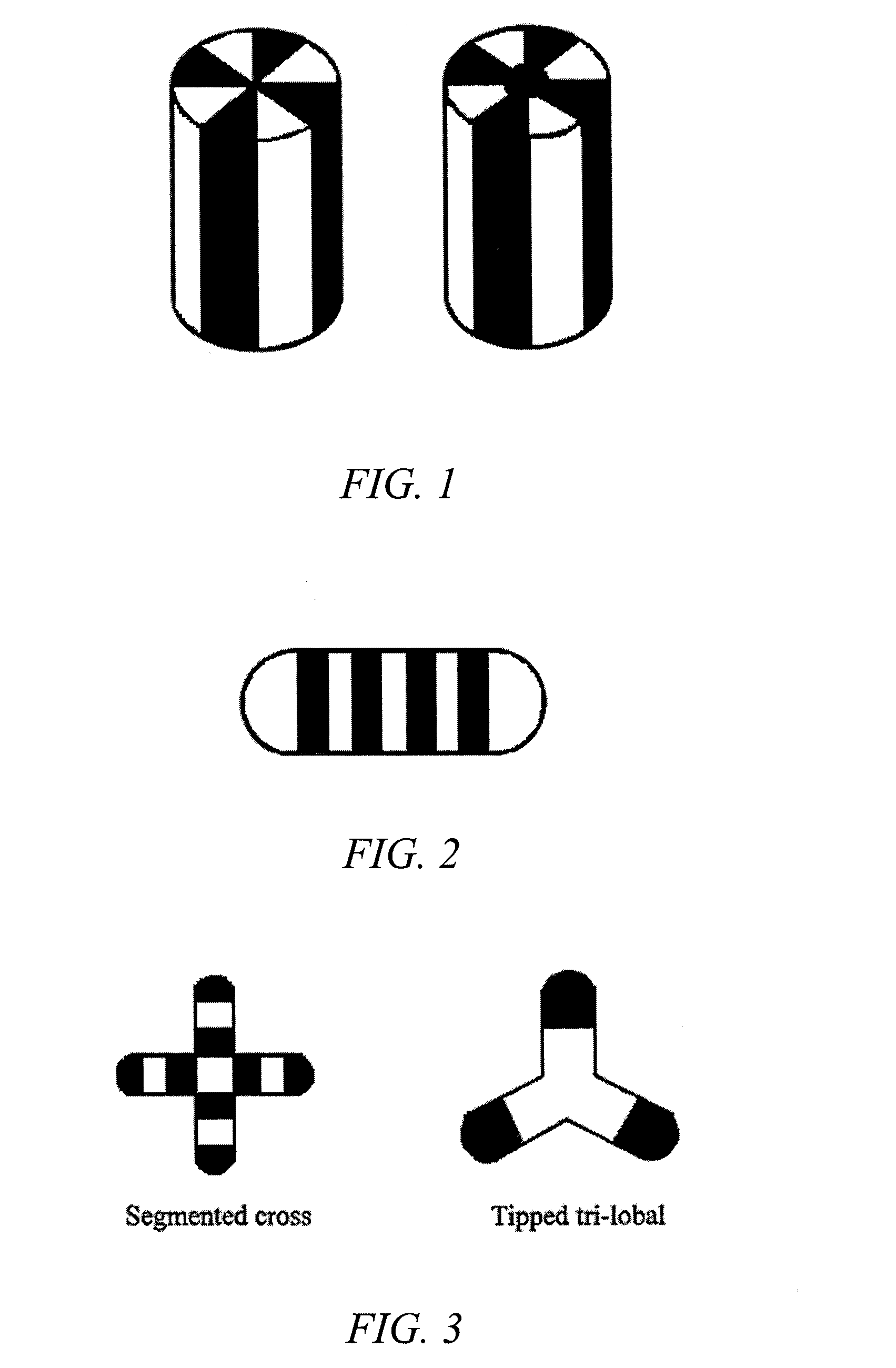
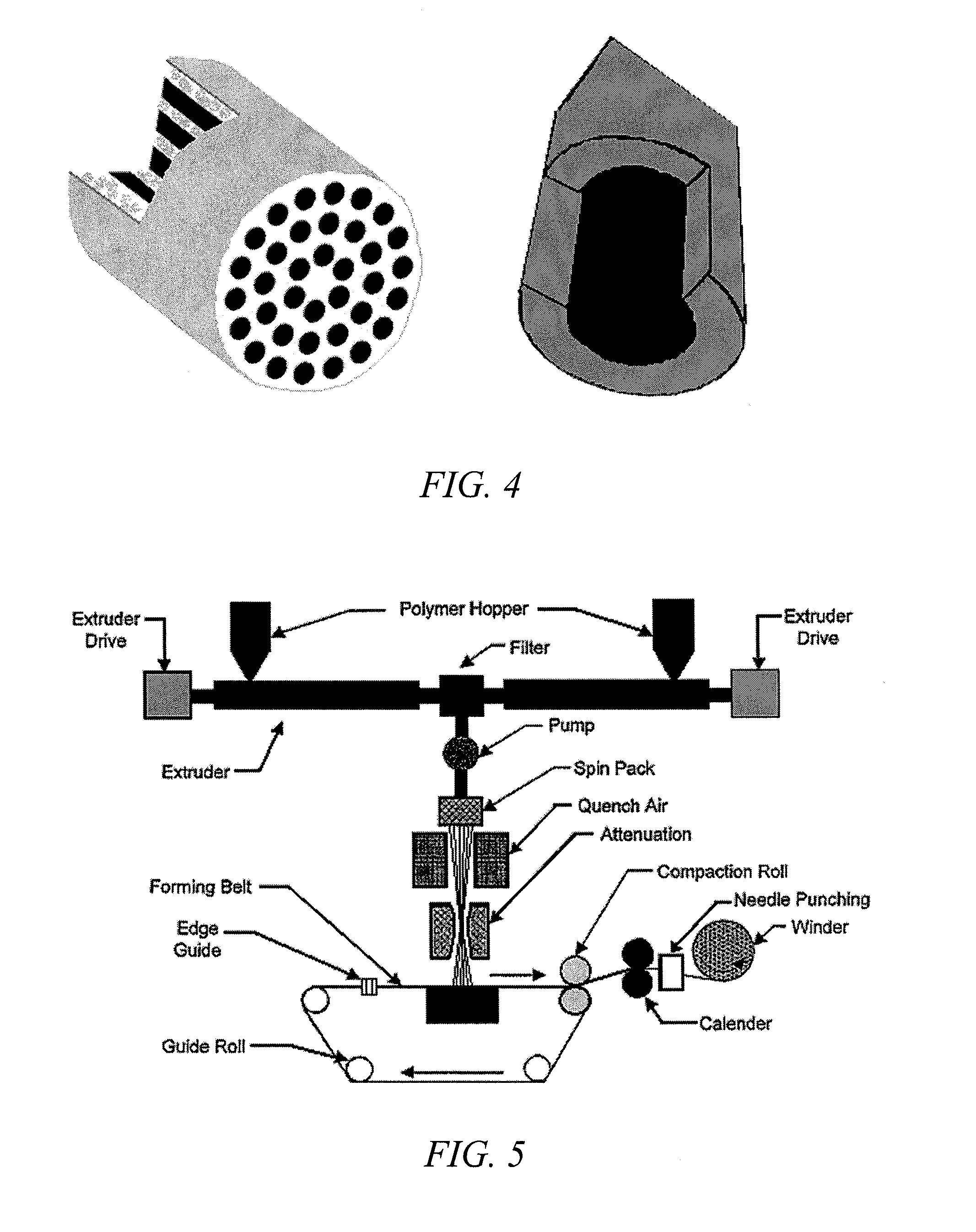
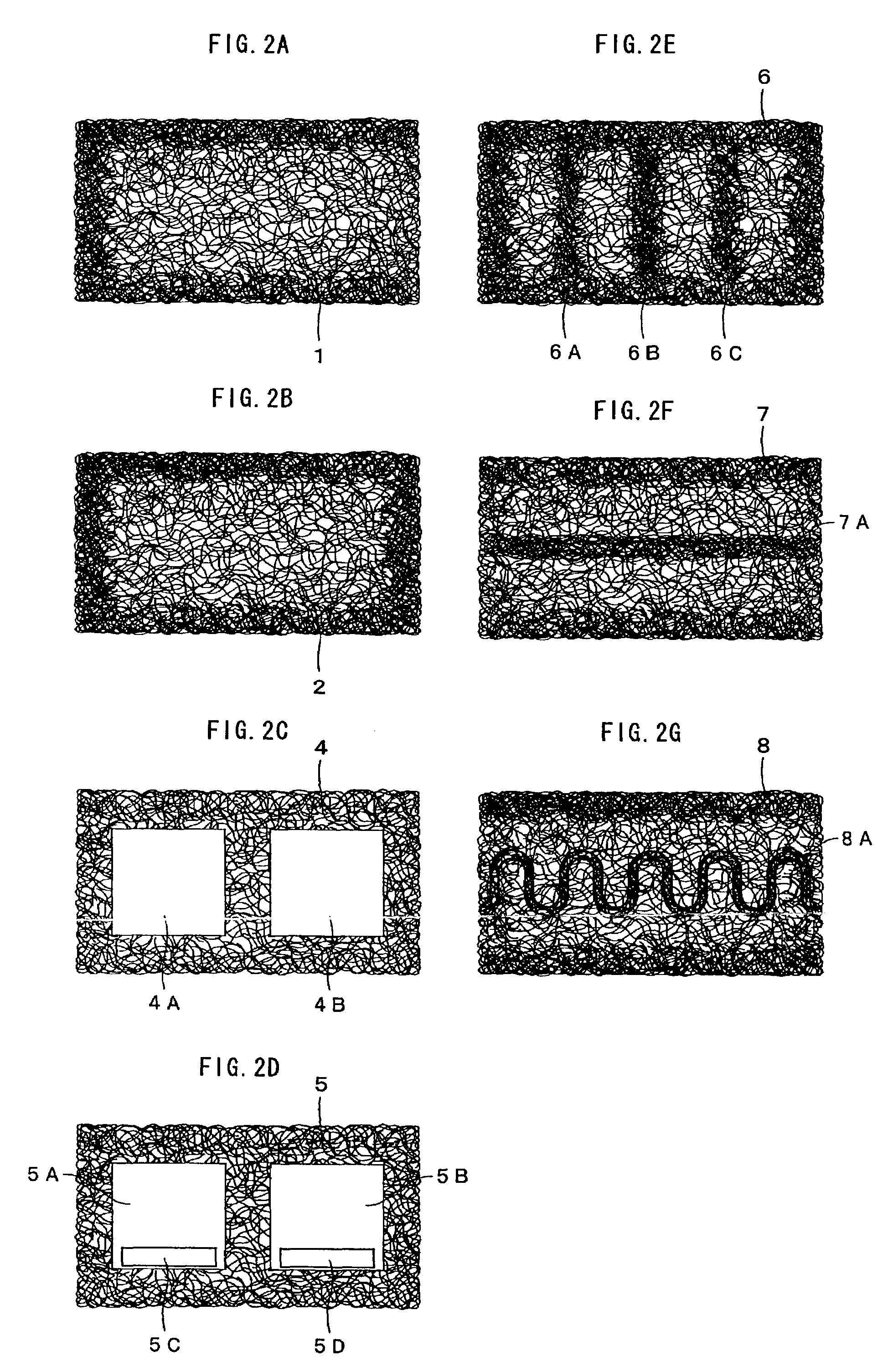
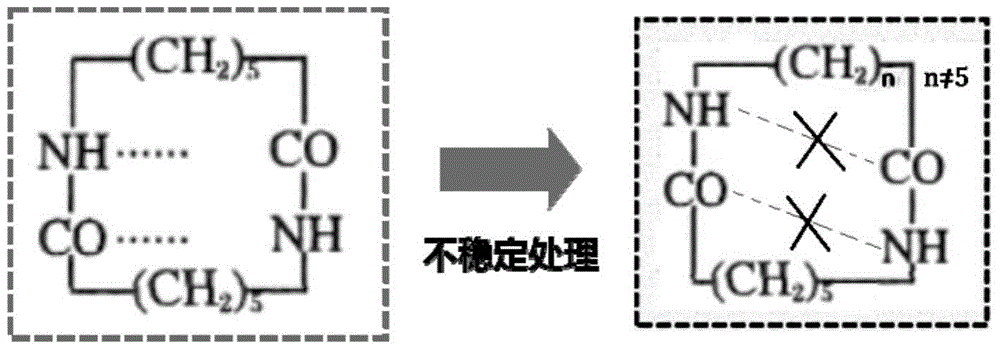
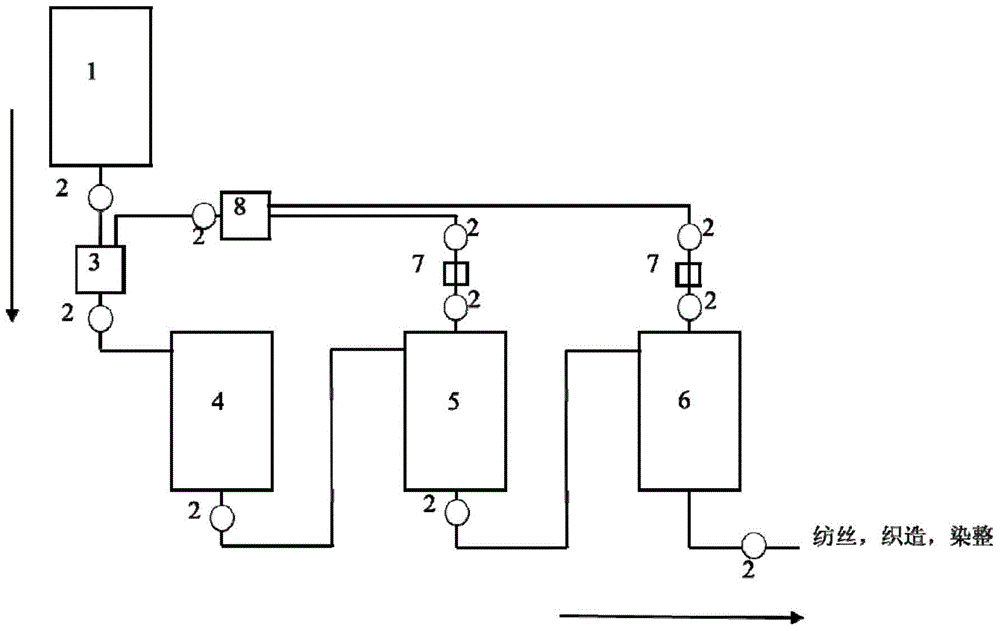
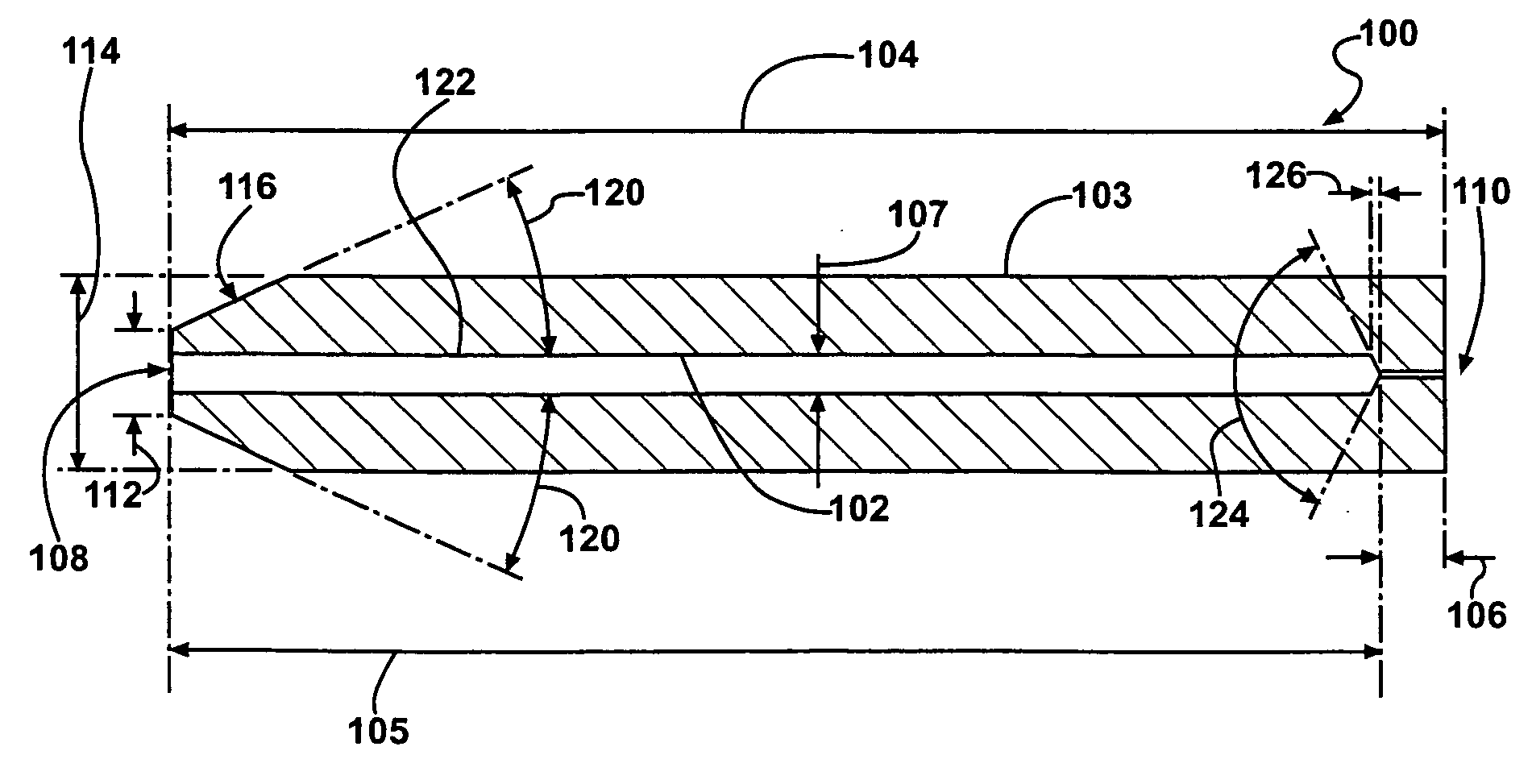
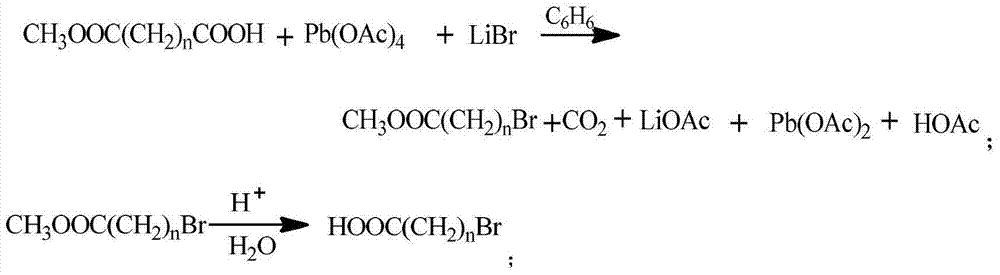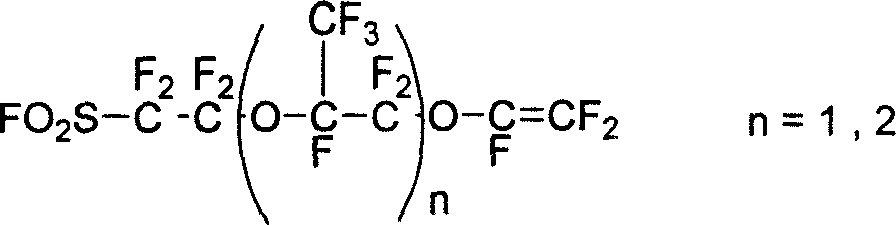Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5753results about "Melt spinning methods" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Preparation method of porous fiber non-woven fabric
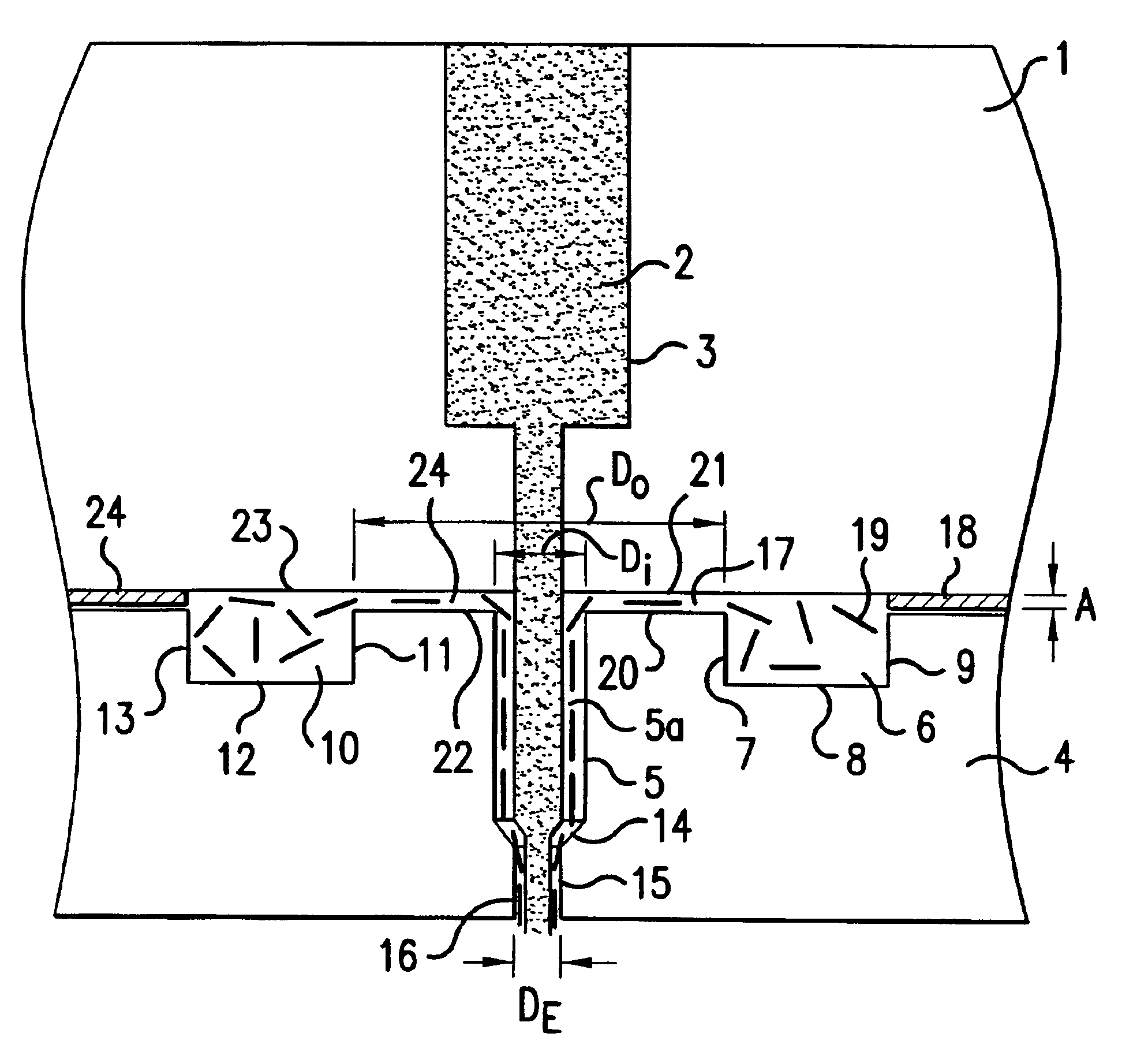
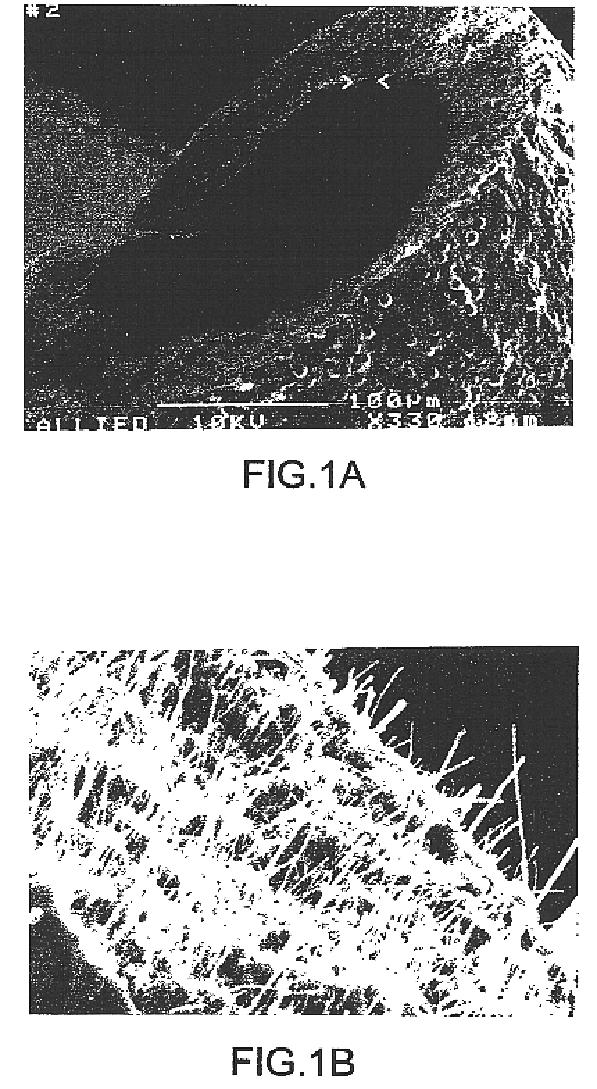
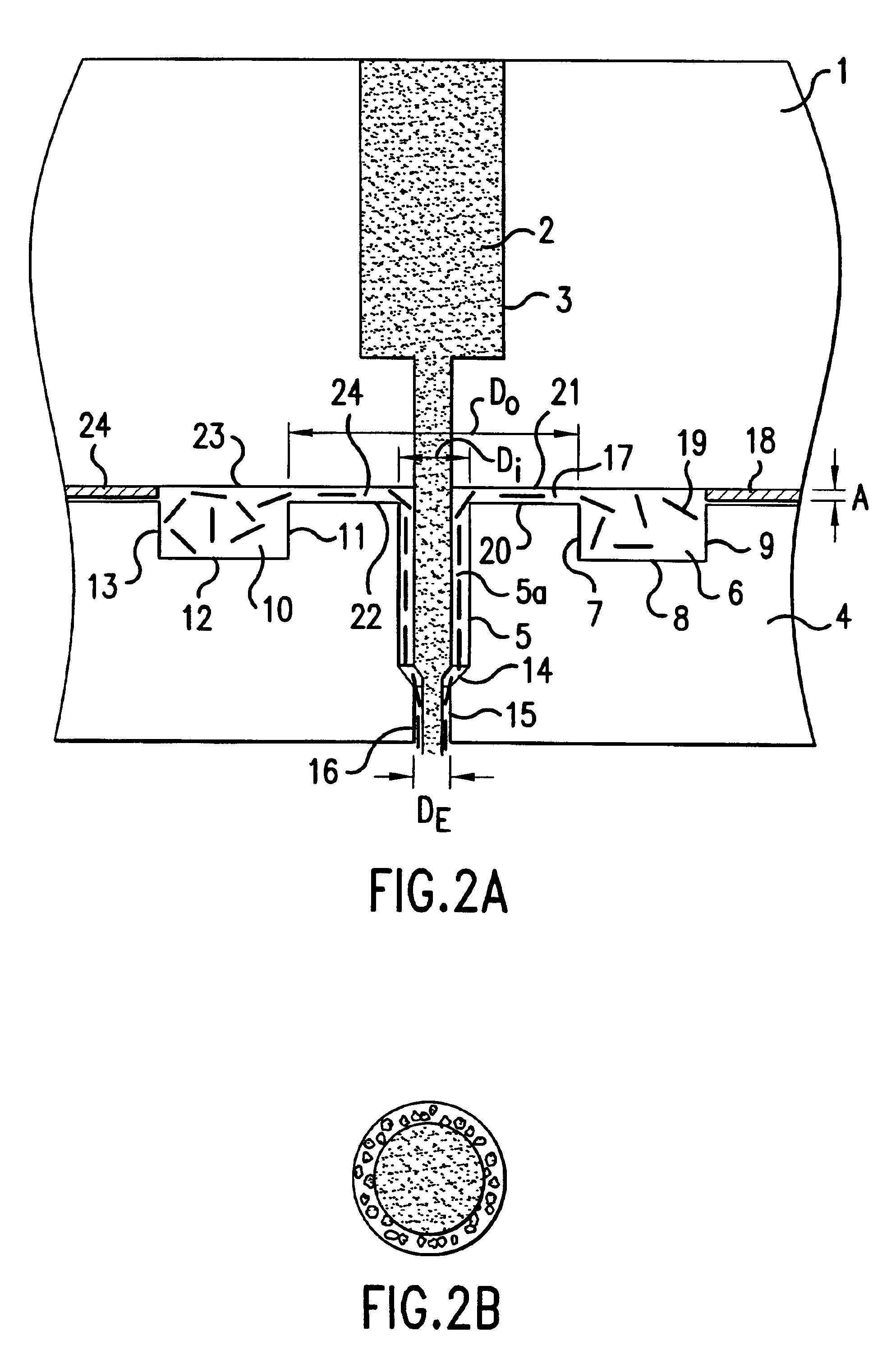
ActiveCN103981635AReduce melt viscosityReduce degradationFilament forming substance formingMelt spinning methodsDiluentNonwoven fabric
The invention relates to a preparation method of a porous fiber non-woven fabric. The aim of the preparation method is to improve the product performance of the conventional non-woven fabric, so that the non-woven fabric meets the requirements on high-precision and high-performance filter. The technical scheme is that the preparation method of the porous fiber non-woven fabric comprises the following steps in sequence: (1) uniformly mixing a polymer and a diluent to obtain a blend with 10 to 60 percent of polymer; (2) melting and extruding the blend in the step (1) by adopting a screw extruder granulator, and directly cooling and granulating in air; (3) producing master batches in the step (2) by melt-down equipment to obtain a primary non-woven fabric; (4) extracting to remove the diluent from the primary non-woven fabric in the step (3), performing pore-forming on fibers in the non-woven fabric, and drying to obtain the porous fiber non-wave fabric; (5) recovering mixed waste liquid of the diluent and an extraction agent for reuse.
Owner:浙江省轻工业品质量检验研究院
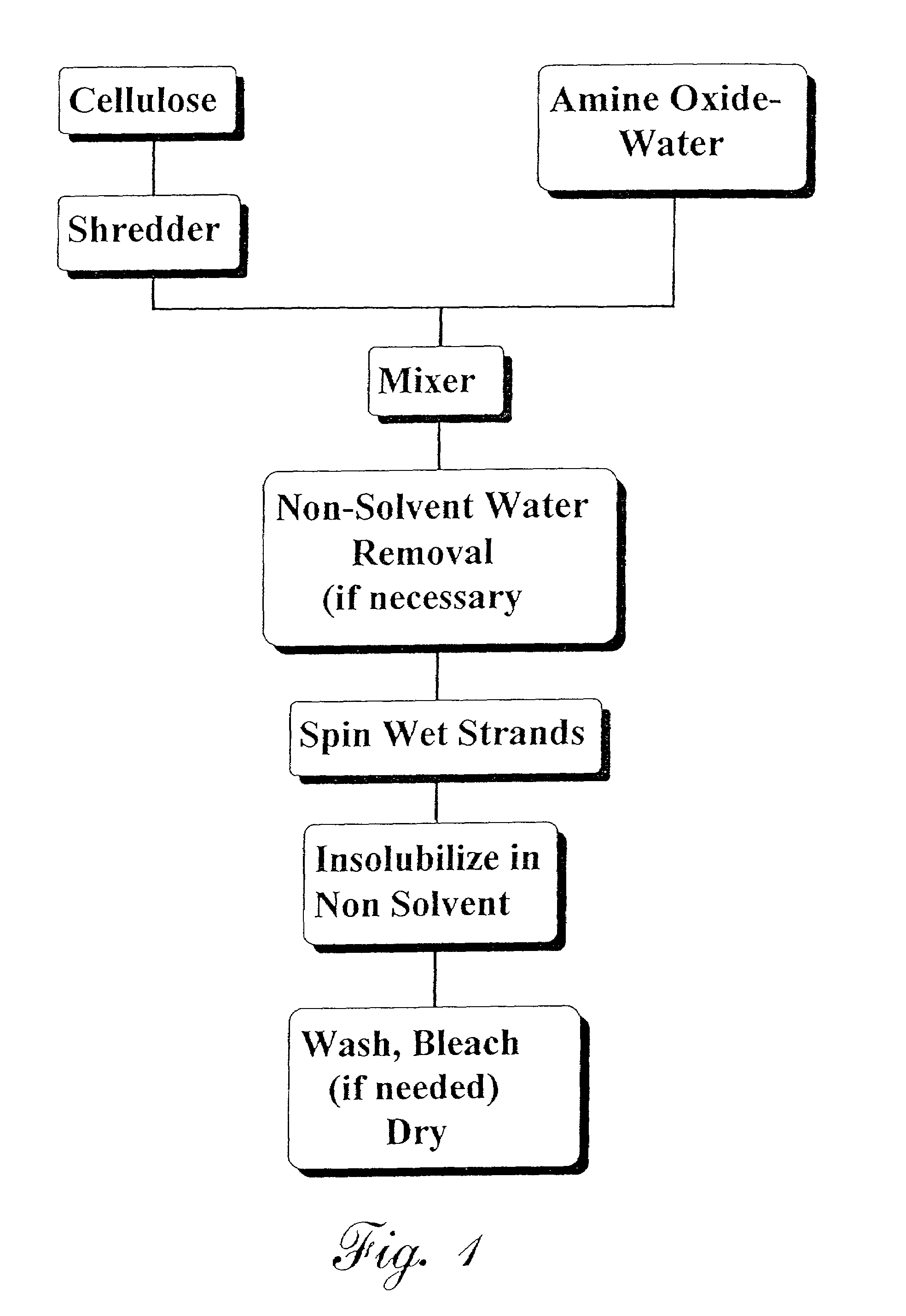
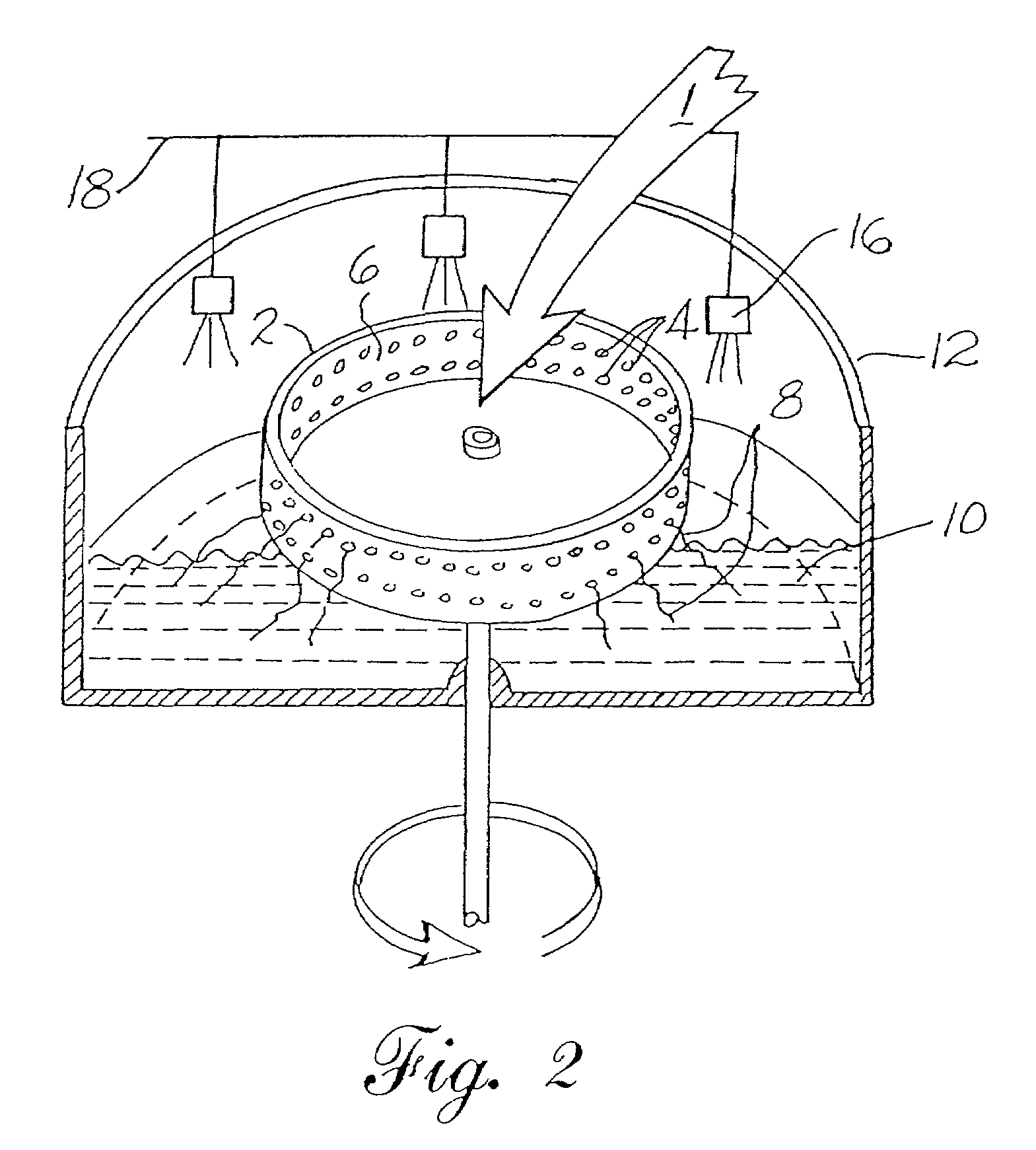
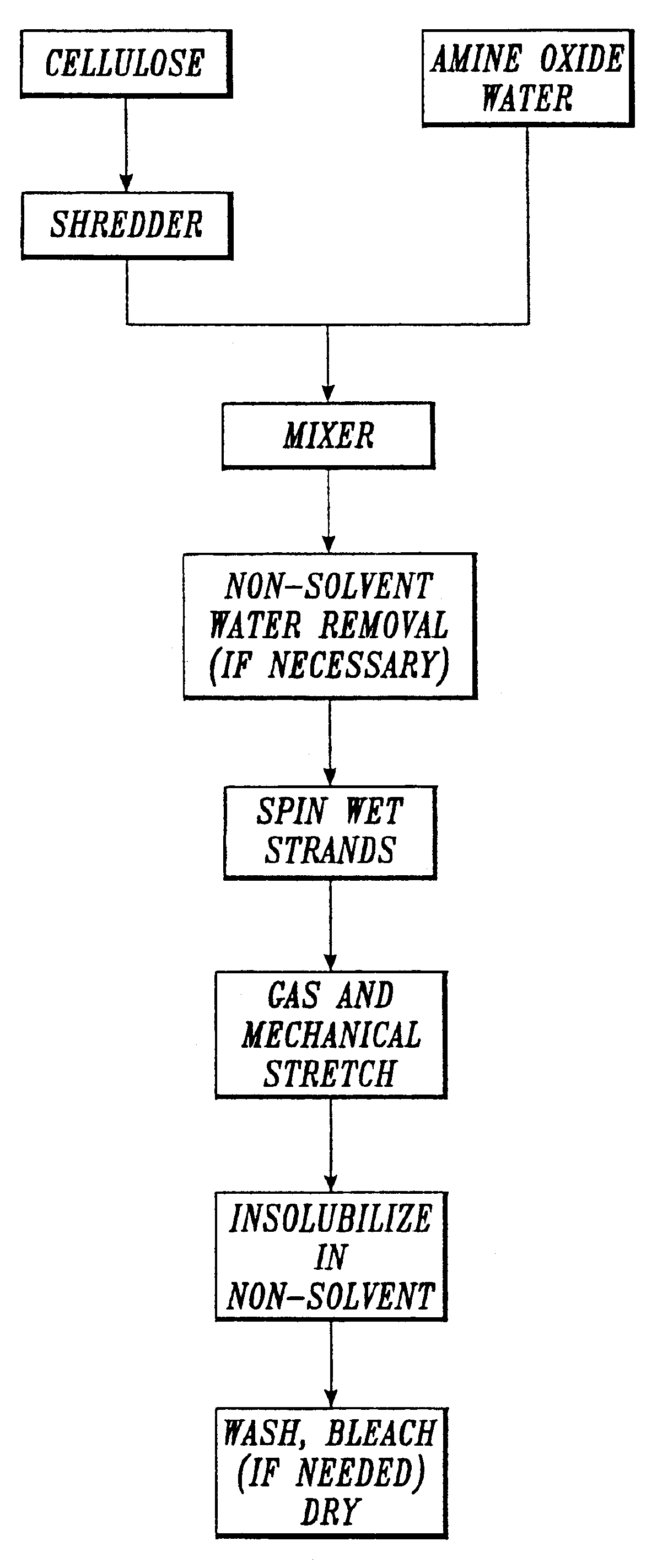
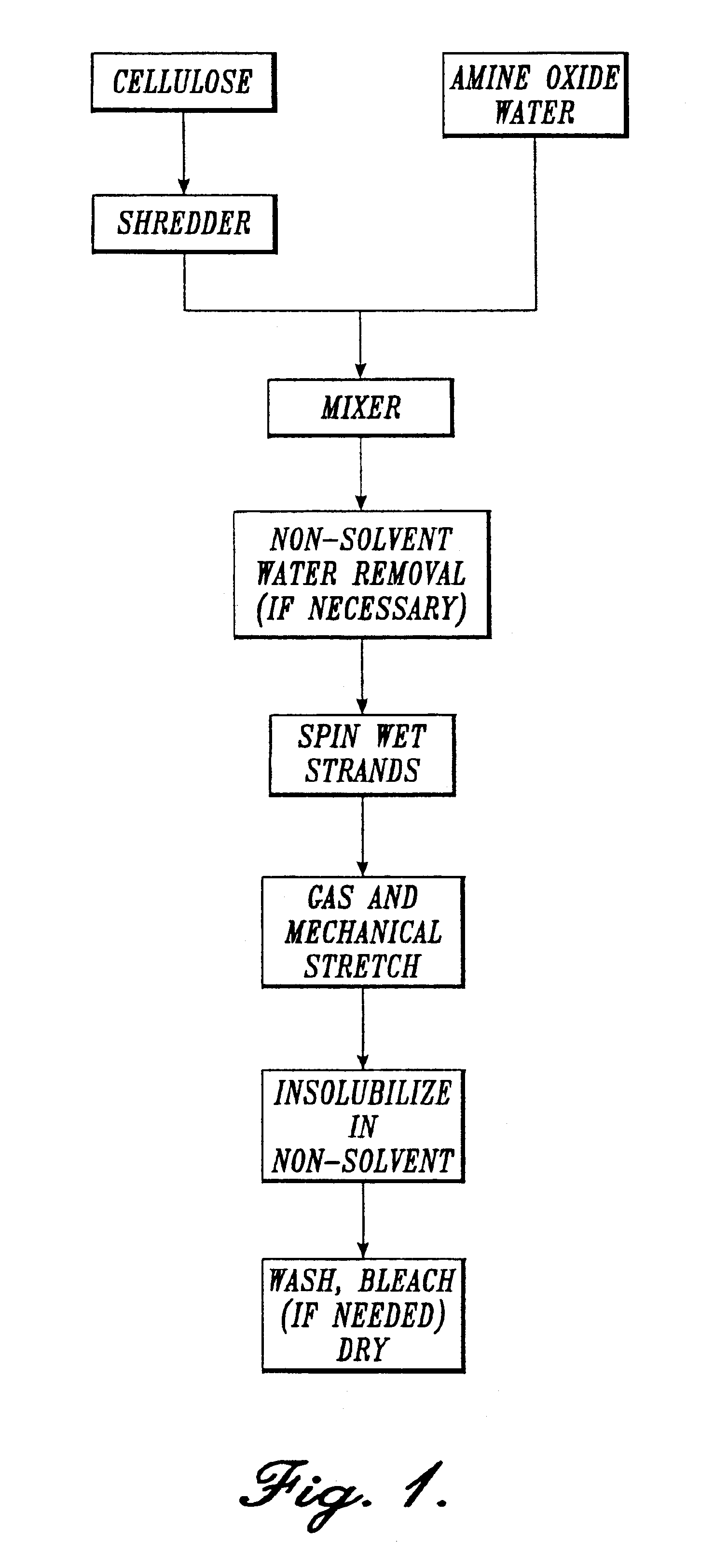
Process for forming micro-fiber cellulosic nonwoven webs from a cellulose solution by melt blown technology and the products made thereby
InactiveUS20050056956A1Artificial filament washing/dryingLoose filtering material filtersNon solventEngineering
This invention relates to a process of melt blowing a cellulose solution through a concentric melt blown die with multiple rows of spinning nozzles to form cellulosic microfiber webs with different web structures. The process comprises the steps of (a) extruding a cellulose solution (dope) through a melt blown spinneret with multiple rows of spinning nozzles; (b) drawing each individual extrudate filament to fine fiber diameter by its own air jet; (c) coagulating and entangling the fine fibers with a series of pressured hydro needling jets of recycling solution of the mixture of cellulose solvent and non-solvent in the spin-line; (d) collecting the stream of microfibers, air and needling jets on a moving collecting surface to form cellulosic fiber web; (e) hydro-entangling the said pre-bonded web downstream with at least one set of hydro needling jets of recycling solvent / non-solvent solution for forming well bonded nonwoven web; (f) regenerating the fine fibers in at least one bath for at least 5 seconds; (g) further regenerating and washing the fine fibers in another bath for at least 5 seconds; (h) pinching the well bonded melt blown cellulosic nonwoven with pressure rollers to remove major portions of the non-solvent; (i) drying the nonwoven web by heat, or vacuum or both, and (j) winding the nonwoven web into rolls.
Owner:BIAX FIBERFILM CORP
Bondable, oriented, nonwoven fibrous webs and methods for making them
InactiveUS6916752B2Improve adhesionImprove strength propertiesDecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsFiberEngineering
Nonwoven fibrous webs comprise fibers of uniform diameter that vary in morphology along their length. The variation provides longitudinal segments that exhibit distinctive softening characteristics during a bonding operation. Some segments soften under the conditions of the bonding operation and bond to other fibers of the web, and other segments are passive during the bonding operation. Webs as described can be formed by a method that comprises a) extruding filaments of fiber-forming material; b) directing the filaments through a processing chamber in which the filaments are subjected to longitudinal stress; c) subjecting the filaments to turbulent flow conditions after they exit the processing chamber; and d) collecting the processed filaments; the temperature of the filaments being controlled so that at least some of the filaments solidify while in the turbulent field.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Dissolvable Fibrous Web Structure Article Comprising Active Agents
The personal care compositions of the present invention are in the form of an Article comprising a dissolvable fibrous web structure. The fibers of the dissolvable fibrous web structure comprise a surfactant; a water soluble polymeric structurant; and a plasticizer. Additionally the ratio of the water soluble water soluble polymeric structurant to the active agent in the fiber is 3.5 or less.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Lyocell nonwoven fabric
InactiveUS7067444B2Powerful solventLow tendency to fibrillatePulp properties modificationMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentMelt blowingNonwoven fabric
A lyocell nonwoven fabric having fibers characterized by pebbled surfaces and variable cross sections and diameters along the fibers and from fiber to fiber, is disclosed. The lyocell nonwoven fabric is produced by centrifugal spinning, melt blowing or spunbonding. The lyocell nonwoven fabric has fibers that can be made in the microdenier range with average weights as low as one denier or less. The lyocell nonwoven fabric has fibers with low gloss, a reduced tendency to fibrillate and have enhanced dye receptivity.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
Low emission polymer compositions
InactiveUS6331264B1Improve stabilityEmission reductionCeramic shaping apparatusMelt spinning methodsMolten stateMolten salt
The invention comprises polymer compositions containing 3-hydroxypropanoxy terminated polymer that exhibit reduced levels of degradation product emissions during processing, by contacting the polymer in the molten state with a melt stable, organic nitrogen-containing stabilizing compound, such as polyamide.
Owner:DUPONT IND BIOSCIENCES USA LLC
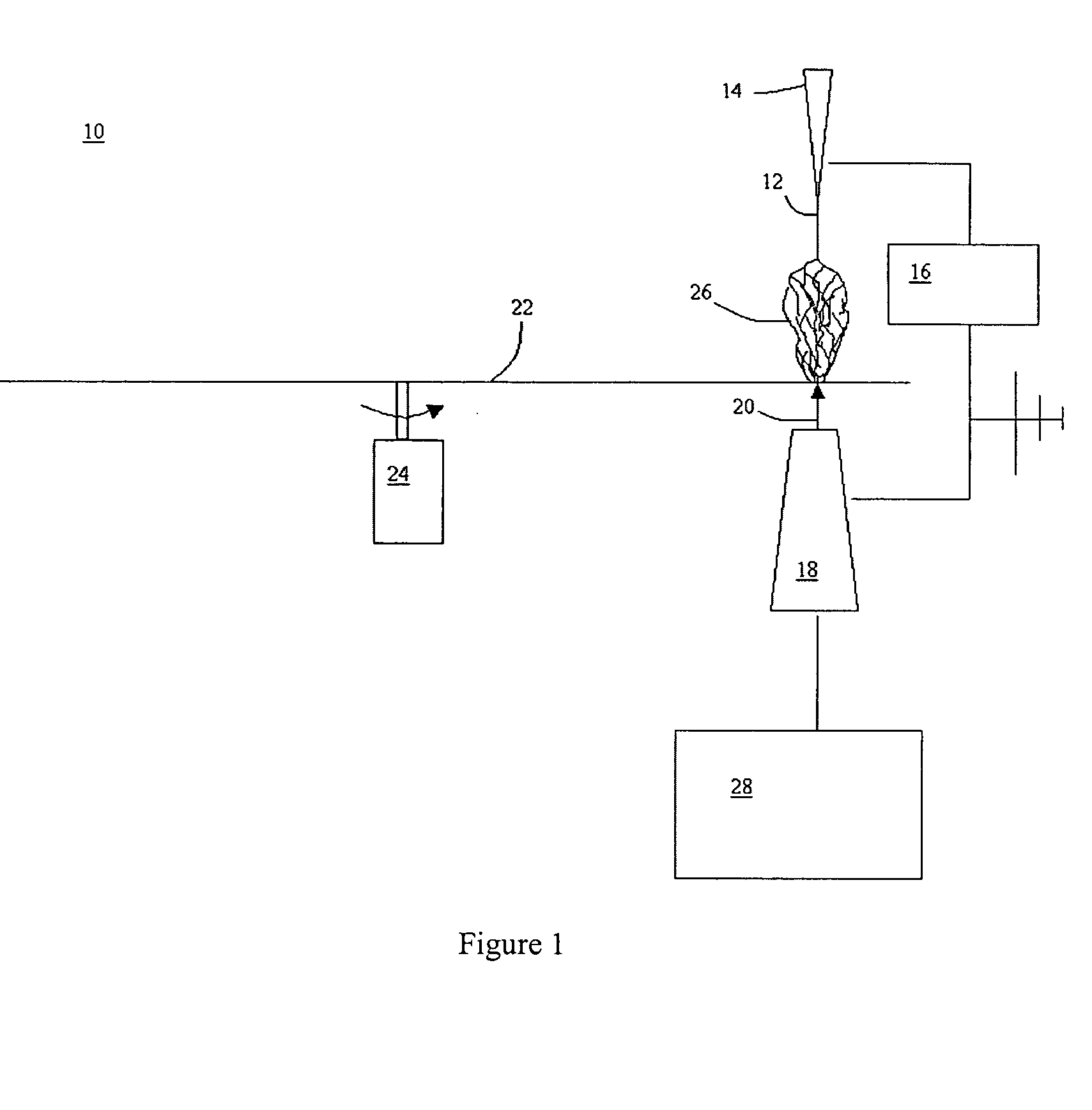
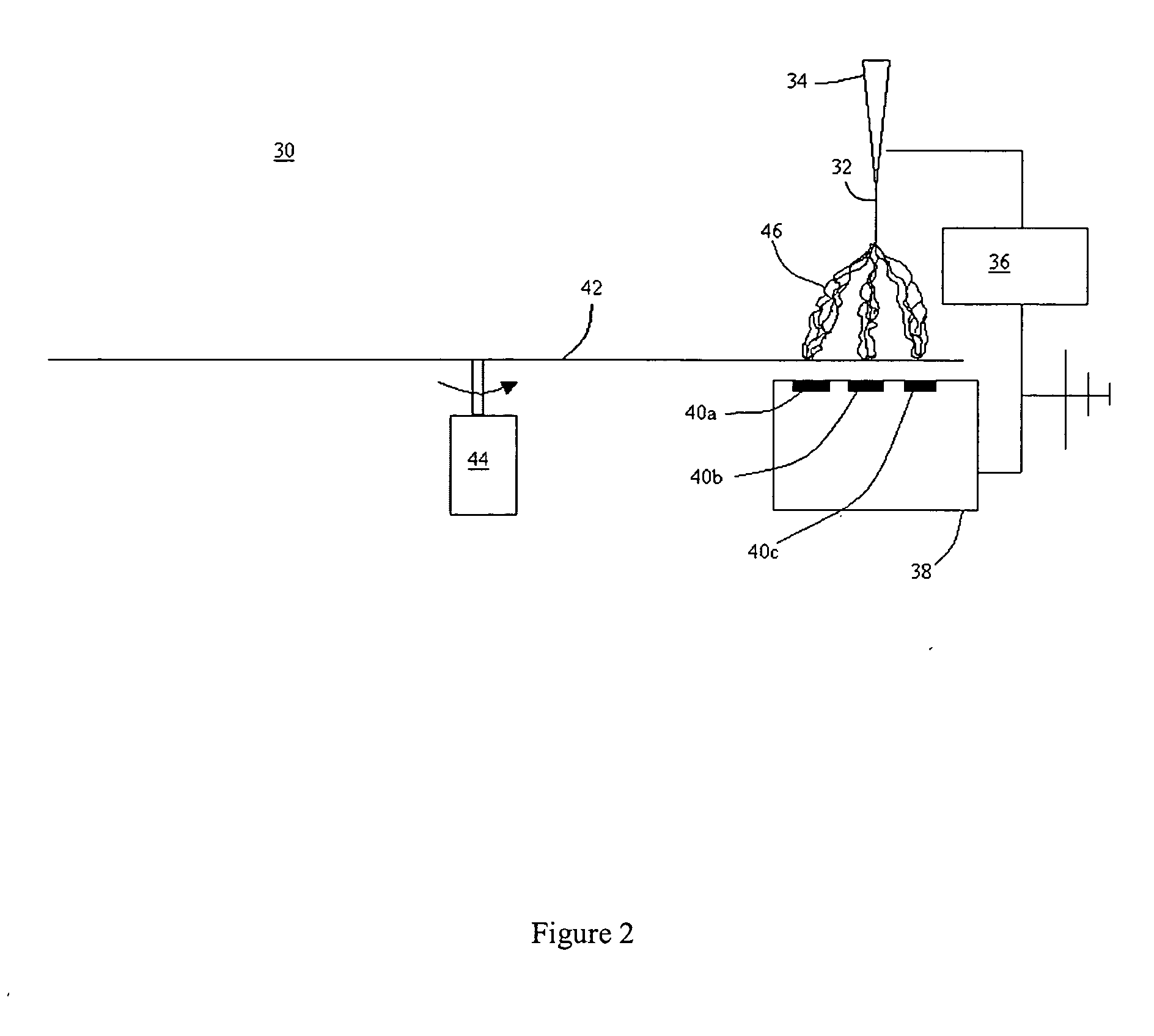
Patterned electrospinning
A polymer is directed from a source electrode into an electric field that drives the formation of electrospun fibers that are deposited onto a collecting surface to thereby form a patterned polymer structure. The collecting surface can be a counterelectrode or a collecting surface that is between the source electrode and a counterelectrode. Apparatus employed to conduct the method include an electrospinning source that directs polymer into an electric field formed by source and counterelectrodes. A collecting surface, such as the counterelectrode or a surface interposed between the source and counterelectrodes, collects electrospun fibers. Articles of manufacture formed by the method of apparatus include, for example, a structure of patterned electrospun fibers comprising multiple aggregations of polymeric electrospun fibers.
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
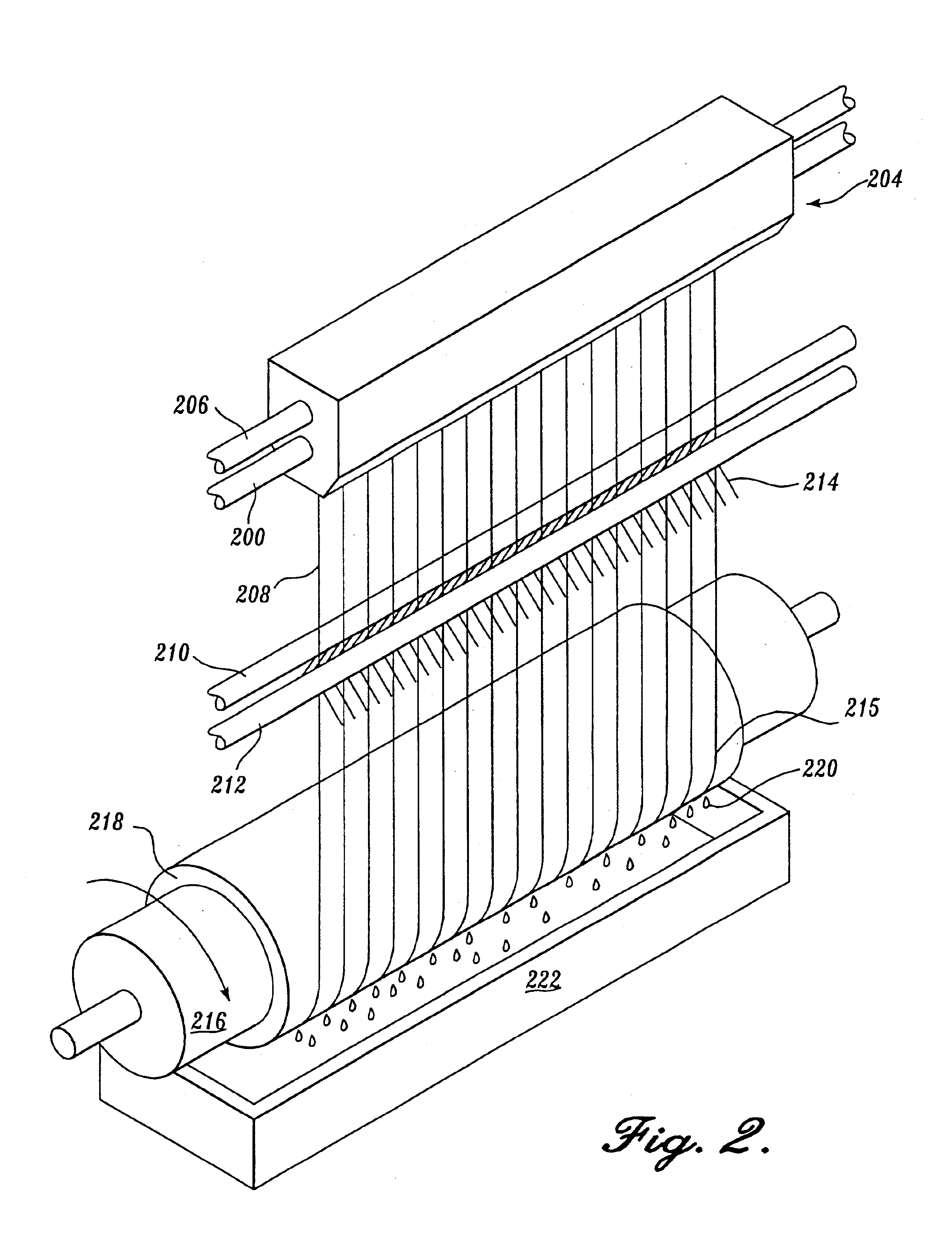
Method and device for the production of an essentially continous fine thread
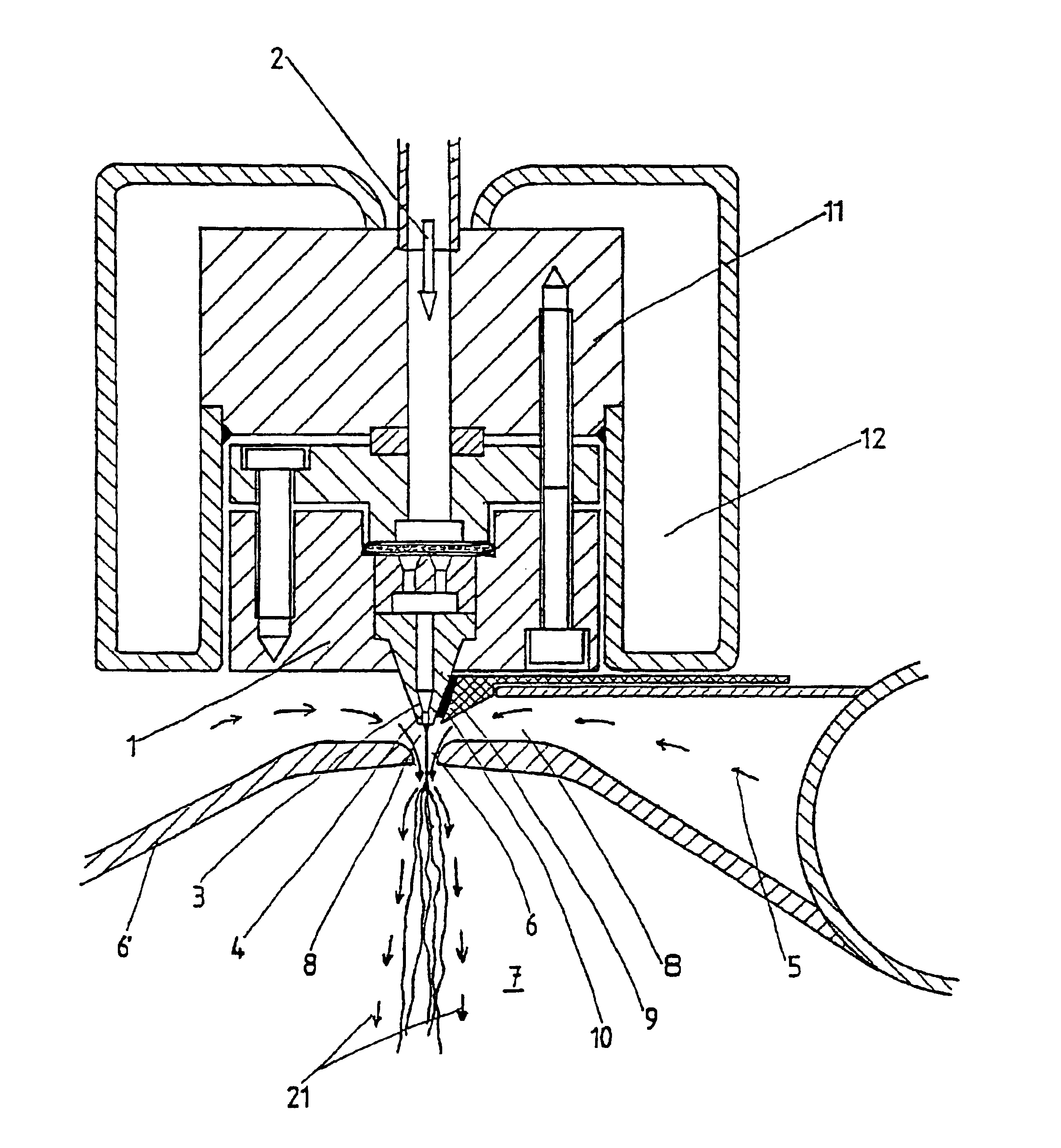
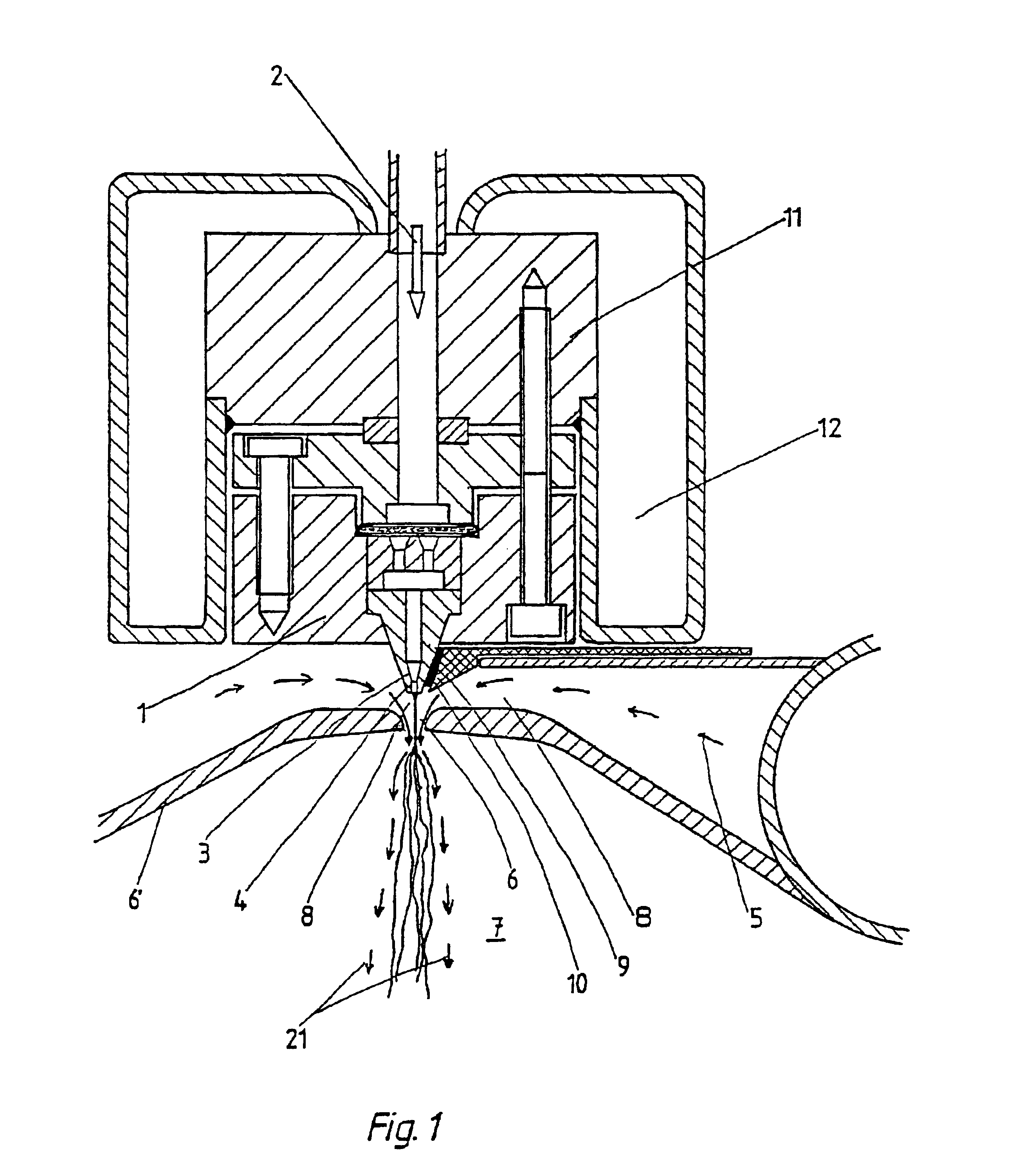
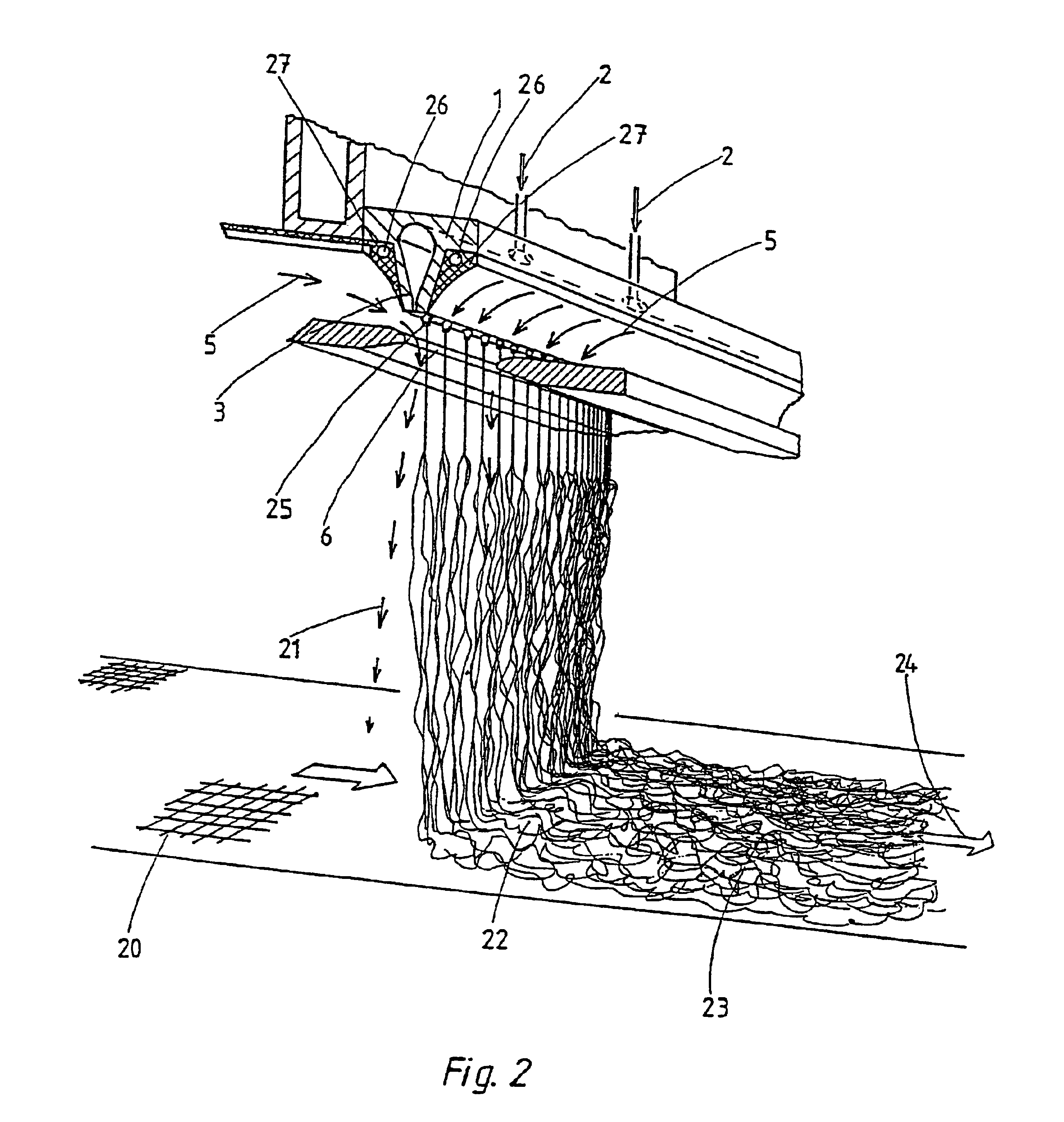
InactiveUS6800226B1Simple and economical mannerReduced strengthSpinnerette packsMelt spinning methodsFine lineYarn
The invention relates to a method and a device for the production of essentially continuous fine threads made of meltable polymers. The polymer melt is spun from at least one spin hole (5) and the spun thread is attenuated using gas flows which are accelerated to achieve high speeds by means of a Laval nozzle (6). As a result of the specific geometry of the melt hole (4) and the position thereof in respect to the Laval nozzle (6), the temperature of the polymer melt, the throughout per spin hole and the pressures determining the velocity of the gas flow upstream and downstream from the Laval nozzle (6) are controlled in such a way that the thread reaches an internal hydrostatic pressure before solidifying, whereby said thread bursts into a plurality of fine threads.
Owner:GERKING LUDER
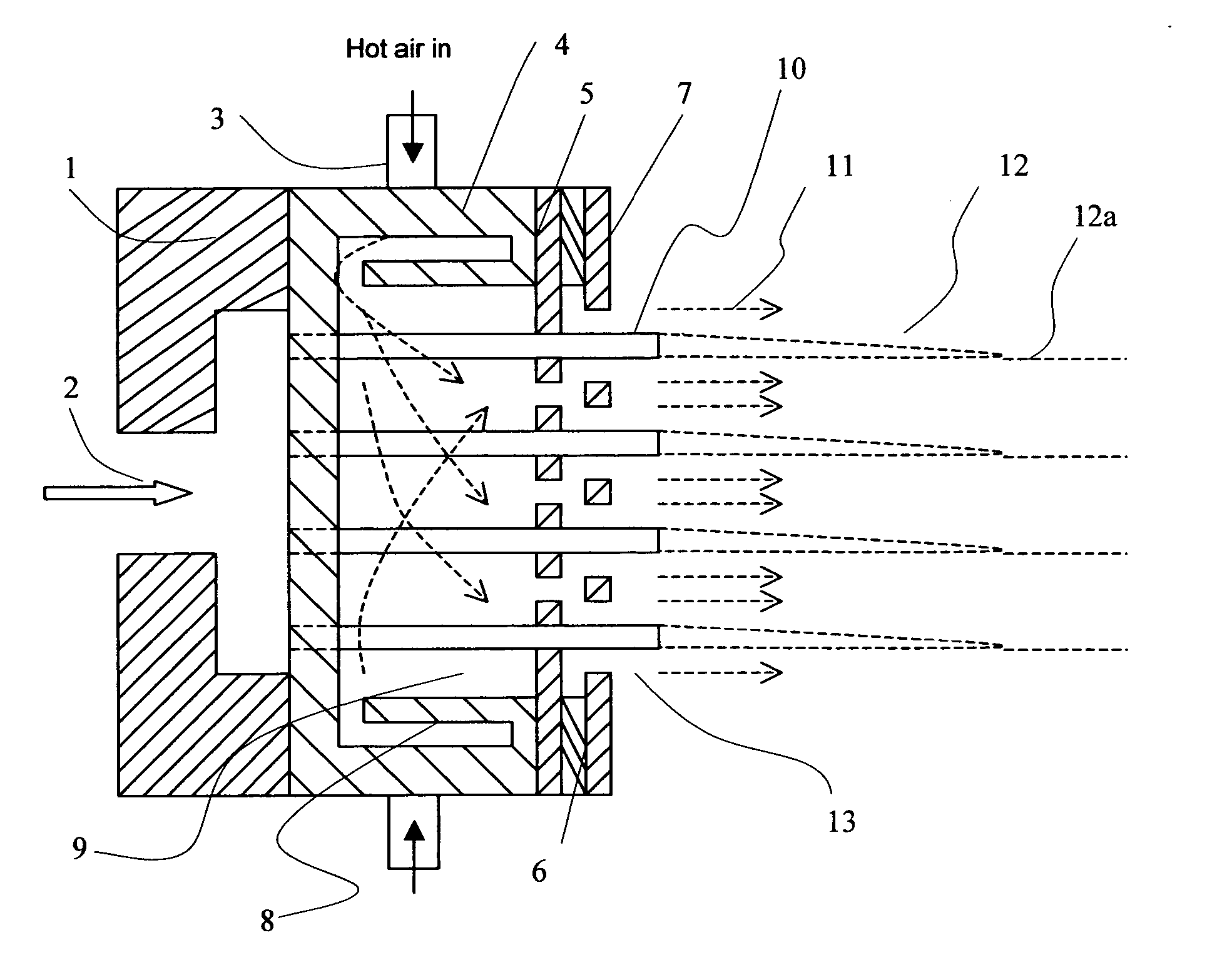
Melt-blown non-woven fabric, and nozzle piece for producing the same
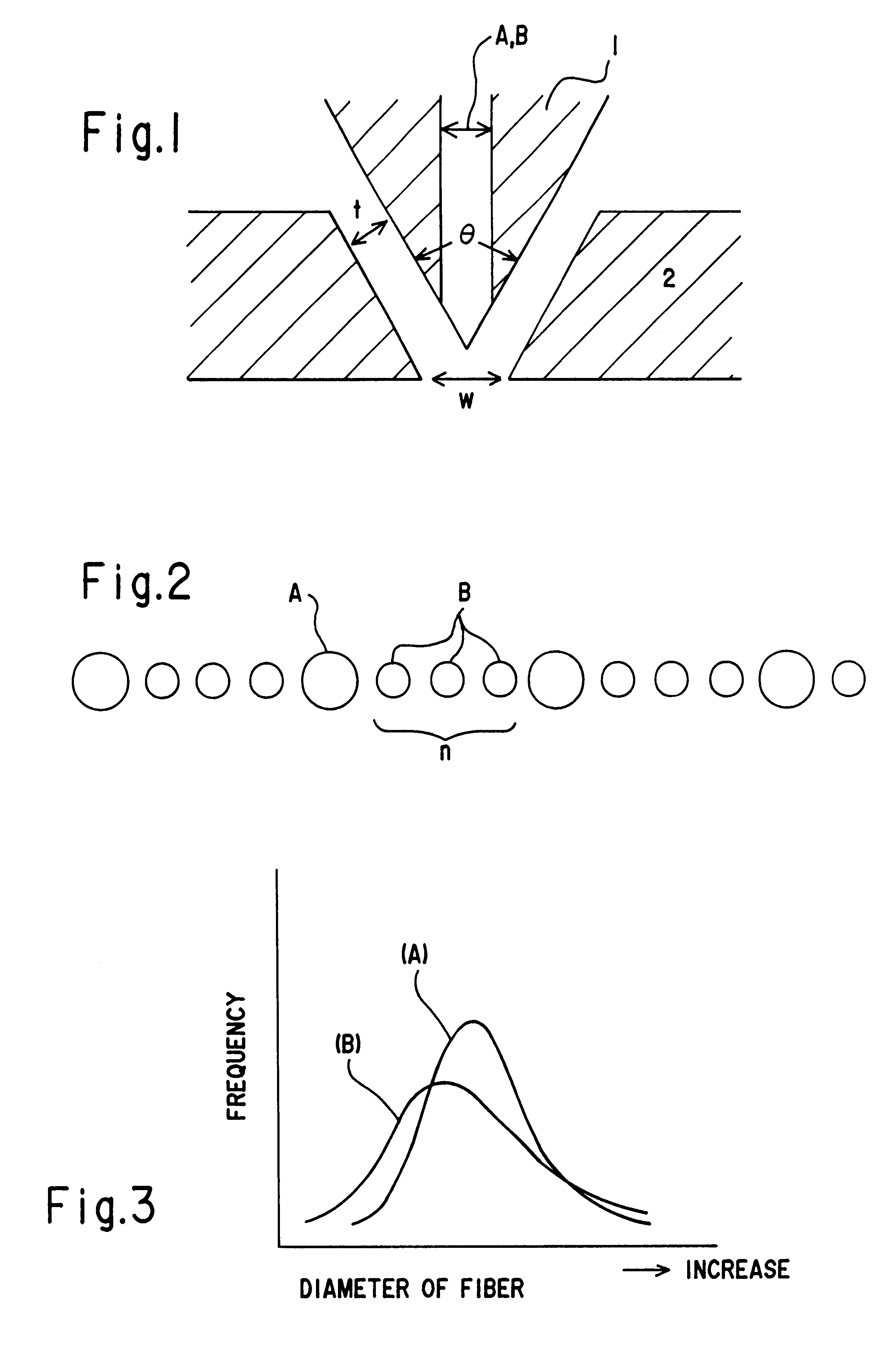
InactiveUS6319865B1Efficient productionLayered productsMelt spinning methodsEngineeringFiber diameter
The nozzle piece of the present invention is provided with circular cross sectional nozzles having different sizes disposed in a row in front of the die, with n-numbered smaller nozzles B (hole diameter: Db) between adjacent larger nozzles A (hole diameter: Da). It gives melt-blown non-woven fabric of monolithic structure in one step, composed of fine fibers having a diameter in a range from 1 to 10 mum diameter Variance ratio F of 2.0 or more and wide fiber diameter distribution.
Owner:TONEN TAPYRUS
Water-dispersible and multicomponent fibers from sulfopolyesters
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Vascular prosthesis and method for production thereof
A vascular prosthesis comprising a first layer having a predetermined first porosity and a second layer having a predetermined second porosity, wherein the first layer and the second layer are each made of first and second electrospun polymer fibers.
Owner:NICAST LTD
Electro-blowing technology for fabrication of fibrous articles and its applications of hyaluronan
InactiveUS20050073075A1Improve the situationHigh productElectric discharge heatingFibre chemical featuresFiberNanofiber
A method for electroblowing fibers is provided which involves the steps of: forcing a polymer fluid through a spinneret in a first direction towards a collector located a first distance from the spinneret, while simultaneously blowing a gas through an orifice that is substantially concentrically arranged around the spinneret, wherein the gas is blown substantially in the first direction; wherein an electrostatic differential is generated between the spinneret and the collector; and collecting the fibers, and its use in preparing submicron scale fibers of various types, particularly hyaluronan fibers, and the hyaluronan nanofibers thus formed.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method of nanofibres production from a polymer solution using electrostatic spinning and a device for carrying out the method
ActiveUS7585437B2High quality and uniformity of layerSpinnerette packsNanotechnologyPotential differenceElectrospinning
A method of nanofibers production from a polymer solution uses electrostatic spinning in an electric field created by a potential difference between a charged electrode and a counter electrode. The polymer solution for spinning is supplied into the electric field using the surface of a rotating charged electrode. On a part of the circumference of the charged electrode near to the counter electrode, a spinning surface is created for attaining a high spinning capacity. In a device for carrying out the method, the charged electrode is pivoted and part of its circumference is immersed in the polymer solution. The free part of the circumference of the charged electrode is positioned opposite the counter electrode.
Owner:TECHNICKA UNIVEZITA V LIBERCI
High-strength activated polyester industry yarn and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104499080AGood flexibilityGood compatibilityNew-spun product collectionMelt spinning methodsPolyesterChemistry
The invention relates to a high-strength activated polyester industry yarn and a preparation method thereof. The high-strength activated polyester industry yarn is a modified polyester industry yarn of which the surface is coated with an activating agent and the high-strength activated polyester industry yarn is prepared from modified polyesters through spinning; the modified polyester is composed of polyester and aminoadipic acid gylcol ester, hydrogen-bond interaction exists between the aminoadipic acid gylcol ester and the molecular chains of the polyester, and the relative position of the aminoadipic acid gylcol ester and the molecular chains of the polyester is fixed; the free volume of the fiber is increased when the high-strength activated polyester industry yarn is at 70-80 DEG C, a part of activating agent molecules are dispersed into fiber gaps, more -OHs and -NHs with strong activity are introduced into the polyester molecules, a firm resinoid coating is formed on the surface of a polyester cord thread and the reactivity of the polyester fiber is improved; and the high-strength activated polyester industry yarn can be applied to triangular belt cords, radial tire cord fabrics and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU HENGLI CHEM FIBER
Modified Polylactic Acid Fibers
ActiveUS20120040582A1Improve responseMelt spinning methodsWoven fabricsChain scissionGlass transition
A method for forming biodegradable fibers is provided. The method includes blending polylactic acid with a polyepoxide modifier to form a thermoplastic composition, extruding the thermoplastic composition through a die, and thereafter passing the extruded composition through a die to form a fiber. Without intending to be limited by theory, it is believed that the polyepoxide modifier reacts with the polylactic acid and results in branching of its polymer backbone, thereby improving its melt strength and stability during fiber spinning without significantly reducing glass transition temperature. The reaction-induced branching can also increase molecular weight, which may lead to improved fiber ductility and the ability to better dissipate energy when subjected to an elongation force. To minimize premature reaction, the polylactic acid and polyepoxide modifier are first blended together at a relatively low temperature(s). Nevertheless, a relatively high shear rate may be employed during blending to induce chain scission of the polylactic acid backbone, thereby making more hydroxyl and / or carboxyl groups available for subsequent reaction with the polyepoxide modifier. Once blended, the temperature(s) employed during extrusion of the blended composition can be selected to both melt the composition and initiate a reaction of the polyepoxide modifier with hydroxyl and / or carboxyl groups of the polylactic acid. Through selective control over this method, the present inventors have discovered that the resulting fibers may exhibit good mechanical properties, both during and after melt spinning.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Mixed fibers and nonwoven fabrics made from the same
ActiveUS20090042475A1Improve breathabilityIncrease flexibilityLaminationLamination apparatusFiltrationSubject matter
The subject matter disclosed herein relates generally to the production of a predetermined ratio of multicomponent fibers in combination with monocomponent fibers or other multicomponent fibers, preferably through a spunbonding process. After extrusion, these fibers can produce a fiber network that is subsequently bonded to produce a nonwoven fabric comprising multiple types of fibers. The multicomponent fibers within the network may be processed to remove one component by dissolution or to split the individual components into separate fibers. As a result, the fabric will be comprised of fibers with a range of diameters (micro- or nano-denier fibers as well as higher denier fibers) such that the fibers will not pack as tightly as in a homogeneous nonwoven fabric produced from one type of monocomponent or multicomponent fiber. The present invention additionally relates to methods for producing nonwoven fabrics with increased loft, breathability, strength, compressive properties, and filtration efficiency.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Composite material comprising oriented carbon nanotubes in a carbon matrix and process for preparing same
Fiber spinning of two polymer compositions wherein one of the compositions contains carbon nanotubes produces structures such as fibers, ribbons, yarns and films of carbon nanotubes. The polymers are removed and stabilization of the carbon nanotube material is achieved by post-spinning processes. The advances disclosed herein enable the carbon nanotube composites to be used in actuators, supercapacitors, friction materials and in devices for electrical energy harvesting.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method of making regenerated cellulose microfibers and absorbent products incorporating same
ActiveUS20080173419A1High yieldLow costNon-fibrous pulp additionElectric discharge heatingPolymer sciencePersonal Care Product
A method of making regenerated cellulose microfibers includes forming segmented fibers with multiple longitudinally-extending segments of slightly different composition such that there is defined splittable interfaces between juxtaposed segments of the fibers which are then split into microfibers at yields of greater than 50%. Fibers so produced may be incorporated into absorbent sheet with other papermaking fibers to provide strength, softness, bulk and absorbency to tissue, towel, and personal care products.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Nonwoven fabrics with advantageous properties
InactiveUS7060149B2Increasing the thicknessIncrease opening spacingEnvelopes/bags making machineryLaminationEngineeringNonwoven fabric
This invention relates to nonwoven fabrics with advantageous characteristics and the method to produce these fabrics. Advantageously, the fabrics of the subject invention have increased thickness (loft) compared to conventional nonwoven fabrics and have high air permeability and open space while maintaining softness and strength at the same basis weight.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Composite material comprising oriented carbon nanotubes in a carbon matrix and process for preparing same
Fiber spinning of two polymer compositions wherein one of the compositions contains carbon nanotubes produces structures such as fibers, ribbons, yarns and films of carbon nanotubes. The polymers are removed and stabilization of the carbon nanotube material is achieved by post-spinning processes. The advances disclosed herein enable the carbon nanotube composites to be used in actuators, supercapacitors, friction materials and in devices for electrical energy harvesting.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Polymer of containing fluorin, and application as material of ion exchange fiber
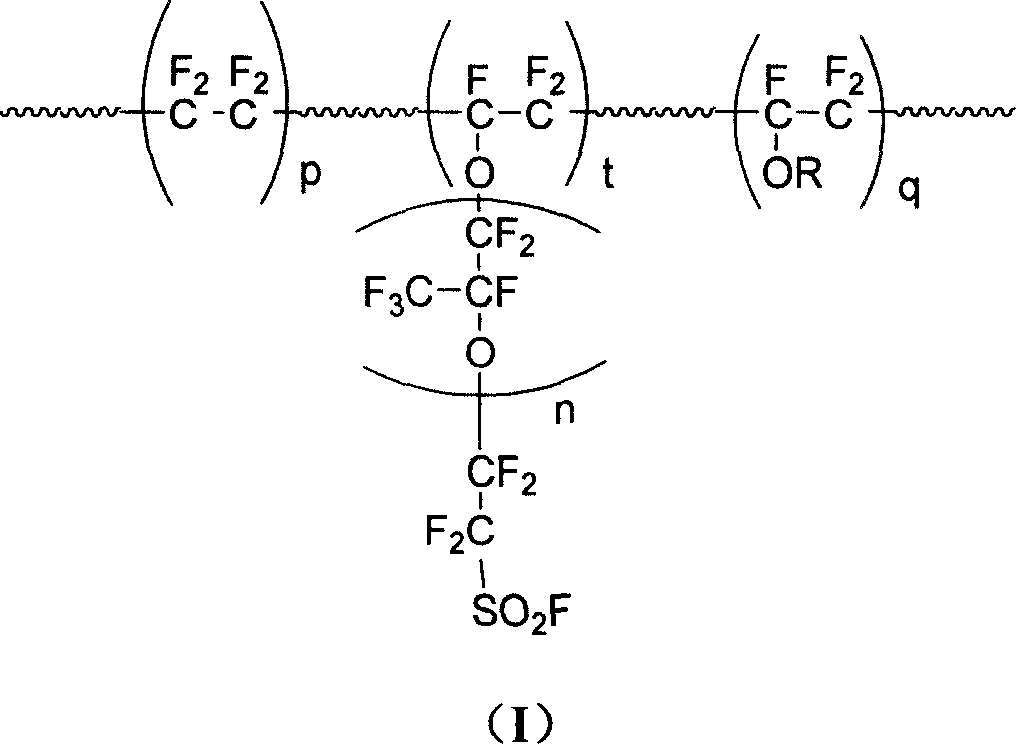
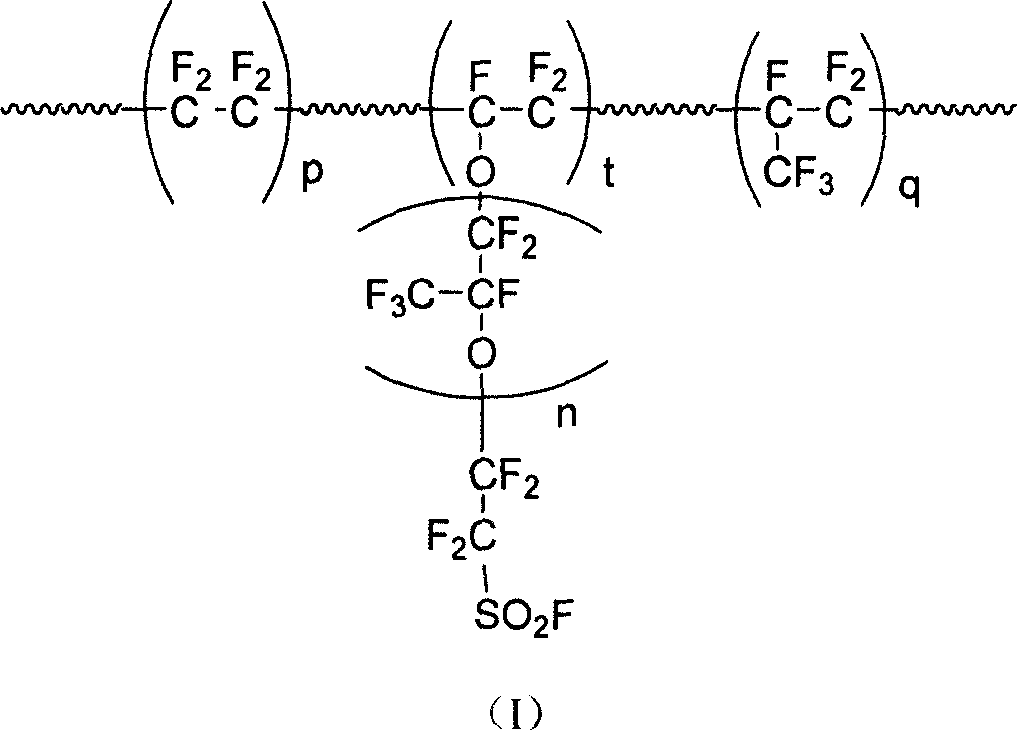
InactiveCN101003588AIncrease the effective areaLower resistanceMelt spinning methodsVinyl etherAlkali ions
This invention discloses a fluorine-containing polymer and its application as ion exchange fiber material. The fluorine-containing polymer is a perfluoro resin containing sulfonylfluoride groups, and is shown in formula 1. The fluorine-containing polymer has ion exchange function, and is prepared by free radical copolymerization of perfluorosulfonyl vinyl ether, tetrafluoroethylene and hexafluoropropylene in the presence of dispersant, solvent and initiator. The dispersant / solvent is mixed solution of melamine derivative containing linear perfluoro hydrocarbon and water. The fluorine-containing polymer can be melt-spun into polymer fibers, which can be woven into fiber network that can be used as the reinforcing network material for ion exchange membranes and chlor-alkali ion membrane to reinforce and improve the ion exchange ability.
Owner:SHANDONG HUAXIA SHENZHOU NEW MATERIAL
Three-dimensional net-like structure, and method and device for producing three dimensional net-like structure
ActiveUS7625629B2Efficient use ofIncrease rangeWeft knittingSynthetic resin layered productsVolumetric Mass DensityEngineering
A method of and an apparatus for manufacturing a three-dimensional netted structure which is capable of rendering it unnecessary to carry out a finishing operation in a later stage, improving the degree of straightness of the side surfaces of the netted structure, meeting a demand for finishing the netted structure to modified shapes, and improving the durability of the netted structure. A three-dimensional netted structure (1) using thermoplastic resin as a raw material or a main raw material is characterized by a three-dimensional plate type netted structure, in which a plurality of filaments are helically and randomly entangled and partly and thermally bonded together. The density of any of at least three surfaces or four surfaces on the outer periphery of the three-dimensional netted structure is preferably relatively higher than the density of the other portion excluding these surfaces, and flaked or chipped PET bottles are used as a raw material or a main raw material for thermoplastic resin, such PET bottles being directly crushed and then melted to provide flakes, suiting to recycling promoting age, working well in waste disposal cost reduction, the uses of the three-dimensional netted structure (1) including, chiefly, shock absorbing materials, cushioning materials, and sound-absorbing materials.
Owner:C ENG CO LTD
Nylon 6 polymerization method and direct spinning method of melt of polymer obtained with nylon 6 polymerization method
ActiveCN105669969AIncrease profitReduce manufacturing costFlame-proof filament manufactureHollow filament manufacturePolymer sciencePolyamide
The invention relates a nylon 6 polymerization method and a direct spinning method of a melt of a polymer obtained with the nylon 6 polymerization method. A polyamide 6 prepolymer is prepared at the low temperature, the content of oligomers in the melt is controlled in advance, polymerization is completed before a large quantity of cyclic oligomers are generated with a condensation polymerization dynamic strengthening method, a nylon 6 polymer melt with certain molecular weight is acquired, the content of extracts in the product is smaller than or equal to 1.5 wt%, and the content of cyclic dipolymers is smaller than or equal to 0.2wt%; then, direct melt spinning forming is performed after condensation polymerization dynamic strengthening ends. The process is simple, energy consumption is further reduced while the utilization rate of caprolactam is increased, the obtained melt can be directly used for melt spinning, high-capacity large-scale production is easy to realize, a modifier can be added in the polymerization process, flexible production of nylon 6 is realized, and the nylon 6 can be applied to fibers for clothes, industrial filaments, engineering plastics and other fields.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HENGYI PETROCHEMICAL RES INST CO LTD
Process for forming polymeric micro and nanofibers
Polymers that have extremely high melt viscosities are very difficult to extrude and stretch making it difficult to synthesize fibers of such polymers via conventional methods. A process is provided for producing a polymer fiber which involves blowing a mixture of a polymer and a gas through a nozzle such that polymer micro- and / or nano-fibers are produced. The polymer fibers are characterized in that they have a diameter less than the diameter of the outlet aperture of the nozzle.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
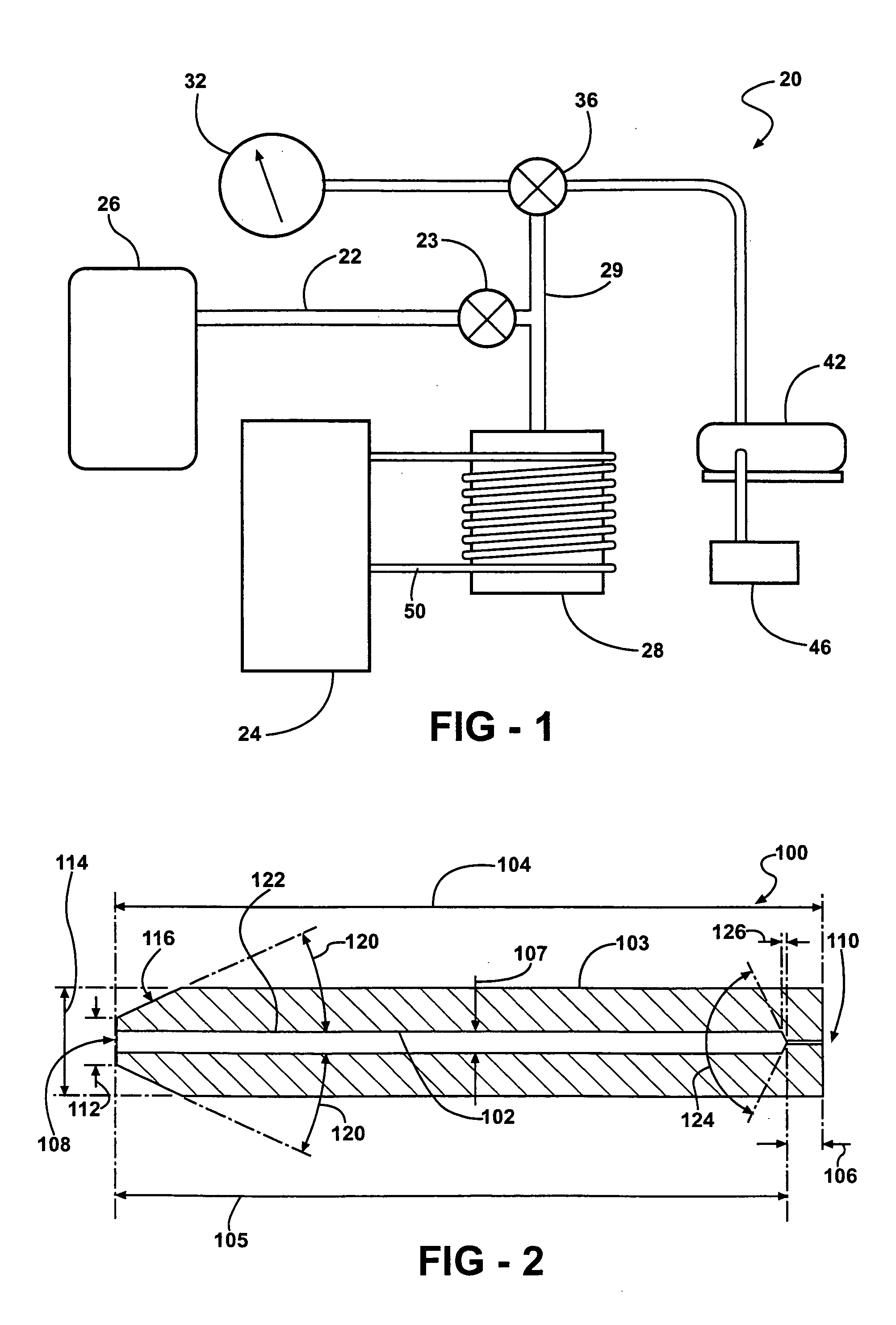
Electrohydrodynamic printing and manufacturing
ActiveUS20090233057A1Liquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge heatingFiberManufacturing technology
An stable electrohydrodynamic filament is obtained by causing a straight electrohydrodynamic filament formed from a liquid to emerge from a Taylor cone, the filament having a diameter of from 10 nm to 100 μm. Such filaments are useful in electrohydrodynamic printing and manufacturing techniques and their application in liquid drop / particle and fiber production, colloidal deployment and assembly, and composite materials processing.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Composite fiber filter comprising nan0-materials, and manufacturing method and apparatus thereof
InactiveUS20080217807A1Improve efficiencyPronounced antibacterial activityLayered productsWood working apparatusYarnElectrospinning
Disclosed herein is a method for manufacturing a composite fiber filter having high efficiency and high functionality, the method comprising: melt-spinning microfiber yarns on a forming rod, which is made of a conductive material, grounded at one end thereof and rotatably driven, using a melt-spinning device, to form on the forming layer a microfiber layer consisting of the microfiber yarns; and electrospinning on the microfiber layer an electrospinnable polymer solution having a given dielectric constant, using an electrospinning device, so as to form on the microfiber layer a nanofiber layers consisting of nanofiber yarns, wherein the microfiber yarns of the microfiber layer and the nanofiber yarns of the nanofiber layer contain silver nanoparticles so as to have an antibacterial function.
Owner:LEE BONG DAE +2
Meltblown process with mechanical attenuation
InactiveUS6773648B2High speed spinningImprove productivityPulp properties modificationArtificial filament physical treatmentCelluloseUltrasound attenuation
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER NR CO
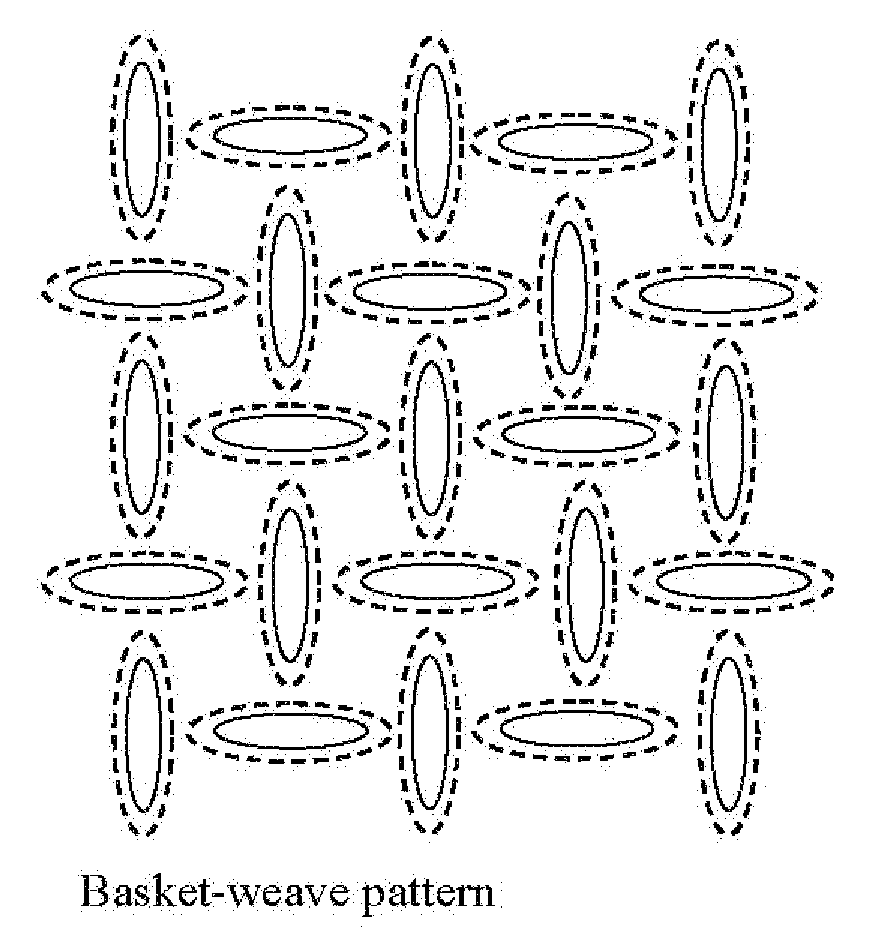
Nonwoven bonding patterns producing fabrics with improved abrasion resistance and softness
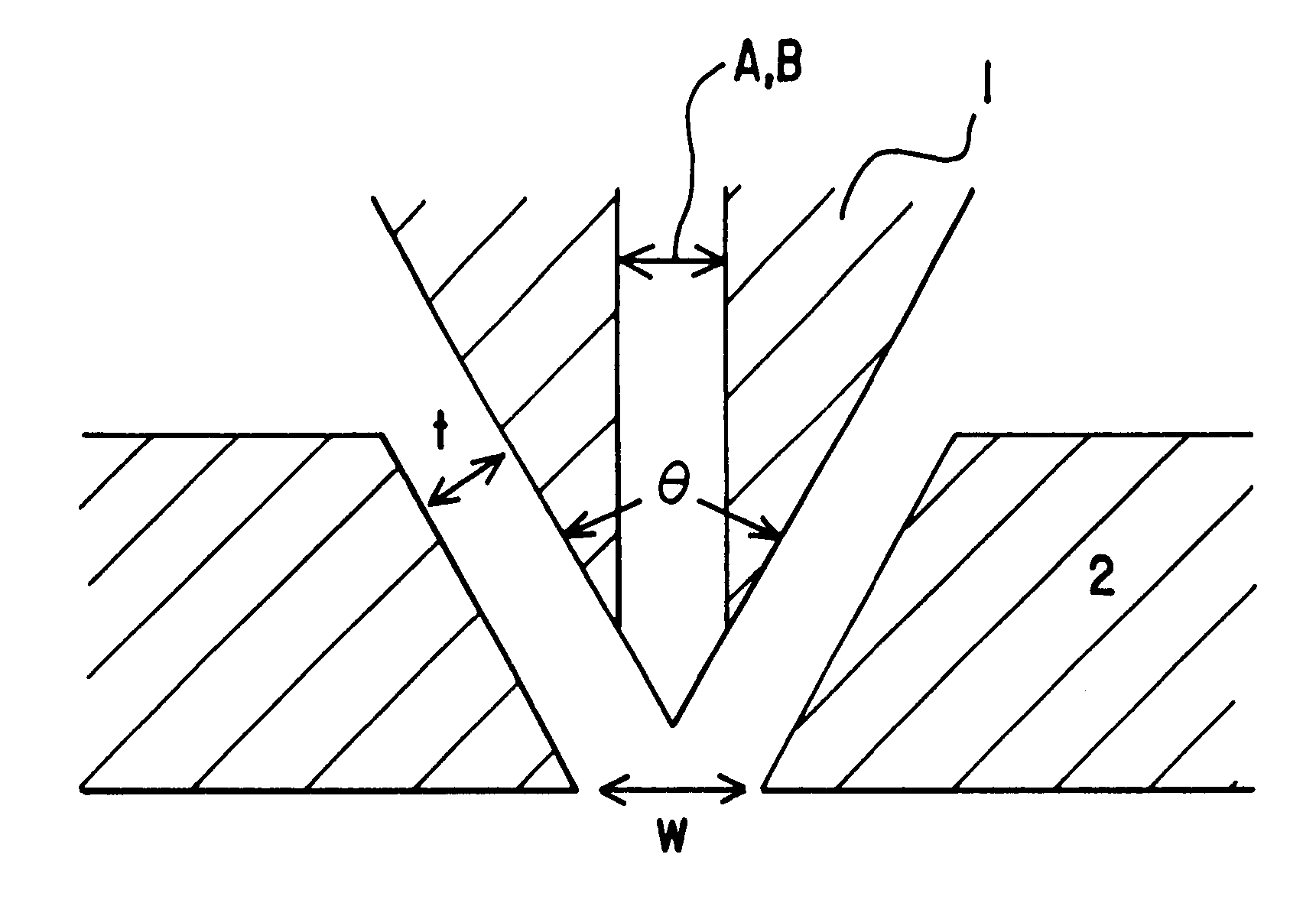
ActiveUS20080268194A1Excellent abrasion resistanceHigh strengthStampsWrappersEngineeringNonwoven fabric
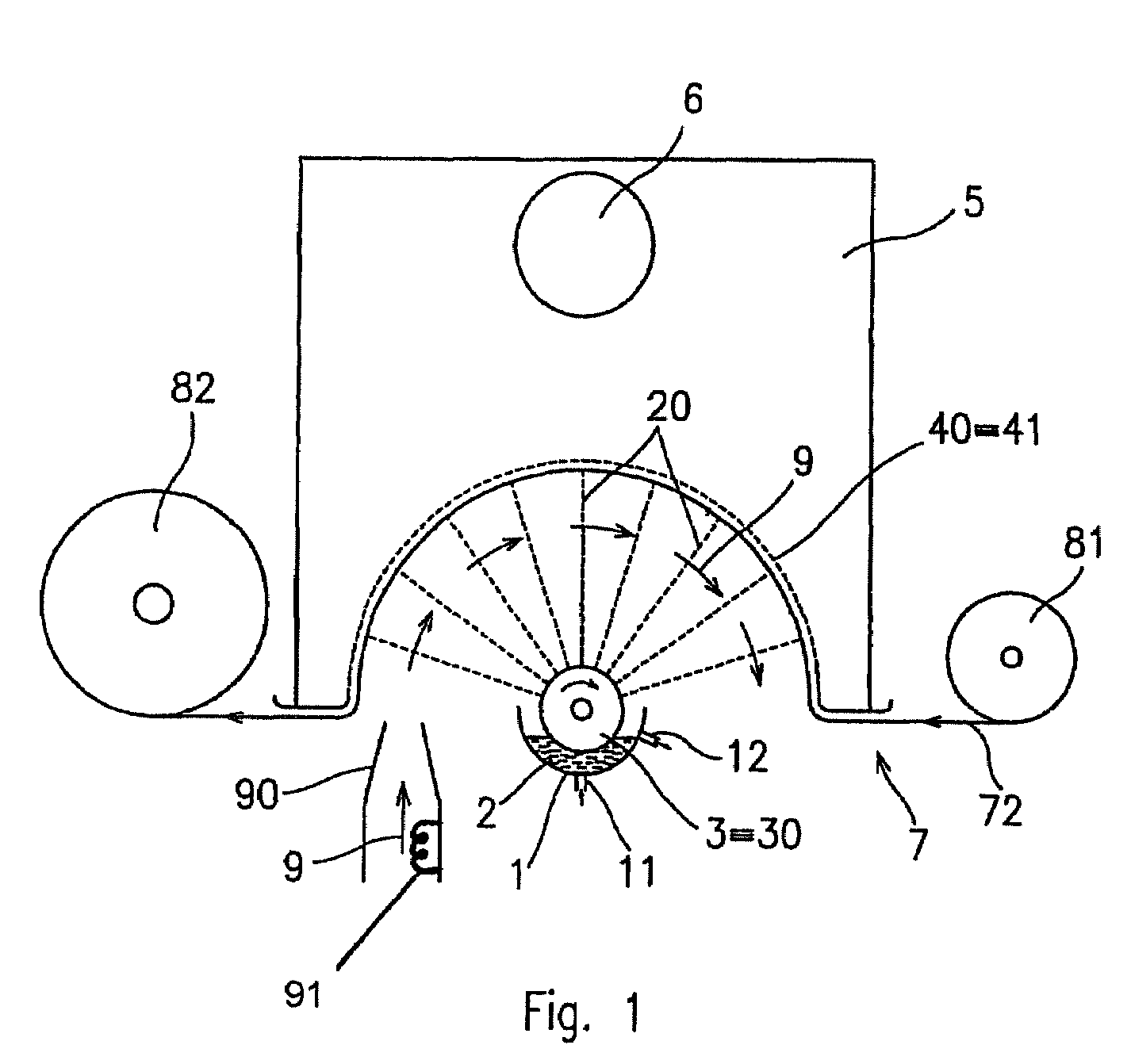
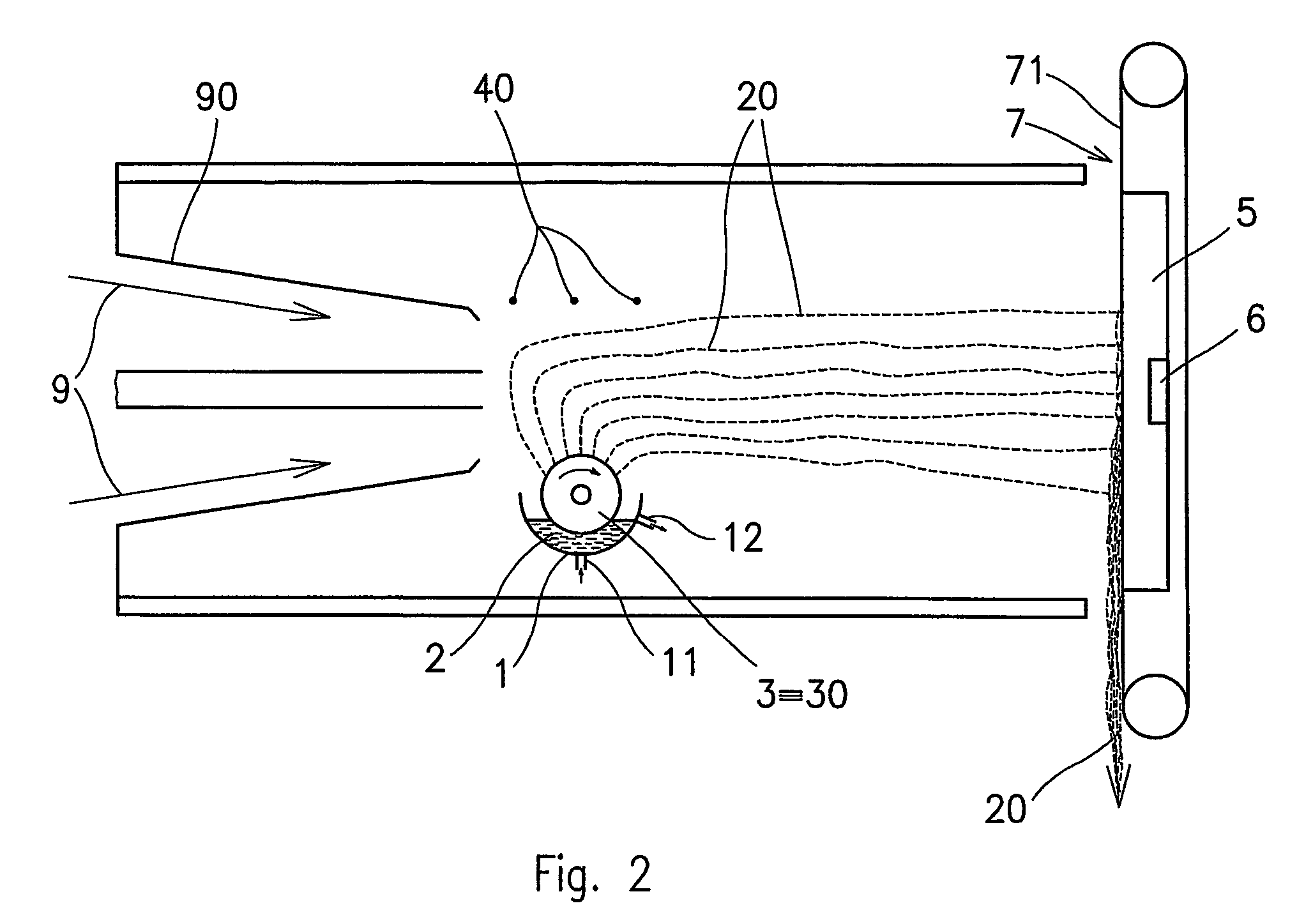
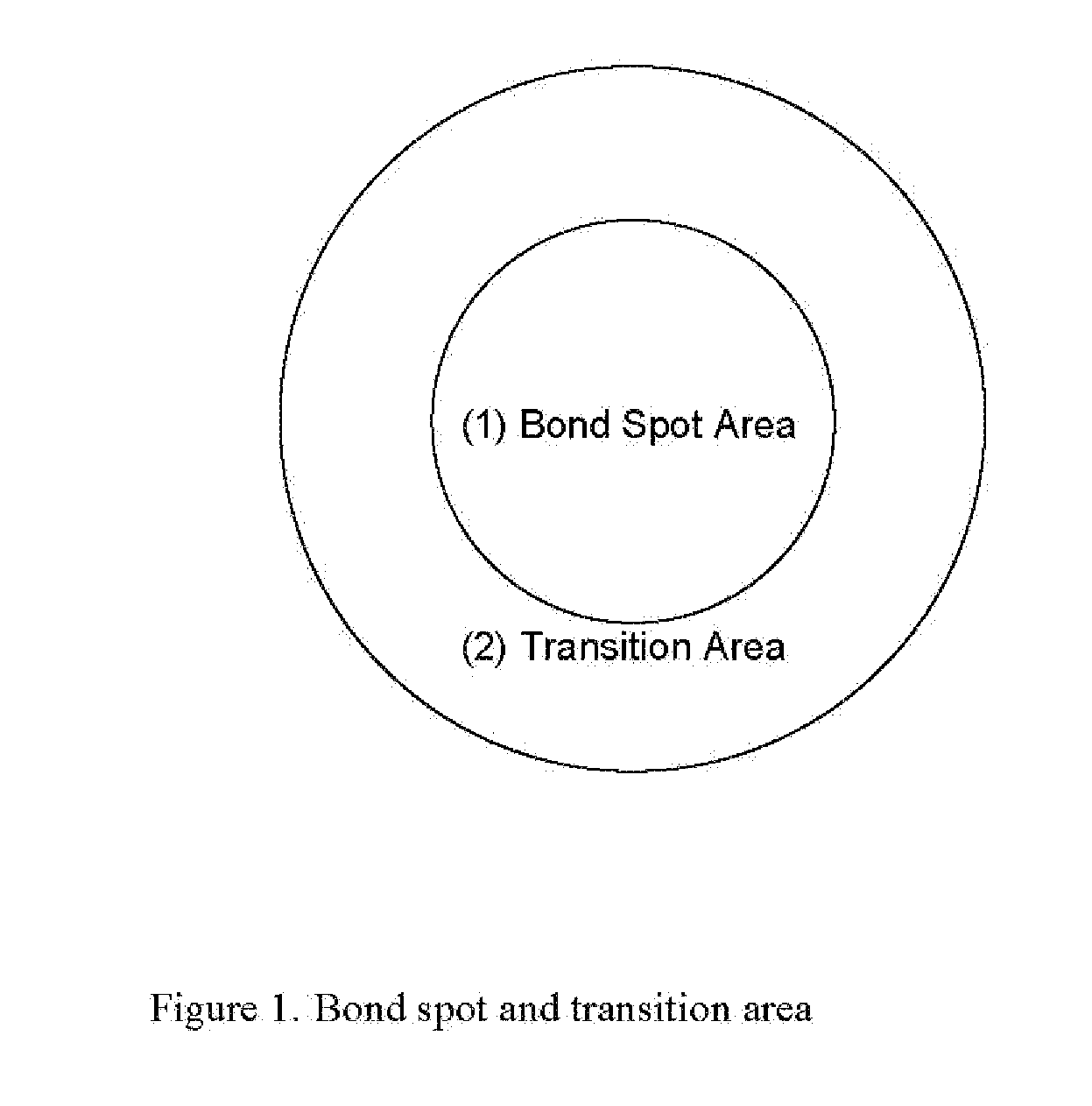
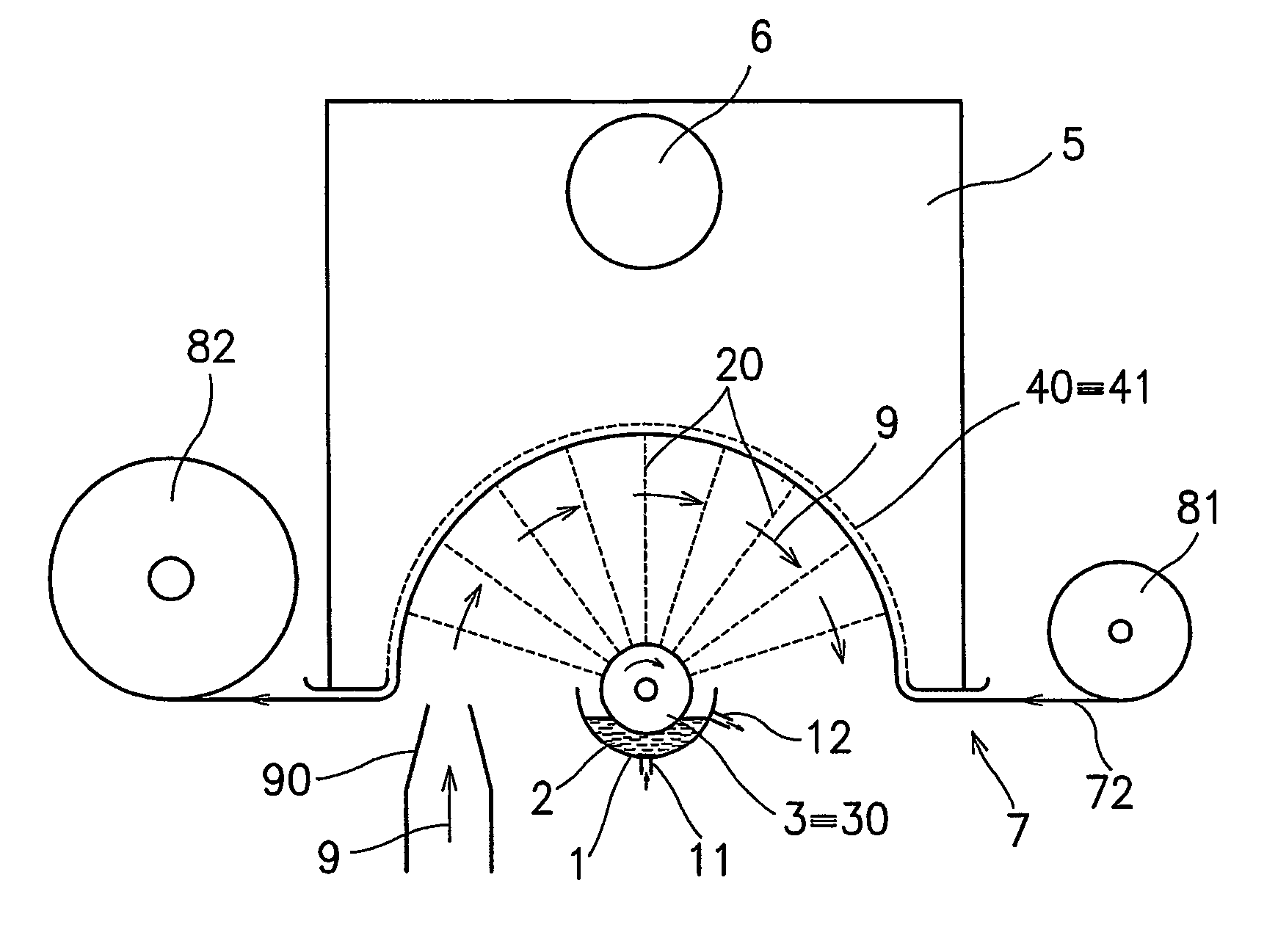
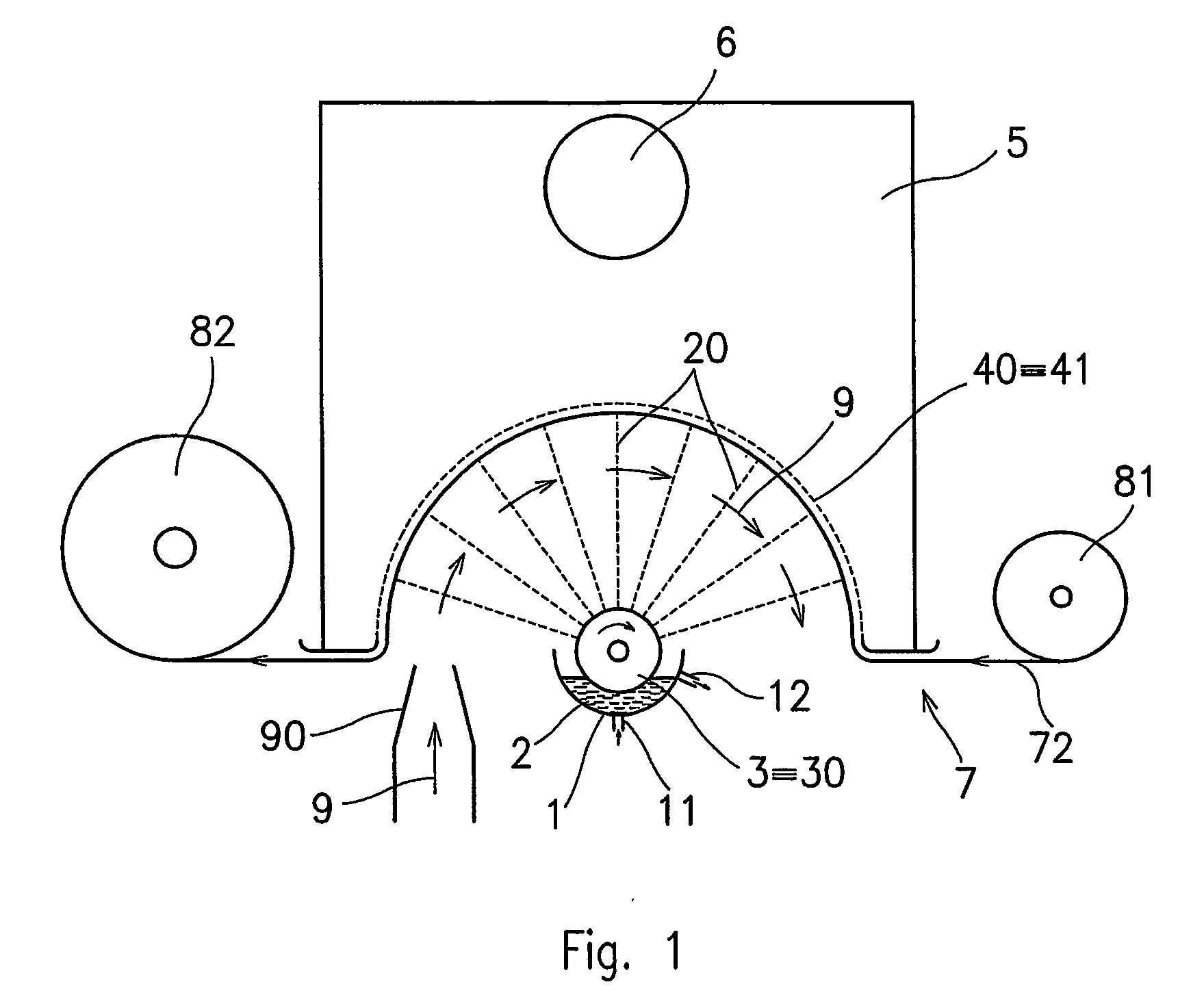
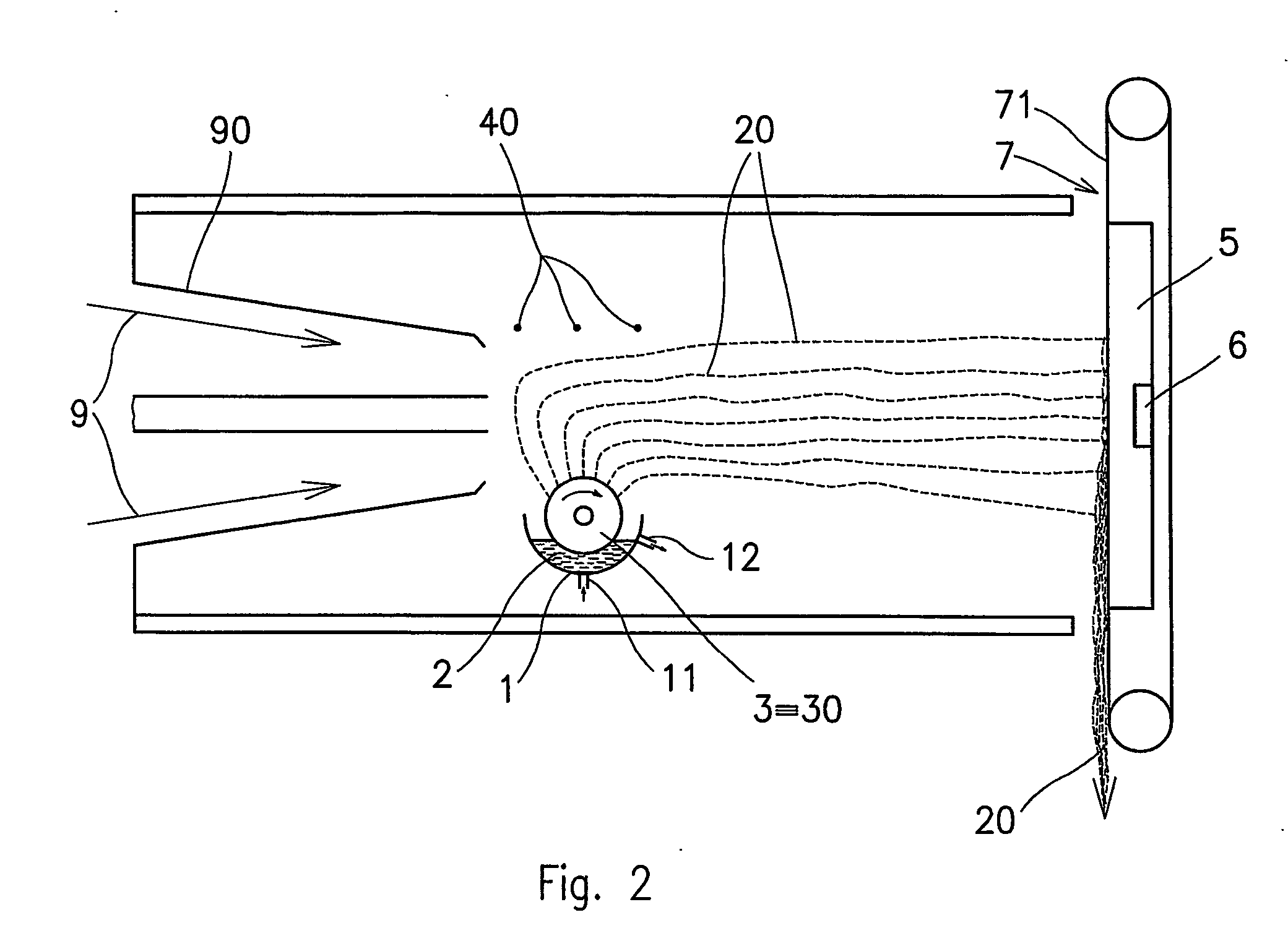
A thermal bonding pattern for nonwoven fabric possessing improved abrasion resistance while retaining softness, comprising a basket-weave pattern or other pattern having a transition area (2) equal to at least 10% of bonding spot area (1) in FIG. 1, more preferably a transition area (2) equal to at least 50% of bonding spot area (1), and most preferably a transition area (2) equal to at least 100% of bonding spot area.
Owner:A AHLSTROM CORP
Spunbond fibers and fabrics from polyolefin blends
The invention described relates to a polyolefin blend composition suitable for spunbond fiber or filament compositions, and to fabric compositions and composite constructions therefrom, said blend comprising a) from 60-98 wt % of at least one random propylene copolymer having a comonomer content of from 8 to 25 wt % and a crystalline melting point (Tm) as determined by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) of from about 40° C. to about 110° C.; and b) from 2-40 wt % of at least one substantially isotactic polypropylene homopolymer or copolymer comprising one or more C2 and / or C4-C8 comonomer, having a crystalline melting point (Tm) as determined by DSC greater than or equal to 120° C. The blends of the present invention typically have a melt flow rate (MFR) of from 100 g / 10min to about 500 g / 10min.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Method of nanofibres production from a polymer solution using electrostatic spinning and a device for carrying out the method
ActiveUS20060290031A1Quality improvementImprove uniformityElectric discharge heatingSpinnerette packsElectrospinningPotential difference
The invention relates to a method of nanofibres production from a polymer solution using electrostatic spinning in an electric field created by a potential difference between a charged electrode and a counter electrode. The polymer solution (2) is for spinning supplied into the electric field using the surface of the rotating charged electrode (30), while on a part of the circumference of the charged electrode (30) near to the counter electrode (40) is a spinning surface created, by which is a high spinning capacity reached. Further the invention relates to a device for carrying out the method, where the charged electrode (30) is pivoted and by its (bottom) part of its circumference it is immersed in the polymer solution (2), while against the free part of the circumference of the charged electrode (30) is positioned the counter electrode (40).
Owner:TECHNICKA UNIVEZITA V LIBERCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com