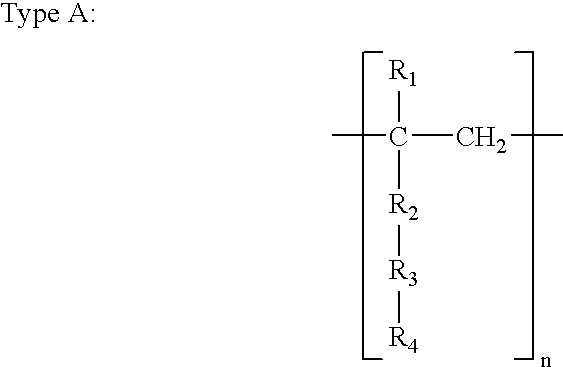
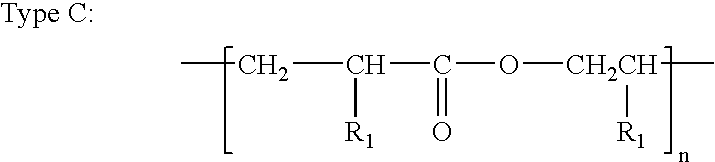
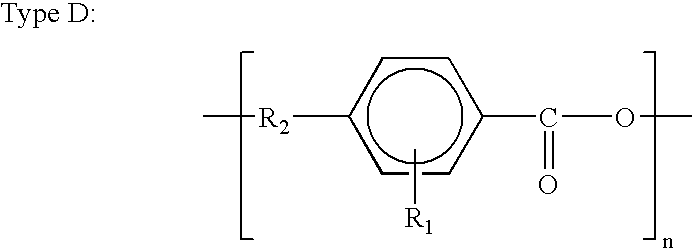
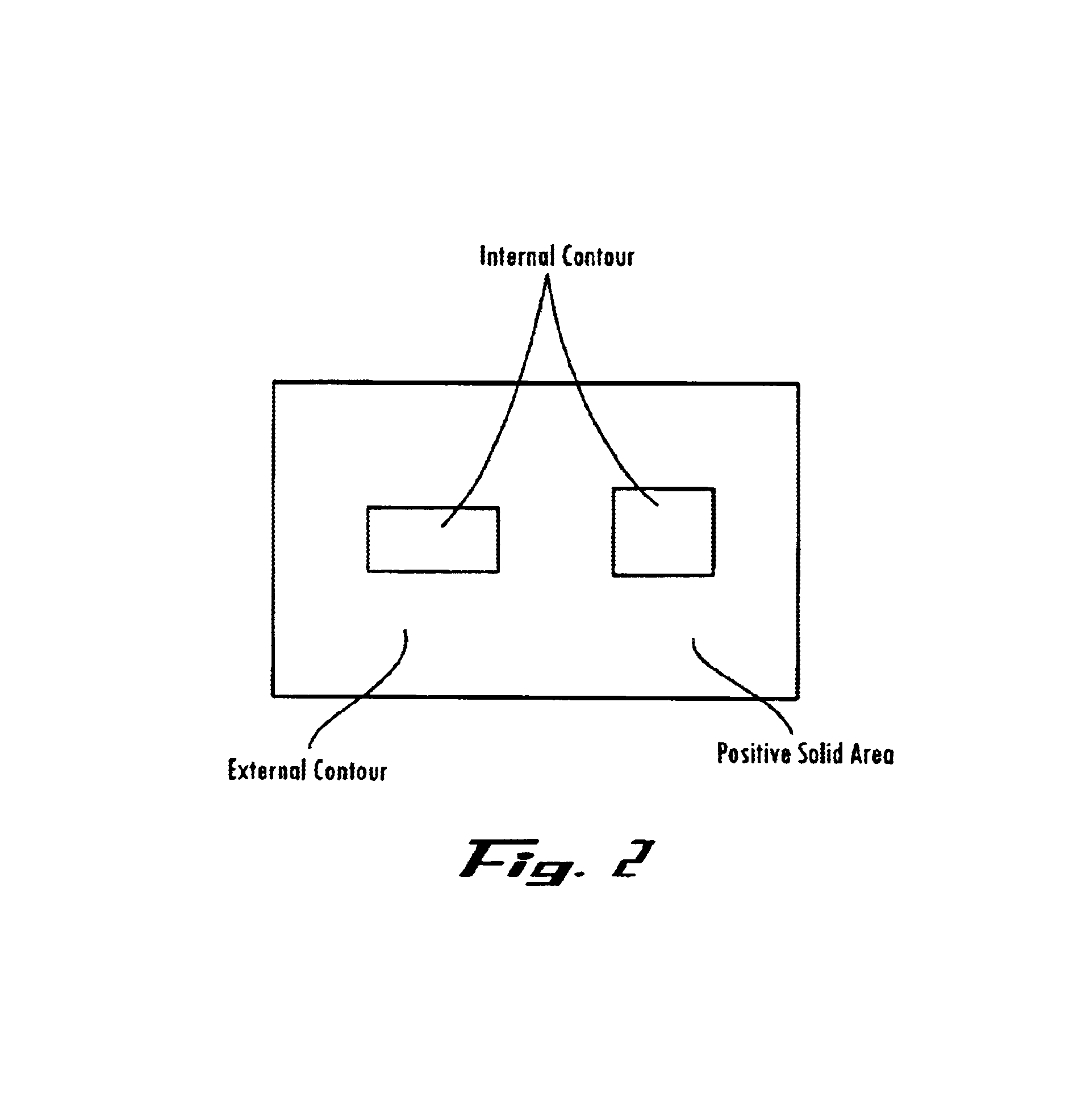
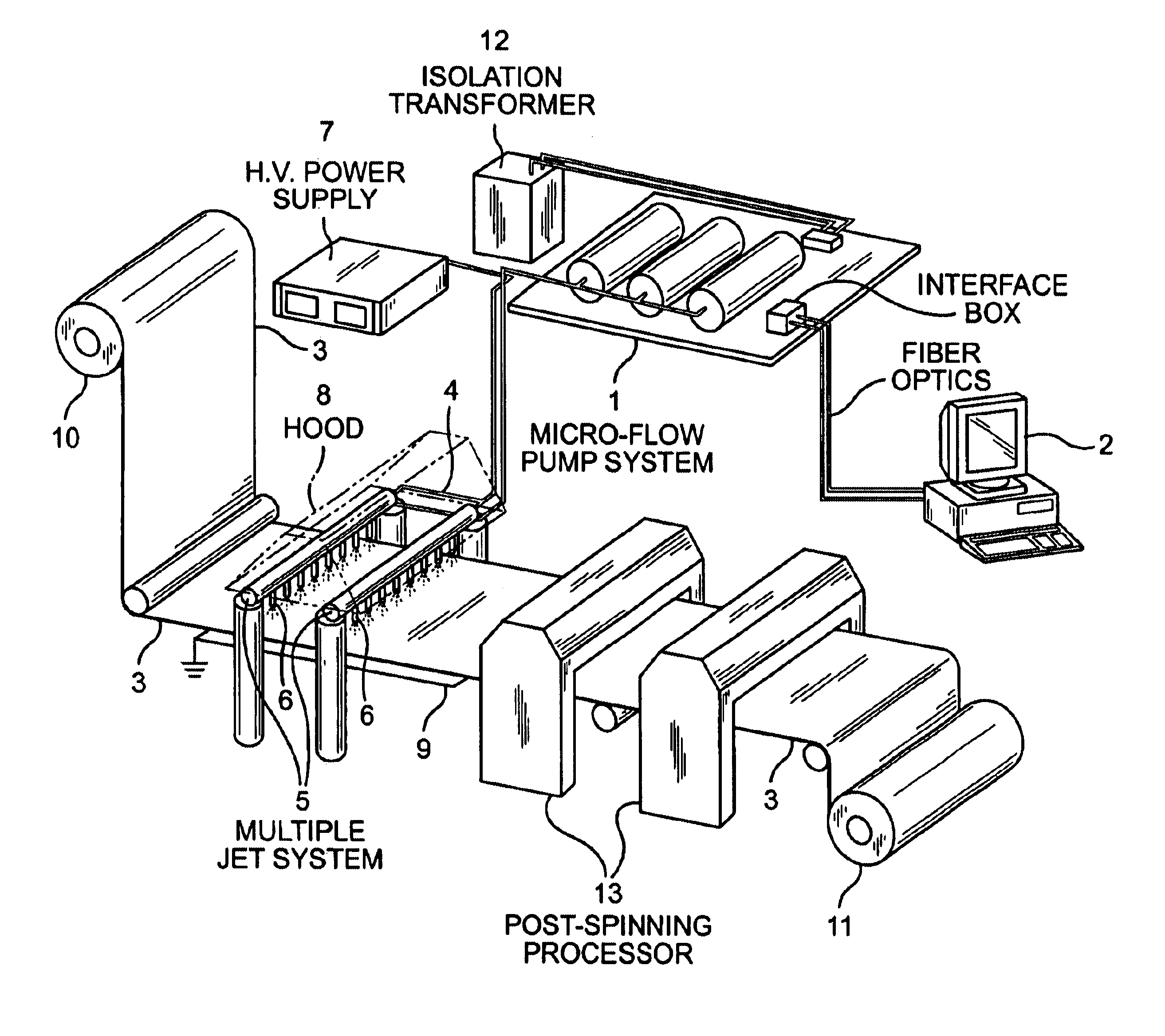
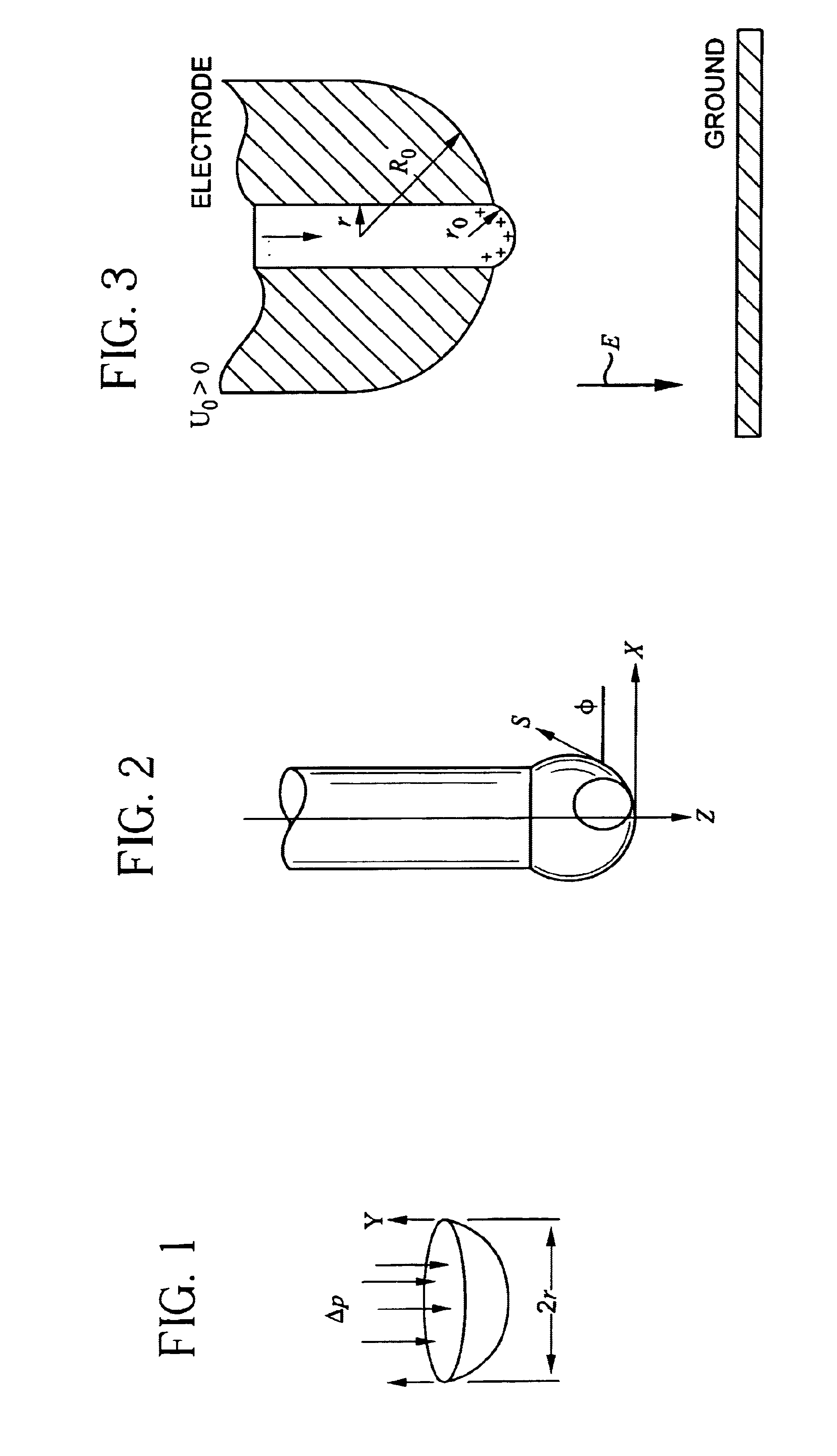
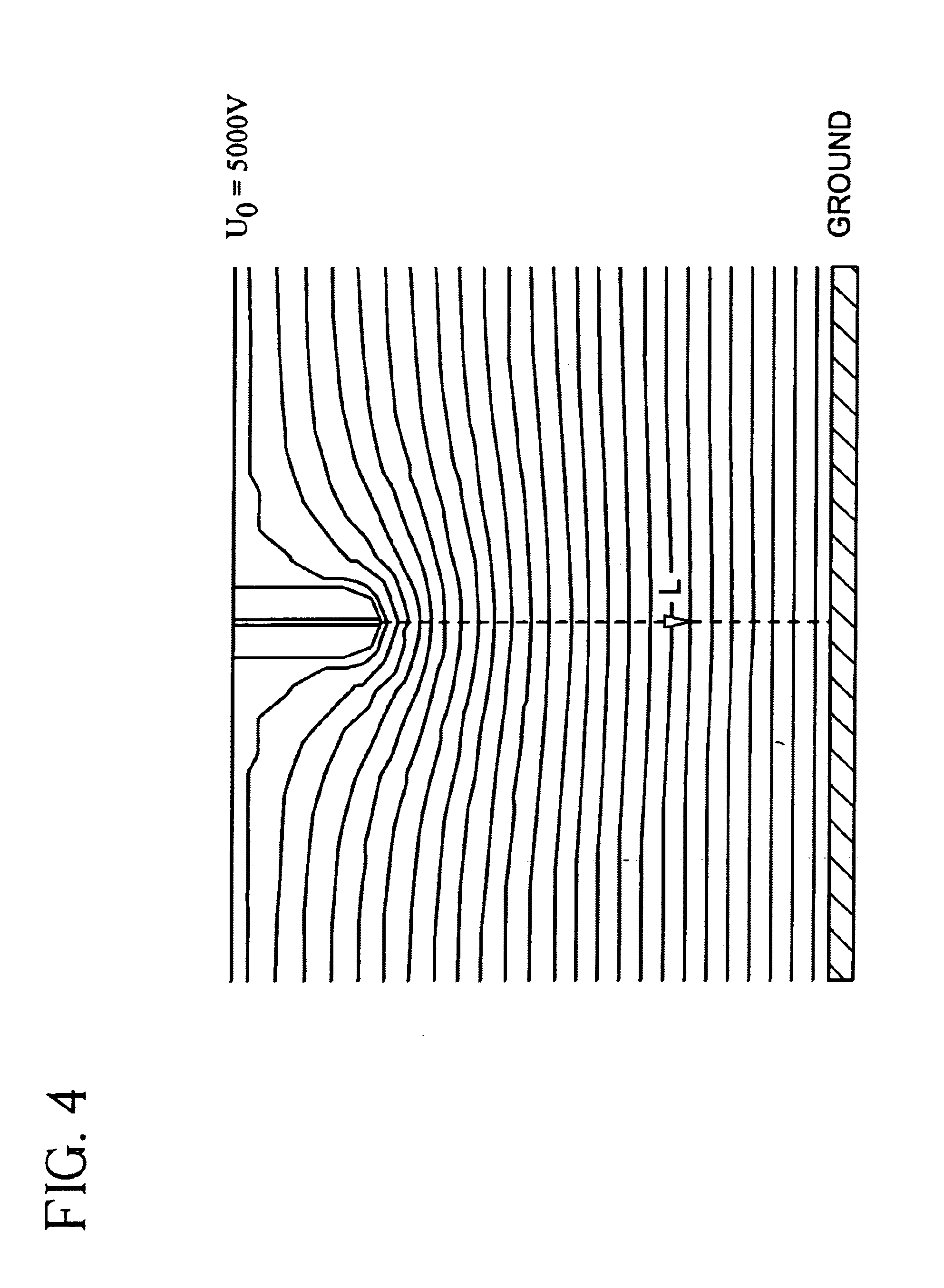
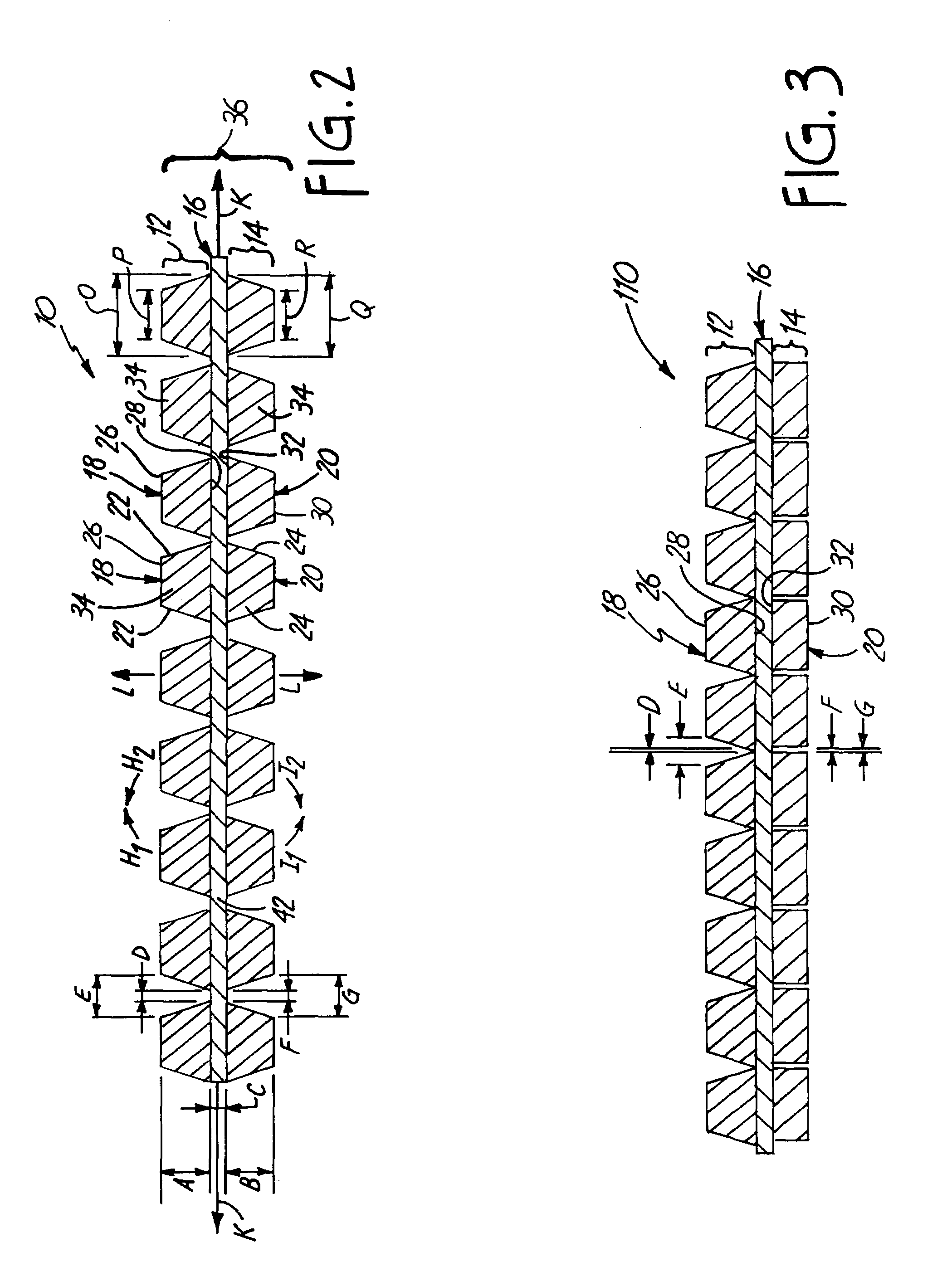
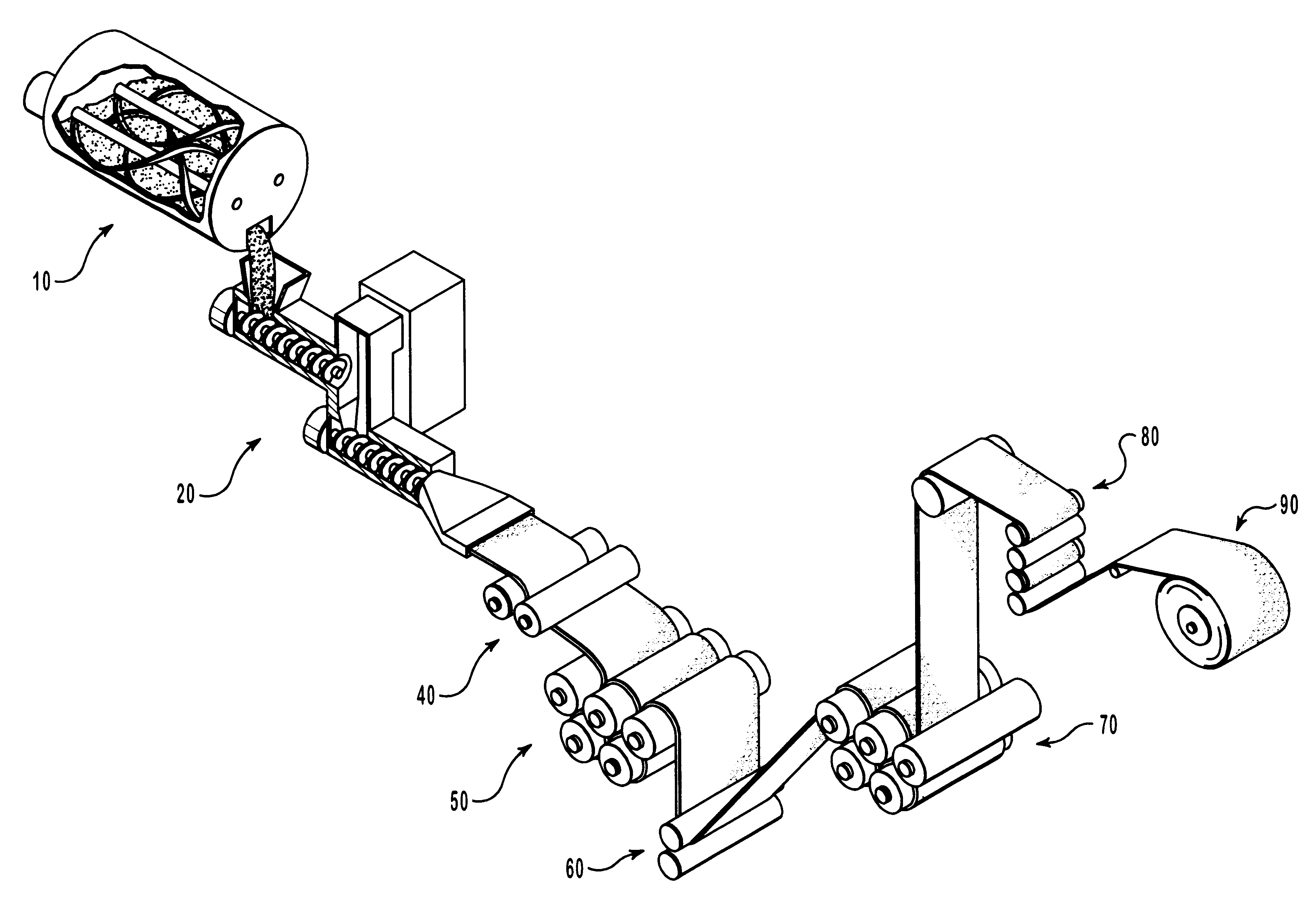
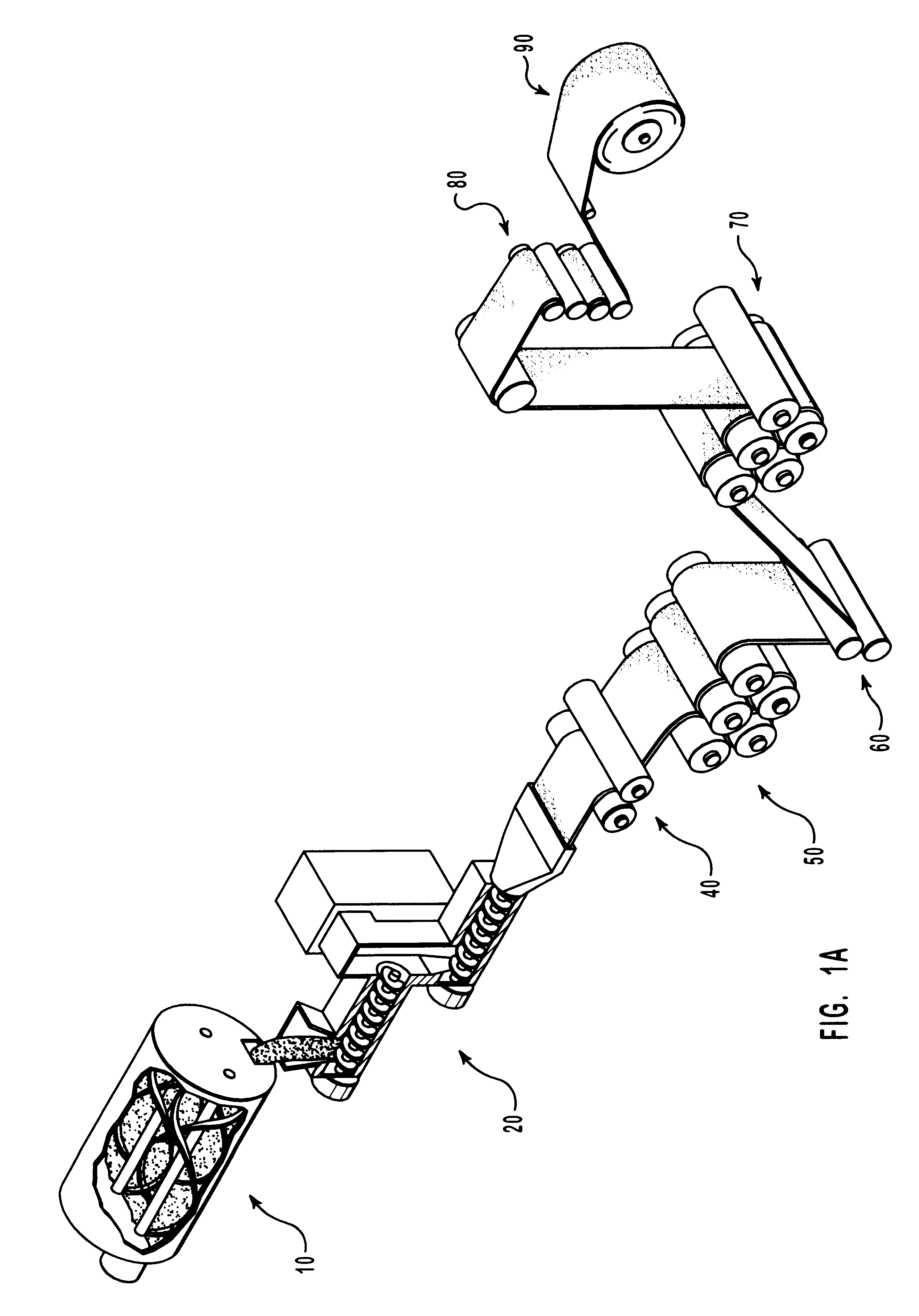
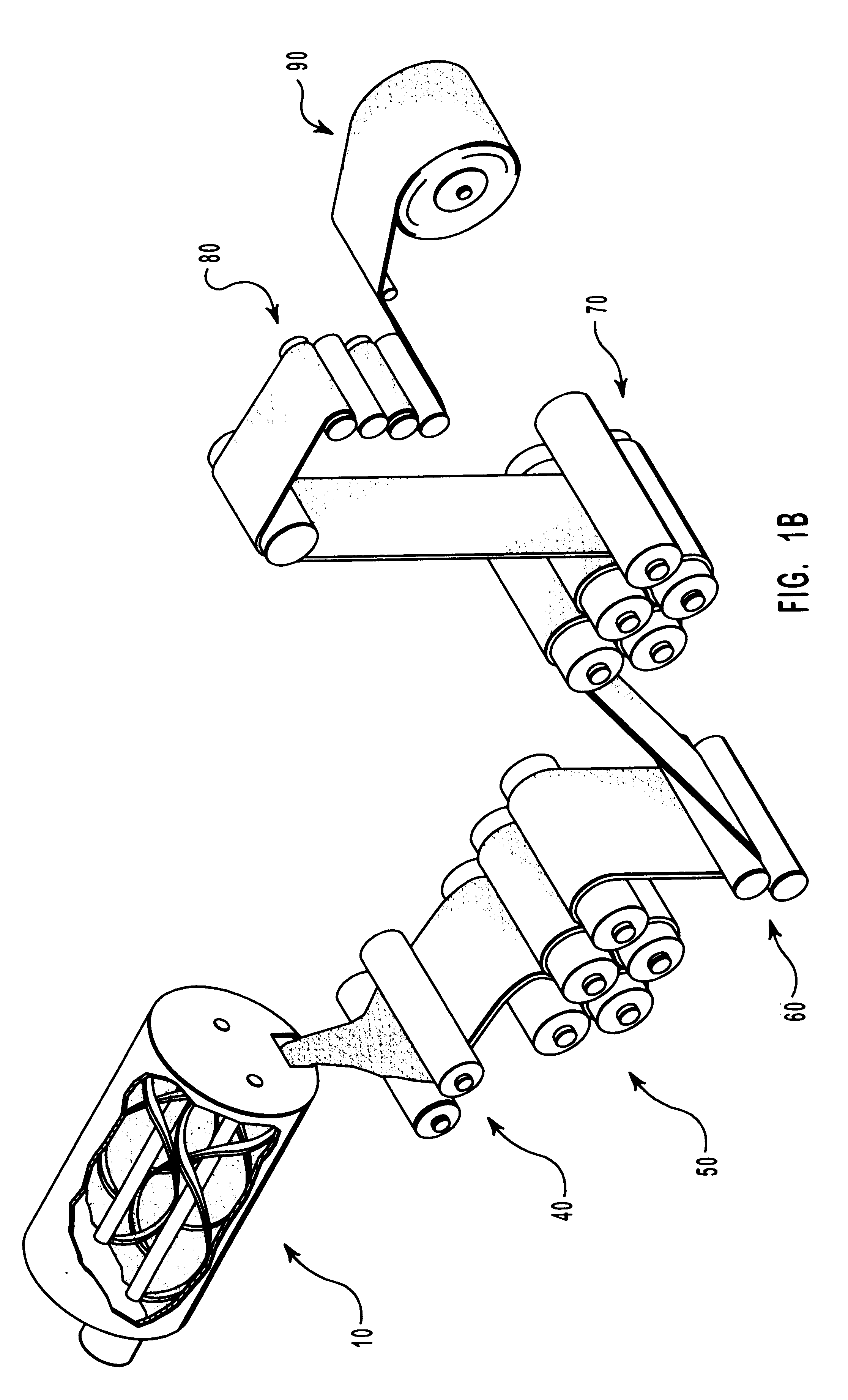
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
24099results about "Flat articles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
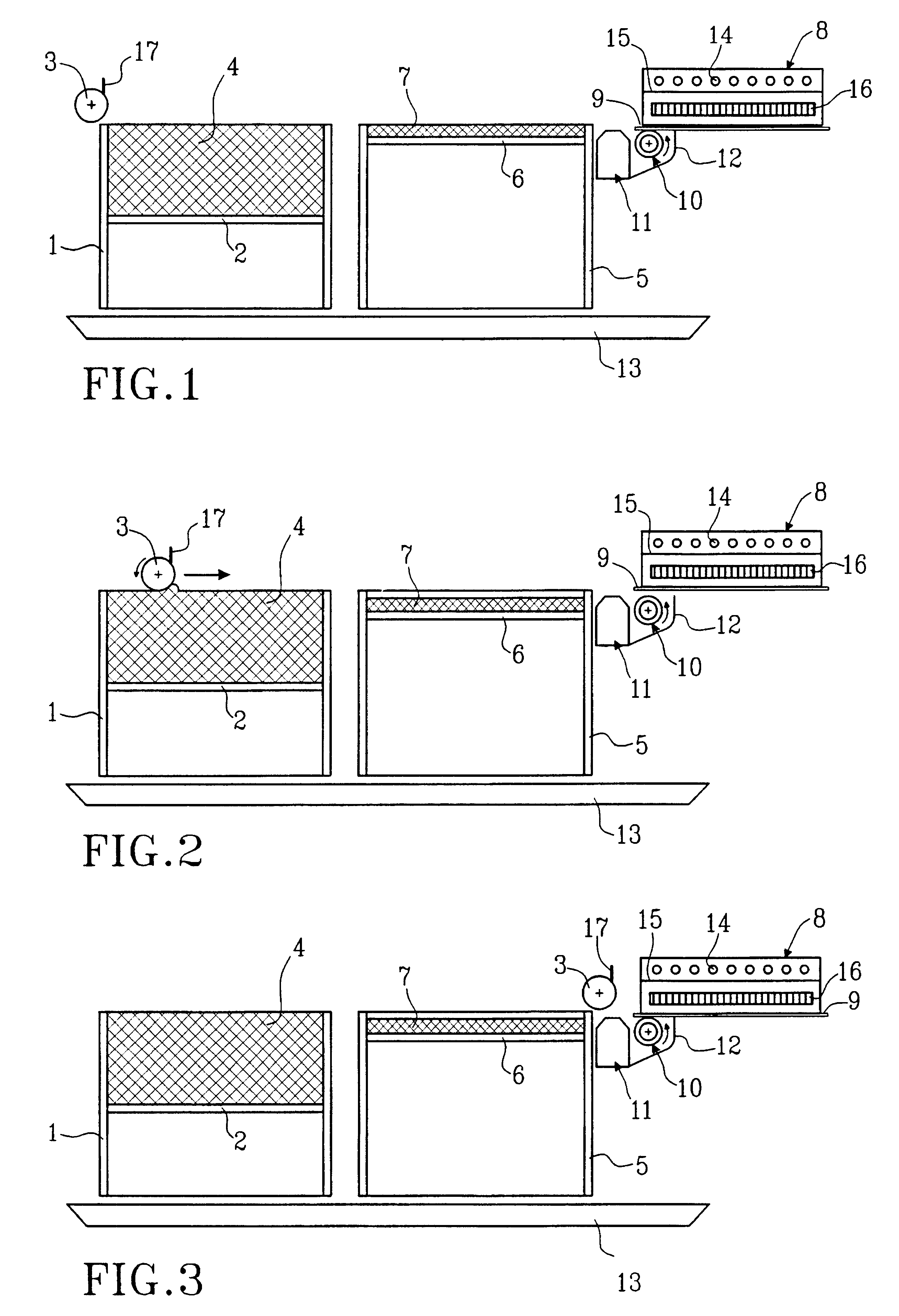
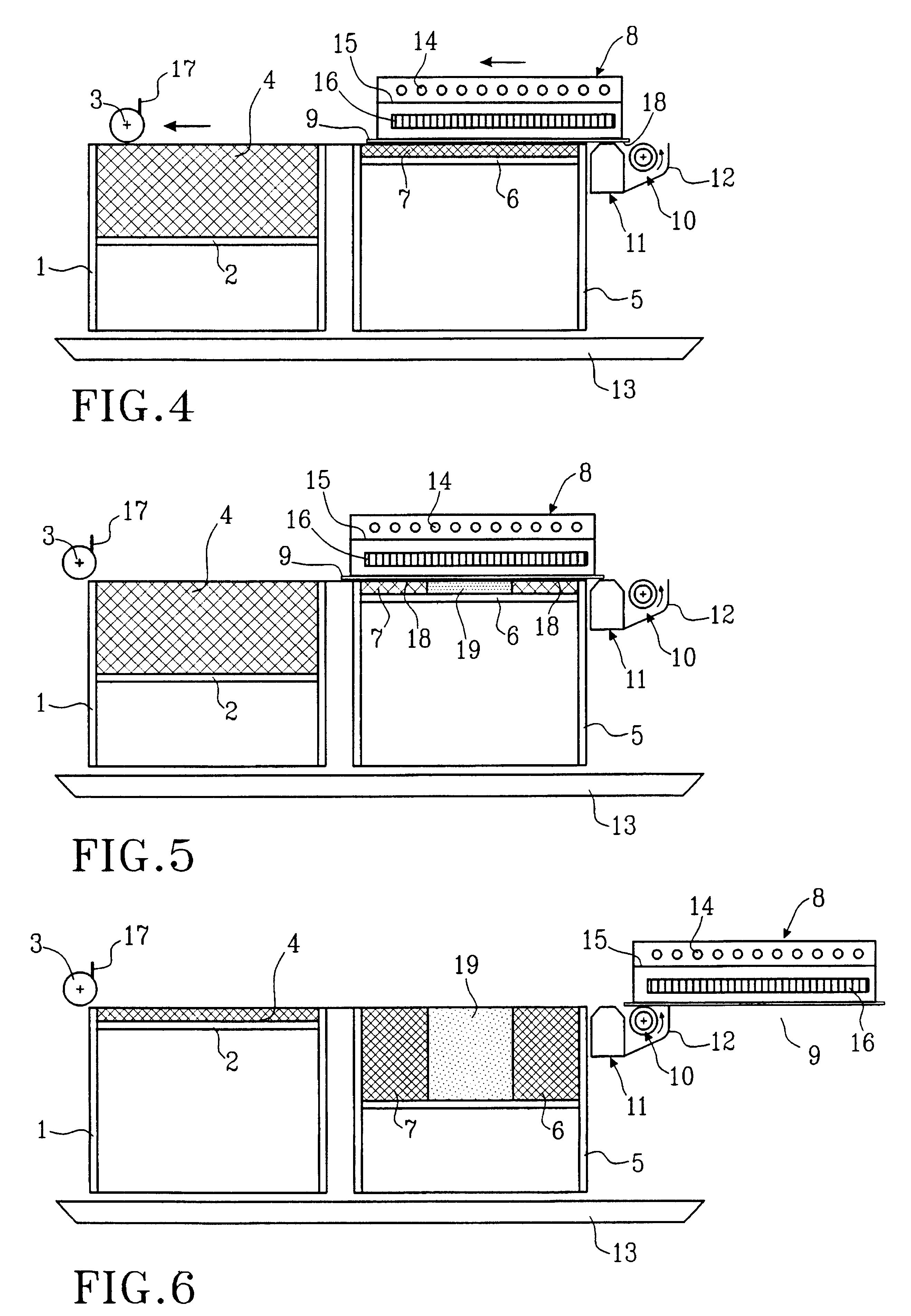
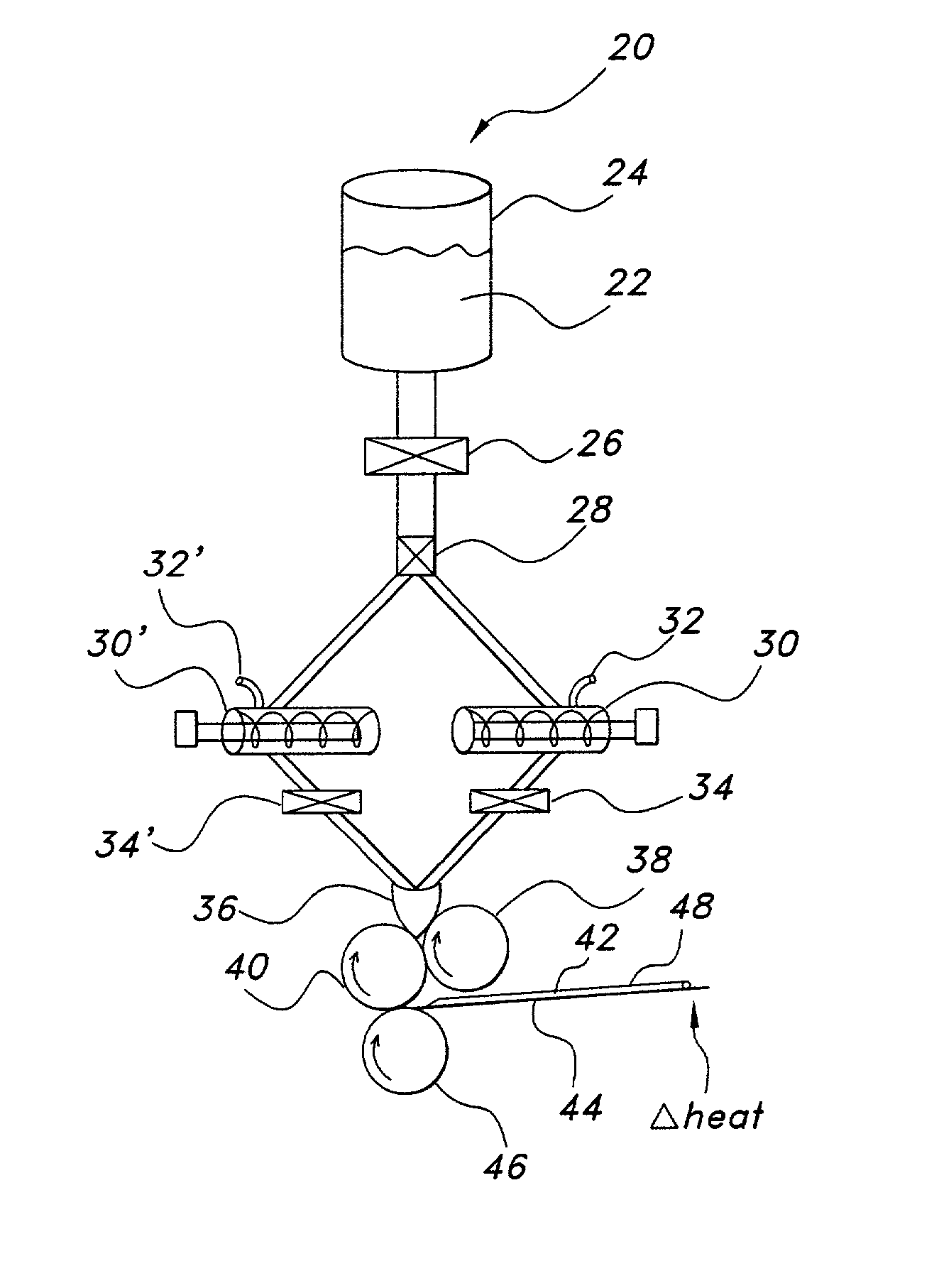
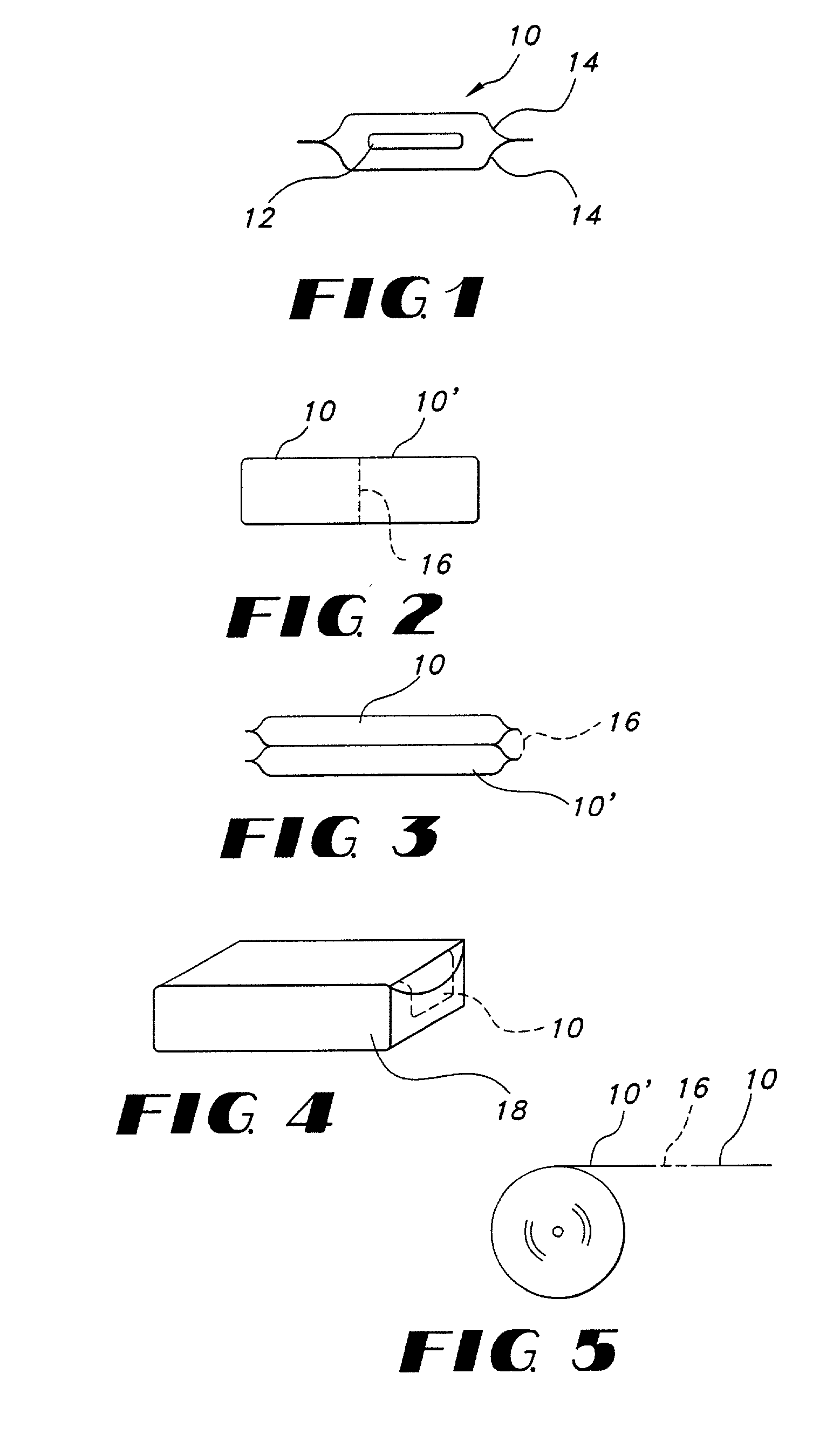
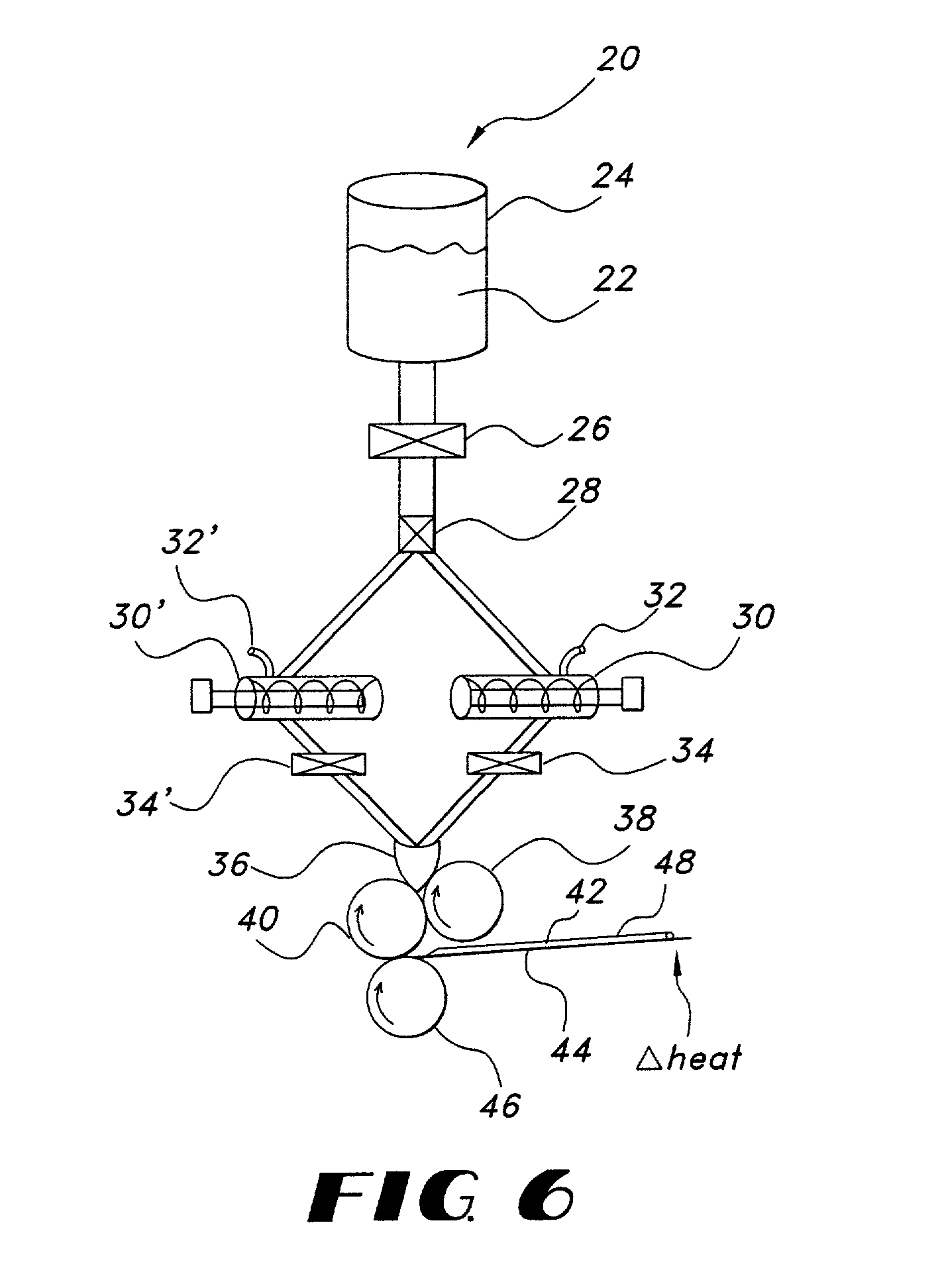
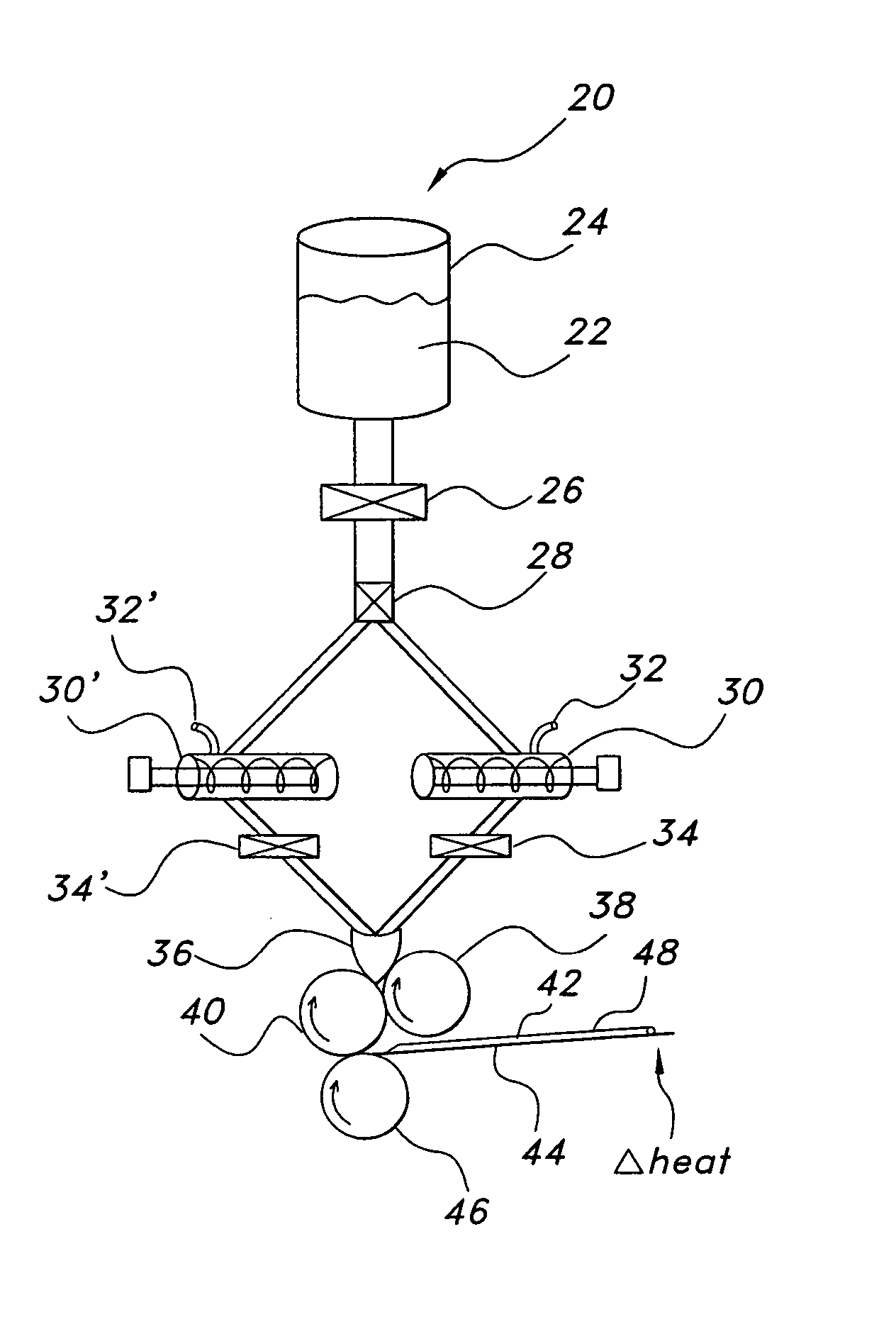
Wound closure material
Articles are provided having no orientation or a multi-directional orientation. Such articles may be in the form of films, ribbons, sheets, and / or tapes and may be utilized as buttresses with a surgical stapling apparatus or as reinforcing means for suture lines.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Method of making an embolic filter
Embolic protection filters and methods of making and using such devices are disclosed. An illustrative method of making a device for filtering embolic debris from a body may include the steps of molding a filter assembly that includes a distal tip and a filter portion, forming a plurality of apertures within the filter portion, and coupling a support member to the filter assembly that is adapted to shift the filter portion between a collapsed configuration and an expanded configuration.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
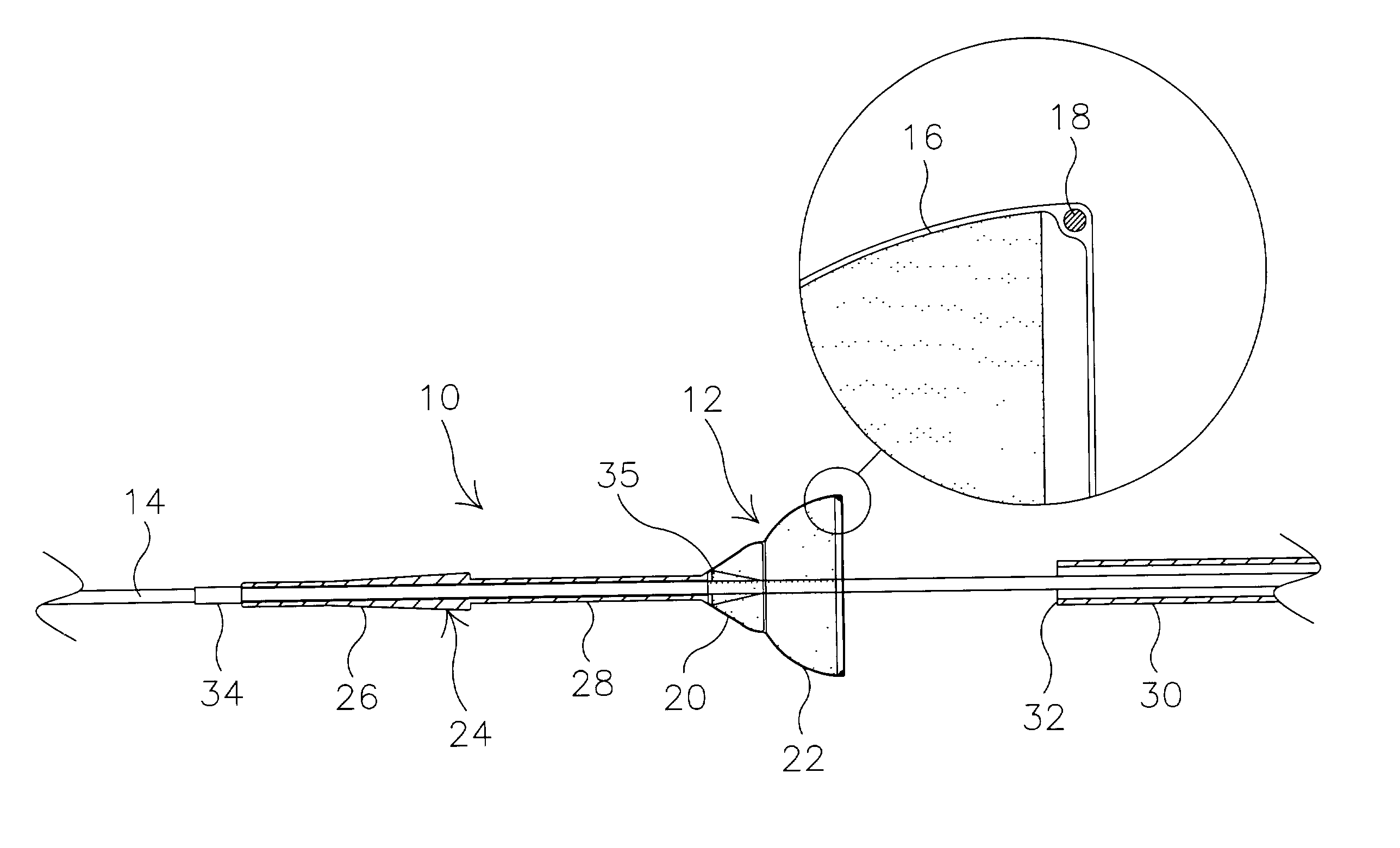
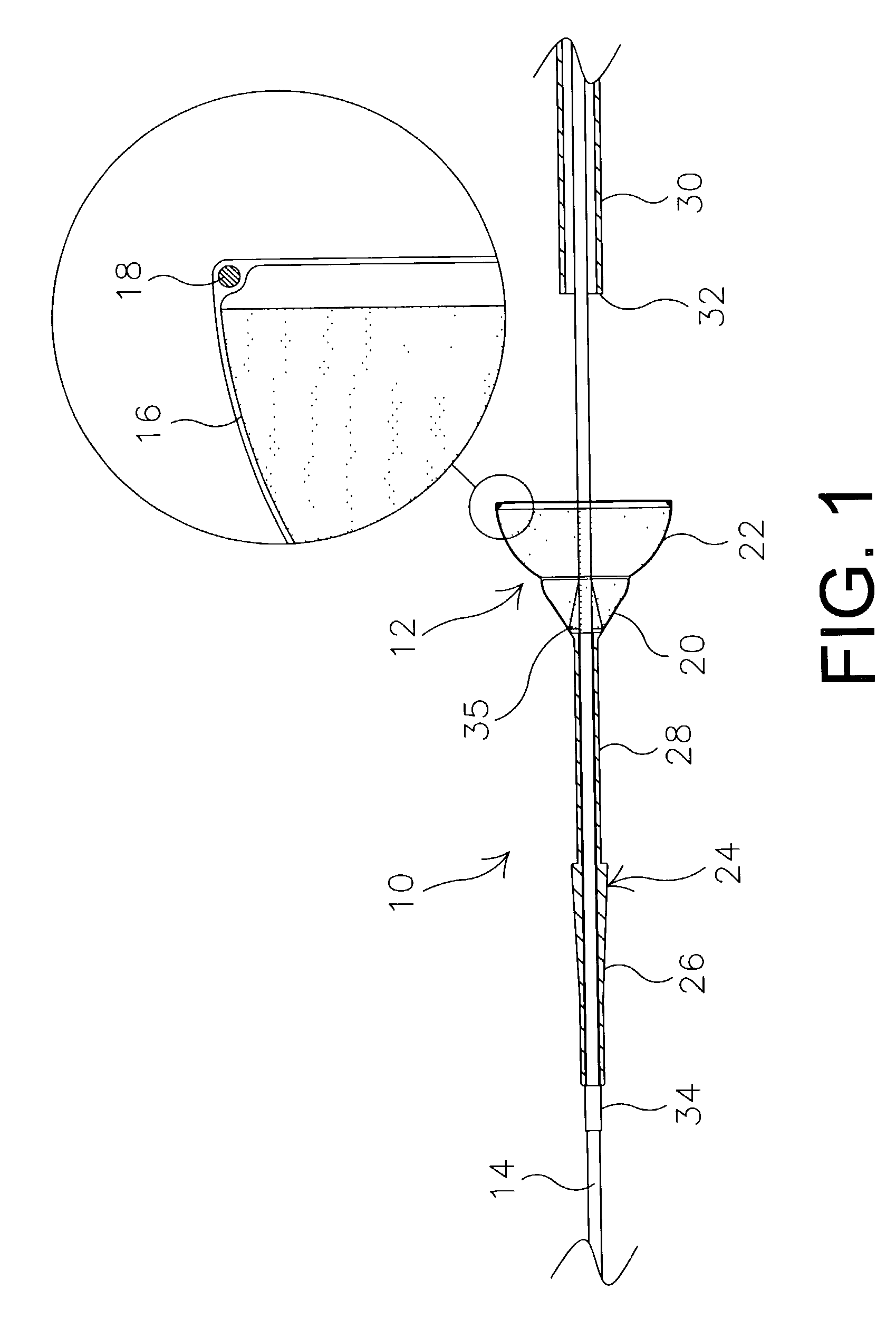
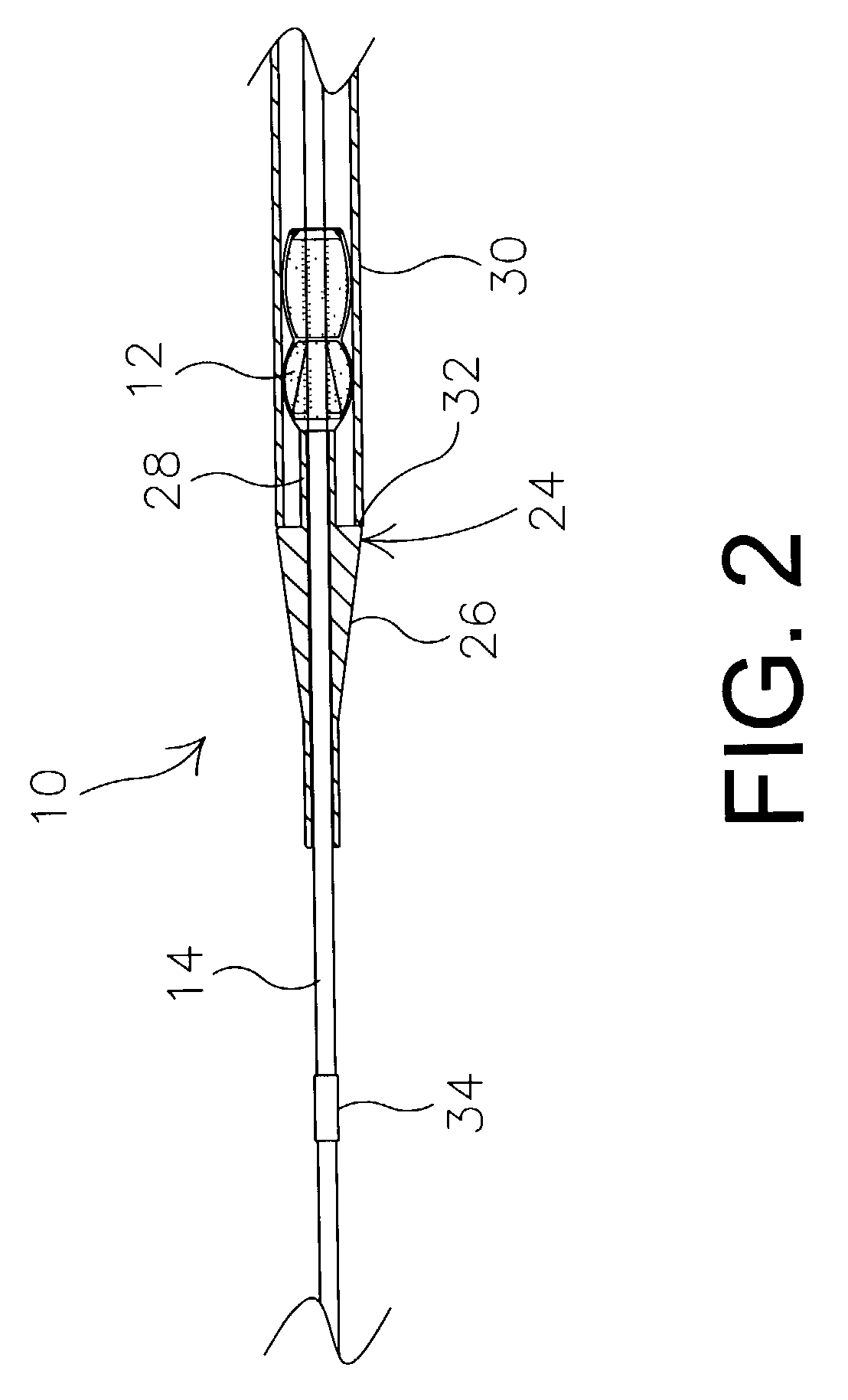
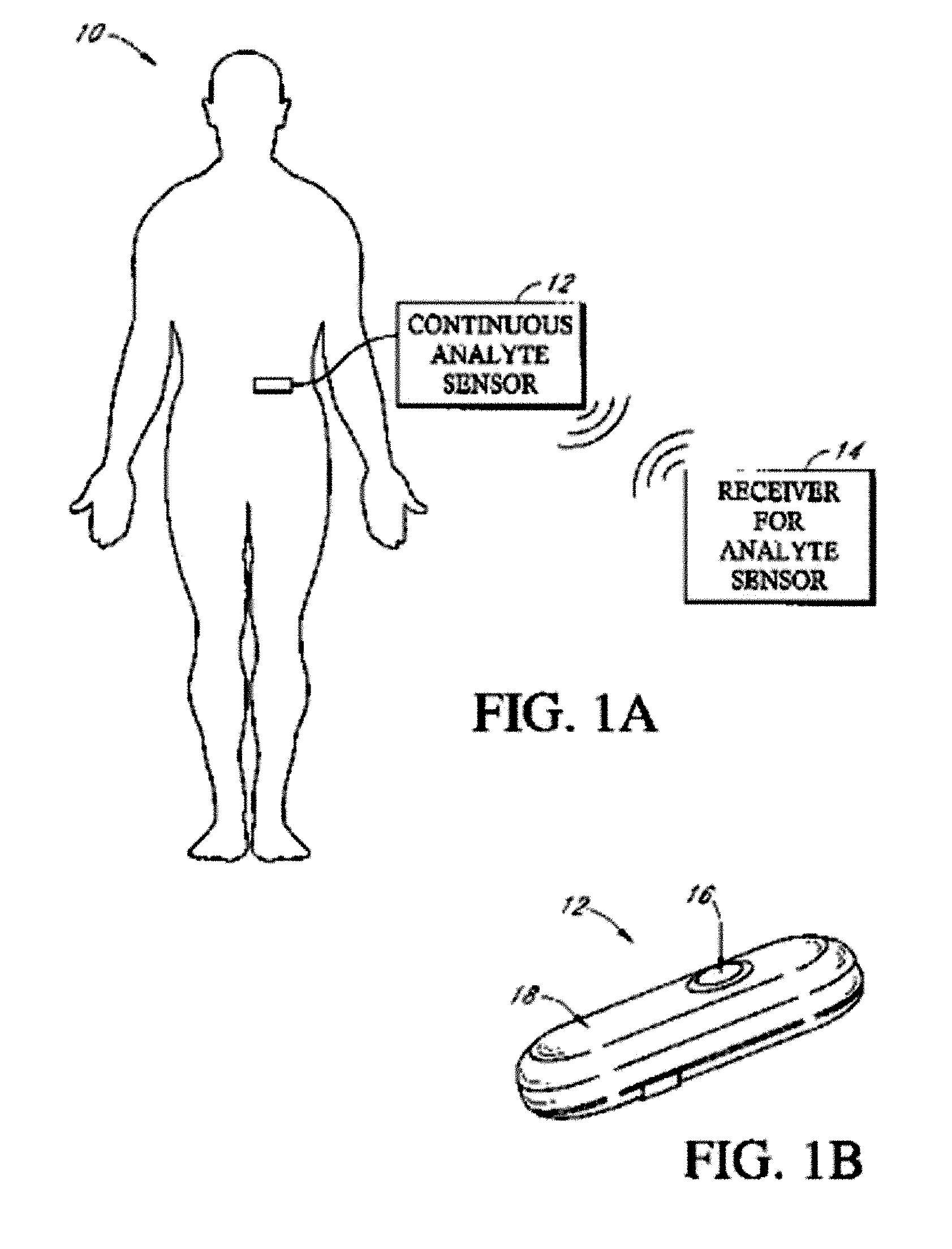
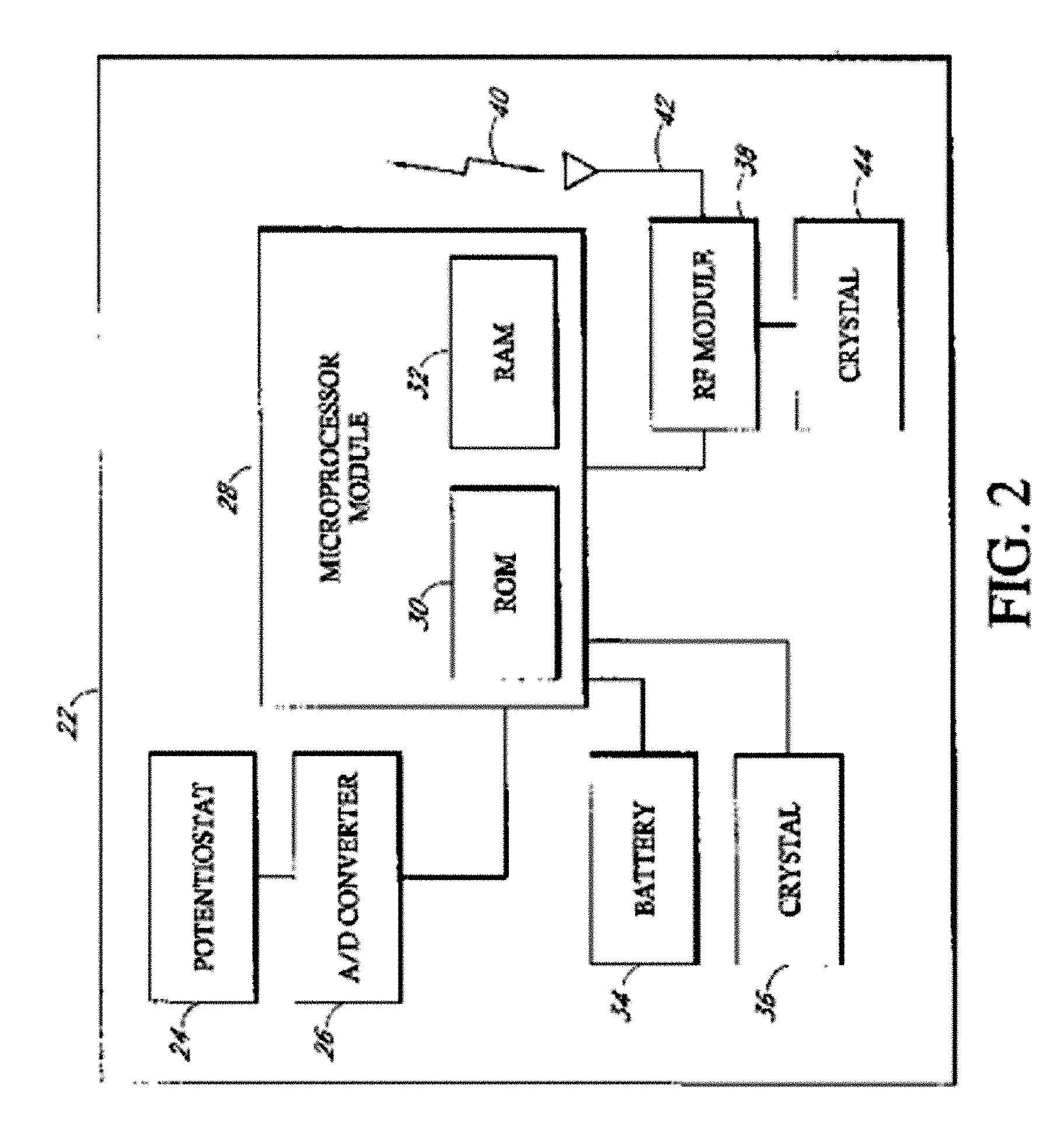
Implantable analyte sensor
ActiveUS20050242479A1Improved patient convenienceConvenient careImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteMiniaturization
Abstract of the DisclosureAn implantable analyte sensor including a sensing region for measuring the analyte and a non-sensing region for immobilizing the sensor body in the host. The sensor is implanted in a precisely dimensioned pocket to stabilize the analyte sensor in vivo and enable measurement of the concentration of the analyte in the host before and after formation of a foreign body capsule around the sensor. The sensor further provides a transmitter for RF transmission through the sensor body, electronic circuitry, and a power source optimized for long-term use in the miniaturized sensor body.
Owner:DEXCOM
Method And Apparatus For Making Disposable Absorbent Article With Absorbent Particulate Polymer Material And Article Made Therewith
A method for making a disposable absorbent core comprises depositing absorbent particulate polymer material from a plurality of reservoirs in a printing roll onto a substrate disposed on a grid of a support which includes a plurality of cross bars extending substantially parallel to and spaced from one another so as to form channels extending between the plurality of cross bars. The plurality of reservoirs in the first peripheral surface are arranged in an array comprising rows extending substantially parallel to and spaced from one another. The support and printing roll are arranged such that the plurality of cross bars are substantially parallel to the rows of the plurality of reservoirs and the absorbent particulate polymer material is deposited on the substrate in a pattern such that the absorbent particulate polymer material collects in rows on the first substrate formed between the first plurality of cross bars. A thermoplastic adhesive material is deposited on the absorbent particulate polymer material and the substrate to cover the absorbent particulate polymer material on the substrate and form an absorbent layer. A disposable absorbent article and apparatus for making an absorbent article are also disclosed.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method and apparatus for making an apertured web
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Polymer solution for nanoimprint lithography to reduce imprint temperature and pressure
InactiveUS20040110856A1Reduce pressureReduce the temperatureNanostructure manufactureDecorative surface effectsCross-linkVitrification
A method of forming features on substrates by imprinting is provided. The method comprises: (a) forming a polymer solution comprising at least one polymer dissolved in at least one polymerizable monomer; and (b) depositing the polymer solution on a substrate to form a liquid film thereon; and then either: (c) curing the liquid film by causing the monomer(s) to polymerize and optionally cross-linking the polymer(s) to thereby form a polymer film, the polymer film having a glass transition temperature (Tg); and imprinting the polymer film with a mold having a desired pattern to form a corresponding negative pattern in the polymer film, or (d) imprinting the liquid film with the mold and curing it to form the polymer film. The temperature of imprinting is as little as 10° C. above the Tg, or even less if the film is in the liquid state. The pressure of the imprinting can be within the range of 100 to 500 psi.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Three-Dimensional Adhesive Device Having a Microelectronic System Embedded Therein
InactiveUS20080275327A1Simple and inexpensive wayModerate viscosityWave amplification devicesLayered productsCapacitanceElectronic systems
Accordingly, the present invention relates to a three-dimensional adhesive device to be attached to the body surface of a mammal comprising a microelectronic sensing system characterized by(a) a three-dimensional adhesive body made of a pressure sensitive adhesive having an upper surface and a bottom surface;(b) a microelectronic system embedded in the body of the pressure sensitive adhesive;(c) one or more cover layer(s) attached to the upper surface; and(d) optionally a release liner releasable attached to the bottom surface of the adhesive device.Suitably the microelectronic system is a microelectronic sensing system capable of sensing physical input such as pressure, vibration, sound, electrical activity (e.g. from muscle activity), tension, blood-flow, moisture, temperature, enzyme activity, bacteria, pH, blood sugar, conductivity, resistance, capacitance, inductance or other chemical, biochemical, biological, mechanical or electrical properties.
Owner:BRAEMAR MFG +2
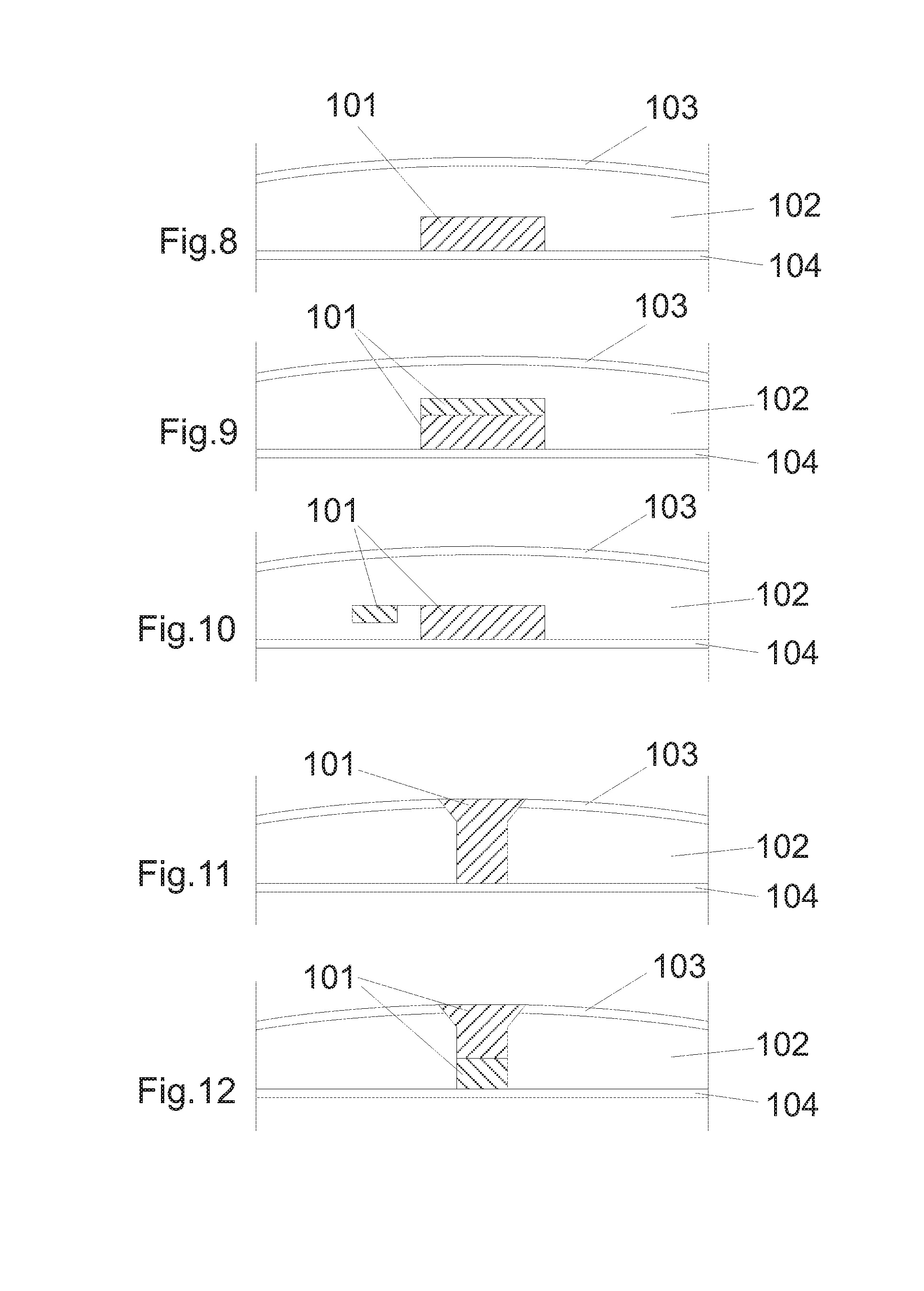
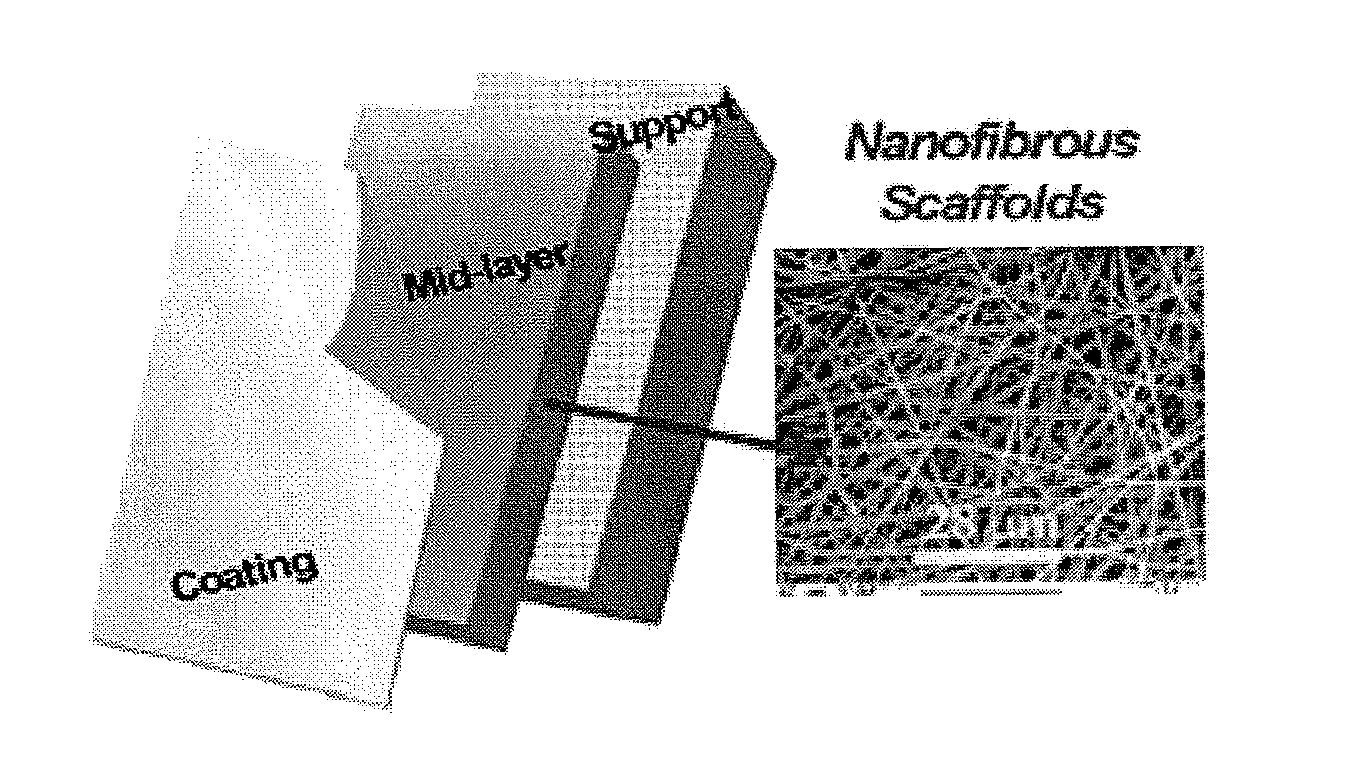
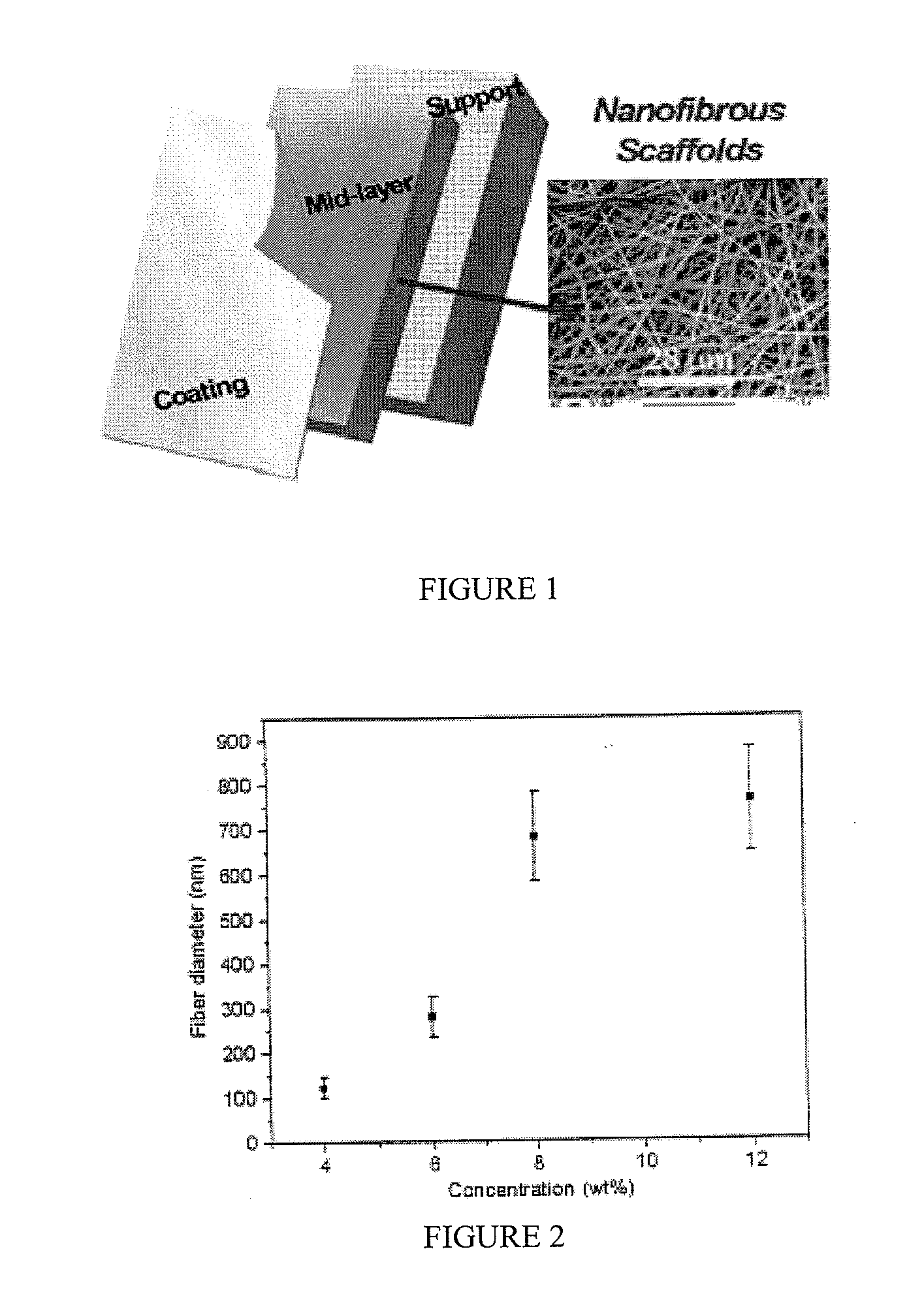
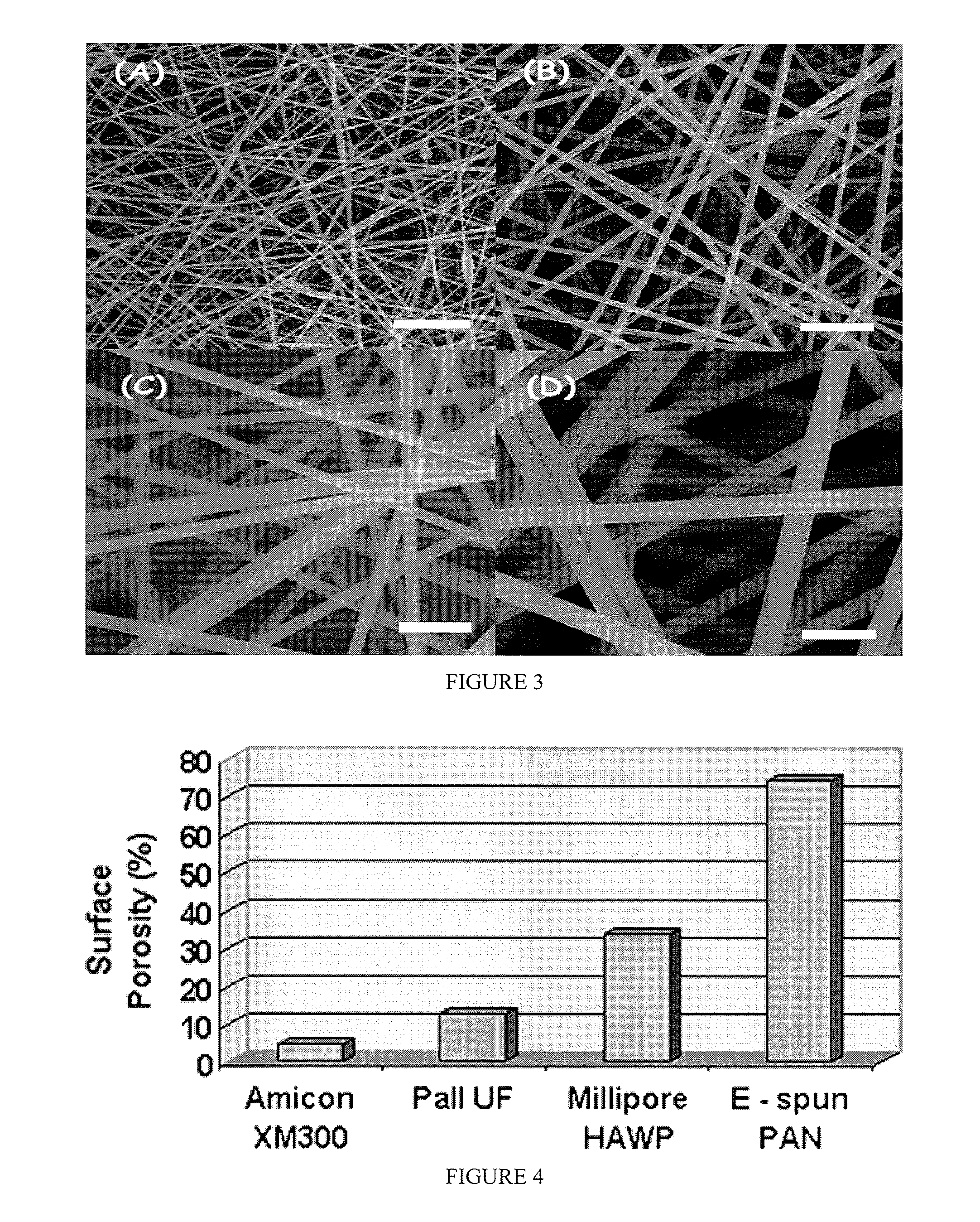
Articles Comprising a Fibrous Support
Articles comprising a fibrous support of nanofibers and an interfacially polymerized polymer layer disposed on a surface of the fibrous support are useful, e.g., as fluid separation membranes.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method for manufacturing susceptor
ActiveUS20100163524A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSusceptorMetallurgy
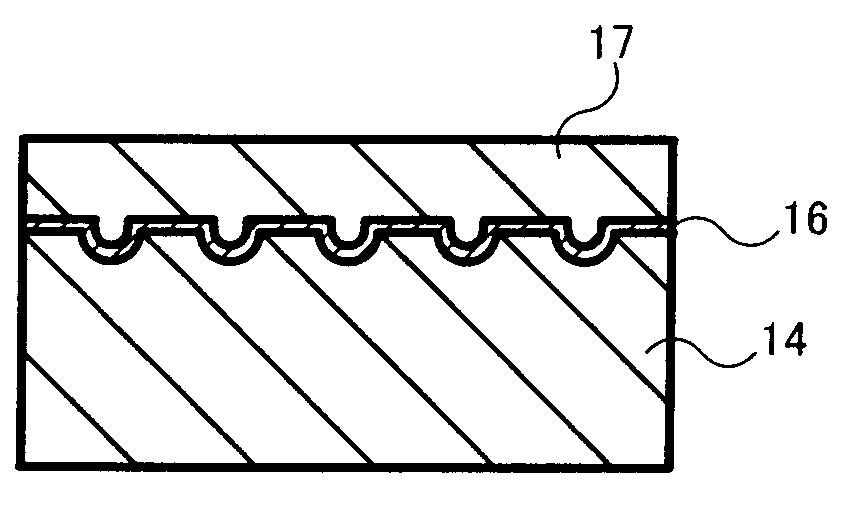
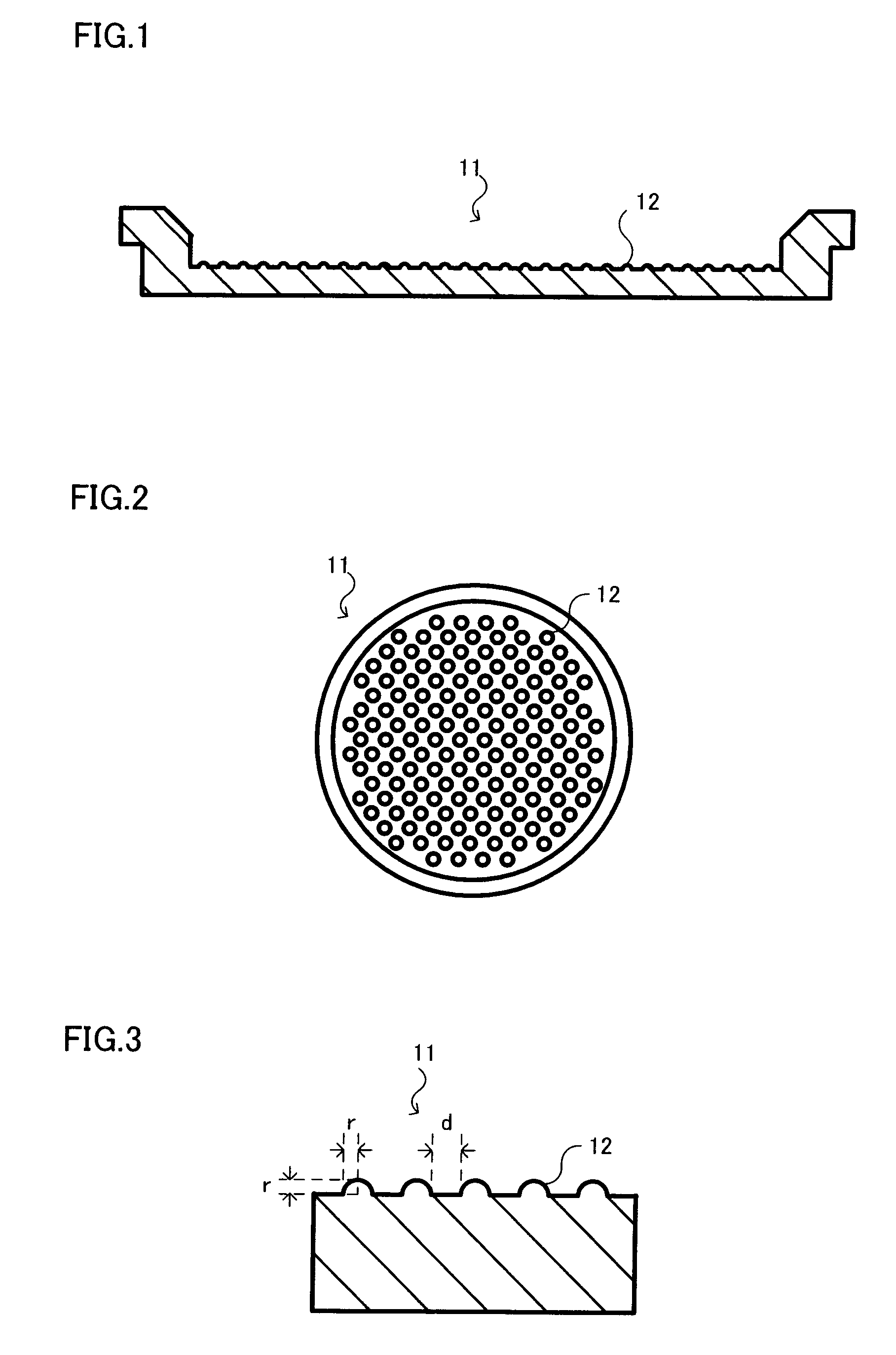
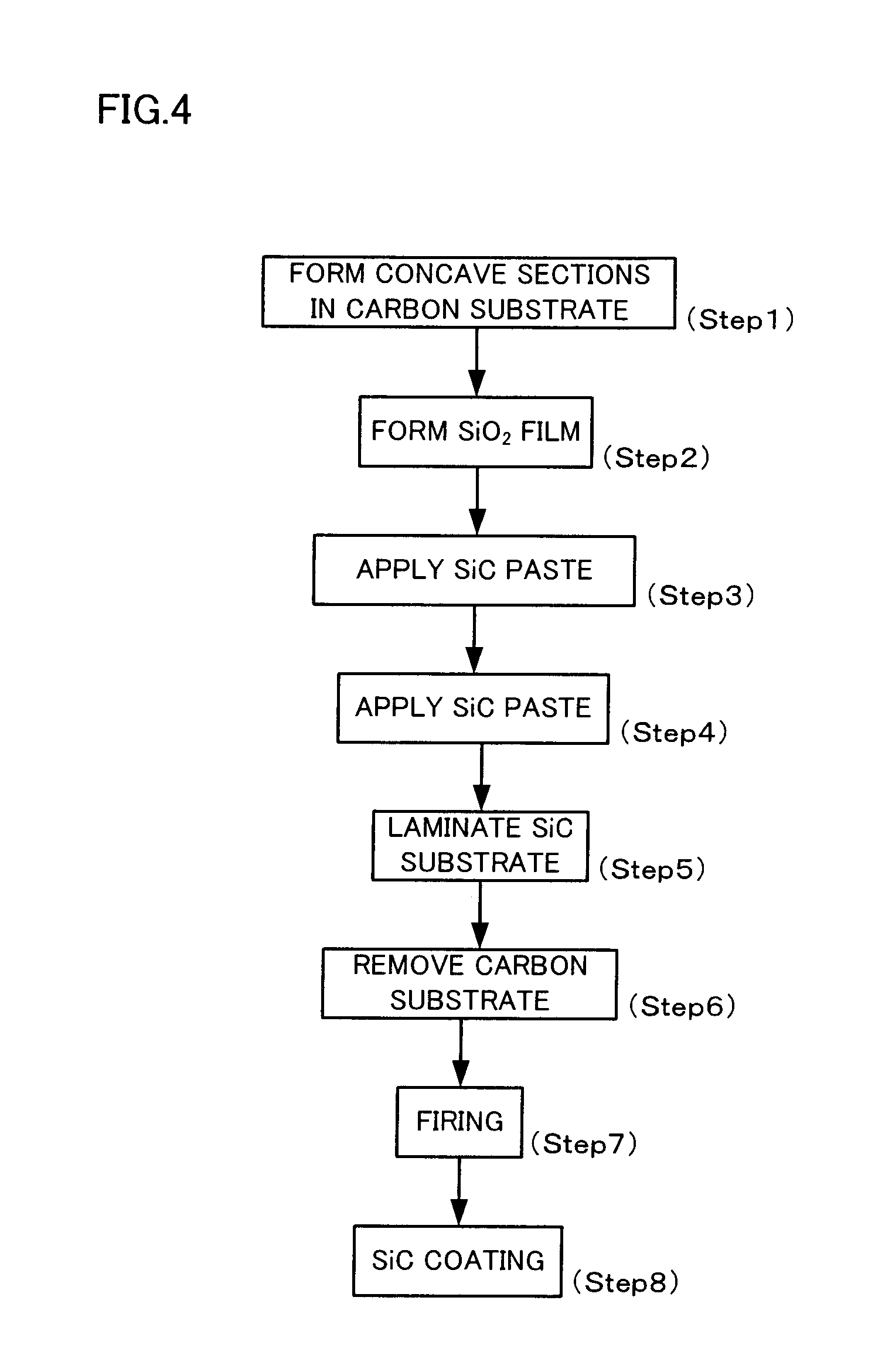
A method for manufacturing a susceptor includes: forming a concave pattern in a surface of a substrate to be processed; applying a SiC paste containing a SiC powder and a sintering agent to the surface of the substrate to be processed to fill the concave pattern to form a SiC coating layer; laminating a SiC substrate on the SiC coating layer; and firing the SiC coating layer to form a SiC layer having at least one convex section on the surface of the SiC substrate.
Owner:NUFLARE TECH INC
Reinforced composite stamp for dry transfer printing of semiconductor elements
ActiveUS7927976B2Easy to controlPrecise and repeatable vertical motionTurning machine accessoriesMouldsSemiconductor structureContact force
Provided are reinforced composite stamps, devices and methods of making the reinforced composite stamps disclosed herein. Reinforced composite stamps of certain aspects of the present invention have a composition and architecture optimized for use in printing systems for dry transfer printing of semiconductor structures, and impart excellent control over relative spatial placement accuracy of the semiconductor structures being transferred. In some embodiments, for example, reinforced composite stamps of the present invention allow for precise and repeatable vertical motion of the patterned surface of the printing apparatus with self-leveling of the stamp to the surface of a contacted substrate. Reinforced composite stamps of certain aspect of the present invention achieve a uniform distribution of contact forces between the printing apparatus patterned surface and the top surface of a substrate being contacted by the reinforced composite stamp of the printing apparatus.
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD
Method and apparatus for manufacturing composite structures
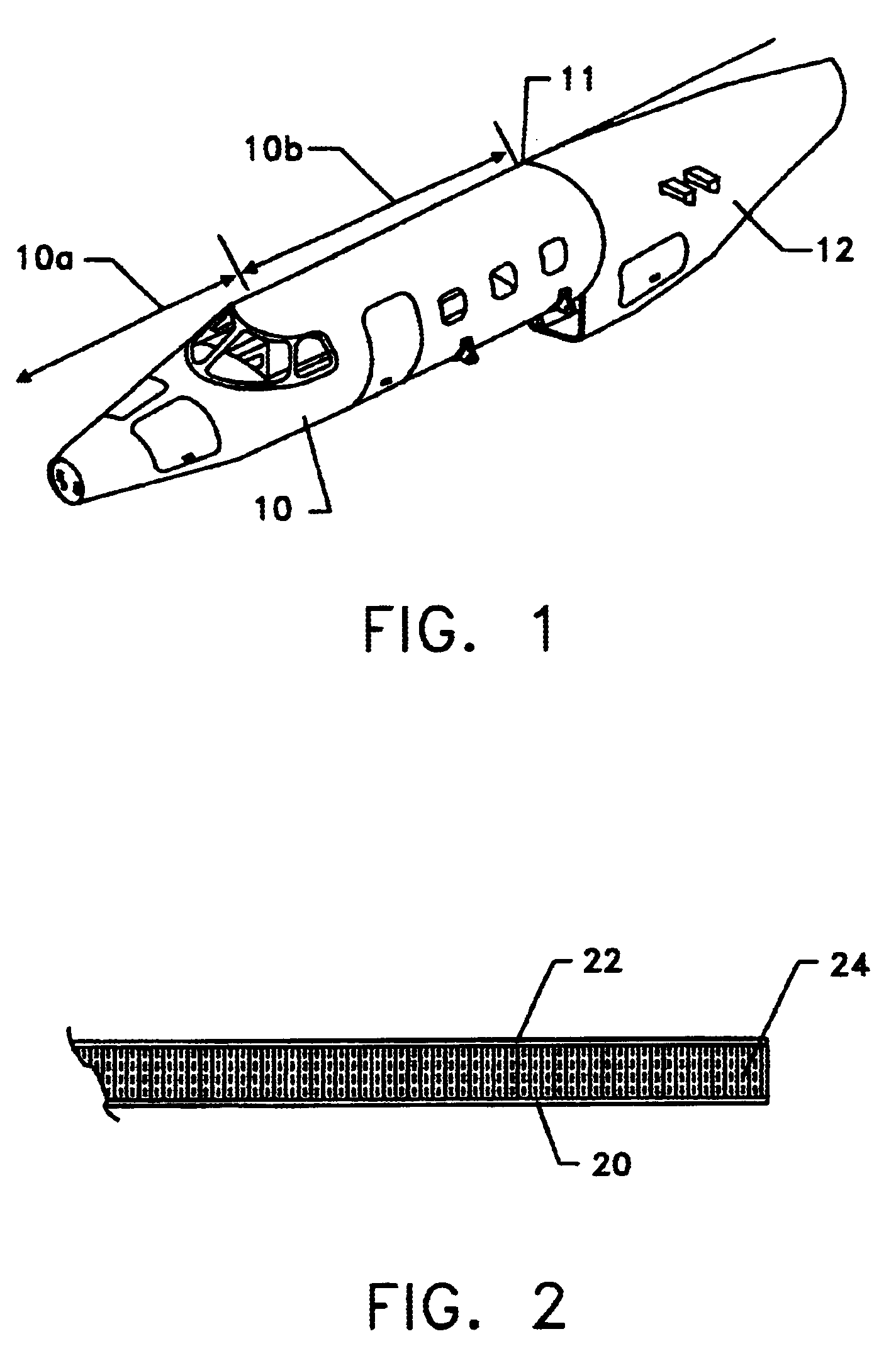
Composite structures having a single continuous skin may be formed using automated fiber placement methods. These composite structures include frameless aircraft fuselage components offering an increased interior cabin width over conventional fuselage components. The composite structures may be constructed of multiple layers of fibers and other materials placed on a fiber placement tool that includes a mandrel body surrounded by a bladder or an integral bladder / caul sheet having expansion spaces created within the caul sheet section. Uncured composite structures may be created by placing fibers around the fiber placement tool in a plurality of discontinuous segments that are capable of moving or sliding in relation to each other so that the uncured composite structure is expandable from within. Fluid openings may be provided in the outer surface of the mandrel body for the application of vacuum and / or fluid pressure to secure the bladder to the mandrel body and to assist in the removal of the bladder from the mandrel body, respectively. Uncured composite structures may be sealed between the bladder and is clam shell molds. The uncured structures may be expanded against the inner surface of the molds by creating a vacuum between the bladder and molds.
Owner:BEECHCRAFT
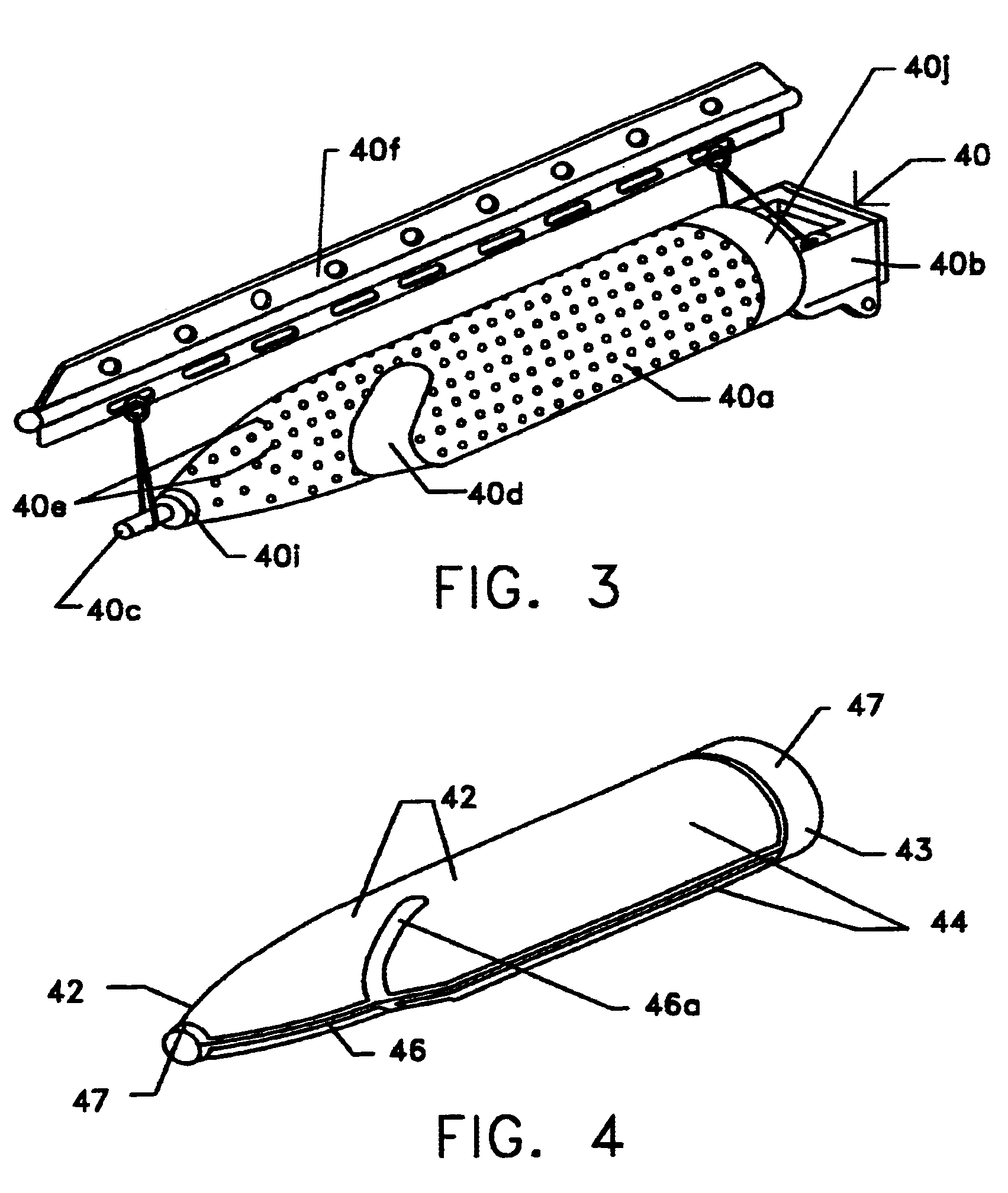
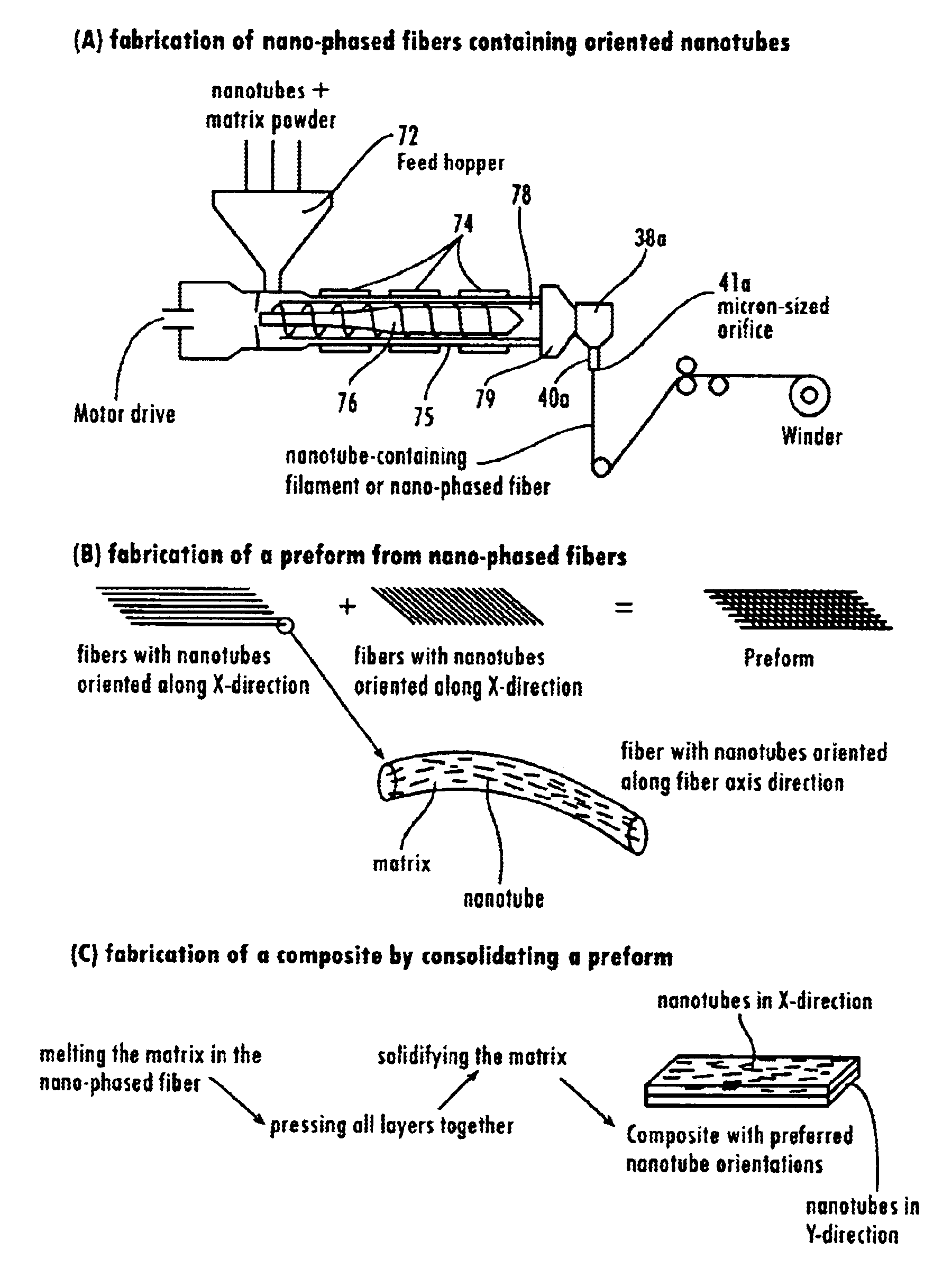
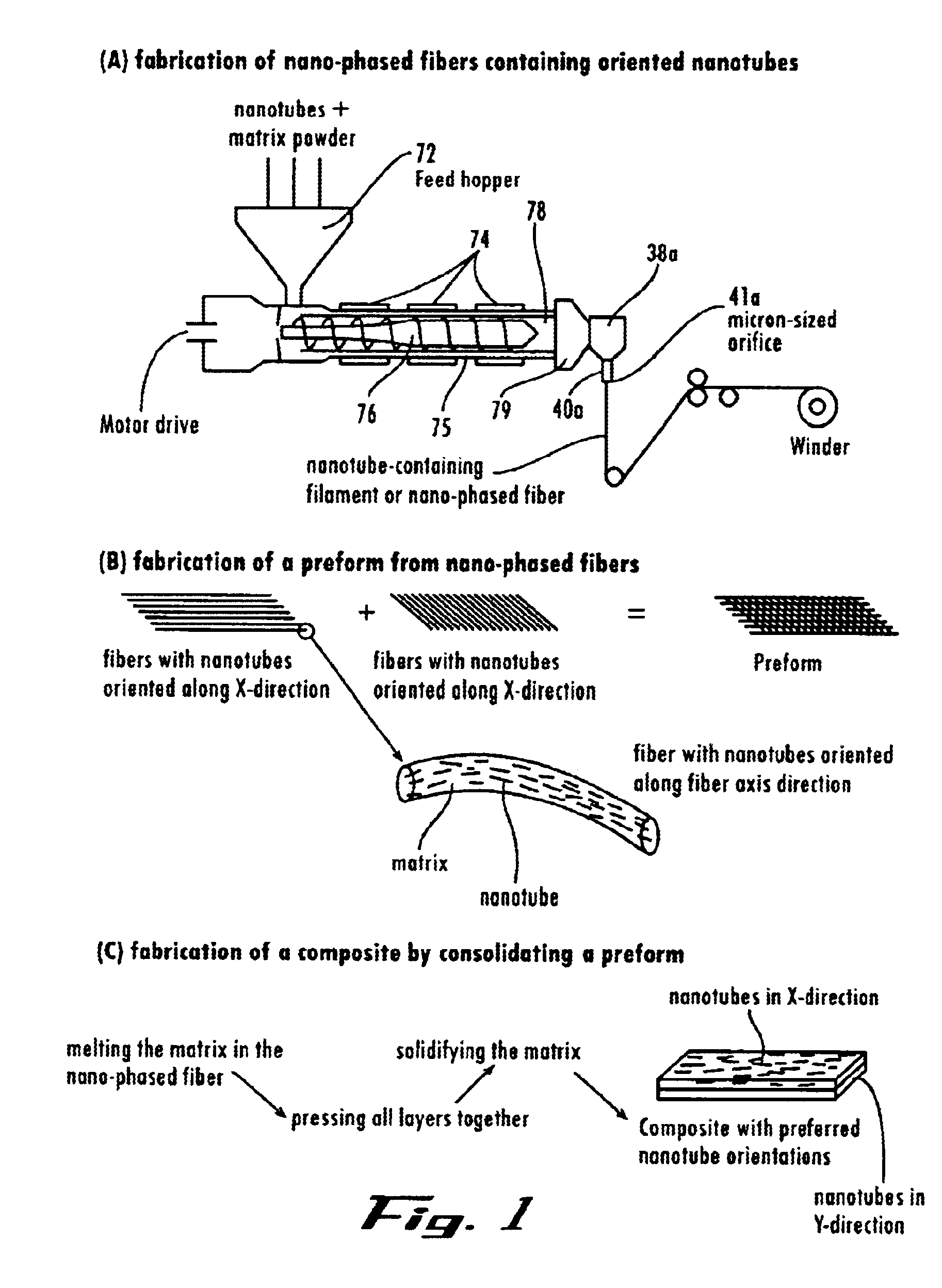
Nanotube fiber reinforced composite materials and method of producing fiber reinforced composites
InactiveUS6934600B2Requires minimizationGenerate efficientlyMaterial nanotechnologyAdditive manufacturing apparatusFiber-reinforced compositeMotion controller
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Apparatus and methods for electrospinning polymeric fibers and membranes
InactiveUS6713011B2Easy to controlLarge specific surface areaElectric discharge heatingConfectioneryFiberElectrospinning
An apparatus and method for electrospinning polymer fibers and membranes. The method includes electrospinning a polymer fiber from a conducting fluid in the presence of a first electric field established between a conducting fluid introduction device and a ground source and modifying the first electric field with a second electric field to form a jet stream of the conducting fluid. The method also includes electrically controlling the flow characteristics of the jet stream, forming a plurality of electrospinning jet streams and independently controlling the flow characteristics of at least one of the jet streams. The apparatus for electrospinning includes a conducting fluid introduction device containing a plurality of electrospinning spinnerets, a ground member positioned adjacent to the spinnerets, a support member disposed between the spinnerets and the ground member and movable to receive fibers formed from the conducting fluid, and a component for controlling the flow characteristics of conducting fluid from at least one spinneret independently from another spinneret.
Owner:RES FOUND THE
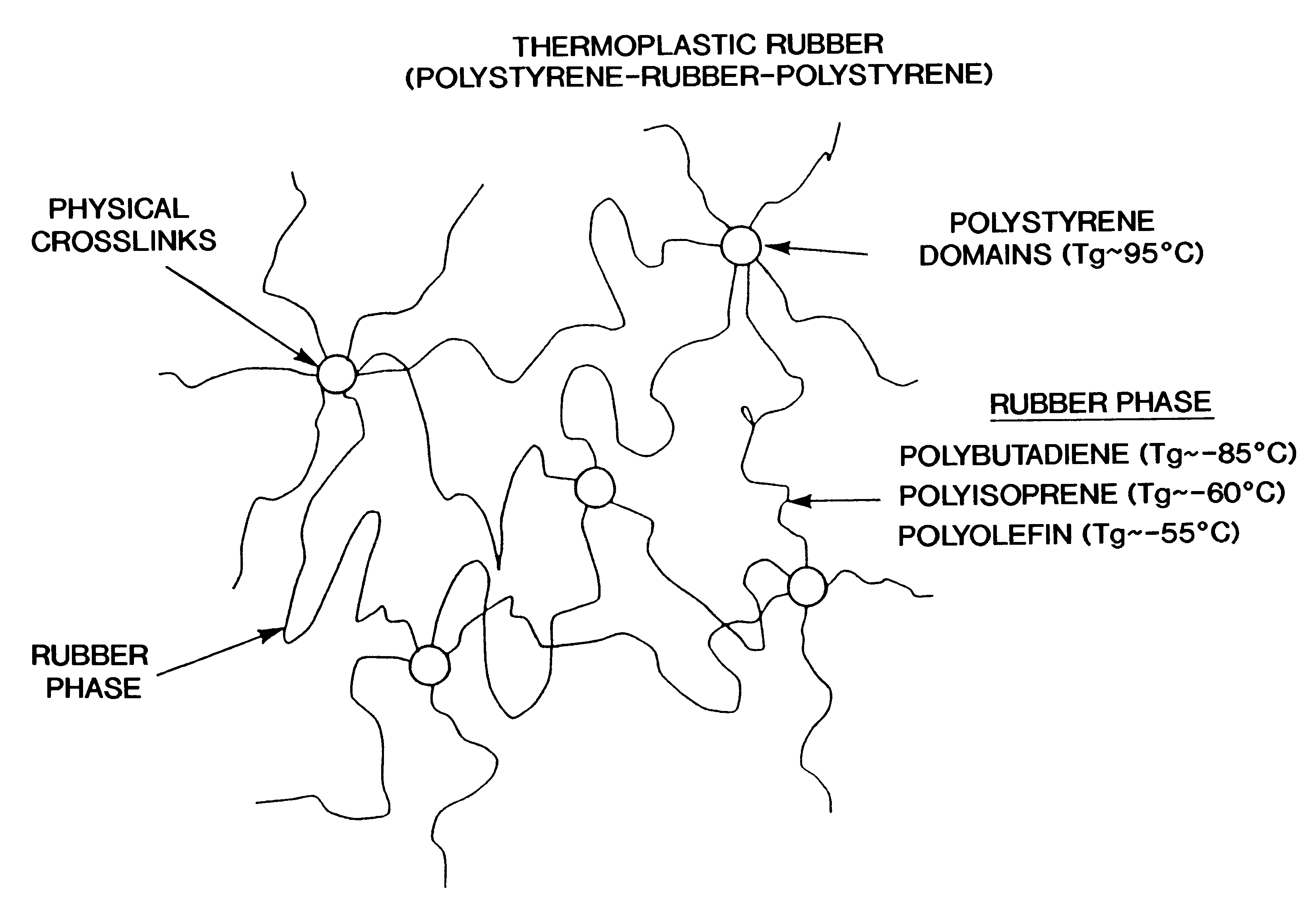
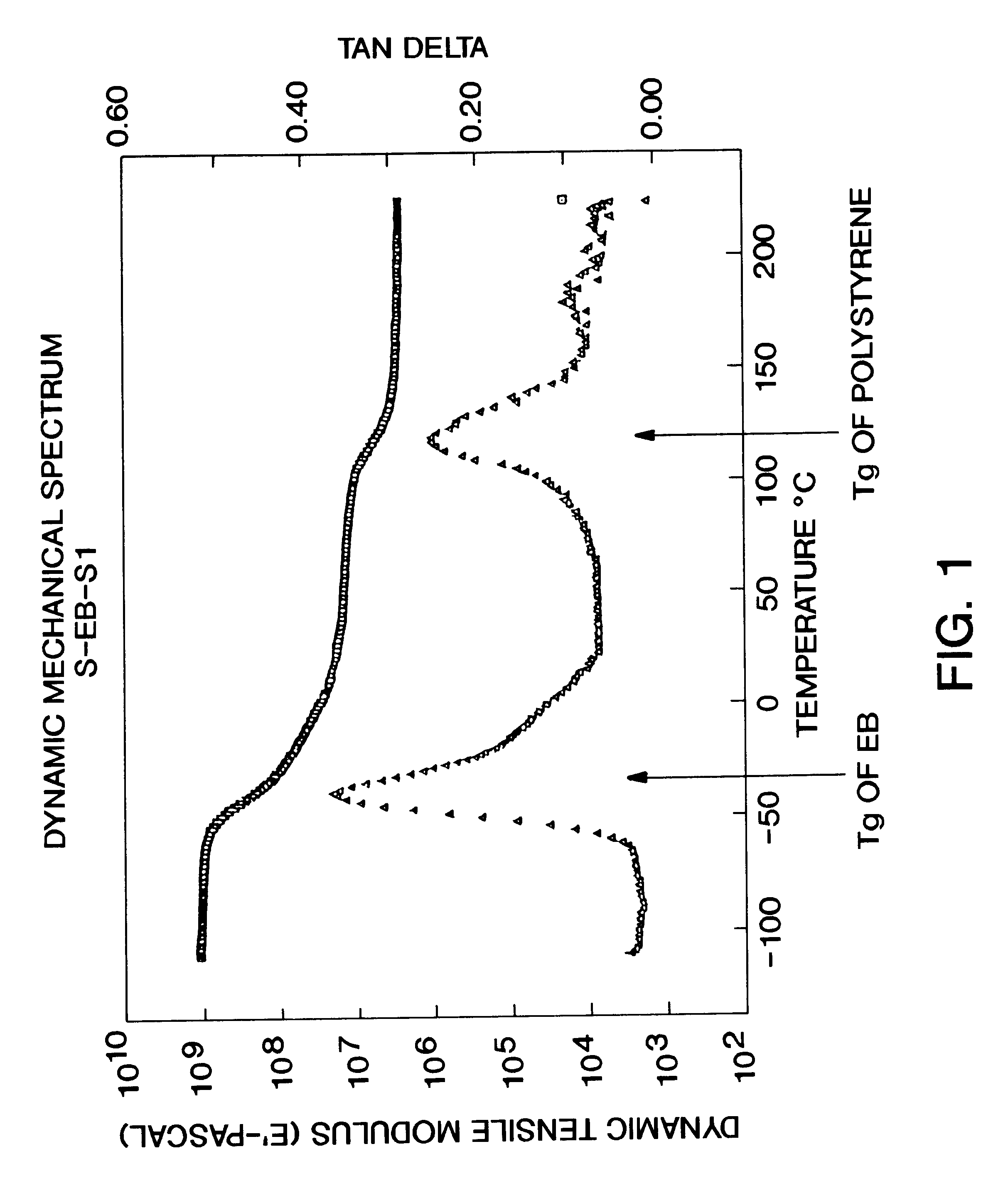
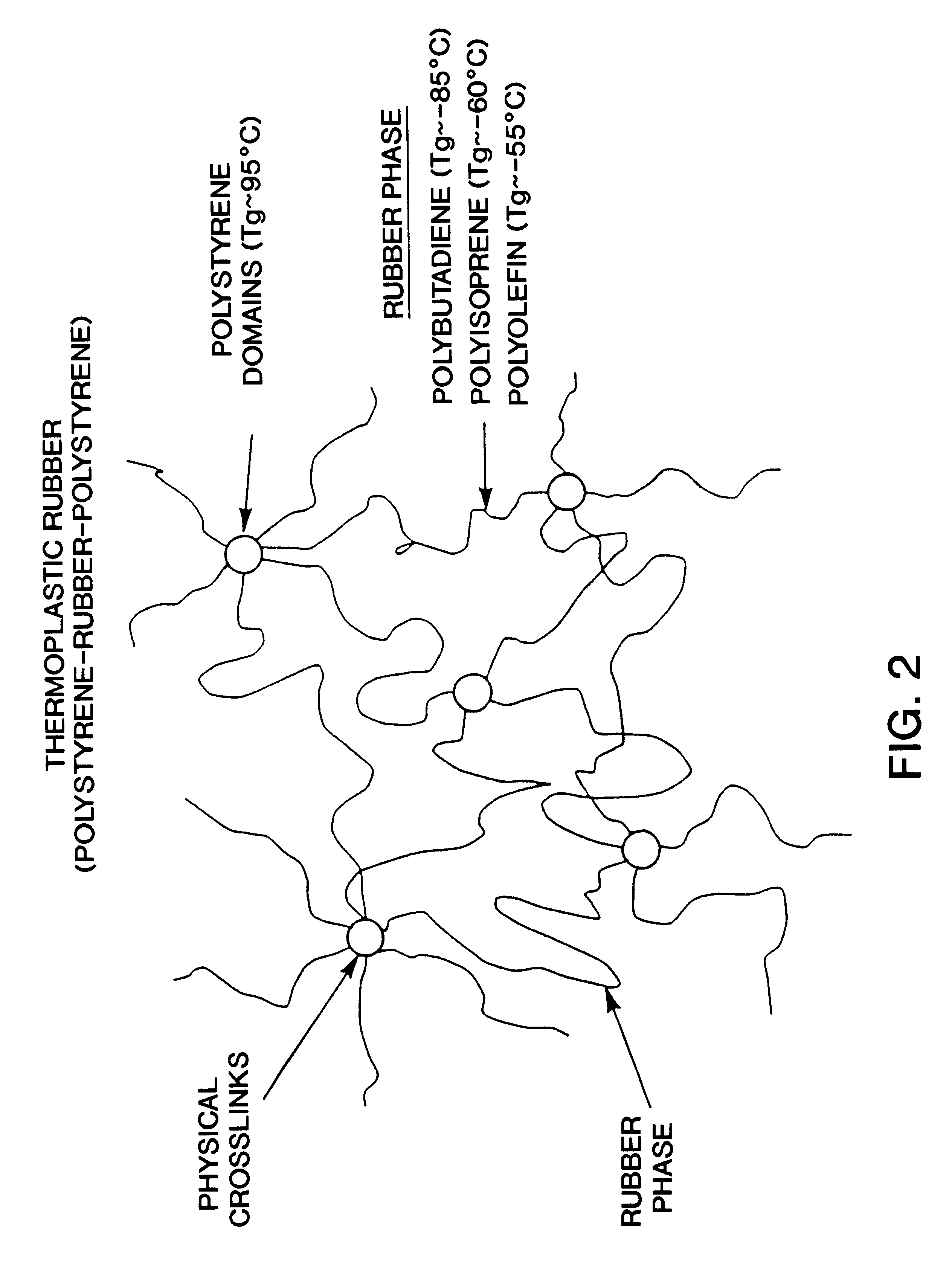
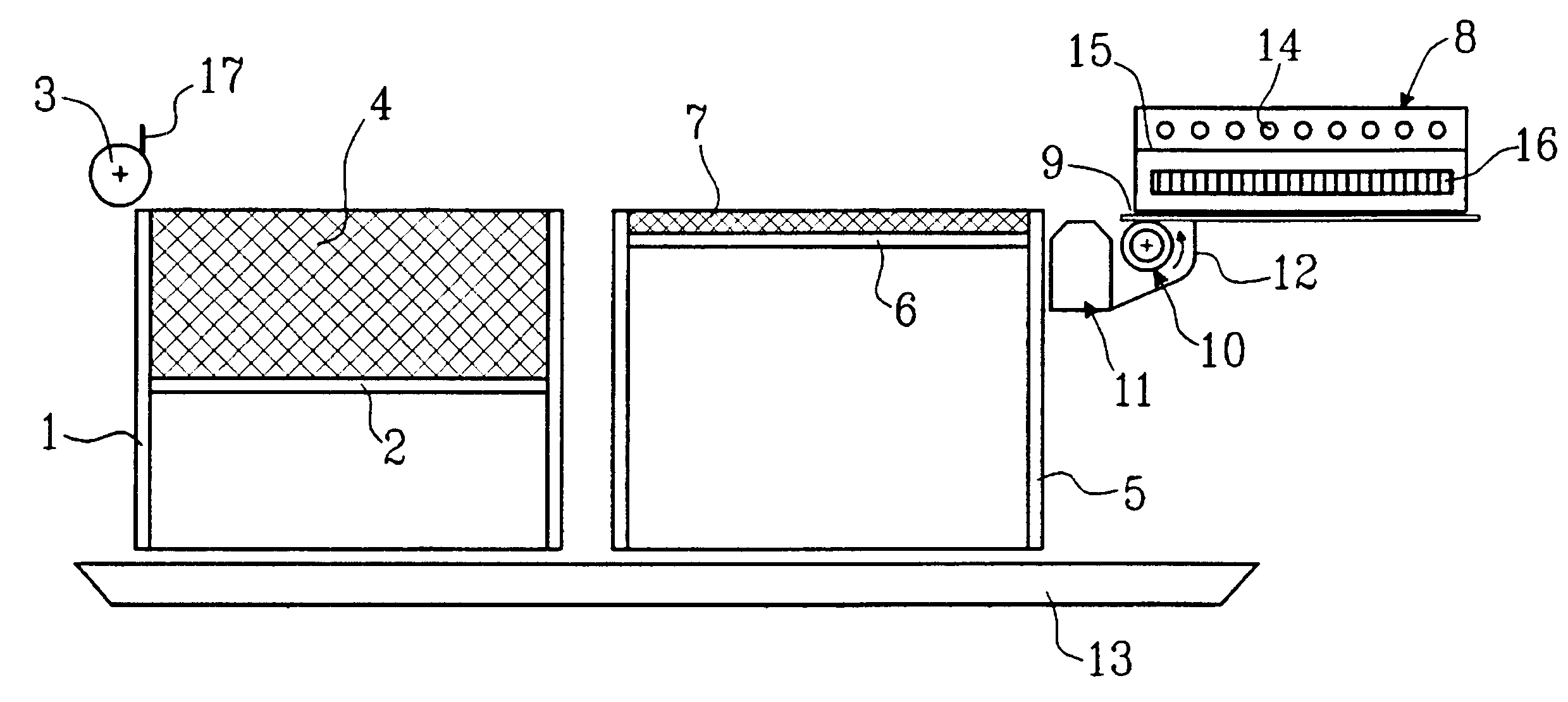
Dimensionally stable, breathable, stretch-thinned, elastic films
A method for producing a stretch-thinned elastic article having dimensional stability over time and at elevated temperatures in which a thermoplastic block copolymer is melt-processed into a stretchable article such as a film or fiber. The article is then conditioned at an elevated temperature greater than or equal to a glass transition temperature (Tg) of a hard phase of the thermoplastic block copolymer. The article is stretch-thinned at the elevated temperature to a desired percentage stretch, forming a stretch-thinned article, after which it is cooled to a temperature below the glass transition temperature of the hard phase of the thermoplastic block copolymer. Films produced by this method are suitable for use in durable and disposable articles including personal care articles such as diapers, incontinence wear, training pants, and feminine care articles, as well as wound dressings, wipes, towels, napkins, and protective apparel.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Method and device for manufacturing three-dimensional bodies
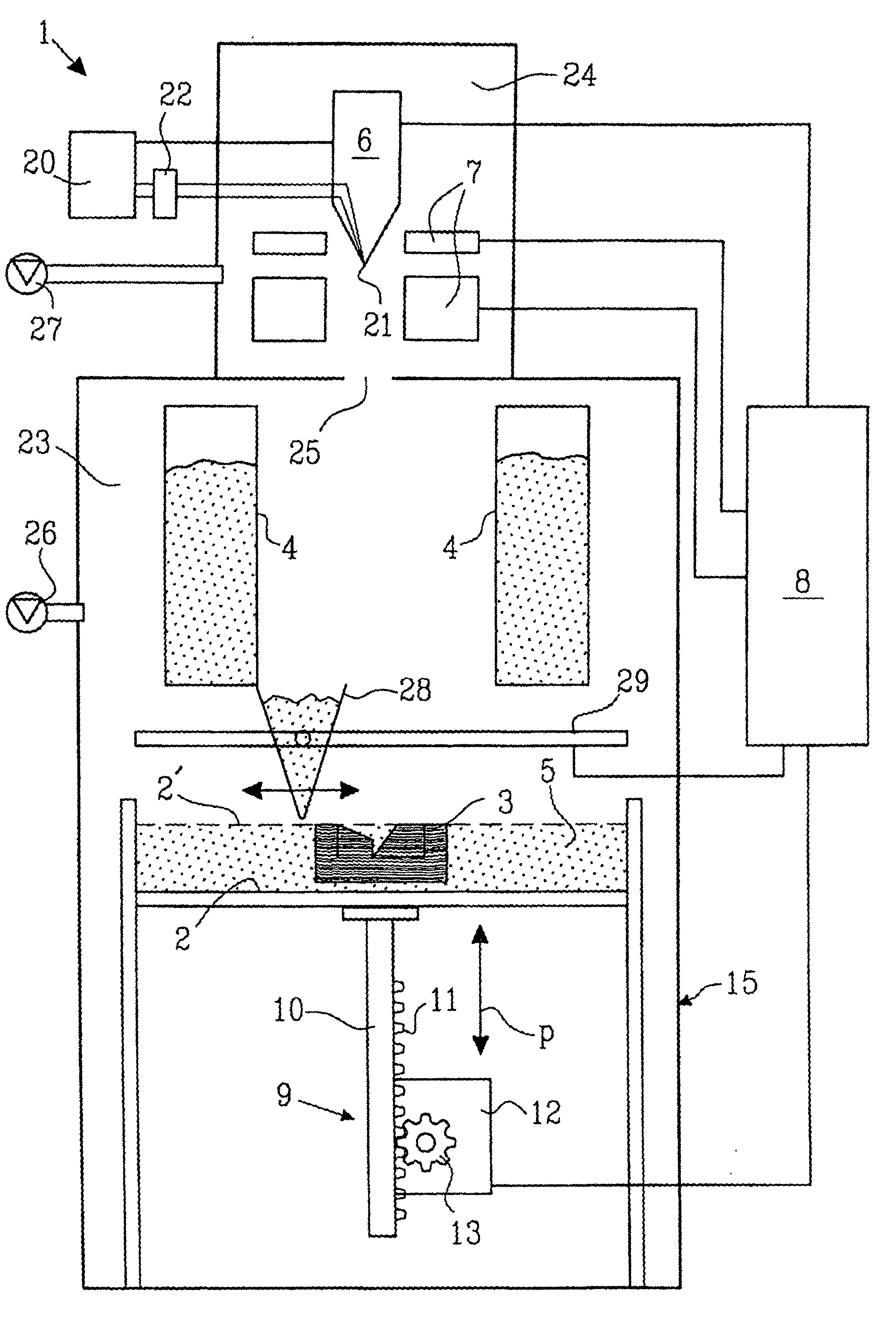
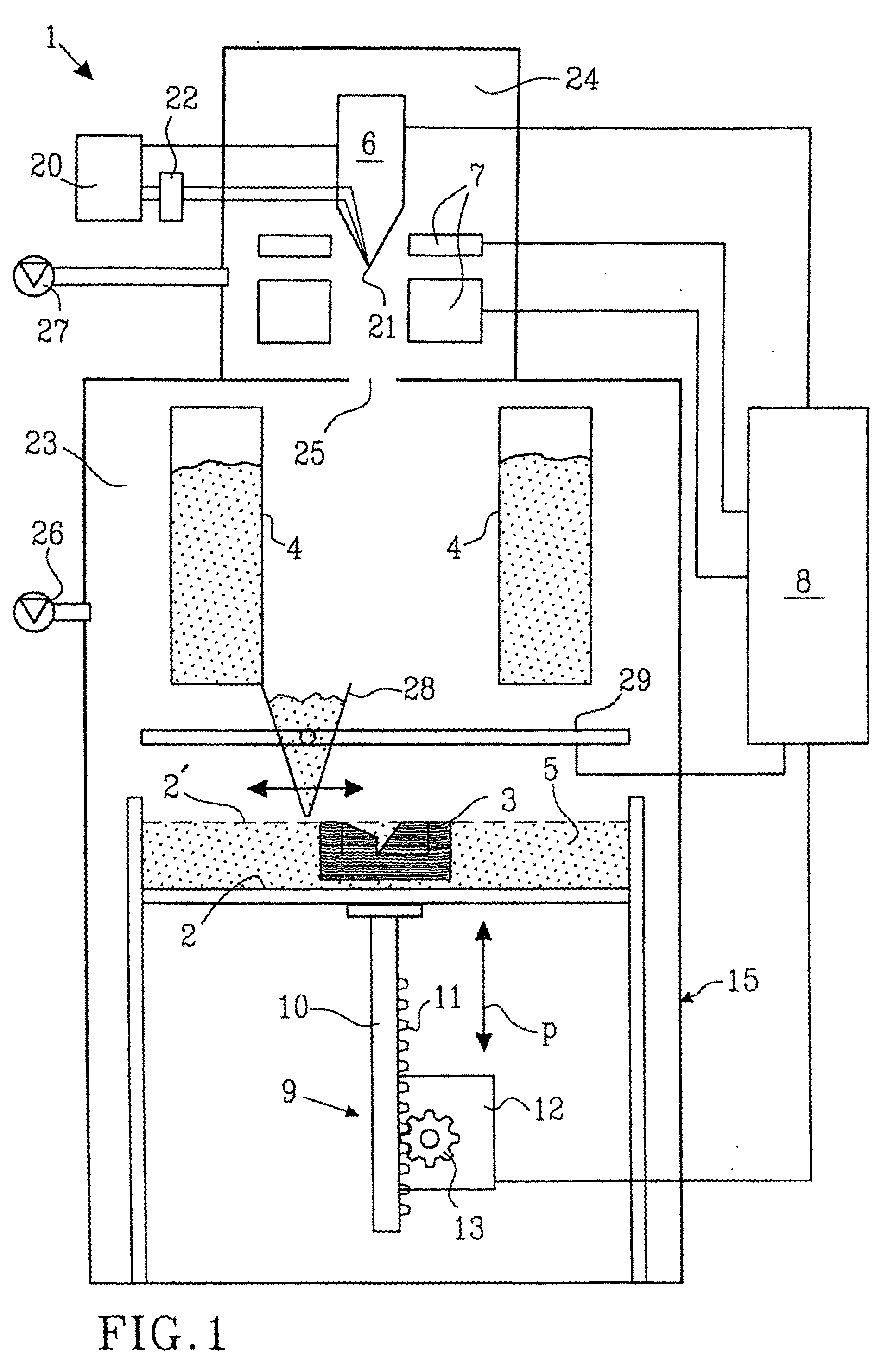
A method for producing three-dimensional bodies of a large number of mutually connected layers of a particle-shaped material such as a powder, and where the information of the appearance of each layer is achieved from a computer's CAD-unit or similar. An essentially even particle layer (7) of building material is applied on a support base (6) and on a masking device (9) is arranged a masking pattern in accordance with the information from the CAD-unit, which masking device is led over said particle layer and close to it. A radiation producer (8) is arranged or is led over the masking device (9), whereby the particles which are not covered by the masking pattern are exposed for radiation and thereby are attached to each other. The masking pattern is removed from the masking device and new sequences in accordance with the above are carried through until the three-dimensional body (19) is produced.
Owner:SPEED PART RP
Pattern forming method and pattern forming apparatus
Owner:CANON KK
Methods of cutting or forming cavities in a substrate for use in making optical films, components or wave guides
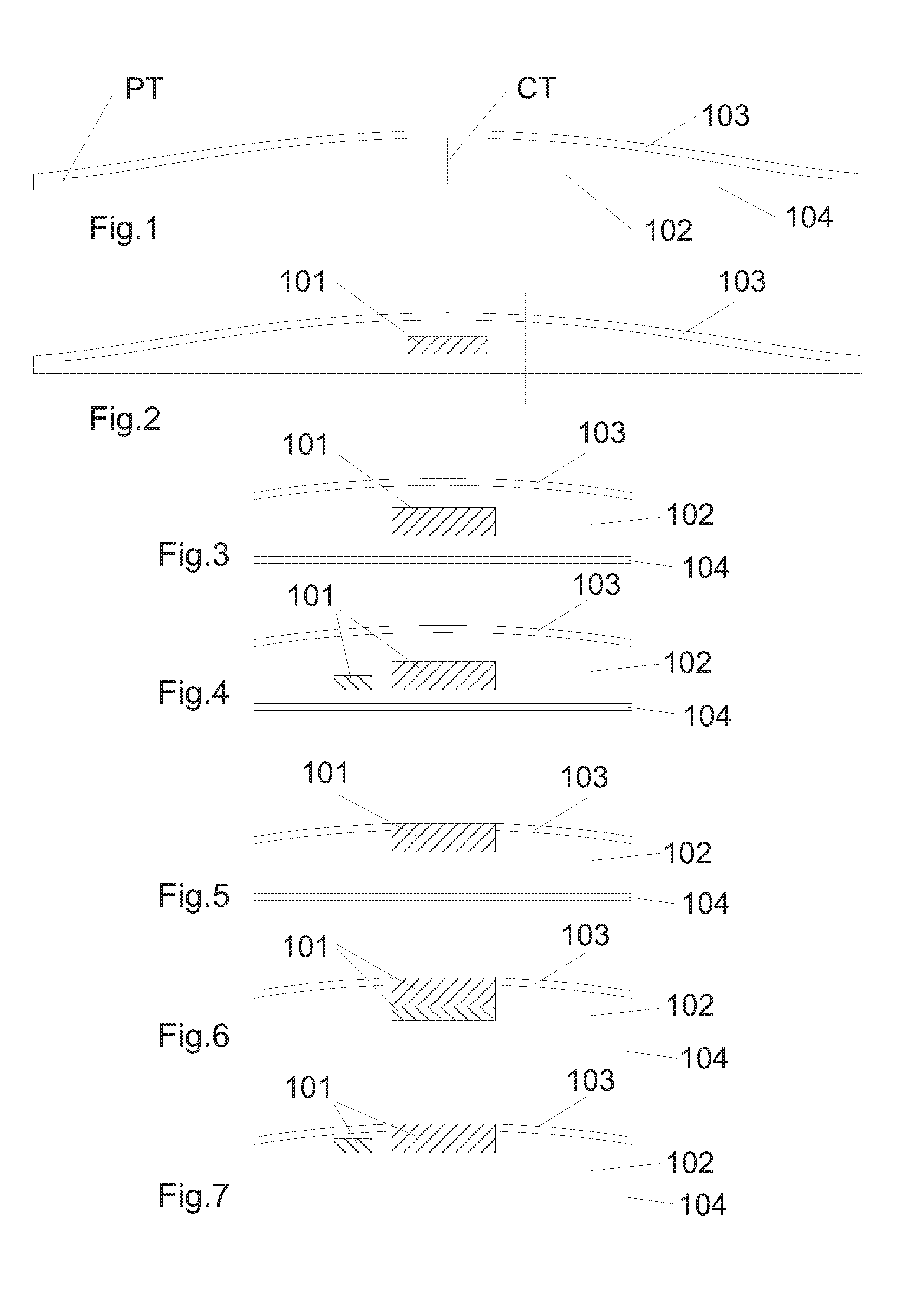
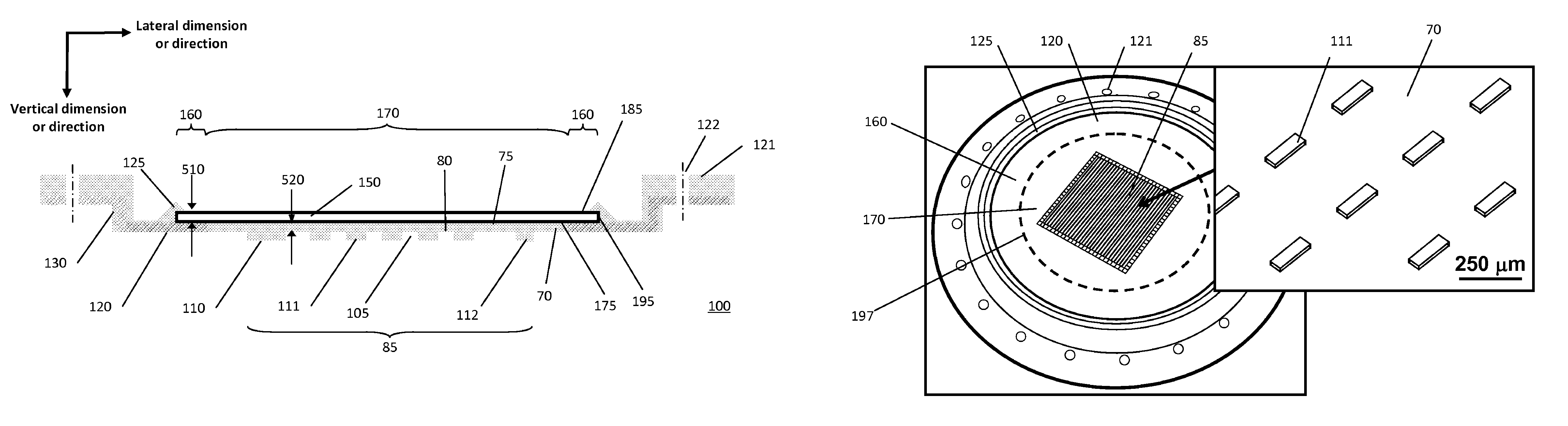
InactiveUS20050024849A1Small in in lengthSmall in widthMechanical apparatusFlat articlesEngineeringRidge
The methods involve using a tool to cut or form multiple optical element shaped cavities in a surface of a substrate without rotating the tool or substrate during the cutting or forming process. At least some of the cavities are cut or formed to have at least two surfaces that come together to form a ridge and that are quite small relative to the length and width of the substrate. Thereafter the substrate is used to form optical films, components or wave guides having multiple optical elements on at least one surface corresponding to the cavities in the substrate.
Owner:SOLID STATE OPTO
Synthetic fiber
InactiveUS6135987AFormed easily and efficientlyCeramic shaping apparatusBaby linensPolyesterVitrification
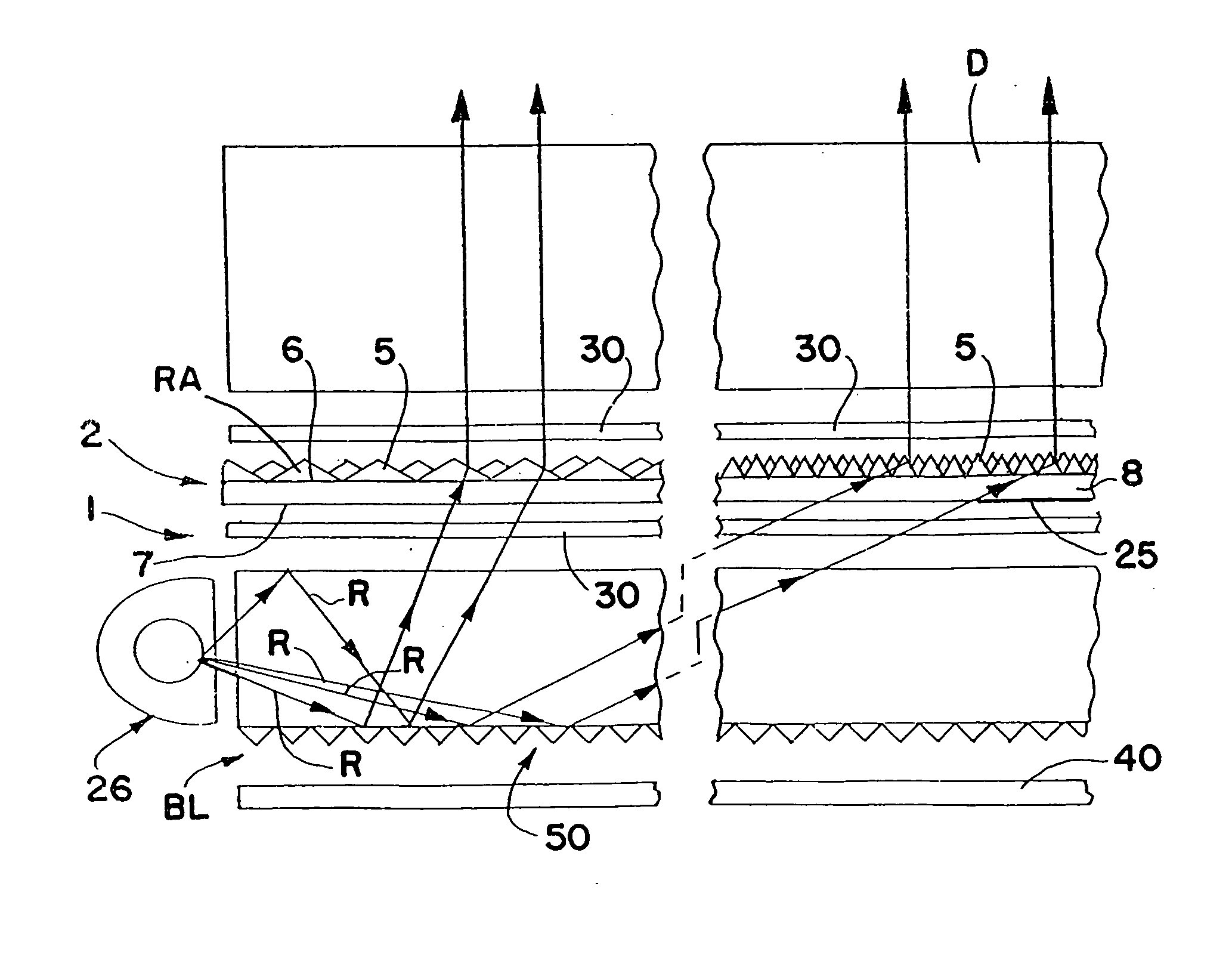
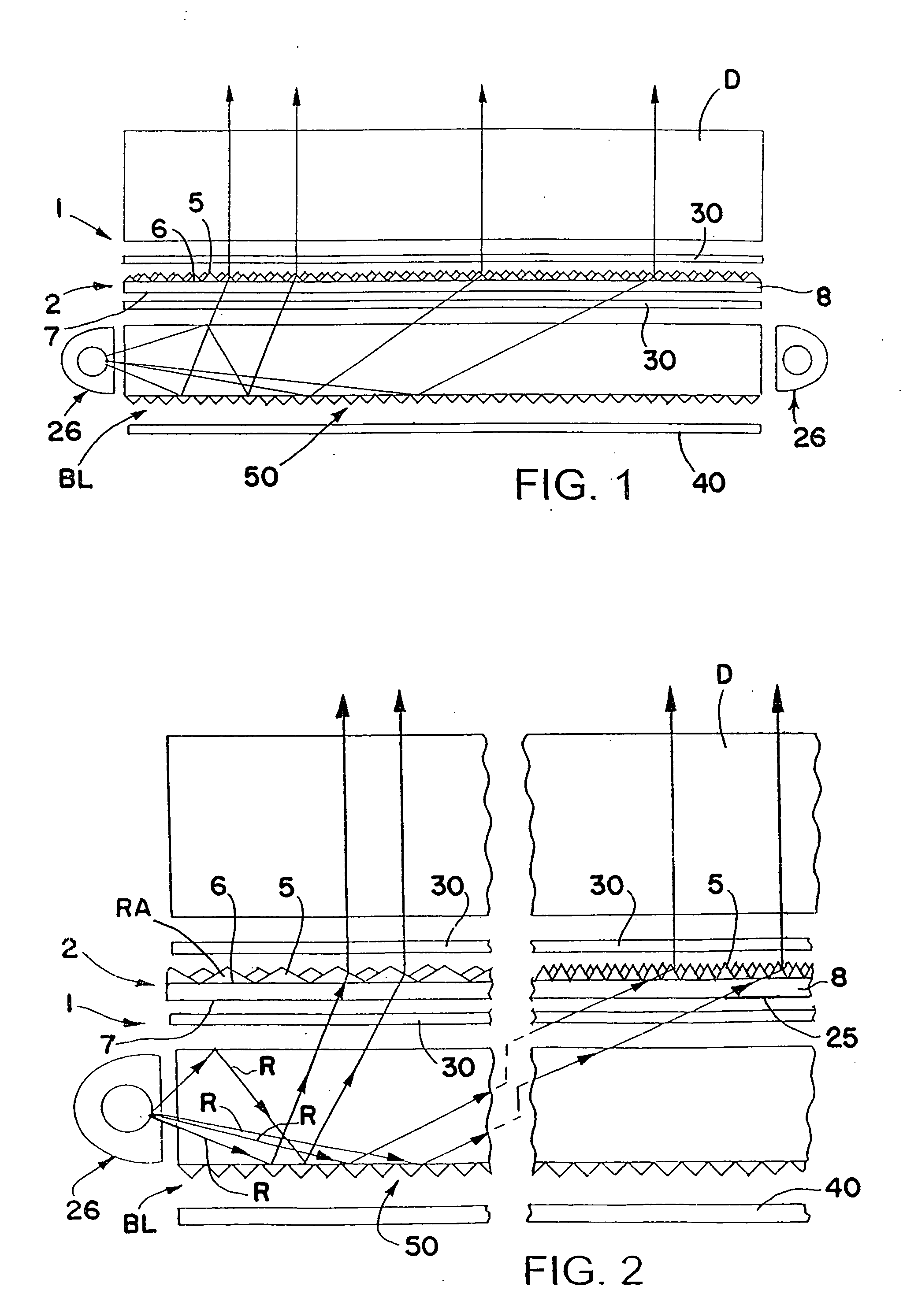
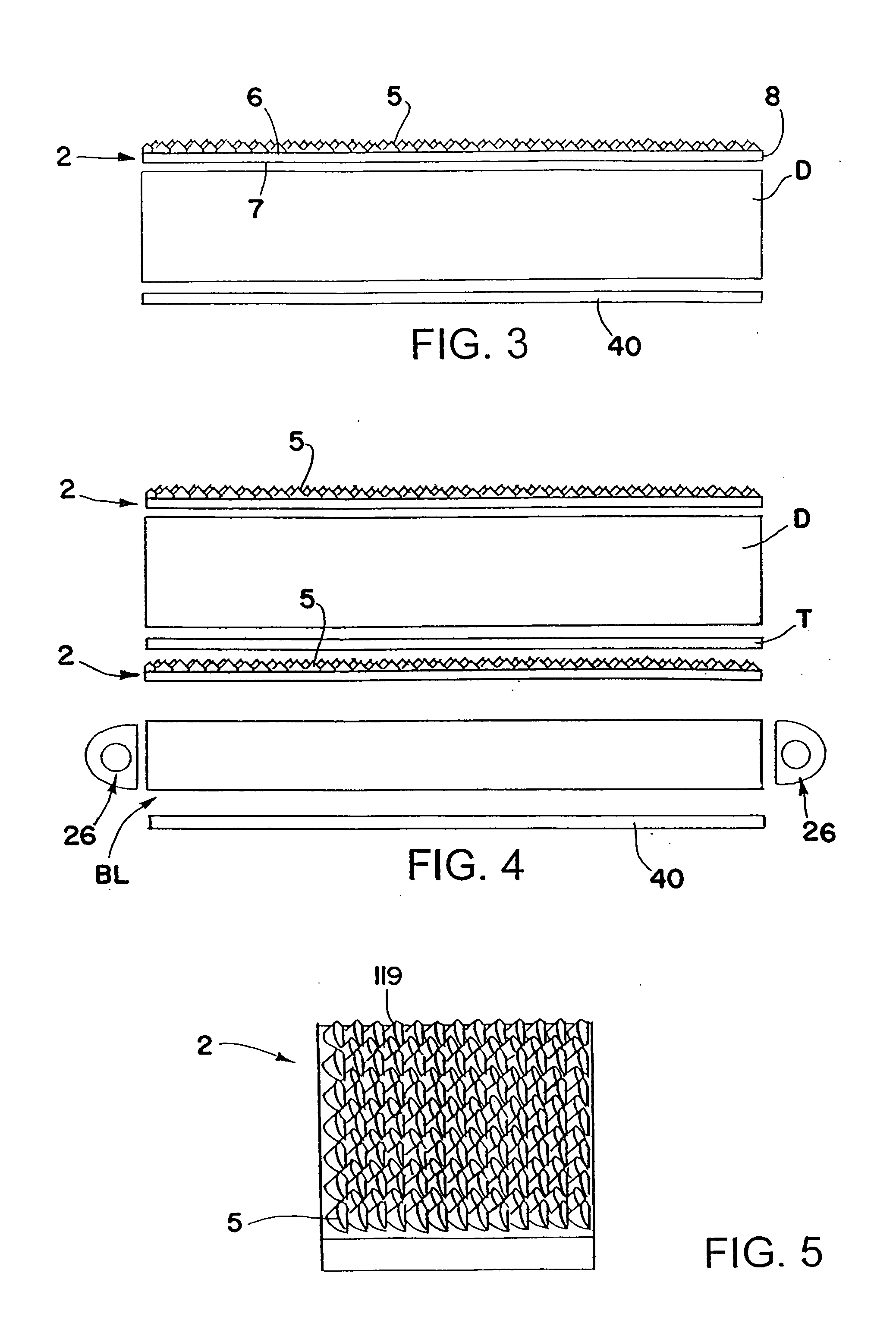
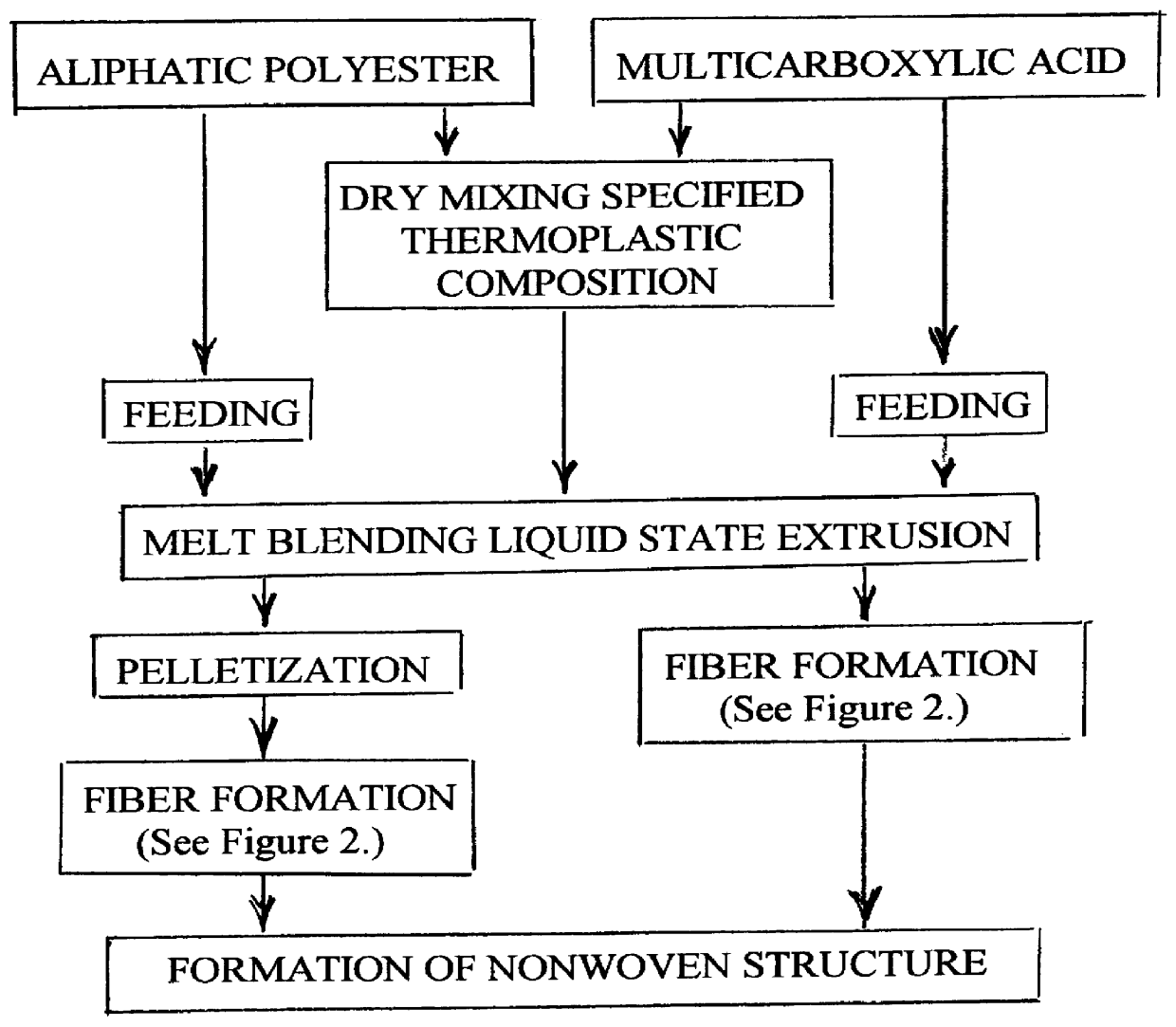
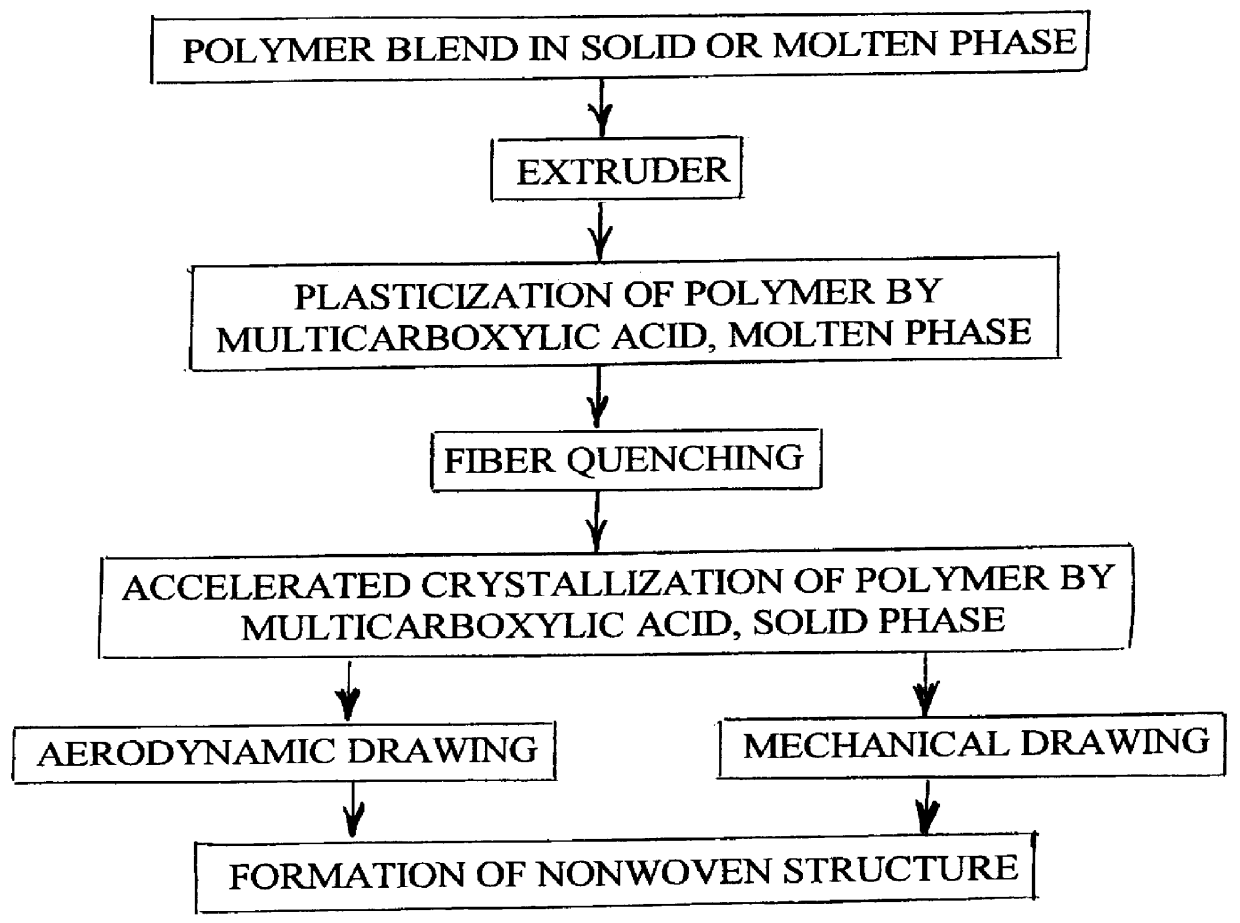
A process is disclosed for forming a synthetic fiber including providing a first component of an aliphatic polyester polymer a second component of a multicarboxylic acid, mixing the first component aliphatic polyester polymer and the second component multicarboxylic acid to form an unreacted specified thermoplastic composition, and melt blending the unreacted specified thermoplastic composition in an extruder or a mixer. The second component multicarboxylic acid lubricates the extruder and provides a nucleating agent for crystallizing the specified thermoplastic composition to form a mean crystal size less than about 120 Angstroms. Fiber composed of the specified thermoplastic composition has a mean crystal size less than about 120 Angstroms. The fiber has a glass transition temperature (Tg) less than about 55 DEG C. In one aspect, a first component of polylactic acid and a second component of adipic acid provide synthetic fibers in a nonwoven structure used in a biodegradable and compostable disposable absorbent product for the absorption and removal of body fluids.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Graphite-based heat sink
InactiveUS6503626B1Improve cooling effectIncreased anisotropyLayered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNuclear engineeringGraphite
The present invention relates to a system for managing the heat from a heat source like an electronic component. More particularly, the present invention relates to a system effective for dissipating the heat generated by an electronic component using a heat sink formed from a compressed, comminuted particles of resin-impregnated flexible graphite mat or sheet.
Owner:GRAFTECH INT HLDG INC
Thin film with non-self-aggregating uniform heterogeneity and drug delivery systems made therefrom
The invention relates to the film products and methods of their preparation that demonstrate a non-self-aggregating uniform heterogeneity. Desirably the films disintegrate in water and may be formed by a controlled drying process, or other process that maintains the required uniformity of the film.
Owner:AQUESTIVE THERAPEUTICS INC
Polyethylene oxide-based films and drug delivery systems made therefrom
The invention relates to the film products and methods of their preparation that demonstrate a non-self-aggregating uniform heterogeneity. Desirably, the films disintegrate in water and may be formed by a controlled drying process, or other process that maintains the required uniformity of the film. The films contain a polymer component, which includes polyethylene oxide optionally blended with hydrophilic cellulosic polymers. Desirably, the films also contain a pharmaceutical and / or cosmetic active agent with no more than a 10% variance of the active agent pharmaceutical and / or cosmetic active agent per unit area of the film.
Owner:AQUESTIVE THERAPEUTICS INC
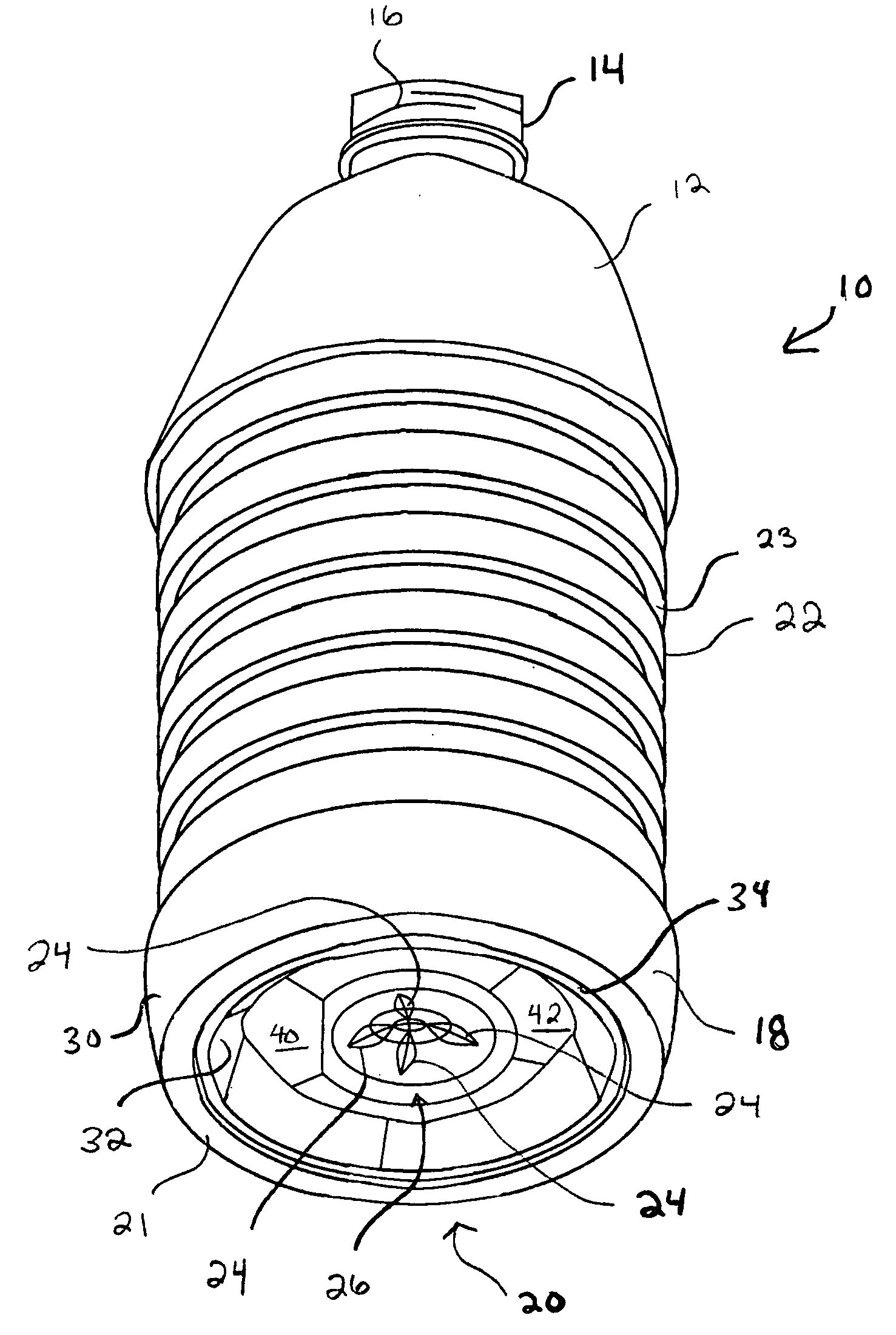
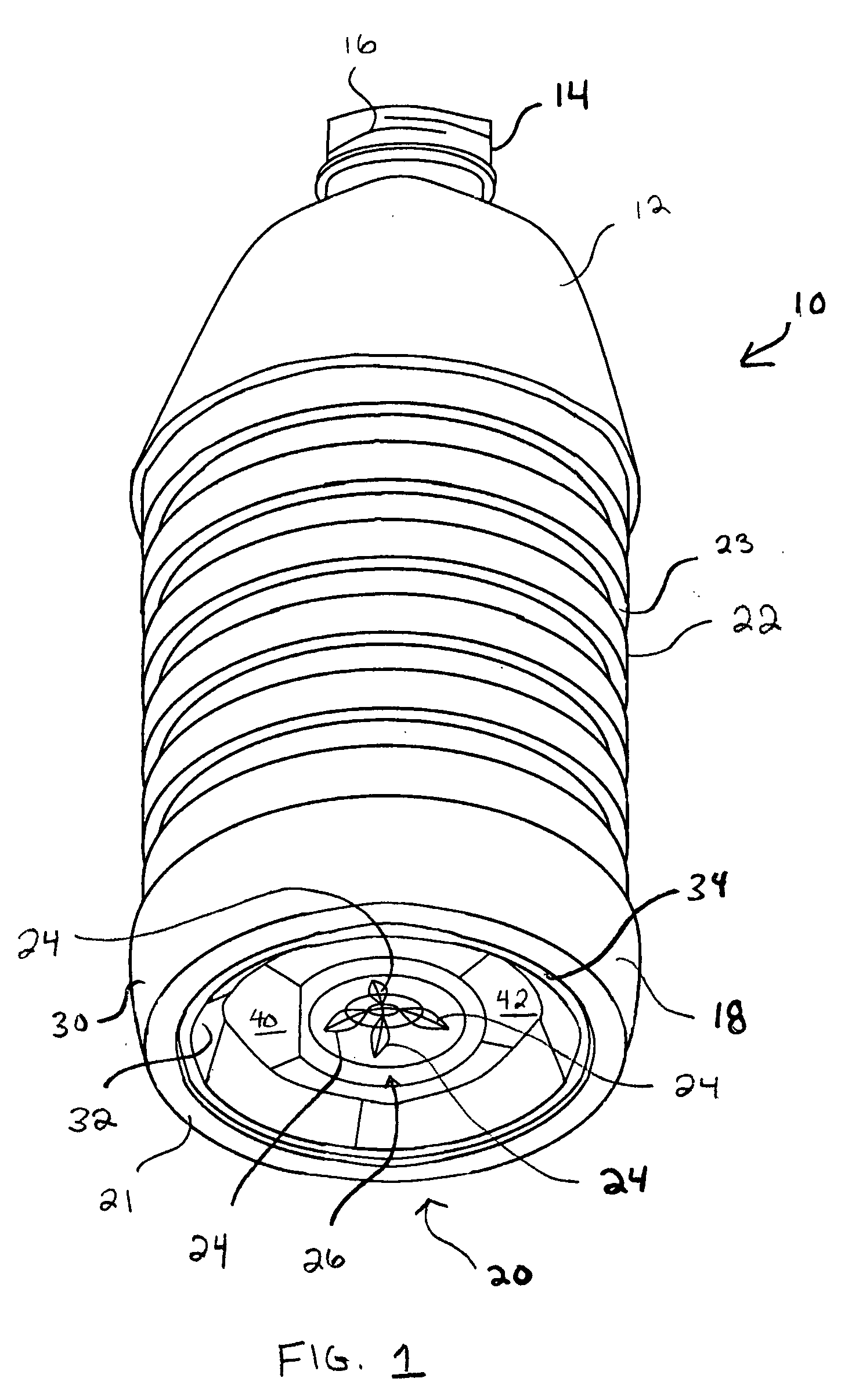
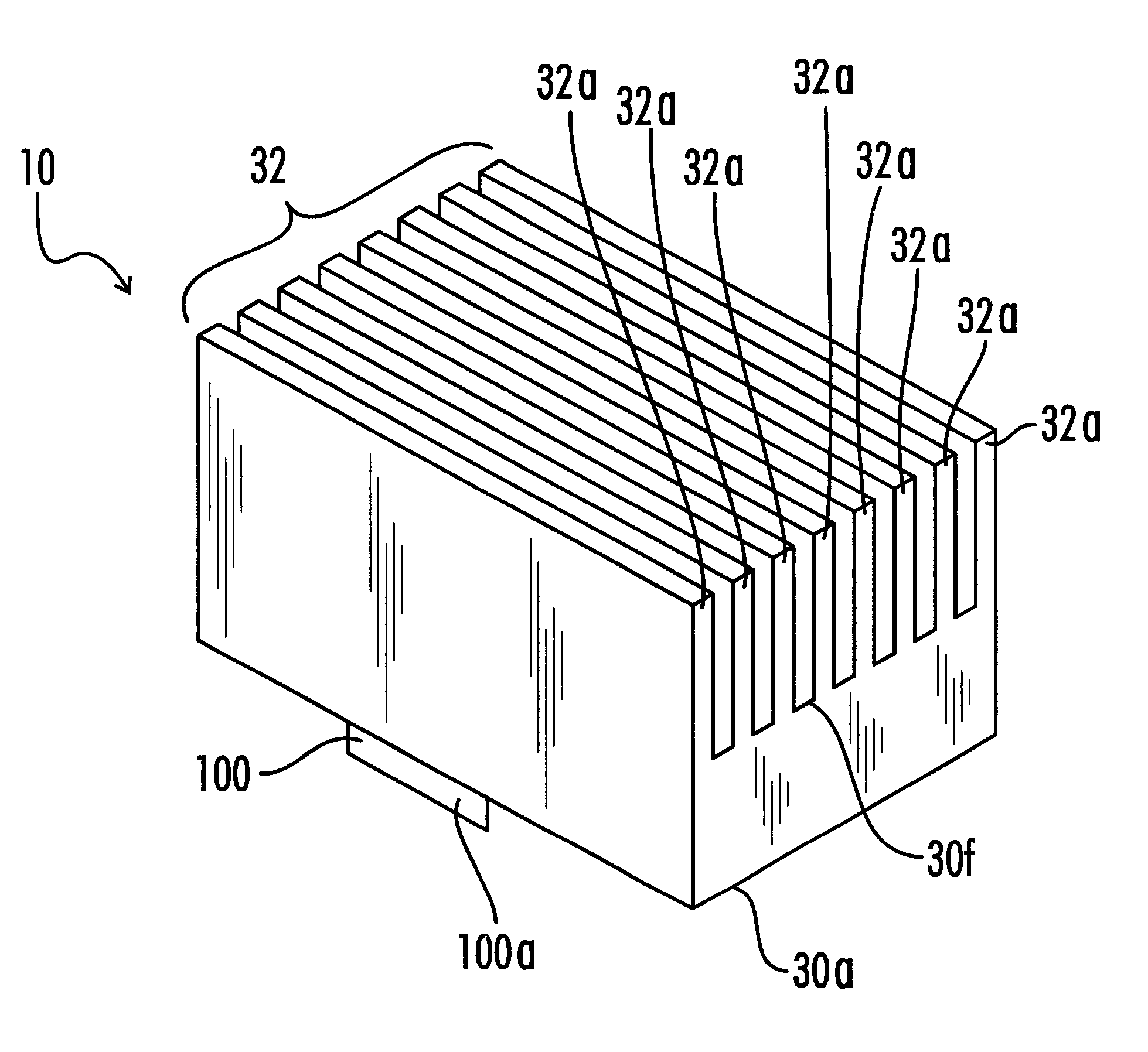
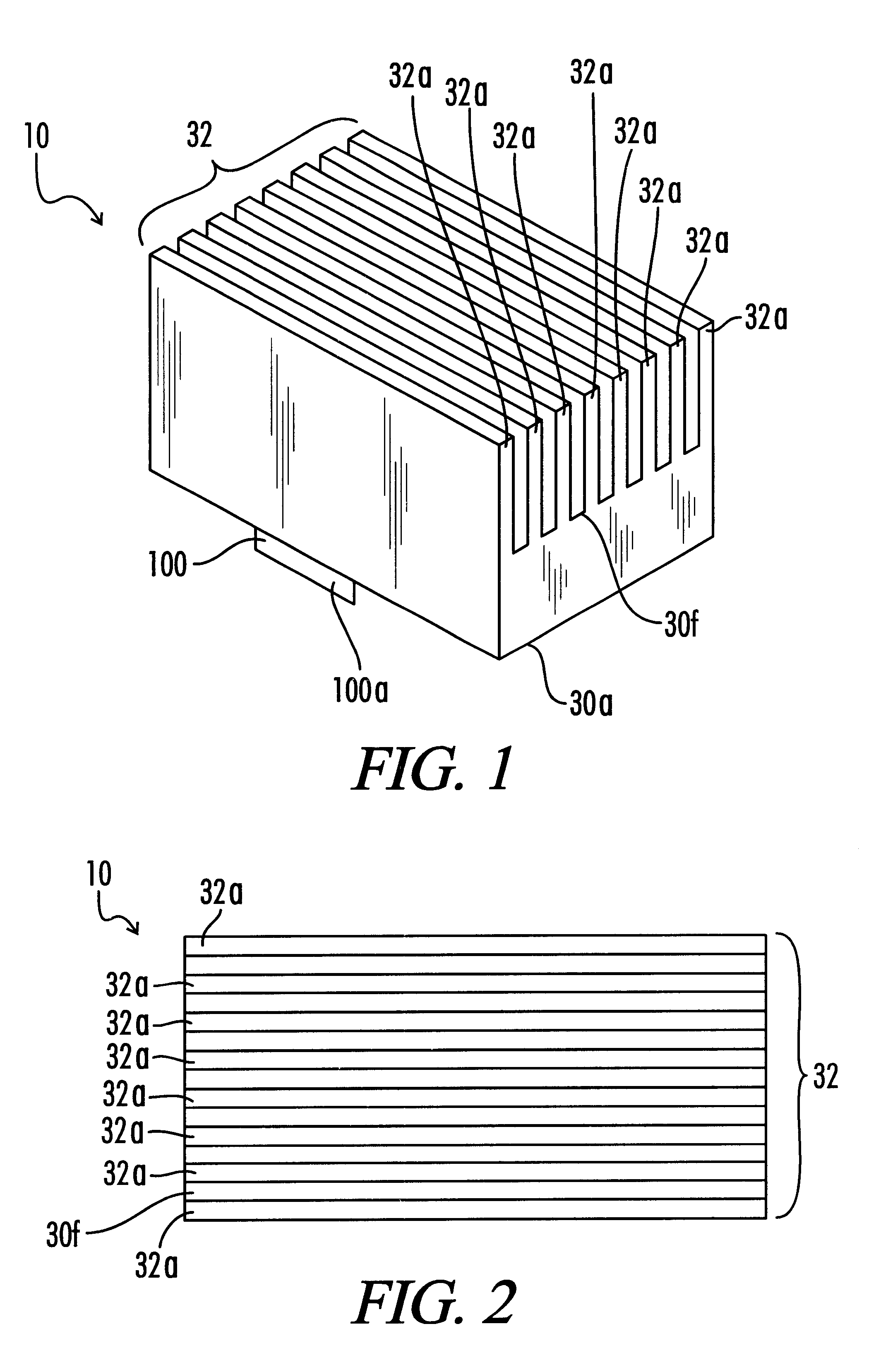
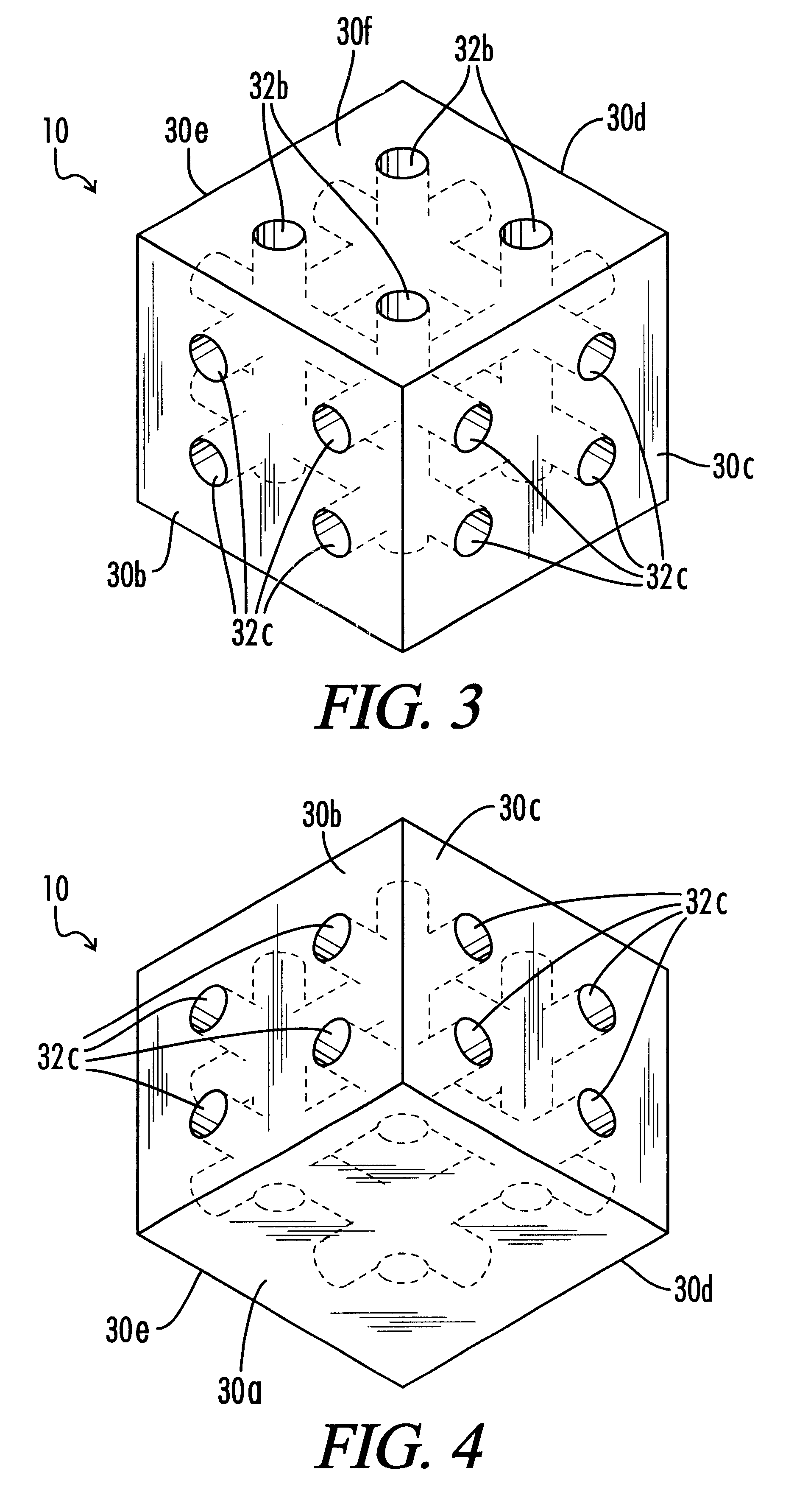
Impact absorbing composite
An impact absorbing composite structure (10), the impact absorbing composite structure including a plurality of impact absorbing members (18) and a flexible layer (16), each impact absorbing member (18) integral with the flexible layer (16).
Owner:GOLDFINE ANDREW A
Methods for the manufacture of sheets having a highly inorganically filled organic polymer matrix
Compositions and methods for manufacturing sheets having a highly inorganically filled matrix. Suitable inorganically filled mixtures are prepared by mixing together an organic polymer binder, water, one or more inorganic aggregate materials, fibers, and optional admixtures in the correct proportions in order to form a sheet which has the desired performance criteria. The inorganically filled mixtures are formed into sheets by first extruding the mixtures and the passing the extruded materials between a set of rollers. The rolled sheets are dried in an accelerated manner to form a substantially hardened sheet, such as by heated rollers and / or a drying chamber. The inorganically filled sheets may have properties substantially similar to sheets presently made from traditional materials like paper, cardboard, polystyrene, plastic, or metal. Such sheets can be rolled, pressed, scored, perforated, folded, and glued. They have especial utility in the mass production of containers, particularly food and beverage containers.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
Process for forming micro-fiber cellulosic nonwoven webs from a cellulose solution by melt blown technology and the products made thereby
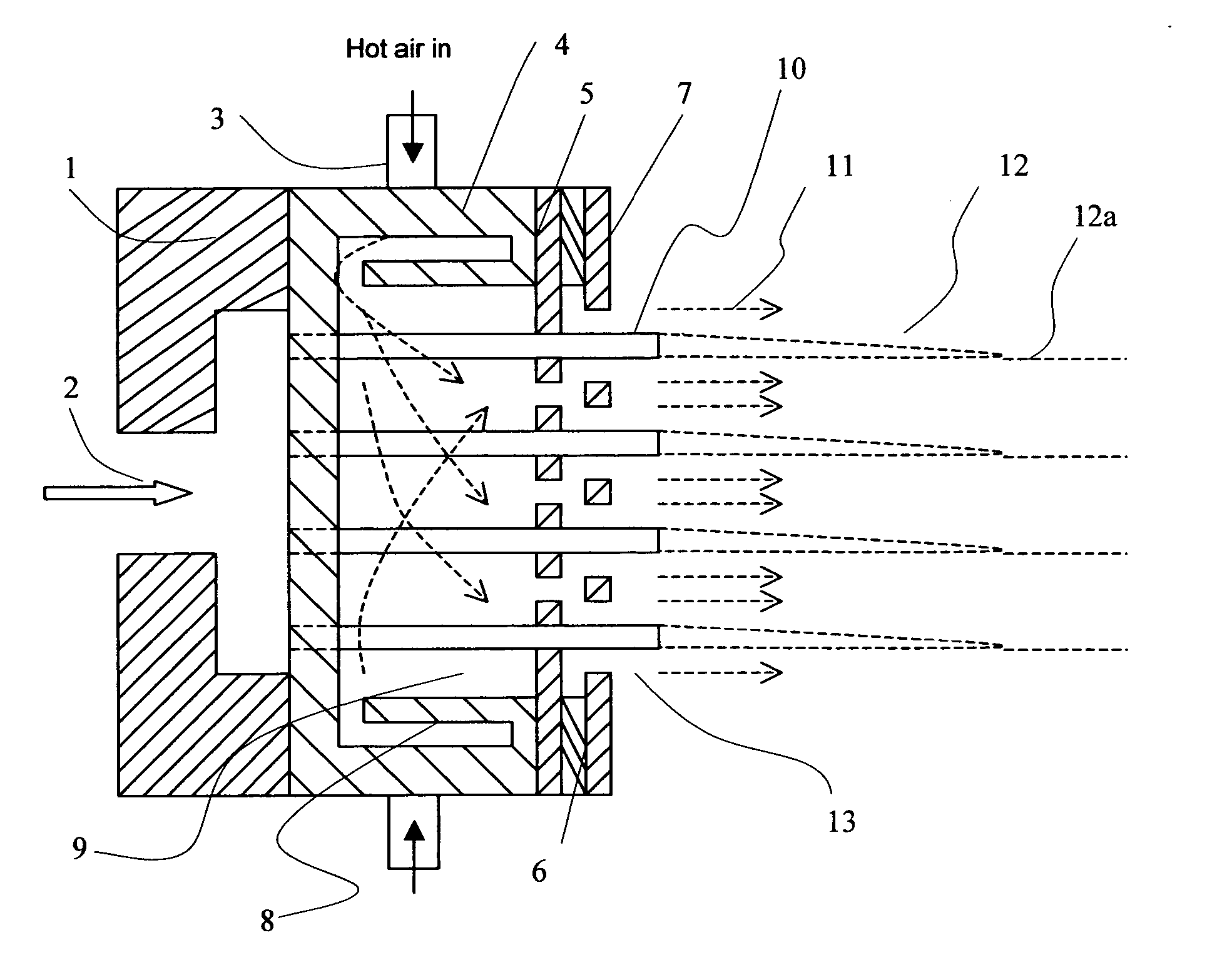
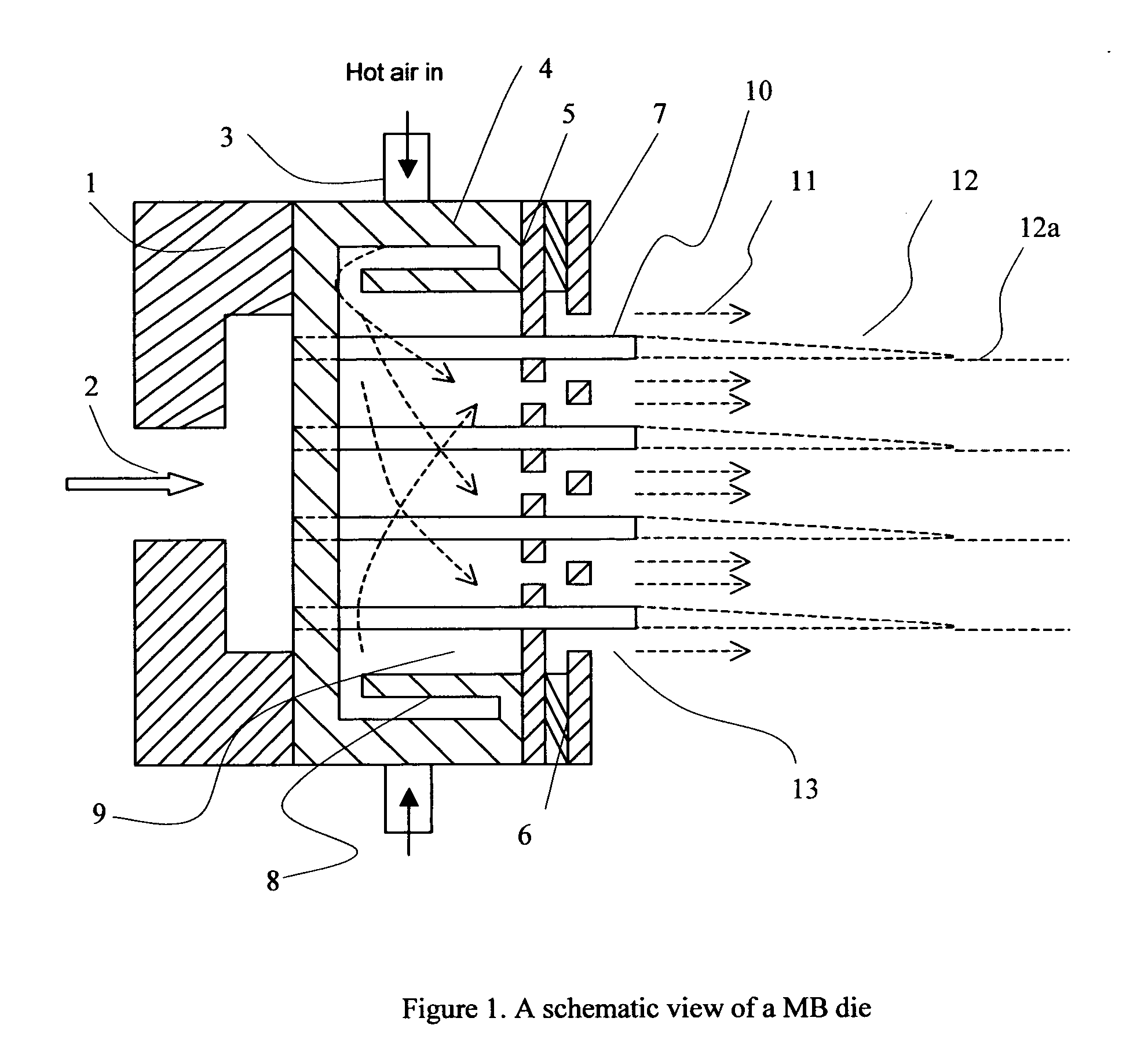
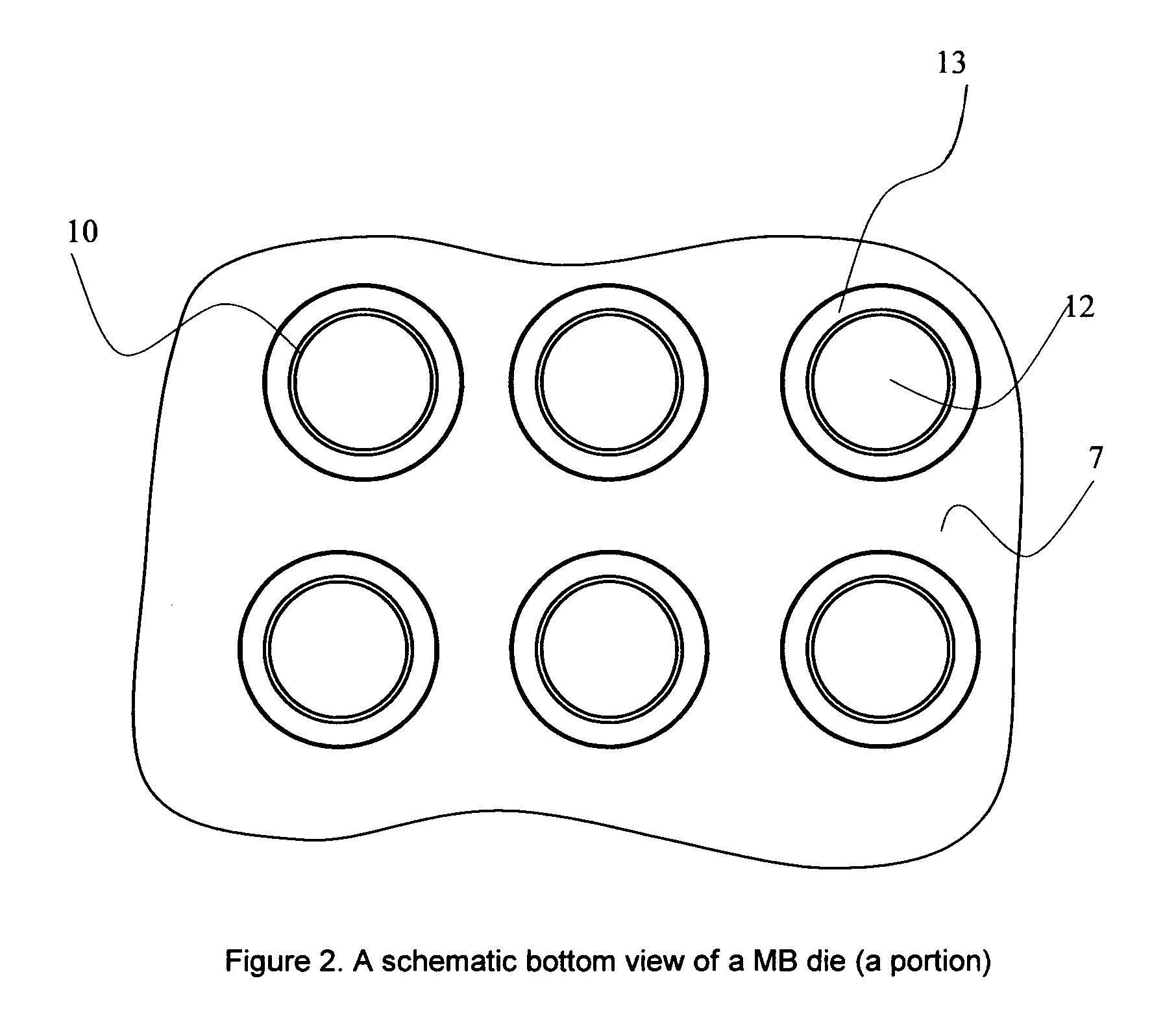
InactiveUS20050056956A1Artificial filament washing/dryingLoose filtering material filtersNon solventEngineering
This invention relates to a process of melt blowing a cellulose solution through a concentric melt blown die with multiple rows of spinning nozzles to form cellulosic microfiber webs with different web structures. The process comprises the steps of (a) extruding a cellulose solution (dope) through a melt blown spinneret with multiple rows of spinning nozzles; (b) drawing each individual extrudate filament to fine fiber diameter by its own air jet; (c) coagulating and entangling the fine fibers with a series of pressured hydro needling jets of recycling solution of the mixture of cellulose solvent and non-solvent in the spin-line; (d) collecting the stream of microfibers, air and needling jets on a moving collecting surface to form cellulosic fiber web; (e) hydro-entangling the said pre-bonded web downstream with at least one set of hydro needling jets of recycling solvent / non-solvent solution for forming well bonded nonwoven web; (f) regenerating the fine fibers in at least one bath for at least 5 seconds; (g) further regenerating and washing the fine fibers in another bath for at least 5 seconds; (h) pinching the well bonded melt blown cellulosic nonwoven with pressure rollers to remove major portions of the non-solvent; (i) drying the nonwoven web by heat, or vacuum or both, and (j) winding the nonwoven web into rolls.
Owner:BIAX FIBERFILM CORP
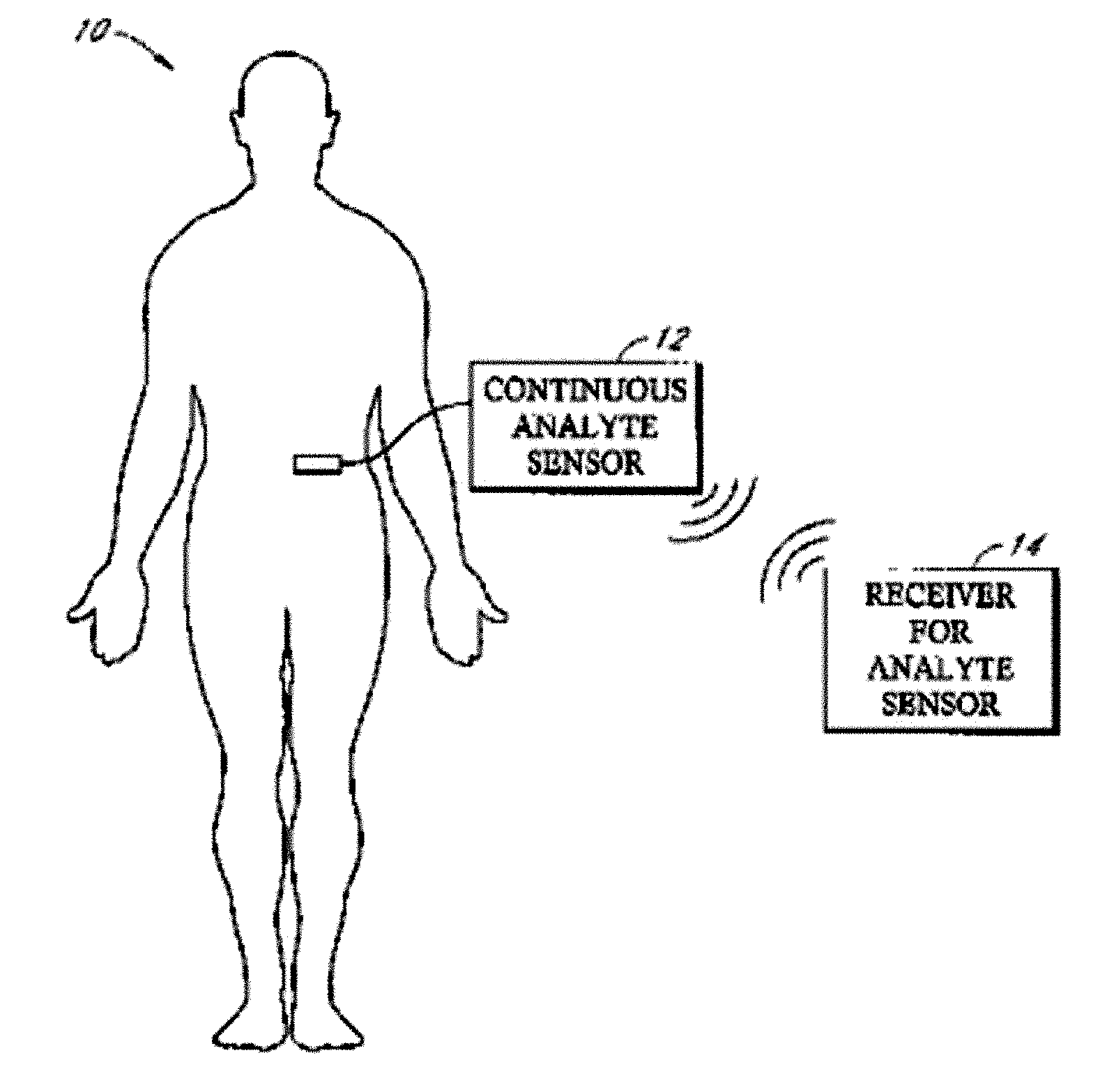
Implantable analyte sensor
ActiveUS8277713B2Improve convenienceMinimize movementImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteMiniaturization
An implantable analyte sensor including a sensing region for measuring the analyte and a non-sensing region for immobilizing the sensor body in the host. The sensor is implanted in a precisely dimensioned pocket to stabilize the analyte sensor in vivo and enable measurement of the concentration of the analyte in the host before and after formation of a foreign body capsule around the sensor. The sensor further provides a transmitter for RF transmission through the sensor body, electronic circuitry, and a power source optimized for long-term use in the miniaturized sensor body.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Device and arrangement for producing a three-dimensional object
InactiveUS20040026807A1Reduced form requirementsSmall sizeConfectioneryWood working apparatusThin layerRunning time
A device for manufacturing a three-dimensional product, which device comprises a work table on which said three-dimensional product is to be built, a powder dispenser which is arranged to lay down a thin layer of powder on the work table for the formation of a powder bed, a ray gun for giving off energy to the powder whereby fusion of the powder takes place, members for controlling of the beam released by the ray gun across said powder bed for the formation of a cross section of said three-dimensional product through fusion of parts of said powder bed, and a controlling computer in which information about successive cross sections of the three-dimensional product is stored, which cross sections build the three-dimensional product, the controlling computer intended to control said members for guiding the ray gun across the powder bed according to a running schedule forming a cross section of said three-dimensional body, whereby said three-dimensional product is formed by successive fusion of successively formed cross sections from powder layers successively laid down by the powder dispenser.
Owner:ARCAM AB
Polarizing film, optical film and liquid crystal display using polarizing film
InactiveUS6961178B2Solve the real problemImprove adhesionSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationTectorial membraneLiquid-crystal display
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
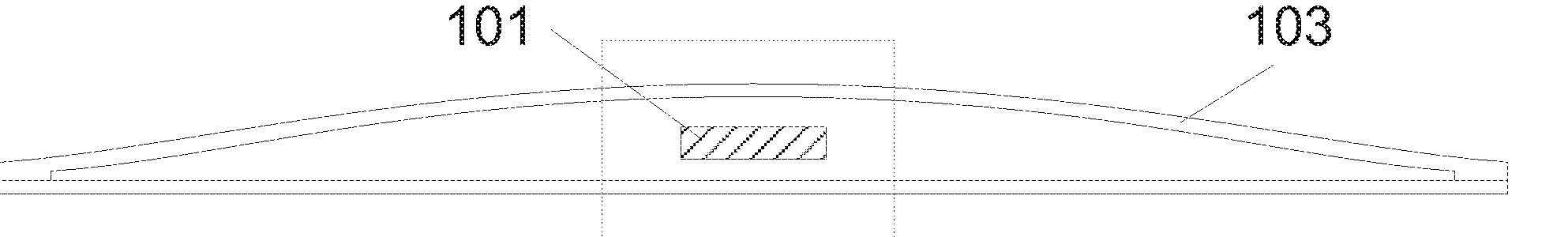
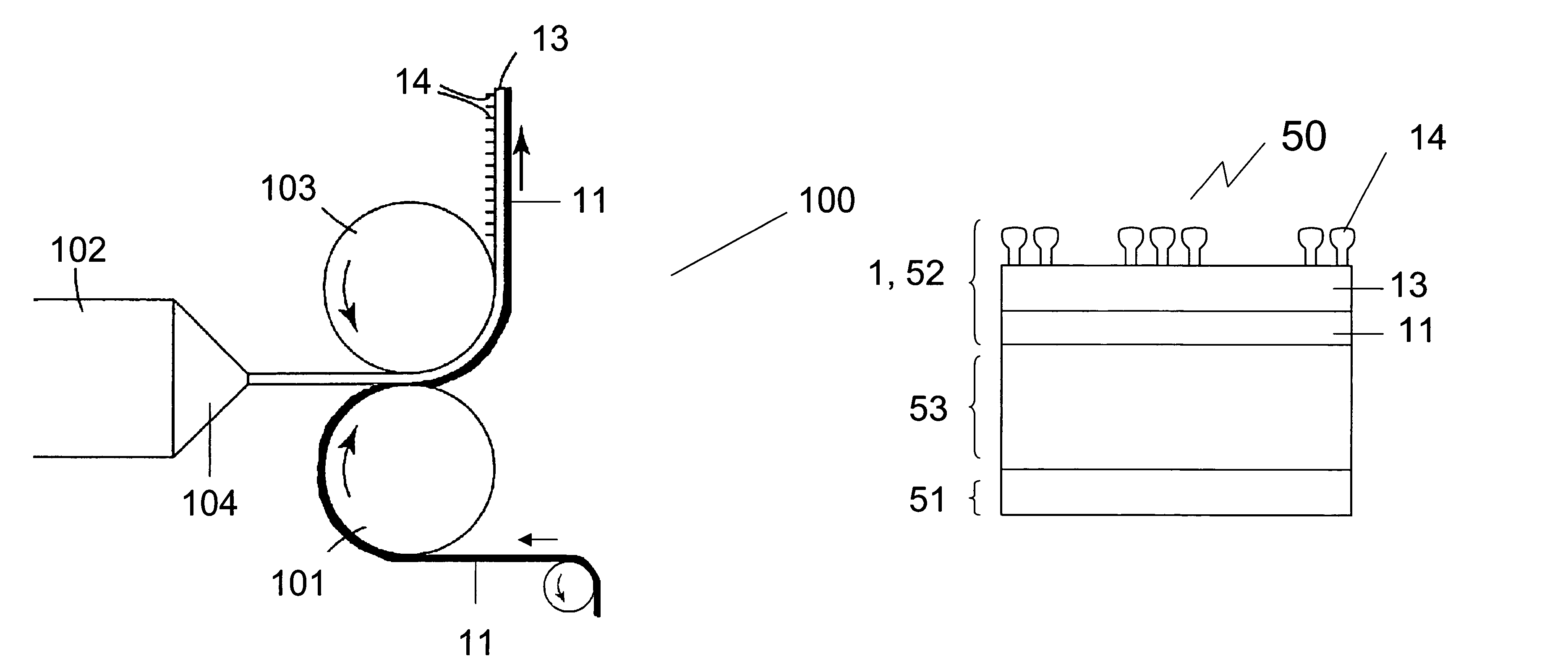
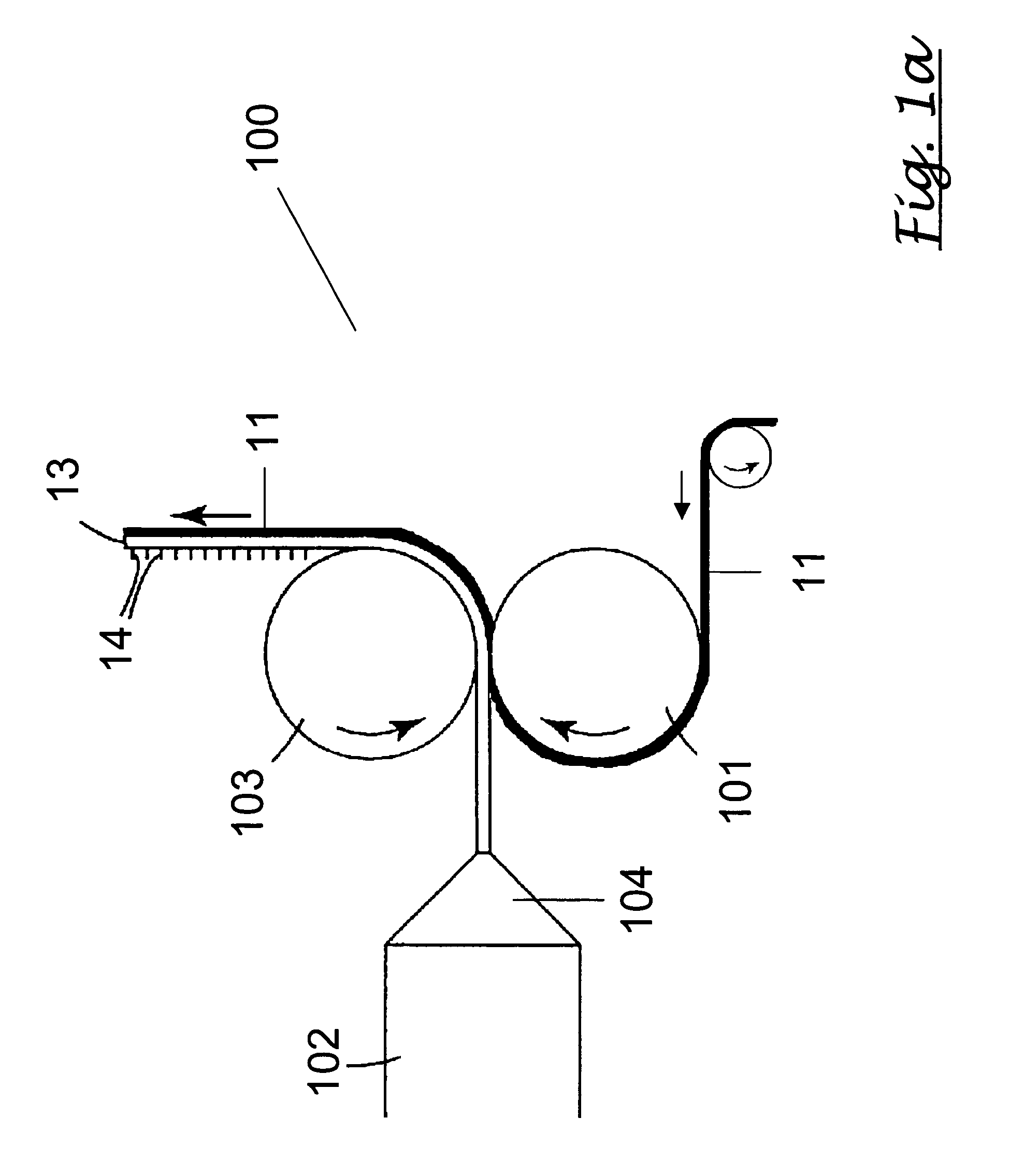
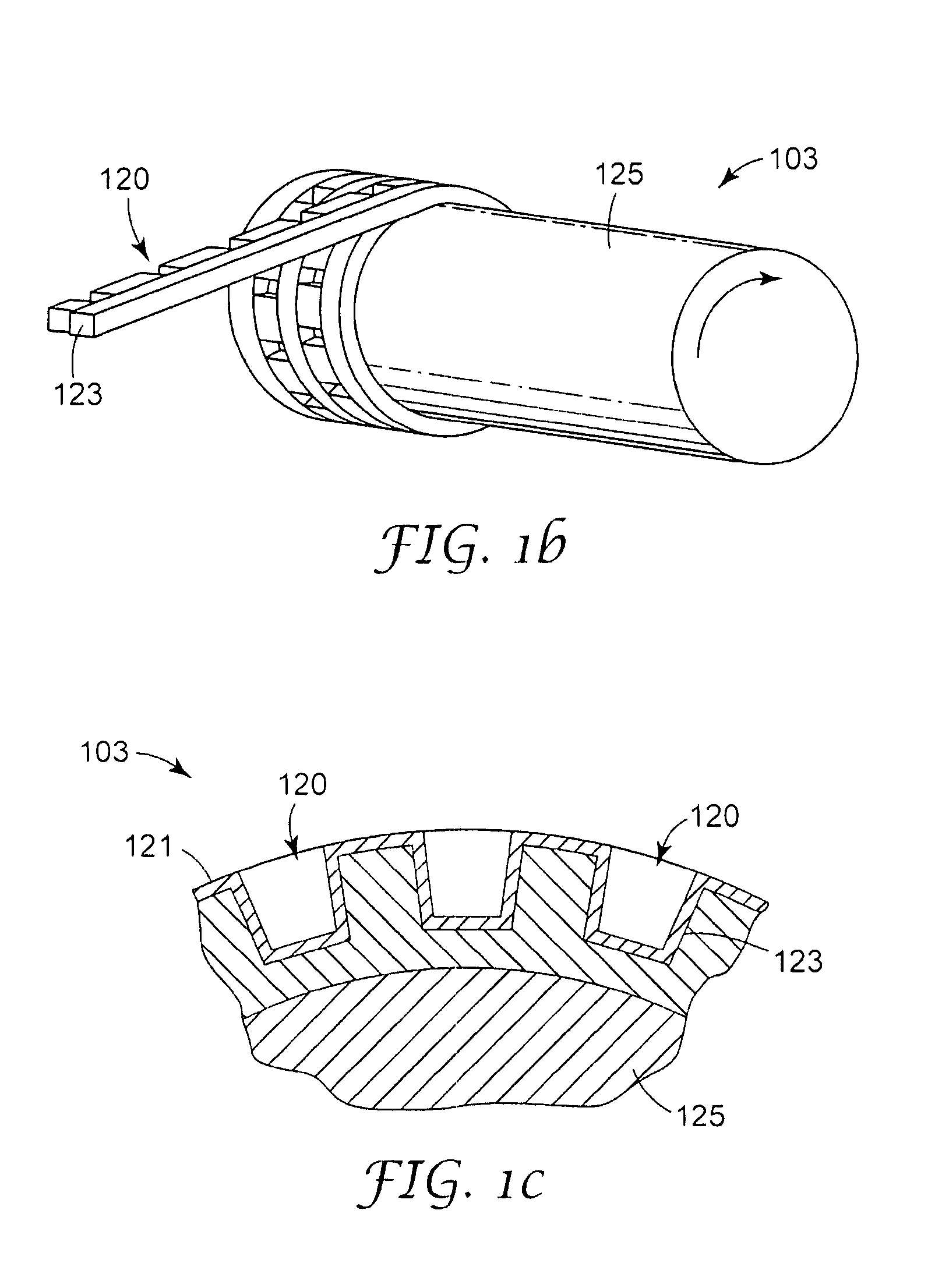
Methods of manufacturing a stretched mechanical fastening web laminate
InactiveUS7897078B2Reduce basis weightSnap fastenersWood working apparatusFiberVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing a stretched mechanical fastening web laminate (1) comprising a thermoplastic web layer (13) having two major surfaces, one of the major surfaces bearing a multitude of male fastening elements (14) suitable for engagement with a corresponding female fastening material, and on its other major surface a fibrous web layer (11), said method comprising the steps of(i) providing the fibrous web layer (11) having an initial basis weight,(ii) passing the fibrous web layer (11) through a nip formed by two rolls (101), (103), one of them having cavities (120) that are the negatives of a plurality of male fastening elements (14), introducing a molten thermoplastic resin into the cavities (120) in excess of an amount that would fill the cavities (120) which excess forms the thermoplastic web layer (13), allowing the resin to at least partially solidify and stripping of a precursor web laminate (10) thus formed comprising the fibrous web layer (11) and the thermoplastic web layer (13) bearing a plurality of male fastening elements (14), from the cylindrical roll (103) having cavities (120) whereby the thermoplastic web layer (13) has an initial thickness and an initial hook density, and(iii) stretching the precursor web laminate (10) monoaxially or biaxially thereby decreasing the basis weight of the fibrous web layer (11) and the thickness of the thermoplastic web layer (13) from their respective initial values to provide a stretched mechanical fastening laminate (1) having a basis weight of less than 100 g·m−2.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Wood fibre based panels with a thin surface layer
ActiveUS20100092731A1Large market shareImprove impact resistanceLiquid surface applicatorsCovering/liningsSurface layerWood fibre
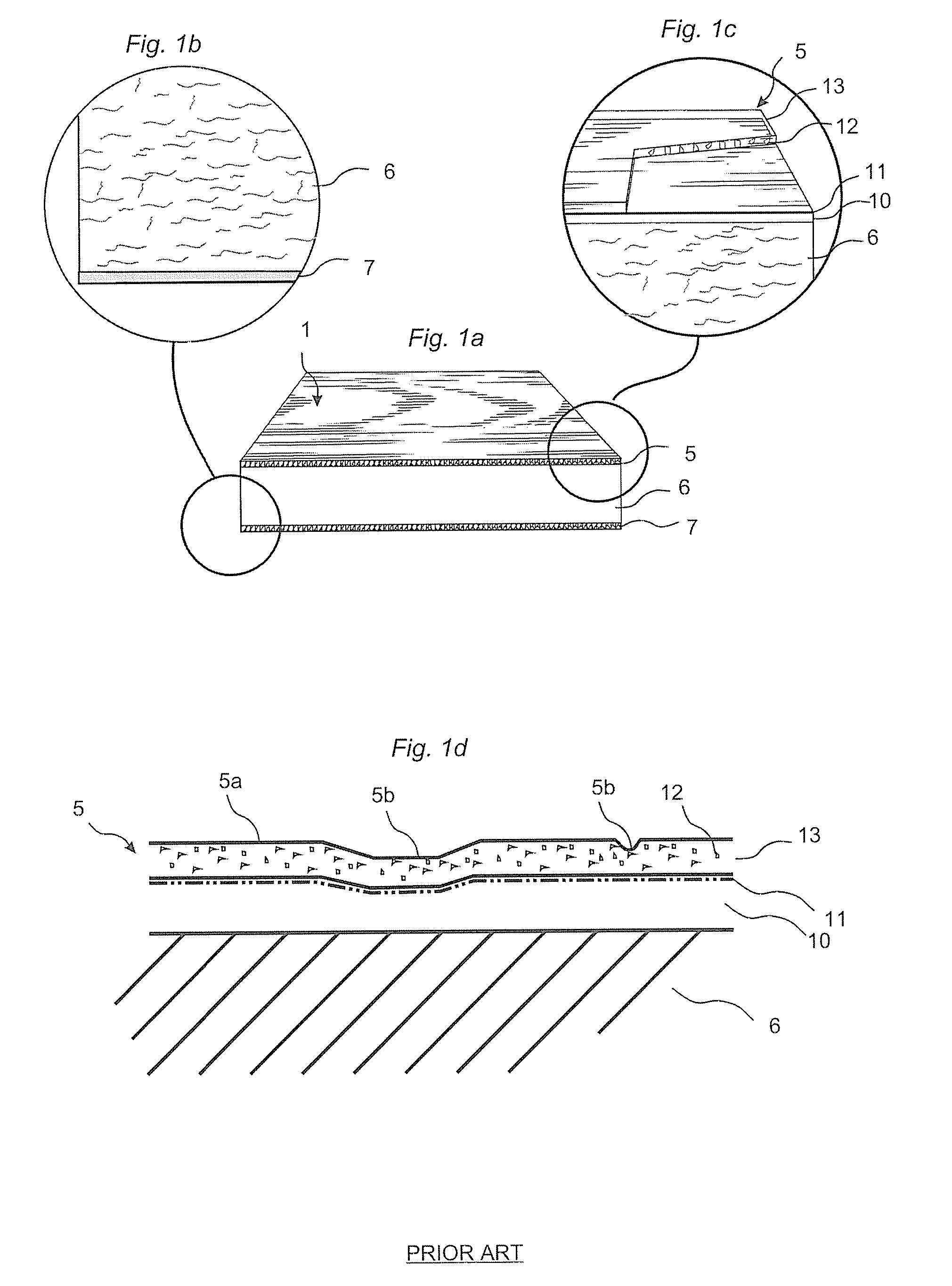
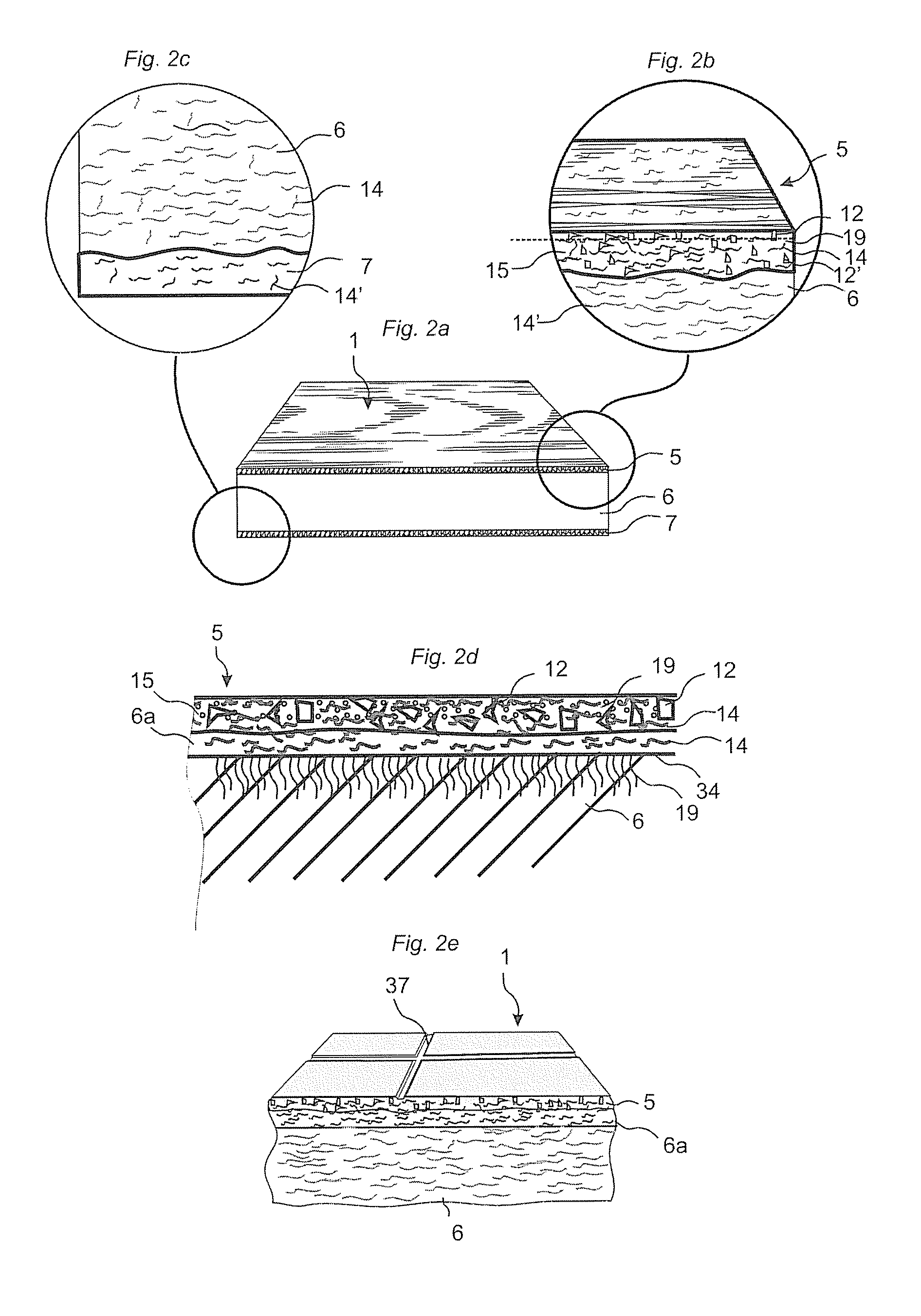
Building panels with a thin and embossed surface layer and a sub layer between a surface layer and a core.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com