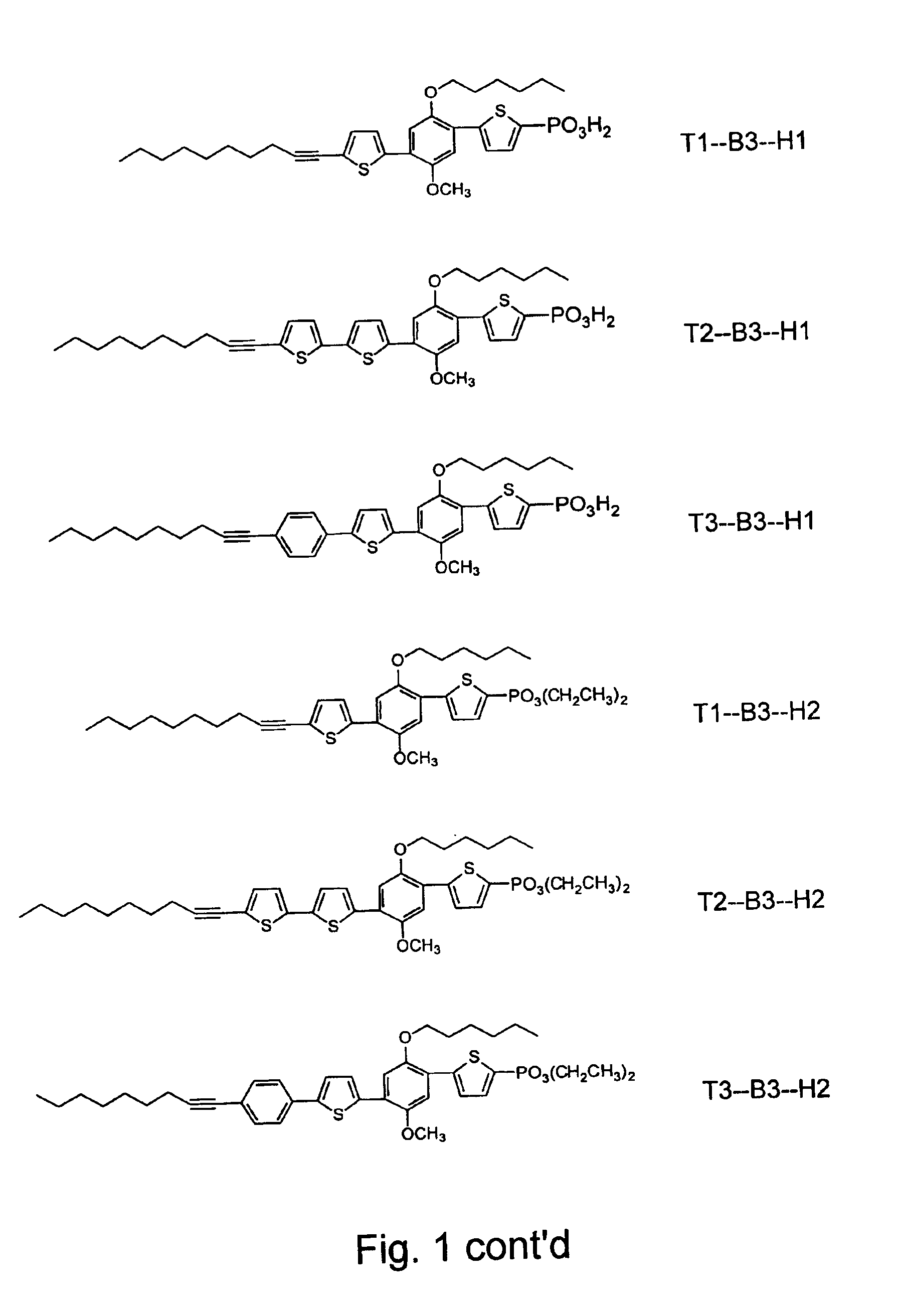
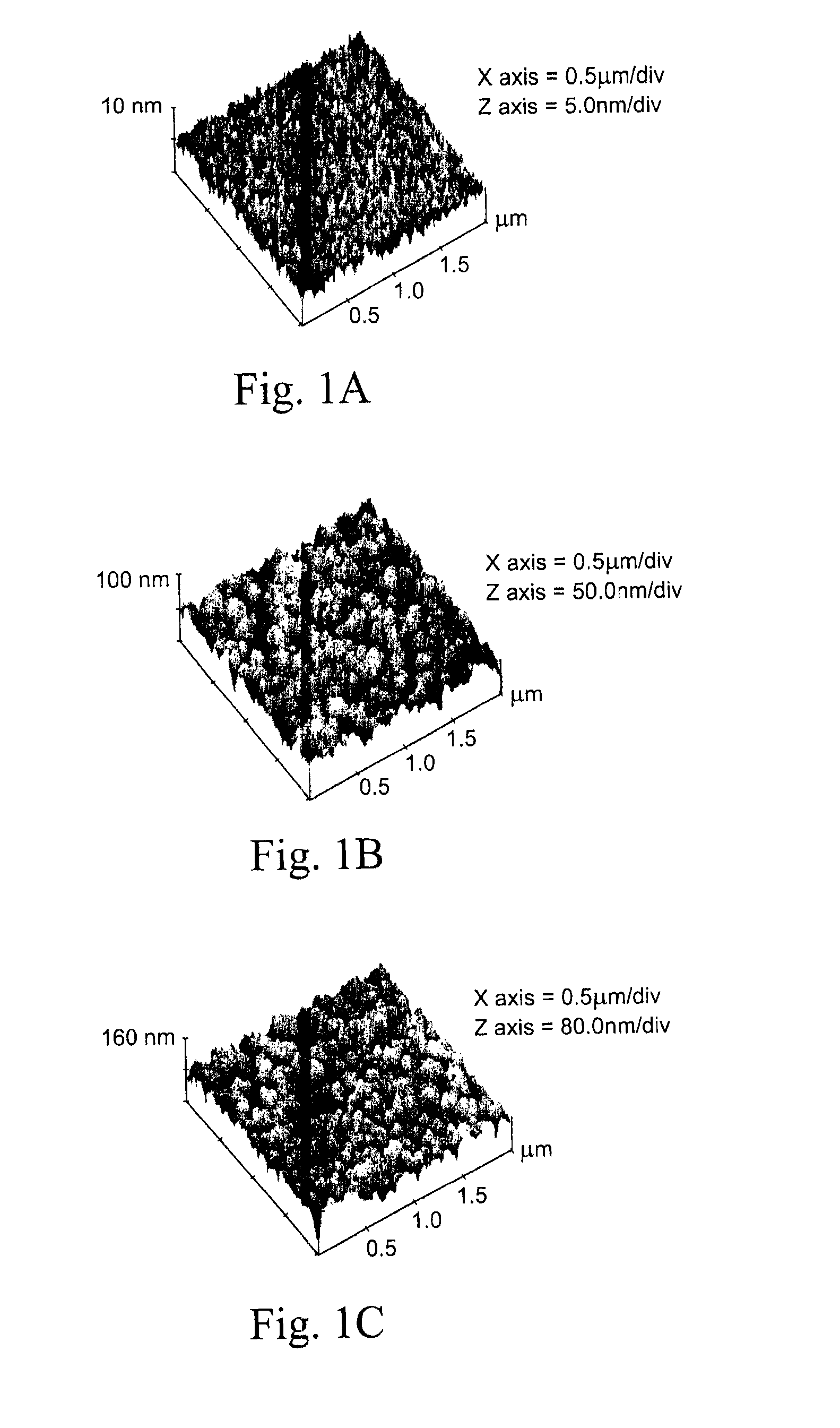
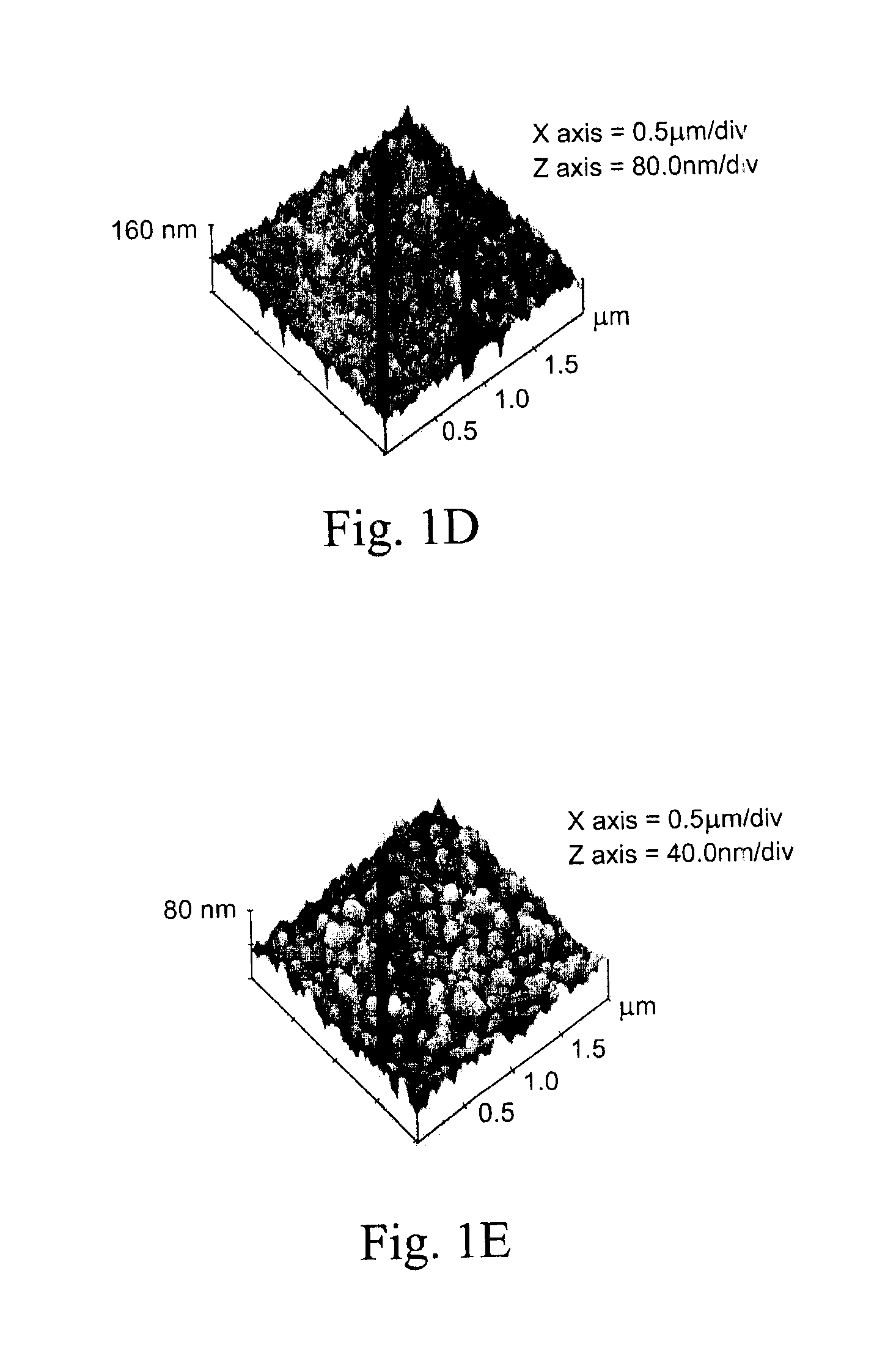
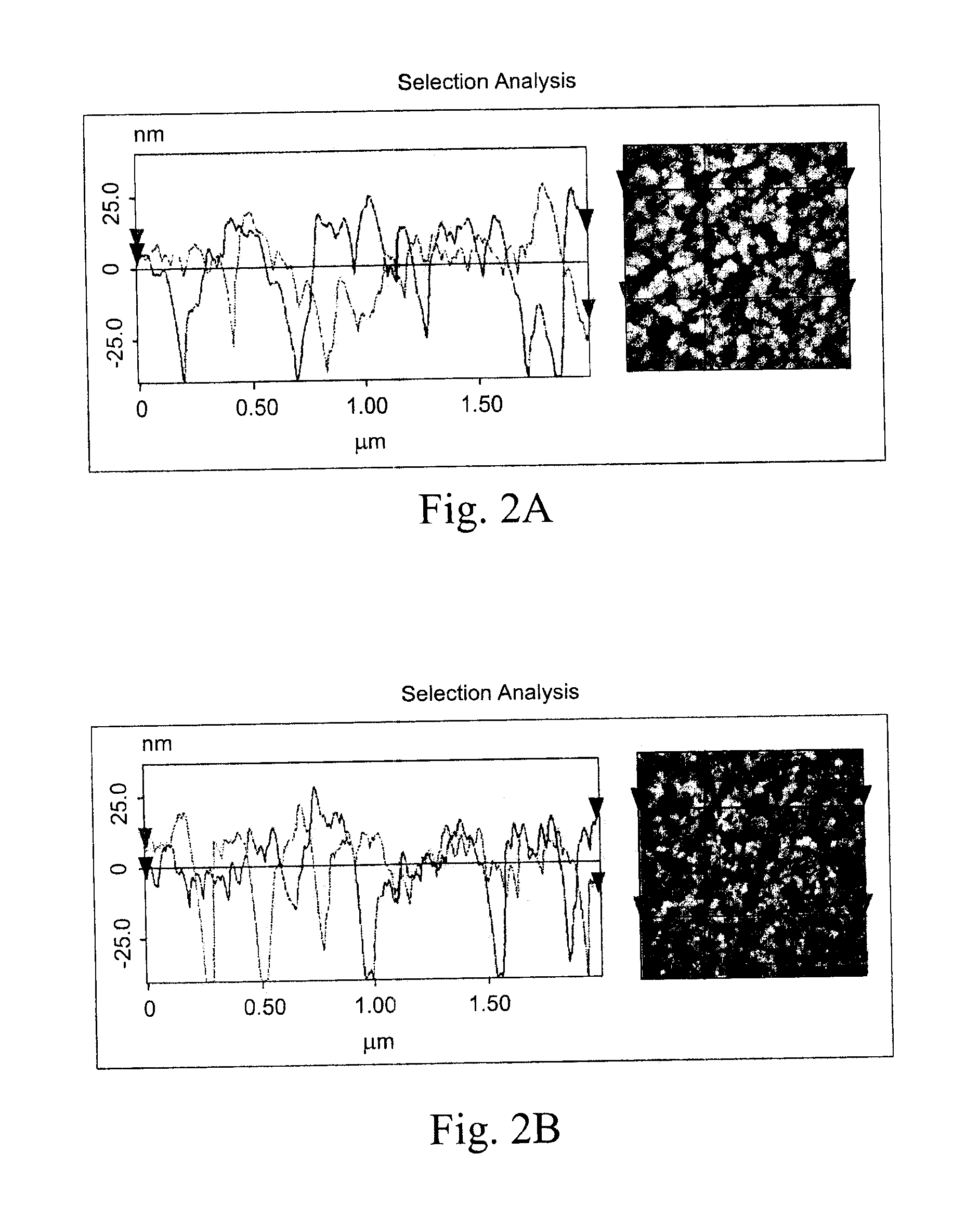
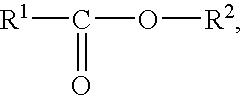
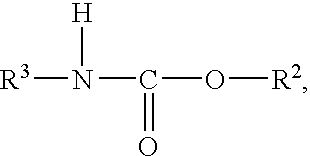
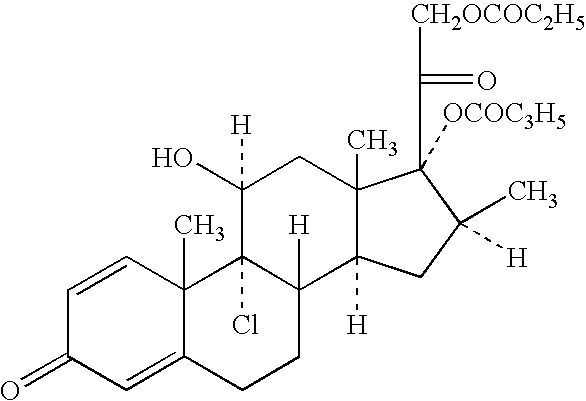
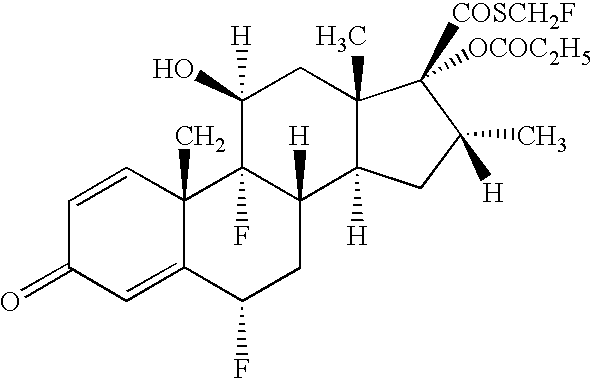
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5024results about "Nanostructure manufacture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Free-standing and aligned carbon nanotubes and synthesis thereof
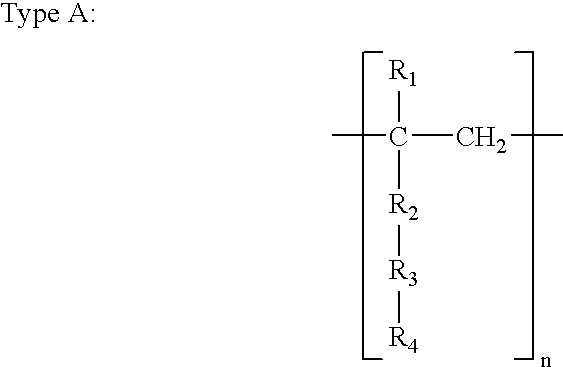
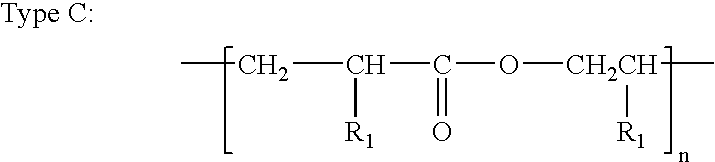
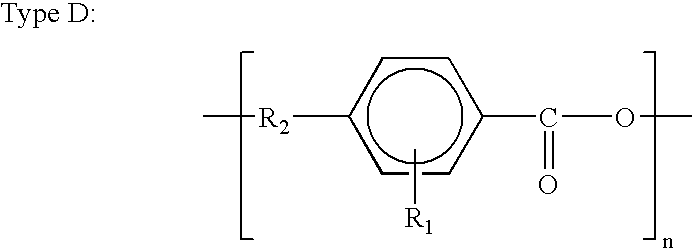
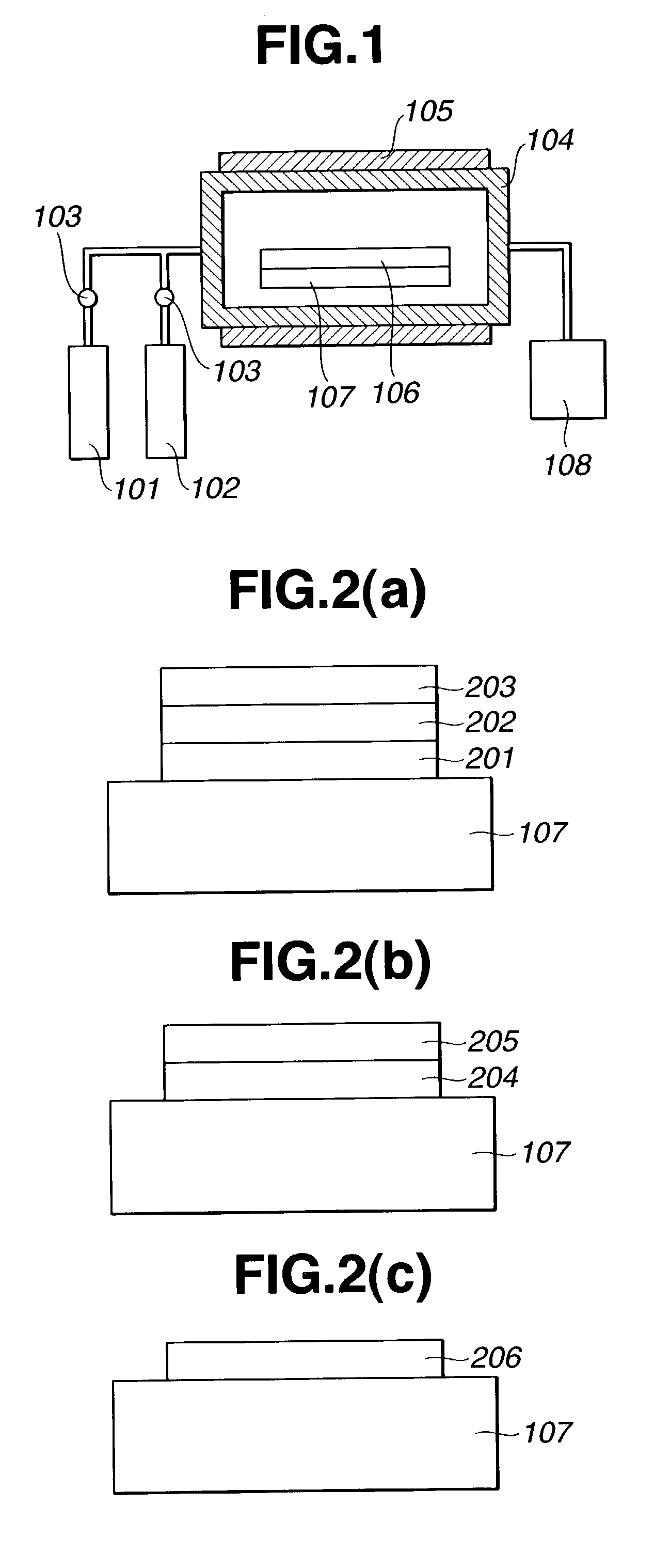
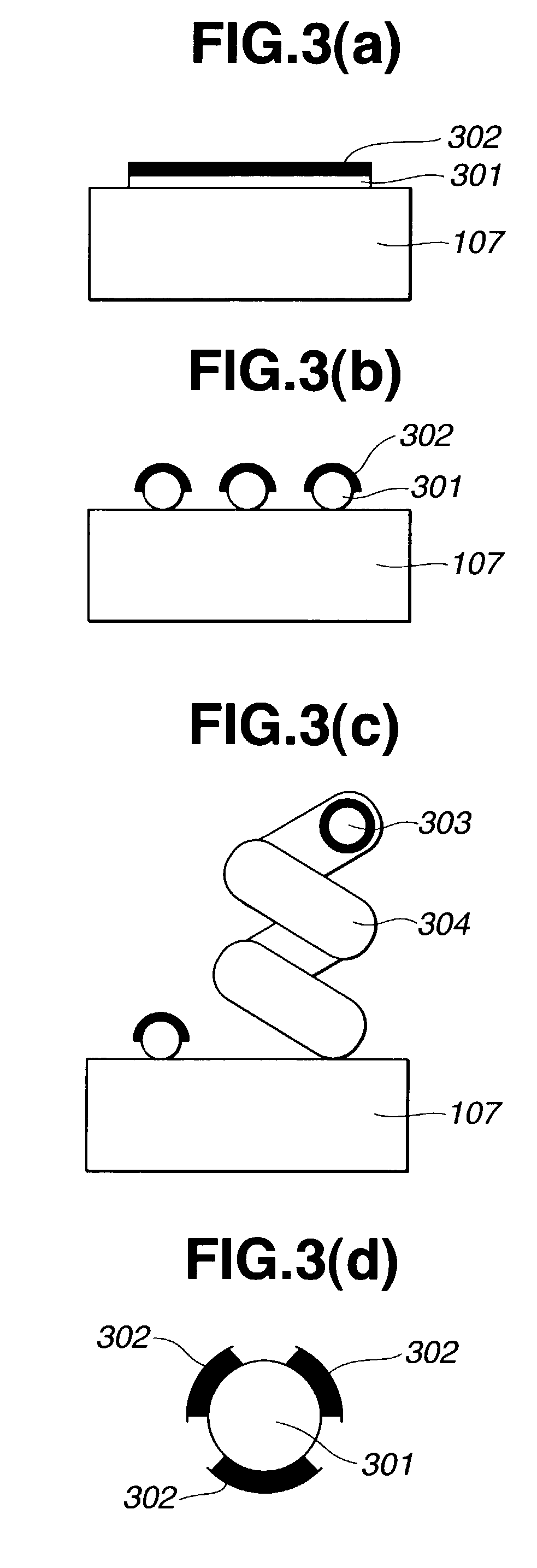
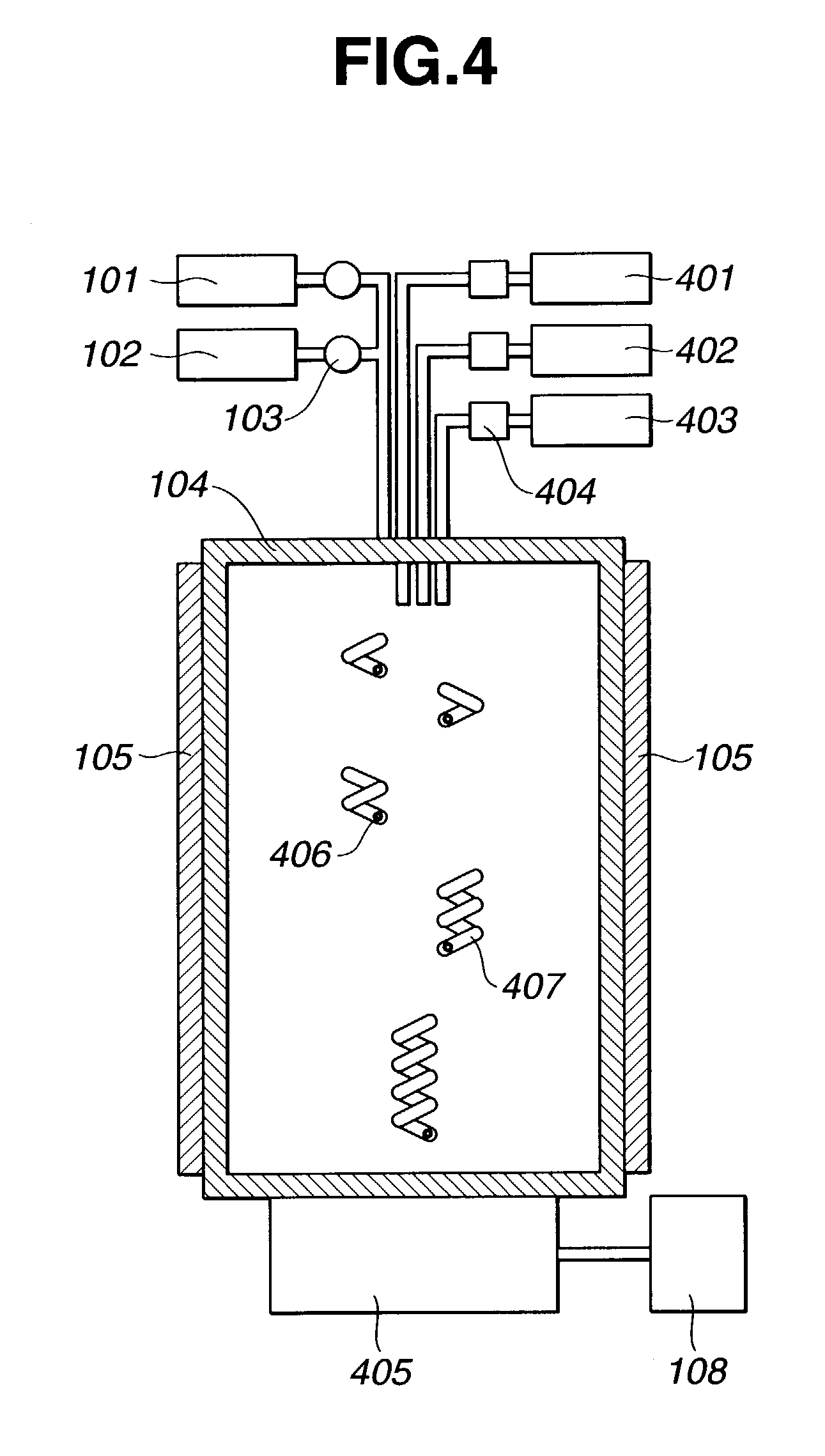
One or more highly-oriented, multi-walled carbon nanotubes are grown on an outer surface of a substrate initially disposed with a catalyst film or catalyst nano-dot by plasma enhanced hot filament chemical vapor deposition of a carbon source gas and a catalyst gas at temperatures between 300° C. and 3000° C. The carbon nanotubes range from 4 to 500 nm in diameter and 0.1 to 50 μm in length depending on growth conditions. Carbon nanotube density can exceed 104 nanotubes / mm2. Acetylene is used as the carbon source gas, and ammonia is used as the catalyst gas. Plasma intensity, carbon source gas to catalyst gas ratio and their flow rates, catalyst film thickness, and temperature of chemical vapor deposition affect the lengths, diameters, density, and uniformity of the carbon nanotubes. The carbon nanotubes of the present invention are useful in electrochemical applications as well as in electron emission, structural composite, material storage, and microelectrode applications.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Methods of positioning and/or orienting nanostructures
Methods of positioning and orienting nanostructures, and particularly nanowires, on surfaces for subsequent use or integration. The methods utilize mask based processes alone or in combination with flow based alignment of the nanostructures to provide oriented and positioned nanostructures on surfaces. Also provided are populations of positioned and / or oriented nanostructures, devices that include populations of positioned and / or oriented nanostructures, systems for positioning and / or orienting nanostructures, and related devices, systems and methods.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
Polymer solution for nanoimprint lithography to reduce imprint temperature and pressure
InactiveUS20040110856A1Reduce pressureReduce the temperatureNanostructure manufactureDecorative surface effectsCross-linkVitrification
A method of forming features on substrates by imprinting is provided. The method comprises: (a) forming a polymer solution comprising at least one polymer dissolved in at least one polymerizable monomer; and (b) depositing the polymer solution on a substrate to form a liquid film thereon; and then either: (c) curing the liquid film by causing the monomer(s) to polymerize and optionally cross-linking the polymer(s) to thereby form a polymer film, the polymer film having a glass transition temperature (Tg); and imprinting the polymer film with a mold having a desired pattern to form a corresponding negative pattern in the polymer film, or (d) imprinting the liquid film with the mold and curing it to form the polymer film. The temperature of imprinting is as little as 10° C. above the Tg, or even less if the film is in the liquid state. The pressure of the imprinting can be within the range of 100 to 500 psi.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Carbon nanotube hybrid system using carbide-derived carbon, a method of making the same, an electron emitter comprising the same, and an electron emission device comprising the electron emitter
InactiveUS20080248310A1Improve uniformityLong life-timeMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureHybrid systemHalogen
A carbon nanotube hybrid system includes: a carbide-derived carbon prepared by reacting a carbide compound and a halogen group containing gas to extract elements of the carbide compound except carbons; metals supported on the carbide-derived carbon or remaining in the carbide-derived carbon; and carbon sources from which carbon nanotubes are grown from the carbide-derived carbon. A method of preparing the carbon nanotube hybrid system includes preparing the carbide-derived carbon, extracting elements therefrom, and growing carbon nanotubes from the carbide-derived carbon. The carbon nanotube hybrid system has excellent uniformity and a long lifetime. An electron emitter having improved electron emitting properties can be inexpensively prepared using the carbon nanotube hybrid system compared to conventional carbon nanotubes. An electron emission device having excellent electron emitting properties can be prepared using the electron emitter.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Method of manufacturing inorganic nanotube
InactiveUS7005391B2Material nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthInorganic materialsAtomic layer deposition
A method of manufacturing an inorganic nanotube using a carbon nanotube (CNT) as a template, includes preparing a template on which a CNT or a CNT array is formed, forming an inorganic thin film on the CNT by depositing an inorganic material on the template using atomic layer deposition (ALD), and removing the CNT to obtain an inorganic nanotube or an inorganic nanotube array, respectively.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of preparing catalyst for manufacturing carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20070020167A1Improve uniformityMinimize agglomerationMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureFreeze-dryingCarbon nanotube
A novel method of forming catalyst particles, on which carbon nanotubes grow based, on a substrate with increased uniformity, and a method of synthesizing carbon nanotubes having improved uniformity are provided. A catalytic metal precursor solution is applied to a substrate. The applied catalytic metal precursor solution is freeze-dried, and then reduced to catalytic metal. The method of forming catalyst particles can minimize agglomeration and / or recrystallization of catalyst particles when forming the catalyst particles by freeze-drying the catalyst metal precursor solution. The catalyst particles formed by the method has a very uniform particle size and are very uniformly distributed on the substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Organic species that facilitate charge transfer to or from nanostructures
InactiveUS6949206B2Facilitates injection and extractionMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureOligomerNanocrystal
The present invention provides compositions (small molecules, oligomers and polymers) that can be used to modify charge transport across a nanocrystal surface or within a nanocrystal-containing matrix, as well as methods for making and using the novel compositions.
Owner:SHOEI CHEM IND CO LTD
Method of preparing nano-structured surface coatings and coated articles
InactiveUS7892606B2Improve adhesionMore readily manufacturableMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureCross-linkNano structuring
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
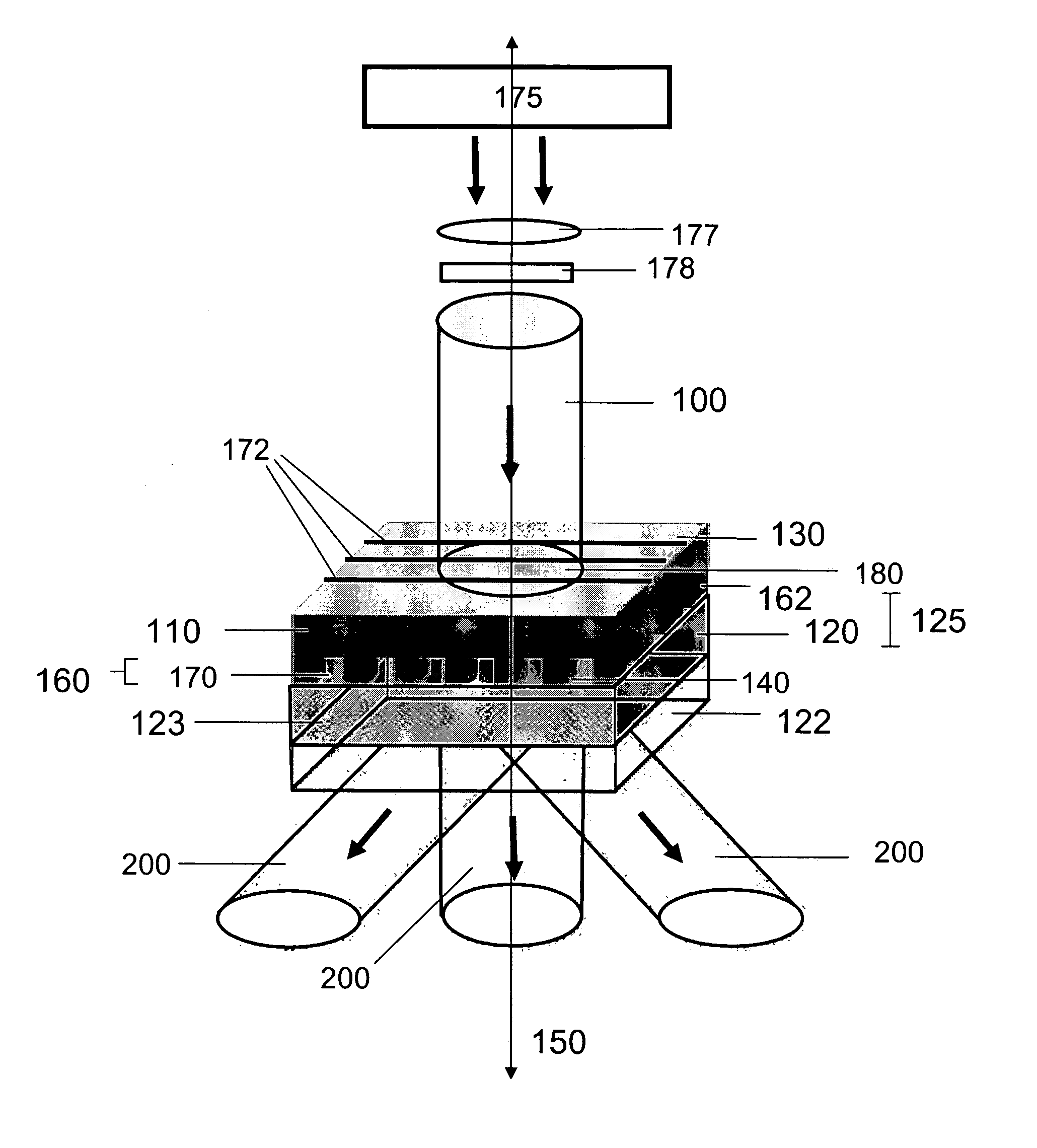
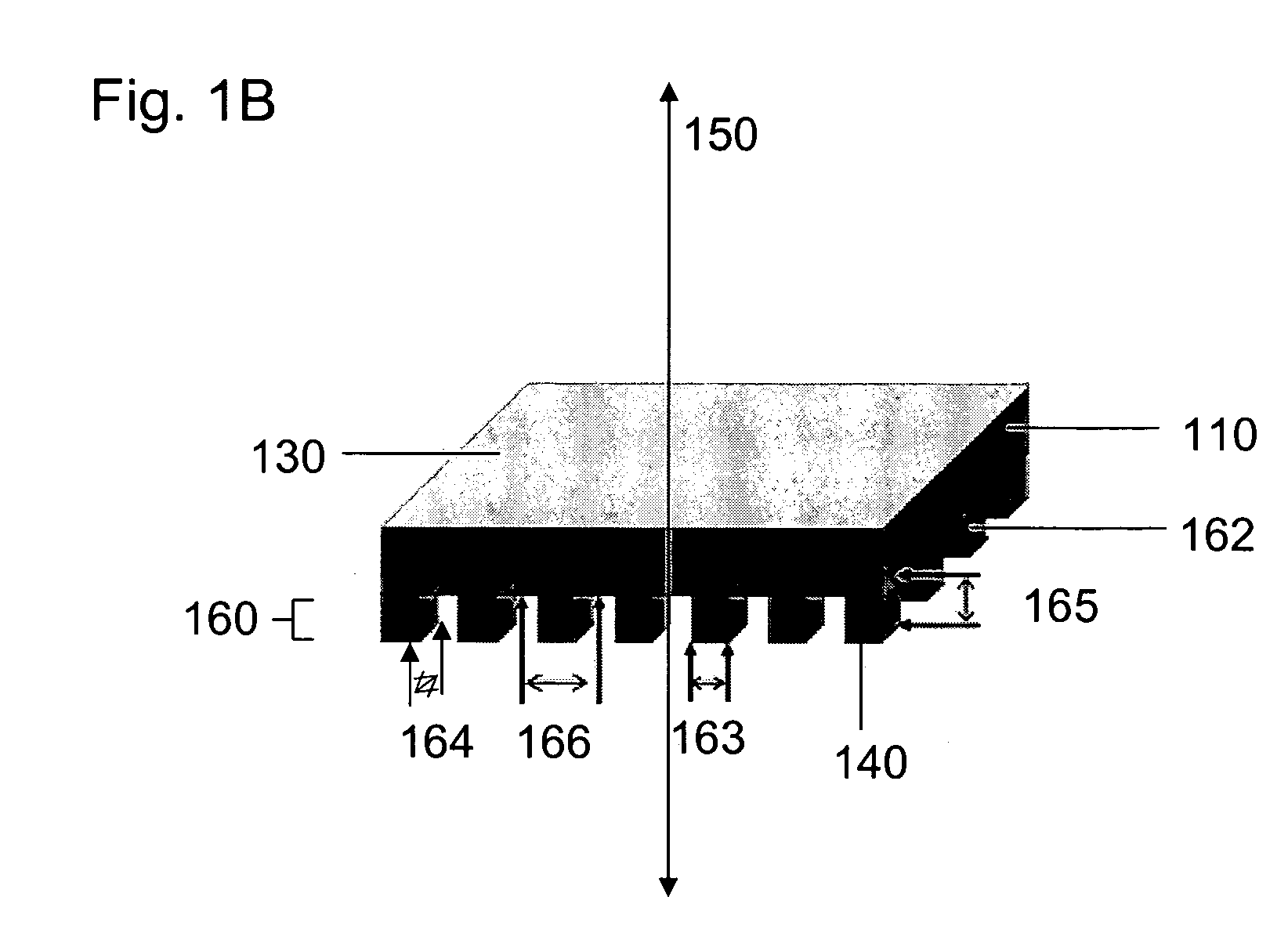
Methods and devices for fabricating three-dimensional nanoscale structures
ActiveUS7704684B2Convenient ArrangementEfficiently patternMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureEngineeringElectromagnetic radiation
The present invention provides methods and devices for fabricating 3D structures and patterns of 3D structures on substrate surfaces, including symmetrical and asymmetrical patterns of 3D structures. Methods of the present invention provide a means of fabricating 3D structures having accurately selected physical dimensions, including lateral and vertical dimensions ranging from 10s of nanometers to 1000s of nanometers. In one aspect, methods are provided using a mask element comprising a conformable, elastomeric phase mask capable of establishing conformal contact with a radiation sensitive material undergoing photoprocessing. In another aspect, the temporal and / or spatial coherence of electromagnetic radiation using for photoprocessing is selected to fabricate complex structures having nanoscale features that do not extend entirely through the thickness of the structure fabricated.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Solution-based fabrication of photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS20050183767A1Improve overall utilizationLow costMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanoparticleSolar cell
An ink for forming CIGS photovoltaic cell active layers is disclosed along with methods for making the ink, methods for making the active layers and a solar cell made with the active layer. The ink contains a mixture of nanoparticles of elements of groups IB, IIIA and (optionally) VIA. The particles are in a desired particle size range of between about 1 nm and about 500 nm in diameter, where a majority of the mass of the particles comprises particles ranging in size from no more than about 40% above or below an average particle size or, if the average particle size is less than about 5 nanometers, from no more than about 2 nanometers above or below the average particle size. The use of such ink avoids the need to expose the material to an H2Se gas during the construction of a photovoltaic cell and allows more uniform melting during film annealing, more uniform intermixing of nanoparticles, and allows higher quality absorber films to be formed.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Replication and transfer of microstructures and nanostructures
InactiveUS6849558B2Facilitates pattern transferCheap to makeNanostructure manufactureDecorative surface effectsEngineeringMicroscopic scale
A method for the duplication of microscopic patterns from a master to a substrate is disclosed, in which a replica of a topographic structure on a master is formed and transferred when needed onto a receiving substrate using one of a variety of printing or imprint techniques, and then dissolved. Additional processing steps can also be carried out using the replica before transfer, including the formation of nanostructures, microdevices, or portions thereof. These structures are then also transferred onto the substrate when the replica is transferred, and remain on the substrate when the replica is dissolved. This is a technique that can be applied as a complementary process or a replacement for various lithographic processing steps in the fabrication of integrated circuits and other microdevices.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Aqueous dispersions of polymer-enclosed particles, related coating compositions and coated substrates
ActiveUS20060251896A1Nanostructure manufactureSynthetic resin layered productsNanoparticleMaterials science
Disclosed are aqueous dispersions of polymer-enclosed particles, such as nanoparticles. Also disclosed are methods for making an aqueous dispersion of polymer-enclosed particles, polymerizable polymers useful in such a method, powder coating compositions formed from such an aqueous dispersion, substrates at least partially coated with such a composition, and reflective surfaces comprising a non-hiding coating layer deposited from such a composition.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Transformable pressure sensitive adhesive tape and use thereof in display screens
InactiveUS20060100299A1Easy and safe applicationLow level of VOC 'sNanostructure manufactureGas-filled discharge tubesDisplay deviceLight-emitting diode
A transformable pressure sensitive adhesive composition comprised of from about 15 to about 80% by weight of a polymer having a softening point greater than 60° C.; from about 20 to about 85% by weight of a polymerizable resin having a softening point less than 30° C.; a latent initiator in an amount sufficient to cause a reaction between said polymer and said resin; and optionally, a crosslinking agent. The transformable pressure sensitive adhesive has particular applicability in connection with organic light emitting diode display devices, light emitting diode display devices, medical diagnostic testing devices, flexible or rigid LCD display devices, plasma display devices, and electrochromic devices.
Owner:ADHESIVES RES
Photovoltaic devices fabricated from nanostructured template
Photovoltaic devices, such as solar cells, and methods for their manufacture are disclosed. A device may be characterized by an architecture having a nanostructured template made from an n-type first charge transfer material with template elements between about 1 nm and about 500 nm in diameter with about 1012 to 1016 elements / m2. A p-type second charge-transfer material optionally coats the walls of the template elements leaving behind additional space. A p-type third charge-transfer material fills the additional space volumetrically interdigitating with the second charge transfer material.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Purification of biologically-produced 1,3-propanediol
InactiveUS20050069997A1Reduce the amount of waterFermented solutions distillation/rectificationMembranesEscherichia coliDistillation
A process for purifying 1,3-propanediol from the fermentation broth of a cultured E. coli that has been bioengineered to synthesize 1,3-propanediol from sugar is provided. The basic process entails filtration, ion exchange and distillation of the fermentation broth product stream, preferably including chemical reduction of the product during the distillation procedure. Also provided are highly purified compositions of 1,3-propanediol.
Owner:DUPONT IND BIOSCIENCES USA LLC +1
Electrode Including Nanostructures for Rechargeable Cells
InactiveUS20100285358A1Lower resistanceNanostructure manufactureMicroscopic fiber electrodesRechargeable cellSilicon nanowires
A lithium ion battery electrode includes silicon nanowires used for insertion of lithium ions and including a conductivity enhancement, the nanowires growth-rooted to the conductive substrate.
Owner:AMPRIUS INC
Nanoscale patterning for the formation of extensive wires
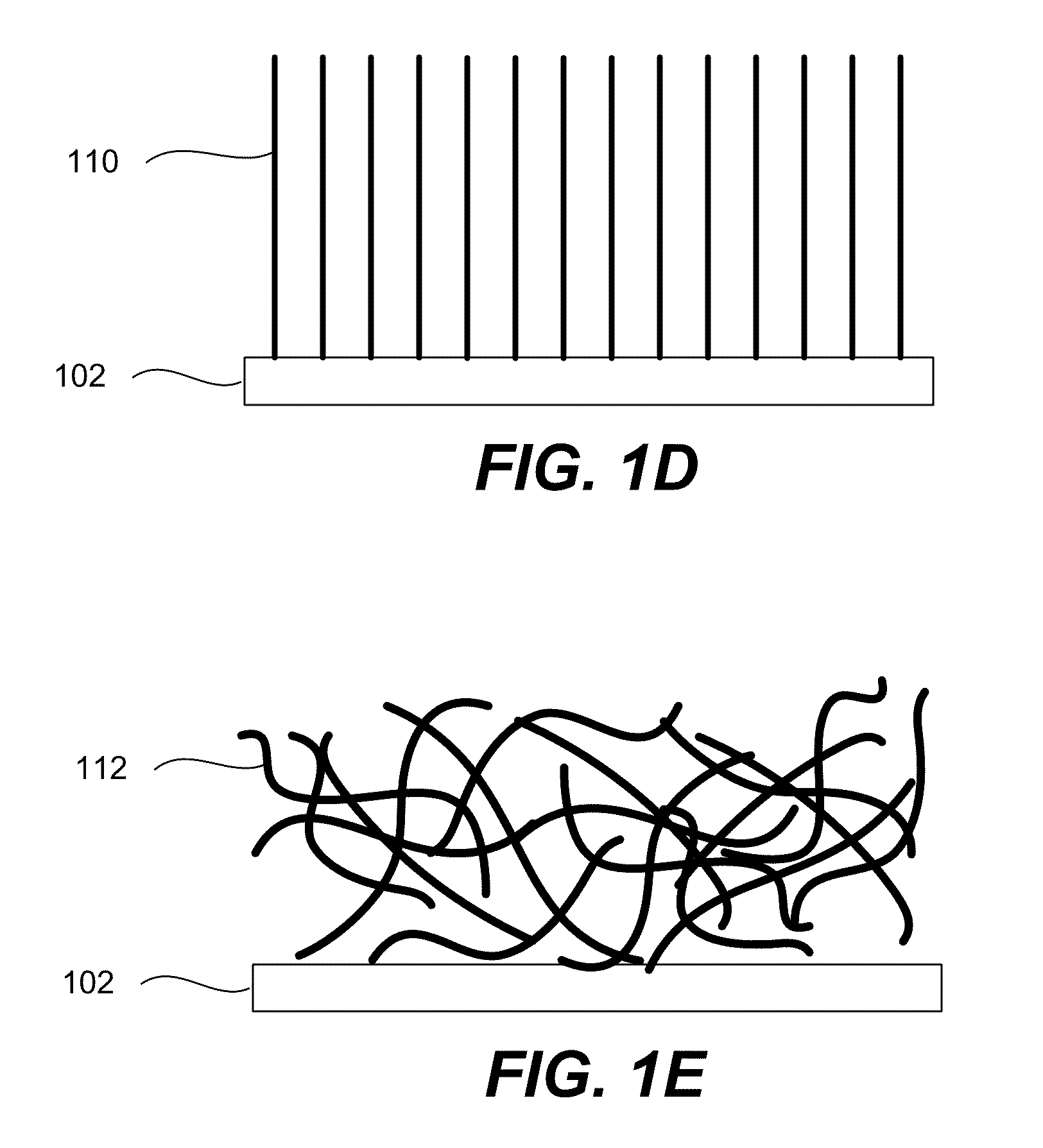
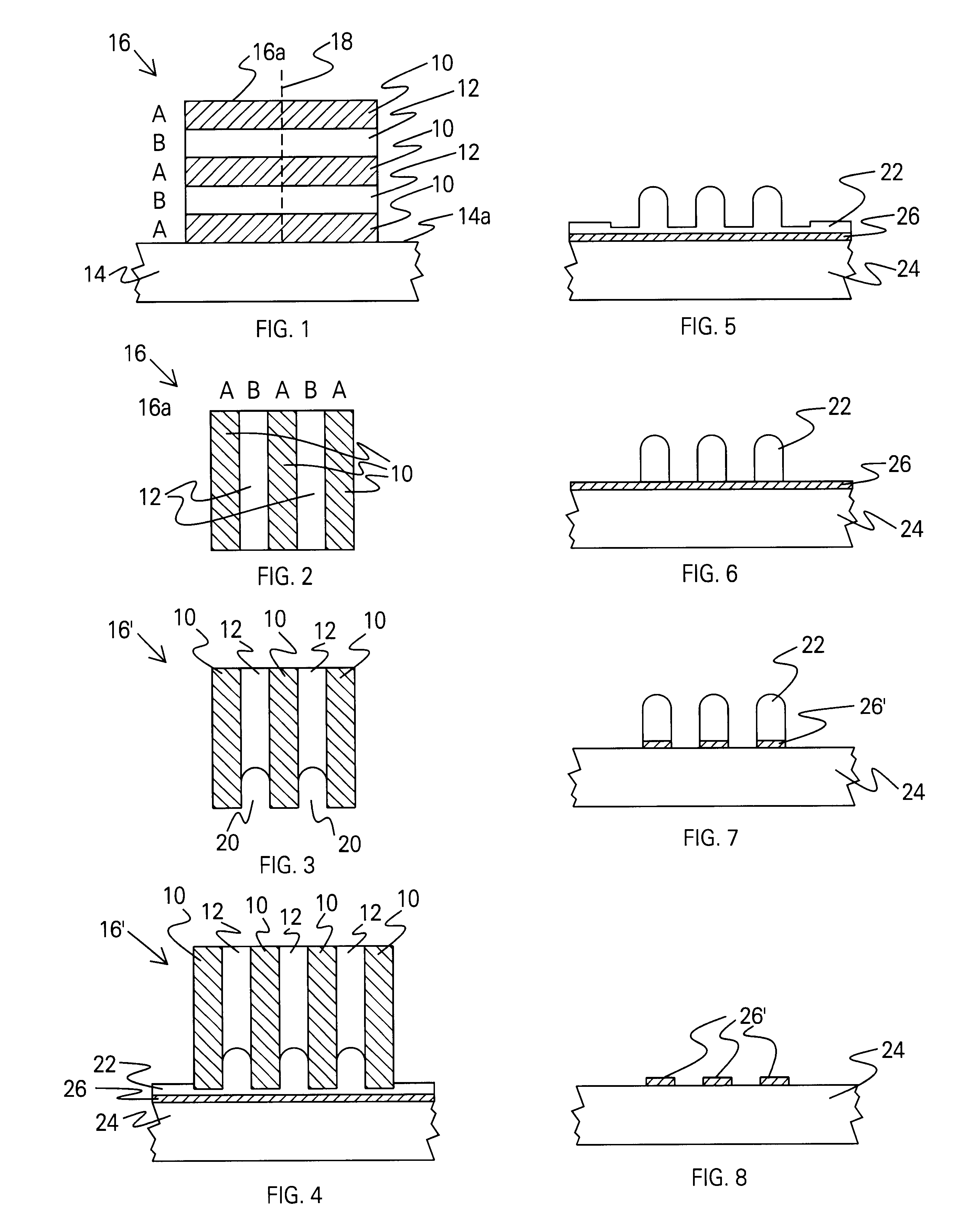
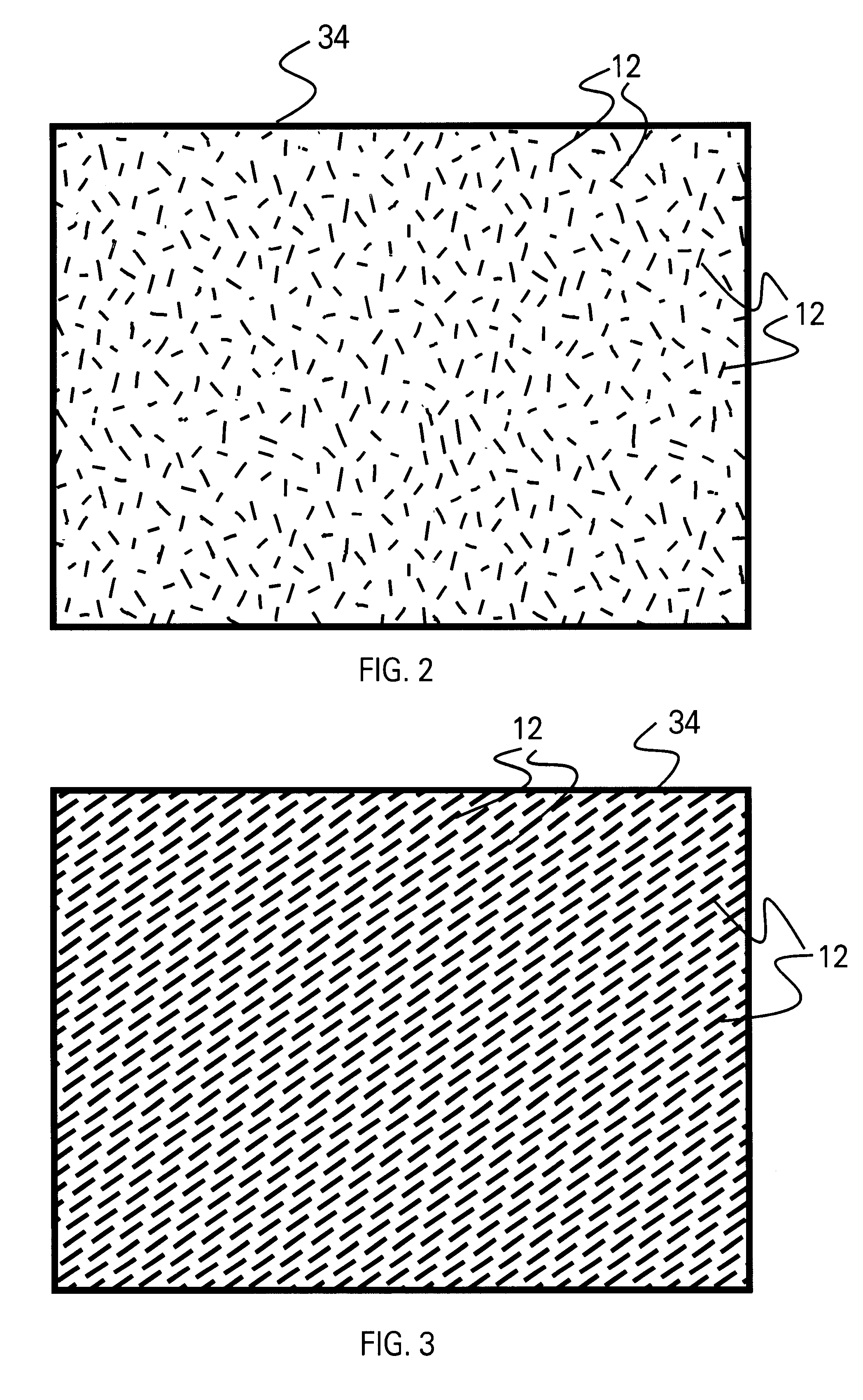
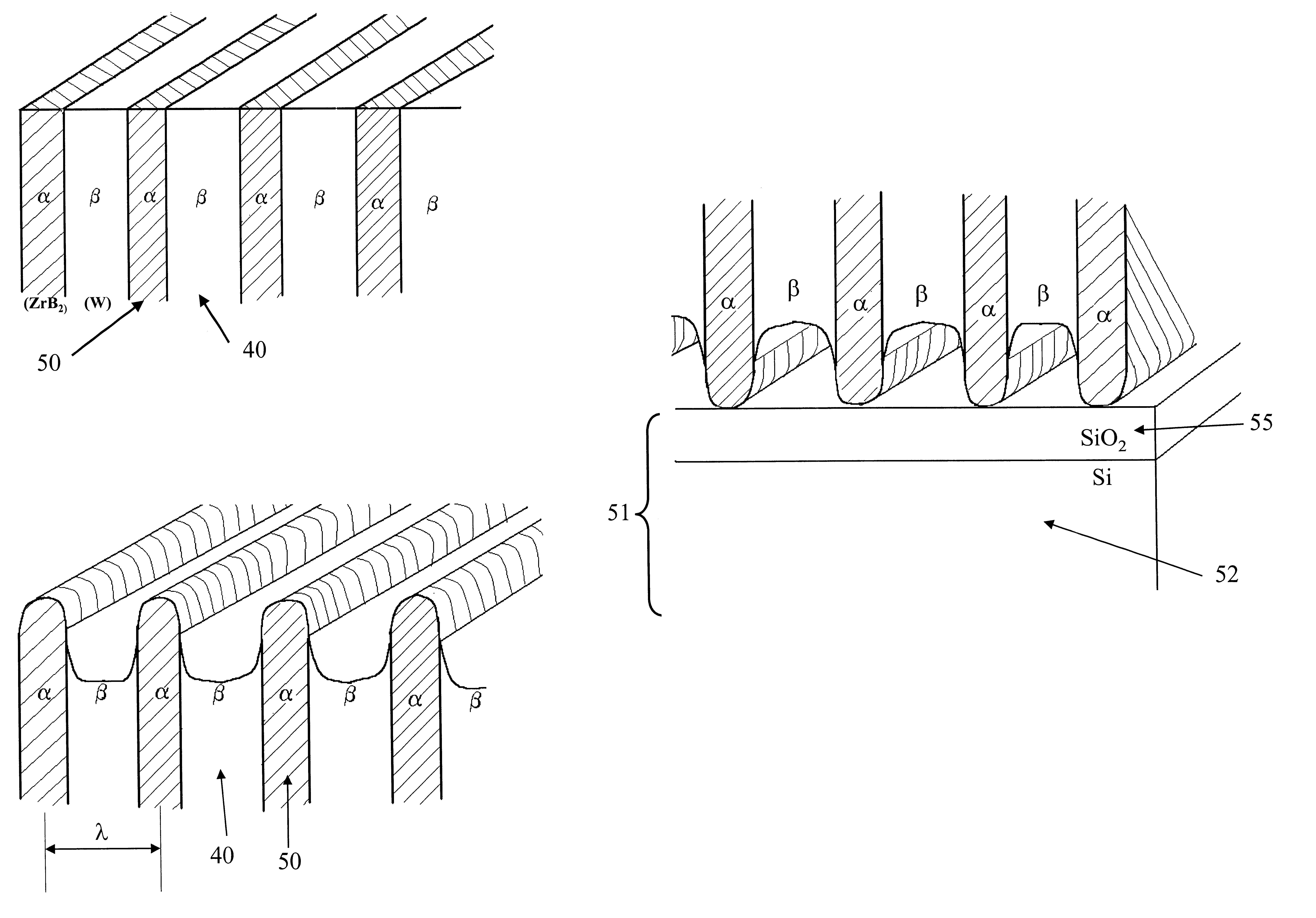
A method for forming a platen useful for forming nanoscale wires for device applications comprises: (a) providing a substrate having a major surface; (b) forming a plurality of alternating layers of two dissimilar materials on the substrate to form a stack having a major surface parallel to that of the substrate; (c) cleaving the stack normal to its major surface to expose the plurality of alternating layers; and (d) etching the exposed plurality of alternating layers to a chosen depth using an etchant that etches one material at a different rate than the other material to thereby provide the surface with extensive strips of indentations and form the platen useful for molding masters for nano-imprinting technology. The pattern of the platen is then imprinted into a substrate comprising a softer material to form a negative of the pattern, which is then used in further processing to form nanowires. The nanoscale platen thus comprises a plurality of alternating layers of the two dissimilar materials, with the layers of one material etched relative the layers of the other material to form indentations of the one material. The platen is then oriented such that the indentations are parallel to a surface to be imprinted.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
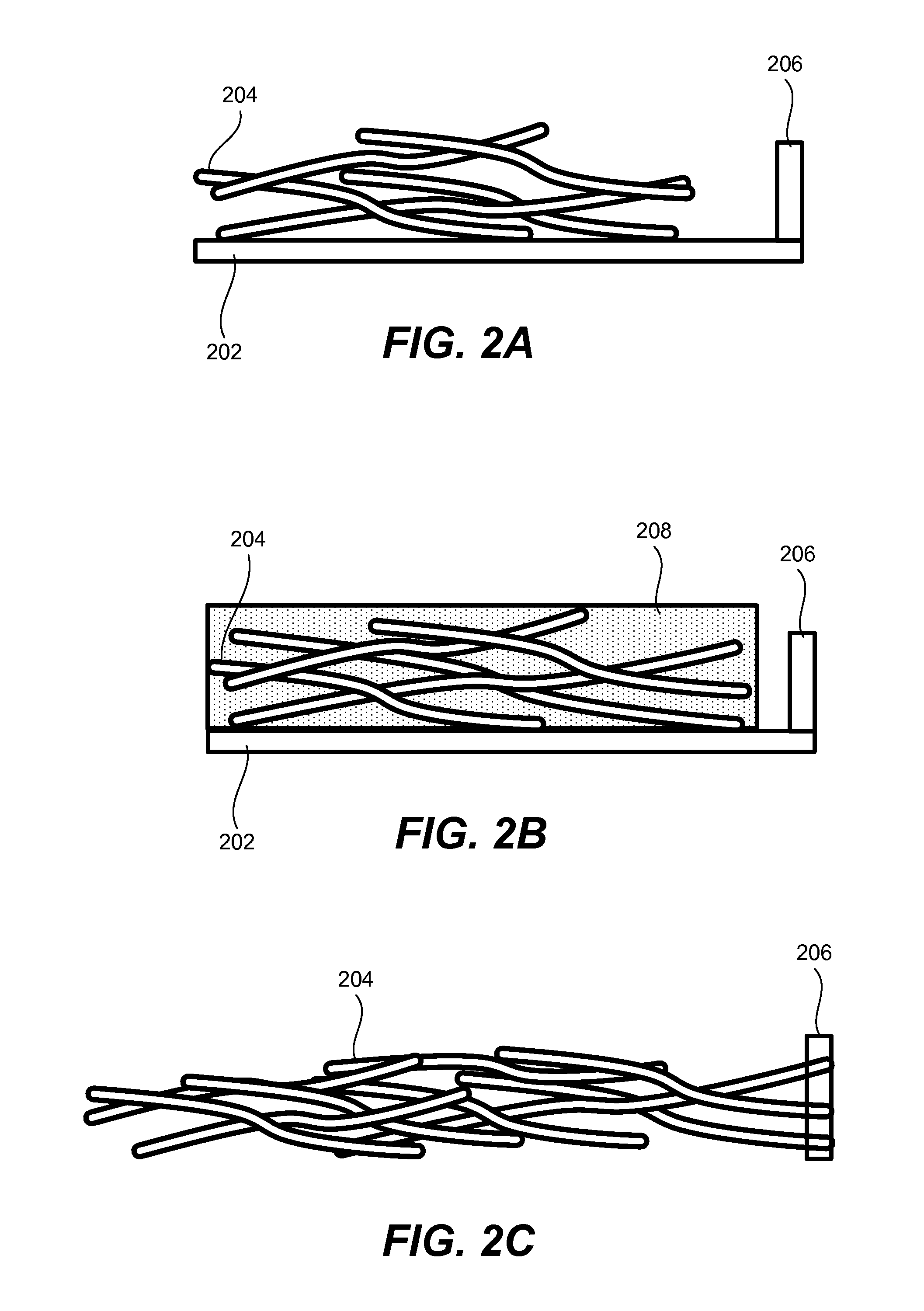
Method of aligning nanowires
A method of aligning nanowires on a substrate is provided. First, a plurality of the nanowires is formed on the substrate, then the plurality of nanowires is exposed to a flux of energetic ions, e.g., argon at an ion energy of 5 KV and an integrated flux density of about 6x1015 ions / cm2. The flux of energetic ions serves to align the nanowires parallel to each other. The flux of energetic ions may also be used to align the nanowires parallel to the substrate surface.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for making a nano-stamp and for forming, with the stamp, nano-size elements on a substrate
The stamping process and a method of fabrication of nano-stamps with characteristic dimensions below 1 nm and up to 100 nm intended for usage in making patterns of characteristic dimensions the same as those of the nano-stamp on surface of a substrate is provided. In the process a very hard stamp is fabricated by first depositing alternating layers of two materials, one of which has very high hardness, on some sacrificial substrate via PVD, CVD or any other deposition procedure that produces alternating layers of selected thickness, from sub 1 nm to above 100 nm. The layered film is then polished to an atomically smooth finish perpendicular to the plane of the layers and etched to produce dips in the softer layers. These steps produce a grid of parallel elevations and valleys on the etched surface, which now can be used as a stamp to stamp out patterns on a substrate of lower hardness than the hardness of the elevated layers. If the substrate is stamped twice with a turning of the stamp 90 degrees between first and second stampings, a square pattern of elevations or hills and valleys is formed, which can be used for magnetic memory storage by subsequently sputtering magnetic material on the tops of the elevations or hills.
Owner:VIGIL THOMAS R +1
Devices and methods for pattern generation by ink lithography
InactiveUS20080055581A1Improve fidelityIncrease resistanceNanostructure manufactureNanoinformaticsElastomerLithographic artist
The present invention provides methods, devices and device components for fabricating patterns on substrate surfaces, particularly patterns comprising structures having microsized and / or nanosized features of selected lengths in one, two or three dimensions and including relief and recess features with variable height, depth or height and depth. Composite patterning devices comprising a plurality of polymer layers each having selected mechanical and thermal properties and physical dimensions provide high resolution patterning on a variety of substrate surfaces and surface morphologies. Gray-scale ink lithography photomasks for gray-scale pattern generation or molds for generating embossed relief features on a substrate surface are provided. The particular shape of the fabricated patterned can be manipulated by varying the three-dimensional recess pattern on an elastomeric patterning device which is brought into conformal contact with a substrate to localize patterning agent to the recess portion of the pattern.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Microparticles
InactiveUS6669961B2Minimal deformationHardening of the spheresPowder deliveryNanostructure manufactureMicroparticleNanometre
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Nanofibrillar structure and applications including cell and tissue culture
ActiveUS20050095695A1Reduce usageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanostructure manufactureLipid formationNanofiber
A nanofibrillar structure for cell culture and tissue engineering is disclosed. The nanofibrillar structure can be used in a variety of applications including methods for proliferating and / or differentiating cells and manufacturing a tissue. Also disclosed is an improved nanofiber comprising a lipid, lipophilic molecule, or chemically modified surface. The nanofibers can be used in a variety of applications including the formation of nanofibrillar structures for cell culture and tissue engineering.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Functionalized matrixes for dispersion of nanostructures
ActiveUS20100276638A1High quantum yieldFacilitate device fabricationMaterial nanotechnologyGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsAnti-reflective coatingVolumetric Mass Density
Matrixes doped with semiconductor nanocrystals are provided. In certain embodiments, the semiconductor nanocrystals have a size and composition such that they absorb or emit light at particular wavelengths. The nanocrystals can comprise ligands that allow for mixing with various matrix materials, including polymers, such that a minimal portion of light is scattered by the matrixes. The matrixes are optionally formed from the ligands. The matrixes of the present invention can also be utilized in refractive index matching applications. In other embodiments, semiconductor nanocrystals are embedded within matrixes to form a nanocrystal density gradient, thereby creating an effective refractive index gradient. The matrixes of the present invention can also be used as filters and antireflective coatings on optical devices and as down-converting layers. Processes for producing matrixes comprising semiconductor nanocrystals are also provided. Nanostructures having high quantum efficiency, small size, and / or a narrow size distribution are also described, as are methods of producing indium phosphide nanostructures and core-shell nanostructures with Group II-VI shells.
Owner:NANOSYS INC
Sterilized nanoparticulate glucocorticosteroid formulations
InactiveUS20070178051A1Readily heat sterilizedImprove the heating effectOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryPediatric patientMicroparticle
The invention is directed sterile to compositions of glucocorticosteroids useful in the prophylaxis and chronic treatment of asthma and other allergic and inflammatory conditions in adults and pediatric patients.
Owner:ELAN PHRMA INT LTD
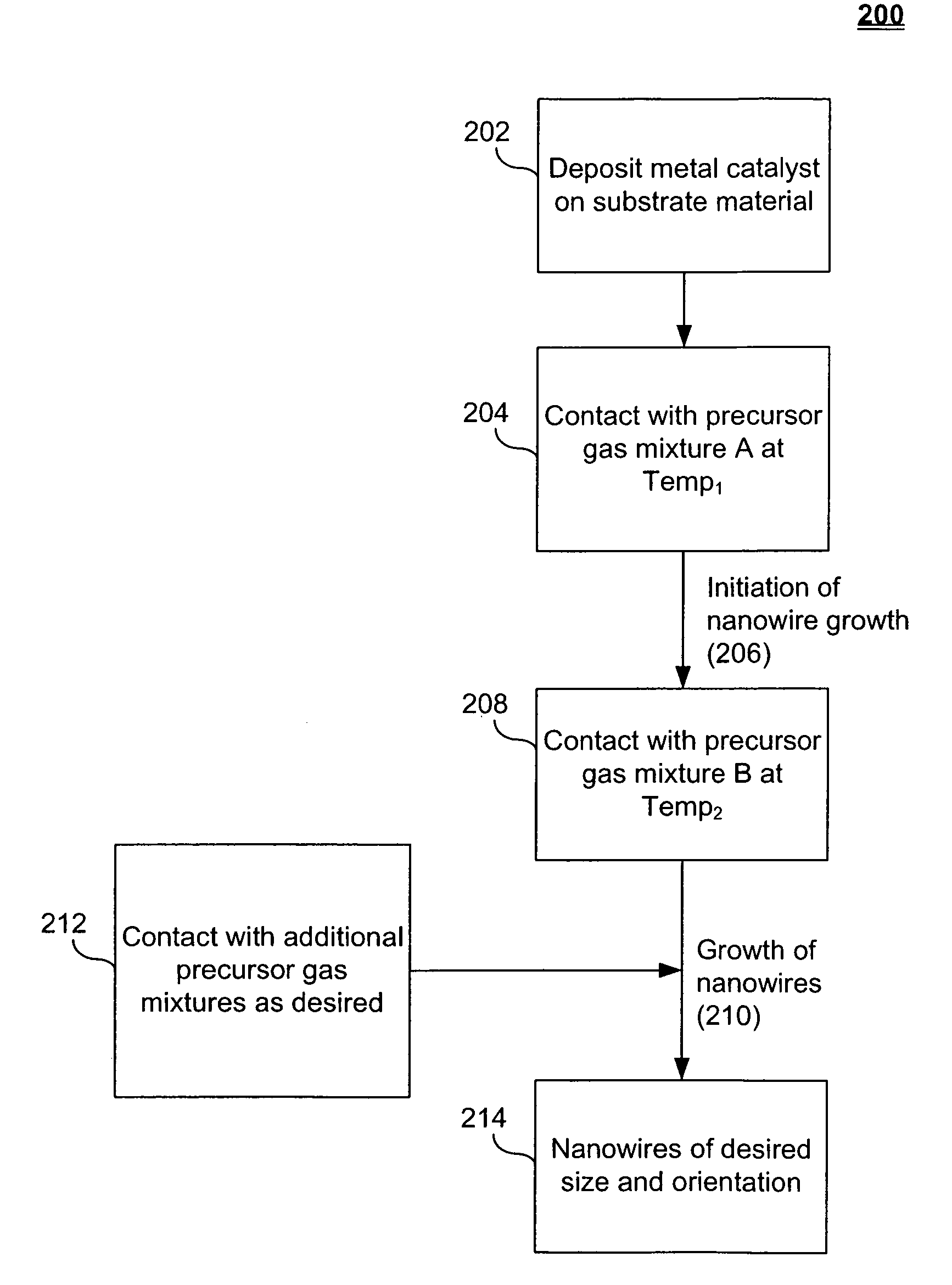
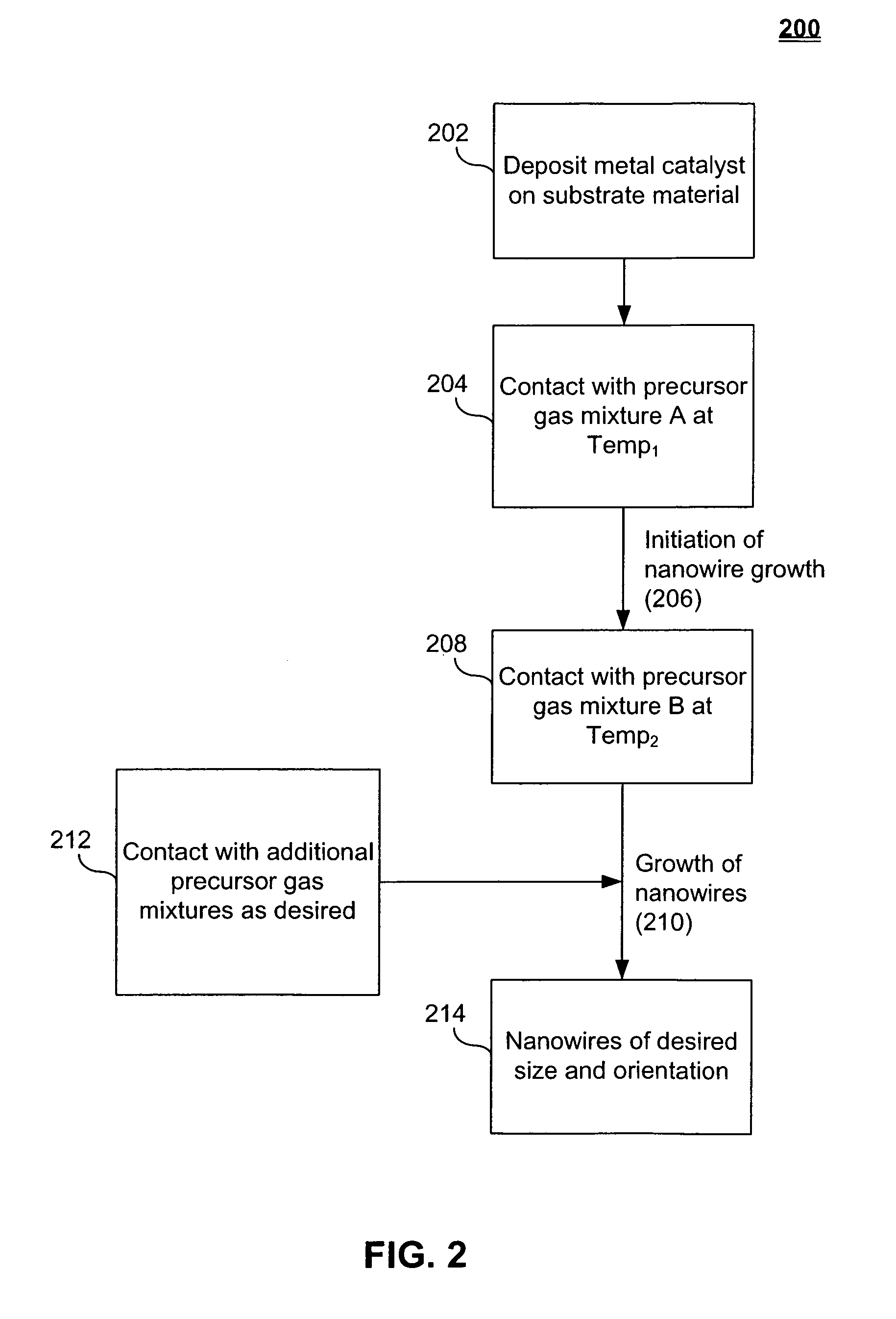
Systems and methods for nanowire growth and harvesting
ActiveUS7105428B2Minimize diffusionIncrease depositionMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanowireSilicon
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
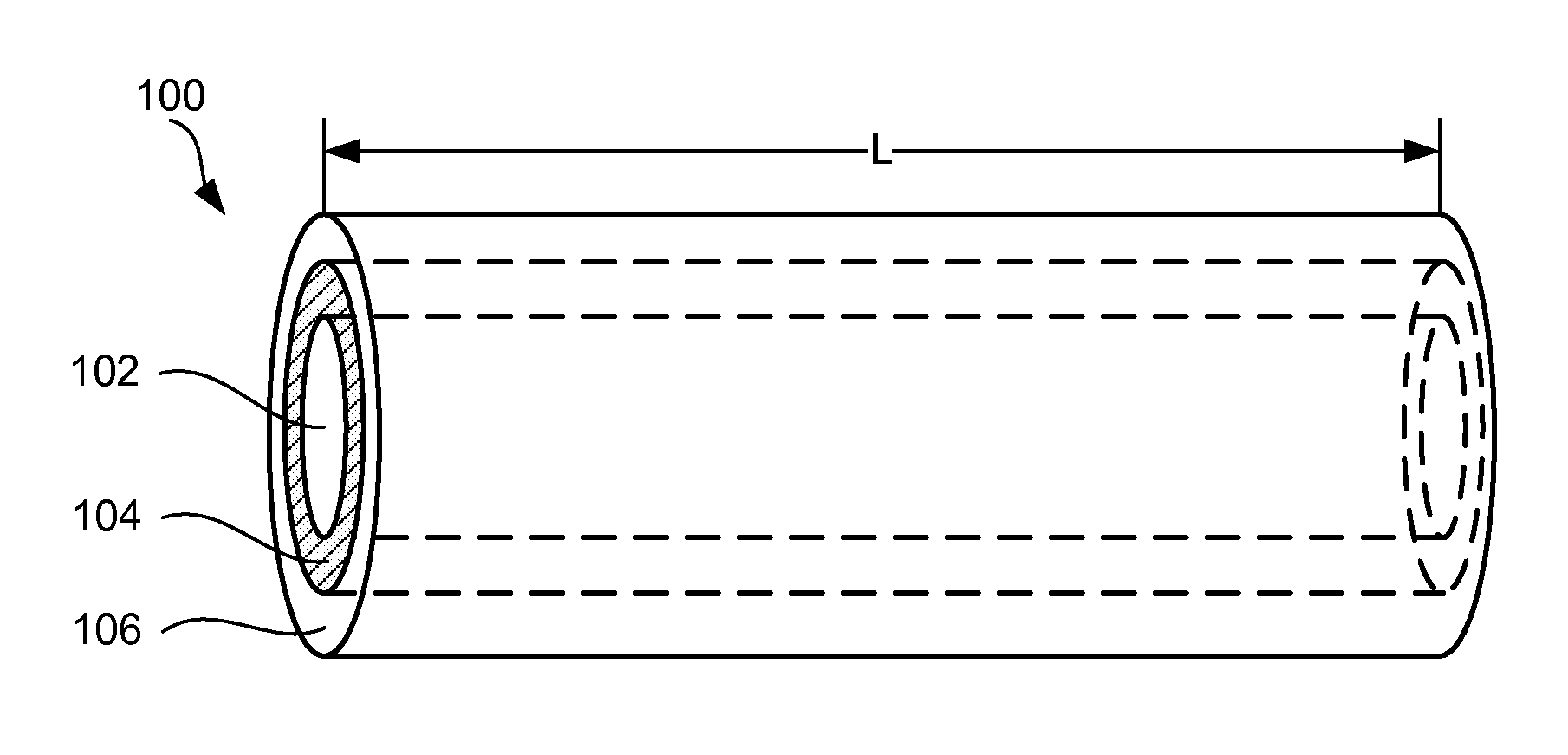
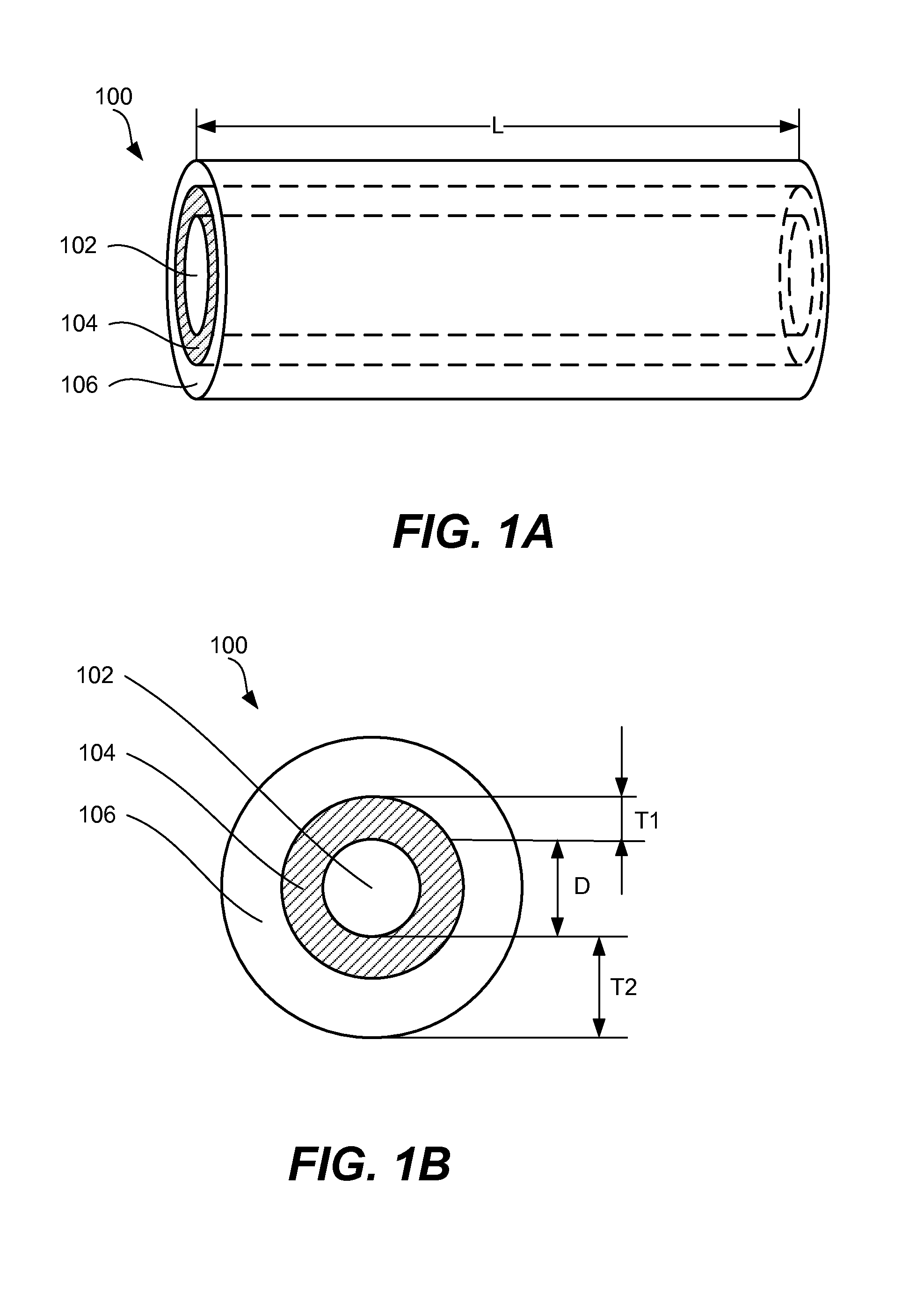
Core-shell high capacity nanowires for battery electrodes
InactiveUS20100330421A1Large capacityInhibition formationMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanowireElectrochemistry
Provided are nanostructures containing electrochemically active materials, battery electrodes containing these nanostructures for use in electrochemical batteries, such as lithium ion batteries, and methods of forming the nanostructures and battery electrodes. The nanostructures include conductive cores, inner shells containing active materials, and outer shells partially coating the inner shells. The high capacity active materials having a stable capacity of at least about 1000 mAh / g can be used. Some examples include silicon, tin, and / or germanium. The outer shells may be configured to substantially prevent formation of Solid Electrolyte lnterphase (SEI) layers directly on the inner shells. The conductive cores and / or outer shells may include carbon containing materials. The nanostructures are used to form battery electrodes, in which the nanostructures that are in electronic communication with conductive substrates of the electrodes.
Owner:AMPRIUS INC
Method for preparing nano-carbon fiber and nano-carbon fiber
A carbon nano-fiber, particularly twisted carbon nano-fiber such as a carbon nano-coil, carbon nano-twist, carbon nano-rope is produced by means of a catalyst CVD method using carbon-containing gas as a raw material and a catalyst comprising one or plural components selected from the group consisting of Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni and oxide thereof and one or plural components selected from the group consisting of Cu, Al, Si, Ti, V, Nb, Mo, Hf, Ta, W and oxide thereof is used.
Owner:FUTABA CORPORATION
Methods, devices and compositions for depositing and orienting nanostructures
ActiveUS20050066883A1Readily apparentMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthNanostructureMaterials science
Methods and systems for depositing nanomaterials onto a receiving substrate and optionally for depositing those materials in a desired orientation, that comprise providing nanomaterials on a transfer substrate and contacting the nanomaterials with an adherent material disposed upon a surface or portions of a surface of a receiving substrate. Orientation is optionally provided by moving the transfer and receiving substrates relative to each other during the transfer process.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
Fabrication of molecular electronic circuit by imprinting
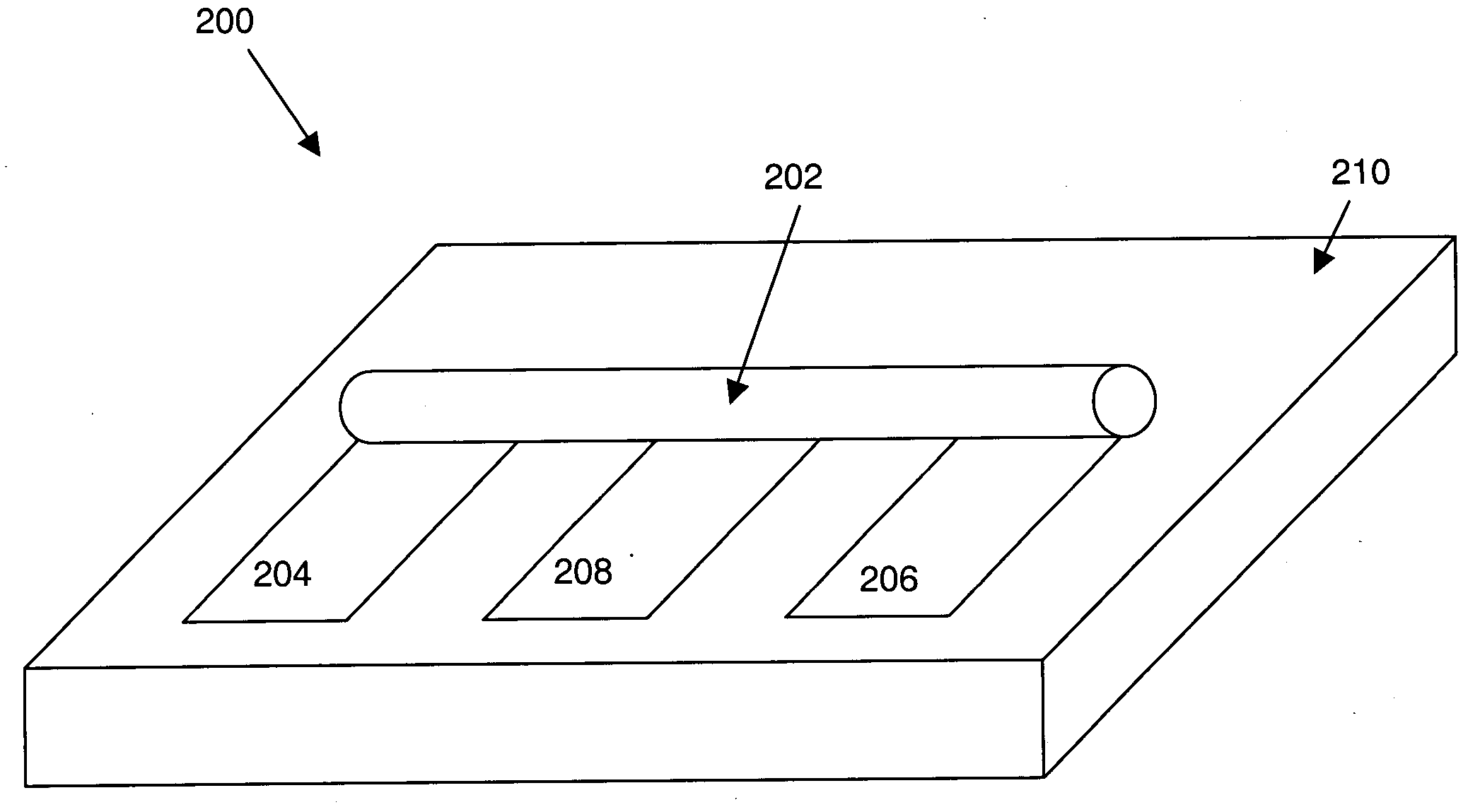
A method of fabricating a molecular electronic device or crossbar memory device is provided. The device comprises at least one pair of crossed wires and a molecular switch film therebetween. The method comprises: (a) forming at least one bottom electrode on a substrate by first forming a first layer on the substrate and patterning the first layer to form the bottom electrode by an imprinting technique; (b) forming the molecular switch film on top of the bottom electrode; (c) optionally forming a protective layer on top of the molecular switch film to avoid damage thereto during further processing; (d) coating a polymer layer on top of the protective layer and patterned the polymer layer by the imprinting method to form openings that expose portions of the protective layer; and (e) forming at least one top electrode on the protective layer through the openings in the polymer layer by first forming a second layer on the polymer layer and patterning the second layer. The imprinting method can be used to fabricate nanoscale patterns over a large area at high speeds acceptable in industrial standards. Consequently, it can be used to fabricate nanoscale molecular devices, e.g., crossbar memory circuits.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
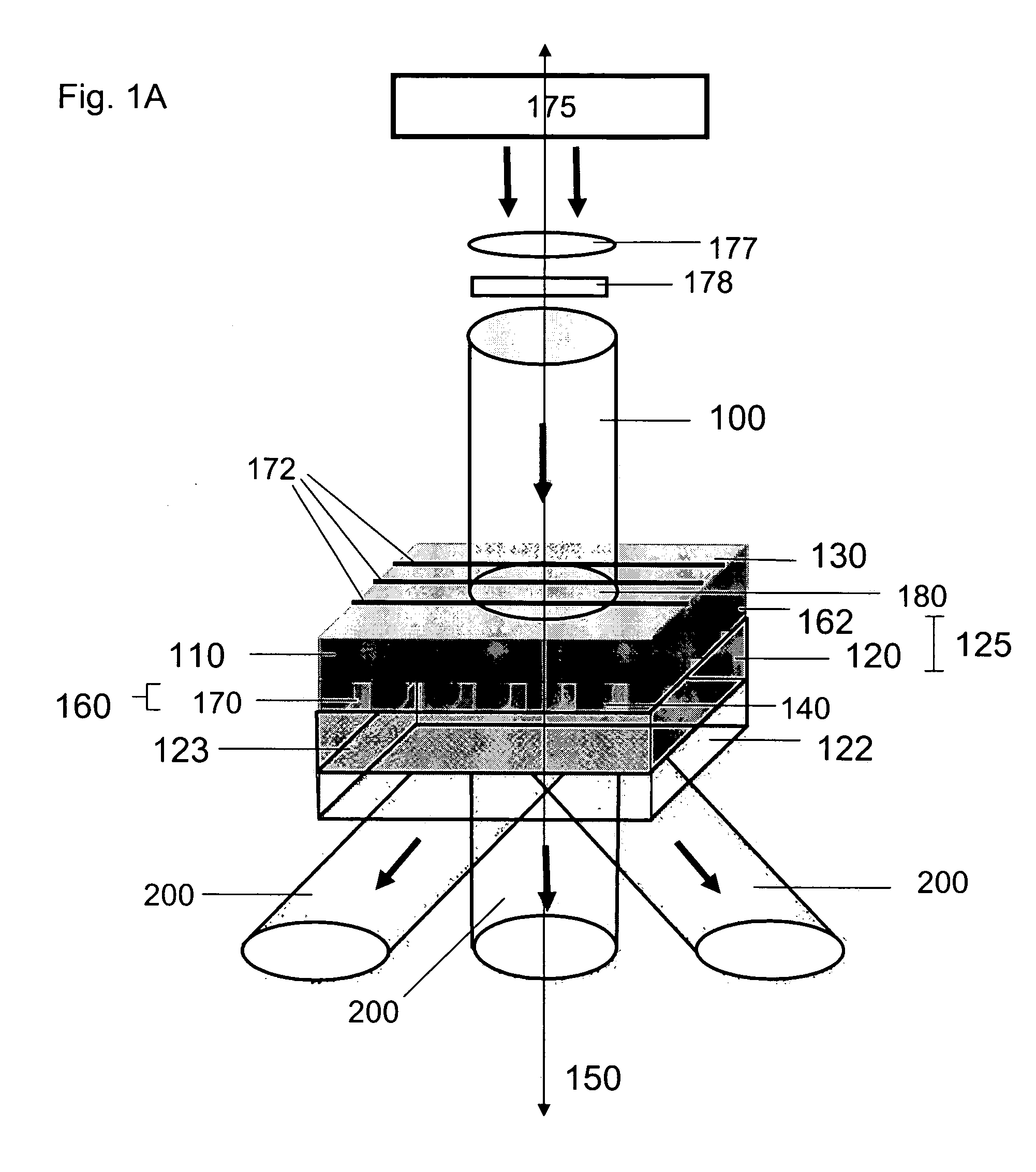
Methods and devices for fabricating three-dimensional nanoscale structures
ActiveUS20060286488A1Simple optical arrangementConvenient ArrangementMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureEngineeringElectromagnetic radiation
The present invention provides methods and devices for fabricating 3D structures and patterns of 3D structures on substrate surfaces, including symmetrical and asymmetrical patterns of 3D structures. Methods of the present invention provide a means of fabricating 3D structures having accurately selected physical dimensions, including lateral and vertical dimensions ranging from 10 s of nanometers to 1000 s of nanometers. In one aspect, methods are provided using a mask element comprising a conformable, elastomeric phase mask capable of establishing conformal contact with a radiation sensitive material undergoing photoprocessing. In another aspect, the temporal and / or spatial coherence of electromagnetic radiation using for photoprocessing is selected to fabricate complex structures having nanoscale features that do not extend entirely through the thickness of the structure fabricated.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com