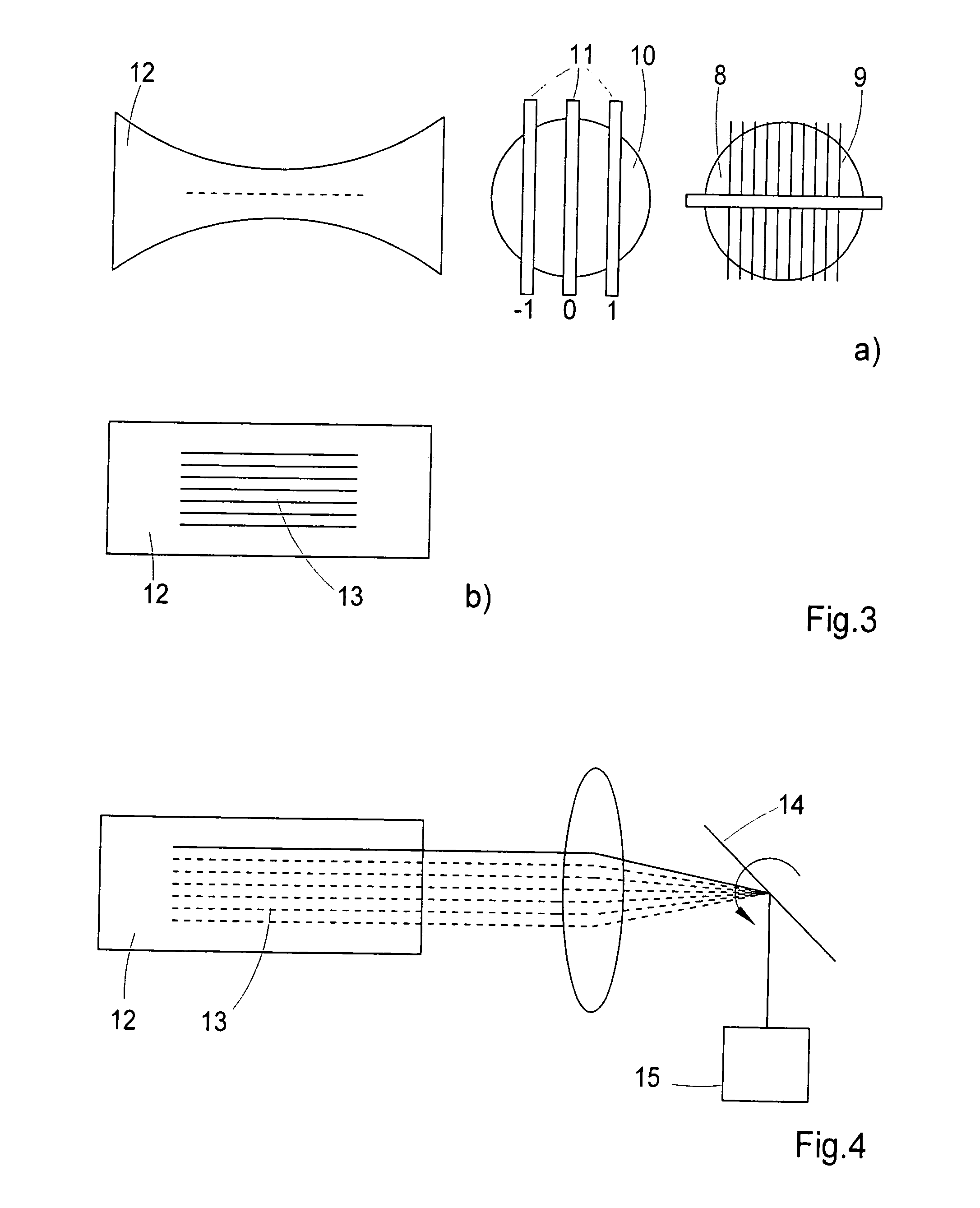
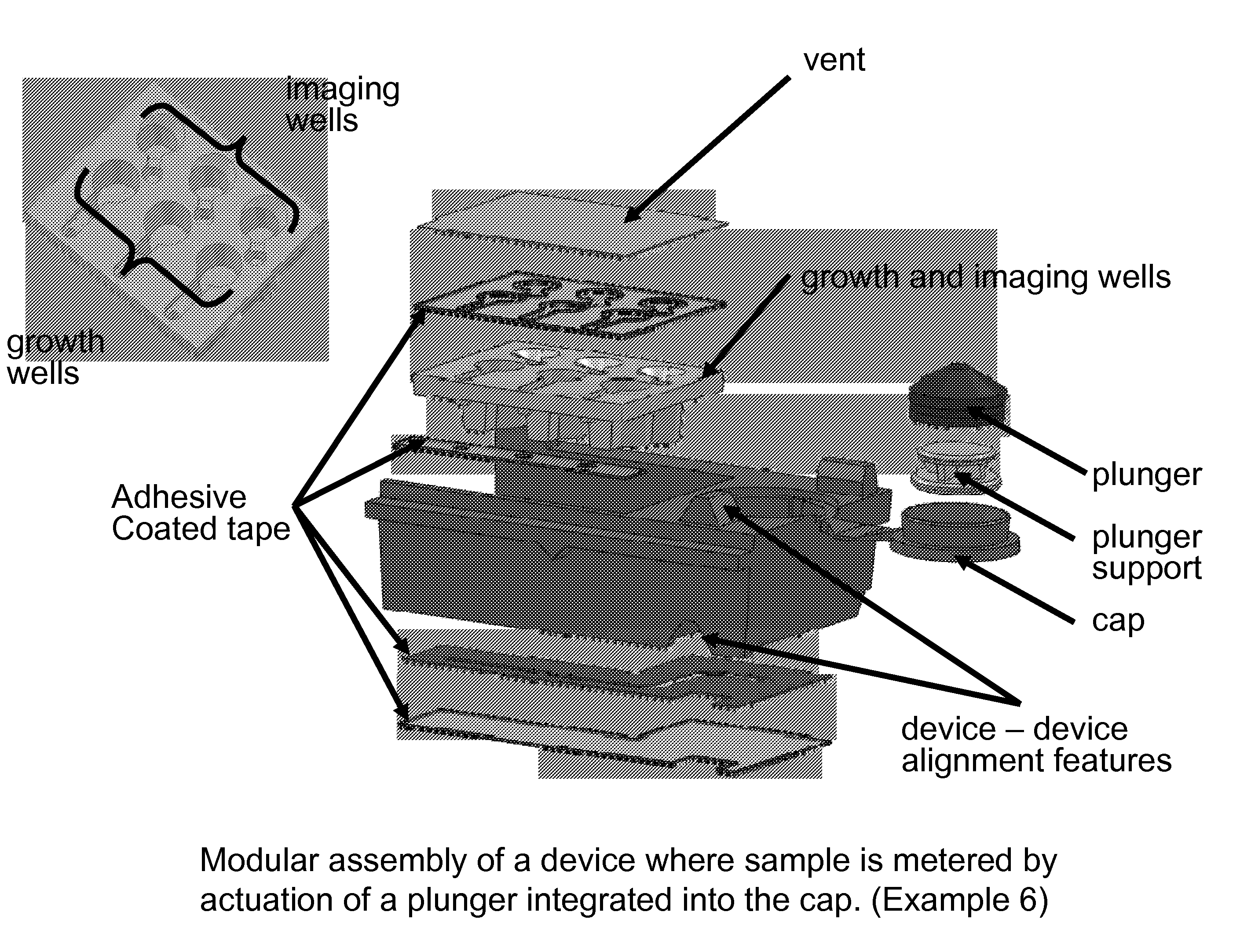
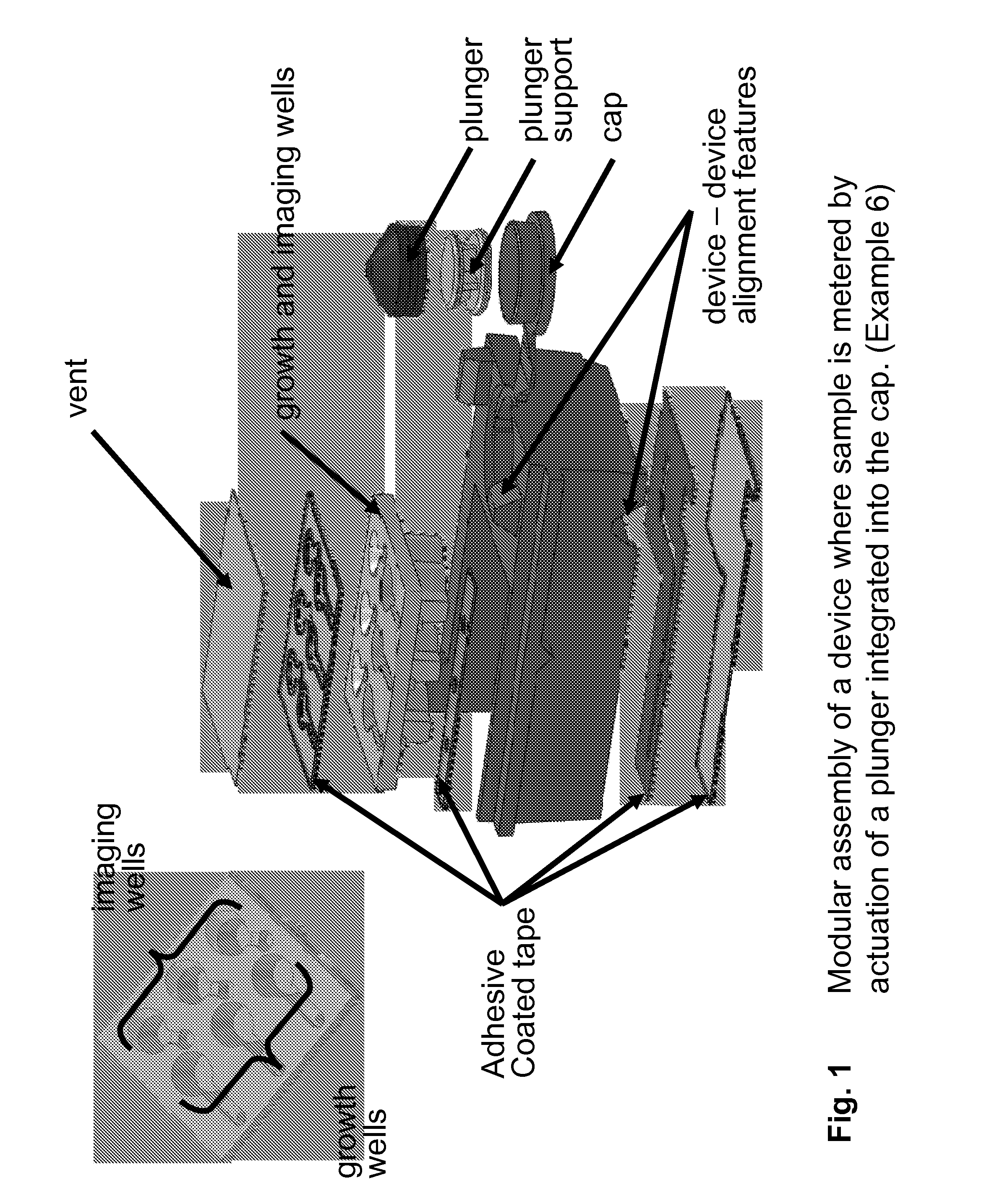
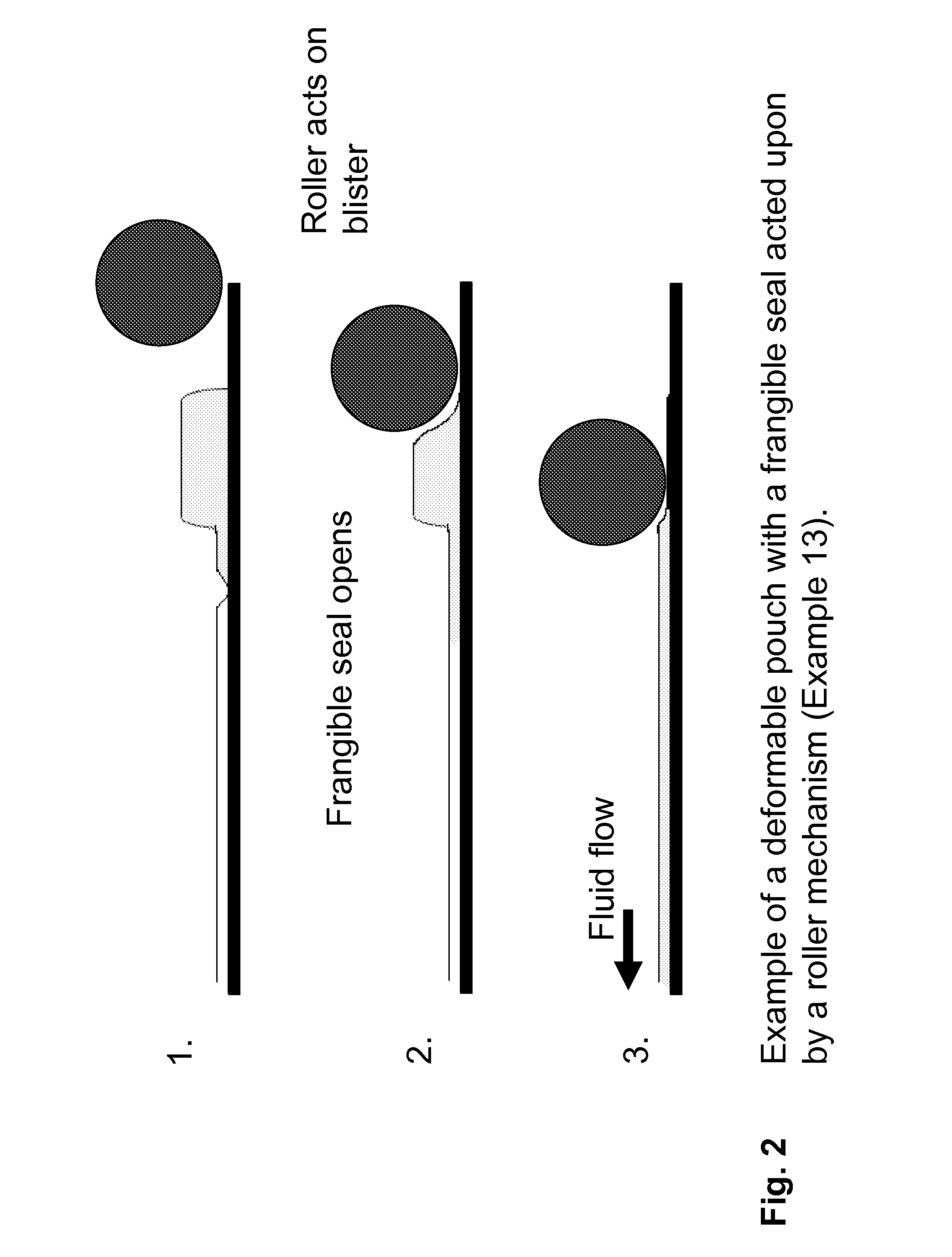
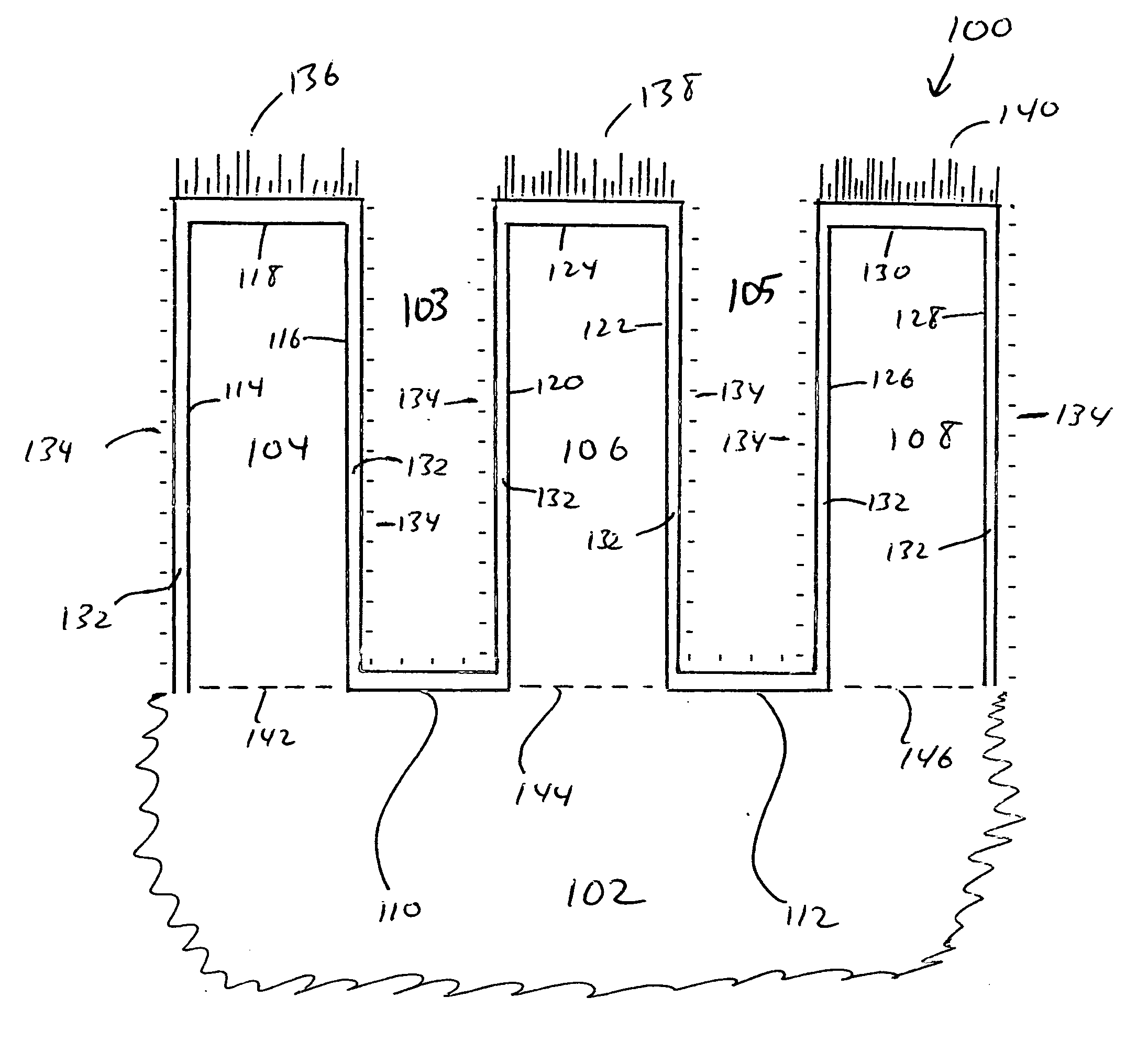
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1136 results about "Microscopic scale" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The microscopic scale (from Greek: μικρός, mikrós, "small" and σκοπέω, skopéō "look") is the scale of objects and events smaller than those that can easily be seen by the naked eye, requiring a lens or microscope to see them clearly. In physics, the microscopic scale is sometimes regarded as the scale between the macroscopic scale and the quantum scale. Microscopic units and measurements are used to classify and describe very small objects. One common microscopic length scale unit is the micrometre (also called a micron) (symbol: μm), which is one millionth of a metre.
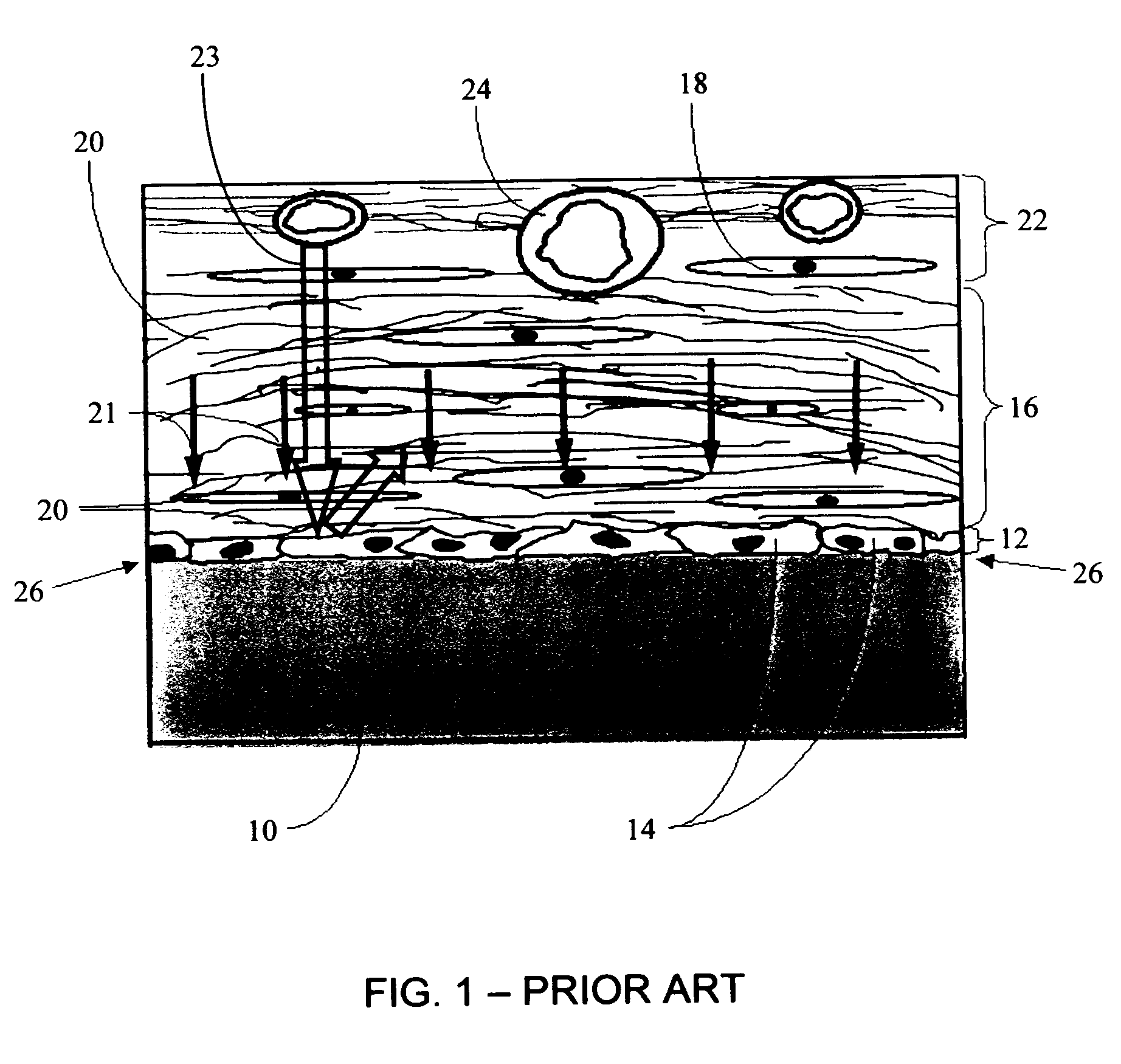
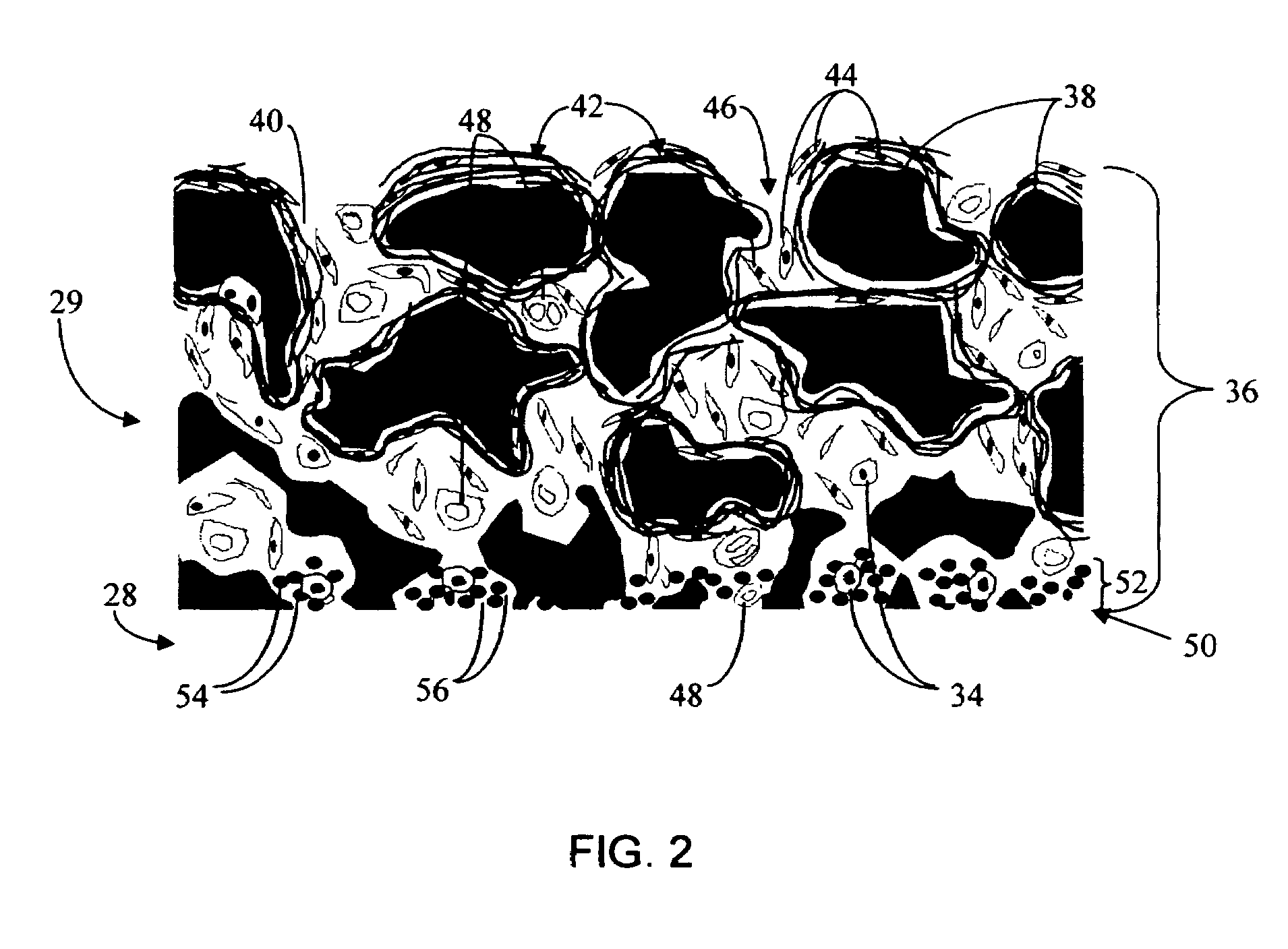
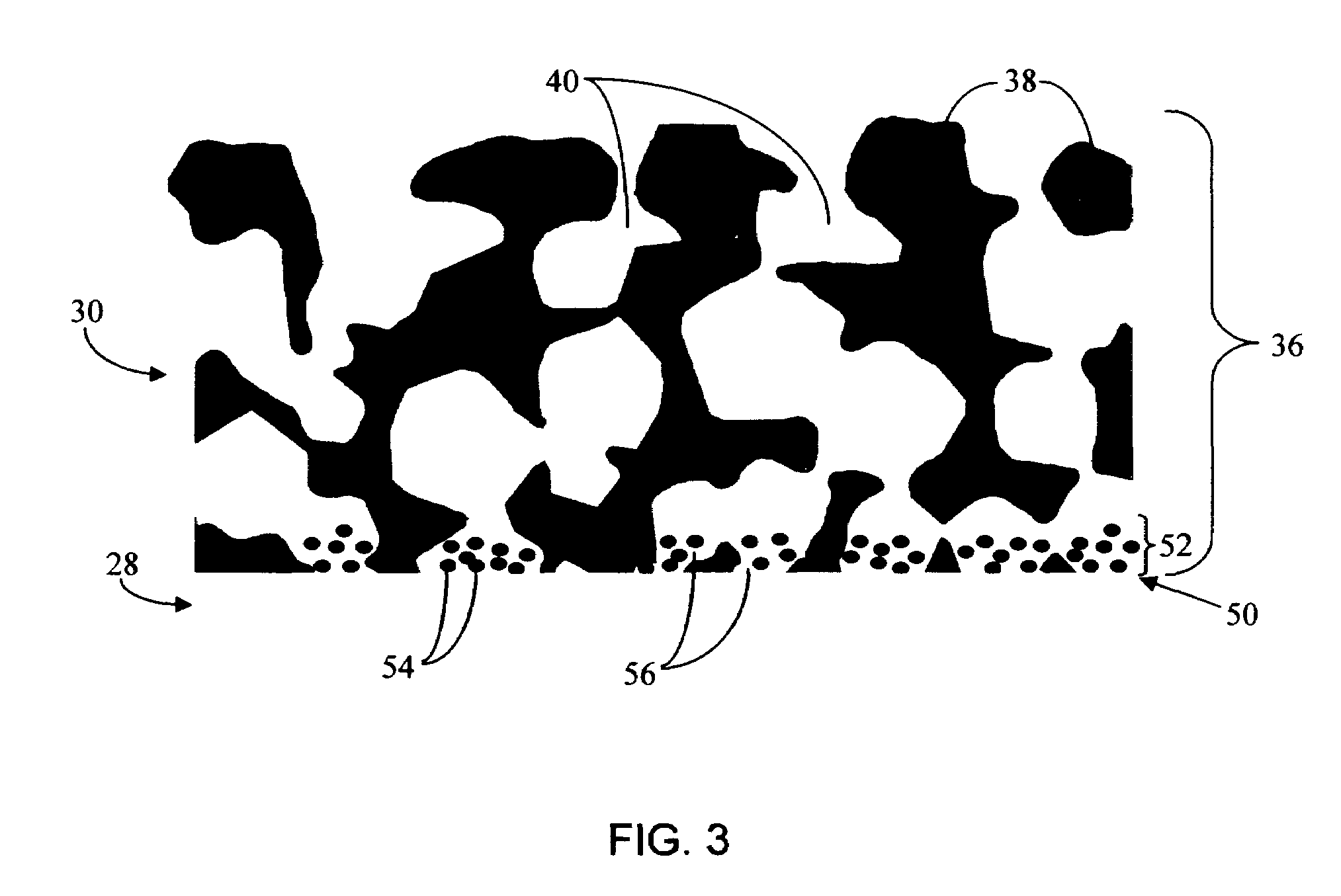
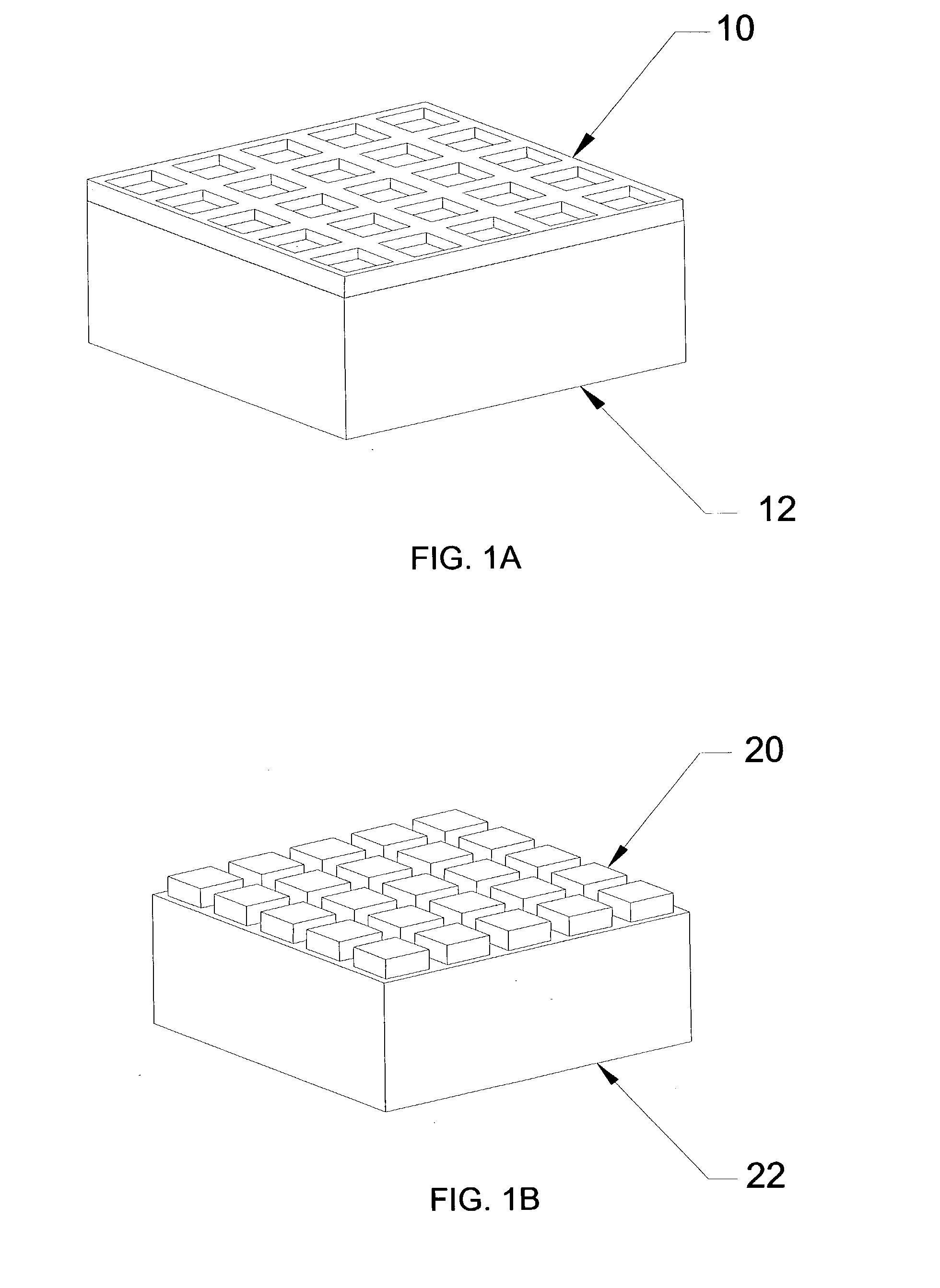
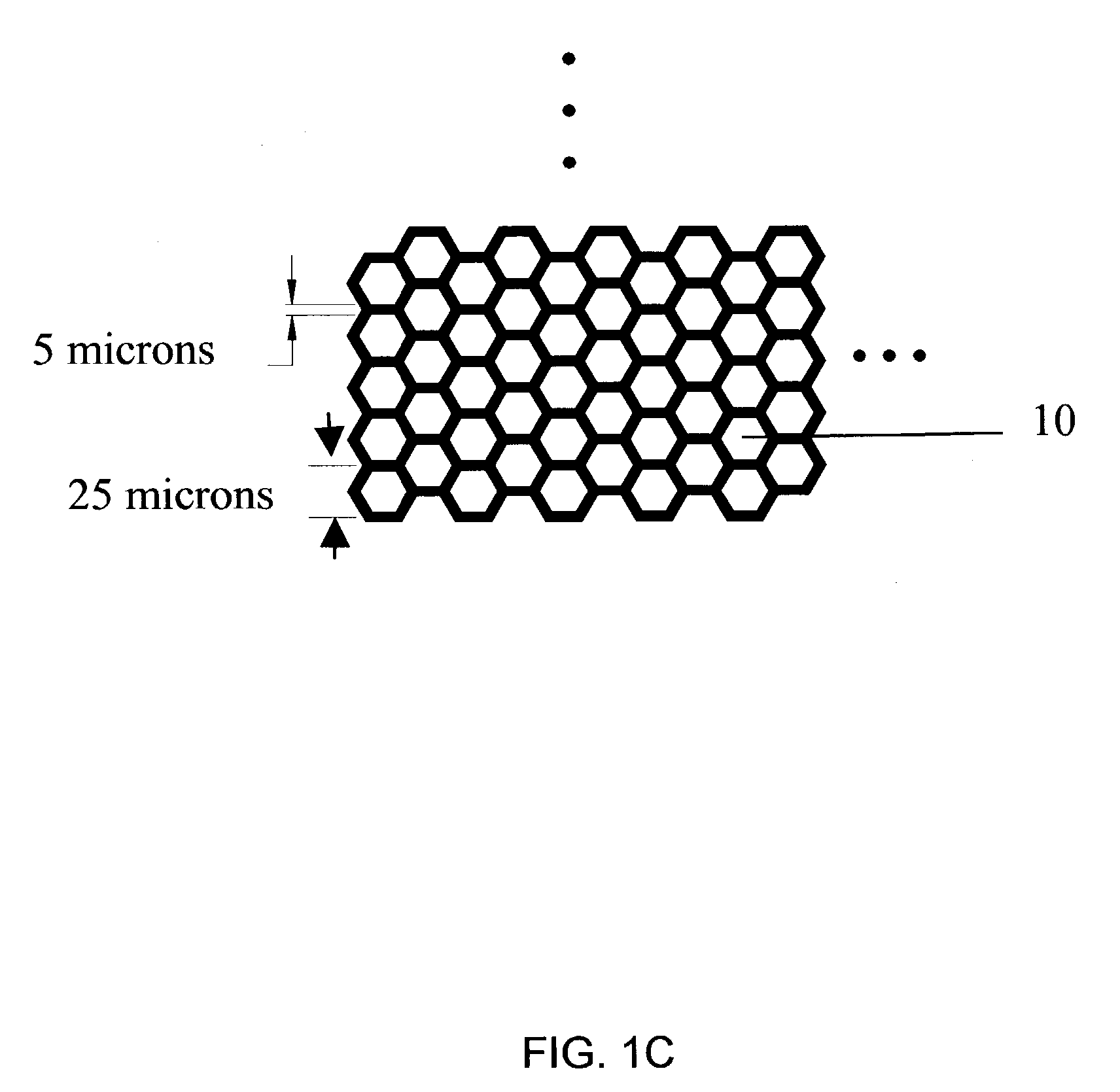
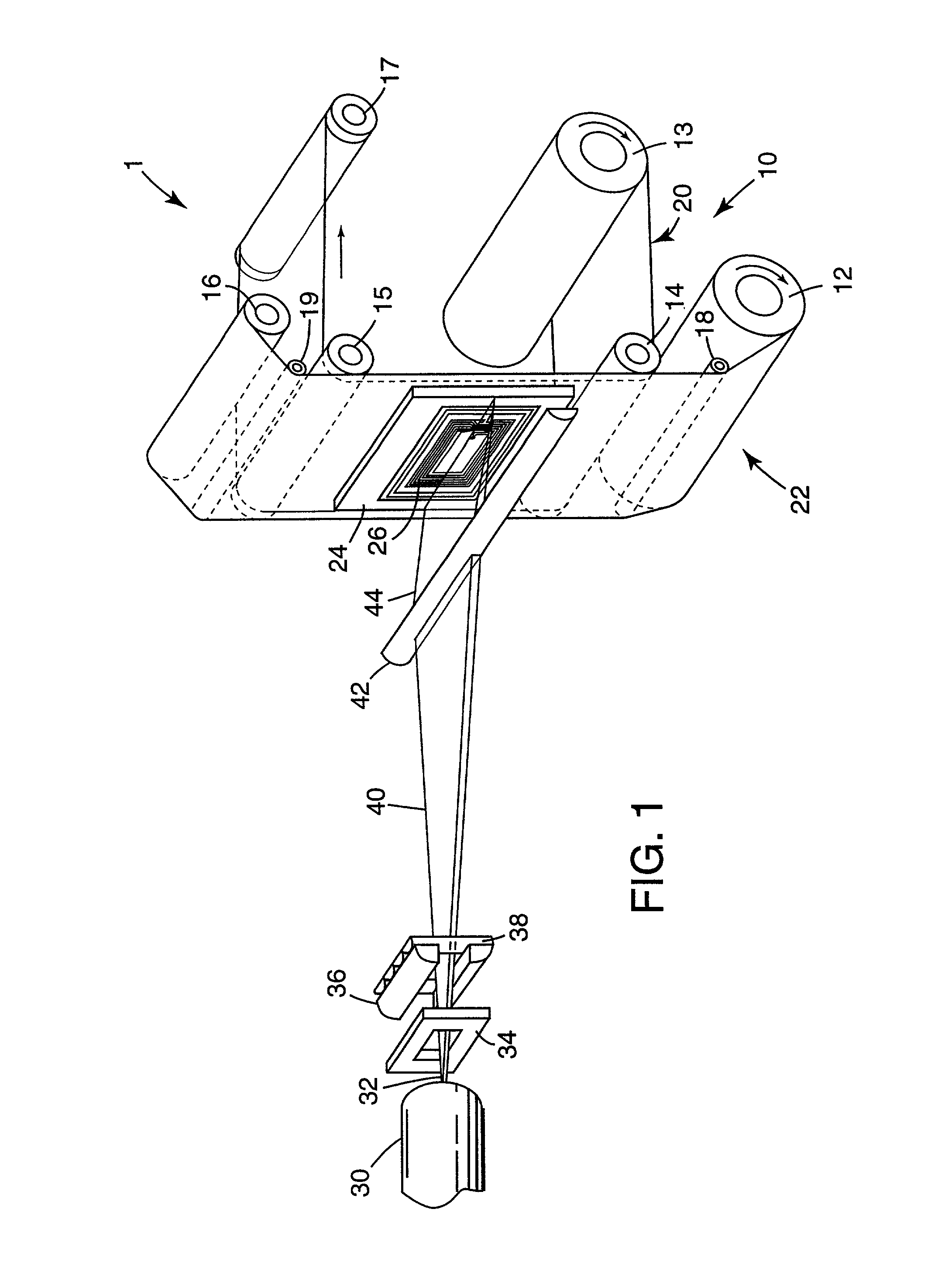
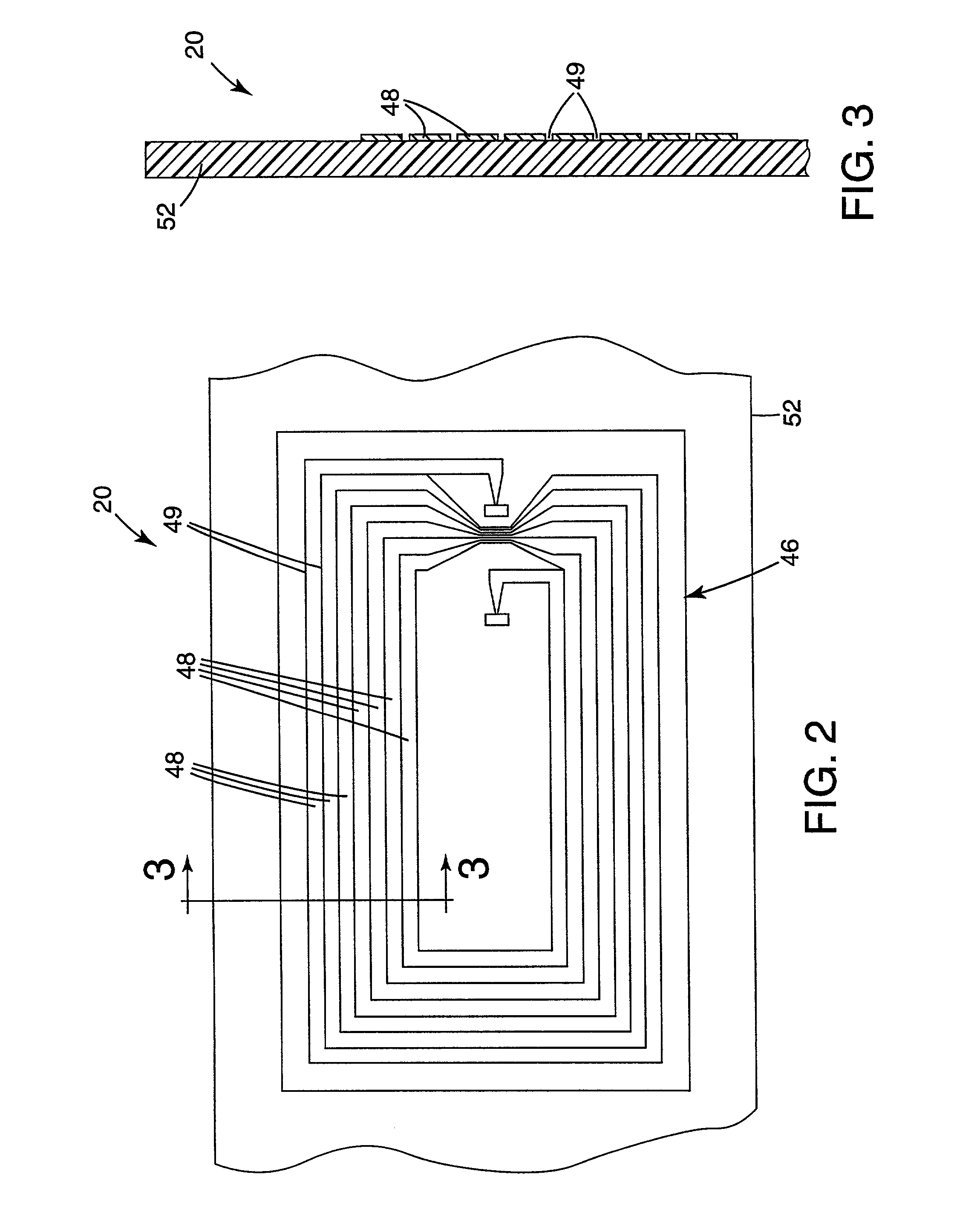
Biointerface membrane with macro-and micro-architecture
Disclosed herein are biointerface membranes including a macro-architecture and a micro-architecture co-continuous with and bonded to and / or located within at least a portion of the macro-architecture. The macro- and micro-architectures work together to manage and manipulate the high-level tissue organization and the low-level cellular organization of the foreign body response in vivo, thereby increasing neovascularization close to a device-tissue interface, interfering with barrier cell layer formation, and providing good tissue anchoring, while reducing the effects of motion artifact, and disrupting the organization and / or contracture of the FBC. The biointerface membranes of the preferred embodiments can be utilized with implantable devices such as devices for the detection of analyte concentrations in a biological sample (for example, from a body), cell transplantation devices, drug delivery devices, electrical signal delivering or measuring devices, and / or combinations thereof.
Owner:DEXCOM
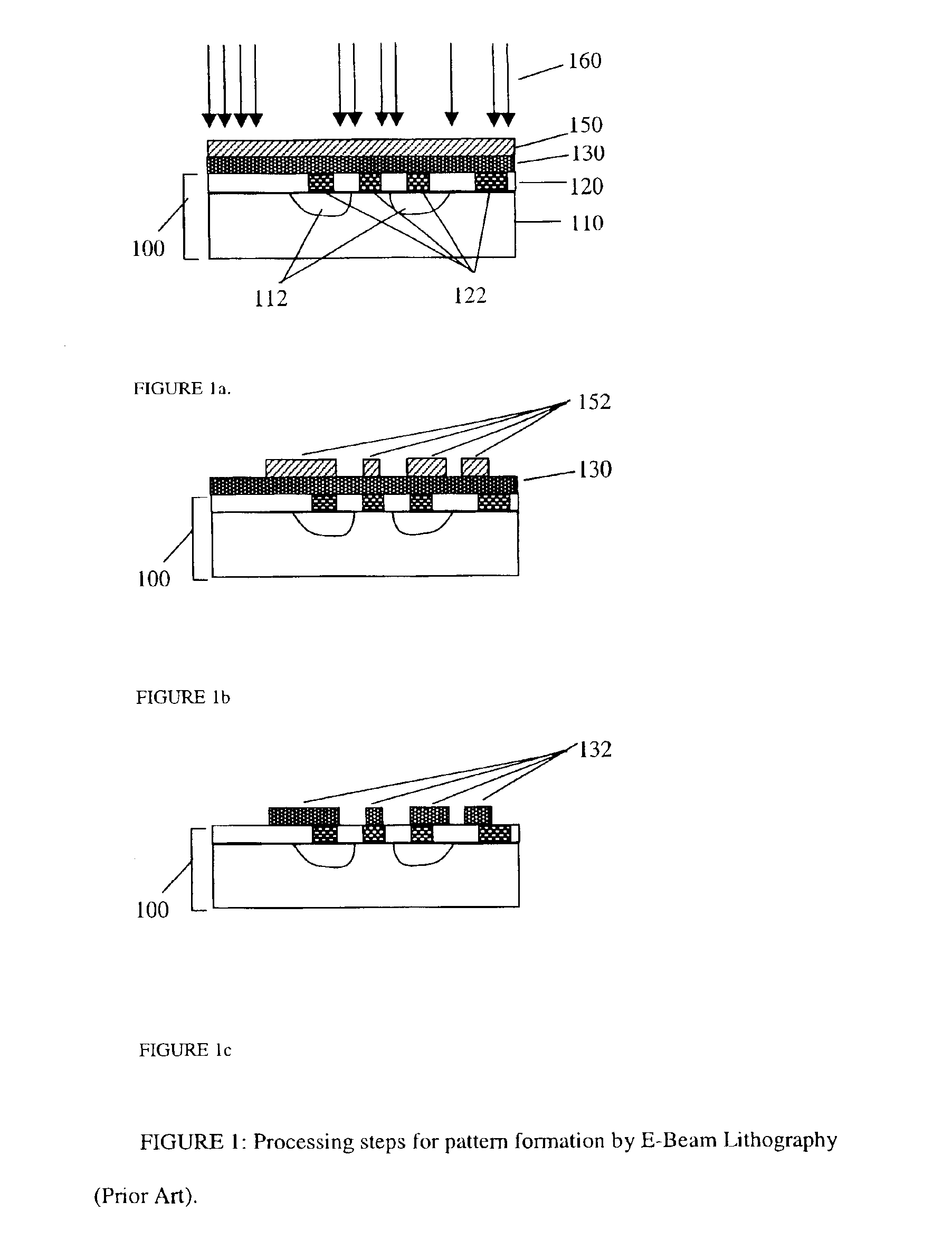
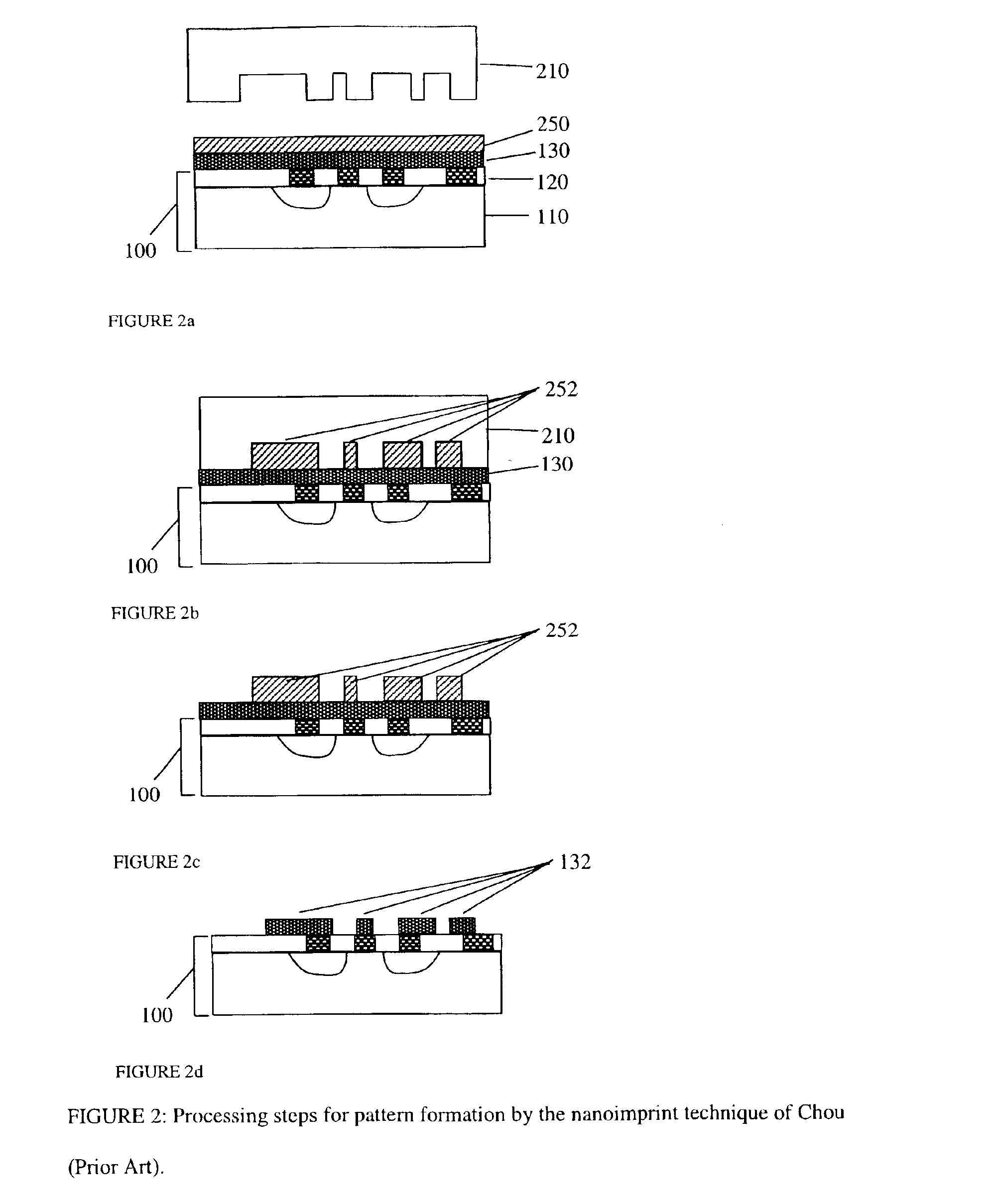
Replication and transfer of microstructures and nanostructures
InactiveUS6849558B2Facilitates pattern transferCheap to makeNanostructure manufactureDecorative surface effectsEngineeringMicroscopic scale
A method for the duplication of microscopic patterns from a master to a substrate is disclosed, in which a replica of a topographic structure on a master is formed and transferred when needed onto a receiving substrate using one of a variety of printing or imprint techniques, and then dissolved. Additional processing steps can also be carried out using the replica before transfer, including the formation of nanostructures, microdevices, or portions thereof. These structures are then also transferred onto the substrate when the replica is transferred, and remain on the substrate when the replica is dissolved. This is a technique that can be applied as a complementary process or a replacement for various lithographic processing steps in the fabrication of integrated circuits and other microdevices.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
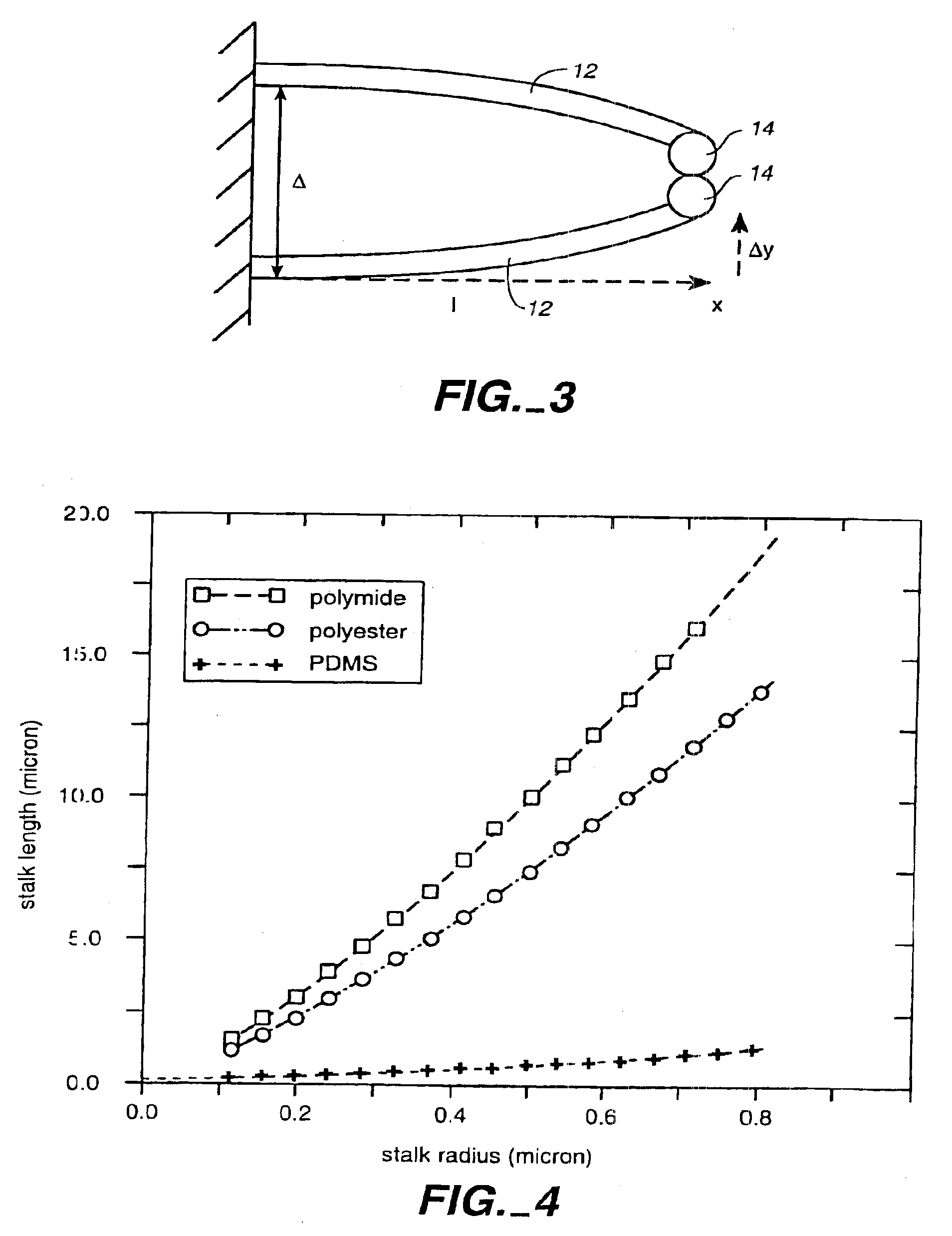
Adhesive microstructure and method of forming same
InactiveUS6872439B2Improve adhesionEasy to disengageSnap fastenersMaterial nanotechnologyMicroscopic scaleOblique angle
A fabricated microstructure comprising at least one protrusion capable of providing an adhesive force at a surface of between about 60 and 2,000 nano-Newtons. A stalk supports the protrusion at an oblique angle relative to a supporting surface. The microstructure can adhere to different surfaces.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Overlay alignment measurement of wafers
InactiveUS6079256AMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementControl systemEngineering
The present invention is a method and apparatus that uses a microscopic height variation positioned relative to a semiconductor device to scan a target on the device to produce an electrical signal representative of height variations of first and second periodic structures of the target in a selected path across the device, and a computing and control system to provide translation between the microscopic height variation detector and the target on the device in a selected path, and to calculate any offset between the first periodic structure and the second periodic structure of the target from the electrical signals from the microscopic height variation detector. The first periodic structure of the target is on a first layer of the device, and the second periodic structure, that complements the first periodic structure, is on a second layer of the device at a location that is adjacent the first periodic structure.
Owner:KLA INSTR
Imaged article on polymeric substrate
InactiveUS6203952B1Increasing the thicknessSmooth peelingAntenna supports/mountingsLoop antennasResistPolymer substrate
Patterned articles, such as RFID antenna, are made by subablation, a process comprising the steps of:A. providing a substrate having a coating, such as a metal or metal oxide, and an interface comprising the thin region where the coating and the substrate are closest to each other;B. exposing at least one part of the total area of the coating to a flux of electromagnetic energy, such as a focused excimer laser beam, sufficient to disrupt the interface but insufficient to ablate the coating; andC. removing the parts of the coating in registry with the portion of the interface area that was disrupted, by means such as ultrasonic agitation.The process has advantages over photo-resist processes in that there is no residual chemical resist left on the product and no undercutting of the pattern or image. It has advantages over laser ablation processes in that higher throughput is possible at the same energy level and there is no microscopic debris left on the product surface.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
High surface area substrates for microarrays and methods to make same
InactiveUS7195872B2Small dimensionImprove analytical precisionSequential/parallel process reactionsFixed microstructural devicesPolymer scienceMicroscopic scale
The present invention is directed to a substrate having a plurality of microfeatures that provide a high surface area and are open to provide ready access to fluids and components therein. Methods of making the high surface area substrates are described and include generating microfeatures and / or microstructures on the surface of the substrate.
Owner:BIOMICROARRAYS +1
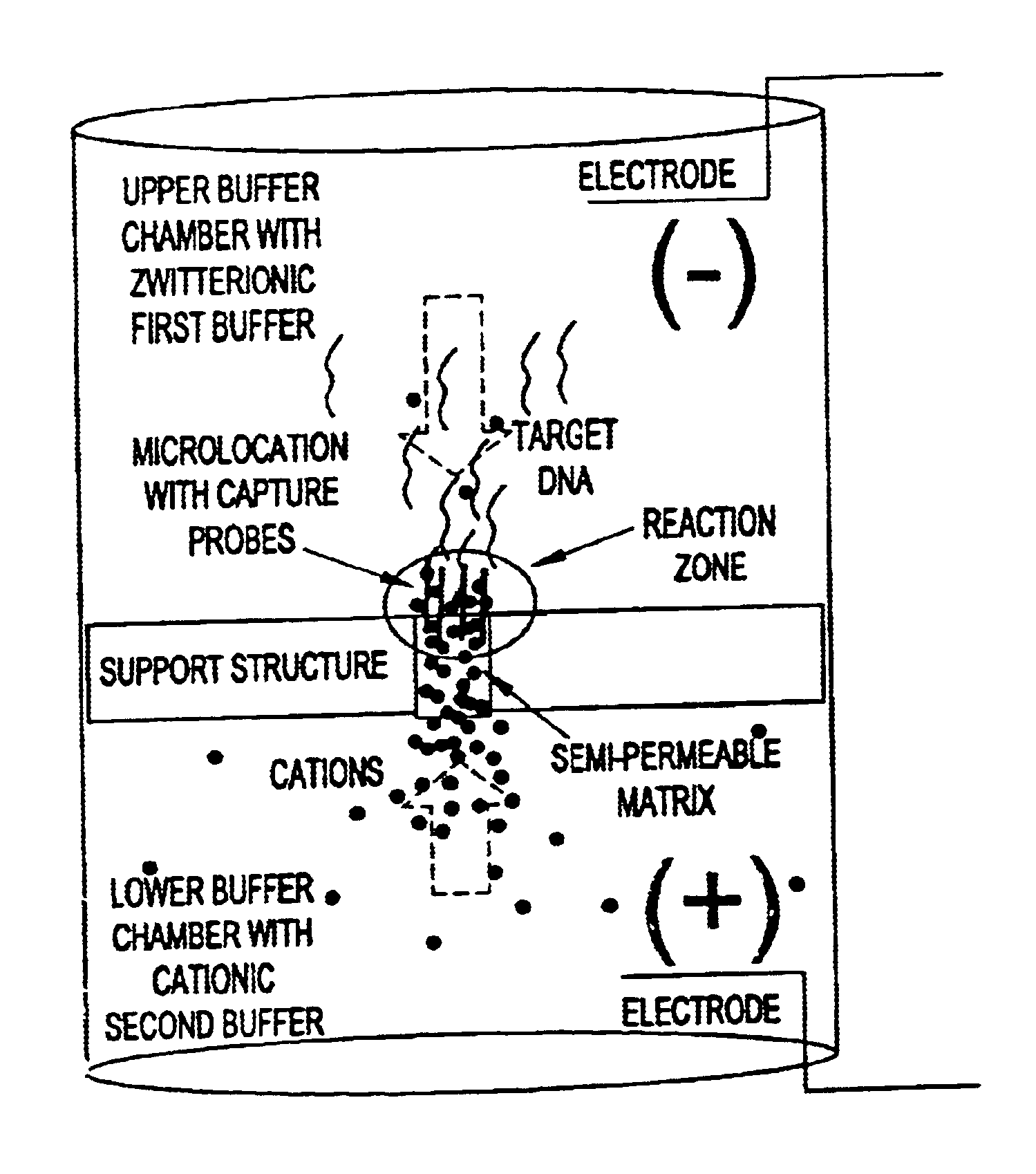
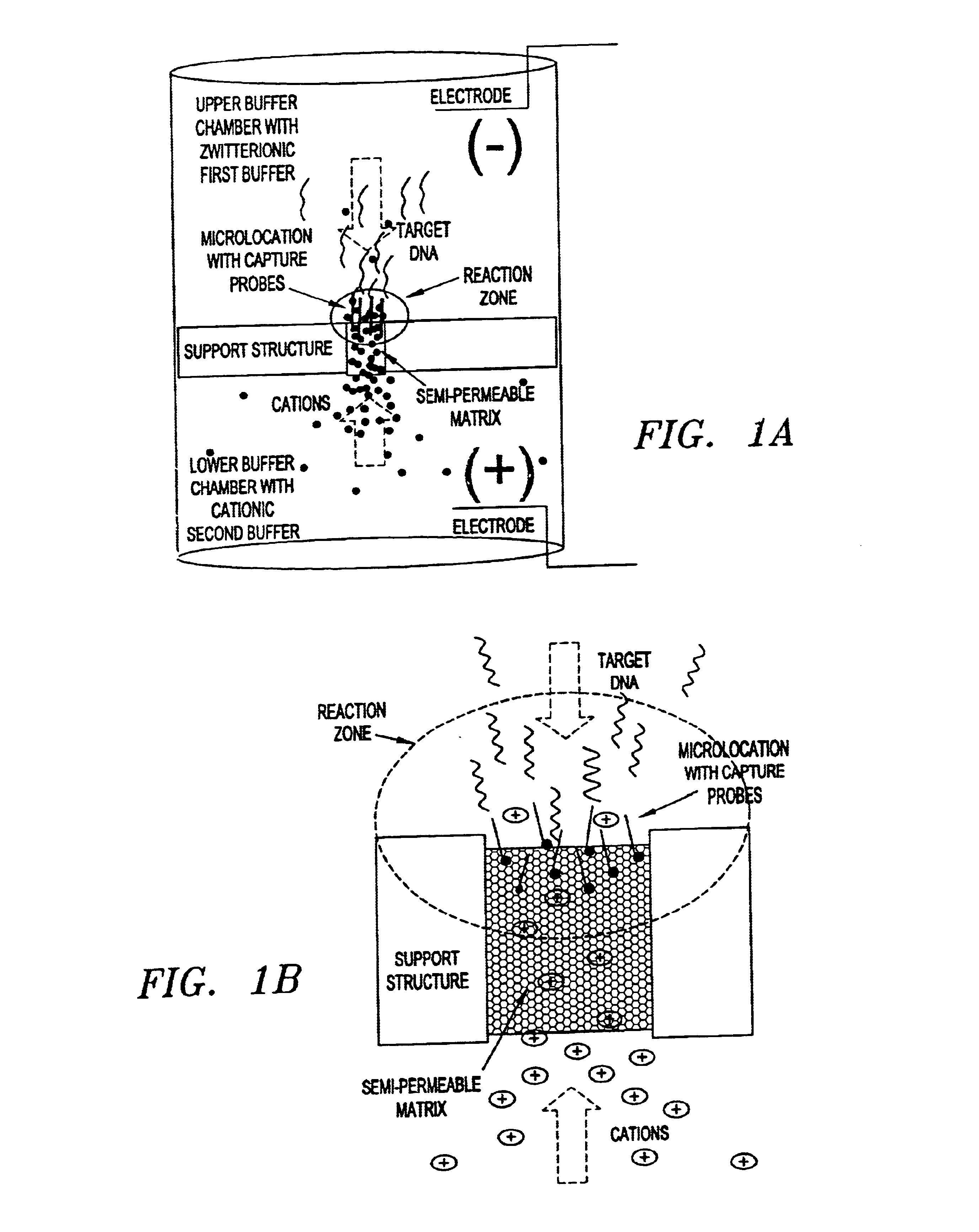
Electronic systems and component devices for macroscopic and microscopic molecular biological reactions, analyses and diagnostics
InactiveUS6780584B1Favorable zoneImprove responseMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsAntigenElectronic systems
This invention pertains to the design, fabrication, and uses of an electronic system which can actively carry out and control multi-step and multiplex reactions in macroscopic or microscopic formats. In particular, these reactions include molecular biological reactions, such as nucleic acid hybridizations, nucleic acid amplification, sample preparation, antibody / antigen reactions, clinical diagnostics, combinatorial chemistry and selection, drug screening, oligonucleotide and nucleic acid synthesis, peptide synthesis, biopolymer synthesis and catalytic reactions. A key feature of the present invention is the ability to control the localized concentration of two or more reaction-dependant molecules and their reaction environment in order to greatly enhance the rate and specificity of the molecular biological reaction.
Owner:ADOR DIAGNOSTICS SRL +1
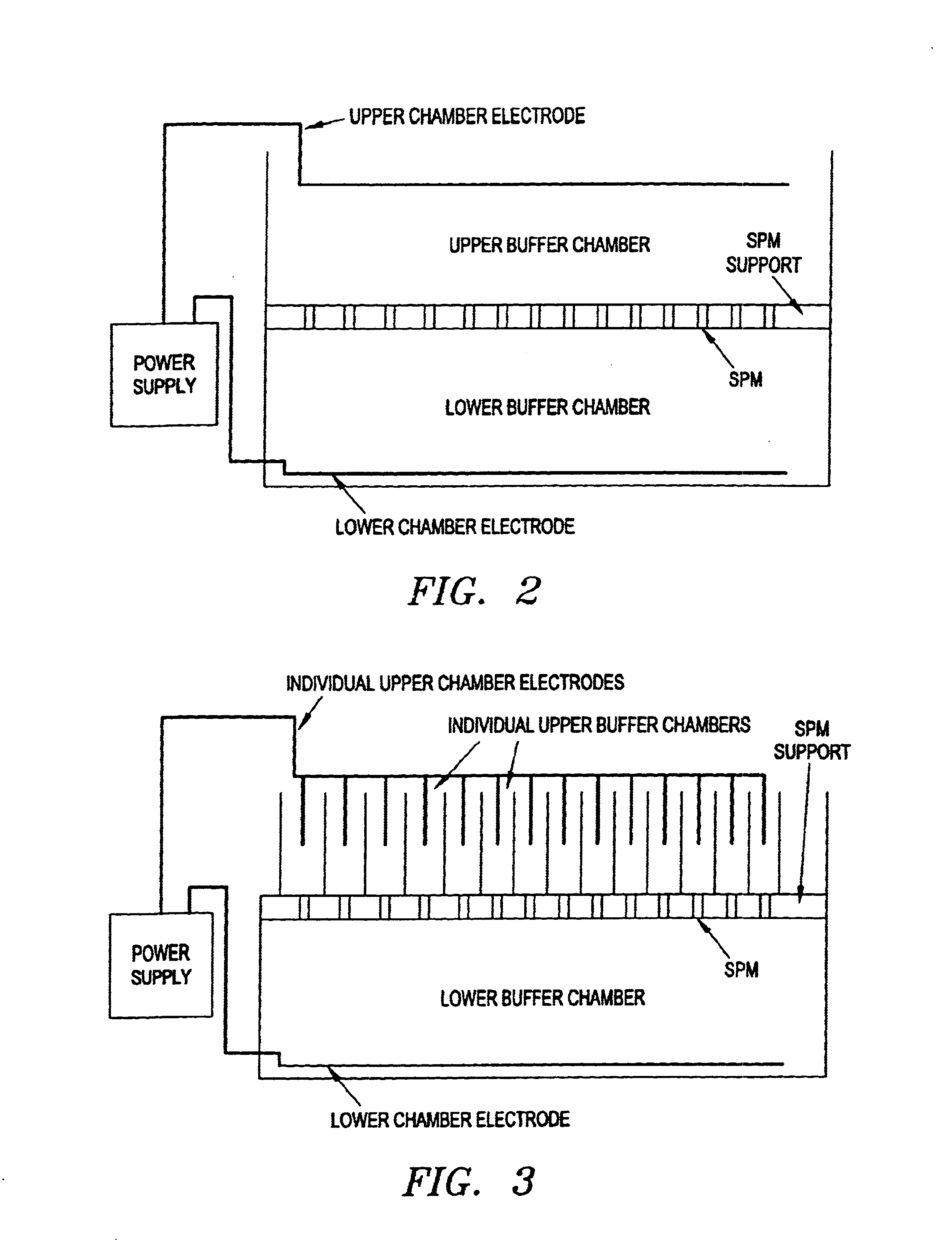
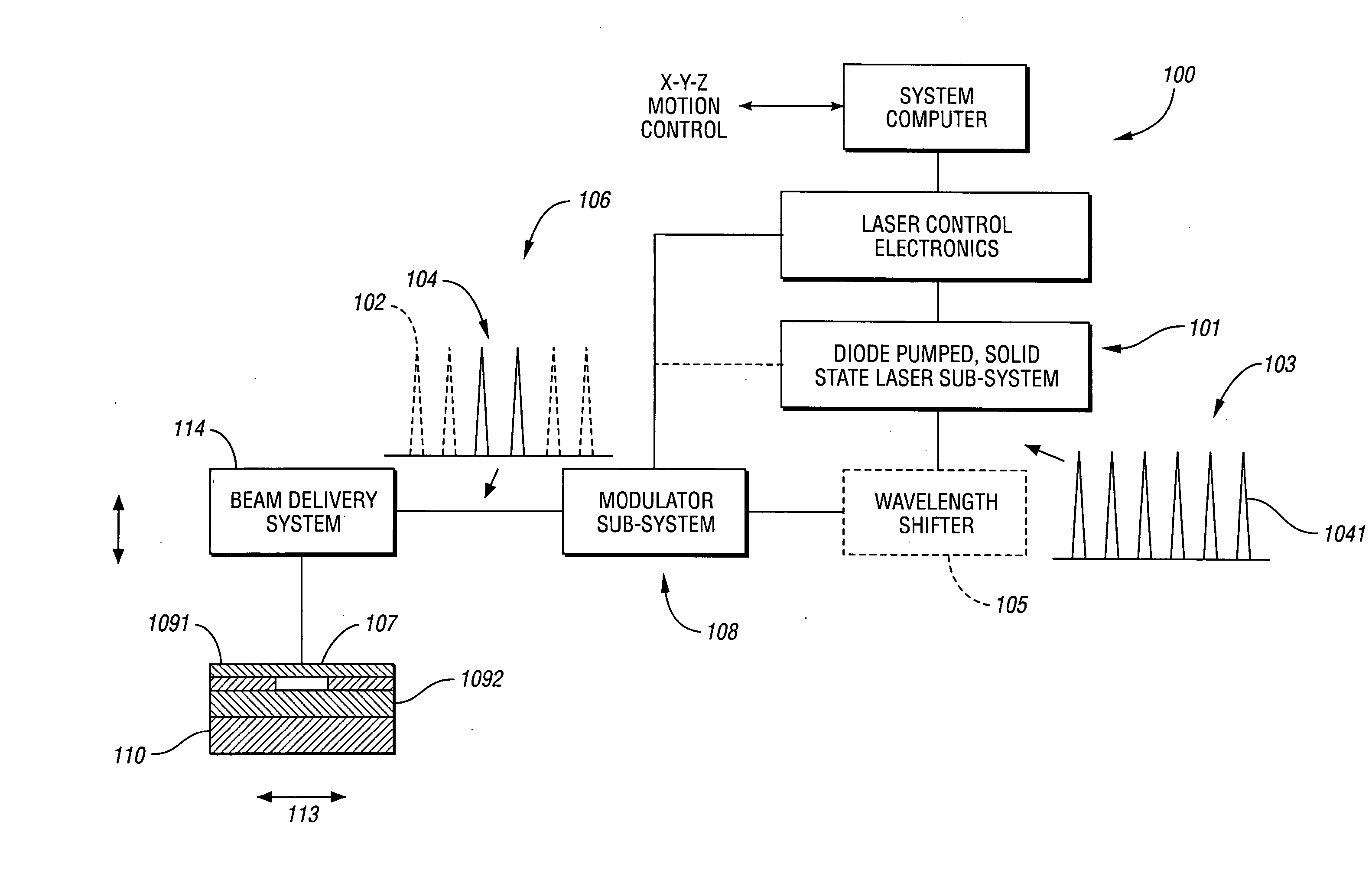
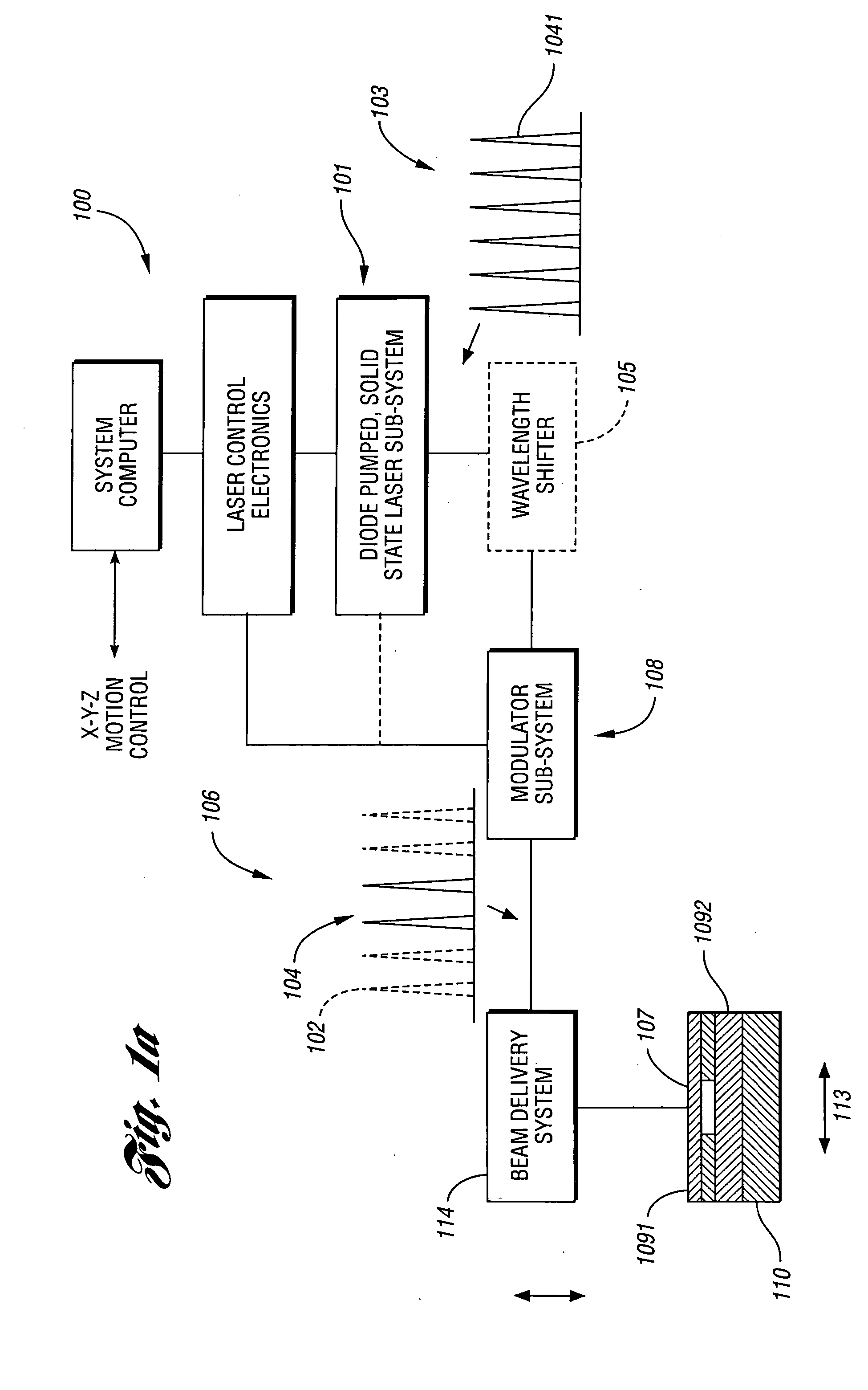
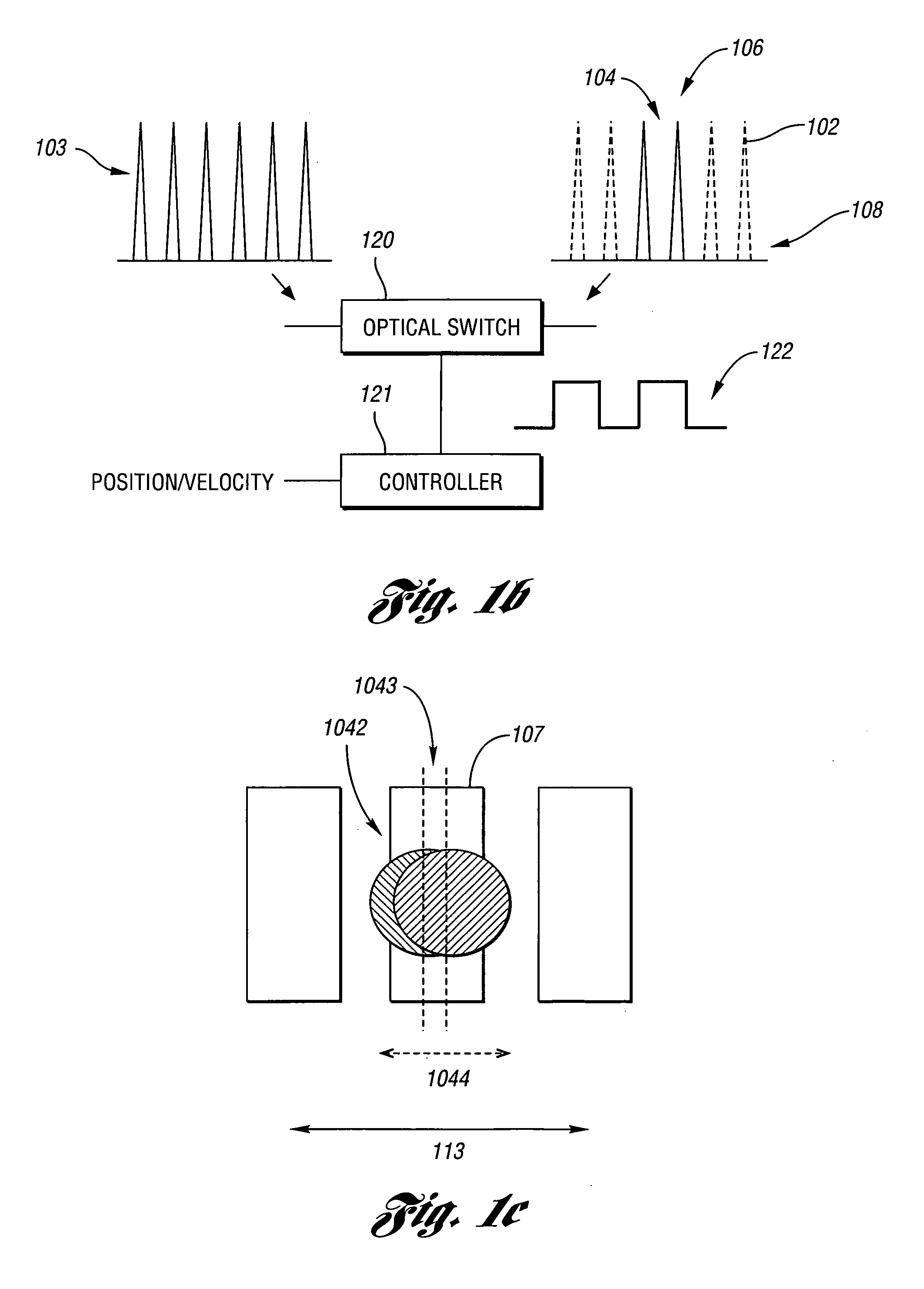
Laser-based system for memory link processing with picosecond lasers
InactiveUS20040134894A1Quality improvementReduce reflectivitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPicosecond laserMicroscopic scale
A laser-based system for processing target material within a microscopic region without causing undesirable changes in electrical or physical characteristics of at least one material surrounding the target material, the system includes a seed laser, an optical amplifier, and a beam delivery system. The seed laser for generating a sequence of laser pulses having a first pre-determined wavelength. The optical amplifier for amplifying at least a portion of the sequence of pulses to obtain an amplified sequence of output pulses. The beam delivery system for delivering and focusing at least one pulse of the amplified sequence of pulses onto the target material. The at least one output pulse having a pulse duration in the range of about 10 picoseconds to less than 1 nanosecond. The pulse duration being within a thermal processing range. The at least one focused output pulse having sufficient power density at a location within the target material to reduce the reflectivity of the target material and efficiently couple the focused output into the target material to remove the target material.
Owner:GSI LUMONICS CORP
Tape data carrier, method and device for manufacturing the same
A tape data carrier for protecting articles and documents from counterfeiting and copying is formed by a polymer structure including at least one polymer layer of which at least one layer has at least one of through-perforations and pits. These through-perforations and pits are preferably between 0.001 mum and 20 mum in size and can be filled with different materials. The data carriers can carry concealed and visible macro-and micro- images created by heavy-ion bombardment of the polymer film, subsequent exposure of the bombarded film to ultraviolet radiation, and etching of the polymer film in a solvent. A device for manufacturing a data carrier of this type includes the following elements configured in series: a heavy ion source; a heavy ion beam-formation system; an ion guide; a three-dimensional amplitude modulation unit; and a target which is destined to become the data carrier. The three-dimensional amplitude modulation unit is designed to hold a matrix of wafers and is connected to a drive for rotating and translating the wafers. The drive is connected via a control unit to the three-dimensional amplitude modulation unit for positioning the target.
Owner:BELOUSOV BORIS ILICH +3
Microfluidic chips and assay systems
ActiveUS20070166200A1Efficient executionSimple designValve arrangementsHeating or cooling apparatusFluid transportEngineering
The systems and methods described herein include a microfluidic chip having a plurality of microfeatures interconnected to provide a configurable fluid transport system for processing at least one reagent. Inserts are provided to removably interfit into one or more of the microfeatures of the chip, wherein the inserts include sites for interactions with the reagent. As will be seen from the following description, the microfluidic chip and the inserts provide an efficient and accurate approach for conducting parallel assays.
Owner:RHEONIX
Birefringent reflectors using isotropic materials and form birefringence
Multilayer thin film reflectors, such as mirrors and reflective polarizers, are described in which form birefringent optical layers are incorporated into a plurality of optical repeat units in the film. The form birefringent layers exhibit birefringence as a result of microscopic structures that have a dimension that is small compared to the wavelength of light but large compared to molecular distances. The optical layers within the optical repeat units have out-of-plane indices of refraction that are tailored to produce desired effects as a function of incidence angle for p-polarized light. The multilayer reflectors can be made by conventional vacuum deposition techniques using known inorganic optical materials, but can also be made entirely with polymeric materials by co-extrusion or other processes.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Ophthalmic lens synthesized from its specification
InactiveUS6464355B1Less aberrationImprove optical qualityEye diagnosticsOptical partsRough surfaceMicroscopic scale
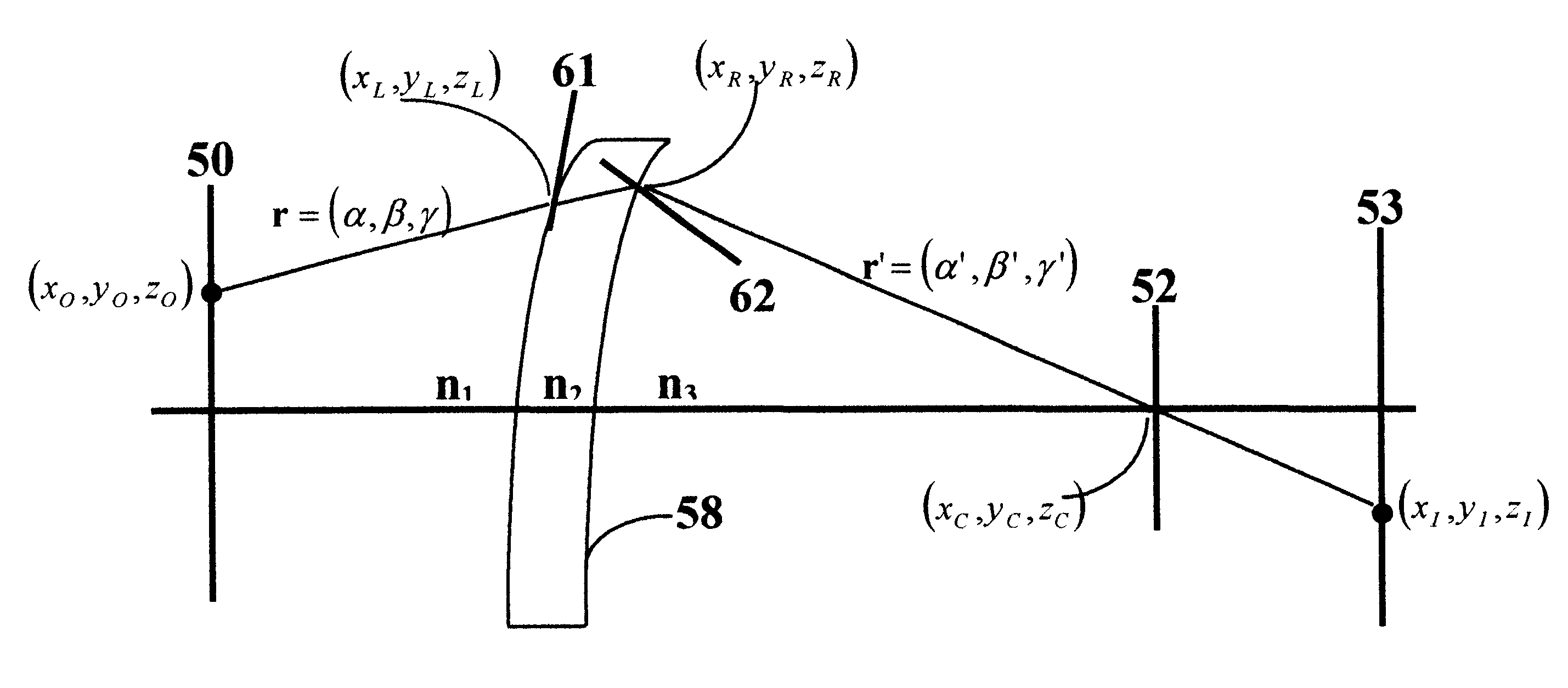
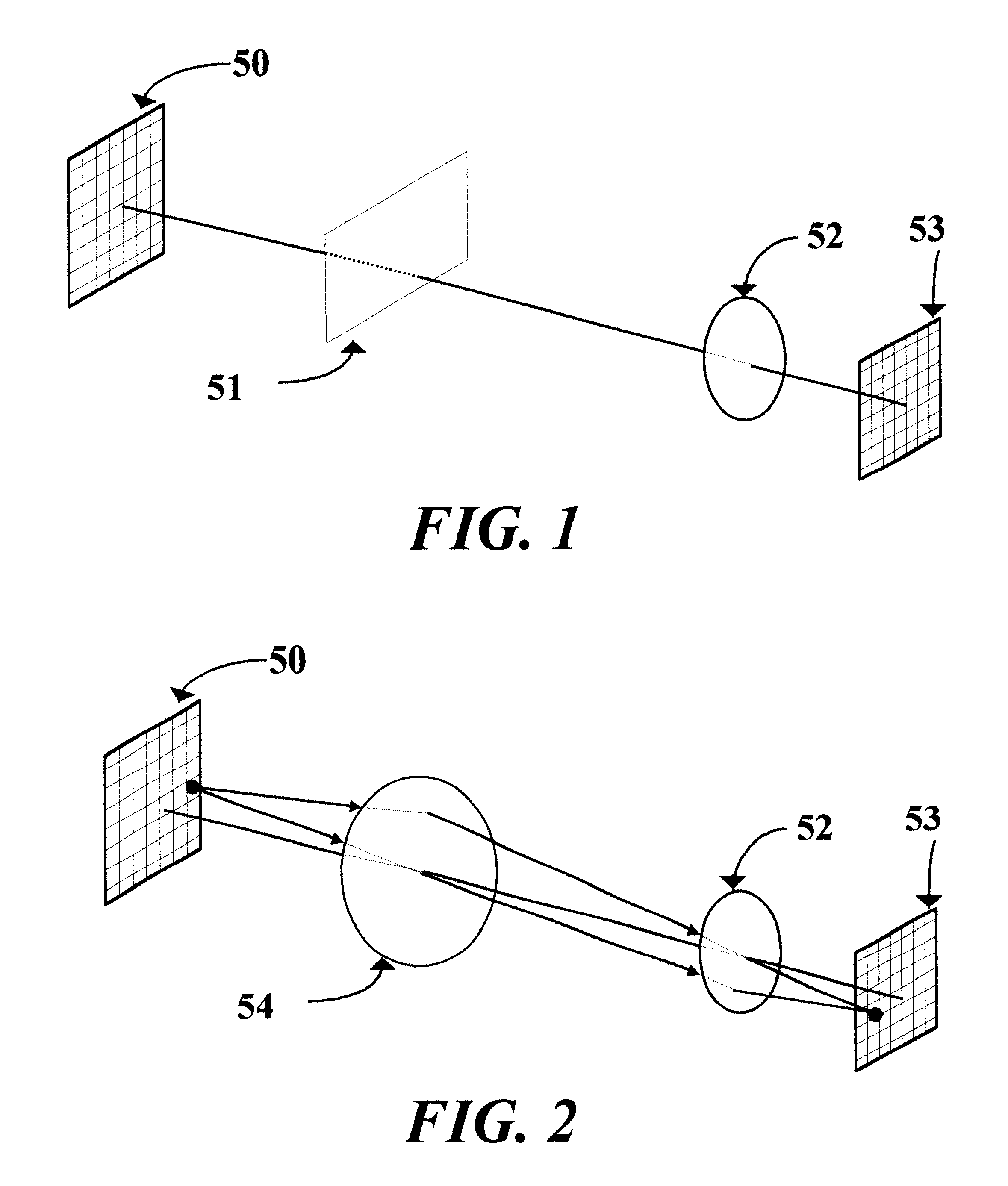
This invention relates to a novel prescription lens (58), mainly suited for ophthalmic applications. The lens designer defines the macroscopic surfaces of the lens (59, 60) as desired. The design process assumes that the location of the object (50), the lens (51), and the required image (53) are known. By using Ray-tracing technique we calculate the microscopic normals to the lens that will form the required image. From those microscopic normals we calculate microscopic surface by a process of summation the slopes with geometric pattern conditions. The final surface is not smooth but contains plenty of dense microscopic shapes that look like saw-teeth. That rough surface enables the lens to have almost any desired shape and thickness.
Owner:GIL THIEBERGER
Variable property electrodepositing of metallic structures
ActiveUS20090159451A1Increase floor spaceAdd equipmentCellsElectrolytic coatingsParticulatesMetallic materials
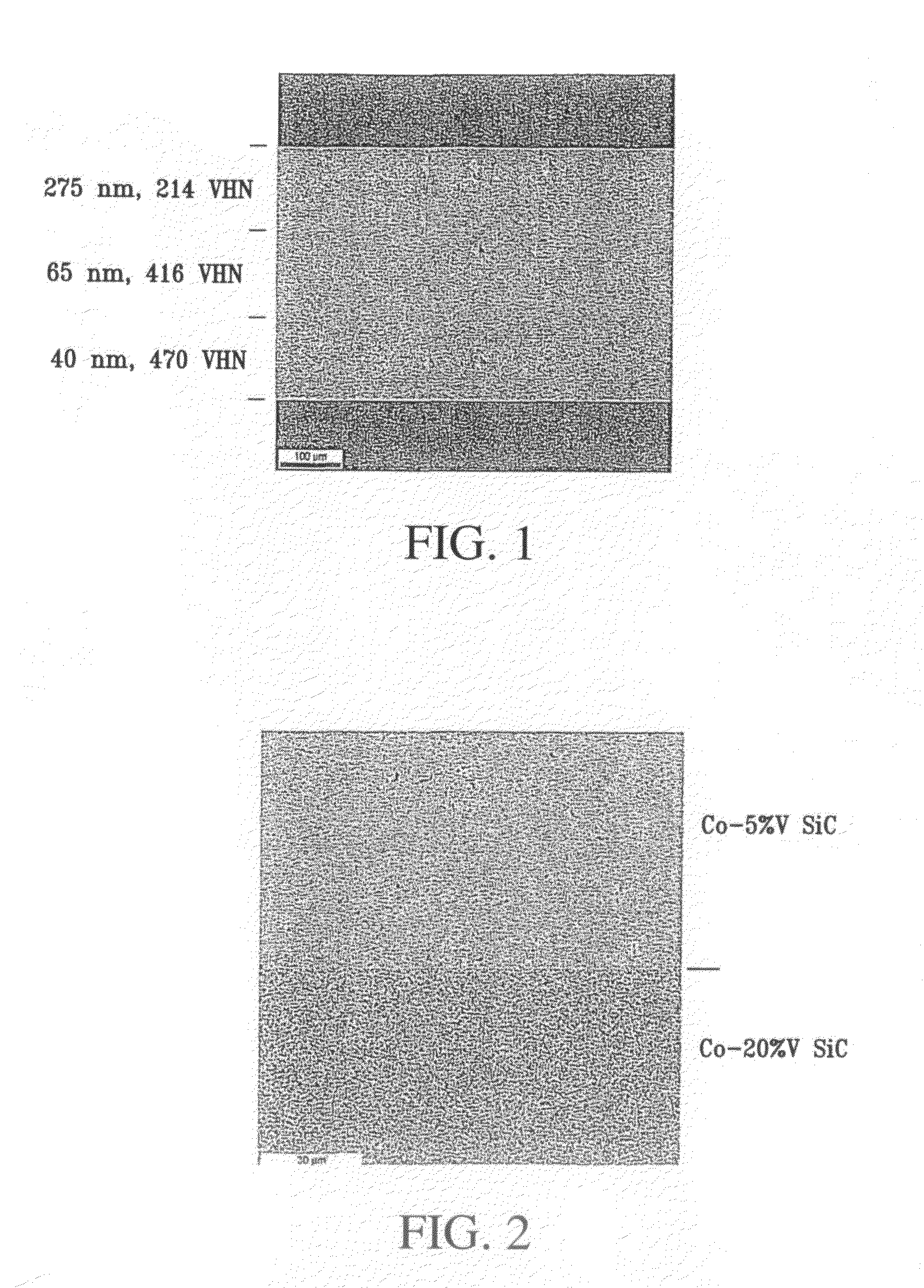
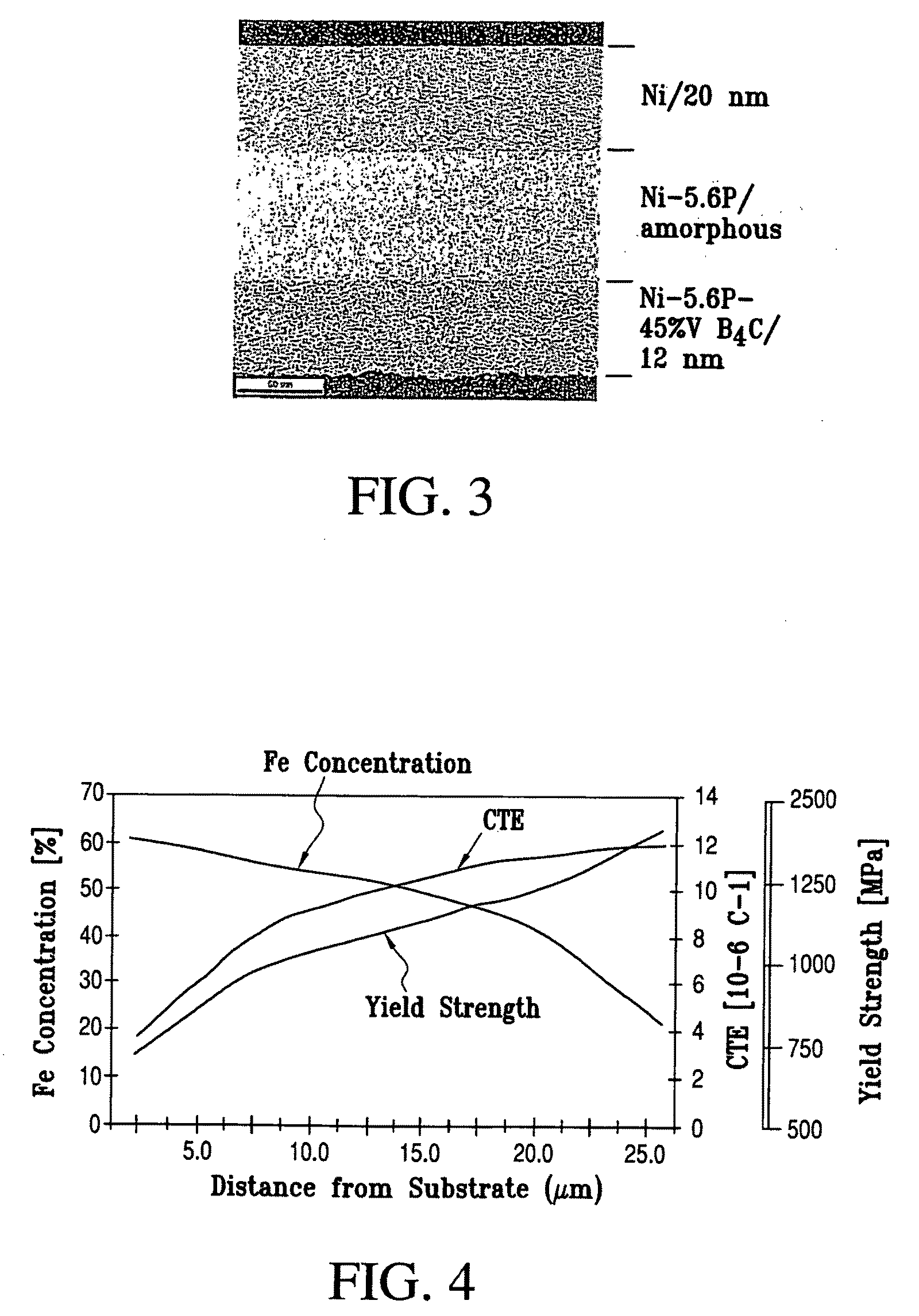
Variable property deposit, at least partially of fine-grained metallic material, optionally containing solid particulates dispersed therein, is disclosed. The electrodeposition conditions in a single plating cell are suitably adjusted to once or repeatedly vary at least one property in the deposit direction. In one embodiment denoted multidimension grading, property variation along the length and / or width of the deposit is also provided. Variable property metallic material deposits containing at least in part a fine-grained microstructure and variable property in the deposit direction and optionally multidimensionally, provide superior overall mechanical properties compared to monolithic fine-grained (average grain size: 2 nm-5 micron), entirely coarse-grained (average grain size: >20 micron) or entirely amorphous metallic material deposits.
Owner:INTEGRAN TECH
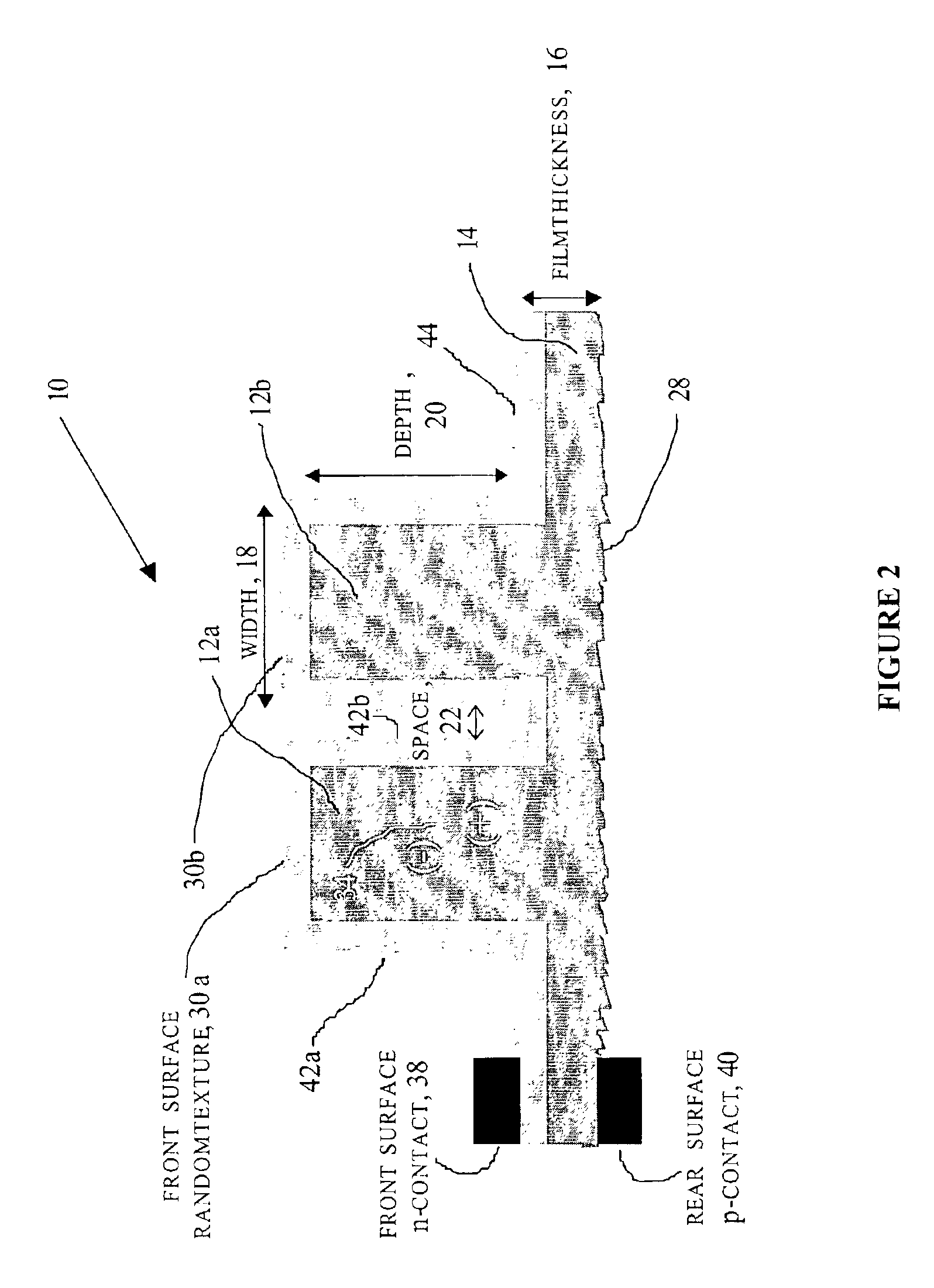
Method of making an enhanced optical absorption and radiation tolerance in thin-film solar cells and photodetectors
InactiveUS7109517B2Promote absorptionImprove toleranceFinal product manufacturePhotoelectric discharge tubesDiffraction orderPhotodetector
Subwavelength random and periodic microscopic structures are used to enhance light absorption and tolerance for ionizing radiation damage of thin film and photodetectors. Diffractive front surface microscopic structures scatter light into oblique propagating higher diffraction orders that are effectively trapped within the volume of the photovoltaic material. For subwavelength periodic microscopic structures etched through the majority of the material, enhanced absorption is due to waveguide effect perpendicular to the surface thereof. Enhanced radiation tolerance of the structures of the present invention is due to closely spaced, vertical sidewall junctions that capture a majority of deeply generated electron-hole pairs before they are lost to recombination. The separation of these vertical sidewall junctions is much smaller than the minority carrier diffusion lengths even after radiation-induced degradation. The effective light trapping of the structures of the invention compensates for the significant removal of photovoltaic material and substantially reduces the weight thereof for space applications.
Owner:ZAIDI SALEEM H
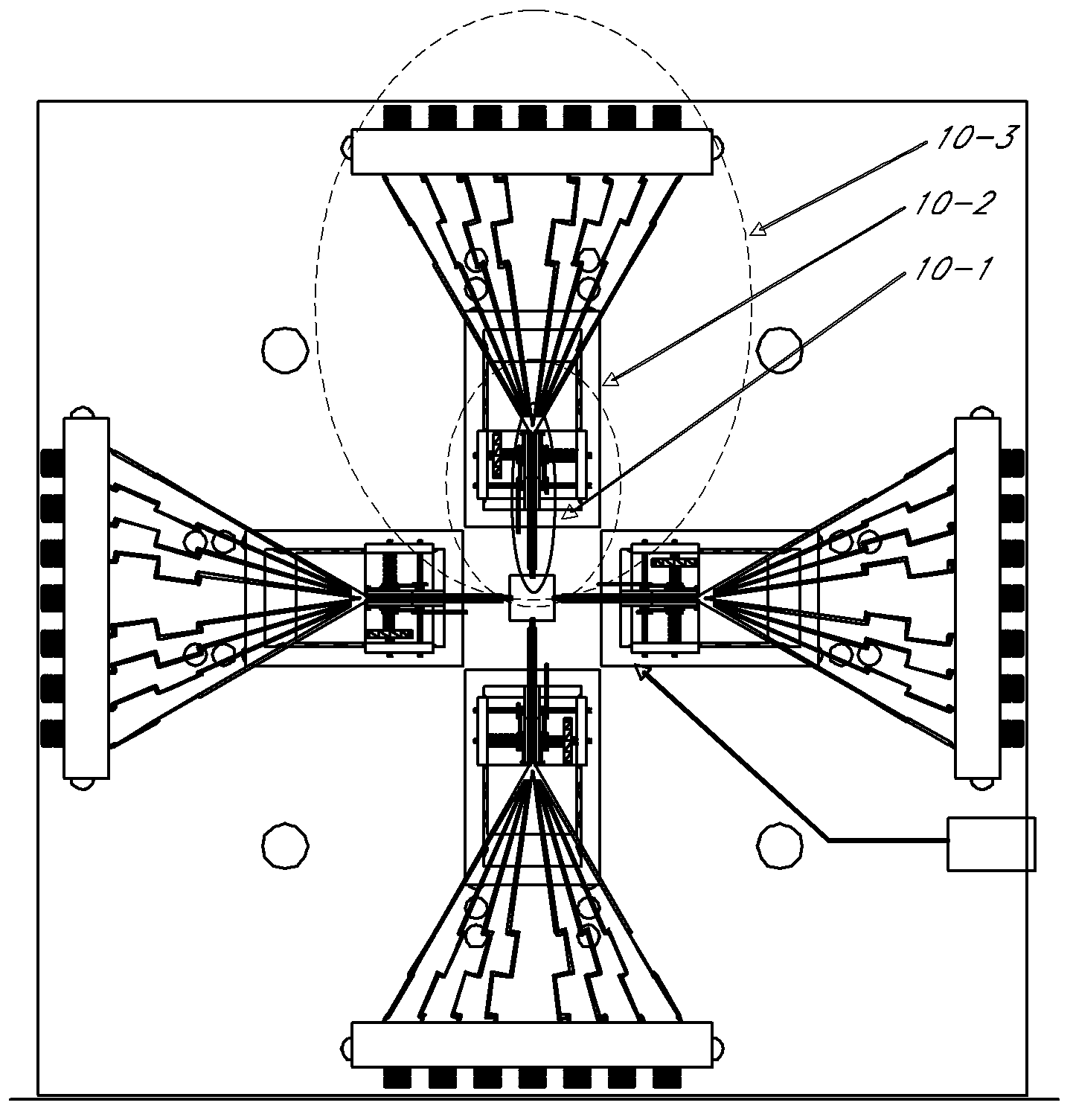
Scalable wideband probes, fixtures, and sockets for high speed IC testing and interconnects
ActiveUS20080265919A1Reducing cross talk and prasiticsIncrease speedElectrical measurement instrument detailsSolid-state devicesRadiation lossPicosecond
We introduce a new Periodic micro coaxial transmission line (PMTL) that is capable of sustaining a TEM propagation mode up to THz band. The PMTL can be manufactured using the current photolithographic processes. This transmission line can be embedded in microscopic layers that allow many new applications. We use the PMTL to develop a wideband highly scalable connector that is then used in a Probe that can be used for connecting to microscopic scale Integrated Circuits with picoseconds High Speed Digital and near THz Analogue performance in various stages of development from R&D to production testing. These probes, in one embodiment, provide a thin pen-like vertical probe tip that matches the die pad pattern precisely that can be as agile as a high speed plotter pen, connecting on the fly to any die pattern on a wafer. This approach allows the most valuable part of the test, namely the wafer to remain stationary and safe, and the least costly part of the test, namely the probe to take most of the wear and tear. We further use the embedded PMTL to develop a modular, scaleable and fully automated Universal Test Fixture for testing chips in various stages of development mainly for digital IC chips that can be utilized in production lines with pick and place of chips on tape to test every chip before insertion into circuits. One embodiment includes a low profile wideband Signal Launcher and an alligator type RF Clip that can be used at the edge of PCB's directly for validation broads. The Signal Launcher is used to develop a new versatile Flush Top Test Fixtures for individual device testing in various stages of development from die, to packaged, to Module, to Circuit Boards. The PMTL can also provide Confined Field Interconnects (CFI) between various elements on semiconductor wafers to reduce parasitic and radiation losses and practically eliminating cross talk, thus, increasing the speed of digital IC's. The PMTL is also used to develop a Universal Test Socket, and a Hand Probe with performance up to 220 GHz.
Owner:WAYMO LLC
Processes for hermetically packaging wafer level microscopic structures
InactiveUS6936494B2AdaptableImprove integrityDecorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesEtchingLithographic artist
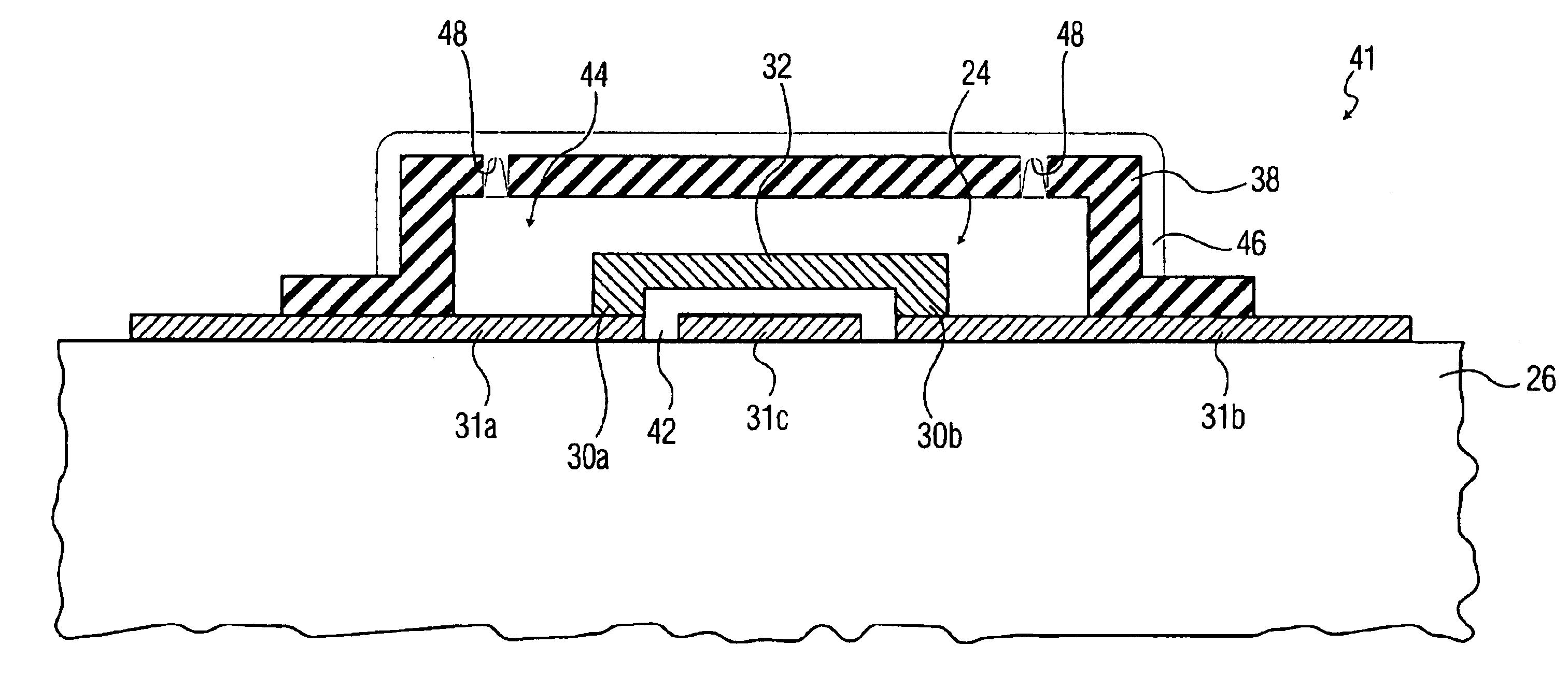
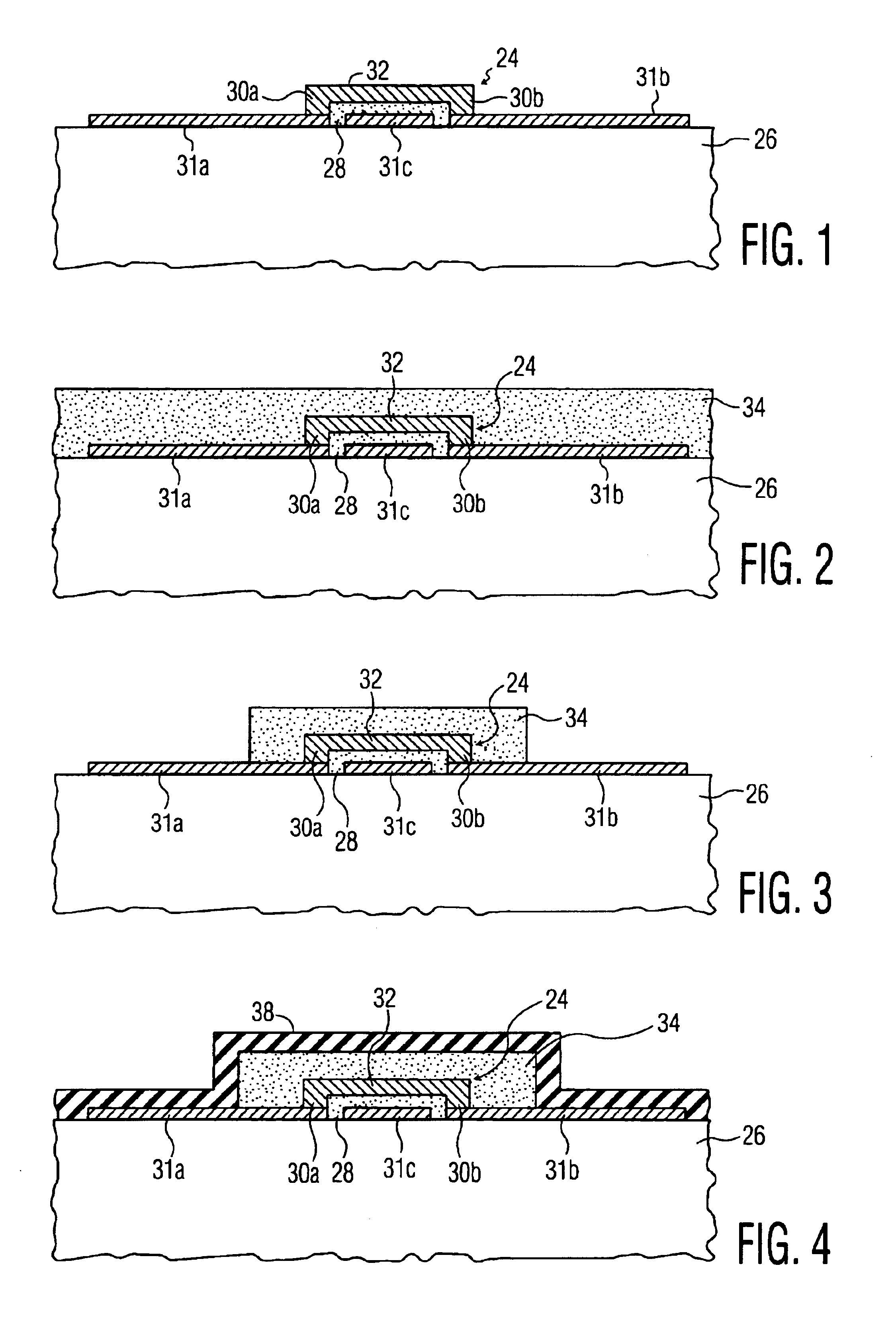
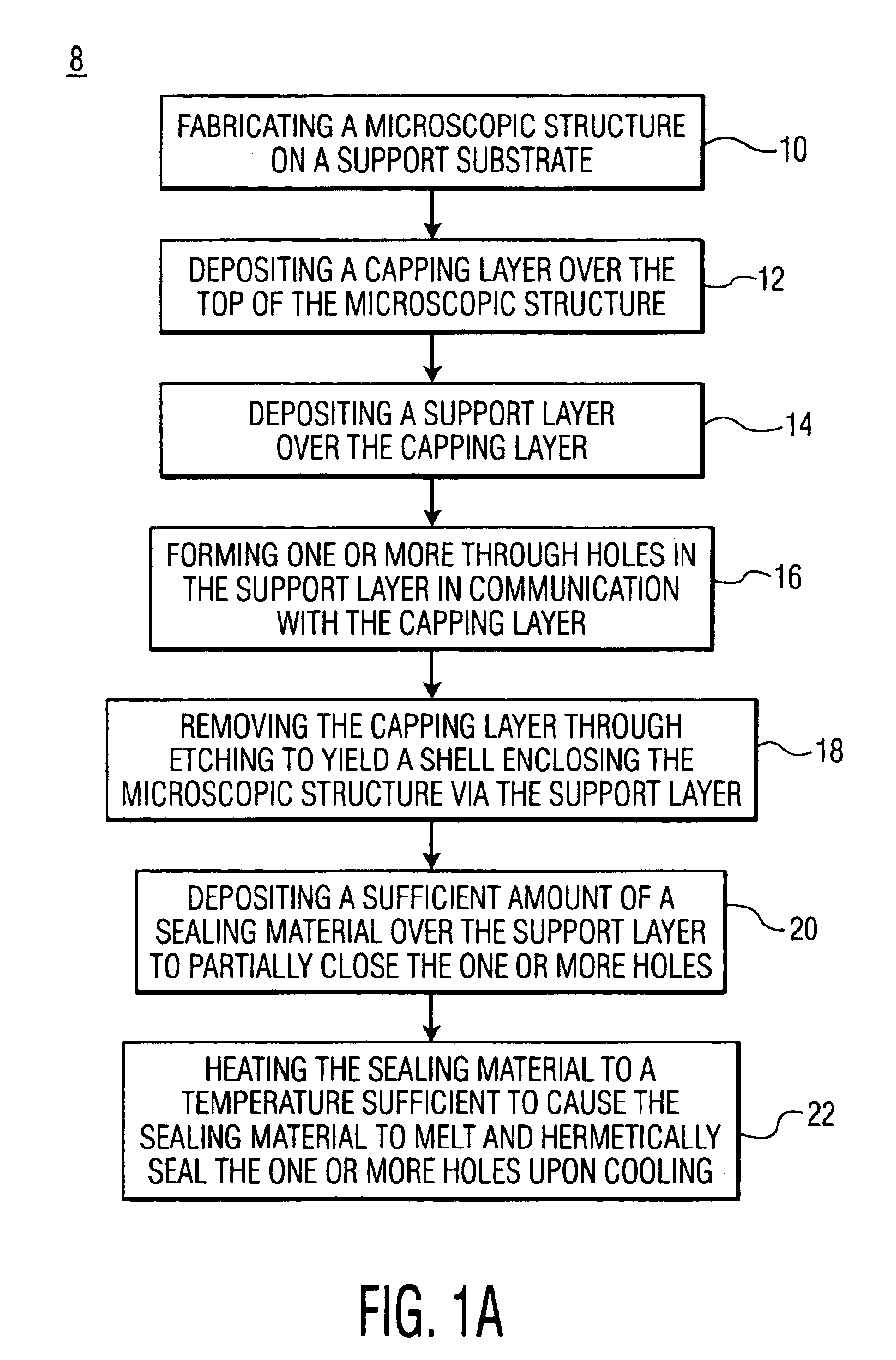
A process for hermetically packaging a microscopic structure including a MEMS device is provided. The process for the present invention includes the steps of depositing a capping layer of sacrificial material patterned by lithography over the microscopic structure supported on a substrate, depositing a support layer of a dielectric material patterned by lithography over the capping layer, providing a plurality of vias through the support layer by lithography, removing the capping layer via wet etching to leave the support layer intact in the form of a shell having a cavity occupied by the microscopic structure, depositing a metal layer over the capping layer that is thick enough to provide a barrier against gas permeation, but thin enough to leave the vias open, and selectively applying under high vacuum a laser beam to the metal proximate each via for a sufficient period of time to melt the metal for sealing the via.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Systems and methods for computationally developing manufacturable and durable cast components
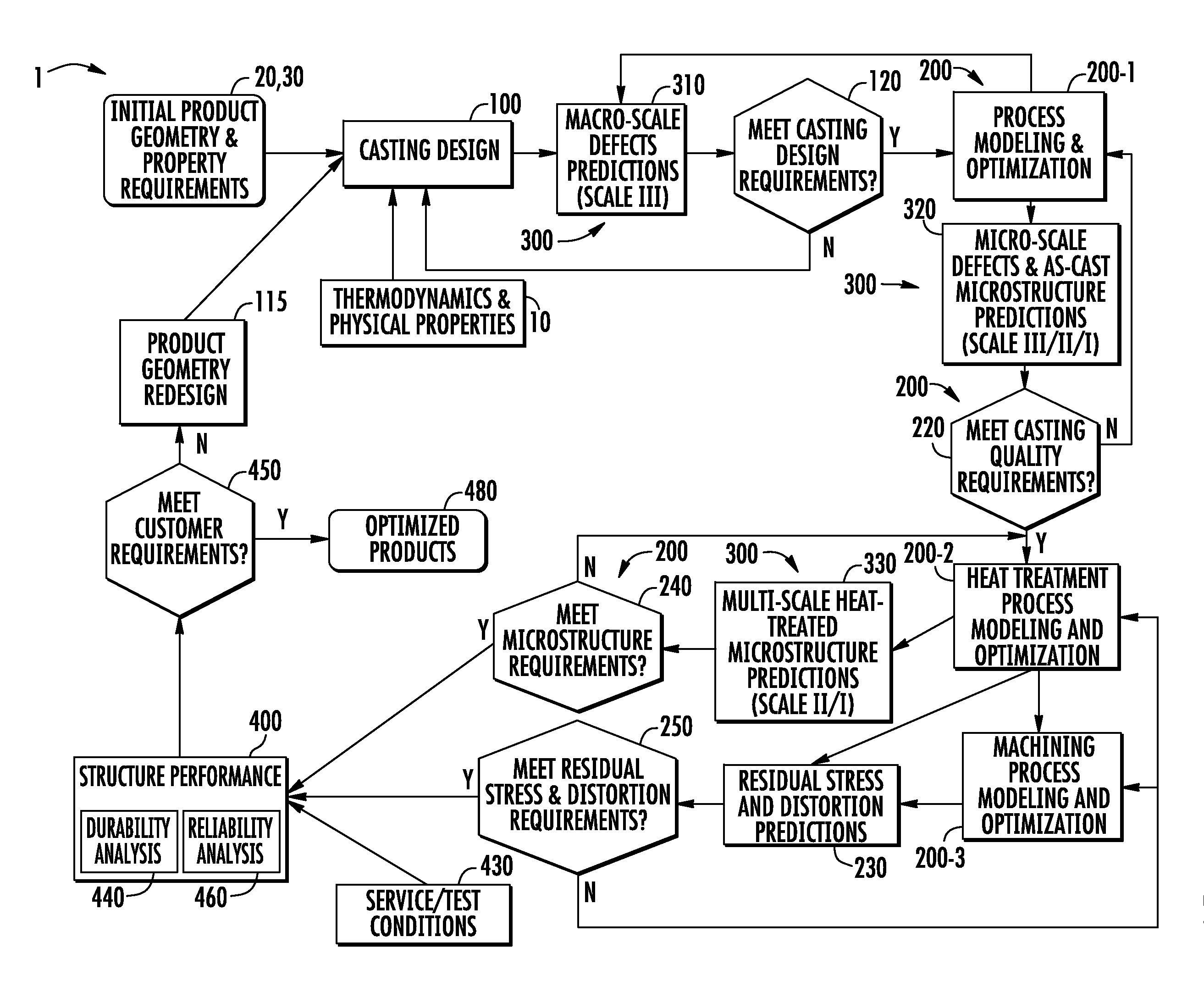
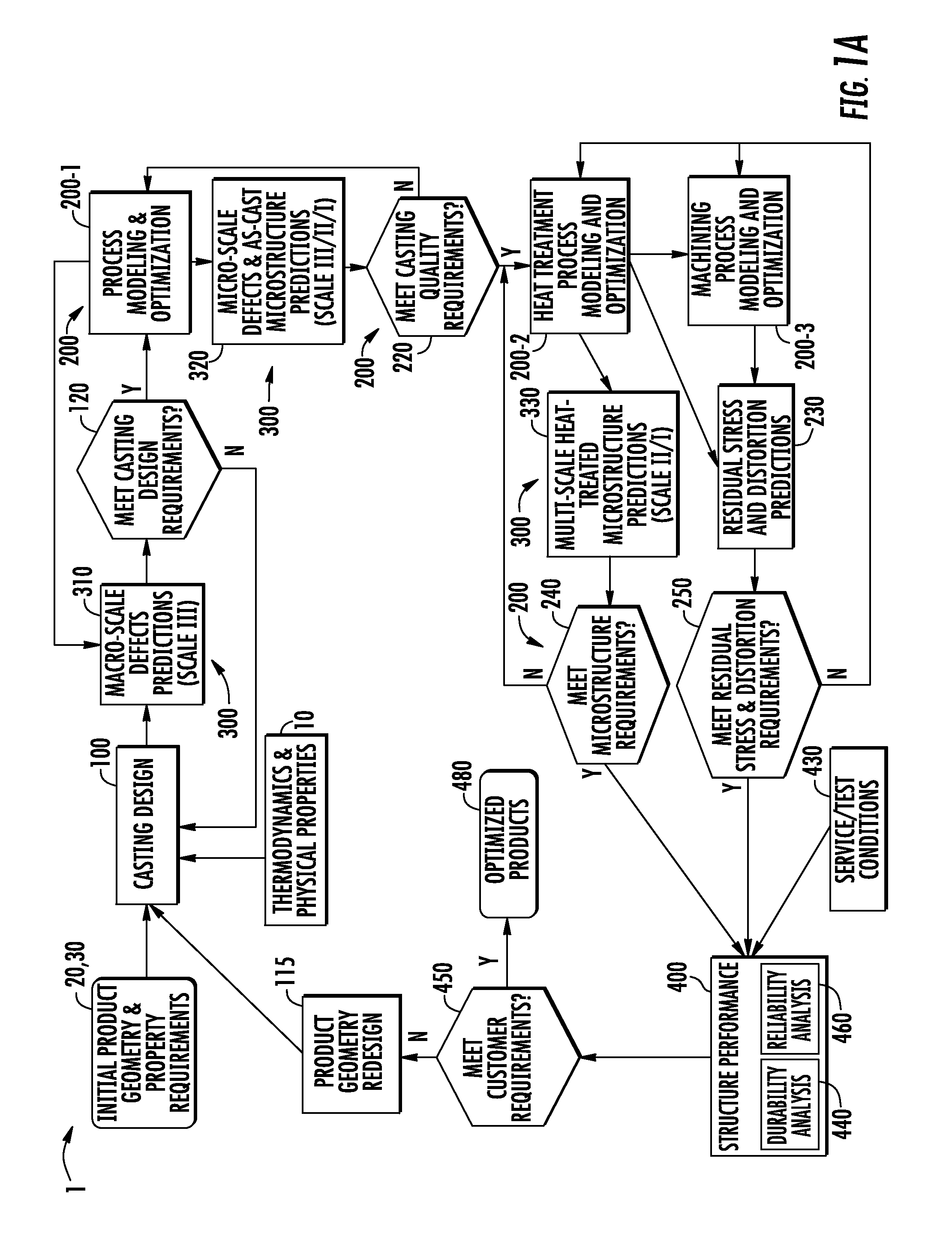
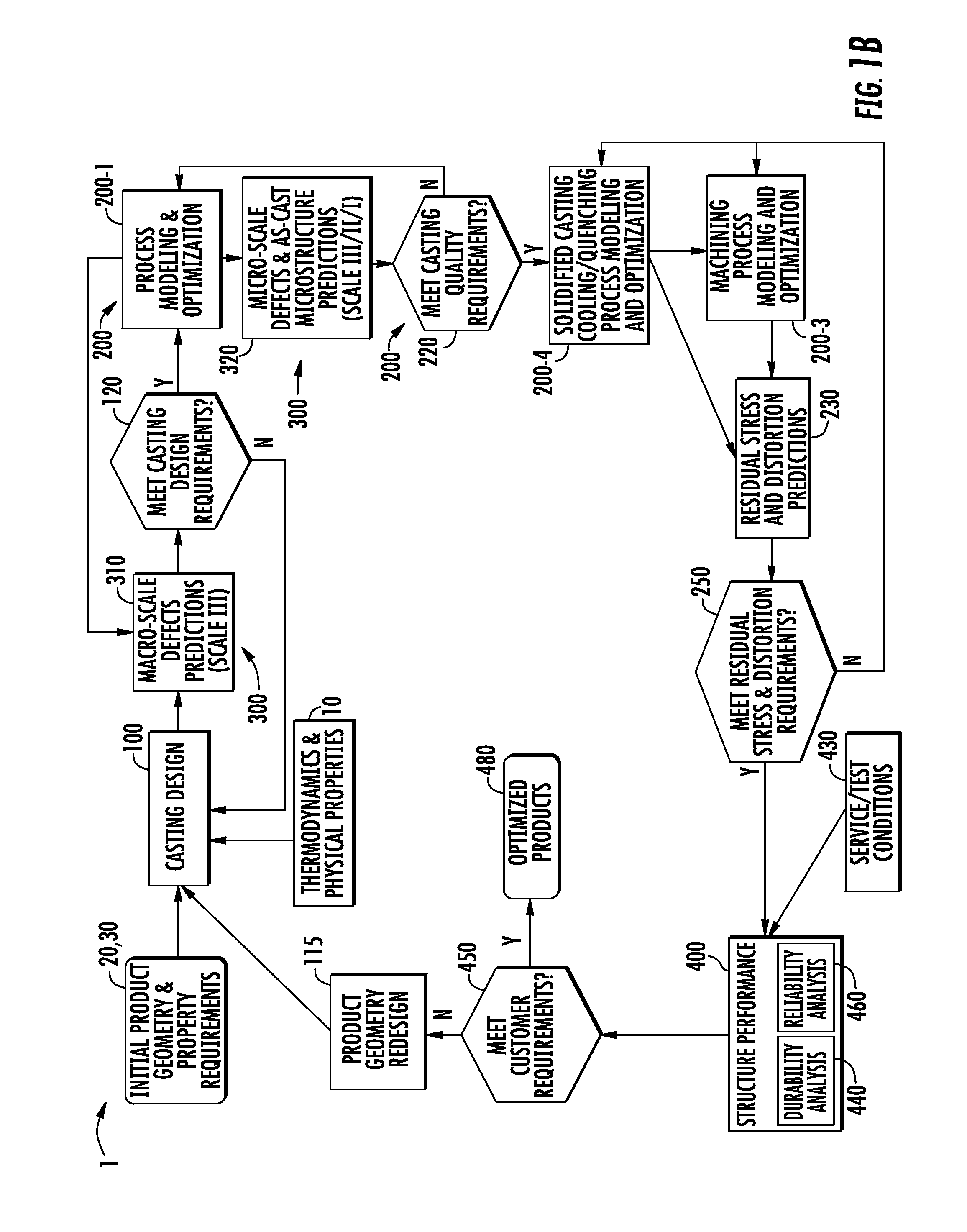
A method and system for optimizing a simulated casting of a light weight alloy component. The simulation includes passing component design data through various computational modules relating to casting designs, process modeling and optimization, material microstructure and defects and product performance. Variations in microstructure and defects across various very small size scales are extended to increasingly larger scales to permit structural performance calculations of the cast component to take such non-uniformities into consideration. At least some of the modules employ an expert system-based approach to achieve the optimized results. The results can be compared to end user needs to determine if redesign of the part geometry or manufacturing process is needed.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
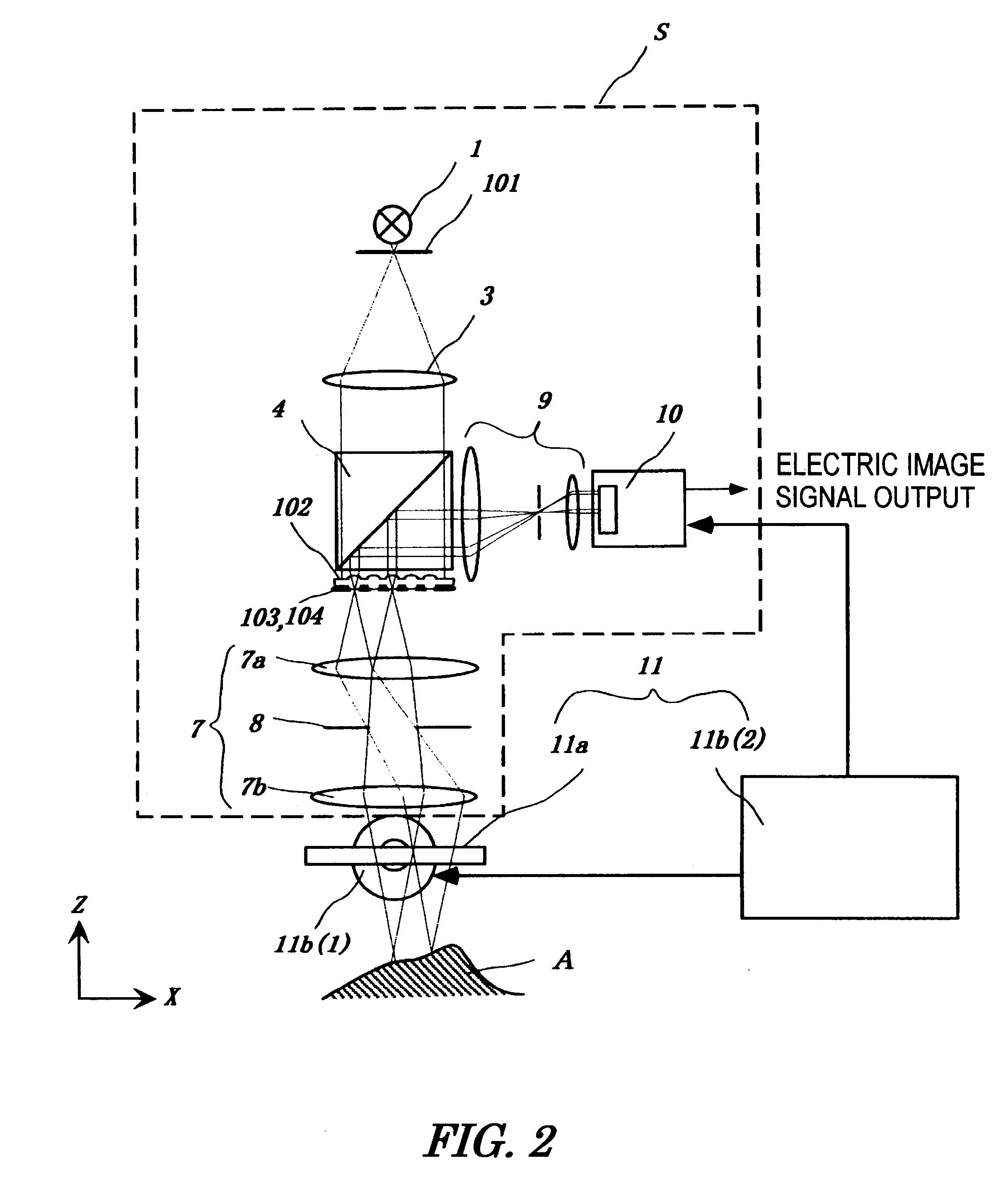
Micro-scanning multislit confocal image acquisition apparatus
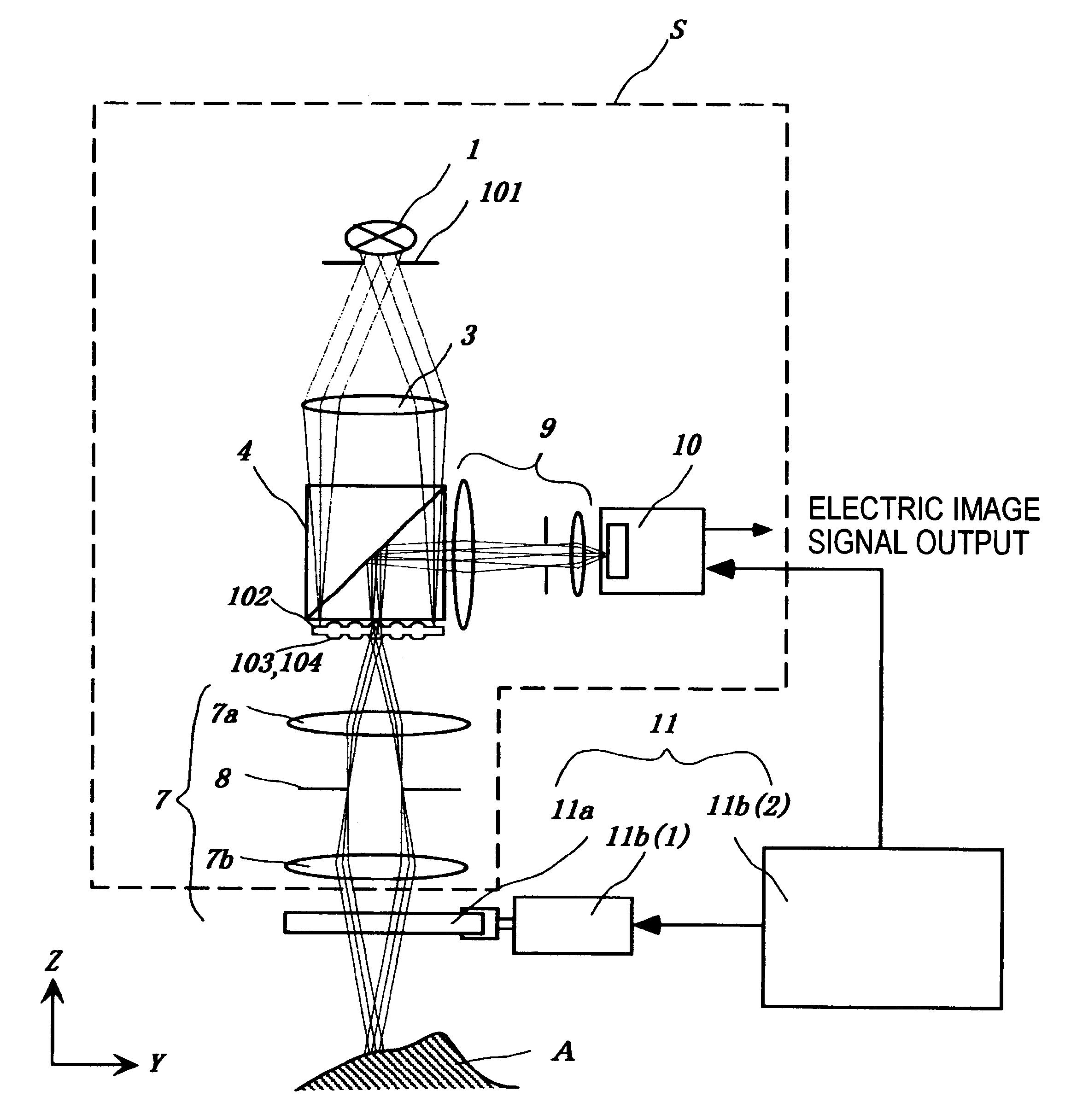
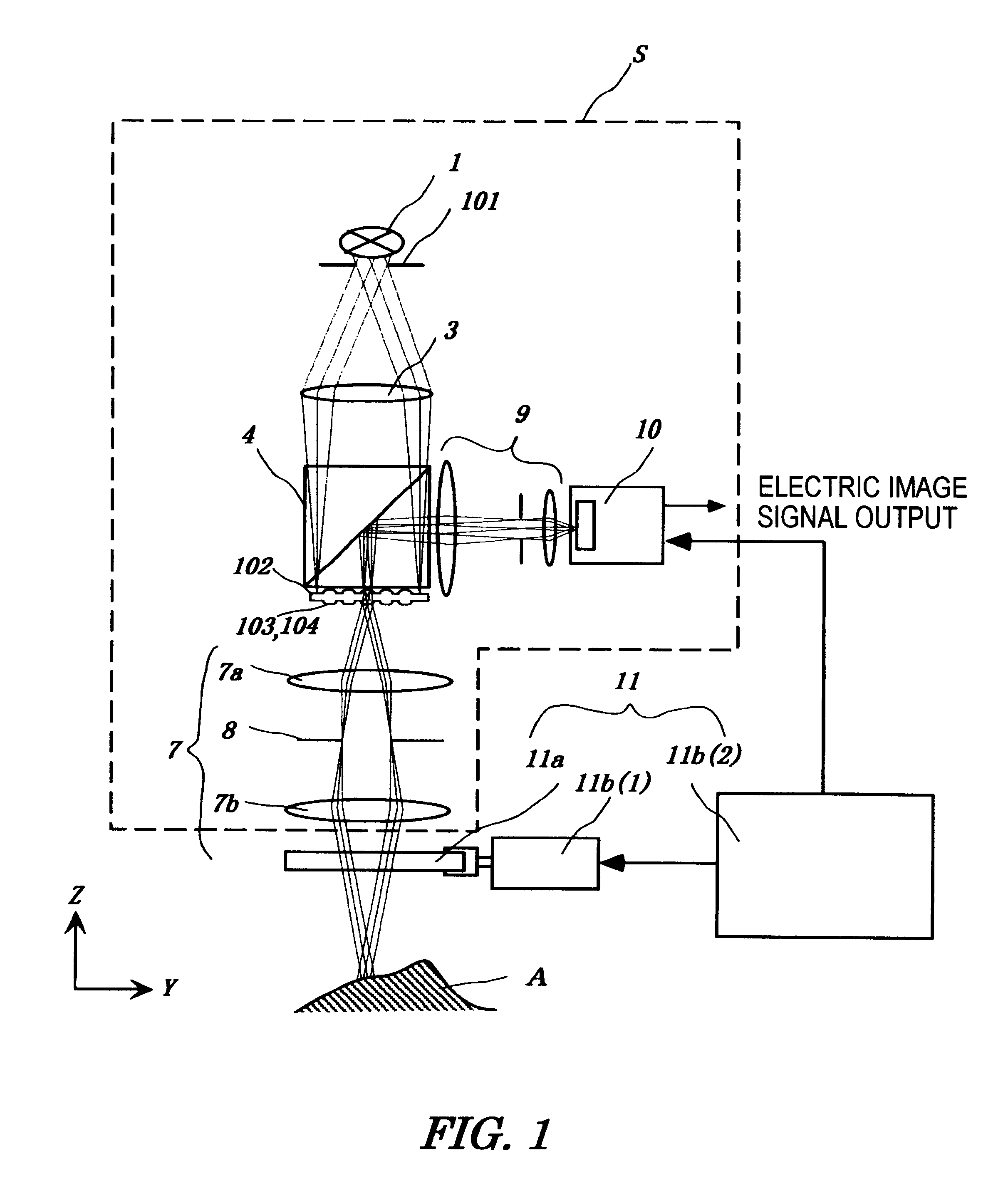
InactiveUS6288382B1Reduce the impactReduce impactRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
The micro-scanning multislit confocal image acquisition apparatus of the present invention is a confocal image acquisition apparatus that comprises a nonscanning multislit confocal image acquisition system using a slit array instead of a pinhole array and a multislit-image microscanning mechanism for moving the image of the slit array in a small back and forth motion with respect to the object during each exposure of the two-dimensional arrayed photodetector in one complete measurement. Microscanning the image of the slit array with an amplitude equal to half the distance between adjacent slits increase the aperture ratio of the pixels to 100 percent, reducing blind regions to zero. As a result, this apparatus can measure a small object that cannot be measured by a conventional nonscanning confocal image acquisition apparatus because of blind regions. Microscanning the image of the slit array can also reduce the effect of speckles, another problem of a conventional nonscanning confocal image acquisition apparatus, by averaging the reflected light passing through each aperture of the slit array.
Owner:TAKAOKA ELECTRIC MFG
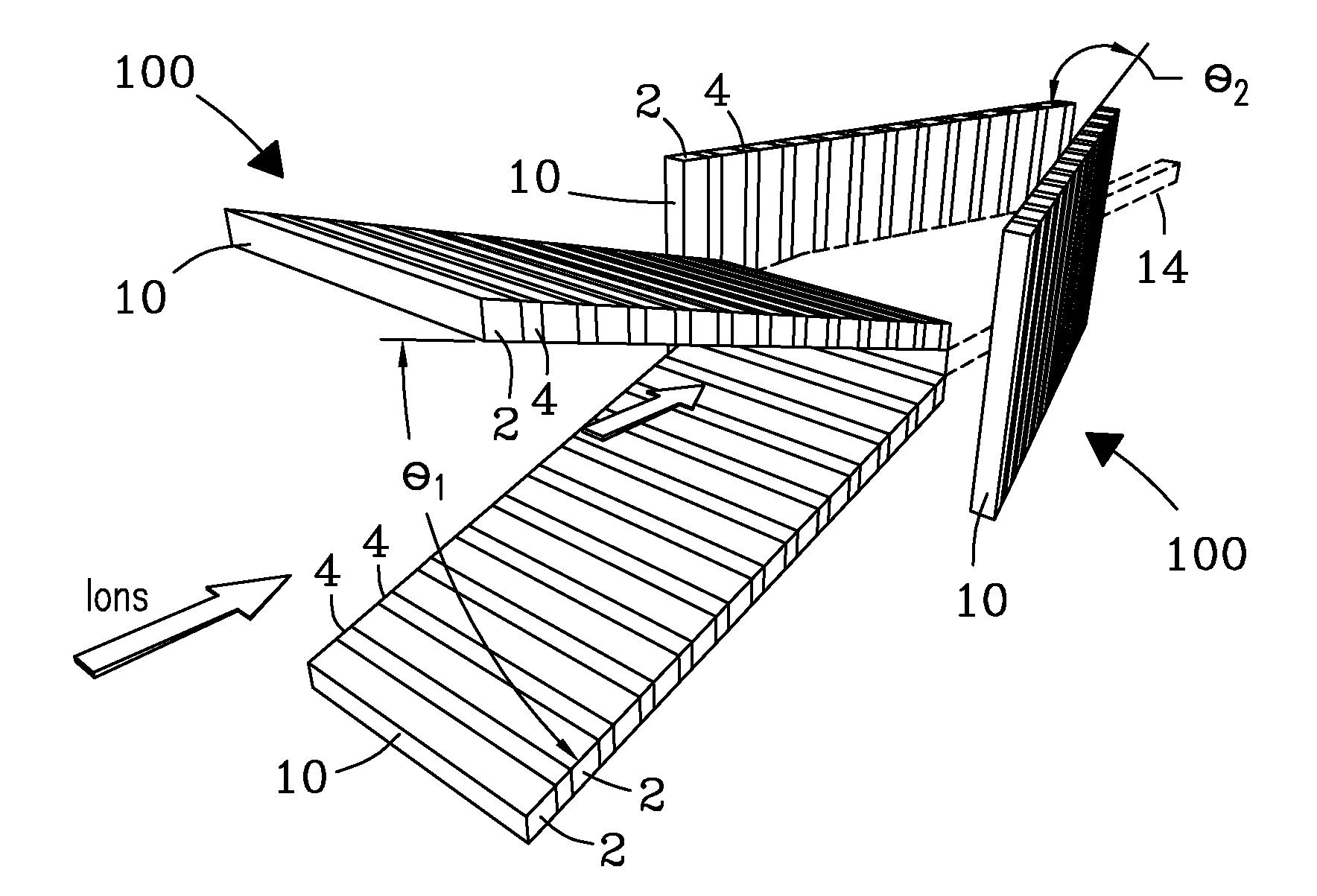
Microchip and wedge ion funnels and planar ion beam analyzers using same
ActiveUS20120261570A1Time-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionMicroscopic scaleMeasurement precision
Electrodynamic on funnels confine, guide, or focus ions in gases using the Dehmelt potential of oscillatory electric field. New funnel designs operating at or close to atmospheric gas pressure are described. Effective on focusing at such pressures is enabled by fields of extreme amplitude and frequency, allowed in microscopic gaps that have much higher electrical breakdown thresholds in any gas than the macroscopic gaps of present funnels. The new microscopic-gap funnels are useful for interfacing atmospheric-pressure ionization sources to mass spectrometry (MS) and on mobility separation (IMS) stages including differential IMS or FAIMS, as well as IMS and MS stages in various configurations. In particular, “wedge” funnels comprising two planar surfaces positioned at an angle and wedge funnel traps derived therefrom can compress on beams in one dimension, producing narrow belt-shaped beams and laterally elongated cuboid packets. This beam profile reduces the ion density and thus space-charge effects, mitigating the adverse impact thereof on the resolving power, measurement accuracy, and dynamic range of MS and IMS analyzers, while a greater overlap with coplanar light or particle beams can benefit spectroscopic methods.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Xerographic micro-assembler
ActiveUS7332361B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesObject basedImage transfer
Xerographic micro-assembler systems and methods are disclosed. The systems and methods involve manipulating charge-encoded micro-objects. The charge encoding identifies each micro-object and specifies its orientation for sorting. The micro-objects are sorted in a sorting unit so that they have defined positions and orientations. The sorting unit has the capability of electrostatically and magnetically manipulating the micro-objects based on their select charge encoding. The sorted micro-objects are provided to an image transfer unit. The image transfer unit is adapted to receive the sorted micro-objects, maintain them in their sorted order and orientation, and deliver them to a substrate. Maintaining the sorted order as the micro-objects are delivered to the substrate may be accomplished through the use of an electrostatic image, as is done in xerography. The substrate with the micro-objects is further processed to interconnect the micro-objects—through electrical wiring, for example—to form the final micro-assembly.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Porous and non-porous nanostructures
ActiveUS20110266521A1Material nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsHigh resistivity siliconMicroscopic scale
Disclosed are a variety of porous and non-porous wire-like structures of microscopic and nanoscopic scale. For instance, disclosed are structures that comprise a porous object that comprises: (i) a first region; and (ii) a second region adjacent to the first region along an axis of the object, where the first region has at least one porous property different from that of the second region. Also disclosed are structures that include: (i) a high resistivity silicon; and (ii) a cross-section that is substantially perpendicular to an axis of the object. Also disclosed are methods of making and using such structures. For instance, the present invention provides methods of making a porous object by: (i) obtaining an etchable substrate; (ii) forming on a surface of the substrate a patterned porosification assisting metal layer that has at least one opening; and (iii) subsequently exposing the substrate to a first etching solution and a second etching solution to form respectively a first region and a second region of a porous object.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
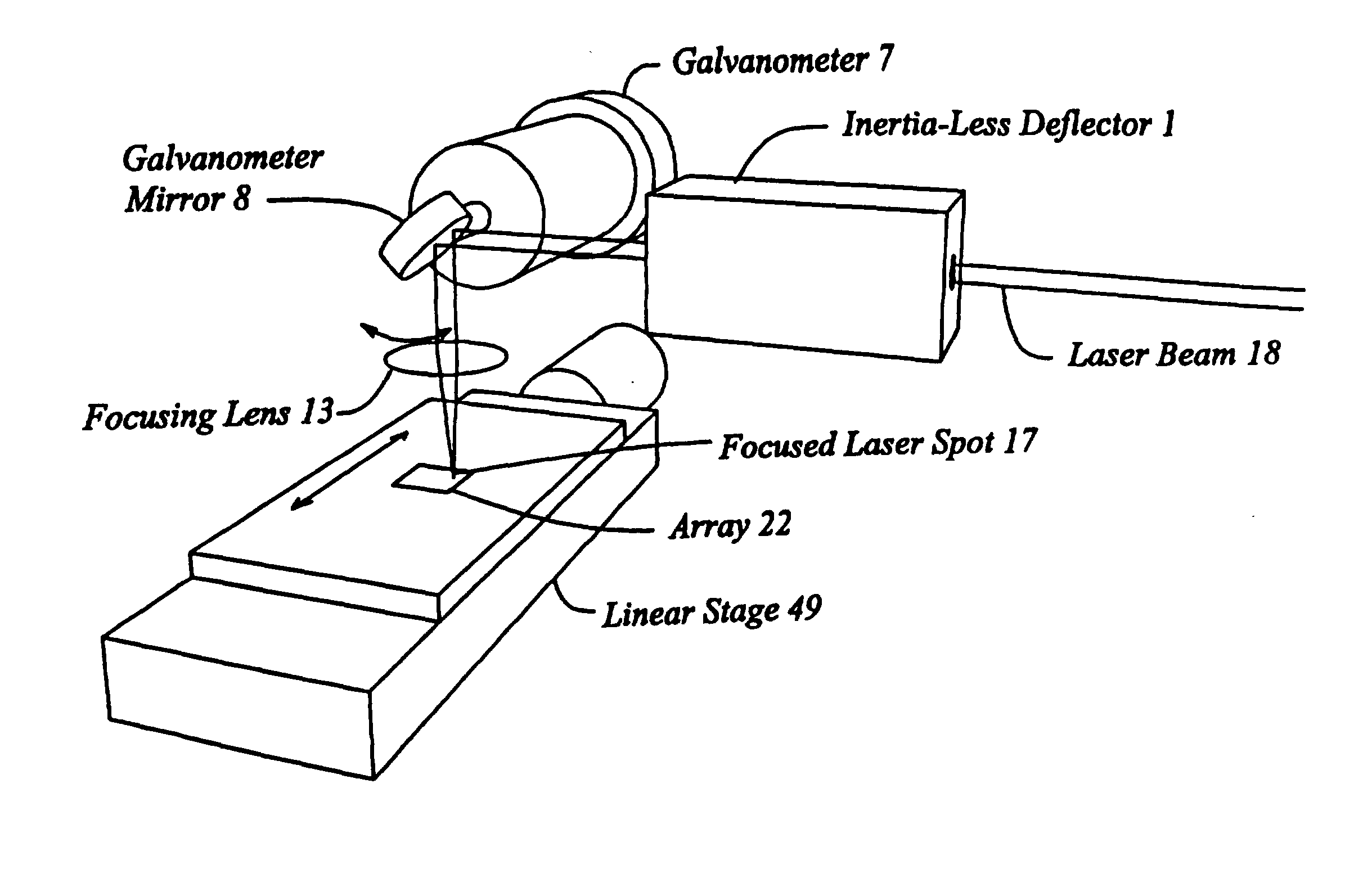
Scanning microscopy, fluorescence detection, and laser beam positioning
InactiveUS20030156323A1Diameter of to varyEnsure high efficiency and accuracyMirrorsMaterial analysis by optical meansWide areaGrating
High speed, wide area microscopic scanning or laser positioning is accomplished with an inertia-less deflector (for example an acousto-optic or electro-optic deflector) combined with a high speed wide area microscopic scanning mechanism or laser positioner mechanism that has inertia, the motion of the inertia-less deflector specially controlled to enable a focused spot to stabilize, for example to stop and dwell or be quickly aimed. It leads to improved data acquisition from extremely small objects and higher speed operation. In the case of fluorescence reading of micro-array elements, dwelling of fluorophore-exciting radiation in a spot that is relatively large enables obtaining the most fluorescent photons per array element, per unit time, a winning criterion for reducing fluorophore saturation effects. The same inertia-less deflector performs stop and dwell scanning, edge detection and raster scans. Automated mechanism for changing laser spot size enables selection of spot size optimal for the action being performed.
Owner:OVERBECK JAMES W
Microfluidic chips and assay systems
ActiveUS7959875B2Efficient executionSimple designValve arrangementsHeating or cooling apparatusFluid transportEngineering
The systems and methods described herein include a microfluidic chip having a plurality of microfeatures interconnected to provide a configurable fluid transport system for processing at least one reagent. Inserts are provided to removably interfit into one or more of the microfeatures of the chip, wherein the inserts include sites for interactions with the reagent. As will be seen from the following description, the microfluidic chip and the inserts provide an efficient and accurate approach for conducting parallel assays.
Owner:RHEONIX INC
Method for patterning thin films
InactiveUS20010006766A1Great throughput and outputReduce impactPhotography auxillary processesAntenna supports/mountingsResistMicroscopic scale
Patterned articles, such as RFID antenna, are made by subablation, a process comprising the steps of: A. providing a substrate having a coating, such as a metal or metal oxide, and an interface comprising the thin region where the coating and the substrate are closest to each other; B. exposing at least one part of the total area of the coating to a flux of electromagnetic energy, Such as a focused excimer laser beam, sufficient to disrupt the interface but insufficient to ablate the coating, and C. removing the parts of the coating in registry with the portion of the interface area that was disrupted, by means such as ultrasonic agitation. The process has advantages over photo-resist processes in that there is no residual chemical resist left on the product and no undercutting of the pattern or image. It has advantages over laser ablation processes in that higher throughput is possible at the same energy level and there is no microscopic debris left on the product surface.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
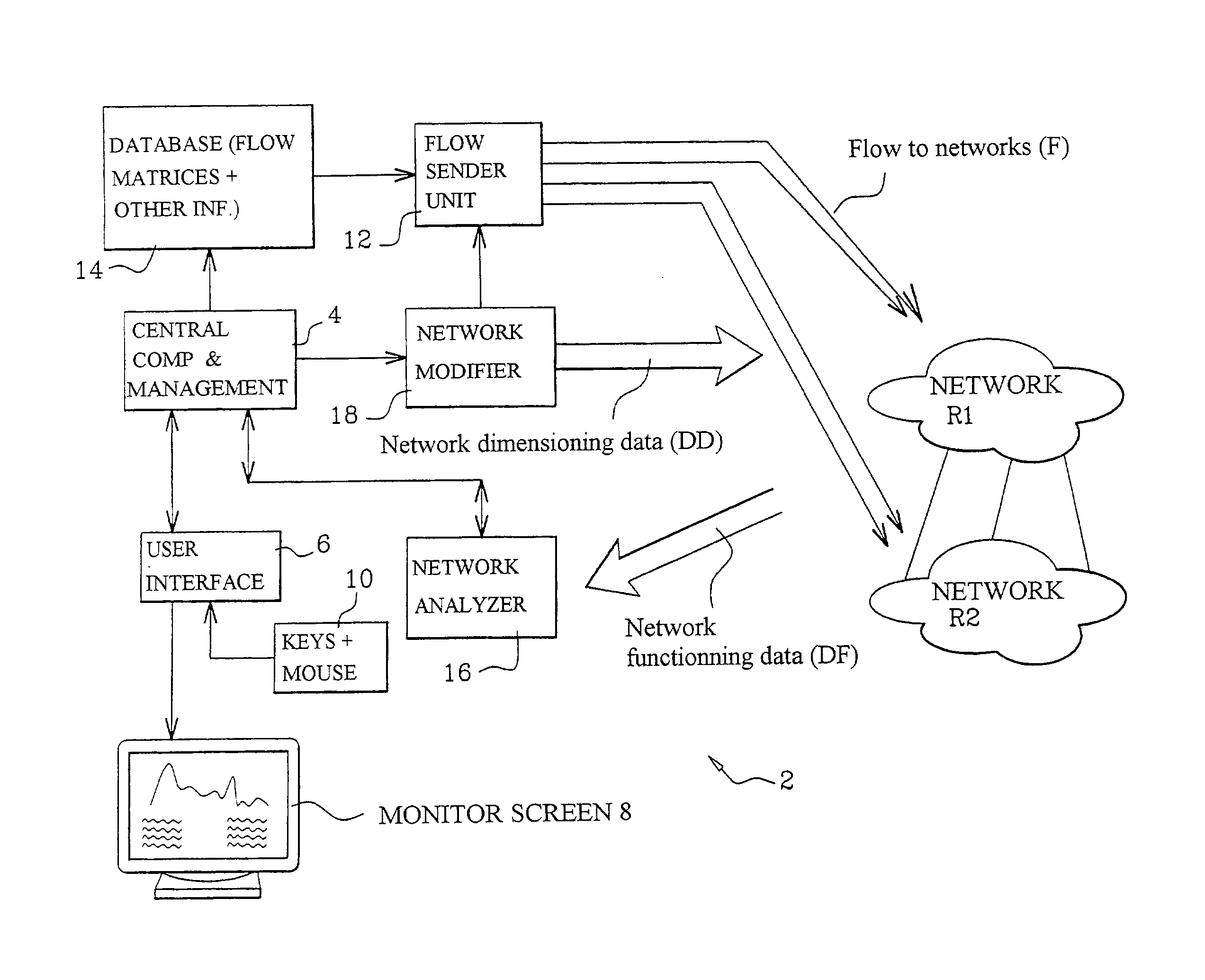
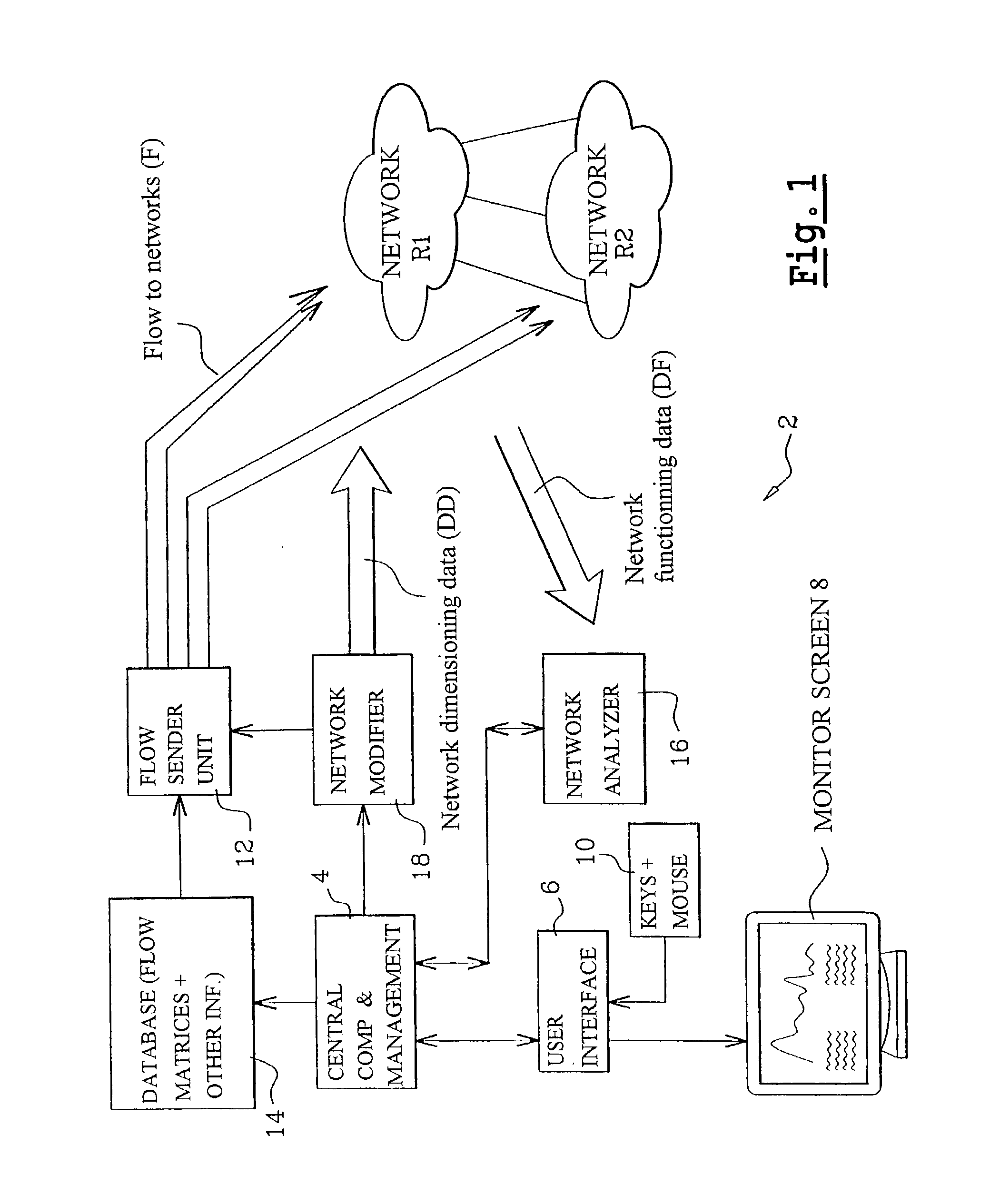
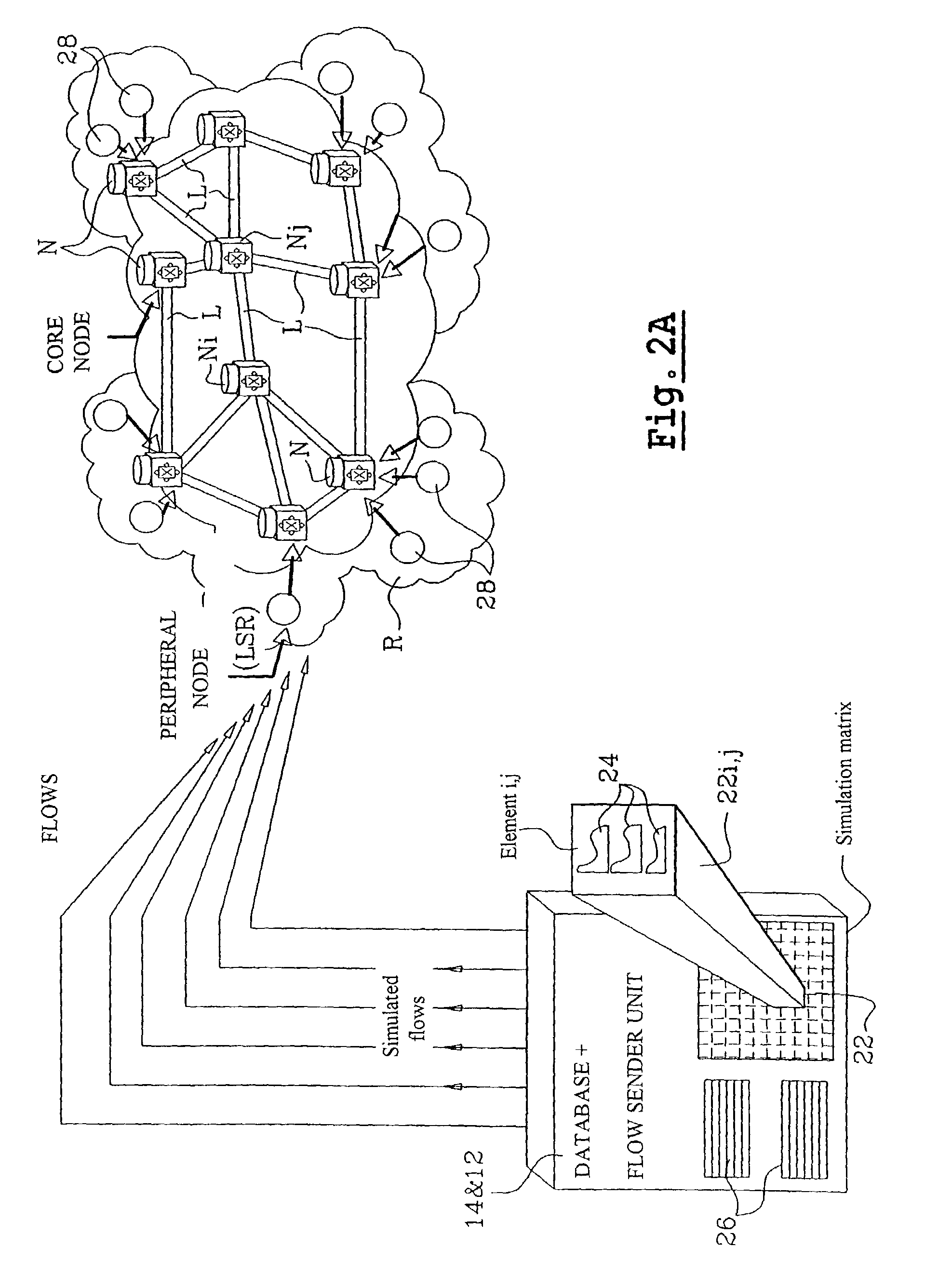
Method and a system for simulating the behavior of a network and providing on-demand dimensioning
InactiveUS20030061017A1Data switching networksSpecial data processing applicationsTraffic intensityMicroscopic scale
The invention simulates the behavior of a network including a set of network elements by introducing into the network a parametered flow intended to simulate a constraint on a network element. The flow can model the variation in time of the traffic intensity in the network in relation to the or each element to which a flow is addressed in the context of the simulation, and can feature a modulation on a macroscopic timescale and stochastic fluctuations on a microscopic scale. The invention further provides on-demand dimensioning of a network by uprating, during the simulation, the levels of performance of elements that have manifested a weakness in relation the flow at the time of the simulation. The field of application targets any type of network: circuit mode or packet mode data, electronic or optical networks, and even networks for transporting material or nonmaterial commodities.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
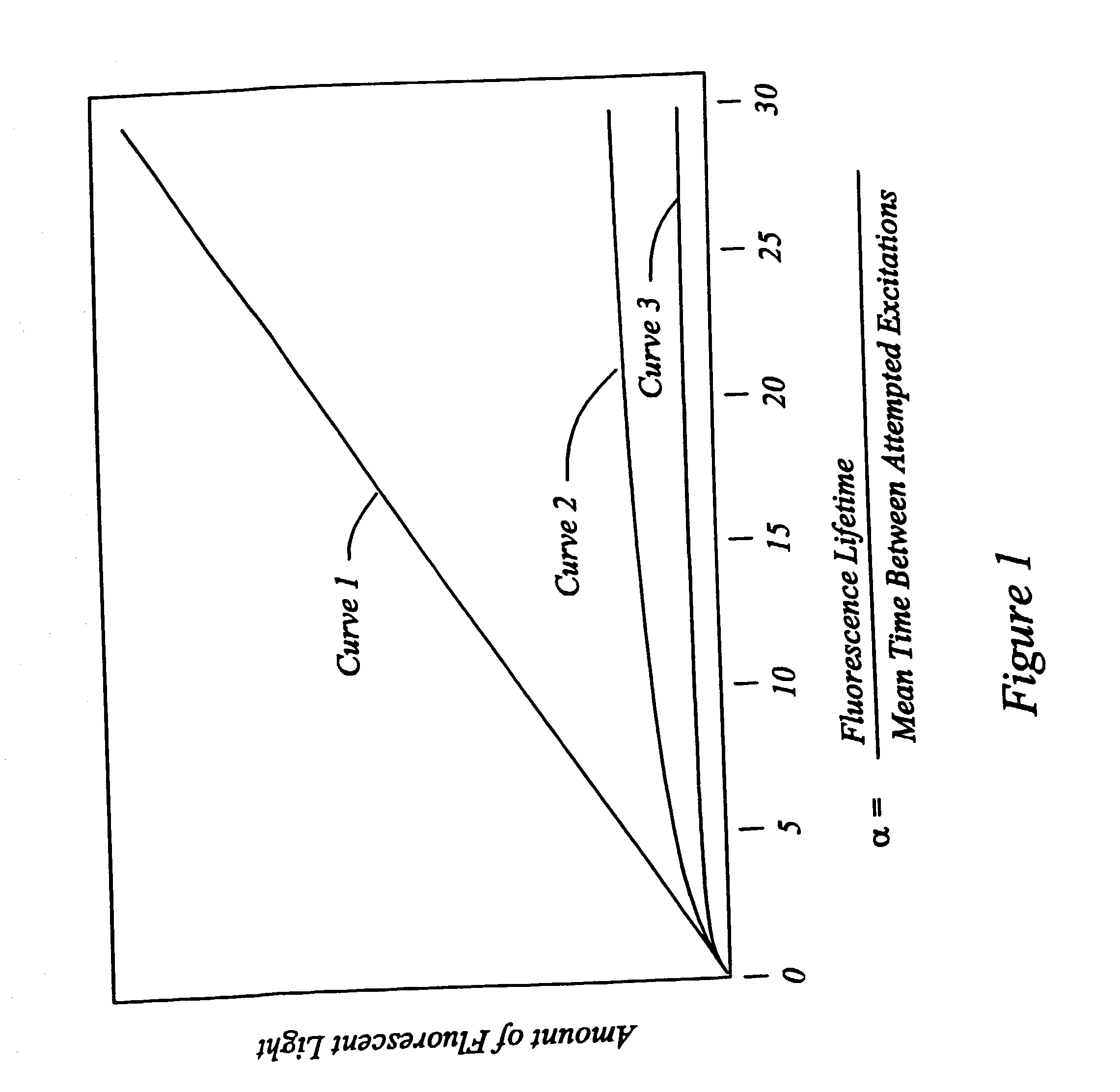
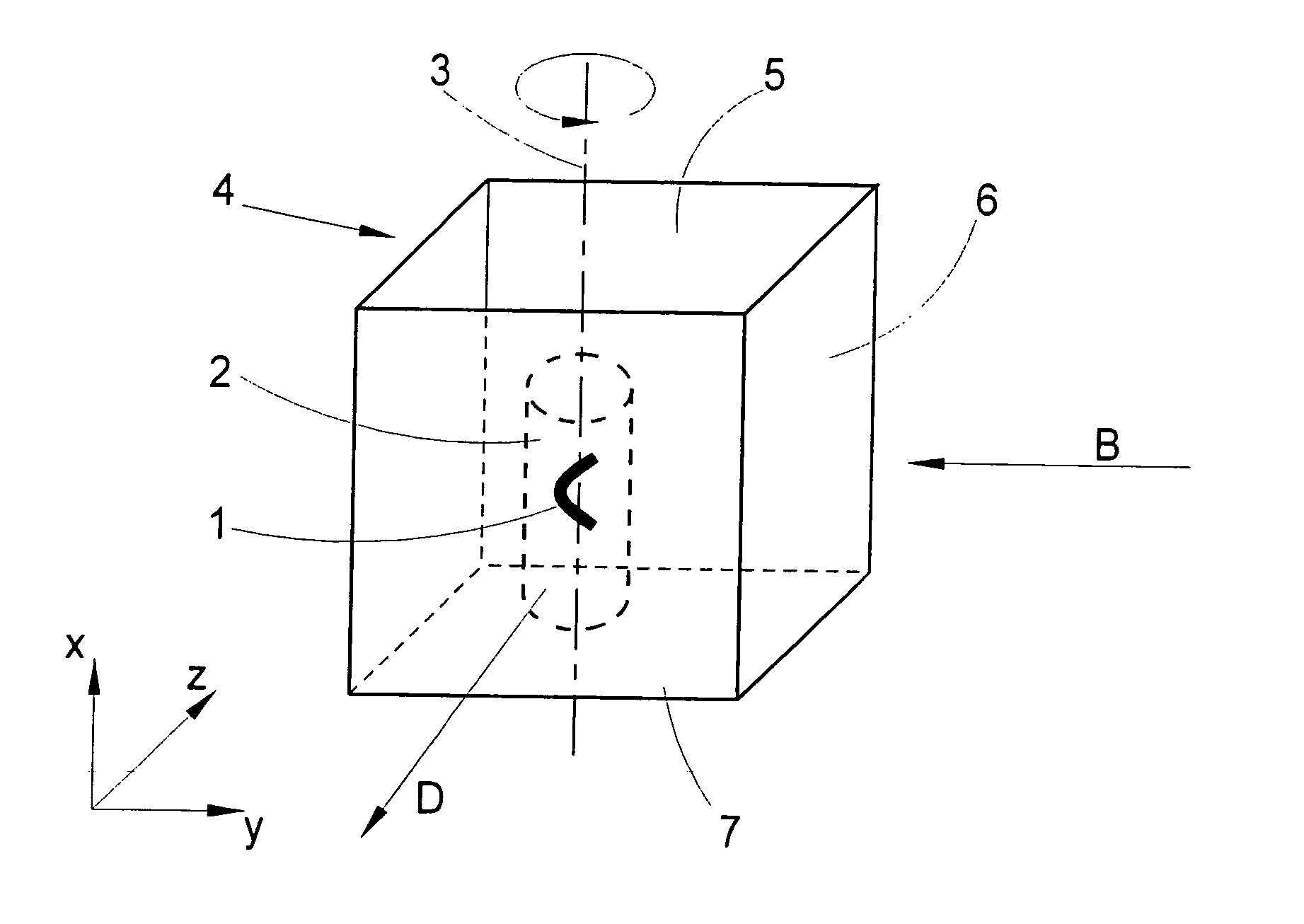
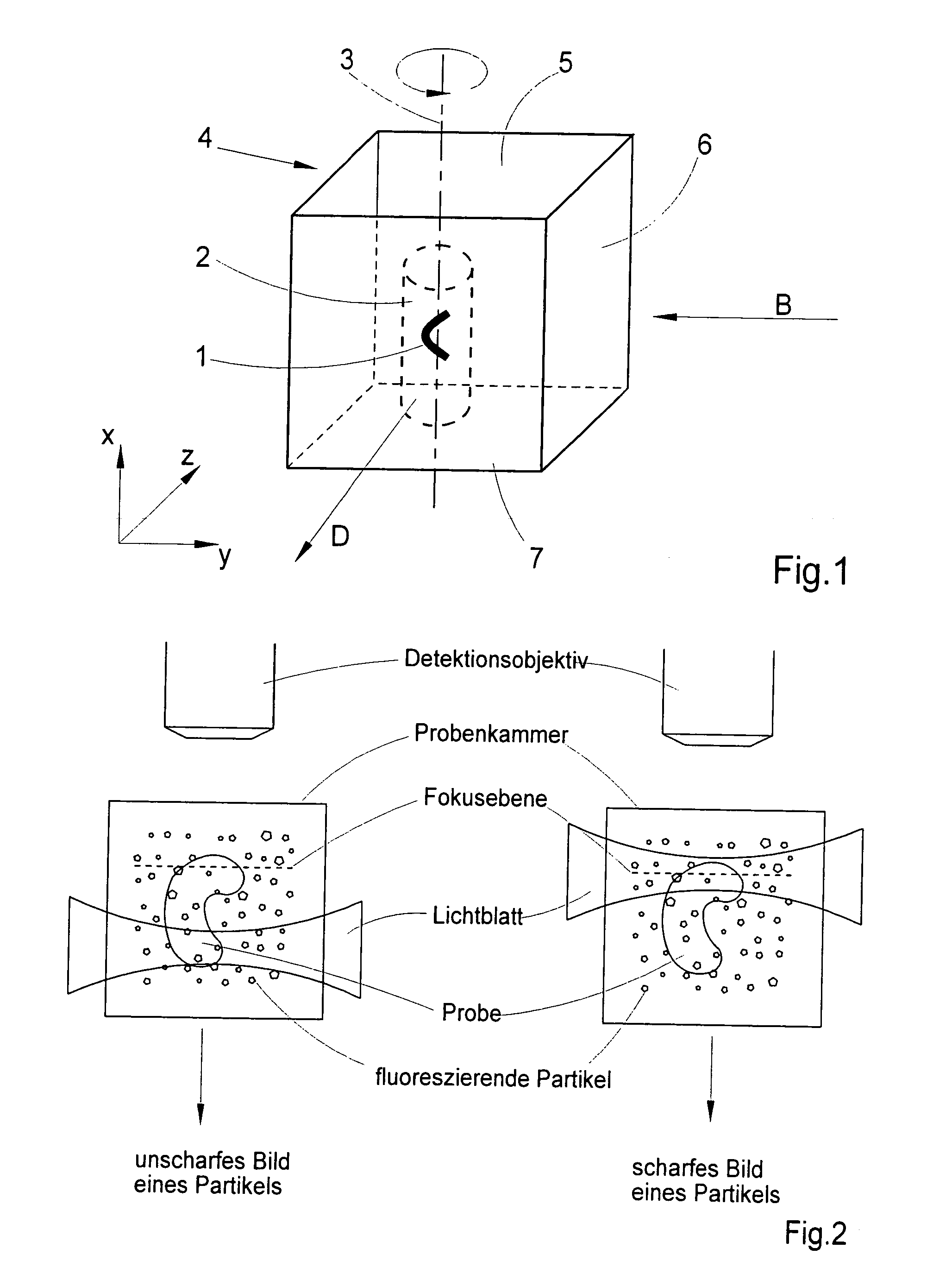
Method for the microscopic three-dimensional reproduction of a sample
InactiveUS20100201784A1Avoid shadow effectMore resolutionImage analysisMicroscopesSpatially resolvedFluorescence
A method for the three-dimensional imaging of a sample in which image information from different depth planes of the sample is stored in a spatially resolved manner, and the three-dimensional image of the sample is subsequently reconstructed from this stored image information is provided. A reference structure is applied to the illumination light, at least one fluorescing reference object is positioned next to or in the sample, images of the reference structure of the illumination light, of the reference object are recorded from at least one detection direction and evaluated. The light sheet is brought into an optimal position based on the results and image information of the reference object and of the sample from a plurality of detection directions is stored. Transformation operators are obtained on the basis of the stored image information and the reconstruction of the three-dimensional image of the is based on these transformation operators.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
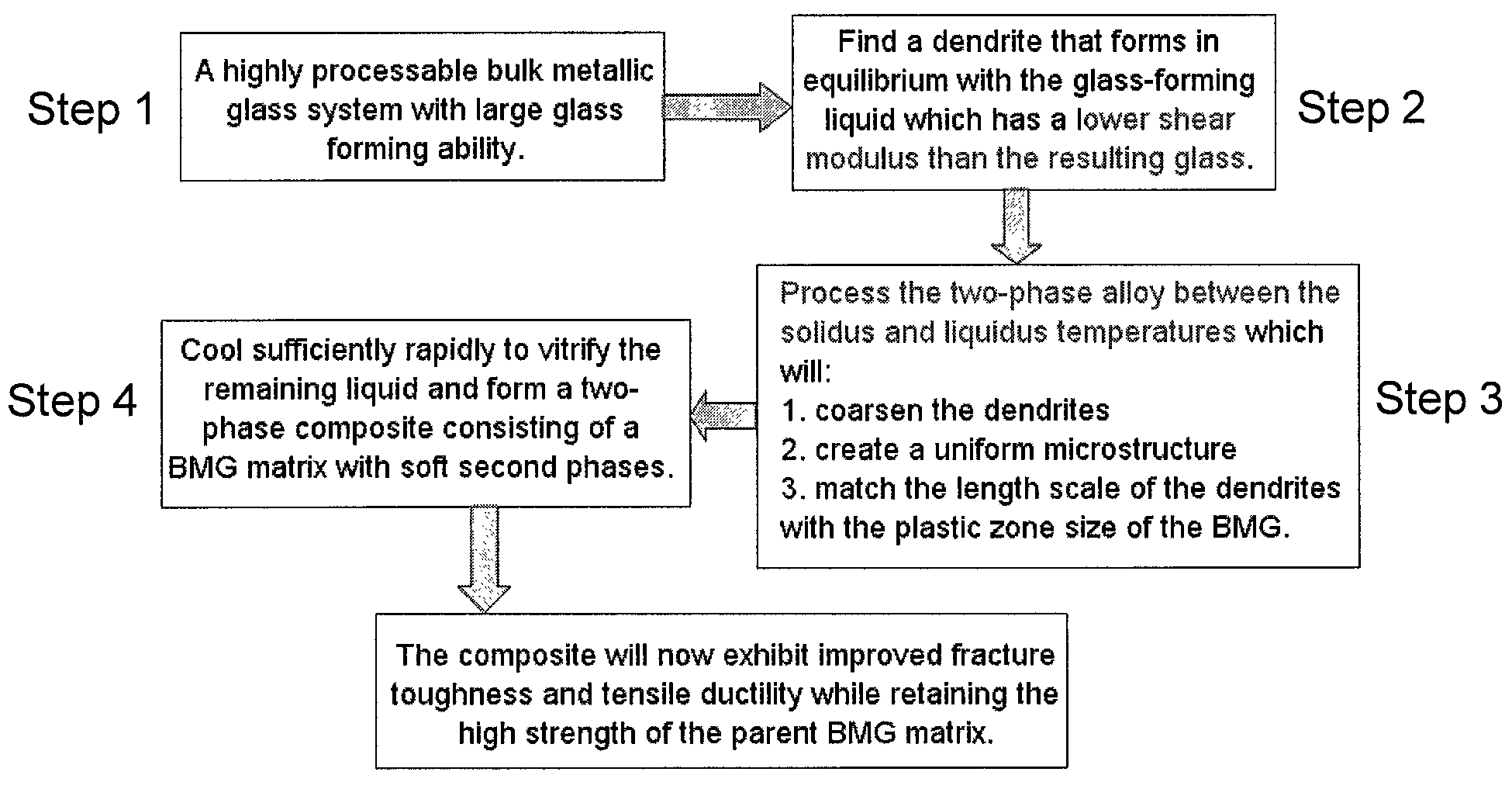
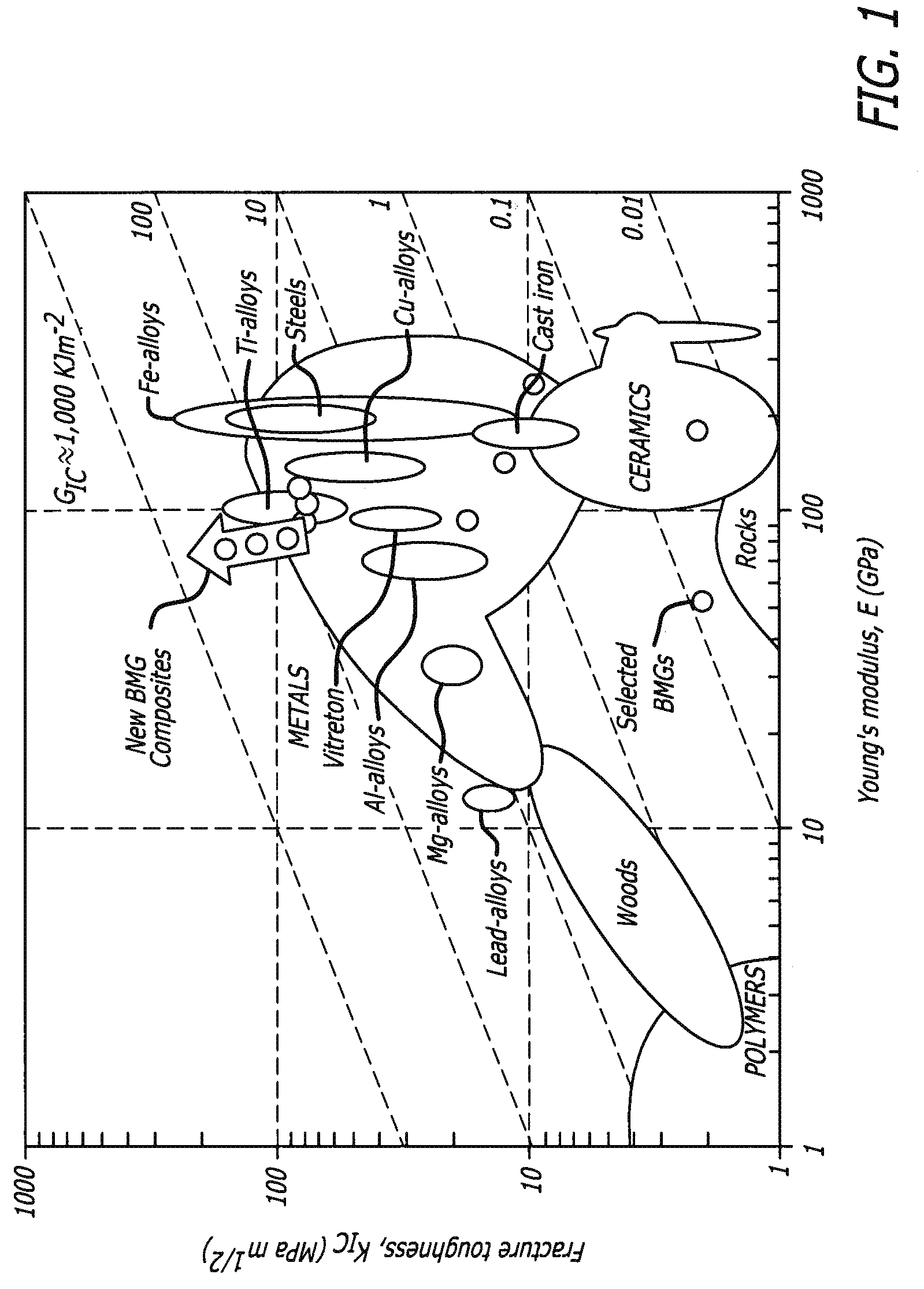
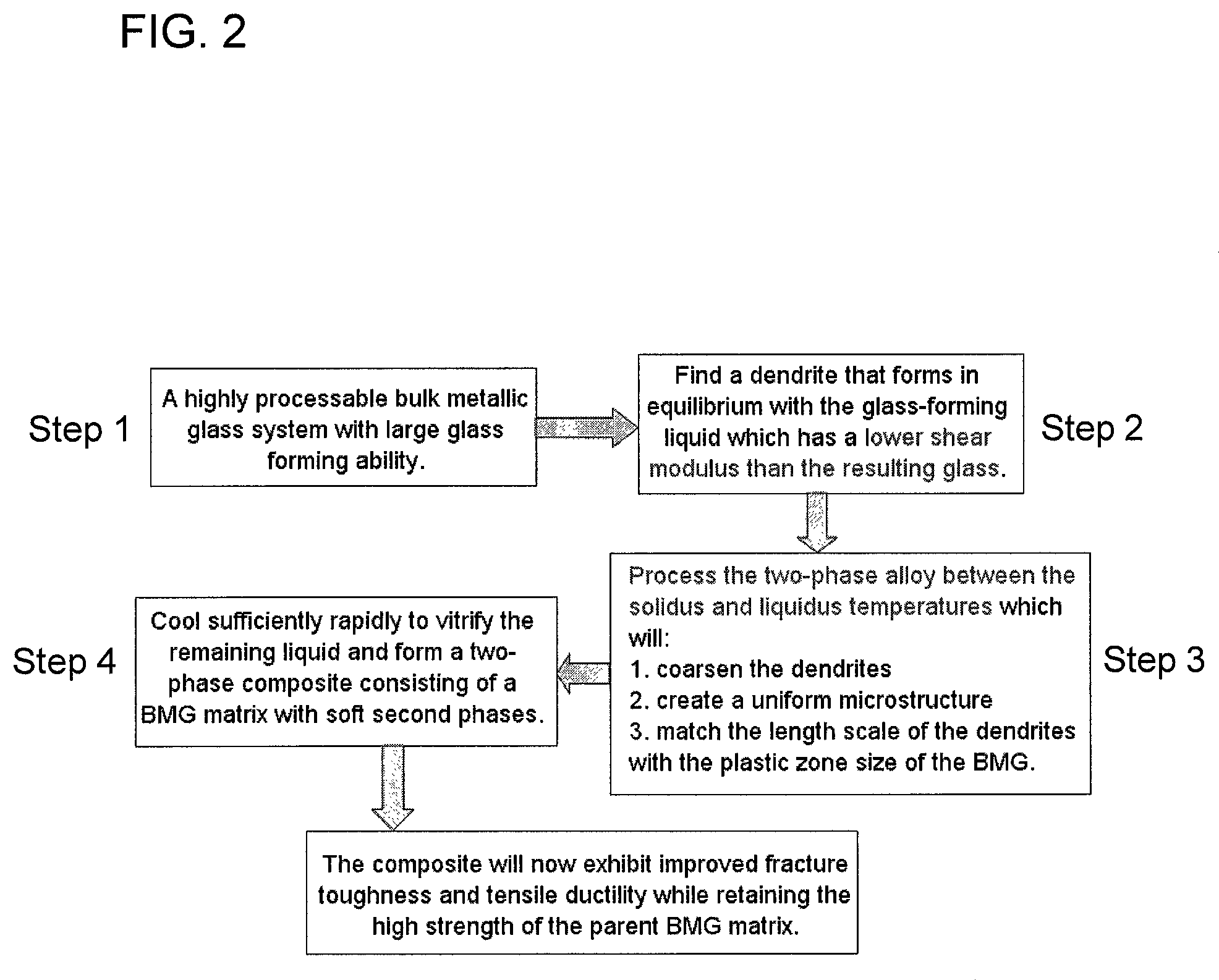
Semi-solid processing of bulk metallic glass matrix composites
A method of forming bulk metallic glass engineering materials, and more particularly a method for forming coarsening microstructures within said engineering materials is provided. Specifically, the method forms ‘designed composites’ by introducing ‘soft’ elastic / plastic inhomogeneities in a metallic glass matrix to initiate local shear banding around the inhomogeneity, and matching of microstructural length scales (for example, L and S) to the characteristic length scale RP (for plastic shielding of an opening crack tip) to limit shear band extension, suppress shear band opening, and avoid crack development.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Kits and devices for detecting analytes
ActiveUS20120045826A1Easy to operate manuallyLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSpecific detectionAnalyte
The invention provides devices that improve tests for detecting specific cellular, viral, and molecular targets in clinical, industrial, or environmental samples. The invention permits efficient detection of individual microscopic targets at low magnification for highly sensitive testing. The invention does not require washing steps and thus allows sensitive and specific detection while simplifying manual operation and lowering costs and complexity in automated operation. In short, the invention provides devices that can deliver rapid, accurate, and quantitative, easy-to-use, and cost-effective tests.
Owner:FIRST LIGHT BIOSCI INC
Reversibly adaptive rough micro- and nano-structures
Reversibly adaptive rough structures, comprising: a substrate; a plurality of raised elements on the substrate, the raised elements mutually spaced apart by channel regions on the substrate, each of the raised elements having a lateral surface and a distal end; the lateral surface, the distal end and the channel regions having hydrophobic molecules thereon; and the distal end having reversibly adaptive bristles thereon, the reversibly adaptive bristles being convertible between relatively hydrophilic and hydrophobic states by the application of an external stimulus. Techniques for making reversibly adaptive rough structures.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Direct Nanoscale Patterning of Metals Using Polymer Electrolytes
InactiveUS20090050487A1Improve throughputRobust and commercially attractive manufacturing pathwayMachining electrodesMaterial nanotechnologySpatial OrientationsElectrical conductor
Disclosed herein are electrochemical fabrication platforms for making structures, arrays of structures and functional devices having selected nanosized and / or microsized physical dimensions, shapes and spatial orientations. Methods, systems and system components use an electrochemical stamping tool such as solid state polymeric electrolytes for generating patterns of relief and / or recessed features exhibiting excellent reproducibility, pattern fidelity and resolution on surfaces of solid state ionic conductors and in metal. Electrochemical stamping tools are capable high throughput patterning of large substrate areas, are compatible with commercially attractive manufacturing pathways to access a range of functional systems and devices including nano- and micro-electromechanical systems, sensors, energy storage devices, metal masks for printing, interconnects, and integrated electronic circuits.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com