Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
14812results about "Microscopes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and system for drying a substrate
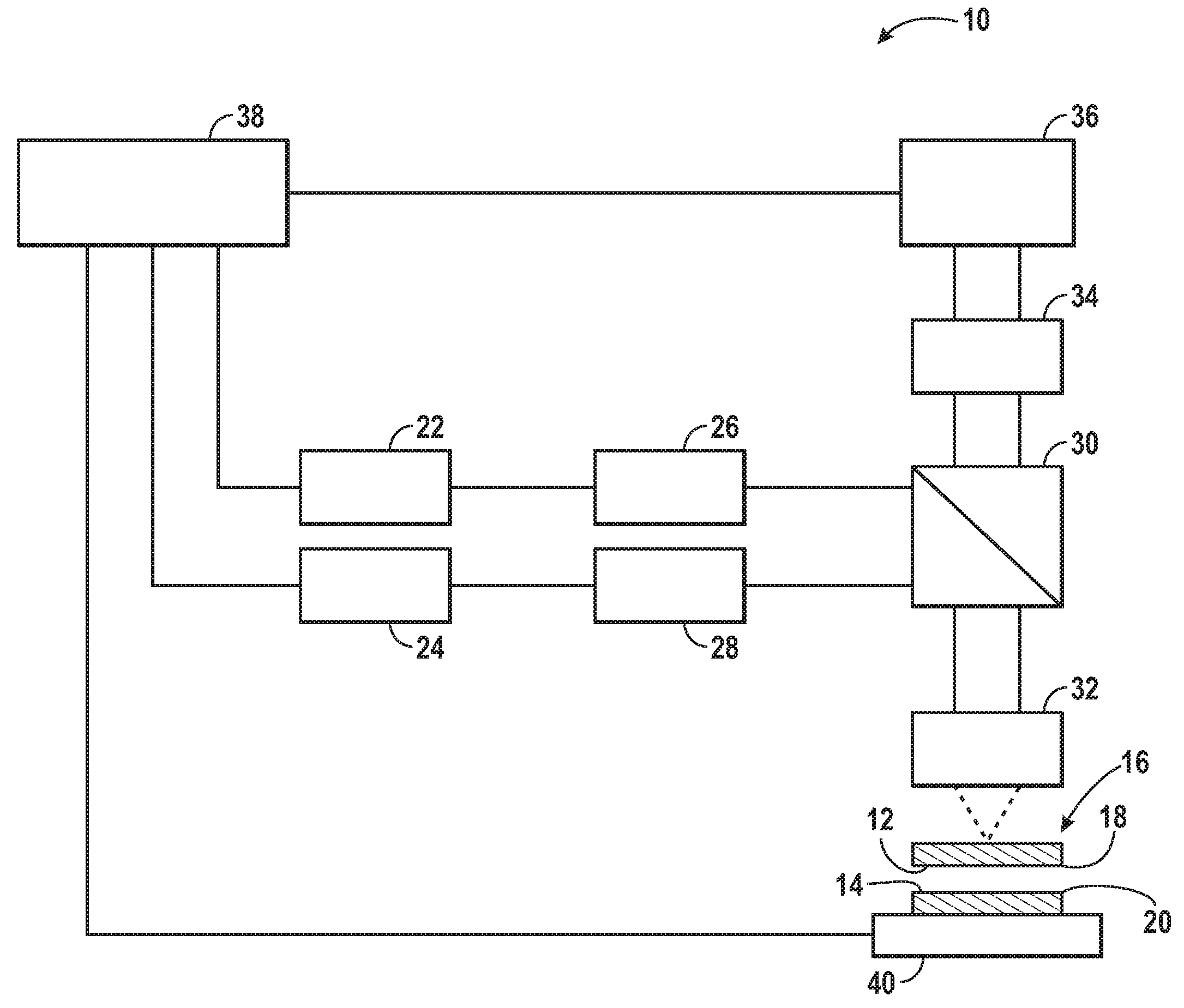
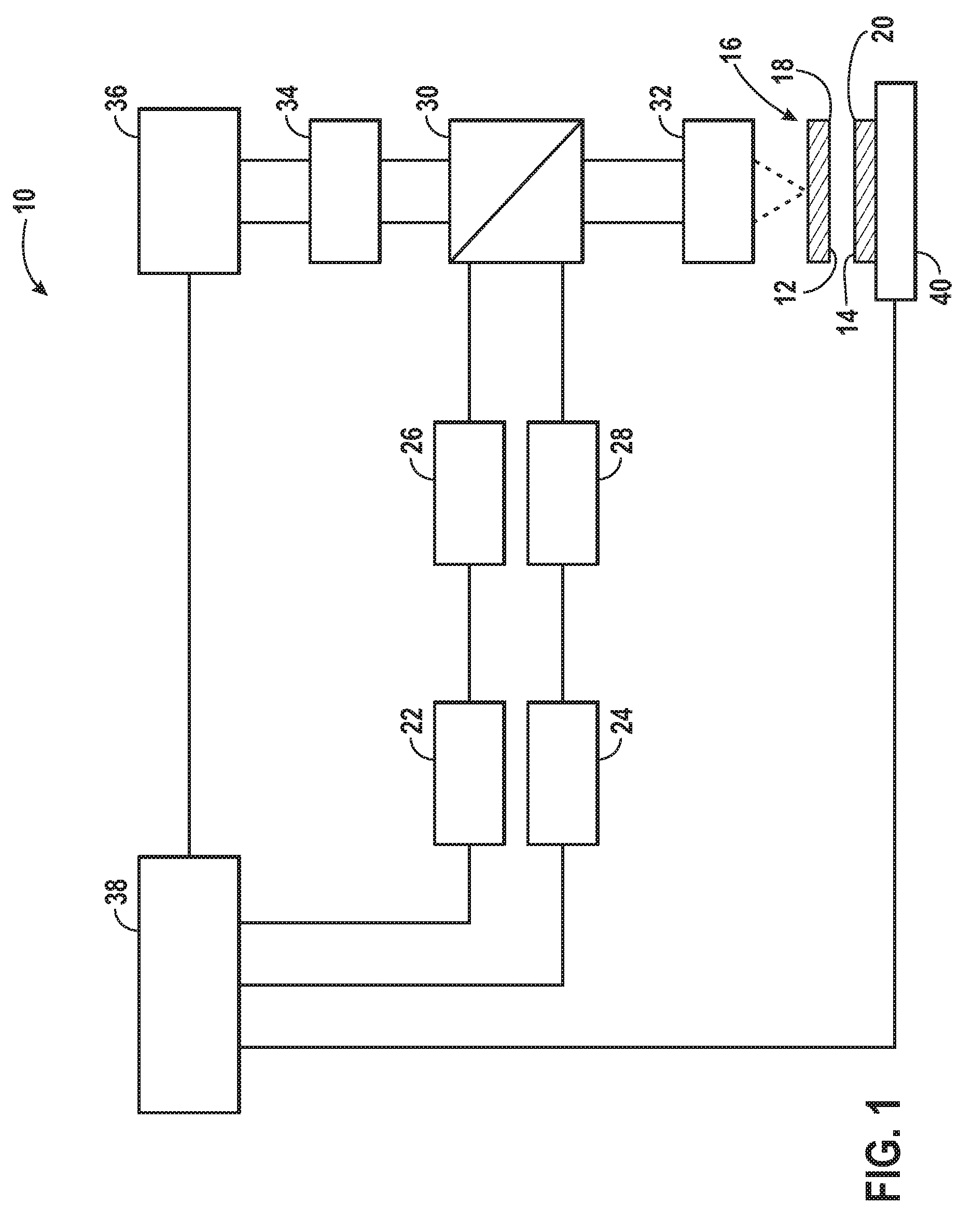
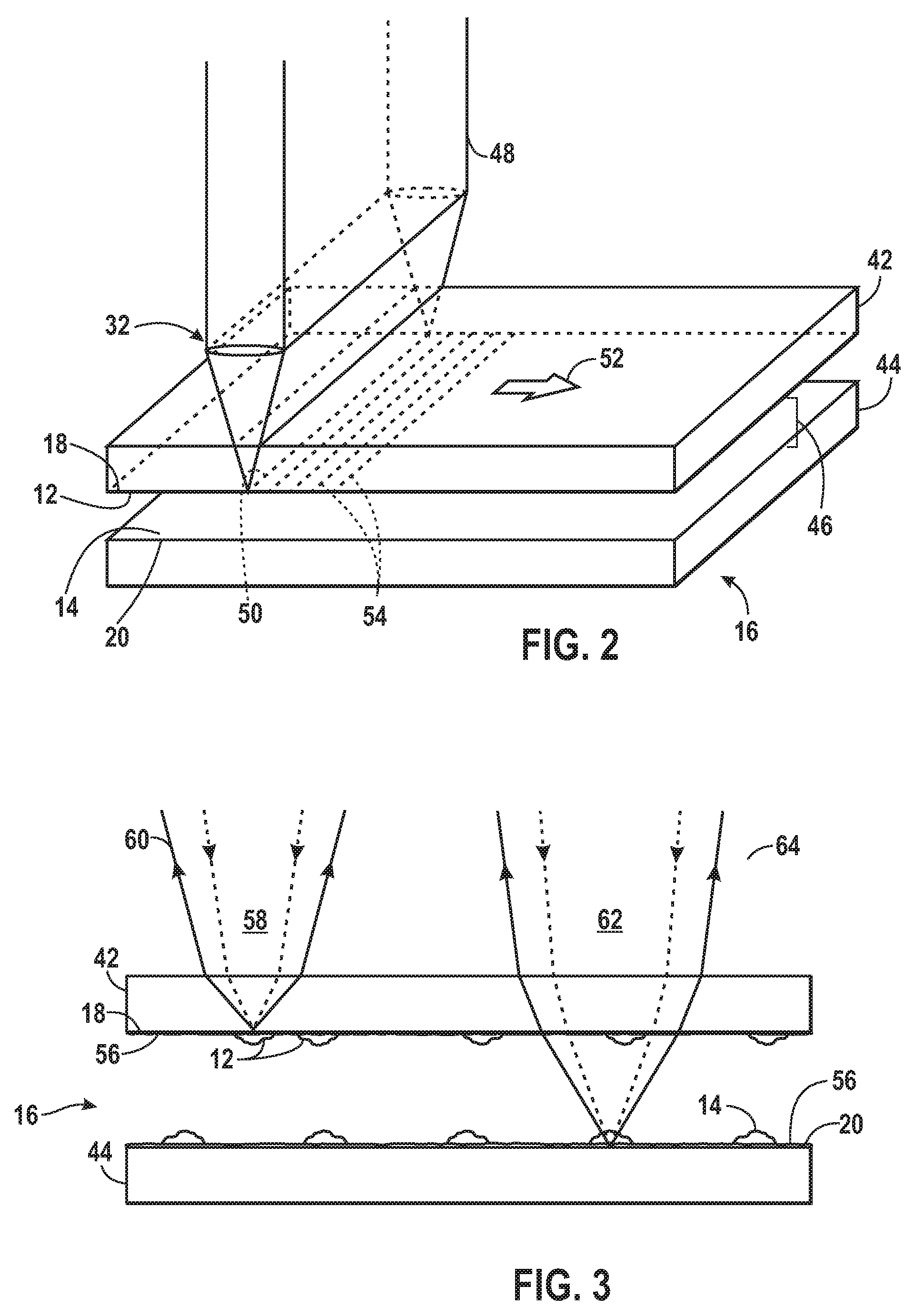
ActiveUS20050046934A1Good pattern uniformityImprove uniformityMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusCooking & bakingThin membrane
A method and system is described for drying a thin film on a substrate following liquid immersion lithography. Drying the thin film to remove immersion fluid from the thin film is performed prior to baking the thin film, thereby reducing the likely hood for interaction of immersion fluid with the baking process. This interaction has been shown to cause non-uniformity in critical dimension for the pattern formed in the thin film following the developing process.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
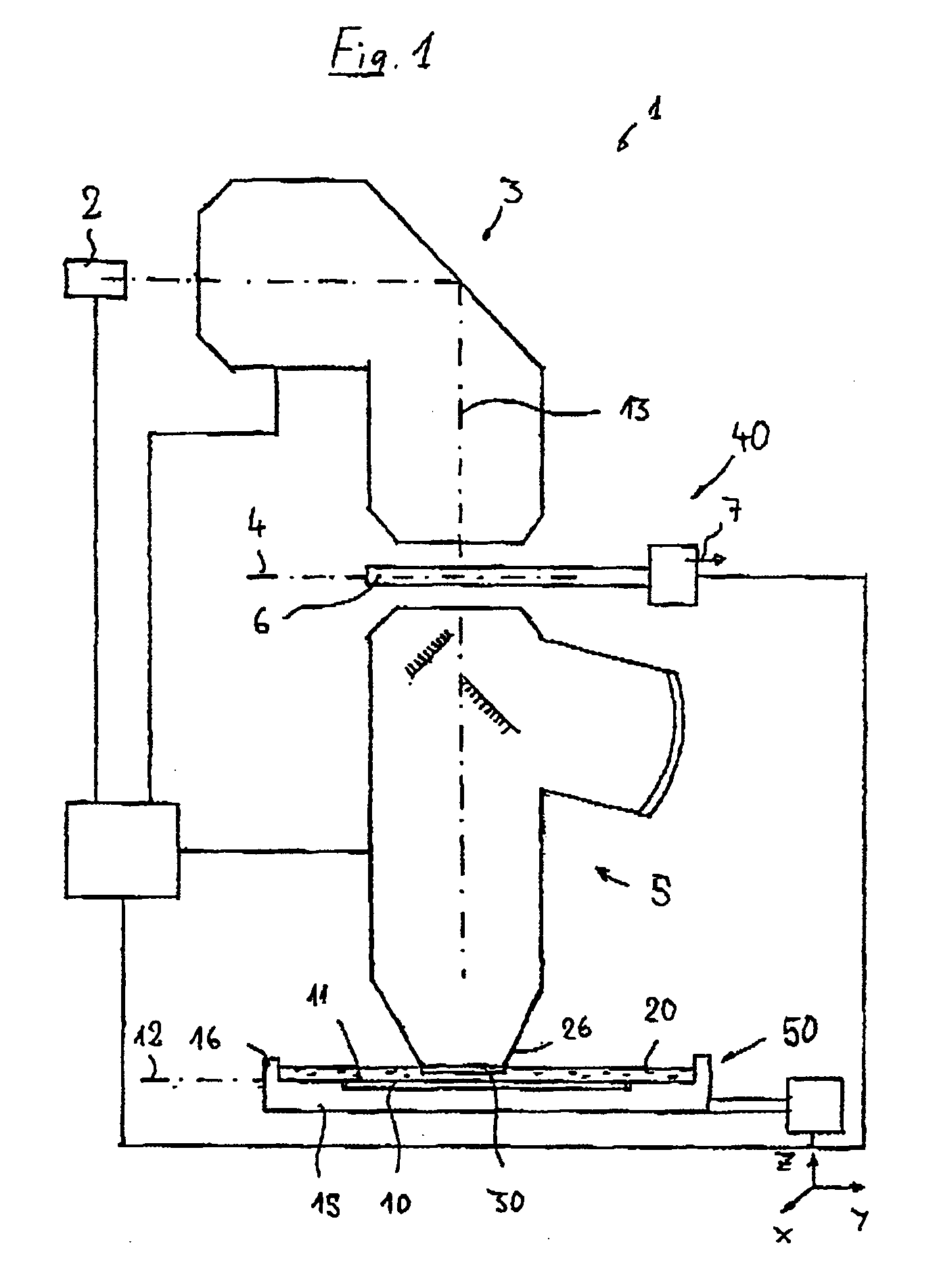
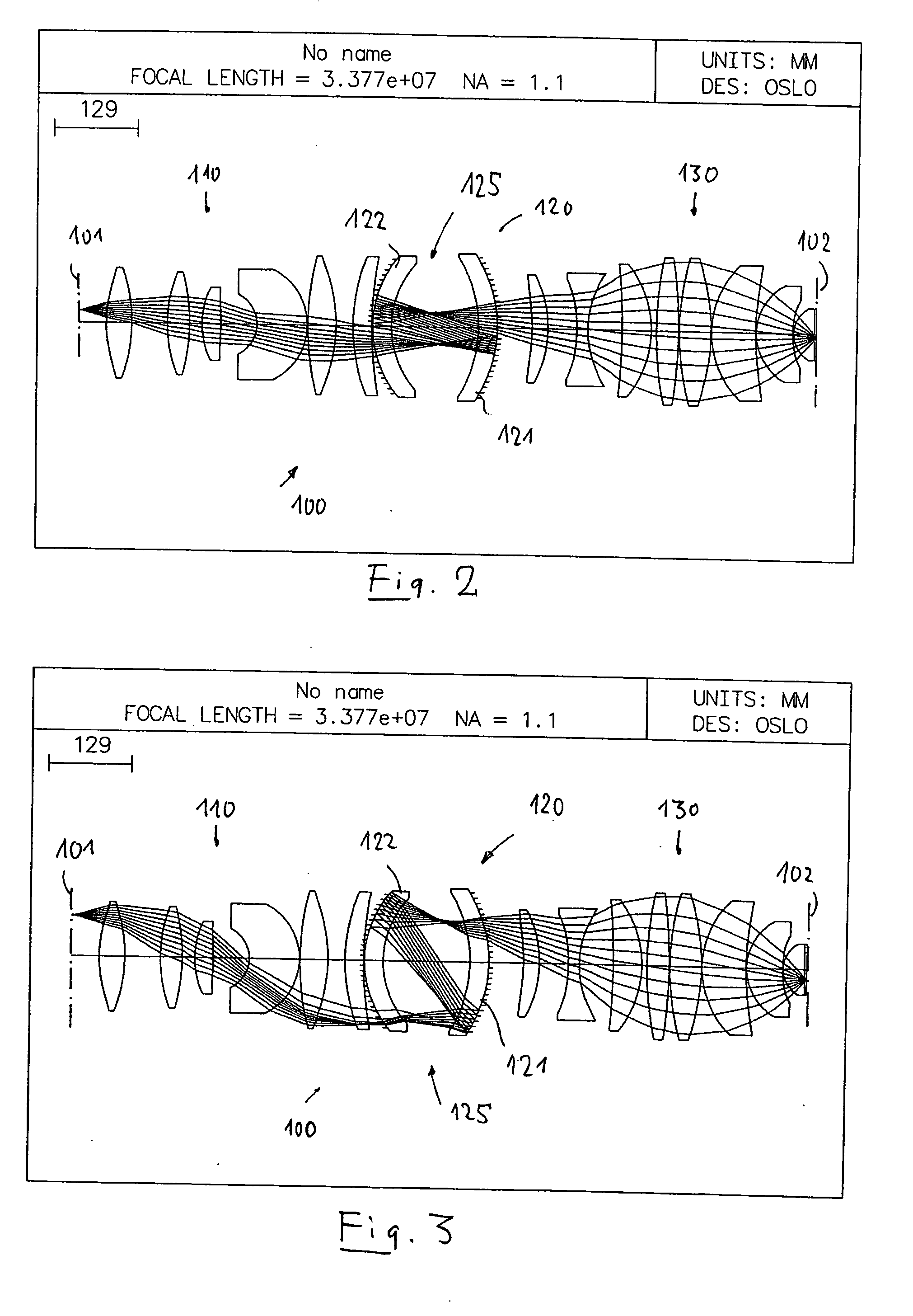
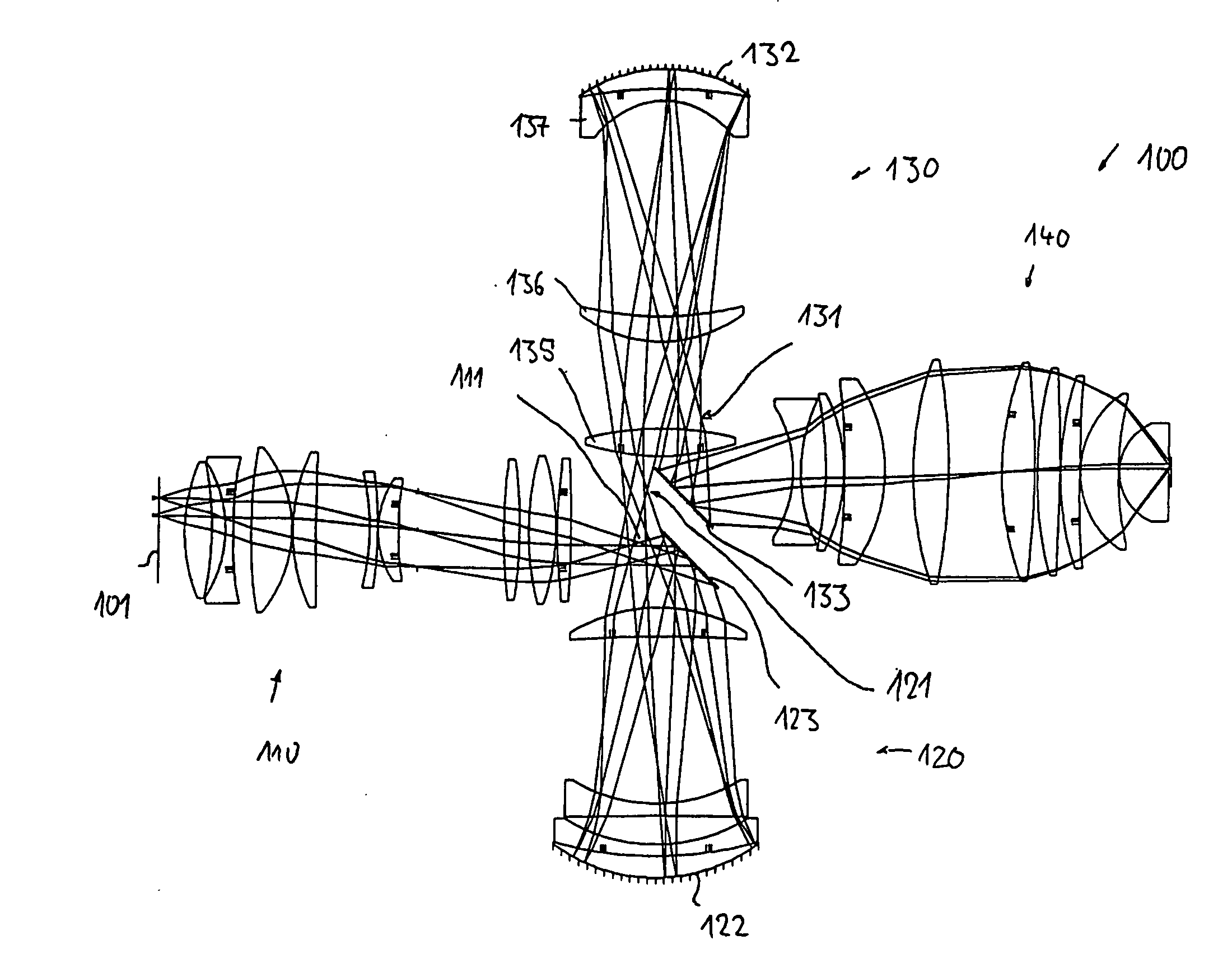
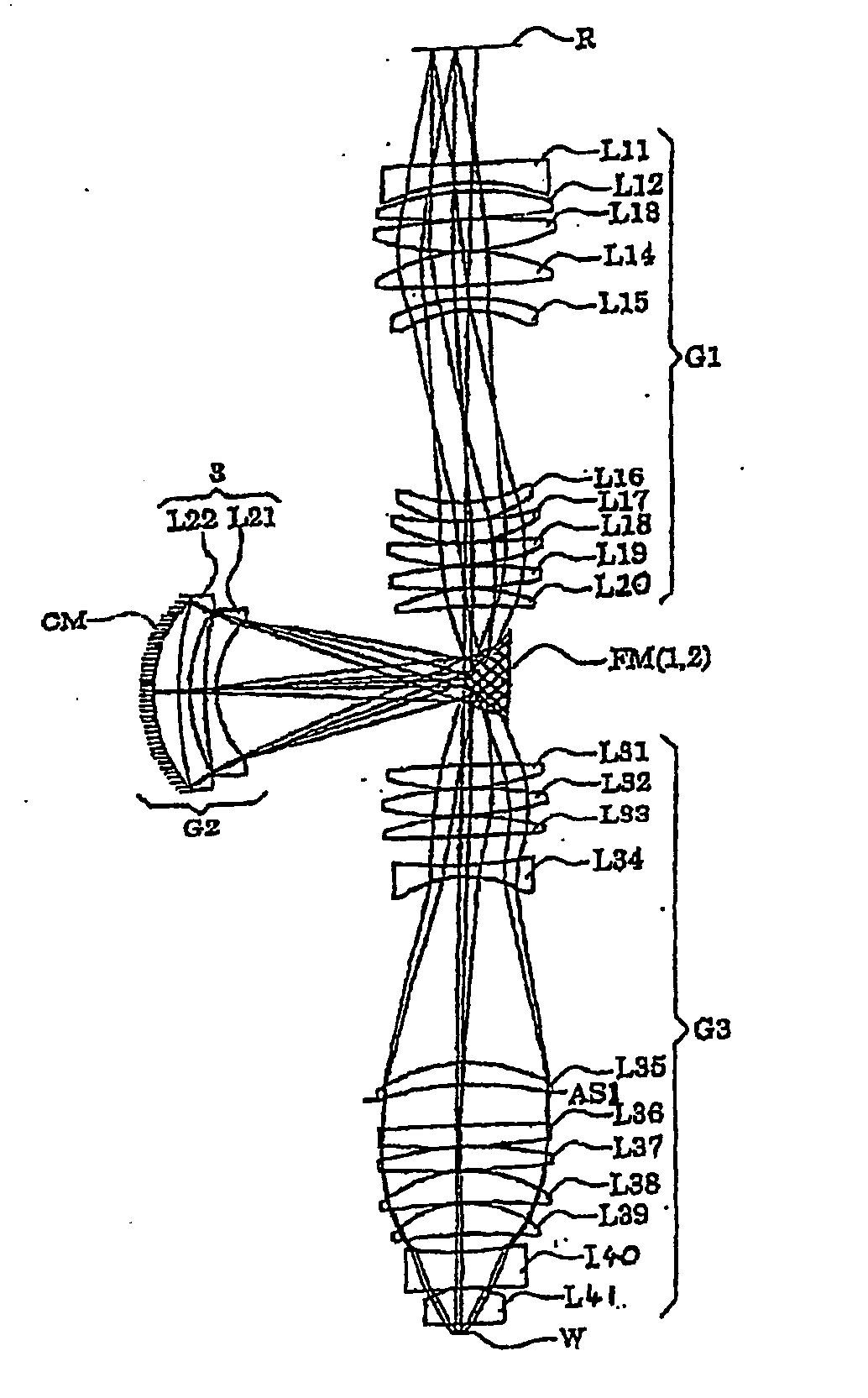
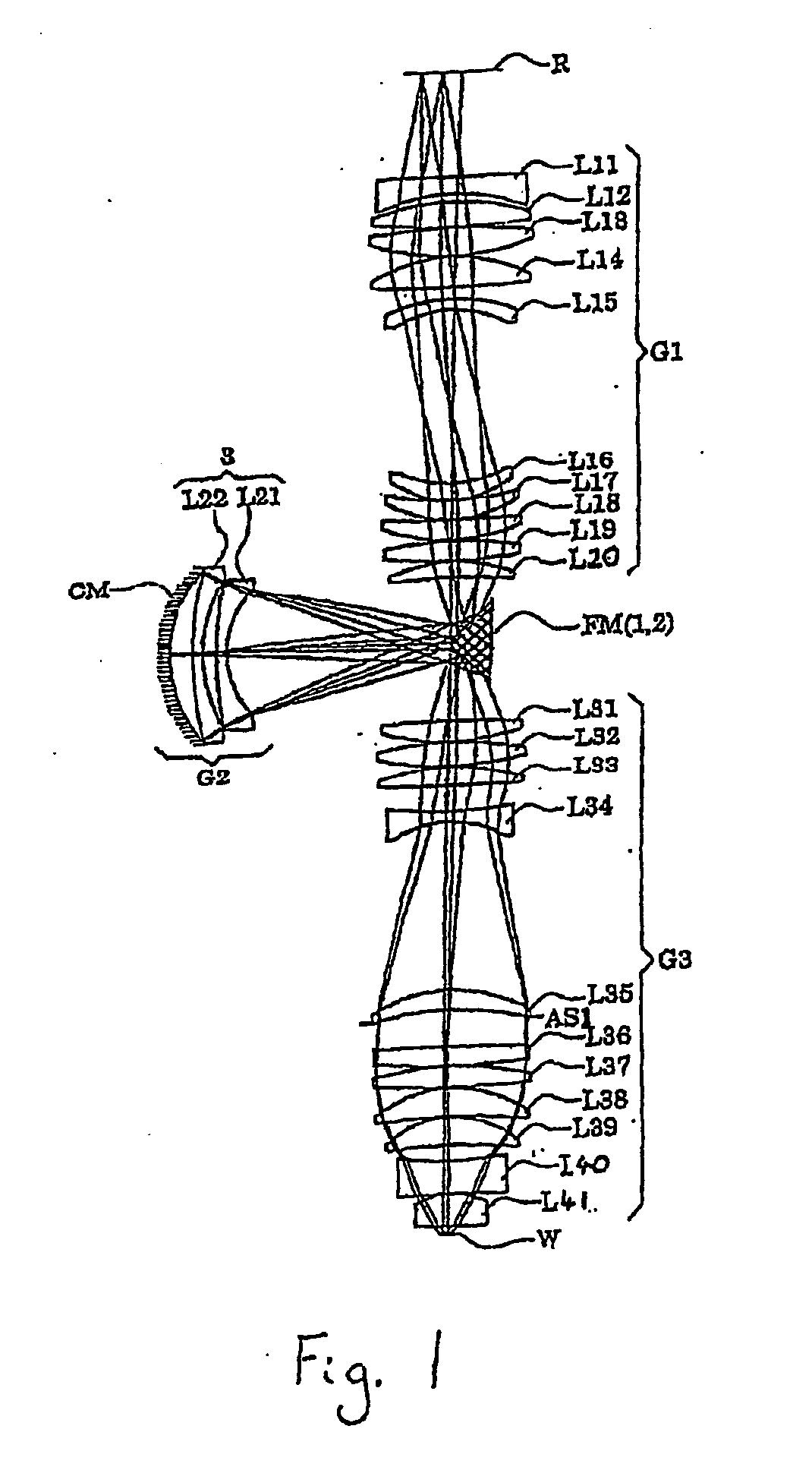
Catadioptric projection objective with geometric beam splitting
InactiveUS20050117224A1Good engineering qualityEasy to installMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntermediate imageOptical axis
A catadioptric projection objective is used to project a pattern arranged in an object plane of the projection objective into an image plane of the projection objective with the formation of at least one real intermediate image and has an image-side numerical aperture NA>0.7. The projection objective comprises an optical axis and at least one catadioptric objective part that comprises a concave mirror and a first folding mirror. There are a first beam section running from the object plane to the concave mirror and a second beam section running from the concave mirror to the image plane. The first folding mirror is arranged with reference to the concave mirror in such a way that one of the beam sections is folded at the first folding mirror and the other beam section passes the first folding mirror without vignetting, the first beam section and the second beam section crossing one another in a cross-over region.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
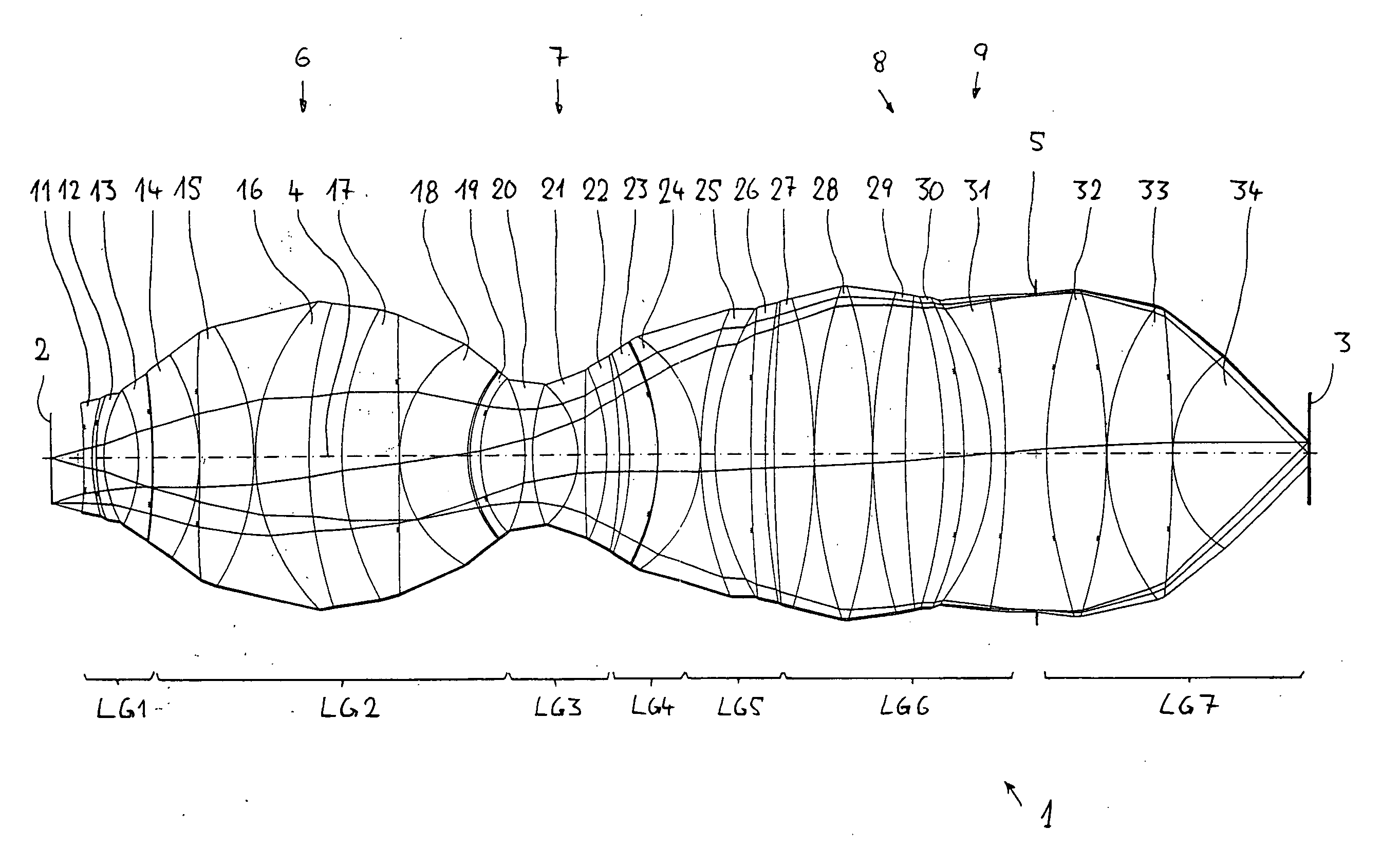
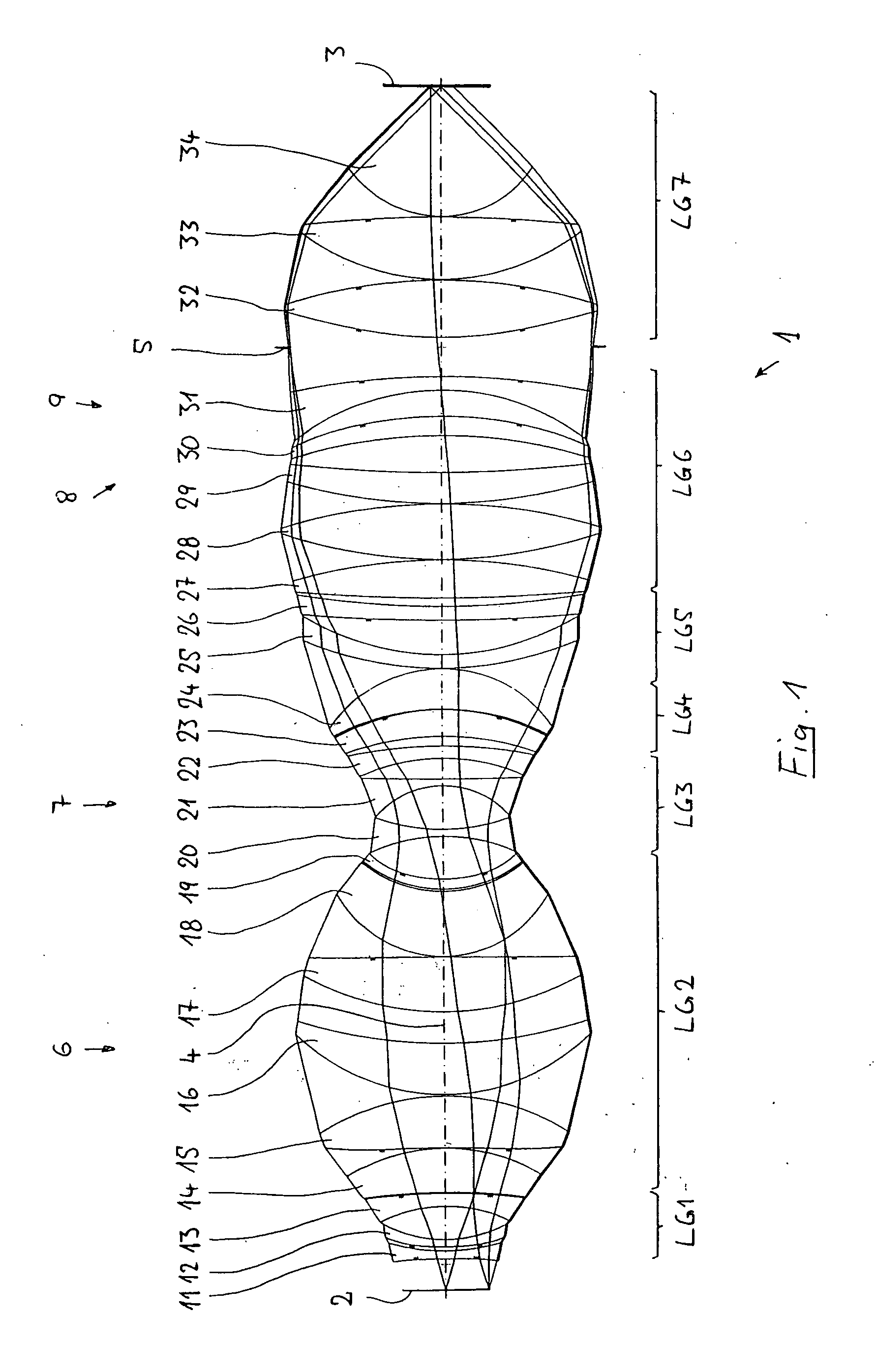
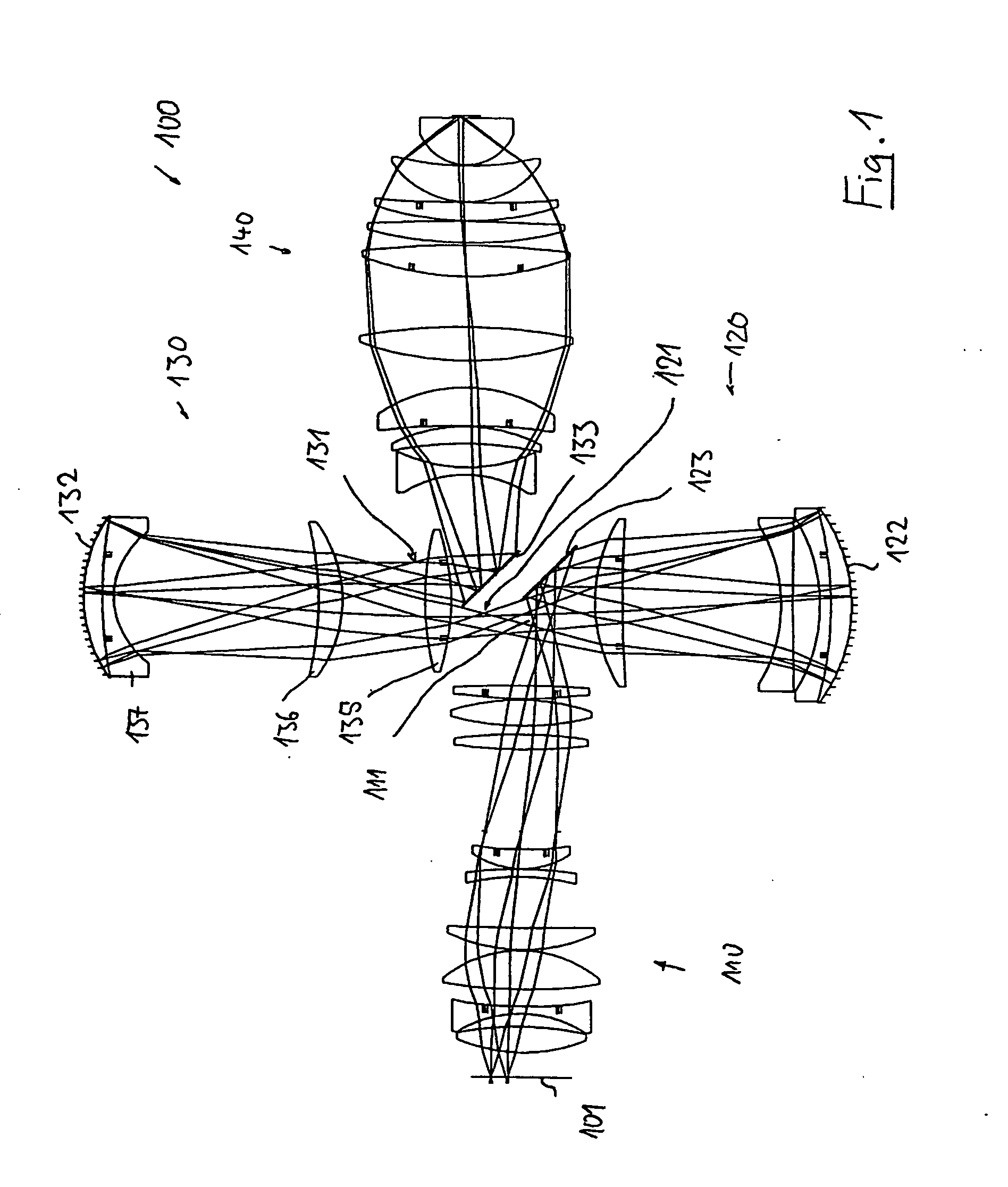
Catadioptric projection objective
ActiveUS20050190435A1High image side numerical apertureSmall amountSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicroscopesIntermediate imageHigh numerical aperture
A catadioptric projection objective for imaging a pattern provided in an object plane of the projection objective onto an image plane of the projection objective comprises: a first objective part for imaging the pattern provided in the object plane into a first intermediate image; a second objective part for imaging the first intermediate imaging into a second intermediate image; a third objective part for imaging the second intermediate imaging directly onto the image plane; wherein a first concave mirror having a first continuous mirror surface and at least one second concave mirror having a second continuous mirror surface are arranged upstream of the second intermediate image; pupil surfaces are formed between the object plane and the first intermediate image, between the first and the second intermediate image and between the second intermediate image and the image plane; and all concave mirrors are arranged optically remote from a pupil surface. The system has potential for very high numerical apertures at moderate lens material mass consumption.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
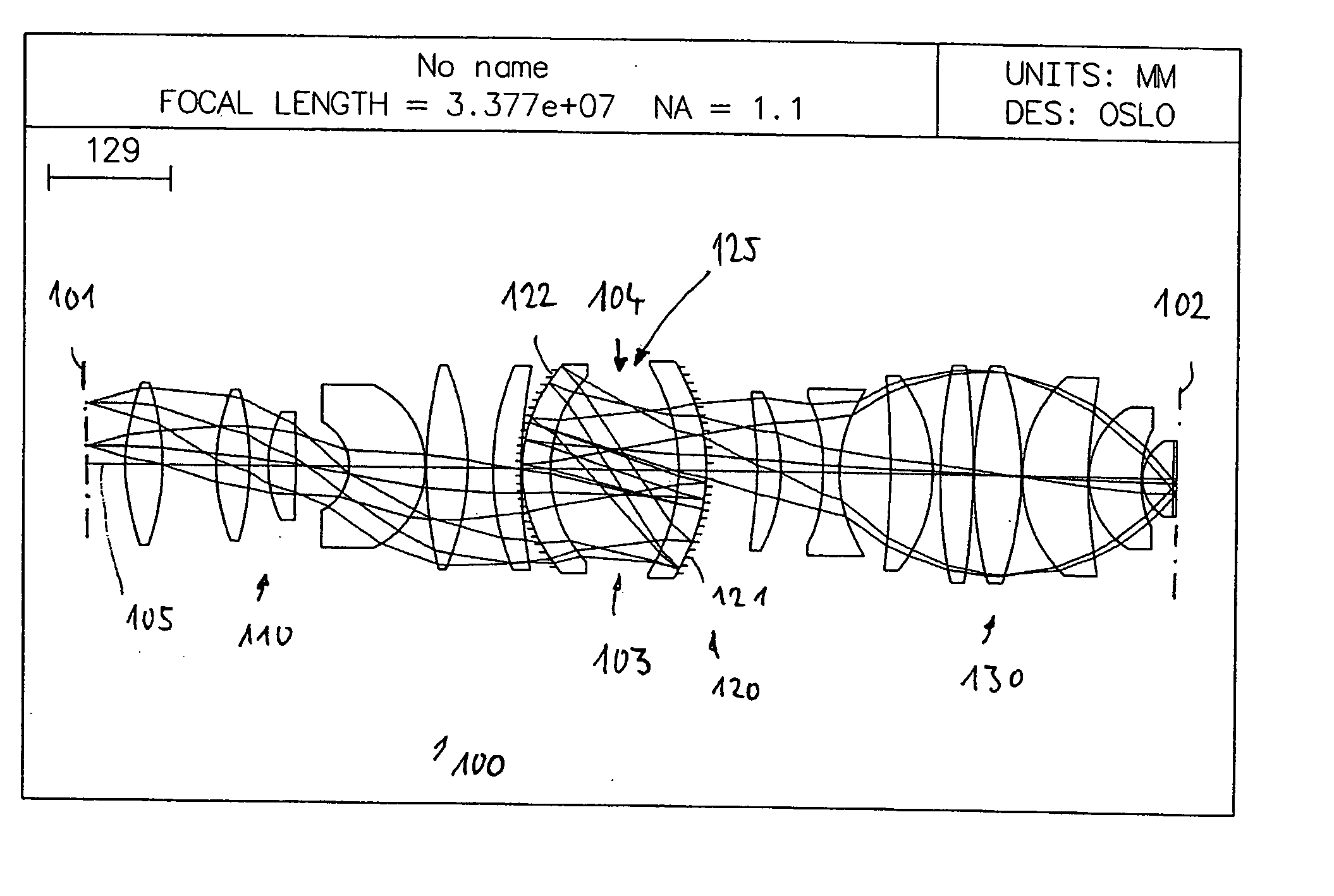
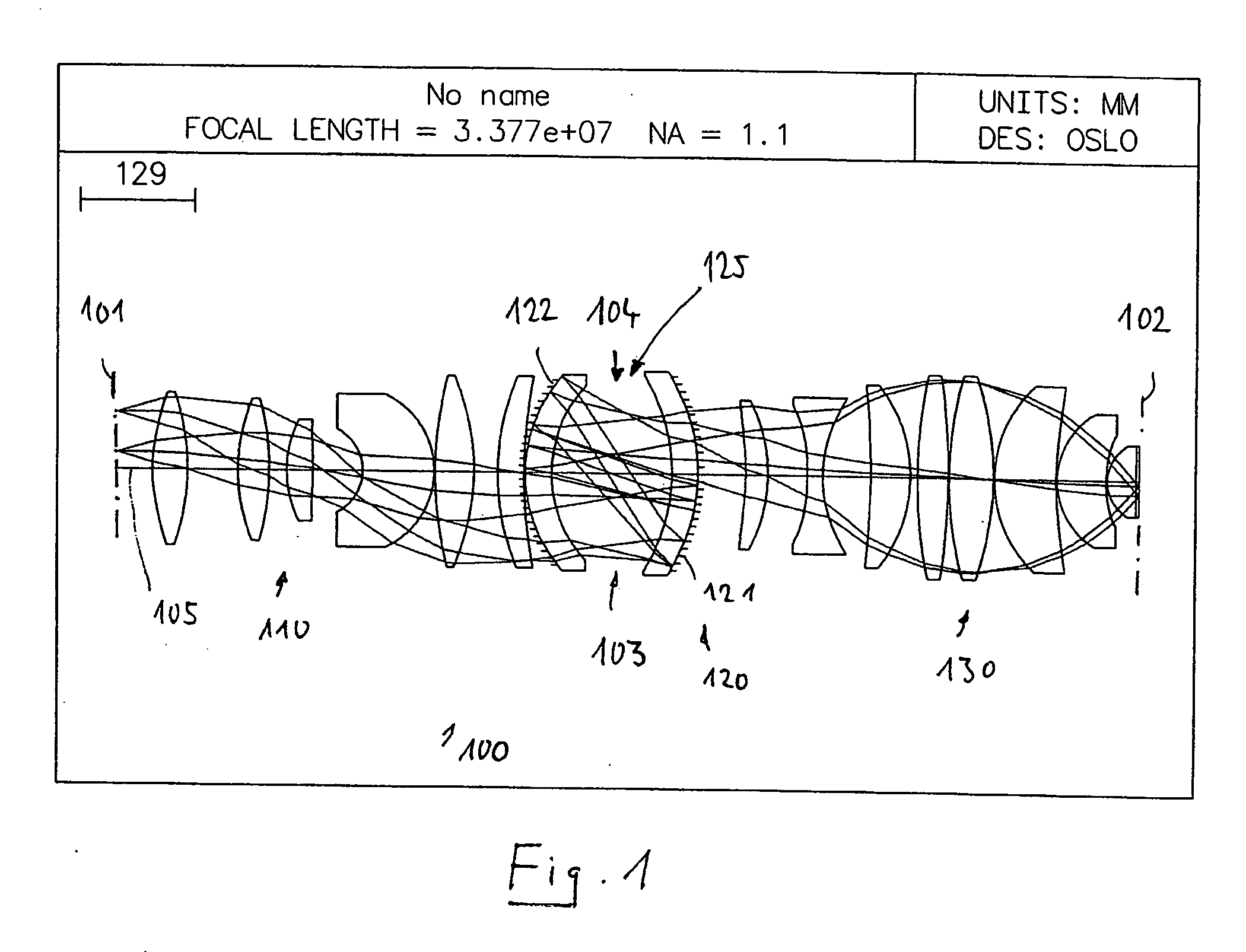
Very high-aperture projection objective
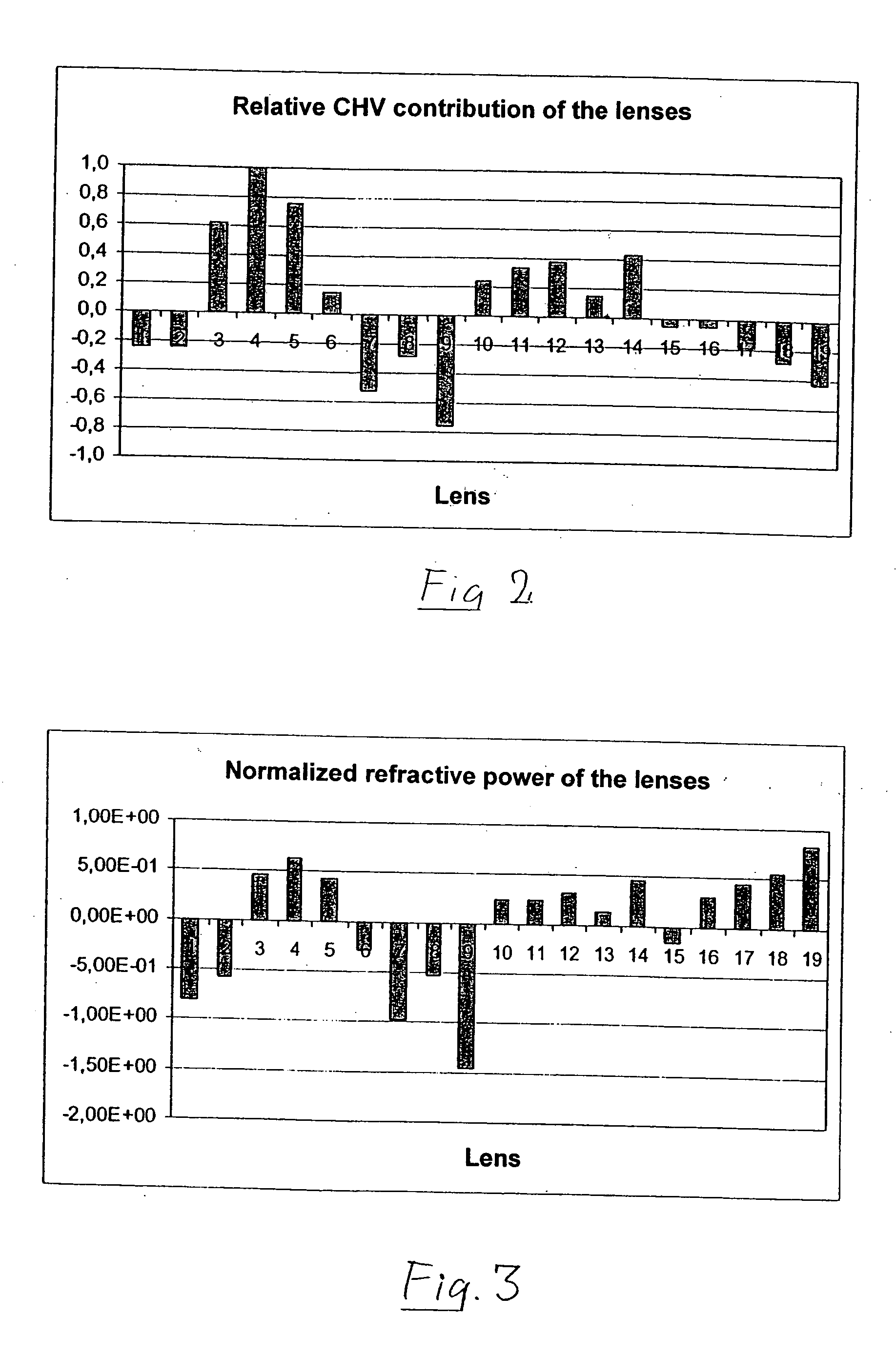
InactiveUS20050141098A1Guaranteed true stateIncrease the number ofSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicroscopesSpherical shapedOptic system
A very high-aperture, purely refractive projection objective having a multiplicity of optical elements has a system diaphragm (5) arranged at a spacing in front of the image plane. The optical element next to the image plane (3) of the projection objective is a planoconvex lens (34) having a substantially spherical entrance surface and a substantially flat exit surface. The planoconvex lens has a diameter that is at least 50% of the diaphragm diameter of the system diaphragm (5). It is preferred to arrange only positive lenses (32, 33, 34) between the system diaphragm (5) and image plane (3). The optical system permits imaging in the case of very high apertures of NA≧0.85, if appropriate of NA≧1.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
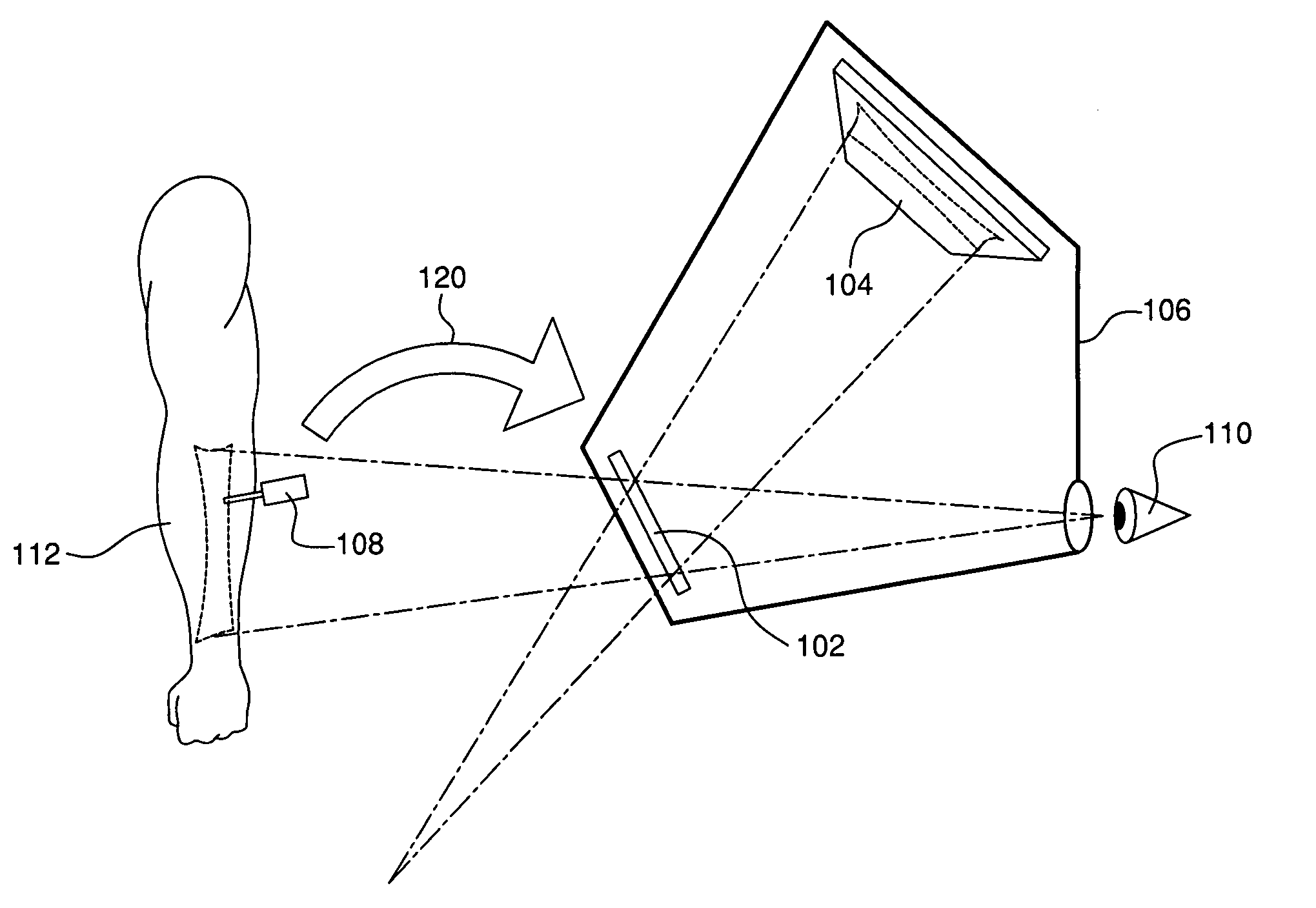
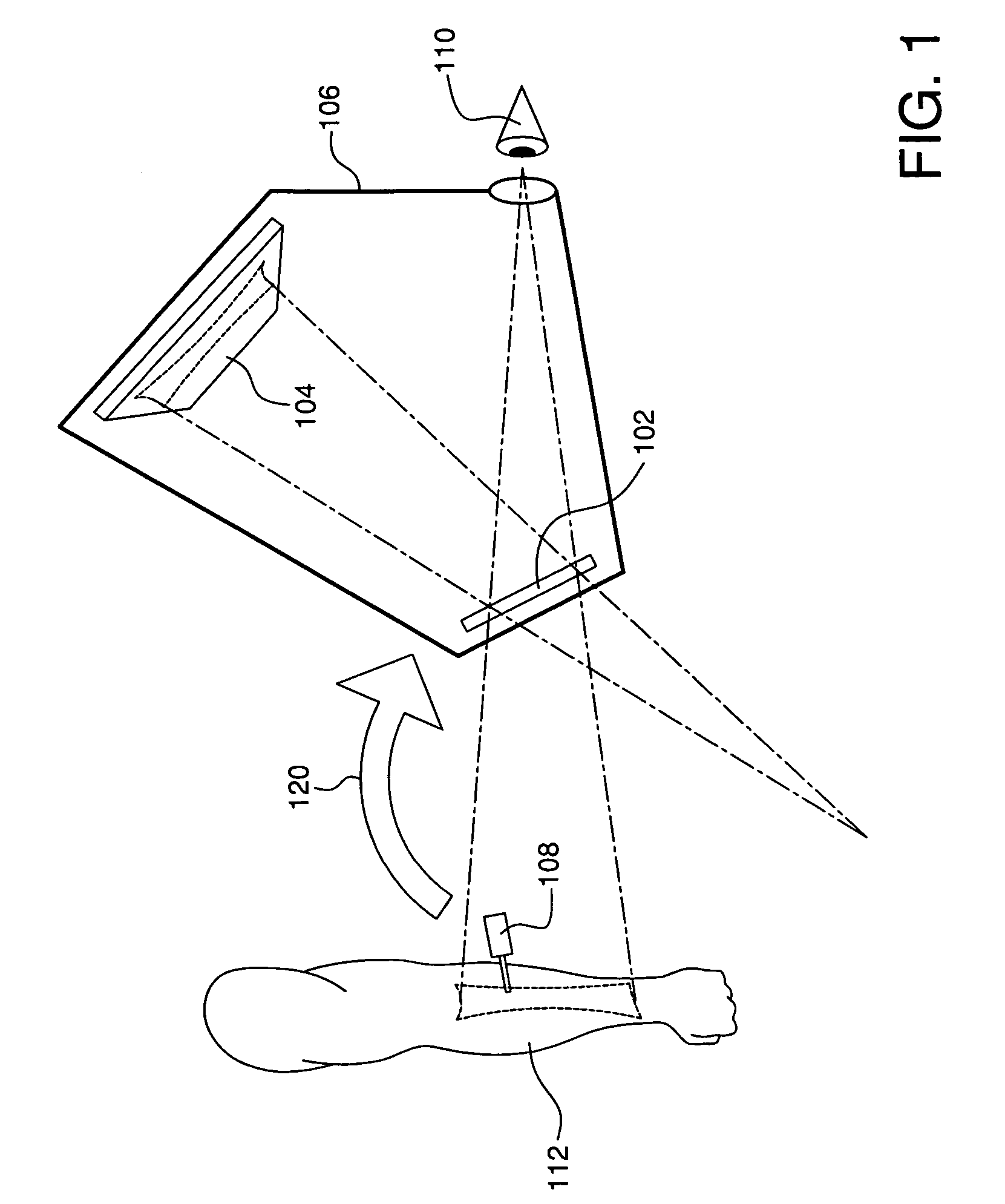
Augmented reality device and method
InactiveUS20060176242A1Precise alignmentUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using lightEyepieceDisplay device
An augmented reality device to combine a real world view with an object image. An optical combiner combines the object image with a real world view of the object and conveys the combined image to a user. A tracking system tracks one or more objects. At least a part of the tracking system is at a fixed location with respect to the display. An eyepiece is used to view the combined object and real world images, and fixes the user location with respect to the display and optical combiner location.
Owner:BLUE BELT TECH
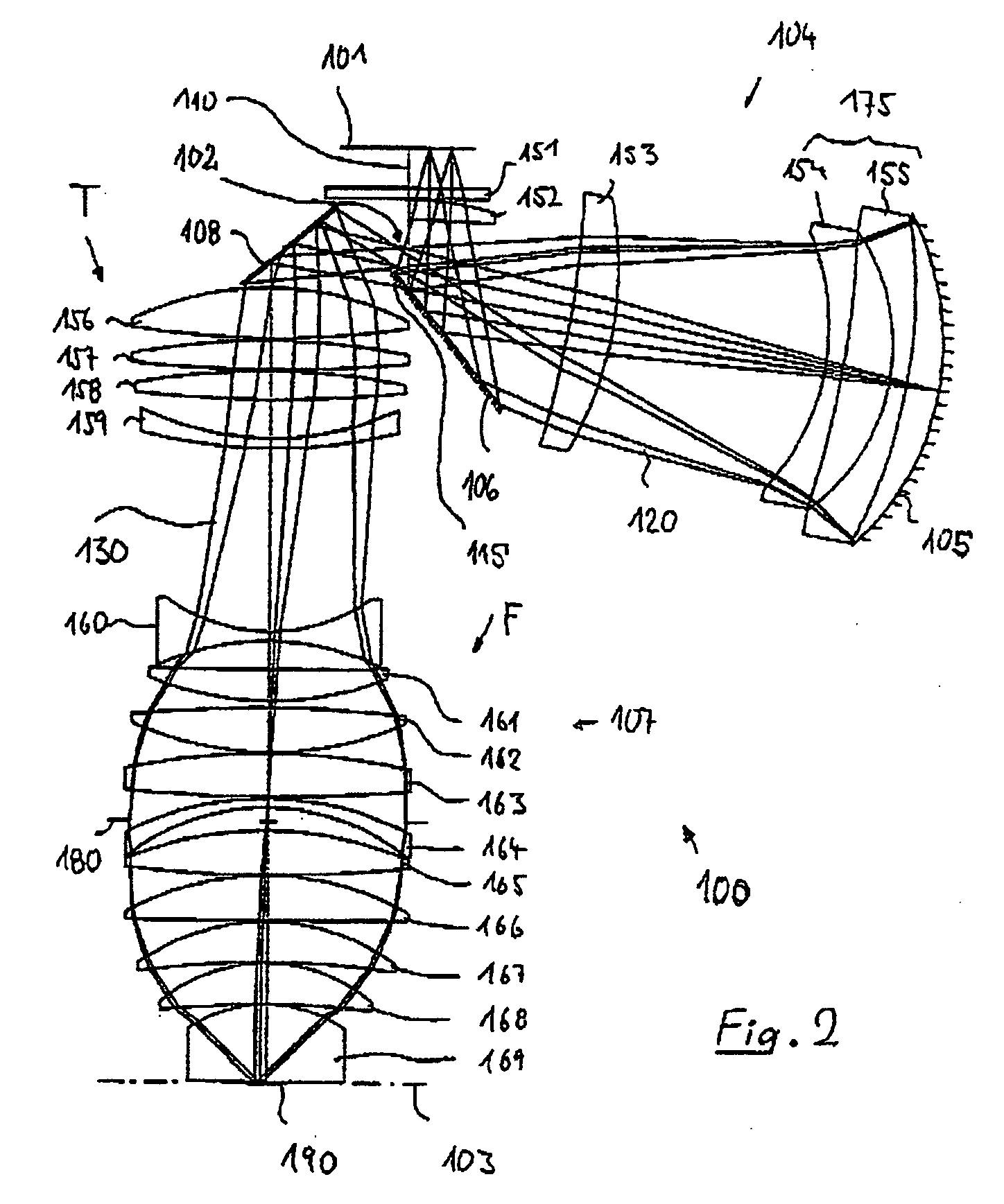
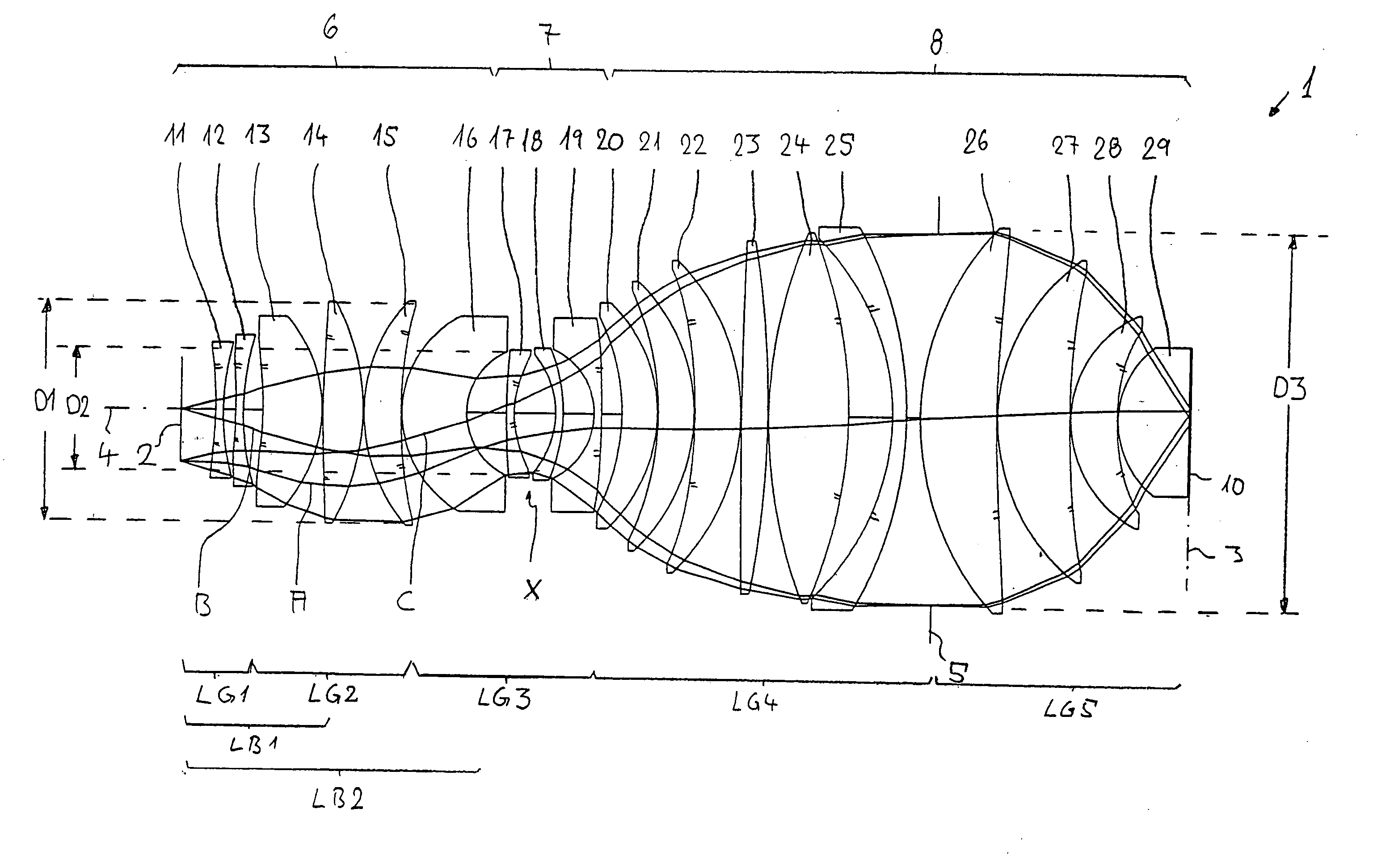
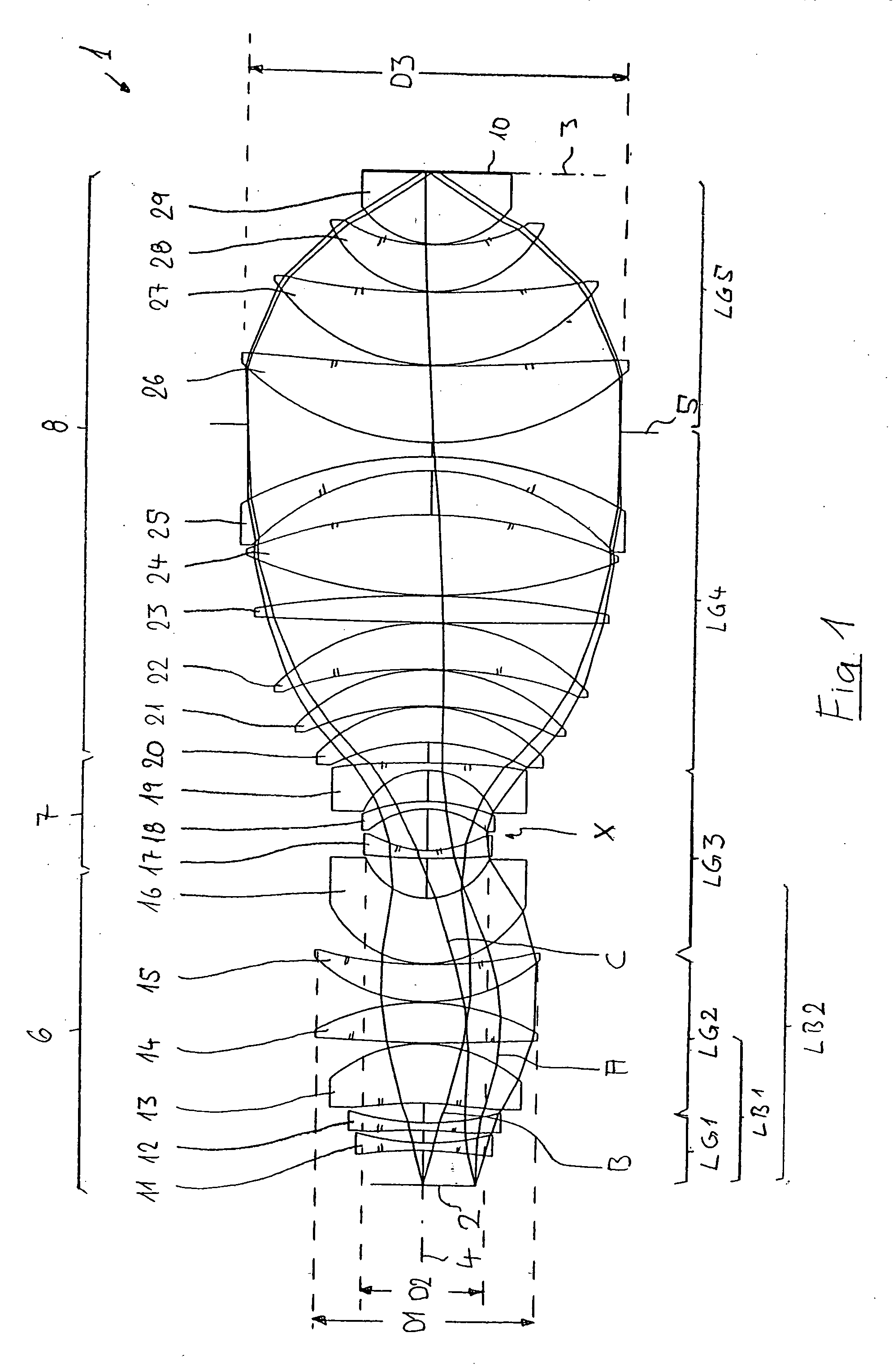
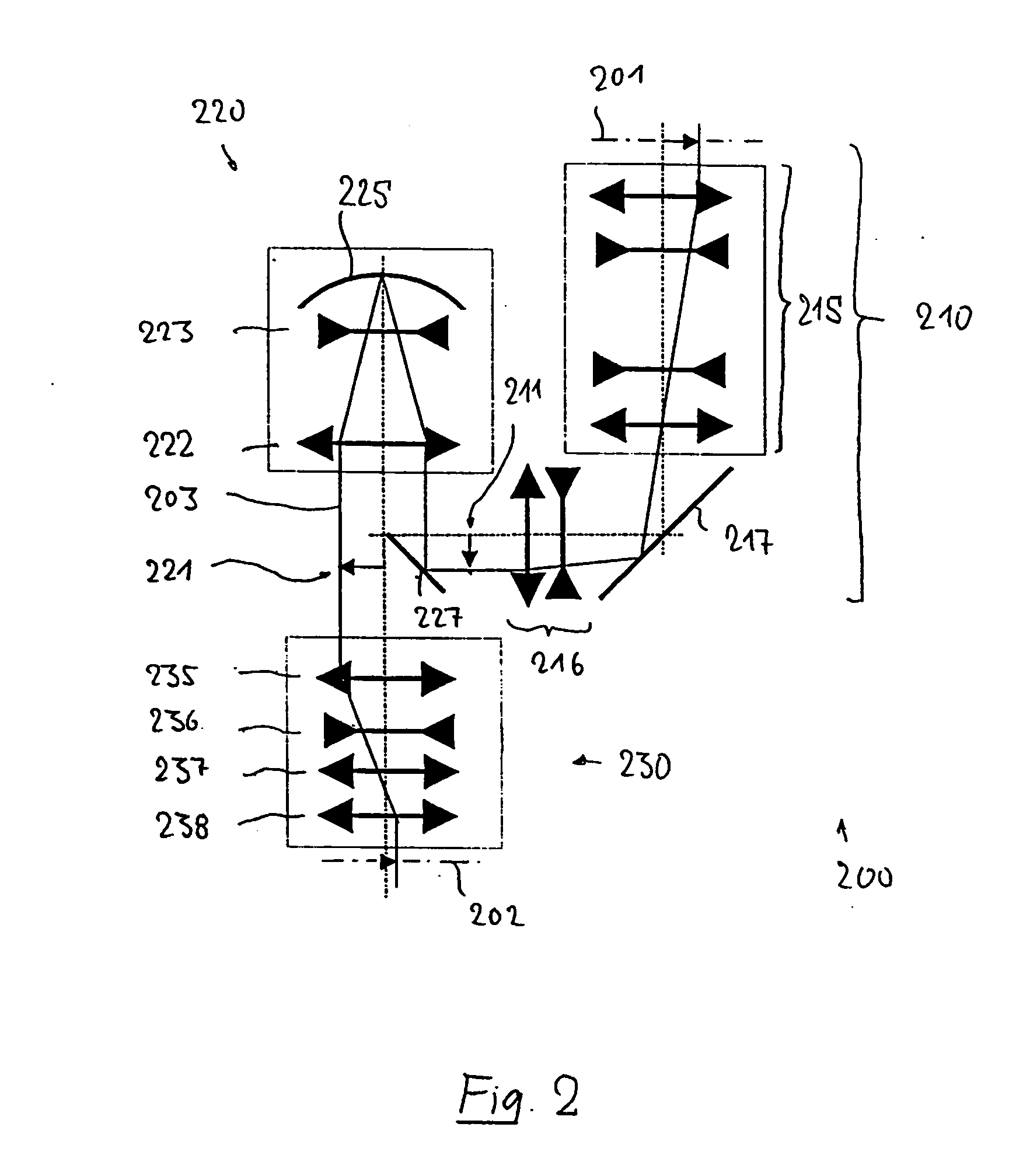
Refractive projection objective for immersion lithography
InactiveUS20050190455A1Small sizeGood correction stateMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusHigh numerical apertureOptoelectronics
A purely refractive projection objective suitable for immersion microlithography is designed as a single-waist system with five lens groups, in the case of which a first lens group with negative refractive power, a second lens group with positive refractive power, a third lens group with negative refractive power, a fourth lens group with positive refractive power and a fifth lens group with positive refractive power are provided. A constriction site of narrowest constriction of the beam bundle lies in the region of the waist. A waist distance AT exists between the object plane and the constriction site X. The condition AT / L≦0.4 holds for a distance ratio AT / L between the waist distance AT and an object-image distance L of the projection objective. Embodiments of inventive projection objectives reach very high numerical apertures NA>1.1 in conjunction with a large image field and are distinguished by a compact overall size and good correction of the lateral chromatic aberration.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Catadioptric projection objective with geometric beam splitting
InactiveUS20050185269A1Easy to correctCorrect chromatic aberrationMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntermediate imageBeam splitting
A catadioptric projection objective for imaging a pattern arranged on the object plane of the projection objective, on the image plane of the projection objective, comprising: a first objective part for imaging an object field in a first real intermediate image; a second objective part for producing a second real intermediate image with the radiation coming from the first objective part; and a third objective part for imaging the second real intermediate image on the image plane; wherein at least one of the objective parts is a catadioptric objective part with a concave mirror, and at least one of the objective parts is a refractive objective part and a folding mirror is arranged within this refractive objective part in such a way that a field lens is arranged between the folding mirror and an intermediate image which is closest to the folding mirror.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
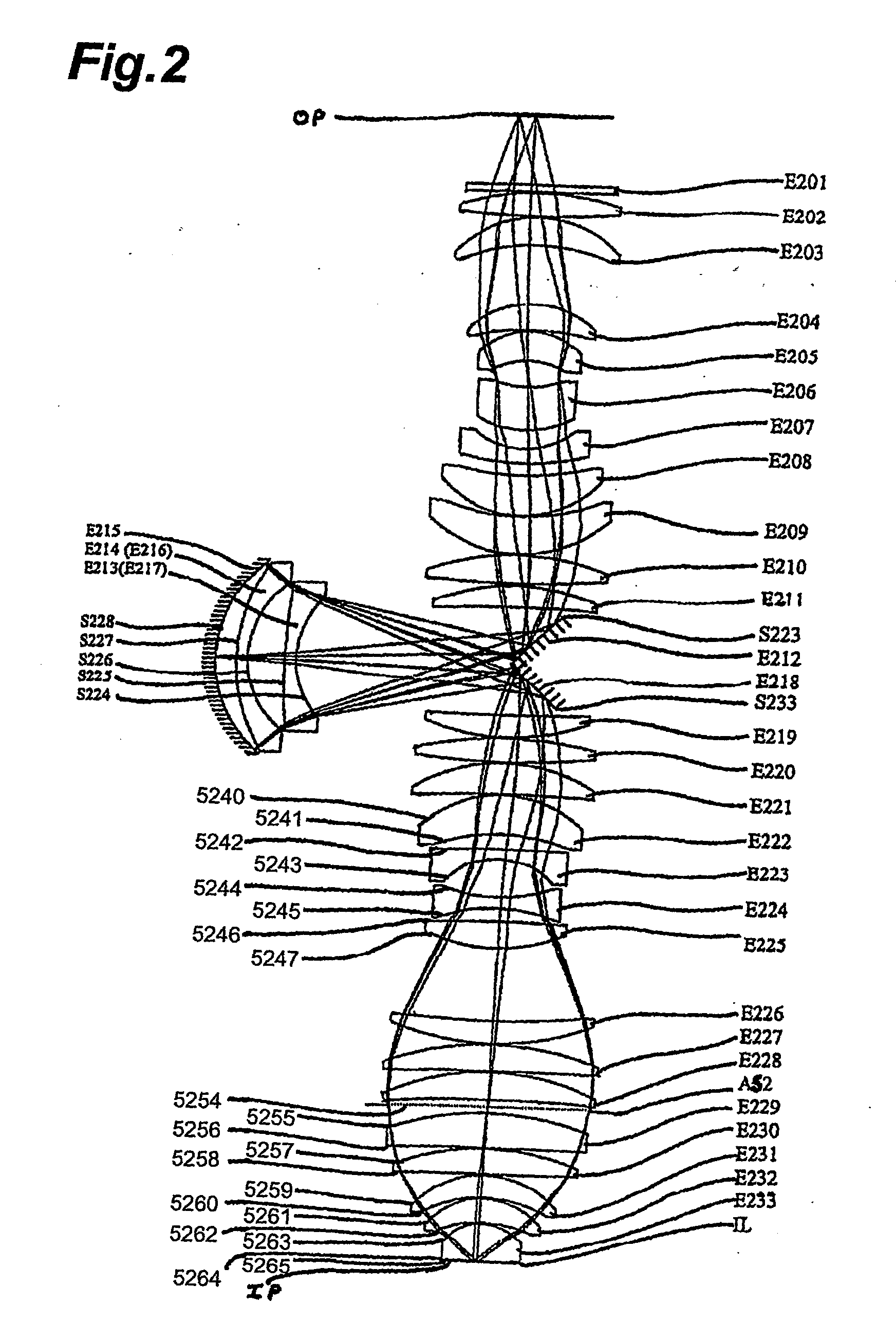
Projection optical system and method for photolithography and exposure apparatus and method using same
InactiveUS20050248856A1Large image-sideWide effective image forming areaSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicroscopesWide fieldProjection system
Optical Projection System and Method for Photolithography. A lithographic immersion projection system and method for projecting an image at high resolution over a wide field of view. The projection system and method include a final lens which decreases the marginal ray angle of the optical path before light passes into the immersion liquid to impinge on the image plane.
Owner:NIKON CORP
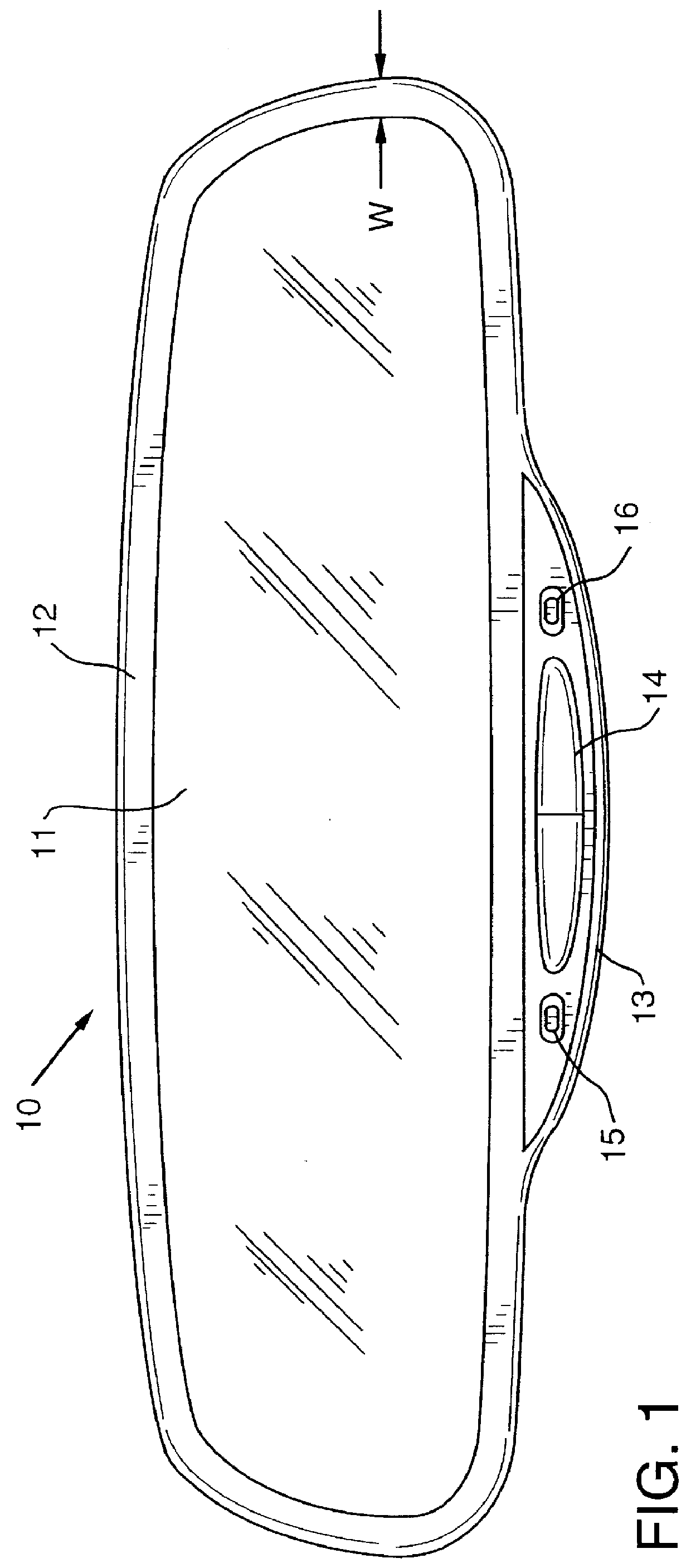
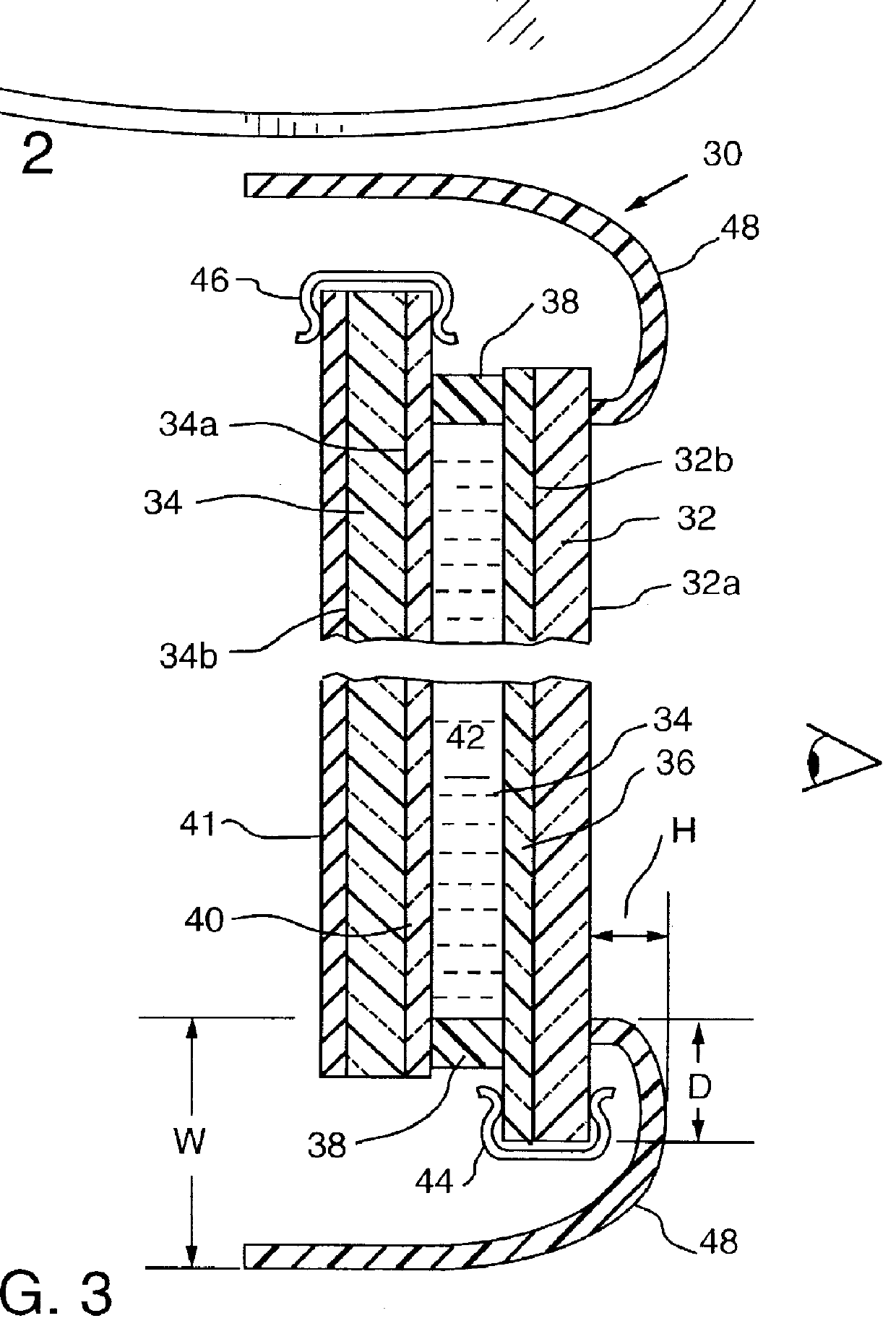
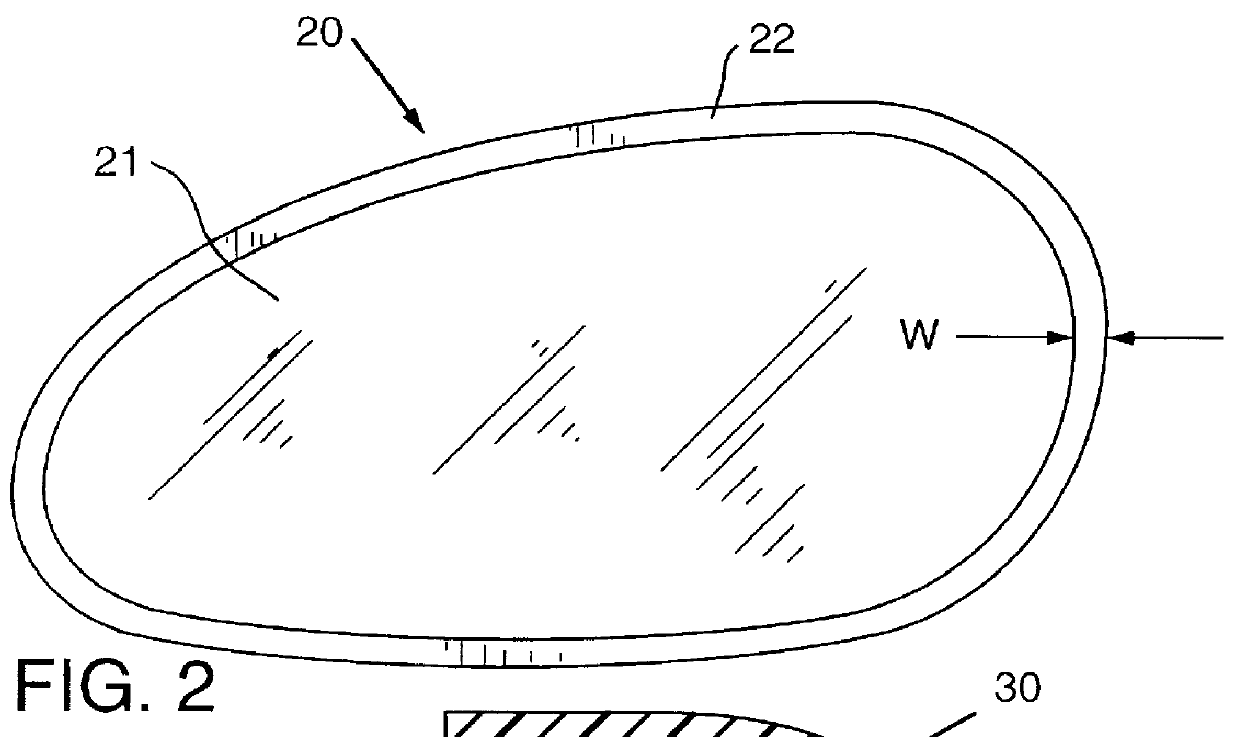
Rearview mirror bezel having reduced apparent size
InactiveUS6102546AControlled lightness valueSmall sizeMirrorsMicroscopesApparent SizeElectrochromism
Electrochromic rearview mirrors having reduced apparent size bezels are disclosed. Visual characteristics of the bezel, such as lightness value, are controlled in order to reduce the apparent size of the bezel. The lightness value of the bezel is preferably matched to the lightness value of the electrochromic mirror. In addition, the color value of the bezel may also be controlled. The electrochromic rearview mirrors may be mounted in the interior or on the exterior of vehicles.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
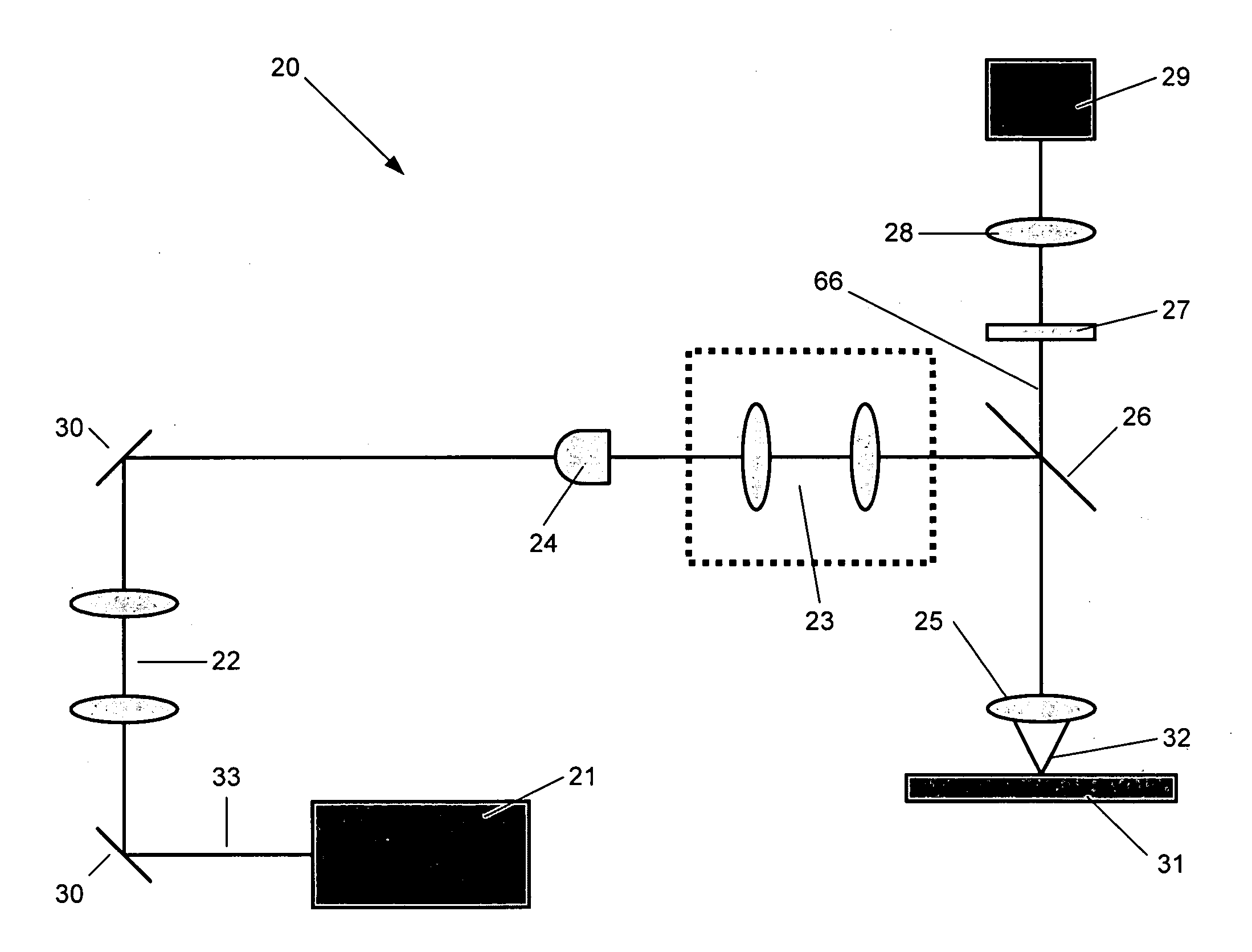
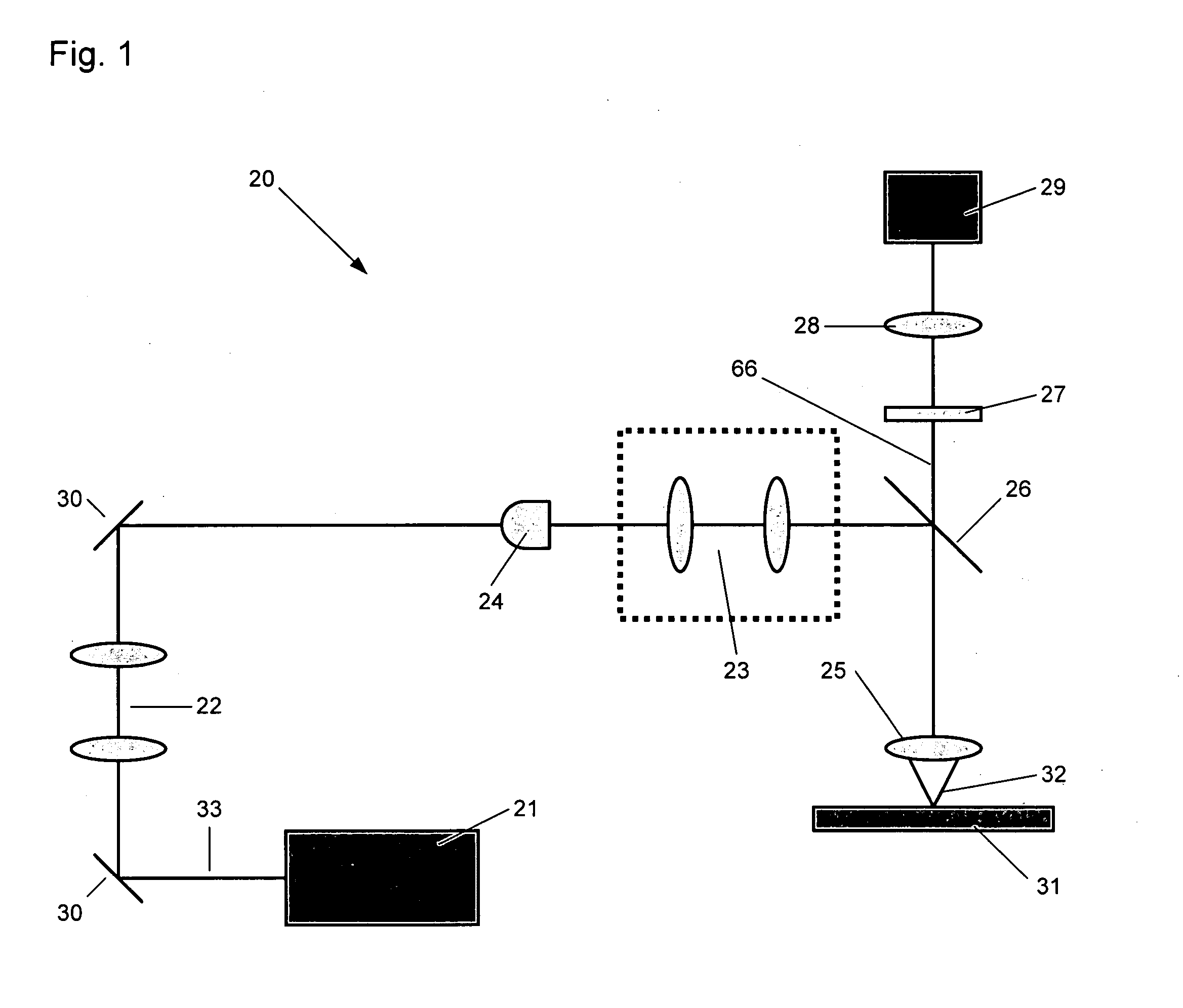
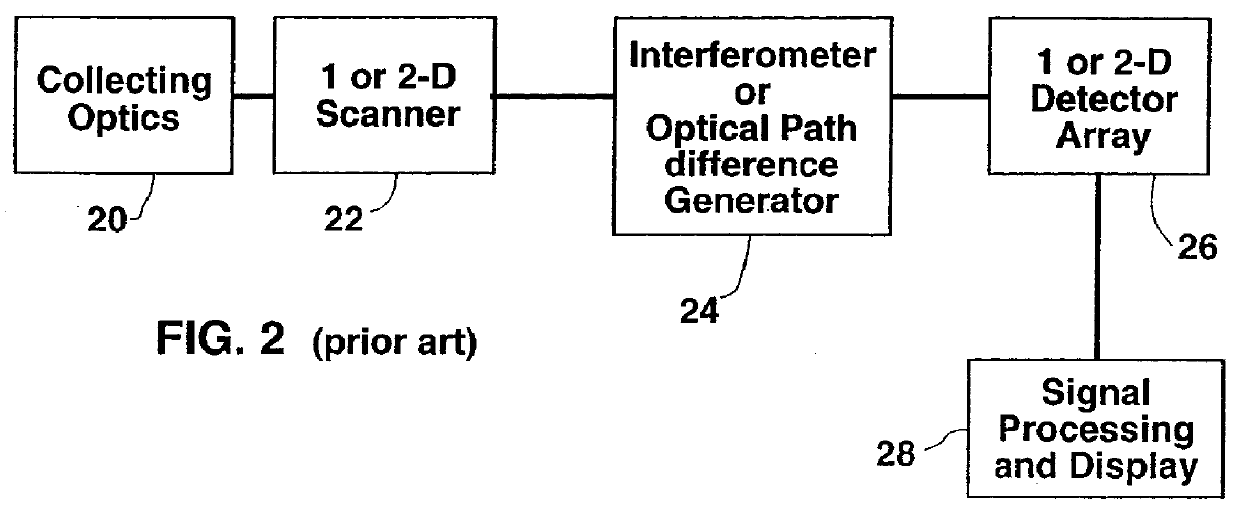
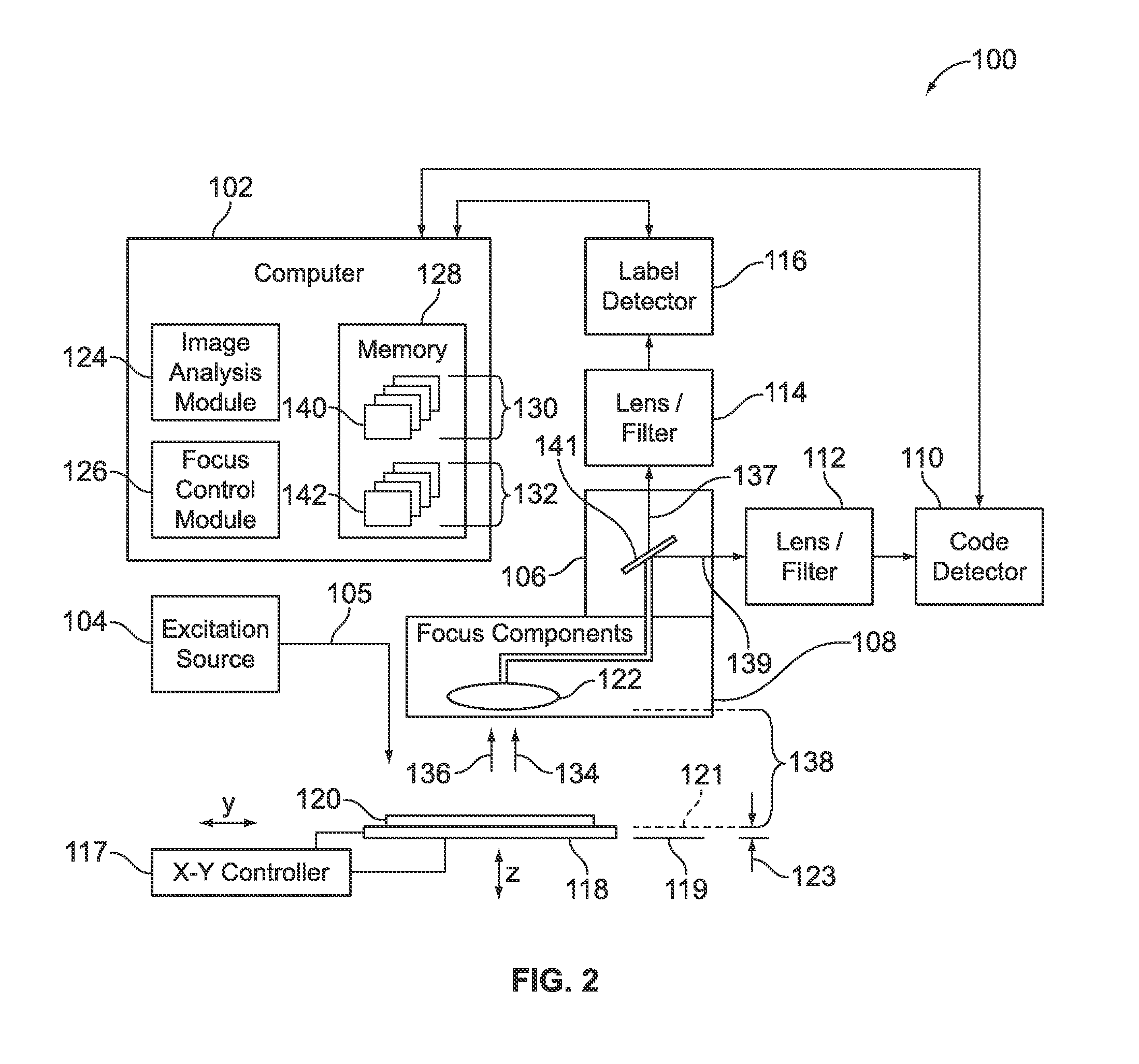
Confocal imaging methods and apparatus
The invention provides imaging apparatus and methods useful for obtaining a high resolution image of a sample at rapid scan rates. A rectangular detector array having a horizontal dimension that is longer than the vertical dimension can be used along with imaging optics positioned to direct a rectangular image of a portion of a sample to the rectangular detector array. A scanning device can be configured to scan the sample in a scan-axis dimension, wherein the vertical dimension for the rectangular detector array and the shorter of the two rectangular dimensions for the image are in the scan-axis dimension, and wherein the vertical dimension for the rectangular detector array is short enough to achieve confocality in a single axis.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Compact folded-optics illumination lens
The present embodiments provide for apparatuses, and methods for manufacturing apparatuses to convert a first distribution of an input radiation to a second distribution of output radiation. The apparatus can be defined in some embodiments by generating a two-dimensional representation of three active optical surfaces including calculating a segment of first, entry and second surfaces based on first second, and third generalized Cartesian ovals, respectively, and successively repeating the calculating of the segments of the first and second surfaces, and rotationally sweeping the two-dimensional representation about a central axis providing a three-dimensional representation. In some embodiments, portion of the first and / or second surfaces can be totally internally reflective.
Owner:LIGHT ENGINE
Camera Adapter Based Optical Imaging Apparatus
ActiveUS20110043661A1Cancel noiseLow costTelevision system detailsInterferometersSpectral bandsFrequency spectrum
The invention describes several embodiments of an adapter which can make use of the devices in any commercially available digital cameras to accomplish different functions, such as a fundus camera, as a microscope or as an en-face optical coherence tomography (OCT) to produce constant depth OCT images or as a Fourier domain (channelled spectrum) optical coherence tomography to produce a reflectivity profile in the depth of an object or cross section OCT images, or depth resolved volumes. The invention admits addition of confocal detection and provides simultaneous measurements or imaging in at least two channels, confocal and OCT, where the confocal channel provides an en-face image simultaneous with the acquisition of OCT cross sections, to guide the acquisition as well as to be used subsequently in the visualisation of OCT images. Different technical solutions are provided for the assembly of one or two digital cameras which together with such adapters lead to modular and portable high resolution imaging systems which can accomplish various functions with a minimum of extra components while adapting the elements in the digital camera. The cost of such adapters is comparable with that of commercial digital cameras, i.e. the total cost of such assemblies of commercially digital cameras and dedicated adapters to accomplish high resolution imaging are at a fraction of the cost of dedicated stand alone instruments. Embodiments and methods are presented to employ colour cameras and their associated optical sources to deliver simultaneous signals using their colour sensor parts to provide spectroscopic information, phase shifting inferometry in one step, depth range extension, polarisation, angular measurements and spectroscopic Fourier domain (channelled spectrum) optical coherence tomography in as many spectral bands simultaneously as the number of colour parts of the photodetector sensor in the digital camera. In conjunction with simultaneous acquistion of a confocal image, at least 4 channels can simultaneously be provided using the three color parts of conventional color cameras to deliver three OCT images in addition to the confocal image.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KENT
Multifocal imaging systems and method
InactiveUS20070057211A1Fast imagingEfficient collectionMaterial analysis by optical meansColor television detailsLow noiseGrating
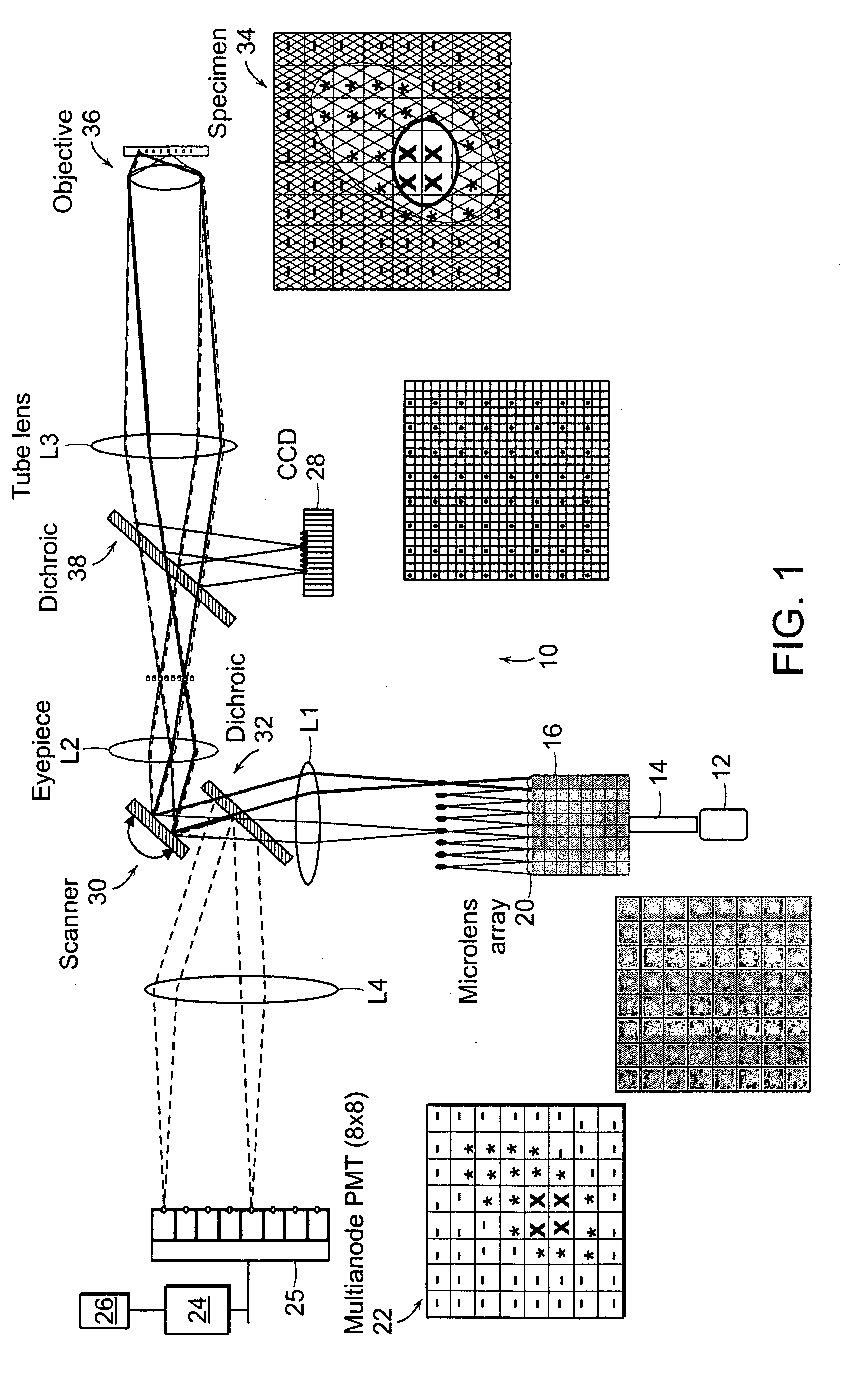
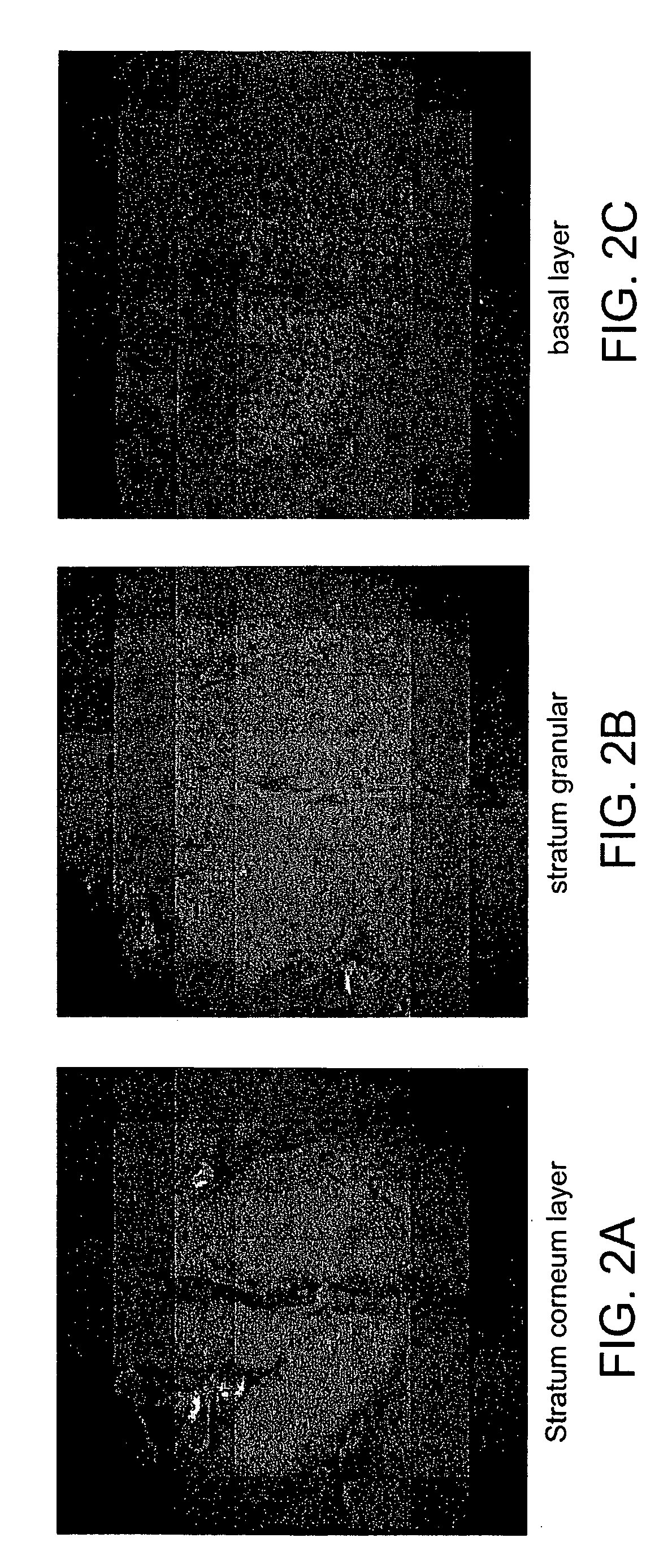
In the systems and methods of the present invention a multifocal multiphoton imaging system has a signal to noise ratio (SNR) that is reduced by over an order of magnitude at imaging depth equal to twice the mean free path scattering length of the specimen. An MMM system based on an area detector such as a multianode photomultiplier tube (MAPMT) that is optimized for high-speed tissue imaging. The specimen is raster-scanned with an array of excitation light beams. The emission photons from the array of excitation foci are collected simultaneously by a MAPMT and the signals from each anode are detected using high sensitivity, low noise single photon counting circuits. An image is formed by the temporal encoding of the integrated signal with a raster scanning pattern. A deconvolution procedure taking account of the spatial distribution and the raster temporal encoding of collected photons can be used to improve decay coefficient. We demonstrate MAPMT-based MMM can provide significantly better contrast than CCD-based existing systems.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
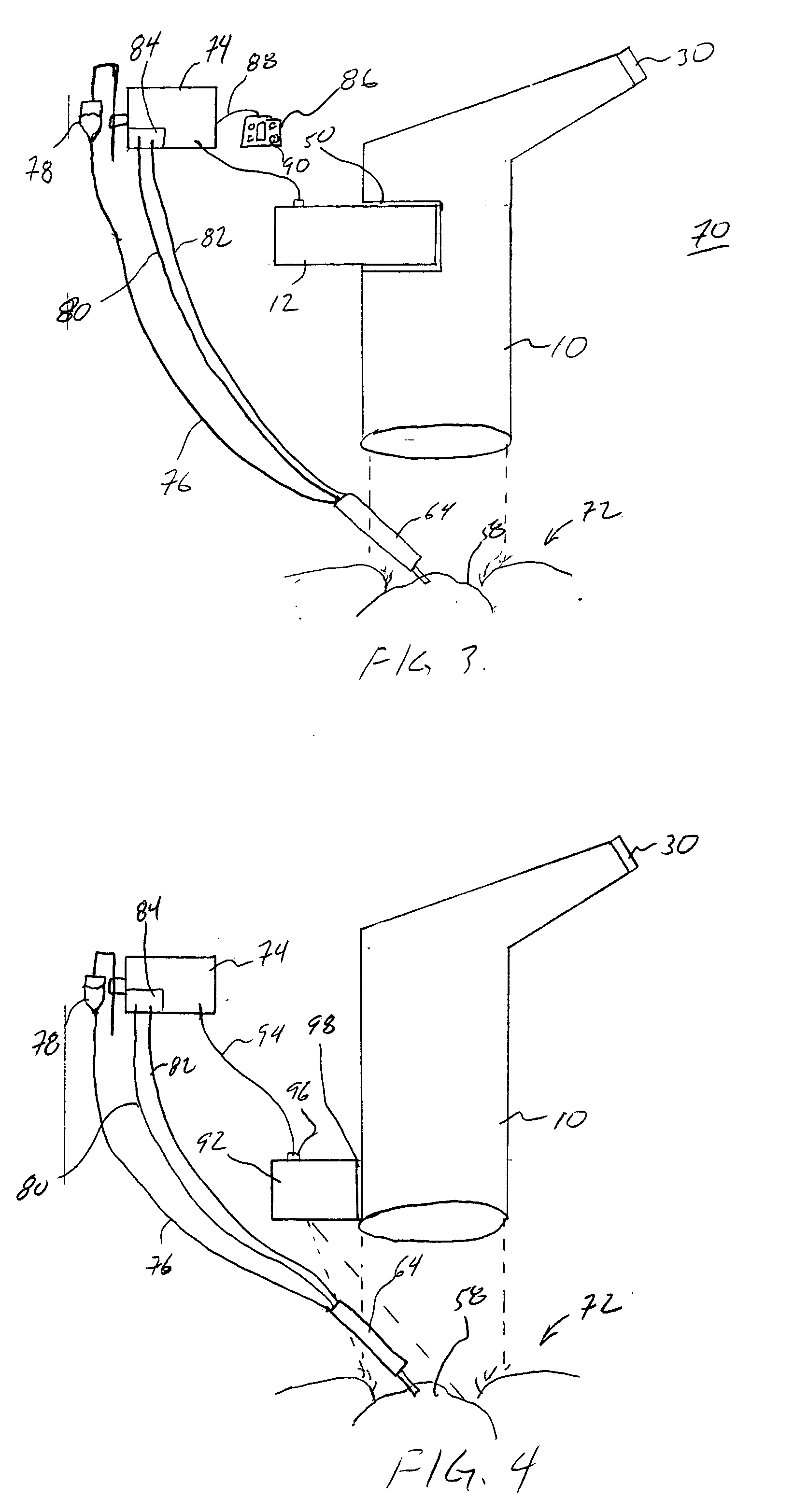
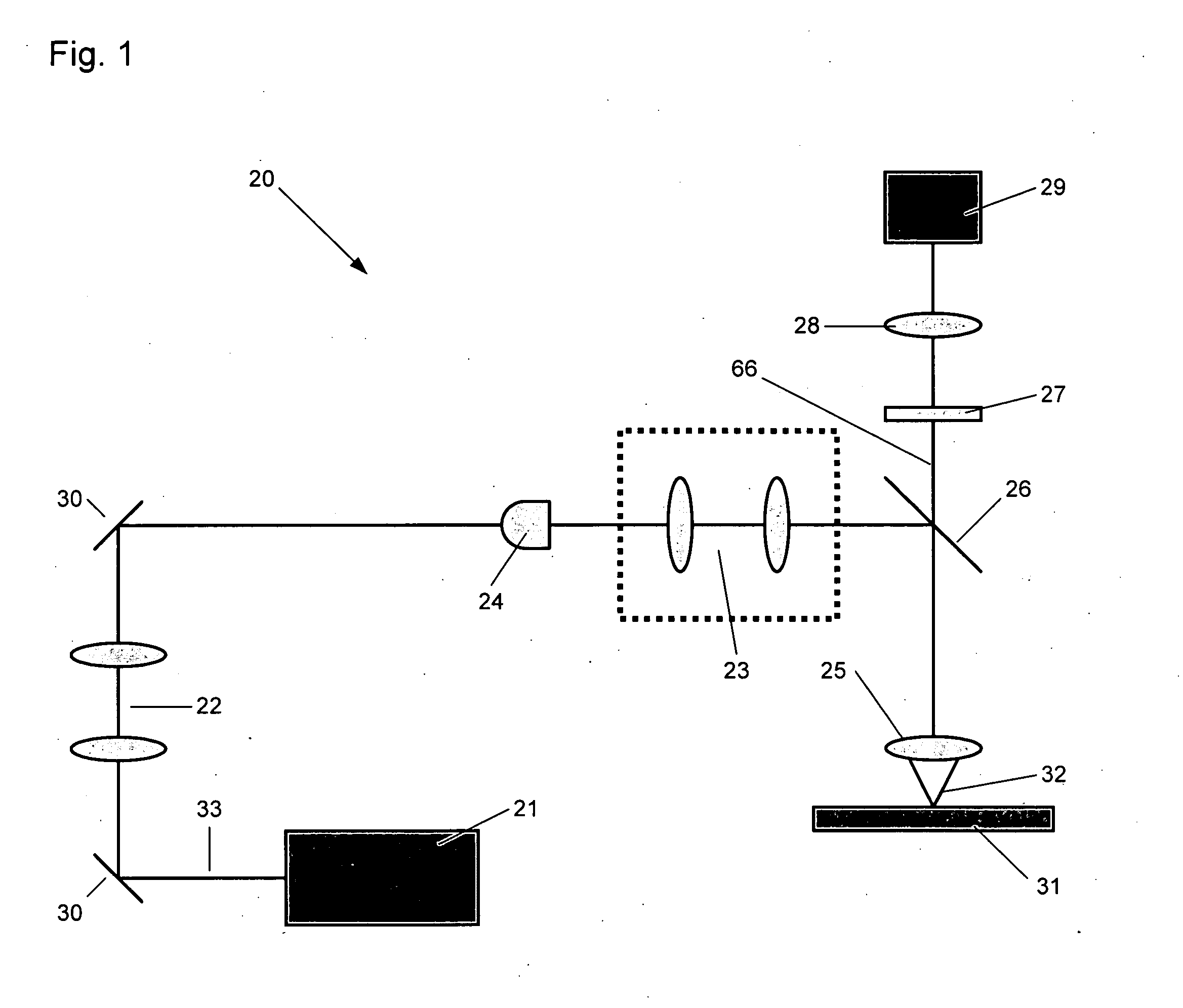
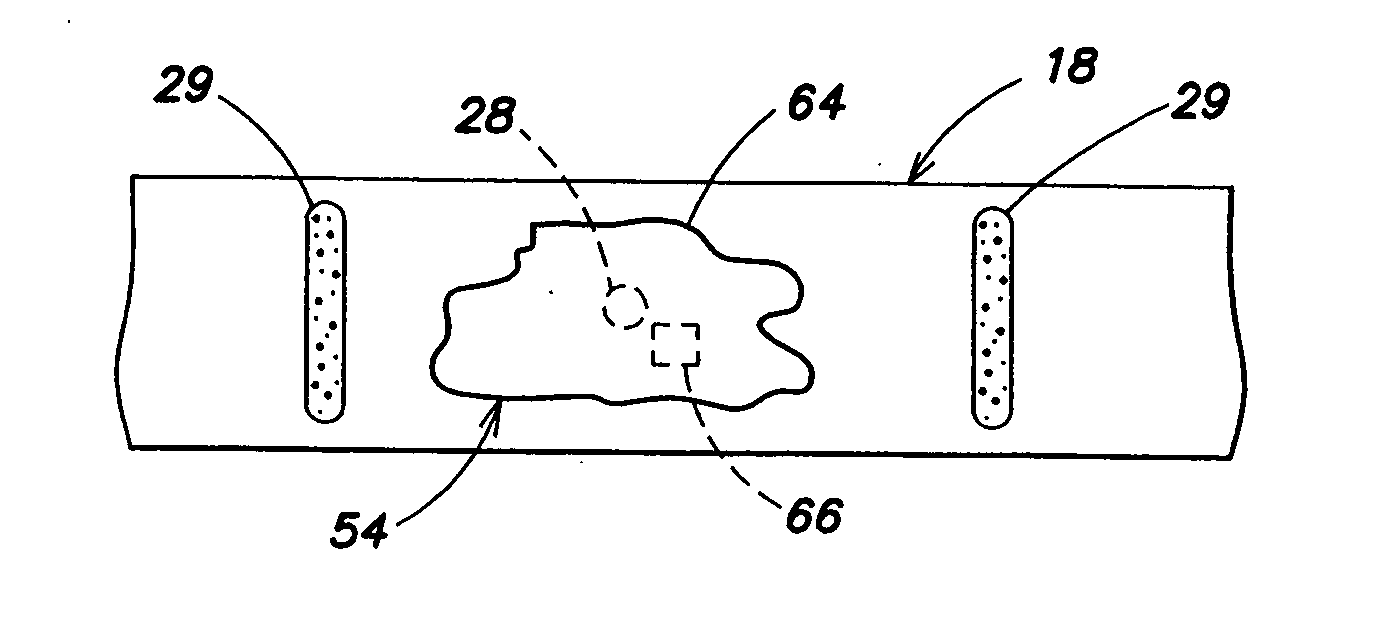
Heads-up display for displaying surgical parameters in a surgical microscope
An ophthalmic surgical system 70 includes a surgery-viewing device 10 for observing a surgical site 72. A surgical console 74 controls at least one surgical instrument 64. The surgical console 74 detects certain surgical parameters during surgery. A heads-up display 12 is connected to each of the surgery-viewing device 10 and the surgical console 74 for displaying at least one of the surgical parameters to a user through the surgery-viewing device 10.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
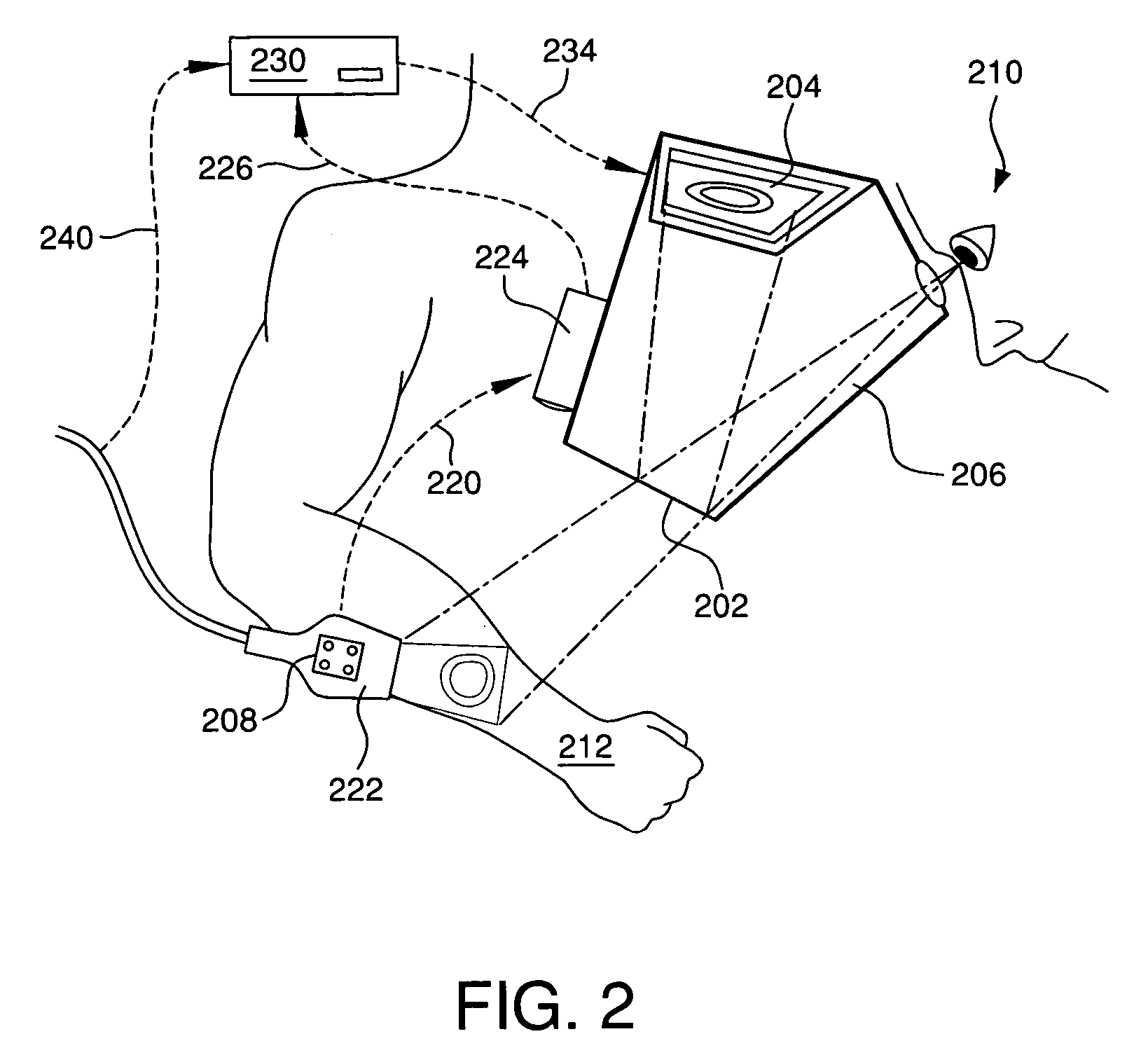
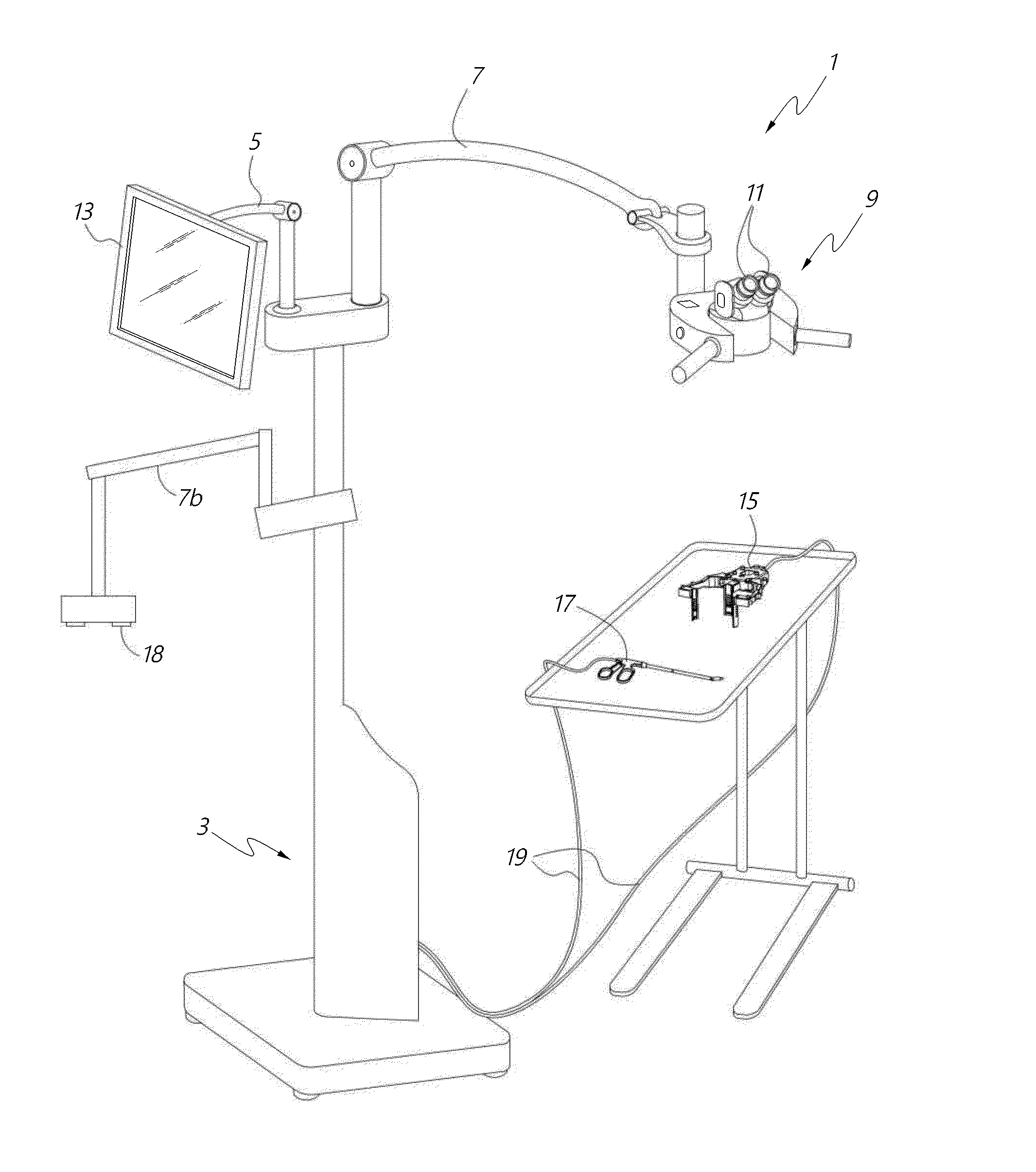
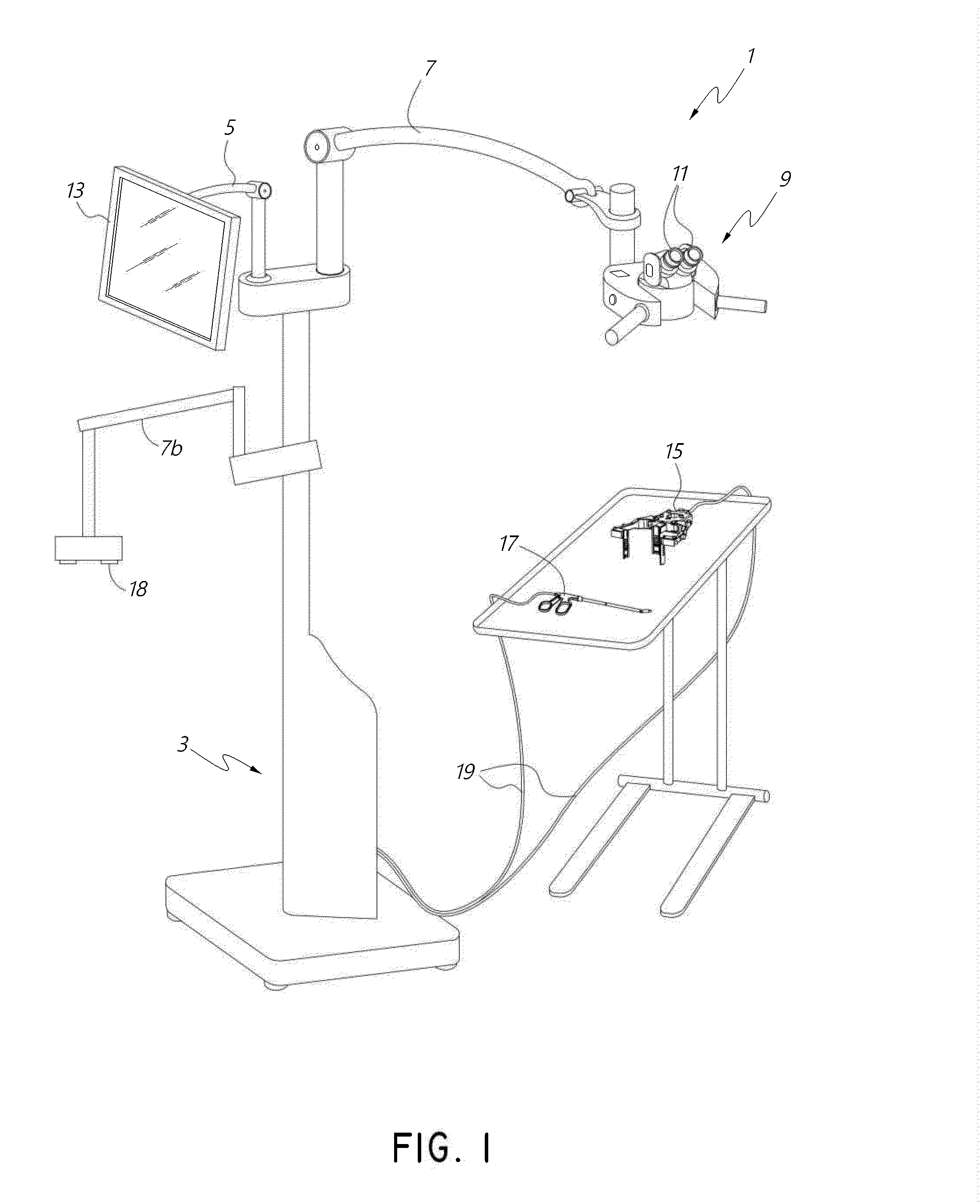
Surgical visualization systems
InactiveUS20150297311A1Minimize and reduce sizeSave spaceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementEyepieceDisplay device
A medical apparatus is described for providing visualization of a surgical site. The medical apparatus includes an electronic display disposed within a display housing, the electronic display configured to produce a two-dimensional image. The medical apparatus includes a display optical system disposed within the display housing, the display optical system comprising a plurality of lens elements disposed along an optical path. The display optical system is configured to receive the two-dimensional image from the electronic display, produce a beam with a cross-section that remains substantially constant along the optical path, and produce a collimated beam exiting the opening in the display housing. The medical apparatus can also include an auxiliary video camera configured to provide an oblique view of a patient on the electronic display without requiring a surgeon to adjust their viewing angle through oculars viewing the electronic display.
Owner:CAMPLEX
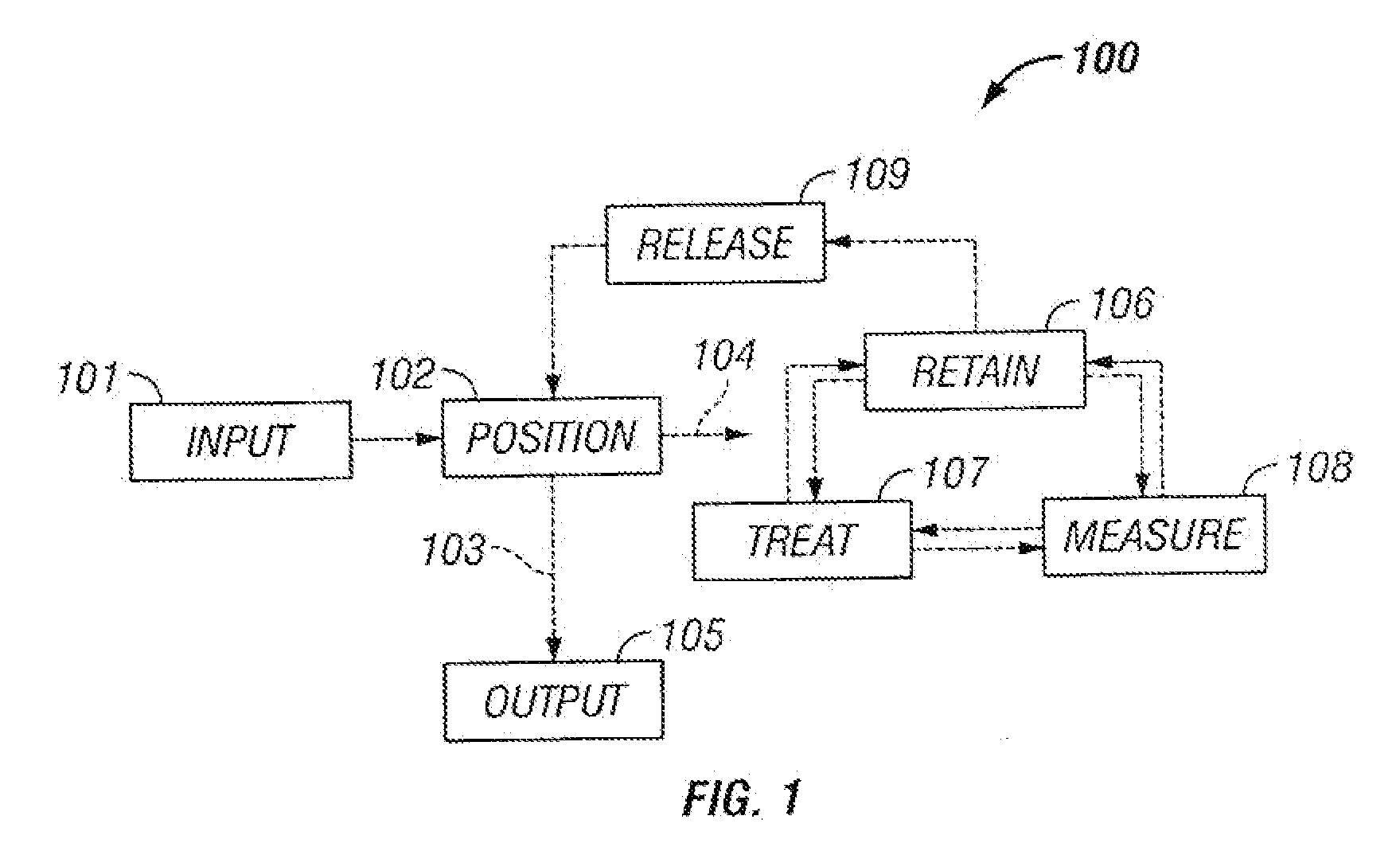
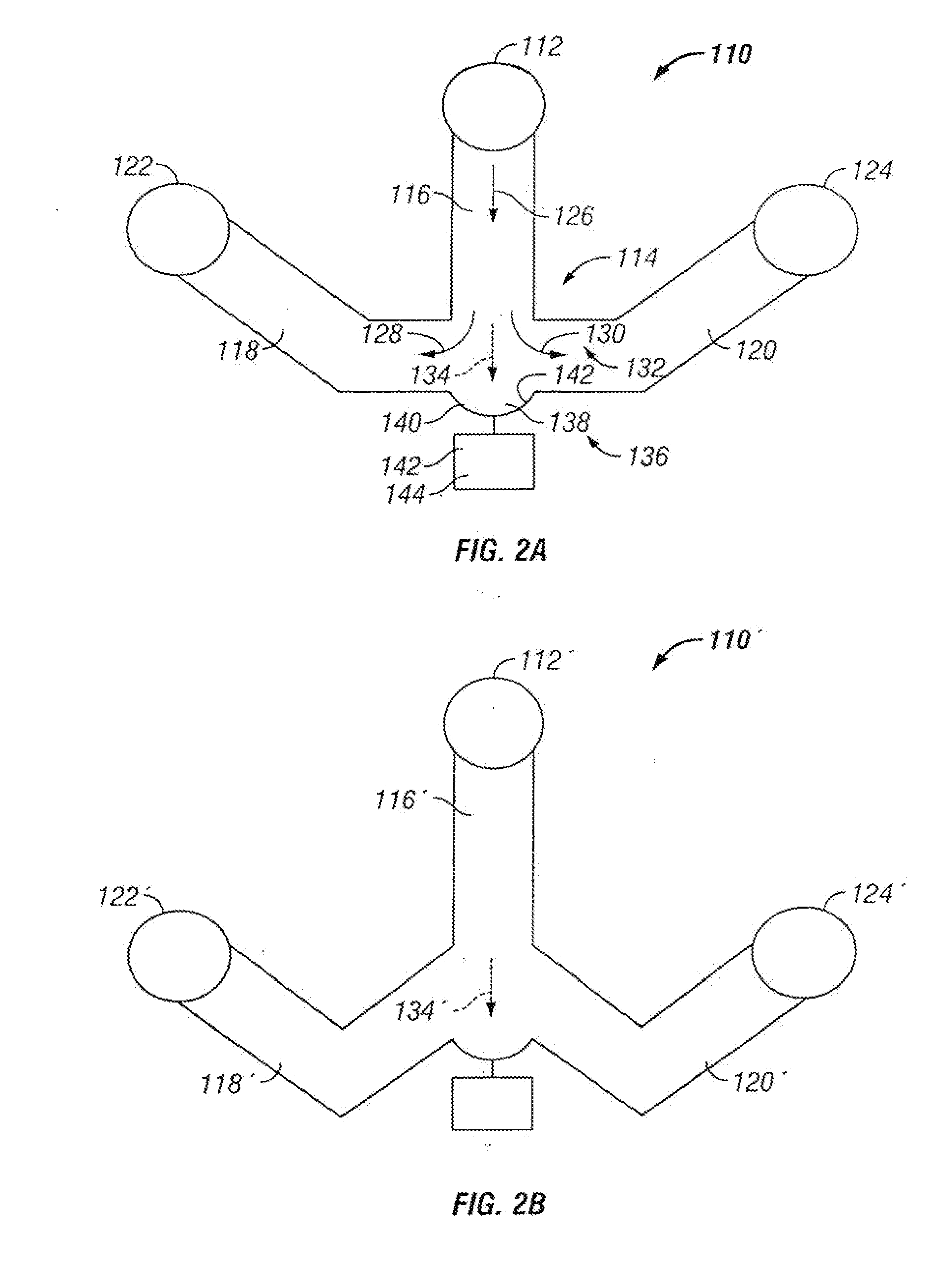
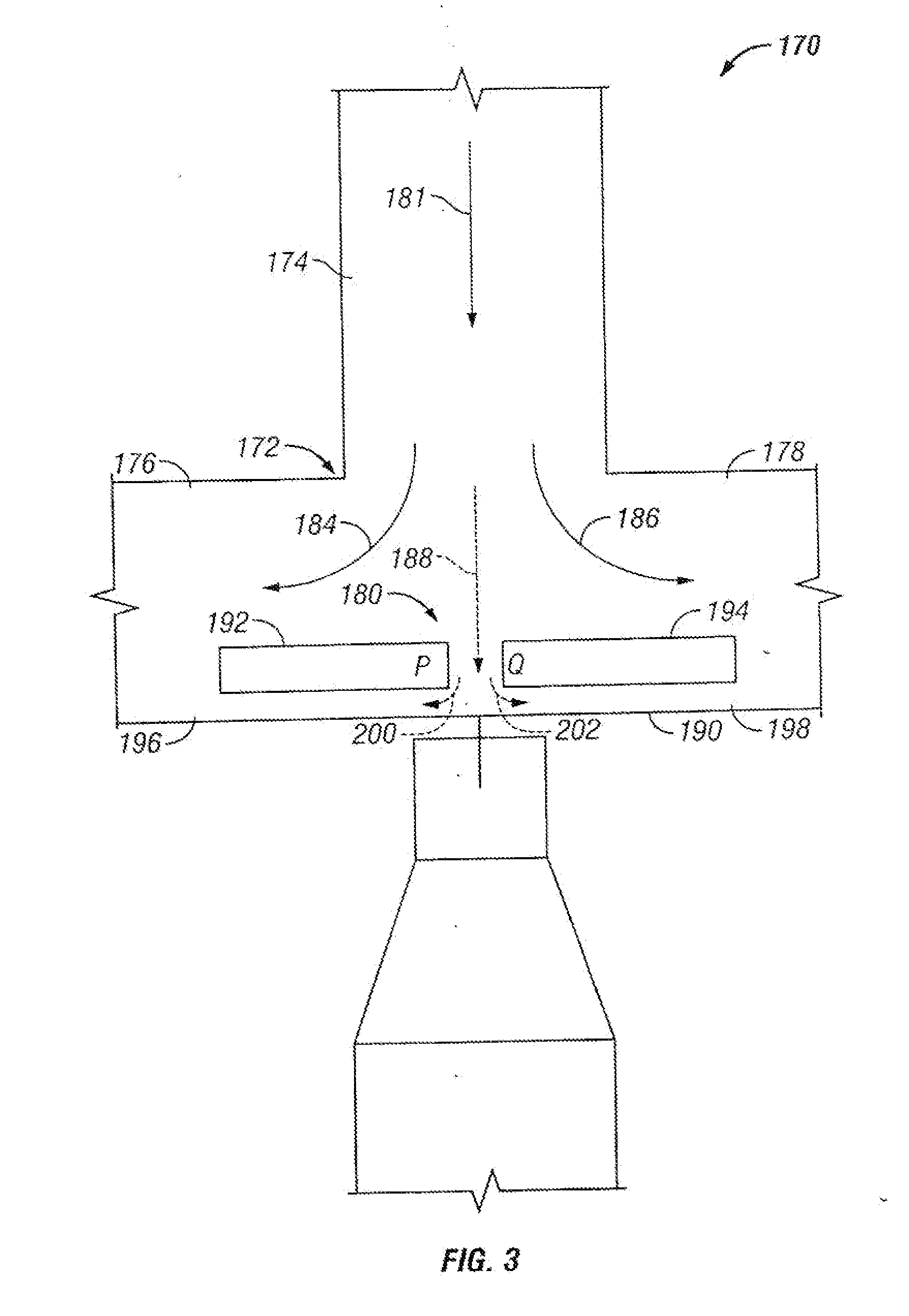
Microfluidic particle-analysis systems
InactiveUS20100120077A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssayMixed group
The invention provides systems, including apparatus, methods, and kits, for the microfluidic manipulation and / or detection of particles, such as cells and / or beads. The invention provides systems, including apparatus, methods, and kits, for the microfluidic manipulation and / or analysis of particles, such as cells, viruses, organelles, beads, and / or vesicles. The invention also provides microfluidic mechanisms for carrying out these manipulations and analyses. These mechanisms may enable controlled input, movement / positioning, retention / localization, treatment, measurement, release, and / or output of particles. Furthermore, these mechanisms may be combined in any suitable order and / or employed for any suitable number of times within a system. Accordingly, these combinations may allow particles to be sorted, cultured, mixed, treated, and / or assayed, among others, as single particles, mixed groups of particles, arrays of particles, heterogeneous particle sets, and / or homogeneous particle sets, among others, in series and / or in parallel. In addition, these combinations may enable microfluidic systems to be reused. Furthermore, these combinations may allow the response of particles to treatment to be measured on a shorter time scale than was previously possible. Therefore, systems of the invention may allow a broad range of cell and particle assays, such as drug screens, cell characterizations, research studies, and / or clinical analyses, among others, to be scaled down to microfluidic size. Such scaled-down assays may use less sample and reagent, may be less labor intensive, and / or may be more informative than comparable macrofluidic assays.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS INC
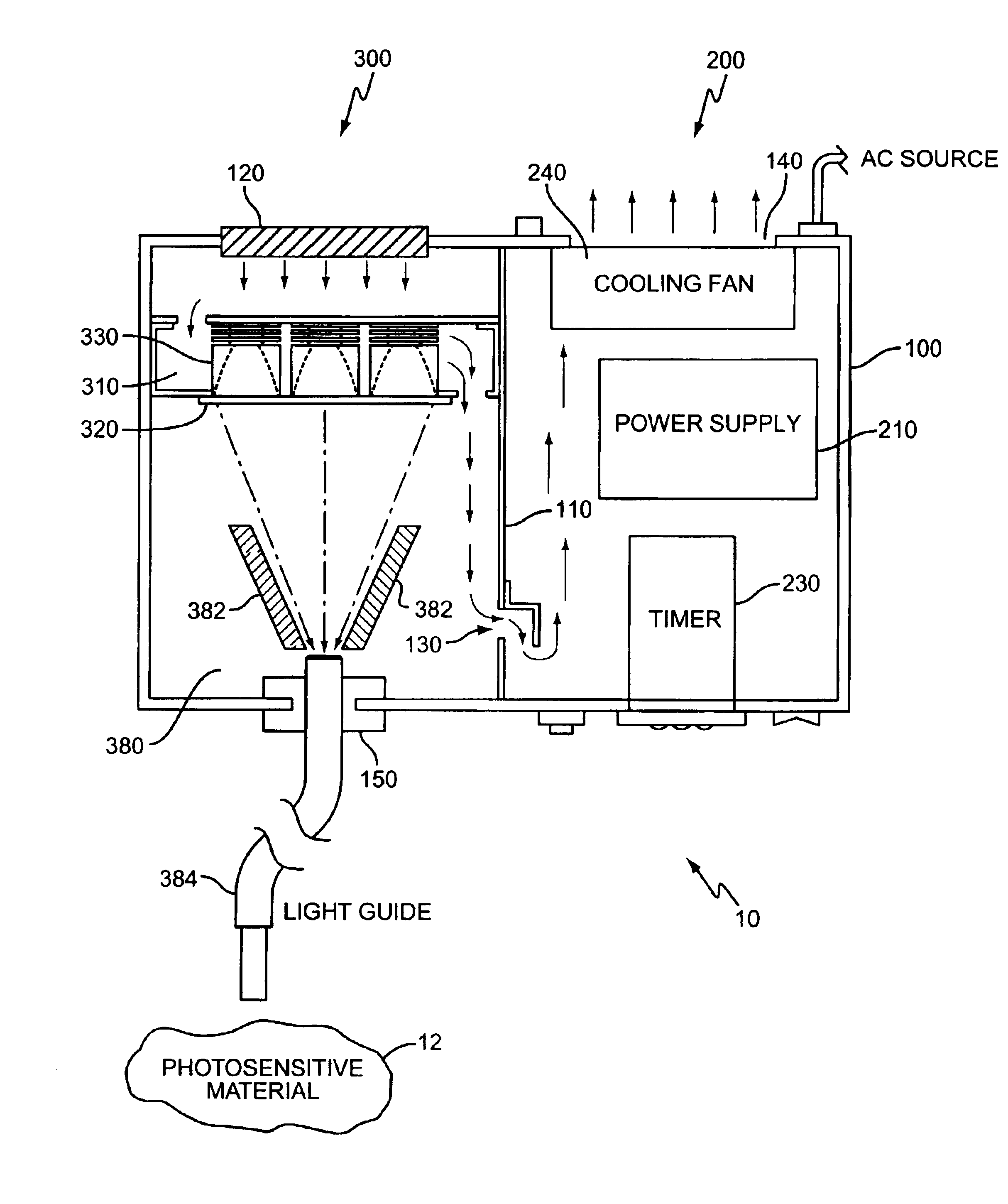
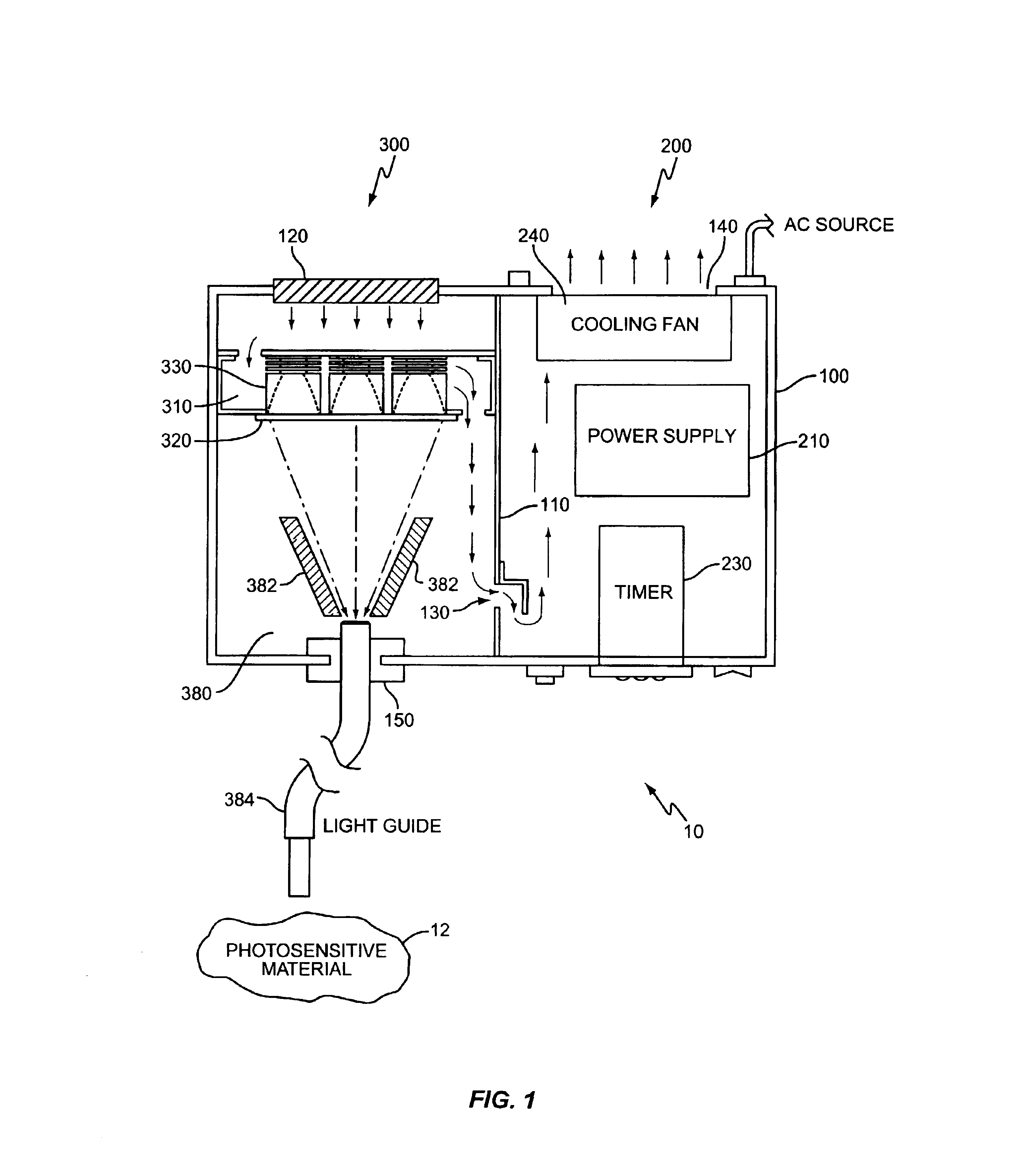
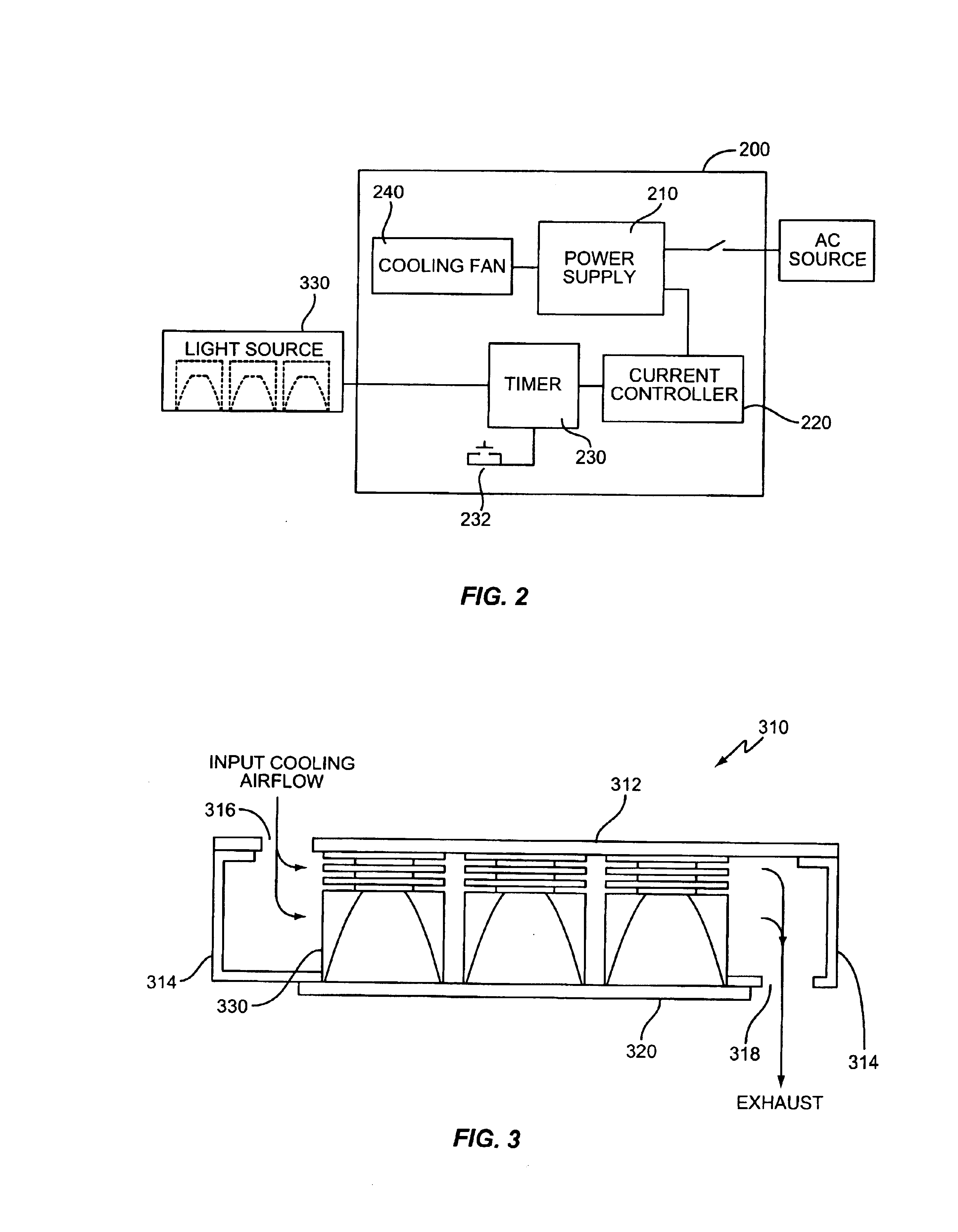
High intensity photocuring system
A method and apparatus for curing photosensitive materials uses LEDs and an optical concentrator to generate high optical power intensities. An LED array, comprising a plurality of LED assemblies, generates collimated light. A collection lens functions as an optical concentrator and focuses the collimated light to a desired spot size at a desired location. The LED assemblies may be at least partially disposed in a cooling plenum, where the cooling plenum is at least partially defined by the collection lens. Each LED assembly within the LED array may be detachably coupled to a mounting surface, enabling easy replacement of individual LED assemblies within the LED array. The photocuring assembly may also include a redirecting assembly disposed between the collection lens and the desired location that may further concentrate the light at the desired location. The photocuring assembly may include more than one of the above features.
Owner:SMD SOFTWARE
Method for simultaneous detection of multiple fluorophores for in situ hybridization and multicolor chromosome painting and banding
InactiveUS6066459AImprove throughputShorten the timeRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryChromosome paintingFluorophore
A spectral imaging method for simultaneous detection of multiple fluorophores aimed at detecting and analyzing fluorescent in situ hybridizations employing numerous chromosome paints and / or loci specific probes each labeled with a different fluorophore or a combination of fluorophores for color karyotyping, and at multicolor chromosome banding, wherein each chromosome acquires a specifying banding pattern, which pattern is established using groups of chromosome fragments labeled with various fluorophore or combinations of fluorophores.
Owner:APPLIED SPECTRAL IMAGING
Microscope with tunable acoustic gradient index of refraction lens enabling multiple focal plan imaging
An apparatus, system and method for microscopy. The apparatus, system and method includes a stage configured to receive an item; a tunable acoustic gradient index of refraction (TAG) lens having a first aspect positioned to image the received item, wherein the first aspect of the TAG lens is configured to have an optical power profile in accordance with an operational frequency of the TAG lens; one or more lenses configured to magnify an image of the received item at a viewing point; and at least one pulsed light source configured to illuminate the received item and to pulse at one or more points within the optical power profile of the TAG lens.
Owner:MITUTOYO OPTICS MFG AMERICA CORP +1
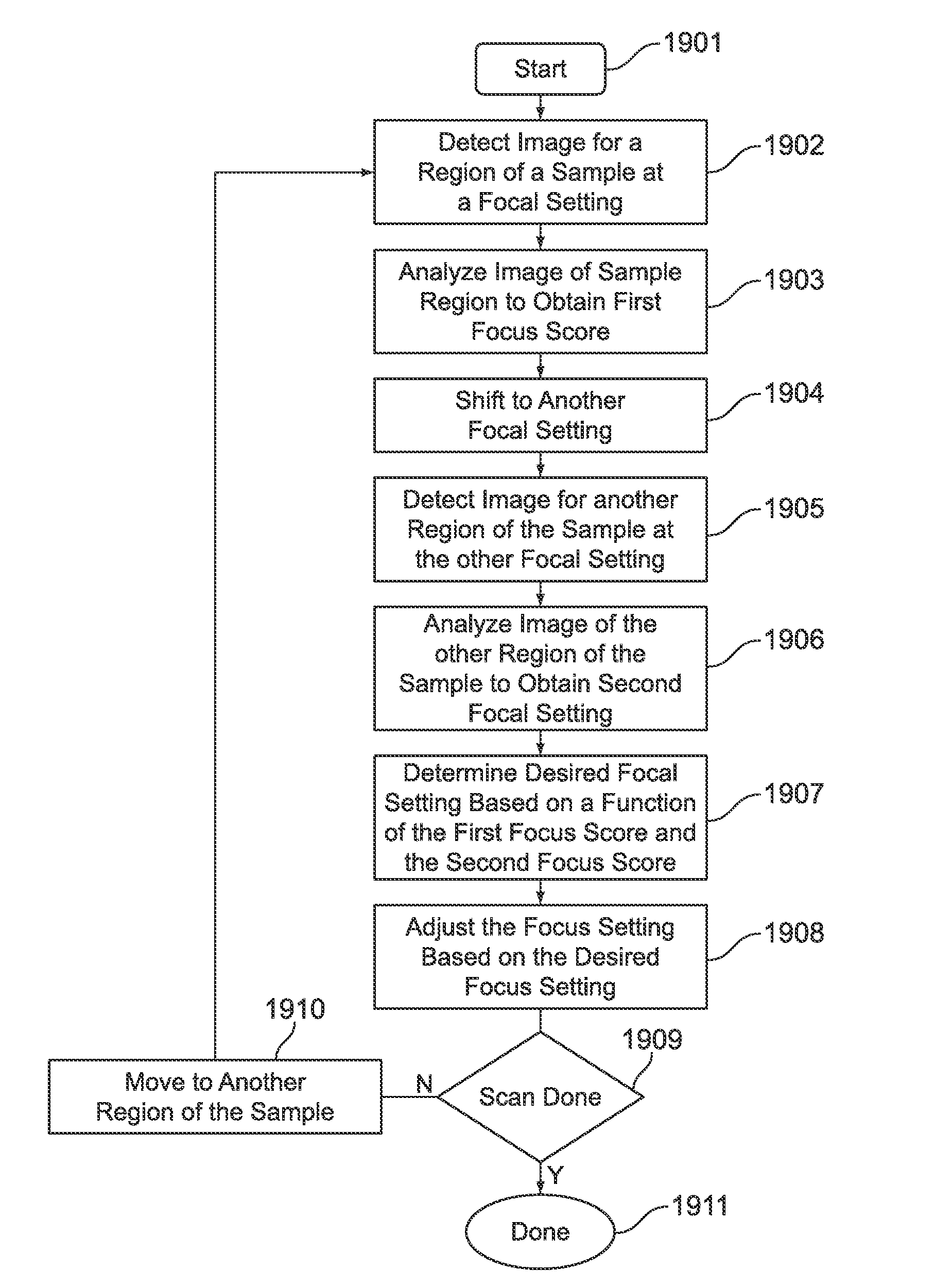
Dynamic autofocus method and system for assay imager
InactiveUS20100157086A1Television system detailsMicrobiological testing/measurementAssayAssociate degree
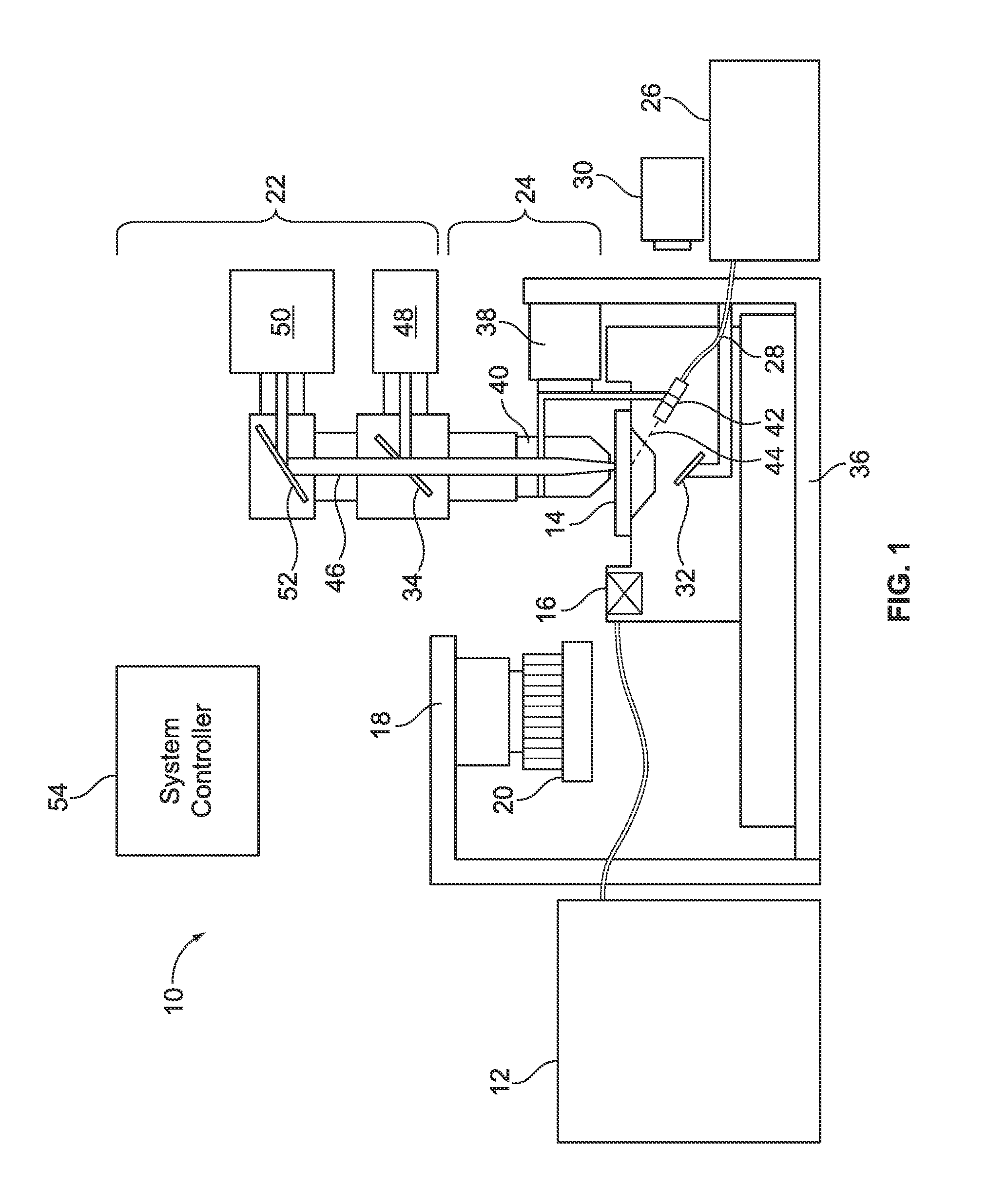
A method and system are provided for controlling focus dynamically of a sample imager. The method comprises scanning a sample with an optical assembly that apportions the sample into regions based on a scan pattern. The optical assembly has a focal setting with respect to the sample. The method further comprises shifting the focal setting of the optical assembly during scanning of the sample, and detecting one or more images representative of one of the regions from the sample. The one or more images have associated degrees of focus corresponding to the focal setting of the optical assembly. The method analyzes the image(s) to obtain a focus score or scores corresponding thereto, where the focus scores represent a degree to which the optical assembly was in focus when detecting the images. The method adjusts the focus setting based on the focus score(s).
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Sterile control unit with a sensor screen
InactiveUS20110235168A1Direct contact guaranteeGood adhesionDiagnosticsSurgical drapesSurgical microscopeIdentification device
The present invention relates to a control unit for an item of medical equipment, particularly a surgical microscope, for controlling equipment functions, comprising a sensor-screen having a sensor-screen surface for displaying image material, the sensor-screen being configured to be operated in contactless manner via a recognition device and to accommodate a sterile transparent control surface in front of the sensor-screen surface.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS (SCHWEIZ) AG
Illumination systems, devices, and methods for biomass production
InactiveUS20090148931A1Sufficient amountMore energySolar heating energyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsLight energyLighting system
Illumination systems, devices, and methods for cultivating biomasses. A bioreactor system is operable for growing photosynthetic organisms. The bioreactor system includes a bioreactor and an illumination system. The illumination system includes one more optical waveguides configured to light at least some of a plurality of photosynthetic organisms retained in the bioreactor. In some embodiments, the one or more optical waveguides include a plurality of structures configured to direct light energy from a solar energy collector, and a plurality of artificial light sources, along the interior of the waveguide. In some embodiments, the one more optical waveguides include a plurality of light-diffusing structures configured to guide at least a portion of the light from the solar energy collector and a plurality of artificial light sources directed along the interior of the waveguide, to the exterior of the waveguide.
Owner:BIONAVITAS
Confocal imaging methods and apparatus
The invention provides imaging apparatus and methods useful for obtaining a high resolution image of a sample at rapid scan rates. A rectangular detector array having a horizontal dimension that is longer than the vertical dimension can be used along with imaging optics positioned to direct a rectangular image of a portion of a sample to the rectangular detector array. A scanning device can be configured to scan the sample in a scan-axis dimension, wherein the vertical dimension for the rectangular detector array and the shorter of the two rectangular dimensions for the image are in the scan-axis dimension, and wherein the vertical dimension for the rectangular detector array is short enough to achieve confocality in a single axis.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Disposable Chamber for Analyzing Biologic Fluids
ActiveUS20070243117A1Accurately determinableUniform heightBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringBiological fluids
Owner:WARDLAW PARTNERS +2
Imaging device and digital camera using the imaging device
InactiveUS20040008271A1Solve the thickerLow costTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensOptical power
An imaging device has a zoom lens system having a plurality of lens units and forming an optical image of an object so as to continuously optically zoom by varying distances between the lens unit; and an image sensor converting the optical image formed by the zoom lens system to an electric signal. The zoom lens system has from an object side, a first lens unit being overall negative and including a reflecting surface that bends a luminous flux substantially 90 degrees; and a second lens unit disposed with a variable air distance from the first lens unit, and having an optical power, and wherein at least one lens element made of resin is included in the entire lens system.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
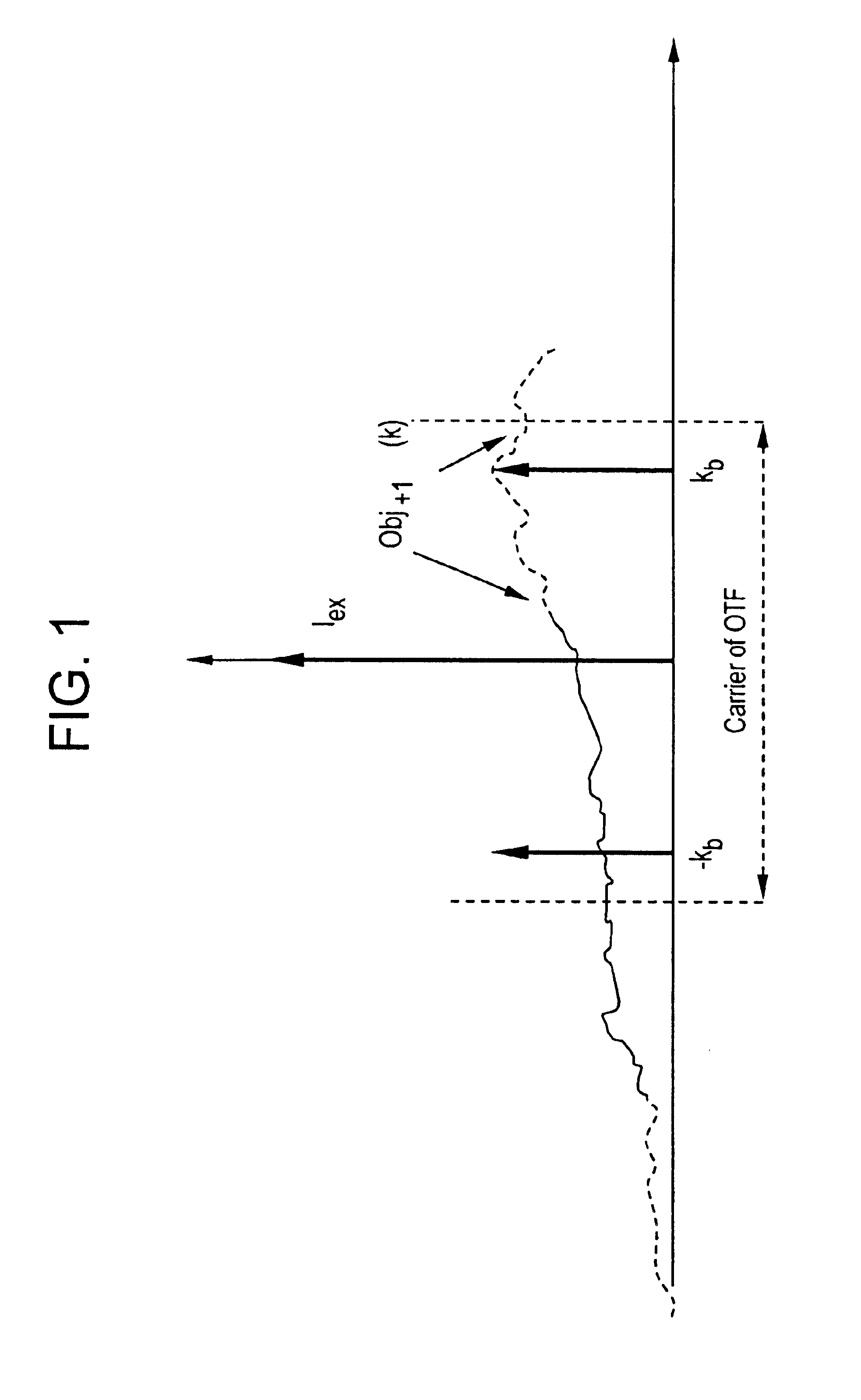
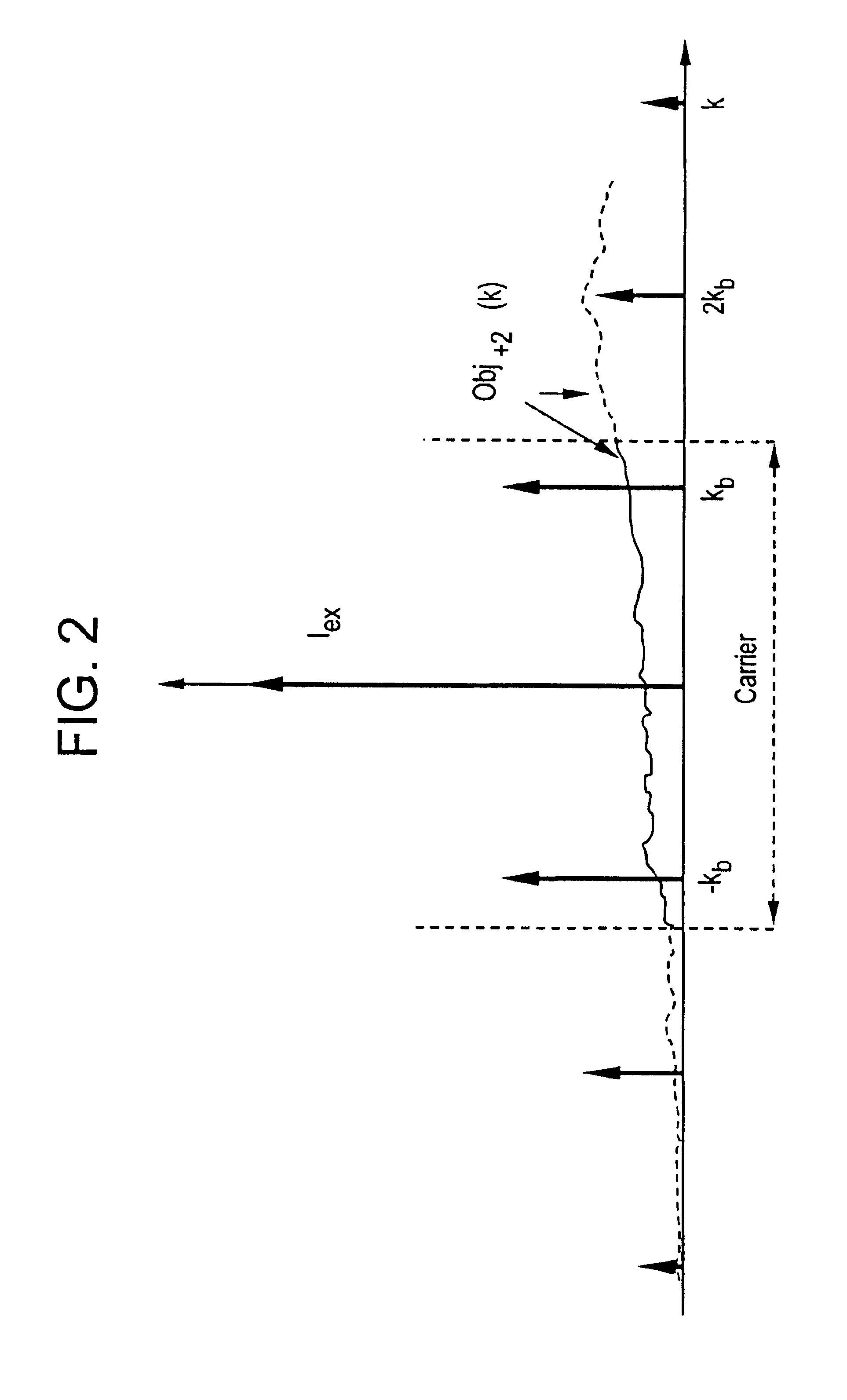
Method and device for representing an object
InactiveUS6909105B1Increased frequency rangeEasy to getImage analysisInvestigating moving sheetsPattern recognitionObject structure
A process for obtaining an object image of at least one object (40) is described, wherein at least two partial images of the object (40) are taken under differing object conditions which are formed on the object with spatial patterns, wherein a non-linear dependence of the light detectable from the object point on the object conditions given at the object point exists and the partial images contain different contributions of various space frequency components of the object structure, and the desired object image is determined from the partial images by reconstruction of the space frequency components. Optical systems for implementing this type of process are also described.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
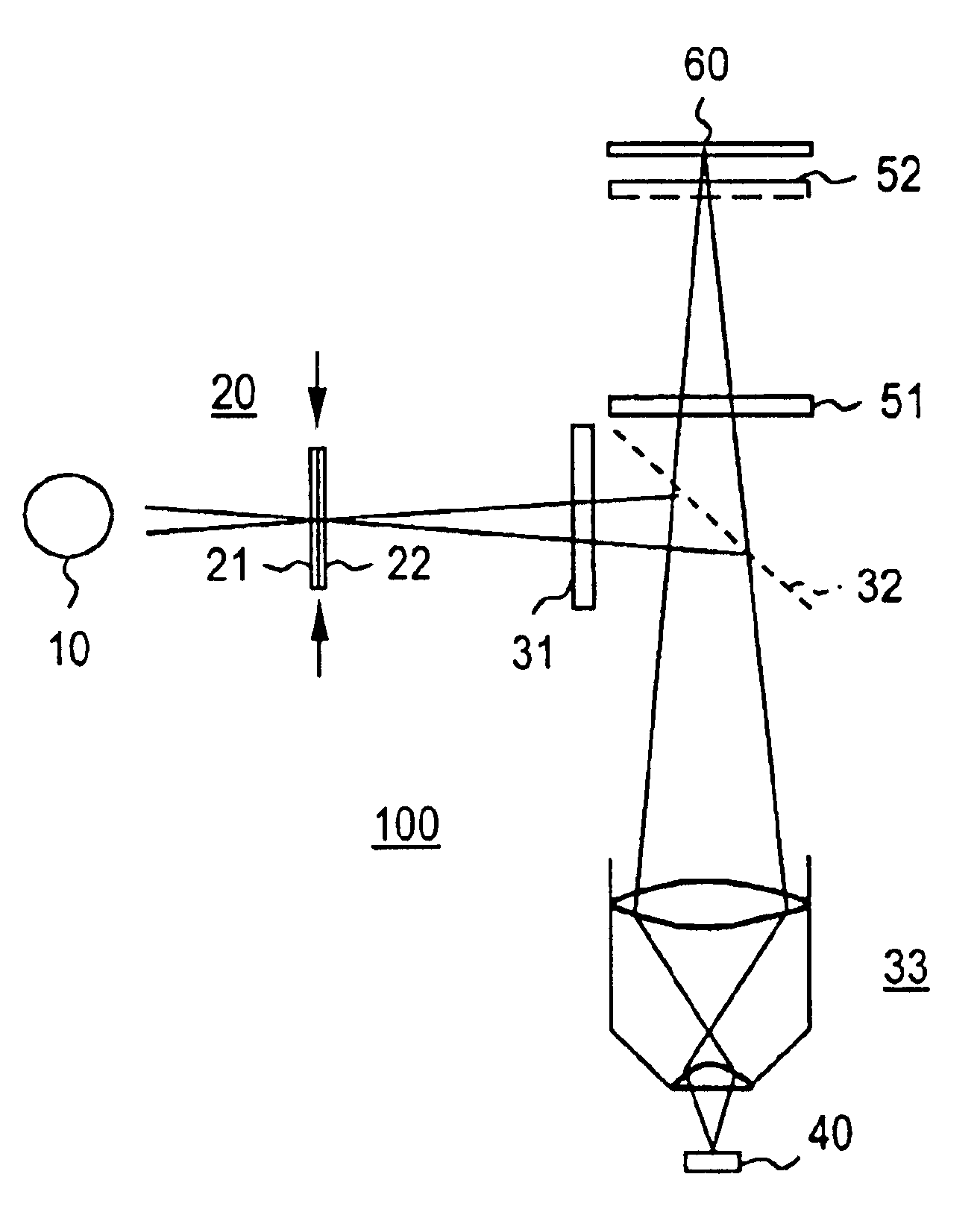
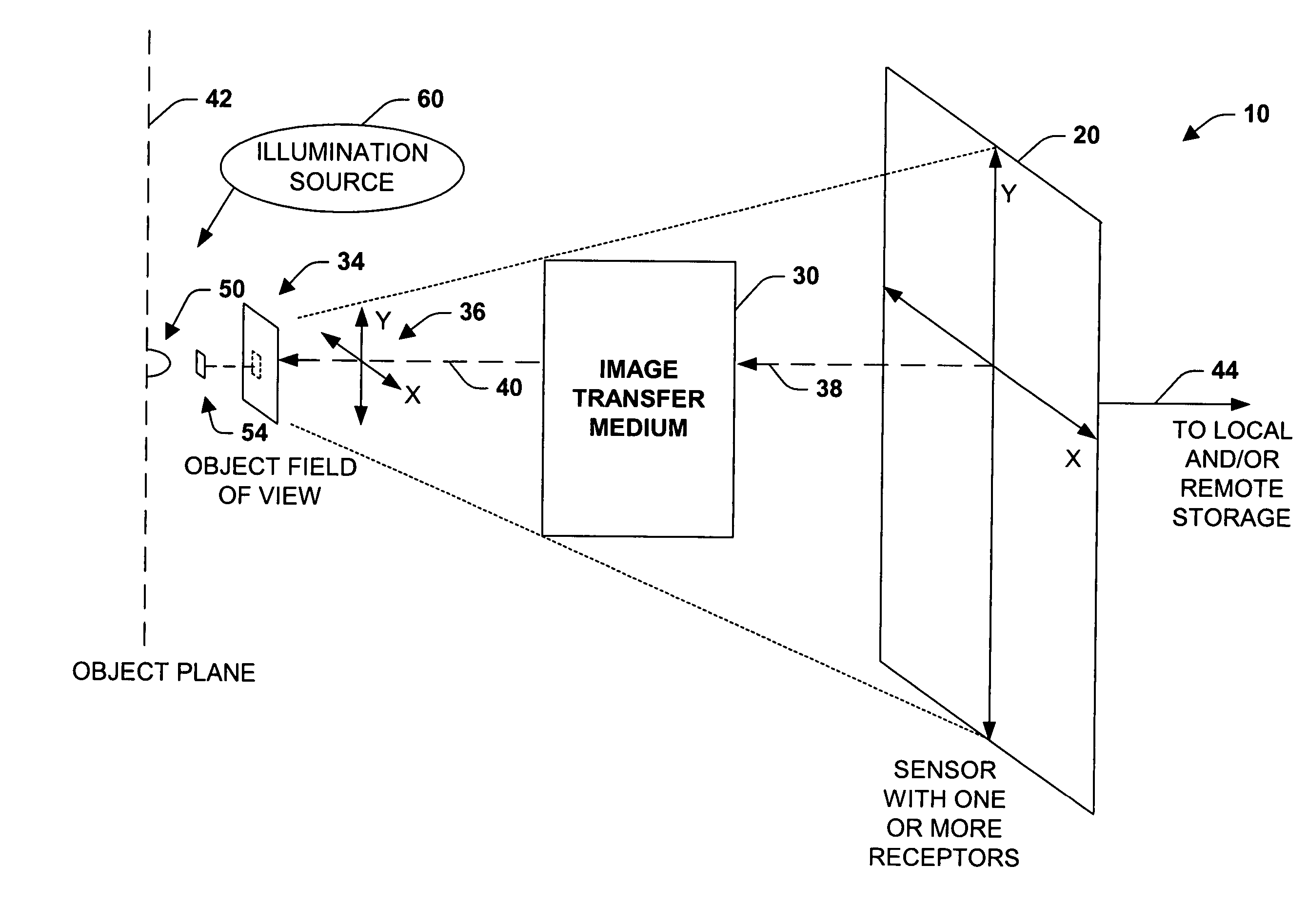
Imaging system and methodology
InactiveUS7151246B2Improve performanceEffectively scaledTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationImage transferDisplay device
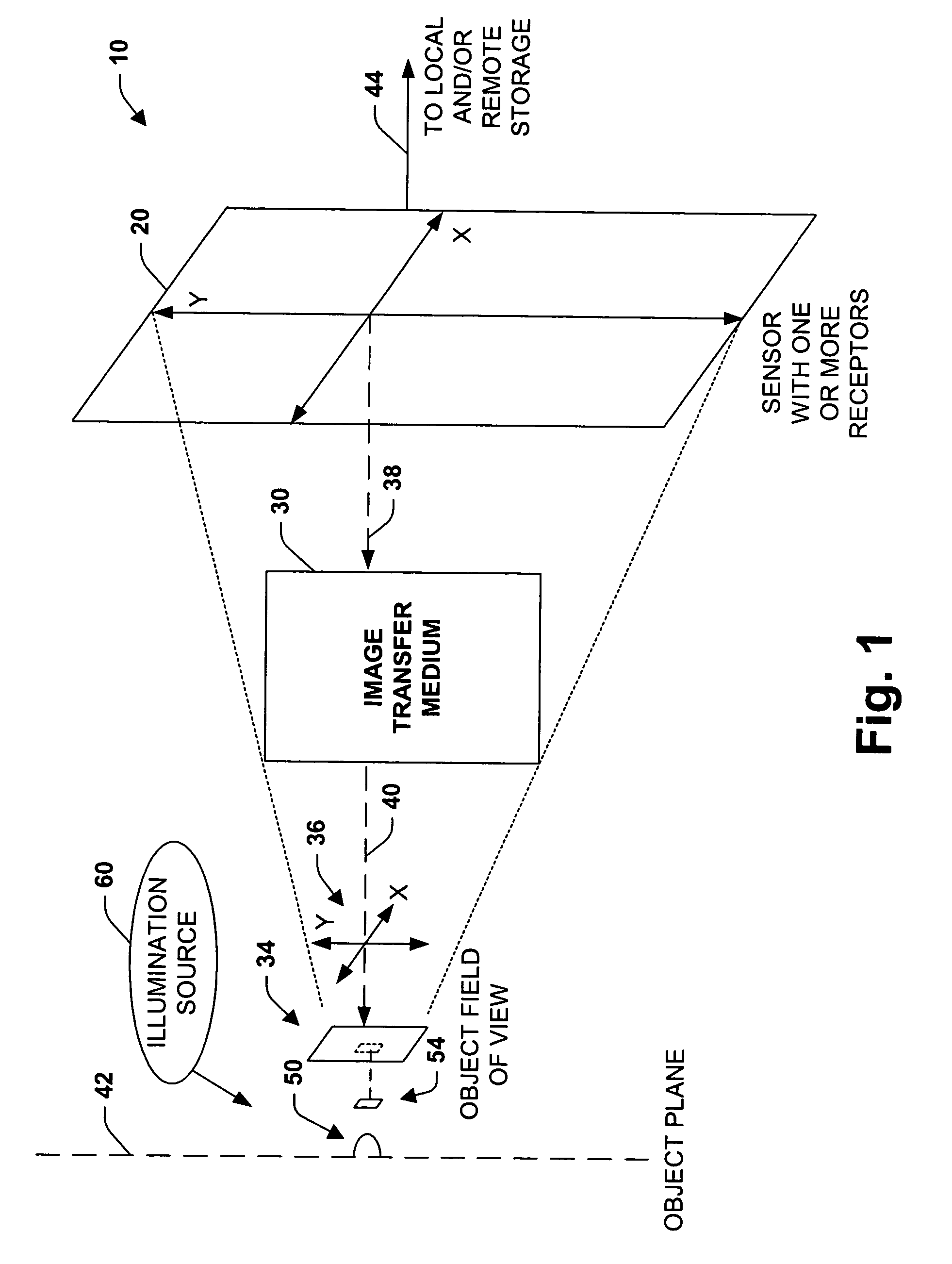
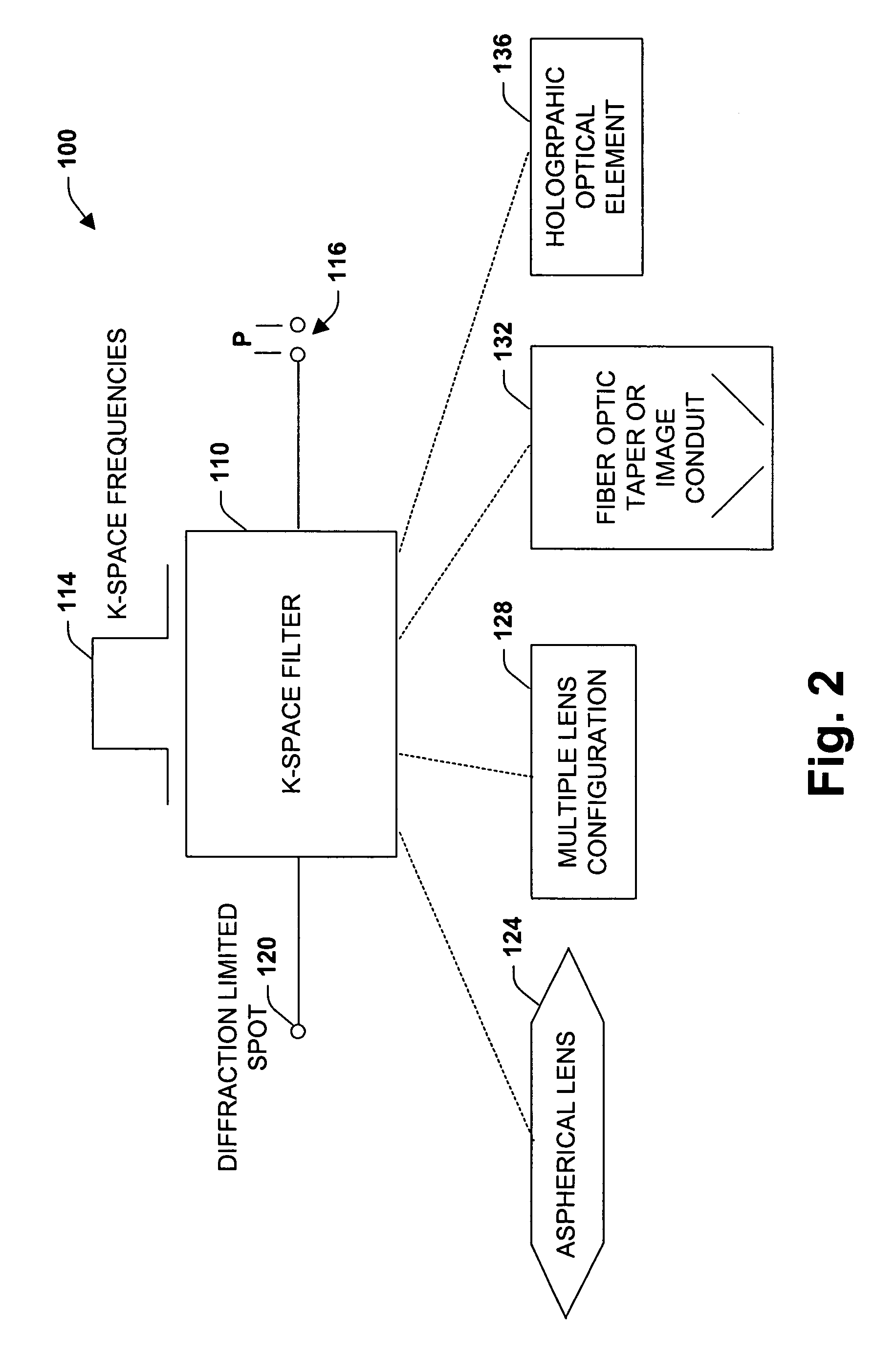
An imaging system, methodology, and various applications are provided to facilitate optical imaging performance. The system contains a sensor having one or more receptors and an image transfer medium to scale the sensor and receptors in accordance with resolvable characteristics of the medium, and as defined with certain ratios. A computer, memory, and / or display associated with the sensor provides storage and / or display of information relating to output from the receptors to produce and / or process an image, wherein a plurality of illumination sources can also be utilized in conjunction with the image transfer medium. The image transfer medium can be configured as a k-space filter that correlates projected receptor size to a diffraction-limited spot associated with the image transfer medium, wherein the projected receptor size can be unit-mapped within a certain ratio to the size of the diffraction-limited spot, both in the object plane.
Owner:HIMANSHU S AMIN +3
Method for correction of relative object-detector motion between successive views
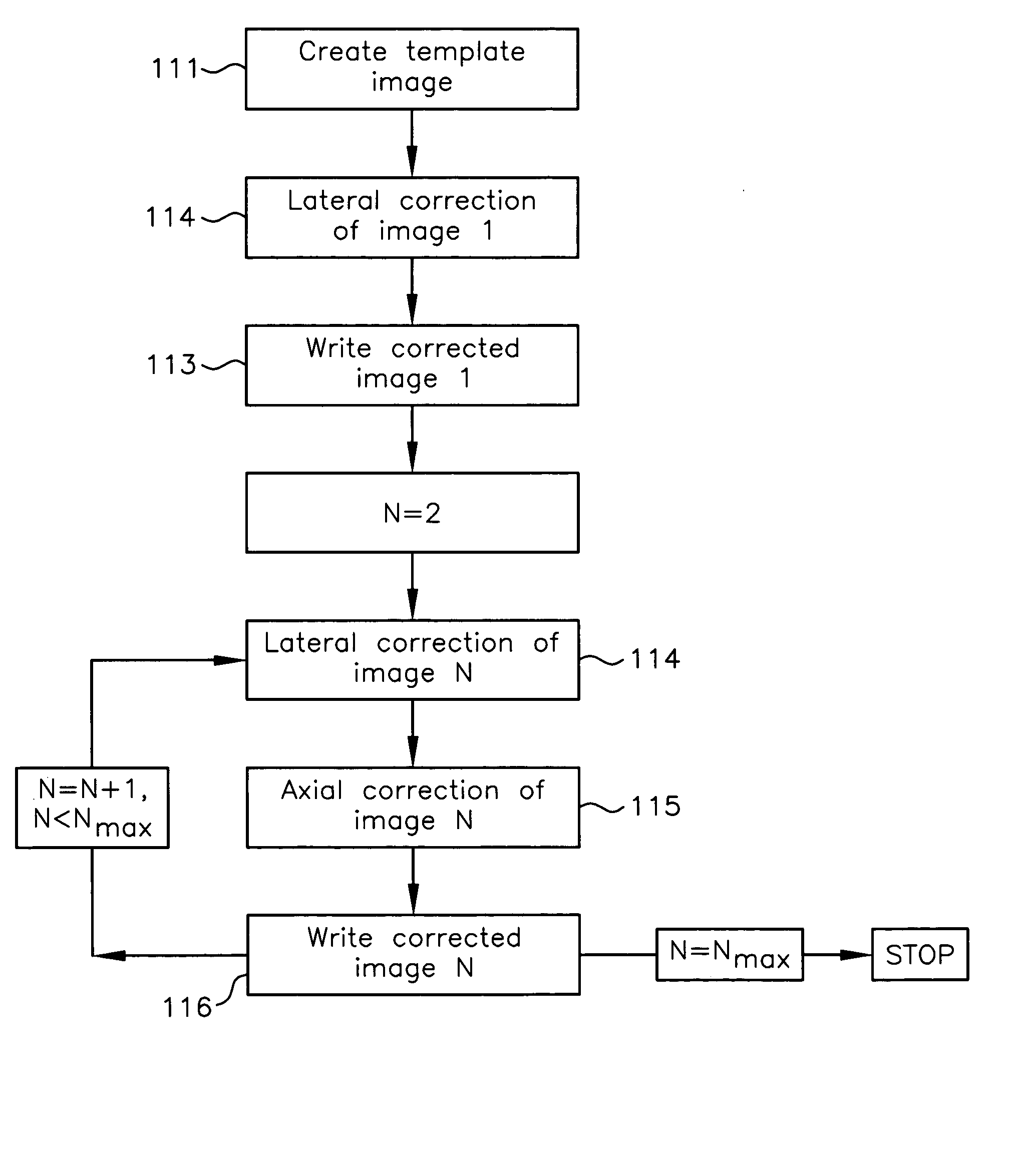
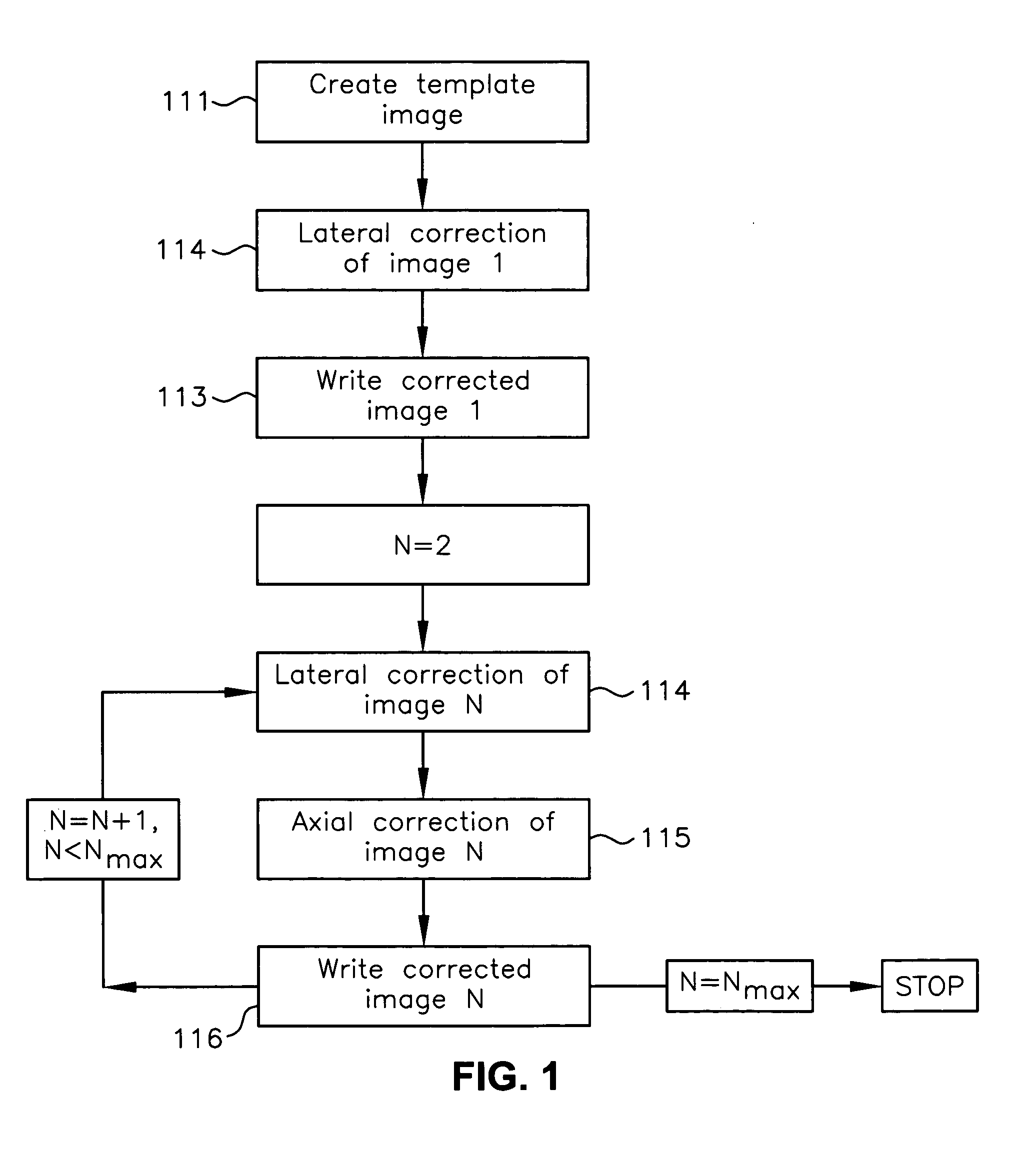
Registration correction for optical tomographic imaging in three dimensions. An object of interest is illuminated to produce an image. A lateral offset correction value is determined for the image. An axial offset correction value is determined for the image. The lateral offset correction value and the axial offset correction value are applied to the image to produce a corrected file image.
Owner:VISIONGATE
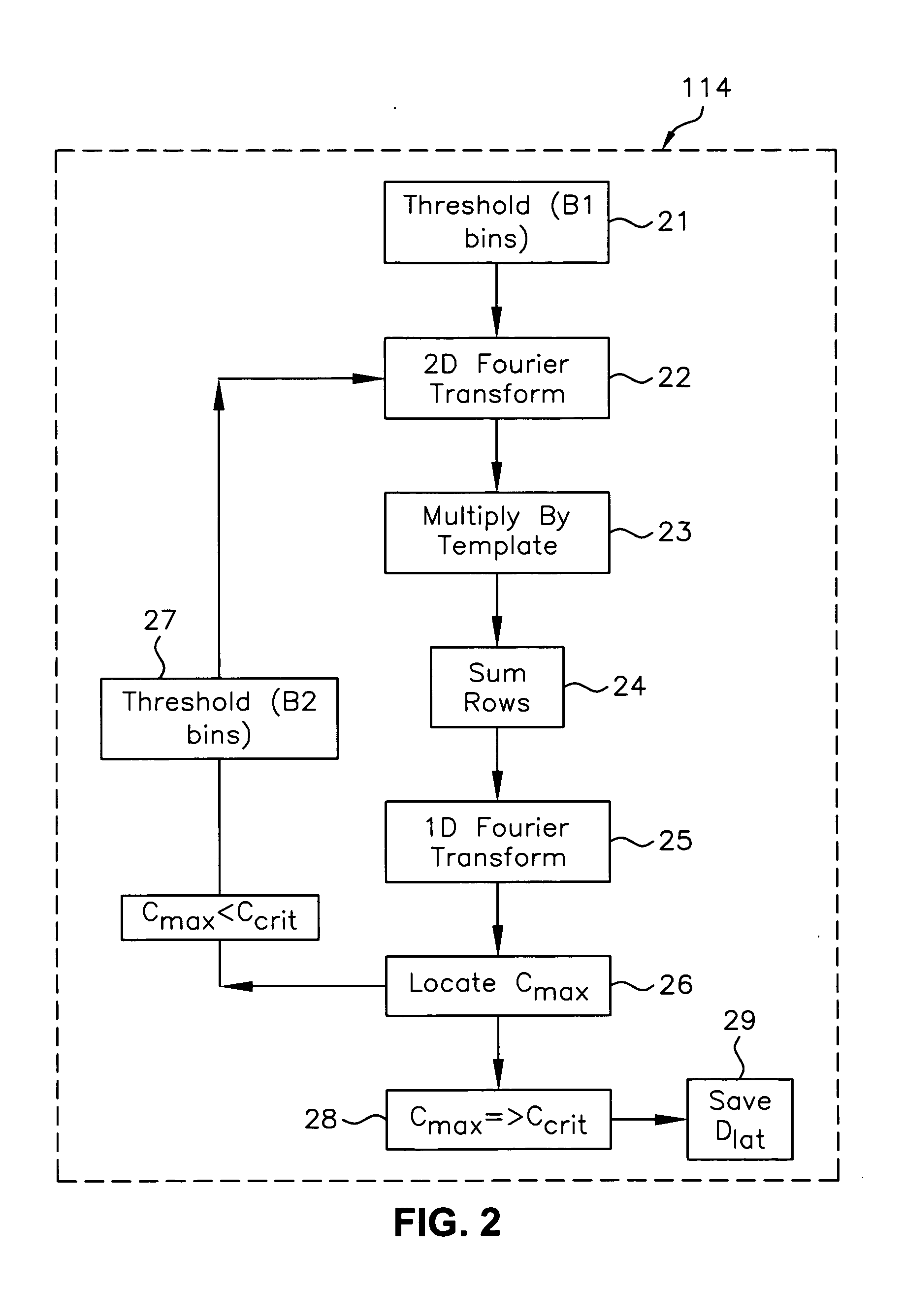
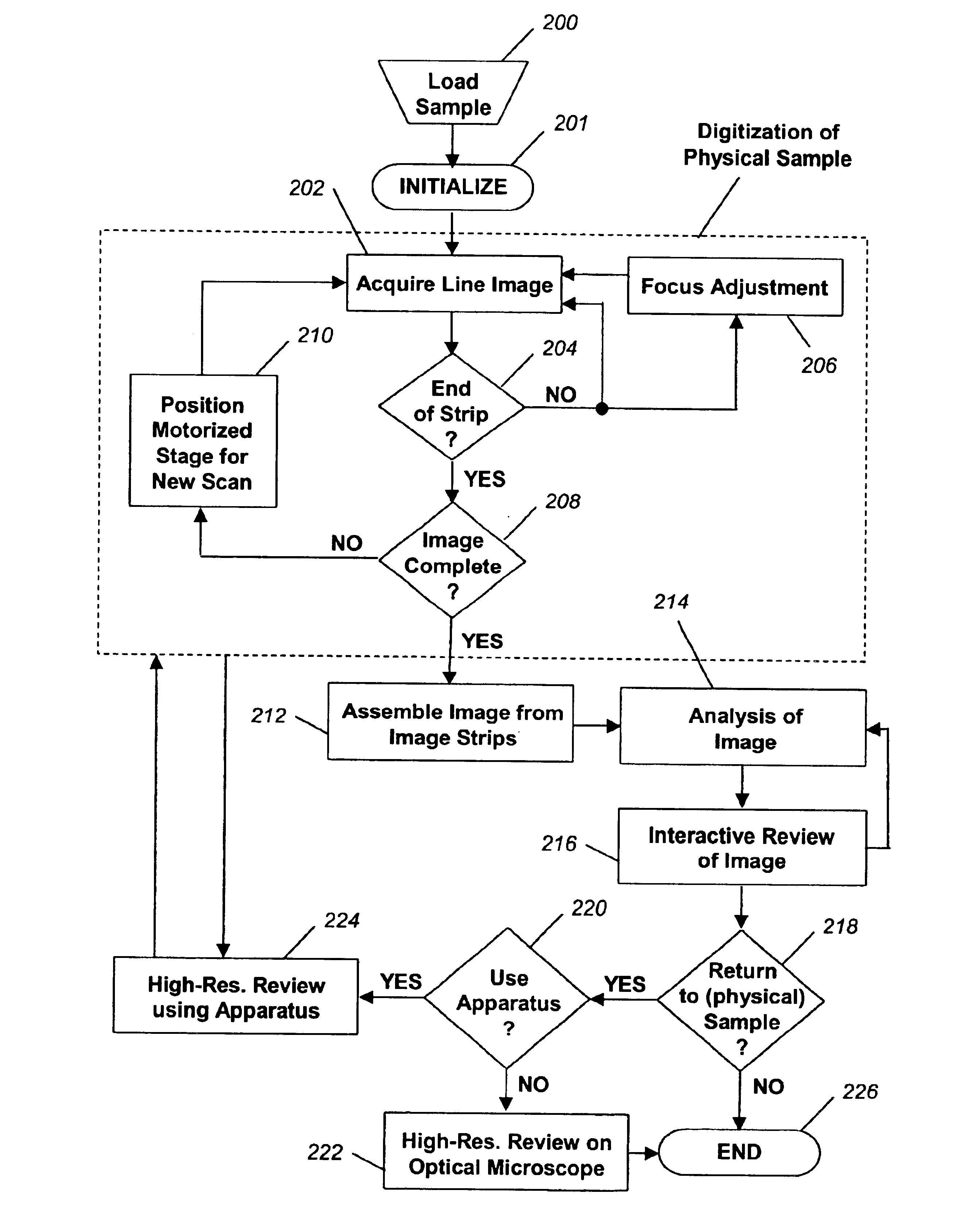
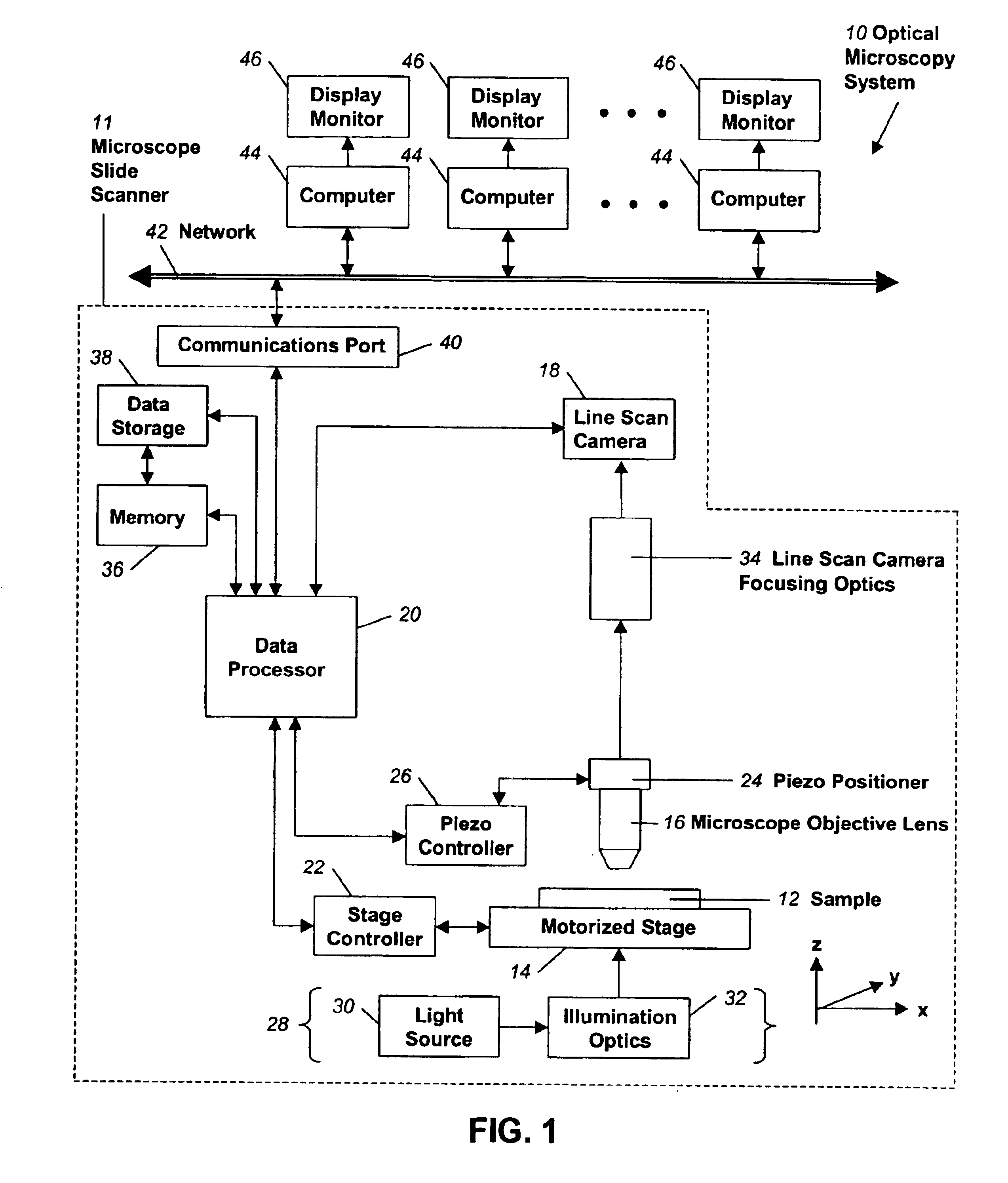
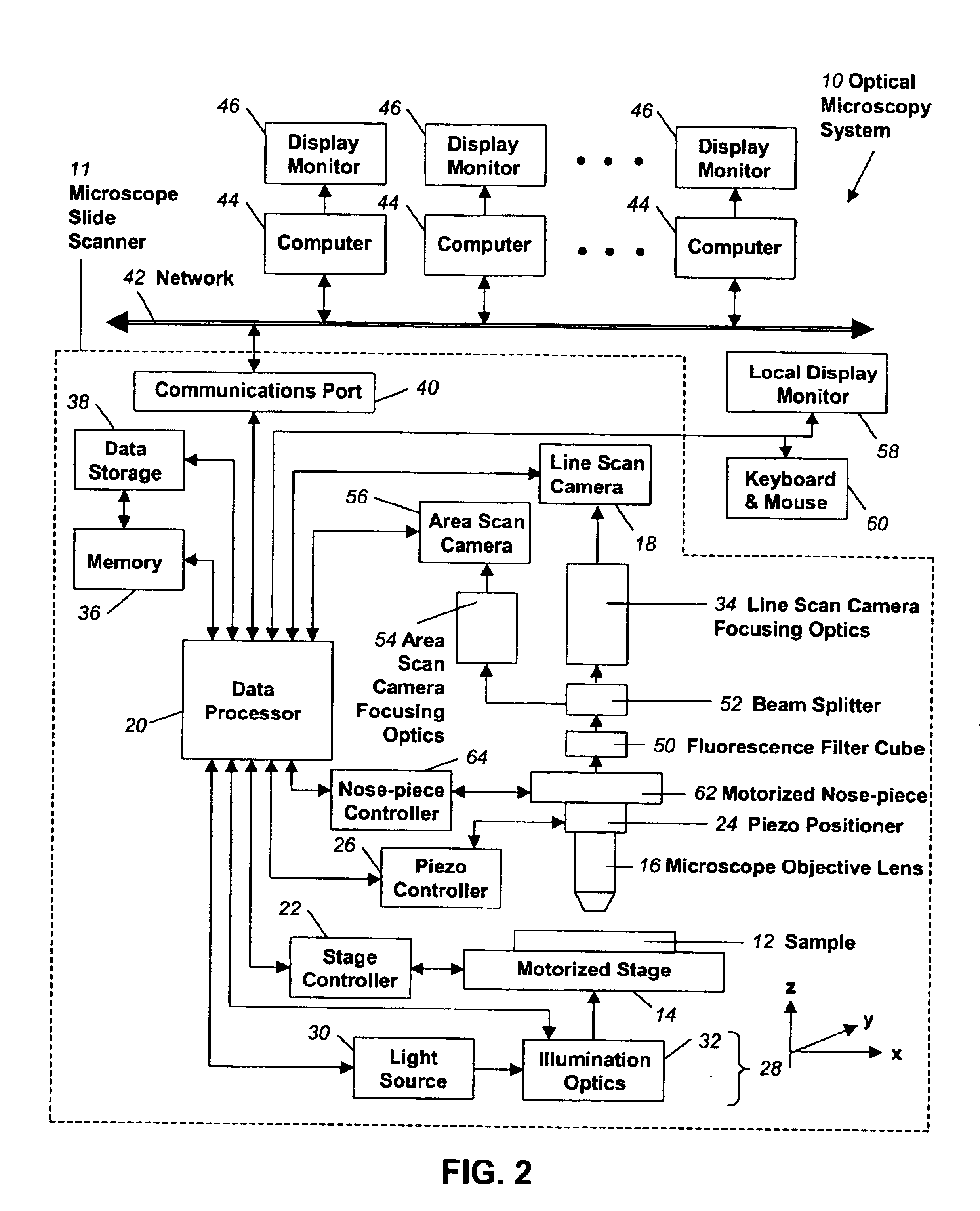
Fully automatic rapid microscope slide scanner
InactiveUS6917696B2Television system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscope slideContinuous scanning
Apparatus for and method of fully automatic rapid scanning and digitizing of an entire microscope sample, or a substantially large portion of a microscope sample, using a linear array detector synchronized with a positioning stage that is part of a computer controlled microscope slide scanner. The invention provides a method for composing the image strips obtained from successive scans of the sample into a single contiguous digital image. The invention also provides a method for statically displaying sub-regions of this large digital image at different magnifications, together with a reduced magnification macro-image of the entire sample. The invention further provides a method for dynamically displaying, with or without operator interaction, portions of the contiguous digital image. In one preferred embodiment of the invention, all elements of the scanner are part of a single-enclosure that has a primary connection to the Internet or to a local intranet. In this embodiment, the preferred sample type is a microscope slide and the illumination and imaging optics are consistent with transmission mode optics optimized for diffraction-limited digital imaging.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
Compensator for multiple surface imaging
ActiveUS20090272914A1Reduce aberrationScattering properties measurementsLuminescent dosimetersTotal internal reflectionFluorescence
A system and method for imaging biological samples on multiple surfaces of a support structure are disclosed. The support structure may, for instance, be a flow cell through which a reagent fluid is allowed to flow and interact with the biological samples. Excitation radiation from at least one radiation source may be used to excite the biological samples on multiple surfaces. In this manner, fluorescent emission radiation may be generated from the biological samples and subsequently captured and detected by detection optics and at least one detector. The captured and detected fluorescent emission radiation may then be used to generate image data. This imaging of multiple surfaces may be accomplished either sequentially or simultaneously. In addition, the techniques of the present invention may be used with any type of imaging system. For instance, both epifluorescent and total internal reflection (TIR) methods may benefit from the techniques of the present invention. In addition, the biological samples imaged may be present on the surfaces of the support structure in a random special pattern and need not be at known locations in order for the imaging to be performed.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com