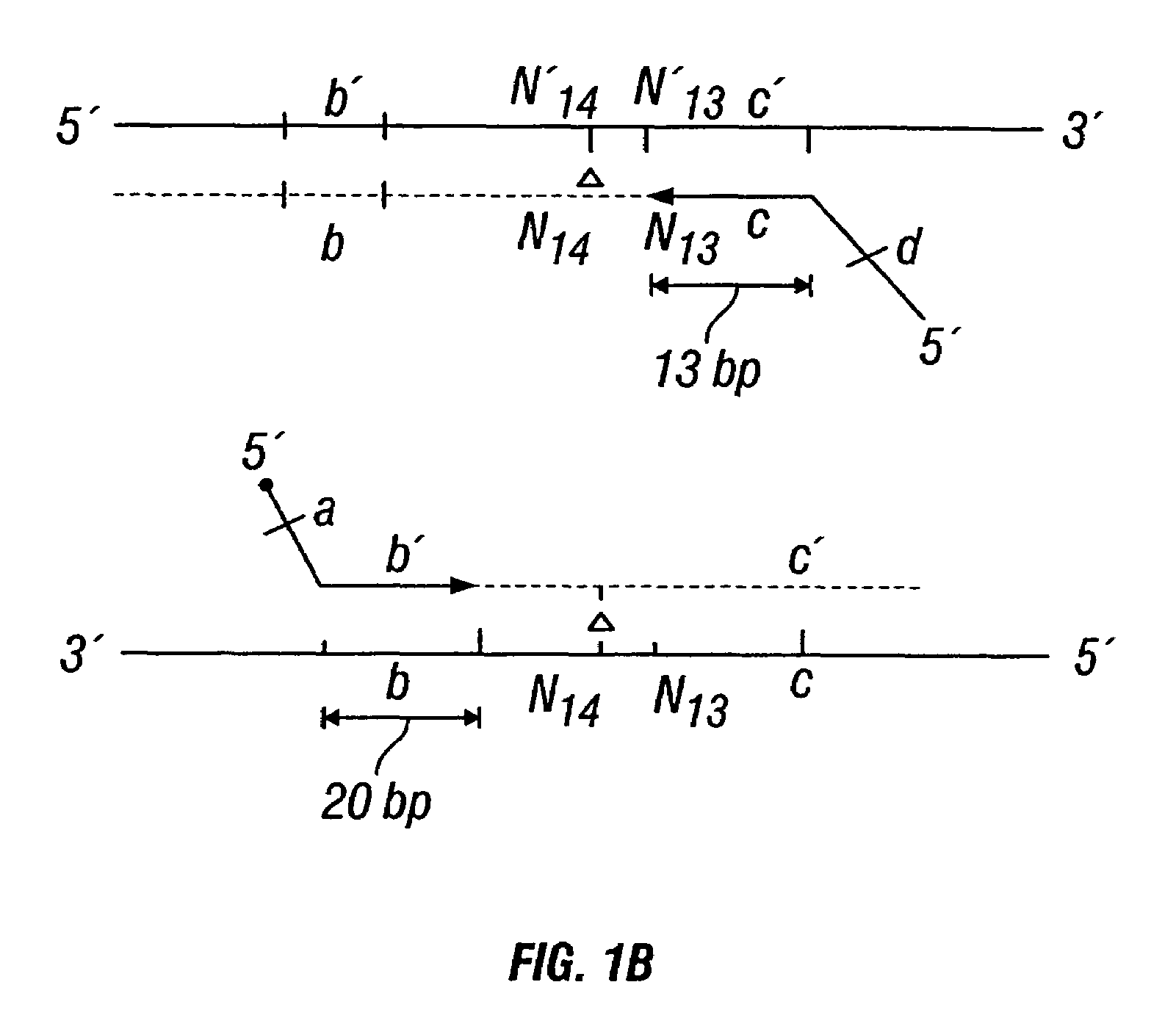
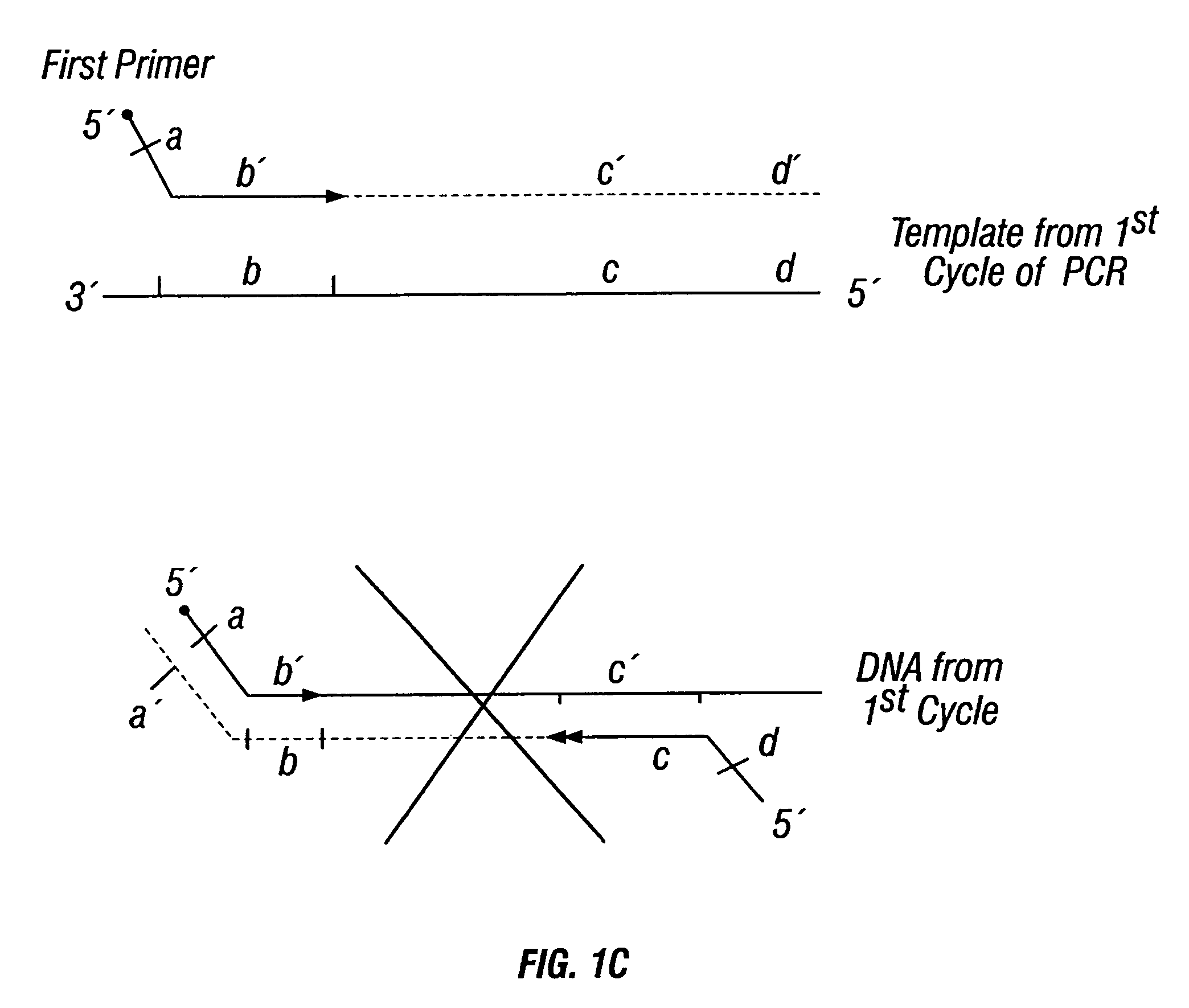
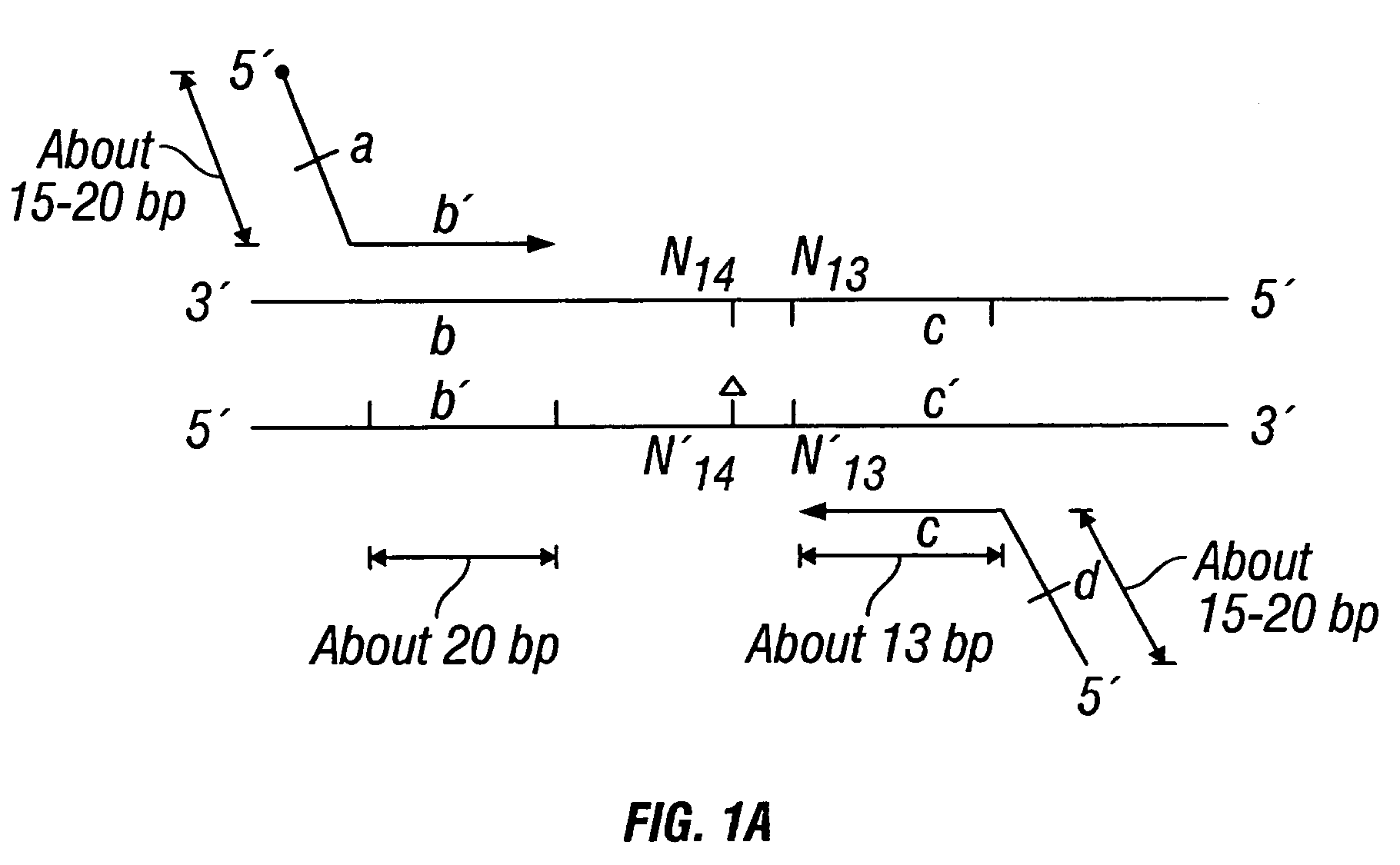
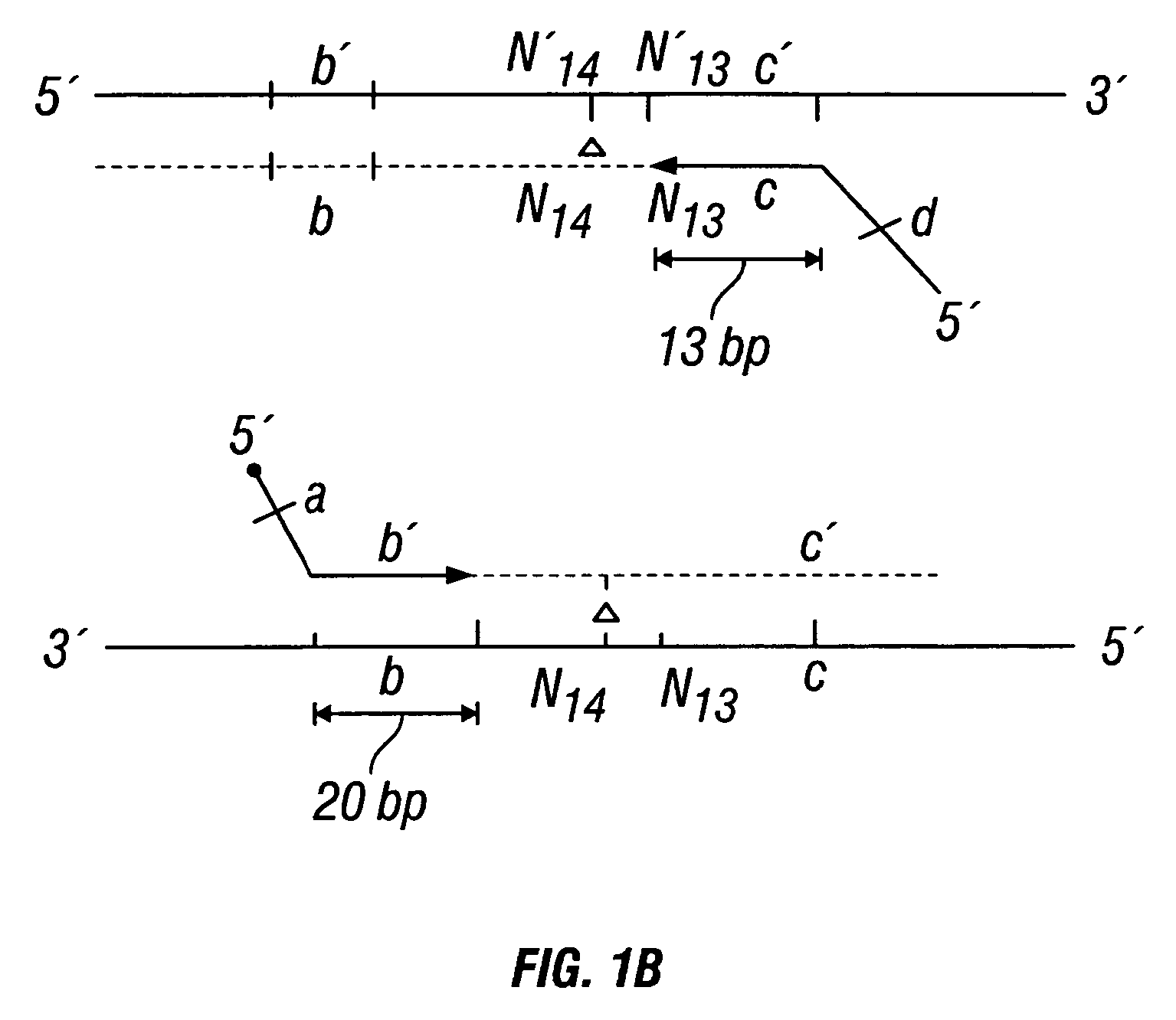
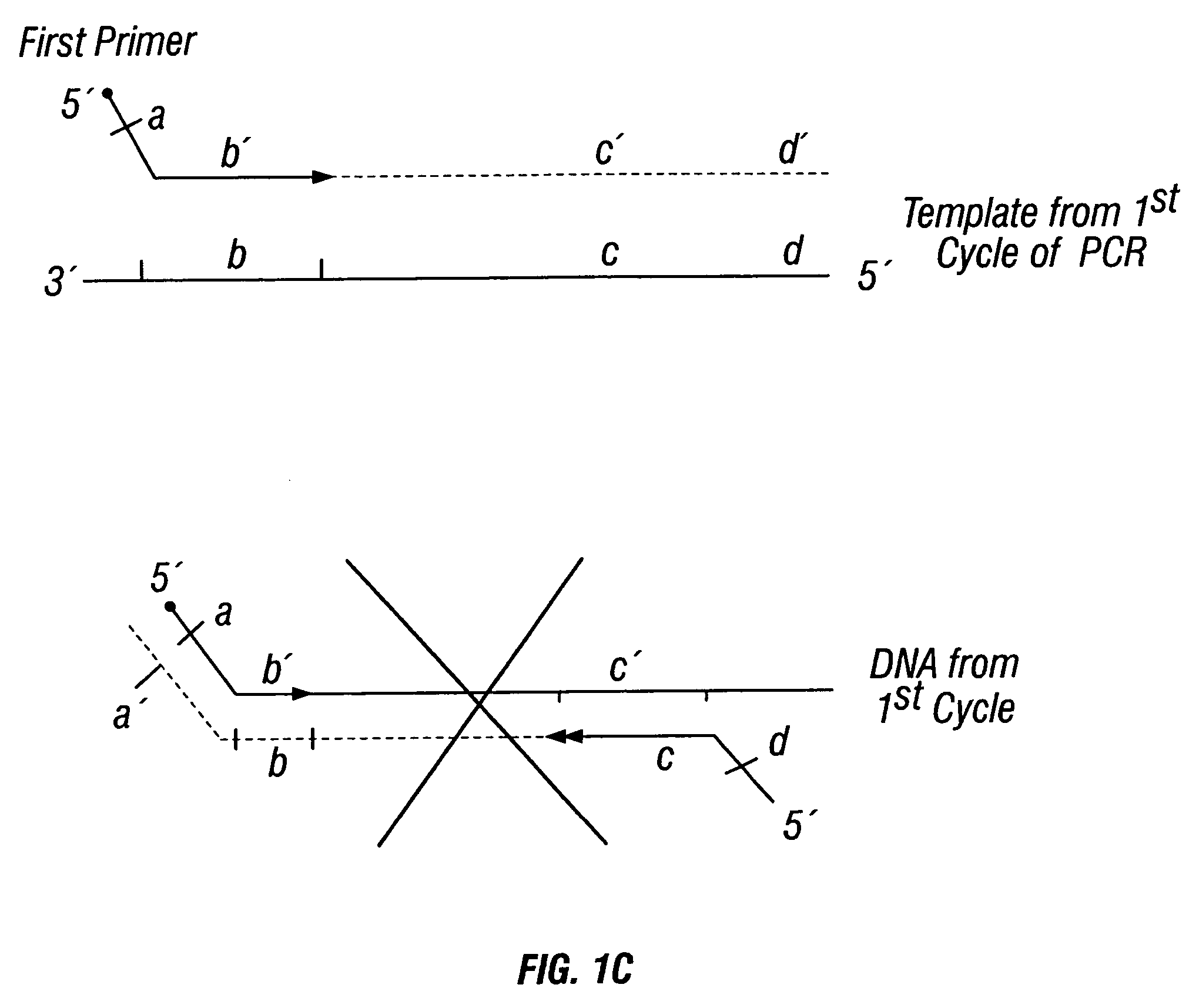
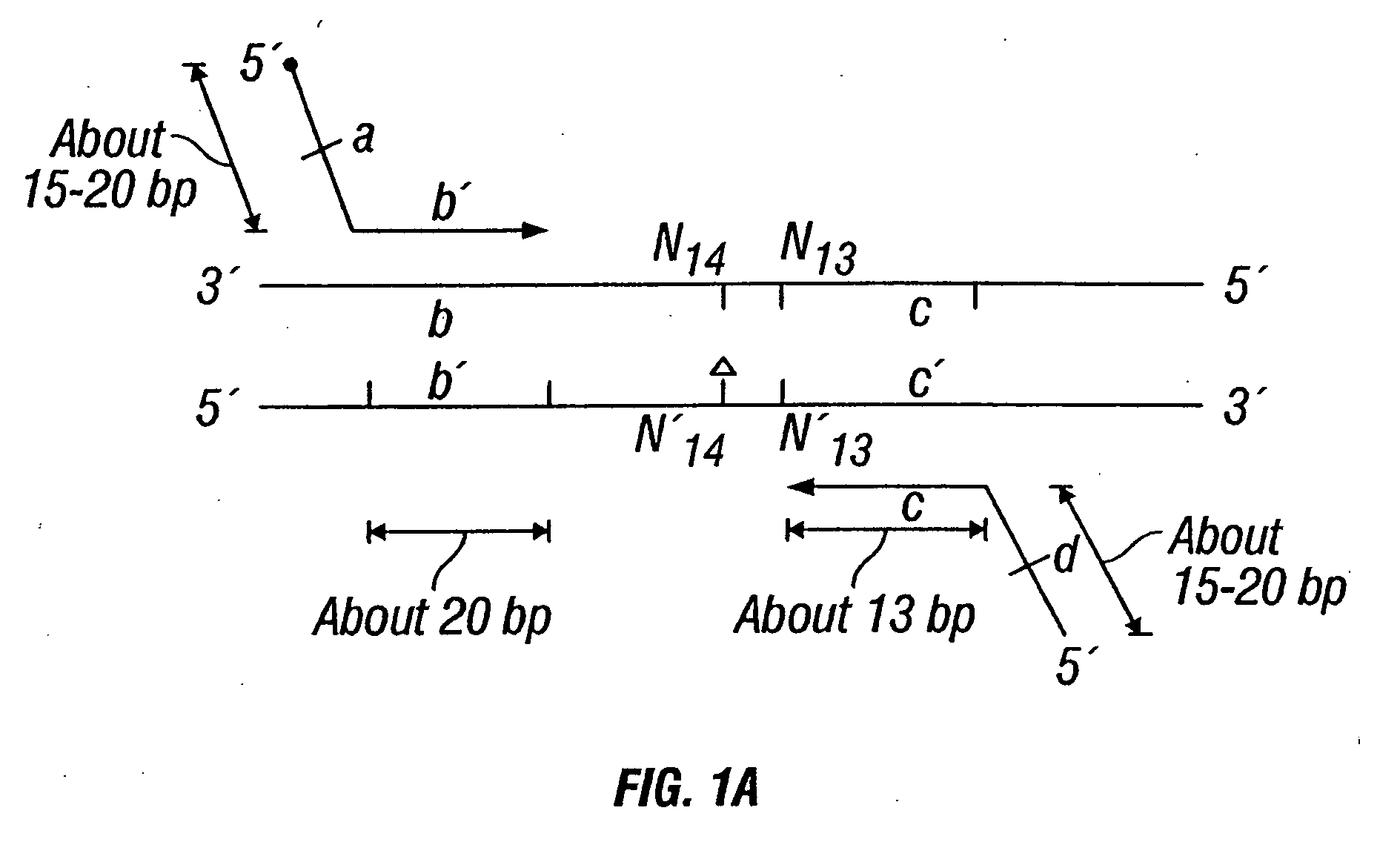
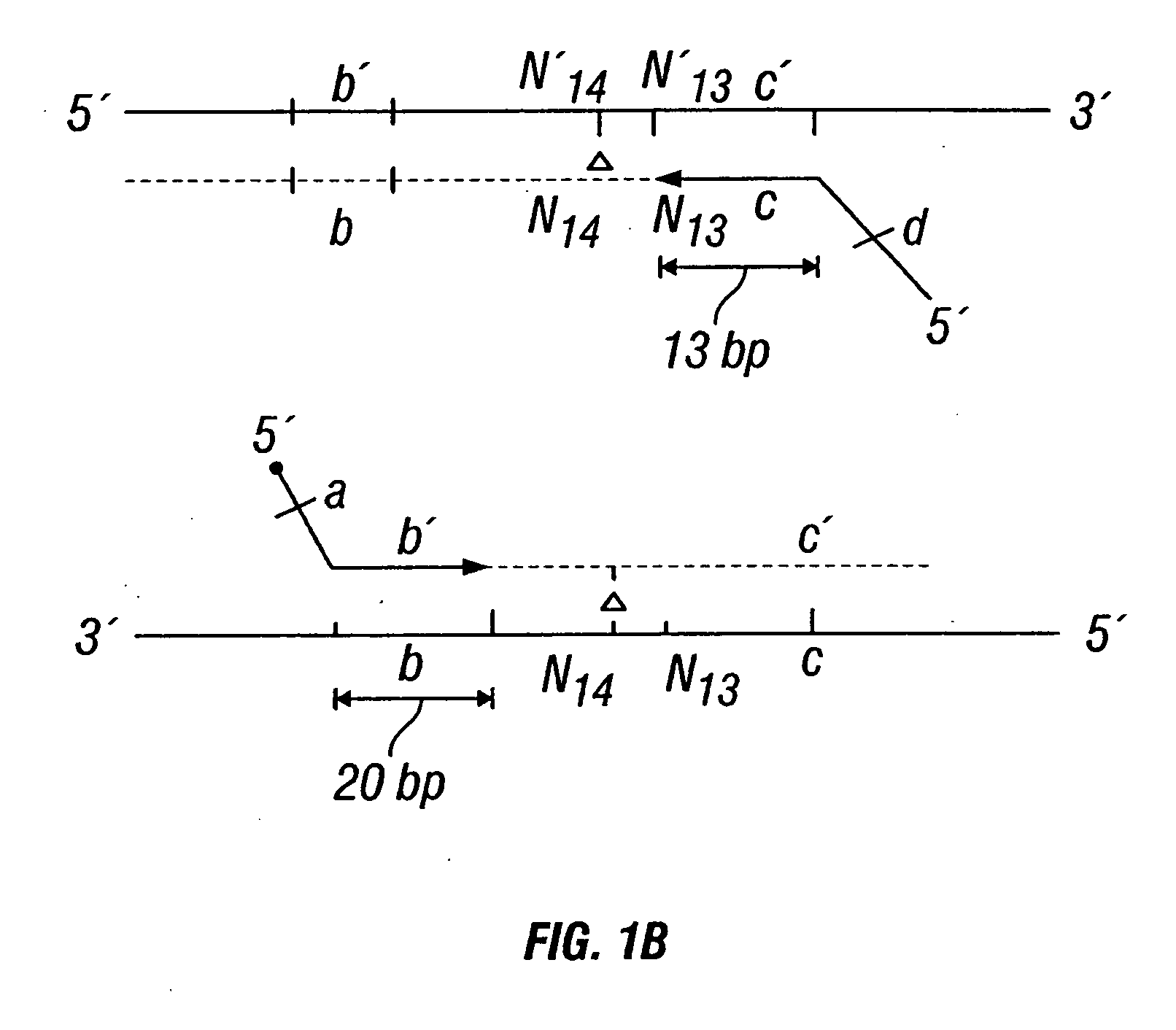
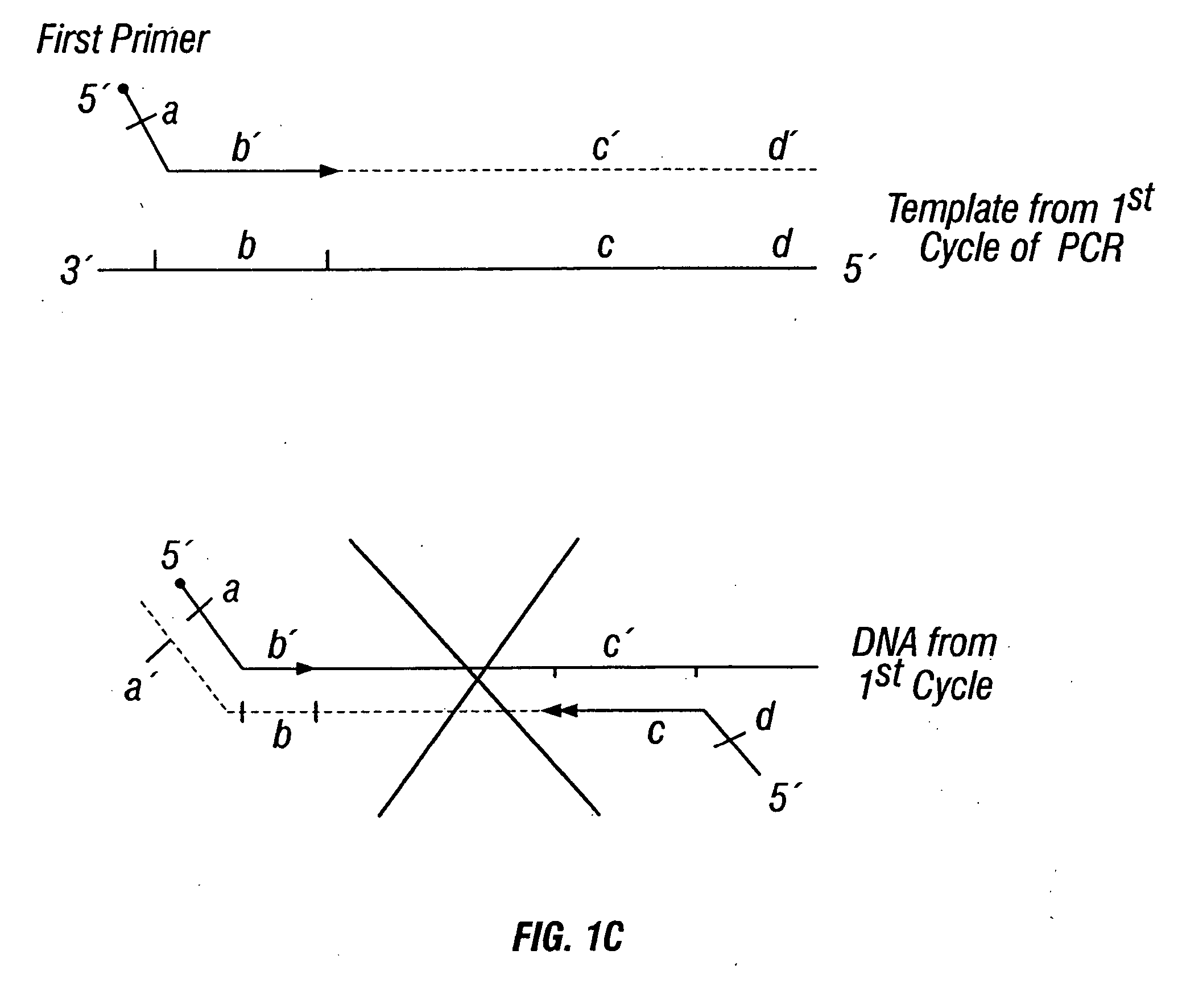
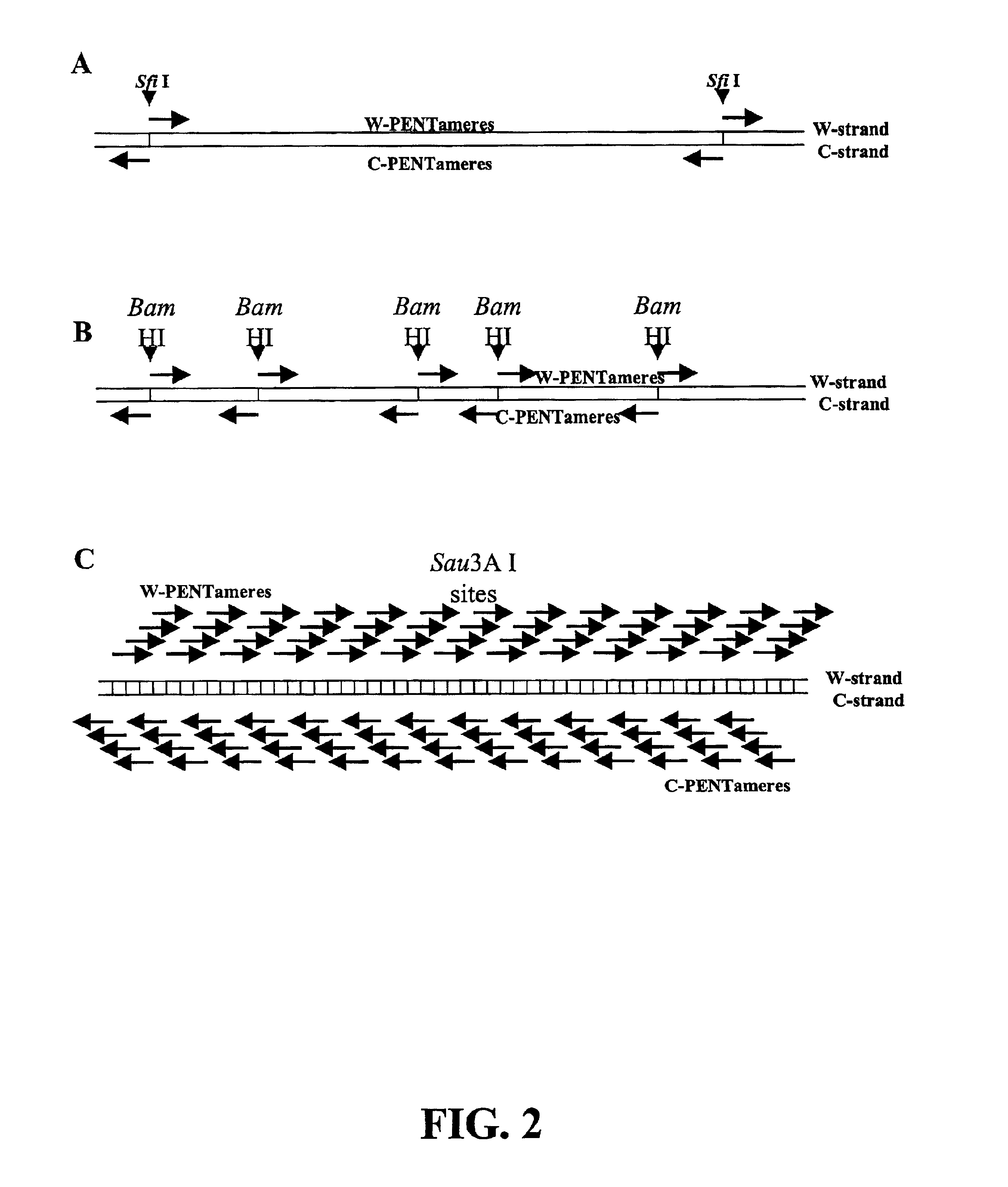
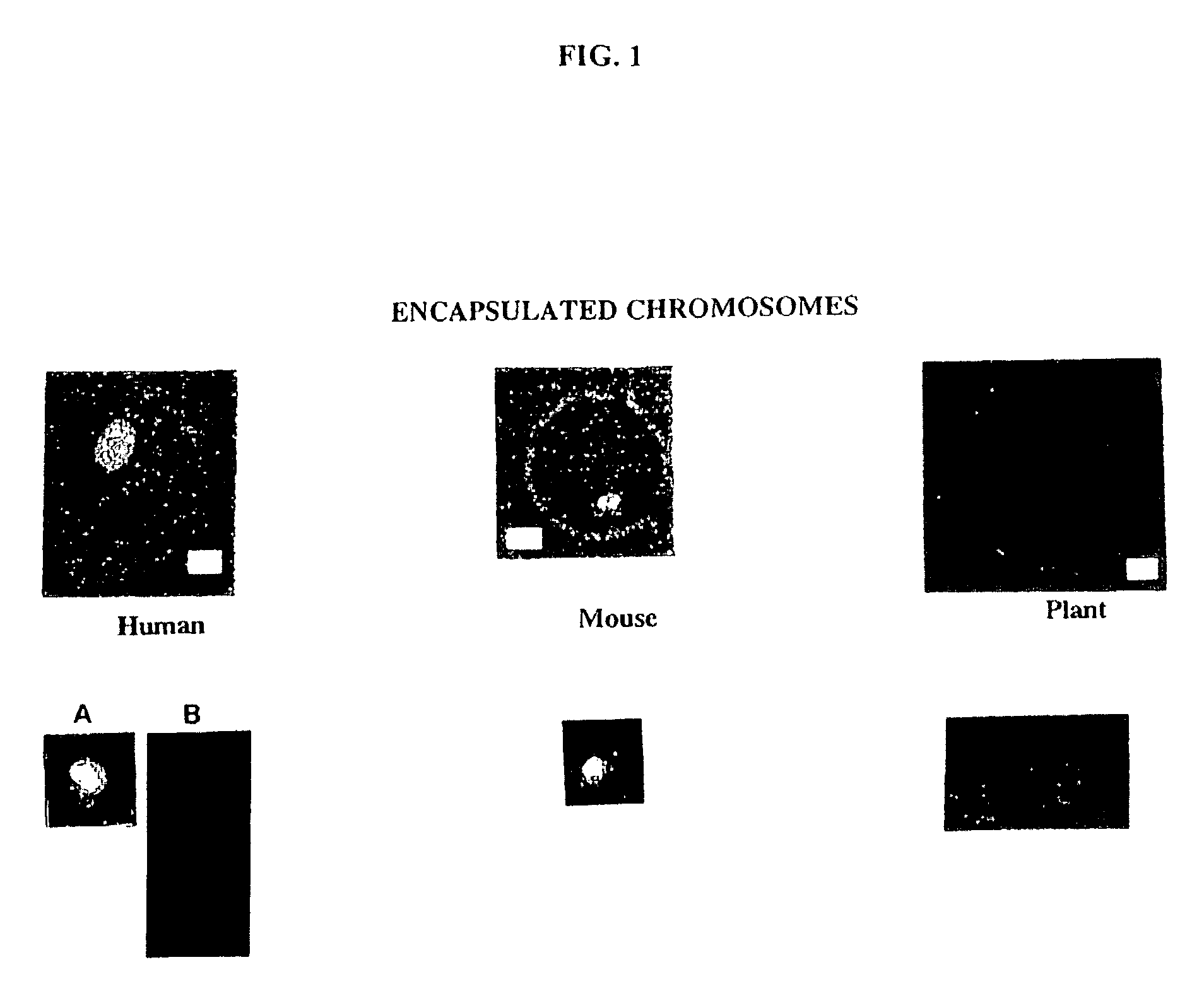
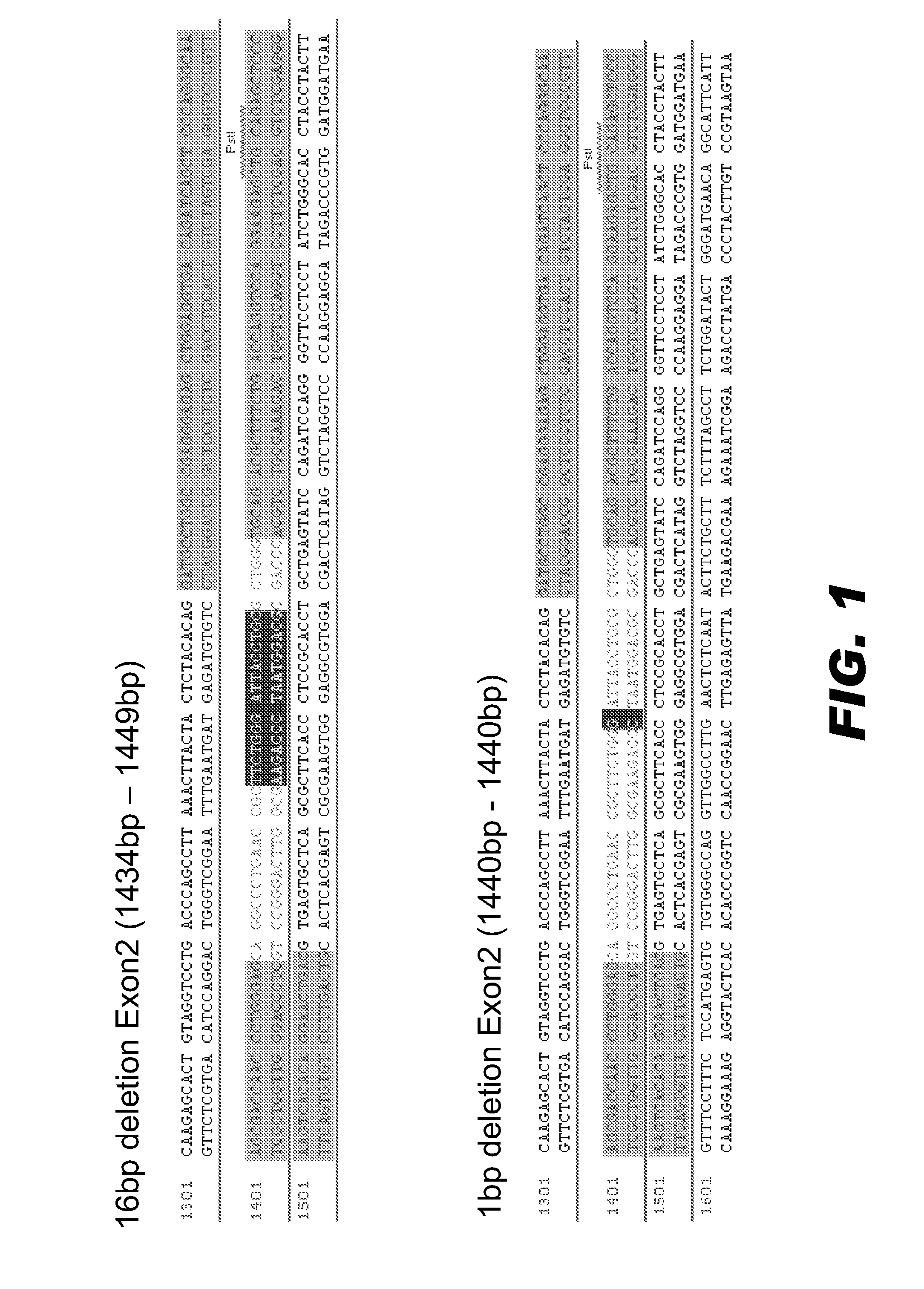
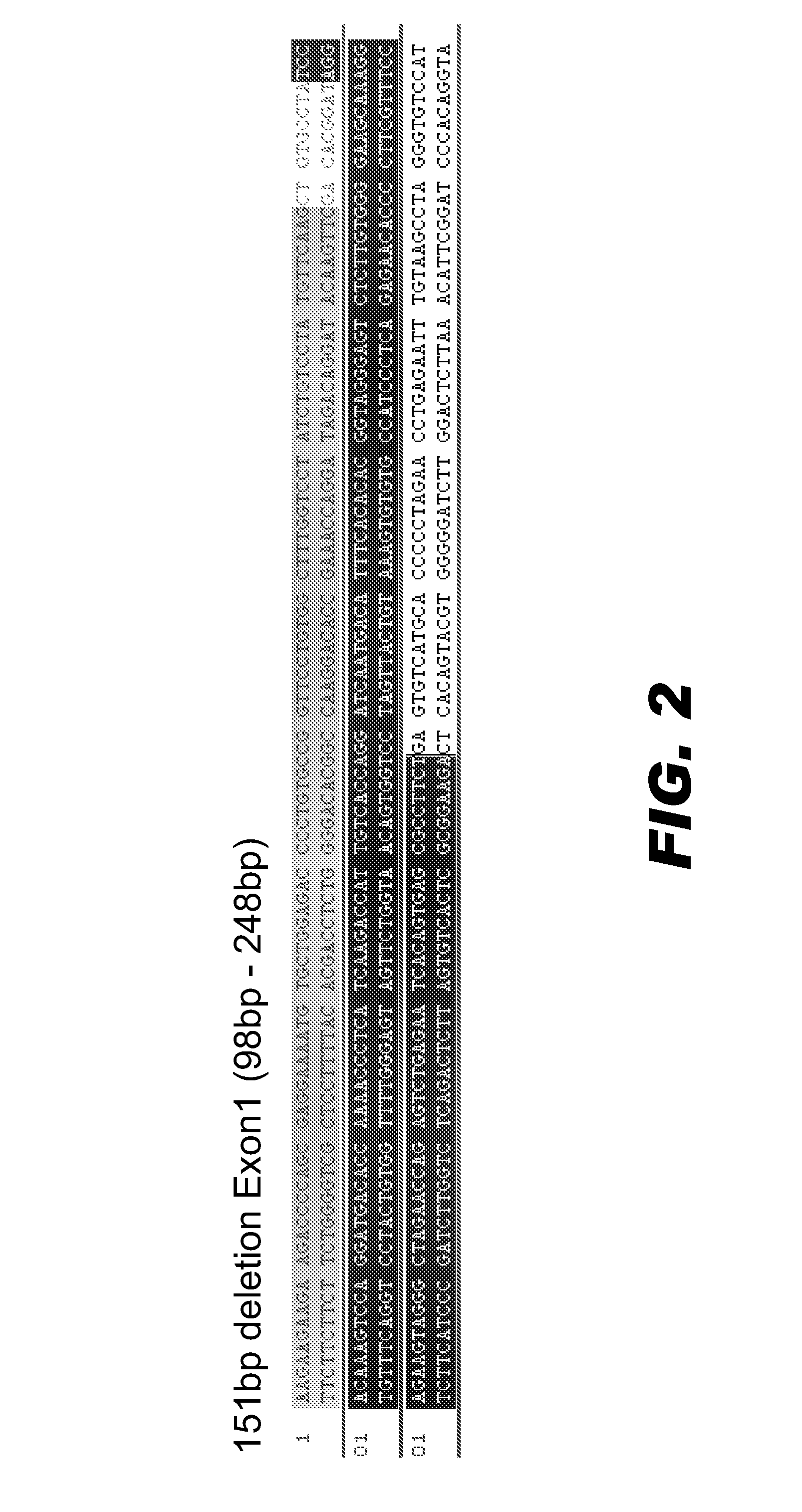
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4937 results about "Chromosome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A chromosome is a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecule with part or all of the genetic material (genome) of an organism. Most eukaryotic chromosomes include packaging proteins which, aided by chaperone proteins, bind to and condense the DNA molecule to prevent it from becoming an unmanageable tangle.
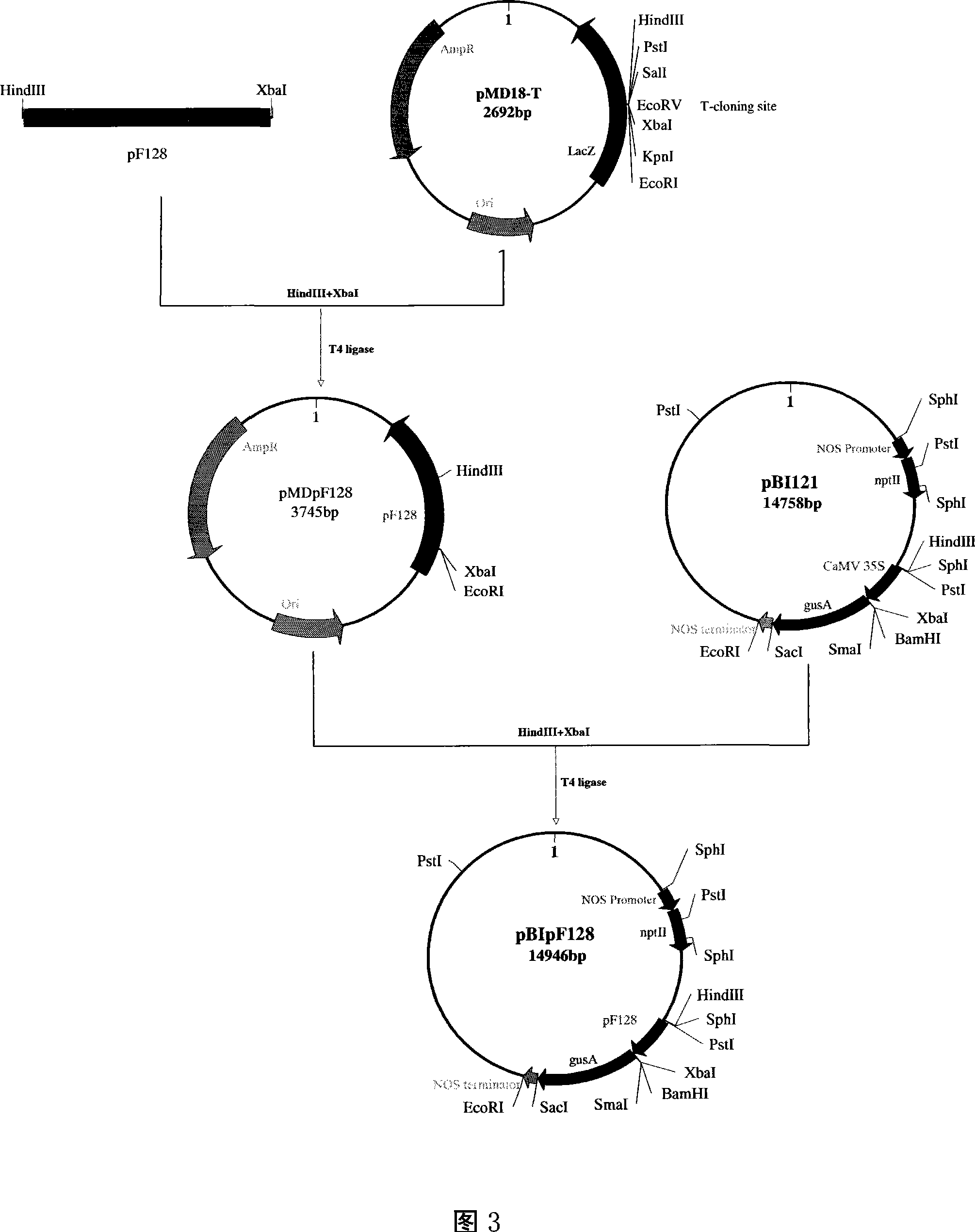
Seed specific highly effective promoter and its application
The invention discloses a special promoter separated from millet, expressing carrier with nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1 host with the expressing carrier and appliance of the promoter, which is characterized by the following: utilizing Tail-PCR (colored body step moving method); getting the special promoter from gene group DNA; possessing nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1; ;linking downstream of the promoter to non-homologous or homologous gene; constructing plant expressing carrier; transferring host plant; driving the downstream gene to high effective and special express goal protein in the seed; realizing genetic modification of plant; or using as effective tool for studying plant and biological reactor.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Seed specificity highly effective promoter and its application
InactiveCN101063139AReduce adverse effectsFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousNucleotide
The invention discloses a special promoter separated from millet, expressing carrier with nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1 host with the expressing carrier and appliance of the promoter, which is characterized by the following: utilizing Tail-PCR (colored body step moving method); getting the special promoter from gene group DNA; possessing nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1; ;linking downstream of the promoter to non-homologous or homologous gene; constructing plant expressing carrier; transferring host plant; driving the downstream gene to high effective and special express goal protein in the seed; realizing genetic modification of plant; or using as effective tool for studying plant and biological reactor.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
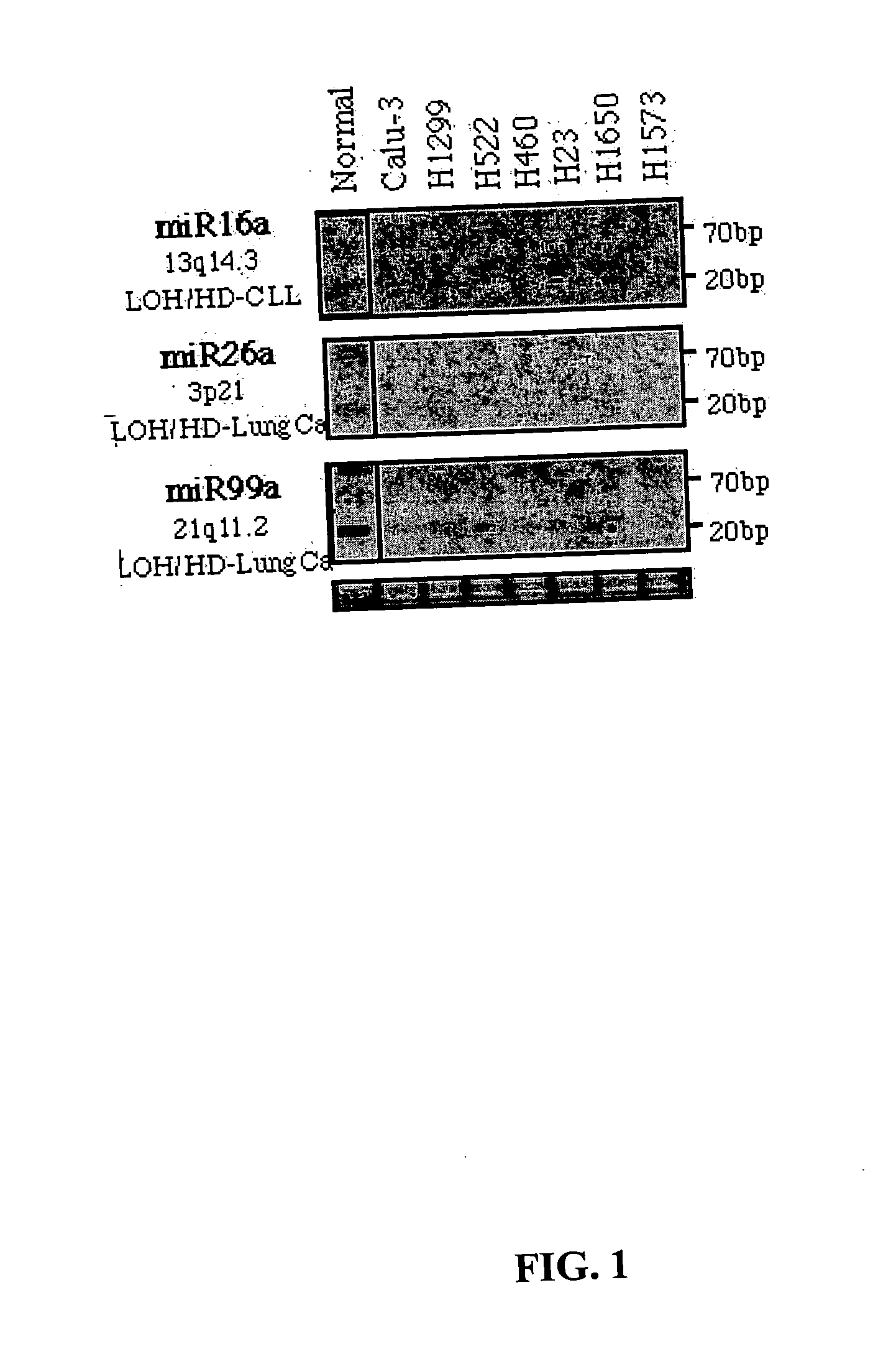
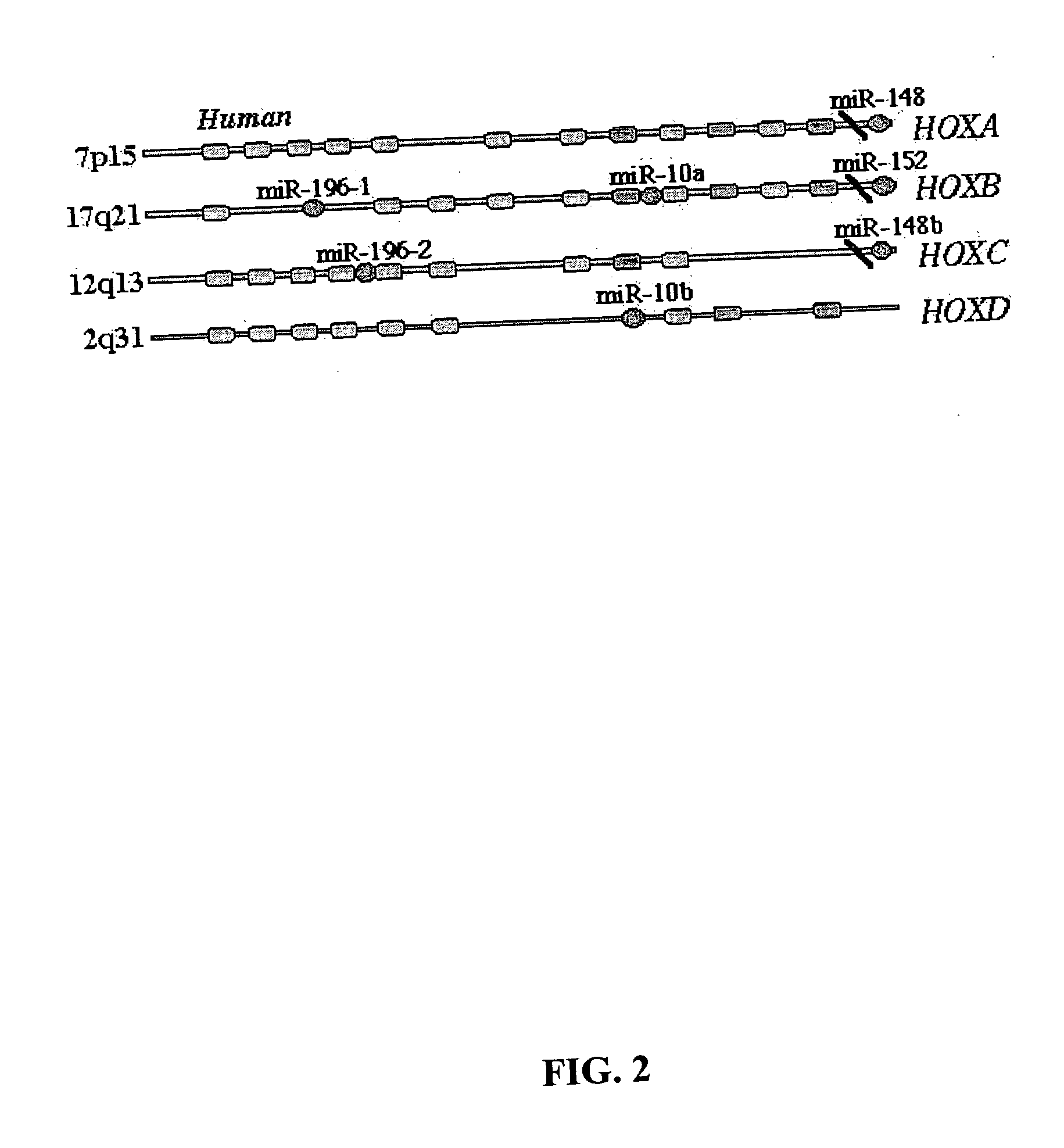
Diagnosis and treatment of cancers with microRNA located in or near cancer associated chromosomal features
InactiveUS20060105360A1Restore levelOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementEtiologyMicroRNA Gene
MicroRNA genes are highly associated with chromosomal features involved in the etiology of different cancers. The perturbations in the genomic structure or chromosomal architecture of a cell caused by these cancer-associated chromosomal features can affect the expression of the miR gene(s) located in close proximity to that chromosomal feature. Evaluation of miR gene expression can therefore be used to indicate the presence of a cancer-causing chromosomal lesion in a subject. As the change in miR gene expression level caused by a cancer-associated chromosomal feature may also contribute to cancerigenesis, a given cancer can be treated by restoring the level of miR gene expression to normal. microRNA expression profiling can be used to diagnose cancer and predict whether a particular cancer is associated with an adverse prognosis. The identification of specific mutations associated with genomic regions that harbor miR genes in CLL patients provides a means for diagnosing CLL and possibly other cancers.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Methods for detection of genetic disorders
InactiveUS7727720B2Maximize efficiencyIncrease delaySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsAllele
The invention provides a method useful for detection of genetic disorders. The method comprises determining the sequence of alleles of a locus of interest, and quantitating a ratio for the alleles at the locus of interest, wherein the ratio indicates the presence or absence of a chromosomal abnormality. The present invention also provides a non-invasive method for the detection of chromosomal abnormalities in a fetus. The invention is especially useful as a non-invasive method for determining the sequence of fetal DNA. The invention further provides methods of isolation of free DNA from a sample.
Owner:RAVGEN INC
Methods for detection of genetic disorders
InactiveUS7442506B2Maximize efficiencyIncrease delaySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsAllele
The invention provides a method useful for detection of genetic disorders. The method comprises determining the sequence of alleles of a locus of interest, and quantitating a ratio for the alleles at the locus of interest, wherein the ratio indicates the presence or absence of a chromosomal abnormality. The present invention also provides a non-invasive method for the detection of chromosomal abnormalities in a fetus. The invention is especially useful as a non-invasive method for determining the sequence of fetal DNA. The invention further provides methods of isolation of free DNA from a sample.
Owner:RAVGEN INC
Methods for detection of genetic disorders
InactiveUS20070178478A1Minimize disruptionMaximize efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGeneticsAllele
The invention provides a method useful for detection of genetic disorders. The method comprises determining the sequence of alleles of a locus of interest, and quantitating a ratio for the alleles at the locus of interest, wherein the ratio indicates the presence or absence of a chromosomal abnormality. The present invention also provides a non-invasive method for the detection of chromosomal abnormalities in a fetus. The invention is especially useful as a non-invasive method for determining the sequence of fetal DNA. The invention further provides methods of isolation of free DNA from a sample.
Owner:RAVGEN INC
Methods for Non-Invasive Prenatal Ploidy Calling
ActiveUS20120270212A1Fill in the blanksMathematical modelsMicrobiological testing/measurementDistribution patternGenotype
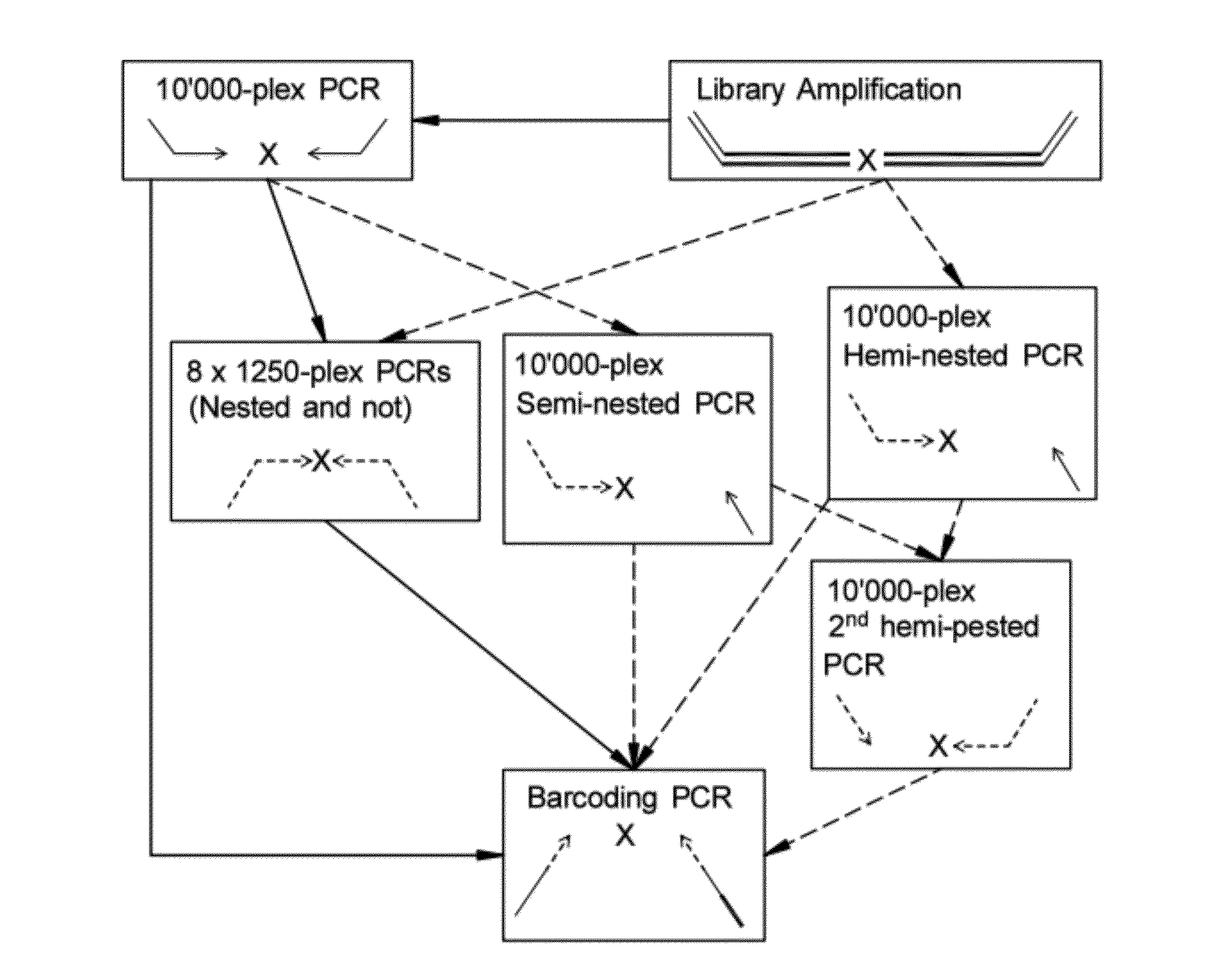
The present disclosure provides methods for determining the ploidy status of a chromosome in a gestating fetus from genotypic data measured from a mixed sample of DNA comprising DNA from both the mother of the fetus and from the fetus, and optionally from genotypic data from the mother and father. The ploidy state is determined by using a joint distribution model to create a plurality of expected allele distributions for different possible fetal ploidy states given the parental genotypic data, and comparing the expected allelic distributions to the pattern of measured allelic distributions measured in the mixed sample, and choosing the ploidy state whose expected allelic distribution pattern most closely matches the observed allelic distribution pattern. The mixed sample of DNA may be preferentially enriched at a plurality of polymorphic loci in a way that minimizes the allelic bias, for example using massively multiplexed targeted PCR.
Owner:NATERA
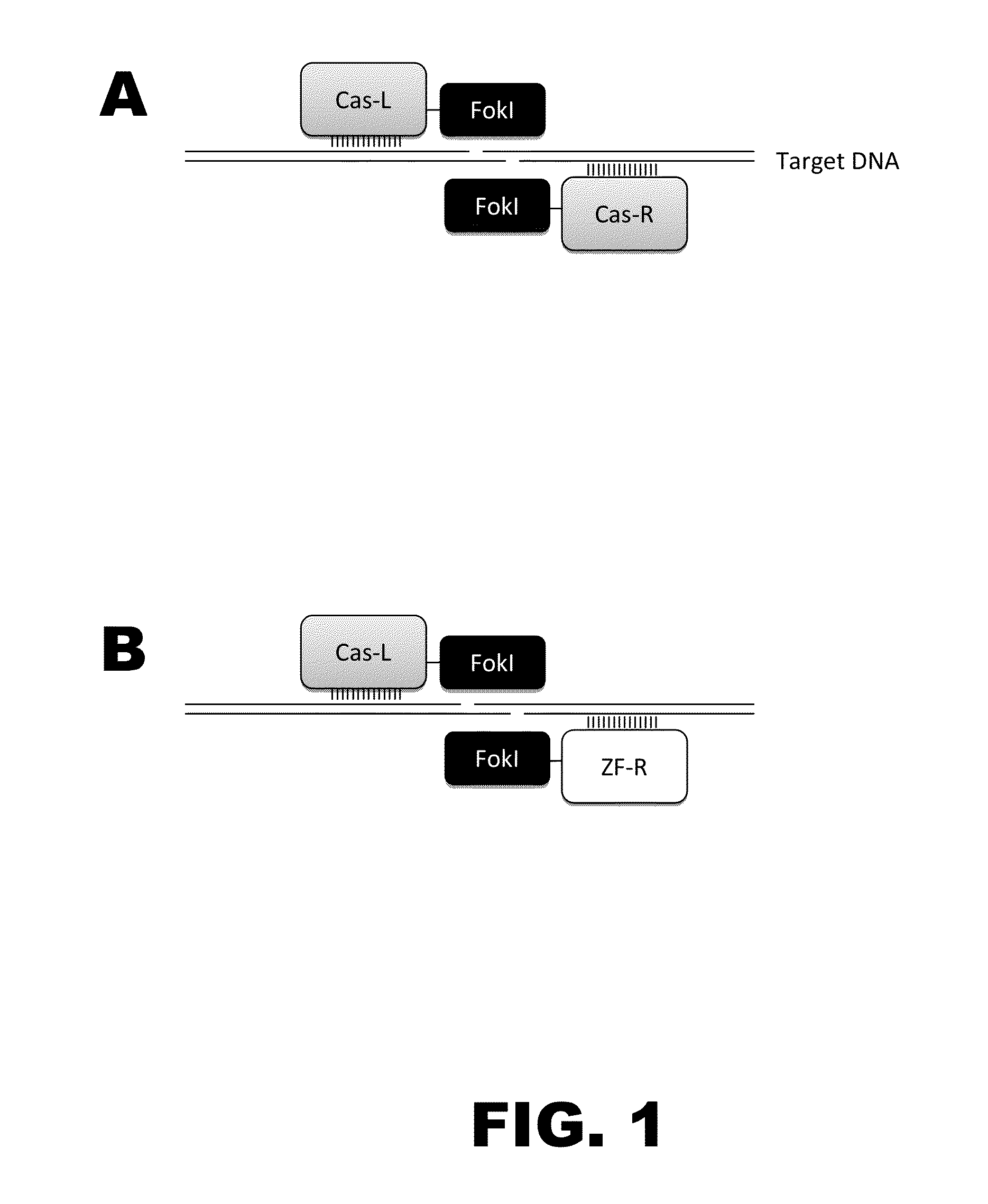
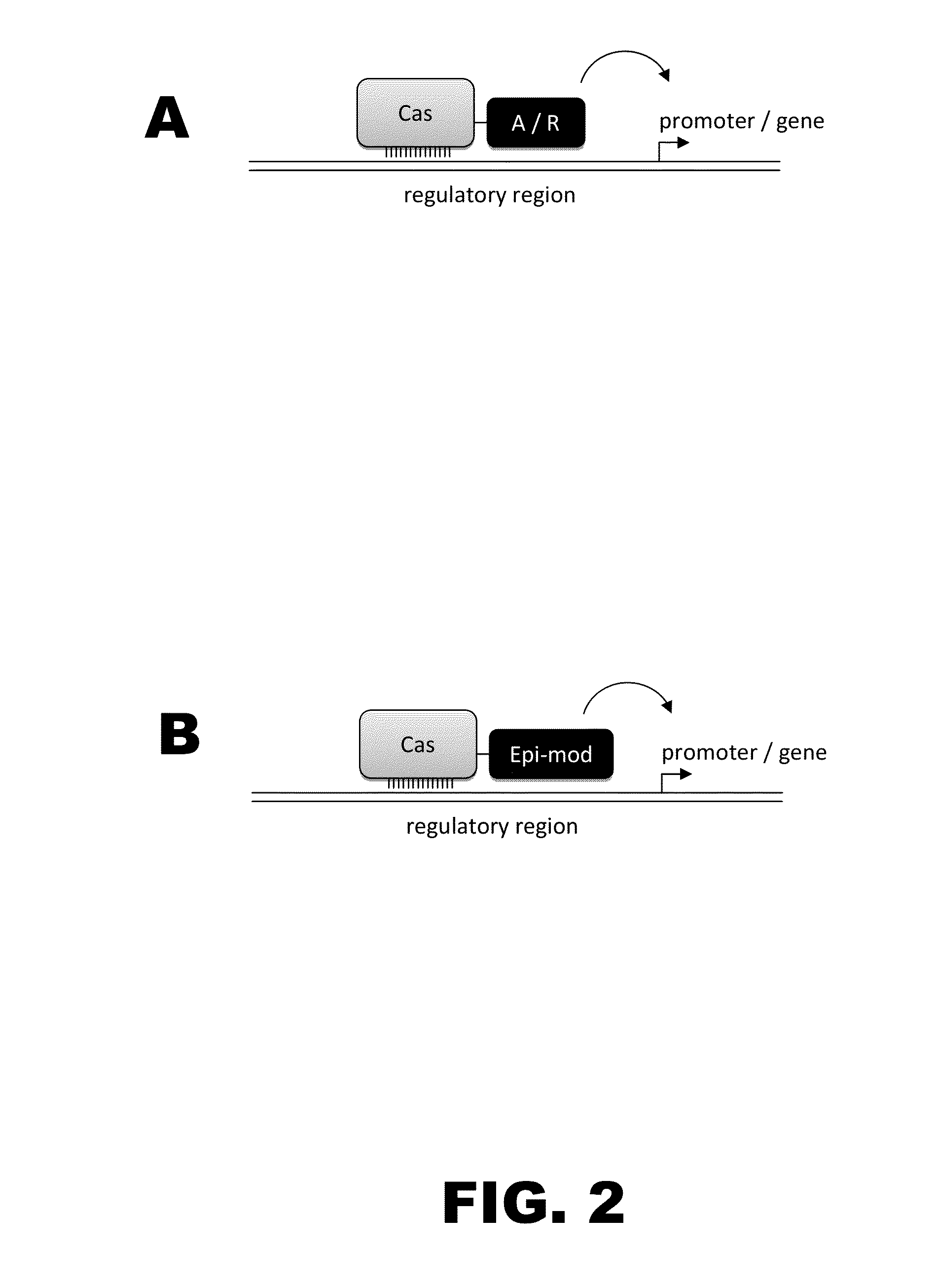
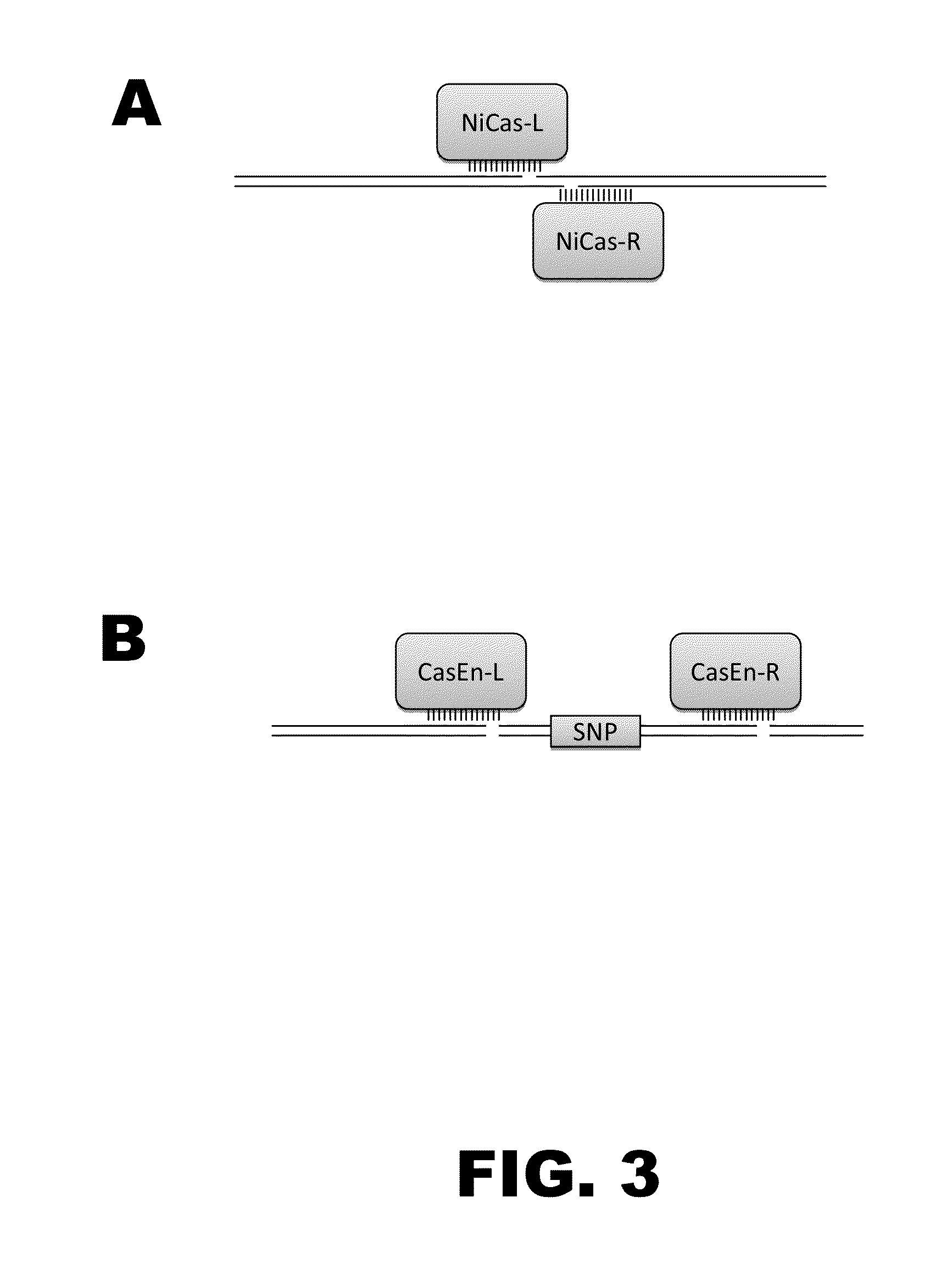
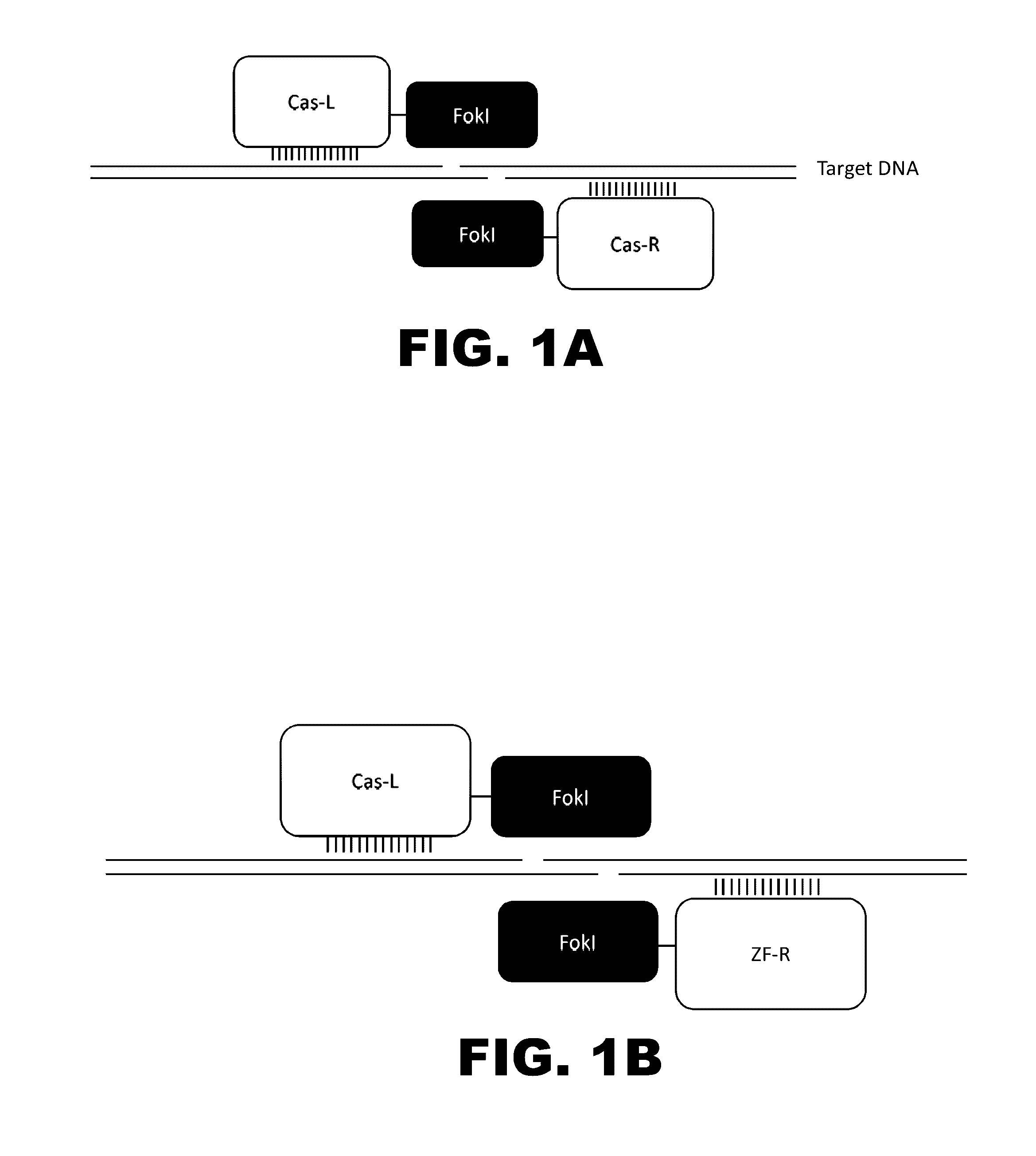
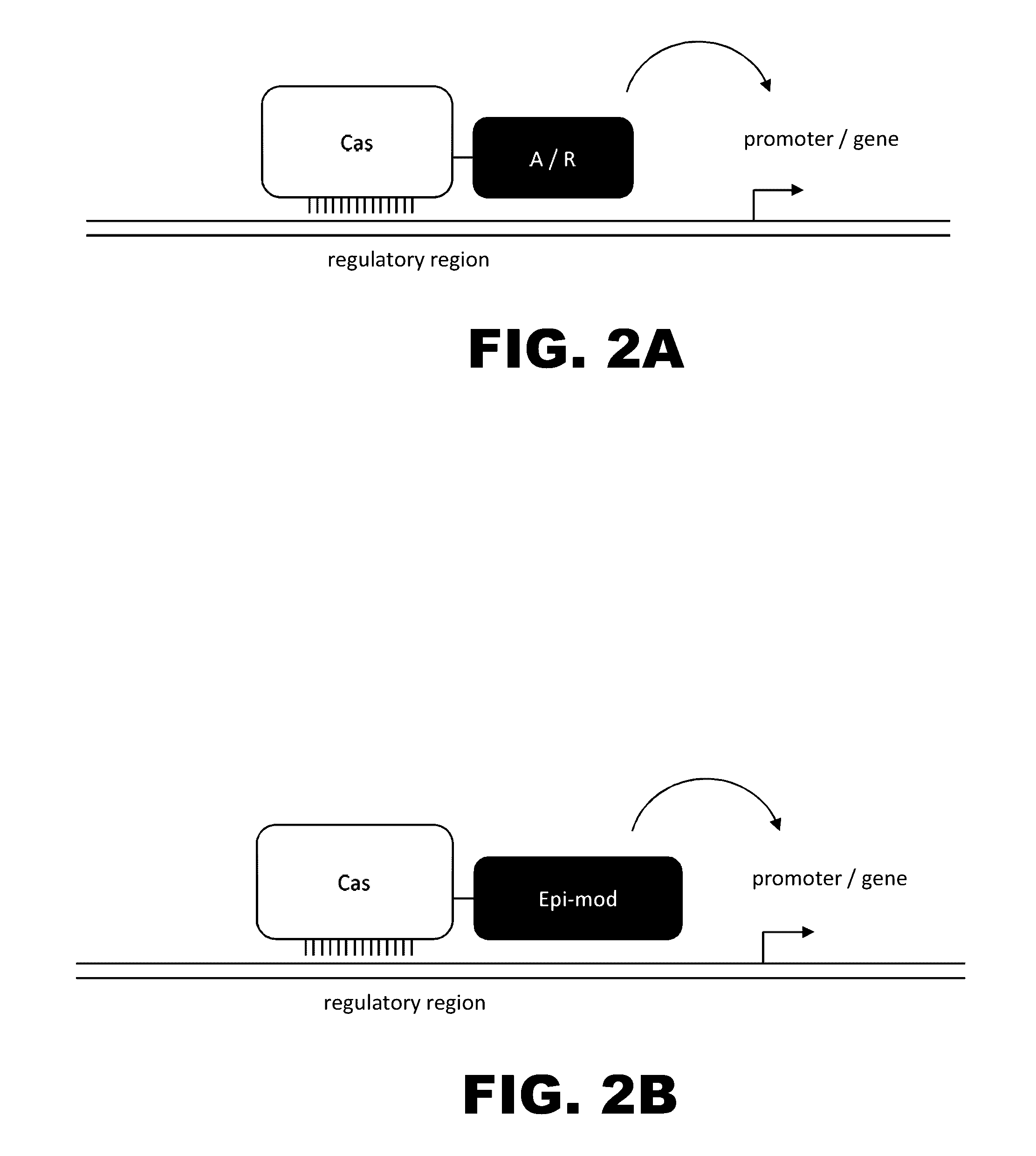
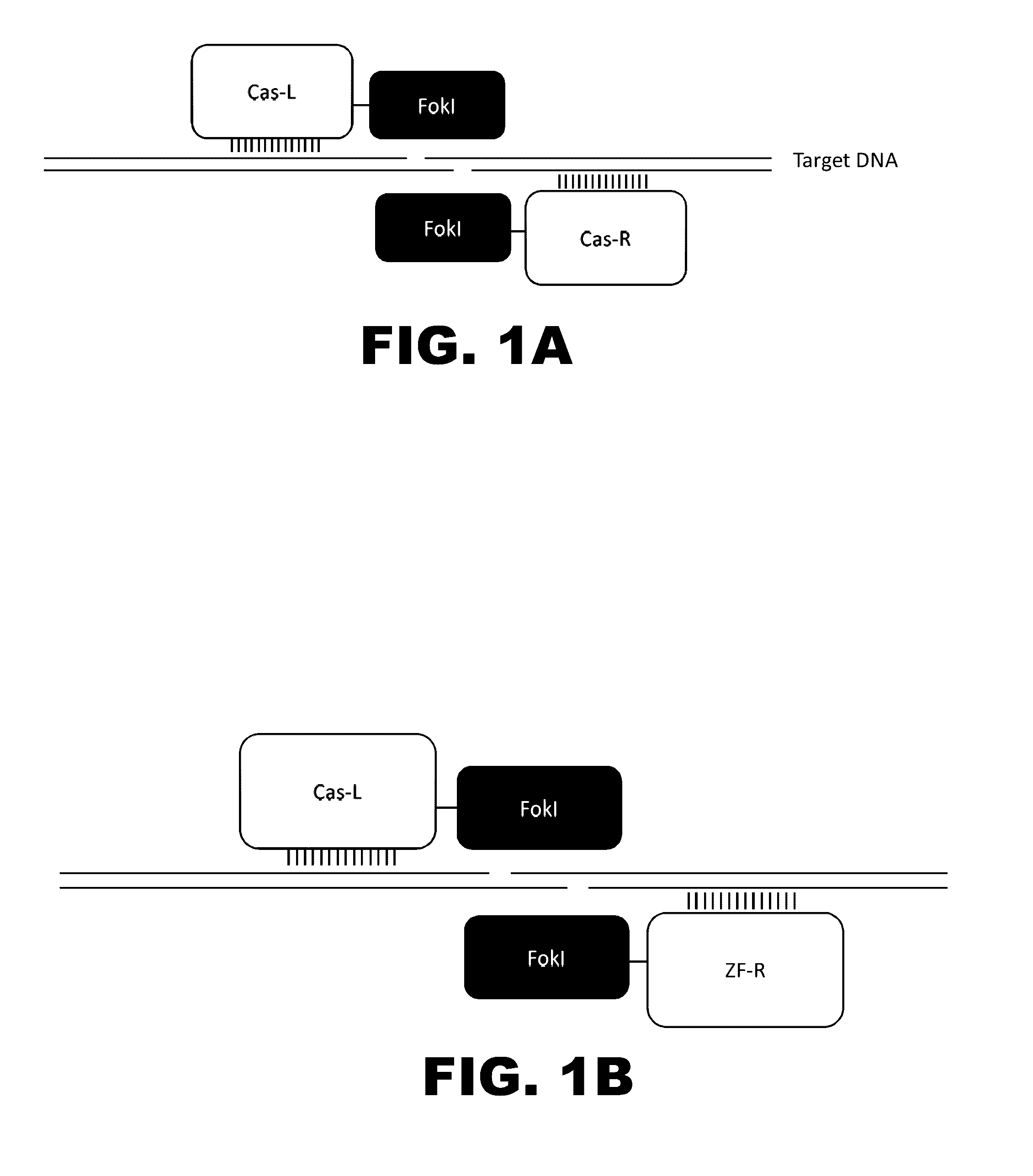
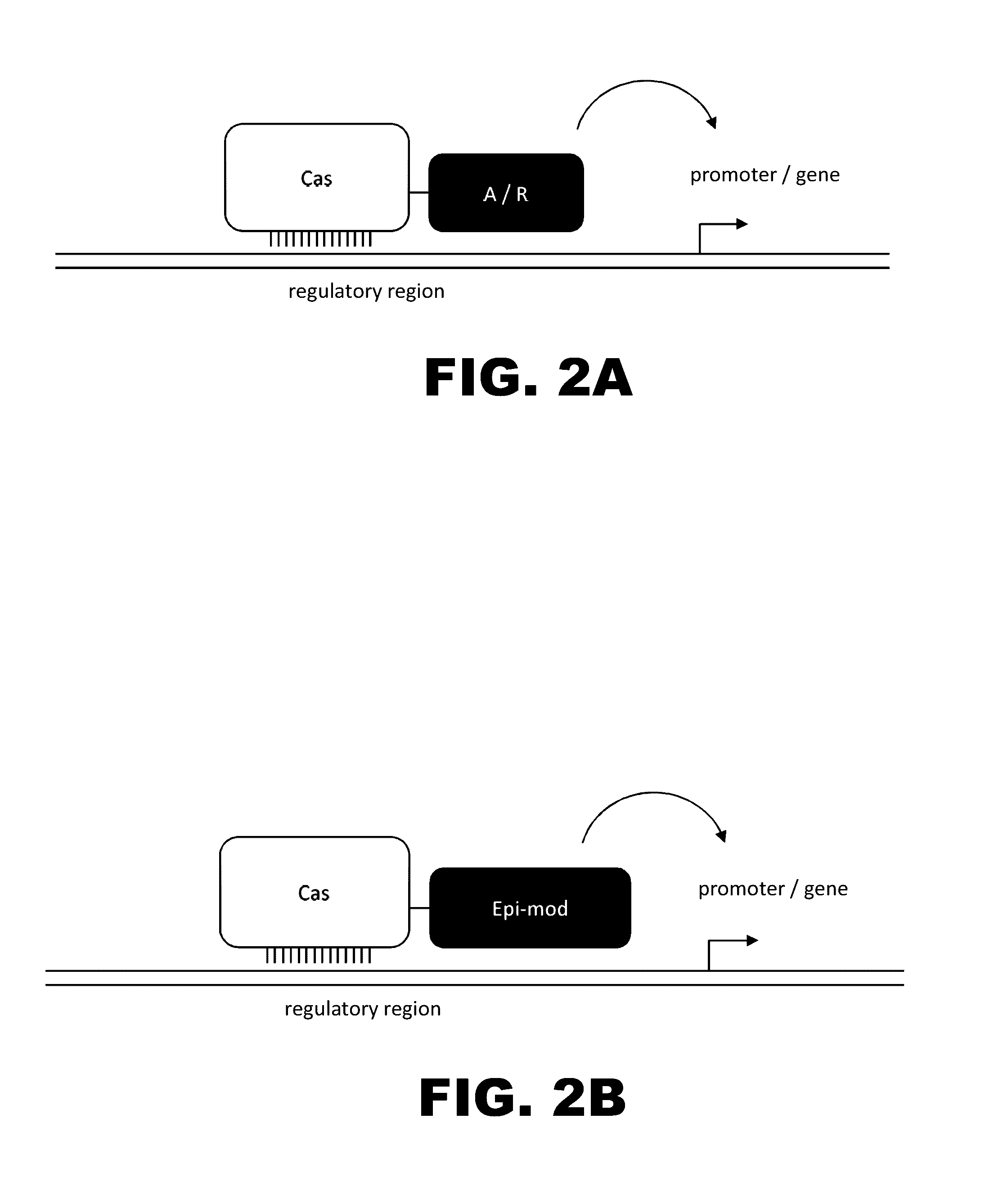
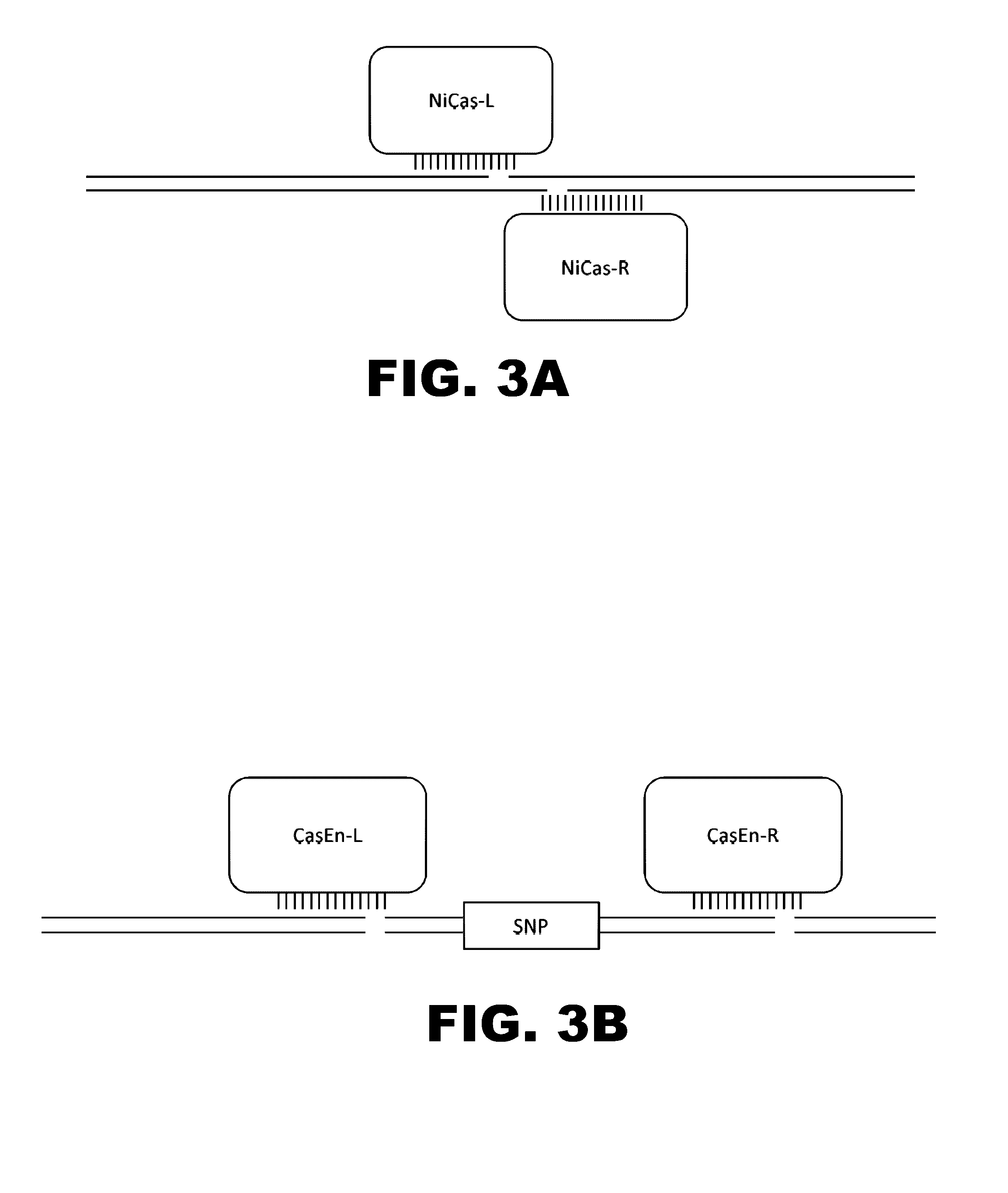
Crispr-based genome modification and regulation
InactiveUS20140273230A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifHydrolasesGenomeDNA Endonuclease
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Crispr-based genome modification and regulation
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
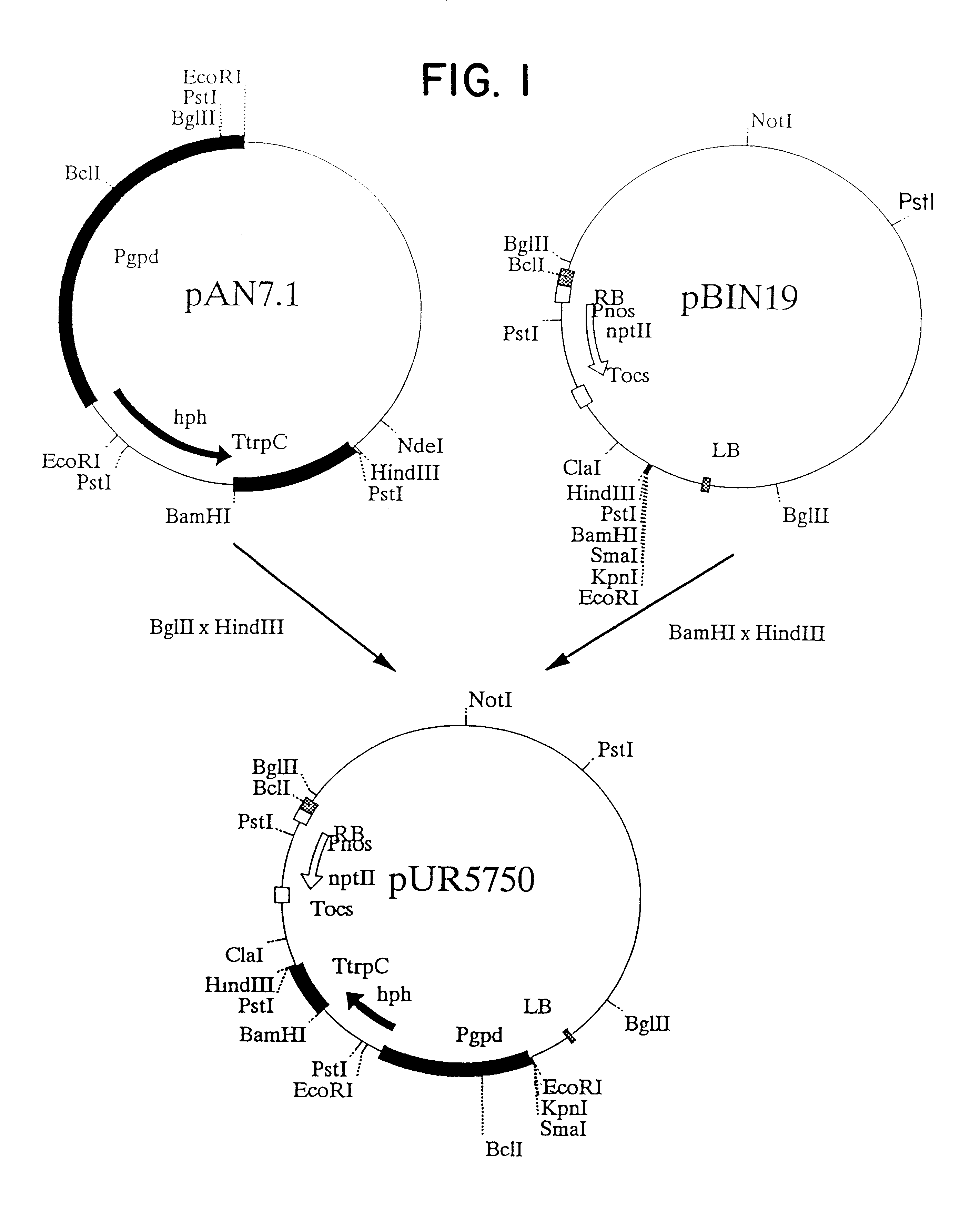
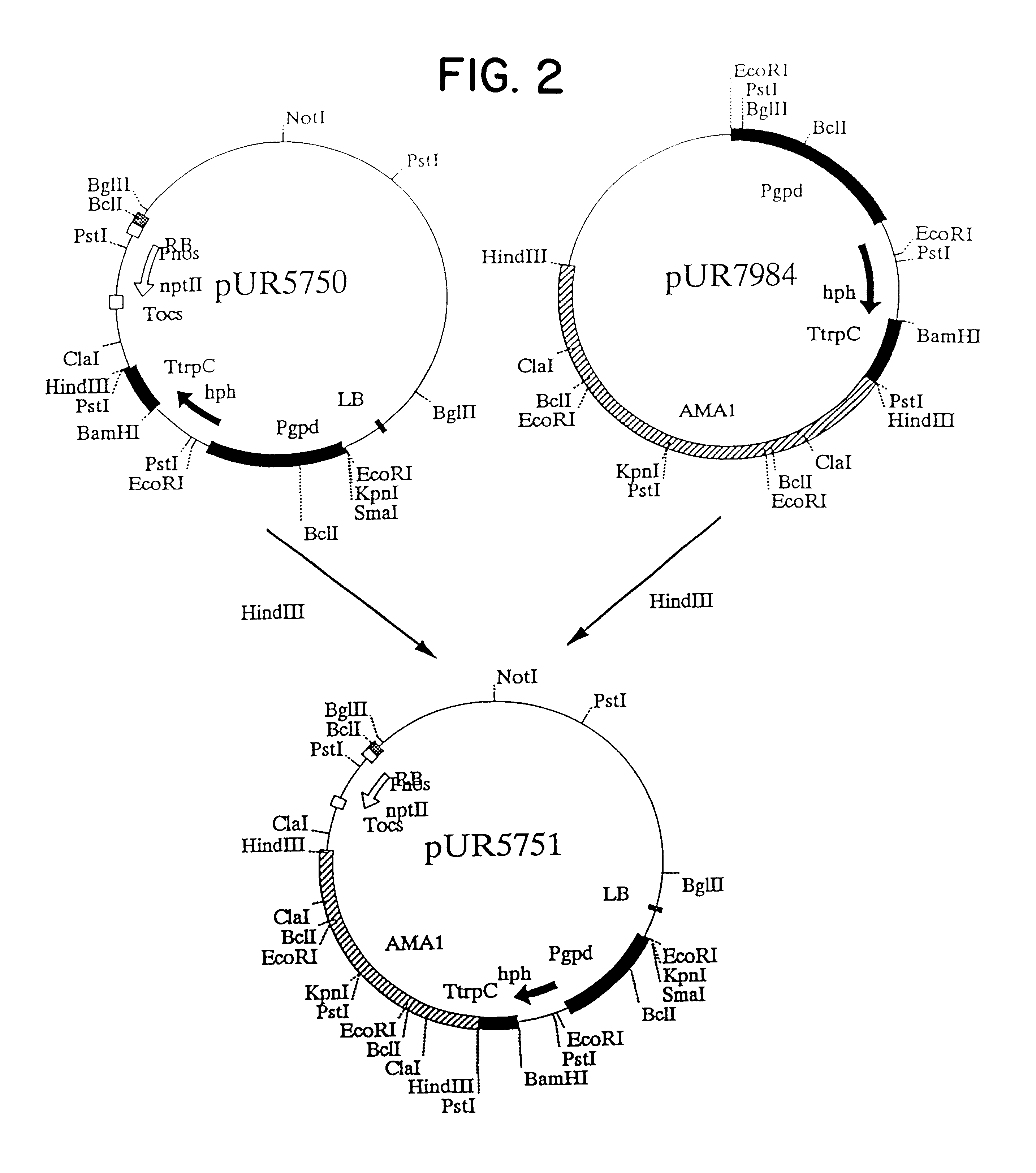
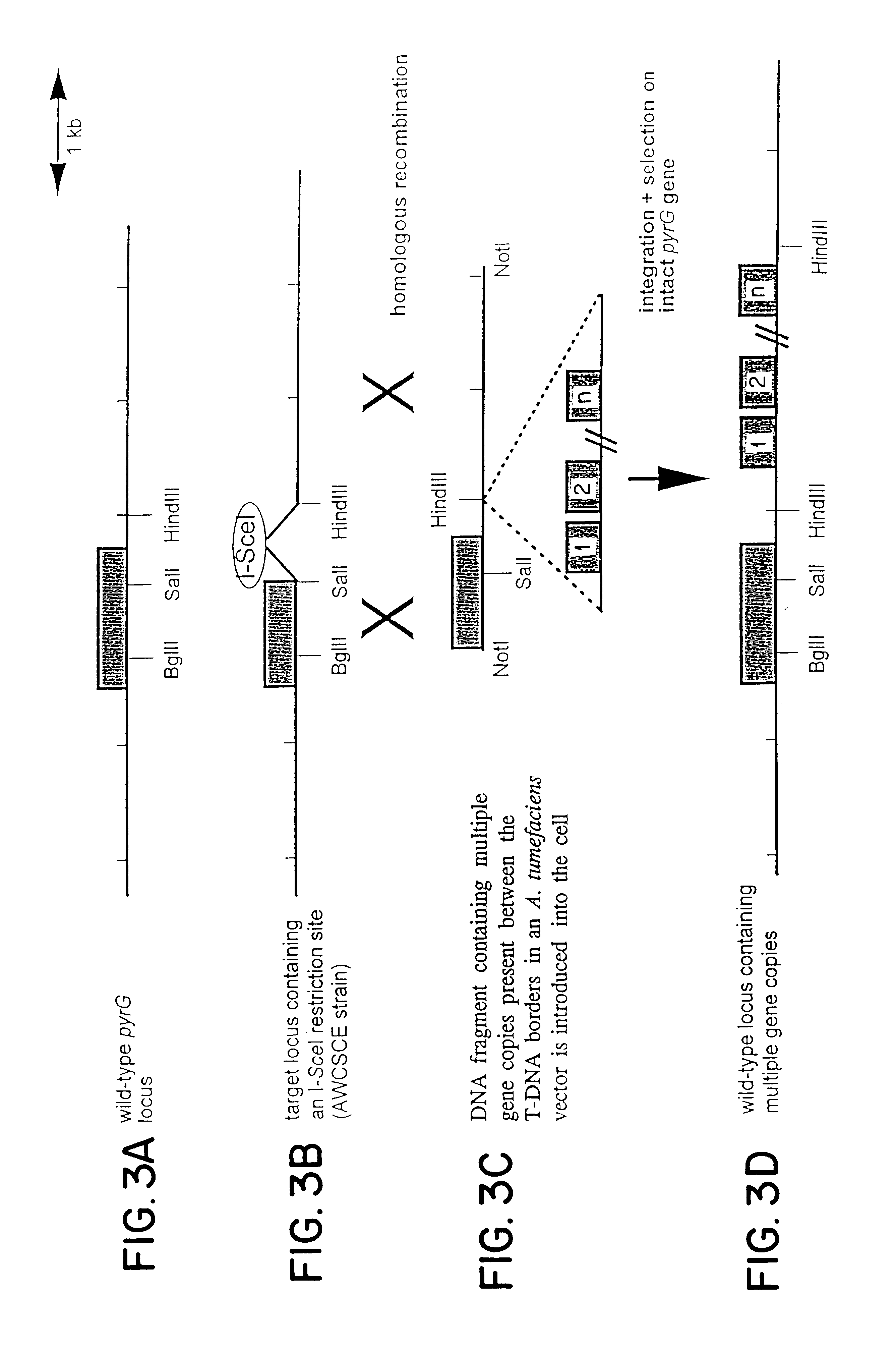
Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds, in particular those belonging to the genus Aspergillus
The invention relates to Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds comprising species of the fungal sub-divisions Ascomycotina, Basidiomycotina, Deuteromycotina, Mastigomycotina, and Zygomycotina.Examples demonstrate the transformation of Aspergillus awamori (both protoplasts and conidia), Aspergillus nidulans, Aspergillus niger, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Fusarium solani pisi, Neurospora crassa, Trichoderma reesei, Pleurotus ostreatus and Agaricus bisporus (all conidia), and Fusarium graminearum (both conidia and rehydrated freeze dried ATCC material).Especially for Aspergillus awamori the transformation frequency is much higher than with conventional mould transformation techniques.It has further been found that not only one expressable gene can be introduced into these moulds, but even multiple copies of such gene, which, moreover, can be targeted e.g. in the chromosomal pyrG locus, as exemplified for A. awamori. These multiple copies can be of a gene encoding a desired, homologous or heterologous, protein.
Owner:UNILEVER PATENT HLDG BV
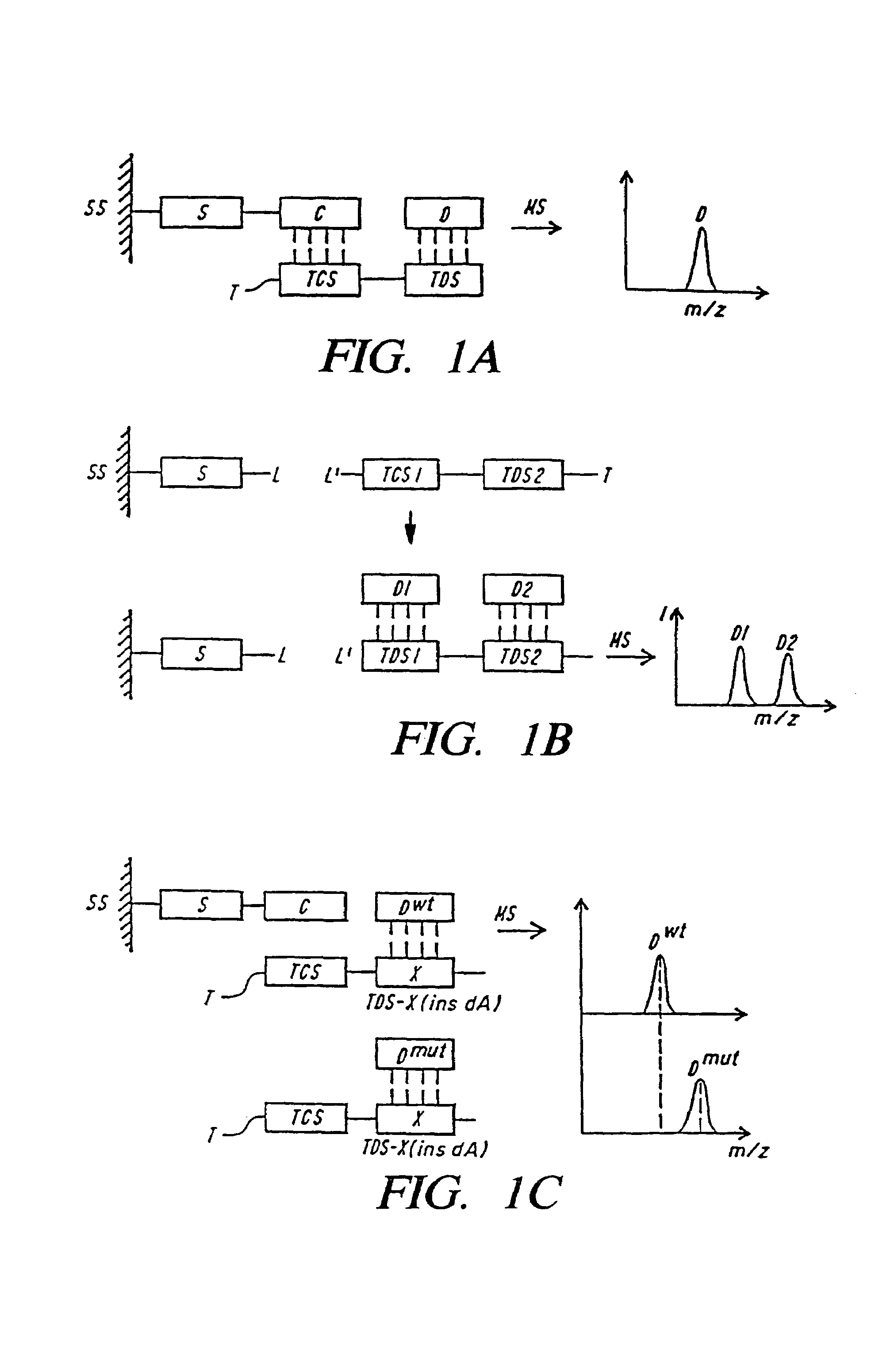
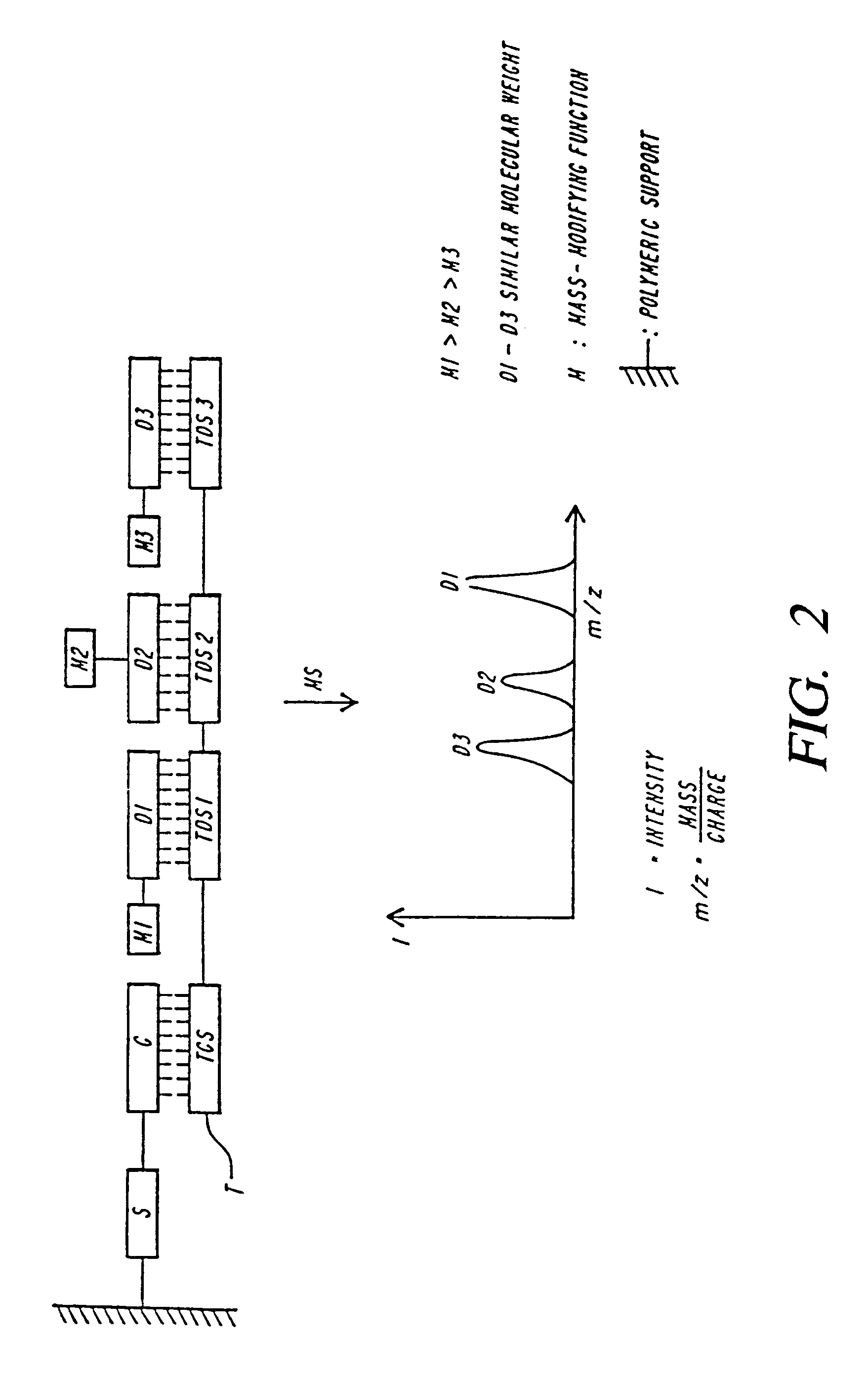
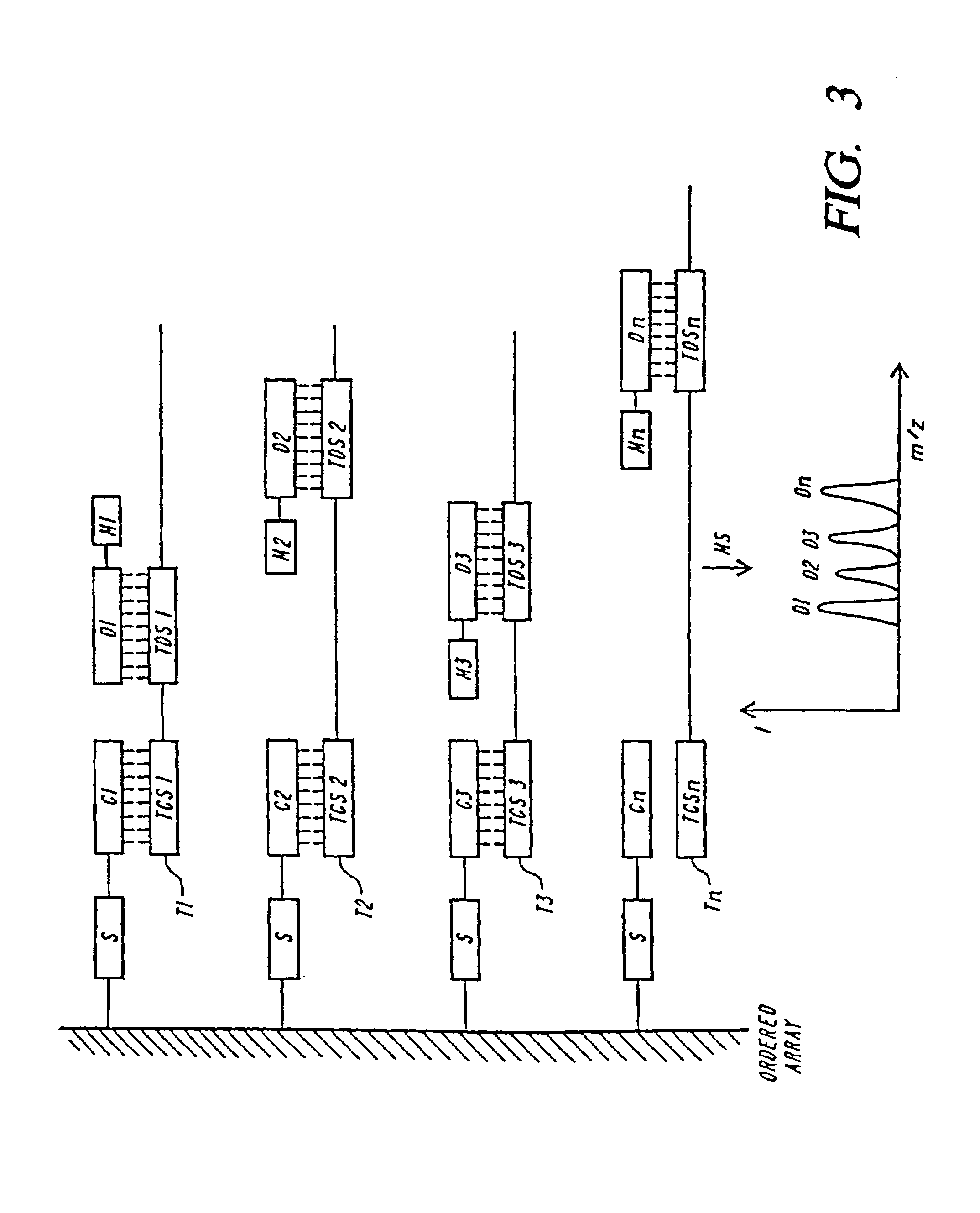
DNA diagnostics based on mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7198893B1Increase mass resolution massIncrease mass mass accuracyPeptide librariesSequential/parallel process reactionsMass spectrometry imagingOrganism
Fast and highly accurate mass spectrometry-based processes for detecting a particular nucleic acid sequence in a biological sample are provided. Depending on the sequence to be detected, the processes can be used, for example, to diagnose a genetic disease or chromosomal abnormality; a predisposition to a disease or condition, infection by a pathogenic organism, or for determining identity or heredity.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
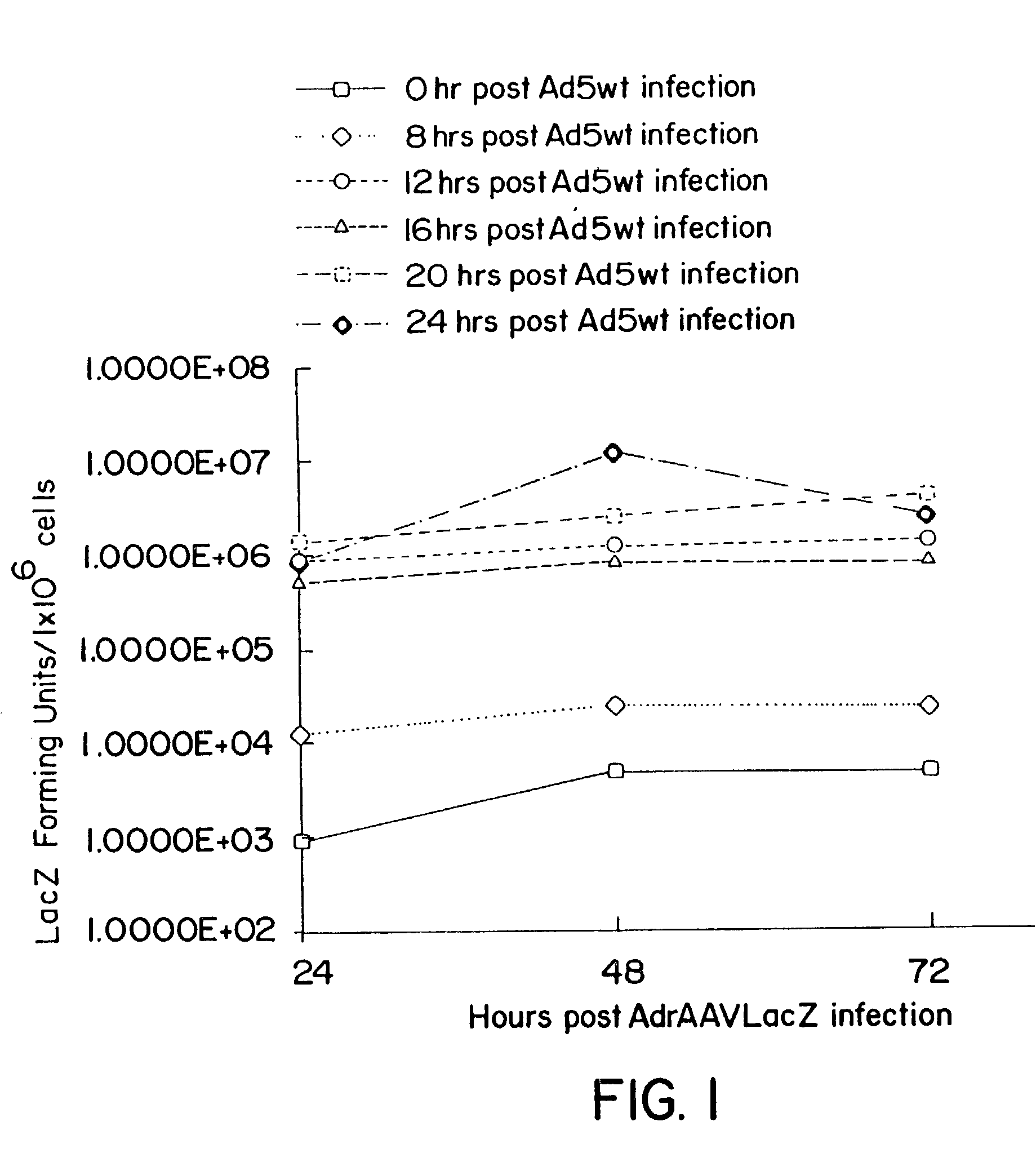
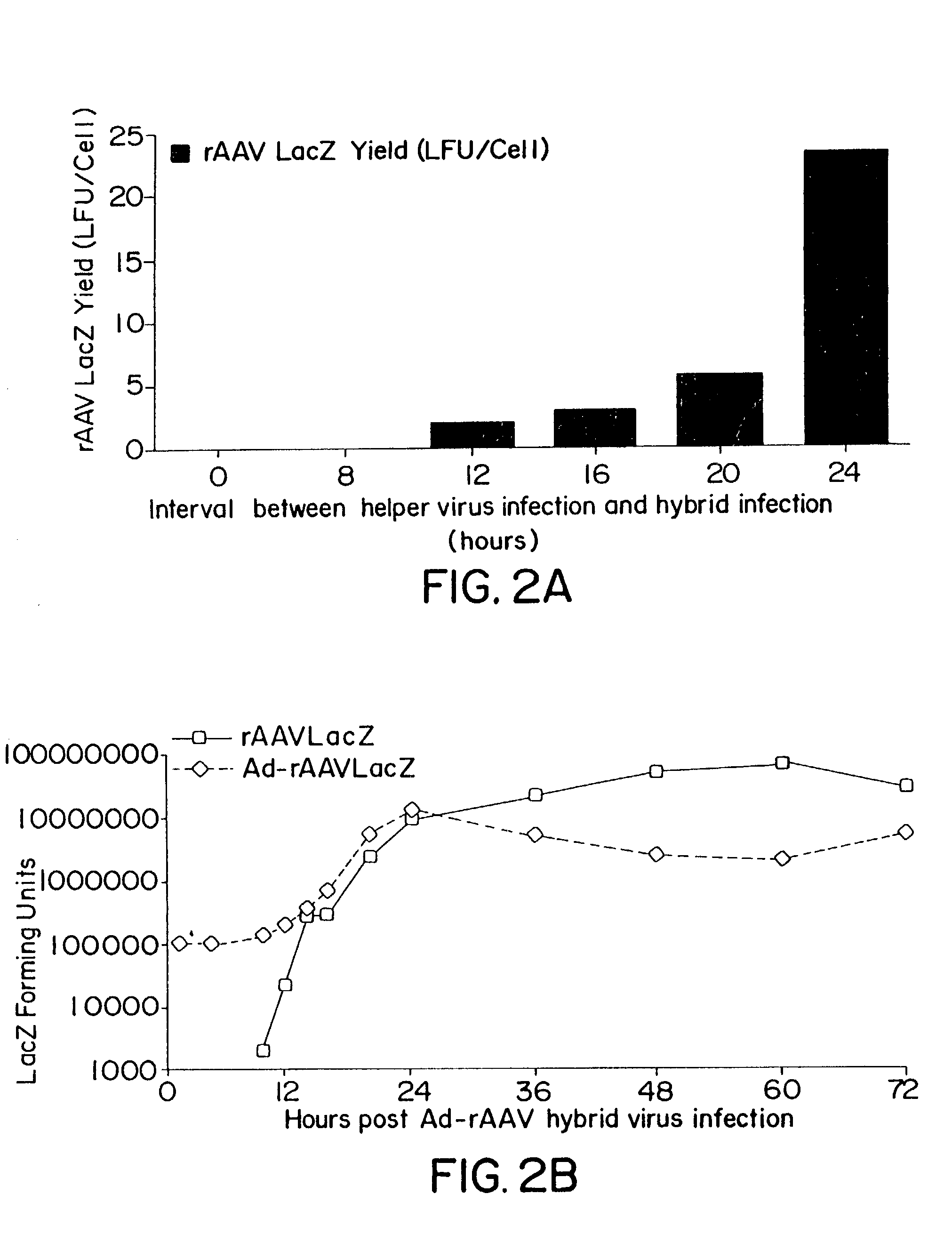
Methods and cell line useful for production of recombinant adeno-associated viruses
InactiveUS7238526B2High yieldInduce expressionGenetically modified cellsGenetic material ingredientsPlasmid VectorAdeno associate virus
Methods for efficient production of recombinant AAV employ a host cell which comprising AAV rep and cap genes stably integrated within the cell's chromosomes, wherein the AAV rep and cap genes are each operatively linked to regulatory sequences capable of directing the expression of the rep and cap gene products upon infection of the cell with a helper virus, a helper gene, and a helper gene product. A method for producing recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) involves infecting such a host cell with a helper virus, gene or gene product and infecting the infected host cell with a recombinant hybrid virus or plasmid vector containing adenovirus cis-elements necessary for replication and virion encapsidation, AAV sequences comprising the 5′ and 3′ ITRs of an AAV, and a selected gene operatively linked to regulatory sequences directing its expression, which is flanked by the above-mentioned AAV sequences.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
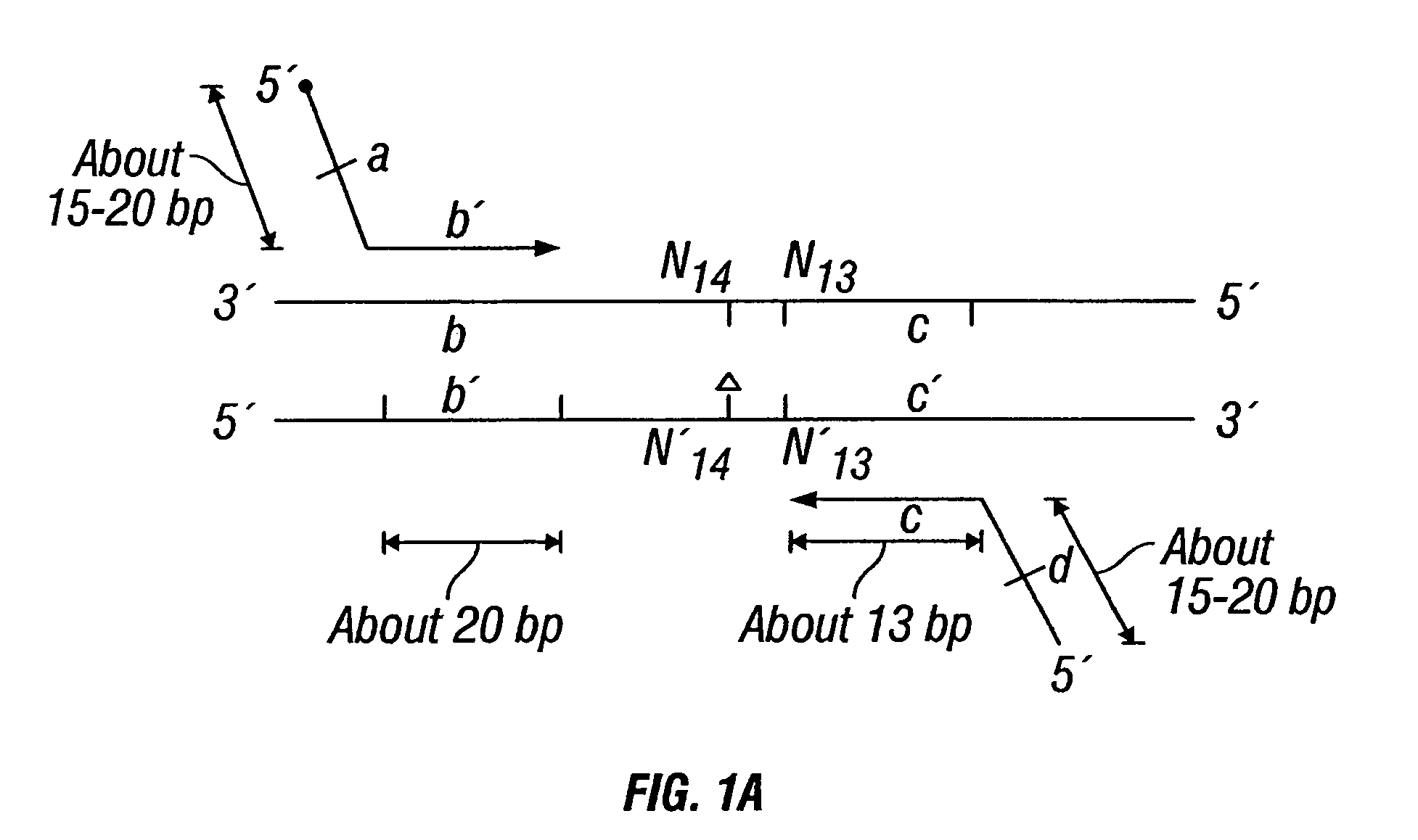
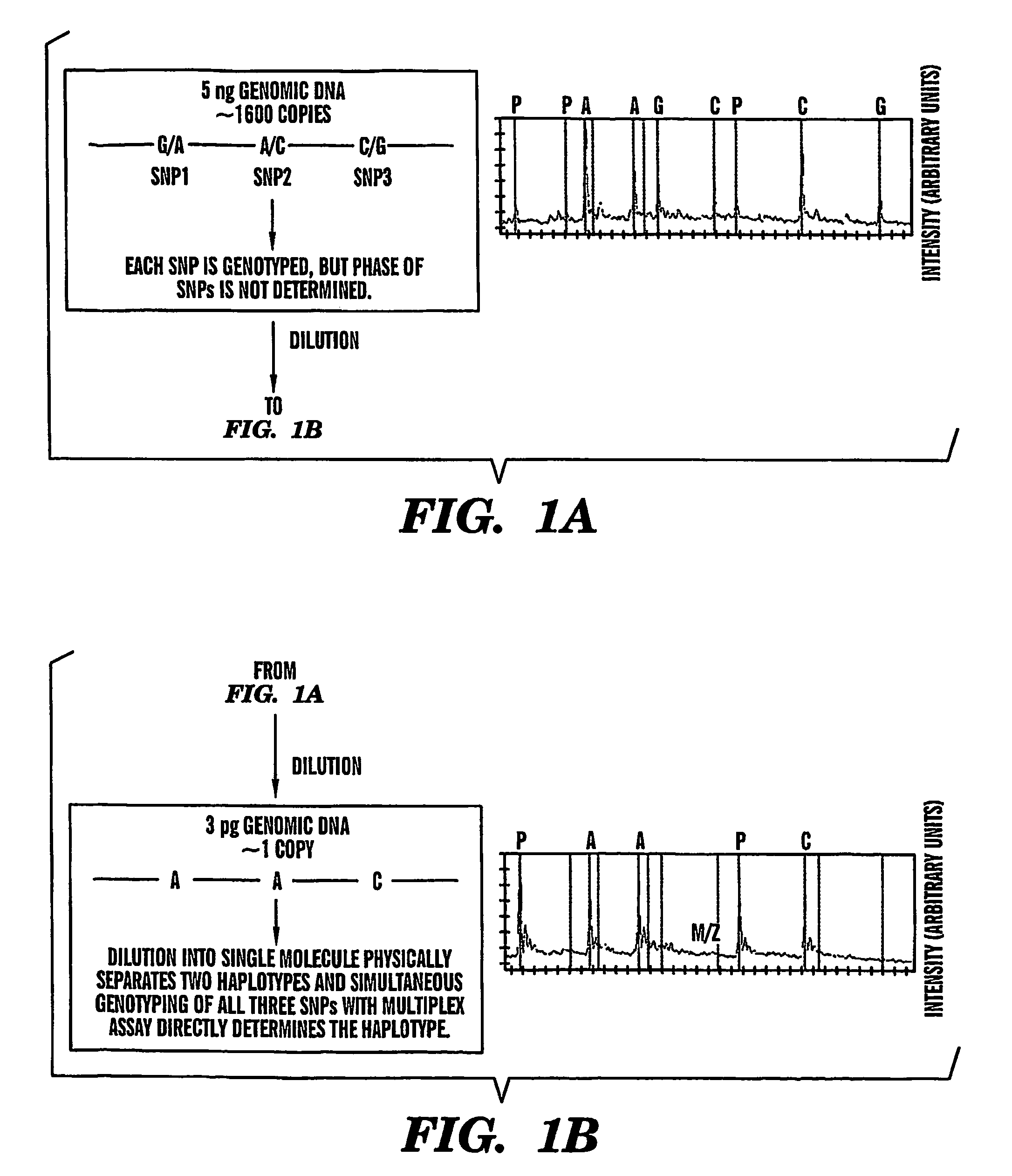
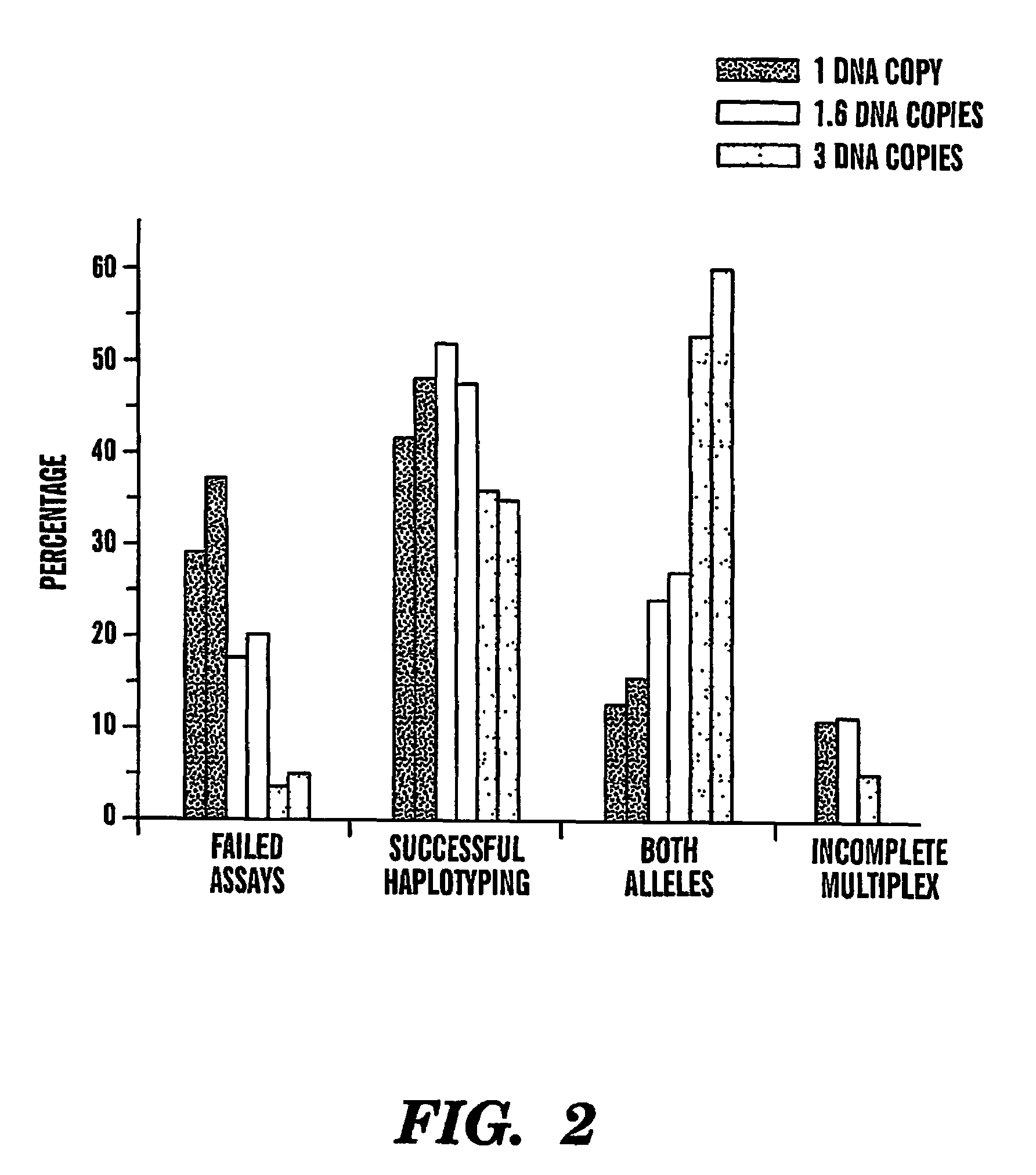
Haplotype analysis
InactiveUS7700325B2High analysisReliable determinationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementStatistical analysisHaplotype
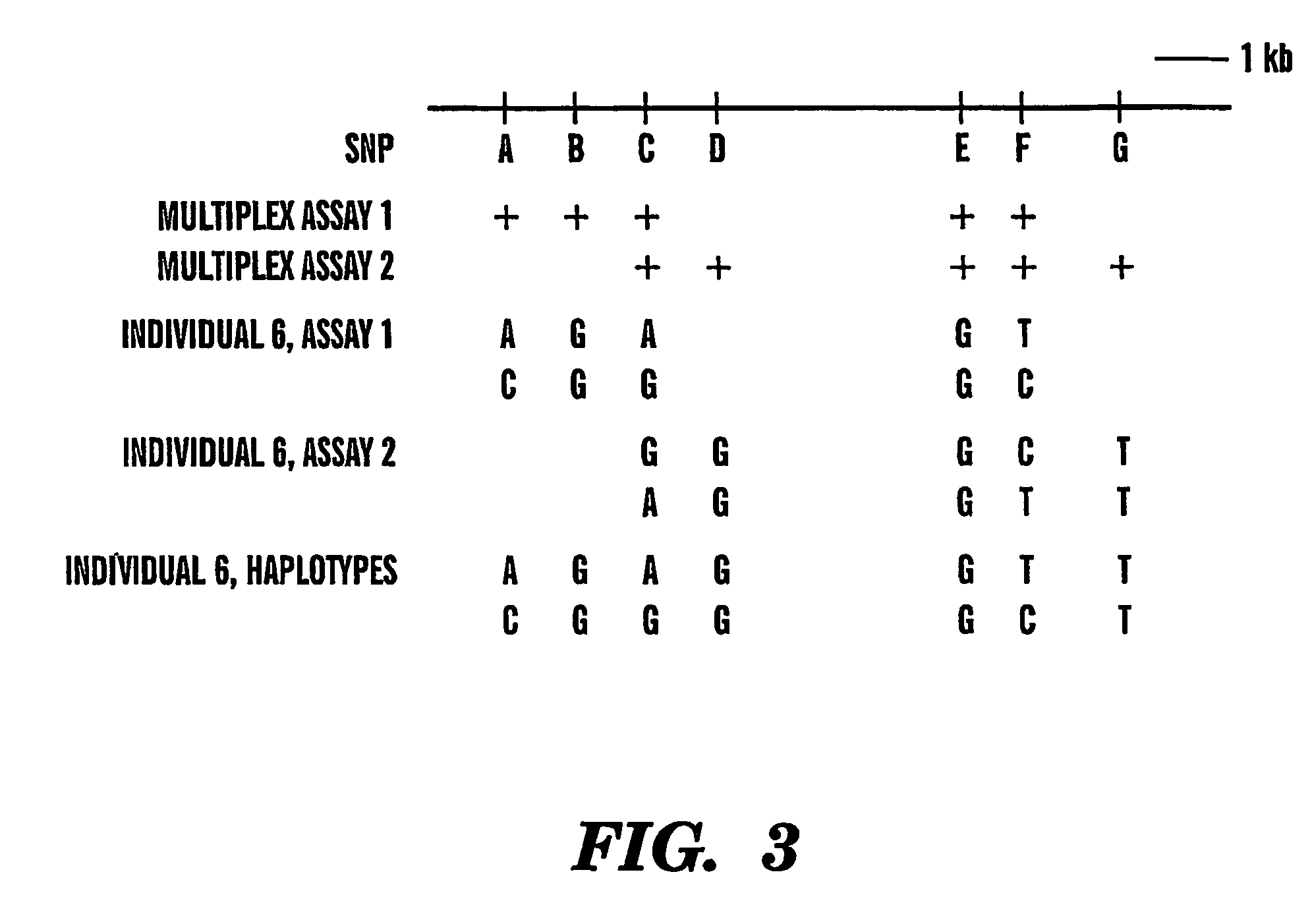
The present invention provides an efficient way for high throughput haplotype analysis. Several polymorphic nucleic acid markers, such as SNPs, can be simultaneously and reliably determined through multiplex PCR of single nucleic acid molecules in several parallel single molecule dilutions and the consequent statistical analysis of the results from these parallel single molecule multiplex PCR reactions results in reliable determination of haplotypes present in the subject. The nucleic acid markers can be of any distance to each other on the chromosome. In addition, an approach wherein overlapping DNA markers are analyzed can be used to link smaller haplotypes into larger haplotypes. Consequently, the invention provides a powerful new tool for diagnostic haplotyping and identifying novel haplotypes.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Gel microdrops in genetic analysis
InactiveUS6586176B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle entityVirus
The invention provides methods of nucleic acid analysis. Such methods entail forming a population of gel microdrops encapsulating a population of biological entities, each entity comprising a nucleic acid, whereby at least some microdrops in the population each encapsulate a single entity. The population of gel microdrops is then contacted with a probe under conditions whereby the probe specifically hybridizes to at least one complementary sequence in the nucleic acid in at least one gel microdrop. At least one gel microdrop is then analyzed or detected. The biological entities can be cells, viruses, nuclei and chromosomes.
Owner:CELLAY
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
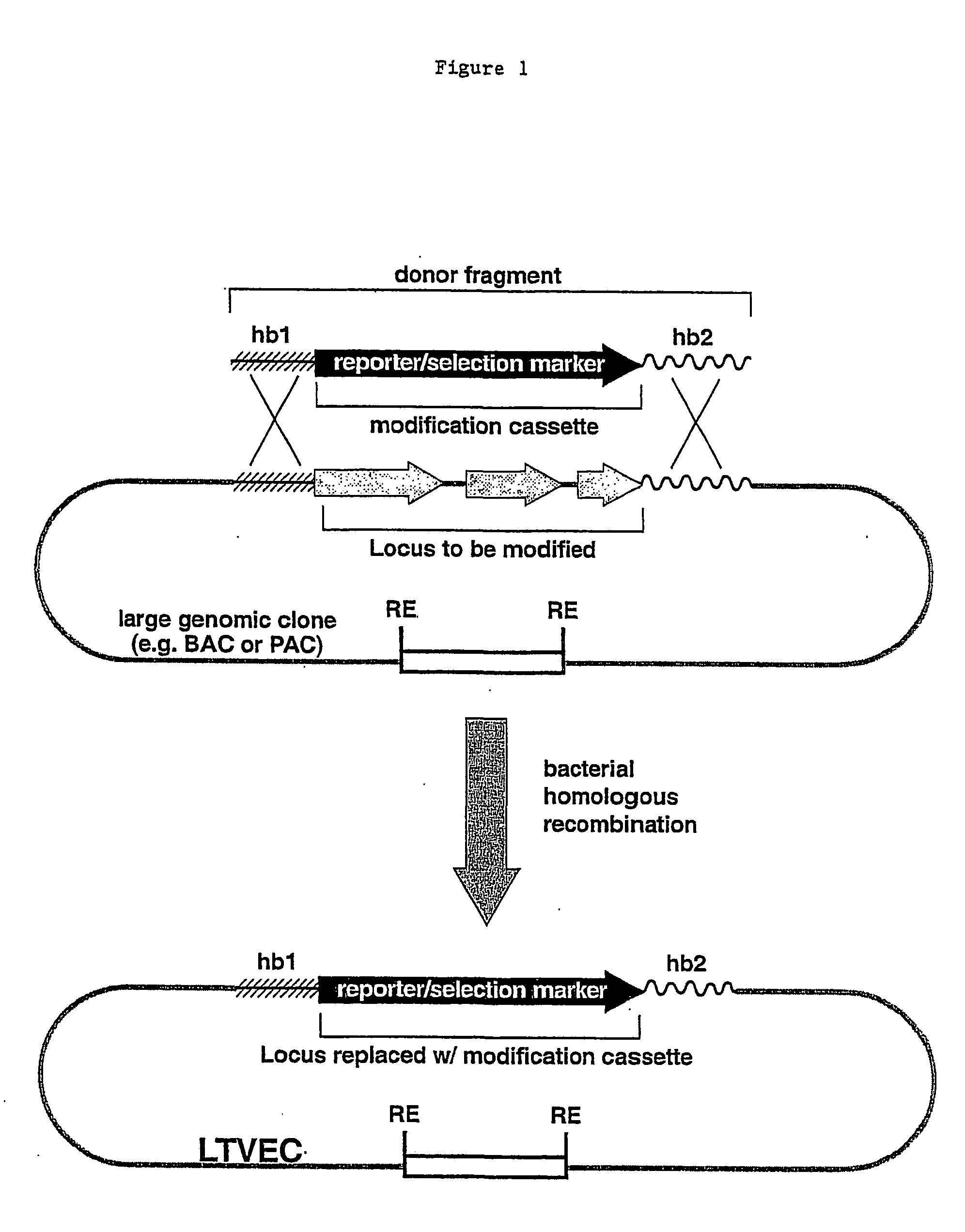
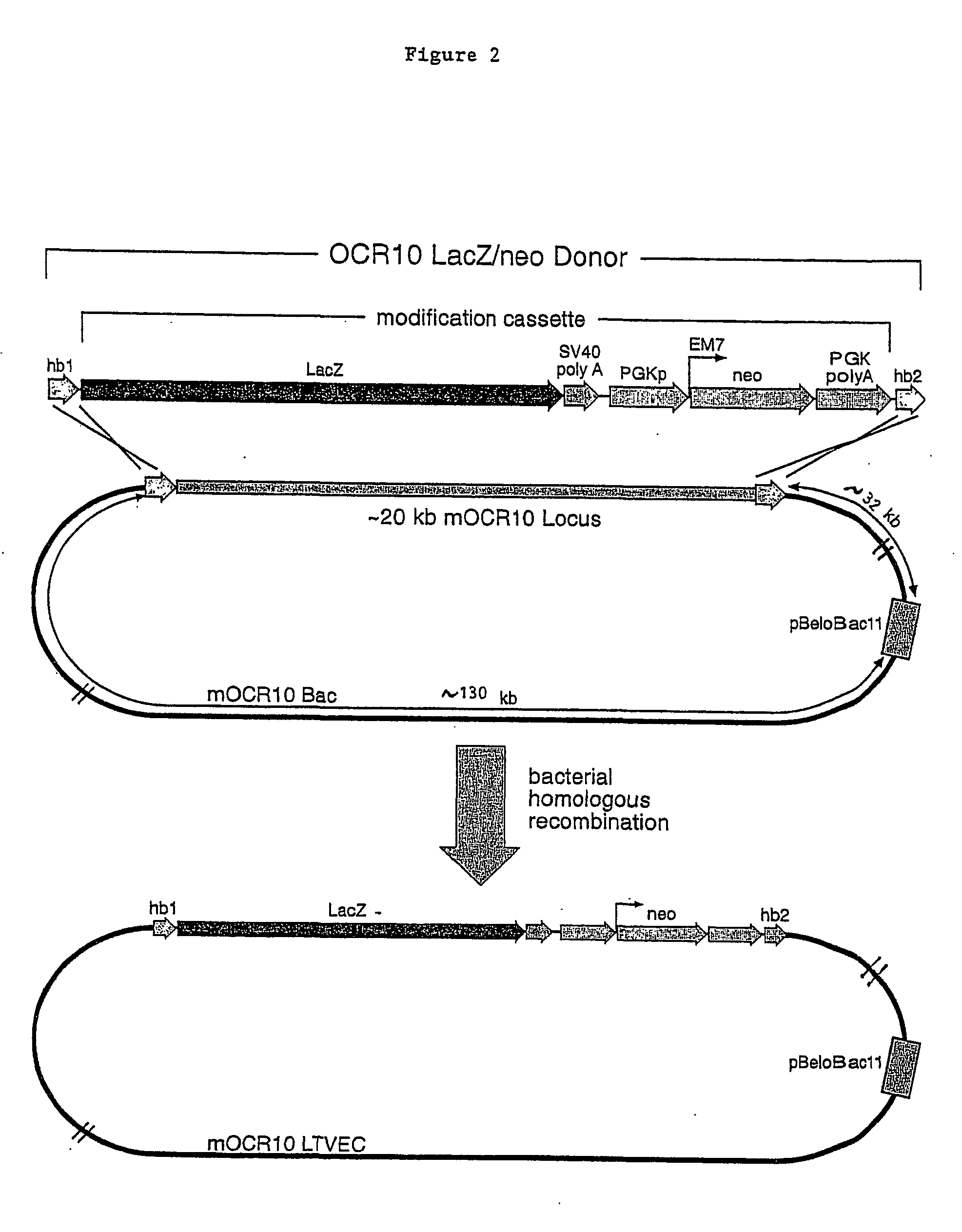
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous genes(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Methods for targeted genomic analysis
ActiveUS20140274731A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecific detectionGene expression profiling
The invention provides a method for genetic analysis in individuals that reveals both the genetic sequences and chromosomal copy number of targeted and specific genomic loci in a single assay. The present invention further provide methods for the sensitive and specific detection of target gene sequences and gene expression profiles.
Owner:RESOLUTION BIOSCI
Risk calculation for evaluation of fetal aneuploidy
The present invention provides processes for determining accurate risk probabilities for fetal aneuploidies. Specifically, the invention provides non-invasive evaluation of genomic variations through chromosome-selective sequencing and non-host fraction data analysis of maternal samples.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Genome editing of genes associated with trinucleotide repeat expansion disorders in animals
InactiveUS20110016540A1Vertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsZinc finger nucleaseChemical toxicity
The present invention provides genetically modified animals and cells comprising edited chromosomal sequences encoding proteins that are associated with trinucleotide repeat expansion disorders. In particular, the animals or cells are generated using a zinc finger nuclease-mediated editing process. Also provided are methods of using the genetically modified animals or cells disclosed herein to screen agents for toxicity and other effects.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
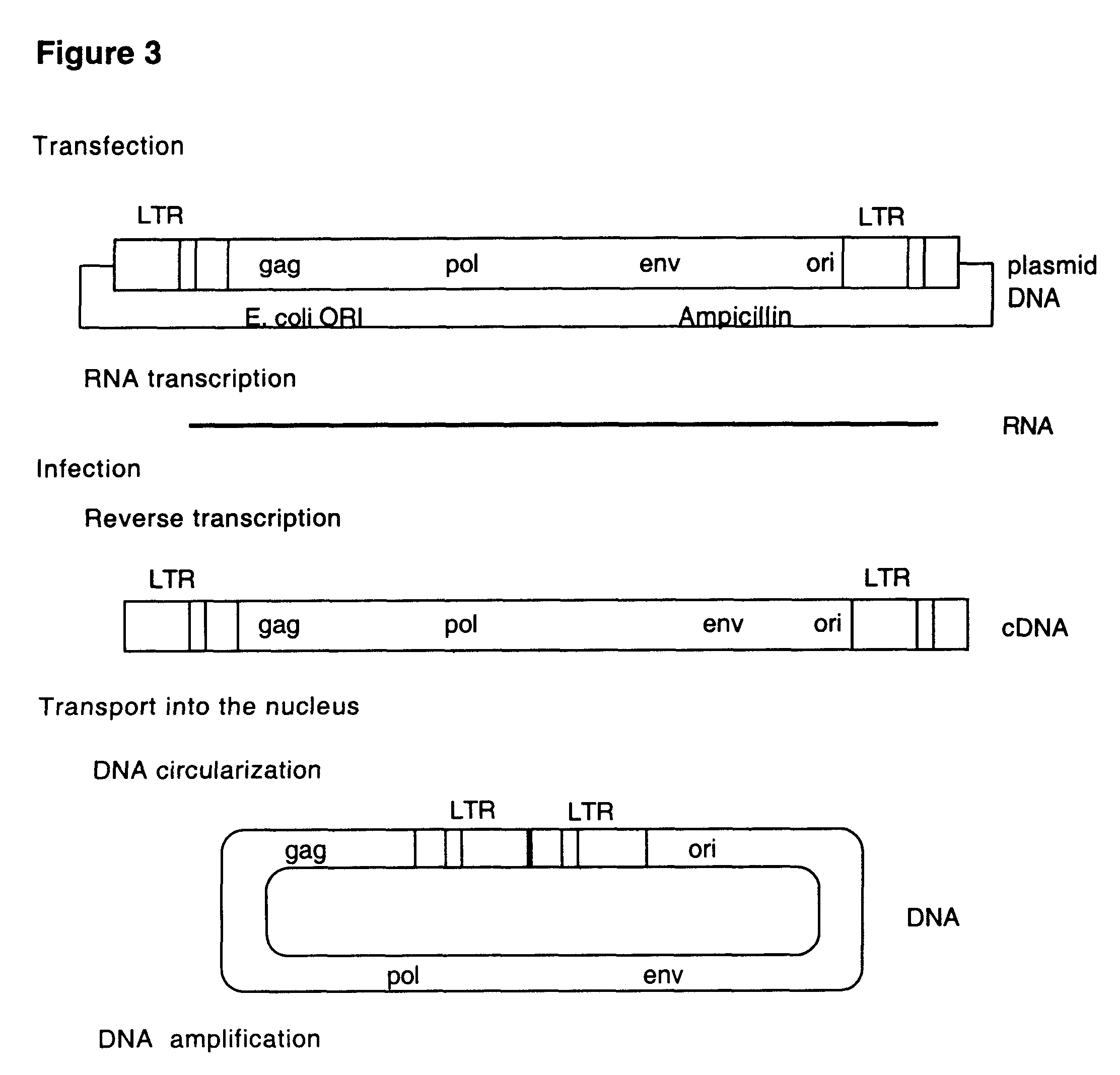
Retrovirus and viral vectors
InactiveUS6635472B1Prevent and attenuate diseaseEnhance immune responseGenetic material ingredientsVirus peptidesVirus-RetrovirusDna viral
This invention relates to the fields of genetic engineering, virus replication and gene transfer. More specifically, this invention relates to polynucleotide construct, recombinant virus, transposon, and their vectors, wherein an ori derived from a DNA virus capable of replicating in vertebrate cells is inserted into the retrovirus, allowing the retrovirus following the reverse transcription to efficiently replicate as extrachromosomal or episomal DNA without the necessity of integration into the host cell chromosome. Additionally, this invention relates to polynucleotide construct, recombinant virus, transposon, and their vectors replicating episomally without aid of an ori and related elements. Also, this invention encompasses preventive, therapeutic, and diagnostic applications employing said constructs, viruses and vectors.
Owner:RUBICON LABS
Novel markers for prenatal diagnosis and monitoring
ActiveUS20070275402A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementObstetricsPrenatal diagnosis
This application provides the use of novel fetal markers for prenatal diagnosis and monitoring of certain pregnancy-related conditions. More specifically, the invention resides in the discovery that certain CpG islands located on fetal chromosome 21 demonstrate a methylation profile that is distinct from that of the corresponding CpG islands located on maternal chromosome 21. This application also provides kits for diagnosing or monitoring of the relevant conditions.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
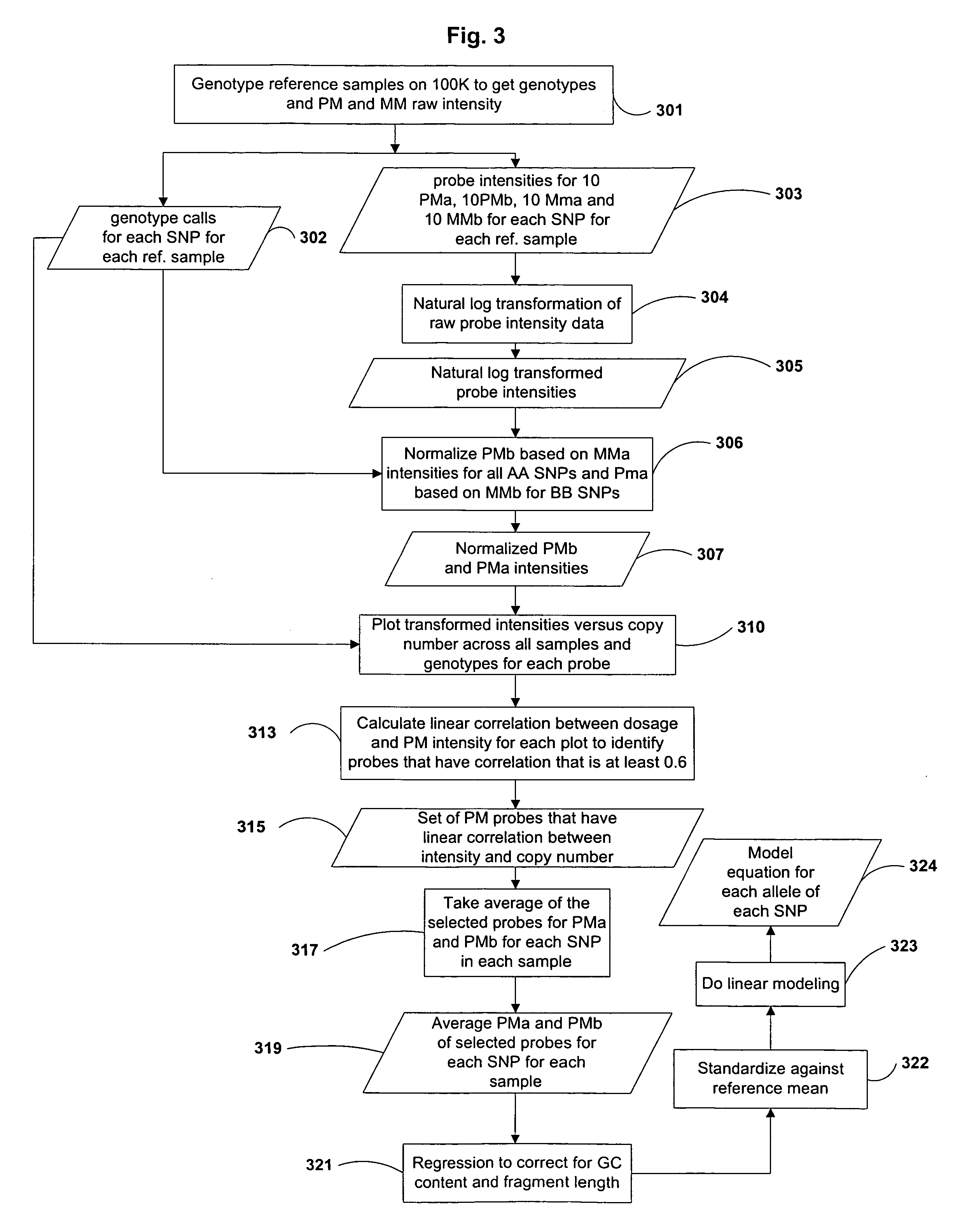
Methods for identifying DNA copy number changes
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
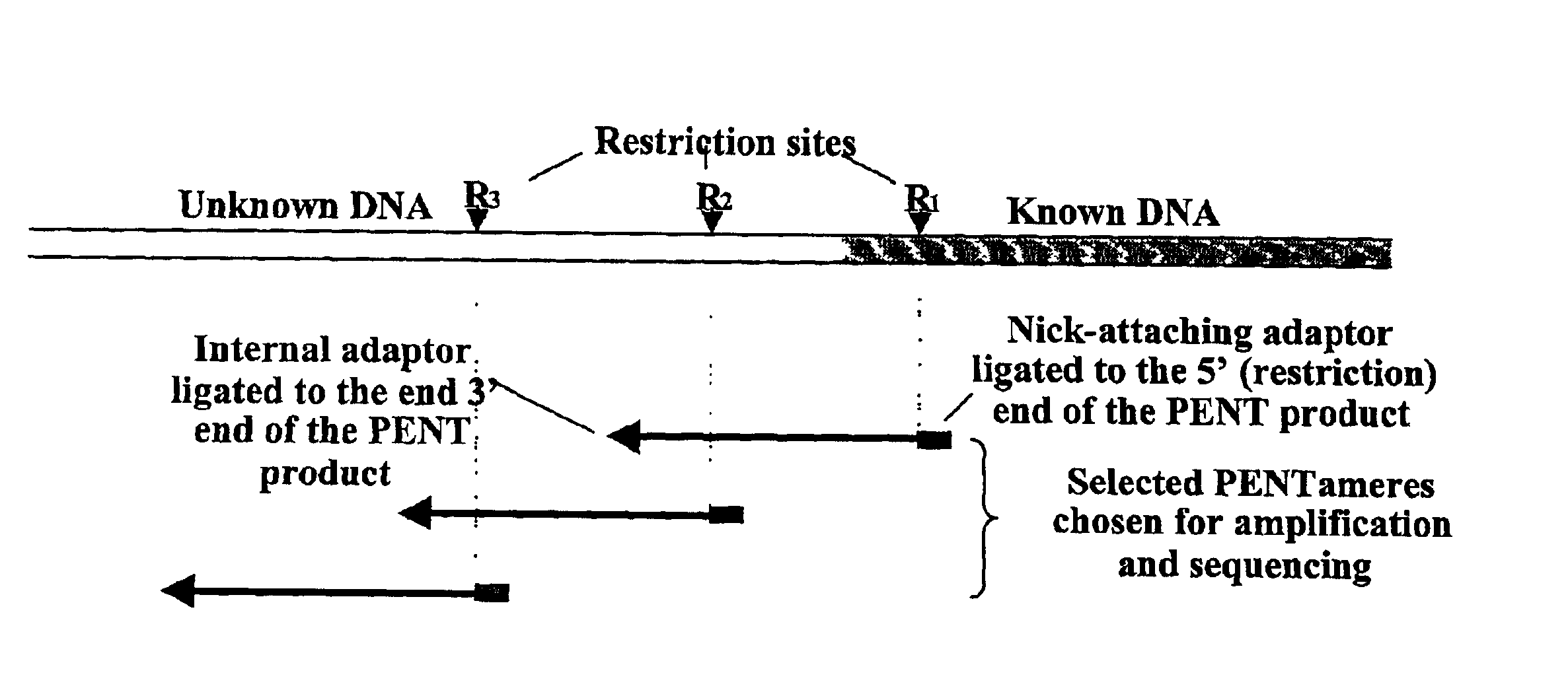
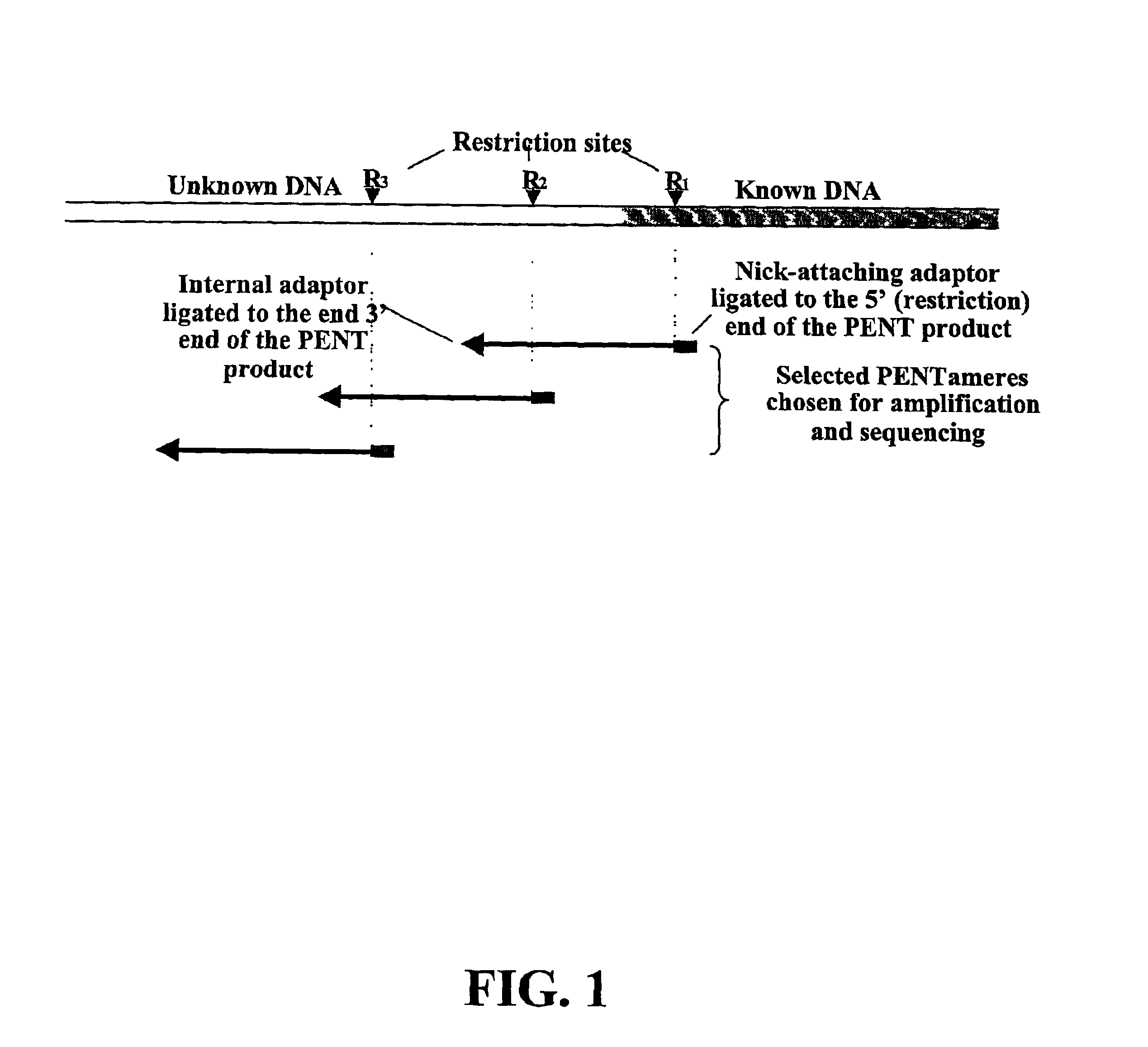
Genome walking by selective amplification of nick-translate DNA library and amplification from complex mixtures of templates
Improved methods and reagents for chromosome walking of nucleic acid are discussed herein. A library of amplifiable nick translation molecules is generated, and a chromosome walk is initiated from a known sequence in the nucleic acid by producing at least one nick translate molecule, sequencing part of the nick translate molecule, and producing a second nick translate molecule by initiating the primer extension from the region of the obtained sequence of the prior nick translate molecule.
Owner:TAKARA BIO USA INC
Gel microdroplets in genetic analysis
InactiveUS20030207260A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVirusSingle entity
Owner:ONE CELL SYST
Methods for identifying DNA copy number changes
InactiveUS20050064476A1Reduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGenomic DNANormal tissue
Methods of identifying changes in genomic DNA copy number are disclosed. Methods for identifying homozygous deletions and genetic amplifications are disclosed. An array of probes designed to detect presence or absence of a plurality of different sequences is also disclosed. The probes are designed to hybridize to sequences that are predicted to be present in a reduced complexity sample. The methods may be used to detect copy number changes in cancerous tissue compared to normal tissue. The methods may be used to diagnose cancer and other diseases associated with chromosomal anomalies.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Crispr-based genome modification and regulation
The present invention provides RNA-guided endonucleases, which are engineered for expression in eukaryotic cells or embryos, and methods of using the RNA-guided endonuclease for targeted genome modification in in eukaryotic cells or embryos. Also provided are fusion proteins, wherein each fusion protein comprises a CRISPR / Cas-like protein or fragment thereof and an effector domain. The effector domain can be a cleavage domain, an epigenetic modification domain, a transcriptional activation domain, or a transcriptional repressor domain. Also provided are methods for using the fusion proteins to modify a chromosomal sequence or regulate expression of a chromosomal sequence.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
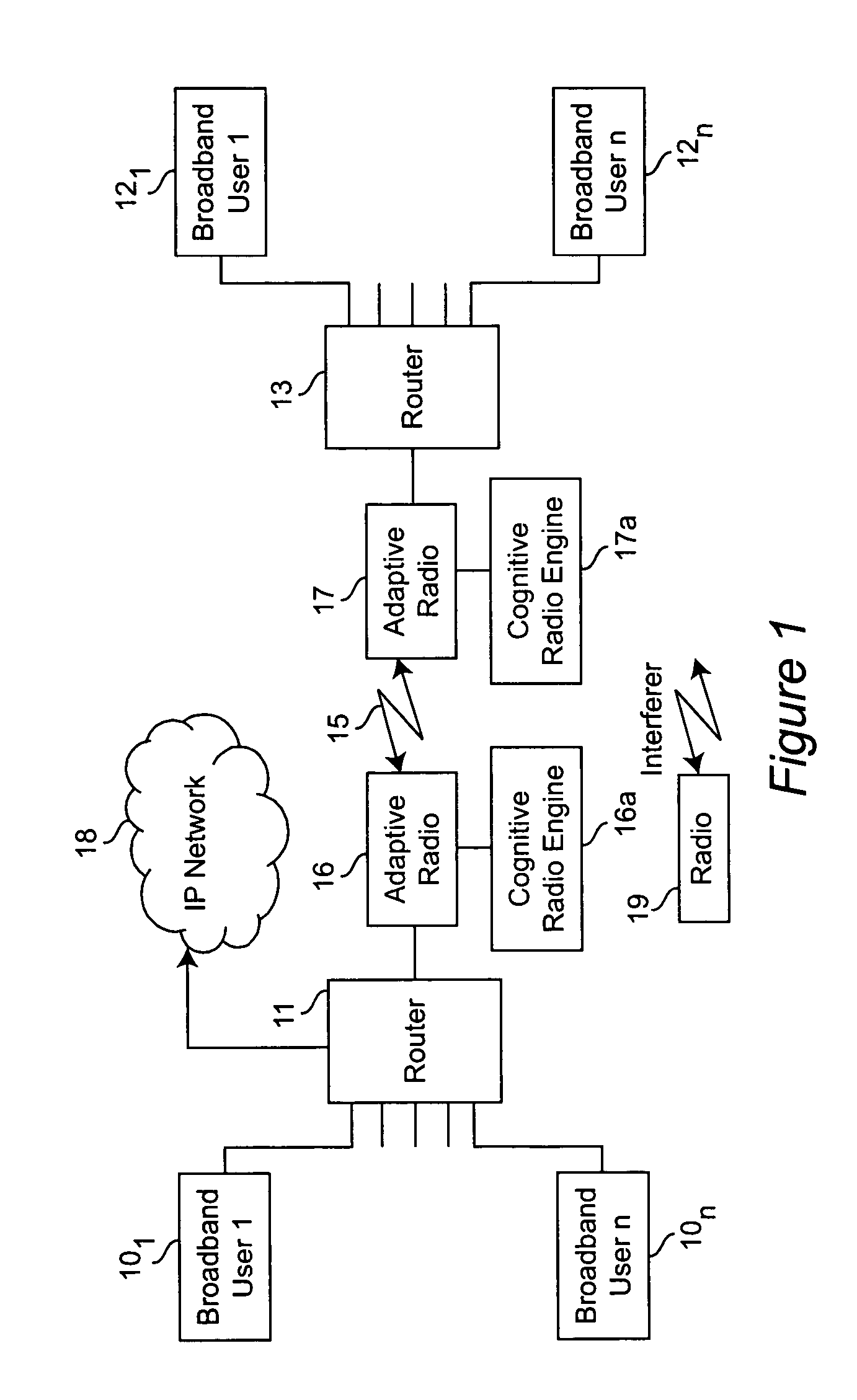
Cognitive radio engine based on genetic algorithms in a network
ActiveUS20060009209A1Enable spontaneous inspiration and creativityNetwork traffic/resource managementGenetic modelsTransmitted powerGenetic algorithm
A genetic algorithm (GA) approach is used to adapt a wireless radio to a changing environment. A cognitive radio engine implements three algorithms; a wireless channel genetic algorithm (WCGA), a cognitive system monitor (CSM) and a wireless system genetic algorithm (WSGA). A chaotic search with controllable boundaries allows the cognitive radio engine to seek out and discover unique solutions efficiently. By being able to control the search space by limiting the number of generations, crossover rates, mutation rates, fitness evaluations, etc., the cognitive system can ensure legal and regulatory compliance as well as efficient searches. The versatility of the cognitive process can be applied to any adaptive radio. The cognitive system defines the radio chromosome, where each gene represents a radio parameter such as transmit power, frequency, modulation, etc. The adaptation process of the WSGA is performed on the chromosomes to develop new values for each gene, which is then used to adapt the radio settings.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
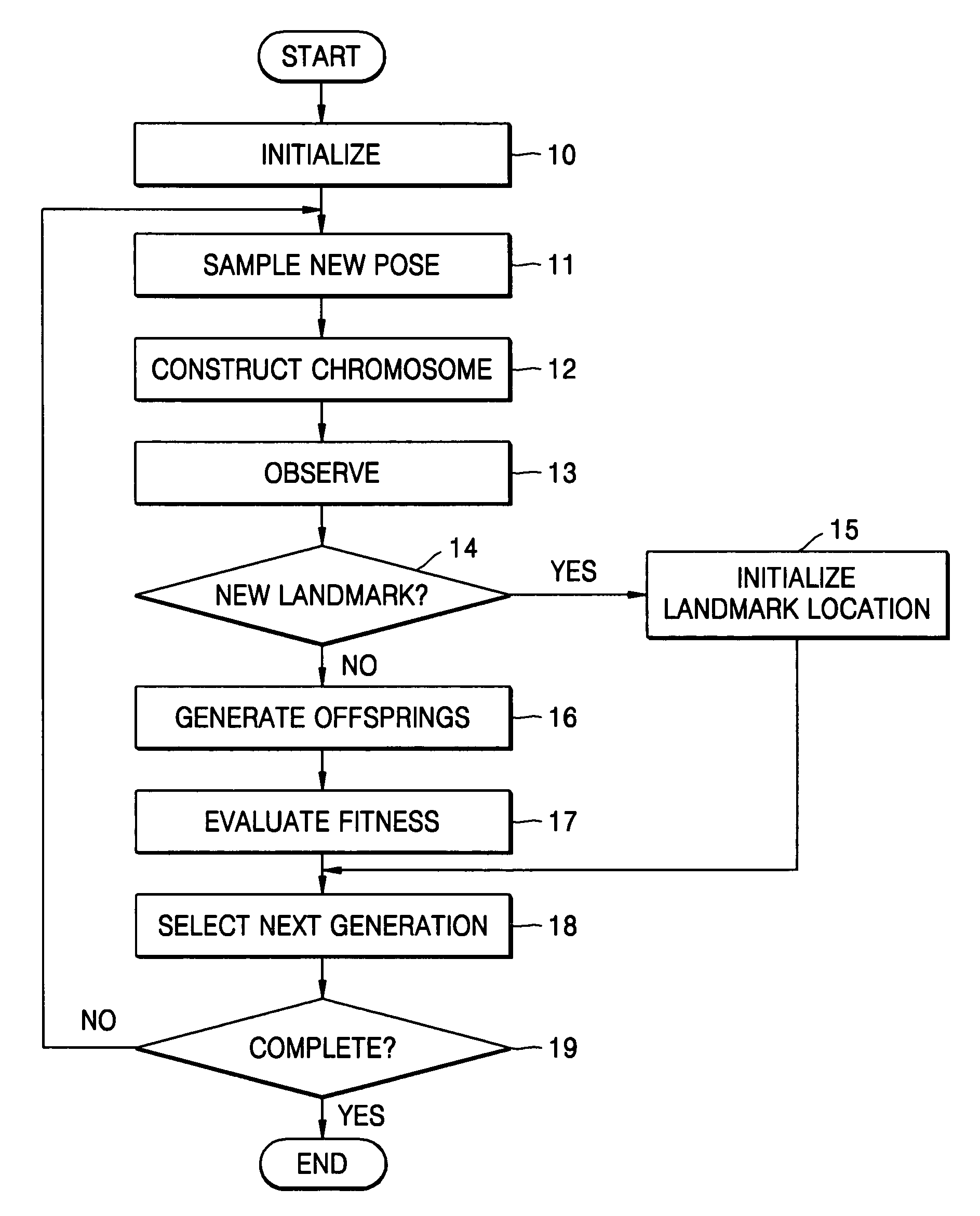
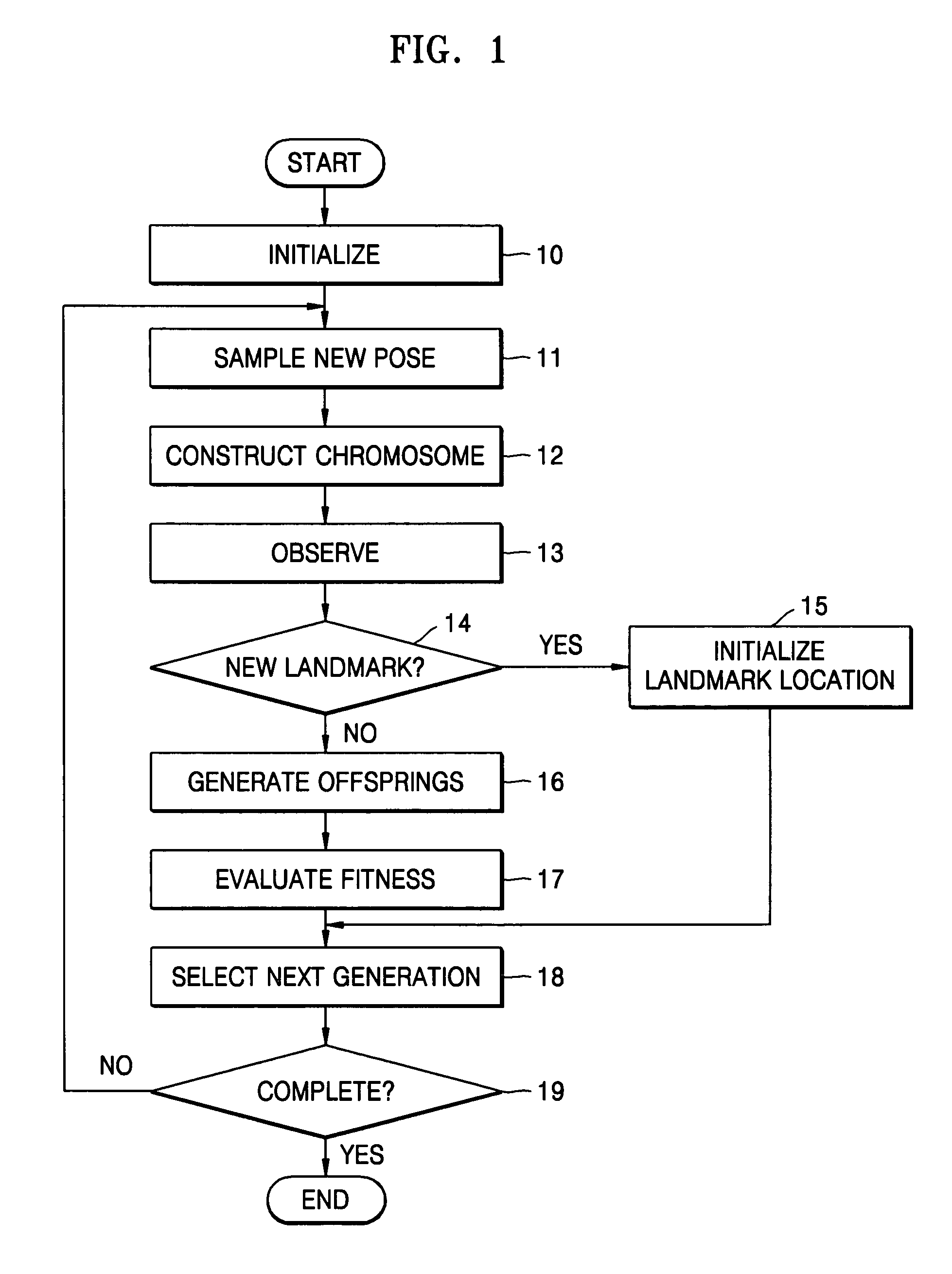
Method used by robot for simultaneous localization and map-building
A method used by a robot for simultaneous localization and map-building, including: initializing a pose of the robot and locations of landmarks; sampling a new pose of the robot during motion of the robot, and constructing chromosomes using the locations of the landmarks; observing the landmarks from a present location of the robot; generating offspring from the chromosomes; and selecting next-generation chromosomes from the chromosomes and the offspring using observation values of the landmarks.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Genomic editing of genes involved in amyotrophyic lateral sclerosis disease
The present invention provides genetically modified animals and cells comprising edited chromosomal sequences encoding proteins that are associated ALS. In particular, the animals or cells are generated using a zinc finger nuclease-mediated editing process. Also provided are methods of using the genetically modified animals or cells disclosed herein to screen agents for toxicity and other effects.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Color display of chromosomes or portions of chromosomes
InactiveUS6055325AMore informationHigh sample throughputRaman/scattering spectroscopyInterferometric spectrometryFluorophoreComputer science
A color display comprising an image of all chromosomes or portions of chromosomes of a cell, each of the chromosomes or portions of chromosomes being painted with a different fluorophore or a combination of fluorophores, the image presenting the chromosomes or portions of chromosomes in different distinctive colors, wherein each of the chromosomes or portions of chromosomes is associated with one of the different distinctive colors.
Owner:APPLIED SPECTRAL IMAGING
Genomic editing of genes involved in cardiovascular disease
The present invention provides genetically modified animals and cells comprising edited chromosomal involved in cardiovascular disease. In particular, the animals or cells are generated using a zinc finger nuclease-mediated editing process. The invention also provides zinc finger nucleases that target chromosomal sequences involved in cardiovascular disease and the nucleic acids encoding said zinc finger nucleases. Also provided are methods of using the genetically modified animals or cells disclosed herein to screen agents for toxicity and other effects.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com