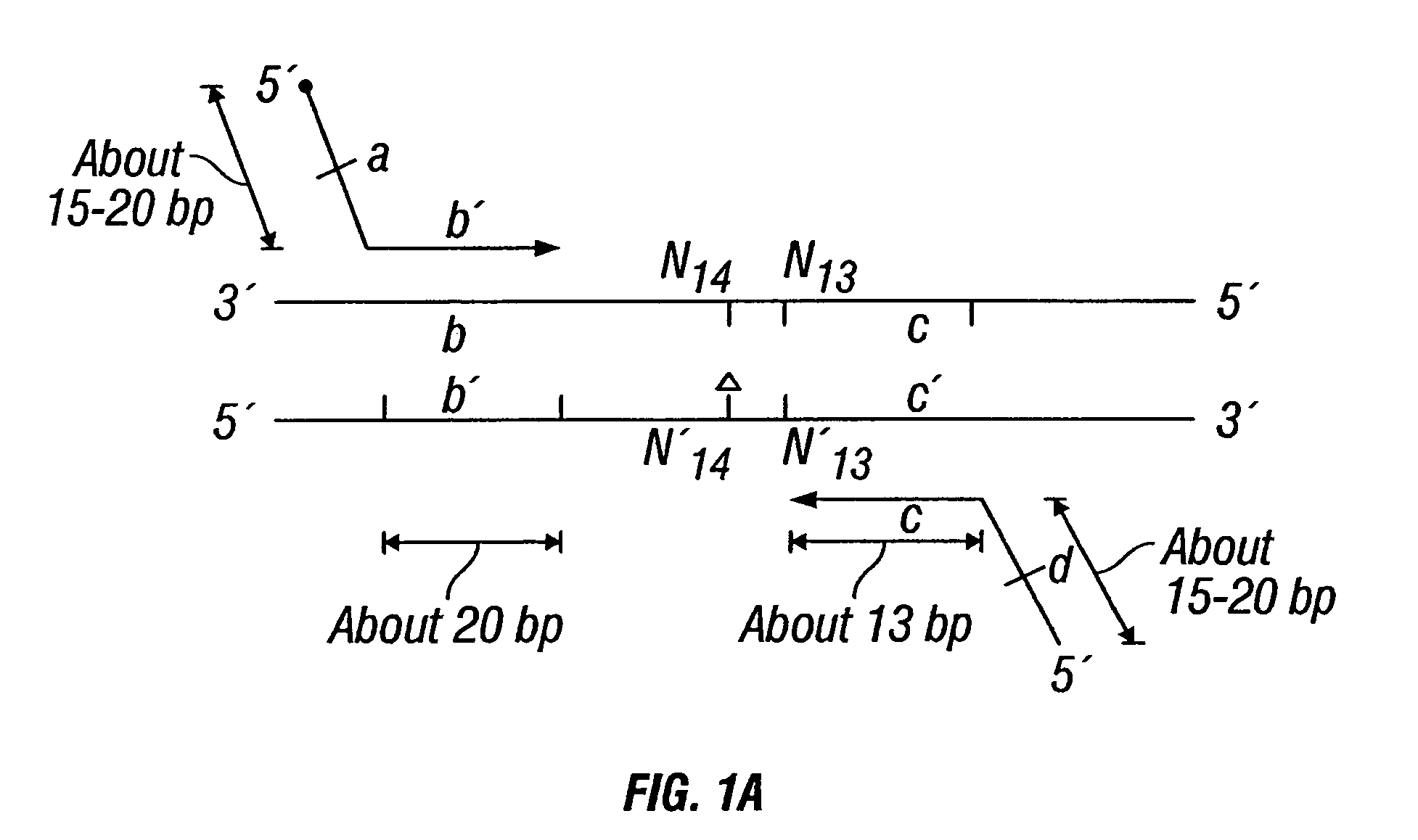
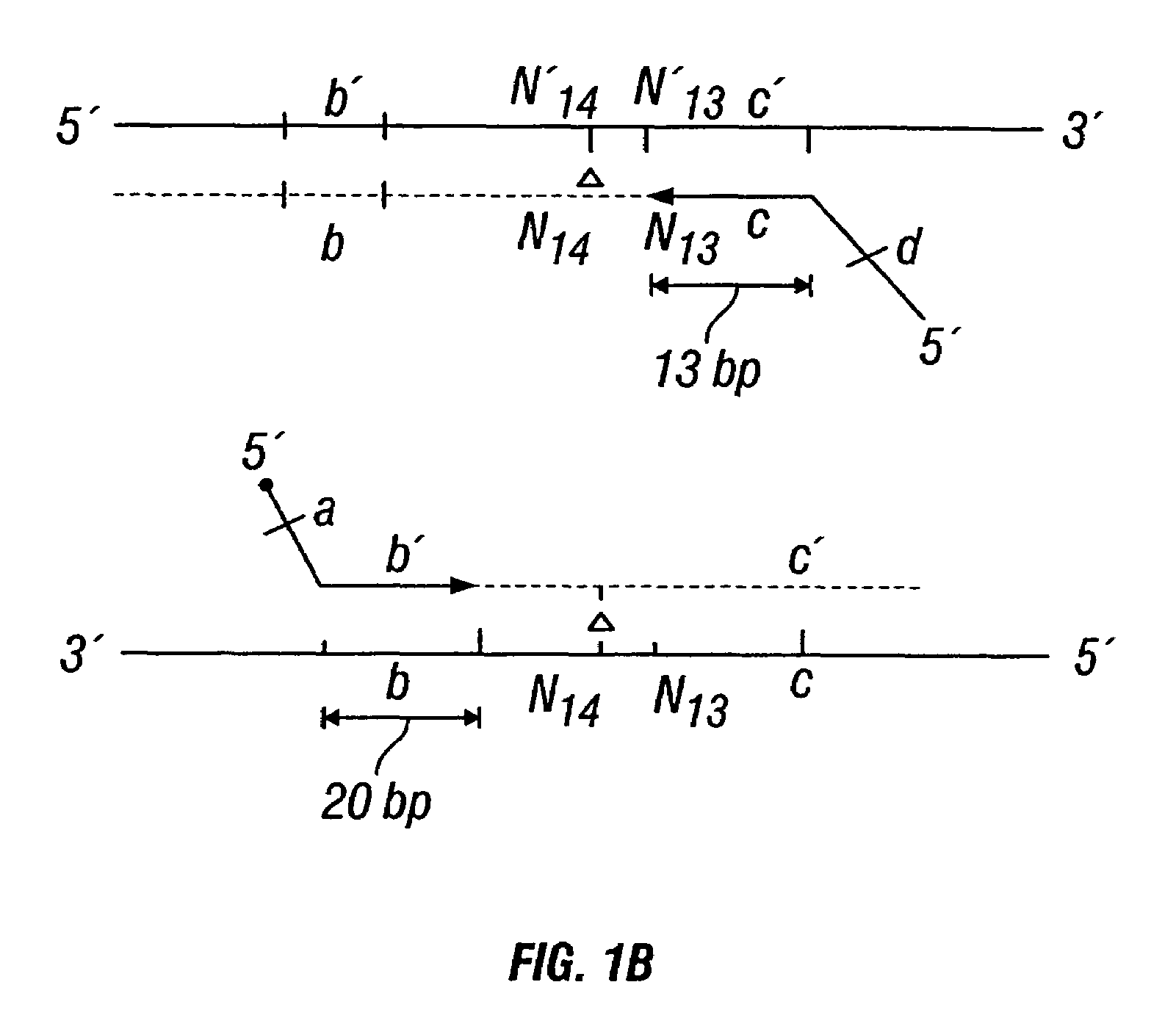
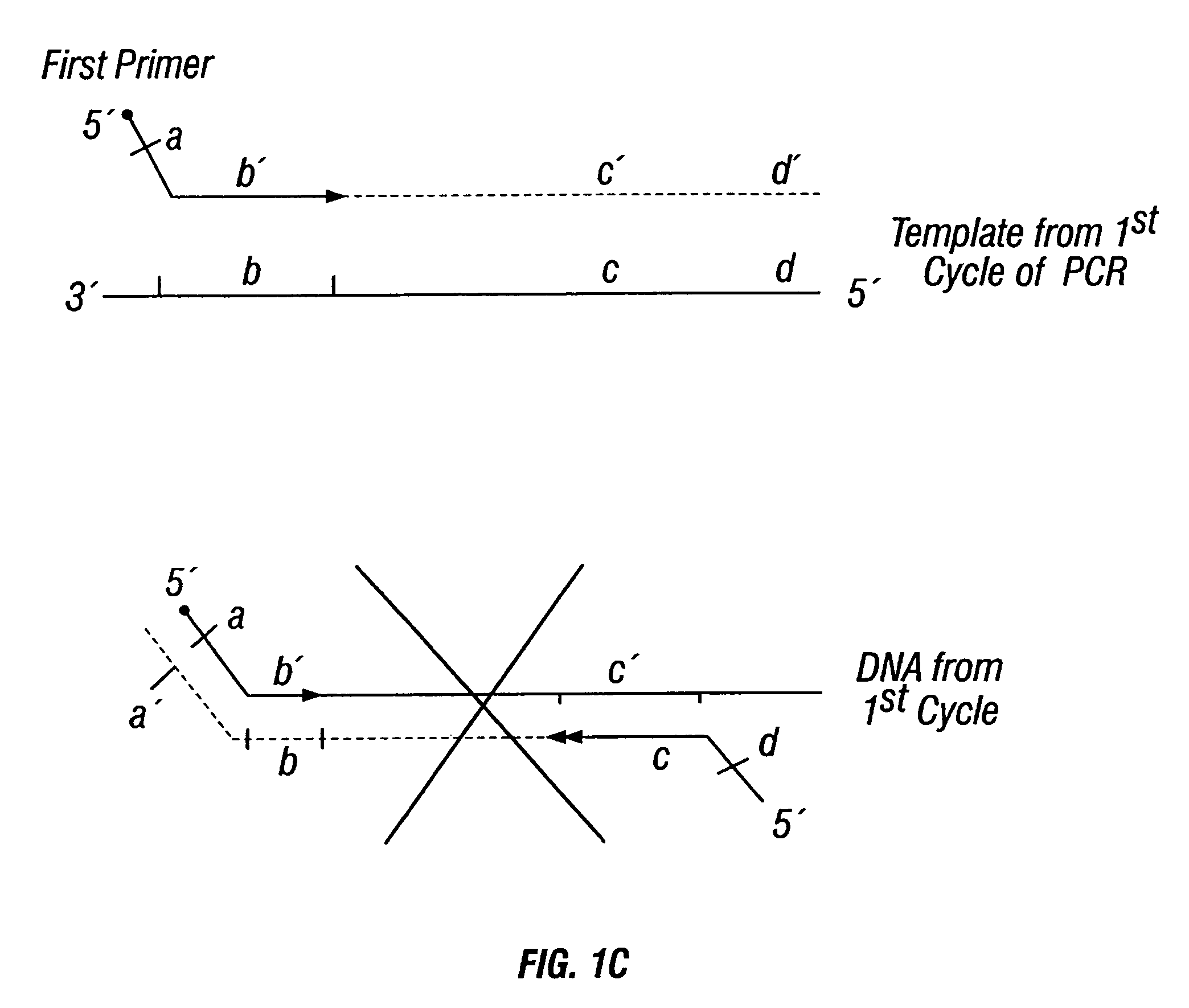
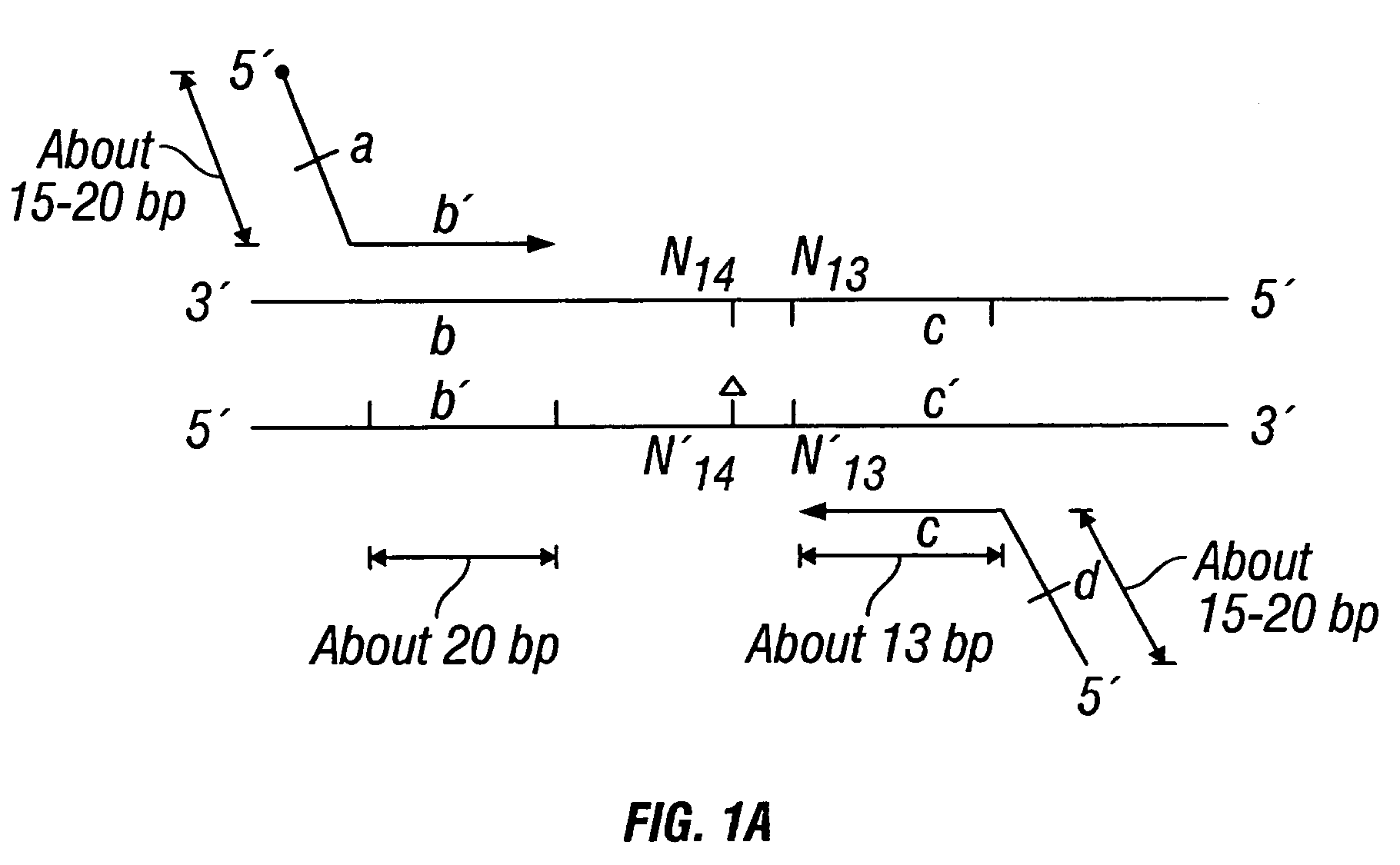
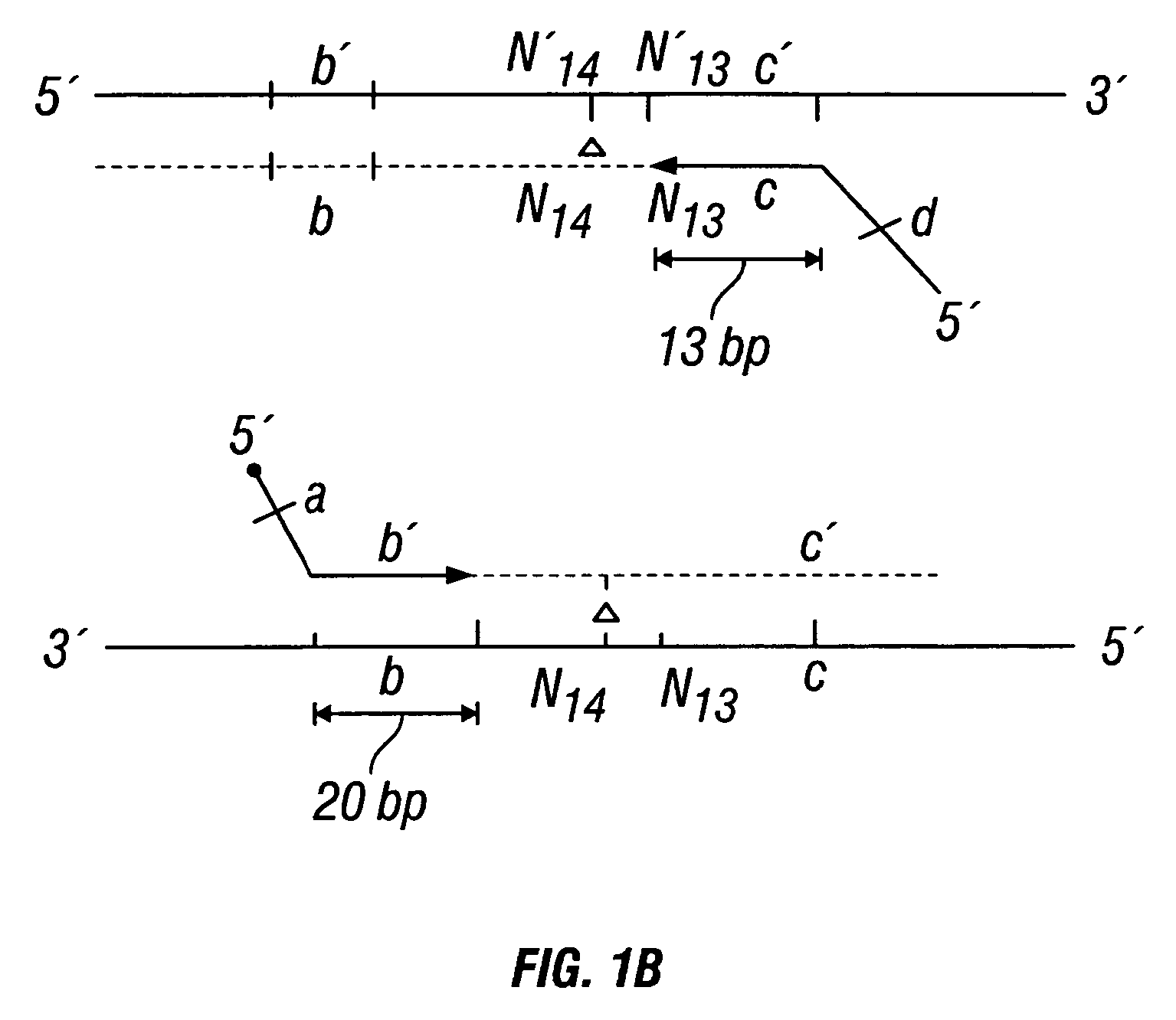
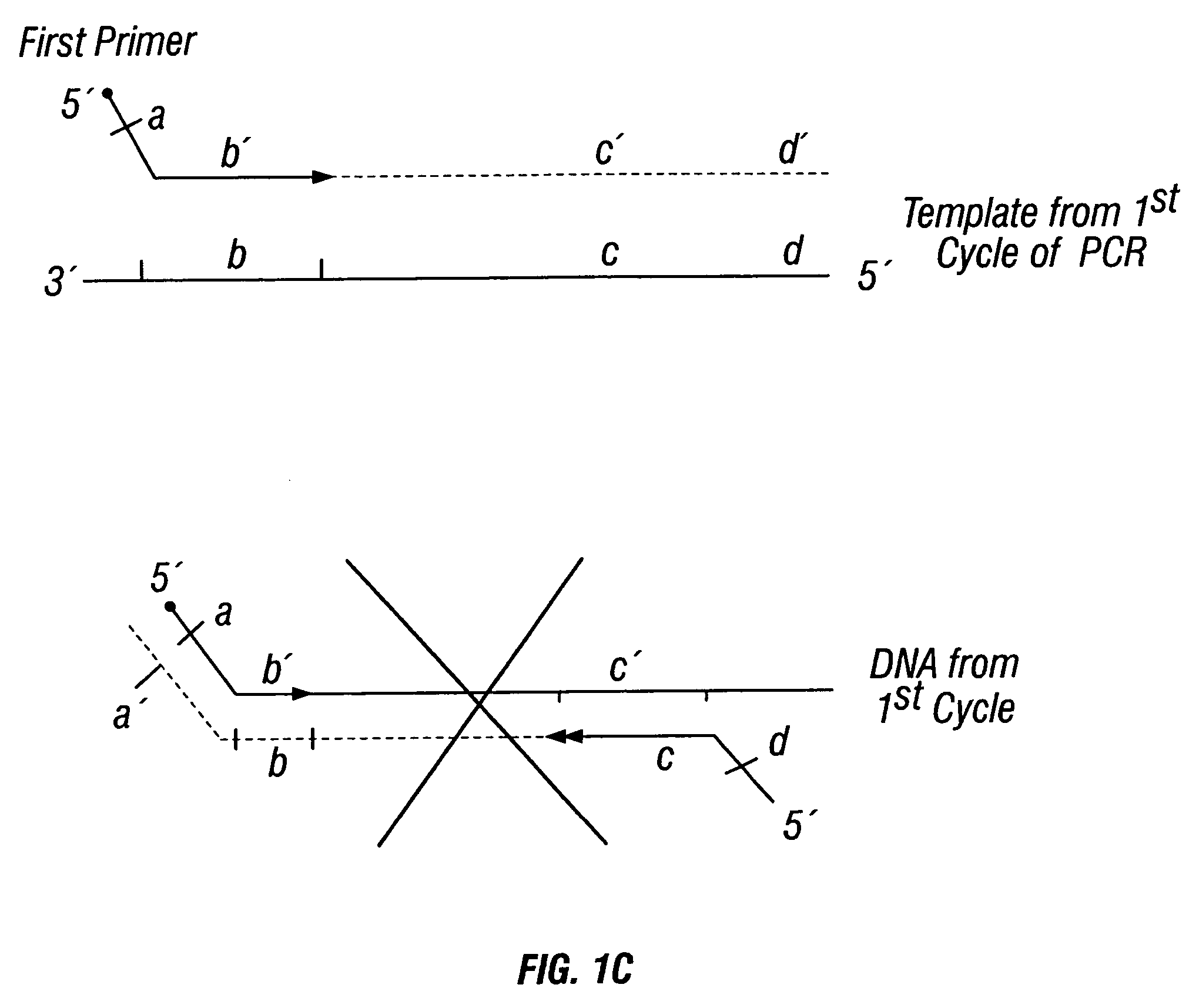
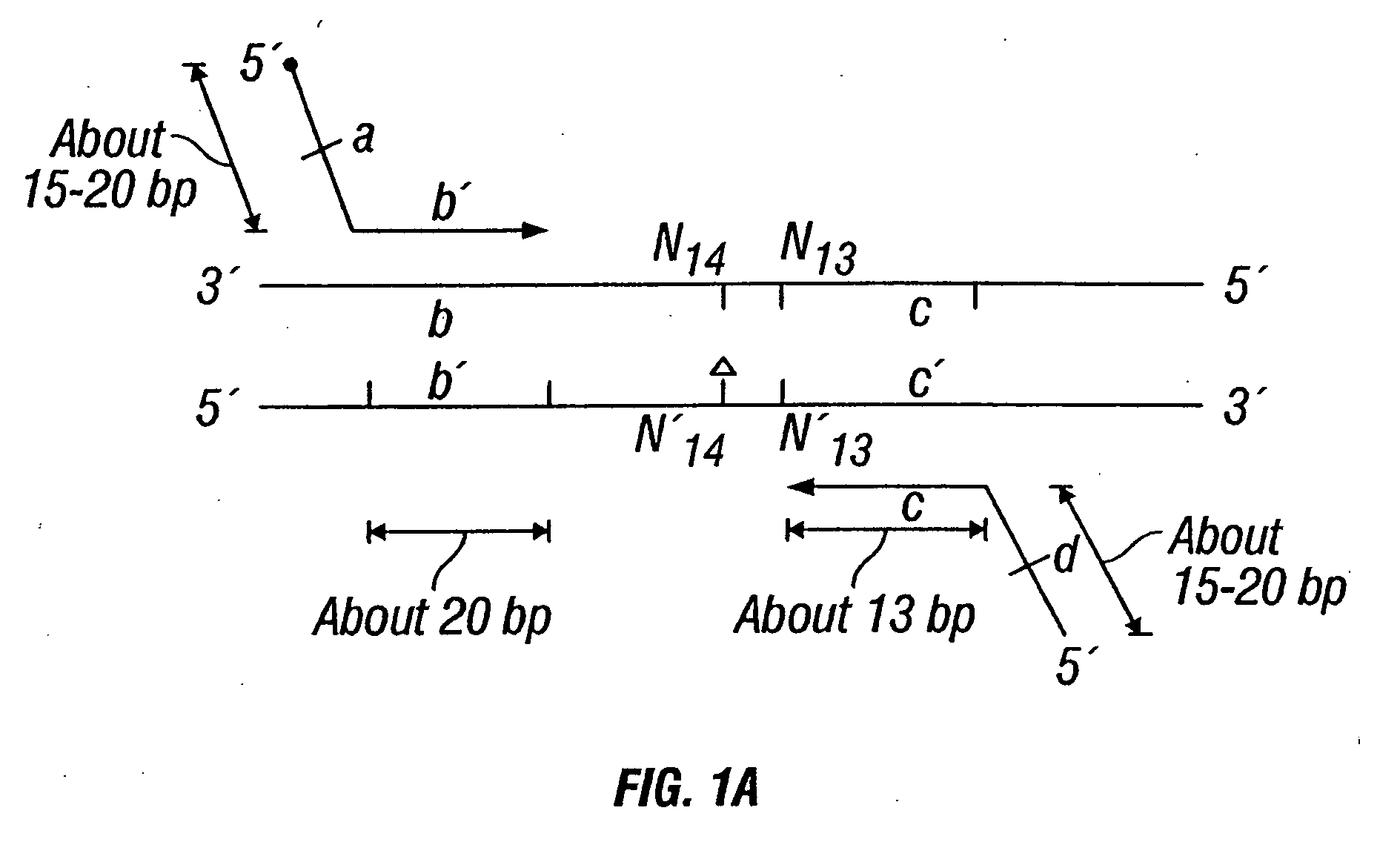
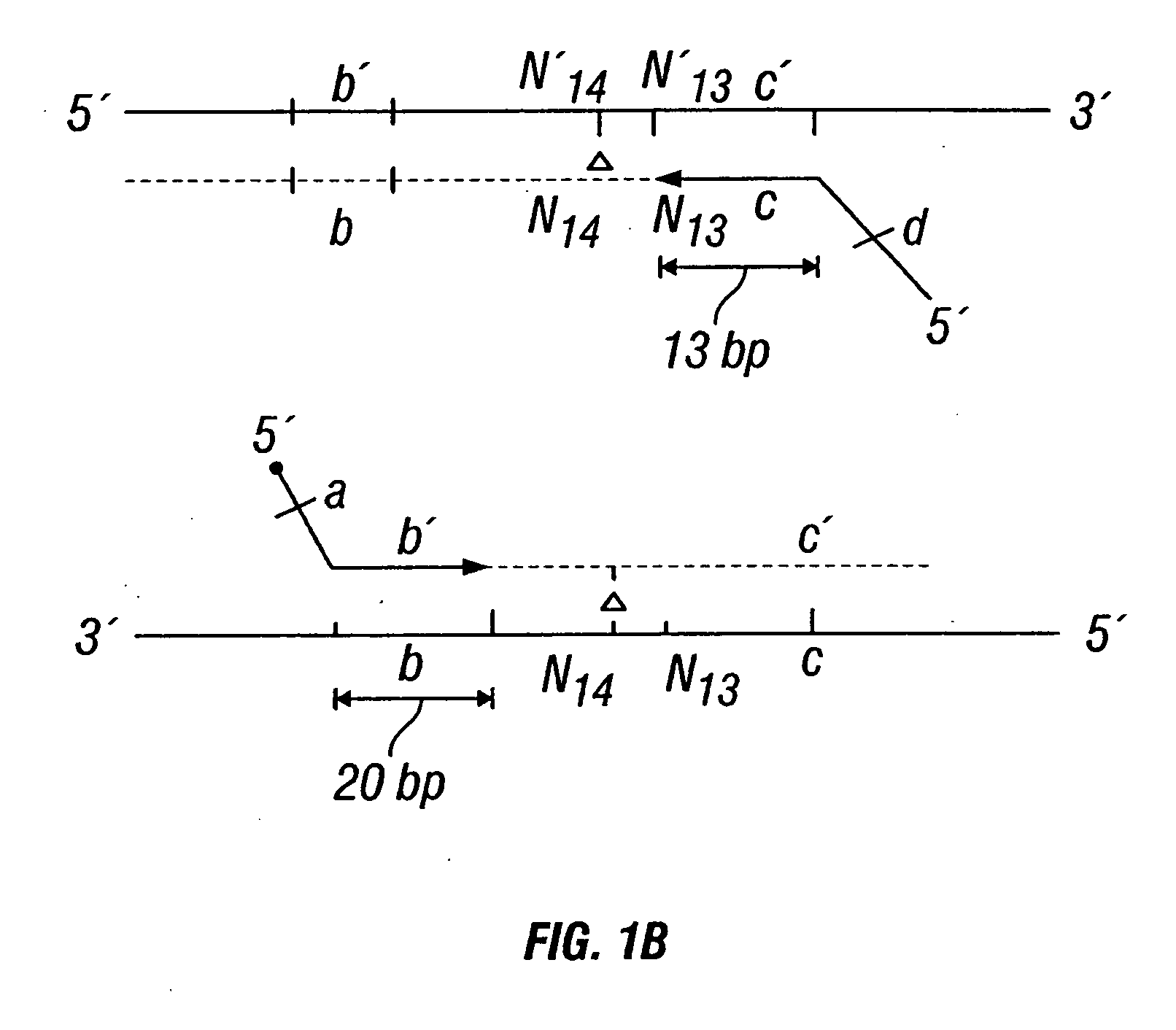
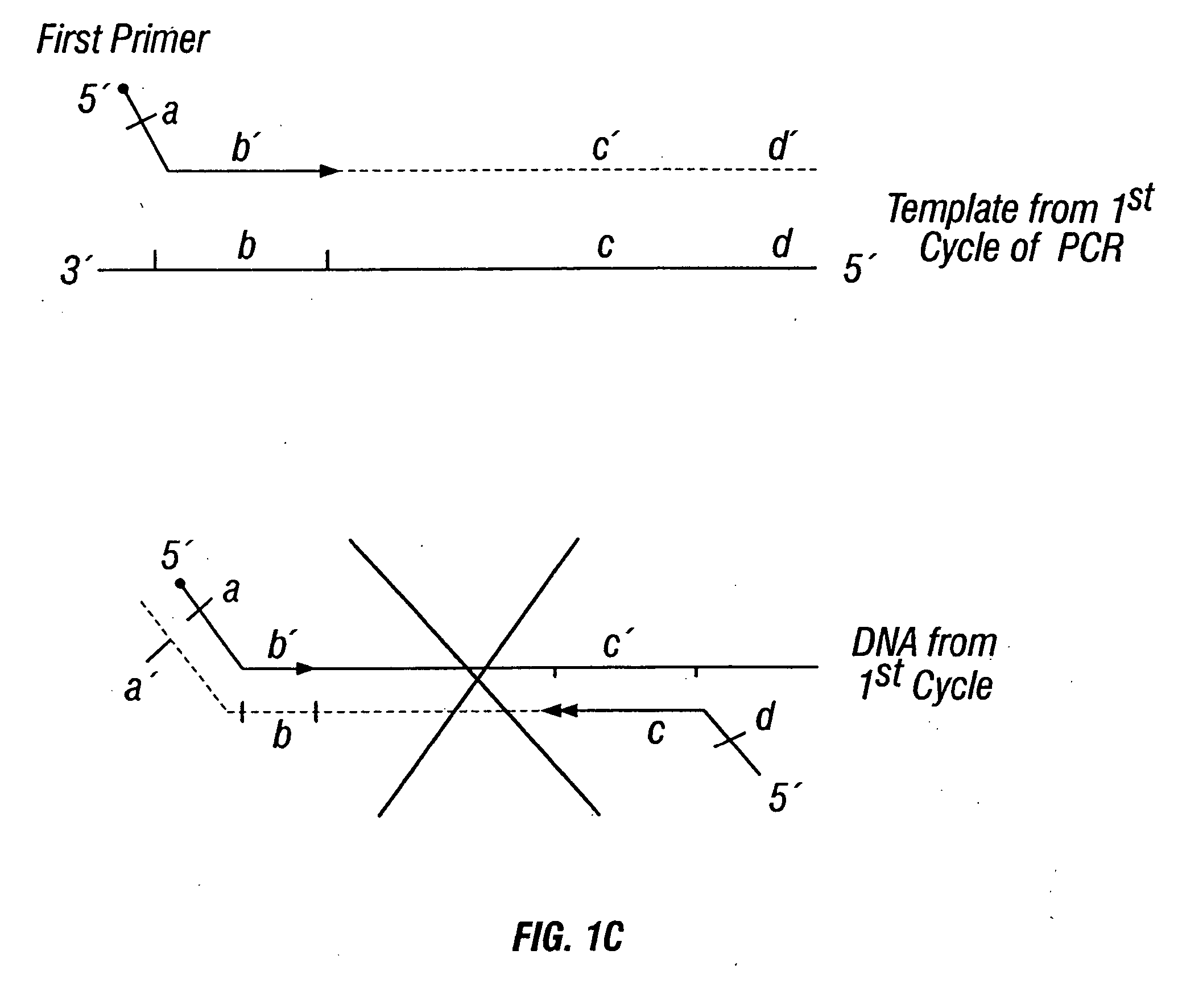
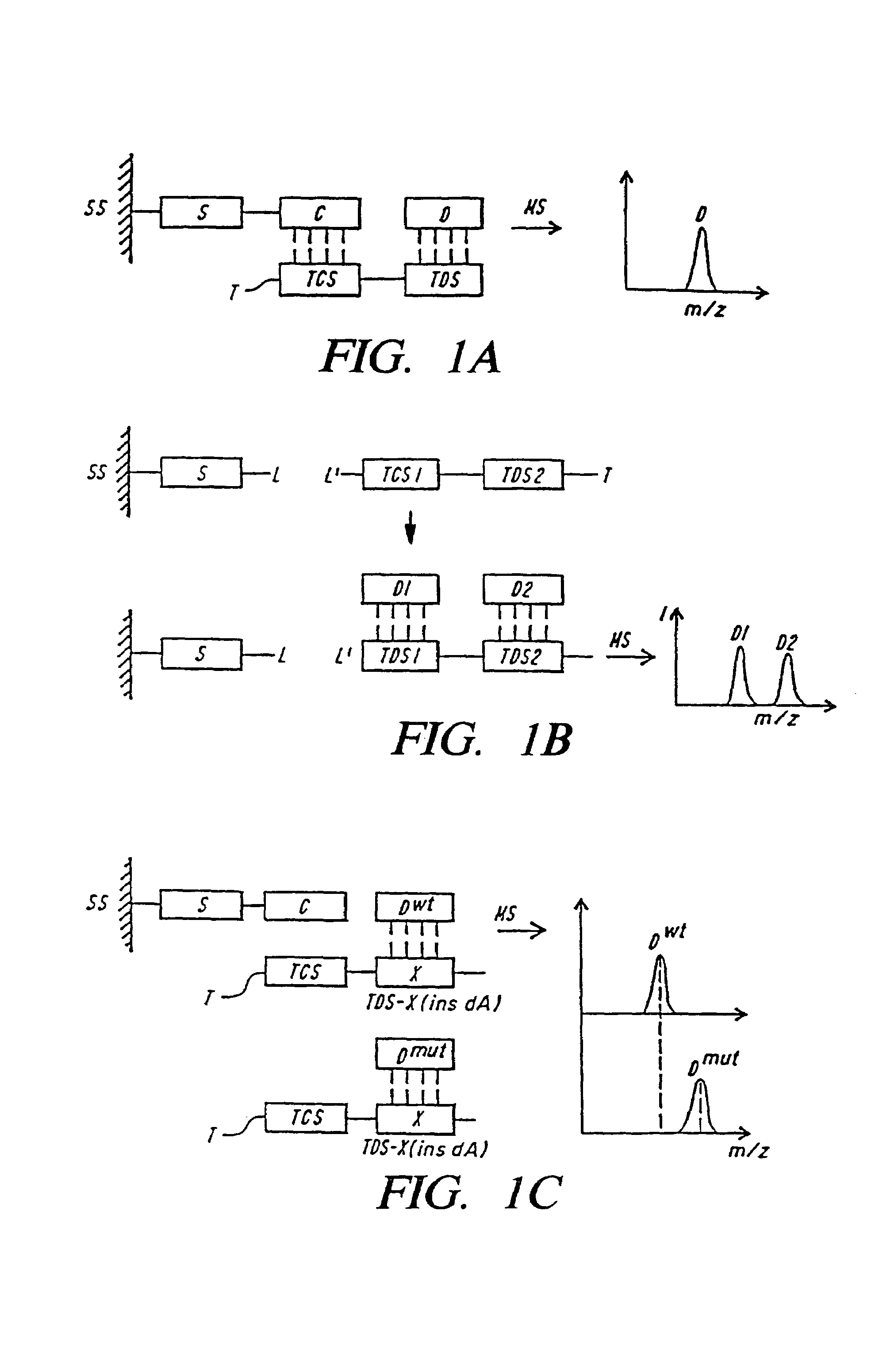
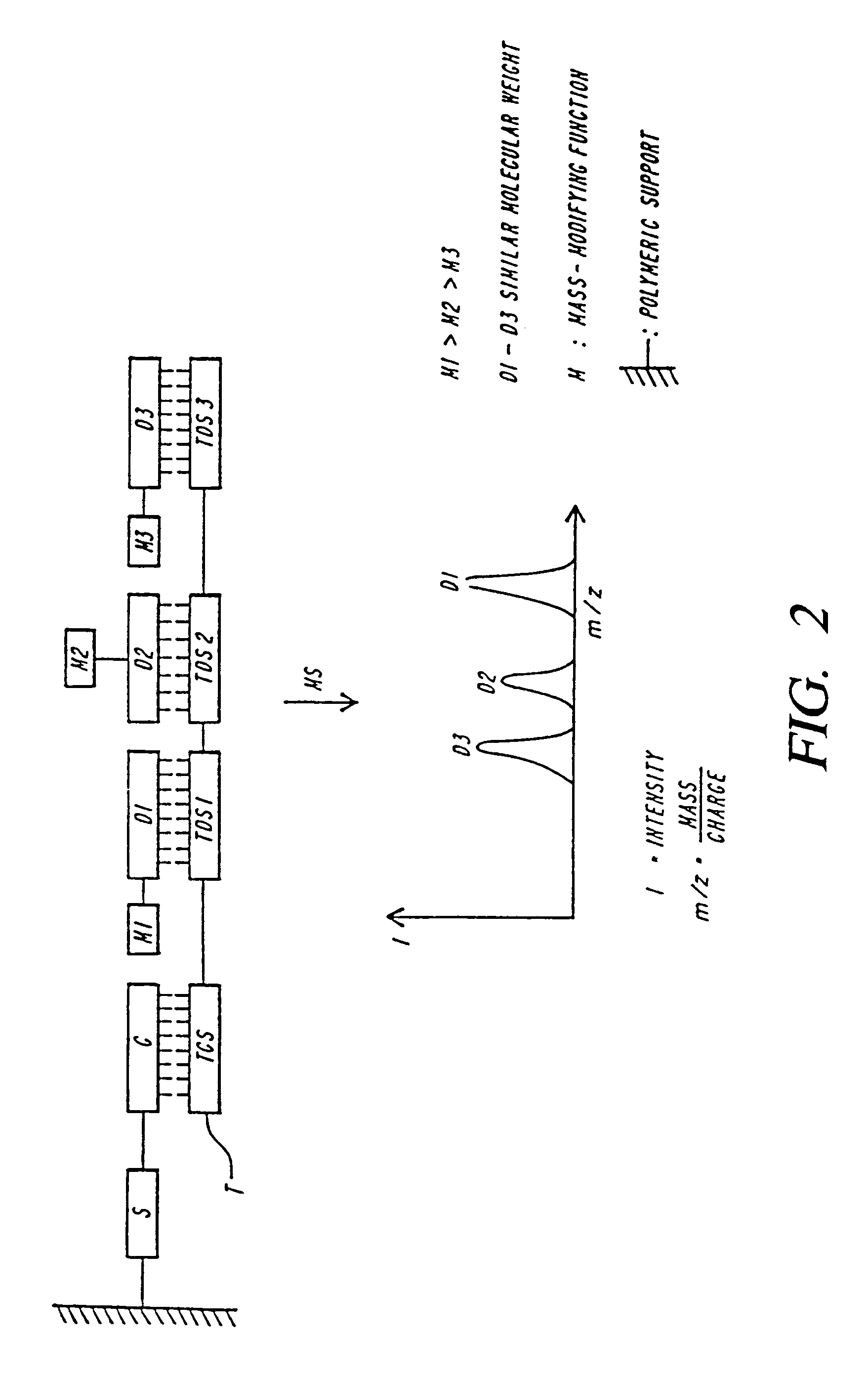
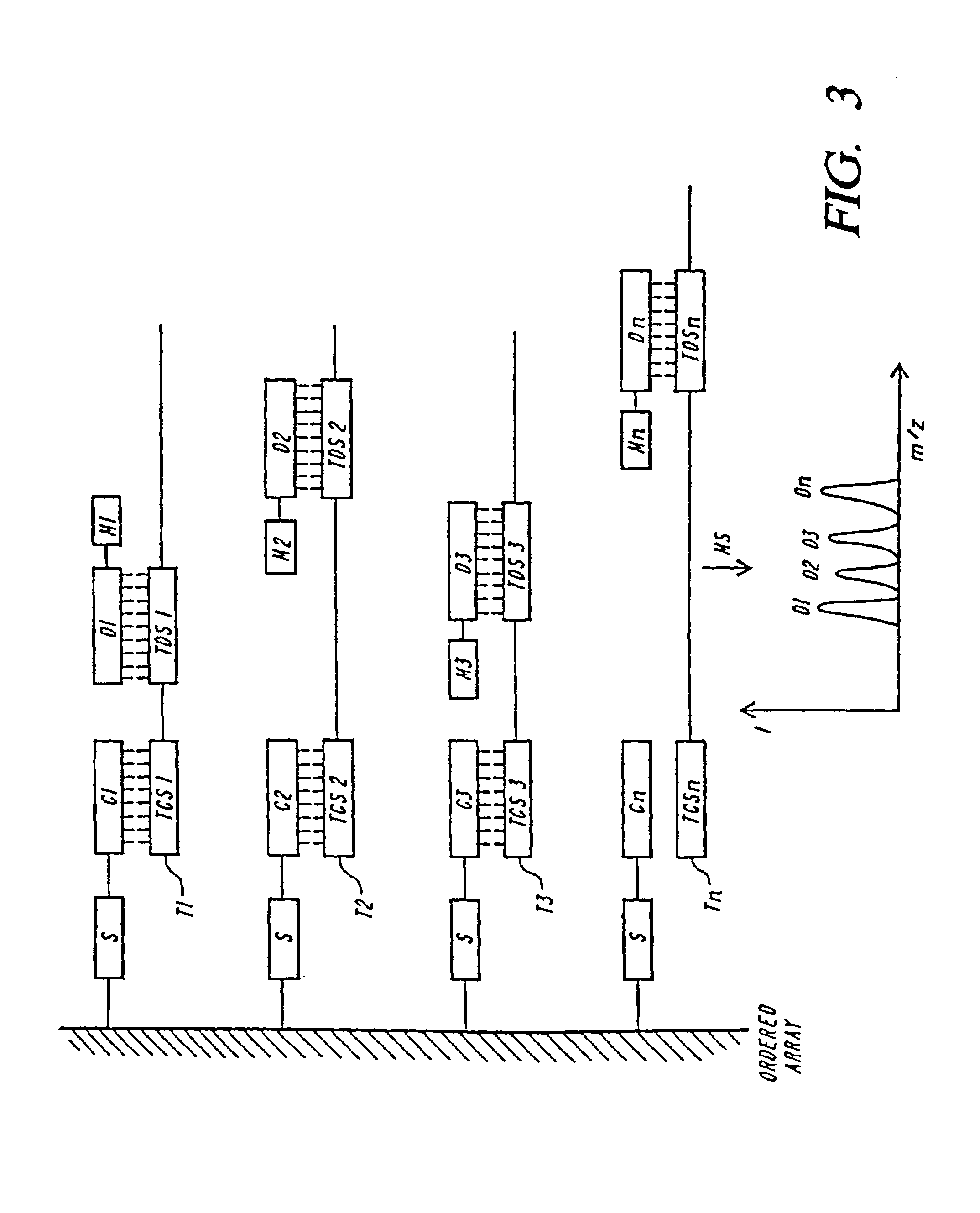
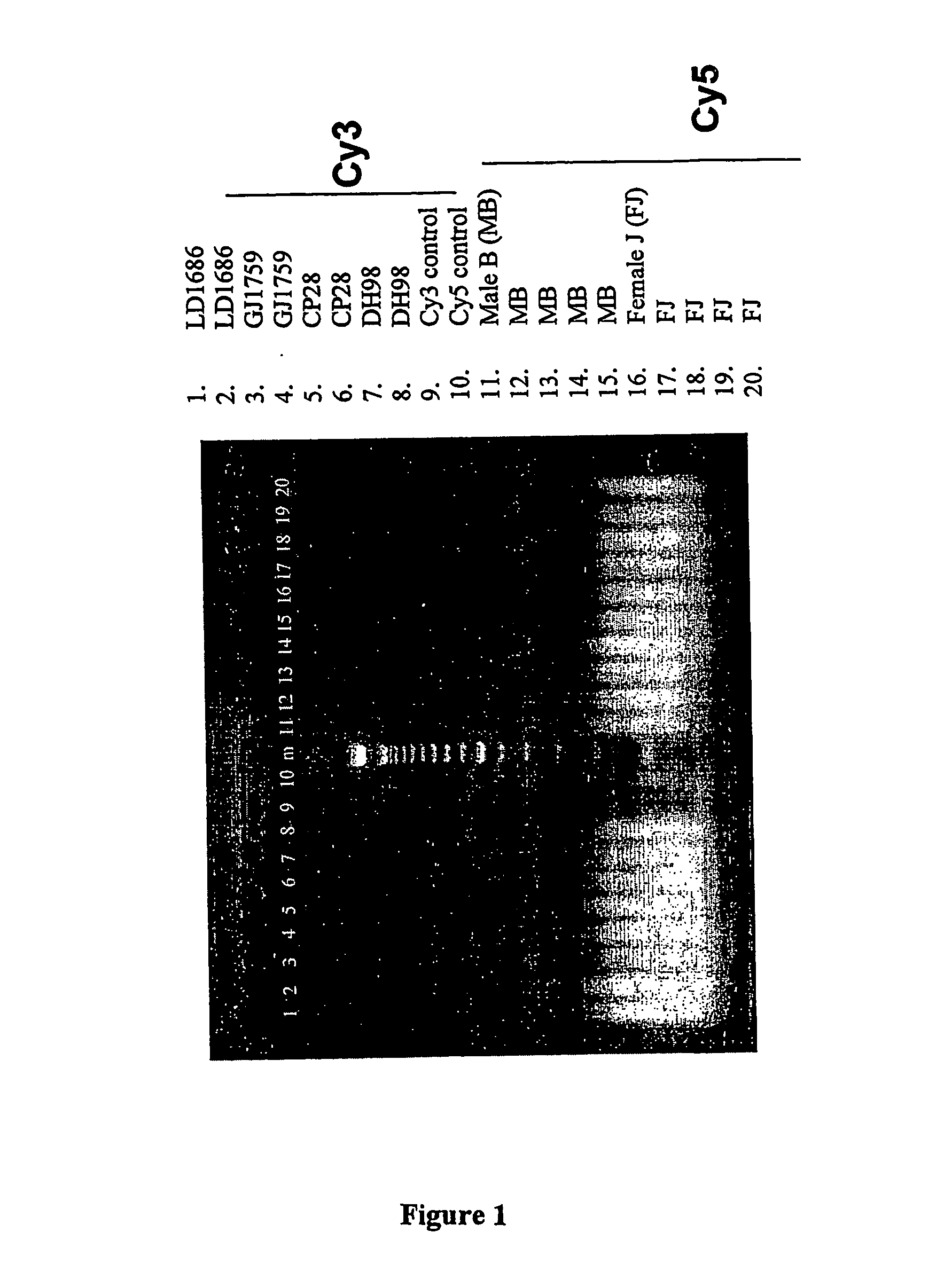
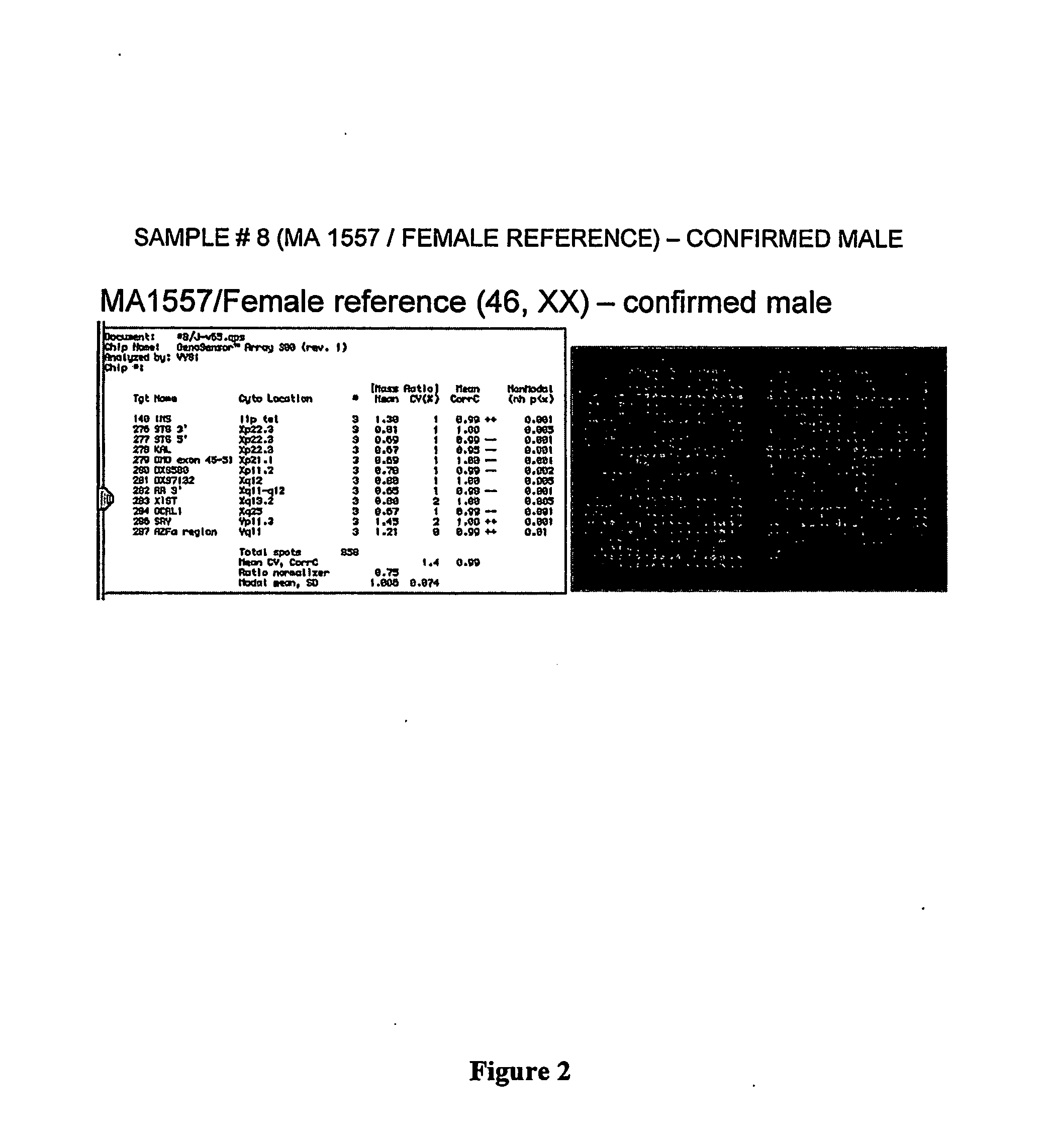
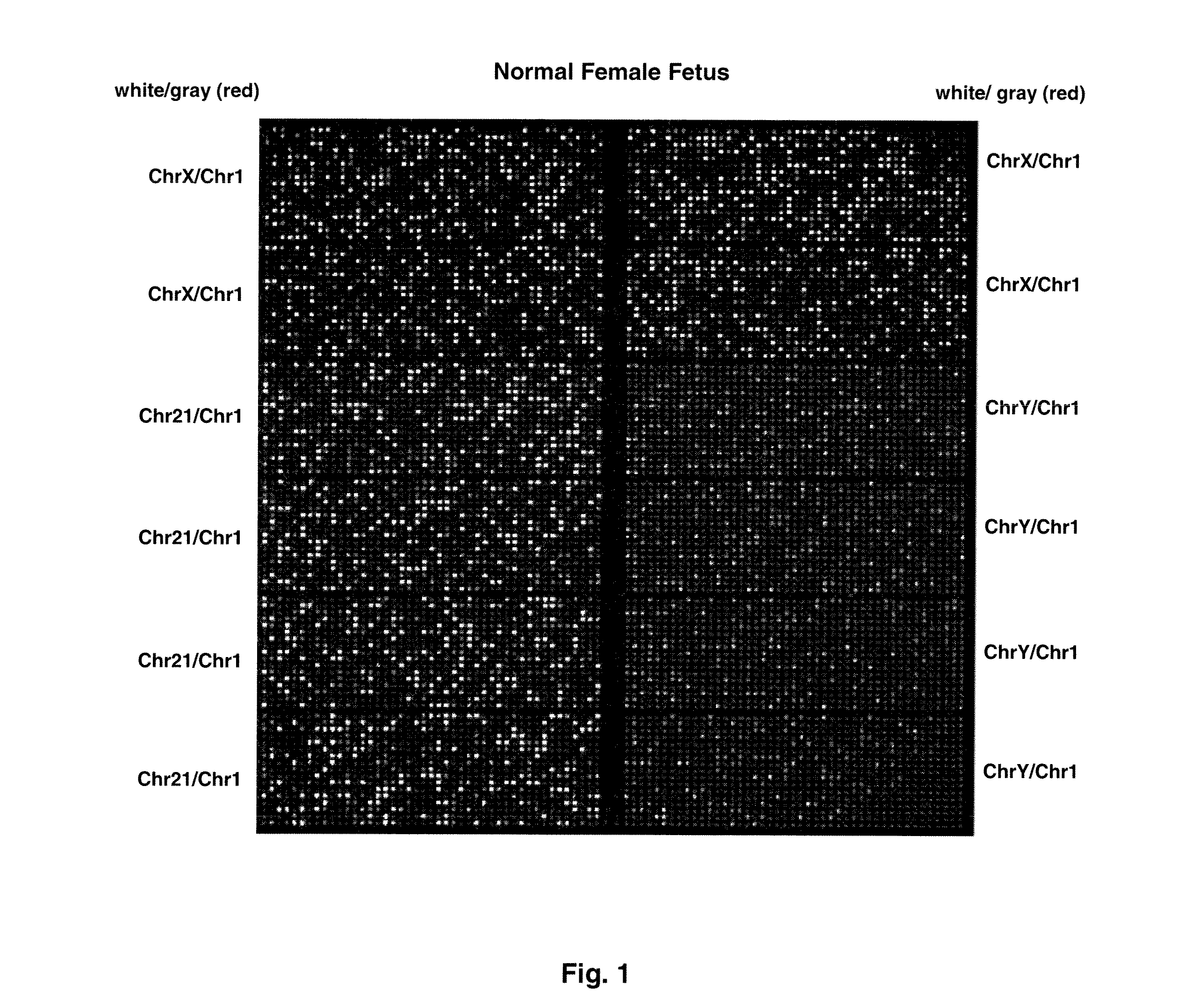
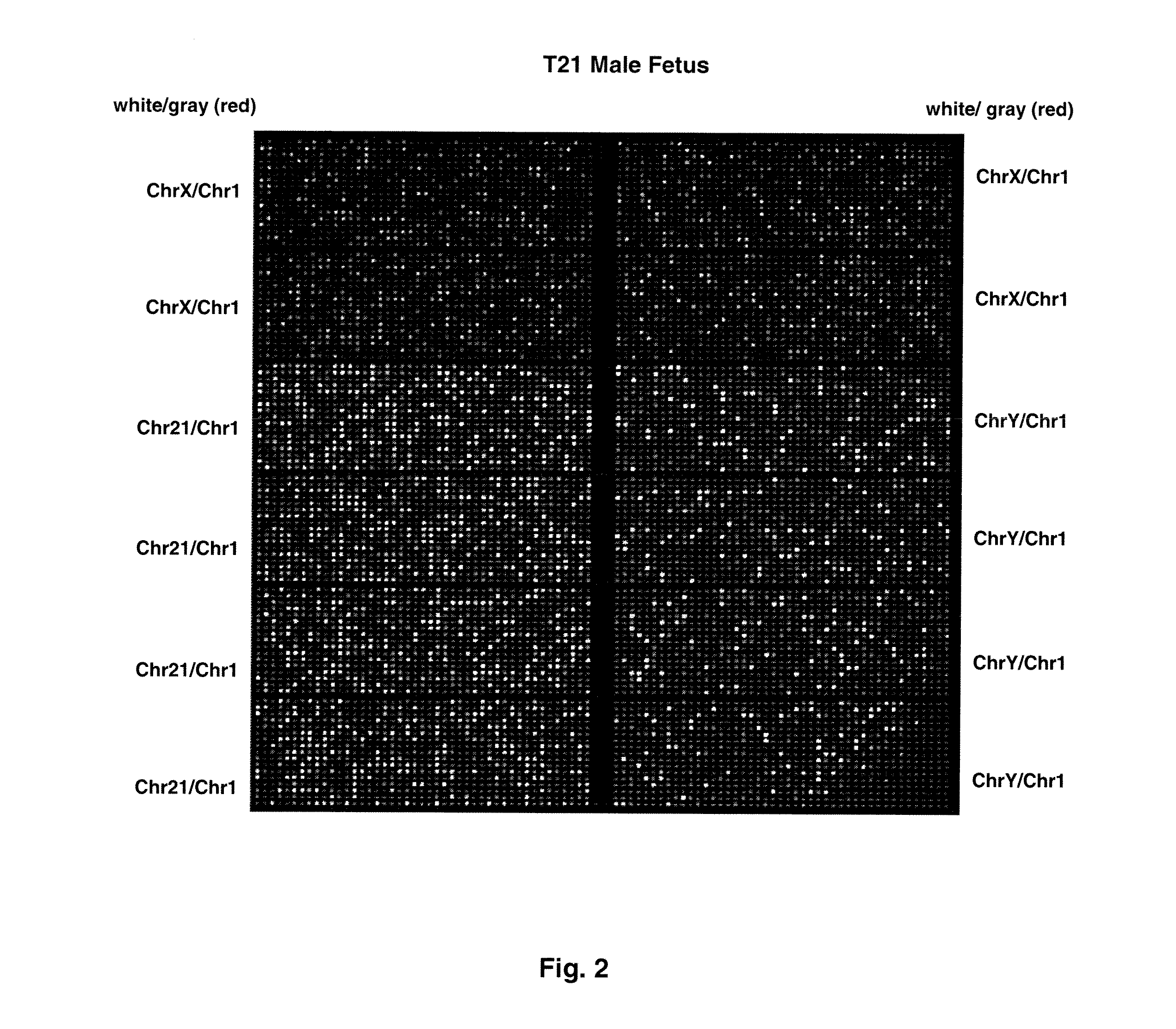
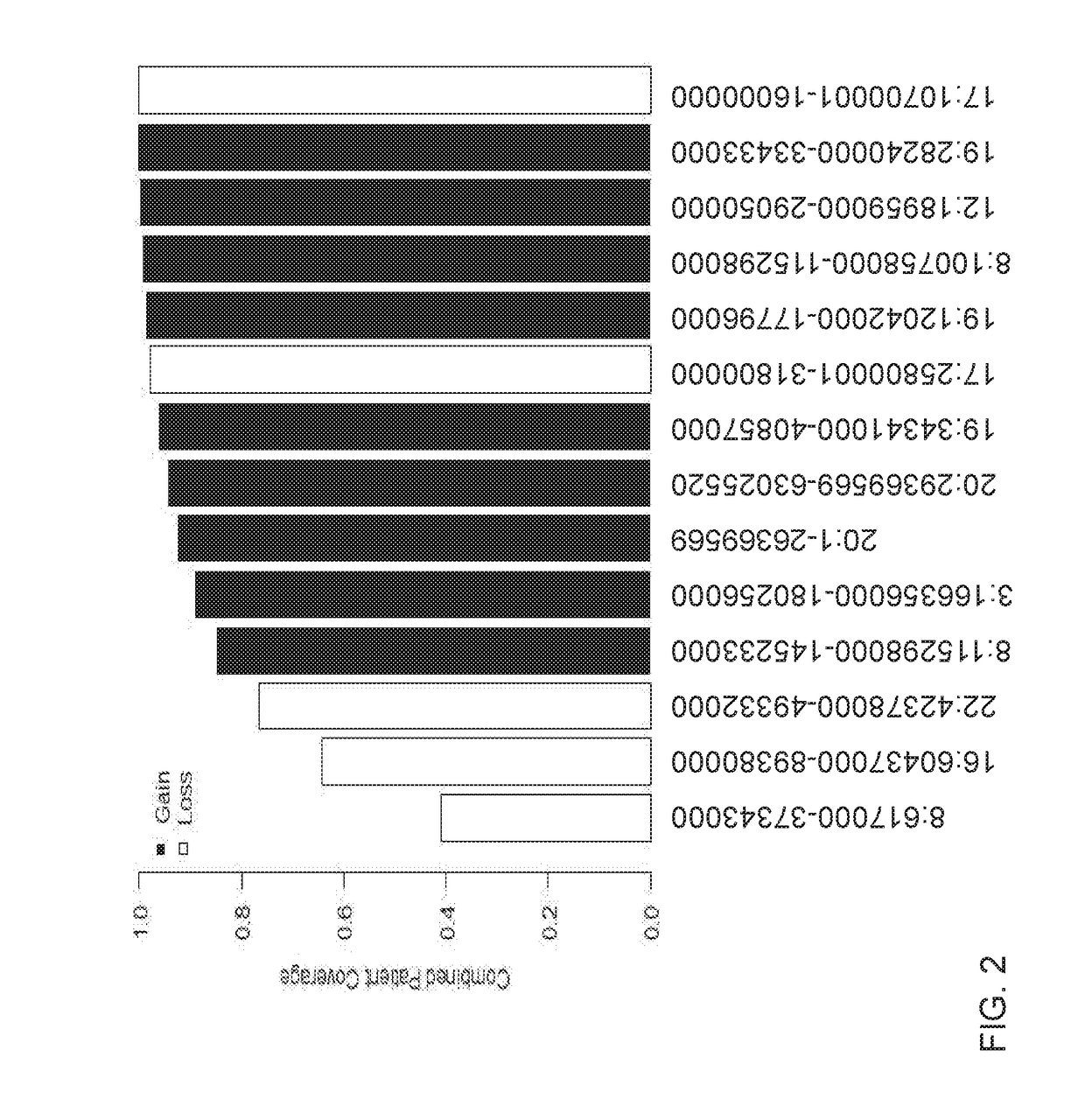
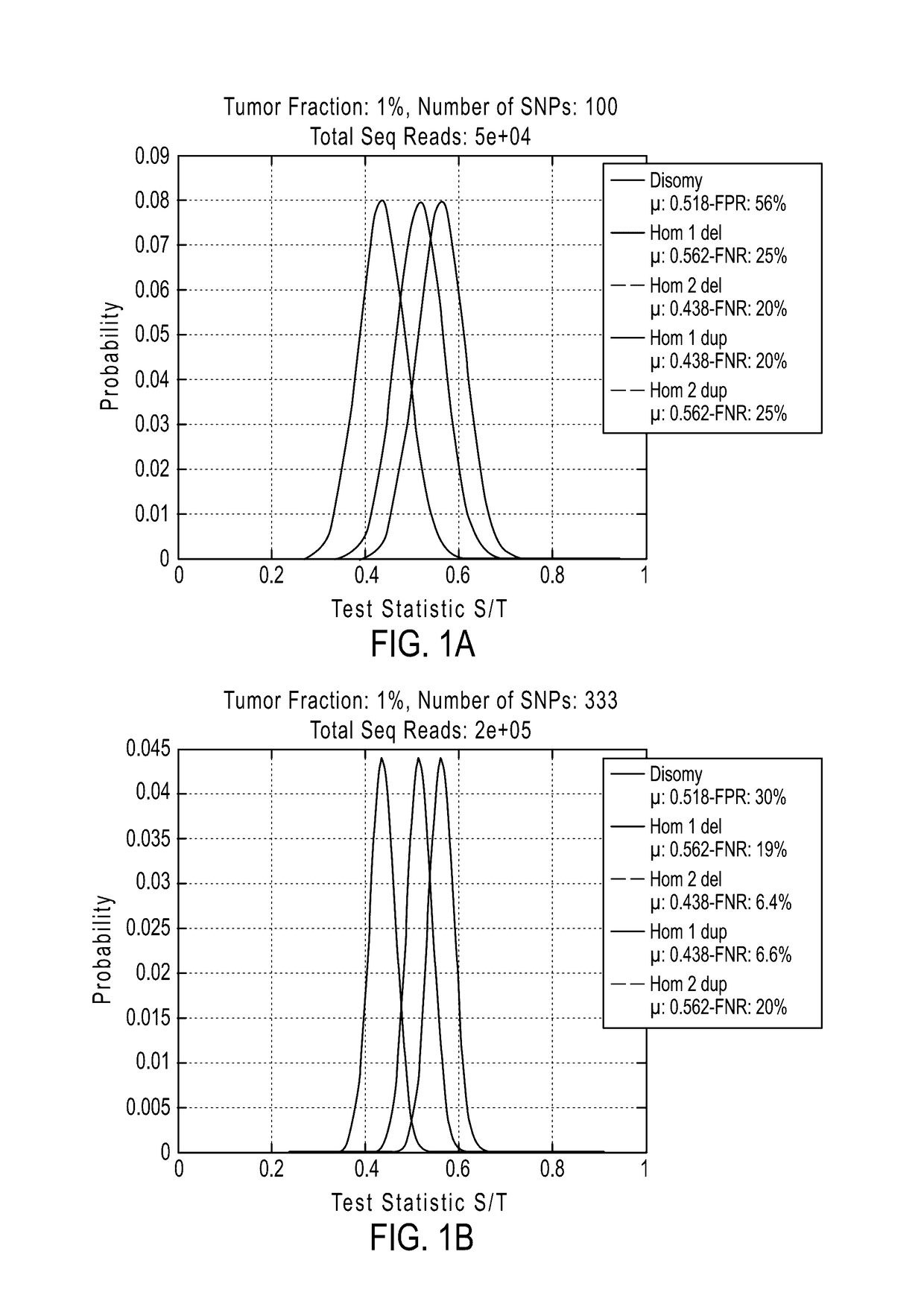
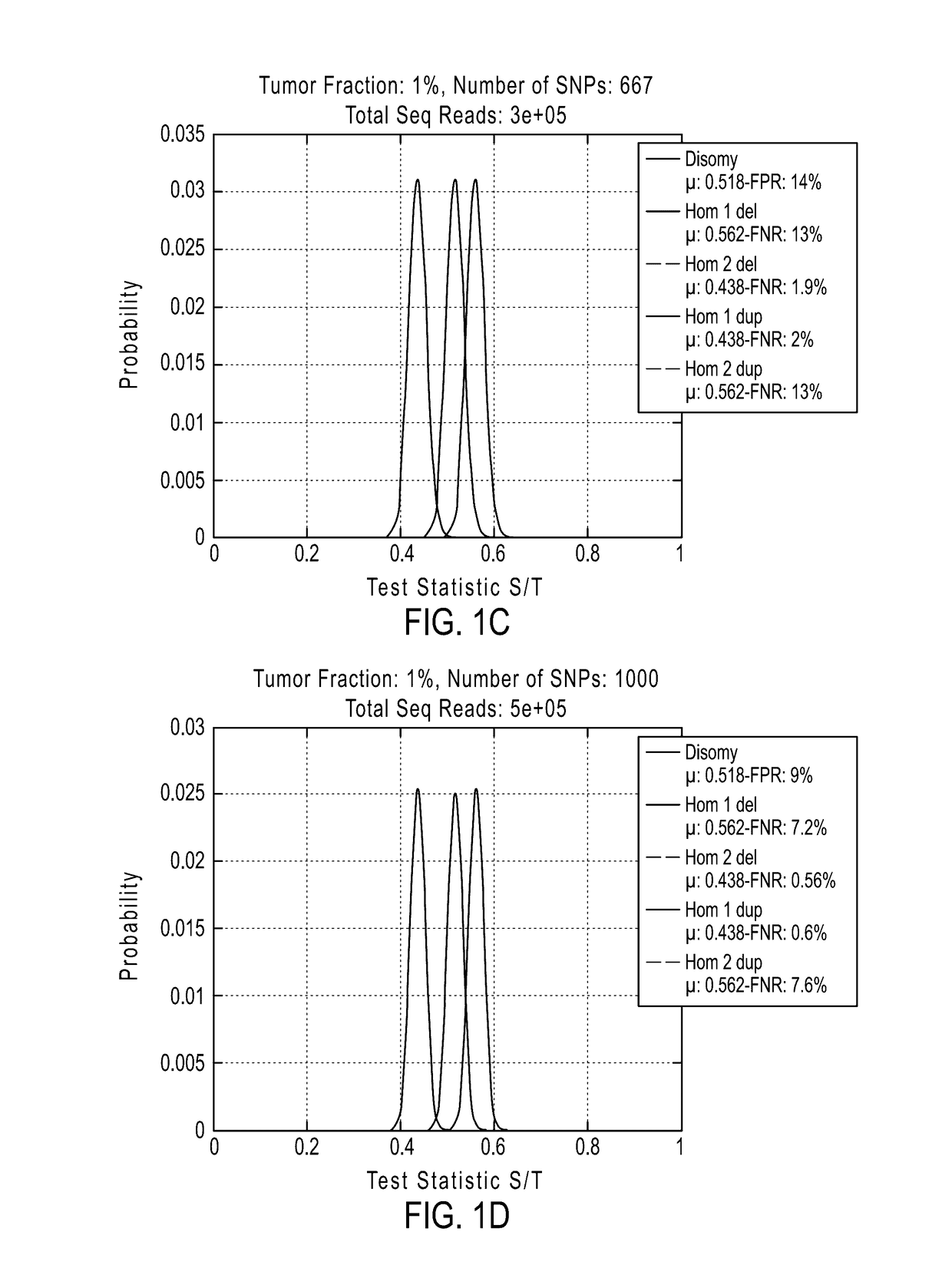
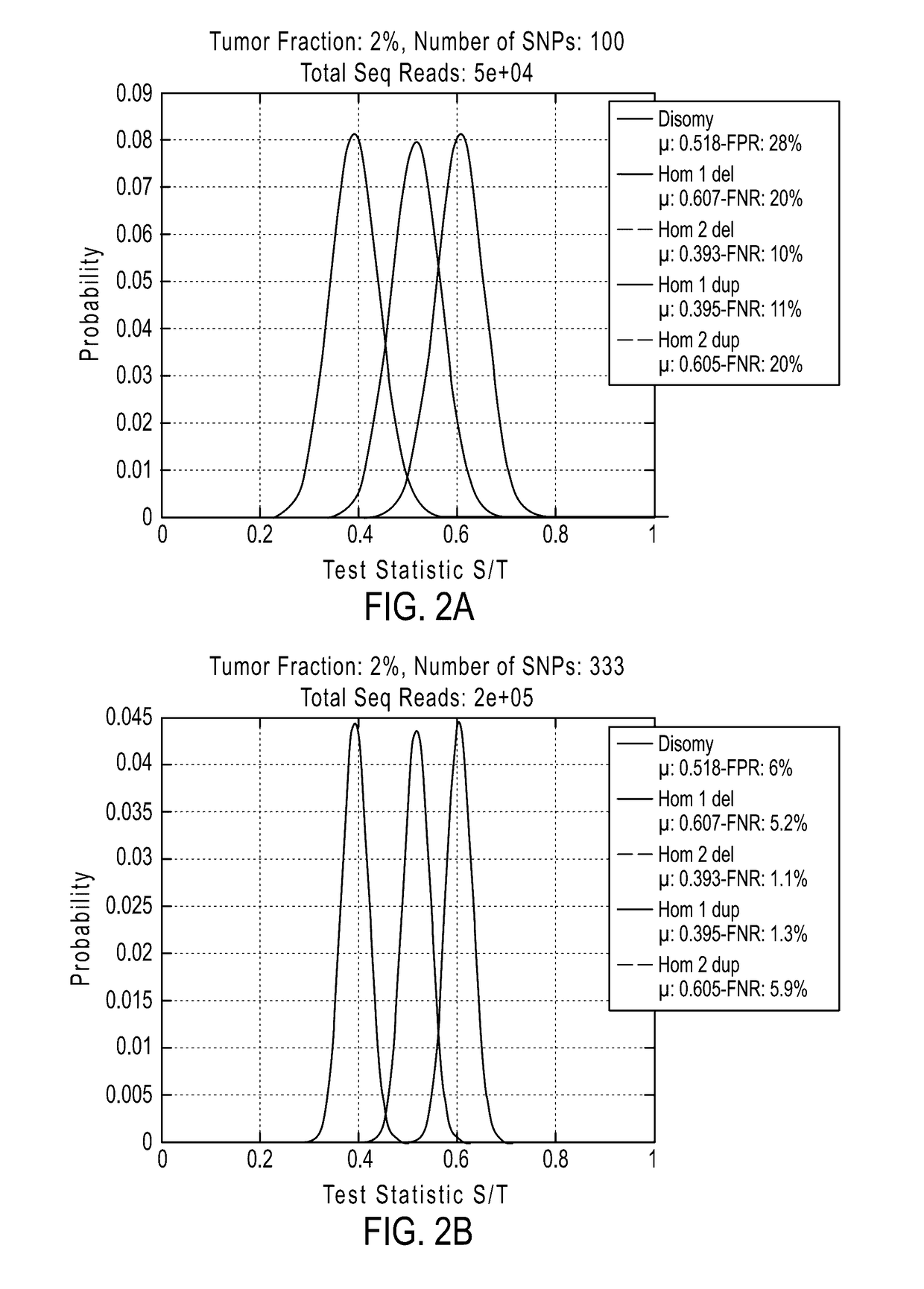
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
105 results about "Chromosomal Abnormality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
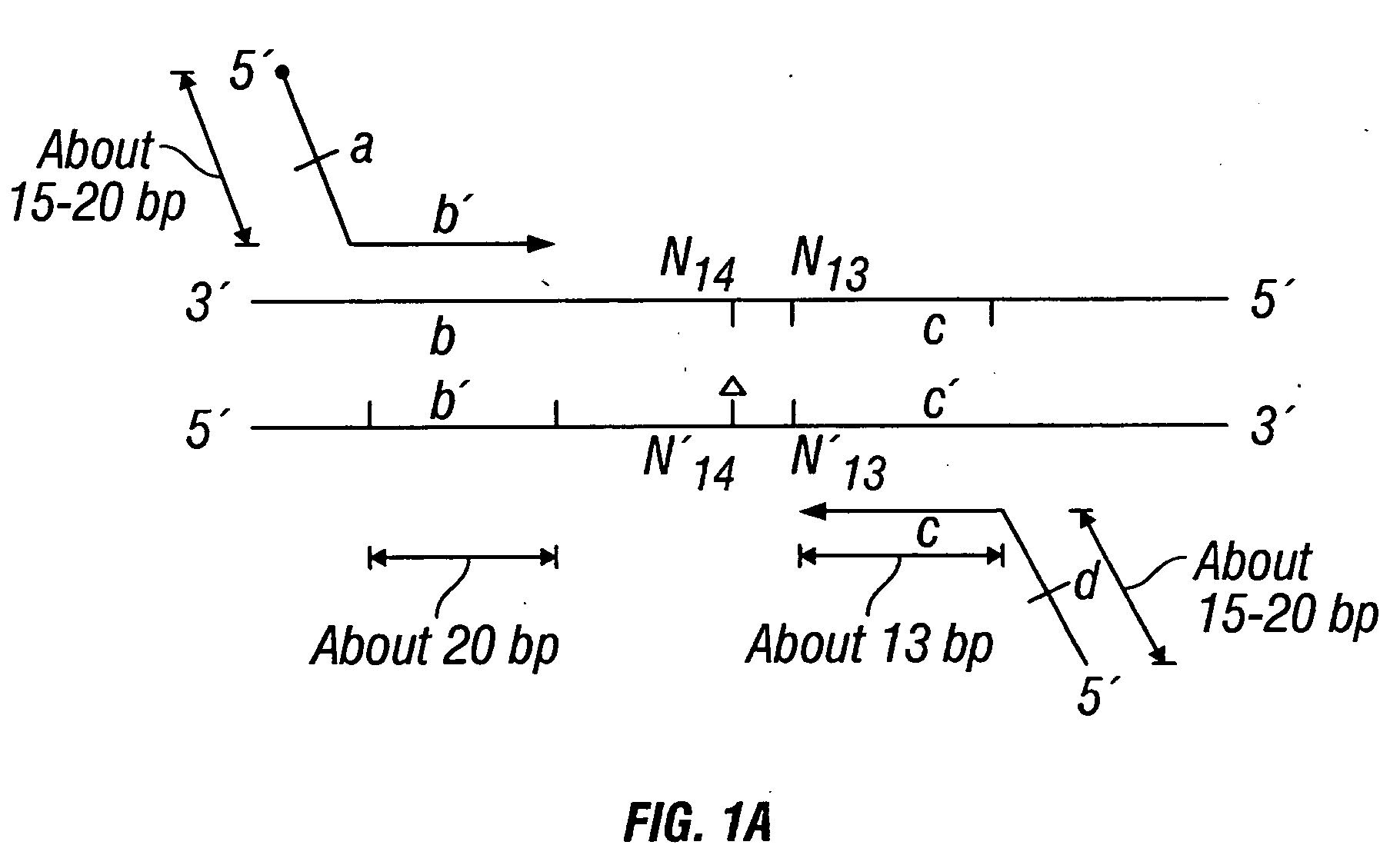
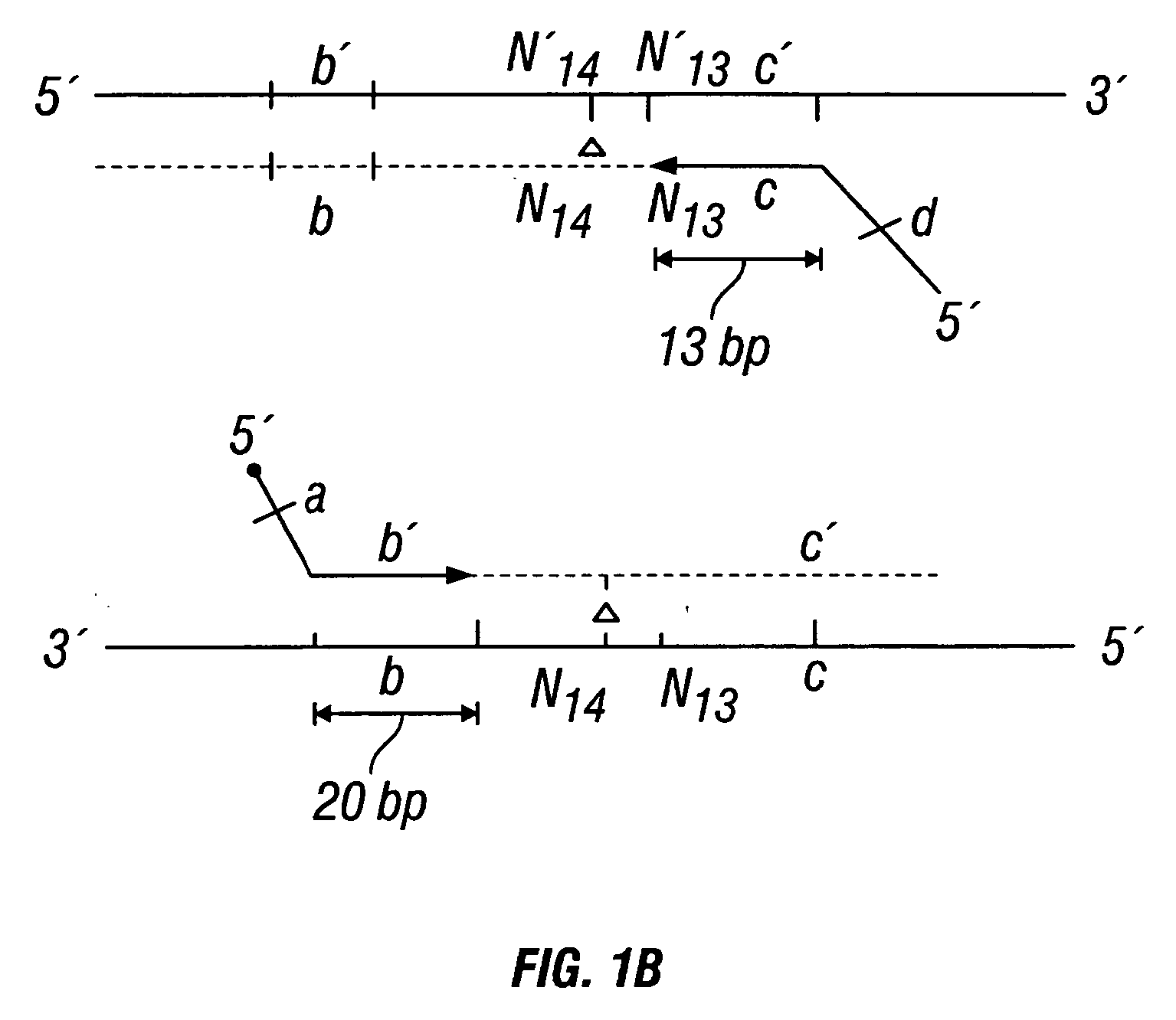
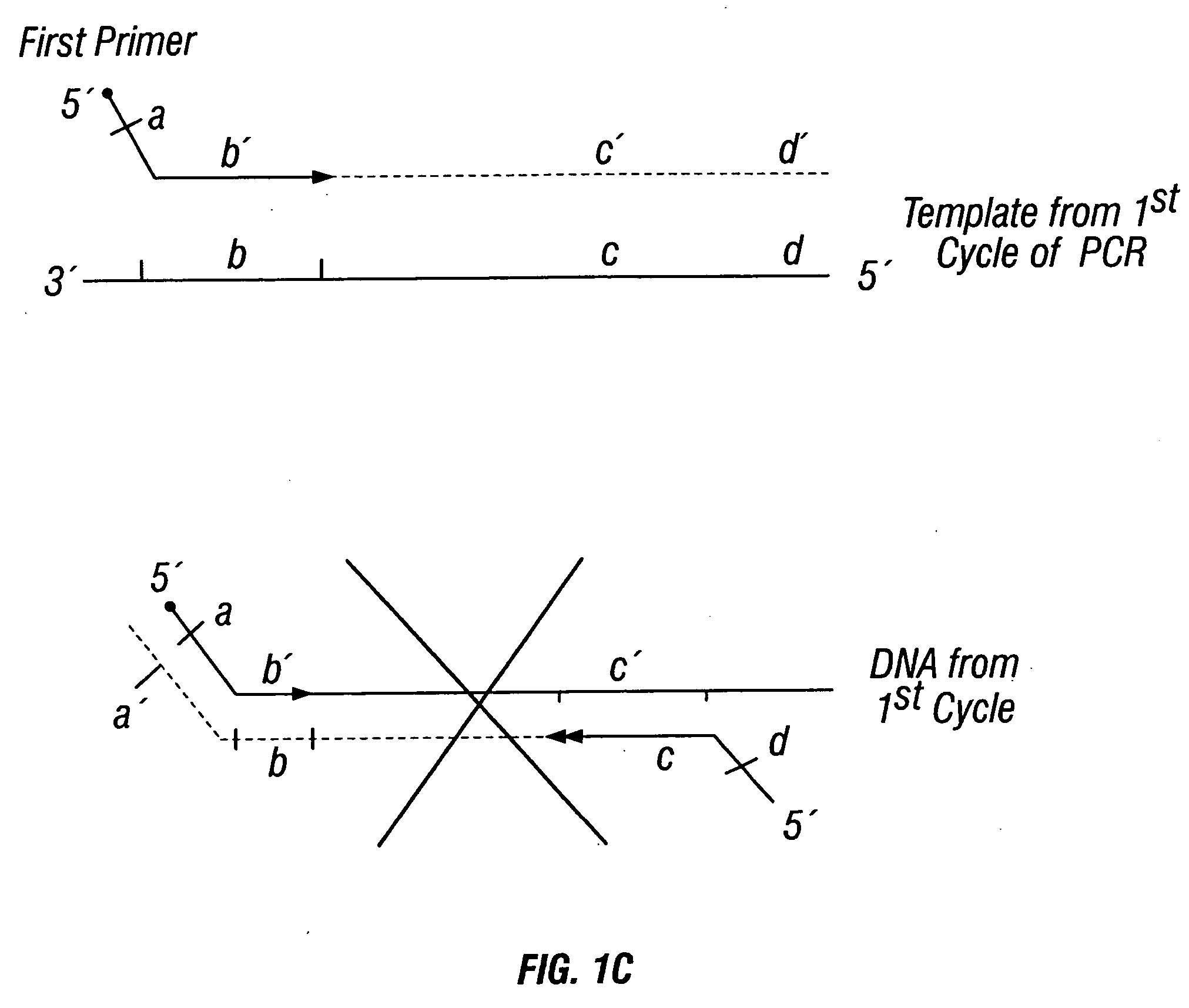
Methods for detection of genetic disorders
InactiveUS7727720B2Maximize efficiencyIncrease delaySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsAllele
The invention provides a method useful for detection of genetic disorders. The method comprises determining the sequence of alleles of a locus of interest, and quantitating a ratio for the alleles at the locus of interest, wherein the ratio indicates the presence or absence of a chromosomal abnormality. The present invention also provides a non-invasive method for the detection of chromosomal abnormalities in a fetus. The invention is especially useful as a non-invasive method for determining the sequence of fetal DNA. The invention further provides methods of isolation of free DNA from a sample.
Owner:RAVGEN INC
Methods for detection of genetic disorders
InactiveUS7442506B2Maximize efficiencyIncrease delaySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsAllele
The invention provides a method useful for detection of genetic disorders. The method comprises determining the sequence of alleles of a locus of interest, and quantitating a ratio for the alleles at the locus of interest, wherein the ratio indicates the presence or absence of a chromosomal abnormality. The present invention also provides a non-invasive method for the detection of chromosomal abnormalities in a fetus. The invention is especially useful as a non-invasive method for determining the sequence of fetal DNA. The invention further provides methods of isolation of free DNA from a sample.
Owner:RAVGEN INC
Methods for detection of genetic disorders
InactiveUS20070178478A1Minimize disruptionMaximize efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGeneticsAllele
The invention provides a method useful for detection of genetic disorders. The method comprises determining the sequence of alleles of a locus of interest, and quantitating a ratio for the alleles at the locus of interest, wherein the ratio indicates the presence or absence of a chromosomal abnormality. The present invention also provides a non-invasive method for the detection of chromosomal abnormalities in a fetus. The invention is especially useful as a non-invasive method for determining the sequence of fetal DNA. The invention further provides methods of isolation of free DNA from a sample.
Owner:RAVGEN INC
DNA diagnostics based on mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7198893B1Increase mass resolution massIncrease mass mass accuracyPeptide librariesSequential/parallel process reactionsMass spectrometry imagingOrganism
Fast and highly accurate mass spectrometry-based processes for detecting a particular nucleic acid sequence in a biological sample are provided. Depending on the sequence to be detected, the processes can be used, for example, to diagnose a genetic disease or chromosomal abnormality; a predisposition to a disease or condition, infection by a pathogenic organism, or for determining identity or heredity.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
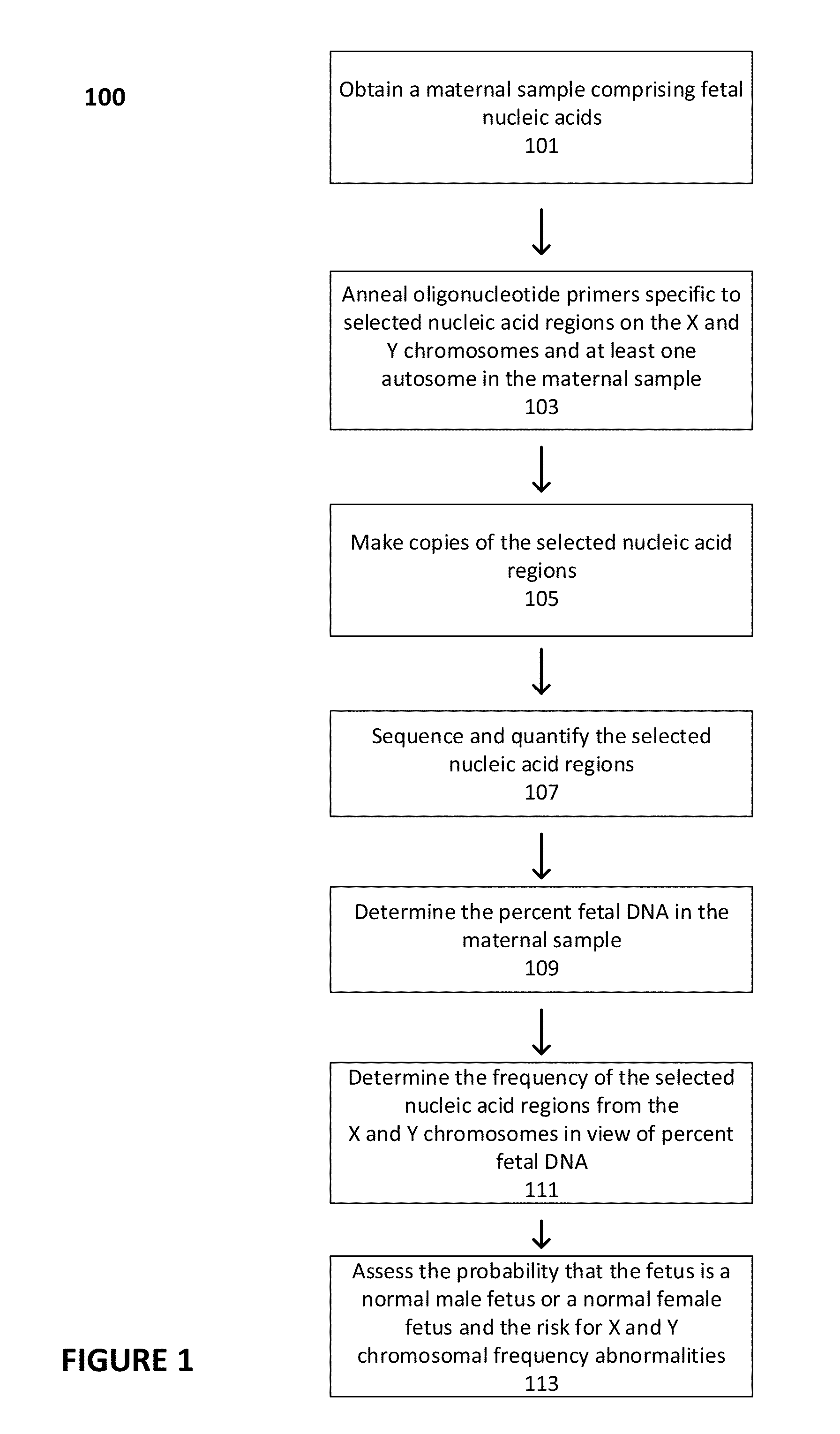
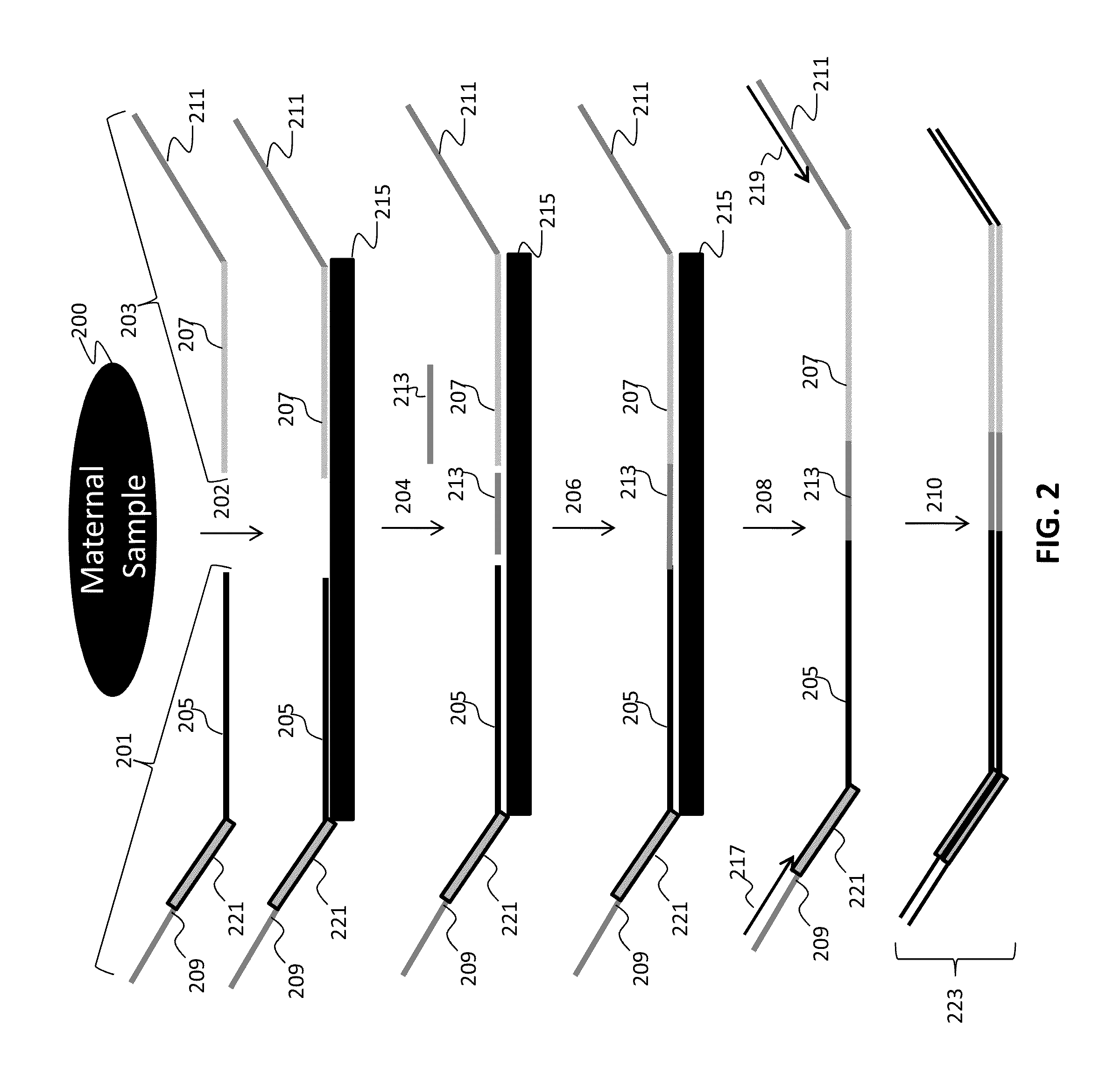
Prenatal Diagnosis Using Cell-Free Fetal DNA in Amniotic Fluid
InactiveUS20070212689A1Rapid determinationAddressing slow performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansCell-free fetal DNAAmniotic fluid
The present invention relates to improved methods of prenatal diagnosis, screening, monitoring and / or testing. The inventive methods include the analysis by array-based hybridization of cell-free fetal DNA isolated from amniotic fluid. In addition to allowing the prenatal diagnosis of a variety of diseases and conditions, and the assessment of fetal characteristics such as fetal sex and chromosomal abnormalities, the new inventive methods provide substantially more information about the fetal genome in less time than it takes to perform a conventional metaphase karyotype analysis. In particular, the enhanced molecular karyotype methods provided by the present invention allow the detection of chromosomal aberrations that are not often detected prenatally such as microdeletions, microduplications and subtelomeric rearrangements.
Owner:BIANCHI DIANA W +2
Methods for prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities
ActiveUS20070059707A1Rapid productionAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDiseaseNon invasive
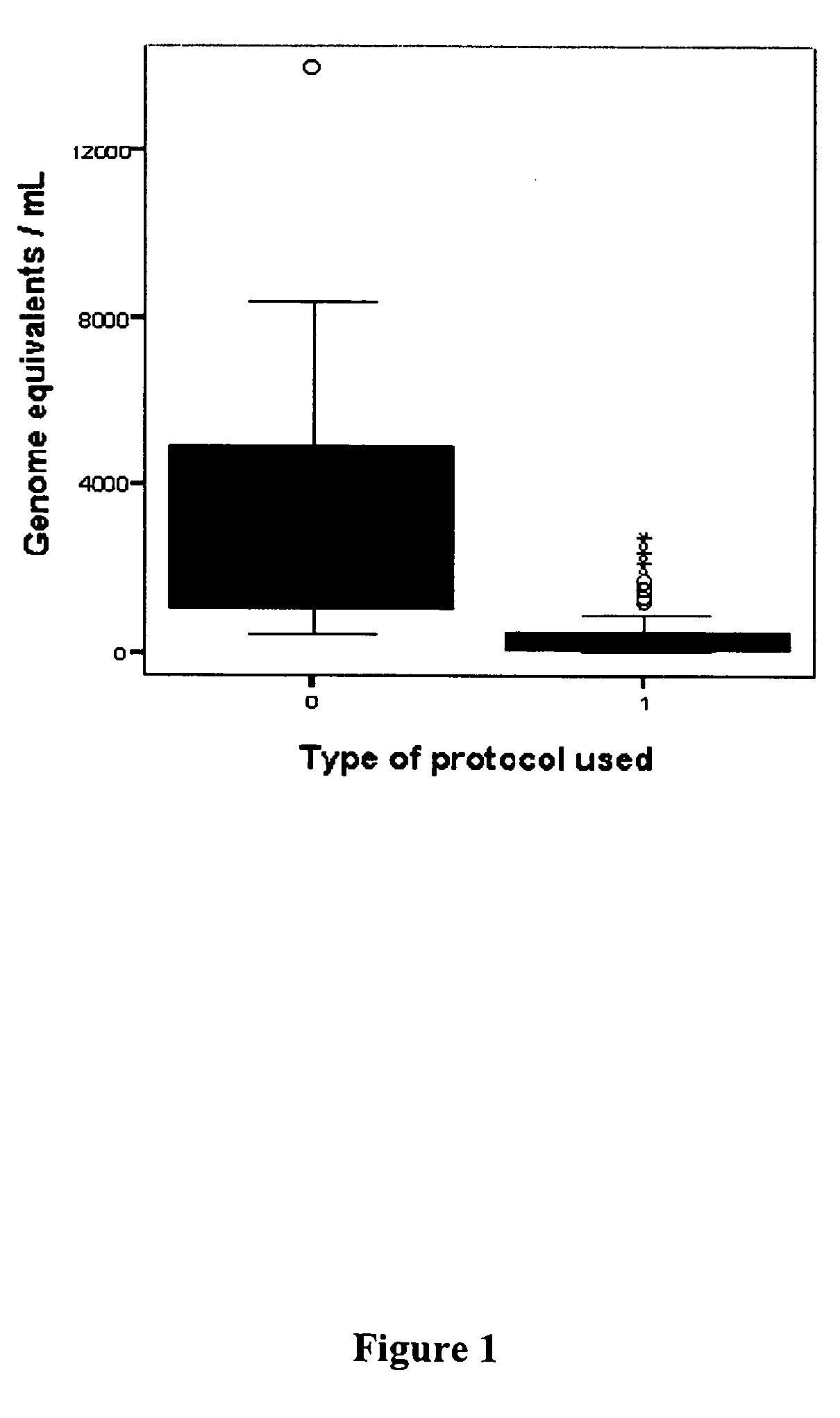
Chromosomal abnormalities are responsible for a significant number of birth defects, including mental retardation. The present invention is related to methods for non-invasive and rapid, prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities based on analysis of a maternal blood sample. The invention exploits the differences in DNA between the mother and fetus, for instance differences in their methylation states, as a means to enrich for fetal DNA in maternal plasma sample. The methods described herein can be used to detect chromosomal DNA deletions and duplications. In a preferred embodiment, the methods are used to diagnose chromosomal aneuploidy and related disorders, such as Down's and Turner's Syndrome.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Direct Molecular Diagnosis of Fetal Aneuploidy
ActiveUS20110151442A1Addressing slow performanceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecific chromosomeFetal tissues
Methods and materials for detection of aneuploidy and other chromosomal abnormalities using fetal tissue are disclosed. Results can be obtained rapidly, without cell culture. The method uses digital PCR for amplification and detection of single target sequences, allowing an accurate count of a specific chromosome or chromosomal region. Specific polynucleic acid primers and probes are disclosed for chromosomes 1, 13, 18, 21, X and Y. These polynucleic acid sequences are chosen to be essentially invariant between individuals, so the test is not dependent on sequence differences between fetus and mother.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods for prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities
ActiveUS7655399B2Rapid productionAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementPlasma samplesNon invasive
Chromosomal abnormalities are responsible for a significant number of birth defects, including mental retardation. The present invention is related to methods for non-invasive and rapid, prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities based on analysis of a maternal blood sample. The invention exploits the differences in DNA between the mother and fetus, for instance differences in their methylation states, as a means to enrich for fetal DNA in maternal plasma sample. The methods described herein can be used to detect chromosomal DNA deletions and duplications. In a preferred embodiment, the methods are used to diagnose chromosomal aneuploidy and related disorders, such as Down's and Turner's Syndrome.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Prenatal diagnosis using cell-free fetal DNA in amniotic fluid
InactiveUS20070111233A1Improved and rapid methodHigh recovery rateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCell-free fetal DNAAmniotic fluid
The present invention relates to improved methods of prenatal diagnosis, screening, monitoring and / or testing. The inventive methods include the analysis by array-based hybridization of cell-free fetal DNA isolated from amniotic fluid. In addition to allowing the prenatal diagnosis of a variety of diseases and conditions, and the assessment of fetal characteristics such as fetal sex and chromosomal abnormalities, the new inventive methods provide substantially more information about the fetal genome in less time than it takes to perform a conventional metaphase karyotype analysis. In particular, the enhanced molecular karyotype methods provided by the present invention allow the detection of chromosomal aberrations that are not often detected prenatally such as microdeletions, microduplications and subtelomeric rearrangements. Also provided are improved methods of extraction of fetal DNA from amniotic fluid.
Chromosome structural abnormality localization with single copy probes
InactiveUS7014997B2Eliminates spurious hybridizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic SegmentHybridization probe
Nucleic acid (e.g., DNA) hybridization probes are described which comprise a labeled, single copy nucleic acid which hybridizes to a deduced single copy sequence interval in target nucleic acid of known sequence. The probes, which are essentially free of repetitive sequences, can be used in hybridization analyses without adding repetitive sequence-blocking nucleic acids. This allows rapid and accurate detection of chromosomal abnormalities. The probes are preferably designed by first determining the sequence of at least one single copy interval in a target nucleic acid sequence, and developing corresponding hybridization probes which hybridize to at least a part of the deduced single copy sequence. In practice, the sequences of the target and of known genomic repetitive sequence representatives are compared in order to deduce locations of the single copy sequence intervals. The single copy probes can be developed by any variety of methods, such as PCR amplification, restriction or exonuclease digestion of purified genomic fragments, or direct synthesis of DNA sequences. This is followed by labeling of the probes and hybridization to a target sequence.
Owner:CHILDRENS MERCY HOSPITAL
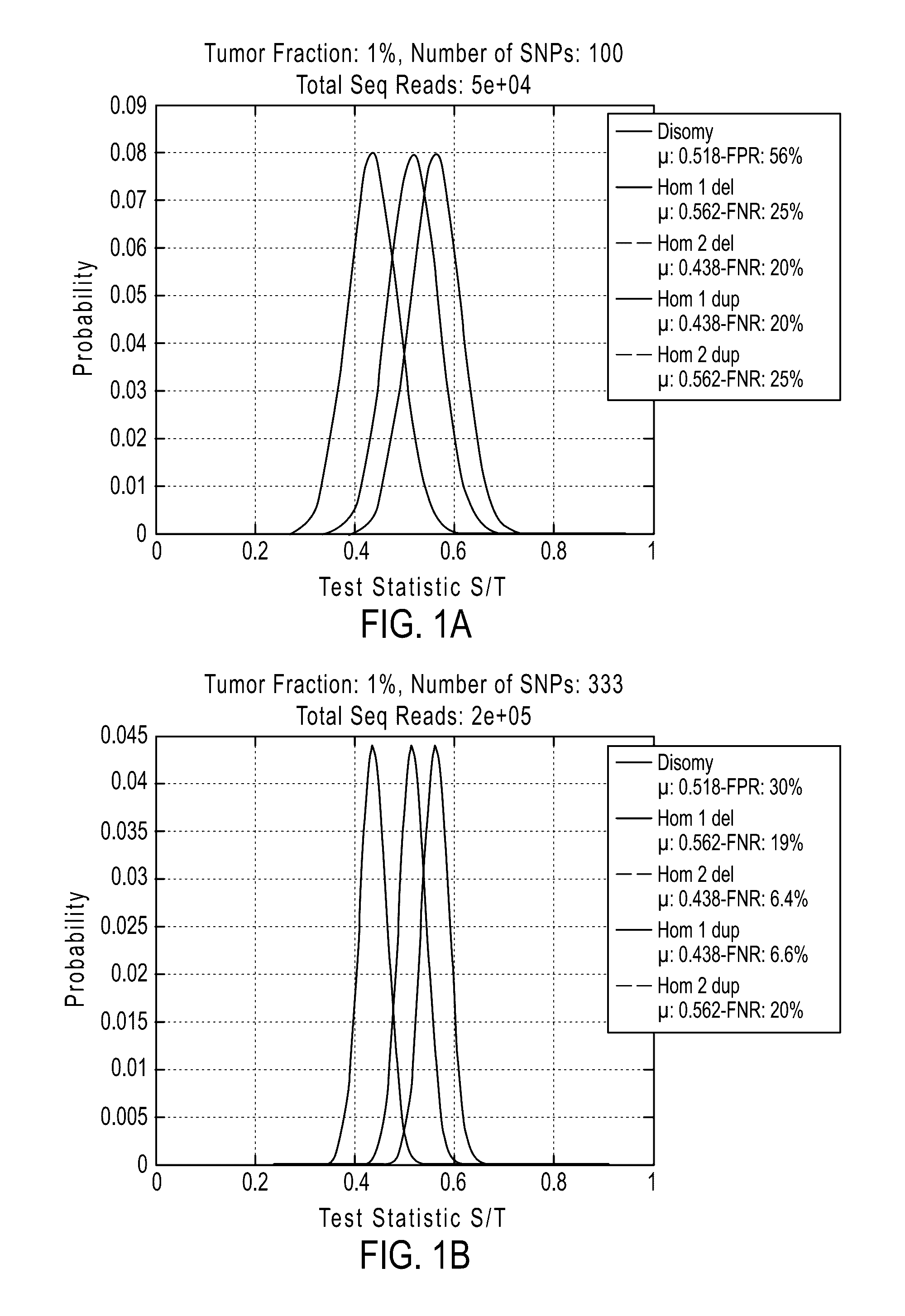
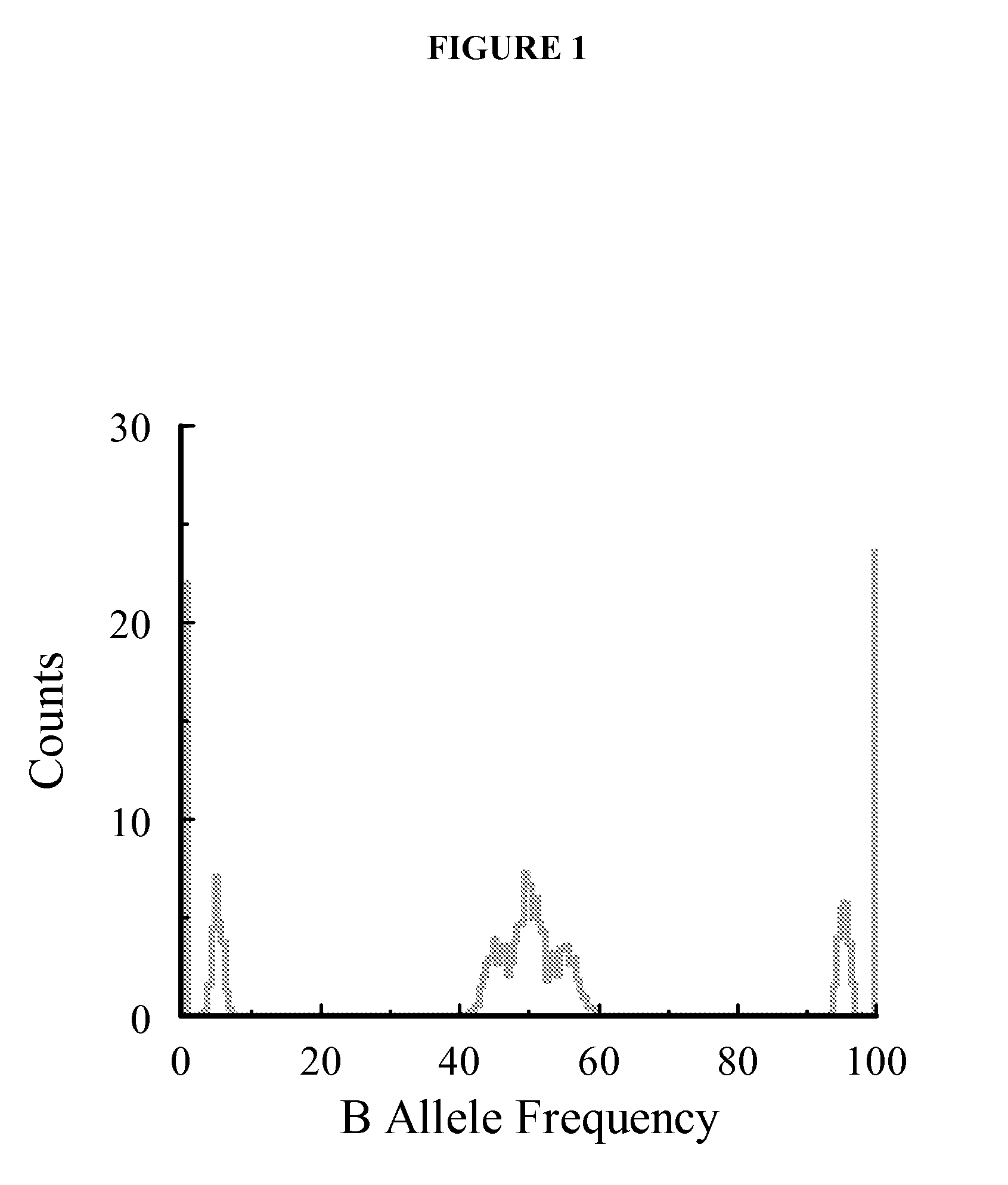
Methods and compositions for determining ploidy
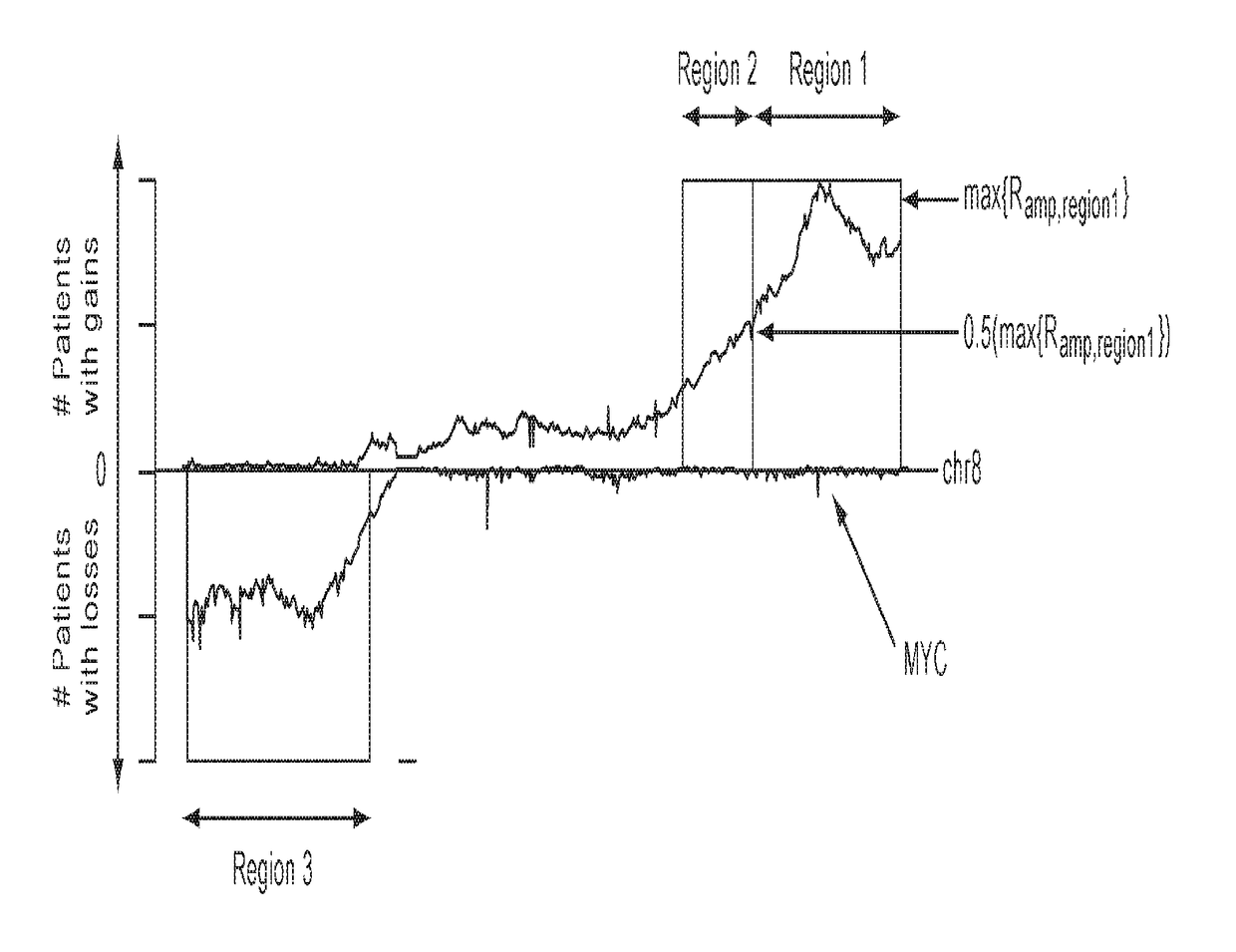
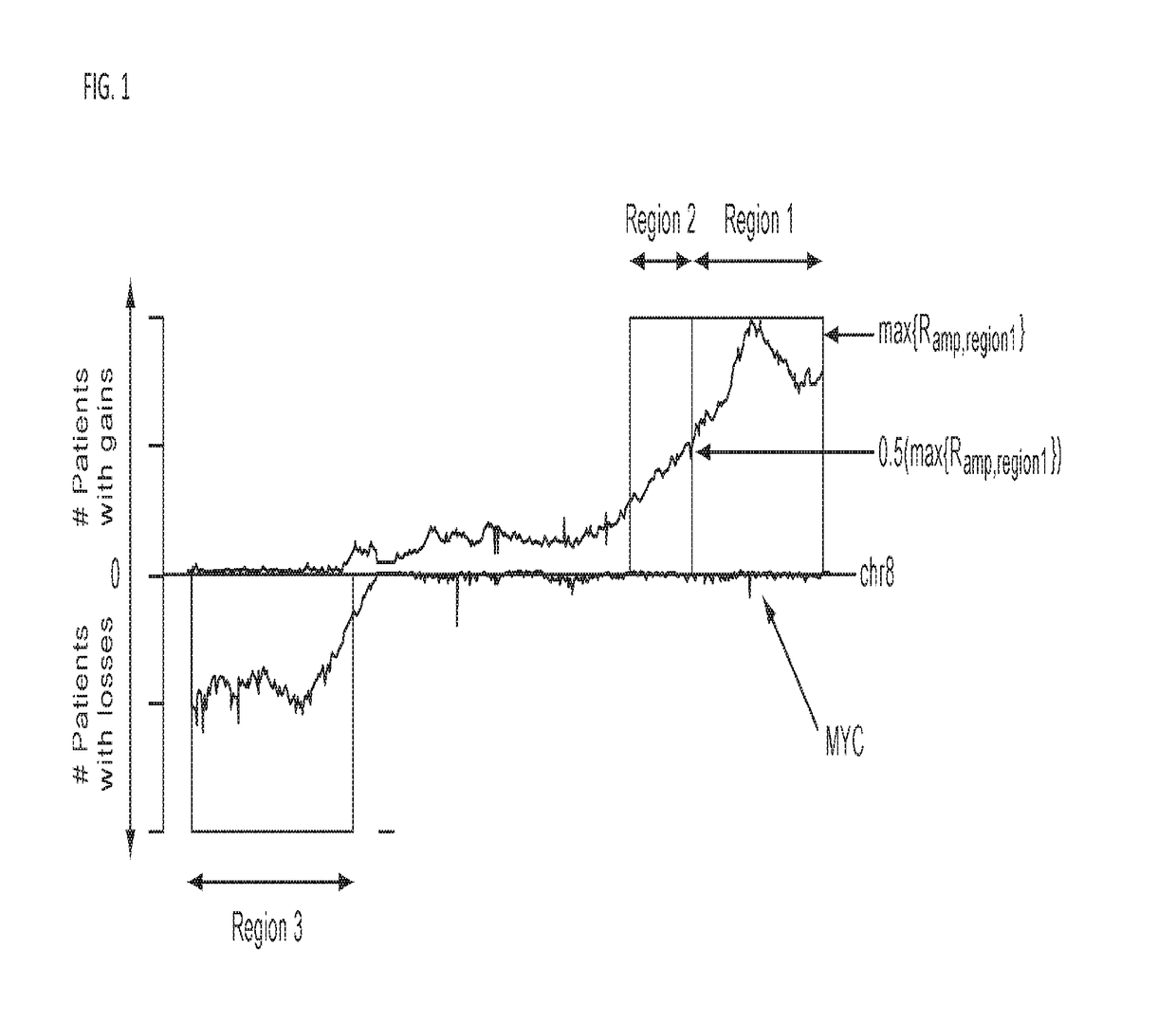
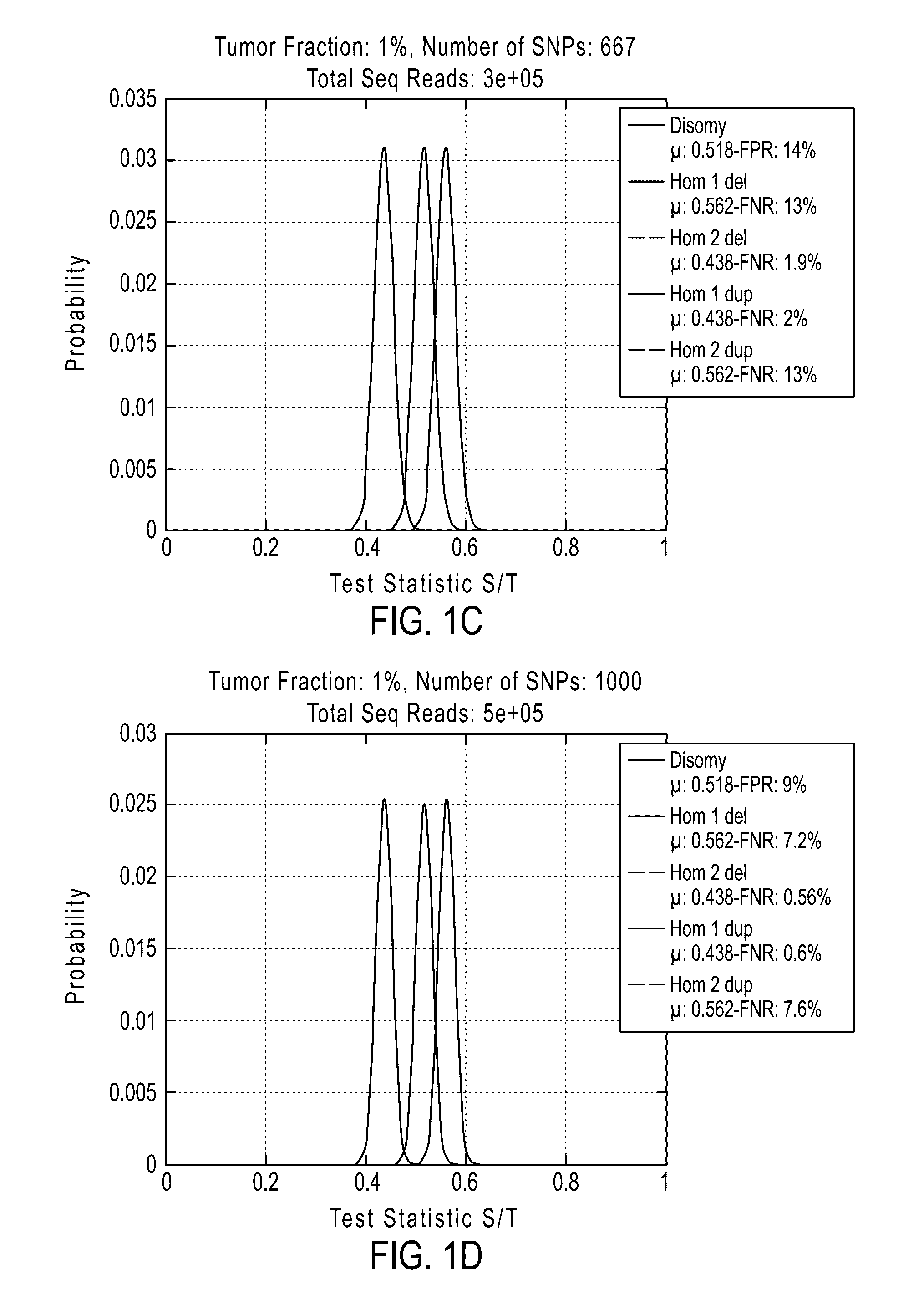
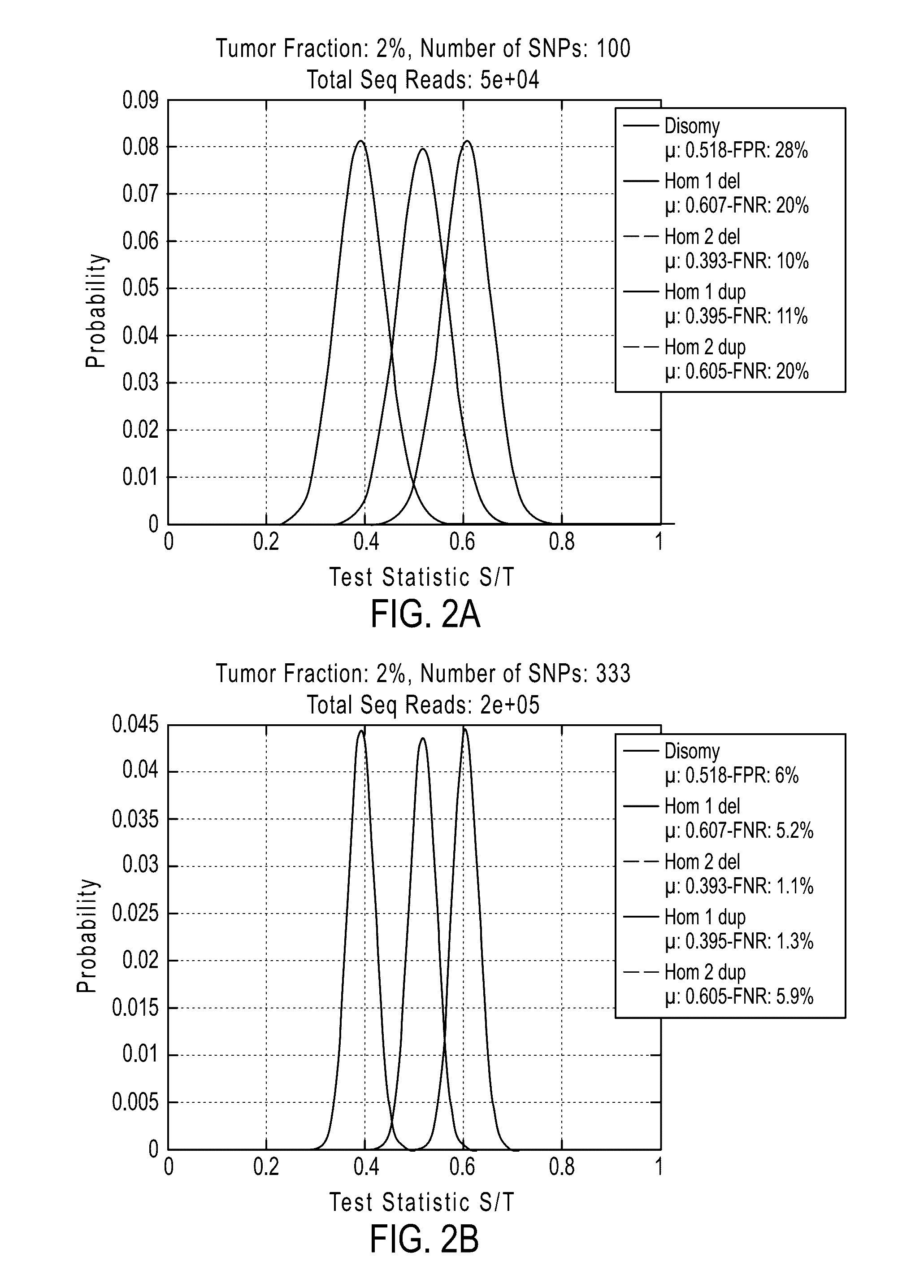
The invention provides improved methods, compositions, and kits for detecting ploidy of chromosome regions, e.g. for detecting cancer or a chromosomal abnormality in a gestating fetus. The methods can utilize a set of more than 200 SNPs that are found within haploblocks and can include analyzing a series of target chromosomal regions related to cancer or a chromosomal abnormality in a gestating fetus. Finally the method may use knowledge about chromosome crossover locations or a best fit algorithm for the analysis. The compositions may comprise more than 200 primers located within haplotype blocks known to show CNV.
Owner:NATERA
Detecting mutations and ploidy in chromosomal segments
ActiveUS20170107576A1Reduce sensitivityIncreased susceptibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsNucleotideBiology
The invention provides methods, systems, and computer readable medium for detecting ploidy of chromosome segments or entire chromosomes, for detecting single nucleotide variants and for detecting both ploidy of chromosome segments and single nucleotide variants. In some aspects, the invention provides methods, systems, and computer readable medium for detecting cancer or a chromosomal abnormality in a gestating fetus.
Owner:NATERA
Methods for detection of genetic disorders
InactiveUS20060160105A1Minimize disruptionMaximize efficiencySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsAllele
Owner:RAVGEN INC
Assay systems for genetic analysis
ActiveUS20120040859A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningPolygenic traitChromosomal Abnormality
Owner:TANDEM DIAGNOSTICS
Method for genotype determination
InactiveUS20040115684A1Enabling detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationReference genesMedicine
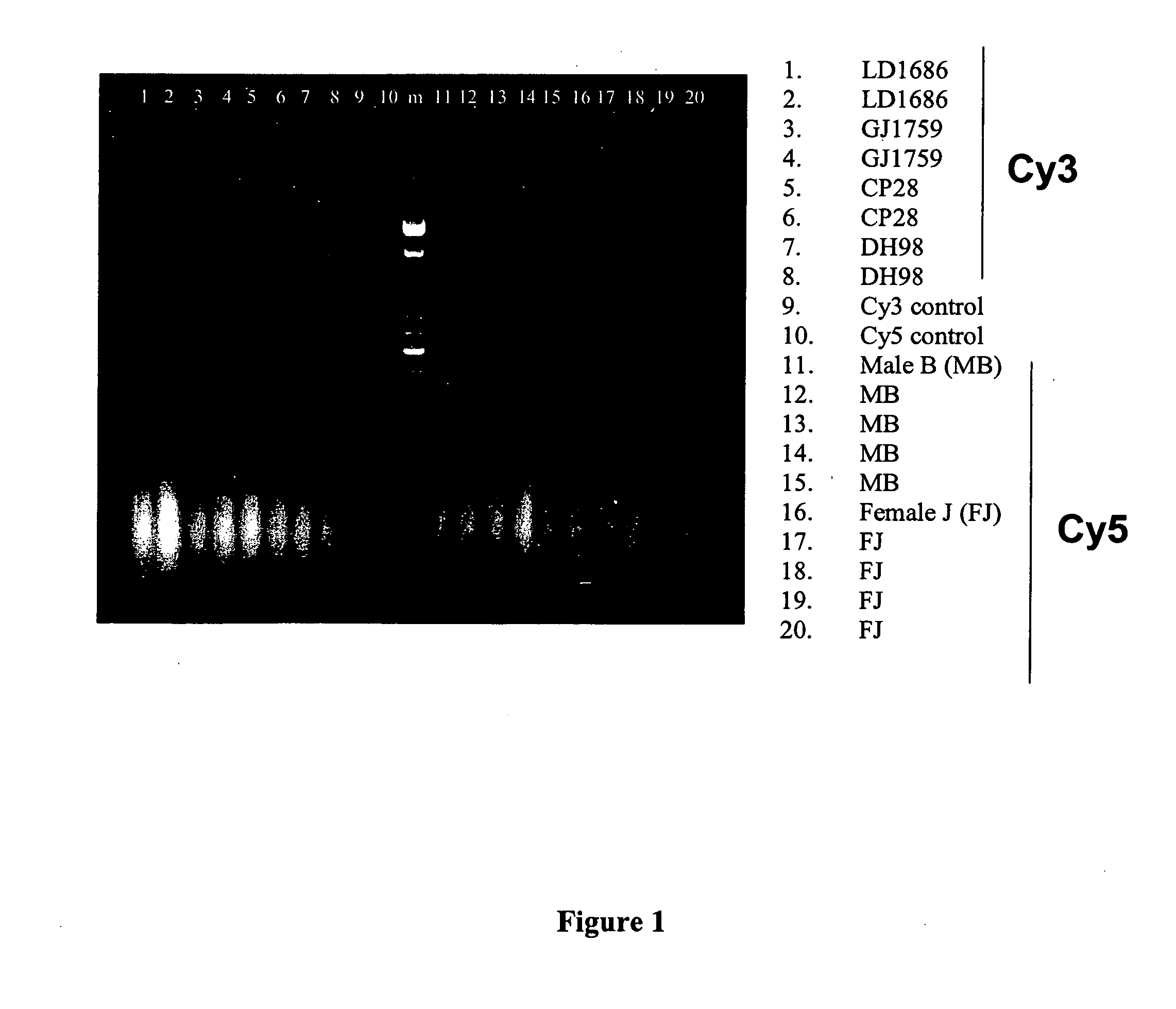
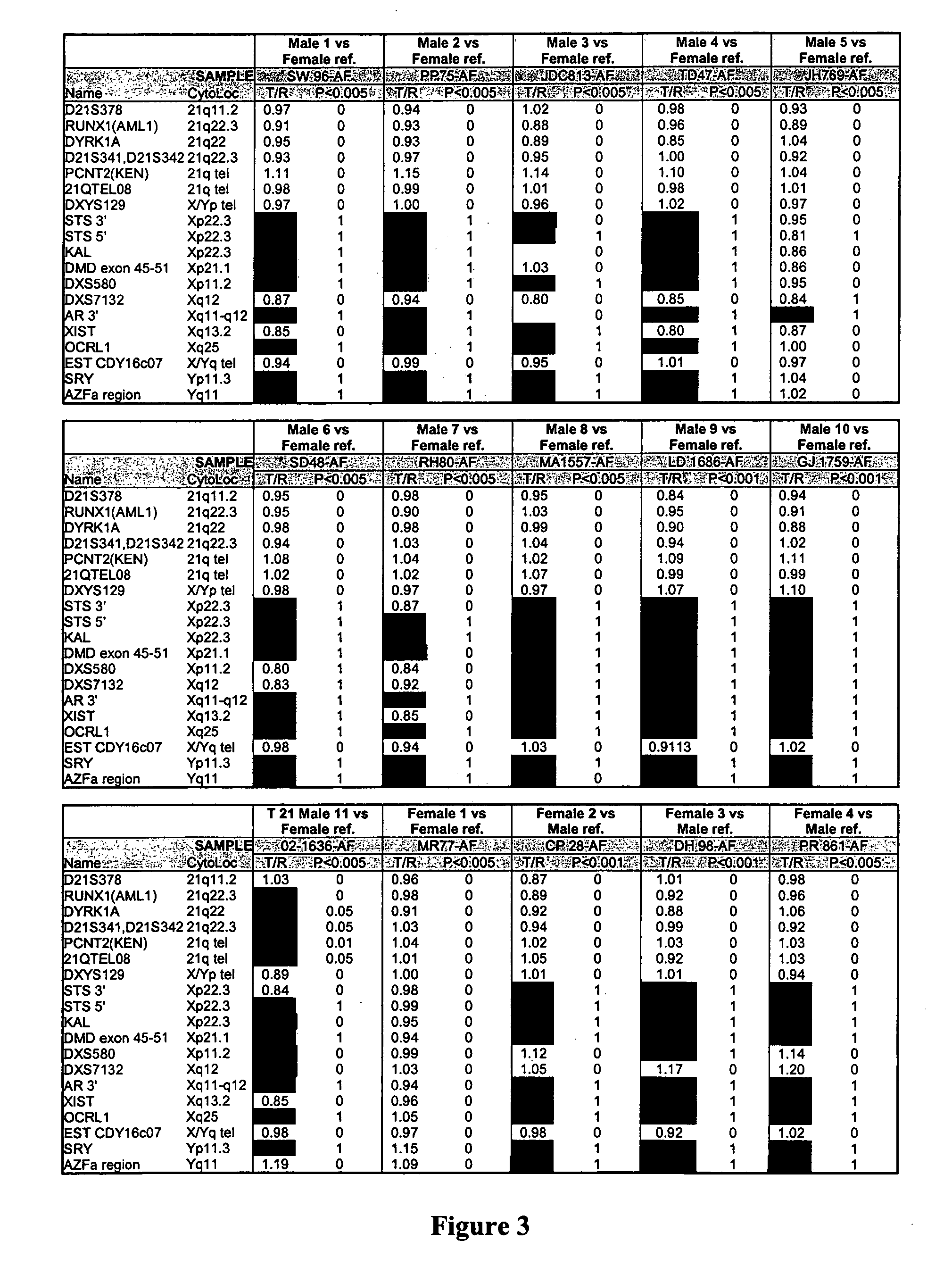
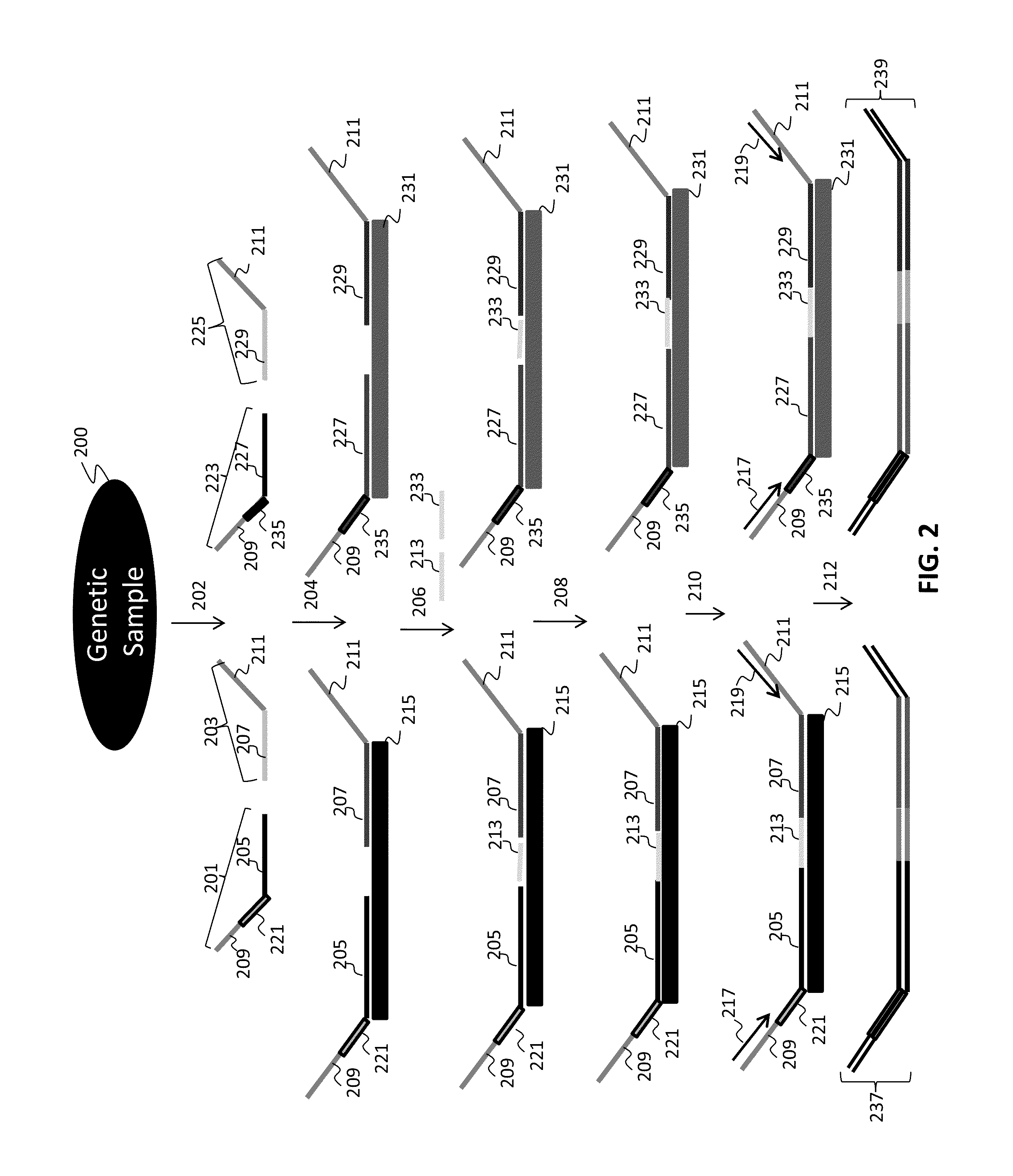
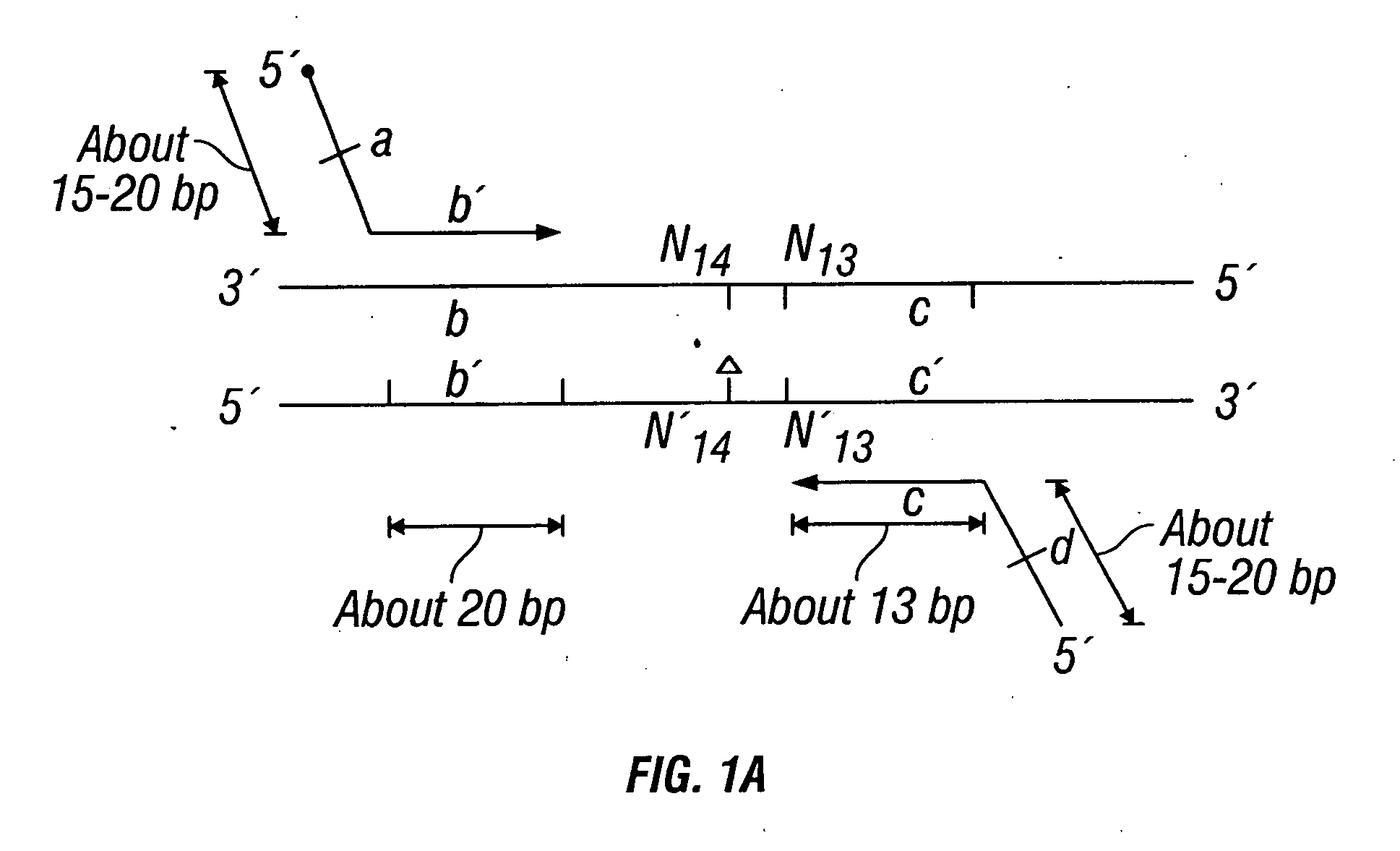
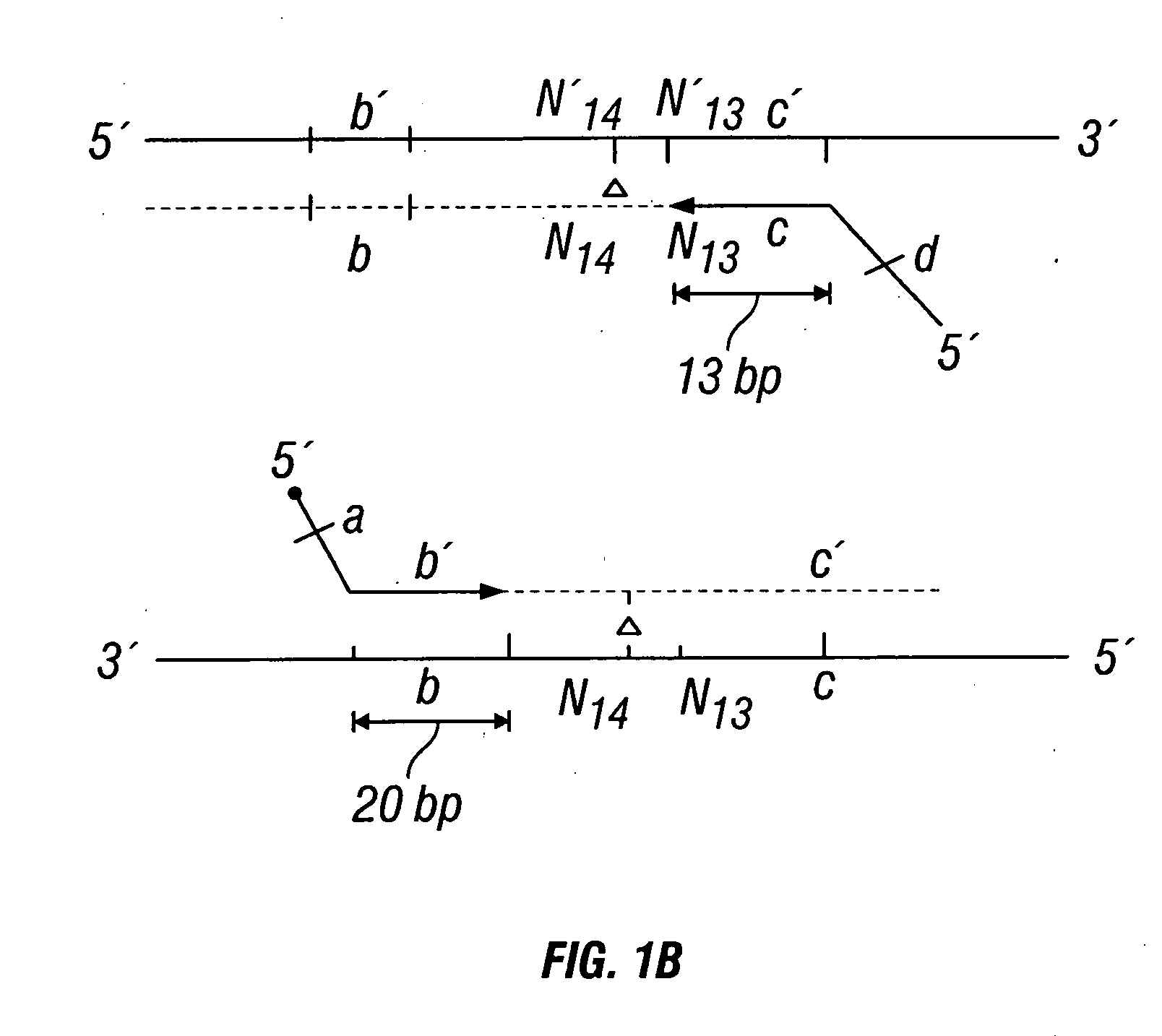
The present invention is directed to a new method for genotype determination at a specific gene locus of an individual or a fetus comprising (i) amplifying a first sequence of said gene locus and a second sequence of a second reference gene locus from DNA originating from a sample containing biological material of said individual or fetus (ii) Monitoring both amplifications preferably in real time and determining the amount of amplification products after each cycle, and (iii) Calculating the ratio between the amount of DNA from the first gene locus and the amount of DNA from the second gene locus. The new method is useful for a variety of applications, especially for detection of chromosomal abnormalities in fetal cells.
Owner:COSTA JEAN MARC
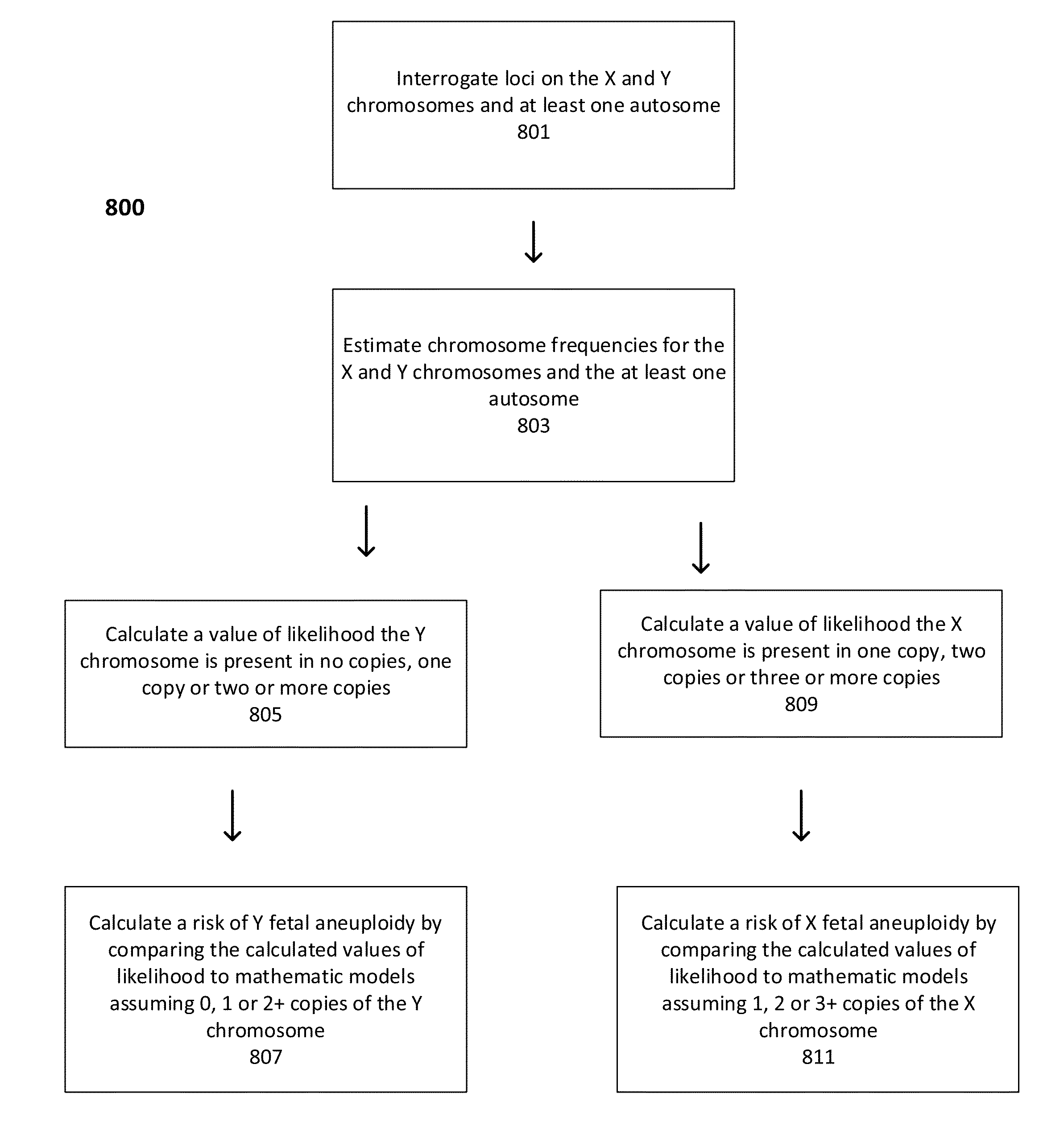
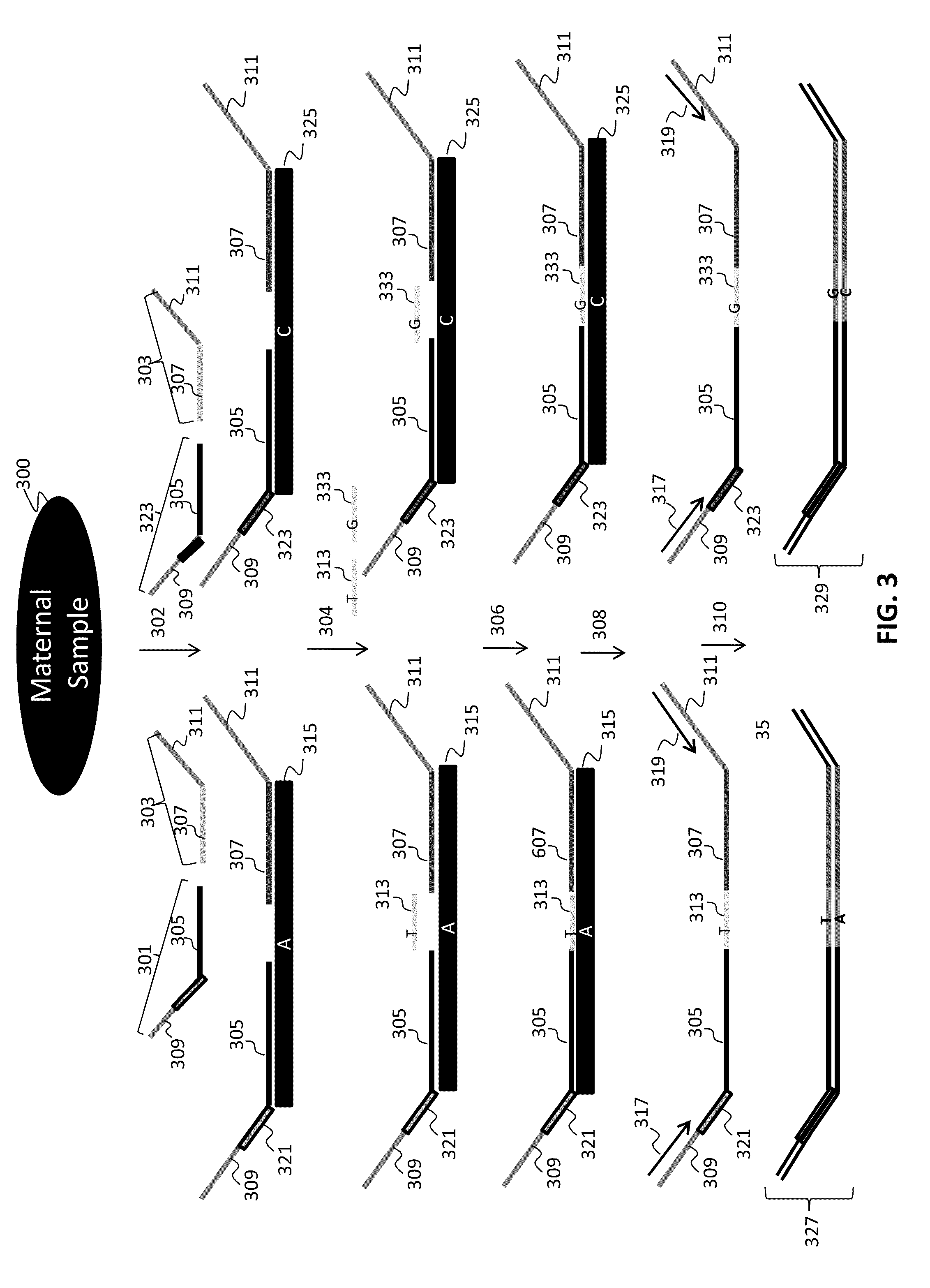
Statistical analysis for non-invasive sex chromosome aneuploidy determination
ActiveUS20130275103A1Increase contentBiostatisticsComputation using non-denominational number representationX chromosomeStatistical analysis
The present invention provides methods for non-invasive determination of X and / or Y chromosomal abnormalities indicative of aneuploidy or sex mosaicisms in a maternal sample by detecting and determining the relative contribution of genetic sequences from the X chromosome and / or the Y chromosome in the maternal sample.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Detecting cancer mutations and aneuploidy in chromosomal segments
ActiveUS20160333416A1Improve throughputIncrease probabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisNucleotideBiology
The invention provides methods, systems, and computer readable medium for detecting ploidy of chromosome segments or entire chromosomes, for detecting single nucleotide variants and for detecting both ploidy of chromosome segments and single nucleotide variants. In some aspects, the invention provides methods, systems, and computer readable medium for detecting cancer or a chromosomal abnormality in a gestating fetus.
Owner:NATERA
Imaging and evaluating embryos, oocytes, and stem cells
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Non-in situ hybridization method for detecting chromosomal abnormalities
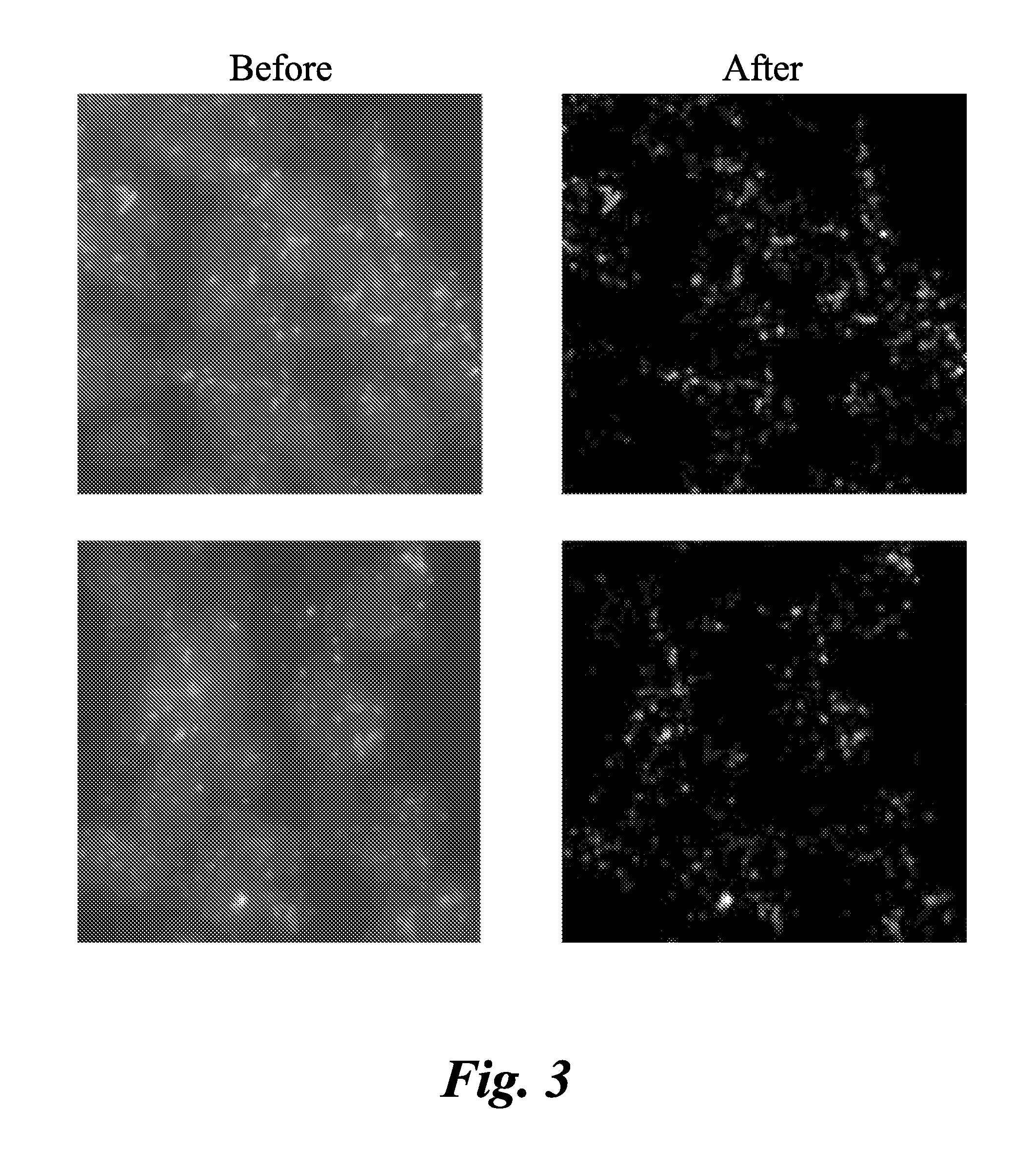
The present invention provides methods of detecting chromosomal or genetic abnormalities associated with various diseases or with predisposition to various diseases. In particular, the present invention provides advanced methods of performing DNA hybridization, capture, and detection on solid support. Invention methods are useful for the detection, diagnosis, predicting response to therapy, detecting minimal residual disease, prognosis, or monitoring of disease treatment or progression of particular disease conditions such as cell proliferative disorders
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
Methods for preparing and analyzing cells having chromosomal abnormalities
InactiveUS20060257884A1Microbiological testing/measurementFluorescenceFluorescence in situ hybridization
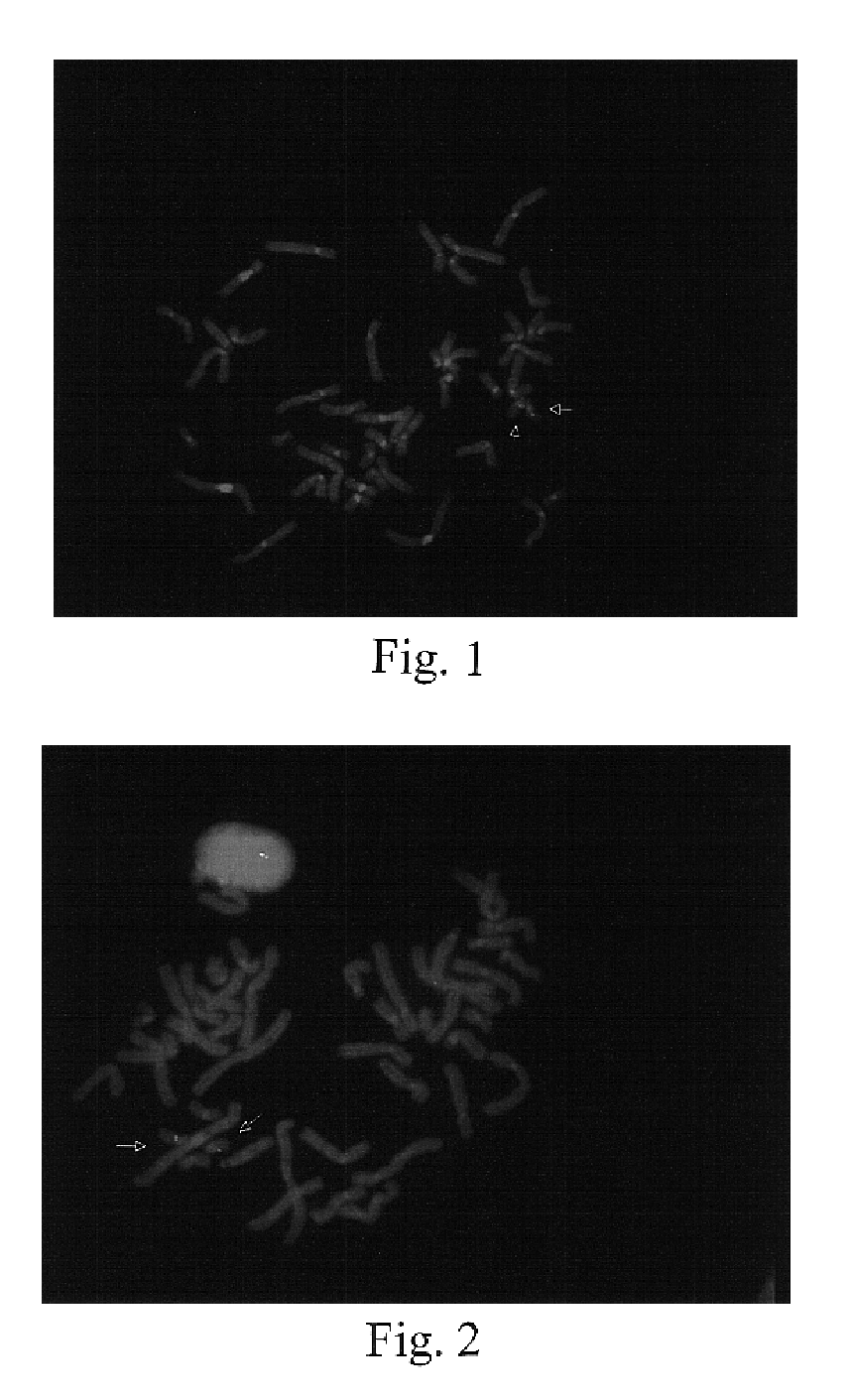
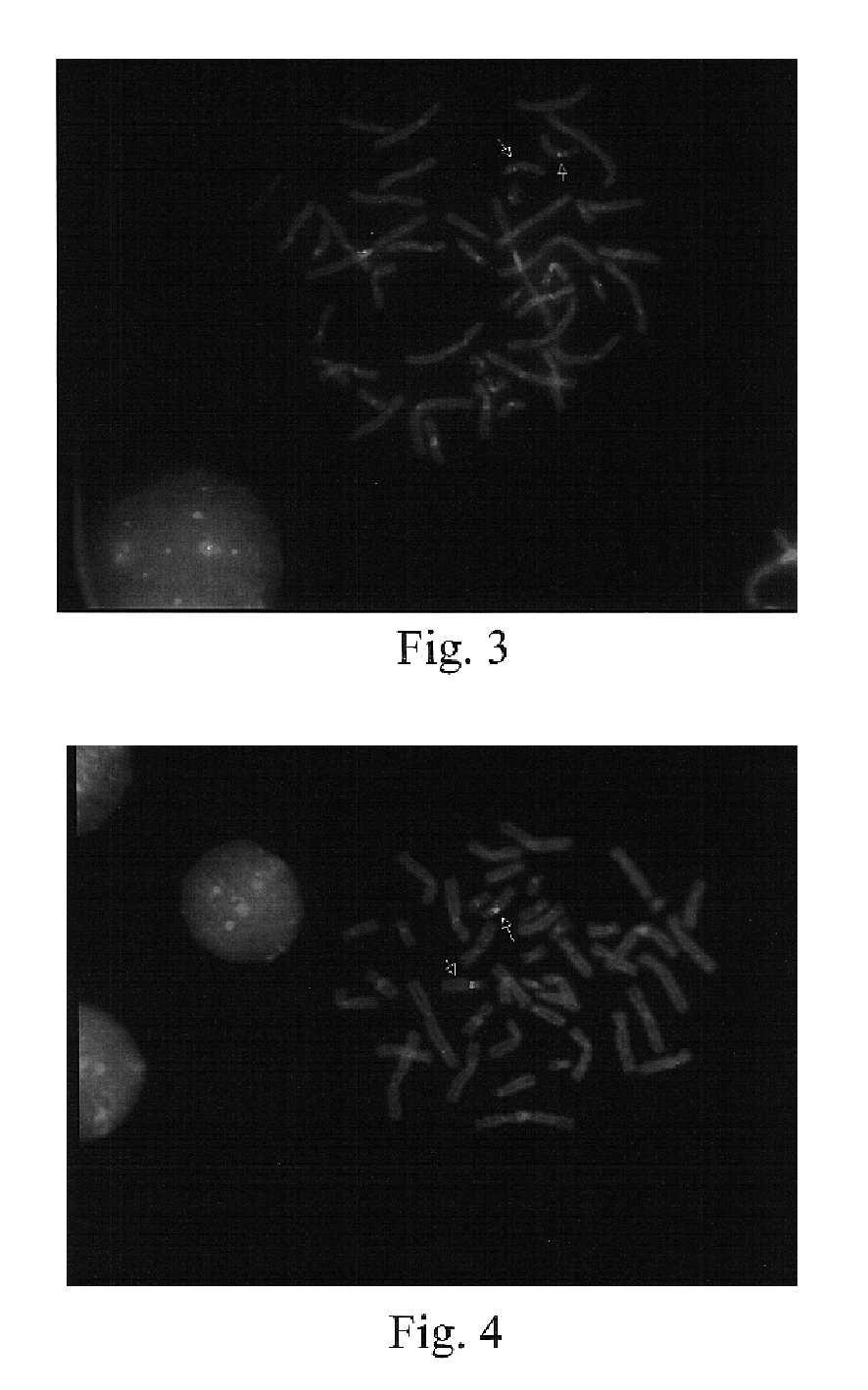
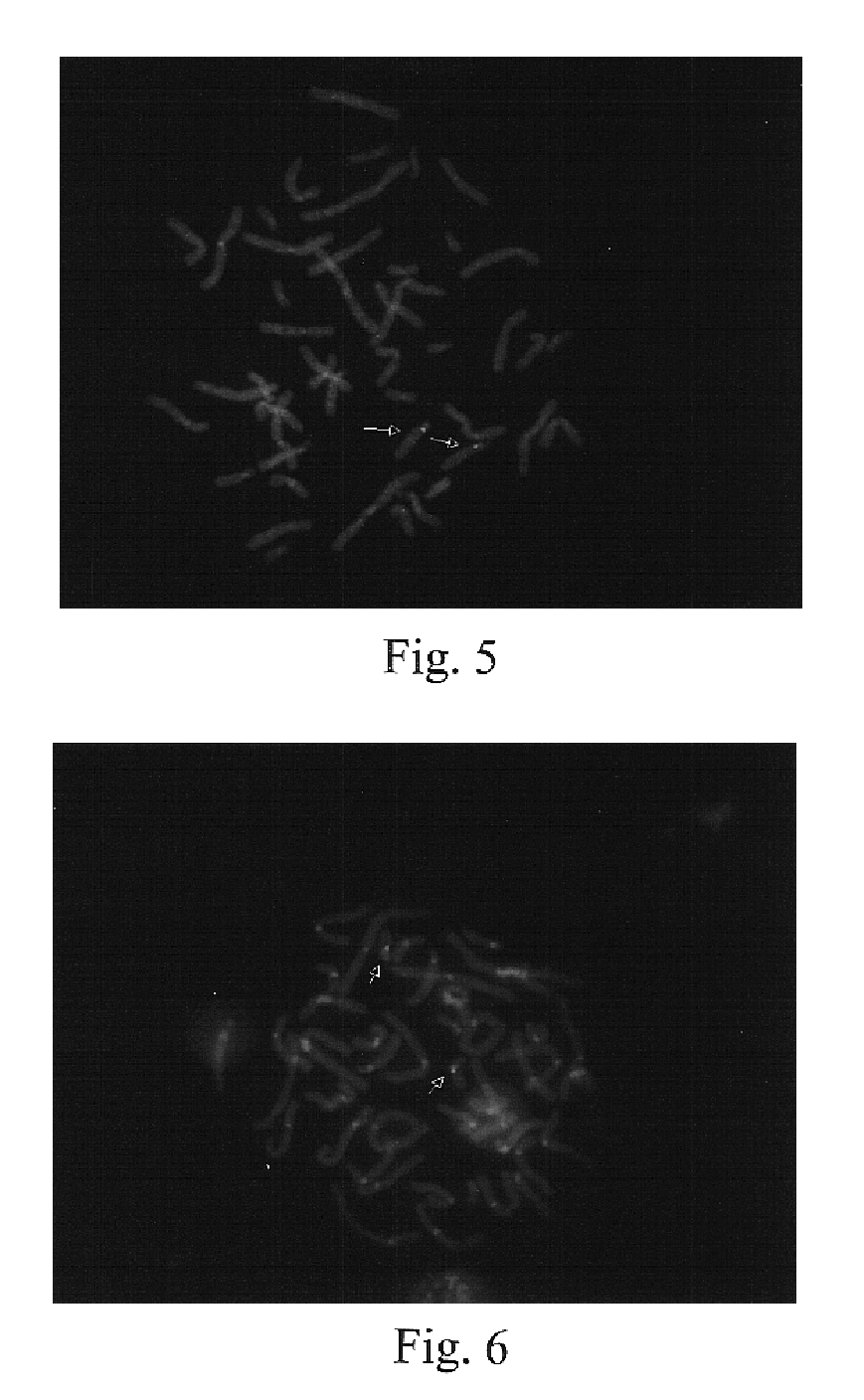
The present invention provides methods for preparing cells with highly condensed chromosomes, such as sperm, and methods for detecting and quantifying specific cellular target molecules in intact cells. Specifically, methods are provided for detecting chromosomes and chromosomal abnormalities, including aneuploidy, in intact cells using fluorescence in situ hybridization of cells in suspension, such as sperm cells.
Owner:AMNIS CORP
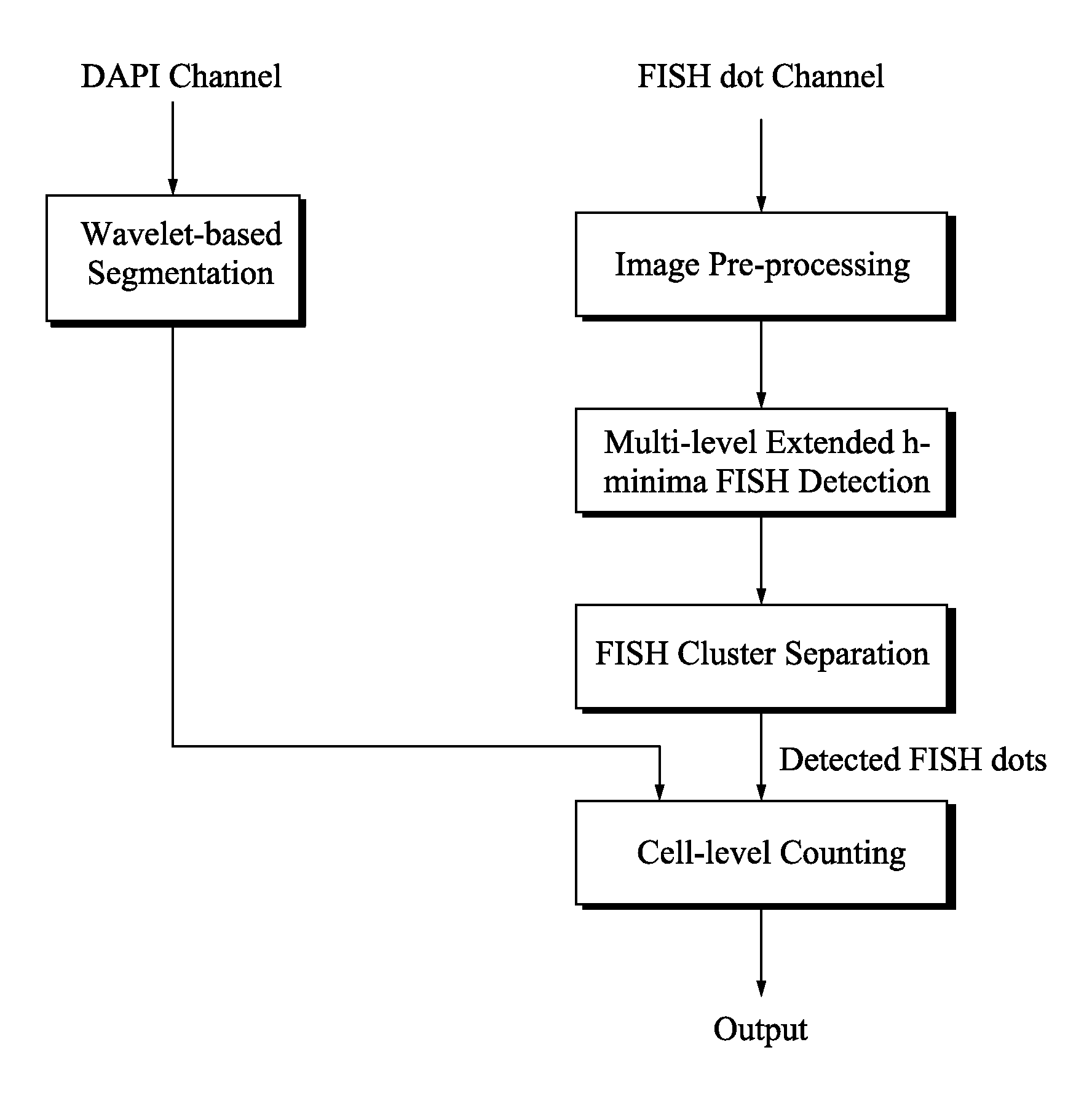
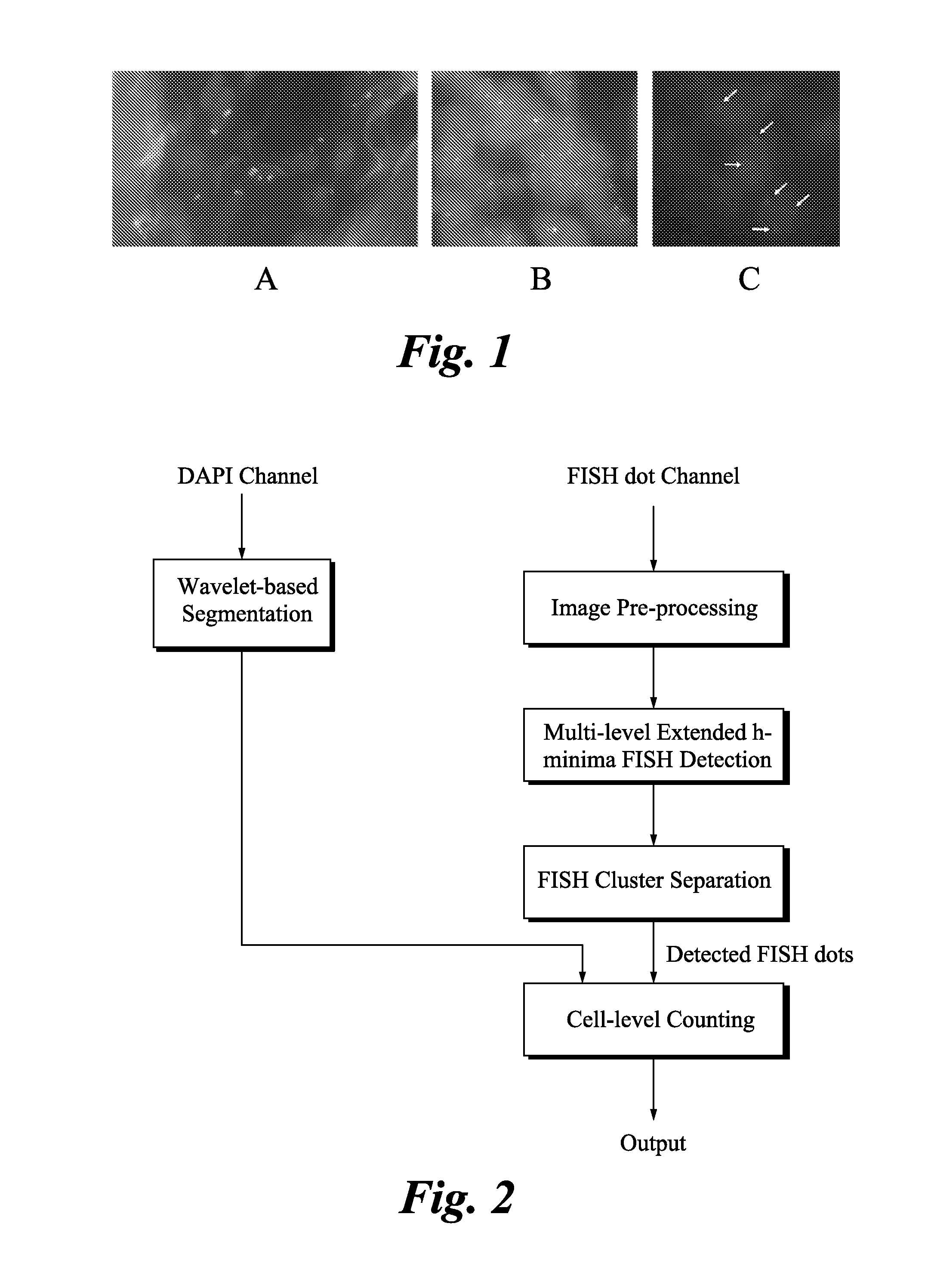
Method and systems for cell-level fish dot counting
The invention relates to a computer implemented method and systems for cell level fish dot counting. FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) dot counting is the process of enumerating chromosomal abnormalities in the cells which can be used in areas of diagnosis and cancer research. The method comprises in part overlaying images of a biological sample comprising a nuclear counterstain mask and a FISH binary mask. The FISH binary mask is extracted using a multi-level extended h-maxima or h-minima.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Assay systems for genetic analysis
ActiveUS20130004950A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssayPolygenic trait
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Amniotic fluid cell-free fetal DNA fragment size pattern for prenatal diagnosis
InactiveUS20070122823A1Rapid prenatal screeningSimple systemMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingFragment sizeChromosomal Abnormality
The present invention relates to improved methods of prenatal diagnosis, screening, monitoring and / or testing. The inventive methods include analysis of the fragment size distribution of cell-free fetal DNA isolated from amniotic fluid. The inventive methods allow for rapid screening of fetal characteristics such as chromosomal abnormalities and for prenatal diagnosis of a variety of diseases and conditions. Since the new methods do not require cell culture, they can be performed more rapidly than conventional fetal karyotypes.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND MEDICAL CENT HOSPITALS
Methods for detection of genetic disorders
InactiveUS20070122835A1Maximize efficiencyIncrease delaySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsAllele
The invention provides a method useful for detection of genetic disorders. The method comprises determining the sequence of alleles of a locus of interest, and quantitating a ratio for the alleles at the locus of interest, wherein the ratio indicates the presence or absence of a chromosomal abnormality. The present invention also provides a non-invasive method for the detection of chromosomal abnormalities in a fetus. The invention is especially useful as a non-invasive method for determining the sequence of fetal DNA. The invention further provides methods of isolation of free DNA from a sample.
Owner:RAVGEN INC
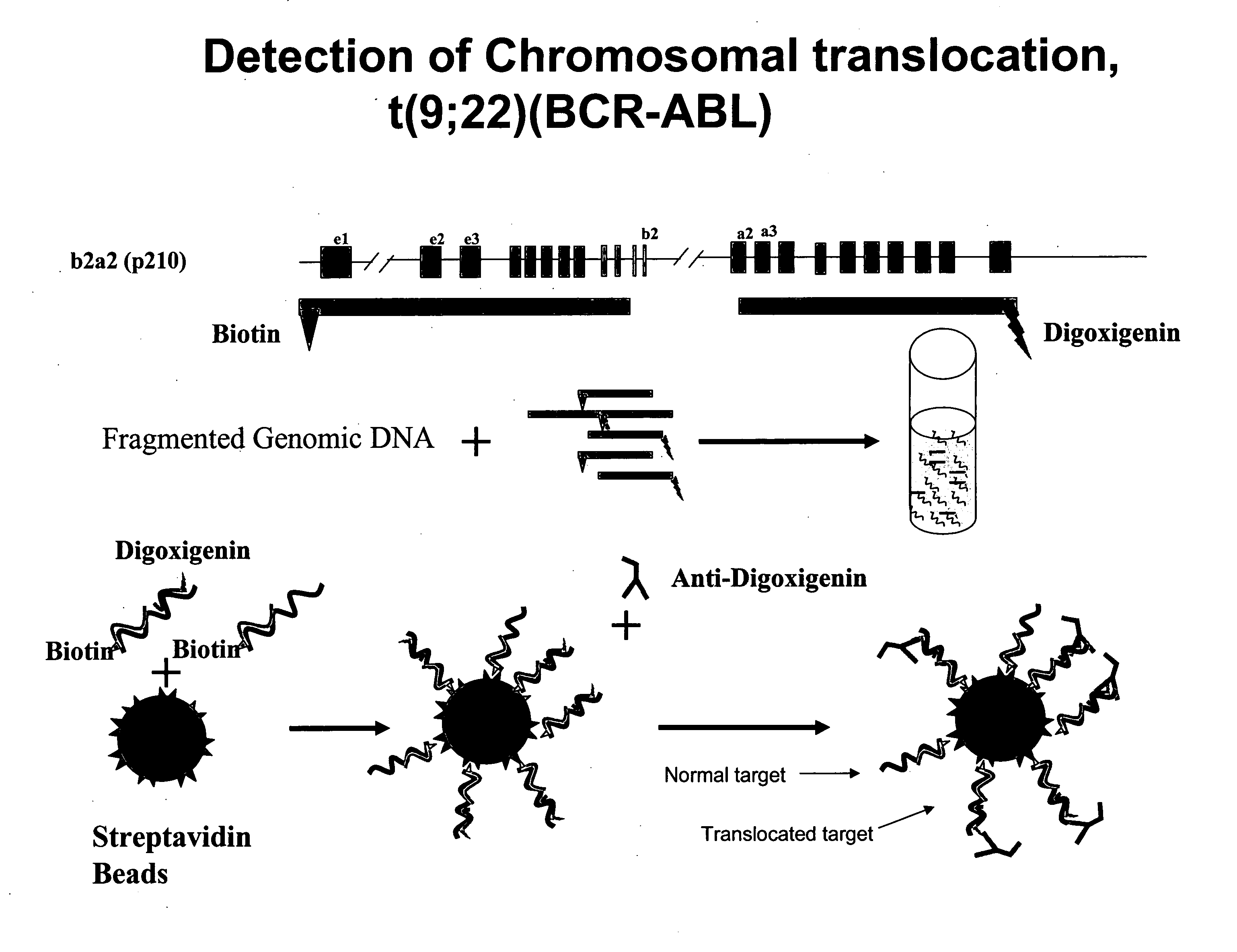
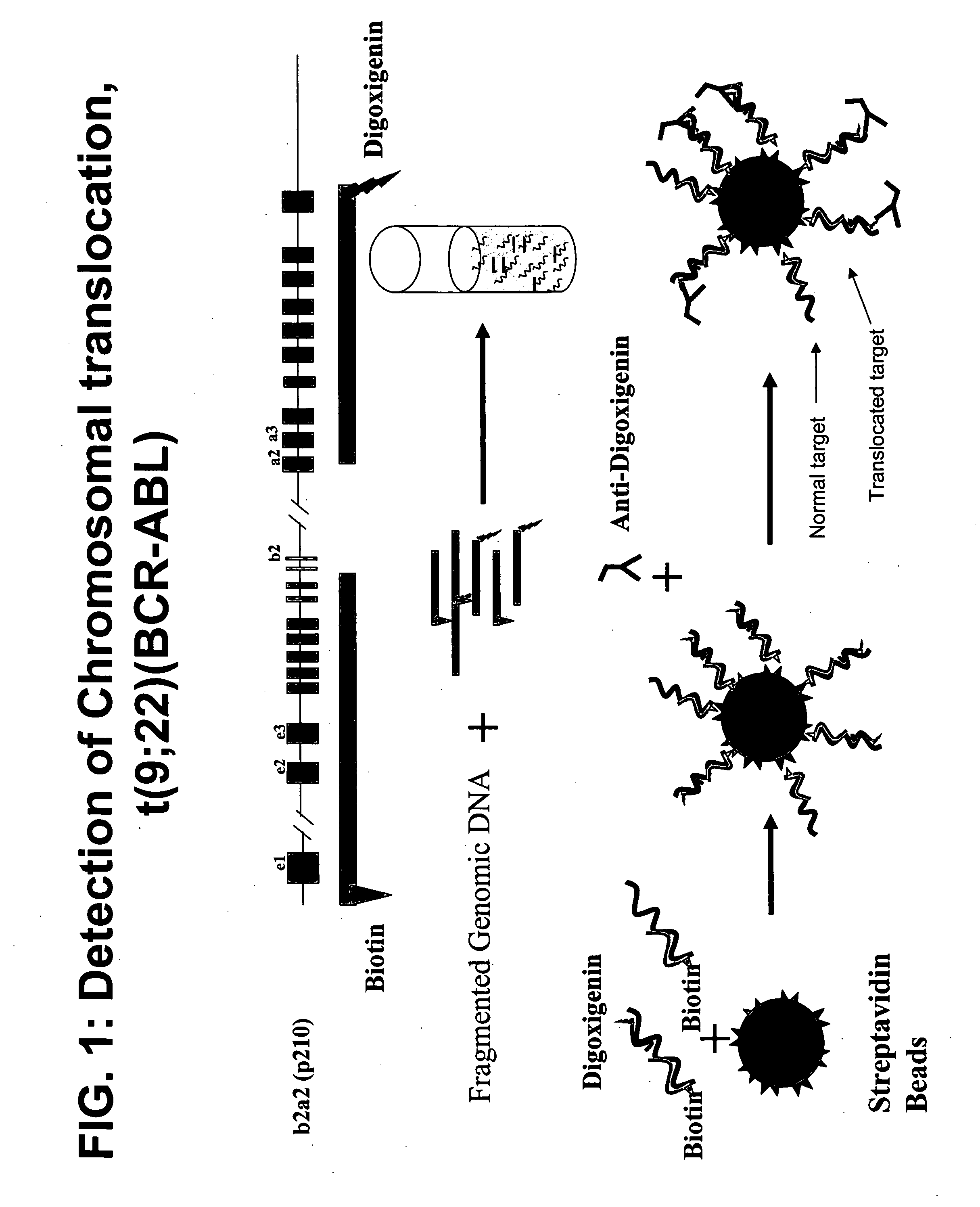
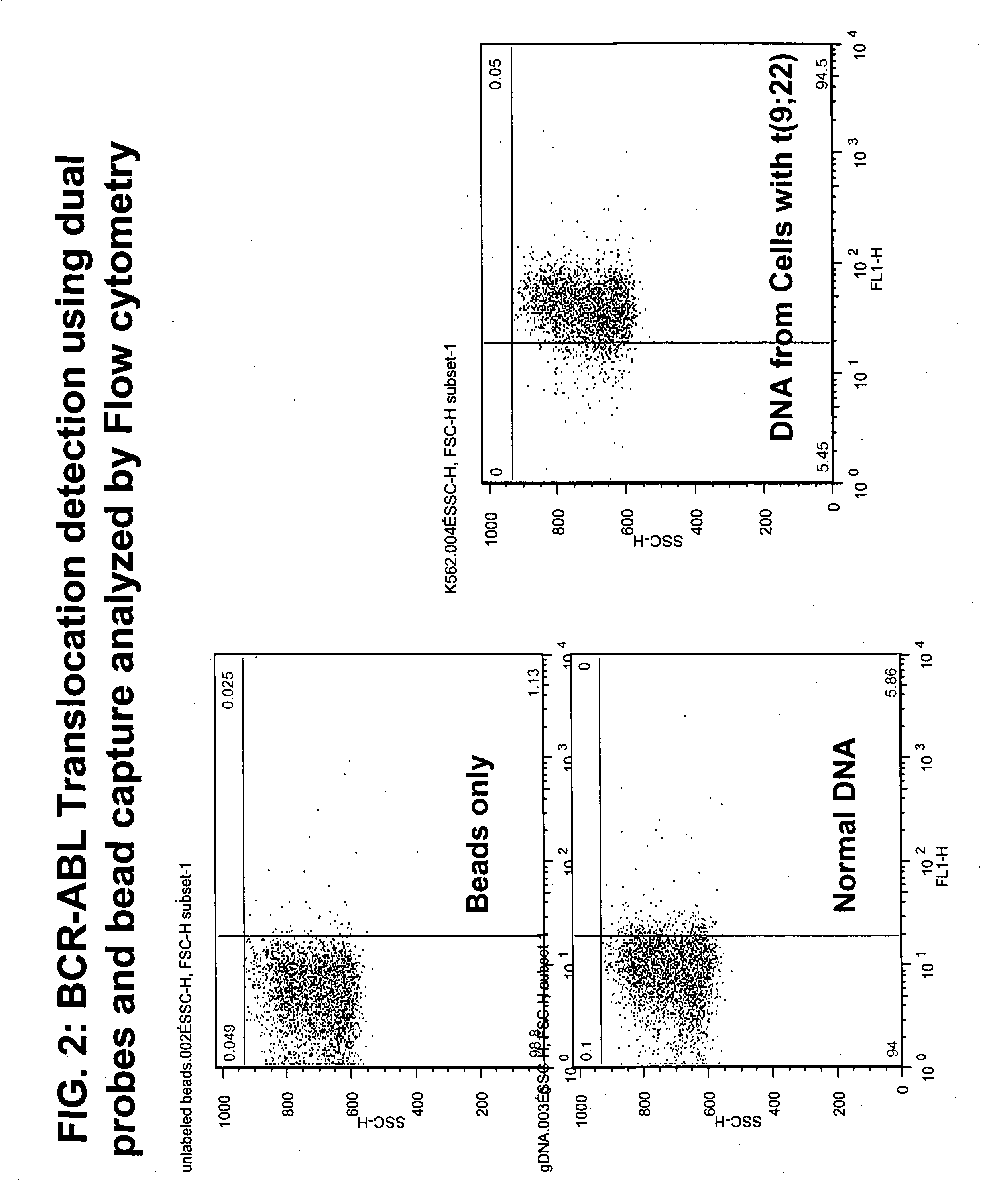
Methods for detecting gene dysregulations
ActiveUS20100304390A1Microbiological testing/measurementHybridisationProtein translocationChromosomal Abnormality
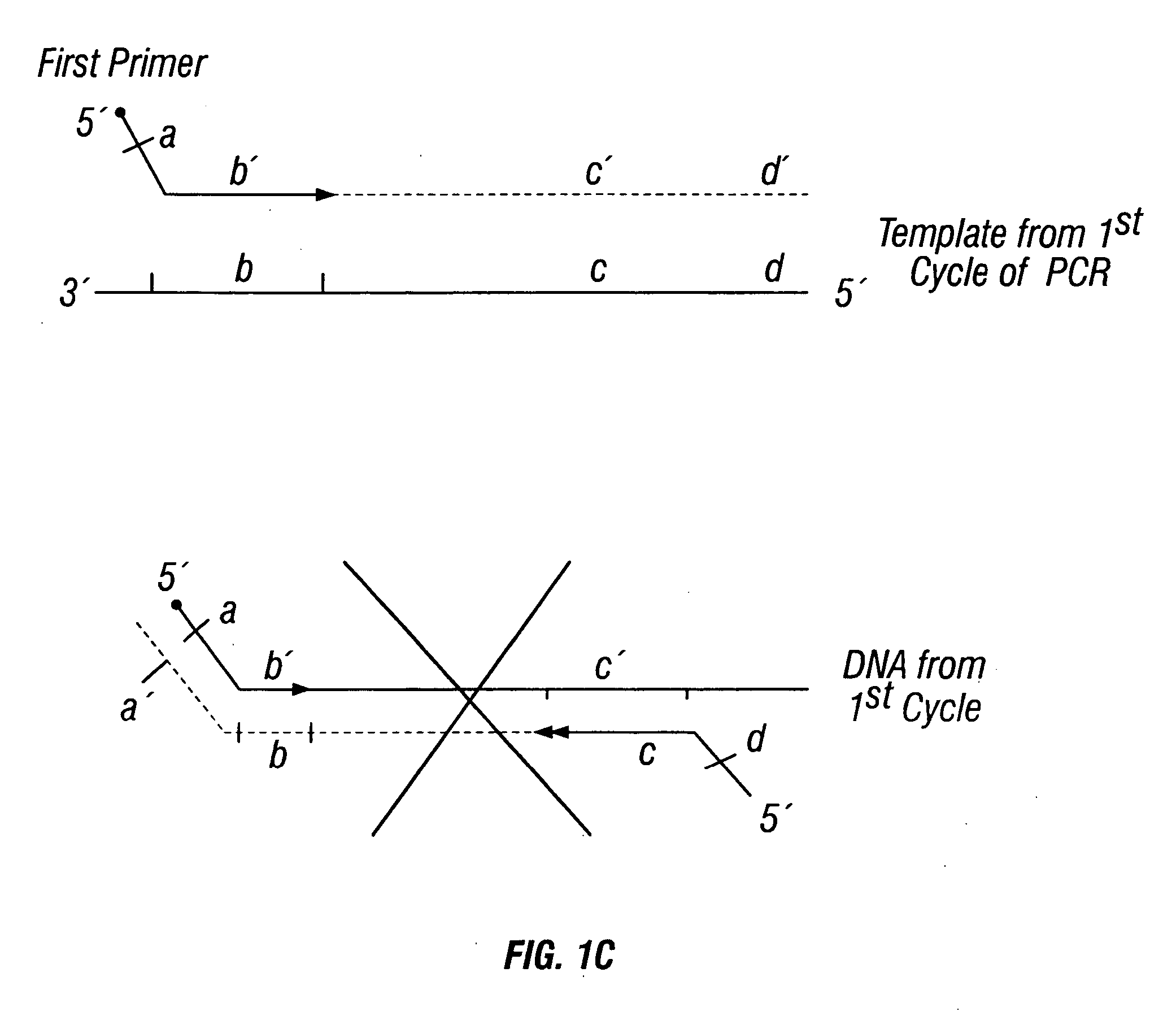
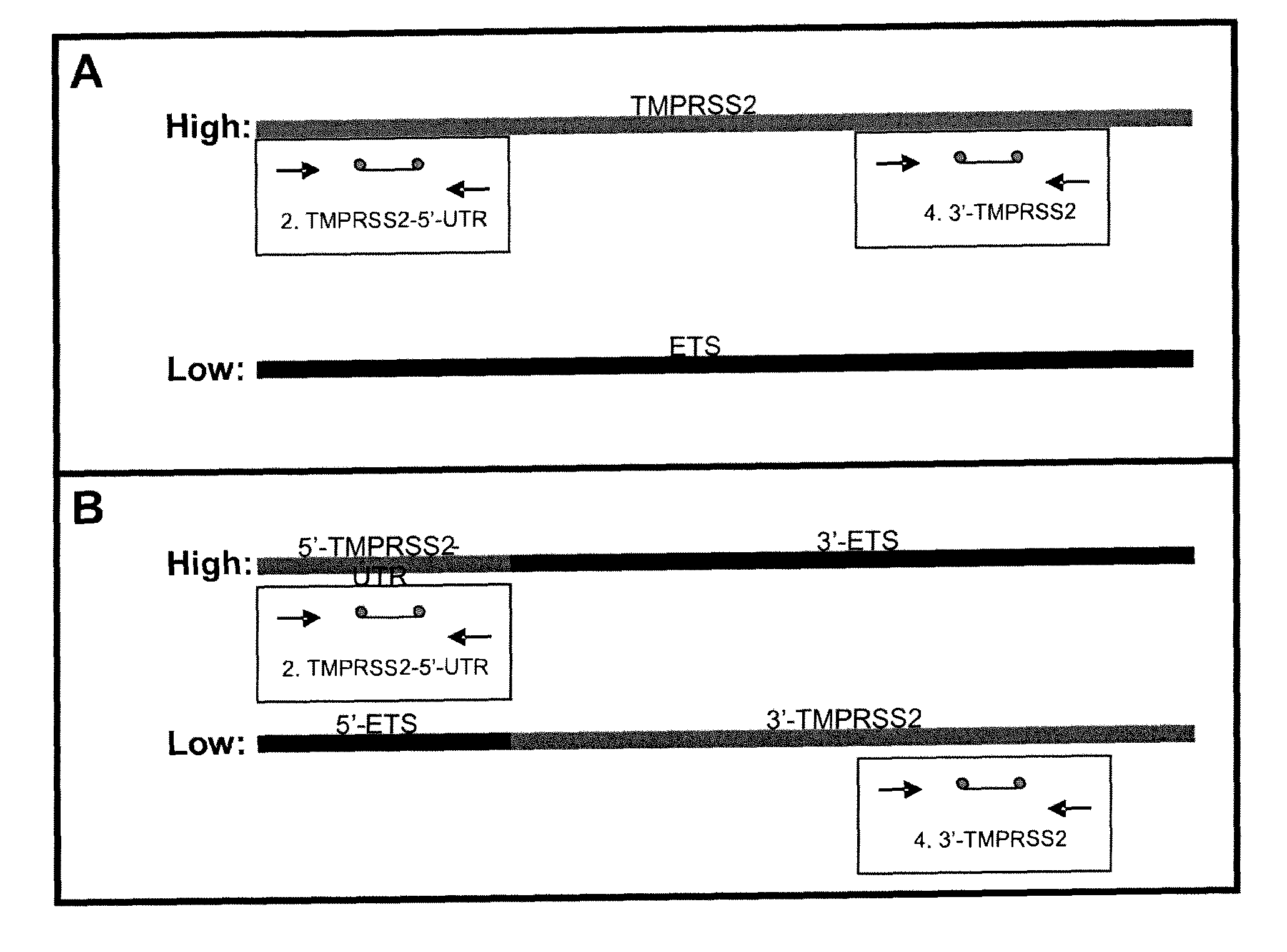
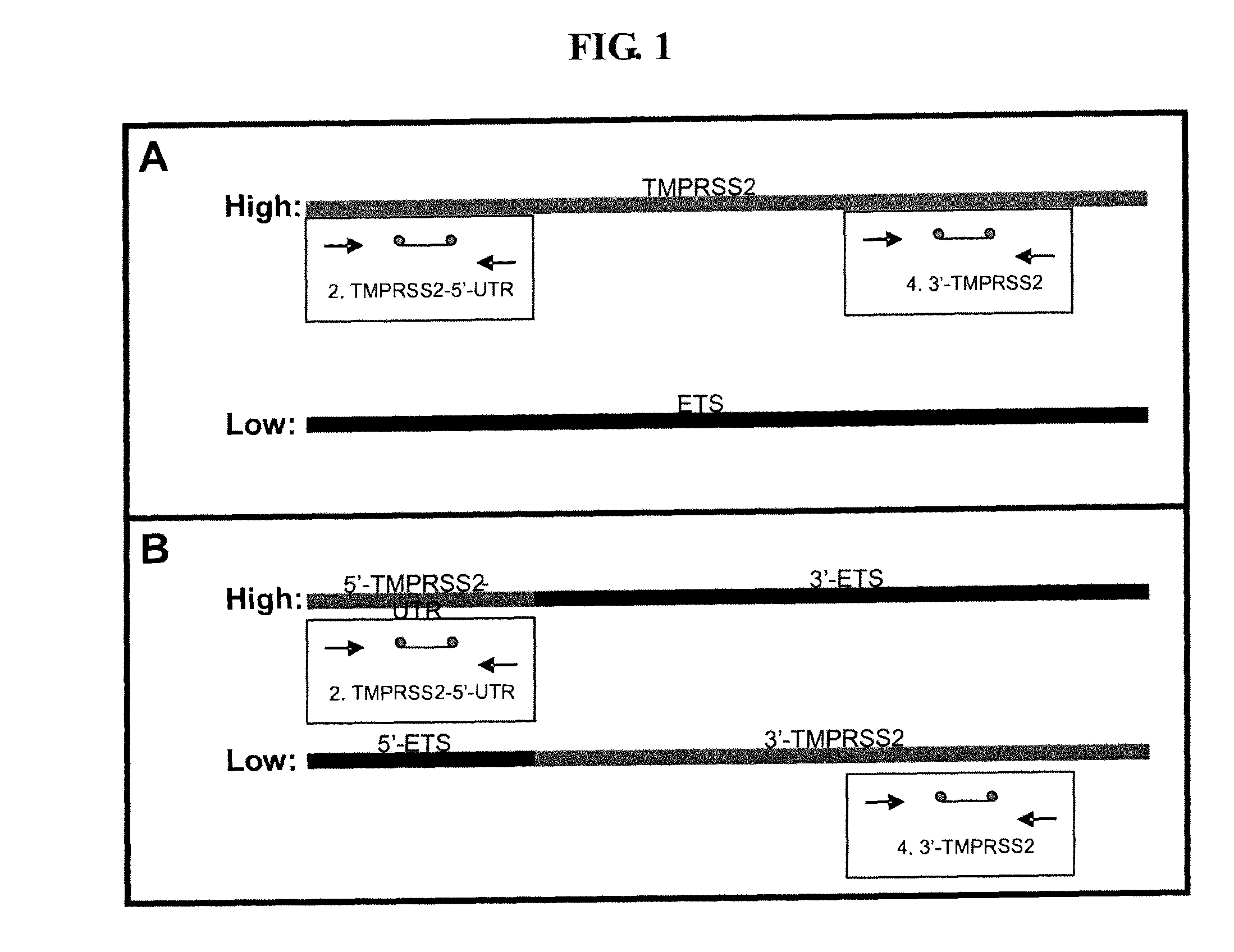
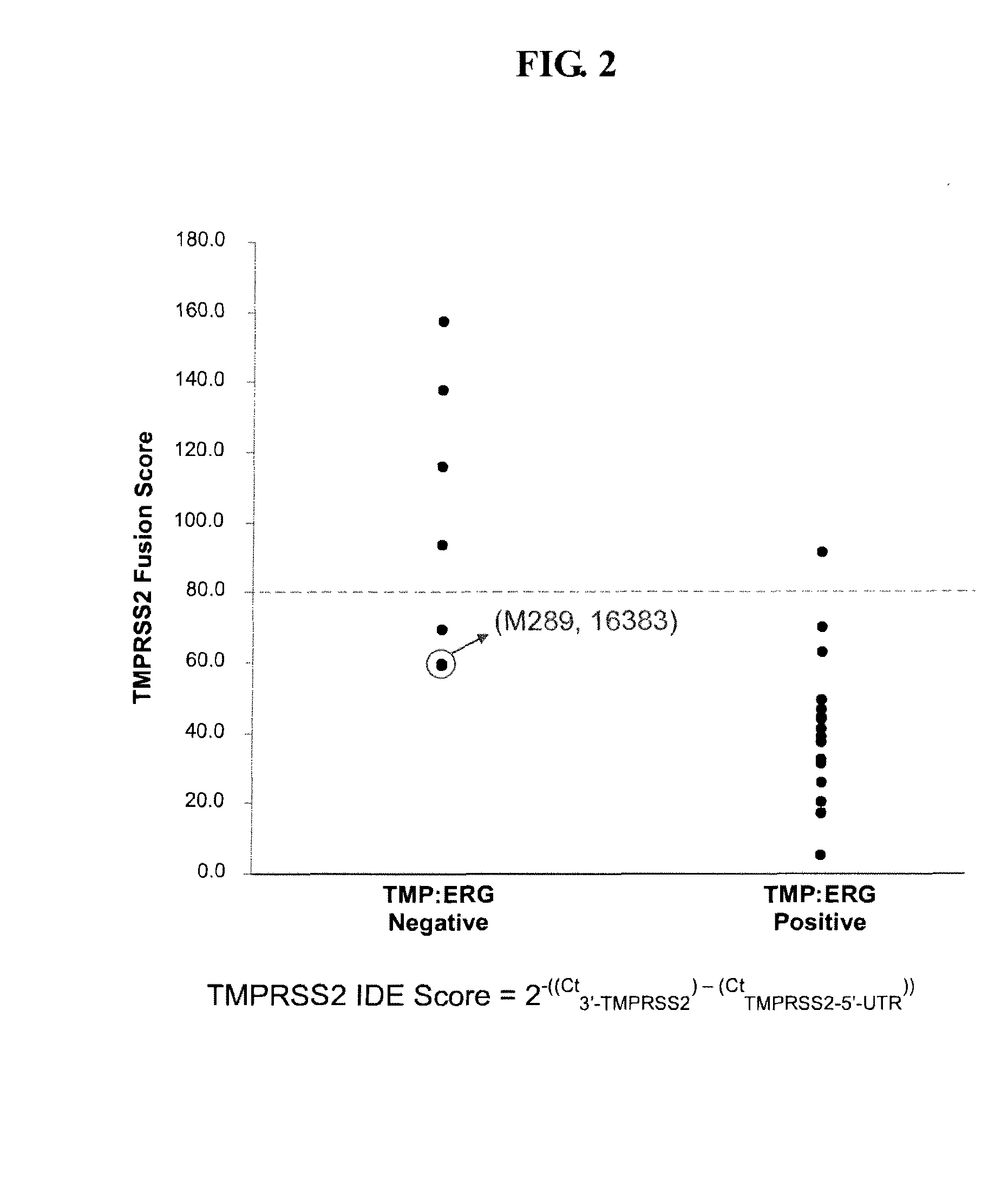
Described herein are methods, compositions and kits directed to the detection of gene dysregulations such as those arising from gene fusions and / or chromosomal abnormalities, e.g. translocations, insertions, inversions and deletions. Samples containing dysregulated gene(s) of interest may show independent expression patterns for the 5′ and 3′ regions of the gene. The methods, compositions and kits are useful for detecting mutations that cause the differential expression of a 5′ portion of a target gene relative to the 3′ region of the target gene.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
Diagnostic methods for determining treatment
ActiveUS20070161008A1Inhibits signaling capability of HER-Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesEffective treatment
The present invention provides methods for identifying cancer patients susceptible to effective treatment with trastuzumab and other medications that function similarly to trastuzumab. The invention is based on the discovery that certain chromosomal abnormalities can be used to selectively identify cancer patients that are likely to be successfully treated with medication that inhibits the signaling capability of the HER-2 receptor protein or otherwise function similarly to trastuzumab. The invention is based on the use of nucleic acid technology where nucleic acid probes are allowed to hybridize to cell samples and the number of copies of particular genetic regions quantified. The present invention also provides kits and sets of probes for use in identifying cancer patients susceptible to effective treatment with trastuzumab and other medications that function similarly to trastuzumab.
Owner:ABBOTT MOLECULAR INC
Method of detecting chromosomal abnormalities
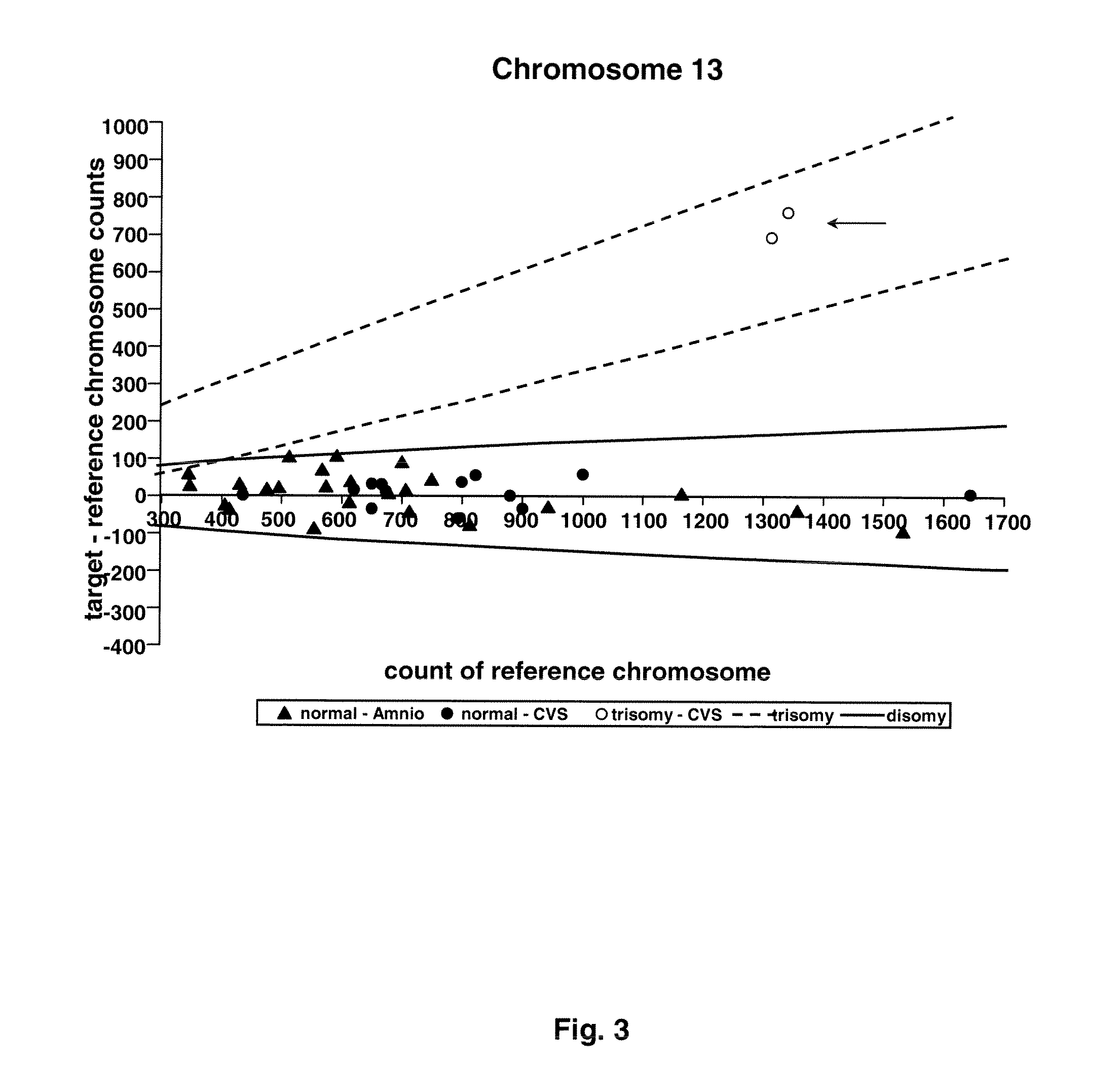
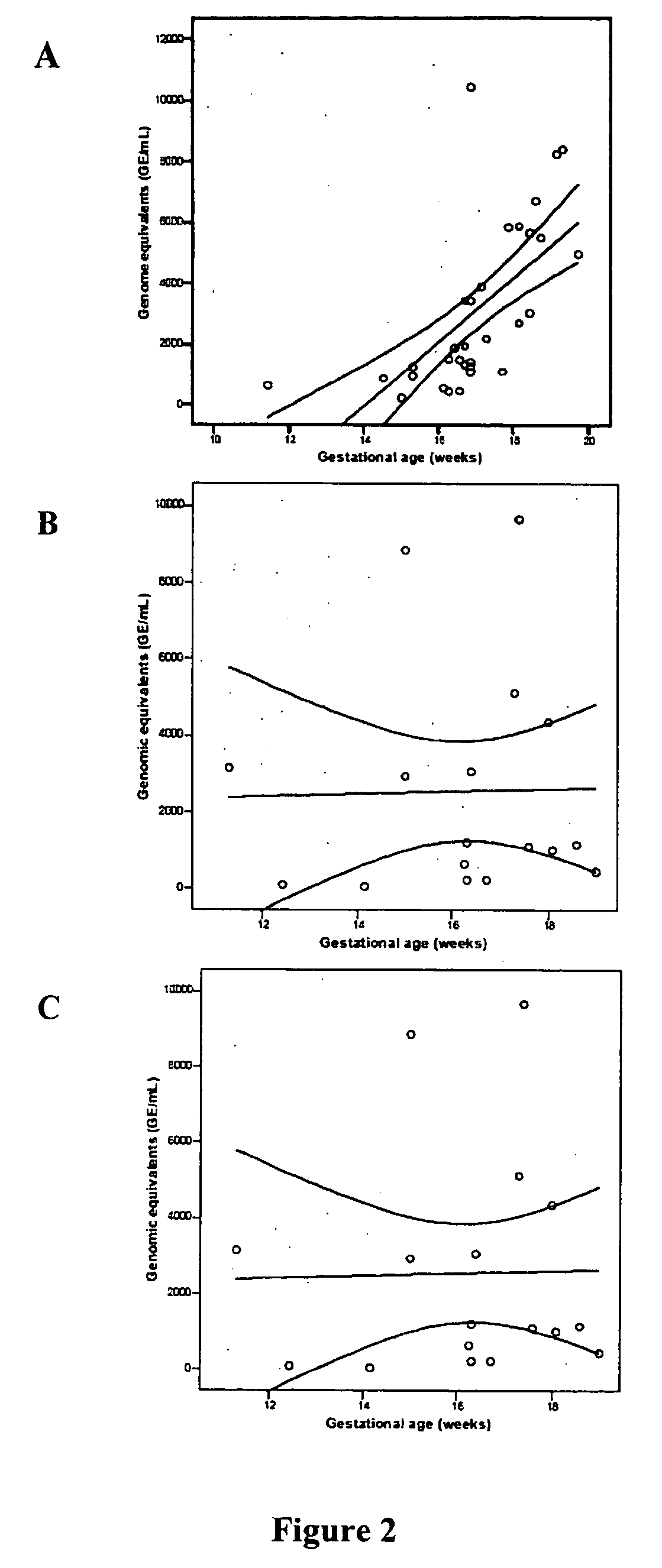
The invention relates to a method of detecting chromosomal abnormalities, in particular, the invention relates to the diagnosis of fetal chromosomal abnormalities such as trisomy 21 (Down's syndrome) which comprises sequence analysis of cell-free DNA molecules in plasma samples obtained from maternal blood during gestation of the fetus.
Owner:PREMAITHA LTD
Cancer Stem Cells And Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080038770A1Useful in treatmentIncreased mortalityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBlastomaIn vivo
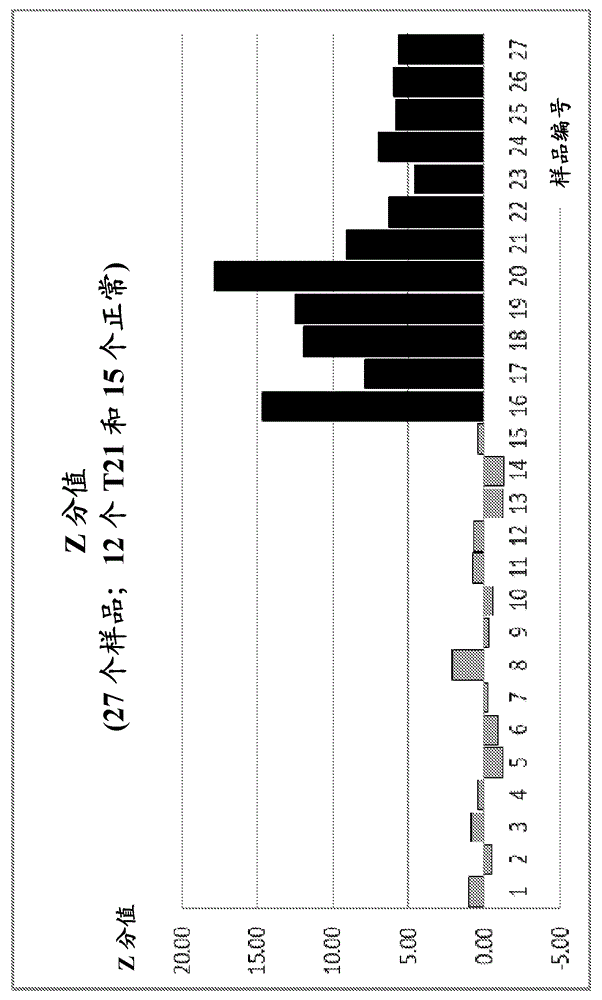
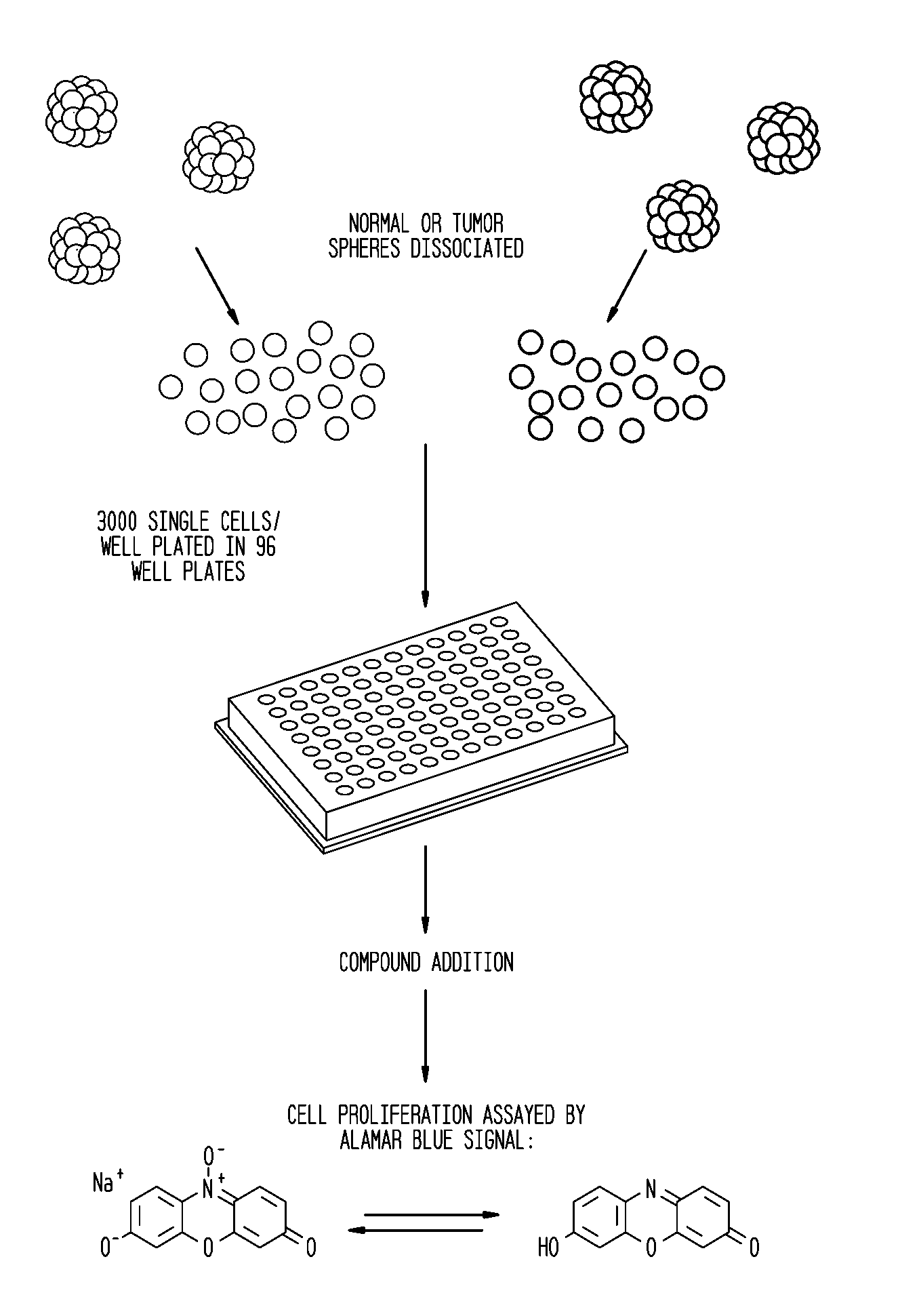
Disclosed are enriched preparations of neuroblastoma tumor initiating cells (NB TICs). The NB TICs are capable of self-renewal, initiating neuroblastoma tumor growth in vivo and are capable of being passaged in high frequency. These NB TICs have chromosomal abnormalities and are capable of giving rise to secondary tumor spheres. Methods are also disclosed for preparing the enriched preparations of NB TICs, such as from neuroblastoma tumor tissue and metastasized bone marrow. Also disclosed are methods of screening candidate substances to identify therapeutic agents for the treatment of neuroblastoma. Methods are also provided for screening a sample for neuroblastoma, as well as for screening a sample to identify the stage of neuroblastoma present. Kits are also provided for selecting appropriate anti-neuroblastoma compounds for a patient, and utilize isolated compositions of the patients' neuroblastoma tumor initiating cells. In this manner, a customized medicinal profile for the patient may be devised.
Owner:HOSPITAL FOR SICK CHILDREN
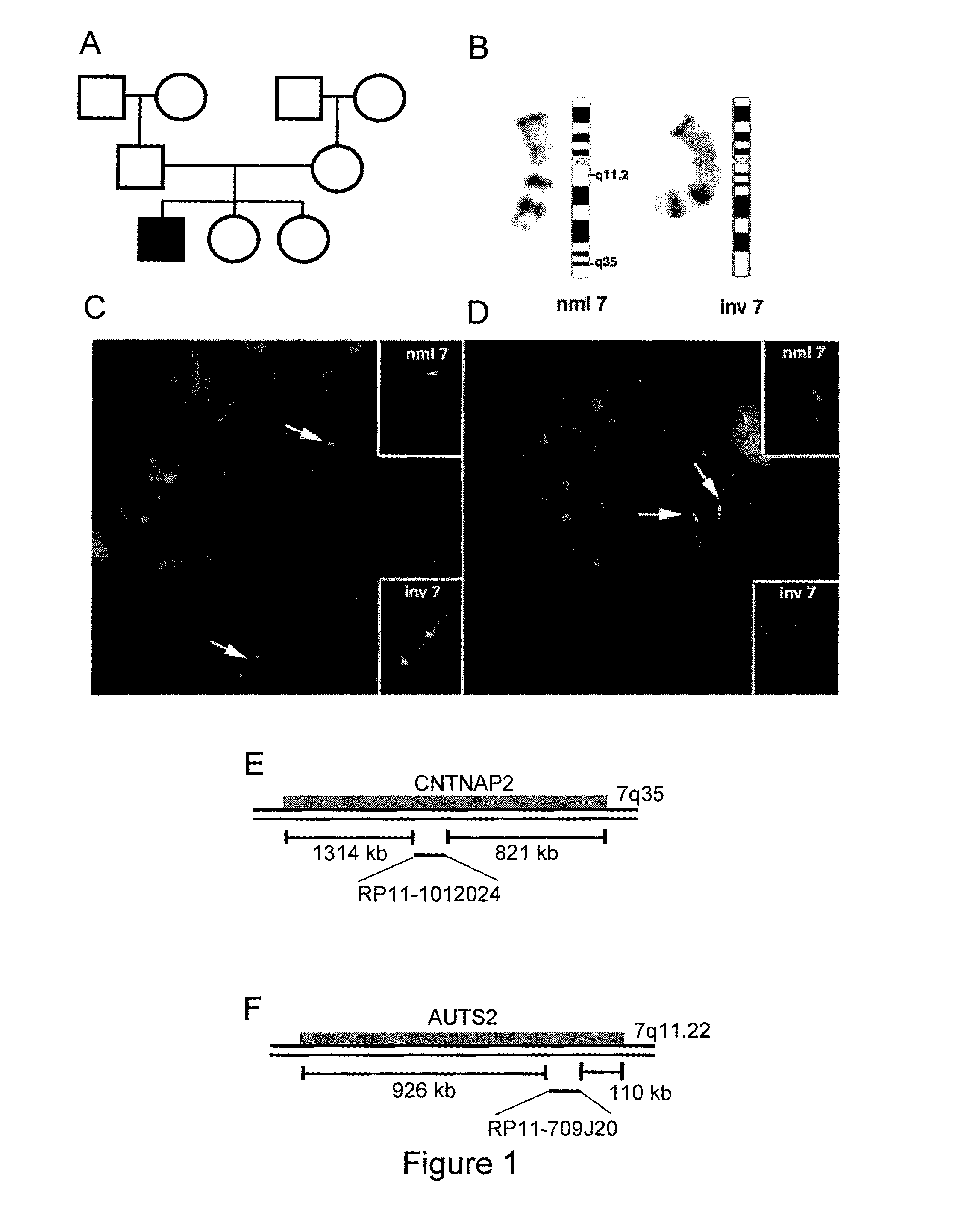
Mutations in Contaction Associated Protein 2 (CNTNAP2) are Associated with Increased Risk for Ideopathic Autism
The present invention provides compositions and methods for the examination of cells, tissues, and fluids, collectively known as body samples, to identify human subjects at-risk of developing Autism Spectrum Disorder by detecting a chromosomal abnormality or variant in the CNTNAP2 gene, the AUTS2 gene, or both.
Owner:YALE UNIV
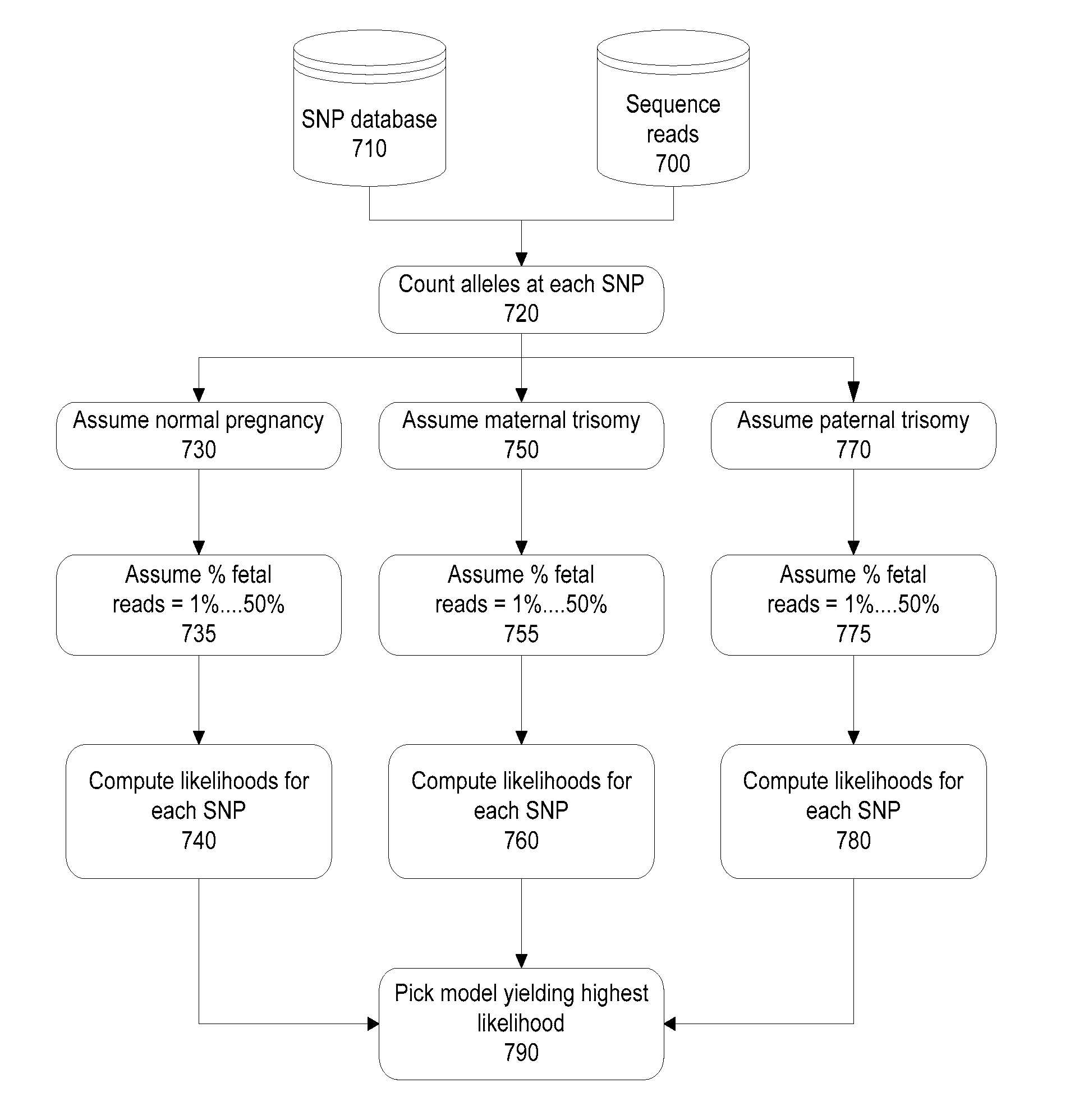
Methods and systems for determining fetal chromosomal abnormalities
InactiveUS20130261984A1Minimize or eliminate false negativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMedical automated diagnosisTrisomyGenotype
The present disclosure provides methods and systems for determining the presence or absence of aneuploidy in a fetus. In particular, the present disclosure provides noninvasive methods and systems for detecting the presence of fetal trisomy and other fetal chromosomal anomalies, paternity of a fetus and fetal genotype.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com