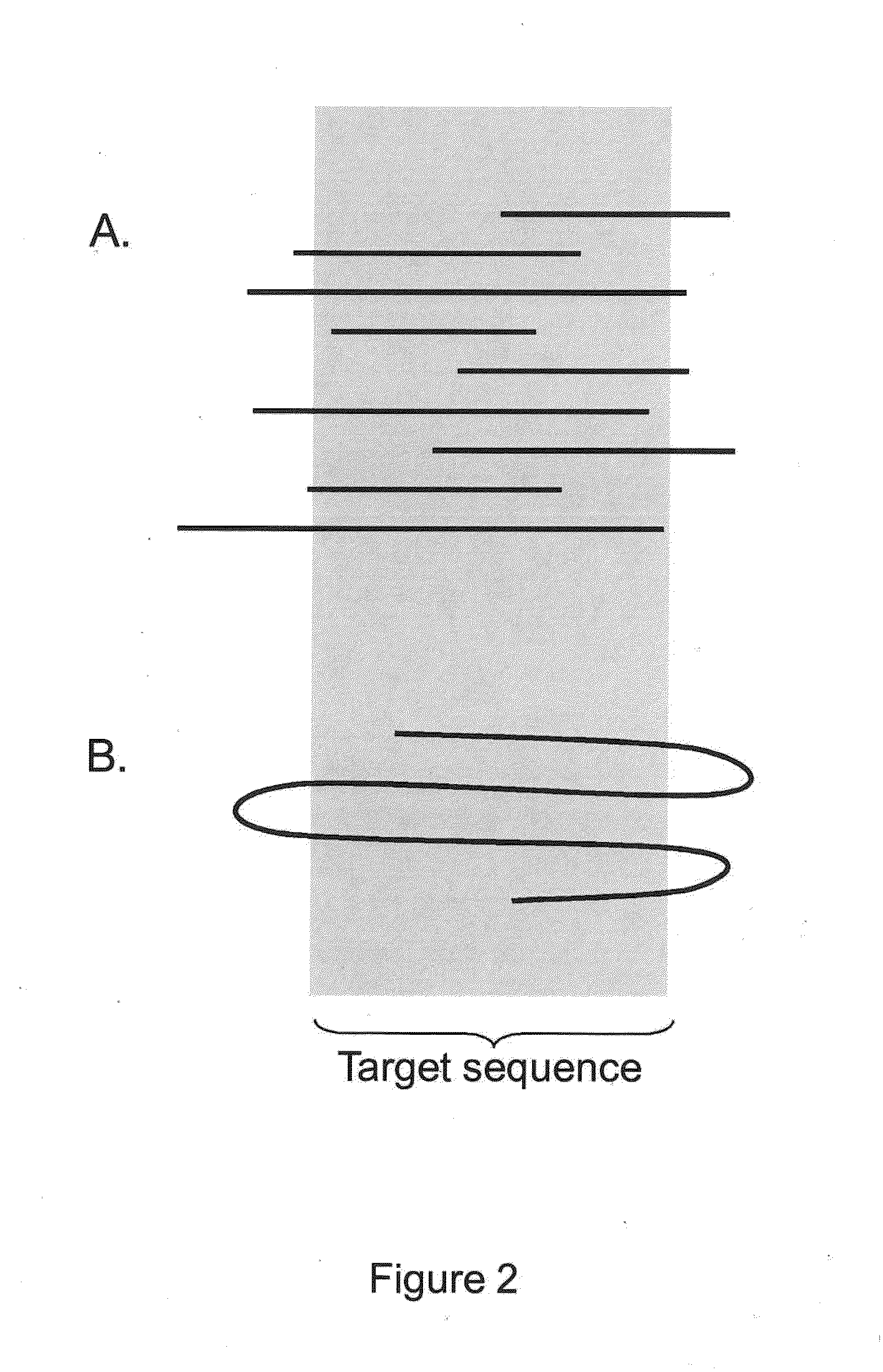
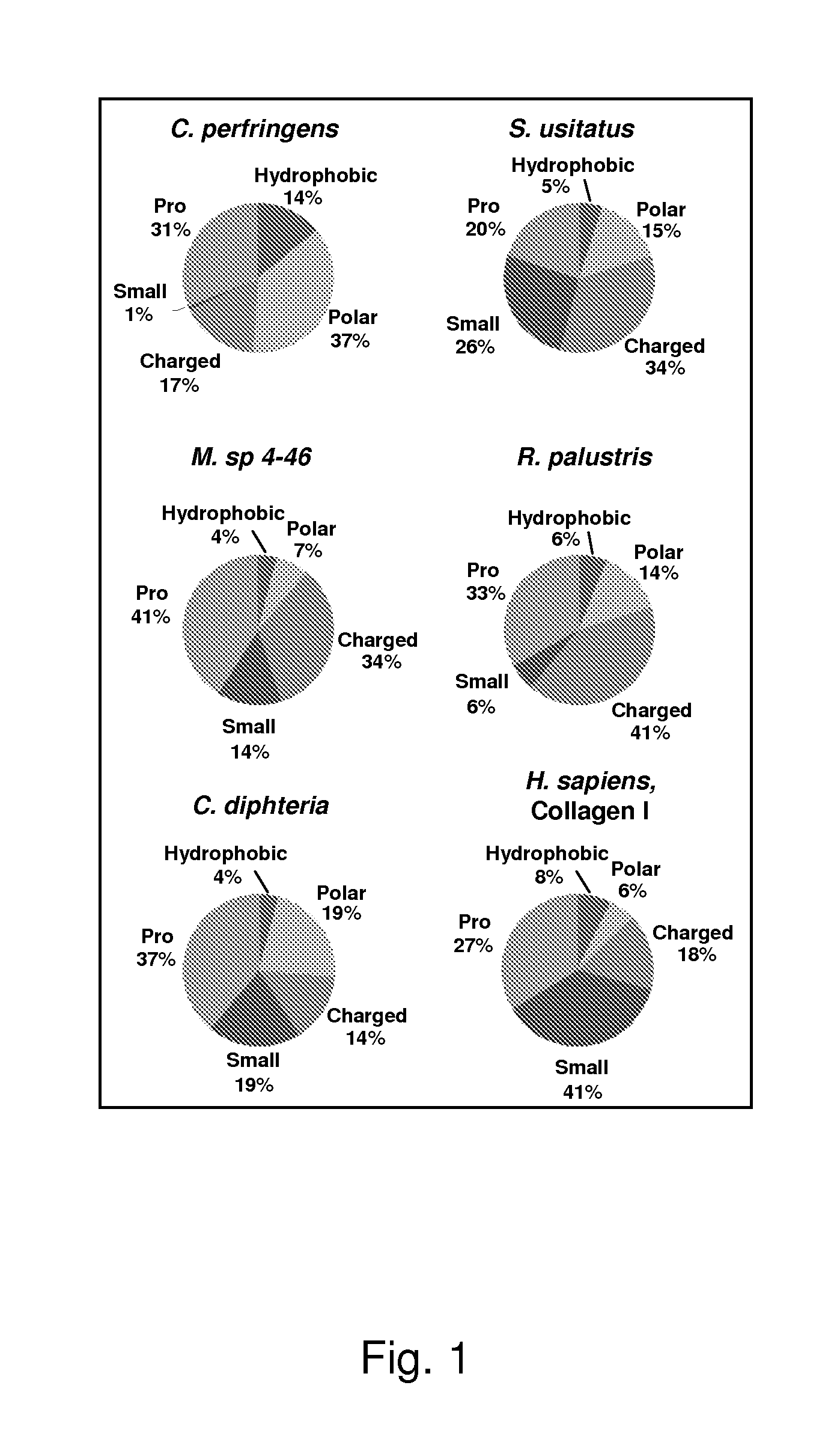
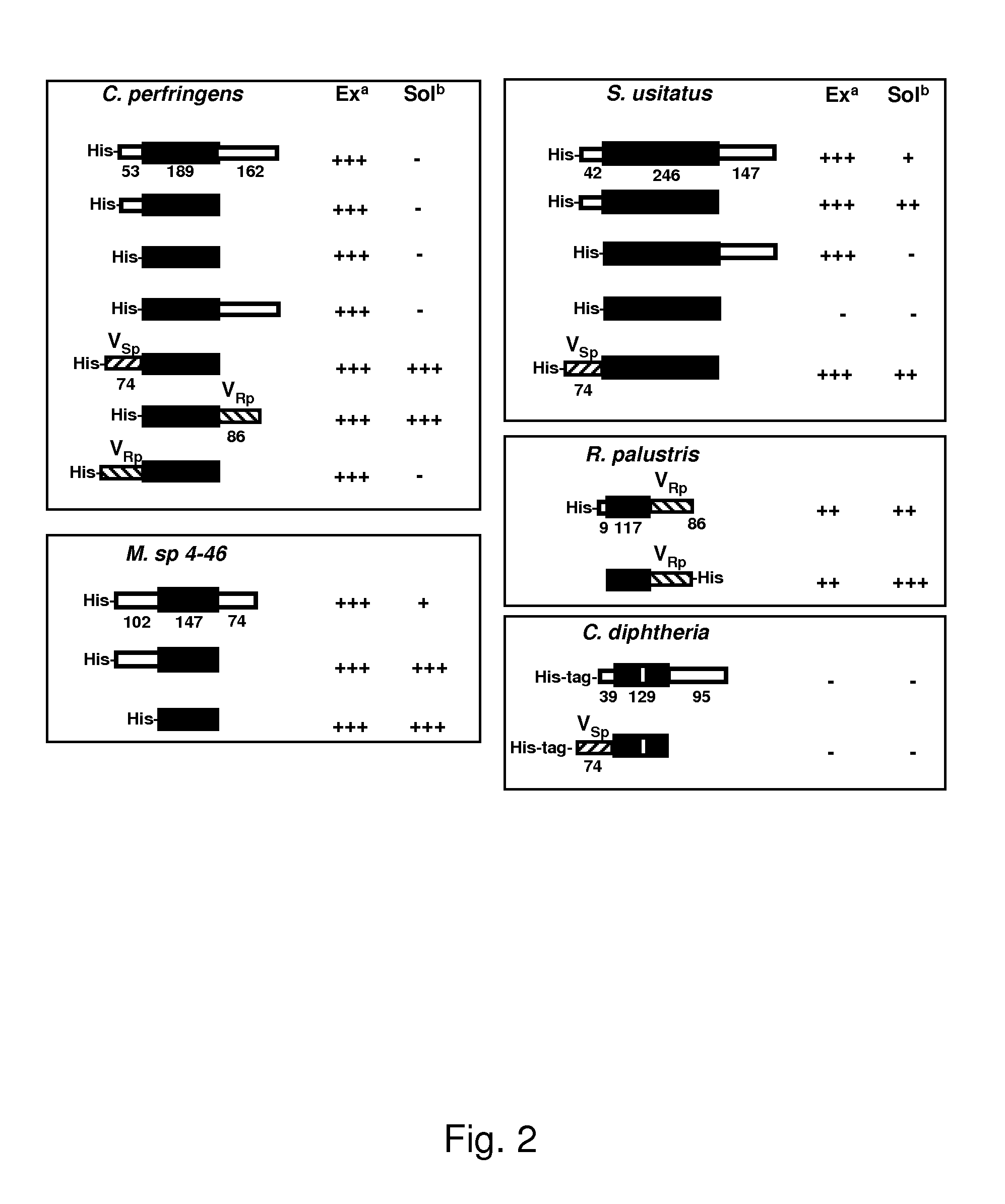
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
203 results about "Repetitive Sequences" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
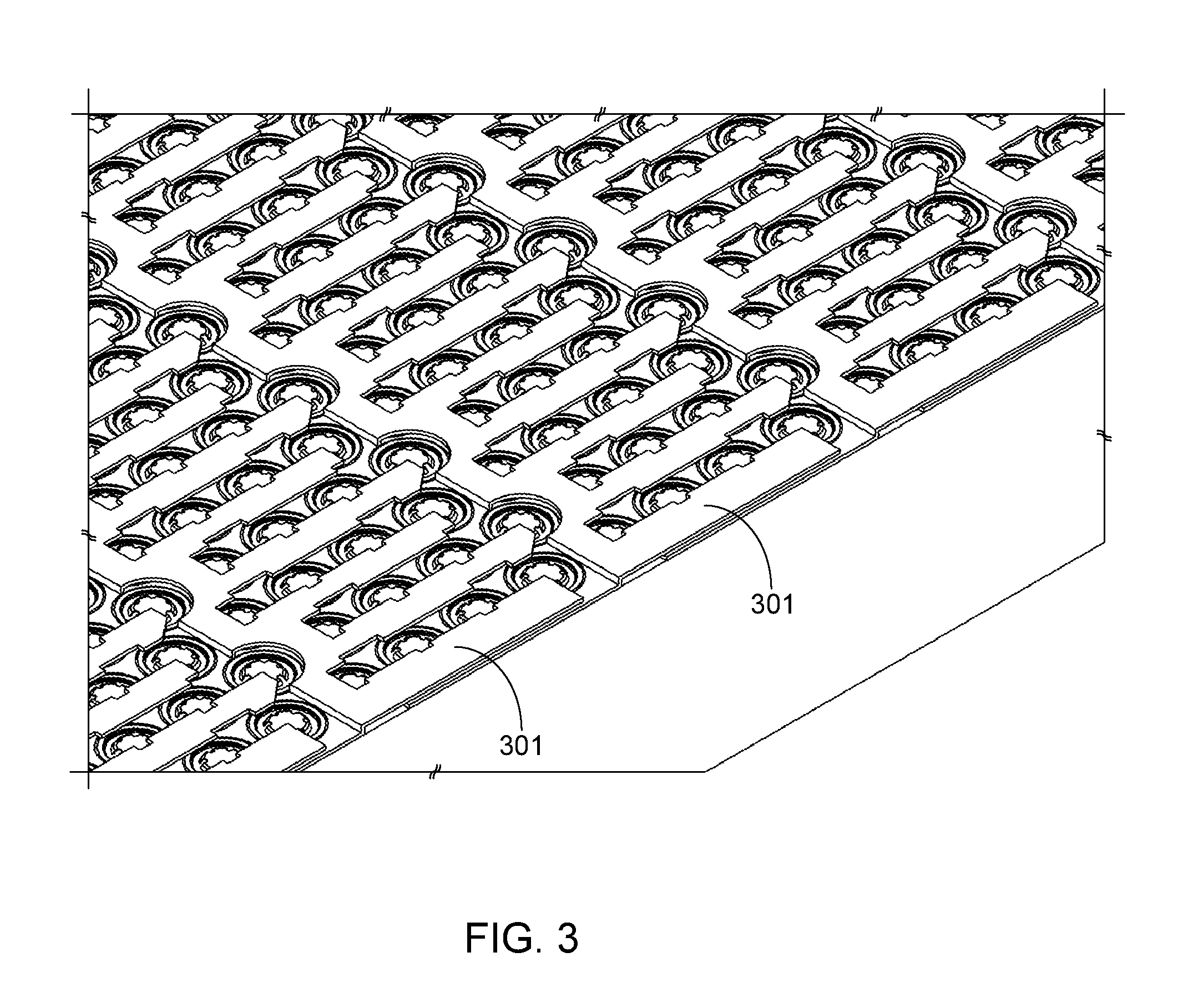
Battery Assembly with Linear Bus Bar Configuration
A battery assembly utilizing a compact and robust bus bar configuration is provided. The batteries within the assembly are divided into groups, where the batteries within each battery group are connected in parallel and the groups are connected in series. The batteries are interconnected using a repetitive sequence of non-overlapping, alternating polarity bus bars. The bus bars, which are integrated into a battery assembly upper tray member, are devoid of contact fingers and positioned such that there is a single bus bar located adjacent to either side of each battery group.
Owner:ATIEVA USA INC
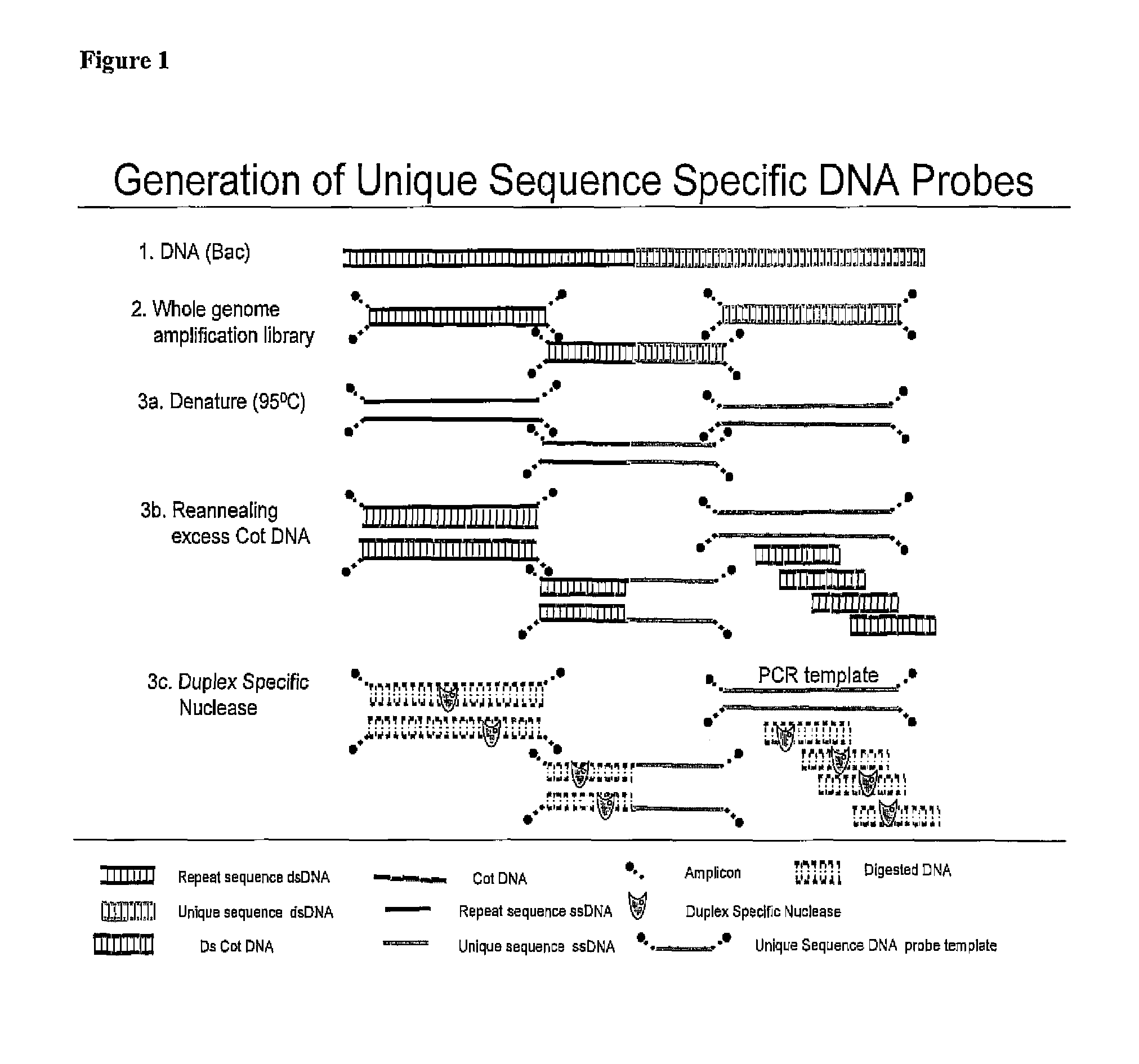
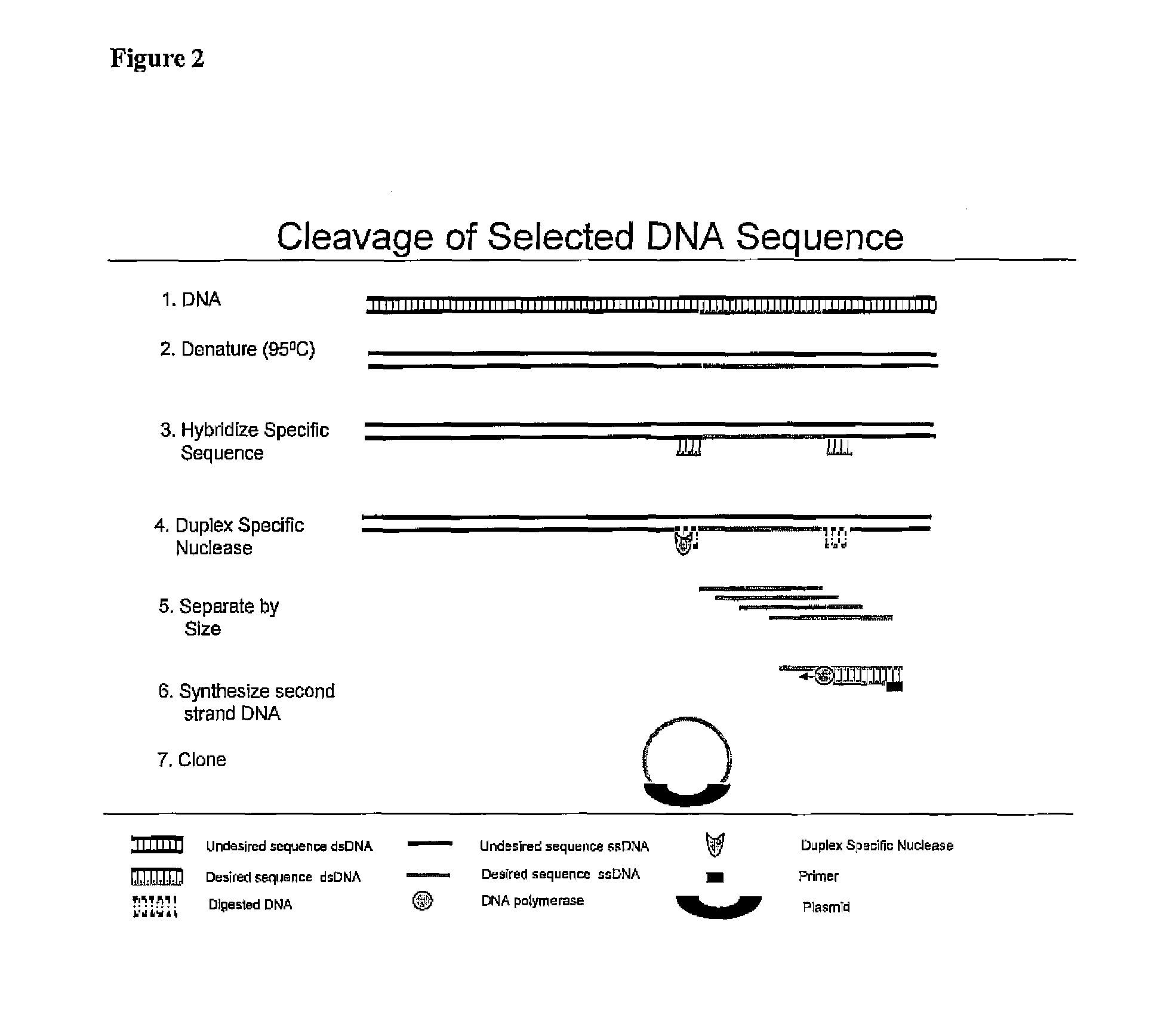
Methods of making repetitive sequences removed probes and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050064450A1Low costSimple protocolSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRepetitive SequencesBioinformatics
The invention discloses novel methods and compositions for the detection of a target nucleic acid molecule in a sample. In particular, the invention provides a method of producing a probe having removed repetitive sequences comprising: (a) providing a source nucleic acid molecule containing repetitive sequences; (b) providing a driver nucleic acid molecule attached to a label and containing repetitive sequences that hybridize with the repetitive sequences of the source nucleic acid molecule; (c) hybridizing the source nucleic acid molecule and the driver nucleic acid molecule in the presence of a molecule that binds the label of step (b) wherein the repetitive sequences of source nucleic acid molecule hybridize with the repetitive sequences of the driver nucleic acid molecule to form a product; (d) subtracting the hybridized repetitive sequences of the product of step (c) by extraction with a protein dissolving solution to remove the hybridized repetitive sequences from the product; and (e) recovering the probe having repetitive sequences removed therefrom.
Owner:LUCAS JOE +1
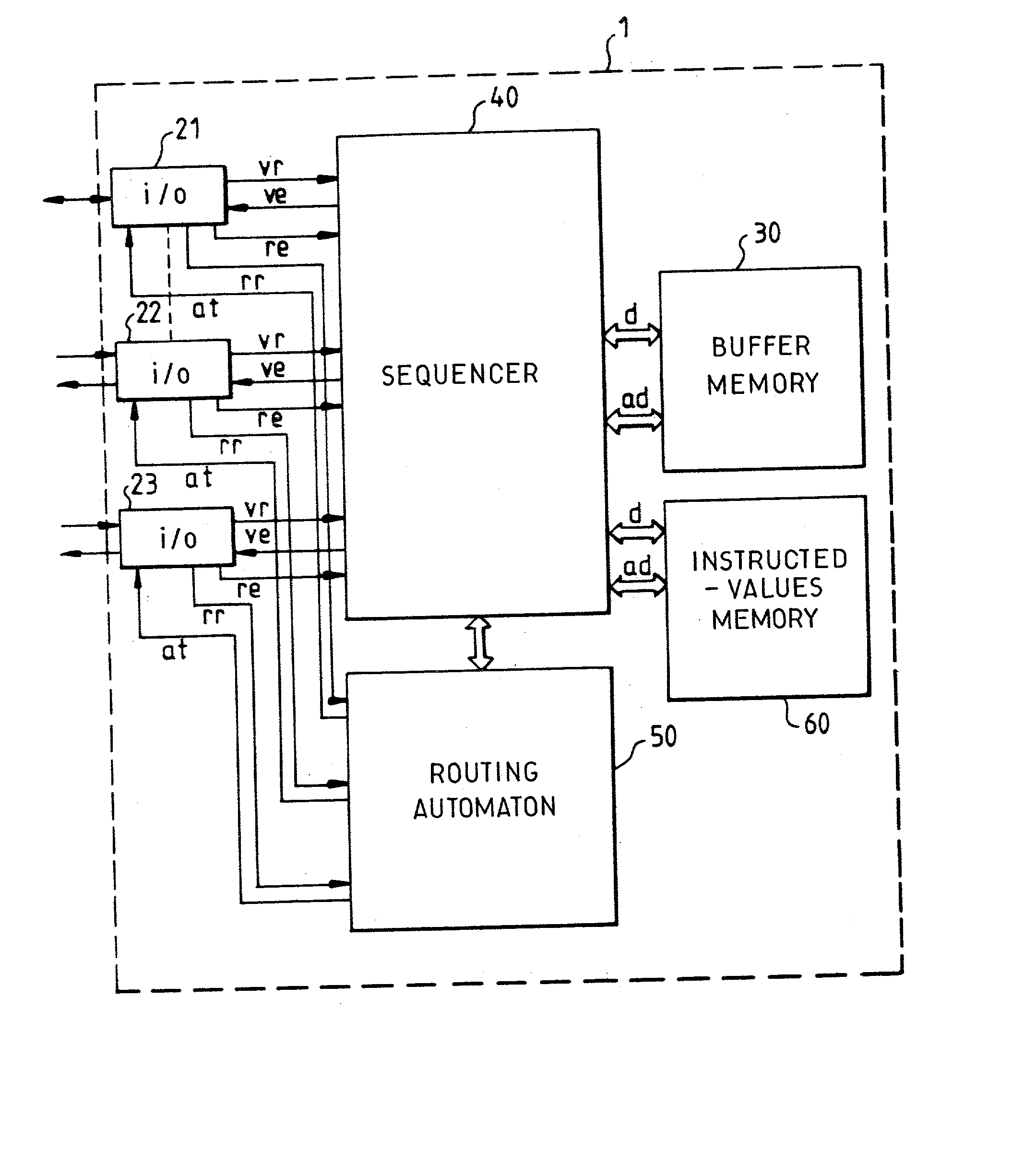
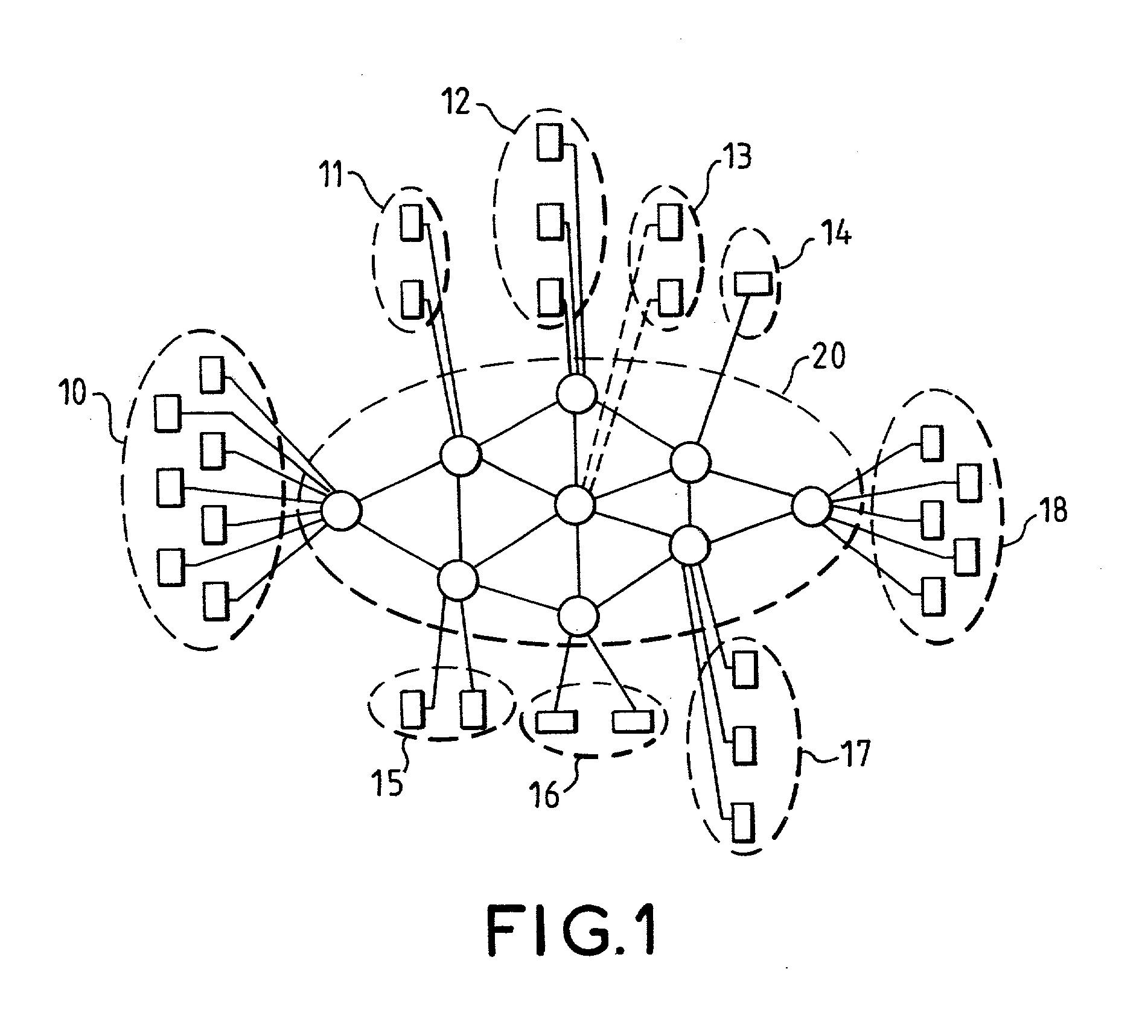
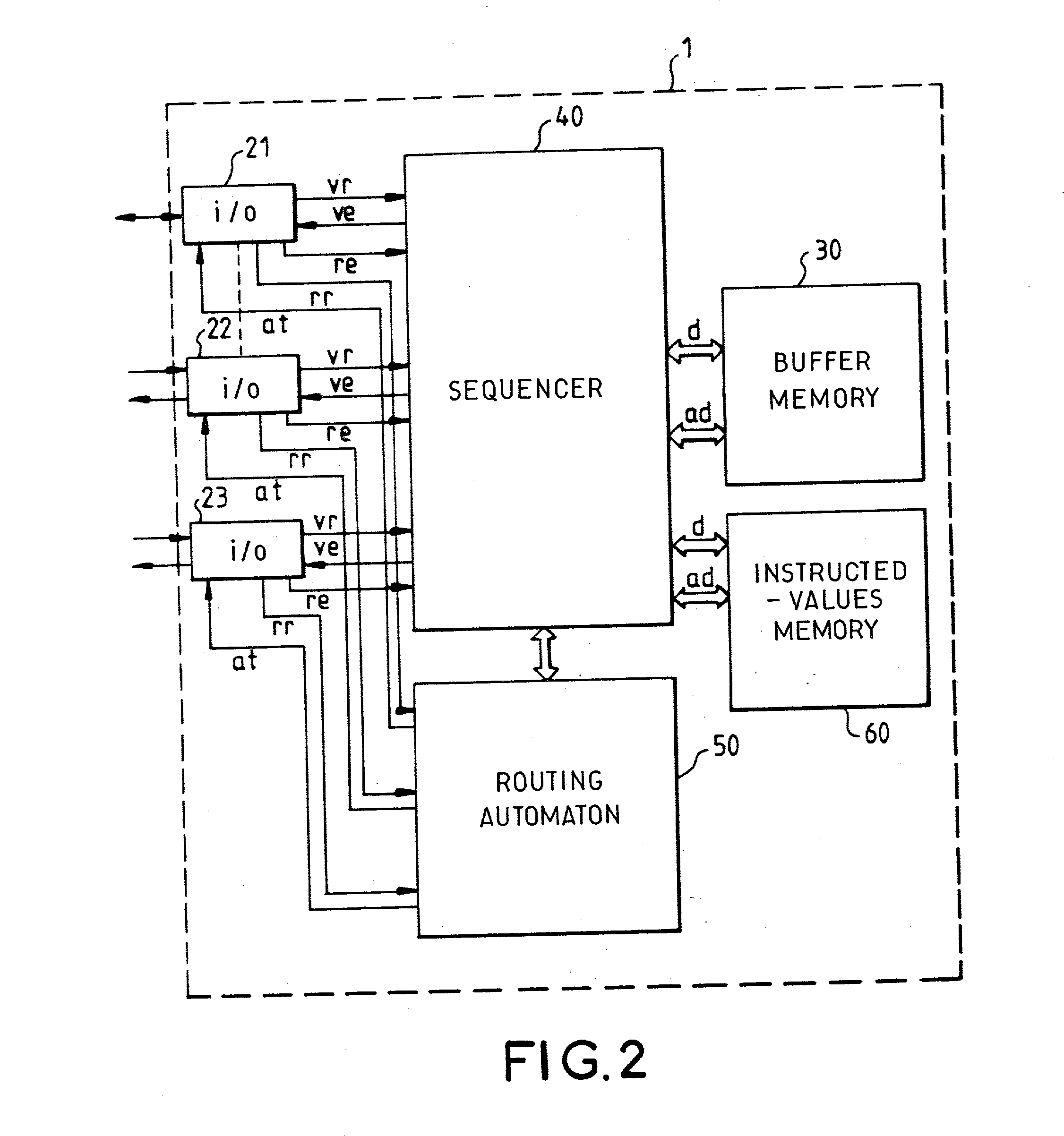
Task management method for a packet switch routing automaton forming part of a secured packet-switching transmission network
ActiveUS20030076780A1Improve network securityReduce wiring timeError preventionTransmission systemsRepetitive SequencesRandom access memory
This method consists in making a routing automaton (50) carry out verifications on the integrity of the packets arriving at the packet switch (1), their periods of stay in the packet switch (1), their matching with the virtual paths that they claim to take as well as the routings proper, within the packet switch (1), of the datagrams that have satisfactorily undergone the verification. The routing automaton (50) is provided with a random access memory of instructed values (60) containing a table of virtual path local descriptors. The processing time of the automaton is divided into a repetitive sequence of time slots individually allocated to the different input ports (21, 22, 23) of the packet switch (1).
Owner:THALES SA
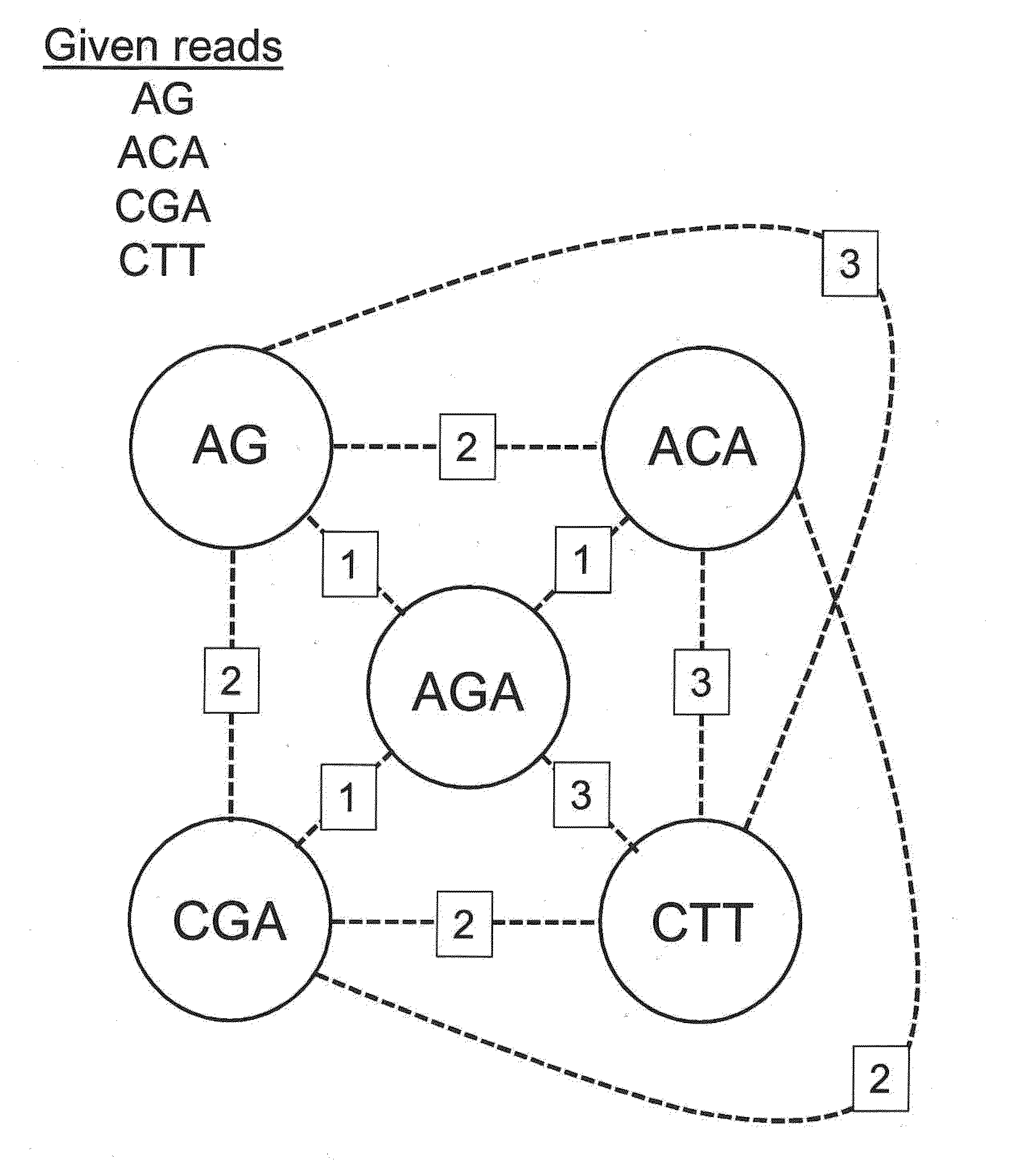
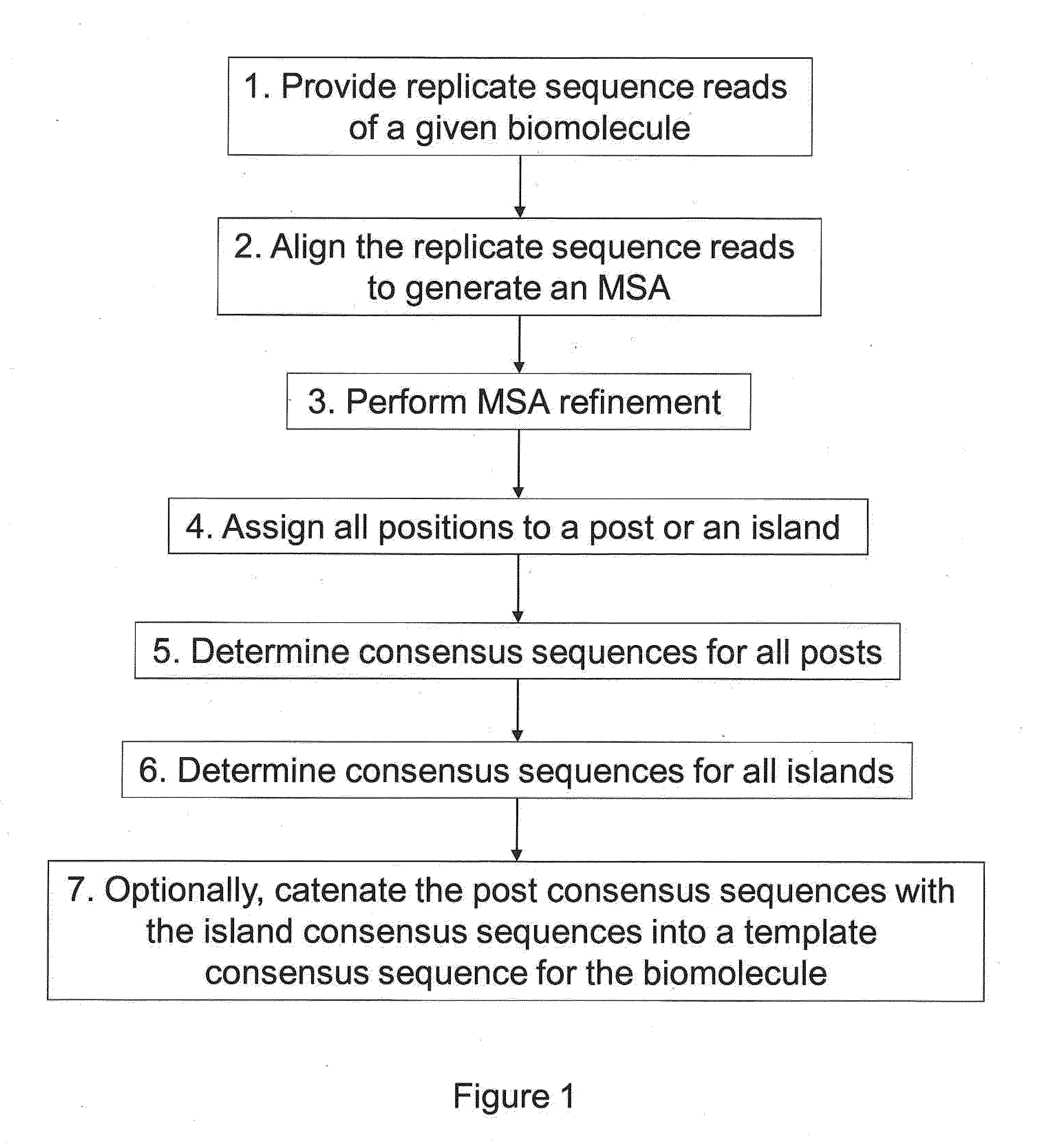
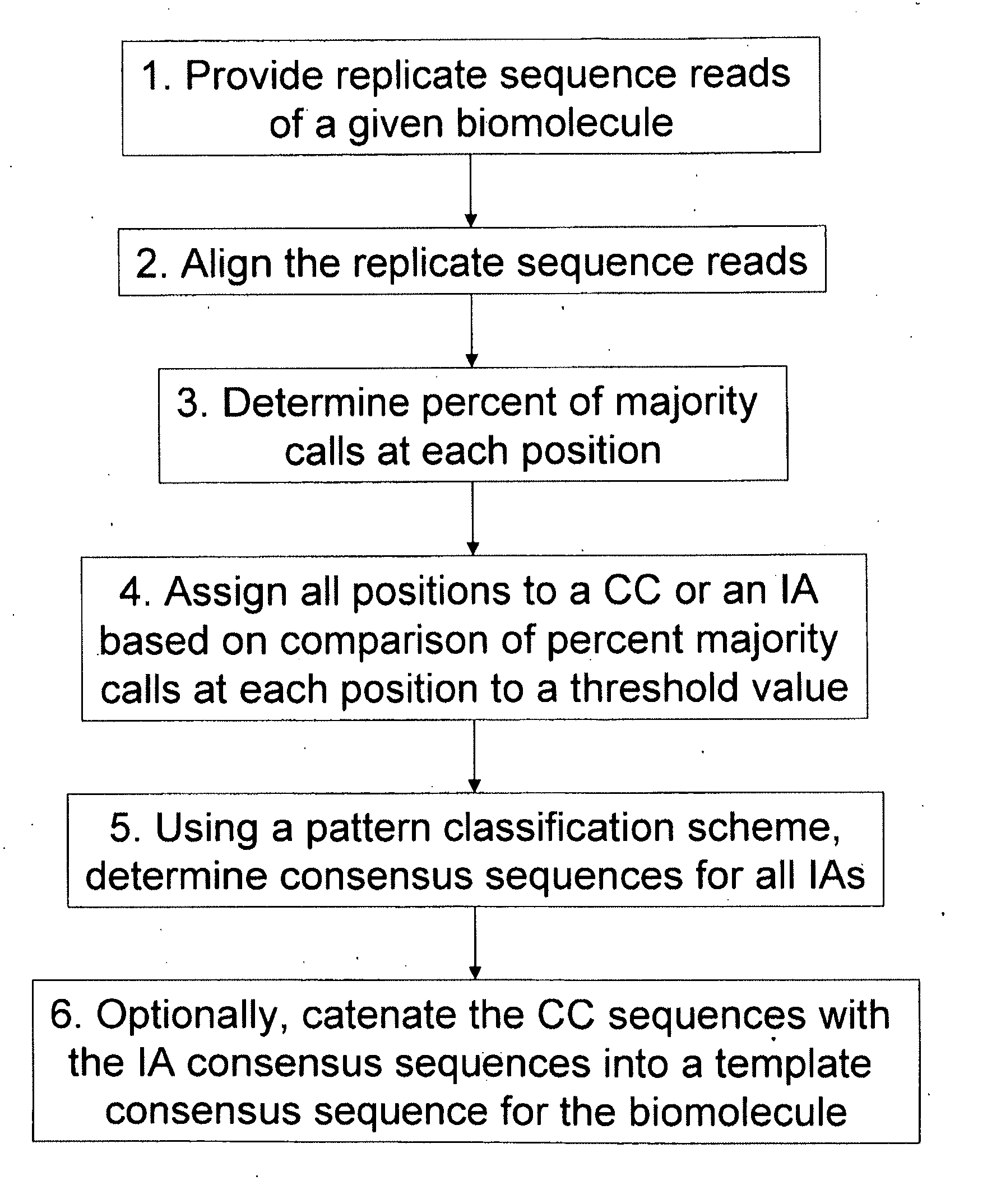
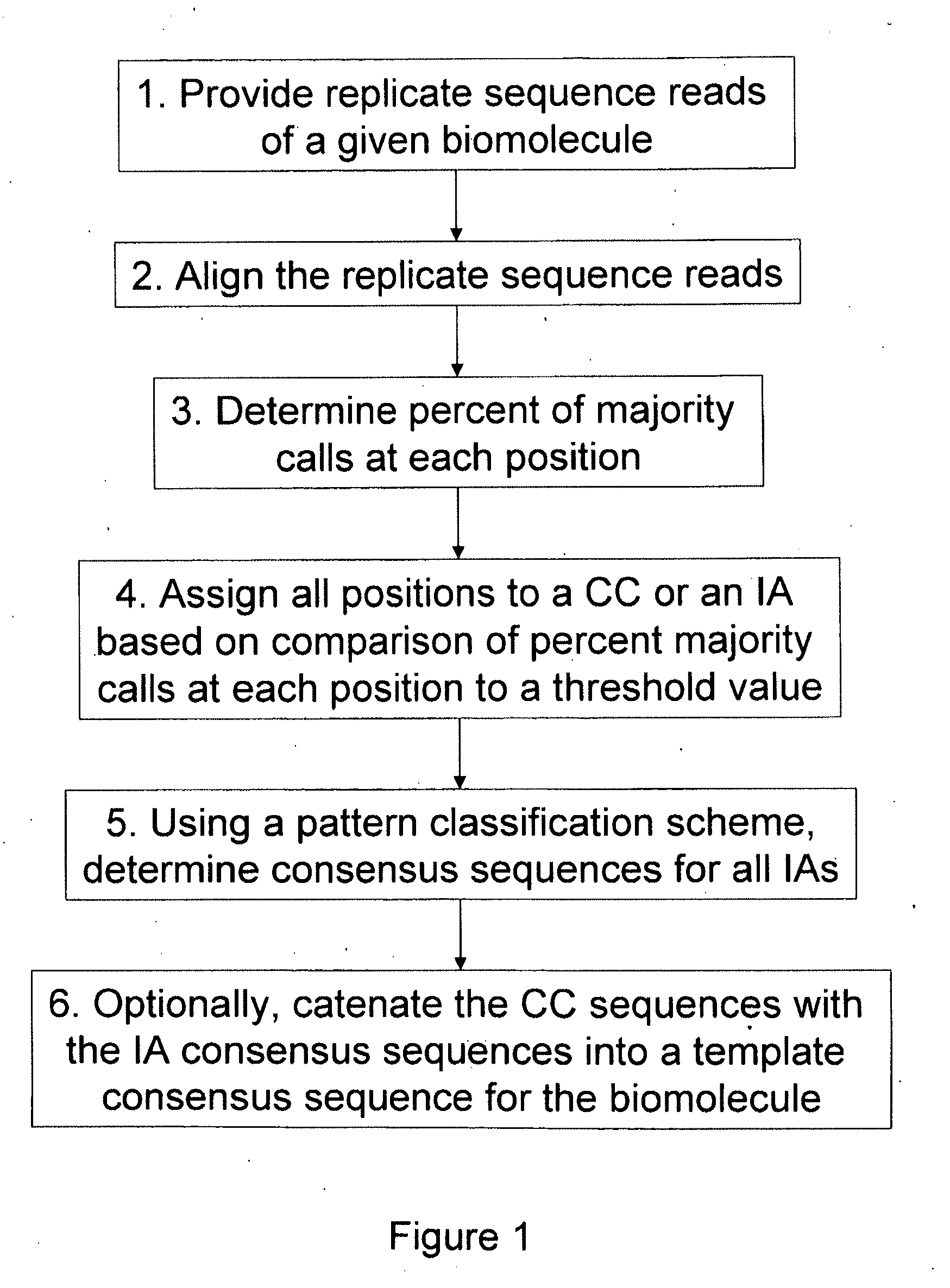
Algorithms for sequence determination
InactiveUS20130138358A1Enhanced authenticationImprove accuracyBiological testingSequence analysisOne passSequence analysis
The present invention is generally directed to powerful and flexible methods and systems for consensus sequence determination from replicate biomolecule sequence data. It is an object of the present invention to improve the accuracy of consensus biomolecule sequence determination from replicate sequence data by providing methods for assimilating replicate sequence into a final consensus sequence more accurately than any one-pass sequence analysis system.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Expression of triple-helical collagen-like products in e.coli
InactiveUS20120116053A1Facilitates protein foldingConnective tissue peptidesCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsRepetitive SequencesCollagenan
Recombinant bacterial triple-helical collagen-like proteins comprising two or more repetitive sequences of Gly-Xaa-Yaa yielding high-stability polymeric constructs without the need for post-translational modifications and which may incorporate one or more functional domains of biological or structural importance. The polymers are capable of high-yield production for a variety of applications
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
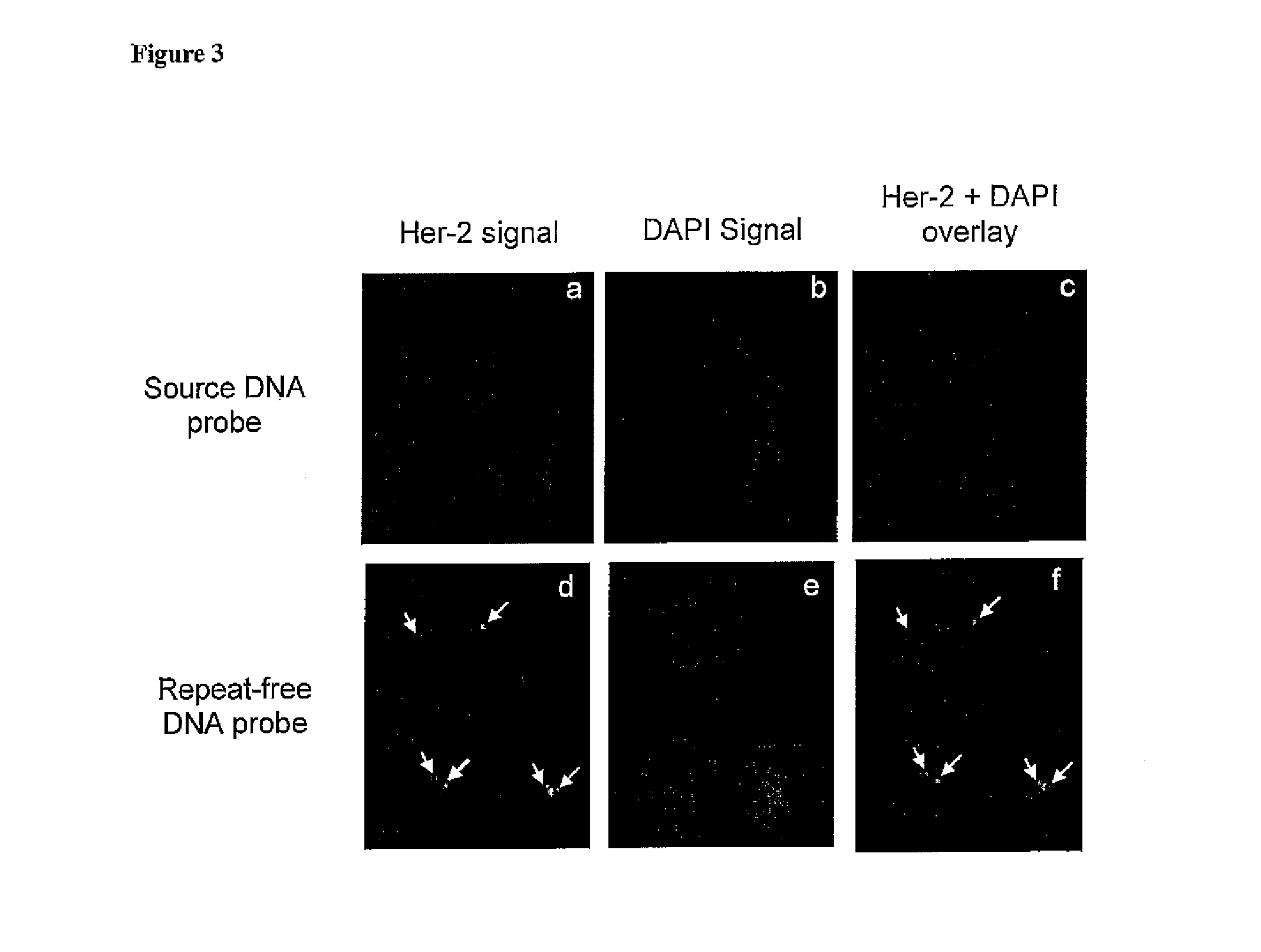
Method of and composite for in situ fluorescent hybridization
InactiveUS6043039AMaximize denaturationReduce concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyHybridization probeSingle strand
A fluorescent in situ hybridization method including the steps of (a) obtaining a chromosome spread of a species; (b) preparing a hybridization composite containing a plurality of chromosomal paints each of the plurality of chromosomal paints being labeled with a different fluorophore-or-combination-of-fluorophores, such that an averaged specific activity of highly repetitive sequences in the hybridization composite substantially equals an averaged specific activity of unique sequences in the hybridization composite; (c) denaturing the hybridization composite and subjecting the hybridization composite to conditions for allowing at least a part of the highly repetitive sequences in the hybridization composite to reanneal while at least a part of the unique sequences in the hybridization composite remaining single stranded; (d) contacting under hybridization conditions the hybridization composite with the chromosome spread; (e) washing away excess of the hybridization composite; and (d) analyzing and presenting images of the now hybridized chromosome spread.
Owner:APPLIED SPECTRAL IMAGING
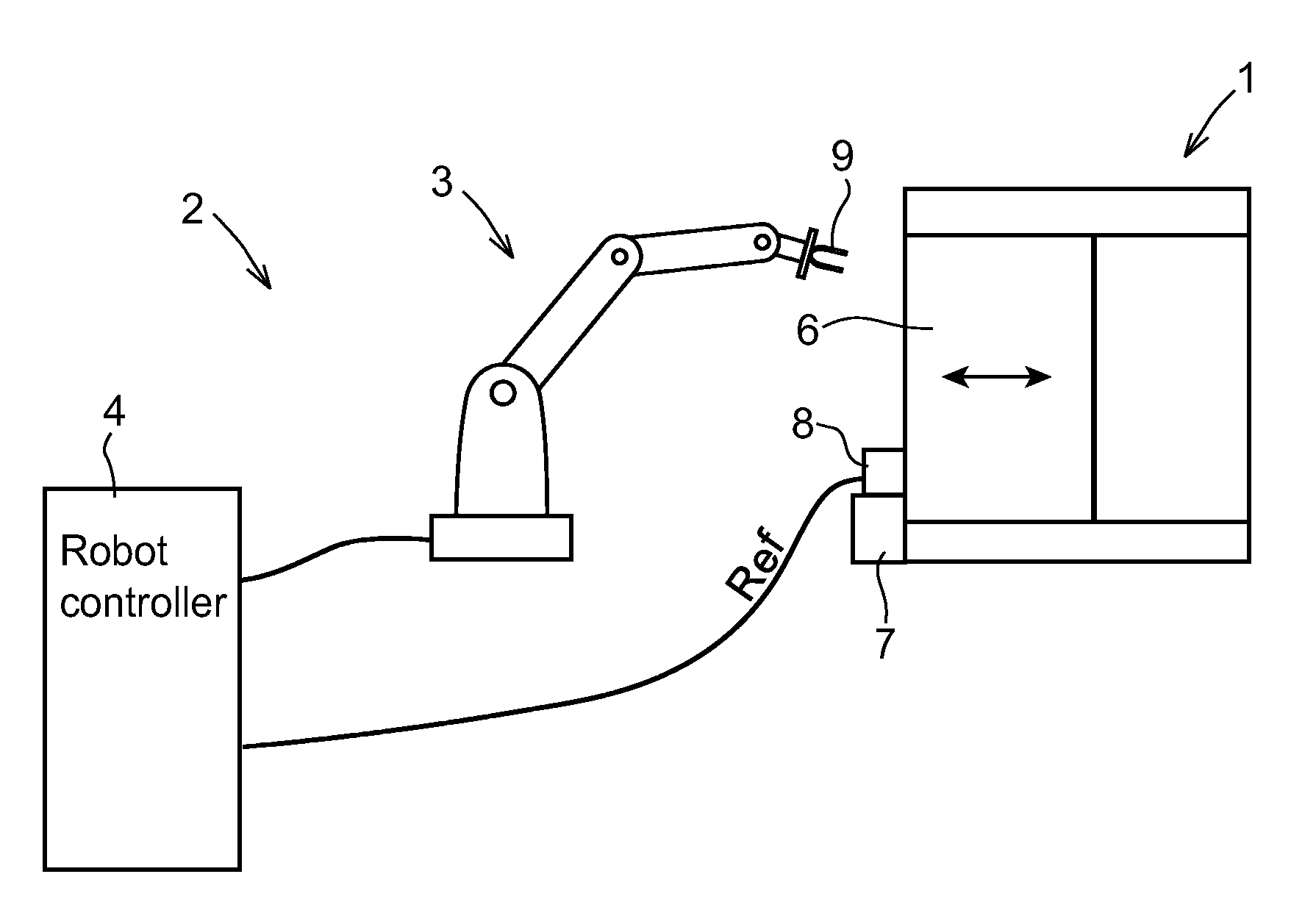
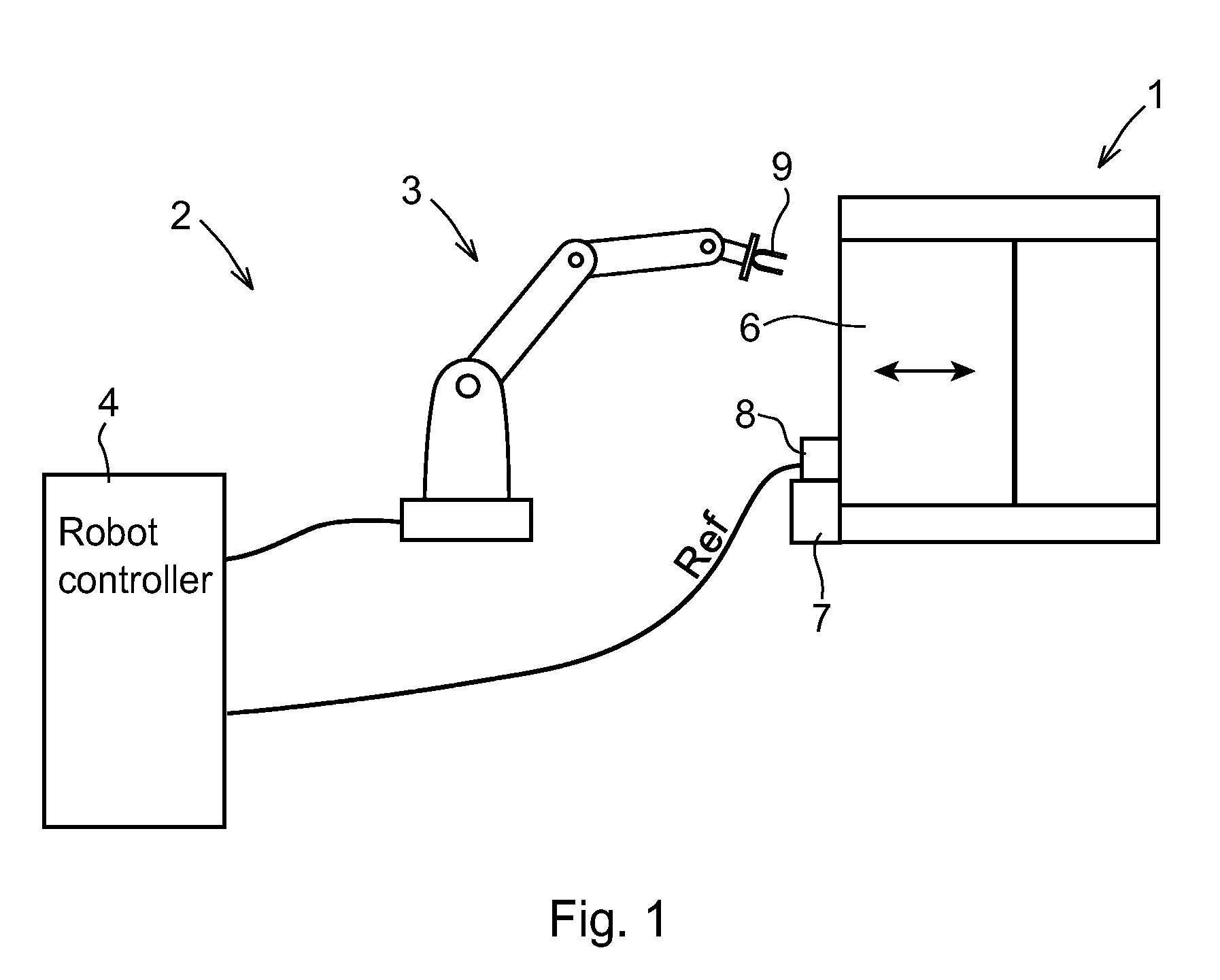
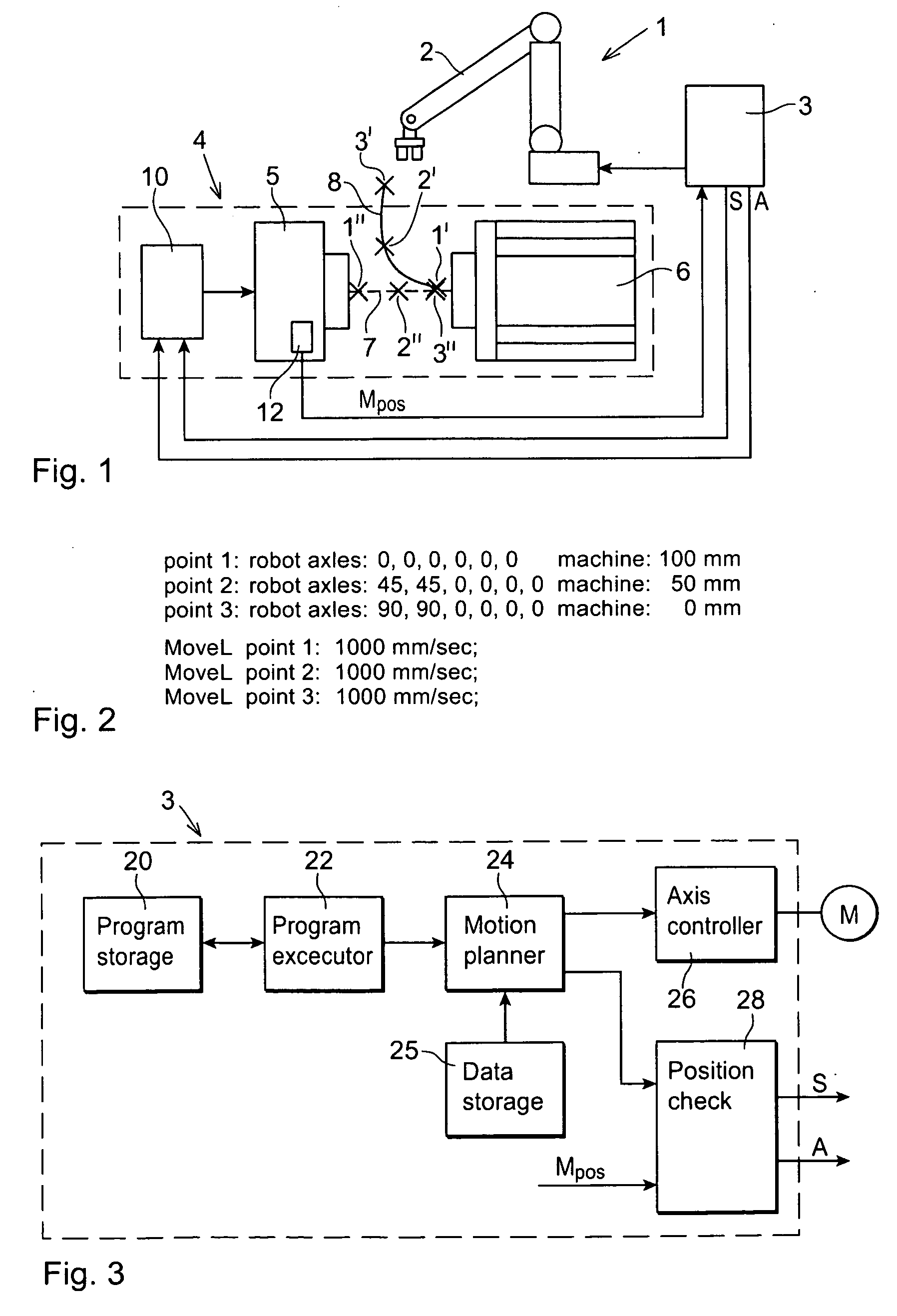
Industrial System Comprising an Industrial Robot and a Machine Receiving Movement Instructions From the Robot Controller
InactiveUS20080275593A1Shorten cycle timeTotal factory controlSpecial data processing applicationsRepetitive SequencesMachine parts
An industrial system including a machine for processing or producing a product. The machine includes at least one actuator providing a repetitive sequence of movements of a machine part, and a regulator controlling the movements of the actuator in response to a reference value. An industrial robot is adapted to tend the machine. The robot includes a drive unit and a robot controller adapted to generate control signals to the drive unit based on a control program including movement instructions for the robot. The robot controller is adapted to generate the reference value to the regulator based on a control program including movement instructions for the machine part. The regulator may also be an integrated part of the robot controller.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Detection of chromosoal abnormalities associated with breast cancer
InactiveUS7094534B2Avoid saturationHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingComparative genomic hybridization
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Human X-chromosome composite amplification system composed of 20 short serially-connected repetitive sequences and applications thereof
ActiveCN105177125AHigh polymorphic informationHigh individual recognition rateMicrobiological testing/measurementRepetitive SequencesX chromosome
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and relates to a human X-chromosome composite amplification system composed of 20 short serially-connected repetitive sequences and applications thereof. The composite amplification system comprises 20 pairs of primers and is capable of amplifying 19 STR sites: DXS6795, DXS6803, DXS6807, DXS9907, DXS7423, GATA172D05, DXS101, DXS9902, DXS7133, DXS9810, GATA31E08, DXS6800, DXS981, DXS10162, DXS6809, GATA165B12, DXS10079, DXS10135, and HPRTB, and one sex recognition site: Amelogenin. Five-color fluorescence labeling is adopted by the system, the size of amplification products is in a range of 85 to 450 bp, the operation is simple, and the individual recognition performance is high. The sites provided by the provided composite amplification system are highly compatible to the conventional commonly-used X-STR kits, moreover, sites with high polymorphism information are provided, and the provided composite amplification system can be applied to paternity identification related with X-chromosome, individual recognition, and auxiliary detection of X-chromosome sex-linked hereditary diseases.
Owner:SUZHOU MICROREAD GENETICS
Electromagnetic fields for systemic effect in therapy
A new mechanism of therapeutic action of electromagnetic fields, based upon systemic effect, applies selected EMF signals to cause efficacious therapeutic effects at sites distant from the point of application. The method of generating specific EMF waveshape and application of this exogeneous signal for therapeutic purposes allows the benefit to be achieved via the systemic effect. The EMF signals take the form of a repetitive sequence of semi sinewaves, resulting in a pulsating waveform occurring at a frequency in the range of from about 50 to about 300 pulses per second. Bridge rectification is applied to a sinusoidal signal, and a resultant therapy signal takes the form of a repetitive sequence of semi sinewaves of up to about 300 pps with a periodically recurring DC component. The shape of alternating pulses in the resultant therapy signal is modified under computer control to achieve therapeutic effects. Flux densities in the range of several hundred Gauss up to several thousand Gauss are generated. The treatment with the resultant therapy signal may be applied to an arm or leg of a therapy recipient for a sufficient length of time to cause the recipient's entire blood volume to be exposed to the therapeutic field such that this can initiate effects in cells, tissues, and organs distant from the point of application
Owner:ELECTROMAGNETIC RESOURCES
FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) probe, kit and detection method for detecting BCR/ABL fusion gene free from repetitive sequence
InactiveCN103409505AHigh detection sensitivityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRepetitive SequencesIn situ hybridisation
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and discloses a FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) probe, a kit and a detection method for detecting BCR / ABL fusion gene free from repetitive sequence. A BCR gene and ABL gene are used as templates to perform polymerase chain reaction on non-repetitive sequence in the BCR gene and ABL gene, the amplification product is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragments with 350-800 different base-pairs, the repetitive sequences in the BCR gene and ABL gene are eliminated so as to form the product free from repetitive sequence; after the product is in fluorescence labeling, the BCR gene and ABL gene free from repetitive FISH are obtained for the BCR gene and ABL gene FISH detection. The BCR / ABL fusion gene FISH probe obtained by the invention can be used for eliminating the repetitive sequence, the non-specific background signal of the FISH probe can be obviously reduced, and the specificity of the FISH probe is improved.
Owner:WUHAN HEALTHCHART BIOLOGICAL TECH
Polypeptide, and production method and application thereof
ActiveCN109593126AHigh yieldHigh purityConnective tissue peptidesBacteriaRepetitive SequencesAqueous solution
The invention relates to a polypeptide, and a production method and the application thereof, belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and provides the polypeptide. The polypeptide comprises n repetitions of the sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1; the n is an integer which is greater than or equal 1; when the n is the integer which is greater than or equal to 2; various repetitive sequences are directly connected with each other. The polypeptide provided by the invention has an excellent adhesion effect, has high stability in an aqueous solution, and can remove endotoxin more easily.
Owner:SHANXI JINBO BIO PHARMA CO LTD
Treatment of genetic disorders associated with DNA repeat instability
ActiveUS20160053254A1Lower Level RequirementsAltered RNA processing and/or splicingNervous disorderGenetic material ingredientsInstabilityGene transcript
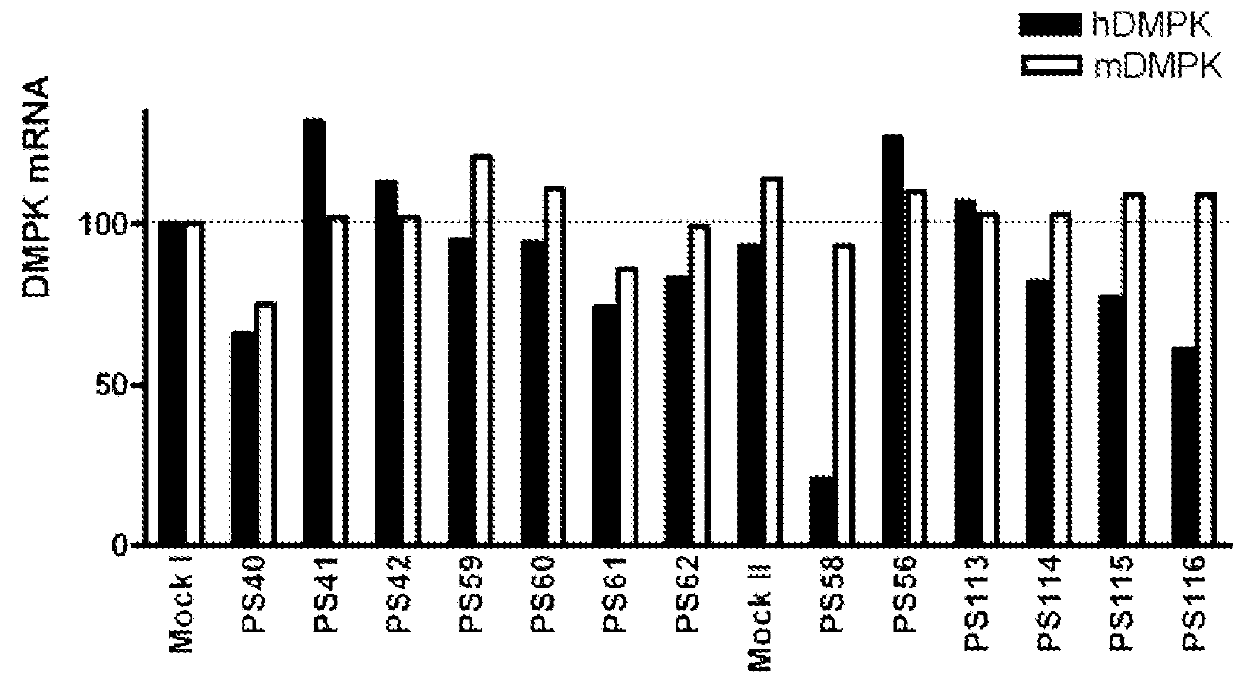
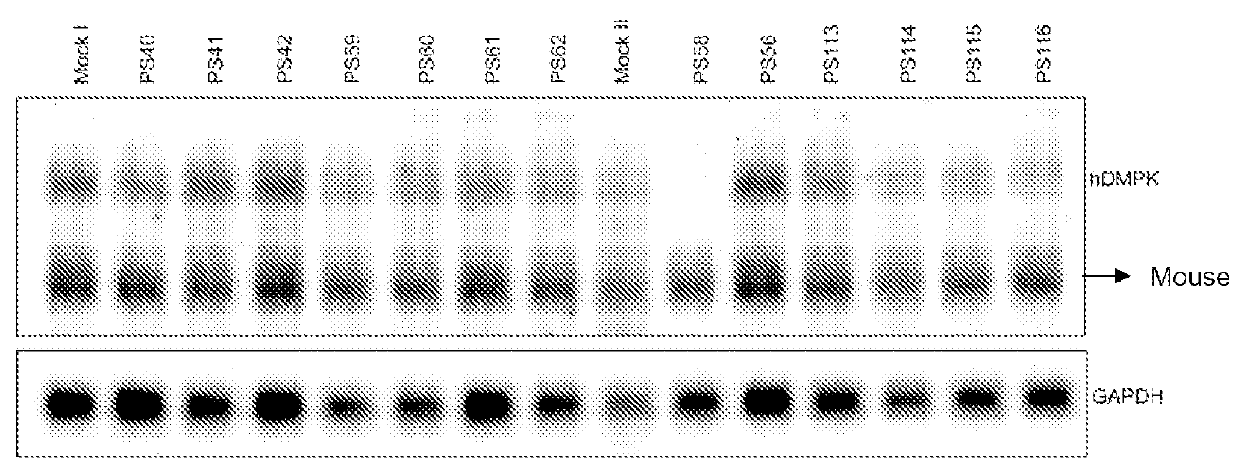
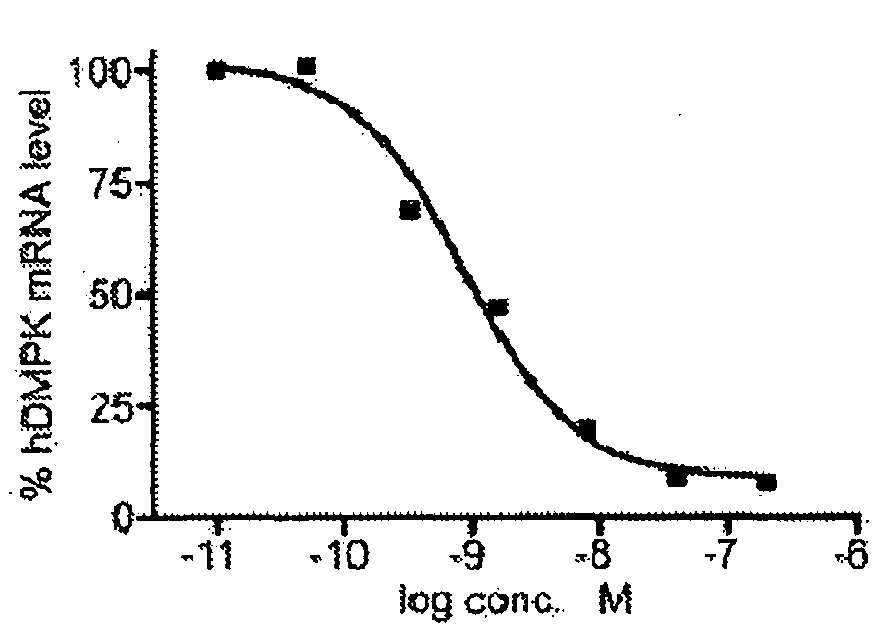
The current invention provides for methods and medicaments that apply oligonucleotide molecules complementary only to a repetitive sequence in a human gene transcript, for the manufacture of a medicament for the diagnosis, treatment or prevention of a cis-element repeat instability associated genetic disorders in humans. The invention hence provides a method of treatment for cis-element repeat instability associated genetic disorders. The invention also pertains to modified oligonucleotides which can be applied in method of the invention to prevent the accumulation and / or translation of repeat expanded transcripts in cells.
Owner:VICO THERAPEUTICS BV
System for the detection and enumeration of suspect target cells in a mixed cell population
ActiveUS9127302B2Strong specificityConfirm the identity of suspect CTCBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMixed cellFluorescence
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
Algorithms for sequence determination
InactiveUS20130217006A1Enhanced authenticationImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSequence analysisRepetitive Sequences
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Spider dragline silk protein optimized expression method
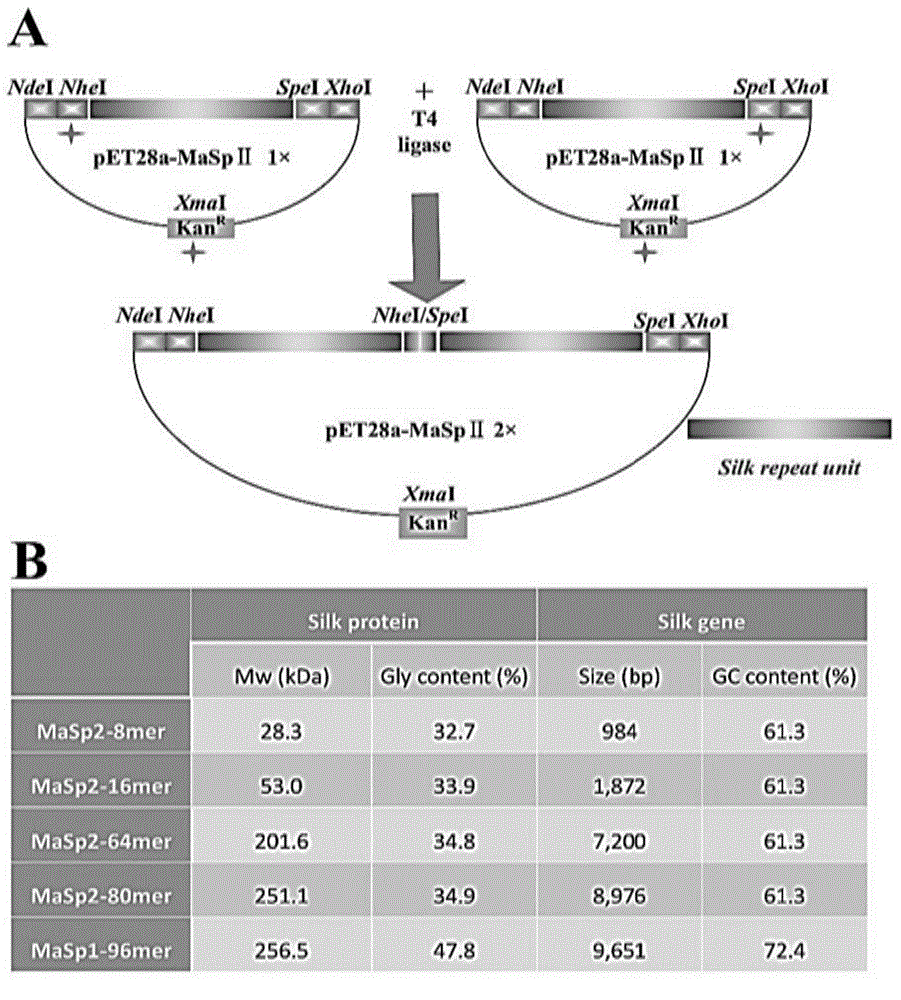
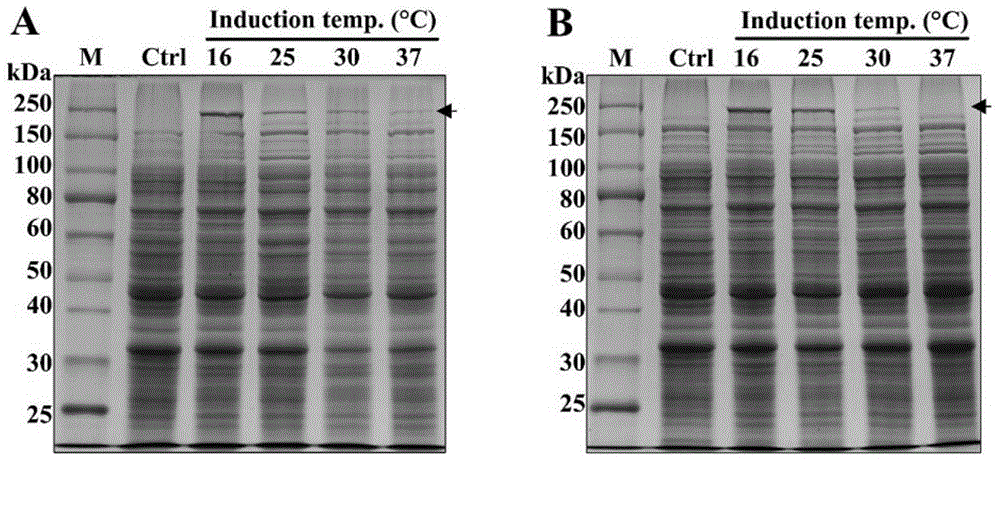
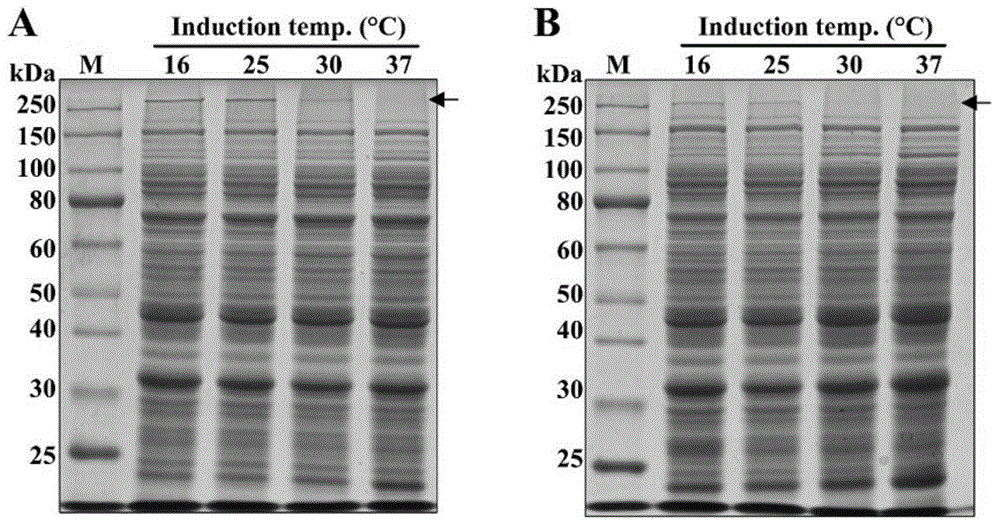
InactiveCN104946710ALower culture temperatureOvercome the defect of low expressionFermentationBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention relates to a spider dragline silk protein optimized expression method, belonging to the field of bioengineering. The method comprises the following steps: constructing high-molecular-weight recombinant spider dragline silk protein grains in Escherichia coli, and carrying out expression production, wherein the protein yield is enhanced by lowering the culture temperature in the protein expression production process; and by using the combined strategy of high-density fermentation and culture temperature lowering on the fermentation tank level, implementing the double enhancement of the cell quantity and expression level. The method can effectively overcome the defects of low expression level of the highly-repetitive recombinant spider dragline silk protein in the production fermentation process, and provides favorable reference meanings for fermentation production study and application of spider silk proteins and similar highly-repetitive sequence proteins.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
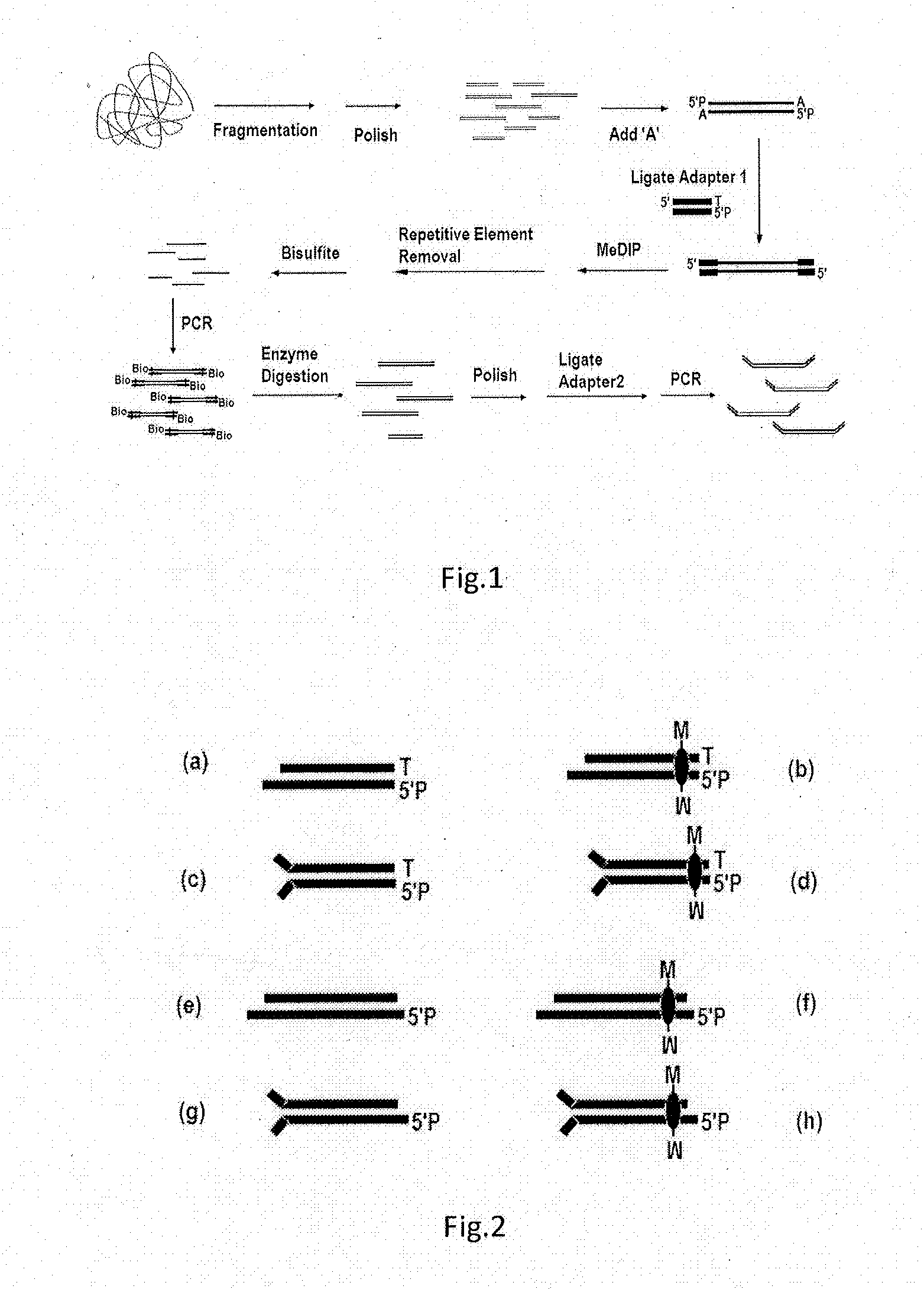
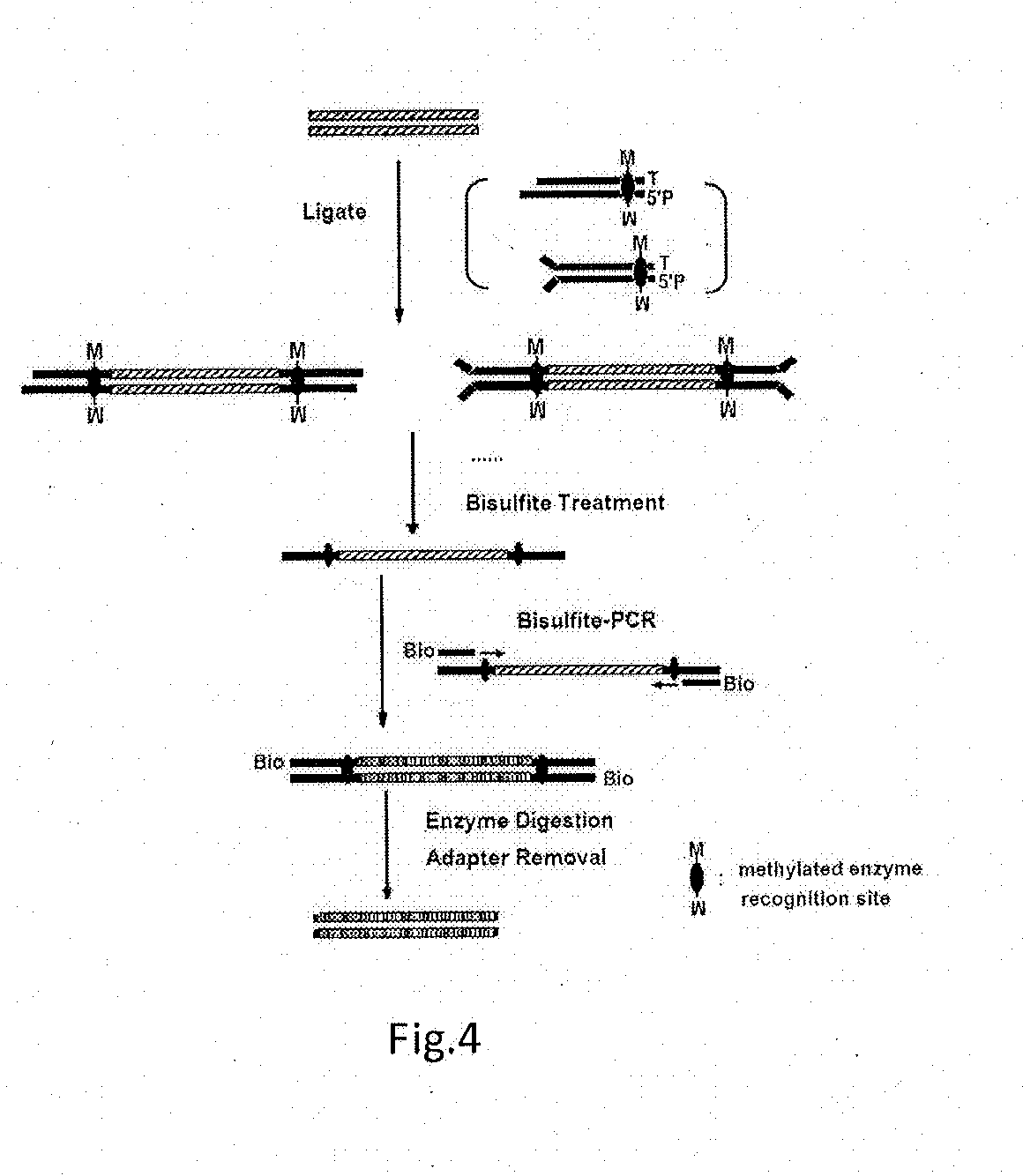
High-throughput sequencing method for methylated DNA and use thereof
ActiveUS20130244885A1Improve digestion efficiencyDigestion efficiencyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementRepetitive SequencesMethylated DNA immunoprecipitation
The present invention provides a high-throughput sequencing method for methylated DNA, and use thereof. Particularly, the present invention provides a high-throughput sequencing method for methylated DNA, which combines methylated DNA immunoprecipitation, removal of repetitive sequences, and bisulfite treatment. The site of sequencing library will be decreased, and the cost will be reduced by using the method disclosed in the present invention.
Owner:INST OF PSYCHOLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Producing repetitive coatings on a flexible substrate
ActiveUS20050274319A1Efficient productionEfficient depositionVacuum evaporation coatingSolid-state devicesRepetitive SequencesMechanical engineering
Apparatus for use in making a device by forming repetitive sequences of coatings on a flexible substrate including defining a path for the flexible substrate; the flexible substrate being disposed about at least a portion of the path; a first deposition source for depositing material located around the path periphery and in cooperative relationship with the surface of the disposed flexible substrate; actuable means effective when actuated for moving the flexible substrate around at least more than one revolution around the path; and actuating the actuable means and the first deposition source so that at least two separate material coatings are provided on the substrate by the deposition source.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Methods and means for treating DNA repeat instability associated genetic disorders
InactiveUS20110184050A1Lower Level RequirementsReduced stabilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderRepetitive SequencesNucleotide
The current invention provides for methods and medicaments that apply an oligonucleotide comprising aninosine and / or an uracile and / or a nucleotide containing a base able to form a wobble base pair, said oligonucleotide being preferably RNAse H substantially independent and being complementary only to a repetitive sequence in a human gene transcript, for the manufacture of a medicament for the diagnosis, treatment or prevention of a cis-element repeat instability associated genetic disorders in humans. The invention hence provides a method of treatment for cis-element repeat instability associated genetic disorders. The invention also pertains to a modified oligonucleotide which can be applied in a method of the invention to prevent the accumulation and / or translation of repeat expanded transcripts in cells.
Owner:PROSENSA HLDG BV +1
Industrial Robot Tending A Machine And A Method For Controlling An Industrial Robot Tending A Machine
InactiveUS20090216375A1Easy programmingAttractive solutionComputer controlSimulator controlRepetitive SequencesMachine parts
An industrial robot for tending a machine includes a machine part providing a repetitive sequence of movements. The robot includes a robot controller having a program storage for storing a path of programmed positions for the robot and a path of programmed positions for the machine part, and a motion planner configured to plan the motion of the robot and the motion of the machine part based on the programmed positions for the robot and the machine part such that the motion of the robot and the motion of the machine part are coordinated with each other.
Owner:ABB TECH AG
Oligonucleotide probe and acquisition method thereof
ActiveCN106566876ASimple designLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationRepetitive SequencesIn situ hybridisation
The invention relates to a method for acquisition of an oligonucleotide probe. The method comprises the following steps: downloading genomic sequence of crop species from a public database, filtering and finding out tandem repeat sequences, screening preliminarily found repetitive sequences, comparing residual tandem repeat sequence and known probe sequence, removing already used probe sequence, comparing residual screened tandem repeat sequences, carrying out probe design and synthesizing and verifying the designed probe sequence so as to obtain effective oligonucleotide sequence. According to the invention, cost is low and efficiency is high. The probe can be used for non-degenerated fluorescence in situ hybridization (ND-FISH) analysis of crop chromosome, determination of distribution of tandem repeat sequences represented by the probe on chromosome, understanding of the structure characteristics of chromosome and establishment of specific landmark of chromosome. Thus, specific chromosome or chromosome region of crops is identified, and the developed new oligonucleotide probe has specificity of chromosome or chromosome region.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
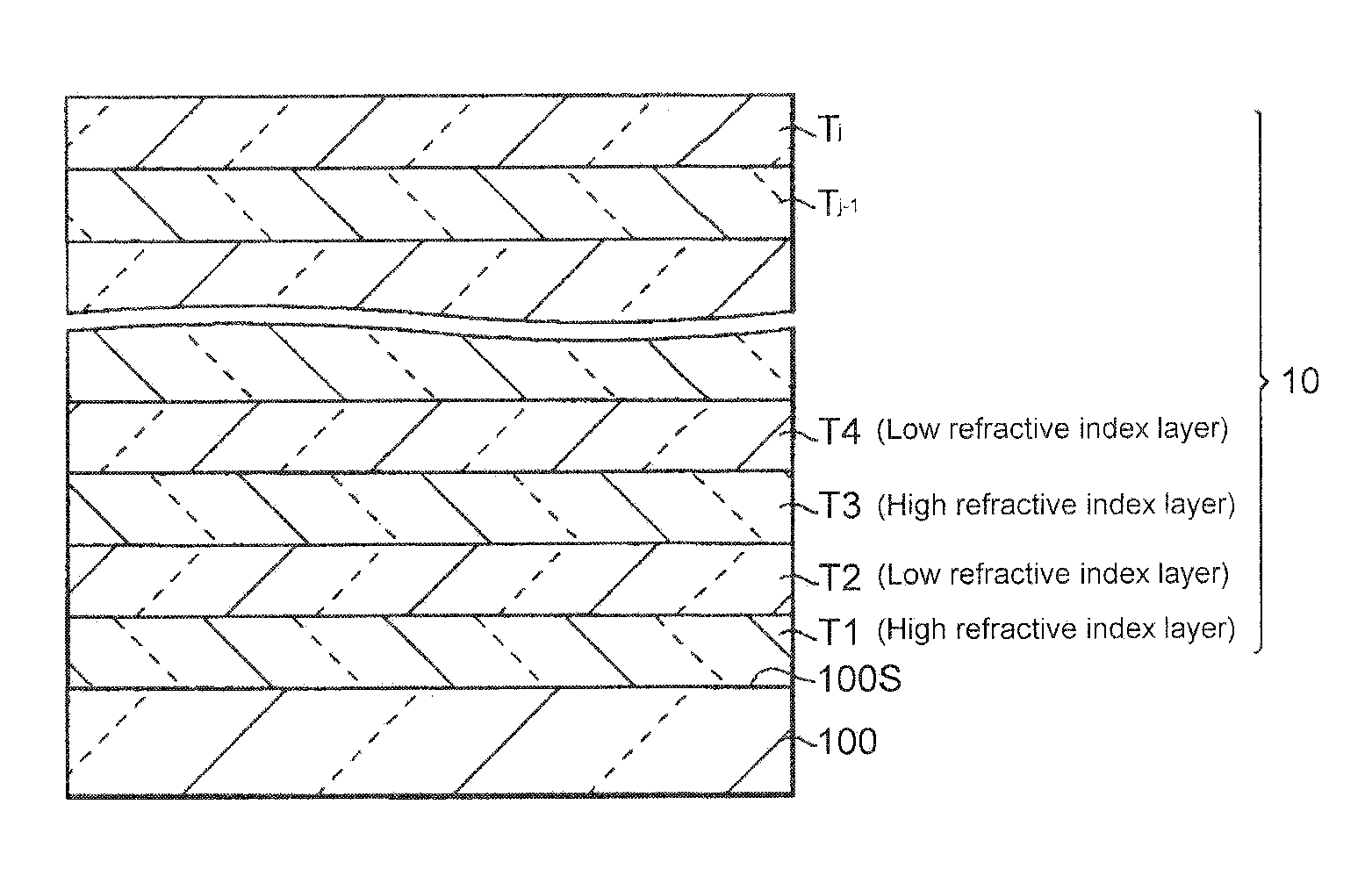
Optical filter
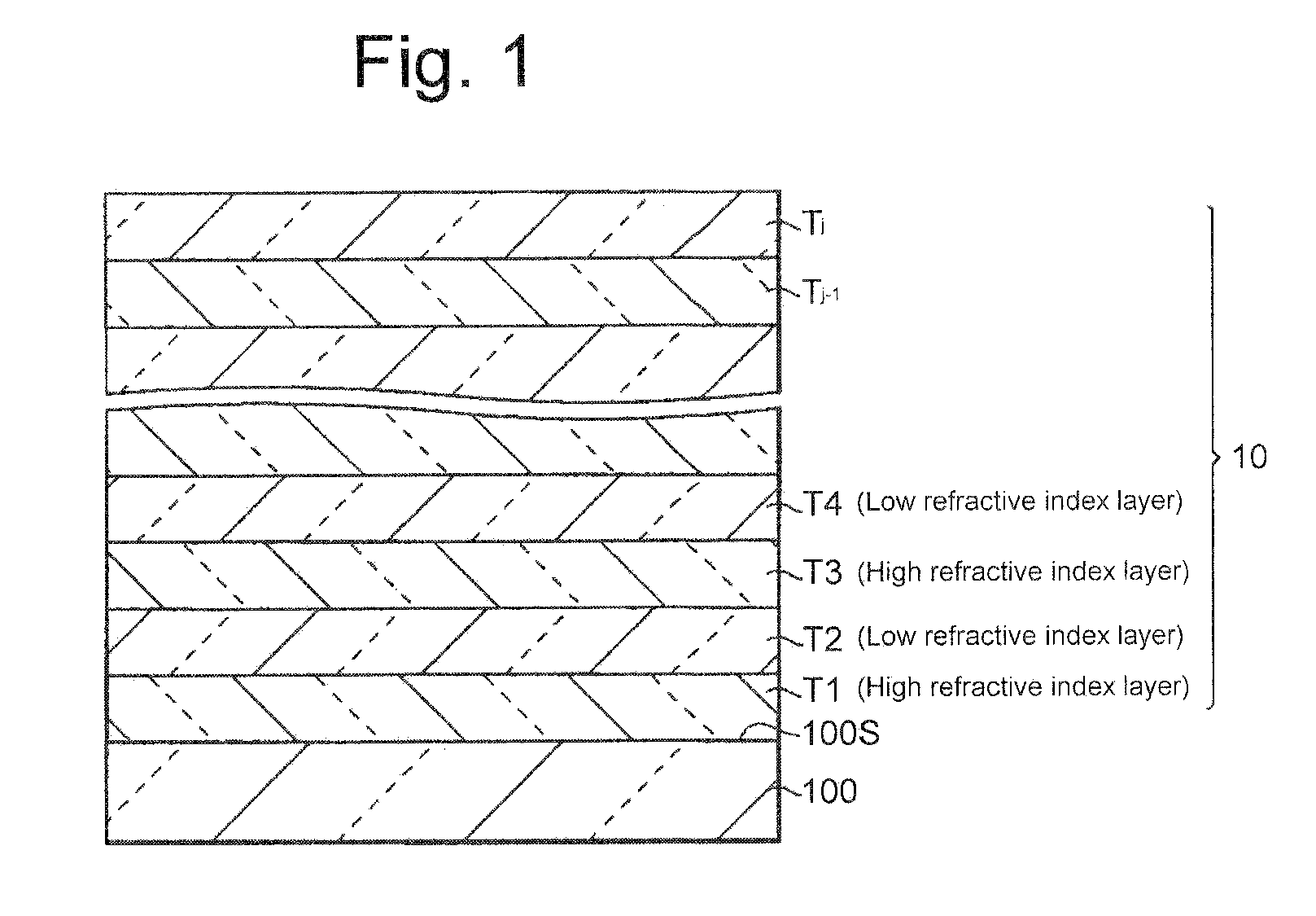
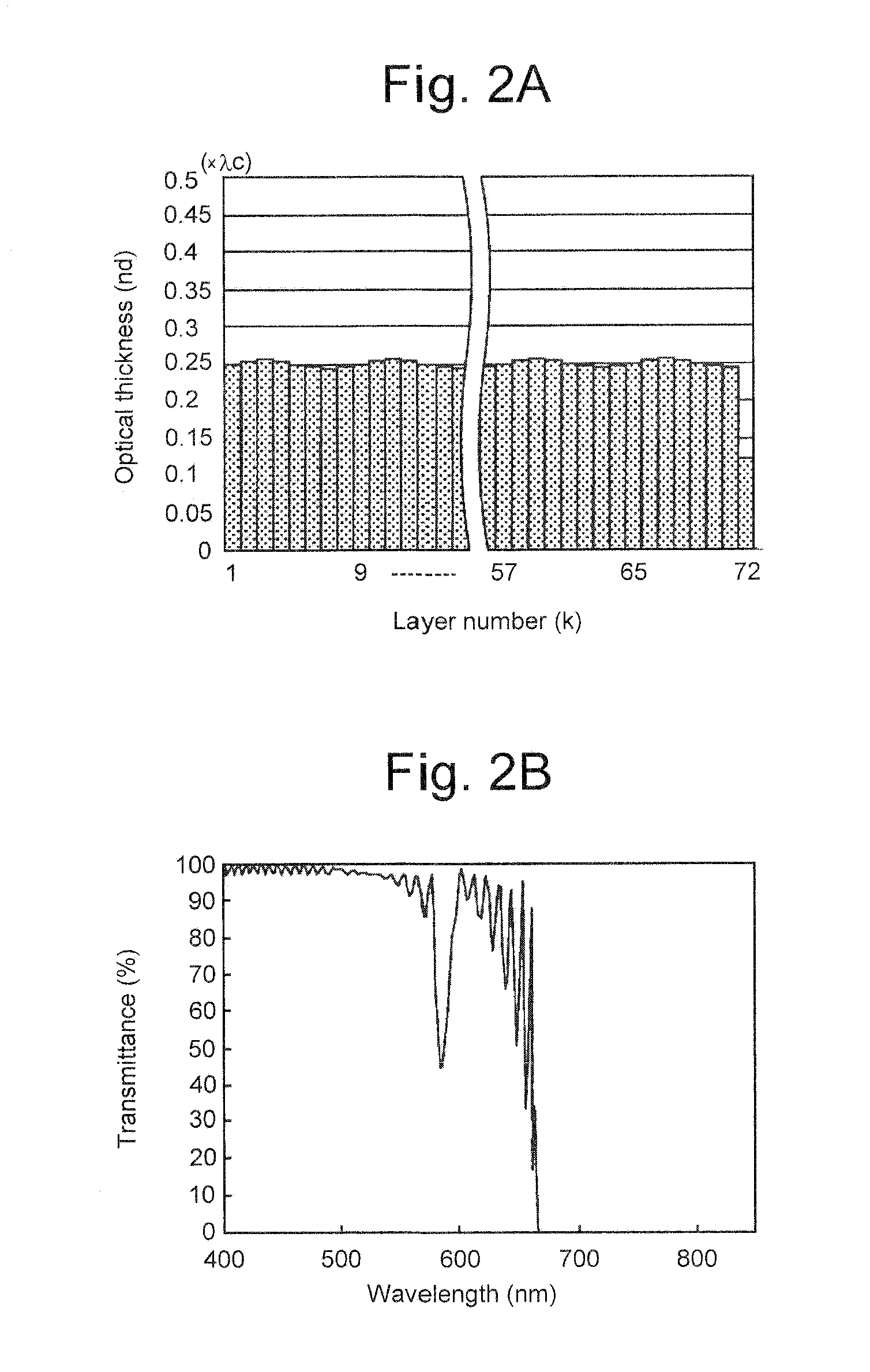
InactiveUS20080239496A1Improve reflectivityHigh design freedomOptical elementsRepetitive SequencesConditional expression
An optical filter has a multilayer thin film comprising first to i-th layers stacked in alternate layers of high and low refractive indices on a transparent substrate. Respective odd-numbered layers (Sigh refractive index layers) and respective even-numbered layers (low refractive index layers) form repetitive sequences of layers each of which cyclically changes in optical thickness throughout the multilayer tin film. Each of k-th from-the-bottom alternate layers of high and low refractive indices has such an optical thicknesses as meet the following conditional expressions (1) and (2), concurrently:n×d=(.c / 4)×[1+sin{(k−1)×}×.] (1)0 . . . <1 (2)where.c is the center wavelength of reflection band,n is the ref ion index of the layer for the d-line,d is the physical thickness of the layer,. is a factor of a pitch angle represented by 2. / the number of layers a one layer-stack,. is the rate of amplitude.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
DNA electrochemical sensor based on target DNA repetitive sequence self enhancement and amplification signal
InactiveCN103175873ARealize highly sensitive detectionHighly conservativeMaterial electrochemical variablesRepetitive SequencesPower flow
The invention discloses a DNA electrochemical sensor based on target DNA repetitive sequence self enhancement and amplification signal. A signal probe is designed by a repetitive sequence clip of a detected target chain, thus, the volume of the signal probes combined with the target sequence is increased, and a compound is formed, when a capture probe on electrode surface is hybridized with the target sequence, the amplified signal probe is combined with the electrode surface, under the affinity function between the biotin treated by end labeling of the signal probe and the avidin modified on the horseradish peroxidase, multiple enzymes are combined with a 'sandwich' structure, finally, under the efficient catalytic action of the enzymes, H2O2 is catalyzed to oxidize the TMB, the oxidative product generates an amplified reduction current signal on the electrode, and the concentration of the target DNA is judged according to the magnitude of the current signal. In the experiment, based on the characteristics of self enhancement and amplification signal of the target chain of the repetitive sequence, the target chain with two sections of repetitive sequences is detected, and the method is high in sensitivity.
Owner:福州市第二医院 +1
Mutation analysis method and device for cell-free DNA (cfDNA) sequencing data
InactiveCN112111565AHigh mutation sensitivityImprove verification accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsRepetitive SequencesSomatic cell
The invention relates to a mutation analysis method and device for cell-free DNA (cfDNA) sequencing data. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preprocessing original sequencing data; 2, comparing the sequencing data with a reference standard genome, identifying and eliminating PCR repetitive sequences, and correcting comparison errors of sequences to obtain an accurate sequence comparisonfile; 3, identifying tumor-related somatic cell variation sites, adopting a Sentieon software TNScope tool, setting parameters to ensure that cfDNA variation sites higher than 5 / 10000 variation abundance can be detected, and obtaining a potential tumor-related somatic cell variation site table; and 4, analyzing and identifying the highly credible low-frequency variation, and finally obtaining an expected positive variation analysis result. The method can achieve ultrahigh mutation sensitivity detection and high verification accuracy.
Owner:上海其明信息技术有限公司
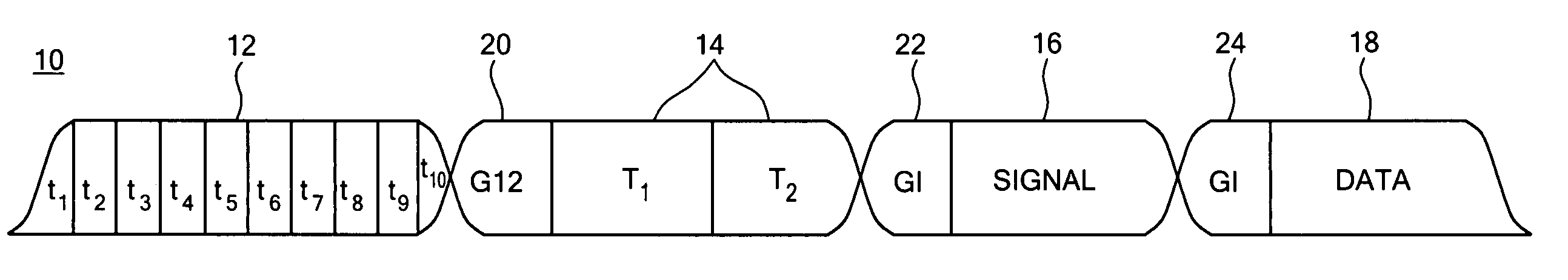
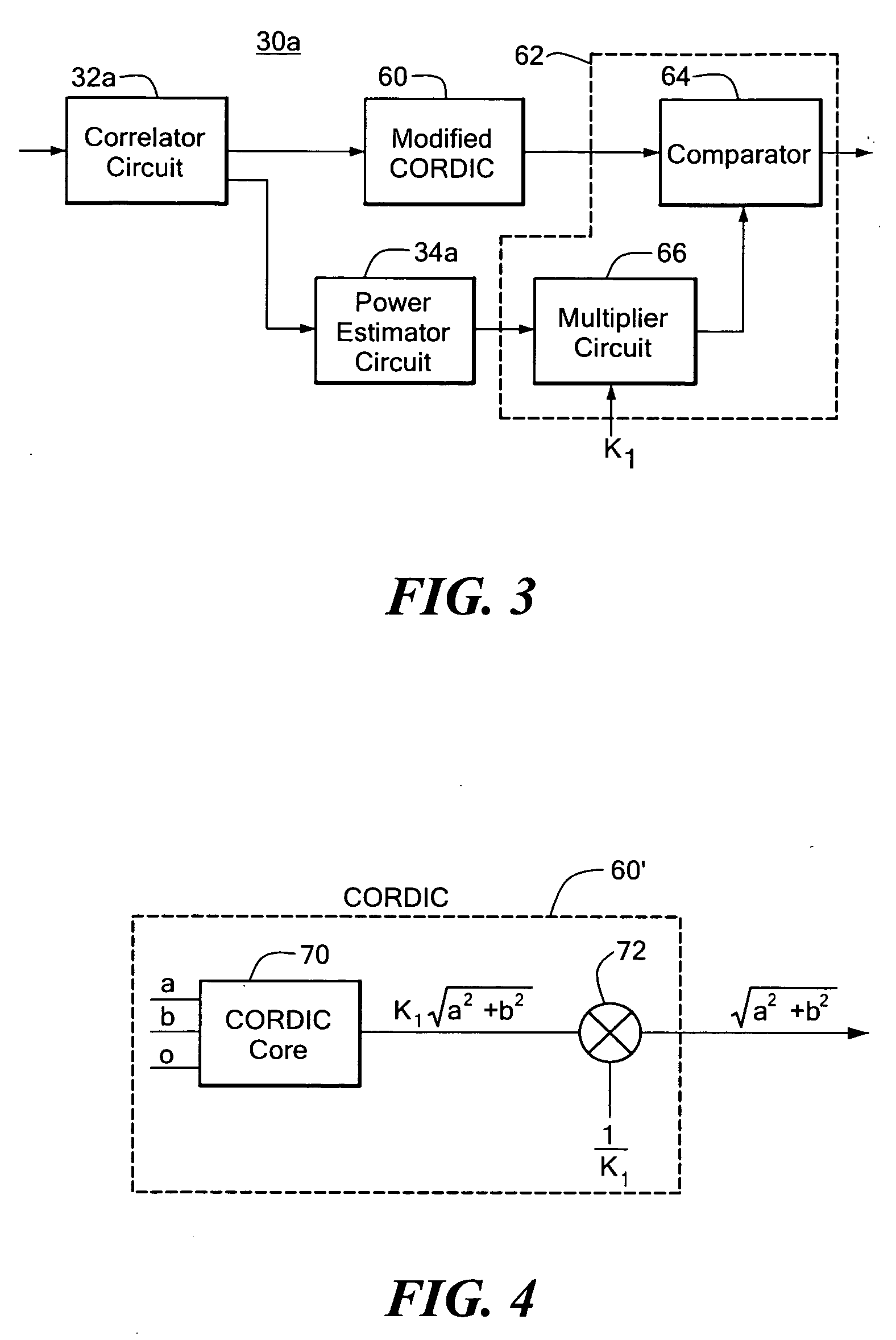
Packet detection system and method
ActiveUS20060031740A1Reduce total powerLess complexError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRepetitive SequencesComputer science
A packet detection technique is disclosed in which an average correlation signal is generated representative of the match between a repetitive sequence of symbols; an average power signal is generated representative of the average power in the sequence of symbols; a scaled magnitude of the average correlation signal scaled by a first predetermined scale factor is produced; and one of the average power signal and scaled magnitude of the average correlation signal are multiplied by the second scale factor and compared to determine whether there is a match between a repetitive sequence of symbols.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
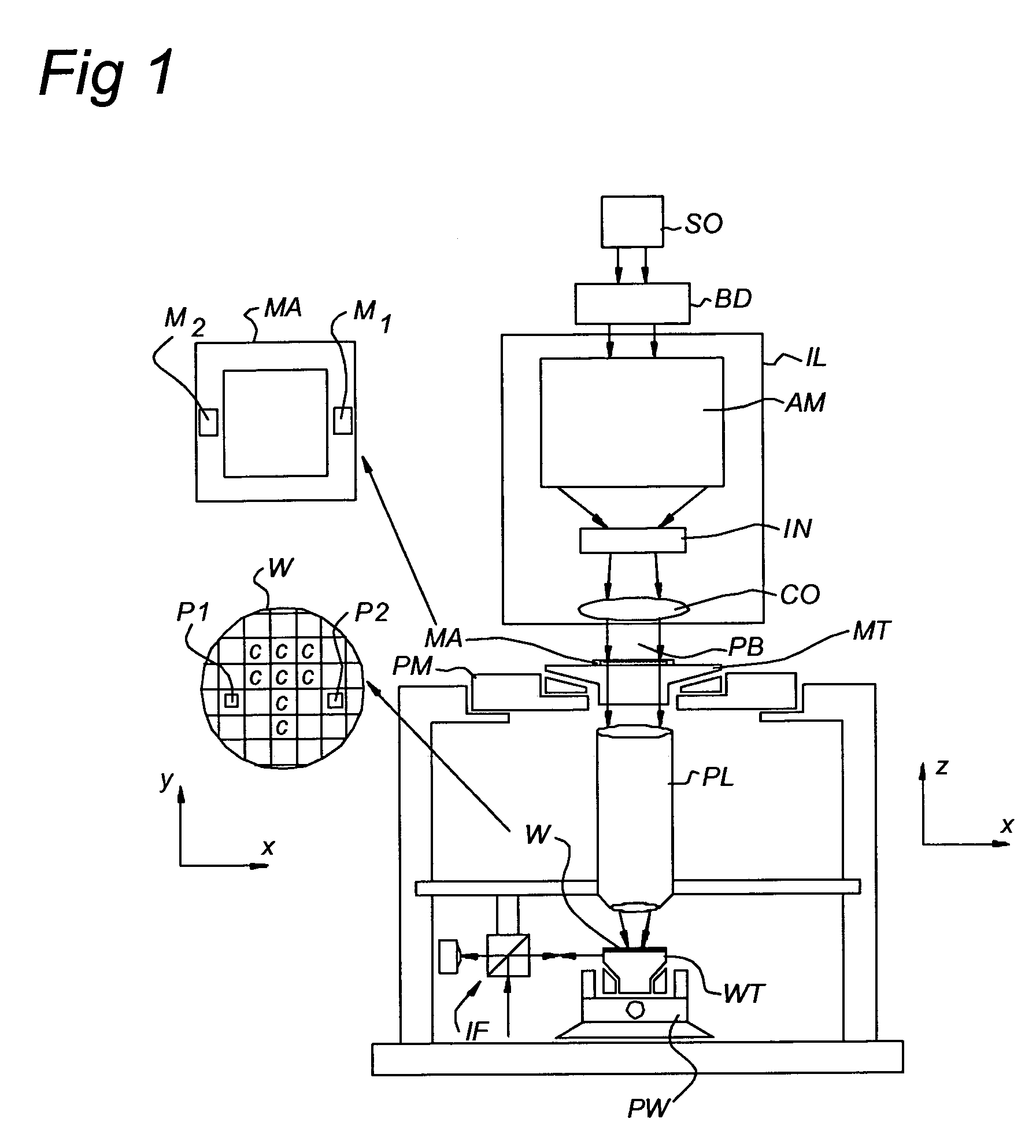
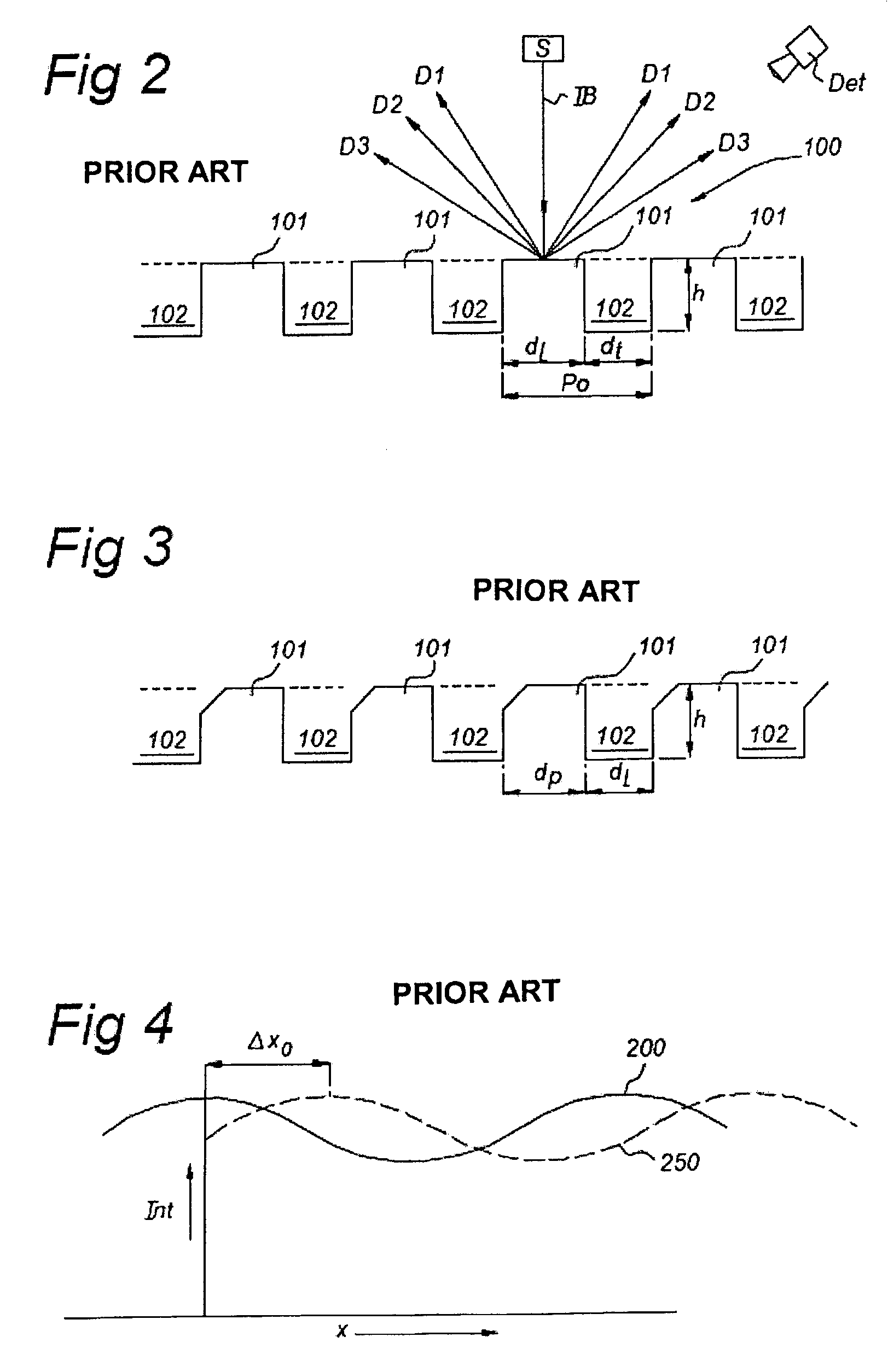
Alignment system and lithographic apparatus equipped with such an alignment system
InactiveUS7283236B2Improve alignment qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRepetitive SequencesLine width
A marker structure on a substrate includes line elements and trench elements, the line elements and trench elements each having a length in a first direction and being arranged in an alternating repetitive sequence in a second direction perpendicular to the first direction, the alternating repetitive sequence having a sequence length, the marker structure having at least one pitch value, the at least one pitch value being the sum of a line width of one line element and a trench width of one trench element. A width of the line elements varies over the sequence length of the marker structure between a minimum line width value and a maximum line width value, while a width of the trench elements likewise varies over the sequence length of the marker structure between a minimum trench width value and a maximum trench width value. A duty cycle of a pair of a line element and an adjacent trench element is substantially constant over the sequence length of the marker structure. Thus, the pitch value varies from a minimum pitch value to a maximum pitch value over the sequence length.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
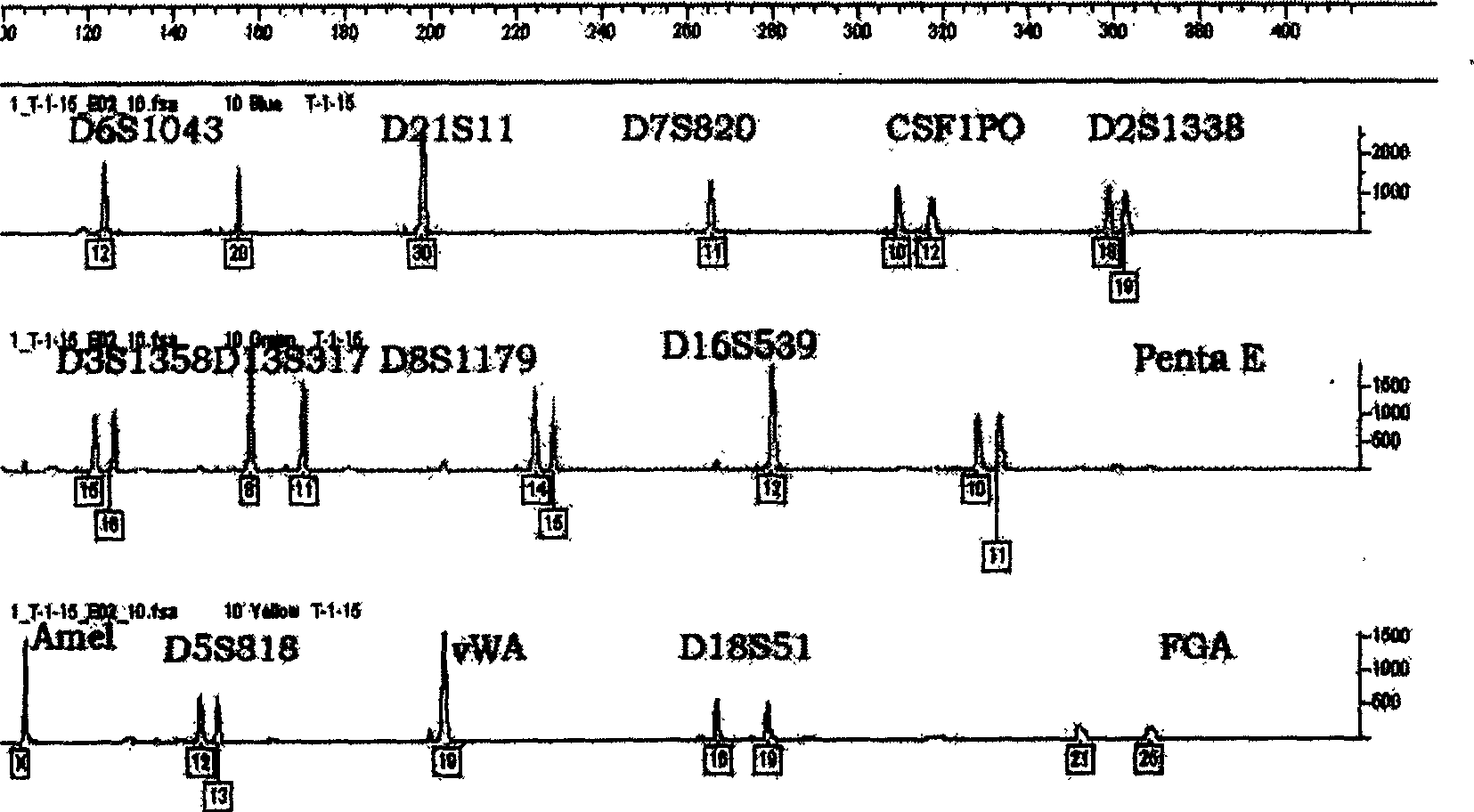
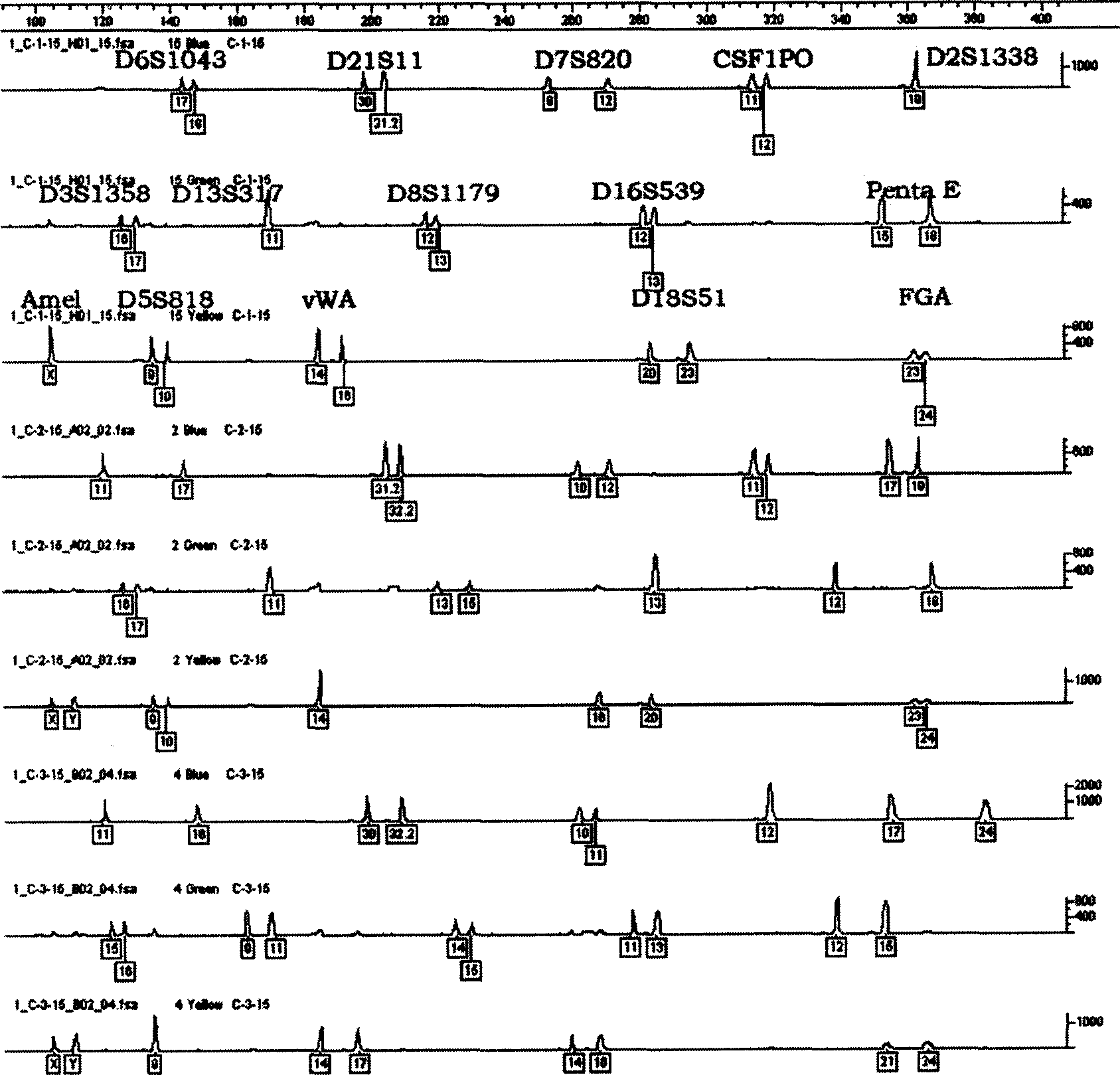
Complex aplification detecting system of fluorescent marker short tandem repetitive sequence gene locus
InactiveCN1724688AHigh sensitivityHigh polymorphismMicrobiological testing/measurementRepetitive SequencesFluorescence
The invention supplies a fluorescence labeling verification system by compounding and expanding 14 short series repeating sequence locus to take personal identification and paternity test. The specific compounding method controls the expanding product in the range of 400 basic groups, and only labeling three fluorescence of the compounding expanding of the 14 locus would be realized. The invention takes a deep research to the gene characteristic of the 14 locus and the allele in five minorities in China, and supplies the compounding expanding verification system. The agent box suited for Chinese throng is researched.
Owner:公安部第二研究所
AETCA (anchored-extension and telomeric complements amplification) detection reagent kit for telomerase and detection method
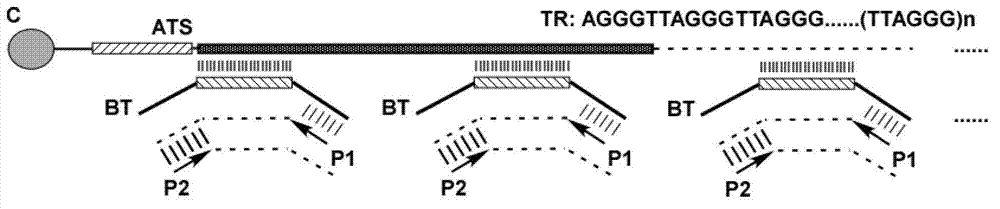
ActiveCN102876792AIncreased sensitivityReduce the possibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementTelomeraseRepetitive Sequences
The invention provides an AETCA (anchored-extension and telomeric complements amplification) detection reagent kit for telomerase and a detection method. The reagent kit comprises an anchored PCR (polymerase chain reaction) tube, a probe BT (SEQ ID No.2), PCR primer, denaturing lysis buffer, extension hybridization buffer, PCR buffer and washing buffer, wherein telomerase primer ATS (SEQ ID No.1) are fixed in the anchored PCR tube. By utilizing a part of probe sequence (the probe BT) complementary with a telomere repetitive sequence as a template, the probe is combined on the telomere repetitive sequence synthesized by the telomerase in a multicopy manner, and accordingly, amplification of the probe BT can be kept in efficient fixed length though the length of the telomere repetitive sequence is not constant, and the defects of the TRAP (tartrate resistant acid phosphatase) method are overcome. The detection method is convenient and easy to operate, sensitivity and specificity of activity detection of the telomerase can be improved, and the detection method is applicable to detection of various sources including cells or tissues of clinical samples such as sputum.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JFK BIOLOGICAL TECH
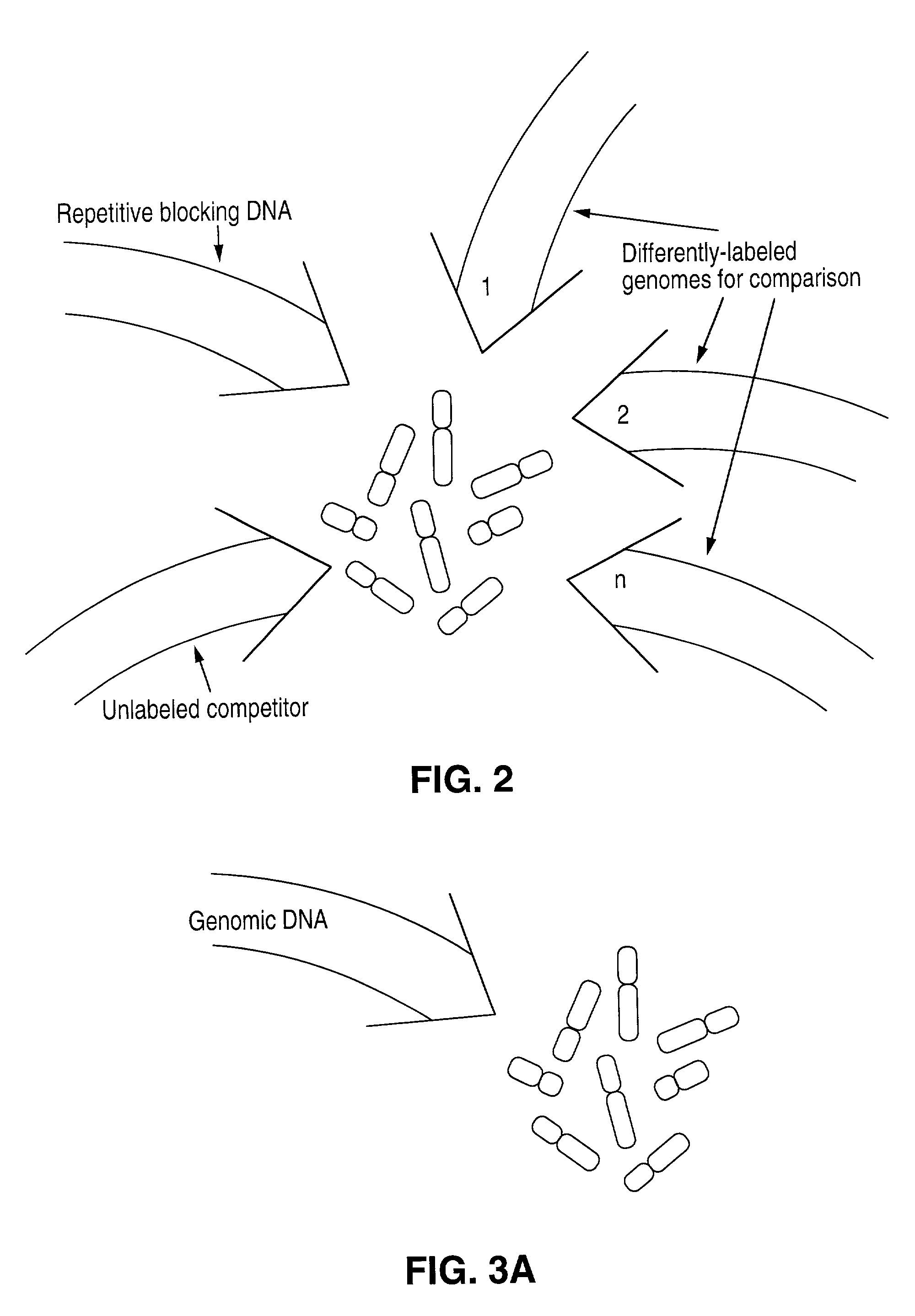
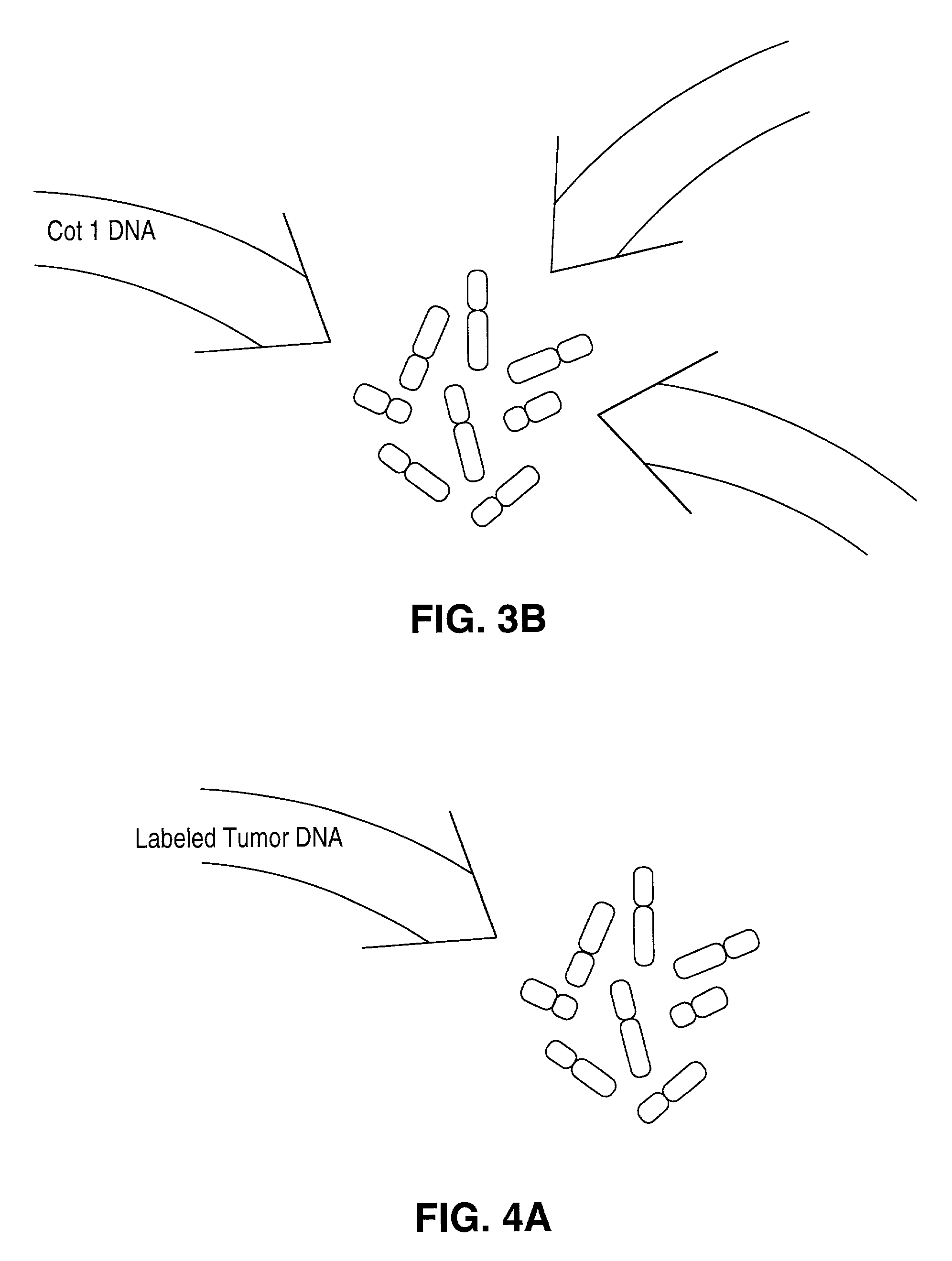
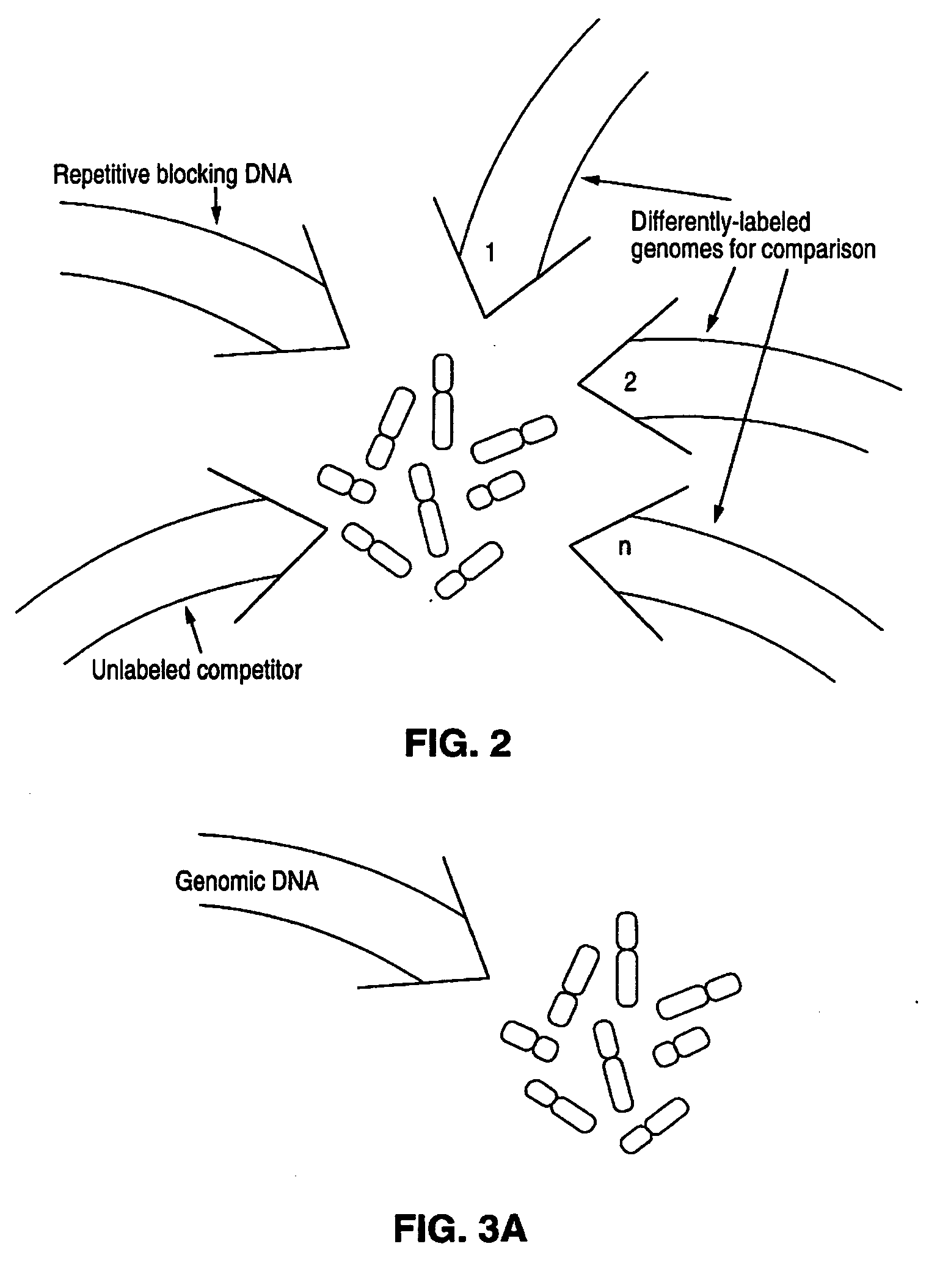
Comparative genomic hybridization
InactiveUS20060292608A1High sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingComparative genomic hybridization
Disclosed are new methods comprising the use of in situ hybridization to detect abnormal nucleic acid sequence copy numbers in one or more genomes wherein repetitive sequences that bind to multiple loci in a reference chromosome spread are either substantially removed and / or their hybridization signals suppressed. The invention termed Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH) provides for methods of determining the relative number of copies of nucleic acid sequences in one or more subject genomes or portions thereof (for example, a tumor cell) as a function of the location of those sequences in a reference genome (for example, a normal human genome). The intensity(ies) of the signals from each labeled subject nucleic acid and / or the differences in the ratios between different signals from the labeled subject nucleic acid sequences are compared to determine the relative copy numbers of the nucleic acid sequences in the one or more subject genomes as a function of position along the reference chromosome spread. Amplifications, duplications and / or deletions in the subject genome(s) can be detected. Also provided is a method of determining the absolute copy numbers of substantially all RNA or DNA sequences in subject cell(s) or cell population(s).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Kit for realizing multiple amplification of 21 short tandem repeats by adopting degenerate primers
InactiveCN105368958AHigh polymorphismHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementRepetitive SequencesTandem repeat
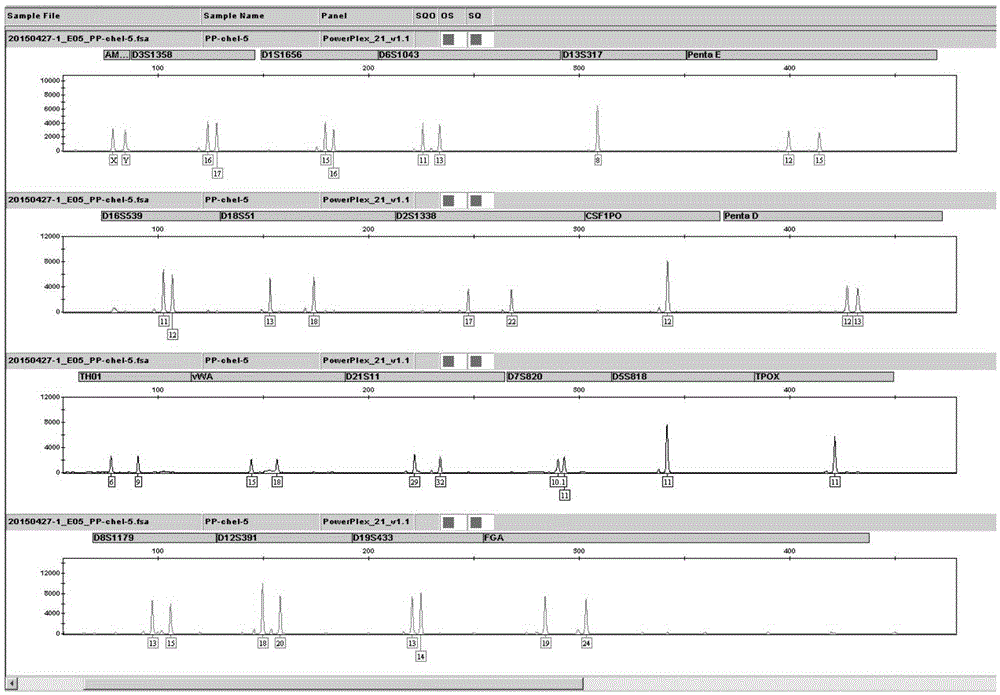
The invention provides a kit for realizing multiple amplification of 21 short tandem repeats by adopting degenerate primers, and belongs to a multiple amplification system for simultaneously analyzing a plurality of STR gene loci. 21 gene loci are amplified in a multiple amplification system simultaneously, and are divided into the following four groups: the first group: D19S433, TH01, D21S11, D18S51 and Penta E; the second group: D3S1358, D13S317, D7S820, D5S818, CSF1PO and Penta D; the third group: Amelogenin, vWA, D8S1179, TPOX, D6S1043 and D1S1656; and the fourth group: D16S539, D12S391, D2S1338 and FGA. Specific primers are respectively designed on flanks of a gene loci repetitive sequence, so that the balance of the peaks of the fragments inside the gene loci groups achieves 40% or above, the four gene loci groups are subjected to multiple amplification, and the concentration of the primer of each gene locus is regulated, so that the integral balance of the peaks of the gene loci achieves 30% or above. With the kit, a balanced and stable multiple amplification result is easily obtained, so that the kit belongs to a multiple amplification system with low cost and high efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING PEOPLESPOT TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com