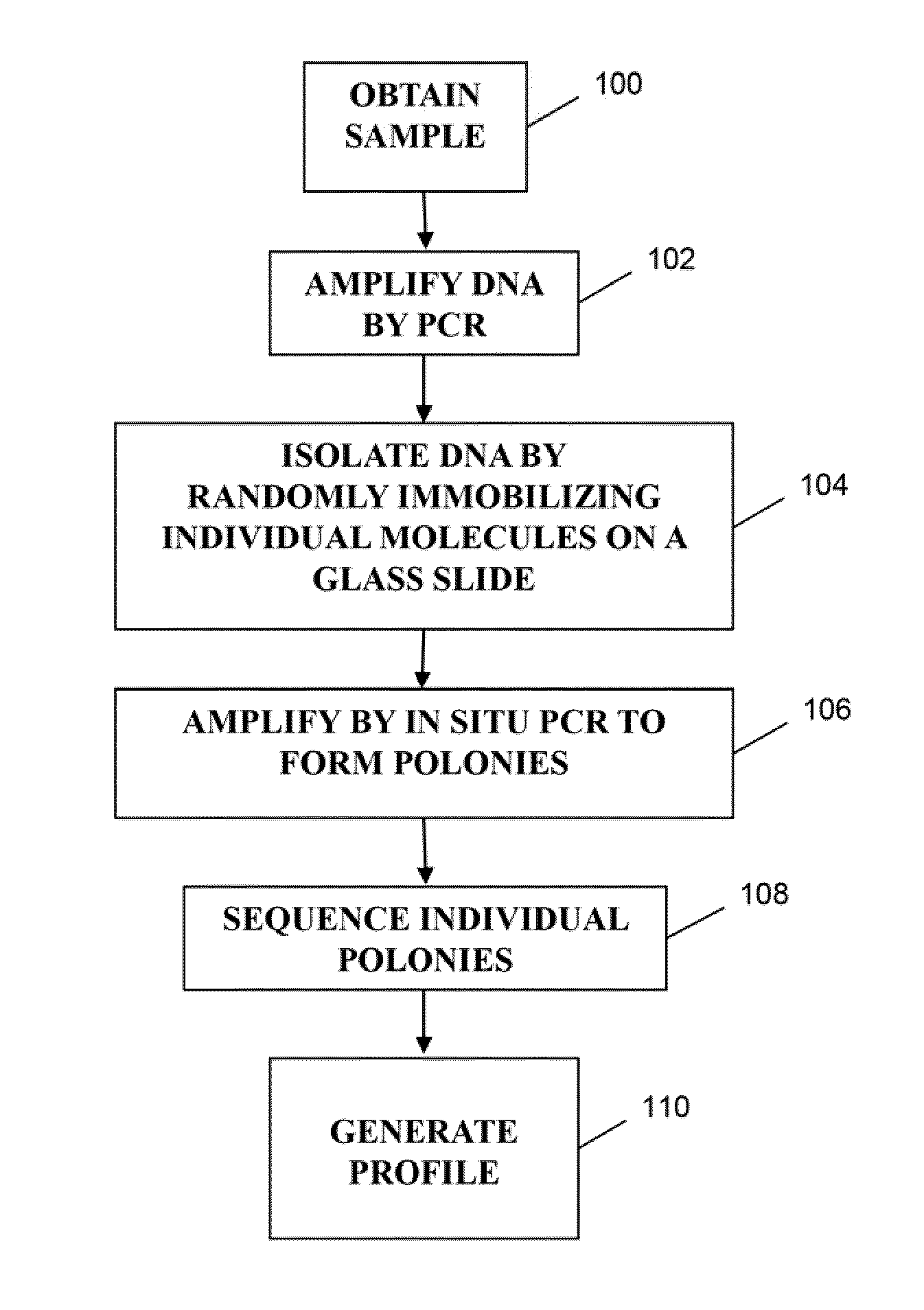
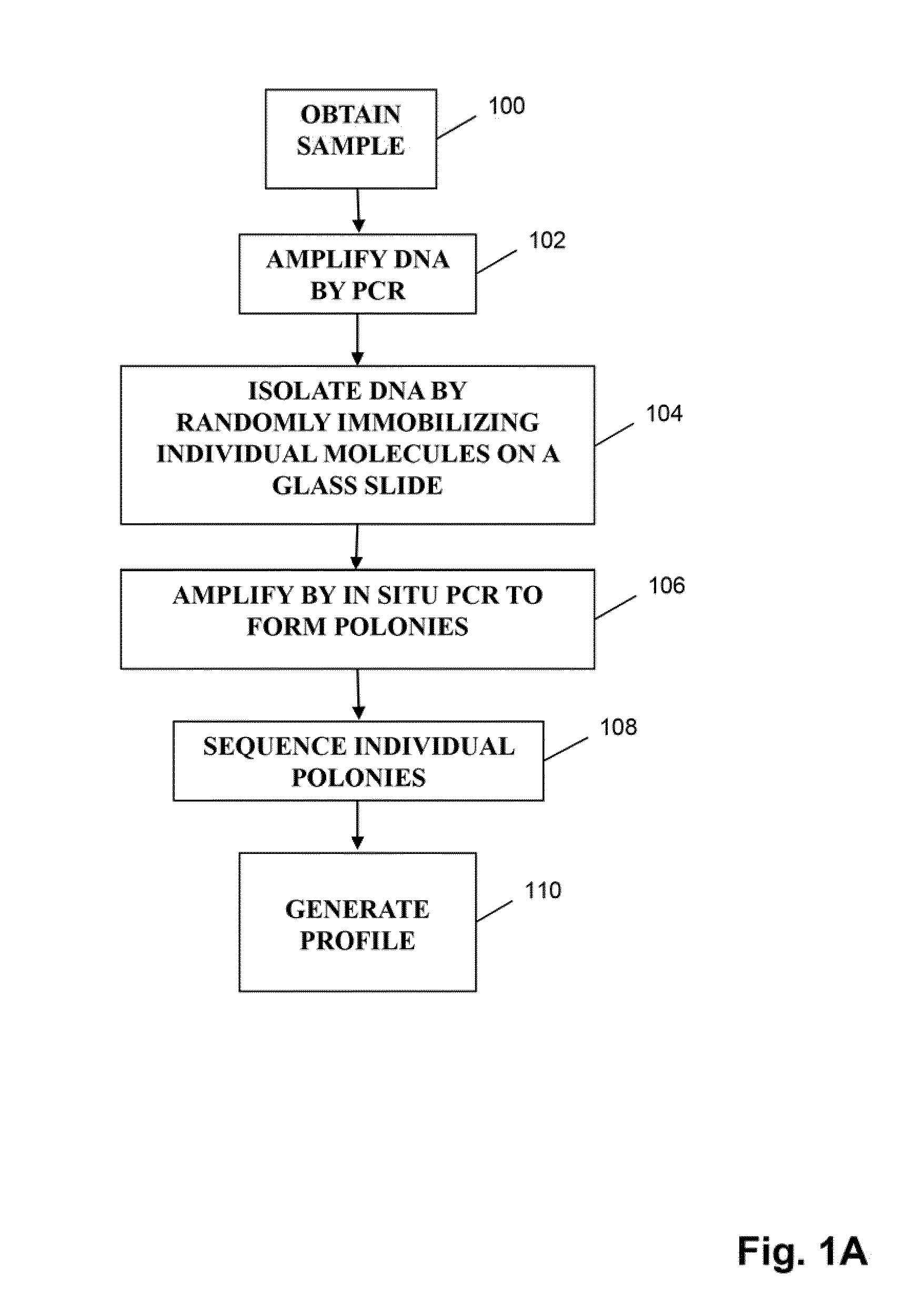
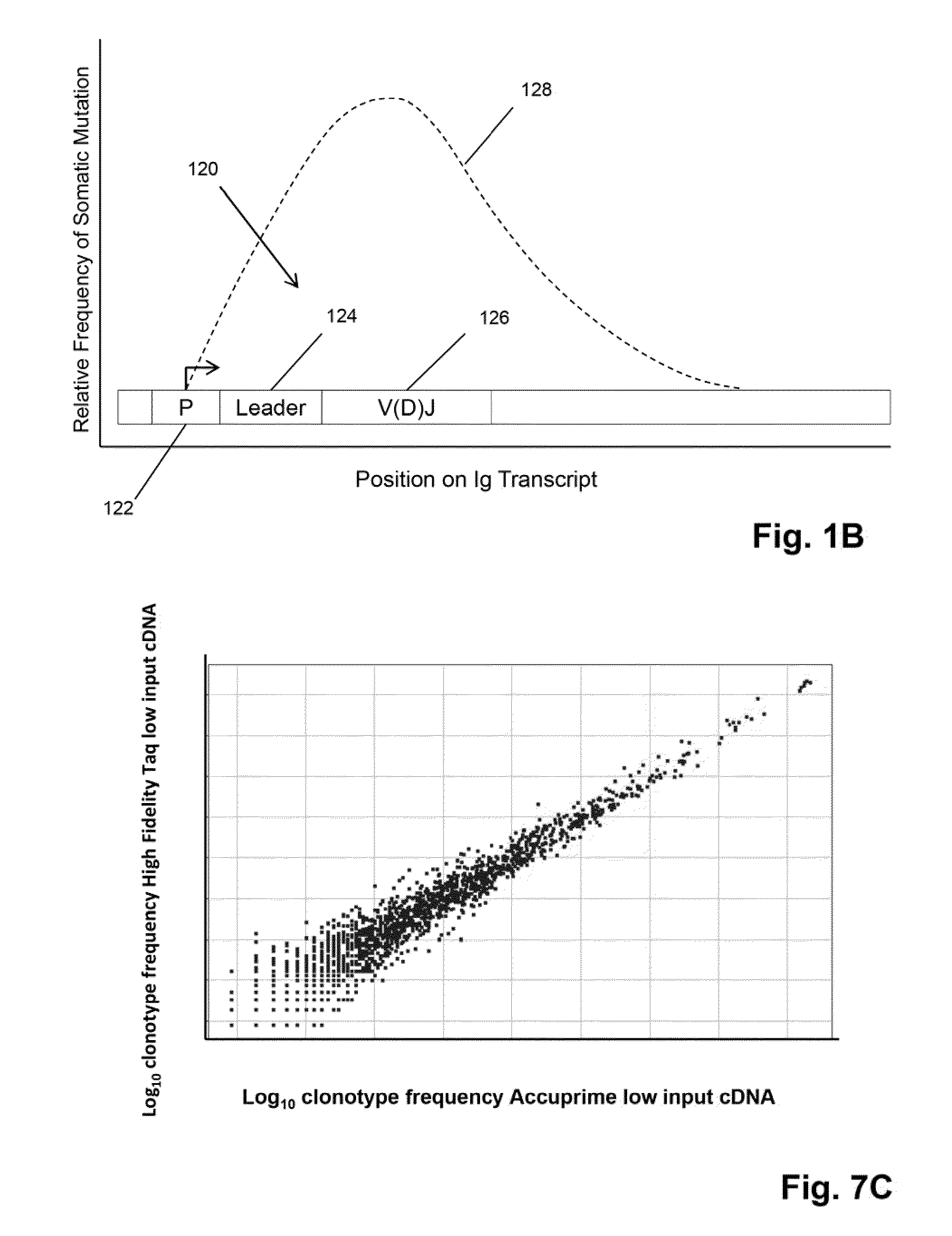
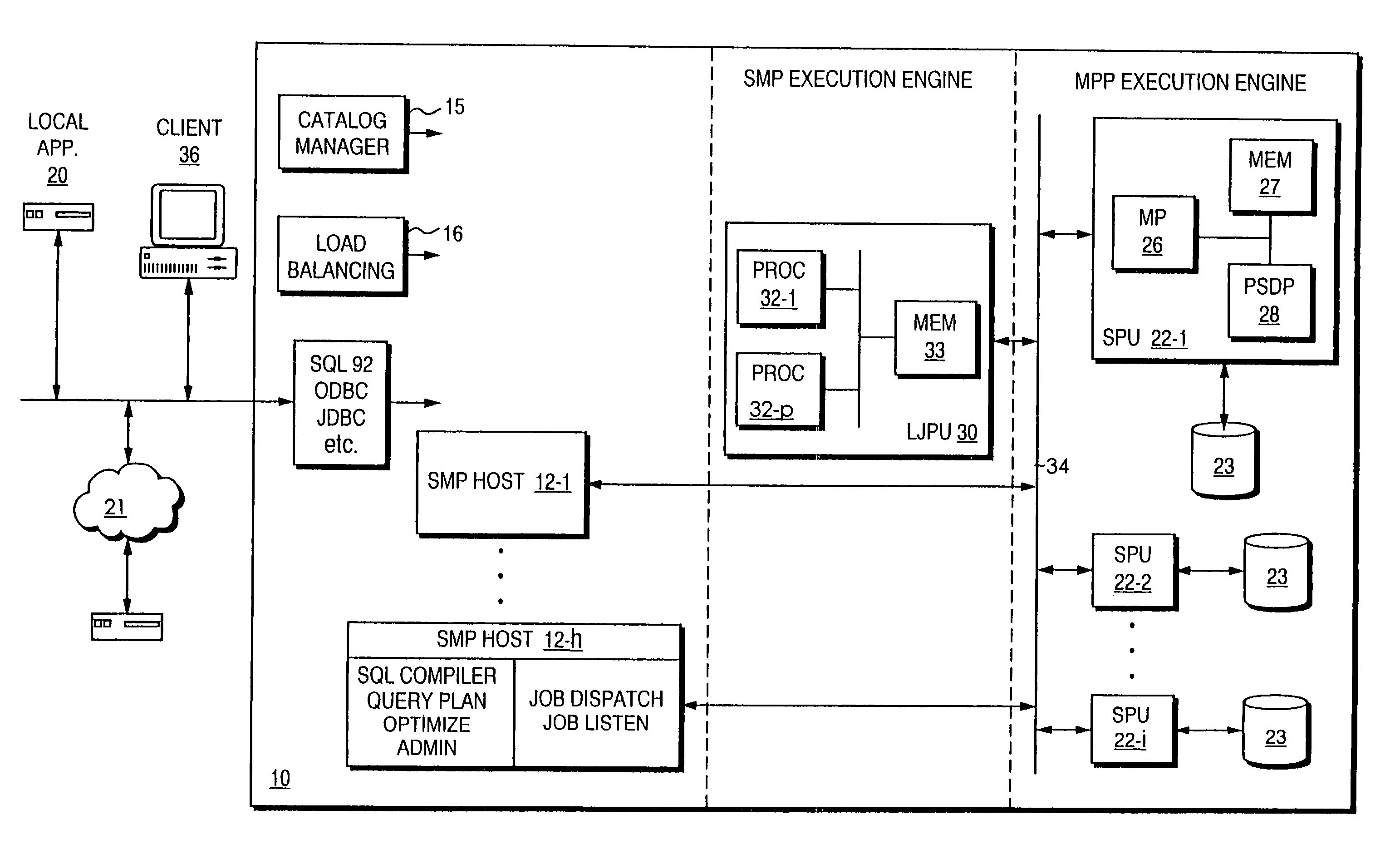
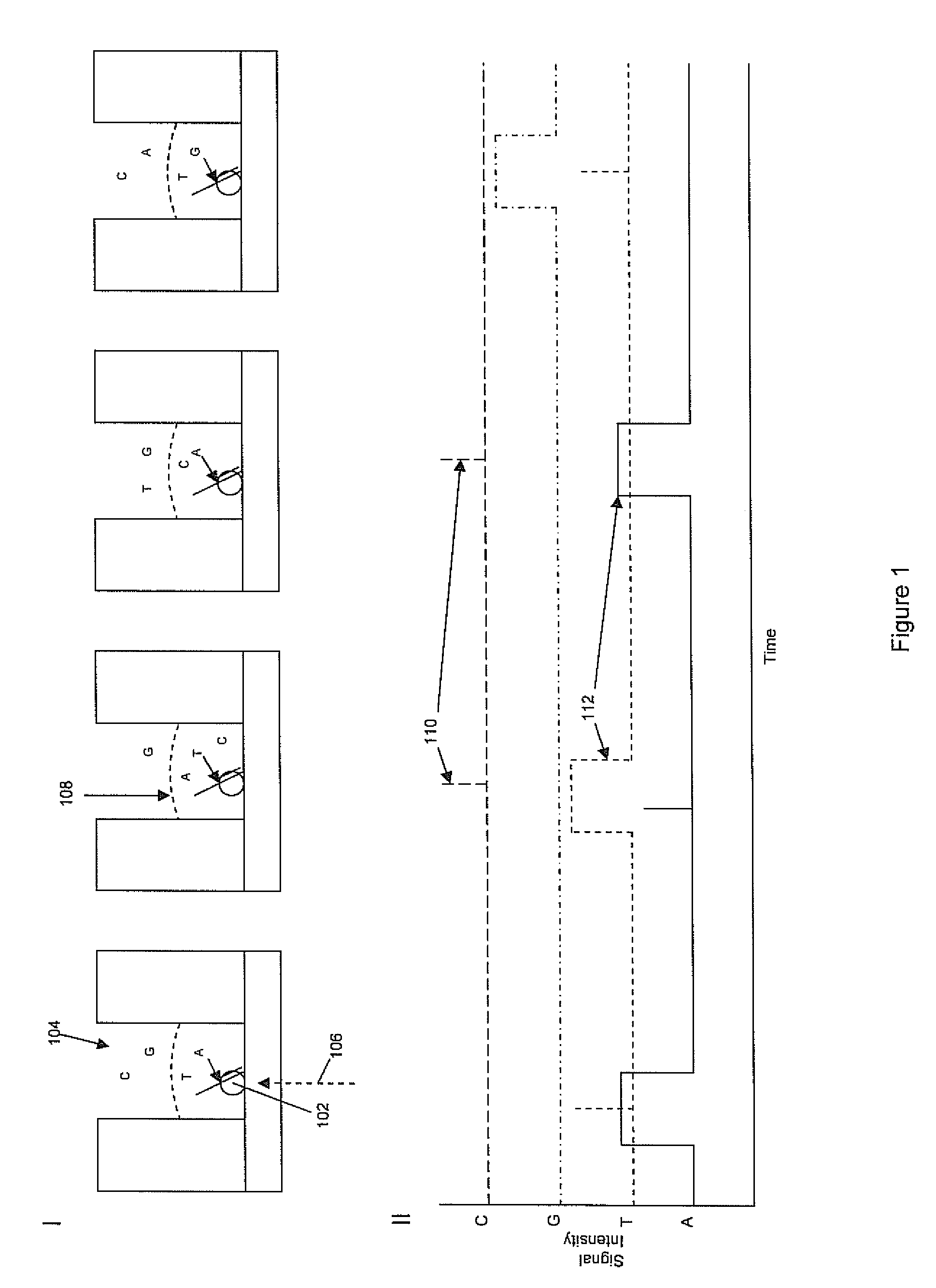
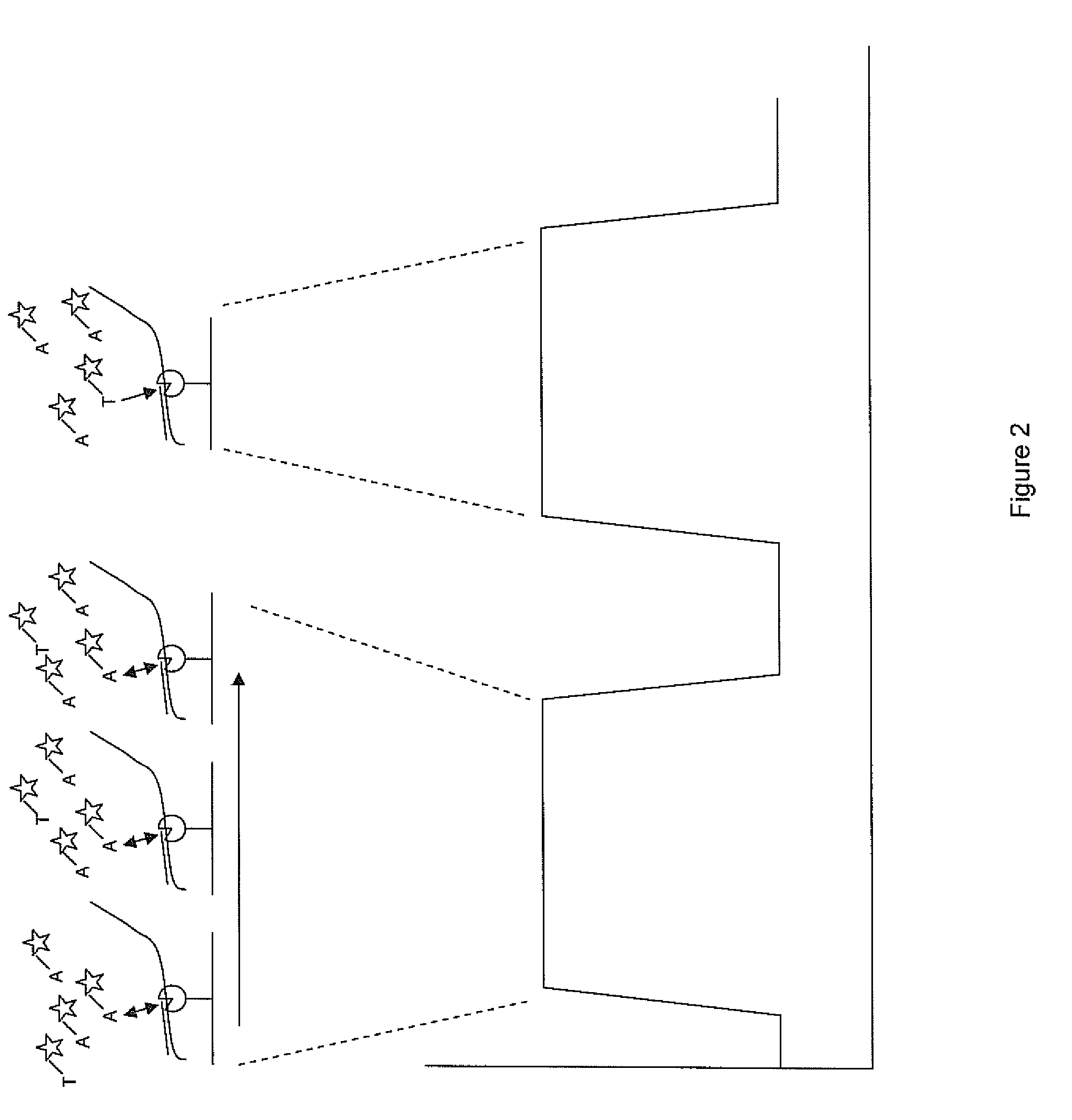
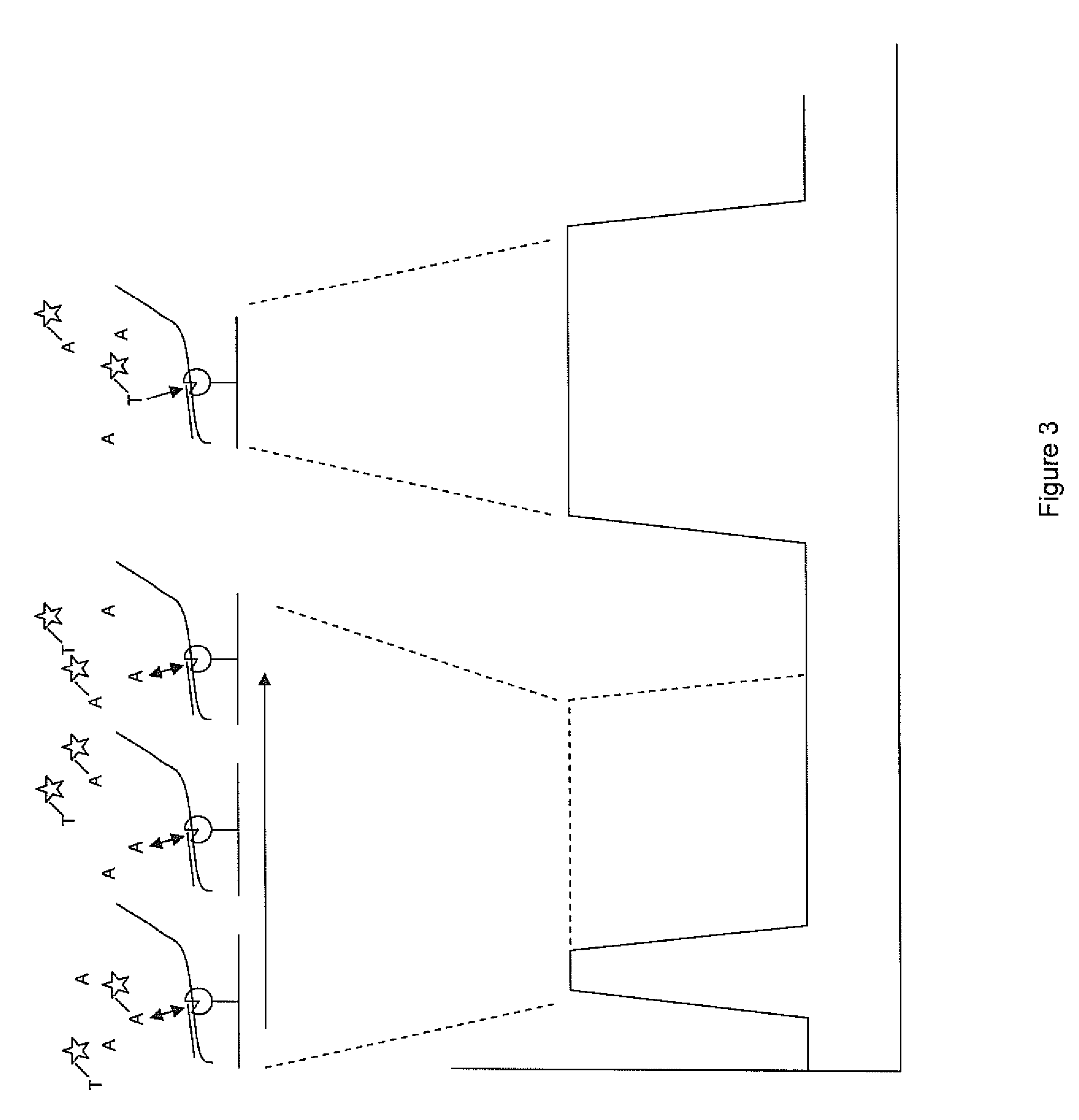
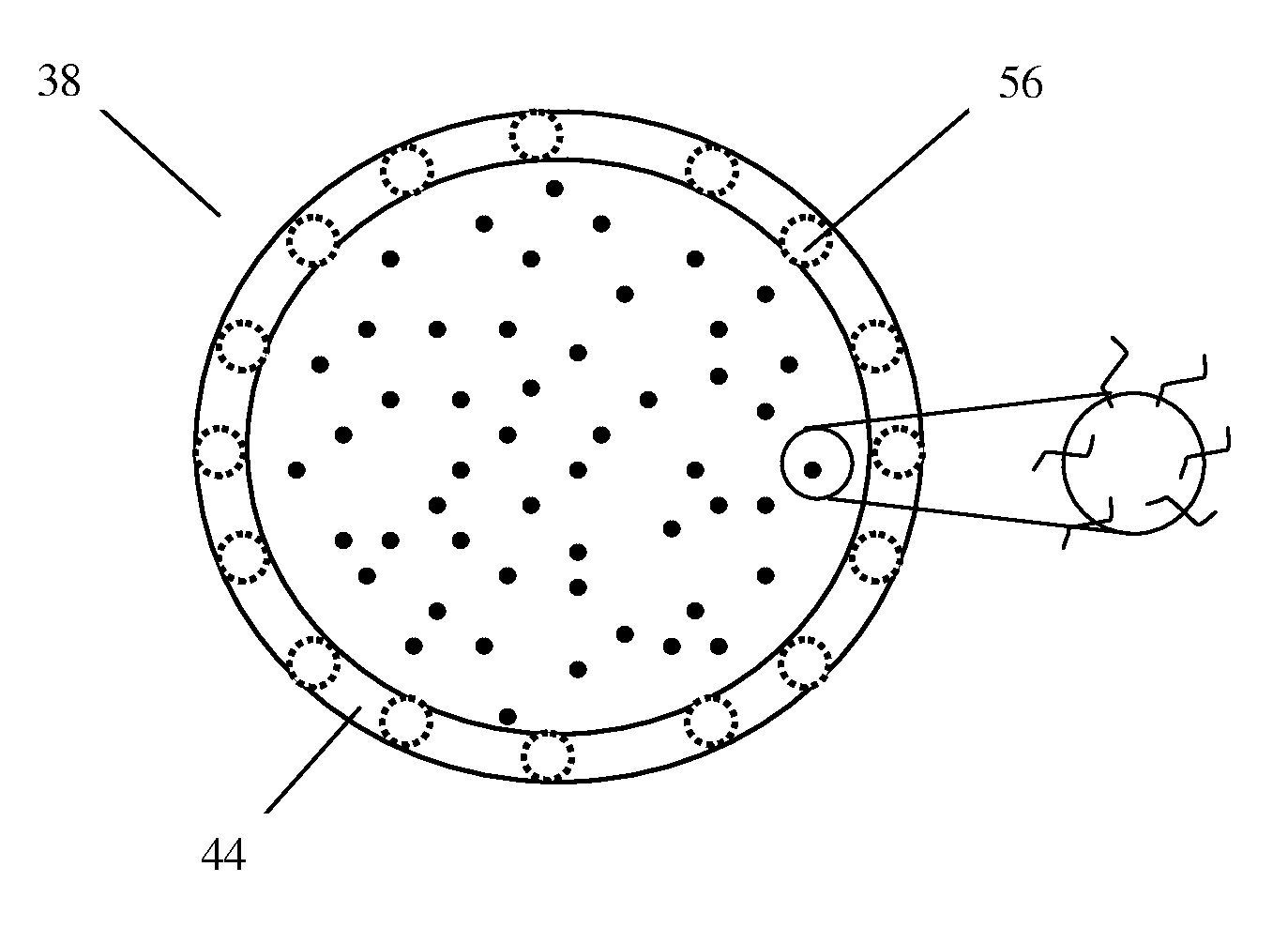
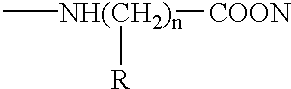Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1222 results about "Sequence analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
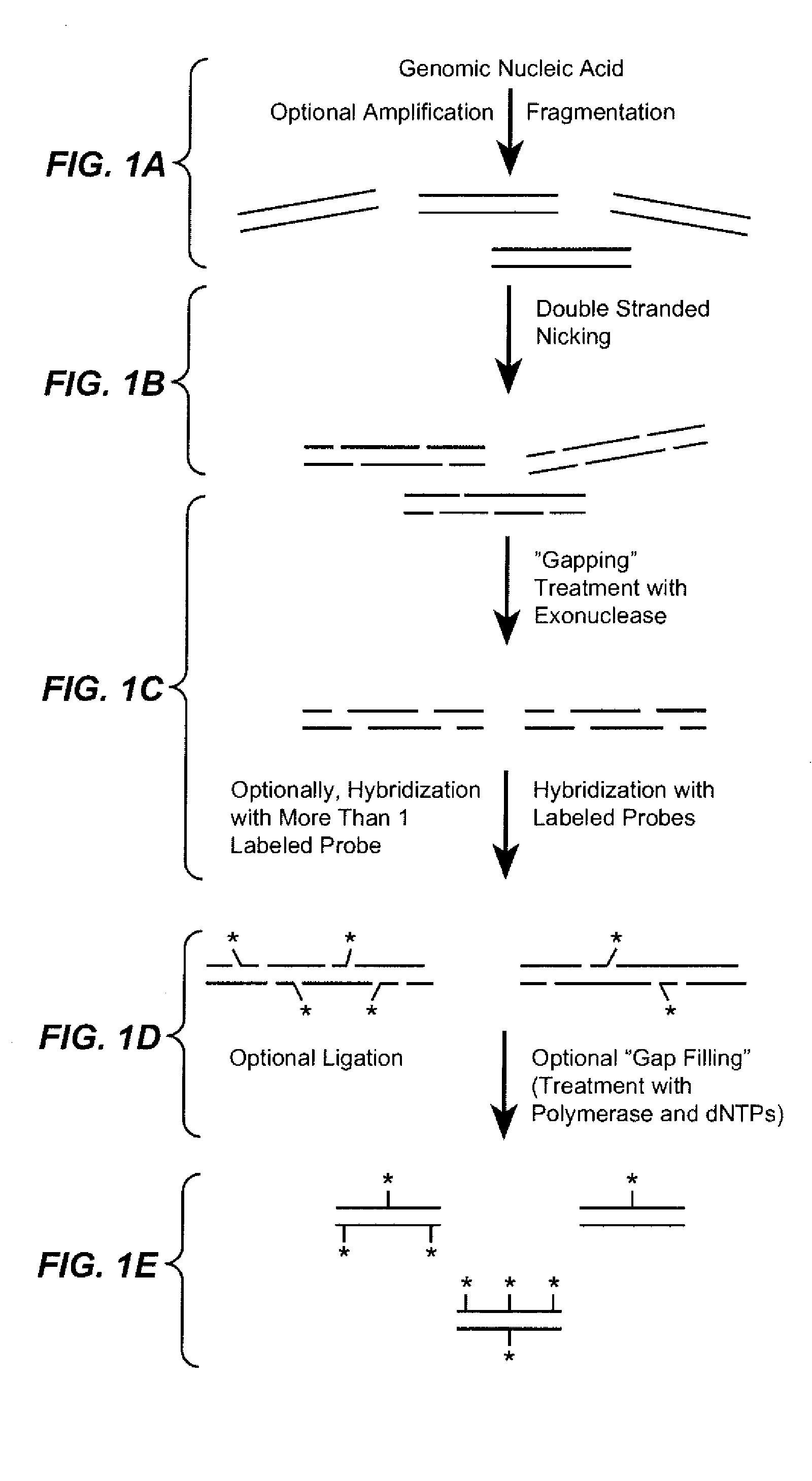
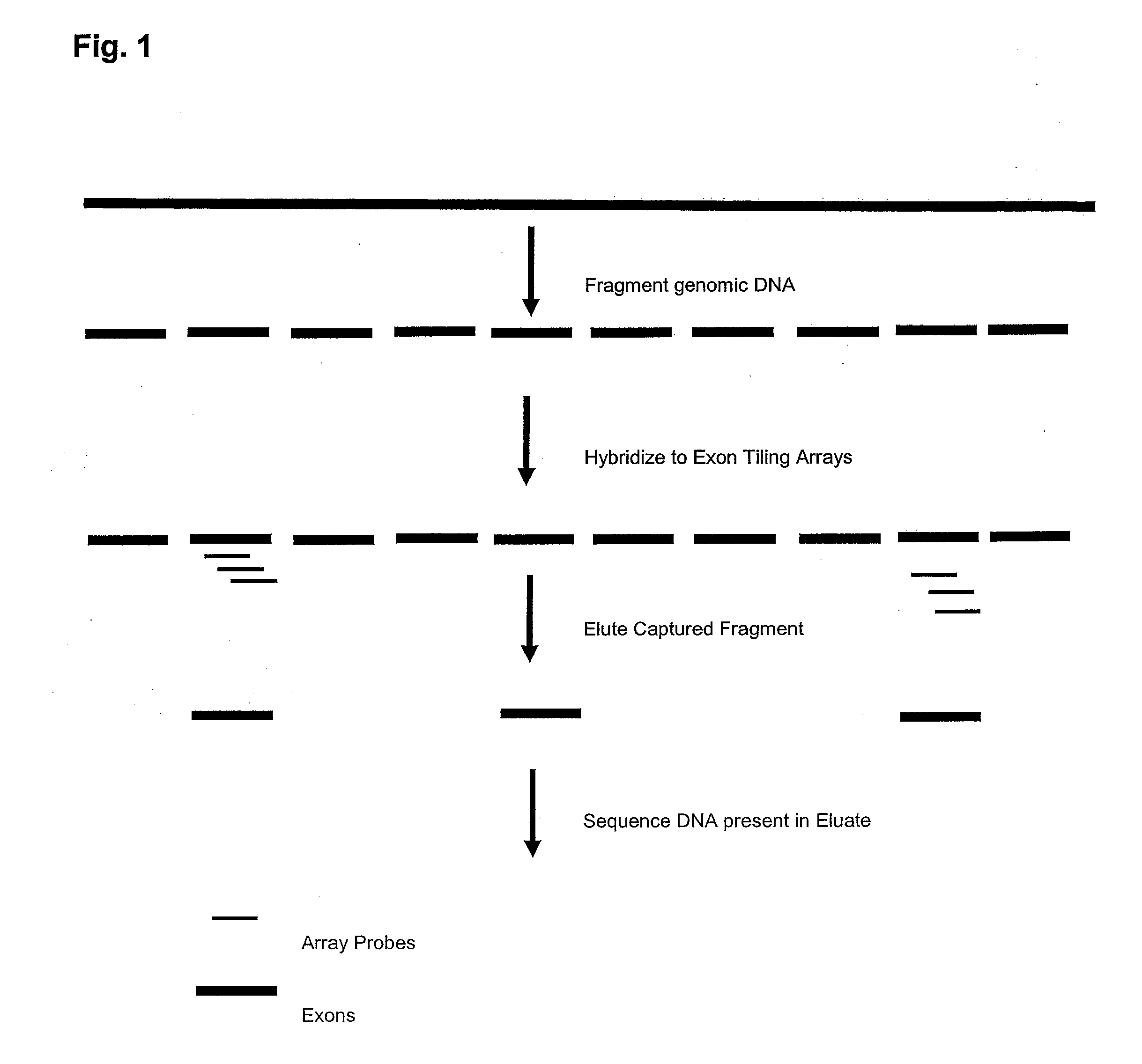
In bioinformatics, sequence analysis is the process of subjecting a DNA, RNA or peptide sequence to any of a wide range of analytical methods to understand its features, function, structure, or evolution. Methodologies used include sequence alignment, searches against biological databases, and others. Since the development of methods of high-throughput production of gene and protein sequences, the rate of addition of new sequences to the databases increased exponentially. Such a collection of sequences does not, by itself, increase the scientist's understanding of the biology of organisms. However, comparing these new sequences to those with known functions is a key way of understanding the biology of an organism from which the new sequence comes. Thus, sequence analysis can be used to assign function to genes and proteins by the study of the similarities between the compared sequences. Nowadays, there are many tools and techniques that provide the sequence comparisons (sequence alignment) and analyze the alignment product to understand its biology.
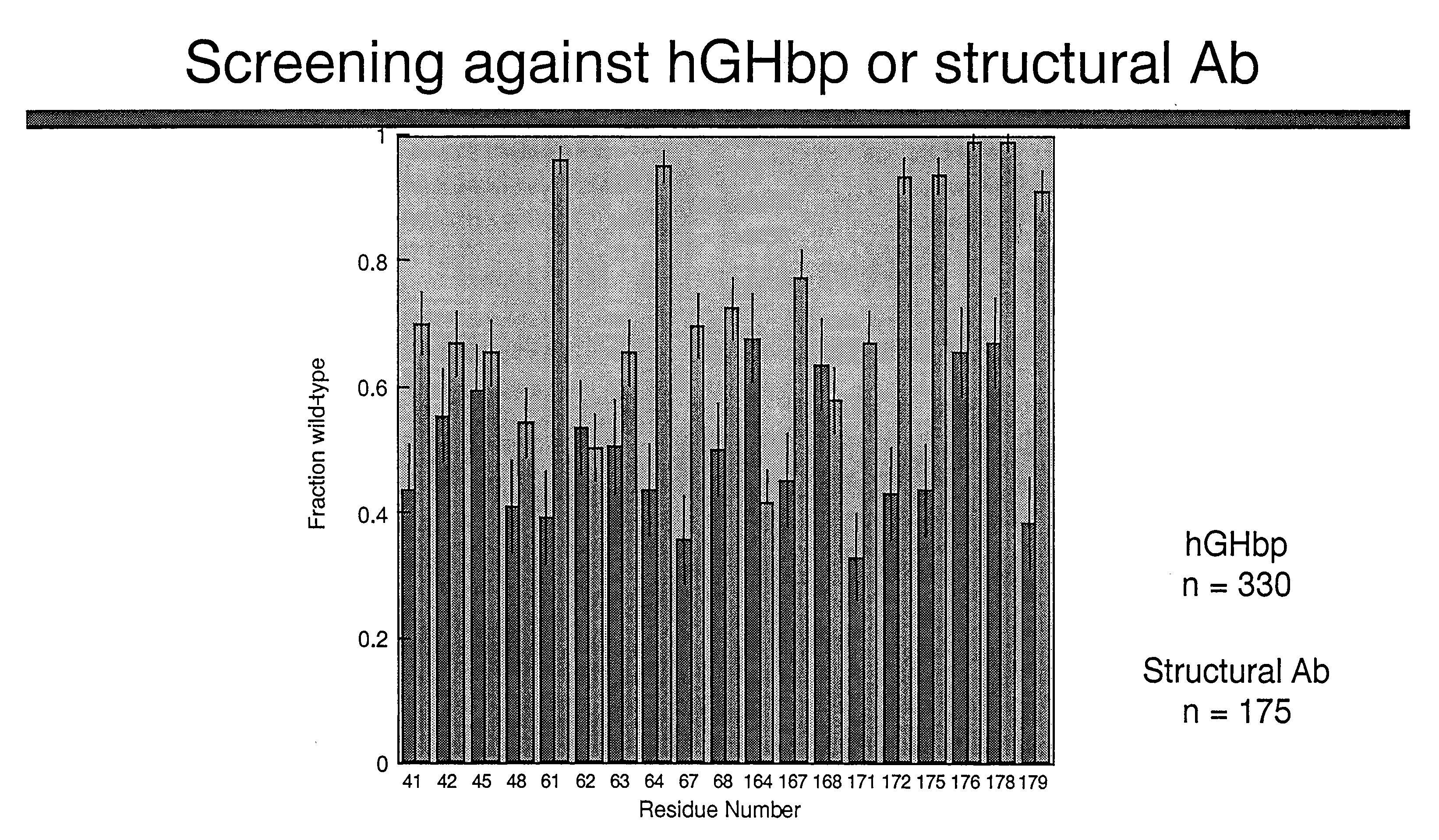
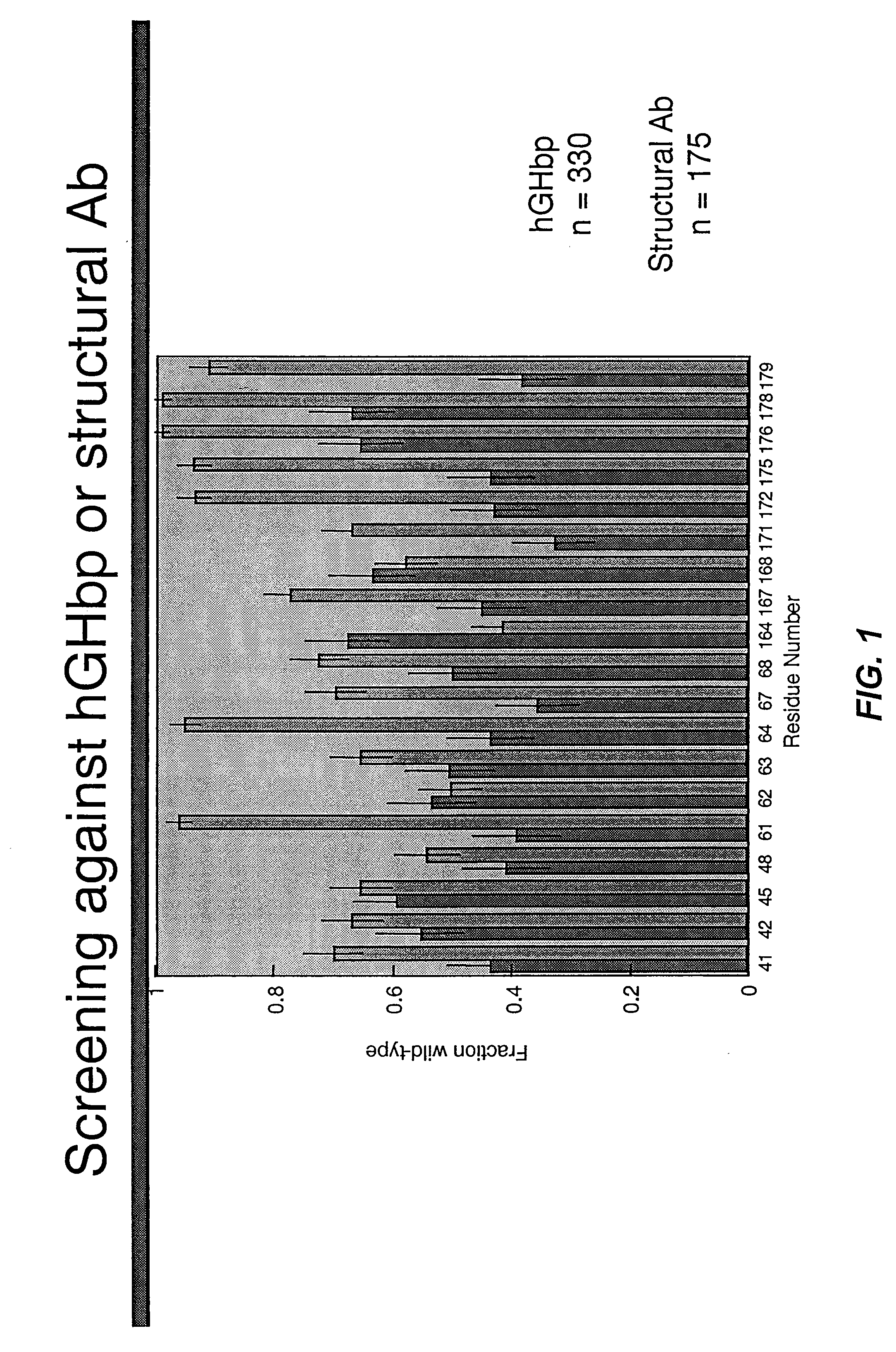
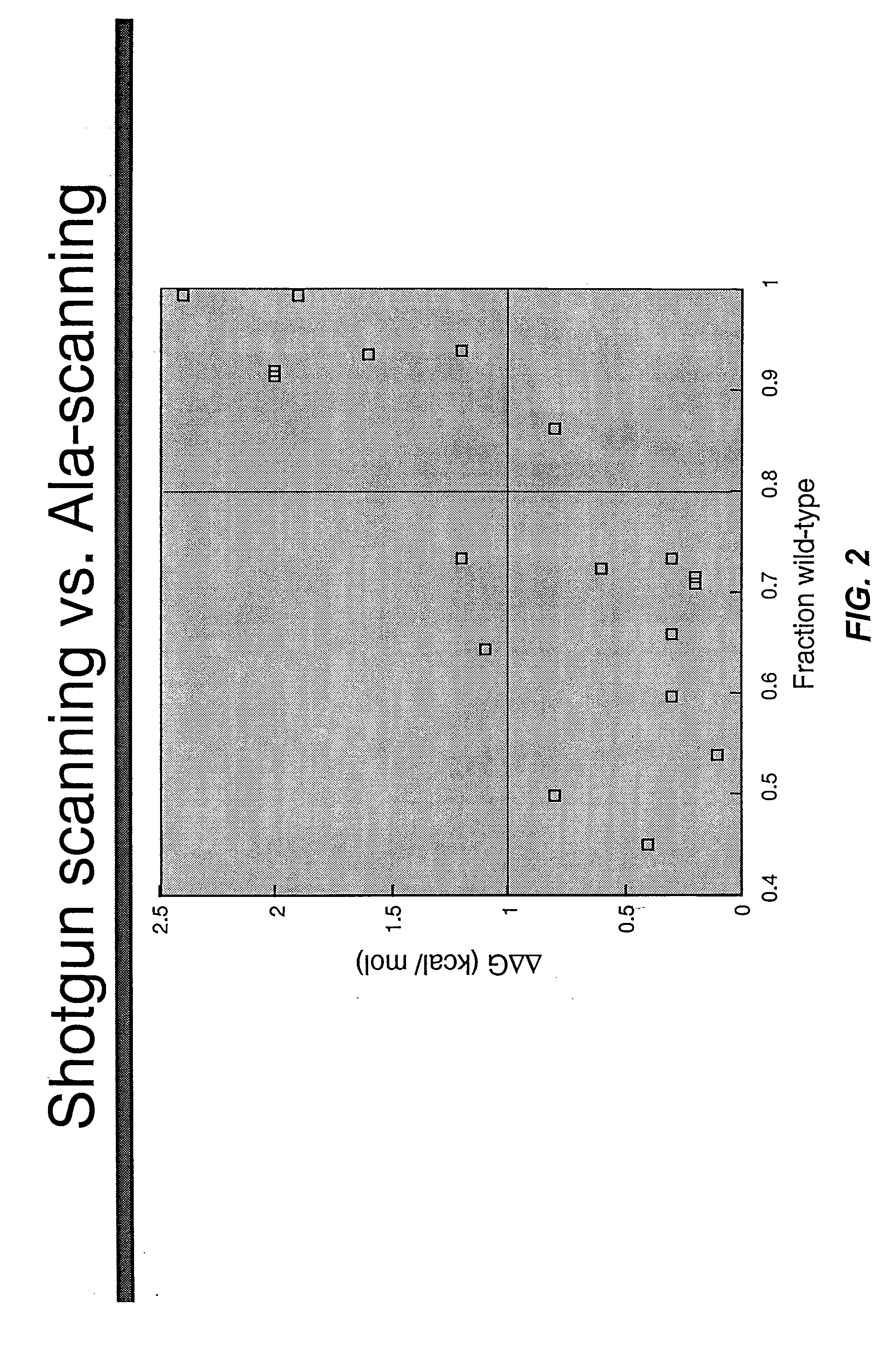
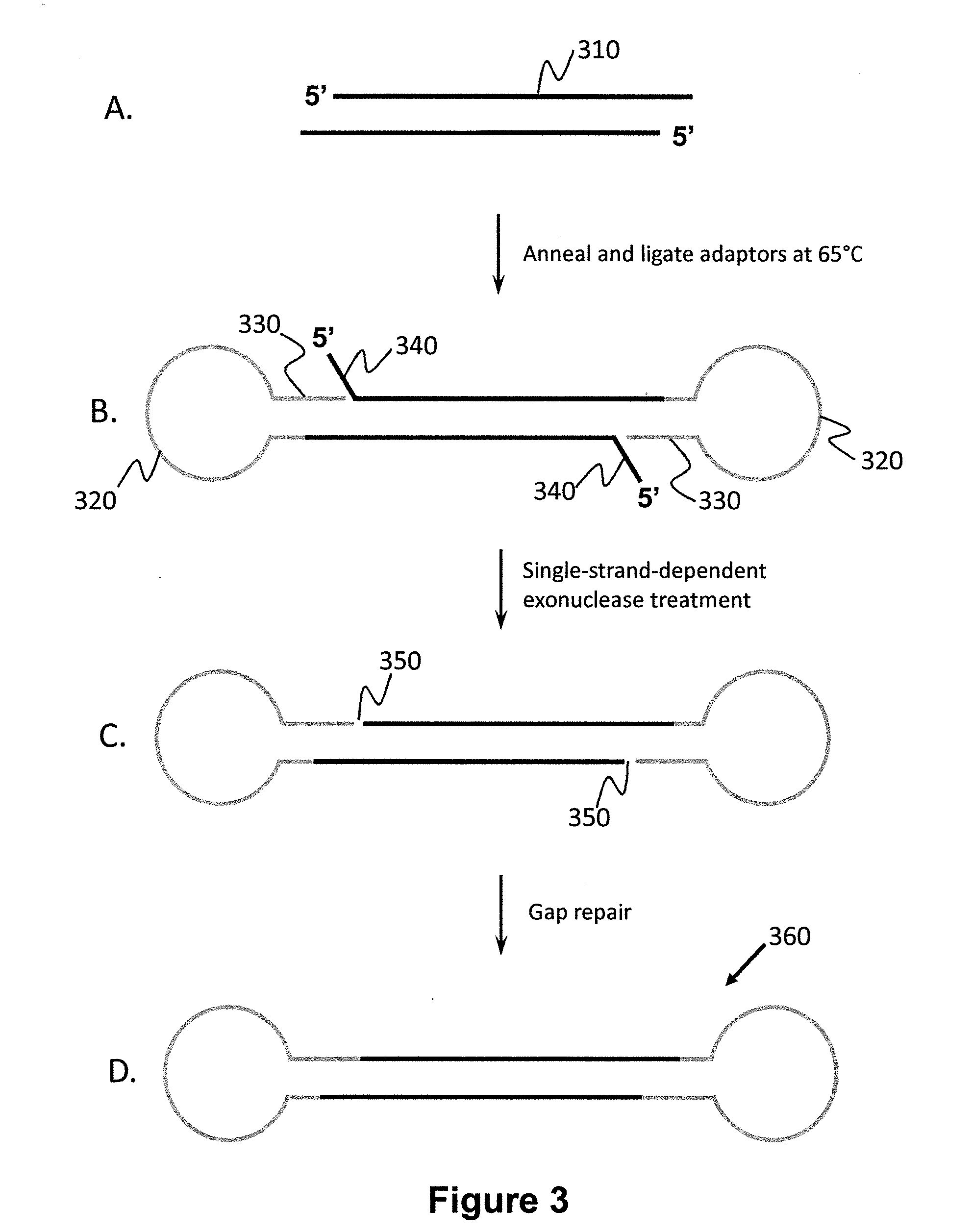
Shotgun scanning
A combinatorial method that uses statistics and DNA sequence analysis rapidly assesses the functional and structural importance of individual protein side chains to binding interactions. This general method, termed “shotgun scanning”, enables the rapid mapping of functional protein and peptide epitopes and is suitable for high throughput proteomics.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Increasing confidence of allele calls with molecular counting
ActiveUS8481292B2Easy to analyzeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisNucleotide
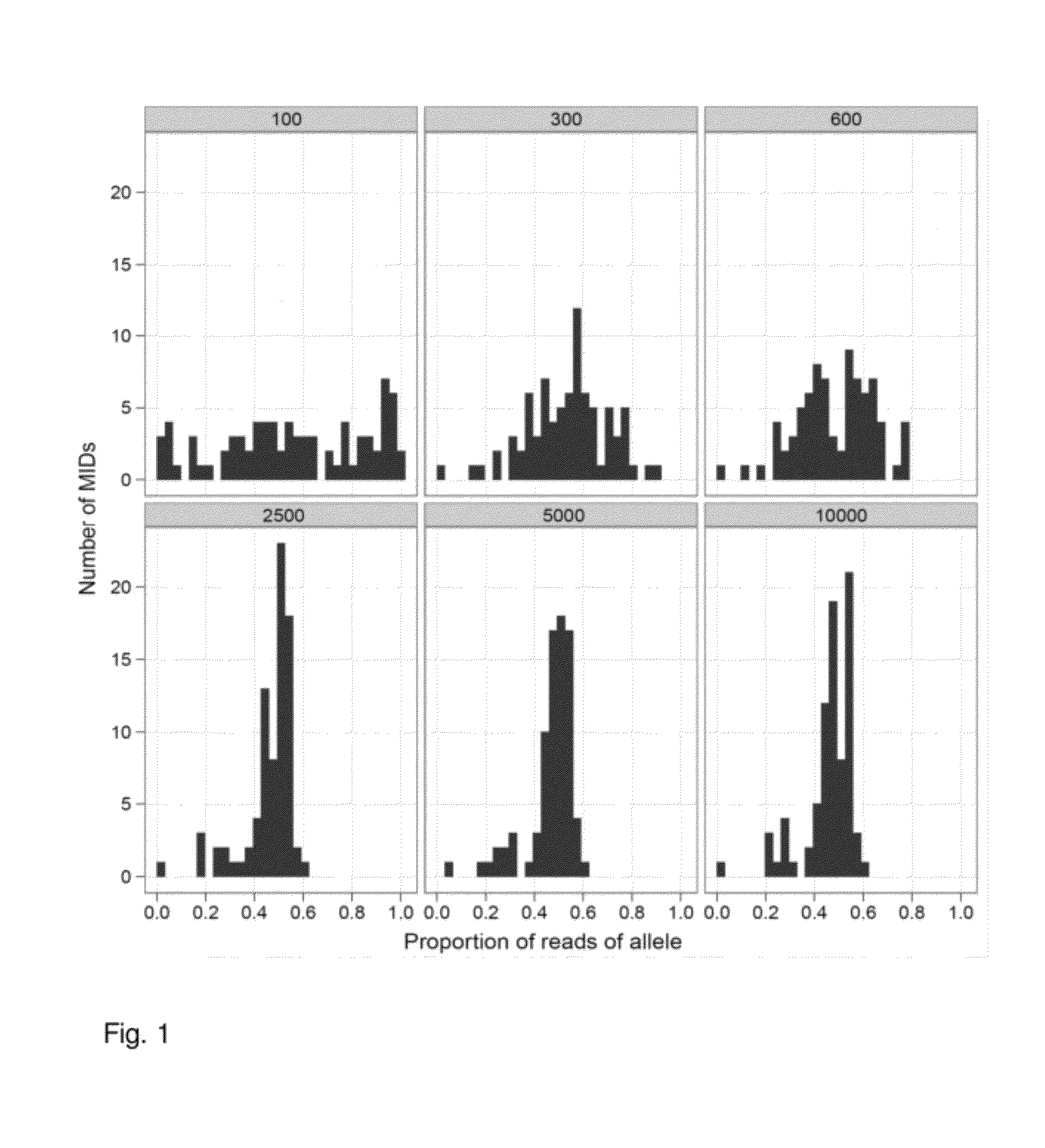
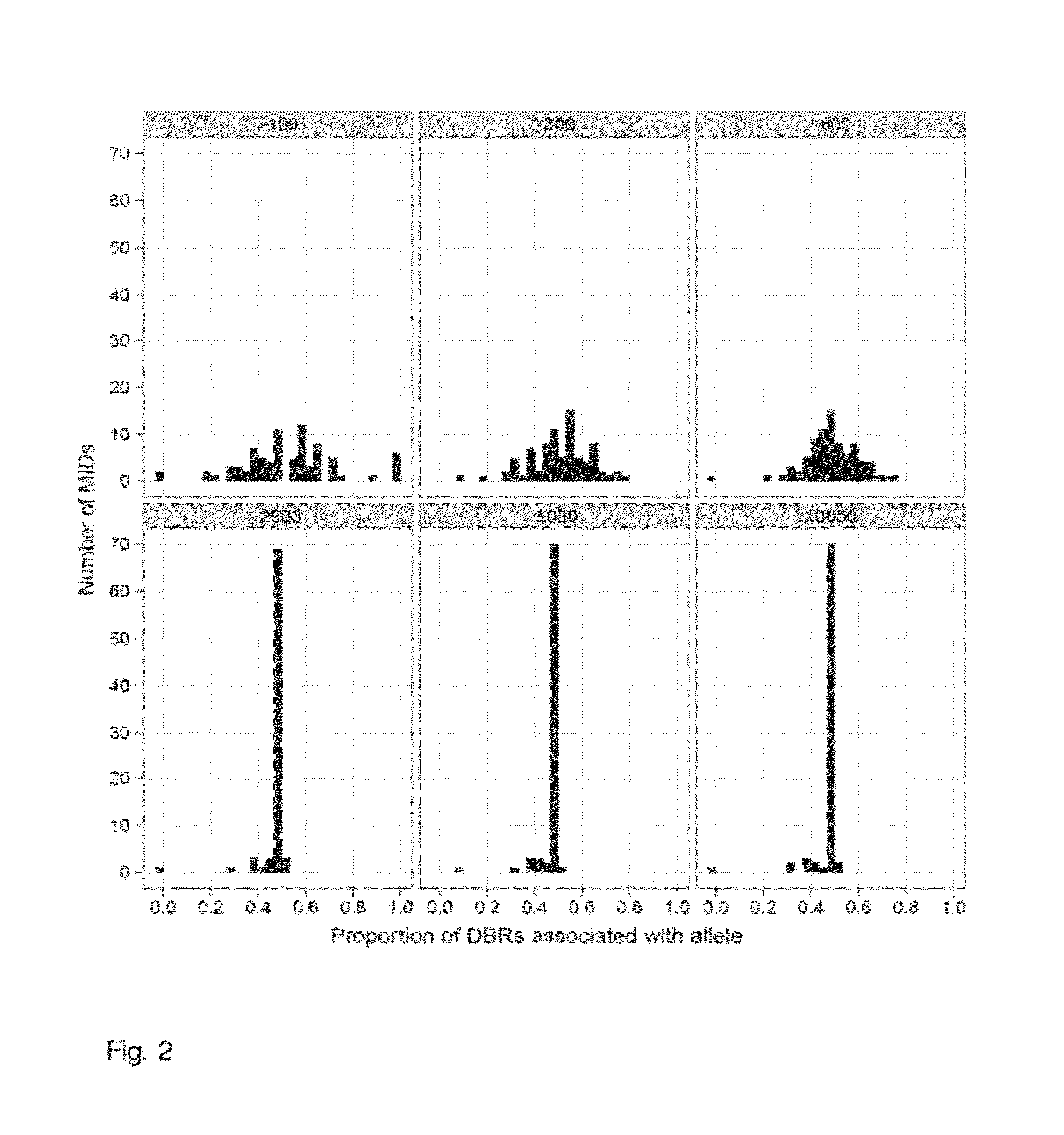
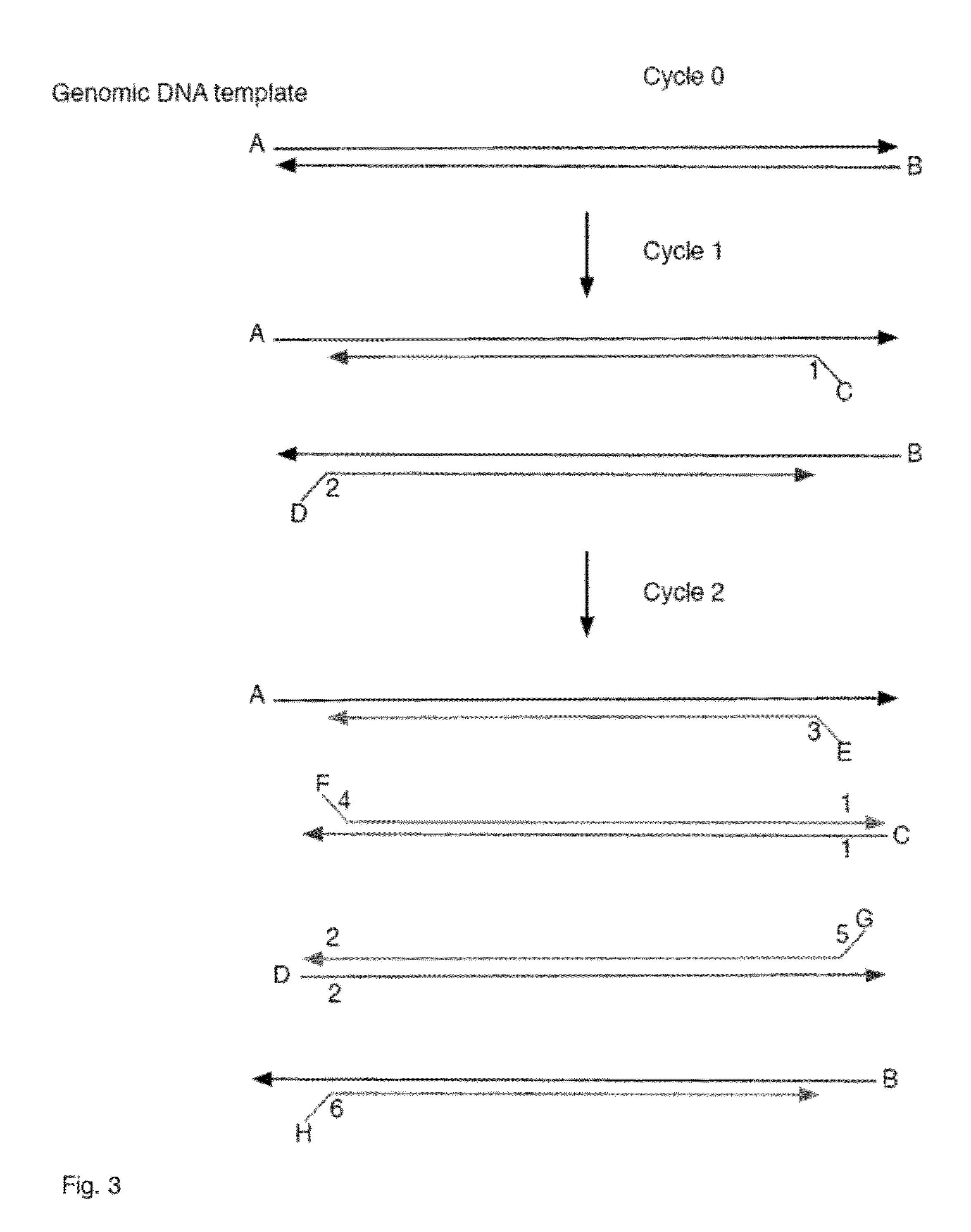
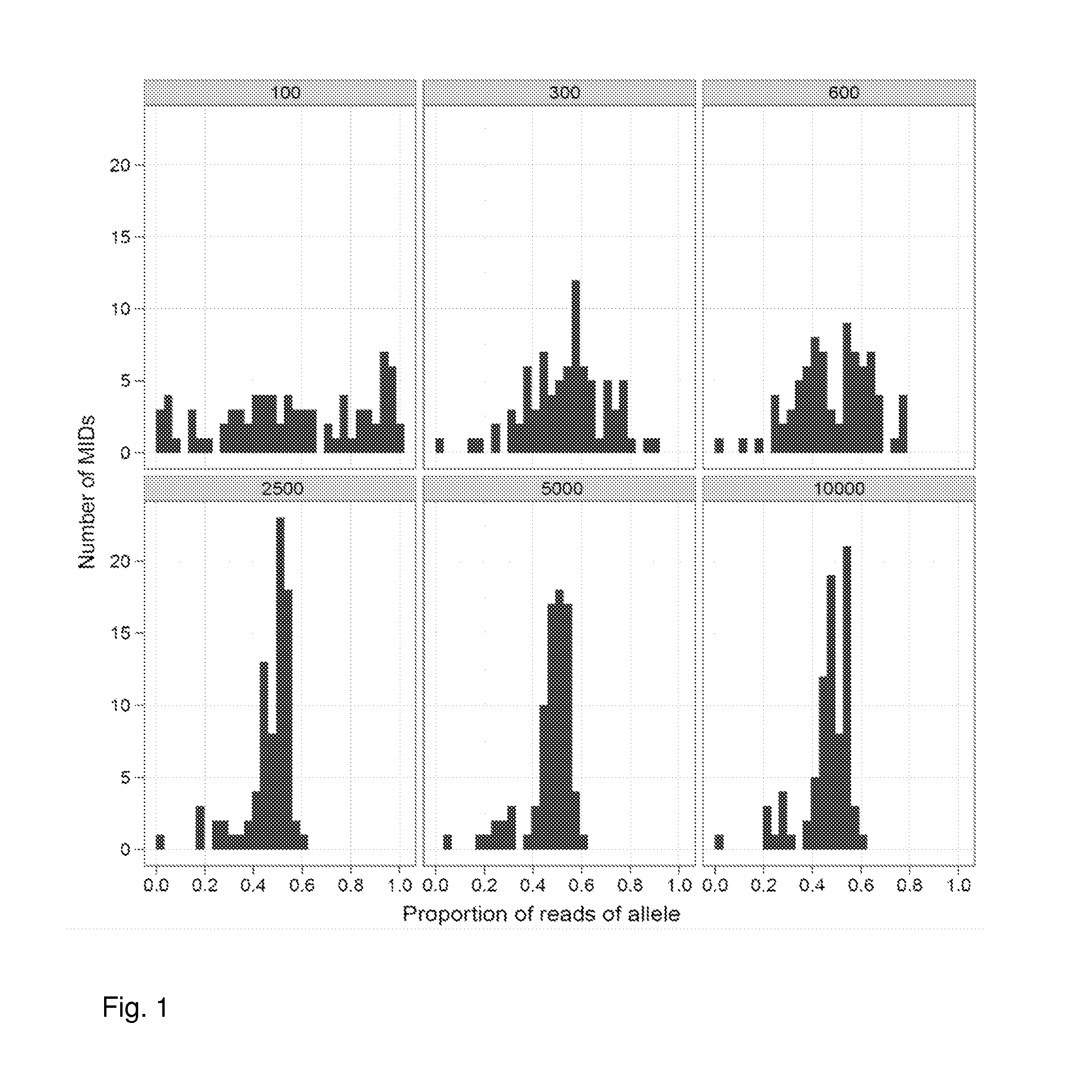
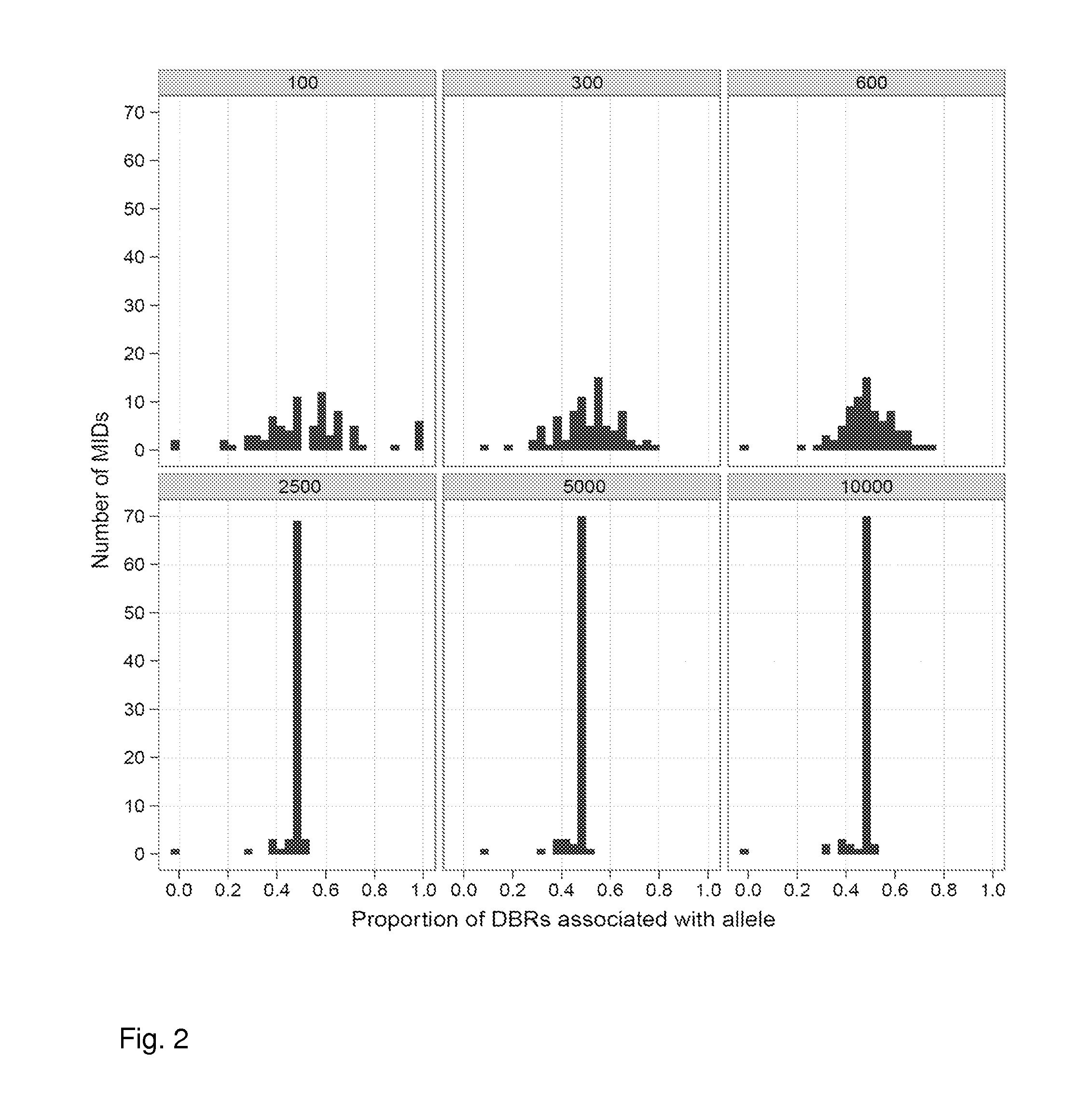
Aspects of the present invention include methods and compositions for determining the number of individual polynucleotide molecules originating from the same genomic region of the same original sample that have been sequenced in a particular sequence analysis configuration or process. In these aspects of the invention, a degenerate base region (DBR) is attached to the starting polynucleotide molecules that are subsequently sequenced (e.g., after certain process steps are performed, e.g., amplification and / or enrichment). The number of different DBR sequences present in a sequencing run can be used to determine / estimate the number of different starting polynucleotides that have been sequenced. DBRs can be used to enhance numerous different nucleic acid sequence analysis applications, including allowing higher confidence allele call determinations in genotyping applications.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Increasing confidence of allele calls with molecular counting
ActiveUS20120071331A1Easy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationSequence analysisAllele
Aspects of the present invention include methods and compositions for determining the number of individual polynucleotide molecules originating from the same genomic region of the same original sample that have been sequenced in a particular sequence analysis configuration or process. In these aspects of the invention, a degenerate base region (DBR) is attached to the starting polynucleotide molecules that are subsequently sequenced (e.g., after certain process steps are performed, e.g., amplification and / or enrichment). The number of different DBR sequences present in a sequencing run can be used to determine / estimate the number of different starting polynucleotides that have been sequenced. DBRs can be used to enhance numerous different nucleic acid sequence analysis applications, including allowing higher confidence allele call determinations in genotyping applications.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Nucleic acid sequence analysis from single cells
ActiveUS20160053253A1Reduce cascadeNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBarcodeNucleic acid sequencing
Presented herein are methods and compositions for multiplexed single cell gene expression analysis. Some methods and compositions include the use of droplets and / or beads bearing unique barcodes such as unique molecular barcodes (UMI).
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Methods of monitoring conditions by sequence analysis
ActiveUS20100151471A1Maximize correlationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSequence analysisAutoimmune disease
There is a need for improved methods for determining the diagnosis and prognosis of patients with conditions, including autoimmune disease and cancer. Provided herein are methods for using DNA sequencing to identify personalized biomarkers in patients with autoimmune disease and other conditions. Identified biomarkers can be used to determine the disease state for a subject with an autoimmune disease or other condition.
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
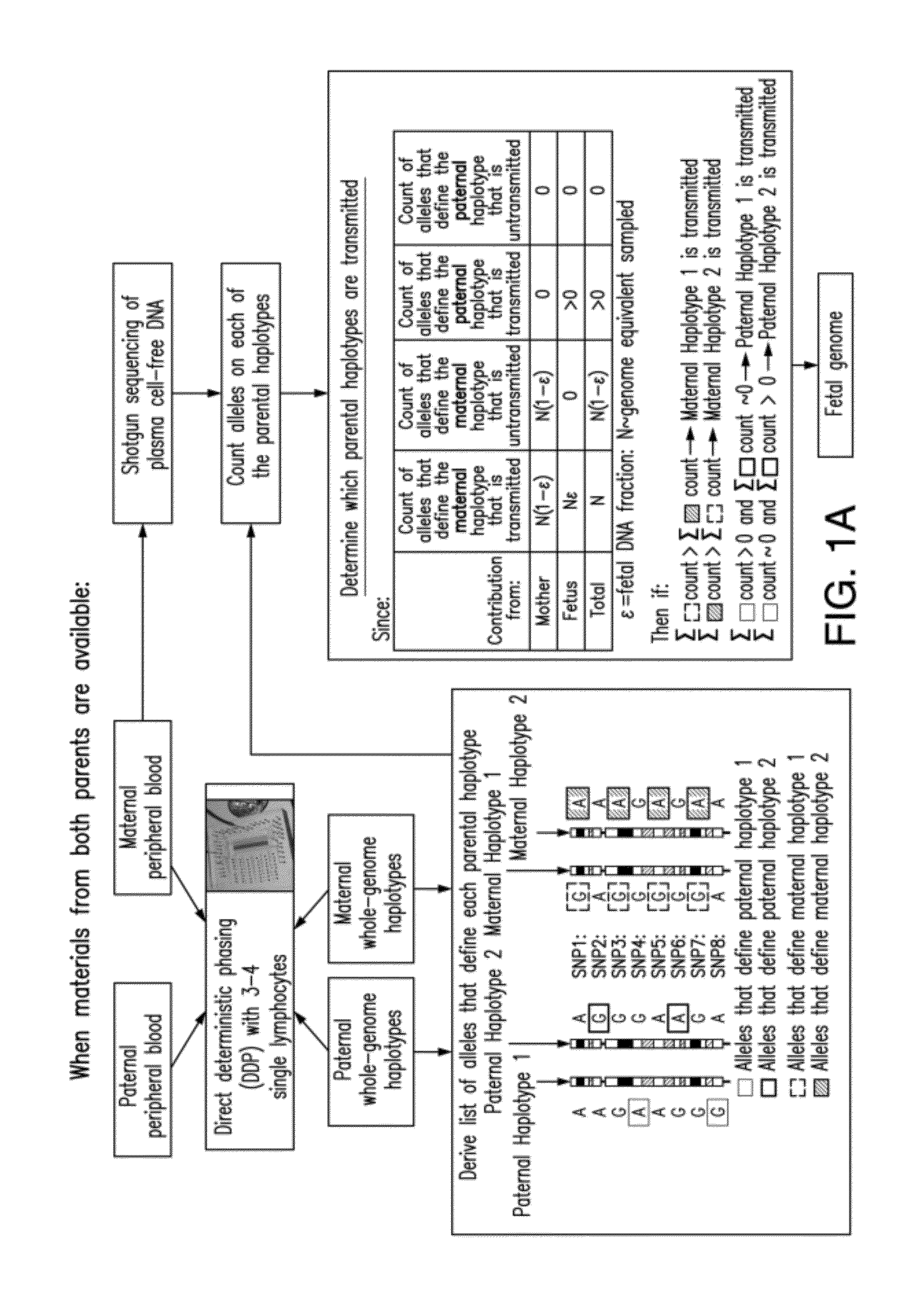
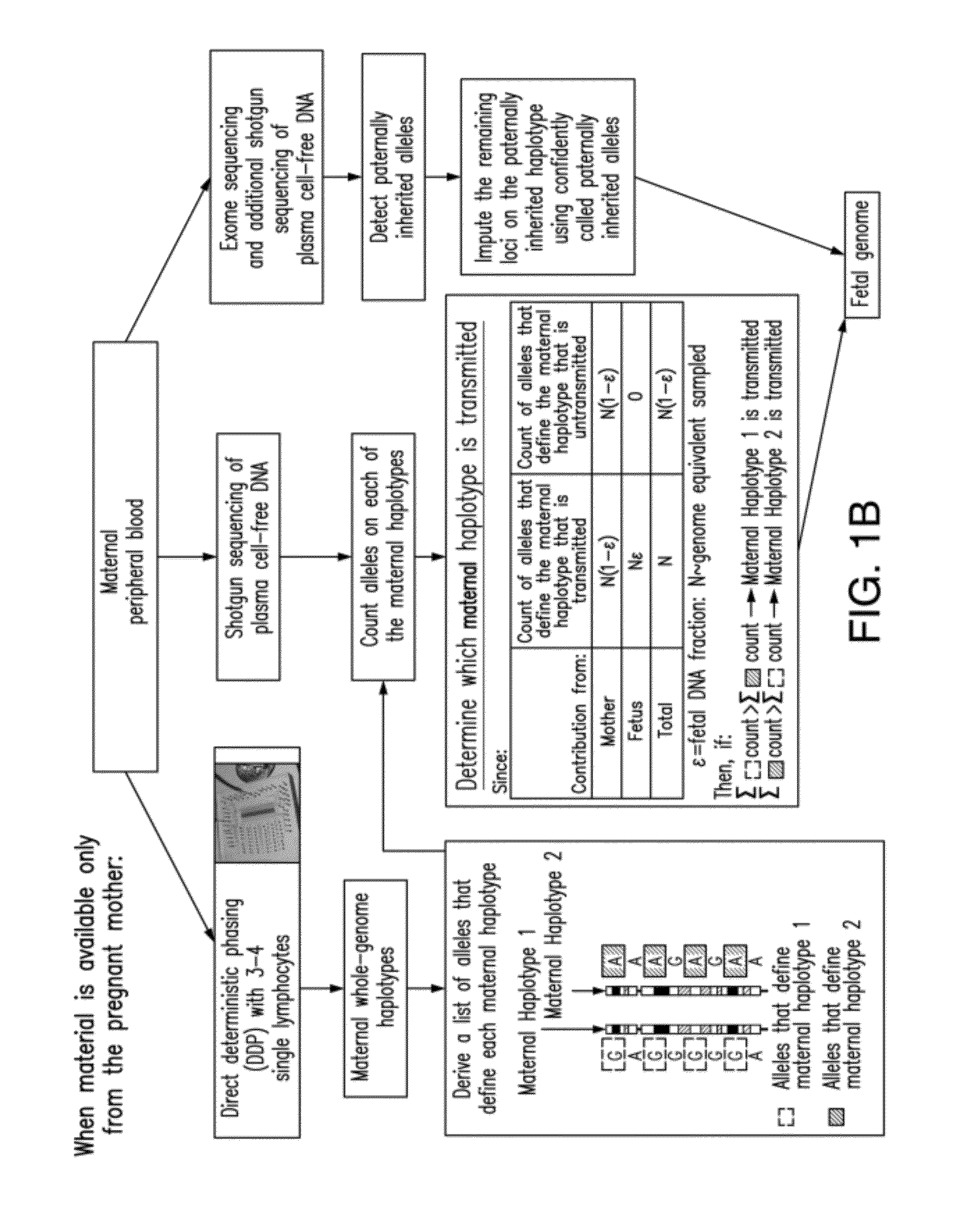
Non-invasive determination of fetal inheritance of parental haplotypes at the genome-wide scale
ActiveUS20120196754A1Reduce riskNon-invasively determiningBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSequence analysisSerum samples
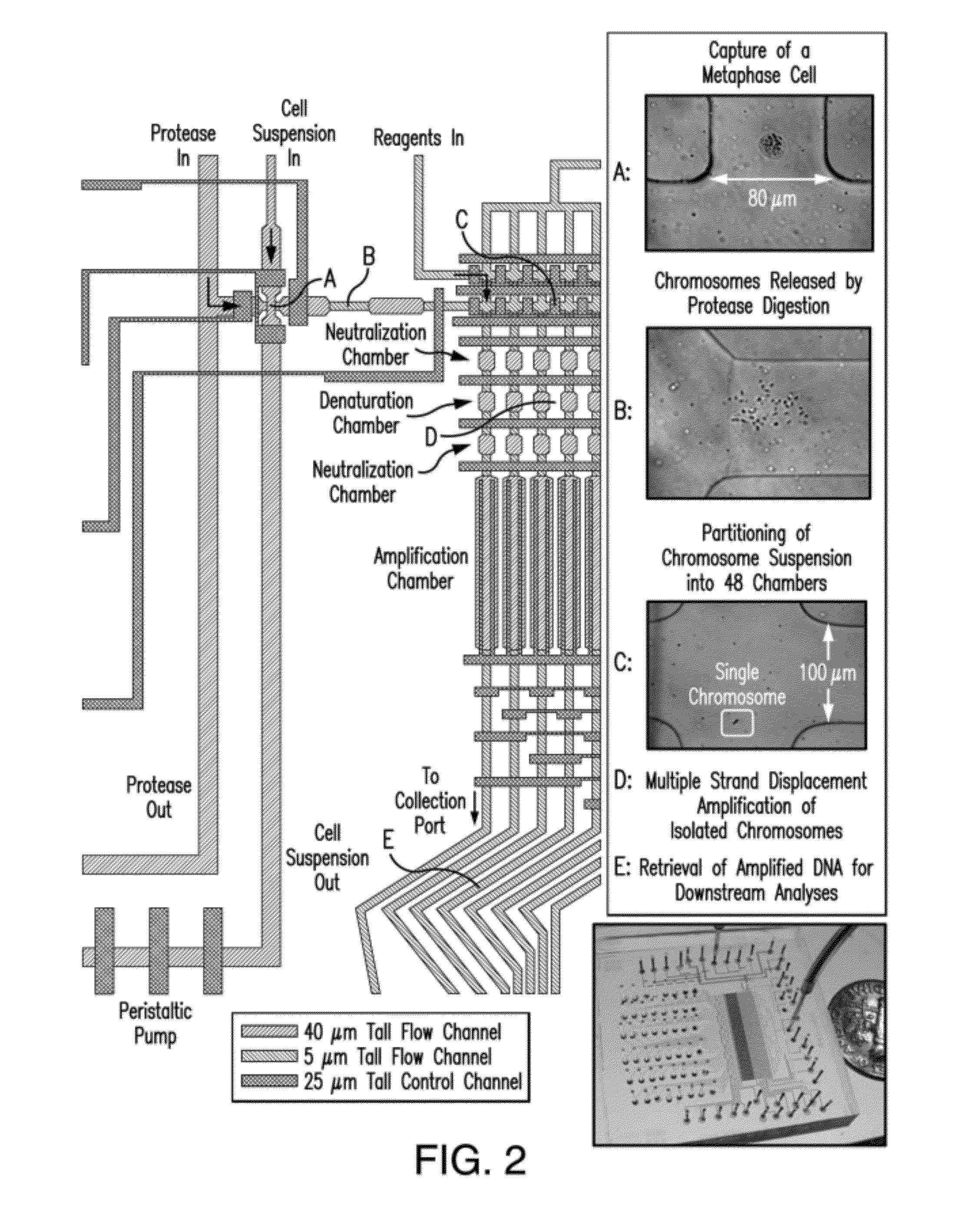
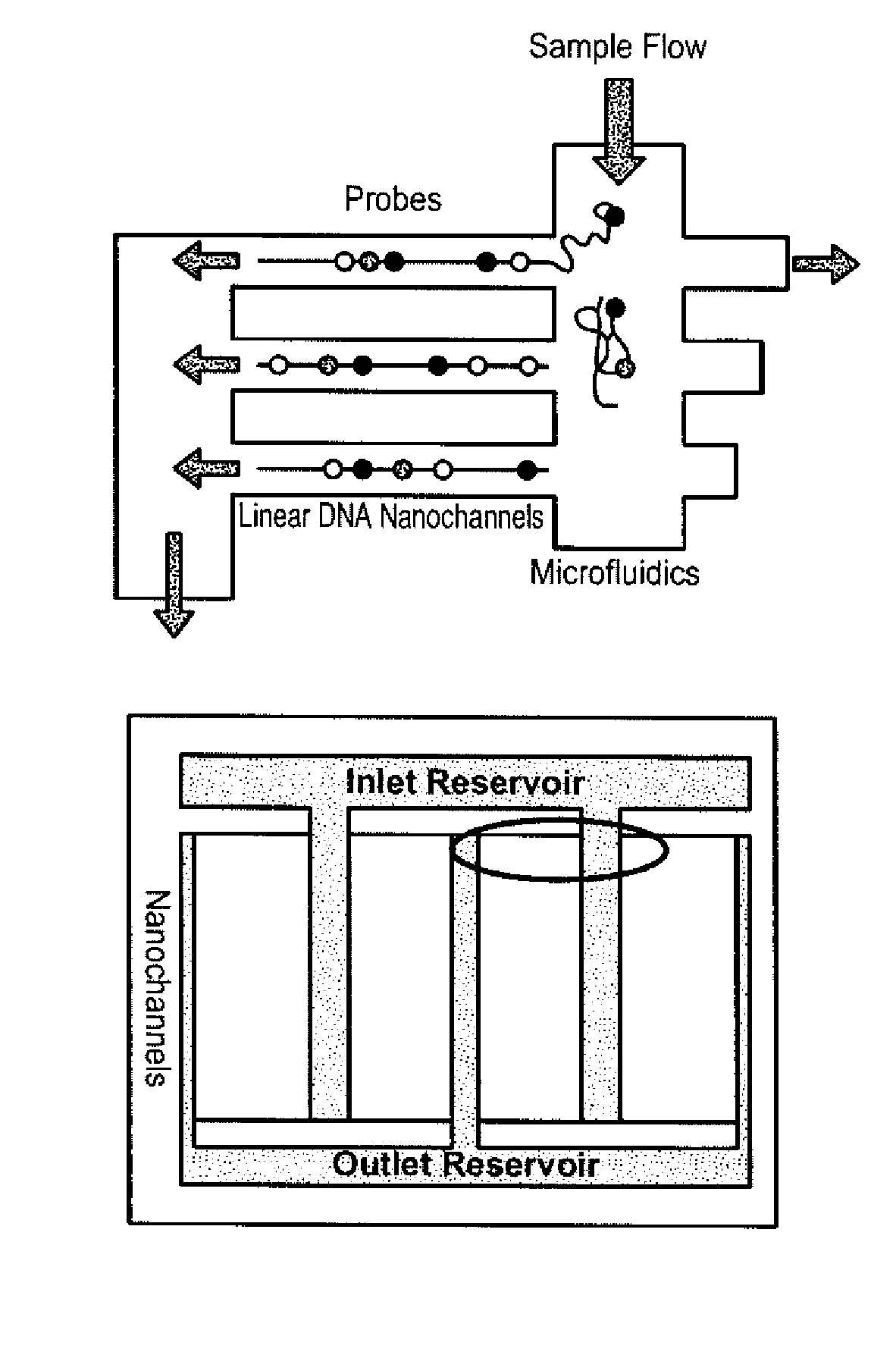
The present invention provides a method, device and a computer program for haplotyping single cells, such that a sample taken from a pregnant female, without directly sampling the fetus, provides the ability to non-invasively determine the fetal genome. The method can be performed by determining the parental and inherited haplotypes, or can be performed merely on the basis of the mother's genetic information, obtained preferably in a blood or serum sample. The novel device allows for sequence analysis of single chromosomes from a single cell, preferably by partitioning single chromosomes from a metaphase cell into long, thin channels where a sequence analysis can be performed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
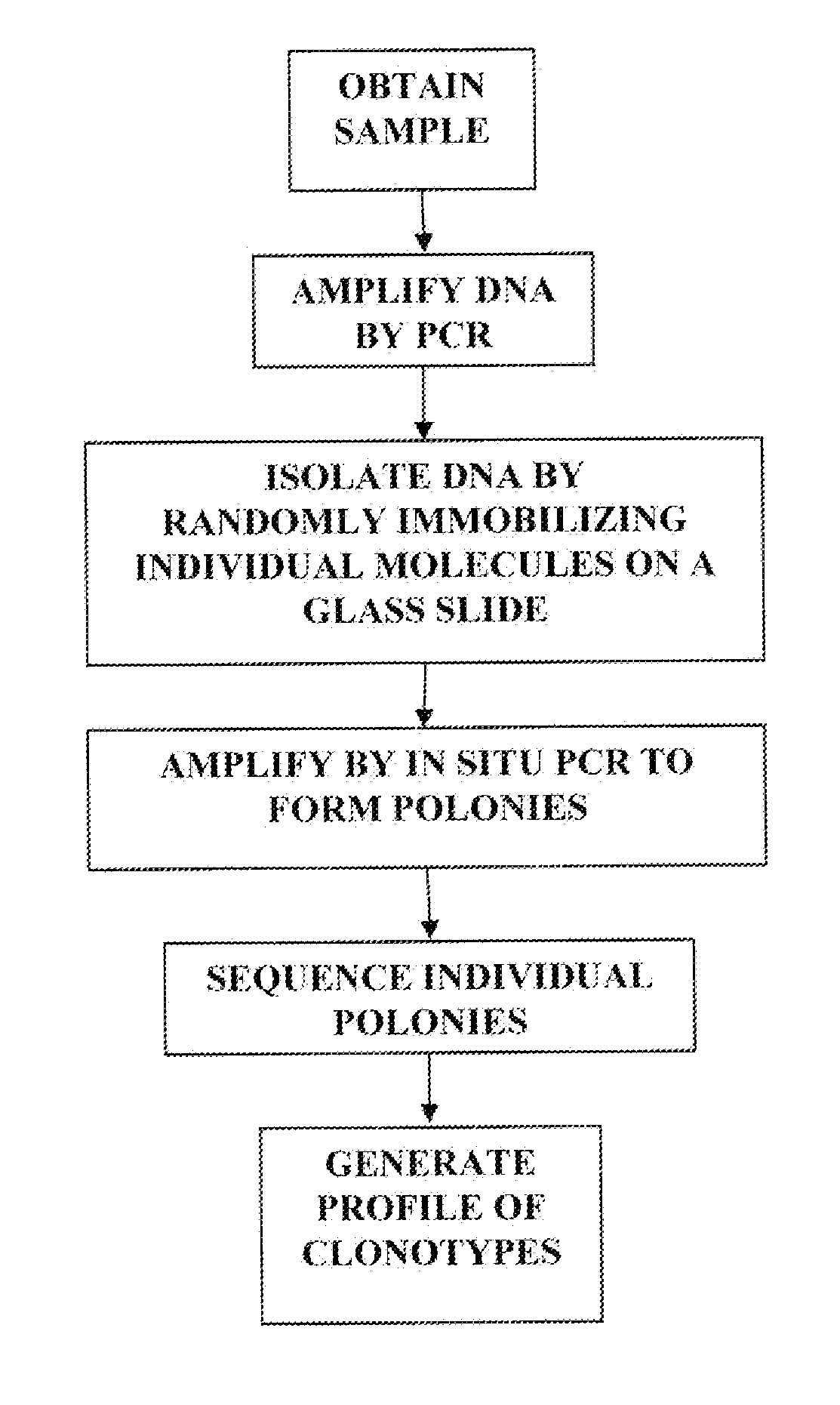
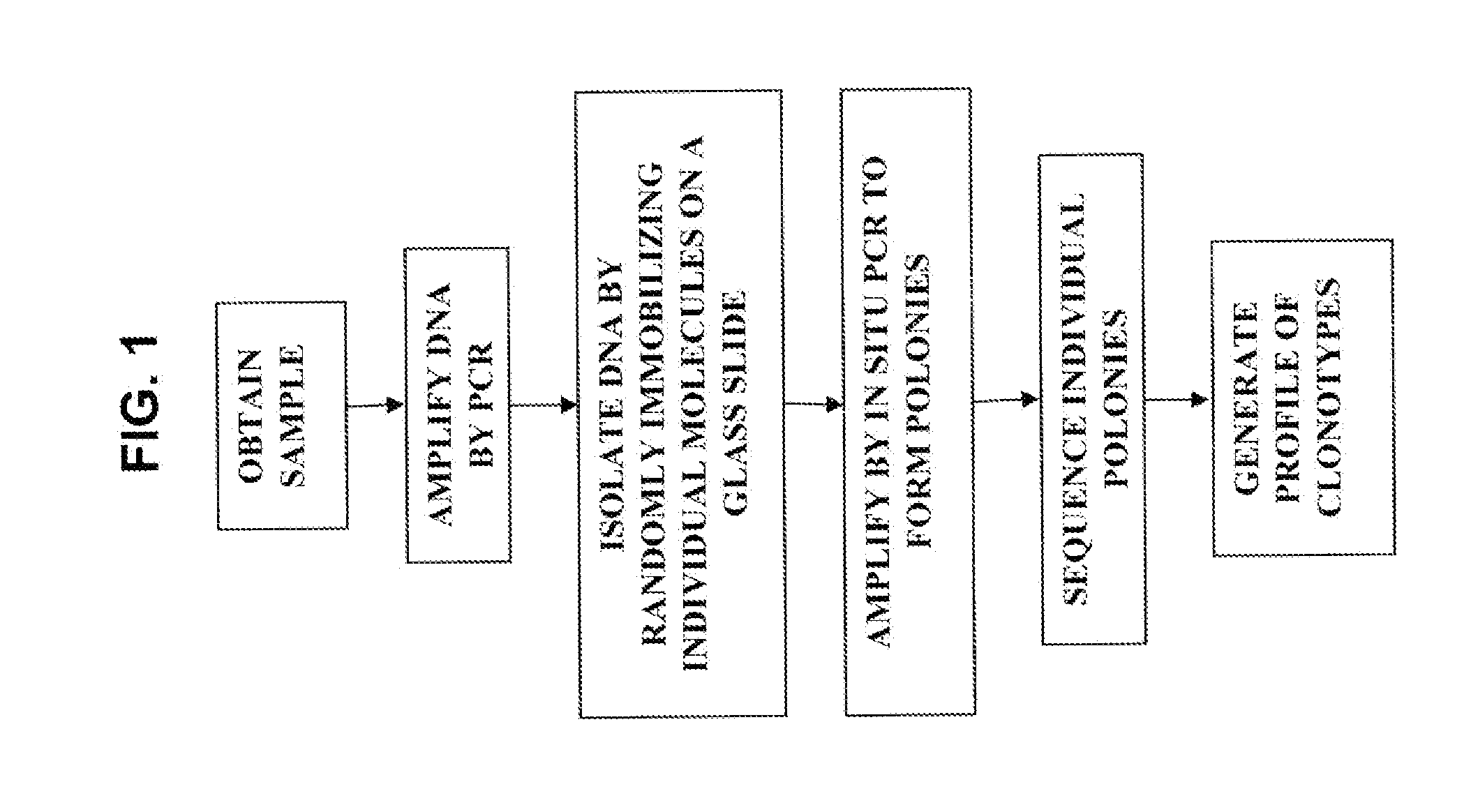
Sequence analysis of complex amplicons
ActiveUS20140315725A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationSequence analysisB-cell receptor
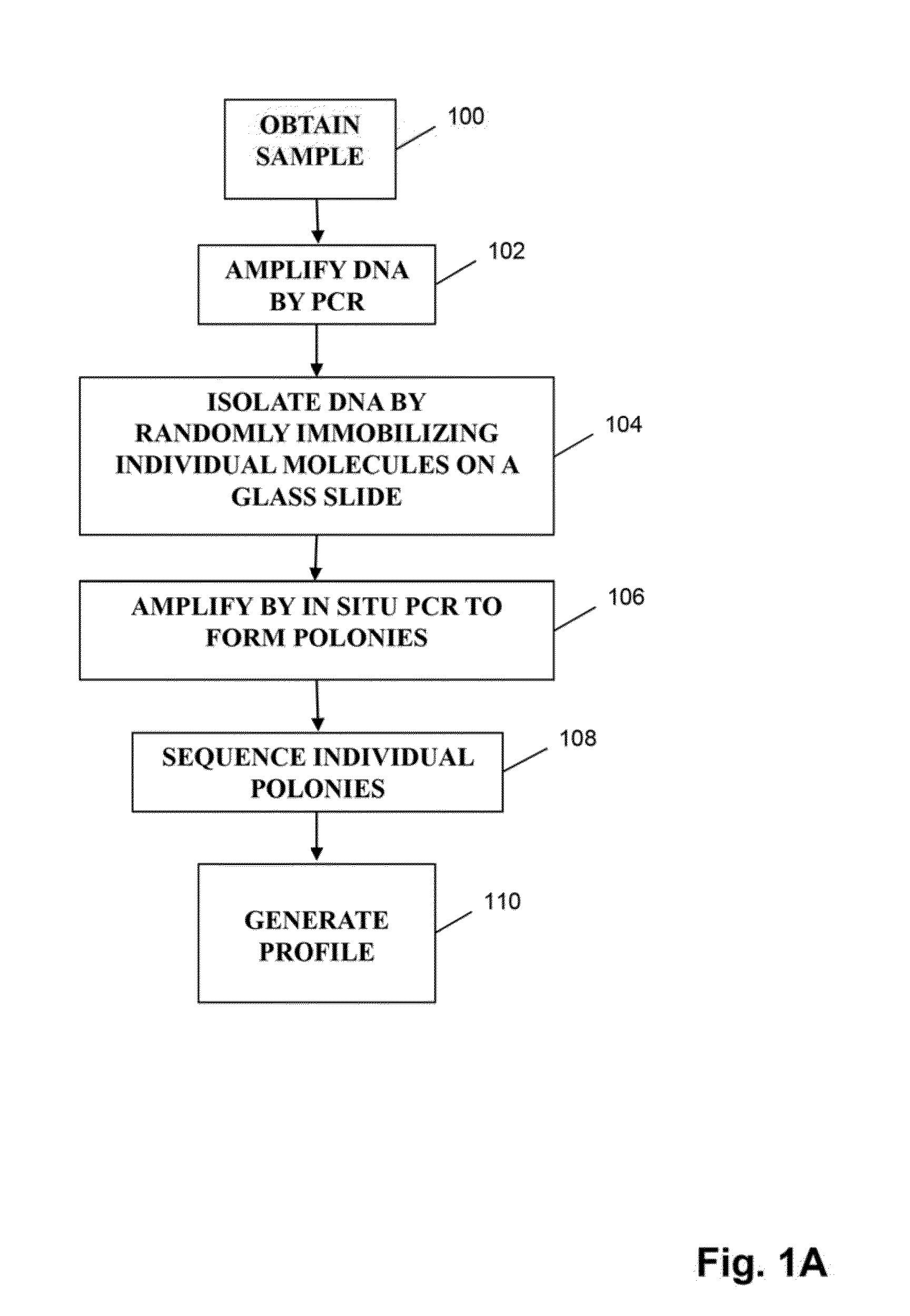
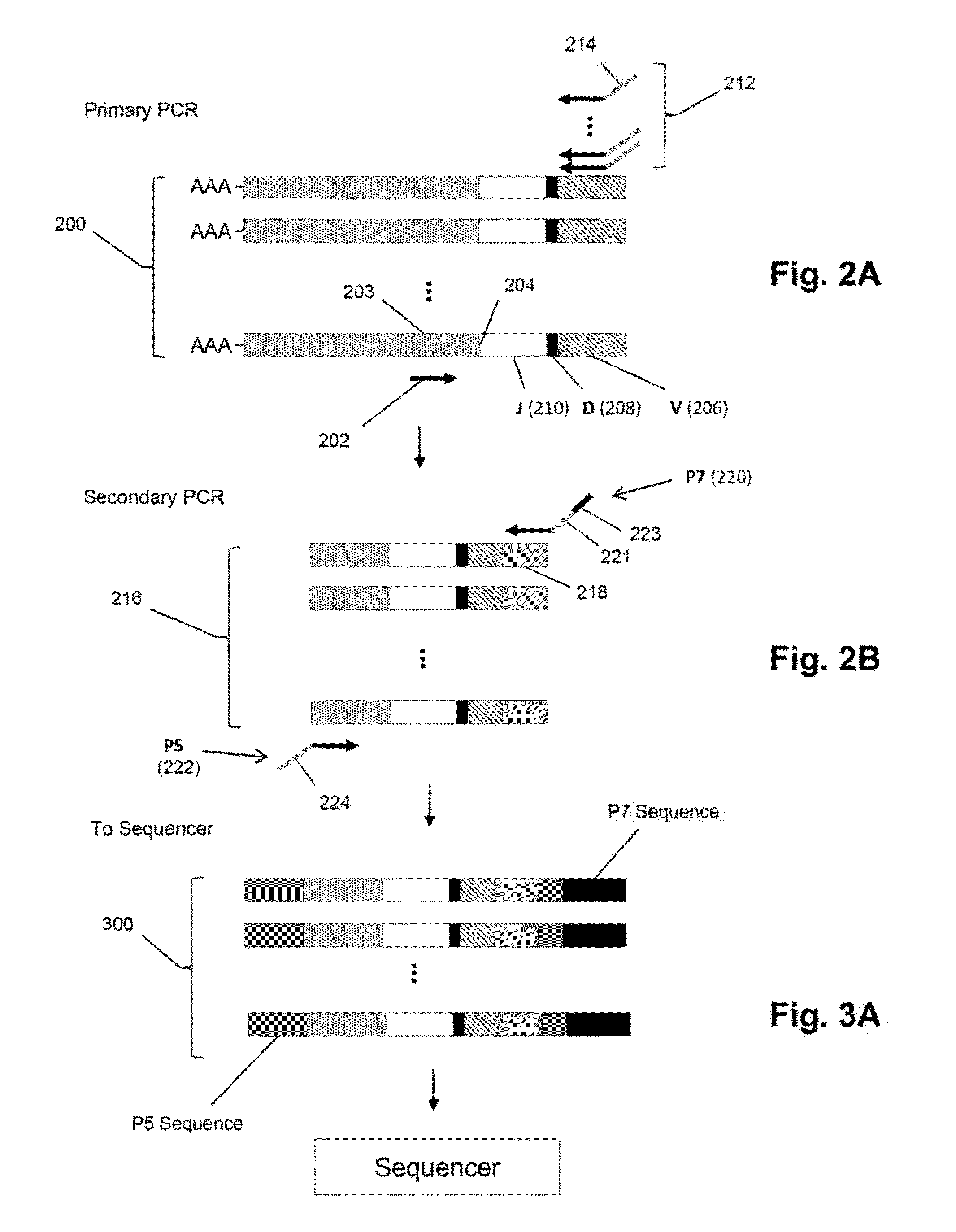
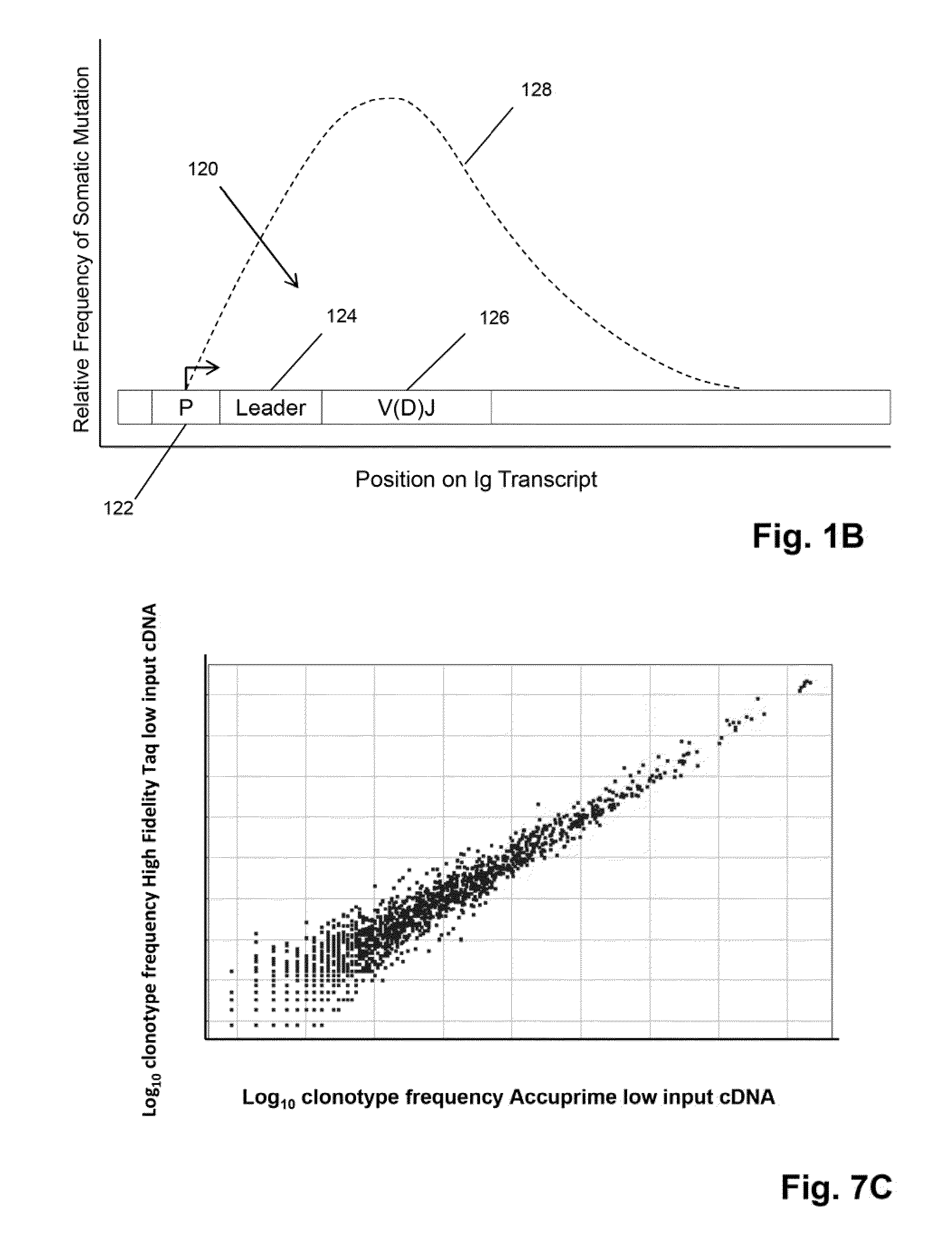
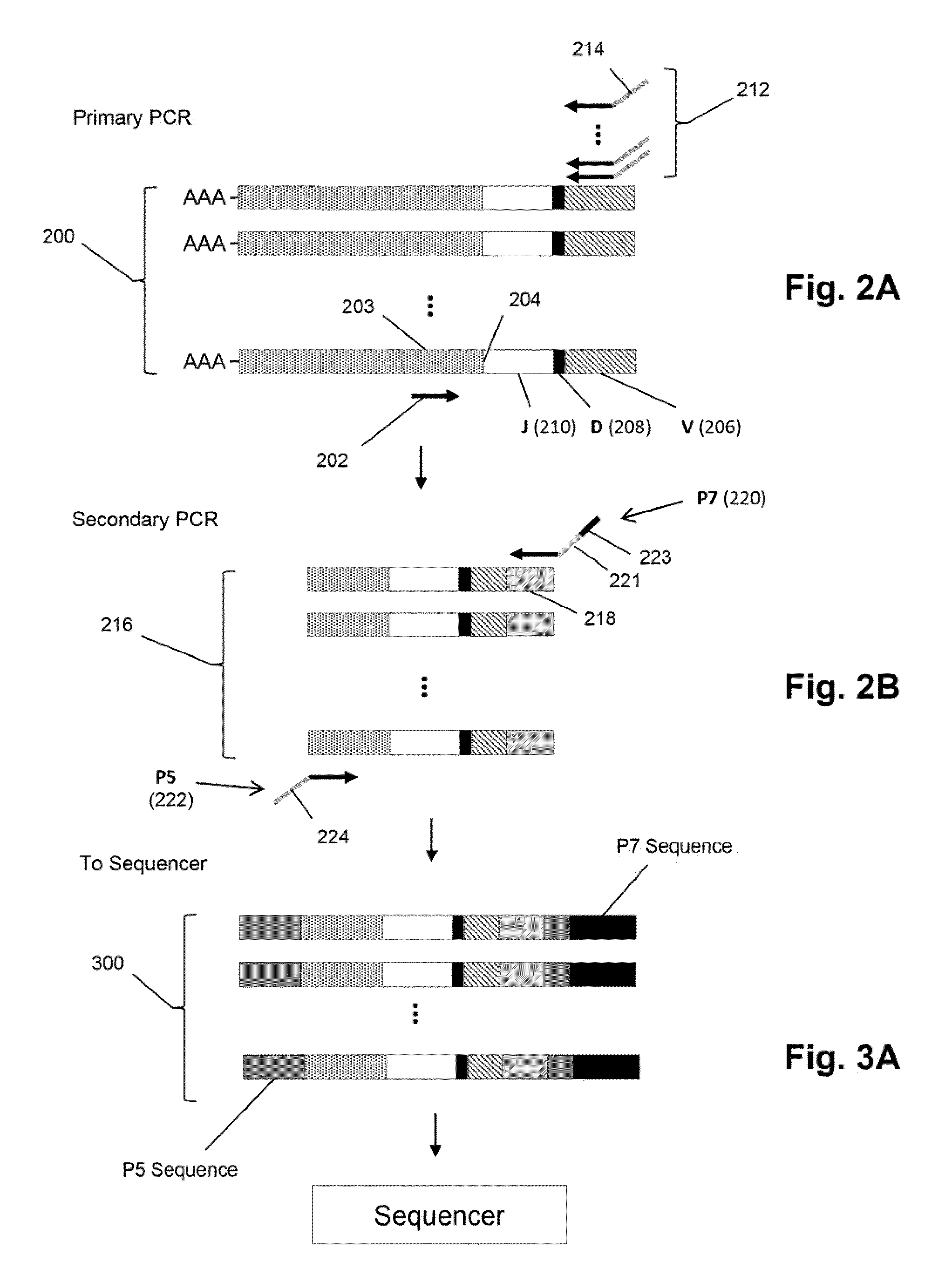
The invention is directed to methods of generating sequence profiles of populations of nucleic acids, whose member nucleic acids contain regions of high variability, such as populations of nucleic acids encoding T cell receptors or B cell receptors. In one aspect, the invention provides pluralities of sets of primers for generating nested sets of templates from nucleic acids in such populations, thereby insuring the production of at least one template from which sequence reads are generated, despite such variability, or despite limited lengths or quality of sequence reads. In another aspect, members of such populations are bidirectionally sequenced so that further sequence information is obtained by analyzing overlapping sequence reads in the zones of highest variability.
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
Methods of monitoring conditions by sequence analysis
ActiveUS20110207135A1Low quality scoreMicrobiological testing/measurementICT adaptationSequence analysisGenetics
The invention is directed to methods of generating sequence profiles of populations of nucleic acids, whose member nucleic acids contain regions of high variability, such as populations of nucleic acids encoding T cell receptors or B cell receptors. In one aspect, the invention provides pluralities of sets of primers for generating nested sets of templates from nucleic acids in such populations, thereby insuring the production of at least one template from which sequence reads are generated, despite such variability, or dispite limited lenghs or quality of sequence reads. In another aspect, members of such populations are bidirectionally sequenced so that further sequence information is obtained by analyzing overlapping sequence reads in the zones of highest variability.
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
Performing sequence analysis as a multipart plan storing intermediate results as a relation
InactiveUS7702610B2Reliable and high performance integrationReduce calculationMedical data miningData processing applicationsProgramming languageSequence analysis
A usage model and the underlying technology used to provide sequence analysis as part of a relational database system. Included components include the semantic and syntactic integration of the sequence analysis with an existing query language, the storage methods for the sequence data, and the design of a multipart execution scheme that runs the sequence analysis as part of a potentially larger database query, especially using parallel execution techniques.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Immobilized nucleic acid complexes for sequence analysis
ActiveUS20100075328A1Use performanceImprove accuracySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisPolymerase L
Provided are methods for sequencing a nucleic acid that include fixing a template to a surface through a template localizing moiety and sequencing the nucleic acid with a sequencing enzyme, e.g. a polymerase or exonuclease. The sequencing enzyme can optionally be exchanged with a second sequencing enzyme, which continues the sequencing of the nucleic acid. The template localizing moiety can optionally anneal with the nucleic acid and / or associate with the sequencing enzyme. Also provided are compositions comprising a nucleic acid fixed to a surface via a template localizing moiety, and a first sequencing enzyme, which can sequence the nucleic acid and optionally exchange with a second sequencing enzyme present in the composition. Compositions in which a template localizing moiety is immobilized on a surface are provided. Compositions for sequencing reactions are provided. Also provided are sequencing systems comprising reaction regions in which or near which template localizing moieties are immobilized.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Sequence analysis using decorated nucleic acids
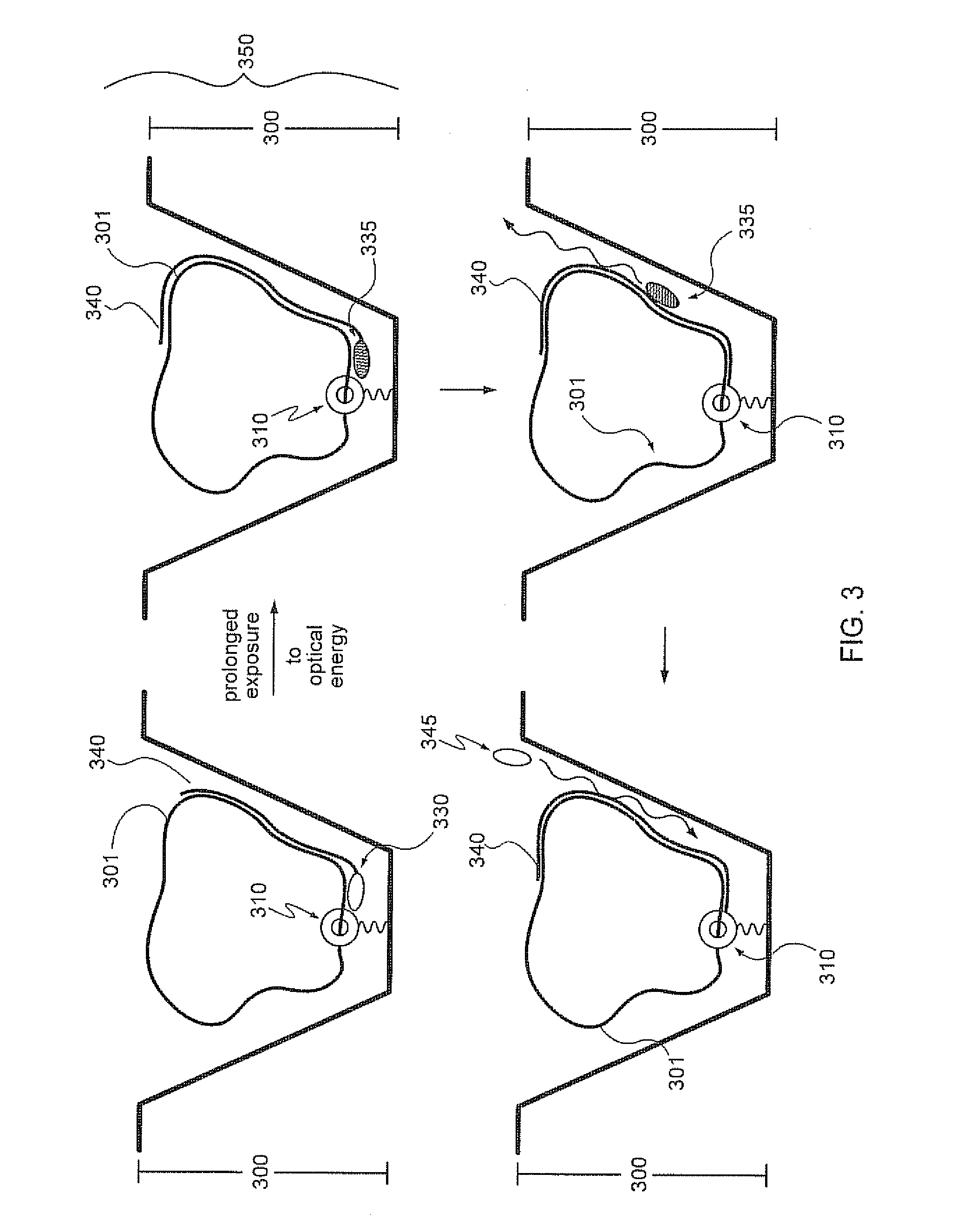
The present invention provides a sequence interrogation chemistry that combines the accuracy and haplotype integrity of long-read sequencing with improved methods of preparing genomic nucleic acids and analyzing sequence information generated from those nucleic acids. The present invention encompasses compositions comprising decorated nucleic acids stretched on substrates. The present invention further encompasses methods of making stretched decorated nucleic acids and methods of using decorated nucleic acids to obtain sequence information.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Sample indexing methods and compositions for sequencing applications
InactiveUS20160314242A1Improve abilitiesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisSequence analysisComputational biology
Compositions, processes and systems are provided for preparing and analyzing sample indexing of nucleic acid libraries for multiplexed sequencing analysis of diverse sample sets.
Owner:10X GENOMICS
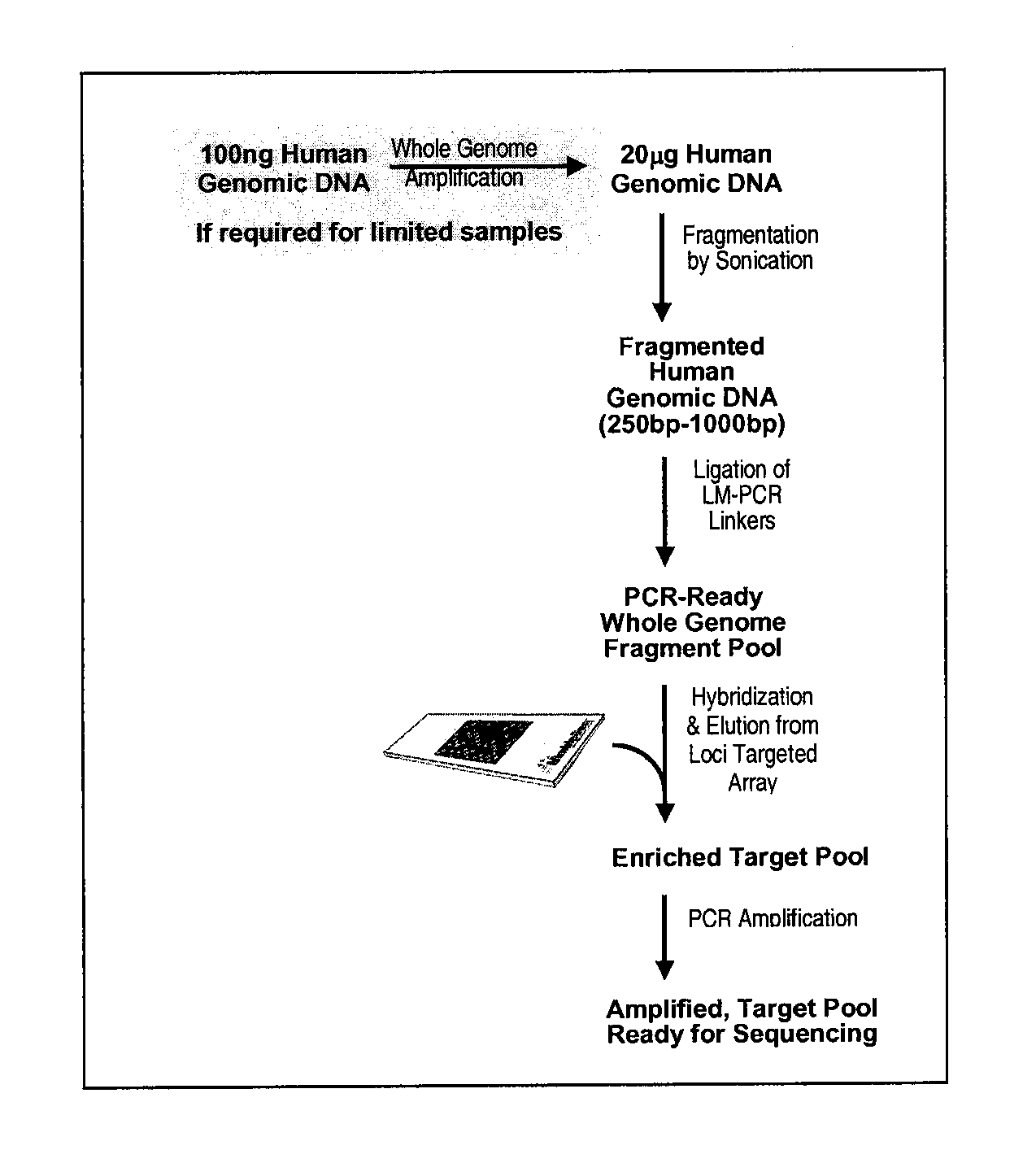
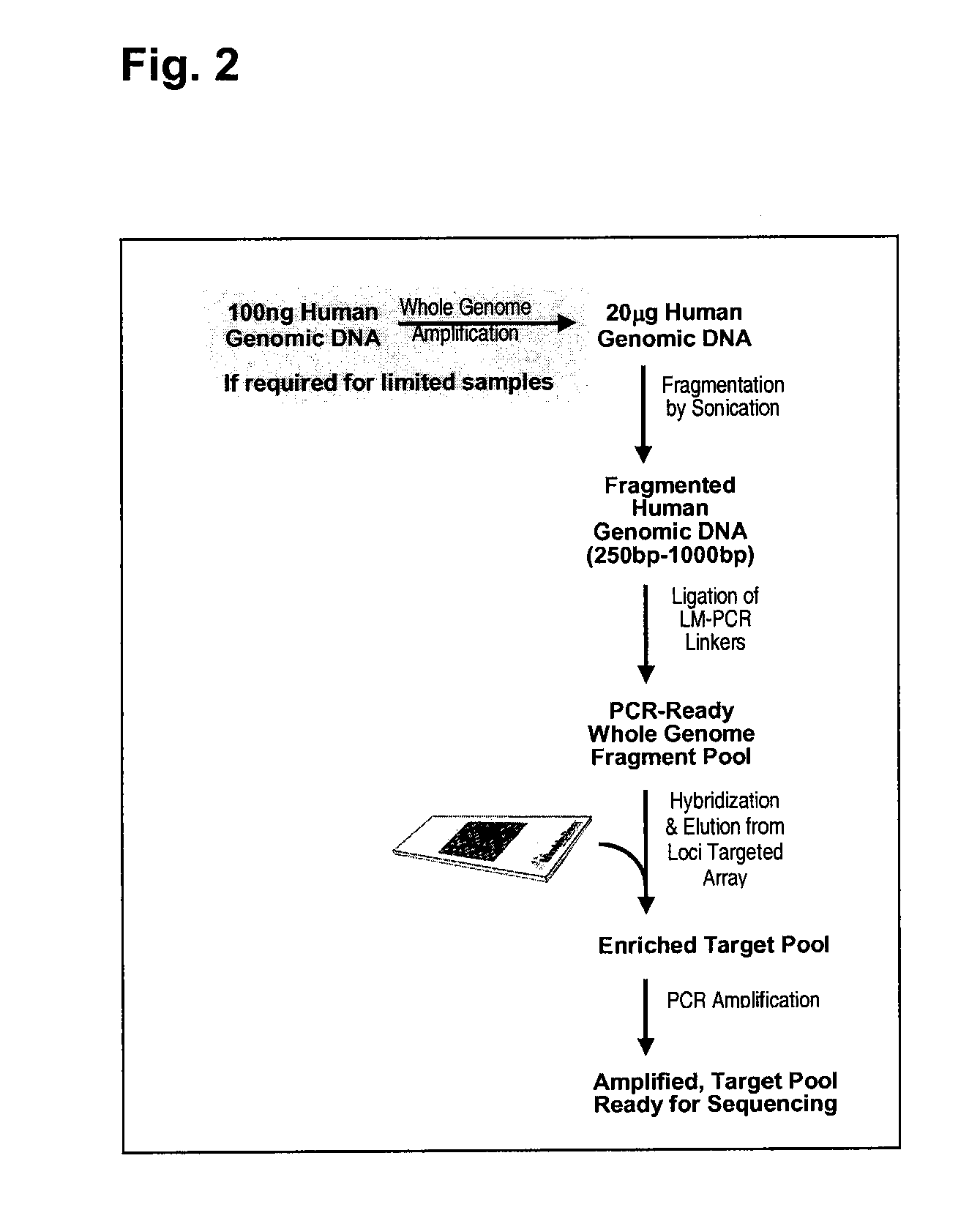
Enrichment and sequence analysis of genomic regions
InactiveUS20080194414A1Significant complexityFacilitate subsequent processingMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningSequence analysisAs Directed
The present invention provides novel methods for reducing the complexity of preferably a genomic sample for further analysis such as direct DNA sequencing, resequencing or SNP calling. The methods use pre-selected immobilized oligonucleotide probes to capture target nucleic acid molecules from a sample containing denatured, fragmented (genomic) nucleic acids for reducing the genetic complexity of the original population of nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:ALBERT THOMAS J +8
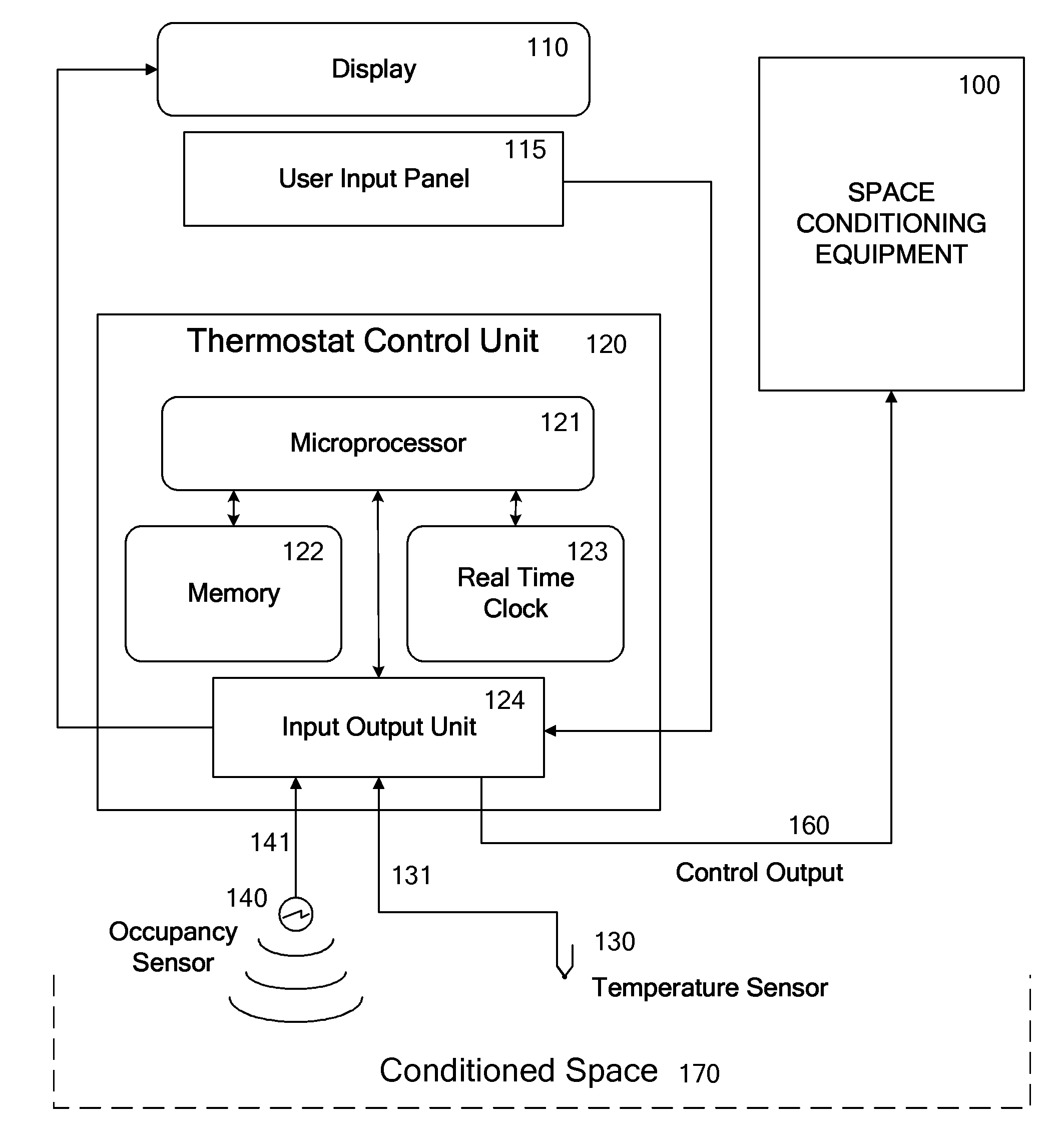
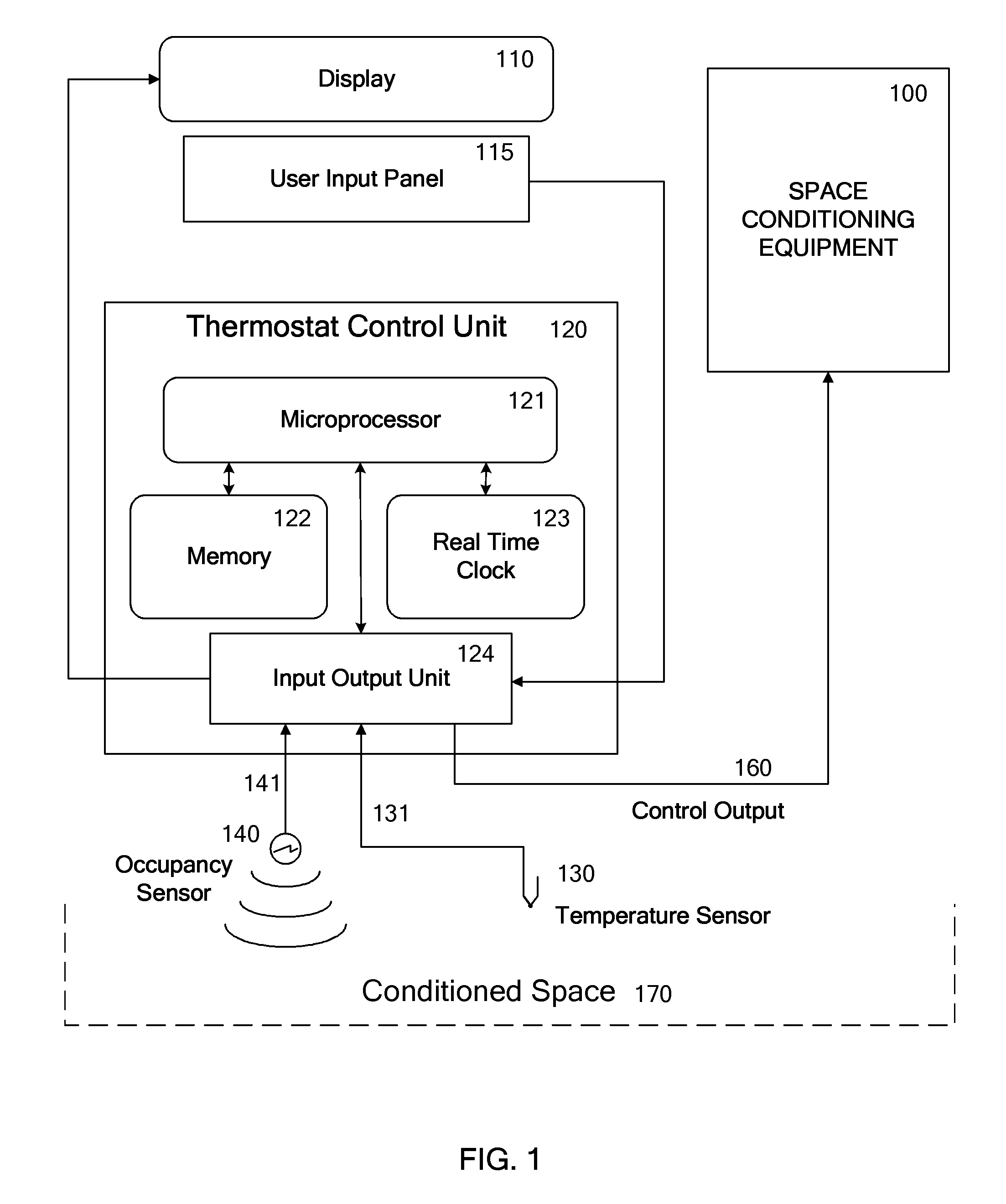
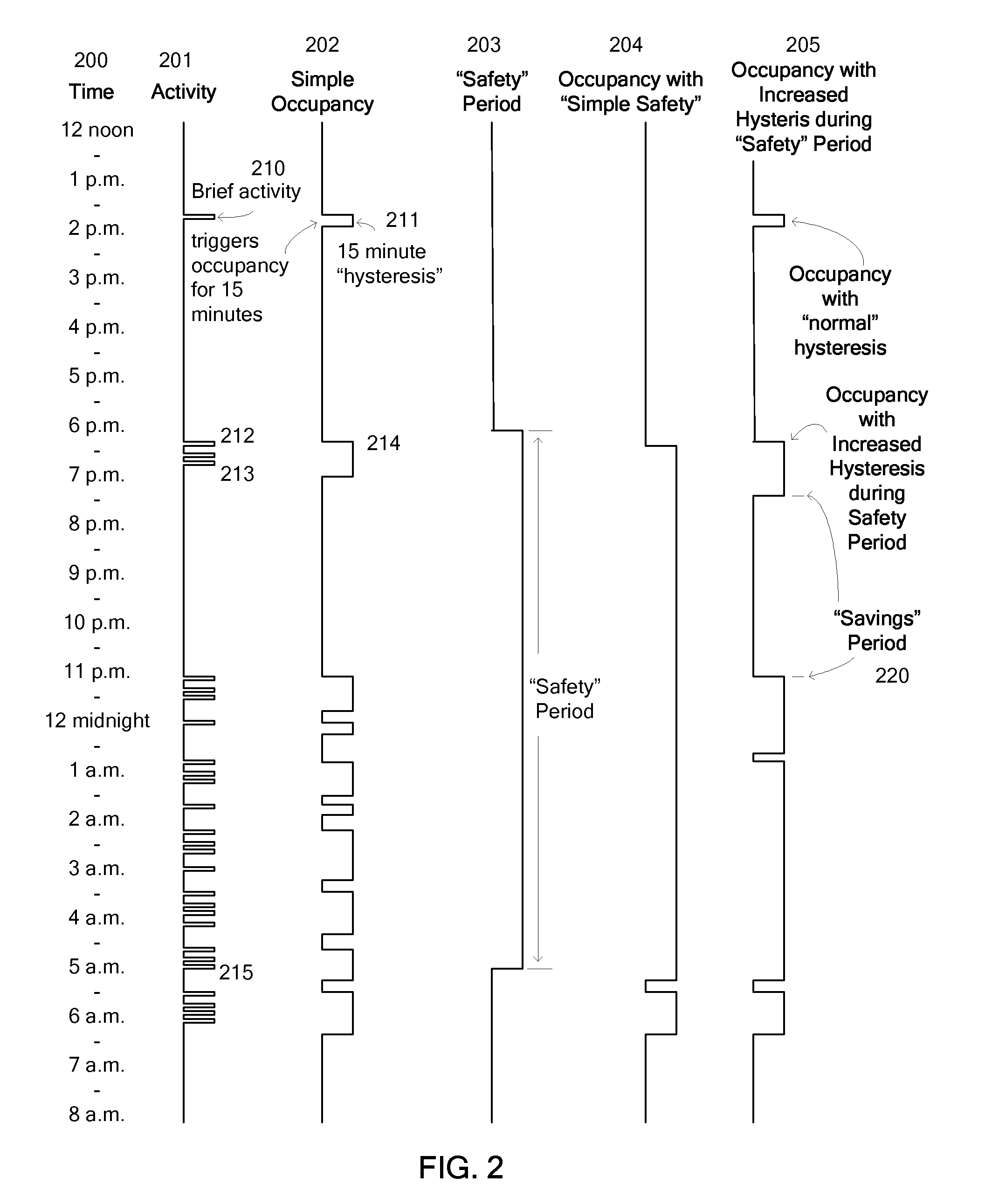
Override of nonoccupancy status in a thermostat device based upon analysis of recent patterns of occupancy
ActiveUS7918406B2Save energyReduce chanceAir-treating devicesMechanical apparatusSequence analysisEngineering
Owner:VERDANT ENVIRONMENTAL TECH INC
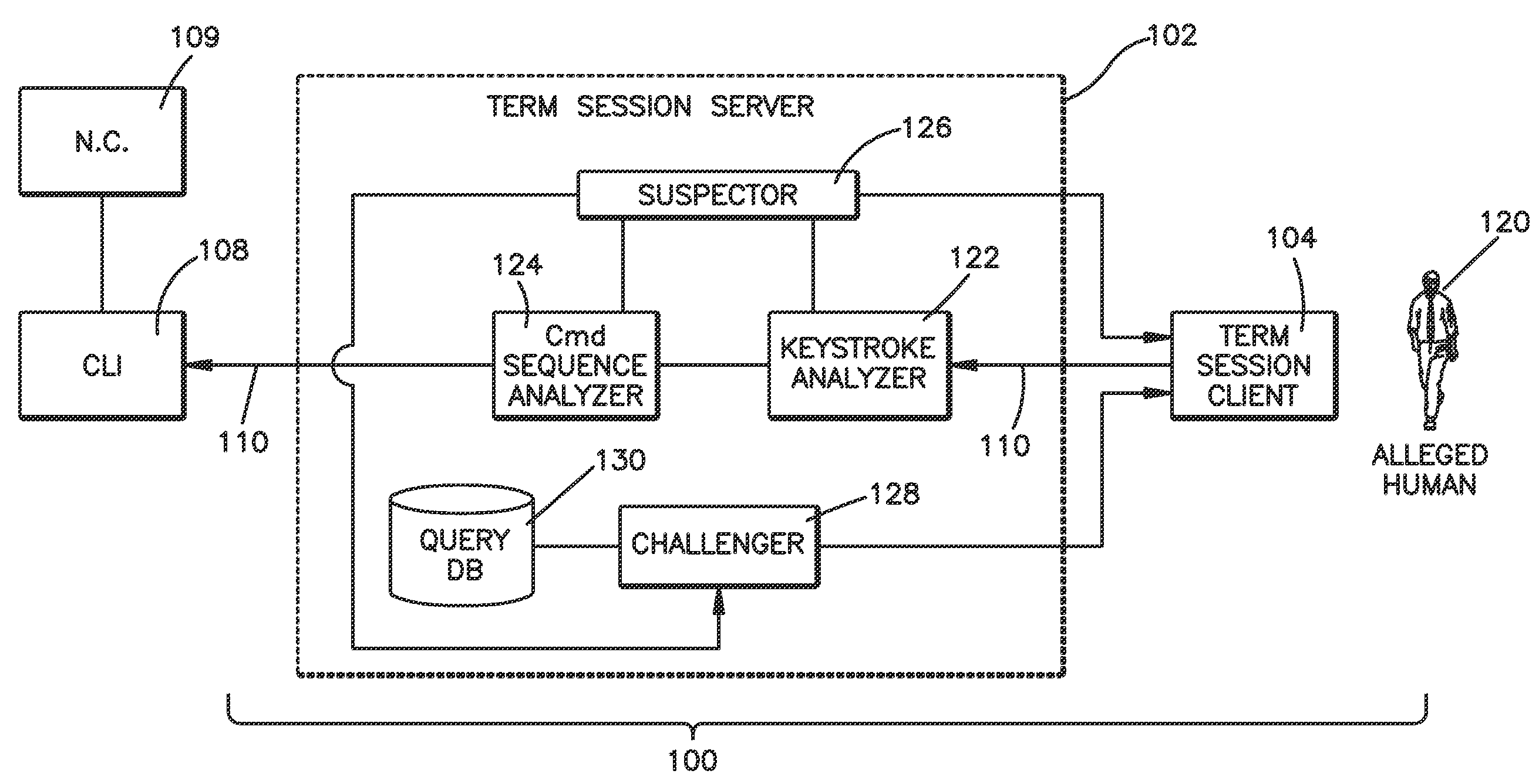
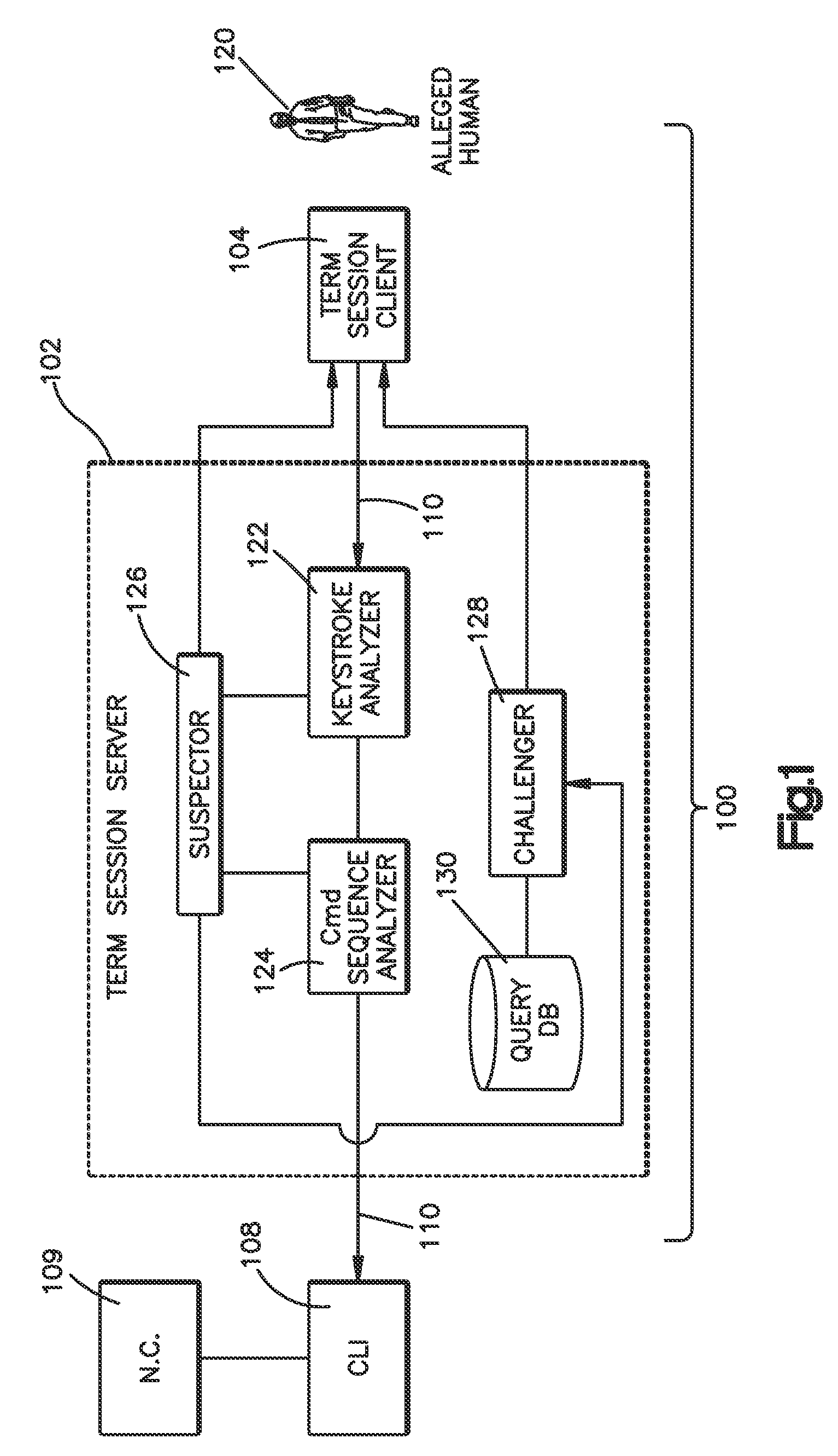
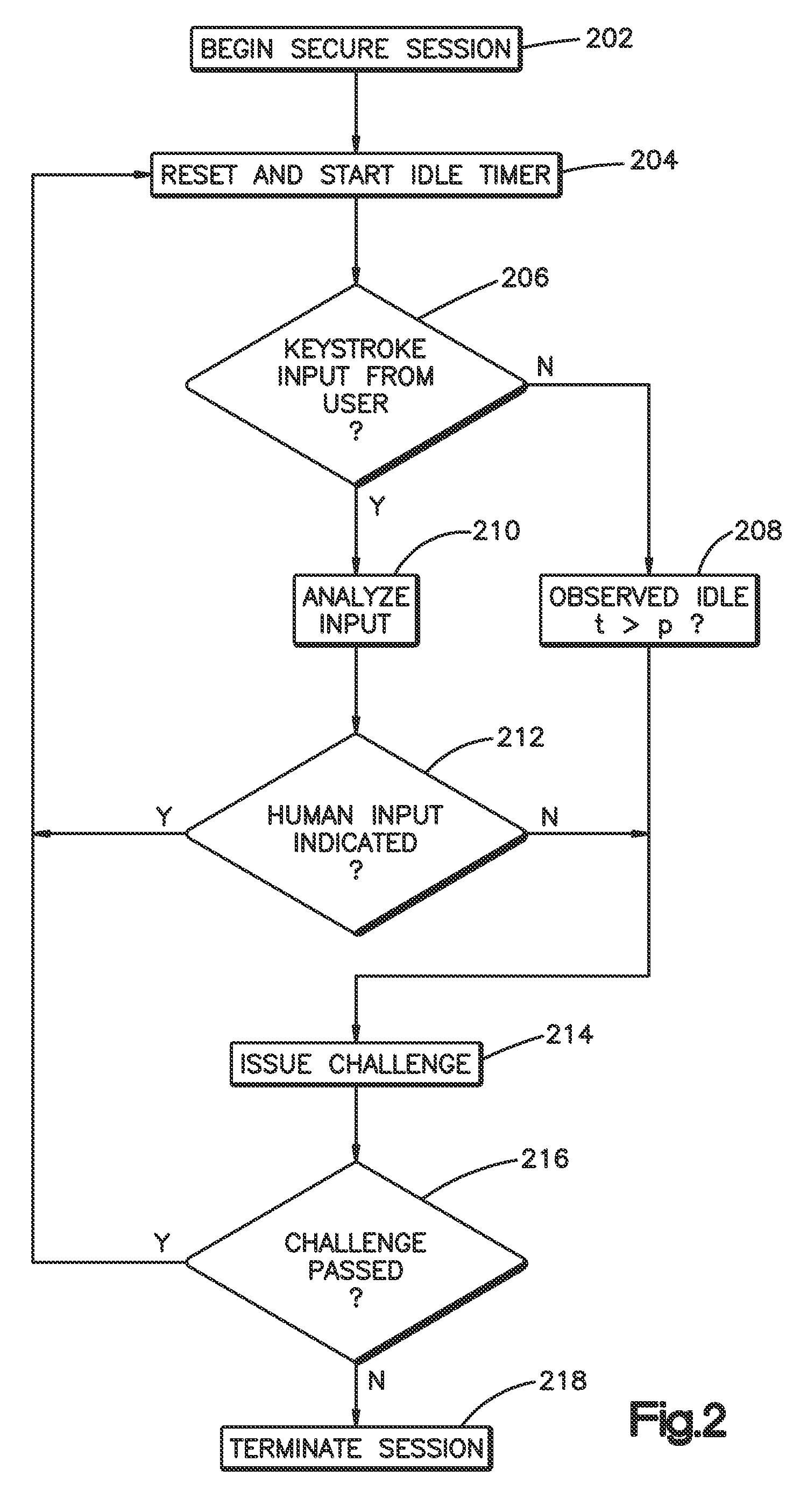
Method and system for validating active computer terminal sessions
InactiveUS20080263636A1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsSequence analysisCommand-line interface
Systems, methods and program codes are provided wherein an analyzer analyzes input from a terminal device; ascertains human-like behavior; and terminates an active session, generates a time-out warning, manipulates an idle session timer or presents a challenge in response to a humanness likelihood determination or to a challenge result. In one aspect a keystroke analyzer and a command sequence analyzer determine whether the terminal device input is likely from a human user or from an automaton. In another aspect a Completely Automated Public Turing Test to tell Computers and Humans Apart challenge is presented. Timing characteristics include maximum generation rate, burstiness, and keystroke sequence delays, and command characteristics include a no-action-required characteristic and a query characteristic. A command sequence analyzer may have an affinity for a command line interface. Weighting algorithms or artificial intelligence routines may be applied to humanness likelihood outputs.
Owner:IBM CORP
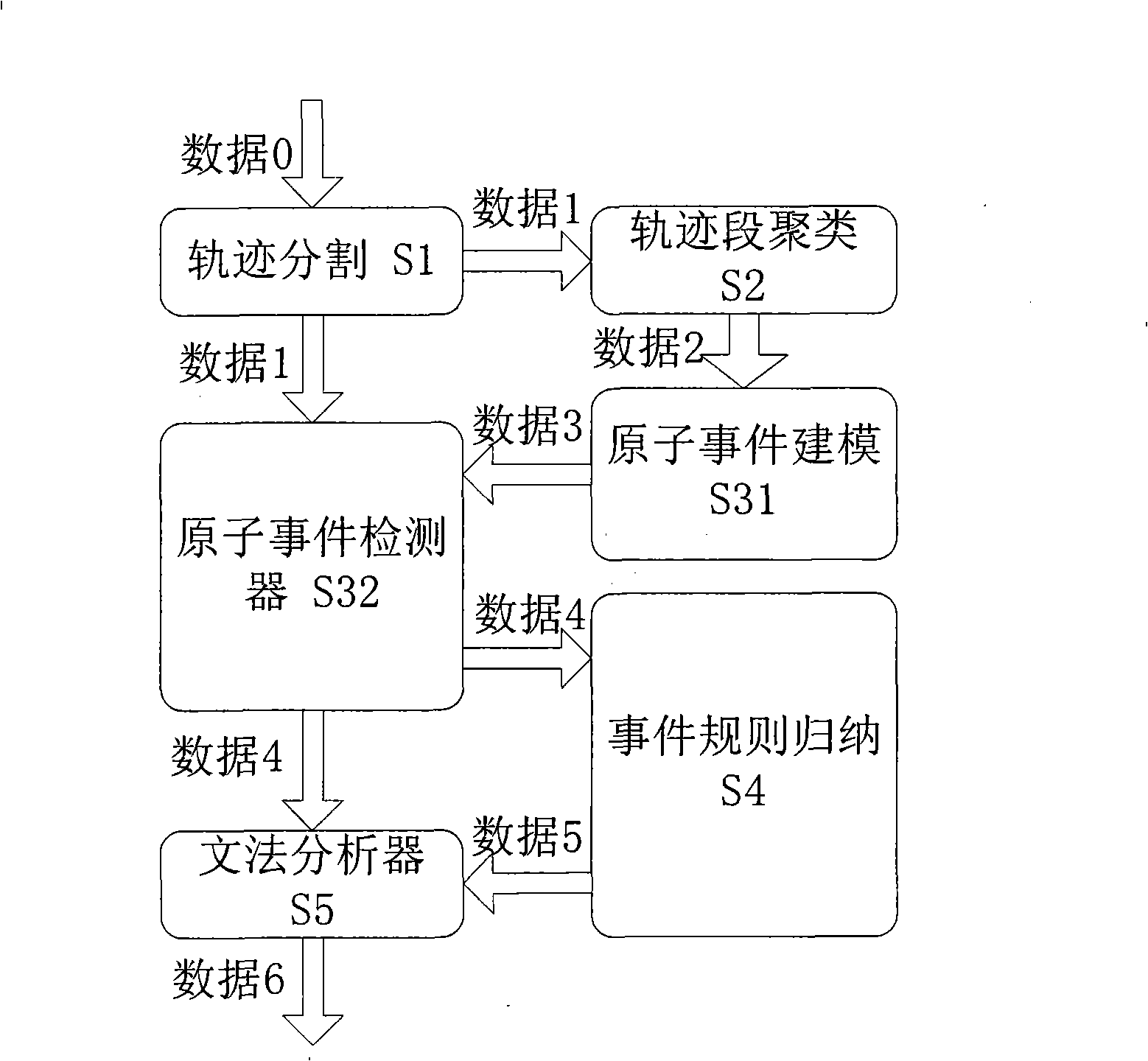
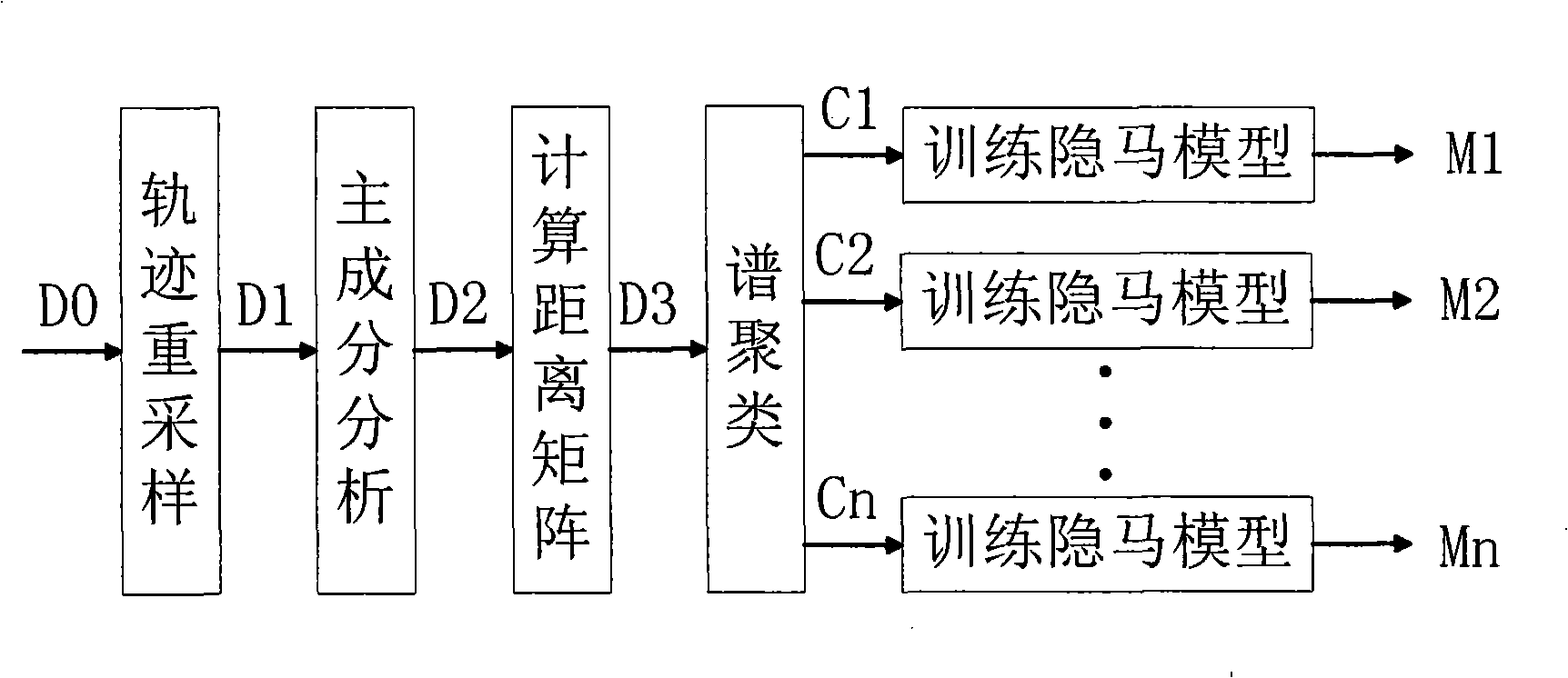
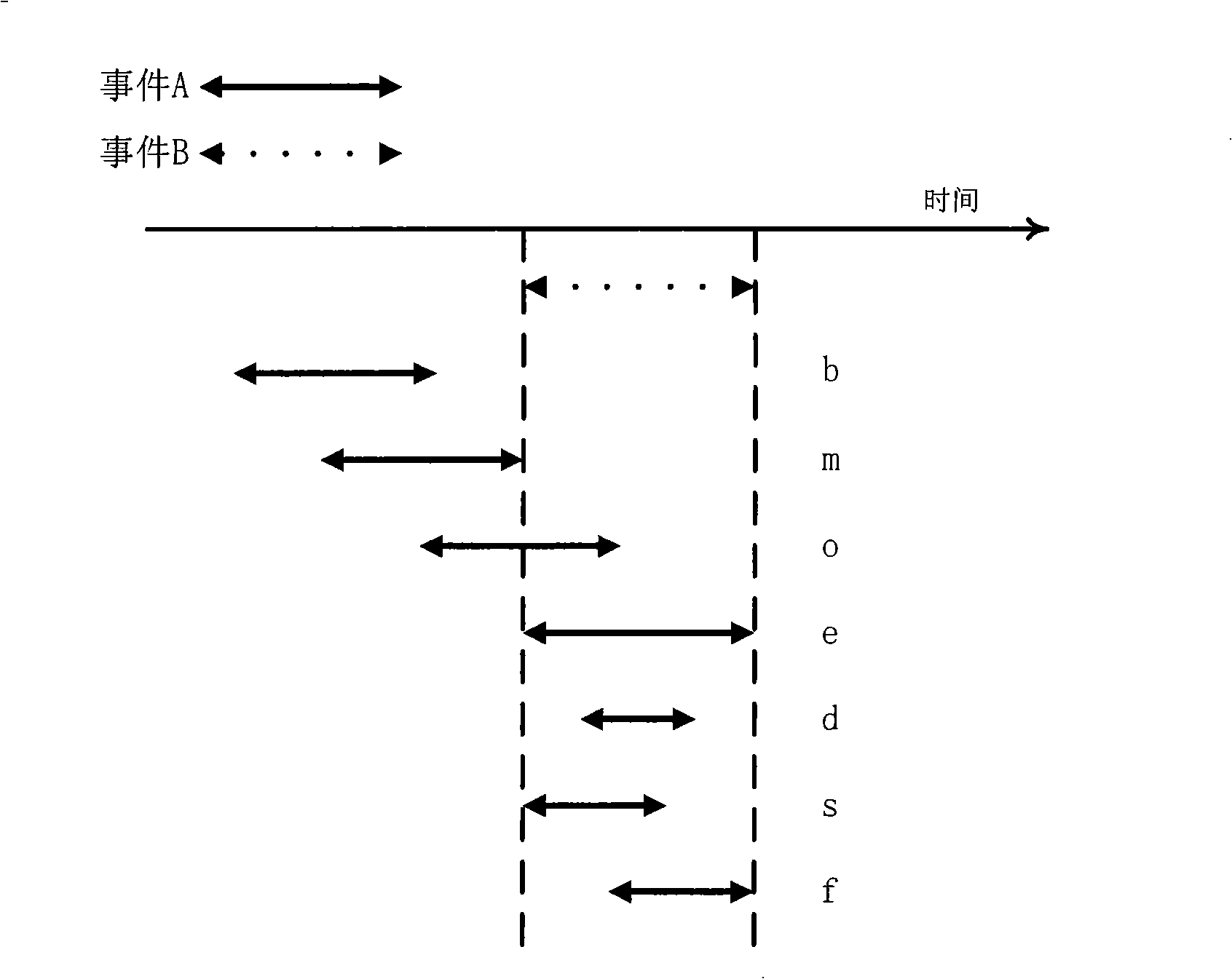
Video frequency behaviors recognition method based on track sequence analysis and rule induction
InactiveCN101334845AReduce manpower consumptionCharacter and pattern recognitionVideo monitoringSequence analysis
The invention discloses a method for identifying the video action based on trajectory sequence analysis and rule induction, which solves the problems of large labor intensity. The method of the invention divides a complete trajectory in a scene into a plurality of trajectory section with basic meaning, and obtains a plurality of basic movement modes as atomic events through the trajectory clustering; meanwhile, a hidden Markov model is utilized for establishing a model to obtain the event rule contained in the trajectory sequence by inducting the algorithm based on the minimum description length and based on the event rule, an expanded grammar analyzer is used for identifying an interested event. The invention provides a complete video action identification frame and also a multi-layer rule induction strategy by taking the space-time attribute, which significantly improves the effectiveness of the rule learning and promotes the application of the pattern recognition in the identification of the video action. The method of the invention can be applied to the intelligent video surveillance and automatic analysis of movements of automobiles or pedestrians under the current monitored scene so as to lead a computer to assist people or substitute people to complete monitor tasks.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compositions and methods for use in analytical reactions
ActiveUS8252911B2Rate of reactionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisPolyphosphate
Compositions, methods, substrates and systems for use in analysis of single molecule reactions and particularly single molecule nucleic acid sequence analysis. Compositions that include non-reactive, distinguishable or undetectable competitive substrates for the reaction system of interest are provided, as well as their use in systems and substrates for such applications, such compounds typically preferably polyphosphate chains or analogous structures.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
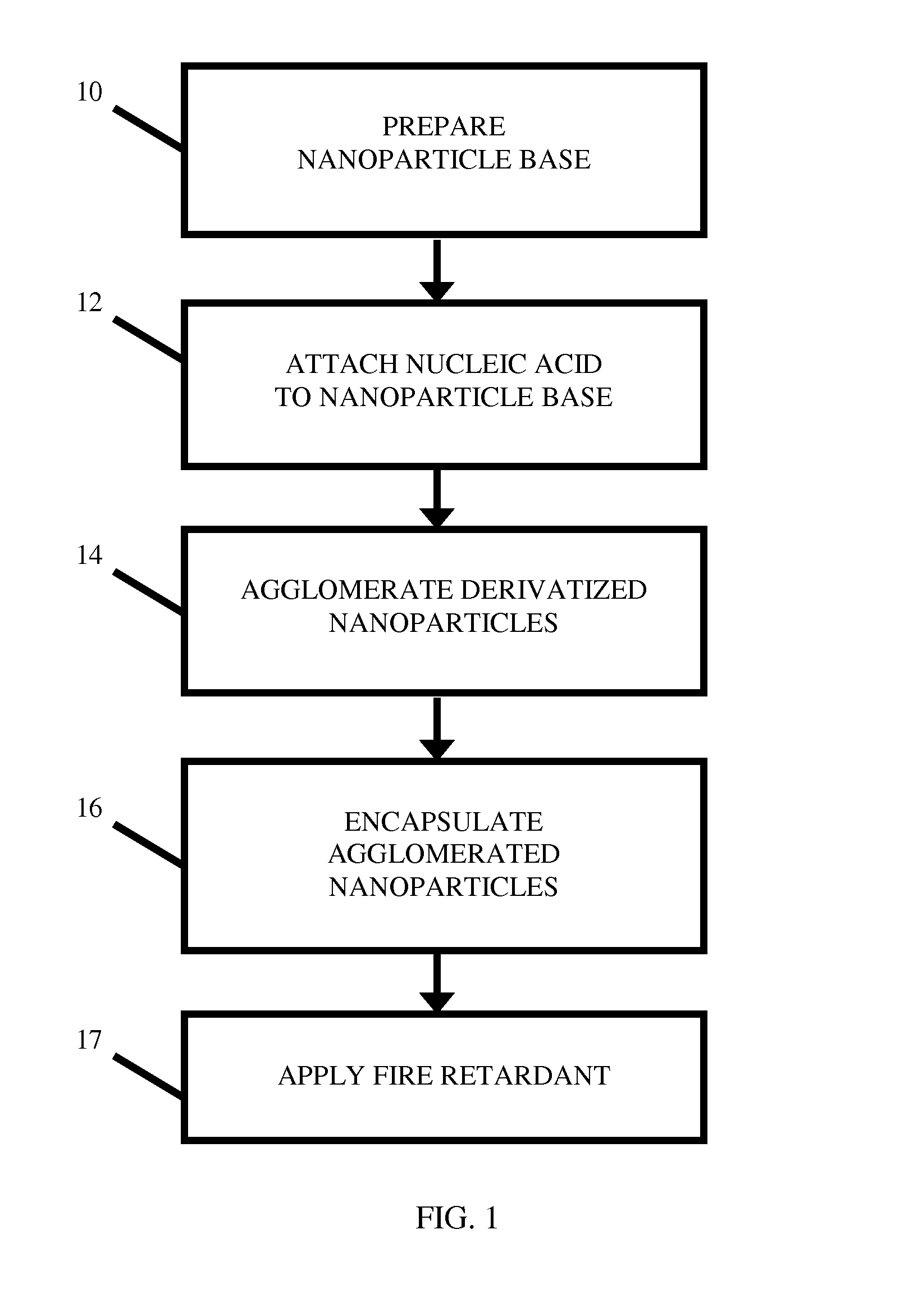
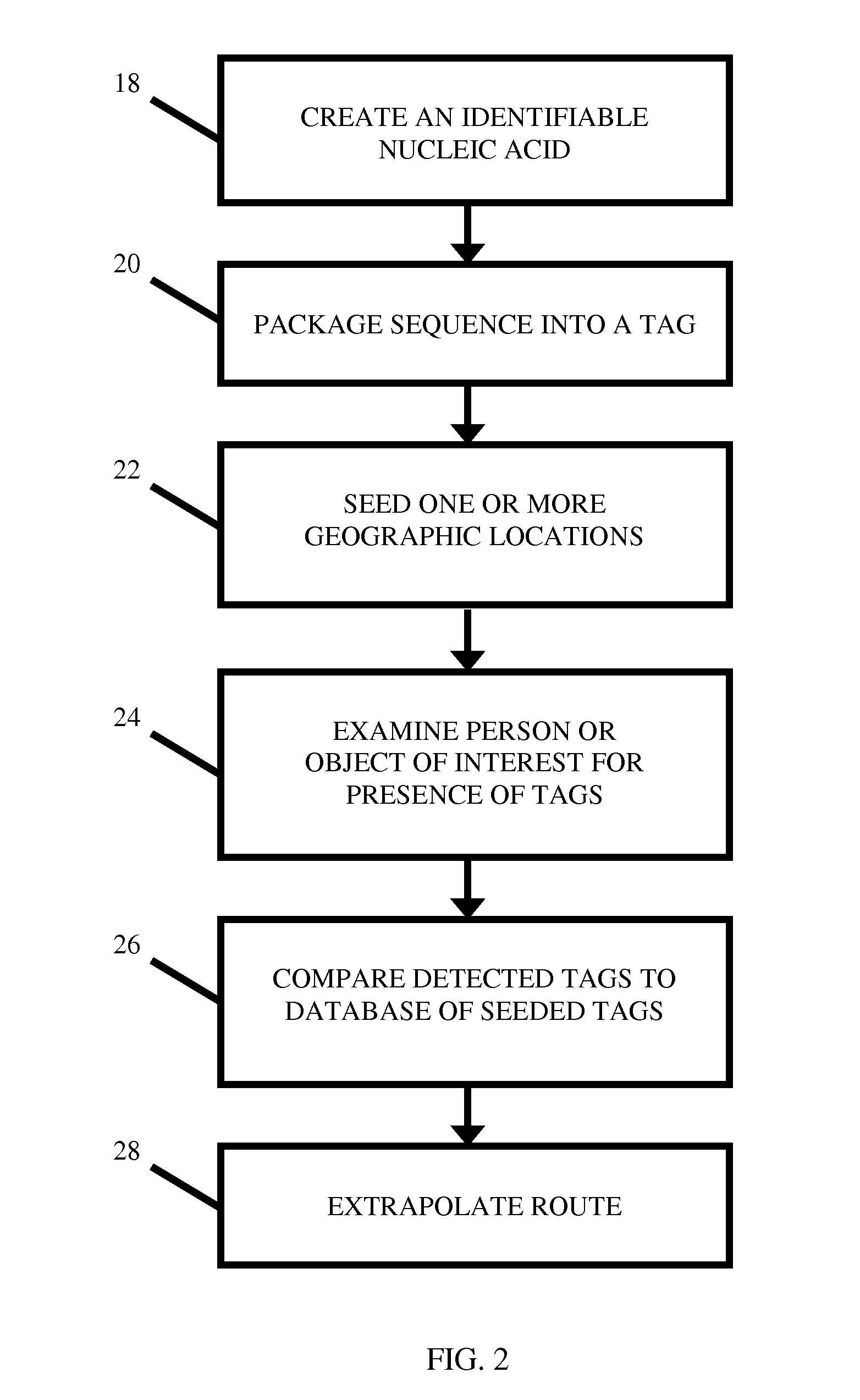
Location Analysis Using Fire Retardant-Protected Nucleic Acid-Labeled Tags
A nucleic acid tag comprising a nucleotide-support platform attached to a nucleic acid molecule, a fire retardant, and an encapsulant. Unique nucleic acid-containing tags containing a fire- or heat-protective element are seeded at one or more geographic locations. Using sequence analysis techniques, the person or object of interest is examined for the presence of one or more of the seeded nucleic acids. The geographic location associated with each detected nucleic acid is used to backtrack the item's path or extrapolate a probable point of origin.
Owner:SRC INC
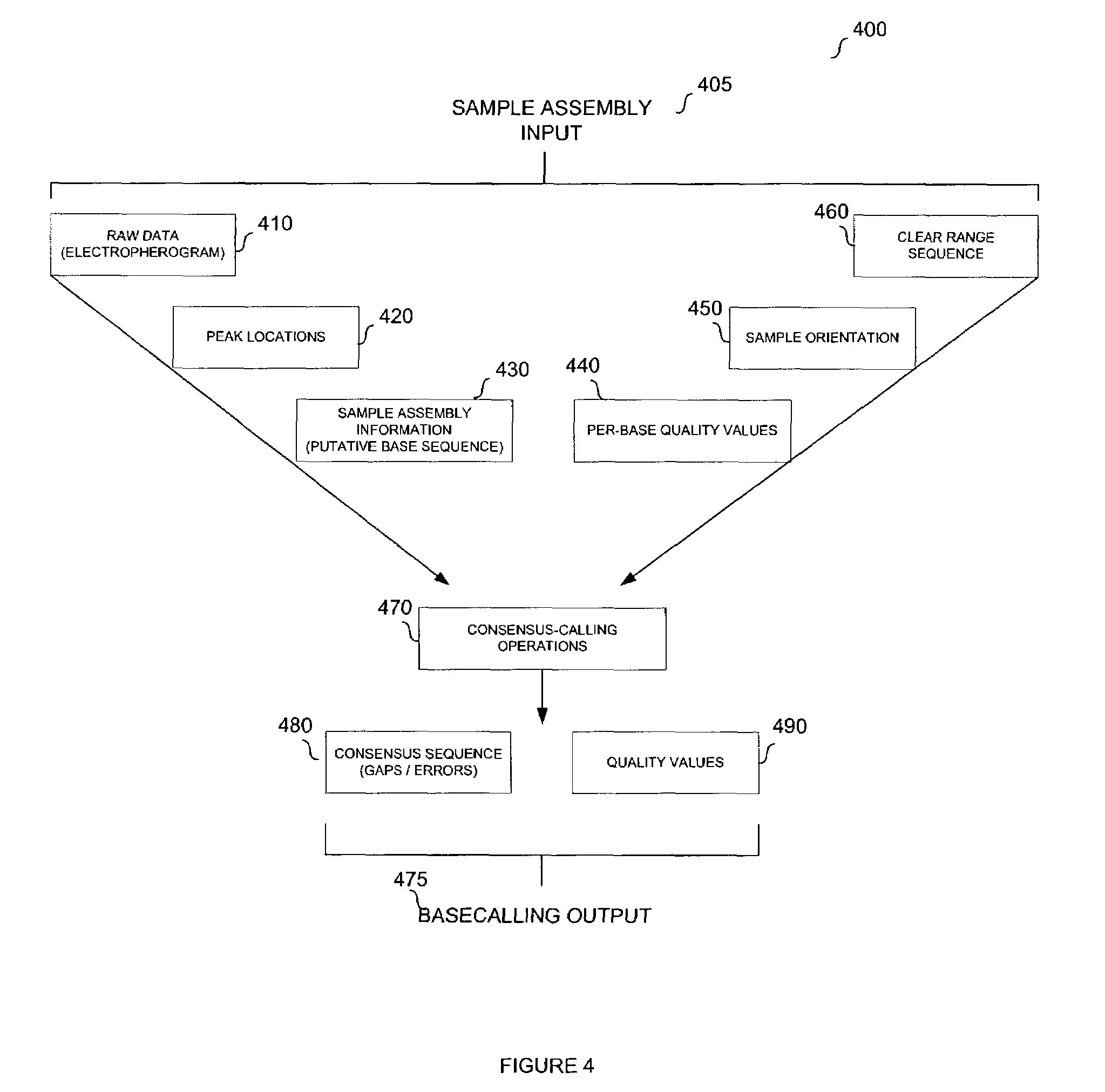
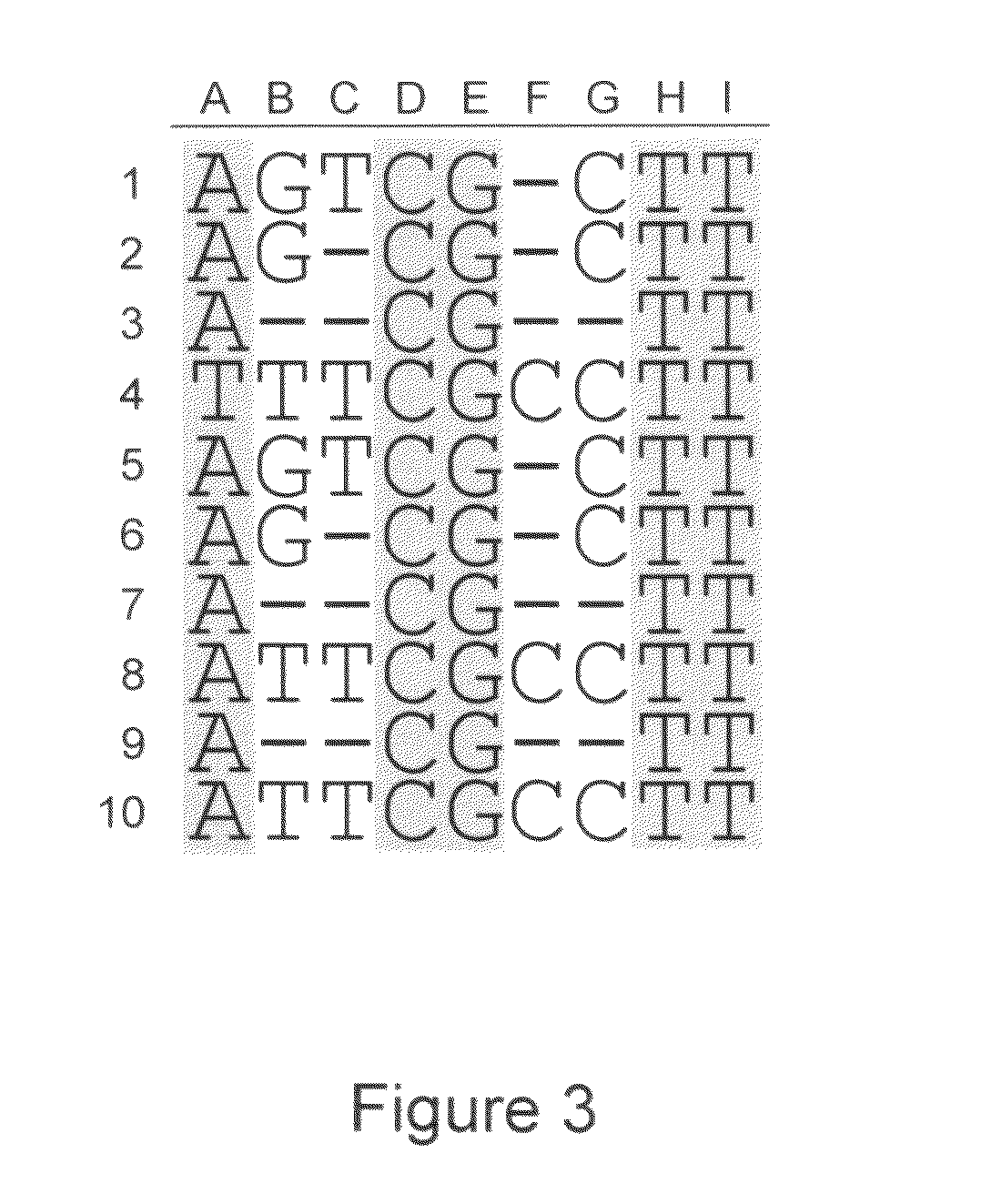
System and method for consensus-calling with per-base quality values for sample assemblies
InactiveUS7406385B2Quality improvementRemove uncertaintyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSequence analysisNucleotide
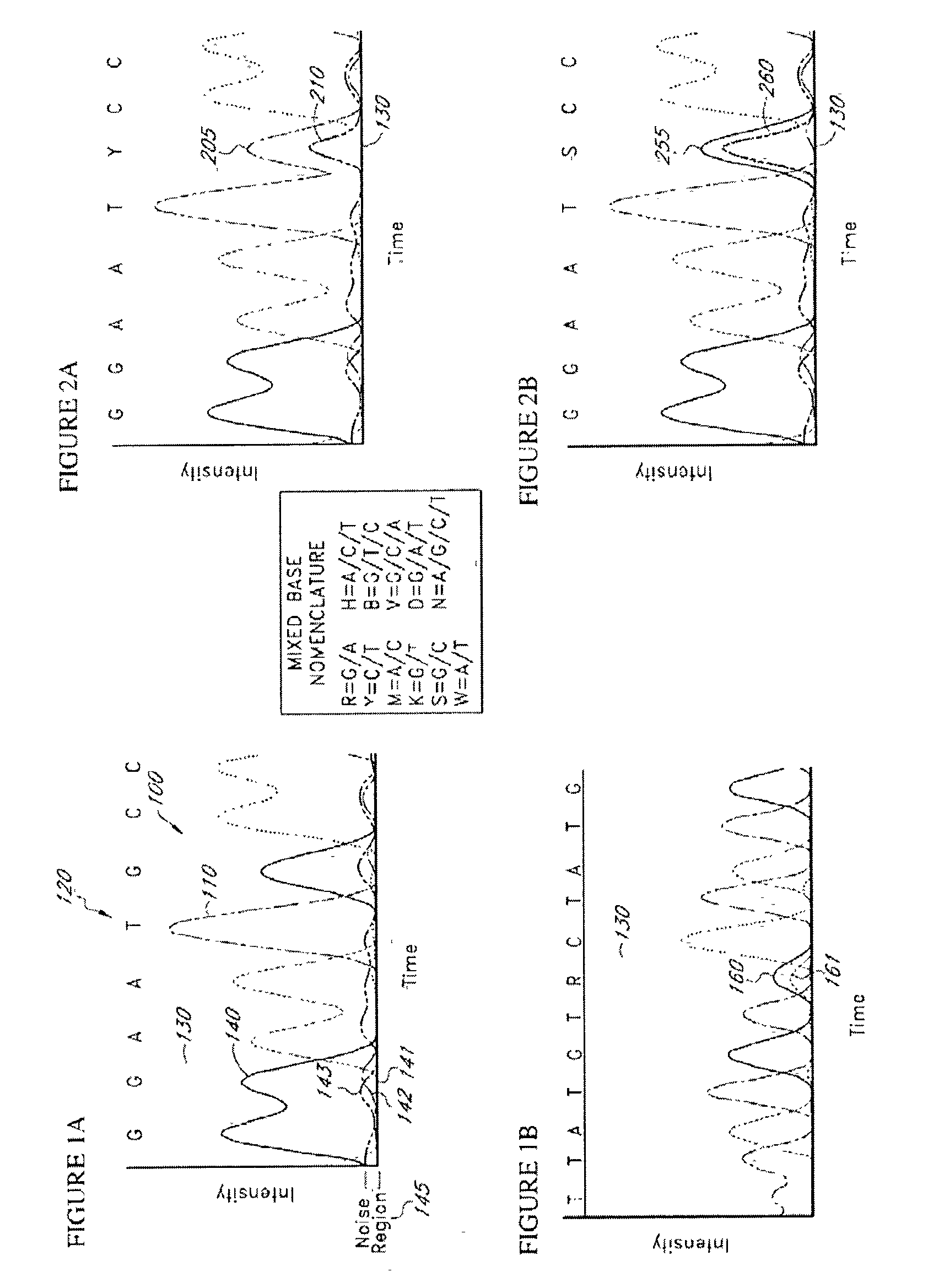
The present teachings disclose a method for evaluation of a polynucleotide sequence using a consensus-based analysis approach. The sequence analysis method utilizes quality values for a plurality of aligned sequence fragments to identify consensus basecalls and calculate associated consensus quality values. The disclosed method is applicable to resolution of single nucleotide polymorphisms, mixed-based sequences, heterozygous allelic variants, and heterogeneous polynucleotide samples.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Sequence analysis of complex amplicons
The invention is directed to methods of generating sequence profiles of populations of nucleic acids, whose member nucleic acids contain regions of high variability, such as populations of nucleic acids encoding T cell receptors or B cell receptors. In one aspect, the invention provides pluralities of sets of primers for generating nested sets of templates from nucleic acids in such populations, thereby insuring the production of at least one template from which sequence reads are generated, despite such variability, or dispite limited lengths or quality of sequence reads. In another aspect, members of such populations are bidirectionally sequenced so that further sequence information is obtained by analyzing overlapping sequence reads in the zones of highest variability.
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
Method for depleting specific nucleic acids from a mixture
InactiveUS20050003369A1Improve the level ofEfficient amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiologyNucleic acid
The presently claimed invention provides methods, compositions, and apparatus for analyzing nucleic acids isolated from blood. Specifically, the present invention provides a method of analyzing blood samples by blocking amplification of selected unwanted RNAs and subsequently analyzing the amplified sample by hybridization to a plurality of probes attached to a solid support. In one embodiment, the invention provides enriching for a population of interest in a complex population by diminishing the presence of an unwanted sequence that may interfere with the analysis of sequences of interest.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Compositions and methods for selection of nucleic acids
ActiveUS20140134610A1Reduce complexityIncreased complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSequence analysisGenomic DNA
Methods are provided for reducing the complexity of a population of nucleic acids prior to performing an analysis of the nucleic acids, e.g., sequence analysis. The methods result in a subset of the initial population enriched for a target region, which is typically located within one or more target fragments. The methods are particularly useful for analyzing populations having a high degree of complexity, e.g., chromosomal-derived DNA, whole genomic DNA, or mRNA populations.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
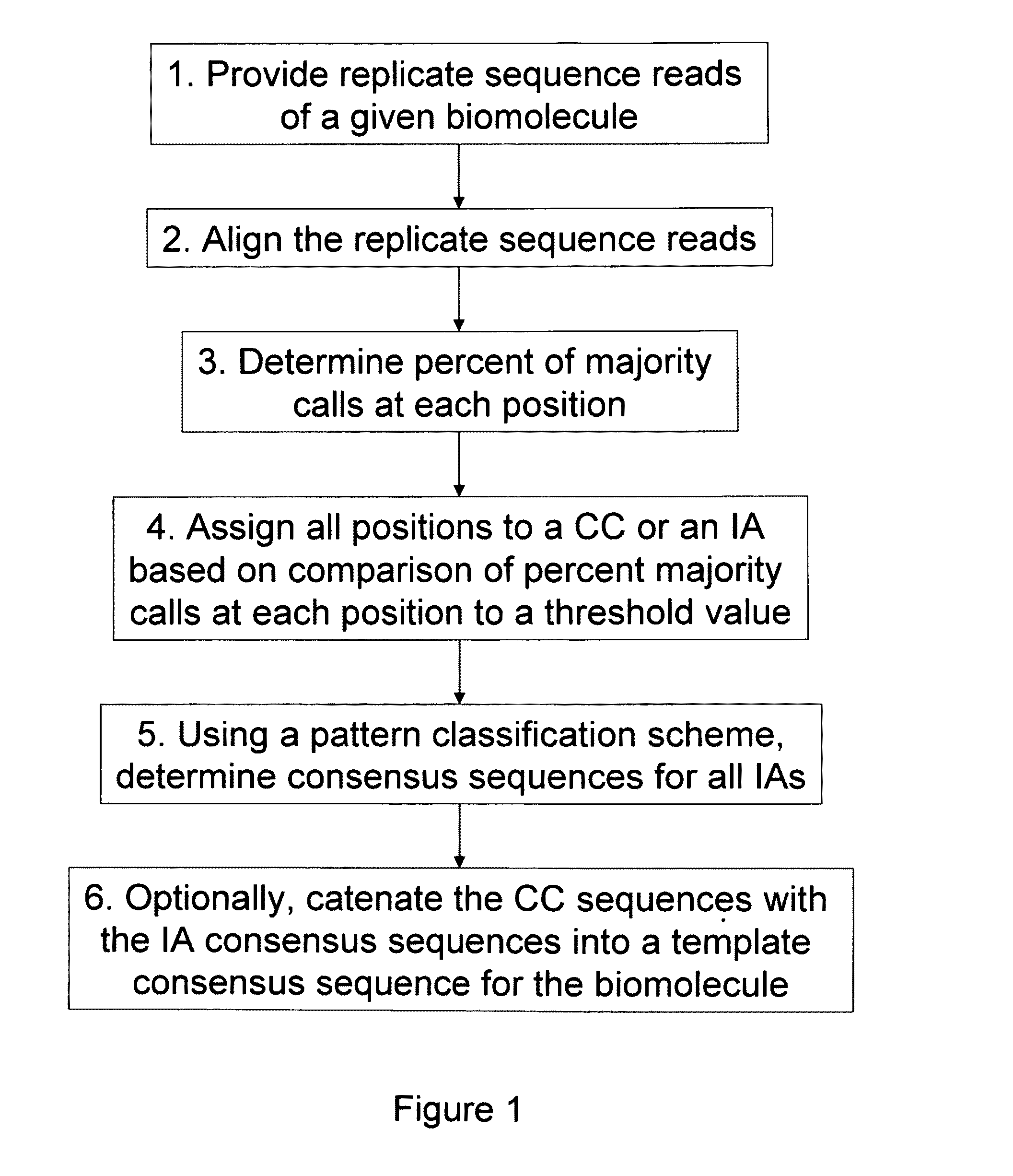
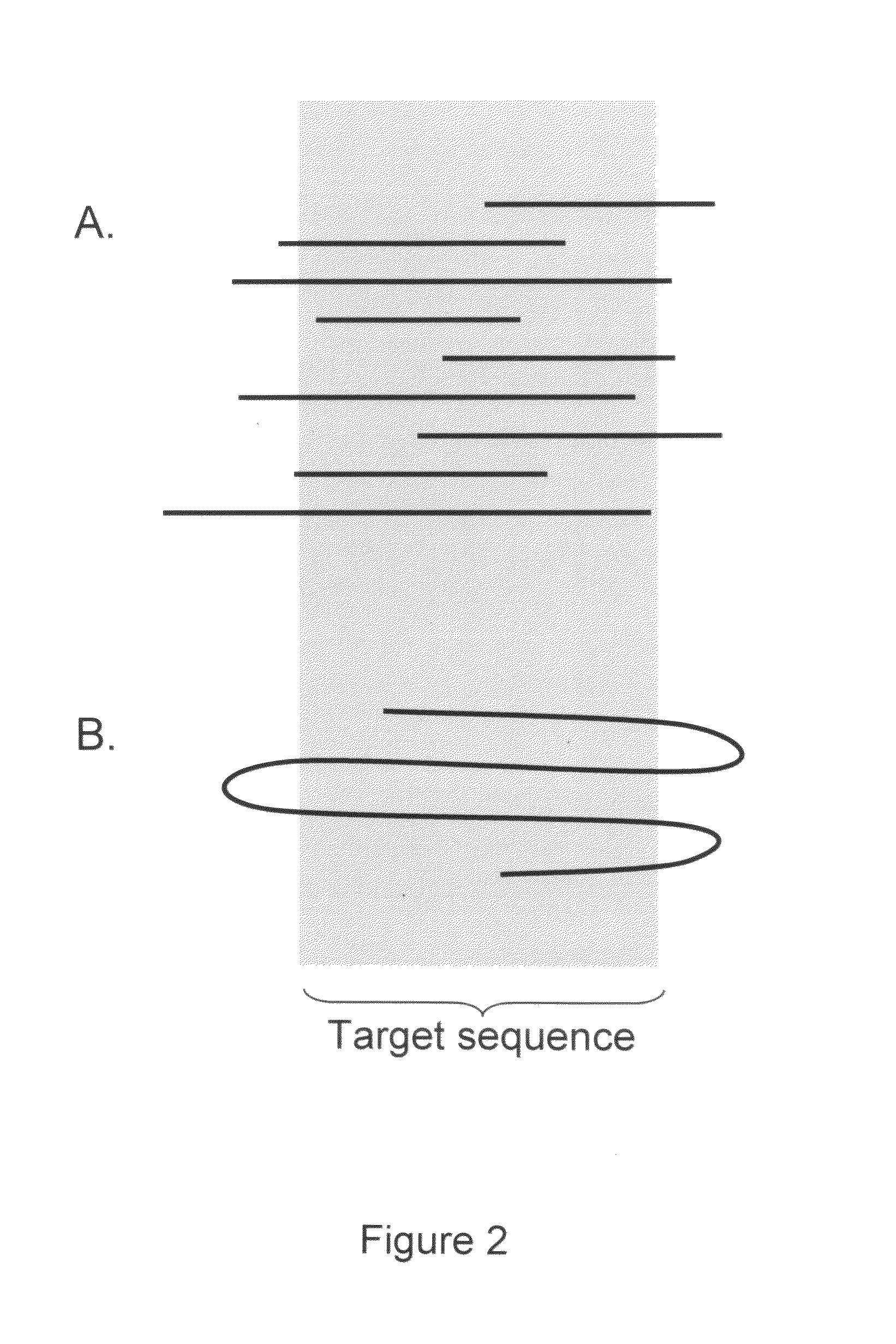
Algorithms for sequence determination
ActiveUS8370079B2Enhanced authenticationImprove accuracyBiological testingSequence analysisOne passSequence analysis
The present invention is generally directed to powerful and flexible methods and systems for consensus sequence determination from replicate biomolecule sequence data. It is an object of the present invention to improve the accuracy of consensus biomolecule sequence determination from replicate sequence data by providing methods for assimilating replicate sequence into a final consensus sequence more accurately than any one-pass sequence analysis system.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Methods and compositions for nucleic acid detection and sequence analysis
InactiveUS20050147977A1Easy to distinguishSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisSignalling molecules
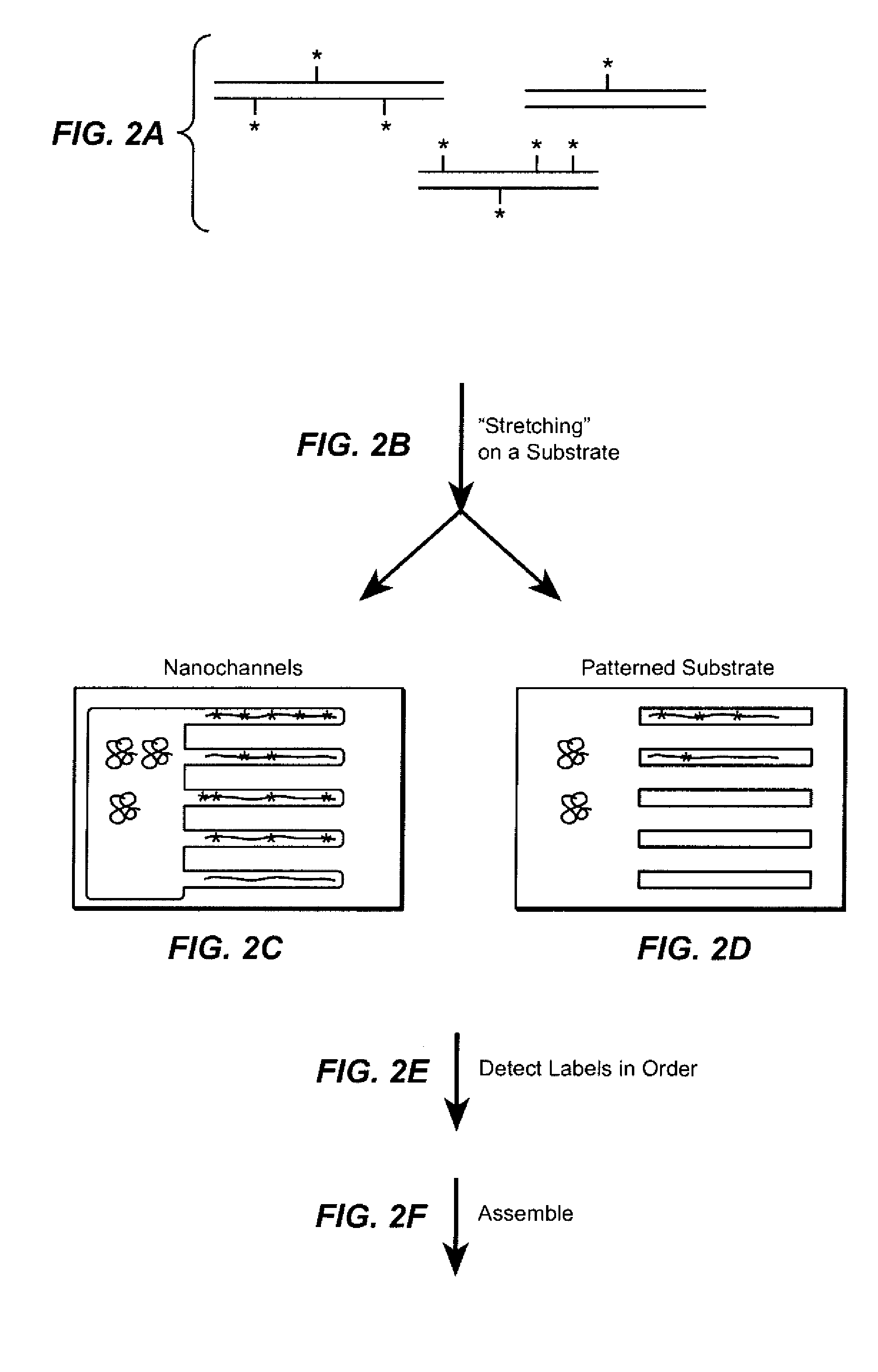
A population of labeled probes is provided that utilize an encoding system in which both the intensity and specific characteristics of a signal molecule are utilized to reduce the number of signal molecules necessary to identify each member of the population of probes. In the population of labeled probes, each labeled probe includes a probe associated with a series of detectably distinguishable signal molecules. The number and type of signal molecules identifies the associated probe, and the number of probes in the population exceeds the number of unique signal molecules. The population of probes are used in methods of the invention and reaction mixtures of the invention, for identifying a target molecule and for sequencing a nucleic acid molecule, for example.
Owner:INTEL CORP
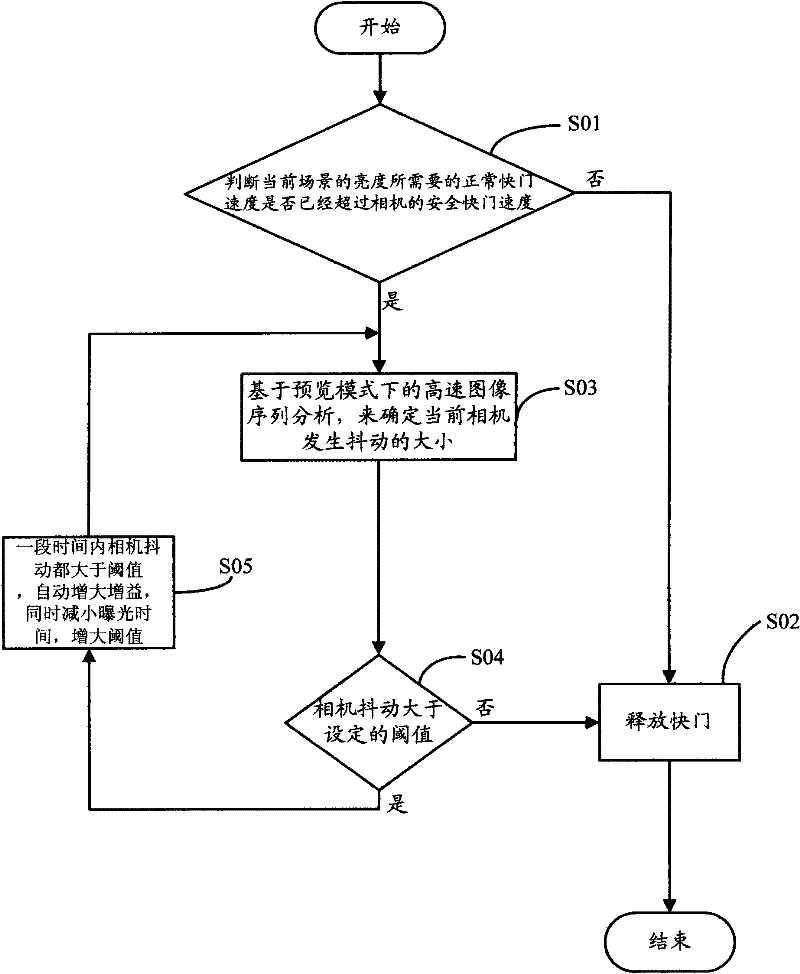
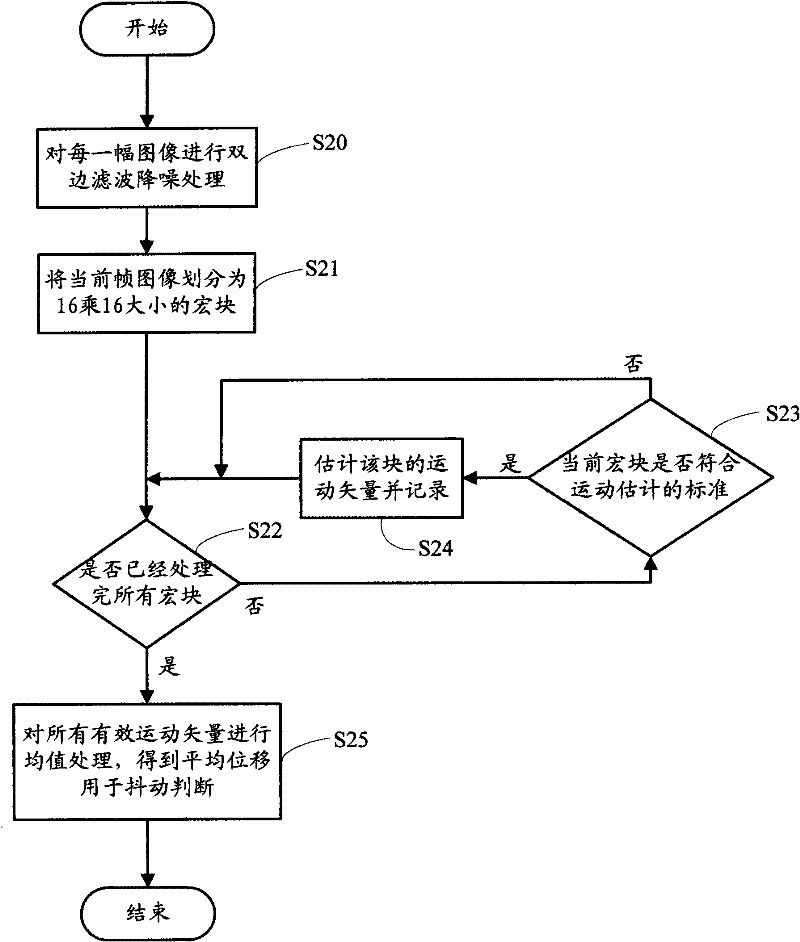
Image shooting anti-shaking manner for handheld camera equipment
ActiveCN102457675ALow costImprove real-time performanceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSequence analysisComputer hardware
The invention relates to a method which can prevent handheld camera equipment from shaking when shooting. The method comprises the following steps of: judging a normal shutter speed needed by brightness on a current scene whether have exceeded a safe shutter speed of the handheld camera equipment or not; if no, directly releasing a shutter for shooting; if so, analyzing high-speed image sequences based on a preview mode to confirm size of the current handheld camera equipment when the equipment is shaking; confirming current shaking whether is larger than a set threshold value according to a preset threshold value range, if the current shaking is smaller than the set threshold value, so a user can be allowed to press down the shutter for shooting; if the shaking continuously becomes larger within a certain time, a condition for shutter releasing is not satisfied, so exposure parameters can be automatically adjusted, namely, gain can be automatically increased, meanwhile, exposure time is reduced, moreover, the threshold value used for judging degree of shaking is correspondingly enlarged, so that the shooting is easier to be reached within an allowable shaking range.
Owner:BEIJING SPREADTRUM HI TECH COMM TECH CO LTD
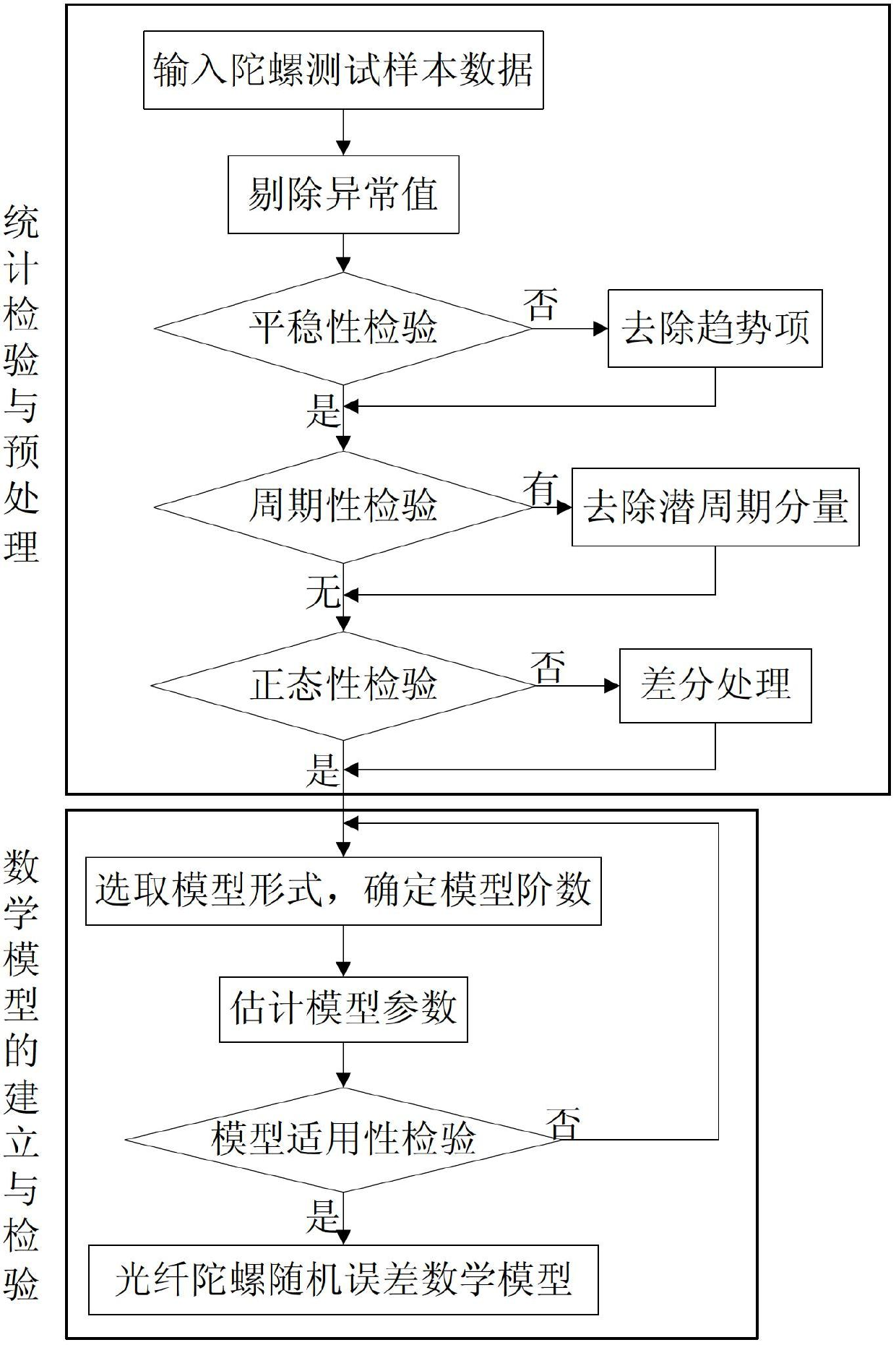
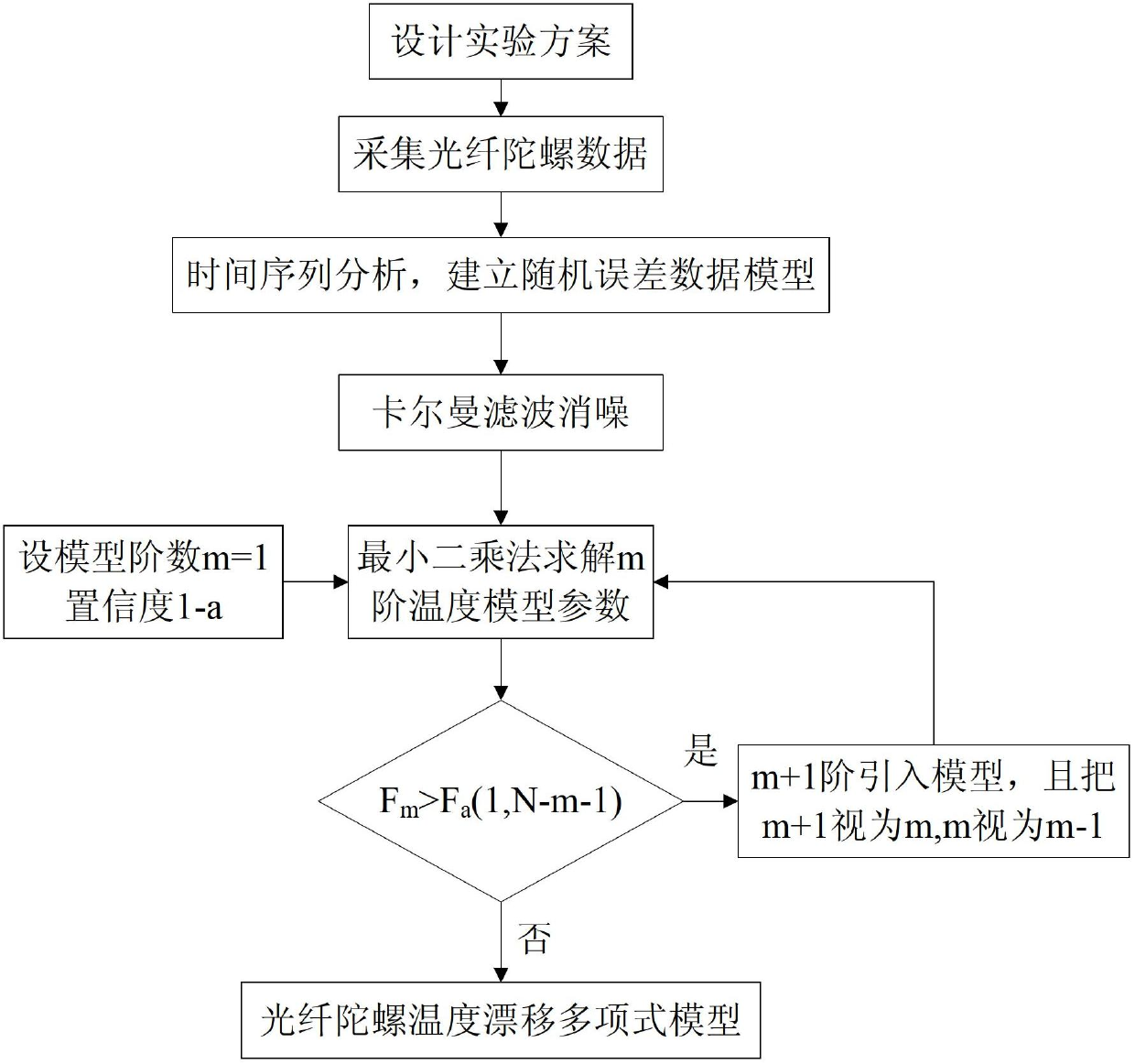
Temperature compensation method for denoising fiber-optic gyroscope on basis of time series analysis
A temperature compensation method for denoising a fiber-optic gyroscope on the basis of time series analysis comprises four steps of: step 1, designing an experimental scheme, performing fixed point low and high temperature testing experiment on the fiber-optic gyroscope, and utilizing acquisition software for data acquisition; step 2, performing time series analysis on the zero offset data of the gyroscope, and establishing the mathematical model of the random error of the fiber-optic gyroscope; step 3, adopting a kalman filtering algorithm to filter random noise in the zero offset data of the fiber-optic gyroscope; and step 4, utilizing the data which is de-noised by the kalman filtering to identify the model structure of the temperature shift error of the fiber-optic gyroscope, and calculating the parameters of the identified model. The method establishes the multinomial model of the static temperature shift error of the fiber-optic gyroscope through time series analysis, kalman filtering denoising treatment and identification of the temperature shift error model structure and parameters. The method completely meets the real-time compensation requirement on the project, and has a better practicable value and a wide application prospect in the technical field of aerospace navigation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Bioinformatics systems, apparatuses, and methods for performing secondary and/or tertiary processing
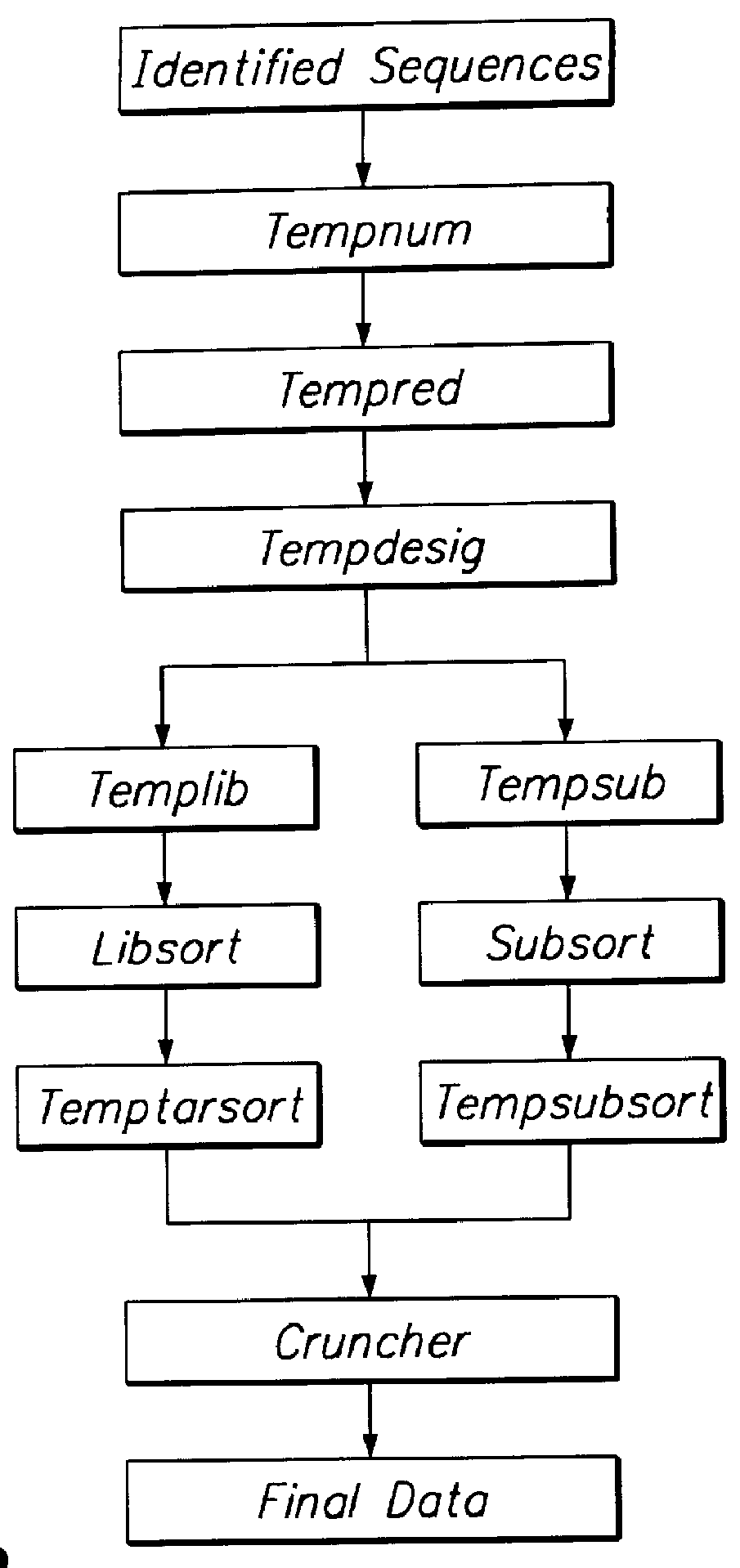
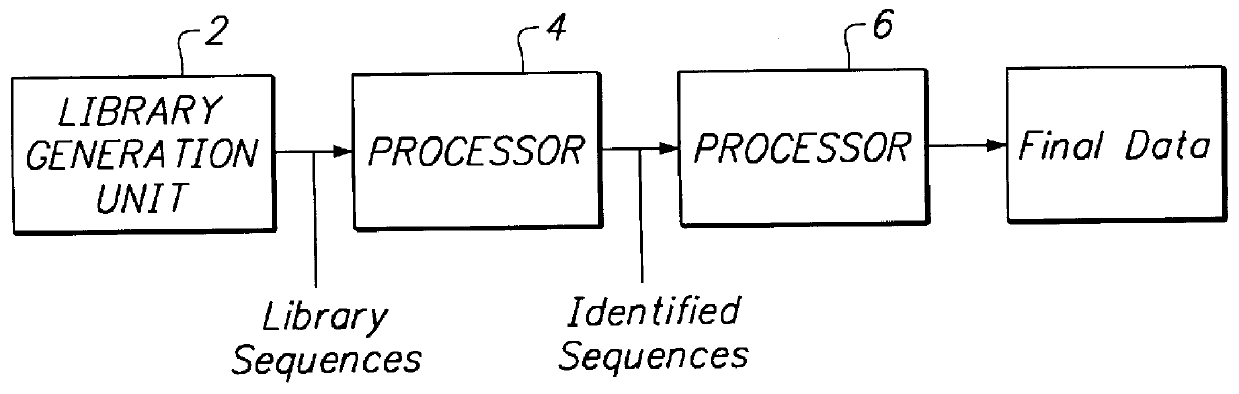
A system, method and apparatus for executing a bioinformatics analysis on genetic sequence data is provided. Particularly, a genomics analysis platform for executing a sequence analysis pipeline is provided. The genomics analysis platform includes one or more of a first integrated circuit, where each first integrated circuit forms a central processing unit (CPU) that is responsive to one or more software algorithms that are configured to instruct the CPU to perform a first set of genomic processing steps of the sequence analysis pipeline. Additionally, a second integrated circuit is also provided, where each second integrated circuit forming a field programmable gate array (FPGA), the FPGA being configured by firmware to arrange a set of hardwired digital logic circuits that are interconnected by a plurality of physical interconnects to perform a second set of genomic processing steps of the sequence analysis pipeline, the set of hardwired digital logic circuits of each FPGA being arranged as a set of processing engines to perform the second set of genomic processing steps. A shared memory is also provided.
Owner:EDICO GENOME
Comparative gene transcript analysis
InactiveUS6114114ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisDisease cause
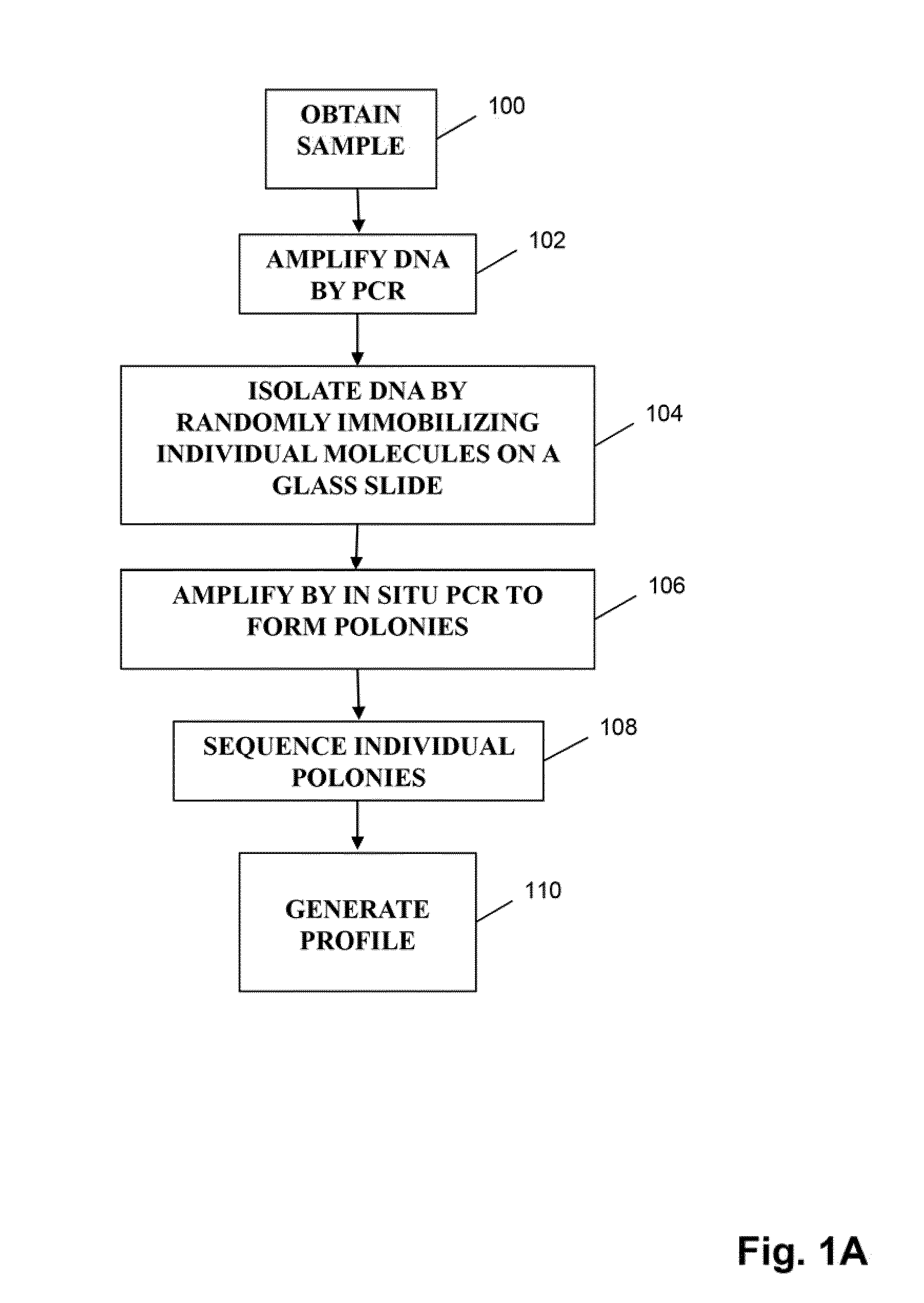
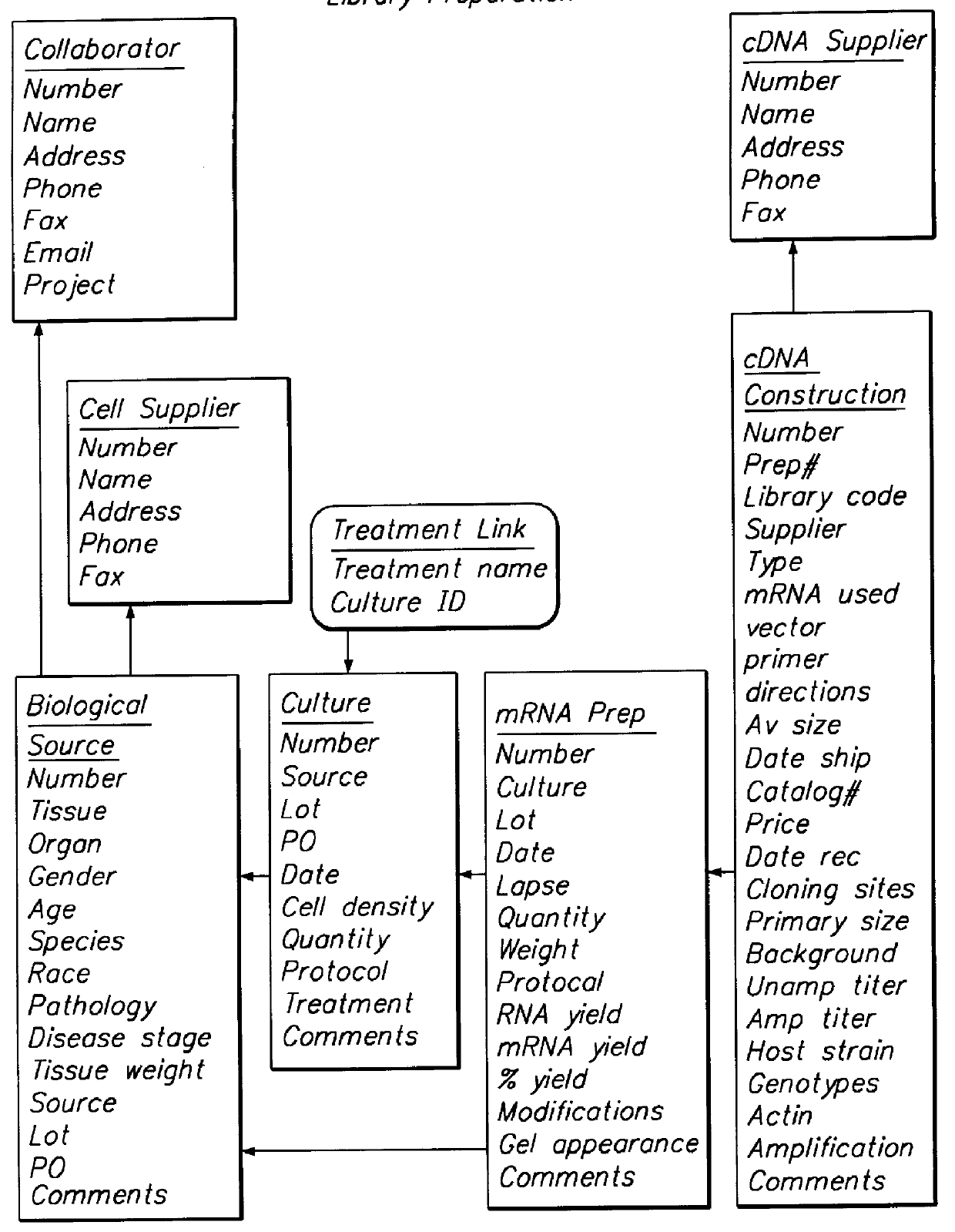
A method and system for quantifying the relative abundance of gene transcripts in a biological sample. One embodiment of the method generates high-throughput sequence-specific analysis of multiple RNAs or their corresponding cDNAs (gene transcript imaging analysis). Another embodiment of the method produces a gene transcript imaging analysis by the use of high-throughput CDNA sequence analysis. In addition, the gene transcript imaging can be used to detect or diagnose a particular biological state, disease, or condition which is correlated to the relative abundance of gene transcripts in a given cell or population of cells. The invention provides a method for comparing the gene transcript image analysis from two or more different biological samples in order to distinguish between the two samples and identify one or more genes which are differentially expressed between the two samples.
Owner:INCYTE PHARMA INC
Fluorescent analysis method
InactiveUS20120126142A1Improve detection efficiencyImprove throughputEmission spectroscopyPhotometrySequence analysisLength wave
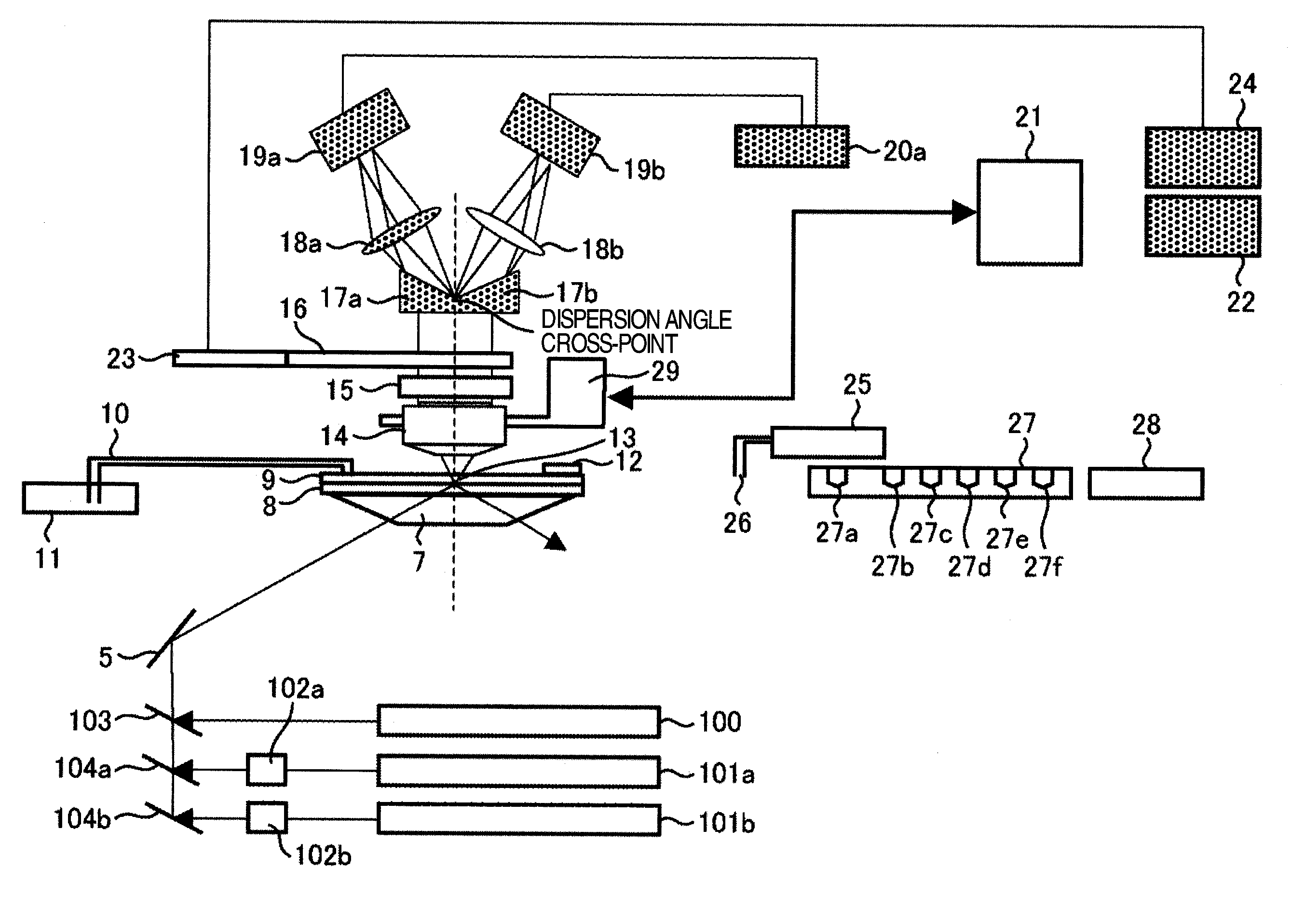
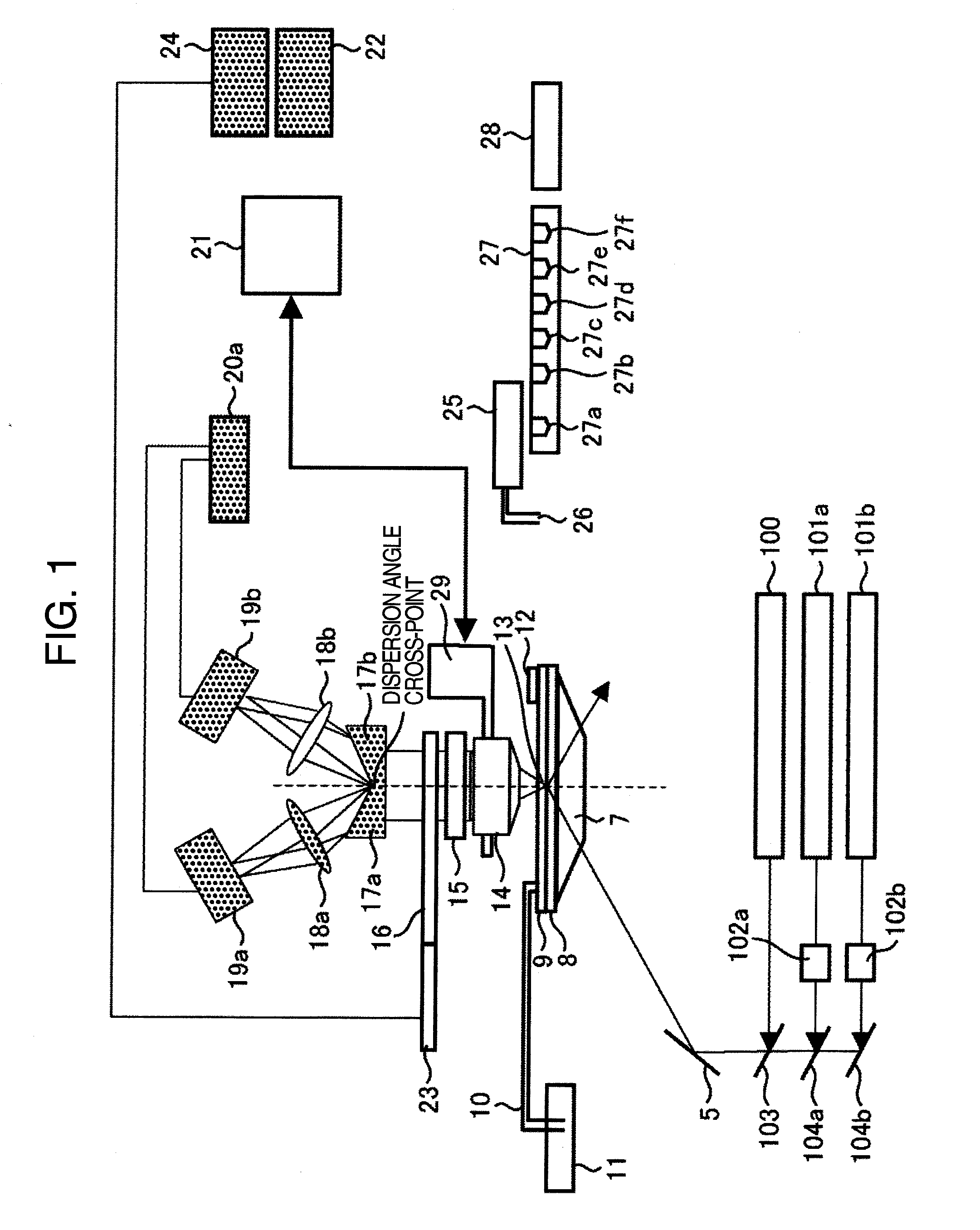
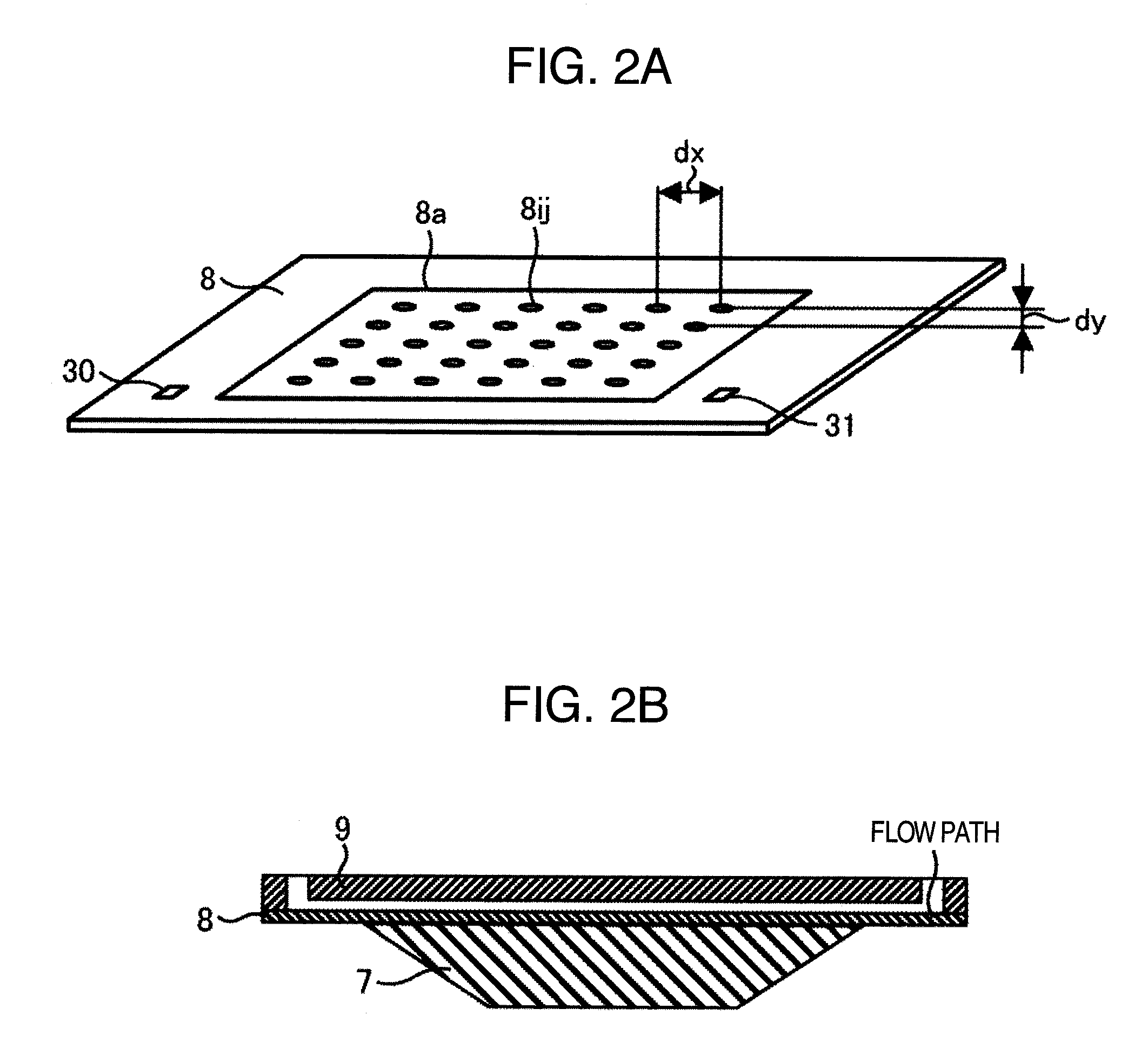
Disclosed is a fluorescent analysis method whereby the throughput in DNA sequence analysis or the like can be improved. The method comprises irradiating a substrate, which carries biological molecules such as oligonucleotides immobilized thereon, with light for fluorescent measuring, collecting the generated fluorescence, dispersing the collected light, forming an image by focusing the light on a two-dimensional sensor, and then detecting the fluorescence with the two-dimensional sensor. In this method, since wavelengths are dispersed in different directions and then detected at the same time, the intensity of each dispersed wavelength and the position of the subject of spectroscopic imaging can be calculated even in the case where the wavelength dispersion distance is longer than the inter-lattice distance.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
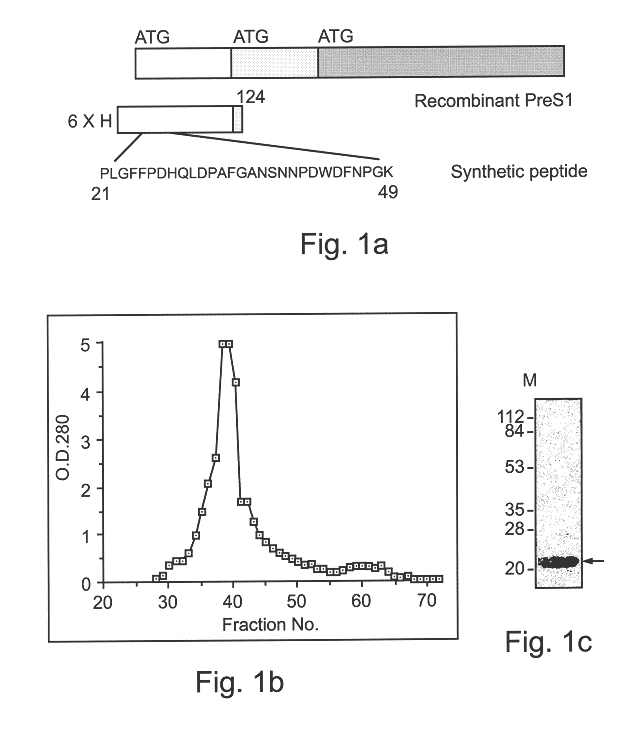
Hepatitis B virus binding proteins and uses thereof
An isolated nucleic acid, a recombinant protein encoded thereby and uses thereof. The isolated nucleic acid including (a) a polynucleotide at least 60% identical to SEQ ID NOs:1, 3, 5 or portions thereof as determined using the Bestfit procedure of the DNA sequence analysis software package developed by the Genetic Computer Group (GCG) at the university of Wisconsin (gap creation penalty-50, gap extension penalty-3); (b) a polynucleotide encoding a polypeptide being at least 60 homologous with SEQ ID NOs:2, 4, 6 or portions thereof as determined using the Bestfit procedure of the DNA sequence analysis software package developed by the Genetic Computer Group (GCG) at the university of Wisconsin (gap creation penalty-50, gap extension penalty-3); or (c) a polynucleotide hybridizable with SEQ ID NOs:1, 3, 5 or portions thereof at 68° C. in 6xSSC, 1% SDS, 5xDenharts, 10% dextran sulfate, 100 mug / ml salmon sperm DNA, and 32p labeled probe and wash at 68° C. with 3xSSC and 0.1% SDS.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com