Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1726results about How to "Reduce calculation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
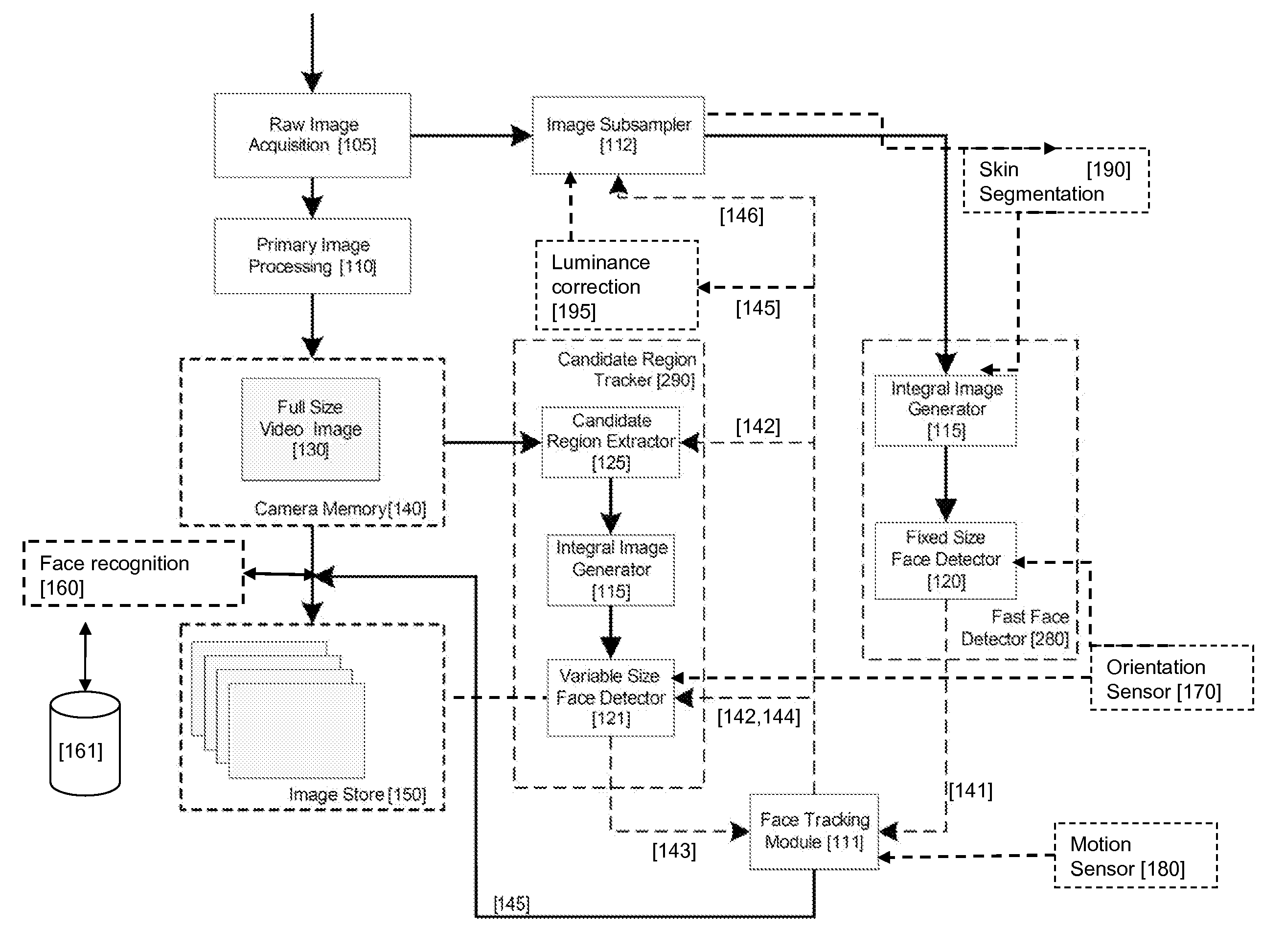
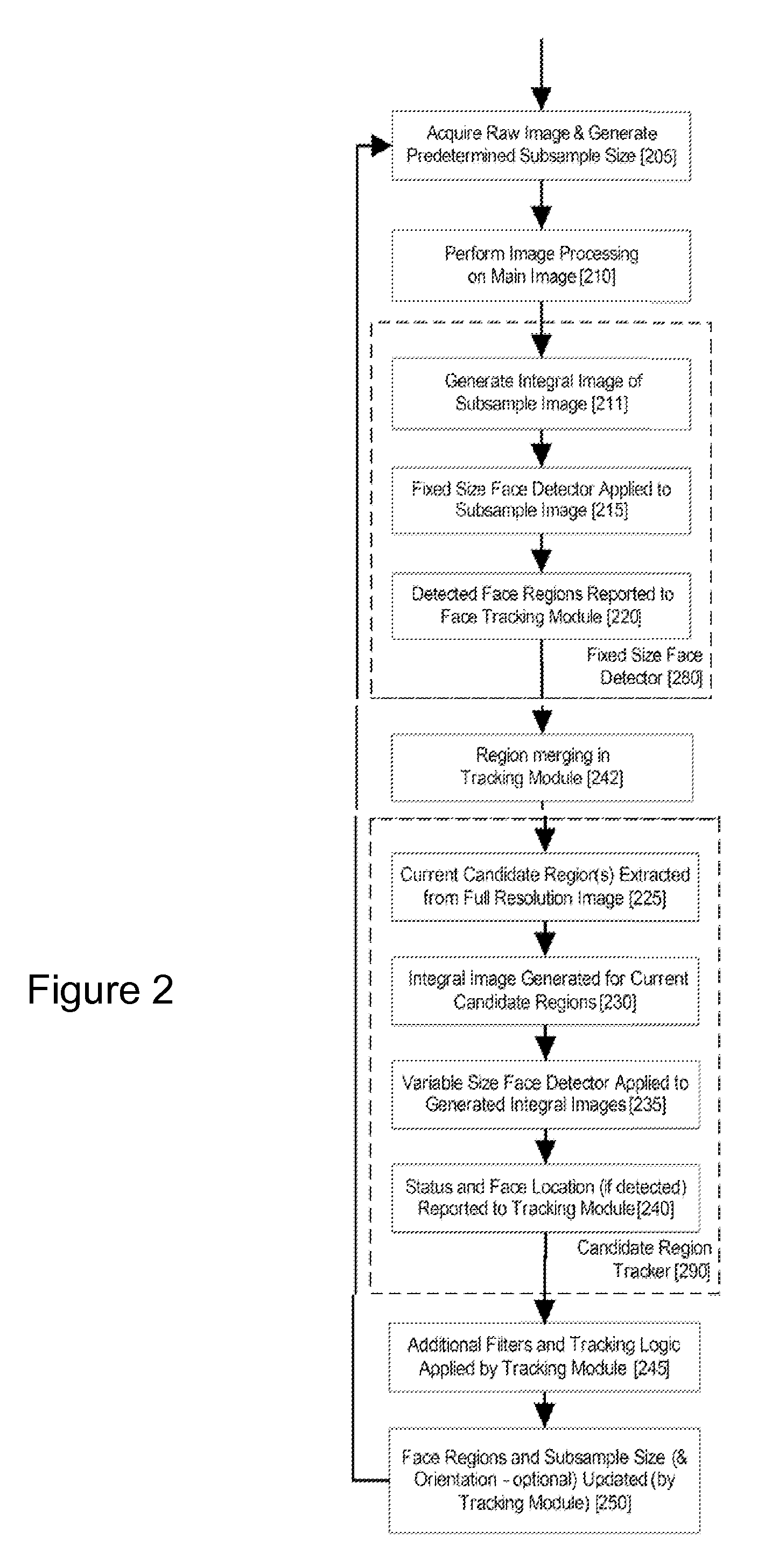
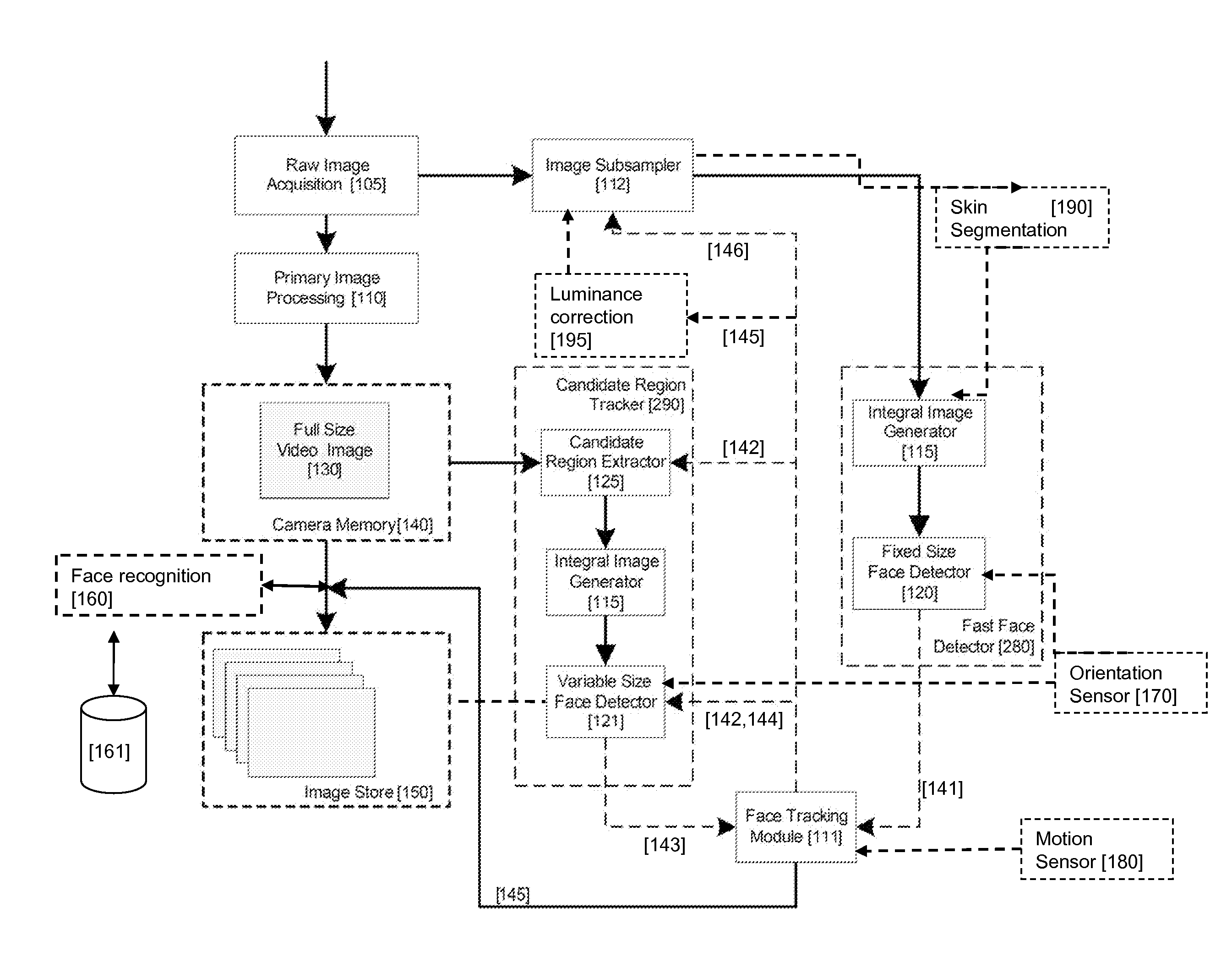
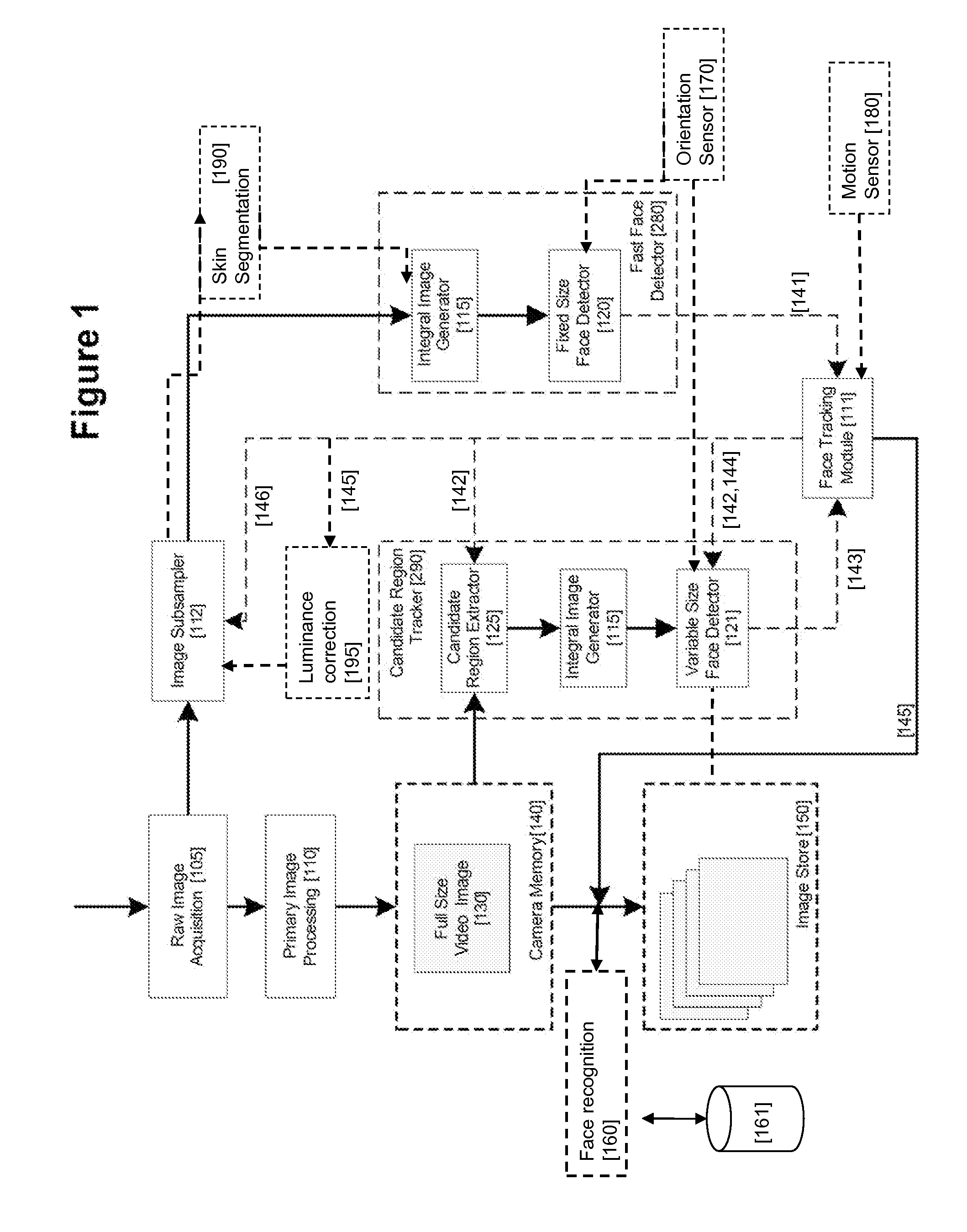
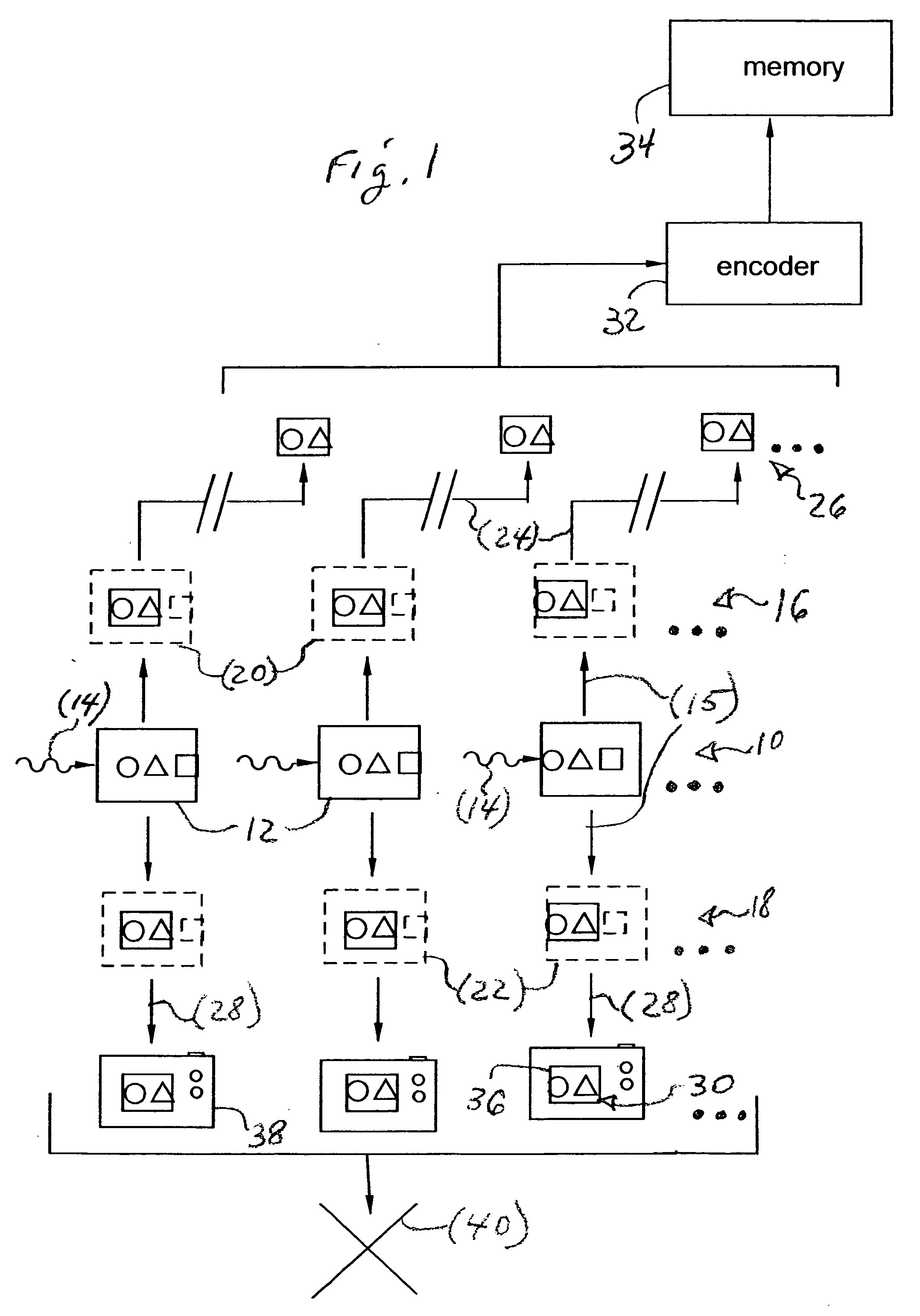
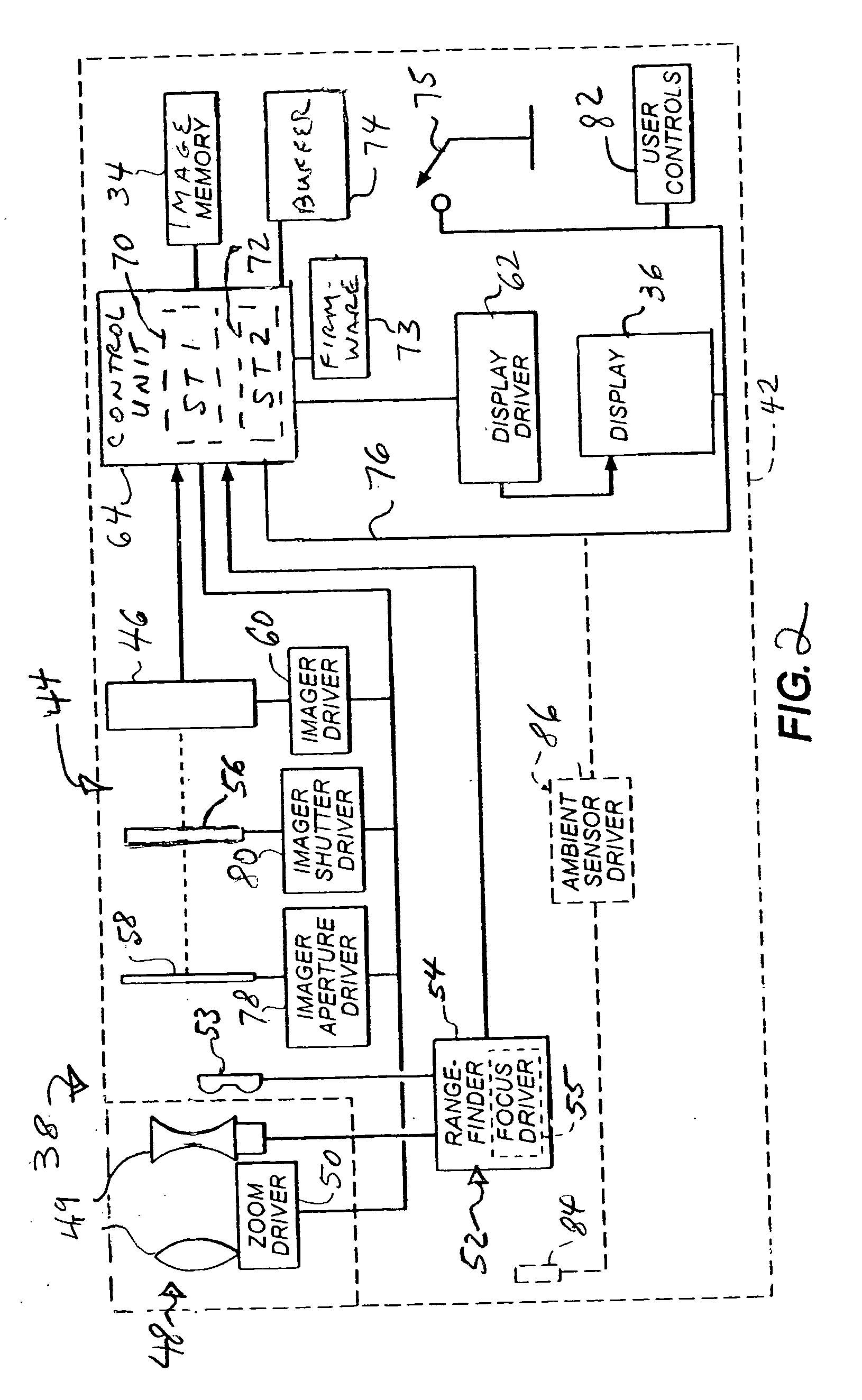
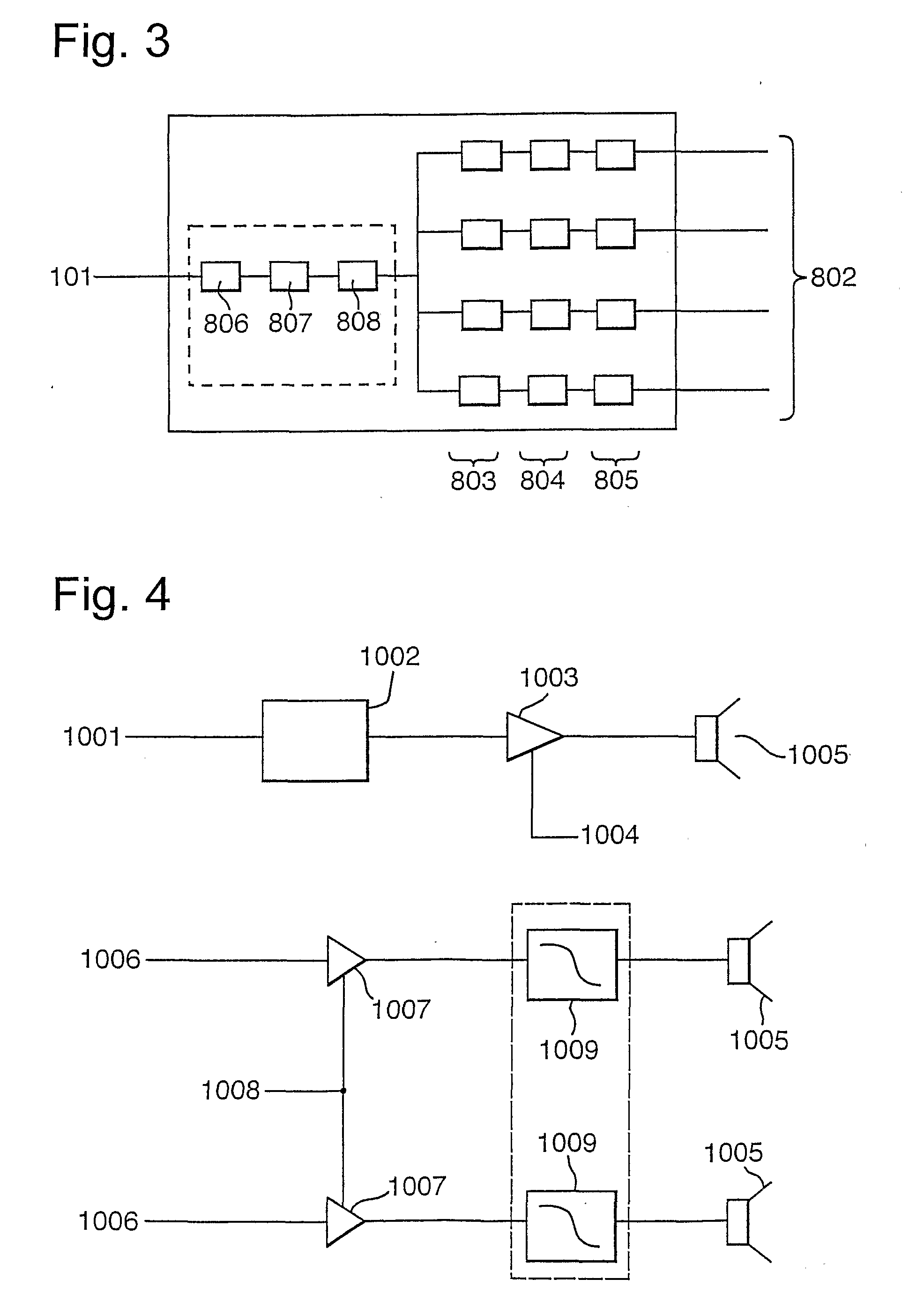
Real-time face tracking in a digital image acquisition device
ActiveUS7315631B1Effectively provide similar quality resultQuick checkTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionImaging processing
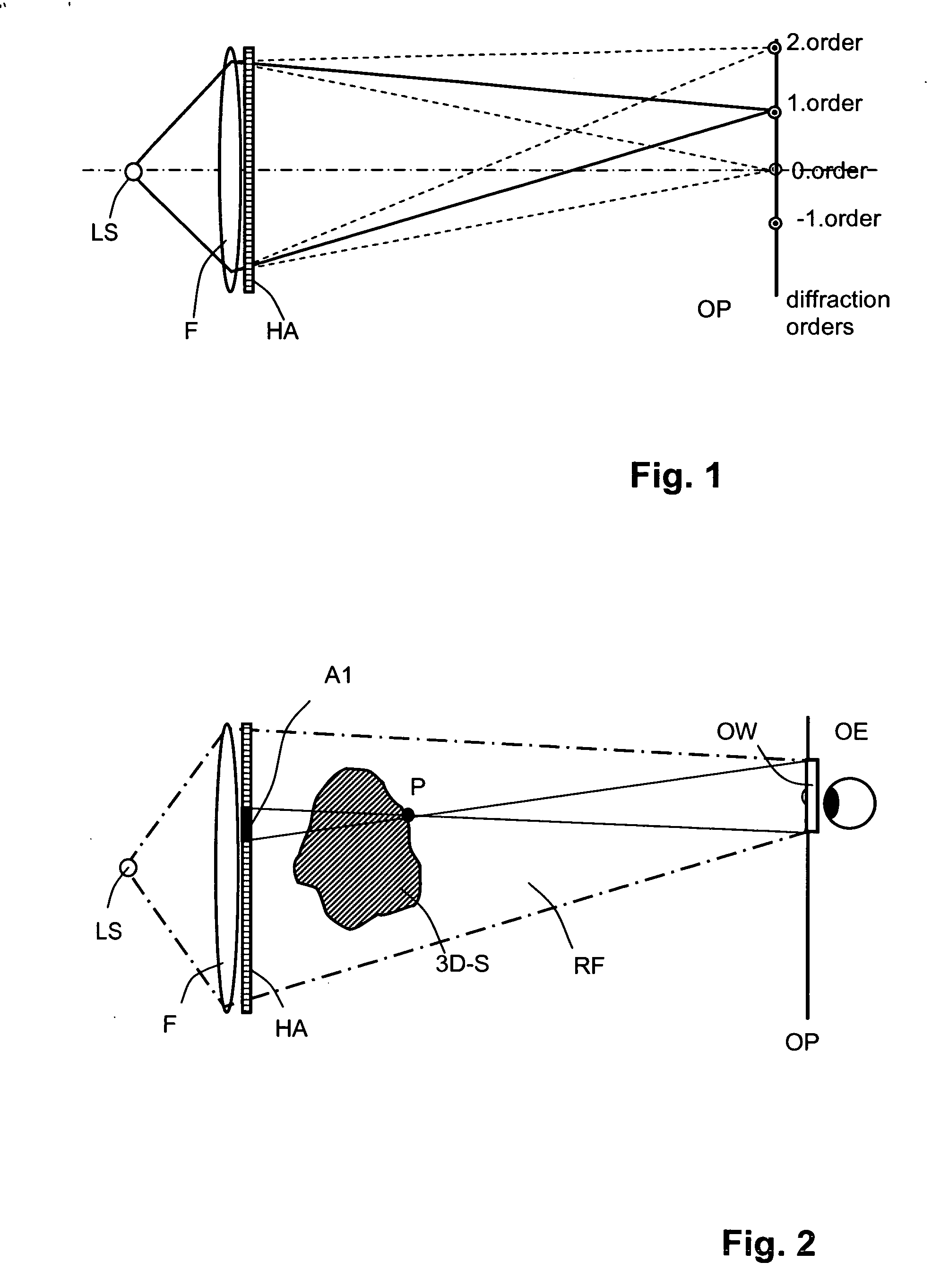
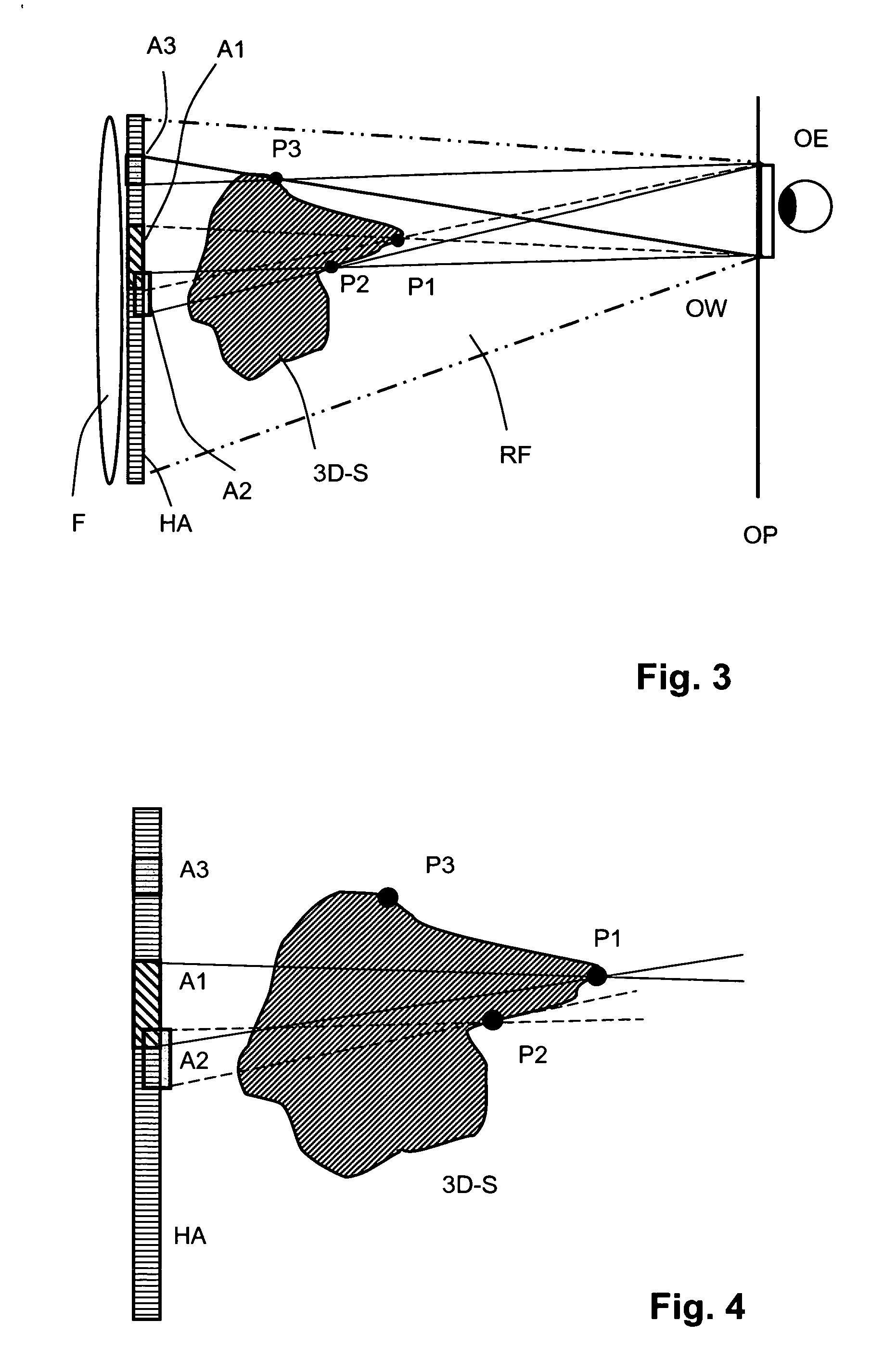
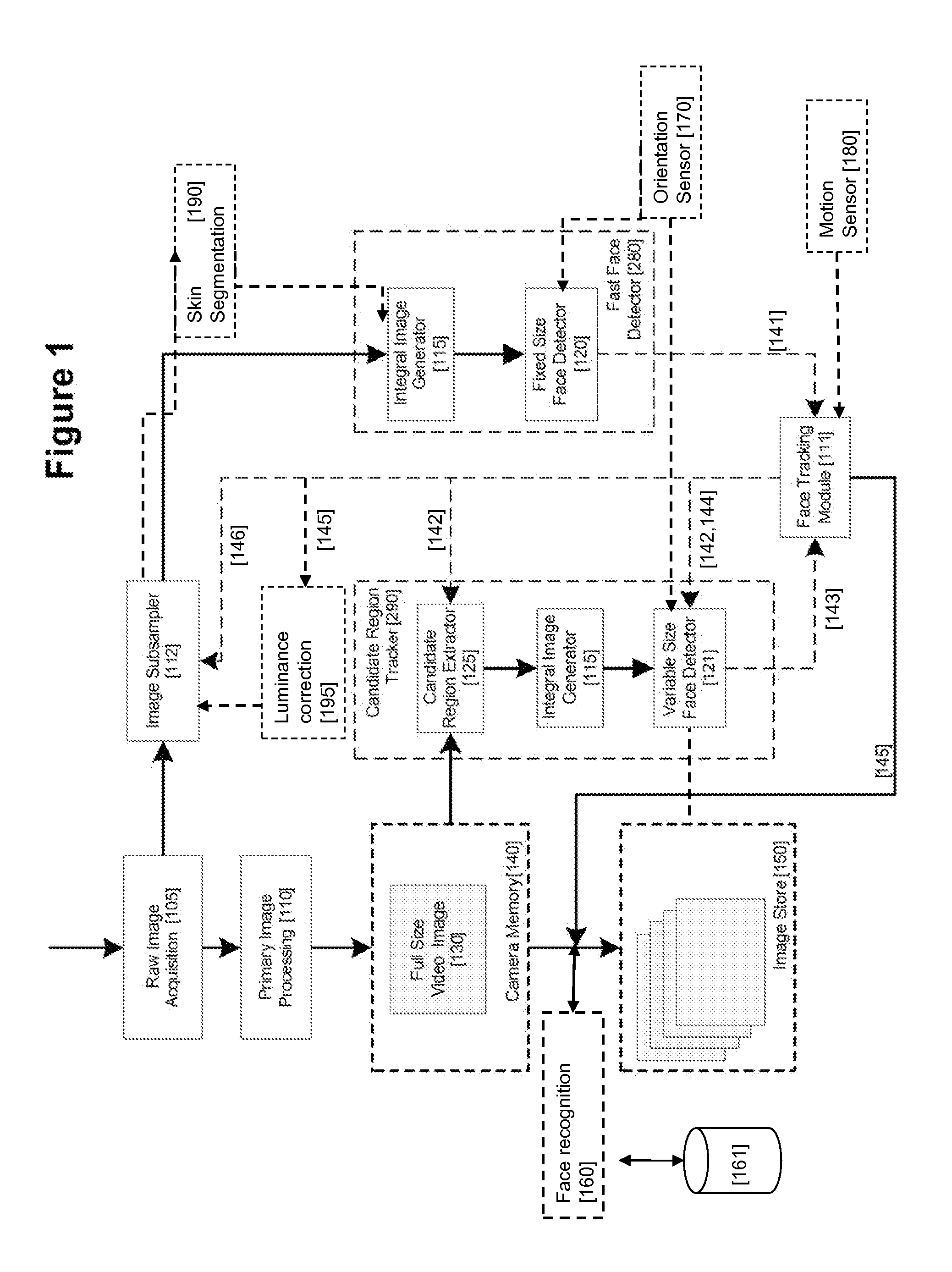
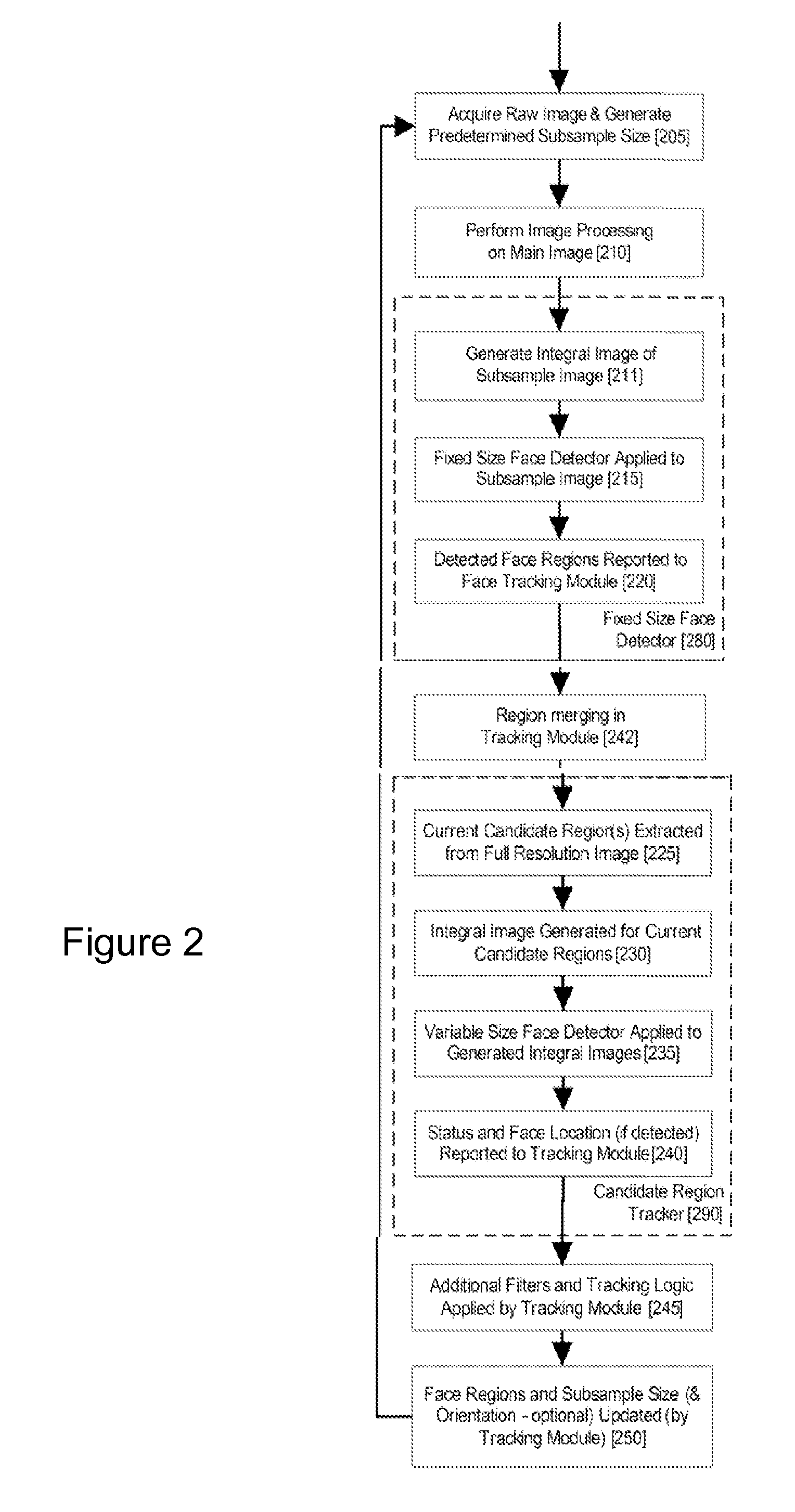
An image processing apparatus for tracking faces in an image stream iteratively receives an acquired image from the image stream potentially including one or more face regions. The acquired image is sub-sampled at a specified resolution to provide a sub-sampled image. An integral image is then calculated for a least a portion of the sub-sampled image. Fixed size face detection is applied to at least a portion of the integral image to provide a set of candidate face regions. Responsive to the set of candidate face regions produced and any previously detected candidate face regions, the resolution is adjusted for sub-sampling a subsequent acquired image.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
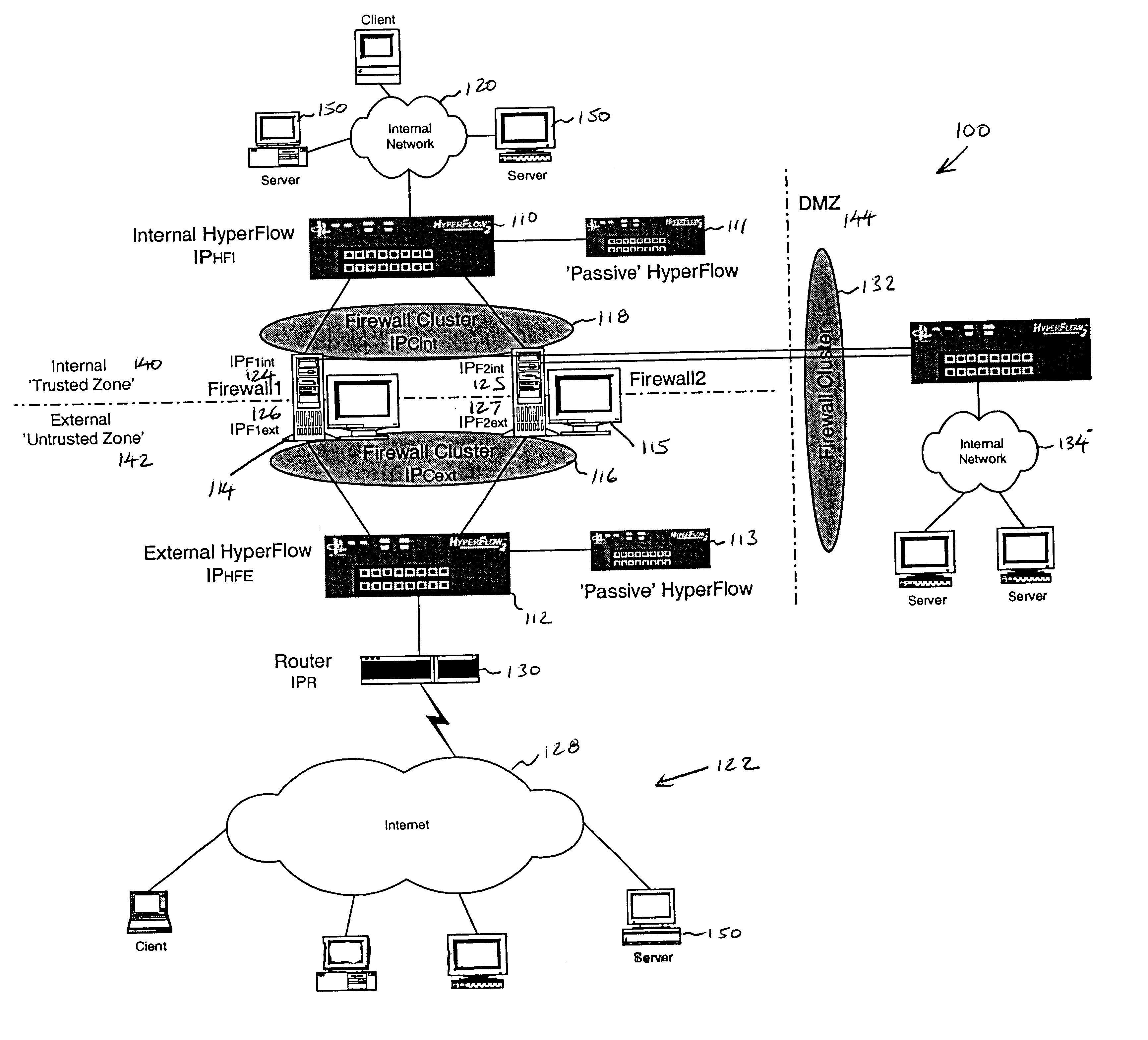
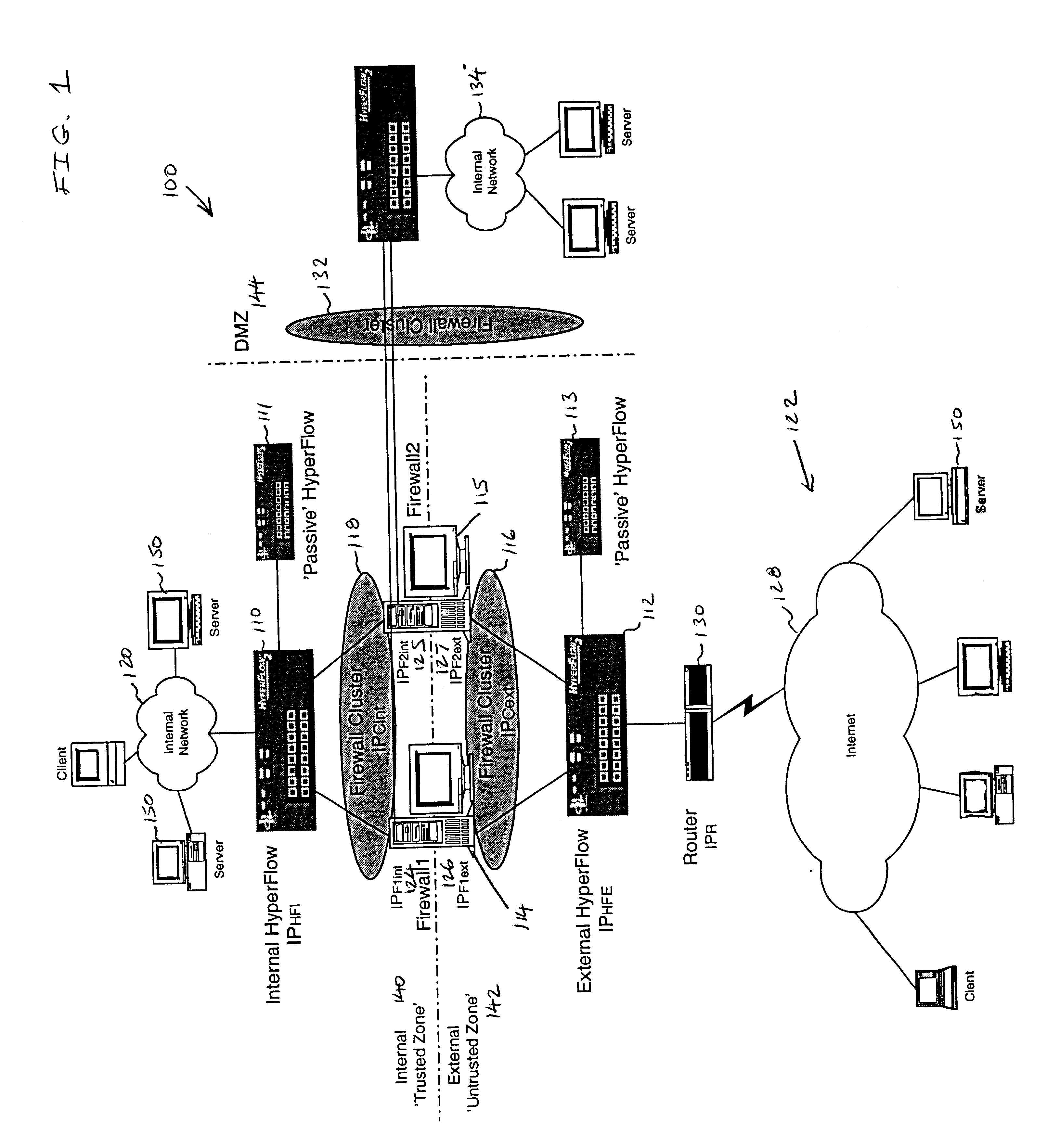
Firewall clustering for multiple network servers
InactiveUS6880089B1Increase capacityReduce calculationMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlTraffic capacityExtensibility
A firewall clustering system connects two or more firewalls between an internal network and an external network. The plurality of two or more firewalls are combined to supply high-availability and scaling of processing capacity. Firewalls maintain client-server state information. Flow controllers are connected to the firewalls and placed on both the internal “trusted” side and the external “untrusted” side of the firewalls. Flow controllers are placed on both sides of the firewalls to ensure that traffic for a given client-server session flows through the same firewall in both inbound and outbound directions. The firewalls perform filtering operations and / or network address translation (NAT) services. In both cases, the flow controllers supply high availability, scalability, and traffic distribution for the firewalls in the firewall cluster.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Overlay alignment metrology using diffraction gratings
InactiveUS20020158193A1Limited space availableOvercome difficultiesBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMetrologyAngle of incidence
Alignment accuracy between two or more patterned layers is measured using a metrology target comprising substantially overlapping diffraction gratings formed in a test area of the layers being tested. An optical instrument illuminates all or part of the target area and measures the optical response. The instrument can measure transmission, reflectance, and / or ellipsometric parameters as a function of wavelength, polar angle of incidence, azimuthal angle of incidence, and / or polarization of the illumination and detected light. Overlay error or offset between those layers containing the test gratings is determined by a processor programmed to calculate an optical response for a set of parameters that include overlay error, using a model that accounts for diffraction by the gratings and interaction of the gratings with each others' diffracted field. The model parameters might also take account of manufactured asymmetries. The calculation may involve interpolation of pre-computed entries from a database accessible to the processor. The calculated and measured responses are iteratively compared and the model parameters changed to minimize the difference.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method and apparatus for controlling uplink transmission power
InactiveUS8918135B2Accurate powerReduce calculationPower managementSite diversityUplink transmissionControl channel
The present description relates to a method for controlling uplink power in a distributed multi-node system, comprising the following steps: receiving reference signals from a plurality of antenna nodes containing at least one antenna; estimating average propagation loss on the basis of the receiving power of the reference signals received from the plurality of antenna nodes; receiving, via a downlink control channel, noise and interference (NI) information from a base station which contains the plurality of antenna nodes; and determining uplink transmission power using the estimated average propagation loss and the received noise and interference information.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
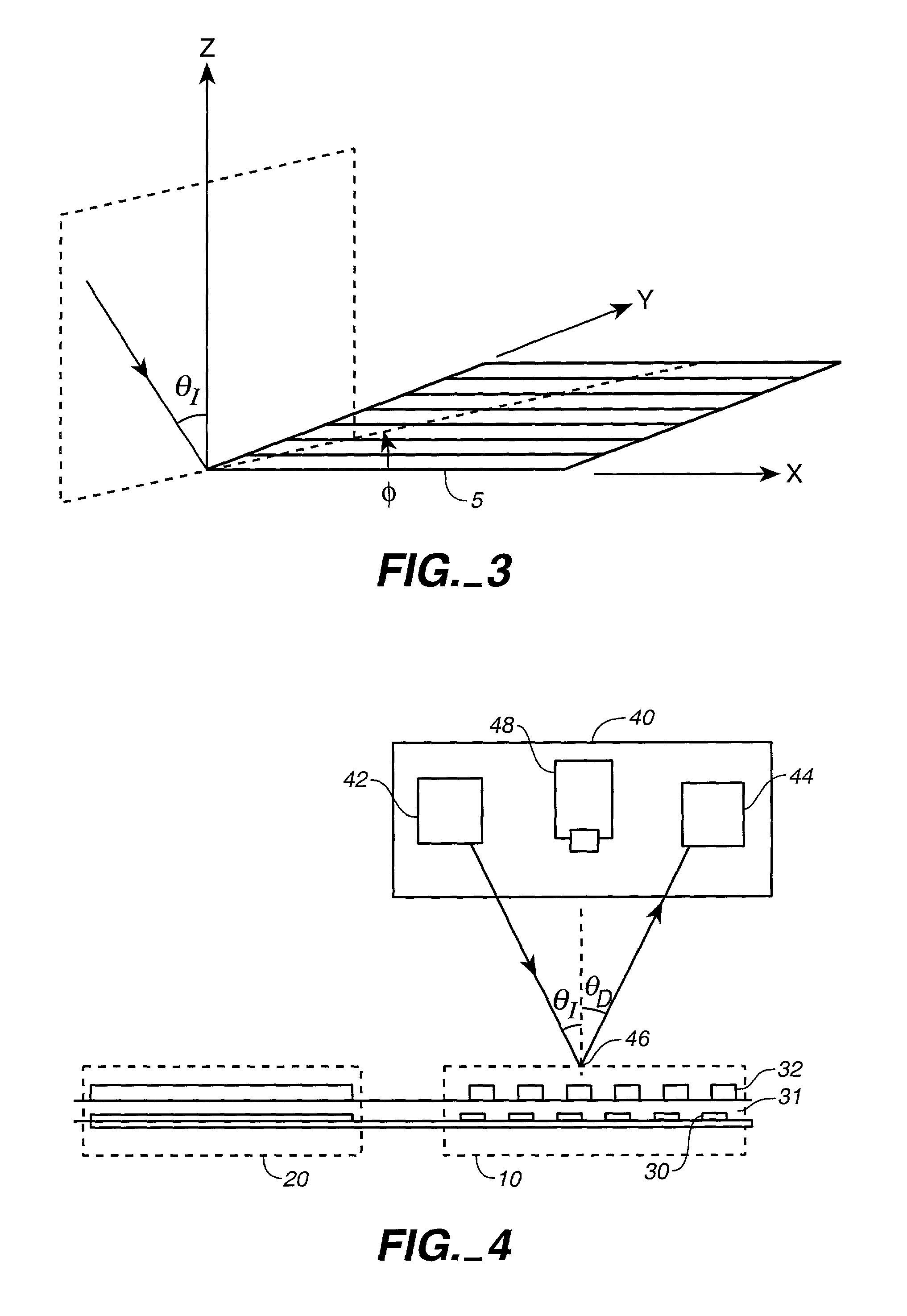
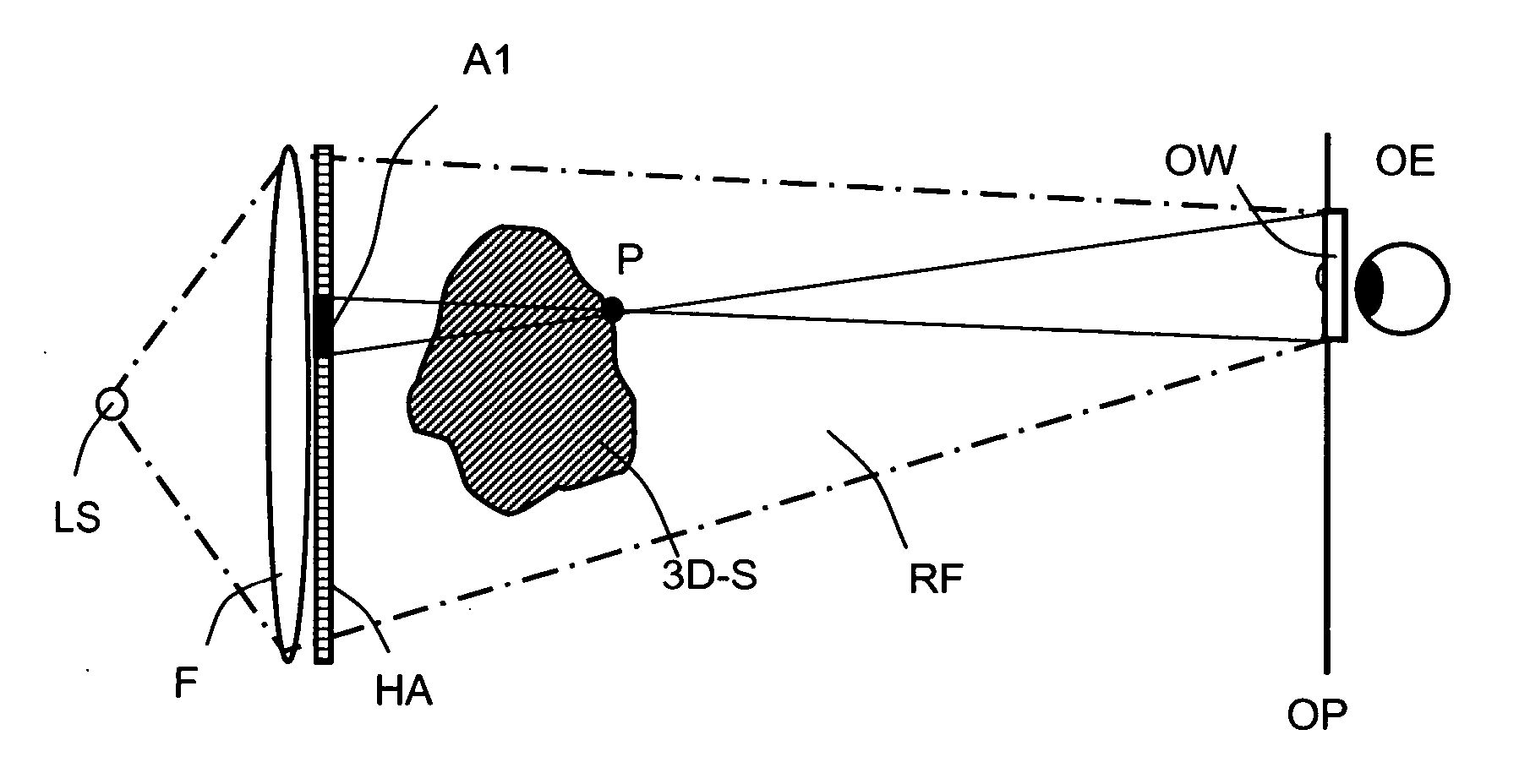
Method of computing a hologram
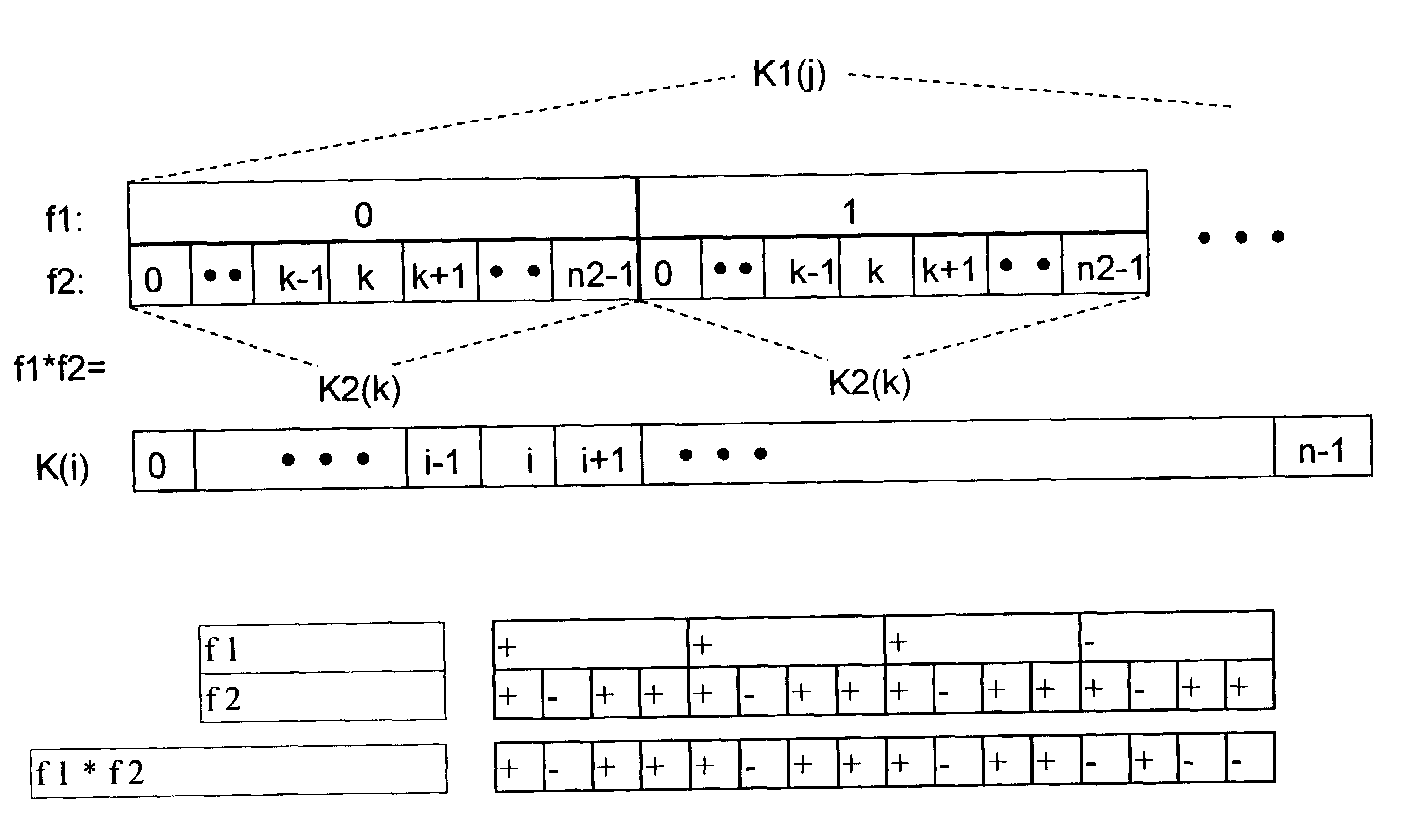
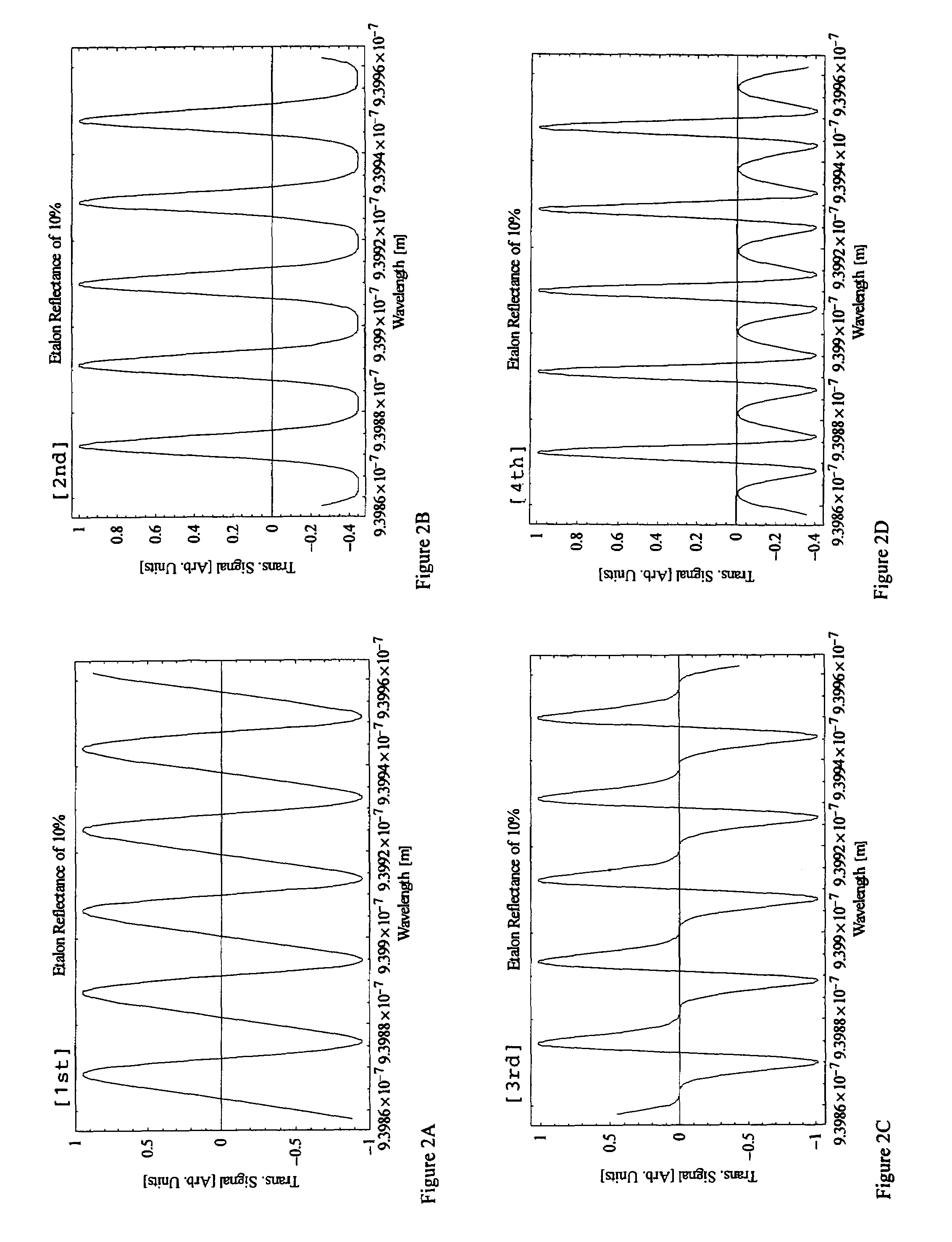
ActiveUS20060139711A1Reduce calculationQuality improvementHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsWavefrontComputer science
A method of computing a hologram by determining the wavefronts at the approximate observer eye position that would be generated by a real version of an object to be reconstructed. In normal computer generated holograms, one determines the wavefronts needed to reconstruct an object; this is not done directly in the present invention. Instead, one determines the wavefronts at an observer window that would be generated by a real object located at the same position of the reconstructed object. One can then back-transforms these wavefronts to the hologram to determine how the hologram needs to be encoded to generate these wavefronts. A suitably encoded hologram can then generate a reconstruction of the three-dimensional scene that can be observed by placing one's eyes at the plane of the observer window and looking through the observer window.
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
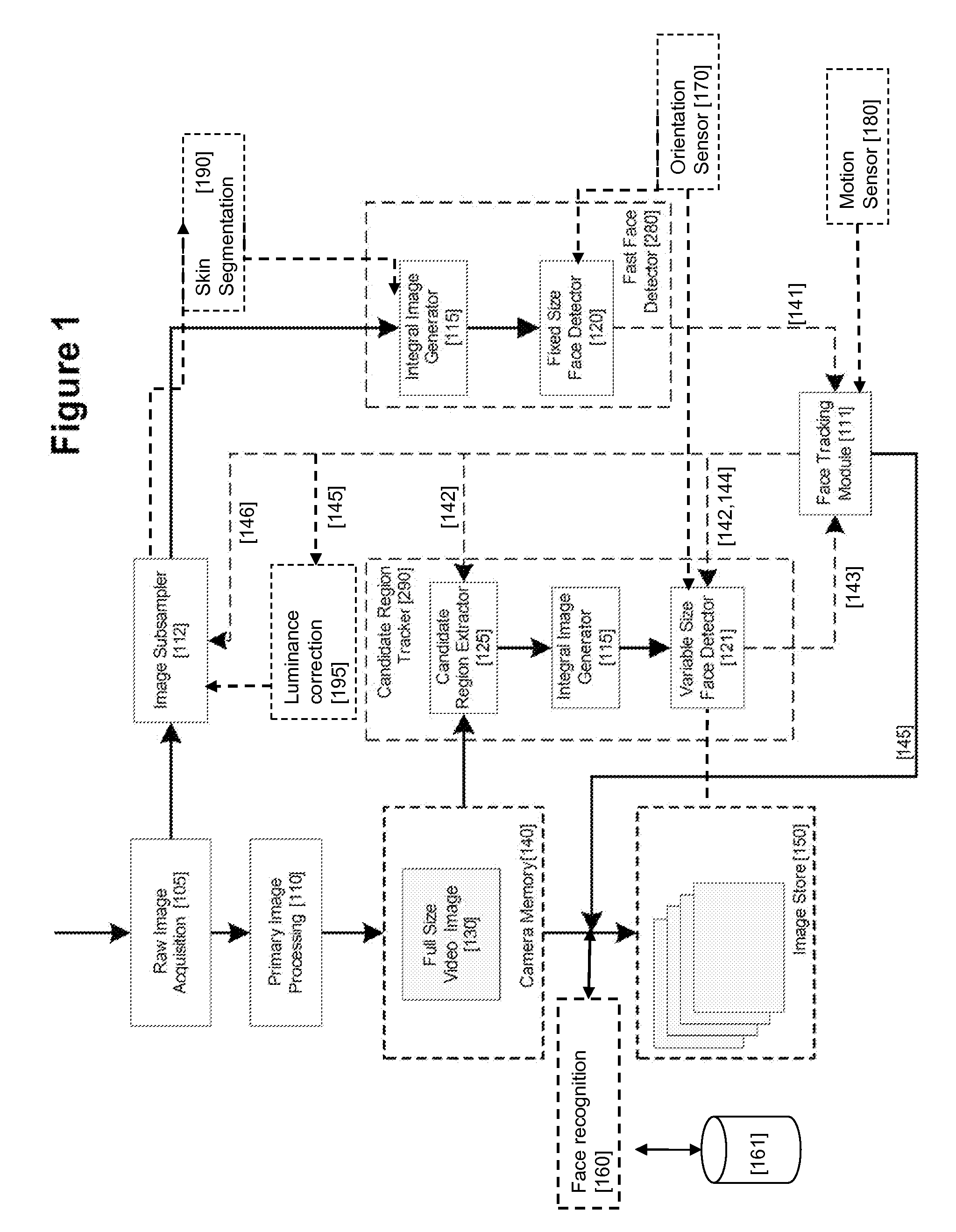
Real-Time Face Tracking in a Digital Image Acquisition Device
ActiveUS20080037839A1Improve performance accuracyReduce calculationTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionImaging processing
An image processing apparatus for tracking faces in an image stream iteratively receives a new acquired image from the image stream, the image potentially including one or more face regions. The acquired image is sub-sampled (112) at a specified resolution to provide a sub-sampled image. An integral image is then calculated for a least a portion of the sub-sampled image. Fixed size face detection (20) is applied to at least a portion of the integral image to provide a set of candidate face regions. Responsive to the set of candidate face regions produced and any previously detected candidate face regions, the resolution at which a next acquired image is sub-sampled is adjusted.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Real-Time Face Tracking in a Digital Image Acquisition Device
ActiveUS20080037827A1Improve performance accuracyReduce calculationTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionImaging processing
An image processing apparatus for tracking faces in an image stream iteratively receives a new acquired image from the image stream, the image potentially including one or more face regions. The acquired image is sub-sampled (112) at a specified resolution to provide a sub-sampled image. An integral image is then calculated for a least a portion of the sub-sampled image. Fixed size face detection (20) is applied to at least a portion of the integral image to provide a set of candidate face regions. Responsive to the set of candidate face regions produced and any previously detected candidate face regions, the resolution at which a next acquired image is sub-sampled is adjusted.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
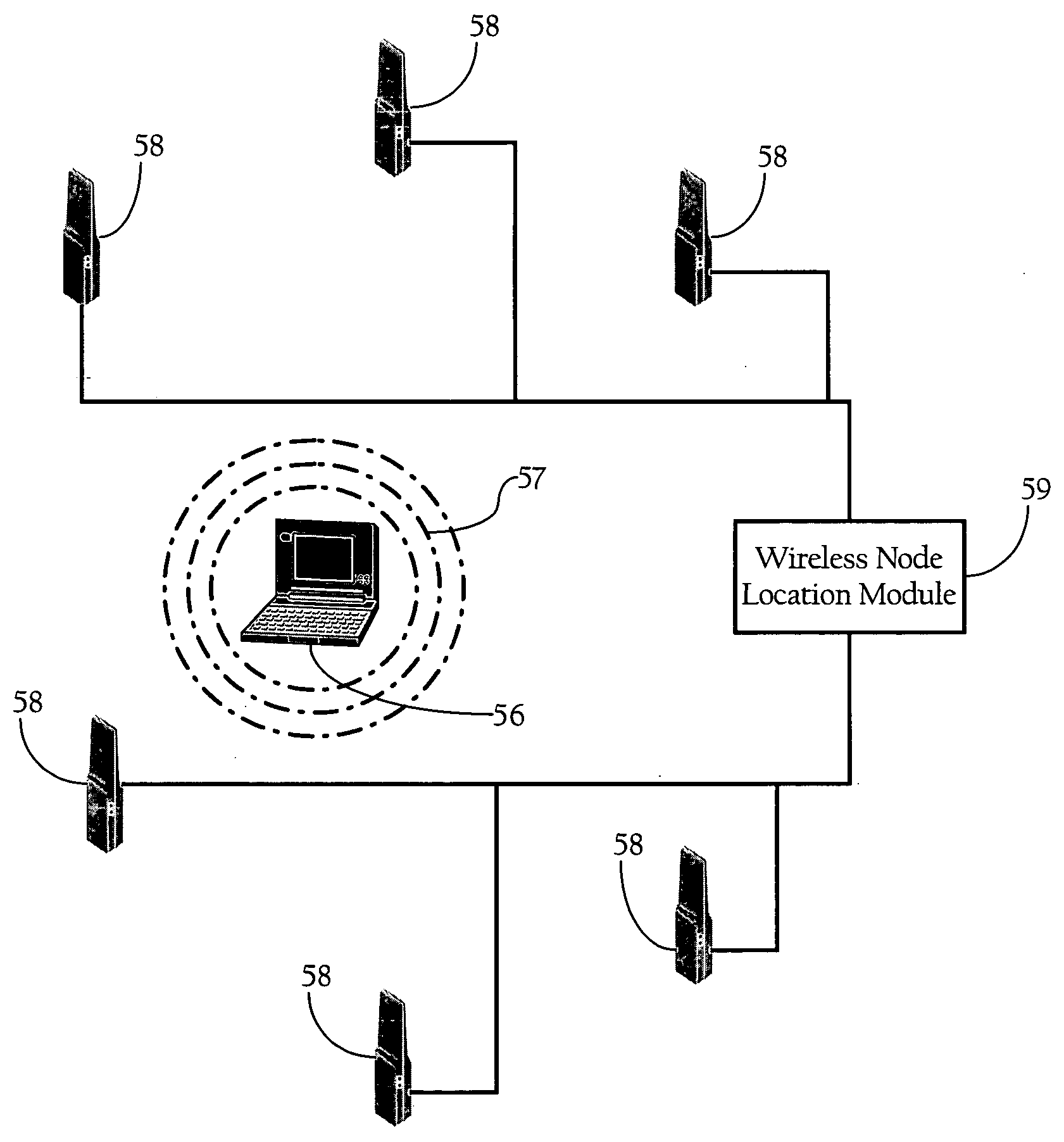
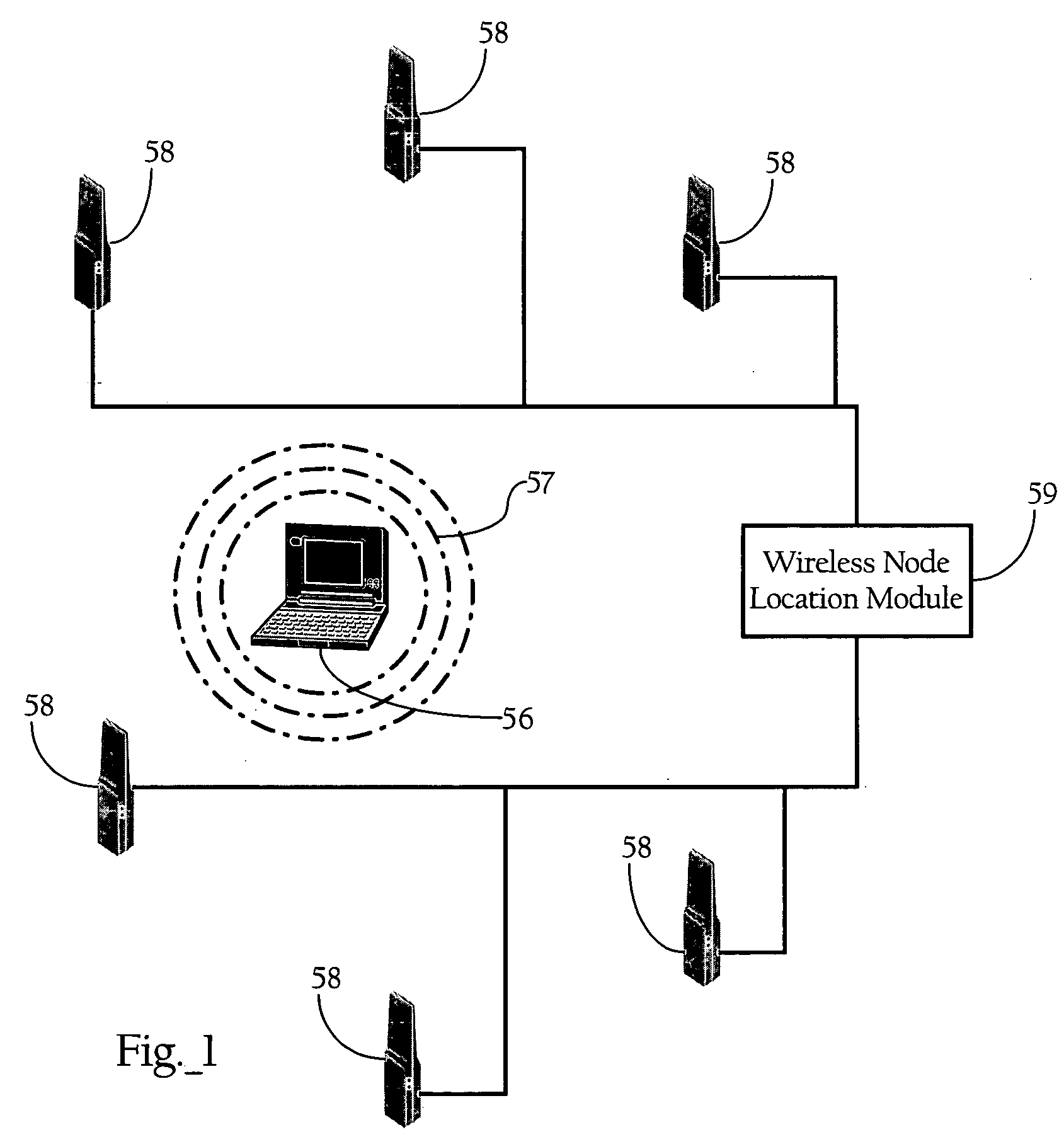
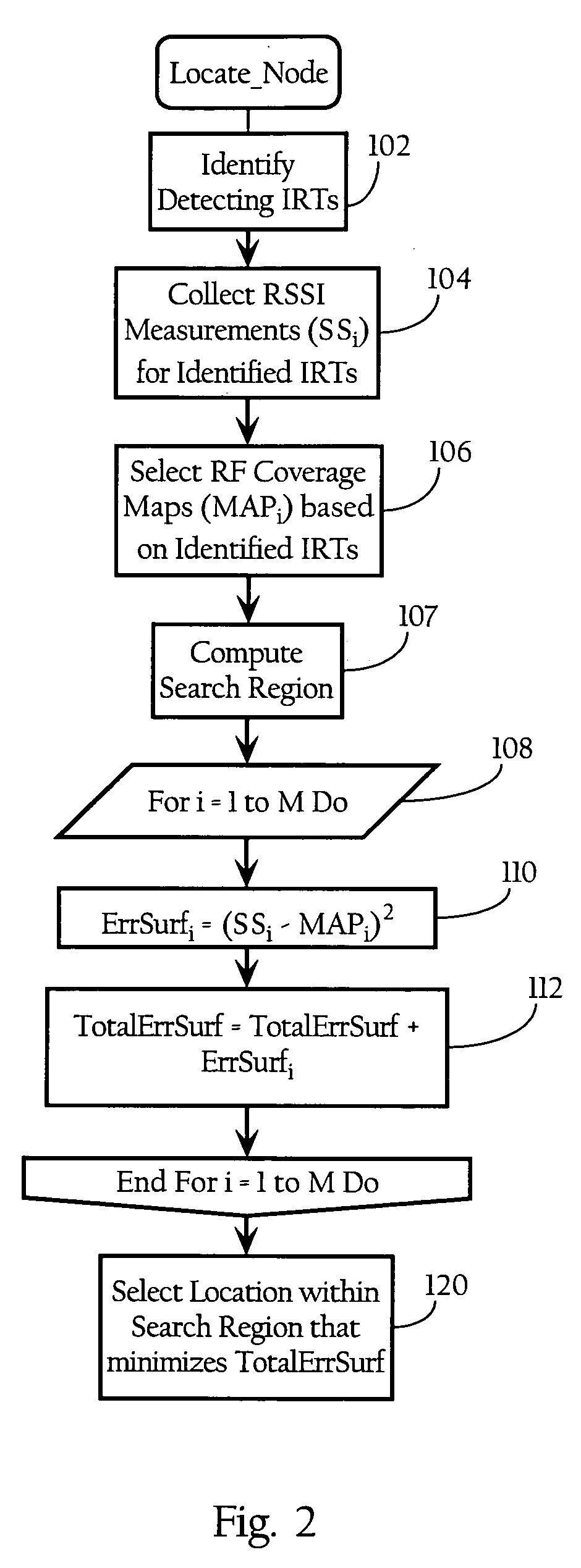
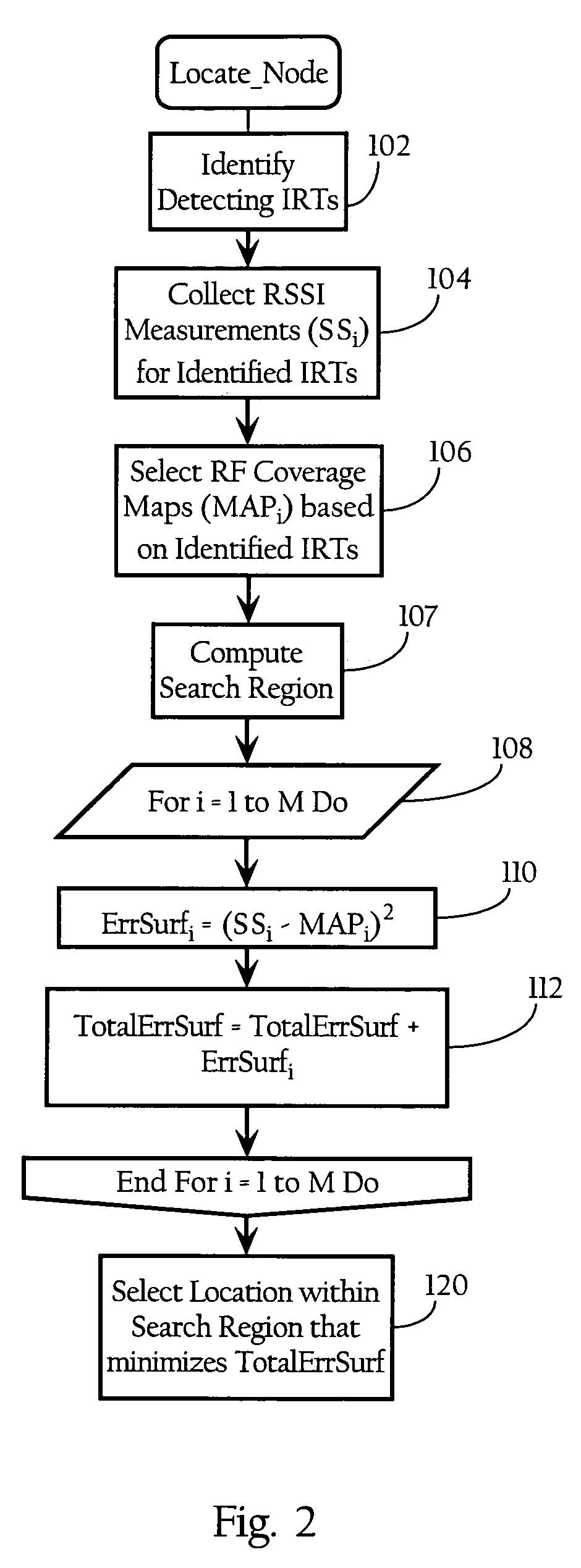
Wireless node location mechanism featuring definition of search region to optimize location computation
ActiveUS20050261004A1Optimize locationReduce total powerDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationRadio receptionRadio receiver
A wireless node location mechanism that defines a search region to optimize the computations associated with estimating the location of a given wireless node. According to one implementation, a coverage map associated with each radio receiver that records signal strength data is defined out to a threshold signal strength level. Before computing the estimated location of a given wireless nodes, a search region is defined based on the intersection of the coverage maps associated with each radio receiver that detects the wireless node. Some implementations use information provided by the fact that certain radio receivers did not detect the wireless node to further optimize the location estimate. By defining a search region, which is a generally small area relative to the space encompassed by an entire RF environment, the present invention provides several advantages, such as reducing the processing time and / or power to compute estimated locations for wireless nodes.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Device and system for calculating 3D seismic classification features and process for geoprospecting material seams
InactiveUS20050171700A1Eliminate needEliminate errorSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsFeature vectorComputer science
A device for calculating 3D seismic classification features constrained to be tangent to a path in a 3D volume is provided as a “geo-operator”. The method has the capability to associate horizontal (2D), vertical (2D) or arbitrary (3D) classification “feature vectors” with the geo-operator output, to allow determining where the geo-operator has sufficient data for the calculation to form a valid output and where the output of the geo-operator indicates a measure to which alternative feature vector prototypes may be present along the path. The geo-operator has the flexibility of using variable crossline, inline and vertical extent and having a direction able to be designated as it traverses the path, from the start point to the endpoint, aligned to be tangent to the path.
Owner:CHROMA ENERGY
Method for synchronizing a base station with a mobile station, a base station and a mobile station
InactiveUS7062002B1Sure easyEasy to useCode division multiplexSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlMobile stationComputer science
Method for forming and determining a signal sequence, a synchronization method, a transmitting unit and a receiving unit, including the formation of signal sequences that are based on partial signal sequences, the second partial signal sequence being repeated and modulated in the process by the first partial signal sequence, and at least one of the signal sequences being a Golay sequence, and use of these partial signal sequences for the purpose of simplified calculation of correlation sums in a two-stage calculation method, with one partial correlation sum sequence being calculated first.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Image sequence stabilization method and camera having dual path image sequence stabilization
InactiveUS20060274156A1Improve performanceReduce calculationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Digital image
In an image sequence stabilization method and a camera, a sequence of input digital images are captured. The sequence of input digital images is replicated to provide a corresponding sequence of archival images and a corresponding sequence of display images. The archival image sequence is automatically stabilized to provide a stabilized archival image sequence. The display image sequence is automatically stabilized to provide a stabilized display image sequence. The stabilization methods used for the two sequences are different, although both can be digital.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Performing sequence analysis as a multipart plan storing intermediate results as a relation
InactiveUS7702610B2Reliable and high performance integrationReduce calculationMedical data miningData processing applicationsProgramming languageSequence analysis
A usage model and the underlying technology used to provide sequence analysis as part of a relational database system. Included components include the semantic and syntactic integration of the sequence analysis with an existing query language, the storage methods for the sequence data, and the design of a multipart execution scheme that runs the sequence analysis as part of a potentially larger database query, especially using parallel execution techniques.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method and apparatus to create a sound field
ActiveUS7515719B2Eliminate the effects ofReduce calculationTelevision system detailsGain controlTransducerVocal tract
The invention generally relates to a method and apparatus for taking an input signal, replicating it a number of times and modifying each of the replicas before routing them to respective output transducers such that a desired sound field is created. This sound field may comprise a directed beam, focussed beam or a simulated origin. In a first aspect, delays are added to sound channels to remove the effects of different travelling distances. In a second aspect, a delay is added to a video signal to account for the delays added to the sound channels. In a third aspect, different window functions are applied to each channel to give improved flexibility of use. In a fourth aspect, a smaller extent of transducers is used top output high frequencies than are used to output low frequencies. An array having a larger density of transducers near the centre is also provided. In a fifth aspect, a line of elongate transducers is provided to give good directivity in a plane. In a sixth aspect, sound beams are focussed in front or behind surfaces to give different beam widths and simulated origins. In a seventh aspect, a camera is used to indicate where sound is directed.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
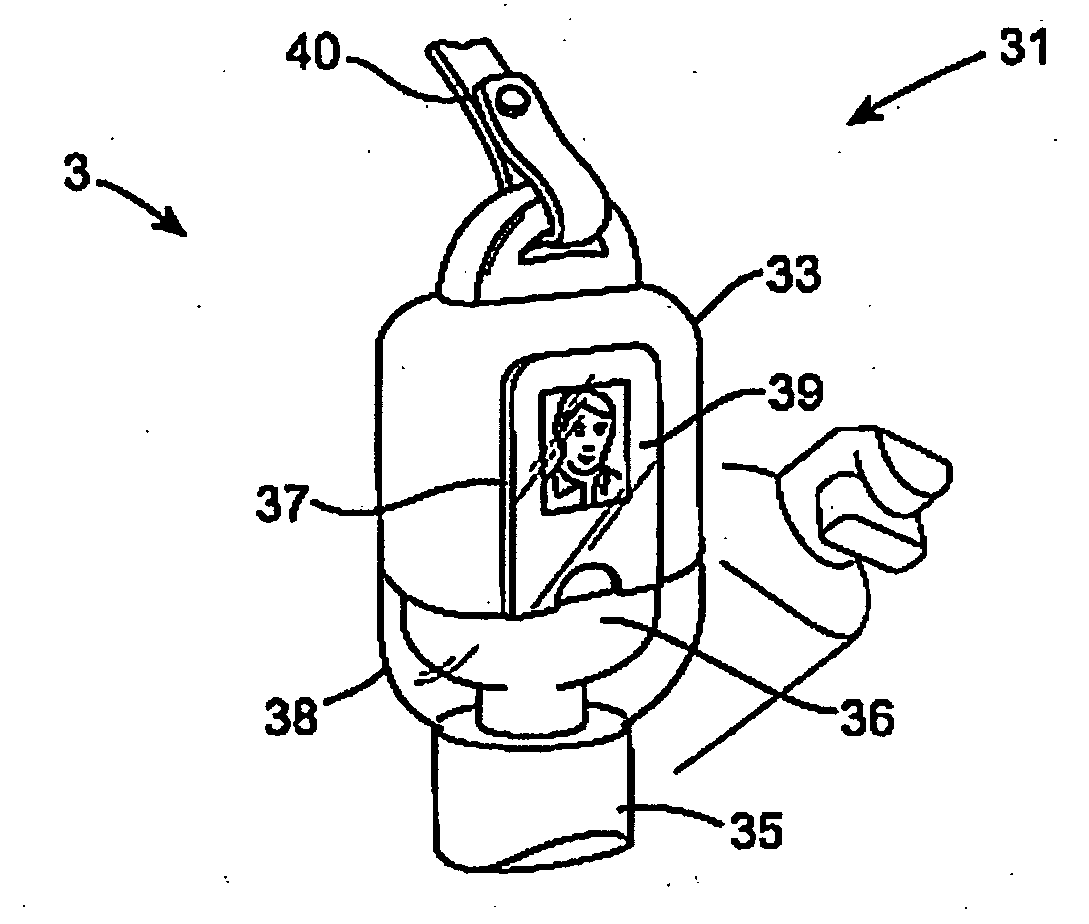
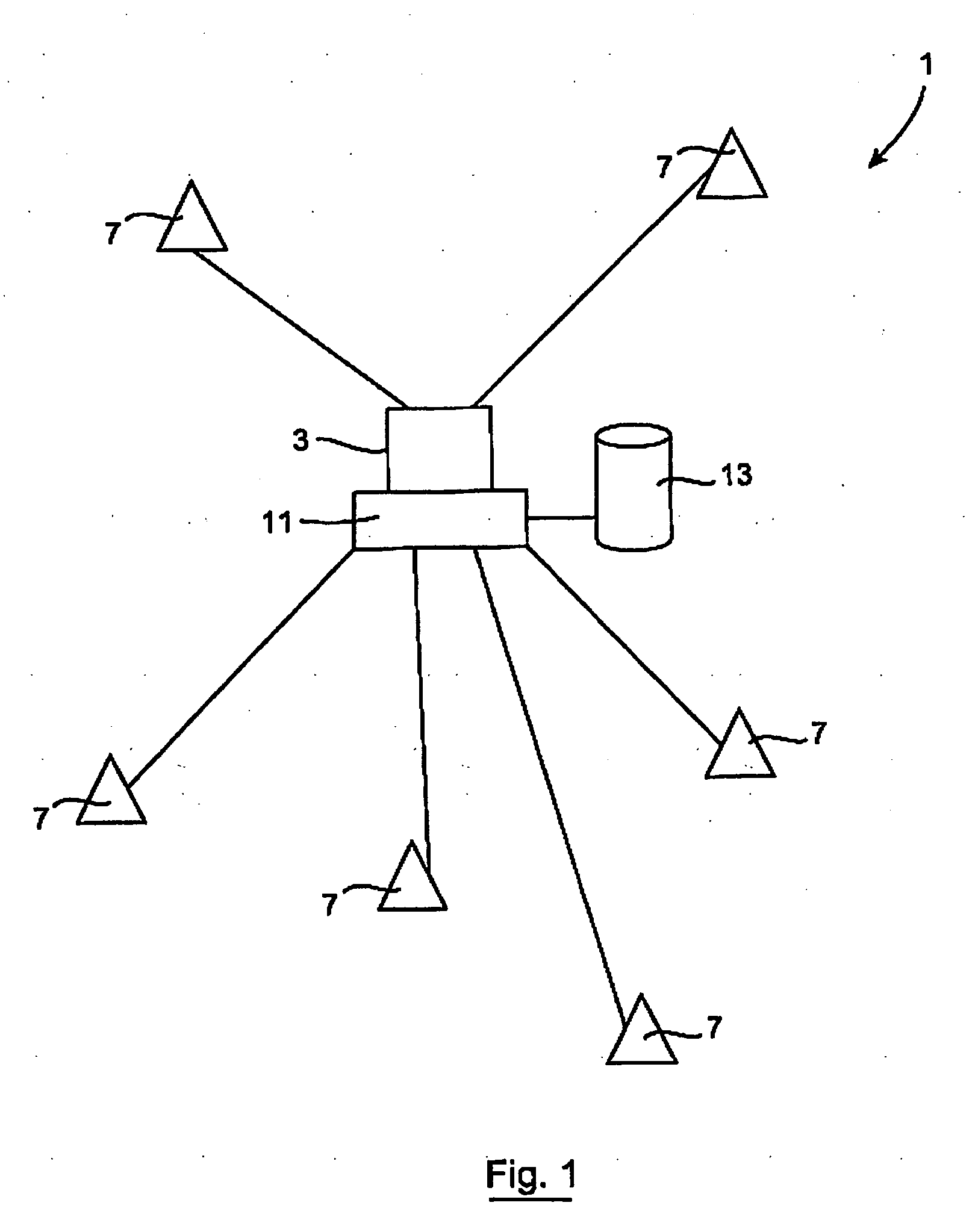
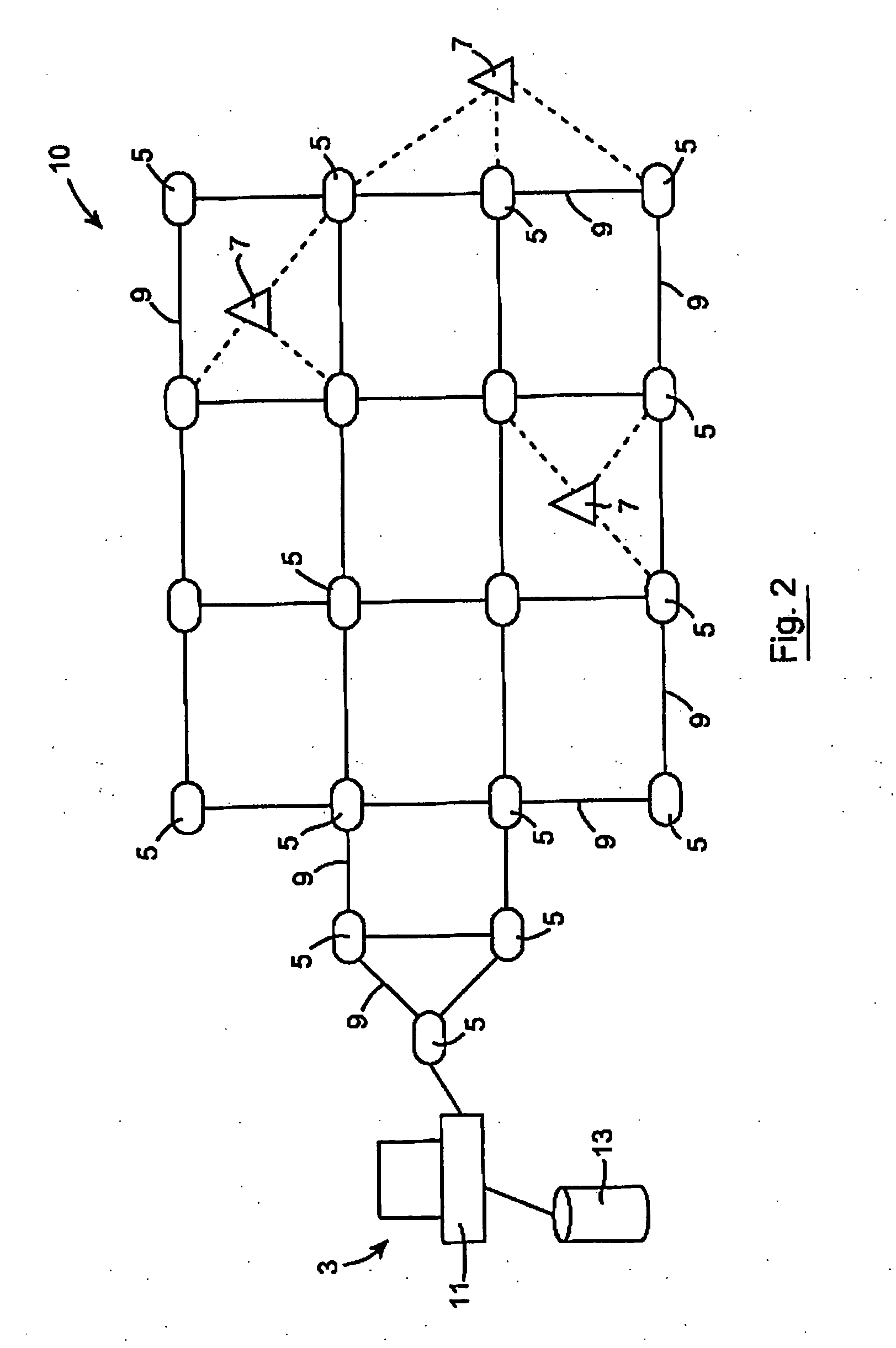
System and Method for Monitoring Hygiene Standards Compliance
InactiveUS20100188228A1Accurate locationStrong signalError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMobile WebHygiene
This invention relates to a system and method of monitoring hygiene standards compliance in a medical facility in which there is provided a surveillance network having a monitoring unit 3 and a plurality of mobile network units 7. There may additionally be provided a plurality of fixed network units 5. The monitoring unit 3, mobile network units 7 and fixed network units 5 are connected by way of a Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN), in this case a ZigBee network. Identification signals are sent from the mobiles network units 7 to the monitoring unit 3 and the monitoring unit stores the identification signals in memory and generates a hygiene standards compliance profile for an individual associated with a particular mobile network unit. The hygiene compliance profile may provide information relating to the number of times that a particular individual washed their hands to information regarding the patients that that individual came into contact with over the course of a shift. Reports on the behaviour of individuals or groups of individuals may be generated.
Owner:HYINTEL
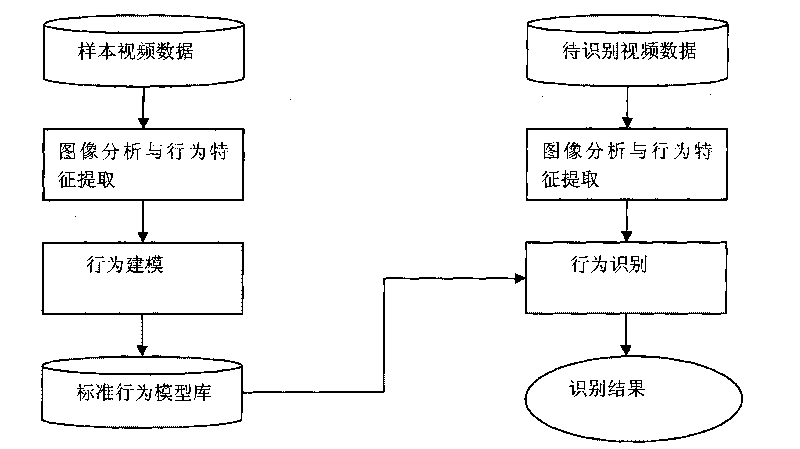
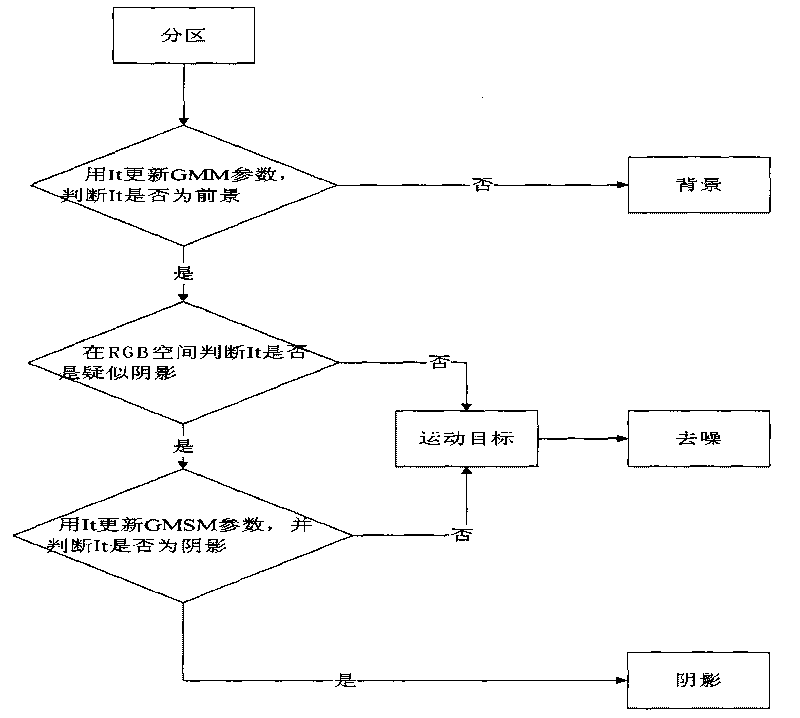
Movement human abnormal behavior identification method based on template matching
InactiveCN101719216AGood effectThe effect is accurateCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual technologyAnomalous behavior
The invention relates to a movement human abnormal behavior identification method based on template matching, which mainly comprises the steps of: video image acquisition and behavior characteristic extraction. The movement human abnormal behavior identification method is a mode identification technology based on statistical learning of samples. The movement of a human is analyzed and comprehended by using a computer vision technology, the behavior identification is directly carried out based on geometric calculation of a movement region and recording and alarming are carried out; the Gaussian filtering denoising and the neighborhood denoising are combined for realizing the denoising, thereby improving the independent analysis property and the intelligent monitoring capacity of an intelligent monitoring system, achieving higher identification accuracy for abnormal behaviors, effectively removing the complex background and the noise of a vision acquired image, and improving the efficiency and the robustness of the detection algorithm. The invention has simple modeling, simple algorithm and accurate detection, can be widely applied to occasions of banks, museums and the like, and is also helpful to improve the safety monitoring level of public occasions.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
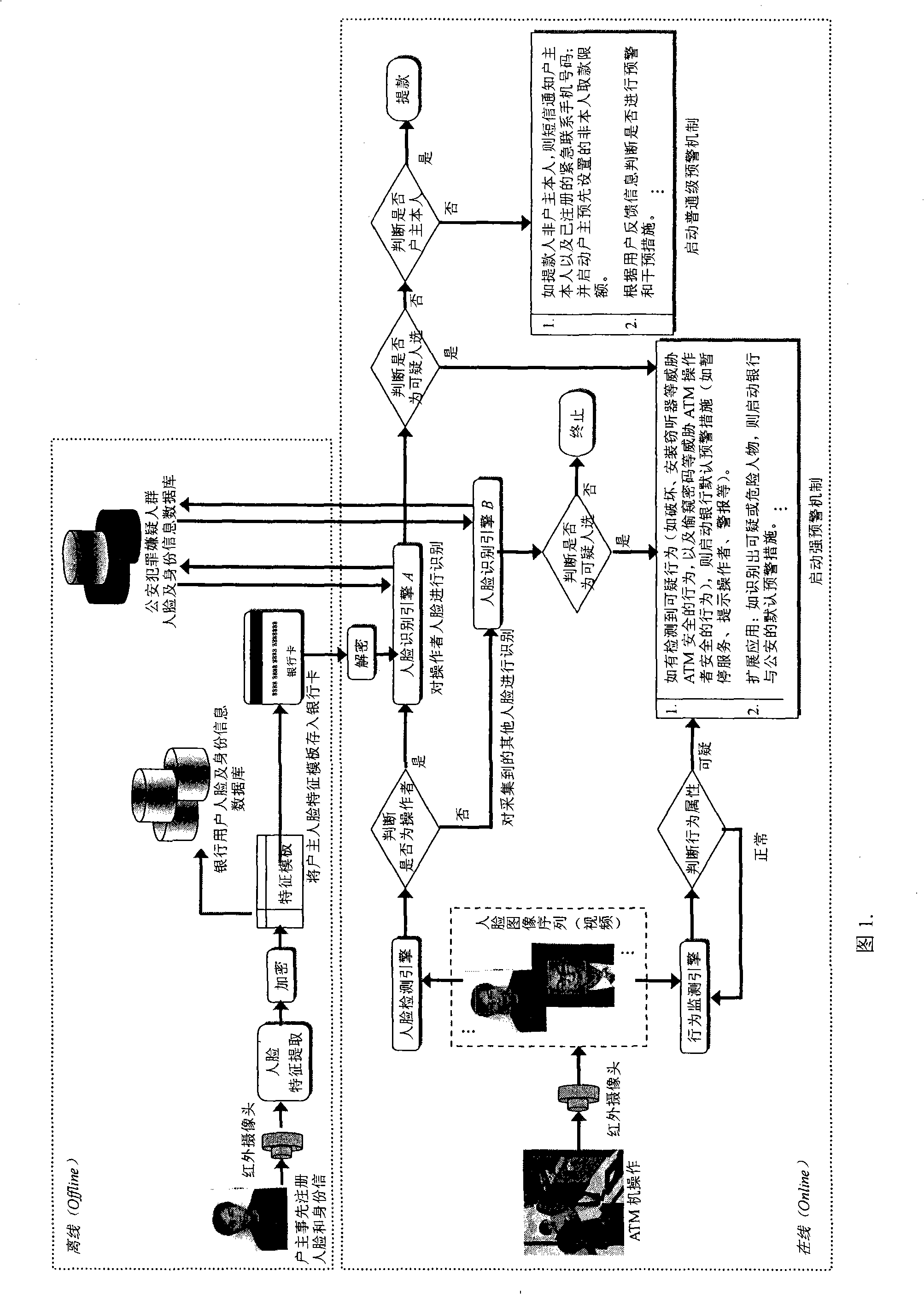
ATM secure authentication and pre-alarming method based on face recognition
ActiveCN101266704AEnsure safetyGuaranteed privacyCharacter and pattern recognitionAlarmsComputer networkAcquisition apparatus
The invention discloses an ATM security certificate and a pre-warning method based on face recognition. The invention introduces face recognition and video detection into the applications of ATM and bank card business for the first time, which can obviously improve the security of ATM financial system, effectively reduce and overawe various ATM fraud and criminal activities. The complete system operation process in the method of the invention is: firstly, registering the face information of a holder at a service window which arranges an infrared face acquisition equipment or with the registration by the users themselves on ATM in bank, and saving the encrypted face information to a bank database and a bank card. Then, determining whether the ATM operator to be recognized is the holder of the bank card or not through verifying the user's identity by a face recognition engine; determining and recognizing whether existing behaviors that threaten ATM and the users though a behavior monitoring engine; and determining whether to trigger corresponding pre-warning mechanism or not according to the recognition result. The invention can extend to the applications of bank book business, public security monitoring and pursuing escaped criminals, etc.
Owner:哈尔滨维科智能系统有限公司
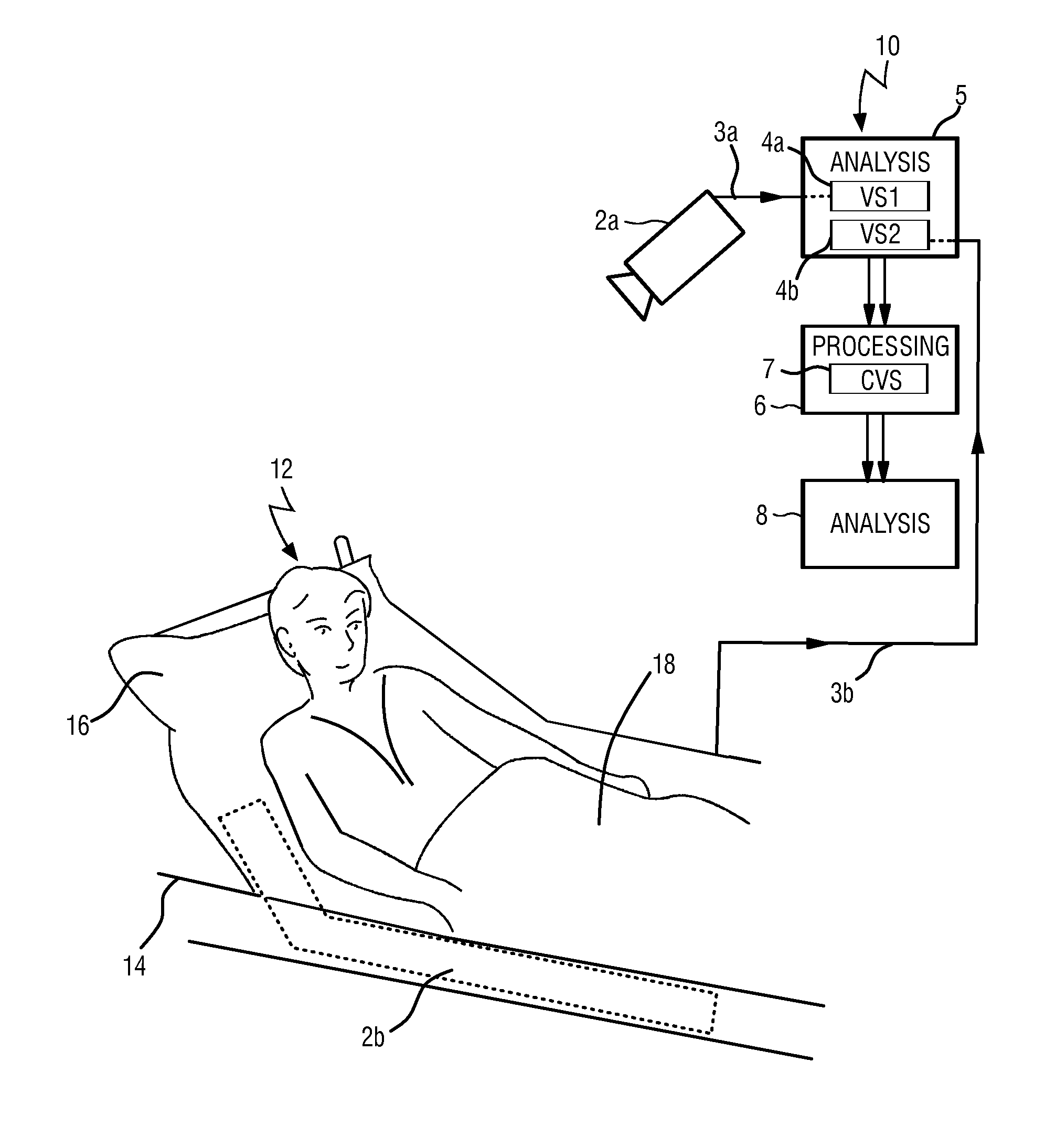
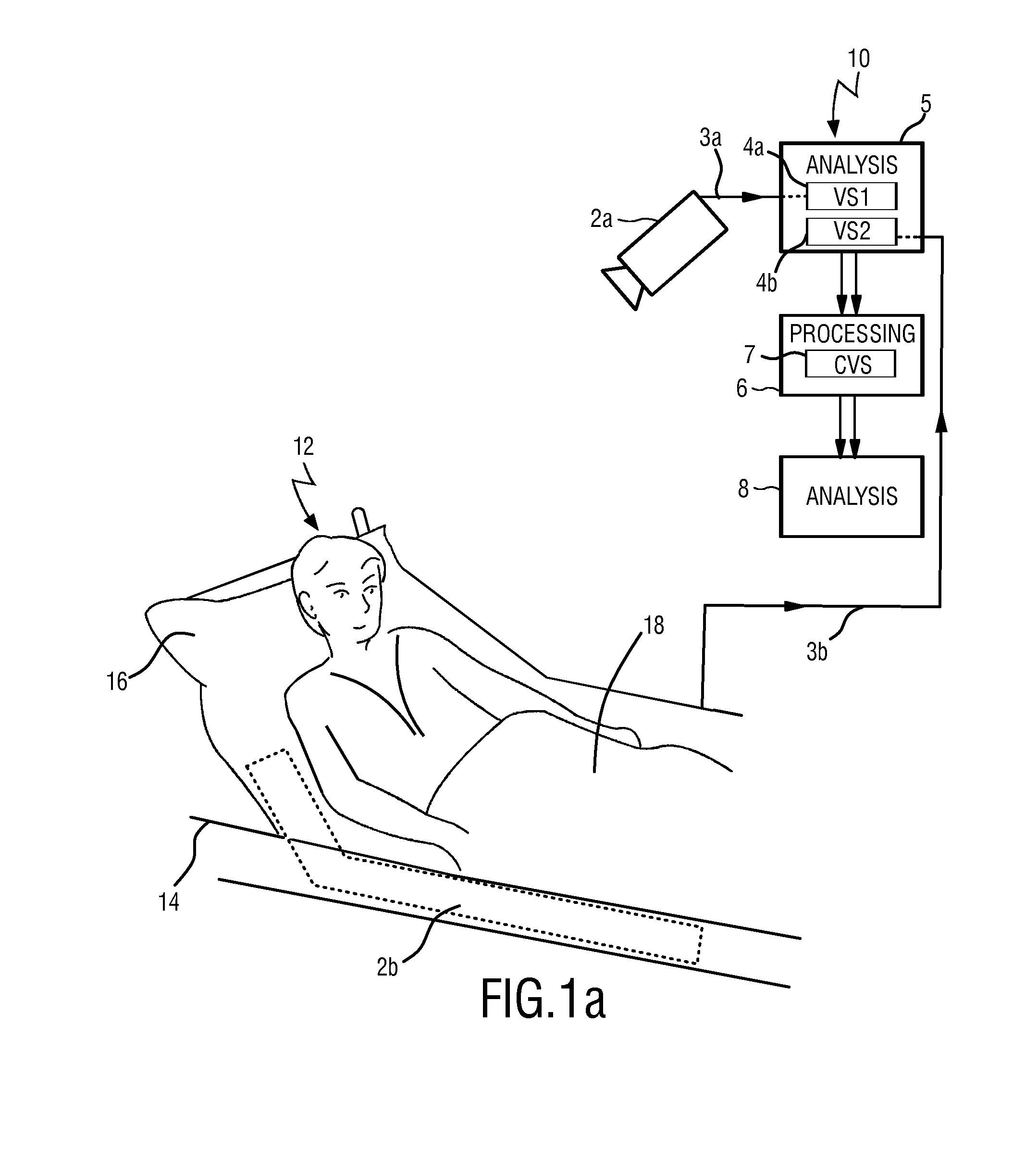
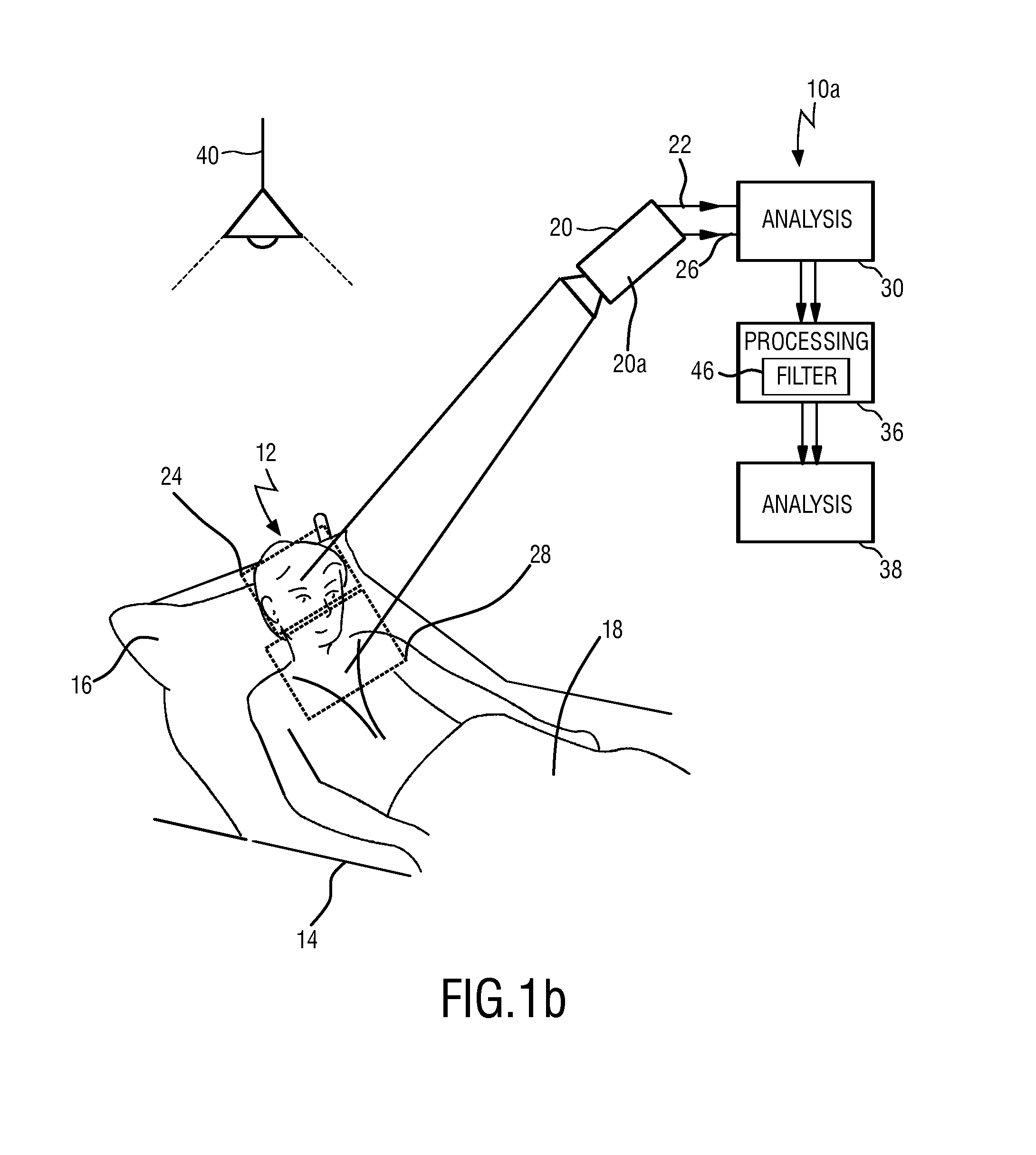
Device and method for obtaining vital sign information of a subject
InactiveUS20140275832A1Lowering intrathoracic pressureDecrease in stroke volumeElectrocardiographyPressure sensorsInternet privacyVital signs
For the measurement of vital sign information such as a respiratory rate and a heart rate a device for obtaining vital sign information of a subject is provided, comprising a first detection unit that acquires first set of detection data allowing the extraction of a first vital sign information signal related to a first vital sign of the subject and a second detection unit that acquires a second set of detection data allowing the extraction of a second vital sign information signal related to a second vital sign of the subject. An analysis unit extracts the first vital sign information signal from the first set of detection data (3a) and extracts the second vital sign information signal from the second set of detection data. A processing unit combines the first vital sign information signal and the second vital sign information signal to obtain a combined vital sign information signal. An extracting unit extracts at least one of the first and second vital signs of the subject from the combined vital sign information signal.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
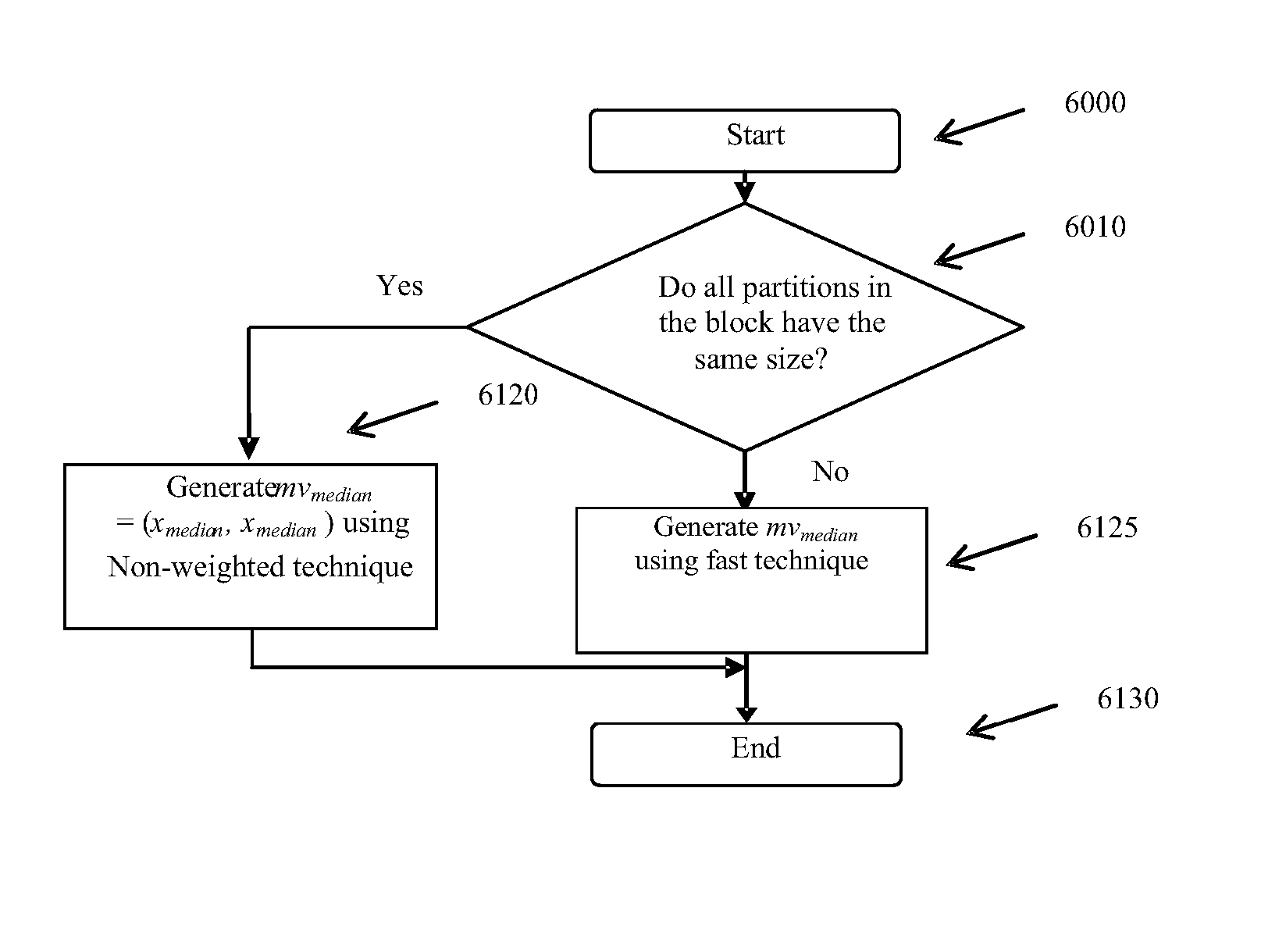
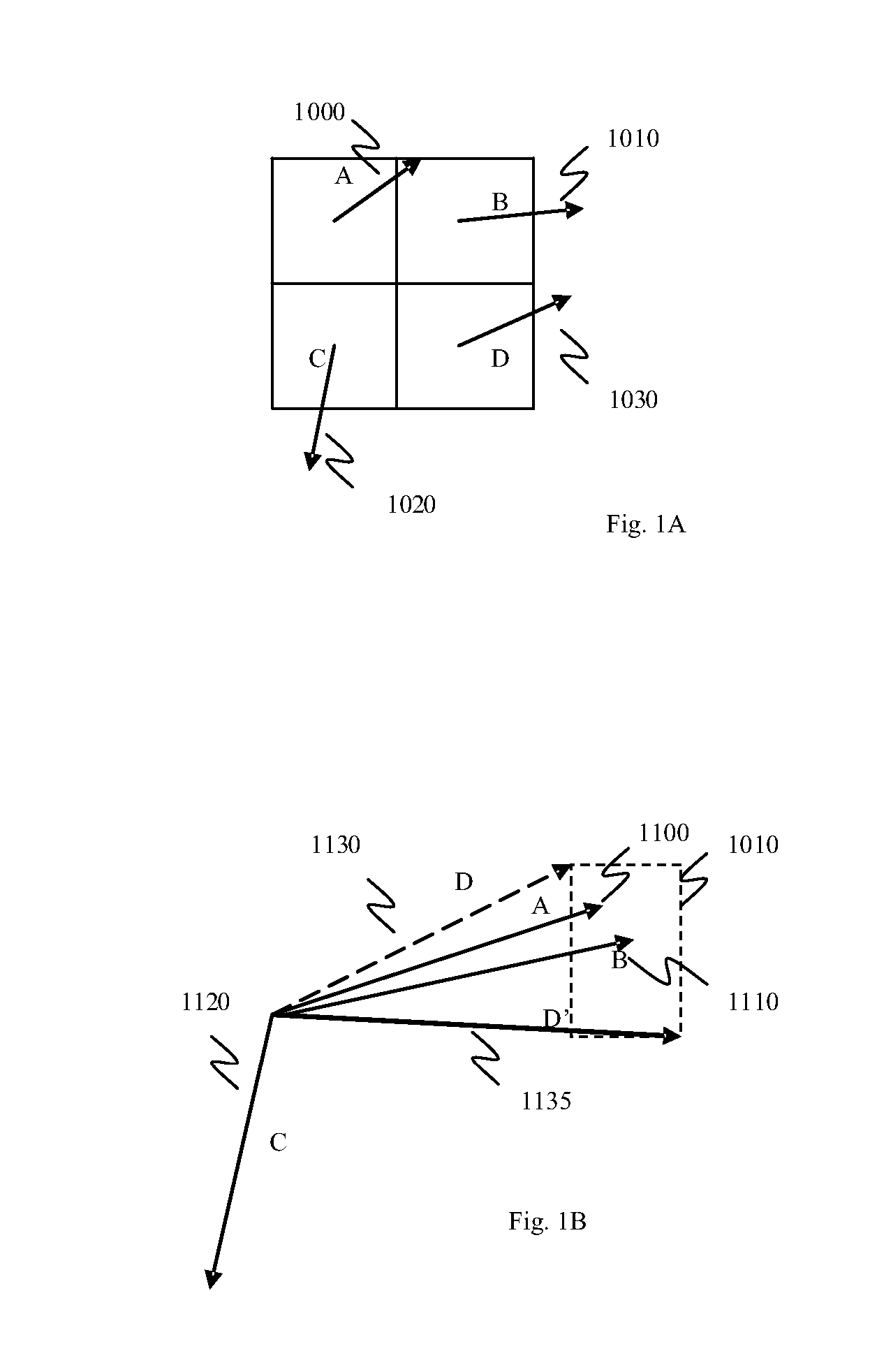
Method and System for Video Encoding and Transcoding
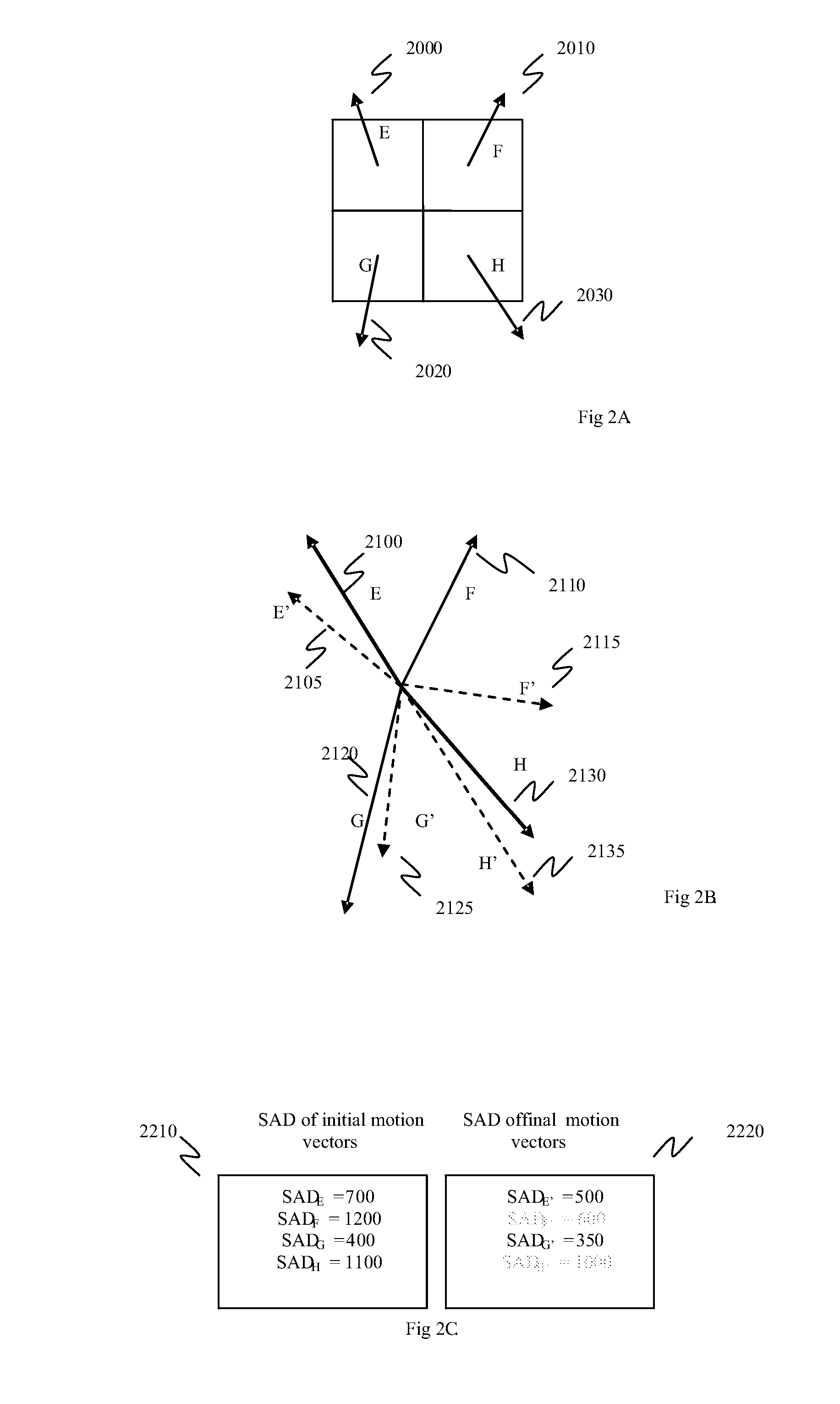
InactiveUS20070286286A1Reduce computationReduce calculationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorTranscoding
A method of removing a motion vector from a group of motion vectors used in an encoding process includes providing a list of motion vectors, selecting an initial motion vector from the list of motion vectors, and providing an intermediate motion vector using a motion vector refinement process. The motion vector refinement process uses, in part, the initial motion vector. The method also includes forming a region defined by one or more parameters associated with the initial motion vector and one or more parameters associated with the intermediate motion vector, selecting an additional motion vector from the list of motion vectors, determining that the additional motion vector points into the region, and modifying a state of the additional motion vector.
Owner:ONMOBILE GLOBAL LTD
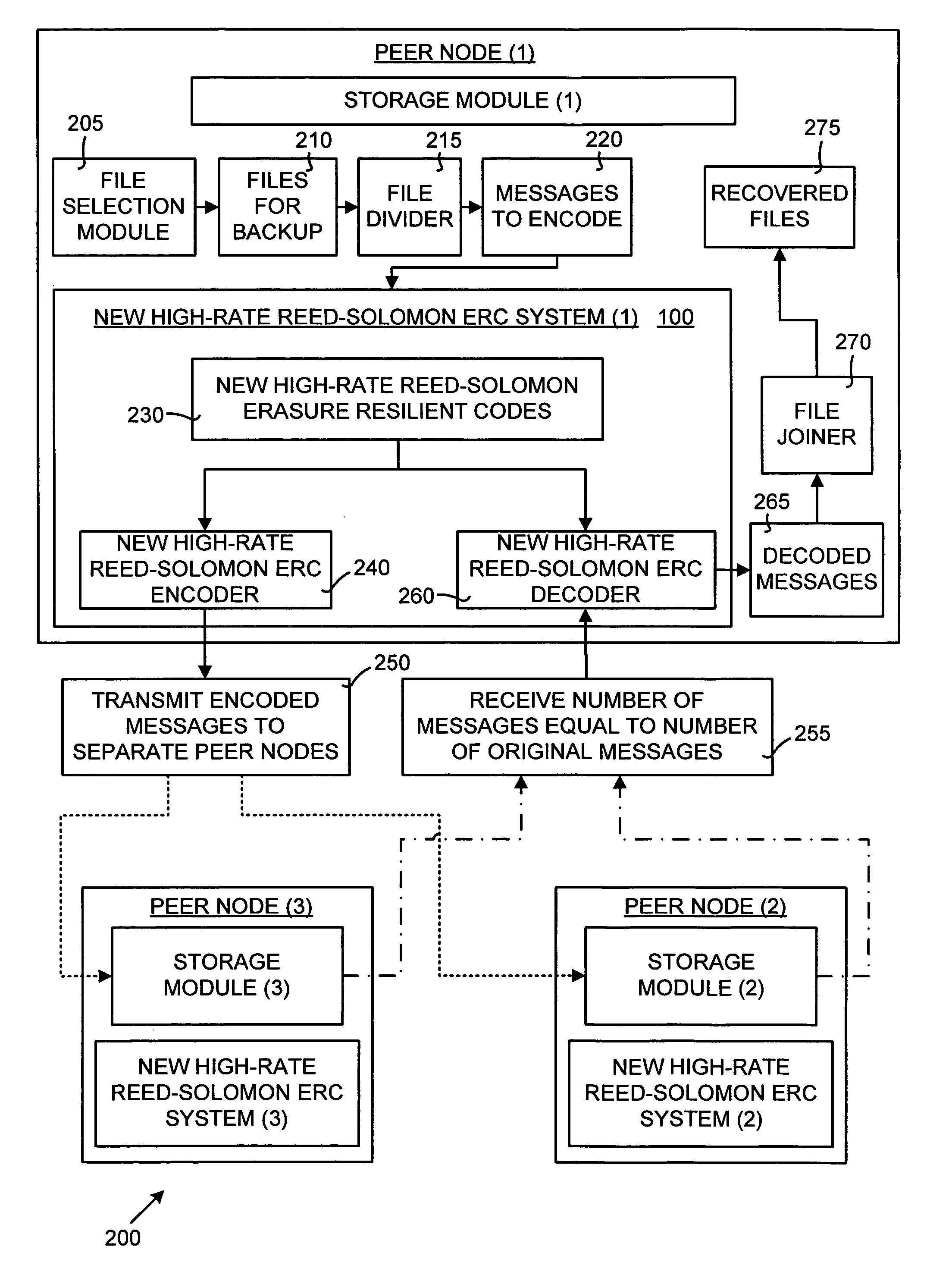
Efficient implementation of reed-solomon erasure resilient codes in high-rate applications
A new high-rate Reed-Solomon erasure resilient codes (ERC) system and method for generating and efficiently implementing novel Reed-Solomon erasure-resilient codes for use in high-rate applications. High-rate applications are applications where the number of coded messages is significantly higher (such as an order of magnitude) than the number of original messages. The new Reed-Solomon ERC system uses a novel scalar vector multiplication and addition technique and a novel direct inversion technique. The direct inversion technique uses specific generator matrices, including a modified Vandermonde Matrix and a Cauchy Matrix, to directly calculate an inverse of the sub-generator matrix of receiving ERC-coded messages, thereby reducing decoding computation. The scalar vector multiplication and addition technique generates new high-rate Reed-Solomon codes and performs scalar vector multiplication and addition on the Galois Field to speed up the Reed-Solomon erasure encoding / decoding operations. In effect, the new Reed-Solomon codes are “tuned” for maximum performance in the high-rate environment.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for rate modulated cardiac therapy utilizing a temperature senor
ActiveUS20150328459A1Controls are responsiveOvercome problemsHeart stimulatorsGeneration rateRate modulation
A cardiac rhythm management system provides an increase in pacing rate as a combination of responses to three characteristics of a relative-temperature signal: a dip, a positive slope, and a positive magnitude. The relative-temperature signal is the difference between a short-term and a long-term temperature average. A dip produces a limited and temporary rate increase having a first proportionality. A positive slope produces a rate increase with a second proportionality. A positive magnitude produces a rate increase with a third proportionality. The dip response seeds the slope response to provide a seamless and immediate rate transition after a dip. The cardiac rhythm management system limits and filters the sum of the rate increases to provide a sensor indicated rate, which is used to stimulate the heart.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method and apparatus for controlling uplink transmission power
InactiveUS20120327804A1Accurate powerReduce calculationPower managementSite diversityUplink transmissionEngineering
The present description relates to a method for controlling uplink power in a distributed multi-node system, comprising the following steps: receiving reference signals from a plurality of antenna nodes containing at least one antenna; estimating average propagation loss on the basis of the receiving power of the reference signals received from the plurality of antenna nodes; receiving, via a downlink control channel, noise and interference (NI) information from a base station which contains the plurality of antenna nodes; and determining uplink transmission power using the estimated average propagation loss and the received noise and interference information.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
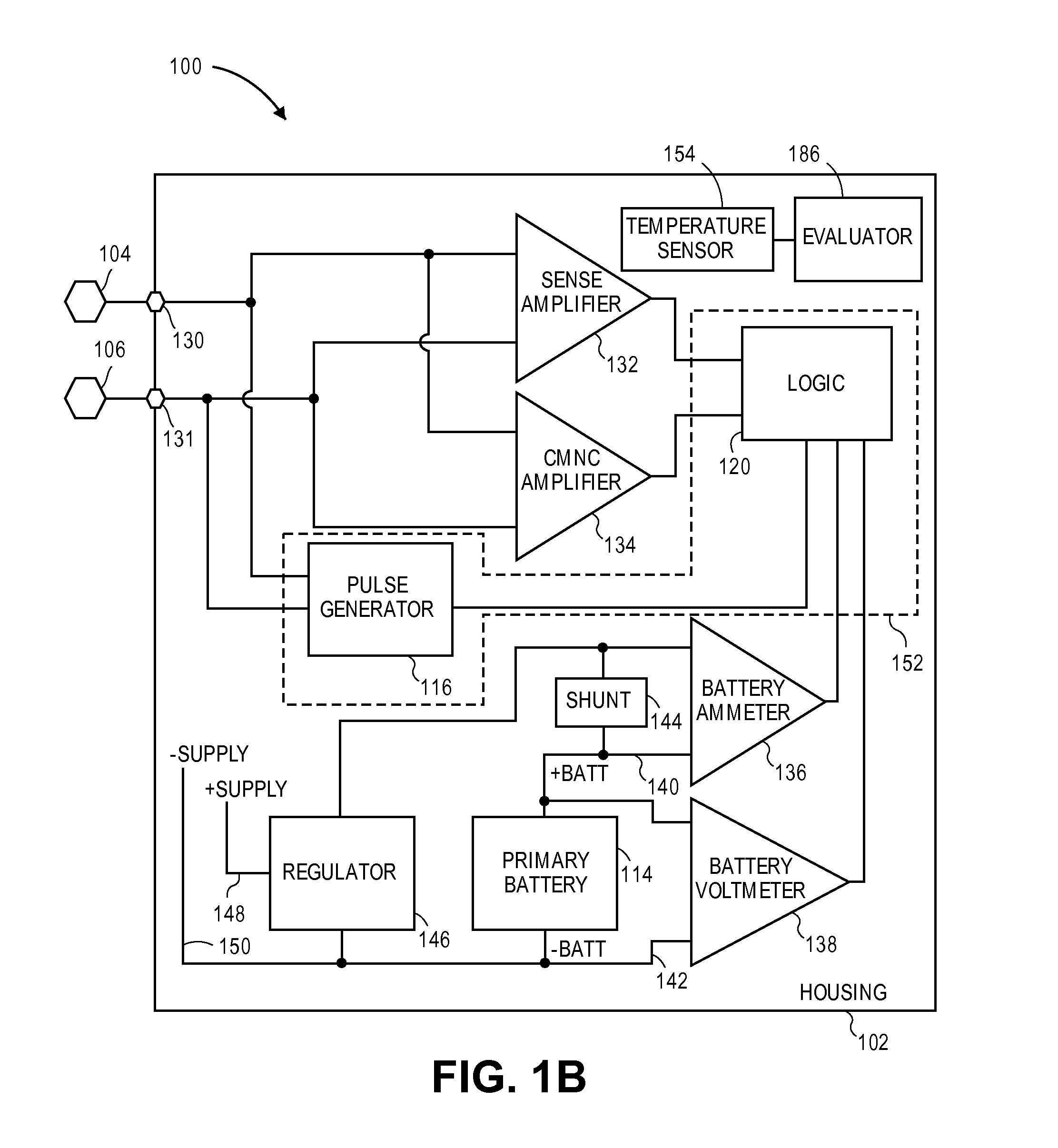
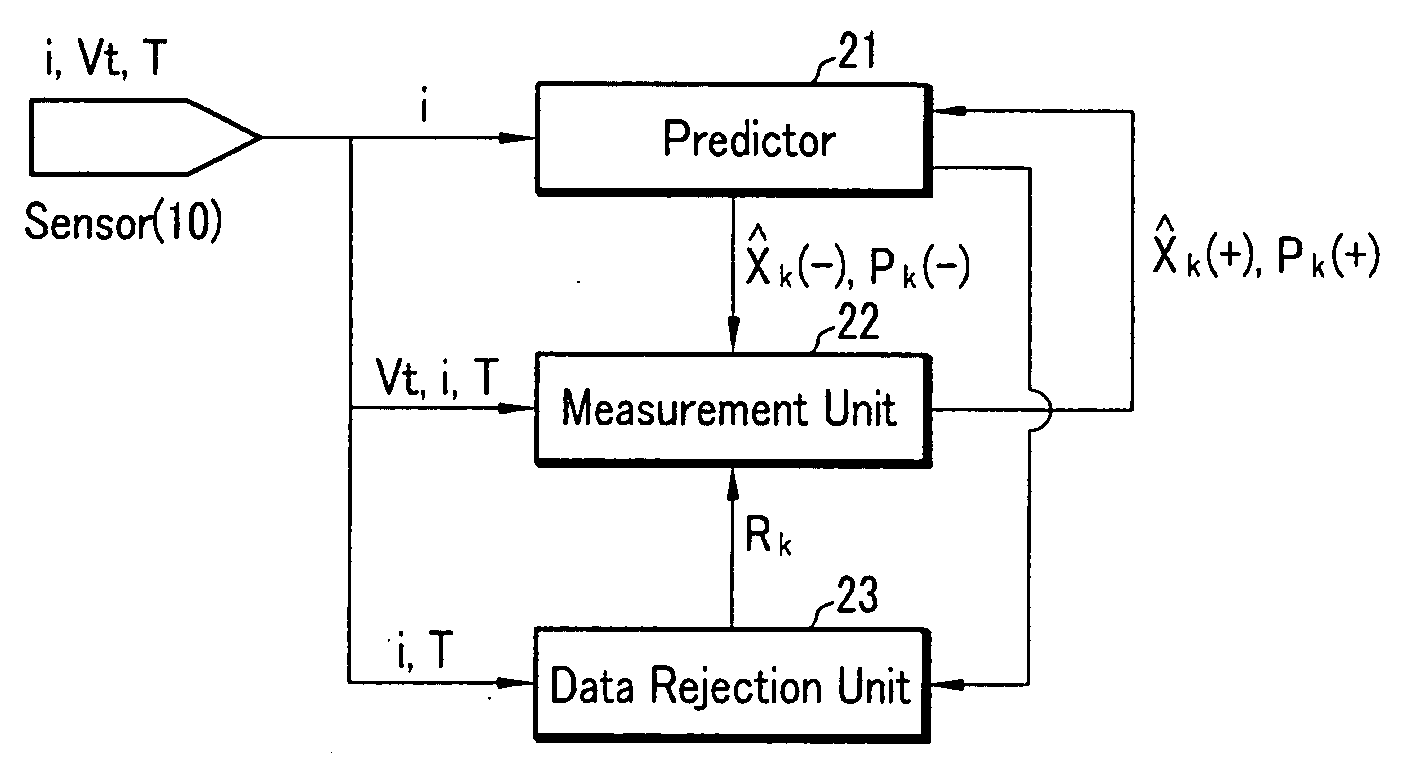
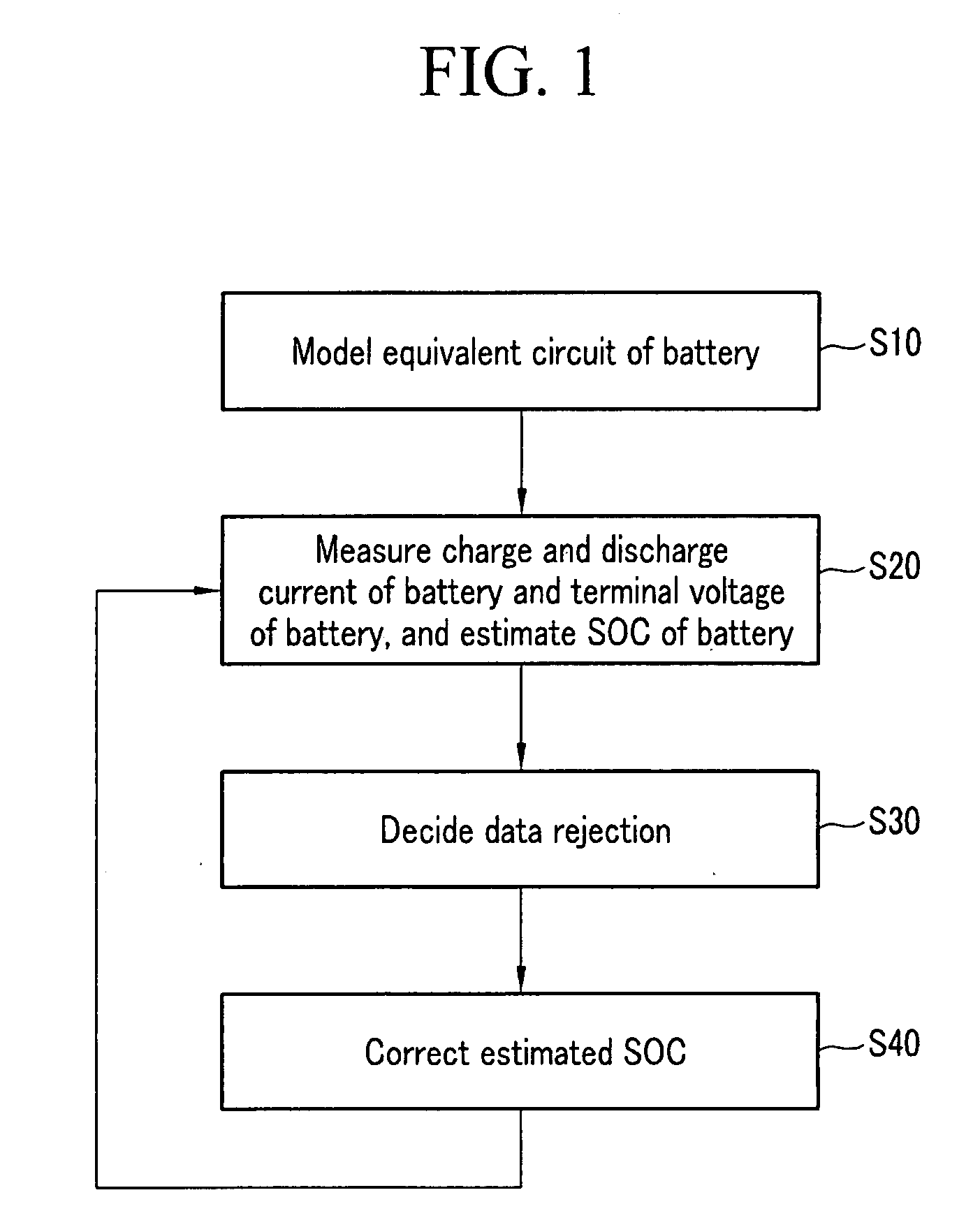
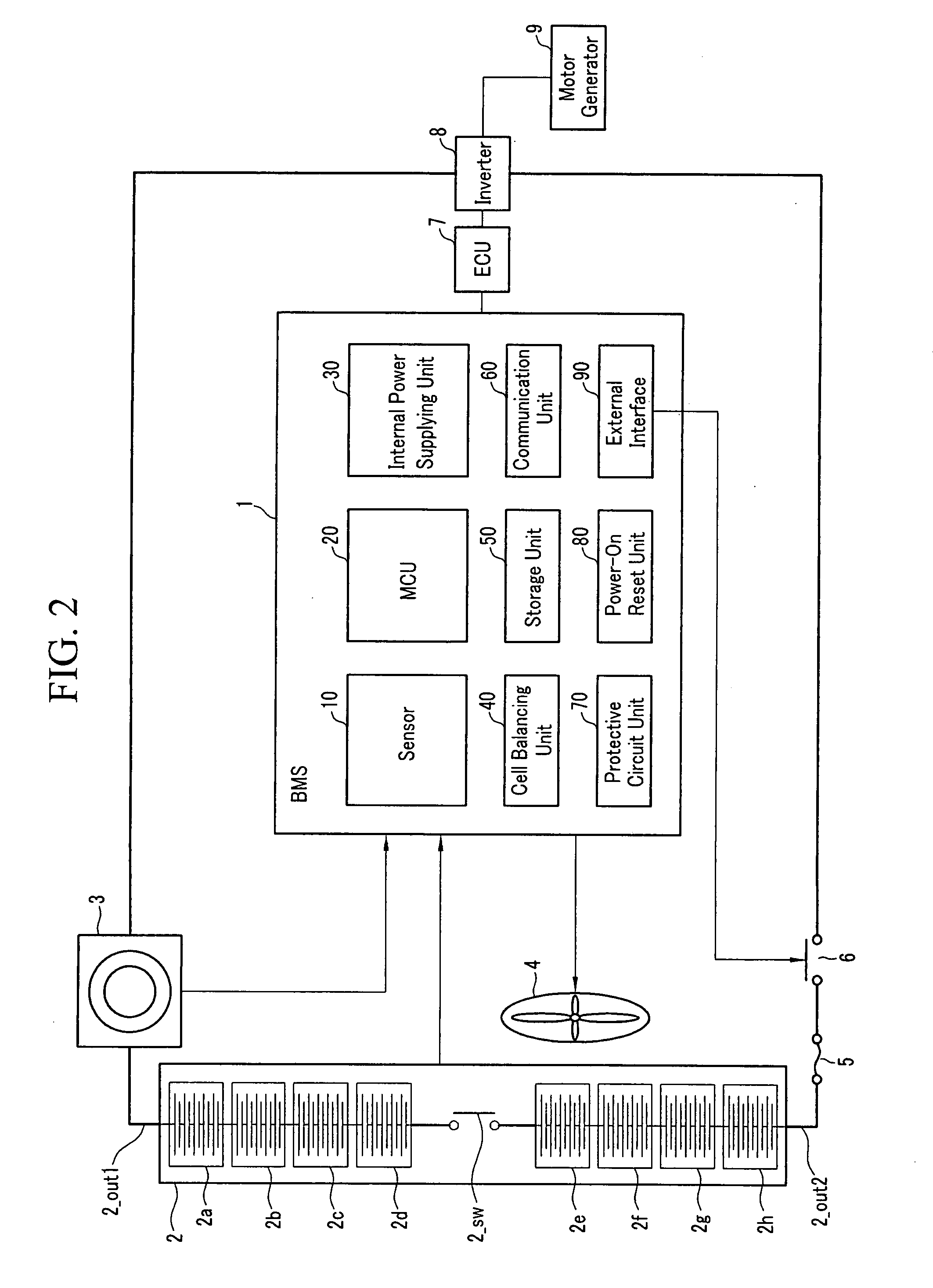
Method for estimating state of charge of battery, battery management system using same, and driving method thereof
ActiveUS20070299620A1Reduce calculationAccurately estimate SOCBatteries circuit arrangementsOperating modesBattery state of chargeElectrical battery
A battery management system using a measurement model modeling a battery, and estimating a SOC (state-of-charge) of the battery, and a battery driving method thereof. The battery management system is constructed with a sensor, a predictor, a data rejection unit, and a measurement unit. The sensor senses a charging and discharging current flowing through the battery, a temperature of the battery, a terminal voltage of the battery. The predictor counts the charging and discharging current, and estimates the state-of-charge of the battery. The data rejection unit generates information associated with an error generated from the measurement model, as a function of at least one of the battery temperature, the charging and discharging current, the state-of-charge, and a dynamic of the charging and discharging current. The measurement unit corrects the estimated state-of-charge of the battery, using the measurement model and the information associated with the error.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD +1
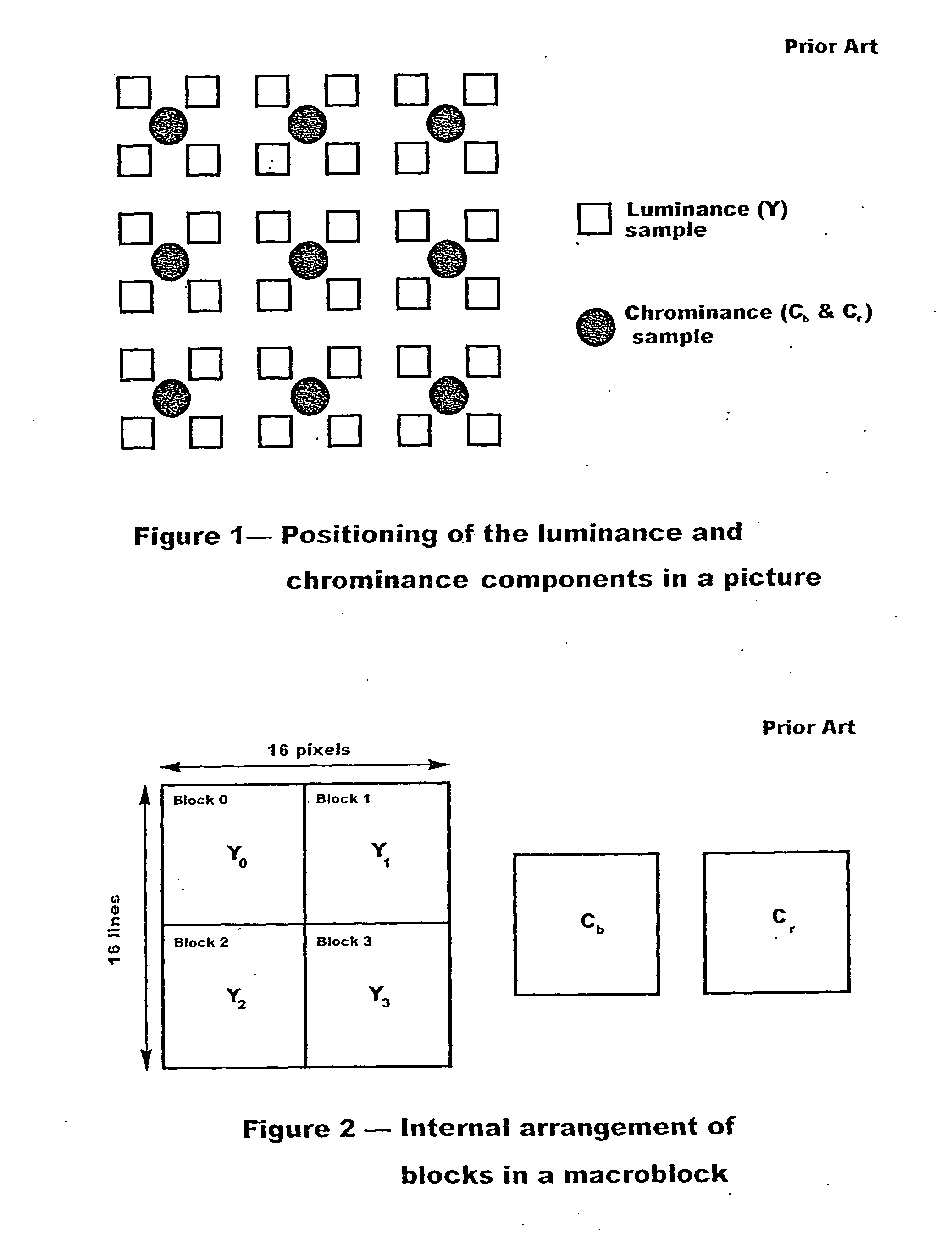
H.264/AVC intra coding algorithms having quality scalability
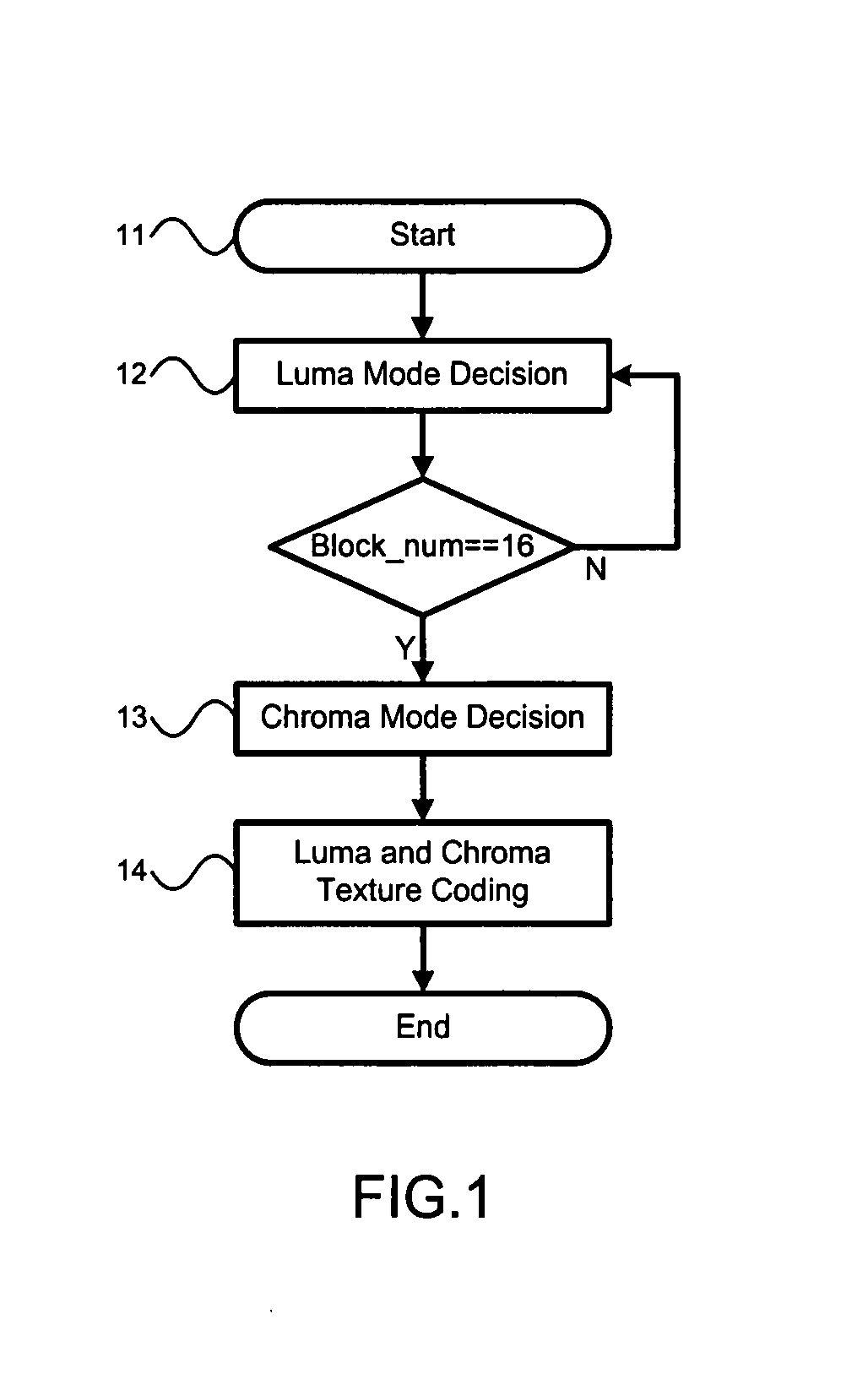
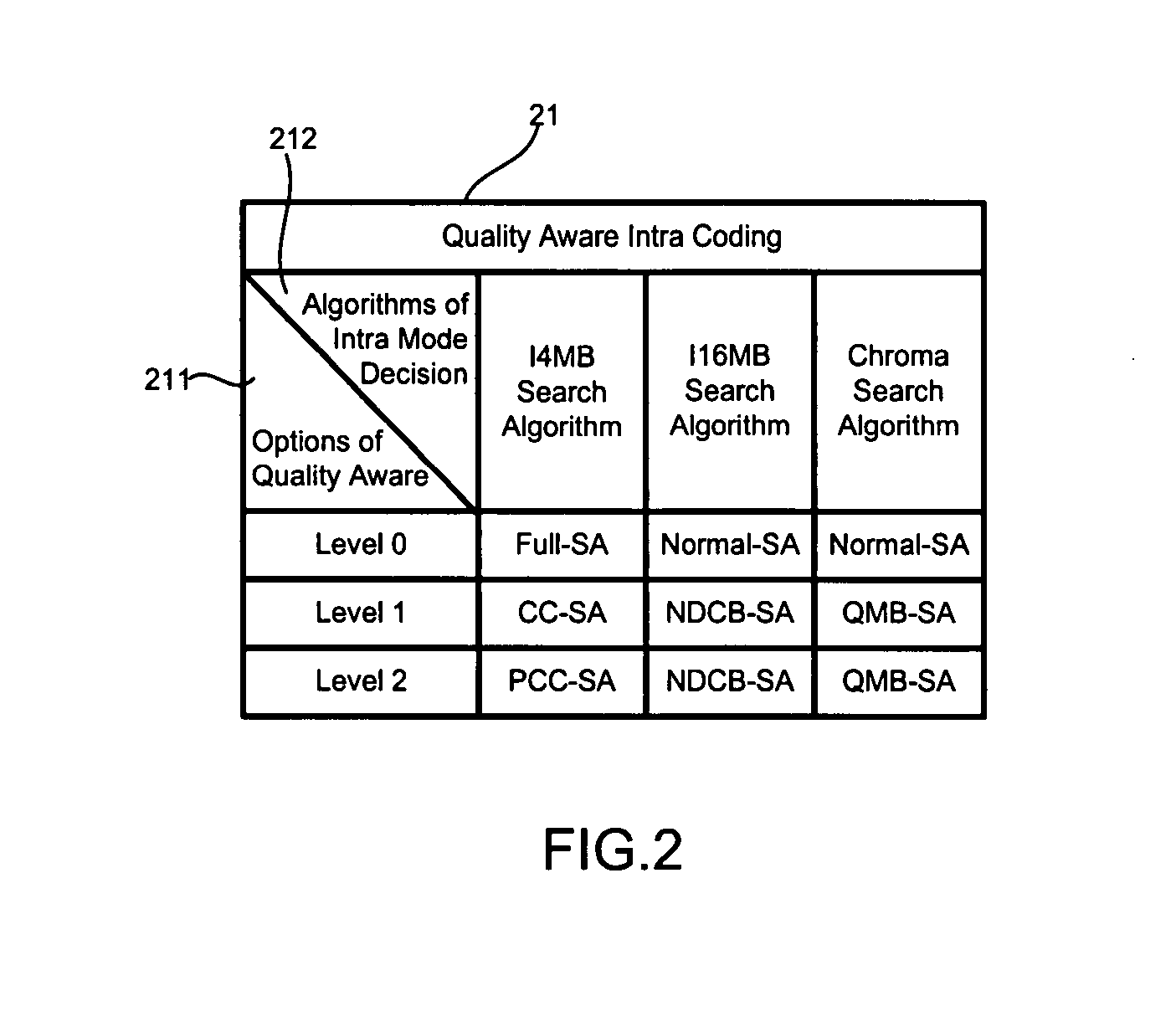
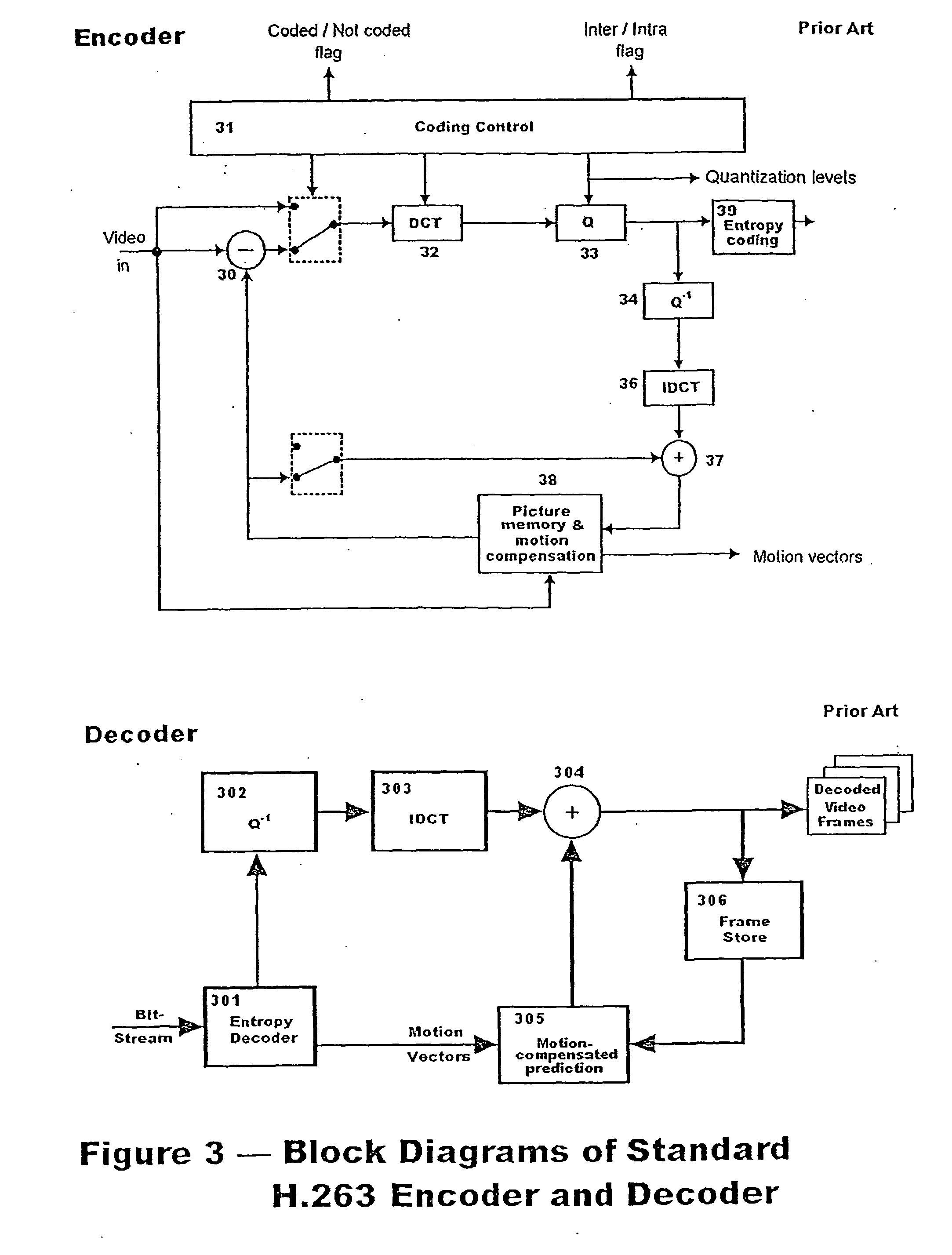
InactiveUS20080219350A1Reduce calculationImprove coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionBasic levelEncoding algorithm
Different algorithms are used in H.264 / AVC intra coding to form three coding levels. Algorithms used in two of the three coding levels reduce calculation complexities and power consumptions. The basic level is an exception, which fully keeps an original picture quality. Thus, various needs can be met by coding in the various levels with the various algorithms.
Owner:NATIONAL CHUNG CHENG UNIV
Device for optical monitoring of constituent in tissue or body fluid sample using wavelength modulation spectroscopy, such as for blood glucose levels
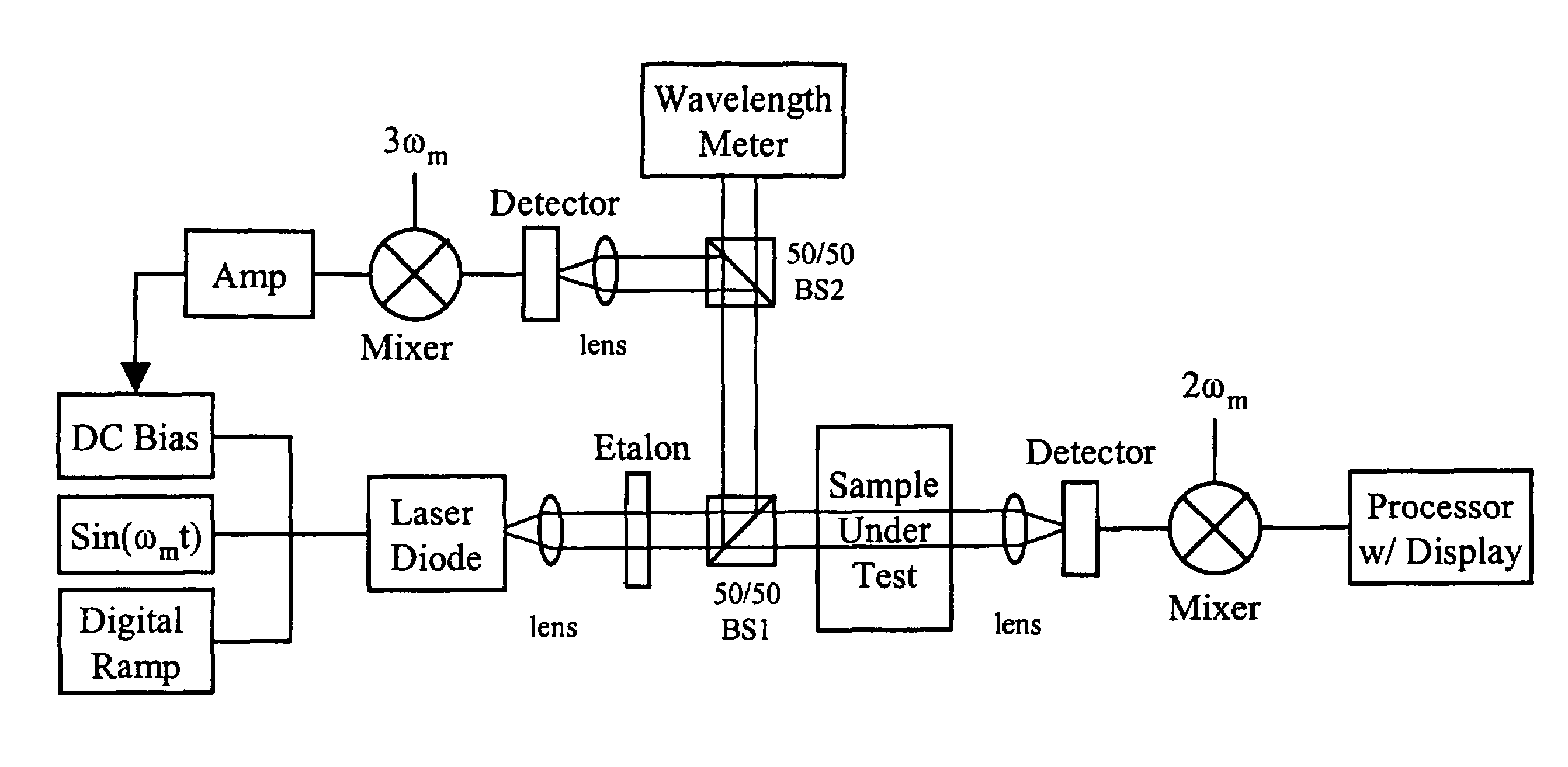
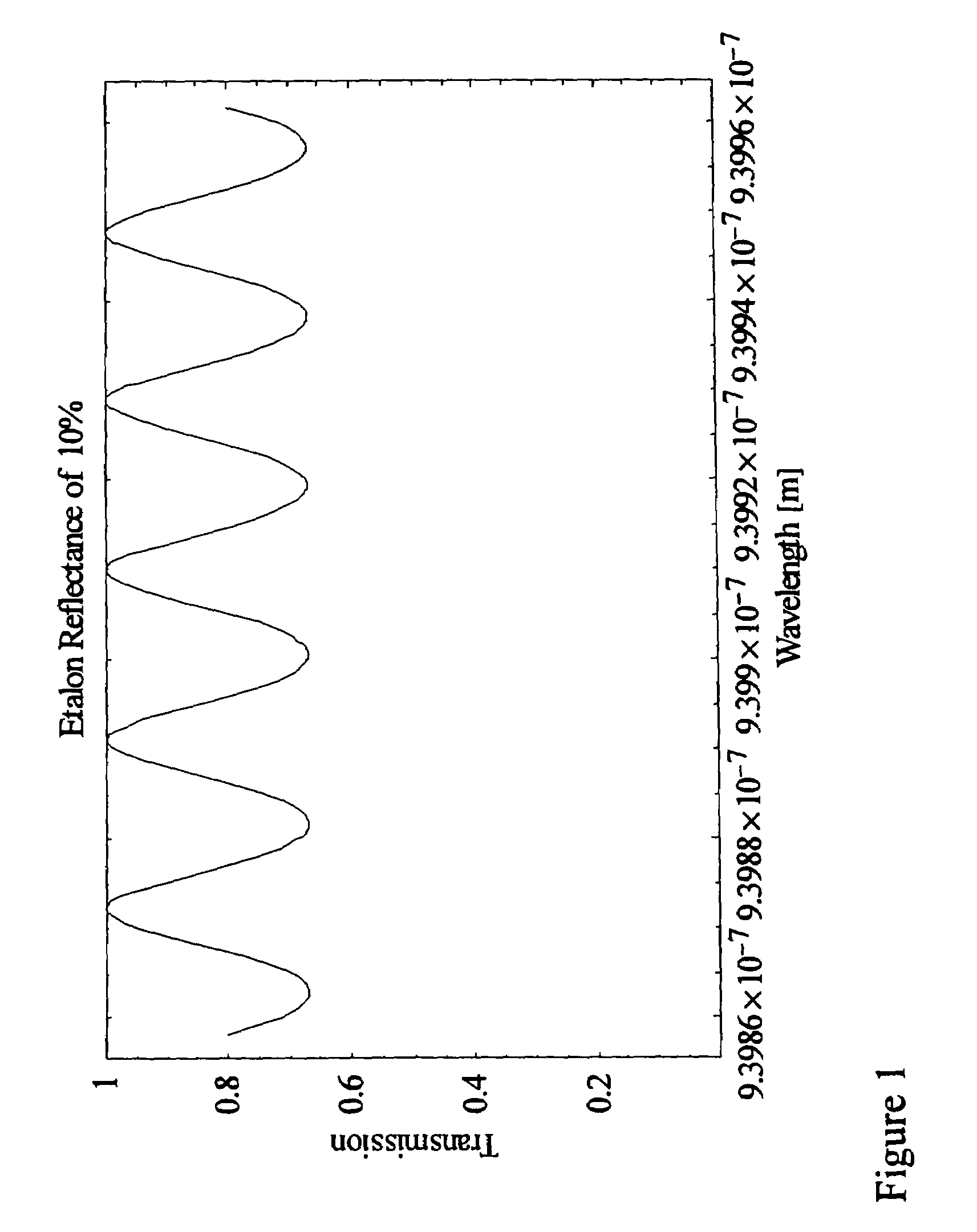
InactiveUS7356364B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce calculationMedical devicesCatheterConcentrations glucosePhotodetector
A device for monitoring the concentration level of a constituent in tissue or a body fluid sample, such as glucose concentration in blood, has a laser light source which is modulated about a center emission frequency to probe the absorption spectrum of the constituent being monitored, a laser driver circuit for tuning and modulating the laser light, a photodetector for detecting light from the laser light source transmitted through the sample as the modulation frequency of the laser is tuned, and a demodulator for demodulating the transmitted light and detecting variations in magnitude at harmonics of the modulation frequency to assess the concentration level of that constituent. The device utilizes short-wavelength near-infrared laser light to monitor blood glucose levels, and could also be used for drug screening and diagnosis of other medical conditions as well. In one embodiment, the device is used to monitor blood glucose level externally from the body and non-invasively by trans-illumination through a thin layer of skin, without the need for physical penetration of the skin. In another embodiment, the device is used as an intravenous sensor deployed through a catheter, and its output can be used to control an insulin pump to stabilize the patient's blood glucose levels.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
Wireless node location mechanism featuring definition of search region to optimize location computation
ActiveUS7433696B2Optimize locationReduce total powerDirection finders using radio wavesTelephonic communicationRadio receiverRadio reception
A wireless node location mechanism that defines a search region to optimize the computations associated with estimating the location of a given wireless node. According to one implementation, a coverage map associated with each radio receiver that records signal strength data is defined out to a threshold signal strength level. Before computing the estimated location of a given wireless nodes, a search region is defined based on the intersection of the coverage maps associated with each radio receiver that detects the wireless node. Some implementations use information provided by the fact that certain radio receivers did not detect the wireless node to further optimize the location estimate. By defining a search region, which is a generally small area relative to the space encompassed by an entire RF environment, the present invention provides several advantages, such as reducing the processing time and / or power to compute estimated locations for wireless nodes.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
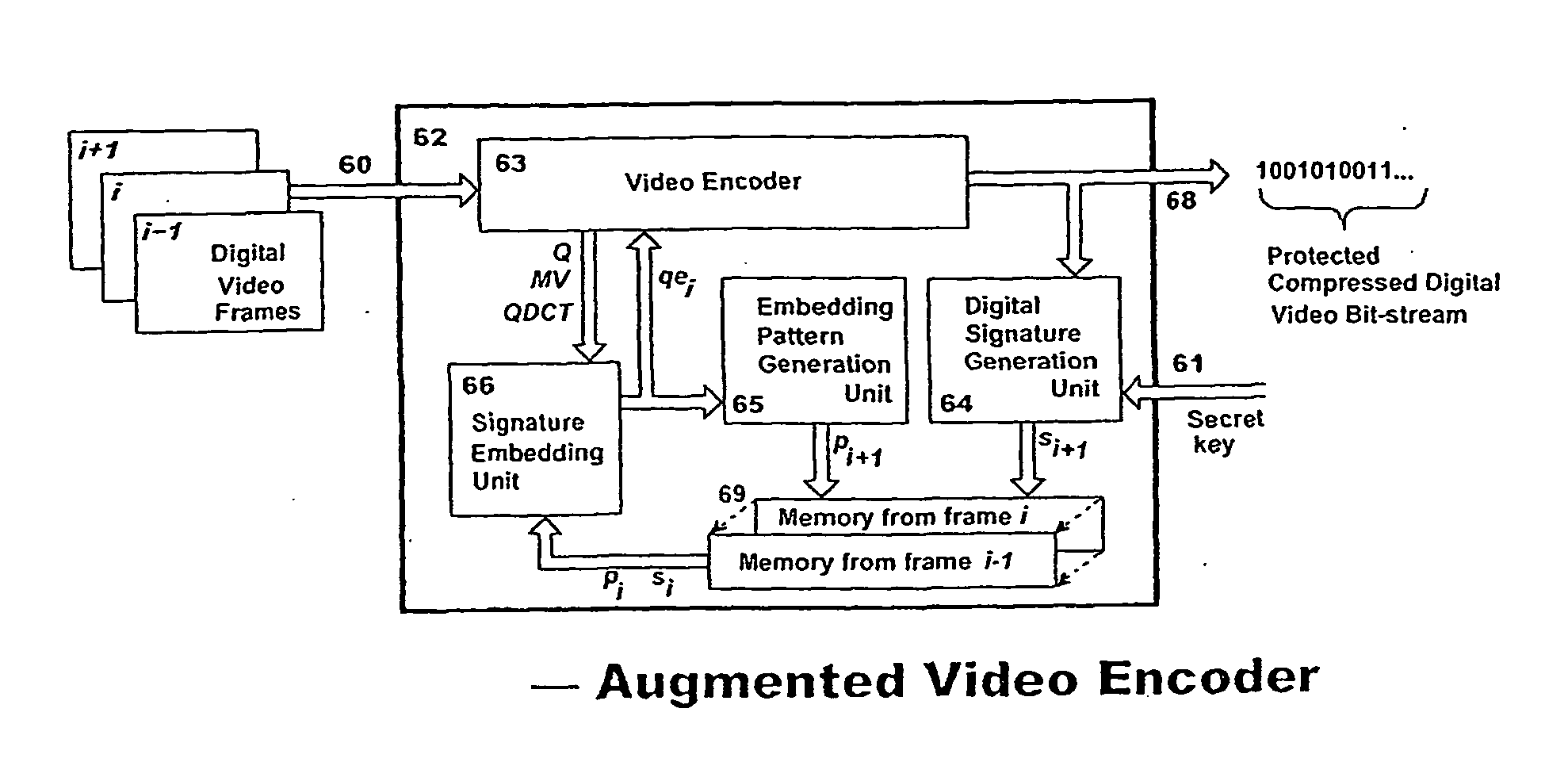
Digital video protection for authenticity verification
ActiveUS20100177891A1Reduce calculationShorten the timeTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDigital videoDigital signature
A method and apparatus for verifying the authenticity and integrity of an ordered sequence of digital video frames, without having access to the original recording, by embedding therein a respective series of digital signatures based on a secret key, or keys, and on the video content of respective frames. Signatures are camouflaged by embedding in transform coefficients of a transformed representation of the video data in parts of the frame corresponding to motion. If there is sufficient motion to contain all of the signature bits, a supplementary technique embeds in high-texture areas of a frame. A final fall-back is to embed in a pre-defined default zone. A method of predicting when supplementary embedding is needed enables the process to be applied in a single pass allowing real-time operation. Verification is done during decoding by comparing, for identity, embedded signatures with signatures calculated anew using the method employed to embed.
Owner:QOGNIFY
Method for Determining the Horizontal Profile of a Flight Plan Complying with a Prescribed Vertical Flight Profile
ActiveUS20080306680A1Reduce computing costReduce calculationInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlCheck pointStraight segment
The present invention relates to the definition, in a flight plan, of the horizontal profile of an air route with vertical flight and speed profile prescribed on departure and / or on arrival, by a stringing together of check-points and / or turn points associated with local flight constraints and called “D-Fix” because they are not listed in a published navigation database like those called “Waypoints”. It consists in charting, on curvilinear distance maps, a direct curvilinear path joining the departure point to the destination point of the air route while complying with vertical flight and speed profiles prescribed on departure and / or on arrival and while guaranteeing a circumnavigation of the surrounding reliefs and compliance with regulated overfly zones, then in approximating the series of points of the direct curvilinear path by a sequence of straight segments complying with an arbitrary maximum deviation threshold relative to the points of the series and an arbitrary minimum lateral deviation threshold relative to the set of obstacles to be circumnavigated and in adopting as “D-Fix” points the points of the intermediate intersections of the rectilinear segments.
Owner:THALES SA
Digital video protection for authenticity verification
ActiveUS7933407B2Maintain qualityImprove security levelTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDigital videoDigital signature
A method and apparatus for verifying the authenticity and integrity of an ordered sequence of digital video frames, without having access to the original recording, by embedding therein a respective series of digital signatures based on a secret key, or keys, and on the video content of respective frames. Signatures are camouflaged by embedding in transform coefficients of a transformed representation of the video data in parts of the frame corresponding to motion. If there is sufficient motion to contain all of the signature bits, a supplementary technique embeds in high-texture areas of a frame. A final fall-back is to embed in a pre-defined default zone. A method of predicting when supplementary embedding is needed enables the process to be applied in a single pass allowing real-time operation. Verification is done during decoding by comparing, for identity, embedded signatures with signatures calculated anew using the method employed to embed.
Owner:QOGNIFY
Method and apparatus to create a sound field
InactiveUS20090161880A1Eliminate the effects ofReduce calculationTelevision system detailsMicrophonesVocal tractTransducer
The invention generally relates to a method and apparatus for taking an input signal, replicating it a number of times and modifying each of the replicas before routing them to respective output transducers such that a desired sound field is created. This sound field may comprise a directed beam, focused beam or a simulated origin. In a first aspect, delays are added to sound channels to remove the effects of different travelling distances. In a second aspect, a delay is added to a video signal to account for the delays added to the sound channels. In a third aspect, different window functions are applied to each channel to give improved flexibility of use. In a fourth aspect, a smaller extent of transducers is used top output high frequencies than are used to output low frequencies. An array having a larger density of transducers near the center is also provided. In a fifth aspect, a line of elongate transducers is provided to give good directivity in a plane. In a sixth aspect, sound beams are focused in front or behind surfaces to give different beam widths and simulated origins. In a seventh aspect, a camera is used to indicate where sound is directed.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE MECHATRONICS
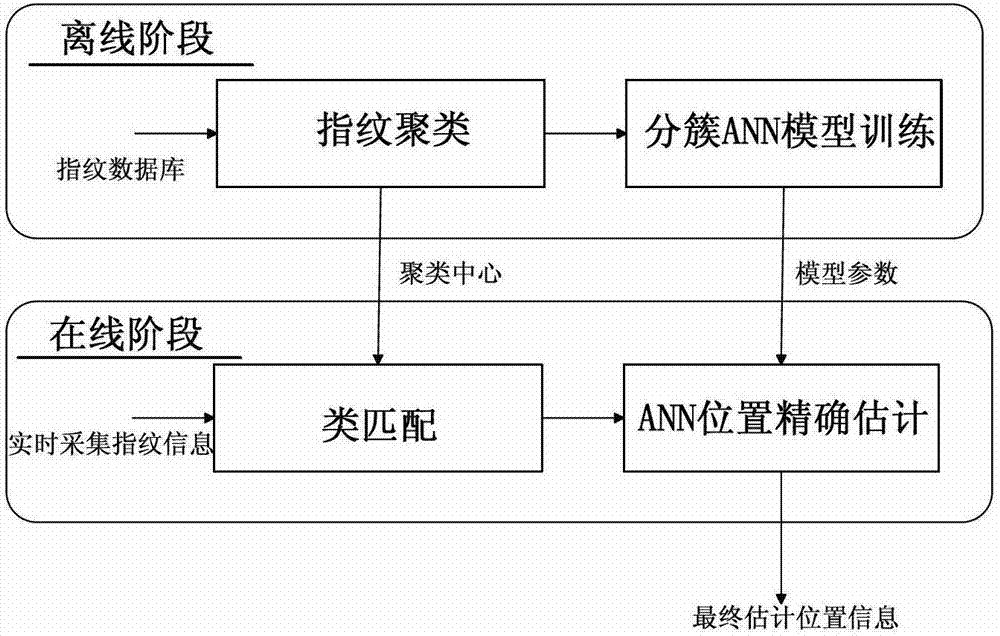
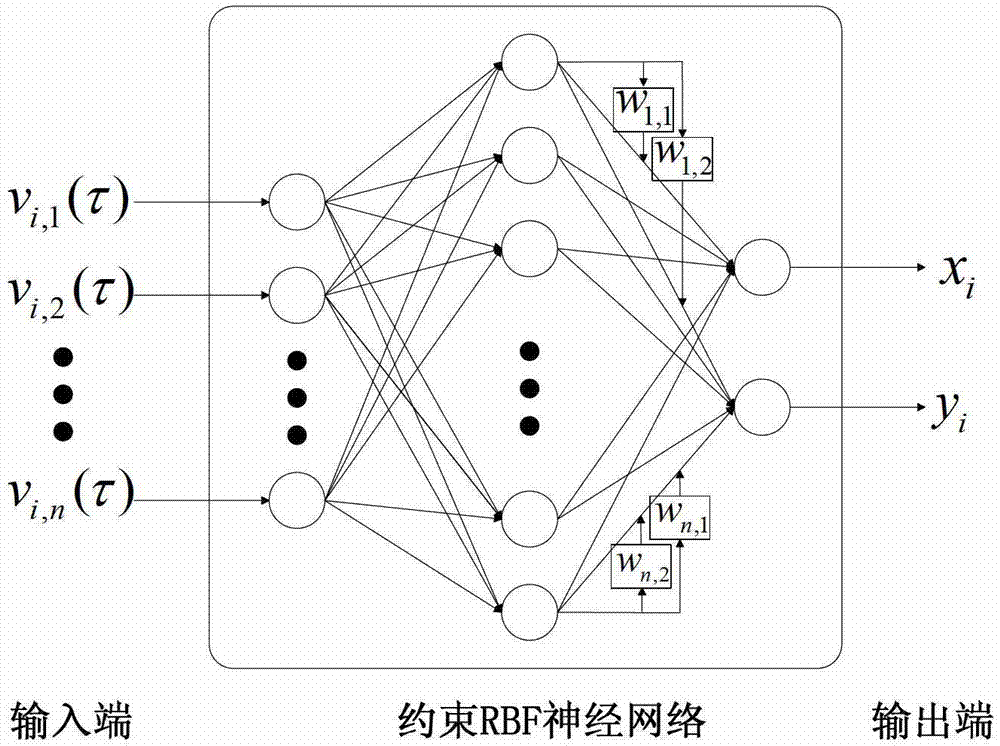
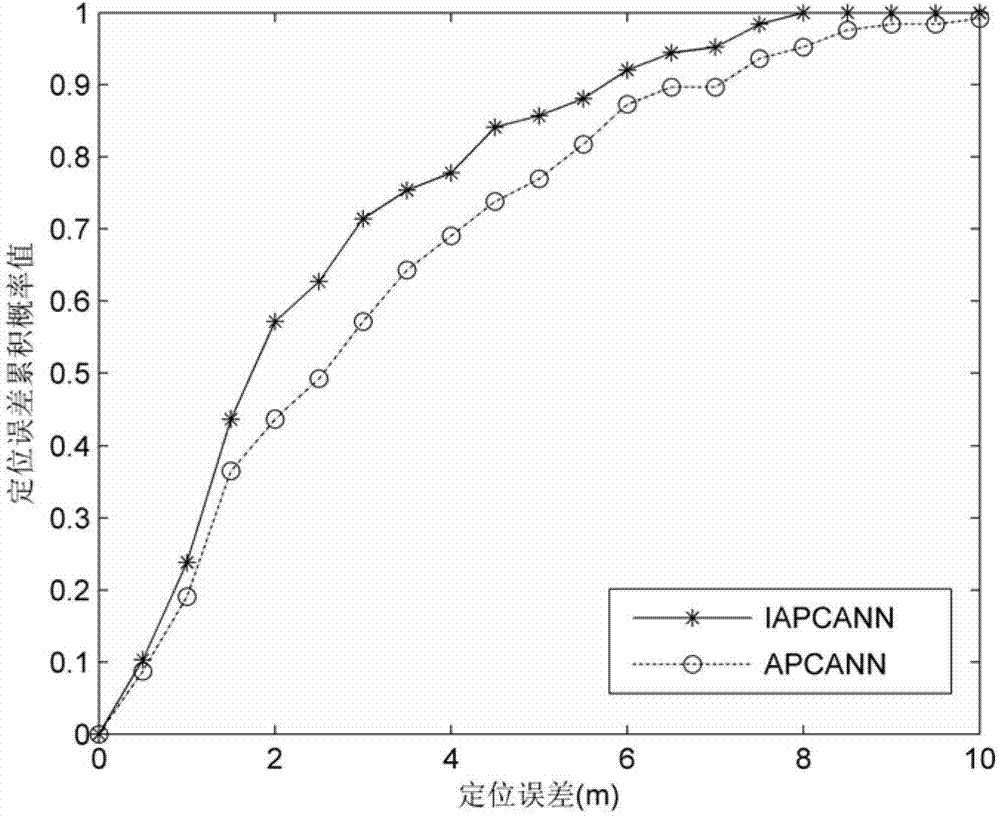
Improved positioning method of indoor fingerprint based on clustering neural network
InactiveCN102932738AReduce calculationReduce storage overheadCharacter and pattern recognitionLocation information based servicePattern recognitionCluster algorithm
The invention discloses the technical field of wireless communication and wireless network positioning, and in particular relates to an improved positioning method of an indoor fingerprint based on a clustering neural network. According to the technical scheme, the positioning method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: an offline phase: constructing a fingerprint database by fingerprint information collected from a reference point, sorting fingerprints in the fingerprint database by utilizing a clustering algorithm, and training the fingerprint and position information of each reference point by utilizing a artificial neural network model to obtain an optimized network model; and an online phase: carrying out cluster matching on the collected real-time fingerprint information and a cluster center in the fingerprint database to determine a primary positioning area, and taking the real-time fingerprint information in the primary positioning area as an input end of the neural network model of the reference point to acquire final accurate position estimation. The method has the advantages that low calculation and storage cost for the clustering artificial neural network fingerprint positioning method can be guaranteed, the positioning accuracy of the clustering artificial neural network fingerprint positioning method can be improved, and accurate positioning information is provided for users.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com