Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
15659results about "Seismic signal processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
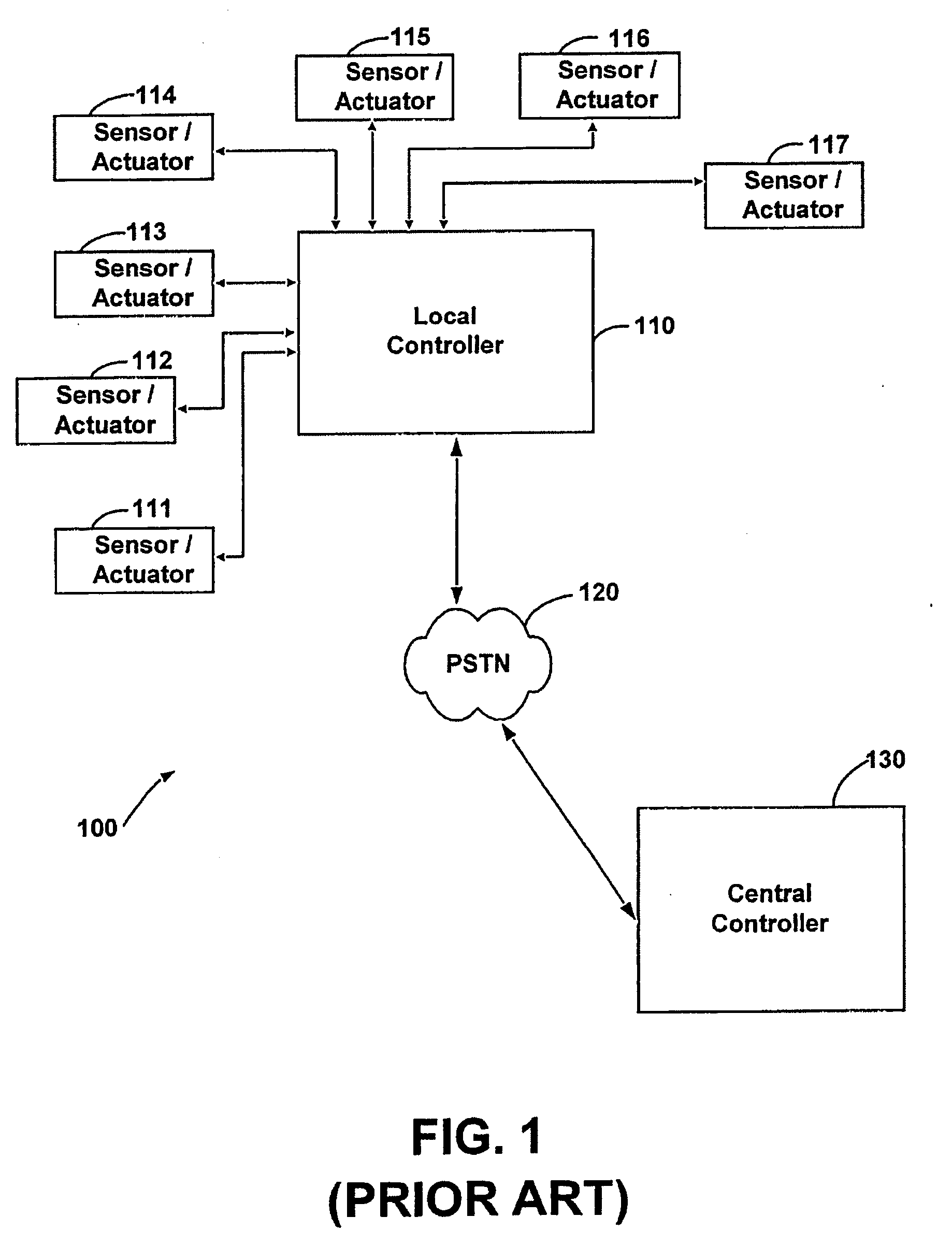
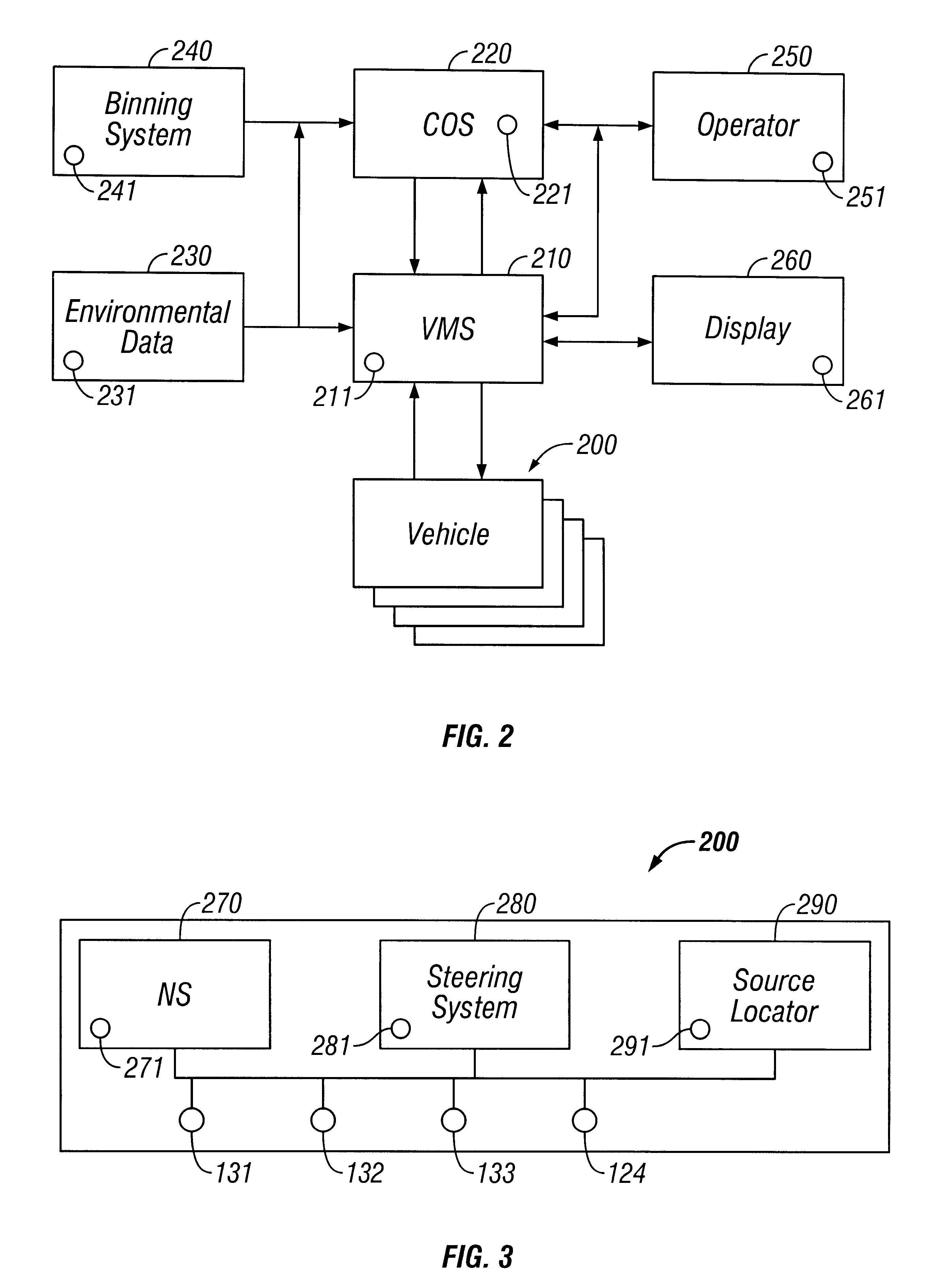
System and method for accessing residential monitoring devices
The present invention is directed to a system and method for accessing home monitoring devices remotely via a distributed wide-area network (WAN). More specifically, the present invention is directed towards smoke detector system, which monitors for the presence of smoke and communicates the smoke condition to a remote location. The smoke detection system comprises a smoke detection device connected to a communication device. The smoke detection device outputs a signal or a change in a signal upon detection of smoke. This signal or change in signal is monitored by the communication device. The smoke condition is then communicated to the remote central location via a message system.
Owner:STARSIGNAL IPC LLC +2
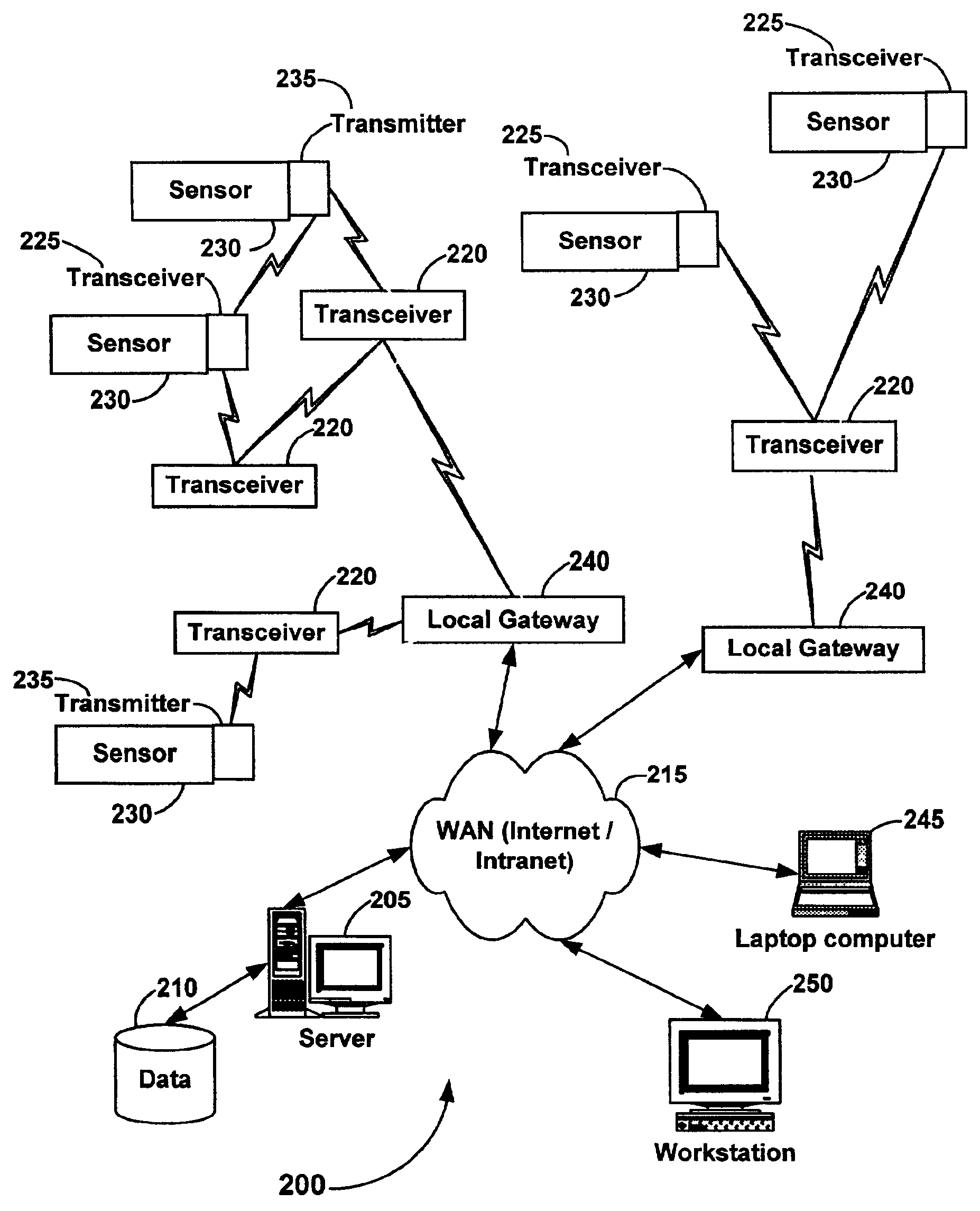
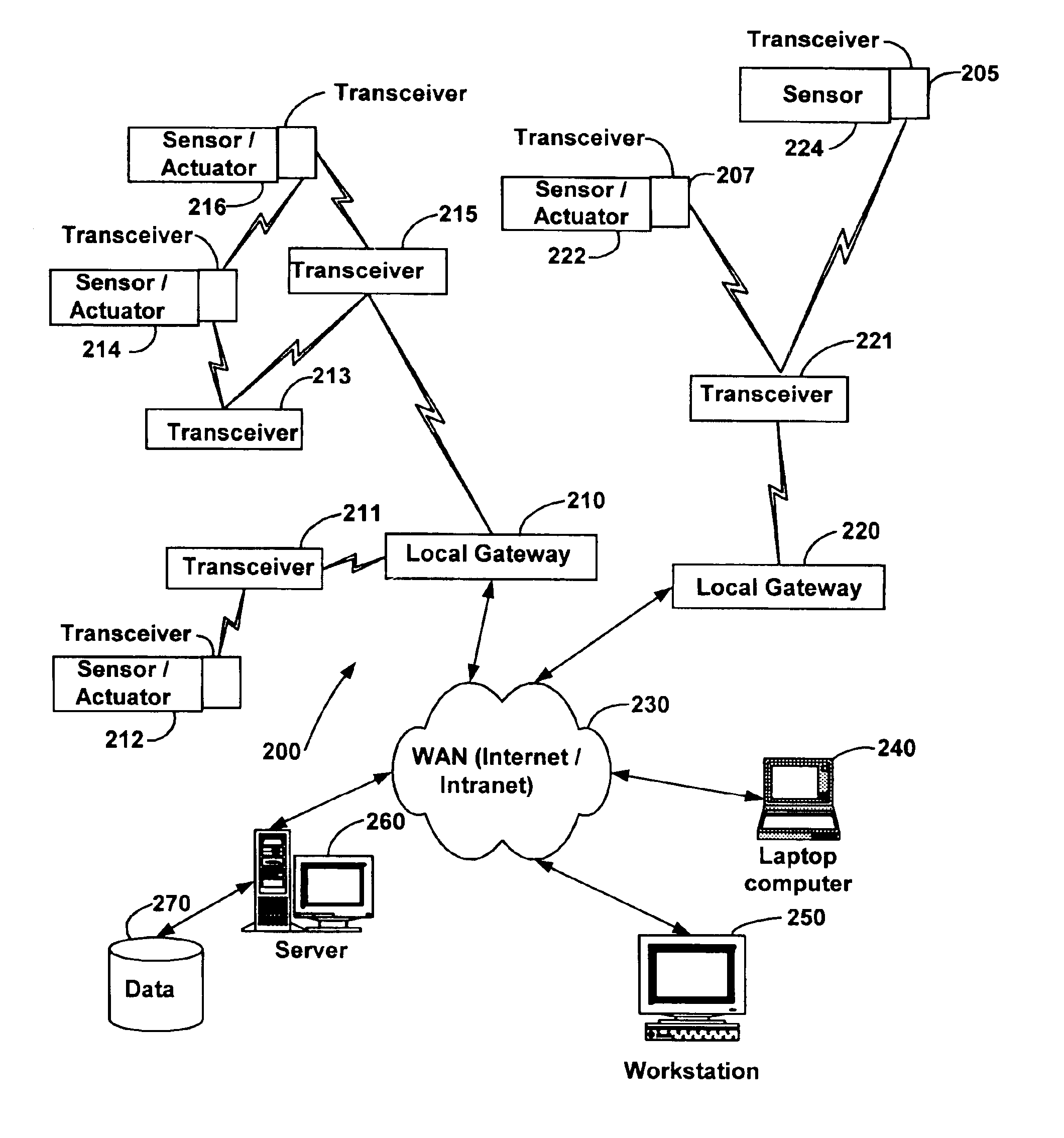
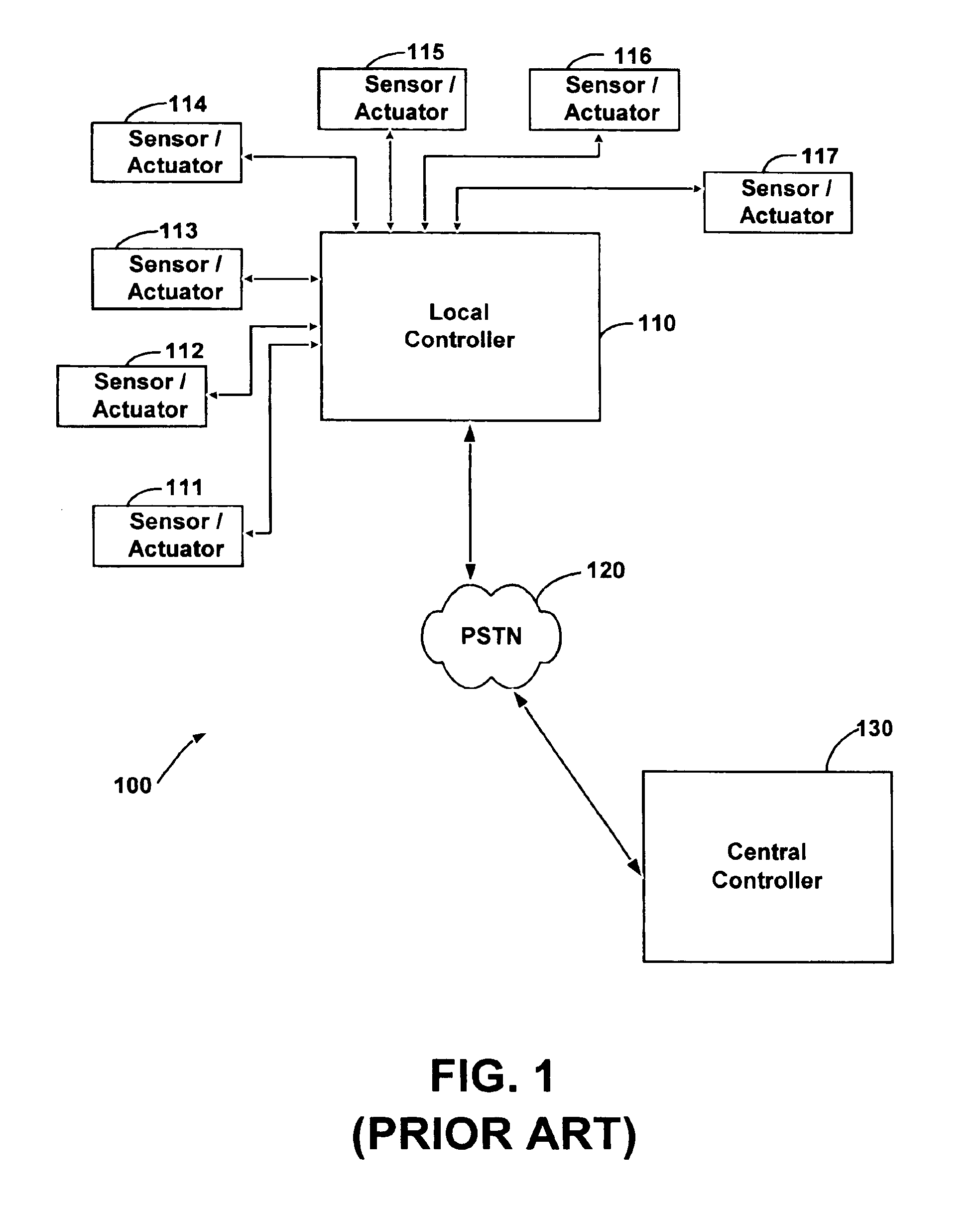
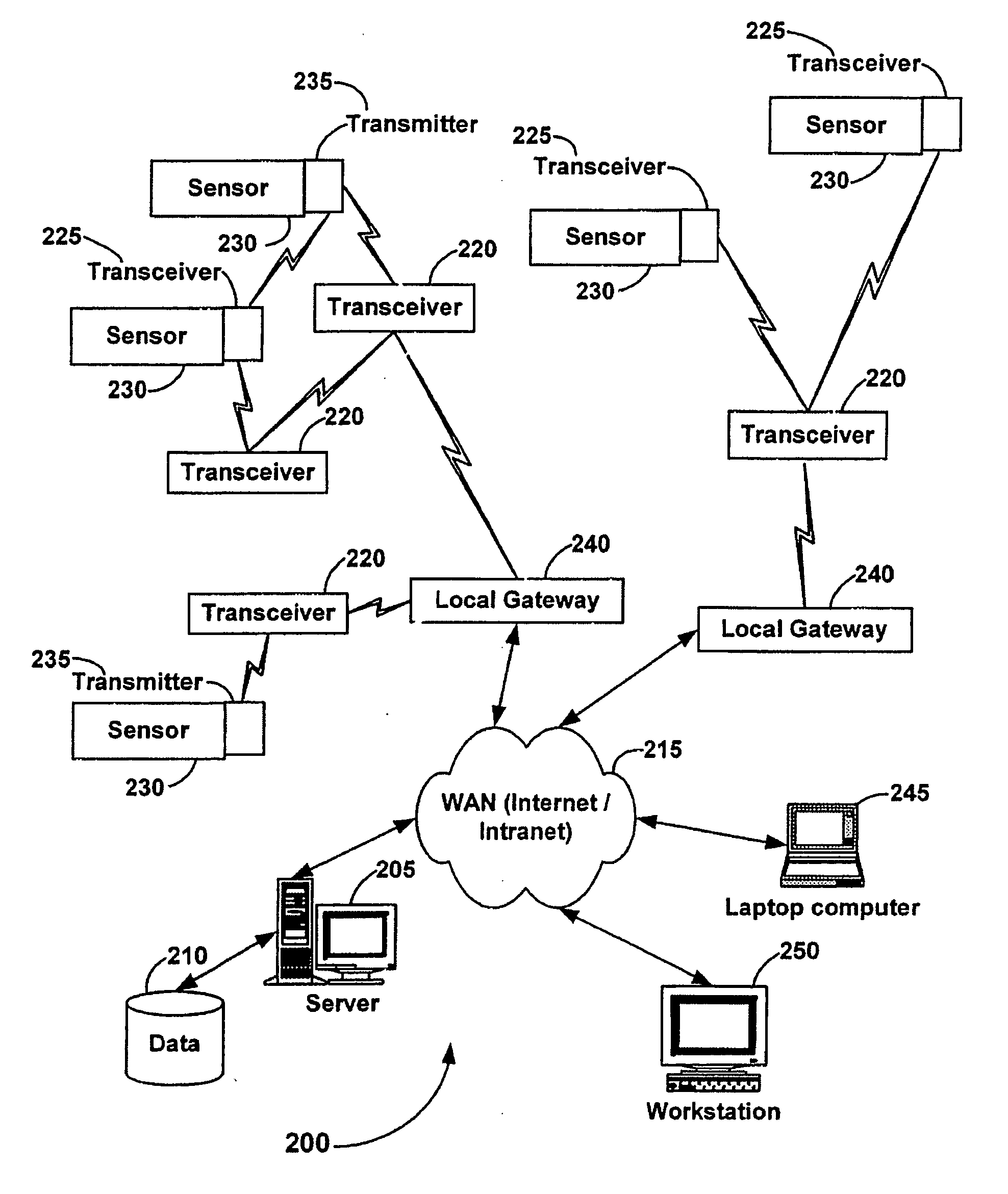
System and method for monitoring and controlling remote devices
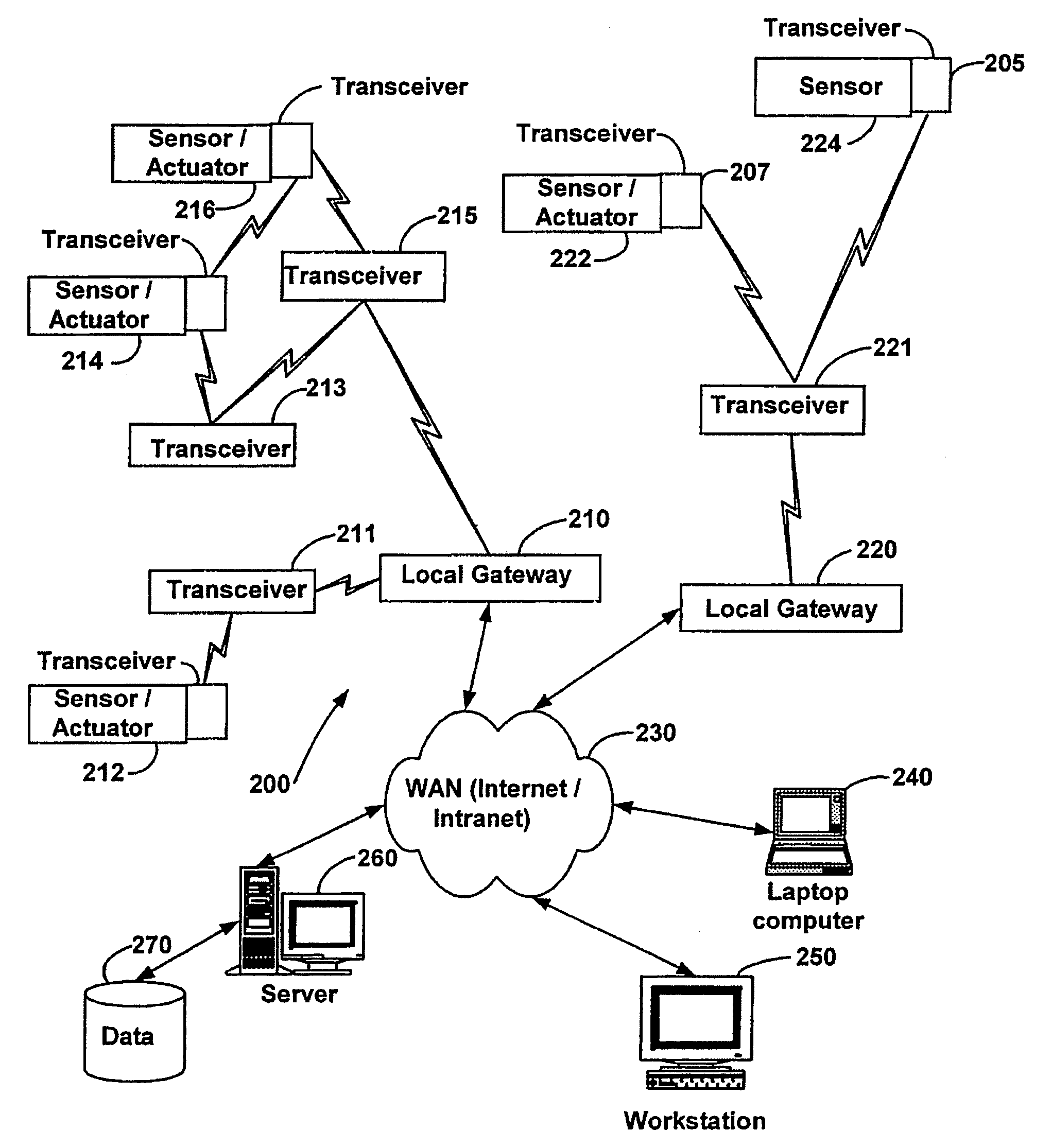
InactiveUS6914893B2Easy to integrateEasily mapped into the packet protocolActive radio relay systemsElectric testing/monitoringTransceiverTelecommunications link
The present system is directed to a computerized system for monitoring and controlling remote devices by transmitting data between the remote systems and a gateway interface via a packet message protocol system. The system comprises one or more remote sensors to be read and possibly one or more actuators to be remotely controlled. The remote sensor(s) / actuator(s) then interface with uniquely identified remote transceivers that transmit and / or receive data. If necessary in individual applications, signal repeaters may relay information between the transceiver(s) and the gateway interface. Communication links between the remote transceivers and the gateway interface are preferably wireless but may also be implemented via a mixture of wireless and wired communication links. To successfully communicate between the transceiver(s) and the gateway interface, the present invention receives a plurality of RF signal transmissions containing a packet protocol via RF signals that includes sender and receiver identifiers, a description of the packet itself, a message number, any commands, the data, and an error detector. In addition, the packet protocol can be easily integrated with alternate data communication protocols for use with systems other than the Internet.
Owner:SIPCO
Simulation gridding method and apparatus including a structured areal gridder adapted for use by a reservoir simulator
InactiveUS6106561AHigh simulationSimulation results are accurateElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingComputation using non-denominational number representationHorizonTriangulation
A Flogrid Simulation Gridding Program includes a Flogrid structured gridder. The structured gridder includes a structured areal gridder and a block gridder. The structured areal gridder will build an areal grid on an uppermost horizon of an earth formation by performing the following steps: (1) building a boundary enclosing one or more fault intersection lines on the horizon, and building a triangulation that absorbs the boundary and the faults; (2) building a vector field on the triangulation; (3) building a web of control lines and additional lines inside the boundary which have a direction that corresponds to the direction of the vector field on the triangulation, thereby producing an areal grid; and (4) post-processing the areal grid so that the control lines and additional lines are equi-spaced or smoothly distributed. The block gridder of the structured gridder will drop coordinate lines down from the nodes of the areal grid to complete the construction of a three dimensional structured grid. A reservoir simulator will receive the structured grid and generate a set of simulation results which are displayed on a 3D Viewer for observation by a workstation operator.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
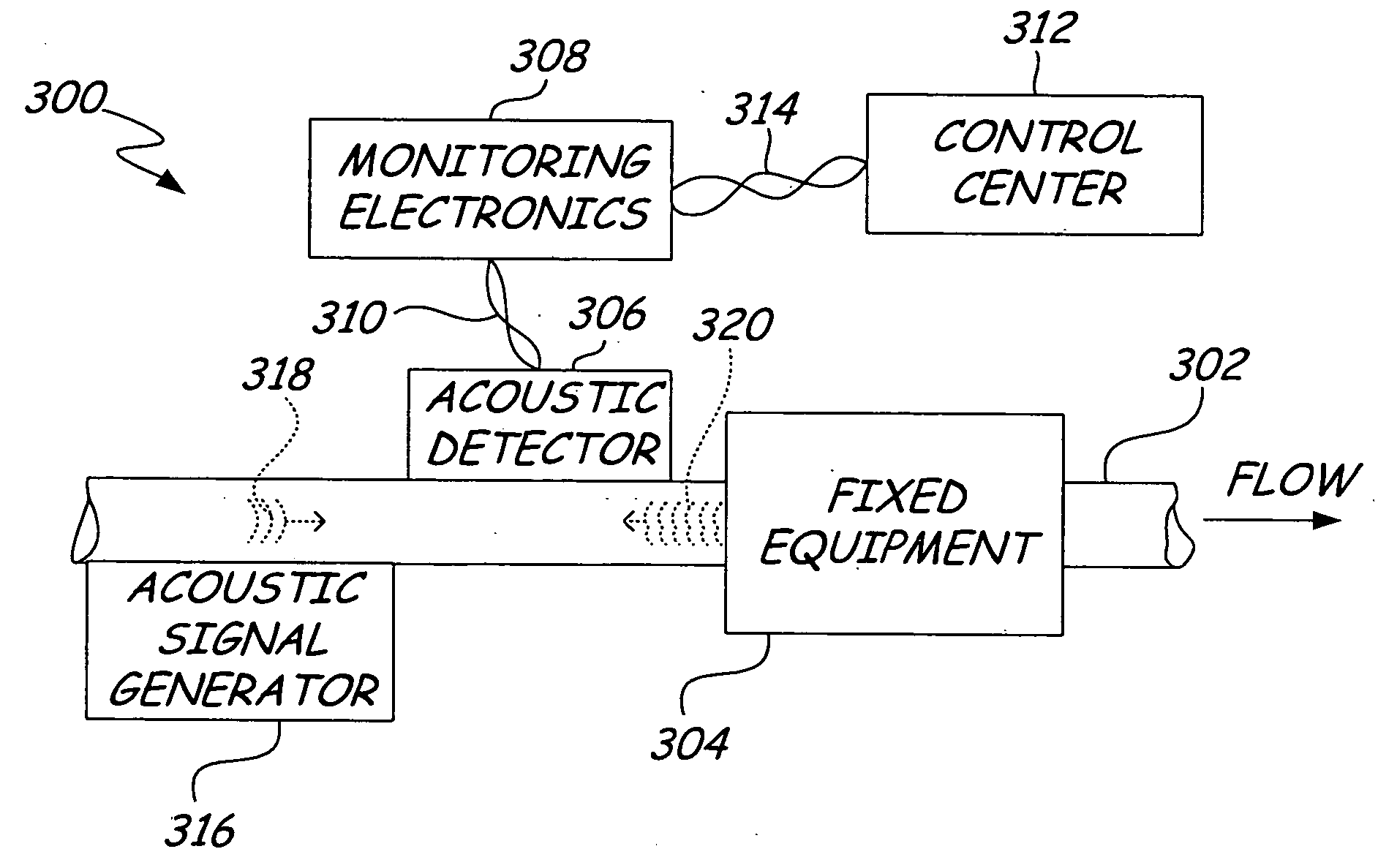
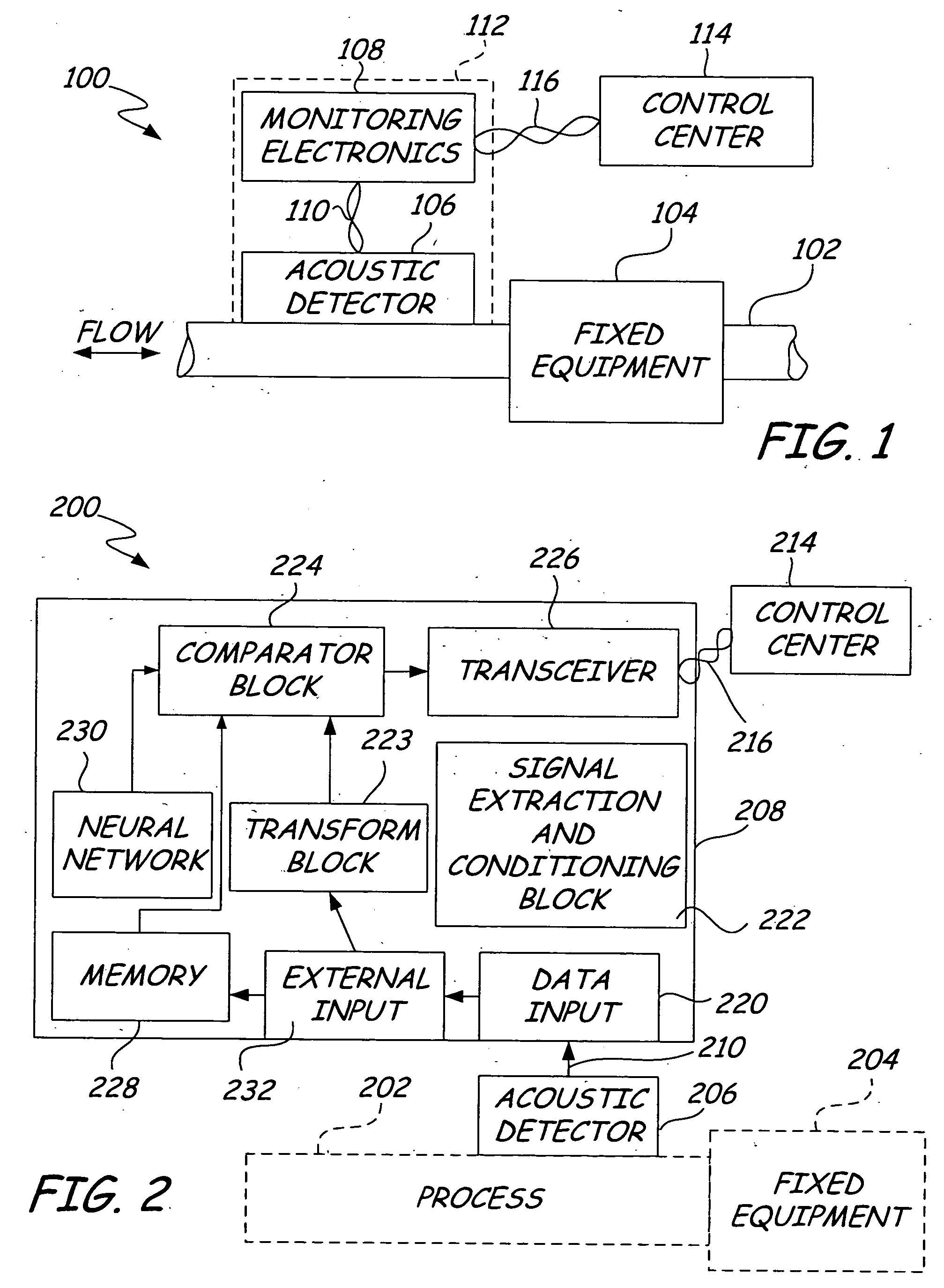
Process diagnostics
ActiveUS20050011278A1Improve abilitiesEasy to useVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTransducerEngineering
A diagnostic device for use in a industrial process includes monitoring electronics or diagnostic circuitry configured to diagnose or identify a condition or other occurrence in the industrial process. The system can be implemented in a process device such as a flowmeter, and in one example an acoustic flowmeter. A transducer can also be used and a frequency response, such as resonant frequency, can be observed.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT INC
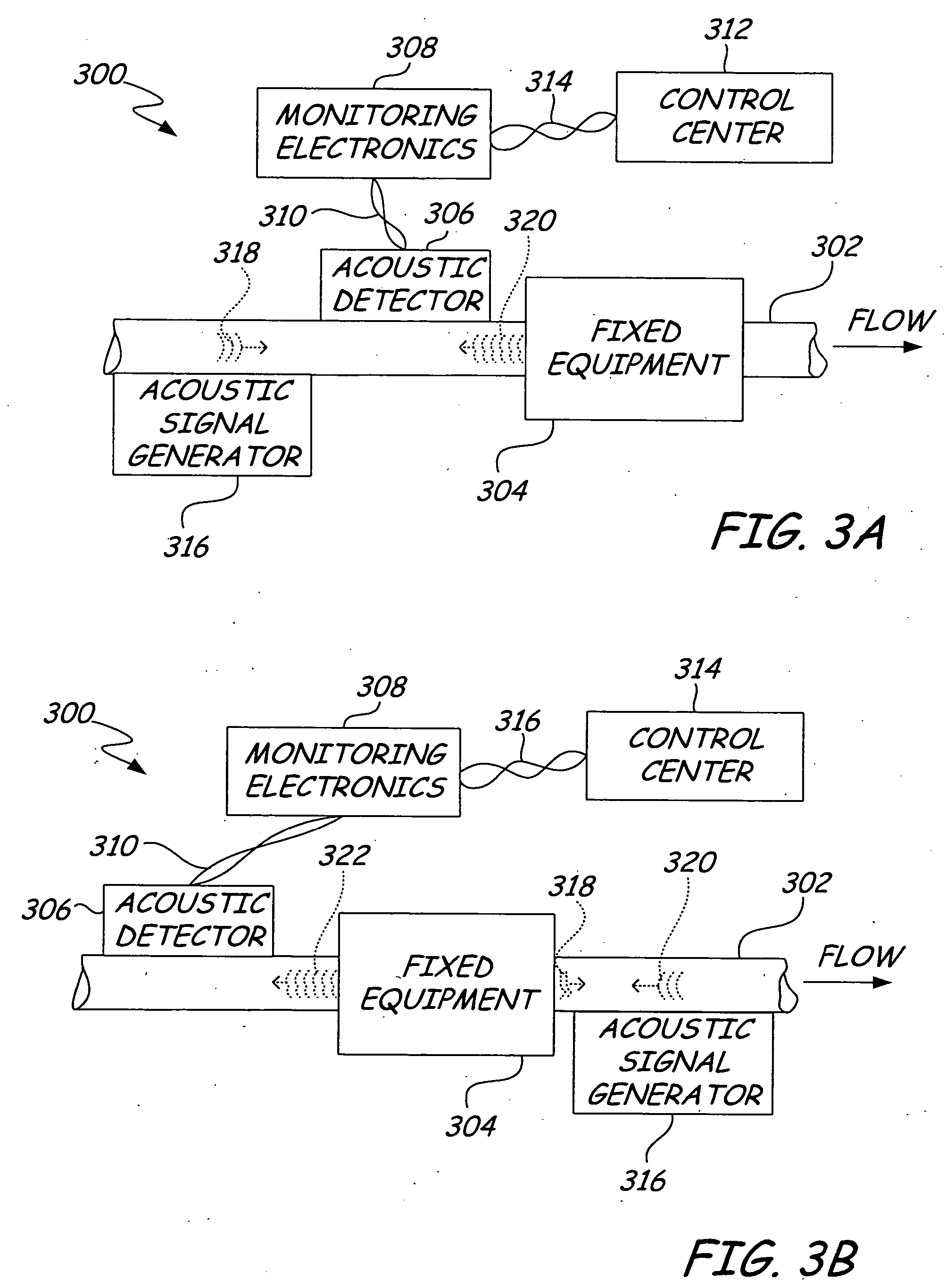
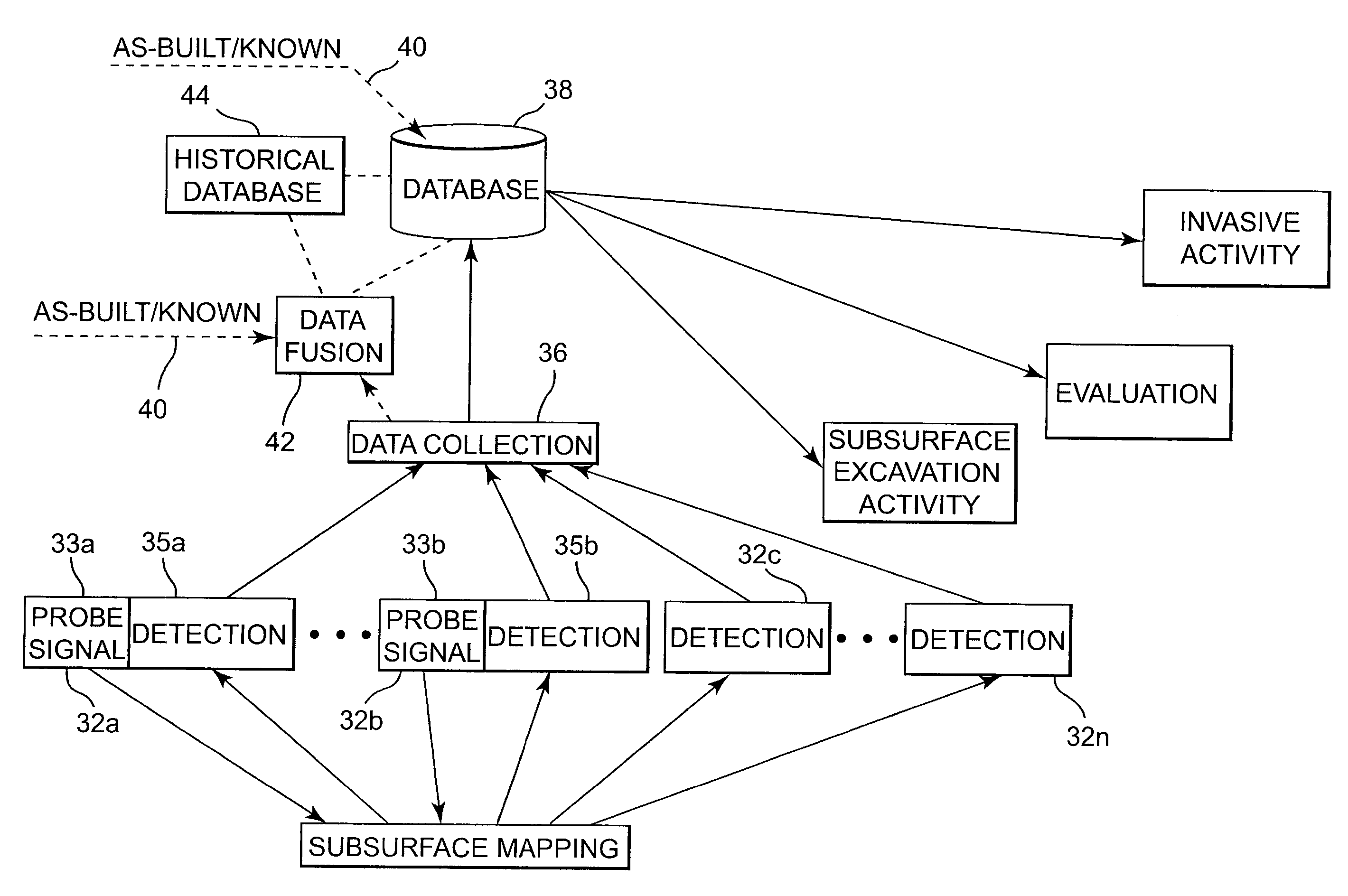
Underground utility detection system and method
Systems and methods provide for detection of one or more underground utilities. Radar waves and seismic waves of about the same wavelength are generated and communicated into a subsurface. Radar and seismic response signals resulting from communication of the radar and seismic waves into the subsurface are concurrently received. Data associated with the received radar and seismic response signals are stored. One or more underground utilities within the subsurface is / are detected using the stored data. The underground utilities may include metallic and non-metallic utilities.
Owner:VERMEER MFG CO
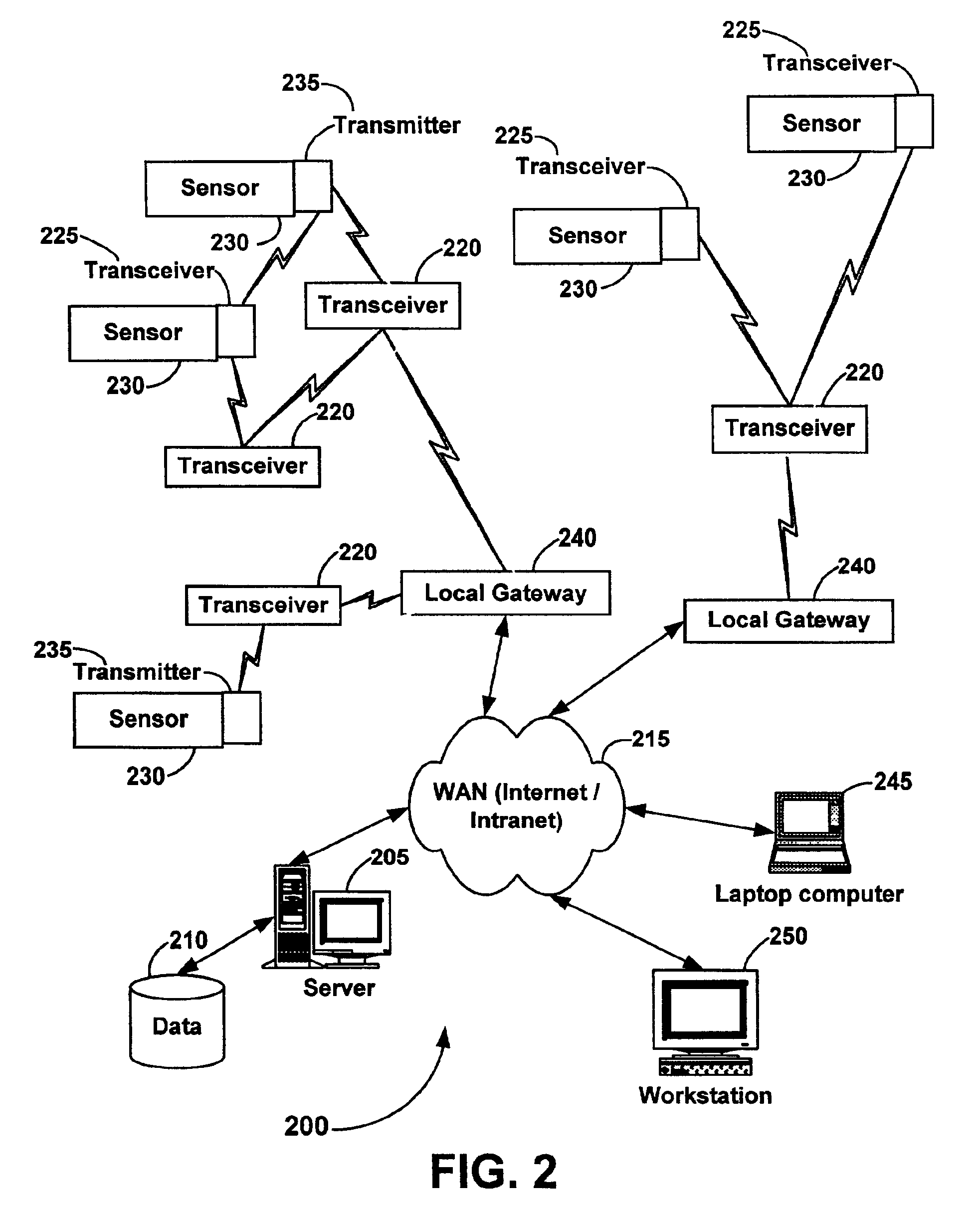
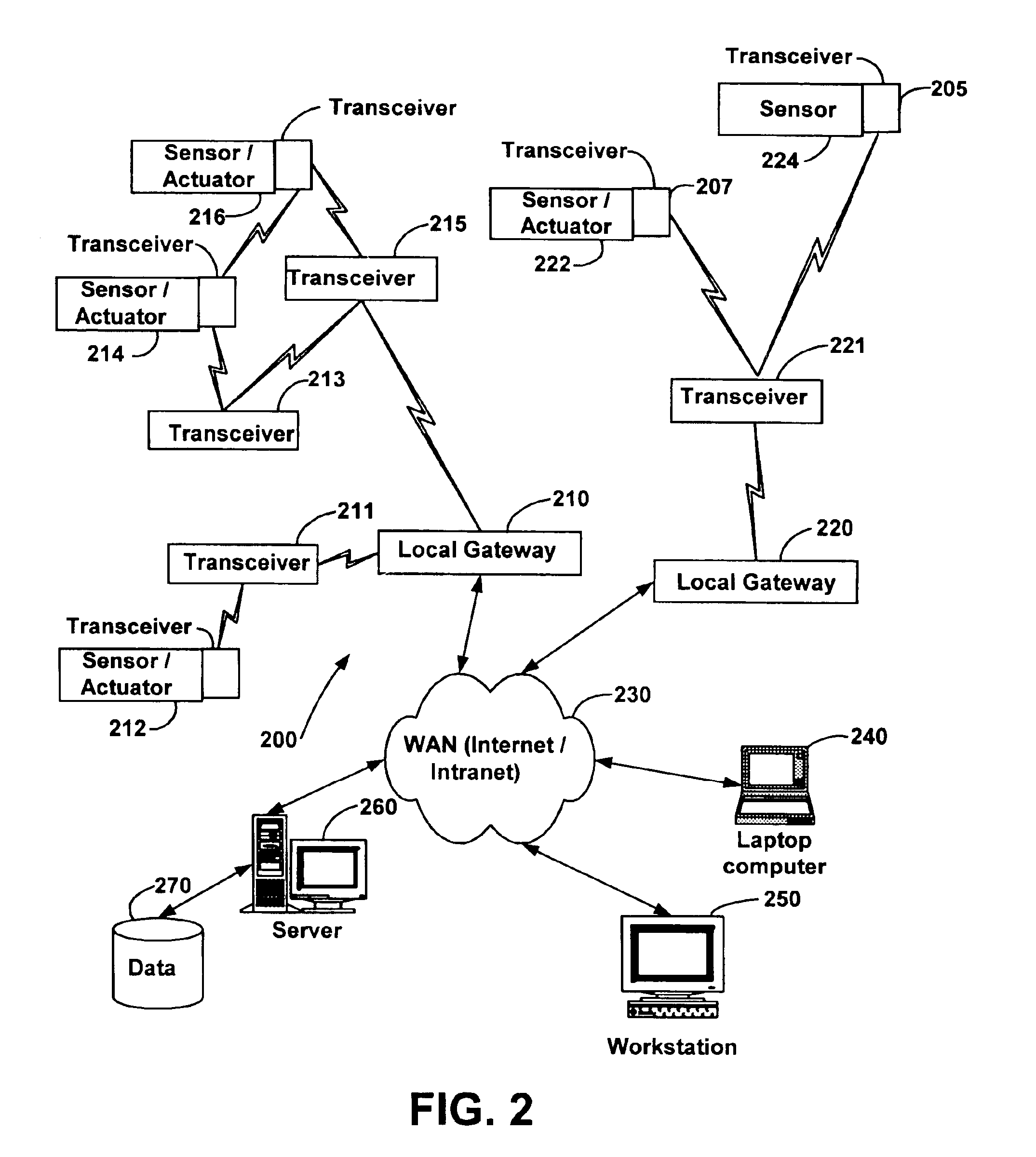
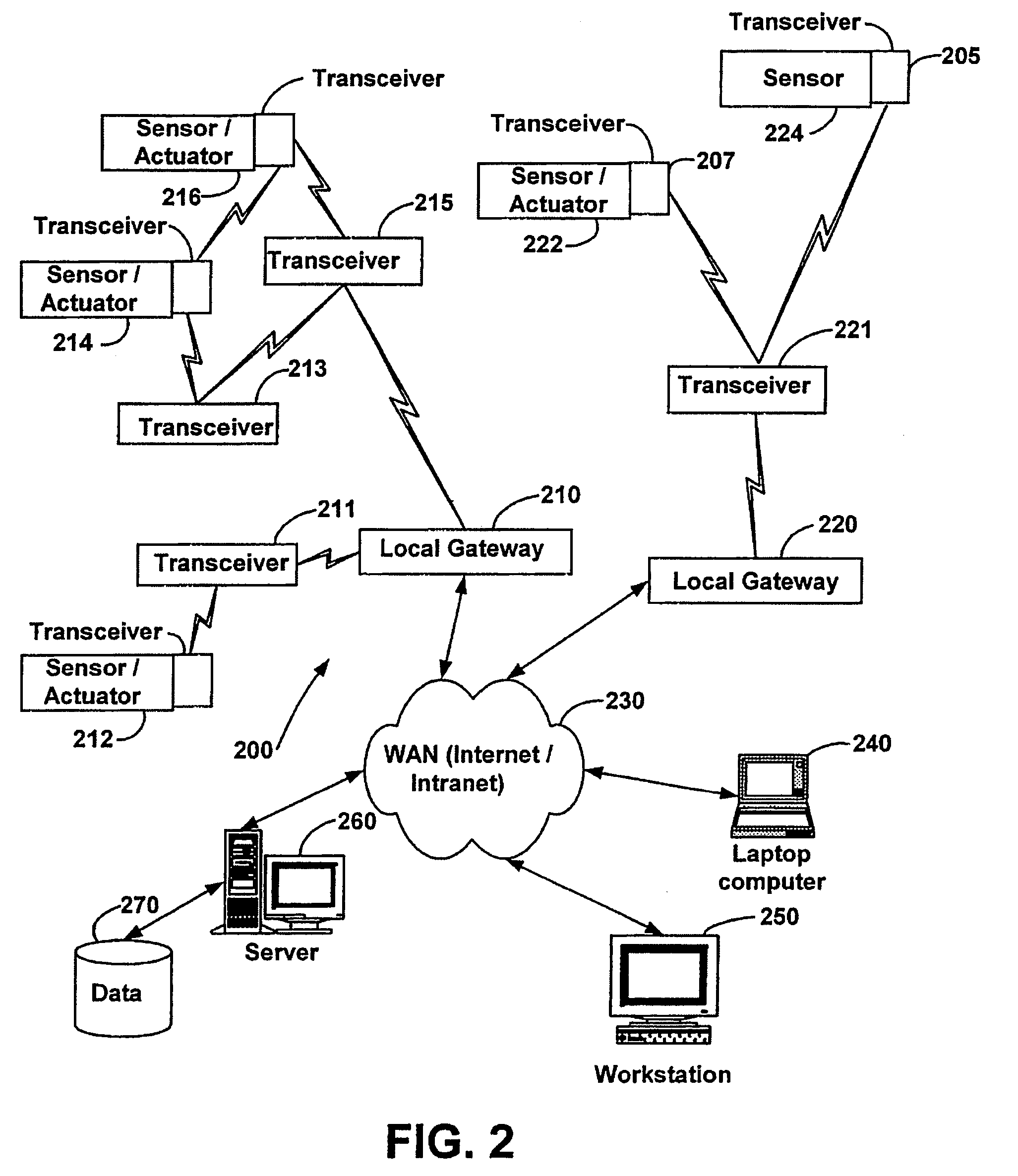
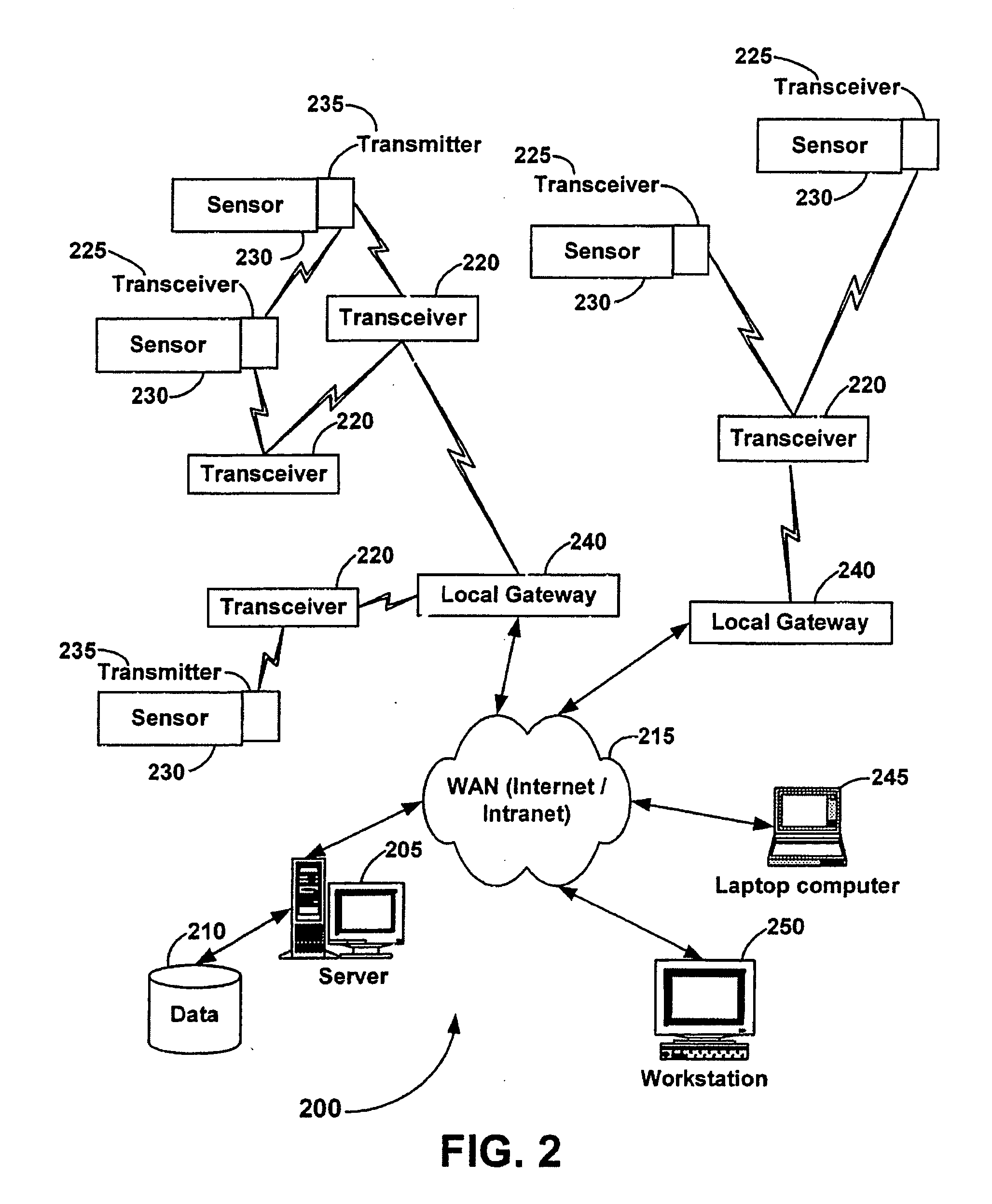
Systems and methods for monitoring and controlling remote devices
InactiveUS20050243867A1Integration into a pre-existingElectric signal transmission systemsActive radio relay systemsTransceiverControl signal
Systems and methods for monitoring and controlling remote devices are provided. In an embodiment, a system can comprise one or more remotely controlled sensors and actuators. The remote sensors / actuators can interface with uniquely identified remote transceivers that transmit and / or receive data. The embodiment can also comprise a plurality of transceivers each having a unique address, and a controller adapted to communicate with at least one of the transceivers in a preformatted message. A sensor can be associated with at least one transceiver to detect a condition and output a data signal to the transceiver, and an actuator can be associated with a transceiver to receive a control signal and activate a device. Other embodiments are also claimed and described.
Owner:HUNT TECH INC +1
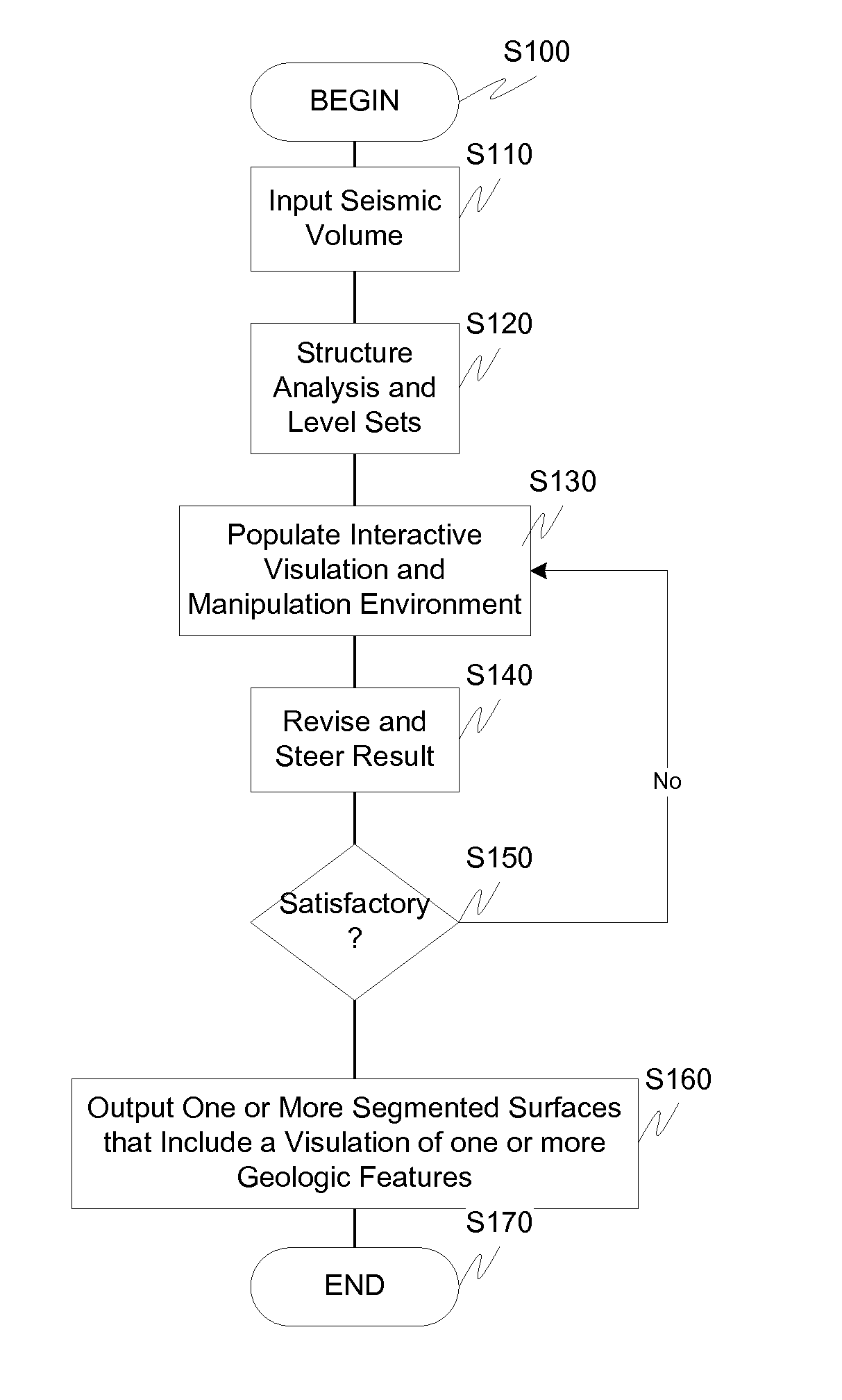
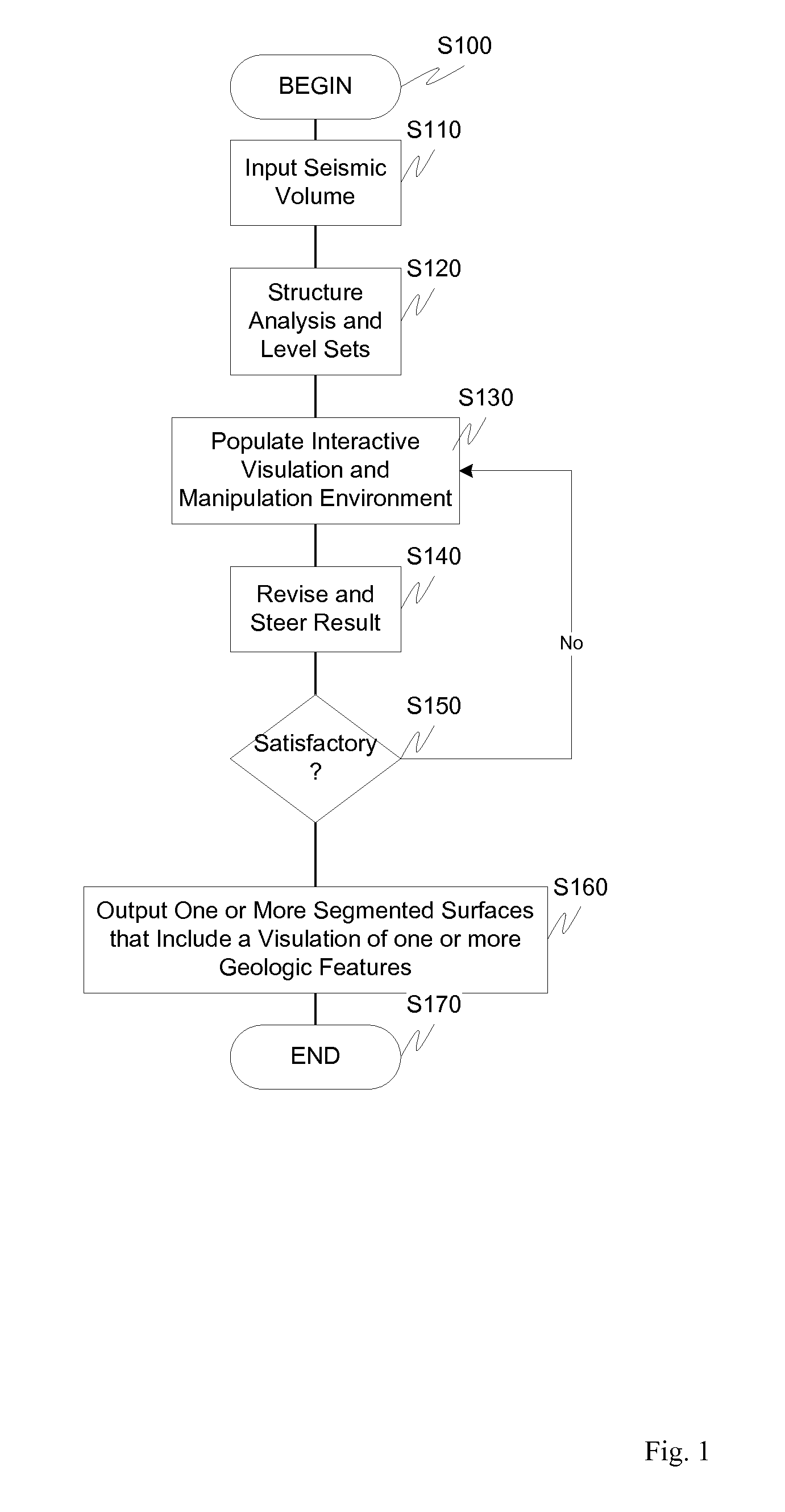
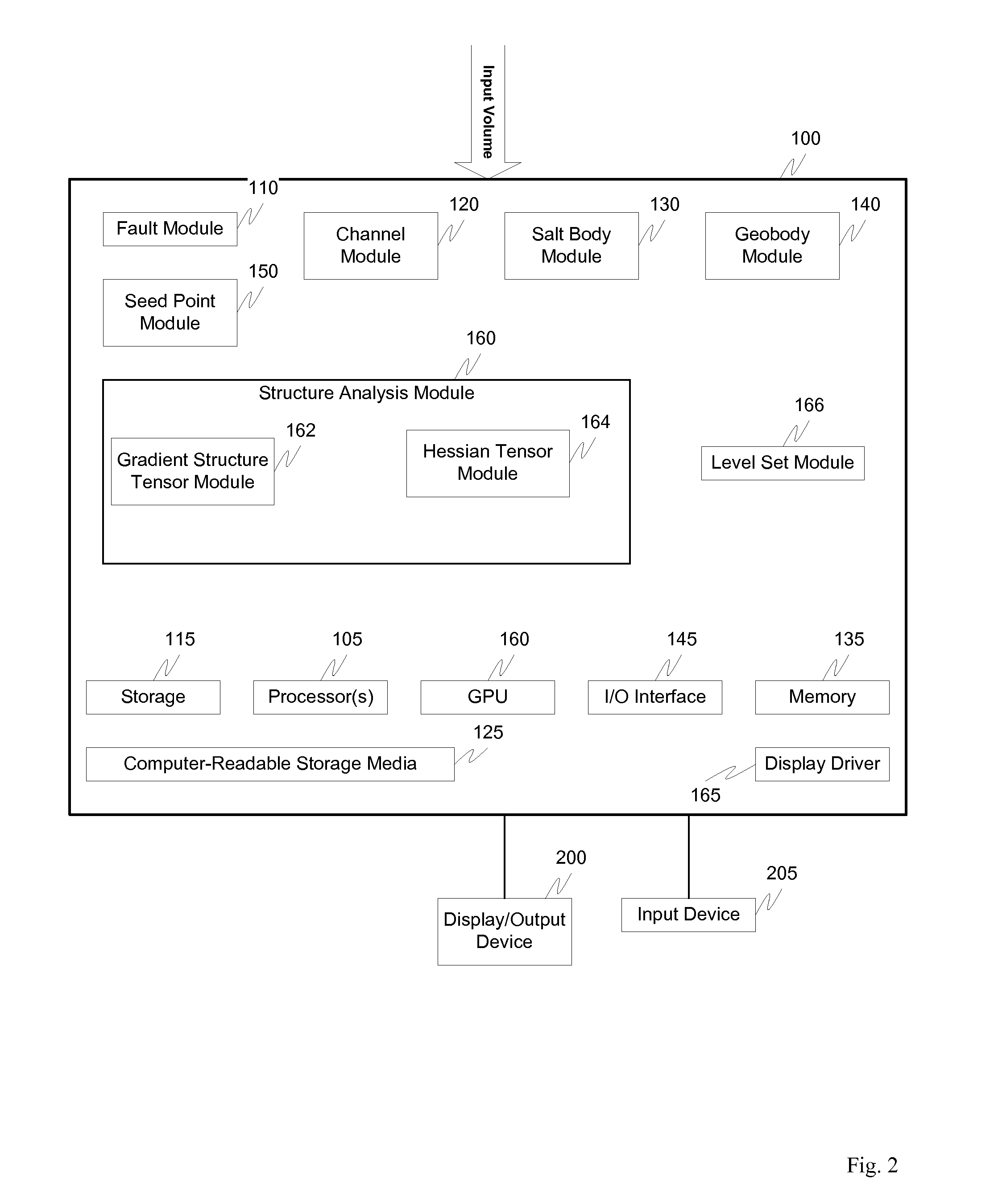
Visulation of geologic features using data representations thereof
InactiveUS20110115787A1Enhance feature structureEasy to divideImage enhancementImage analysisImage structureComputer science
One exemplary embodiment presents a unified approach in the form of an Interactive “Violation” (simultaneous visualization and simulation) Environment (IVE) designed to efficiently segment geologic features with high accuracy. The IVE unifies image structure analysis and implicit surface modeling as a surface-driven solution that assists analysts, such as geoscientists, in the segmentation and modeling of faults, channels, and other geobodies in 3-D data, such as 3-D seismic data.
Owner:CGG JASON NETHERLANDS
Apparatus and methods for multicomponent marine geophysical data gathering
InactiveUS7239577B2Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementFloating cablesGeophoneCubic metre per second
In one embodiment the invention comprises a particle velocity sensor that includes a housing with a geophone mounted in the housing. A fluid that substantially surrounds the geophone is included within the housing. The particle velocity sensor has an acoustic impedance within the range of about 750,000 Newton seconds per cubic meter (Ns / m3) to about 3,000,000 Newton seconds per cubic meter (Ns / m3). In another embodiment the invention comprises method of geophysical exploration in which a seismic signal is generated in a body of water and detected with a plurality of co-located particle velocity sensors and pressure gradient sensors positioned within a seismic cable. The output signal of either or both of the particle velocity sensors or the pressure gradient sensors is modified to substantially equalize the output signals from the particle velocity sensors and the pressure gradient sensors. The output signals from particle velocity sensors and pressure gradient sensors are then combined.
Owner:PGS AMERICA INC
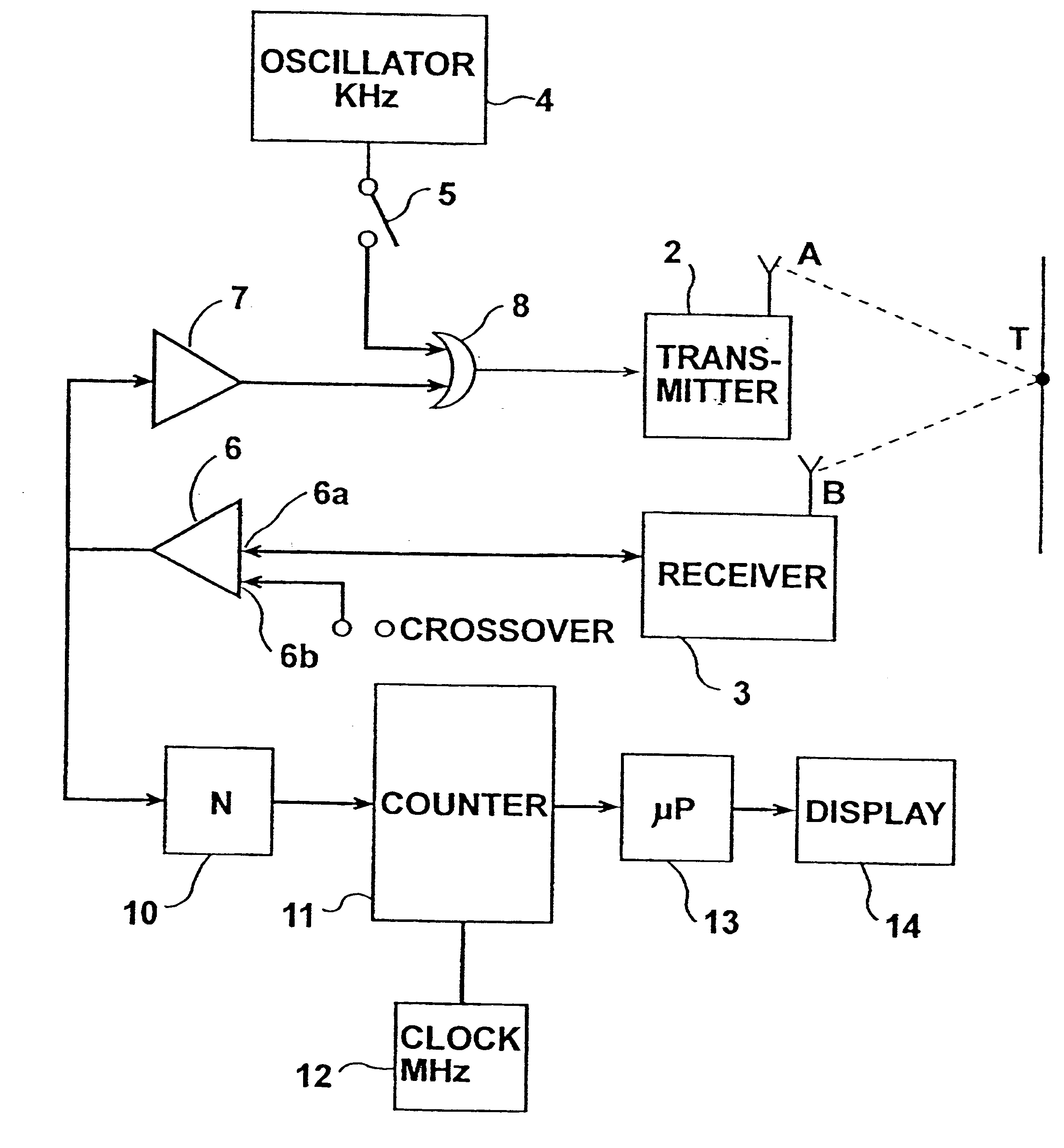
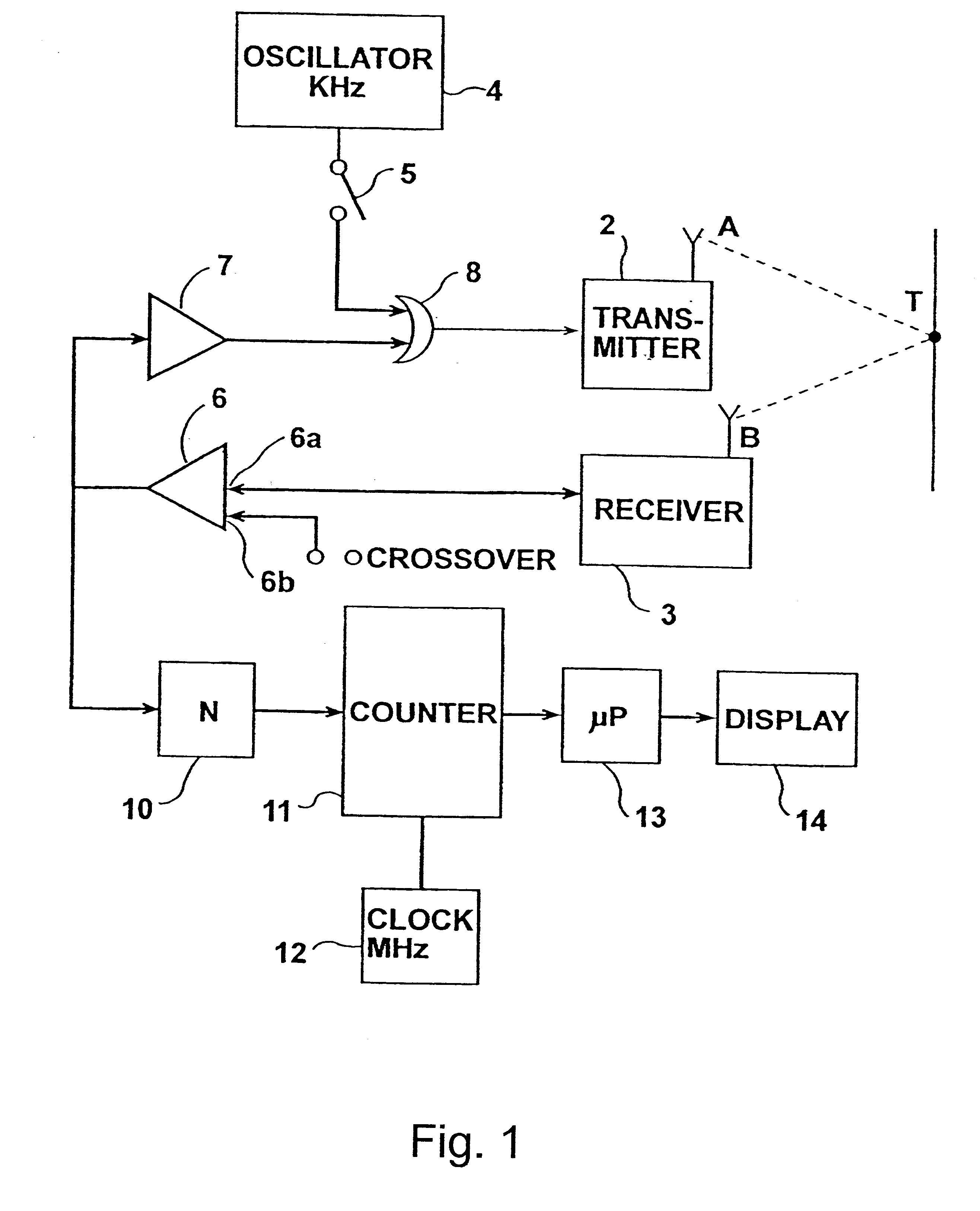
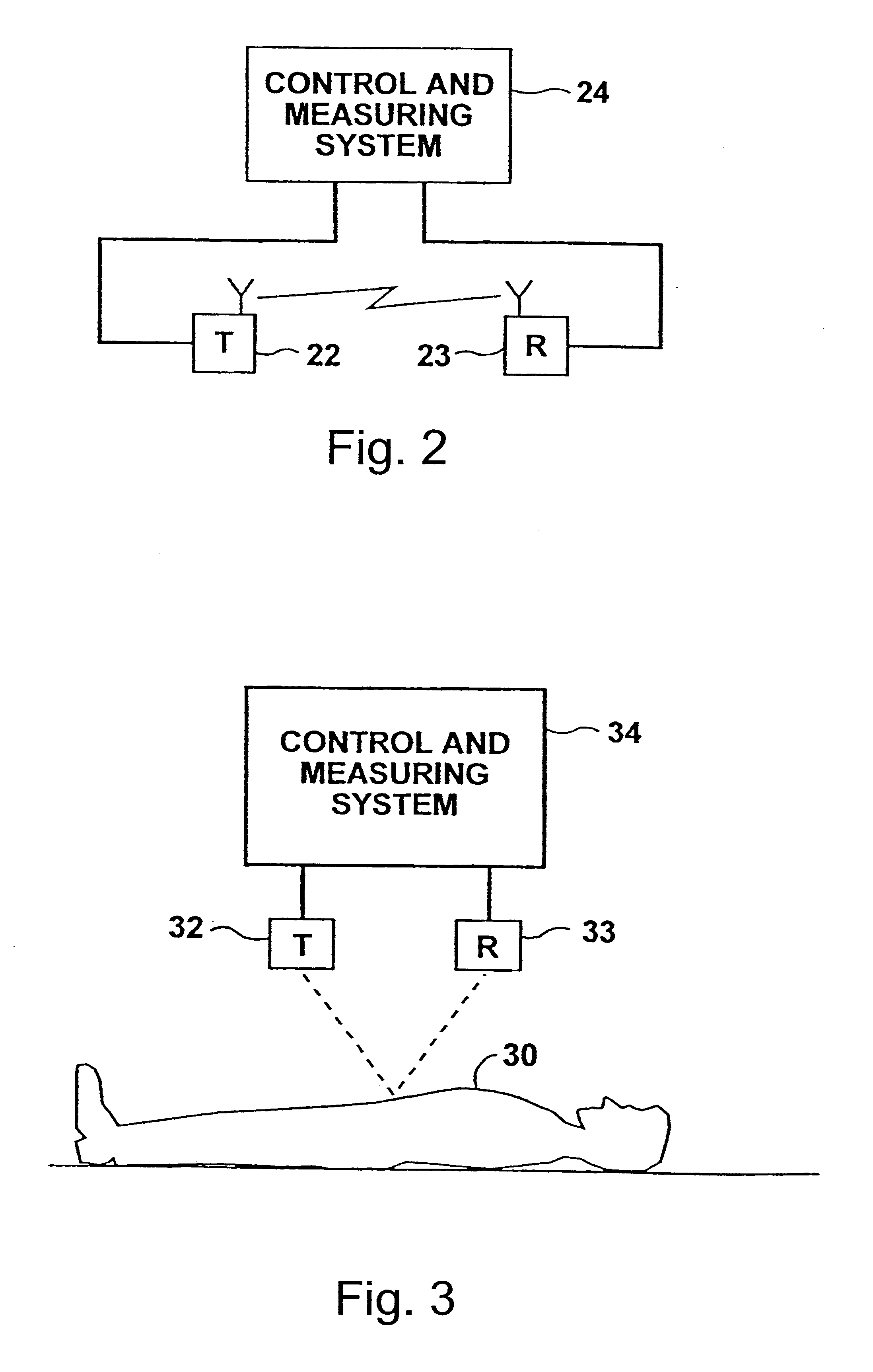
High-precision measuring method and apparatus
InactiveUS6621278B2Low-cost equipmentHigh precisionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEngineeringFiducial points
A method and apparatus of measuring a predetermined parameter having a known relation to the transit time of movement of an energy wave through a medium, by transmitting from a first location in the medium a cyclically-repeating energy wave; receiving the cyclically-repeating energy wave at a second location in the medium; detecting a predetermined fiducial point in the cyclically-repeating energy wave received at the second location; continuously changing the frequency of transmission of the cyclically-repeating energy wave from the first location to the second location in accordance with the detected fiducial point of each received cyclically-repeating energy wave received at the second location such that the number of waves received at the second location from the first location is a whole integer; and utilizing the change in frequency to produce a measurement of the predetermined parameter.
Owner:NEXENSE
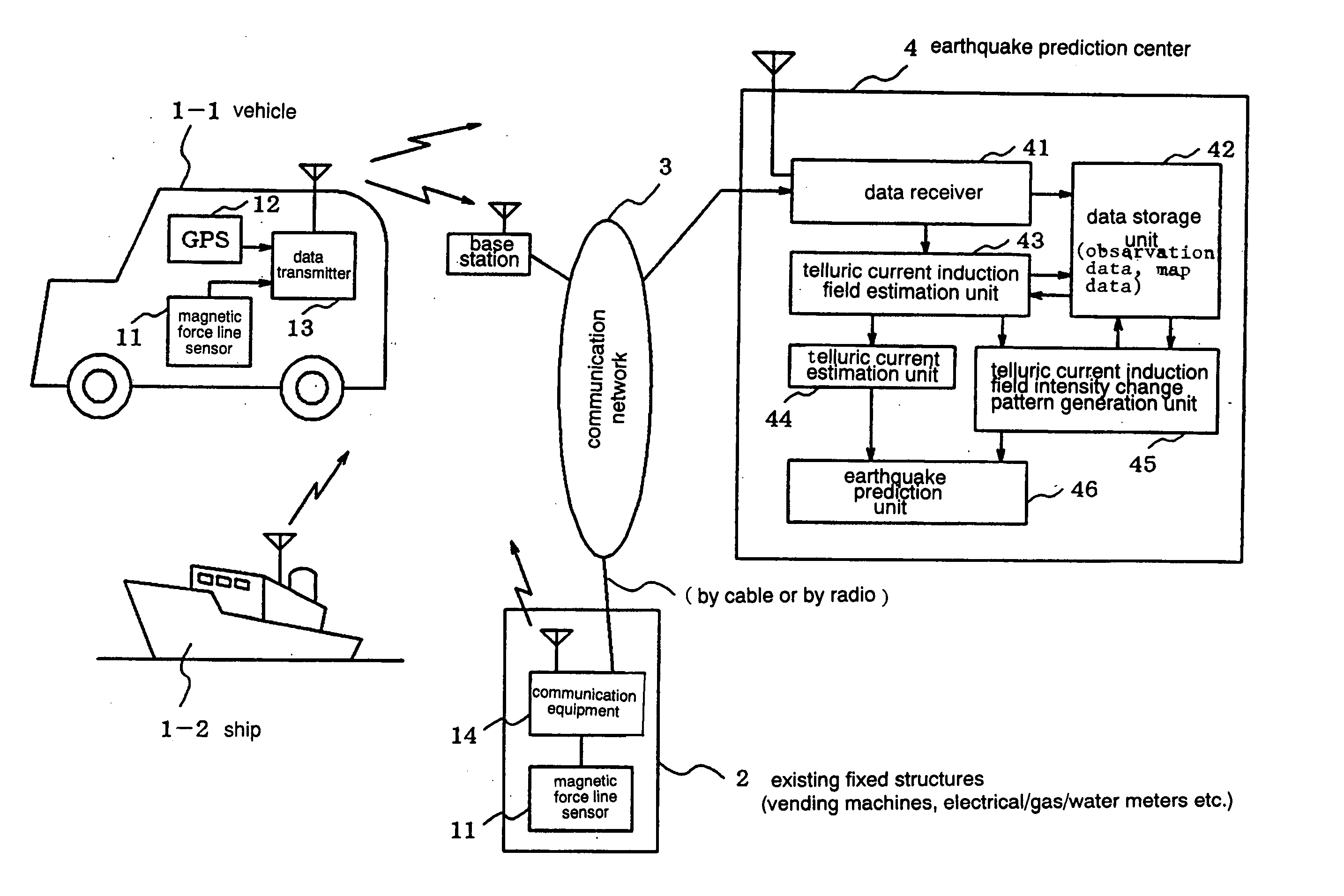
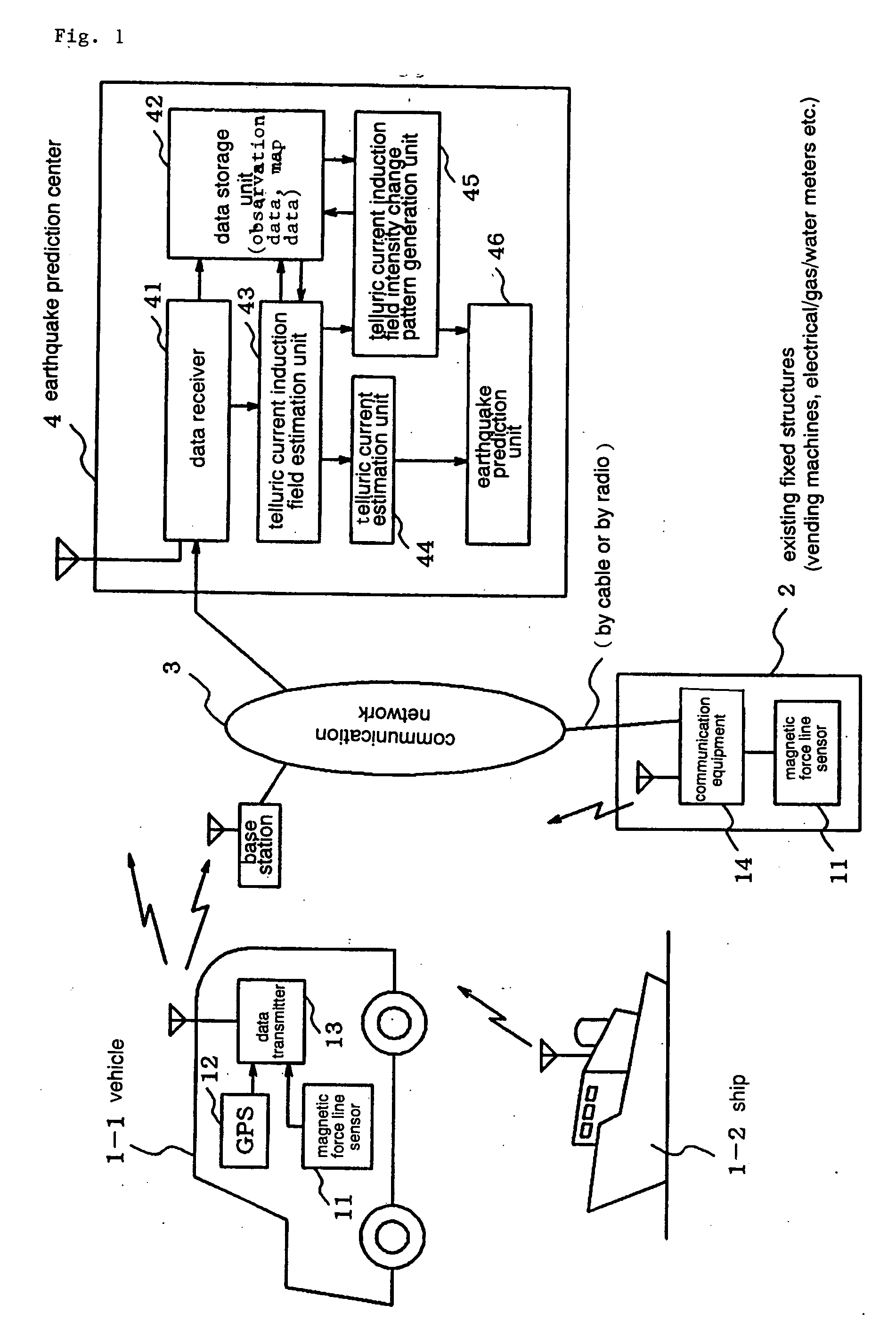
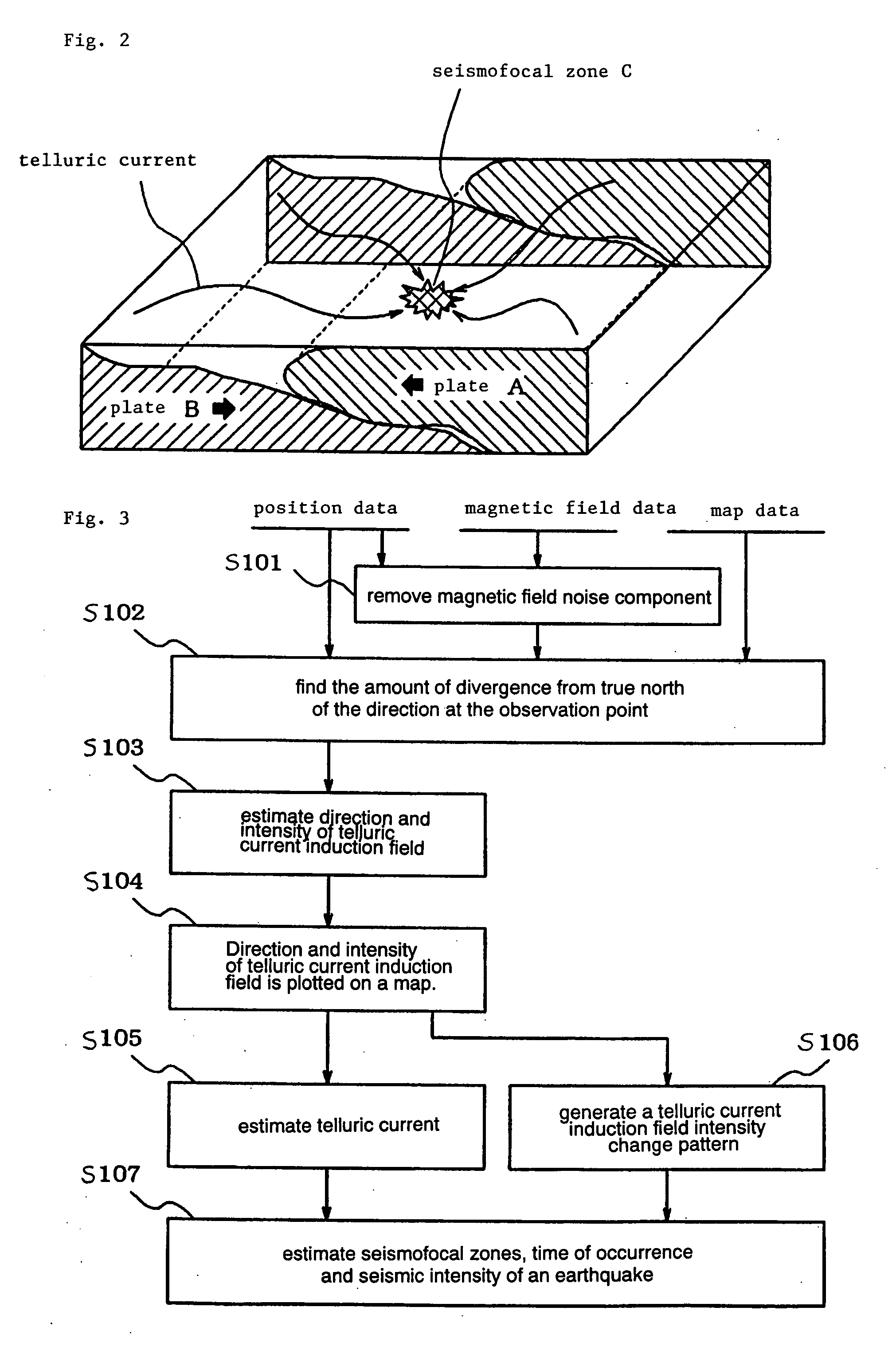
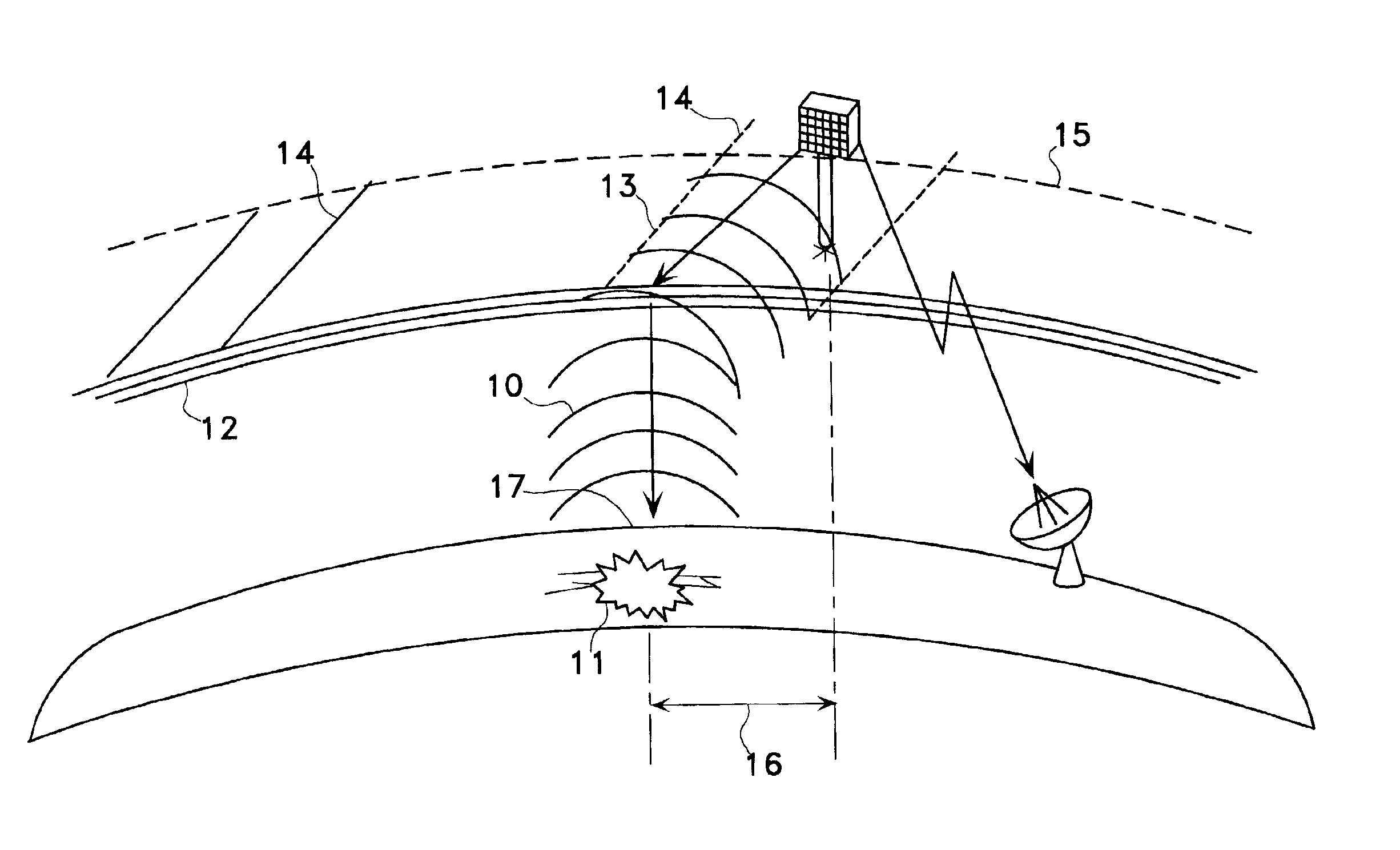
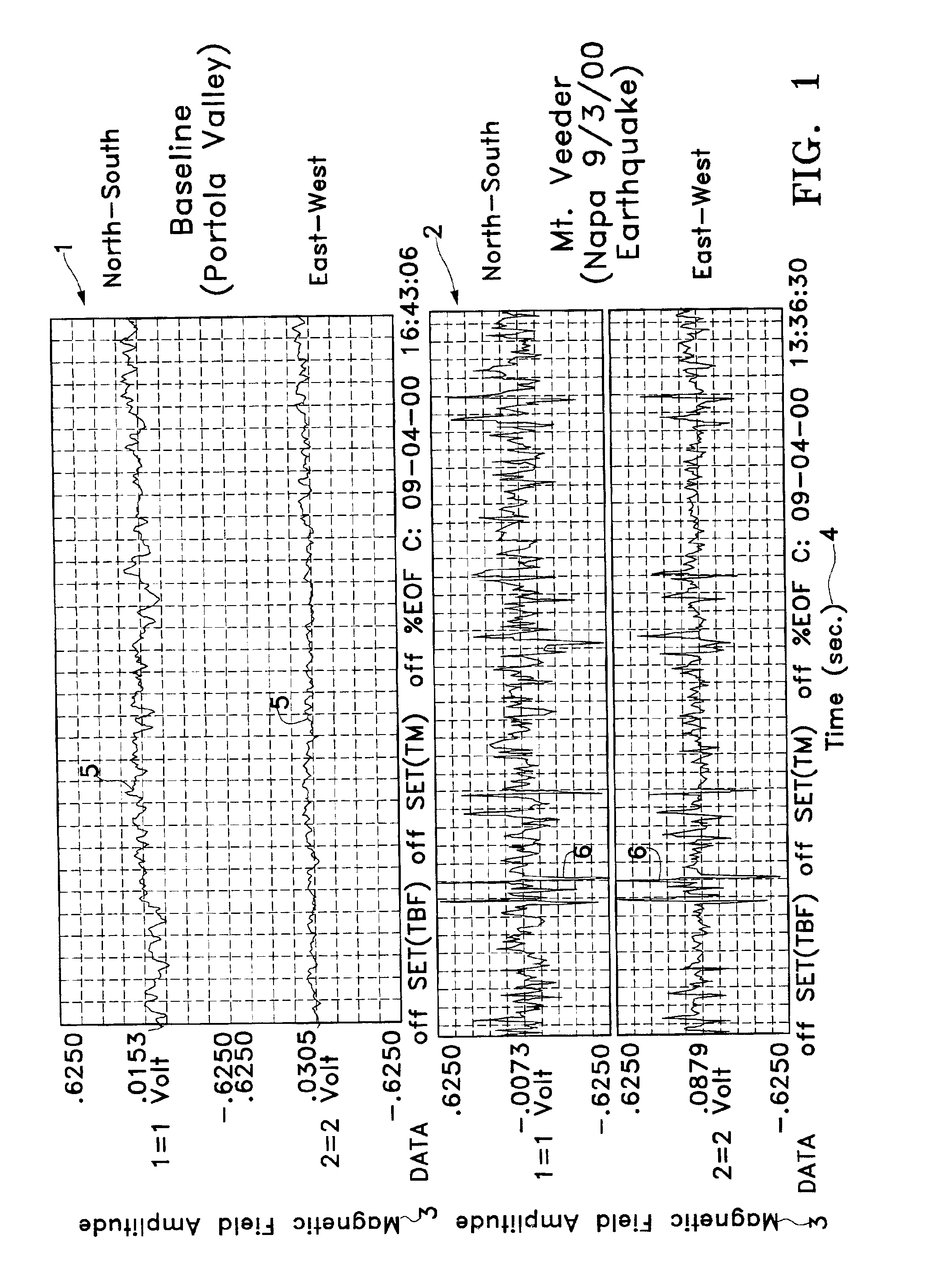
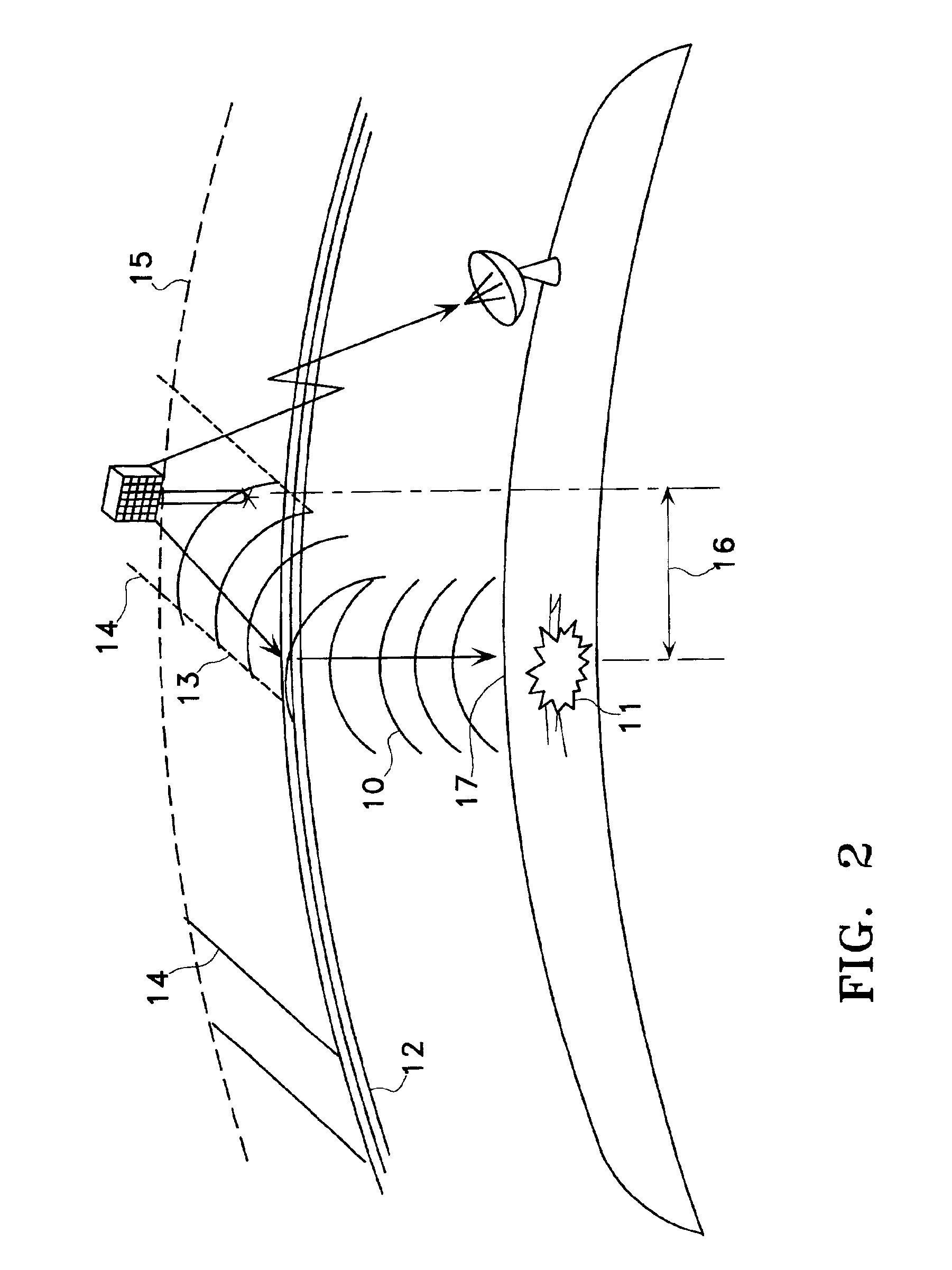
Earthquarke prediction method and system thereof
InactiveUS20050280421A1Low costAccurate predictionEarthquake measurementSeismic signal processingEarthquake predictionTransmitter
Vehicles (1-1) or ships (1-2) each carry a magnetic force line sensor (11), a GPS position detector (12), and a data transmitter (13) and travel within an observation area transmitting magnetic field data and position data of each point to an earthquake prediction center (4). A telluric current induction field estimation unit (43) of the earthquake prediction center (4) estimates telluric current induction fields based on the observation data that it receives and collects. A telluric current estimation unit (44) estimates telluric currents based on the results of estimating the telluric current induction fields. A telluric current induction field intensity change pattern generation unit (45) generates patterns that indicate the change over time of the intensity of telluric current induction fields. An earthquake prediction unit (46) analyzes the state of distribution of the telluric currents and the patterns of change in the intensities of the telluric current induction fields and estimates a seismofocal zone, seismic intensity, and time of occurrence of a seismic event.
Owner:NEC MOBILING LTD
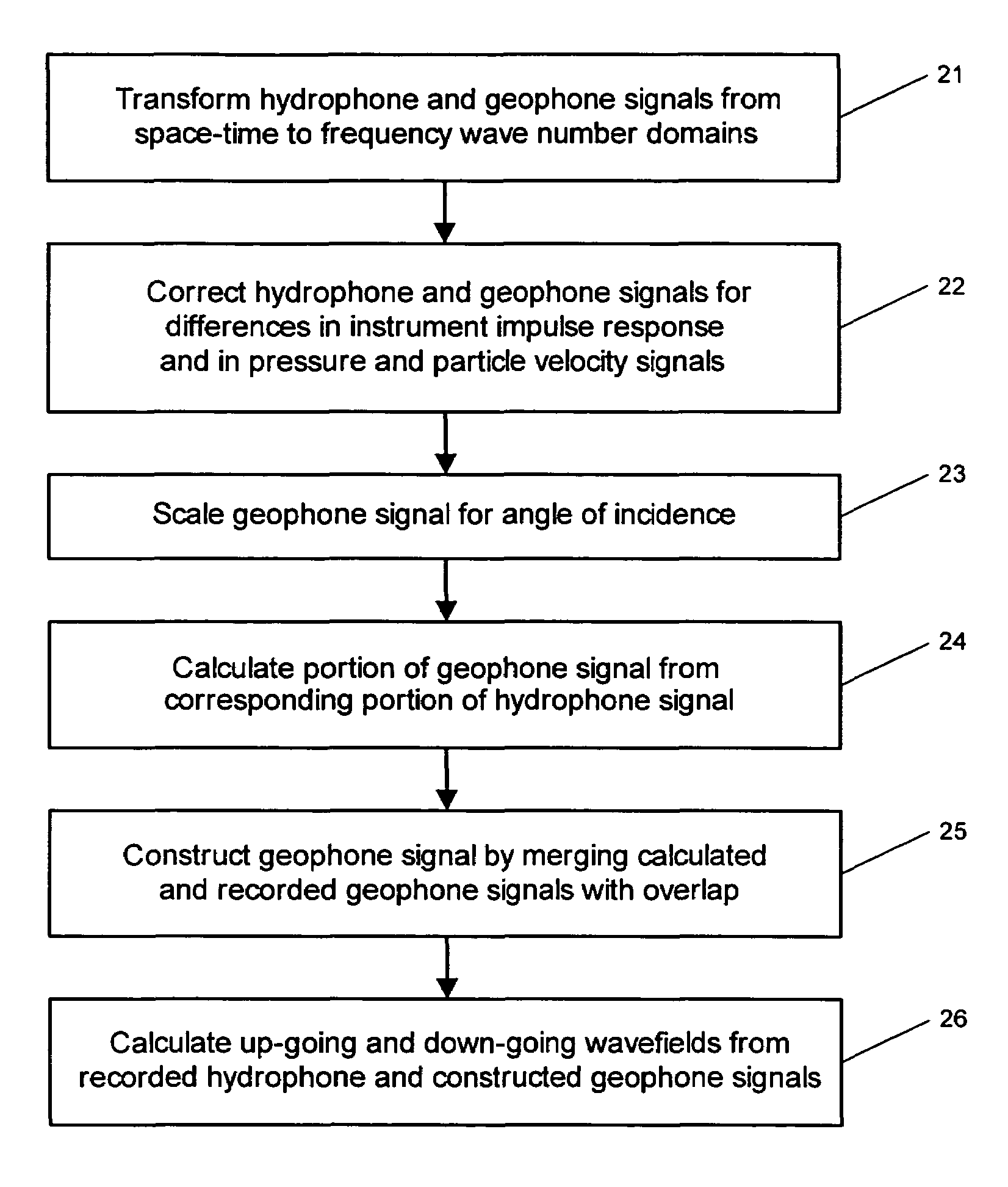
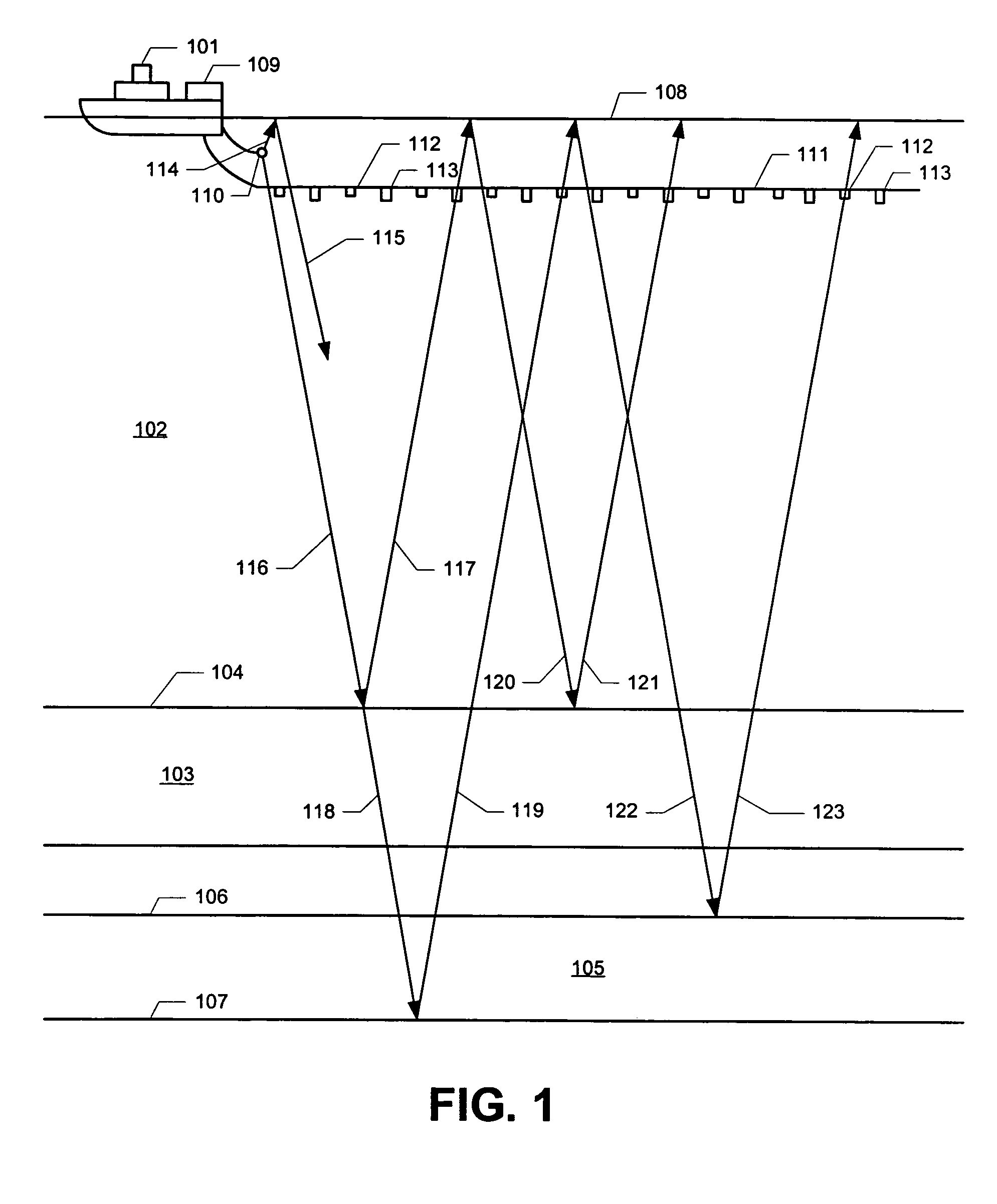
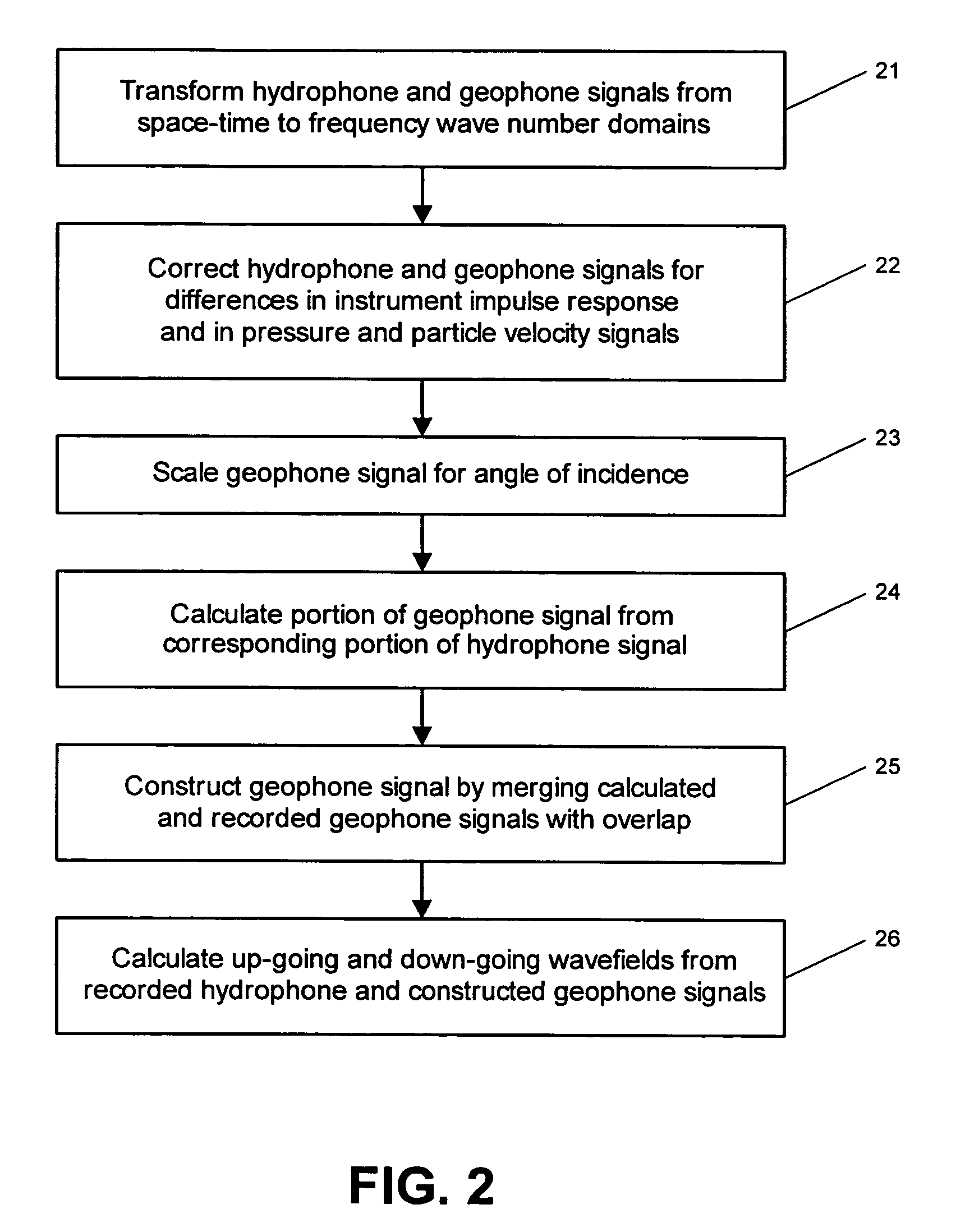
System for combining signals of pressure sensors and particle motion sensors in marine seismic streamers
Signals of pressure sensors and particle motion sensors located in marine seismic streamers are combined to generate pressure sensor data and particle motion data with substantially the same broad bandwidth. The noisy low frequency part of the motion signals are calculated from the recorded pressure signals and merged with the non-noisy motion signals. The two broad bandwidth data sets can then be combined to calculate the full up- and down-going wavefields.
Owner:PGS AMERICA INC
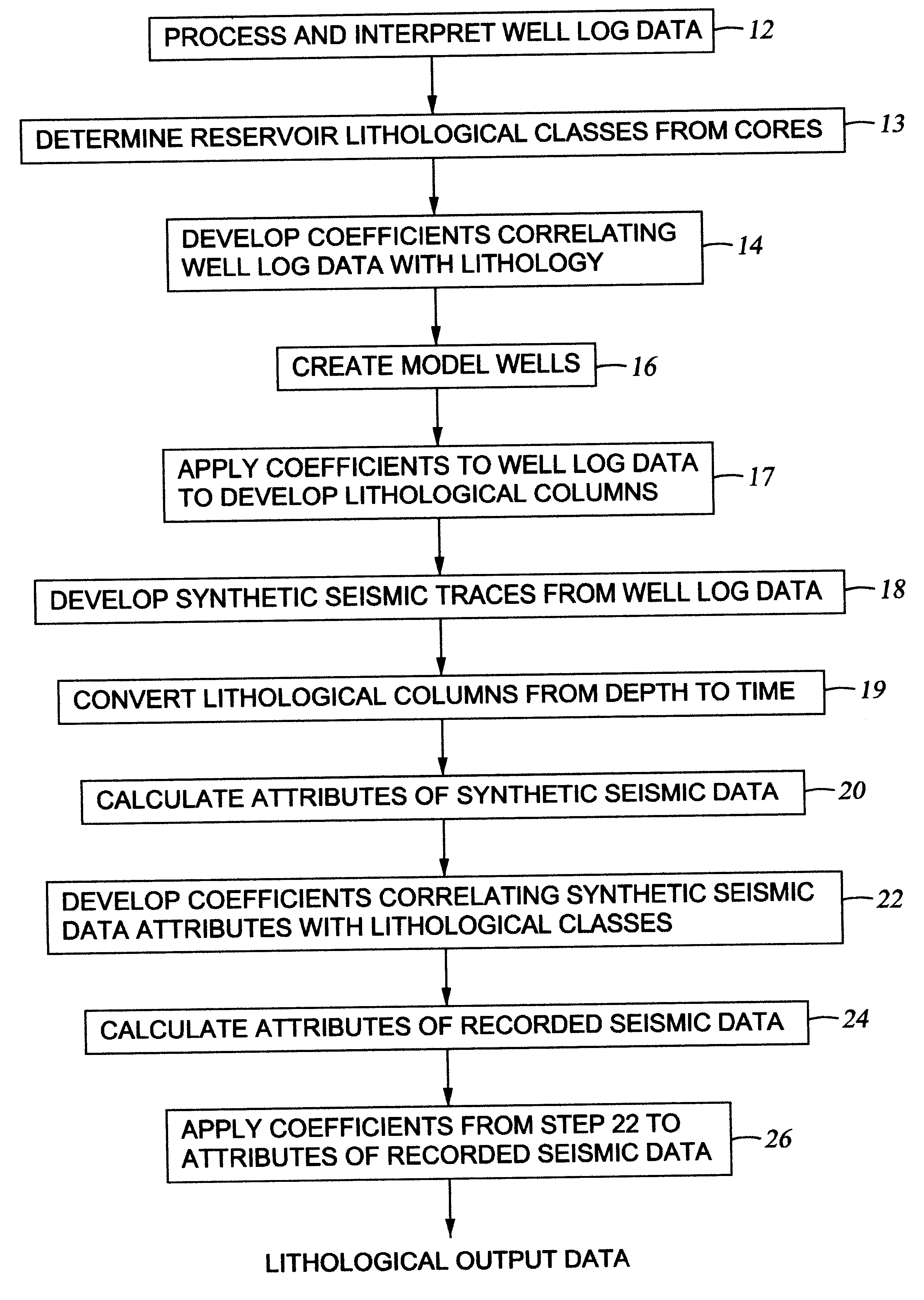
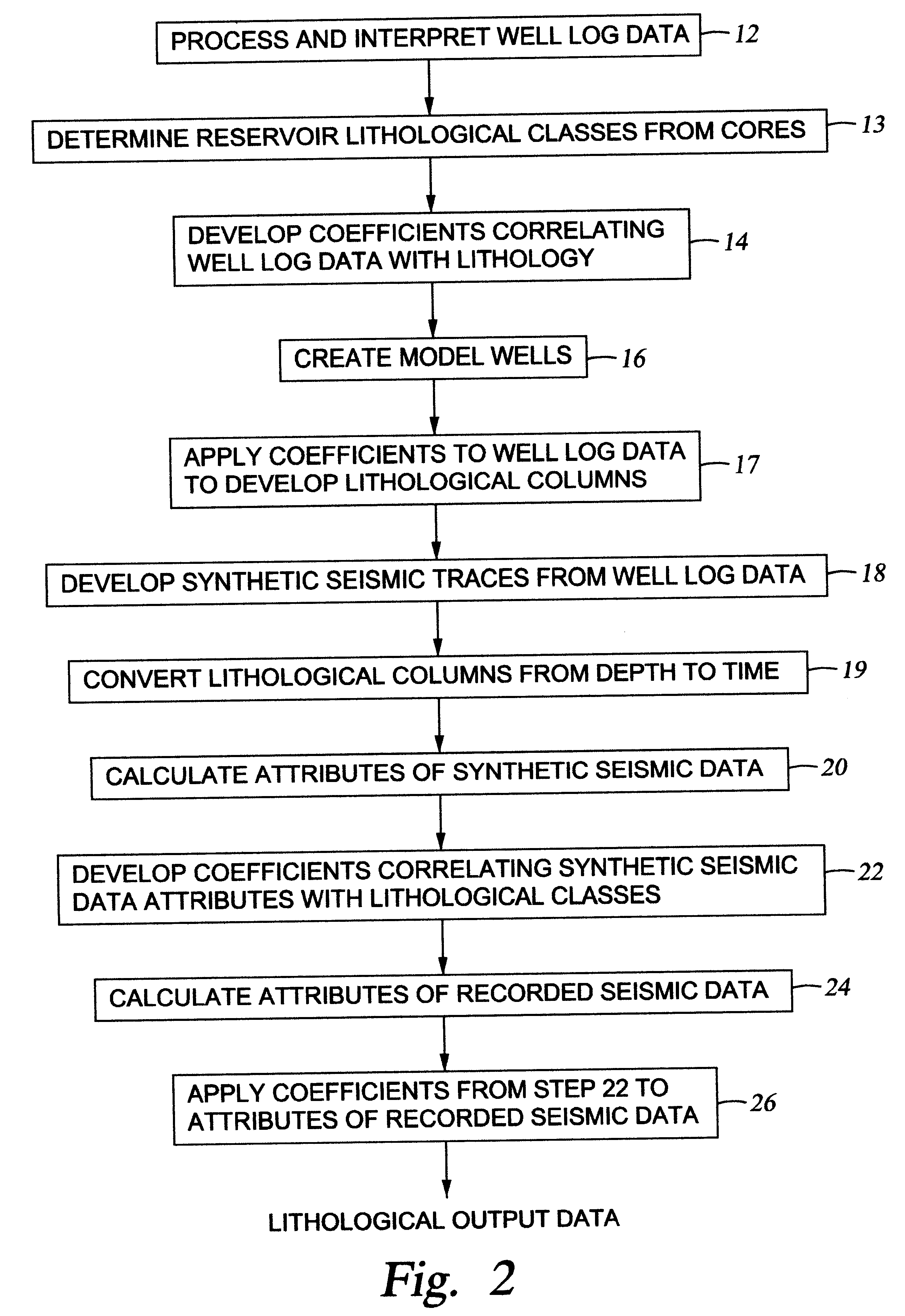
Method for generating an estimate of lithological characteristics of a region of the earth's subsurface
InactiveUS6374185B1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingLithologyWellbore
The invention in a first embodiment comprises a system for generating an estimate of lithological characteristics of a region of the earth's subsurface. A correlation is generated between attributes of synthetic seismic data calculated from log data from at least one wellbore penetrating said region and lithological information from said at least one wellbore. The correlation is then applied to recorded seismic data from the region of the earth's subsurface to generate the estimate.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Apparatus and methods for multicomponent marine geophysical data gathering
InactiveUS20040042341A1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementFloating cablesGeophoneCubic metre per second
In one embodiment the invention comprises a particle velocity sensor that includes a housing with a geophone mounted in the housing. A fluid that substantially surrounds the geophone is included within the housing. The particle velocity sensor has an acoustic impedance within the range of about 750,000 Newton seconds per cubic meter (Ns / m<3>) to about 3,000,000 Newton seconds per cubic meter (Ns / m<3>). In another embodiment the invention comprises method of geophysical exploration in which a seismic signal is generated in a body of water and detected with a plurality of co-located particle velocity sensors and pressure gradient sensors positioned within a seismic cable. The output signal of either or both of the particle velocity sensors or the pressure gradient sensors is modified to substantially equalize the output signals from the particle velocity sensors and the pressure gradient sensors. The output signals from particle velocity sensors and pressure gradient sensors are then combined.
Owner:PGS AMERICA INC
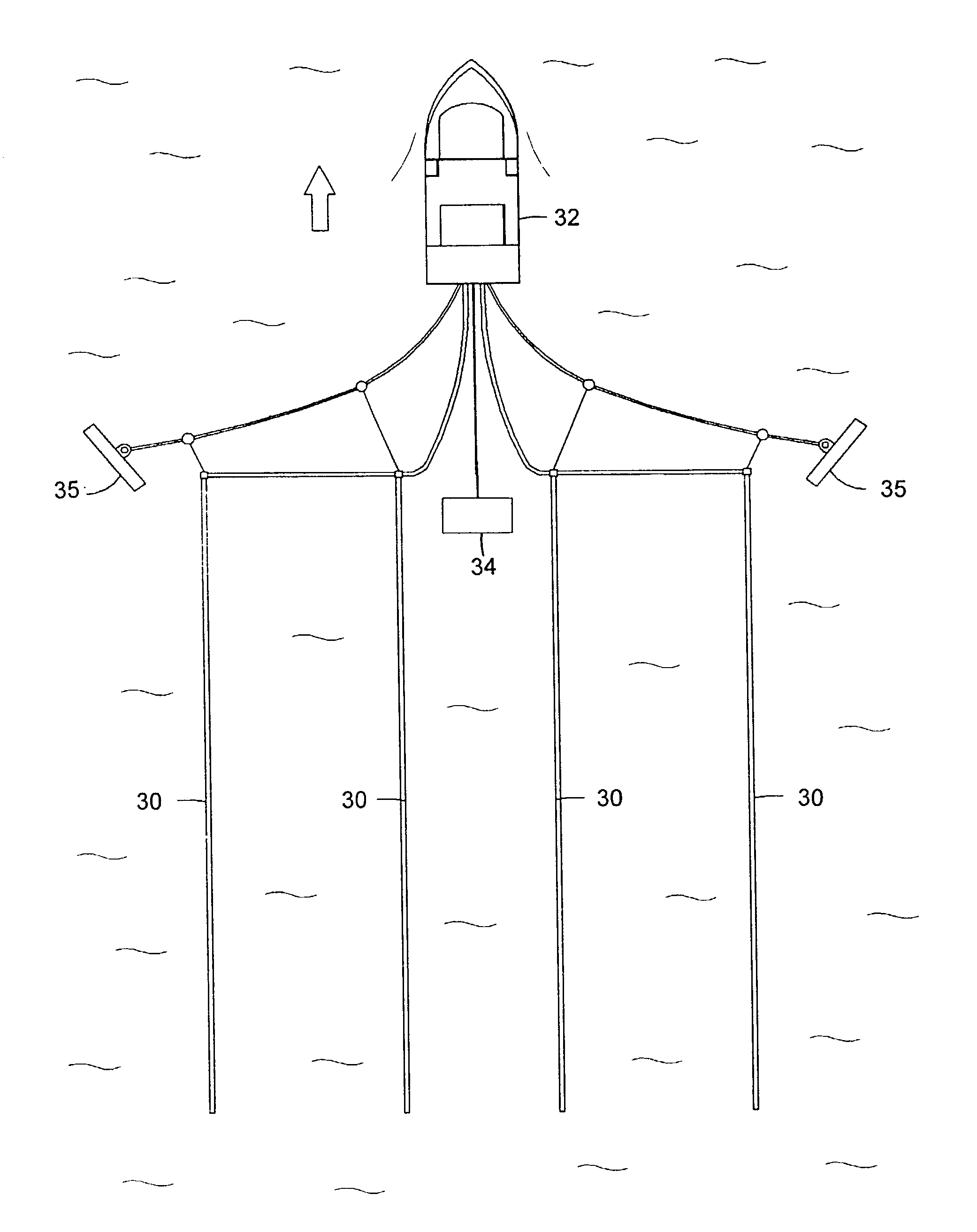
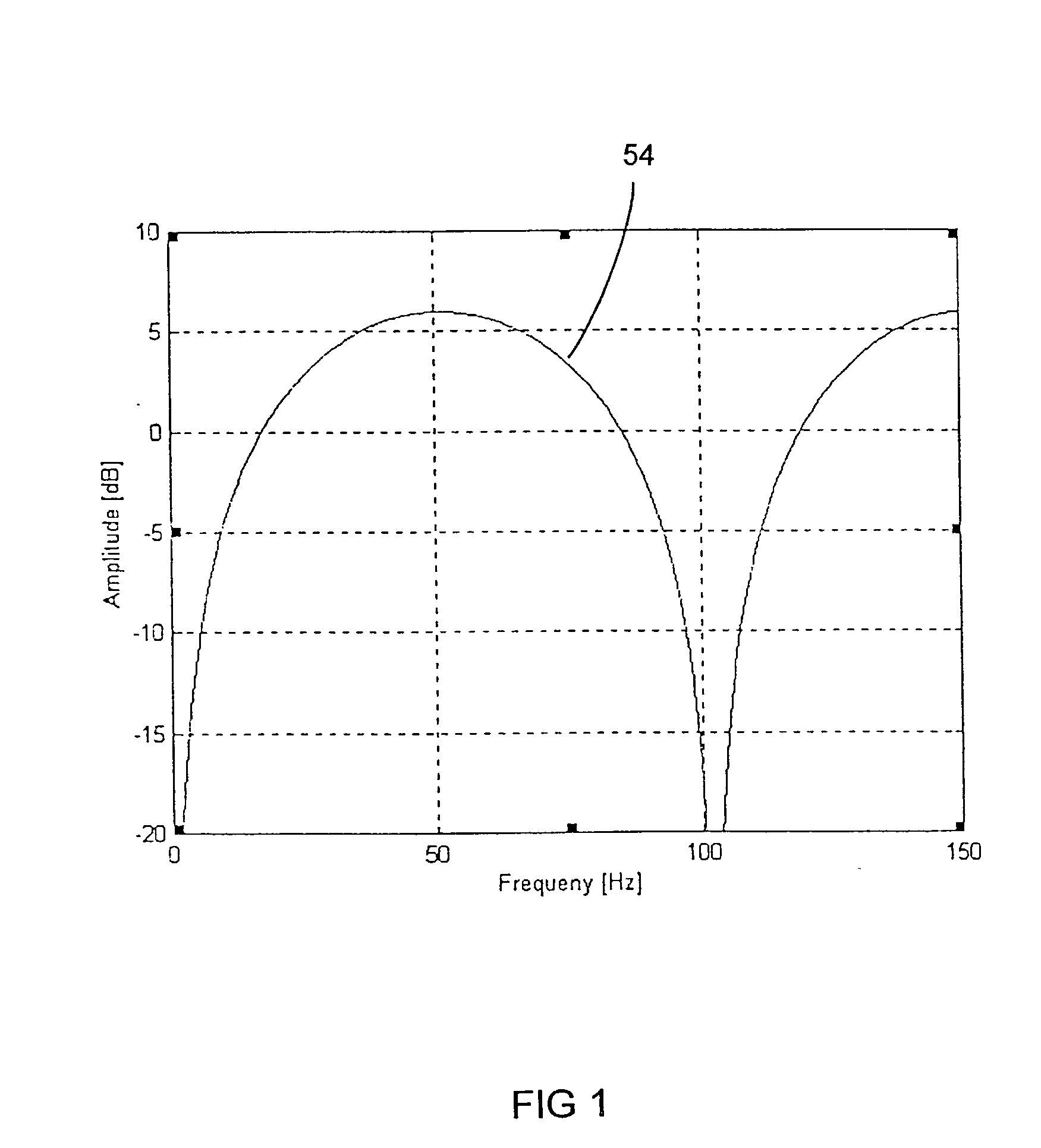
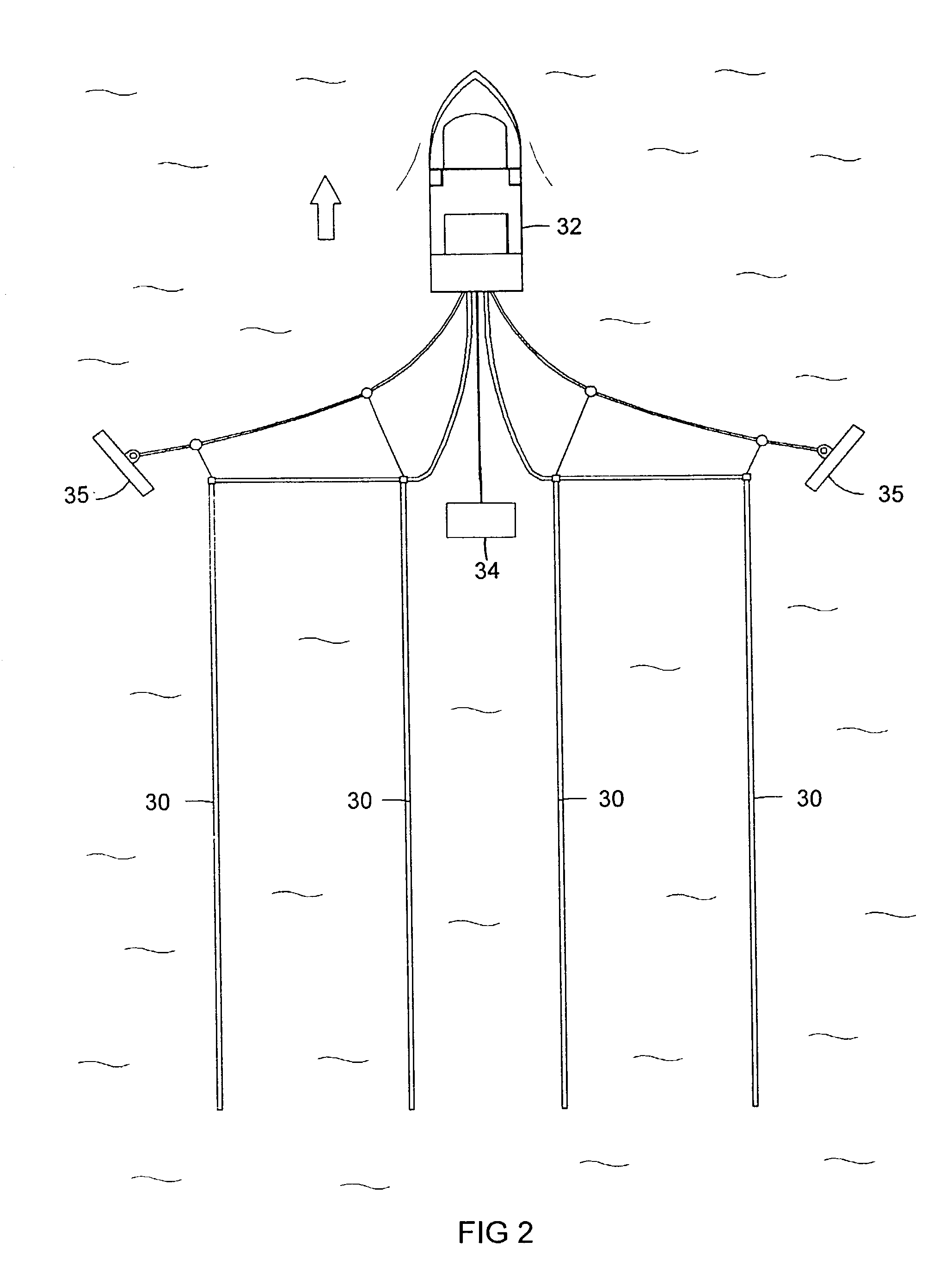
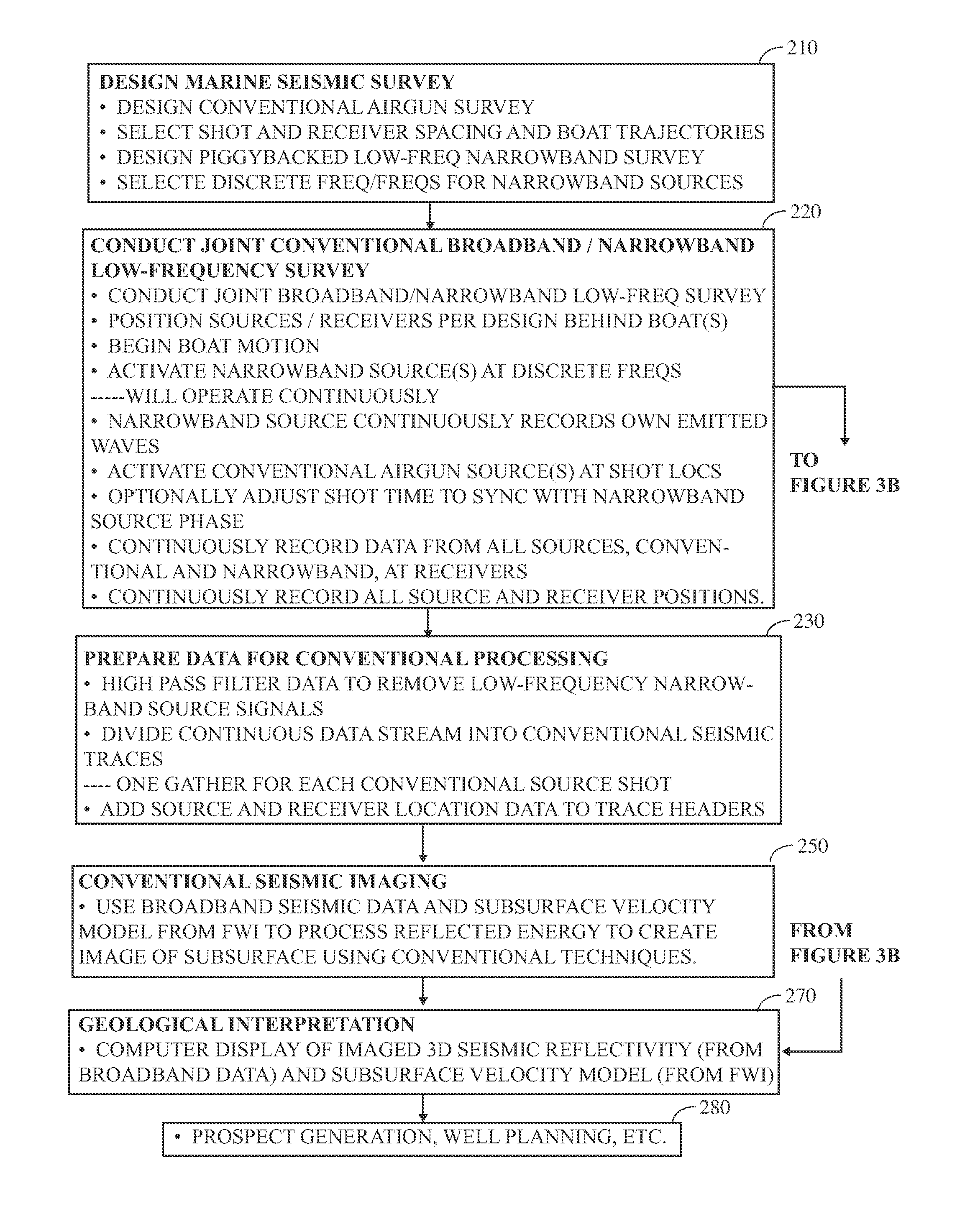
Seismic acquisition using narrowband seismic sources
ActiveUS20120155217A1Reduce crosstalkSpeed up the processSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingMonochromatic colorFull waveform
There is provided herein a system and method of seismic data collection for land and marine data that utilizes narrowband to monochromatic low-frequency non-impulsive sources designed to optimize the ability of migration / inversion algorithms to image the subsurface of the Earth, in particular, full-waveform inversion.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
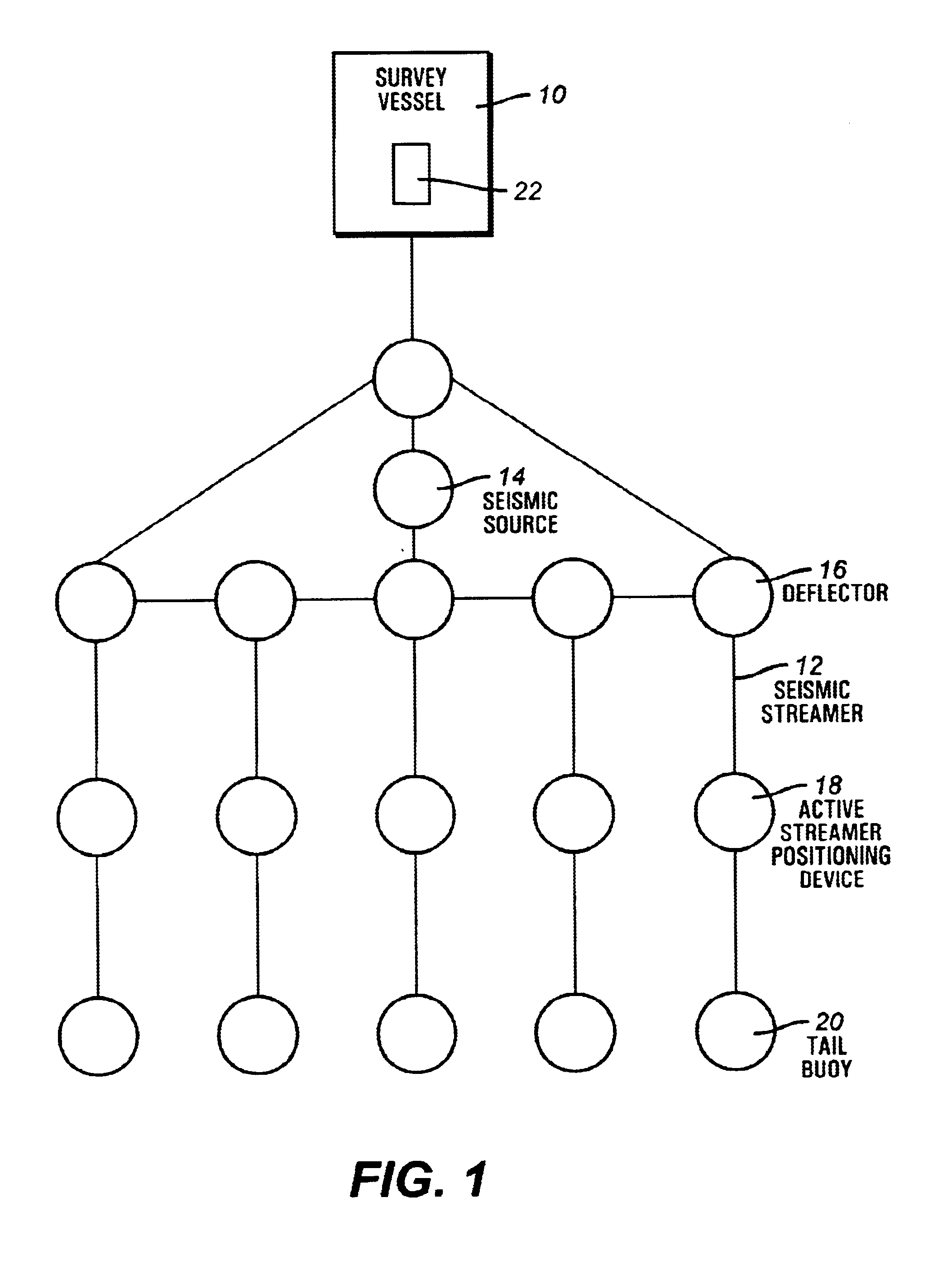
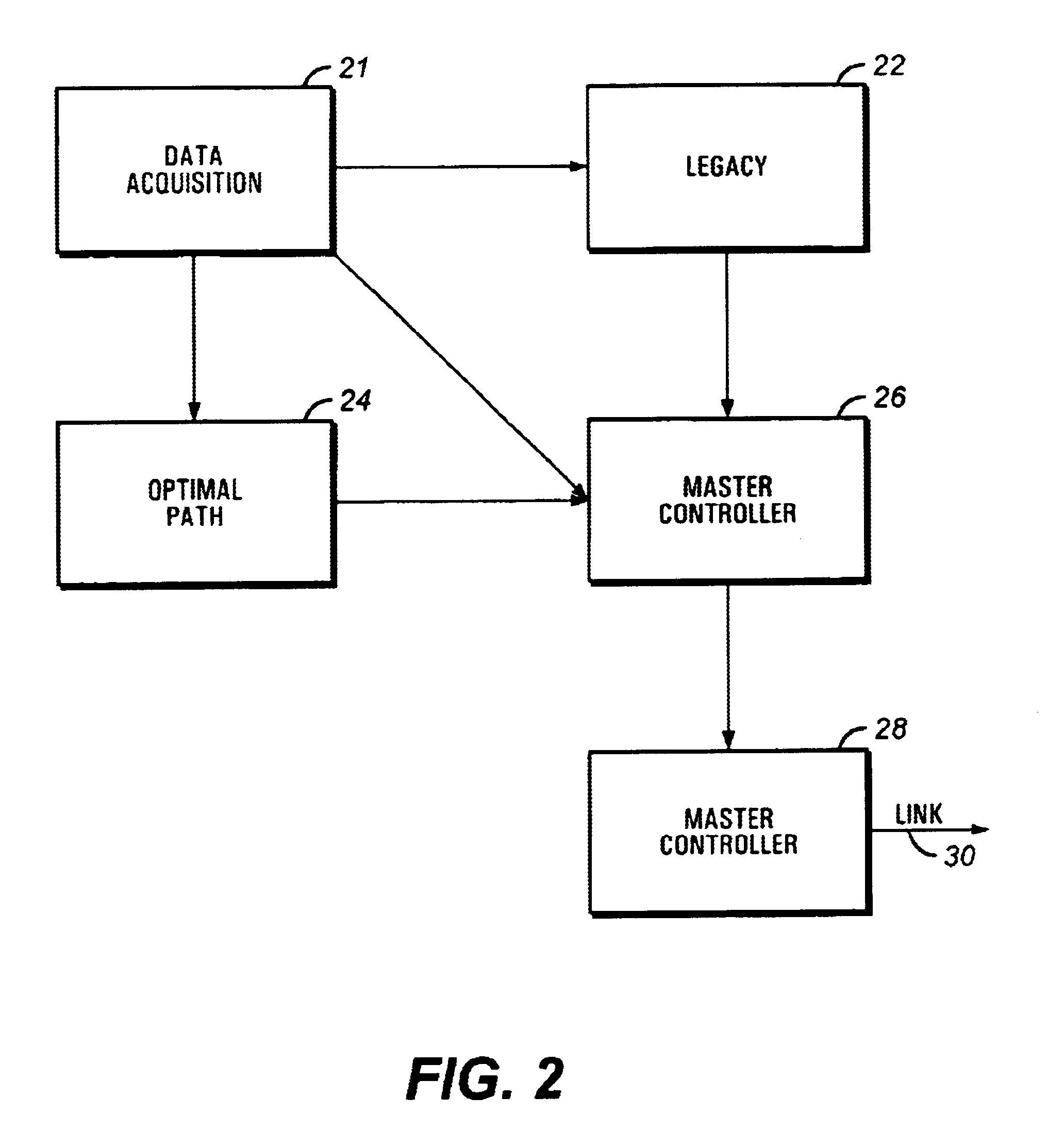
Method and apparatus for controlling and optimizing seismic data acquisition
InactiveUS6590831B1Towing/pushing equipmentSeismic signal processingMarine engineeringData acquisition
A system and method for coordinating the operation of multiple manned, remotely operated or autonomous marine vessels engaged in marine seismic data acquisition to direct cooperating vessels from one point to the next while minimizing deviations in the desired spatial configuration of assets, risk to vessels and seismic assets, and personnel and to obtain optimal midpoint coverage by evaluating inputs from subsystems providing positioning information for cooperating vessels, prospect coverage, vessel capabilities, environmental information, and navigation hazards.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC +1
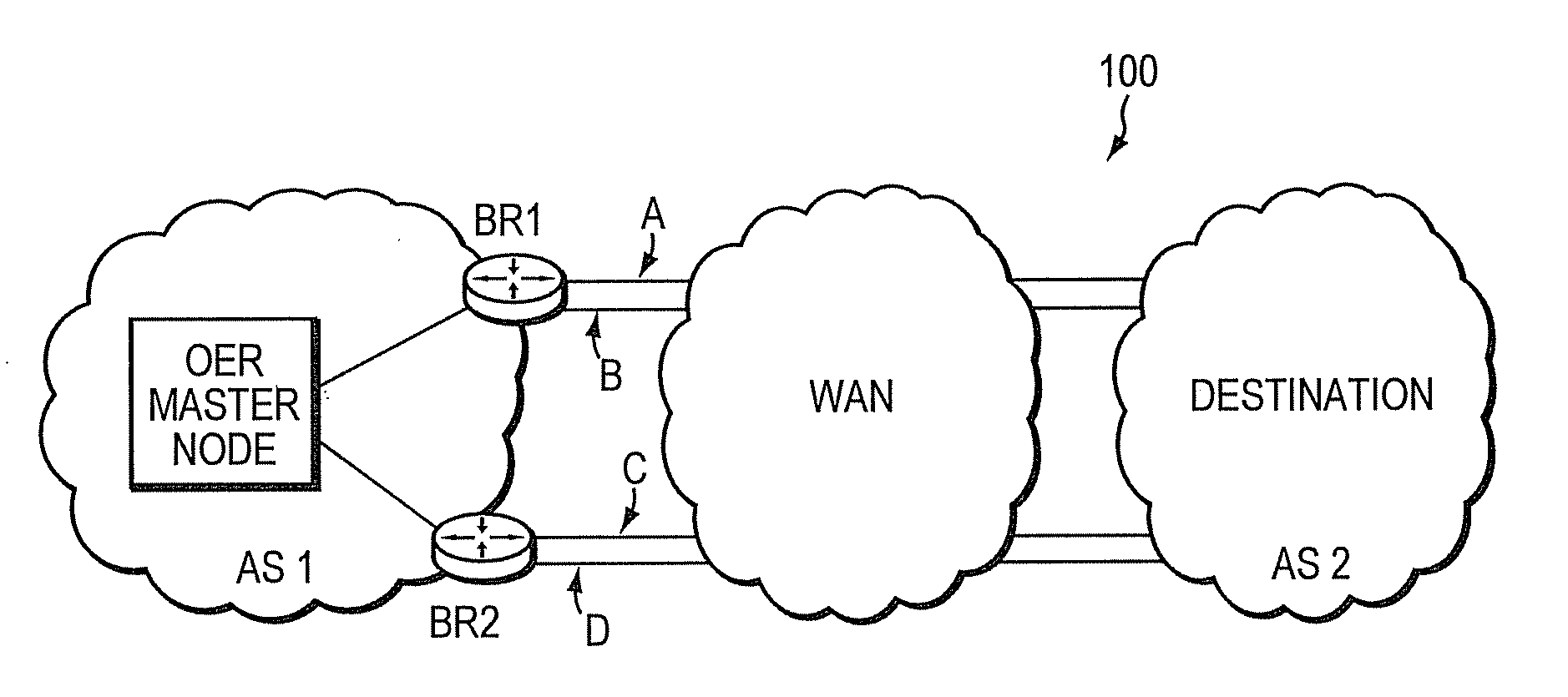
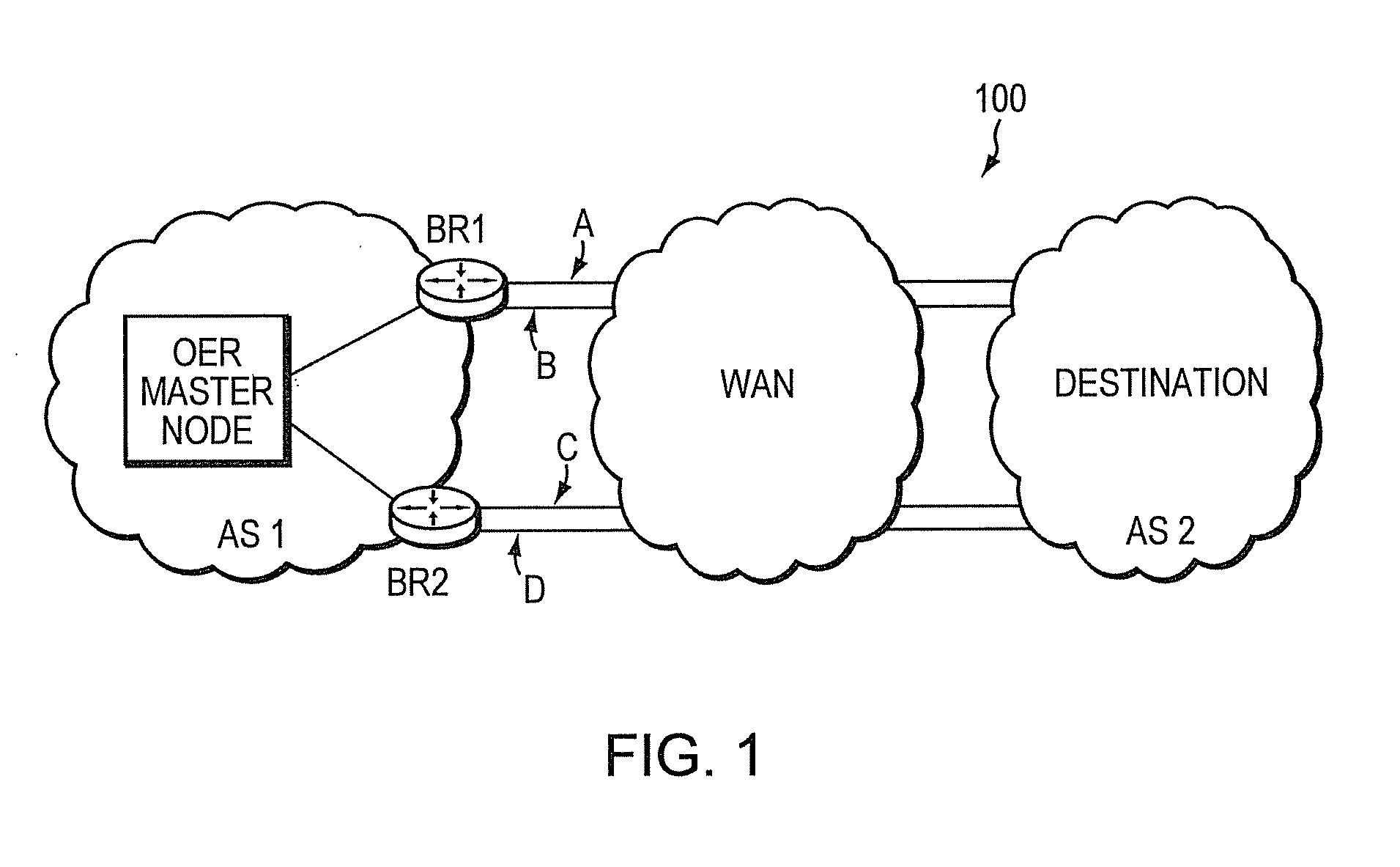
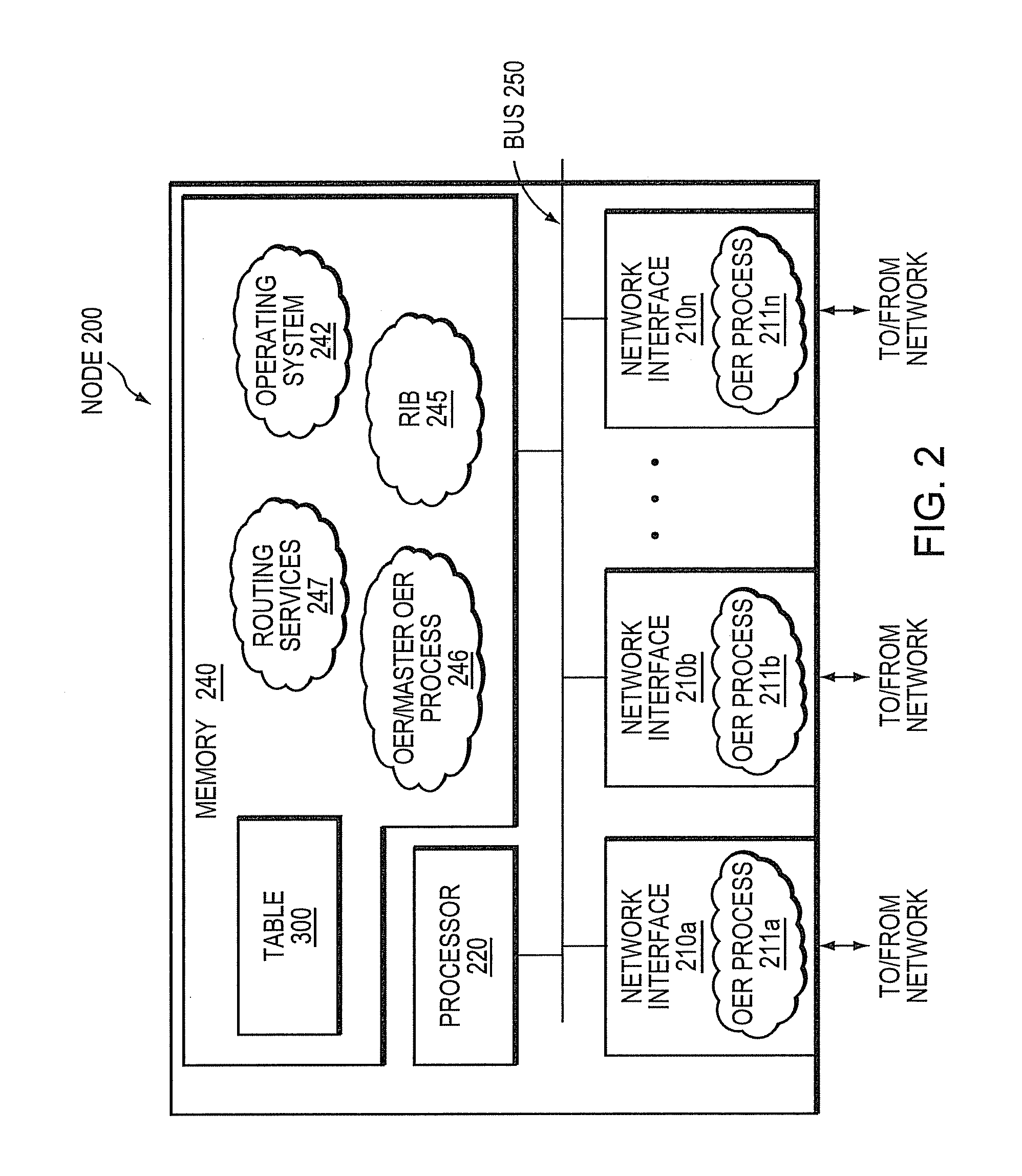
Technique for policy conflict resolution using priority with variance
ActiveUS20100265825A1Reduce varianceError preventionTransmission systemsComputer scienceLower priority
In one embodiment, a value for a option for a particular policy of a plurality of policies that are ranked in a priority order is ascertained. A variance to the value associated with the option for the particular policy is applied to define a range of acceptable values for the particular policy. A determination is made whether one or more other options exist that have values within the range of acceptable values for the particular policy. If no other options exist that have values within the range of acceptable values for the particular policy, the option is selected If other options exist that have values within the range of acceptable values for the particular policy, the ascertaining, applying and determining is repeated for a next lower priority policy of the plurality of policies to consider the other options, the repeating to occur successively until an option is selected.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Satellite and ground system for detection and forecasting of earthquakes
InactiveUS6873265B2Low costSignificant comprehensive benefitsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementEarthquake measurementNatural satelliteWide area
The present invention describes the use of a space-based Extremely Low Frequency (ELF) magnetic field detector in conjunction with ground-based network of ELF magnetic field detectors. In particular, a space based ELF detection system can be used to perform a wide area search and find precursor earthquake signals in both known and unknown earthquake zones, and a ground-based network of ELF detectors can be used to verify that the signals are indeed earthquake generated signals. The use of this invention will minimize cost and manpower necessary to effectuate an accurate and reliable earthquake detection system.
Owner:STELLAR SOLUTIONS
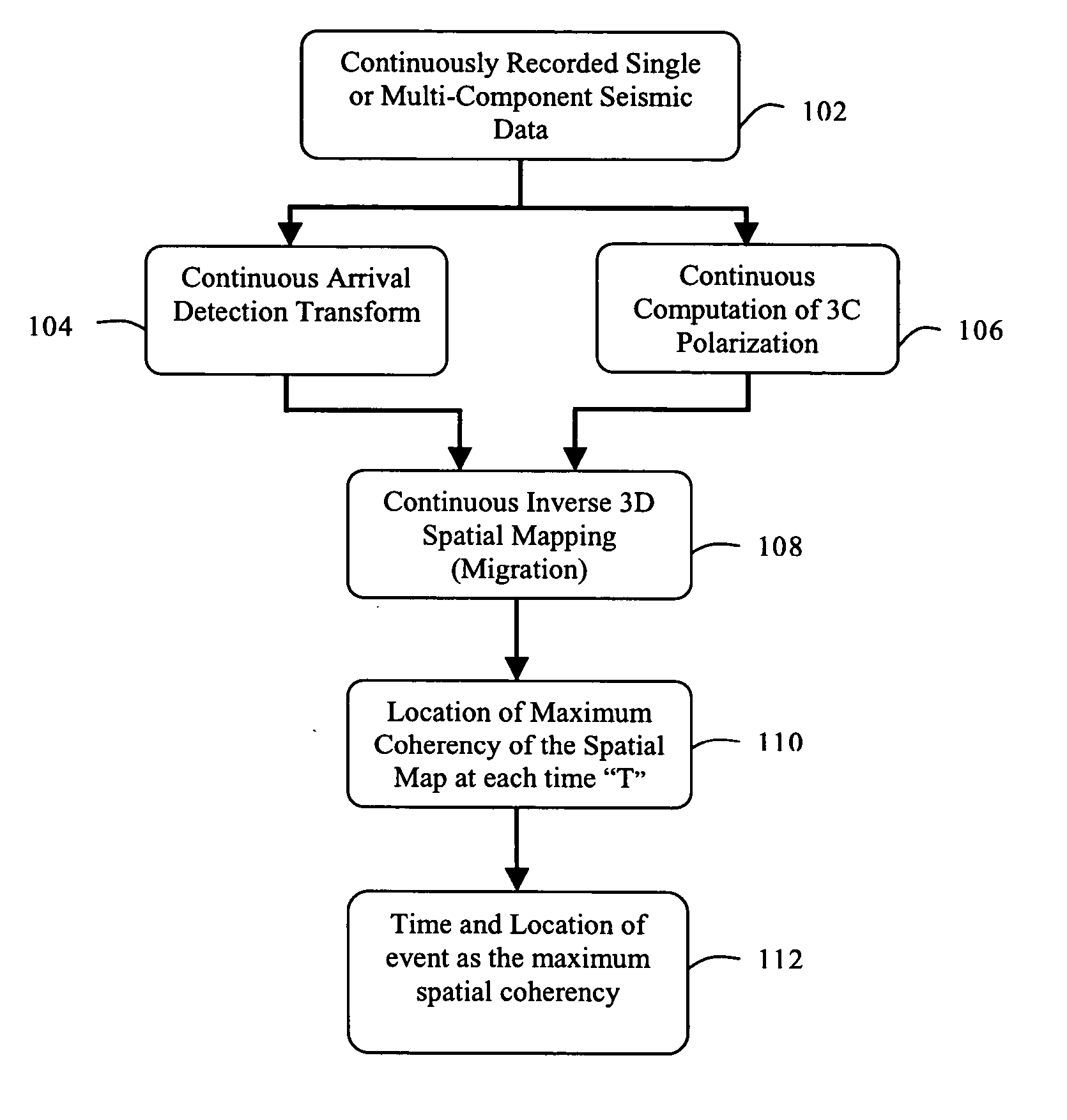
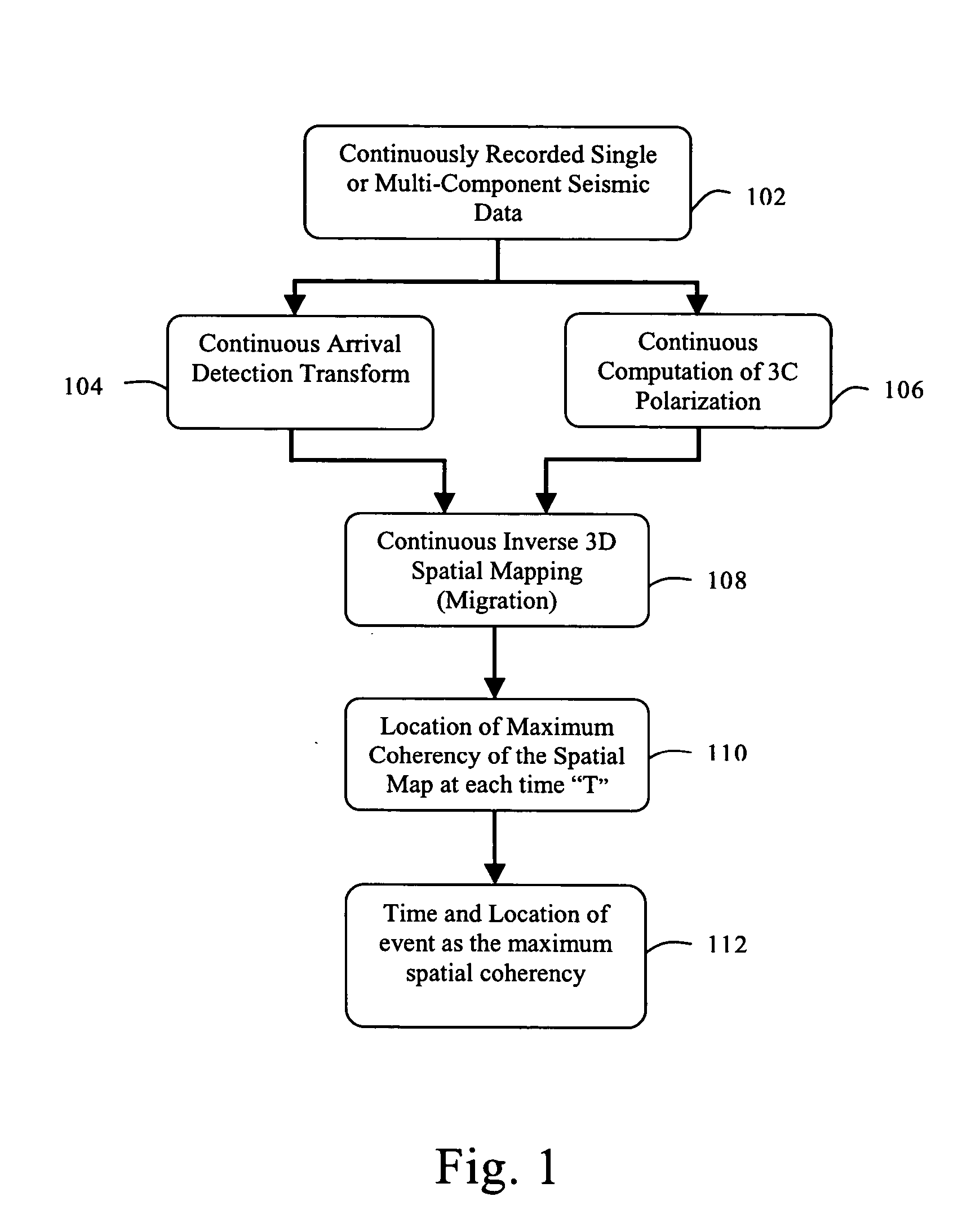
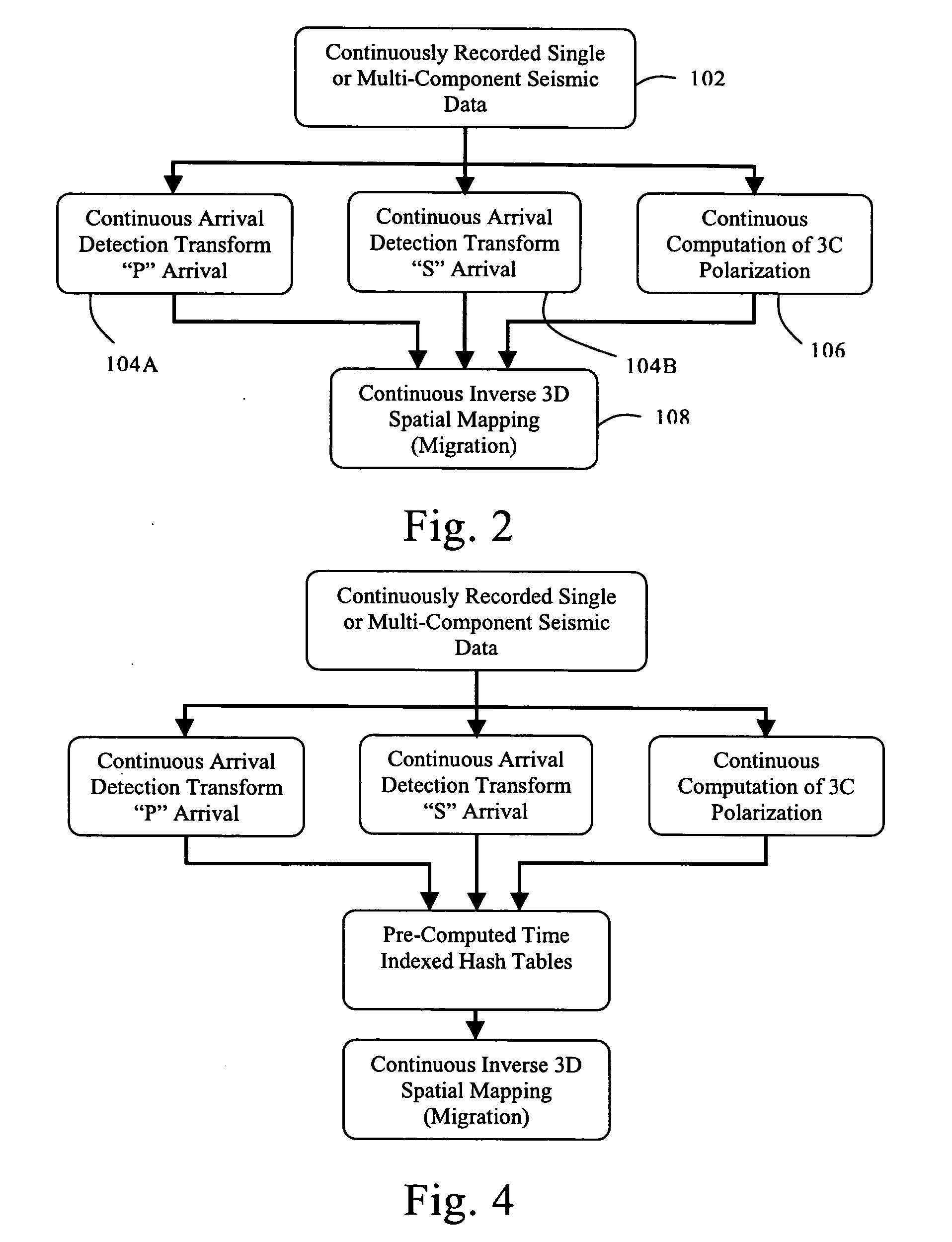
Microseismic event detection and location by continuous map migration
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
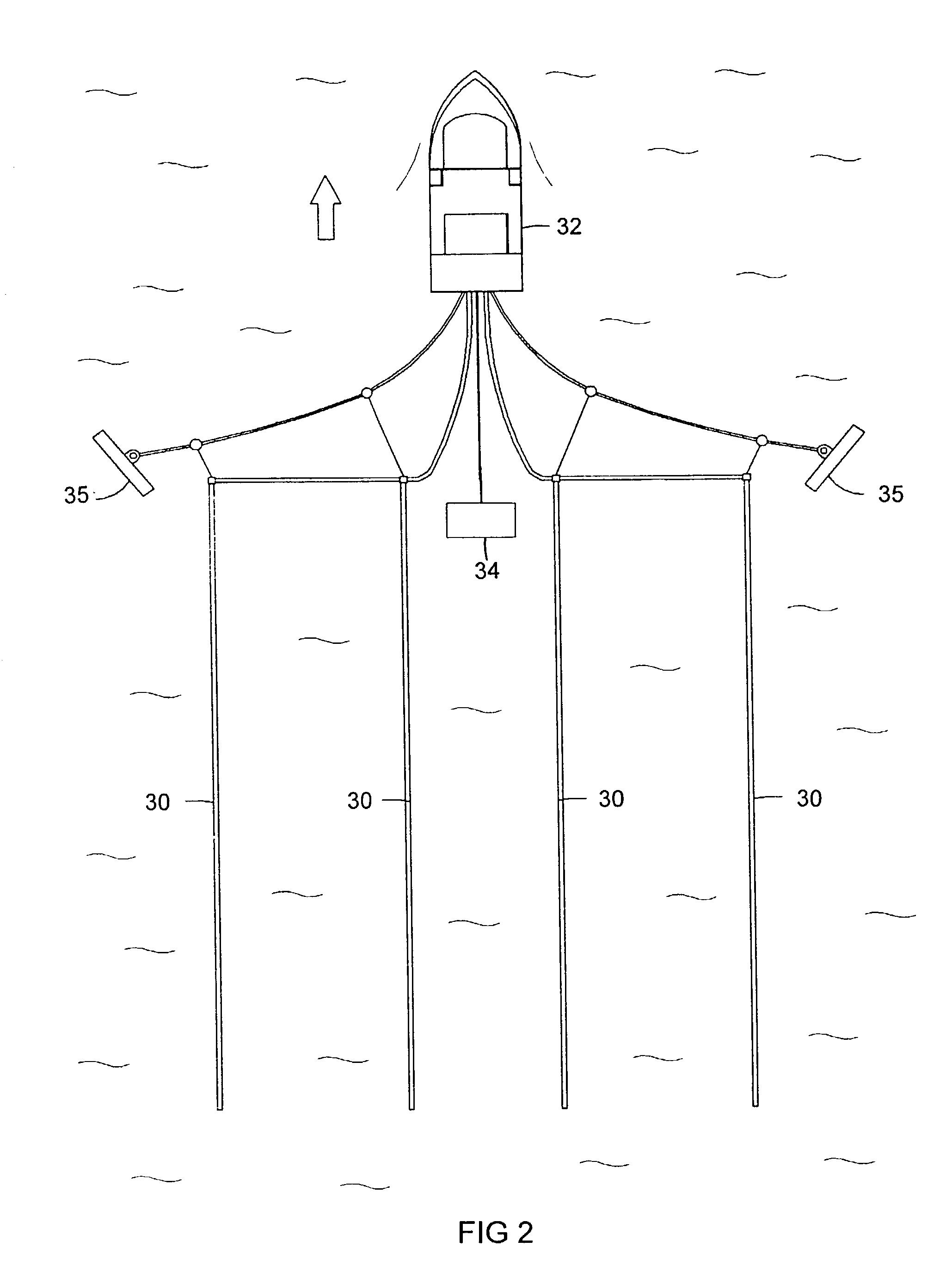
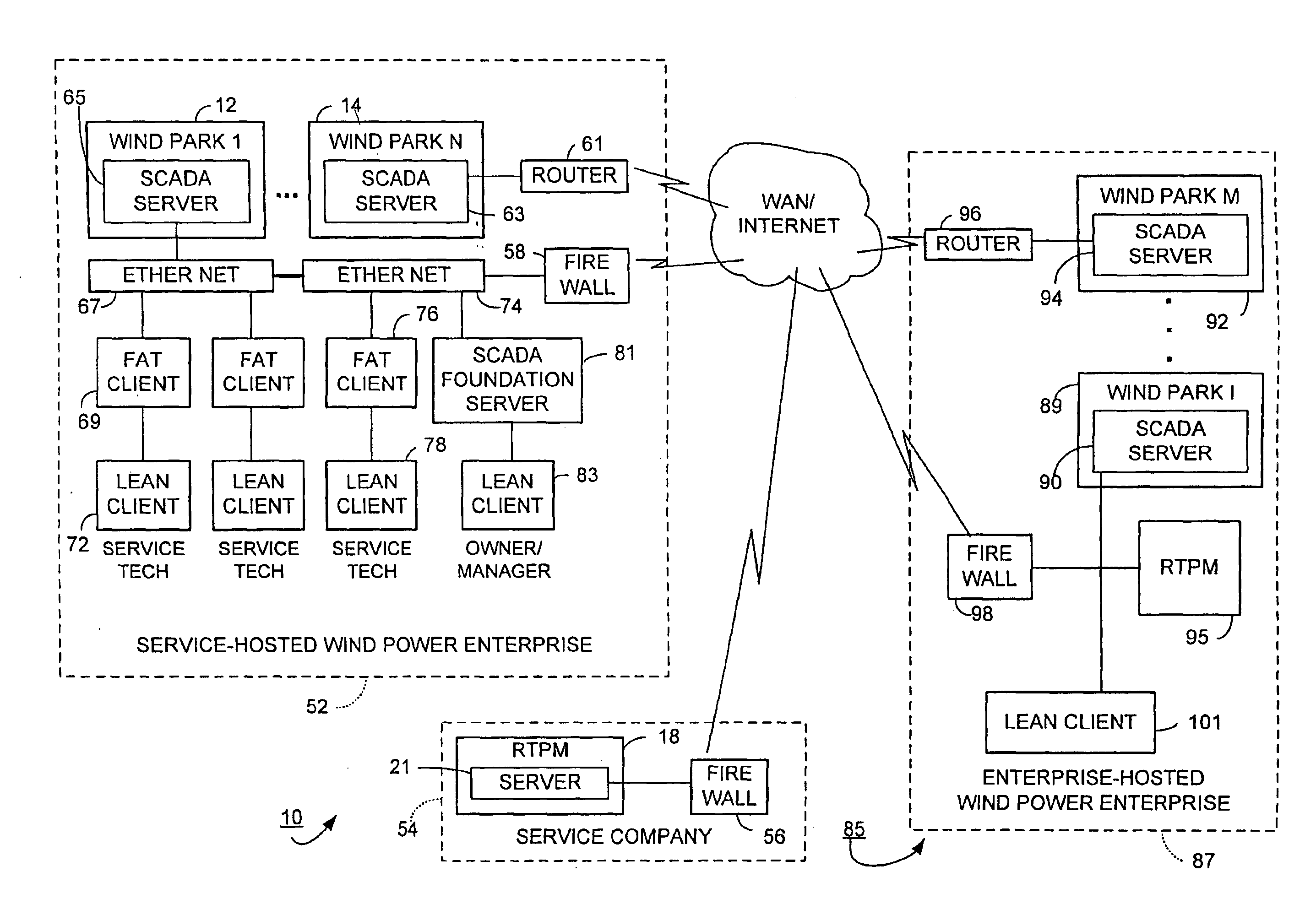
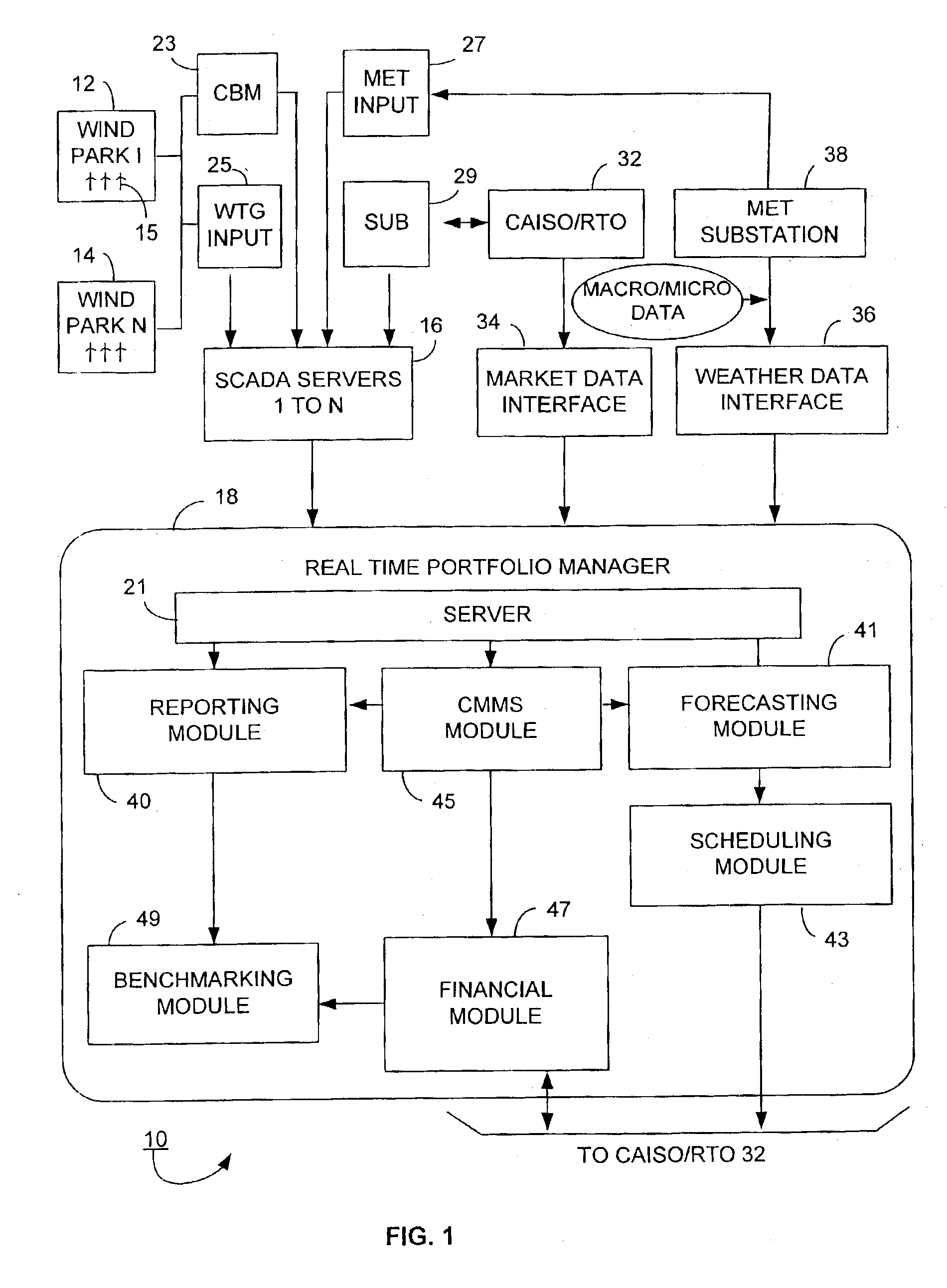
Wind power management system and method
According to certain disclosed embodiments of the invention, there is provided a wind power management system to monitor performance of wind turbine generators situated in wind farms, each having a number of wind turbine generators. A real-time wind power portfolio manager receives and stores in real-time data being produced by the wind turbine generator parks. The manager has a reporting module for generating profile reports for the performance of the wind turbine generators. The manager has a server to provide the reports on-line regarding the wind turbine generators. The server stores the real-time data to enable the reports to be based on the history of the project for each one of the parks.
Owner:SEAWEST HLDG
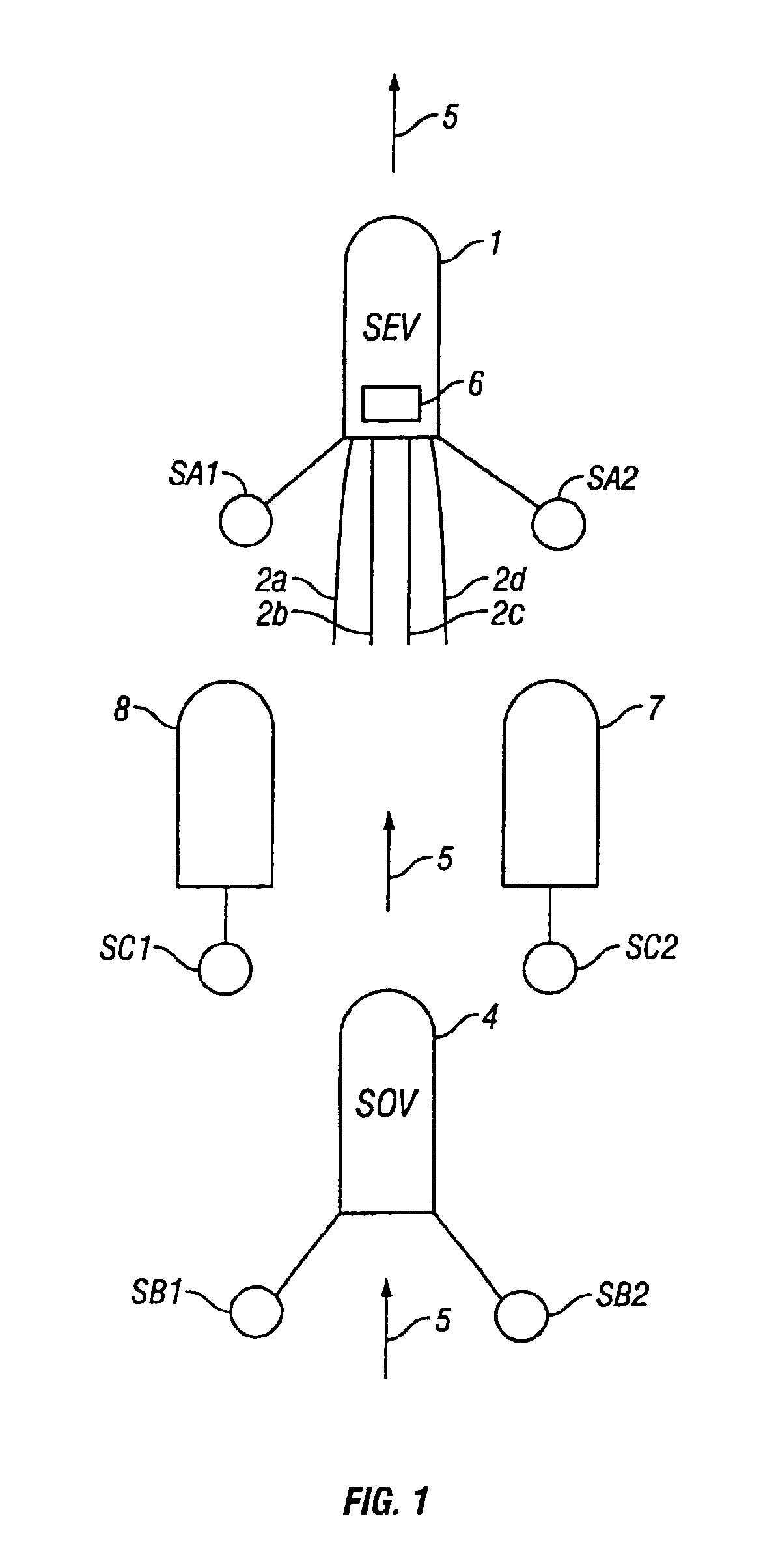
Method and system for acquiring marine seismic data using multiple seismic sources
InactiveUS6906981B2Easy to foldIncrease the lengthSeismic data acquisitionSeismic energy generationSeismic surveySurveyor
A method for seismic surveying is disclosed which includes towing a first seismic energy source and at least one seismic sensor system. A second seismic energy source is towed at a selected distance from the first source. The first seismic energy source and the second seismic energy source are actuated in a plurality of firing sequences. Each of the firing sequences includes firing of the first source, waiting a selected time firing the second source and recording signals generated by the seismic sensor system. The selected time between firing the first source and the second source is varied between successive ones of the firing sequences. The firing times of the first and second source are indexed so as to enable separate identification of seismic events originating from the first source and seismic events originating from the second source in detected seismic signals.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Smoke detection methods, devices, and systems
InactiveUS20050190055A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTelephonic communicationSmoke detectorsEngineering
The present invention is directed to a system and method for accessing home monitoring devices remotely via a distributed wide-area network (WAN). More specifically, the present invention is directed towards a smoke detector system, which monitors for the presence of smoke and communicates the smoke condition to a remote location. The smoke detection system comprises a smoke detection device connected to a communication device. The smoke detection device outputs a signal or a change in a signal upon detection of smoke. This signal or change in signal is monitored by the communication device. The smoke condition is then communicated to the remote central location. Other embodiments are also claimed and described.
Owner:HUNT TECH INC
Active separation tracking and positioning system for towed seismic arrays
InactiveUS6691038B2Facilitate detachment and removalMaintain positionSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasArray data structureControl system
A method and apparatus comprising an active control system for a towed seismic streamer array that enables any relative positional control of any number of towed seismic streamers. The streamer positions are controlled horizontally and vertically using active control units positioned within the seismic array. The three component (x, y, z) position of each streamer element, relative to the vessel and relative to each other is controlled, tracked and stored during a seismic data acquisition run. The present invention enables a seismic array to be maneuvered as the towing vessel maintains course, enables maintenance of specific array position and geometry in the presence of variable environmental factors and facilitates four-dimensional seismic data acquisition by sensing and storing the position of the array and each array element with respect to time.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
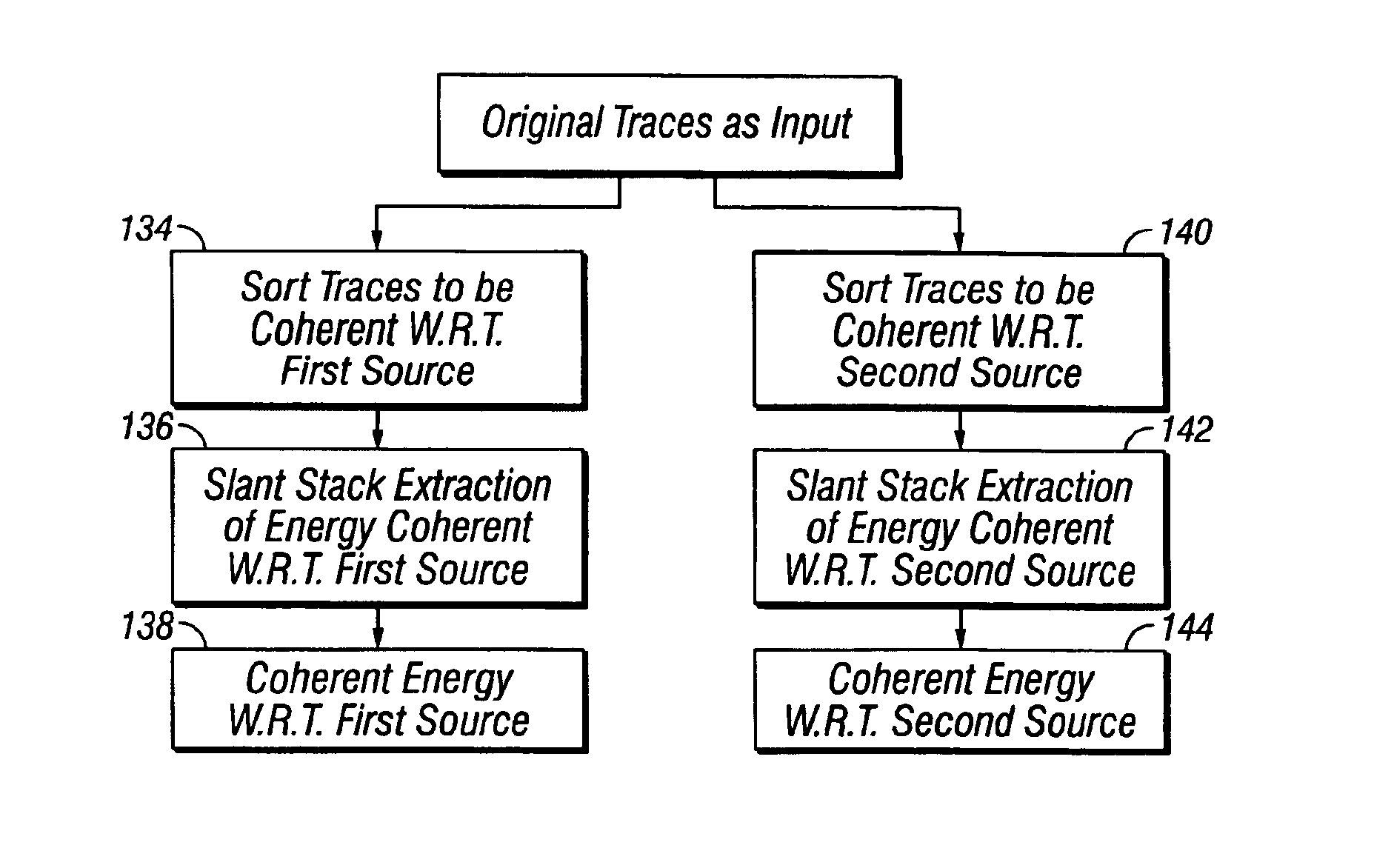
Method for separating seismic signals from two or more distinct sources
InactiveUS6882938B2Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsSpatial directionSeismic energy
A method is disclosed for separating energy resulting from actuating at least two different seismic energy sources from seismic signals. The sources are actuated to provide a variable time delay between successive actuations of a first one and a second one of the sources. The method includes sorting the seismic signals such that events therein resulting from actuations of the first source are substantially coherent in all spatial directions, coherency filtering the first source coherency sorted signals, sorting the seismic signals such that events therein resulting from actuations of the second source are substantially coherent in all spatial directions, and coherency filtering the second source coherency sorted signals.
Owner:PGS AMERICA INC
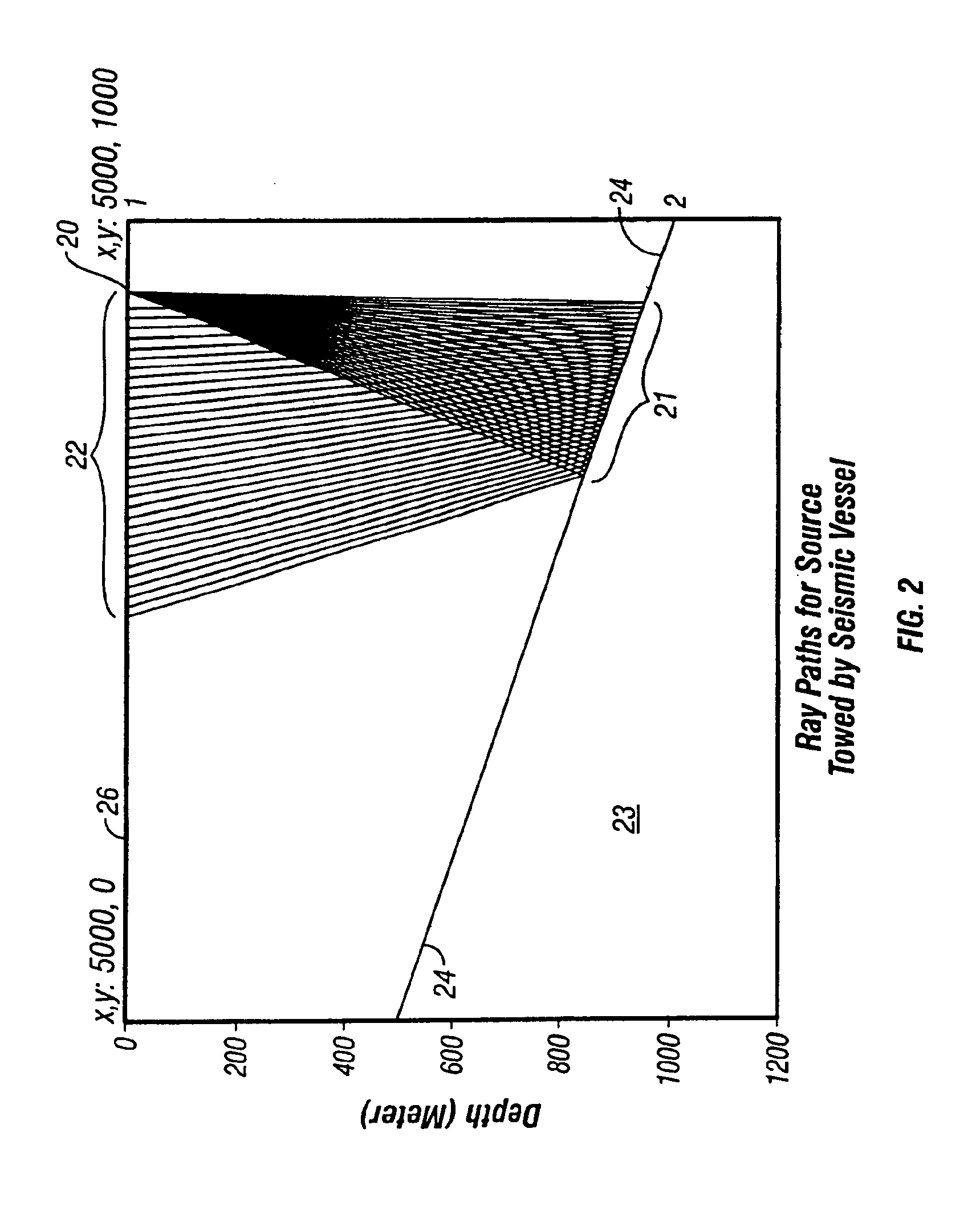
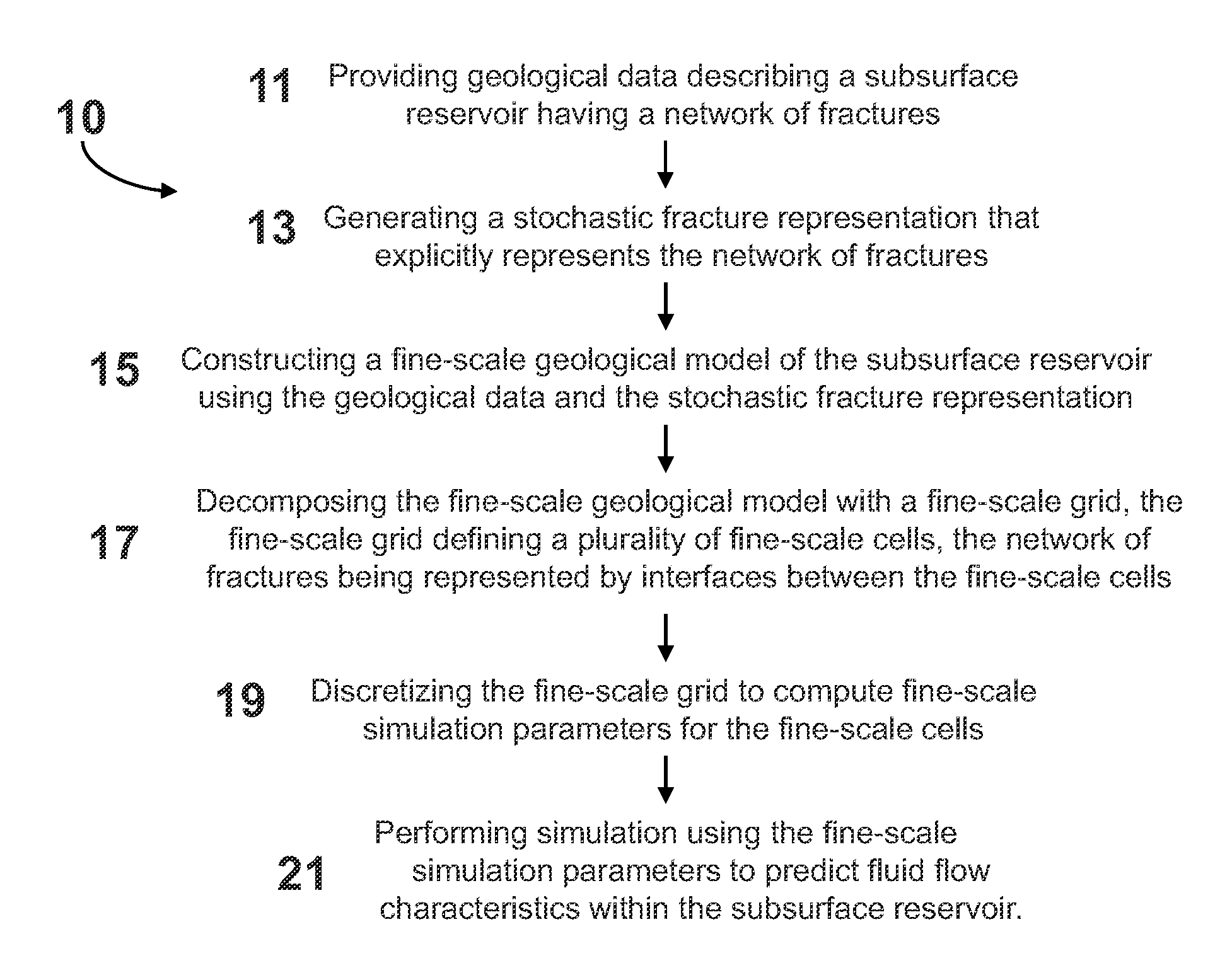
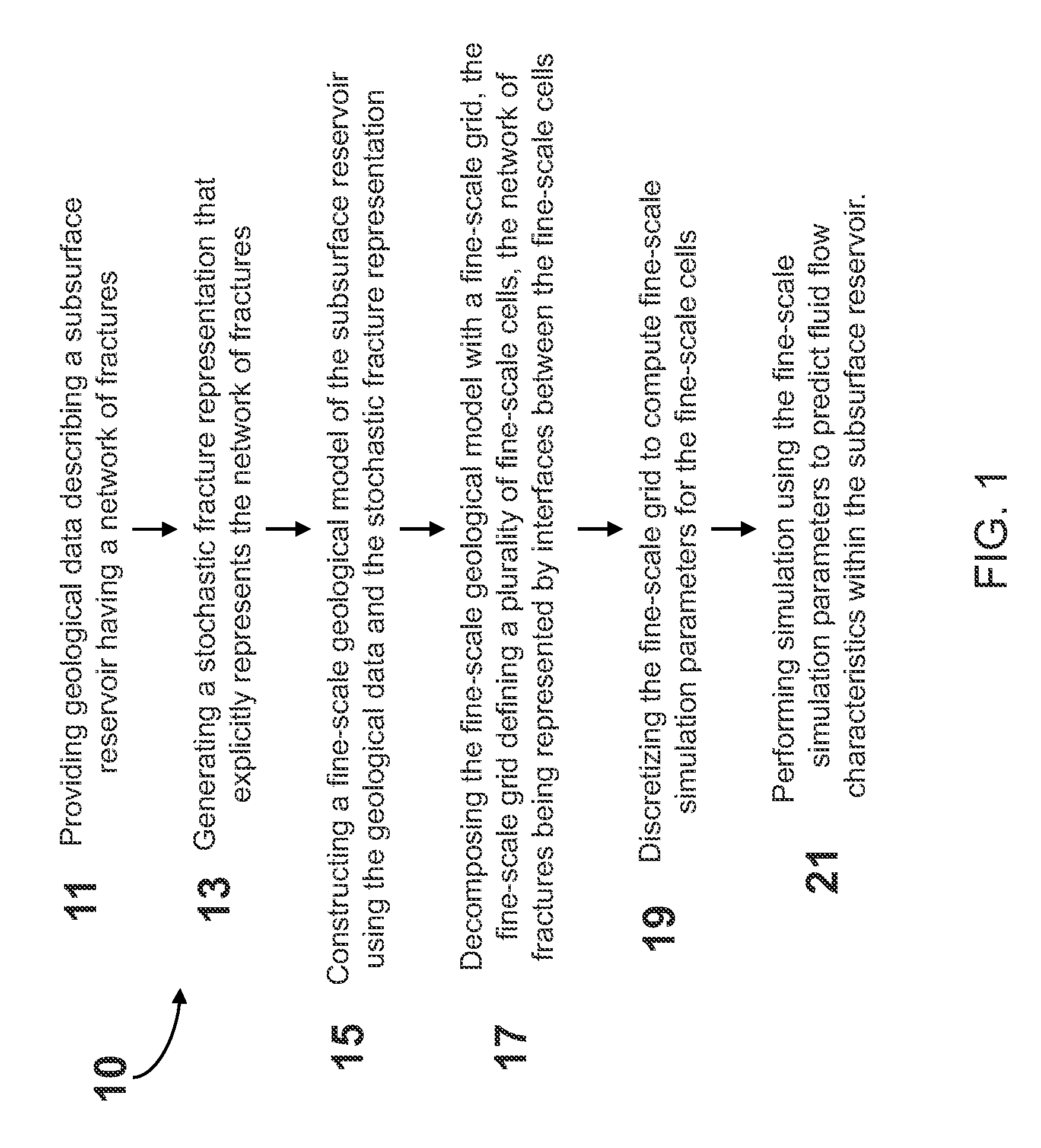
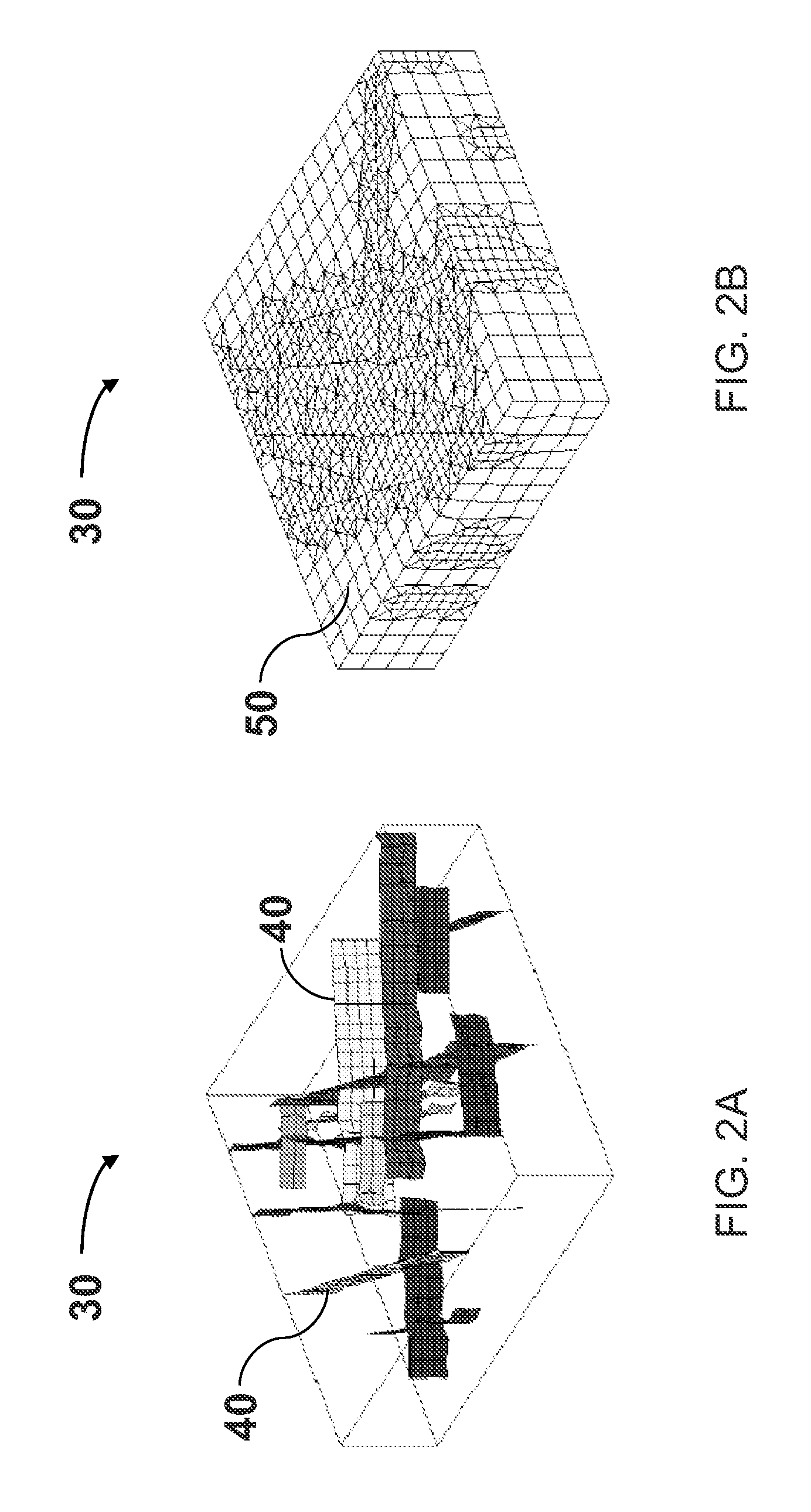
System and method for predicting fluid flow characteristics within fractured subsurface reservoirs
A system and method having application notably towards predicting fluid flow characteristics within fractured subsurface reservoirs. The system and method include steps of reservoir characterization, gridding, discretization, and simulation of geologically realistic models describing the fractured subsurface reservoirs. A stochastic fracture representation that explicitly represents a network of fractures within a subsurface reservoir is constructed and used to build a fine-scale geological model. The model is then gridded such that the network of fractures is represented by interfaces between the fine-scale cells. The model is the discretized and simulated. Simulation can be on a fine-scale or on an upscaled course-scale to produce efficient and reliable prediction of fluid flow characteristics within the subsurface reservoir.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
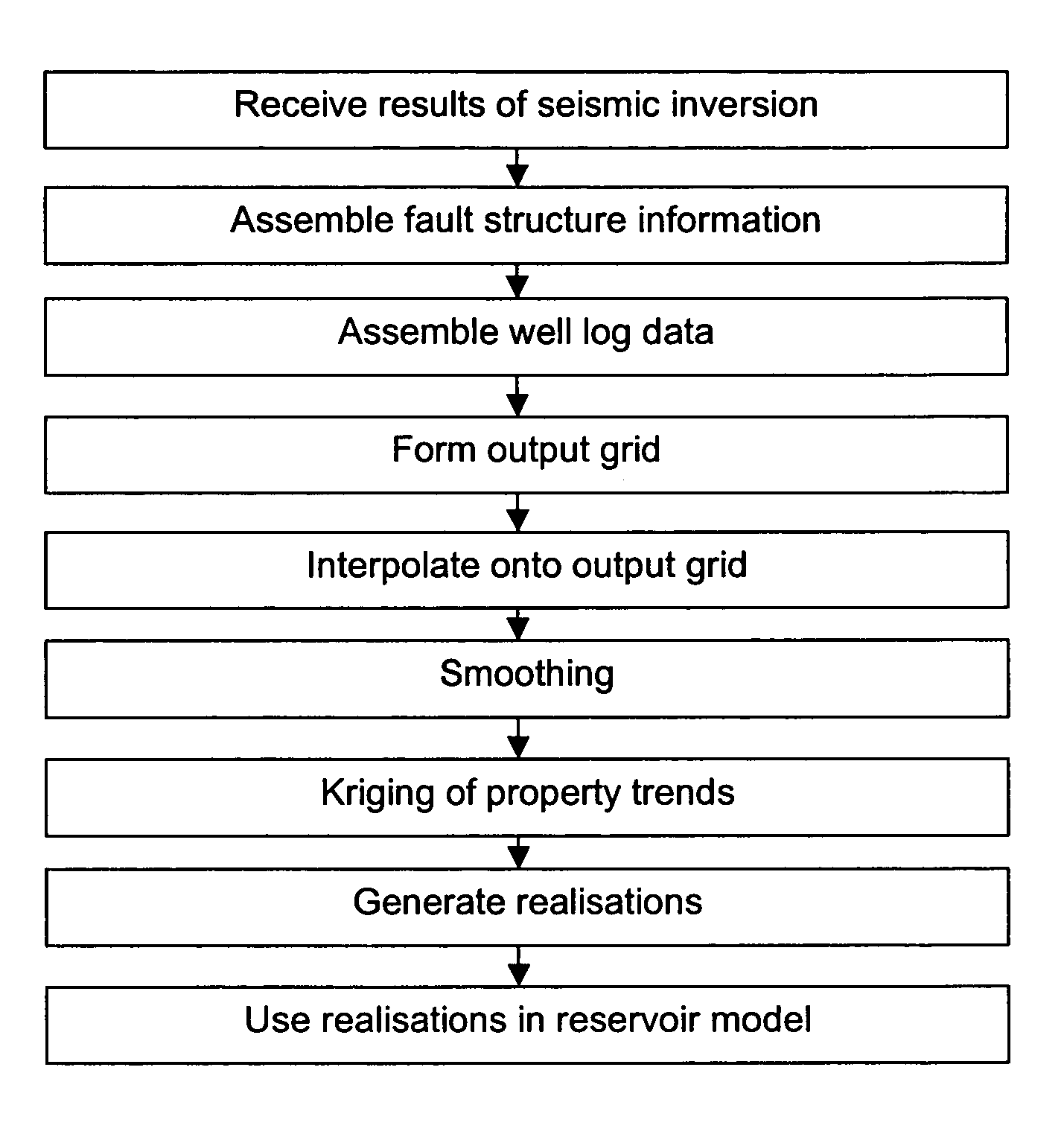
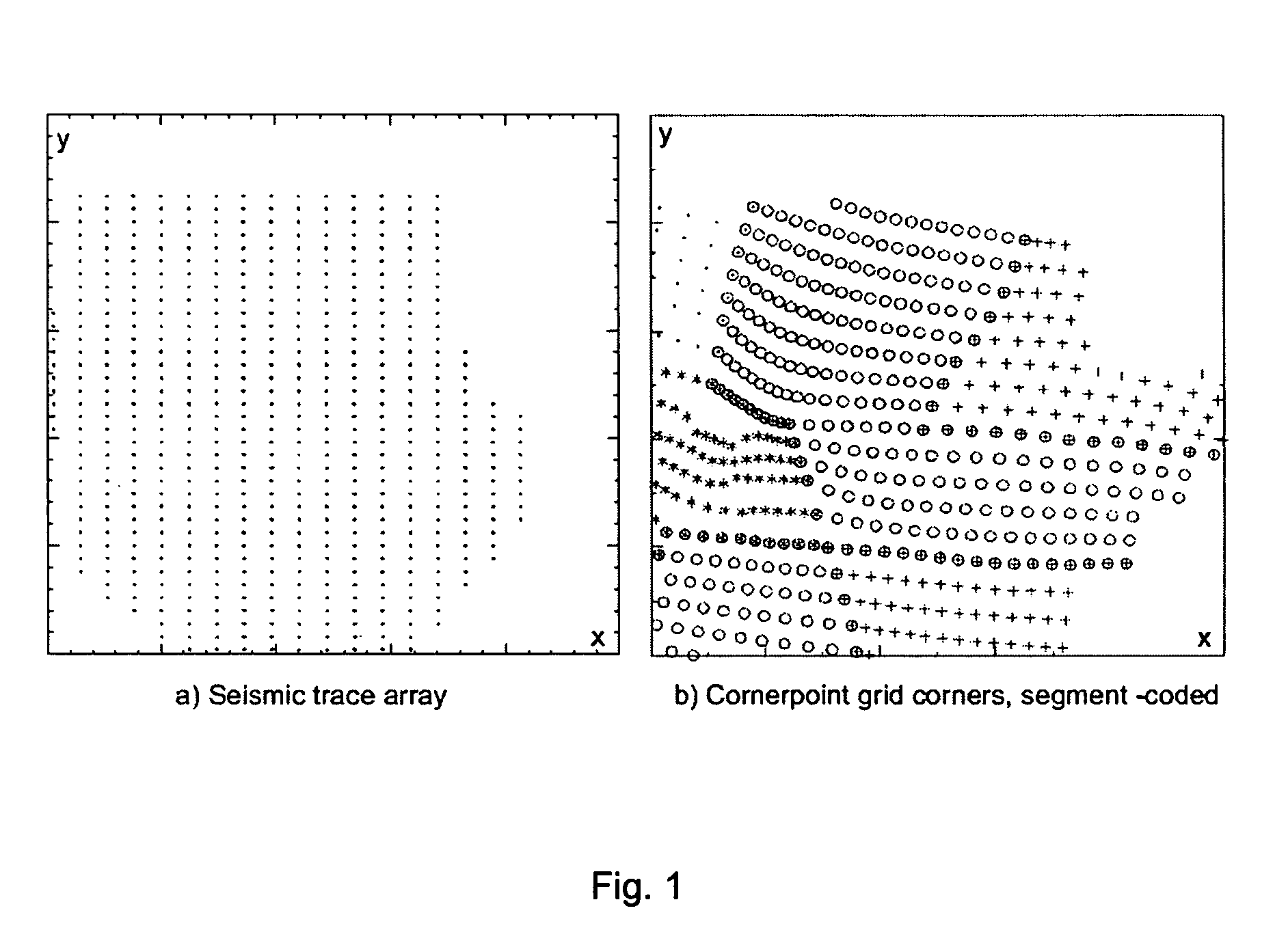
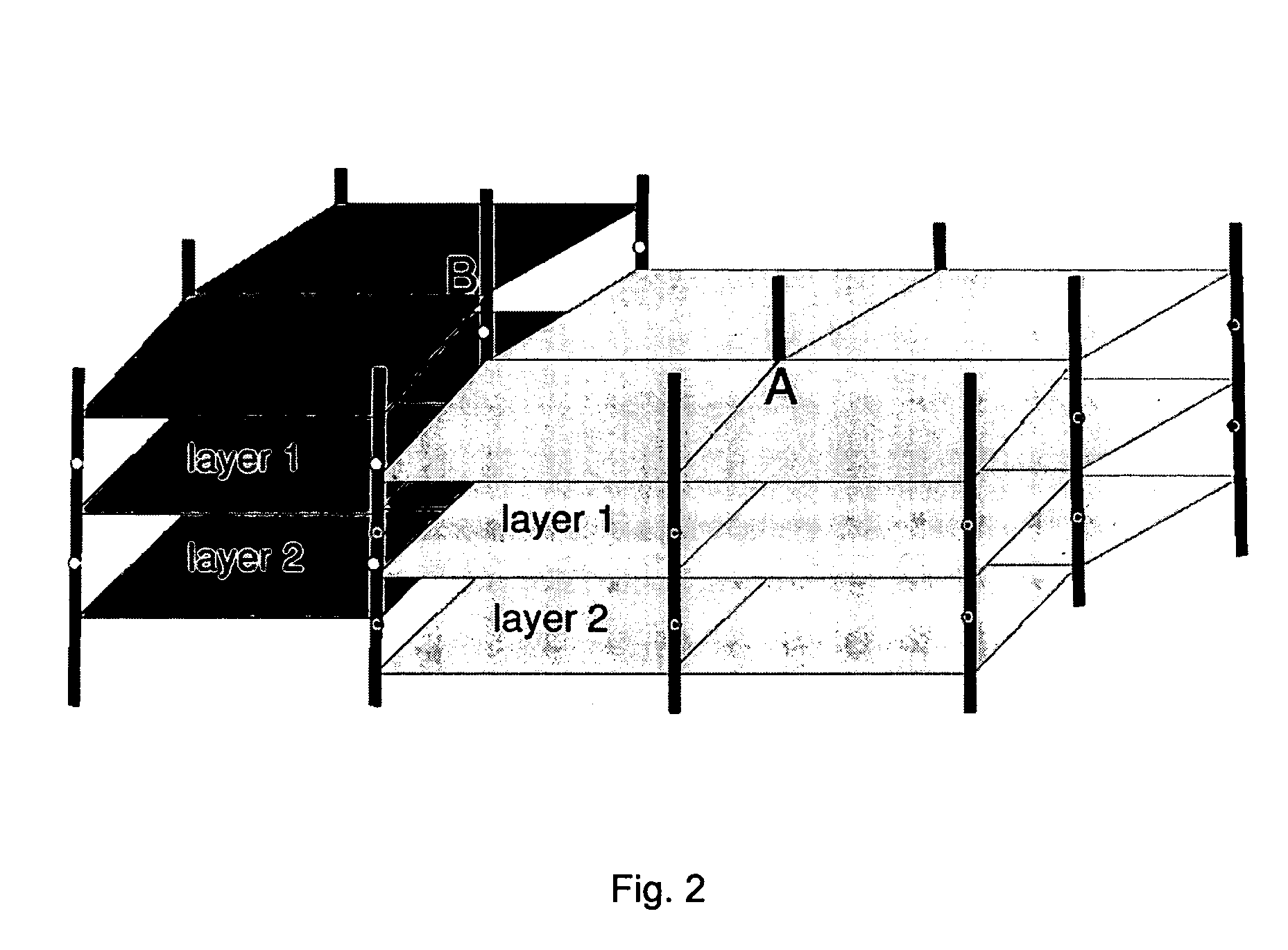
Method for estimating and/or reducing uncertainty in reservoir models of potential petroleum reservoirs
ActiveUS7254091B1Reduce uncertaintyGreat constraintSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsSoil scienceInter layer
A method for estimating and / or reducing uncertainty in reservoir models of potential petroleum reservoirs comprises receiving the results of a stochastic seismic inversion, and transforming the inversion data into a form suitable for reservoir modelling and flow simulations, while honoring inter-property and inter-layer correlations in the inversion data as well as measured well data and other geological constraints.
Owner:BHP BILLITON INNOVATION PTY LTD
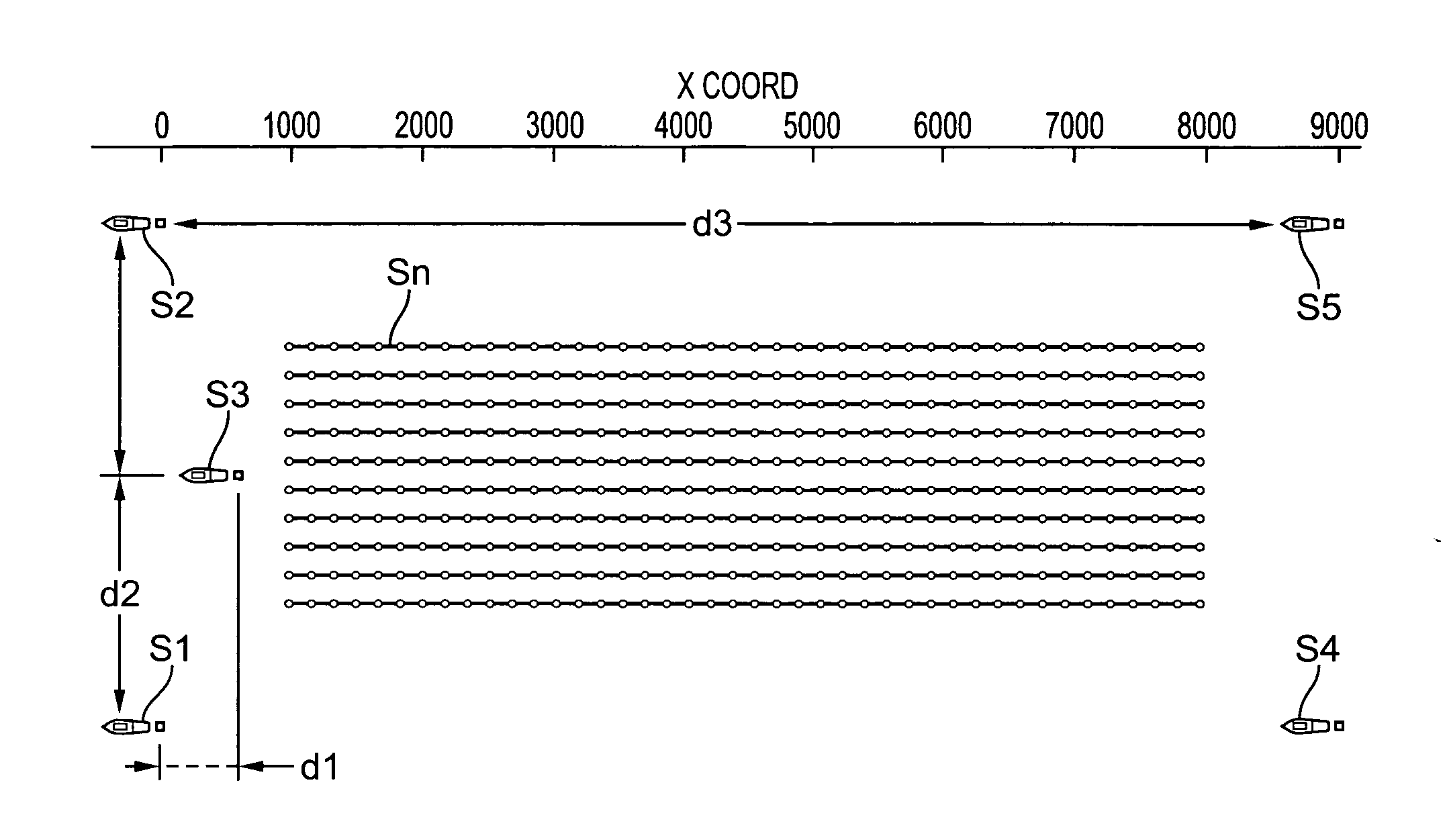
Methods and systems for efficiently acquiring towed streamer seismic surveys
ActiveUS20070165486A1Improved seismic imagingLess timeSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasSurveyorSeismic survey
Methods and systems for efficiently acquiring towed streamer marine seismic data are described. One method and system comprises positioning a plurality of source-only tow vessels and one or more source-streamer tow vessels to acquire a wide- and / or full-azimuth seismic survey without need for the spread to repeat a path once traversed. Another method and system allows surveying a sub-sea geologic feature using a marine seismic spread, the spread smartly negotiating at least one turn during the surveying, and shooting and recording during the turn. This abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract, allowing a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the
Owner:REFLECTION MARINE NORGE AS
Signal interpretation engine
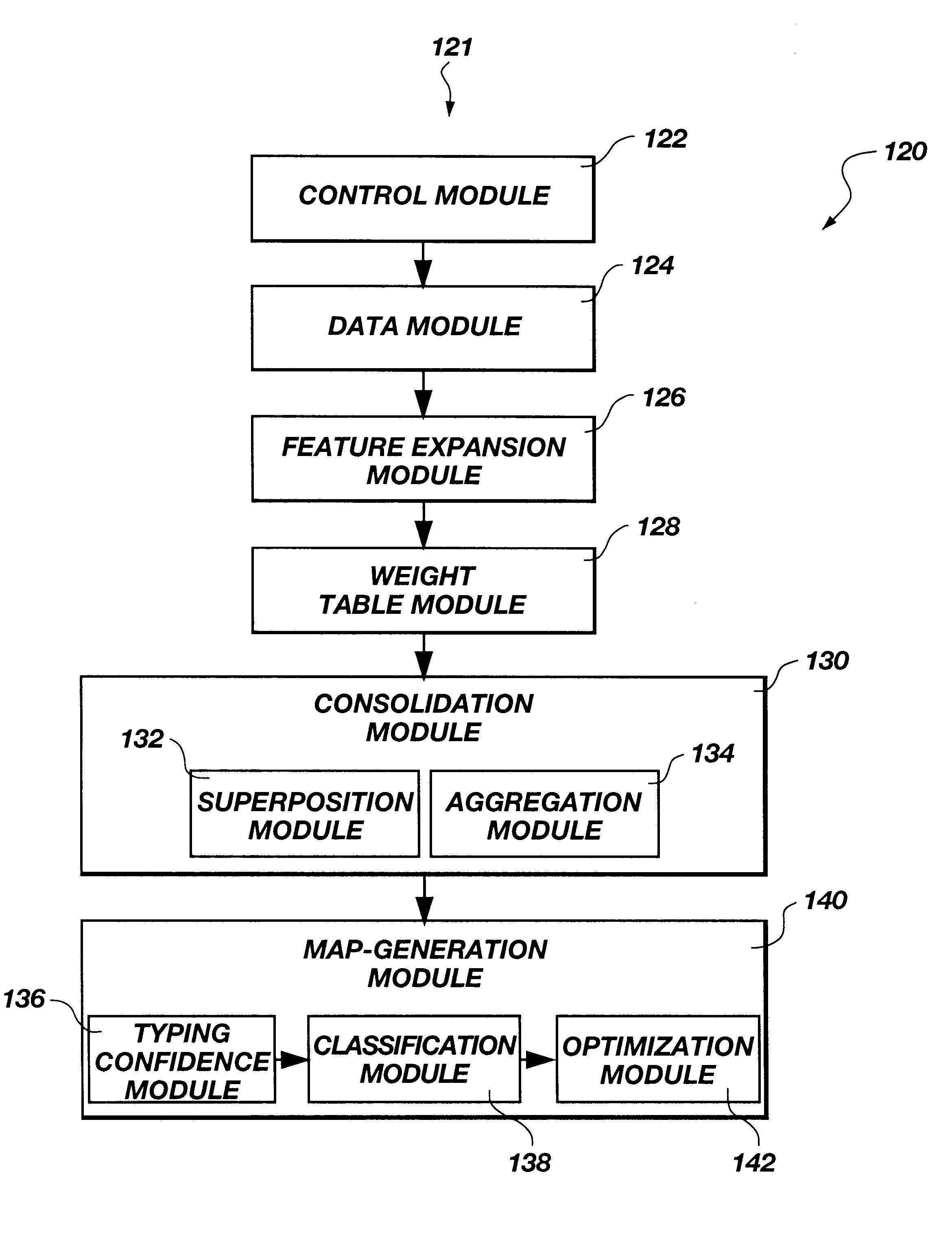
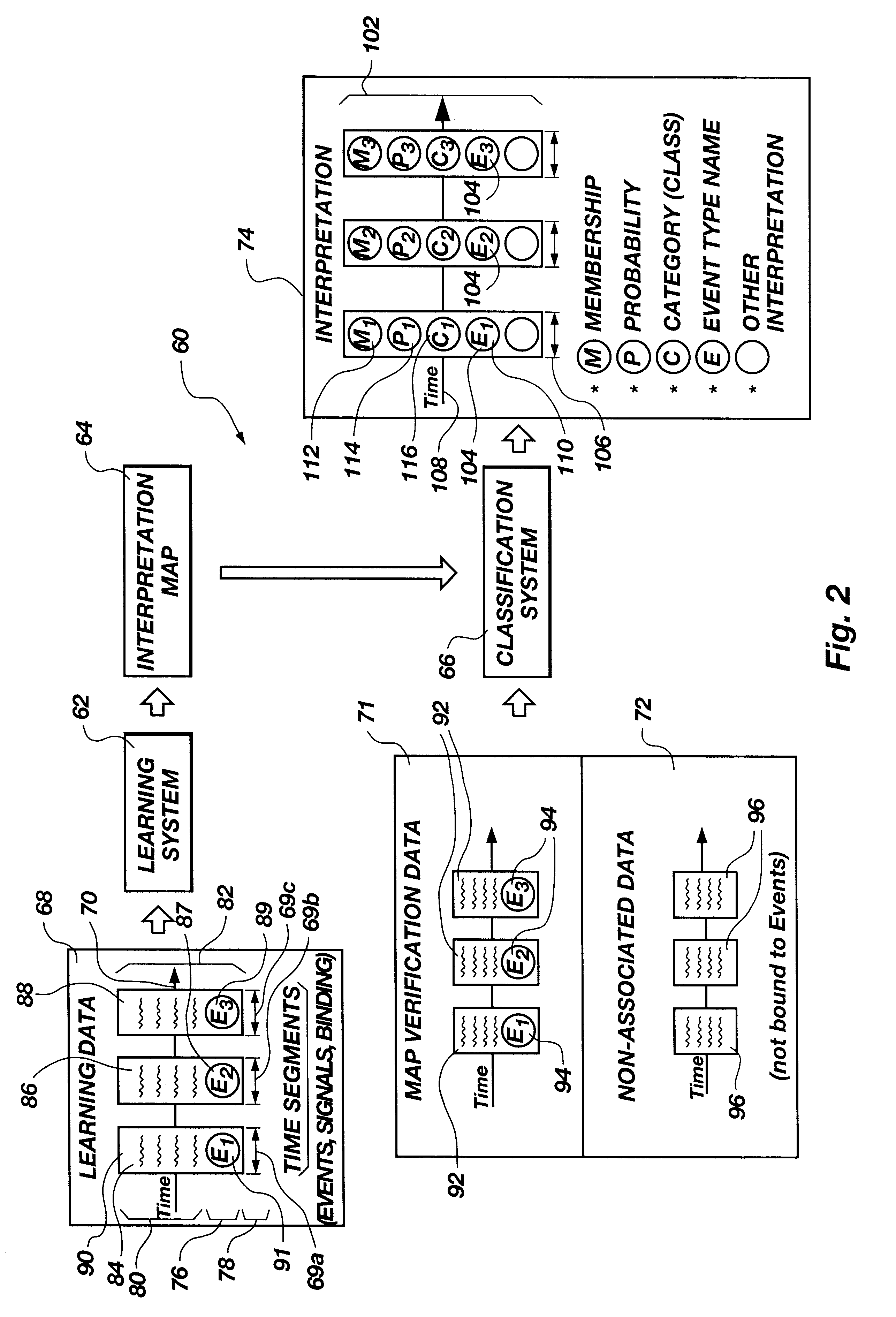
A signal interpretation engine apparatus and method are disclosed in certain presently preferred embodiment as including a computer programmed to run a plurality of modules comprising a feature expansion module, a weight table module, a consolidation module, and a map generation module. The feature expansion module contains feature operators for operating on a signal to expand the signal to form a feature map of feature segments Each feature segment corresponds to a unique representation of the signal created by a feature operator operating on the signal across an epoch. An epoch corresponds to an event occurring within a time segment. The weight table module provides a weight table having weight elements Each weight element has a weight corresponding to a feature segment of the feature map. The consolidation module provides a superposition segment by combining the feature segments of the feature map corresponding to the epoch by forming an inner product of the feature map and the weight table. The consolidation module also applies aggregators to consolidate the inner products or superposition segments into a distribution function representing an attribute over a domain reflecting a selected weight table, aggregator, and event type, corresponding to each value of the attribute. The map generation module produces an interpretation map that reflects a preferred weight table and aggregator to be applied to the signal data to characterize the event.
Owner:BRIGHT IDEAS
Method for acquiring and interpreting seismoelectric and eletroseismic data
InactiveUS20070294036A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsGeophysics
Owner:KJT ENTPR
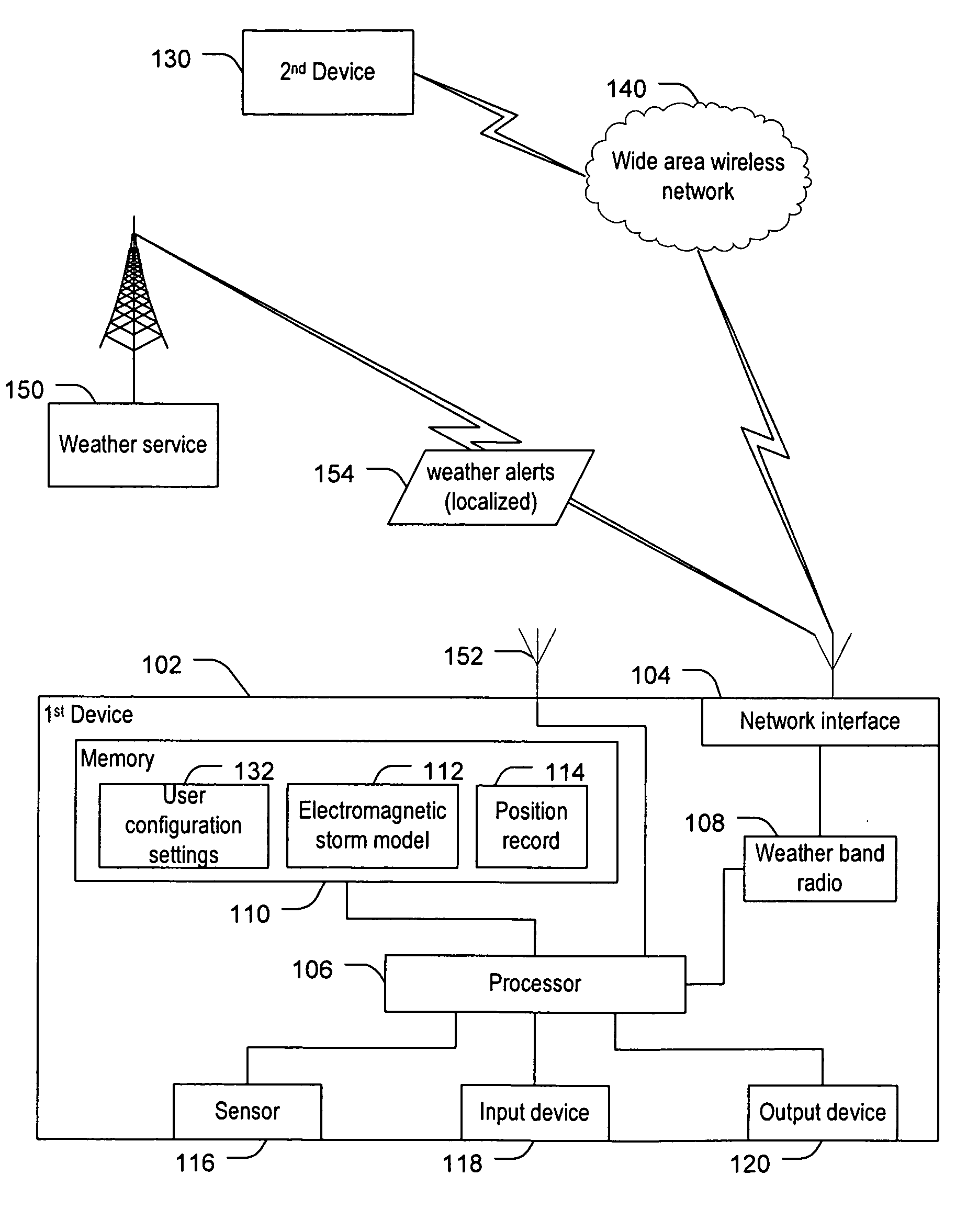
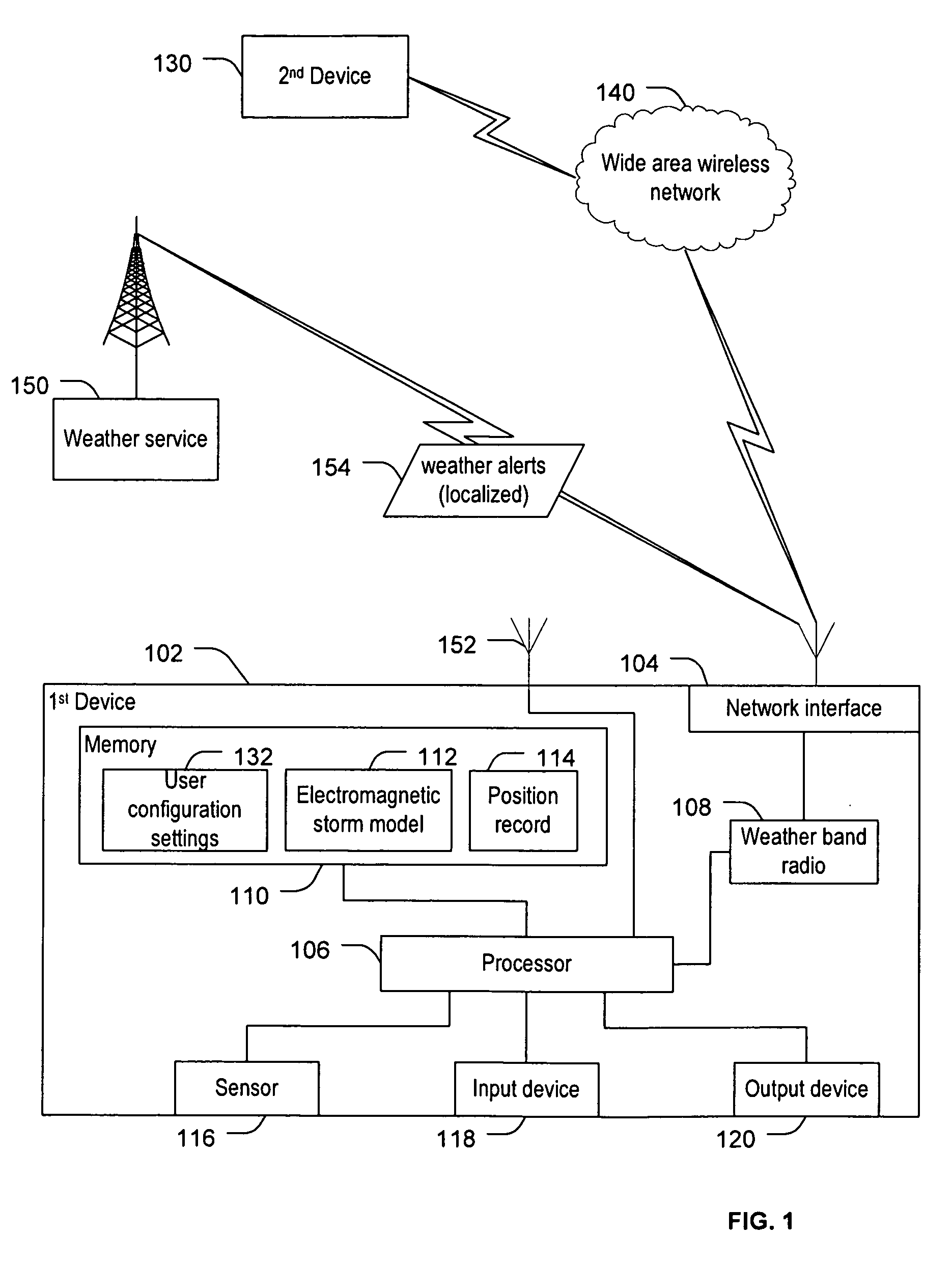
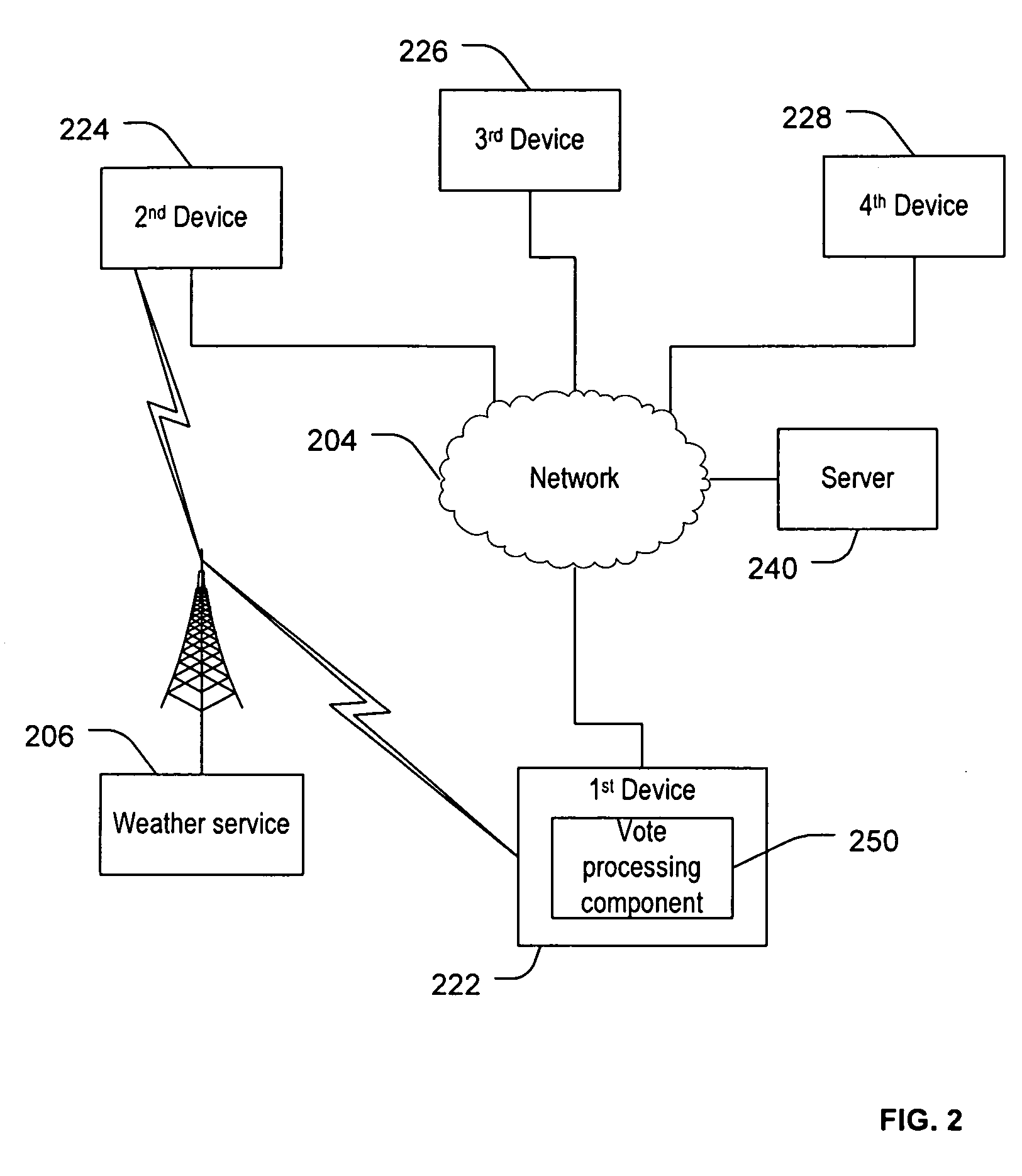
Weather alerts
Systems and methods to generate weather alerts are provided. A particular system includes a weather band radio receiver to receive weather alerts. The system further includes a processor to perform an analysis of the received electromagnetic radiation and to determine based on the analysis whether the electromagnetic radiation indicates rotation in a storm system. The processor initiates an alert when the analysis indicates rotation in the storm system and a weather alert has been received.
Owner:MOORE JASON LEE
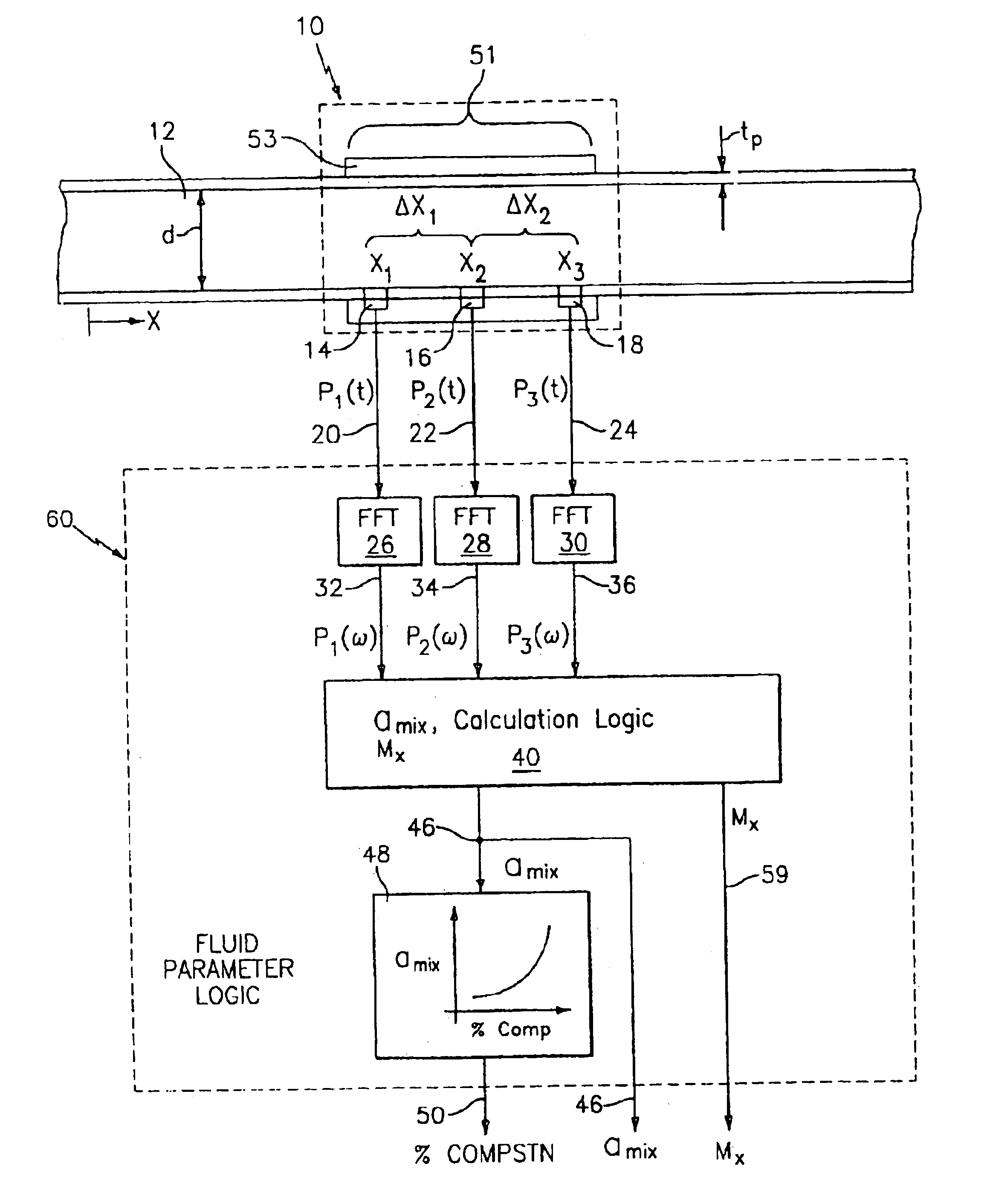
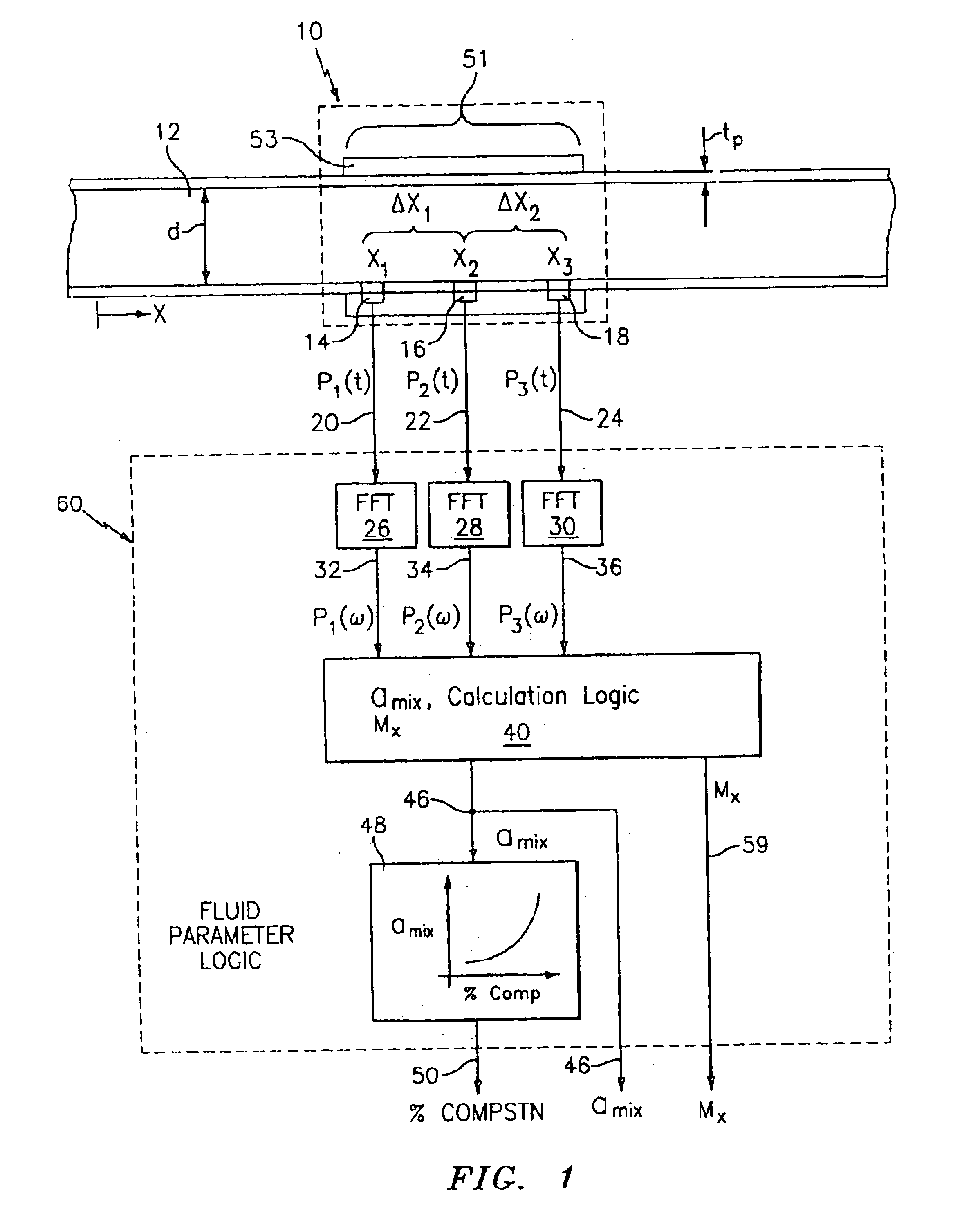
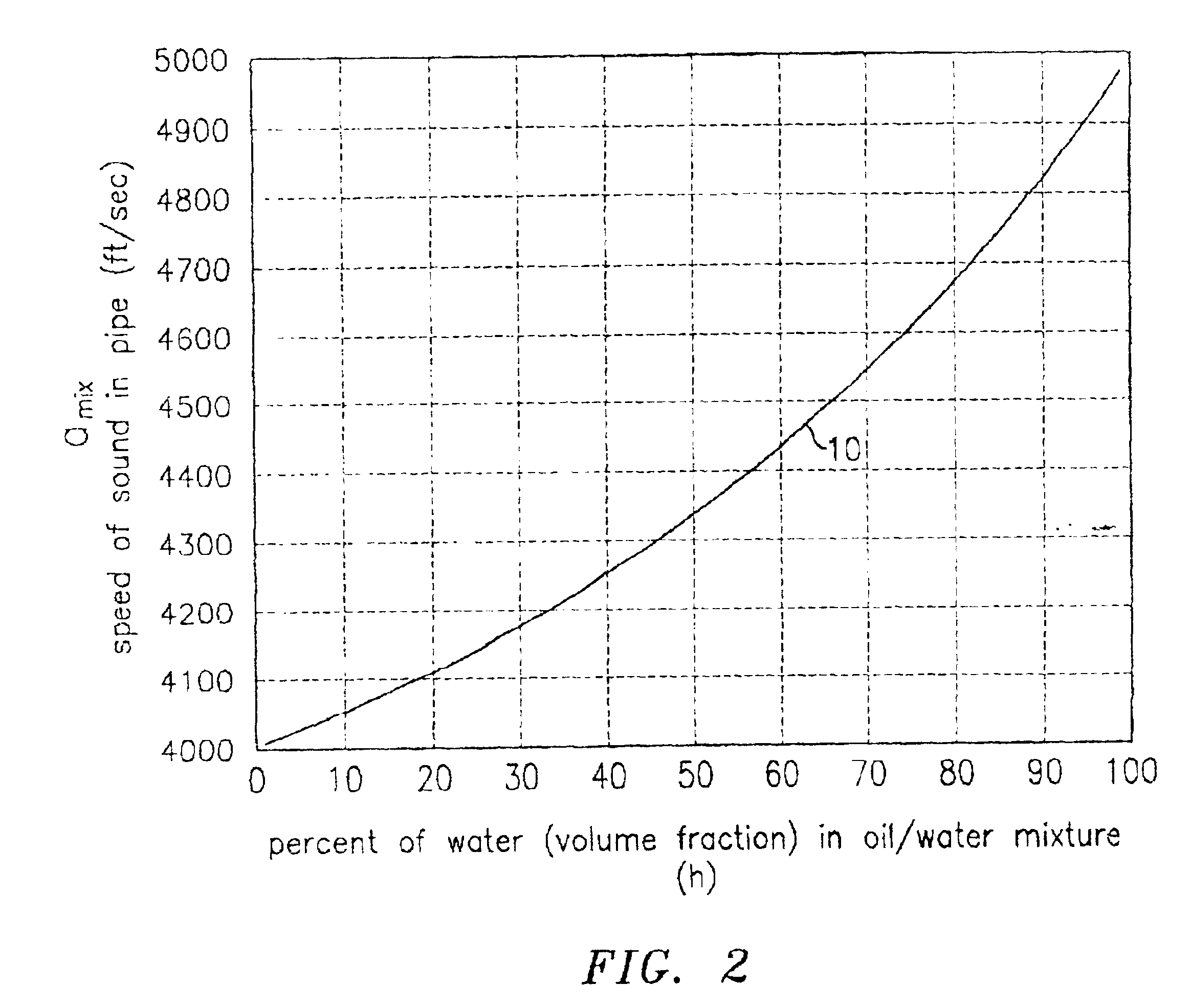
Fluid parameter measurement in pipes using acoustic pressures
InactiveUS6862920B2Less sensitive to static shifts (or errors) in sensingImprove measurement reliabilityAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEngineeringWater fraction
At least one parameter of at least one fluid in a pipe is measured using a spatial array of acoustic pressure sensors placed at predetermined axial locations along the pipe 12. The pressure sensors provide acoustic pressure signals, which are provided to a signal processing system that determines the speed of sound amix of the fluid (or mixture) in the pipe 12 using acoustic spatial array signal processing techniques. Numerous spatial array processing techniques may be employed to determine the speed of sound amix. The speed of sound amix is provided to another logic system that calculates the percent composition of the mixture, e.g., water fraction, or any other parameter of the mixture or fluid which is related to the sound speed amix. The signal processing system may also determine the Mach number Mx of the fluid. The acoustic pressure signals measured are lower frequency (and longer wavelength) signals than those used for ultrasonic flow meters, and thus are more tolerant to inhomogeneities in the flow. No external source is required and thus may operate using passive listening. The invention will work with arbitrary sensor spacing and with as few as two sensors if certain information is known about the acoustic properties of the system.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com