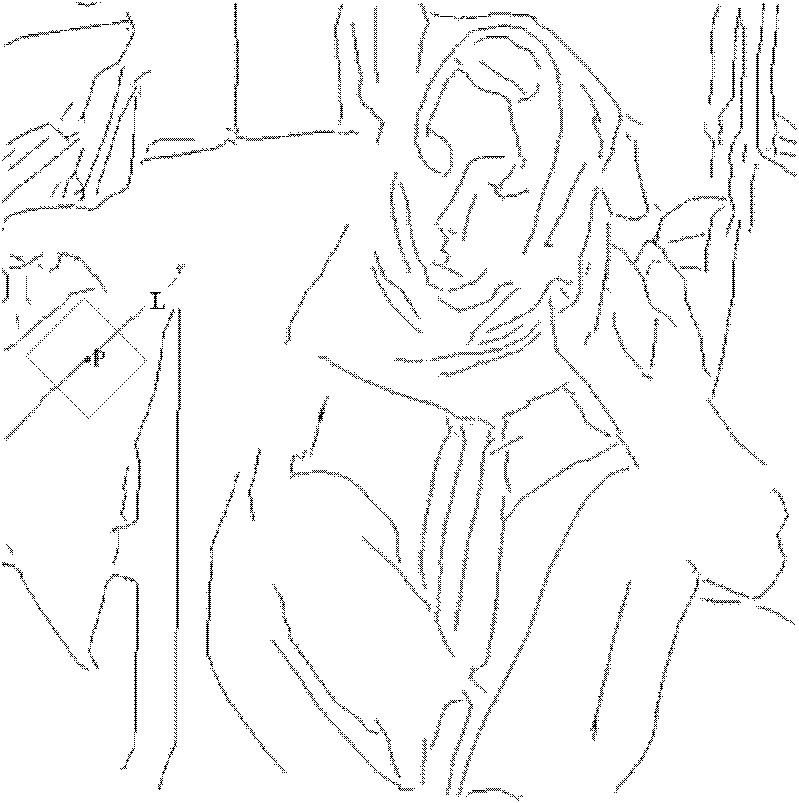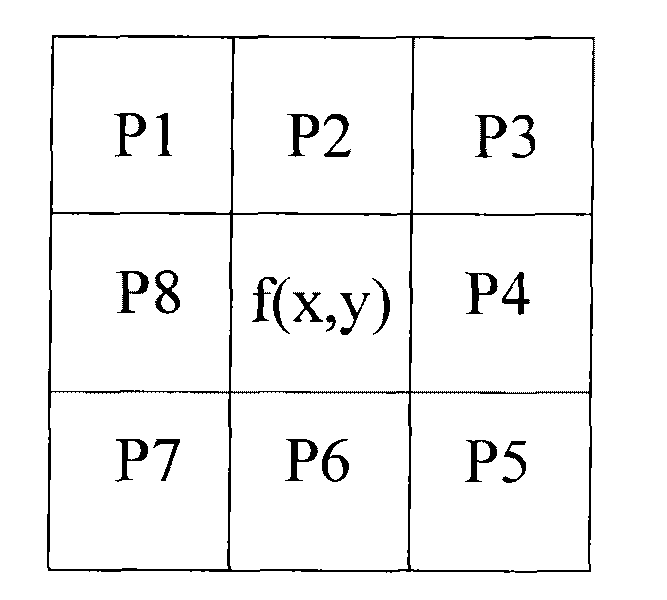Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
644 results about "Image structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
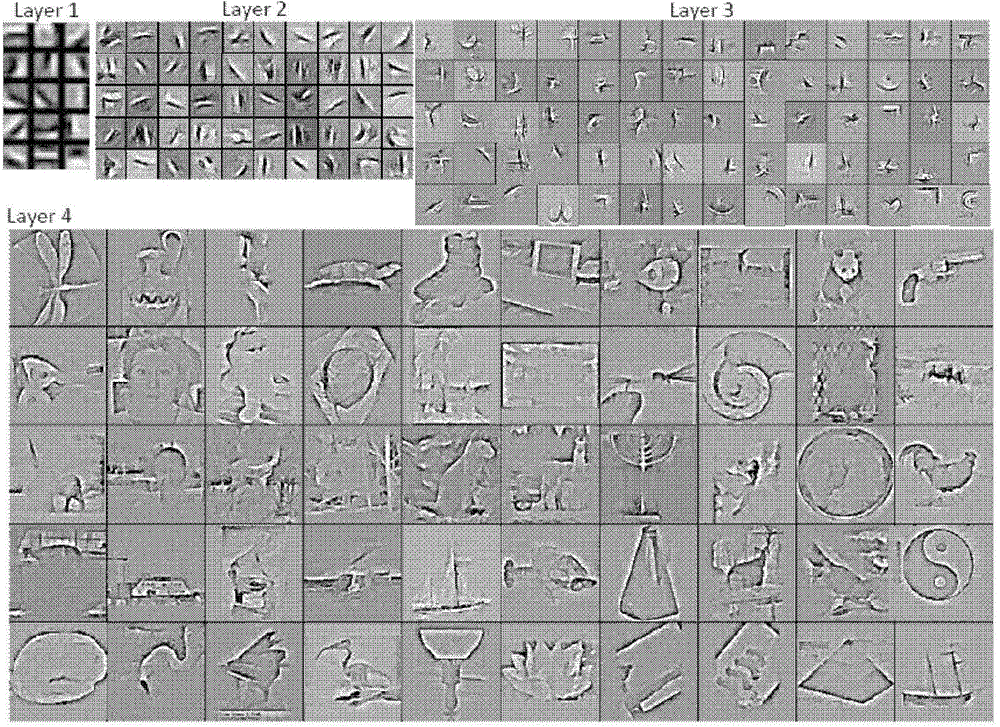
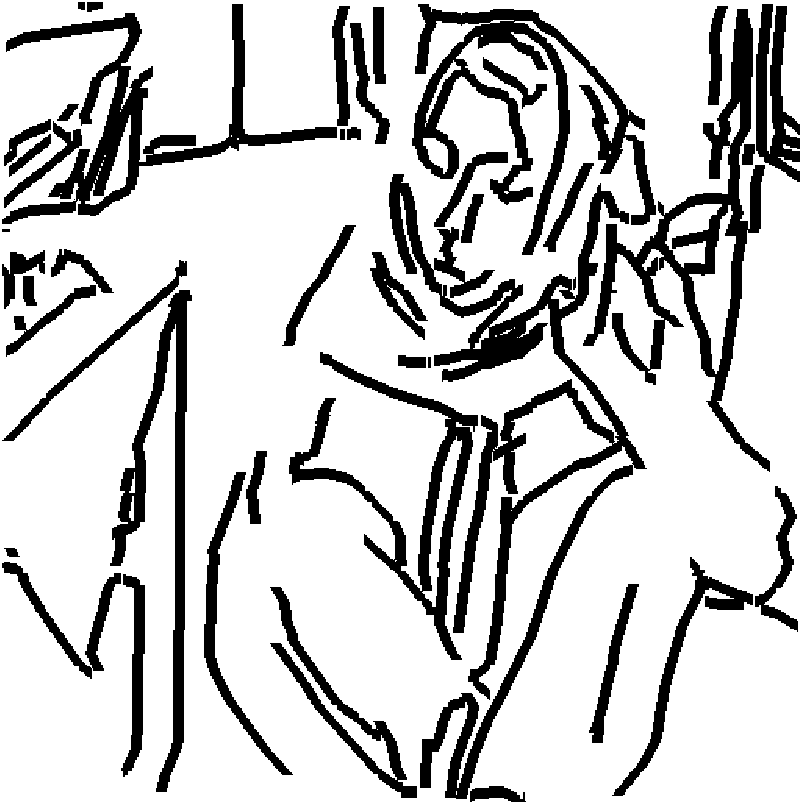
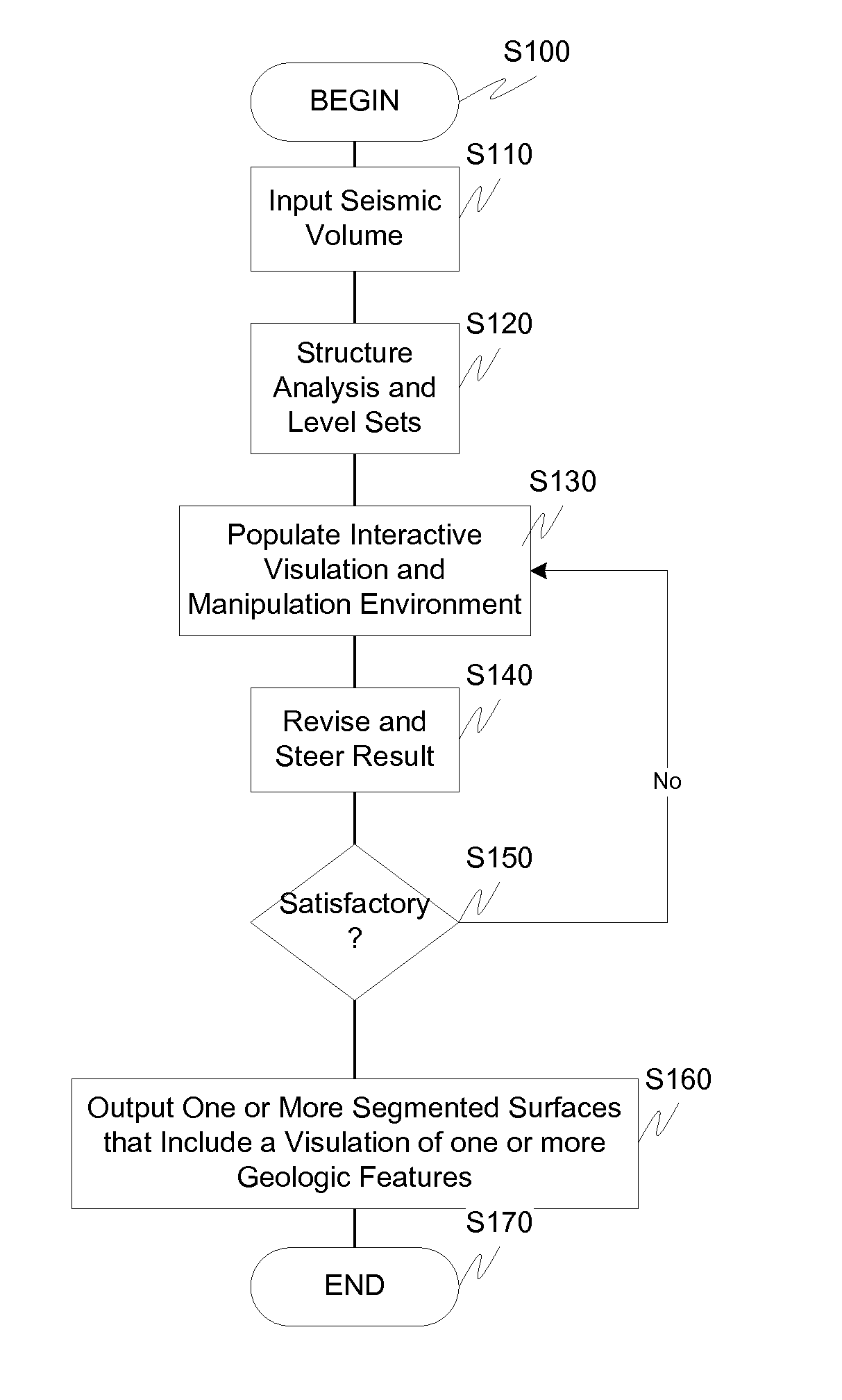
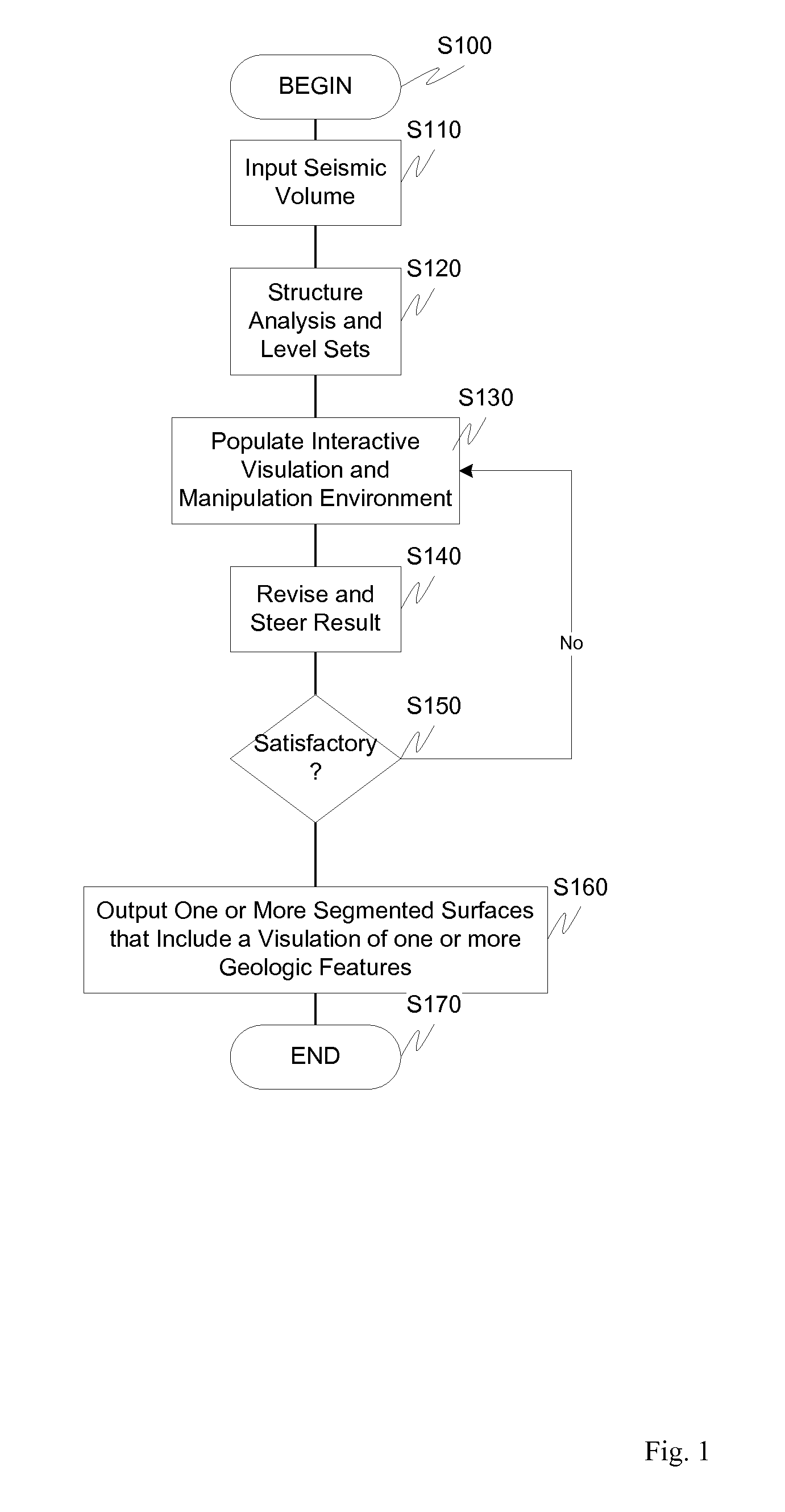
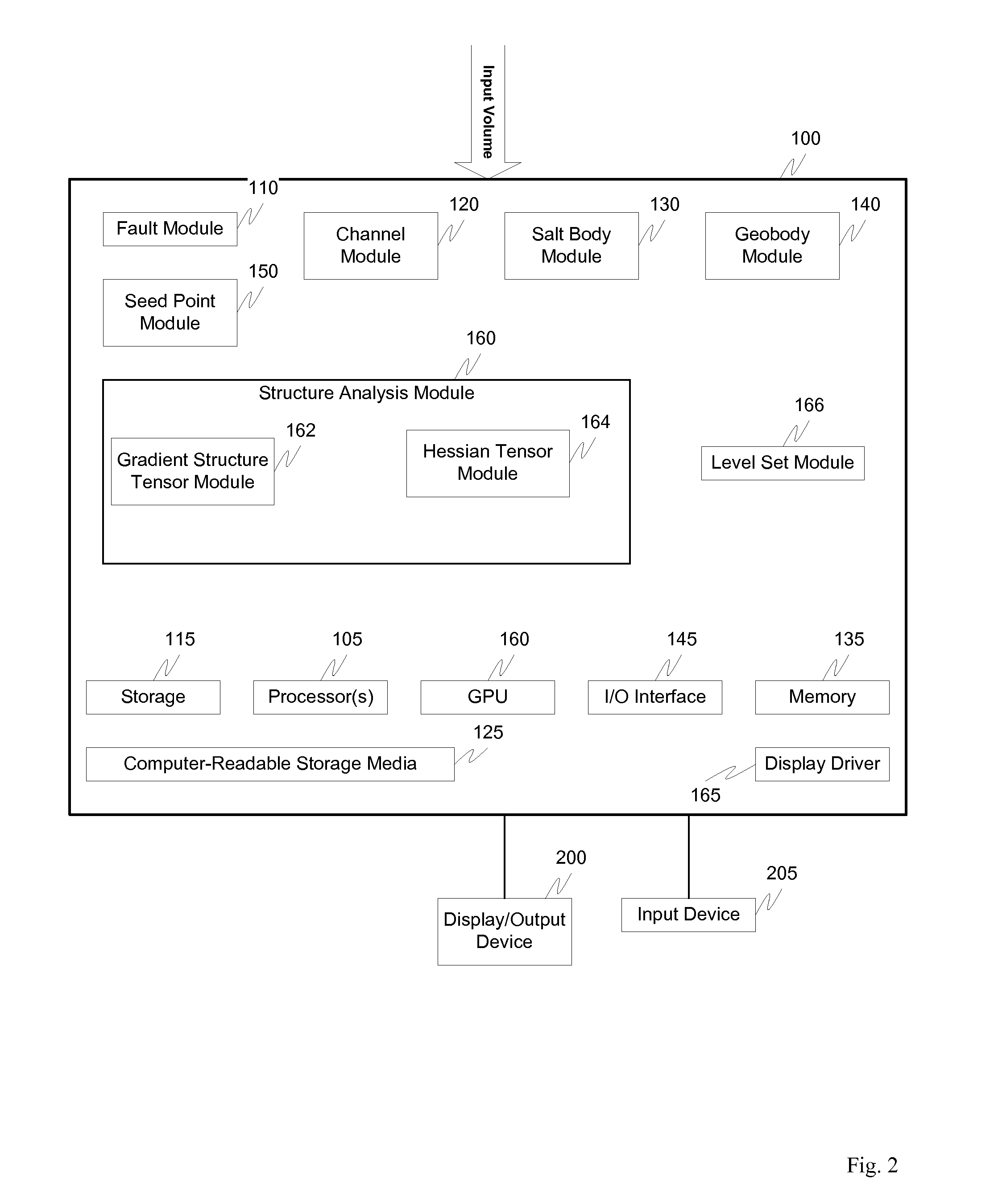
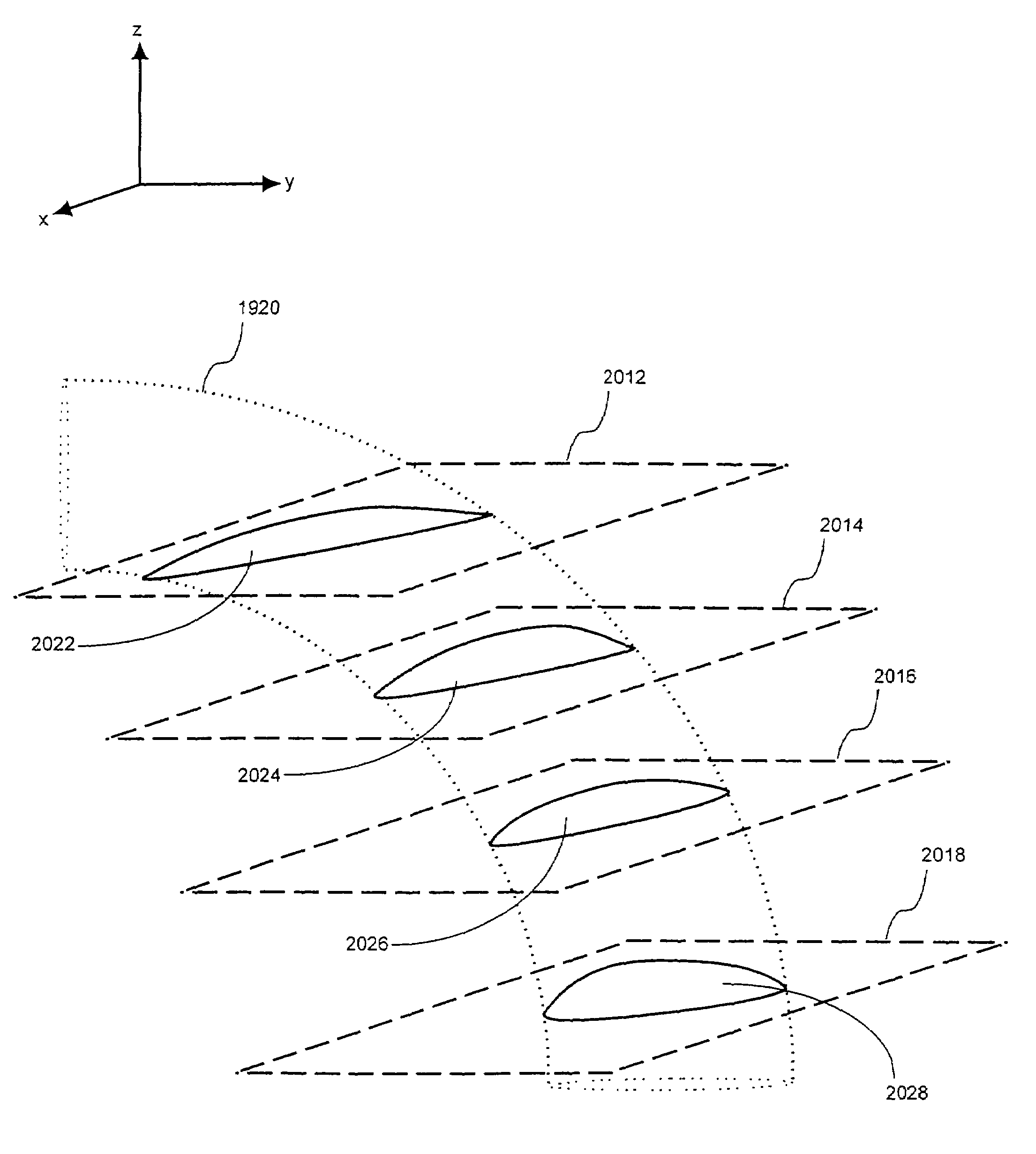
Visulation of geologic features using data representations thereof
InactiveUS20110115787A1Enhance feature structureEasy to divideImage enhancementImage analysisImage structureComputer science
One exemplary embodiment presents a unified approach in the form of an Interactive “Violation” (simultaneous visualization and simulation) Environment (IVE) designed to efficiently segment geologic features with high accuracy. The IVE unifies image structure analysis and implicit surface modeling as a surface-driven solution that assists analysts, such as geoscientists, in the segmentation and modeling of faults, channels, and other geobodies in 3-D data, such as 3-D seismic data.
Owner:CGG JASON NETHERLANDS
Feature quantification from multidimensional image data
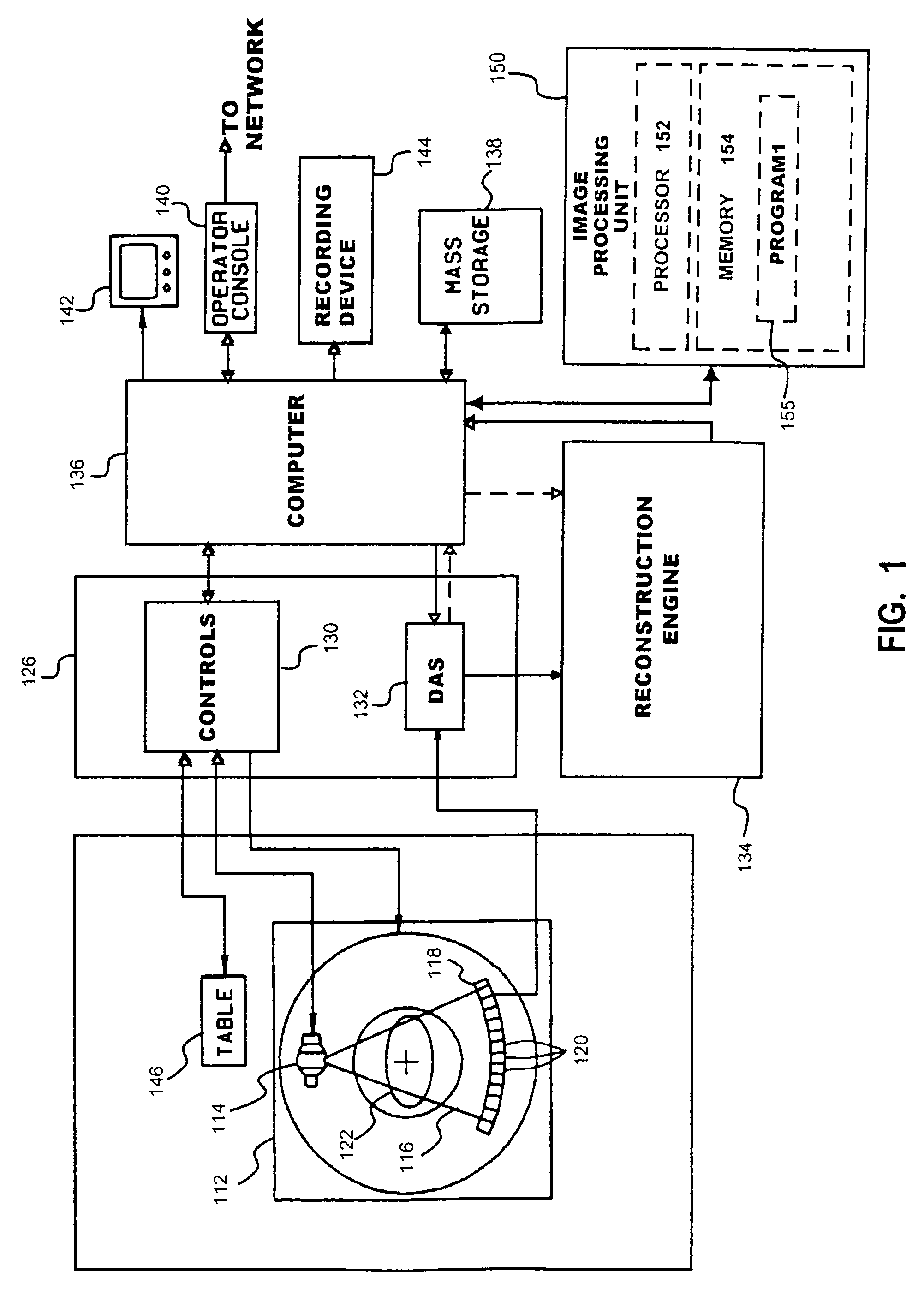
Techniques, hardware, and software are provided for quantification of extensional features of structures of an imaged subject from image data representing a two-dimensional or three-dimensional image. In one embodiment, stenosis in a blood vessel may be quantified from volumetric image data of the blood vessel. A profile from a selected family of profiles is fit to selected image data. An estimate of cross sectional area of the blood vessel is generated based on the fit profile. Area values may be generated along a longitudinal axis of the vessel, and a one-dimensional profile fit to the generated area values. An objective quantification of stenosis in the vessel may be obtained from the area profile. In some cases, volumetric image data representing the imaged structure may be reformatted to facilitate the quantification, when the structural feature varies along a curvilinear axis. A mask is generated for the structural feature to be quantified based on the volumetric image data. A curve representing the curvilinear axis is determined from the mask by center-finding computations, such as moment calculations, and curve fitting. Image data are generated for oblique cuts at corresponding selected orientations with respect to the curvilinear axis, based on the curve and the volumetric image data. The oblique cuts may be used for suitable further processing, such as image display or quantification.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Image processing method for direction dependent low pass filtering
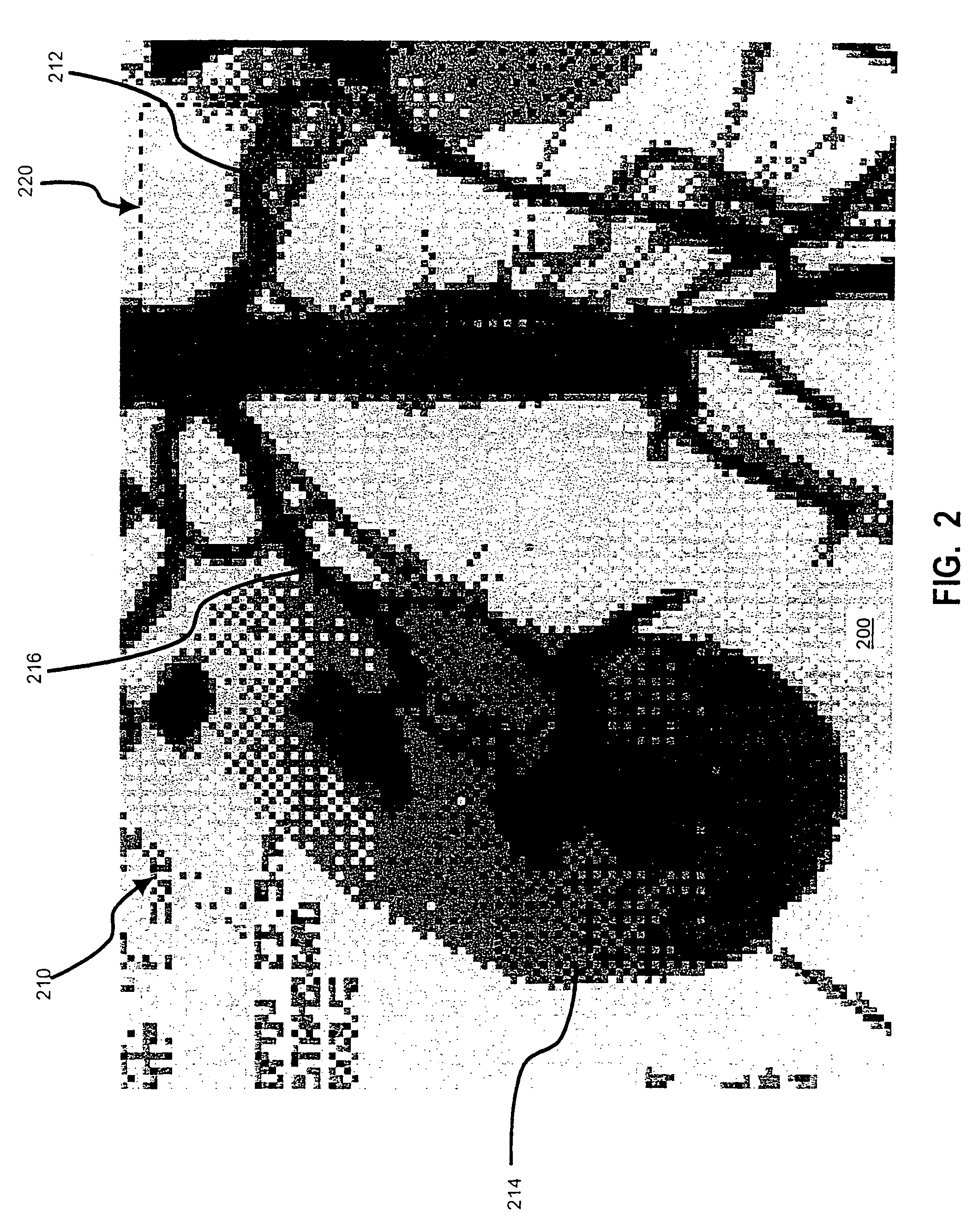
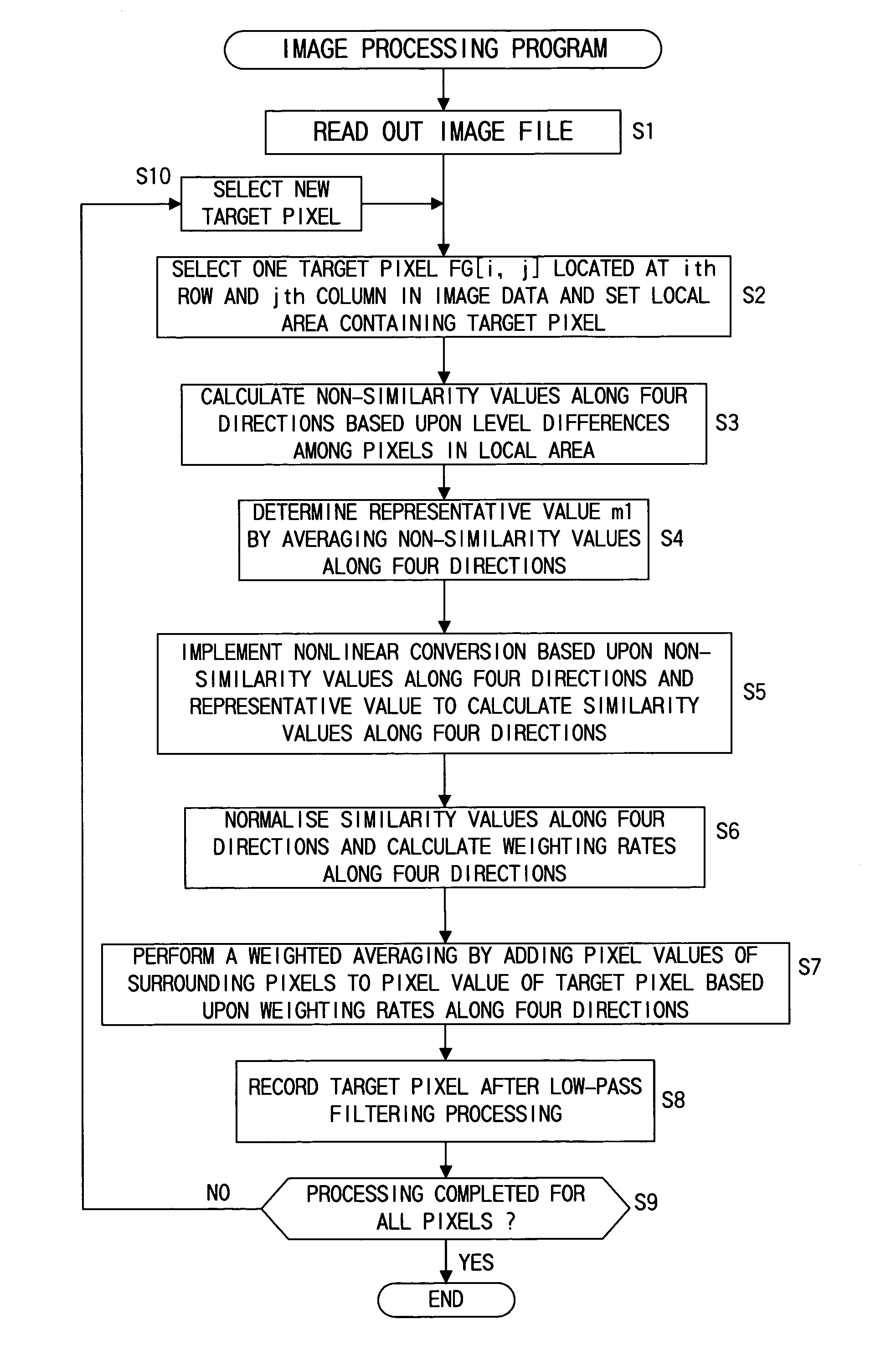
InactiveUS7016549B1Without losing fine structure of imageTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImaging processingJaggies
First similarity values along at least four directions are ascertained within a local area containing a target pixel and weighted averaging is performed by adding the pixel values of pixels around the target pixel value to the pixel value of the target pixel, adding weight along a direction having a small first similarity value (along a direction manifesting a high degree of similarity). By incorporating the pixel value level differences among a plurality of pixels on adjacent lines extending adjacent to the target pixel into the first similarity values, it becomes possible to effectively remove jaggies that are difficult to eliminate in the prior art. Furthermore, by making a judgment on degrees of similarity by incorporating color information such as characteristics differences among different color pixels, a more accurate judgment can be made with regard to the image structure to enable very accurate direction-dependent low-pass filtering.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Generation of high dynamic range images from low dynamic range images in multiview video coding
ActiveUS20130108183A1Easy to identifyEasy to codeImage codingCharacter and pattern recognitionStructure analysis3d image
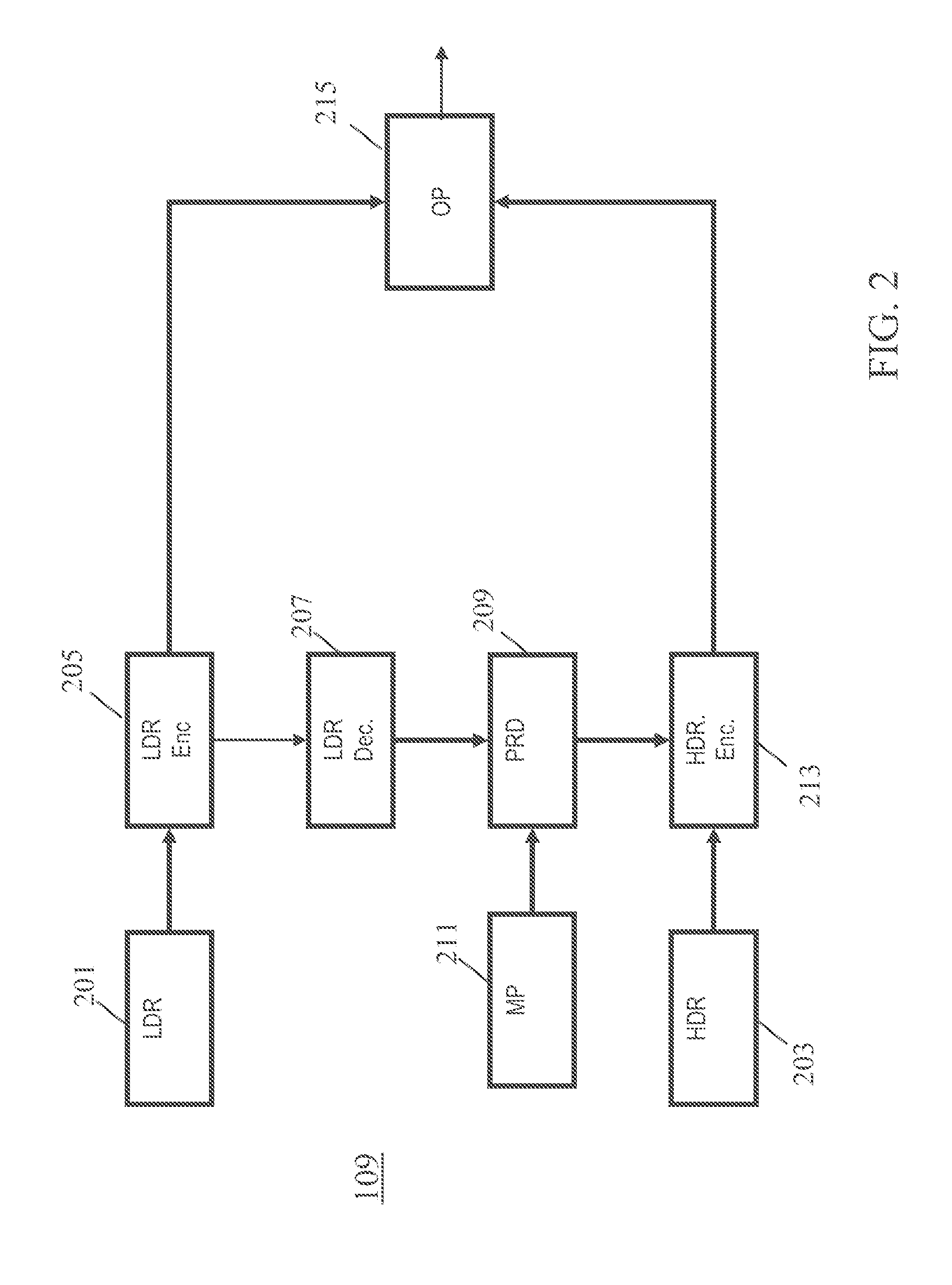
Several approaches are disclosed for combining HDR and 3D image structure analysis and coding, in particular an encoding apparatus for encoding a first view high dynamic range image and a second view high dynamic range image comprising: first and second HDR image receivers (203, 1201) arranged to receive the first view high dynamic range image and a second view high dynamic range image; a predictor (209) arranged to predict the first view high dynamic range image from a low dynamic range representation of the first view high dynamic range image; and a view predictor (1203) to predict the second view high dynamic range image from at least one of the first view high dynamic range image, a low dynamic range representation of the second view high dynamic range image, or a low dynamic range representation of the first view high dynamic range image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Kernel regression for image processing and reconstruction
ActiveUS20070047838A1Improve local image structure informationImproves gradient and pixel valueImage enhancementImage analysisSingular value decompositionKernel regression
A method of image processing using kernel regression is provided. An image gradient is estimated from original data that is analyzed for local structures by computing a scaling parameter, a rotation parameter and an elongation parameter using singular value decomposition on local gradients of the estimated gradients locally to provide steering matrices. A steering kernel regression having steering matrices is applied to the original data to provide a reconstructed image and new image gradients. The new gradients are analyzed using singular value decomposition to provide new steering matrices. The steering kernel regression with the new steering matrices is applied to the noisy data to provide a new reconstructed image and further new gradients. The last two steps are repeated up to ten iterations to denoise the original noisy data and improve the local image structure.
Owner:UNIV OF CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ
Method and a device for managing digital media files
InactiveUS20070016868A1Fast and logical and user-friendly linking and organizingFast and easy imagingDigital data information retrievalProgram controlCamera phoneComputer graphics (images)
A method and an electronic device such as a digital camera or a camera phone for managing digital media files such as photo images. A user of the device may define link areas on the latest image captured via a camera to be automatically associated with the subsequently taken images. Thus image structures called image chains are formed while still continuing the image capturing process. Such chains can be navigated through during the image capturing process or later on.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Transparent-medium-microsphere-based super-resolution microscopic imaging system
InactiveCN102305776AHigh resolution finenessThe image is real and reliableAnalysis by material excitationMicroscopesImage resolutionWhite light
The invention discloses a transparent-medium-microsphere-based super-resolution microscopic imaging system. In the system, a device which is improved on the basis of the traditional wide-field optical microscope system is adopted, namely a micron dimension small transparent ball is placed on the surface of a sample in the traditional wide-field optical microscope system. A method adopted by the system comprises the following steps of: illuminating a sample by using white light, and exciting the surface of the sample to generate surface plasma evanescent waves; coupling the surface plasma evanescent waves by using the micron dimension small transparent ball, and performing spatial amplification to generate an amplified virtual image of the sample; and performing secondary imaging on the virtual image and observing so as to acquire a microscopic image with super-resolution details of the surface of the sample and realize far-field and wide-field super-resolutions on the basis of wide-field illumination of white light. The system has high resolution fineness, is high in image acquisition speed, and can acquire instant dynamic images of observed samples, and acquired images are true and reliable; and the system has a simple structure and is low in cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
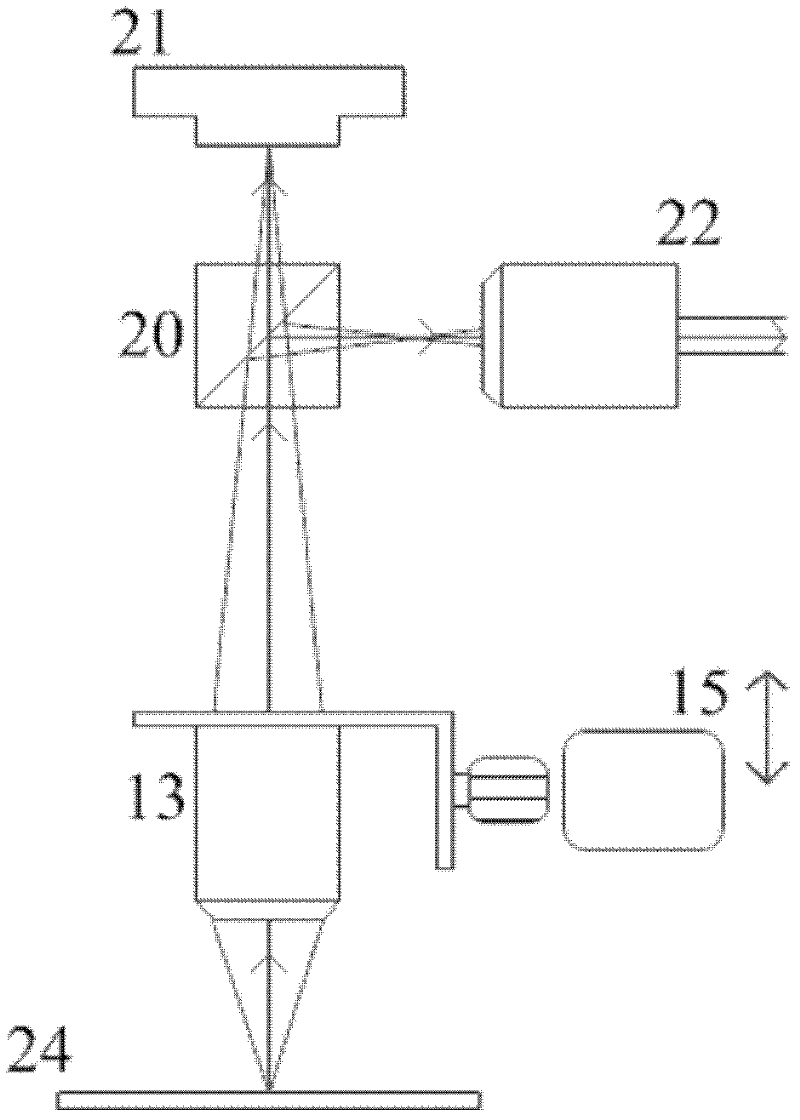
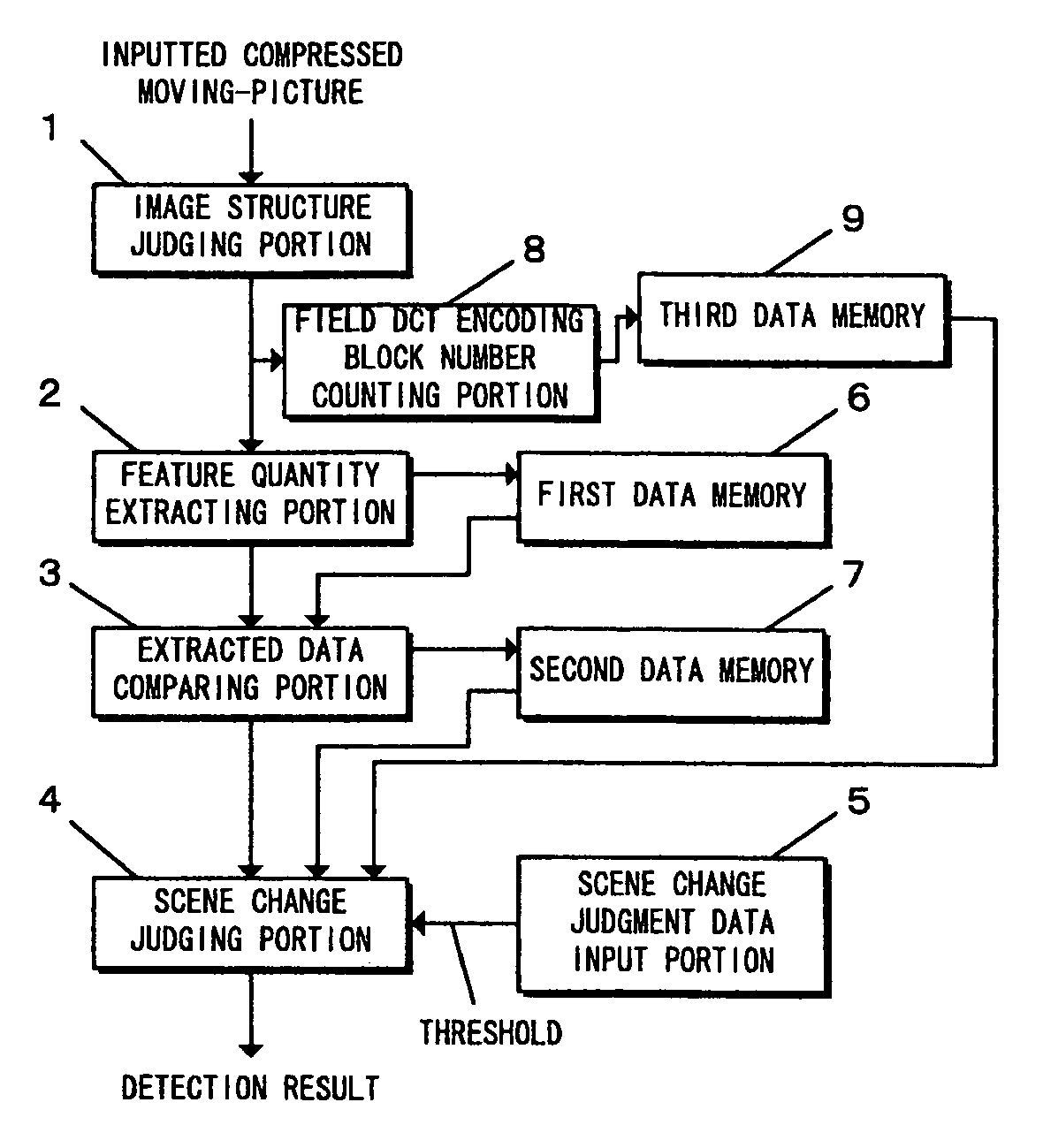
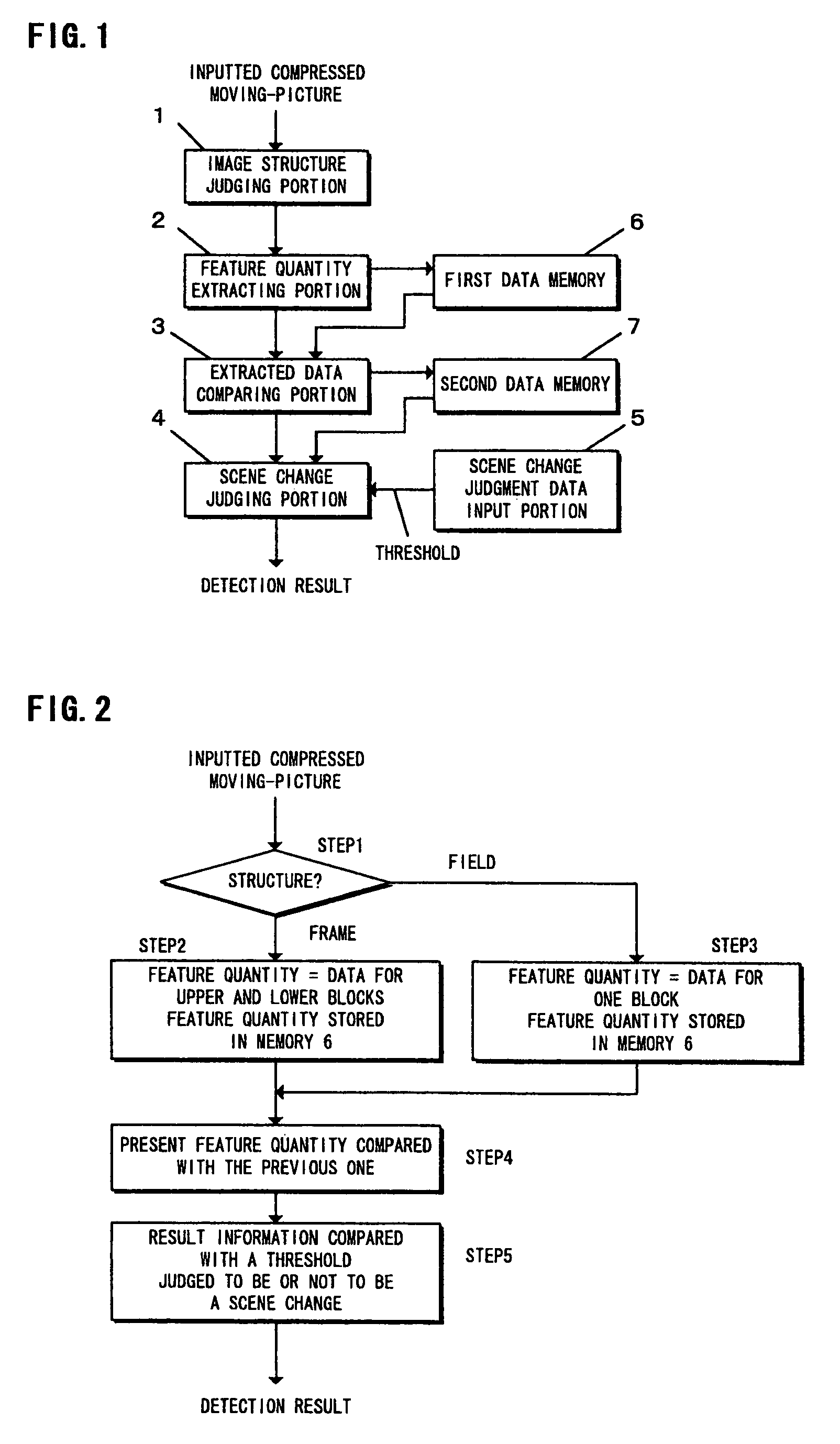
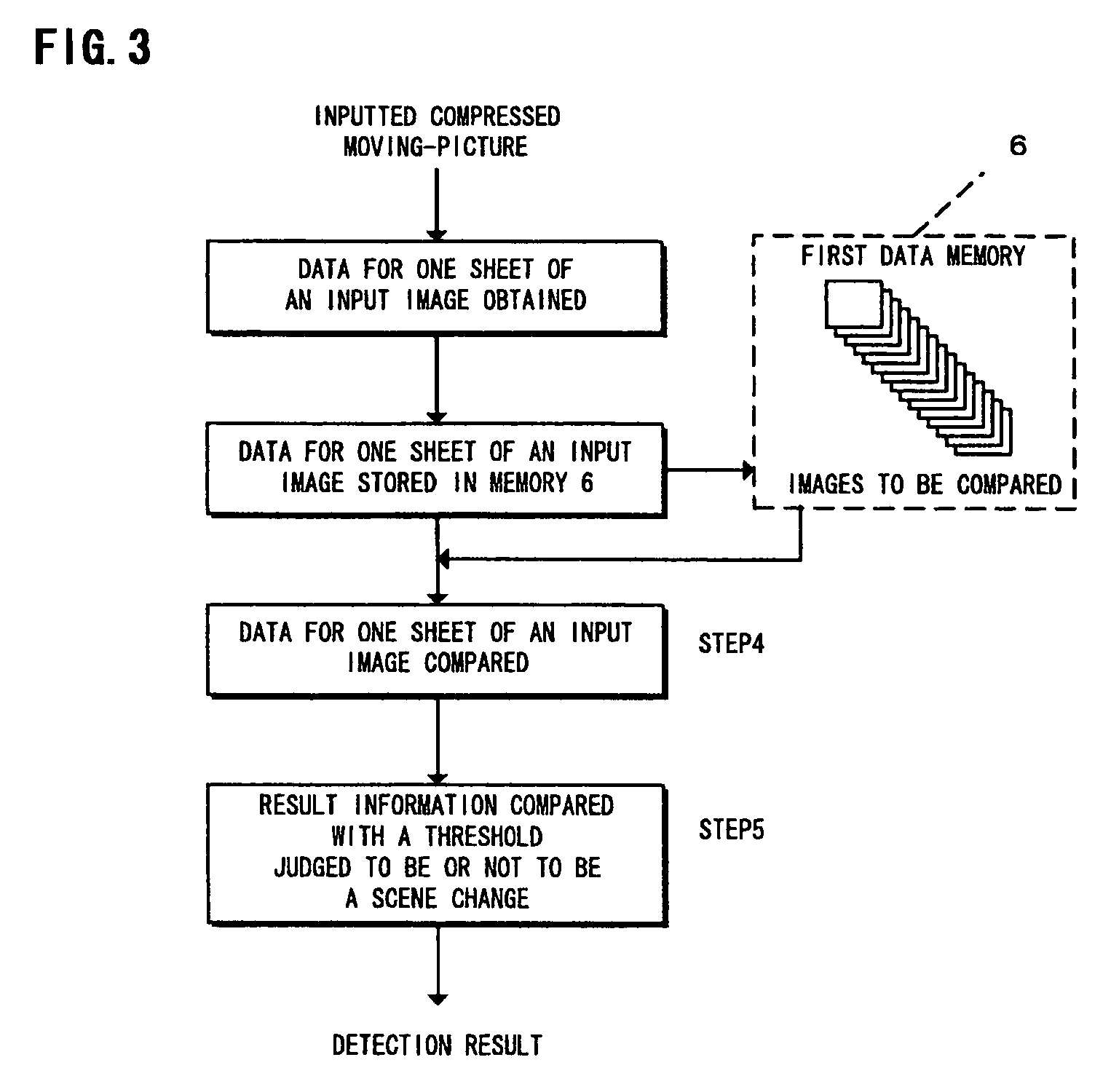
Method and apparatus for detecting scene change of a compressed moving-picture, and program recording medium therefor
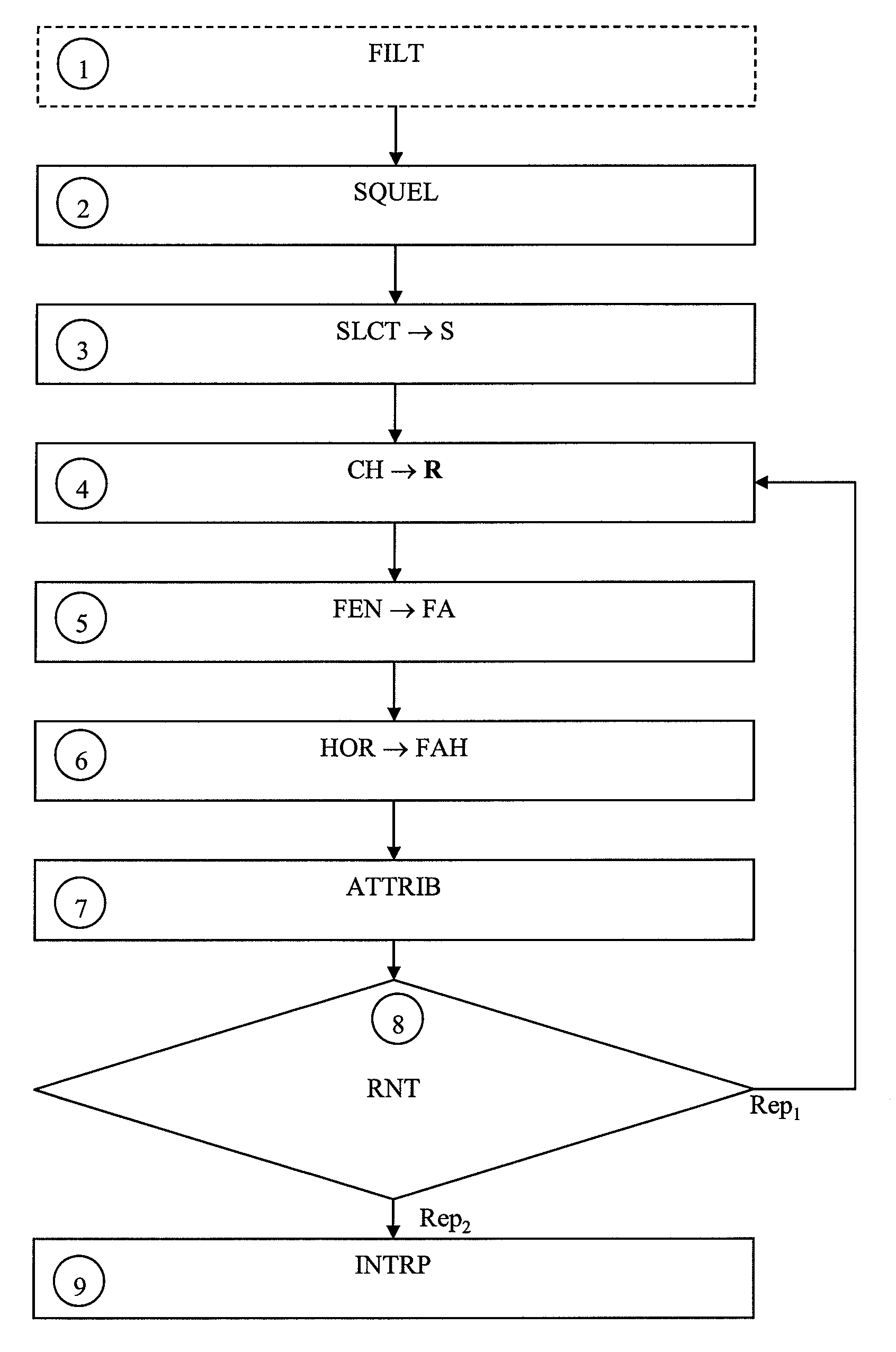
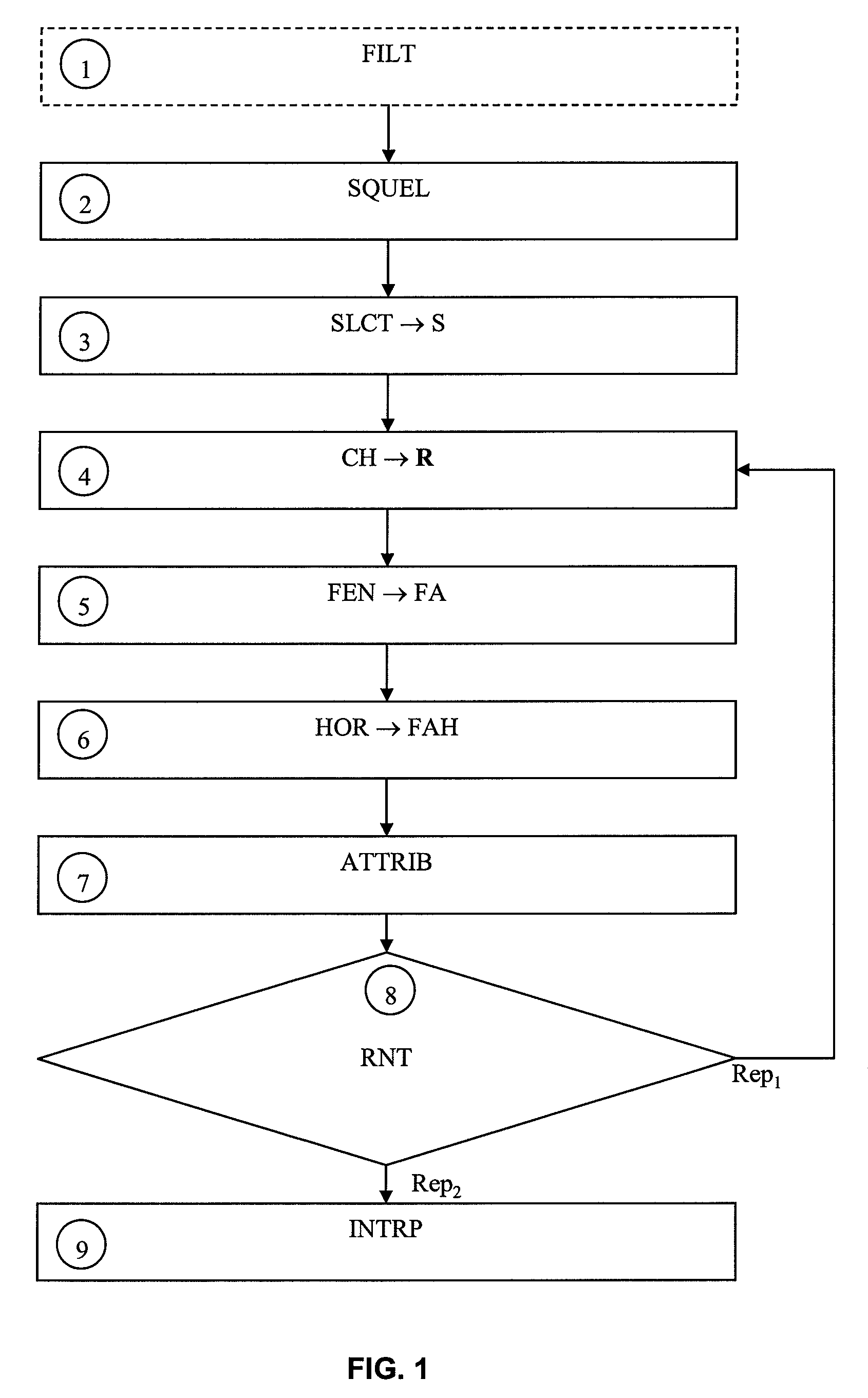
InactiveUS7031385B1Less detection fluctuationQuick checkTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesData memoryImage structure
An apparatus for detecting a scene change in a compressed moving-picture detects the scene change even if frame structure images and field structure images exist together. The apparatus includes an image structure judging portion for judging the image structure of an inputted compressed moving-picture, a feature quantity extracting portion for extracting a feature quantity based on top and bottom double data in vertical direction of the image with respect to a field structure image when the judgment result of the image structure judging portion is a frame structure image, a data memory for storing the data extracted by the feature quantity extracting portion, an extracted data comparing portion for comparing the extracted data and calculating the quantity of variation of a picture, and a scene change judging portion for judging a scene change by the use of the quantity of variation calculated by the extracted data comparing portion.
Owner:BASS AERO PTE LTD +1
Image mutual transfer and succession method of virtual image and real image
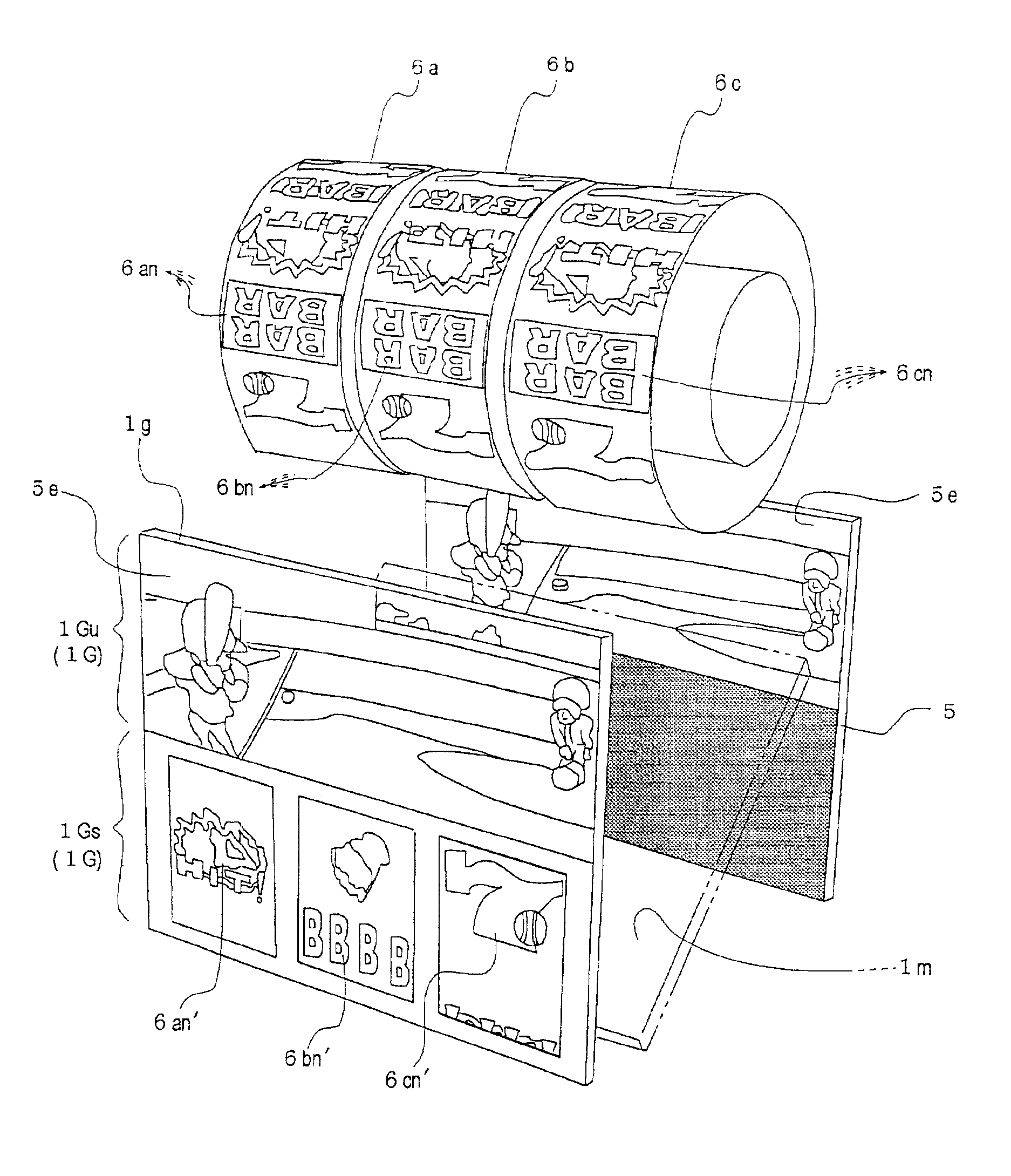
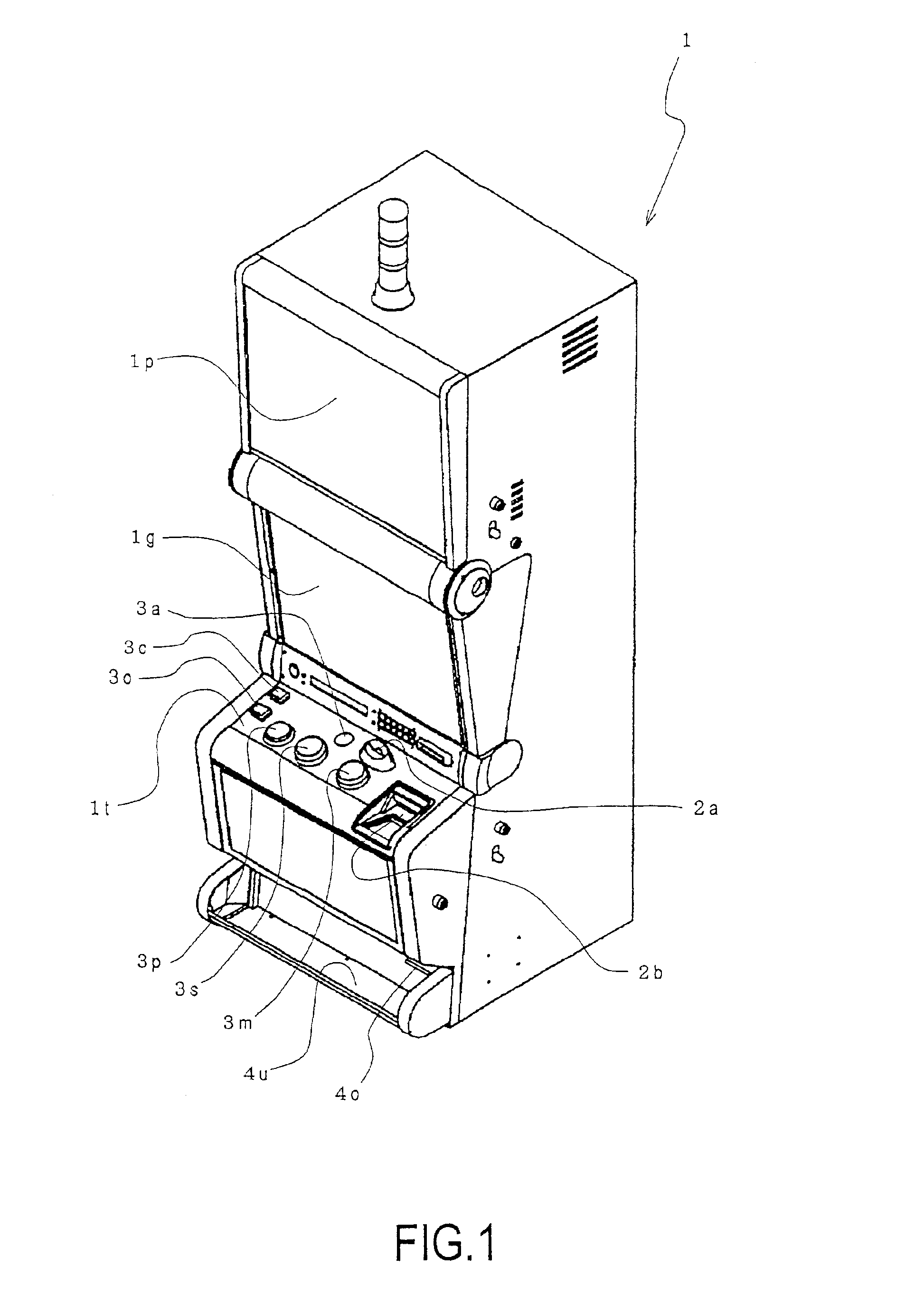
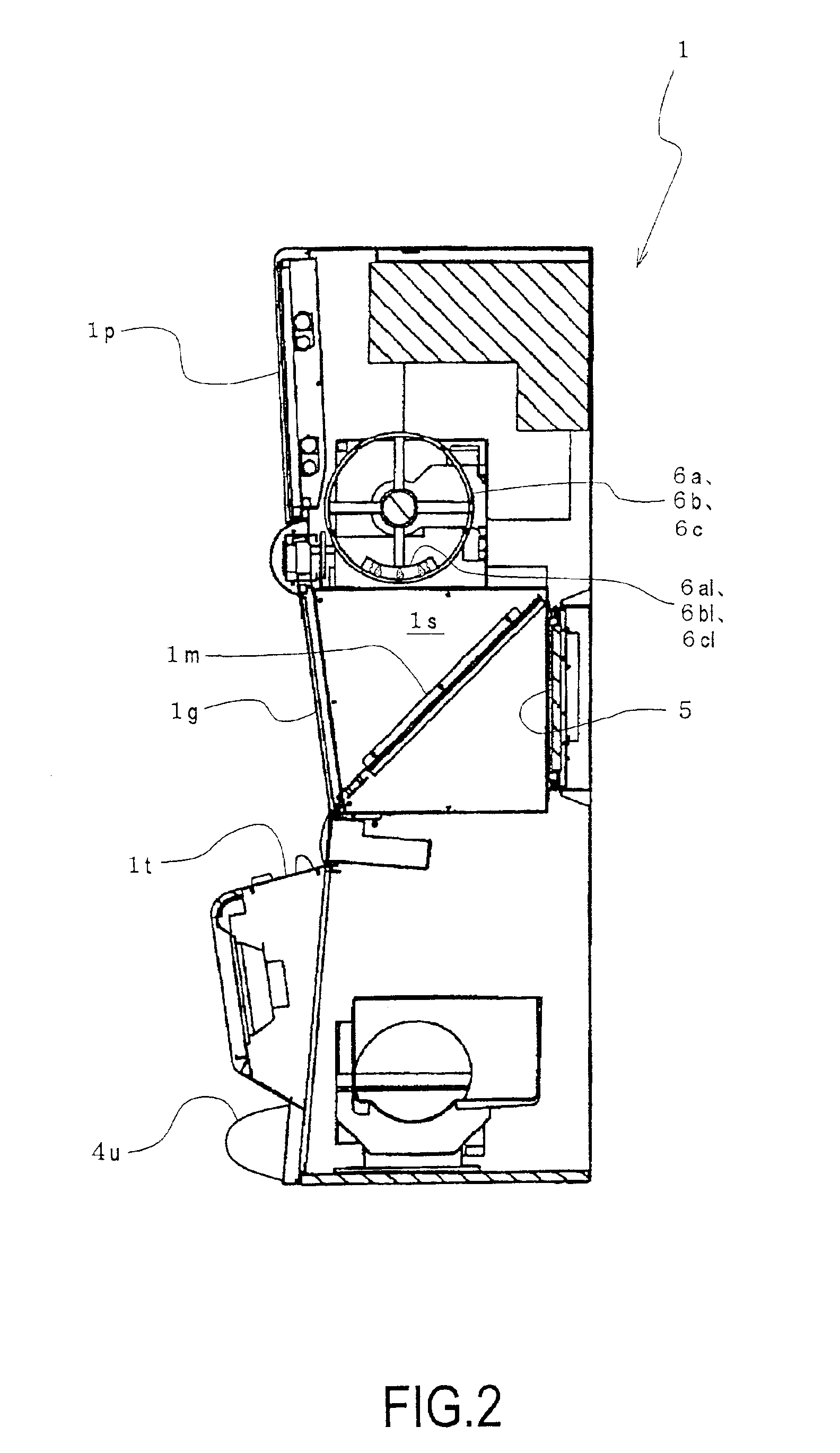
ActiveUS6893345B2Rich representationDifficult to noticeRoulette gamesApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingDisplay deviceImage structure
An object of the present invention is to provide an image mutual transfer and succession method between a virtual image and a real image capable of performing the smooth transfer between the display of a virtual image of a real item and the display of a real image, realizing the successful combination of the reality of the real item and the fantasy of the real image, and enabling a rich representation.The image mutual transfer and succession method between a virtual image and a real image according to the present invention performs take-over control of mutual images by structuring the real image of the display to be apparently identical to the virtual image, displaying the real image on the display in synchronization with the dimming of illumination to the real item when displaying the real image, and brightening the illumination to the real item in synchronization with the stoppage of the real image display on the display device when displaying the virtual image.
Owner:KONAMI DIGITAL ENTERTAINMENT CO LTD
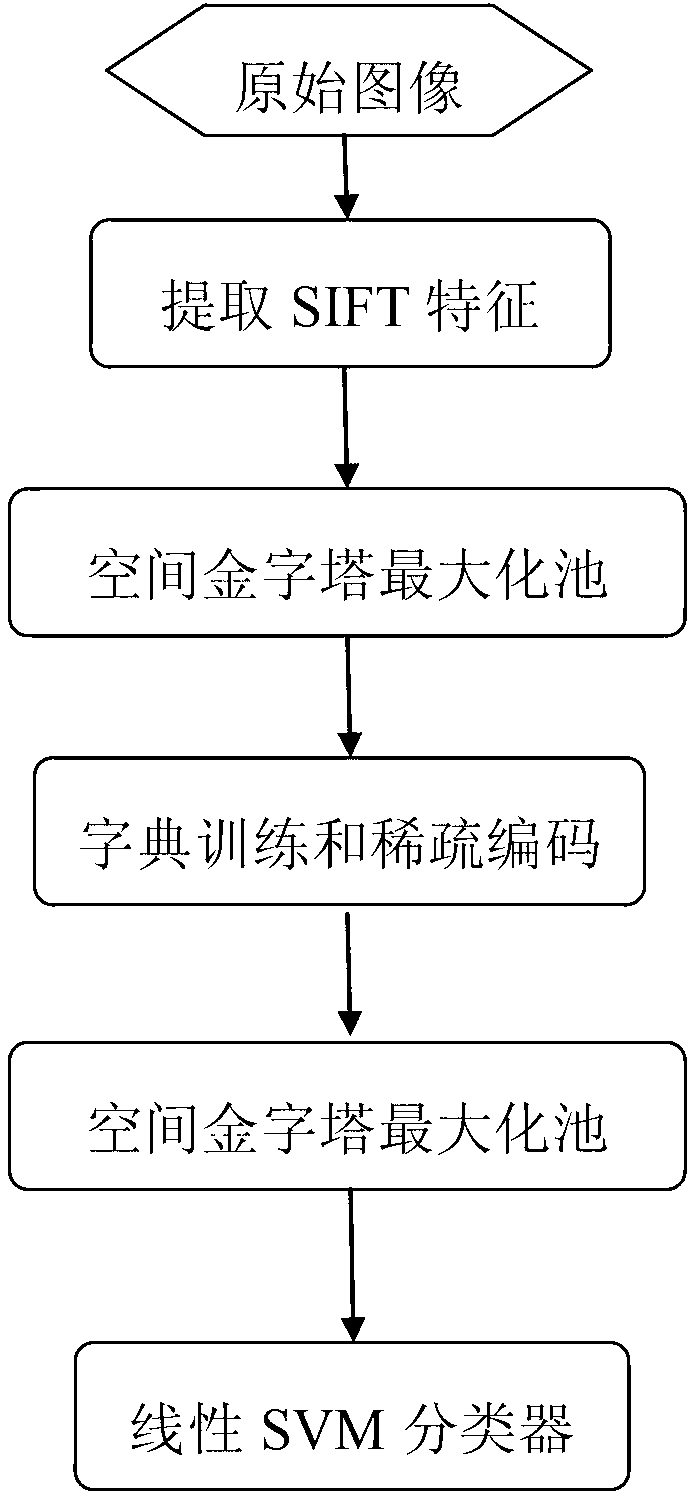
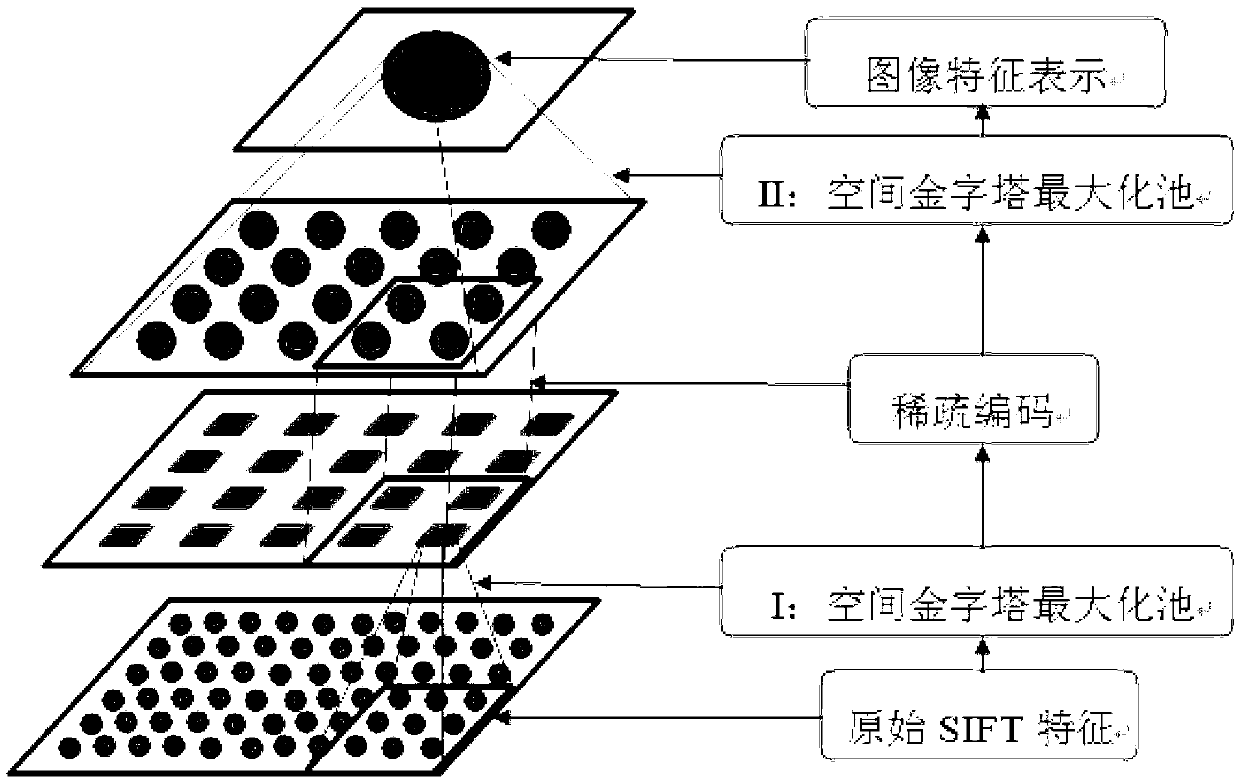
Image classification method based on hierarchical SIFT (scale-invariant feature transform) features and sparse coding
InactiveCN103020647AReduce the dimensionality of SIFT featuresHigh simulationCharacter and pattern recognitionSingular value decompositionData set
The invention discloses an image classification method based on hierarchical SIFT (scale-invariant feature transform) features and sparse coding. The method includes the implementation steps: (1) extracting 512-dimension scale unchanged SIFT features from each image in a data set according to 8-pixel step length and 32X32 pixel blocks; (2) applying a space maximization pool method to the SIFT features of each image block so that a 168-dimension vector y is obtained; (3) selecting several blocks from all 32X32 image blocks in the data set randomly and training a dictionary D by the aid of a K-singular value decomposition method; (4) as for the vectors y of all blocks in each image, performing sparse representation for the dictionary D; (5) applying the method in the step (2) for all sparse representations of each image so that feature representations of the whole image are obtained; and (6) inputting the feature representations of the images into a linear SVM (support vector machine) classifier so that classification results of the images are obtained. The image classification method has the advantages of capabilities of capturing local image structured information and removing image low-level feature redundancy and can be used for target identification.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
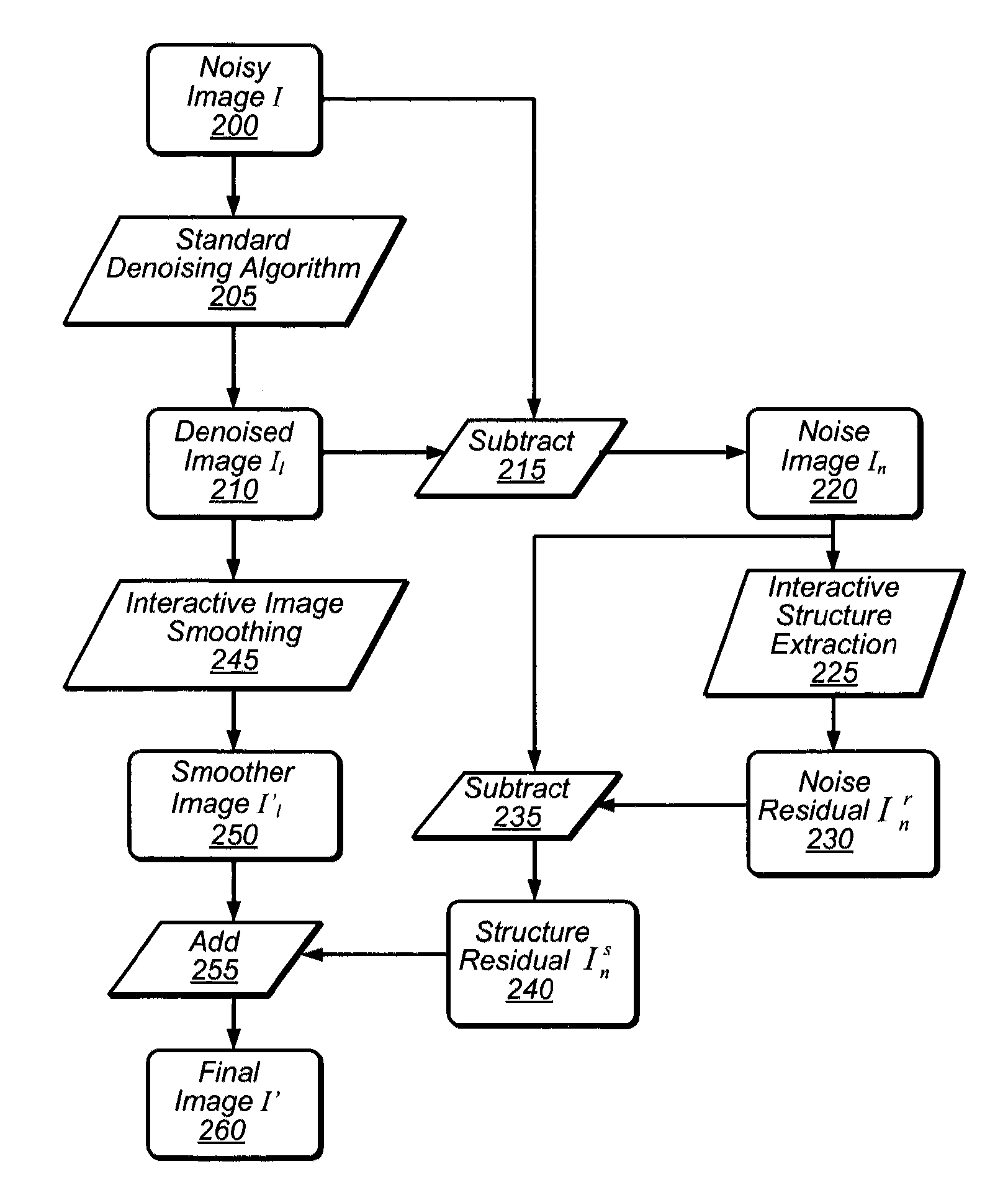
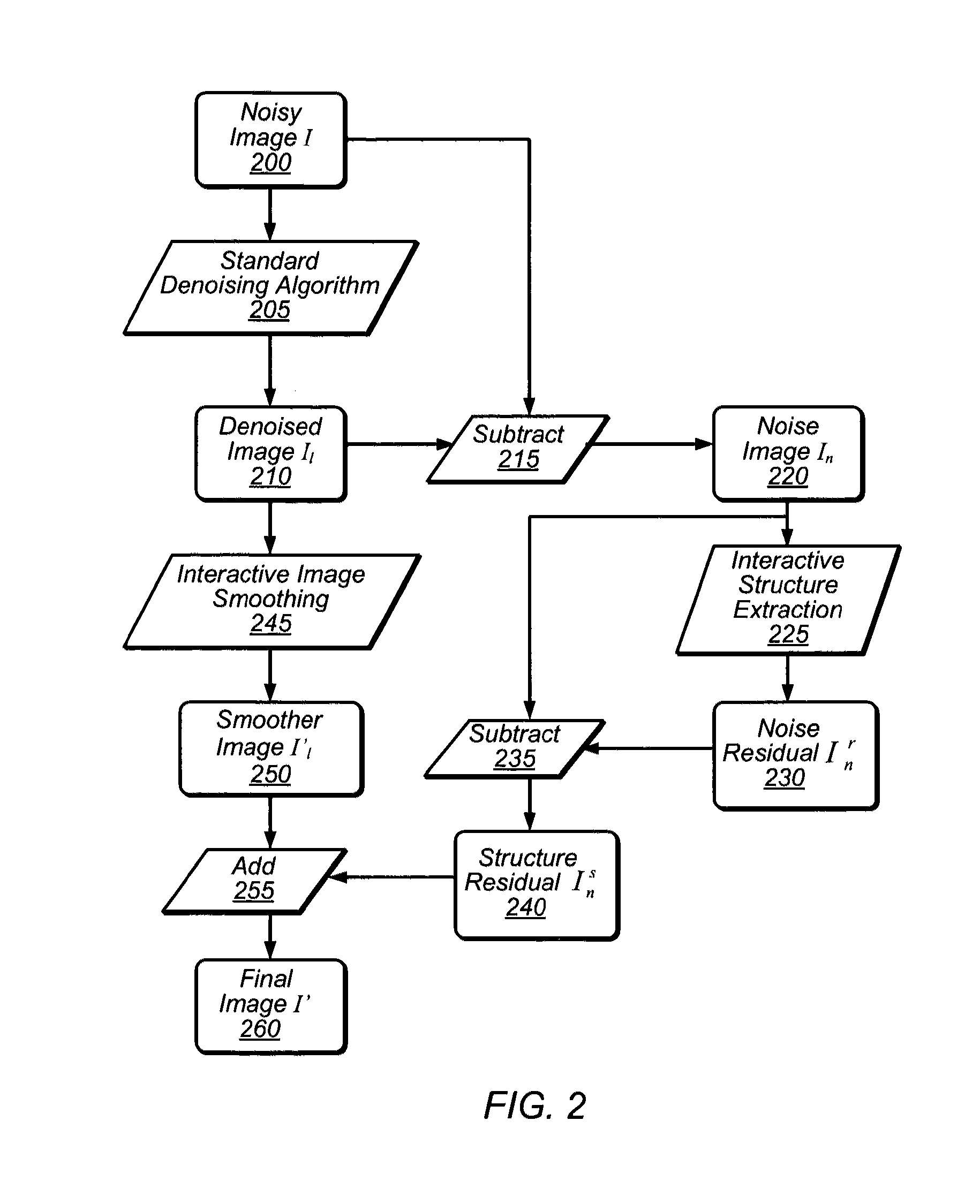
System and method for interactive image-noise separation
ActiveUS8374457B1Improve performanceHigh quality image-noise separation resultImage enhancementImage analysisProgram instructionRandom noise
An interactive system for separating image information from noise information in noisy input images may include a structure-preserving filter capable of separating high- and low-frequency image structures from random noise. The system may access data representing an initially denoised image and a corresponding initial noise layer, apply the structure-preserving filter to the noise layer to extract image structure, and combine the extracted structure with the initially denoised image to produce a refined image, restoring structure incorrectly removed from an image by a previous denoising operation. The system may provide brush tools to identify regions on which to apply the filter and mechanisms to specify filter parameter values. The filter may be applied iteratively to improve results, and may be employed in noise-consistent image editing tasks to preserve original image noise. The filter may be implemented by program instructions stored on a computer readable medium and executable by CPUs and / or GPUs.
Owner:ADOBE INC
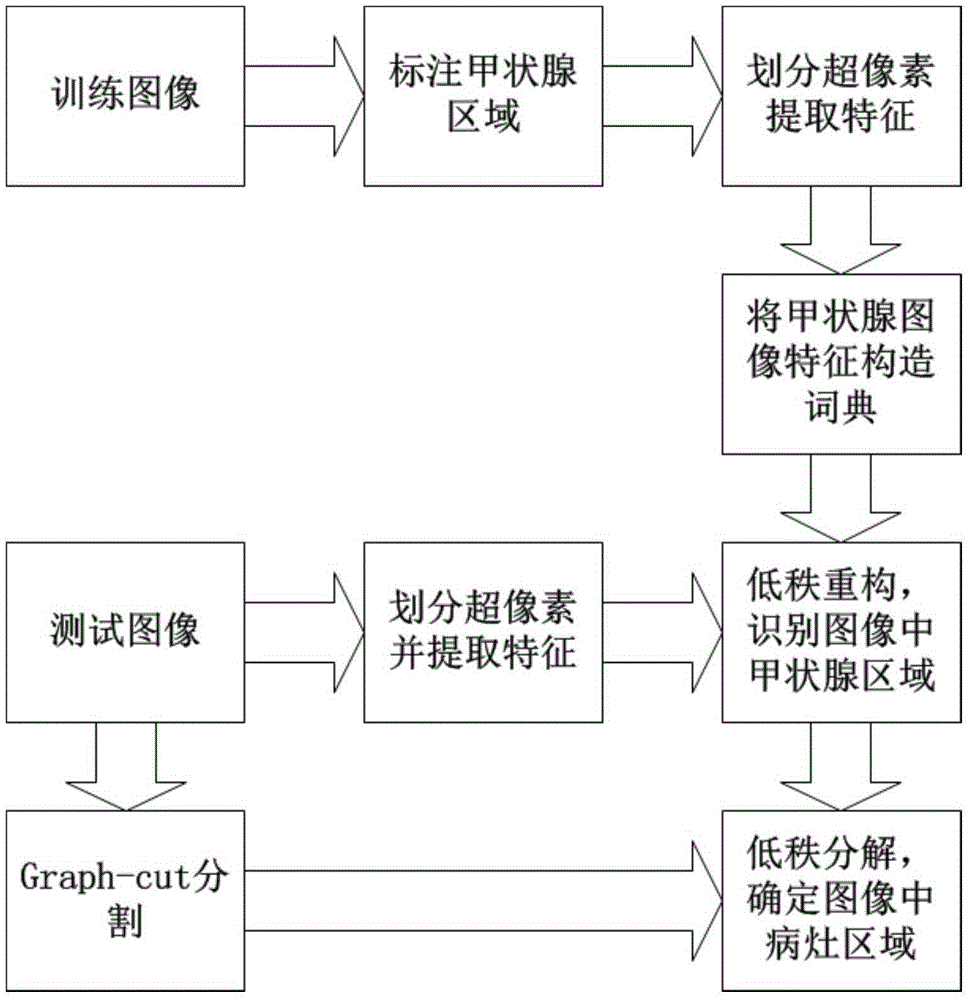
Ultrasonic image low-rank analysis based thyroid lesion image identification method
ActiveCN105427296AEfficient detectionSmall scaleImage enhancementImage analysisSonificationDecomposition
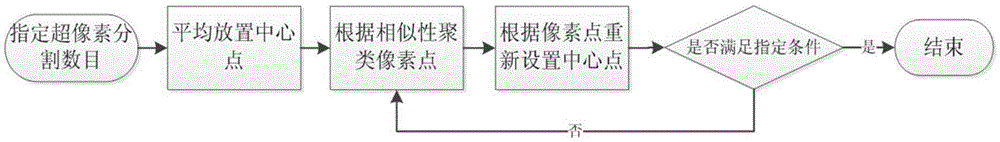
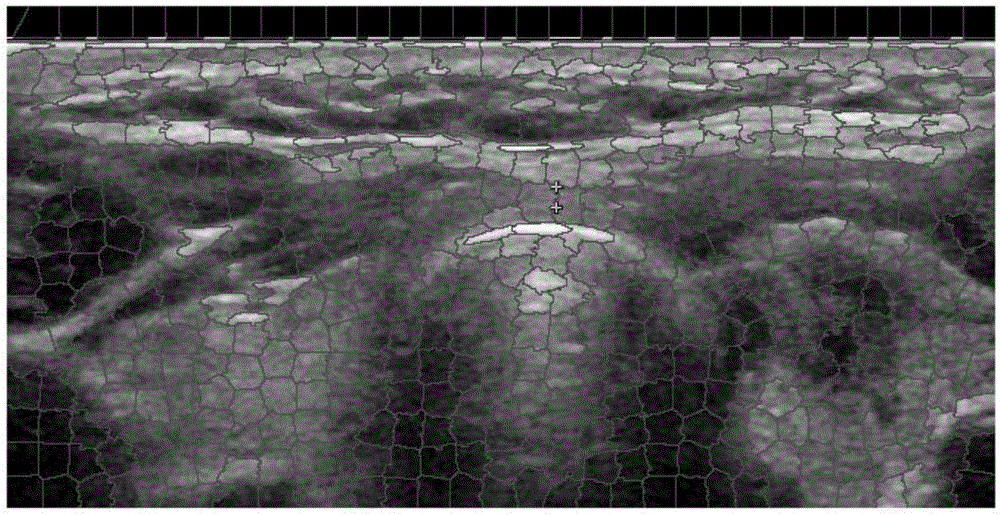
The invention provides an ultrasonic image low-rank analysis based thyroid lesion image identification method. The method comprises three steps of extracting and describing image block-shaped features based on superpixel hierarchy partition: extracting image features in a multi-scale and hierarchical way by taking a superpixel as a unit, removing redundant information of the image by virtue of the superpixel, lowering the complexity of a subsequent image processing task, and giving consideration to acquisition of global and local information; identifying thyroid based on feature space low-rank reconstruction error analysis: according to the low-rank property of image structure information, calculating the similarity between test data and a dictionary in a manner of optimizing a lowest rank, calculating a reconstruction error, and identifying a thyroid region in combination with a graph-cut segmentation algorithm; and detecting a thyroid lesion based on local low-rank decomposition: dividing a data matrix into a matrix with the low-rank property and an error matrix with the sparsity by adopting a low-rank decomposition method, calculating a sparse error, performing significance detection, and determining a lesion region.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Deep deconvolution feature learning network, generating method thereof and image classifying method
ActiveCN104361363AImprove accuracyImprove discrimination abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature learningClassification methods
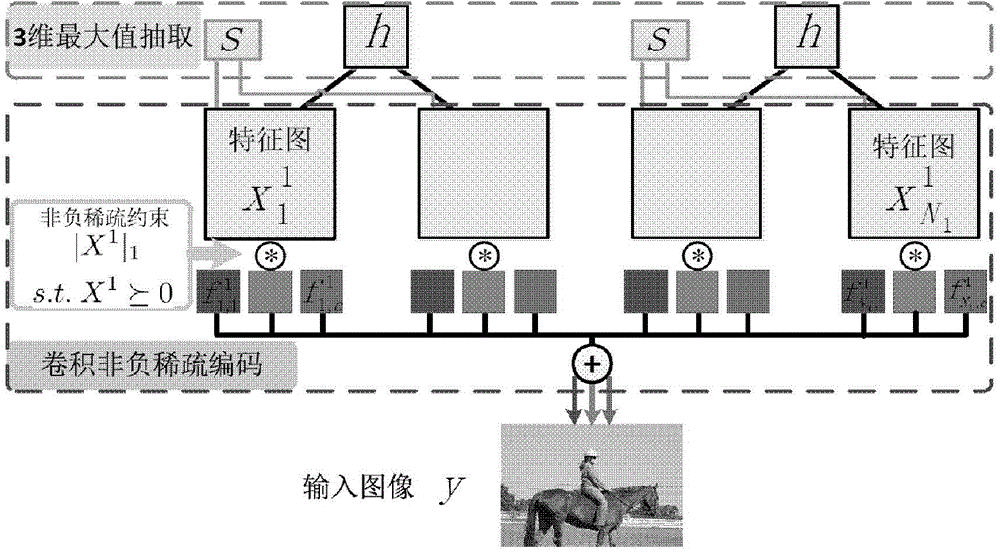
The invention discloses a generating method of a deep deconvolution feature learning network. The generating method comprises the steps that a multi-layer deconvolution feature learning network model is pre-trained in an unsupervised mode; fine adjustment of the learning network model is conducted with object detecting information from top to bottom. The invention further provides the deep deconvolution feature learning network and an image classifying method, wherein the deep deconvolution feature learning network is generated according to the generating method. According to the generating method of the deep deconvolution feature learning network, non-negative sparsity restraints are introduced into the deep feature learning model, the recognition capacity of features is improved, and the image classification accuracy is improved; the object detection information is used as high-level guiding information from top to bottom for fine adjustment of the trained network, so that different nodes in the network have high selectivity for input image structures, especially the nodes on the highest level have different responses to different object types, in this way, obtained high-level features have obvious semantic meaning, and the image classification accuracy is improved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
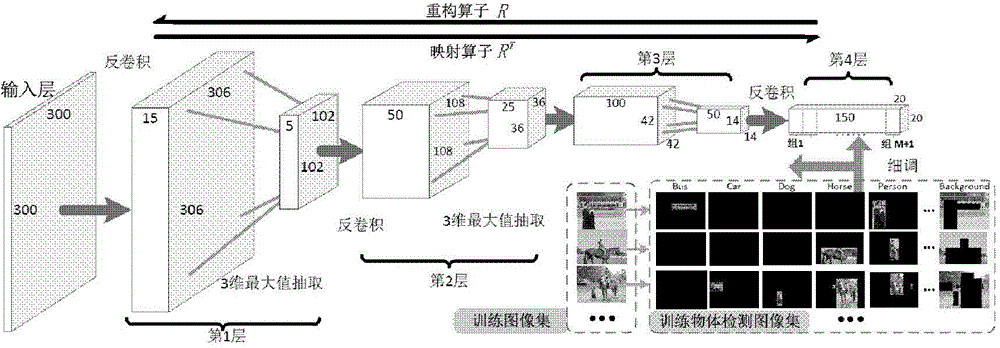
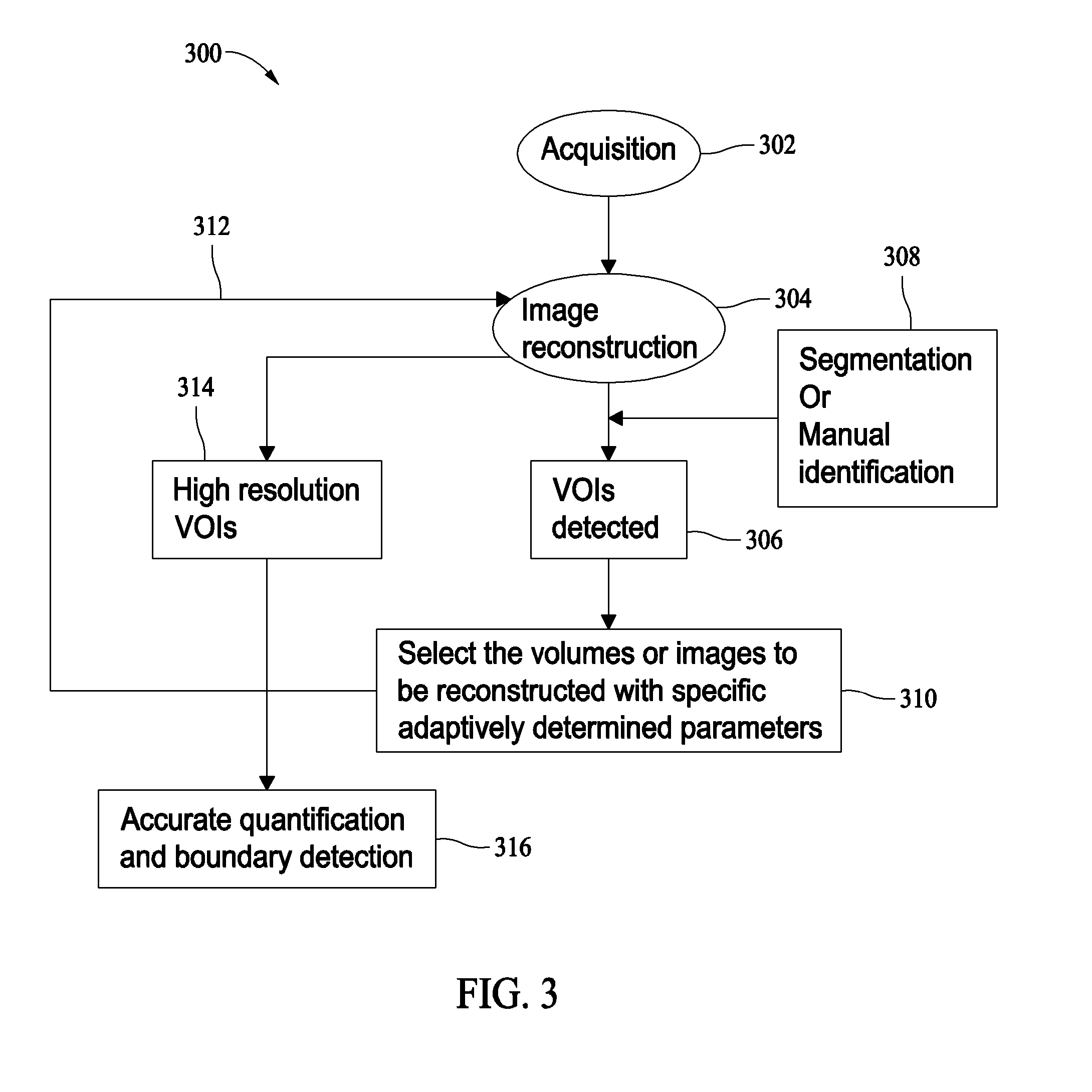
Methods and systems for optimizing high resolution image reconstruction
ActiveUS20080118021A1Image structure is facilitatedEasy to quantifyReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImage resolutionReconstruction method
Methods and apparatus for reconstructing a multiple resolution images of an object are provided. The method includes reconstructing a first three-dimensional image at a first resolution, determining at least one volume of interest in the generated image, and reconstructing a second three-dimensional image of the determined at least one volume of interest at a second resolution, the second resolution being higher than the first resolution such that a quantification of image structures is facilitated.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
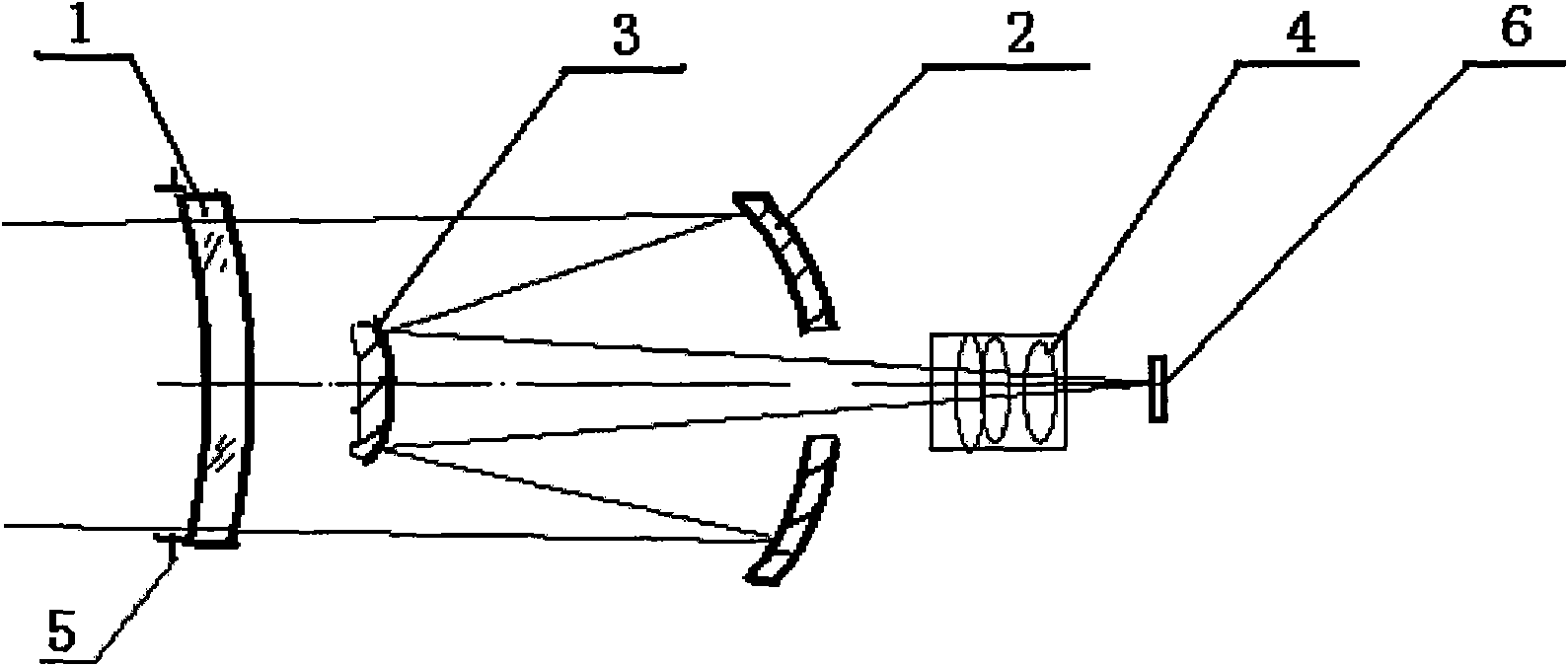
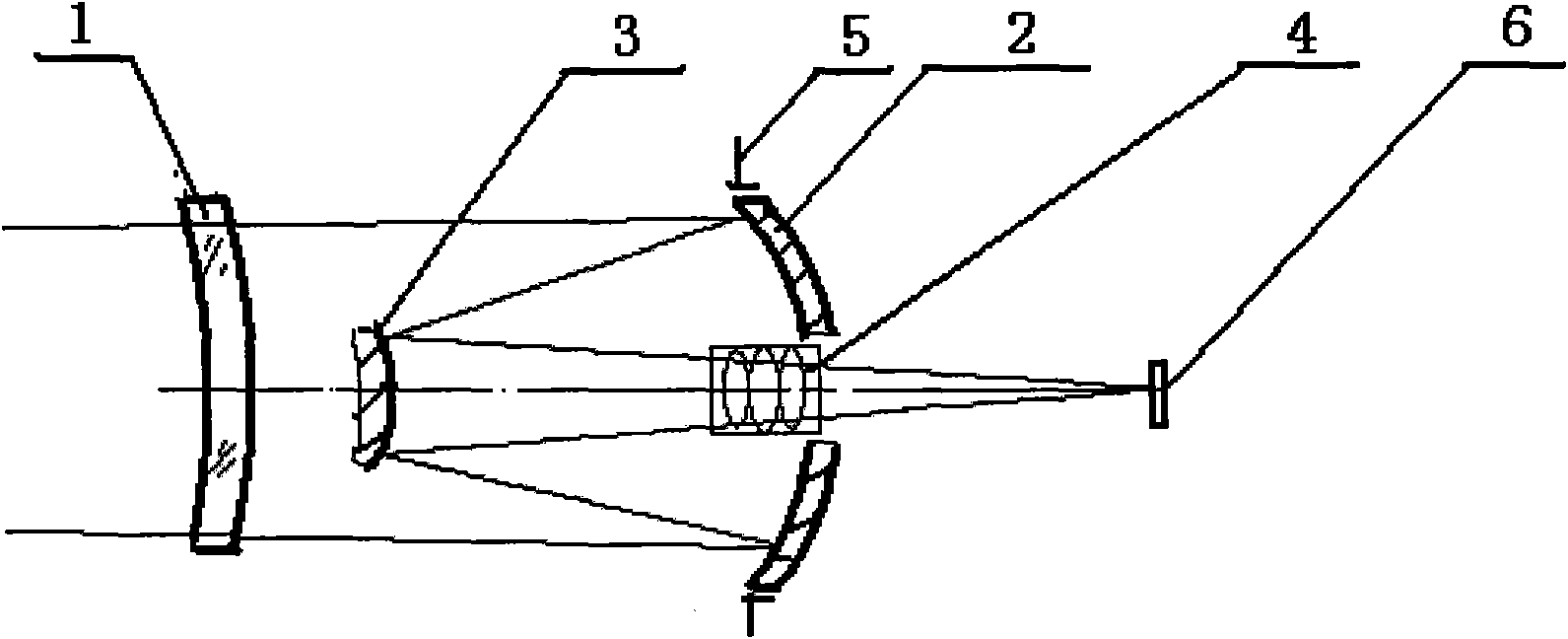
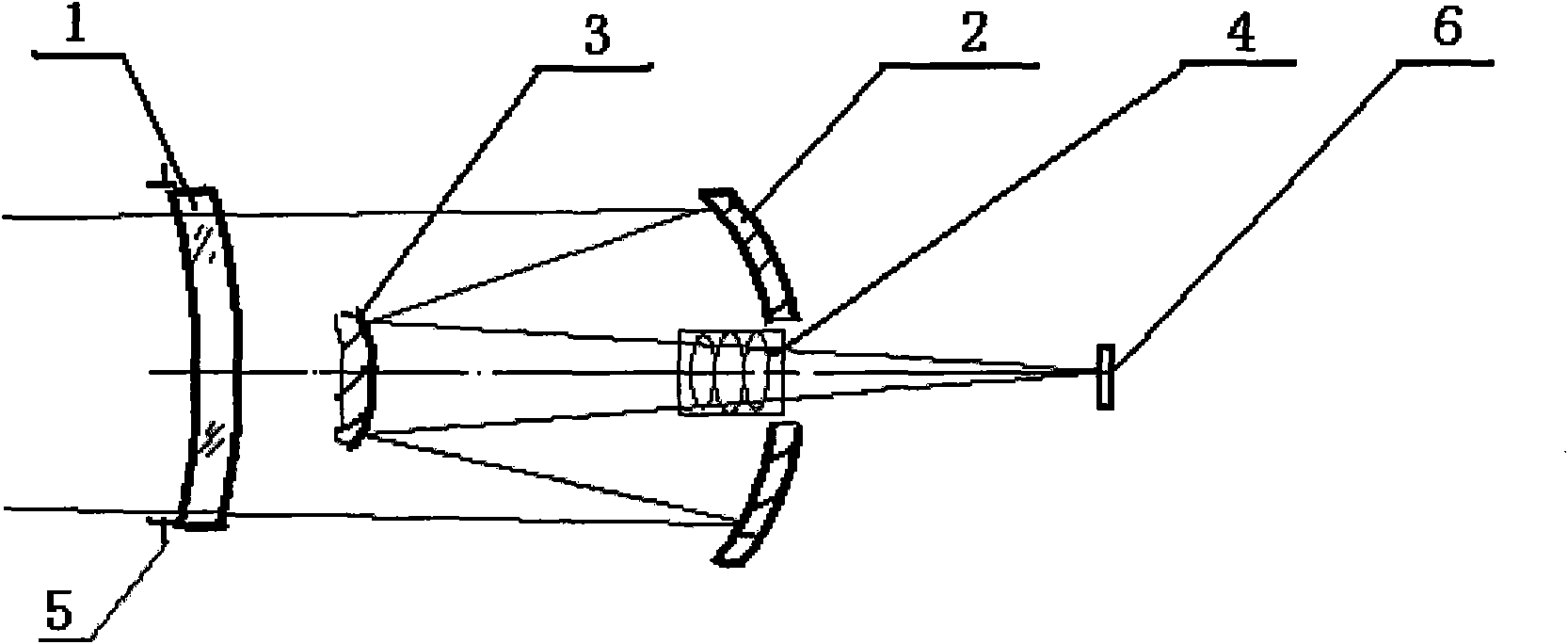
Imaging structure of fixed star sensor
ActiveCN102116926APlay the role of correcting aberrationsReduce processing difficultyNavigation by astronomical meansOptical elementsFixed starsSpace environment
The present invention belongs to the technical field of deep space navigation sensor, specifically discloses an imaging structure of a fixed star sensor, wherein a secondary aspheric surface is applied to an optical surface of an aberration correction lens, which not only can correct the aberration to make system imaging reach a level of near diffraction limit, but can also reduce difficulties ofsystem processing and resetting, and save cost; simultaneously the aberration correction lens can play a part in protecting a window, so as to prevent the system from the damage of space environment,such as irradiation, temperature difference, etc.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Compound soft die for wafer-grade nano imprinting of uneven substrate and manufacturing method
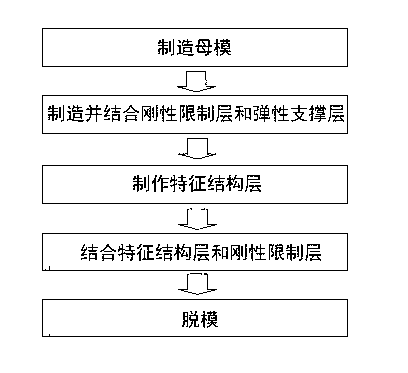
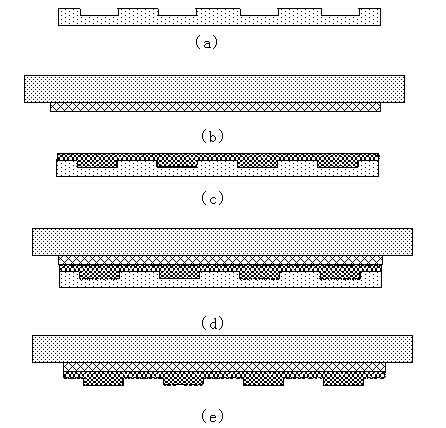
ActiveCN102854741AIncrease elasticityHigh precisionDecorative surface effectsPhotomechanical apparatusMicro nanoPolymer substrate
The invention discloses a compound soft die for wafer-grade nano imprinting of an uneven substrate and a manufacturing method. The compound soft die comprises a characteristic structure layer, a rigid limiting layer and an elastic supporting layer, wherein the characteristic structure layer comprises a micro-nano image structure needing to be copied and is made of a transparent fluorine polymer based material; the rigid limiting layer is located on the characteristic structure layer to limit transverse deformation and vertical deformation of the characteristic structure layer; and the elastic supporting layer is located on the rigid limiting layer. The manufacturing method of the compound soft die comprises the following steps of: (1) manufacturing a female die; (2) manufacturing the rigid limiting layer and the elastic supporting layer, and combining the rigid limiting layer with the elastic supporting layer; (3) manufacturing the characteristic structure layer; (4) combining the characteristic structure layer with the rigid limiting layer; and (5) de-molding. The compound soft die disclosed by the invention has the obvious advantages of high precision, large area, commonly-formed contact capability with the uneven substrate, easiness for de-molding and long service life; and the compound soft die is particularly suitable for a wafer-grade nano imprinting technology of the uneven substrate with a large size and a high resolution.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Memory Based Content Display Interception
In one aspect, the invention relates to a method for blocking or otherwise regulating content. The method includes the steps of intercepting a call to a graphics API; determining if the image meets the requirements for further analysis; and if the image meets the requirements for further analysis, generating a structure to represent the array of pixels in the image; analyzing the image structure for determination of inappropriate content; and preventing the display of the image if the determination is that the content is inappropriate.
Owner:BIOOBSERVATION SYST
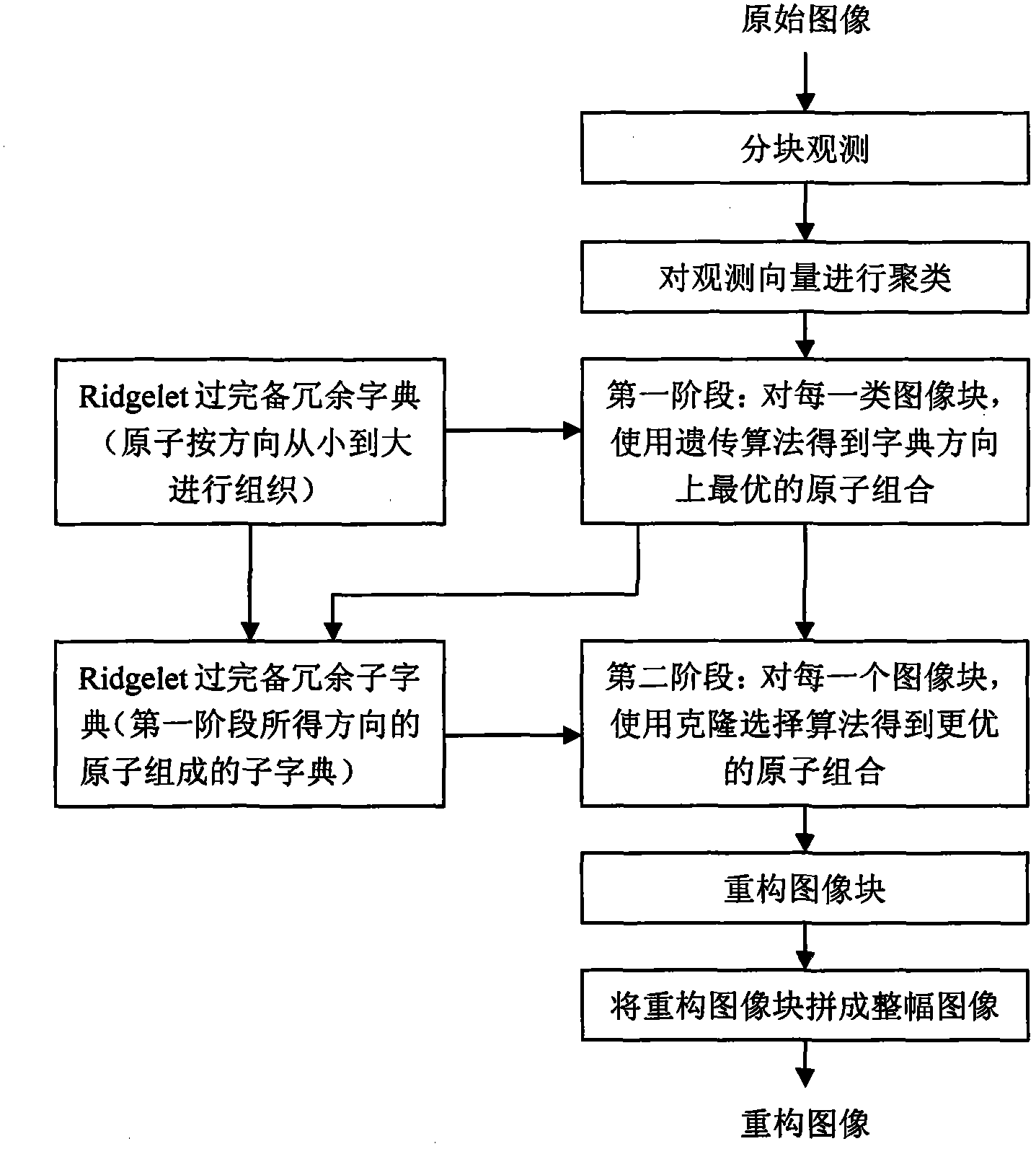
Non-convex compressed sensing image reconstruction method based on redundant dictionary and structure sparsity
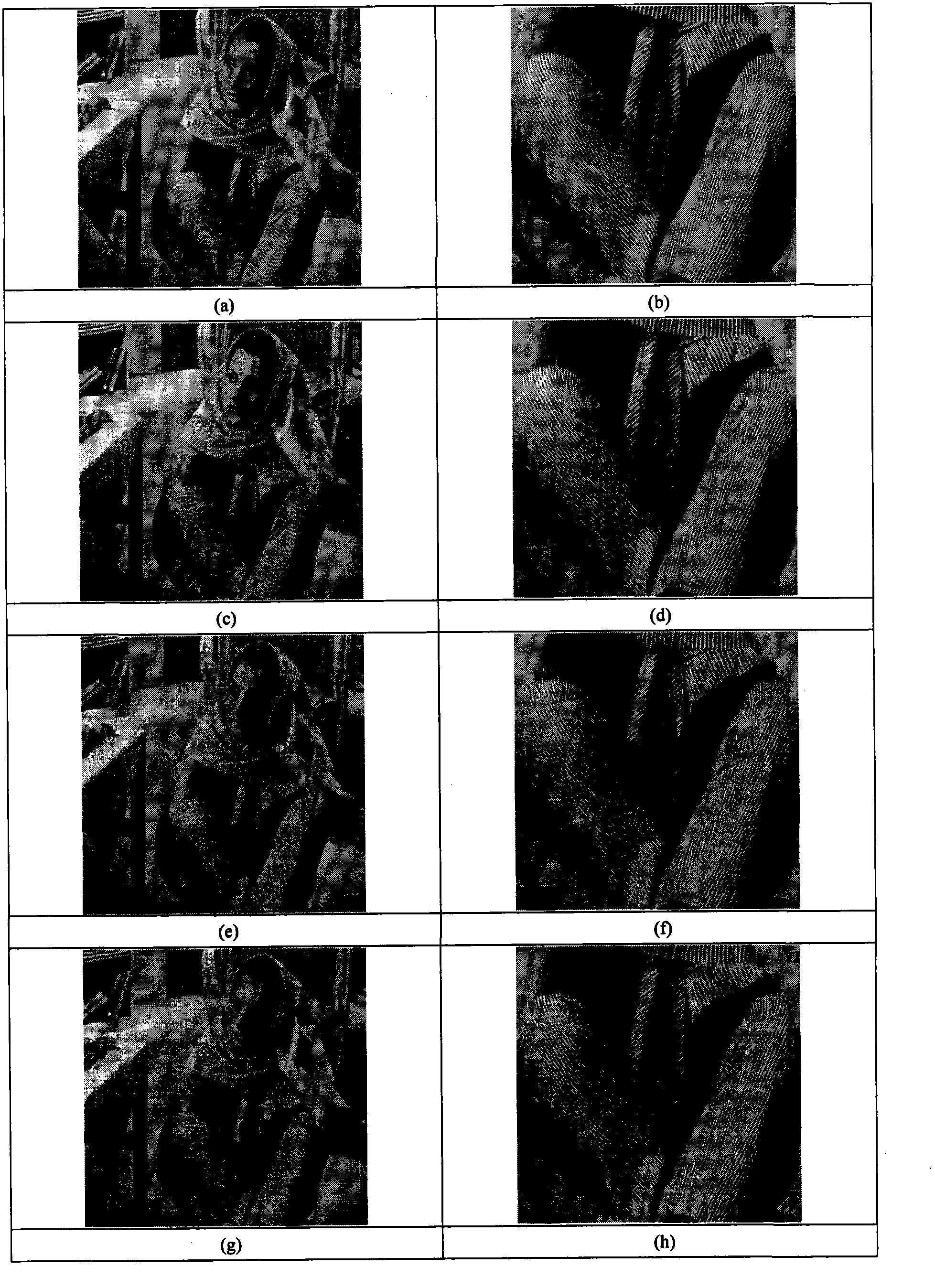
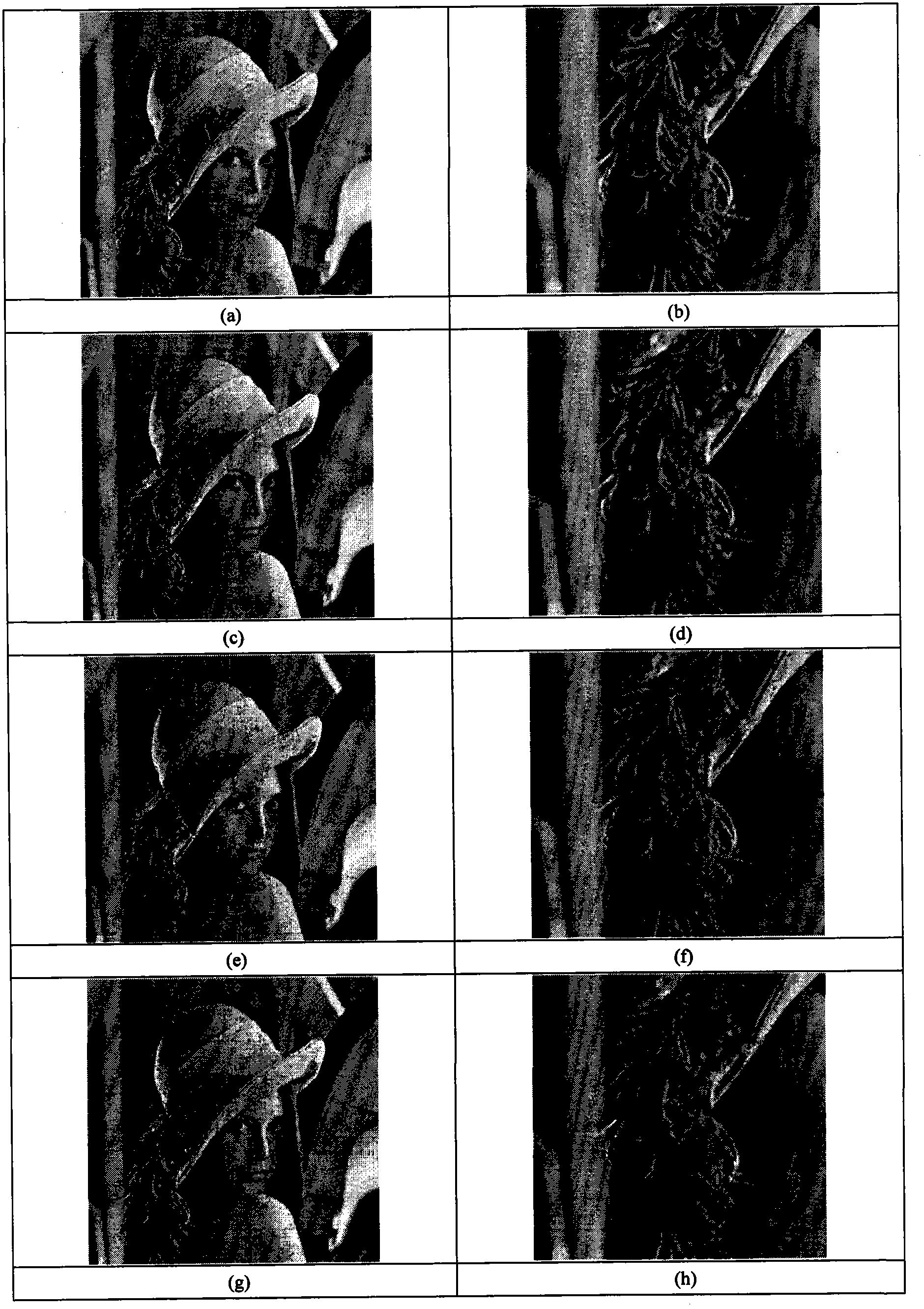
InactiveCN103295198AImprove visual effectsImprove refactoring qualityImage enhancementClonal selection algorithmReconstruction method
The invention discloses a non-convex compressed sensing image reconstruction method based on a redundant dictionary and structure sparsity. A reconstruction process of the method includes: observing original image blocks; using a mutual neighboring technology for clustering observation vectors; using a genetic algorithm for finding optimal atom combinations in a dictionary direction for each class of observation vectors, and preserving species; after species expansion operation is executed on each image block, using a clonal selection algorithm for finding an optimal atom combination on scale and displacement in a determined direction for each image block; reconstructing each image block by the optimal atom combination; and piecing all the constructed image blocks in sequence to form an entire constructed image. Image structure sparsity prior and redundant dictionary direction features are fully utilized, the genetic algorithm is combined with the clonal selection algorithm, and the method is used as a nonlinear optimization reconstruction method to realize image reconstruction. The reconstructed image is good in visual effect, high in peak signal noise ratio and structural similarity, and the method can be used for non-convex compressed sensing reconstruction of image signals.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
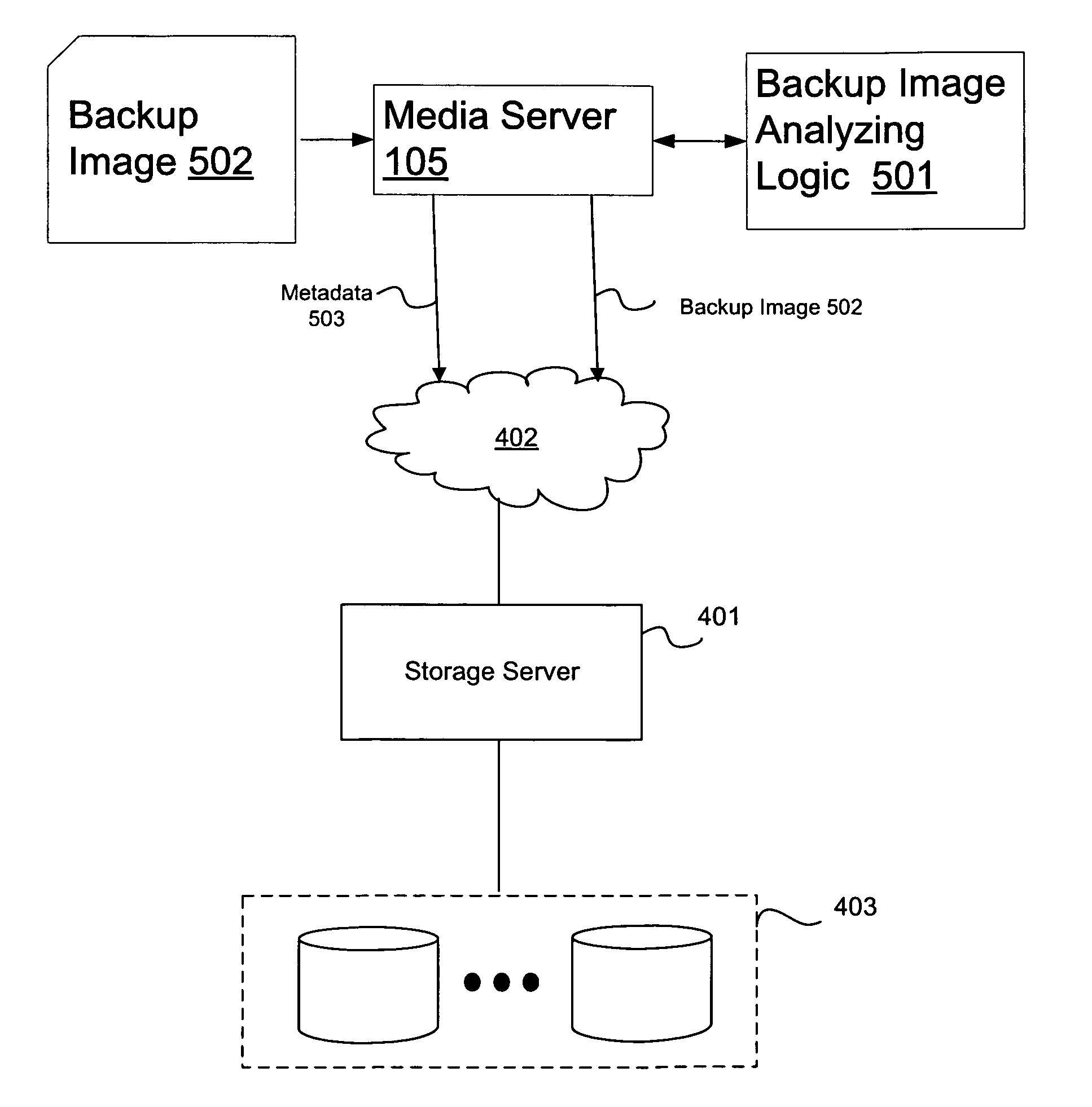
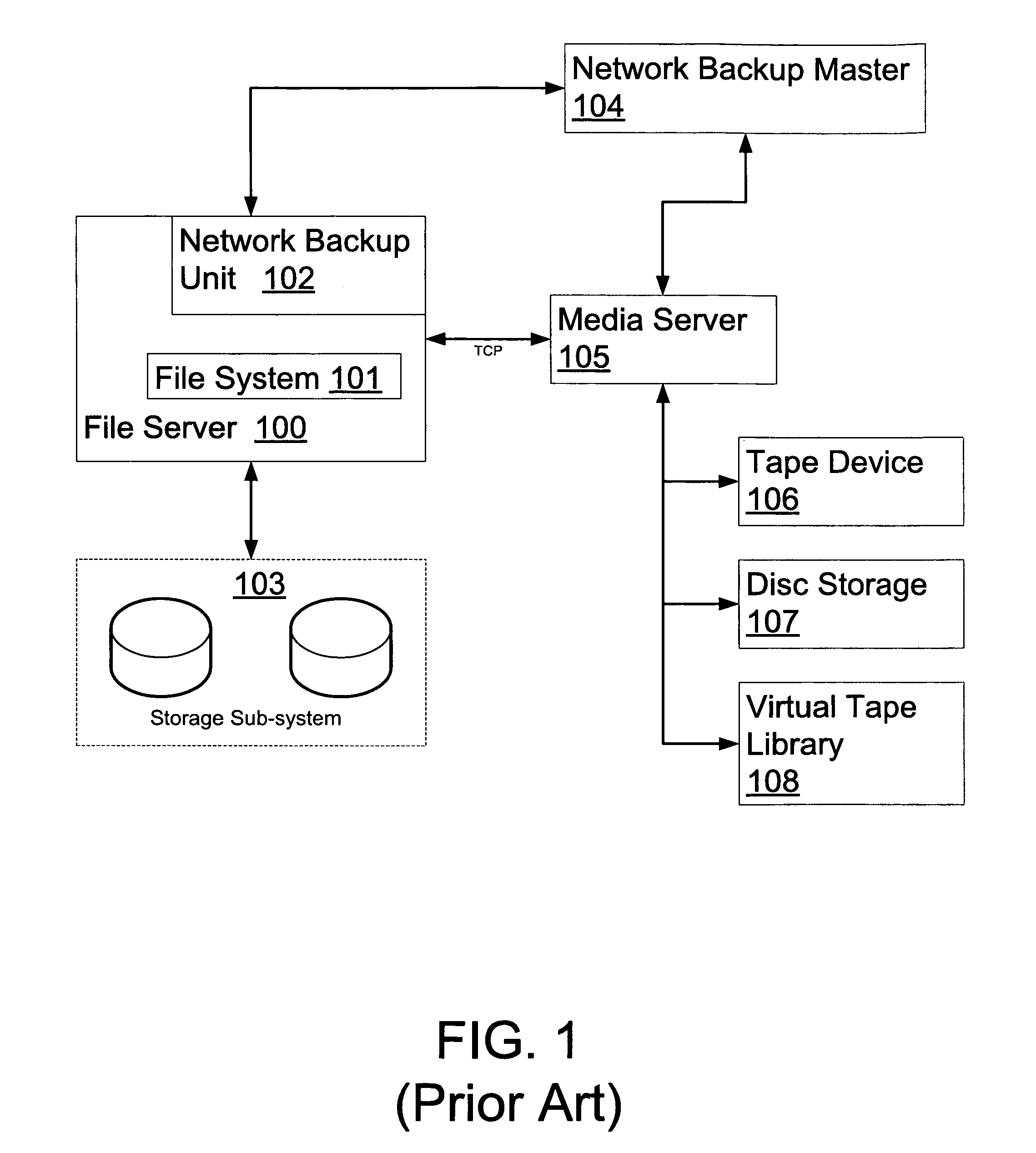
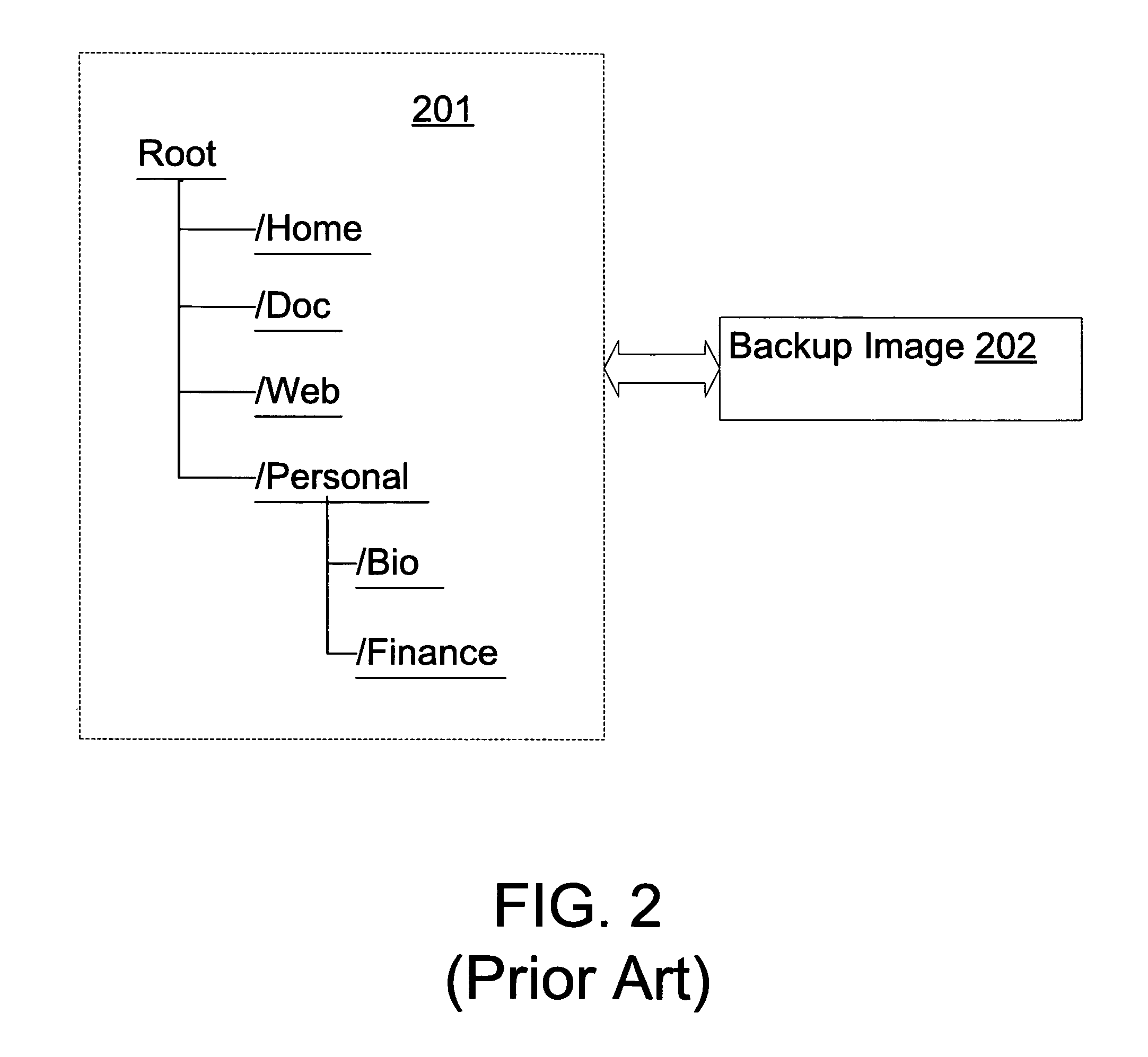
Method and system of using a backup image for multiple purposes
A method for utilizing a backup image of a dataset for multiple purposes, including modifying or deleting any data thereof, yet without changing or modifying the original backup image such that it may be used for backup / restore purposes later. Upon a request to access any part of the backup image, a clone of containing that part is created by using block sharing technology such that the clone and the original part share the same data blocks. In addition, upon a request to view an expanded structure of the backup image, a set of metadata describing the structure of the backup image and providing a basis for accessing and locating data stored therein is accessed to create the expanded view.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Natural image denoising method based on regional division
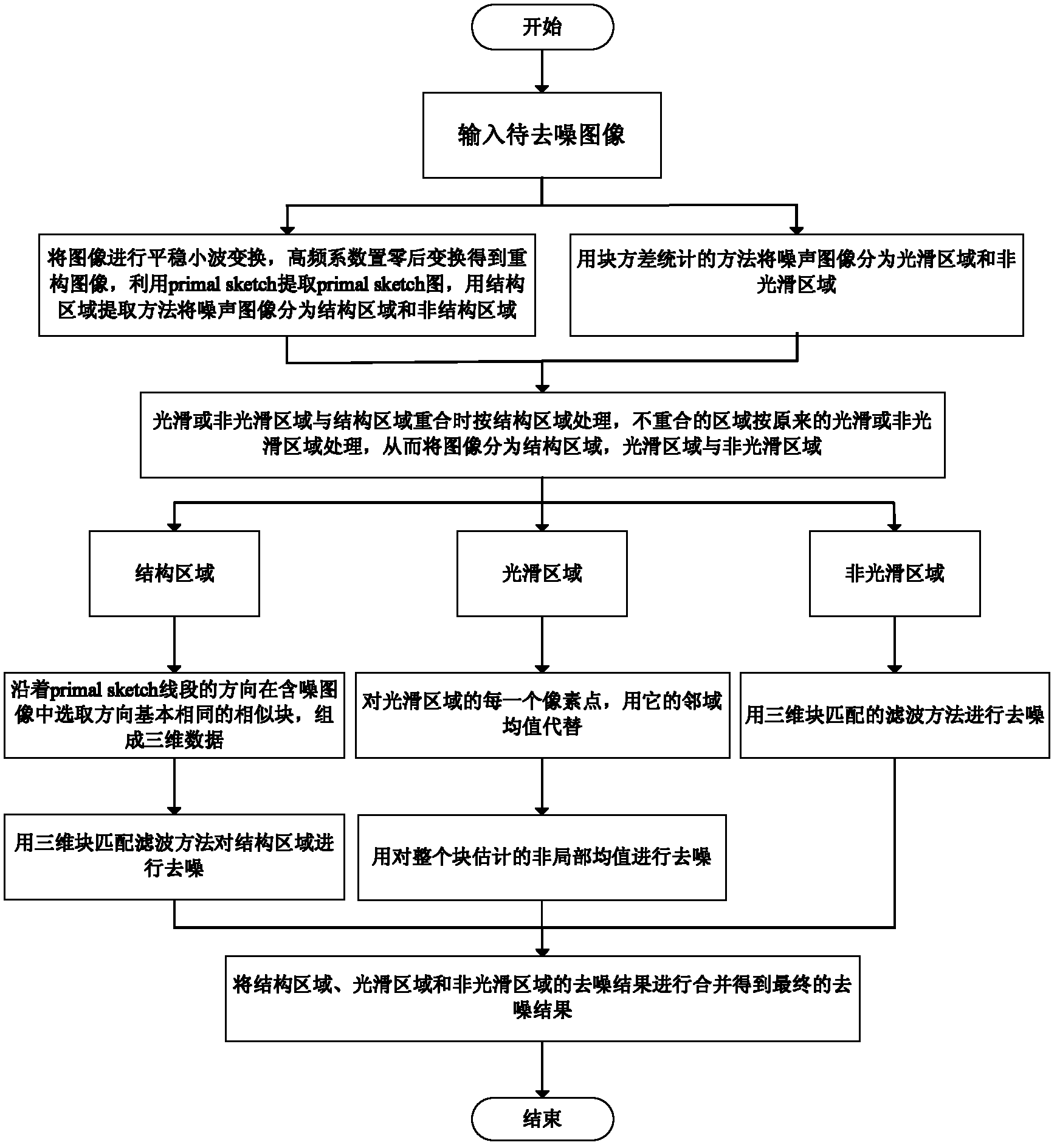
ActiveCN102663702AGood removal effectImprove smoothnessImage enhancementDenoising algorithmBlock match
The invention discloses a natural image denoising method based on the regional division, which mainly solves the problem that patches exist in an image after an image is donoised through the existing three-dimensional block matching denoising algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing two-dimensional stationary wavelet transform on an input image to be denoised, and performing inverse transform on a high frequency coefficient subjected to zero setting, so as to obtain a reconstructed image; secondly, exacting the structural information of the reconstructed image, so as to obtain an image structure sketch; thirdly, dividing the noisy original image into a structure region, a smooth region and a non-smooth region through statistic features of an image block and the image structure sketch; fourthly, performing denoising on the smooth region with an improved non-local mean method, performing denoising on the non-smooth region with a BM3D (Block matching 3D) method, and performing denoising on the structure region with a directional feature-based BM3D method; and fifthly, combining estimated results of the structure region, the smooth region and the non-smooth region, so as to obtain the final denoised image. The method can be used for preprocessing natural images.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for stratigraphic interpretation of seismic images
InactiveUS8027517B2Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging analysisPetroleum exploration
A method for stratigraphic interpretation of a seismic image for determining a sedimentary history of an underground zone having application to petroleum exploration. The seismic reflectors of the image are digitized by means of an applied shape recognition technique. At least one attribute characteristic of the structure of the image in the vicinity of each reflector is calculated for a set of reflectors by means of an image analysis technique. This analysis is based on at least one analysis window whose shape is controlled by the associated reflector. Pertinent reflectors, in the sense of the stratigraphic interpretation, are selected from among this set of reflectors on the basis of this attribute. Finally, the sedimentary history of the underground zone is reconstructed from a stratigraphic interpretation of the reflectors thus selected.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
No-reference image quality evaluation method based on gradient information
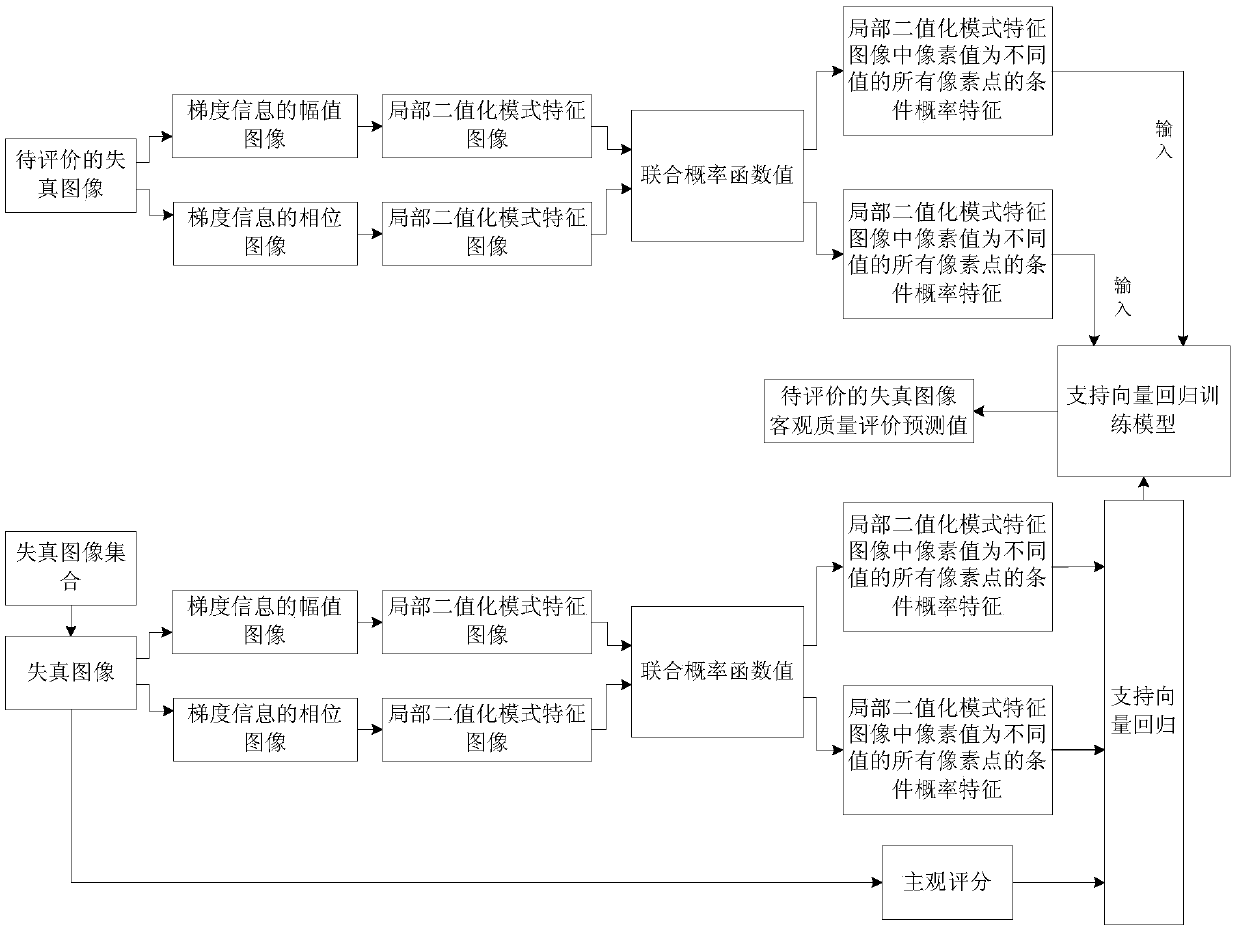
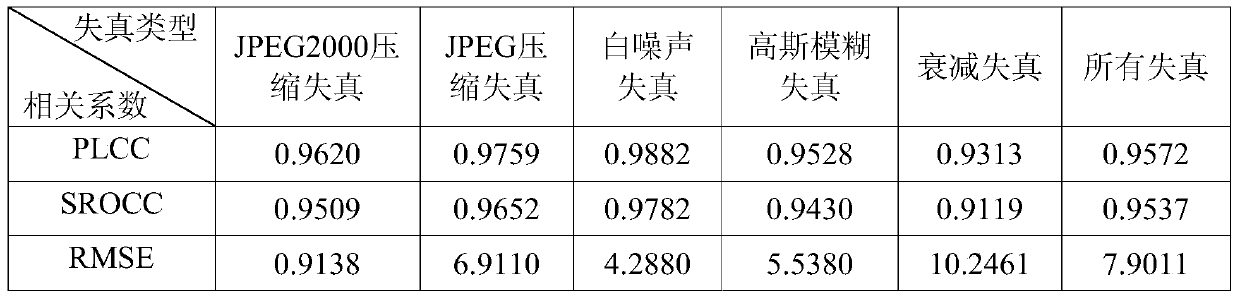
ActiveCN104902267AAccurately reflectImprove relevanceTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationObjective qualityImaging quality
The invention discloses a no-reference image quality evaluation method based on gradient information. Through deep digging of perception characteristics of human vision for image structure, gradient filtering is performed on a distorted image, so as to obtain an amplitude image and a phase image of the gradient information; a local binary pattern operation is performed on the amplitude image and the phase image so as to obtain a local binary pattern characteristic image of the amplitude image and a local binary pattern characteristic image of the phase image; then condition probability characteristics of all pixel points of different pixel values in the amplitude image and the phase image are gained; and finally, according to the condition probability characteristics, an objective quality evaluation prediction value of the distorted image to be evaluated is predicted by use of support vector regression. The method has the advantages that the impact of gradient structure change on visual quality is fully considered, so that the obtained objective quality evaluation prediction value can accurately reflect the subjective perception quality of human vision, and the correlation between an objective evaluation result and subjective perception can be improved effectively.
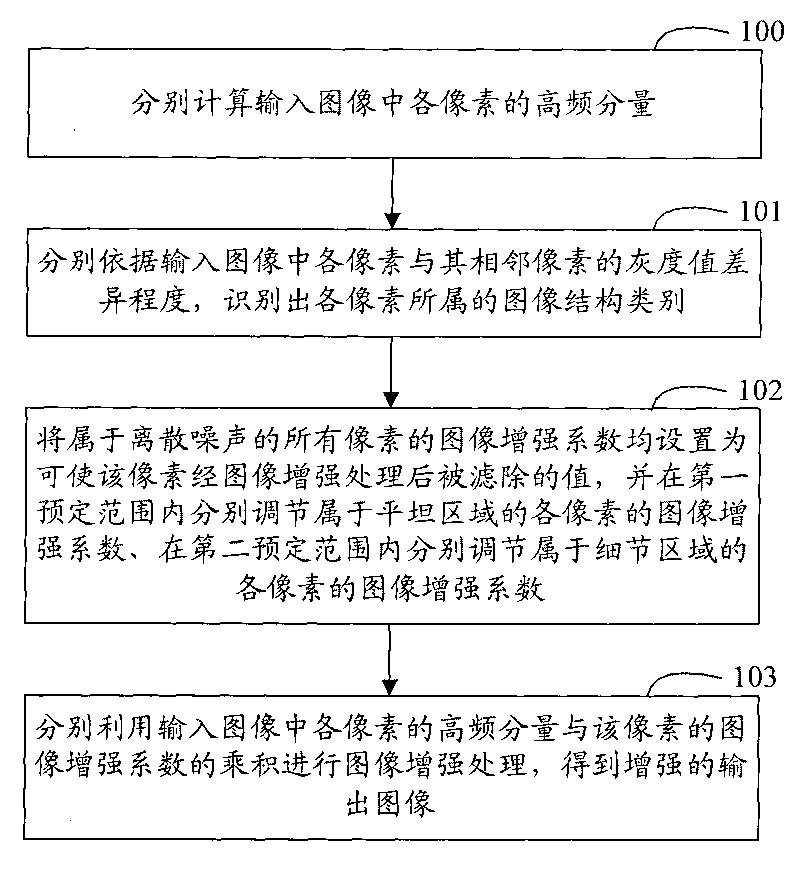
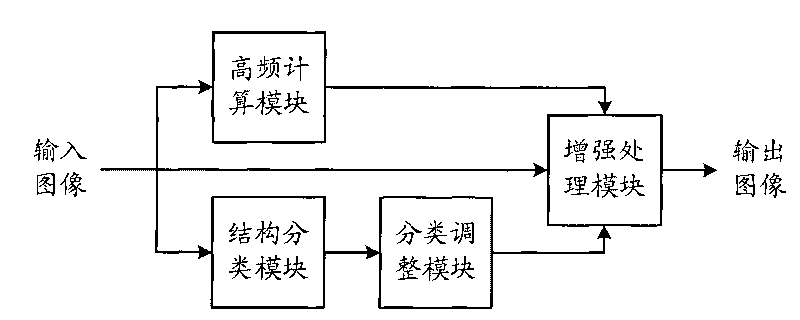
Owner:深圳市深国检珠宝检测有限公司
Metameric security devices using an active material
ActiveUS20130147179A1Not easy to copyImprove performanceOther printing matterCoding/ciphering apparatusElectricityChange color
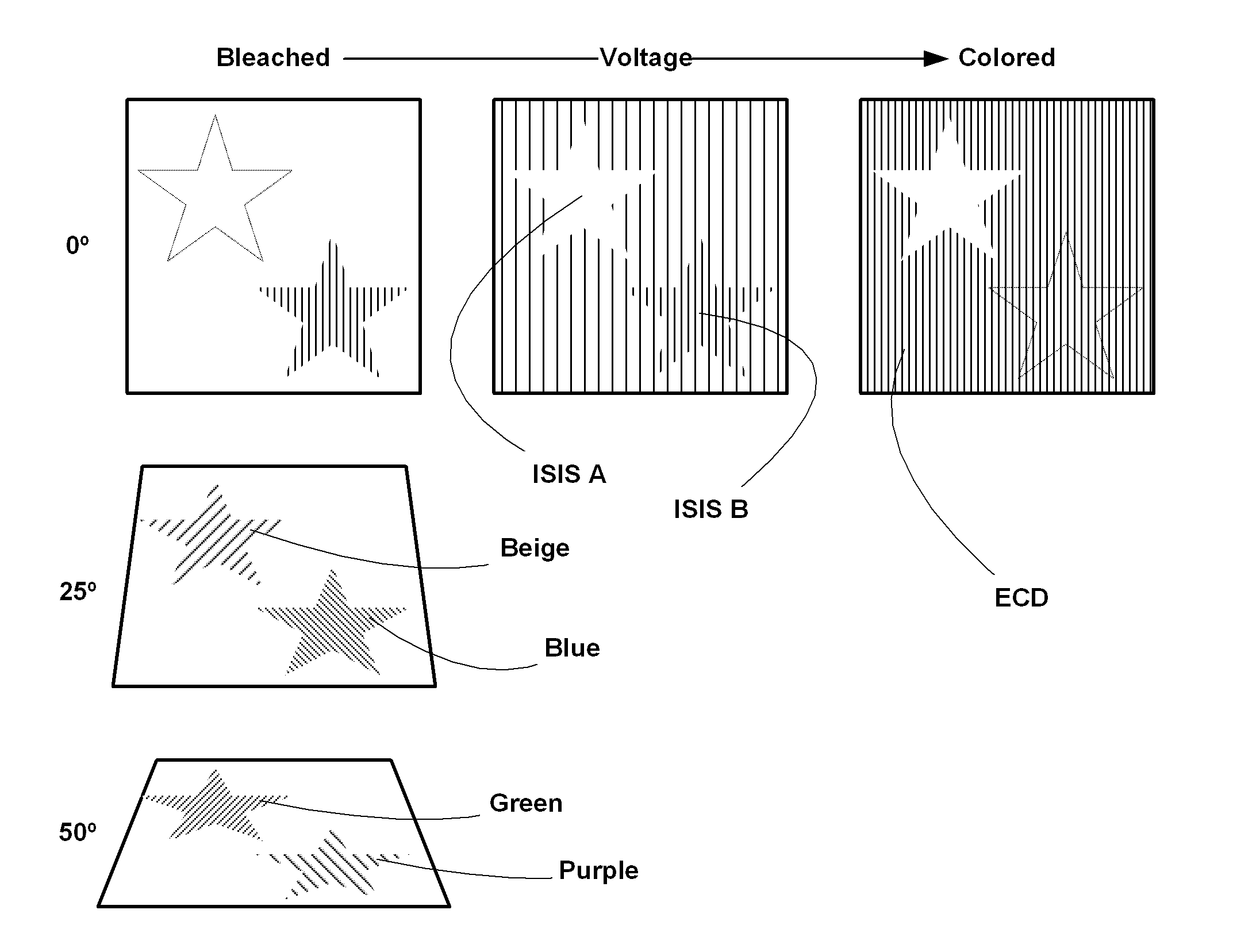
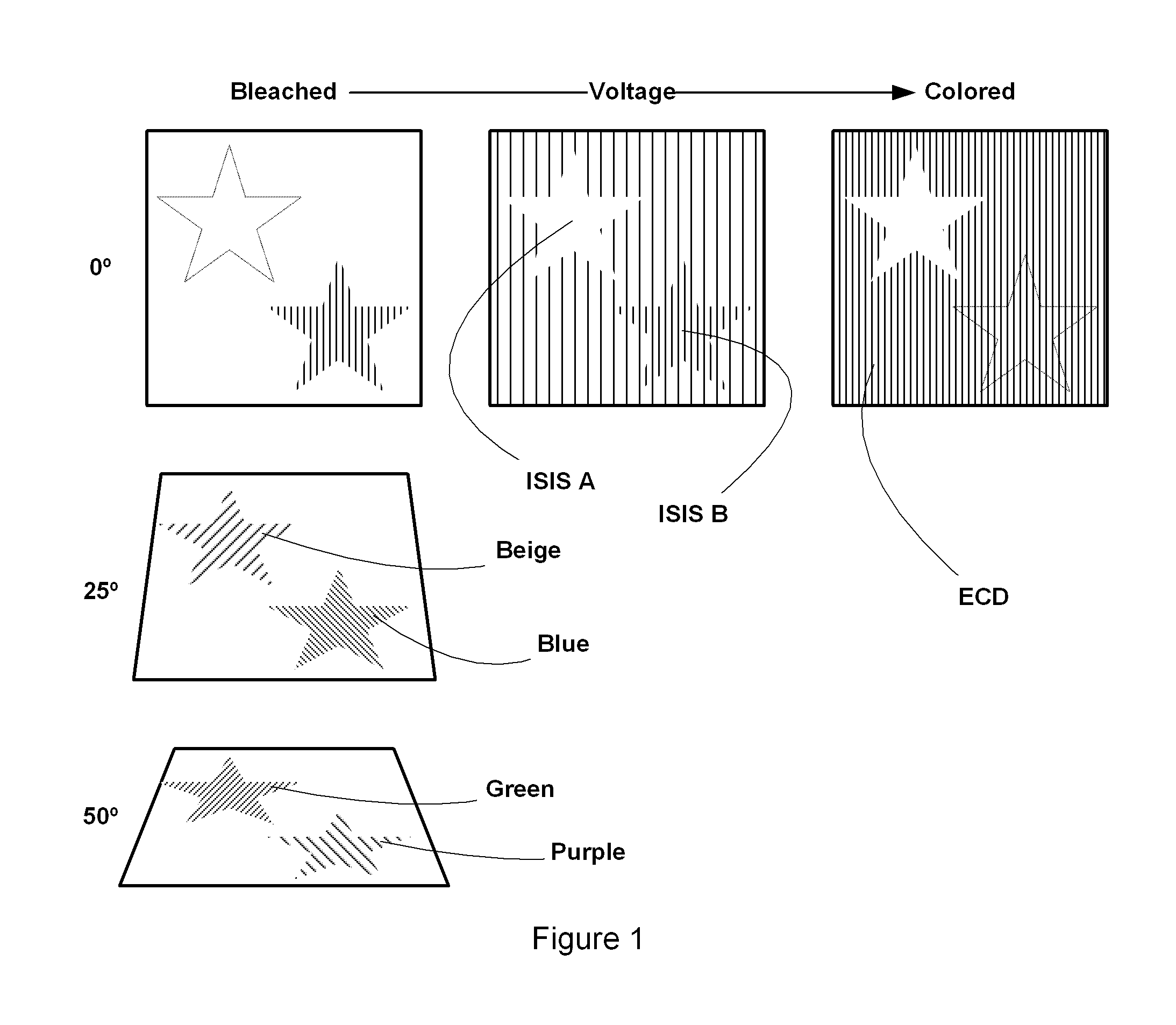
An integrated security structure is provided employing an external source of energy to change the appearance of the structure rendering the structure more challenging to duplicate due to its complexity. The security structure includes a substrate forming part of a bank note, identification document, or other security device; an active device within the substrate changing color between at least two colors wherein a color of the substrate surrounding the active device matches one of the at least two colors to form a metameric device. At least one Interference Security Image Structure (ISIS) is configured to be metameric with a bleached state of the active device and is therefore invisible at normal incidence. Another ISIS is metameric with the colored state of the electrochromic device and consequently becomes invisible during coloration. When the whole device is tilted, both ISIS's change color while the rest of the device essentially remains the same.
Owner:POLYVALOR LP
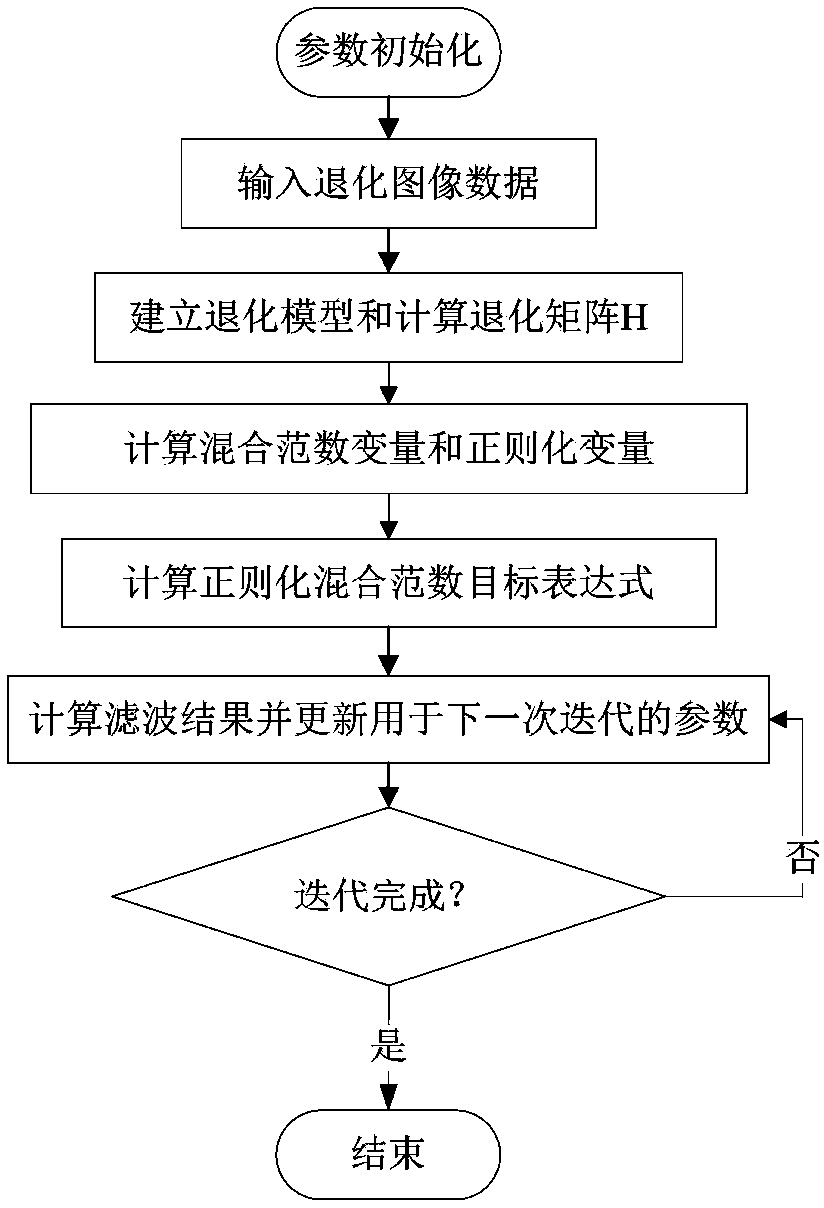
Earthquake image structure guiding noise reduction method based on regularization mixed norm filtering
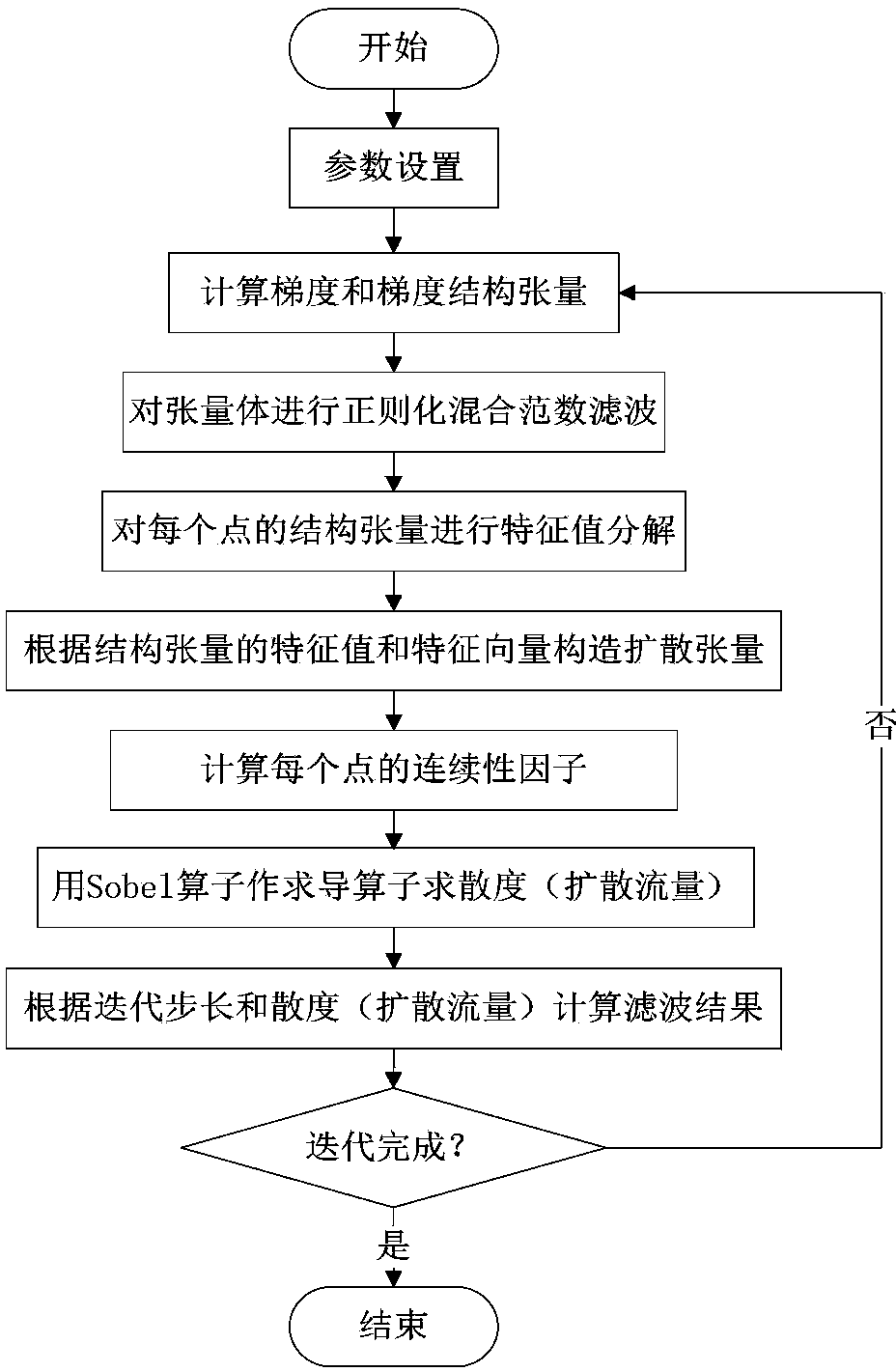
ActiveCN103489163AImprove signal-to-noise ratioPreserve Texture EdgesImage enhancementDiffusionEigenvalues and eigenvectors
The invention discloses an earthquake image structure guiding noise reduction method based on regularization mixed norm filtering. The earthquake image structure guiding noise reduction method includes the following steps that a gradient structure tensor is solved for an input three-dimensional earthquake image; regularization mixed norm filtering is conducted on the gradient structure tensor; a diffusion tensor is designed according to the eigenvalue and eigenvector of the filtered gradient structure tensor; continuity factors are calculated, the continuity factors at the position of a boundary fault feather edge and the like are close to zero, and the maintain performance of the structure is achieved; a sobel operator serves as a derivation operator so that divergence can be calculated. By means of the earthquake image structure guiding noise reduction method based on regularization mixed norm filtering, the textured edge information of earthquake-related data can be reserved, Gaussian noise, ultra Gaussian noise and sub Gaussian noise can be effectively suppressed, and therefore an efficient noise reduction method is achieved.
Owner:OPTICAL SCI & TECH (CHENGDU) LTD
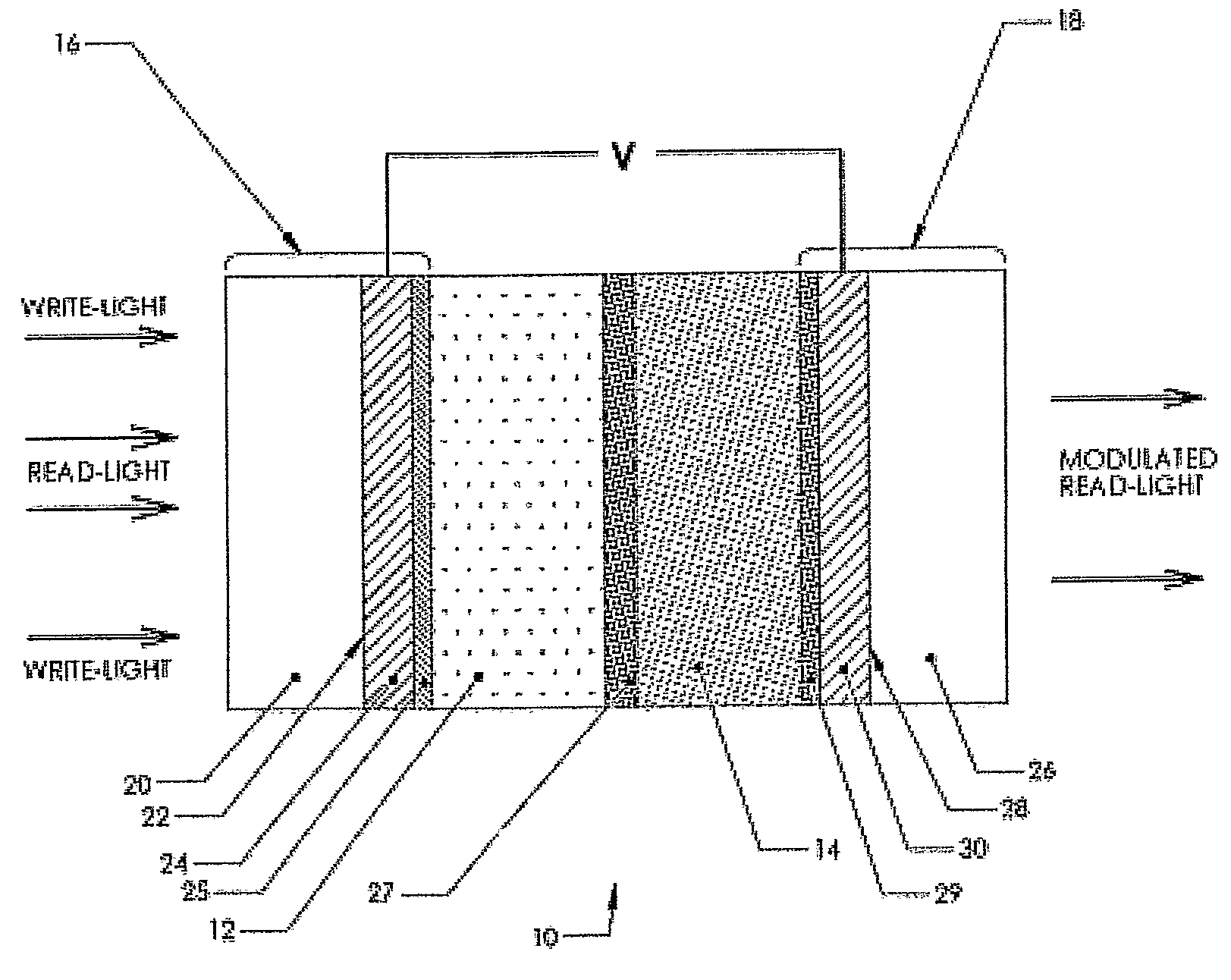
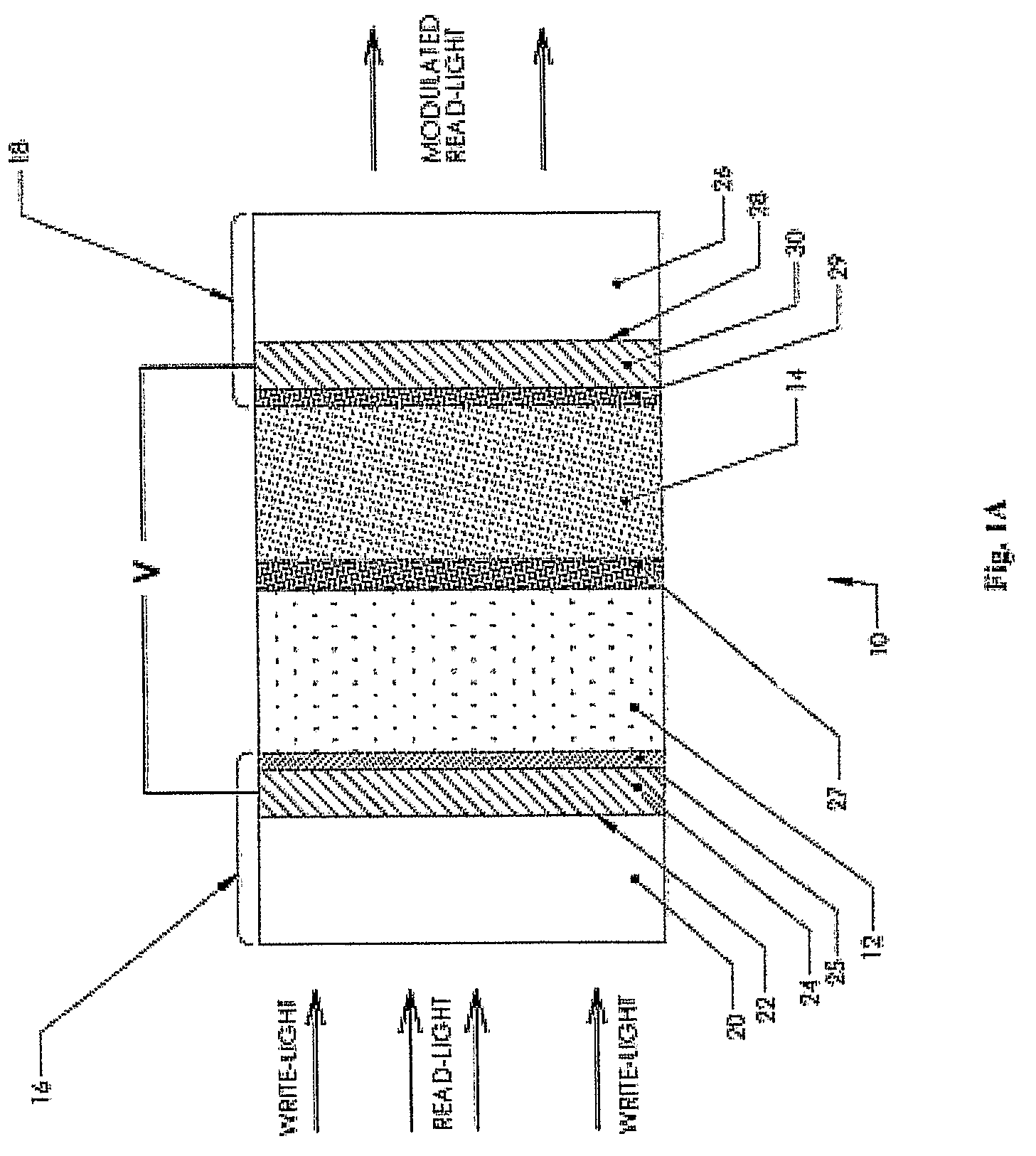
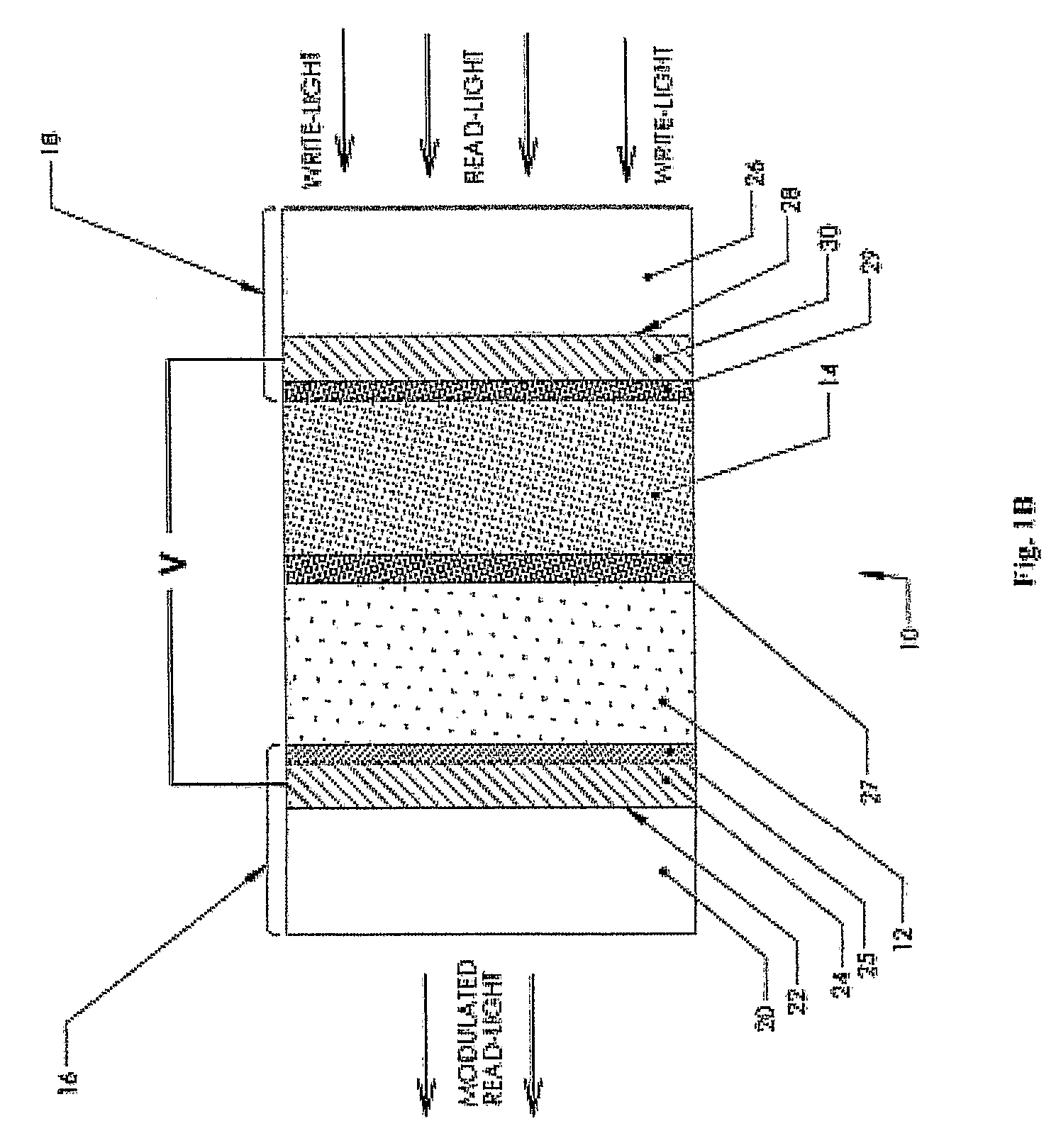
Transmissive, Optically Addressed, Photosensitive Spatial Light Modulators and Color Display Systems Incorporating Same
ActiveUS20080239458A1Sufficient photoconductivityLow costPicture reproducers using projection devicesNon-linear opticsColor imageSpatial light modulator
An optically addressed, photoconductive spatial light modulator (SLM) operates in a transmissive mode and is capable of modulating a wide spectrum of visible light. There is no pixel structure or native pixel resolution in the SLM. The SLM has no photodiodes and does not rectify. A light projection system (100) in which one or more SLMs (128, 130, 132) are placed includes a write (image definition) UV light path (102) and a read (illumination) visible light path (104) to form a color image projection display. The write UV light propagates from an image display pattern source (120) and either sequentially or continuously writes image patterns on the photoconductive SLMs. The read visible light propagates through the SLM and is modulated by an electro-optical material, the optical properties of which change in response to the image structure carried by the write light. The result is a high efficiency display system that delivers high resolution color images through a projection lens (190) onto a display screen.
Owner:SNAP INC
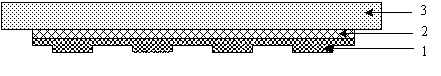
A plane NMR micro-coils micro detector
InactiveCN1971259AHigh sensitivityHigh resolutionAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using NMRPolyimide substrateNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A plane nuclear magnetic resonance micro coil micro detector is disclosed that consists of plane nuclear magnetic resonance micro coil [1] and micro flow channel structure [2]. It adopts the integral design; the plane nuclear magnetic resonance micro coil [1] is processed on the surface of the polyimides substrate [3], the micro flow channel structure [2] is rectangle structure and processed on the other surface of the polyimides substrate [3], it is embedded in the inner of the polyimides substrate [3] which is under the plane nuclear magnetic resonance micro coil [1] by the polyimides slice [4]. When it is working, the plane nuclear magnetic resonance micro coil works as the radio-frequency exciter and the signal receiver at the same time, and actuates the sample to be measured to generate the NMR signal and obtain the NMR wave spectrum. The invention can fulfill the detecting requirements of lossless and real-time, the molecular structure and information of images-structure of detecting sample can be supplied. It can be used in fields of analysis detection of tiny sample, real-time dynamic monitoring of chemical reaction, and biological texture and growth status of cell.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Stepped and repeated illuminating and nano-imprinting device
ActiveCN1800975ALow priceDon't worry about the high cost of preparationPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingControl systemEngineering
The invention discloses a nanometer stamping device of process repeated illumination, which comprises the following parts: pressure driving system, Z-direction calibration system, two-way CCD aligning system, inclined calibration structure, stamper, substrate, XYª working table, substrate bearing piece leveling system, big machine cabinet, control system, big host floor, violet even illuminating system and rack, wherein the bearing piece leveling system is set on the XYª working table to load substrate; the pressure driving system, Z-direction calibration system, inclined calibration structure, two-way CCD aligning system and violet even illuminating system are fixed on the rack. The invention adapts common violet illumination without elastic signet or casting mould as well as adding high temperature, pressure and reducing temperature, which applies the high precise alignment of CCD image to make more complex multiple-layer structure, large effective working area and easy extended nanometer image structure through process repeated manufacturing.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Image enhancement coefficient adjusting method and device thereof and image enhancement method and device thereof
The invention discloses an image enhancement coefficient adjusting method and a device thereof and an image enhancement method and a device thereof; all pixels are distinguished to be the pixels with different image structure categories according to the difference degree of the grey scale of each pixel and the adjacent pixel in an input image, and then adjustment is carried out according to the image enhancement coefficient of the pixels with different image structure categories, so as to lead discrete noise to be filtered, enhance a flat area properly and enhance a detail area greater compared with the flat area, and improve the enhanced image quality in the enhanced image.
Owner:VIMICRO ELECTRONICS CORP
Non-reference image objective quality evaluation method
The invention discloses a non-reference image objective quality evaluation method. The non-reference image objective quality evaluation method comprises the following steps: respectively applying Gaussian smoothing gradient filter and laplace operator Gaussian filter to a distorted image by deeply excavating perception characteristic of human vision to image structure to correspondingly obtain a Gaussian smoothing gradient filter image and a laplace operator Gaussian filter image, then respectively carrying out local binaryzation mode operation on the two filter images to obtain respective local binaryzation mode feature images, then calculating respective marginal probability feature and conditional probability feature of the two local binaryzation mode feature images, and finally forecasting on objective quality evaluation predicted value of the to-be-evaluated distorted images by adopting support vector regression according to the marginal probability feature and conditional probability feature. The obtained objective quality evaluation predicted value can accurately reflect subjective perceived quality of human vision and can be used for effectively improving correlation between objective evaluation result and subjective perception.
Owner:四川济舟信息科技有限公司
Image characteristic extraction method
ActiveCN101770578ASmall amount of calculationImprove performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsImaging processingSelf correlation
The invention discloses an image characteristic extraction method in the technical field of image processing, which comprises the following steps: extracting position information and color information of all pixel points in an image; performing edge area processing on the image, and acquiring position information and color information of each pixel point in the edge area; extracting color self-correlation characteristics from the edge area of the image I, and acquiring a color self-correlation diagram of the edge area; extracting edge direction self-correlation characteristics from all the areas of the image, and acquiring a global edge direction self-correlation diagram; extracting color self-correlation characteristics from all the areas of the image, and acquiring a global color self-correlation diagram; and performing characteristic pre-fusion on the three self-correlation diagrams, and acquiring image characteristics. The image characteristic extraction method realizes more comprehensive image structure-based content description through the characteristic fusion, reduces the computed amount, improves the performance, and has higher accuracy during image retrieval.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com