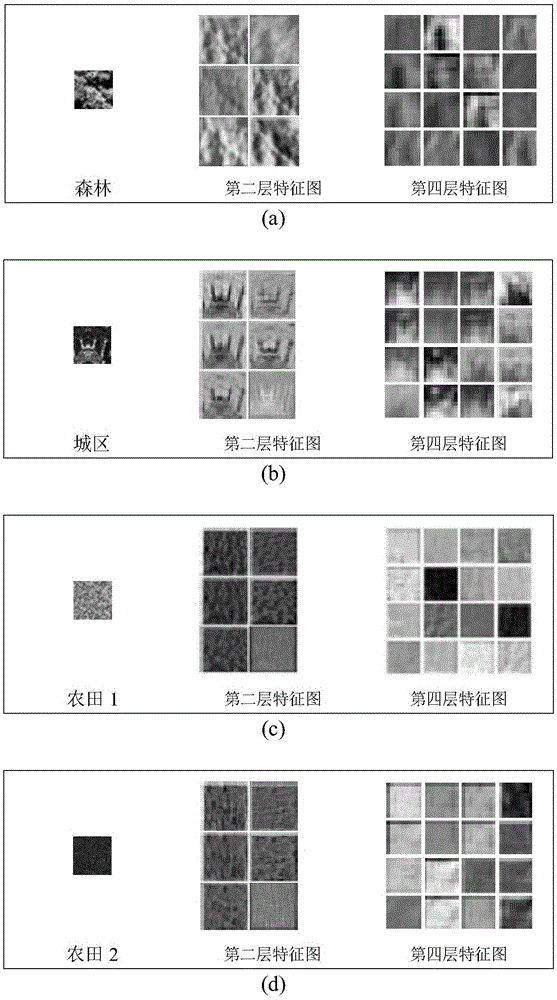
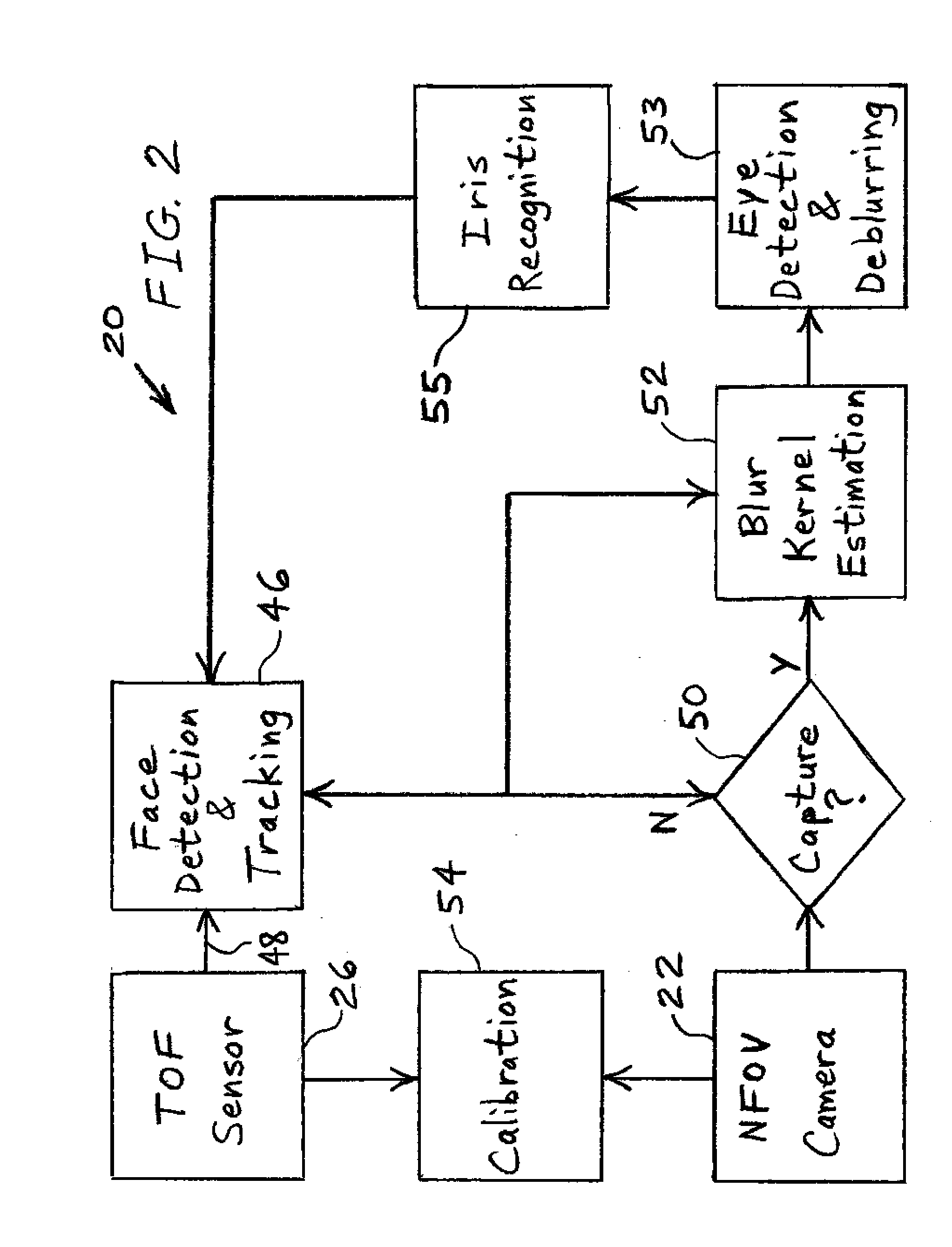
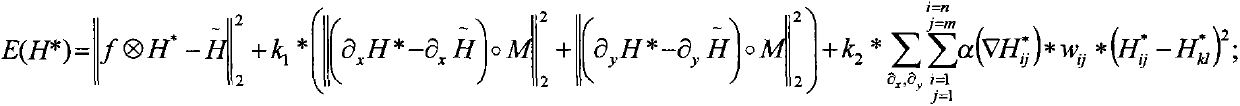Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
509 results about "Image gradient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
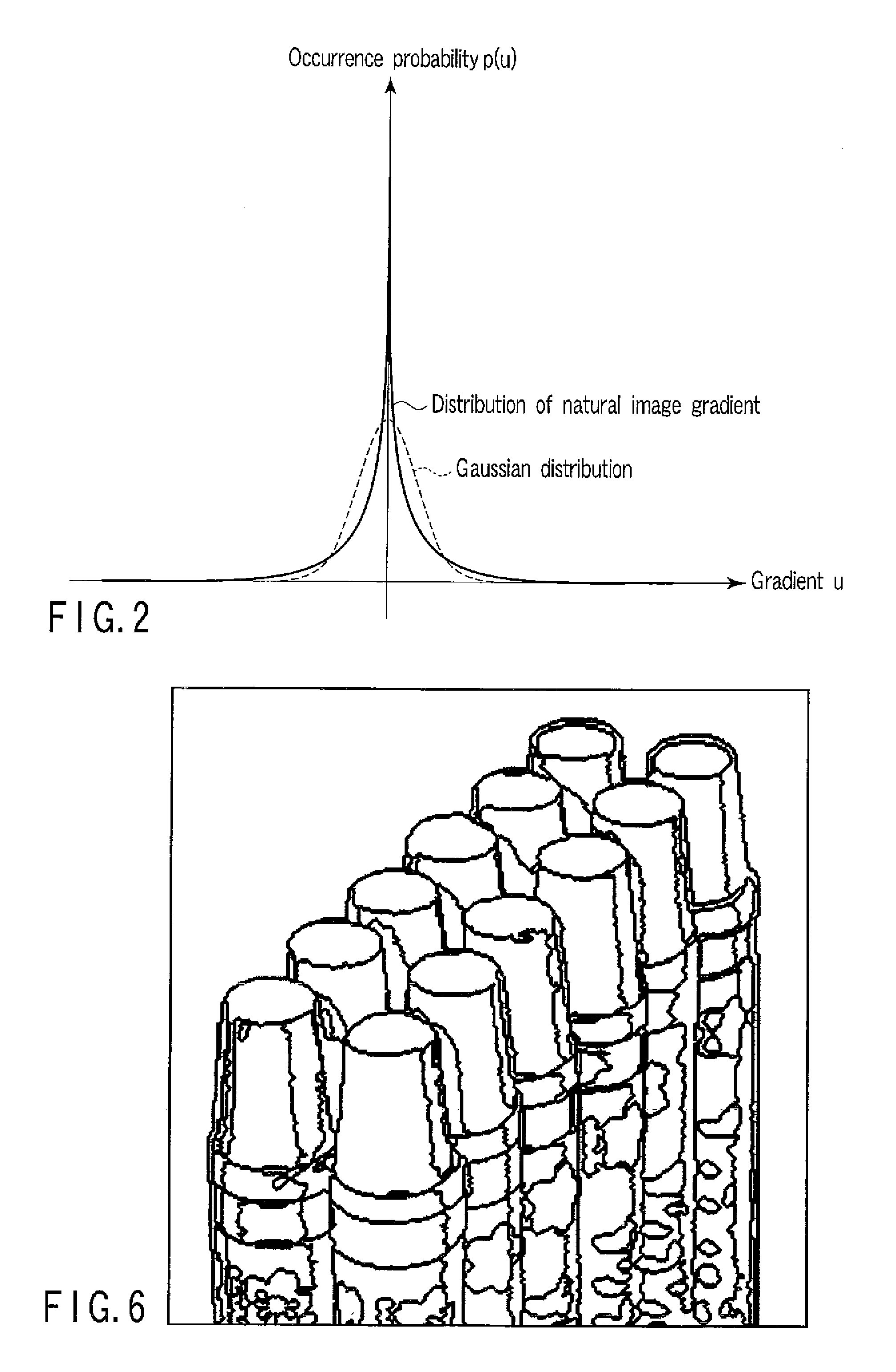
An image gradient is a directional change in the intensity or color in an image. The gradient of the image is one of the fundamental building blocks in image processing. For example, the Canny edge detector uses image gradient for edge detection. In graphics software for digital image editing, the term gradient or color gradient is also used for a gradual blend of color which can be considered as an even gradation from low to high values, as used from white to black in the images to the right. Another name for this is color progression.
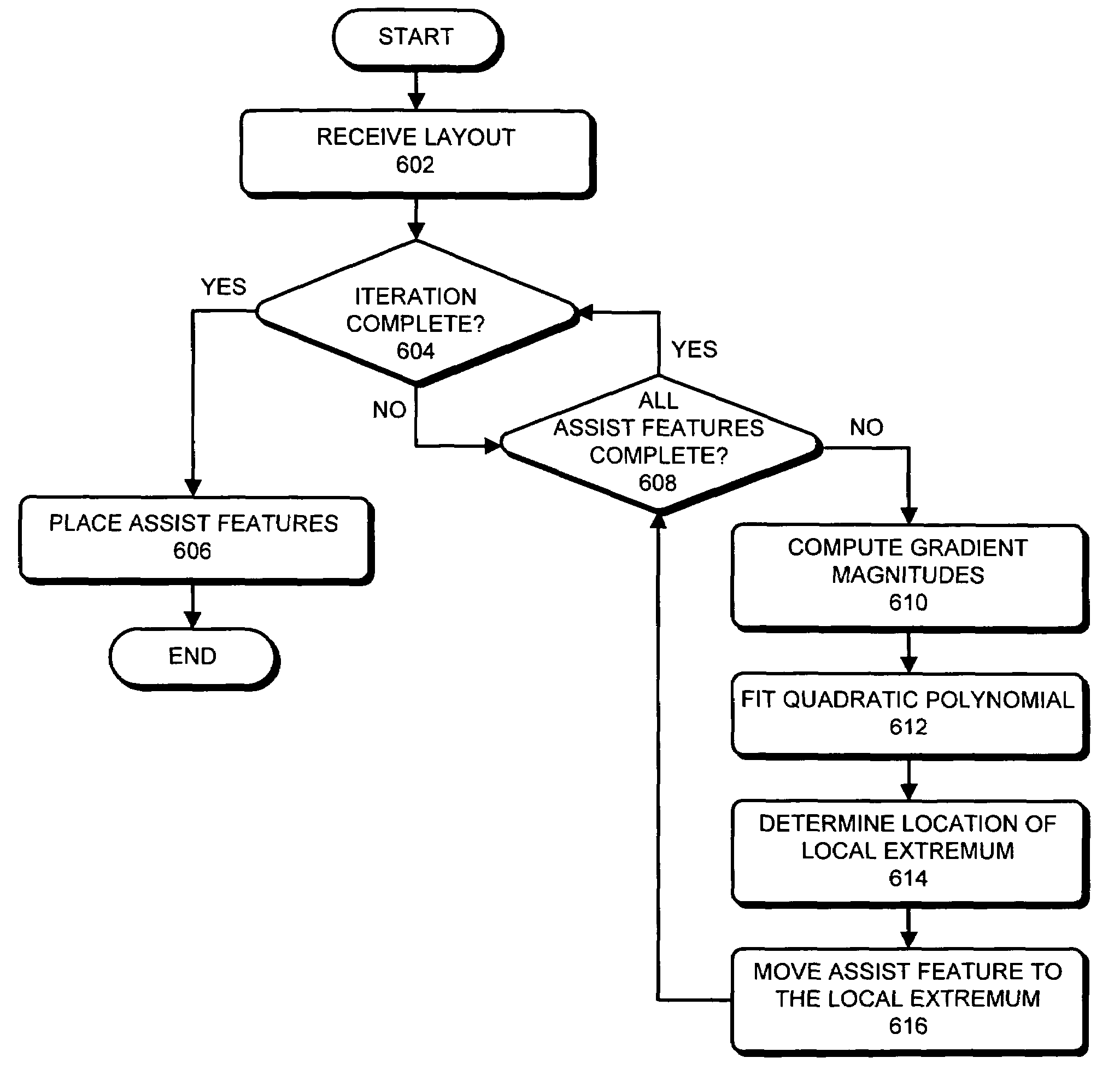
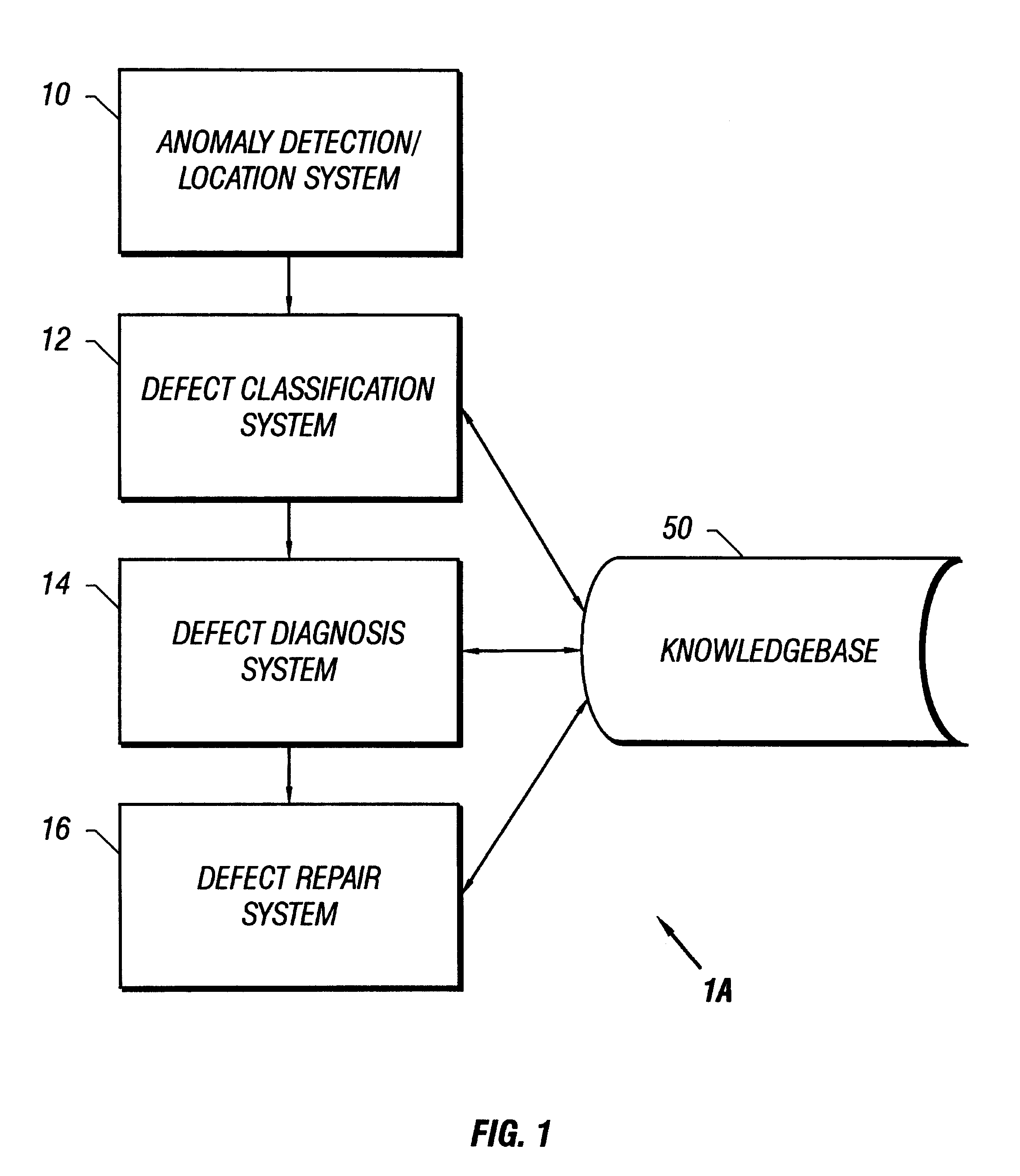
Method and apparatus for placing assist features by identifying locations of constructive and destructive interference
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that determines a location in a layout to place an assist feature. During operation, the system receives a layout of an integrated circuit. Next, the system selects an evaluation point in the layout. The system then chooses a candidate location in the layout for placing an assist feature. Next, the system determines the final location in the layout to place an assist feature by, iteratively, (a) selecting perturbation locations for placing representative assist features in the proximity of the candidate location, (b) computing aerial-images using an image intensity model, the layout, and by placing representative assist features at the candidate location and the perturbation locations, (c) calculating image-gradient magnitudes at the evaluation point based on the aerial-images, and (d) updating the candidate location for the assist feature based on the image-gradient magnitudes.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
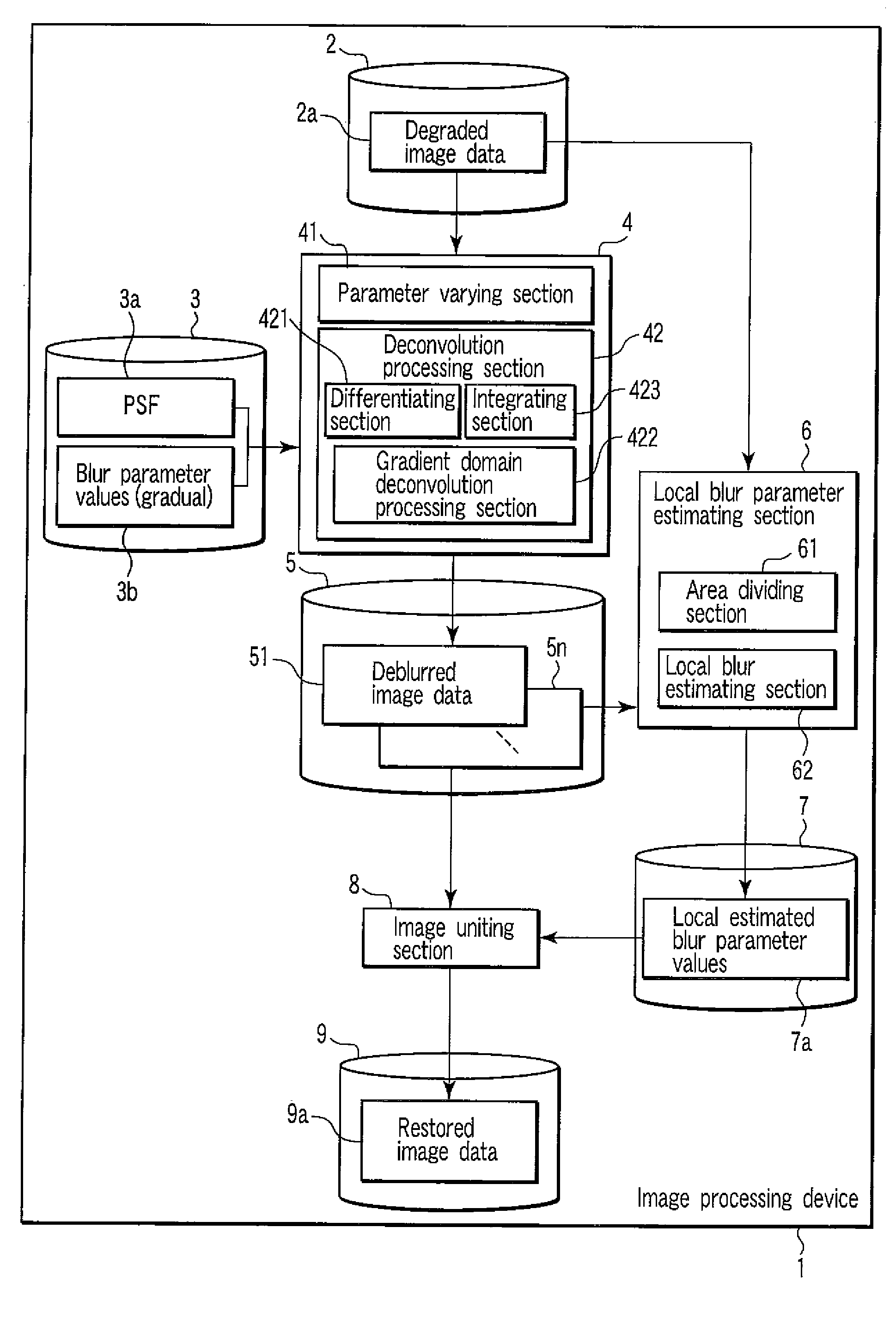
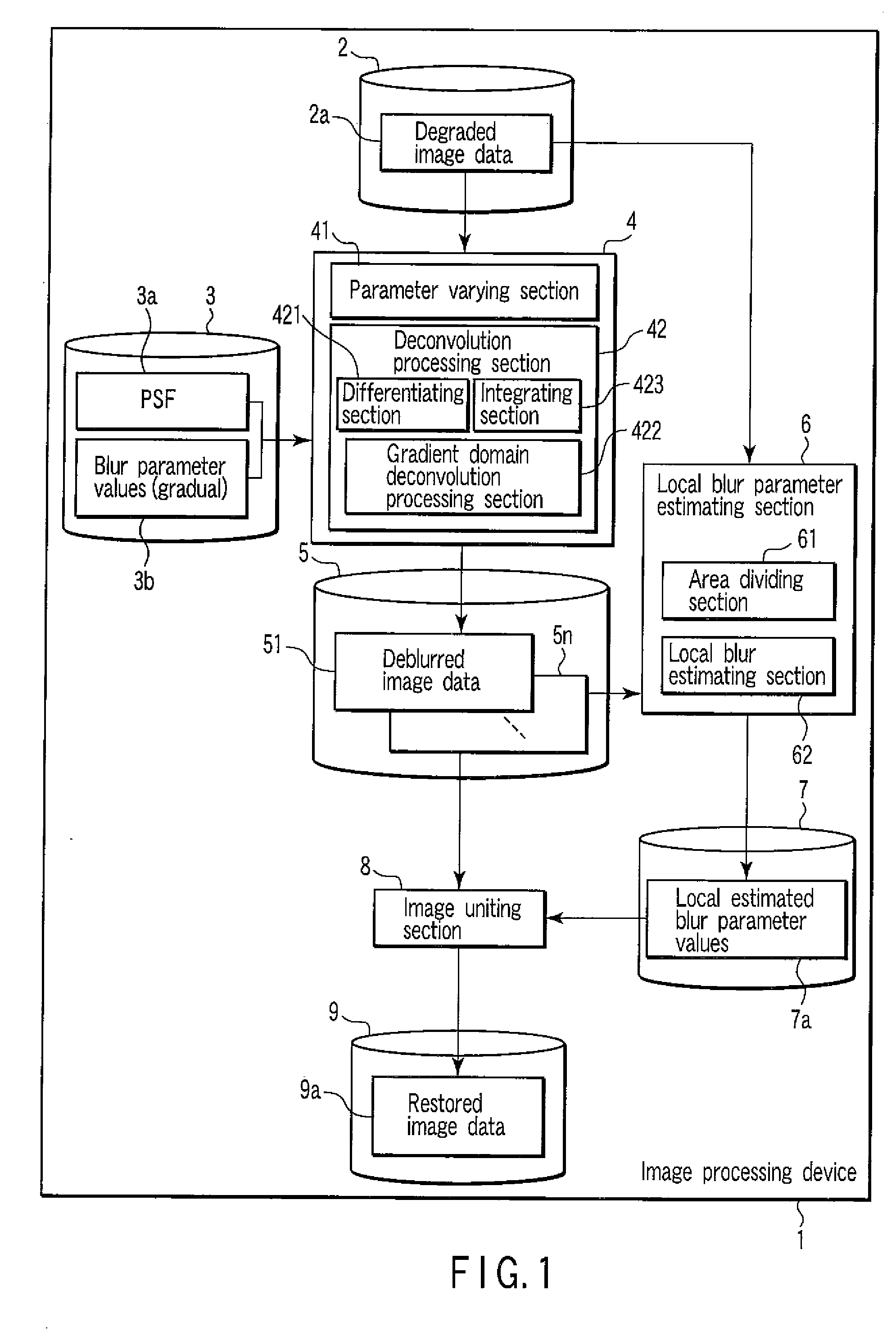
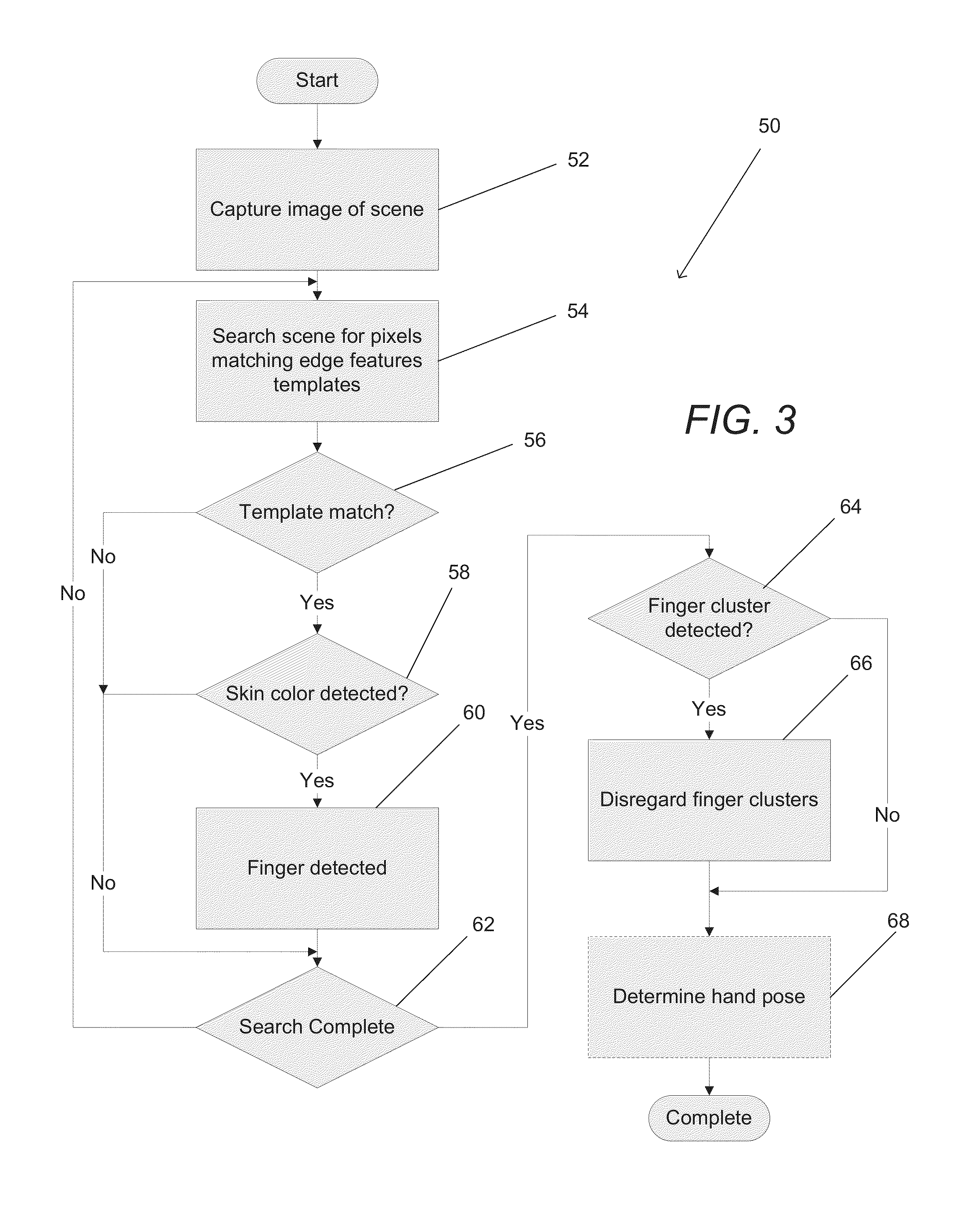
Image Processing Device
InactiveUS20080175508A1Image enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingImage gradient
An image processing device according to an example of the invention comprises a differentiating section which differentiates input image data to generate gradient image data, a gradient domain deconvolution processing section which applies a deconvolution to the gradient image data, the deconvolution performing deblurring corresponding to a prior distribution of an image gradient of an image to generate deconvolved data, and an integrating section which integrates the deconvolved data to generate deblurred image data.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Kernel regression for image processing and reconstruction
ActiveUS20070047838A1Improve local image structure informationImproves gradient and pixel valueImage enhancementImage analysisSingular value decompositionKernel regression
A method of image processing using kernel regression is provided. An image gradient is estimated from original data that is analyzed for local structures by computing a scaling parameter, a rotation parameter and an elongation parameter using singular value decomposition on local gradients of the estimated gradients locally to provide steering matrices. A steering kernel regression having steering matrices is applied to the original data to provide a reconstructed image and new image gradients. The new gradients are analyzed using singular value decomposition to provide new steering matrices. The steering kernel regression with the new steering matrices is applied to the noisy data to provide a new reconstructed image and further new gradients. The last two steps are repeated up to ten iterations to denoise the original noisy data and improve the local image structure.
Owner:UNIV OF CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ
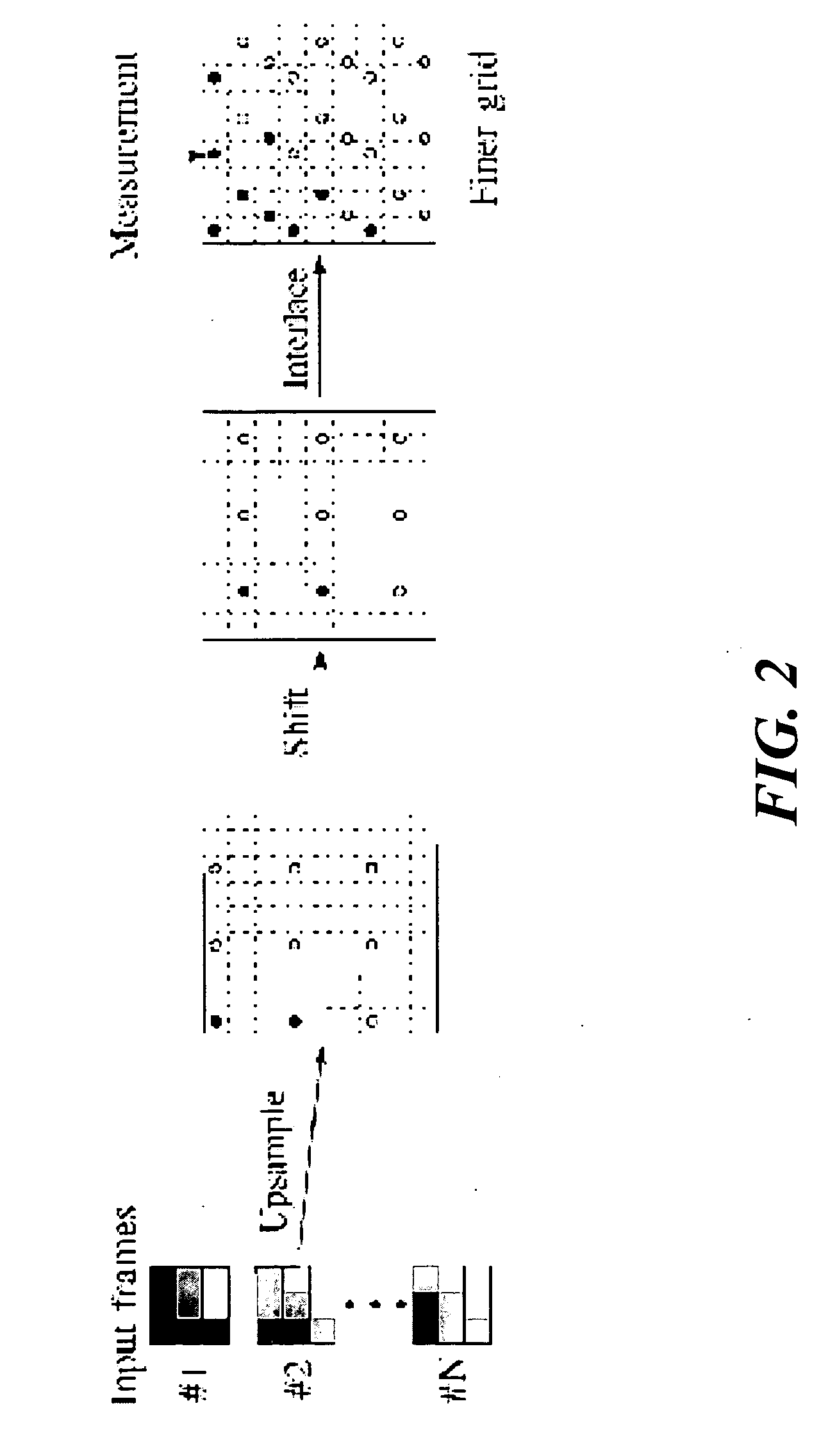
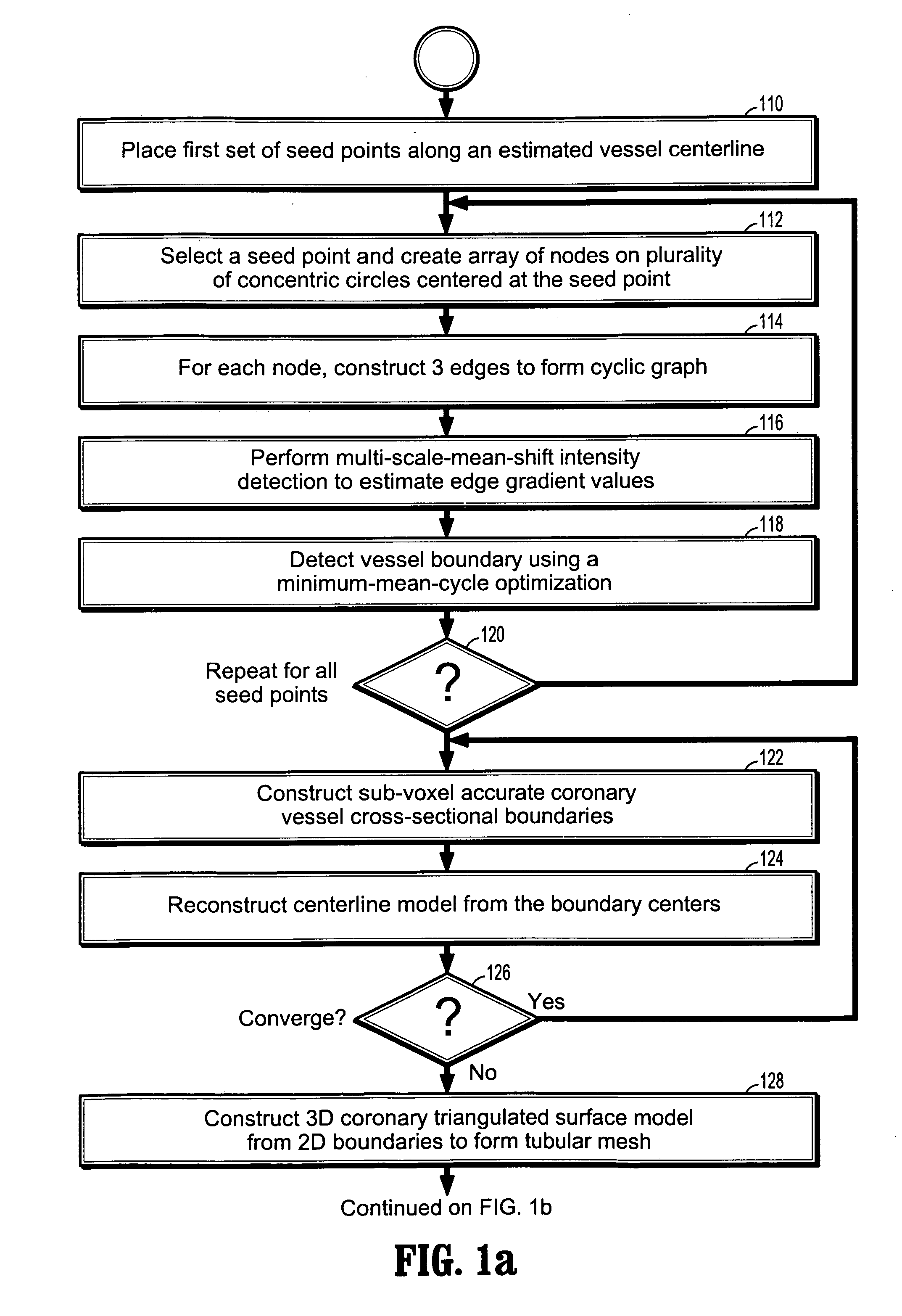
System and method for coronary segmentation and visualization
InactiveUS20080100621A1Eliminating incorrect edgeEliminating incorrect edgesImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelVertical plane
A method of coronary vessel segmentation and visualization includes providing a digitized coronary image, placing a plurality of seed points along an estimated centerline of a coronary vessel, selecting a seed point and constructing a cyclic graph around the seed point in a plane perpendicular to the centerline at the seed point, performing a multi-scale-mean shift filtering in the perpendicular plane to estimate image gradient values, detecting a vessel boundary using a minimum-mean-cycle optimization that minimizes a ratio of a cost of a cycle to a length of a cycle, constructing a sub-voxel accurate vessel boundary about a point on the centerline, and refining the location of the centerline point from the sub-voxel accurate boundary, where the steps of constructing a sub-voxel accurate vessel boundary and refining the centerline point location are repeated until convergence.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Computer method and apparatus for processing image data
InactiveUS20100008424A1Precise cuttingIncrease the compression ratioColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionData compression
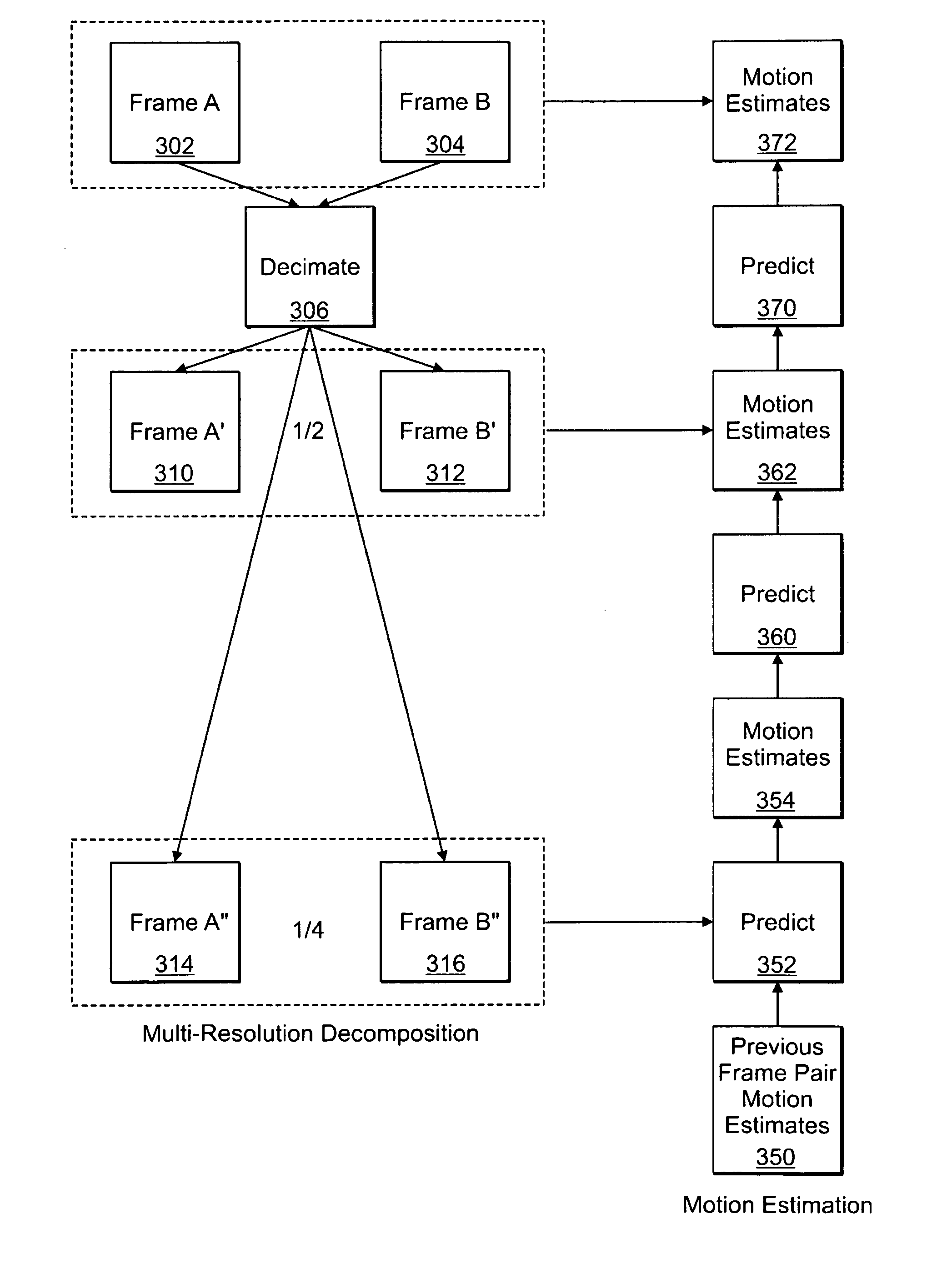
A method and apparatus for image data compression includes detecting a portion of an image signal that uses a disproportionate amount of bandwidth compared to other portions of the image signal. The detected portion of the image signal result in determined components of interest. Relative to certain variance, the method and apparatus normalize the determined components of interest to generate an intermediate form of the components of interest. The intermediate form represents the components of interest reduced in complexity by the certain variance and enables a compressed form of the image signal where the determined components of interest maintain saliency. In one embodiment, the video signal is a sequence of video frames. The step of detecting includes any of: (i) analyzing image gradients across one or more frames where image gradient is a first derivative model and gradient flow is a second derivative, (ii) integrating finite differences of pels temporally or spatially to form a derivative model, (iii) analyzing an illumination field across one or more frames, and (iv) predictive analysis, to determine bandwidth consumption. The determined bandwidth consumption is then used to determine the components of interest.
Owner:EUCLID DISCOVERIES LLC
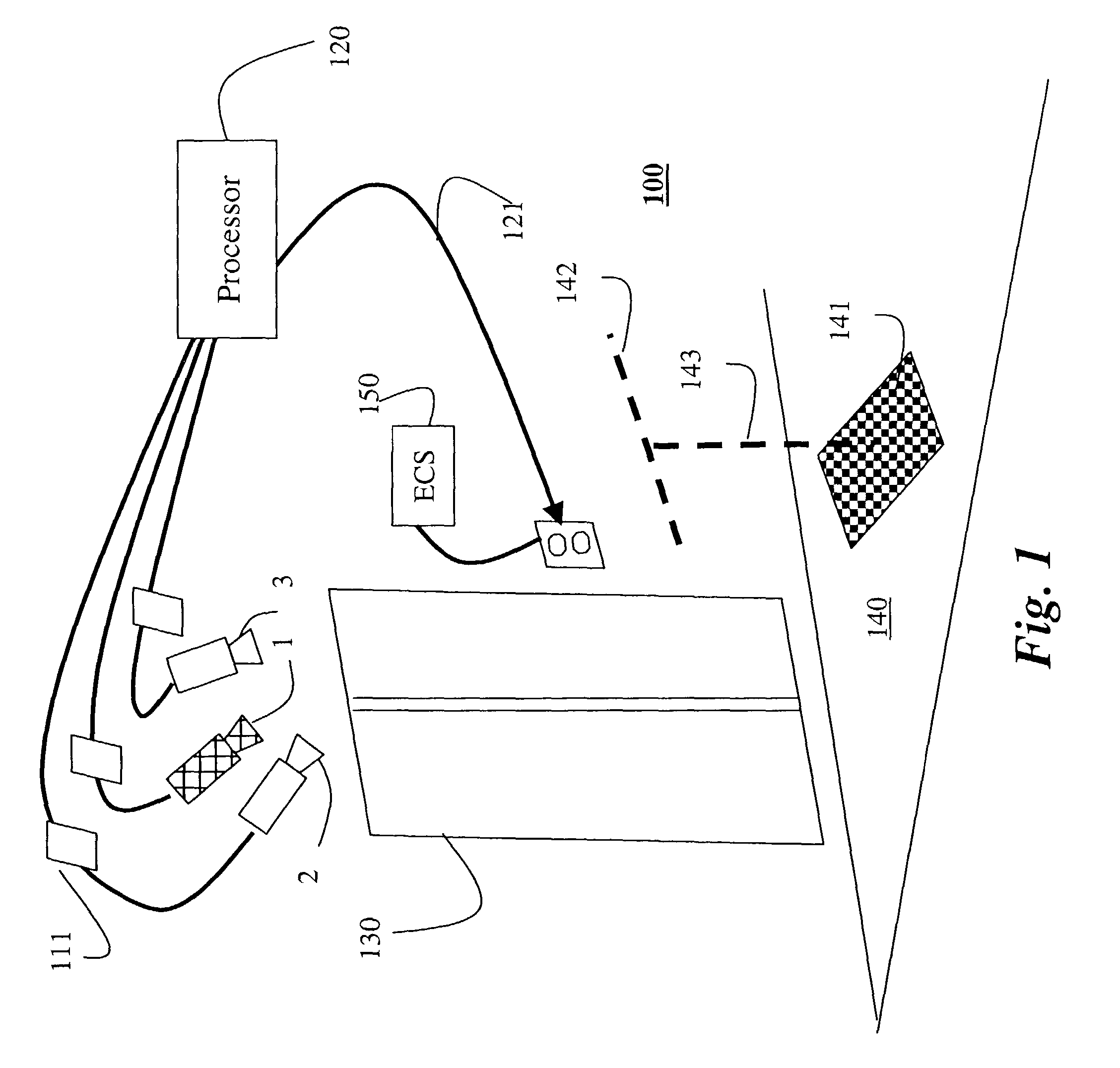
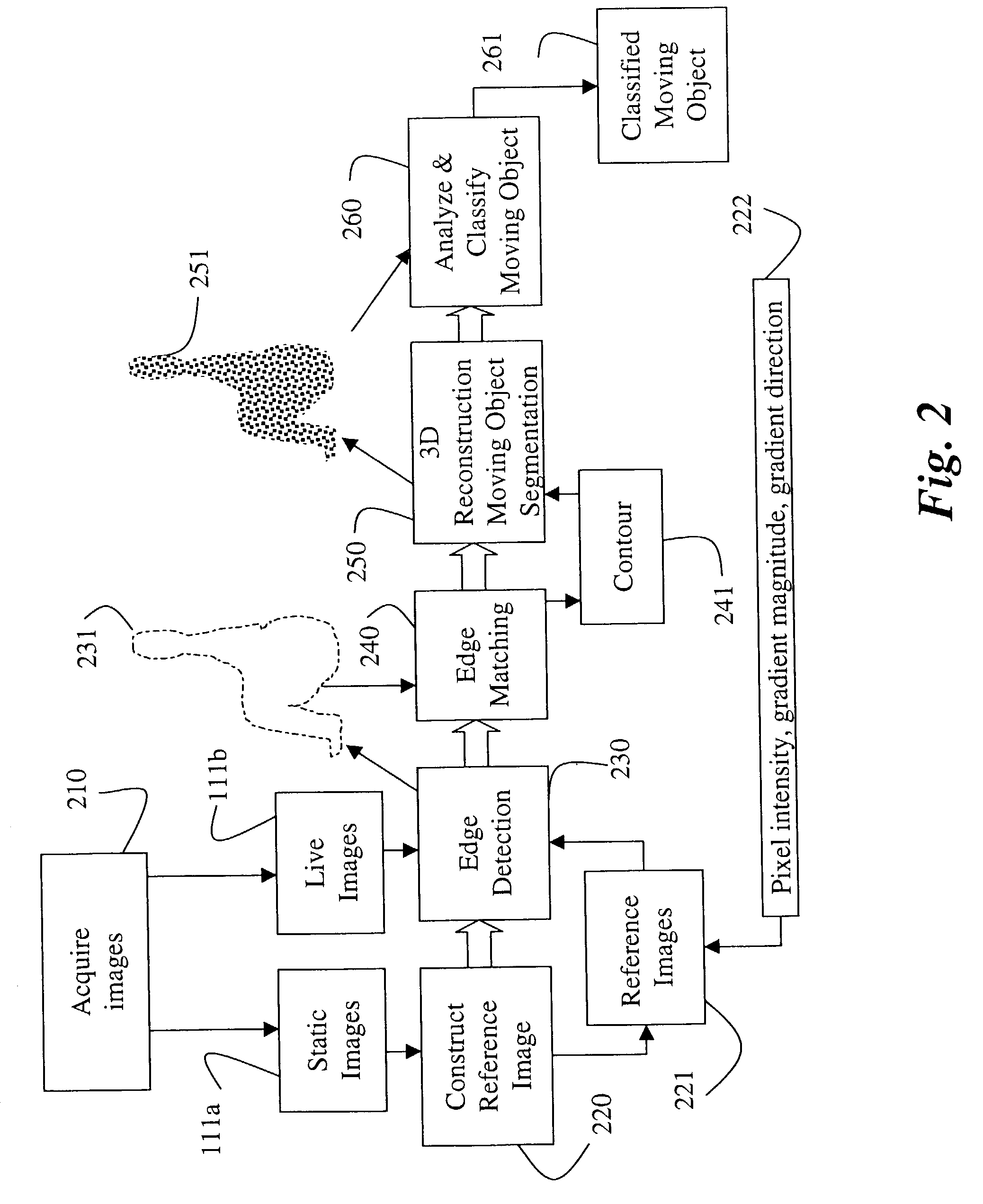
Edge detection based on background change
A method detects edges of an object in a scene by first acquiring a static image of the scene when the scene is static, and a live image of the scene including the object. A reference image is constructed from the static image. Then, image gradients of the reference image are compared with image gradients of the live image to identify edges of the object in the live image.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Novel descriptor for image corresponding point matching
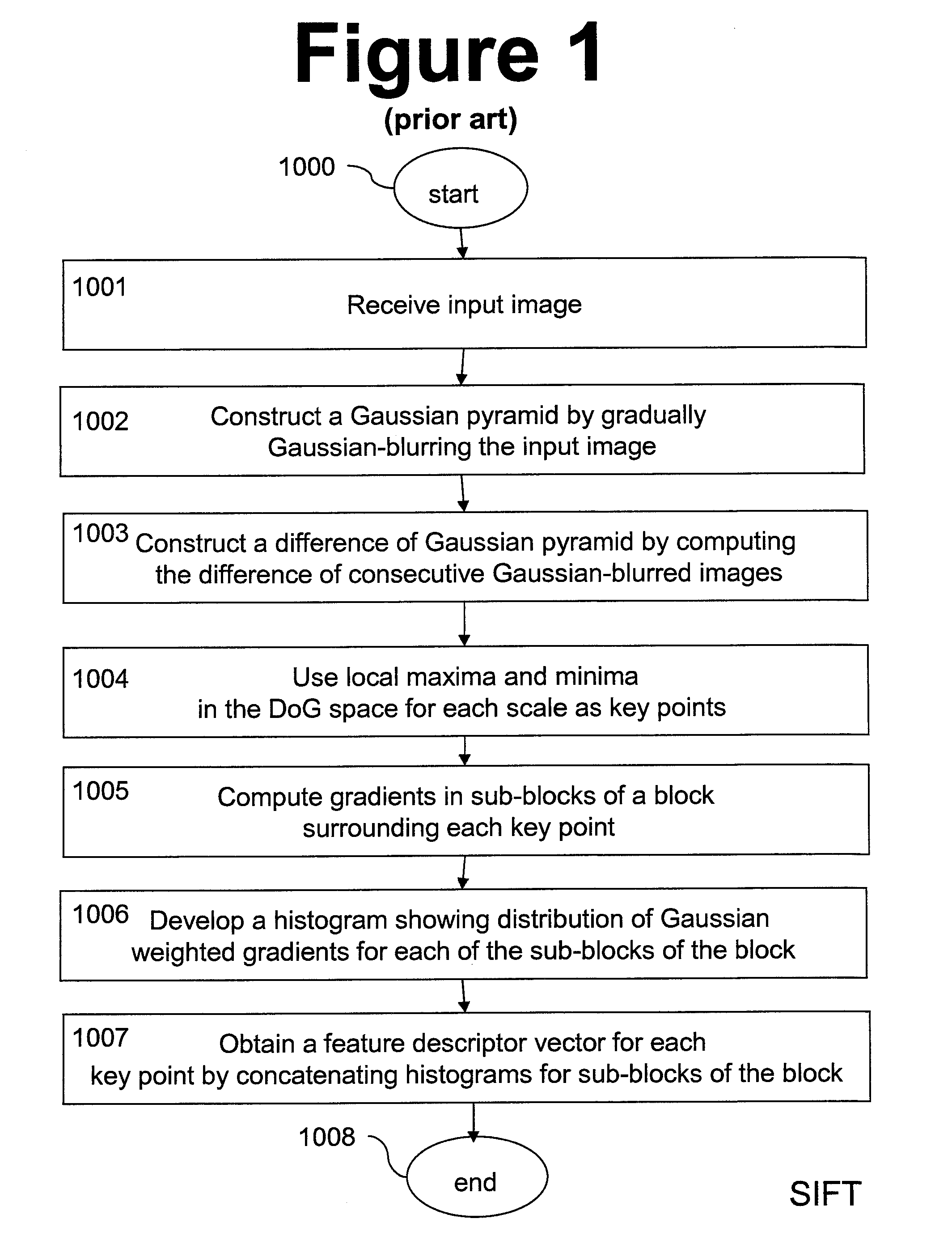
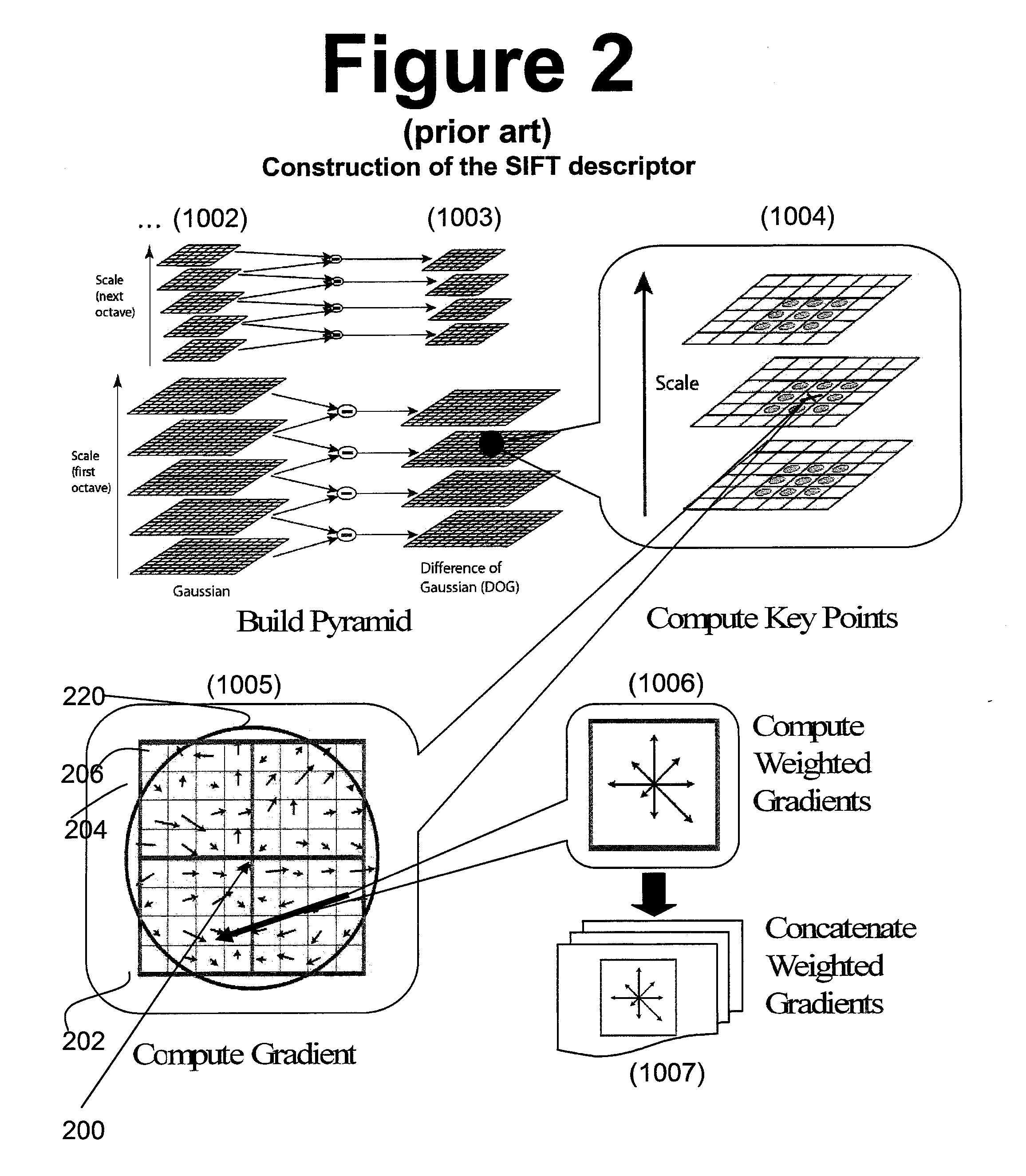
ActiveUS20100080469A1Reduce complexityReduce dimensionalityCharacter and pattern recognitionImage gradientImage identification
System and method of generating feature descriptors for image identification. Input image is Gaussian-blurred at different scales. A difference of Gaussian space is obtained from differences of adjacent Gaussian-blurred images. Key points are identified in the difference-of-Gaussian space. For each key point, primary sampling points are defined with three dimensional relative positions from key point and reaching into planes of different scales. Secondary sampling points are identified for each primary sampling point. Secondary image gradients are obtained between an image at a primary sampling point and images at secondary sampling points corresponding to this primary sampling point. Secondary image gradients form components of primary image gradients at primary sampling points. Primary image gradients are concatenated to obtain a descriptor vector for input image. Descriptor vector thus obtained is scale invariant and requires a number of additions equal to number of primary sampling points multiplied by a number of secondary sampling points.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
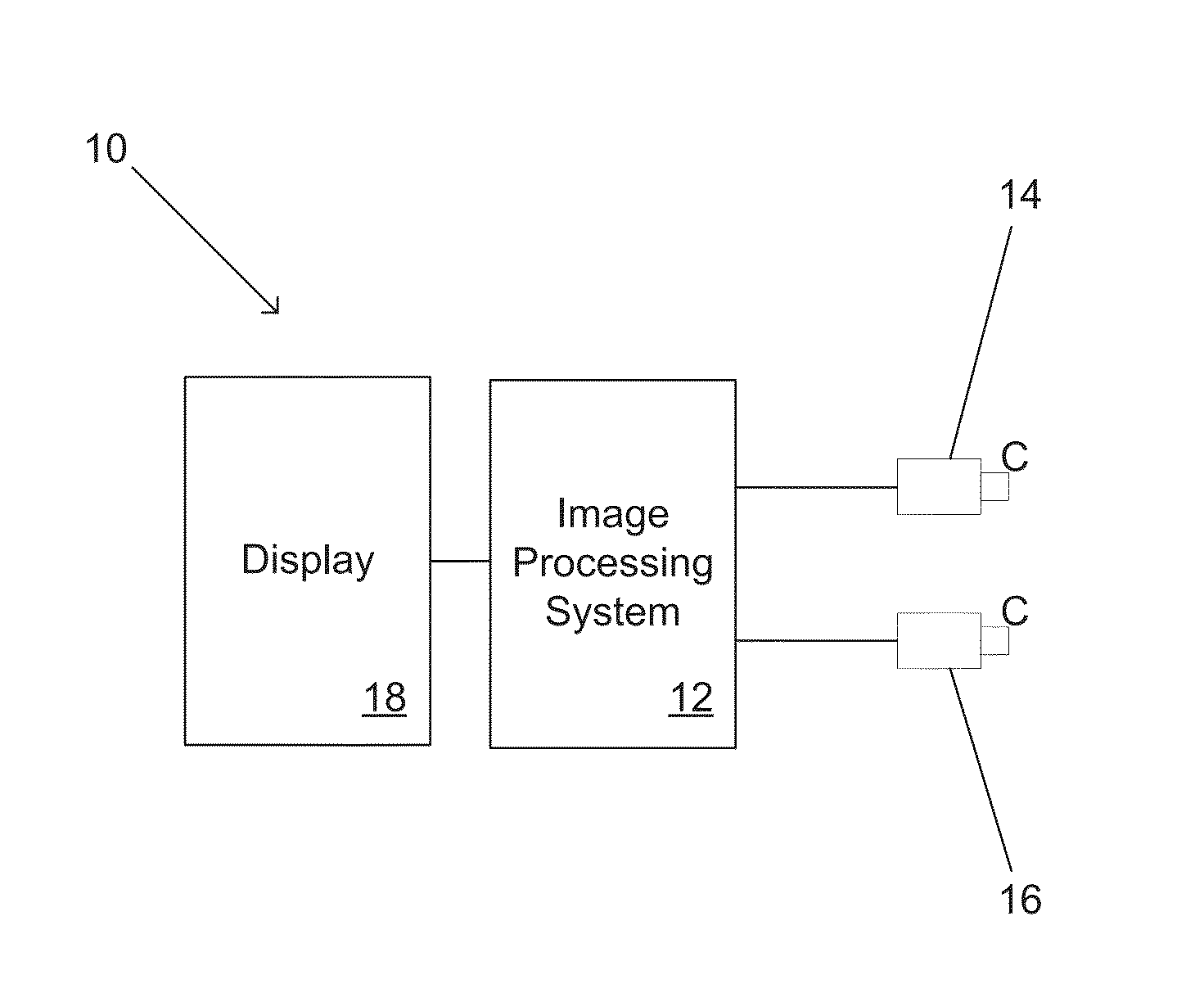
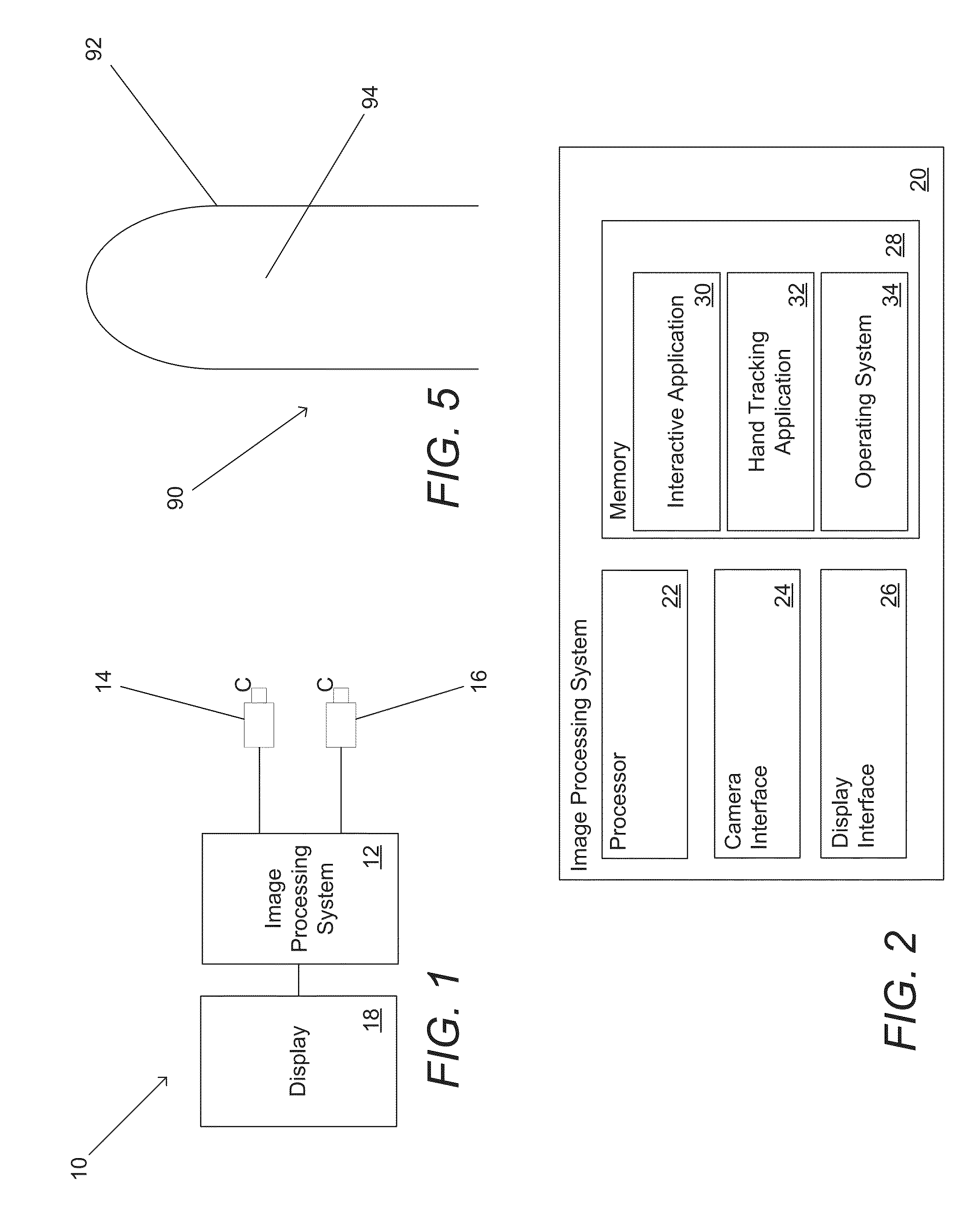
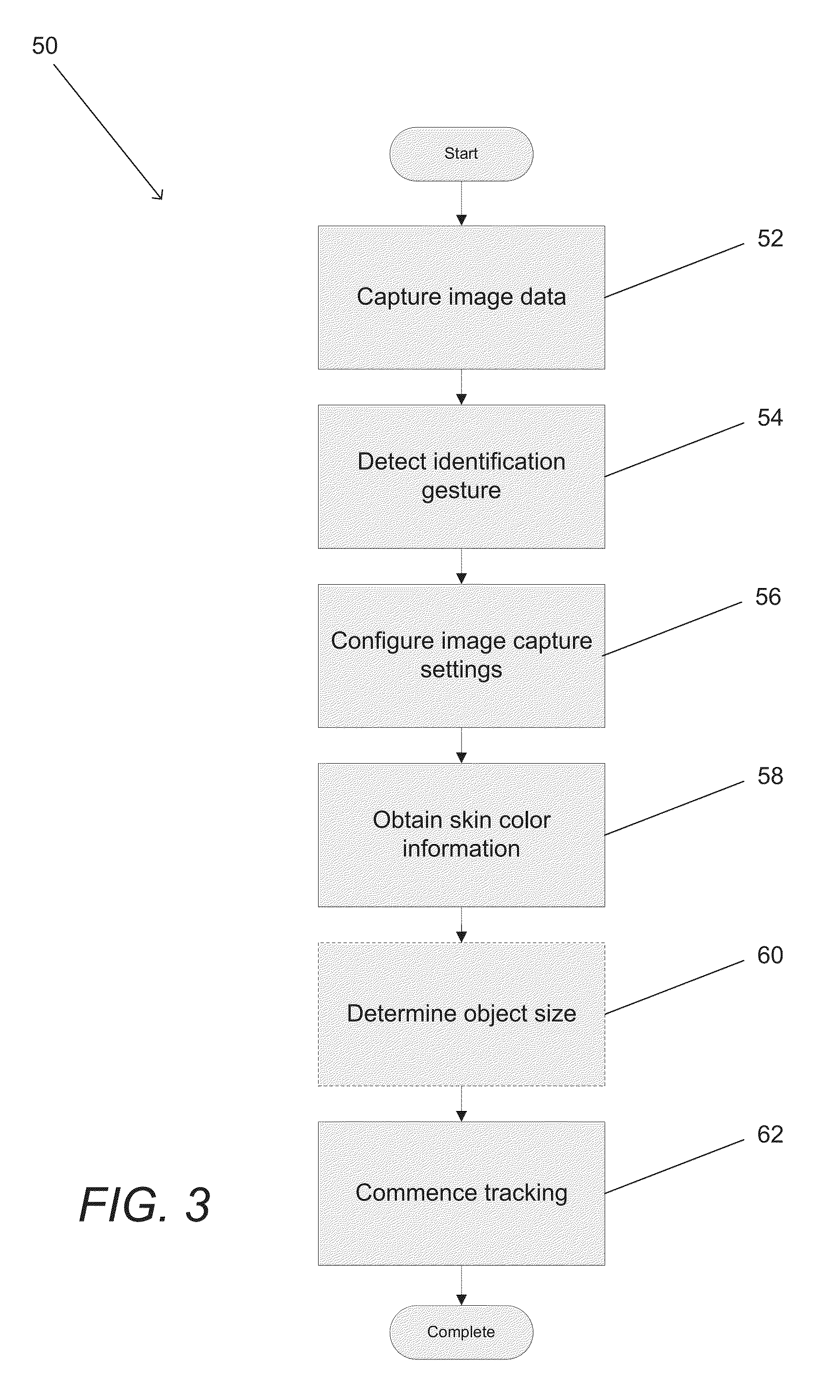
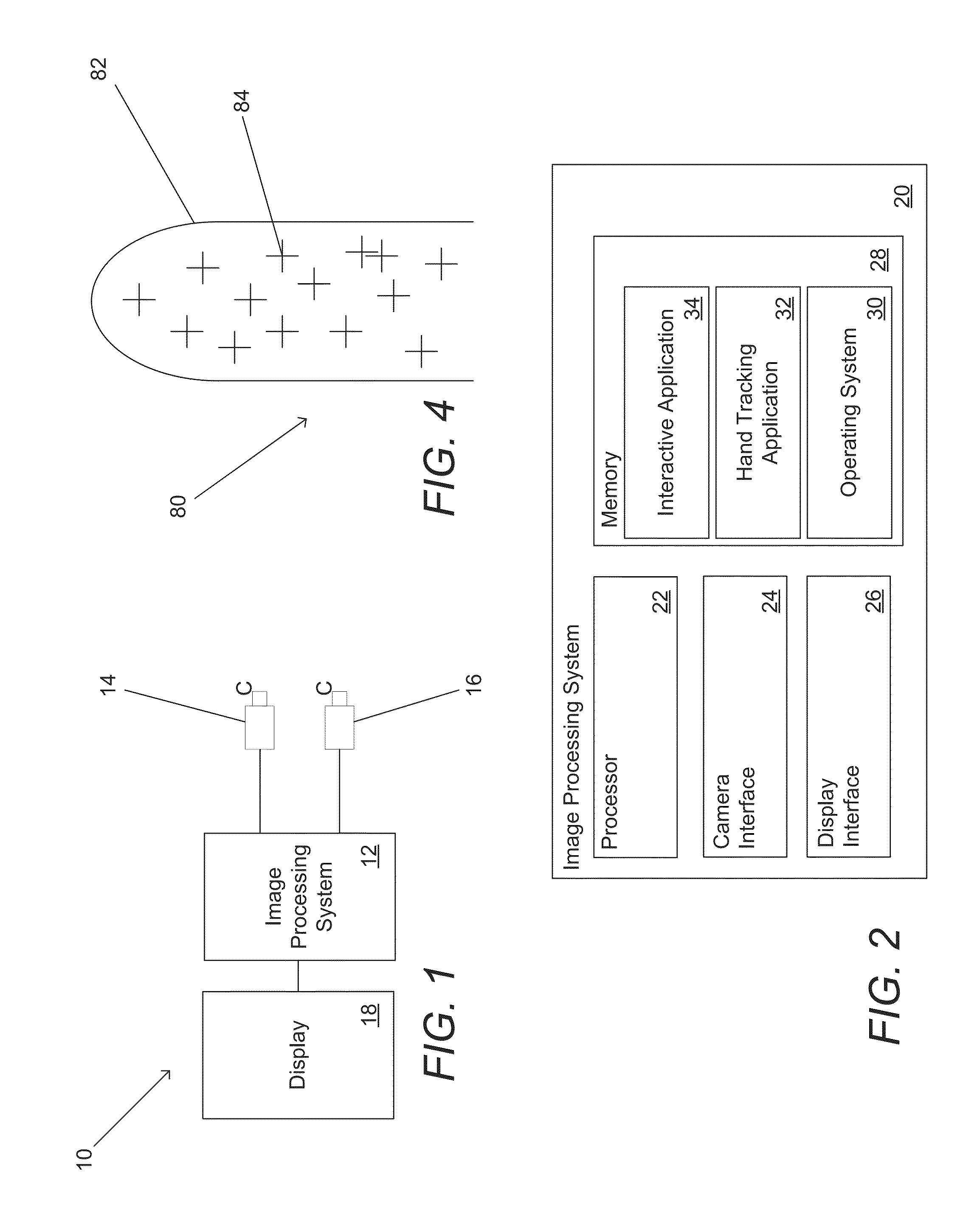
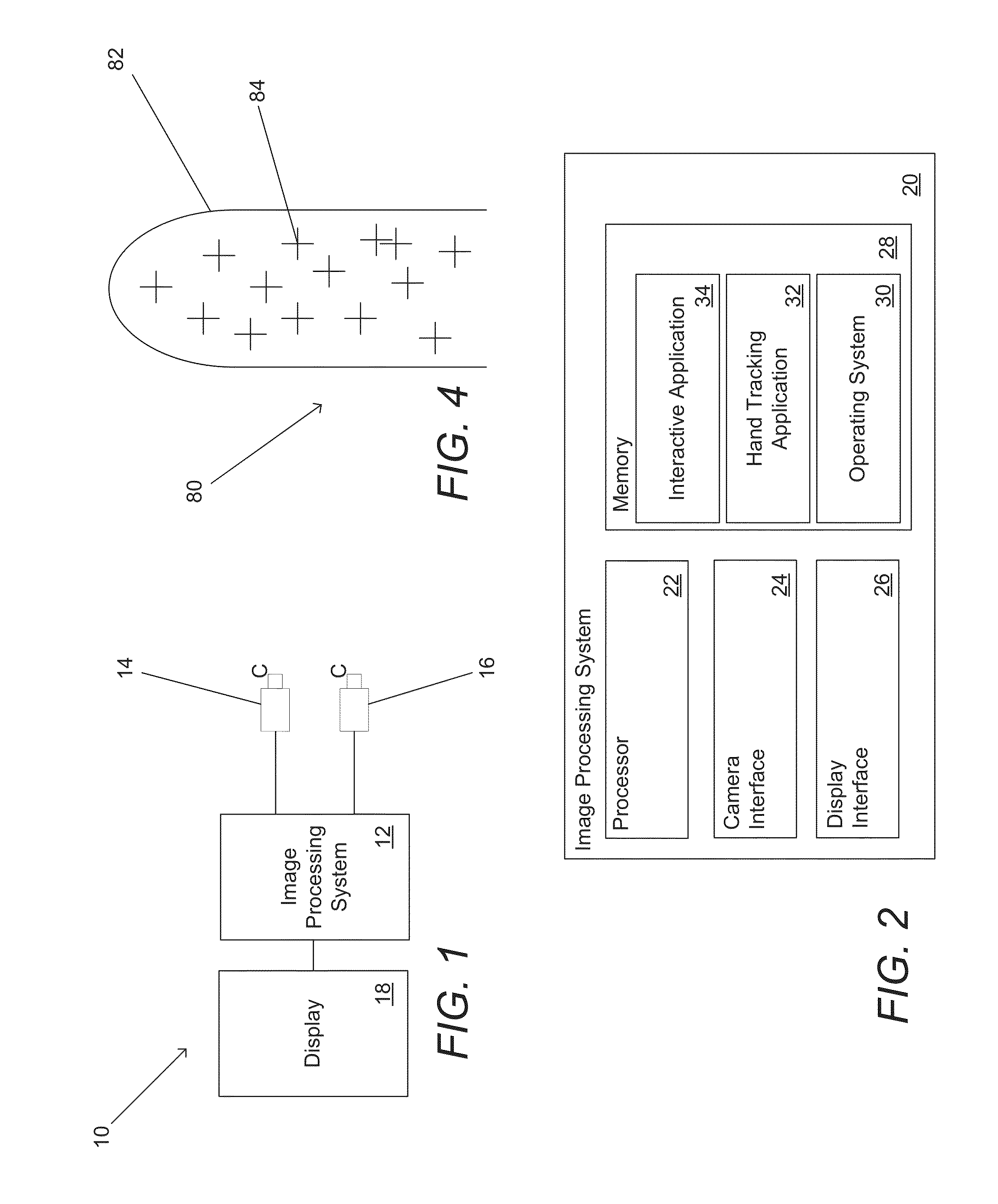
Systems and methods for initializing motion tracking of human hands
ActiveUS20140211991A1Reduce in quantityImage enhancementImage analysisApplication softwareImage gradient
Systems and methods for initializing motion tracking of human hands are disclosed. One embodiment includes a processor; a reference camera; and memory containing: a hand tracking application; and a plurality of edge feature templates that are rotated and scaled versions of a base template. The hand tracking application configures the processor to: determine whether any pixels in a frame of video are part of a human hand, where a part of a human hand is identified by searching the frame of video data for a grouping of pixels that have image gradient orientations that match the edge features of one of the plurality of edge feature templates; track the motion of the part of the human hand visible in a sequence of frames of video; confirm that the tracked motion corresponds to an initialization gesture; and commence tracking the human hand as part of a gesture based interactive session.
Owner:KAYA DYNAMICS LLC
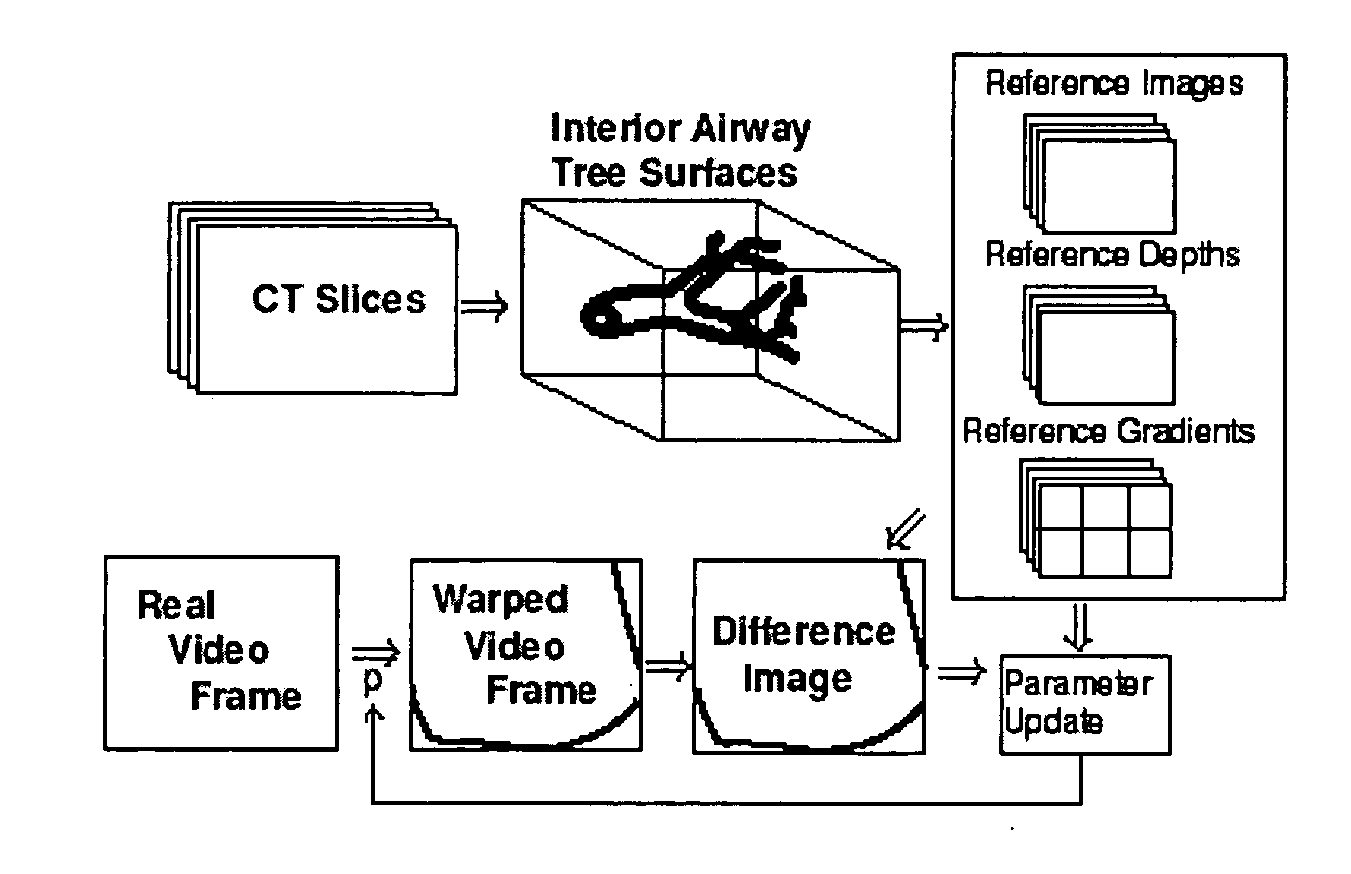
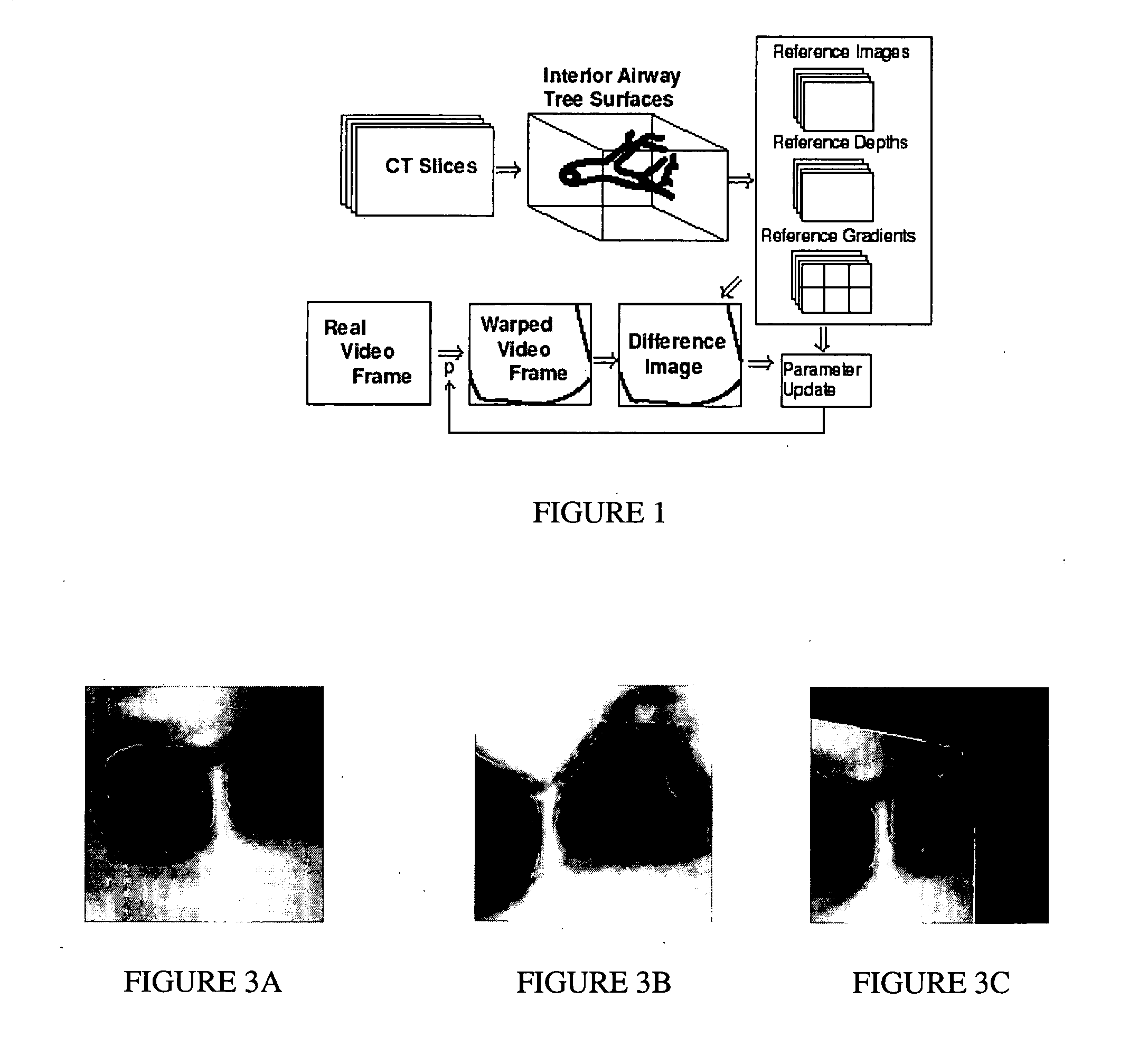
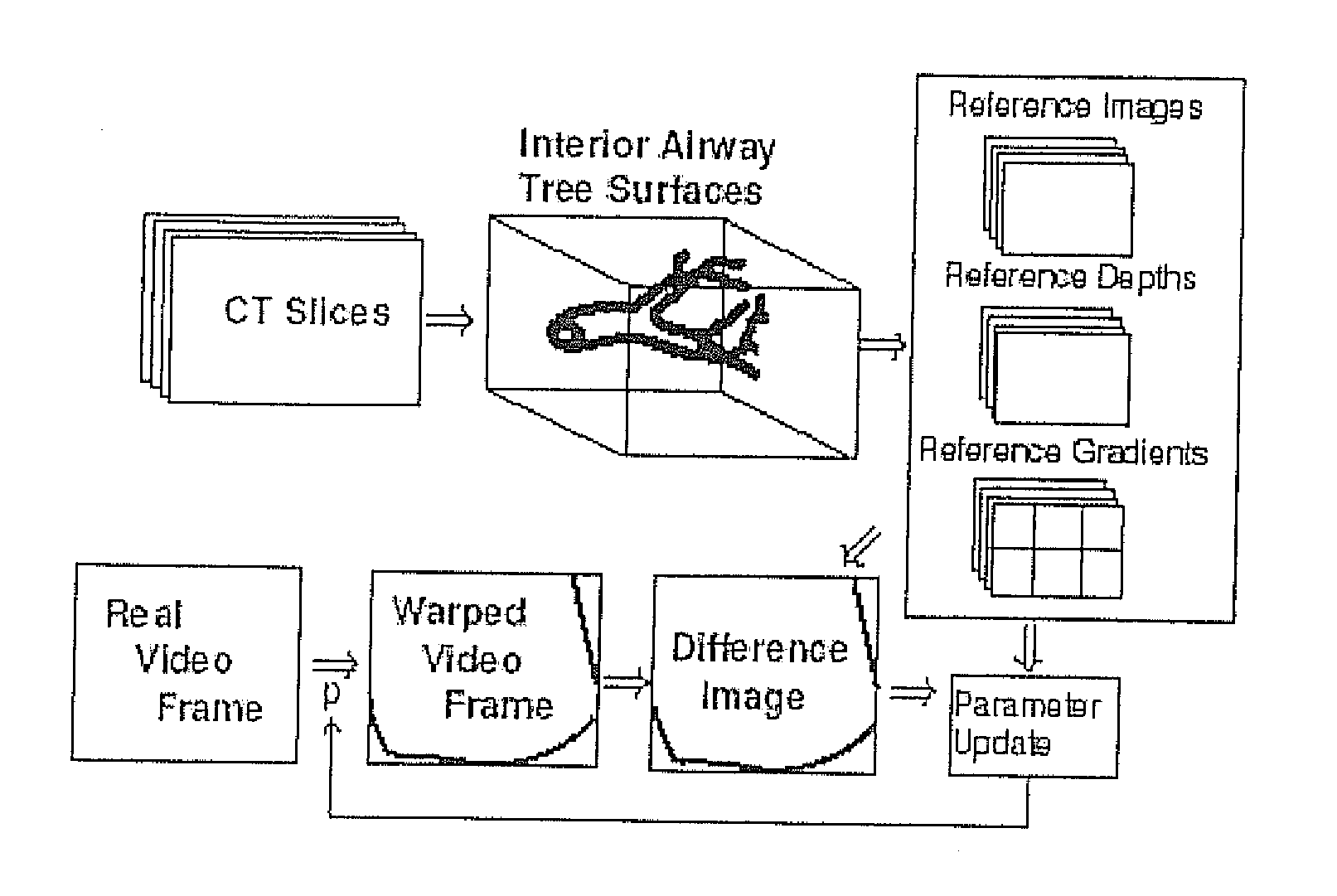
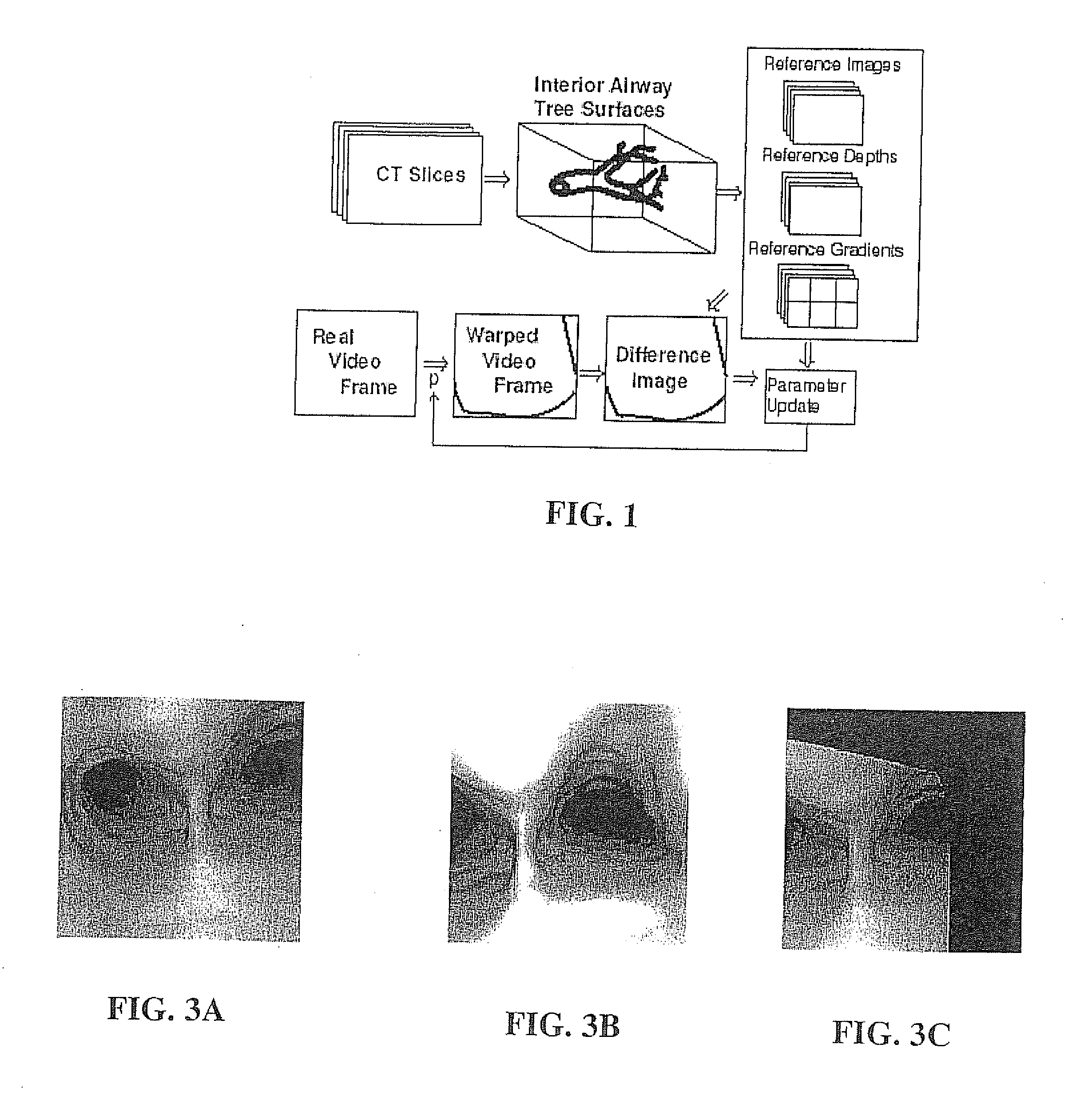
Fast 3D-2D image registration method with application to continuously guided endoscopy
A novel framework for fast and continuous registration between two imaging modalities is disclosed. The approach makes it possible to completely determine the rigid transformation between multiple sources at real-time or near real-time frame-rates in order to localize the cameras and register the two sources. A disclosed example includes computing or capturing a set of reference images within a known environment, complete with corresponding depth maps and image gradients. The collection of these images and depth maps constitutes the reference source. The second source is a real-time or near-real time source which may include a live video feed. Given one frame from this video feed, and starting from an initial guess of viewpoint, the real-time video frame is warped to the nearest viewing site of the reference source. An image difference is computed between the warped video frame and the reference image. The viewpoint is updated via a Gauss-Newton parameter update and certain of the steps are repeated for each frame until the viewpoint converges or the next video frame becomes available. The final viewpoint gives an estimate of the relative rotation and translation between the camera at that particular video frame and the reference source. The invention has far-reaching applications, particularly in the field of assisted endoscopy, including bronchoscopy and colonoscopy. Other applications include aerial and ground-based navigation.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Target detection method and system
InactiveUS7430303B2Simple technologyImprove efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsUltrasound attenuationAlgorithm
A method and system detects candidate targets or objects from a viewed scene by simplifying the data, converting the data to gradient magnitude and direction data which is thresholded to simplify the data. Horizontal edges within the data are softened to reduce their masking of adjacent non-horizontal features. One or more target boxes are stepped across the image data and the number of directions of gradient direction data within the box is used to determine the presence of a target. Atmospheric attenuation is compensated. The thresholding used in one embodiment compares the gradient magnitude data to a localized threshold calculated from the local variance of the image gradient magnitude data. Imagery subsets are containing the candidate targets may then be used to detect and identify features and apply a classifier function to screen candidate detections and determine a likely target.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
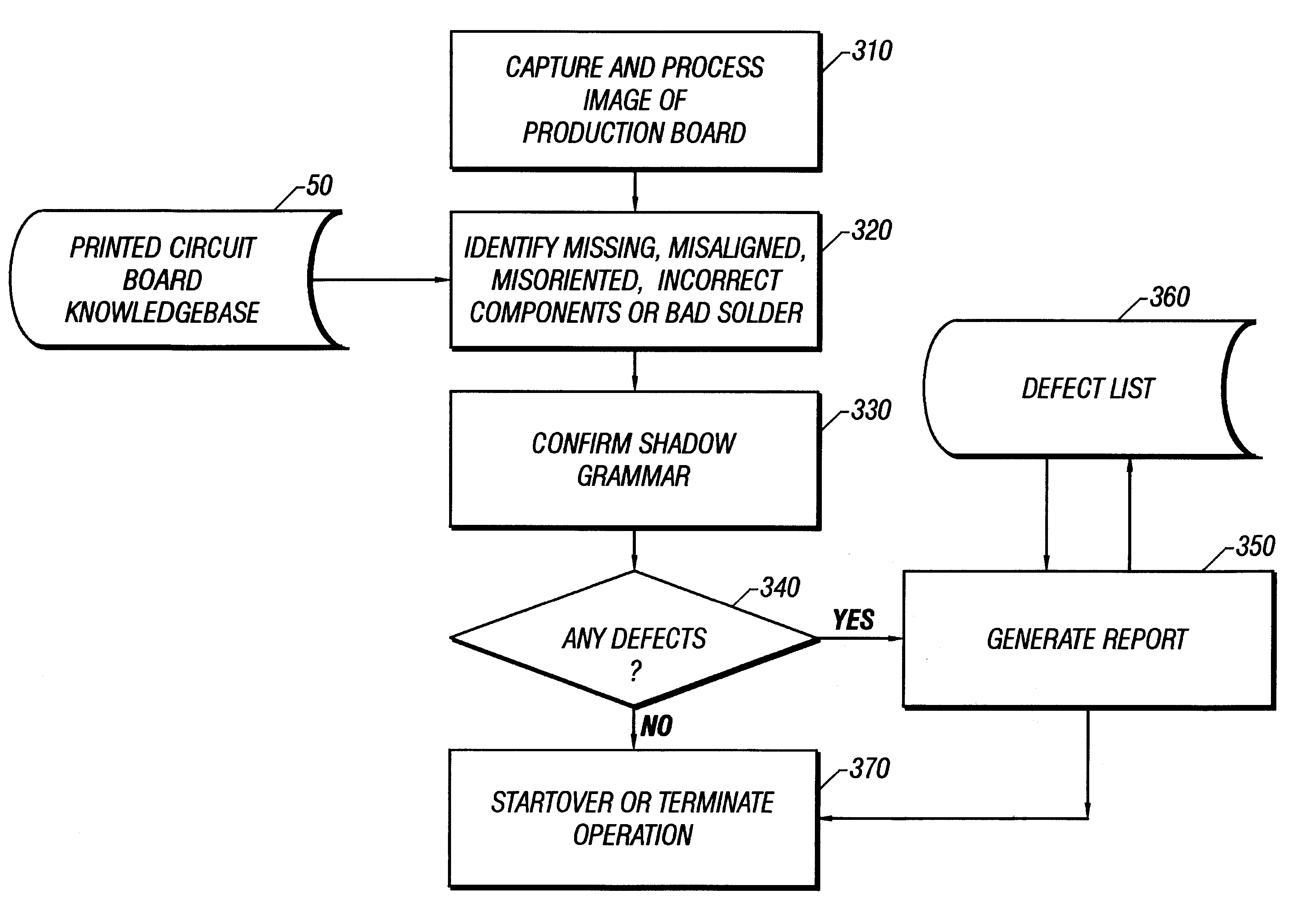
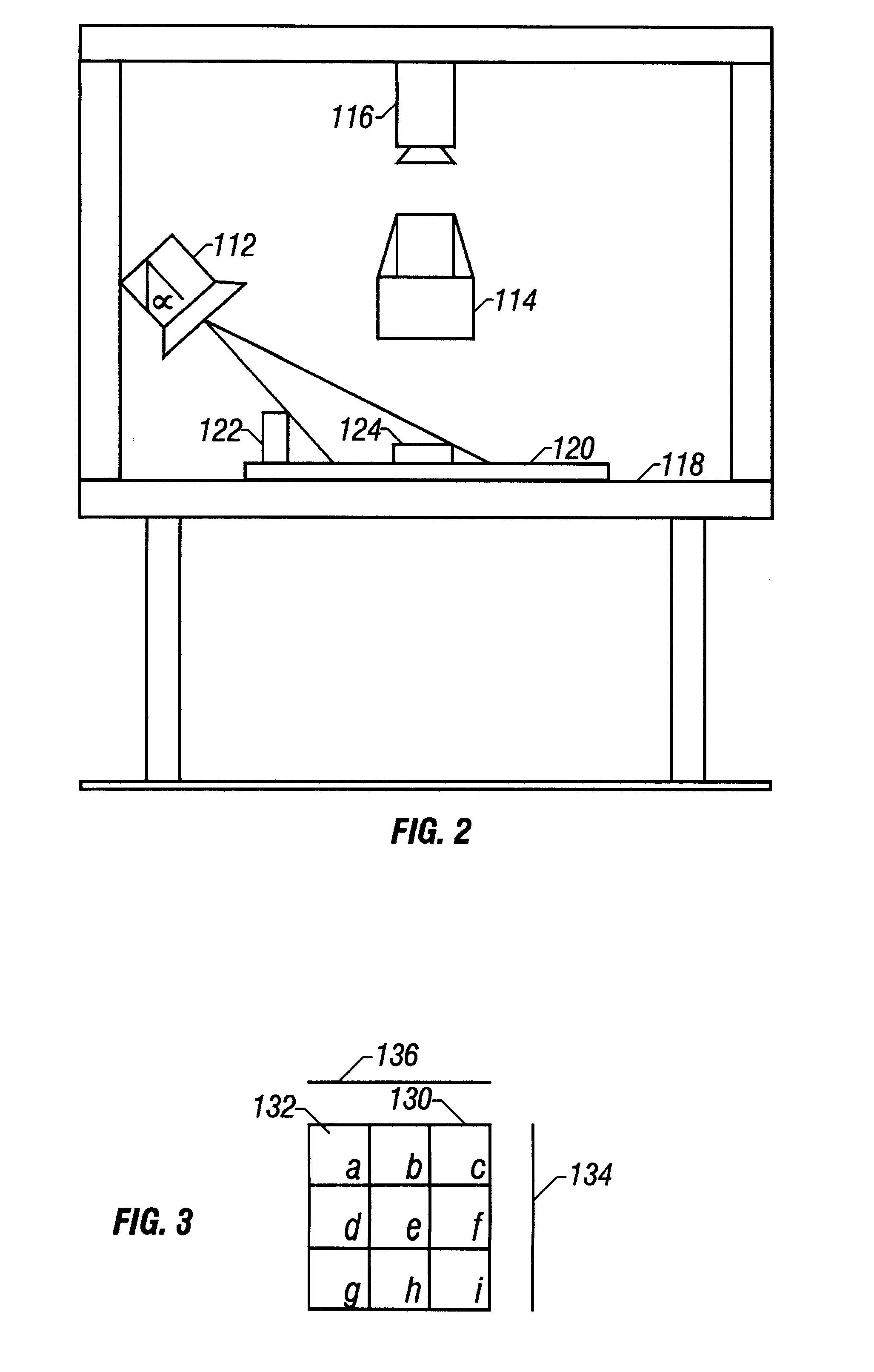
System and method of optically inspecting manufactured devices
An apparatus, system, and method of optically inspecting printed circuit boards (PCBs) for defects, that reliably determines the dimensions of components including those having the same color as the background, and which can detect components which are missing, misoriented, misaligned, or not properly seated. The apparatus uses a camera and a coherent primary light source mounted at an angle away from the vertical so as to produce sharply defined PCB component shadows on the top surface of the PCB. An image of the PCB is captured, the shadow edges are symbolically decomposed into primitives from which gradients are produced, and then compared to a previously captured gradient of a defect-free PCB. Differences in the two image gradients, if any, are used to identify missing, misaligned, misoriented, and improperly seated components, and to detect foreign objects and other PCB defects.
Owner:RUDOLPH TECHNOLOGIES INC
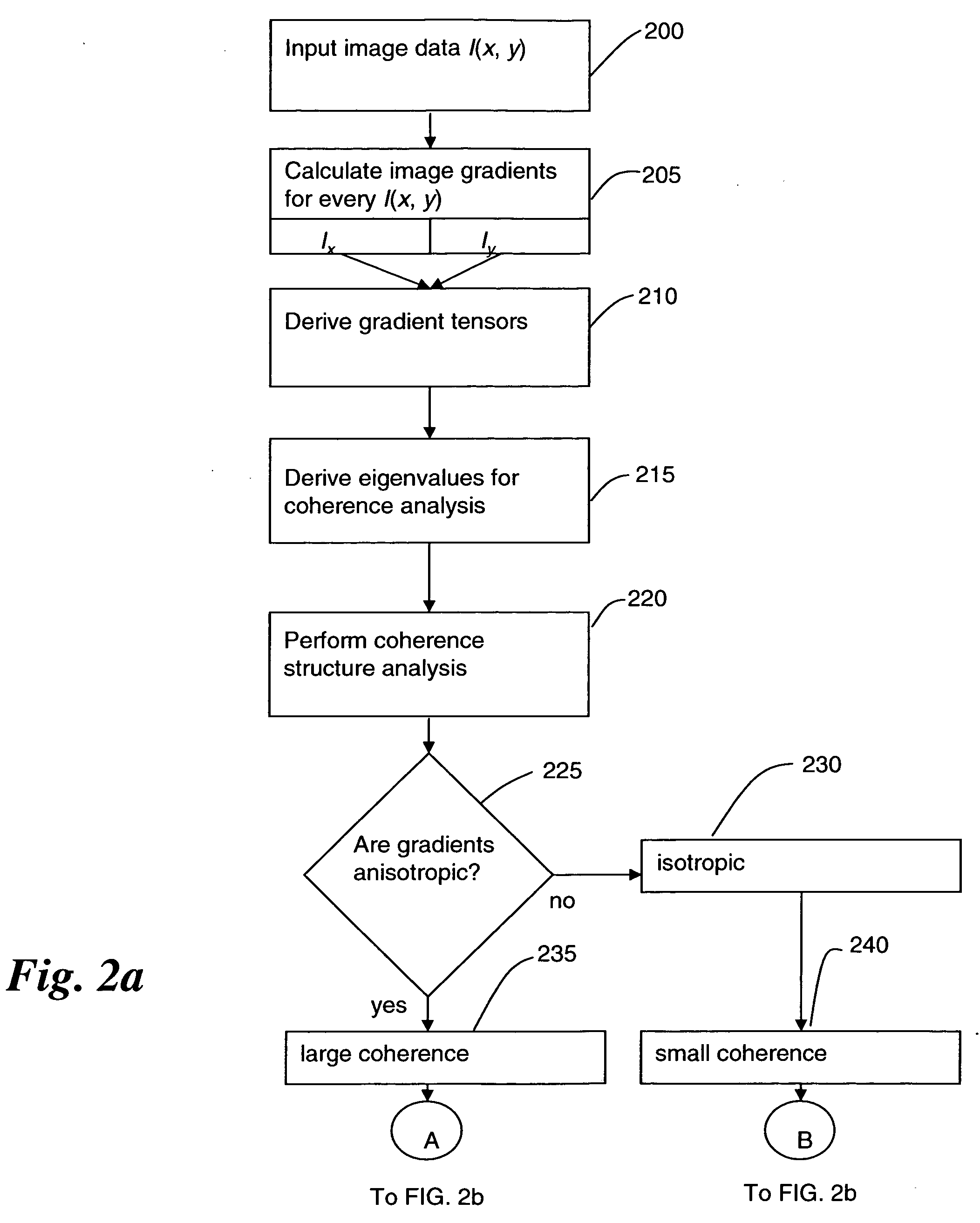
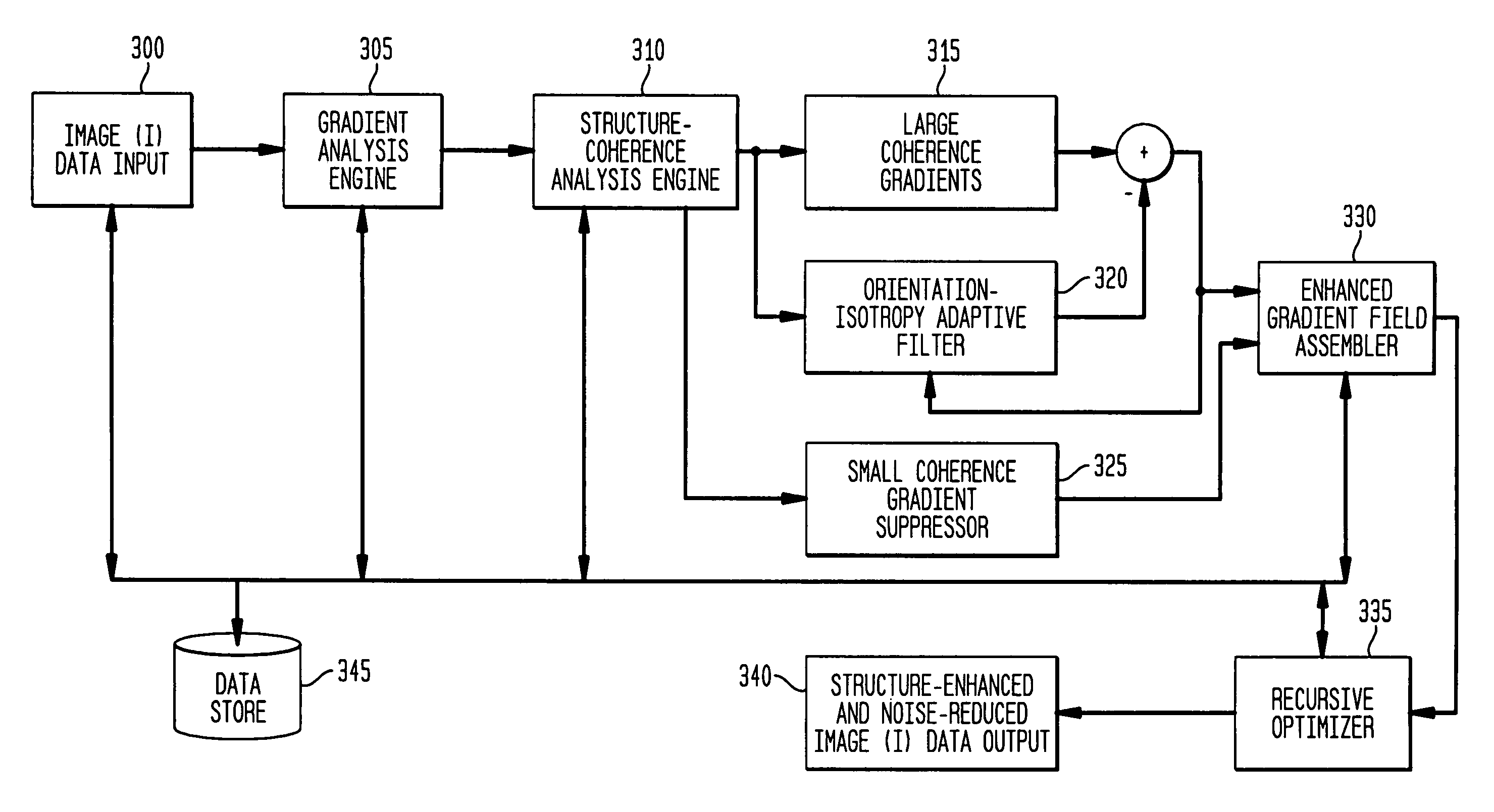
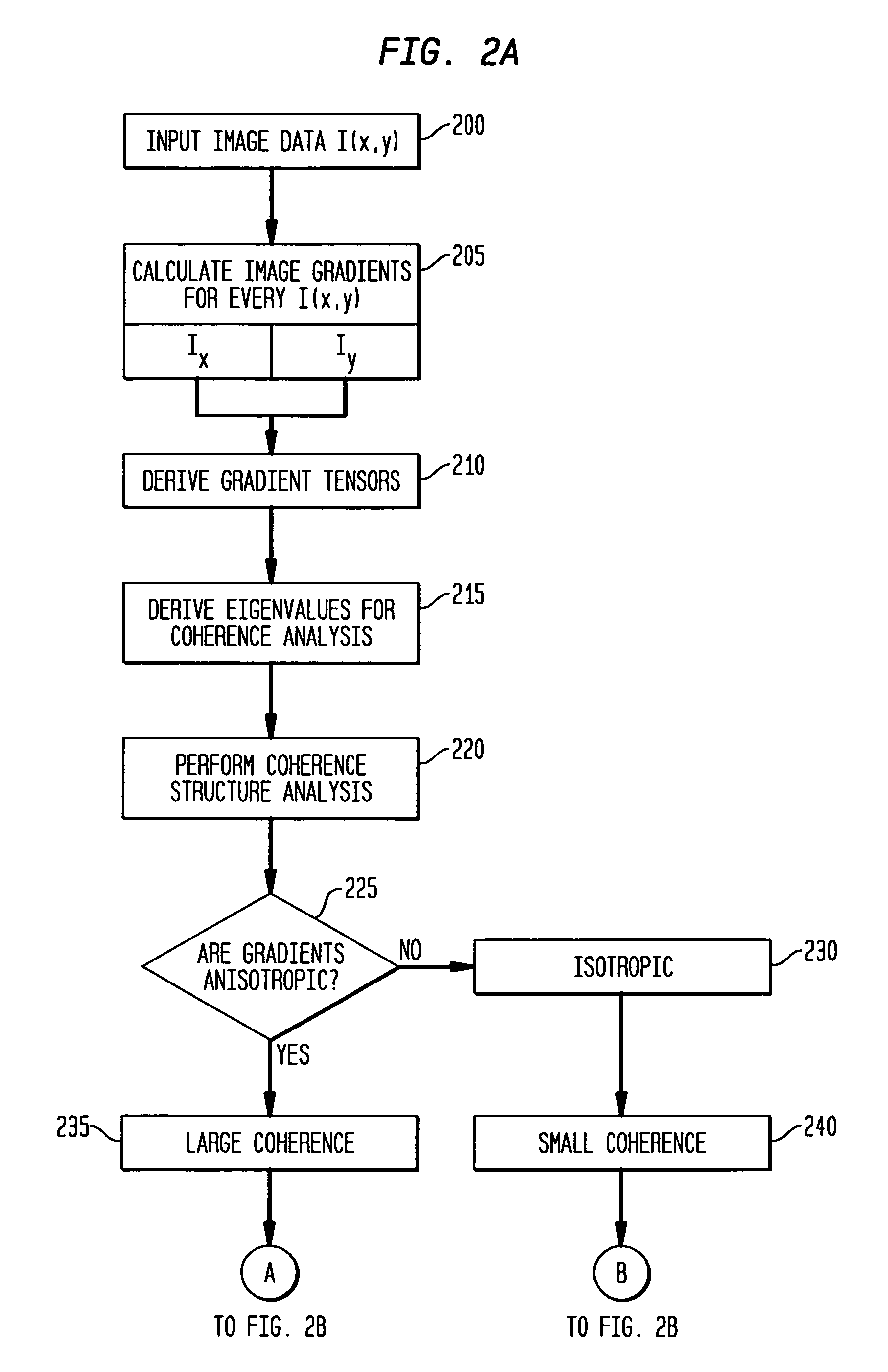
Gradient-based image restoration and enhancement
InactiveUS20060072844A1High gradientSimple structureImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionAdaptive filter
A gradient-based image enhancement and restoration method and system which applies an orientation-isotropy adaptive filter to the gradients of high structured regions, and directly suppresses the gradients in the noise or texture regions. A new gradient field is obtained from which image reconstruction can progress using least mean squares. The method generally comprises: inputting image data; calculating image gradients; defining the gradients as having large or small coherence; filtering the large coherence gradients for edge enhancement; suppressing the small coherence gradients for noise reduction; assembling an enhanced gradient field from the filtered large coherence and suppressed small coherence gradients; and optimizing the assembled gradient field into a restored image.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Sea surface wind measurement method based on X-band marine radar
ActiveCN102681033AImproved wind direction measurement accuracyImproved wind speed accuracyIndication of weather conditions using multiple variablesIndication/recording movementNormalized radar cross sectionSea temperature
The invention discloses a sea surface wind measurement method based on an X-band marine radar and belongs to the technical field of marine dynamic environment remote sensing. The measurement method comprises three parts of radar image preprocessing, wind direction measurement and wind speed measurement. In the wind direction measurement indexes, image gradient, gray level and smoothing item are organically combined, the proportion of the image gradient, the gray level and the smoothing item is adjusted through proportionality factor and a model suitable for the sea surface wind characteristic is established, compared with the prior art, the wind direction measurement precision is improved by 68.4 percent. In the wind speed measurement indexes, when the radar is used for measuring individually, normalized radar cross section (NRCS), the actually measured wind direction and signal to noise ratio (SNR) serve as back propagation (BP) network input, compared with the traditional algorithm, the wind speed measurement precision is improved by over 84 percent. In the wind speed measurement indexes, sea boundary layer parameters serve as addition input of the BP network, so that the wind speed measurement precision of the marine radar can be further improved, and the measurement precision is improved by over 48 percent by taking air-sea temperature difference, salinity, sea level and atmospheric pressure into consideration.
Owner:哈尔滨哈船导航技术有限公司
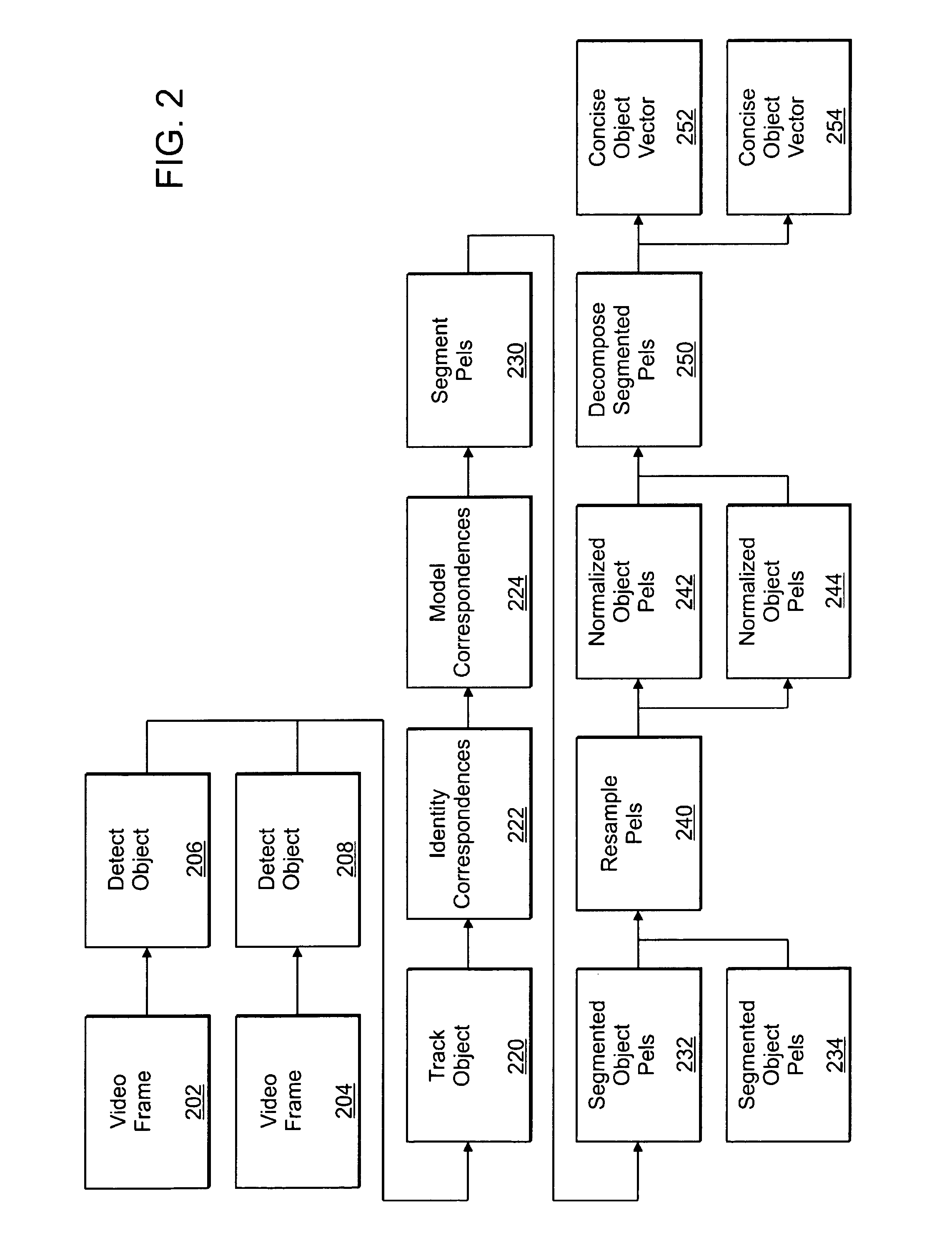
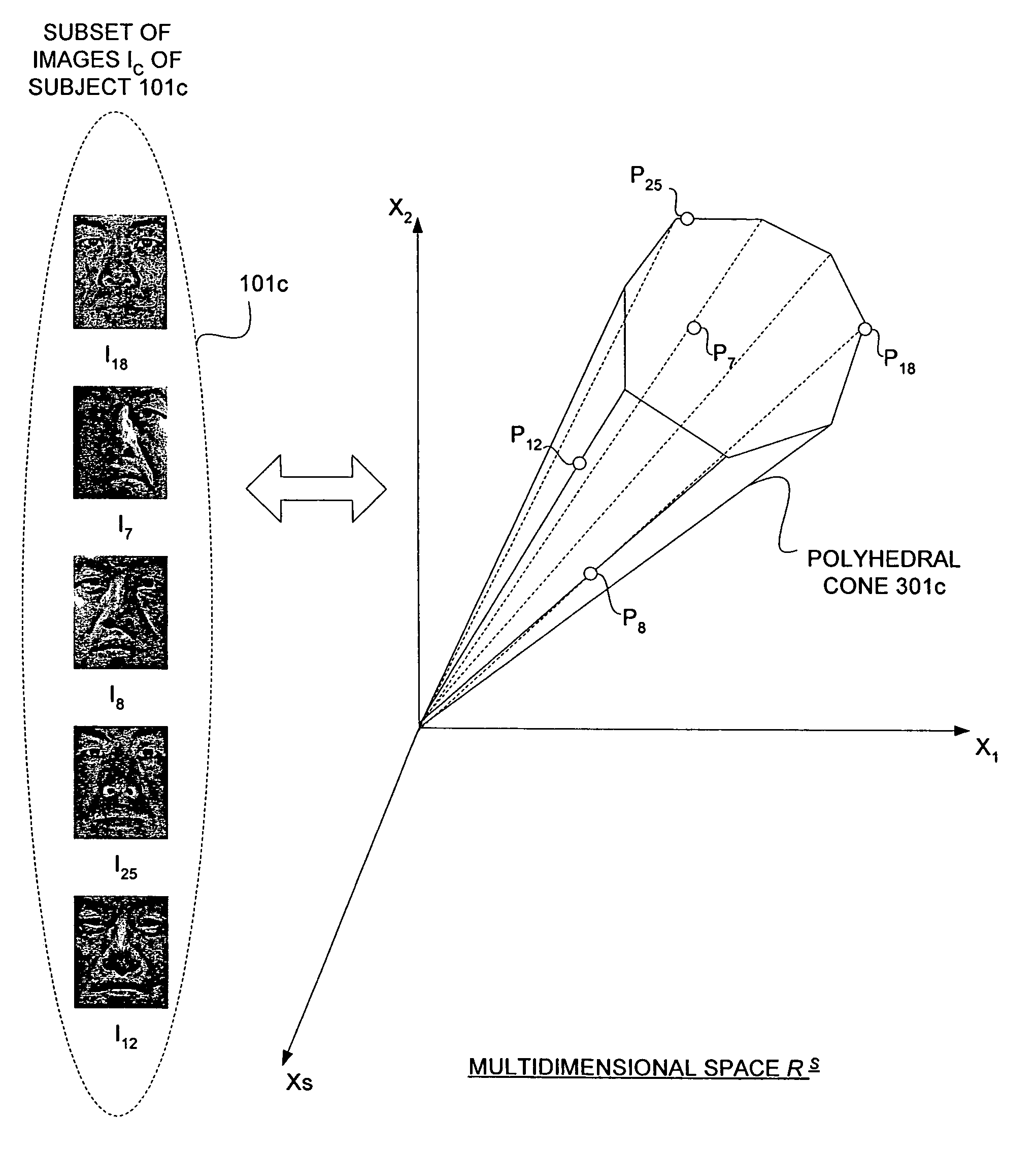
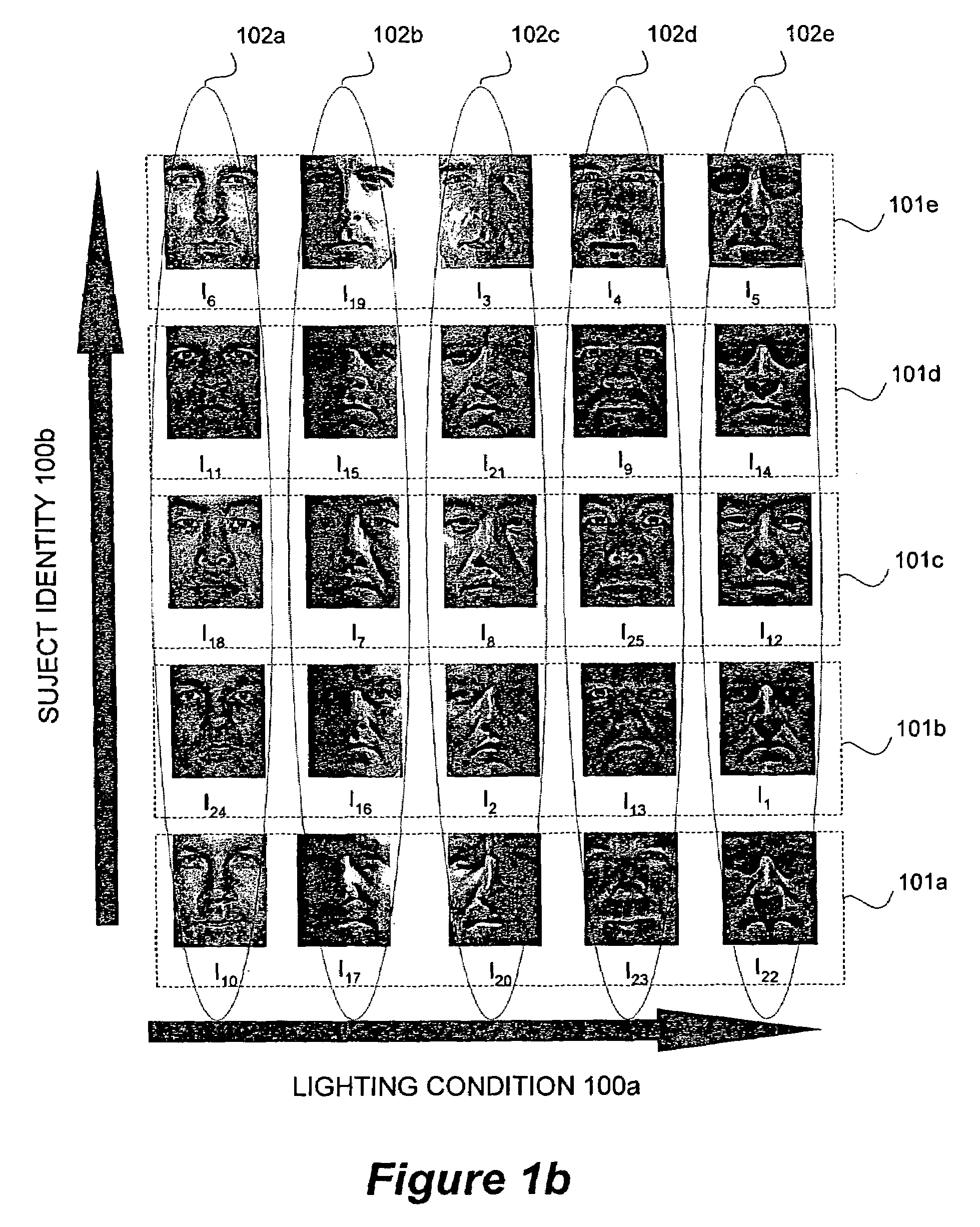
Clustering appearances of objects under varying illumination conditions
ActiveUS7103225B2Efficiently determinedImplementation is particularly straightforwardCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging conditionHigh dimensional
Taking a set of unlabeled images of a collection of objects acquired under different imaging conditions, and decomposing the set into disjoint subsets corresponding to individual objects requires clustering. Appearance-based methods for clustering a set of images of 3-D objects acquired under varying illumination conditions can be based on the concept of illumination cones. A clustering problem is equivalent to finding convex polyhedral cones in the high-dimensional image space. To efficiently determine the conic structures hidden in the image data, the concept of conic affinity can be used which measures the likelihood of a pair of images belonging to the same underlying polyhedral cone. Other algorithms can be based on affinity measure based on image gradient comparisons operating directly on the image gradients by comparing the magnitudes and orientations of the image gradient.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
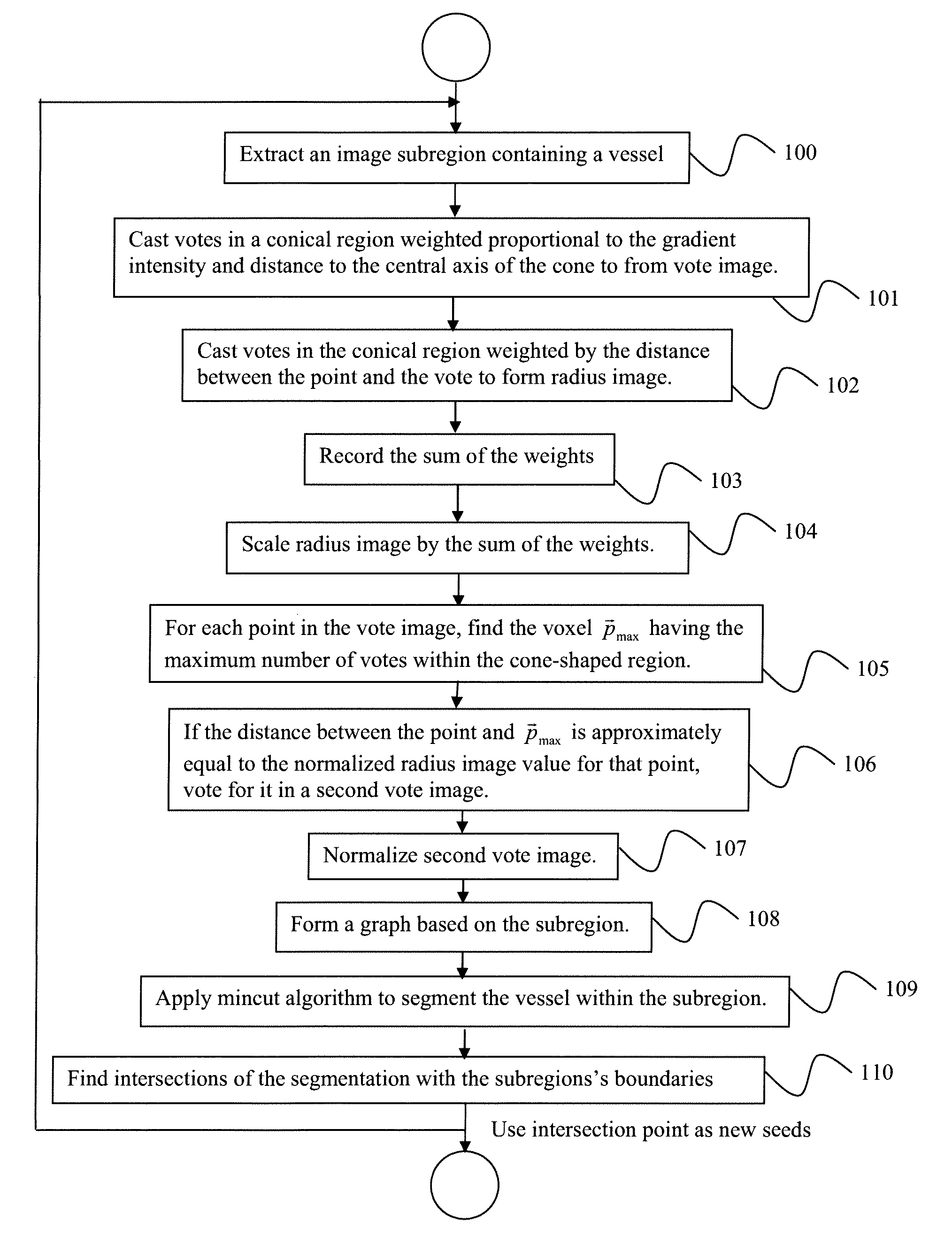
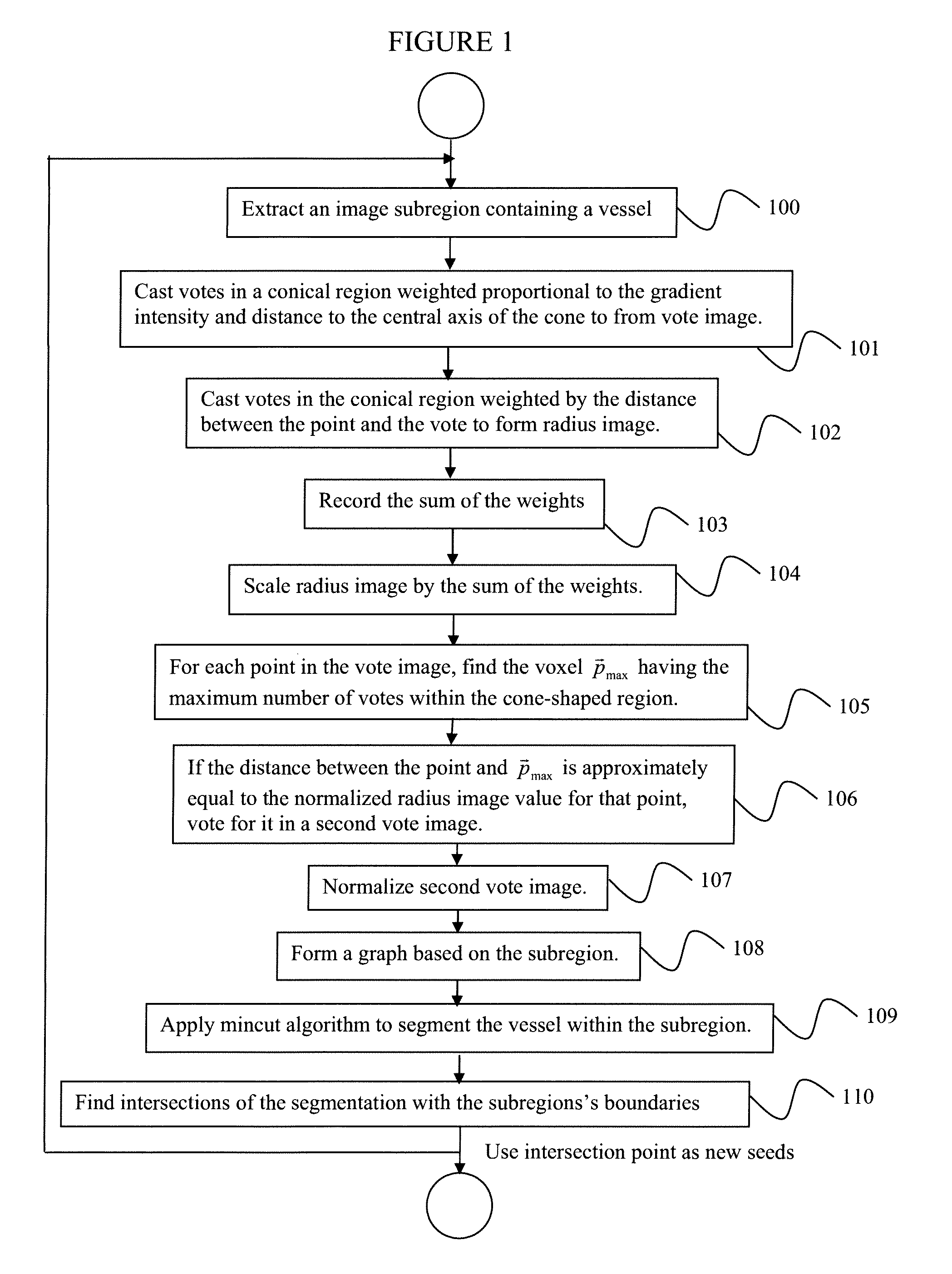
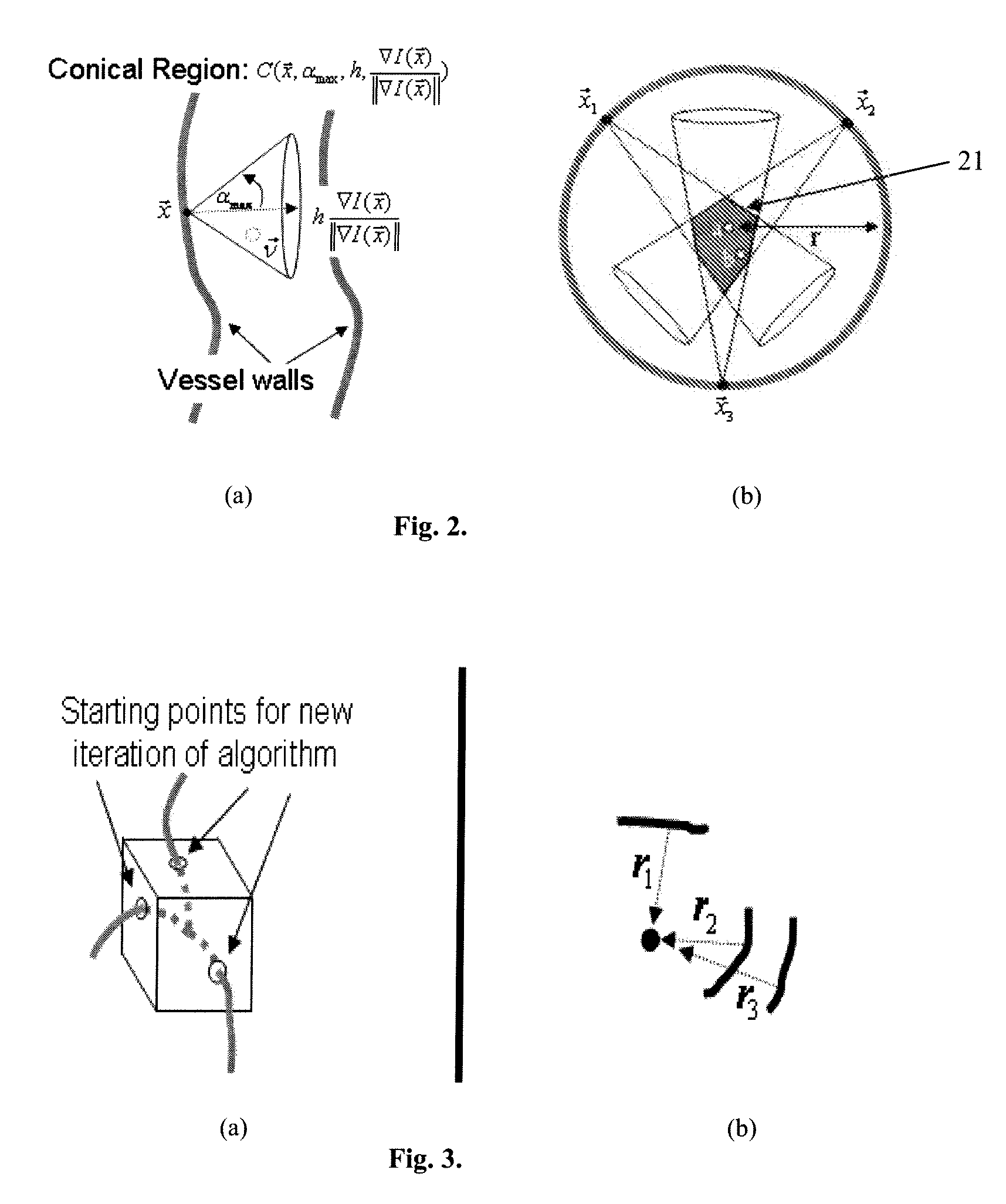
System and method for 3D vessel segmentation with minimal cuts
ActiveUS20090279758A1Minimizing energyFacilitates simple and intuitiveImage enhancementImage analysisGraphicsVoxel
A method for segmenting tubular structures in digital medical images includes extracting a subregion from a 3-dimensional (3D) digital image volume containing a vessel of interest, identifying potential vessel centerpoints for each voxel in the subregion by attaching to each voxel a tip of a 3D cone that is oriented in the direction of the voxel's image gradient and having each voxel within the cone vote for those voxels most likely to belong to a vessel centerline, selecting candidates for a second vote image that are both popular according to a first vote image, as well as being consistently voted upon by a radius image, reconfiguring the subregion as a graph where each voxel is represented by a node that is connected to 26 nearest neighbors by n-link edges, and applying a min-cut algorithm to segment the vessel within the subregion.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
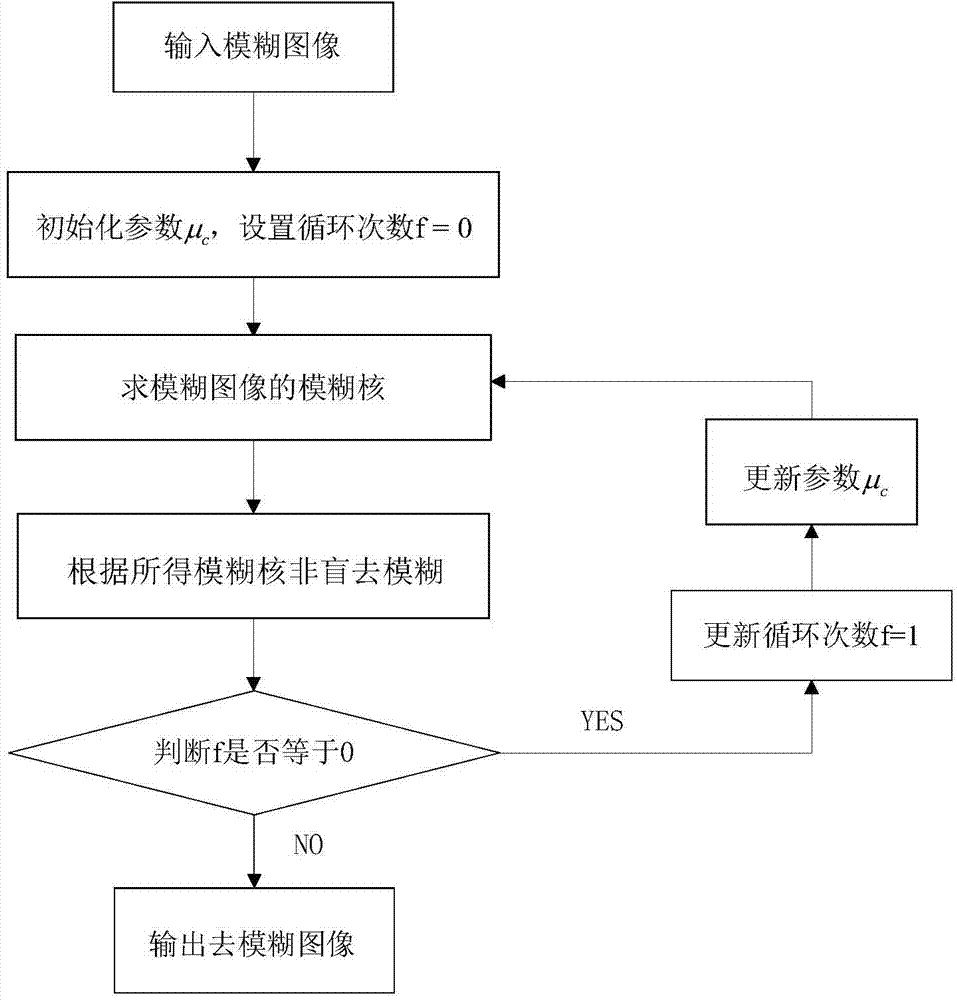
Systems and methods for tracking human hands by performing parts based template matching using images from multiple viewpoints
ActiveUS20130343610A1Character and pattern recognitionDigital data authenticationTemplate matchingView camera
Systems and methods for tracking human hands by performing parts based template matching using images captured from multiple viewpoints are described. One embodiment includes a processor, a reference camera, an alternate view camera, and memory containing: a hand tracking application; and a plurality of edge feature templates that are rotated and scaled versions of a finger template that includes an edge features template. In addition, the hand tracking application configures the processor to: detect at least one candidate finger in a reference frame, where each candidate finger is a grouping of pixels identified by searching the reference frame for a grouping of pixels that have image gradient orientations that match one of the plurality of edge feature templates; and verify the correct detection of a candidate finger in the reference frame by locating a grouping of pixels in an alternate view frame that correspond to the candidate finger.
Owner:AQUIFI
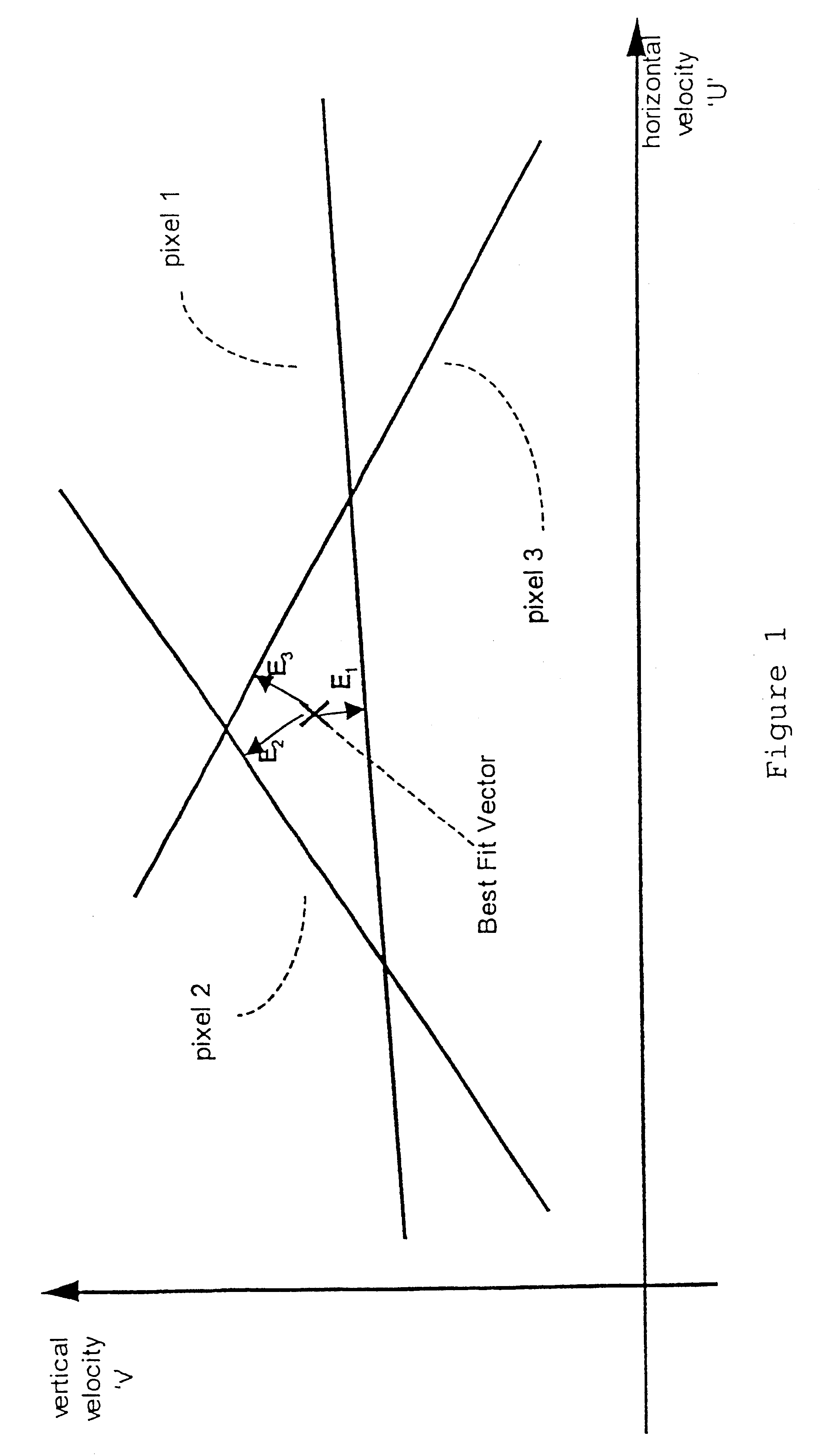
Motion vector field error estimation
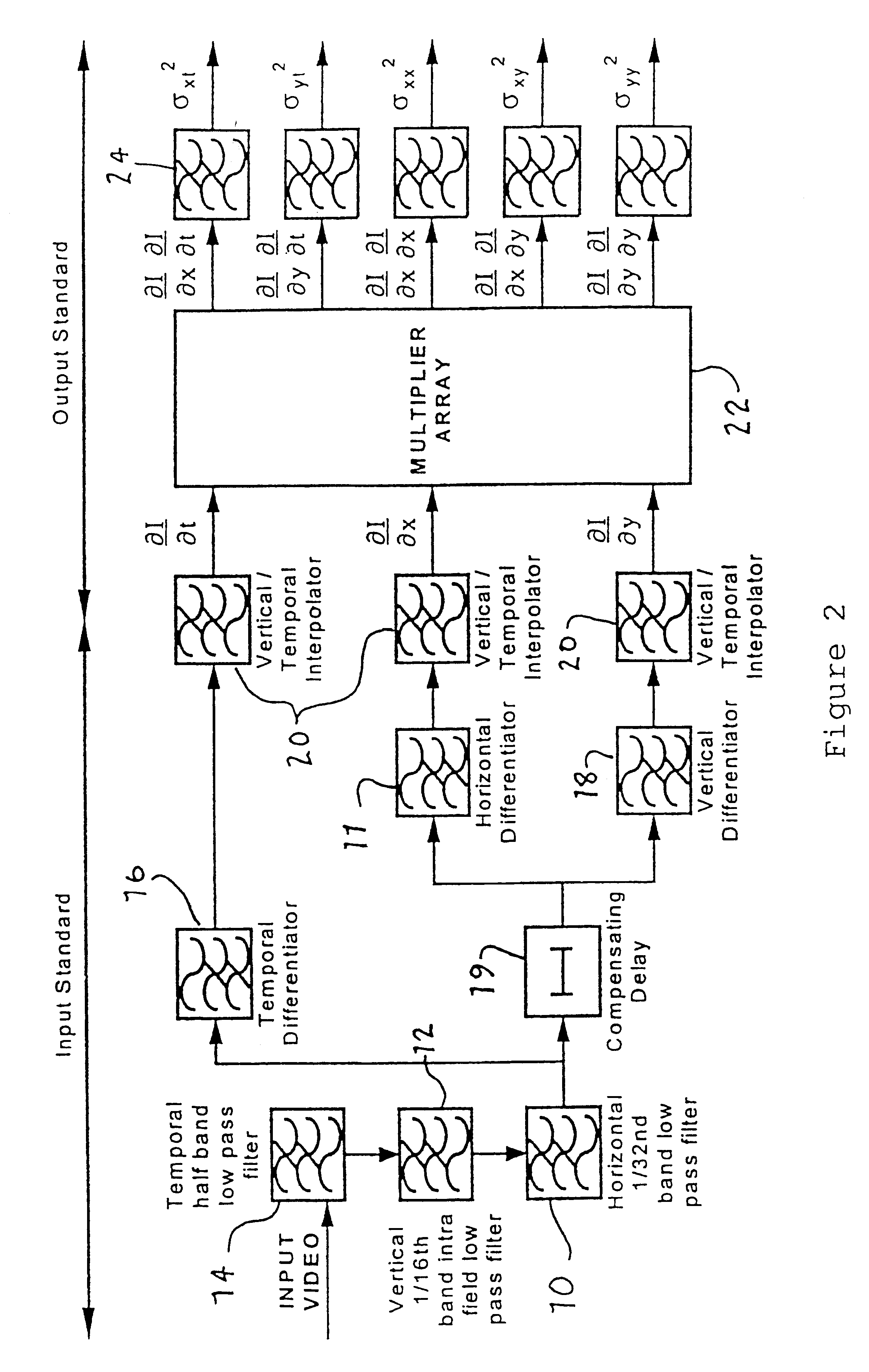
InactiveUS6442202B1Less accurateSimple technologyTelevision system detailsImage analysisObservational errorMotion vector
A technique is disclosed for estimating the measurement error in motion vectors used for example in a motion compensated video signal process. For each motion vector corresponding to a region of an image a plurality of temporal and spatial image gradients are calculated corresponding to that region. From the constraint equations of the image gradients a plurality of error values can be calculated for each motion vector and a parameter generated describing the size of the distribution of motion vector measurement errors. Subsequent processing of the video signals using the motion vectors can then be adapted, for example by graceful fallback in motion compensated interpolation, depending on the accuracy of each motion vector. The "confidence' in the accuracy of each motion vector can be described by a parameter calculated in relation to the size of the error distribution and the motion vector speed.
Owner:HB COMM UK LTD
Fast 3d-2d image registration method with application to continuously guided endoscopy
A novel framework for fast and continuous registration between two imaging modalities is disclosed. The approach makes it possible to completely determine the rigid transformation between multiple sources at real-time or near real-time frame-rates in order to localize the cameras and register the two sources. A disclosed example includes computing or capturing a set of reference images within a known environment, complete with corresponding depth maps and image gradients. The collection of these images and depth maps constitutes the reference source. The second source is a real-time or near-real time source which may include a live video feed. Given one frame from this video feed, and starting from an initial guess of viewpoint, the real-time video frame is warped to the nearest viewing site of the reference source. An image difference is computed between the warped video frame and the reference image. The viewpoint is updated via a Gauss-Newton parameter update and certain of the steps are repeated for each frame until the viewpoint converges or the next video frame becomes available. The final viewpoint gives an estimate of the relative rotation and translation between the camera at that particular video frame and the reference source. The invention has far-reaching applications, particularly in the field of assisted endoscopy, including bronchoscopy and colonoscopy. Other applications include aerial and ground-based navigation.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Gradient-based image restoration and enhancement
A gradient-based image enhancement and restoration method and system which applies an orientation-isotropy adaptive filter to the gradients of high structured regions, and directly suppresses the gradients in the noise or texture regions. A new gradient field is obtained from which image reconstruction can progress using least mean squares. The method generally comprises: inputting image data; calculating image gradients; defining the gradients as having large or small coherence; filtering the large coherence gradients for edge enhancement; suppressing the small coherence gradients for noise reduction; assembling an enhanced gradient field from the filtered large coherence and suppressed small coherence gradients; and optimizing the assembled gradient field into a restored image.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Intelligent multifunctional belt surface patch edge detection method
InactiveCN103208117AAccurate transmissionExtended service lifeImage analysisImage gradientImage edge
The invention discloses an intelligent multifunctional belt surface patch edge detection method which is characterized by including steps: (1) two direction templates are adopted to have neighborhood convolution with images in an image space to complete image gradient magnitude calculation; (2) the gradient value and the gradient direction of edge pixel points are calculated, and edge searching is performed according to the gradient direction information to obtain accurate conveying belt spot image edge point information; and (3) target edge sub pixel positioning is achieved through quadratic polynomial interpolation in the edge point gradient direction. The intelligent multifunctional belt surface patch edge detection method completely eradicates potential safety hazards of conveying belts, reduces irregular maintenance and shutdown overhaul time of the conveying belts, improves production efficiency, has a protection effect for safety production, has important practical significances for promoting the economic development, has a wide application prospect, and can be used for belt surface abrasion detection and surface greasy dirt detection.
Owner:袁景
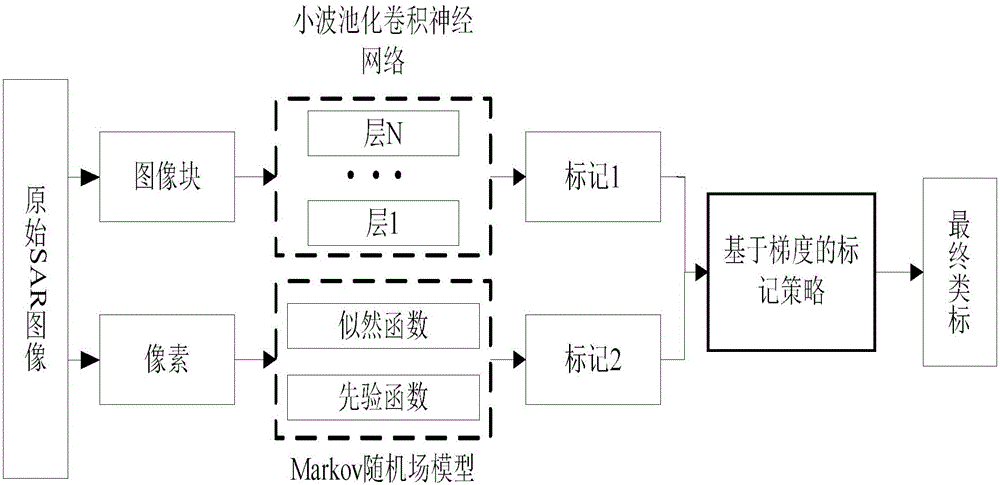
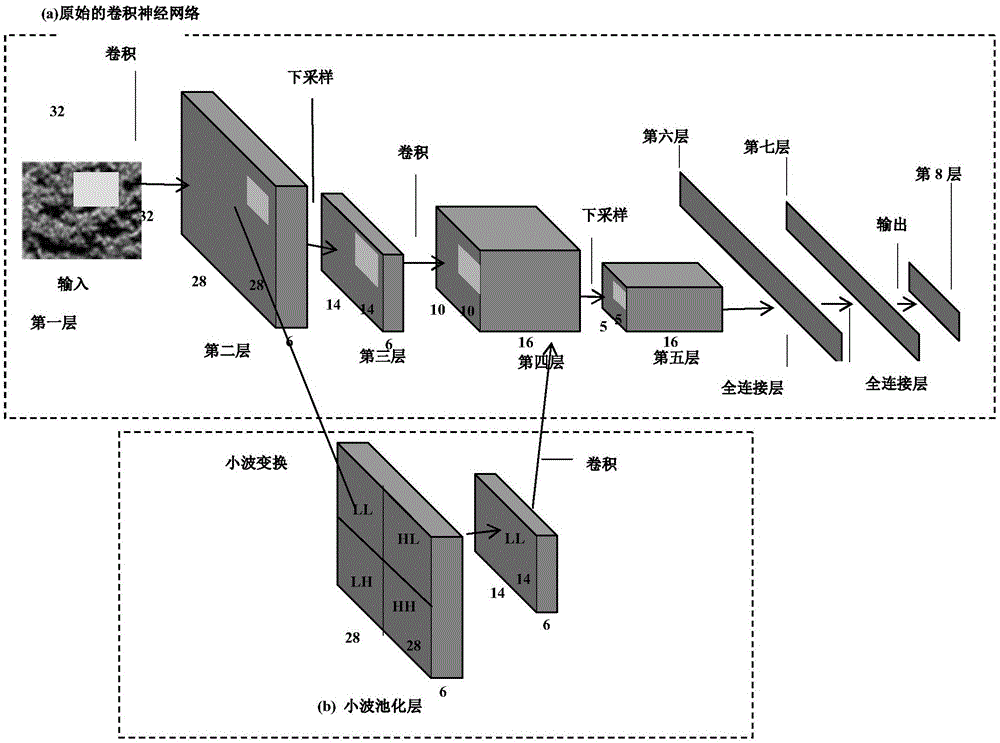
SAR image segmentation method based on wavelet pooling convolutional neural networks
ActiveCN105139395AWith noise reduction functionMaintain structural featuresImage analysisSar image segmentationImage gradient
The invention discloses an SAR image segmentation method based on wavelet pooling convolutional neural networks. The SAR image segmentation method comprises 1. constructing a wavelet pooling layer and forming wavelet pooling convolutional neural networks; 2. selecting image blocks and inputting the image blocks into the wavelet pooling convolutional neural networks, and training the image blocks; 3. inputting all the image blocks into the trained networks, and testing the image blocks to obtain a first class mark of an SAR image; 4. performing superpixel segmentation of the SAR image, and blending the superpixel segmentation result with the first class mark of the SAR image to obtain a second class mark of the SAR image; 5. obtaining a third class mark of the SAR image according to a Markov random field model, and blending the third class mark of the SAR image with the superpixel segmentation result to obtain a fourth class mark of the SAR image; and 6. blending the second class mark of the SAR image with the fourth class mark of the SAR image according to an SAR image gradient map to obtain the eventual segmentation result. The SAR image segmentation method based on wavelet pooling convolutional neural networks improves the segmentation effect of the SAR image and can be used for target detection and identification.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
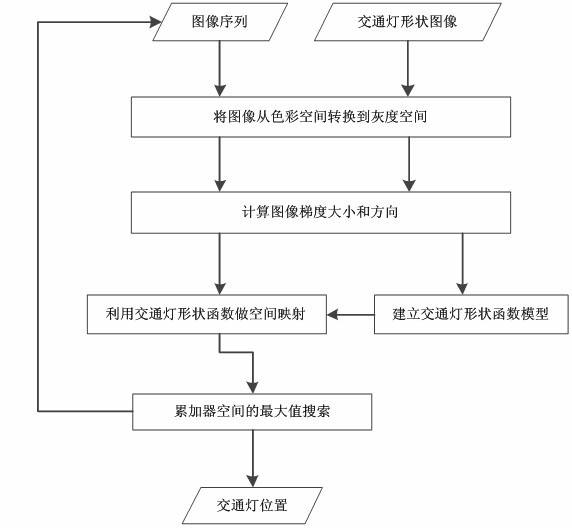
General Hough transformation-based method for detecting position of traffic signal lamp
ActiveCN102354457APrecise positioningEasy to replaceCharacter and pattern recognitionTraffic control supervisionPattern recognitionTraffic signal
The invention belongs to the technical field of digital image processing and pattern recognition and discloses a general Hough transformation-based method for detecting the position of a traffic signal lamp, which comprises the following steps: by taking an image sequence as input, calculating image gradient information by adopting a first-order differential operator on an image by using image gradation; establishing a traffic lamp shape describing function; defining mapping from an image point to the space of an accumulator; and searching the extreme value of the space of the accumulator to acquire the coordinates of the traffic lamp to provide positional information for traffic lamp state identification. The general Hough transformation-based method for detecting the position of the traffic signal lamp can cope with the significant change of illumination, is insensitive to the influence caused by image sampling color cast and can cope with the traffic lamp with various common shapes.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
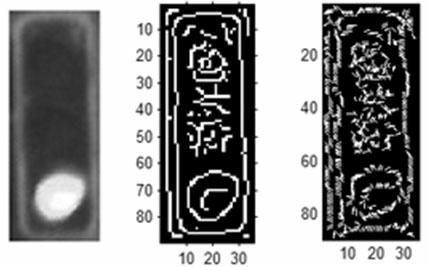
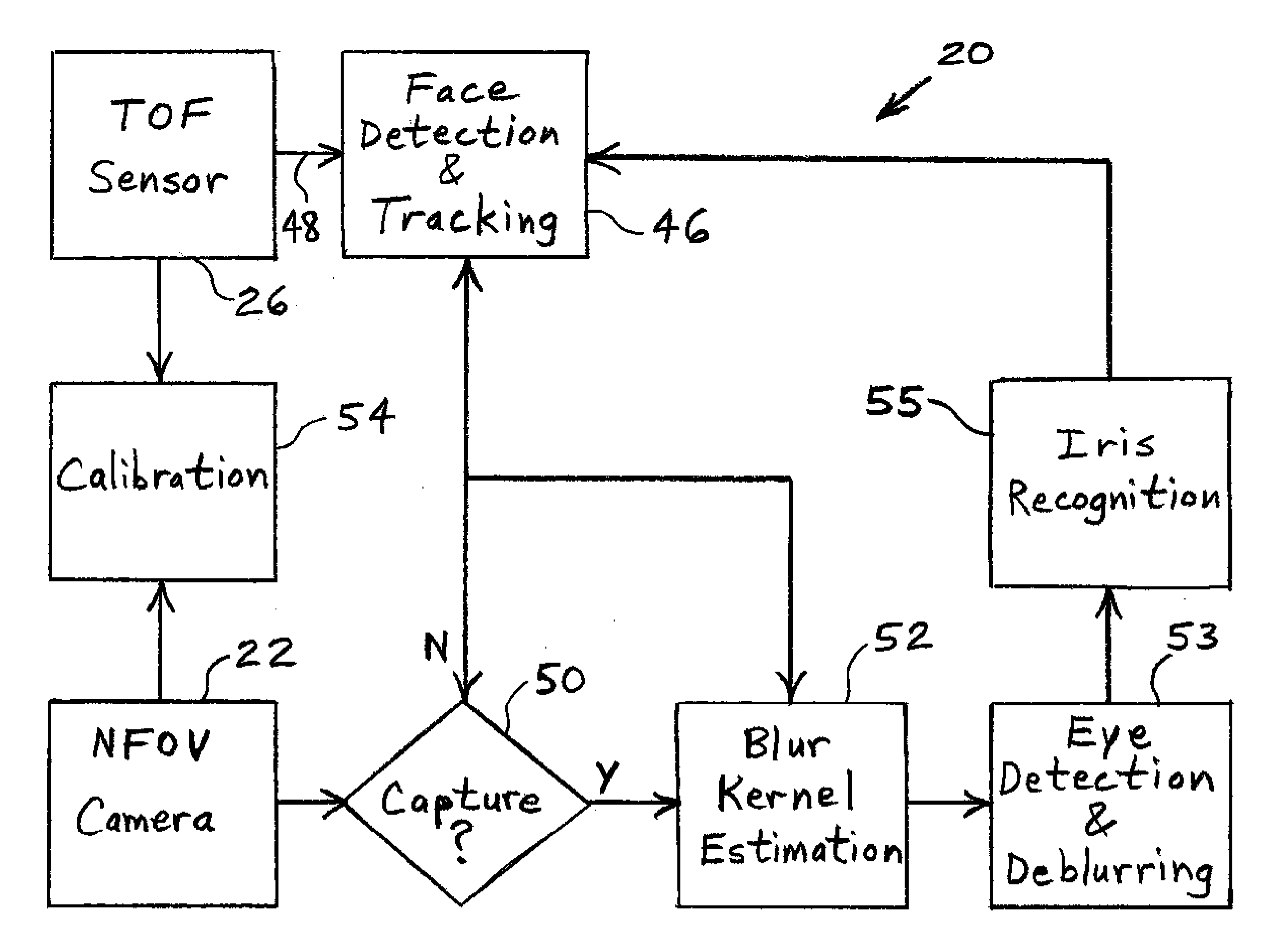
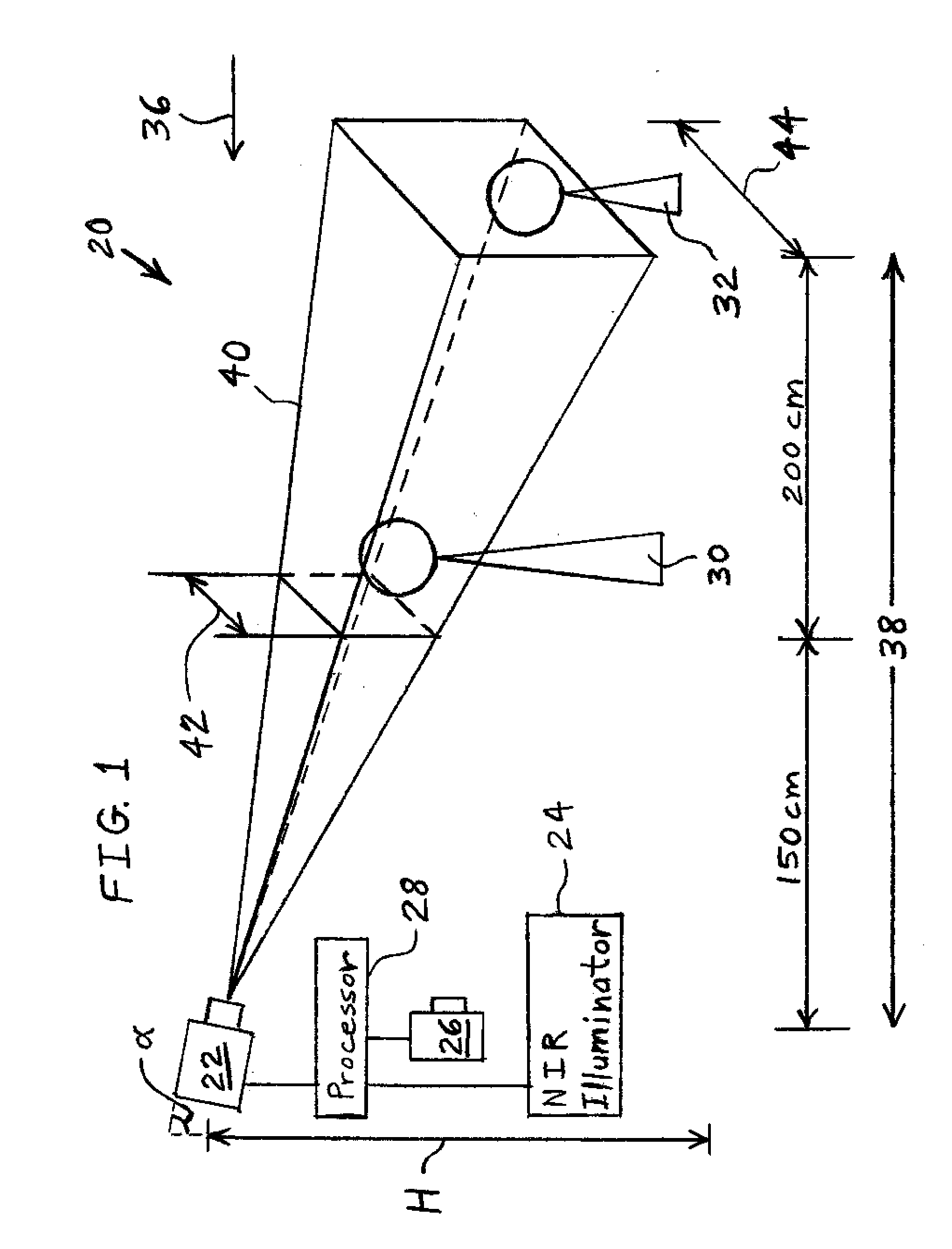
Iris deblurring method based on global and local iris image statistics
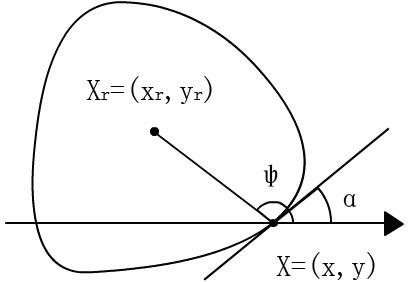
A method of identifying a living being includes using a camera to capture a blurred visual image of an iris of the living being. The blurred visual image is digitally unblurred based on a distribution of eye image gradients in an empirically-collected sample of eye images and characteristics of pupil region. The unblurred image is processed to determine an identity of the living being.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
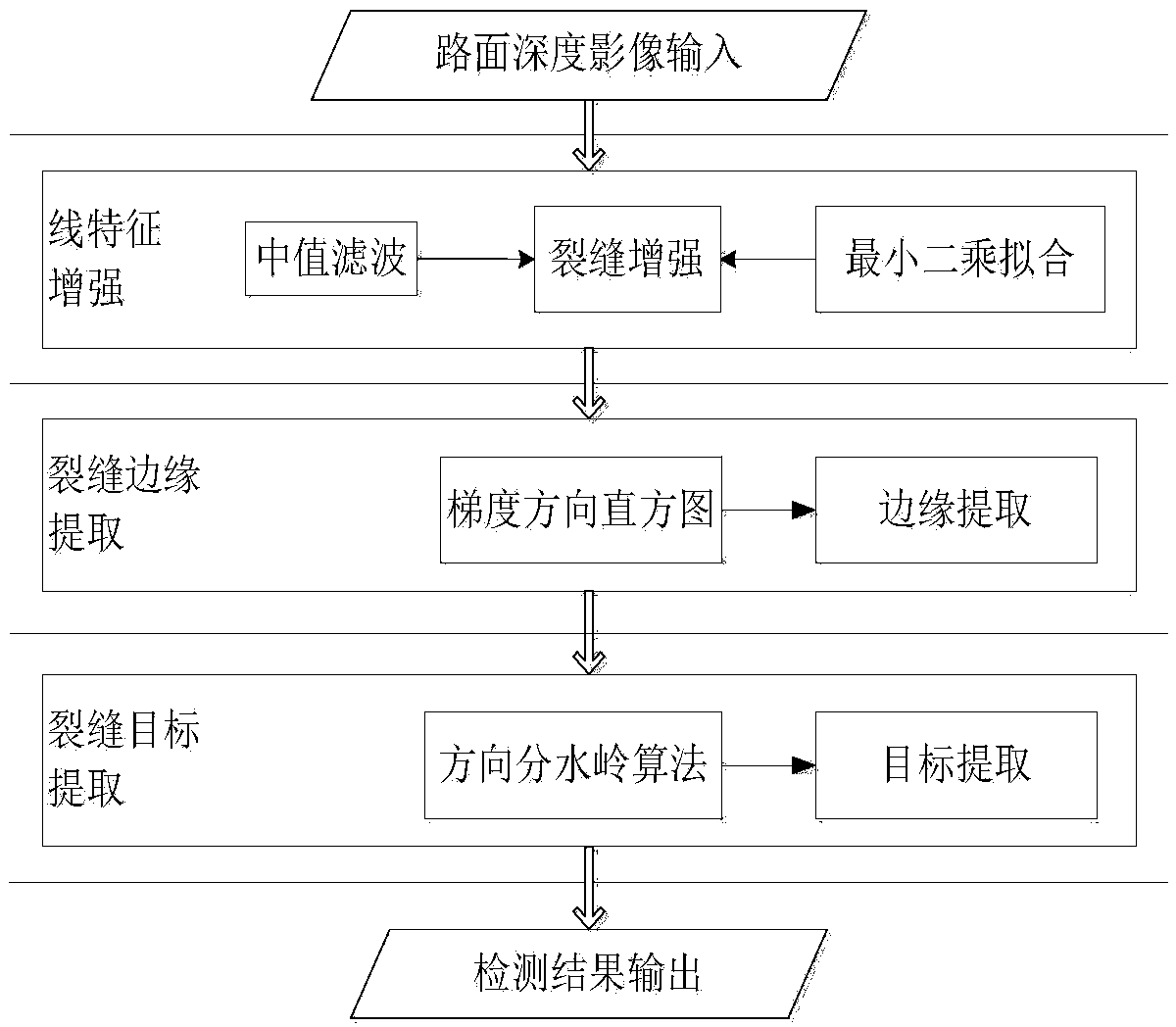
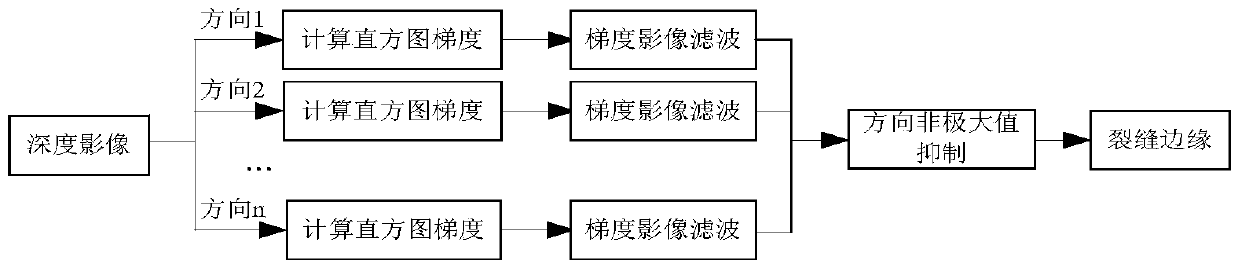
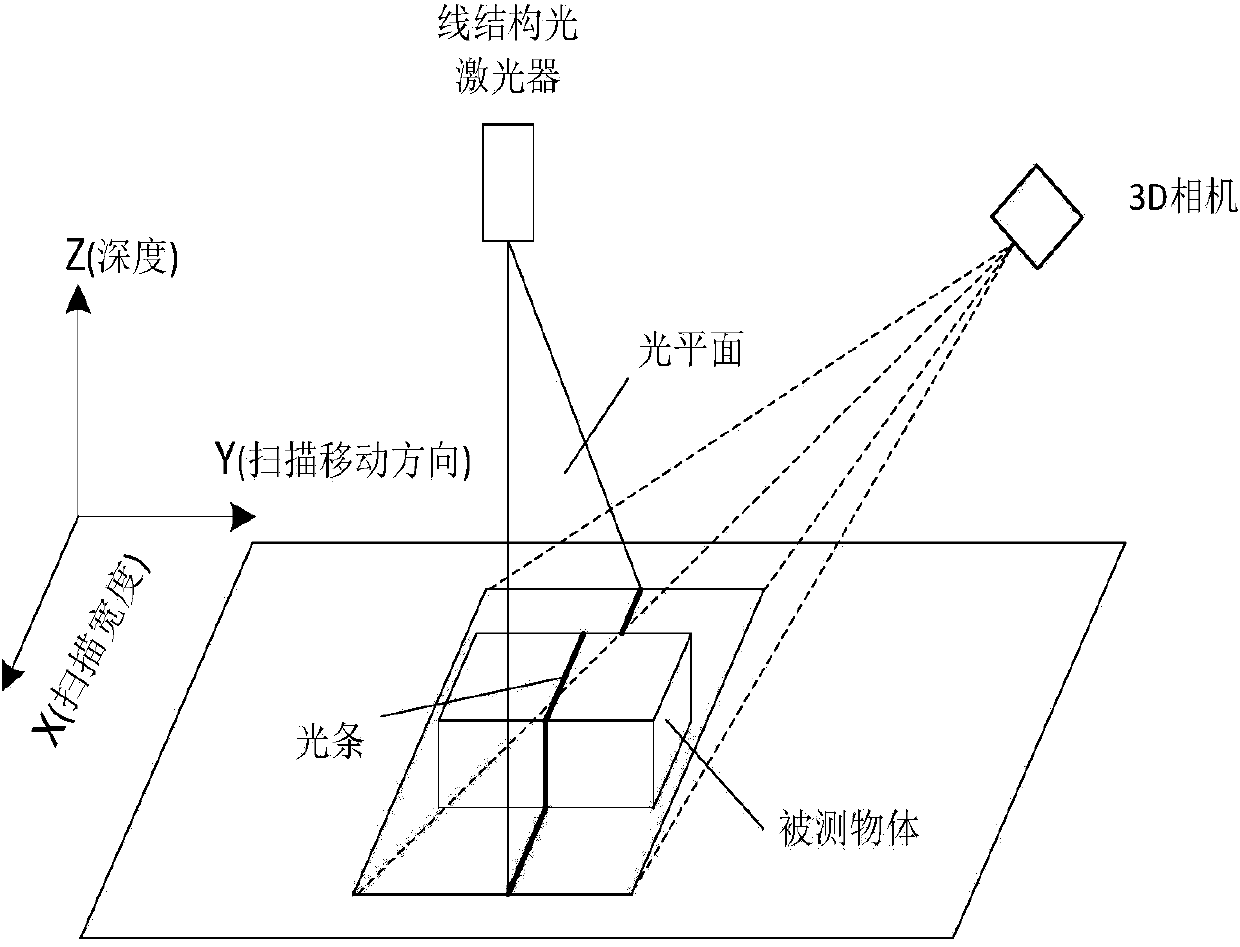
Crack detection method with image gradient direction histogram and watershed method conflated
ActiveCN104008553AGuaranteed growthSolve the puzzle of closure as a region targetImage enhancementImage analysis3d cameraImage gradient
The invention discloses a crack detection method with an image gradient direction histogram and watershed method conflated. The method includes the following steps that 1, the surface to be detected is illuminated by a light source of line structured light, light bar images of the surface to be measured is filmed through a 3D camera, the depth of each pixel point of the surface to be detected is obtained, the depth data are converted into grey level data, and a depth image of the surface to be detected is formed; 2, the gradients of the depth image in eight directions are worked out, and the gradient image of the surface to be detected is obtained; 3, the direction non-maximum suppression of the gradient image is worked out, and the edge image of the surface to be detected is obtained; 4, by adoption of watershed conversion, the connected domain of a crack is obtained, the boundaries of the connected domain are marked, and the closed boundaries of the crack are obtained.
Owner:WUHAN WUDA ZOYON SCI & TECH
Binocular visual image stereo matching method
InactiveCN105528785AImprove matching accuracyThe matching result is reasonableImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxMatrix solution
The present invention discloses a binocular visual image stereo matching method, relating to image data processing. The method comprises the steps of the acquisition and pre-processing of a binocular image, the image gradient matrix solution of the binocular image, the obtainment of an initial disparity map, and the obtainment and output of a final disparity map and the completion of the binocular visual image stereo matching. According to the method, the defect of low matching precision and insufficient real-time performance of the existing binocular stereo matching technology is overcome.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Non-reference image quality evaluation method based on gradient relevance
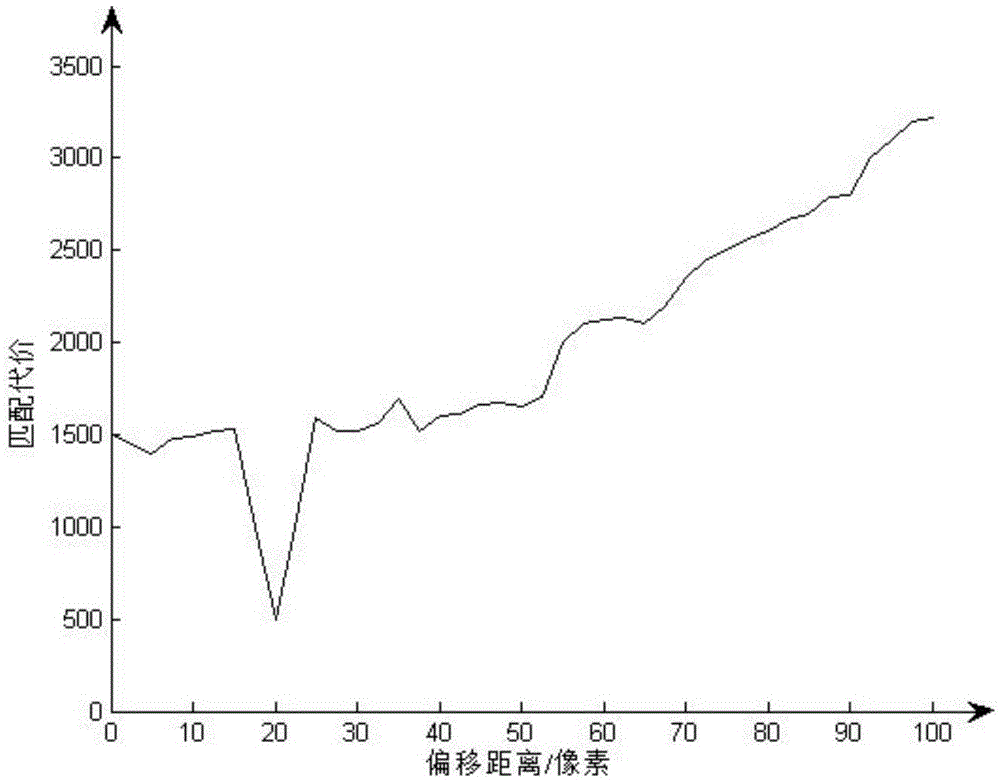
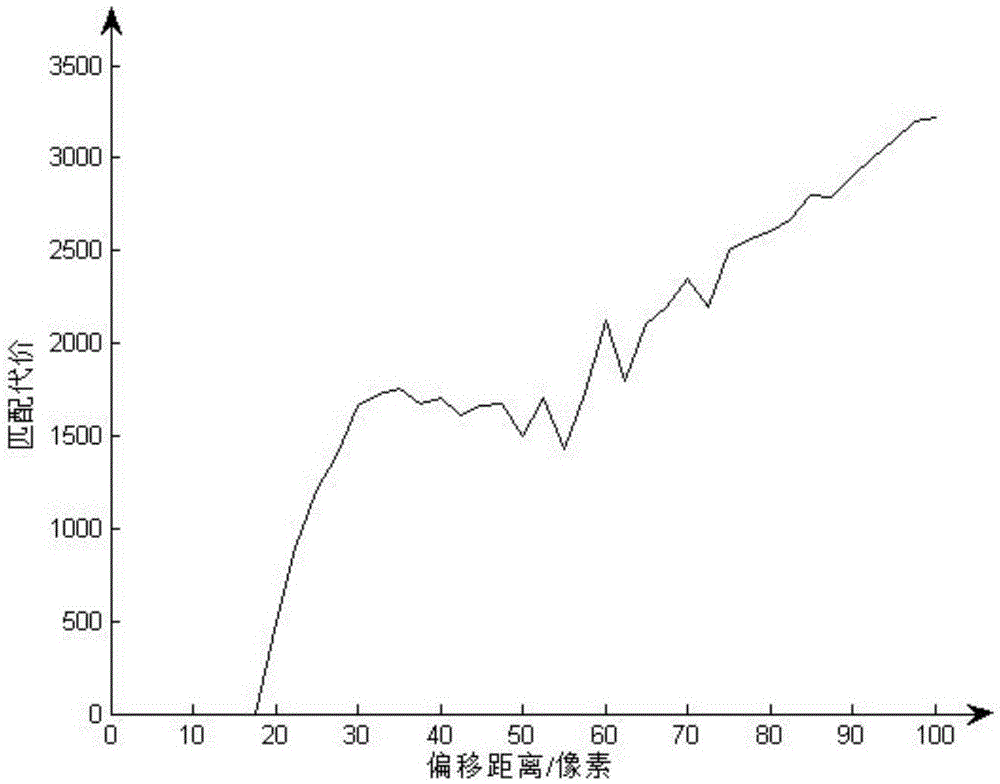
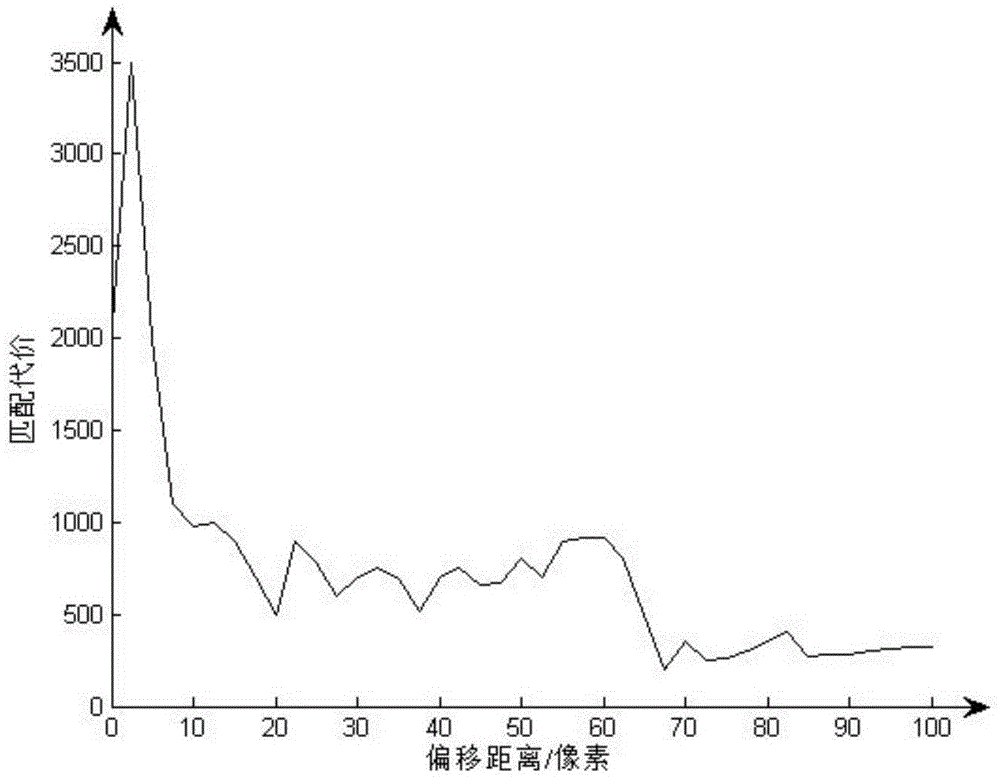
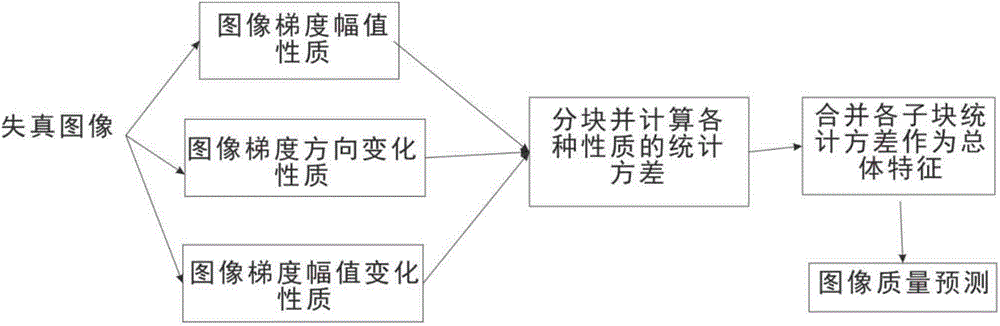
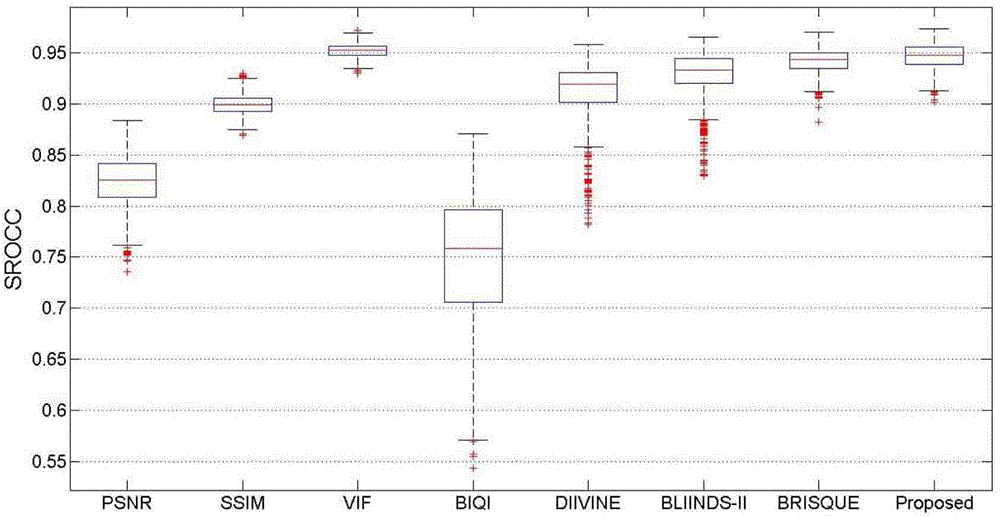
InactiveCN104023230AHigh subjective consistencySmall time complexityTelevision systemsSupport vector machineImaging quality
The invention provides a non-reference image quality evaluation method based on gradient relevance, and belongs to computer image analysis. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, determining three sub-characters, namely, an image gradient amplitude character, an image gradient direction change character and an image gradient amplitude change character, which are easily influenced by distortion in an image gradient; performing M*M image blocking on the three characters, and determining a statistic variance of the three characters in each image block, wherein the average number of the statistic variances of all the image blocks in the whole image is taken as an image characteristic; and finally, determining the image quality by combining a support vector with a two-step frame in image quality evaluation. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of being small in time complexity, high in subjective consistency, low in image feature dimension and good in universality; the method can be applied to applications related to small computer devices or image quality, and is high in practical value.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
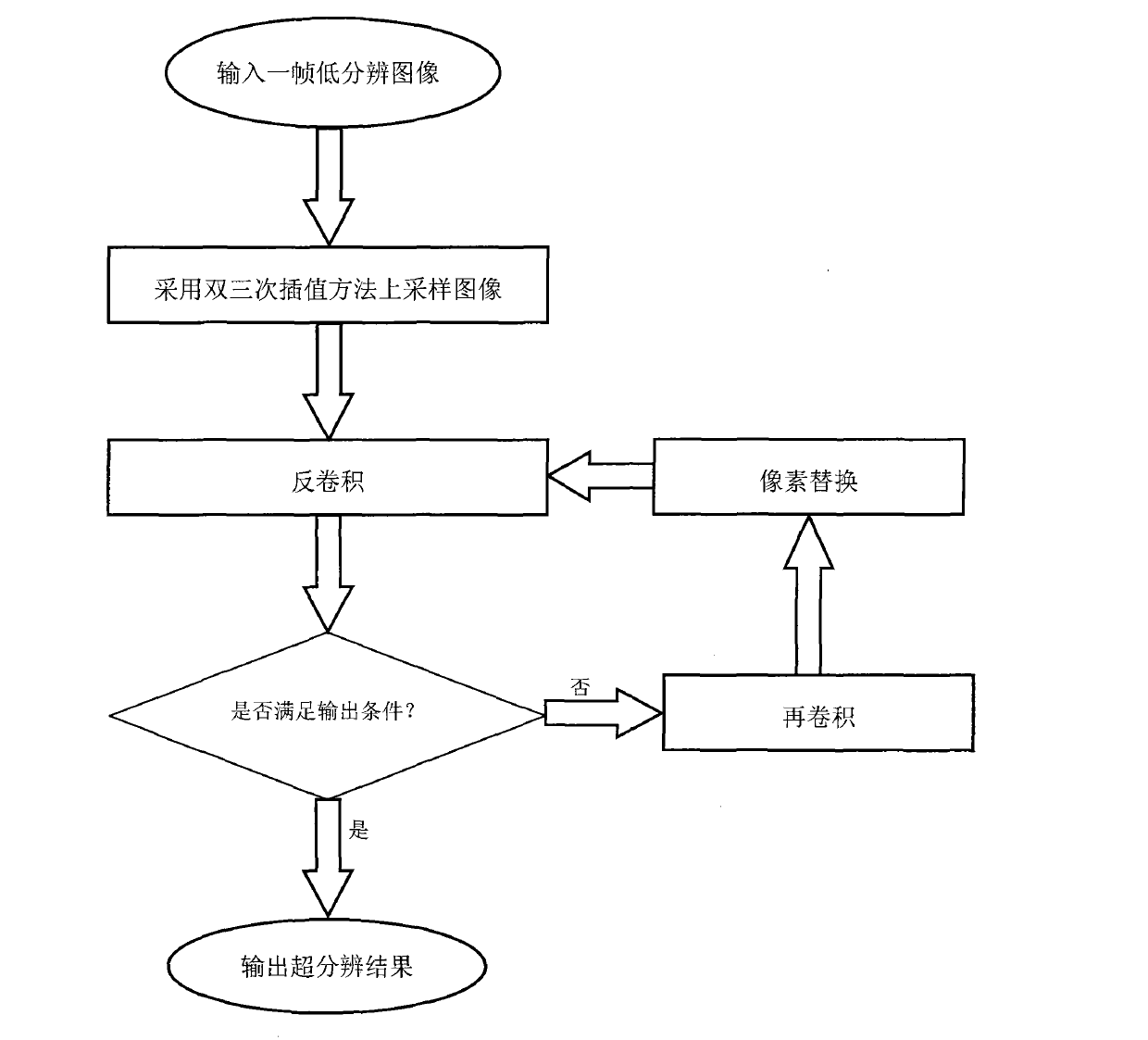
Super resolution image reconstruction method based on gradient consistency and anisotropic regularization
InactiveCN103136727ARecover image detail informationImage enhancementGeometric image transformationHigh resolution imageLow contrast
The invention discloses a super resolution image reconstruction method based on gradient consistency and anisotropic regularization. The super resolution image reconstruction method based on the gradient consistency and the anisotropic regularization is used for solving super resolution image reconstruction self-adaption to maintain high-frequency image information, and recovering image detail information. The steps includes inputting a low resolution image, obtaining an interpolation image by using dual-three interpolation methods to sample the input image, adopting gradient consistency and anisotropic regularization (GCAR) conditions to restrain an objective function, performing a deconvolution operation for the interpolation image, judging a deconvoluted image whether to meet output requirements, outputting a super resolution result if the deconvoluted image meets the output requirements, otherwise, performing reconvuluting and pixel replacement for the deconvoluted image, going to a next deconvolution operation, and iterating like those until the output requirements are met. The super resolution image reconstruction method based on the gradient consistency and the anisotropic regularization has the advantages of maintaining the gradient consistency of low contrast image area low resolution images and corresponding high resolution images, and capable of recovering image detail information in a self-adaption mode and being used for the field of video applications.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Systems and methods for tracking human hands by performing parts based template matching using images from multiple viewpoints
ActiveUS20130343606A1Character and pattern recognitionDigital data authenticationTemplate matchingView camera
Systems and methods for tracking human hands by performing parts based template matching using images captured from multiple viewpoints are described. One embodiment of the invention includes a processor, a reference camera, an alternate view camera, and memory containing: a hand tracking application; and a plurality of edge feature templates that are rotated and scaled versions of a finger template that includes an edge features template. In addition, the hand tracking application configures the processor to: detect at least one candidate finger in a reference frame, where each candidate finger is a grouping of pixels identified by searching the reference frame for a grouping of pixels that have image gradient orientations that match one of the plurality of edge feature templates; and verify the correct detection of a candidate finger in the reference frame by locating a grouping of pixels in an alternate view frame that correspond to the candidate finger.
Owner:KAYA DYNAMICS LLC
Image blind deblurring method based on edge self-adaption
The invention discloses an image blind deblurring method based on edge self-adaption. To solve the problems that as for an existing total variation deblurring algorithm, edges and details of images are easily blurred, a de-mean gradient total variation canonical model is built, weighting coefficients are calculated in an iterated mode by means of local variance self-adaption of gradients of the images, and the ability of the deblurring algorithm to restore the edges and the details of the images. The image blind deblurring method comprises the following steps that (1) a blurred image is input, solutions to a gradient-region clear image and a blurring kernel are obtained alternately, and the initial blurring kernel of the blurred image is obtained; (2) the initial blurring kernel is used for conducting primary non-blind deblurring on the blurred image, and an initial clear image is obtained; (3) clustering is conducted on the initial clear image, the mean value and the weighting coefficient in the de-mean canonical model are updated, and a solution to the blurring kernel is obtained again; (4) the new blurring kernel is used for conducting secondary non-blind deblurring so as to obtain a clear image. Experimental results show that the image blind deblurring method based on edge self-adaption has better deburring effect than the prior art and can be used for image restoration.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Wireless multimedia sensor network-oriented video compression method
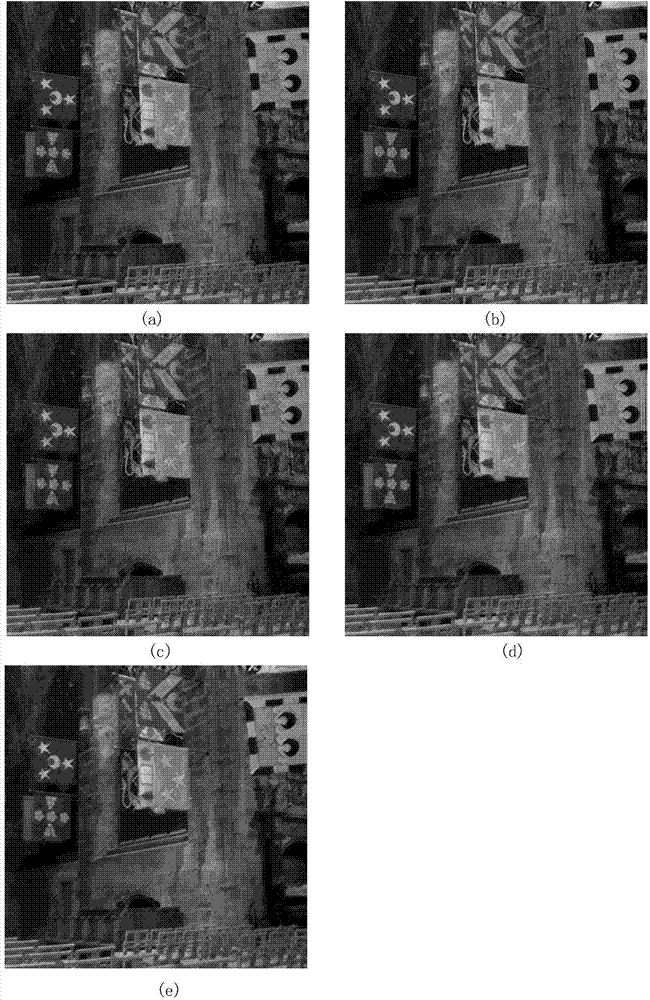
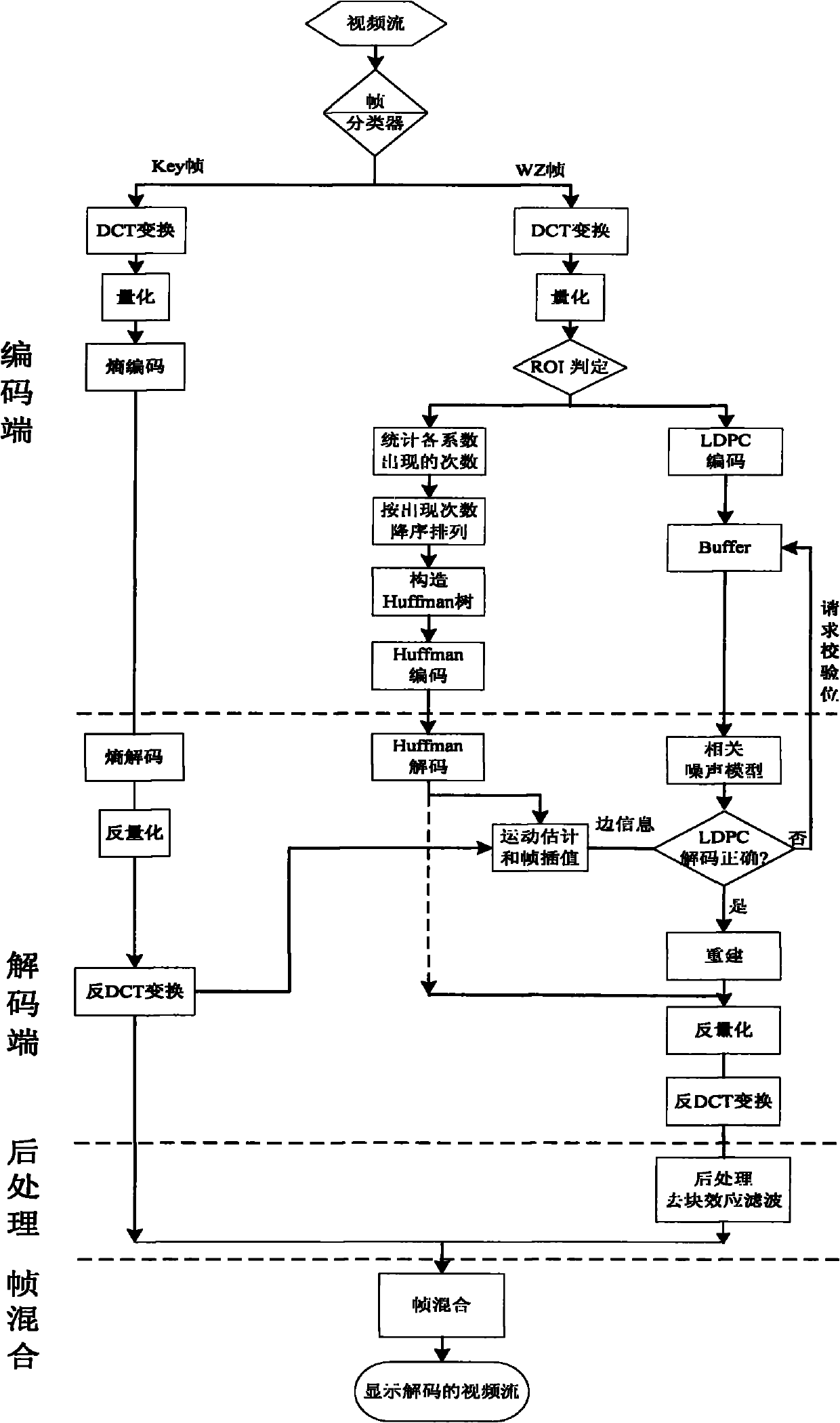
InactiveCN101854548AImprove subjective qualityMeet visual requirementsTelevision system detailsNetwork topologiesVideo encodingDeblocking filter
The invention provides a wireless multimedia sensor network-oriented video compression method, which solves the problem of large data volume in video application. Due to the adoption of the method, code rate is reduced and the quality of a decoded image is improved at the same time, and at last, the energy consumption of a node of the sensor is reduced, so that the life cycle of a network is prolonged. In the method, encoding in a strenuous motion area and in a motion edge area is enhanced by adopting an ROI distinguishing algorithm, and the decoded image is postprocessed by adopting a deblocking filter, so that the subjective quality of the decoded image is further improved. On the basis of a Wyner-Ziv distributed video encoding scheme, the strenuous motion area is extracted through an ROI judging criterion based on an image gradient field and based on Huffman encoding and decoding compression is preformed, and the other areas are encoded and decoded based on the LDPC distribution type, so that the method has the advantages of reducing code rate, improving the quality of the decoded image, reducing the processing and transmission energy consumption of the nodes, implementing the optimized transmission of video and prolonging the life cycle of the whole network.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
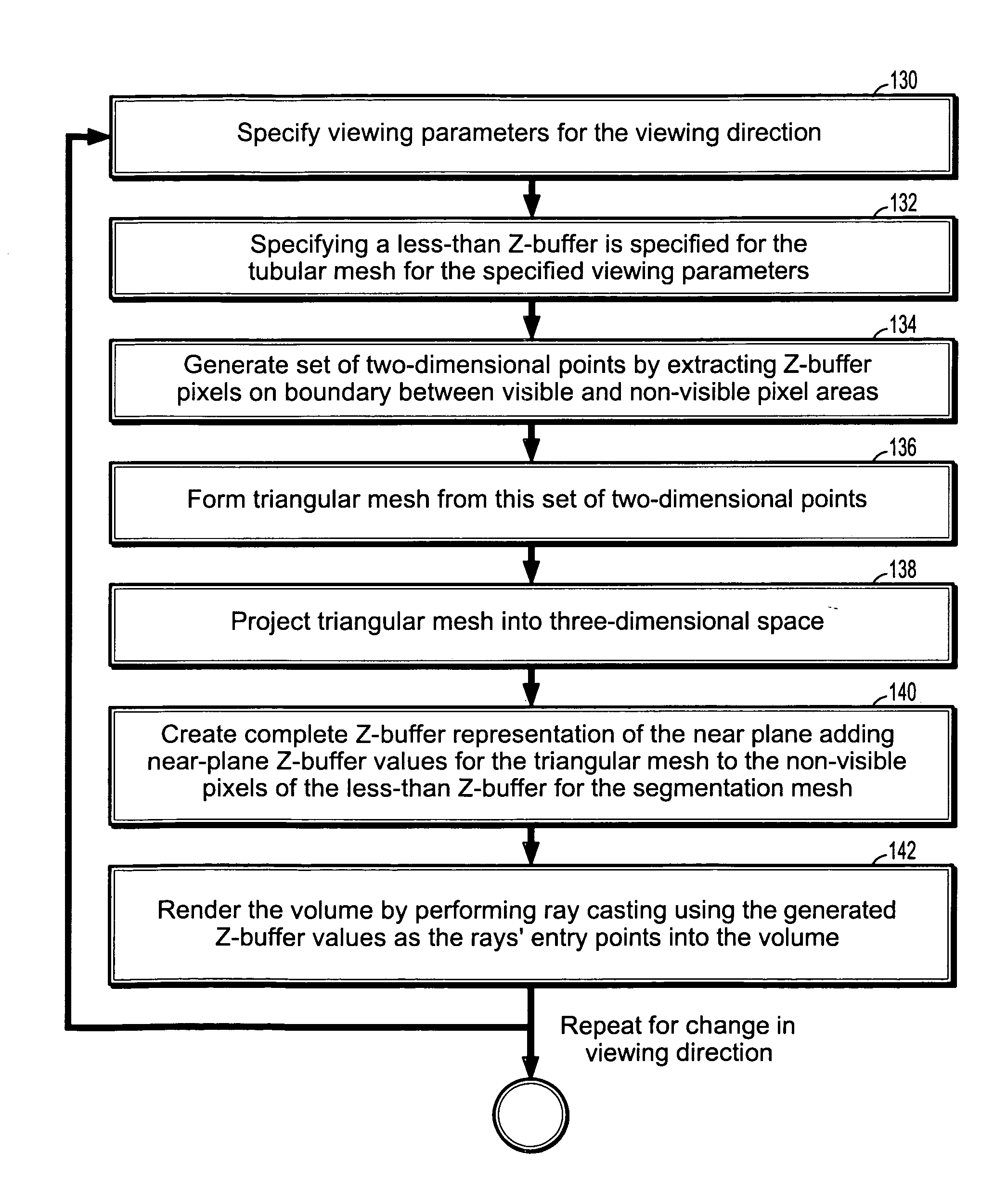
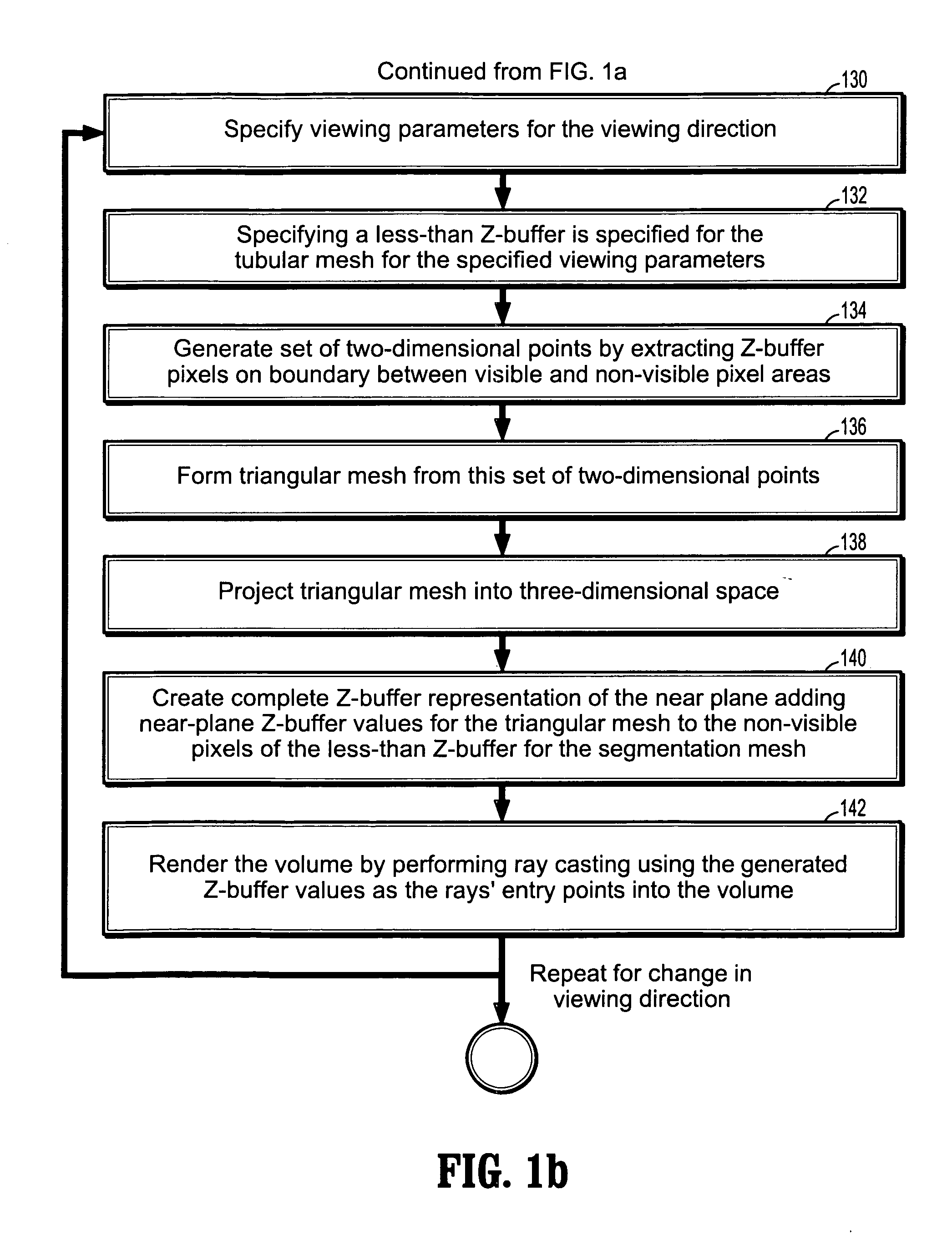
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com