Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4319 results about "Support vector machine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
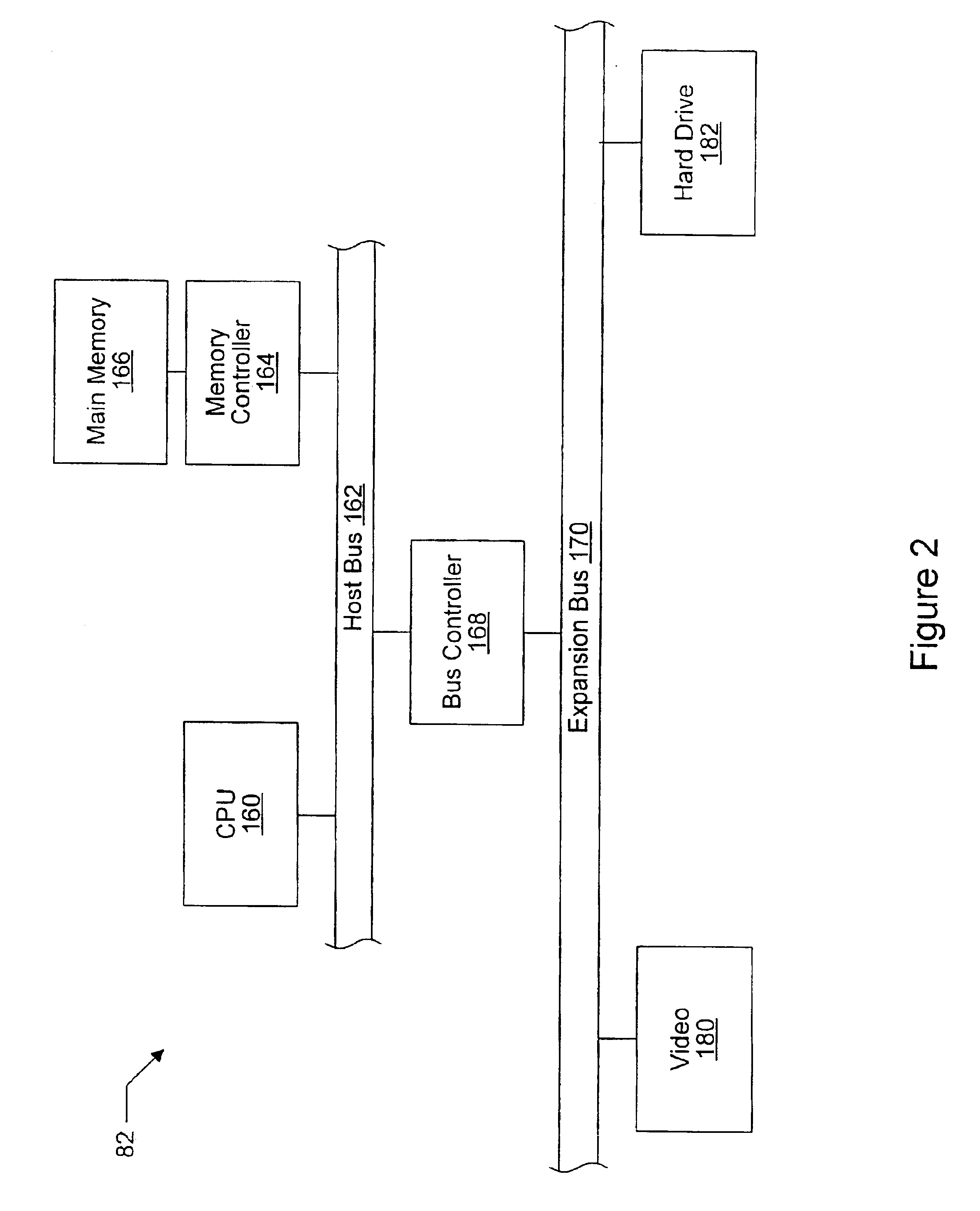
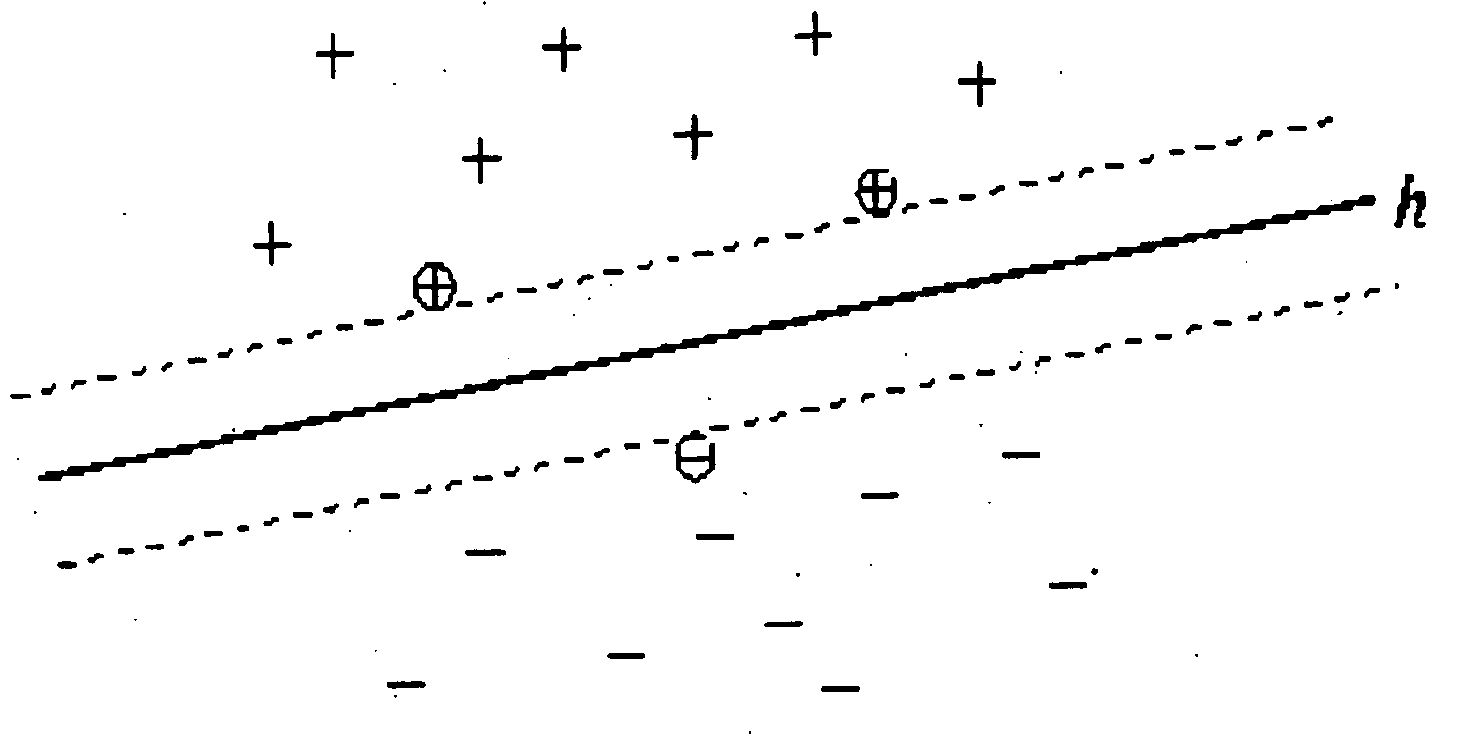
In machine learning, support-vector machines (SVMs, also support-vector networks) are supervised learning models with associated learning algorithms that analyze data used for classification and regression analysis. Given a set of training examples, each marked as belonging to one or the other of two categories, an SVM training algorithm builds a model that assigns new examples to one category or the other, making it a non-probabilistic binary linear classifier (although methods such as Platt scaling exist to use SVM in a probabilistic classification setting). An SVM model is a representation of the examples as points in space, mapped so that the examples of the separate categories are divided by a clear gap that is as wide as possible. New examples are then mapped into that same space and predicted to belong to a category based on the side of the gap on which they fall.
Computer-aided image analysis
InactiveUS6996549B2Improve abilitiesGreat dimensionalityMedical data miningImage analysisLearning machineComputer-aided
Digitized image data are input into a processor where a detection component identifies the areas (objects) of particular interest in the image and, by segmentation, separates those objects from the background. A feature extraction component formulates numerical values relevant to the classification task from the segmented objects. Results of the preceding analysis steps are input into a trained learning machine classifier which produces an output which may consist of an index discriminating between two possible diagnoses, or some other output in the desired output format. In one embodiment, digitized image data are input into a plurality of subsystems, each subsystem having one or more support vector machines. Pre-processing may include the use of known transformations which facilitate extraction of the useful data. Each subsystem analyzes the data relevant to a different feature or characteristic found within the image. Once each subsystem completes its analysis and classification, the output for all subsystems is input into an overall support vector machine analyzer which combines the data to make a diagnosis, decision or other action which utilizes the knowledge obtained from the image.
Owner:HEALTH DISCOVERY CORP +1
Systems and method for malware detection
ActiveUS20110320816A1Avoid bottlenecksReduce dimensionalityMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsFeature vectorSupport vector machine
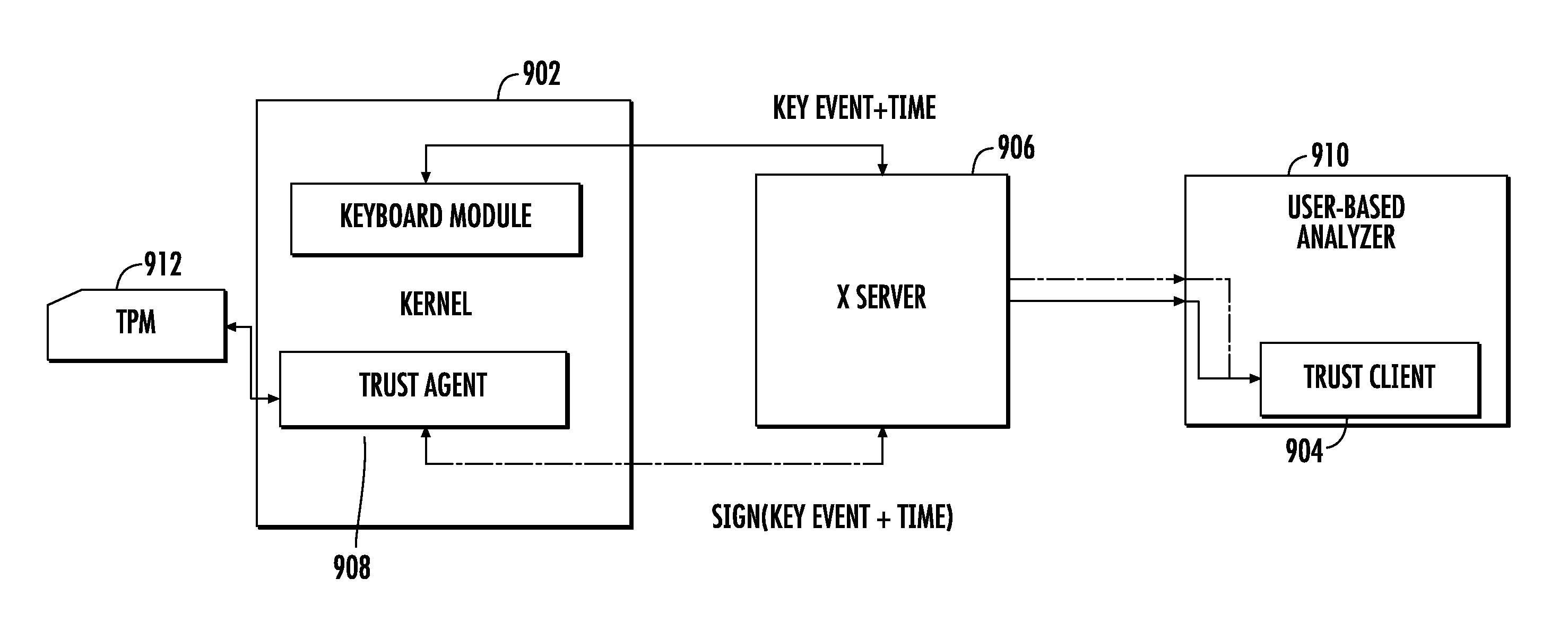
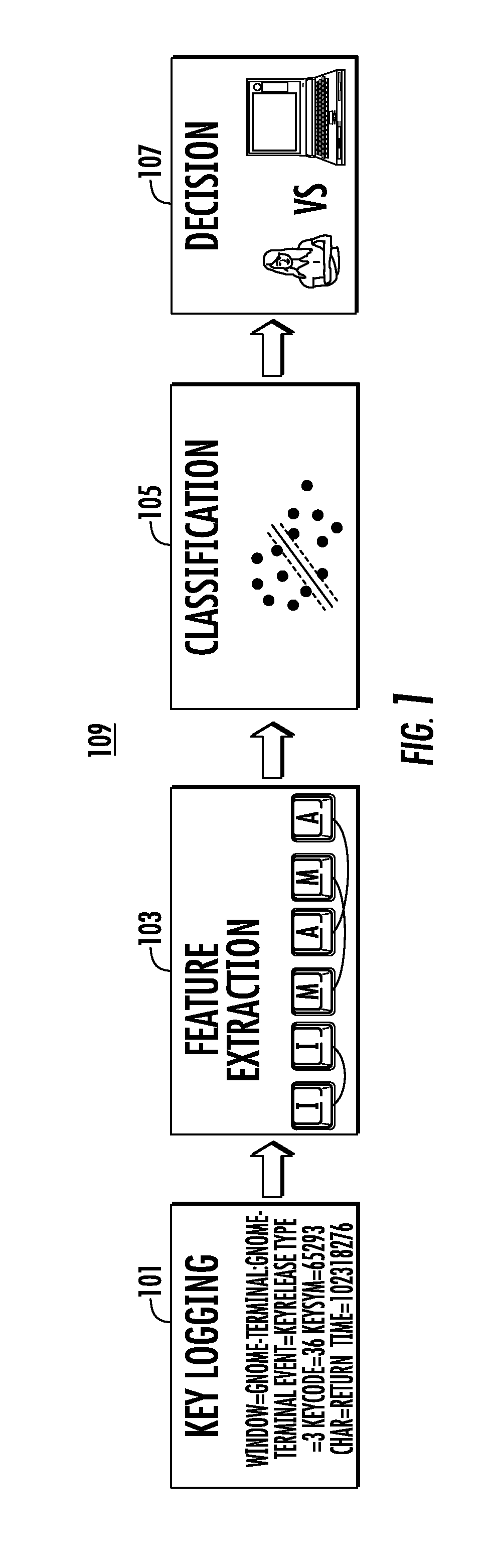
A system and method for distinguishing human input events from malware-generated events includes one or more central processing units (CPUs), one or more input devices and memory. The memory includes program code that when executed by the CPU causes the CPU to obtain a first set of input events from a user utilizing the input device. The first input events are used to obtain or derive a feature indicative of the user, such as a multi-dimensional feature vector as provided by a support vector machine. Second input events are then obtained, and the second input events are classified against the feature to determine if either the user or malware initiated the second input events.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Text emotion classification method based on the joint deep learning model
InactiveCN106599933AImprove classification performanceGreat photo effectCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsSupport vector machineCurse of dimensionality
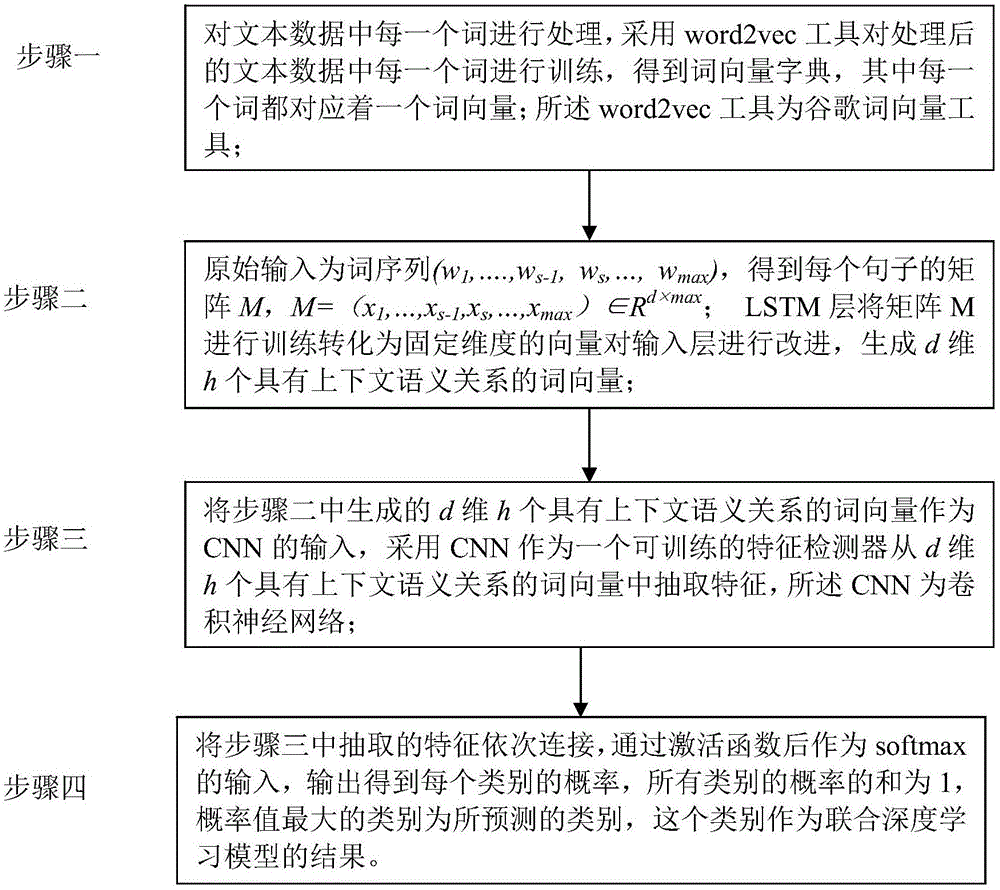
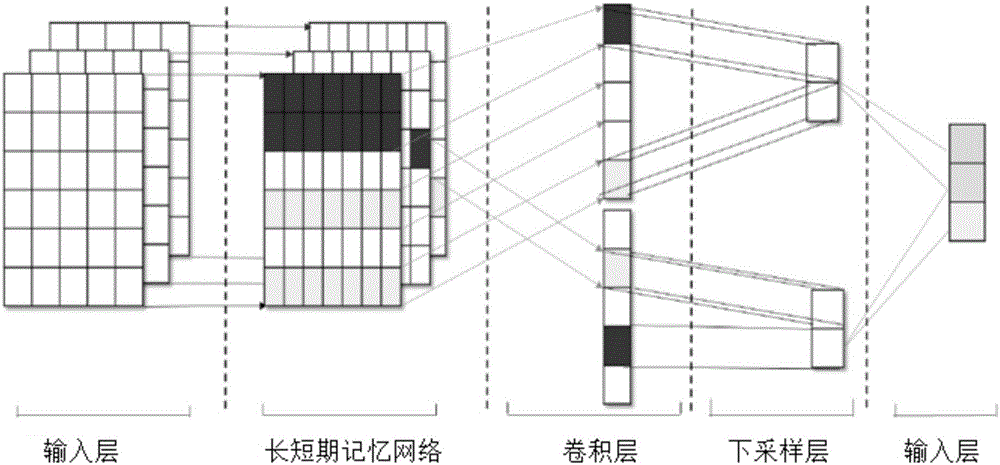
The invention provides a text emotion classification method based on the joint deep learning model which relates to the text emotion classification method. The method is designed with the object of solving the problems with the dimension disaster and sparse data incurred from the existing support vector machine and other shallow layer classification methods. The method comprises: 1) processing each word in the text data; using the word2vec tool to train each processed word in the text data so as to obtain a word vector dictionary; 2) obtaining the matrix M of each sentence; training the matrix M by the LSTM layer and converting it into vector with fixed dimensions; improving the input layer; generating d-dimensional h word vectors with context semantic relations; 3) using a CNN as a trainable characteristic detector to extract characteristics from the d-dimensional h word vectors with context semantic relations; and 4) connecting the extracted characteristics in order; outputting to obtain the probability of each classification wherein the classification with the maximal probability value is the predicated classification. The invention is applied to the natural language processing field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
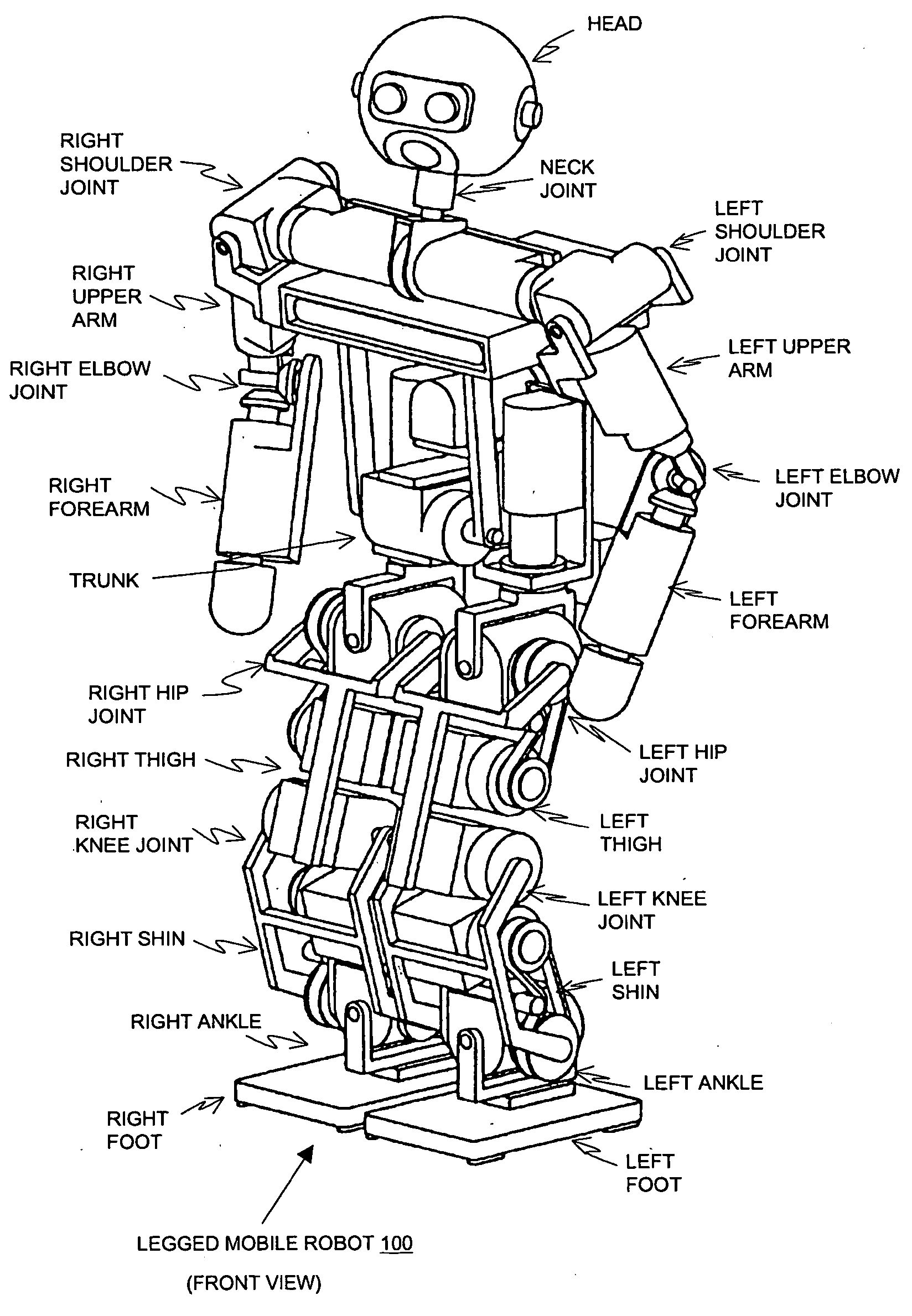
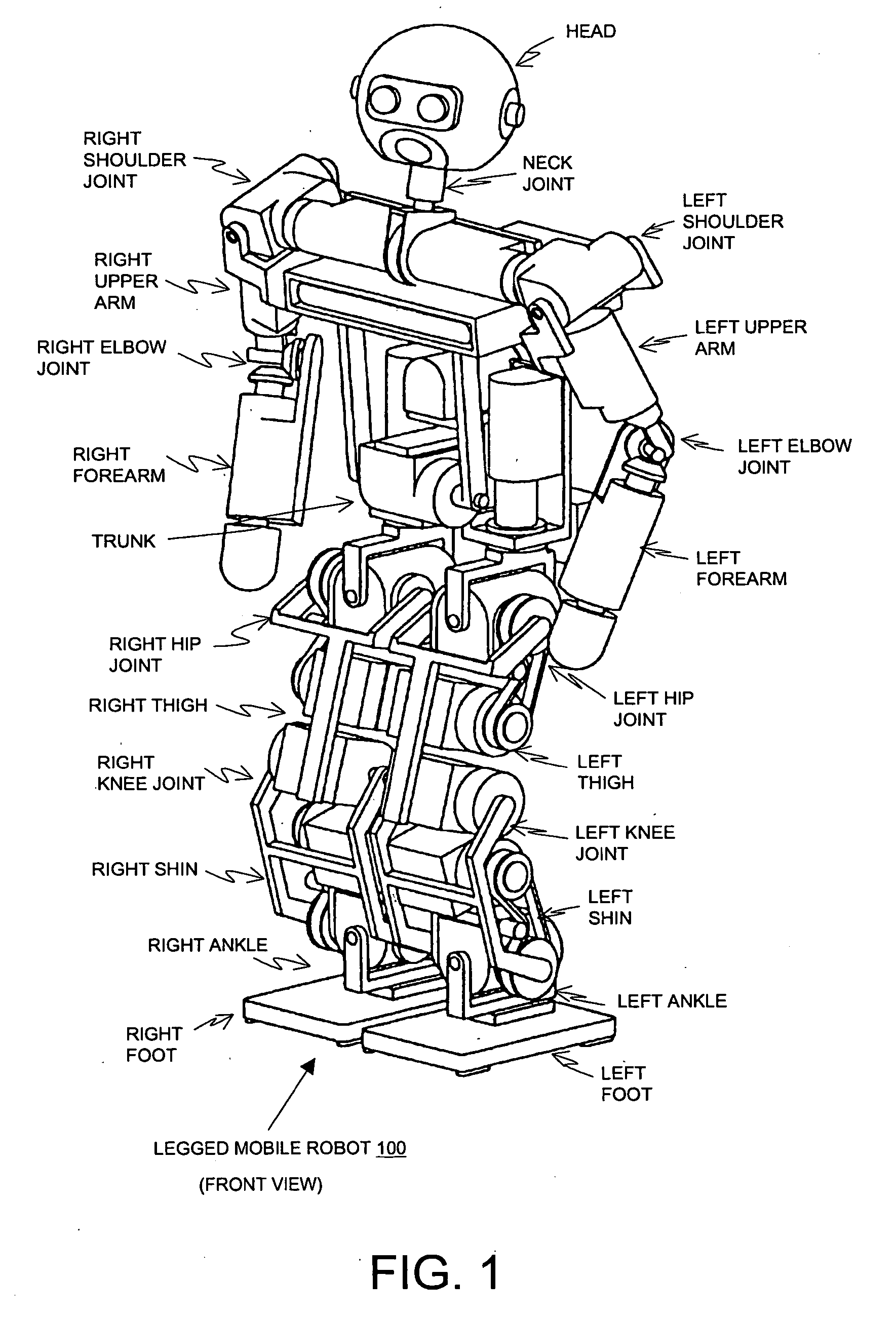
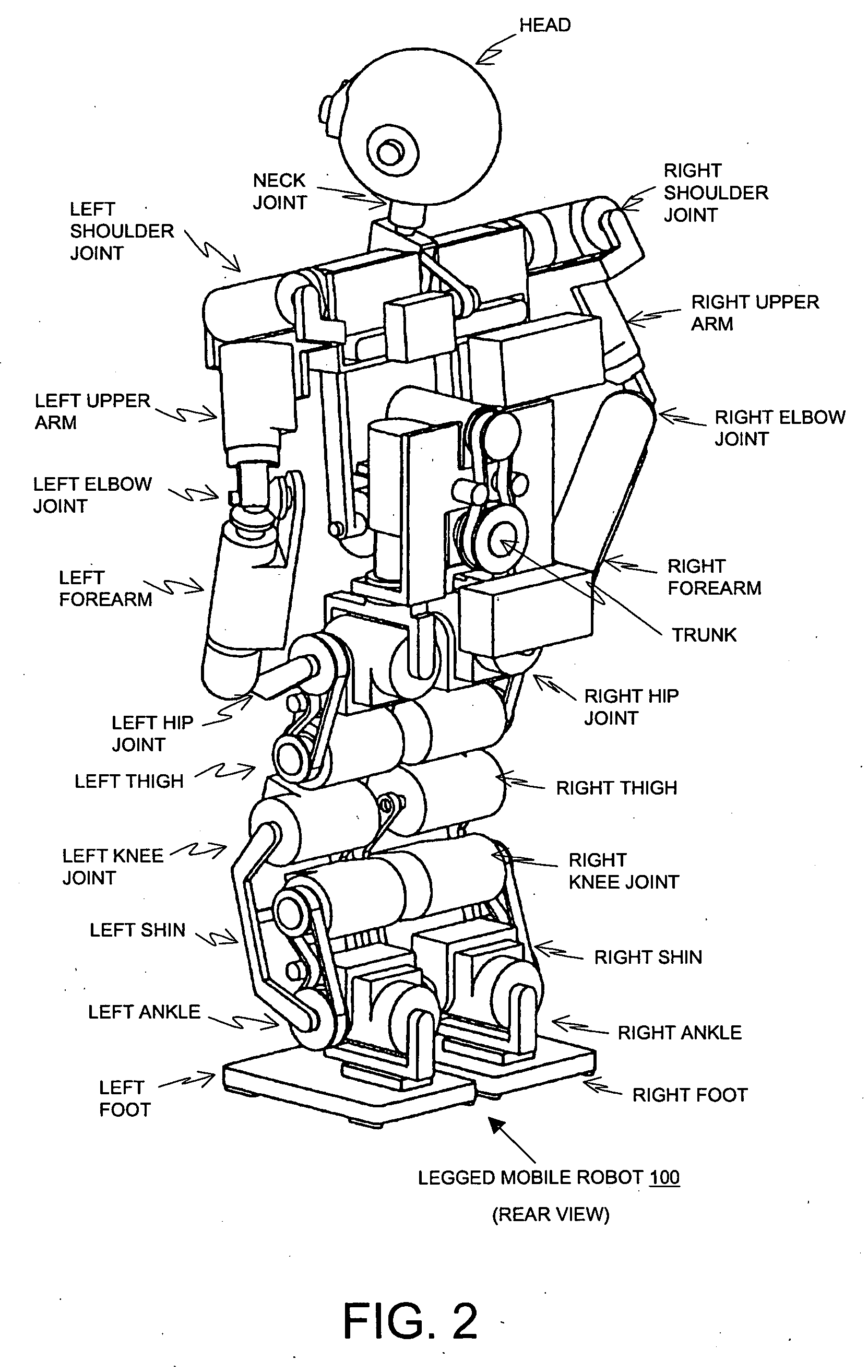
Object detector, object detecting method and robot
InactiveUS20050069208A1Quick checkLimited resourceImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionTemplate matchingSupport vector machine
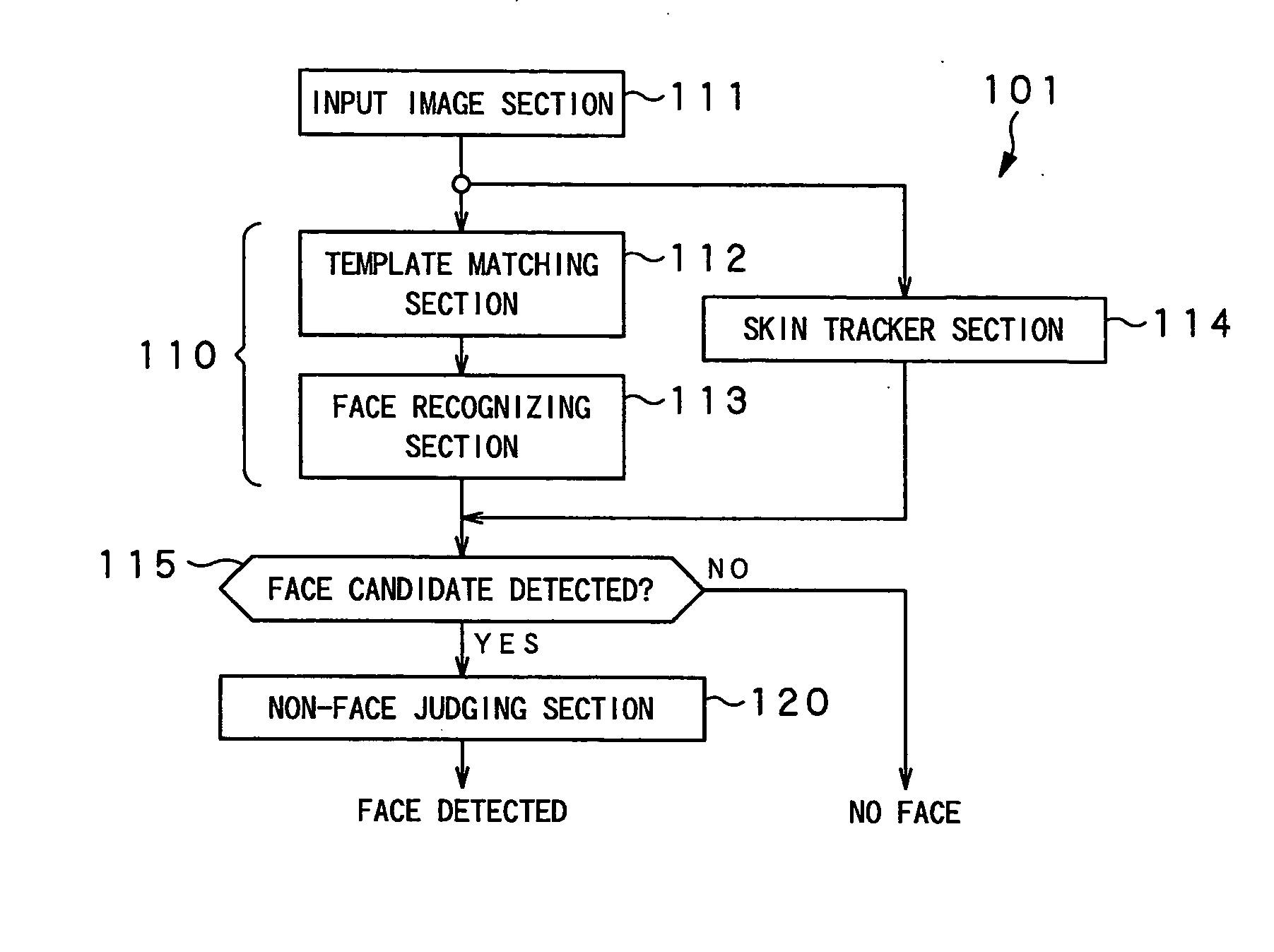
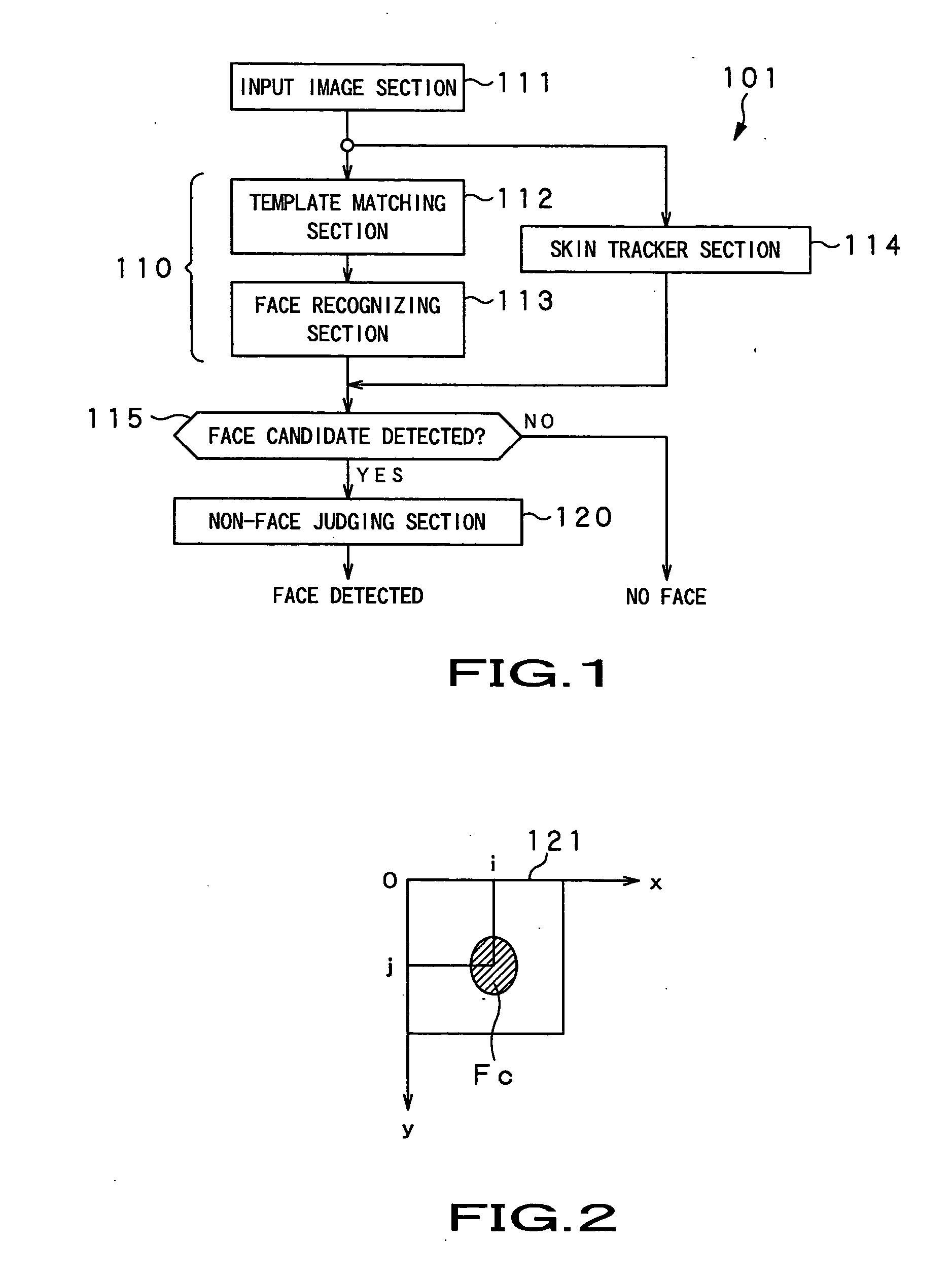
An object detector, an object detecting method and a robot can reduce diction errors of detecting wrong objects without increasing the volume of the computational operation to be performed to detect the right object. A face detector 101 comprises a face detecting section 110 that operates like a conventional face detecting section and is adapted to roughly select face candidates from an input image by template matching and detect face candidates by means of a support vector machine for face recognition, a non-face judging section 120 that detects non-face candidates that are judged to be non-faces and removes them from the face candidates selected by the face detecting section 110 and a skin tracker section 114 for tracking a face region after the non-face judgment. When the assumed distance between the face detector and the face as computed from the input image and the measured distance as measured by a distance sensor show a large difference, when the color variance of the face candidate is small, when the occupancy ratio of the skin color region is large and when the change in the size of the face region is large after the elapse of a predetermined time, the non-face judging section 120 judges such face candidates as non-faces and removes them from the face candidates.
Owner:SONY CORP
Robot apparatus, face recognition method, and face recognition apparatus
A robot includes a face extracting section for extracting features of a face included in an image captured by a CCD camera, and a face recognition section for recognizing the face based on a result of face extraction by the face extracting section. The face extracting section is implemented by Gabor filters that filter images using a plurality of filters that have orientation selectivity and that are associated with different frequency components. The face recognition section is implemented by a support vector machine that maps the result of face recognition to a non-linear space and that obtains a hyperplane that separates in that space to discriminate a face from a non-face. The robot is allowed to recognize a face of a user within a predetermined time under a dynamically changing environment.
Owner:SONY CORP
Machine learning methods and systems for identifying patterns in data
ActiveUS20100063948A1Reduce dimensionalityPromote resultsDigital data processing detailsKernel methodsData classSupport vector machine
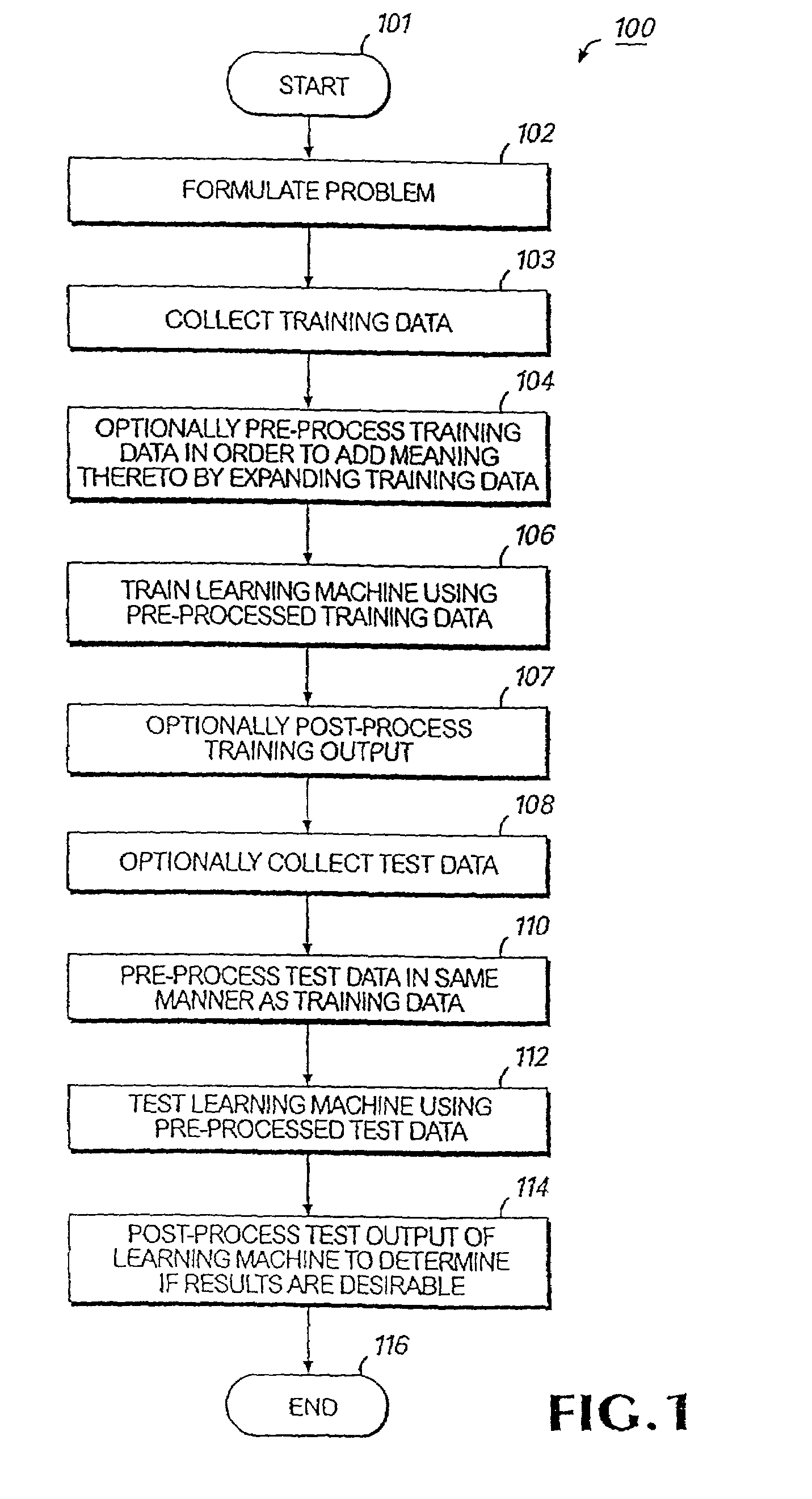
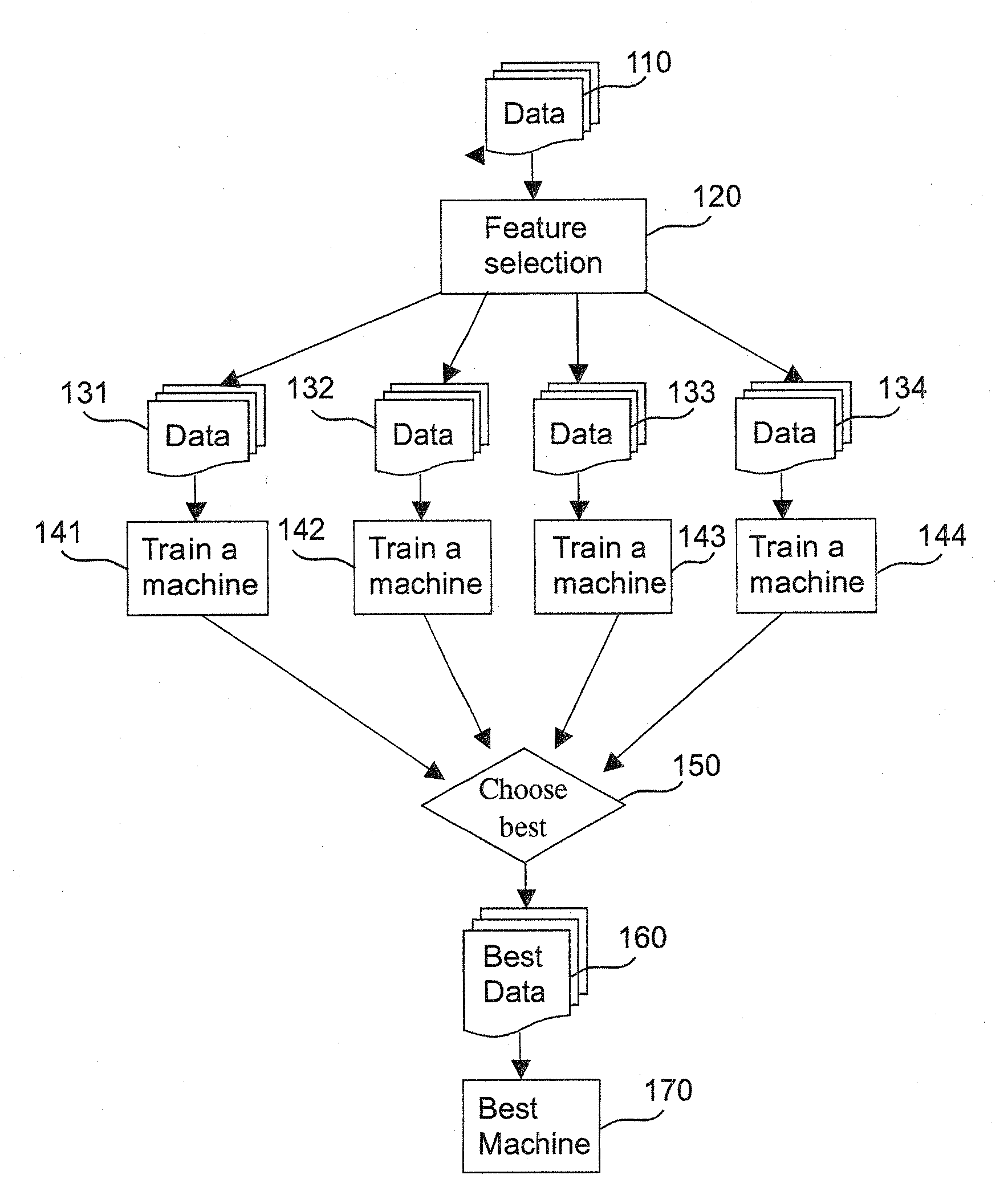
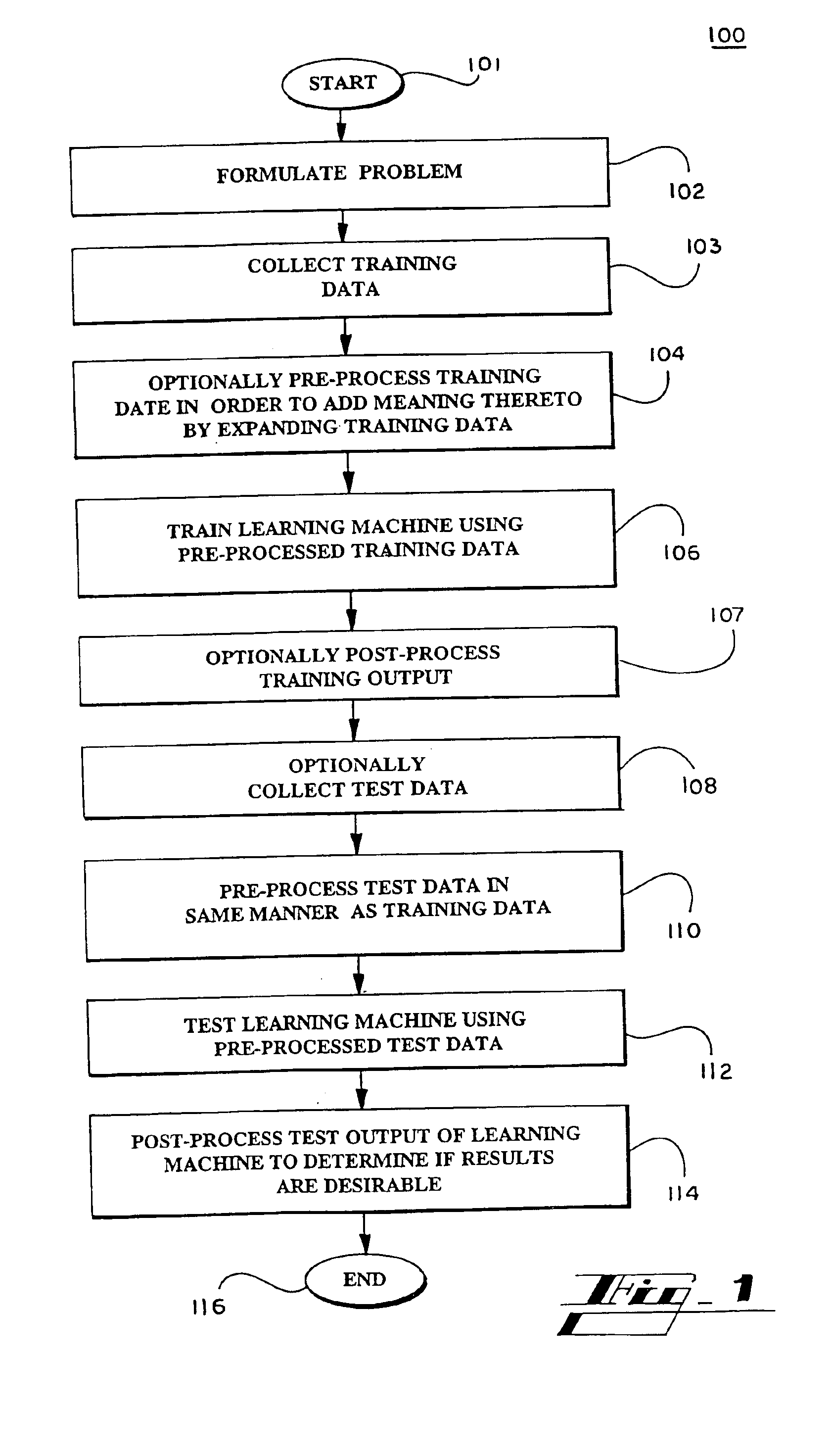
Methods for training machines to categorize data, and / or recognize patterns in data, and machines and systems so trained. More specifically, variations of the invention relates to methods for training machines that include providing one or more training data samples encompassing one or more data classes, identifying patterns in the one or more training data samples, providing one or more data samples representing one or more unknown classes of data, identifying patterns in the one or more of the data samples of unknown class(es), and predicting one or more classes to which the data samples of unknown class(es) belong by comparing patterns identified in said one or more data samples of unknown class with patterns identified in said one or more training data samples. Also provided are tools, systems, and devices, such as support vector machines (SVMs) and other methods and features, software implementing the methods and features, and computers or other processing devices incorporating and / or running the software, where the methods and features, software, and processors utilize specialized methods to analyze data.
Owner:DIGITAL INFUZION
Methods of identifying biological patterns using multiple data sets
InactiveUS6882990B1Improve abilitiesGreat dimensionalityImage analysisDigital data processing detailsSupport vector machineLearning machine
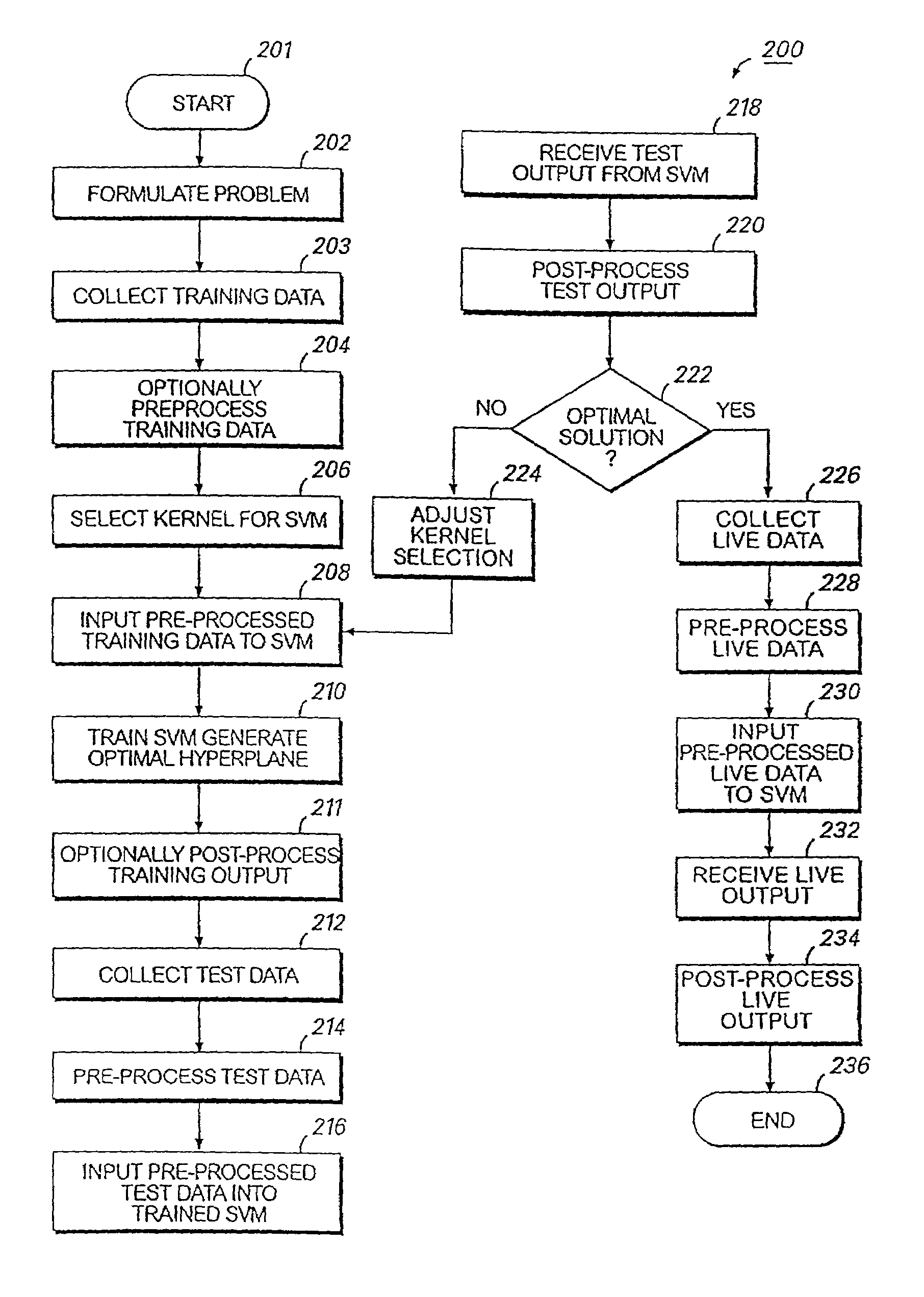
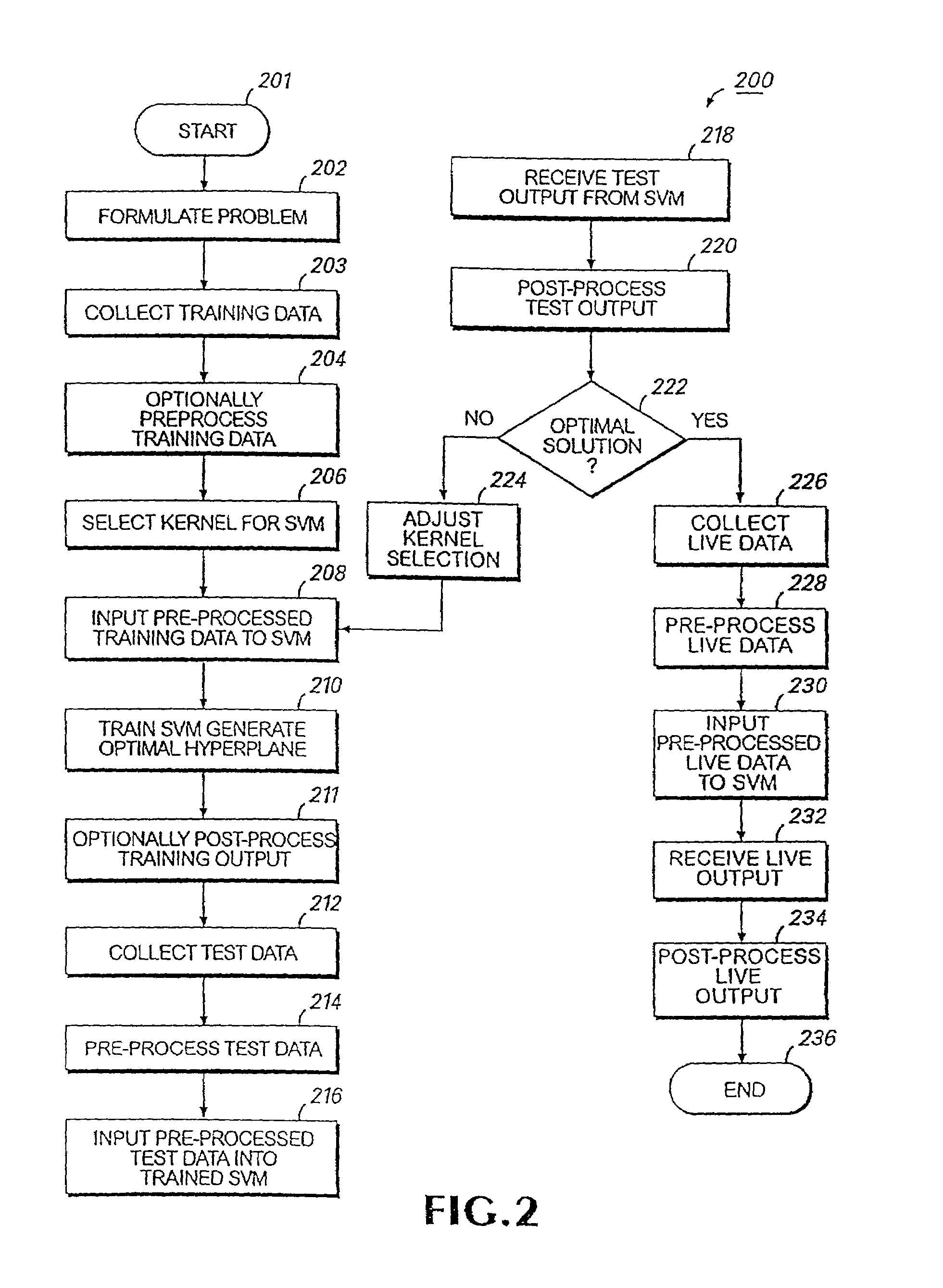
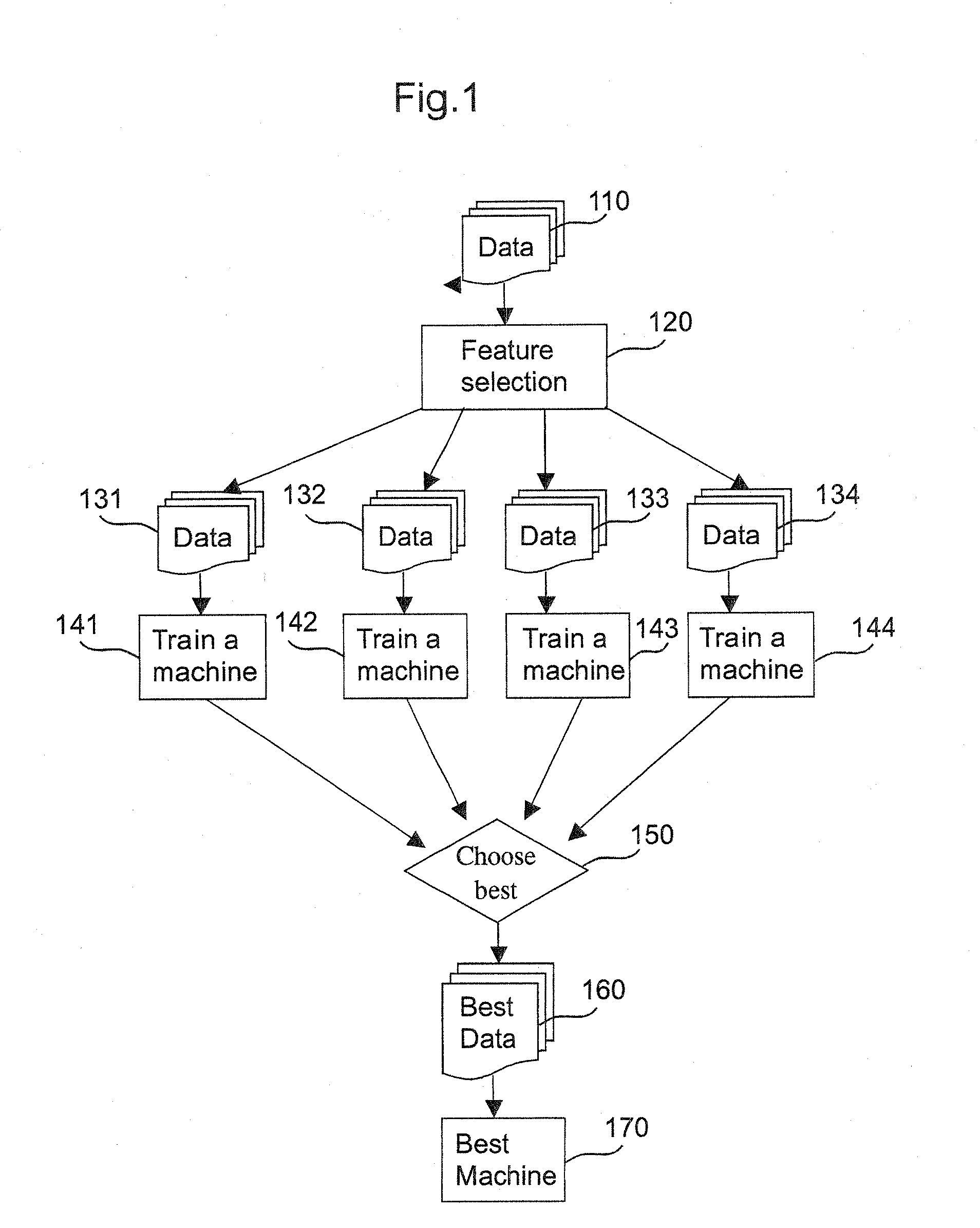
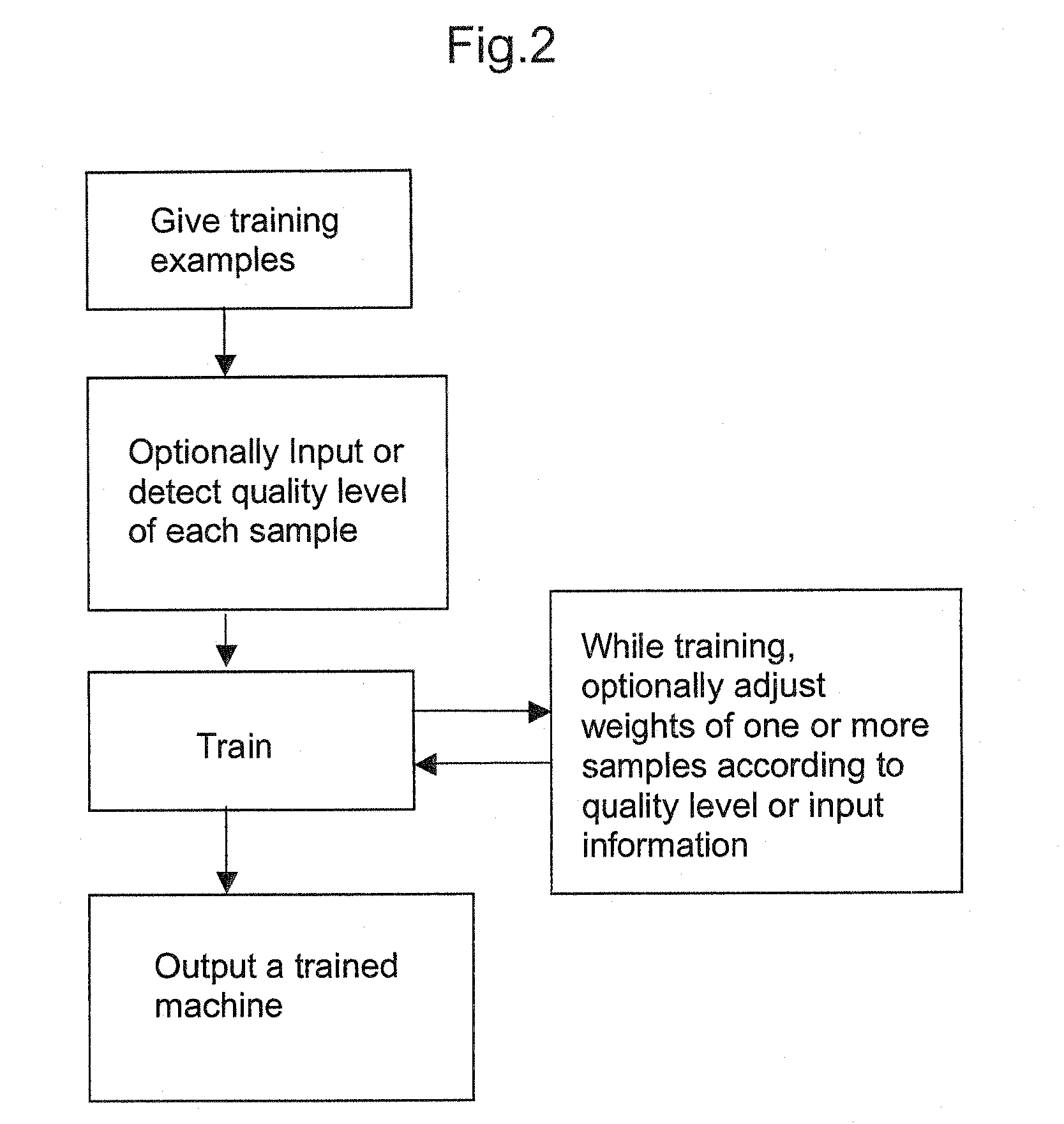
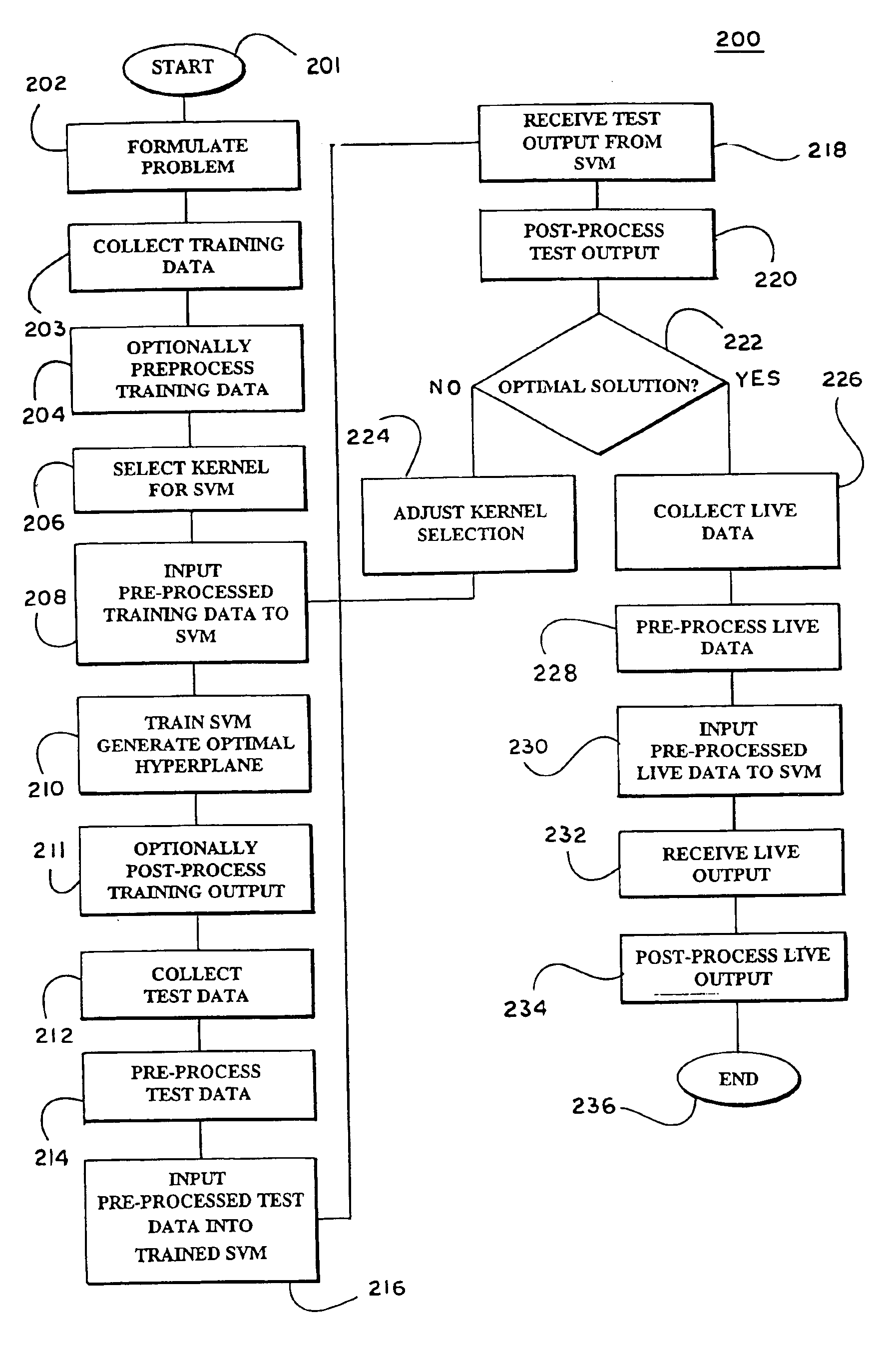
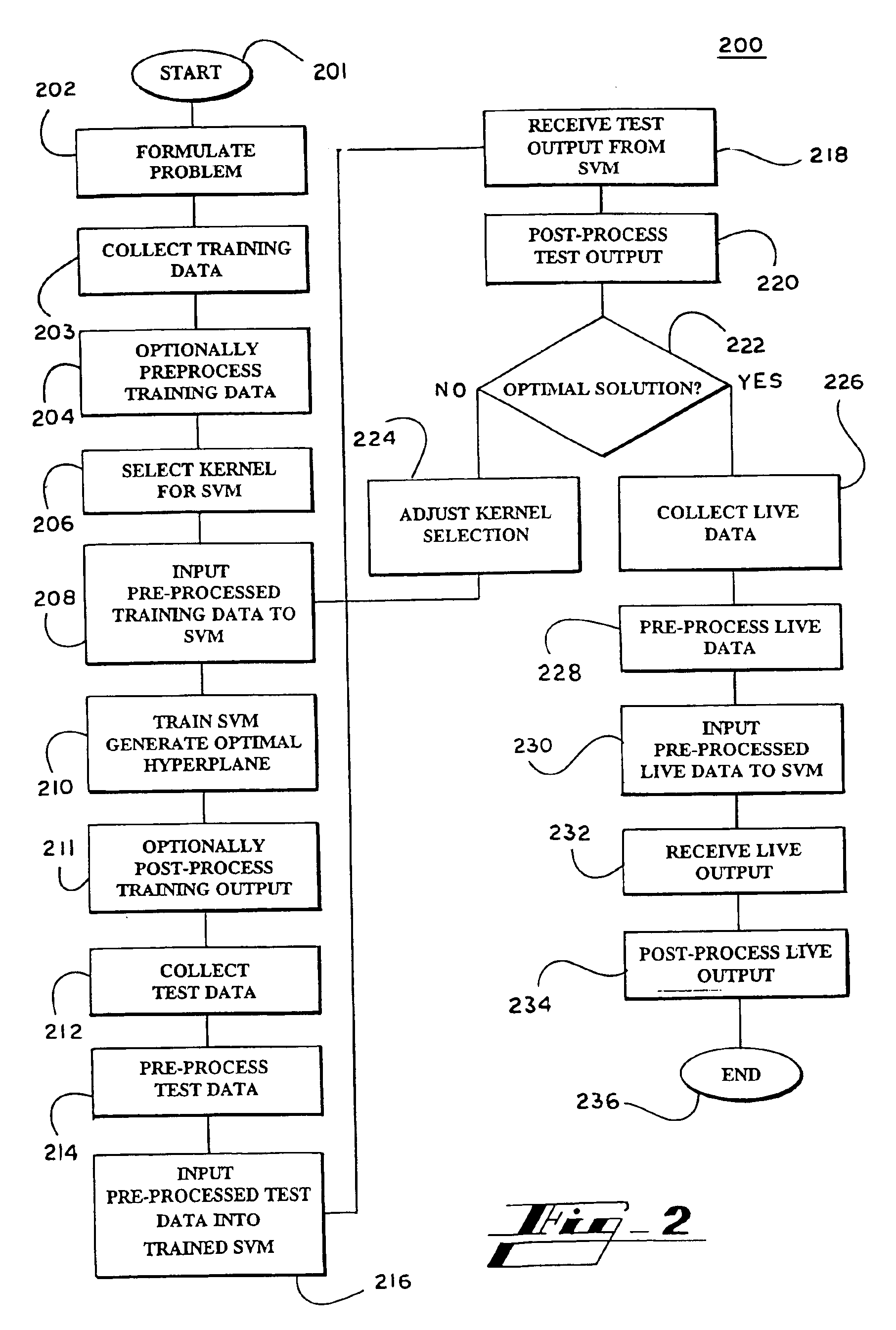
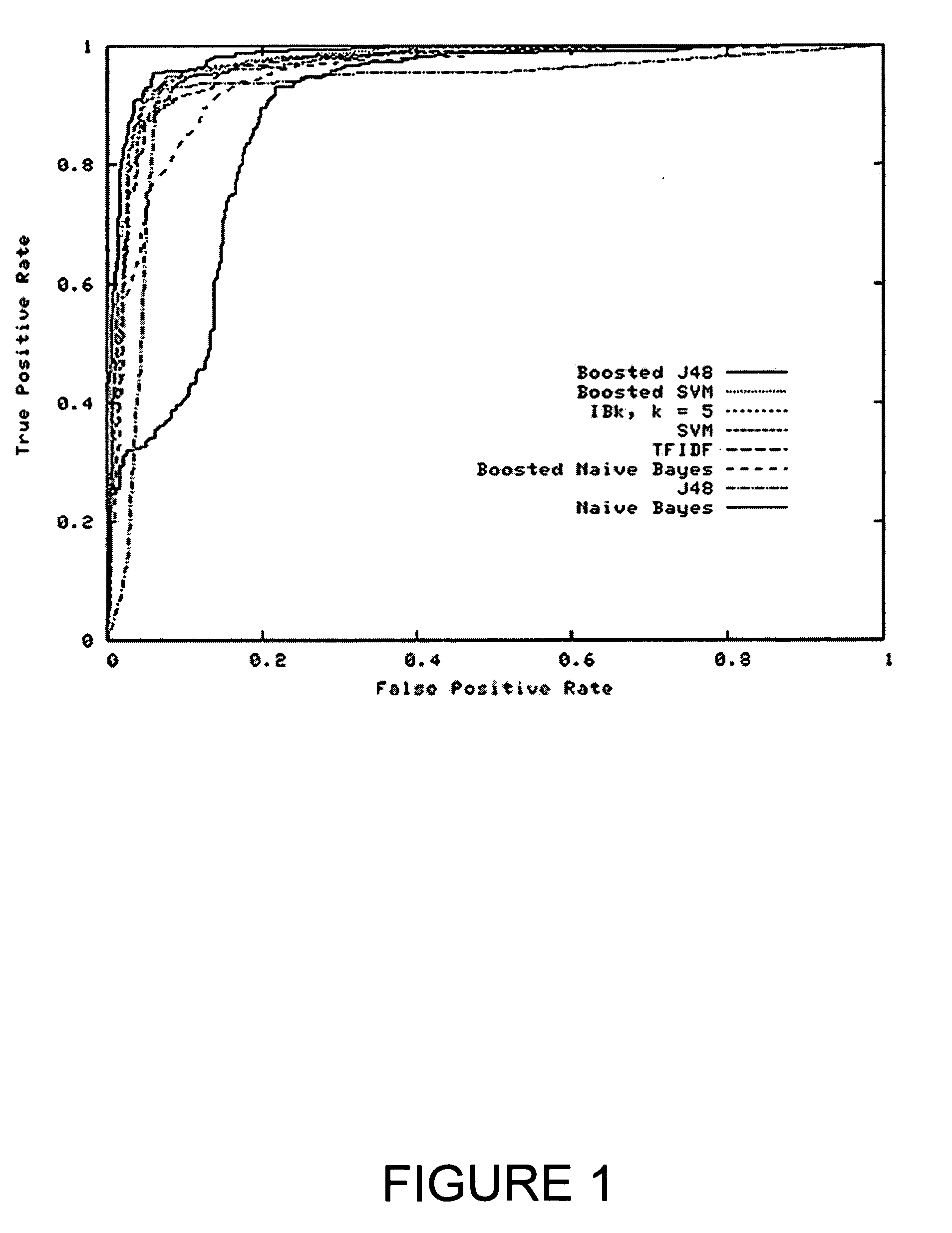
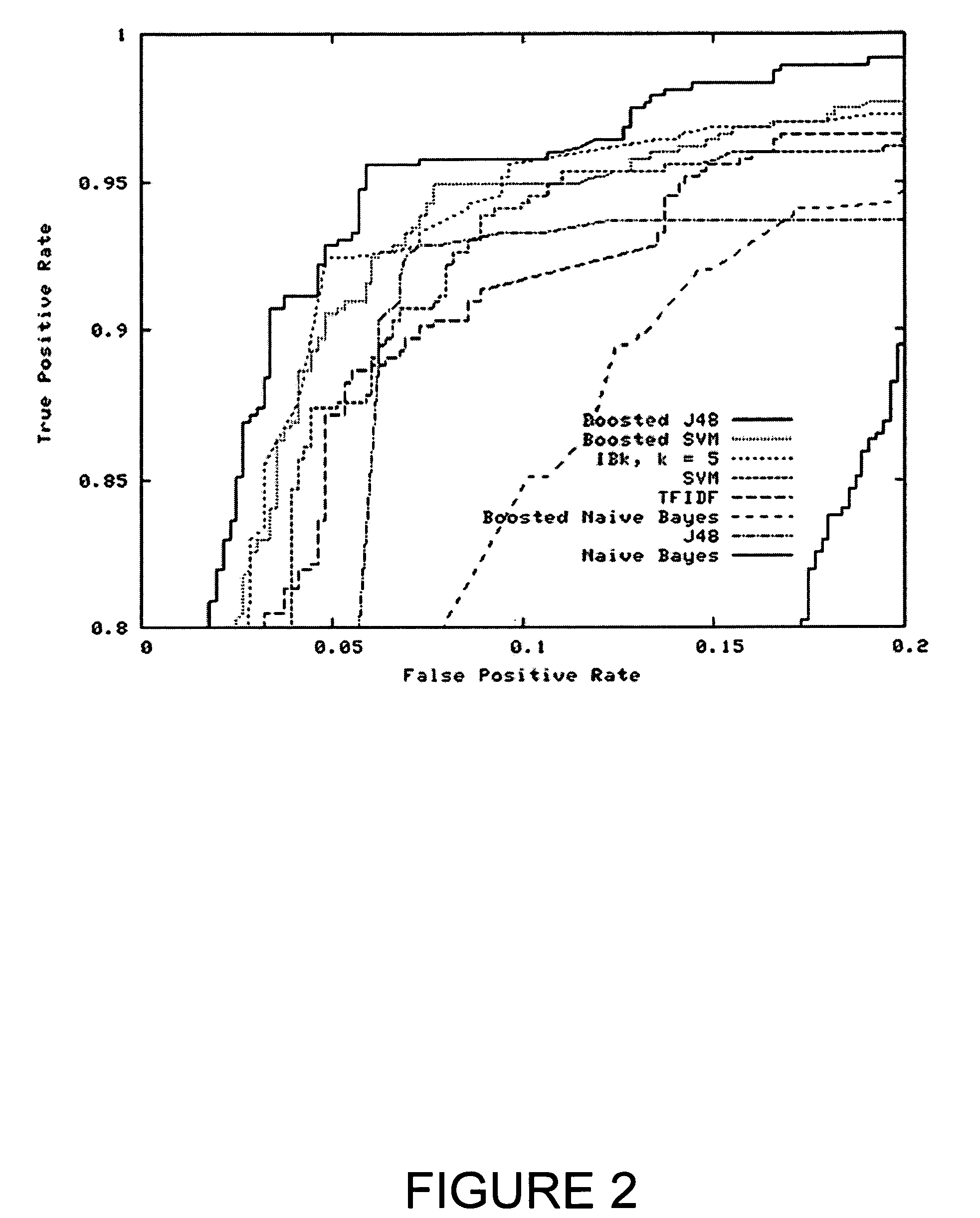
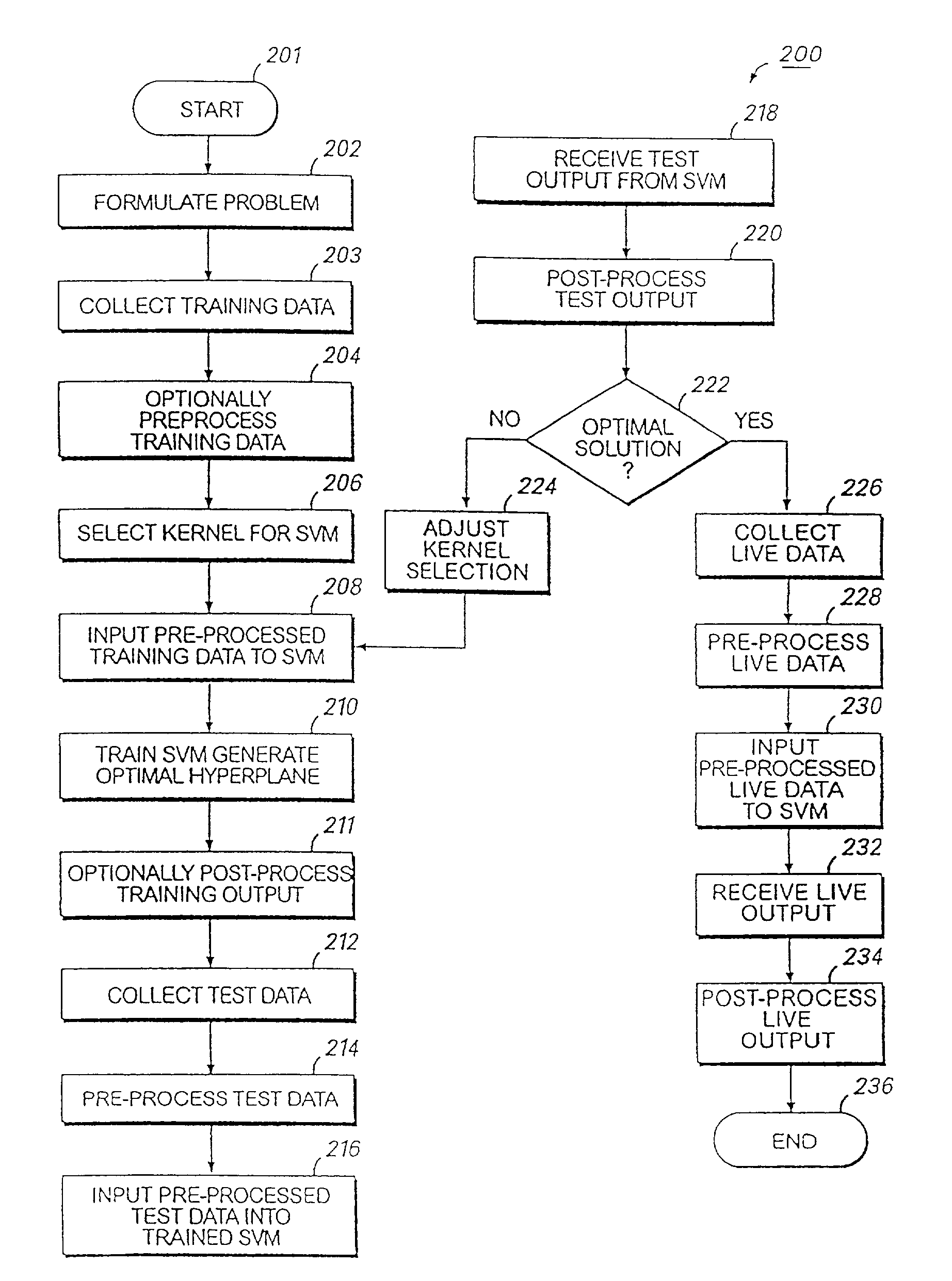
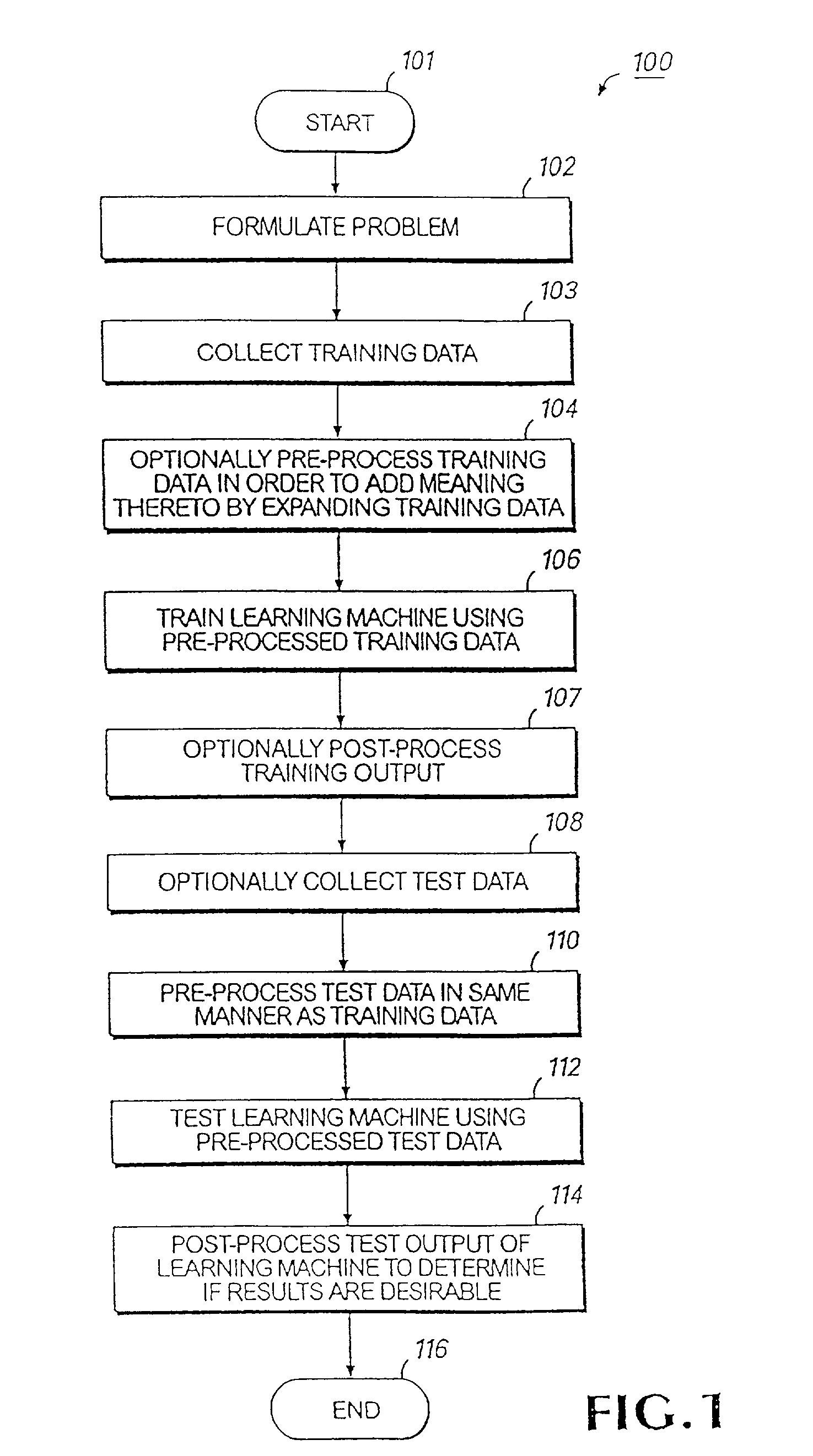
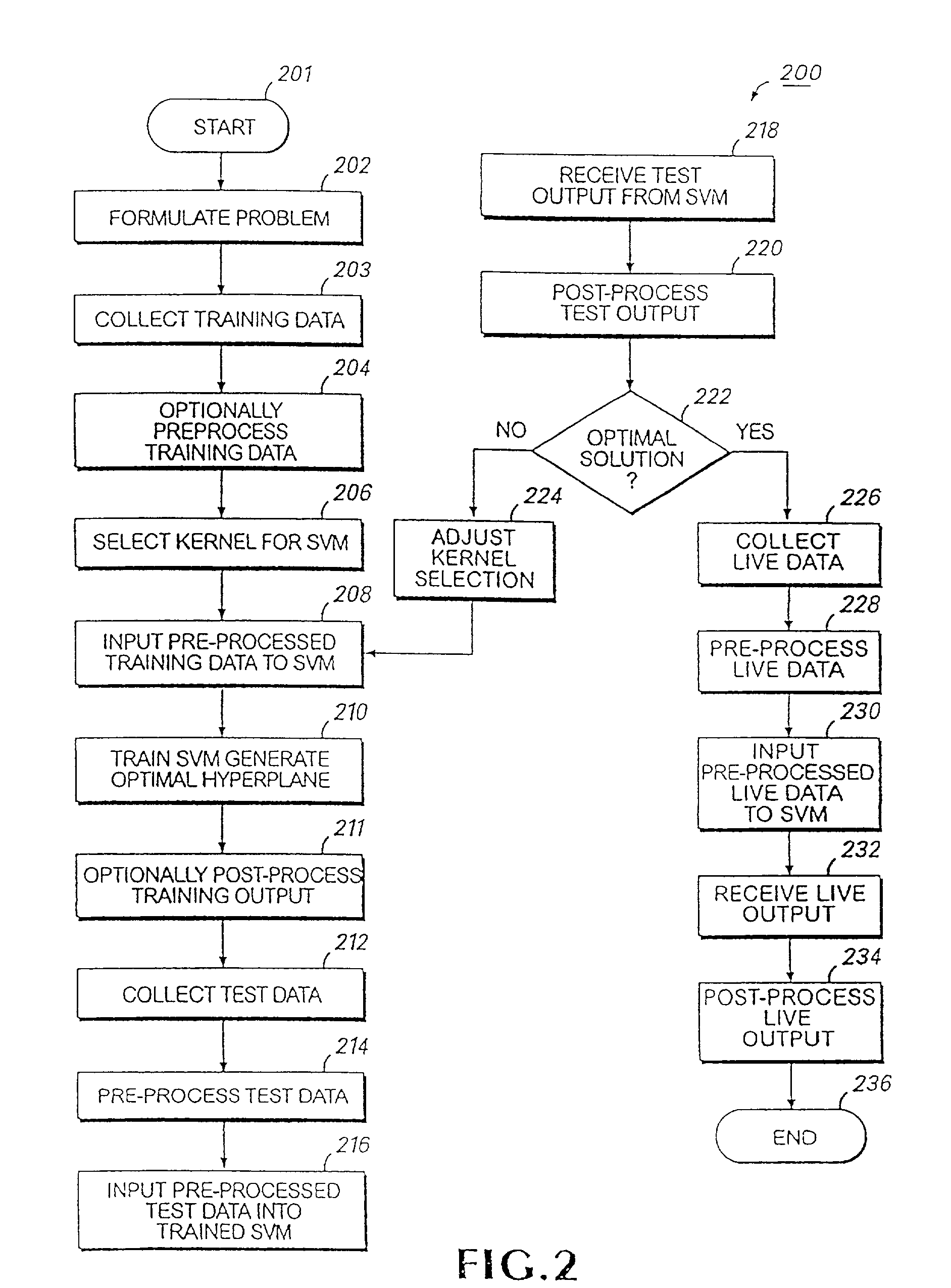
Systems and methods for enhancing knowledge discovery from data using multiple learning machines in general and multiple support vector machines in particular. Training data for a learning machine is pre-processed in order to add meaning thereto. Multiple support vector machines, each comprising distinct kernels, are trained with the pre-processed training data and are tested with test data that is pre-processed in the same manner. The test outputs from multiple support vector machines are compared in order to determine which of the test outputs if any represents a optimal solution. Selection of one or more kernels may be adjusted and one or more support vector machines may be retrained and retested. Optimal solutions based on distinct input data sets may be combined to form a new input data set to be input into one or more additional support vector machine. The methods, systems and devices of the present invention comprise use of Support Vector Machines for the identification of patterns that are important for medical diagnosis, prognosis and treatment. Such patterns may be found in many different datasets. The present invention also comprises methods and compositions for the treatment and diagnosis of medical conditions.
Owner:HEALTH DISCOVERY CORP +1
Imaging based symptomatic classification and cardiovascular stroke risk score estimation
InactiveUS20110257545A1Improve accuracyMaximum accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementGround truthCross modality
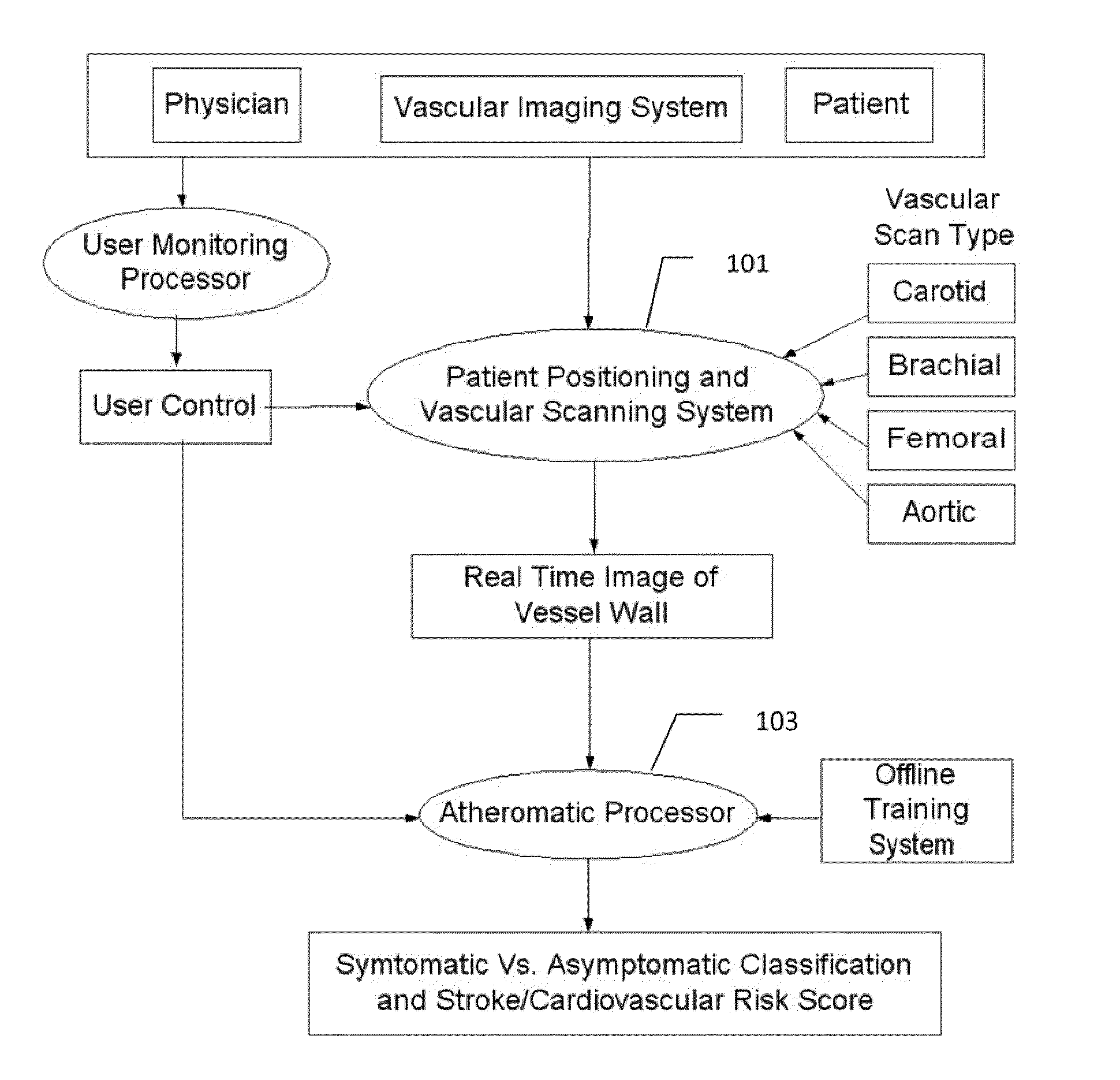
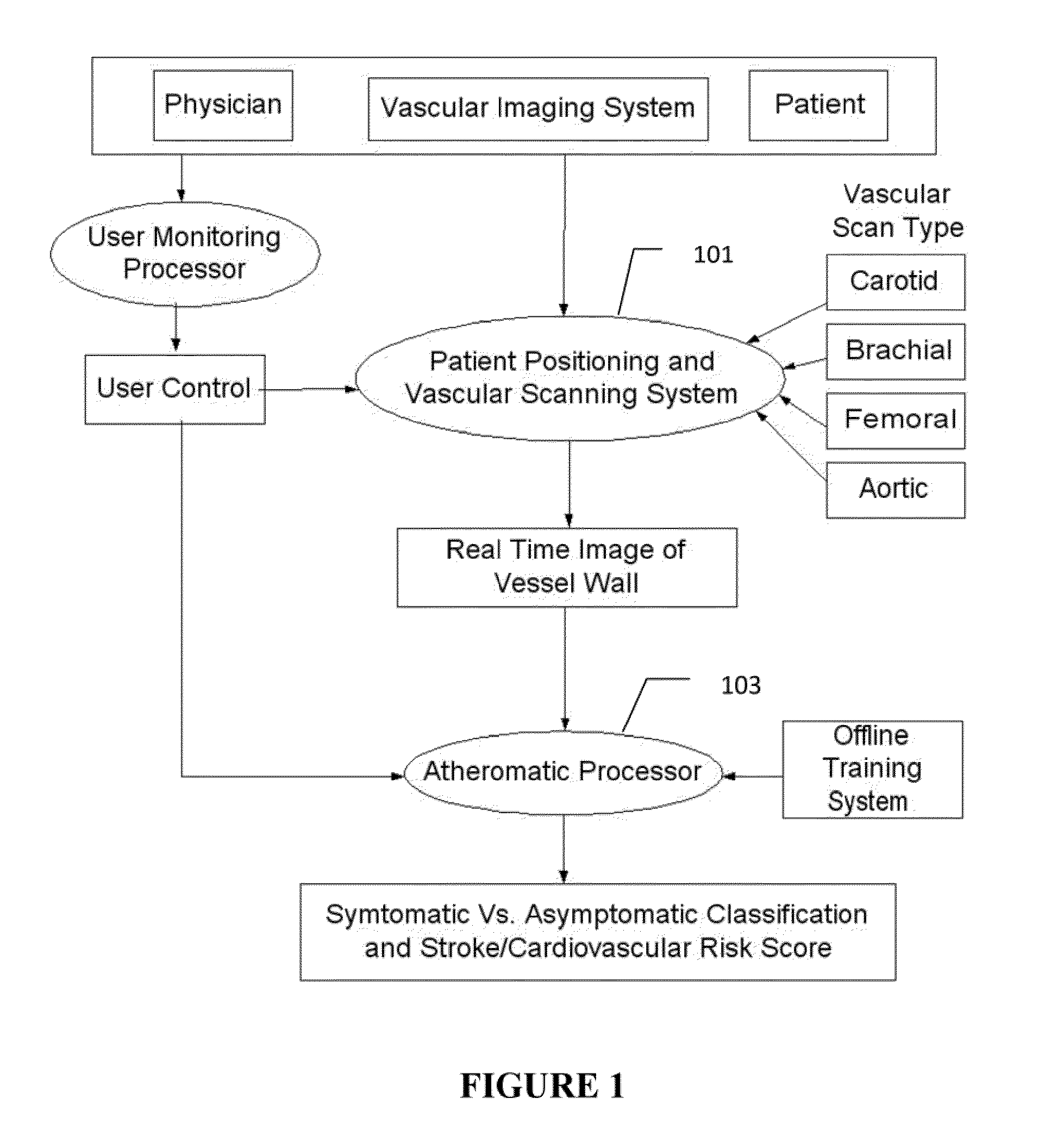
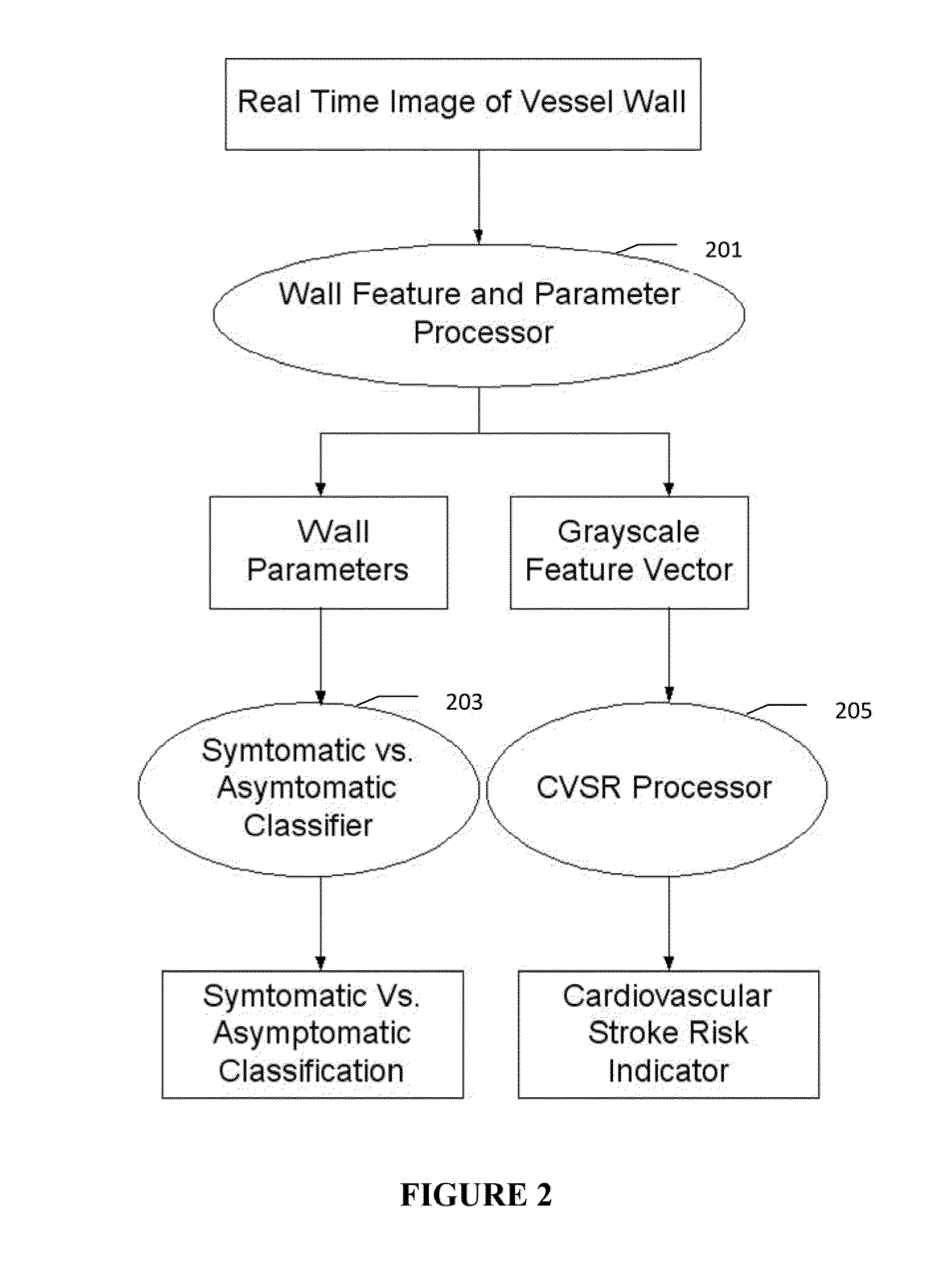
Characterization of carotid atherosclerosis and classification of plaque into symptomatic or asymptomatic along with the risk score estimation are key steps necessary for allowing the vascular surgeons to decide if the patient has to definitely undergo risky treatment procedures that are needed to unblock the stenosis. This application describes a statistical (a) Computer Aided Diagnostic (CAD) technique for symptomatic versus asymptomatic plaque automated classification of carotid ultrasound images and (b) presents a cardiovascular stroke risk score computation. We demonstrate this for longitudinal Ultrasound, CT, MR modalities and extendable to 3D carotid Ultrasound. The on-line system consists of Atherosclerotic Wall Region estimation using AtheroEdge™ for longitudinal Ultrasound or Athero-CTView™ for CT or Athero-MRView from MR. This greyscale Wall Region is then fed to a feature extraction processor which computes: (a) Higher Order Spectra; (b) Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT); (c) Texture and (d) Wall Variability. The output of the Feature Processor is fed to the Classifier which is trained off-line from the Database of similar Atherosclerotic Wall Region images. The off-line Classifier is trained from the significant features from (a) Higher Order Spectra; (b) Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT); (c) Texture and (d) Wall Variability, selected using t-test. Symptomatic ground truth information about the training patients is drawn from cross modality imaging such as CT or MR or 3D ultrasound in the form of 0 or 1. Support Vector Machine (SVM) supervised classifier of varying kernel functions is used off-line for training. The Atheromatic™ system is also demonstrated for Radial Basis Probabilistic Neural Network (RBPNN), or Nearest Neighbor (KNN) classifier or Decision Trees (DT) Classifier for symptomatic versus asymptomatic plaque automated classification. The obtained training parameters are then used to evaluate the test set. The system also yields the cardiovascular stroke risk score value on the basis of the four set of wall features.
Owner:SURI JASJIT S
Brain wave analysis method
InactiveCN101690659AReal-time evaluationTargetedSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringSupport vector machineFeature extraction
The invention provides a brain wave analysis method. The method uses classical time-frequency domain analysis and principal component analysis methods to solve the problem of electroencephalographic feature extraction, successfully extracts time-frequency domain parameters closely related to the tension, fatigue and relaxation of human bodies, maps the time-frequency domain parameters into principal component space, and uses a support vector machine to efficiently analyze non-linear relation in the principal component space so as to improve the accuracy and validity of interpretation.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
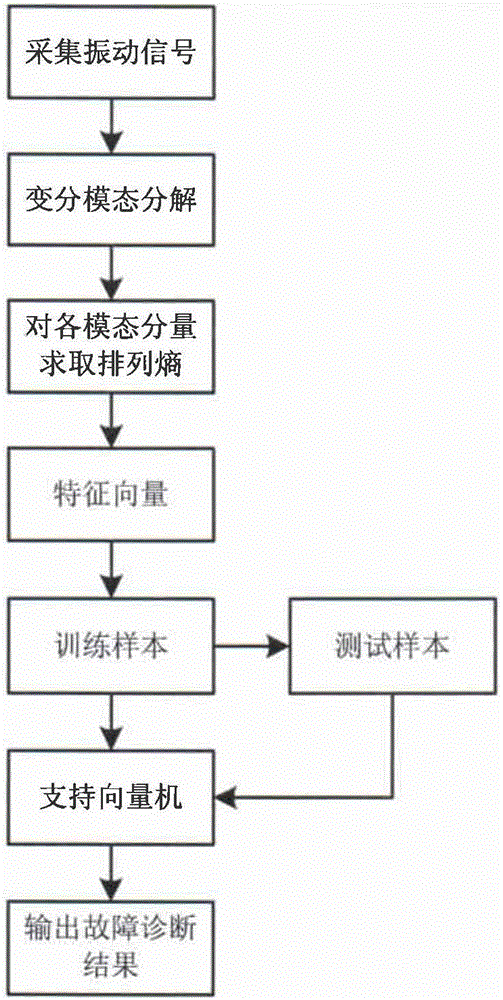
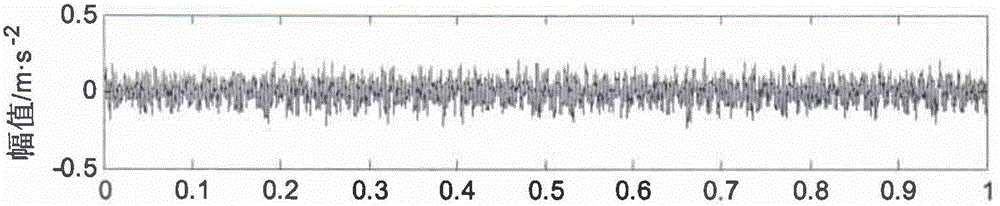
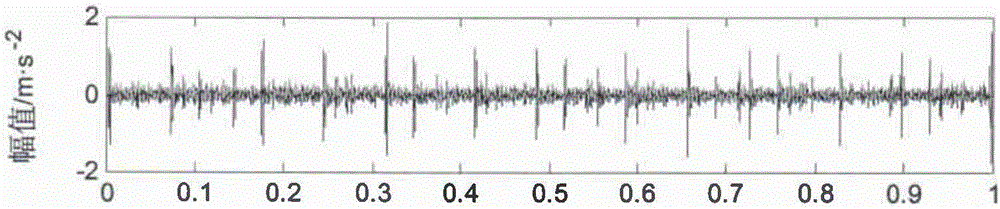
Rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on variation mode decomposition and permutation entropy
InactiveCN105758644AImplement fault diagnosisImprove recognition accuracyMachine bearings testingCharacter and pattern recognitionSupport vector machineDecomposition
The invention relates to a rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on variation mode decomposition and permutation entropy. Vibration signals are decomposed with a variation mode decomposition method, so that reactive components and mode aliasing are effectively reduced, all the mode components include characteristic information of different time scales of original signals, and effective multi-scale components are provided for subsequent signal characteristic extraction. With the combination of the features that permutation entropy is simple in calculation, high in noise resisting ability and the like, bearing fault characteristics of all the mode components are extracted from multi-scale angles. Compared with single permutation entropy analysis of rolling bearing vibration, the characteristic information of the signals can be more comprehensively represented through the permutation entropy characteristic extracting method based on multiple scales, the recognition accuracy of a support vector machine is improved, and fault diagnosis of rolling bearings is better achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
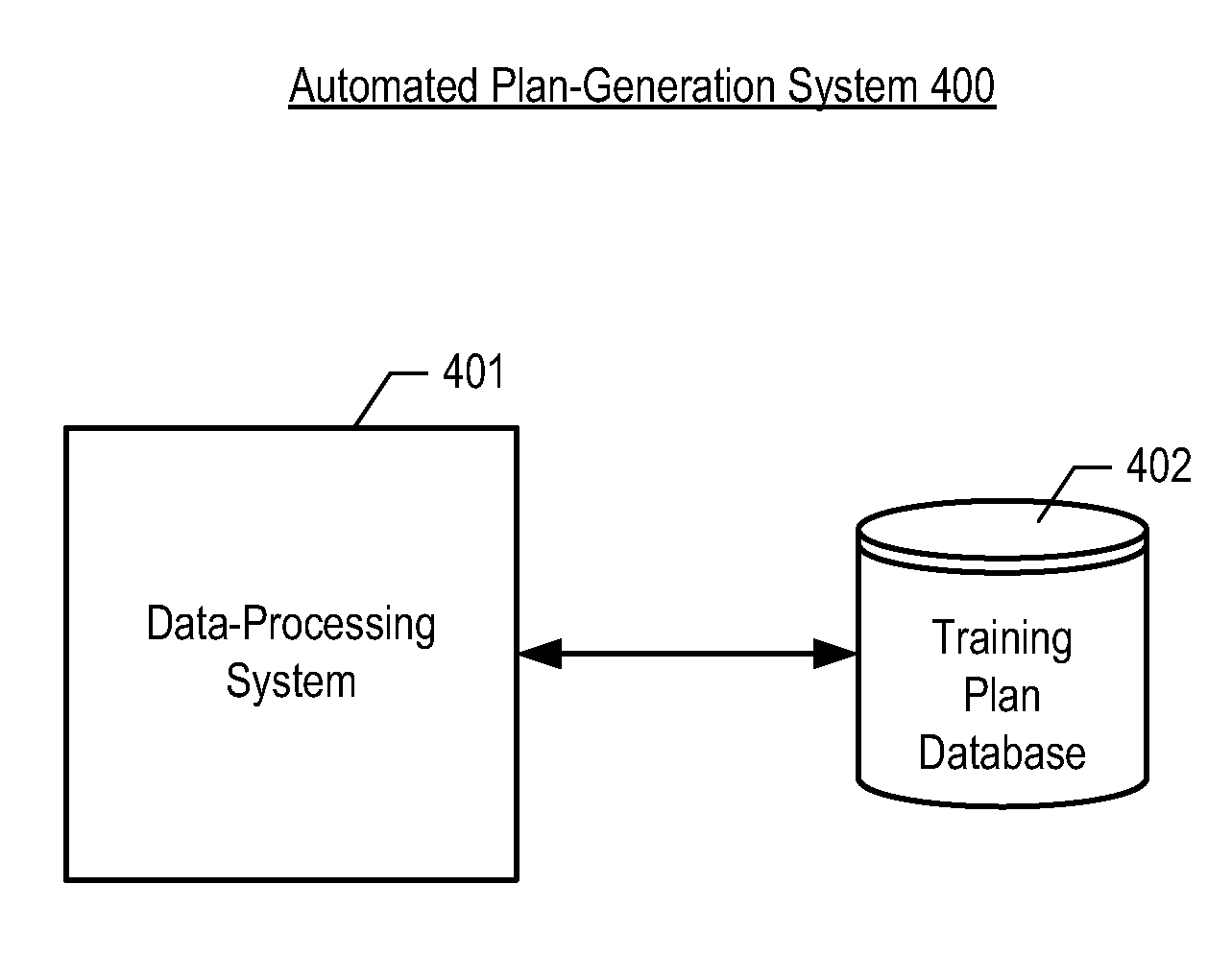
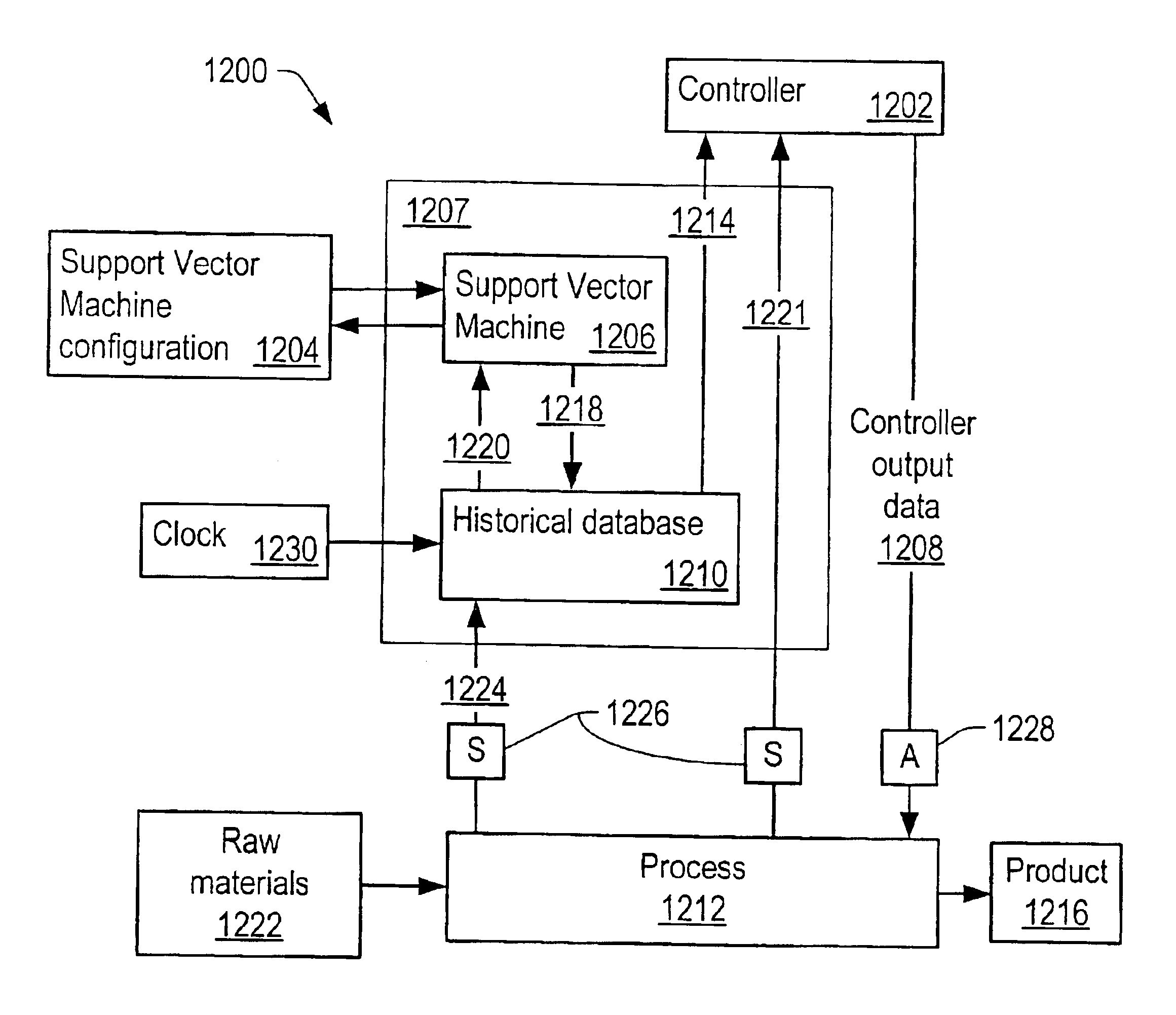
System and method for historical database training of support vector machines
InactiveUS20030101161A1Data processing applicationsComputer controlSupport vector machineData stream
A system and method for historical database training of a support vector machine (SVM). The SVM is trained with training sets from a stream of process data. The system detects availability of new training data, and constructs a training set from the corresponding input data. Over time, many training sets are presented to the SVM. When multiple presentations are needed to effectively train the SVM, a buffer of training sets is filled and updated as new training data becomes available. Once the buffer is full, a new training set bumps the oldest training set from the buffer. The training sets are presented one or more times each time a new training set is constructed. A historical database of time-stamped data may be used to construct training sets for the SVM. The SVM may be trained retrospectively by searching the historical database and constructing training sets based on the time-stamped data.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
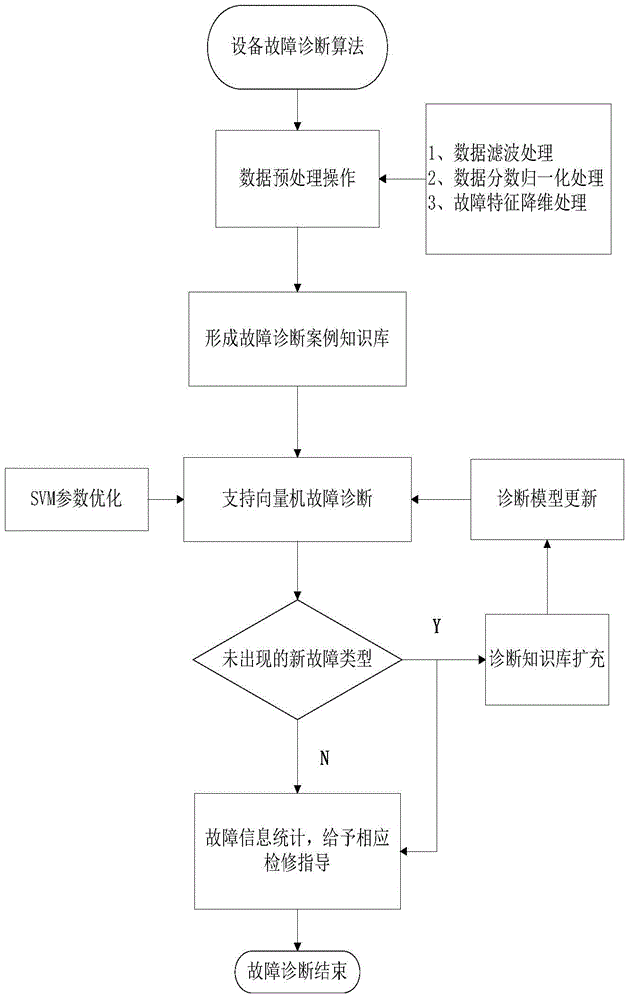
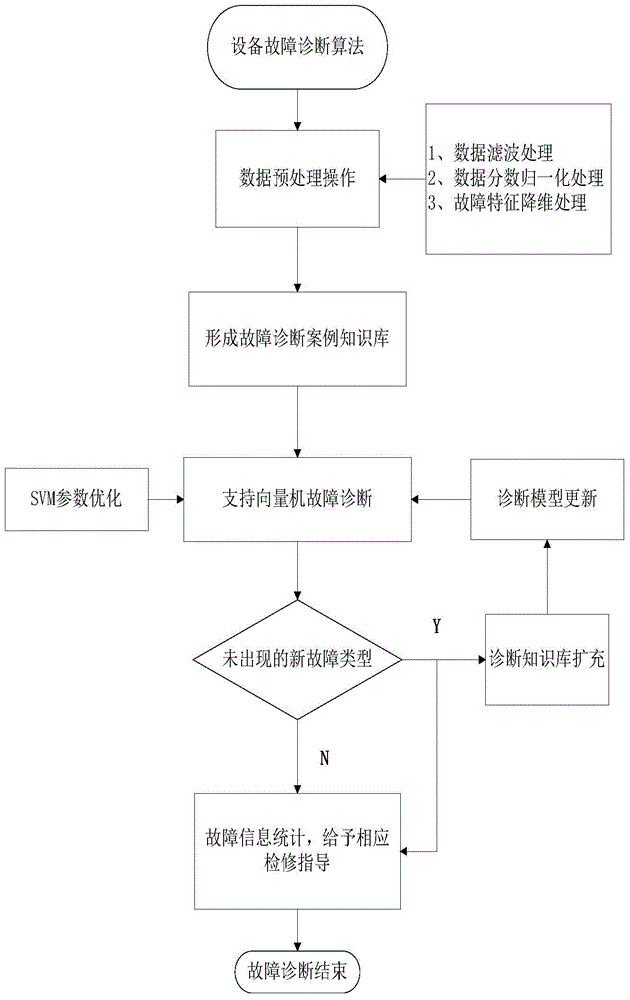
Intelligent device failure diagnosis method based on support vector machine
ActiveCN104462846AHigh speedHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsSupport vector machineKnowledge base
The invention provides an intelligent device failure diagnosis method based on a support vector machine. The method includes the steps that preprocessing operation is conducted on device data; a failure diagnosis case knowledge base is built; failure diagnosis is conducted on the support vector machine; the failure information is obtained, and troubleshooting guide is conducted. By means of the intelligent device failure diagnosis method based on the support vector machine, the failure feature of a device is highlighted to the maximum degree, the situations that the device data are incomplete and imprecise are reduced, the method provides the possibility for building a precise and reliable failure diagnosis model, the problem of aging of the diagnosis model along with the runtime of the device is solved, the misdiagnosis rate of the failure diagnosis model is reduced, and the correct rate and speed of the device failure diagnosis are increased to the maximum degree.
Owner:SHANDONG LUNENG SOFTWARE TECH
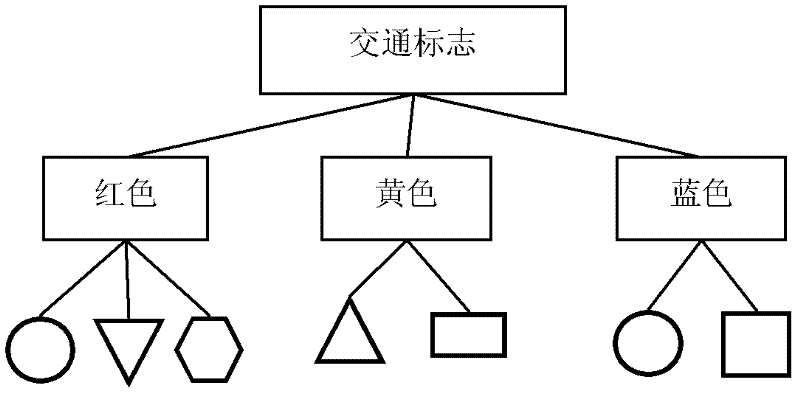
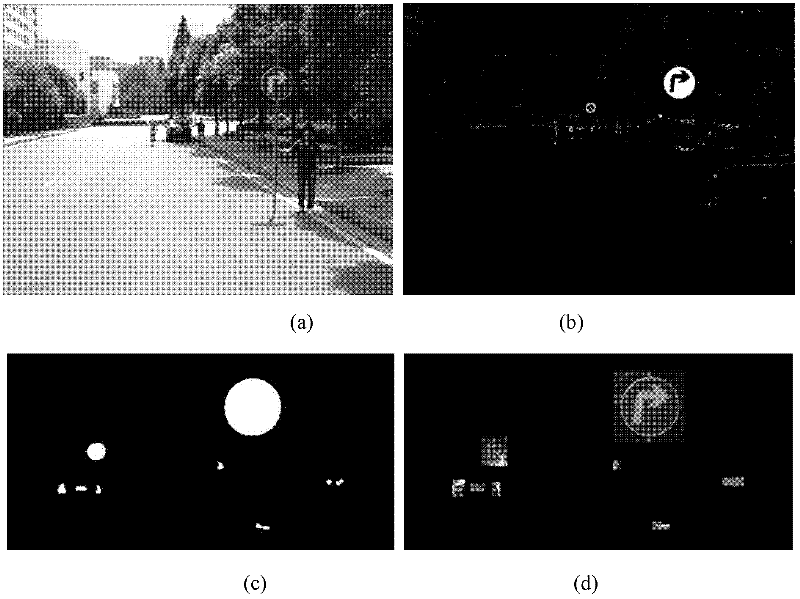
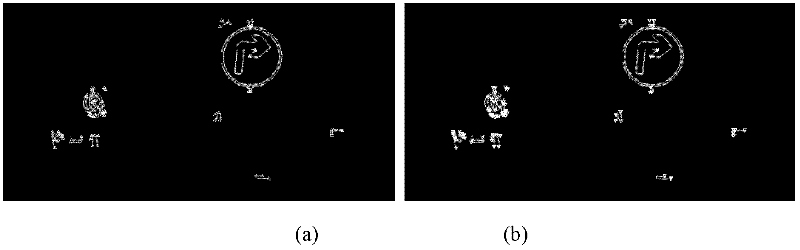
Method for recognizing road traffic sign for unmanned vehicle
InactiveCN102542260AFast extractionFast matchingDetection of traffic movementCharacter and pattern recognitionClassification methodsNear neighbor
The invention discloses a method for recognizing a road traffic sign for an unmanned vehicle, comprising the following steps of: (1) changing the RGB (Red, Green and Blue) pixel value of an image to strengthen a traffic sign feature color region, and cutting the image by using a threshold; (2) carrying out edge detection and connection on a gray level image to reconstruct an interested region; (3) extracting a labeled graph of the interested region as a shape feature of the interested region, classifying the shape of the region by using a nearest neighbor classification method, and removing a non-traffic sign region; and (4) graying and normalizing the image of the interested region of the traffic sign, carrying out dual-tree complex wavelet transform on the image to form a feature vector of the image, reducing the dimension of the feature vector by using a two-dimension independent component analysis method, and sending the feature vector into a support vector machine of a radial basis function to judge the type of the traffic sign of the interested region. By using the method, various types of traffic signs in a running environment of the unmanned vehicle can be stably and efficiently detected and recognized.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
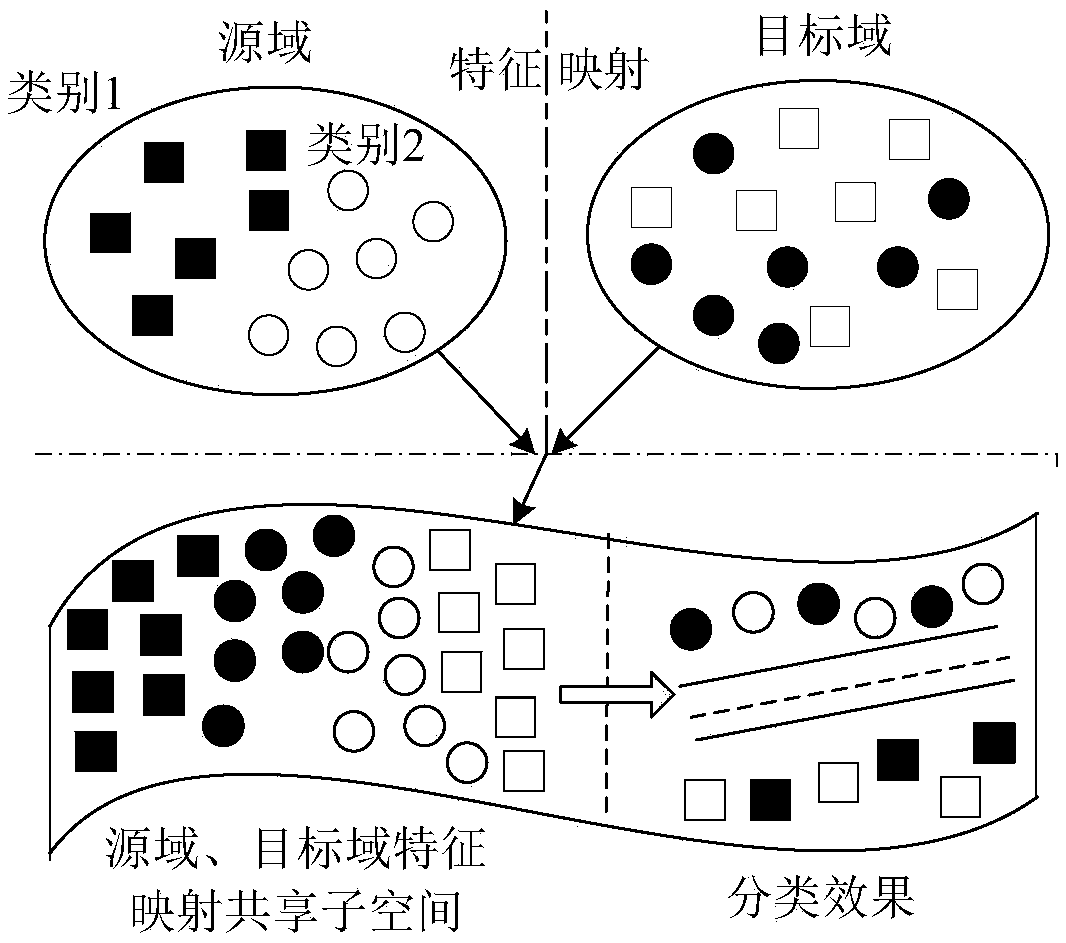
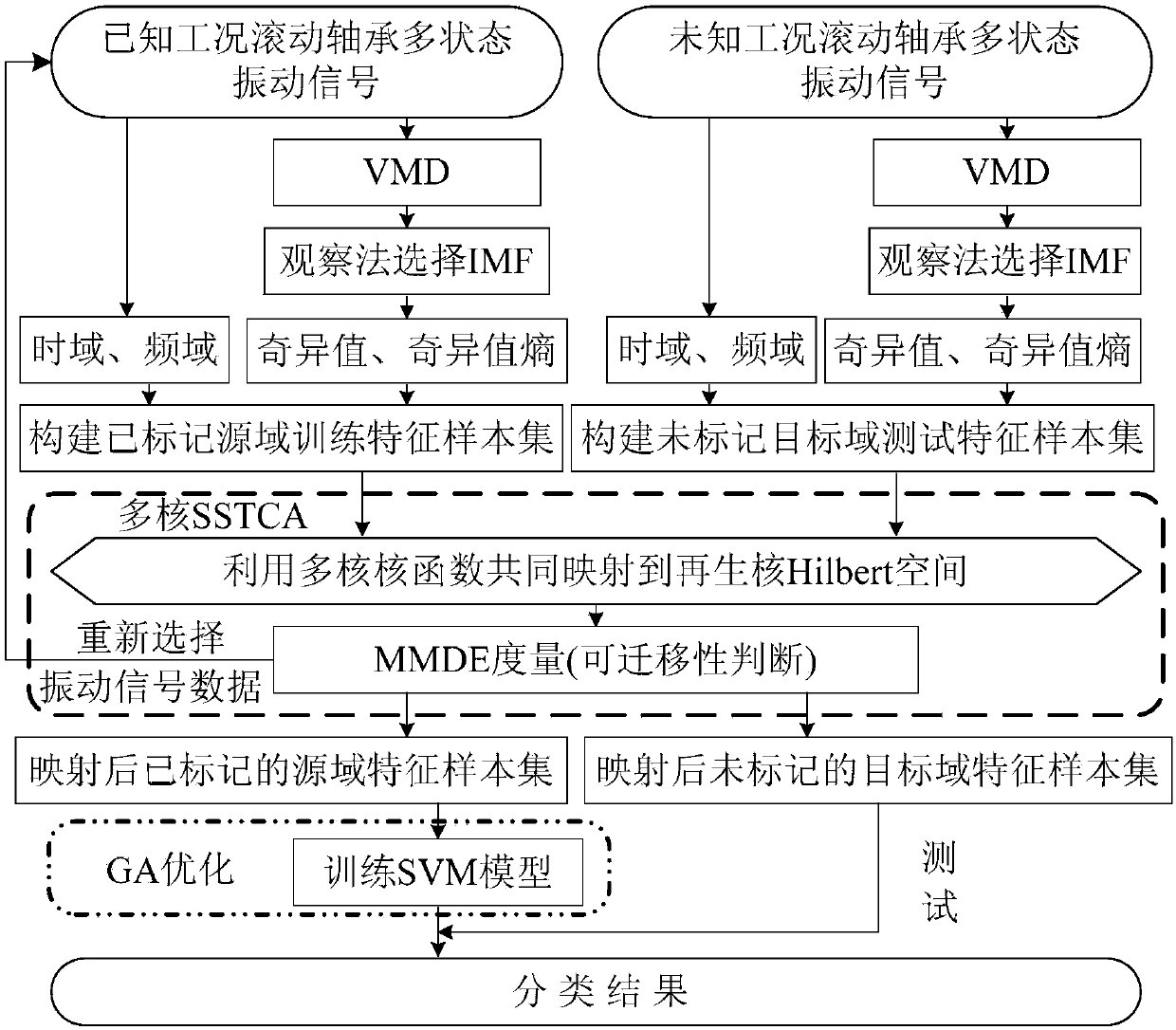
Rolling bearing fault diagnosis method in various working conditions based on feature transfer learning
ActiveCN108414226ABest mapped kernel matrixImprove accuracyMachine bearings testingSingular value decompositionDecomposition
The present invention provides a rolling bearing fault diagnosis method in various working conditions based on feature transfer learning, and relates to the field of fault diagnosis. The objective ofthe invention is to solve the problem that a rolling bearing, especially to various working conditions, is low in accuracy of diagnosis. The method comprise the steps of: employing a VMD (VariationalMode Decomposition) to perform decomposition of vibration signals of a rolling bearing in each state to obtain a series of intrinsic mode functions, performing singular value decomposition of a matrixformed by the intrinsic mode functions to solve a singular value or a singular value entropy, combining time domain features and frequency domain features of the vibration signals to construct a multi-feature set; introducing a semisupervised transfer component analysis method to perform multinuclear construction of a kernel function thereof, sample features of different working conditions are commonly mapped to a shared reproducing kernel Hilbert space so as to improve the data intra-class compactness and the inter-class differentiation; and employing the maximum mean discrepancy embedding to select more efficient data as a source domain, inputting source domain feature samples into a SVM (Support Vector Machine) for training, and testing target domain feature samples after mapping. Therolling bearing fault diagnosis method in various working conditions has higher accuracy in the rolling bearing multi-state classification in various working conditions.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
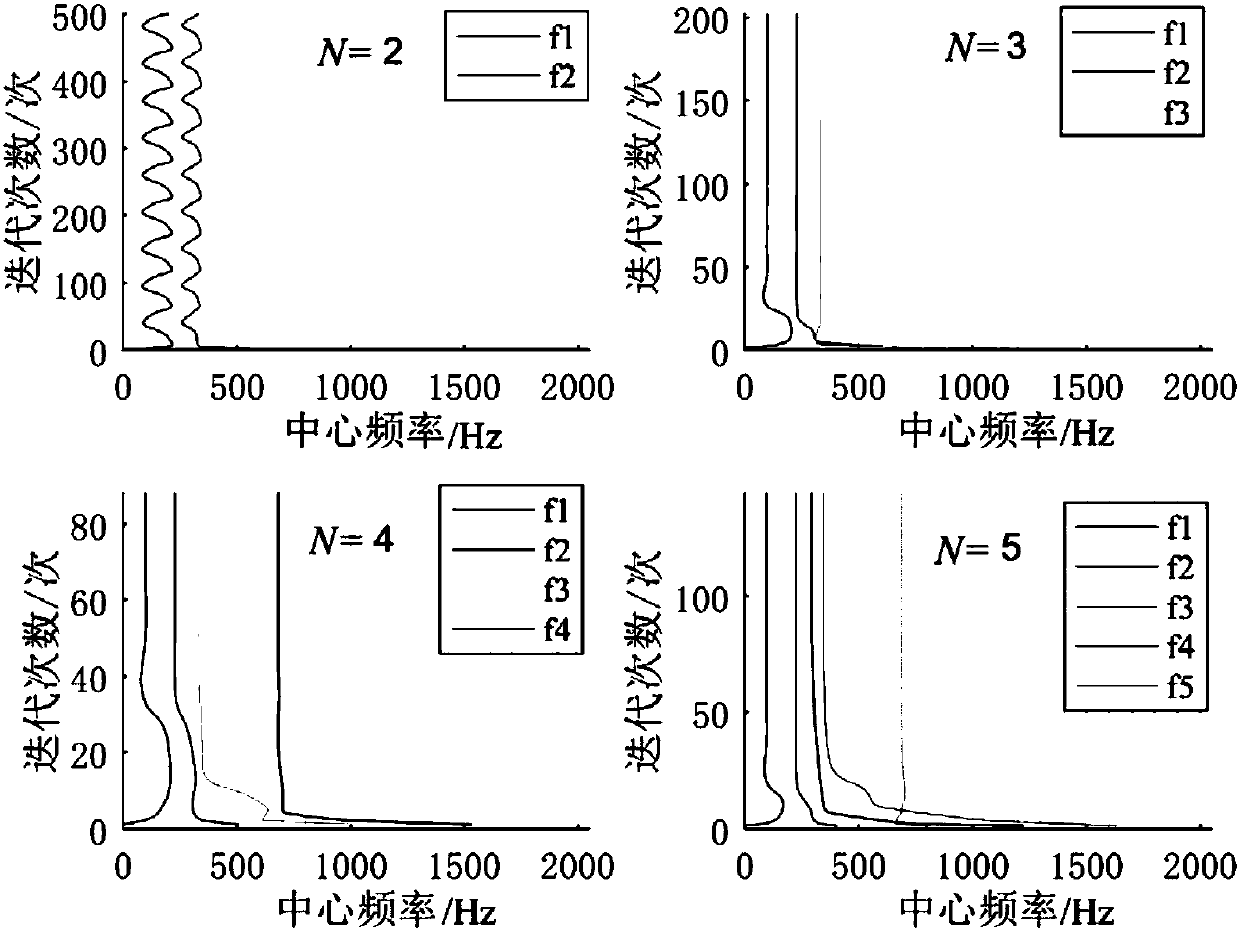
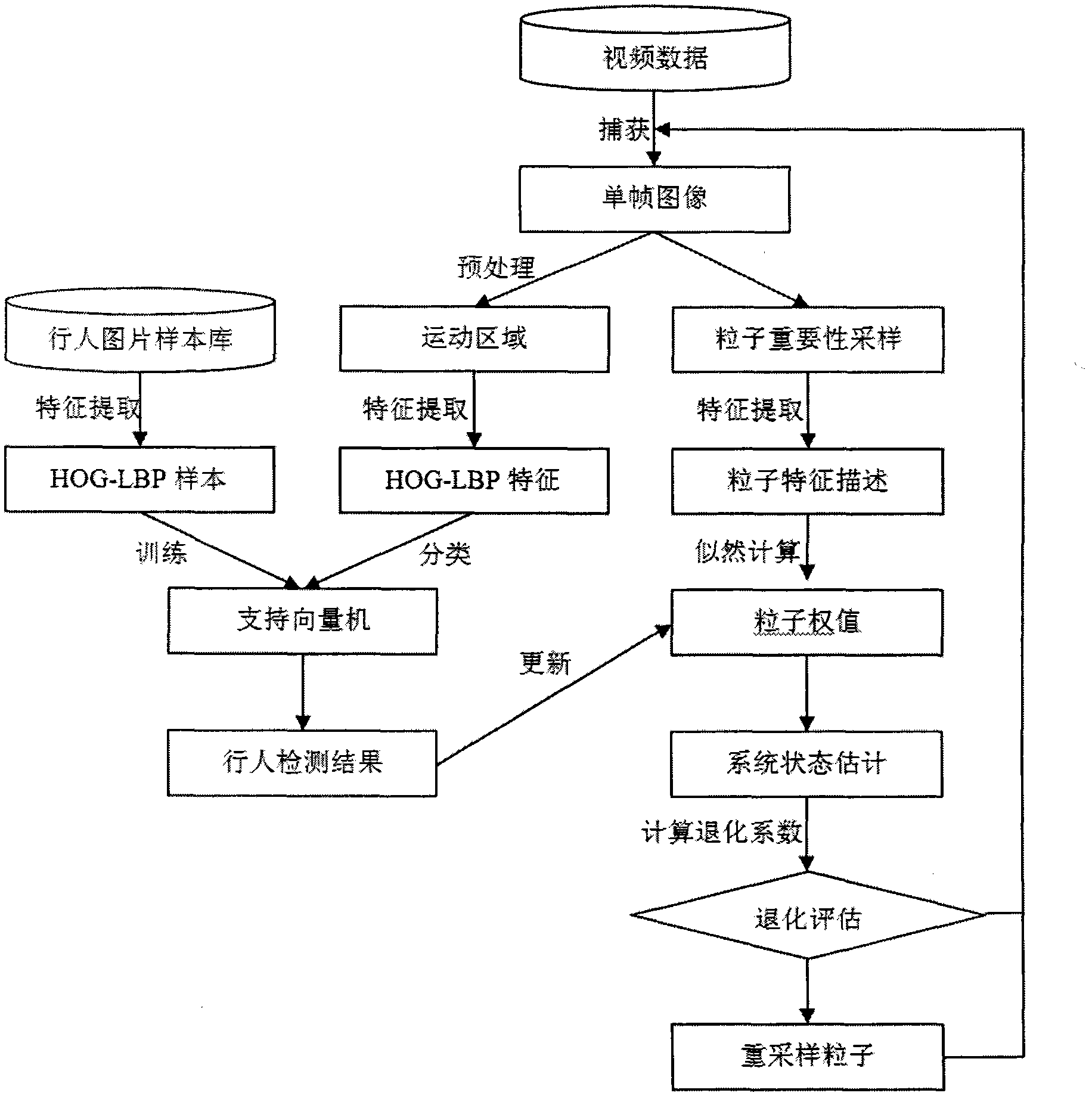
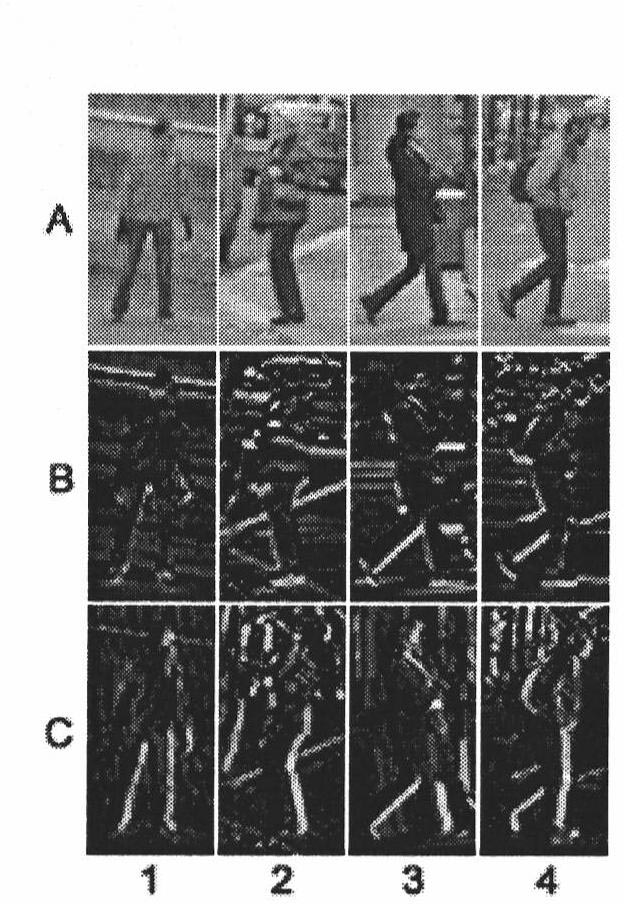
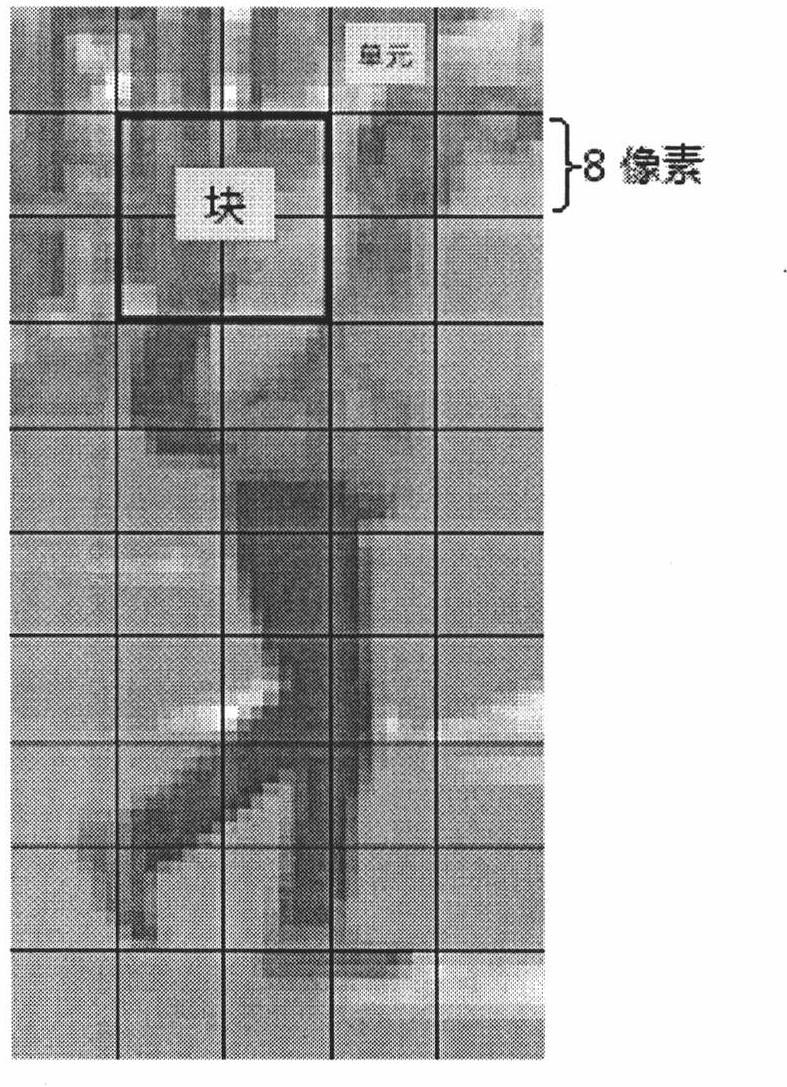
Pedestrian tracking method based on HOG-LBP
InactiveCN102663409AAvoid environmental impactOvercome occlusionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionSupport vector machineFeature extraction
The invention discloses a pedestrian tracking method based on HOG-LBP, comprising the following steps of, A1, sample establishment; A2, feature extraction; A3, SVM model establishment; A4, classifier training; A5, video capture and pretreatment; A6, video pedestrian examination; A7, video pedestrian tracking: applying a particle filtering tracking method based on an HOG-LBP feature to track the pedestrian examined in step A6. The method firstly learns an image pedestrian mode through a support vector machine, and then classifies a moving area in a video sequence and inputs the result to a particle filtering machine to update the particle status, and finally realizes continuous tracking to pedestrian movement in the scene. Because the method collects pedestrian feature by adopting HOG-LBP and uses the particle filtering to track movement, it has good adaptability and stability to movement interleave and sheltering phenomenon in a scene and non-linear feature presented by the movement.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
System and method for detecting malicious executable code
ActiveUS20060037080A1Boosted SVMsFacilitate decision-makingMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionSupport vector machineInductive method
A system and method for detecting malicious executable software code. Benign and malicious executables are gathered; and each are encoded as a training example using n-grams of byte codes as features. After selecting the most relevant n-grams for prediction, a plurality of inductive methods, including naive Bayes, decision trees, support vector machines, and boosting, are evaluated.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
Methods of identifying patterns in biological systems and uses thereof
InactiveUS7117188B2Enhancing knowledge discoveryLarge amount of informationKernel methodsDigital computer detailsSupport vector machineData set
The methods, systems and devices of the present invention comprise use of Support Vector Machines and RFE (Recursive Feature Elimination) for the identification of patterns that are useful for medical diagnosis, prognosis and treatment. SVM-RFE can be used with varied data sets.
Owner:HEALTH DISCOVERY CORP +1
Method and system for authenticating shielded face
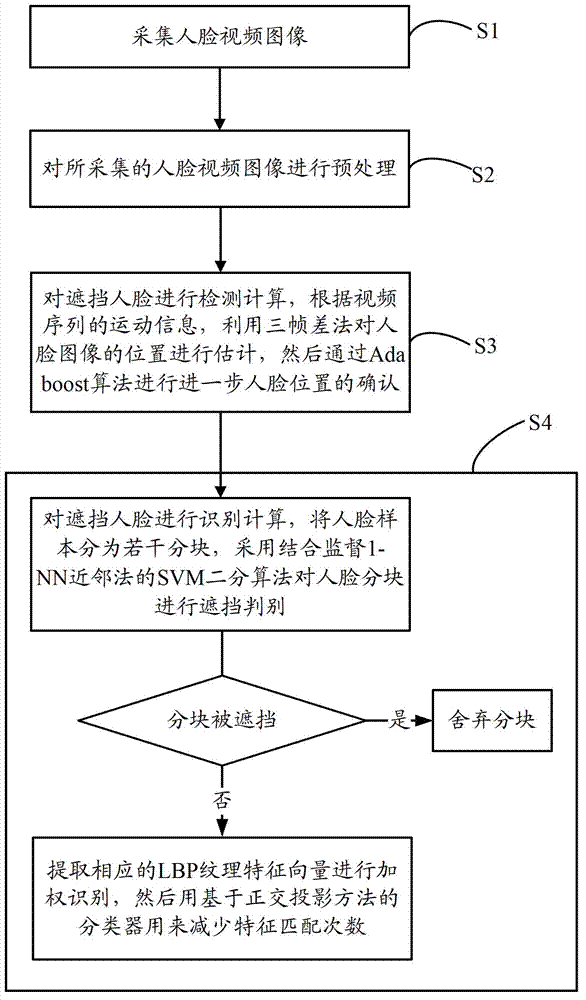
InactiveCN102855496AReduce training timeEasy to detectCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionSupport vector machine
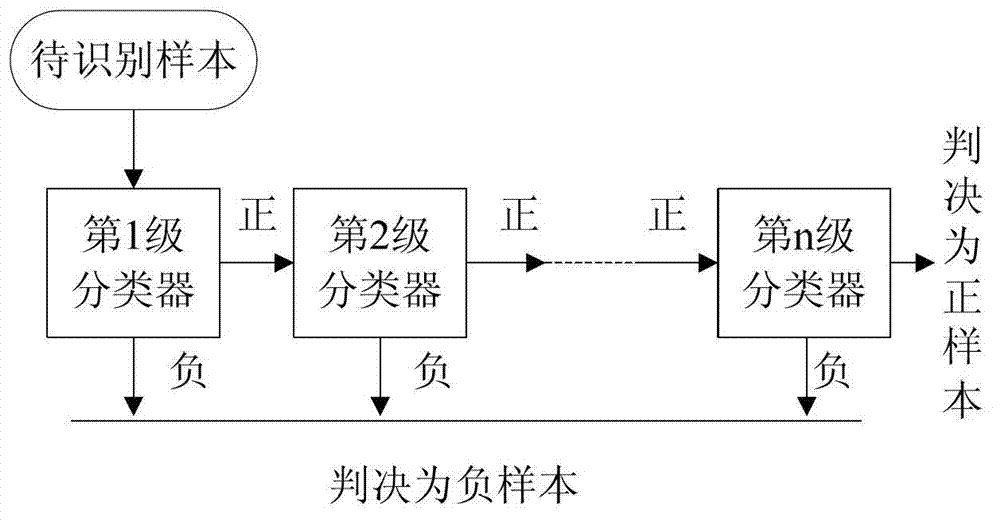
The invention discloses a method and a system for authenticating a shielded face, wherein the method comprises the following steps: S1) collecting a face video image; S2) preprocessing the collected face video image; S3) performing detection calculation on the shielded face, evaluating a position of a face image by utilizing a three-frame difference method according to motion information of a video sequence, and further confirming the position of the face according to an Adaboost algorithm; and S4) performing authenticating calculation on the shielded face, dividing a face sample into a plurality of sub-blocks, performing shielding distinguishment on the sub-blocks of the face by adopting a SVM(Support Vector Machine) binary algorithm combined with a supervising 1-NN k-Nearest neighbor method, if the sub-blocks are shielded, directly abandoning the sub-blocks, and if the sub-blocks are not shielded, extracting a corresponding LBP (Length Between Perpendiculars) textural feature vector for performing weighting identification, and then using a classifier based on a rectangular projection method to reduce feature matching times. According to the method for authenticating the shielded face, the detection rate and the detection speed for the local shielded face are effectively increased.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Automatic Generation of Patient-Specific Radiation Therapy Planning Parameters
An apparatus and method for automatically generating radiation treatment planning parameters are disclosed. In accordance with the illustrative embodiment, a database is constructed that stores: (i) patient data and past treatment plans by expert human planners for these patients, and (ii) optimal treatment plans that are generated using multi-objective optimization and Pareto front search and that represent the best tradeoff opportunities of the patient case, and a predictive model (e.g., a neural network, a decision tree, a support vector machine [SVM], etc.) is then trained via a learning algorithm on a plurality of input / output mappings derived from the contents of the database. During training, the predictive model is trained to identify and infer patterns in the treatment plan data through a process of generalization. Once trained, the predictive model can then be used to automatically generate radiation treatment planning parameters for new patients.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
System and method for historical database training of support vector machines
A system and method for historical database training of a support vector machine (SVM). The SVM is trained with training sets from a stream of process data. The system detects availability of new training data, and constructs a training set from the corresponding input data. Over time, many training sets are presented to the SVM. When multiple presentations are needed to effectively train the SVM, a buffer of training sets is filled and updated as new training data becomes available. Once the buffer is full, a new training set bumps the oldest training set from the buffer. The training sets are presented one or more times each time a new training set is constructed. A historical database of time-stamped data may be used to construct training sets for the SVM. The SVM may be trained retrospectively by searching the historical database and constructing training sets based on the time-stamped data.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Automatic biometric identification based on face recognition and support vector machines
ActiveUS20090074259A1Less resourcesHigh level of recognitionCharacter and pattern recognitionGeometric image transformationSupport vector machineFace perception
An automatic biometric identification method based on face recognition and support vector machines, includes enrolling a user to generate a user's reference template; and identifying the user based on the user's reference template, wherein generating a user's reference template includes acquiring a number of user's face images, and training a one-class support vector machine based on the user's face images only.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Management system for enhanced RFID system performance
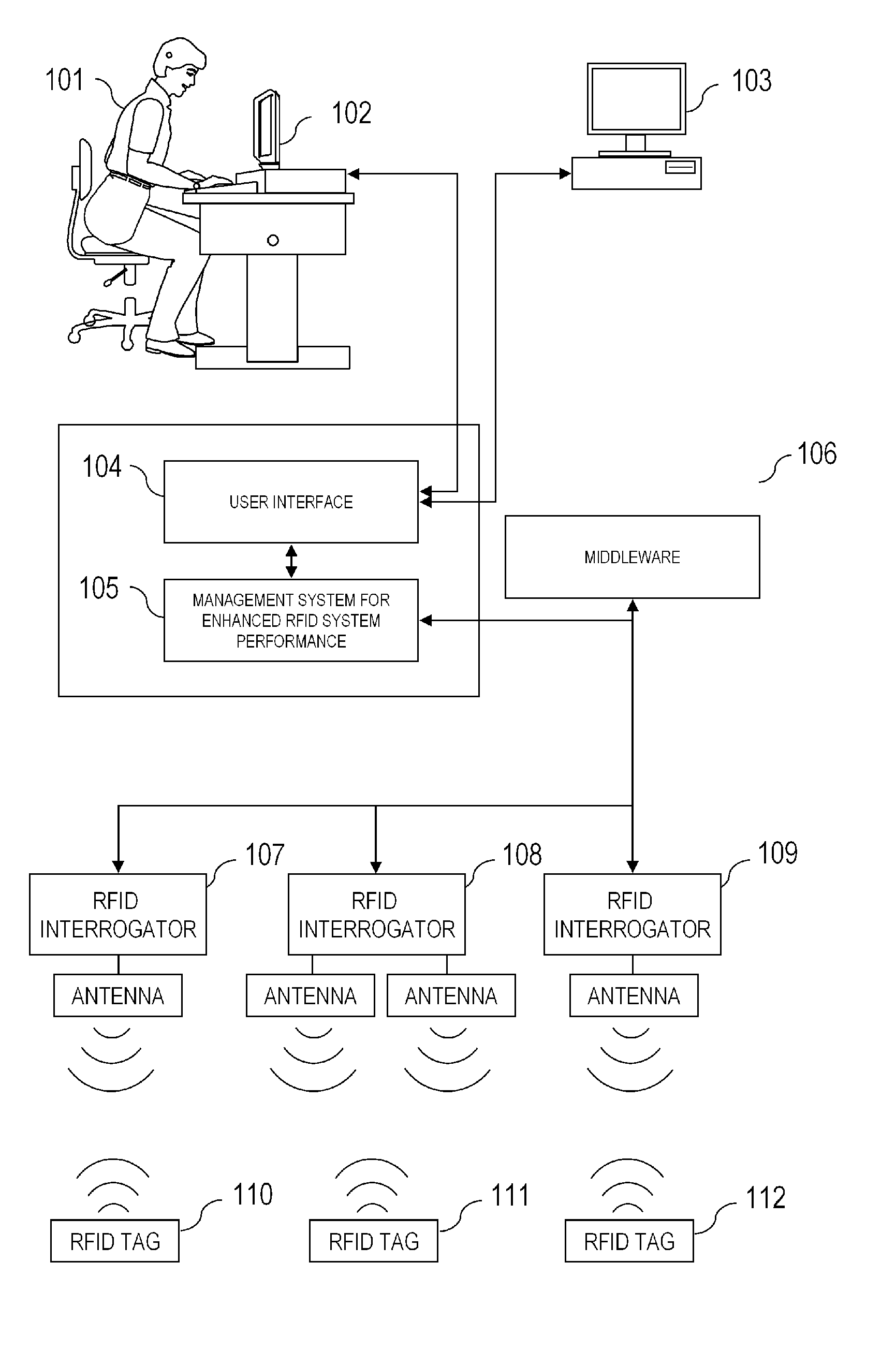
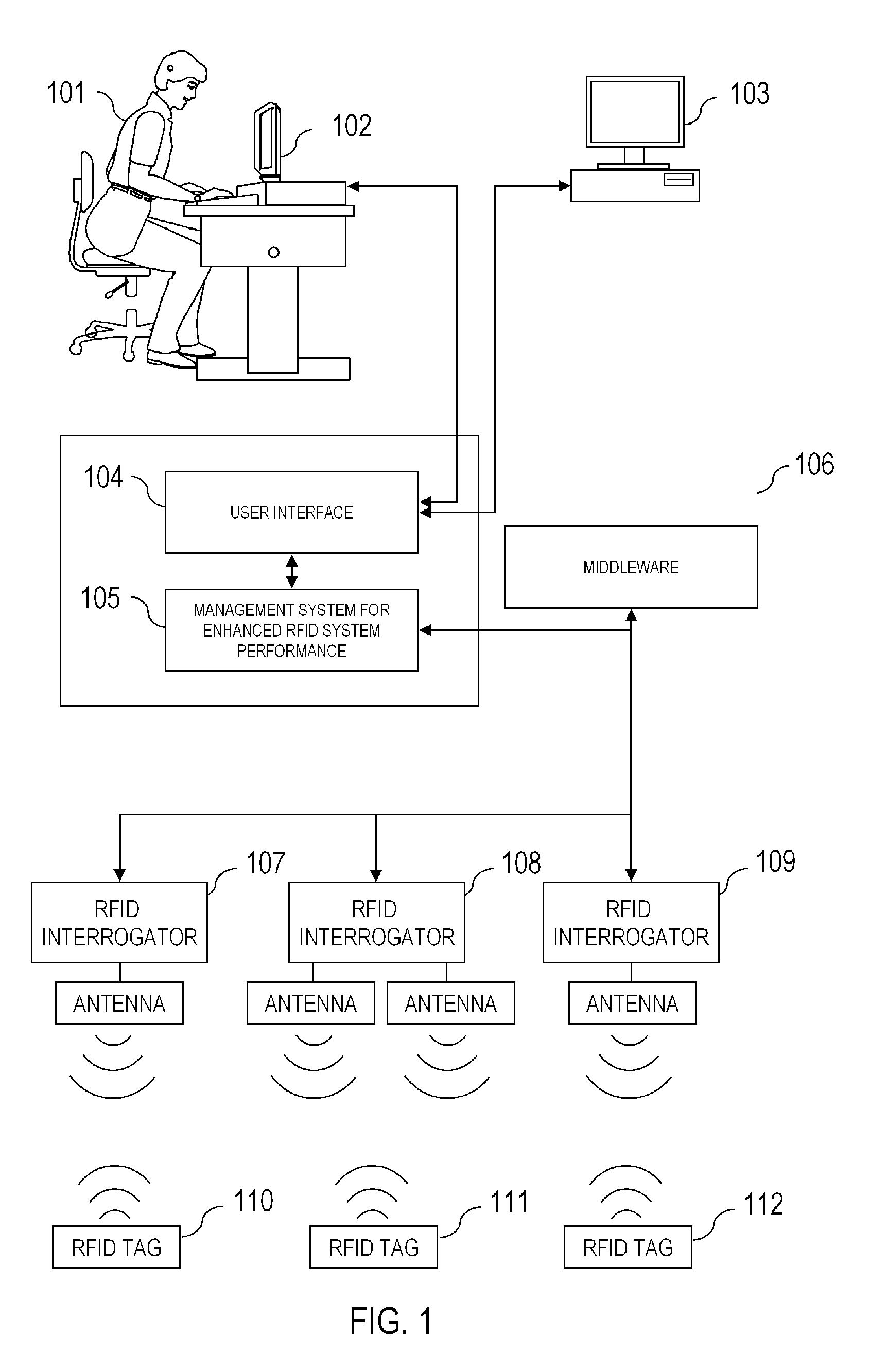
InactiveUS20060082444A1Improve performanceMonitor performance of systemIndividual entry/exit registersSubscribers indirect connectionInformation processingSmart technology
A method and system managing radio frequency identification (RFID) systems. The system monitors the performance of systems that use RFID tags and readers. It operates at multiple levels to ensure the optimal performance of readers, tags, antennae, and the information processing systems that acquire and convey tag data. The management system may employ artificial intelligence techniques such as genetic algorithms, fuzzy logic, neural networks, Bayesian networks, support vector machines or statistical methods to develop, maintain and exploit models of RFID system behavior. By comparing the actual performance of RFIDs and related components, the management system can detect and report failures and partial failures of components. The management system may also send signals to components to enhance performance of the overall RFID system.
Owner:QUAKE GLOBAL
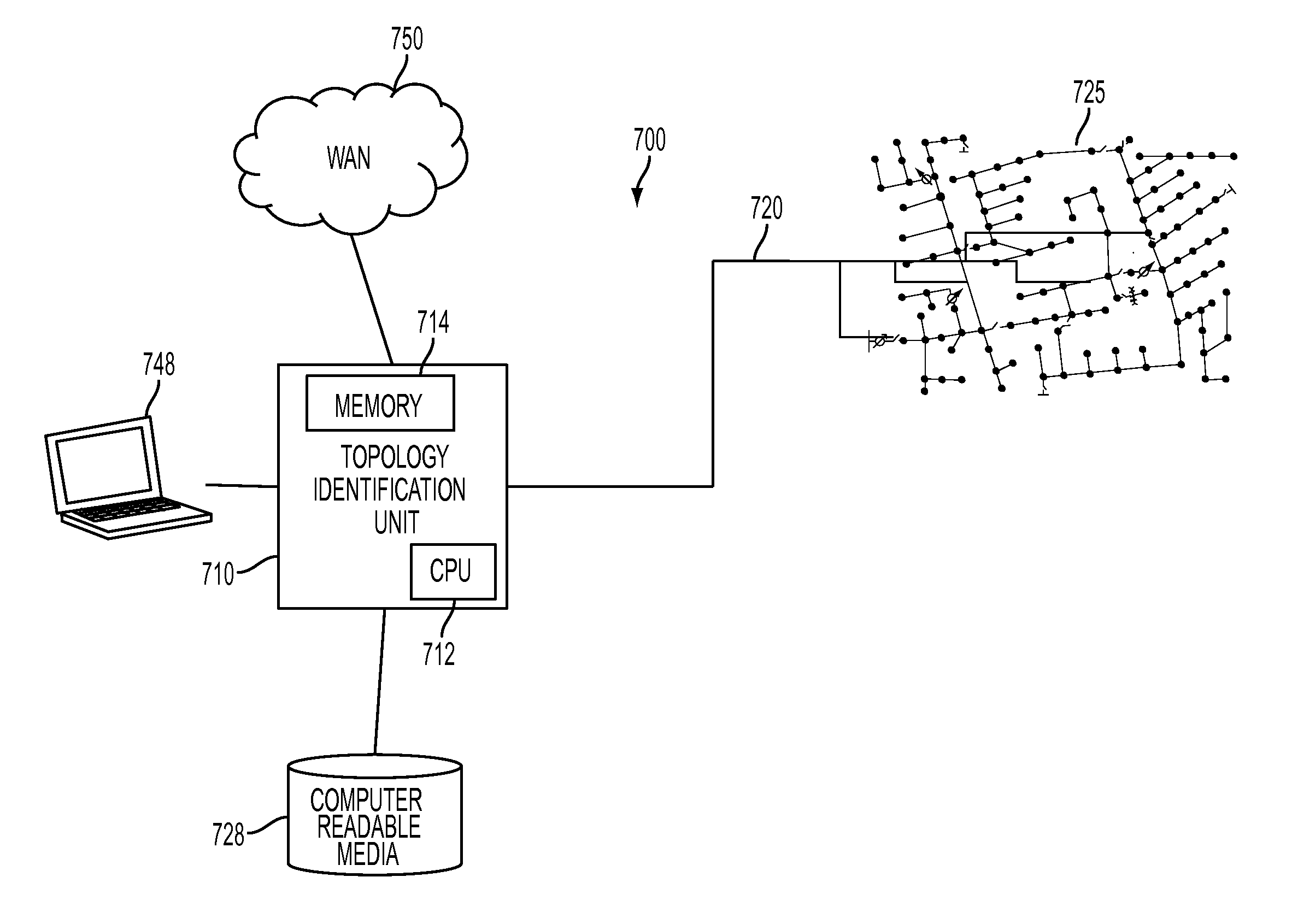
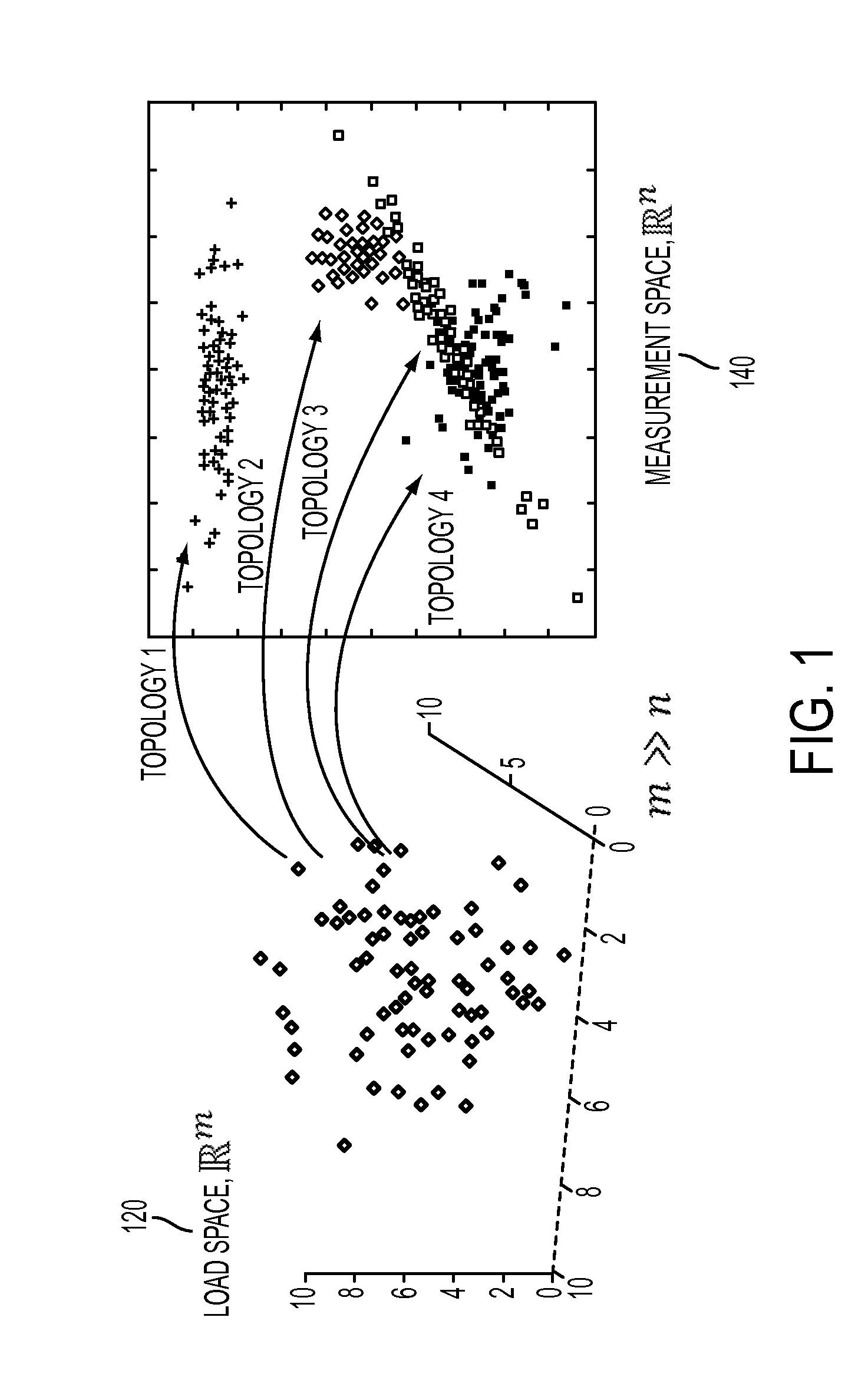
Topology identification in distribution network with limited measurements
A statistical technique is used to estimate the status of switching devices (such as circuit breakers, isolator switches and fuses) in distribution networks, using scares (i.e., limited or non-redundant) measurements. Using expected values of power consumption, and their variance, the confidence level of identifying the correct topology, or the current status of switching devices, is calculated using any given configuration of real time measurements. Different topologies are then compared in order to select the most likely topology at the prevailing time. The measurements are assumed as normally distributed random variables, and the maximum likelihood principle or a support vector machine is applied.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
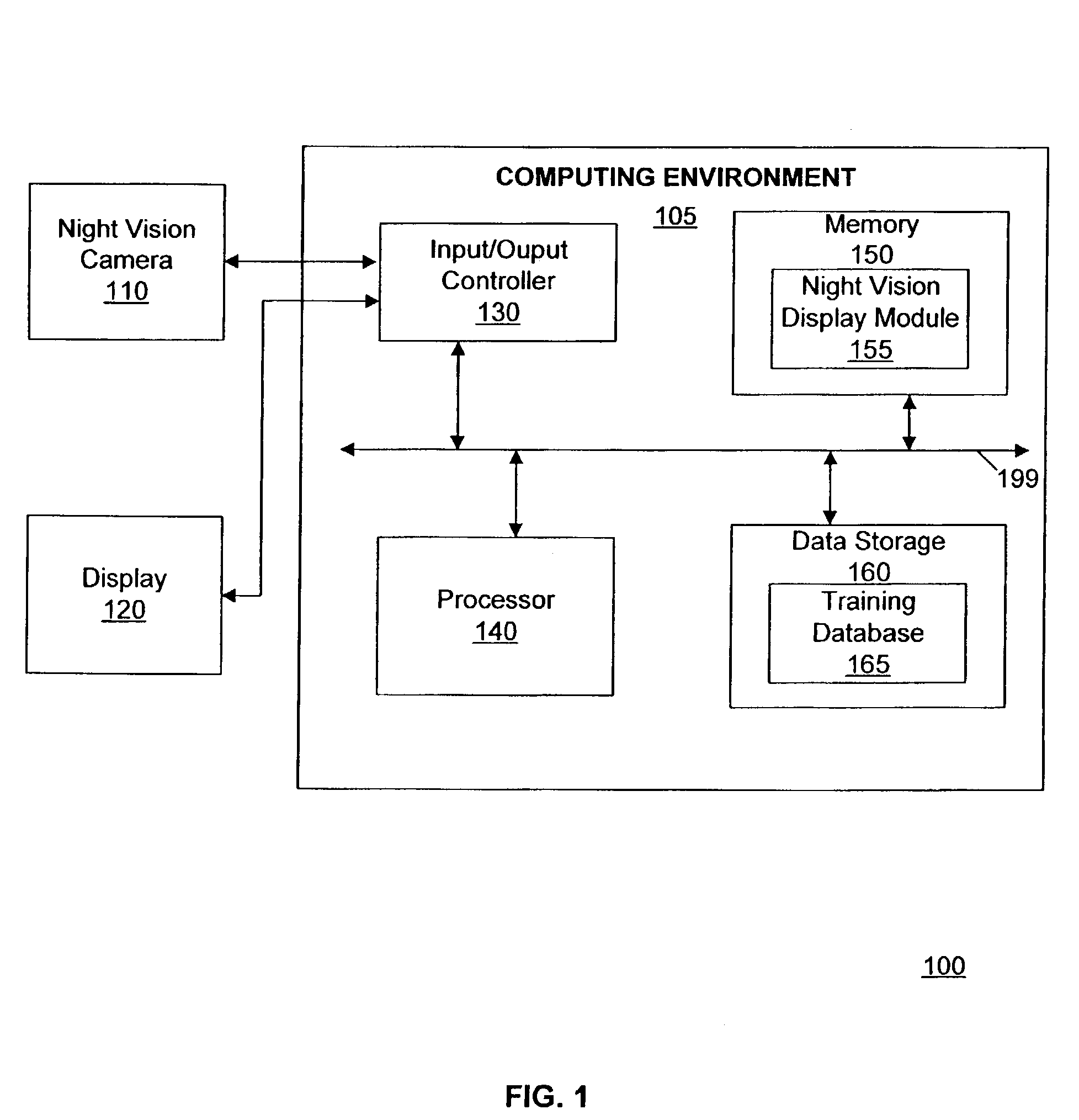
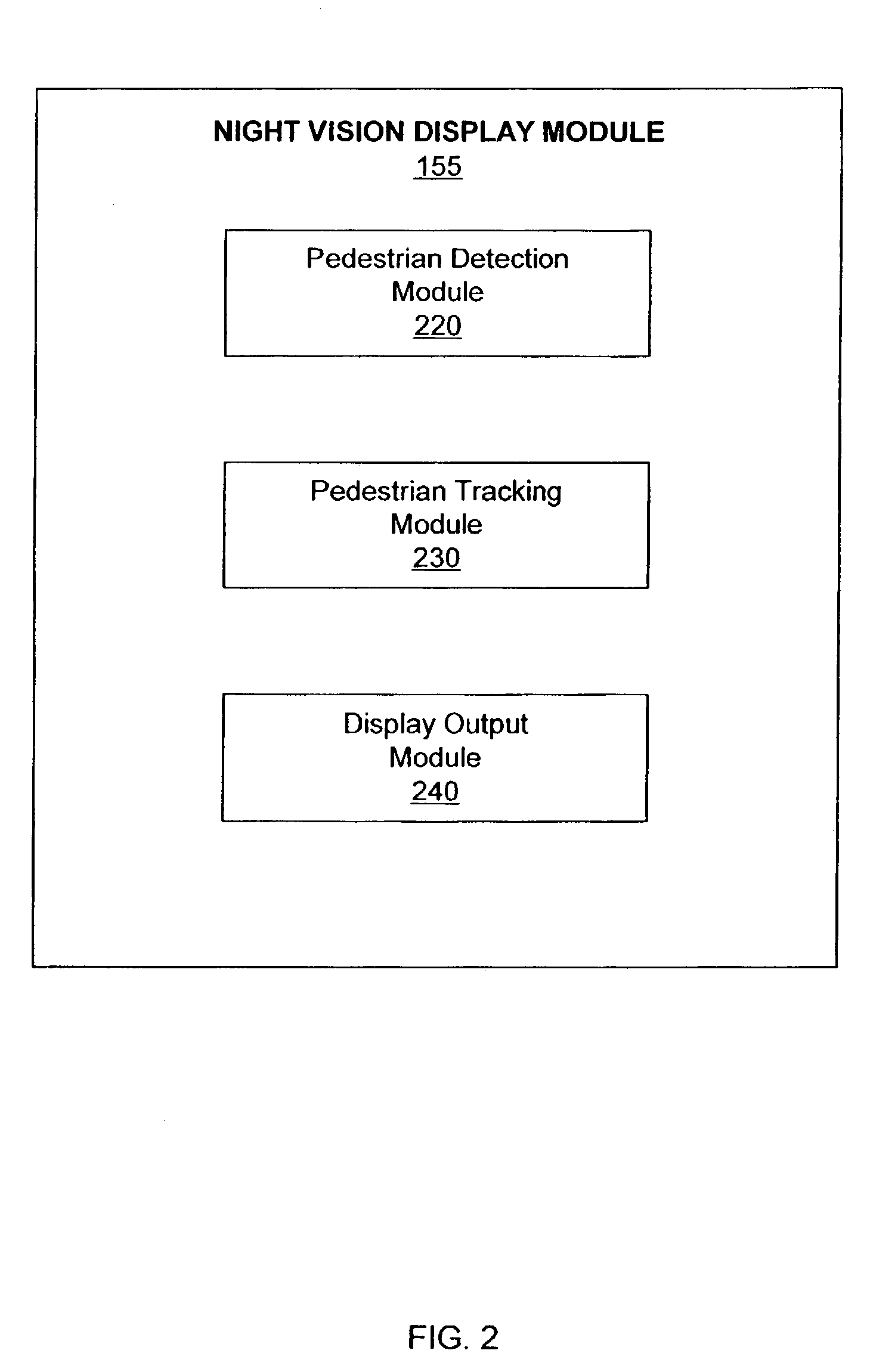
Pedestrian detection and tracking with night vision
Owner:VEONEER SWEDEN AB +1
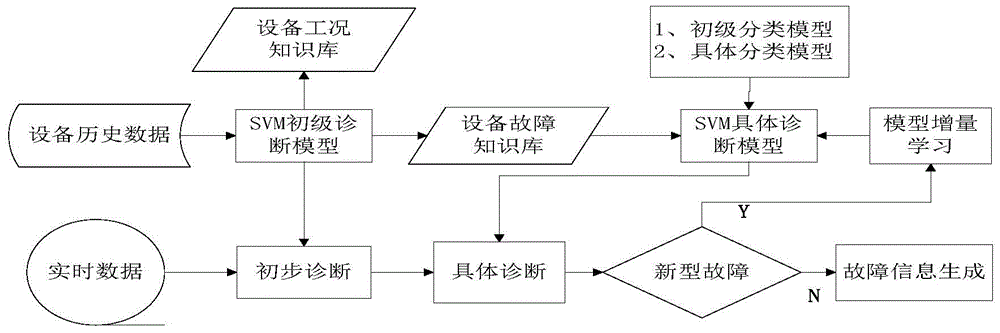
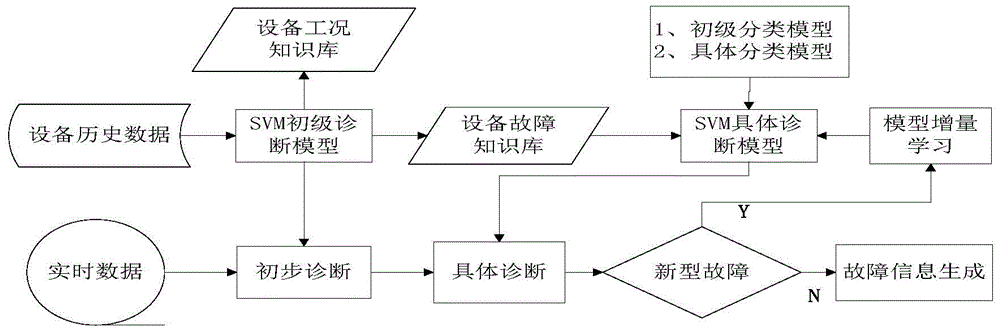
SVM classification model-based equipment fault diagnosing method
ActiveCN104573740AHigh speedHigh precisionDetecting faulty computer hardwareCharacter and pattern recognitionSupport vector machineDiagnosis methods
The invention discloses an SVM classification model-based equipment fault diagnosing method. The method comprises the following steps: performing a preprocessing operation on equipment data; constructing a fault diagnosis case knowledge base; performing fault diagnosis on a support vector machine on the basis of an SVM classification model; acquiring fault information and performing maintenance guide. According to the support vector machine-based intelligent equipment fault diagnosis method, the fault features of equipment are highlighted to the maximum degree; the situations that the equipment data are incomplete and inaccurate are reduced; the possibility is provided for constructing an accurate and reliable fault diagnosis model; the problem that the diagnosis model ages along with the operating time of the equipment is solved; the misdiagnosis rate of the fault diagnosis is reduced; the accuracy and the speed of the equipment fault diagnosis are greatly improved.
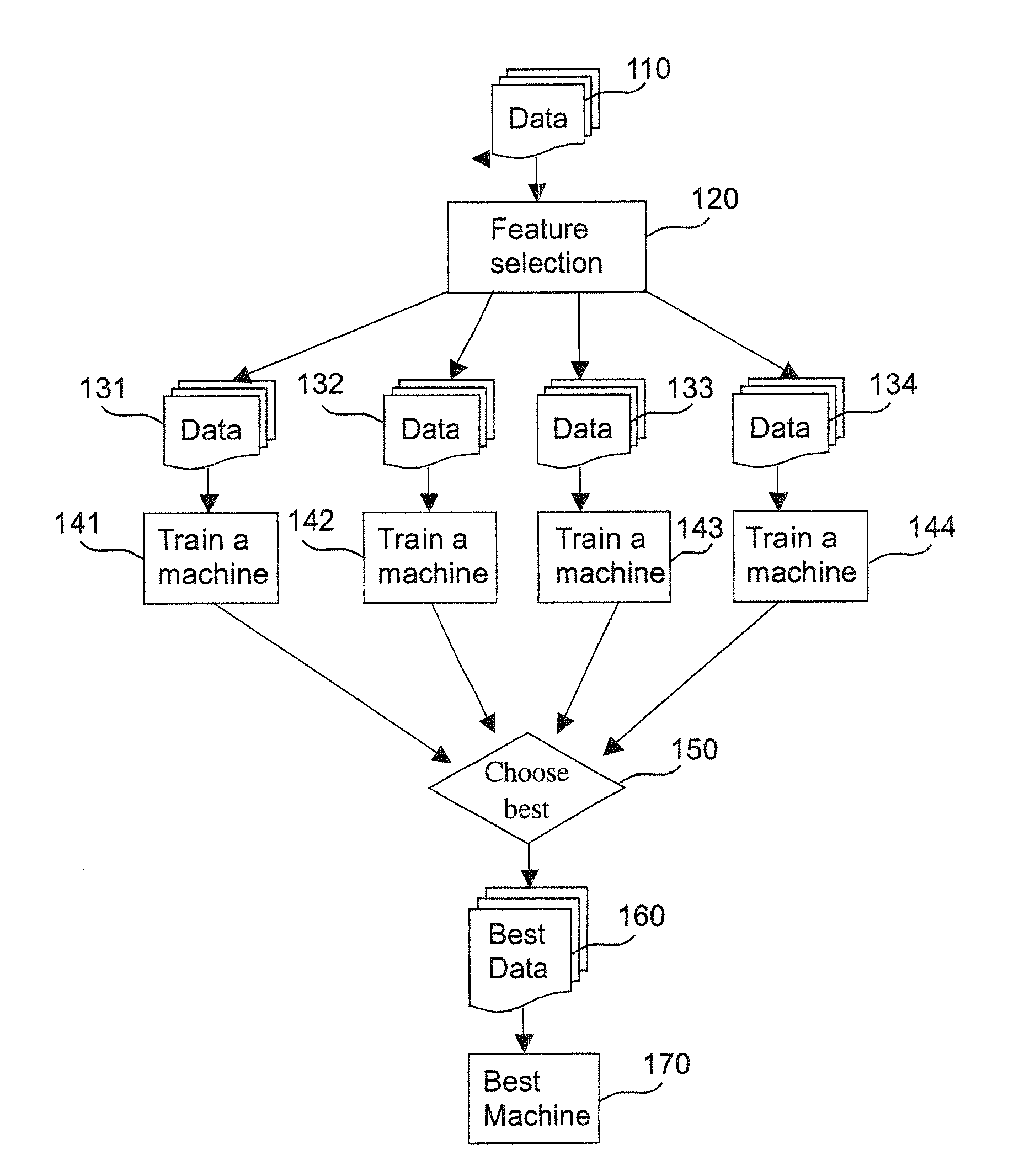
Owner:SHANDONG LUNENG SOFTWARE TECH
Machine learning methods and systems for identifying patterns in data using a plurality of learning machines wherein the learning machine that optimizes a performance function is selected
Methods for training machines to categorize data, and / or recognize patterns in data, and machines and systems so trained. More specifically, variations of the invention relates to methods for training machines that include providing one or more training data samples encompassing one or more data classes, identifying patterns in the one or more training data samples, providing one or more data samples representing one or more unknown classes of data, identifying patterns in the one or more of the data samples of unknown class(es), and predicting one or more classes to which the data samples of unknown class(es) belong by comparing patterns identified in said one or more data samples of unknown class with patterns identified in said one or more training data samples. Also provided are tools, systems, and devices, such as support vector machines (SVMs) and other methods and features, software implementing the methods and features, and computers or other processing devices incorporating and / or running the software, where the methods and features, software, and processors utilize specialized methods to analyze data.
Owner:DIGITAL INFUZION
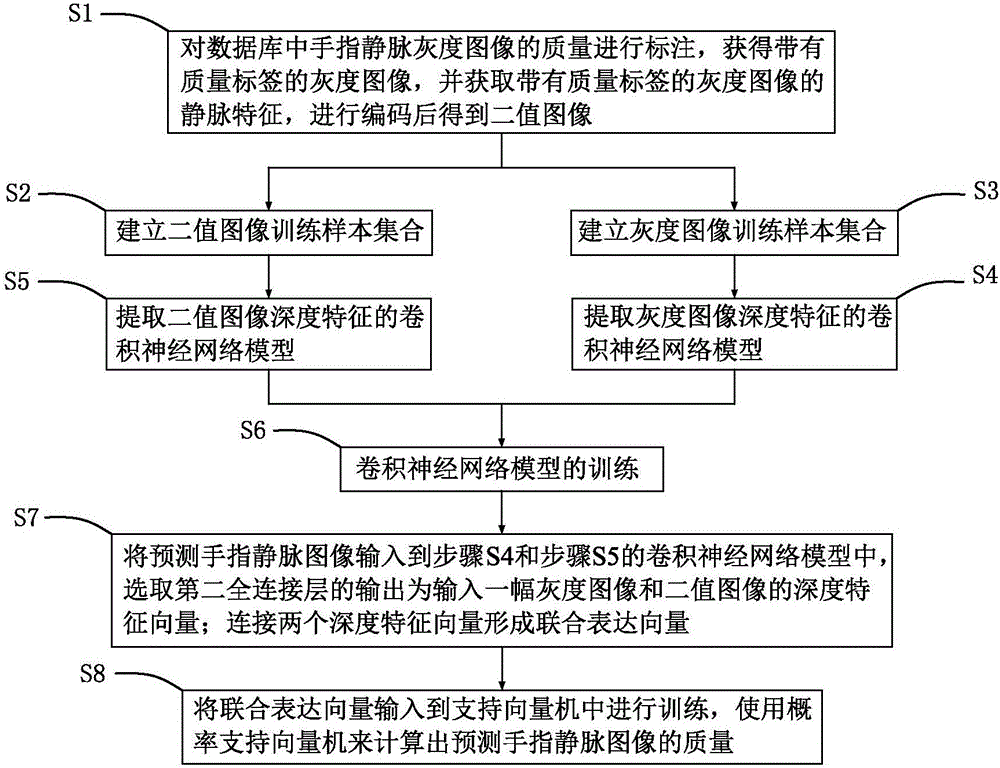
Finger-vein image quality evaluation method and system based on convolutional neural network
ActiveCN106326886AEasy to identifyHigh precisionNeural architecturesMatching and classificationSupport vector machineFeature vector
The invention provides a finger-vein image quality evaluation method and system based on a convolutional neural network. The method includes: labeling the quality of finger-vein gray images, building a training sample set, and using the training sample set to train the convolutional neural network; inputting one optional gray image and a binary image into trained models, selecting the output of second full connection layers in two convolutional neural network models as the depth feature vectors of the input gray image and the binary image; connecting the two depth feature vectors to form a united expression vector, inputting the united expression vector into a support vector machine for training, and using a probability support vector machine to calculate the quality of a predicted finger-vein image. By the evaluation method and system, finger-vein image quality evaluation precision can be increased to a large extent, and the identification performance of a certification system can be improved.
Owner:重庆金融科技研究院 +1
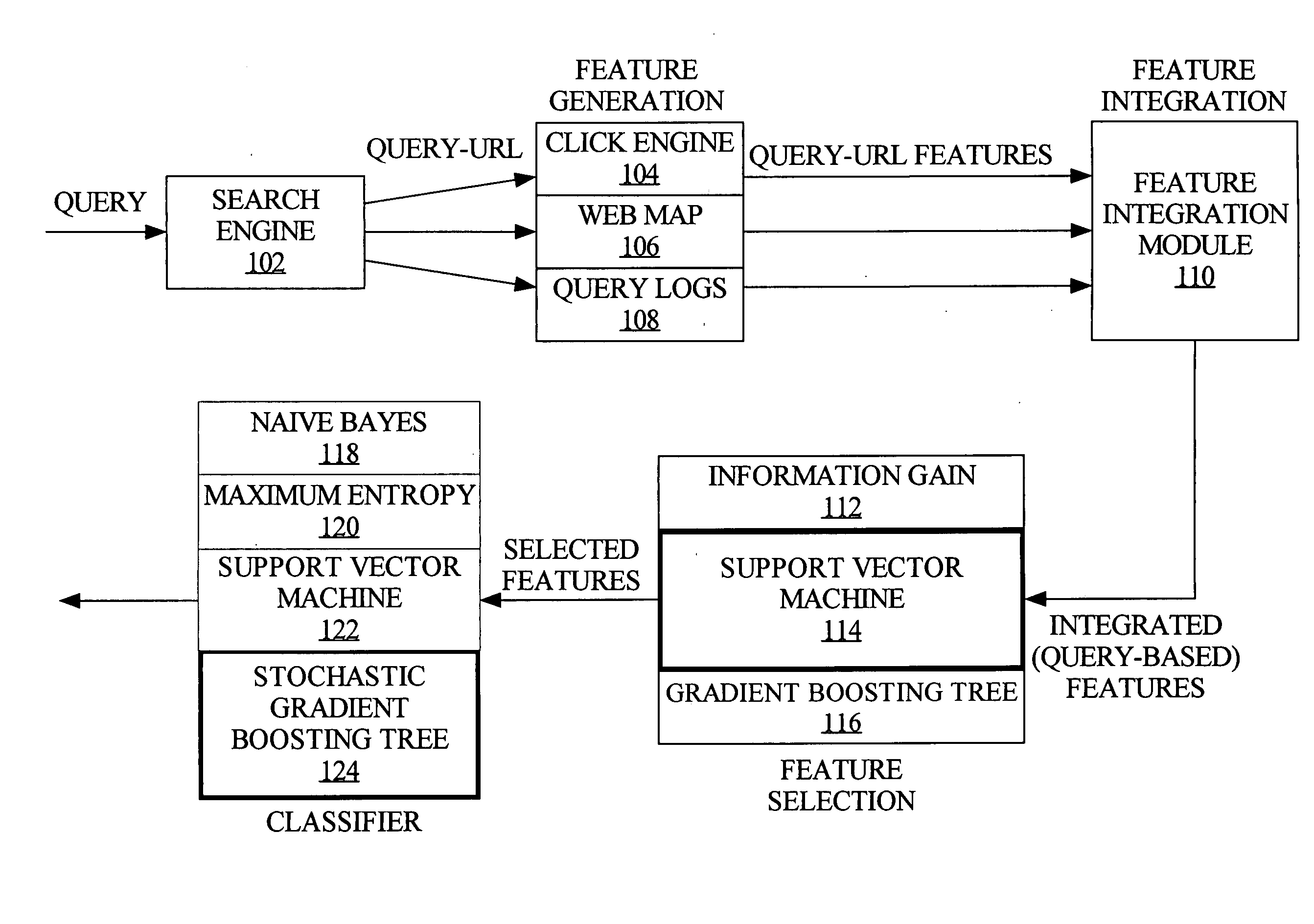
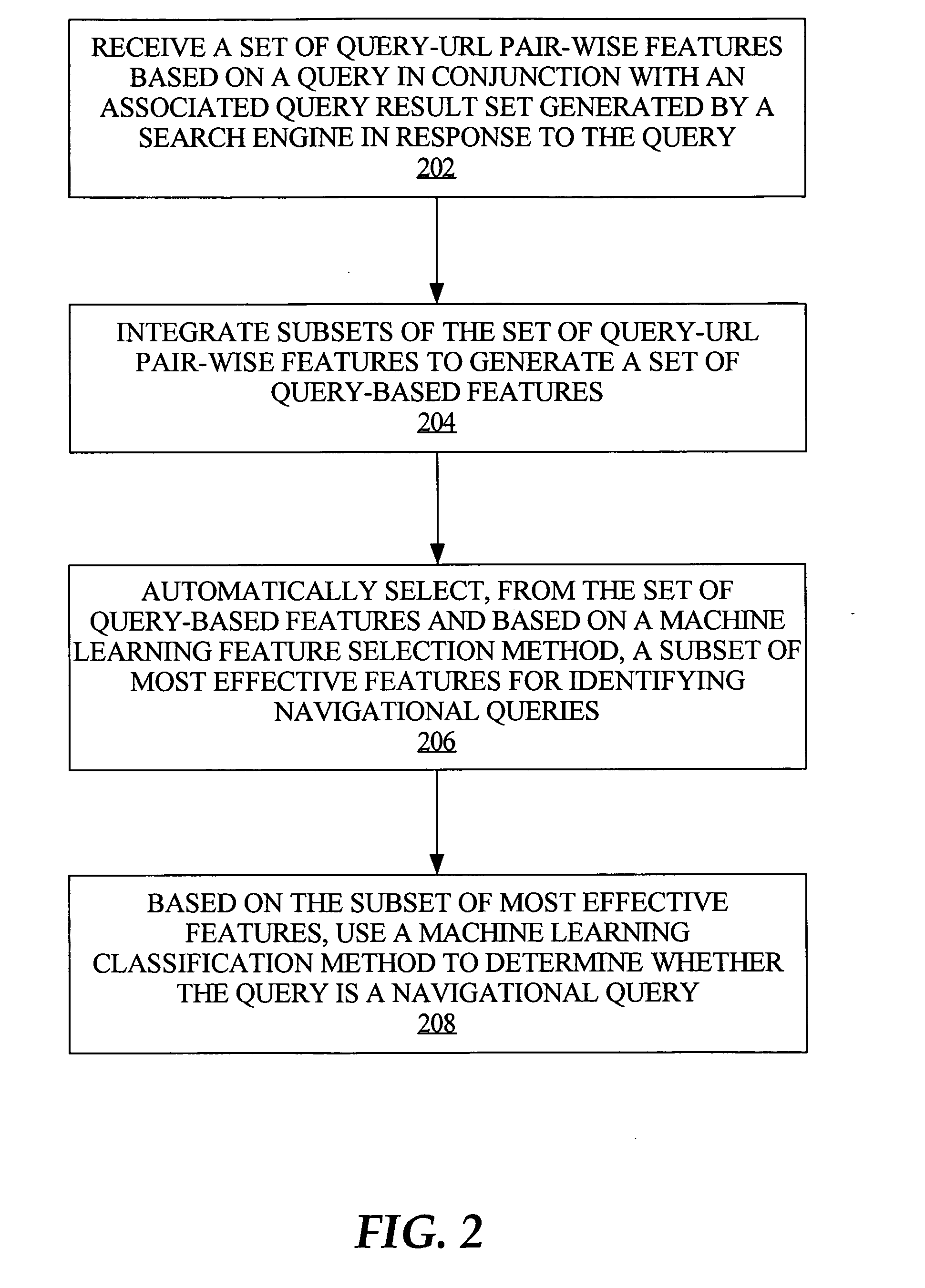
Techniques for navigational query identification
InactiveUS20080059508A1Web data indexingDigital data processing detailsThree levelSupport vector machine
To accurately classify a query as navigational, thousands of available features are explored, extracted from major commercial search engine results, user Web search click data, query log, and the whole Web's relational content. To obtain the most useful features for navigational query identification, a three level system is used which integrates feature generation, feature integration, and feature selection in a pipeline. Because feature selection plays a key role in classification methodologies, the best feature selection method is coupled with the best classification approach to achieve the best performance for identifying navigational queries. According to one embodiment, linear Support Vector Machine (SVM) is used to rank features and the top ranked features are fed into a Stochastic Gradient Boosting Tree (SGBT) classification method for identifying whether or not a particular query is a navigational query.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
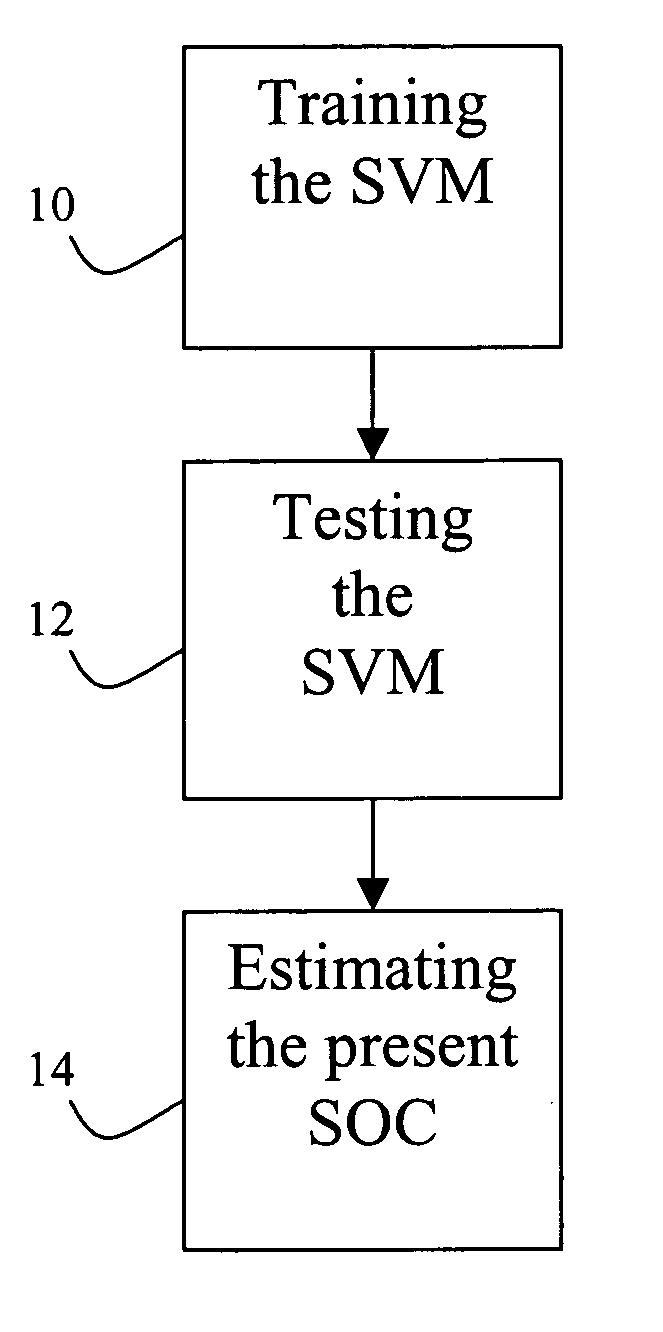
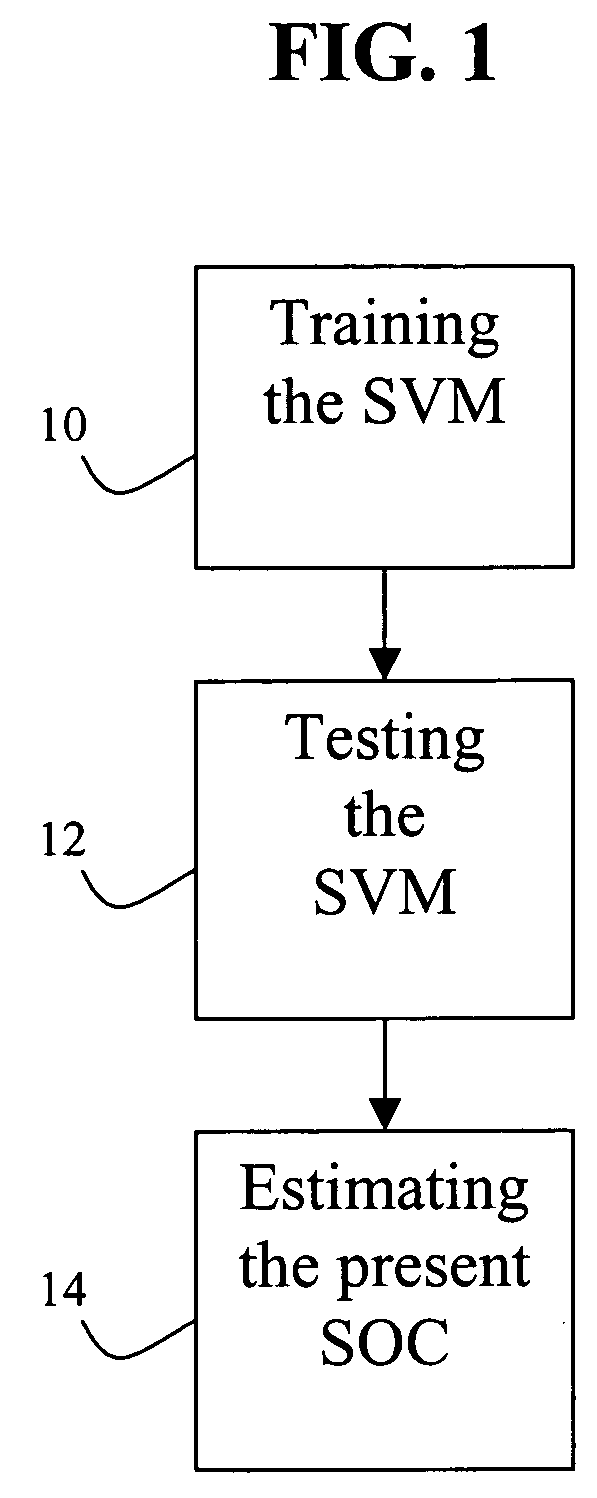
Apparatus and method for estimating battery state of charge
ActiveUS7197487B2Batteries circuit arrangementsDigital computer detailsBattery state of chargeSupport vector machine
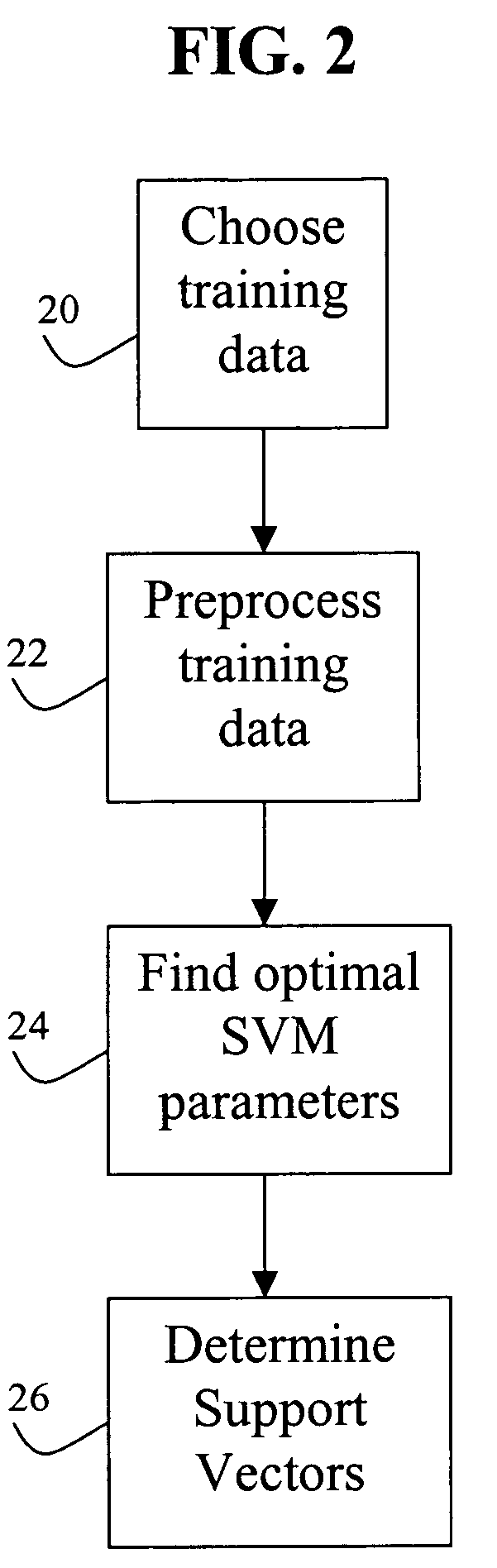
A method for training a support vector machine to determine a present state of charge of an electrochemical cell system includes choosing a training data, preprocessing the training data, finding an optimal parameter of the support vector machine, and determining support vectors.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Fundus image classification method and device of retinopathy
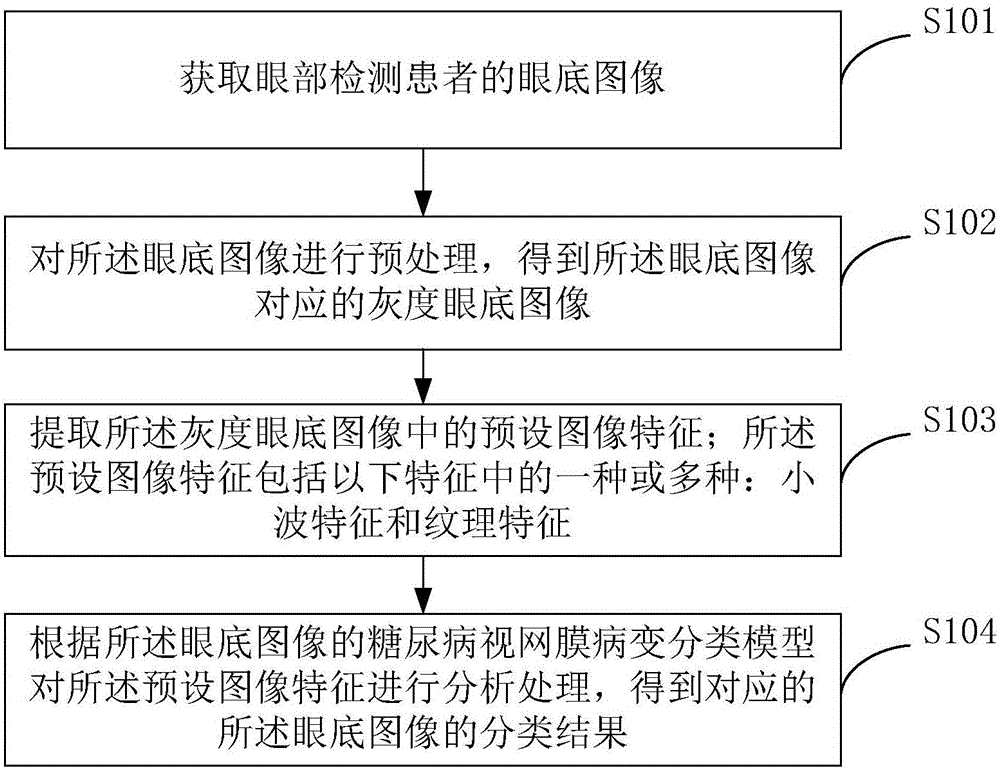
InactiveCN106530295AReduce workloadReduce high standardsImage enhancementImage analysisSupport vector machineDiabetes retinopathy
The present invention provides a fundus image classification method and device of retinopathy. The method comprises a step of obtaining the fundus image of an eye detection patient, a step of preprocessing the fundus image and obtaining a corresponding grey fundus image, a step of extracting a preset image characteristic in the grey fundus image, a step of analyzing the preset image characteristic according to the diabetic retinopathy classification model of the fundus image, and obtaining the classification result of the corresponding fundus image, a step of extracting the preset image characteristic in the preprocessed grey fundus image, and carrying out prediction classification on the above preset image characteristic through the diabetic retinopathy classification model established according to a support vector machine and a deep neural network so as to obtain a final classification result. The artificial participation is not needed in the whole process, the workload of doctors is reduced, the high standard requirement of the medical qualification level of the doctor is reduced, the accuracy of classification is improved, and the method and the device have great significance for specific applications and medical research.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com