Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4045 results about "Troubleshooting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Troubleshooting is a form of problem solving, often applied to repair failed products or processes on a machine or a system. It is a logical, systematic search for the source of a problem in order to solve it, and make the product or process operational again. Troubleshooting is needed to identify the symptoms. Determining the most likely cause is a process of elimination—eliminating potential causes of a problem. Finally, troubleshooting requires confirmation that the solution restores the product or process to its working state.
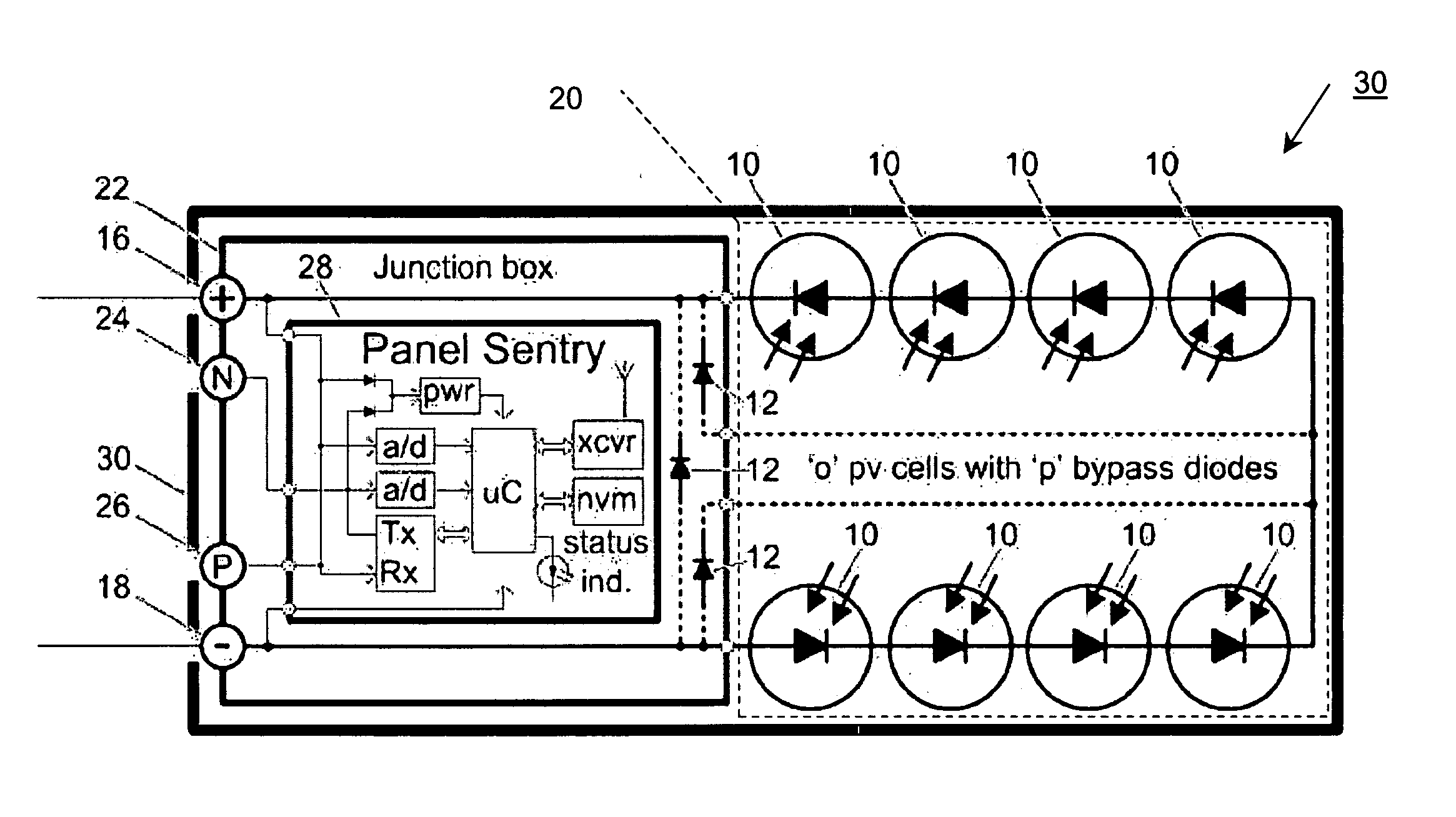
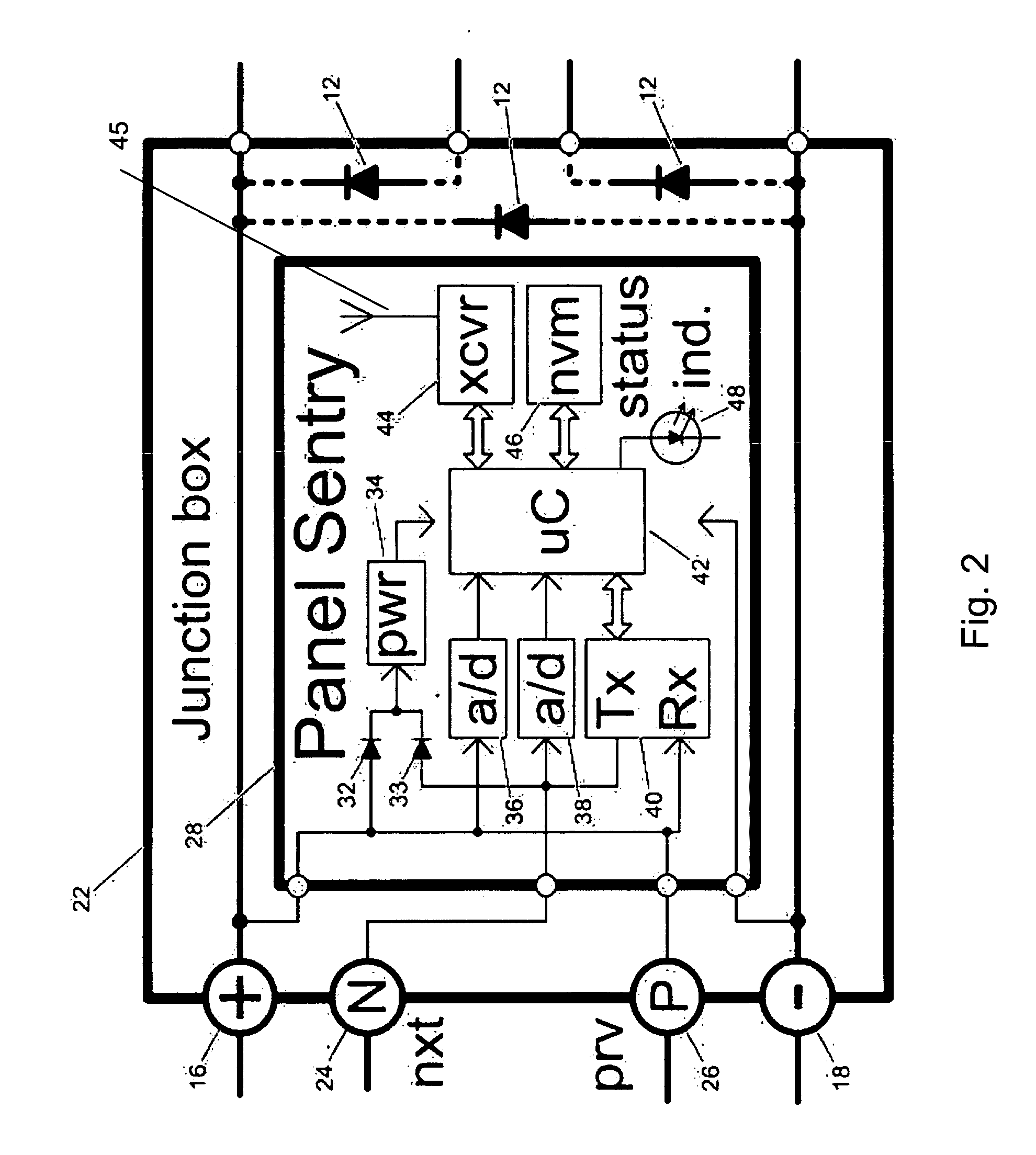
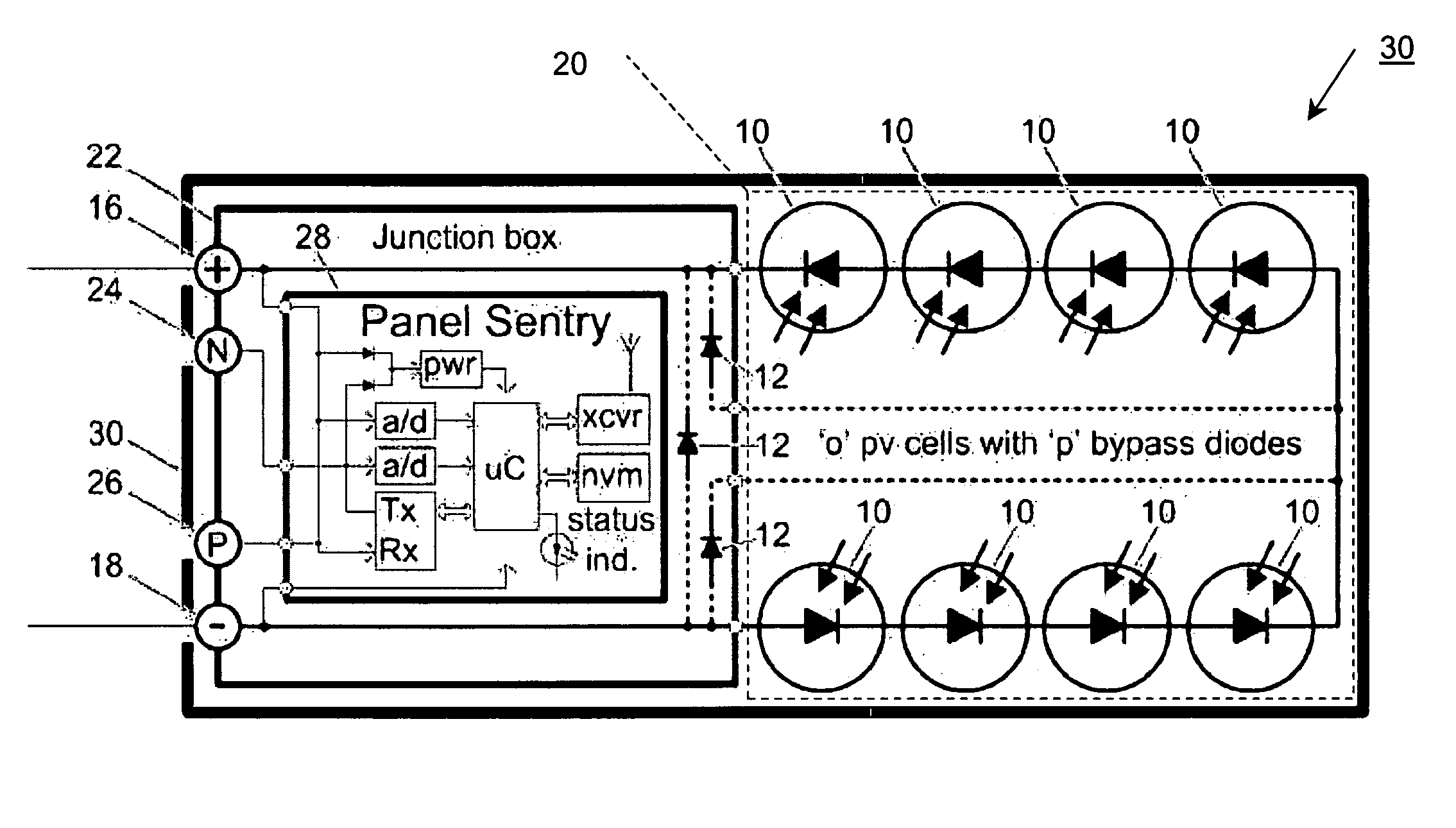
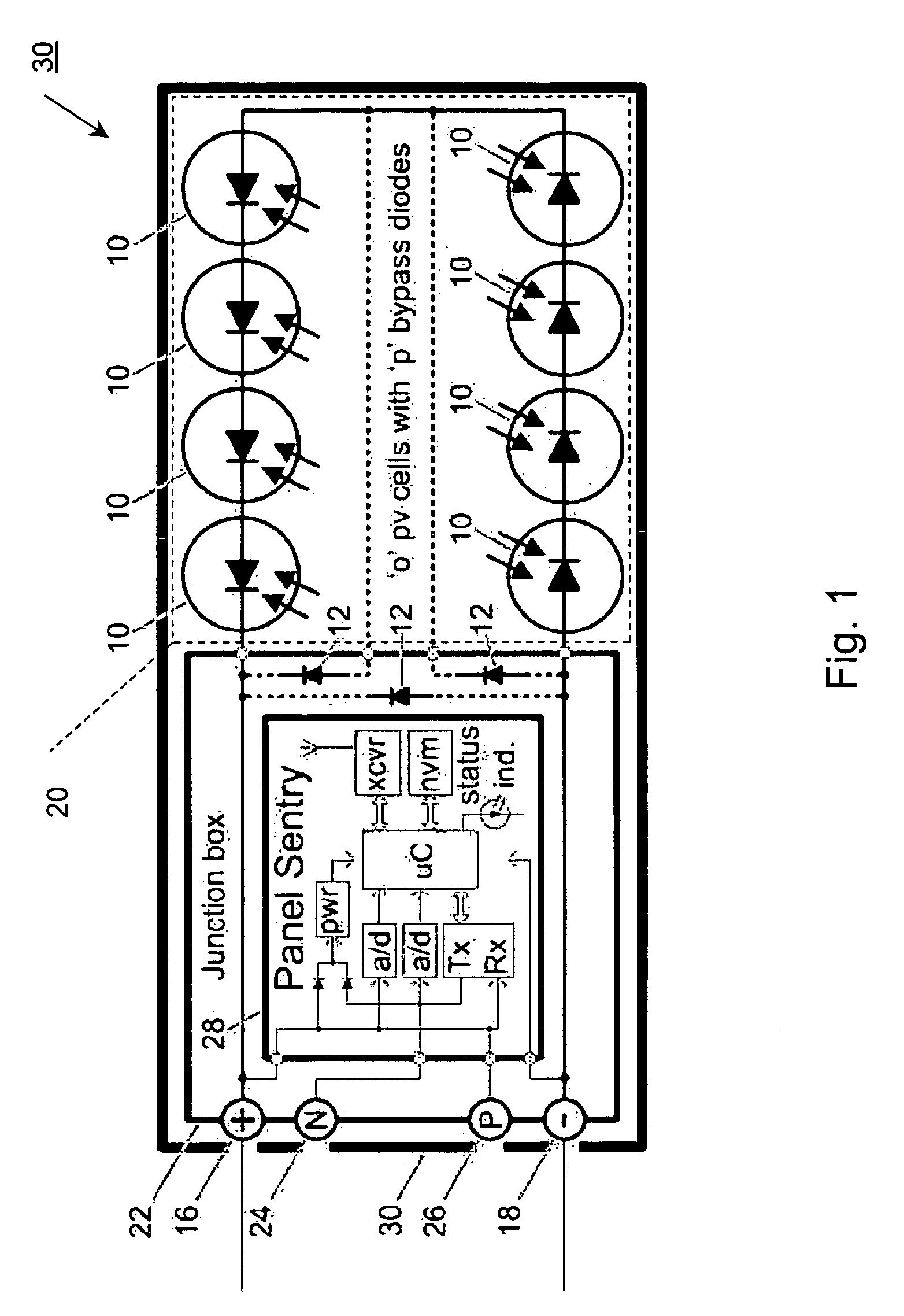
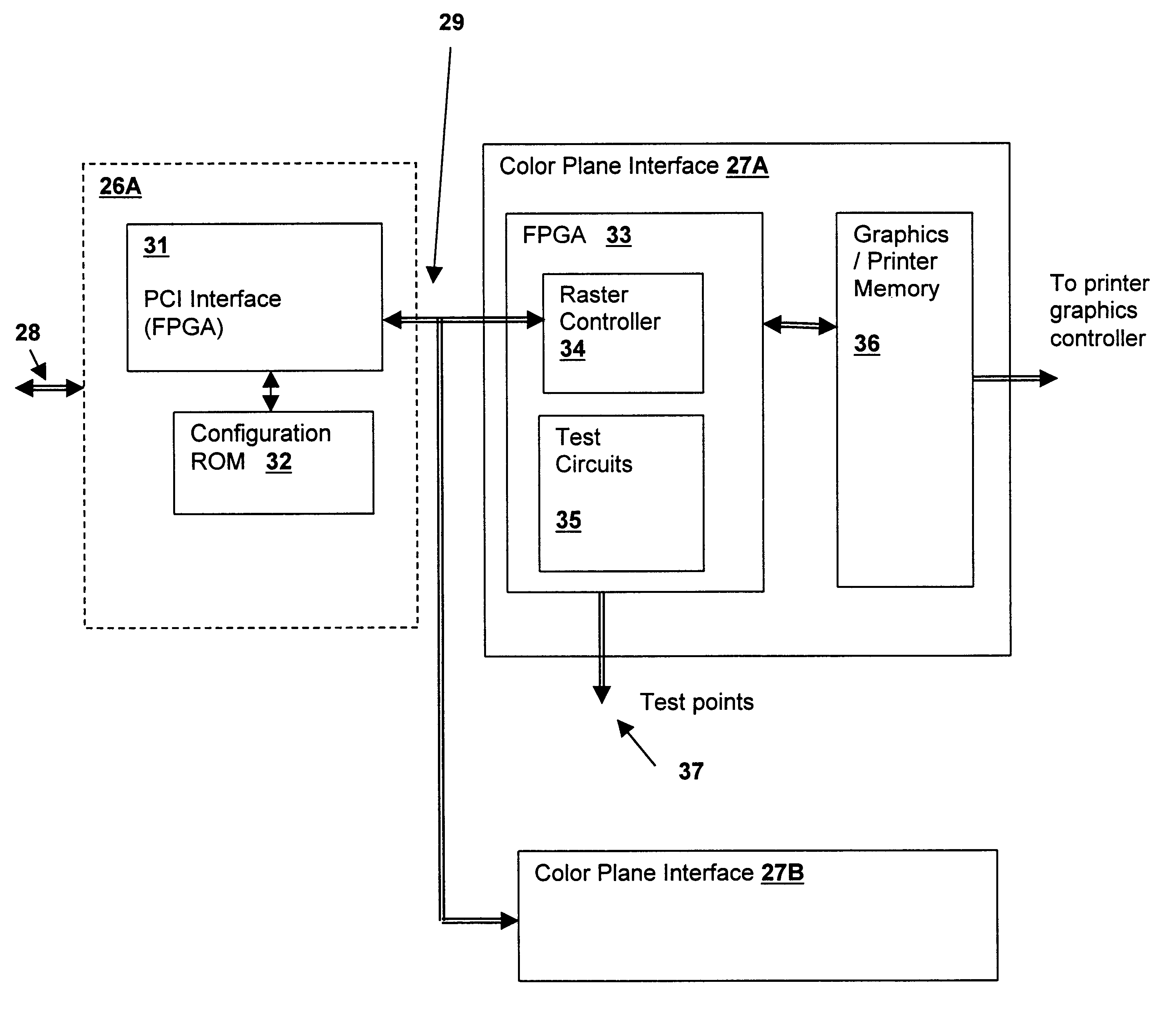
System and method for monitoring photovoltaic power generation systems
InactiveUS20060162772A1Batteries circuit arrangementsPhotovoltaic monitoringDiagnostic dataEngineering
A system and method for monitoring photovoltaic power generation systems or arrays, both on a local (site) level and from a central location. The system includes panel and string combiner sentries or intelligent devices, in bidirectional communication with a master device on the site to facilitate installation and troubleshooting of faults in the array, including performance monitoring and diagnostic data collection.
Owner:SOLAR SENTRY
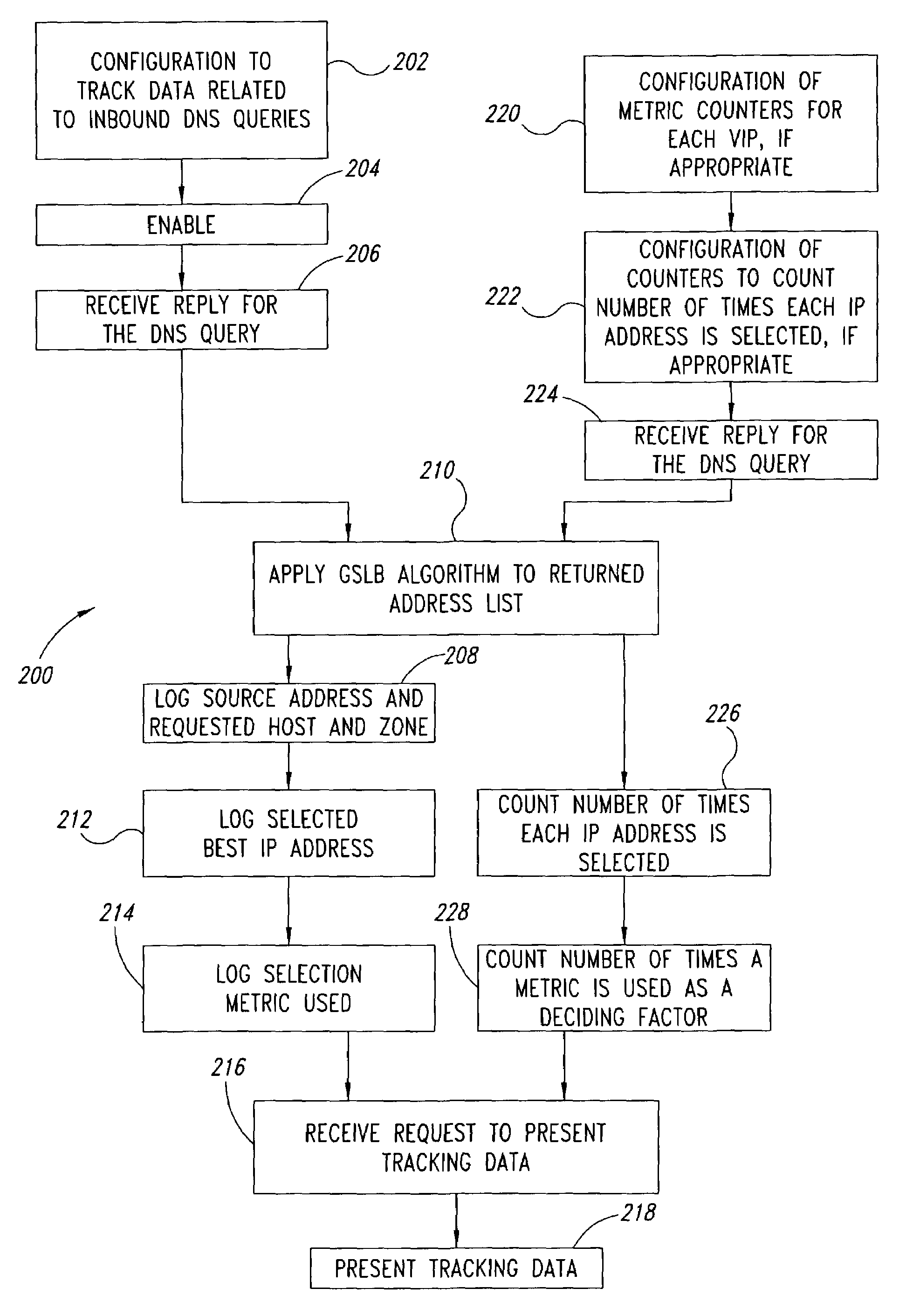
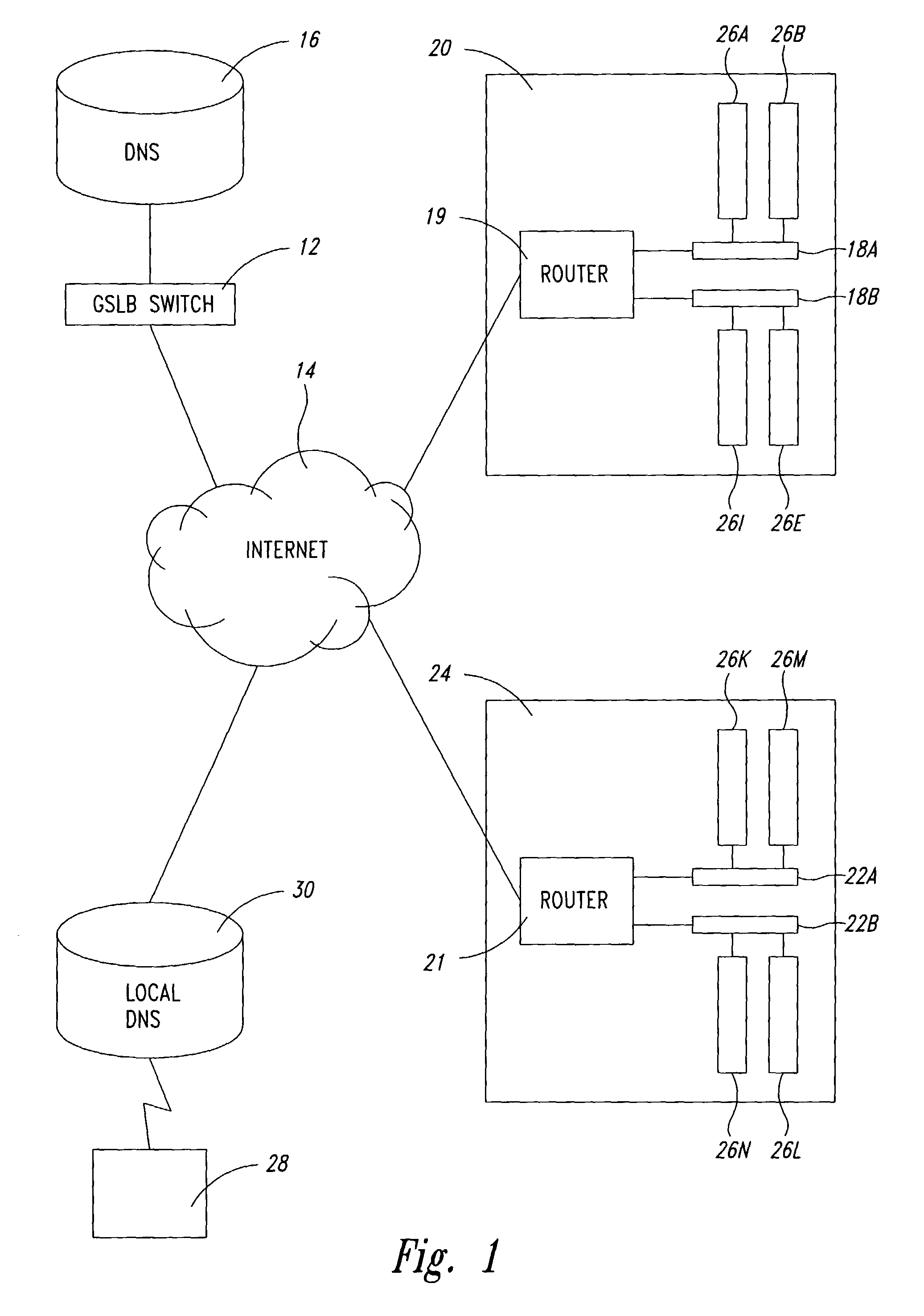
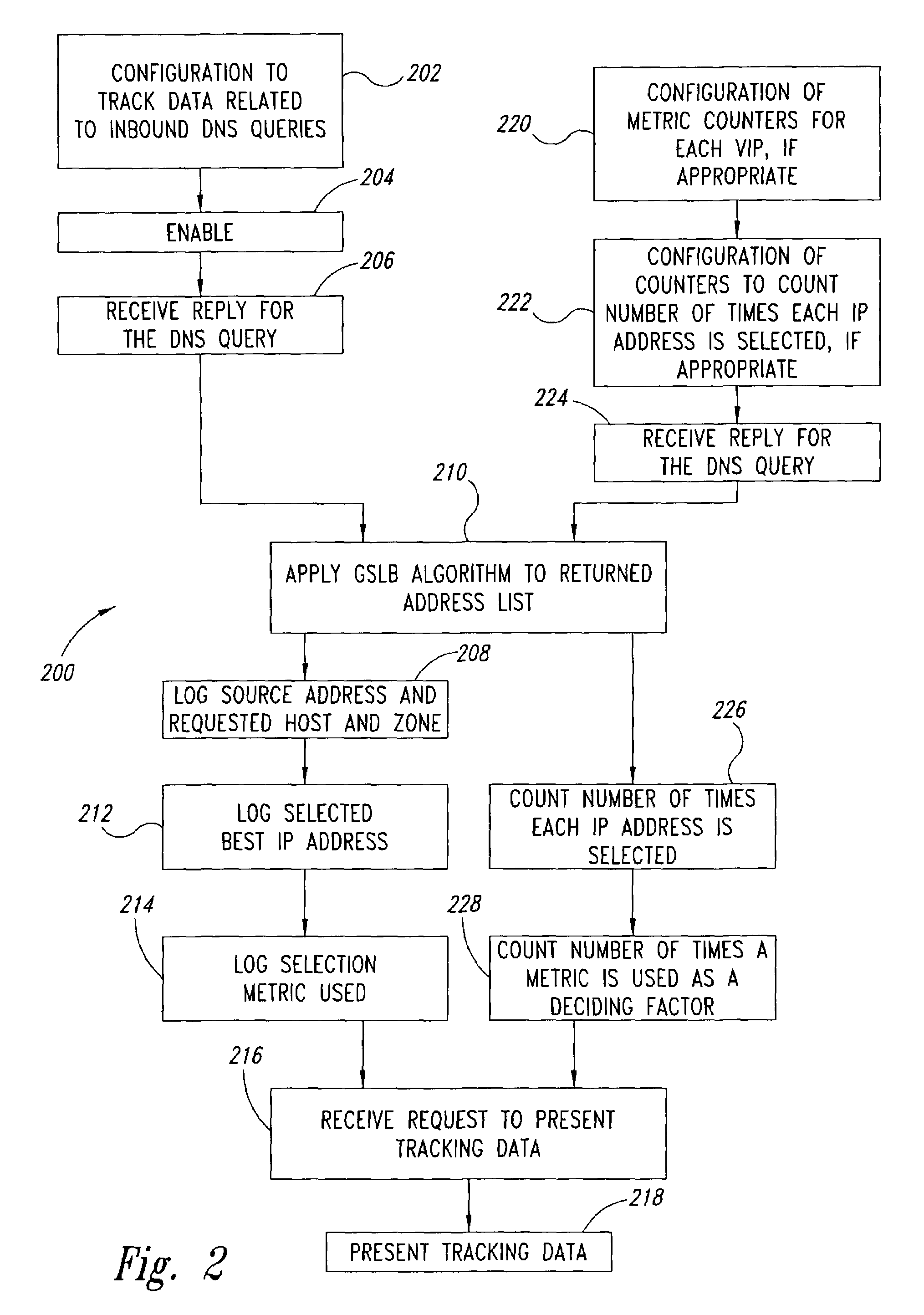
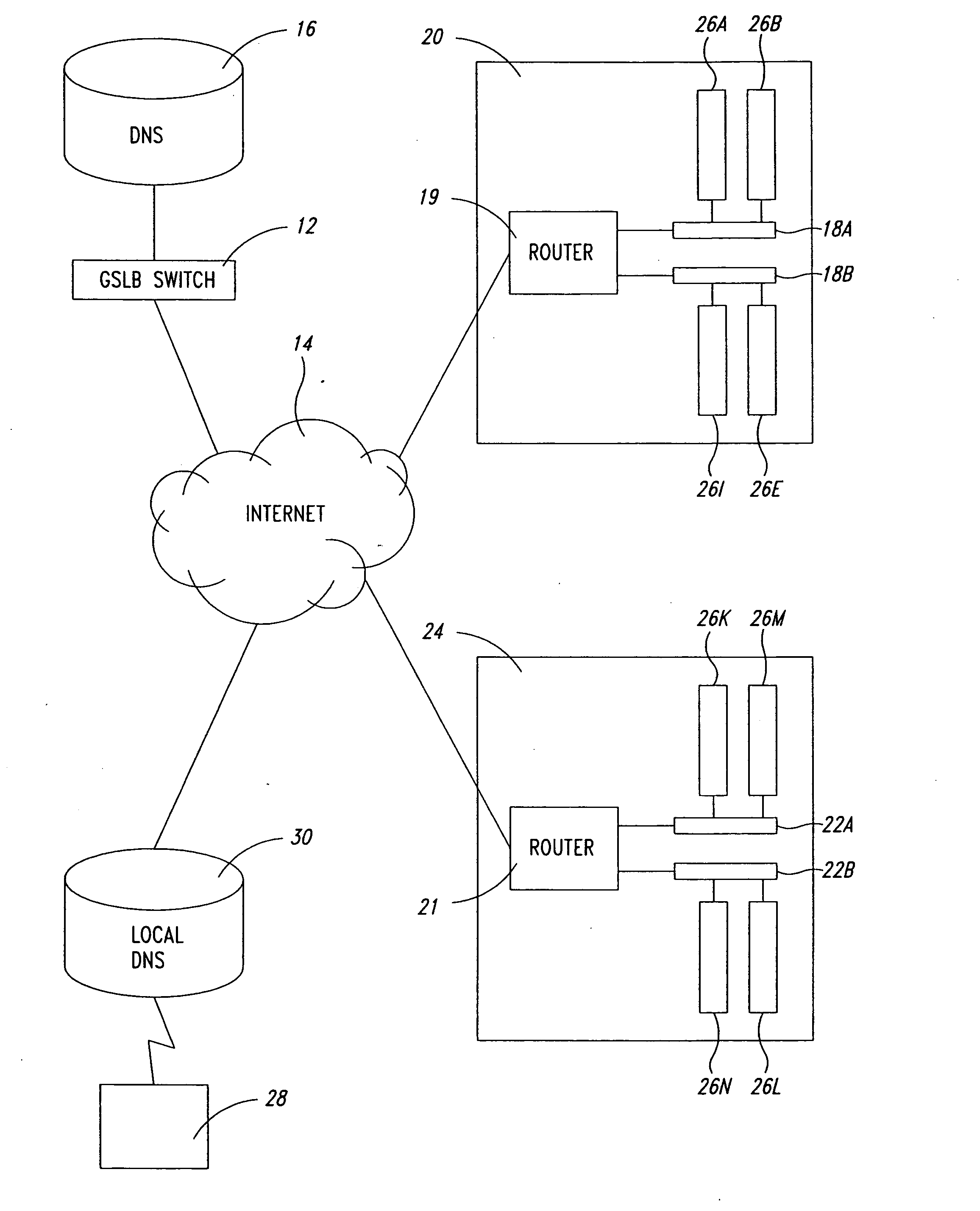
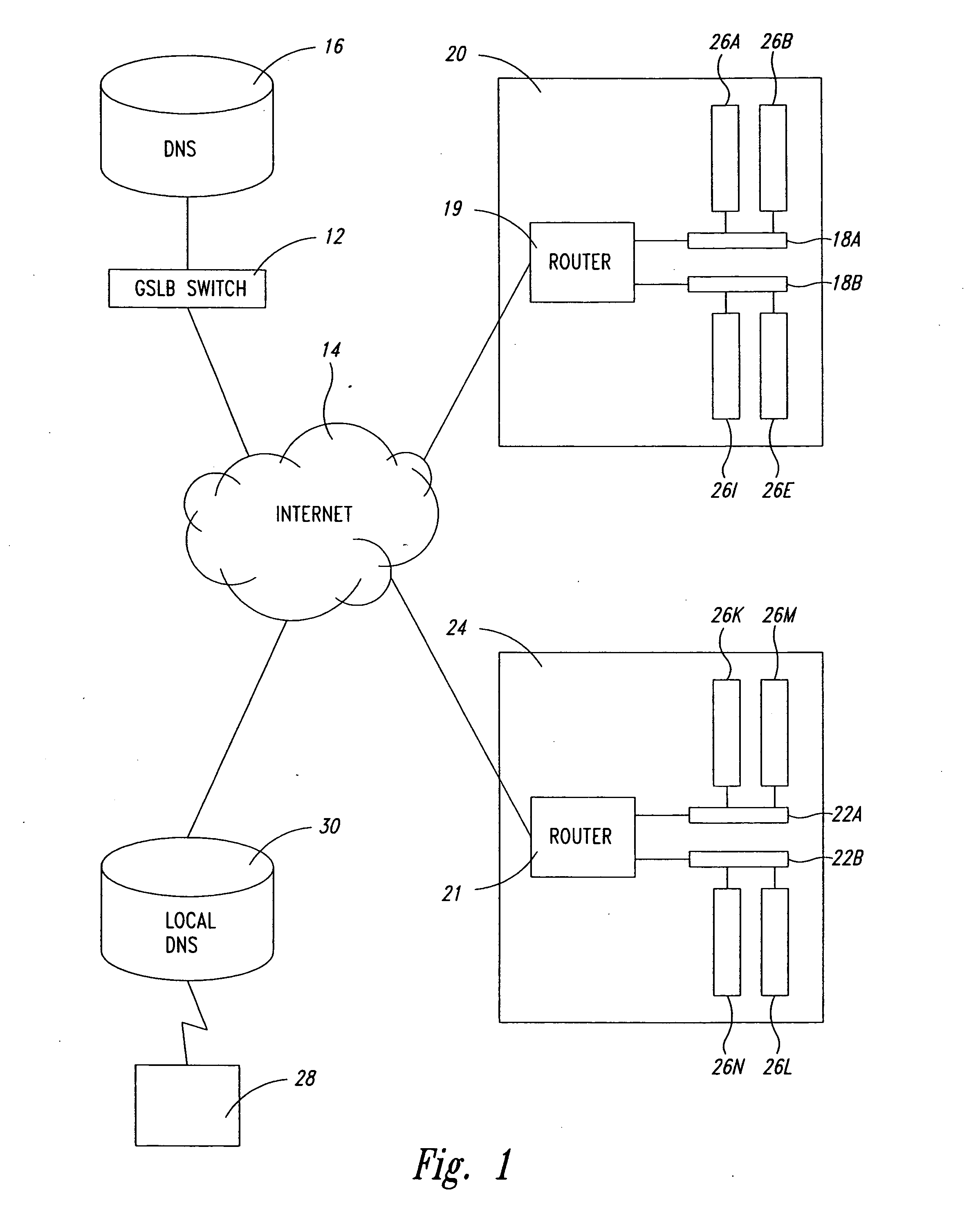
Statistical tracking of global server load balancing for selecting the best network address from ordered list of network addresses based on a set of performance metrics
ActiveUS7086061B1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsPolicy decisionIp address
Server load-balancing operation-related data, such as data associated with a system configured for global server load balancing (GSLB) that orders IP addresses into a list based on a set of performance metrics, is tracked. Such operation-related data includes inbound source IP addresses (e.g., the address of the originator of a DNS request), the requested host and zone, identification of the selected “best” IP addresses resulting from application of a GSLB algorithm and the selection metric used to decide on an IP address as the “best” one. Furthermore, the data includes a count of the selected “best” IP addresses selected via application of the GSLB algorithm, and for each of these IP addresses, the list of deciding performance metrics, along with a count of the number of times each of these metrics in the list was used as a deciding factor in selection of this IP address as the best one. This tracking feature allows better understanding of GSLB policy decisions (such as those associated with performance, maintenance, and troubleshooting) and intelligent deployment of large-scale resilient GSLB networks.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
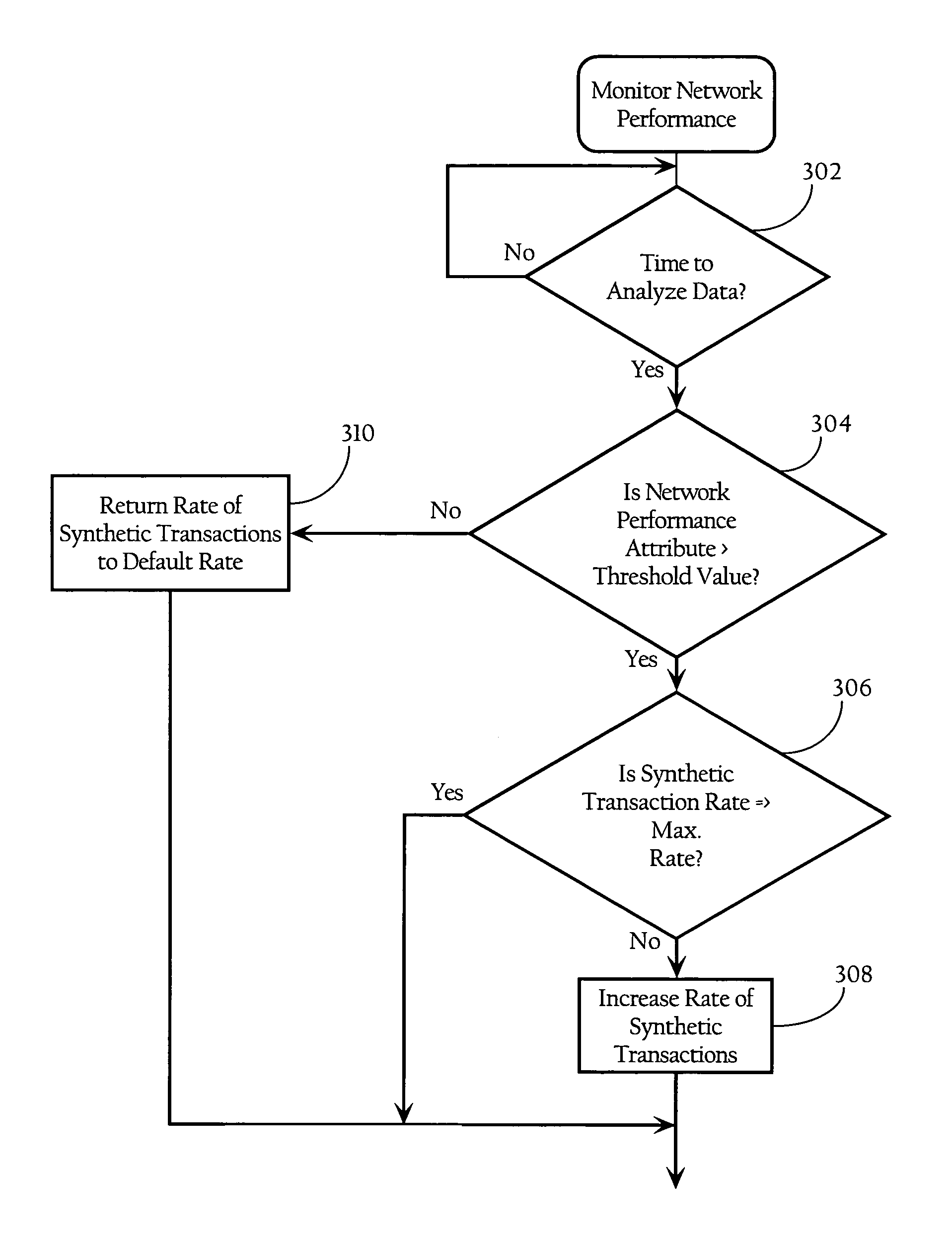
Adaptive correlation of service level agreement and network application performance
InactiveUS7822837B1Easy to useReduce network loadDigital computer detailsData switching networksService-level agreementWeb tracking
Methods, apparatuses and systems directed to adaptive monitoring of network application performance. In one implementation, the present invention improves processes used by enterprises to track, manage, and troubleshoot performance of network applications across distributed networks. In one implementation, the present invention allows for a network application performance monitoring scheme that tracks end-to-end performance of selected network applications on a passive basis, while selectively engaging more invasive (synthetic) approaches to tracking performance and troubleshooting issues when needed.
Owner:CA TECH INC
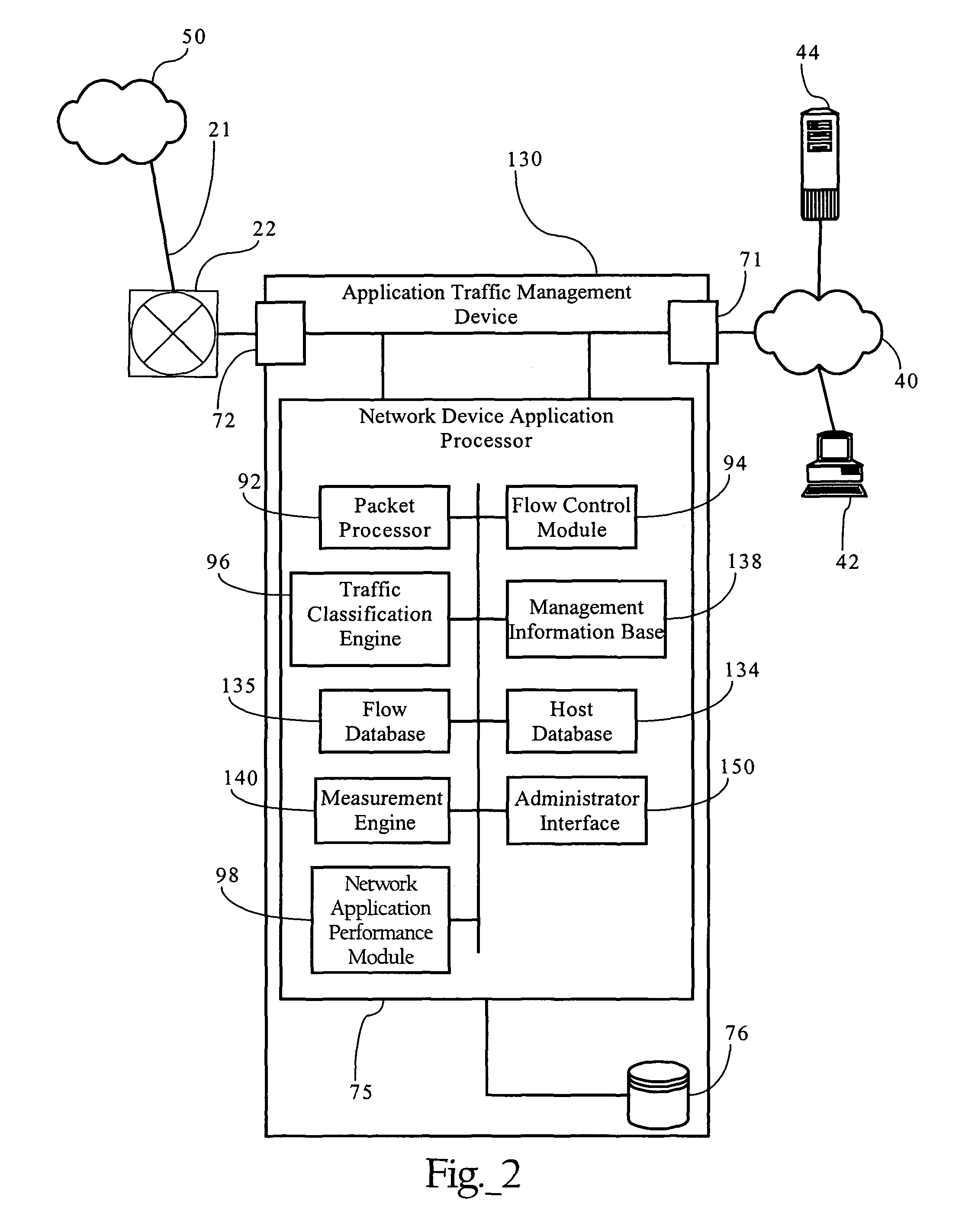
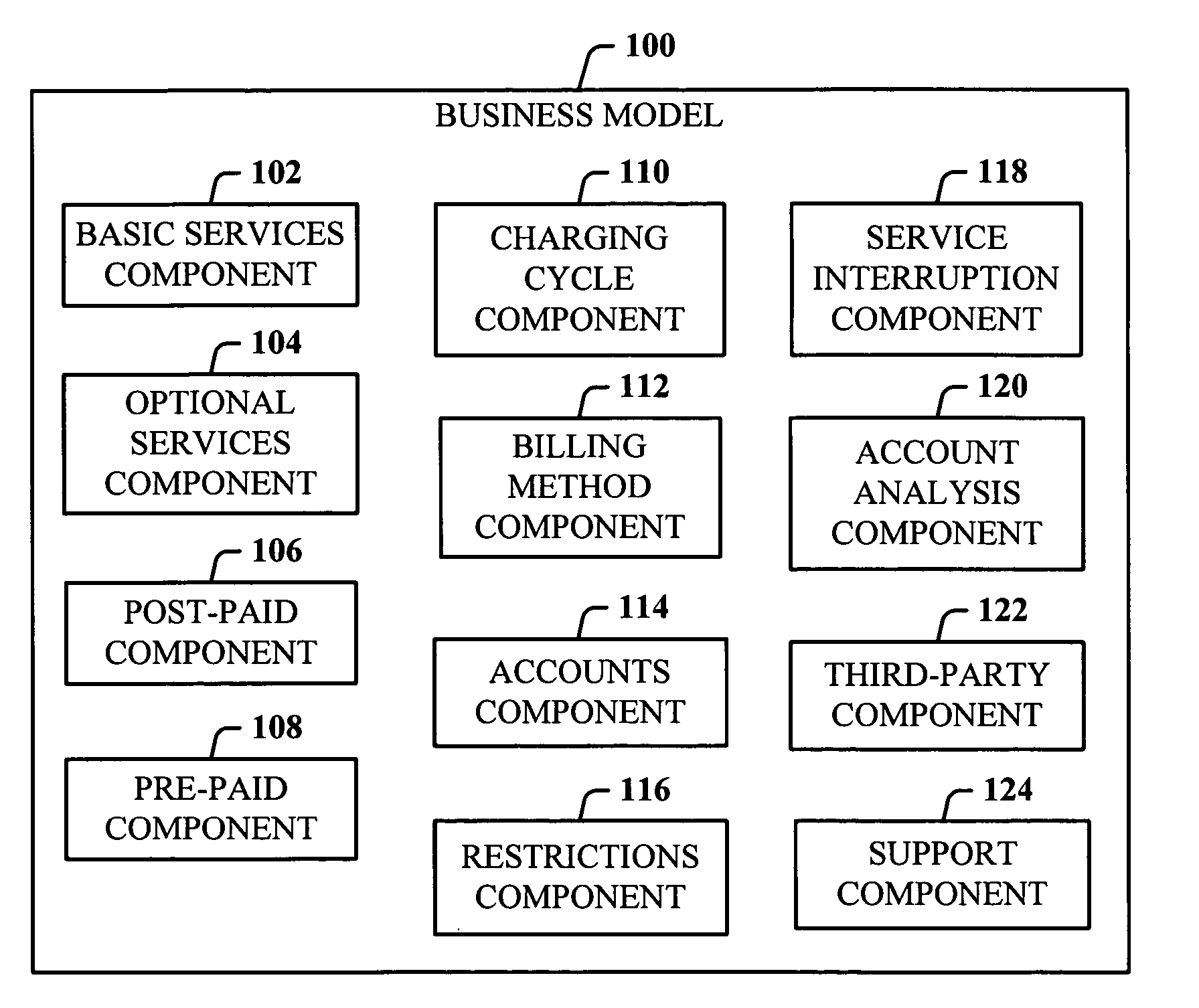
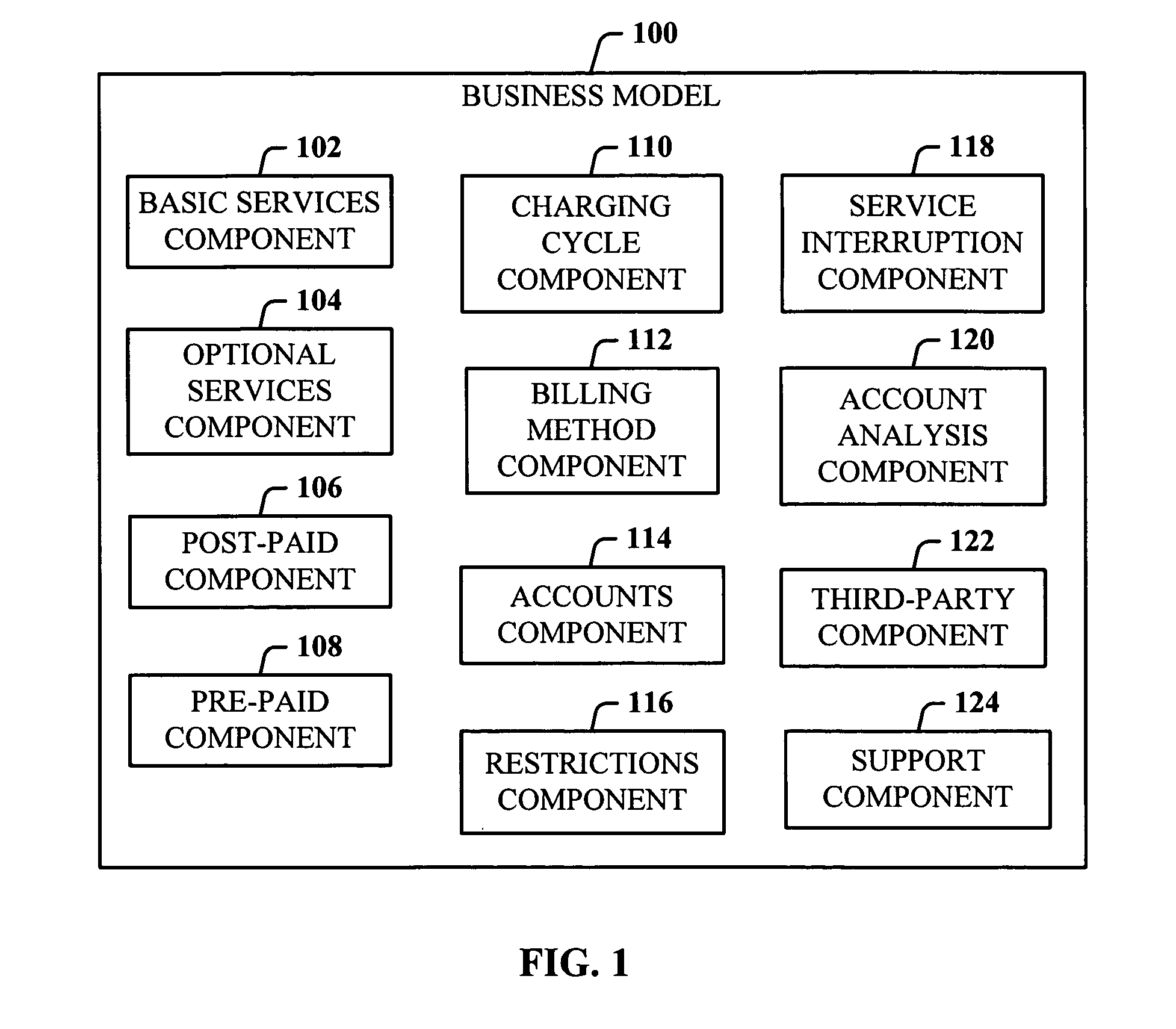
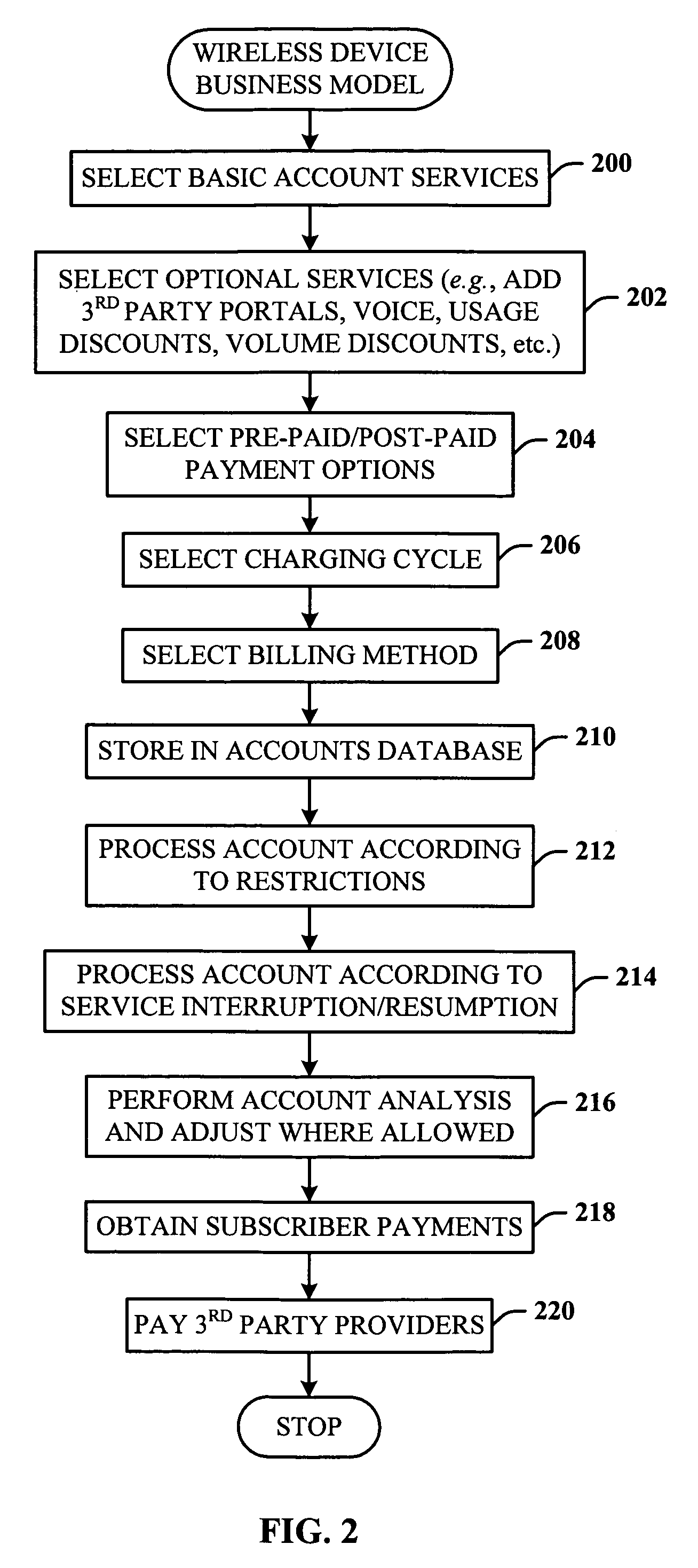
Dedicated wireless device business method
InactiveUS20060019632A1Easy accessAccounting/billing servicesTelephonic communicationThird partyComputer compatibility
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
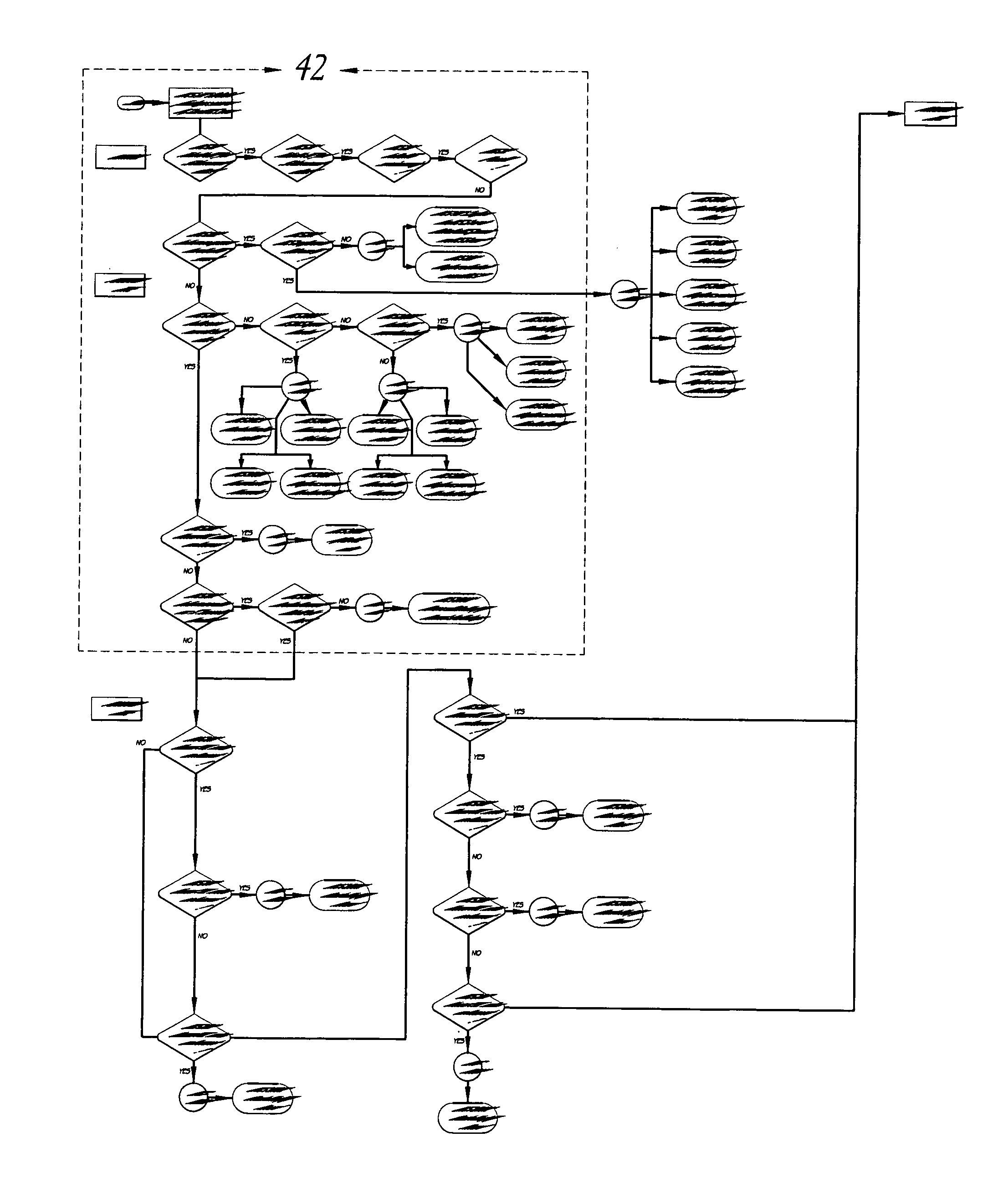
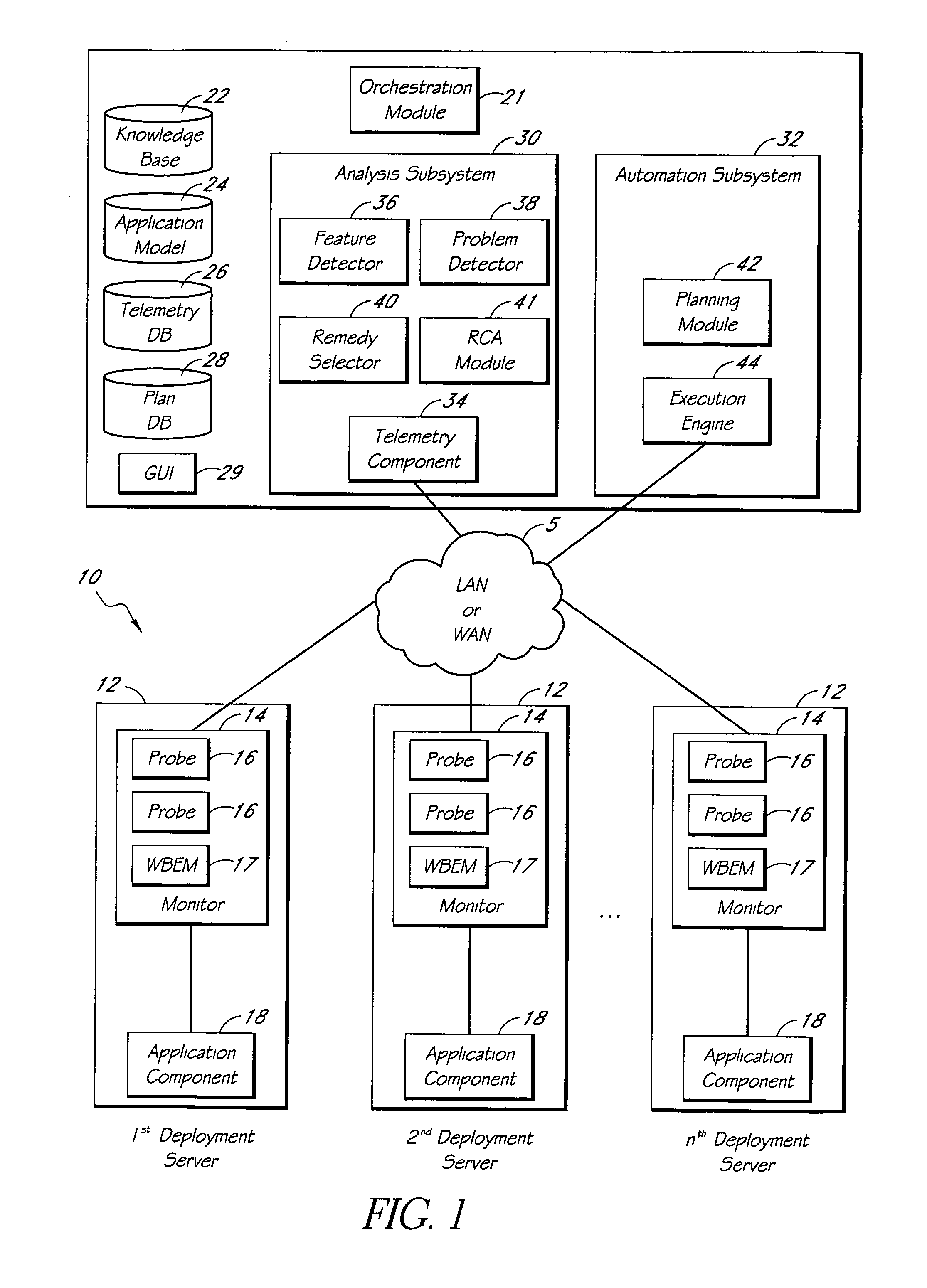
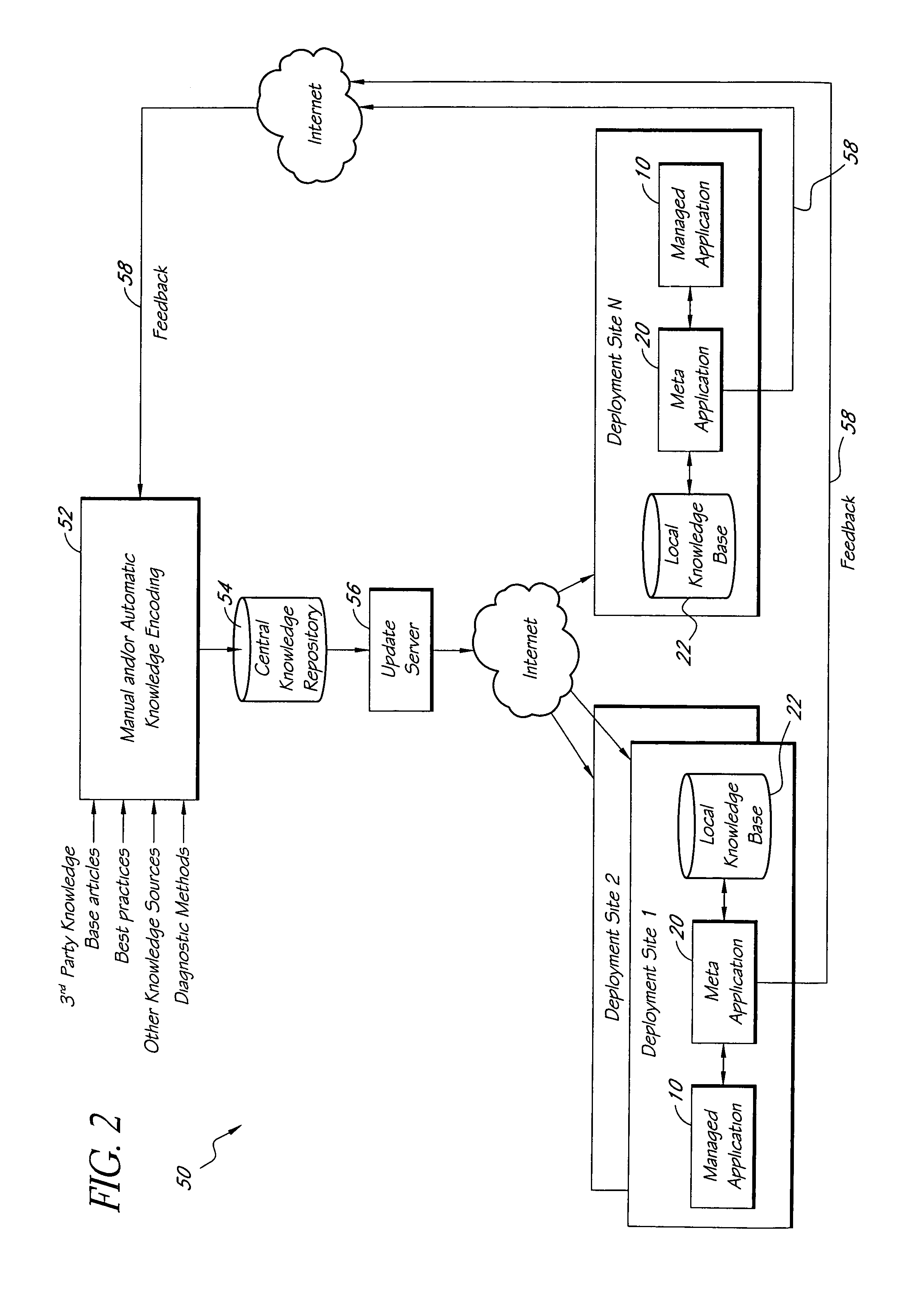
Systems and methods for encoding knowledge for automated management of software application deployments
ActiveUS7490073B1Efficient mappingGreat leverageError detection/correctionChaos modelsKnowledge sourcesSoftware
A method of encoding knowledge is disclosed, which can be used to automatically detect problems in software application deployments. The method includes accessing a source of knowledge describing a problem known to occur in deployments of a particular software application, and which identifies a plurality of conditions associated with the problem. An encoded representation of the knowledge source is generated according to a predefined knowledge encoding methodology. The encoded representation is adapted to be applied automatically by a computer to analyze data representing a current state of a monitored deployment of the software application to detect whether the conditions and the problem exist therein. In various implementations, the encoded representation of the knowledge can include queries for deployment information, information concerning the relative importance of the conditions to a detection of the problem, and / or logical constructs for computing a confidence value in the existence of the problem and for determining whether to report the problem if some of the conditions are not true. The knowledge source can comprise a text document (such as a knowledge base article), a flowchart of a diagnostic troubleshooting method, and the like. Also disclosed are methods of at least partially automating the encoding process.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
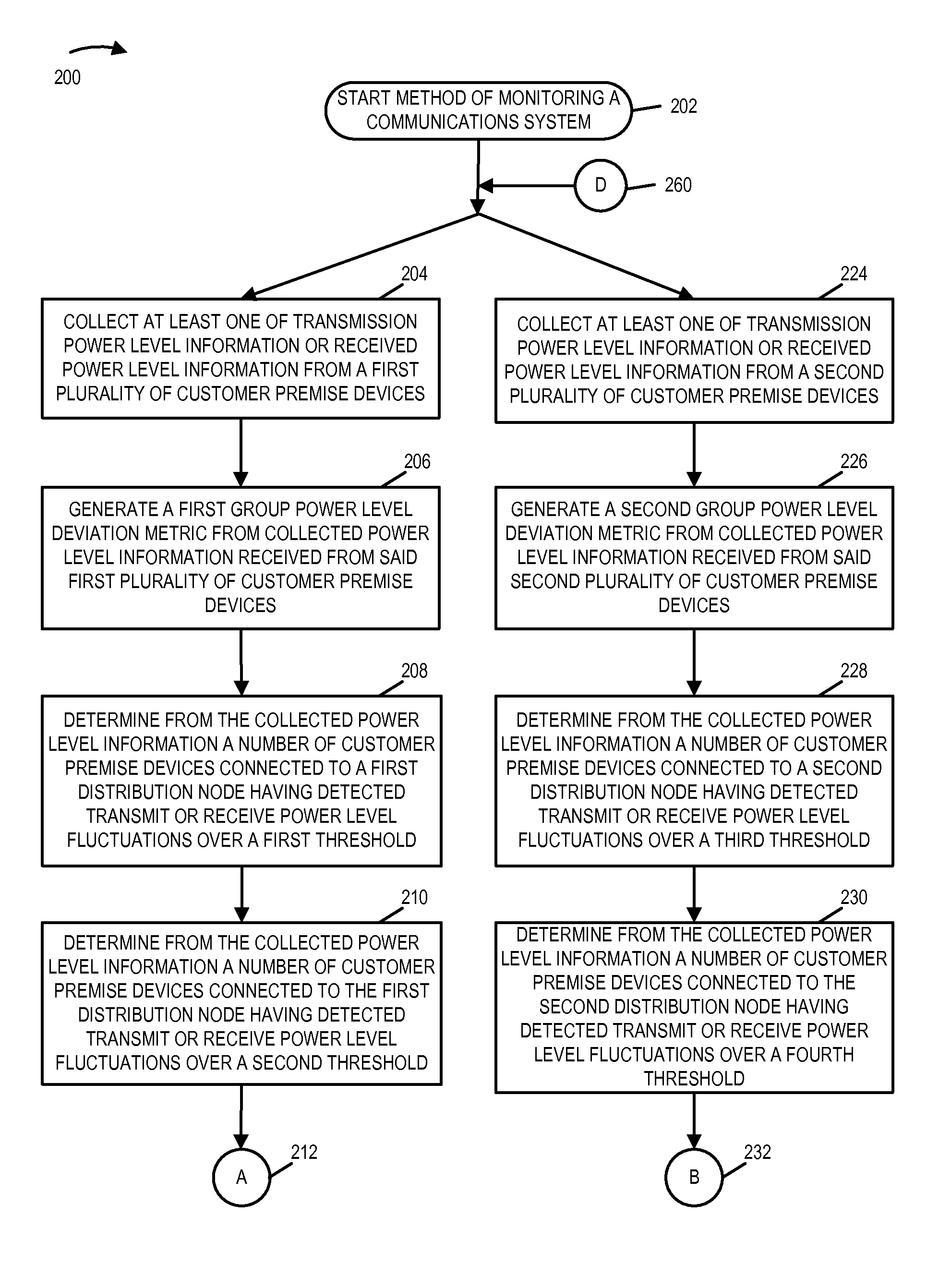
Power fluctuation detection and analysis
ActiveUS20150358222A1Easy to identifyEasy to detectError preventionTransmission systemsEngineeringClient-side
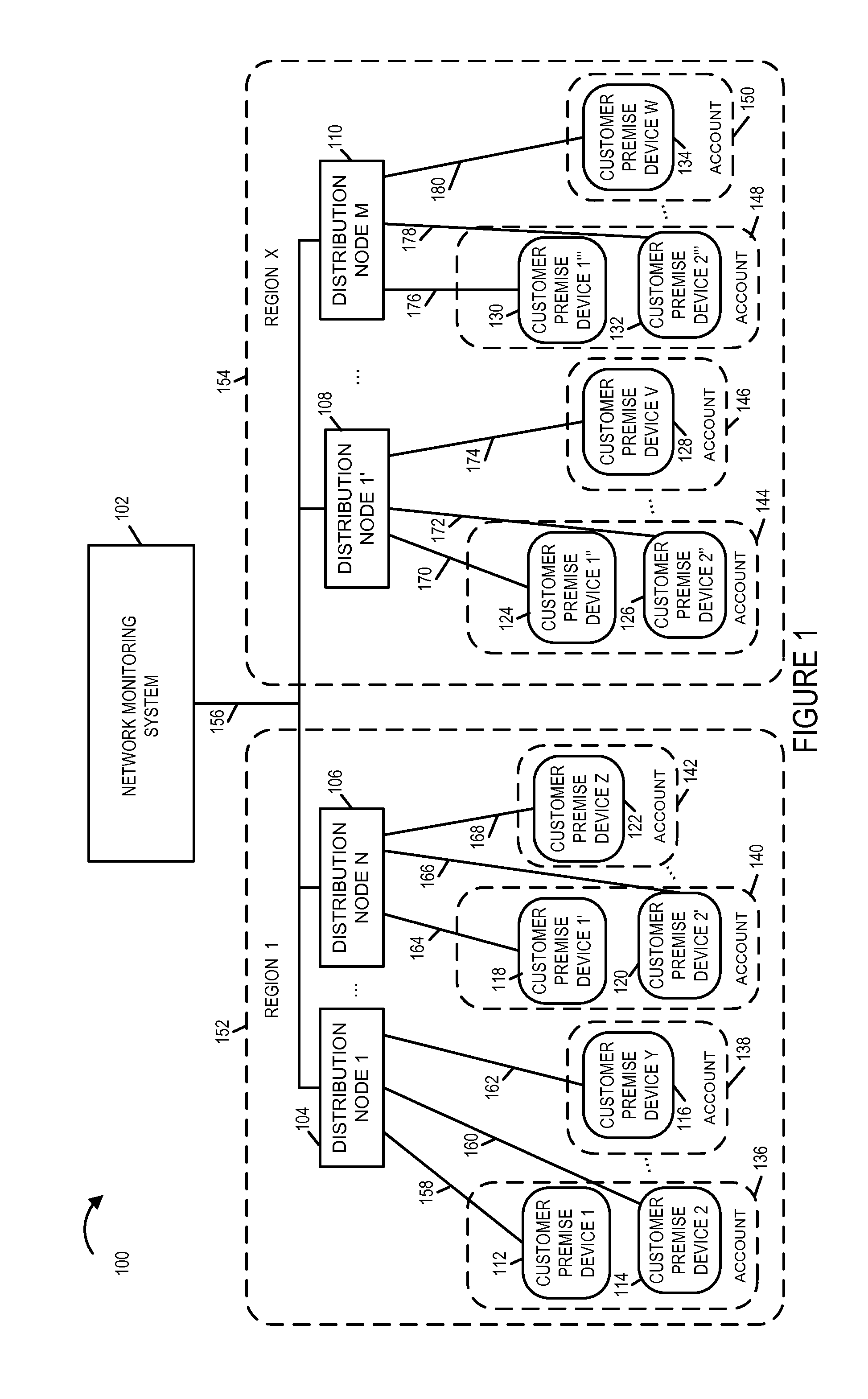
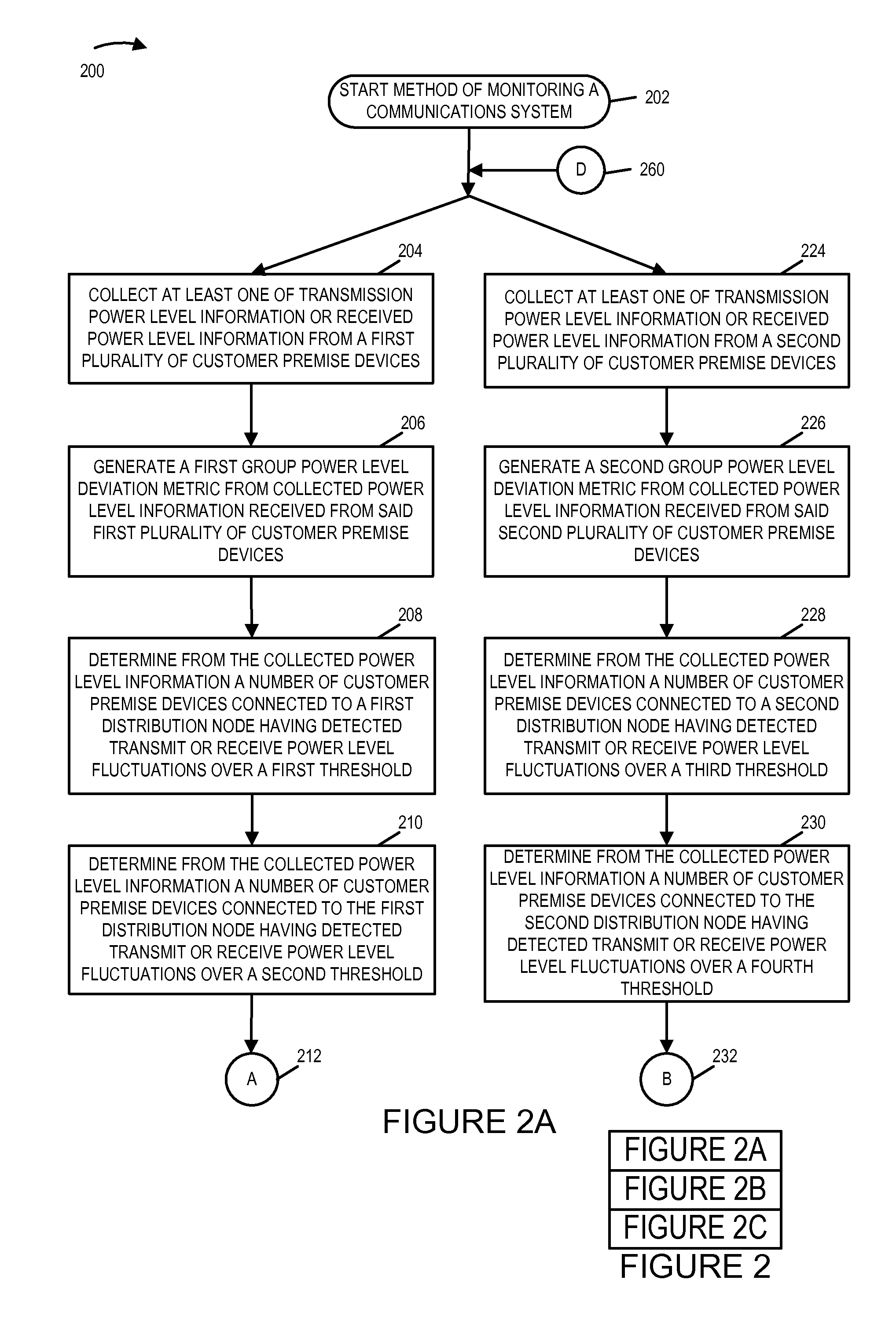
The network monitoring system collects transmission and / or receive power level information from a plurality of customer premise devices connected to the same distribution node for each of a plurality of network distribution nodes. For an individual network distribution node, the network monitoring system calculates a set of fluctuation parameters including a group power level deviation metric, e.g., a modified standard deviation ratio. The network monitoring system evaluates the generated fluctuation parameters and responds, e.g., outputting a fluctuations report, modifying a data collection profile being used by a set of customer premise devices corresponding to a distribution node, commanding diagnostics to be performed on a portion of the network and / or directing a service technician. The network monitoring system compares generated fluctuation parameters corresponding to different distribution nodes, and uses the results of the comparison to assign priority with regard to the assignment of limited available troubleshooting and repair resources.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
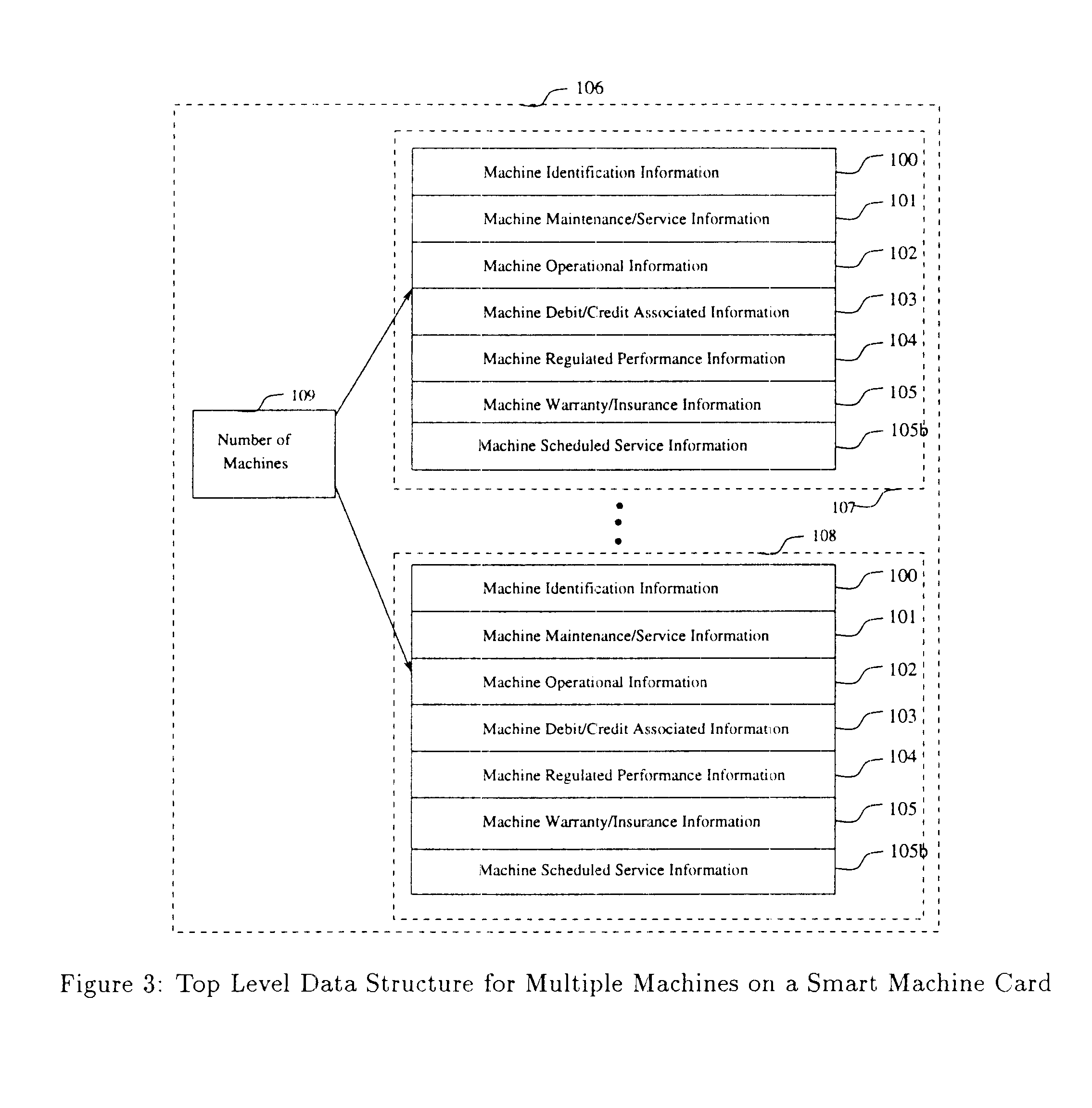
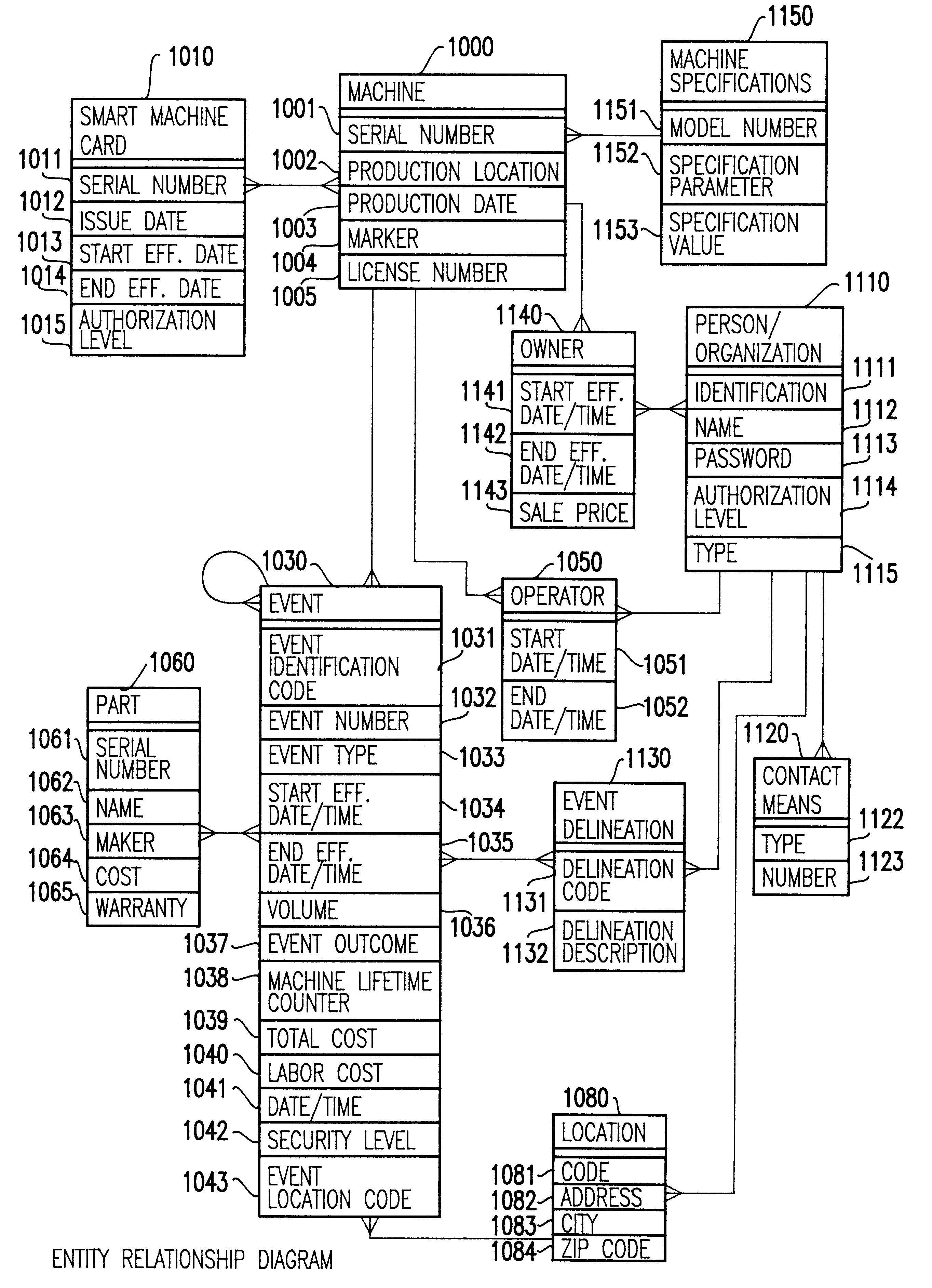
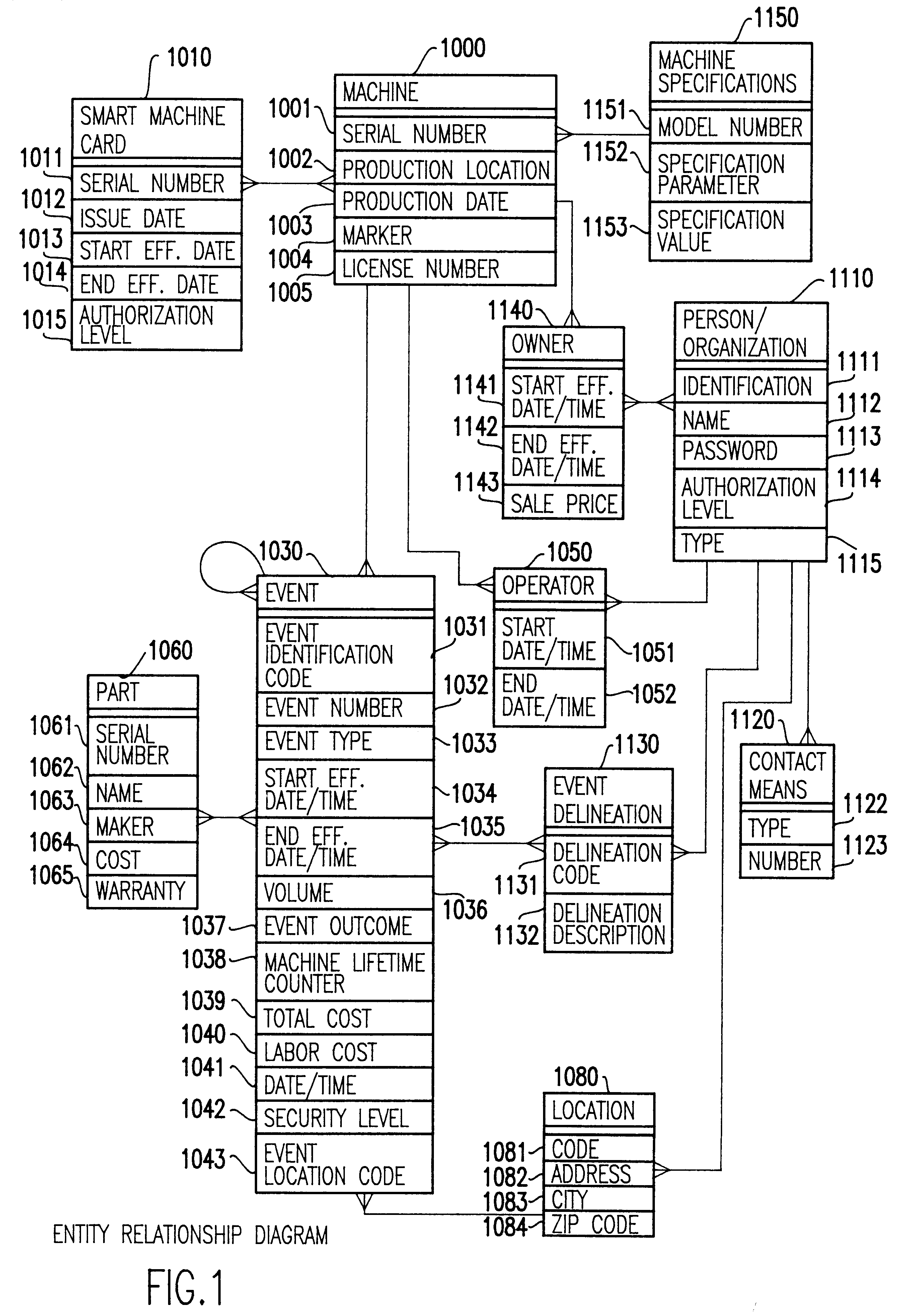
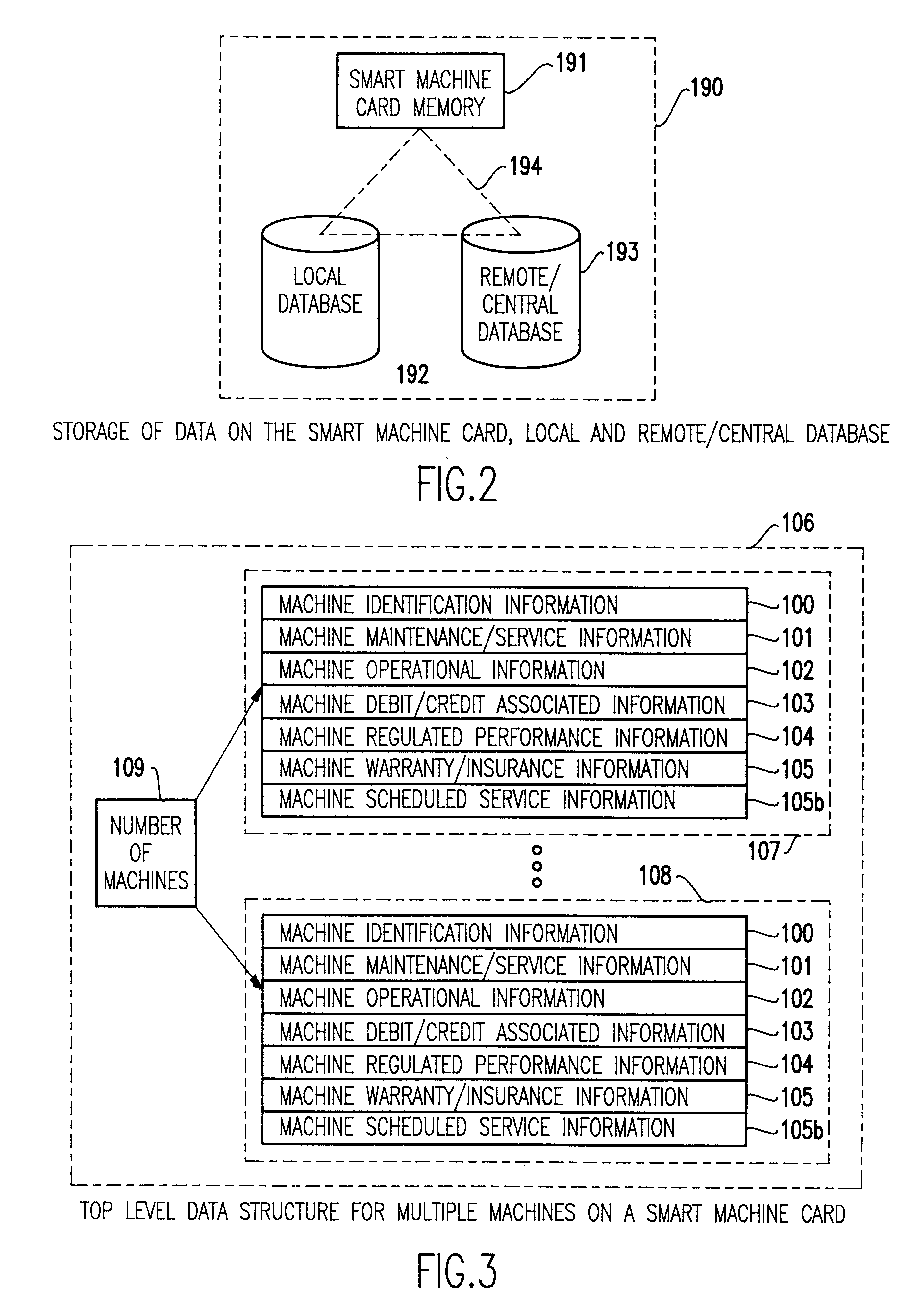
Smart card for recording identification, and operational, service and maintenance transactions
InactiveUS6557752B1Registering/indicating working of vehiclesRegistering/indicating working of machinesTelecommunications linkCommunication link
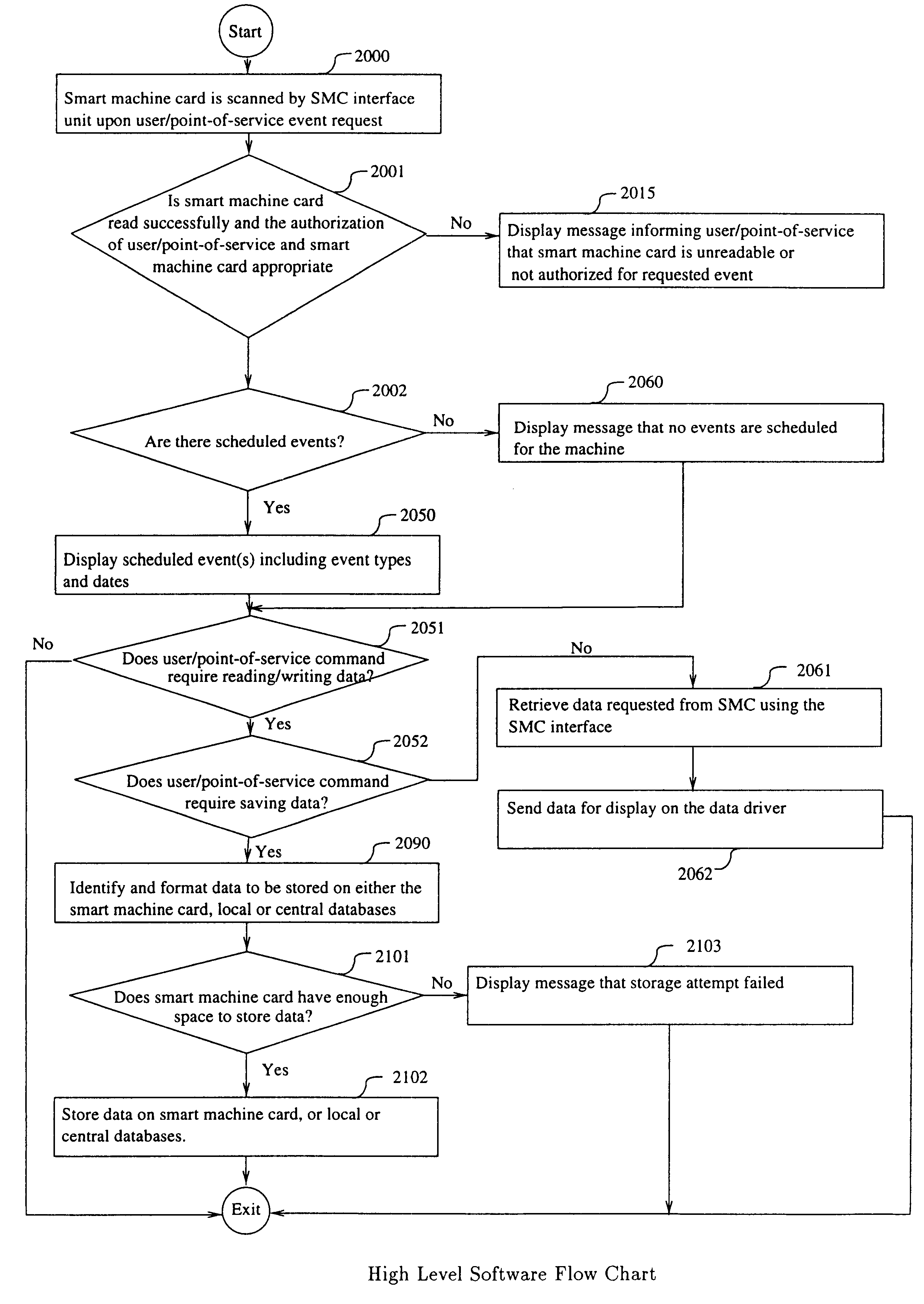
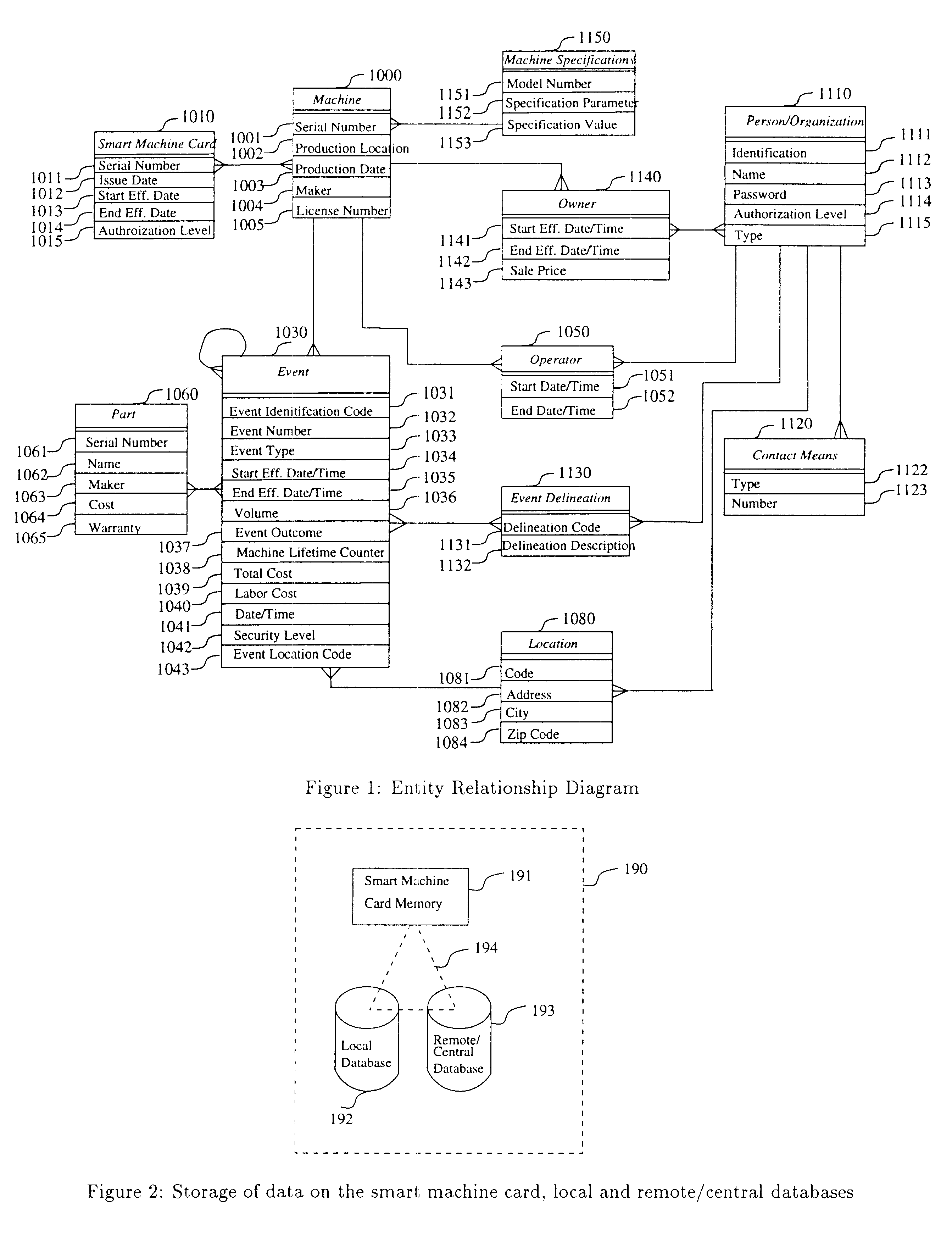
A computerized "smart card" which has a read / write memory and formatted data storage blocks is used to track the life history of one or more associated machine(s) (e.g., vehicles, medical instrumentation and apparatus, business and copying machines, etc.). The smart card can store a variety of information including machine identification, hardware / software specifications, debit / credit, regulated performance, warranty / insurance, maintenance / service and operational transactions that might impact the hardware, software or the intended operation or performance of the machine. The smart card will be equipped to interact with any of a plurality of autonomous reader / writer smart card units and computer-based reader / writer smart card units that may be equipped to interact with any of the plurality of computer databases through the utilization of land or wireless communications links. Preferably, each smart card will be associated with one or more specific machines at the time of sale of the machines, and will be periodically updated at each transaction (e.g., repair, scheduled maintenance, transfer of title, etc.) using reader / writer units operated by service technicians, repair shops, insurance agents, or the like. Thus, upon transfer of title of the machine, the smart card will also be transferred to provide the new owner with a complete life history for the machine. The stored life history can be used for valuation, maintenance scheduling, problem trouble shooting, and other applications. In the case of a single card being associated with a group of machines (e.g., a company with a fleet of cars, trucks or buses, or a company with several photocopiers, etc.), the card can also be used to track the scheduled replacement of individual machines within the group. Provisions are also made to associate new cards with existing machines to track the future life history of a particular machine.
Owner:Q INT
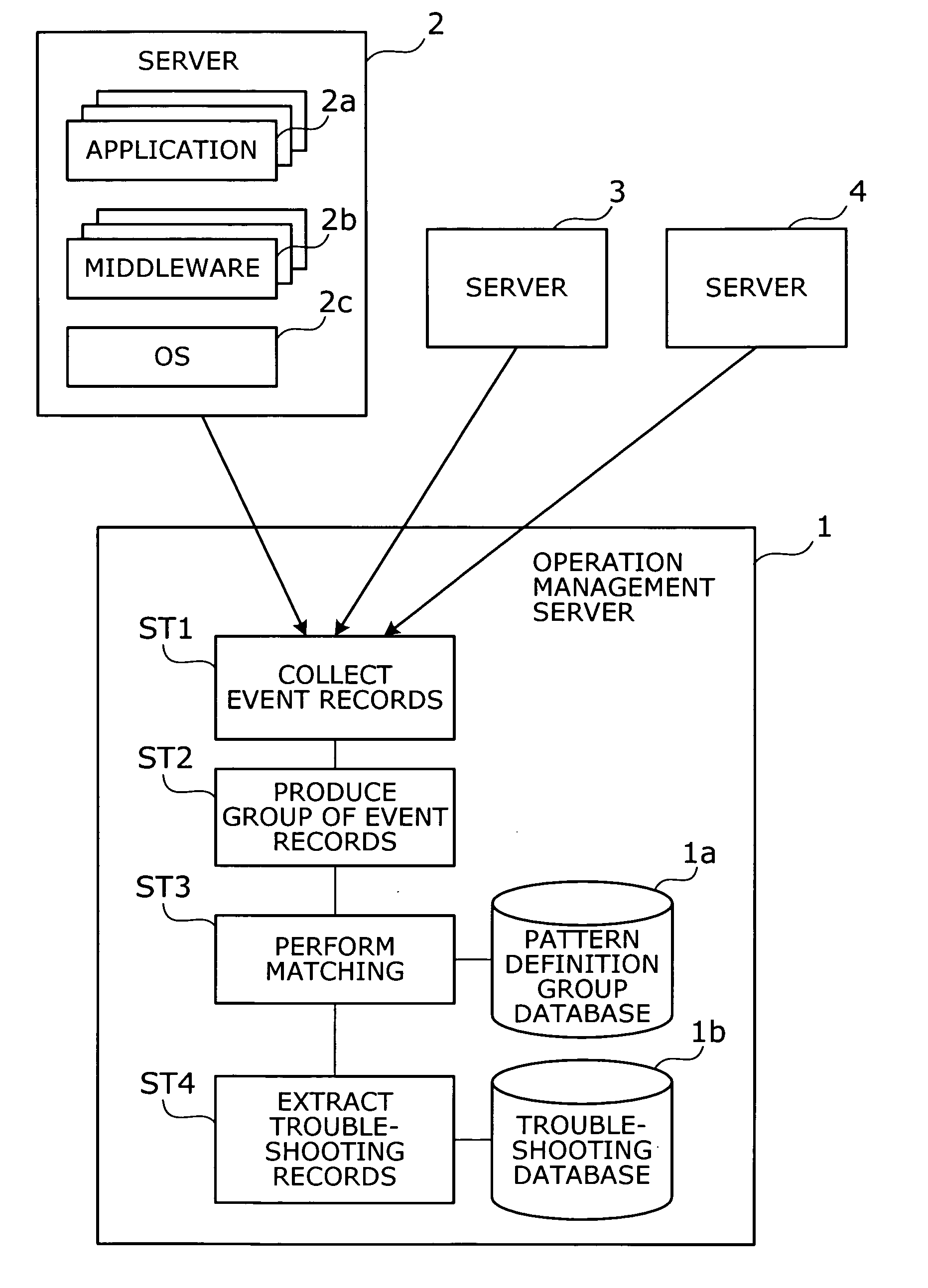
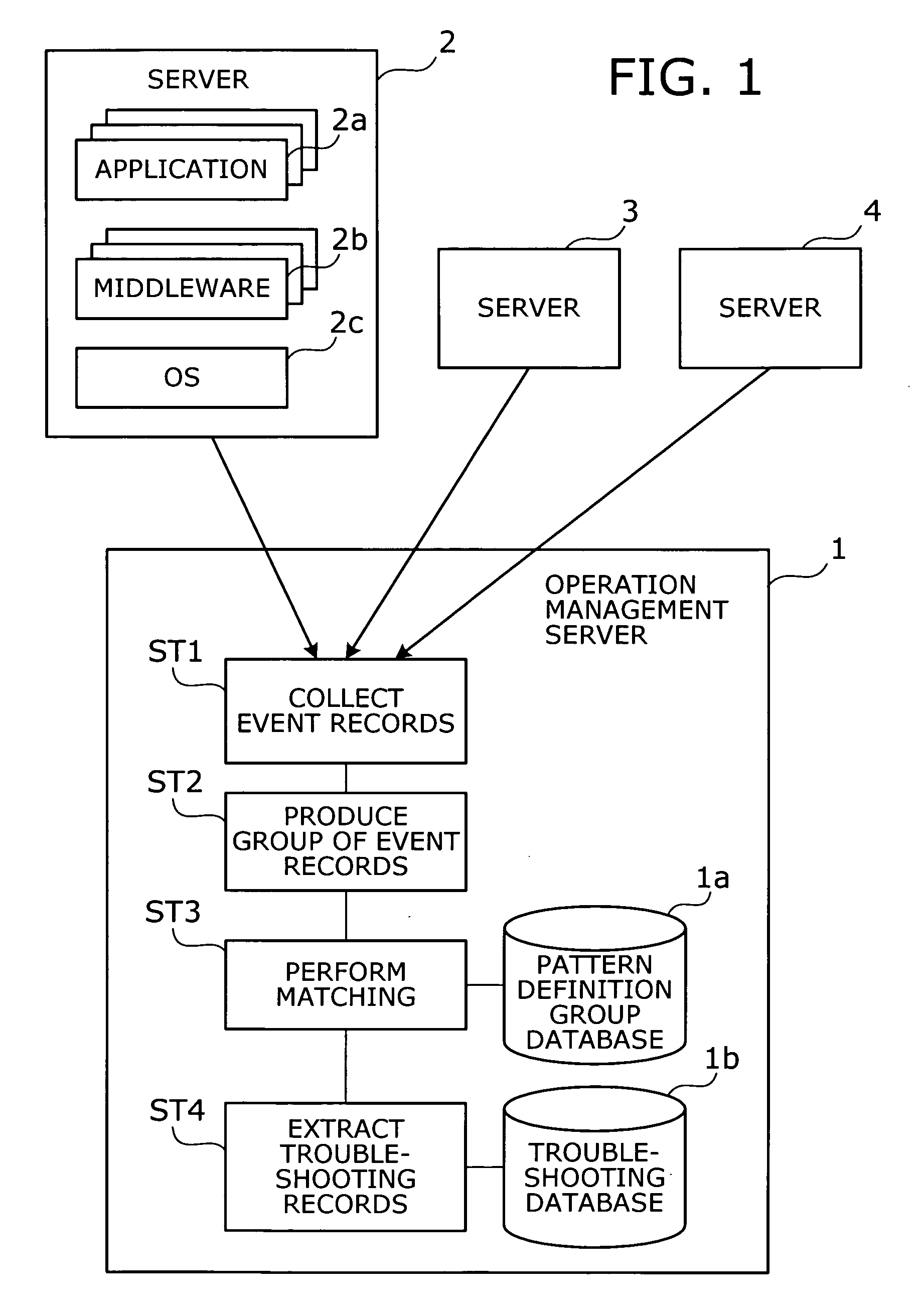
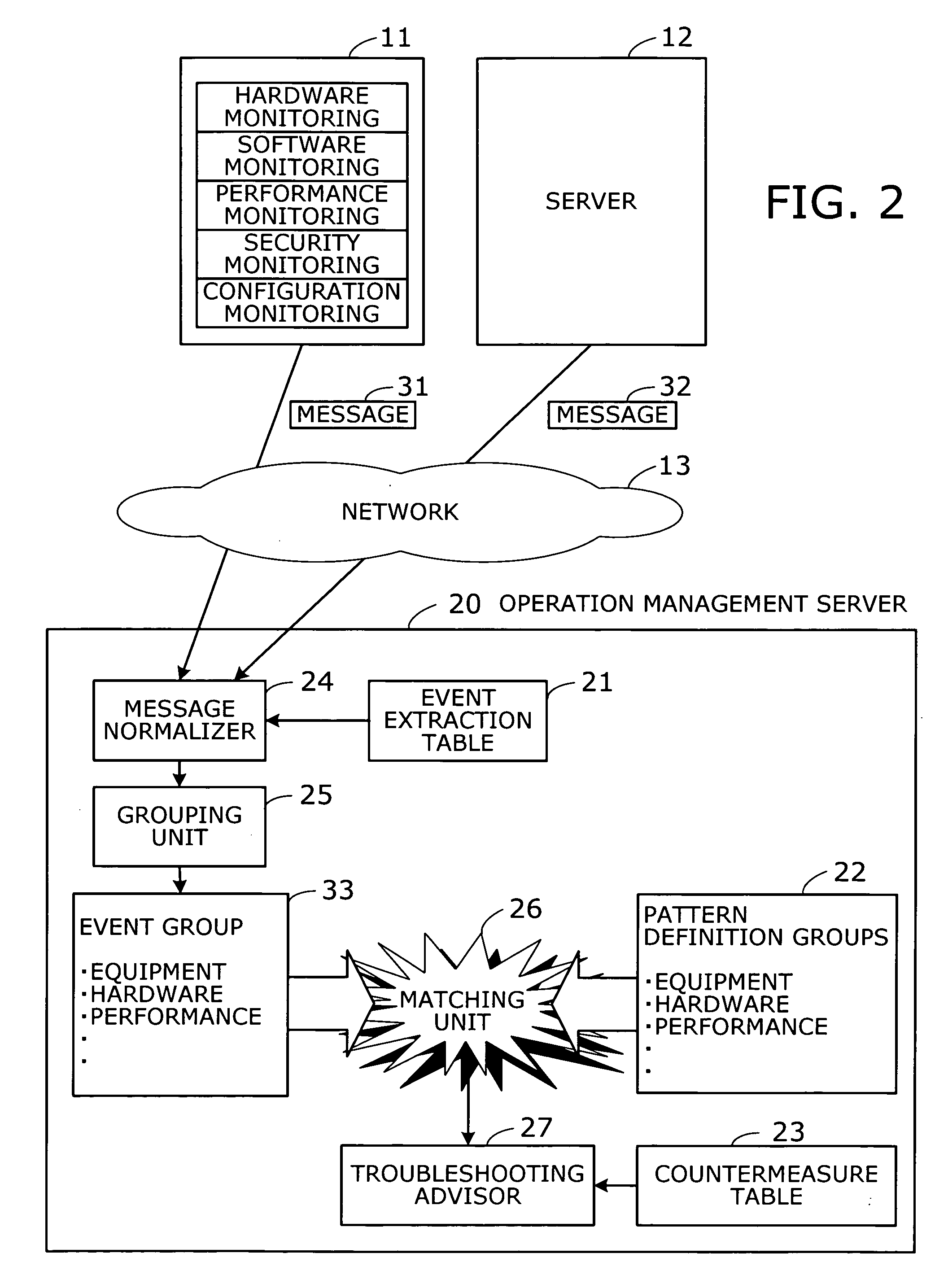
Operation management method and operation management server
InactiveUS20050172162A1Data processing applicationsDetecting faulty computer hardwareSoftwareReal-time computing
A method is provided to point out which software program is causing a problem. Event records are collected from target objects being monitored. An event group is then produced by grouping the collected event records. The event group is compared with a plurality of pattern definition groups in terms of occurrence patterns of event records, where each pattern definition group defines a pattern of event records that would be produced upon occurrence of a particular problem. Subsequently a troubleshooting record is extracted. This troubleshooting record has previously been associated with a pattern definition group resembling the event group in terms of occurrence patterns of event records.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
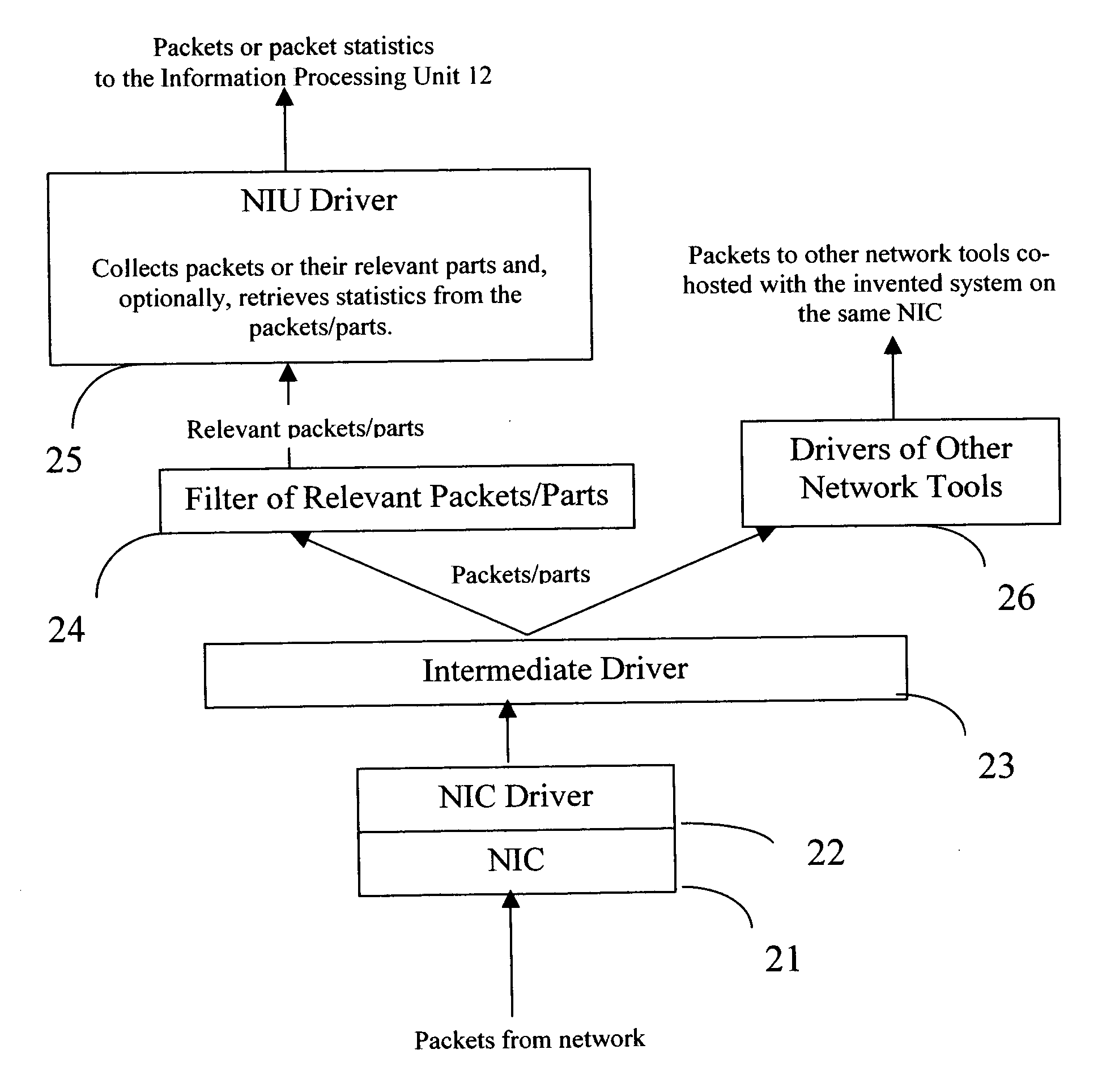
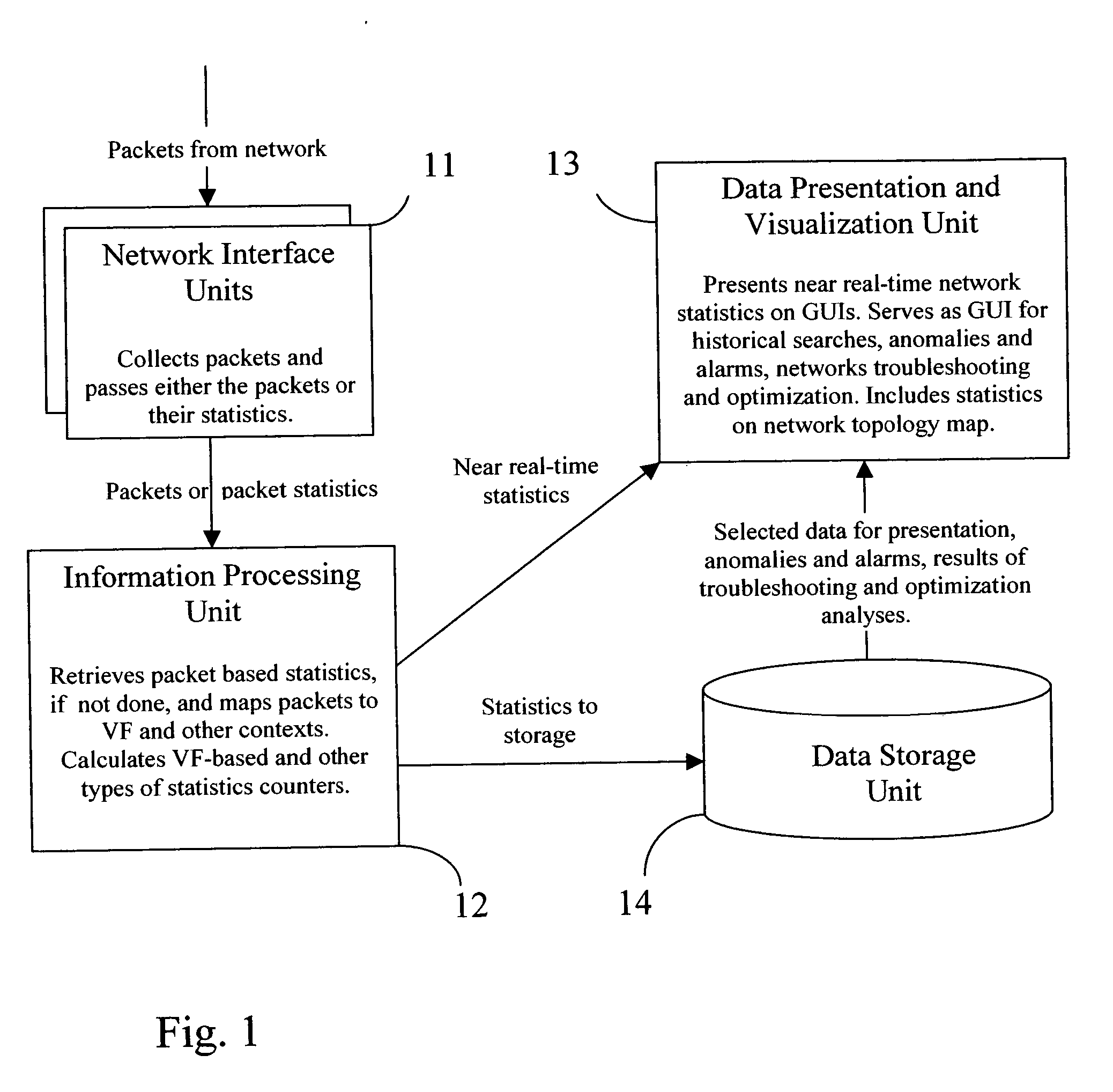
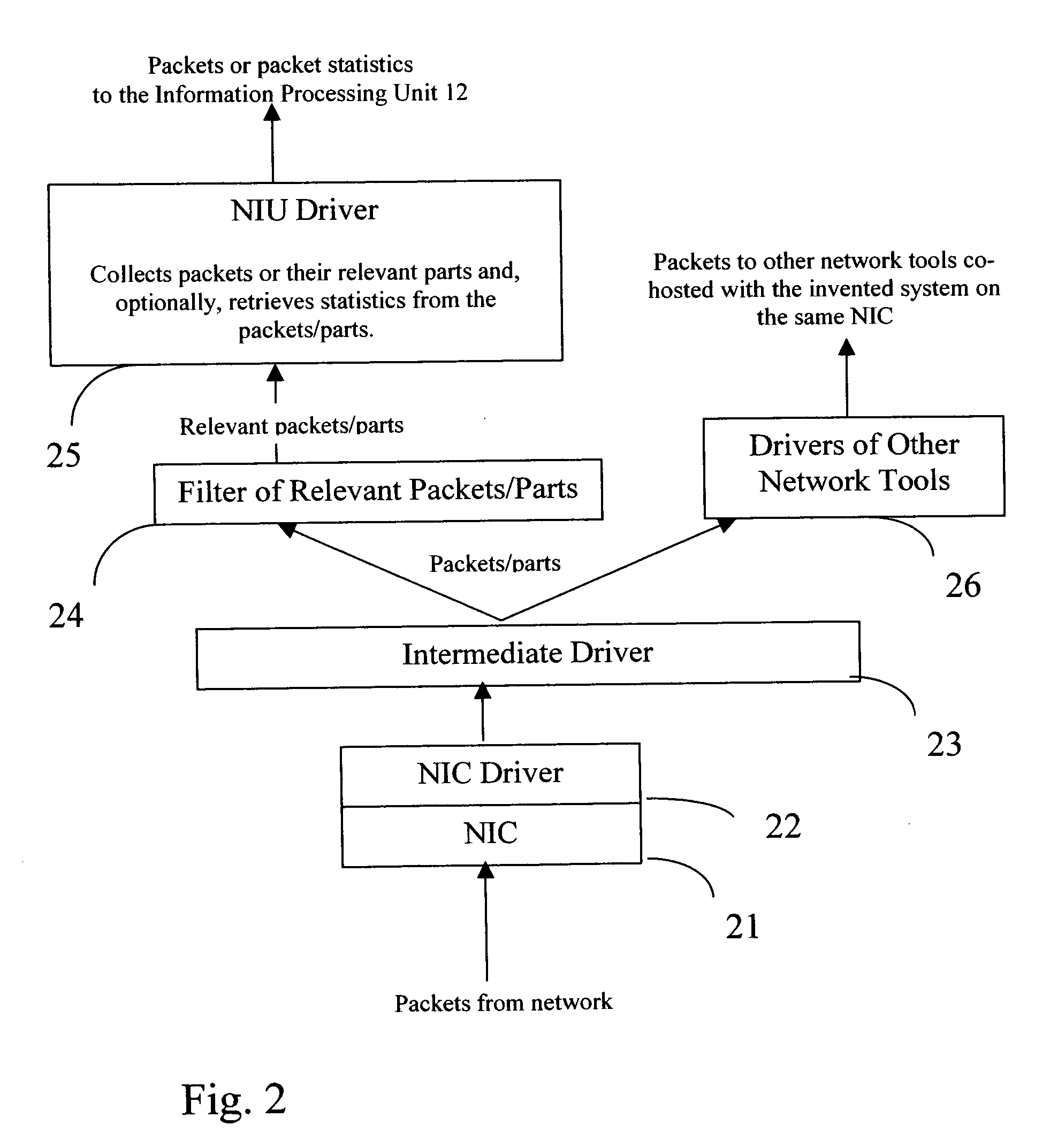
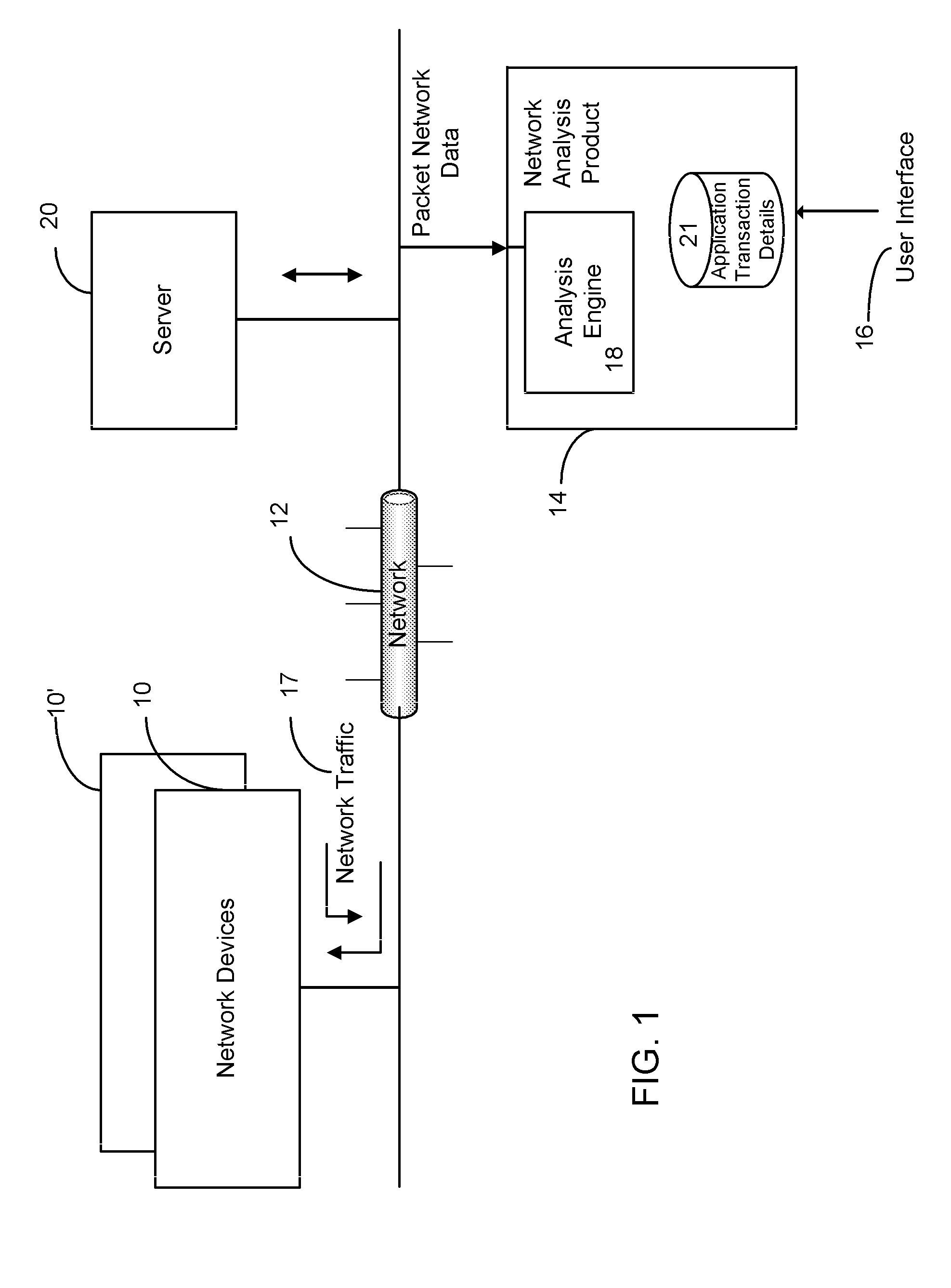
Flows based visualization of packet networks with network performance analysis, troubleshooting, optimization and network history backlog
InactiveUS20060028999A1Improve network securityEasy to highlightError preventionTransmission systemsProcess informationStreamflow
The present invention is a computer system and a method for gathering, processing and analysis of network information resulting in presentation and visualization of packet networks in the form of individual virtual flows, sometimes also called connections or sessions, containing their statistical characteristics in a time-sampled dynamics. The system, deployed as a separate device or co-hosted with other network devices, collects and processes information from all valid packets in network, classifies and maps gathered statistics to the statistics of relevant virtual flows. The statistical information is further processed by the system to provide near-real presentation, as well as stored in a searchable database for future analyses. The invention to be used by network engineers and administrators as a tool for a near real-time control of network traffic, as an analytical tool for solving network bottlenecks, network performance optimization and troubleshooting analyses, cutting costs by optimizing network layout, appropriate organization of traffic and intelligent configuration of QoS, routers and other network devices.
Owner:IAKOBASHVILI ROBERT +1
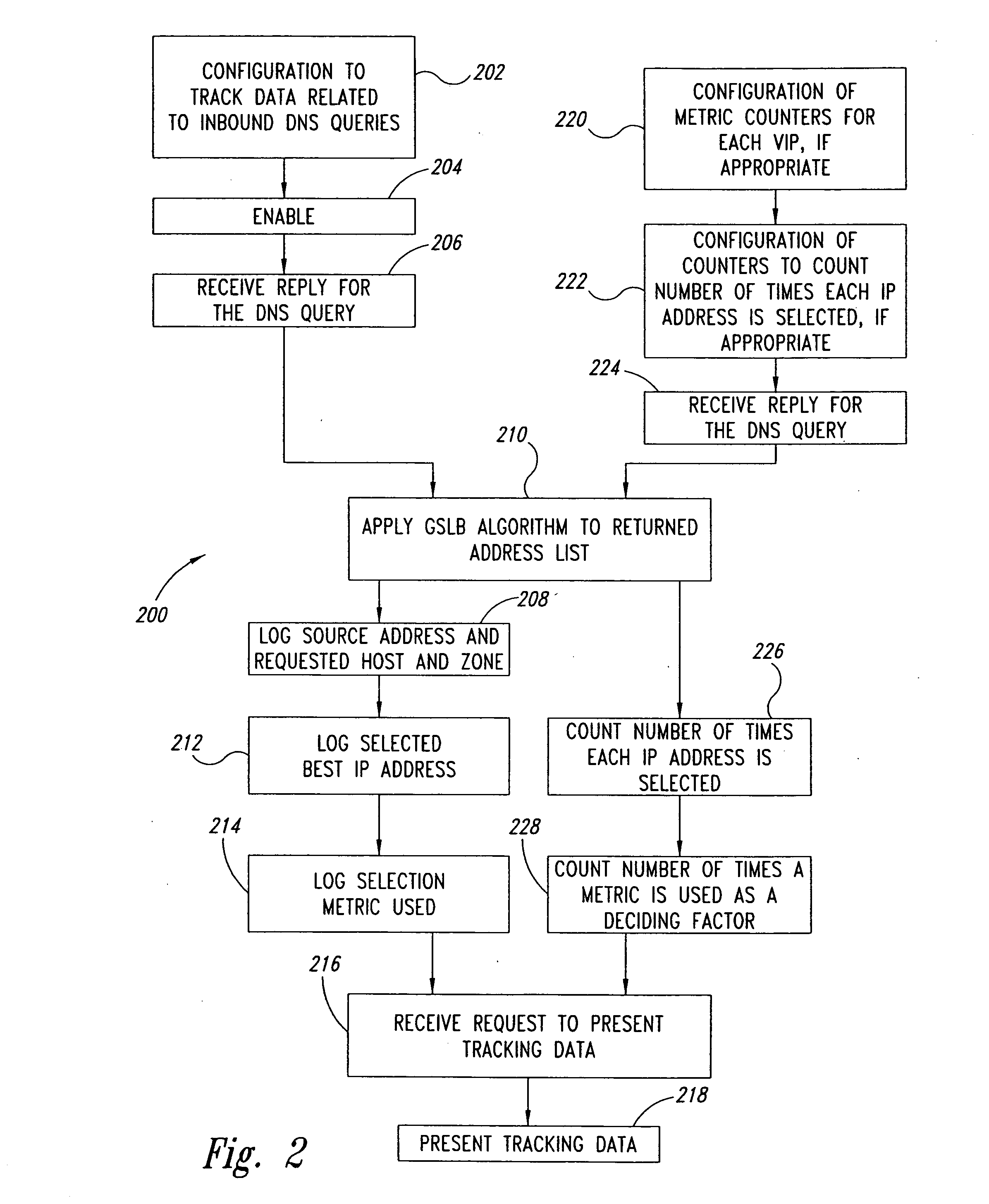
Statistical tracking for global server load balancing
InactiveUS20100223621A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsPolicy decisionIp address
Server load-balancing operation-related data, such as data associated with a system configured for global server load balancing (GSLB) that orders IP addresses into a list based on a set of performance metrics, is tracked. Such operation-related data includes inbound source IP addresses (e.g., the address of the originator of a DNS request), the requested host and zone, identification of the selected “best” IP addresses resulting from application of a GSLB algorithm and the selection metric used to decide on an IP address as the “best” one. Furthermore, the data includes a count of the selected “best” IP addresses selected via application of the GSLB algorithm, and for each of these IP addresses, the list of deciding performance metrics, along with a count of the number of times each of these metrics in the list was used as a deciding factor in selection of this IP address as the best one. This tracking feature allows better understanding of GSLB policy decisions (such as those associated with performance, maintenance, and troubleshooting) and intelligent deployment of large-scale resilient GSLB networks.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
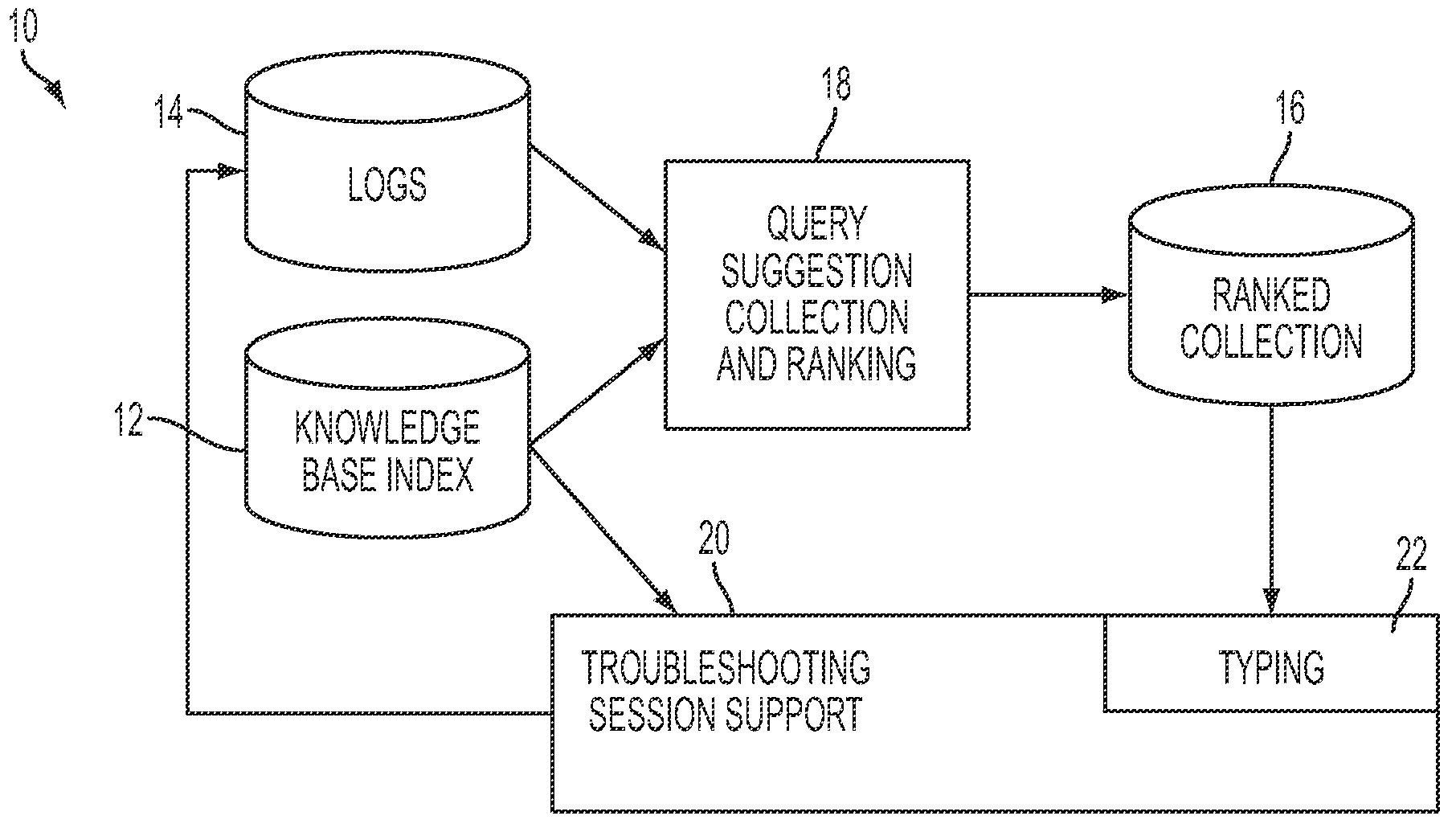
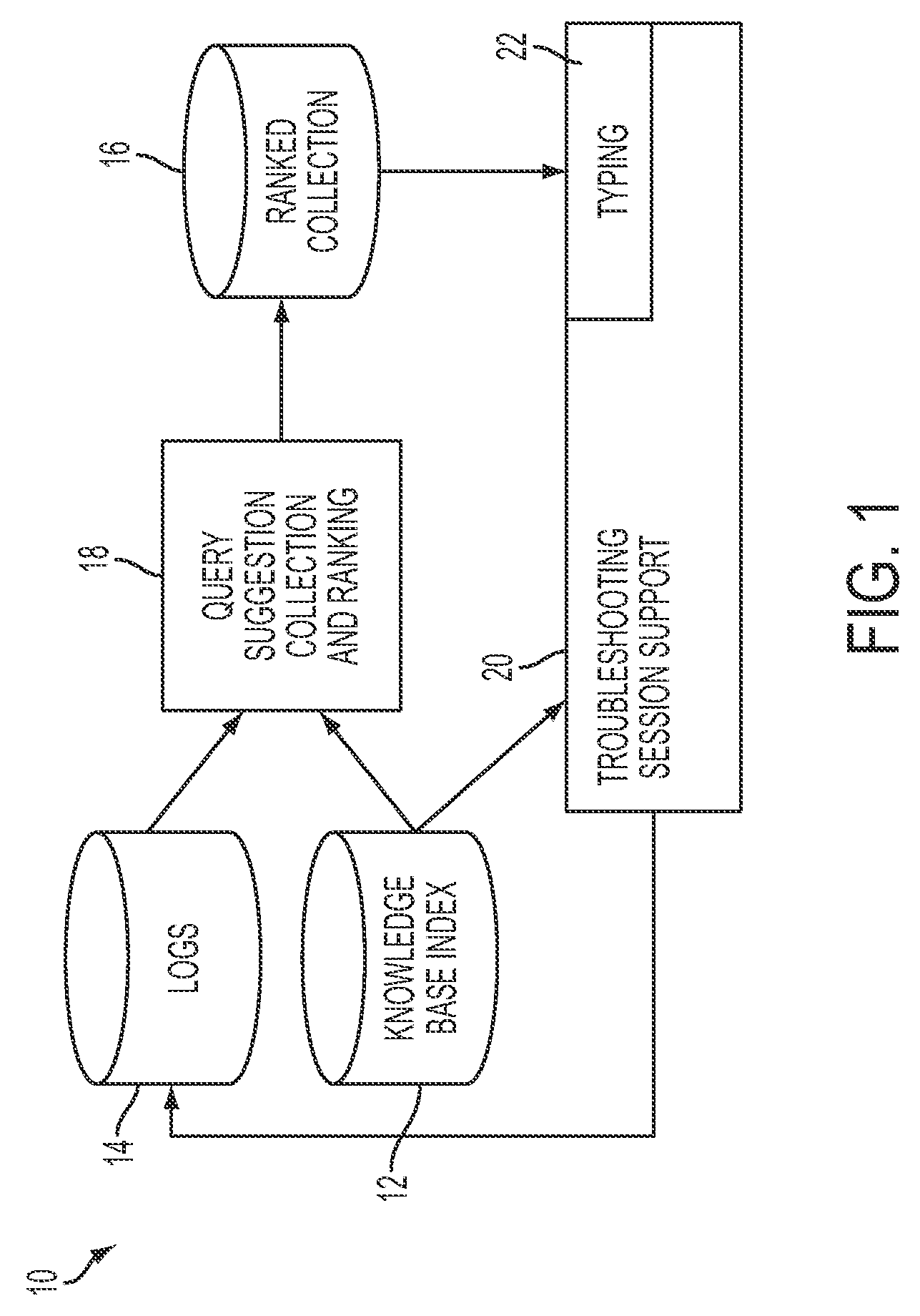
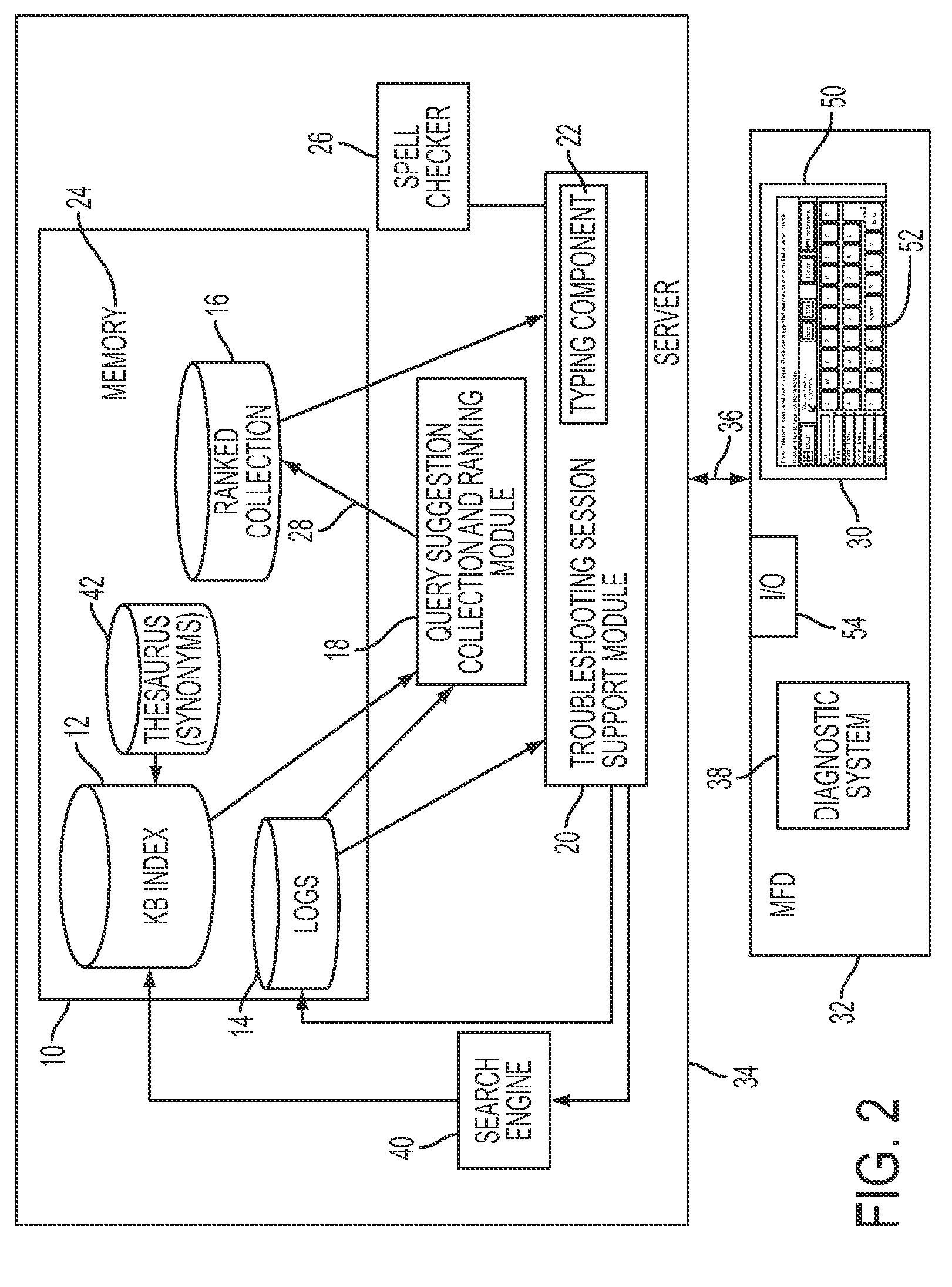
Real-time query suggestion in a troubleshooting context
ActiveUS20090106224A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsRankingKnowledge base
A method for assisting a user to develop a query in a natural language includes receiving a user's query in a natural language and, while the user's query is being entered, presenting a subset of ranked query suggestions from a collection of ranked query suggestions to the user as candidates for user queries. The subset is based on that portion of the user's query already entered. The query suggestions in the subset of query suggestions are presented according to their respective rankings in the collection. Each of the query suggestions in the collection is formulated to retrieve at least one responsive instance in the knowledge base. The rankings of the query suggestions in the collection are based at least in part on stored logs of prior user sessions in which user queries were input to a search engine for retrieving responsive instances from the knowledge base.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
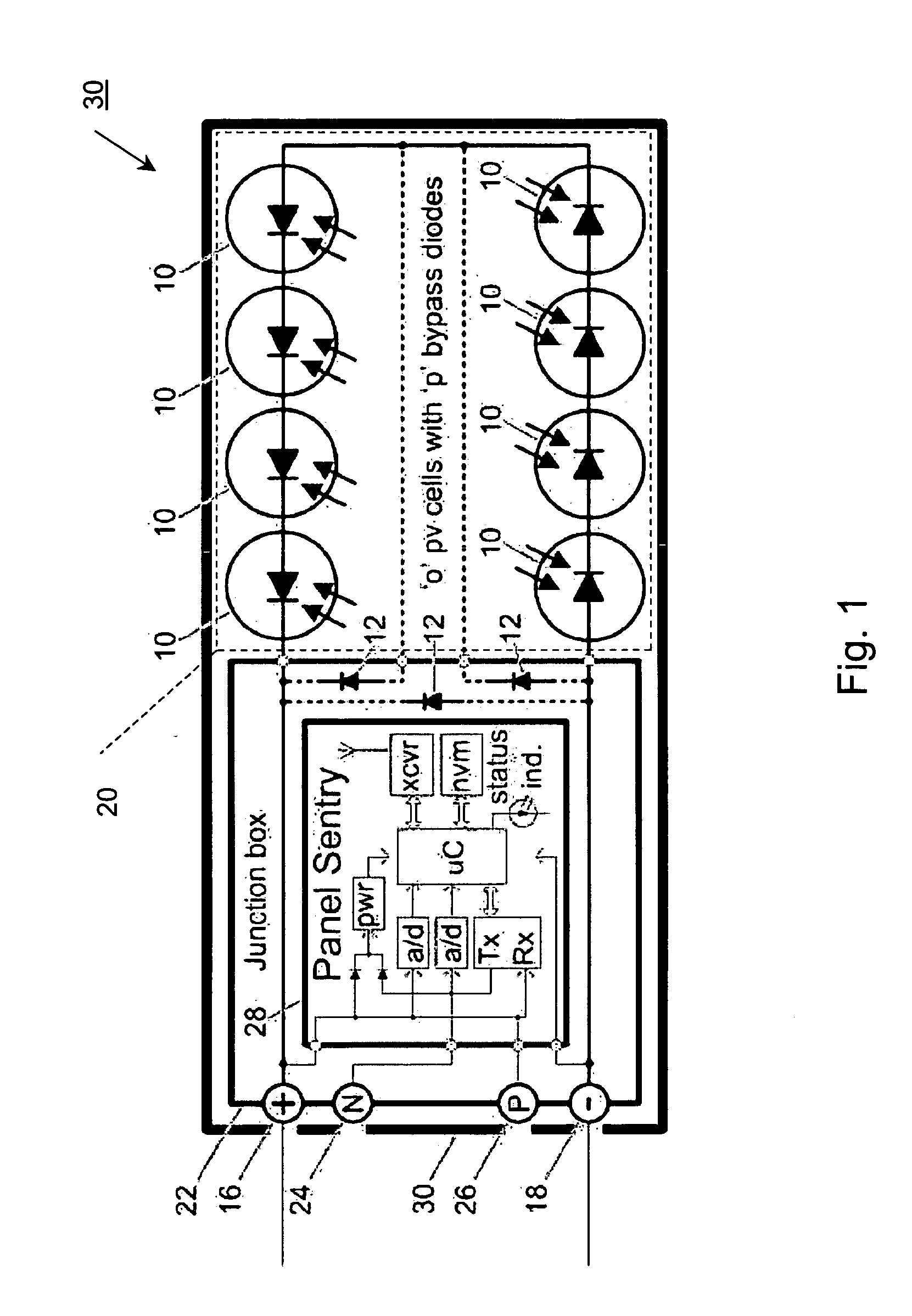
System and method for monitoring photovoltaic power generation systems
InactiveUS8204709B2Batteries circuit arrangementsPhotovoltaic monitoringDiagnostic dataIntelligent equipment
A system and method for monitoring photovoltaic power generation systems or arrays, both on a local (site) level and from a central location. The system includes panel and string combiner sentries or intelligent devices, in bidirectional communication with a master device on the site to facilitate installation and troubleshooting of faults in the array, including performance monitoring and diagnostic data collection.
Owner:SOLAR SENTRY
Method for using a smart card for recording operations, service and maintenance transactions and determining compliance of regulatory and other scheduled events
InactiveUS6170742B1Specific performanceRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesRegistering/indicating working of machinesTelecommunications linkSmart card
A computerized "smart card" which has a read / write memory and formatted data storage blocks is used to track the life history of one or more associated machine(s) (e.g., vehicles, medical instrumentation and apparatus, business and copying machines, etc.). The smart card can store a variety of information including machine identification, hardware / software specifications, debit / credit, regulated performance, warranty / insurance, maintenance / service and operational transactions that might impact the hardware, software or the intended operation or performance of the machine. The smart card will be equipped to interact with any of a plurality of autonomous reader / writer smart card units and computer-based reader / writer smart card units that may be equipped to interact with any of the plurality of computer databases through the utilization of land or wireless communications links. Preferably, each smart card will be associated with one or more specific machines at the time of sale of the machines, and will be periodically updated at each transaction (e.g., repair, scheduled maintenance, transfer of title, etc.) using reader / writer units operated by service technicians, repair shops, insurance agents, or the like. The stored life history can be used for valuation, maintenance scheduling, problem trouble shooting, and other applications.
Owner:Q INT
Network path tracing method
Systems and methods for gathering troubleshooting information through one or more networks are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises a switch port configured to receive a frame that has information added by another switch. As the frame traverses the network, control logic in the switch adds additional information into the frame from the current switch.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Systems and methods for remote testing of wireless LAN access points
InactiveUS20100246416A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMonitoring systemWireless lan
The present disclosure describes systems and methods for remote testing and troubleshooting of a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) using one or more distributed WLAN sensors and one or more servers. Specifically, the invention describes a method to test WLAN access points (APs) for connectivity and performance in the field. In an exemplary embodiment, the one or more distributed WLAN sensors and one or more servers can include a wireless monitoring system, such as a wireless intrusion prevention or detection system. The present invention utilizes a distributed network of WLAN sensors that typically operate to monitor the WLAN, and as needed, the present invention converts the monitoring sensors to WLAN clients capable to connecting and remotely testing one or more WLAN APs.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
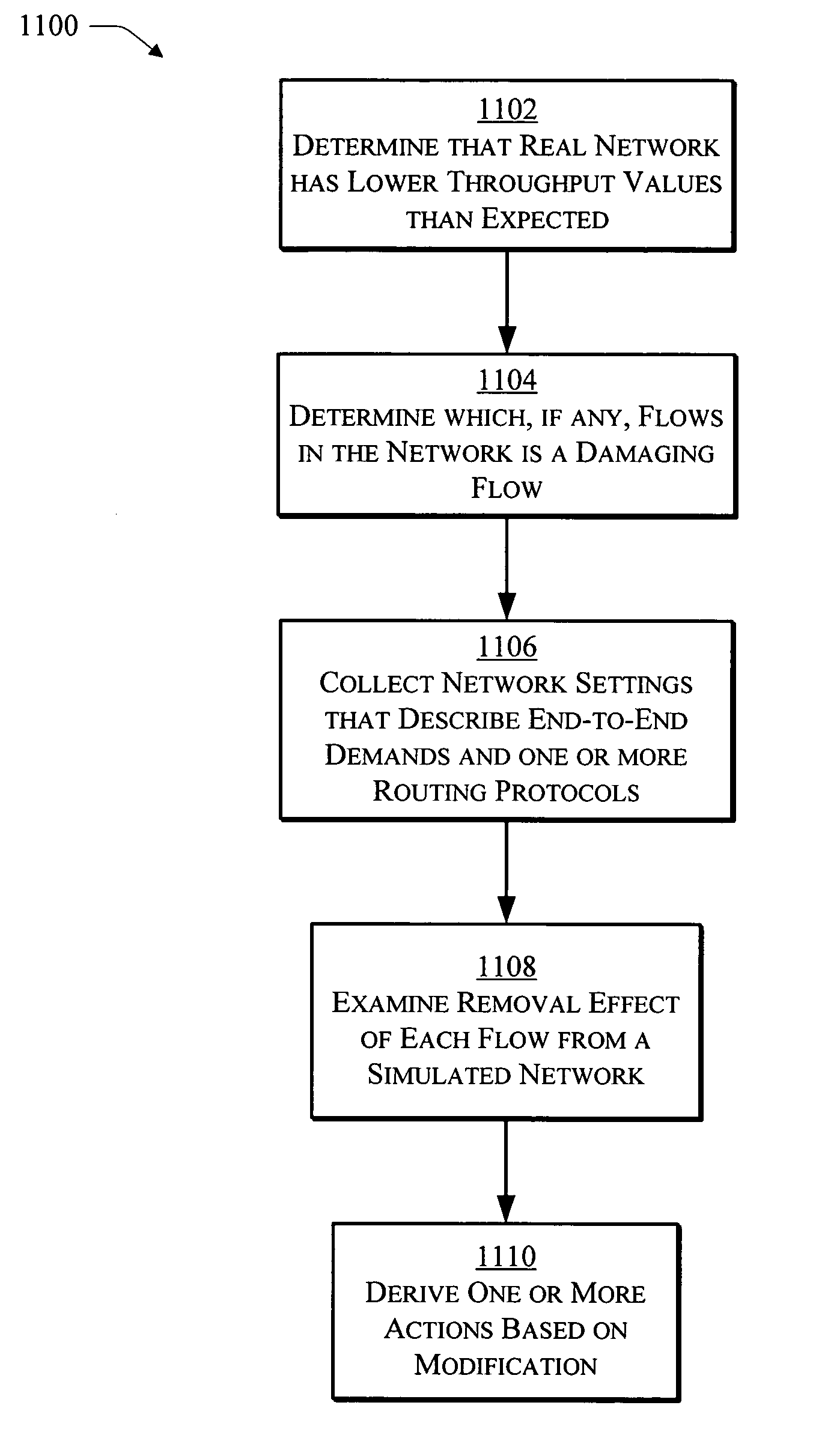
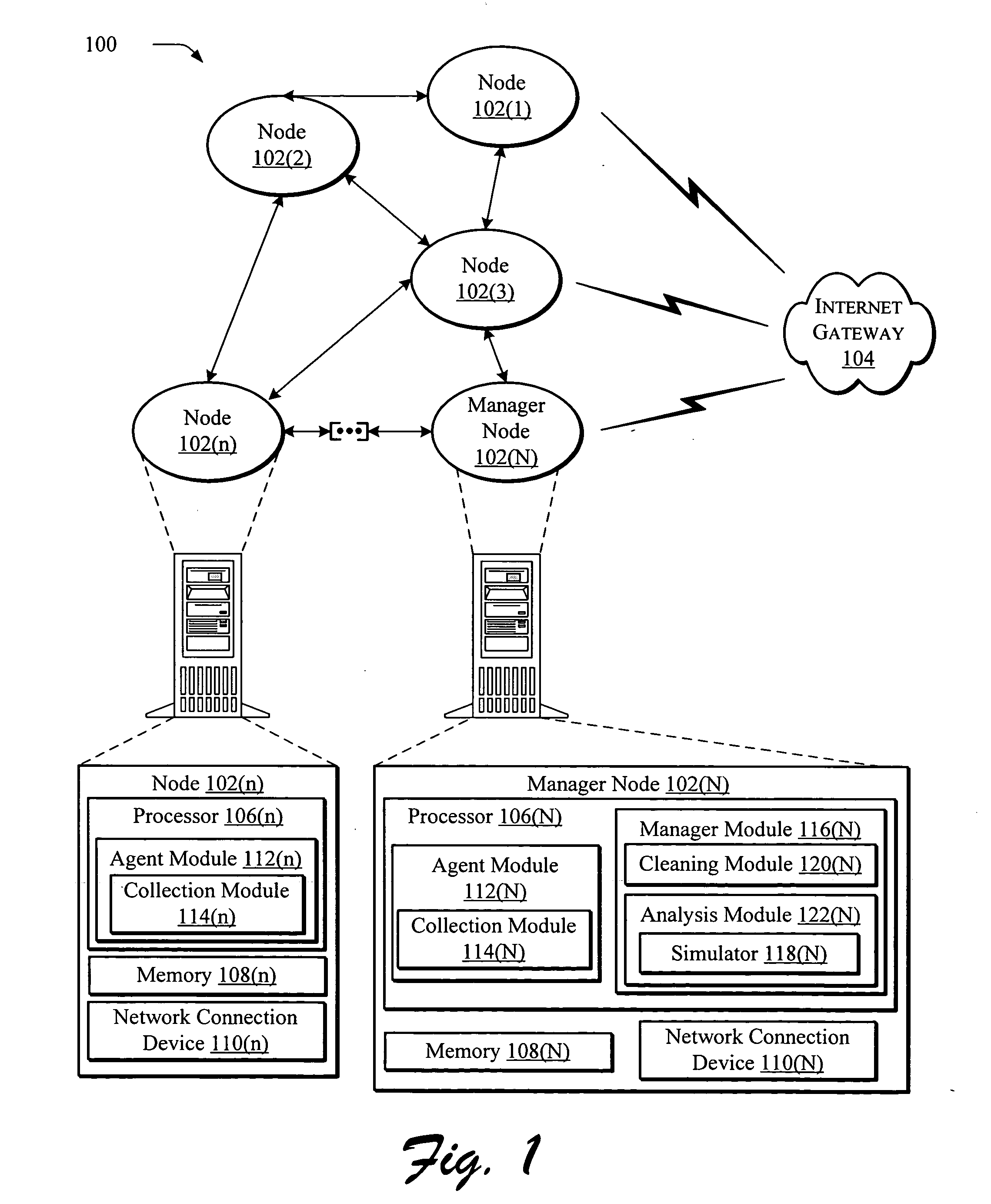
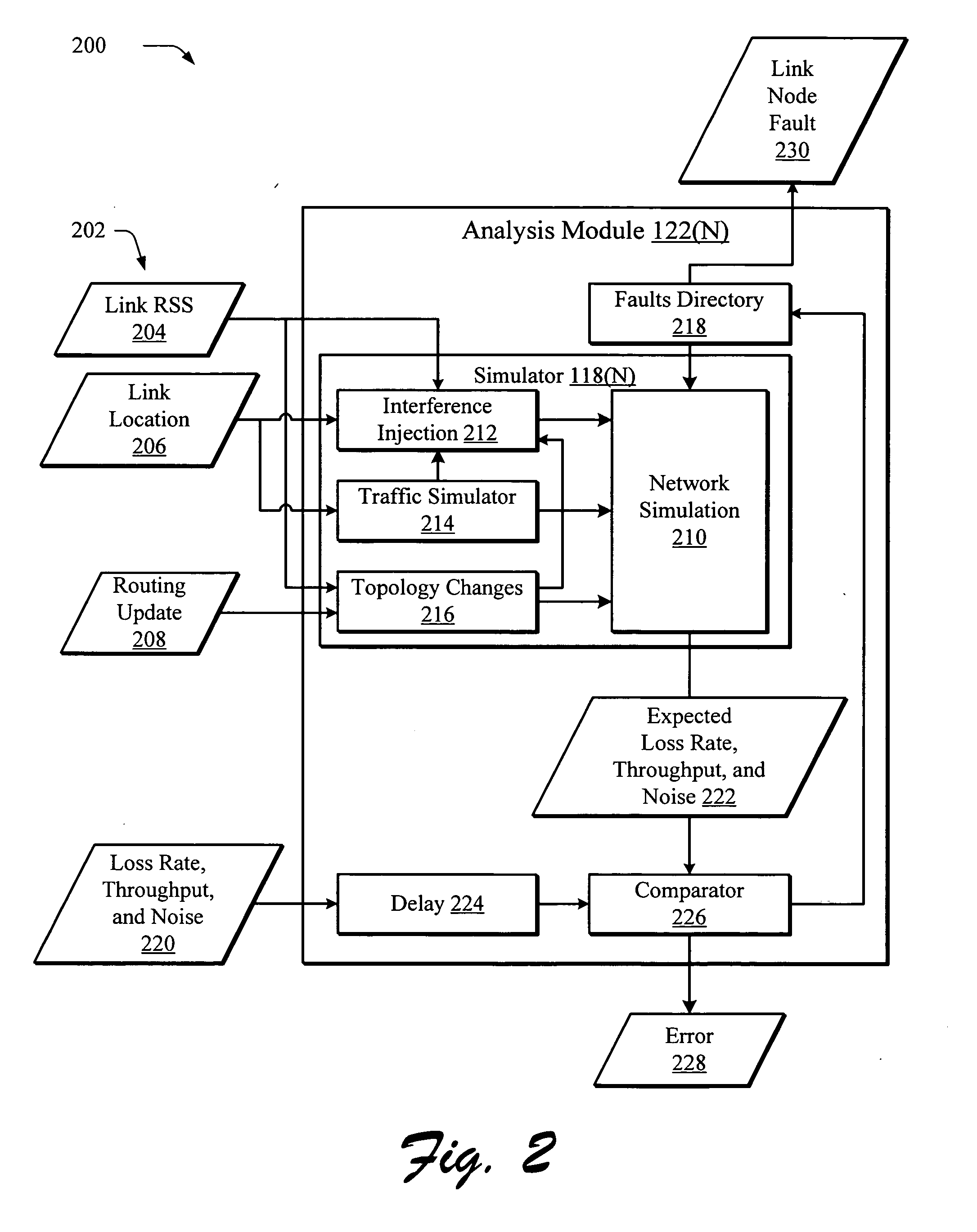
What-if analysis for network diagnostics
InactiveUS20050169186A1Improve network performanceProvide feedbackError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork simulationNetwork performance
A network troubleshooting framework is described. In an implementation, a method includes generating a first estimation of network performance by a simulator based on network settings obtained from a network, estimating the new performance under an alternative setting by providing the alternative setting to the network simulation and observing the simulation output, repeating the procedure for other alternative settings, and suggesting the alternative setting that improves network performance.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
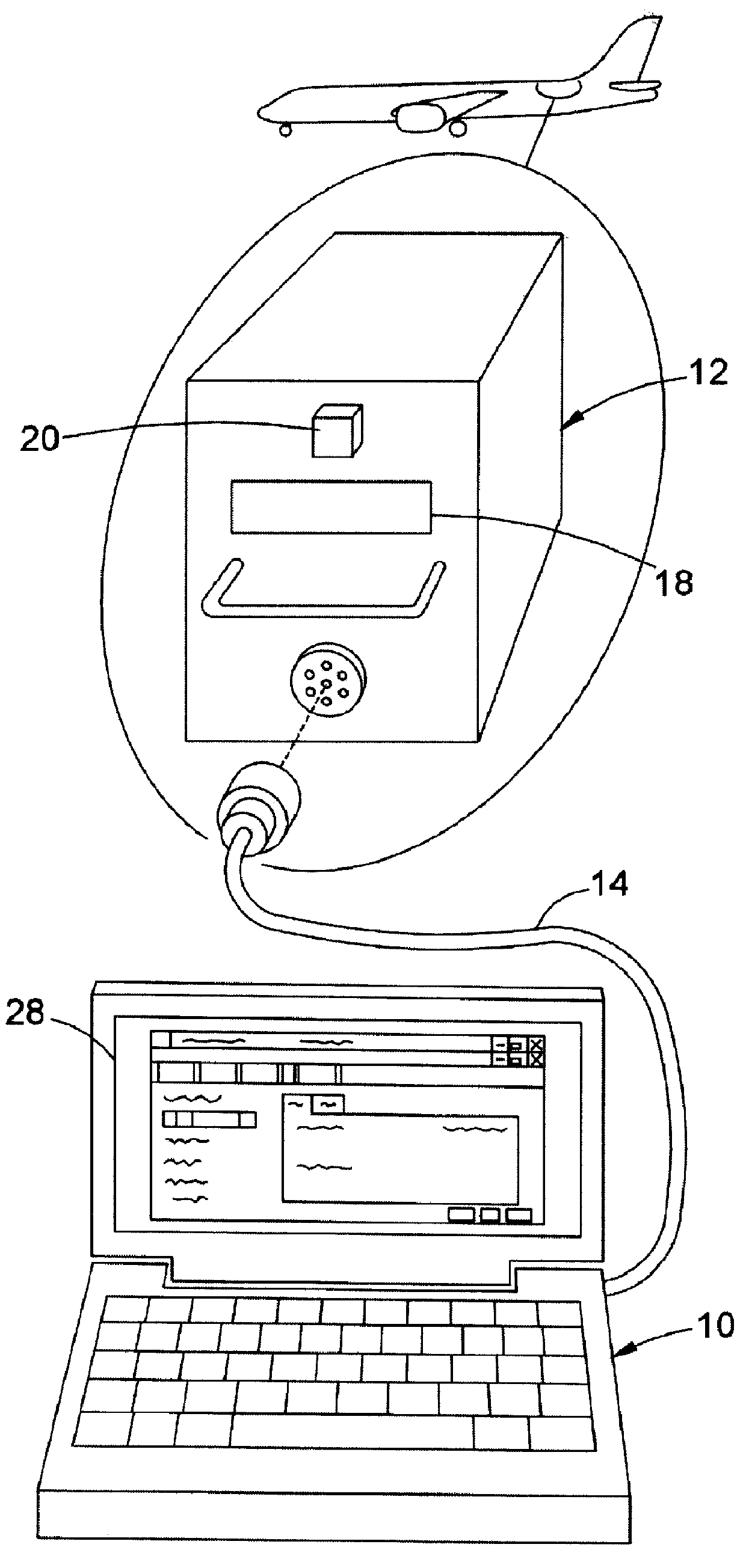
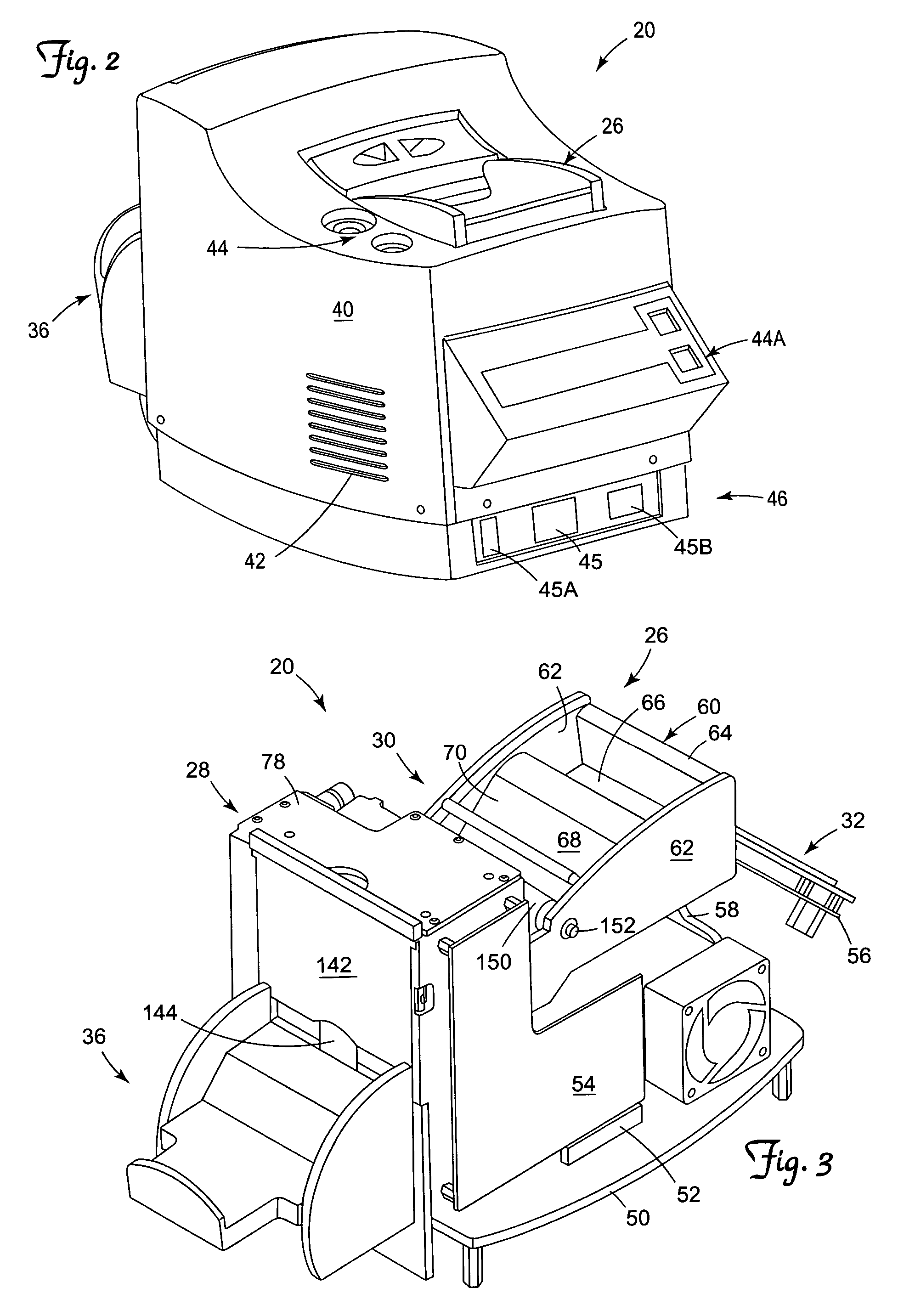
APU troubleshooting system
InactiveUS6122575AVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDisplay deviceAuxiliary power unit
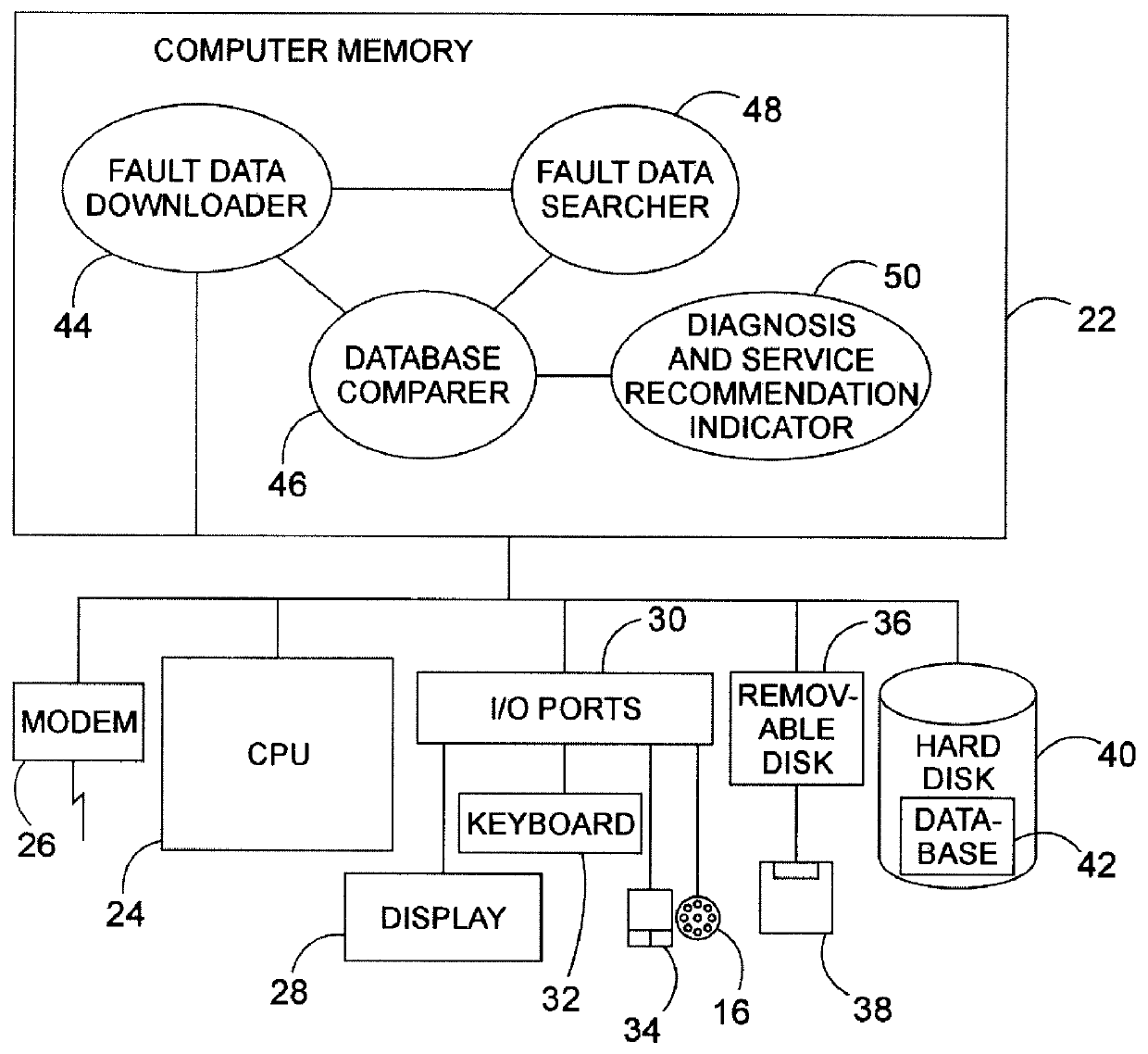
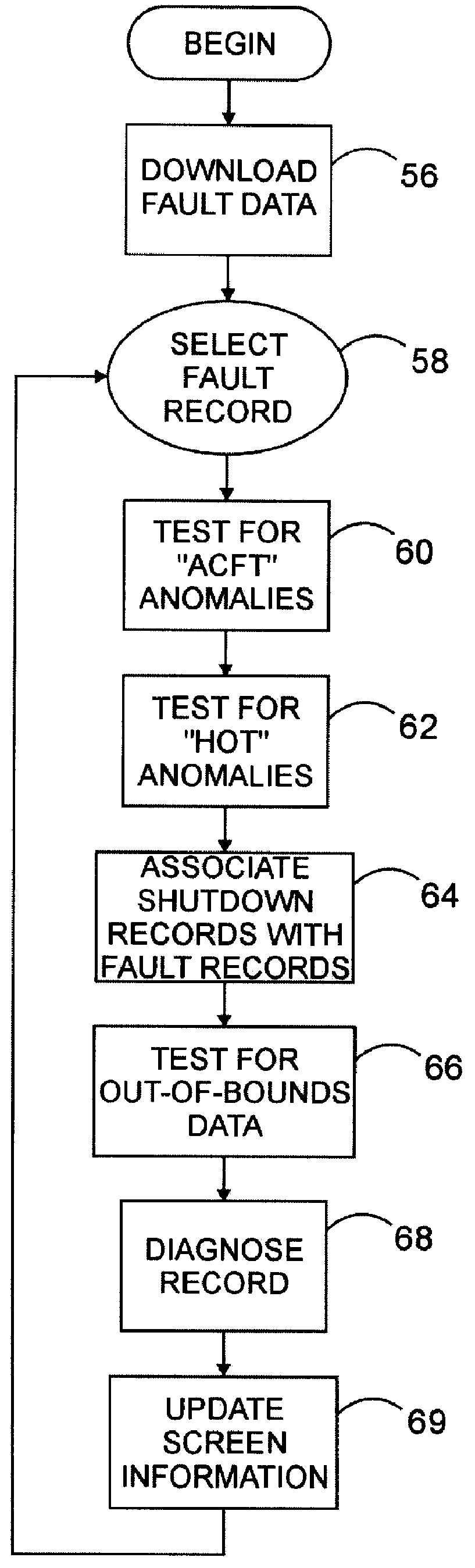
A system, method, and computer program product assist a technician in troubleshooting an aircraft auxiliary power unit (APU). A portable computer is couplable of download the fault data captured in a memory of the ECU. The fault data corresponds to one or more instances of APU failure. The computer is further programmed to compare the fault data to predetermined fault patterns stored in a database. Each record of the database has one of the fault patterns, a corresponding fault indication, and a corresponding service recommendation indication. The computer is further programmed so that when a record in which the fault pattern matches the fault data is found, the corresponding fault indication and service recommendation are retrieved from the database and provided to the technician via the computer's display or other suitable output mechanism.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Fluorescent light and motion detector with quick plug release and troubleshooting capabilities
InactiveUS6091200APromote repairEasy maintenanceEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsElongate light sourcesMotion detectorLED display
An energy saving fluorescent light fixture for small confined areas predominant in residential settings, having a motion detector with a quick plug connector capable of attaching and detaching the detector from the light fixture base. Additional trouble-shooting capabilities are provided by dedicated electronic circuitry and LED display indicators. The LED display indicators signal a nontechnical consumer when maintenance is required, and isolate the failures to the sub-system level, i.e., the detector or fixture base circuitry. The detector is attached through the quick plug connector and concurrently supported by either an elbow joint with rigid wire supporting segments, a flexible arm, or a ball-swivel joint with rigid wire supporting segment. The supporting means enables the user to control the sensor viewing area. A simplified trouble-shooting method enabling the user to use the LED display indicators and quick plug connector facilitates sub-system replacement by nontechnical operators.
Owner:LENZ MARK
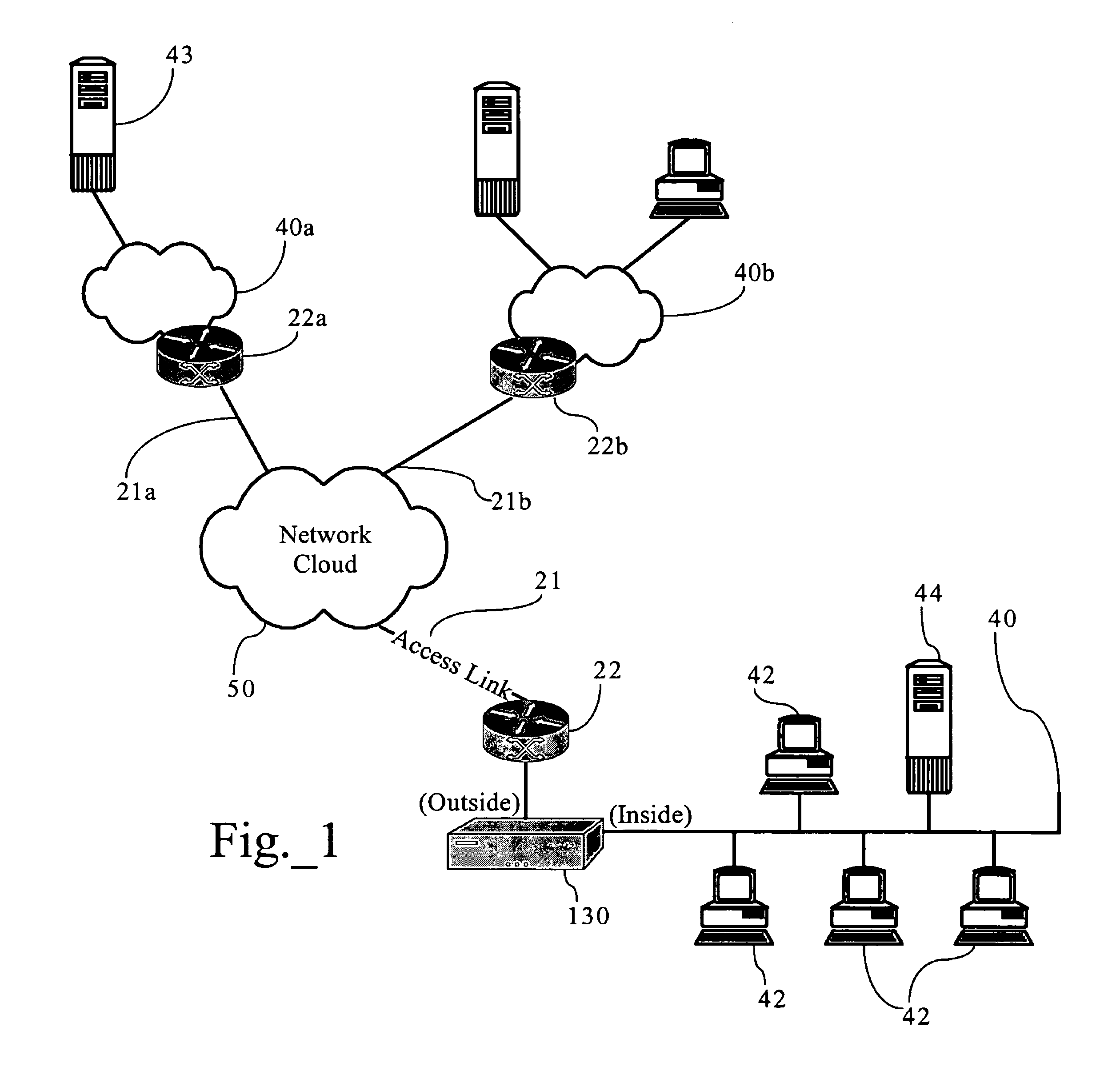
Arrangement for automated fault detection and fault resolution of a network device
ActiveUS7080141B1Minimal loss of serviceAccurate identificationMultiple digital computer combinationsNon-redundant fault processingDevice statusClient-side
Each network device includes a monitoring agent configured for generating a notification message based upon an event where device operations exceed prescribed monitored parameters. A troubleshooting resource at the customer premises requests selected device state attributes from the network device and that are forwarded to a data collection resource that serves as an interface to the manufacturer's back-end infrastructure. The troubleshooting system accesses databases that store the configuration information for the affected network device, and uses the configuration information for accessing problem / resolution information. The rules based troubleshooting system, upon correlating the databases for the problem / resolution information, provides a service notification message as a response to the event, and selectively includes the problem / resolution information for the network device.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for tracing hardware states using dynamically reconfigurable test circuits
A method and apparatus for tracing hardware states using dynamically reconfigurable test circuits provides improved debug and troubleshooting capability for functional logic implemented within field programmable logic arrays (FPGAs). Special test logic configurations may be loaded to enhance the debugging of a system using FPGAs. Registers are used to capture snapshots of internal signals for access by a trace program and a test multiplexer is used to provide real-time output to test pins for use with external test equipment. By retrieving the hardware snapshot information with a trace program running on a system in which the FPGA is used, software and hardware debugging are coordinated, providing a sophisticated model of overall system behavior. Special test circuits are implemented within the test logic configurations to enable detection of various events and errors. Counters are used to capture count values when system processor execution reaches a hardware trace point or when events occur. Comparators are used to detect specific data or address values and event detectors are used to detect particular logic value combinations that occur within the functional logic.
Owner:IBM CORP
Processing a user inquiry
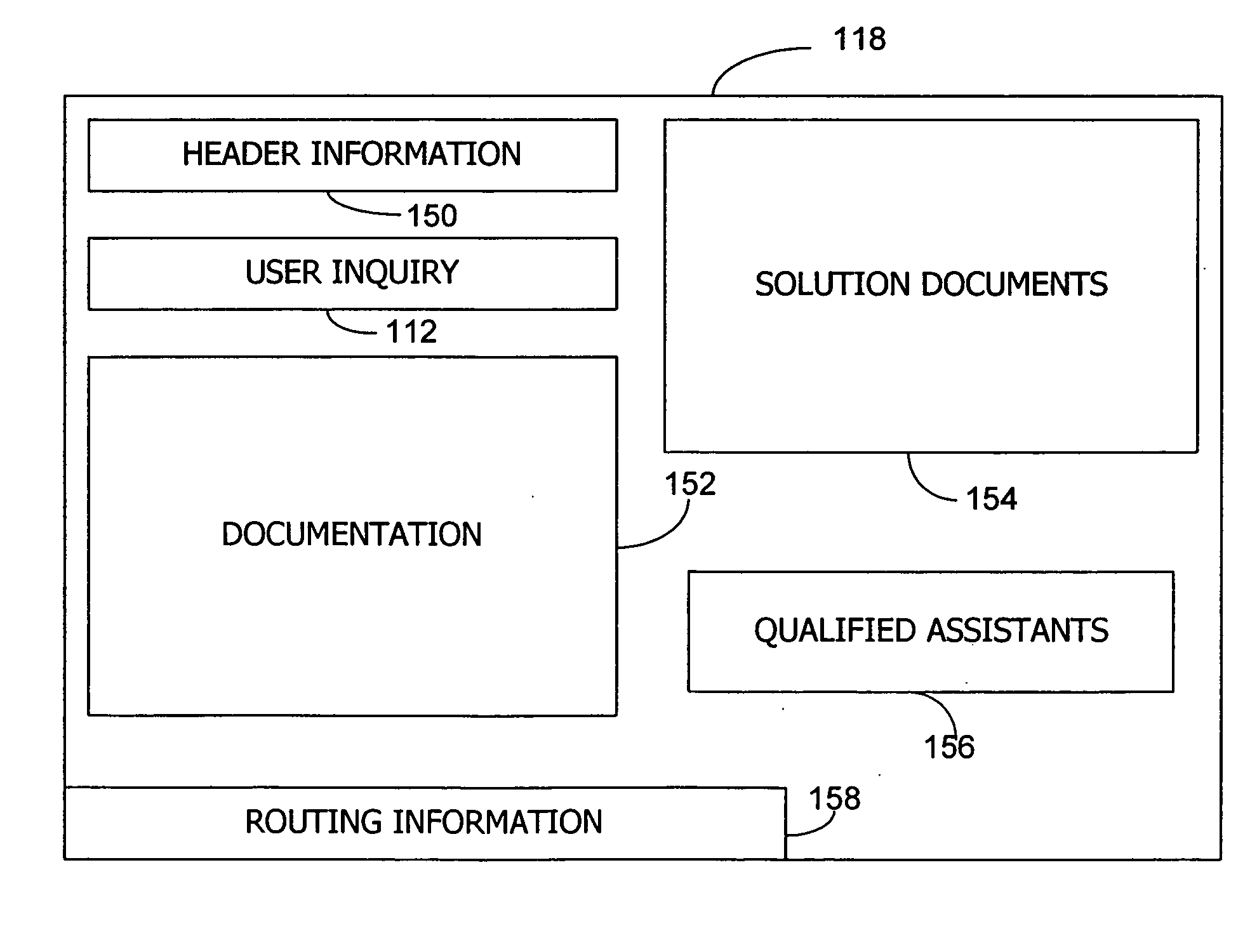
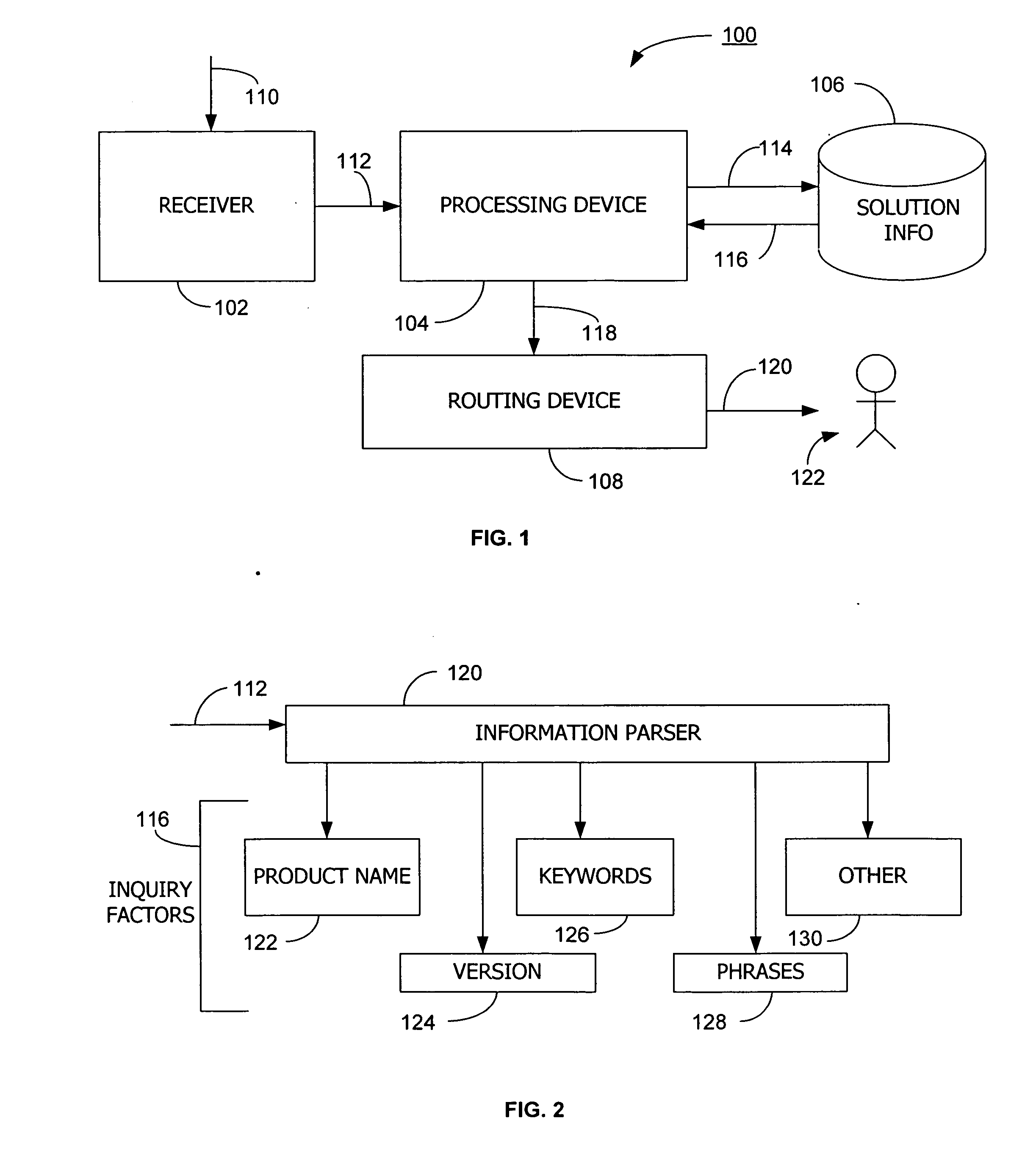
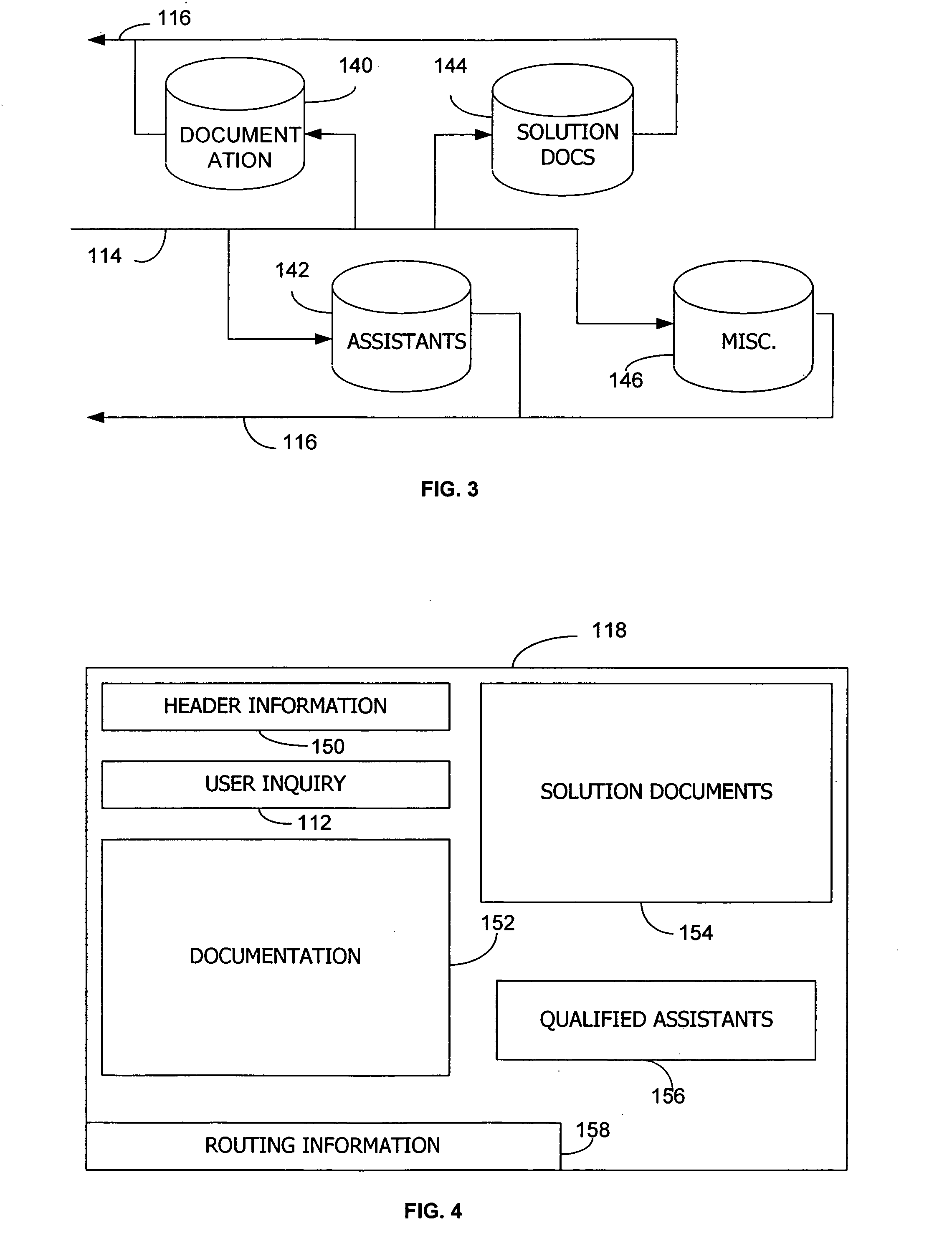
InactiveUS20070136342A1Digital data processing detailsExecution for user interfacesInformation processingPaper document
Processing a user inquiry includes receiving the user inquiry from an input source. The inquiry may then be processed by a processing device to determine various inquiry factors. These factors provide an indication of the content of the inquiry, such as words associated with particular problems, the software or hardware at issue, version information, and other information. The processing device then searches a database using the inquiry factors to retrieve solution information. This solution information includes information regarding troubleshooting and fixing different problems that the user may have encountered. A solution document is generated using this solution information. Using a routing device, the solution document and the user inquiry is thereupon provided to a support assistant to provide directed support to the user.
Owner:SAP AG
Unified event monitoring system
InactiveUS20060178898A1Eliminates the duplicative, time-consuming, paper and fax-intensive processesOffice automationCommerceExtensibilityNetwork management
The present invention provides a system that integrates requests and responses thereto for Operation and Business Support Systems (OSS / BSS) that comprise many discrete and non-inclusive systems with disparate interfaces. The integration of these systems poses a complex problem. Moreover, costs of licenses, maintenance fees, and training for day-to-day use are prohibitively expensive. The present invention is an open and inclusive system that interfaces easily with existing OSS / BSS systems to provide visibility into all network elements and events. It is an advanced, multi-vendor management system designed to increase efficiency and productivity and reduce network administration costs by providing an integrated system for monitoring, troubleshooting, and managing the network. The present invention has as an objective to unite different systems under one common platform. The present invention collects and manipulates information centrally, within a single system, enabling critical data to be shared seamlessly between applications. This provides for Data Consolidation, Data Extendibility, and Reduced Cost. In addition, this solution is robust, as it is expandable and considerate of new systems and technologies as they emerge.
Owner:INTRACOMM
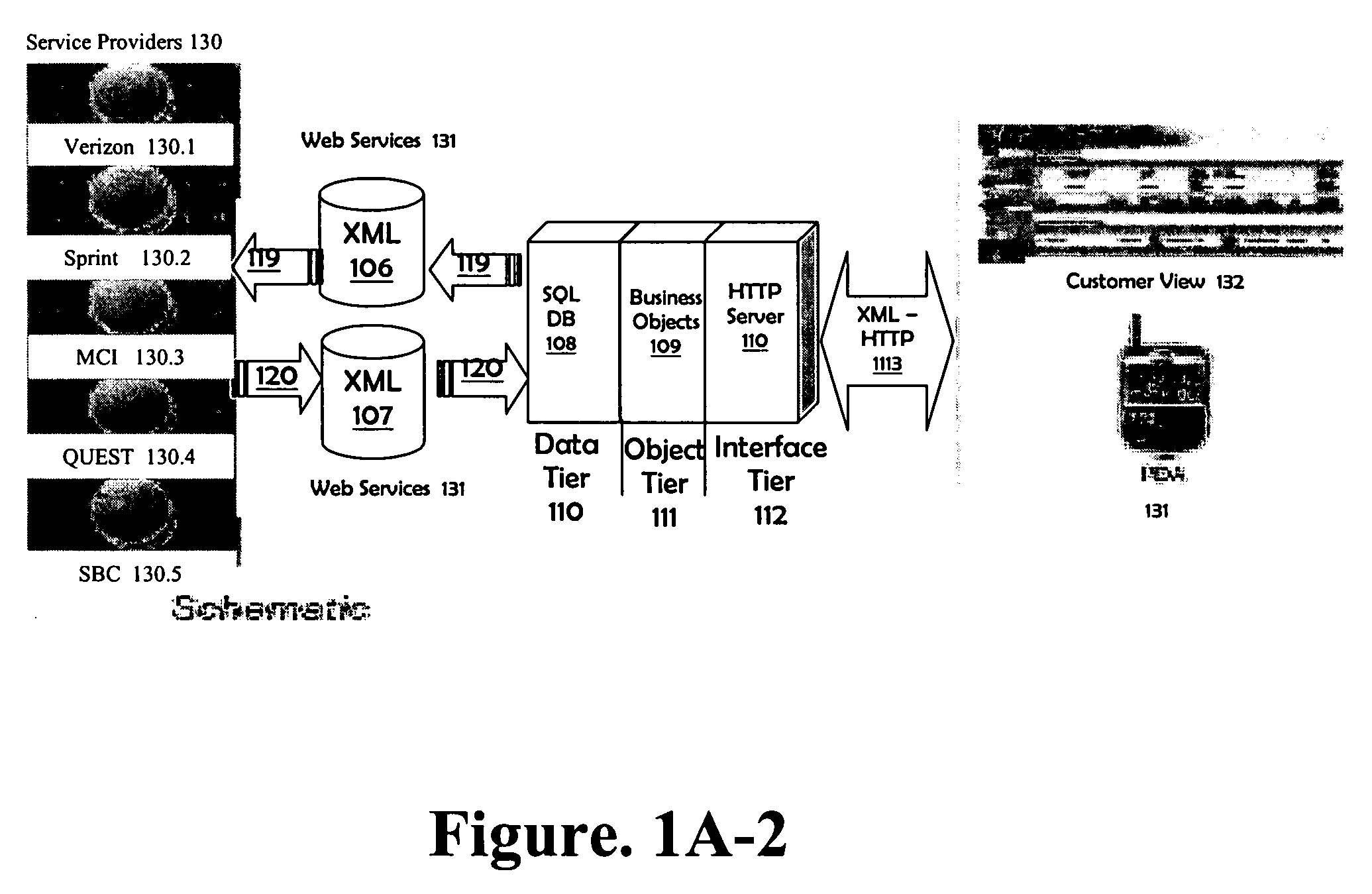
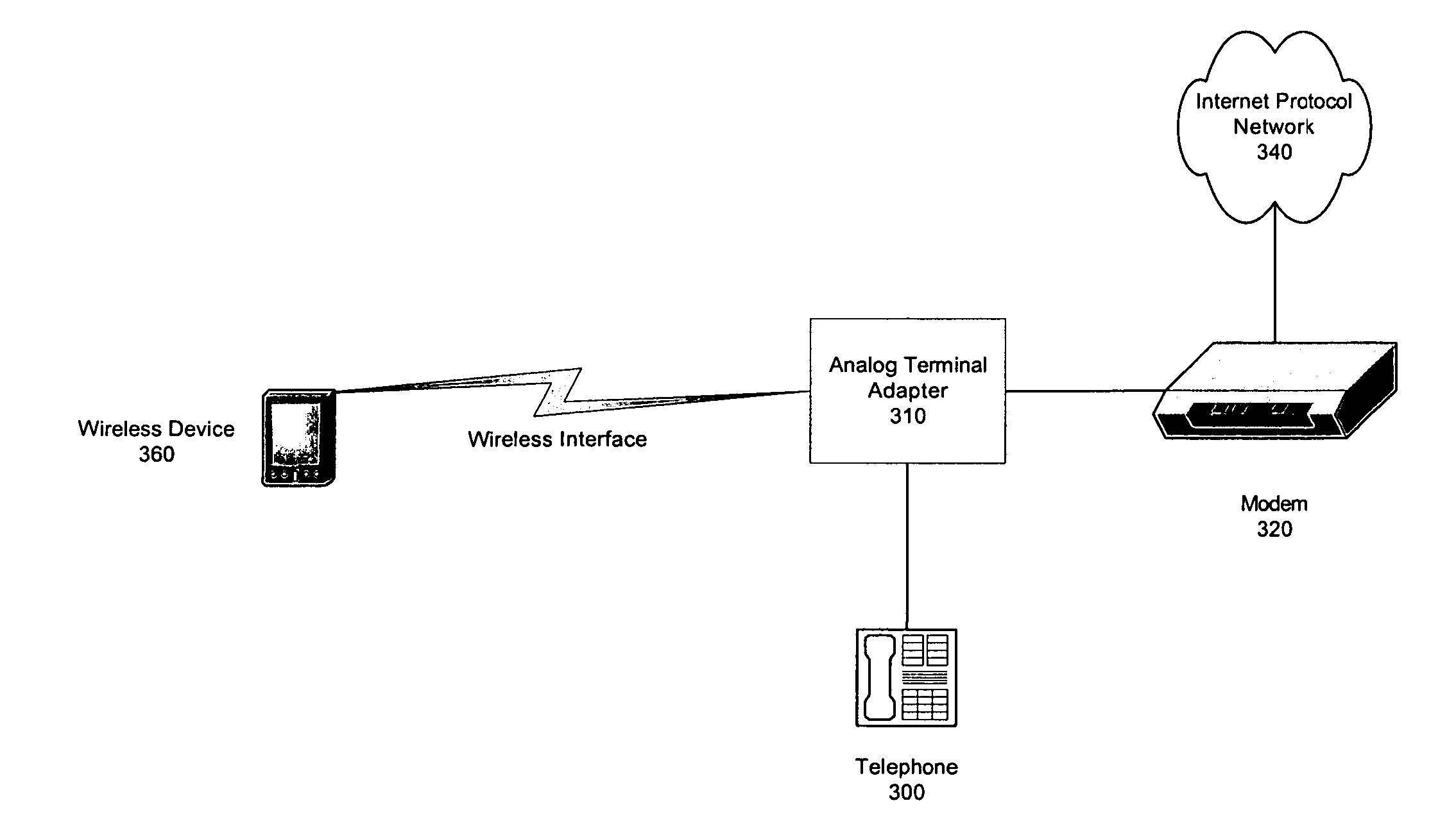
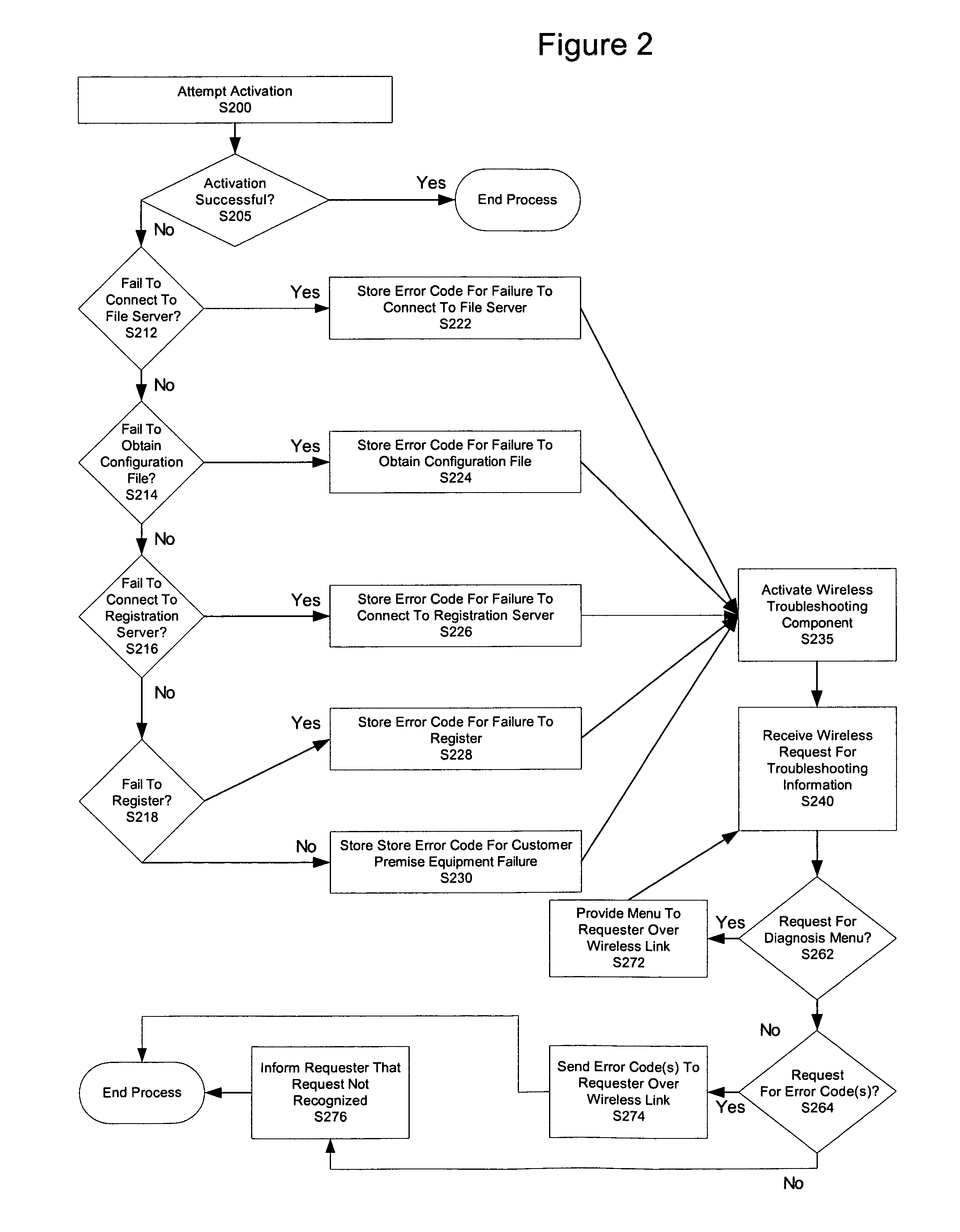
Wireless based troubleshooting of customer premise equipment installation
InactiveUS20070064714A1Network traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationEngineeringCustomer-premises equipment
Troubleshooting of customer premise equipment installation includes receiving a request for troubleshooting information over a wireless link. The troubleshooting also includes providing information relating to an attempt to activate the customer premise equipment over the wireless link in response to receiving the request for troubleshooting information over the wireless link.
Owner:SBC KNOWLEDGE VENTURES LP
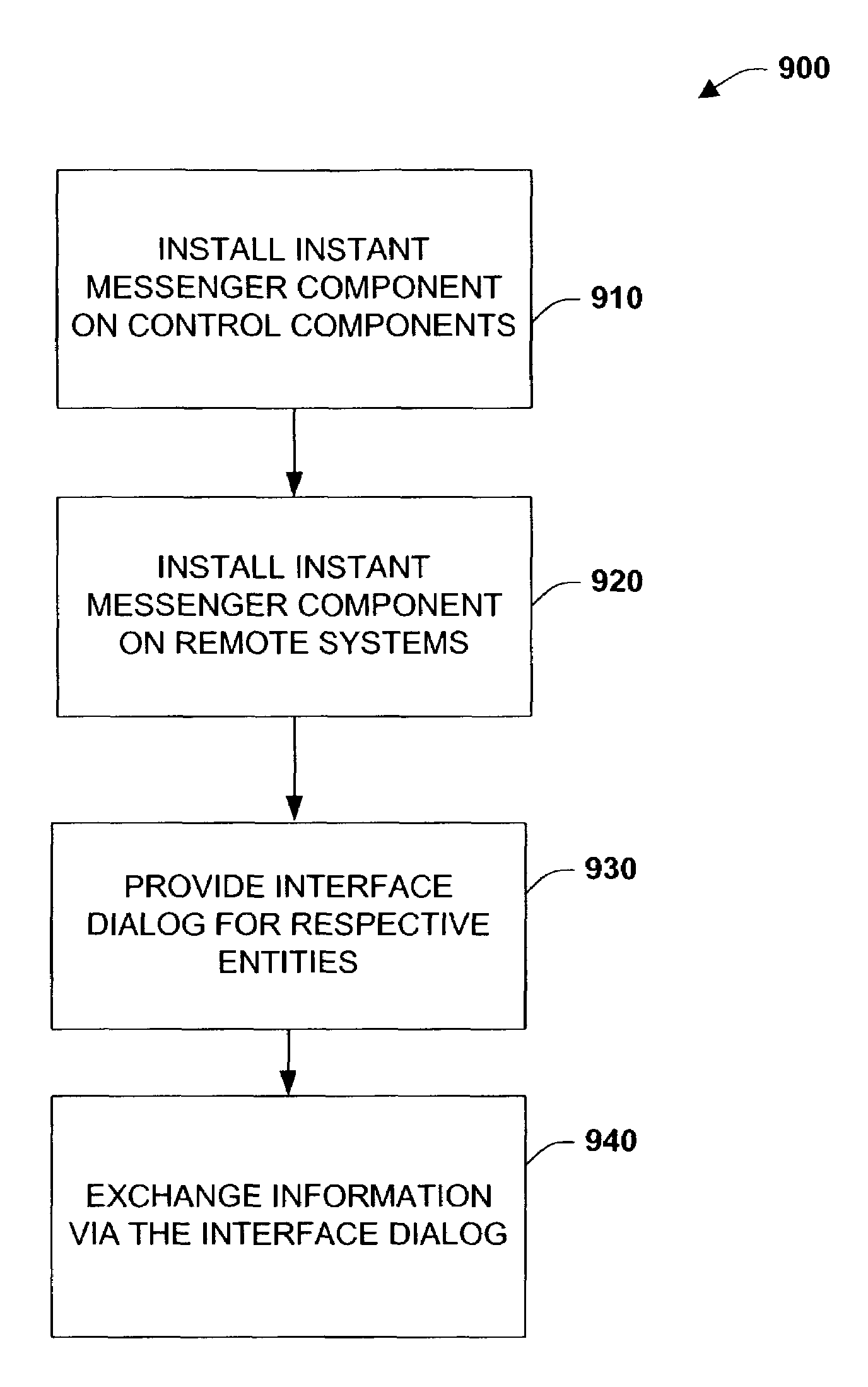
Instant messaging for event notification and exchanging data in an industrial controller environment
ActiveUS7539724B1Facilitate real time message transactionSimple interfaceComputer controlError detection/correctionRemote systemThe Internet
The present invention relates to systems and methods for distributing control information such as event notifications and status in a substantially real time manner. Such information can be provided in a parallel and concurrent manner to many locations / devices and / or users. In addition, multi-directional network communications are provided to facilitate system diagnosis, status, and troubleshooting among various parties and / or devices. In one aspect of the present invention, messaging components may be installed on local control components and remote diagnostic equipment that communicate across a network such as the Internet. If an event is detected, various parties can be contacted by the control components, wherein the parties may communicate in a concurrent manner while receiving control information from the control components. In this manner, diagnosis, troubleshooting, and / or routine maintenance can be performed collaboratively between various control components and remote systems / parties interacting therewith.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Method and system for providing a user-customized electronic book
InactiveUS7236966B1Precise positioningSatisfies needDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsRelevant informationElectronic book
One embodiment of the present invention enables an individual to selectively choose an area(s) of interest and automatically scan a database to intelligently retrieve the relevant information and filter out the irrelevant information. Next, the relevant information may then be collated and made available in an electronic “book” format for ease of distribution. For example, a network administrator may go to his / her company's web page and utilize the present embodiment to download an electronic “book” pertaining to troubleshooting his / her particular network configuration. It is appreciated that the present embodiment may be utilized in a broad number of different areas since it covers any application where there may be a huge database of information and only a part of which may be of interest to selected parties. For example, the present embodiment may be quite useful in areas such as, but not limited to, pharmaceutical, manufacturing, medical, defense, and computer networking.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
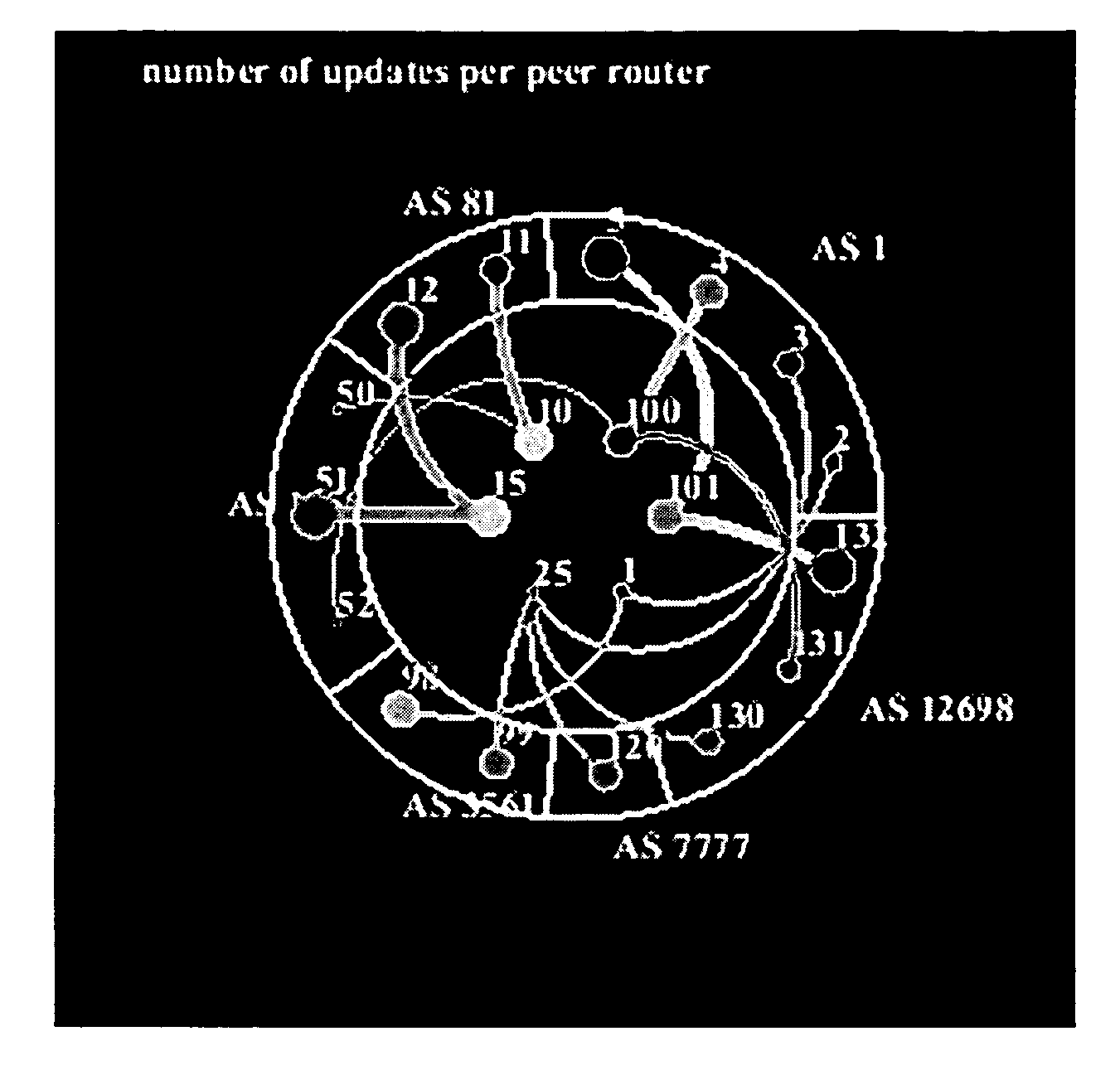
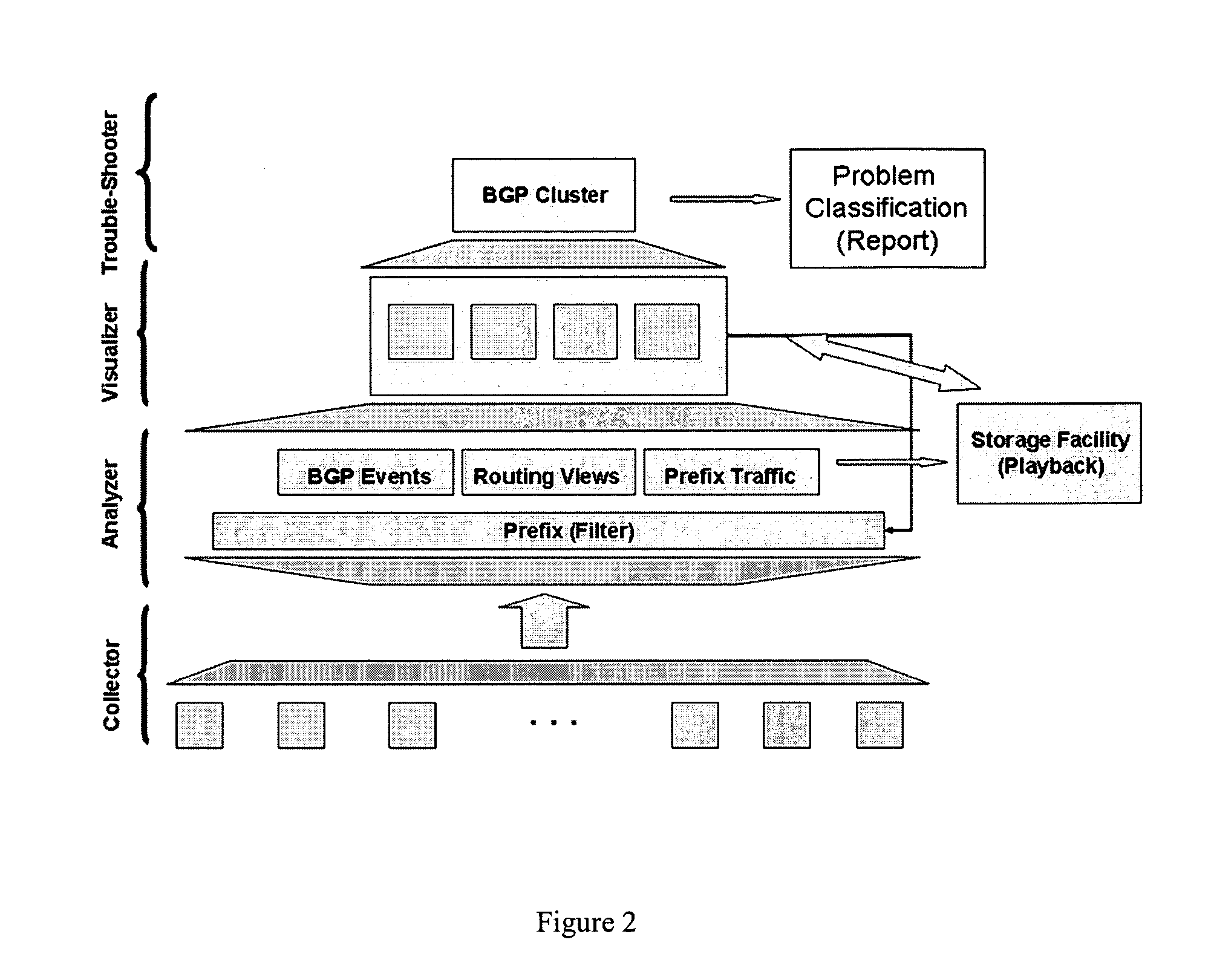
Method for real-time visualization of BGP analysis and trouble-shooting
InactiveUS7945658B1Efficient identificationEfficient reportingError preventionTransmission systemsThe InternetProblem identification
The present invention comprises a multi-tier system. Major goals of the system are to 1) clearly visualize BGP dynamics and alert / report important deviation of BGP dynamics to avoid overwhelming the operators with too much information and 2) analyze the root cause of the problems by using a multi-tier approach, with a light-computational analysis and high-level classification for a real-time problem identification followed by a more rigorous off-line analysis for a further and more detailed trouble shooting. An example embodiment is provided that comprises four modules. The first module comprises a distributed family of collectors in charge of collecting real-time network information. The second module filters out non-relevant prefixes and extracts and profiles key features of the network information. The third module monitors BGP activity from both an Internet-AS and single-AS perspectives by displaying the data in real time and highlighting major shifts or divergence from historical baselines with comprehensive layouts. The forth module is run off-line to focus on a few relevant events that are selected through the first three modules. This is usually a time-consuming phase of the process due to the different temporal and / or spatial correlation that must be run across several sets of data. During this phase, the system can spend more time to better identify the real cause of the problem.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Playing card shuffler with differential hand count capability
A programmable card handling machine with a display and appropriate inputs for adjusting the machine to any of a number of games comprises inputs including a number of cards per hand selector, a card game selector, a number of hands delivered selector and a trouble-shooting input. These features also provide for interchangeability of the apparatus for many different games, for many types of cards or decks and in different locations thereby reducing the number of back-up machines or units required at a casino. The display may include a game mode or game selected display, and use a cycle rate and / or hand count monitor and display for determining or monitoring the usage of the machine. The card-handling machine is capable of randomly selecting numbers of cards to be delivered in a hand of cards to players and the dealer during a round of a casino table card game.
Owner:LNW GAMING INC
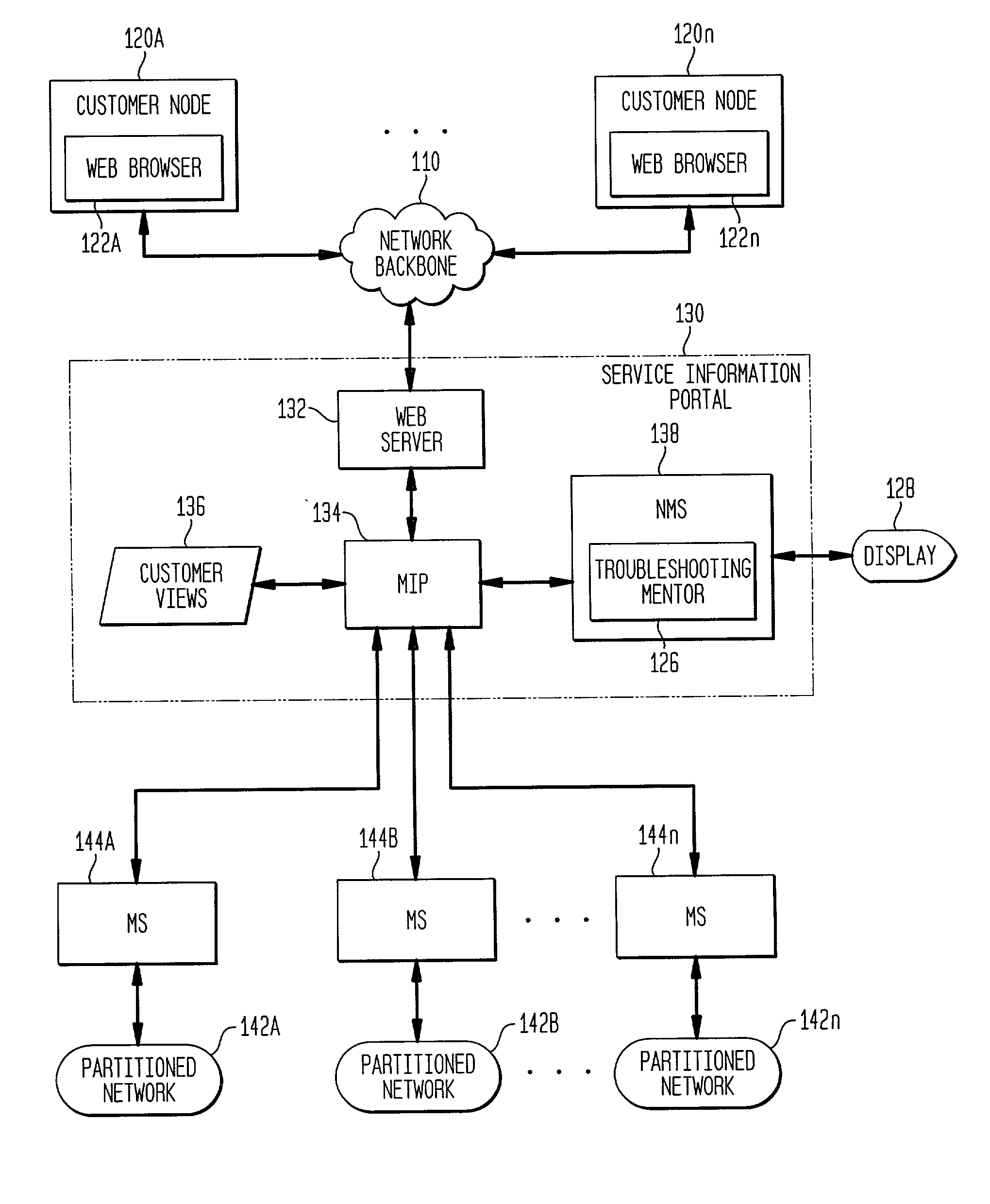
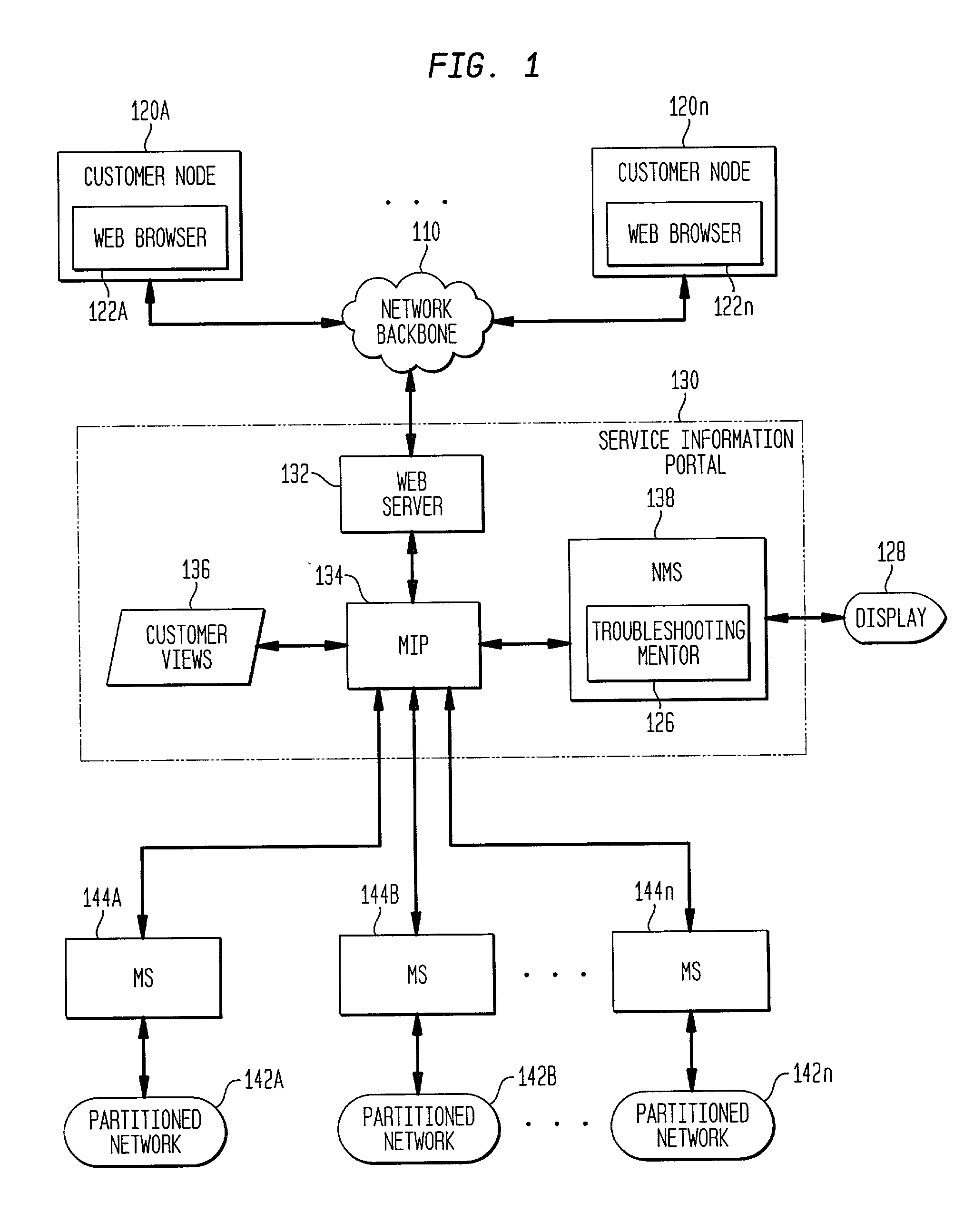
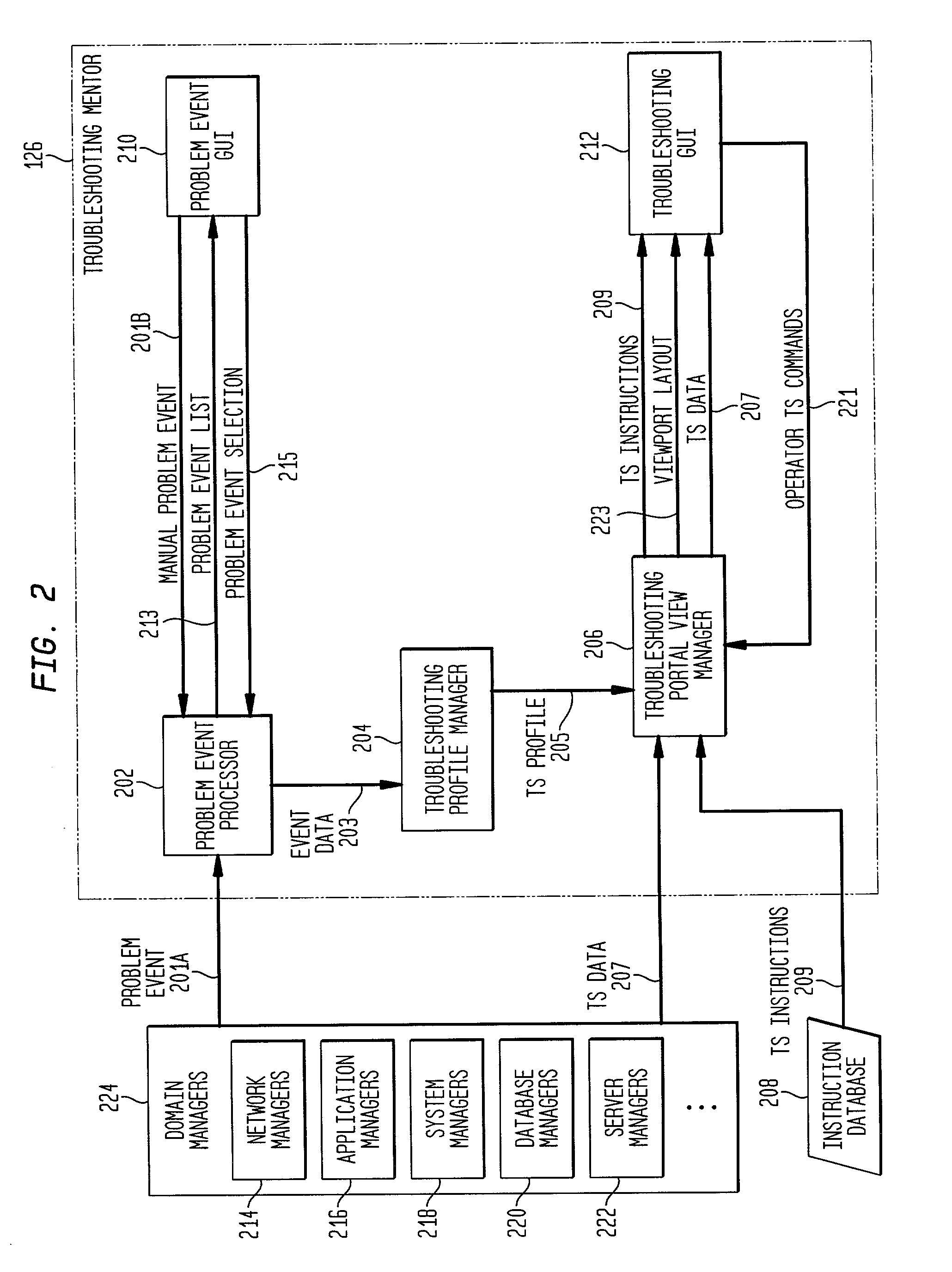
Dynamic generation of context-sensitive data and instructions for troubleshooting problem events in information network systems
InactiveUS20020161875A1Easy diagnosisEliminate needError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsDiagnostic dataRelevant information
A system and method for dynamically providing information to an administrator of a computing environment such as an administrator of a network system that is relevant to a particular problem event. This information includes contextual instructions and diagnostic data that will assist the network administrator in the analysis of the problem event. Generally, the invention automatically obtains from relevant computing environment entities pertinent information likely to be necessary to troubleshoot the particular problem event. The context-sensitive information is presented dynamically on a display for consideration and interaction by the network administrator. Specifically, the invention includes a database of executable troubleshooting (TS) profiles each specifically designed for a particular type of problem event. Each such TS profile references one or more troubleshooting data miner modules included in a library of such modules that accesses particular hardware or software entities in the network system for particular information. When a TS profile is invoked to assist a network administrator troubleshoot a particular type of problem event, the referenced data miner modules are executed and generate or cause the generator of troubleshooting instructions and diagnostic data which is then displayed to the network administrator.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
Playing card shuffler with differential hand count capability
A programmable card handling machine with a display and appropriate inputs for adjusting the machine to any of a number of games comprises inputs including a number of cards per hand selector, a card game selector, a number of hands delivered selector and a trouble-shooting input. These features also provide for interchangeability of the apparatus for many different games, for many types of cards or decks and in different locations thereby reducing the number of back-up machines or units required at a casino. The display may include a game mode or game selected display, and use a cycle rate and / or hand count monitor and display for determining or monitoring the usage of the machine. The card-handling machine is capable of randomly selecting numbers of cards to be delivered in a hand of cards to players and the dealer during a round of a casino table card game.
Owner:LNW GAMING INC
Method and apparatus of measuring and reporting data gap from within an analysis tool
ActiveUS20090296593A1Enhanced authenticationAccurately determineError preventionTransmission systemsInternet trafficNetwork tap
Network data gap is determined and reported to enable a user to validate that all the traffic that was intended to be monitored is being monitored in monitoring and / or troubleshooting tools for observation of network traffic and network installation and maintenance. Span port oversubscription, incomplete span configuration, incorrectly placed network taps and monitoring device packet drop may thereby be detected and reported as data gap.
Owner:NETSCOUT SYSTEMS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com