Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
133 results about "Knowledge sources" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
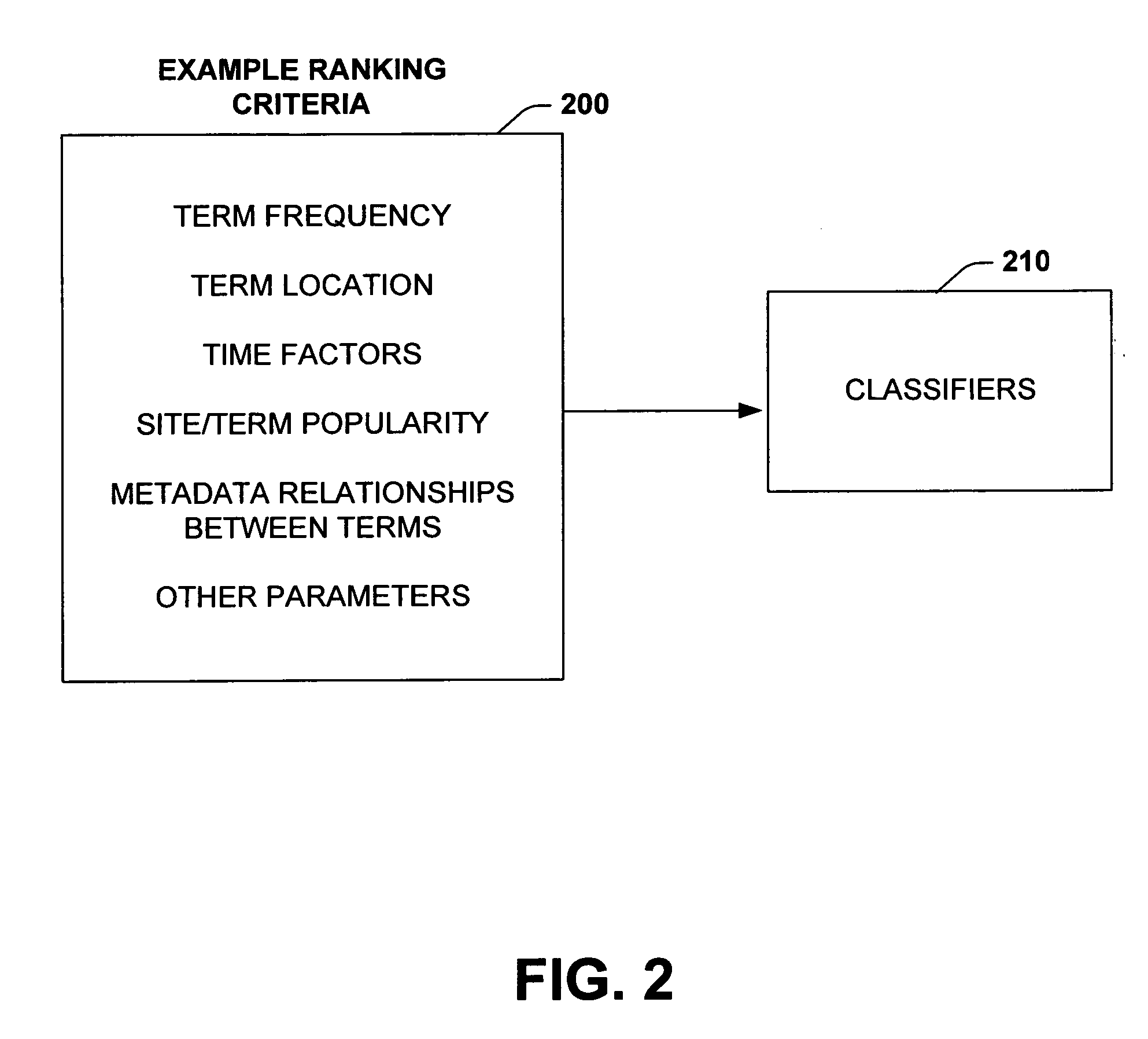
What is Knowledge Source. 1. A source of data, information, or knowledge, which can be explicitly specified. 2. An individual who provides content to a knowledge repository. 3. A source from which knowledge, with practical applications can be obtained, such as know how, know what, know where, and so forth.
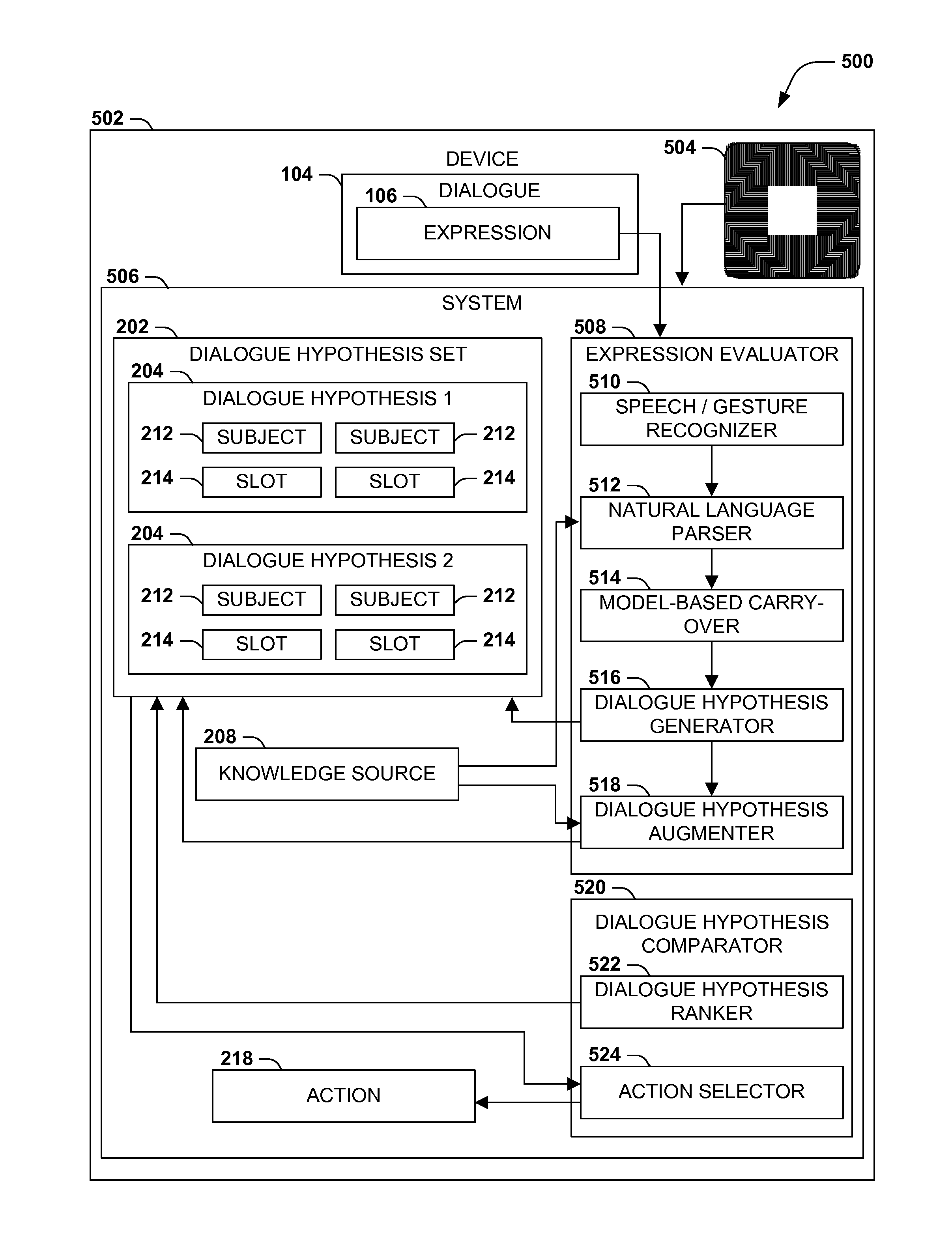
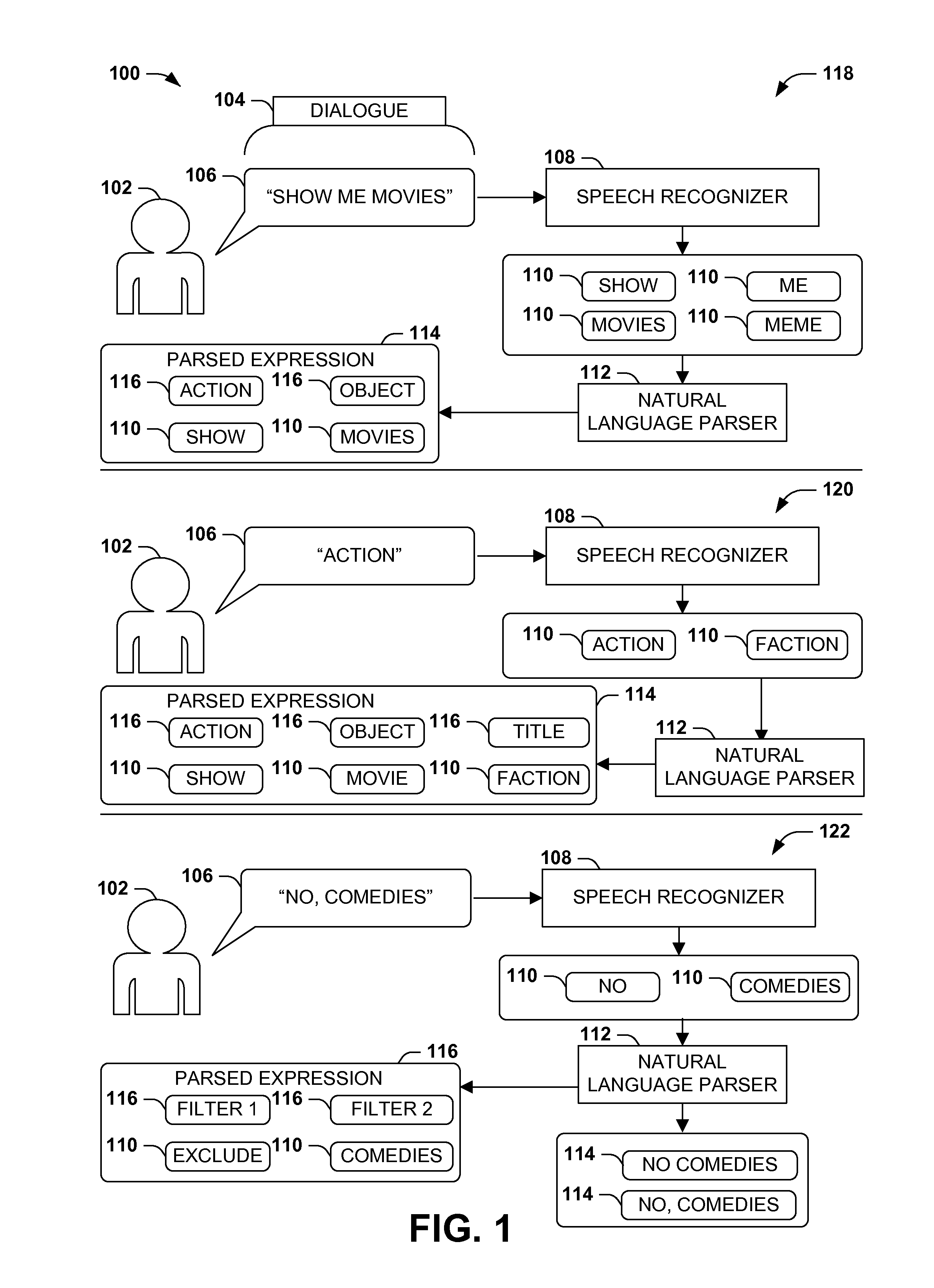
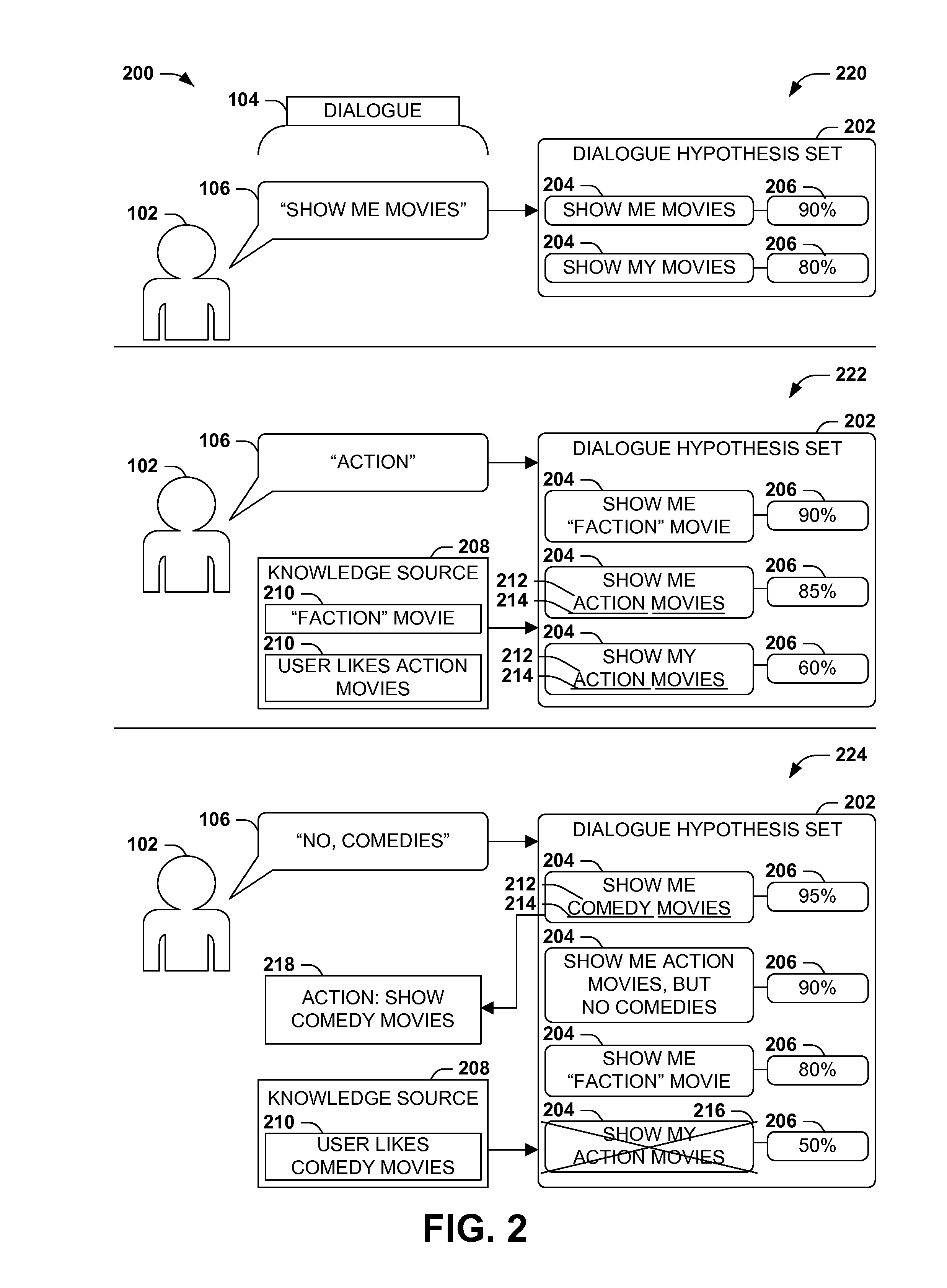
Dialogue evaluation via multiple hypothesis ranking
ActiveUS20150142420A1Reduce settingsNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionKnowledge sourcesMultiple hypothesis
In language evaluation systems, user expressions are often evaluated by speech recognizers and language parsers, and among several possible translations, a highest-probability translation is selected and added to a dialogue sequence. However, such systems may exhibit inadequacies by discarding alternative translations that may initially exhibit a lower probability, but that may have a higher probability when evaluated in the full context of the dialogue, including subsequent expressions. Presented herein are techniques for communicating with a user by formulating a dialogue hypothesis set identifying hypothesis probabilities for a set of dialogue hypotheses, using generative and / or discriminative models, and repeatedly re-ranks the dialogue hypotheses based on subsequent expressions. Additionally, knowledge sources may inform a model-based with a pre-knowledge fetch that facilitates pruning of the hypothesis search space at an early stage, thereby enhancing the accuracy of language parsing while also reducing the latency of the expression evaluation and economizing computing resources.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
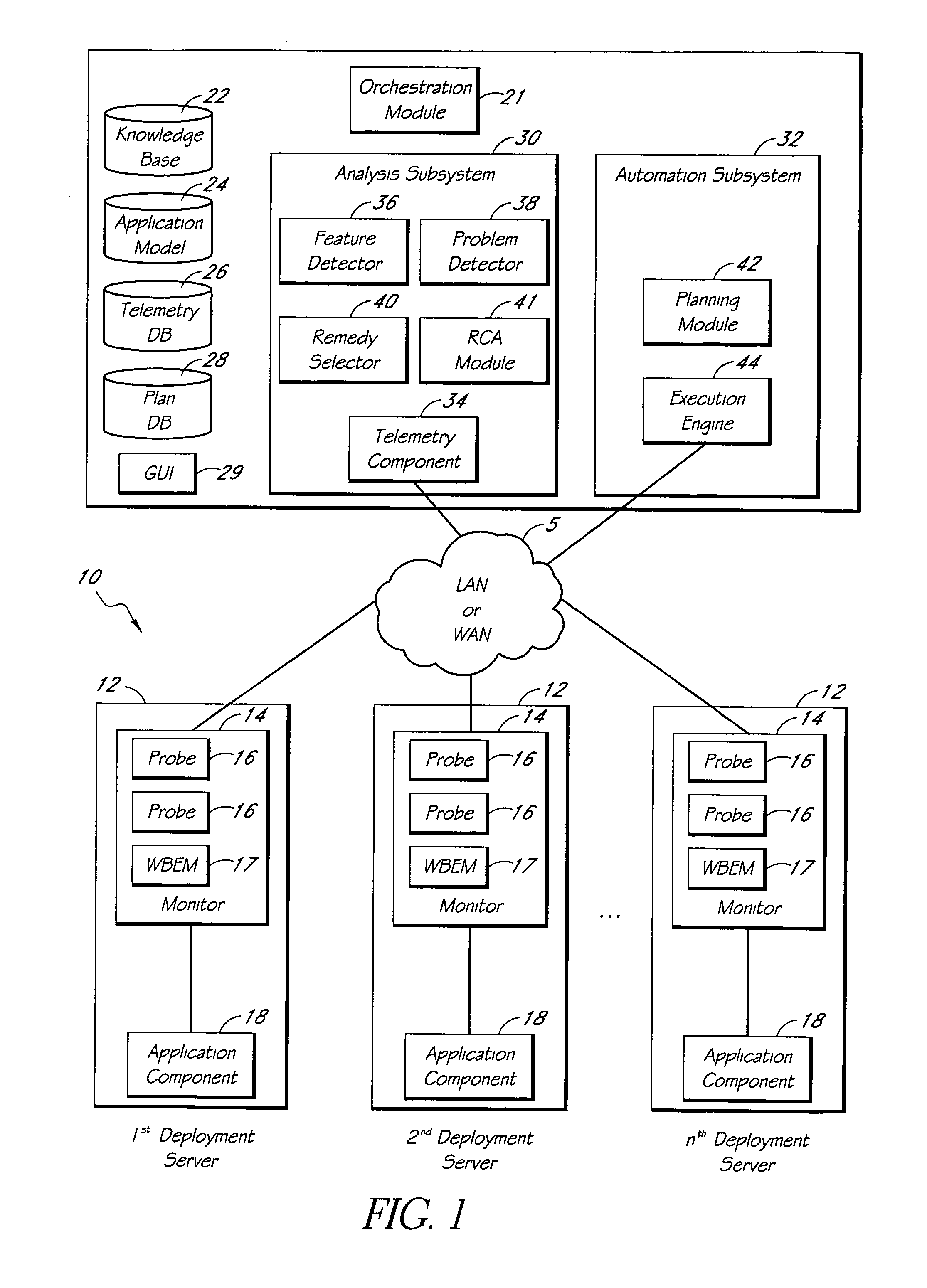
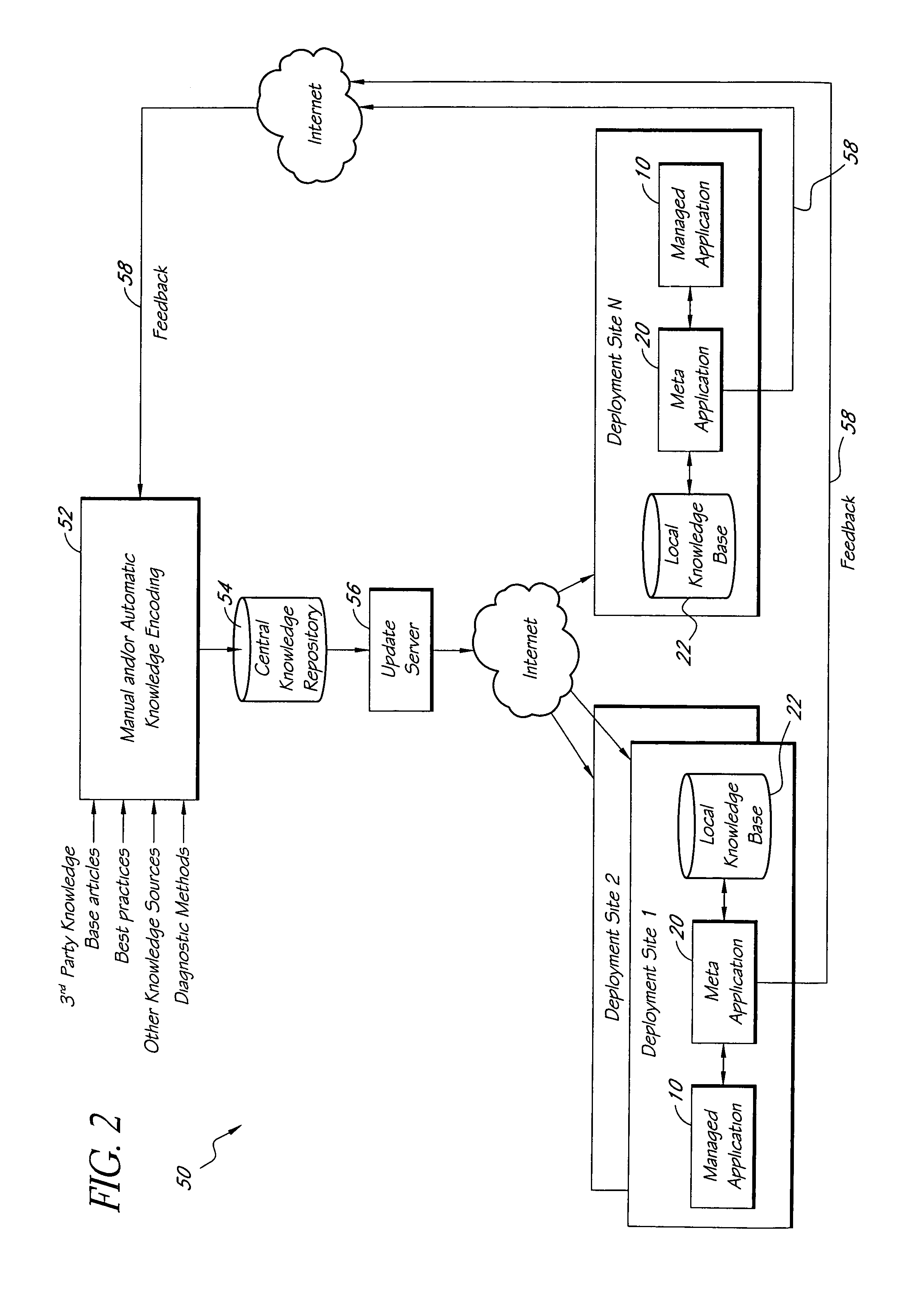
Systems and methods for encoding knowledge for automated management of software application deployments
ActiveUS7490073B1Efficient mappingGreat leverageError detection/correctionChaos modelsKnowledge sourcesSoftware
A method of encoding knowledge is disclosed, which can be used to automatically detect problems in software application deployments. The method includes accessing a source of knowledge describing a problem known to occur in deployments of a particular software application, and which identifies a plurality of conditions associated with the problem. An encoded representation of the knowledge source is generated according to a predefined knowledge encoding methodology. The encoded representation is adapted to be applied automatically by a computer to analyze data representing a current state of a monitored deployment of the software application to detect whether the conditions and the problem exist therein. In various implementations, the encoded representation of the knowledge can include queries for deployment information, information concerning the relative importance of the conditions to a detection of the problem, and / or logical constructs for computing a confidence value in the existence of the problem and for determining whether to report the problem if some of the conditions are not true. The knowledge source can comprise a text document (such as a knowledge base article), a flowchart of a diagnostic troubleshooting method, and the like. Also disclosed are methods of at least partially automating the encoding process.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
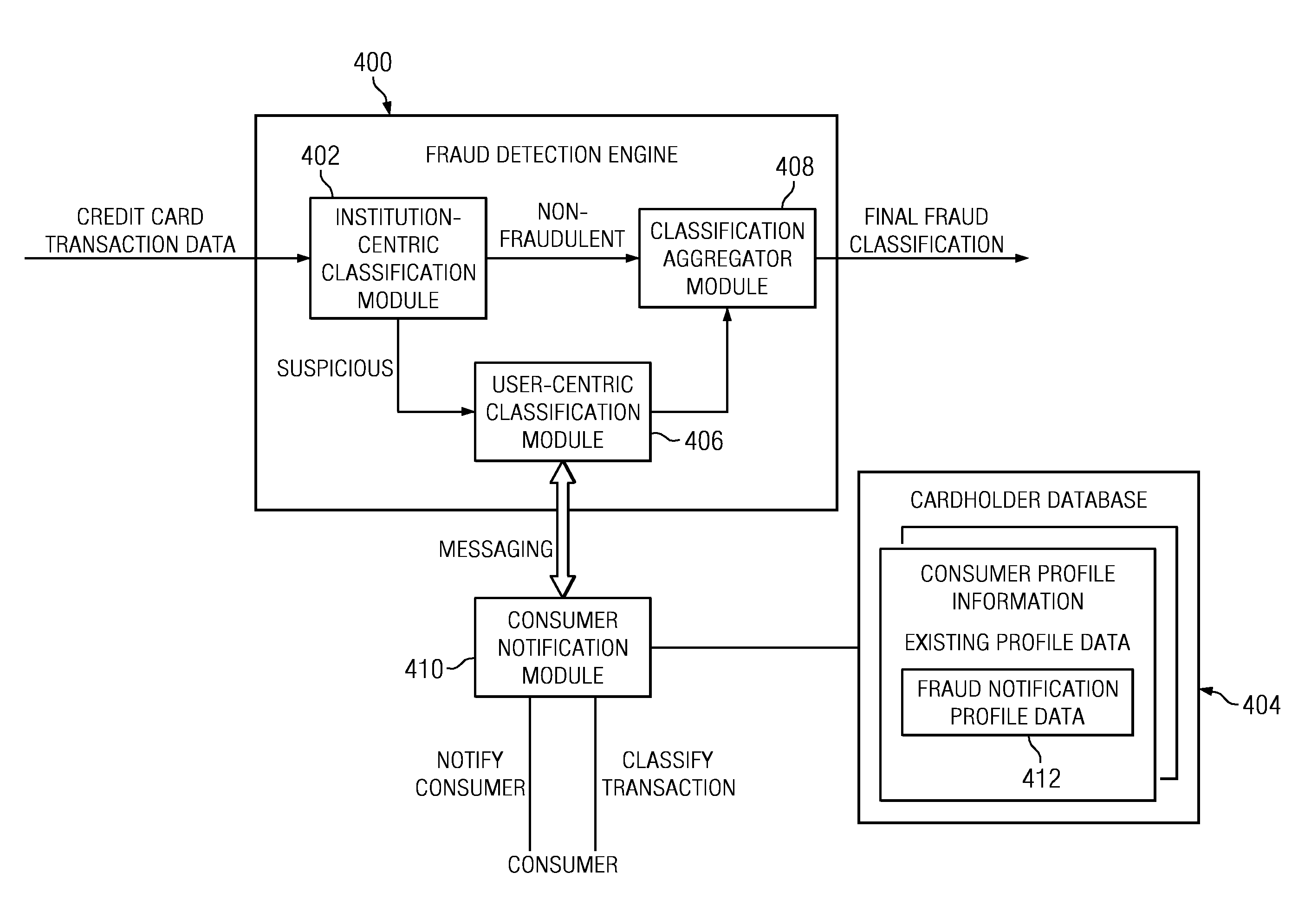
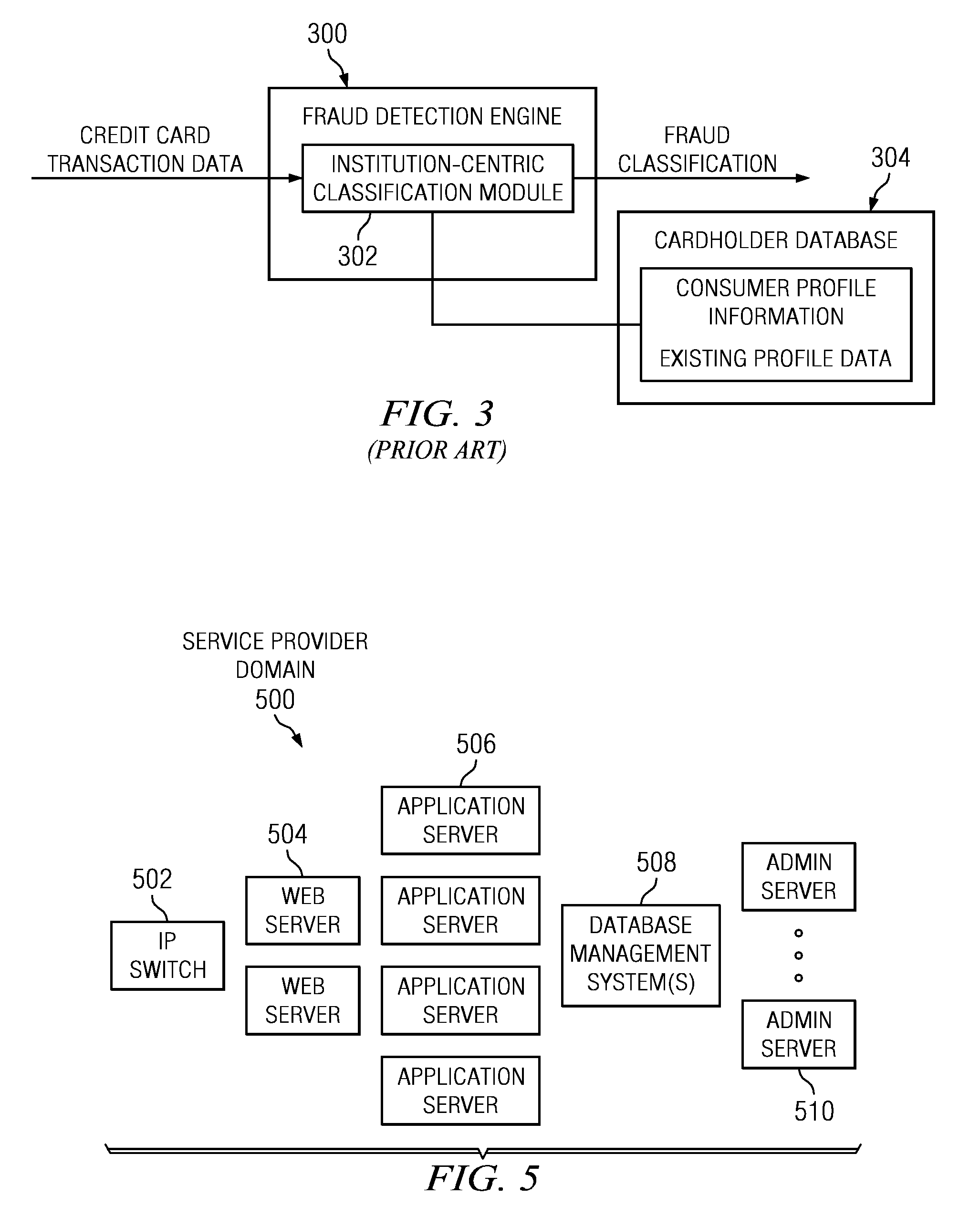
Method and System for Identification By A Cardholder of Credit Card Fraud
A method for fraud detection leverages an existing financial institution's fraud classification functionality, which produces a first level detection, with a “user-centric” classification functionality, which produces a “second” or more fine-grained detection regarding a potentially fraudulent transaction. After passing through an existing (“institution-centric”) fraud detection technique, a transaction that has been identified as potentially fraudulent is then subject to further analysis and classification at the “user” level, as it is the user is presumed to be the best source of knowledge of the legitimate credit card use. Information about the transaction is shared with the consumer, preferably via one or more near real-time mechanisms, such as SMS, email, or the like. Based on the user's response (or lack thereof, as the case may be), one or more business rules in the institution's fraud detection system can then take an appropriate action (e.g., no action, reverse the transaction if complete, deny the transaction if in-progress, or the like).
Owner:IBM CORP
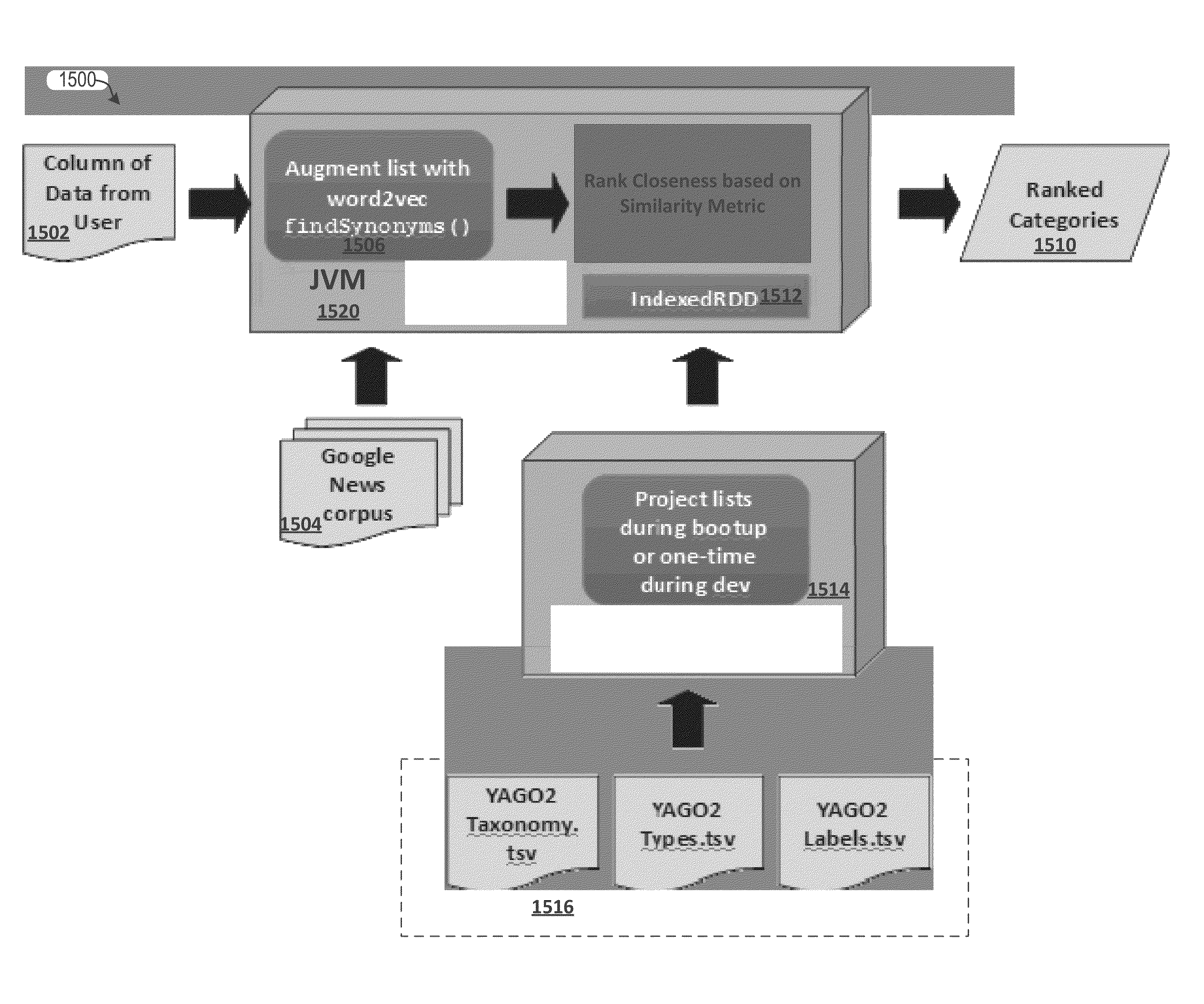
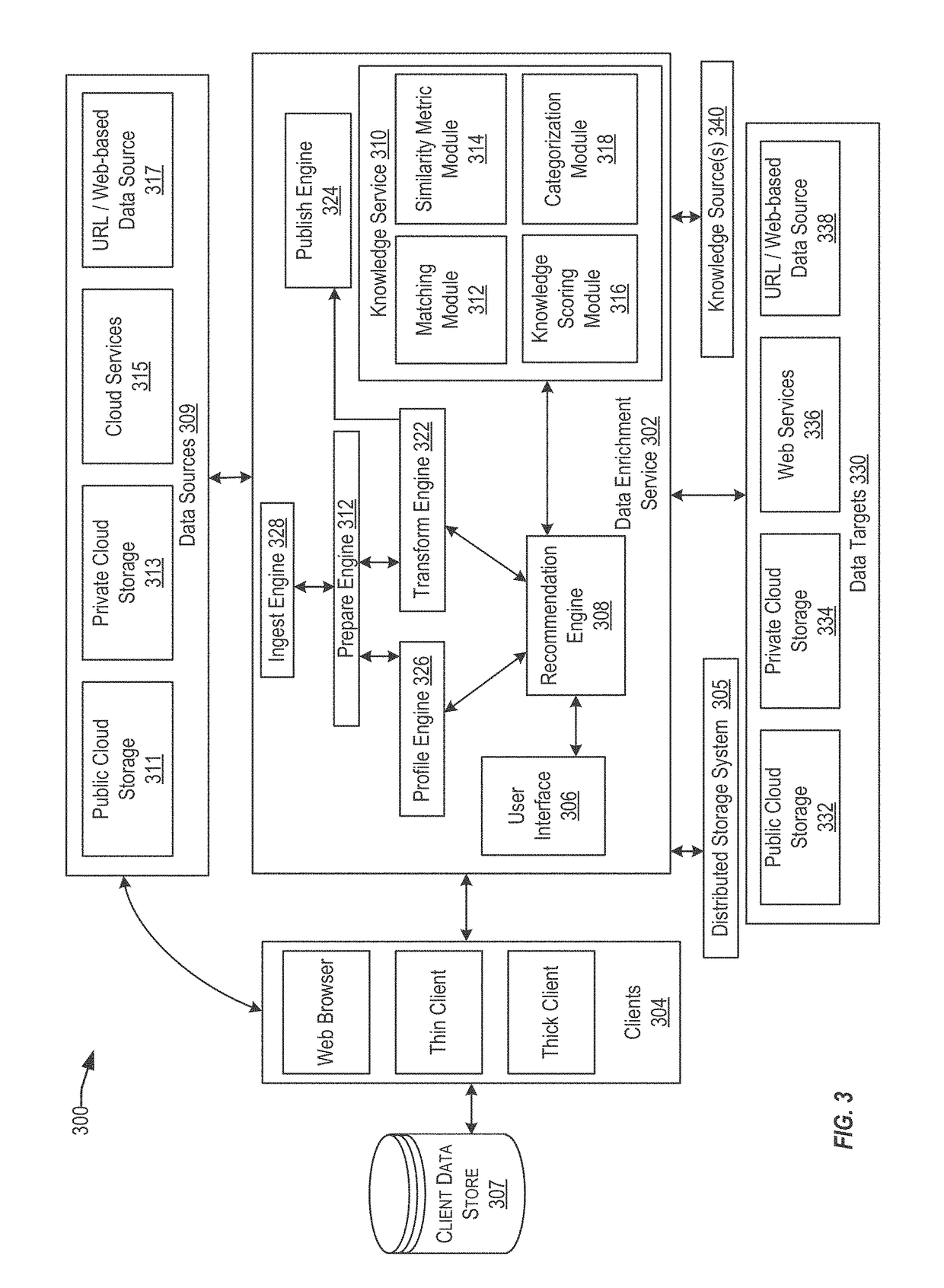
Techniques for similarity analysis and data enrichment using knowledge sources
ActiveUS20160092557A1Accurate resolutionAccurate labelingDigital data processing detailsRelational databasesKnowledge sourcesData set
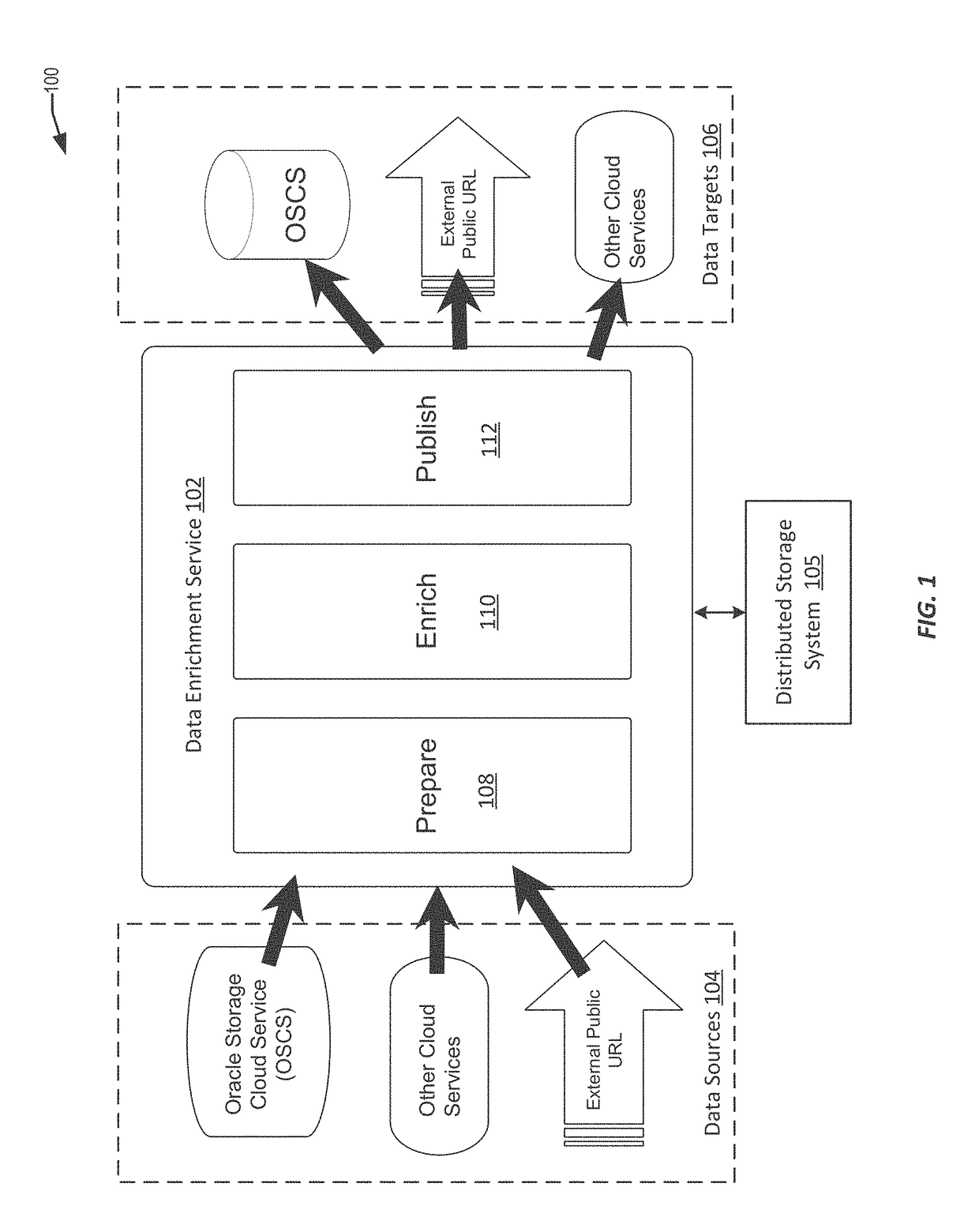
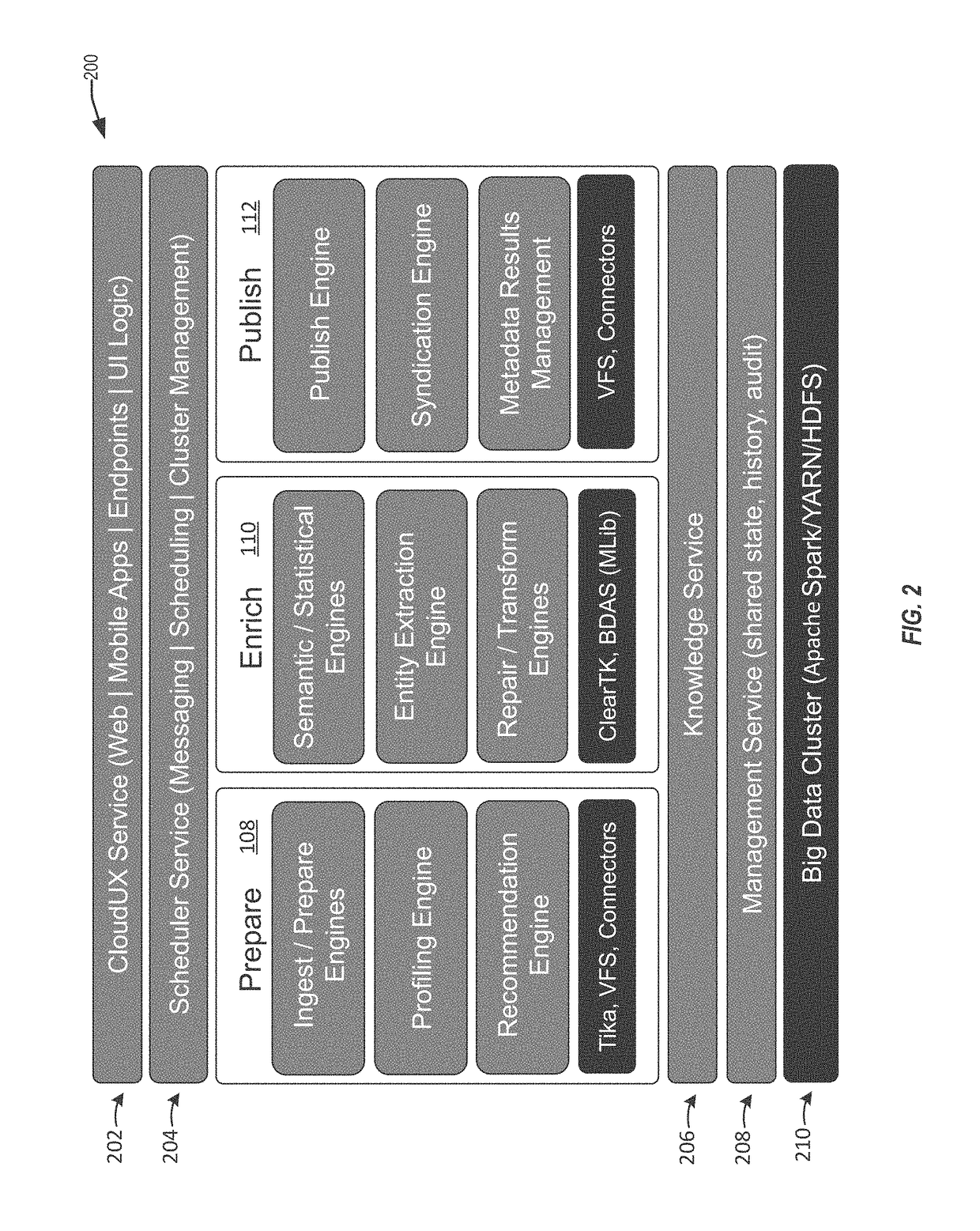
The present disclosure relates to performing similarity metric analysis and data enrichment using knowledge sources. A data enrichment service can compare an input data set to reference data sets stored in a knowledge source to identify similarly related data. A similarity metric can be calculated corresponding to the semantic similarity of two or more datasets. The similarity metric can be used to identify datasets based on their metadata attributes and data values enabling easier indexing and high performance retrieval of data values. A input data set can labeled with a category based on the data set having the best match with the input data set. The similarity of an input data set with a data set provided by a knowledge source can be used to query a knowledge source to obtain additional information about the data set. The additional information can be used to provide recommendations to the user.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
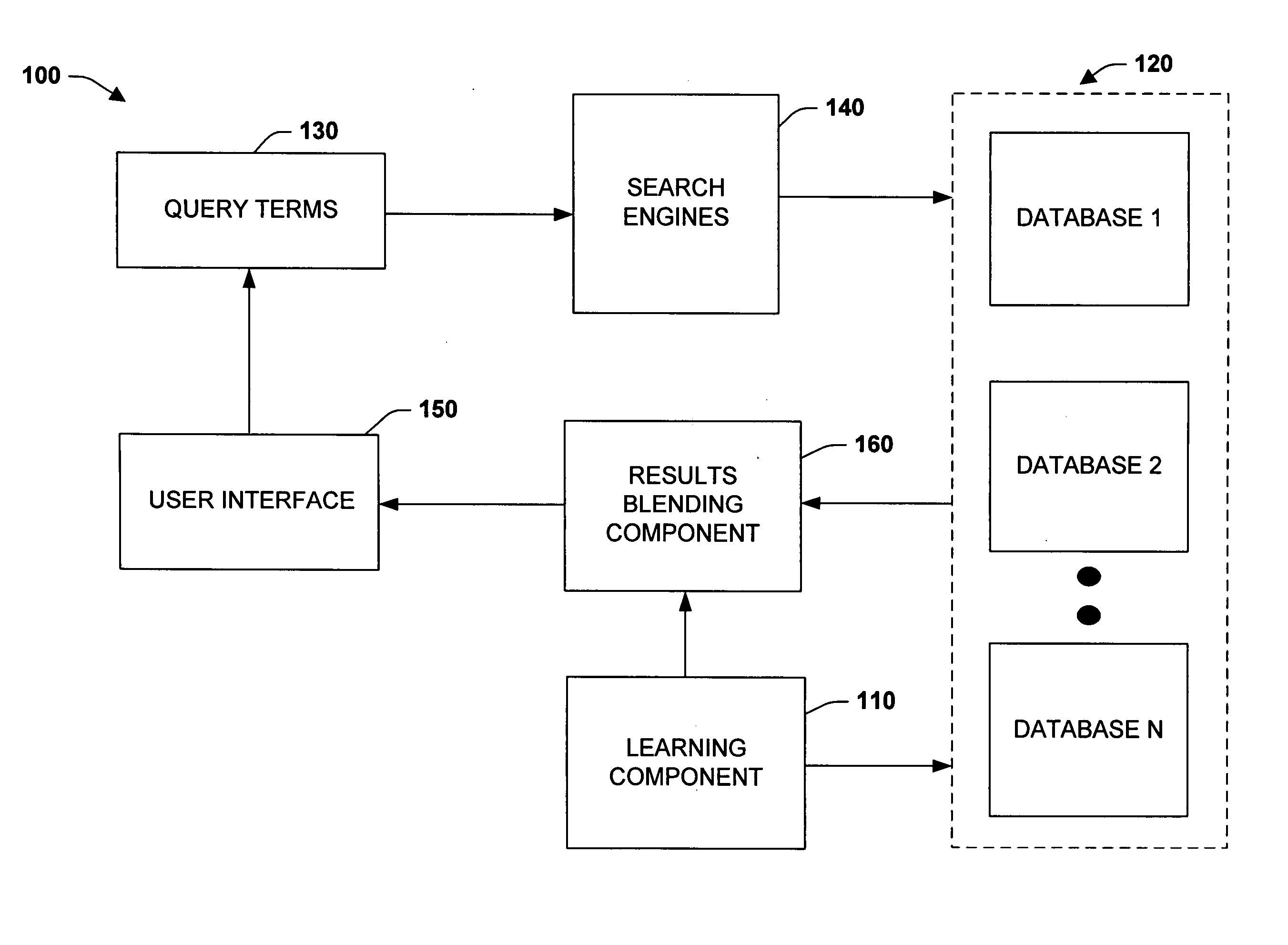
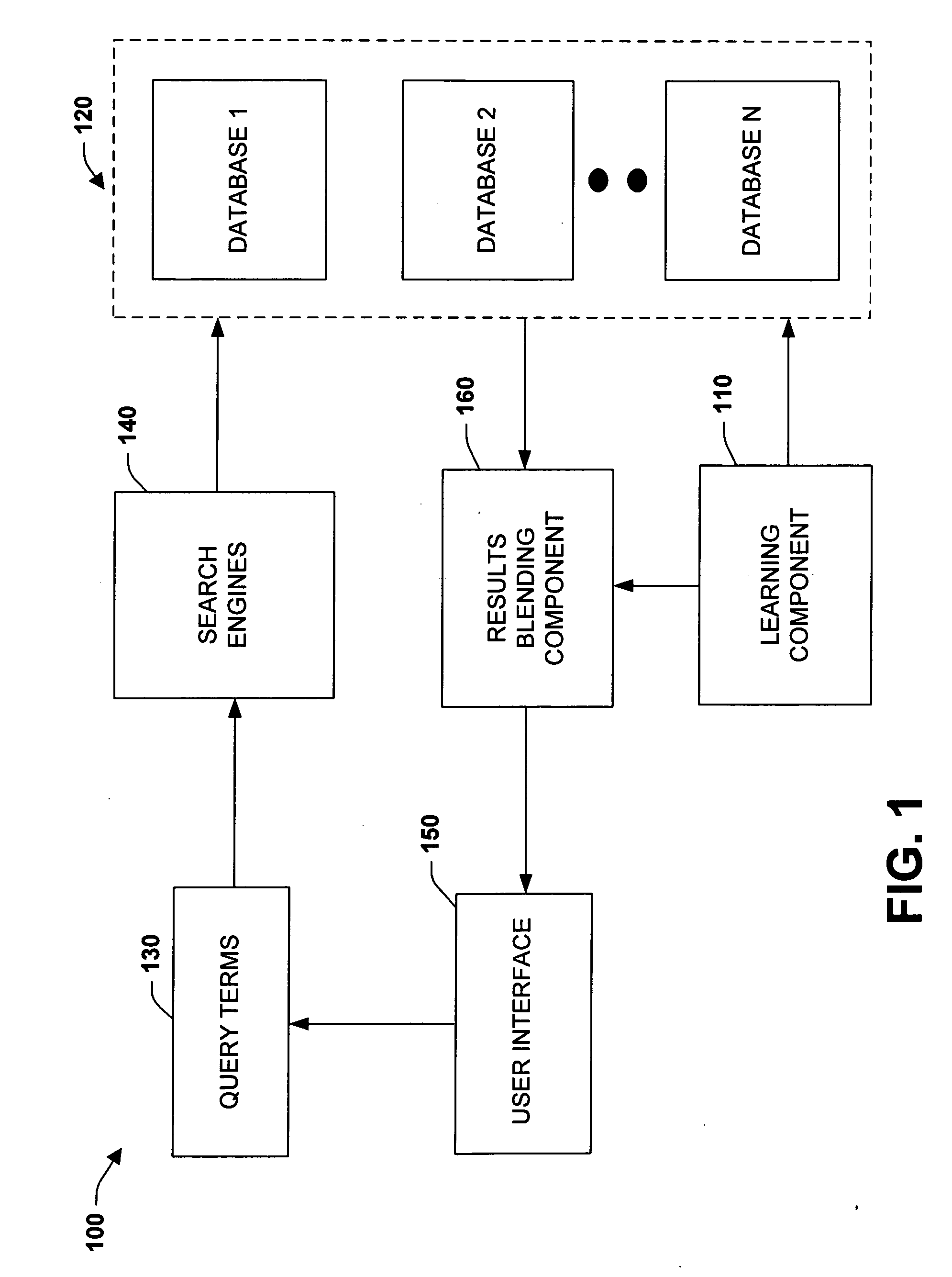
Intelligent search results blending
InactiveUS20060287980A1Well formedShorten the timeWeb data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsKnowledge sourcesRanking
The subject invention relates to systems and methods that automatically combine or interleave received search results from across knowledge databases in a uniform and consistent manner. In one aspect, an automated search results blending system is provided. The system includes a search component that directs a query to at least two databases. A learning component is employed to rank or score search results that are received from the databases in response to the query. A blending component automatically interleaves or combines the results according to the rank in order to provide a consistent ranking system across differing knowledge sources and search tools.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Automatic inquiring and answering method and system
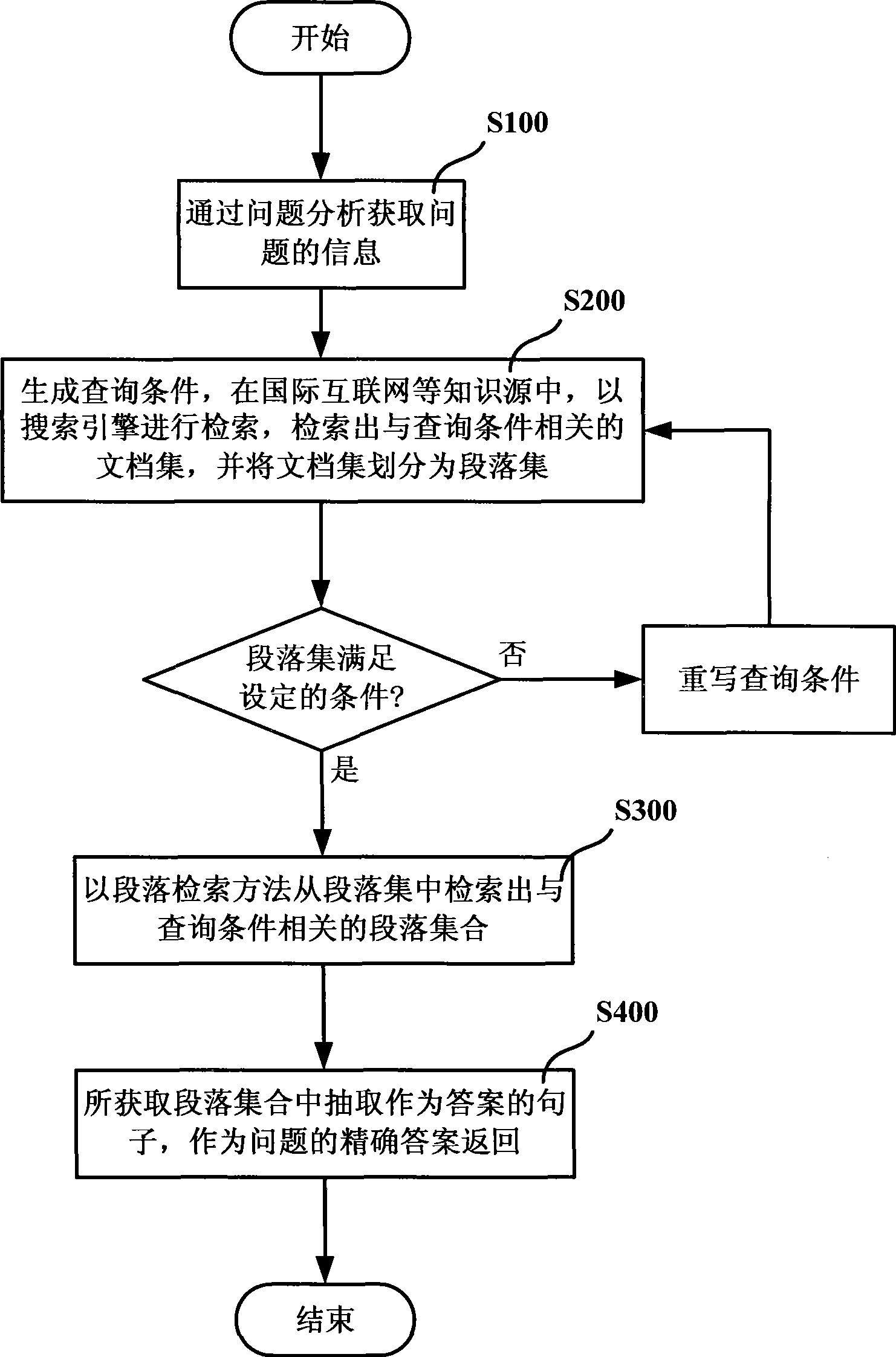
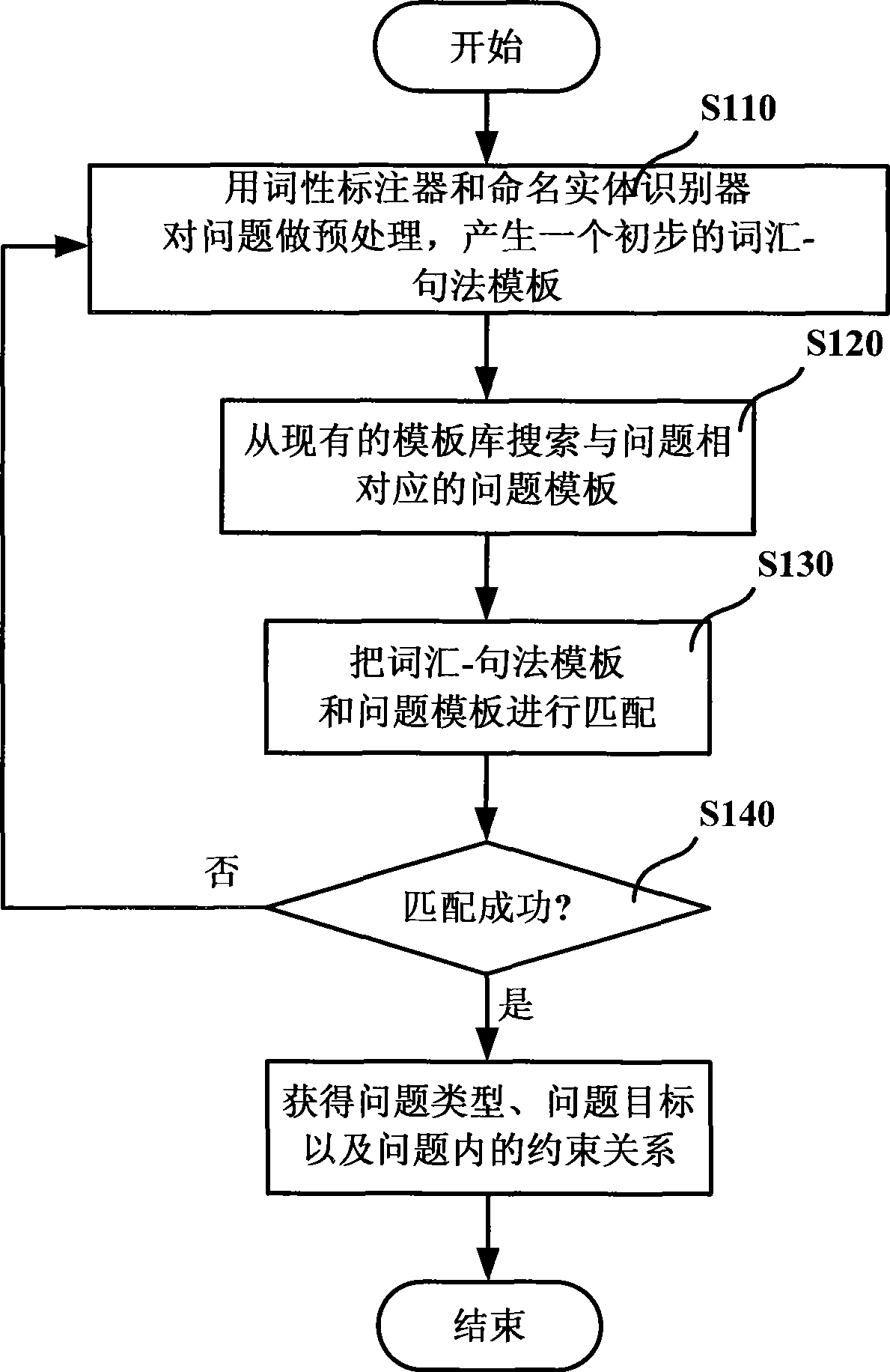
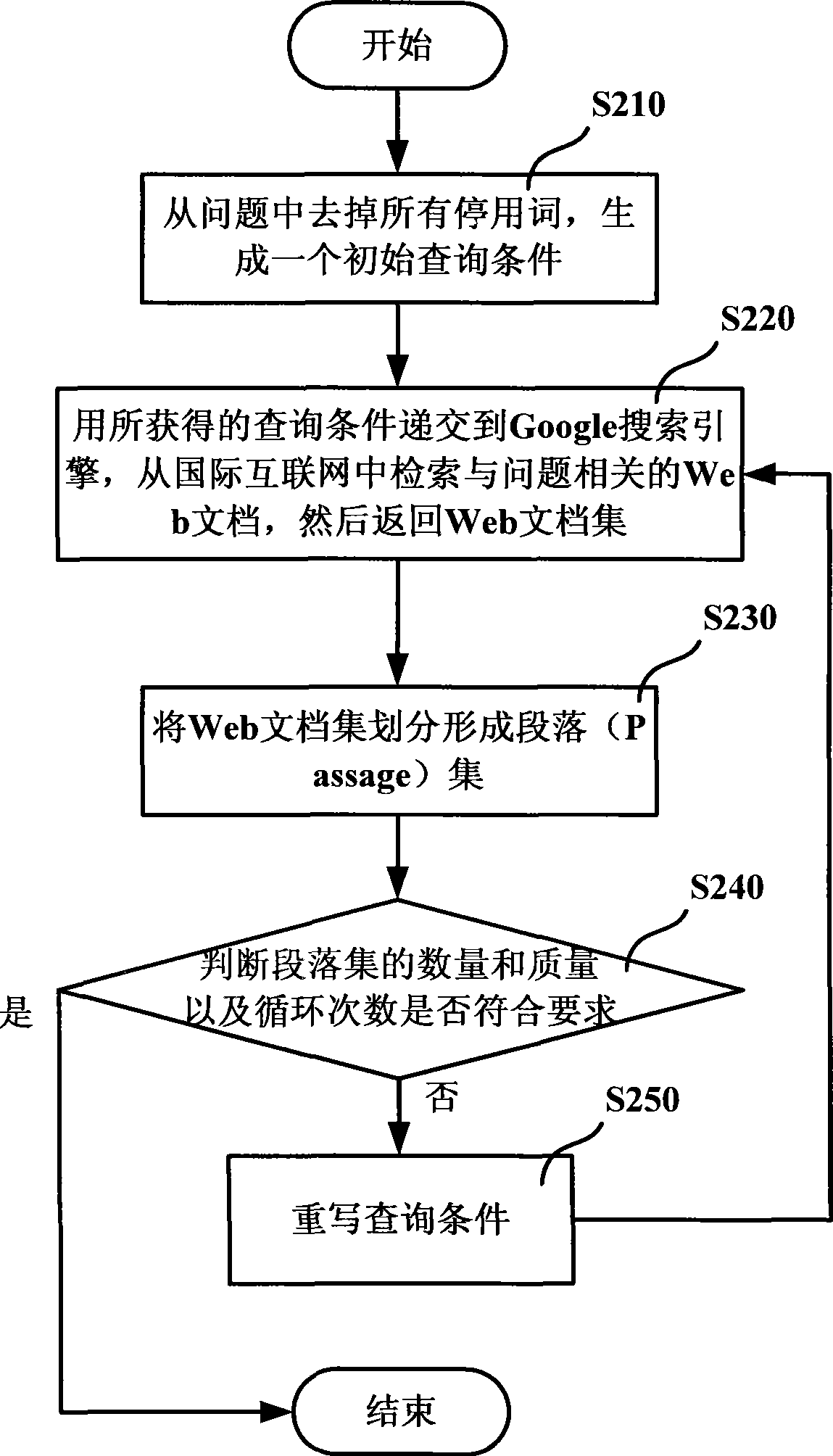
InactiveCN101377777ASpeed up searchReduce sizeKnowledge representationSpecial data processing applicationsKnowledge sourcesQuestion analysis
The invention discloses an automatic question answering method and a system thereof. The automatic question answering method comprises the following steps: step A, the information of a question is acquired through the analysis of the question; step B, the query criterion is generated according to the analysis results of the question for retrieval by using the search engine in knowledge source, thus searching out the file collection relating to the query criterion; the file collection is divided into paragraph collections; step C, paragraph collections relating to the query criterion are retrieved in a centralized way from the paragraphs by using the paragraph retrieval method according to the file retrieval results; and the answer of the question is returned from the paragraph collections. The automatic question answering method and the system improve the accuracy of answers and the precision of returning correct results.
Owner:北京百问百答网络技术有限公司
Using computational engines to improve search relevance
ActiveUS20120005219A1Improve relevanceHighly relevantDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsKnowledge sourcesRecommender system
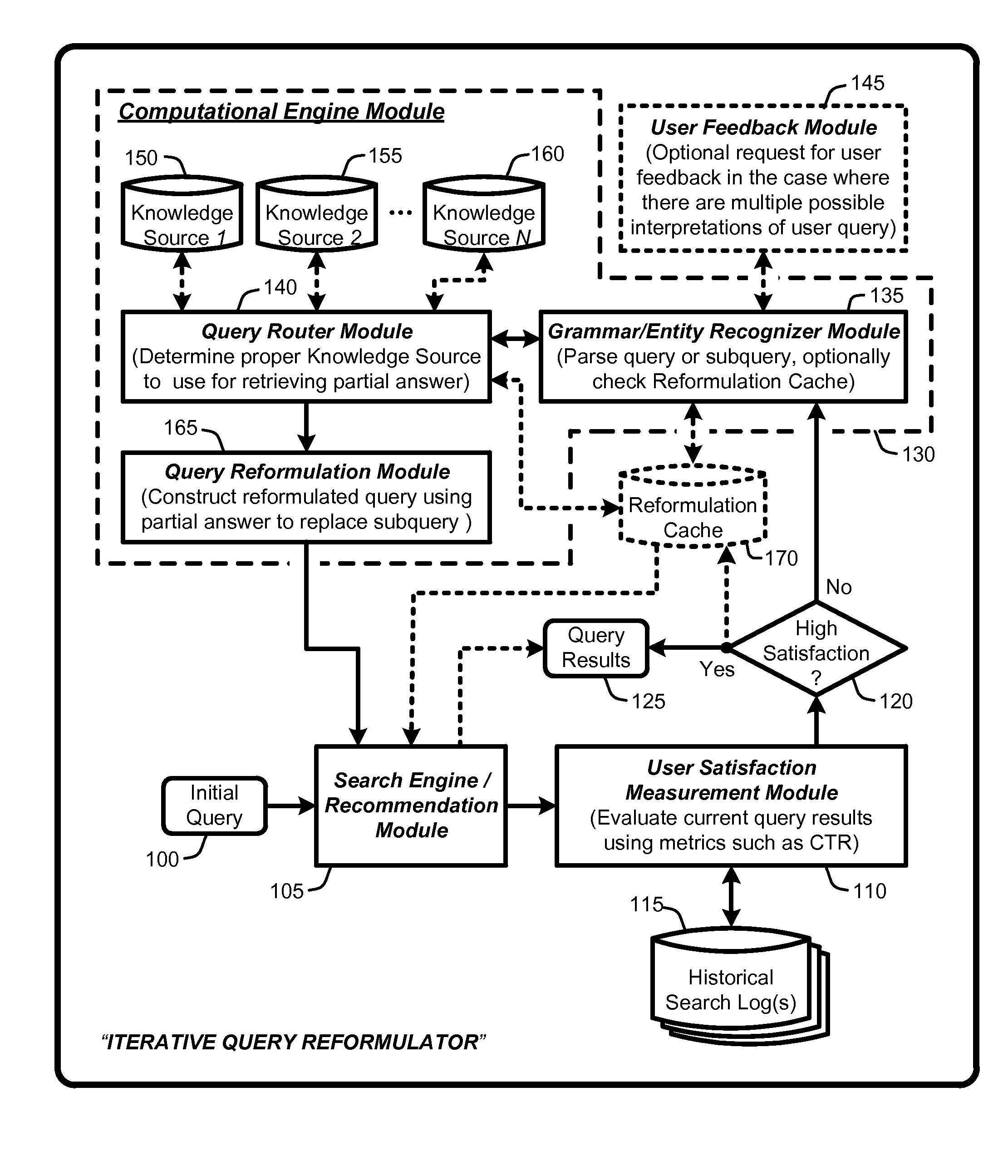
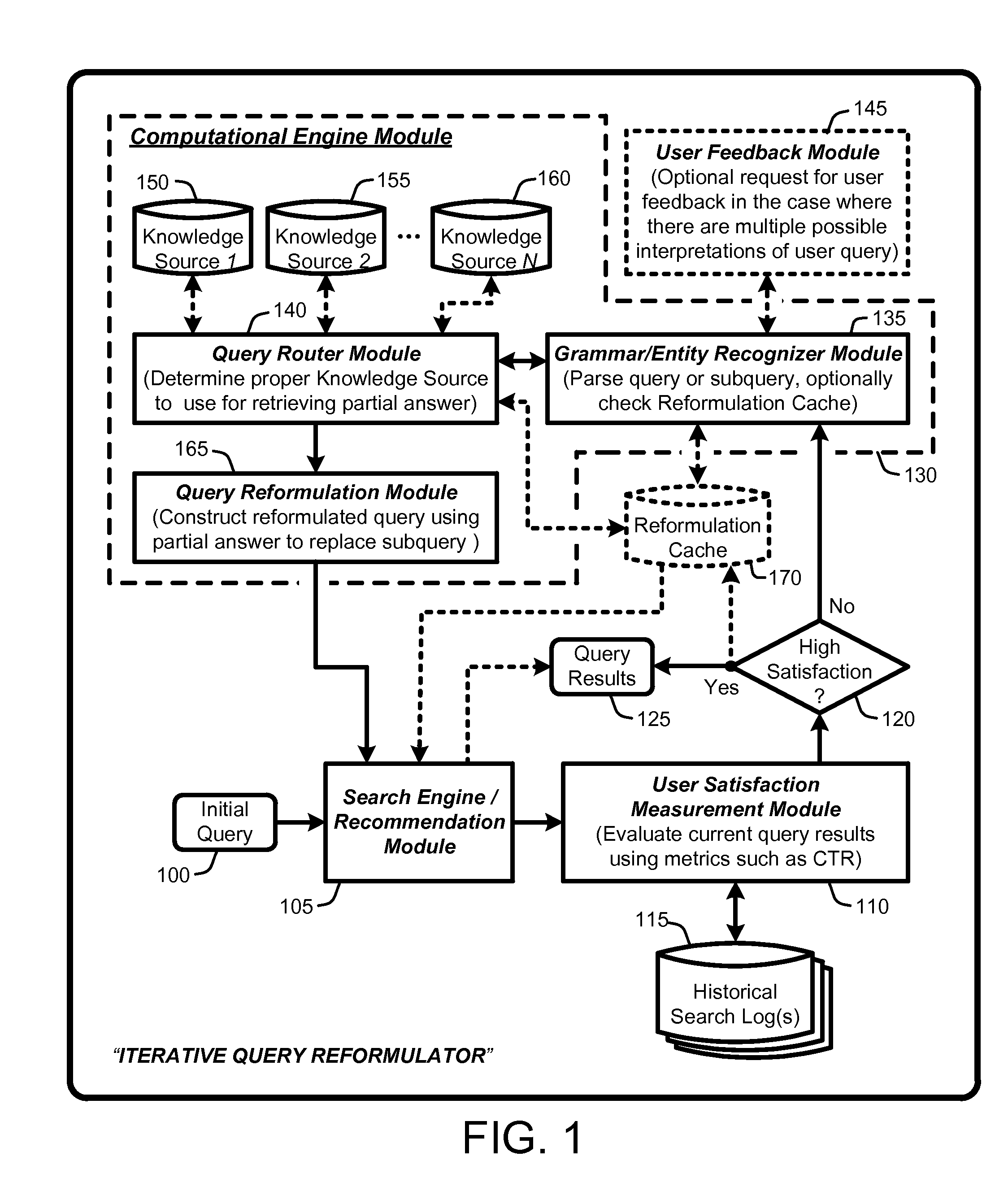
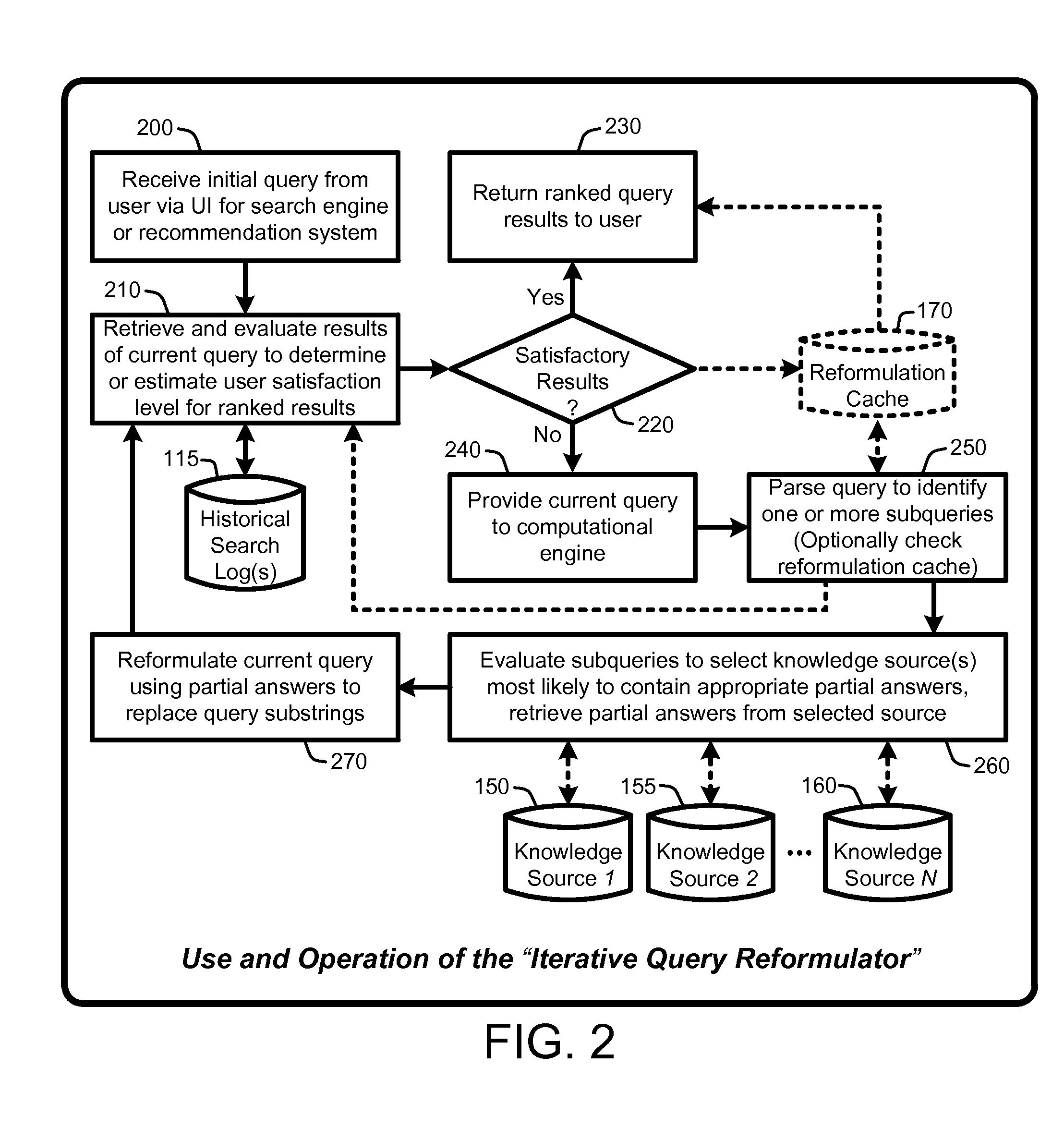
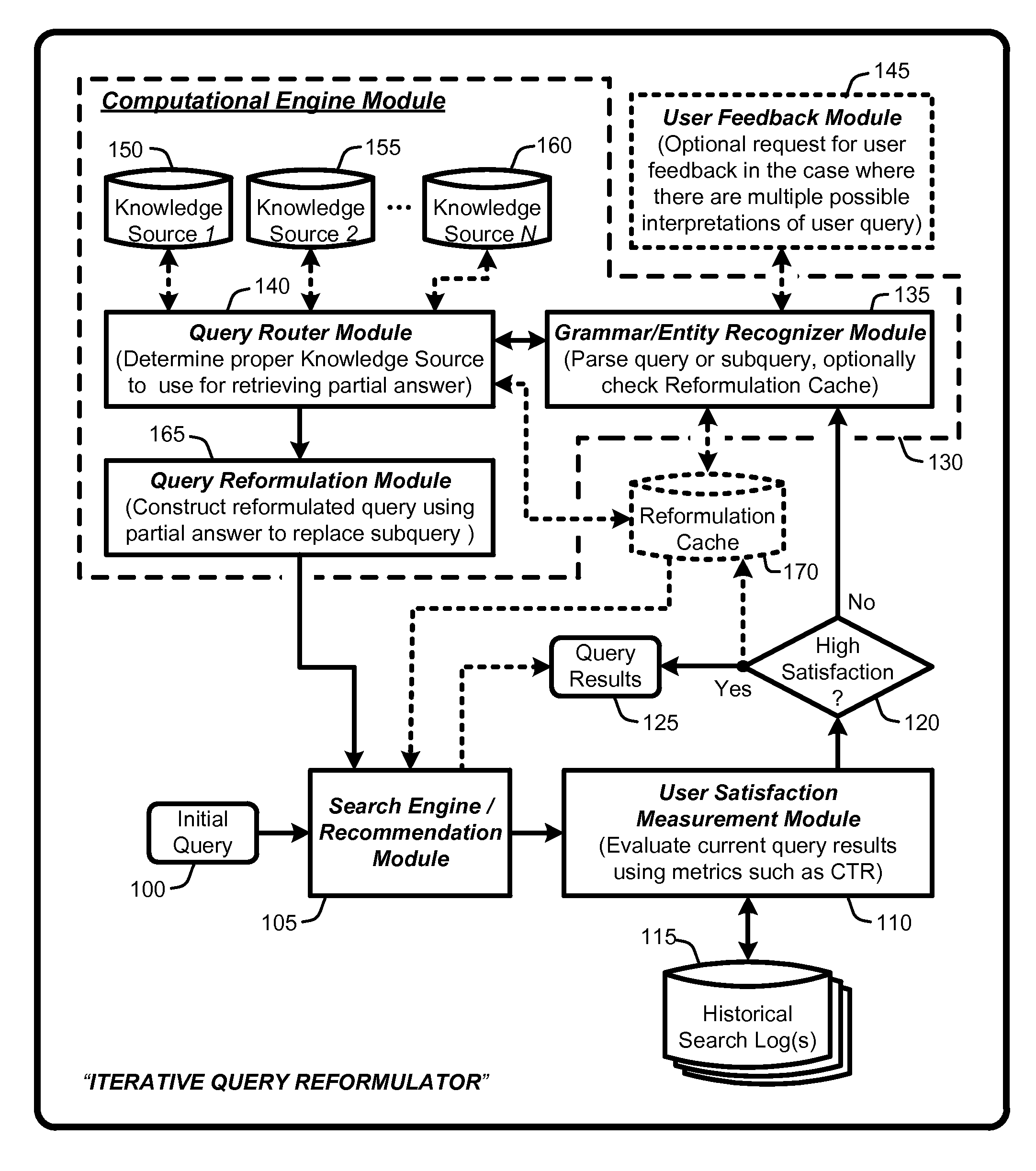
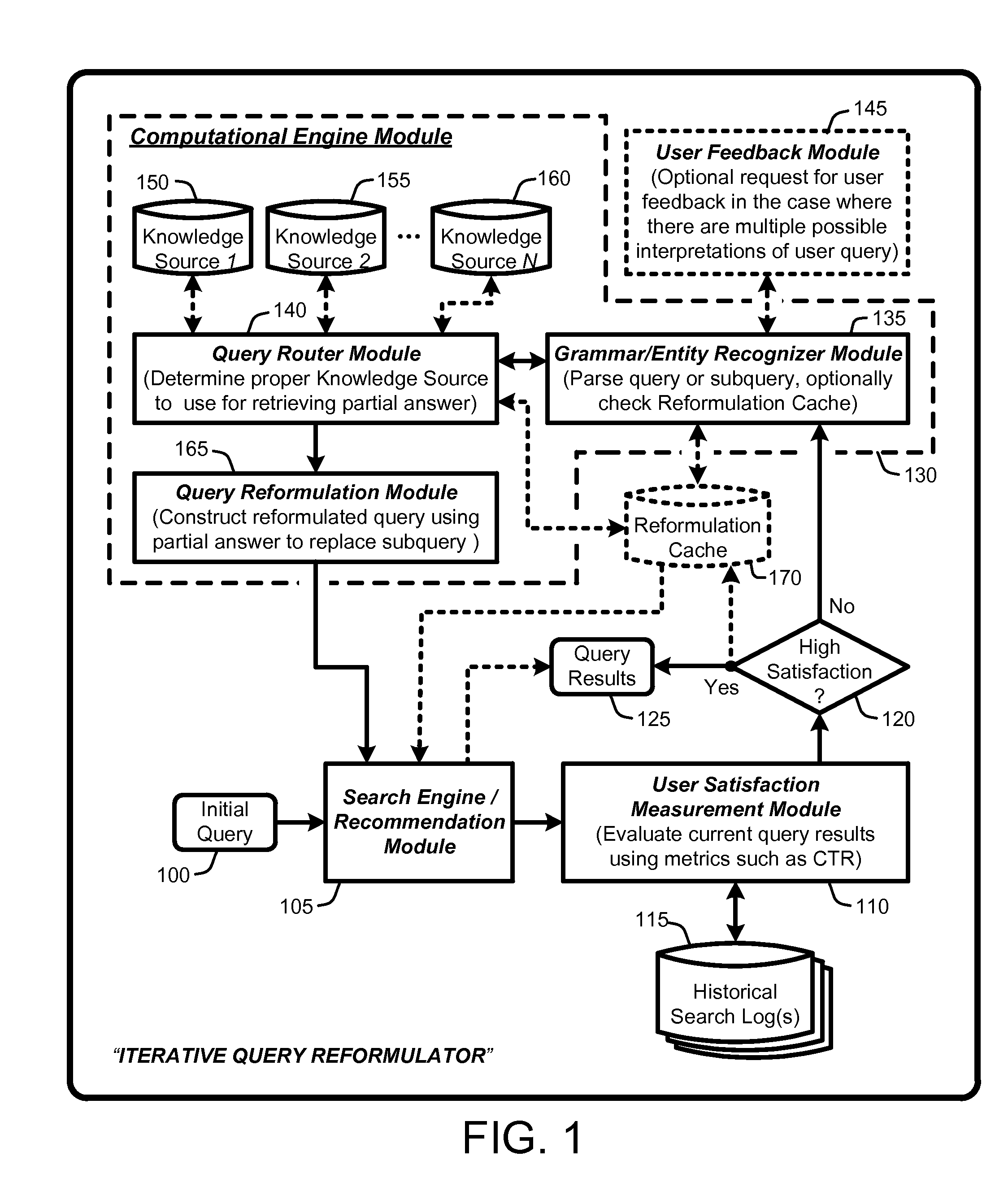
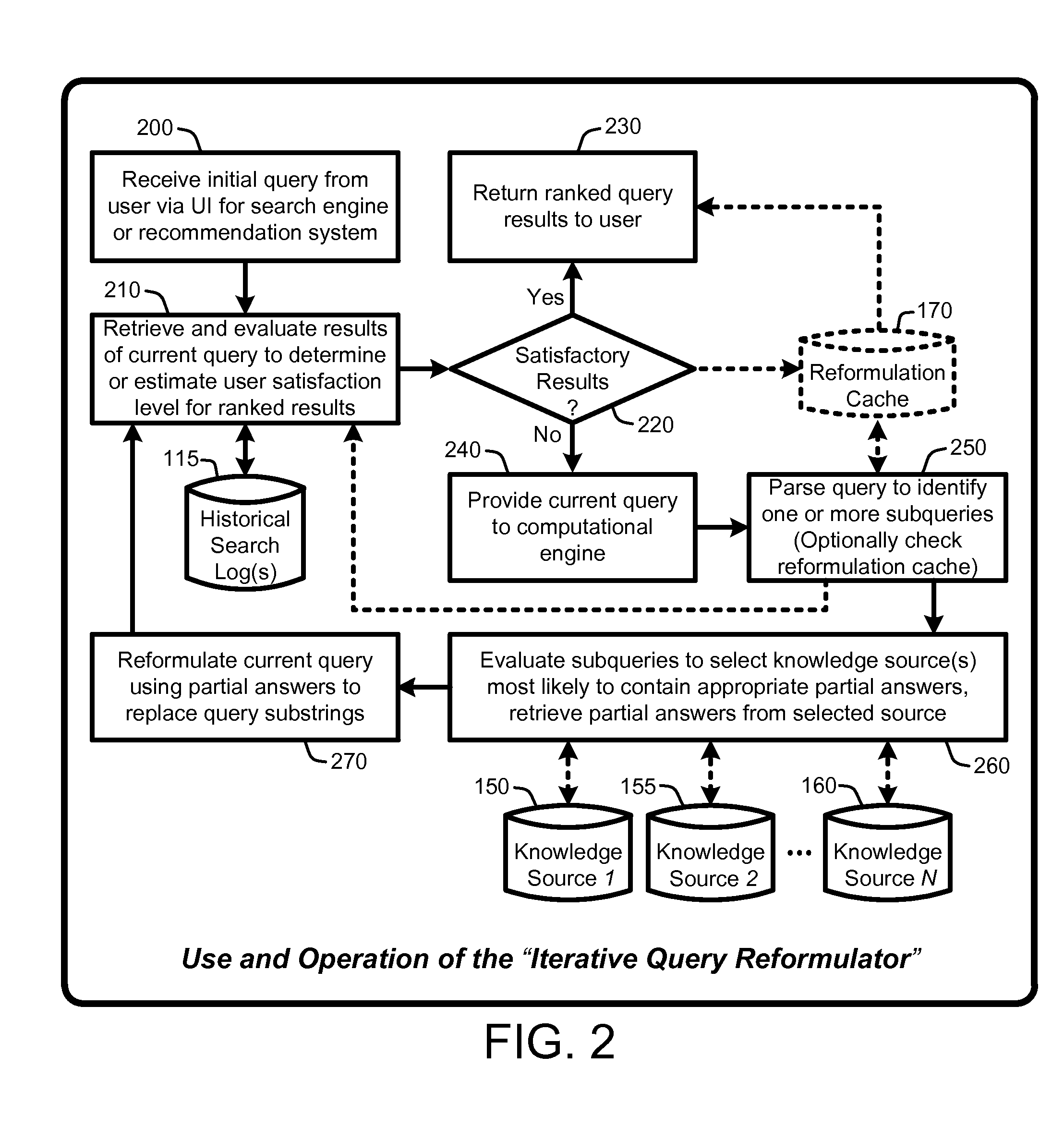
An “Iterative Query Reformulator” provides various techniques for using a computational engine to reformulate initial queries through one or more iterations. This query reformulation process ensures that results returned from search engines or recommendation systems using a reformulated query have improved relevance relative to results that would have been returned using only the initial query. More specifically, the Iterative Query Reformulator provides an end to end solution that uses computations from one or more knowledge databases or knowledge sources to find “partial answers” to subqueries derived or extracted from an initial query. These partial answers are then used to reformulate the initial query, with the reformulated query being used by the search engines or recommendations systems to provide results that are highly relevant to the initial query. Determinations of whether to continue reformulation iterations are based on evaluating user metrics from historical search logs having queries that match reformulated queries.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Extracting sentence translations from translated documents
InactiveUS7054803B2Efficient use ofReduce memory consumptionNatural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsKnowledge sourcesMemory footprint
A system extracts translations from translated texts, such as sentence translations from translated versions of documents. A first and a second text are accessed and divided into a plurality of textual elements. From these textual elements, a sequence of pairs of text portions is formed, and a pair score is calculated for each pair, using weighted features. Then, an alignment score of the sequence is calculated using the pair scores, and the sequence is systematically varied to identify a sequence that optimizes the alignment score. The invention allows for fast, reliable and robust alignment of sentences within large translated documents. Further, it allows to exploit a broad variety of existing knowledge sources in a flexible way, without performance penalty. Further, a general implementation of dynamic programming search with online memory allocation and garbage collection allows for treating very long documents with limited memory footprint.
Owner:XEROX CORP
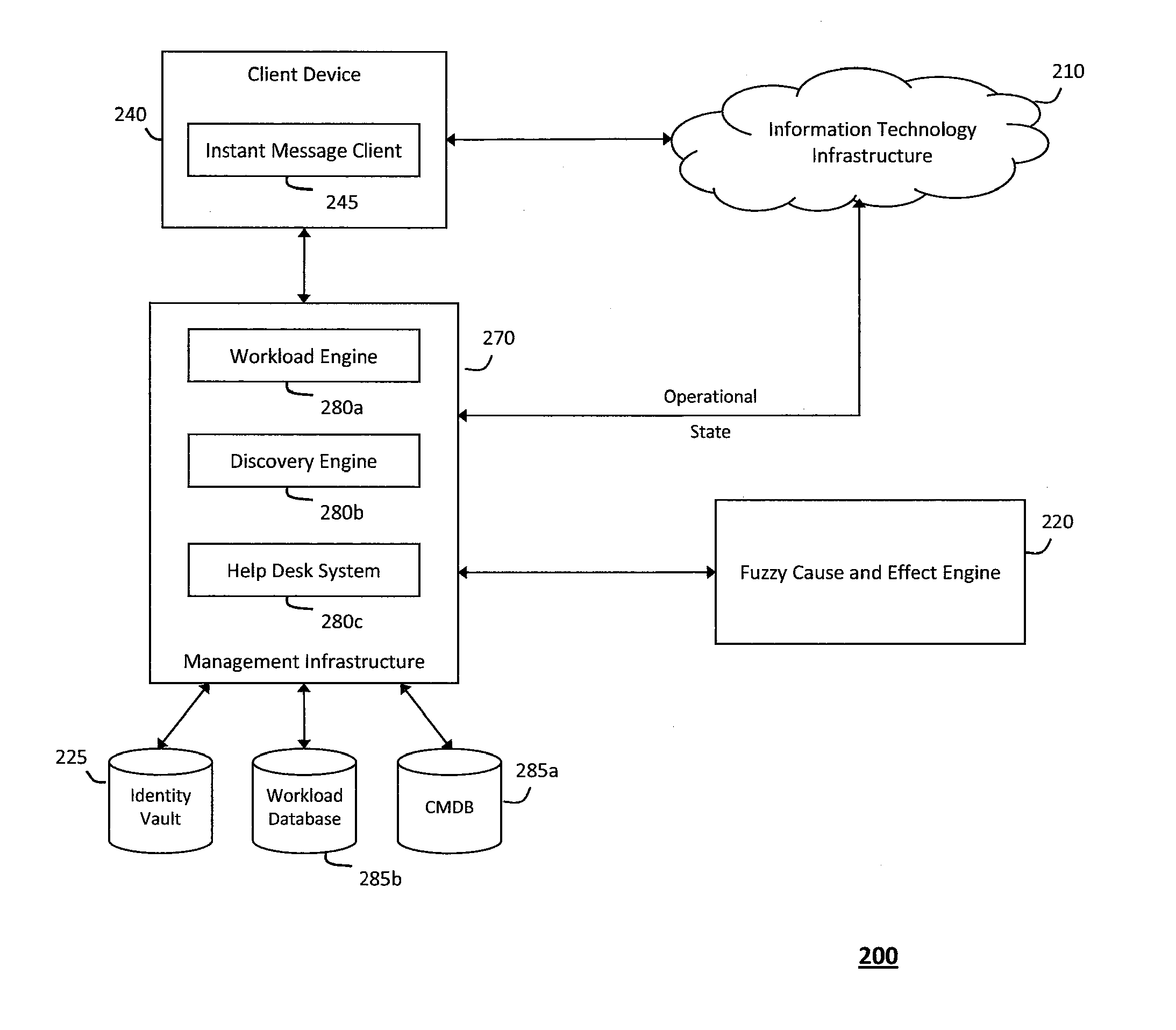
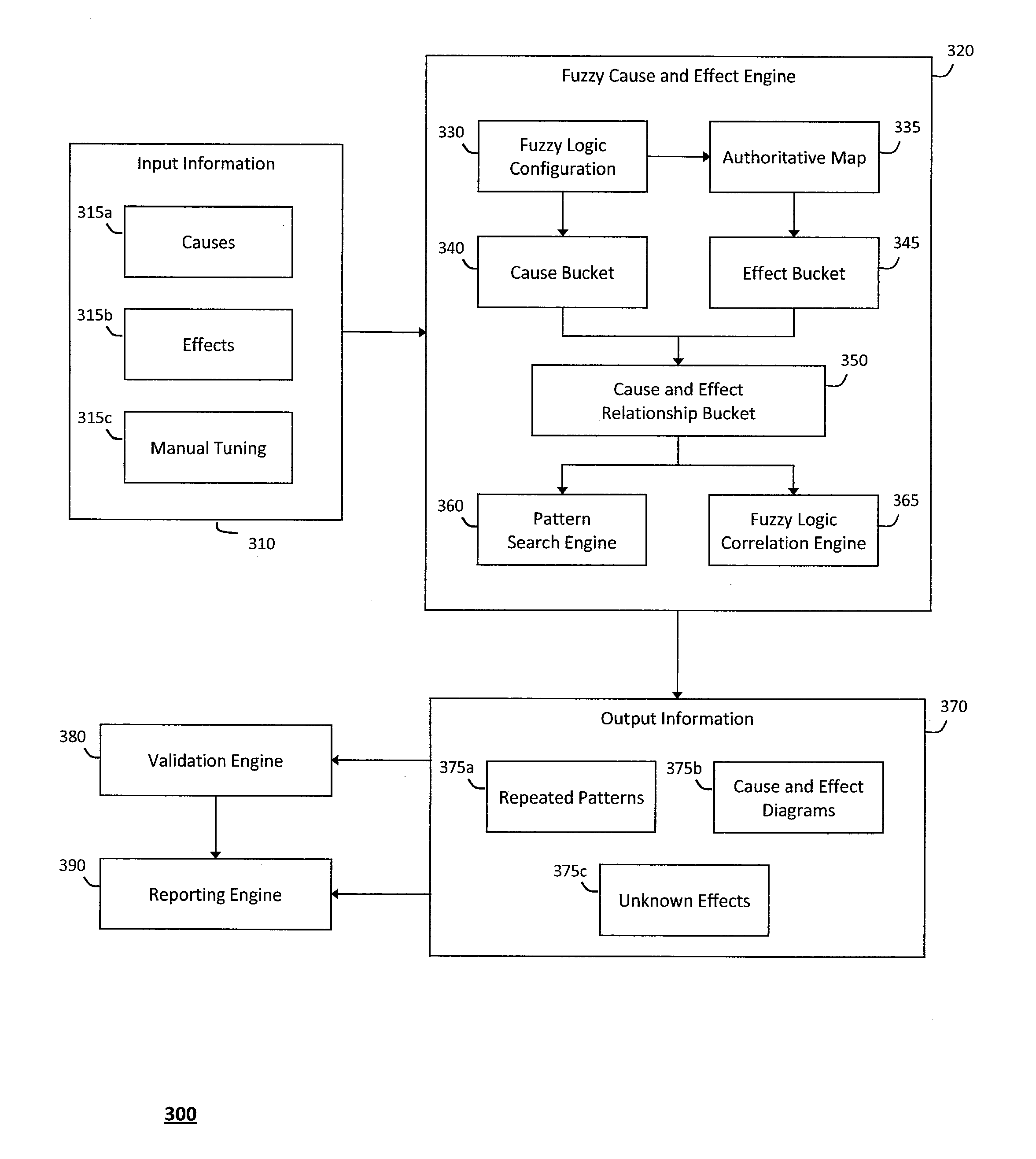
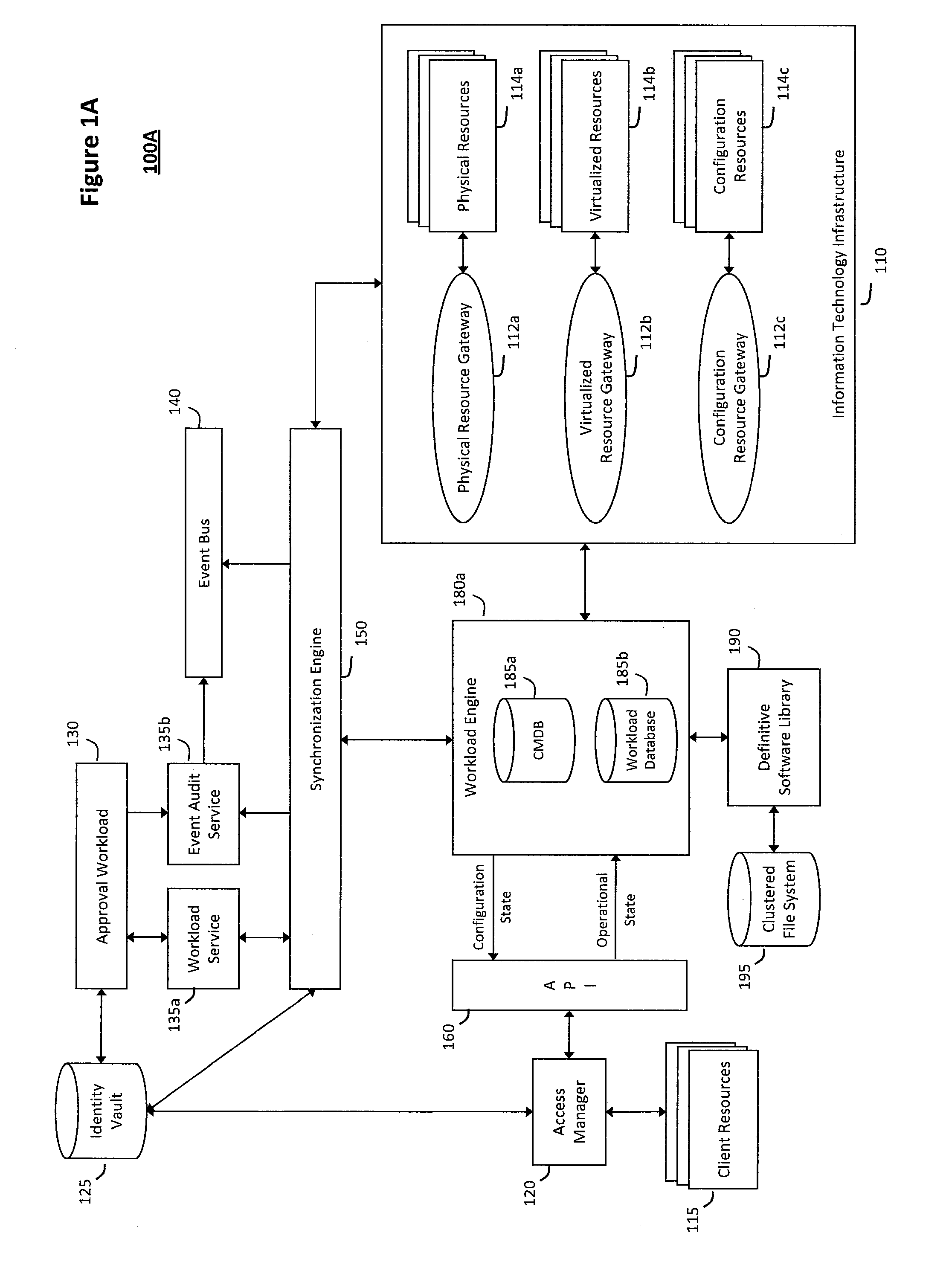
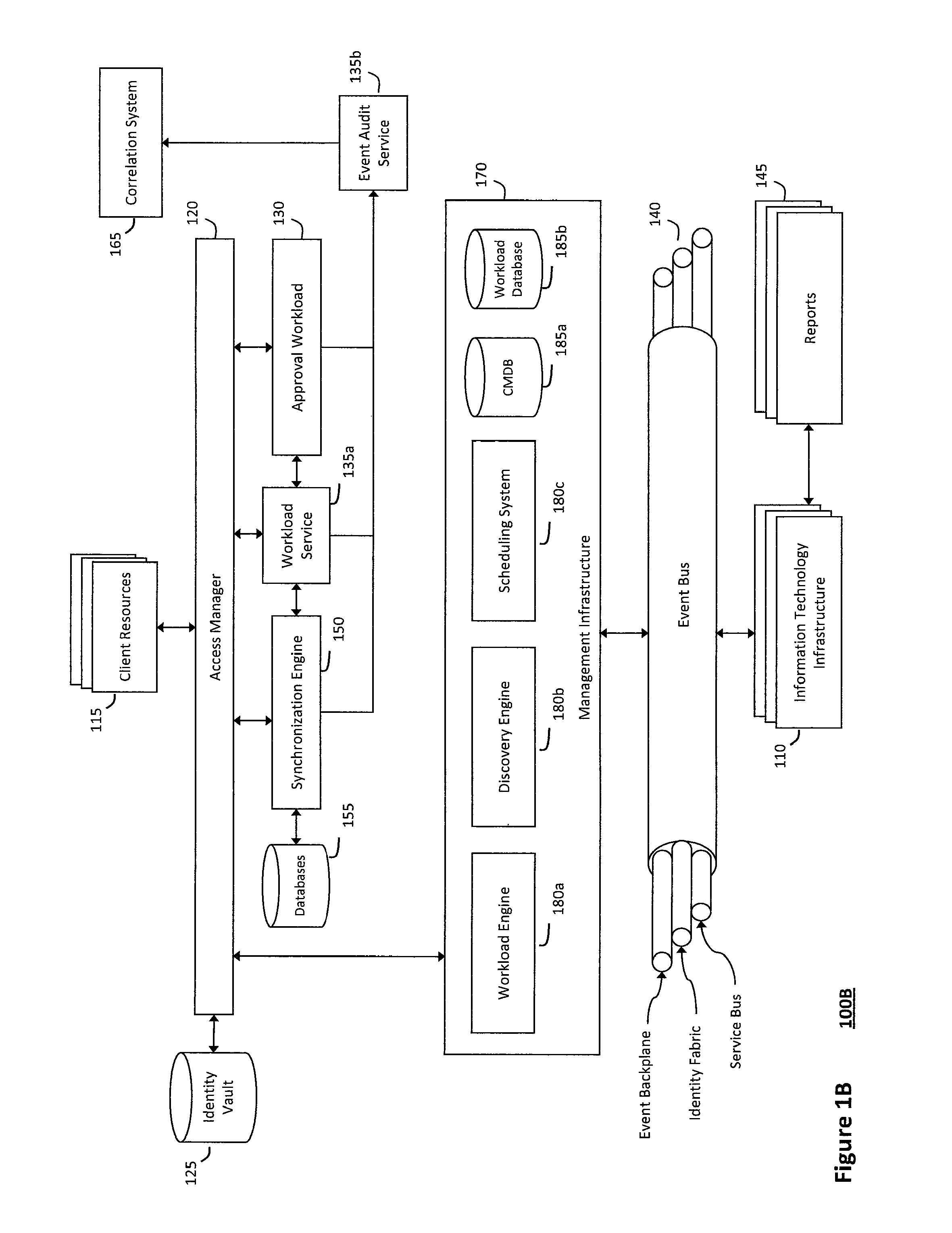
System and method for determining fuzzy cause and effect relationships in an intelligent workload management system
InactiveUS20120130936A1Determine relationshipEnable agilityFuzzy logic based systemsKnowledge representationKnowledge sourcesPotential effect
The system and method for determining fuzzy cause and effect relationships in an intelligent workload management system described herein may combine potential causes and effects captured from various different sources associated with an information technology infrastructure with substantially instantaneous feedback mechanisms and other knowledge sources. As such, fuzzy correlation logic may then be applied to the combined information to determine potential cause and effect relationships and thereby diagnose problems and otherwise manage interactions that occur in the infrastructure. For example, information describing potential causes and potential effects associated with an operational state of the infrastructure may be captured and combined, and any patterns among the information that describes the multiple potential causes and effects may then be identified. As such, fuzzy logic may the be applied to any such patterns to determine possible relationships among the potential causes and the potential effects associated with the infrastructure operational state.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS SOFTWARE INC
Data source integration system and method
InactiveUS7533107B2Easy to addData processing applicationsDatabase management systemsKnowledge sourcesData source
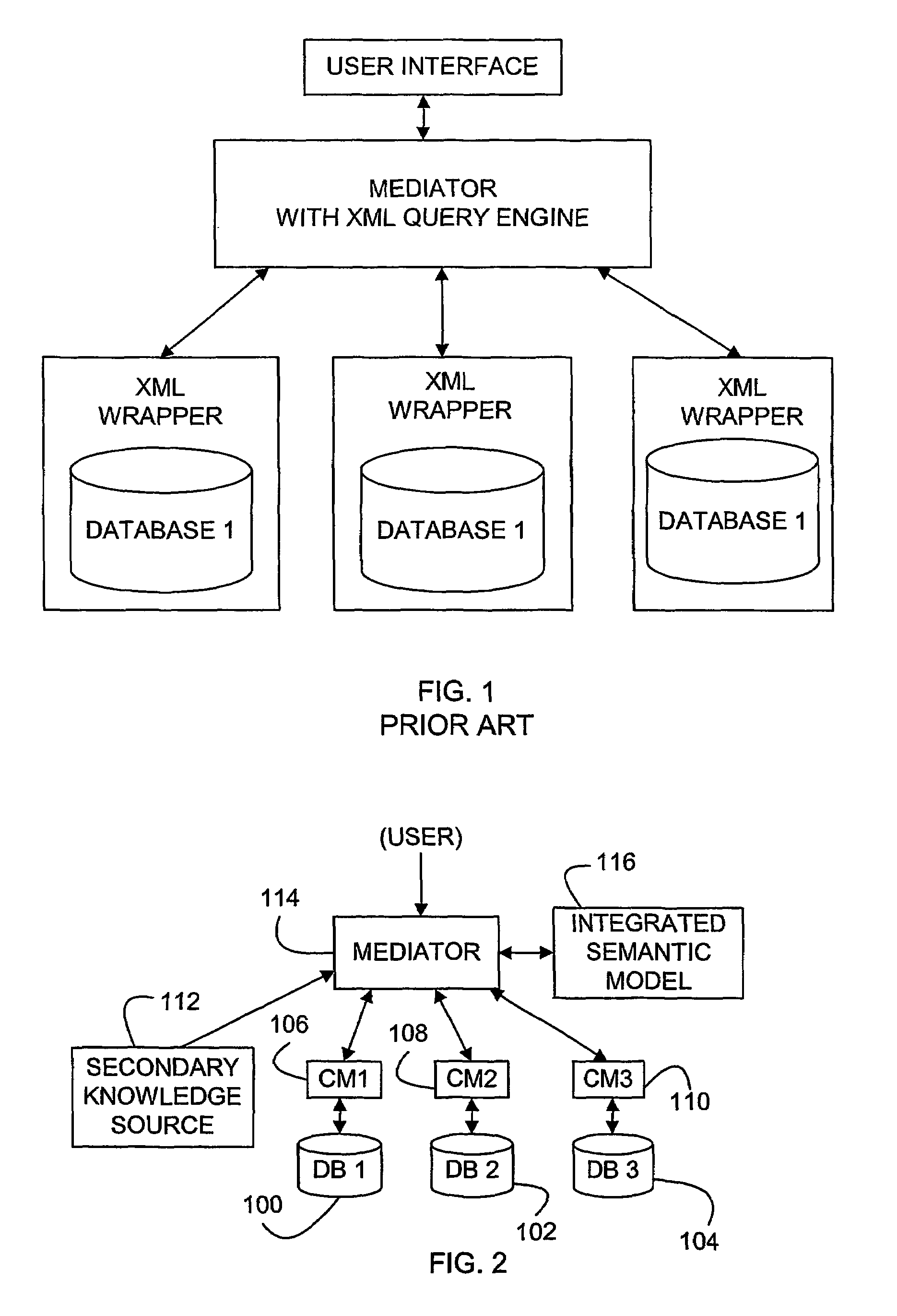
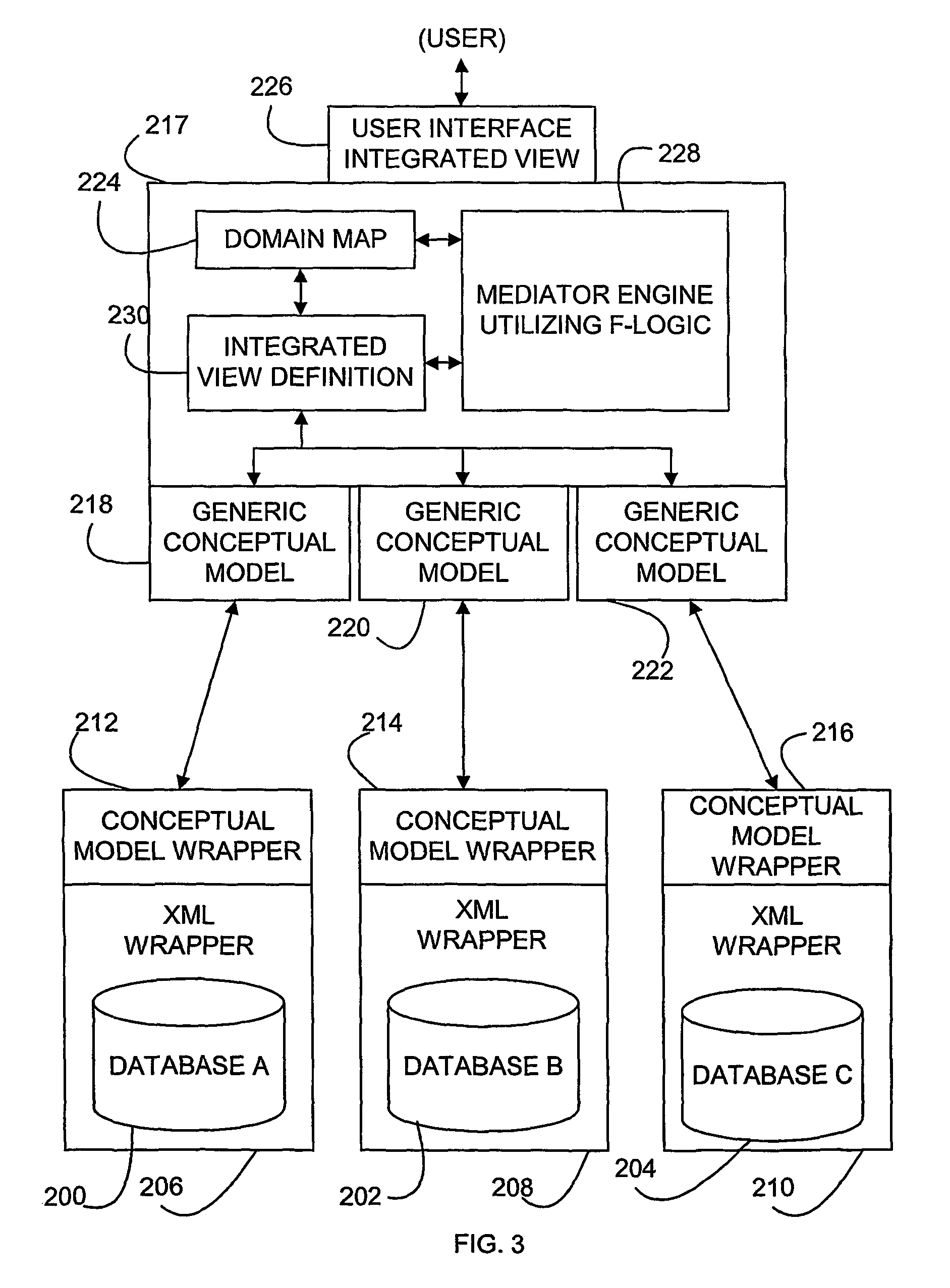
A method and program product for integrating different data sources has steps of obtaining semantic information from each of the different data sources (200, 202, 210), creating a conceptual model of (218, 220, 22) the data source using the semantic information, and accessing one or more secondary knowledge sources. The secondary information sources contain information regarding the relations of data from different of the databases, so that an integrated semantic model of all of the databases (200, 202, 210) may be created. Queries can then be processed using the integrated semantic model.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Techniques for similarity analysis and data enrichment using knowledge sources
ActiveUS10210246B2Accurate resolutionAccurate labelingRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsKnowledge sourcesData set
The present disclosure relates to performing similarity metric analysis and data enrichment using knowledge sources. A data enrichment service can compare an input data set to reference data sets stored in a knowledge source to identify similarly related data. A similarity metric can be calculated corresponding to the semantic similarity of two or more datasets. The similarity metric can be used to identify datasets based on their metadata attributes and data values enabling easier indexing and high performance retrieval of data values. A input data set can labeled with a category based on the data set having the best match with the input data set. The similarity of an input data set with a data set provided by a knowledge source can be used to query a knowledge source to obtain additional information about the data set. The additional information can be used to provide recommendations to the user.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
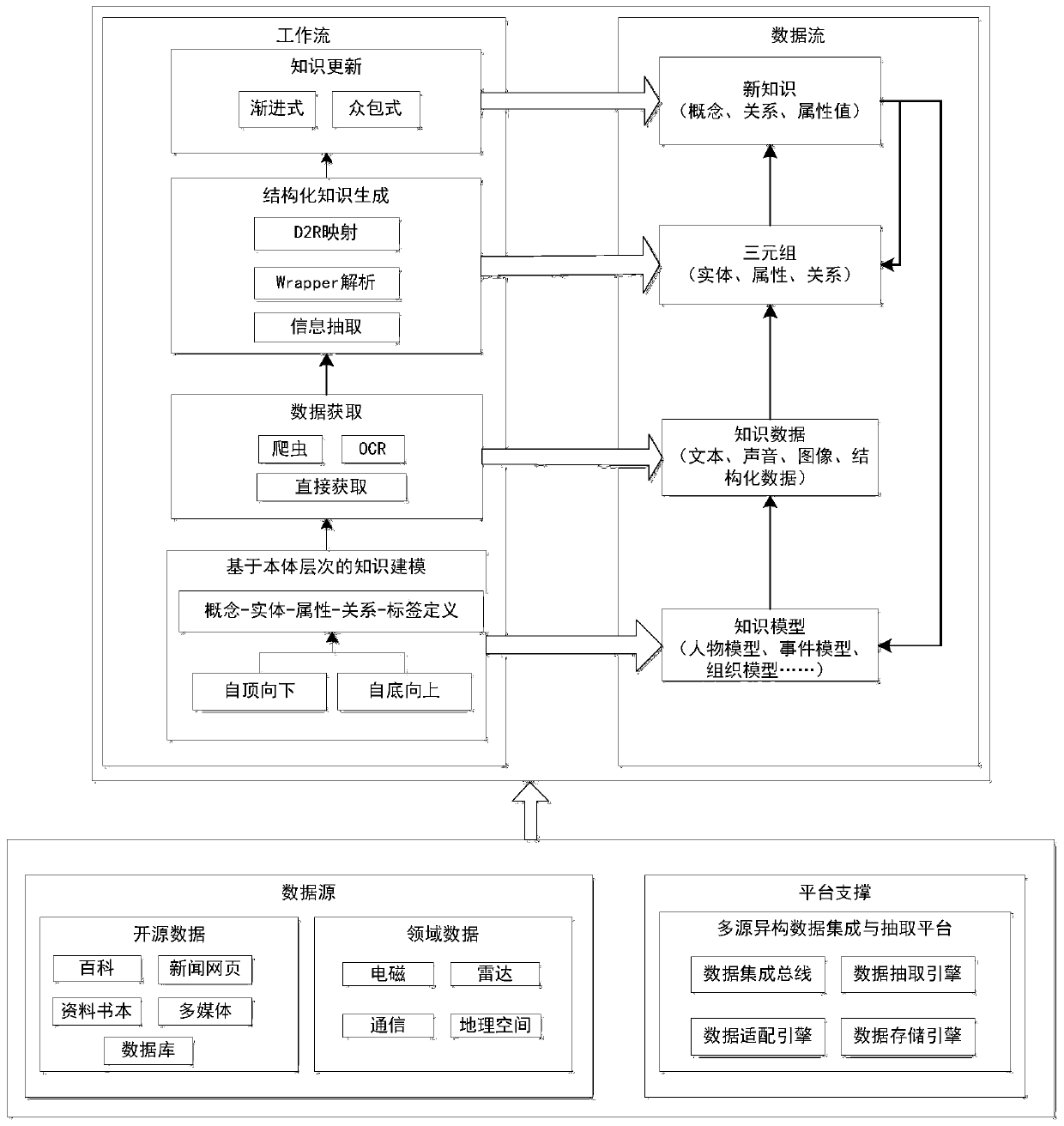
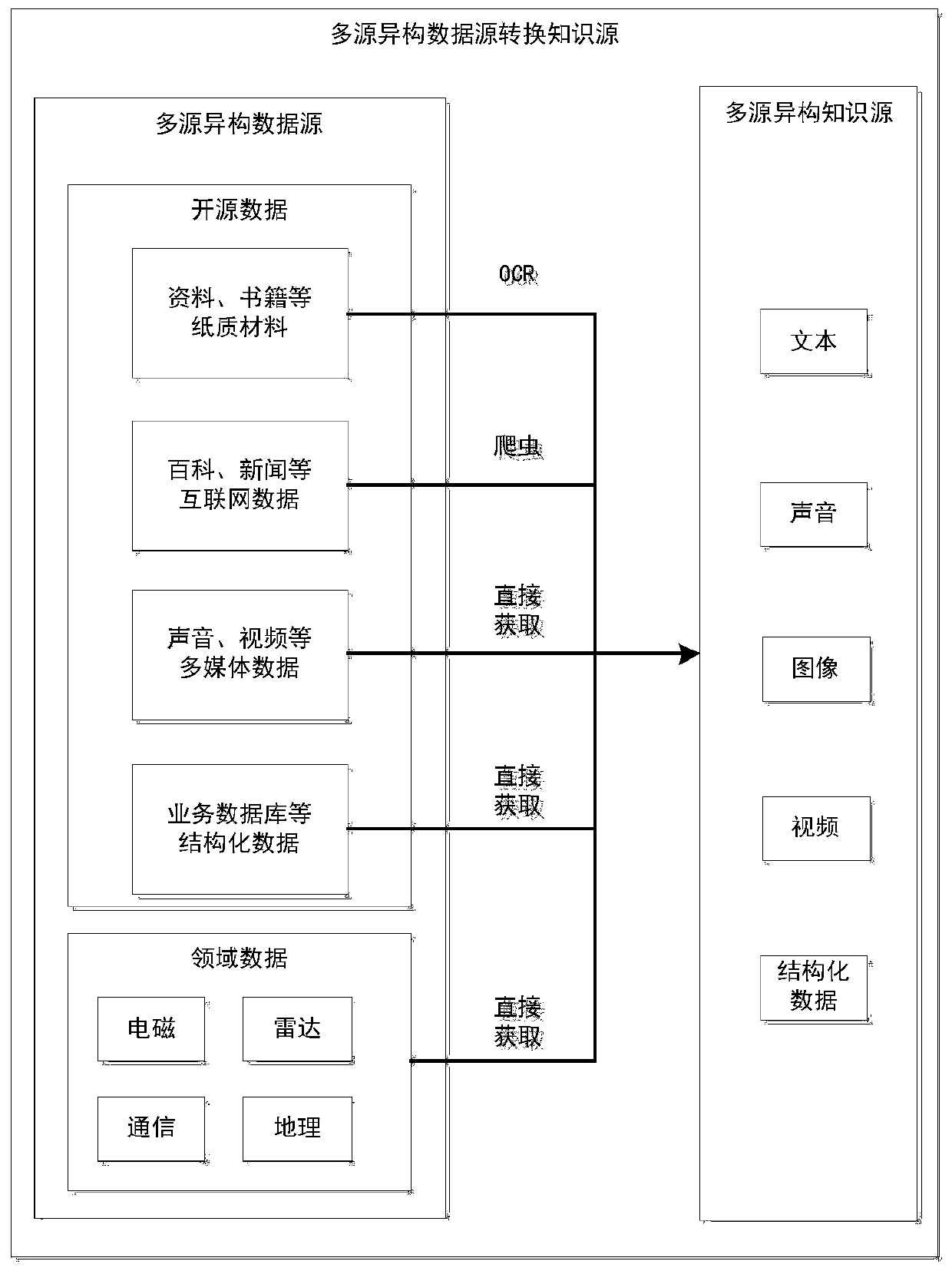
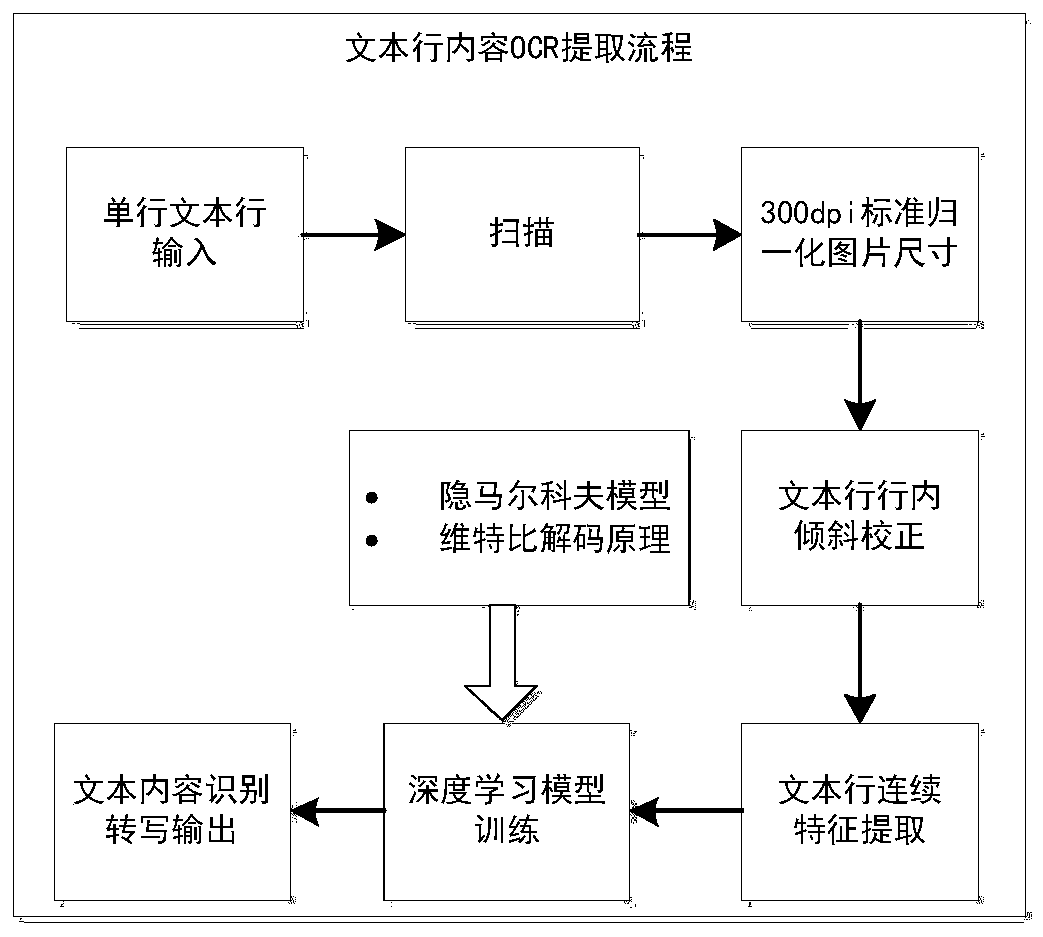
Method for automatically acquiring multi-source heterogeneous data knowledge
ActiveCN110489395AIntegrityImplement associative storageDatabase management systemsRelational databasesKnowledge sourcesData source
The invention discloses a method for automatically acquiring multi-source heterogeneous data knowledge, and aims to provide a method which has better integrity, universality and convenience and is beneficial to knowledge transmission. The method of the invention is realized through the following technical scheme: the method comprises the following steps: 1, processing; a concept-entity-attribute-relation-label is defined from top to bottom or from bottom to top, a knowledge model of an entity object is obtained, then data is obtained through direct data storage and crawler software, OCR and other recognition software, knowledge data is obtained, and conversion from a heterogeneous data source to a heterogeneous knowledge source is completed; obtaining entity-attribute-relationship triad instantiation under a known knowledge mode through a structured knowledge generation method; and updating knowledge and knowledge models by using a long-short-term memory network model (LSTM model) anda publisher-accomplisher cooperation mode to obtain a workflow for expanding and supplementing new knowledge, and obtaining a data flow accommodating concept, entity, relationship and attribute valueinstantiation triples by using the knowledge model formed by knowledge modeling.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
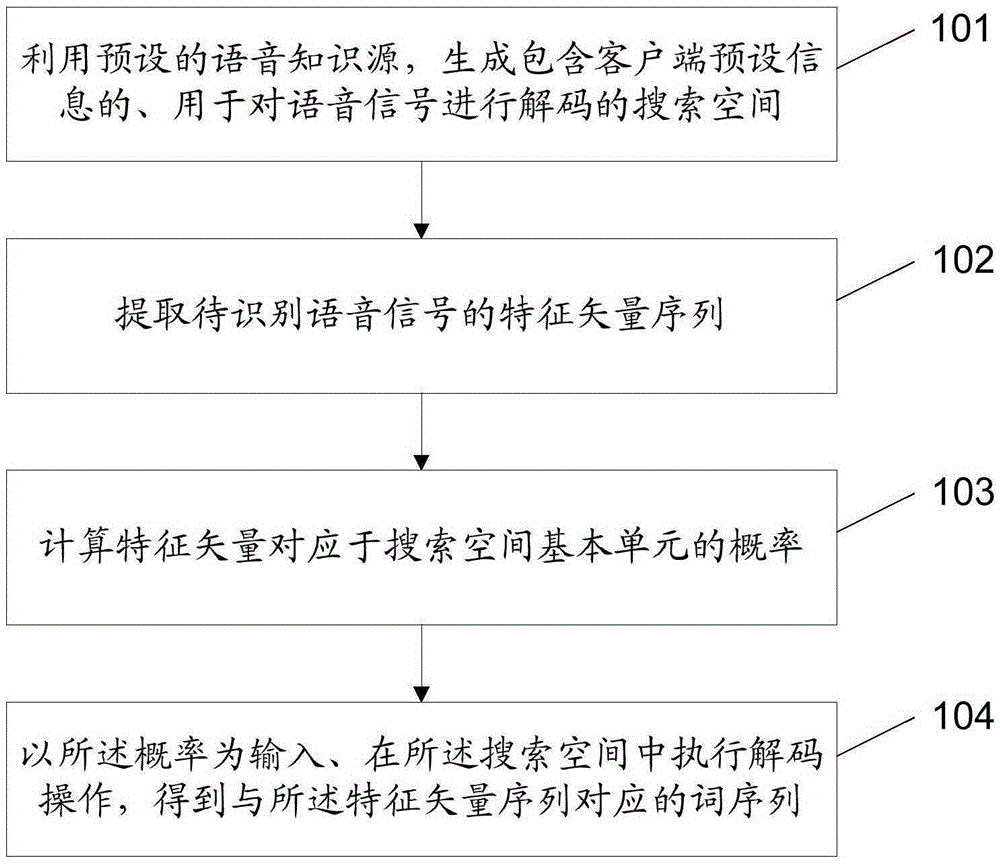
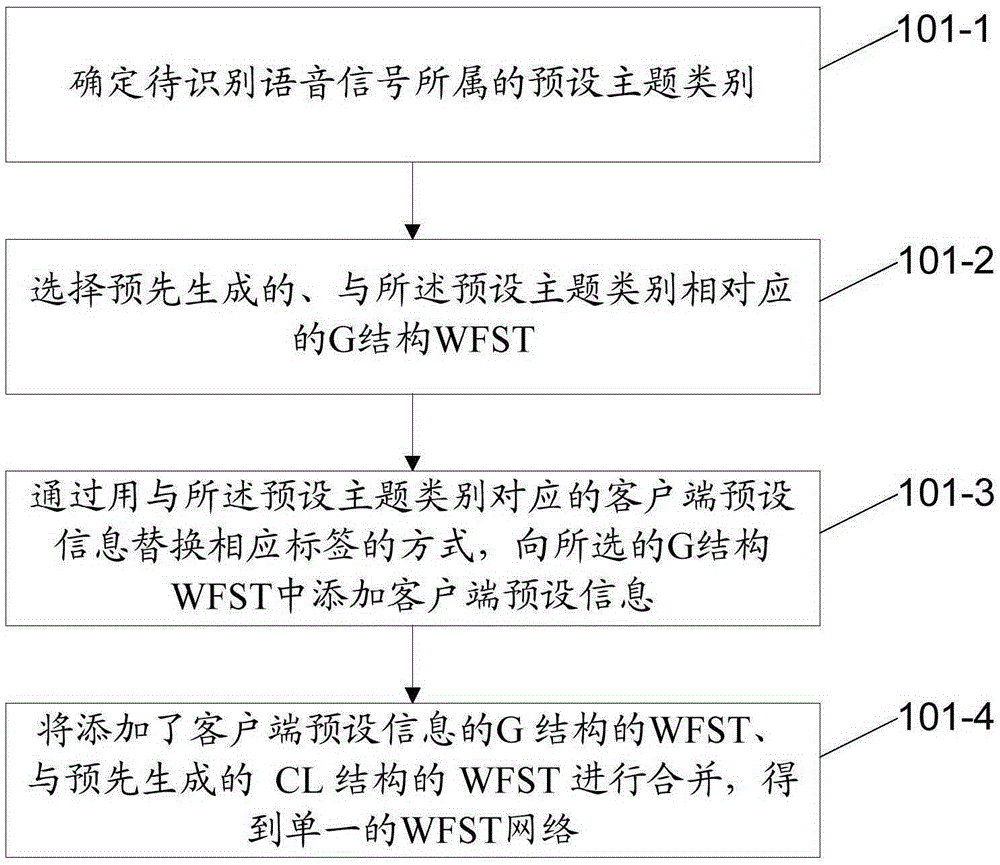
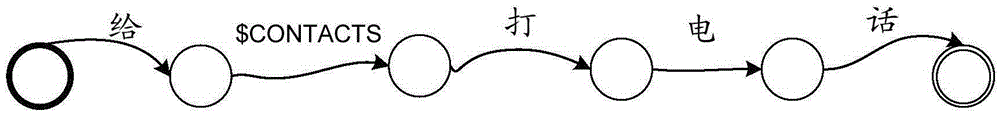
Method and device for recognizing voice
ActiveCN106683677AImprove accuracyImprove user experienceSpeech recognitionFeature vectorKnowledge sources
The invention discloses a method of recognizing voice. The method comprises steps: a preset voice knowledge source is used to generate searching space containing preset information of a client and used for decoding voice signals; a to-be-recognized voice signal feature vector sequence is extracted; the possibility that the feature vector is corresponding to a searching space basic unit is calculated; and with the possibility as input, decoding operation is executed in the searching space to obtain a word sequence corresponding to the feature vector sequence. The invention also provides a device for recognizing voice, and another method and another device for recognizing voice. By adopting the method provided by the invention, as the preset information of the client is included while the searching space for decoding is generated, information related to the client can be accurately recognized while the voice signals acquired by the client are recognized, and thus, the voice recognition accuracy can be improved, and the use experience of the user is enhanced.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
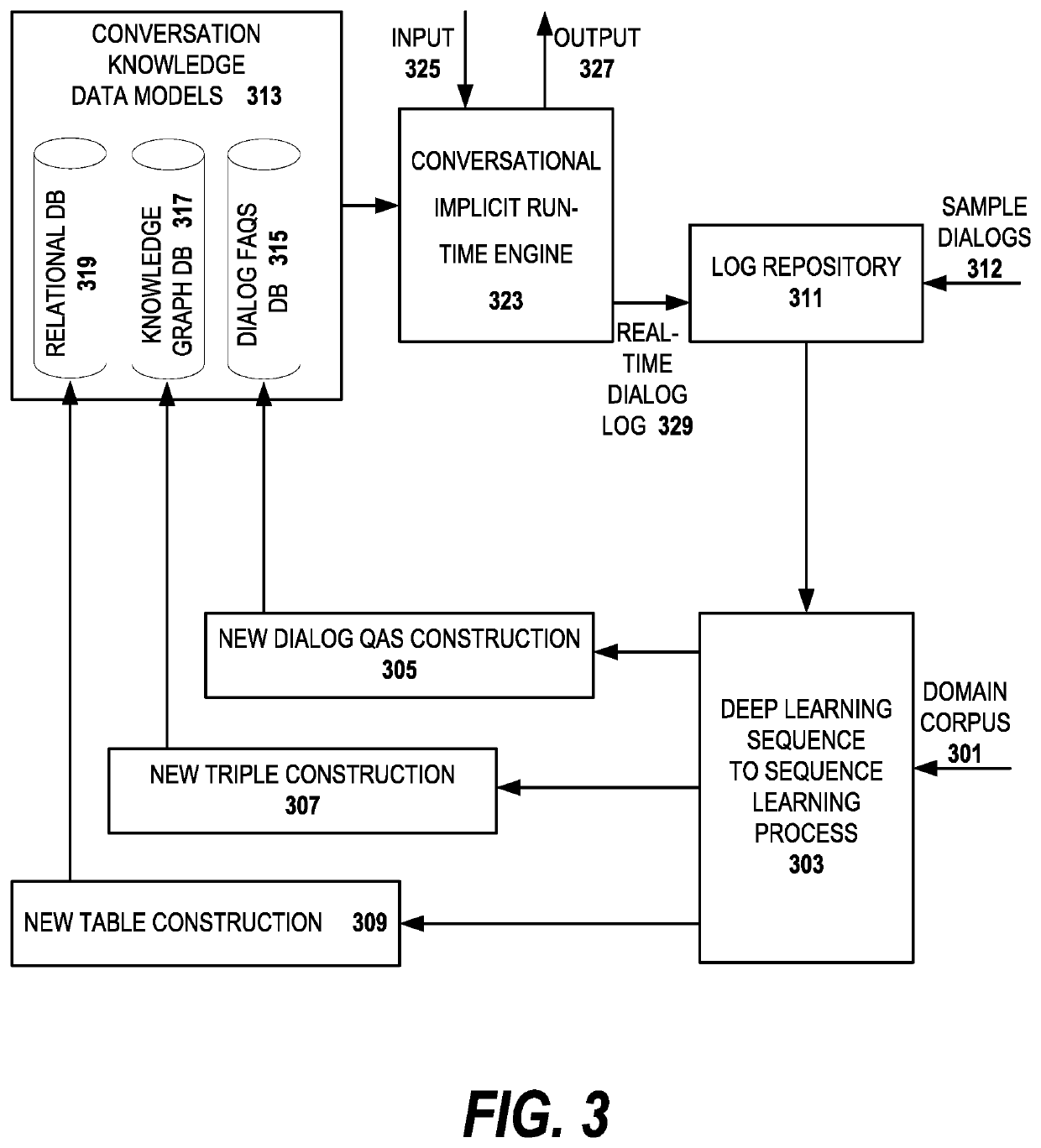
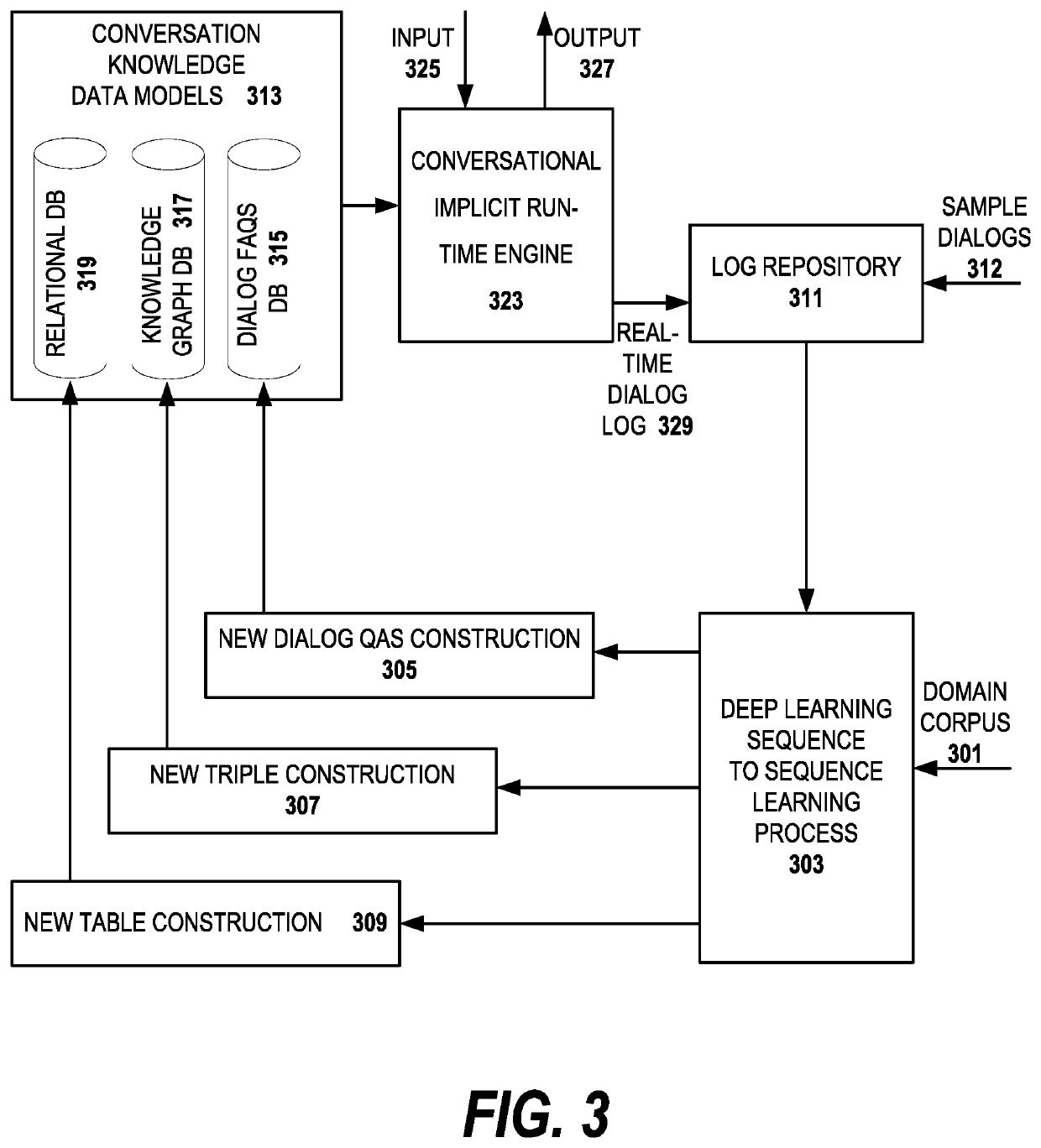
Implicit dialog approach for creating conversational access to web content
A method, apparatus and computer program product for creating a dialog system for web content is described. Knowledge is extracted from a target web application for the dialog system. The knowledge includes an organizational structure of the target web application and domain knowledge pertinent to the target web application. A deep learning process associates the domain knowledge with the organization structure of the target application. A plurality of knowledge sources of different respective types are created from the domain knowledge and the organizational structure. Each of the knowledge sources is used for providing answers to user queries to the dialog system. As part of the invention, a semantic matcher is provided to select among the answers provided by the plurality of knowledge sources for a best answer to a user query.
Owner:IBM CORP
Creating a Training Data Set Based on Unlabeled Textual Data
InactiveUS20170060993A1Machine learningSpecial data processing applicationsKnowledge sourcesData set
A system and method are disclosed for obtaining a plurality of unlabeled text documents; obtaining an initial concept; obtaining keywords from a knowledge source based on the initial concept; scoring the plurality of unlabeled documents based at least in part on the initial keywords; determining a categorization of the documents based on the scores; performing a first feature selection and creating a first vector space representation of each document in a first category and a second category, the first and second categories based on the scores, the first vector space representation serving as one or more labels for an associated unlabeled textual document; and generating the training set including a subset of the obtained unlabeled textual documents, the subset of the obtained unlabeled documents including a documents belonging to the first category and documents belonging to the second category.
Owner:SKYTREE INC
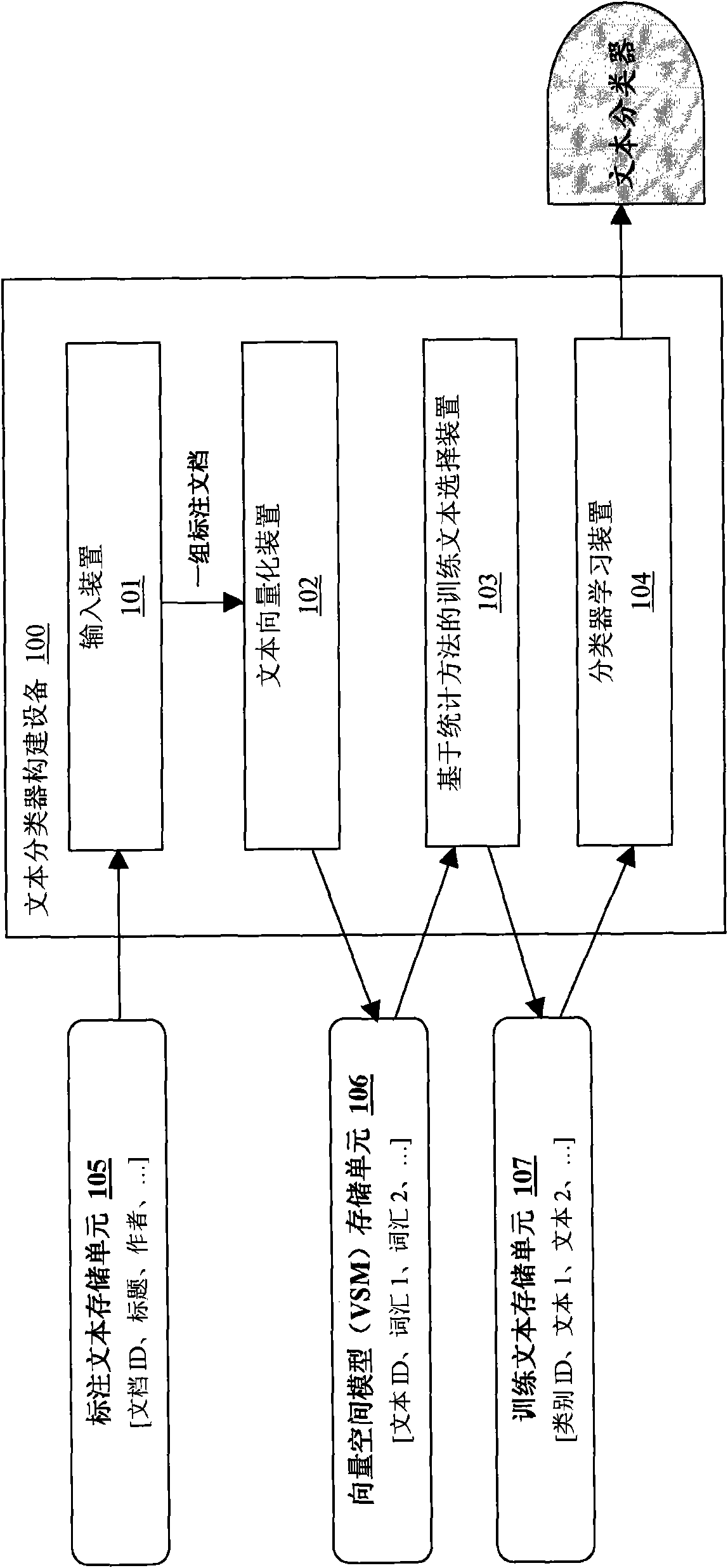
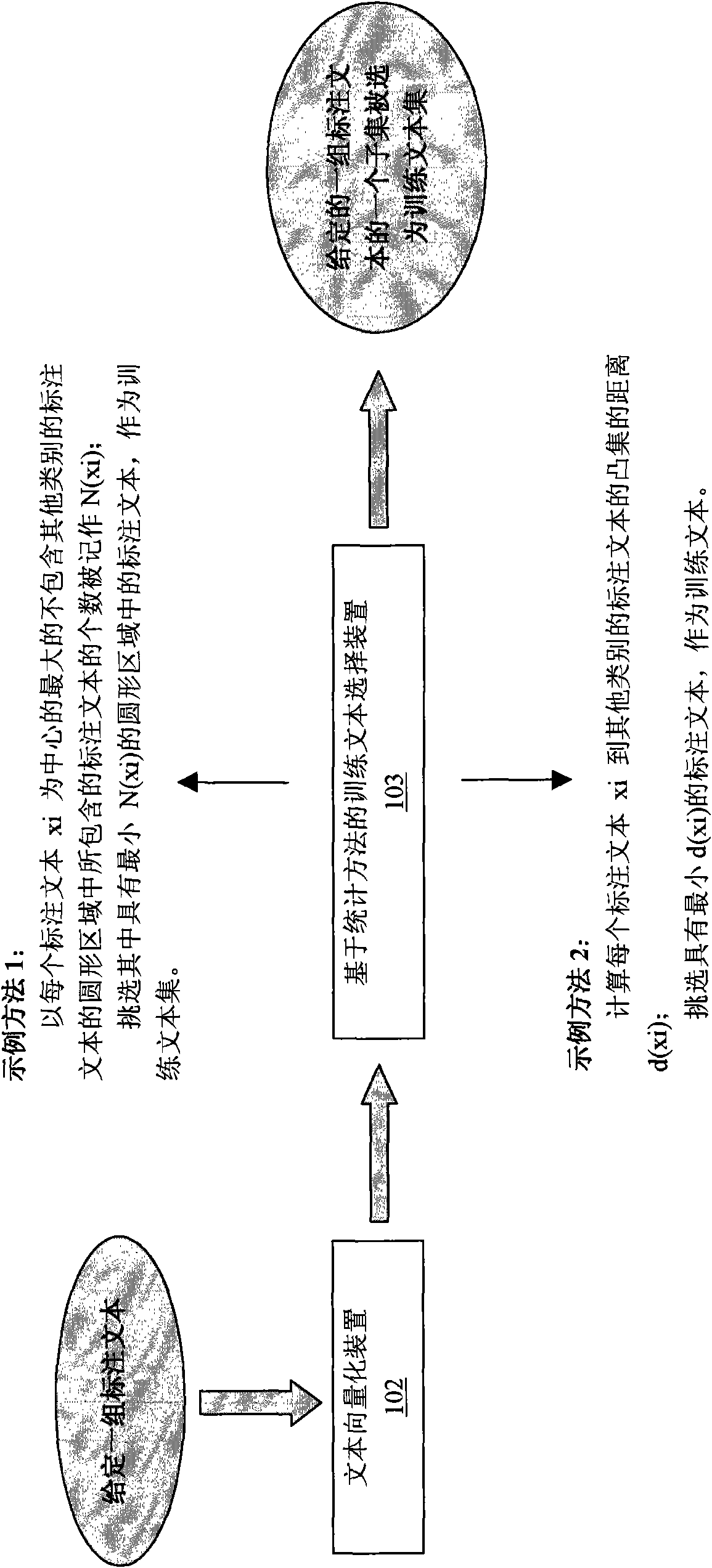
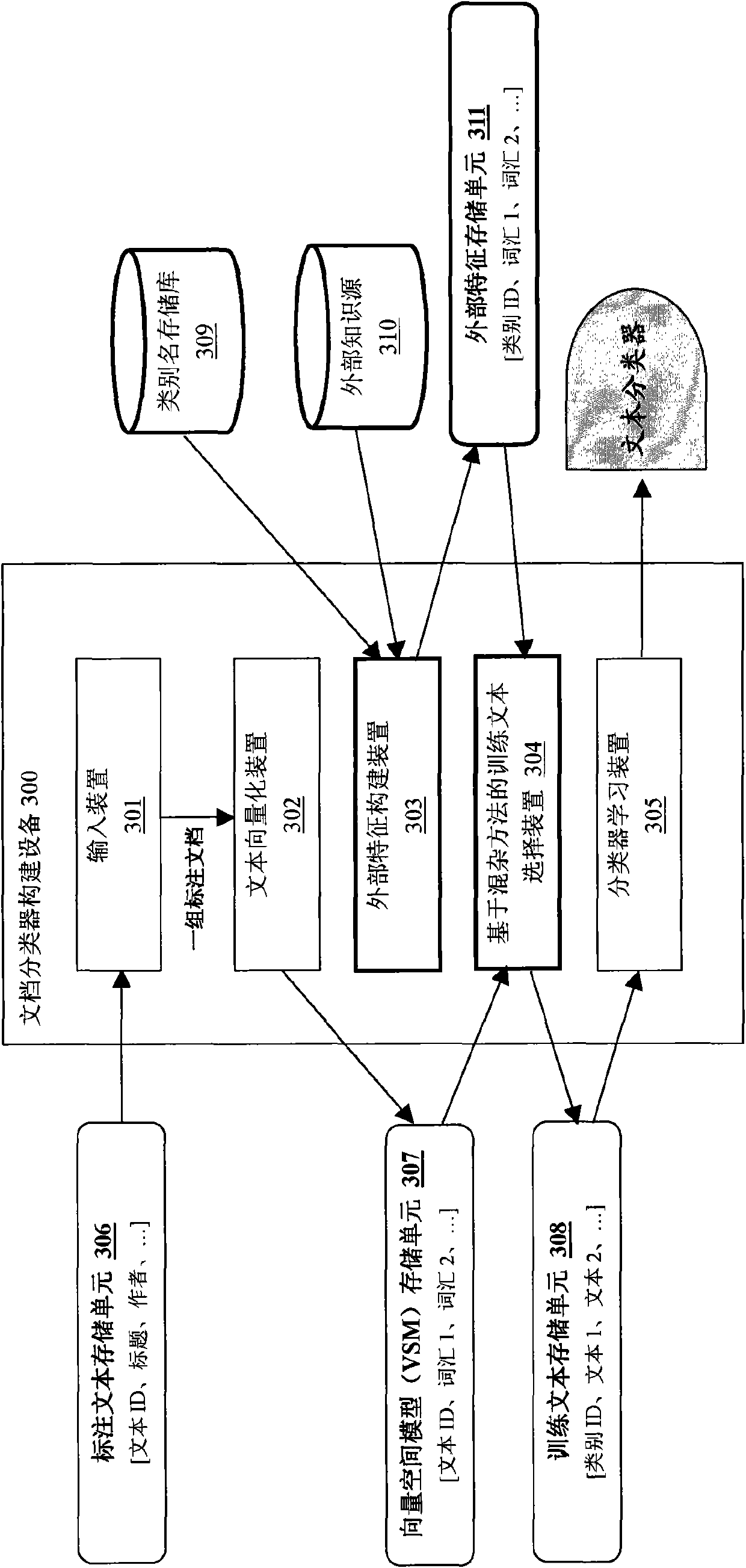
Method and equipment for constructing text classifier by referencing external knowledge
InactiveCN102023986AImprove category representationIncrease differentiationSpecial data processing applicationsNatural language processingKnowledge sources
The invention provides a method and equipment for constructing a text classifier by referencing external knowledge. The method comprises the steps of: inputting a label text set; extracting internal characteristics of the label text set; constructing external characteristics of the label text set by referencing an external knowledge source (such as a dictionary); comprehensively considering the internal characteristics and the external characteristics of the label text set, and selecting training texts from the label text set; and learning the generation of the text classifier by using the selected training texts. According to the invention, sample distribution deviation generated by the label text set can be possibly regulated by the external characteristics automatically generated by the external knowledge source, and therefore, the finally trained classifier has better generalization capability and robustness.
Owner:NEC (CHINA) CO LTD
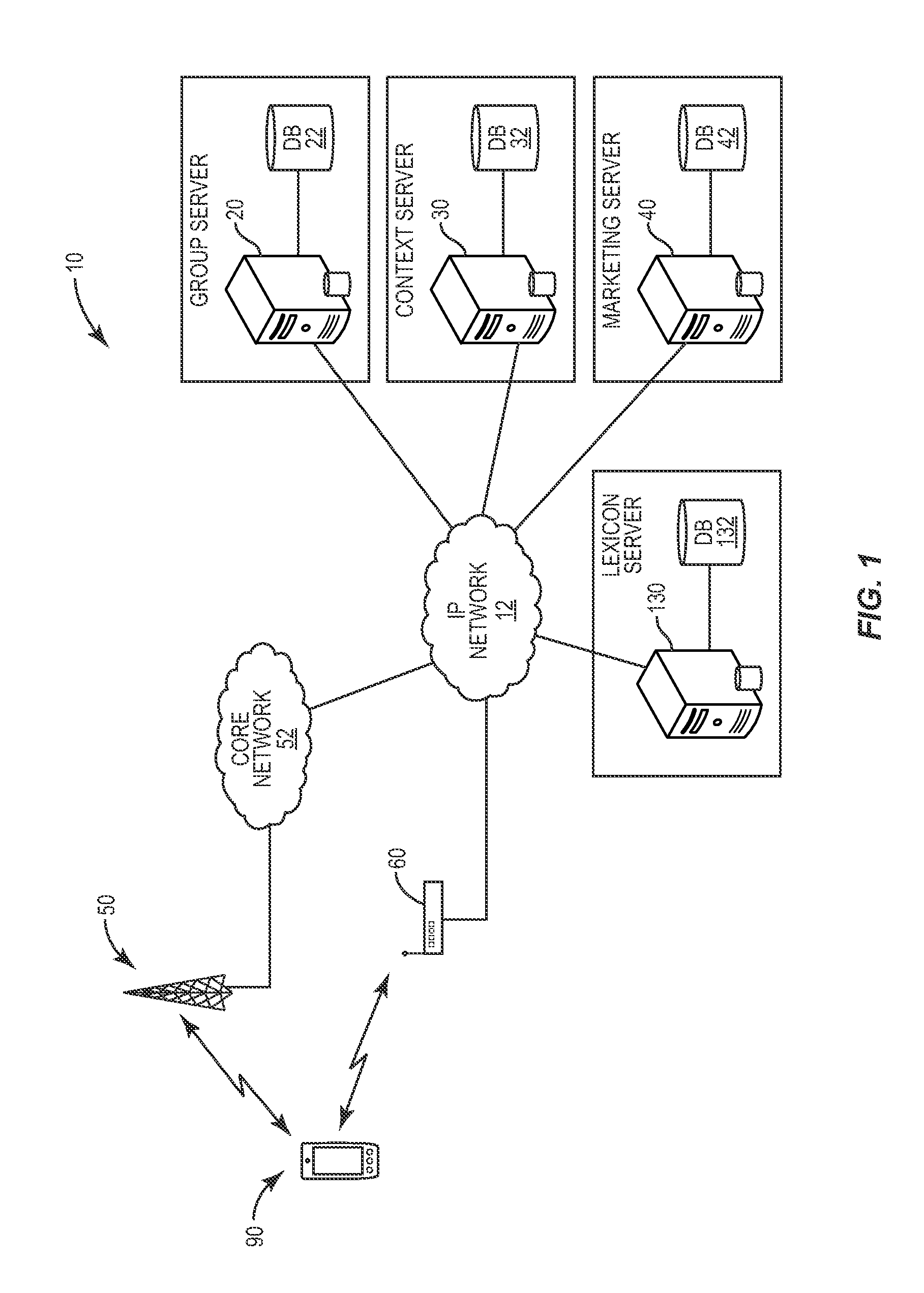
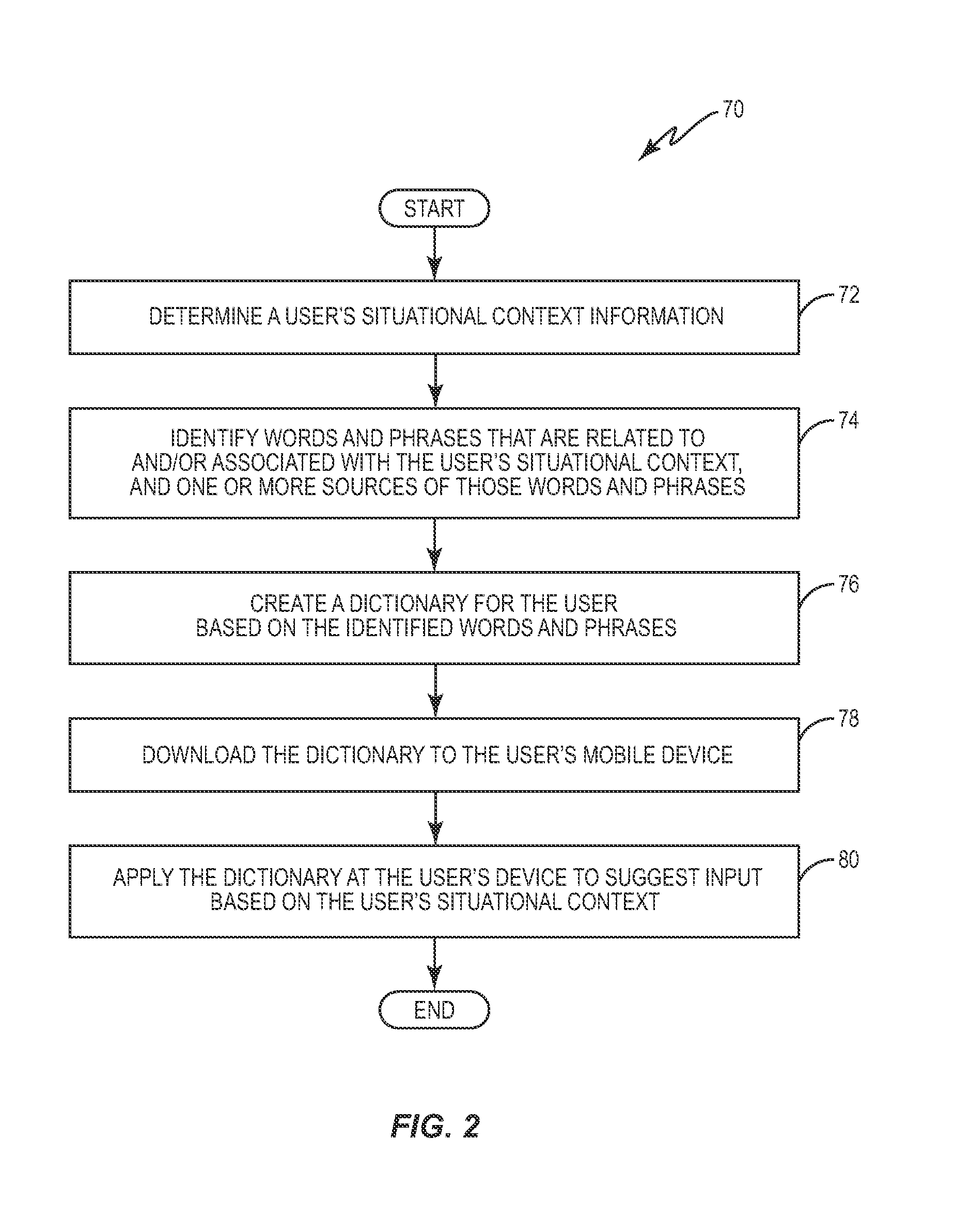
System and method for dynamically generating group-related personalized dictionaries
InactiveUS20130158987A1Natural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsKnowledge sourcesPersonalization
A user device communicates with a network server that has access to one or more knowledge sources. Based on a current situational context for a user of the device, the network server dynamically generates a group-related personalized dictionary using information retrieved from the knowledge sources and provides the dictionary to the user device. Applications executing on the user device can then use the dictionary to suggest or predict words, terms, or symbols to the user in response to receiving user input.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
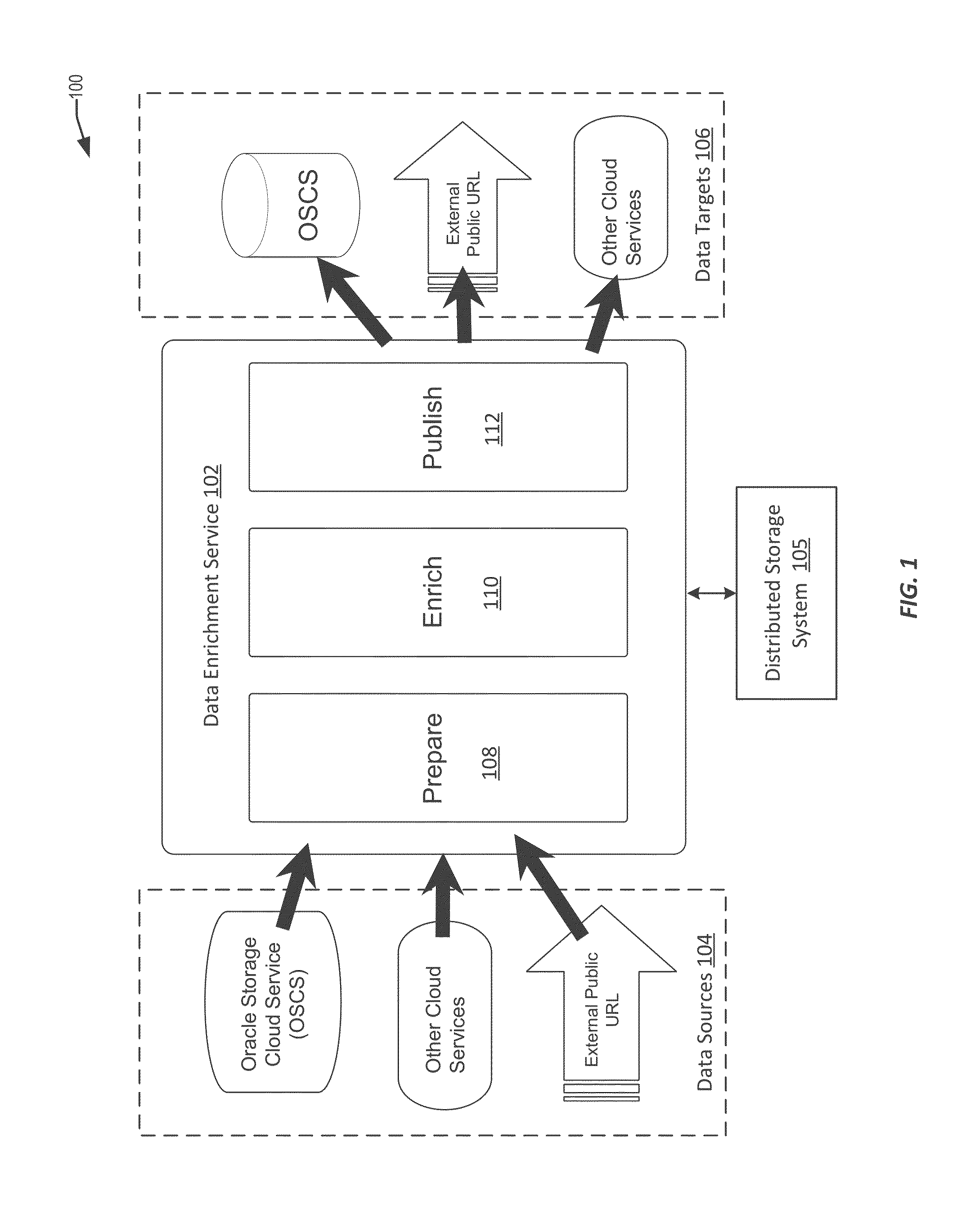
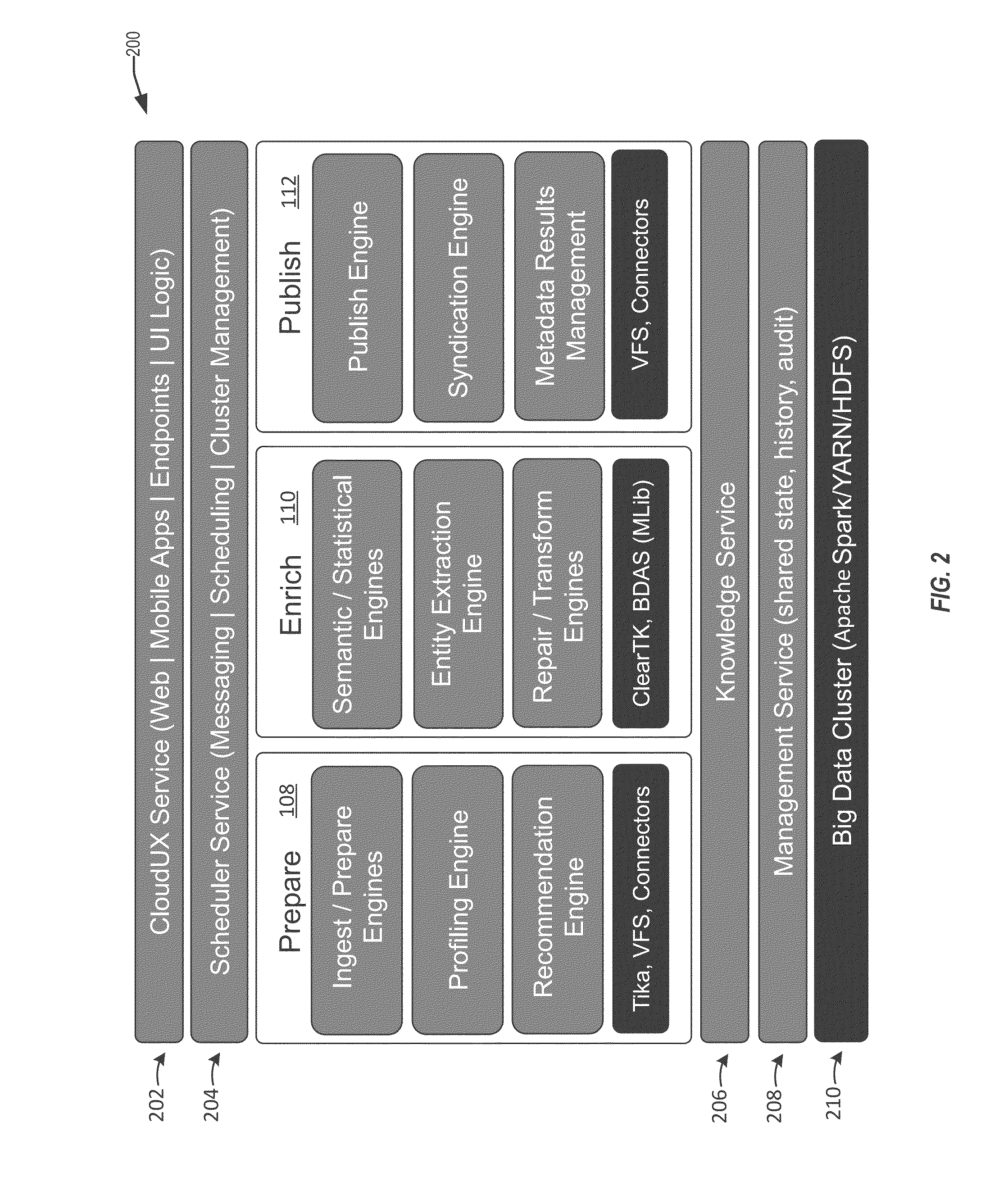
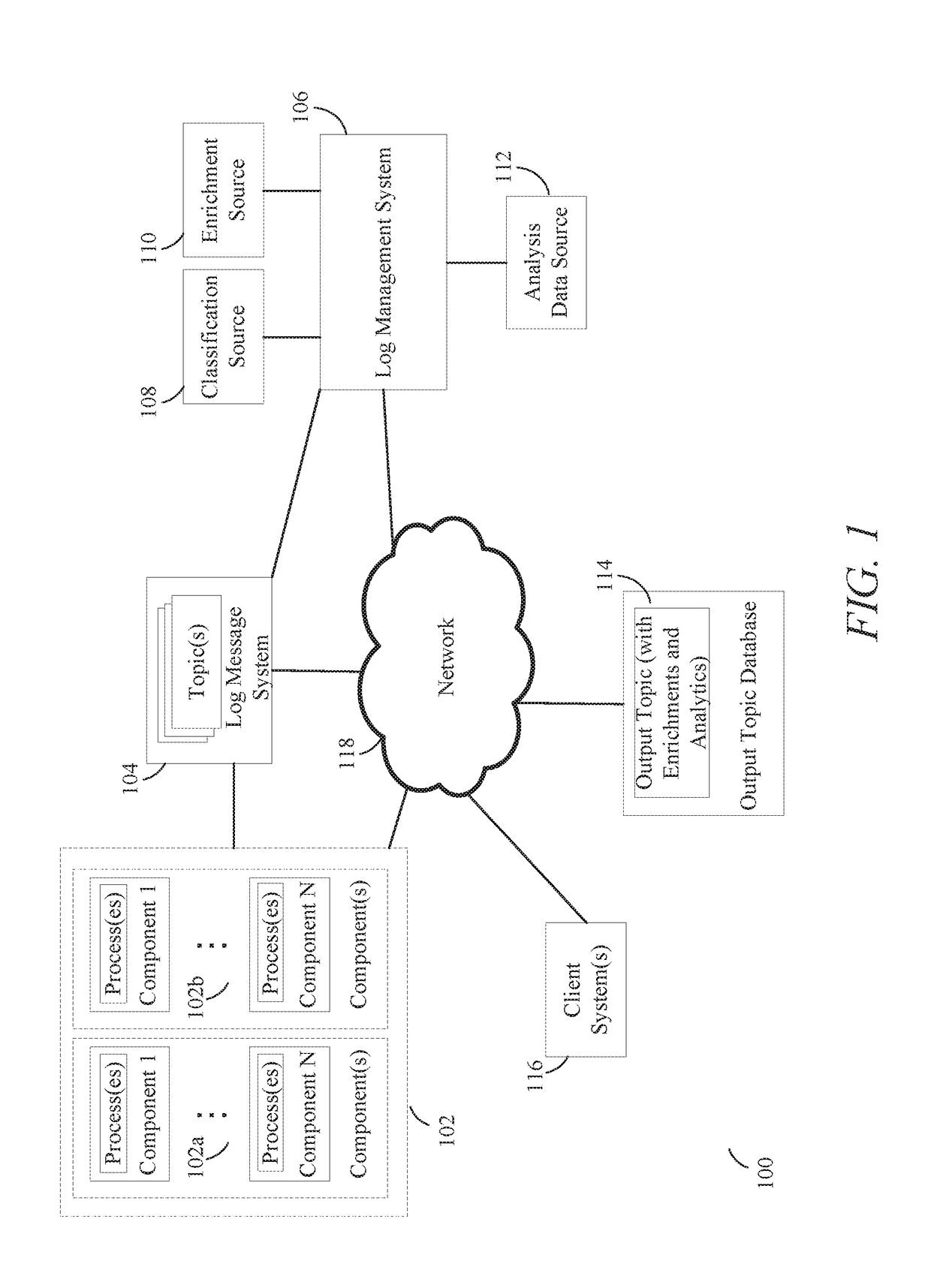
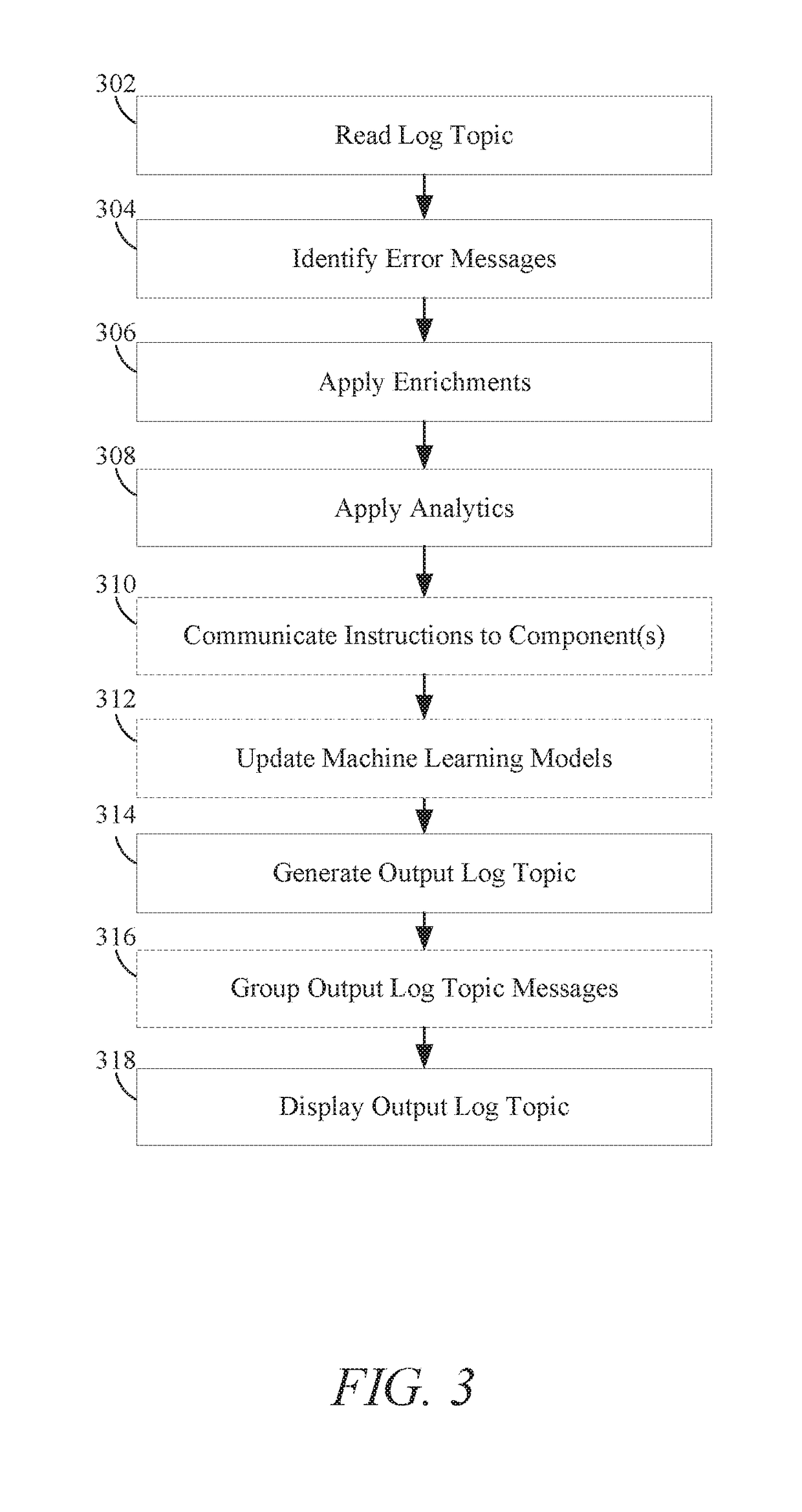
Techniques for managing and analyzing log data
In order to provide effective diagnostics and logging of error messages produced during the execution of processes across multiple components, systems and methods are disclosed for the generating, managing, and processing centralized logs containing those error messages. In particular, the components may write error messages to a centralized log instead of writing the error messages to local log files. These error messages may include exception messages and diagnostics messages. These various error messages in the centralized log can be read, identified, and organized. Furthermore, enrichments and / or analytics may be applied to the error messages based on information from a knowledge source or the application of one or more machine learning models. The organized error messages, enrichments, and analytics can be stored in an output log that can be easily retrieved and viewed through a graphical interface. The organized error messages, enrichments, and analytics may work together to allow for more effective diagnosing of execution errors.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
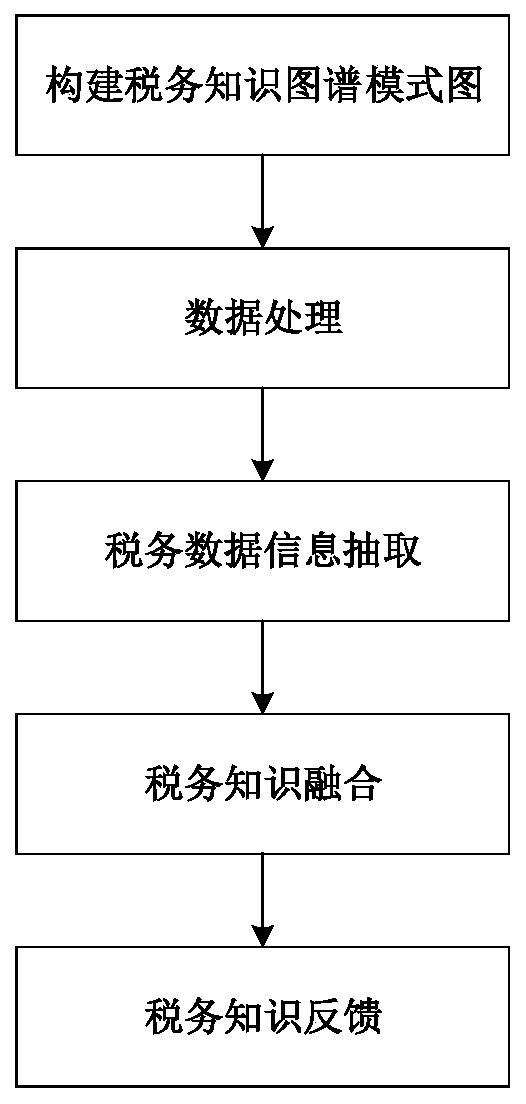
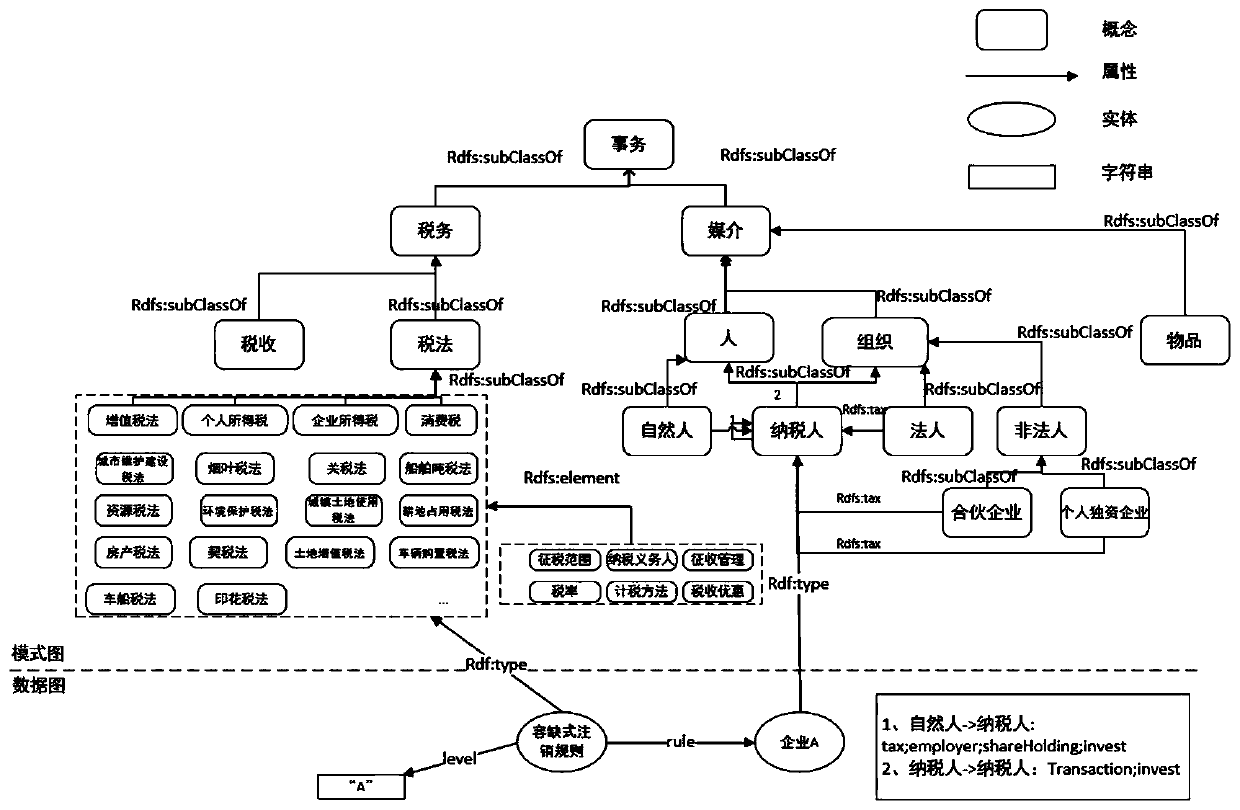
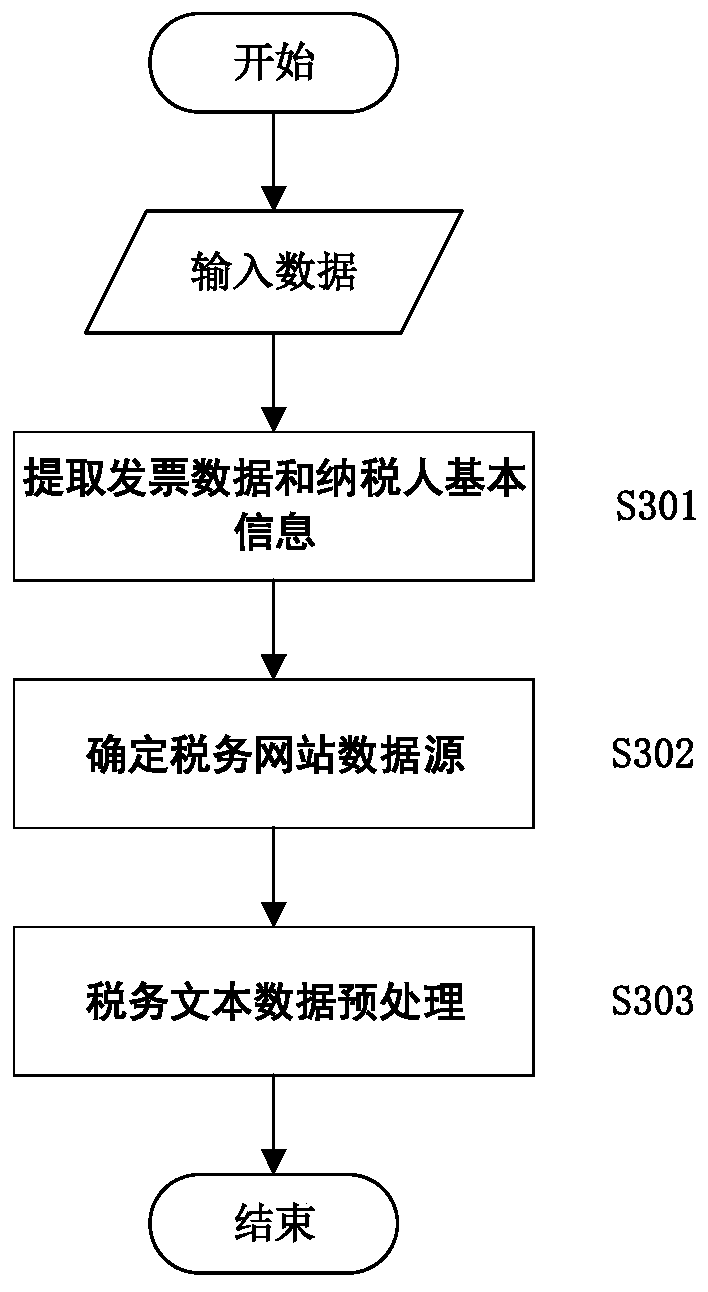
Tax domain-oriented knowledge graph construction method
The invention discloses a tax domain-oriented knowledge graph construction method. According to the construction method, a top-down and bottom-up combined mode is adopted. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing a tax knowledge graph mode based on tax knowledge in a tax expert system; then, data processing including tax data source selection and acquisition, data cleaning and the like is carried out; then information extraction is carried out, and information extraction is carried out on the processed data according to different types and a mode diagram; tax knowledge fusion is carried out, knowledge sources in a tax knowledge graph are different, problems of knowledge repetition, relationship redundancy and the like need to be subjected to mode matching, entity alignment and the like, and knowledge is stored in a knowledge base after knowledge fusion is completed. And finally, knowledge feedback is carried out, and knowledge conflicts in intelligent tax model construction are solved by using a tax expert system. And finally, the problem of untight combination of the knowledge graph and the tax scene is solved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
System and method for determining fuzzy cause and effect relationships in an intelligent workload management system
InactiveUS8620851B2Enable agilityEnable flexibilityFuzzy logic based systemsKnowledge representationKnowledge sourcesPotential effect
The system and method for determining fuzzy cause and effect relationships in an intelligent workload management system described herein may combine potential causes and effects captured from various different sources associated with an information technology infrastructure with substantially instantaneous feedback mechanisms and other knowledge sources. As such, fuzzy correlation logic may then be applied to the combined information to determine potential cause and effect relationships and thereby diagnose problems and otherwise manage interactions that occur in the infrastructure. For example, information describing potential causes and potential effects associated with an operational state of the infrastructure may be captured and combined, and any patterns among the information that describes the multiple potential causes and effects may then be identified. As such, fuzzy logic may the be applied to any such patterns to determine possible relationships among the potential causes and the potential effects associated with the infrastructure operational state.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS SOFTWARE INC
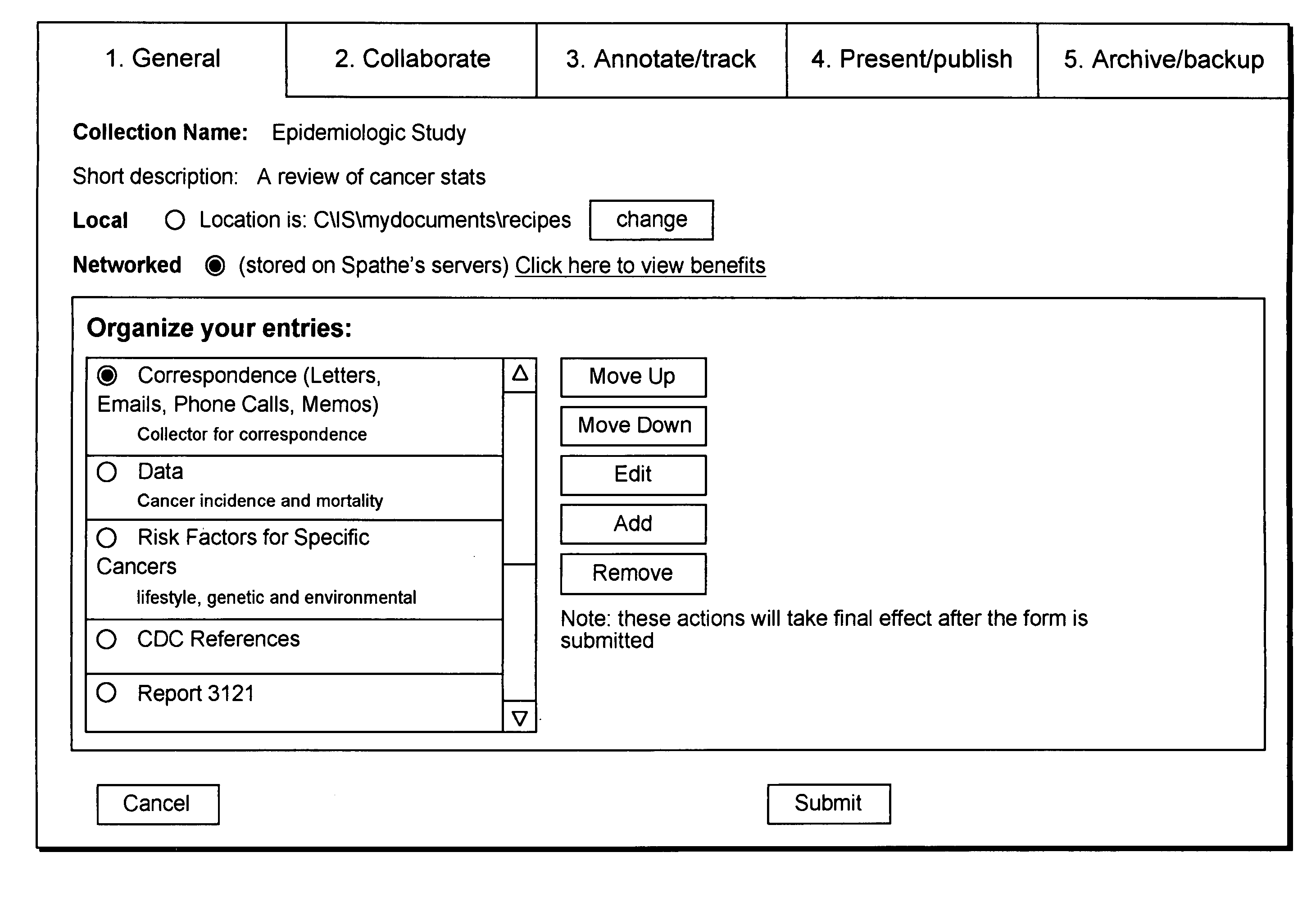
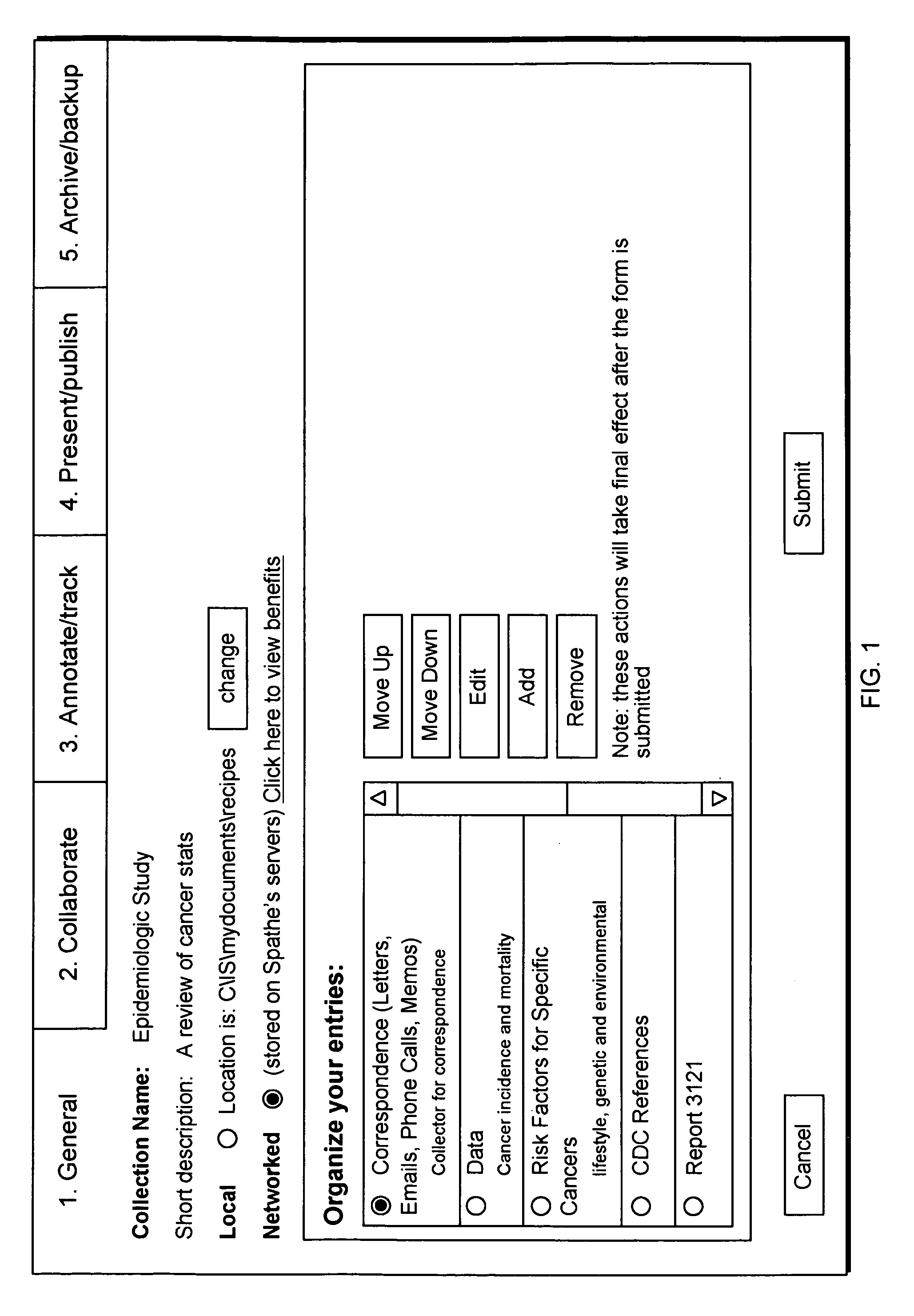
Method or corresponding system employing templates for creating an organizational structure of knowledge
InactiveUS20080222074A1Efficient accessMetadata text retrievalNatural language data processingKnowledge sourcesElectronic document
As the amount of knowledge availability to a user grows, user become overwhelmed with information from sources, such as Web pages, electronic documents, media files, or links to online syndication services. The present invention solves this problem by creating an information collection with efficient knowledge access. In particular, a process selects a collection template and allows a user to determine at least one attribute for the collection template. Next, using a user's intended activity (e.g., a construction project) the process obtains data from all available knowledge sources to include in a collection and creates the collection using the collection template, at least one attribute, and the data. Thus, the process creates a collection with information directed to an intended activity from a vast amount of resources.
Owner:SPATHE
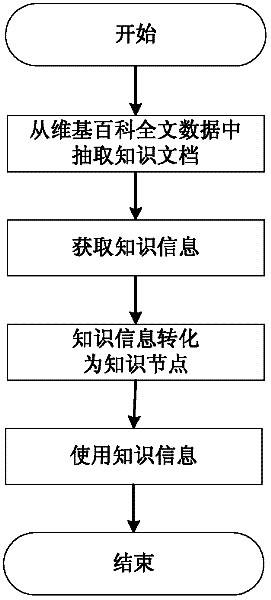
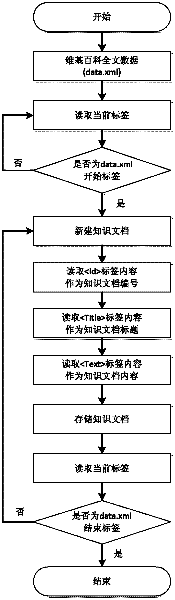
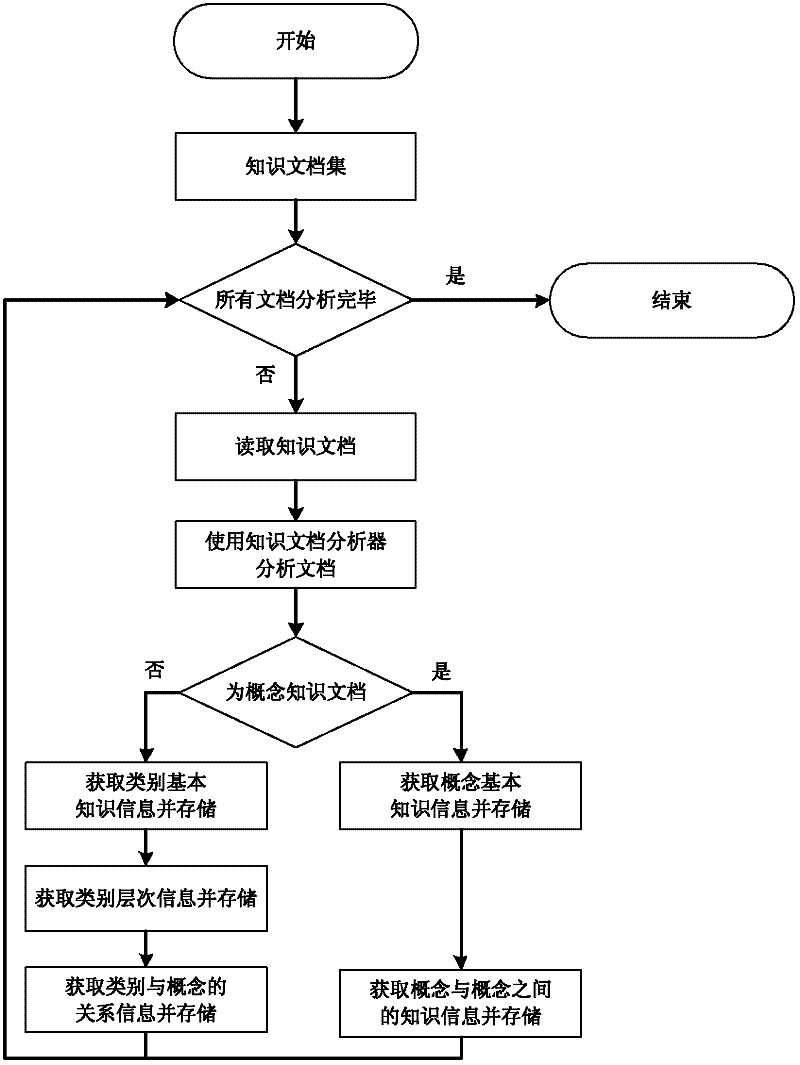
Method for building conceptual knowledge map based on Wikipedia
InactiveCN102609449AReal-time newReal-time updateSpecial data processing applicationsKnowledge sourcesExtensibility
The invention discloses a method for building a conceptual knowledge map based on Wikipedia, which includes steps: firstly, extracting knowledge documents from a Wikipedia full-text database and classifying and storing the extracted documents; secondly, analyzing each knowledge document to obtain knowledge information and storing the knowledge information in a database; thirdly, transforming the knowledge information into corresponding conceptual knowledge nodes and category knowledge nodes on the basis of standards in a knowledge node format description library and storing the knowledge nodes in file format locally; fourthly, building an index to provide a function of knowledge information searching via key words and displaying the searching results. The conceptual knowledge map is applicable to a plurality of fields, the knowledge information can be updated along with Wikipedia, obtaining knowledge source is easy, knowledge information is comprehensive, extensible markup language is adopted to describe the knowledge node information, and accordingly, the conceptual knowledge map is high in extensibility and can be applied to multiple platforms.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Implicit dialog approach operating a conversational access interface to web content
A method, apparatus and computer program product for presenting a user interface for a conversational system is described. A user input is received in a dialog between a user and the conversational system, the user input in a natural language. A domain trained semantic matcher is used to determine a set of entities and a user intent from the user input. One or more queries is generated to selected ones of a plurality of knowledge sources, the knowledge sources created from domain specific knowledge. The results from the one or more queries are ranked based on domain specific knowledge. A system response is presented in the dialog based on at least a highest ranked result from the plurality of knowledge sources.
Owner:IBM CORP
Session context modeling for conversational understanding systems
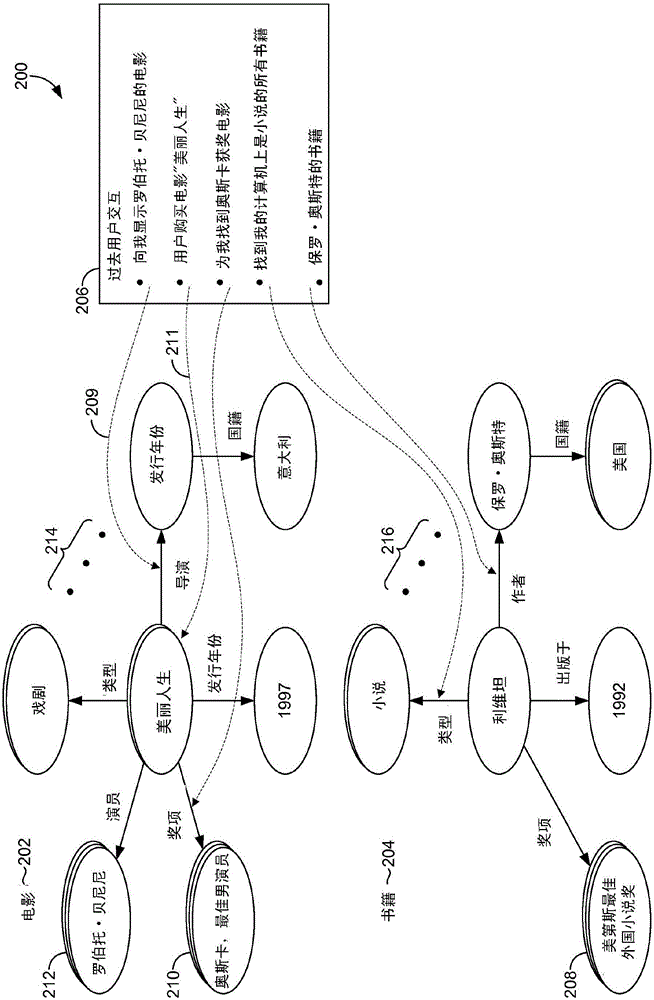
Systems and methods are provided for improving language models for speech recognition by adapting knowledge sources utilized by the language models to session contexts. A knowledge source, such as a knowledge graph, is used to capture and model dynamic session context based on user interaction information from usage history, such as session logs, that is mapped to the knowledge source. From sequences of user interactions, higher level intent sequences may be determined and used to form models that anticipate similar intents but with different arguments including arguments that do not necessarily appear in the usage history. In this way, the session context models may be used to determine likely next interactions or "turns" from a user, given a previous turn or turns. Language models corresponding to the likely next turns are then interpolated and provided to improve recognition accuracy of the next turn received from the user.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
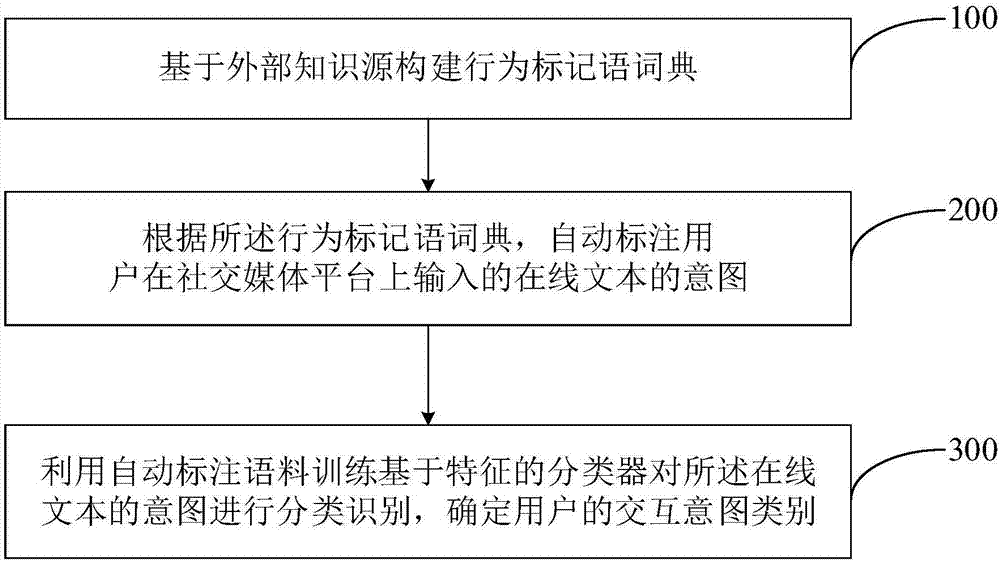
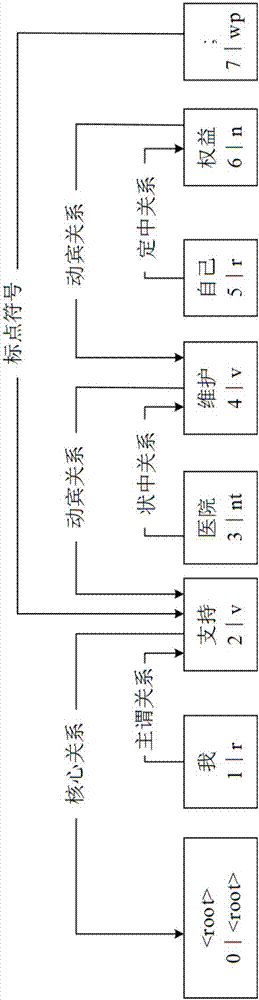
User interaction intention recognition method and system based on speech act theory
InactiveCN107153672AEfficient identificationImprove recognition accuracySemantic analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionKnowledge sourcesSocial media
The invention relates to a user interaction intention recognition method and system based on a speech act theory. The user interaction intention recognition method comprises the steps of constructing a behavior discourse marker dictionary based on an external knowledge source; automatically labeling the intention of an online text input by a user on a social media platform according to the behavior discourse marker dictionary; using an automatic tagged corpus to train a classifier based on features and conduct classified recognition on the intention of the online text to determine the interaction intention category of the user. According to the user interaction intention recognition method based on the speech act theory, by constructing the behavior discourse marker dictionary corresponding to different intention categories based on the external knowledge source, automatically labeling and expanding the corpus based on the behavior discourse marker dictionary, and conducting recognition on feature classification, the interaction intention of the user in a social media can be effectively recognized, the recognition accuracy is high, the user interaction intention recognition method and system can be used for intention analysis and recognition in the field of business intelligence, social situations, comment situations, decision evaluation and the like, and thus the application range is wide.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method and system for maximum-informativeness information extraction using a domain-specific ontology
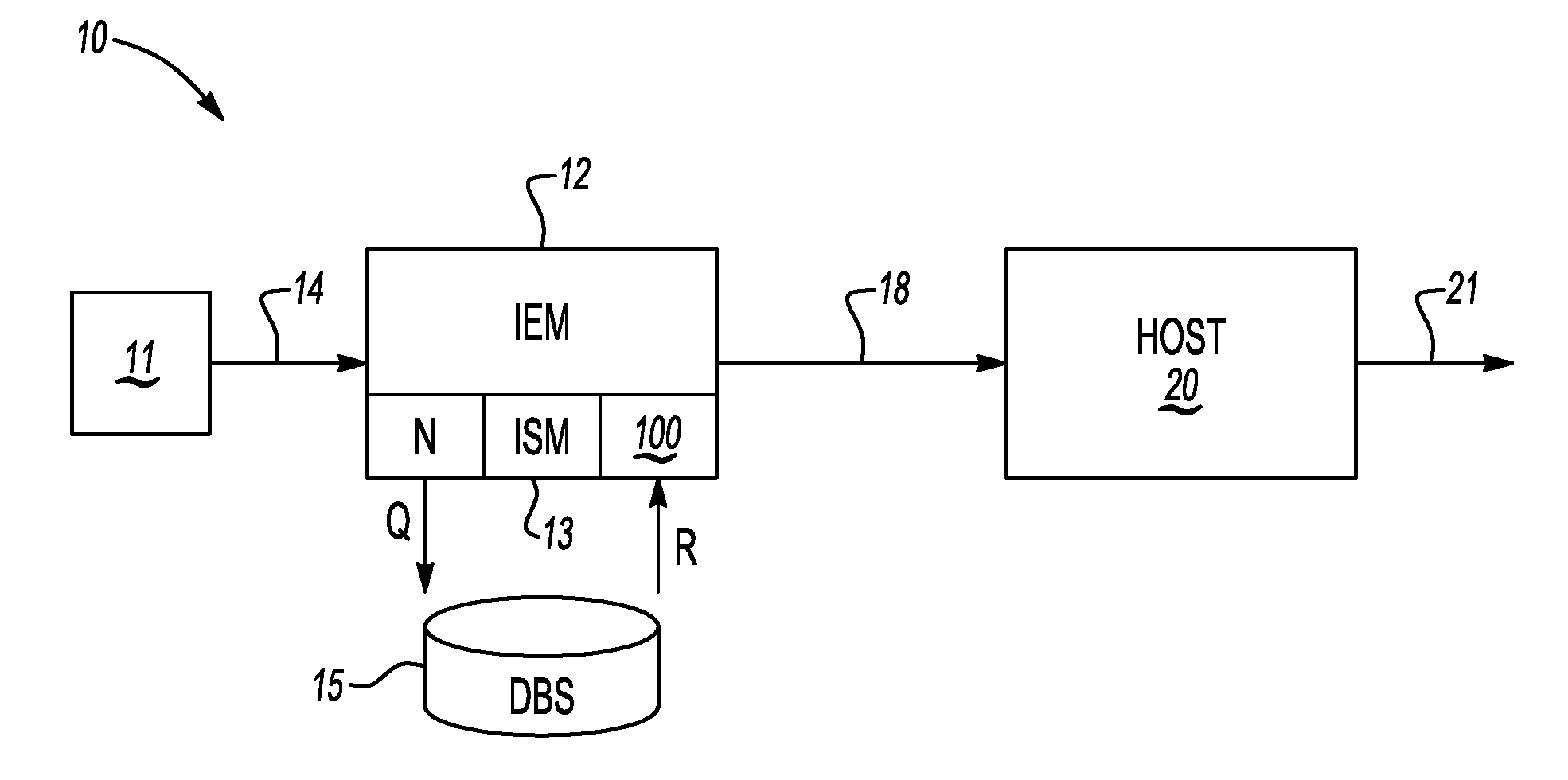
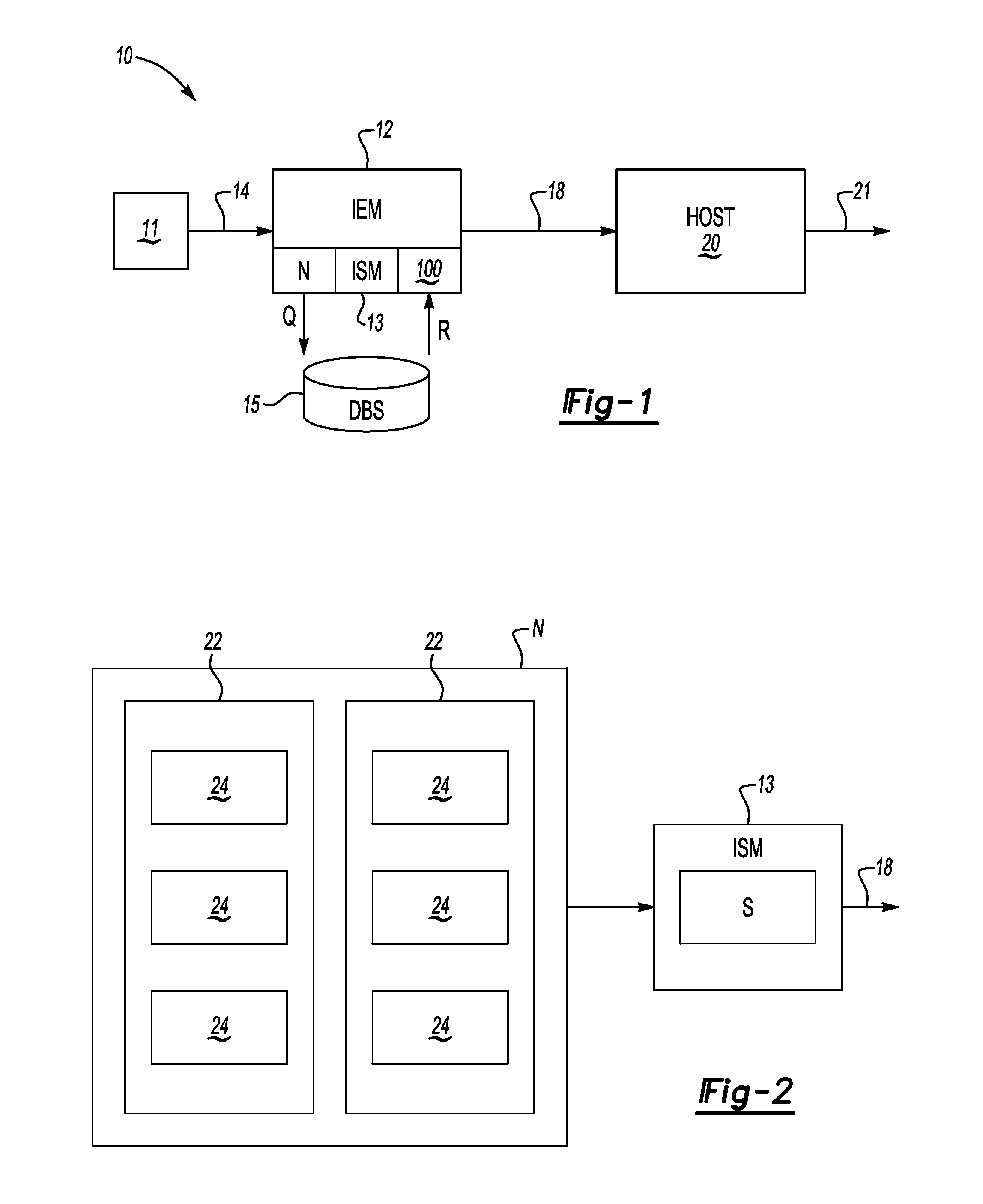
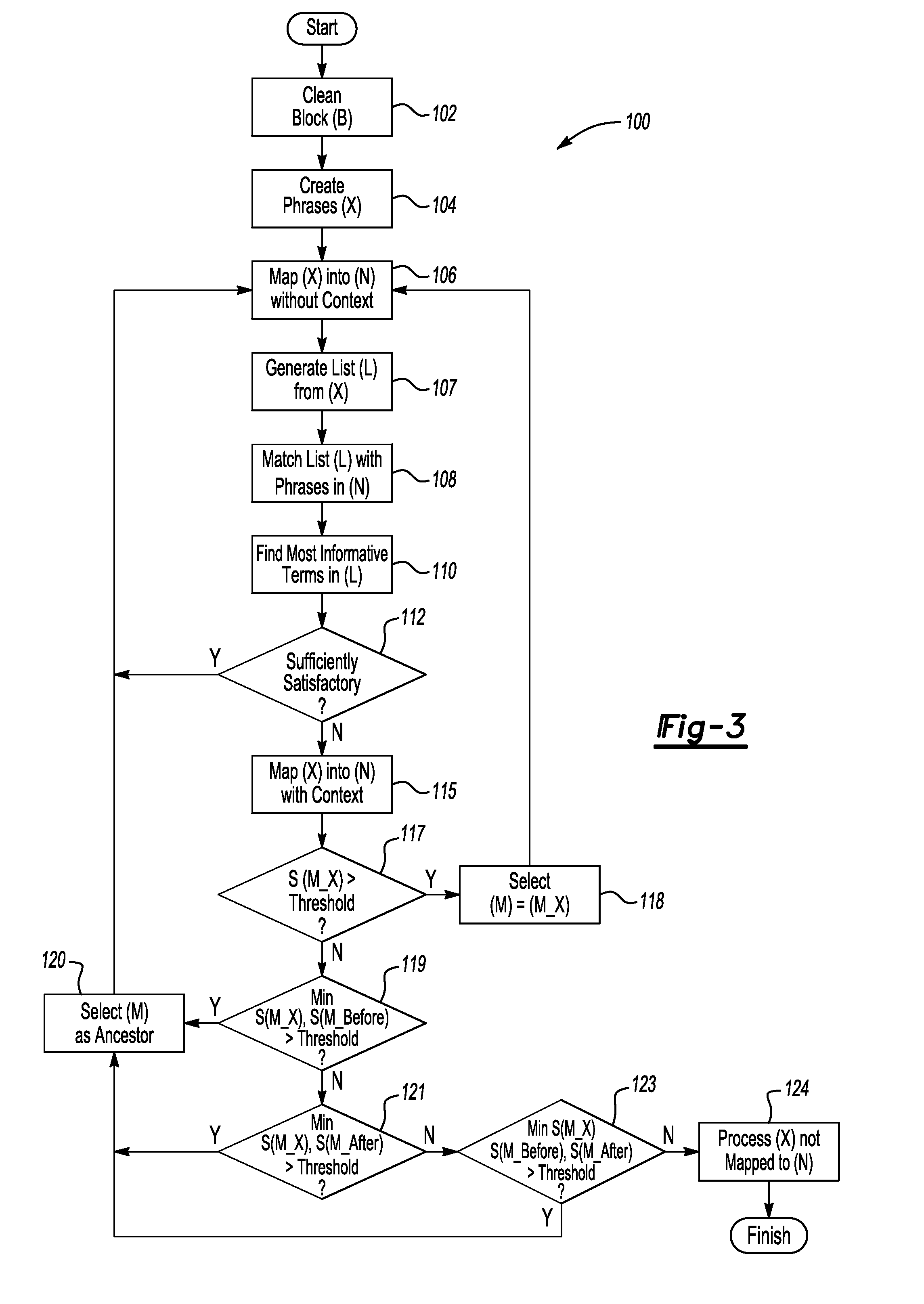
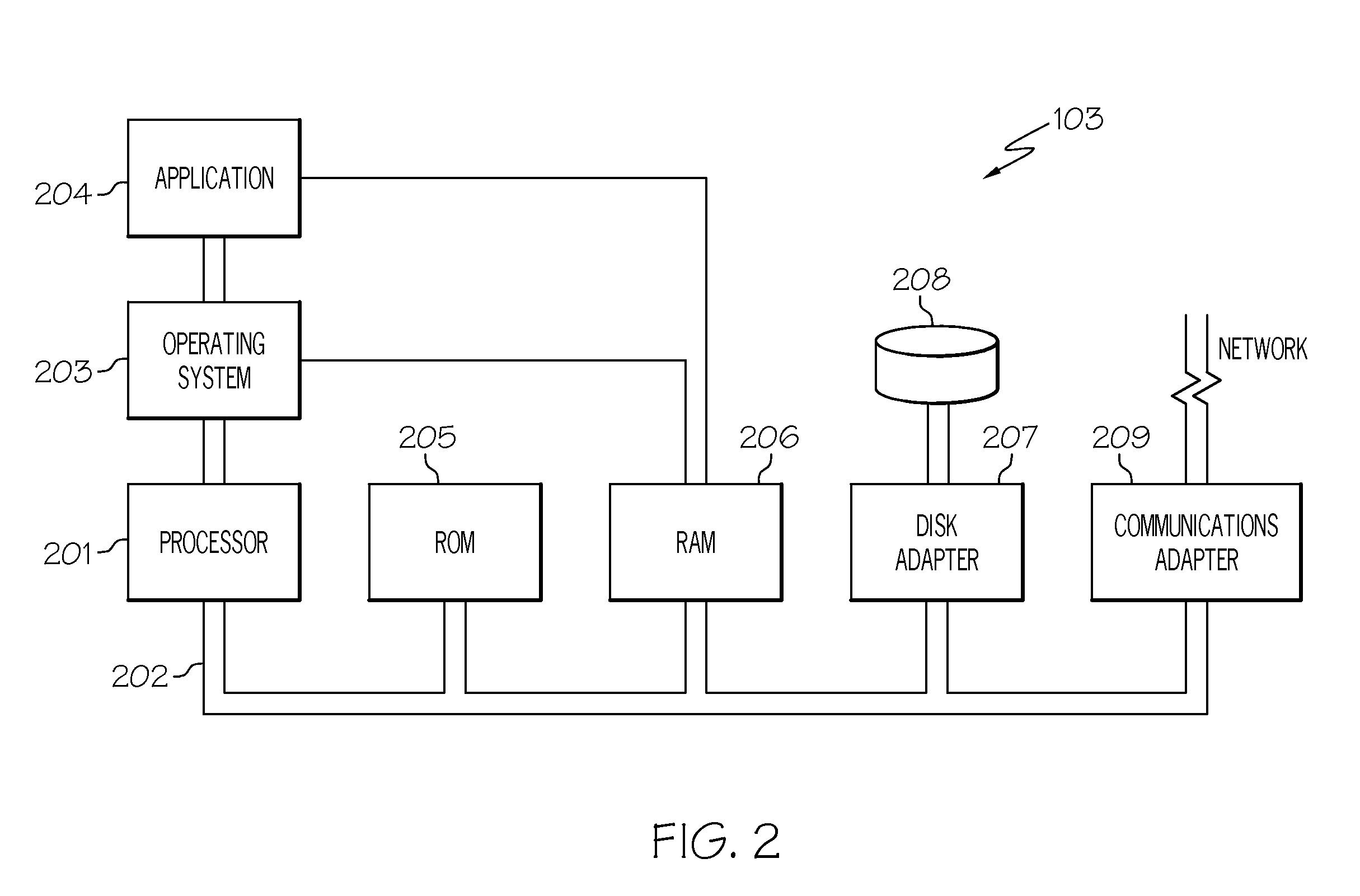
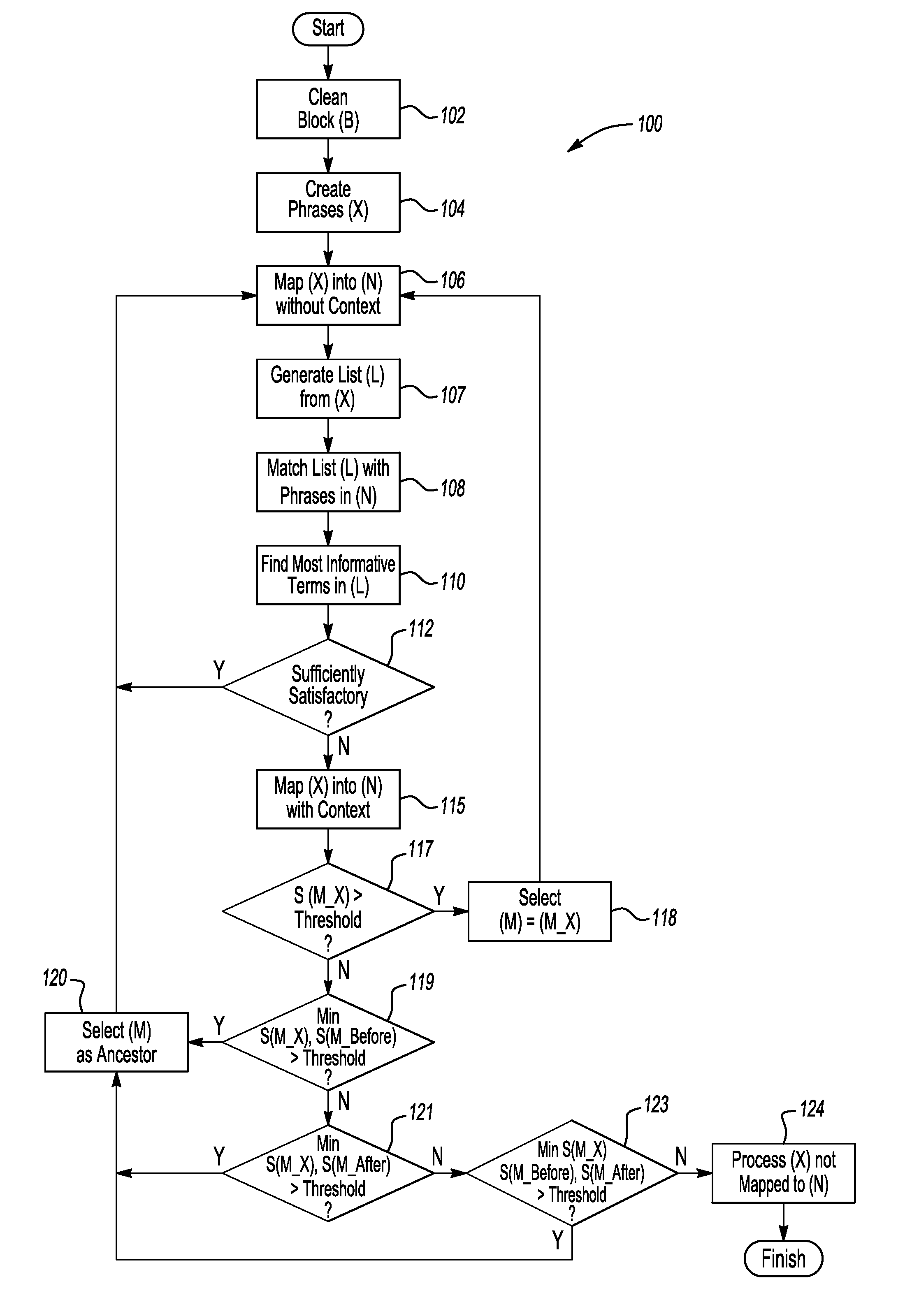
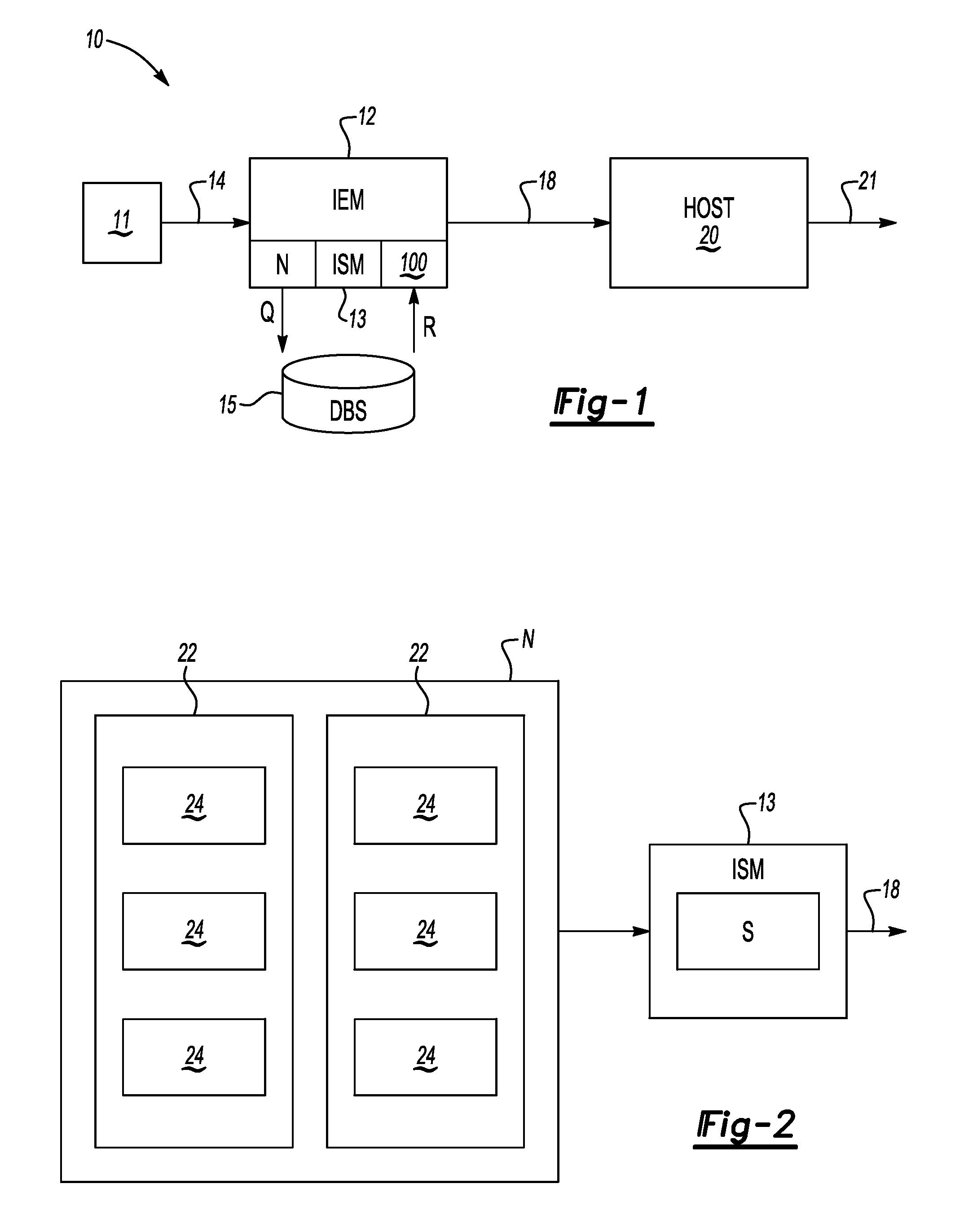
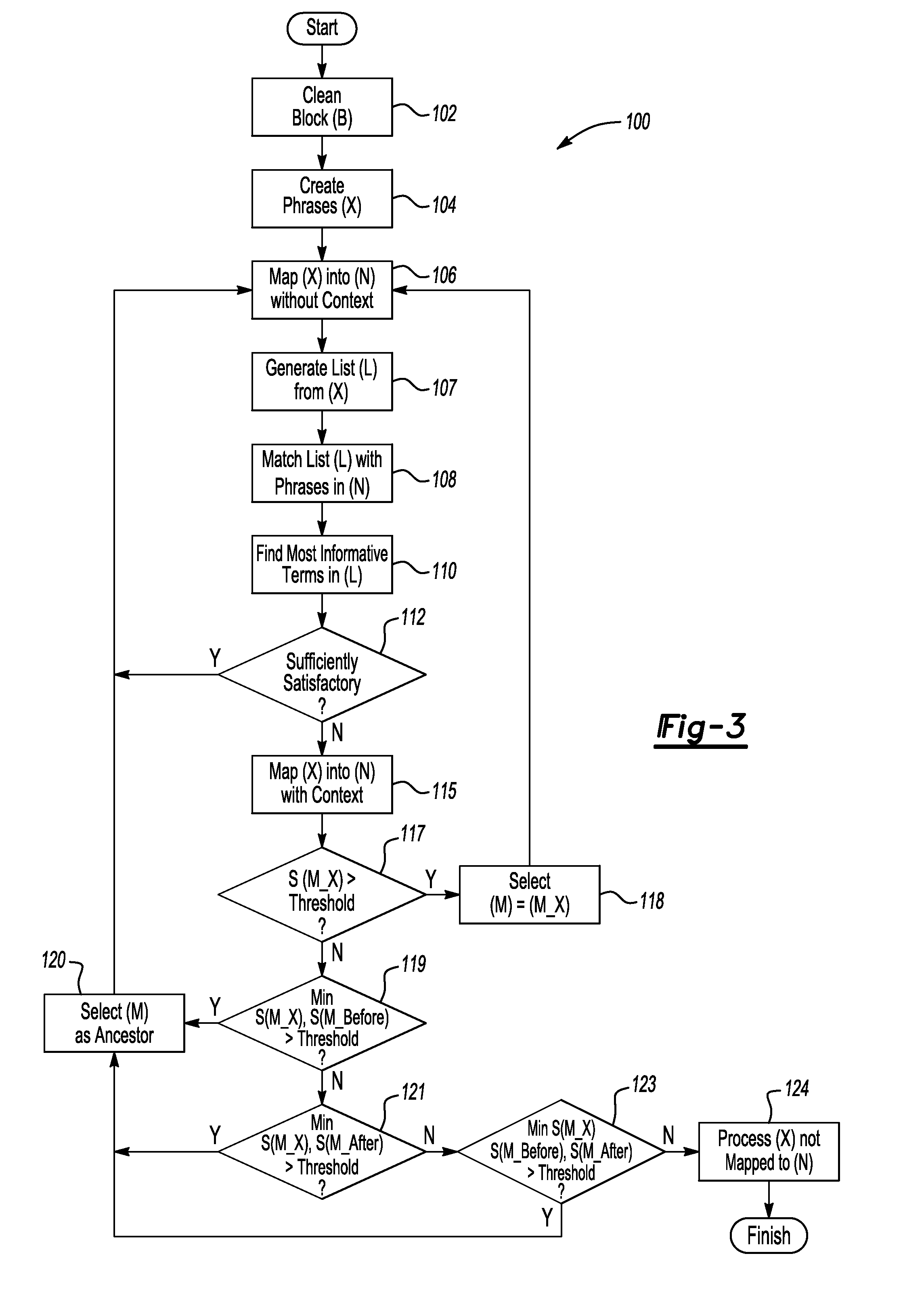
ActiveUS20110113069A1Low recallAvoid High Precision RequirementsDigital data processing detailsNatural language data processingKnowledge sourcesA domain
A method transforms unstructured text into structured data in a domain-specific ontology. The method includes recording an input block of text using an information extraction module (IEM), accessing a domain-specific ontology and supplemental data in a knowledge source(s) via the IEM, processing the input text block, and using the IEM to generate a plurality of nodes in the domain-specific ontology. Each node classifies the unstructured text to corresponding objects of interest, thereby transforming the unstructured text into the structured data. An IEM is also provided having a computer device and an algorithm executable thereby to transform unstructured text into structured data in a domain-specific ontology. The IEM is adapted for recording a text phrase using the computer device, accessing and retrieving the domain-specific ontology and supplemental data from a knowledge source(s), and processing the text block using the computer device to generate a plurality of nodes in the domain-specific ontology.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Using computational engines to improve search relevance
ActiveUS8606739B2Highly relevantImprove relevanceDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsKnowledge sourcesRecommender system
An “Iterative Query Reformulator” provides various techniques for using a computational engine to reformulate initial queries through one or more iterations. This query reformulation process ensures that results returned from search engines or recommendation systems using a reformulated query have improved relevance relative to results that would have been returned using only the initial query. More specifically, the Iterative Query Reformulator provides an end to end solution that uses computations from one or more knowledge databases or knowledge sources to find “partial answers” to subqueries derived or extracted from an initial query. These partial answers are then used to reformulate the initial query, with the reformulated query being used by the search engines or recommendations systems to provide results that are highly relevant to the initial query. Determinations of whether to continue reformulation iterations are based on evaluating user metrics from historical search logs having queries that match reformulated queries.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
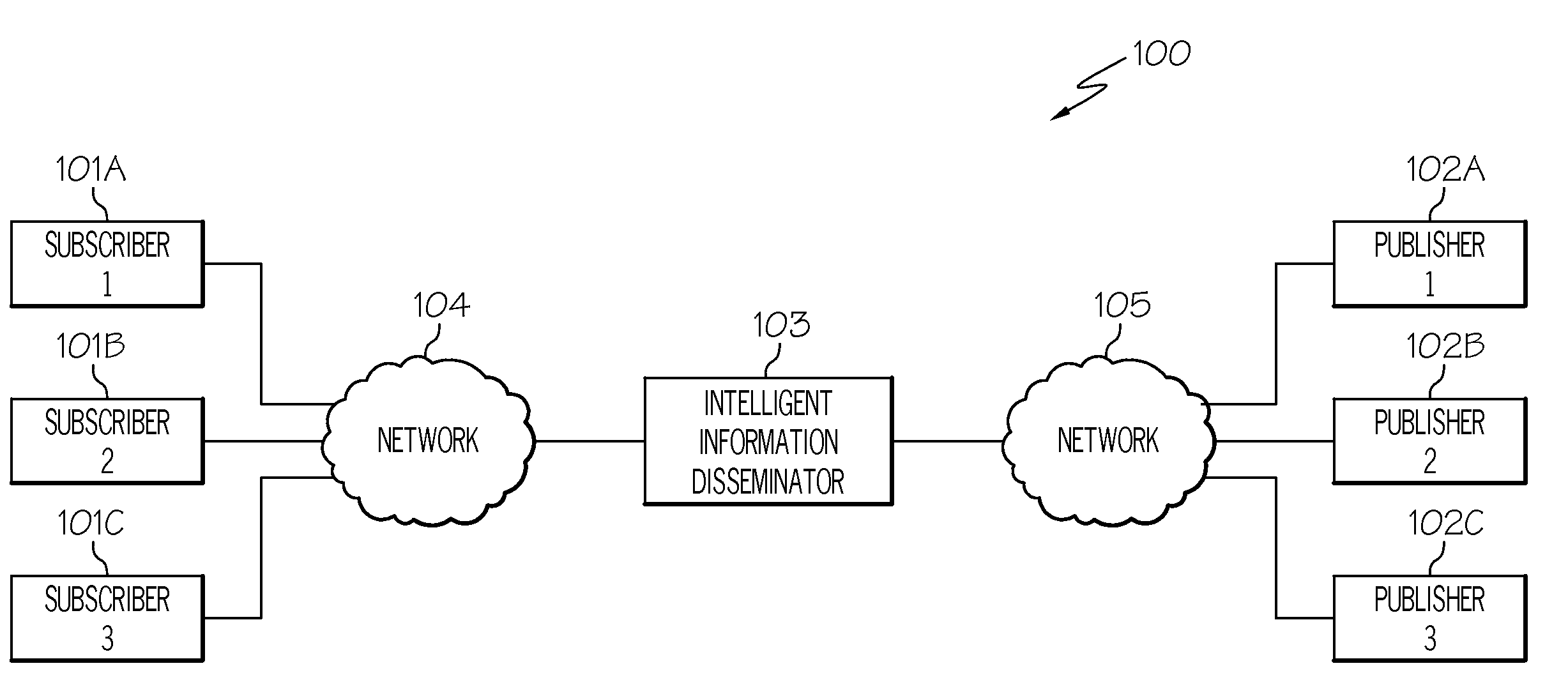
Identifying and routing of documents of potential interest to subscribers using interest determination rules
InactiveUS20100299140A1Office automationSpecial data processing applicationsDocument preparationKnowledge sources
A method, system and computer program product for identifying documents of interest. A profile of a subscriber is created based on information obtained about the subscriber. Subscriber-interest determination rules are used to identify potential topics of interest of the subscriber based on the subscriber's profile as well as based on external knowledge sources. Each potential interest of the subscriber may be represented by a pointer that references a concept. Additionally, concepts in the documents published by the publishers are identified. A comparison may be made between the concepts identified in the documents published by the publishers with those concepts representing the potential topics of interests of the subscriber. Those documents with matching concepts may then be identified as potentially being of interest for the subscriber. In this manner, documents of interest are more accurately identified for the document seeker.
Owner:CYCORP
Method and system for maximum-informativeness information extraction using a domain-specific ontology
ActiveUS8176048B2Digital data processing detailsNatural language data processingKnowledge sourcesA domain
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
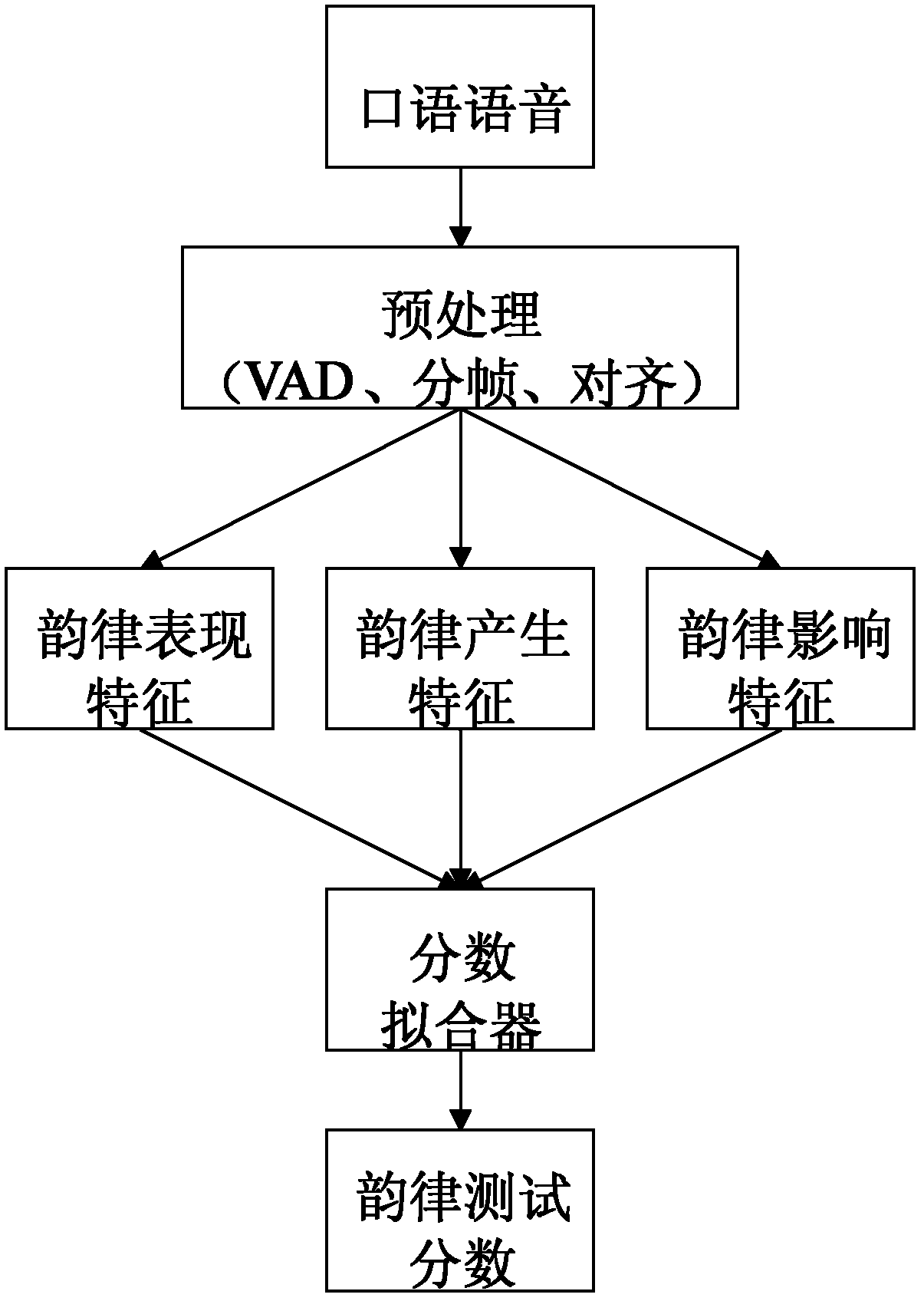
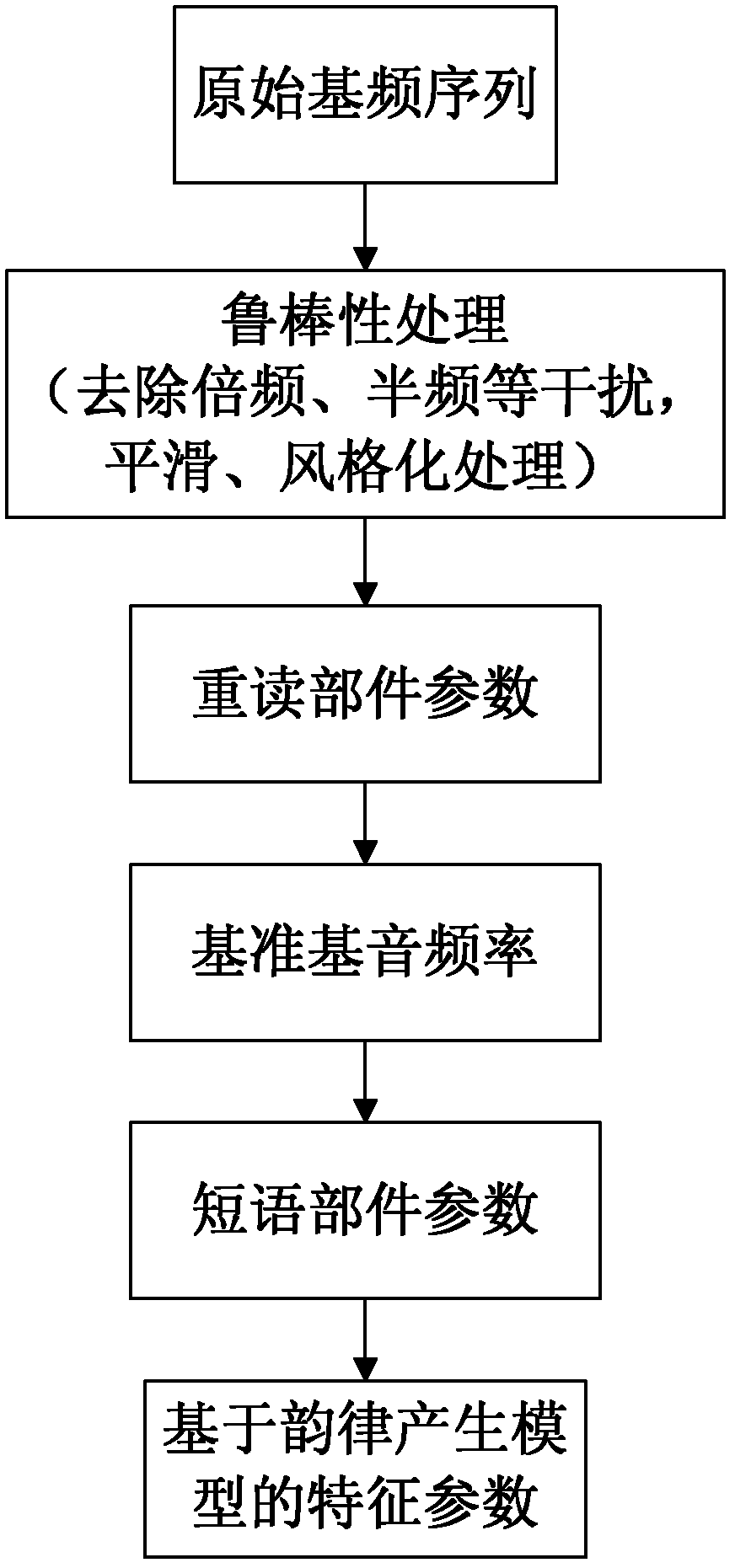
Method for testing rhythm level of spoken English
ActiveCN102426834AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilitySpeech analysisKnowledge sourcesSpoken language
The invention discloses a method for testing the rhythm level of spoken English. The method comprises the following steps of: A, preprocessing an original English speech signal; B, extracting multi-knowledge-source characteristic parameters used for a rhythm test from the preprocessed original English speech signal, wherein the multi-knowledge-source characteristic parameters comprise rhythm performance characteristics, rhythm generation characteristics and rhythm influence characteristics; and C, acquiring a rhythm level test score of original English sounds by using most of the multi-knowledge-source characteristic parameters. By the method for testing the rhythm level of spoken English, a better test result is obtained by using a strategy in which multi-knowledge information is used for thinning and merging, and the objectivity and the accuracy of the test are improved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com