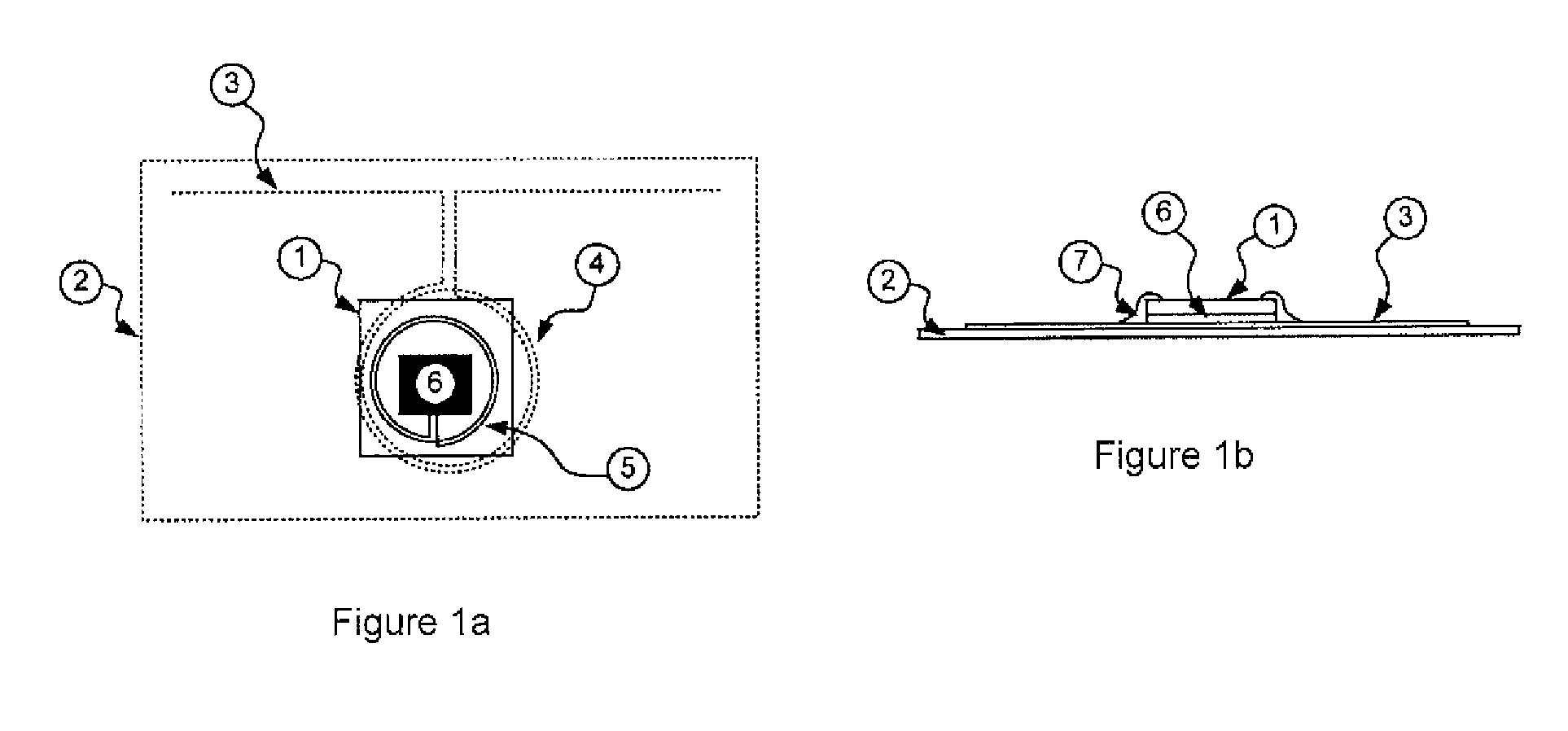
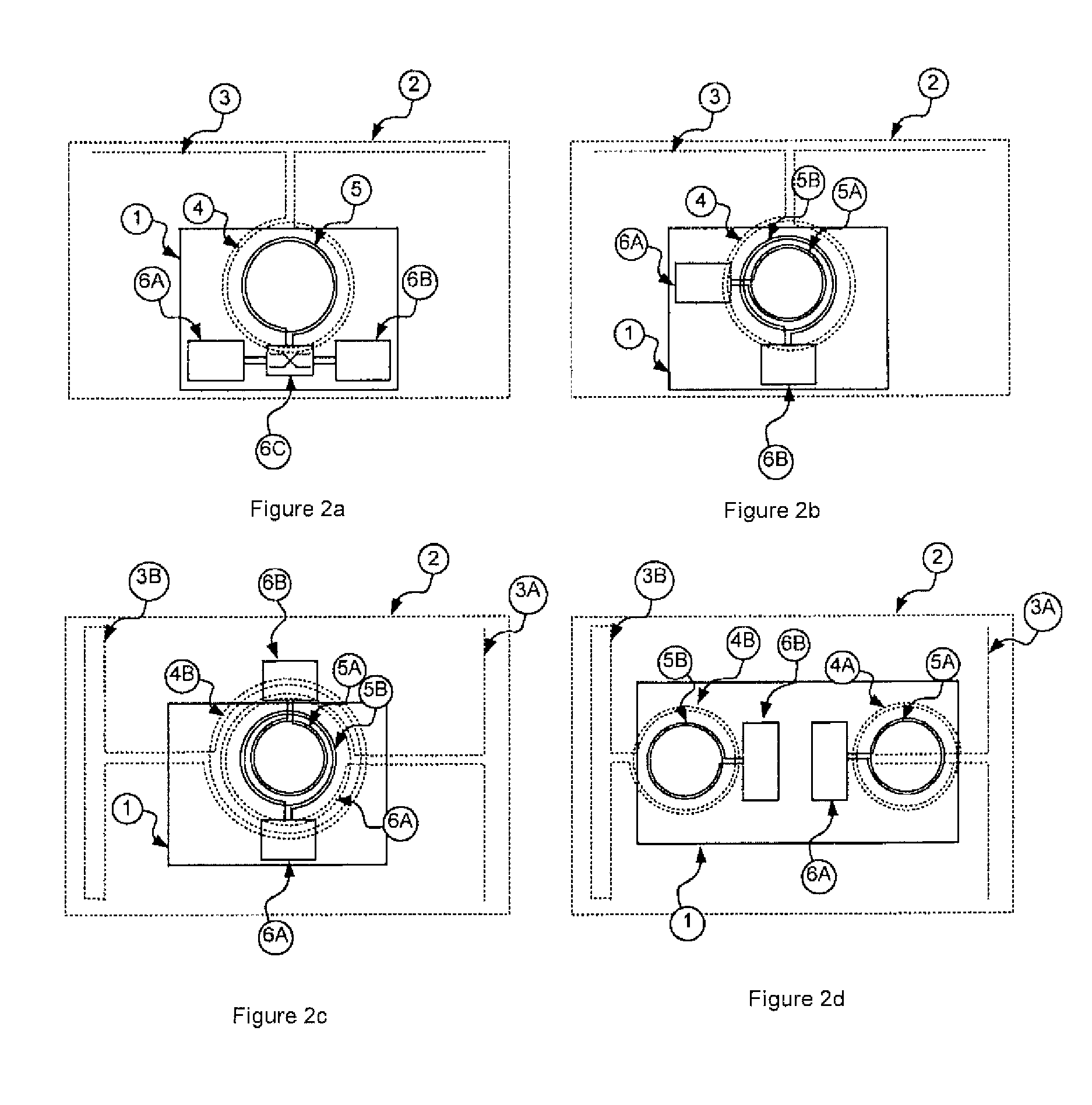
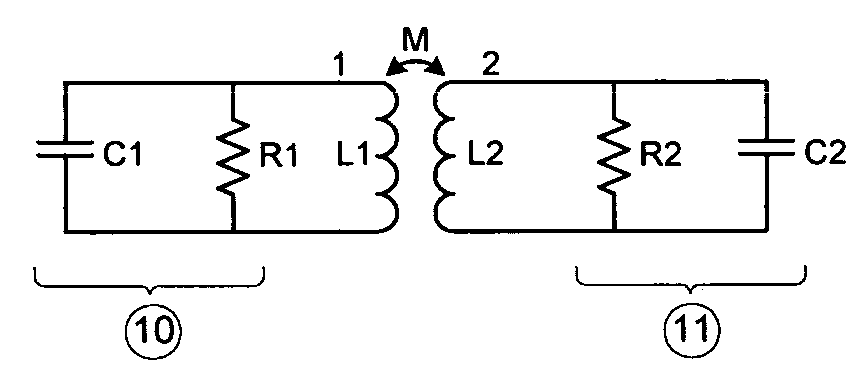
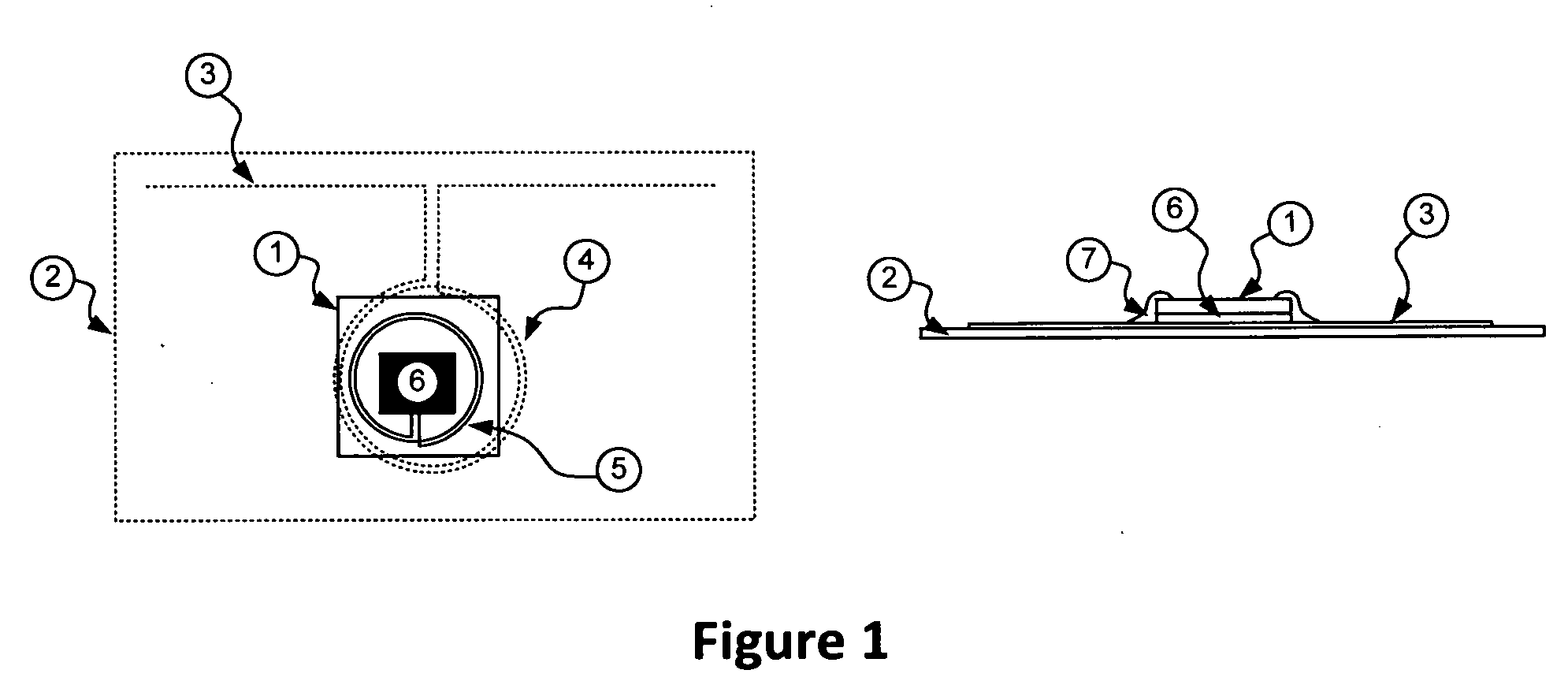
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58results about How to "Avoid High Precision Requirements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
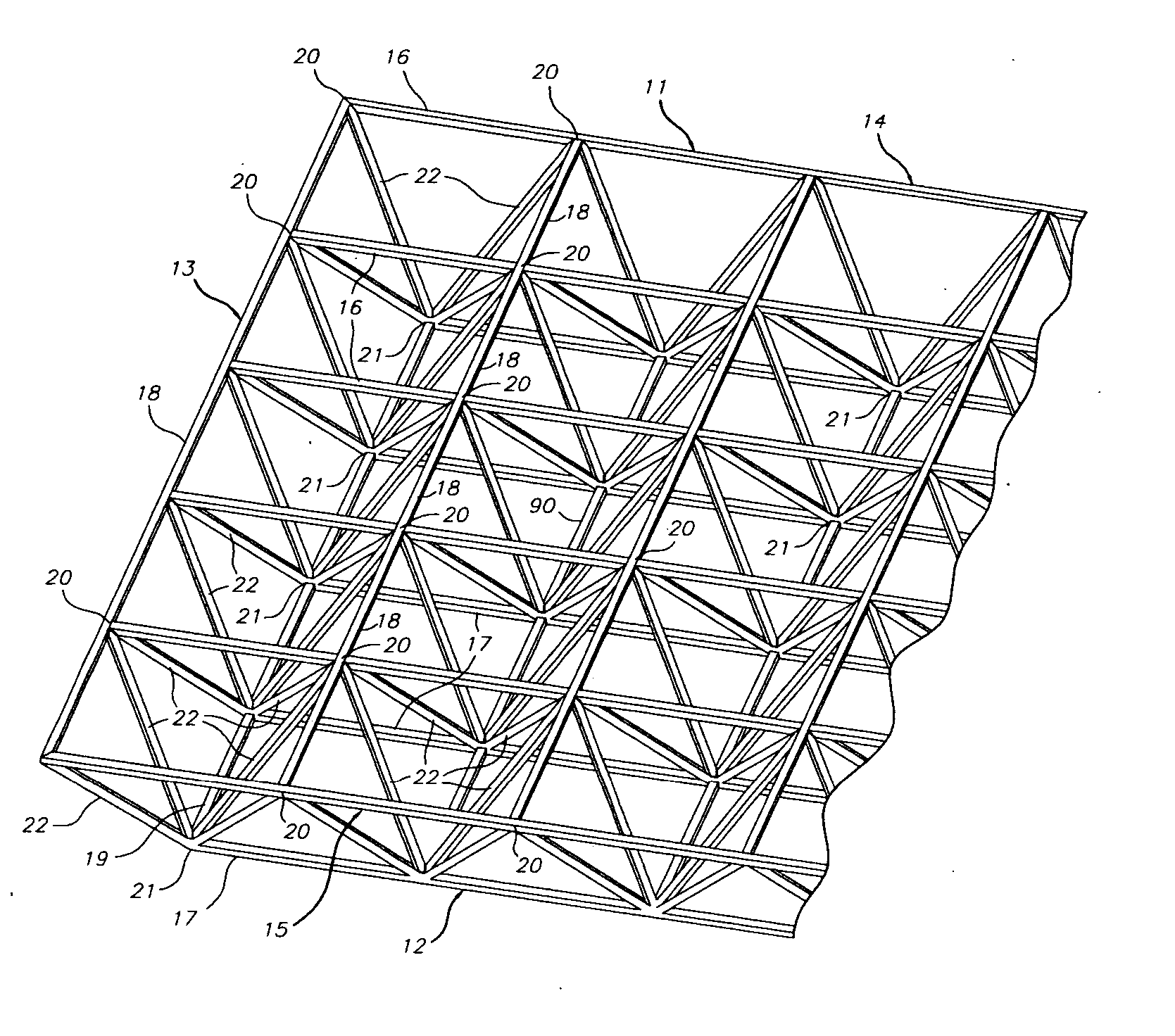
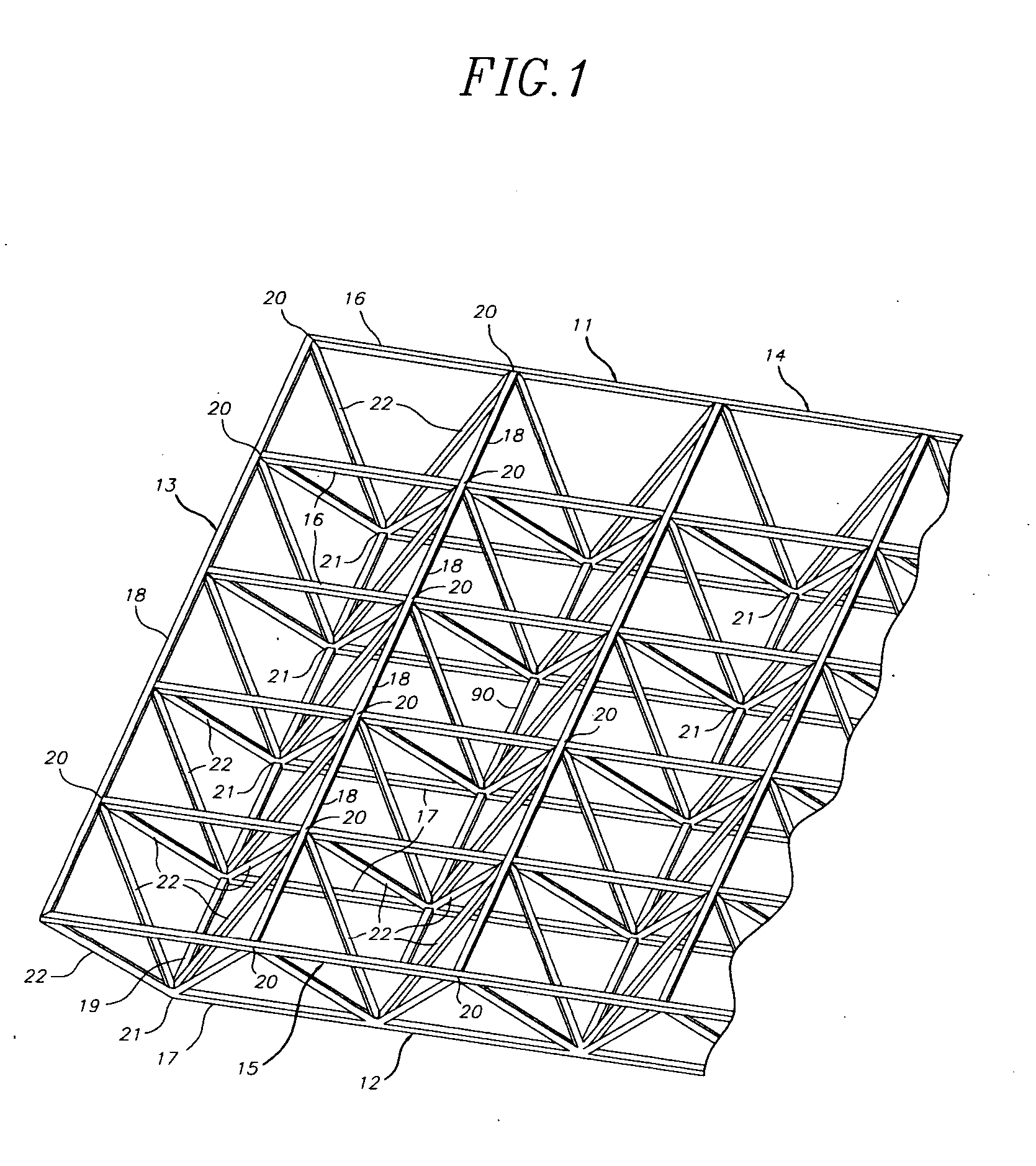
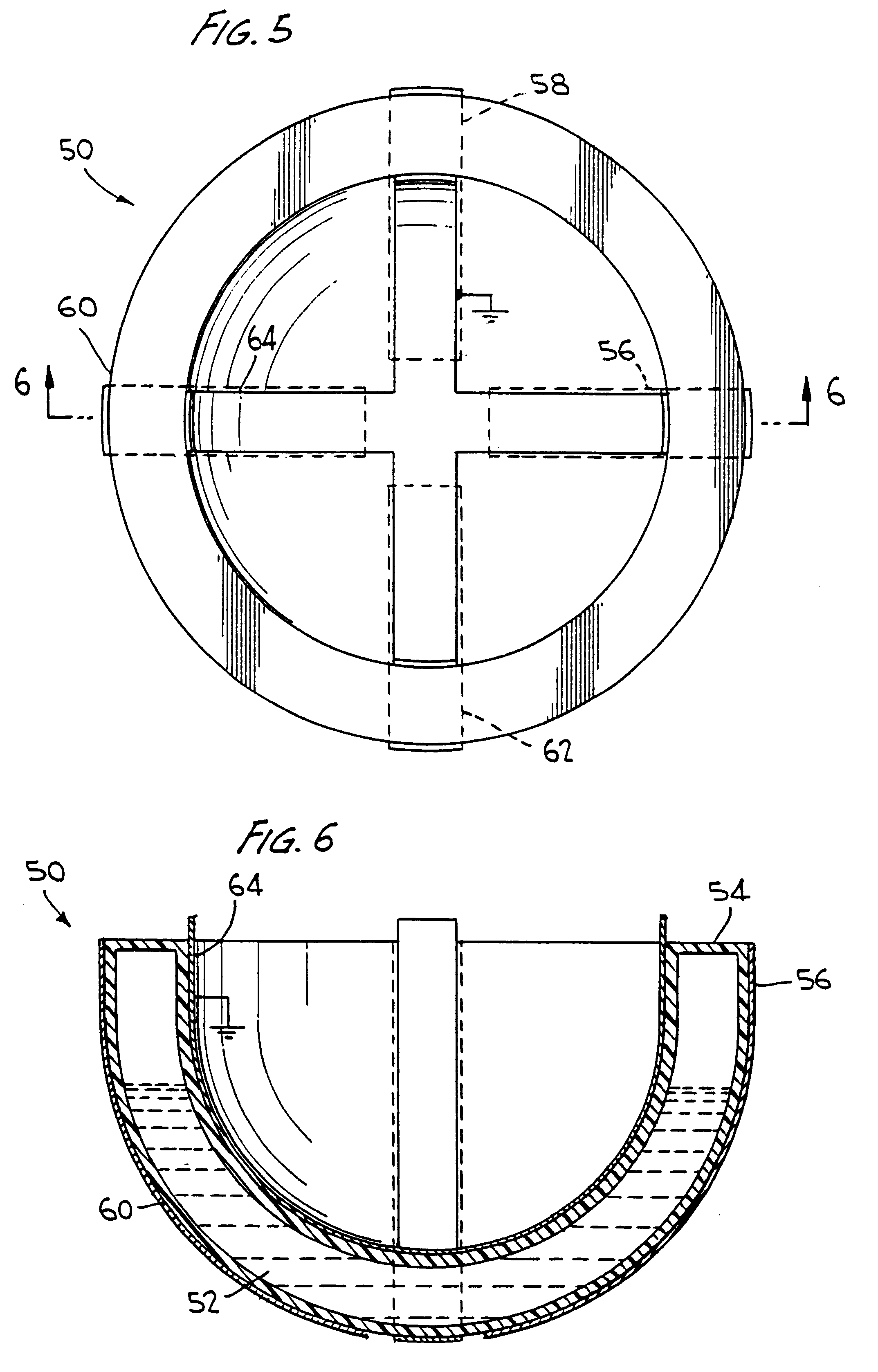
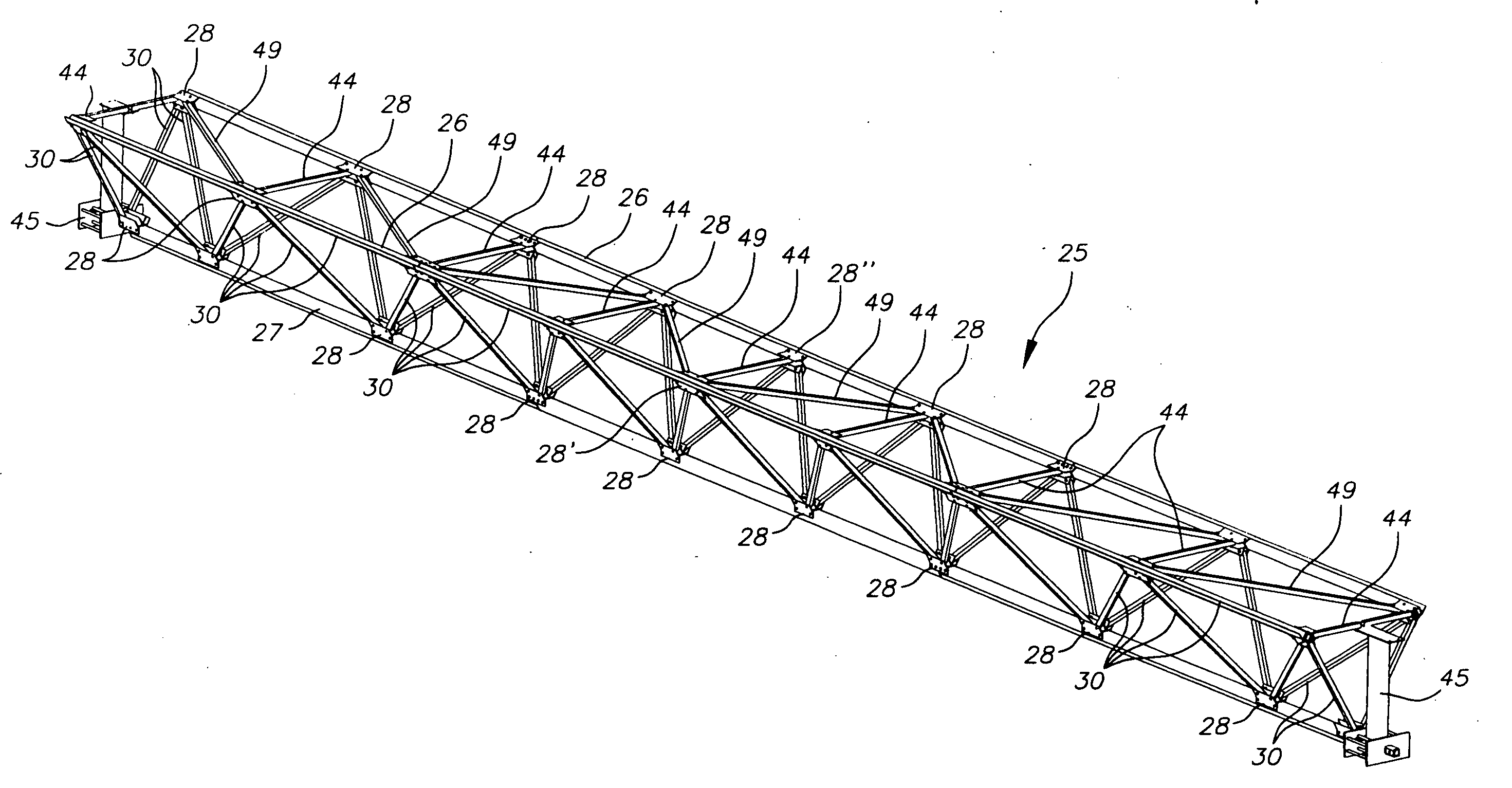
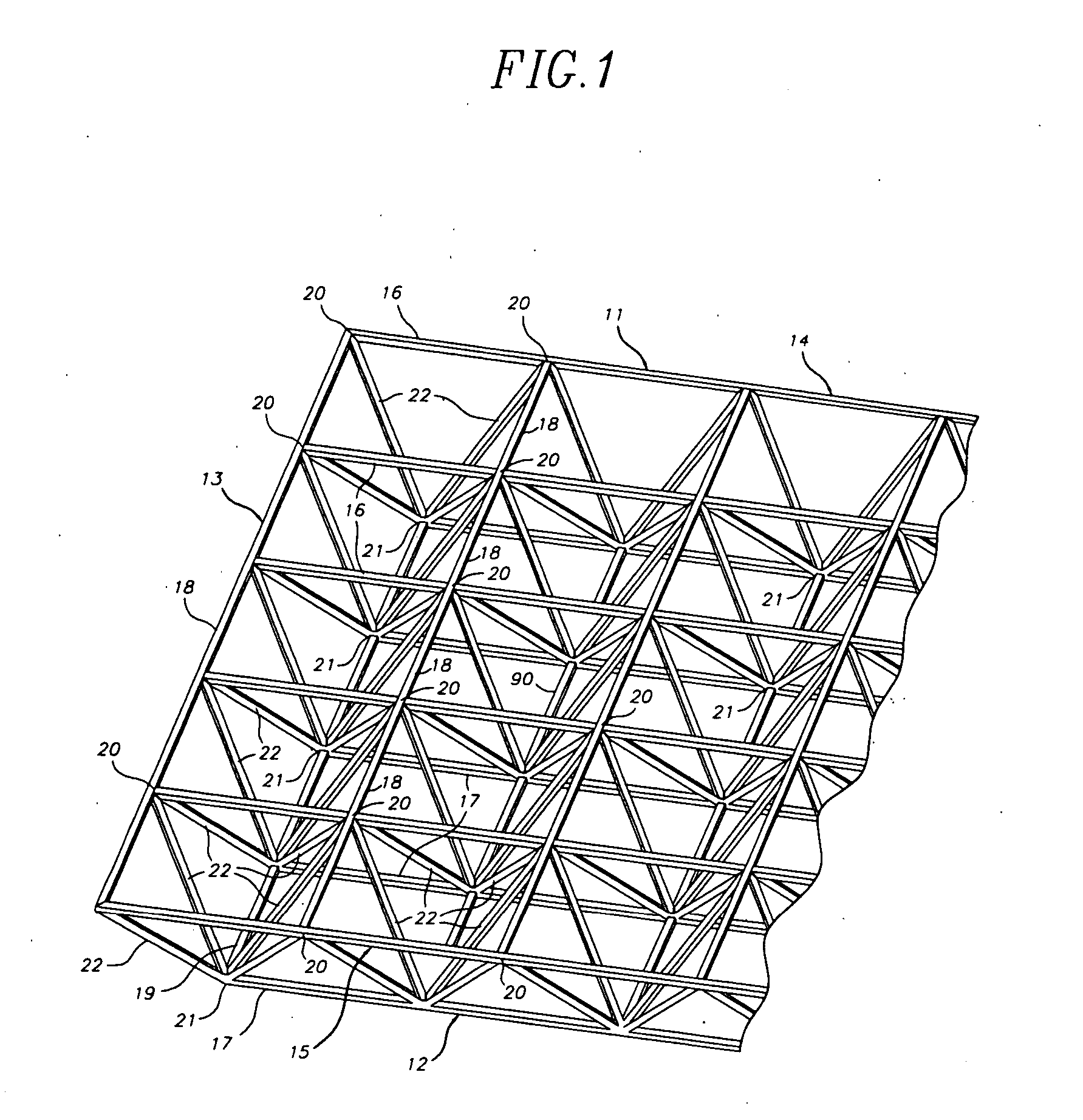
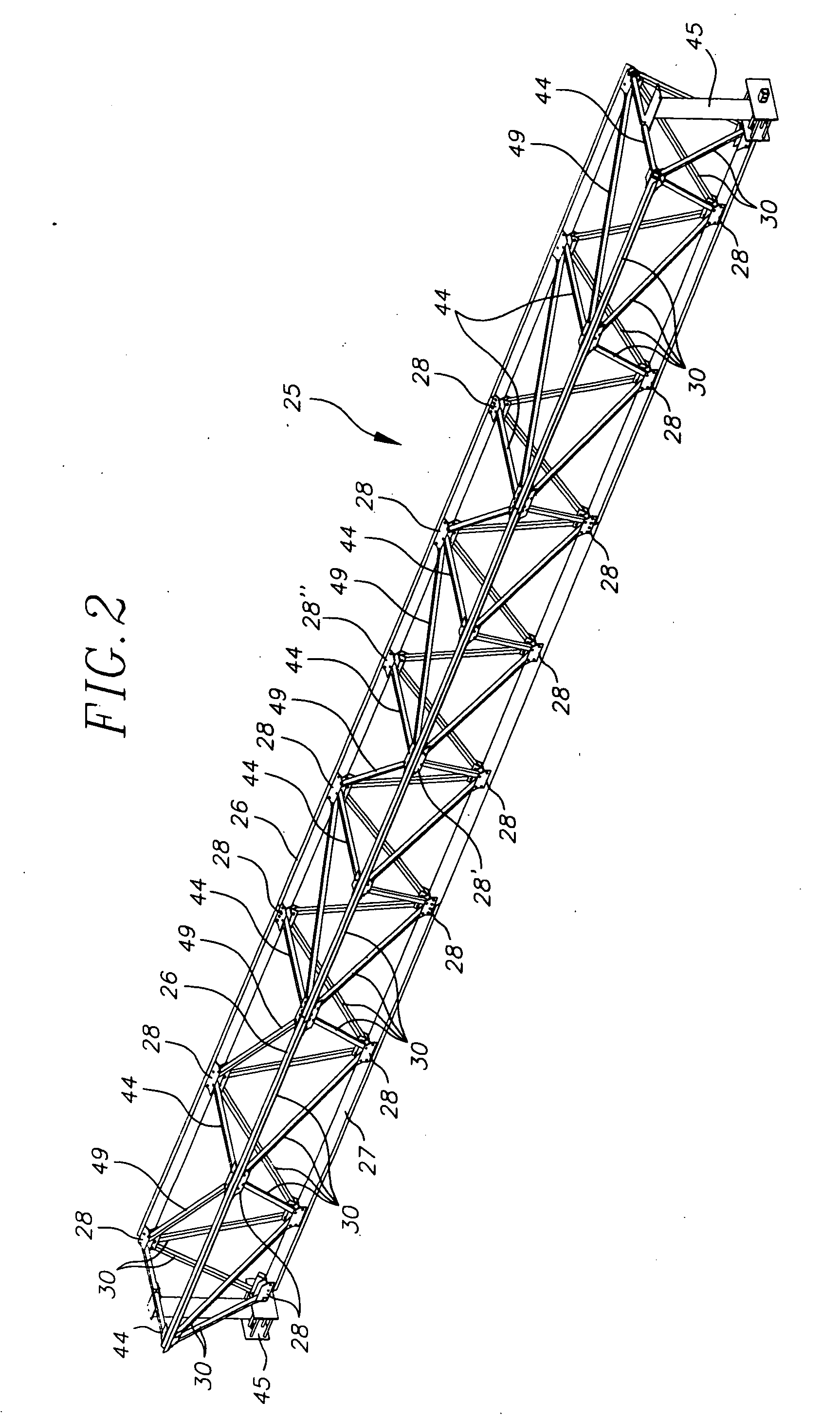
Space frames and connection node arrangement for them
ActiveUS20070011983A1Easy to useEfficiently carry design loadSolar heating energySolar heat devicesEngineeringSpace frame
A node connector in a double layer grid-type of space frame preferably is an extrusion which includes an open-ended tubular portion for snugly at least substantially encircling a frame chord member of desired cross-sectional configuration which is disposable in the passage. The node connector has fixed external elements which extend along the connector parallel to the passage. Those elements define facing parallel flat surfaces arranged in at least two pairs of such surfaces. The surfaces of each pair lie equidistantly from a center plane between them. Each center plane is parallel to the passage axis and preferably includes the passage axis. Each pair of facing flat surfaces of the node connector can cooperate closely with opposite flat surfaces at the end of each of other frames framing member placed between the facing surfaces. The node connector can be secured to a chord member in its passage and to ends of other framing members by shear pins which have zero clearances in node connector holes and in holes or passages through the respective framing members. The space frame can be a movable armature for a curved solar reflector, the space frame having a V-shaped major surface. At least some of the framing members can be thin wall tubes modified to have opposing, flat-exterior wall zones along the length of each tube and in which the wall thickness is locally increased and through which shear pin holes are defined.
Owner:GOSSAMER SPACE FRAMES
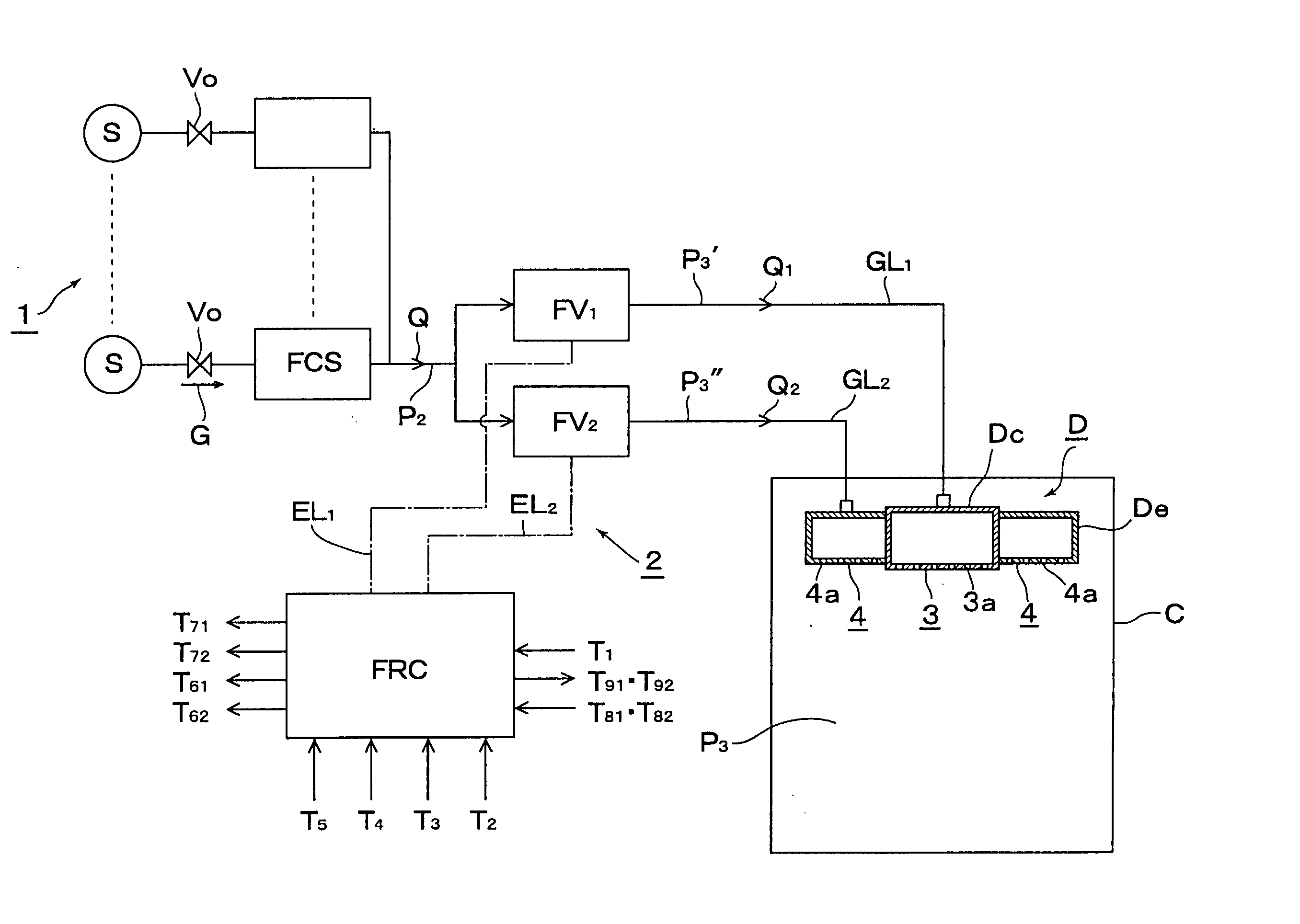
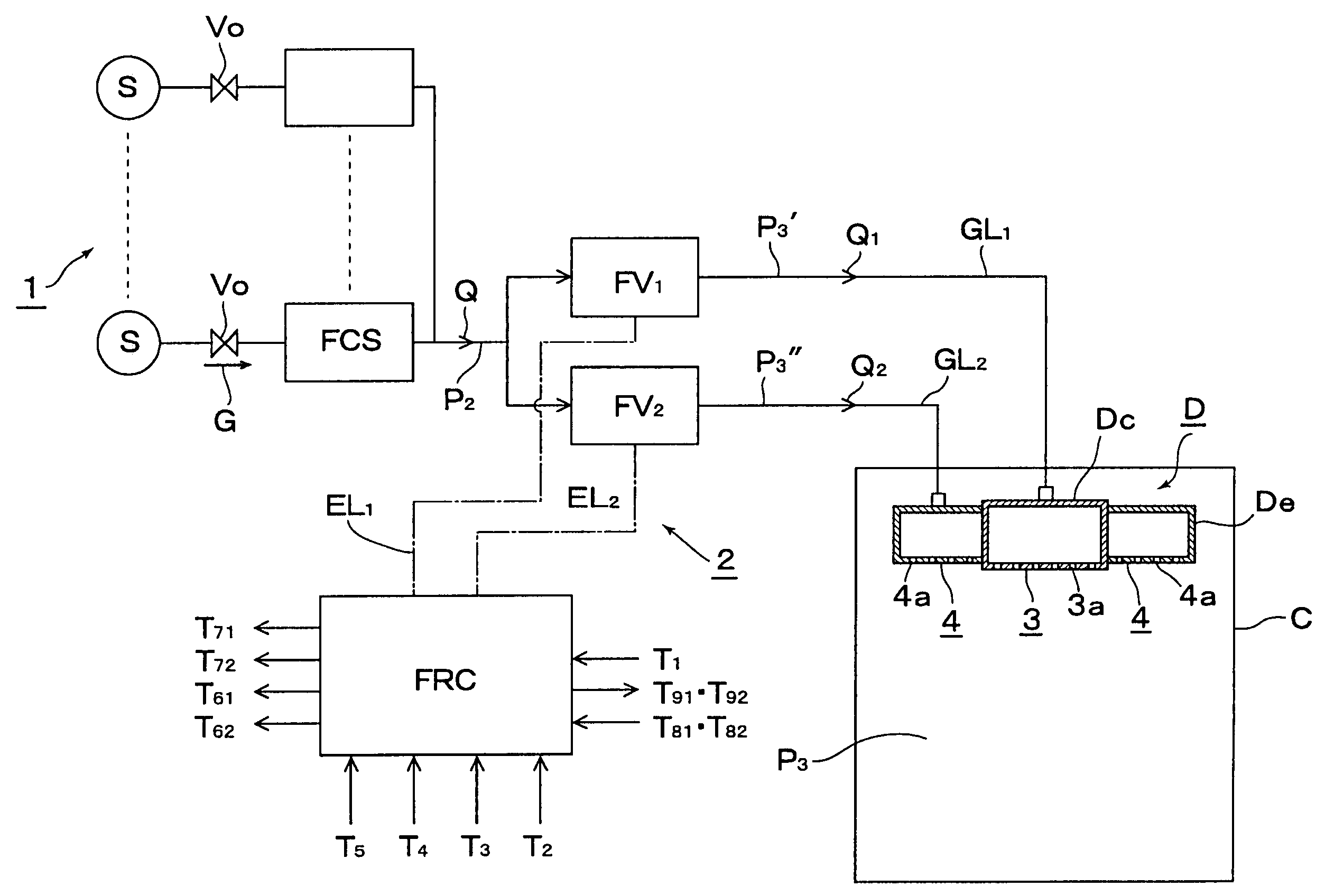
Method for supplying gas while dividing to chamber from gas supply facility equipped with flow controller
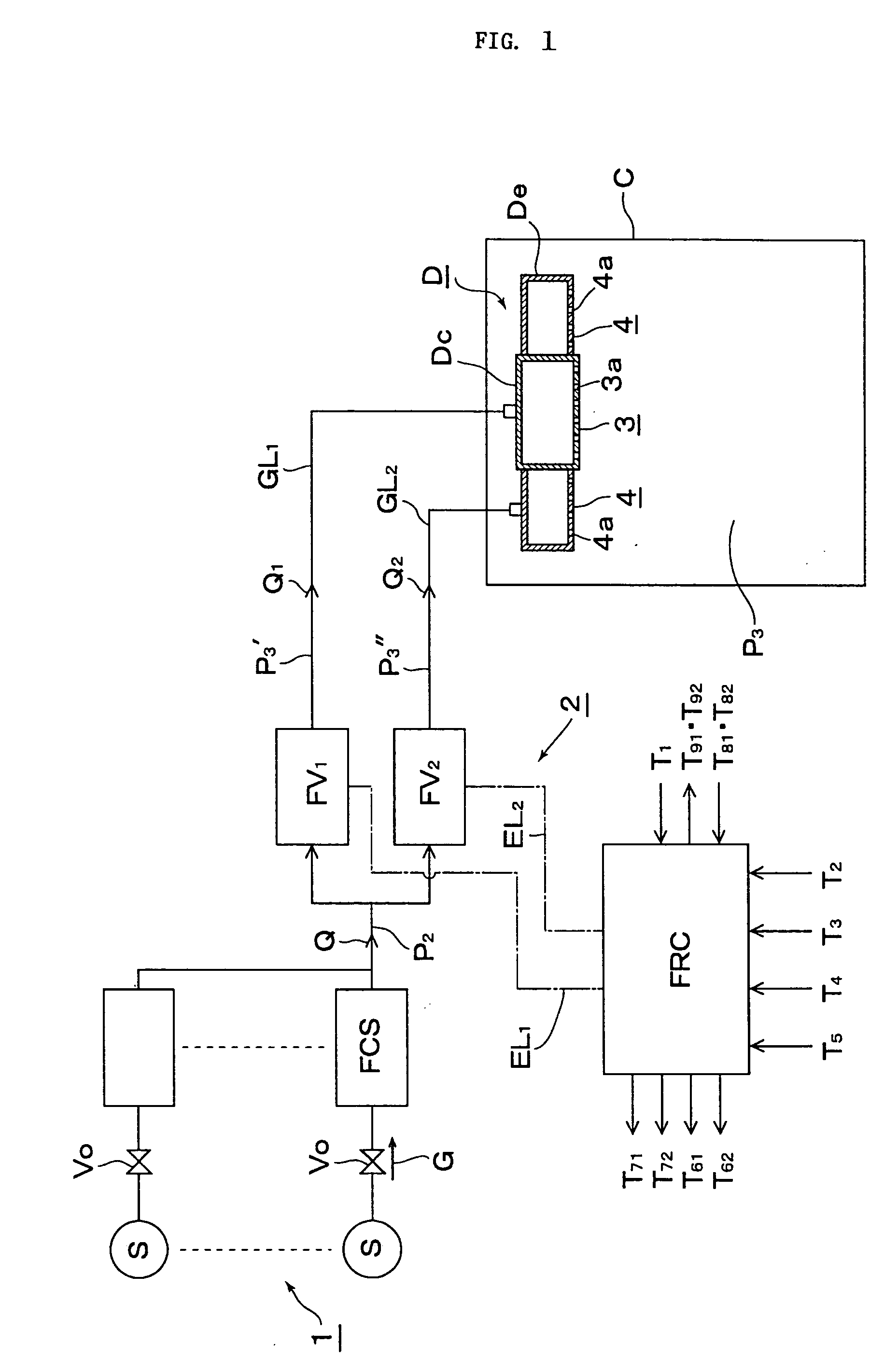
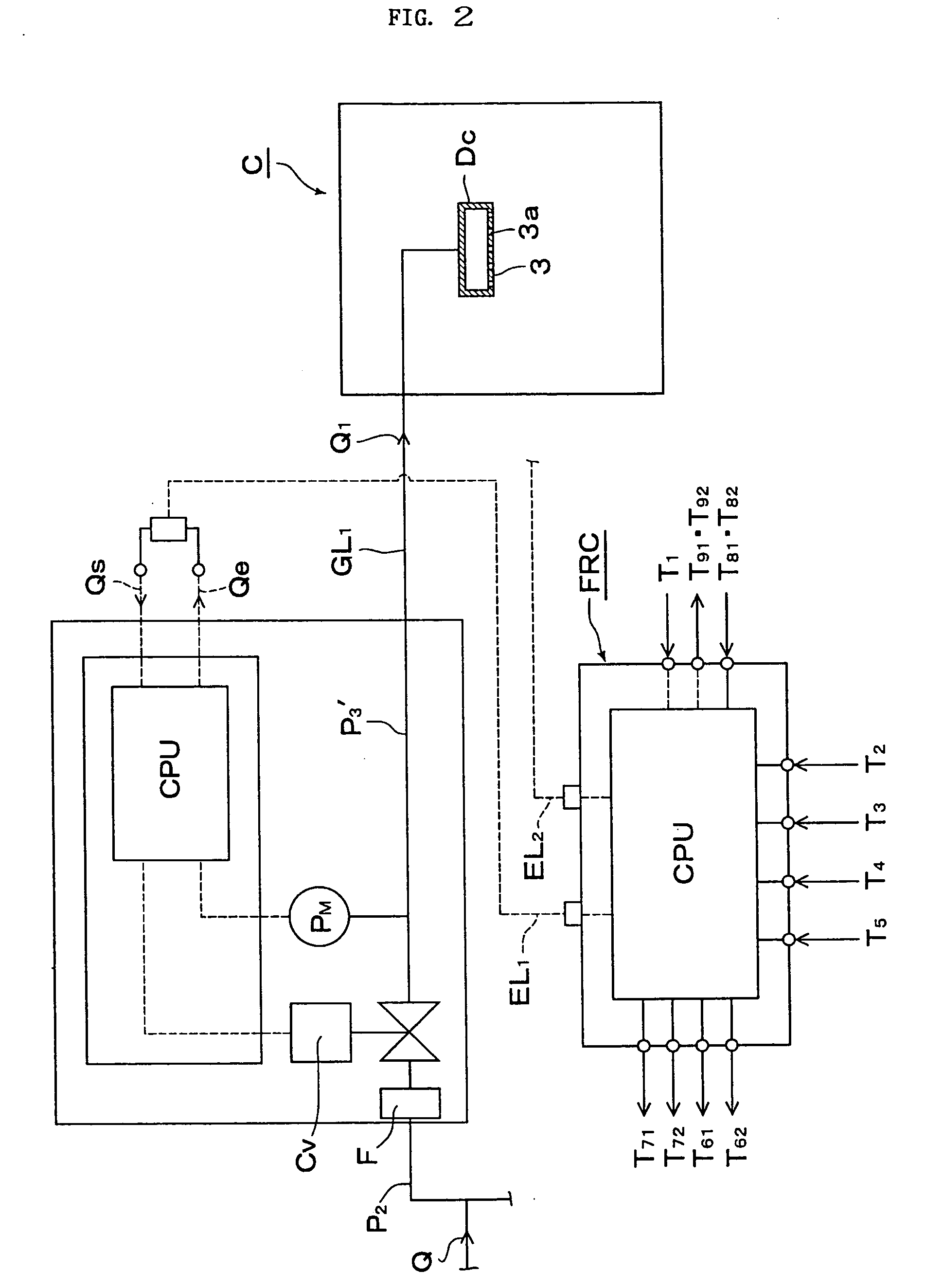
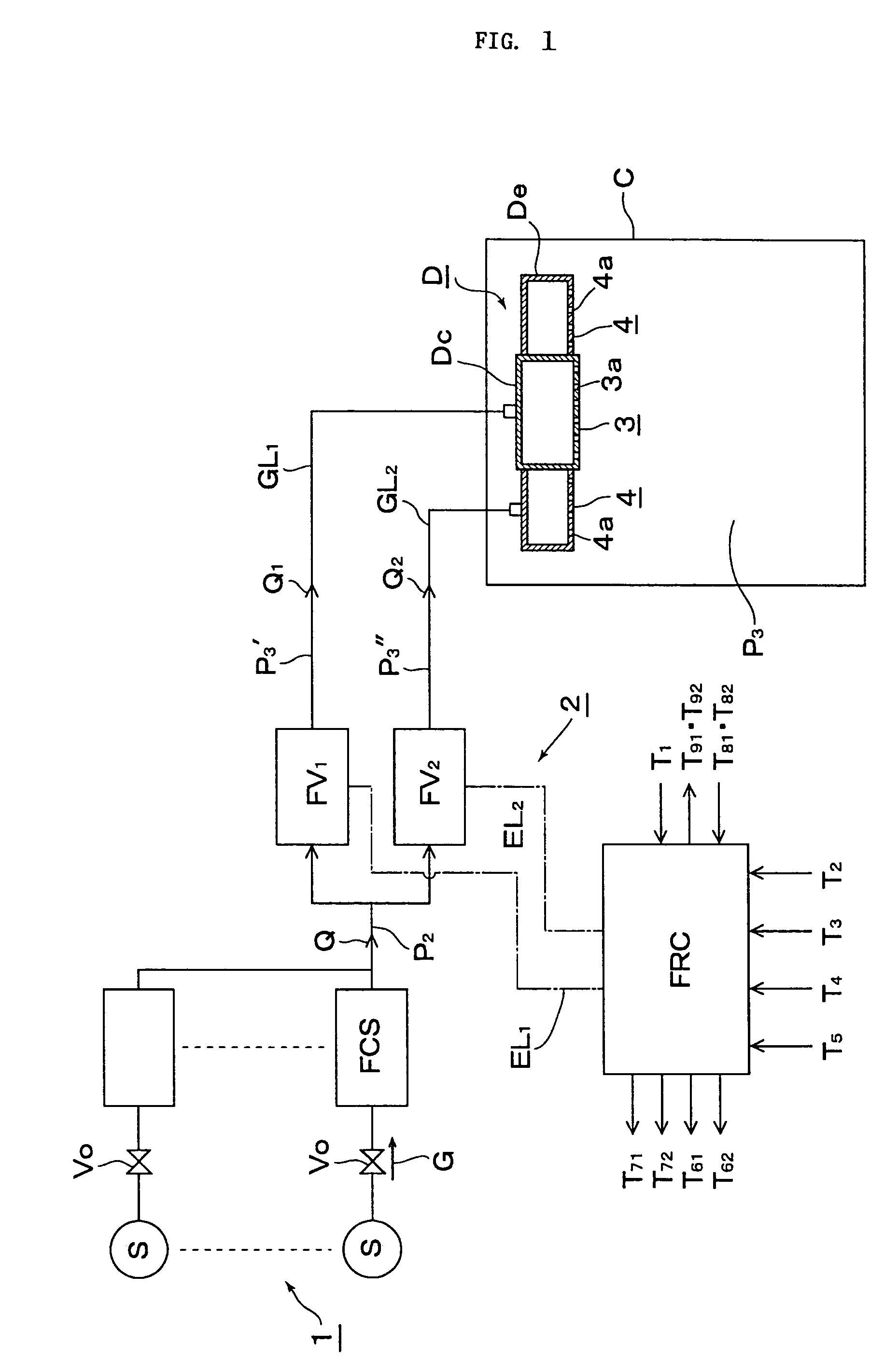
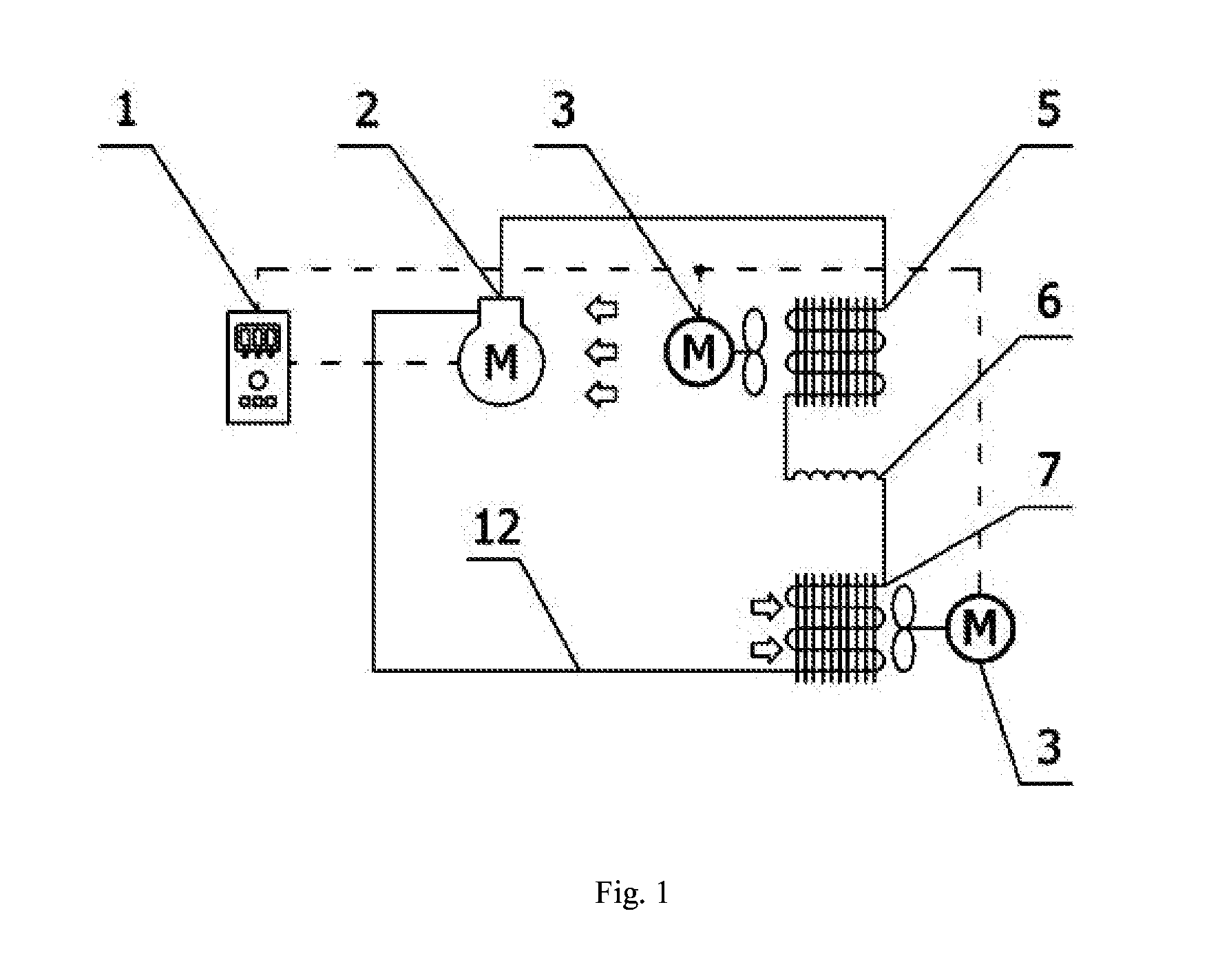
ActiveUS20050005994A1Avoid High Precision RequirementsGood precisionOperating means/releasing devices for valvesLiquid fillingStream flowProcess engineering
A method for supplying a specified quantity Q of processing gas while dividing at a desired flow rate ratio Q1 / Q2 accurately and quickly from a gas supply facility equipped with a flow controller into a chamber. When a specified quantity Q of gas is supplied while being divided at a desired flow rate ratio Q1 / Q2 from a gas supply facility equipped with a flow controller into a reduced pressure chamber C through a plurality of branch supply lines and shower plates fixed to the ends thereof, pressure type division quantity controllers FV1 and FV2 are provided in the plurality of branch supply lines GL1 and GL2. Opening control of both division quantity controllers FV1 and FV2 is started by an initial flow rate set signal from a division quantity control board FRC for fully opening the control valve CV of the pressure type division quantity controller having a higher flow rate and pressures P3′ and P3″ on the downstream side of the control valve CV are regulated thus supplying a total quantity Q=Q1+Q2 of gas while dividing into the chamber C through orifice holes (3a, 4a) made in shower plates (3, 4) at desired division quantities Q1 and Q2 represented by formulas Q1=C1P3′ and Q2=C2P3″ (where, C1 and C2 are constants dependent on the cross-sectional area of the orifice hole or the gas temperature on the upstream side thereof).
Owner:FUJIKIN INC +1
Inclinometer and inclinometer network
InactiveUS6449857B1Low costAvoid High Precision RequirementsResistance/reactance/impedencePlumb lines for surveyingElectrical resistance and conductanceGraphics
An electronic inclinometer and a centrally controlled network of inclinometers are disclosed. A resistive or capacitive inclinometer sensor measures inclination in two orthogonal axes. Measuring electrodes can be provided on the exterior of a dielectric sensor cell isolated from a sensor fluid. In another embodiment, measuring electrodes comprise pins partially immersed in a cell fluid contained in a metal housing and reference electrodes are provided to compensate for temperature and electrochemical changes in the sensor. Sensor signals are converted to frequency signals that are processed by a microprocessor having a unique logical address and preferably having an external solid state memory. A plurality of inclinometers can be arranged in multiple logical branches to be centrally controlled. The controller operates the network in real time or in a programmable timed autonomous mode. Network data can be presented in a graphical 3D format using software provided on the controller.
Owner:QUINLAN DAVID +1
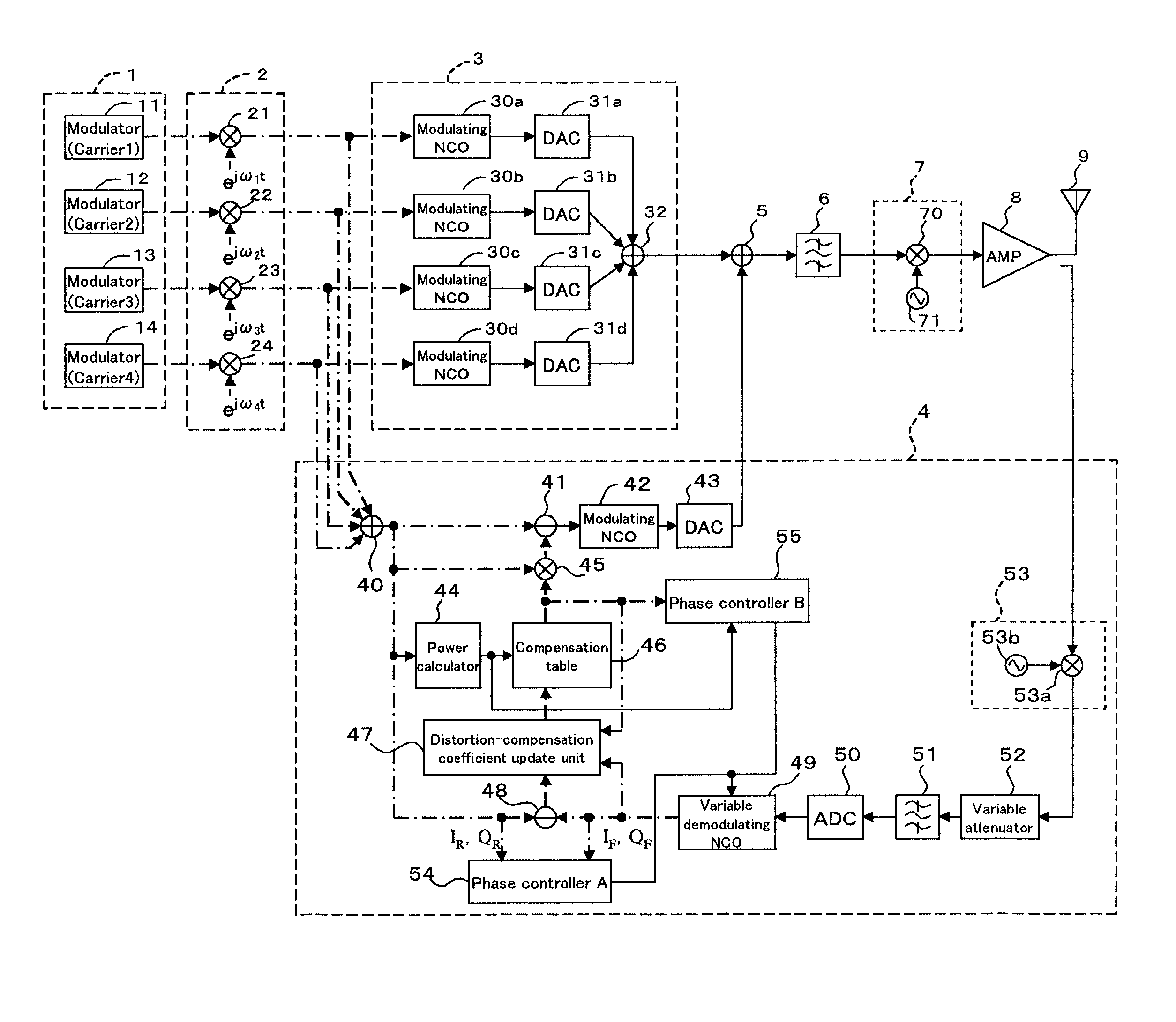
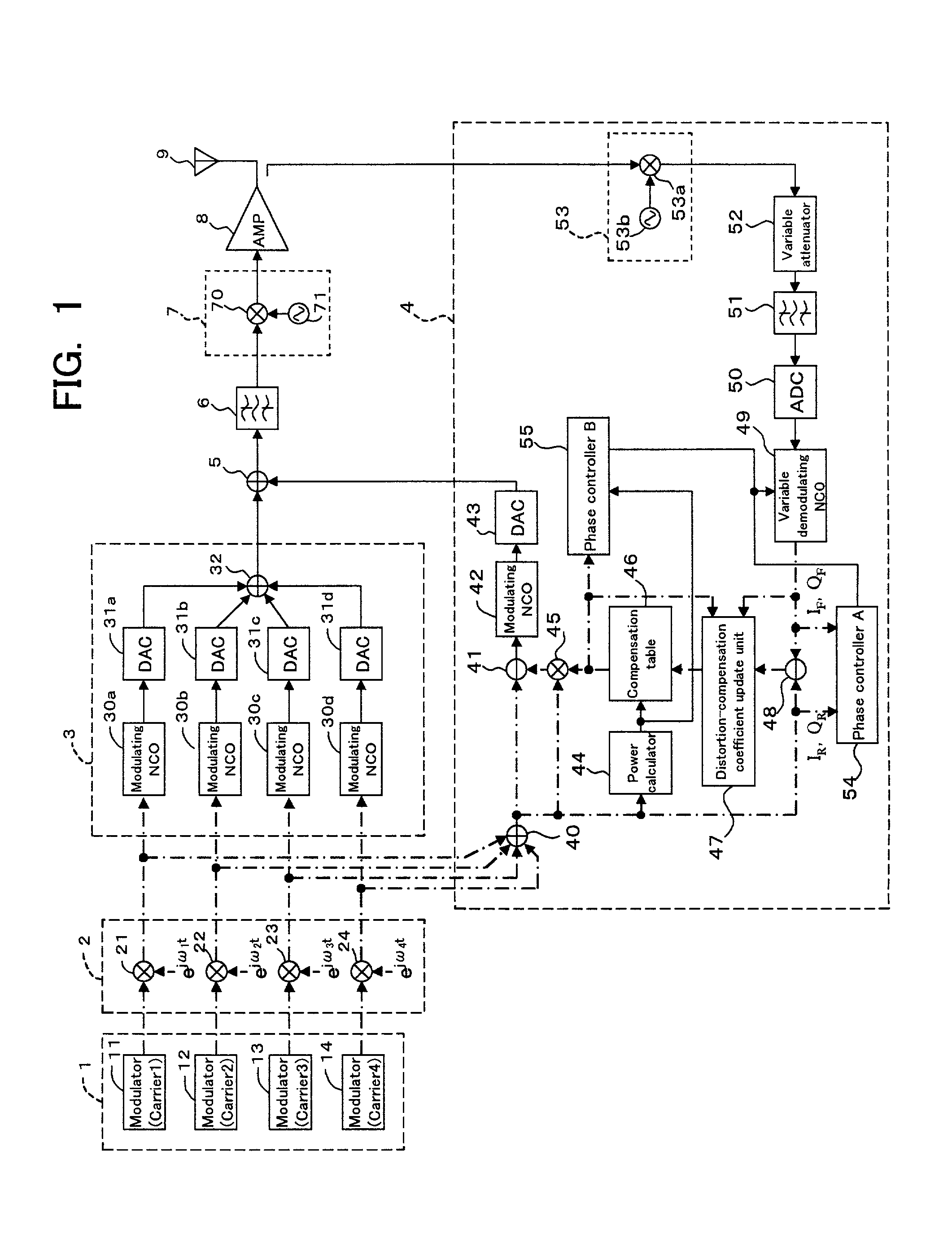
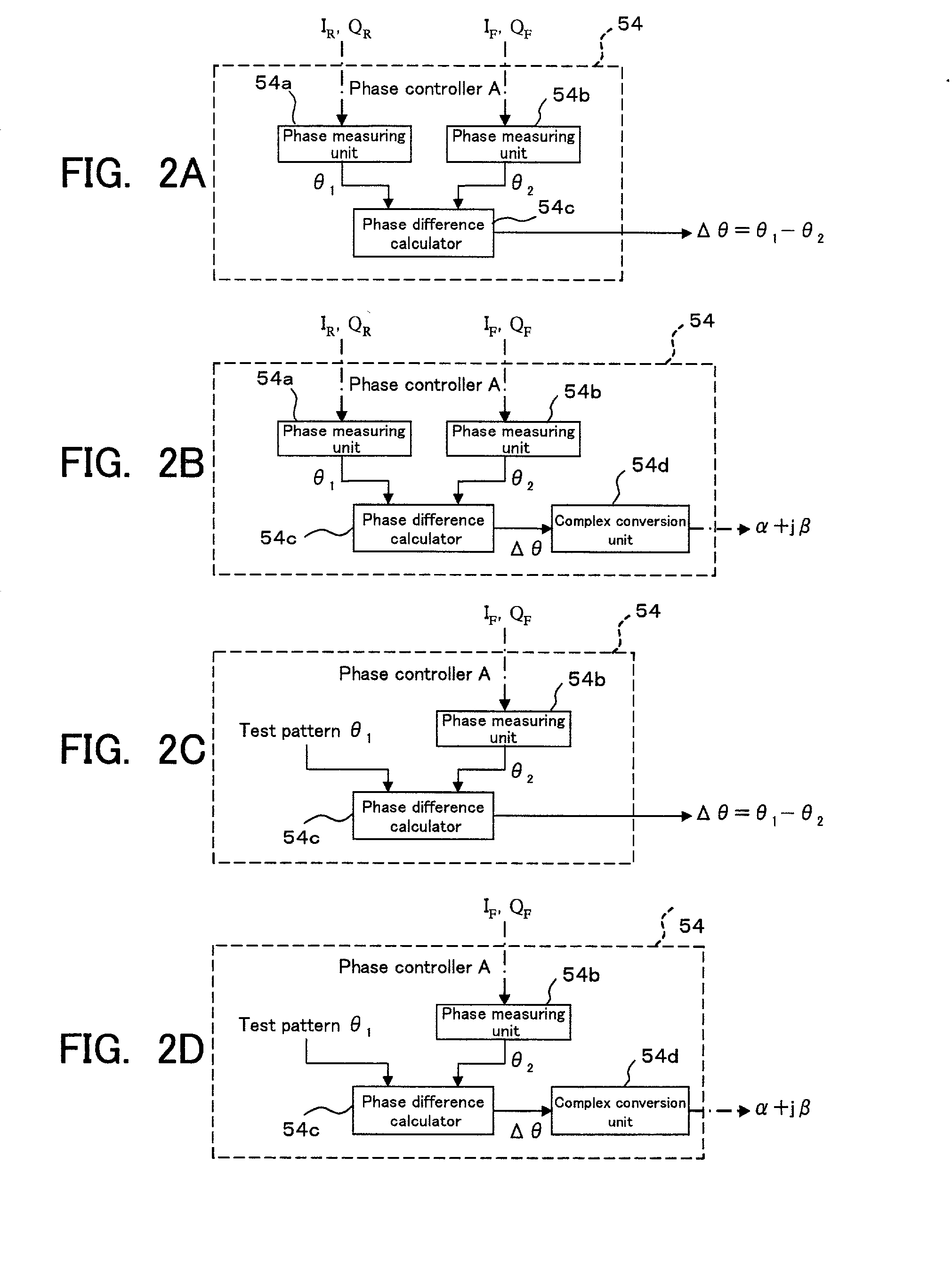
Transmission device and transmission method
InactiveUS20020097811A1Quick conversionReliable compensationAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionEqualisersAudio power amplifierDigital input
The present invention provides a transmission device for predistorting a digital signal in order to compensate distortion, then amplifying and transmitting it. A digital input signal is converted to a first analog signal by a first D / A converter. Separately, the digital input signal is also subjected to predistortion. A compensating signal is then generated from the digital input signal and the predistorted signal. The compensating signal generated thereby is converted into a second analog signal by a second D / A converter. The first analog signal and second analog signal are then added, this addition operation giving a compensated analog transmission signal. This analog transmission signal is supplied to the amplifier for amplification, and then transmitted via an antenna.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Tubular structural member with non-uniform wall thickness
InactiveUS20080072516A1Easy to useEfficiently carry design loadSolar heating energySolar heat devicesExterior dimensionNeutral axis
A tubular structural member has substantially constant cross-sectional size and configuration along its length between its opposite ends. The member has a pair of parallel oppositely aligned flat areas in its exterior surface. The member has substantially uniform wall thickness except in a selected portion of each the opposing areas where the member's wall thickness is a selected amount greater than the uniform wall thickness. The increase wall thickness preferably is manifested in the interior of the tubular member. The cross-sectional area of the member can have orthogonal neutral axes, and the exterior dimension of the member along one of those axes can be greater than the exterior dimension of the member along the other of those axes which is normal to the exterior flat areas; the amount and distribution of the thickening of the member's walls over the uniform thickness can be defined to cause the section modular of the member about each of the neutral axes to be substantially equal.
Owner:REYNOLDS GLENN A +2
Method of supplying divided gas to a chamber from a gas supply apparatus equipped with a flow-rate control system
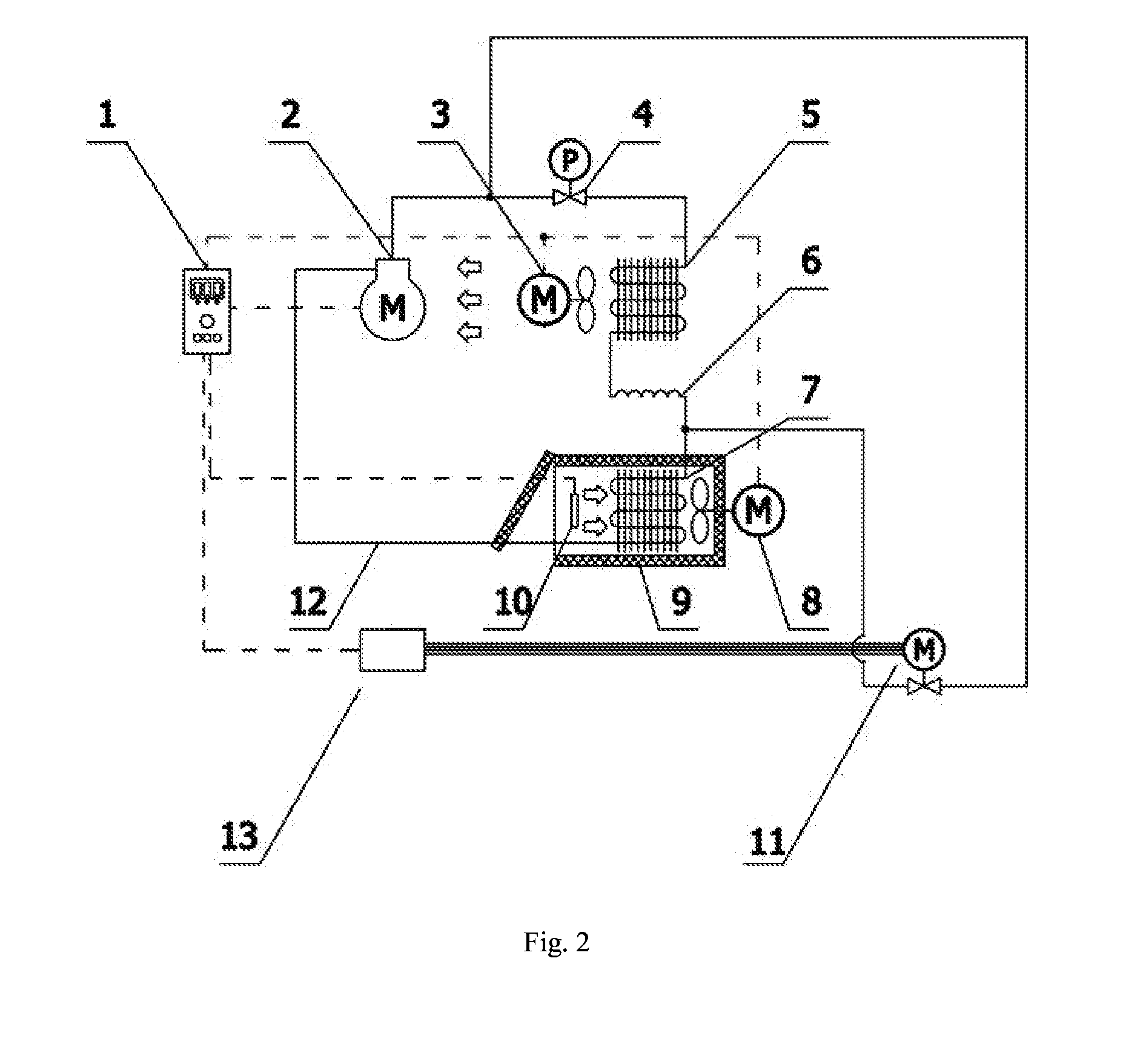
InactiveUS7059363B2Avoid High Precision RequirementsMany timesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesLiquid fillingControl systemProcess engineering
A method for supplying a specified quantity Q of processing gas while dividing at a desired flow rate ratio Q1 / Q2 accurately and quickly from a gas supply facility equipped with a flow controller into a chamber. When a specified quantity Q of gas is supplied while being divided at a desired flow rate ratio Q1 / Q2 from a gas supply facility equipped with a flow controller into a reduced pressure chamber C through a plurality of branch supply lines and shower plates fixed to the ends thereof, pressure type division quantity controllers FV1 and FV2 are provided in the plurality of branch supply lines GL1 and GL2. Opening control of both division quantity controllers FV1 and FV2 is started by an initial flow rate set signal from a division quantity control board FRC for fully opening the control valve CV of the pressure type division quantity controller having a higher flow rate and pressures P3′ and P3″ on the downstream side of the control valve CV are regulated thus supplying a total quantity Q=Q1+Q2 of gas while dividing into the chamber C through orifice holes (3a, 4a) made in shower plates (3, 4) at desired division quantities Q1 and Q2 represented by formulas Q1=C1P3′ and Q2=C2P3″ (where, C1 and C2 are constants dependent on the cross-sectional area of the orifice hole or the gas temperature on the upstream side thereof).
Owner:FUJIKIN INC +1
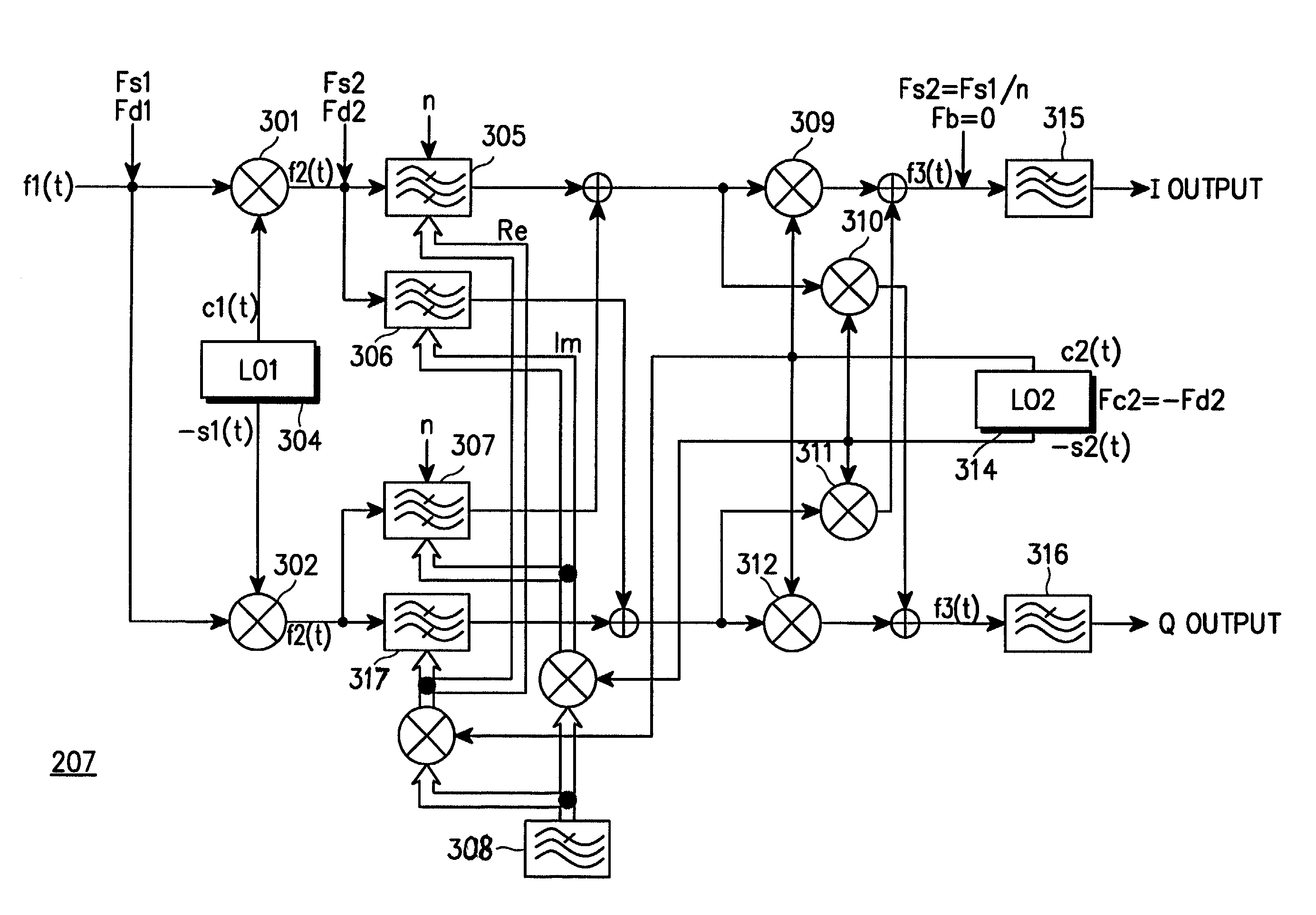
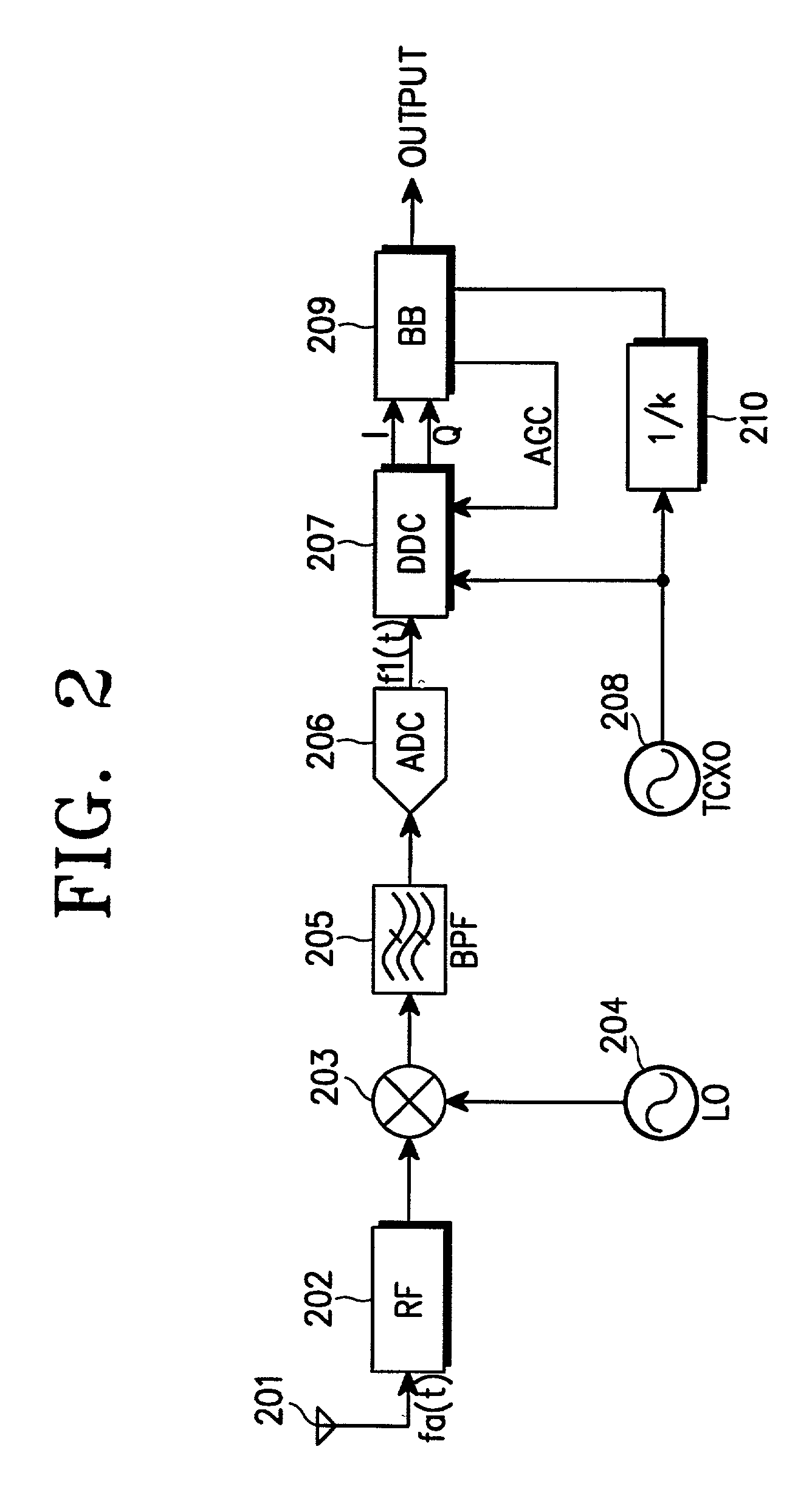
Receiver in a radio communication system
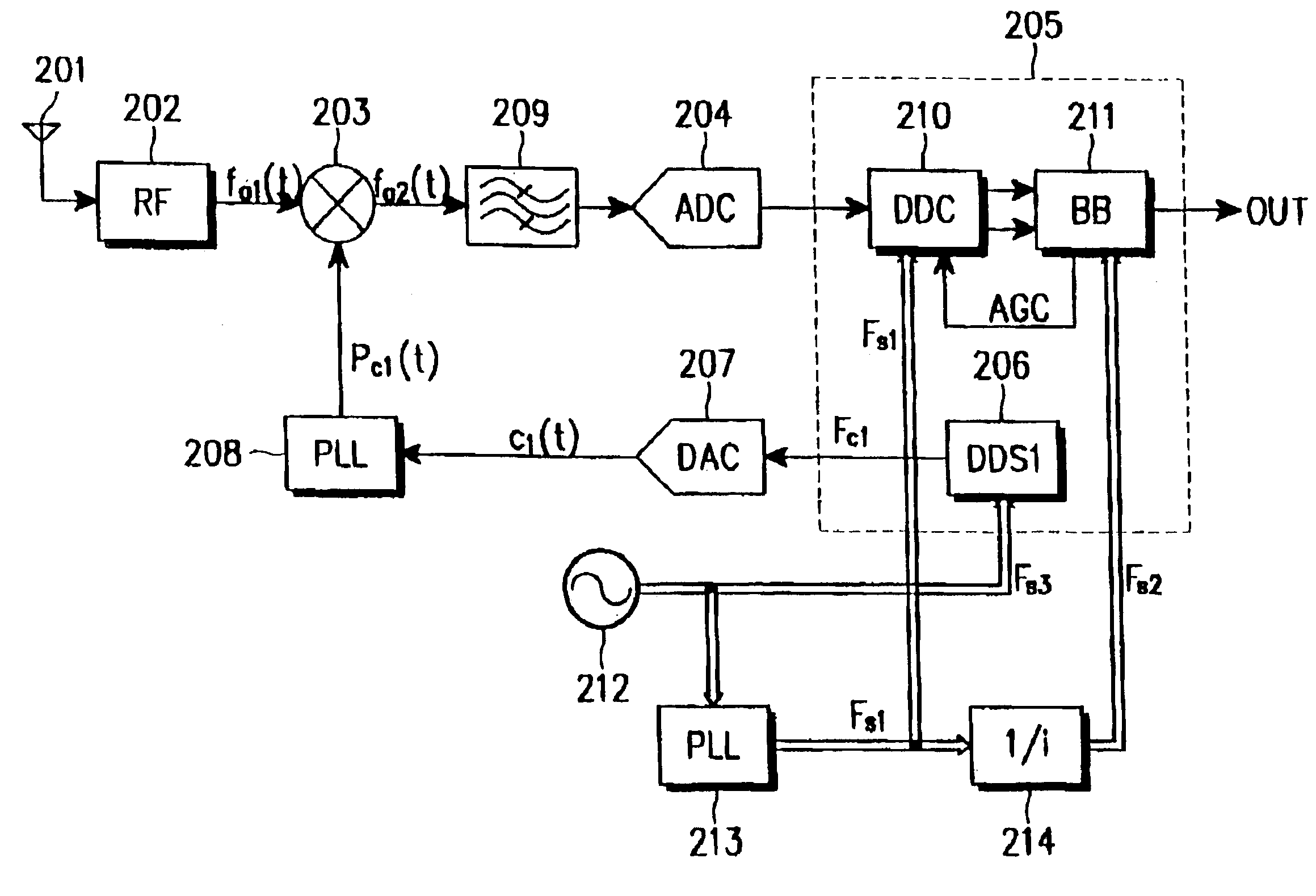
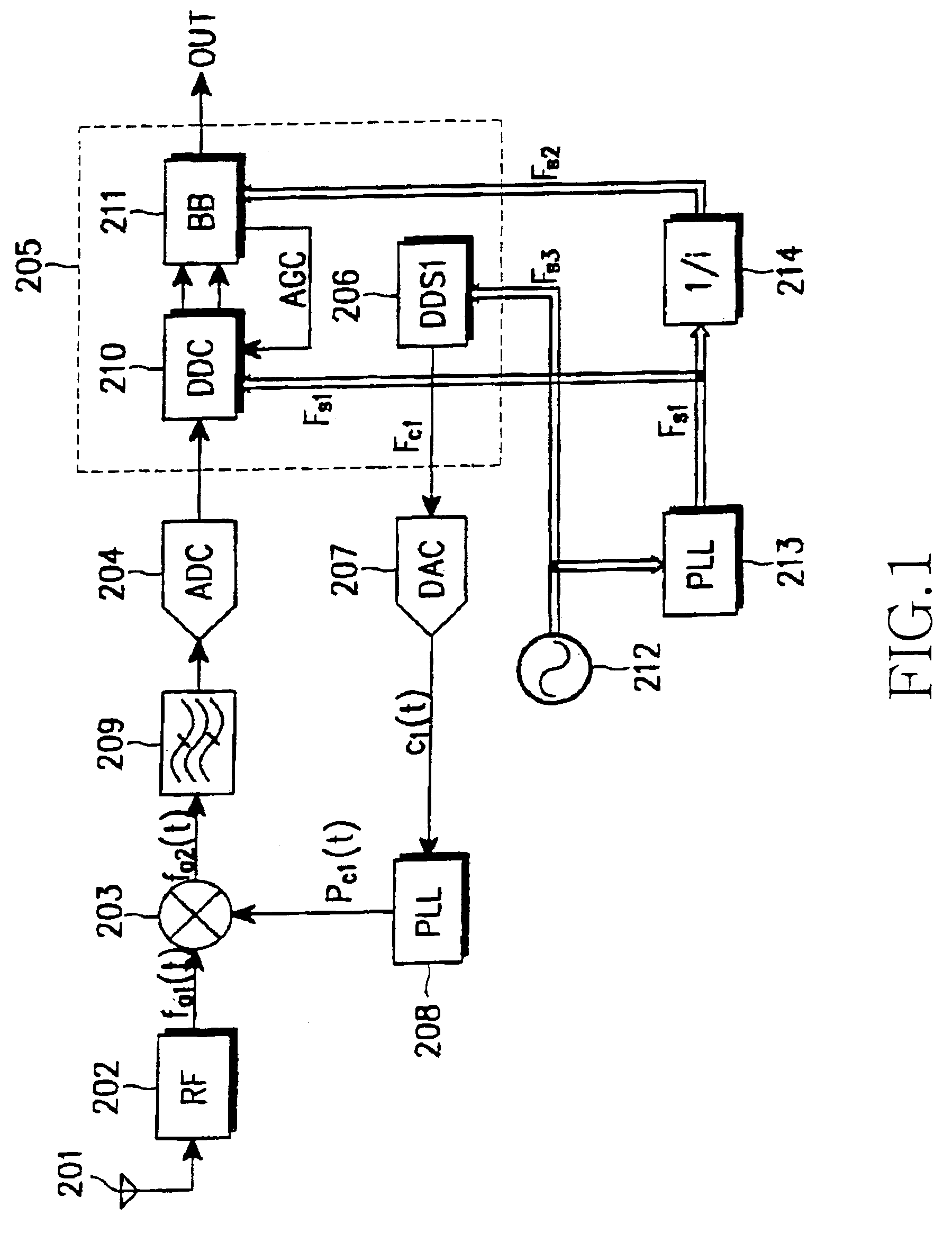
InactiveUS7139329B2Low spurious levelAvoid High Precision RequirementsDigital technique networkAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsBandpass filteringIntermediate frequency
A receiver has a low spurious level and a high frequency precision without increasing power consumption of a local oscillator. The receiver comprises first and second local oscillators; a phase locked loop operating based on an output of the first local oscillator; a first mixer for receiving an RF signal or an IF signal, and converting the received signal to a second IF signal according to an output signal of the phase locked loop; an analog-to-digital converter for converting an output signal of the first mixer to a digital signal; a second mixer for converting the digital signal to a detection process frequency according to an output of the second local oscillator; and a filter for bandpass filtering, interposed between the first mixer and the analog-to-digital converter or between the analog-to-digital converter and the second mixer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
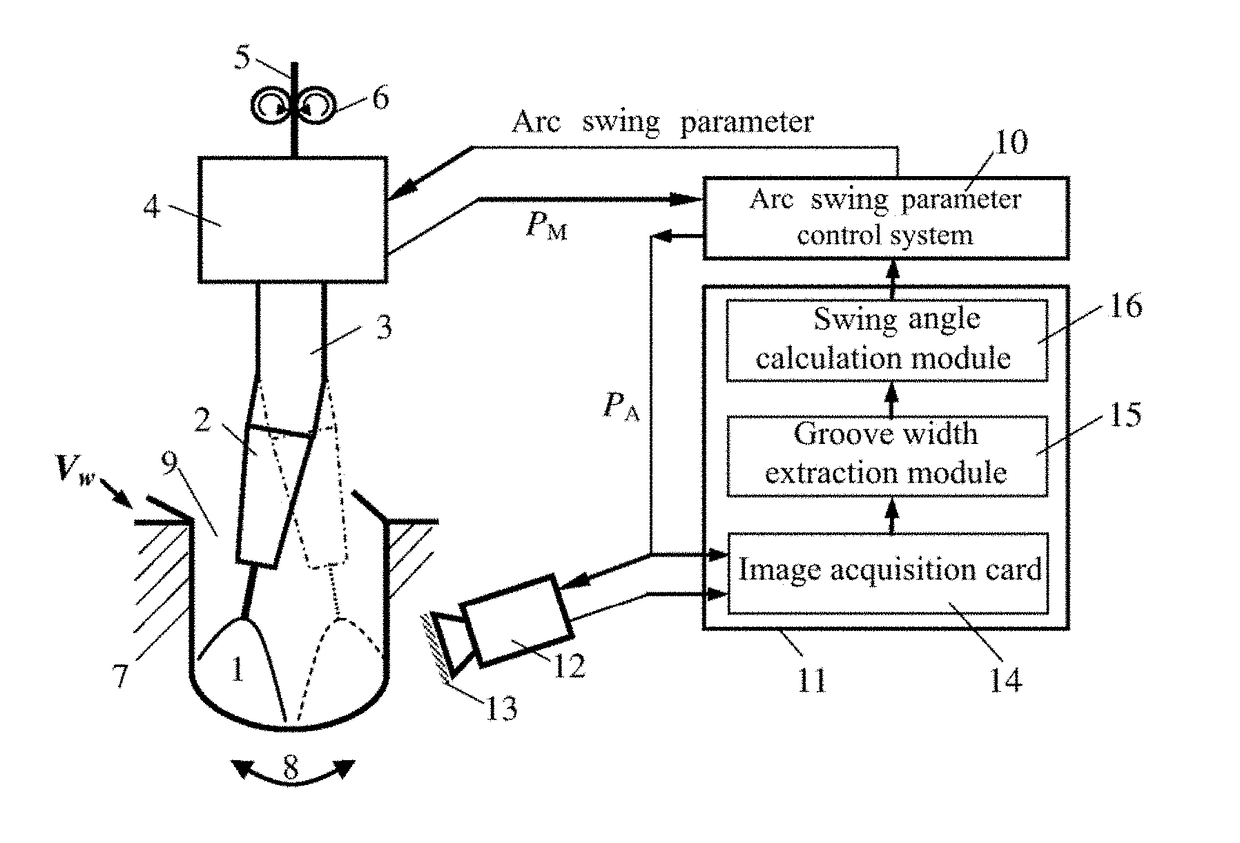
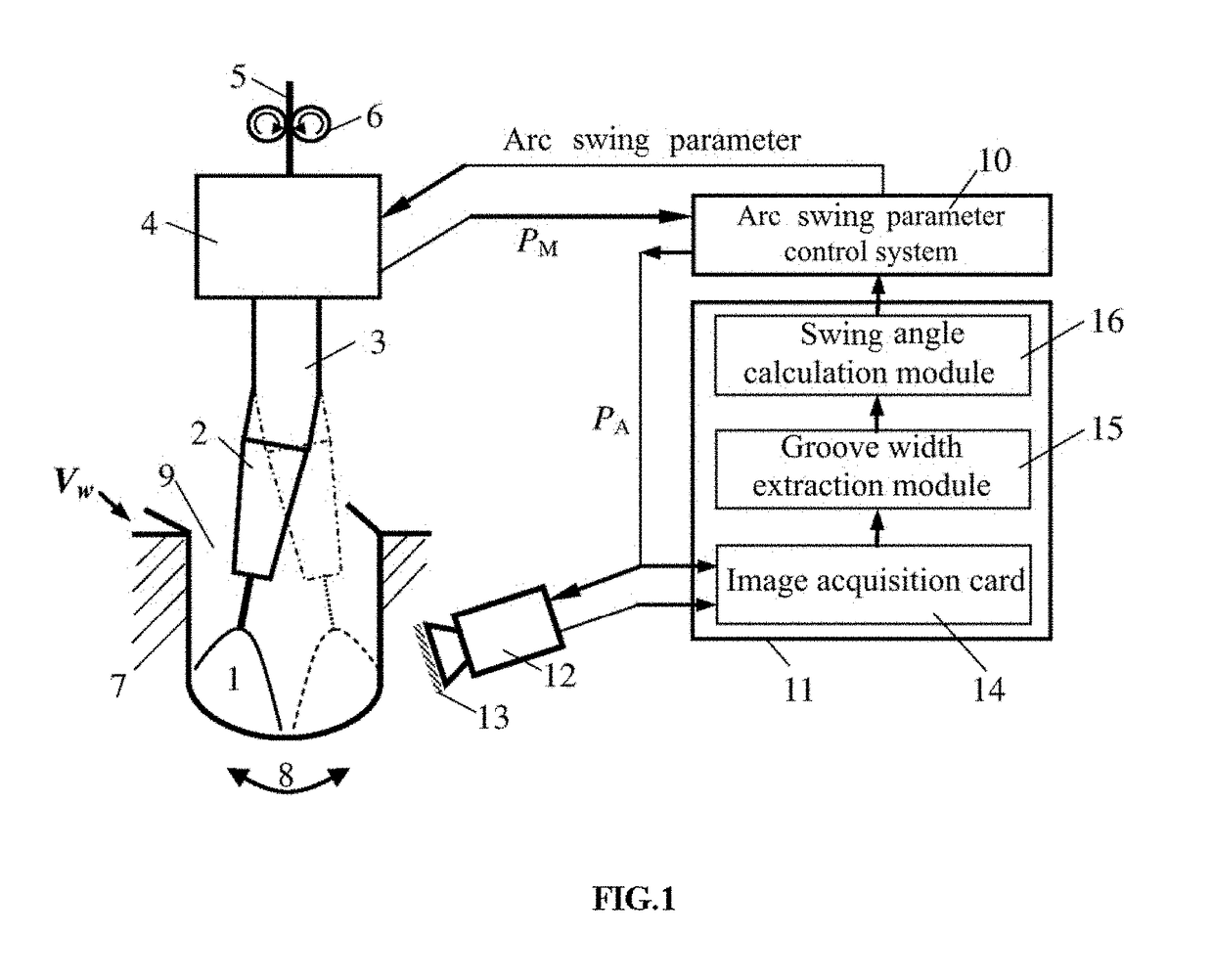
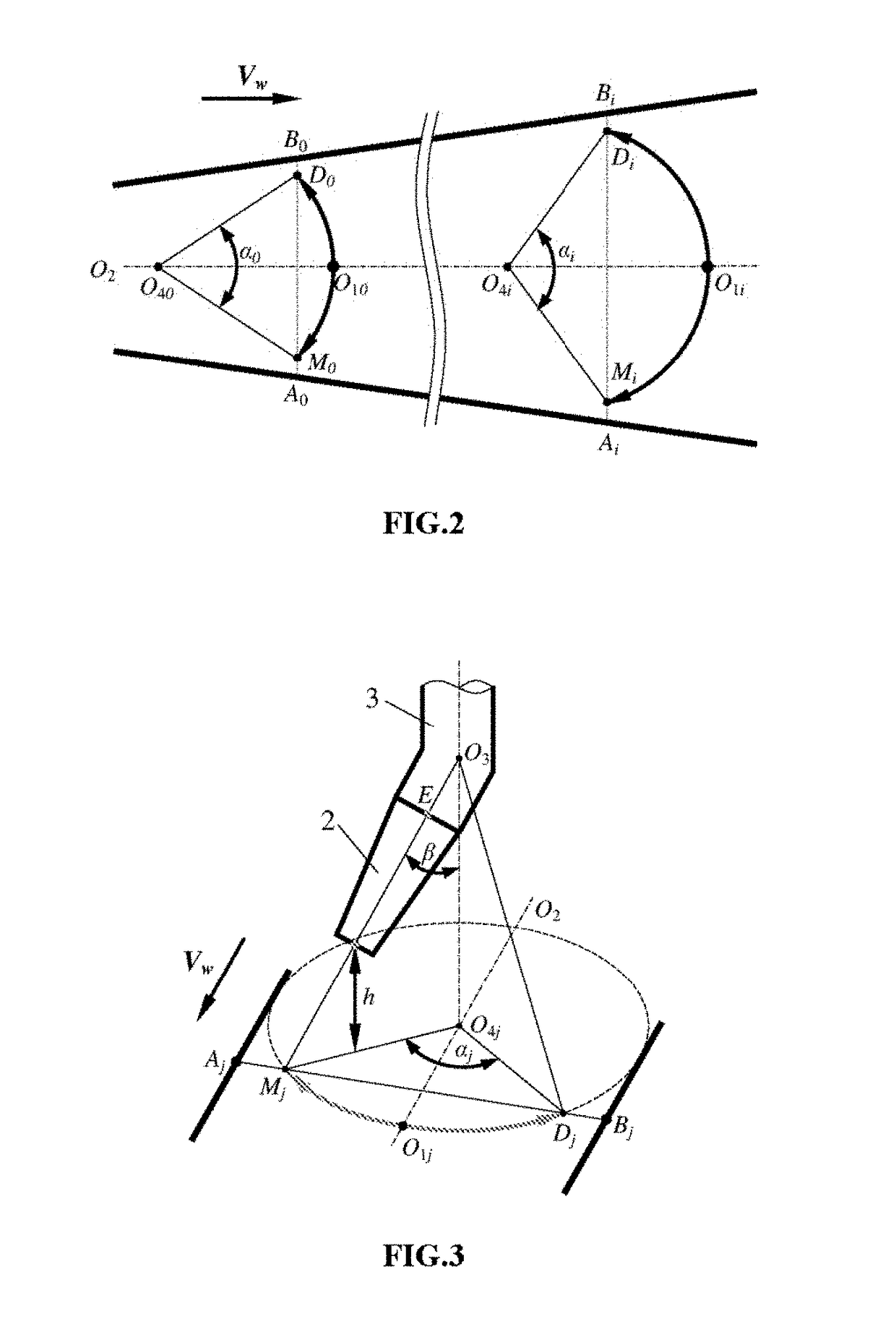
Adaptive control method and equipment of arc swing in narrow gap welding
ActiveUS20180147647A1Desirable synchronizationHigh detection sensitivityArc welding apparatusGroove widthMotor drive
Disclosed are an adaptive control method and equipment of arc swing in narrow gap welding. The control equipment is composed of an infrared camera system, a computer image processing system, an arc swing parameter control system, a bent-conducting-rod-type swing arc torch and the like. The infrared camera system acquires, in an external triggering manner, an infrared image of welding area when an arc is deviated towards the left or the right side wall groove, extracts information about the width of the groove in real time after image processing by a computer, and calculates an arc swing angle target value. The arc swing parameter control system controls a motor drive mechanism to rotate a bent conducting rod, and drives the welding arc to conduct circular arc swing according to the swing angle target value, thereby realizing the adaptive control for the arc swing angle according to changes of the groove width.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
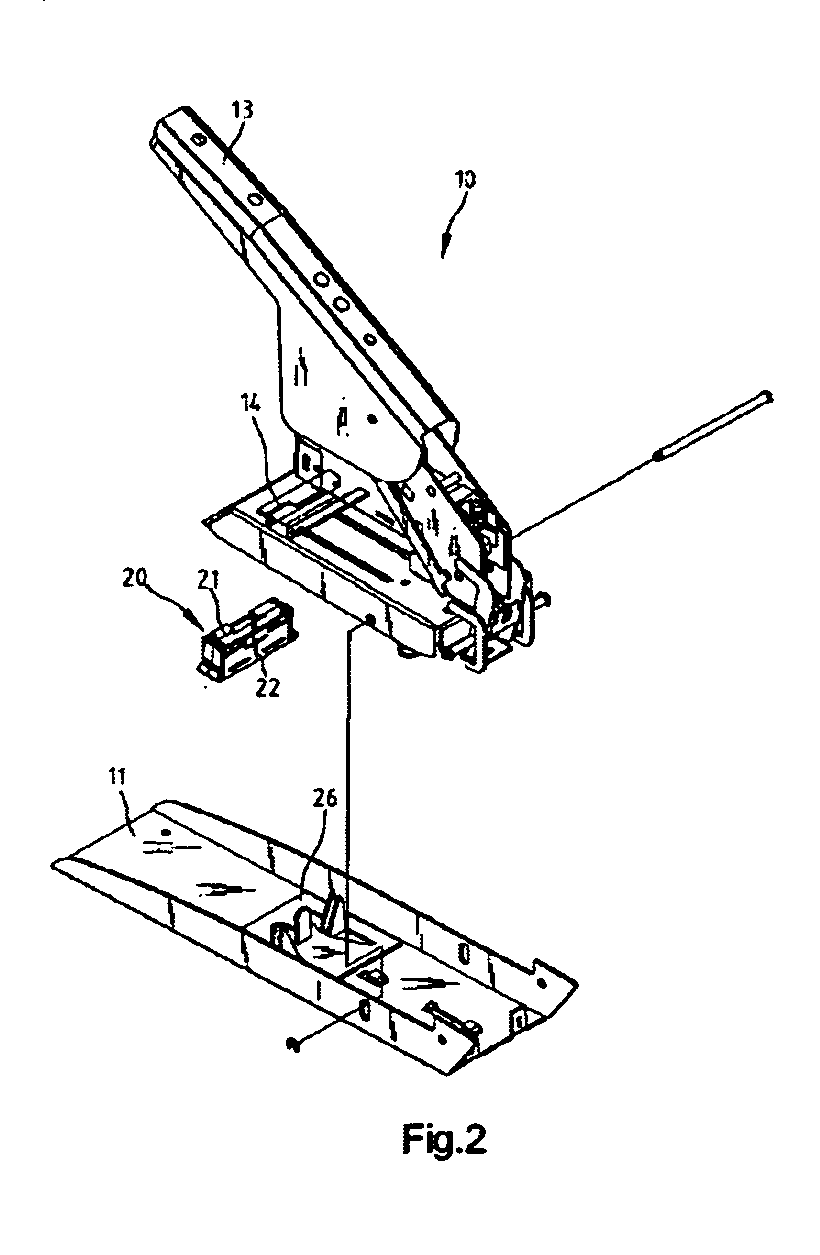
Stapler capable of cutting staple legs
InactiveUS20060266789A1Low costAvoid High Precision RequirementsStapling toolsNailingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A stapler includes a base, a cover put movably on the base, a feeding device for feeding staples, and a bending and cutting device provided between the base and the cover for bending and cutting the legs of each staple. The cutting device includes a seat provided on the base and a housing attached to the cover. The seat includes two wedges formed thereon and a pusher formed thereon. A stationary cutting element is provided in the housing. Two movable cutting elements are provided movably in the housing and on the two wedges so that they are moved towards the stationary cutting element in order to cut the legs of each staple as they are moved towards the seat together with the housing. A spring is put between the movable cutting elements in a tendency to push the movable cutting elements from the stationary cutting element. Two bending elements are provided movably and pivotally in the housing above the movable cutting elements so that they are pushed by the pusher in order to bend the legs of each staple after the stationary cutting element and the movable cutting elements cut the legs of each staple.
Owner:APEX MFG
Method for holding brazing material during a brazing operation
InactiveUS20150360328A1Low costAvoid High Precision RequirementsTurbinesBlade accessoriesMetalWire mesh
A method for holding a sintering filler material during a brazing / sintering operation for repairing a damaged area of a component wherein the component is in either a bonding face down position, bonding face vertical position or bonding face up position. The method includes providing a wire mesh and attaching the wire mesh to the component in a location corresponding to the damaged area. Further, the method includes forming a gap between the wire mesh and the component. Moreover, the sintering filler material may be inside the wire mesh or both inside and outside the wire mesh in order to secure the sintering filler material to the damaged area.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
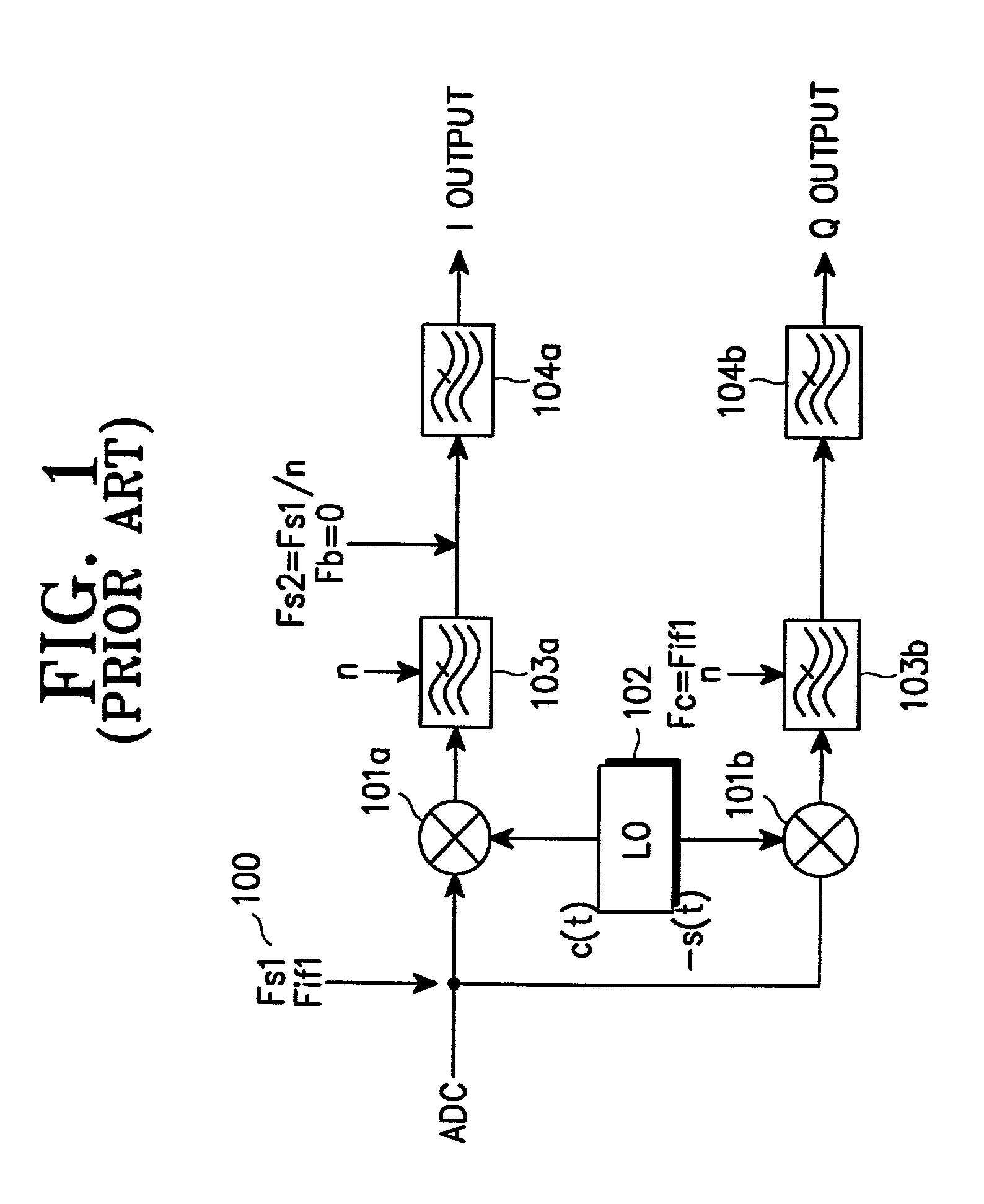
Digital down-converter
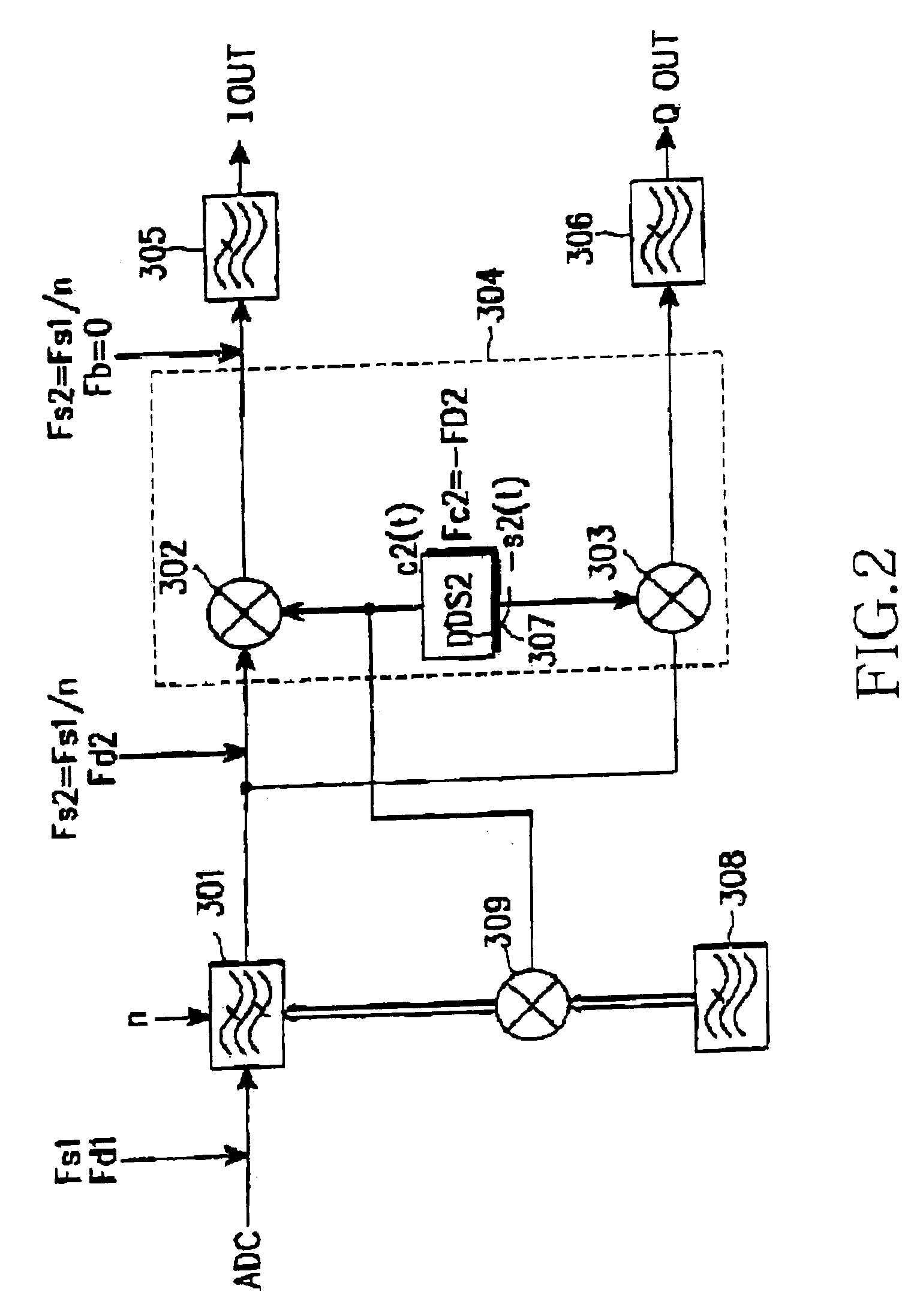
InactiveUS7127227B2Low spurious levelAvoid High Precision RequirementsCode conversionPhase-modulated carrier systemsFrequency changerDigital down converter
A digital down-converter having a low spurious level and a high frequency precision without increasing power consumption of a local oscillator. A first mixer receives, as a first IF input signal, a digital signal obtained by sampling a received signal with an RF signal or an IF signal, and converts the first IF input signal to a second IF signal using the first local oscillator. A digital filter suppresses an outband signal of the second IF signal provided from the first mixer. A second mixer converts an output of the digital filter to a detection process frequency using the second local oscillator. An available frequency step of the first local oscillator is larger than an available frequency step of the second local oscillator.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
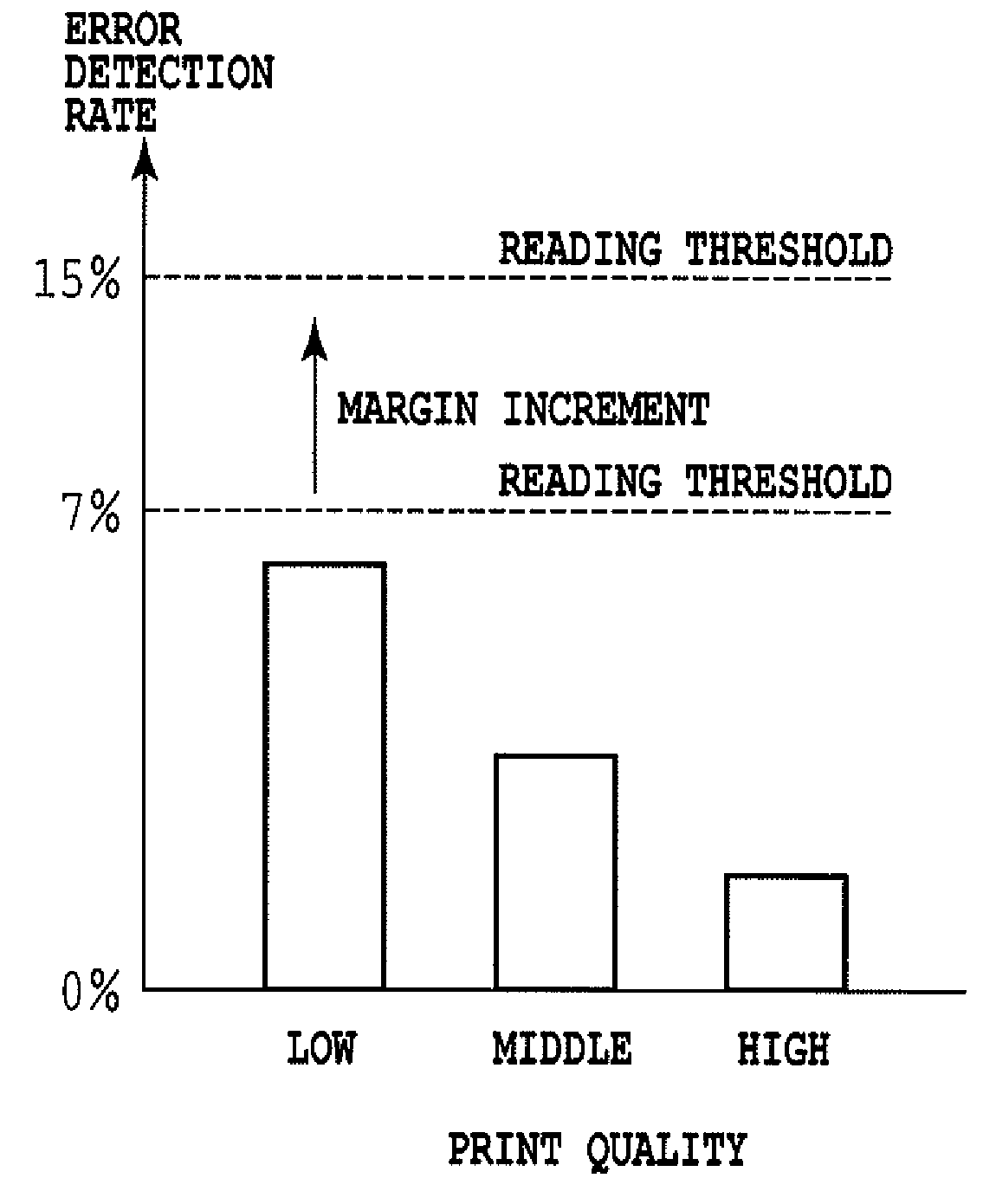
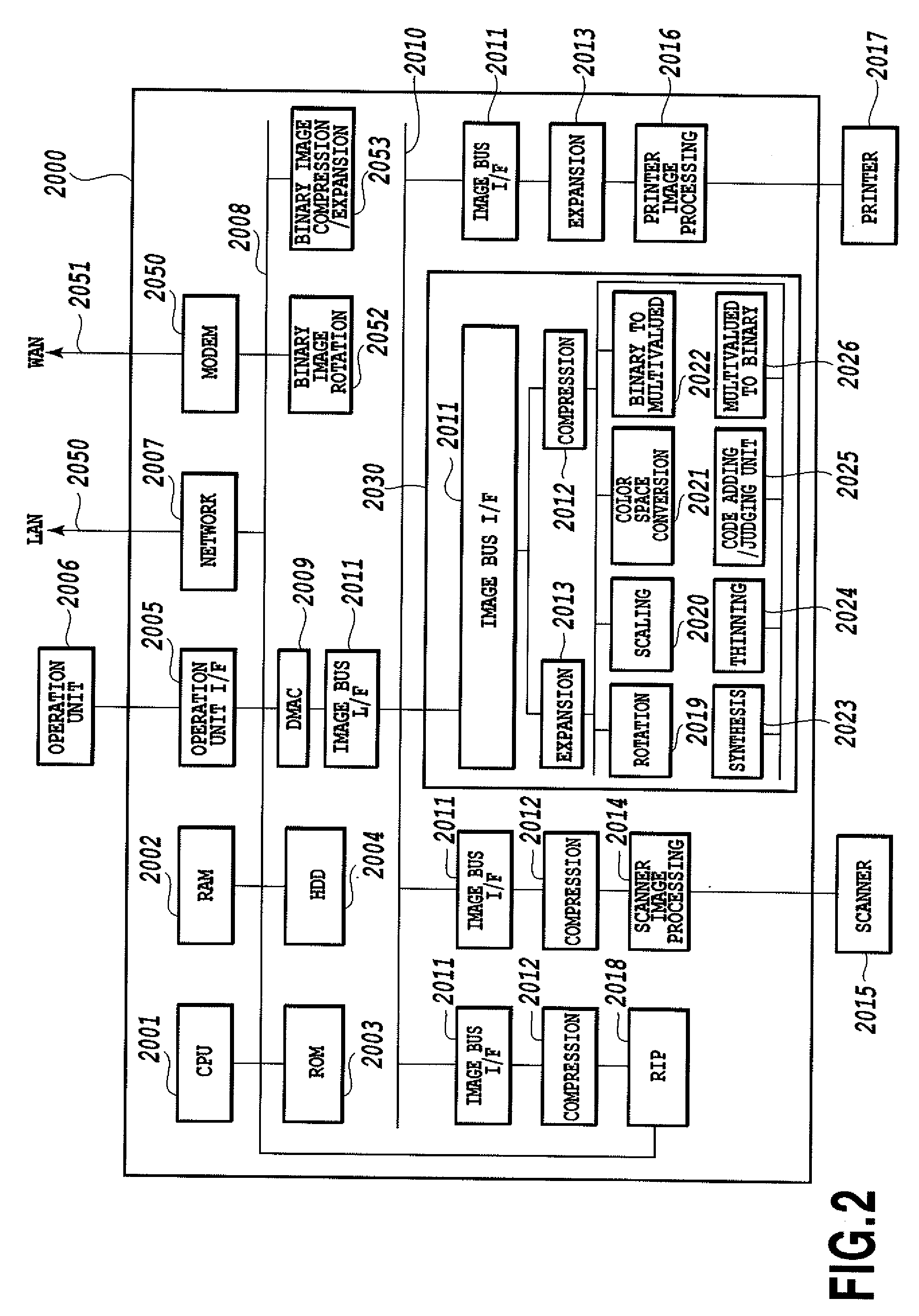
Image forming system, image processing apparatus, determination device, and image processing method
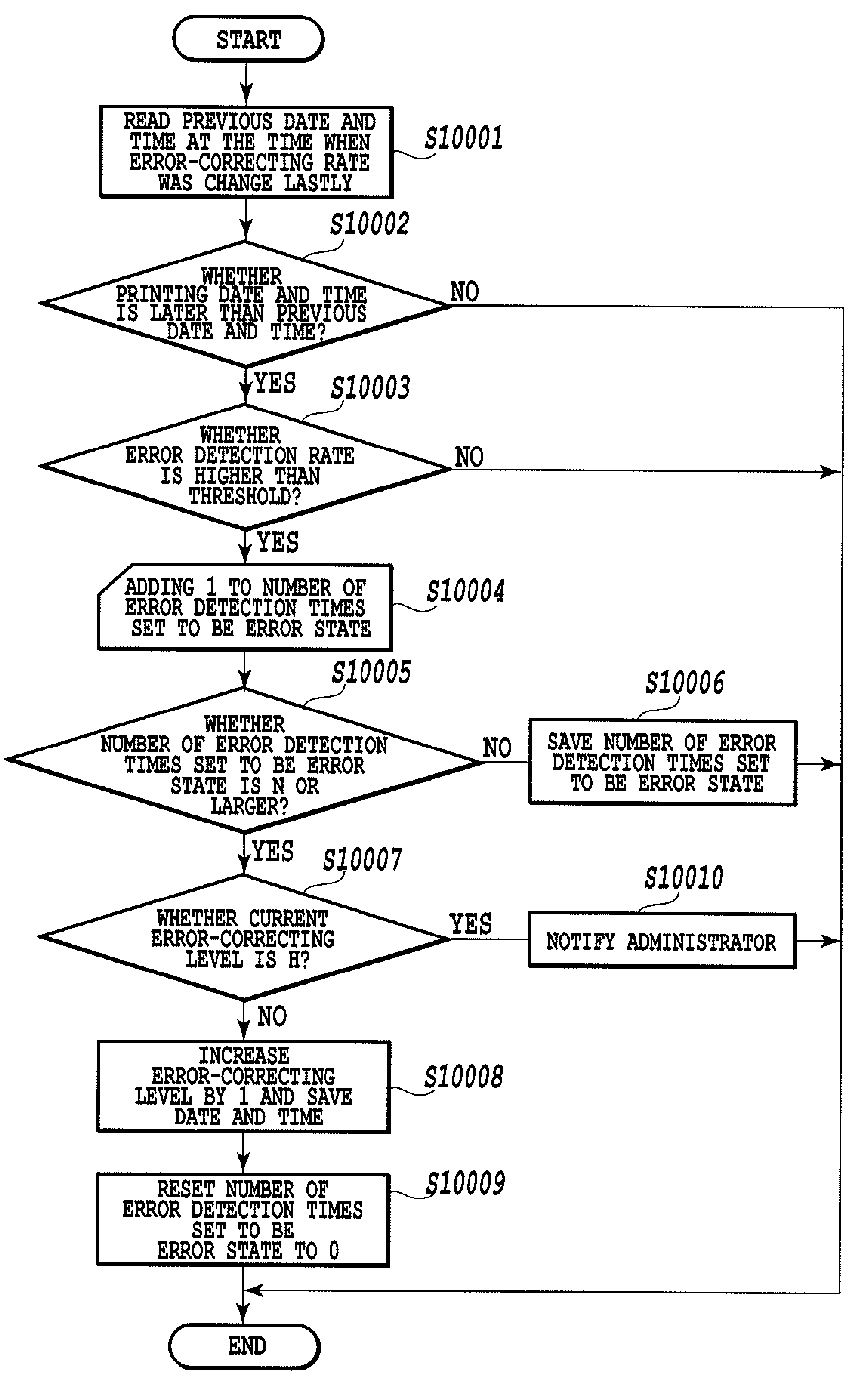
InactiveUS20080222462A1Convenience is hamperedLow print precisionError detection/correctionCode conversionImaging processingImage formation
An object of the present invention is to provide an image forming system, an image processing apparatus, a determination device, and image processing method that are capable of preventing users' convenience from reducing even when an image forming apparatus prints a coded image with a low print precision. A first MFP is connected through a LAN to a second MFP for performing error-correcting coding of original information, for creating a coded image by imaging the original information with the error-correcting code, and for forming the created coded image on a sheet. The first MFP extracts the original information from the coded image on the sheet obtained by reading the sheet on which the coded image is formed. Thereafter, the first MFP transmits to the second MFP an error detection rate at the time when the original information is extracted.
Owner:CANON KK
Capacitive input device
ActiveUS20150248180A1Lighten the burden on the circuitImprove accuracyElectronic switchingInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceEngineering
Electrode portions located on both ends are set to detection electrode portions, ground electrode portions are set on the inside thereof, and a plurality of central electrode portions are set to driving detection portions. A coordinate position of a finger can be obtained based on an output difference between the detection electrode portions, and a vertical distance can be obtained based on an output sum. When the vertical distance of the finger is shorter than a first threshold, switching is performed so that an interval between the detection electrode portions is shortened, and when the finger approaches, a touch detection mode is set.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
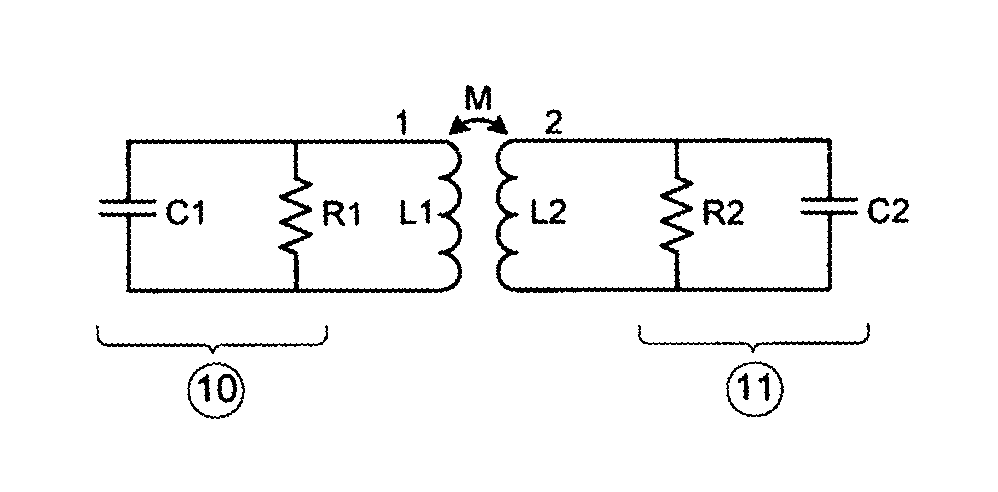
Inductive antenna coupling
ActiveUS8712323B2Small sizeHigh degreeNear-field transmissionRadio transmissionTransformerMiniaturization
This invention pertains to the connection between a radio frequency circuit and its antenna. Miniaturization of radio frequency integrated circuits has made attaching these circuits to their antennas increasingly difficult and costly. This invention uses magnetic coupling, as performed in transformers, between circuits and antennas as a practical solution to reduce cost and effort in attaching the two sides as well as to protect the circuit against electrostatic discharge. Furthermore a simple pre-assembly testing methodology is accounted for as an additional benefit of the method.
Owner:TAGARRAY
Inductive antenna coupling
ActiveUS20090264067A1Small sizeHigh degreeNear-field transmissionRecord carriers used with machinesTransformerMiniaturization
This invention pertains to the connection between a radio frequency circuit and its antenna. Miniaturization of radio frequency integrated circuits has made attaching these circuits to their antennas increasingly difficult and costly. This invention uses magnetic coupling, as performed in transformers, between circuits and antennas as a practical solution to reduce cost and effort in attaching the two sides as well as to protect the circuit against electrostatic discharge. Furthermore a simple pre-assembly testing methodology is accounted for as an additional benefit of the method.
Owner:TAGARRAY
Seven-degrees-of-freedom humanoid robotic arms
ActiveUS20190314979A1Highly bionic designHigh freedom of movementProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsRobotic armDegrees of freedom
The present invention relates to robots and discloses a seven-degrees-of-freedom humanoid robotic arm, including an upper arm component and a forearm component. One end of the upper arm component is provided with a shoulder pitching joint, a shoulder yawing joint and a shoulder rolling joint for connecting with a shoulder. One end of the forearm component is provided with an elbow pitching joint and an elbow rolling joint for connecting with the upper arm component, and the other end of the forearm component is provided with a wrist pitching joint and a wrist yawing joint for connecting with a robotic hand. The seven-degrees-of-freedom humanoid robotic arm of the present invention achieves a highly bionic design of a spherical joint of human shoulder, elbow and wrist joints.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
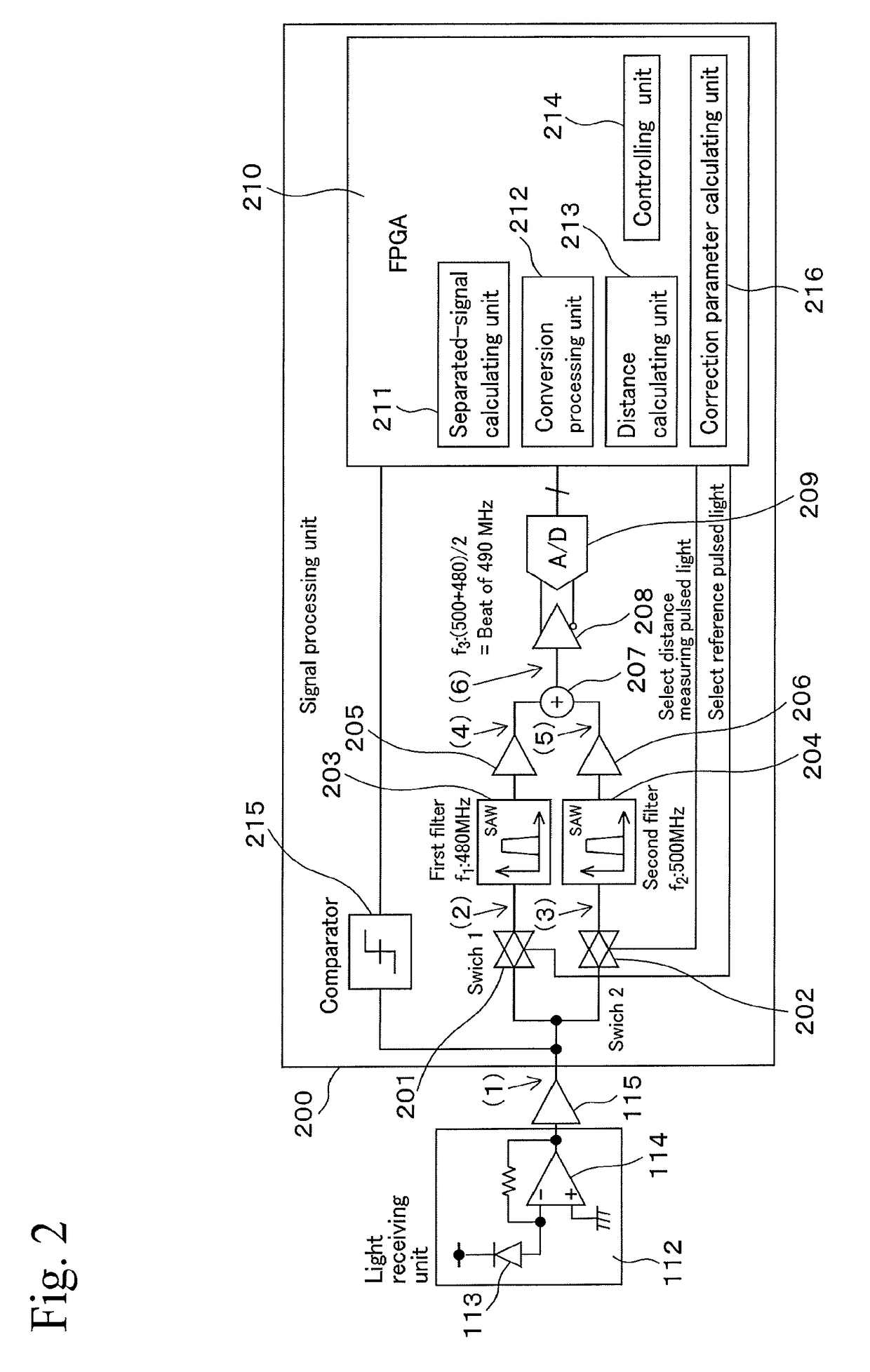
Distance measuring device and method for calibrating the same
ActiveUS20170276773A1Without increase costAvoid High Precision RequirementsElectromagnetic wave reradiationVIT signalsPhase difference
A distance calculating unit includes a first filter for a detection signal of reference pulsed light, a second filter for measuring pulsed light, an adder circuit that adds outputs from the two filters together, an A / D converter that receives output from the adder circuit, a separated-signal calculating unit that analyzes output from the A / D converter and that generates a first separated signal and a second separated signal, a conversion processing unit that converts the phase of at least one of the two separated signals into a phase of a predetermined frequency, and a distance calculating unit that calculates a distance to an object by using a phase difference between the two separated signals and a correction parameter, which is obtained by making the reference pulsed light pass through the first filter and the second filter at the same time and by calculating a phase difference between outputs from these filters.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Anti-shake device for optical instrument
InactiveUS20100002087A1Avoid aberrationsAvoid High Precision RequirementsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical instrumentMechanical engineering
An anti-shake device for positioning an image-capturing unit in an optical instrument. A base includes a shaft pillar. A clamp unit includes a first clamping arm and a second clamping arm. The first and second clamping arms pivot to the shaft pillar of the base and detachably clamp the image-capturing unit. A drive unit is connected to the base and includes a driven member driving the first and second clamping arms of the clamp unit to rotate and shifting between a first mode and a second mode. The first and second clamping arms are separated from each other and the image-capturing unit when the driven member is in the first mode. The first and second clamping arms close and clamp the image-capturing unit when the driven member is in the second mode.
Owner:ASIA OPTICAL INT LTD
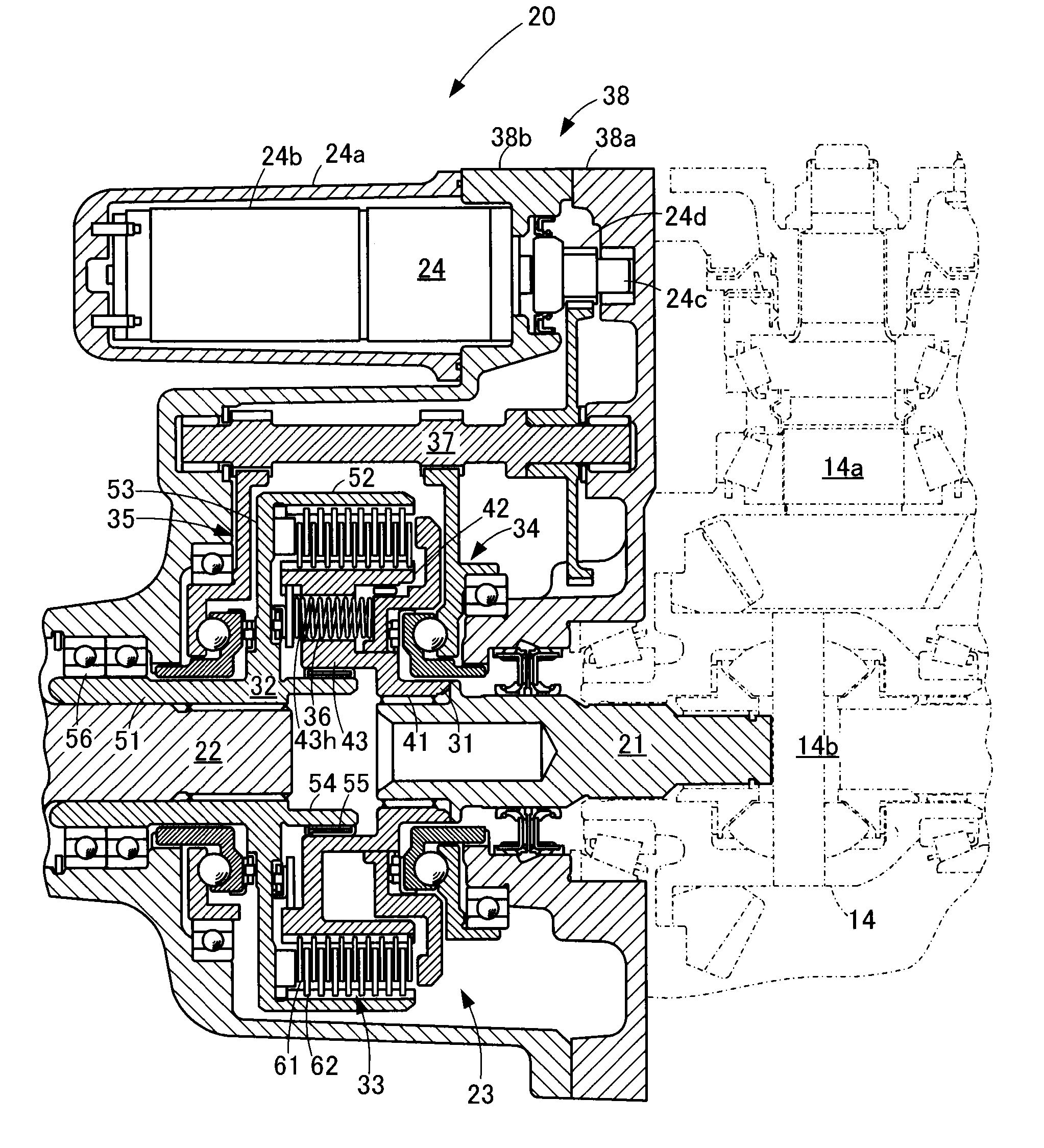
Power transmission apparatus
ActiveUS20150038295A1Avoid High Precision RequirementsReduce the drag torqueFriction clutchesElectrically actuated clutchesDrive shaftEngineering
A power transmission apparatus comprises an input shaft, an output shaft, a clutch device, and an actuator. The clutch device comprises a clutch hub, a clutch housing, a clutch pack, an input side cam mechanism for pressing the clutch pack toward the output shaft, an output side cam mechanism for pressing the clutch pack toward the input shaft, a return spring for urging the clutch pack to have its elements moved away from each other, and a drive shaft having an input side gear for transmitting the driving force of the actuator to the input side cam mechanism, and an output side gear for transmitting the driving force of the actuator to the output side cam mechanism.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
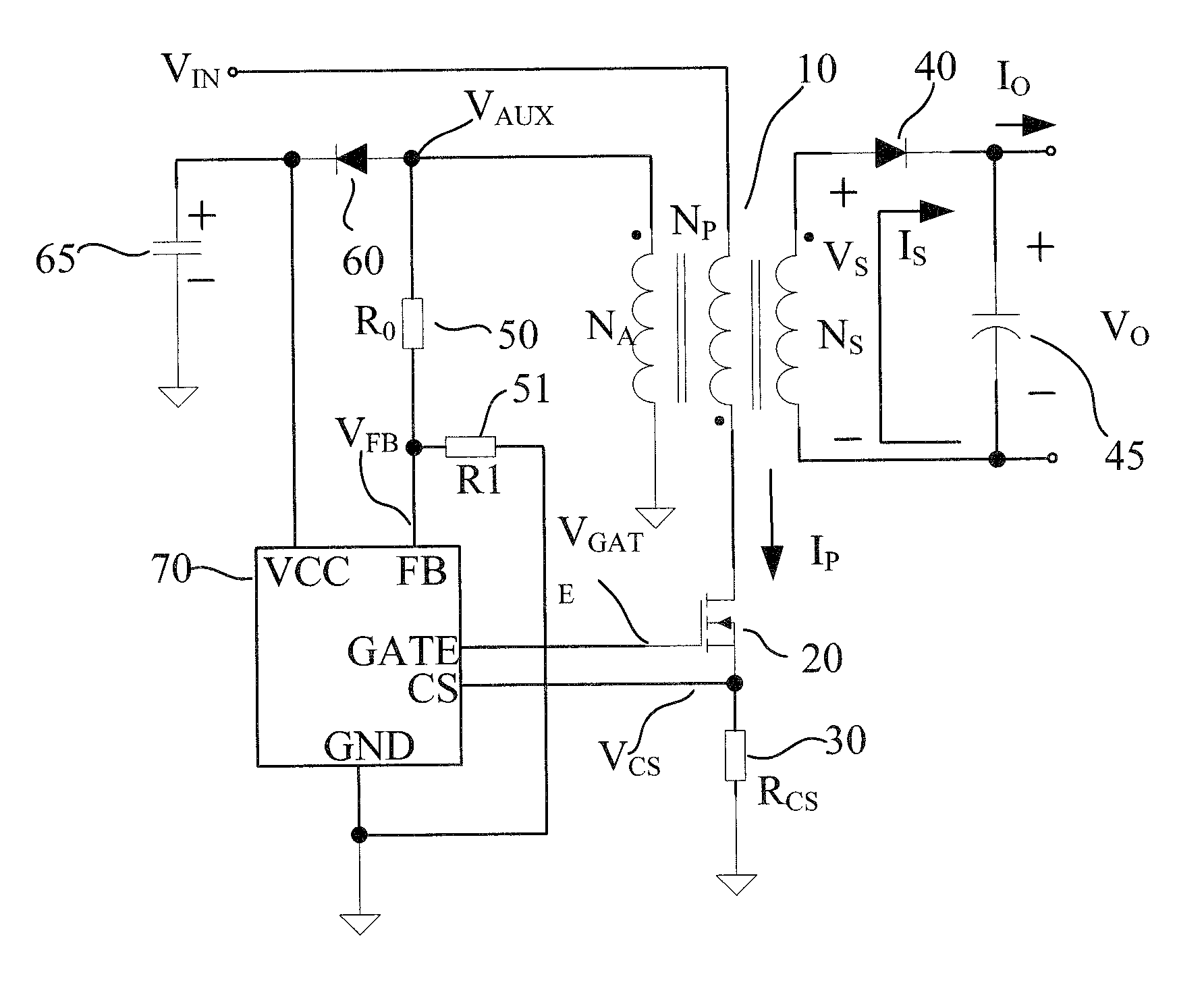
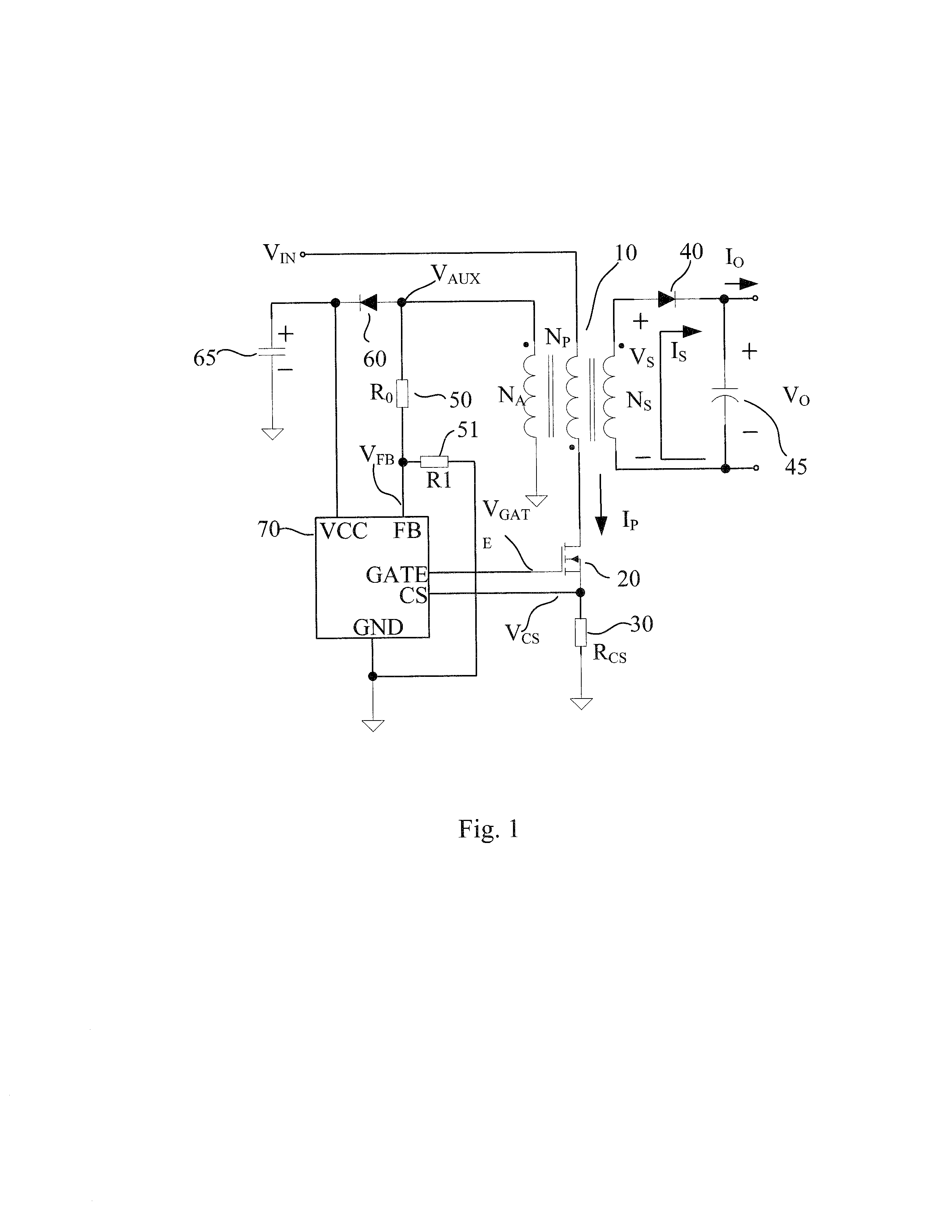
Primary-side feedback controlled ac/DC converter with an improved error amplifier
ActiveUS20130181772A1High output voltage accuracyReduced stabilityDc-dc conversionDifferential amplifiersReducing equivalentEngineering
An error amplifier, a controller using the error amplifier, and a primary-side feedback controlled AC / DC converter using the controller are discussed. When the output voltage of the primary-side feedback controlled AC / DC converter according to present invention changes, the alternating current path enjoys a fast response and adjusts the output voltage quickly with a lower precision, avoiding large voltage fluctuate, then the direct current path functions slowly to reduce equivalent output error. In such a way, the output voltage precision is enhanced while the stability of the primary-side feedback controlled AC / DC converter is maintained.
Owner:FREMONT MICRO DEVICES CORP
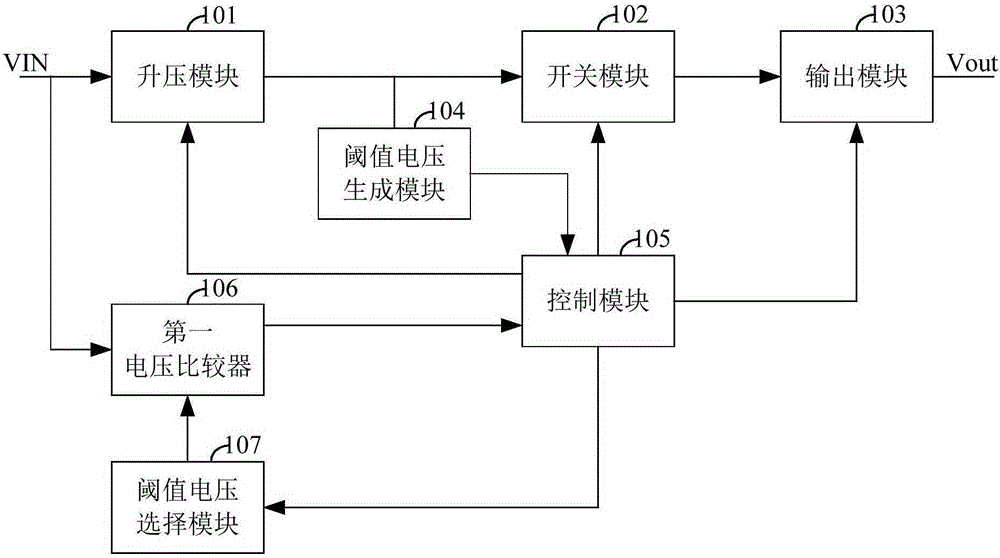
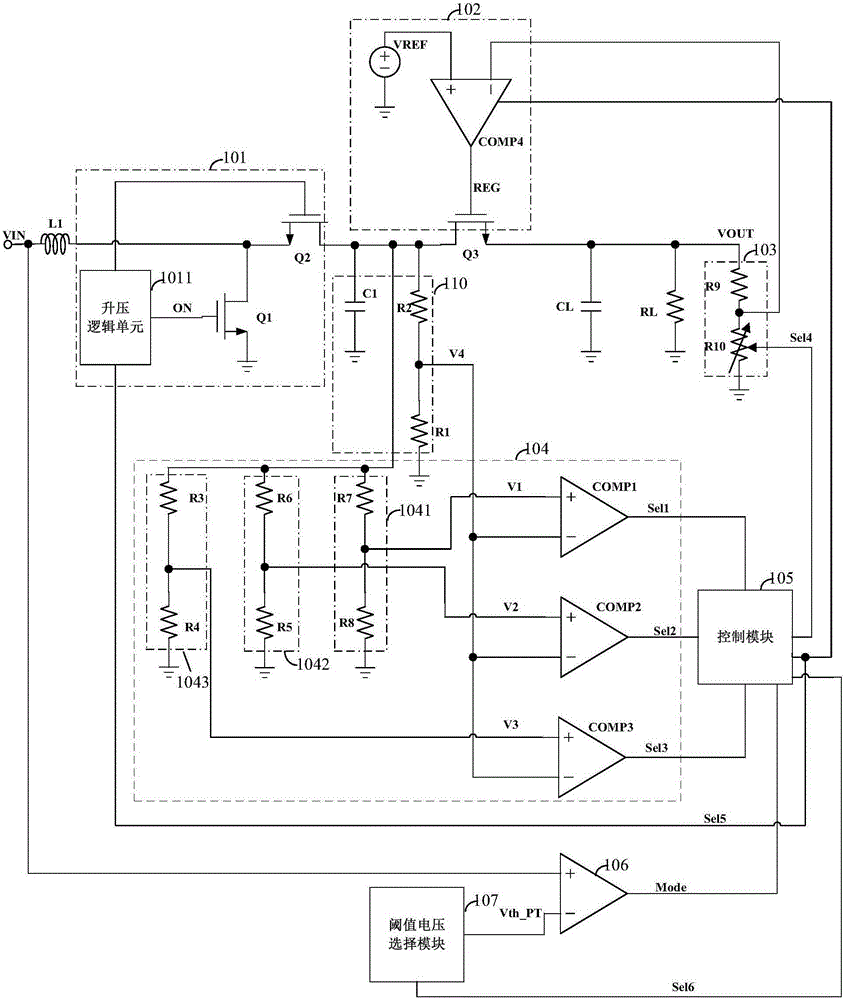
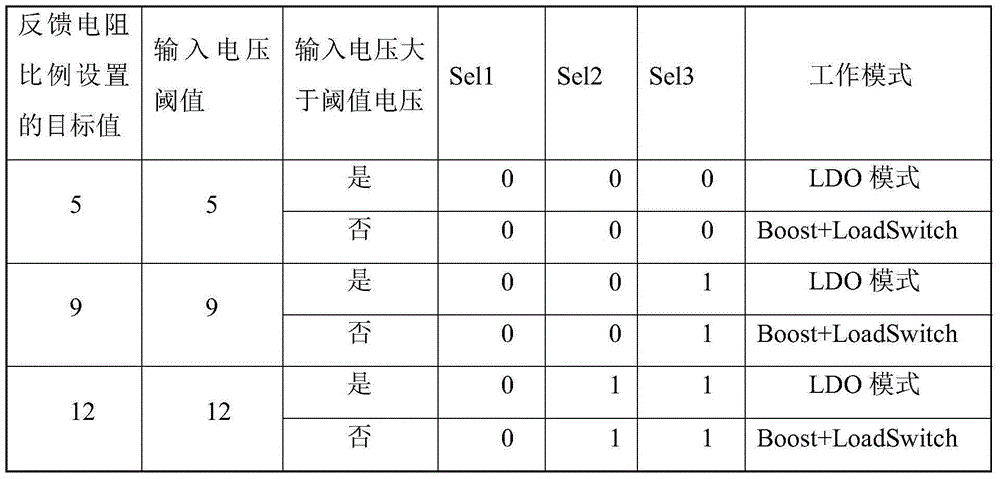
Boost chip
ActiveCN105226945AAvoid high precision requirementsLow costDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationComputer moduleComparator
The invention relates to the technical field of charging and provides a boost chip. The boost chip comprises a boost module, a threshold voltage generation module, a switching module, an output module, a control module, a first voltage comparator and a threshold voltage selection module; when an input voltage is greater than a threshold voltage, the control module controls the boost module to output the input voltage to the switching module according to a comparison result, controls the switching module to be conducted so as to send the input voltage to the output module, and adjusts the output module so that the output module outputs a voltage same as the threshold voltage value according to the input voltage; and when the input voltage is smaller than the threshold voltage, the input voltage is boosted by controlling the boost module and then transmitted to the switching module according to the comparison result, the switching module is controlled to be conducted so that the boosted input voltage is transmitted to the output module, and the output module outputs the voltage. By comparing the input voltage with the threshold voltage, the input voltage is controlled to be boosted or bucked, and thus, the adjustment on the output voltage is achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEWN BAOLI MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method And Device For Material Analysis
ActiveUS20150369765A1Produce easily and cost-effectivelyAvoid High Precision RequirementsMaterial heat developmentMetal working apparatusHeat flowEngineering
Method and thermal analysis device including a sample holder and at least one temperature detector which is assigned to the holder. The invention further relates to a production method for a temperature detector. A heat flow to be detected is conveyed to the temperature detector between a support surface and the sample holder, wherein the support surface and / or the sample holder include elevations or depressions forming contact points, which define a relevant heat flow zone assigned to the support surface. A thermocouple, which includes at least two elements made of different metals, a first metallic element A, with a higher expansion coefficient compared to a second metallic element B, is introduced in a precisely fitting manner into second metallic element B constituted as a hollow profile and the two elements A, B are heated in a first operational step and then cooled again in a second operational step.
Owner:NETZSCH GERATEBAU GMBH
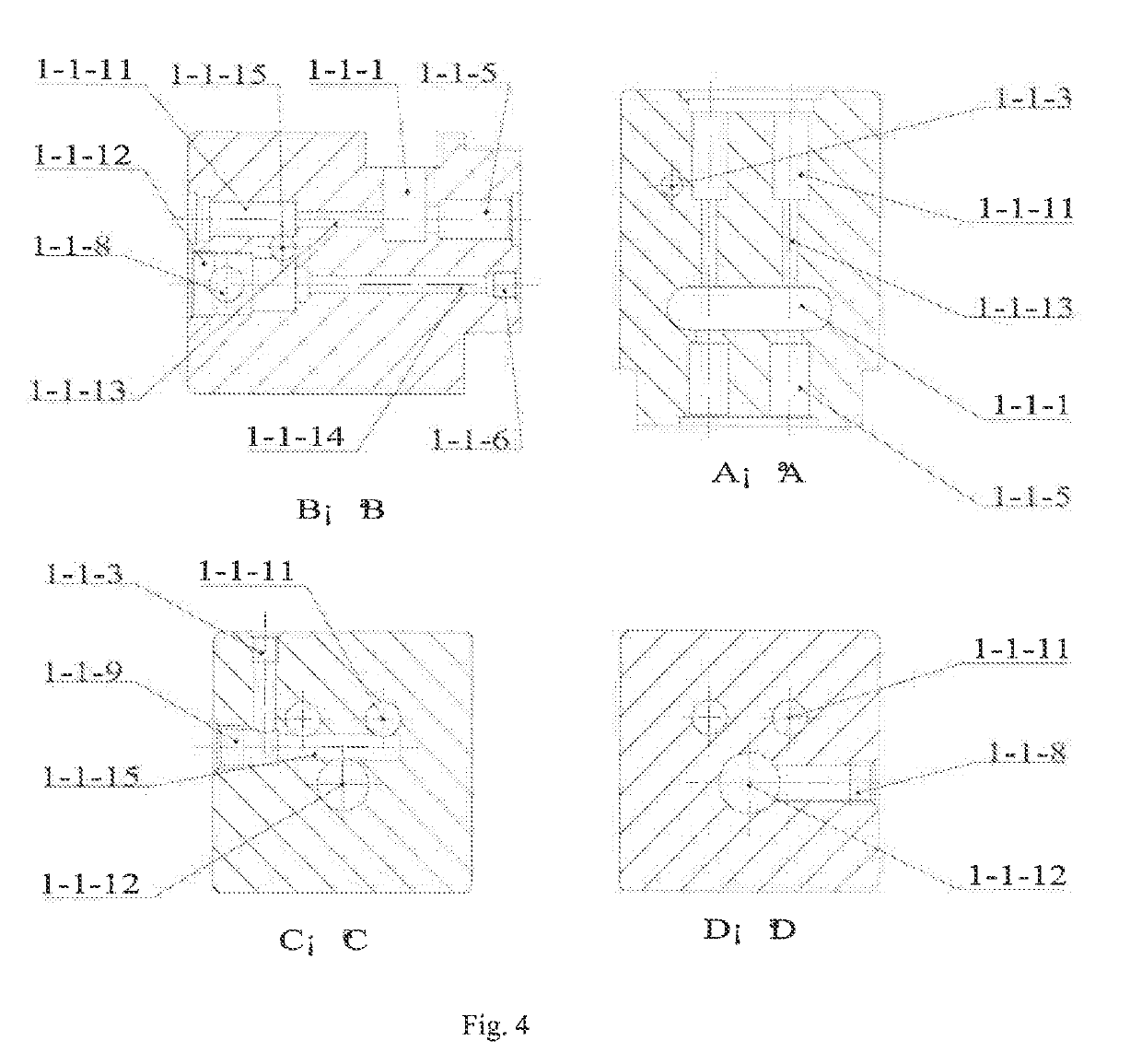
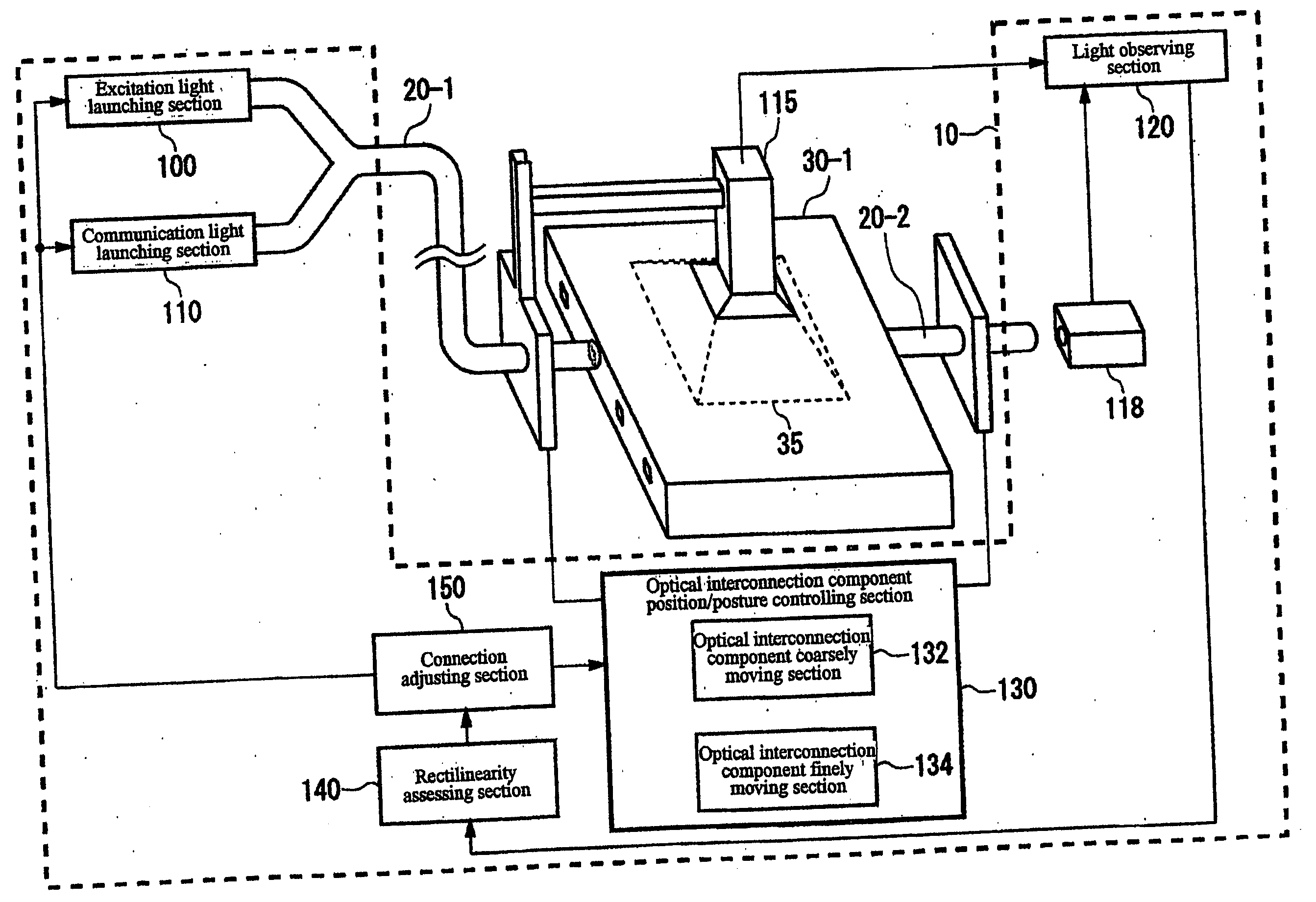
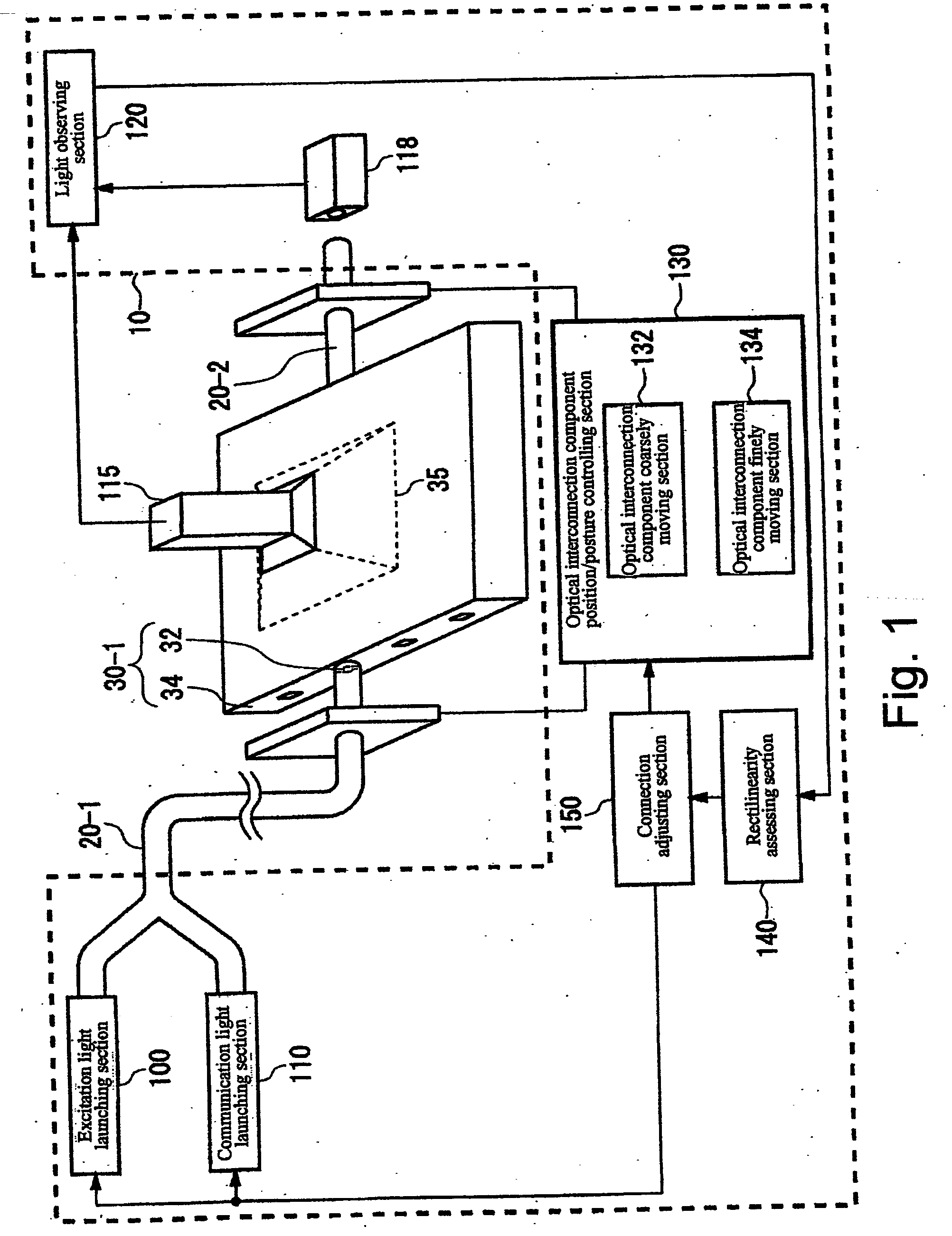
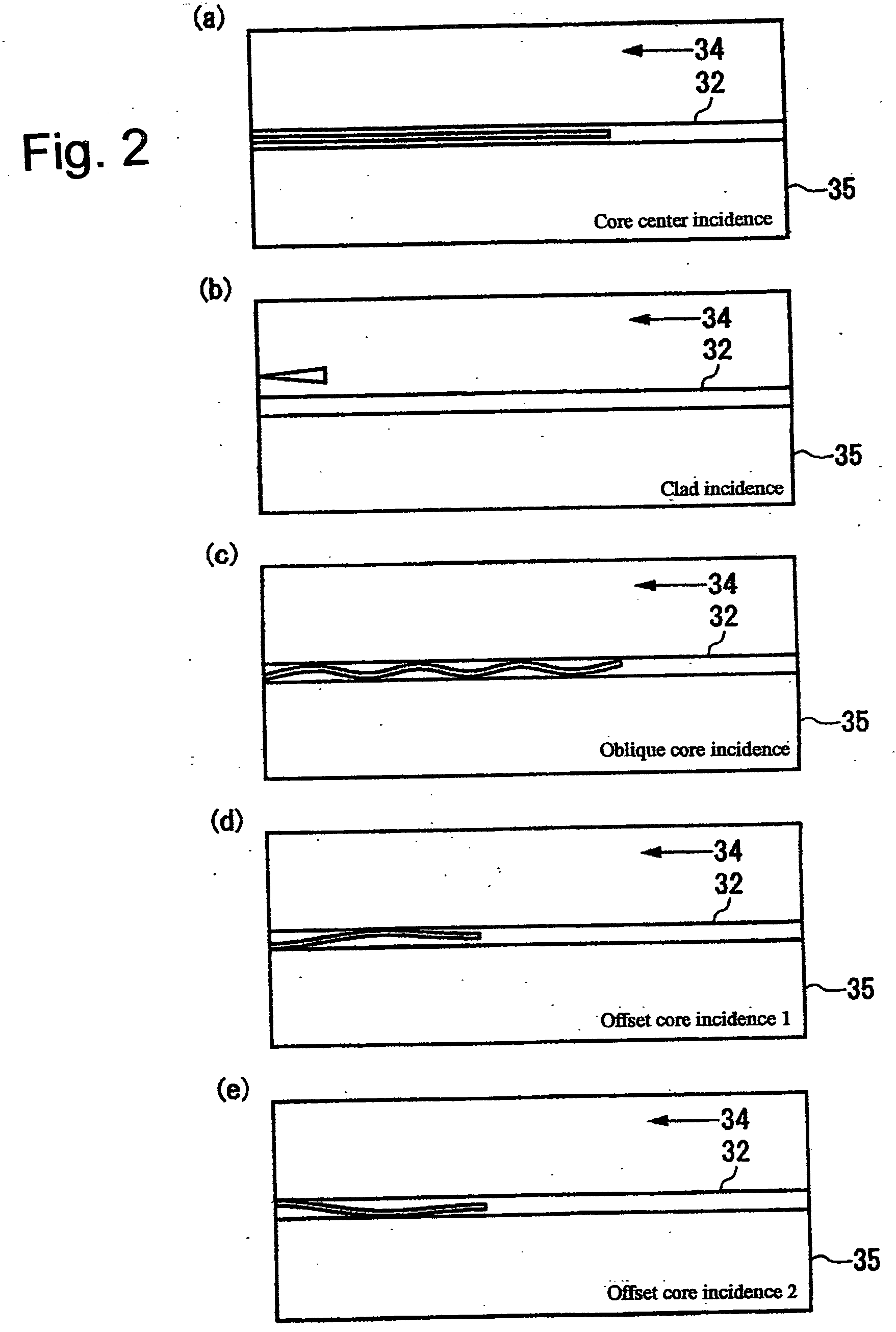
Apparatus and method for connecting optical waveguides
ActiveUS7330247B2Increase in propagation lossAvoid High Precision RequirementsUsing optical meansCoupling light guidesFluorescent lightWaveguide
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Radiation detector comprising an imaging radiation-collimating structure
InactiveUS20100264324A1Easy to manufactureAvoid High Precision RequirementsRadiation/particle handlingSolid-state devicesLow-pass filterDetector array
The invention relates to a radiation detector (3) comprising a detector array (5) having a periodical pattern of detector elements (51). Each detector element (51) comprises a sensor element (53) for converting incident radiation into an electrical charge. The sensor elements (53) are spaced at a sensor-center-to-center distance. Over the detector array (5) an imaging radiation-collimating structure (7) is disposed. The imaging radiation-collimating structure has a periodical pattern of radiation absorbing elements, which radiation absorbing elements are being spaced at a collimator center-to-center distance. The radiation detector (3) comprises a combiner for generating combiner-signals from the electrical charges of the sensor elements (53) of groups of an even number of sensor elements adjacent in a direction of the periodicity of the pattern of the radiation absorbing elements. The collimator center-to-center distance is approximately equal to twice the center-to-center distance of the groups of adjacent sensor elements. The radiation detector (3) further comprises a low-pass filter for receiving the combiner-signals and suppressing components of the combiner-signals with a frequency equal to or higher than a collimator frequency corresponding to the collimator center-to-center distance, thus providing a radiation detector which is easier to manufacture than the known radiation detector and which requires a relatively low degree of precision for the positioning of the radiation absorbing elements of the imaging radiation-collimating structure without introducing visible Moire effects in the image of an object to be imaged by the detector.
Owner:TRIXELL S
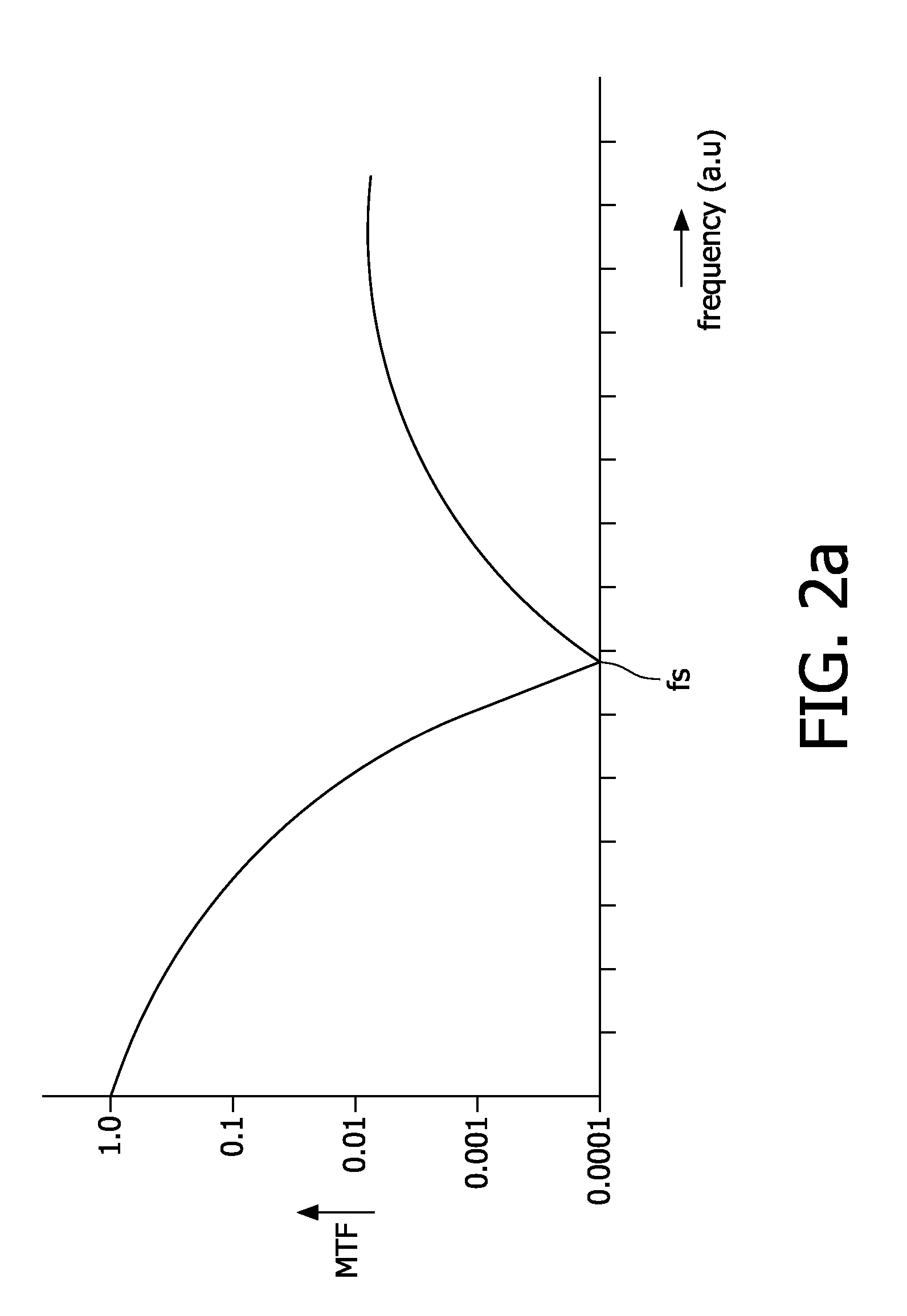
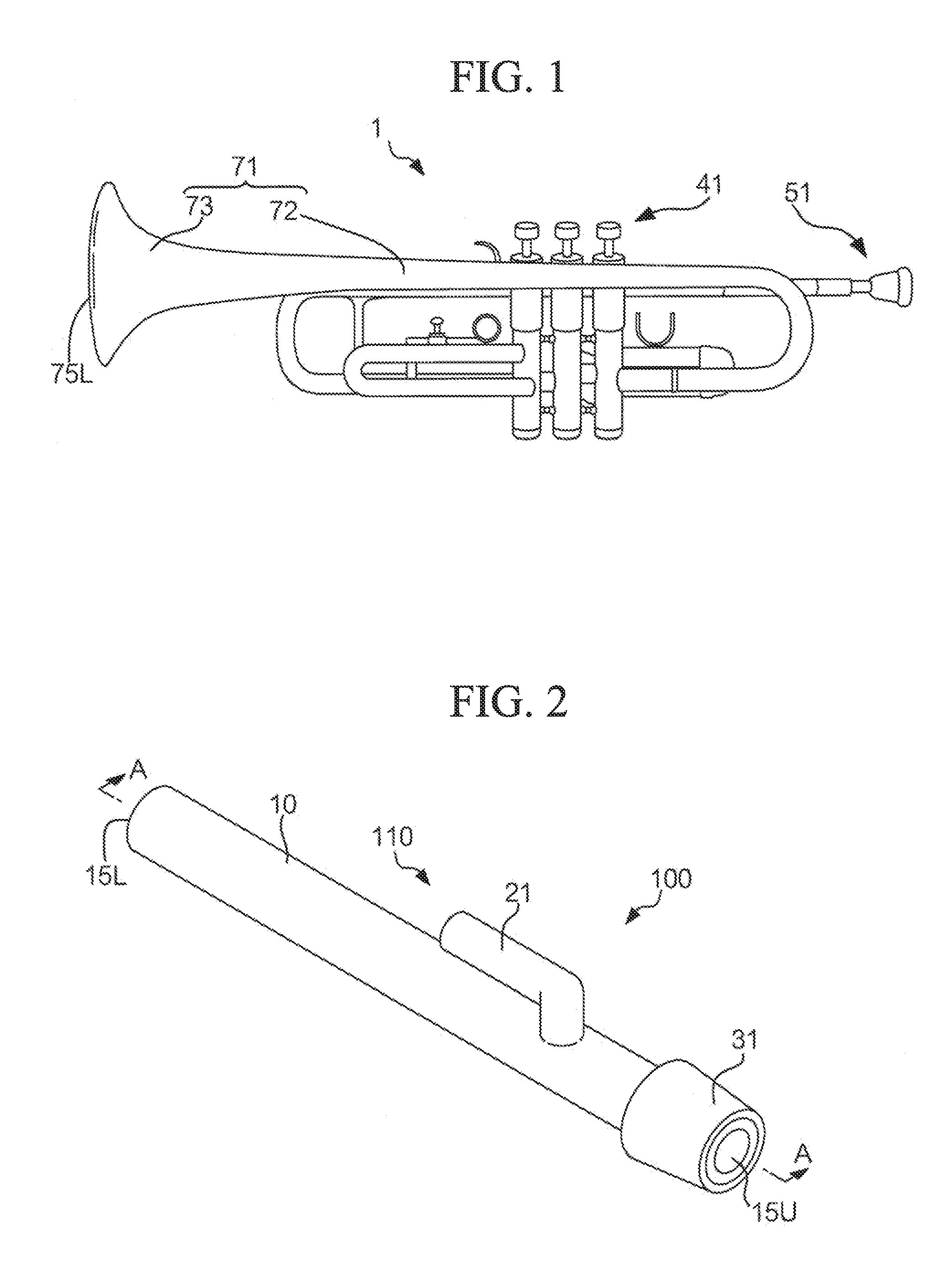
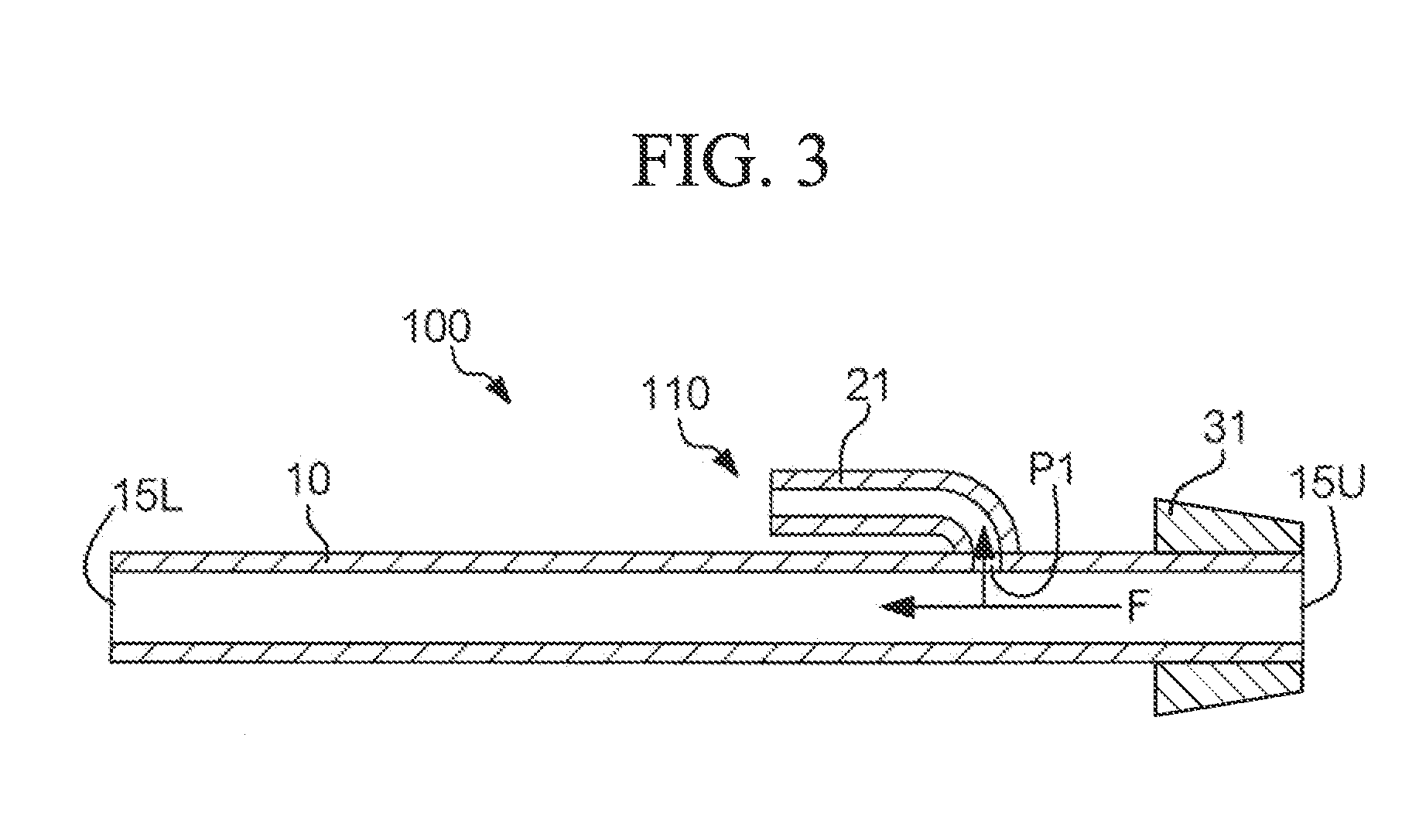
Mute for brass instrument
InactiveUS20130036895A1Improve accuracyLow color requirementWind musical instrumentsEngineeringBrass
A mute detachably attached to a brass instrument includes a fixed part and a plurality of branch pipes, each including a main pipe and an auxiliary pipe. The branch pipes are unified together and inserted into a bell pipe of a brass instrument. The fixed part is attached to the tapered portion of a bell pipe and interposed between the interior of the bell pipe and the exterior of the main pipe. The branch pipe is designed such that the auxiliary pipe is connected to the main pipe at an interconnect part, at which an air flow propagating through the main pipe is partly branched into the auxiliary pipe.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
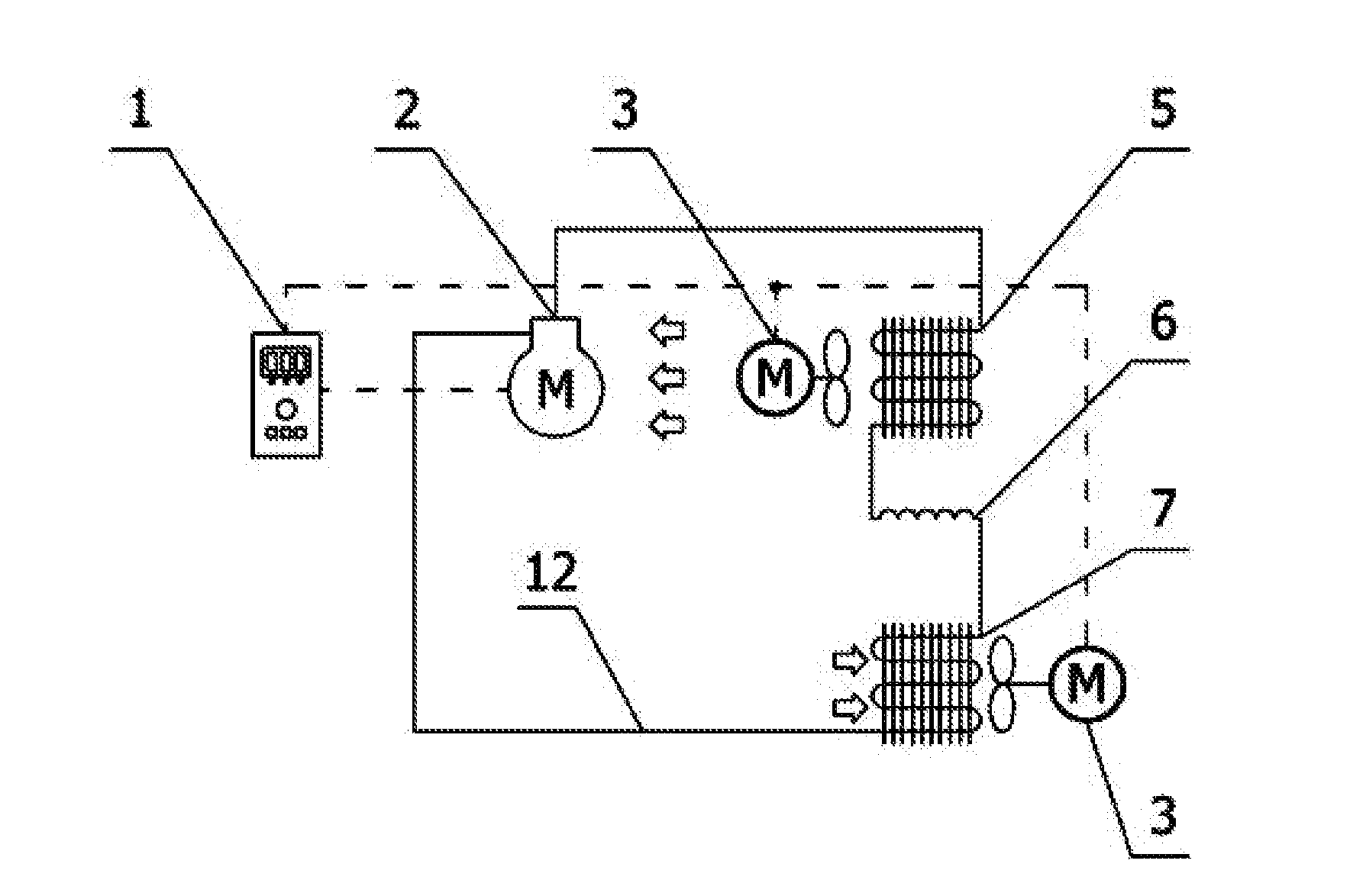
Refrigerating capacity control device, a testing apparatus and a refrigerating control method using the device
InactiveUS20150107283A1Low control precisionGood effectMechanical apparatusCompression machines with non-reversible cycleEngineeringCapacity control
This invention hereof discloses a refrigerating capacity control device, a test apparatus and a refrigerating control method using the device. The refrigerating capacity control device comprises a compressor (2), a condenser (5), an evaporator (7), a controller (1), a pressure regulating valve (4), a throttling device (6), a control panel (13) for driving a hot-gas valve, and a hot-gas valve (11). The controller is connected with the hot-gas valve (11) through the control panel (13) for driving a hot-gas valve; the pressure regulating valve (1) is disposed between an outlet of the compressor (2) and an inlet of the condenser (5) that are arranged in the refrigerating device; the throttling device (6) is disposed between an outlet of the condenser (5) and an inlet of the evaporator (7); one-end of the hot-gas valve (11) is disposed on a pipeline between the outlet of the compressor (2) and the front end of the pressure regulating valve (4), and the other end thereof is disposed on a pipeline that is between the throttling device (6) and an inlet of the evaporator (7).
Owner:XUTEMP TEMPTECH
Image forming system, image processing apparatus, determination device, and image processing method
InactiveUS7818652B2Avoid convenienceAvoid High Precision RequirementsError detection/correctionCode conversionImaging processingImage formation
An object of the present invention is to provide an image forming system, an image processing apparatus, a determination device, and image processing method that are capable of preventing users' convenience from reducing even when an image forming apparatus prints a coded image with a low print precision. A first MFP is connected through a LAN to a second MFP for performing error-correcting coding of original information, for creating a coded image by imaging the original information with the error-correcting code, and for forming the created coded image on a sheet. The first MFP extracts the original information from the coded image on the sheet obtained by reading the sheet on which the coded image is formed. Thereafter, the first MFP transmits to the second MFP an error detection rate at the time when the original information is extracted.
Owner:CANON KK
Solid-state imaging device and electronic apparatus
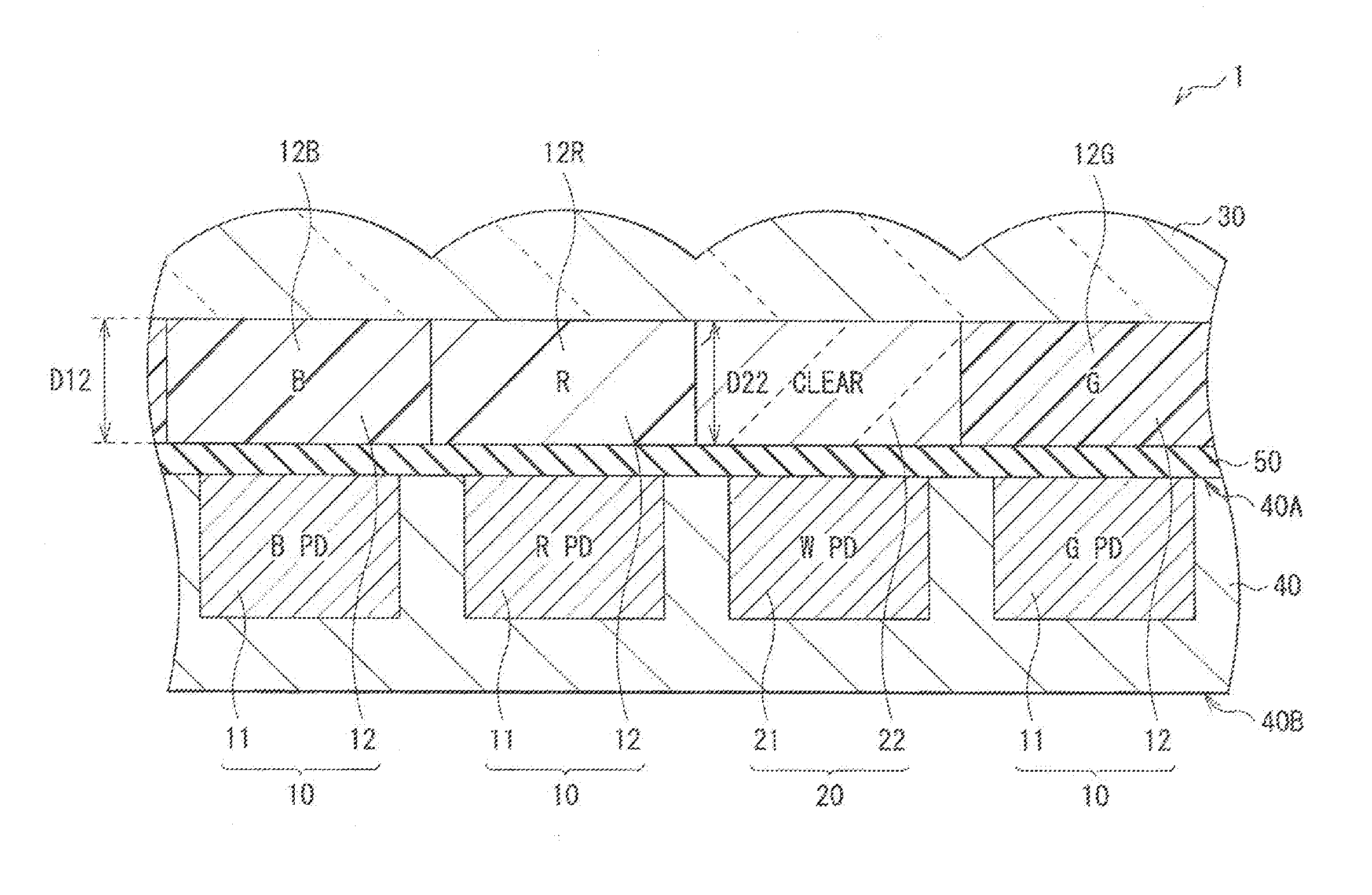
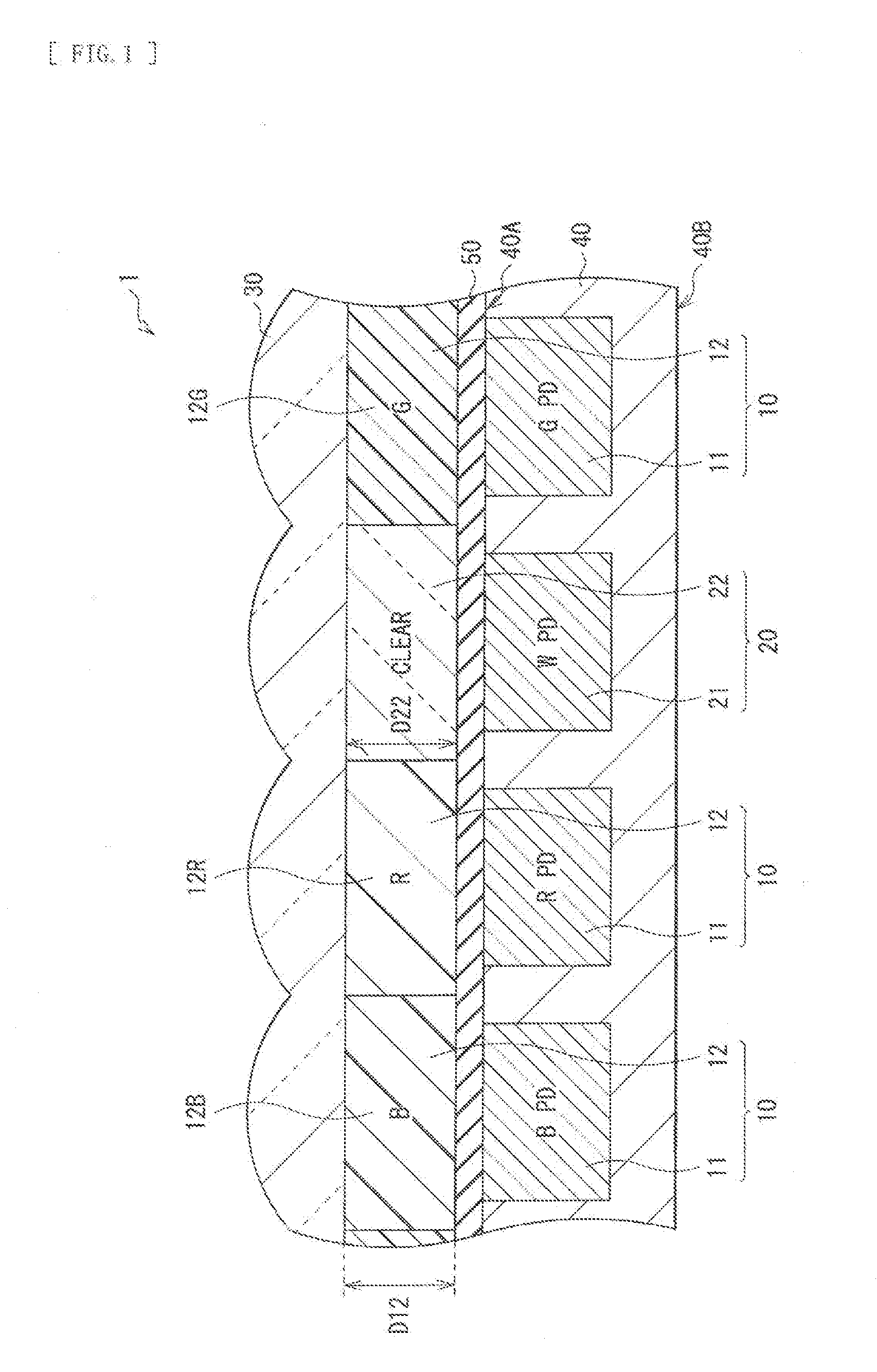
ActiveUS20160197108A1Avoid High Precision RequirementsDifficult to treatSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesClear LayerRefractive index
There is provided a solid-state imaging device that includes: colored pixels each including a first photoelectric conversion element and a colored filler; white pixels each including a second photoelectric conversion element and a clear layer; and an interlayer insulating film provided between the first photoelectric conversion element and the colored filter, and between the second photoelectric conversion element and the clear layer. The colored filter is provided on light-entering side of the first photoelectric conversion element. The clear layer is provided on light-entering side of the second photoelectric conversion element. The clear layer has a higher refractive index than a refractive index of the colored filter, and includes an inorganic dielectric film made of a different material from a material of the interlayer insulating film.
Owner:SONY CORP
Continuous supply precision minimum quantity lubrication pump supporting different lubrication conditions
ActiveUS20190301673A1Improve the lubrication effectFine surfaceEngine pressureLubricating pumpsEmulsionSolenoid valve
A continuous supply precision minimum quantity lubrication pump supporting different lubrication conditions, including a pump system, a gas source processor, a driving system, an oil cup, a water pump, a two-position three-way solenoid valve, a water tank and an emulsion storage tank, wherein the processor is connected with the pump system through a bidirectional joint, the oil cup is connected with the pump system through an oil cup joint, the water pump is installed in a driving box body of the driving system and is connected with the pump system through a hose, the water tank and the emulsion storage tank are connected with the two-position three-way solenoid valve, the two-position three-way solenoid valve is connected with the driving system, and the driving system and the water pump are respectively driven by a stepping motor I and a stepping motor II.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Apparatus and method for connecting optical waveguides
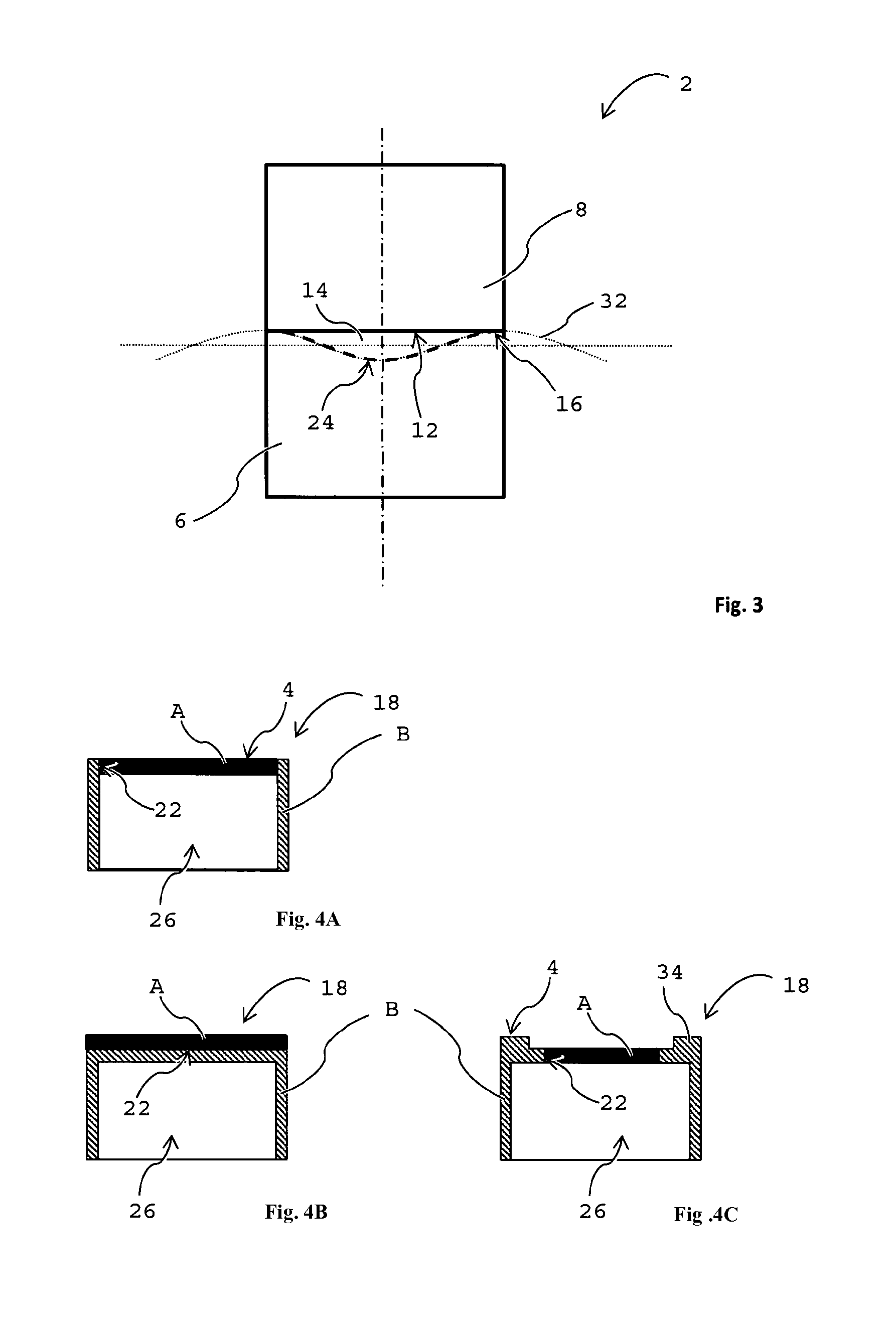
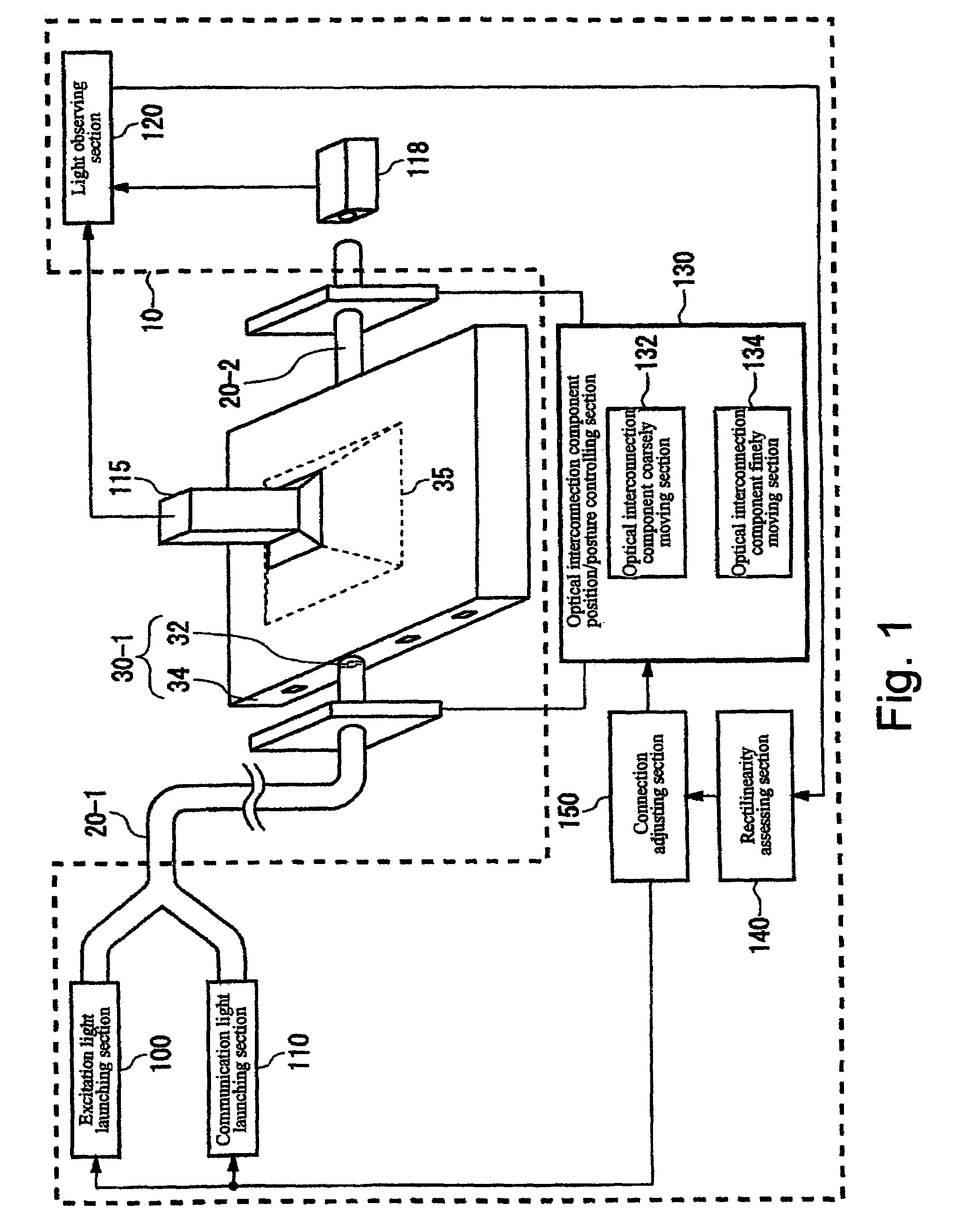
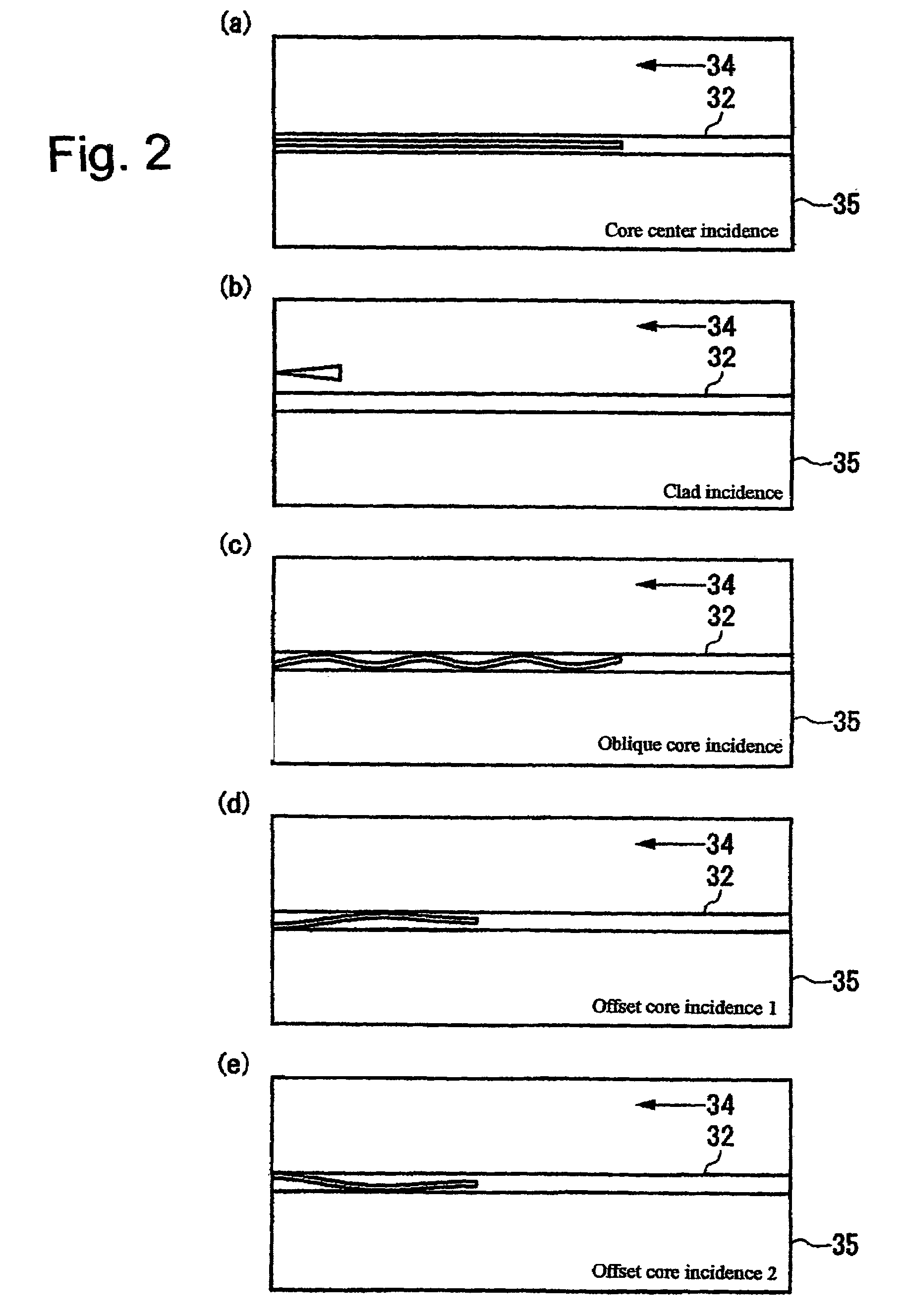
ActiveUS20060067625A1Increase in propagation lossLow optical precisionUsing optical meansCoupling light guidesFluorescent lightWaveguide
Apparatus and method which adjusts an optical connection between a waveguide and an optical interconnection component that launches light into the waveguide or receives light emitted from the waveguide. The apparatus includes: an excitation light element emitting light that causes the waveguide to fluoresce into the waveguide via the optical interconnection component; an observation unit that observes the waveguide from a side face, different from the end face into which light is launched into the waveguide or light having propagated through the waveguide is emitted, and which receives fluorescent light emitted by the waveguide; and a connection adjusting component that adjusts the optical connection between the optical interconnection component and the waveguide based on the intensity of the fluorescent light received at the light observing section.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com