Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
11314 results about "Intermediate frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
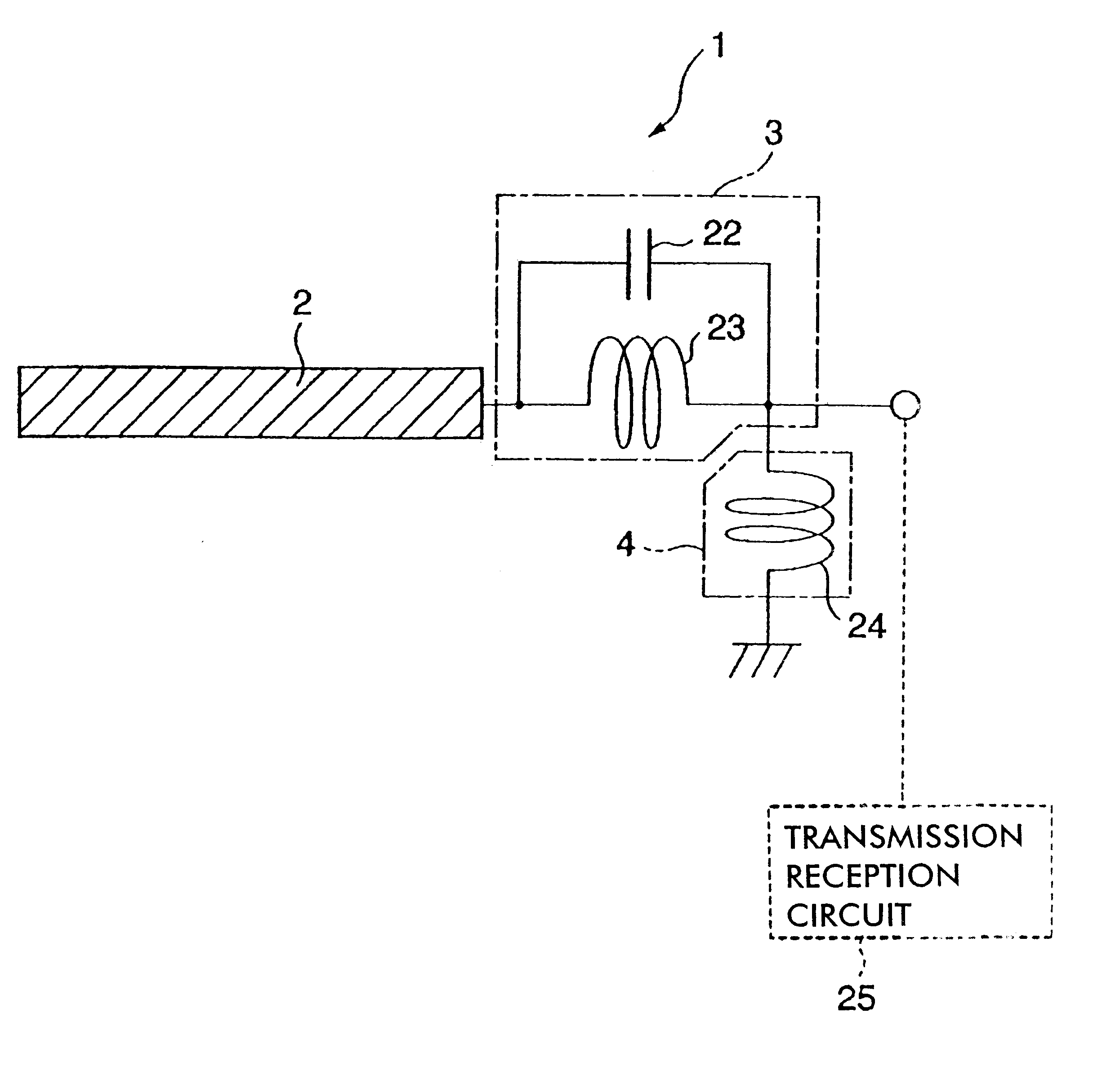
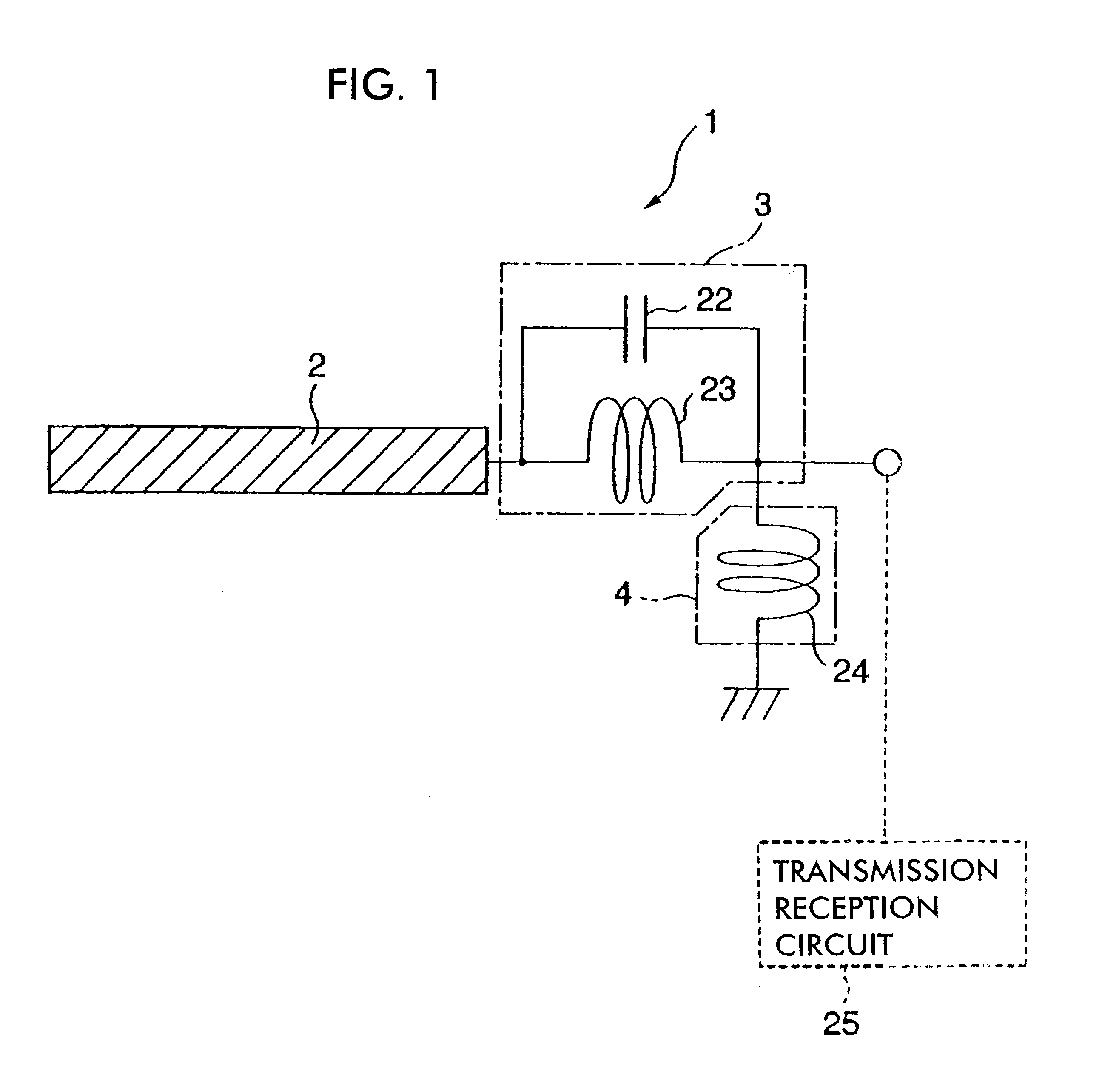
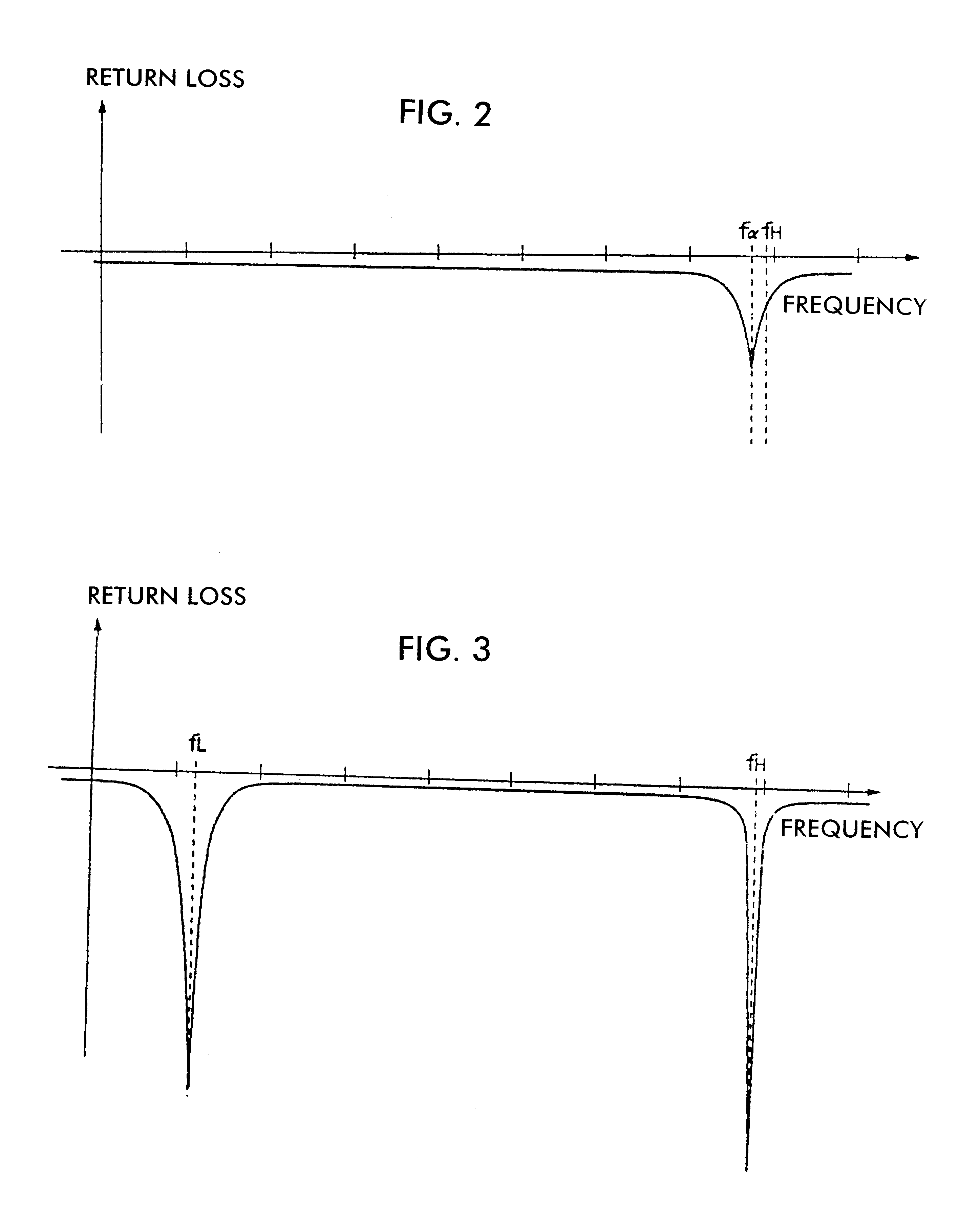
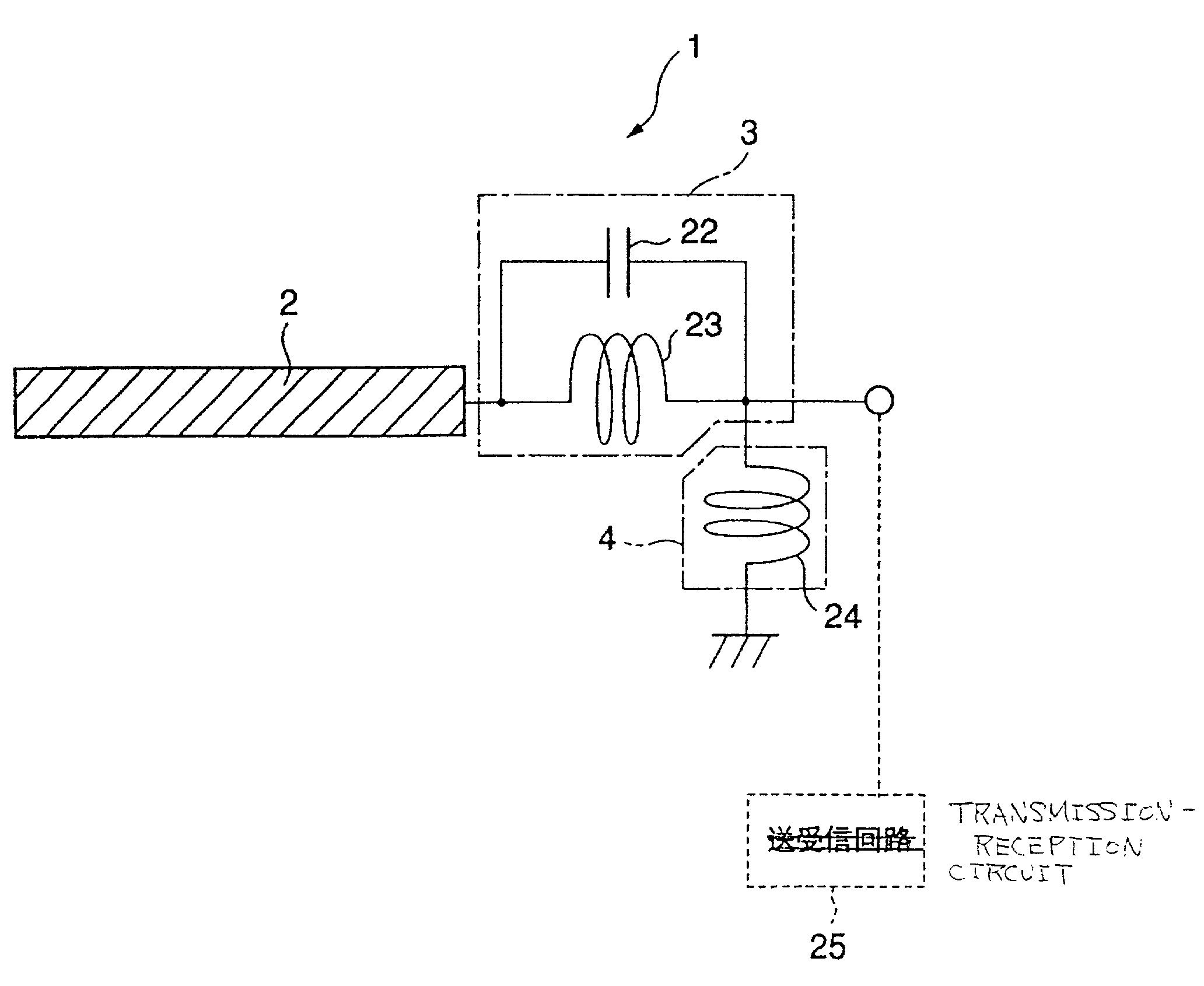
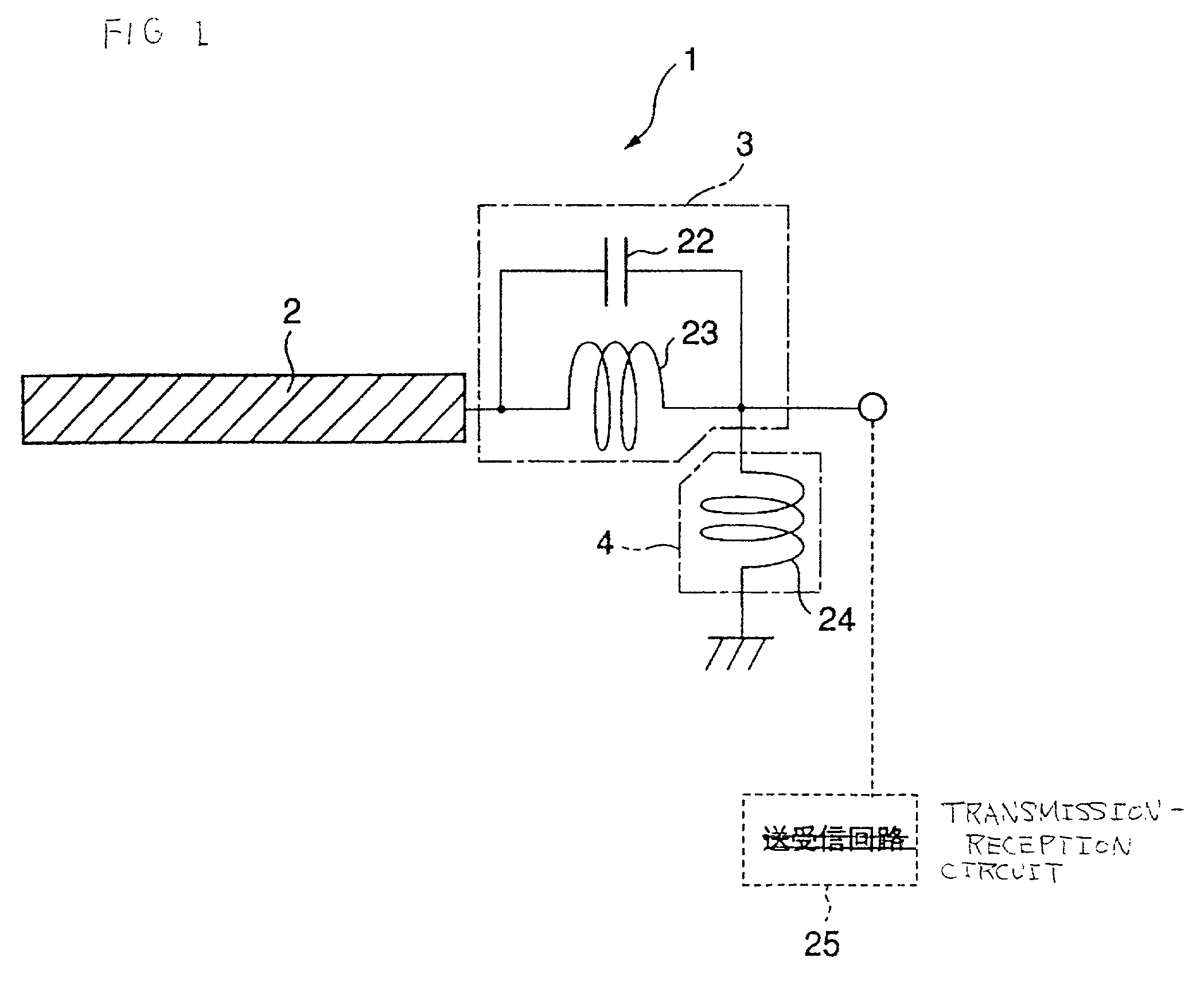
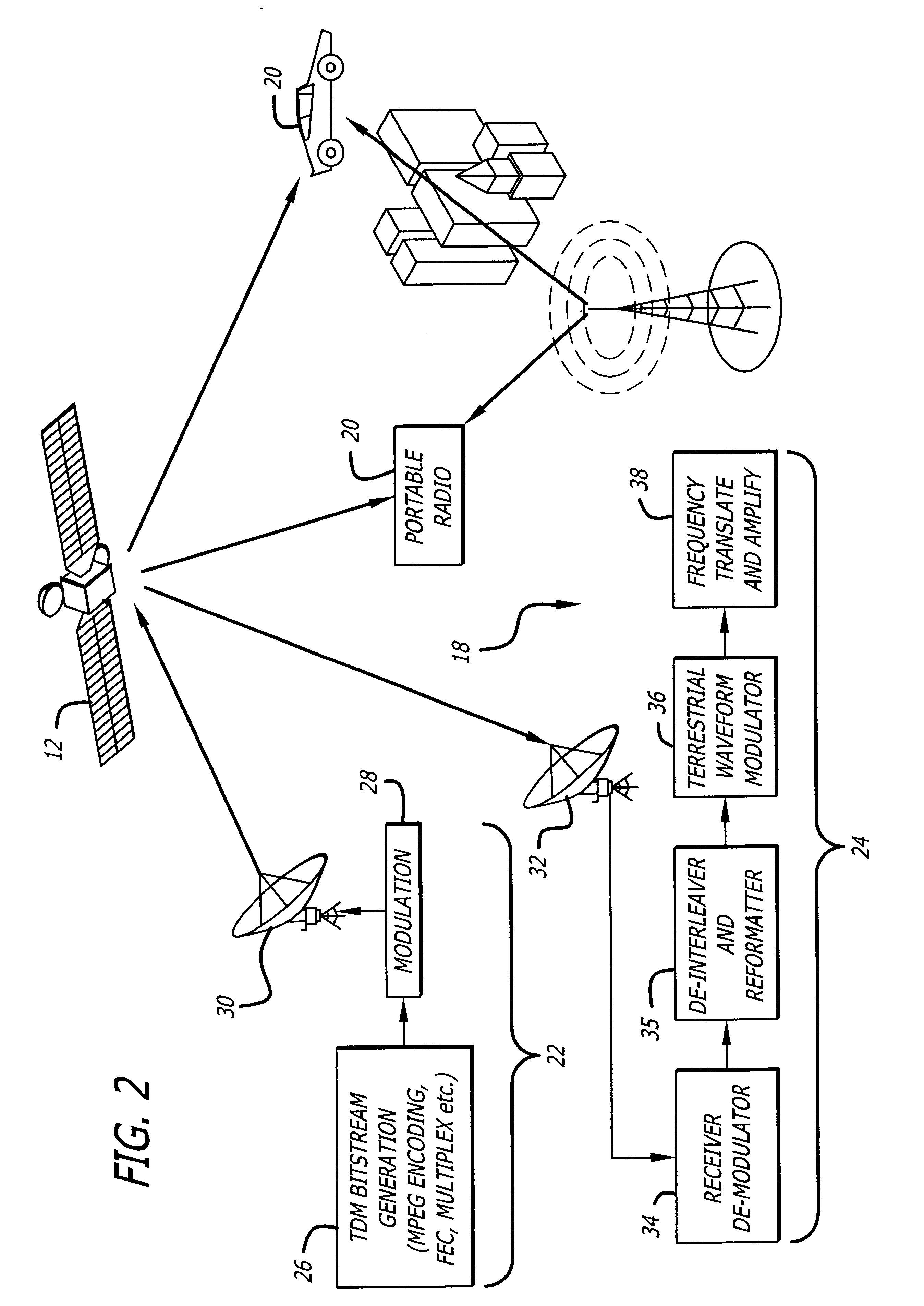
In communications and electronic engineering, an intermediate frequency (IF) is a frequency to which a carrier wave is shifted as an intermediate step in transmission or reception. The intermediate frequency is created by mixing the carrier signal with a local oscillator signal in a process called heterodyning, resulting in a signal at the difference or beat frequency. Intermediate frequencies are used in superheterodyne radio receivers, in which an incoming signal is shifted to an IF for amplification before final detection is done.
Methods for driving electrophoretic displays using dielectrophoretic forces
InactiveUS20080136774A1Significant energy savingStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsElectrical conductorIntermediate frequency
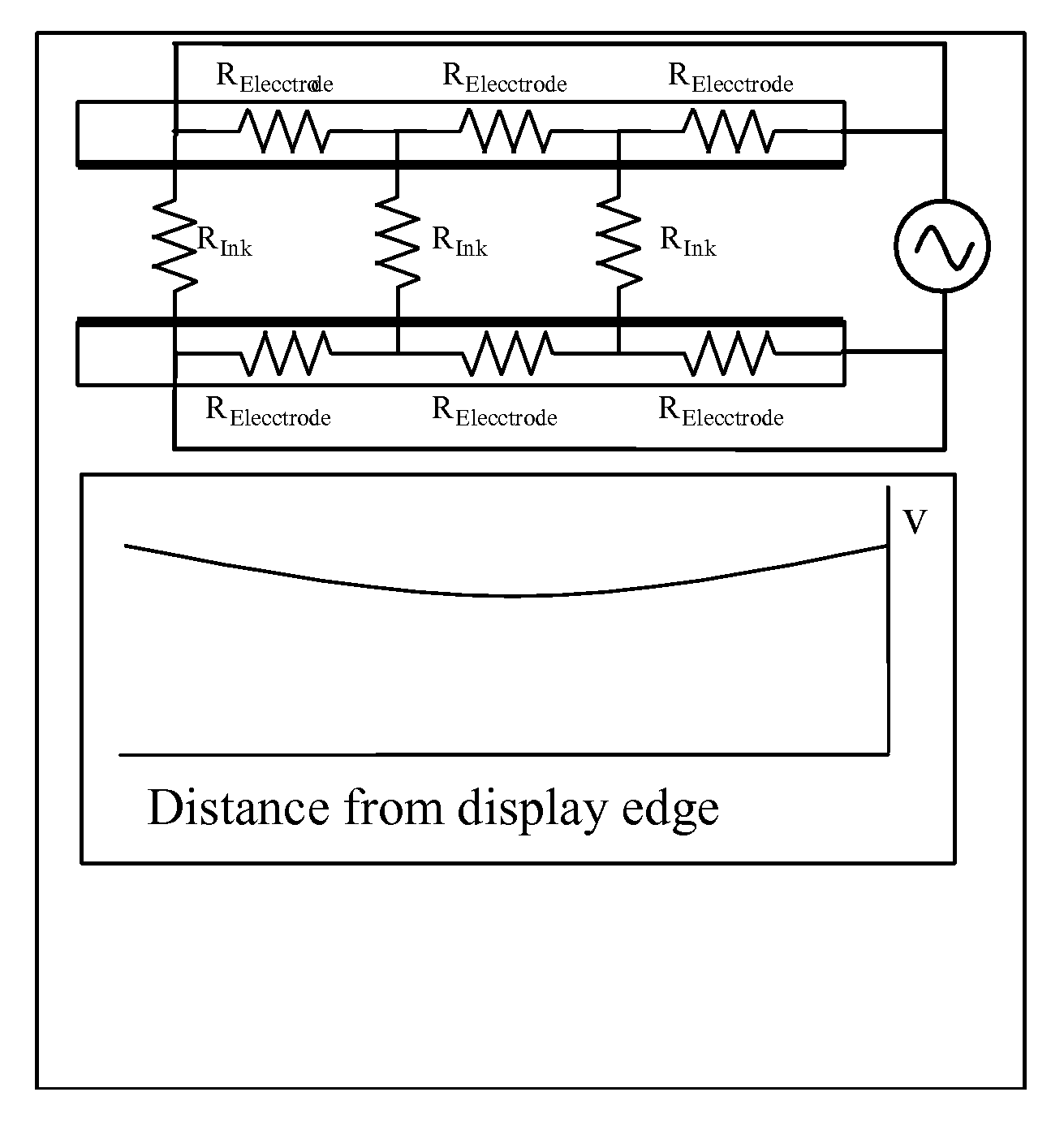
A dielectrophoretic display is shifted from a low frequency closed state to a high frequency open state via at least one, and preferably several, intermediate frequency states; the use of such multiple frequency steps reduces flicker during the transition. A second type of dielectrophoretic display has a light-transmissive electrode through which the dielectrophoretic medium can be viewed and a conductor connected to the light-transmissive electrode at several points to reduce voltage variations within the light-transmissive electrode.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Method and system for down-converting electromagnetic signals
InactiveUS6061551AResonant long antennasModulation transferenceIntermediate frequencyElectromagnetic shielding
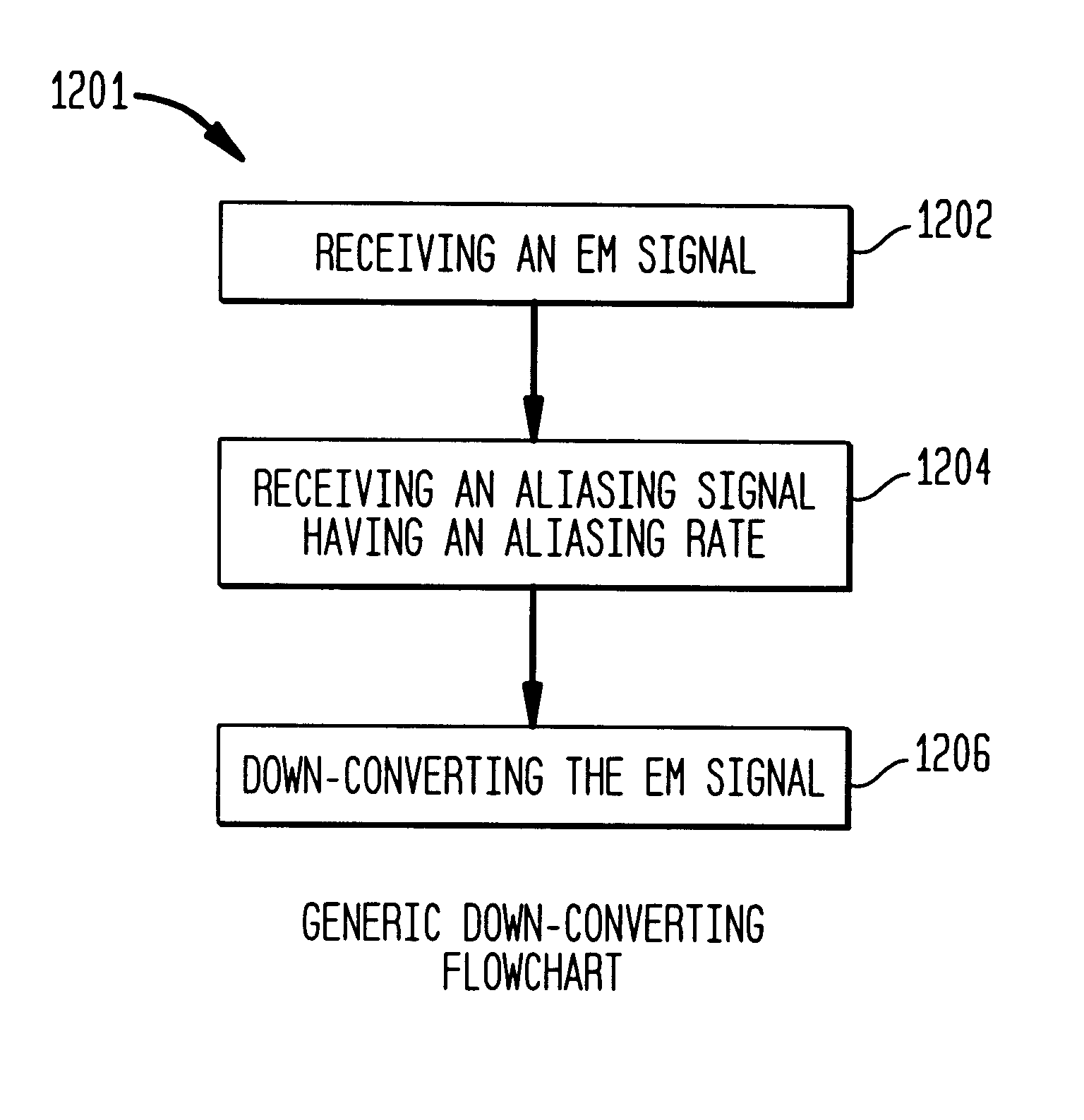
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for down-converting an electromagnetic (EM) signal by aliasing the EM signal are described herein. Briefly stated, such methods, systems, and apparatuses operate by receiving an EM signal and an aliasing signal having an aliasing rate. The EM signal is aliased according to the aliasing signal to down-convert the EM signal. The term aliasing, as used herein, refers to both down-converting an EM signal by under-sampling the EM signal at an aliasing rate, and down-converting an EM signal by transferring energy from the EM signal at the aliasing rate. In an embodiment, the EM signal is down-converted to an intermediate frequency (IF) signal. In another embodiment, the EM signal is down-converted to a demodulated baseband information signal. In another embodiment, the EM signal is a frequency modulated (FM) signal, which is down-converted to a non-FM signal, such as a phase modulated (PM) signal or an amplitude modulated (AM) signal.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
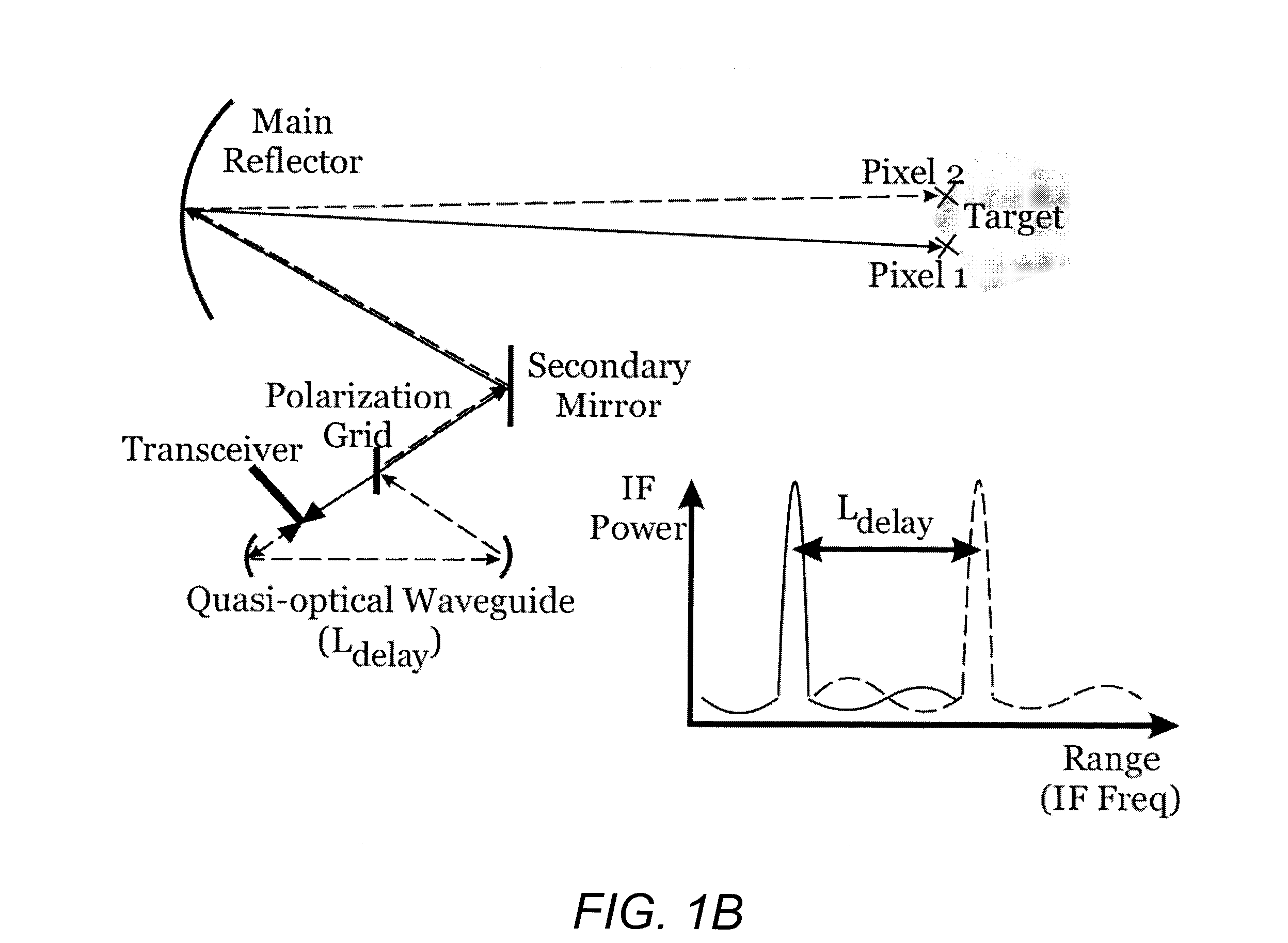
Multi-pixel high-resolution three-dimensional imaging radar
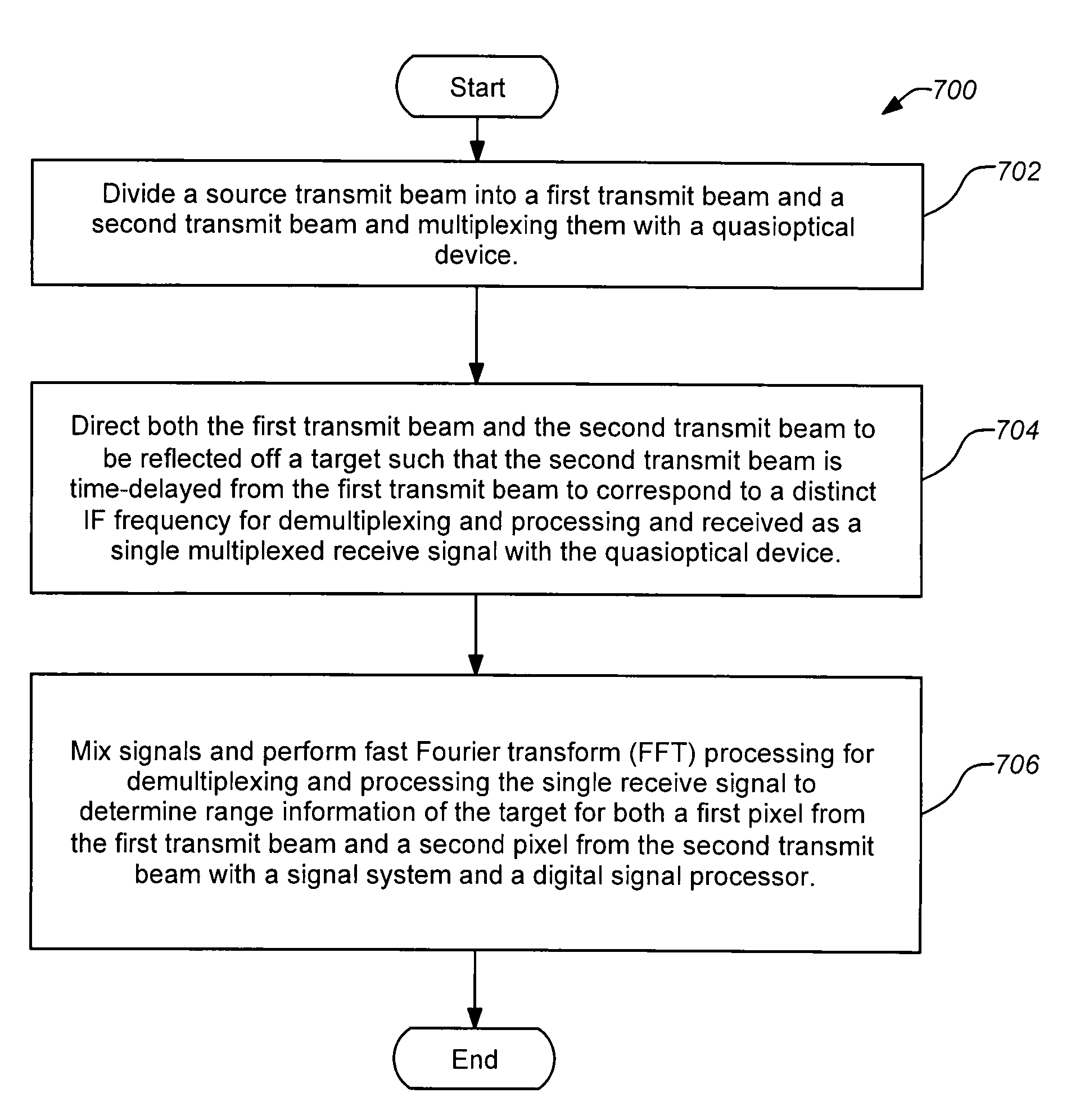
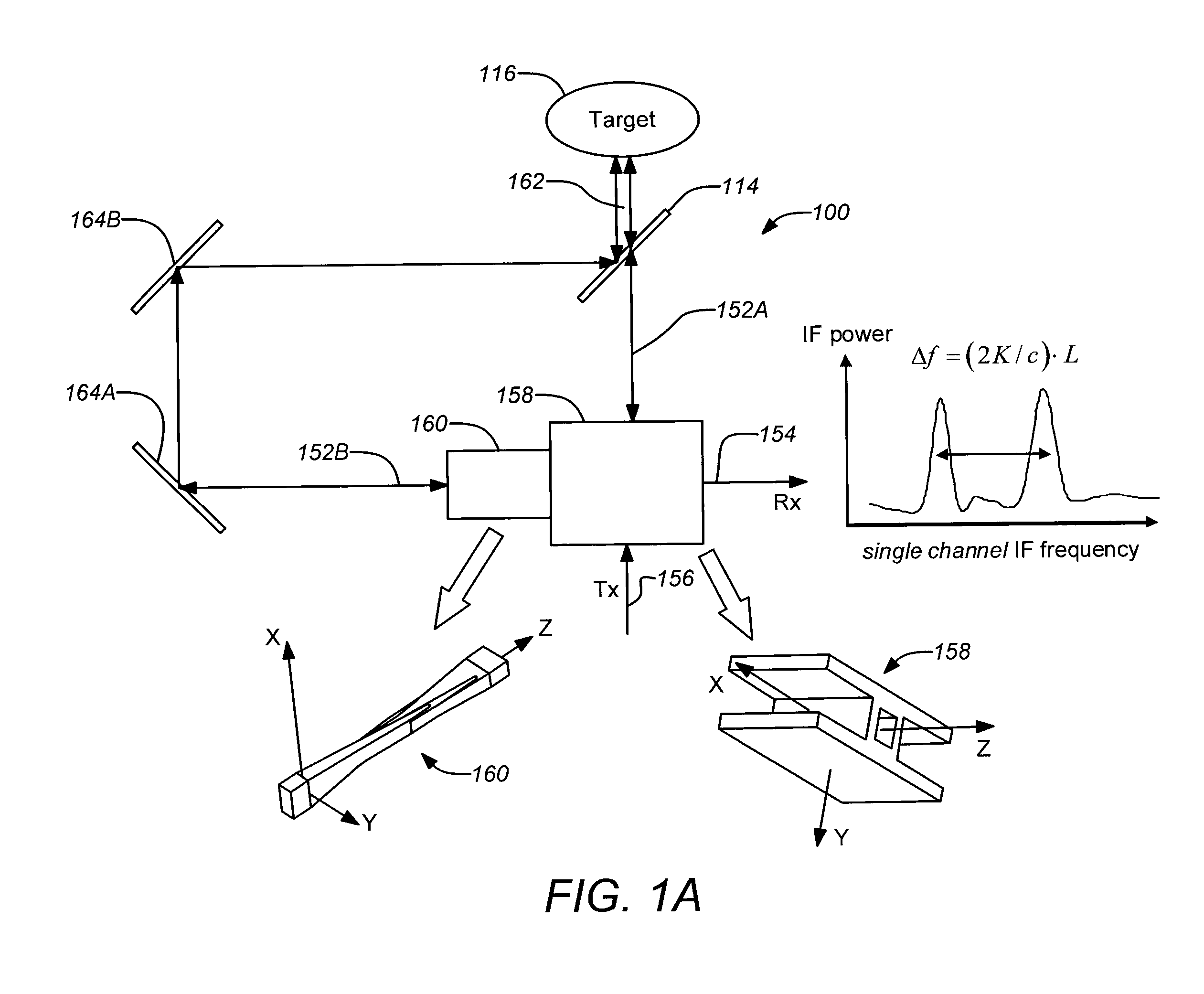
A three-dimensional imaging radar operating at high frequency e.g., 670 GHz radar using low phase-noise synthesizers and a fast chirper to generate a frequency-modulated continuous-wave (FMCW) waveform, is disclosed that operates with a multiplexed beam to obtain range information simultaneously on multiple pixels of a target. A source transmit beam may be divided by a hybrid coupler into multiple transmit beams multiplexed together and directed to be reflected off a target and return as a single receive beam which is demultiplexed and processed to reveal range information of separate pixels of the target associated with each transmit beam simultaneously. The multiple transmit beams may be developed with appropriate optics to be temporally and spatially differentiated before being directed to the target. Temporal differentiation corresponds to a different intermediate frequencies separating the range information of the multiple pixels. Collinear transmit beams having differentiated polarizations may also be implemented.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
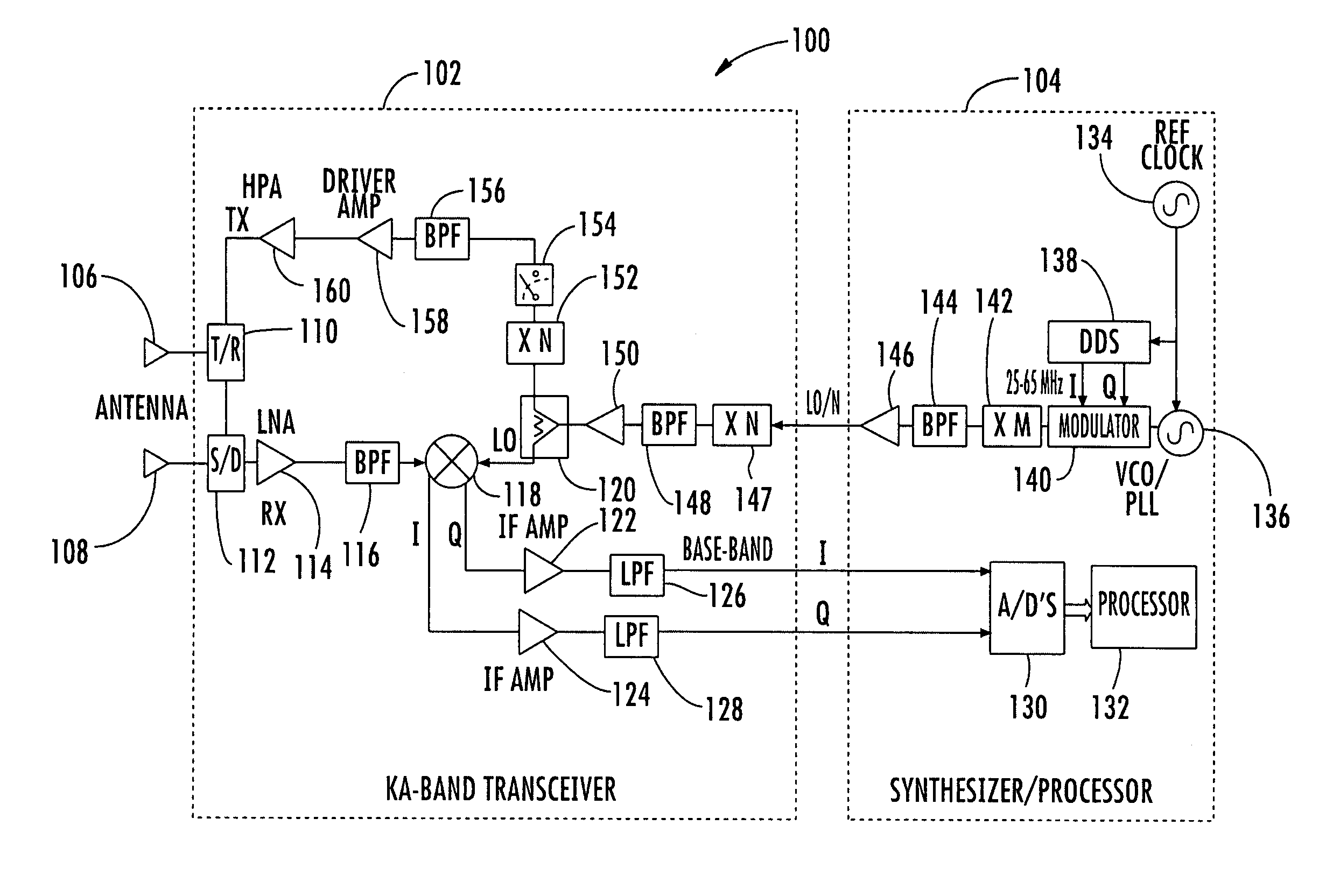
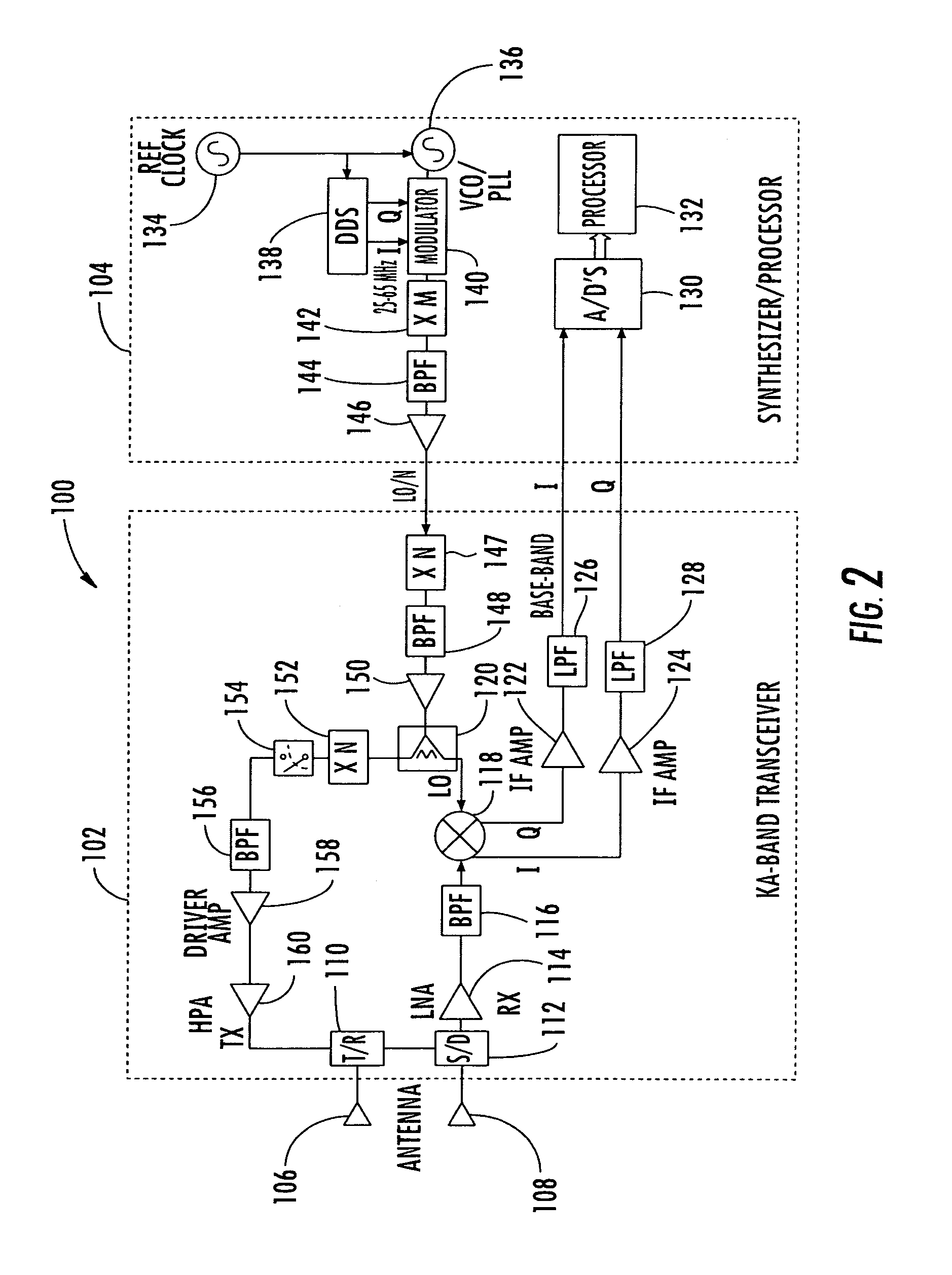
Millimeter wave pulsed radar system
InactiveUS7002511B1Improve efficiencySimplified frequency synthesizer designRadio wave reradiation/reflectionQuadrature modulatorLocal oscillator signal
A millimeter wave pulsed radar system includes a radar synthesizer having a voltage controlled oscillator / phase locked loop (VCO / PLL) circuit, direct digital synthesizer (DDS) circuit and quadrature modulator circuit that are operative to generate an intermediate frequency local oscillator signal (IF / LO signal). A radar transceiver is operative with the radar synthesizer for receiving the IF / LO signal. A transmitter section has a frequency multiplier that multiplies the IF / LO signal up to a millimeter wave (MMW) radar signal and a receiver section and includes a direct conversion mixer that receives a MMW radar signal and the IF / LO signal to produce I / Q baseband signals that are later digitized and processed.
Owner:REVEAL IMAGING
Antenna device and radio equipment having the same
InactiveUS6462716B1Simple circuit configurationReduce conduction lossMultiple-port networksSimultaneous aerial operationsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Antenna device and radio equipment having the same
InactiveUS20020044092A1Simple circuit configurationReduce conduction lossMultiple-port networksSimultaneous aerial operationsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
An LC parallel resonance circuit is connected in series with the power supply side of the antenna conductor portion. The antenna conductor portion is configured so as to resonate at a frequency slightly lower than the center frequency in the higher frequency band of two frequency bands for transmitting and receiving radio waves. The LC parallel resonance circuit is configured so as to resonate substantially at the center frequency in the lower frequency band for transmitting and receiving a radio wave and be capable of providing to the antenna conductor portion a capacitance for causing the antenna conductor portion to resonate at the center frequency in the higher frequency band. Thus, a circuit for changing the upper and lower frequency bands is not needed. Such a change-over circuit, which is complicated, causes problems in that the conduction loss increases, and the antenna sensitivity deteriorates. Without need of the change-over circuit, the conduction loss can be reduced, the antenna sensitivity can be enhanced and costs can be reduced.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
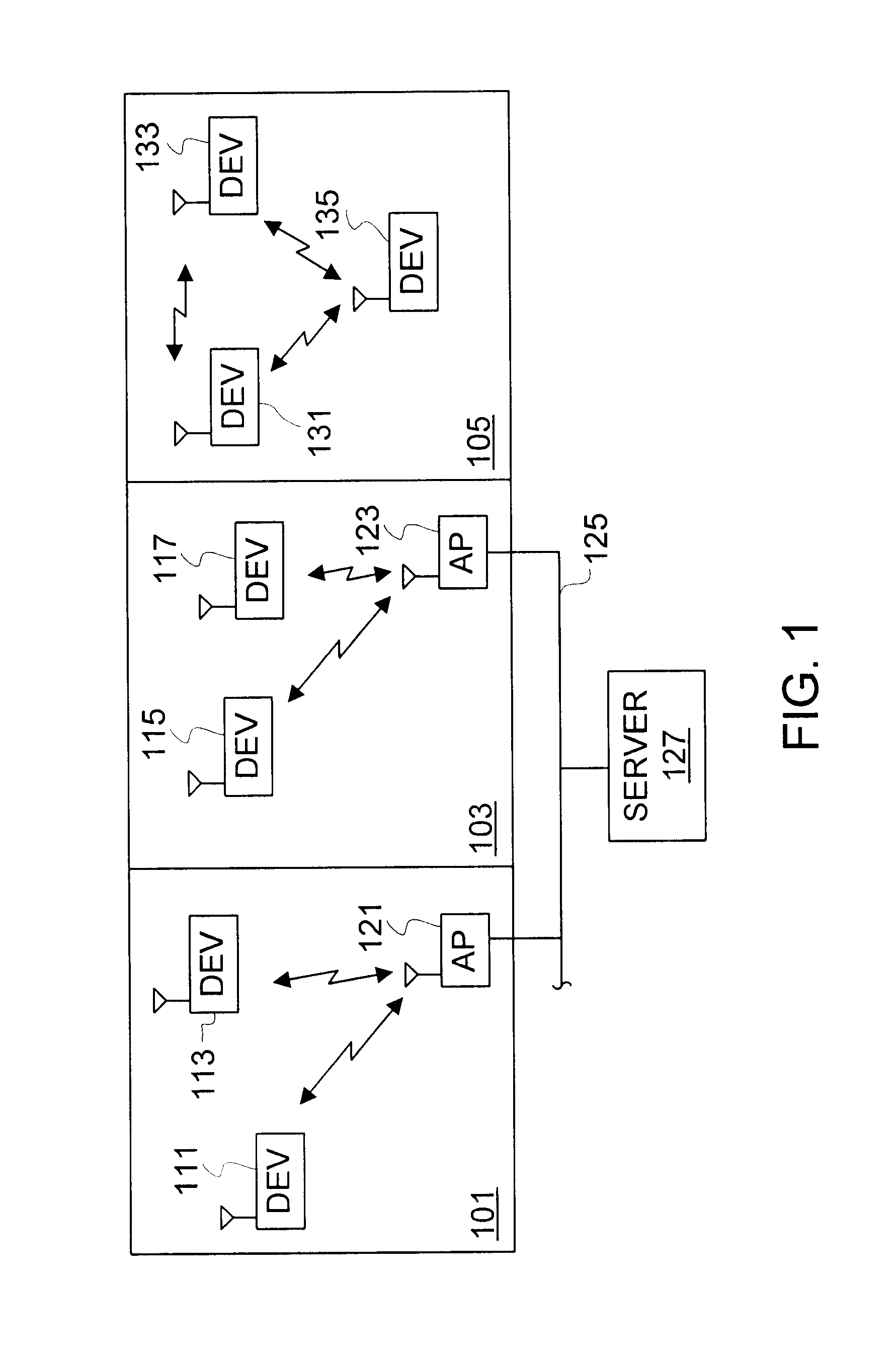
Packet acquisition and channel tracking for a wireless communication device configured in a zero intermediate frequency architecture
A method of controlling operation of a wireless device configured in a zero intermediate frequency architecture including a DC loop and a gain loop. The method includes processing energy in a wireless medium to generate a corresponding receive signal, monitoring the receive signal via a predetermined measurement window, detecting a changed condition in the channel, holding the gain feedback control loop at a constant gain level, and operating the DC loop in an attempt to search a stable DC value for the receive signal while the gain loop is held constant. A first case is DC saturation, where the gain is held constant until DC is controlled. A second case is clear channel assessment, where a prior stored gain setting is applied to the gain loop after detecting the end of the packet. A third case is preparation for receiving an expected acknowledgement packet after transmitting a packet, where again a prior stored gain setting is applied to the gain loop and DC is searched.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Multi-sector in-building repeater
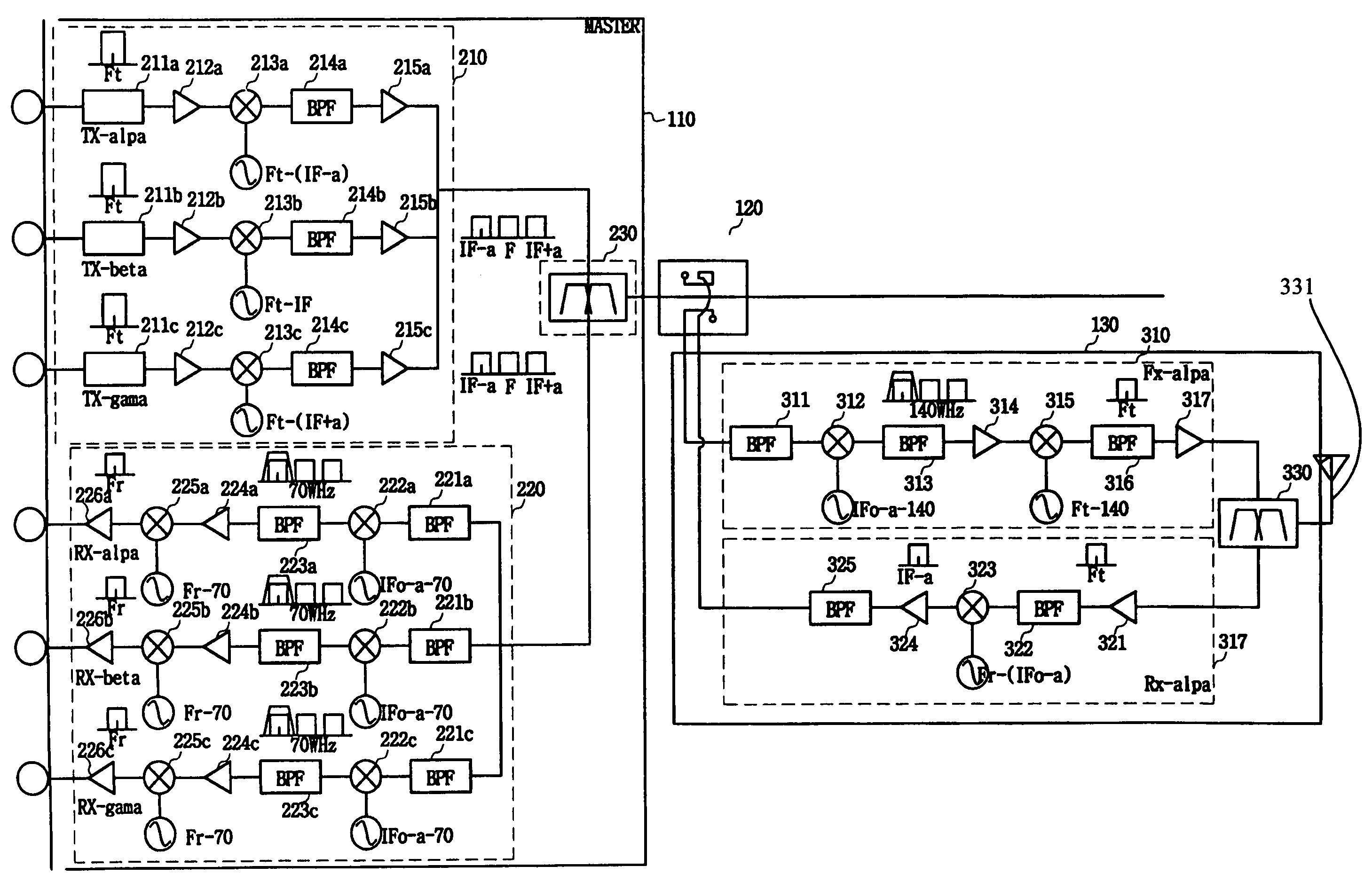
InactiveUS7272362B2Maximize transfer efficiencyHigh frequencyPower distribution line transmissionRepeater/relay circuitsIntermediate frequencyCarrier signal
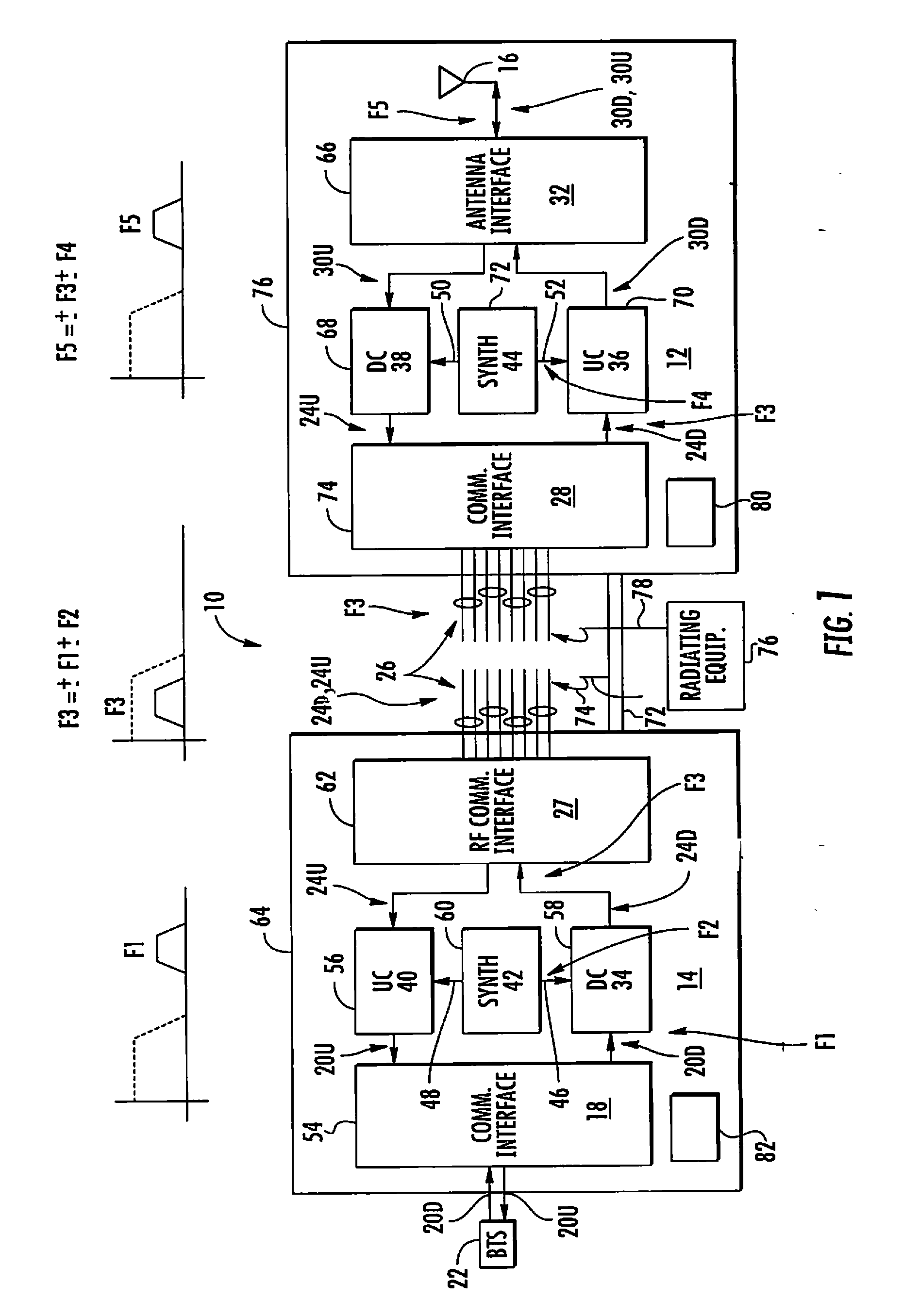
A multi-sector in-building repeater, including: a master transmitting unit for receiving multi-sector signals of a carrier from a base station, mixing the multi-sector signals with different transmission intermediate frequency signals, and outputting mixed multi-sector signals to a same transmission line; a plurality of slave transmitting units for extracting sector signals assigned to the multi-sector signals from the master transmitting unit, converting extracted sector signals into high frequency signals, and transmitting converted high frequency signals through an antenna to a mobile terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
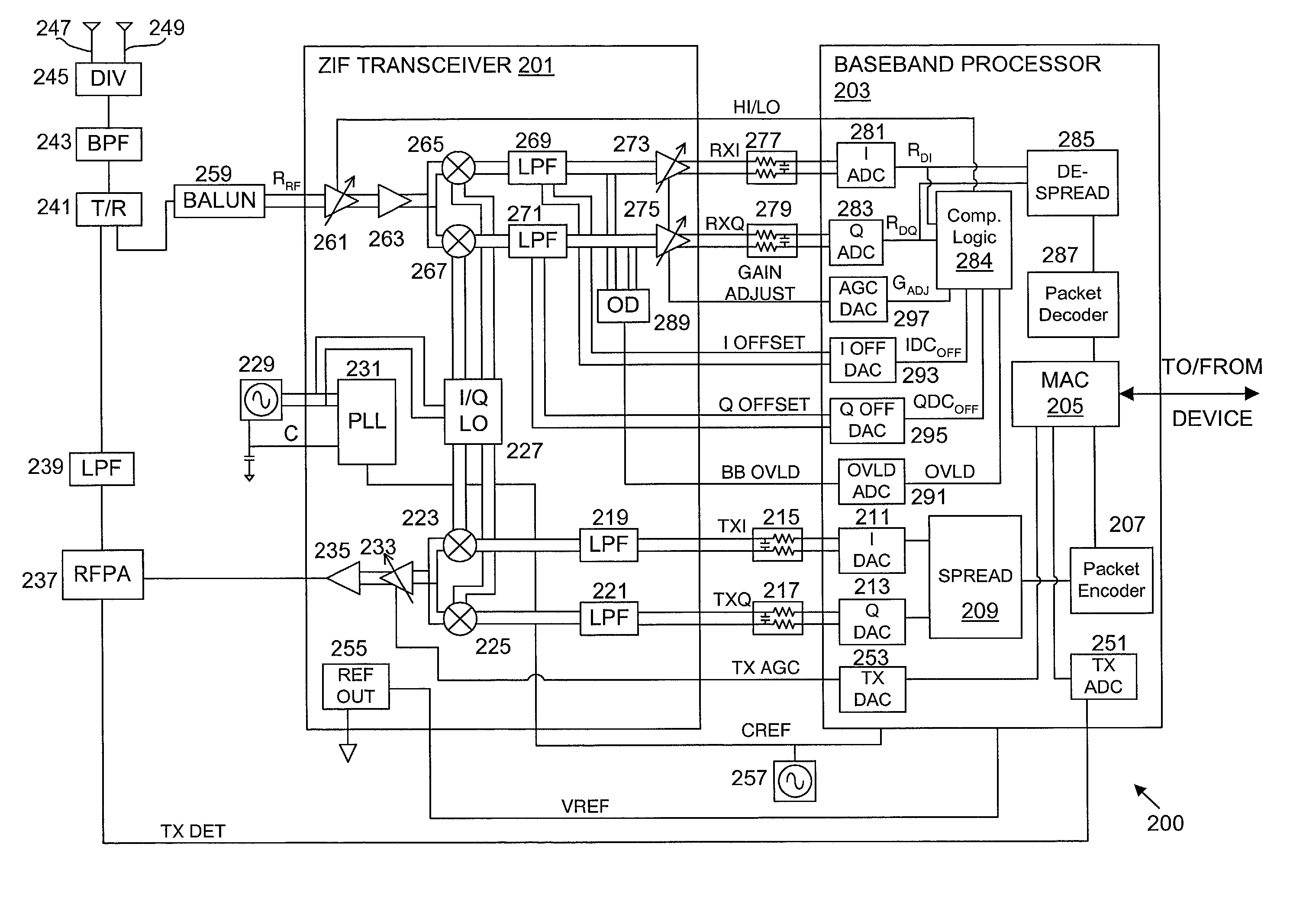
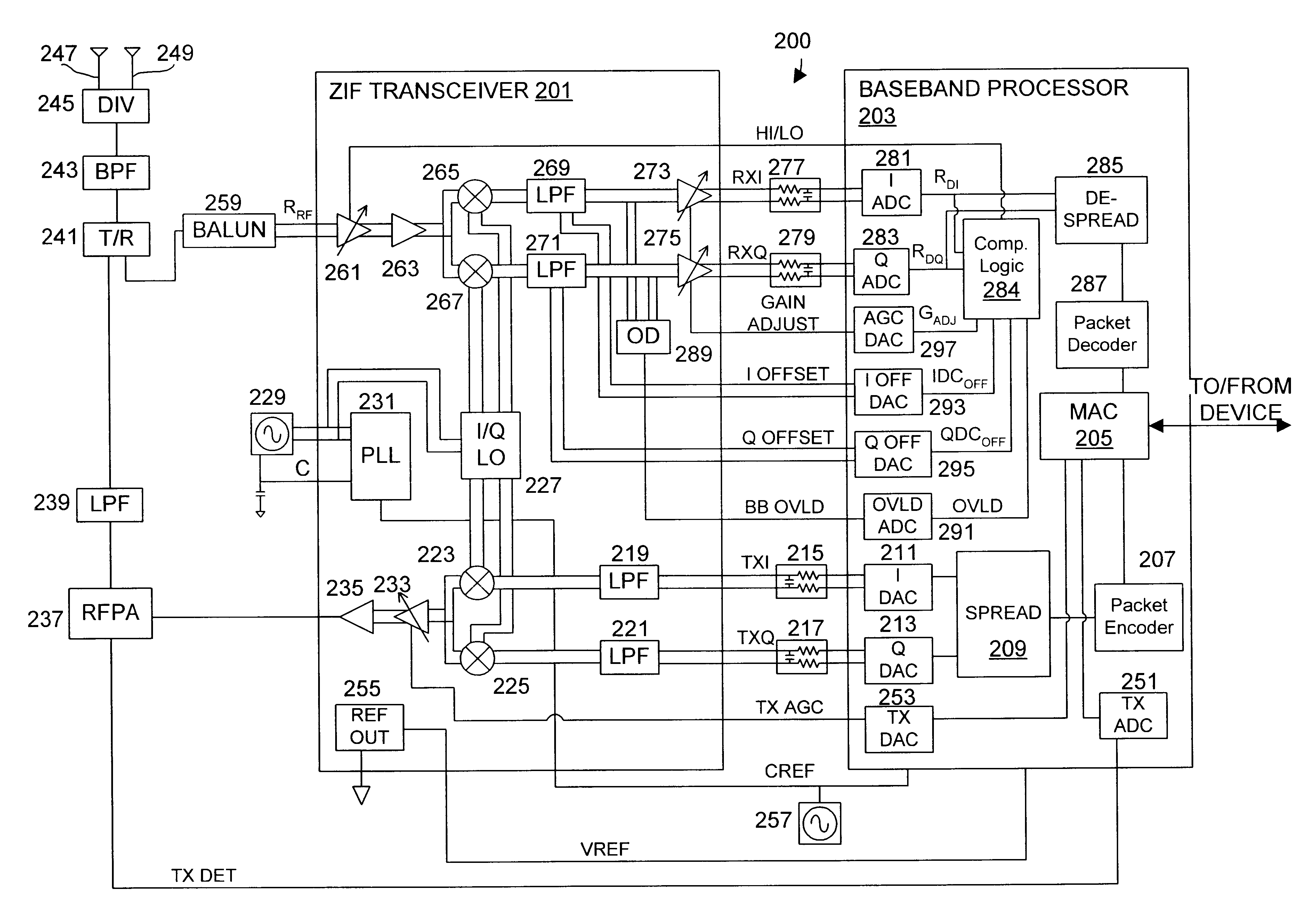
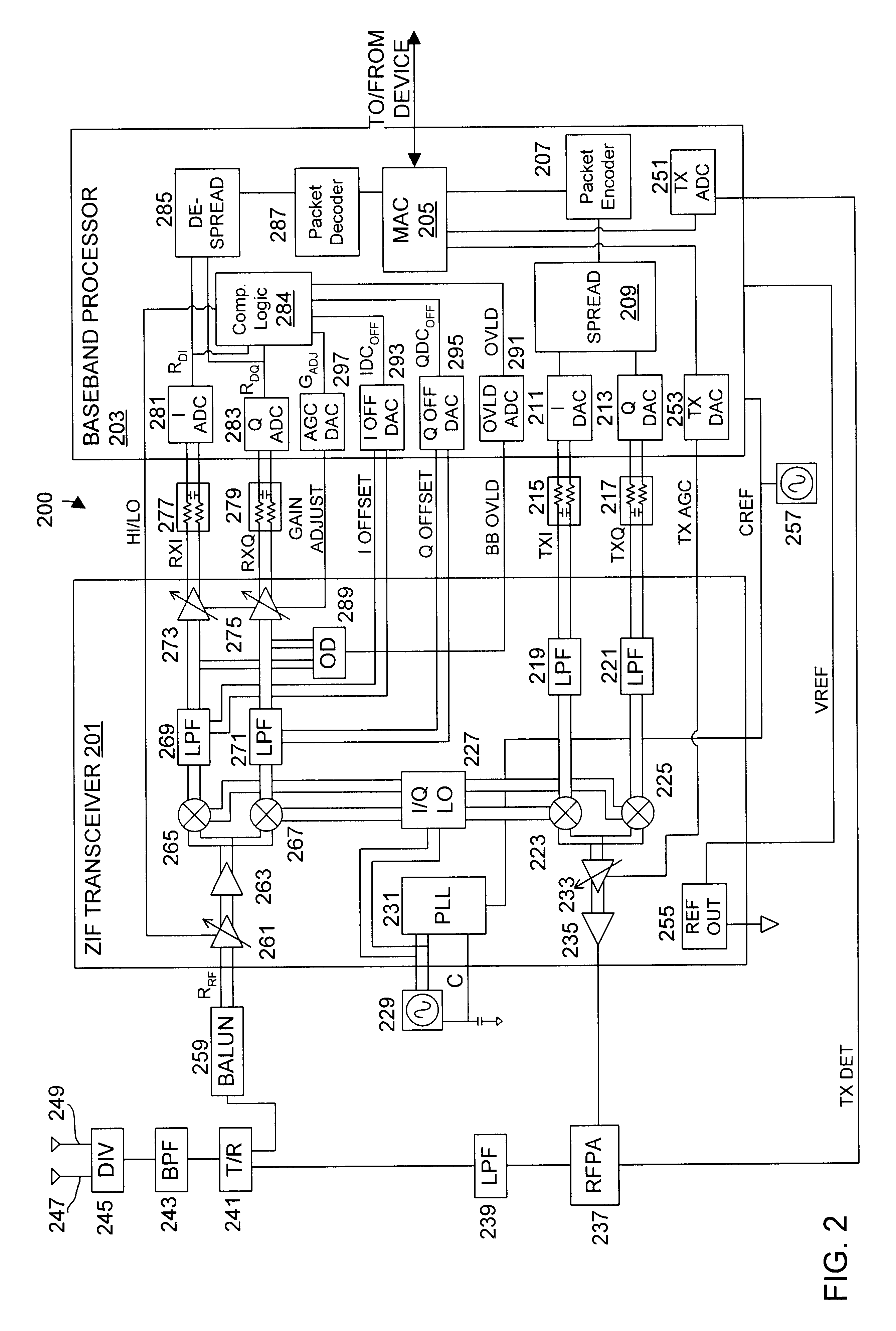
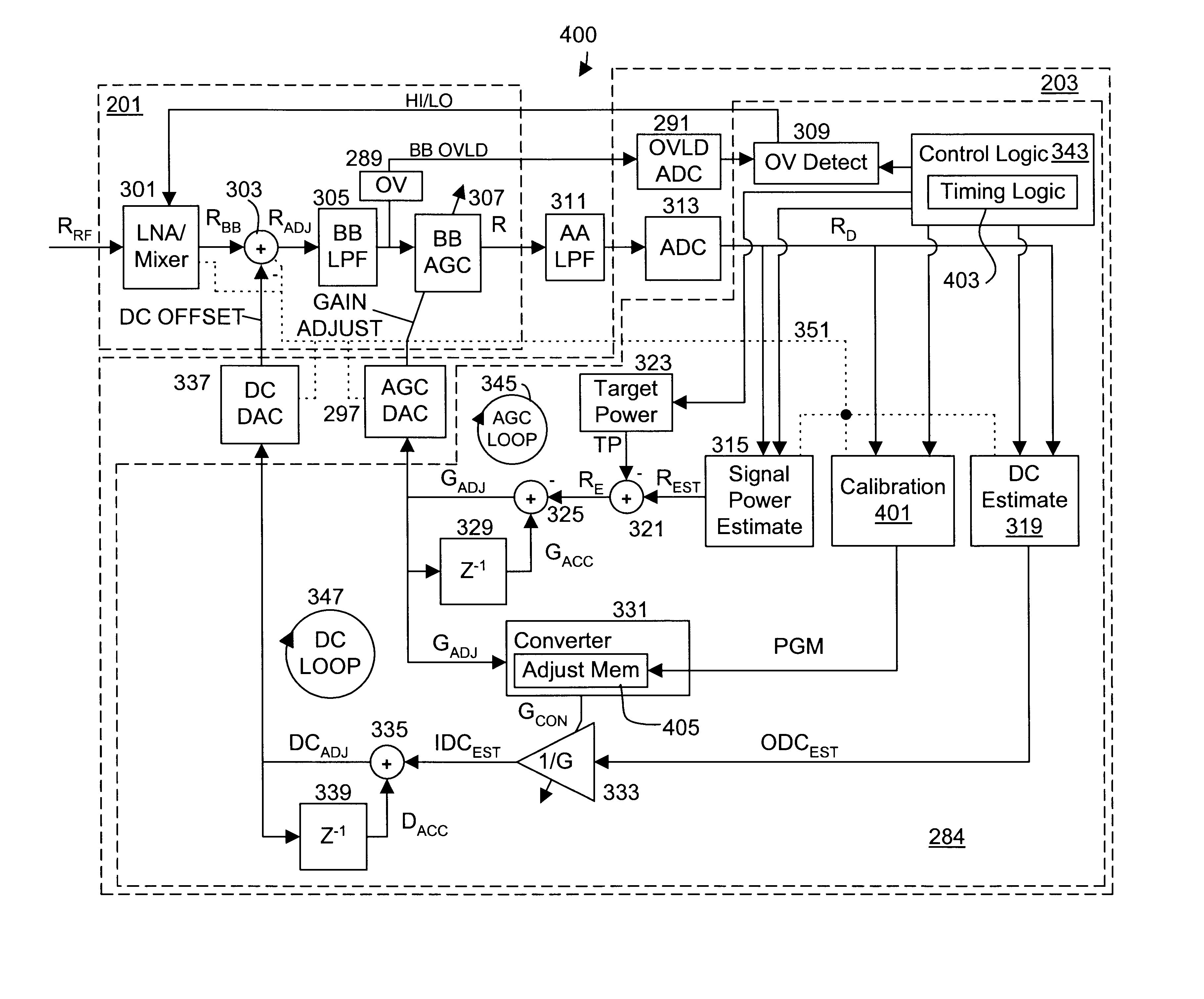
DC compensation system for a wireless communication device configured in a zero intermediate frequency architecture
InactiveUS6560448B1Low costMaximum performanceGain controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransceiverAudio power amplifier
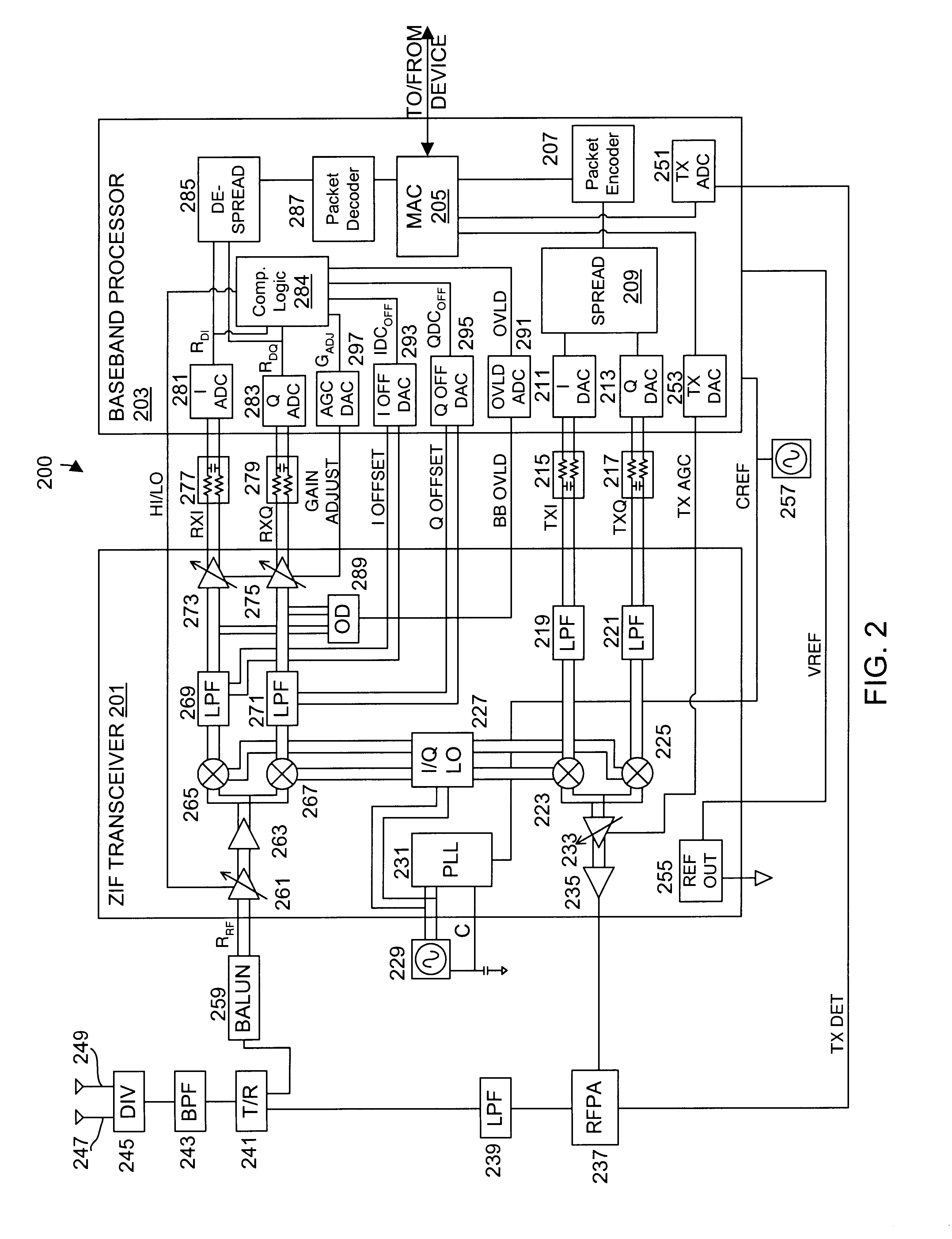
A wireless communication device including a radio frequency (RF) circuit, a ZIF transceiver and a baseband processor. The ZIF transceiver includes an RF mixer circuit that converts the RF signal to a baseband input signal, a summing junction that subtracts a DC offset from the baseband input signal to provide an adjusted baseband input signal, and a baseband amplifier that receives the adjusted baseband input signal and that asserts an amplified input signal based on a gain adjust signal. The baseband processor includes gain control logic, DC control logic and a gain interface. The gain control logic receives the amplified input signal, estimates input signal power and asserts the gain adjust signal in an attempt to keep the input signal power at a target power level. The DC control logic estimates an amount of DC in the amplified input signal and provides the DC offset in an attempt to reduce DC in the amplified input signal. The gain interface converts gain levels between the gain control logic and the DC control logic. The RF signal may include in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) portions, where the RF mixer circuit splits I and Q baseband input signals from the RF signal. Operation is substantially identical for both I and Q channels. The DC control logic operates to remove or otherwise eliminate DC from the received signal that is provided to decoders in the baseband processor.
Owner:M RED INC
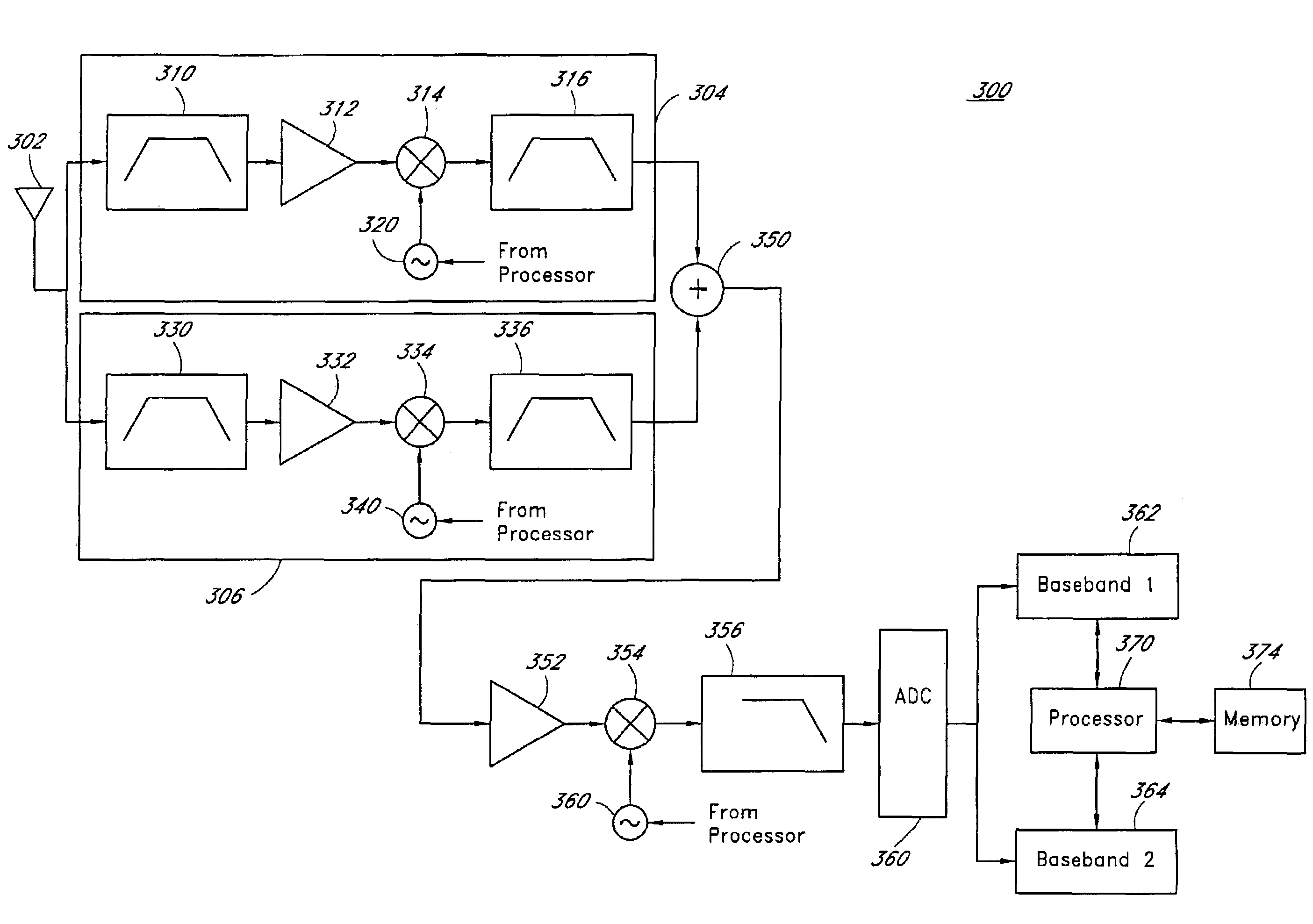
Shared receive path for simultaneous received signals
A method and apparatus are disclosed for a wireless communication device to simultaneously receive at least two signals. Two receiver portions are provided in the wireless communication device. A first receiver portion is configured to receive a first communication signal. A second receiver portion is configured to receive a second communication signal. The two receiver portions are configured to convert the first and second communication signals to a common frequency band. The common frequency band may be an intermediate frequency band or baseband frequency band. The converted first and second communication signals are combined in the common frequency band using an adder or other signal combiner. The combined signal is processed in a single signal processor. The communication device is able to resolve each of the received signals when the first communication signal is a narrowband signal and the second communication signal is a wideband signal, such as a spread spectrum signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
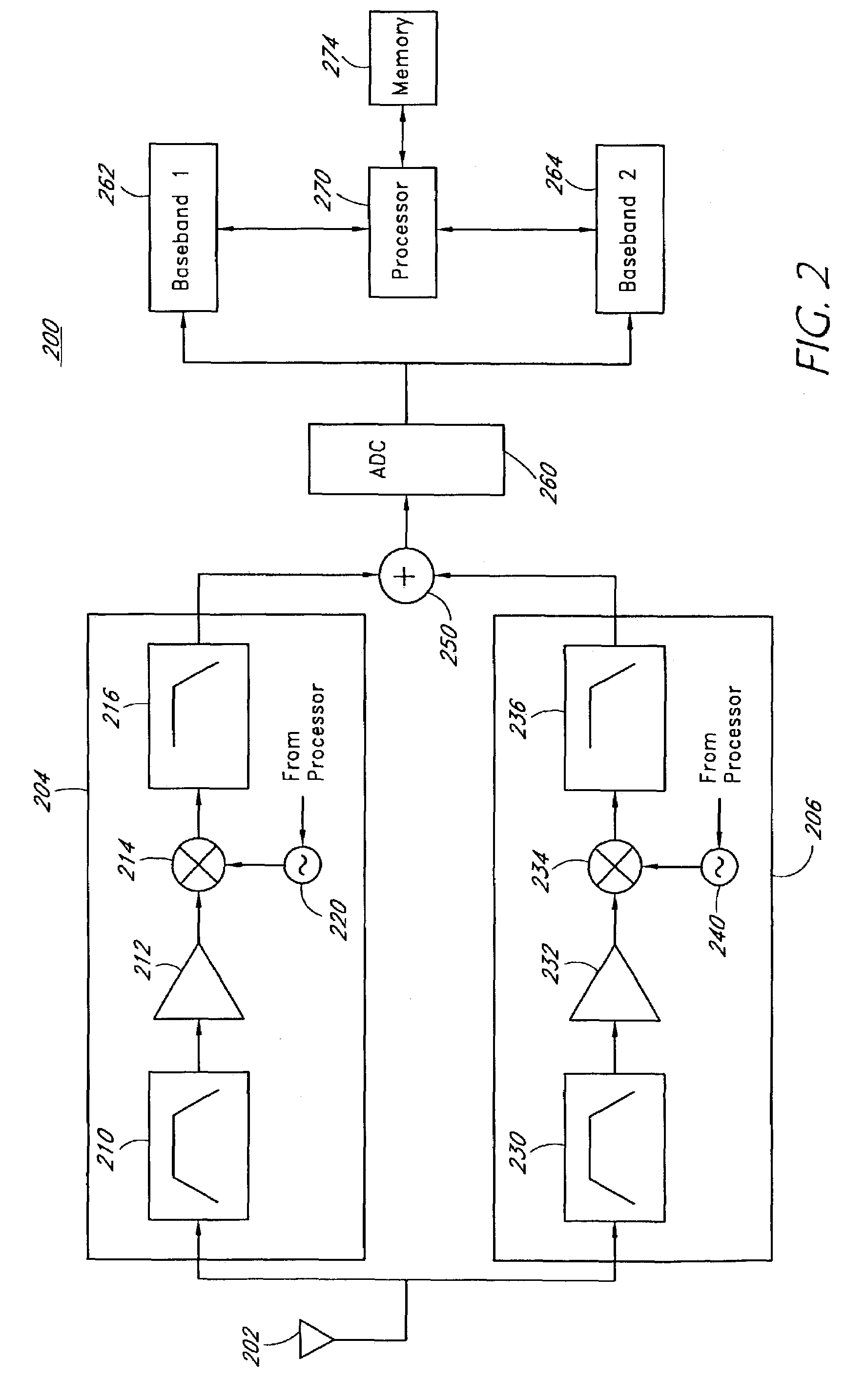
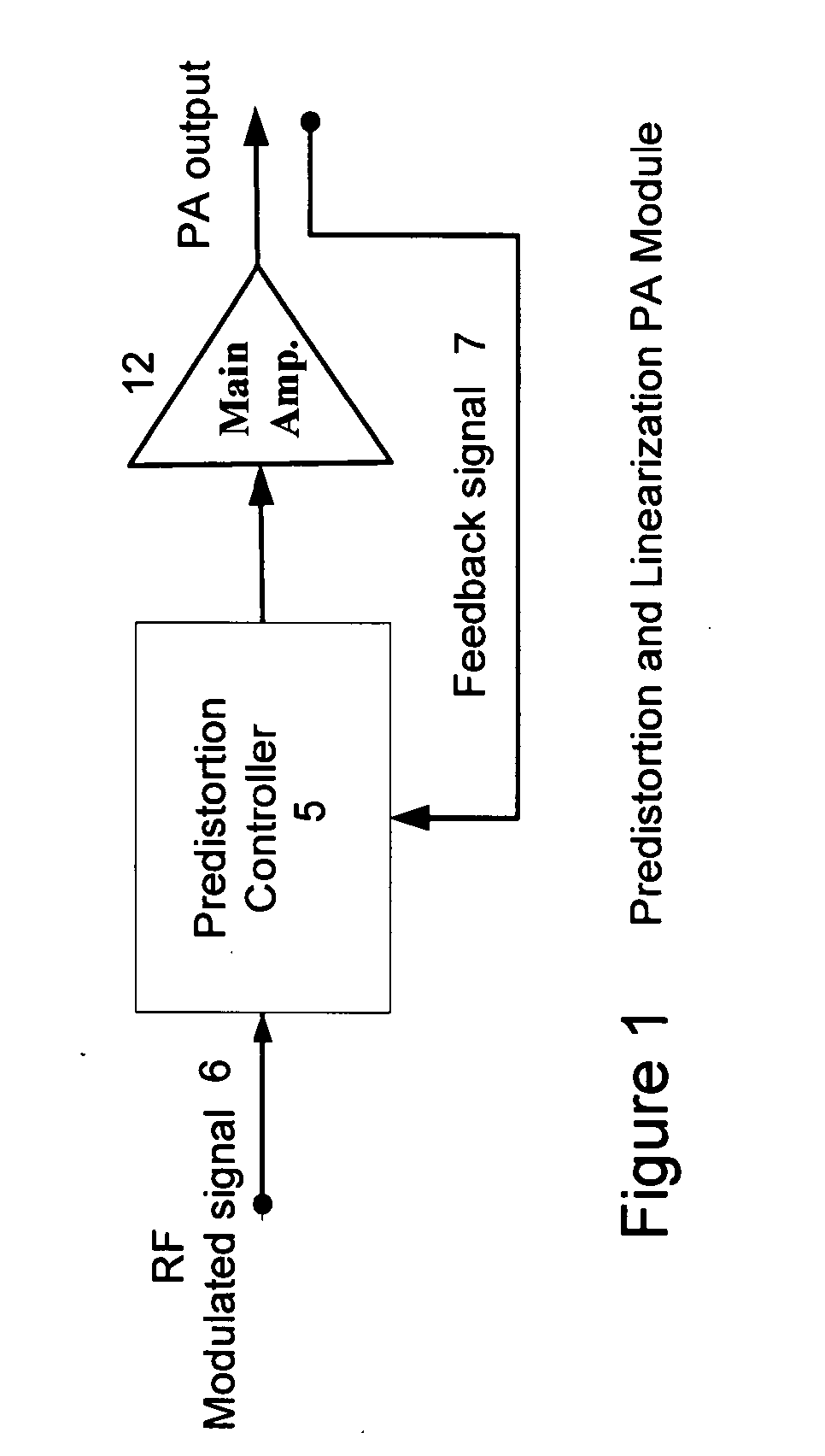
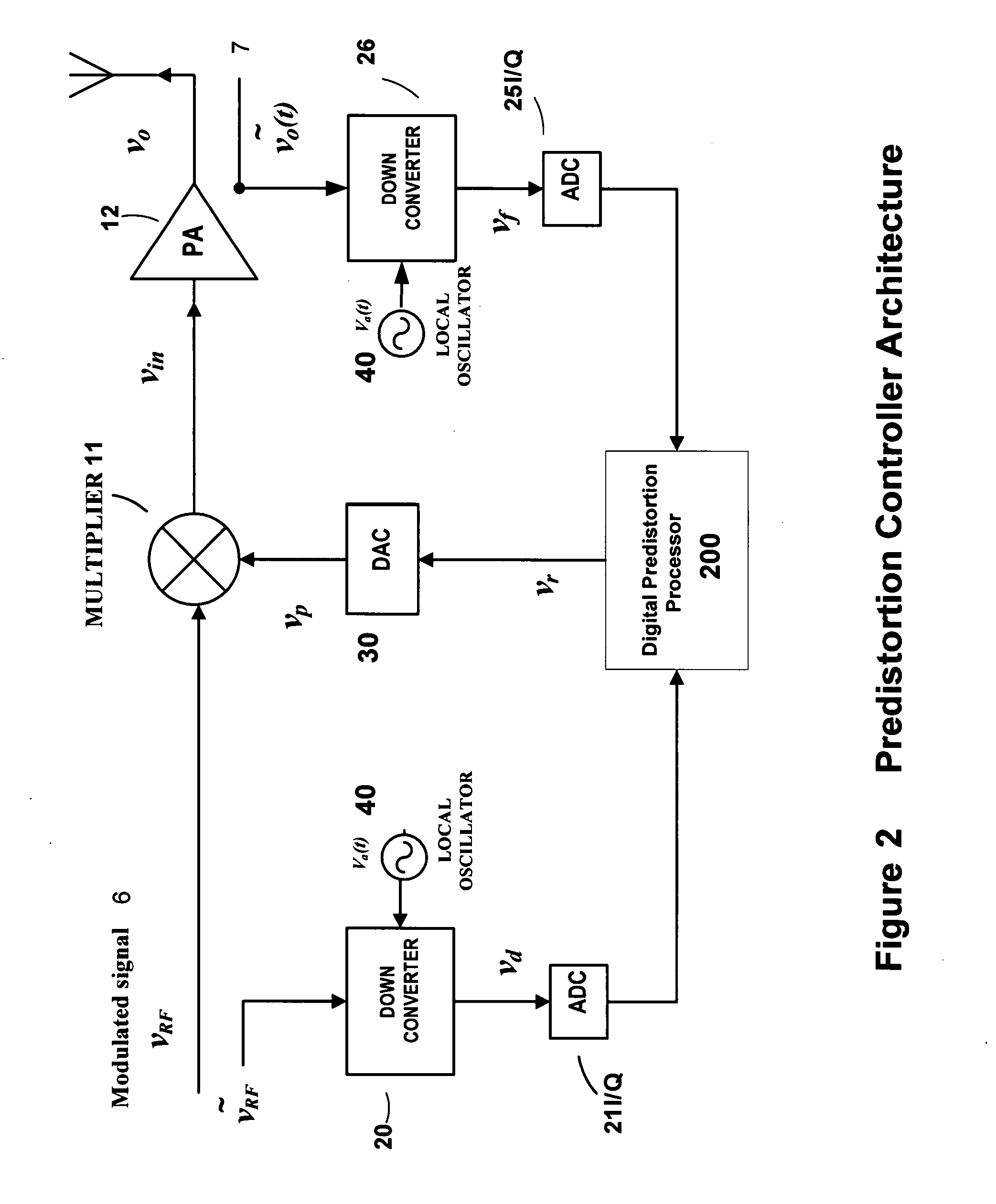
High efficiency linearization power amplifier for wireless communication
ActiveUS20070241812A1Improve efficiencyImprove linearityEnergy efficient ICTAmplifier details to increase power/efficiencyFrequency changerControl signal
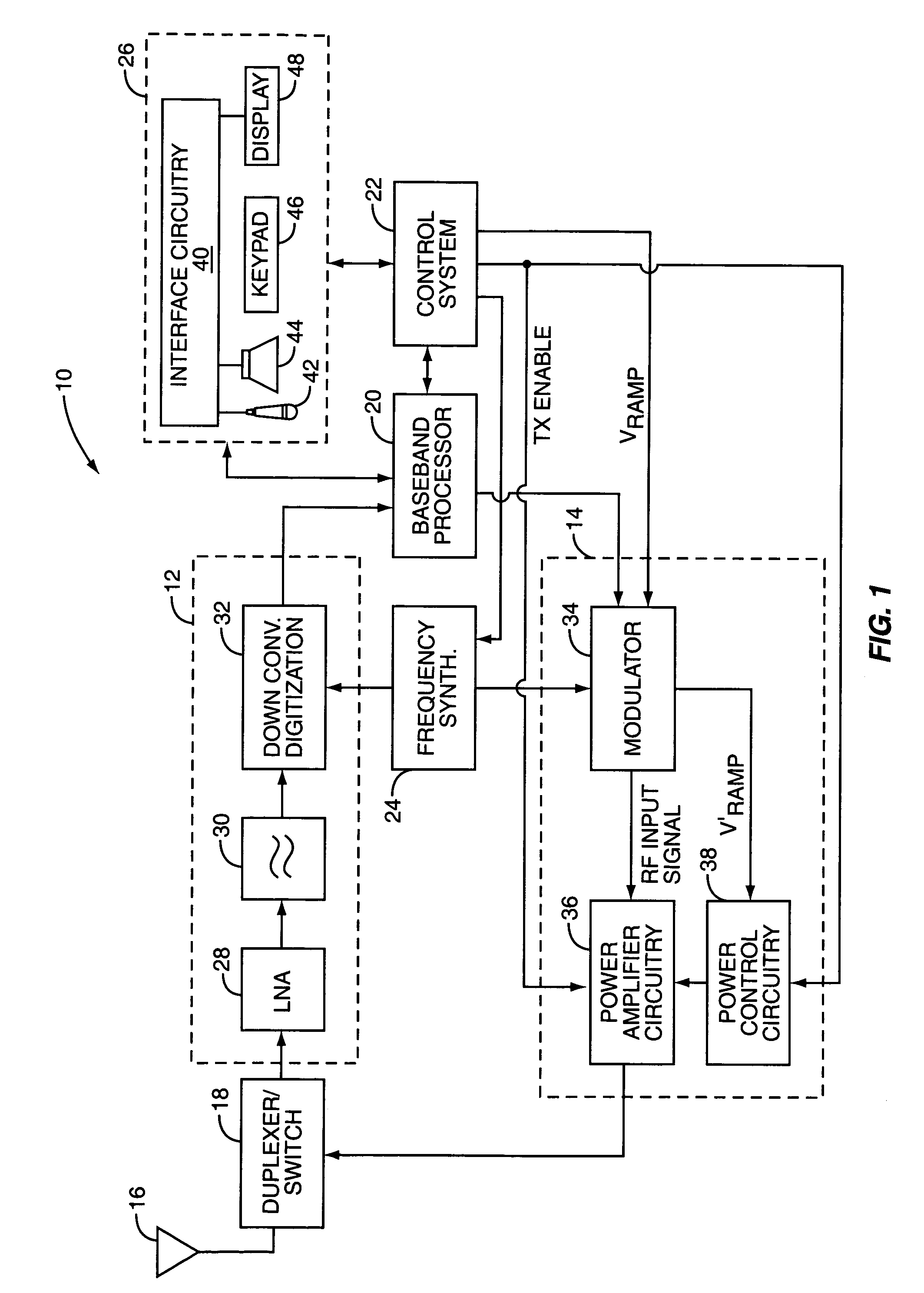
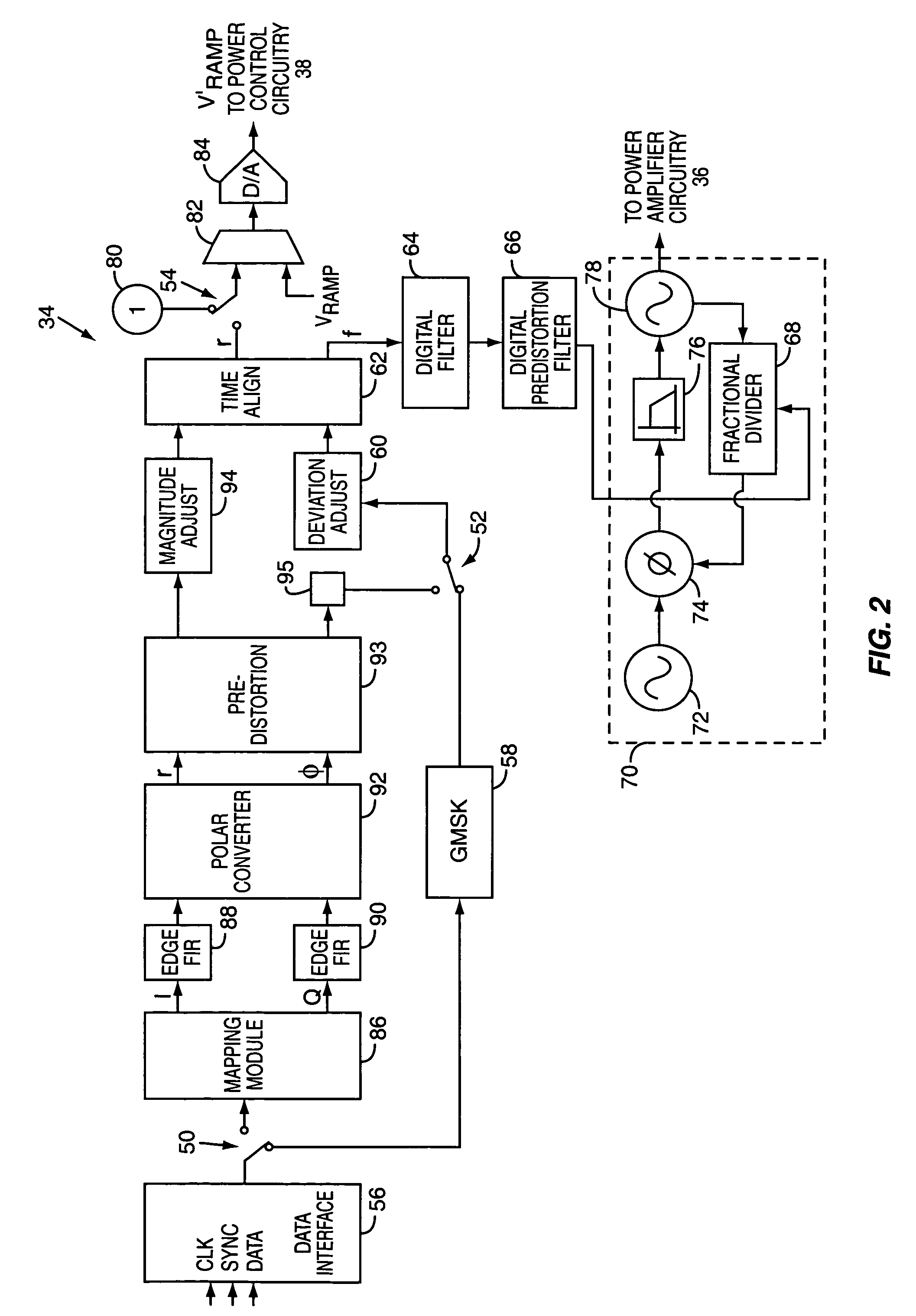
An embodiment of the invention uses a predistortion correction signal to combination the modulated RF signal by an analog multiplier for linearization of power amplifiers having nonlinear characteristics such as those used in wireless RF transmitters. A predistortion controller comprises a plurality of down converters for retrieving both the ideal non-distorted information and the feedback distorted information, together with pre-stored digitally-indexed predistortion information stored, for example, in a look-up table. The digitally-indexed information models nonlinear characteristics of the high power amplifier, and is stored prior to processing of pre-compensation in the power amplifier. When the predistortion information is combined with the modulated RF signal in the analog multiplier, the result is a substantially linear information transmission from the power amplifier. In an embodiment of the system, the modulated RF input signal and the feedback signal from PA output are down-converted, respectively, by analog devices, such as mixers, after which the analog intermediate frequency (IF) signals are digitized by analog-to-digital converters for digital predistortion correction processing, followed by predistortion processing performed by, for example, a DSP or FPGA chip to generate a digital correction control signal, which is then converted to an analog signal by a digital-to-analog converter, followed by combining the analog correction signal with the RF modulated input signal to yield the input to the power amplifier.
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
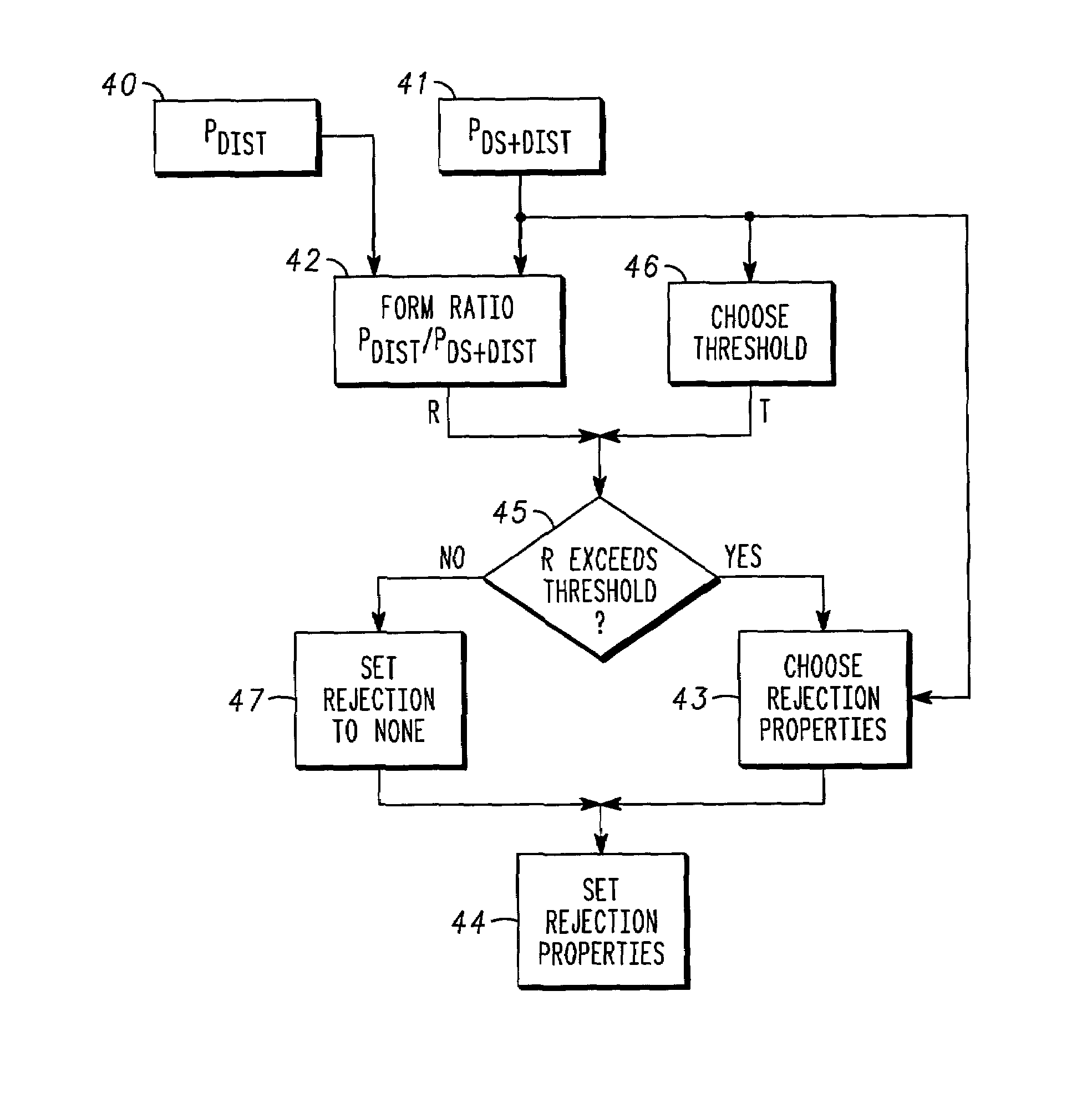
Communications receivers and methods therefor
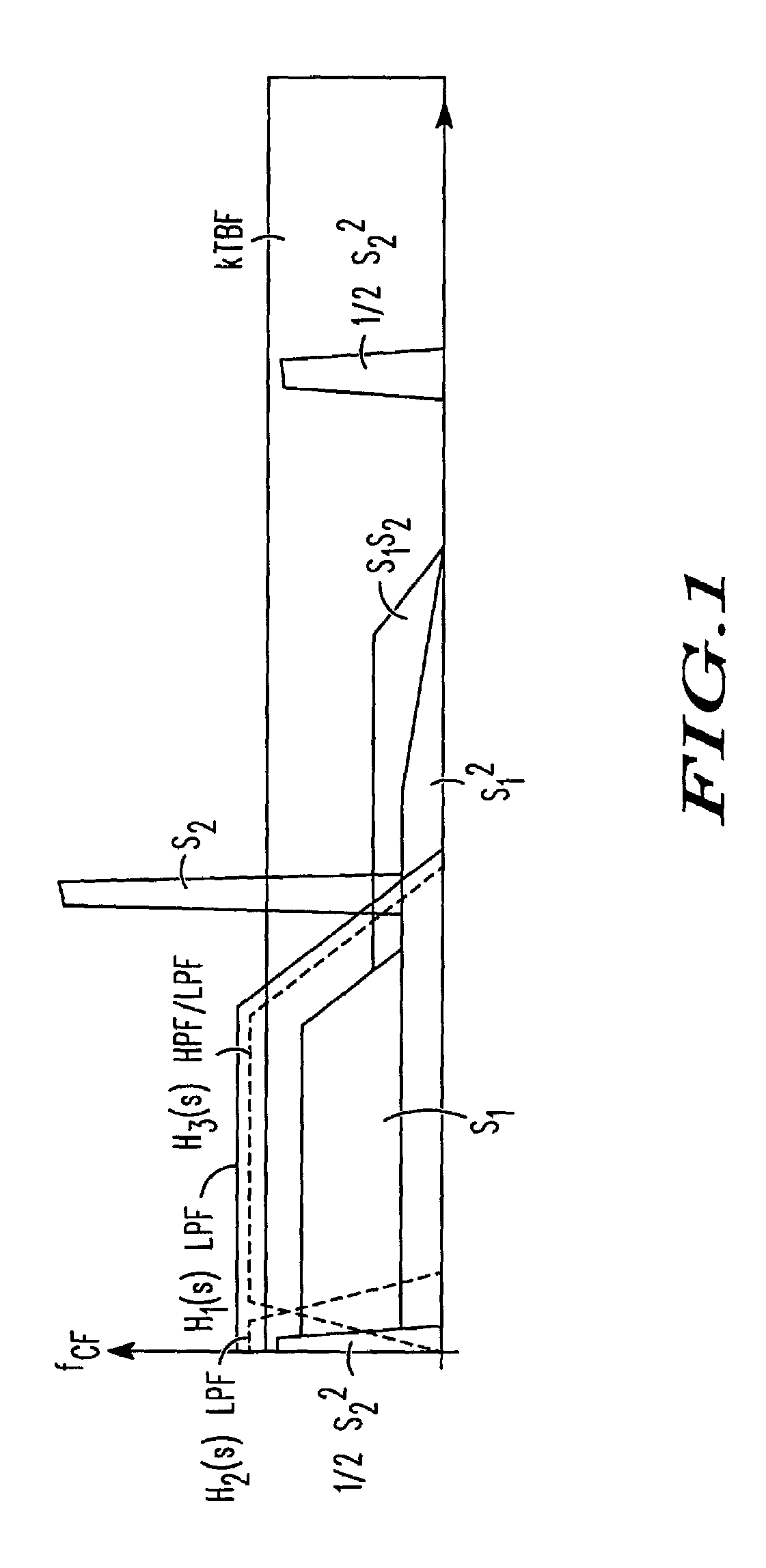
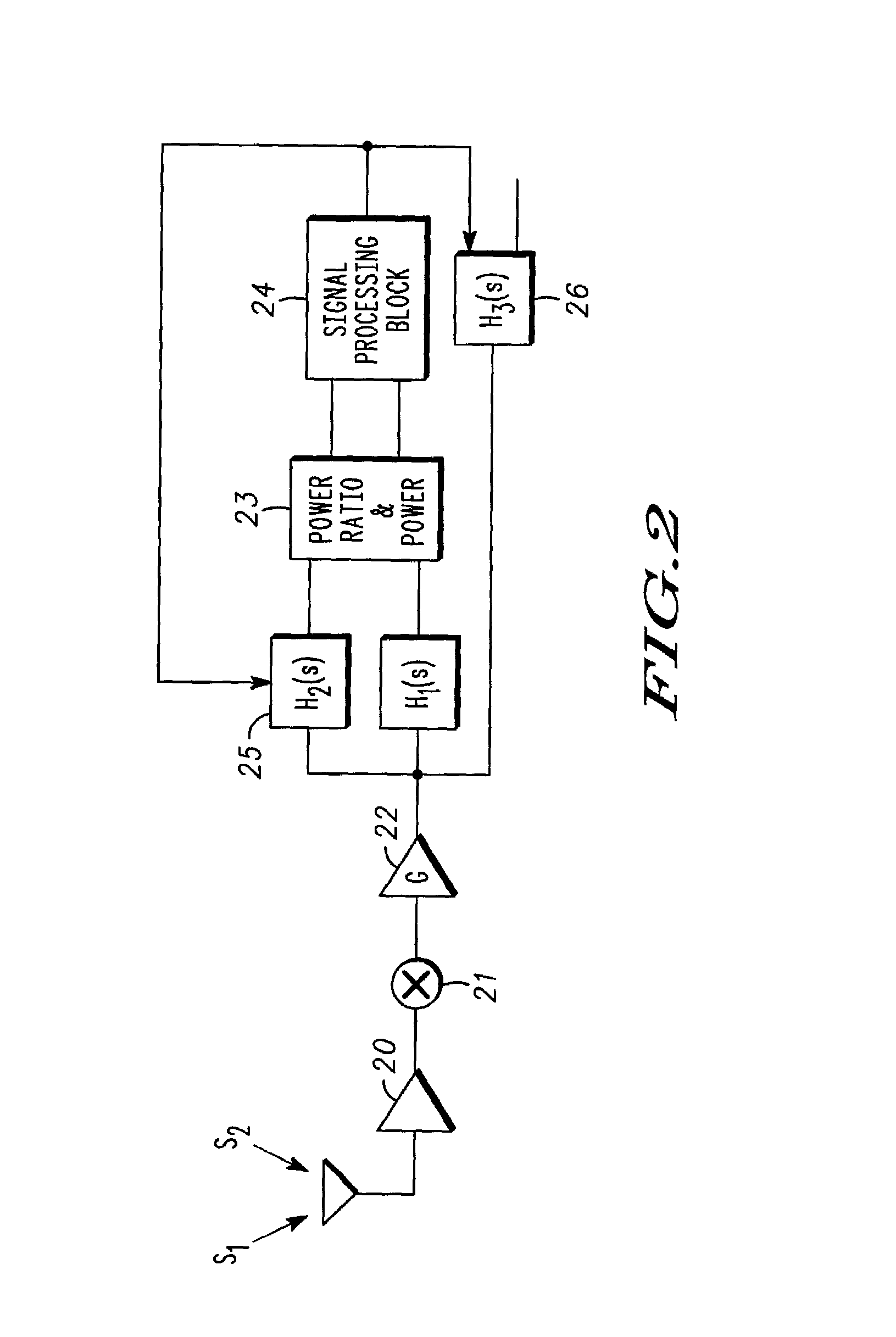
A method in a radio communication device having a receiver receiving a wideband signal in the presence of narrowband blockers method in direct conversion and intermediate frequency RF receivers including determining power for signal distortion products (40), determining power for a desired signal and the distortion products (41), filtering the signal distortion products with a filter having a bandwidth of rejection, and dynamically adjusting a rejection property (43) as a function of the power for both the desired signal and the signal distortion products. In some embodiments, a determination is made whether a ratio of powers exceeds a threshold (45) as a condition for adjusting the rejection property.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Calibrated DC compensation system for a wireless communication device configured in a zero intermediate frequency architecture
InactiveUS6735422B1Low costMaximum performancePulse automatic controlGain controlTransceiverAudio power amplifier
A calibrated DC compensation system for a wireless communication device configured in a zero intermediate frequency (ZIF) architecture. The device includes a ZIF transceiver and a baseband processor, which further includes a calibrator that periodically performs a calibration procedure. The baseband processor includes gain control logic, DC control logic, a gain converter and the calibrator. The gain converter converts gain between the gain control logic and the DC control logic. The calibrator programs the gain converter with values determined during the calibration procedure. The gain converter may be a lookup table that stores gain conversion values based on measured gain of a baseband gain amplifier of the ZIF transceiver. The gain control logic may further include a gain adjust limiter that limits change of a gain adjust signal during operation based on a maximum limit or on one or more gain change limits. A second lookup table stores a plurality of DC adjust values, which are added during operation to further reduce DC offset. The calibration procedure includes sampling an output signal for each gain step of the baseband amplifier at two predetermined range values and corresponding DC offsets using successive approximation. The data is used to calculate gain, DC offset and DC differential values, which are used to determine the conversion values programmed into the lookup tables or the gain adjust limiter.
Owner:M RED INC
N-th order curve fit for power calibration in a mobile terminal
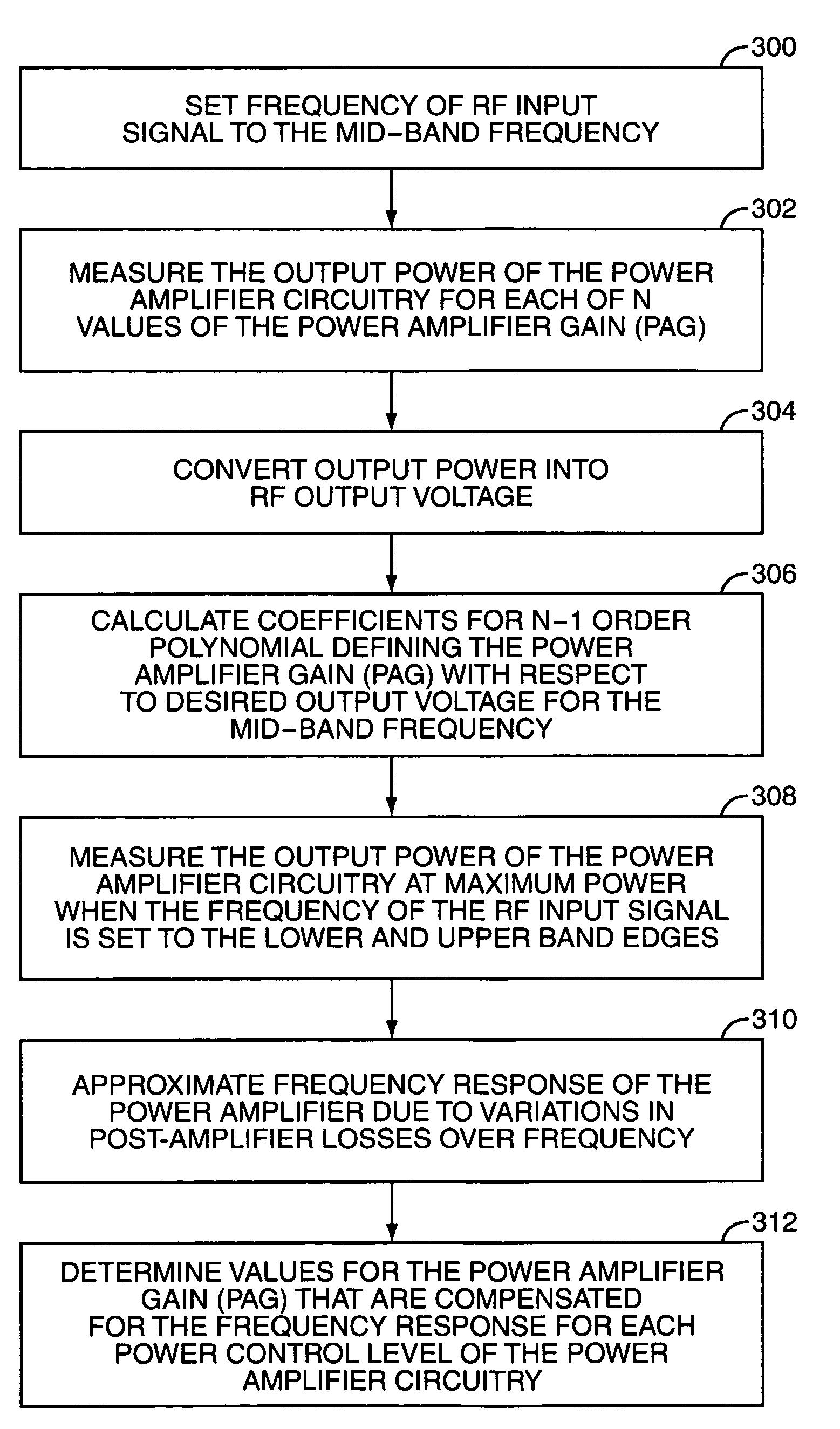
A method for calibrating the output power of a mobile terminal using at least a second order curve fit to describe a power amplifier gain (PAG) setting versus output power characteristic of a power amplifier in a transmitter of the mobile terminal is provided. For each of an upper-band frequency, a mid-band frequency, and a lower-band frequency of a frequency band, multiple measurements of the output power of the mobile terminal are made corresponding to multiple values of the PAG setting, and a curve fit is performed, thereby calculating coefficients defining a polynomial describing the PAG setting versus output power characteristic. Using the polynomials describing the PAG setting versus output power characteristic of the power amplifier for each of the upper-band, mid-band, and lower-band frequencies, values of the PAG setting are determined for each desired output power level for each desired frequency within the frequency band.
Owner:QORVO US INC
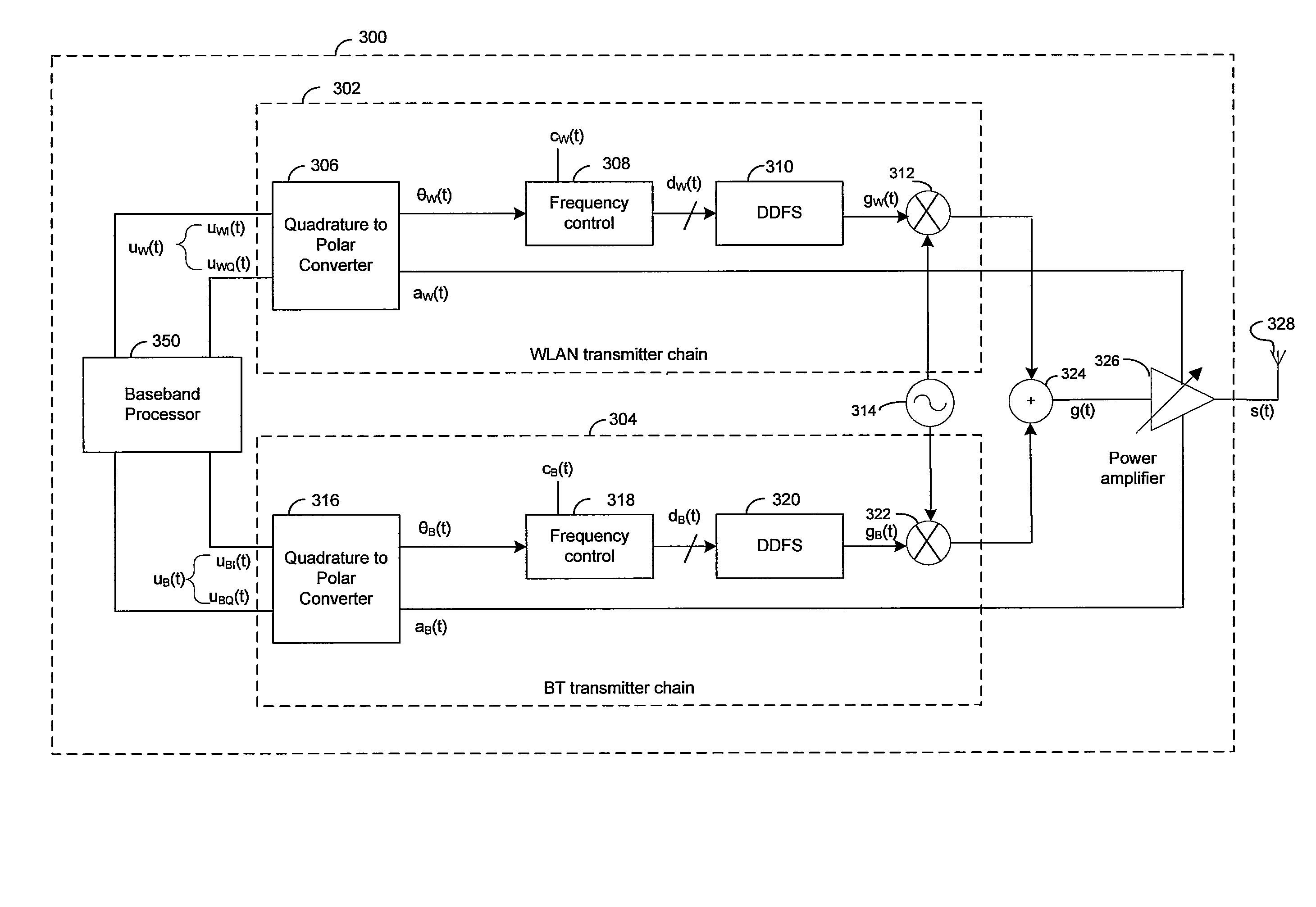
Method and system for a wideband polar transmitter
InactiveUS8036308B2Modulation with suppressed carrierAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsWireless communication protocolIntermediate frequency
Certain aspects of a method and system for a wideband polar transmitter may be disclosed. Aspects of the method may include polar modulating a plurality of signals by generating a plurality of modulated intermediate frequency (IF) signals corresponding to each of a plurality of wireless communication protocols within a transmitter that handles the plurality of wireless communication protocols. The generated plurality of modulated IF signals may be upconverted to a plurality of radio frequency (RF) signals. The plurality of RF signals may be combined and the combined plurality of RF signals may be amplitude modulated.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
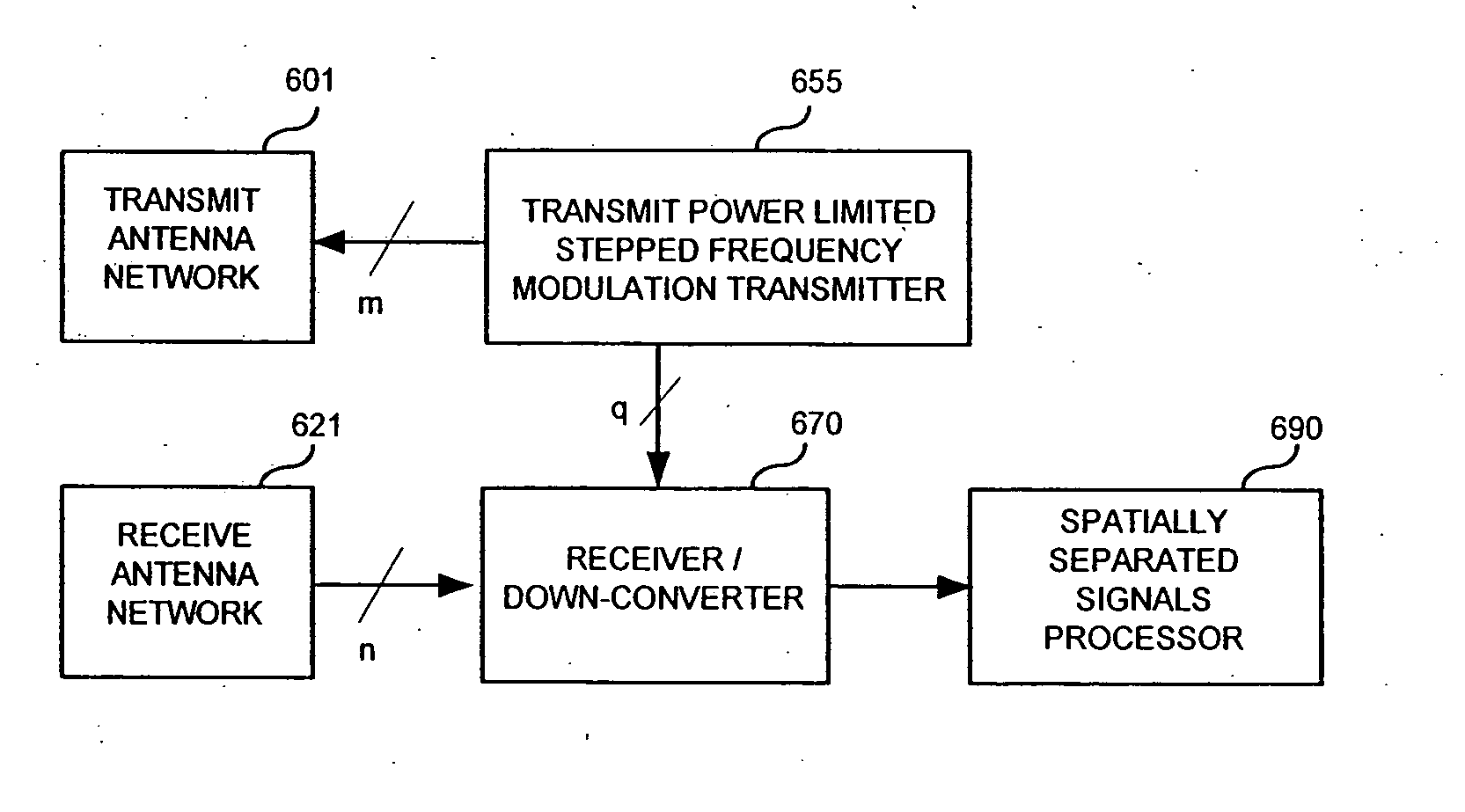
Methods and apparatus for automotive radar sensors
InactiveUS20060262007A1Reduce system costReduce in quantityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionIntermediate frequencyTransmitted power
Methods and apparatus are presented that reduce the overall system cost for automotive radar sensing applications through reduction of the number of the radar sensors required. In accordance with aspects of the present invention, one way sensor count reduction can be achieved is through the combination of target range, direction, and velocity determination capability with wide angular field of view coverage within a single sensor unit. One embodiment combines a transmit-pulsed, linearly stepped frequency modulated, transmit power limited radar architecture with a spatially separated receiver antenna array, intermediate frequency down-conversion, and a digital multi-zone monopulse (DMM) signal processing technique for high-resolution target range, velocity, and azimuth angle determination and fast update rate capability in a low cost, mass-production-capable design.
Owner:CLARIANT TECH
Satellite digital audio radio service tuner architecture for reception of satellite and terrestrial signals
InactiveUS6510317B1Broadcast transmission systemsRadio transmissionIntermediate frequencyRadio receiver
A satellite digital audio radio receiver system and method. The inventive receiver includes a circuit for down-converting a first ensemble in a received combined signal in a first mode of operation and for down-converting a second ensemble from the received combined signal in a second mode of operation. The first ensemble includes a first signal received from a first transmitter, a second signal received from a second transmitter, and a third signal received from a third transmitter. The second ensemble includes a second signal from the first transmitter, a second signal from the second transmitter, and a second signal from the third transmitter. A controller is included to selectively switch the circuit from the first mode to the second mode. The first ensemble comprises first, second and third frequency slots and the second ensemble comprises fourth, fifth, and sixth frequency slots. In the illustrative embodiment, the first and second transmitters are mounted on first and second satellites and the third transmitter is a terrestrial repeater. Both ensembles are transmitted in accordance with the XM frequency plan. The first ensemble is down-converted using low side injection and the second ensemble down-converted using high side injection. The inventive circuit includes a synthesized frequency source. The circuit further includes a first intermediate frequency down-conversion stage with a first mixer for mixing the received combined signals with the output of synthesized frequency source. The circuit further includes first and second surface acoustic wave filters for separating the first and second signals received from the third signals. The inventive circuit further includes a second intermediate frequency down-conversion stage having second and third mixers for mixing the outputs of the first and second filters, respectively, with the output of a local oscillator.
Owner:SIRIUS XM RADIO INC
Method and system for down-converting electromagnetic signals by sampling and integrating over apertures
InactiveUS6266518B1Reduce frequencySufficiently reproducedResonant long antennasModulation transferenceIntermediate frequencyEngineering
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for down-converting an electromagnetic (EM) signal by aliasing the EM signal are described herein. Briefly stated, such methods, systems, and apparatuses operate by receiving an EM signal and an aliasing signal having an aliasing rate. The EM signal is aliased according to the aliasing signal to down-convert the EM signal. The term aliasing, as used herein, refers to both down-converting an EM signal by under-sampling the EM signal at an aliasing rate, and down-converting an EM signal by transferring energy from the EM signal at the aliasing rate. In an embodiment, the EM signal is down-converted to an intermediate frequency (IF) signal. In another embodiment, the EM signal is down-converted to a demodulated baseband information signal. In another embodiment, the EM signal is a frequency modulated (FM) signal, which is down-converted to a non-FM signal, such as a phase modulated (PM) signal or an amplitude modulated (AM) signal.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
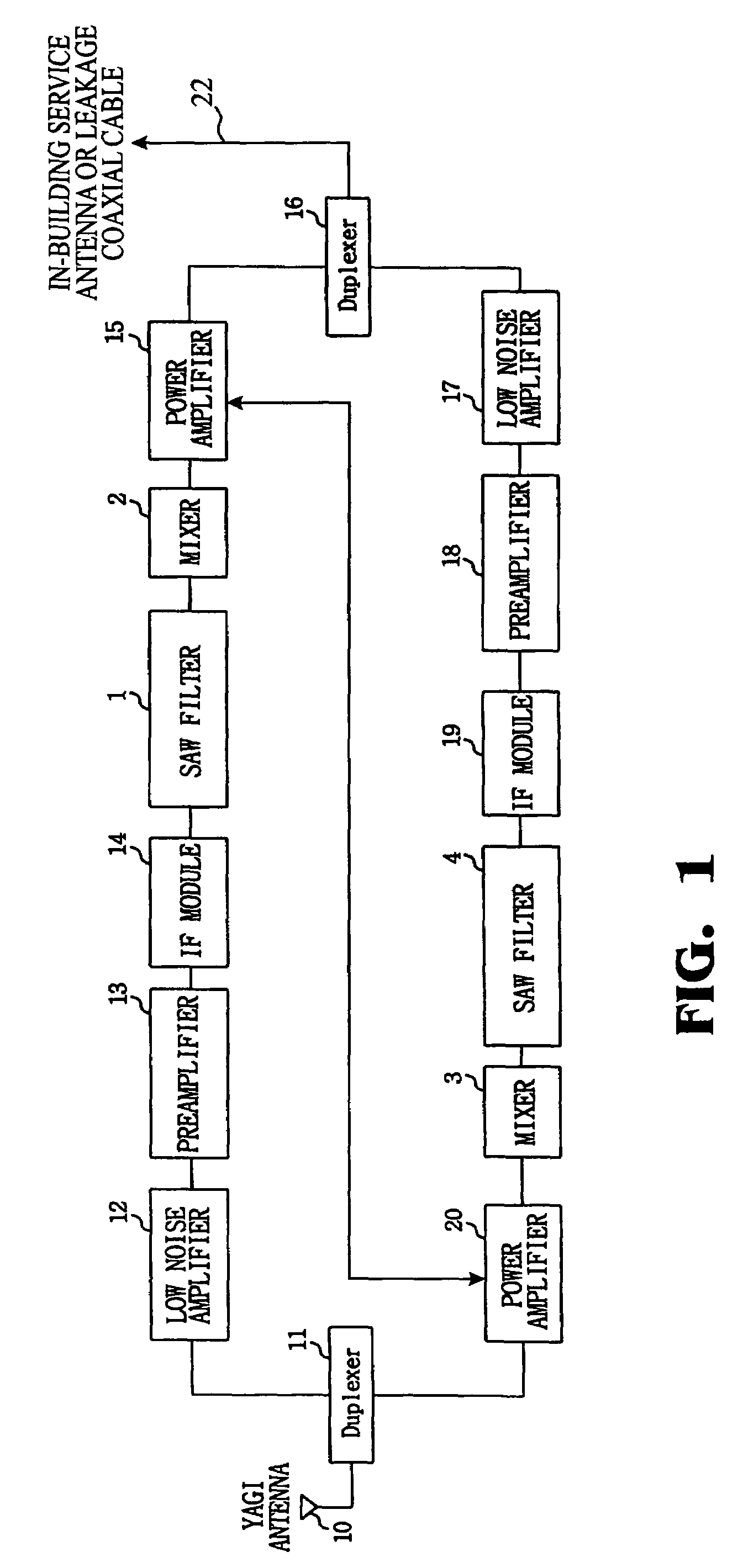
Low cost broadband wireless communication system
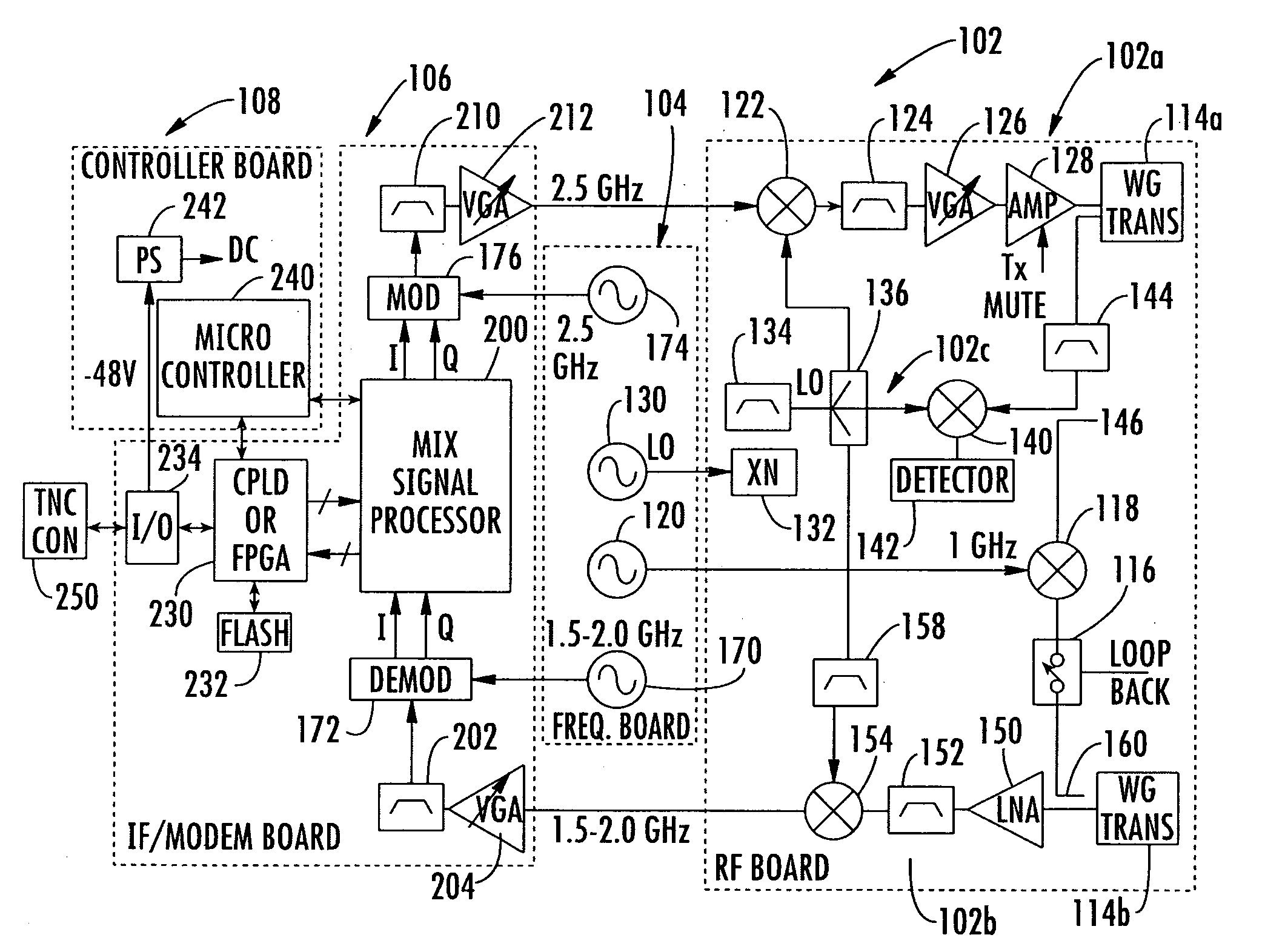
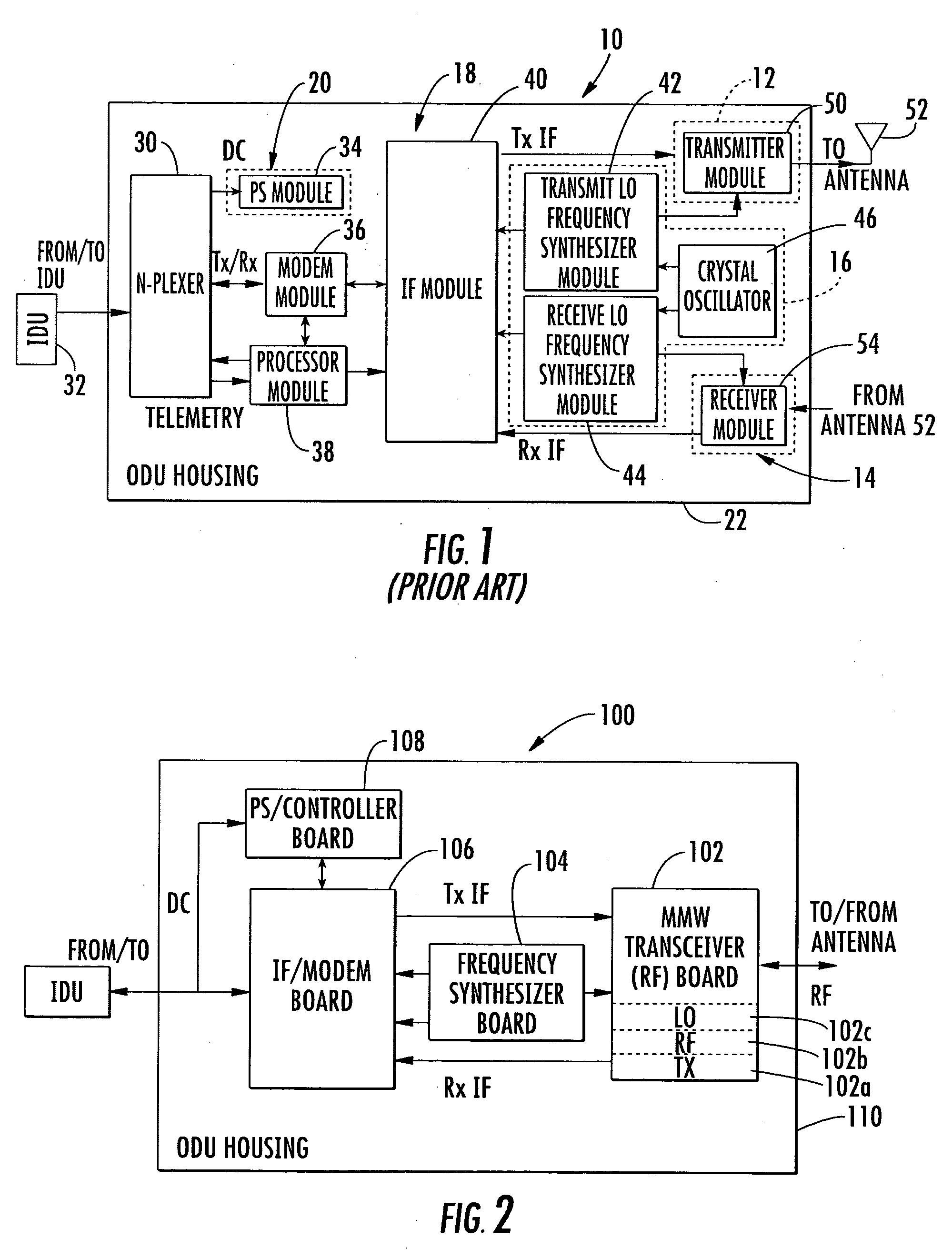
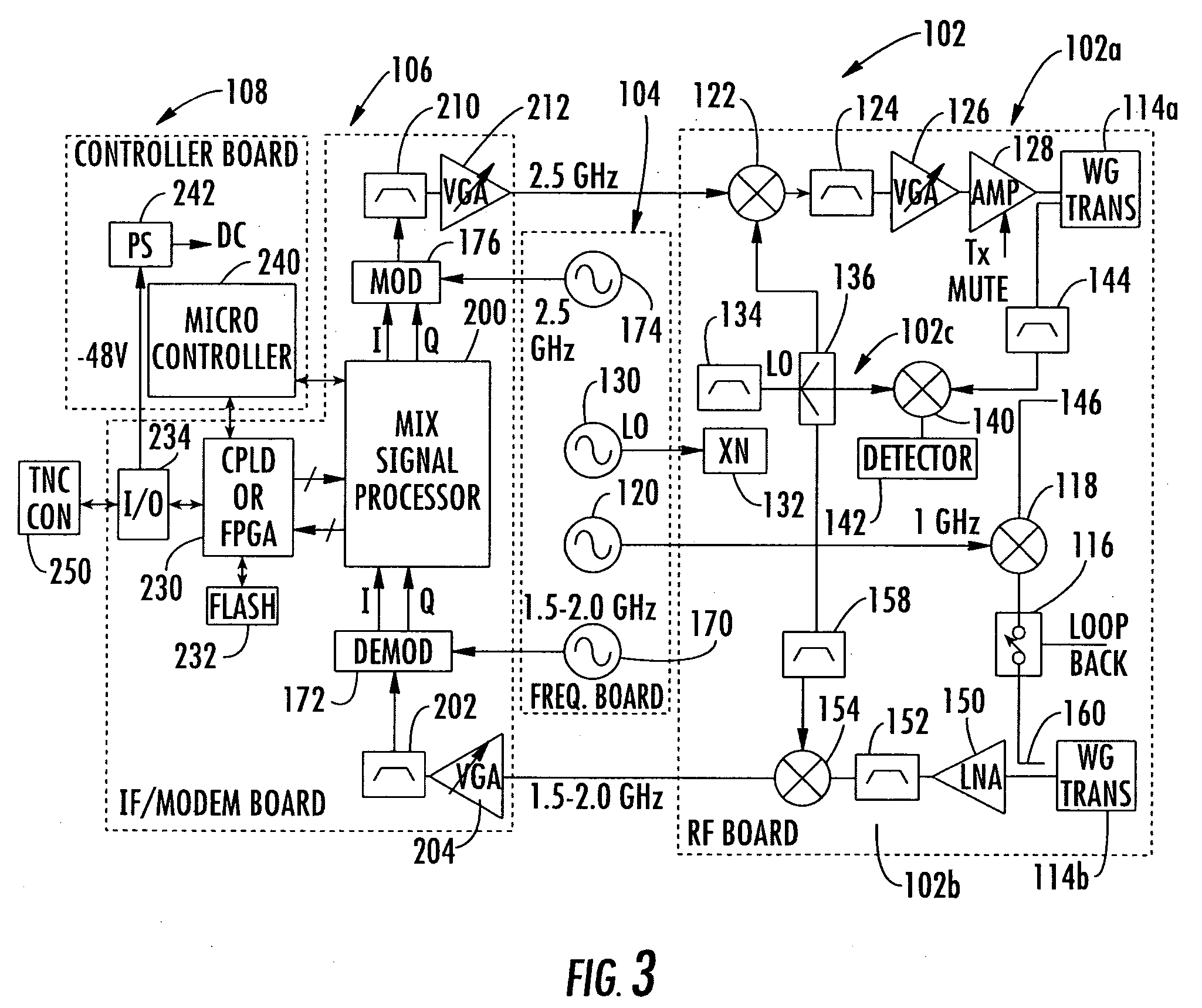
This present invention includes an indoor unit (IDU) and compact outdoor unit (ODU) having an intermediate frequency / modem circuit, millimeter wave transceiver circuit, and digital interface between the IDU and the ODU capable of up to about 100 MBps data rate over at least about a 300 meter cable. The system uses a conversion to the polar coordinate system completes calculations in the polar coordinate system, reducing the computational requirements, and therefore, the size and cost of the system.
Owner:REVEAL IMAGING
Digital beamforming radar system
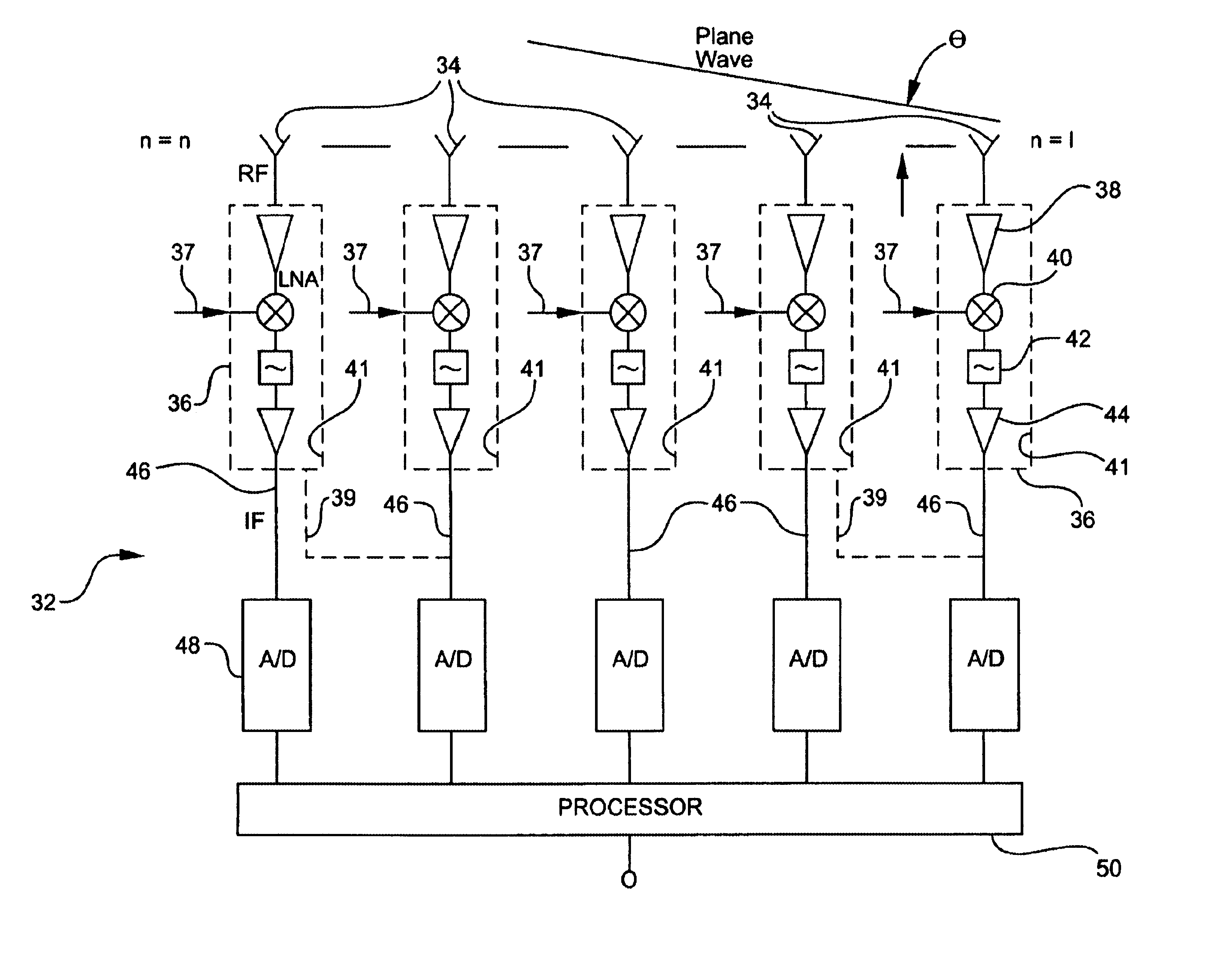
InactiveUS6882311B2Less spaceEasy to manufactureModular arraysTransmissionLow noiseLocal oscillator signal
A receiver for a digital beamforming radar system includes a plurality of antenna elements, low-noise block converters, one or more analog-to-digital converters, and a processor. The antenna elements receive a radar signal and output a received signal. The low-noise block converters are modified commercially available components used in satellite television systems, respond to the received signal from a corresponding antenna element, and output an intermediate frequency signal. The low-noise block converters include at least one amplifier, a mixer, and a local oscillator input. The local oscillator input enables an external local oscillator signal to be inputted to the mixer. The analog-to-digital converters are responsive to the intermediate frequency signal of a corresponding low-noise block converter. The processor is responsive to the digital signals output by the analog-to-digital converters.
Owner:COMM & POWER IND
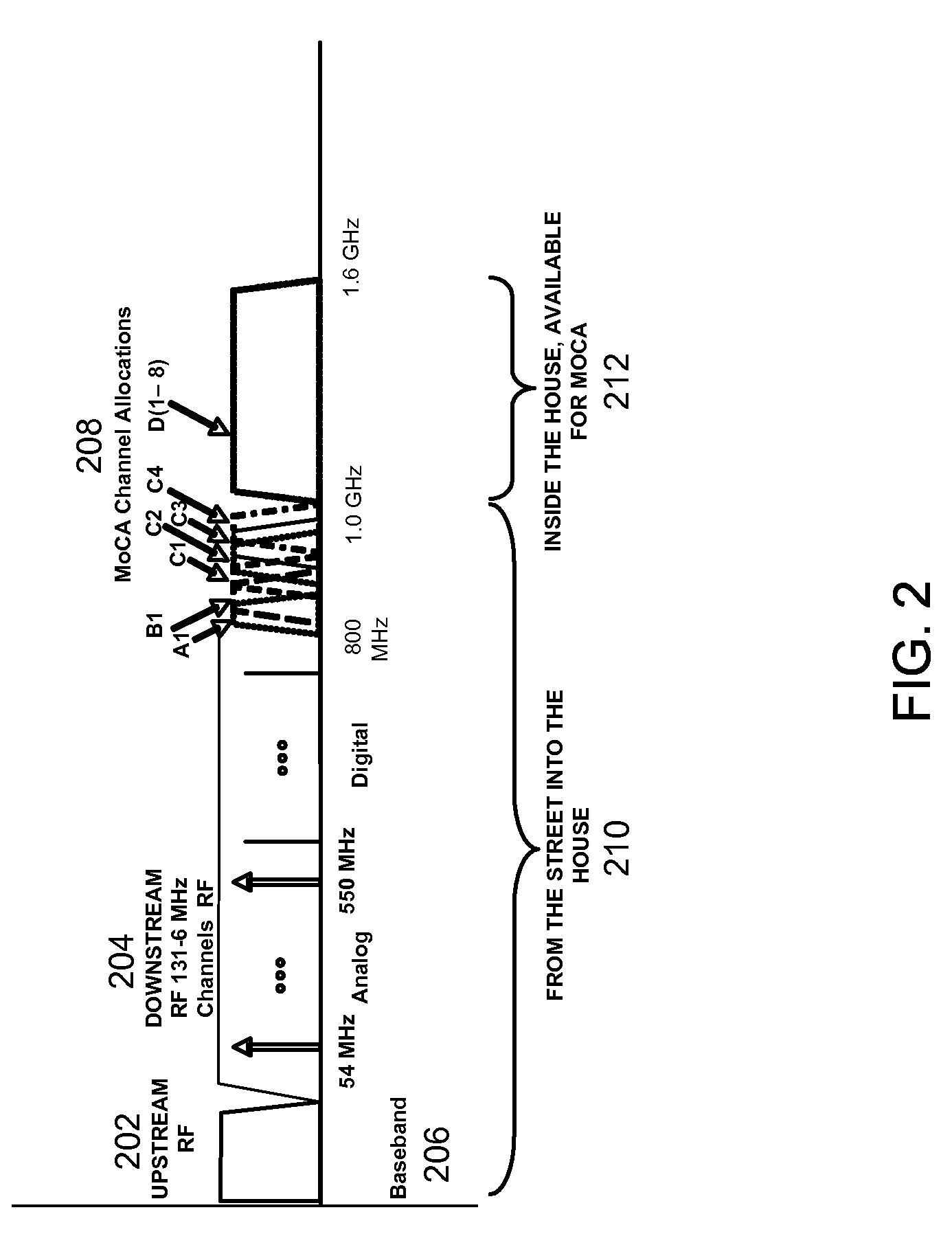
SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR PROVIDING A MoCA COMPATABILITY STRATEGY
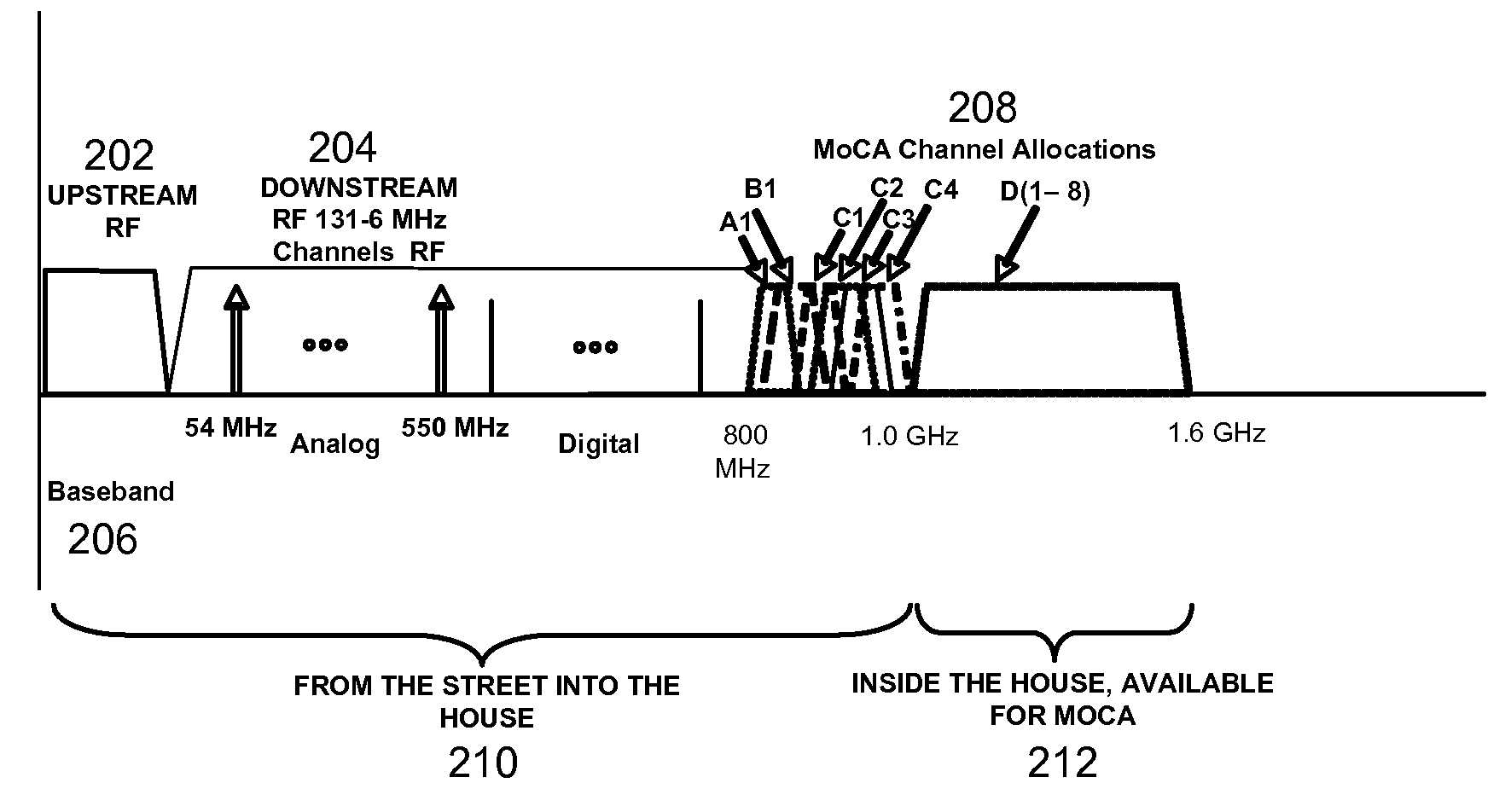
InactiveUS20090165070A1Reduce performance degradationBroadcast transmission systemsCross-talk reductionCoaxial cableIntermediate frequency
Systems and methods for perform a method for reducing interference from Multimedia over Coax Alliance (MOCA) signals in a cable television double conversion tuner are provided. The method may include receiving an indication of the channel in which MoCA signals are operating. When the channel in which the MoCA signals are operating is in the same frequency band as an intermediate frequency of the tuner, the method may require shifting an intermediate frequency of the tuner out of the frequency band occupied by the channel in which the MoCA signals are operating.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
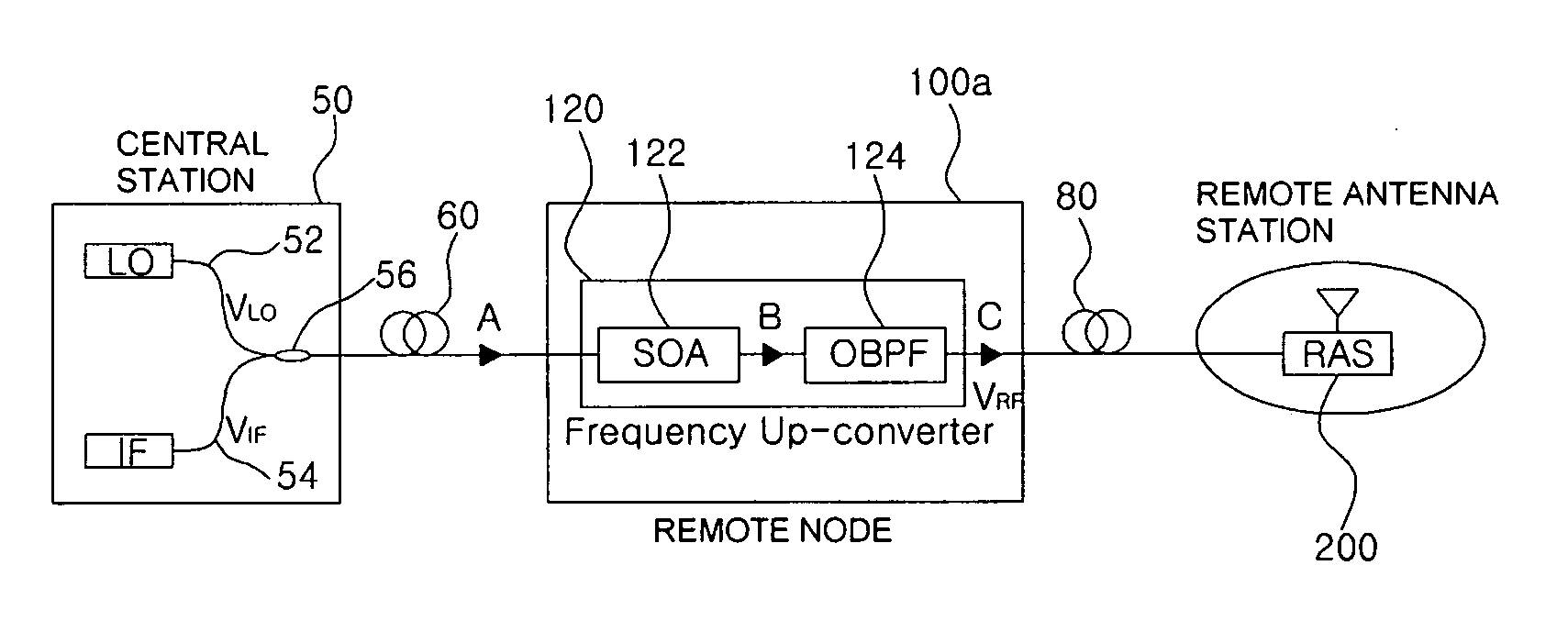
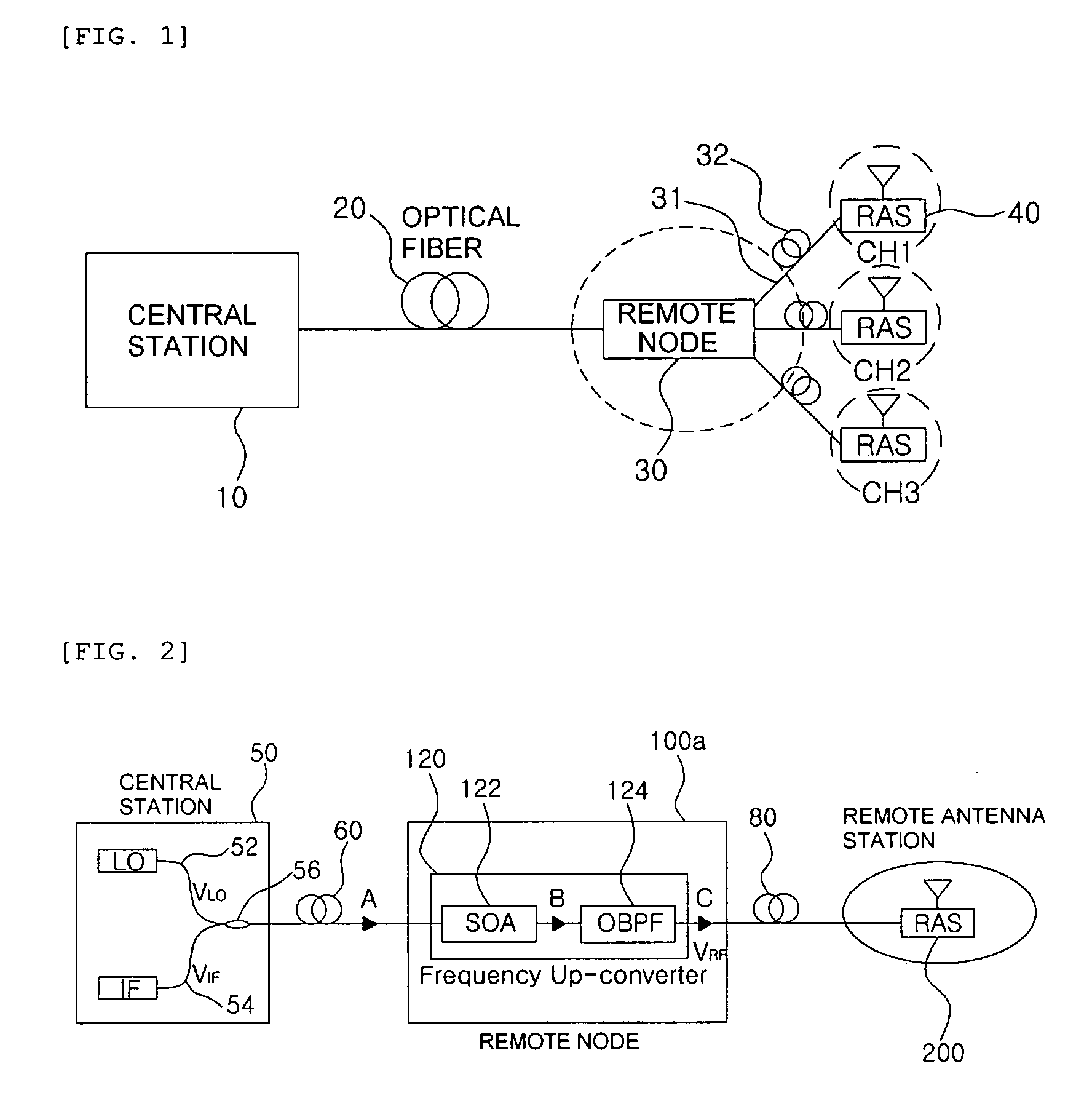
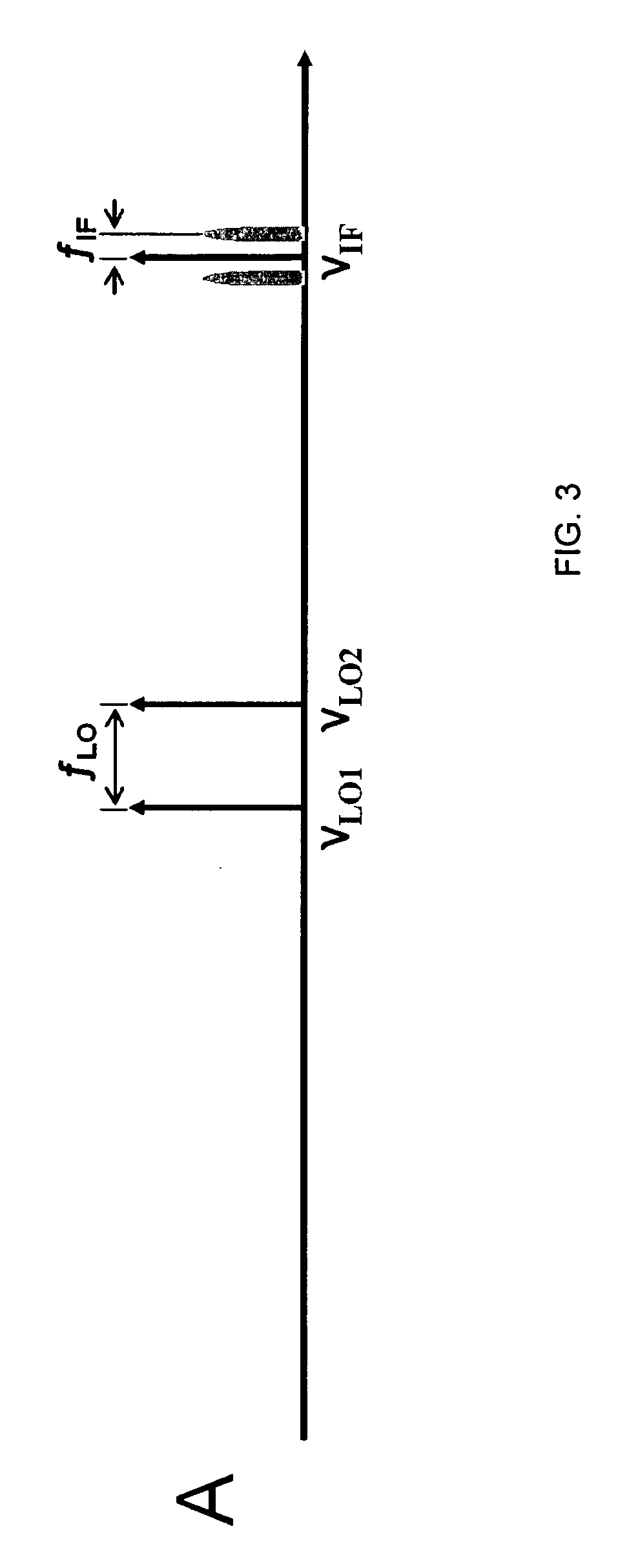
All-optical frequency upconverter and all-optical frequency upconversion method in radio-over-fiber system
InactiveUS20080298813A1Simple configurationRadio-over-fibreElectromagnetic transmittersFrequency changerRadio over fiber
Disclosed is an all-optical frequency upconverter in a radio-over-fiber system that outputs upconverted optical radio frequency (RF) signals using an optical intermediate frequency signal and an optical local oscillation signal. The all-optical frequency upconverter includes a semiconductor optical amplifier that mixes the optical intermediate frequency signal with the optical local oscillation signal through four wave mixing, and an optical filter that filters a plurality of frequency component signals, which are generated through the four wave mixing, to extract optical RF signals. According to the invention the system configuration can be made simple, and wide LO and IF frequency bandwidths can be provided.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
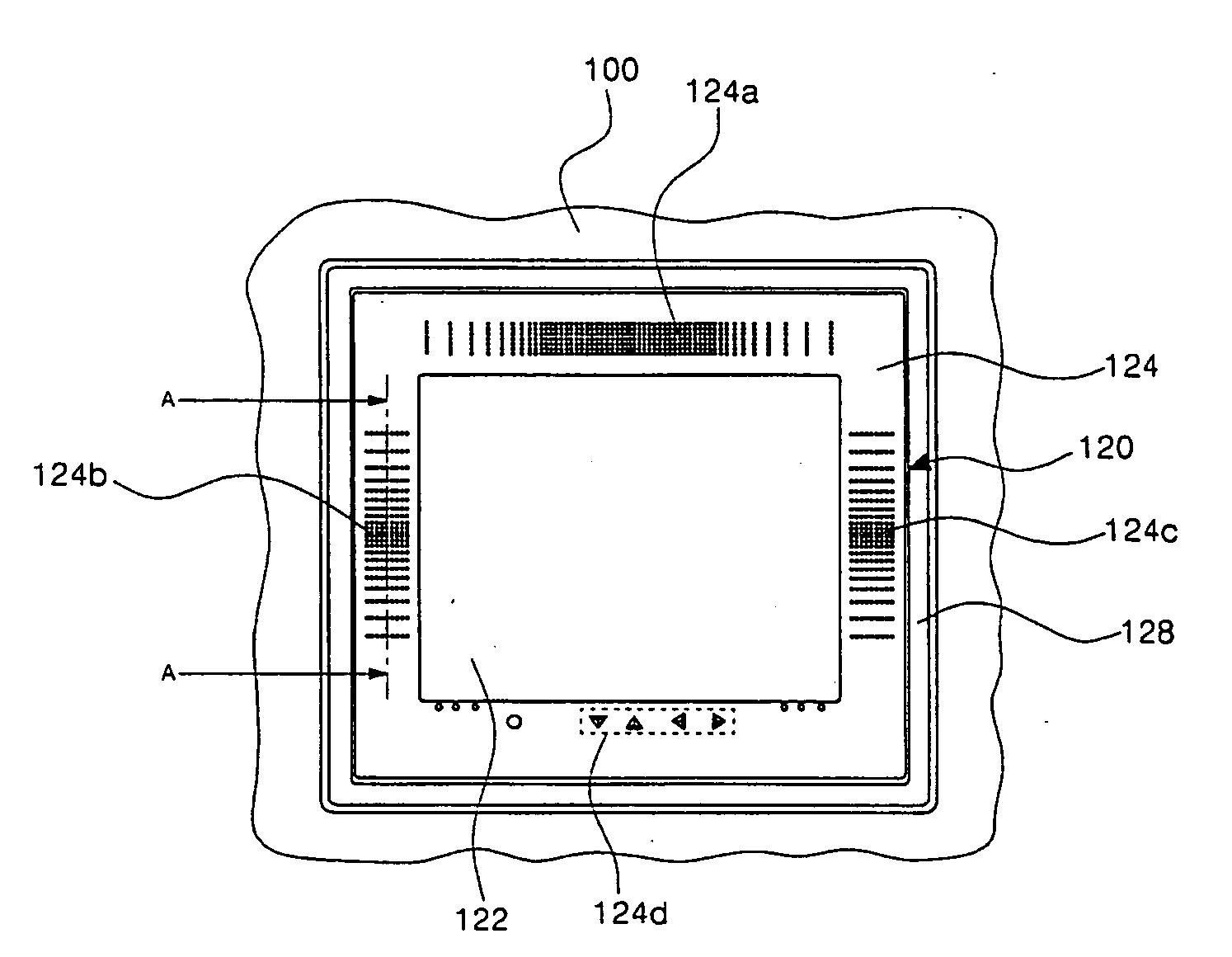
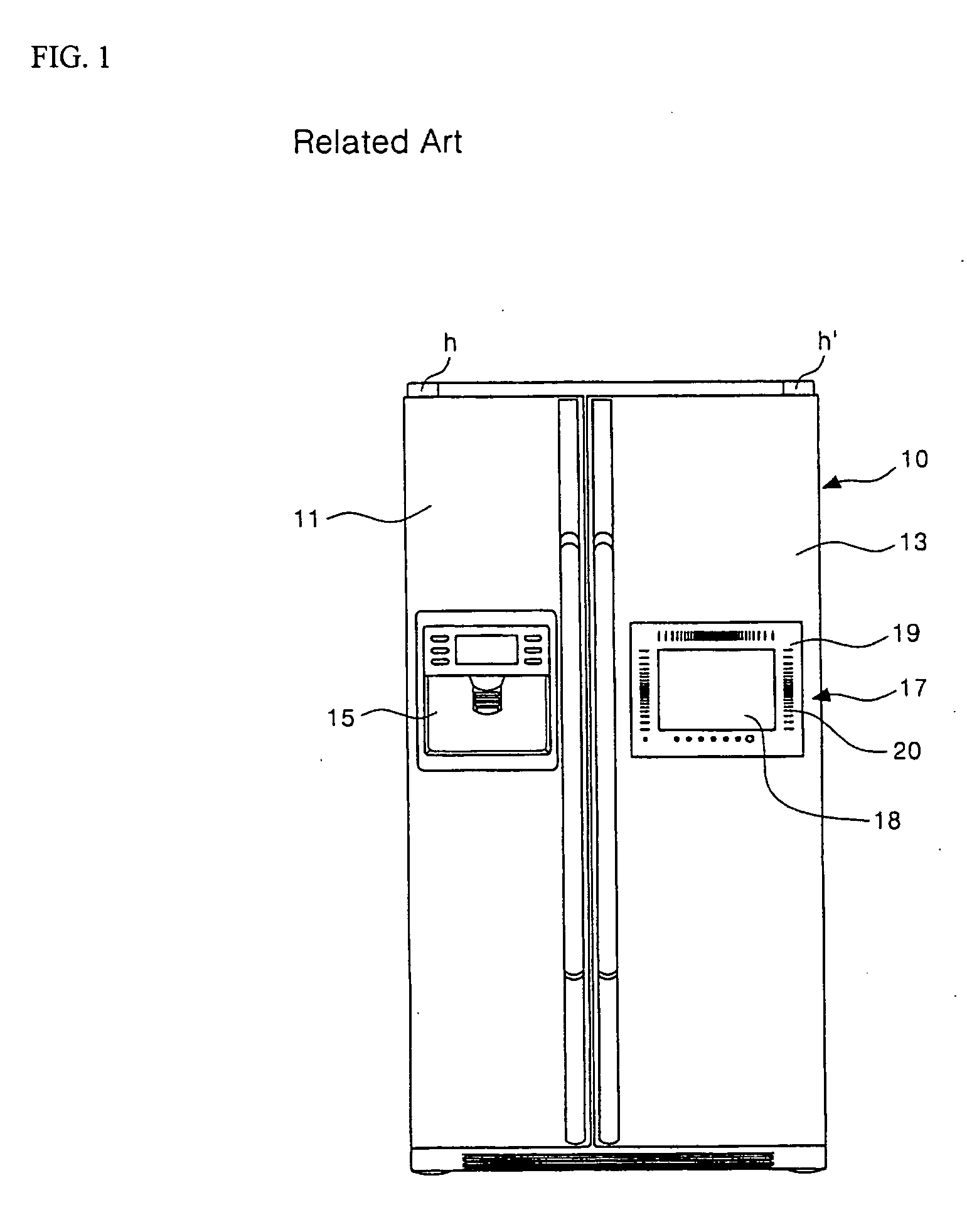
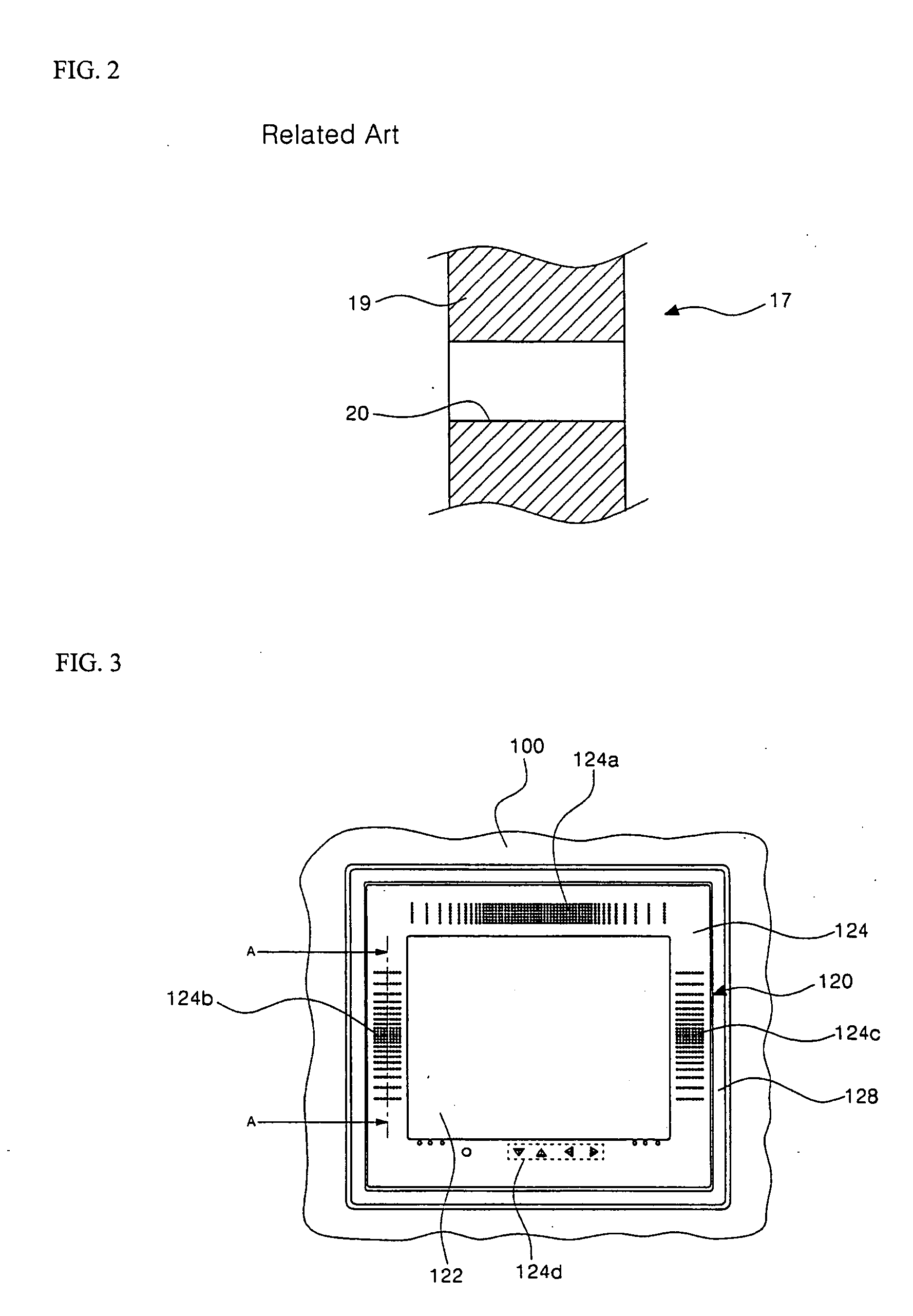
Display unit for refrigerator
ActiveUS20050134472A1Improve sound qualityPrevent penetrationLighting and heating apparatusSignalling system detailsIntermediate frequencyResonance
The present invention relates to a display unit for a refrigerator for improving sound quality. A display having a TV receiving function is installed at a front surface of a refrigerator door. A mounting panel with a plurality of speaker holes formed therein is also installed around an edge of the display. A speaker is mounted to a rear surface of the mounting panel on a portion where the speaker holes are formed. Further, a resonance box is installed to enclose the speaker such that low and middle frequency sound can be transmitted forward to the outside. A sound transmission tube that communicates with the speaker hole is formed at a front portion of the resonance box. In addition, a sound absorbing material is covered on an inner rear surface of the resonance box that faces the rear of the speaker.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
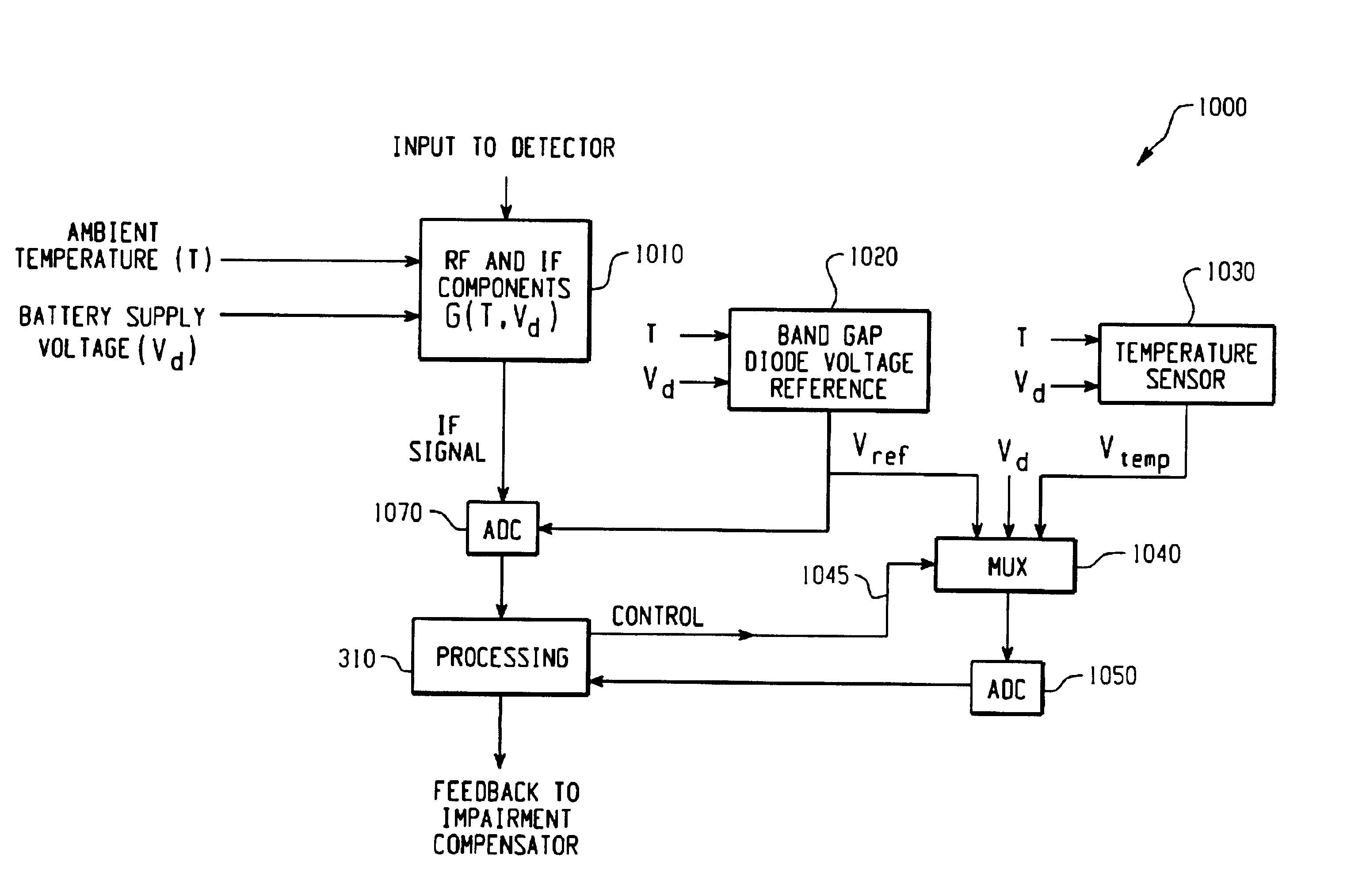
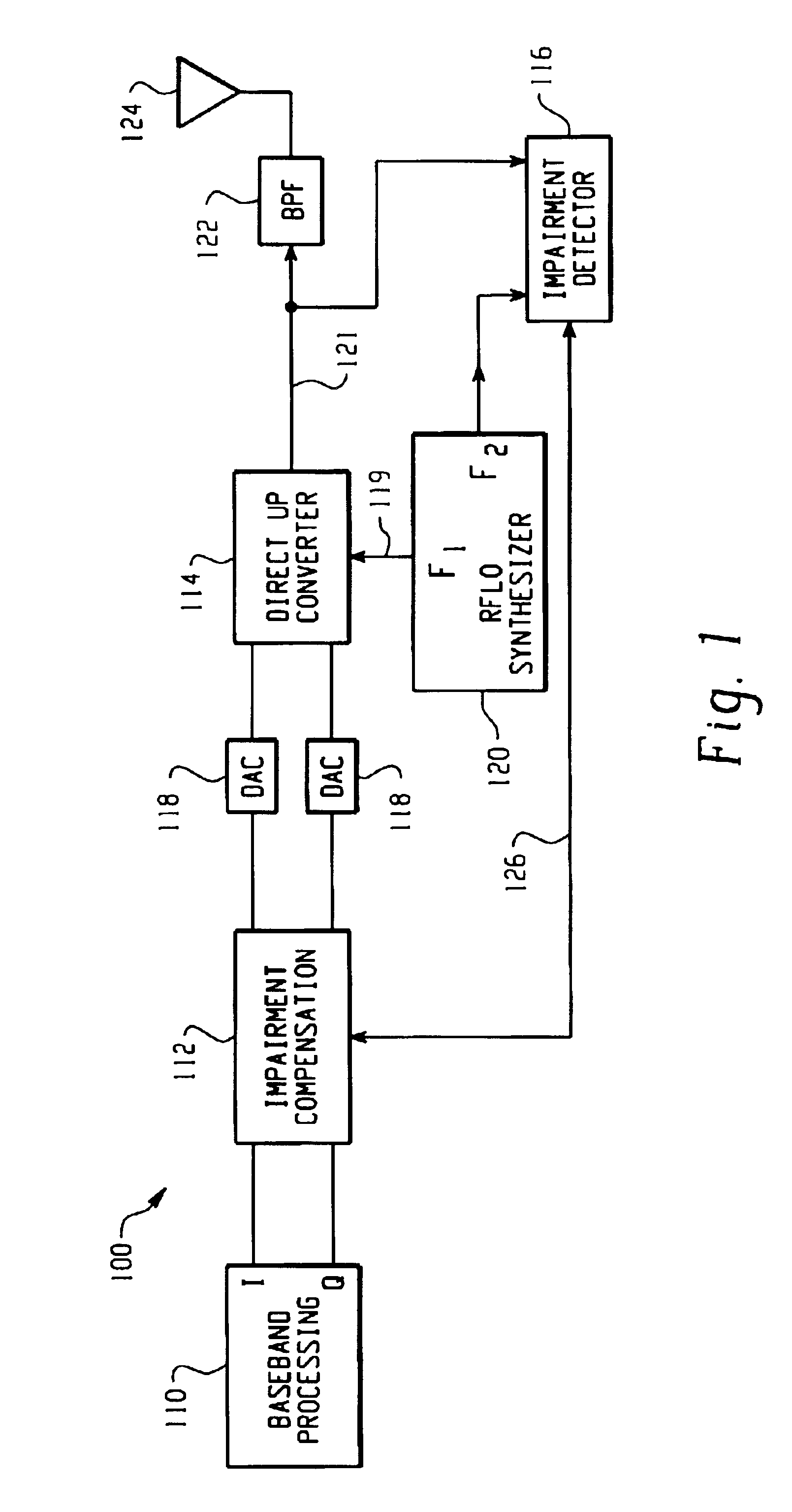
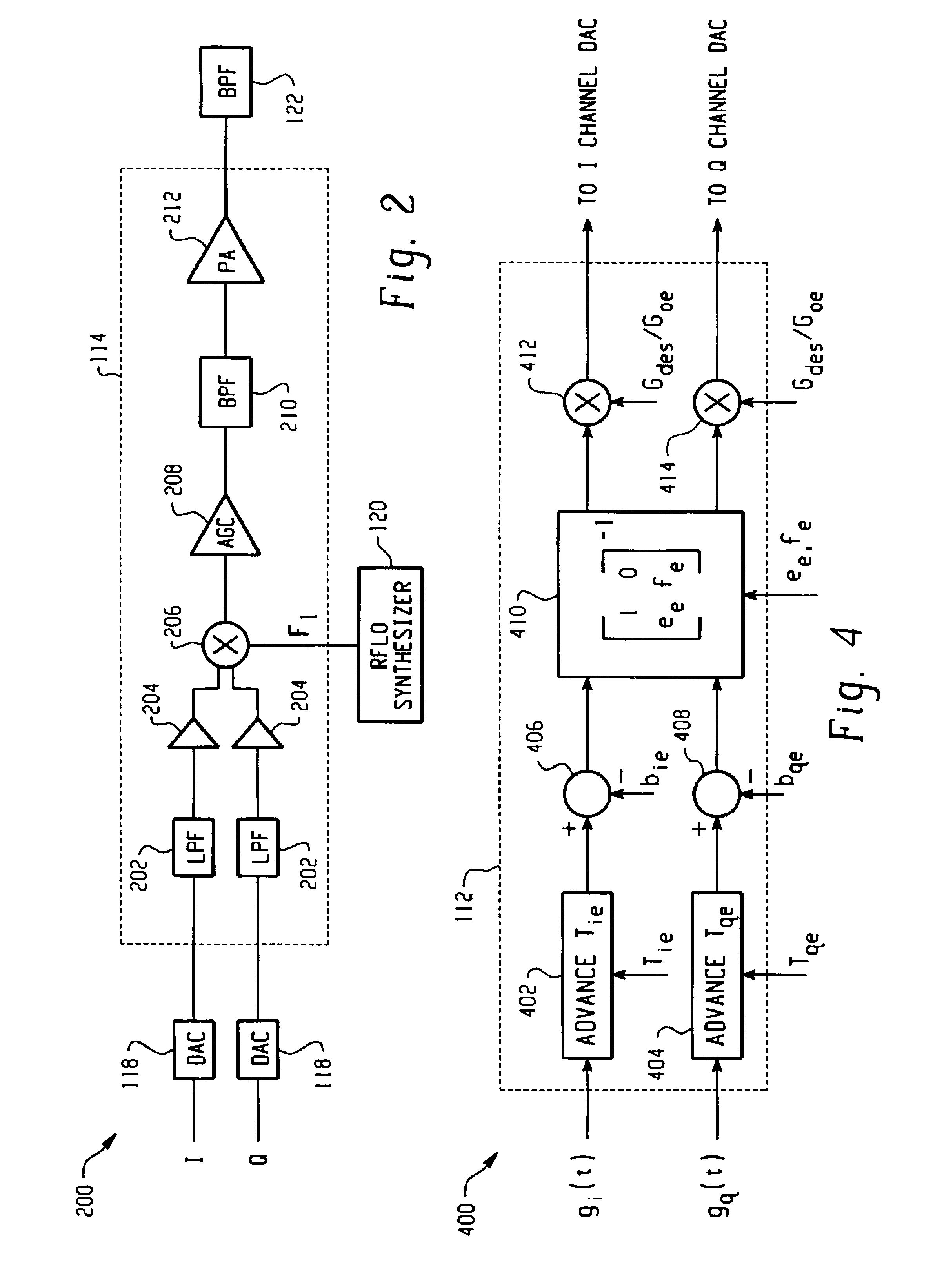
Feedback compensation detector for a direct conversion transmitter
ActiveUS6987954B2Resonant long antennasAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceFrequency changerIntermediate frequency
A feedback compensation detector for a direct conversion transmitter includes a baseband processor, a direct up-converter, an antenna, and an impairment detection and compensation feedback circuit. The baseband processor generates an in-phase (I) baseband signal and a quadrature-phase (Q) baseband signal. The direct up-converter is coupled to the baseband processor, and combines the I and Q baseband signals with an RF carrier signal to generate an RF output signal. The antenna is coupled to the direct up-converter, and transmits the RF output signal. The impairment detection and compensation feedback circuit is coupled to the RF output signal and the I and Q baseband signals. The impairment detection and compensation feedback circuit down-converts the RF output signal to generate an intermediate frequency (IF) signal, measures as least one signal impairment in the IF signal, and pre-distorts the I and Q baseband signals to compensate for the measured signal impairment.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
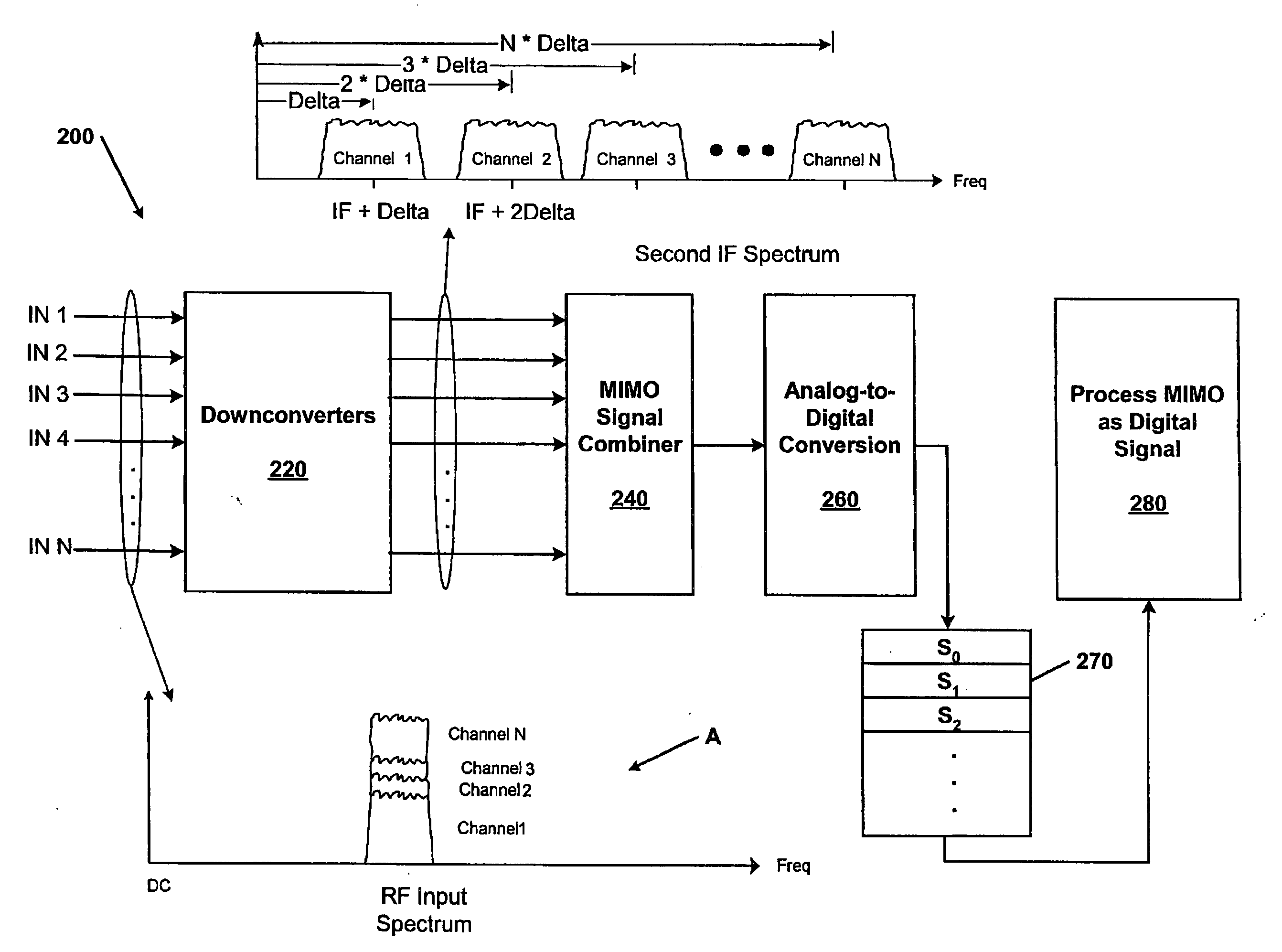
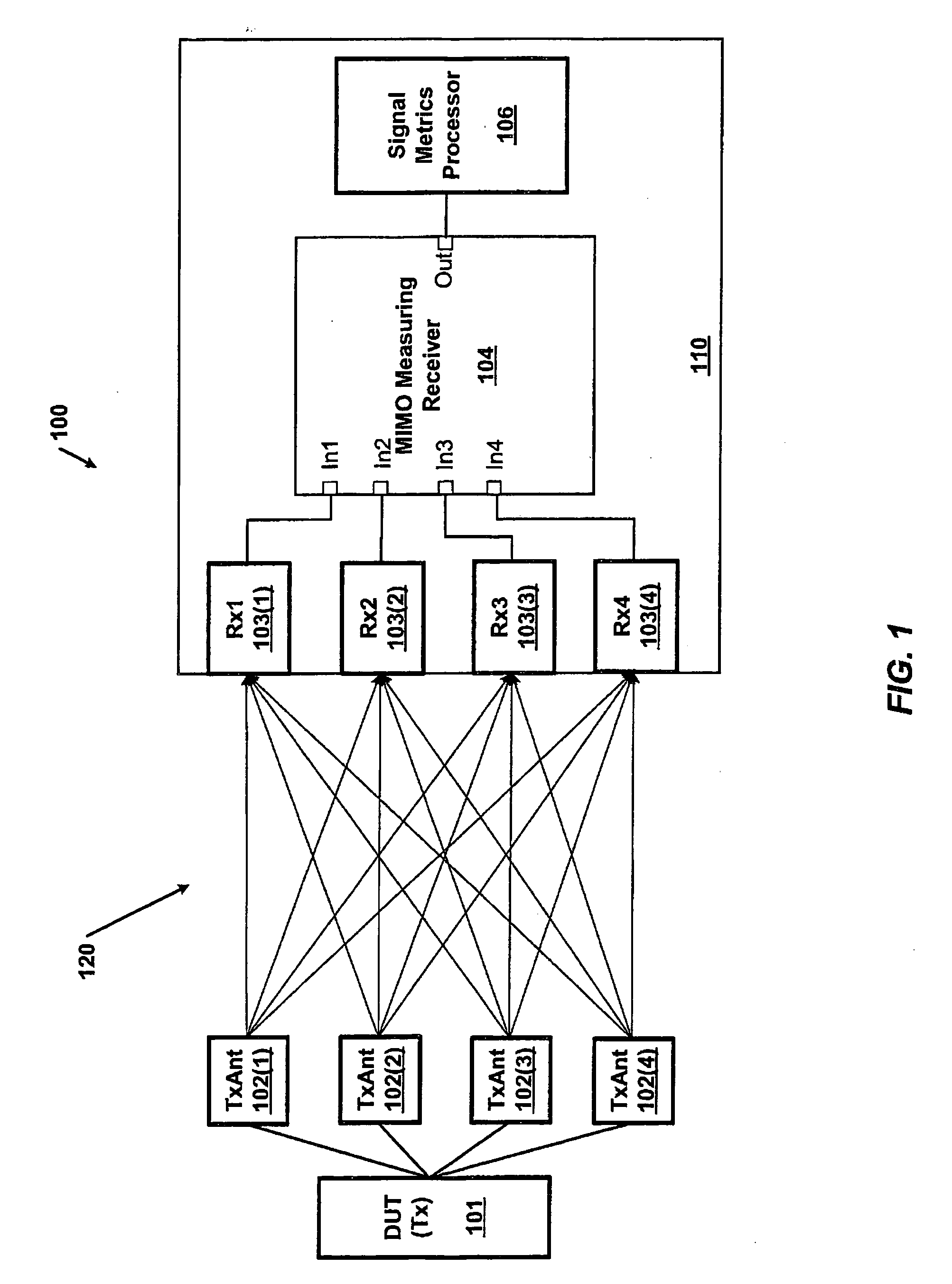
Systems and methods for receiving multiple input, multiple output signals for test and analysis of multiple-input, multiple-output systems
InactiveUS20080084951A1Spatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityFrequency changerIntermediate frequency
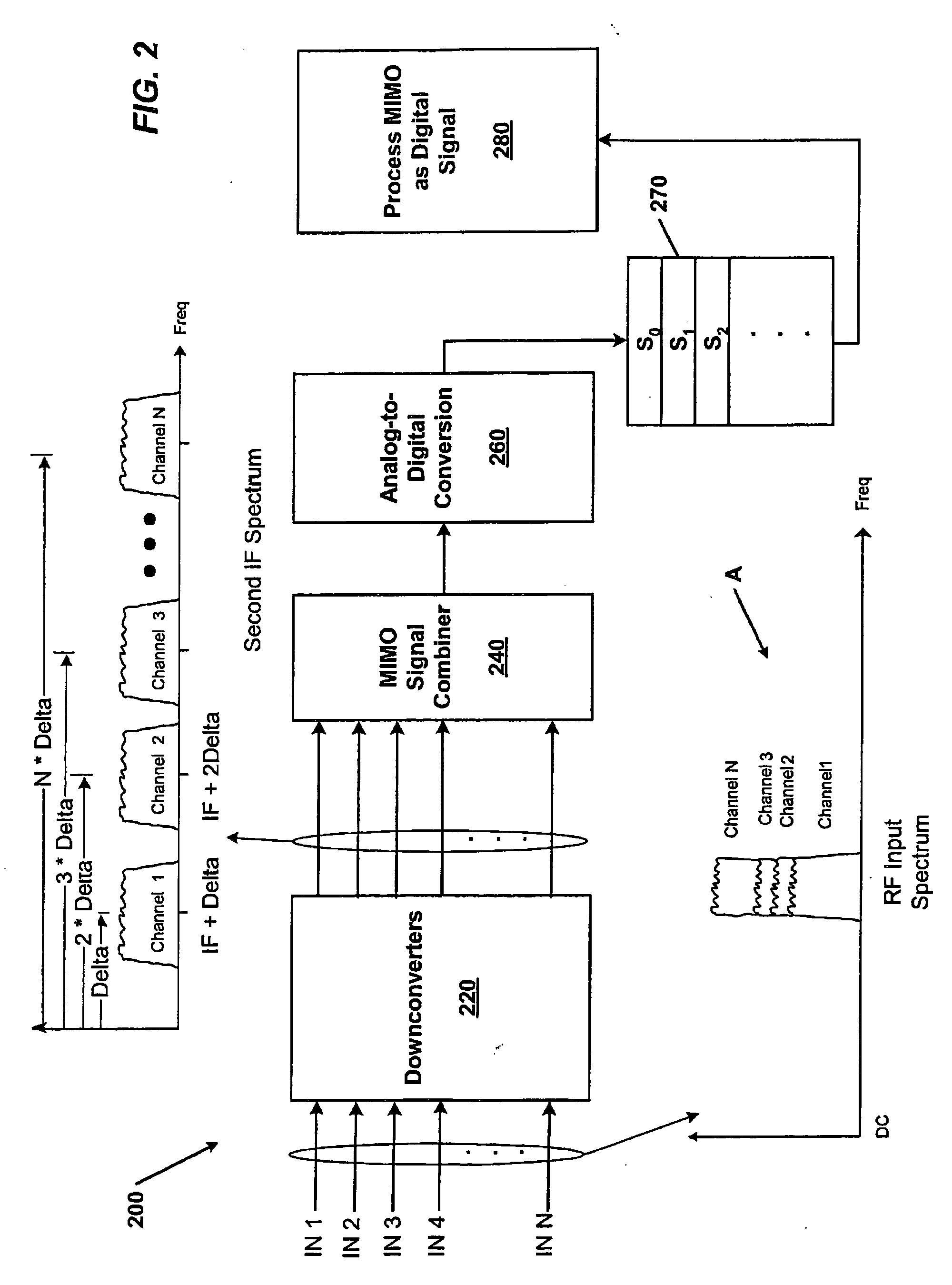
Systems and methods for receiving MIMO signals for testing and analyzing operation of MIMO communications devices. Examples of systems and / or methods for receiving MIMO signals include a measuring receiver with N RF paths consisting of N downconverters. Each downconverter achieves a frequency shift of the input MIMO signal equal to a shifting frequency of a first intermediate frequency (IF) plus a delta determined by the signal bandwidth multiplied by an integer number between 1 and N. The shifted N MIMO signals are combined to generate one combined analog MIMO signal. An analog to digital converter converts the combined analog MIMO signal to a stream of digital samples where the samples may be tested and analyzed with metrics on signals communicated in a MIMO environment. Example systems and method for receiving MIMO signals may also be implemented as a MIMO channel emulator such that samples generated by the ADC may be upconverted to output copies of the original signals to a receiver DUT, for example.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Waiting circuit
A waiting circuit which is utilized in a mobile communication system. The waiting circuit detects a predetermined signal from a base station. The waiting circuit starts other circuits in the mobile communication system which are in a sleep mode when the predetermined signal is received. The predetermined signal is generated in the base station. The predetermined signal has a speed equal to a predetermined symbol rate and is modulated to be an intermediate frequency signal. The intermediate frequency signal is sampled in response to a sampling clock that has a speed equal to an integer times the symbol rate. The sampled intermediate frequency signal is input to a match filter which multiplies the sample signal by a predetermined sequence of coefficients.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
Wireless headset supporting enhanced call functions
ActiveUS20050202857A1Comfortable to wearLess conspicuousInformation formatDevices with wireless LAN interfaceIntermediate frequencyEngineering
A modular wireless headset includes earpiece(s) and microphone(s), where the earpiece and microphone may be physically separate devices. The earpiece renders inbound radio frequencies received from a host device audible. The earpiece may include a receiver module, data recovery module, and speaker module. The receiver module may convert inbound RF signals into low intermediate frequency (IF) signals. The data recovery module recovers audio signals from the low IF signals. The speaker module renders the audio signals audible. The microphone converts received audio signals into outbound RF signals, where the outbound RF signals are transmitted to the host device. The microphone includes an audio input module and a transmitter module. The audio input module is operably coupled to convert received analog audio signals into digital audio signals. The transmitter module is operably coupled to convert the digital audio signals into the outbound RF signals.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Determining noise levels in frequency band(s) in distributed antenna systems and adjusting frequency band(s) of communications signals in response, and related components, systems, and methods
InactiveUS20130295980A1Improve communication performanceTransmission monitoringRadio transmissionFrequency bandIntermediate frequency
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM WIRELESS
Simultaneous tuning of multiple channels using intermediate frequency sub-sampling
ActiveUS6888888B1Improve cooling effectImprove reliabilityTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesAudio power amplifierIntermediate frequency
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
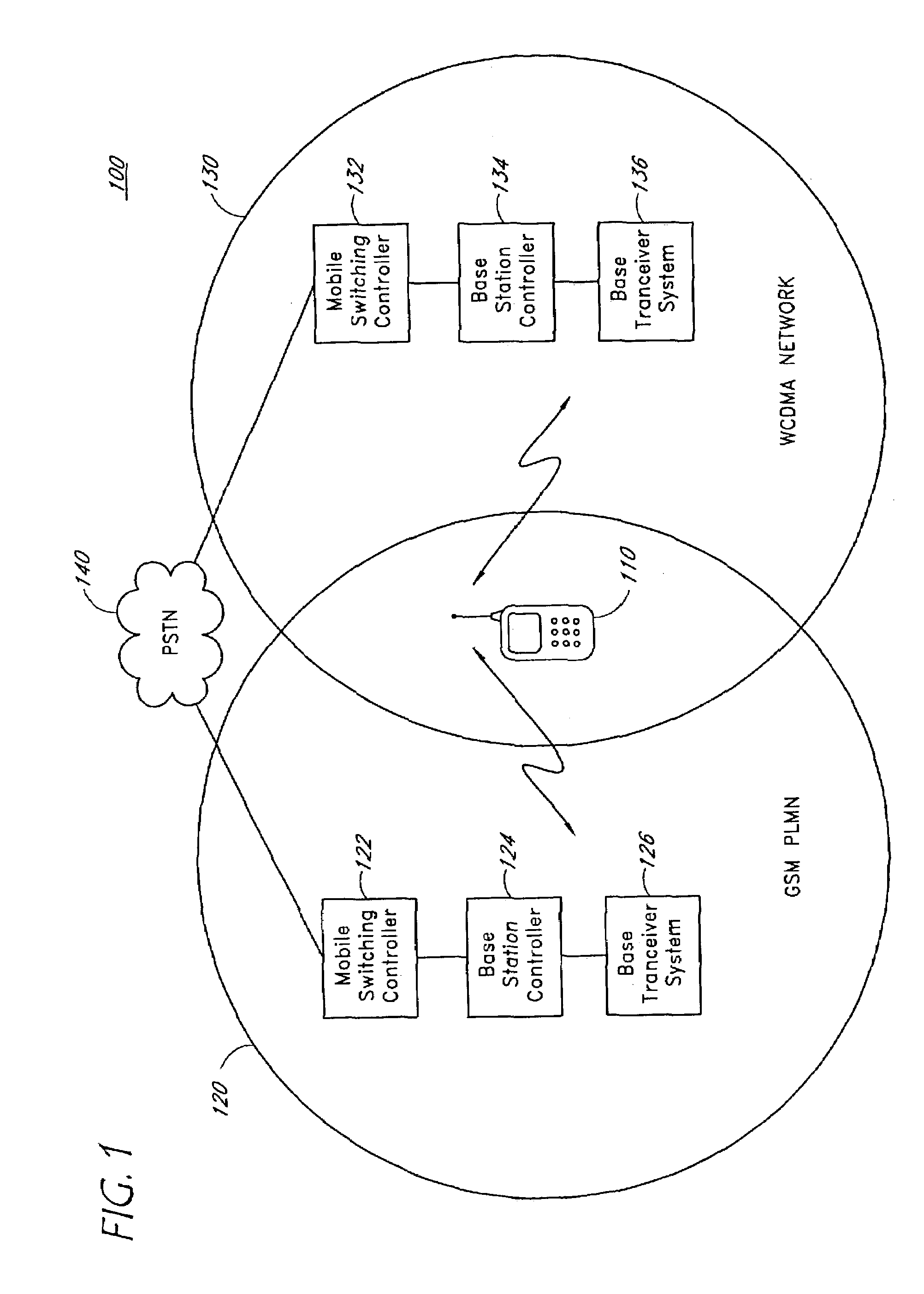
Radio communication apparatus, transmitter apparatus and receiver apparatus
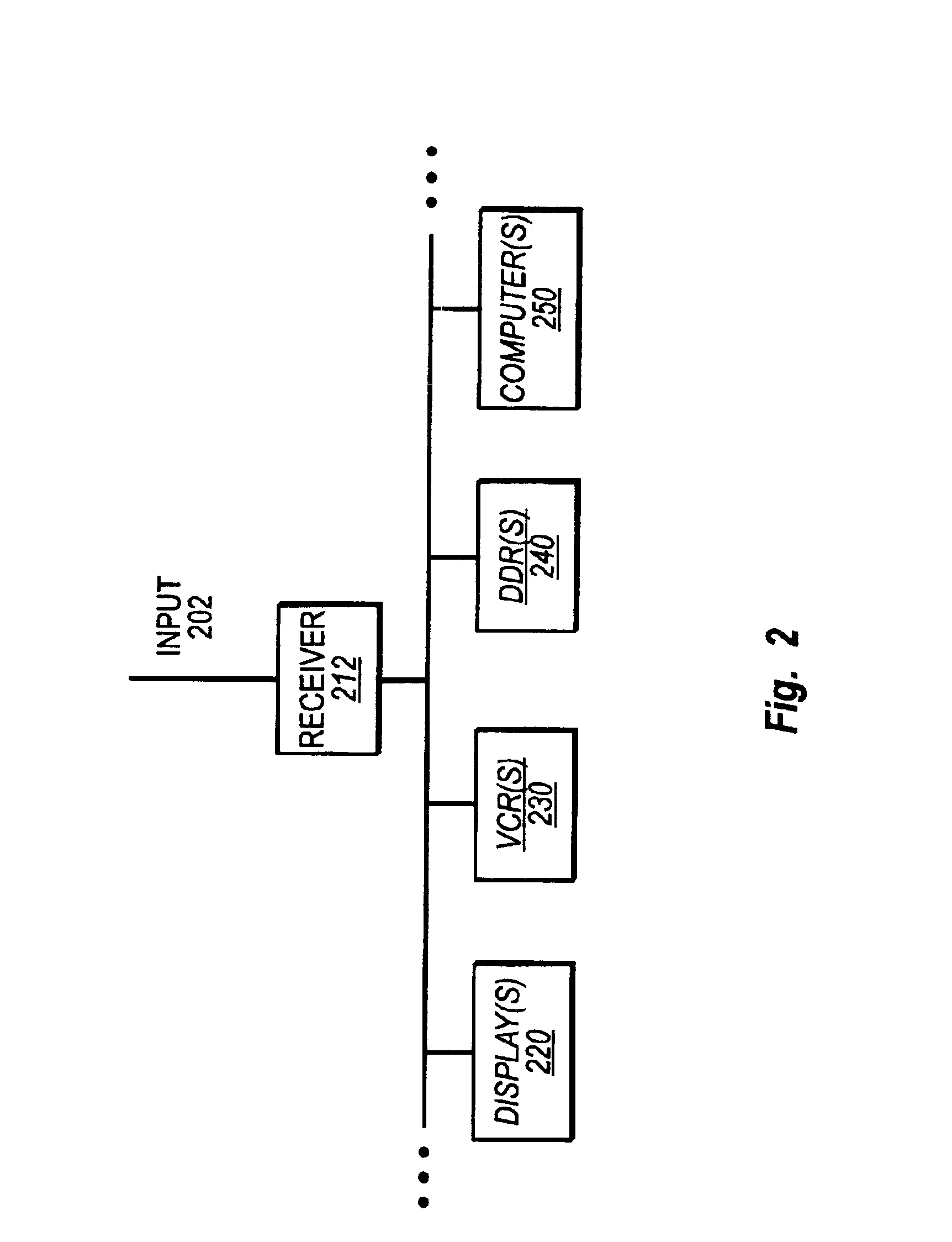
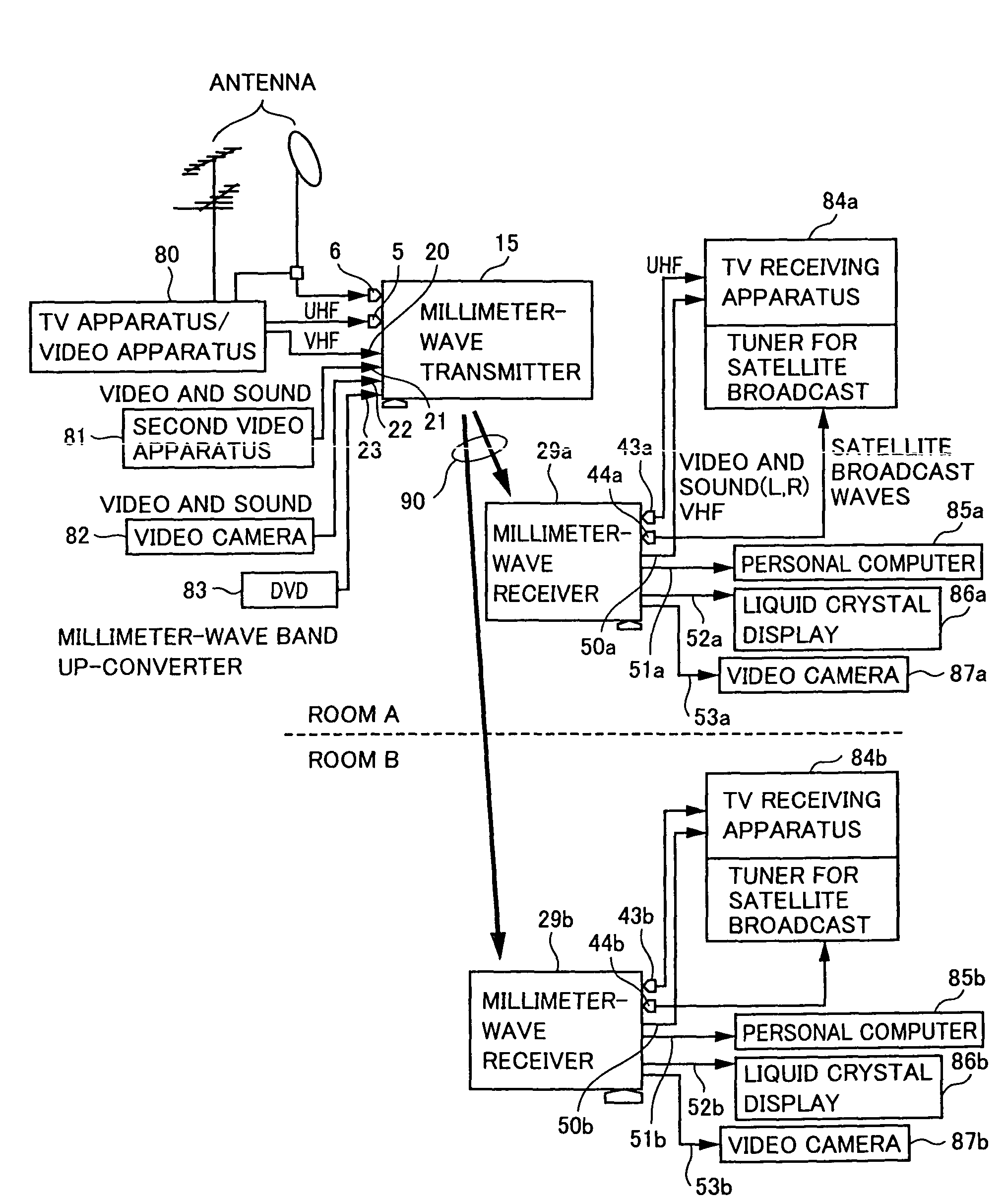
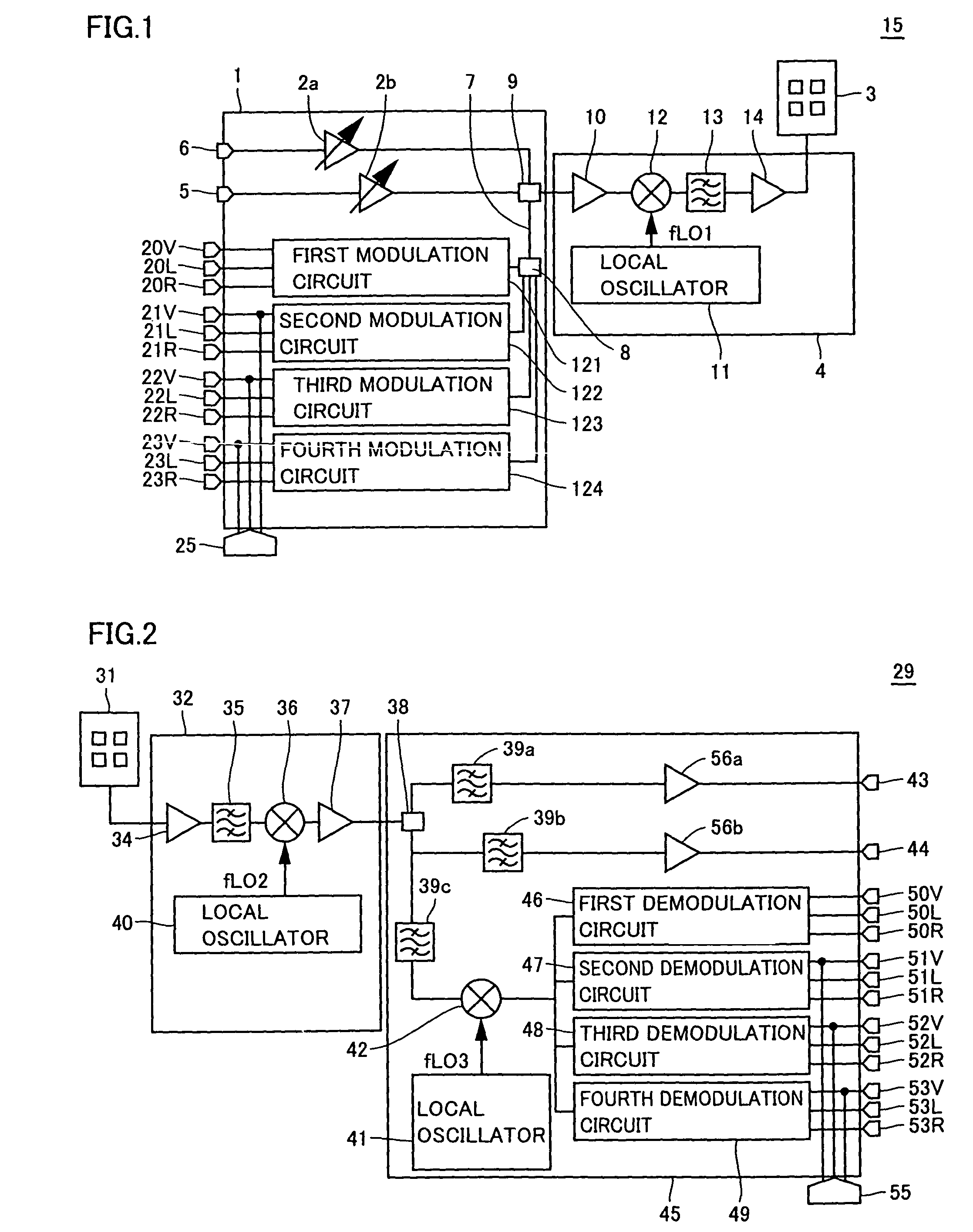
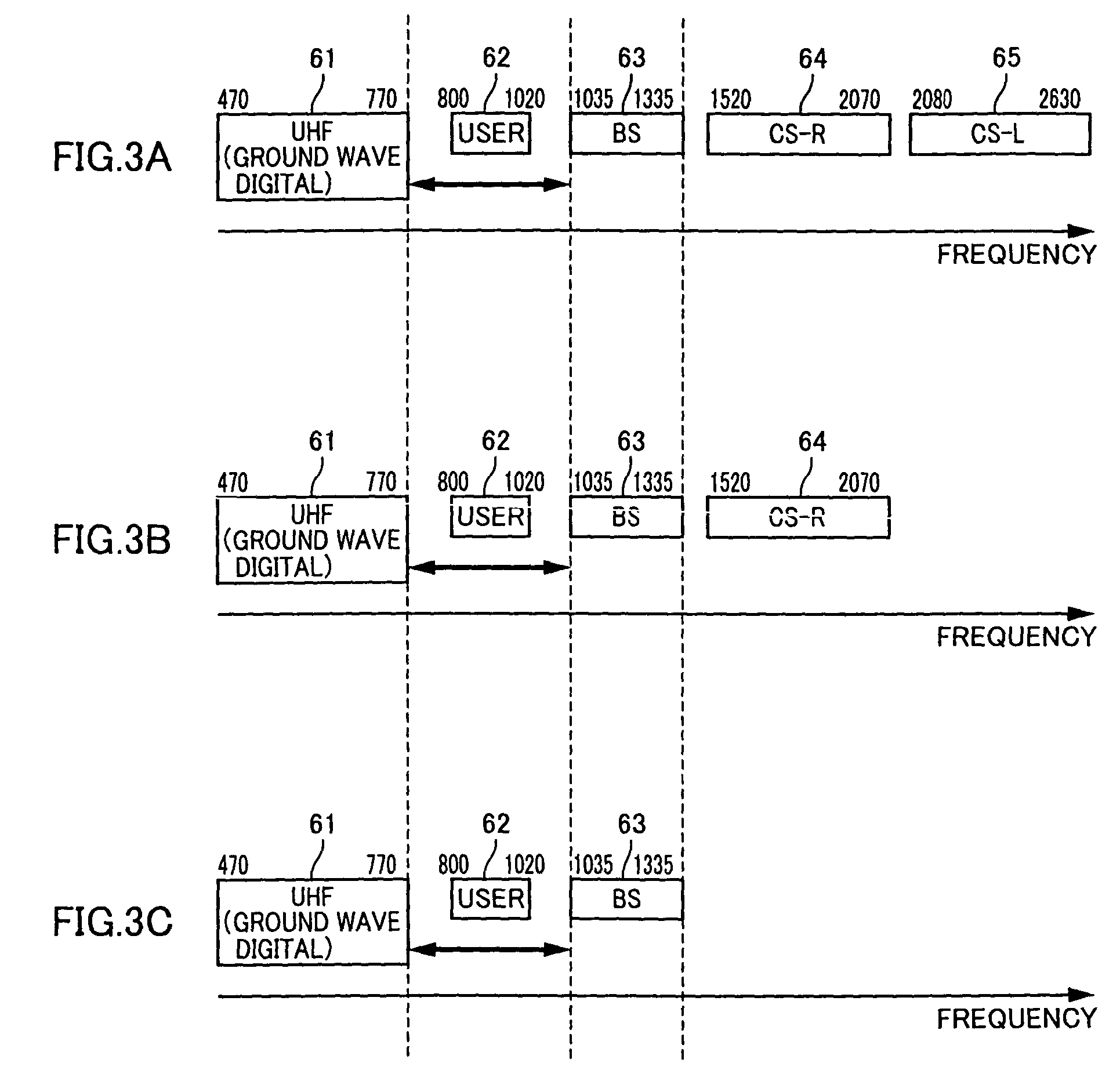
InactiveUS7697574B2Improve frequency stabilityTelevision system detailsActive radio relay systemsMultiplexingSignal wave
The present invention provides a radio communication device, a transmitter and a receiver capable of handling a plurality of signal waves. A radio communication device has a millimeter-wave transmitter (15) and a millimeter-wave receiver (29). Millimeter-wave transmitter (15) includes a multiplexing circuit (1), a millimeter-wave up-converter (4) and an antenna (3), and the millimeter-receiver includes an antenna (31), a millimeter-wave down-converter (32) and an output processing circuit (45). The signal waves dedicated to the user are modulated by a modulation circuit (121 to 124) so as to be allocated between the ground broadcast waves and satellite broadcast waves. The frequencies are multiplexed in an intermediate frequency band, after that, the multiplexed frequencies are converted into a millimeter-wave band and the resultant is transmitted. On the reception side, the multiplexed waves are down-converted, separated to signal waves and demodulated.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com