Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1192 results about "Frequency multiplier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
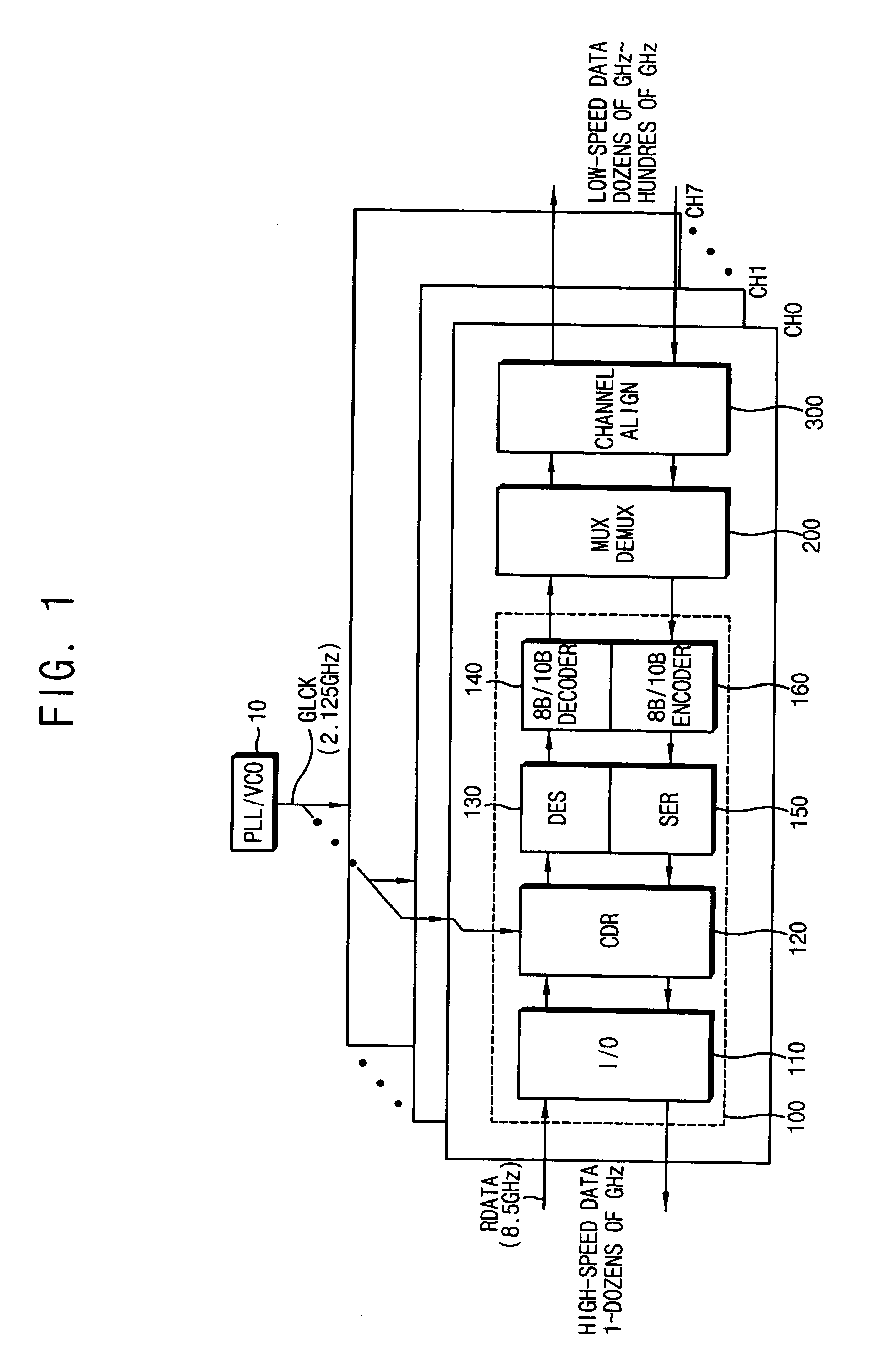
In electronics, a frequency multiplier is an electronic circuit that generates an output signal whose output frequency is a harmonic (multiple) of its input frequency. Frequency multipliers consist of a nonlinear circuit that distorts the input signal and consequently generates harmonics of the input signal. A subsequent bandpass filter selects the desired harmonic frequency and removes the unwanted fundamental and other harmonics from the output.
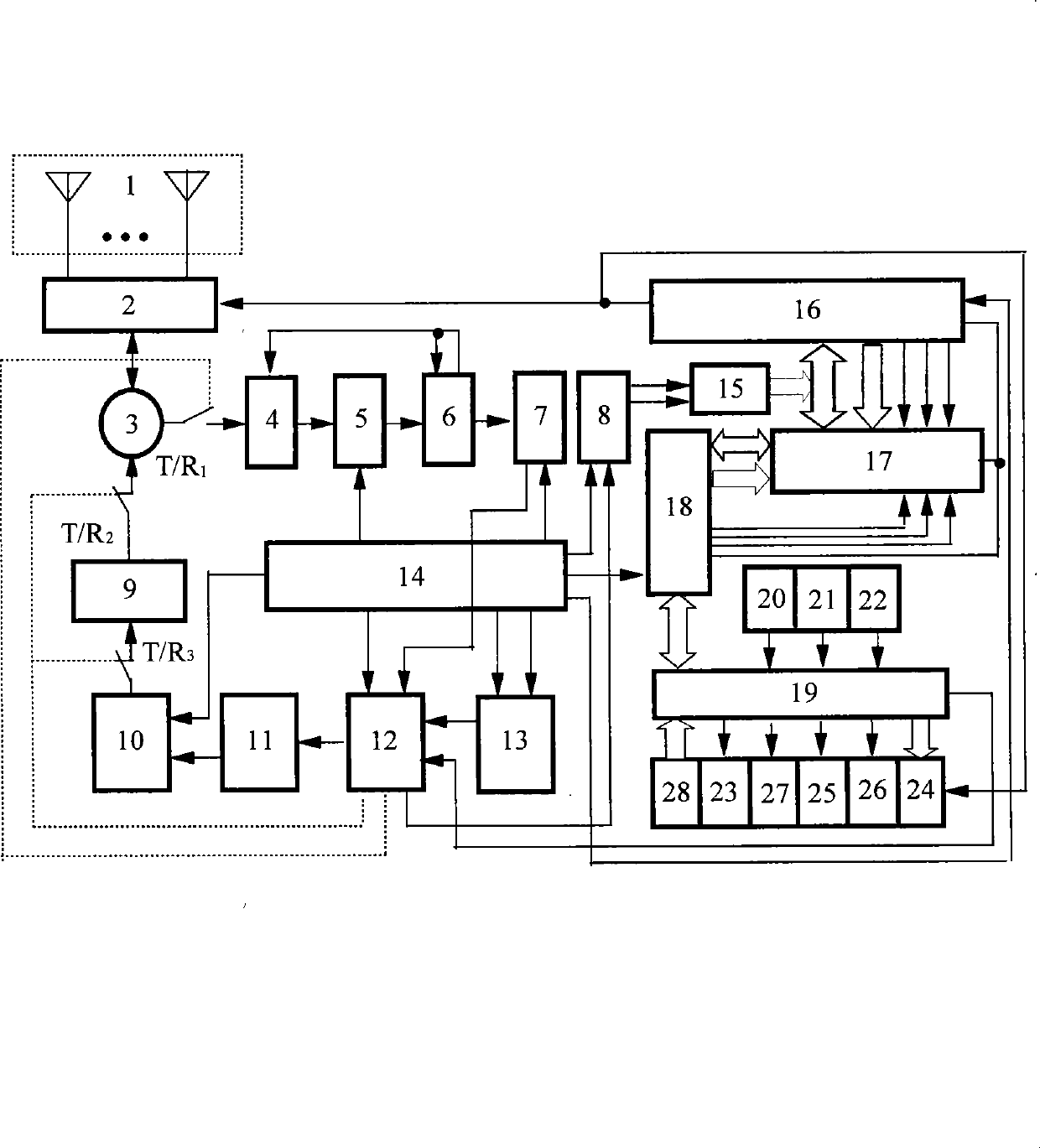
Millimeter wave pulsed radar system
InactiveUS7002511B1Improve efficiencySimplified frequency synthesizer designRadio wave reradiation/reflectionQuadrature modulatorLocal oscillator signal
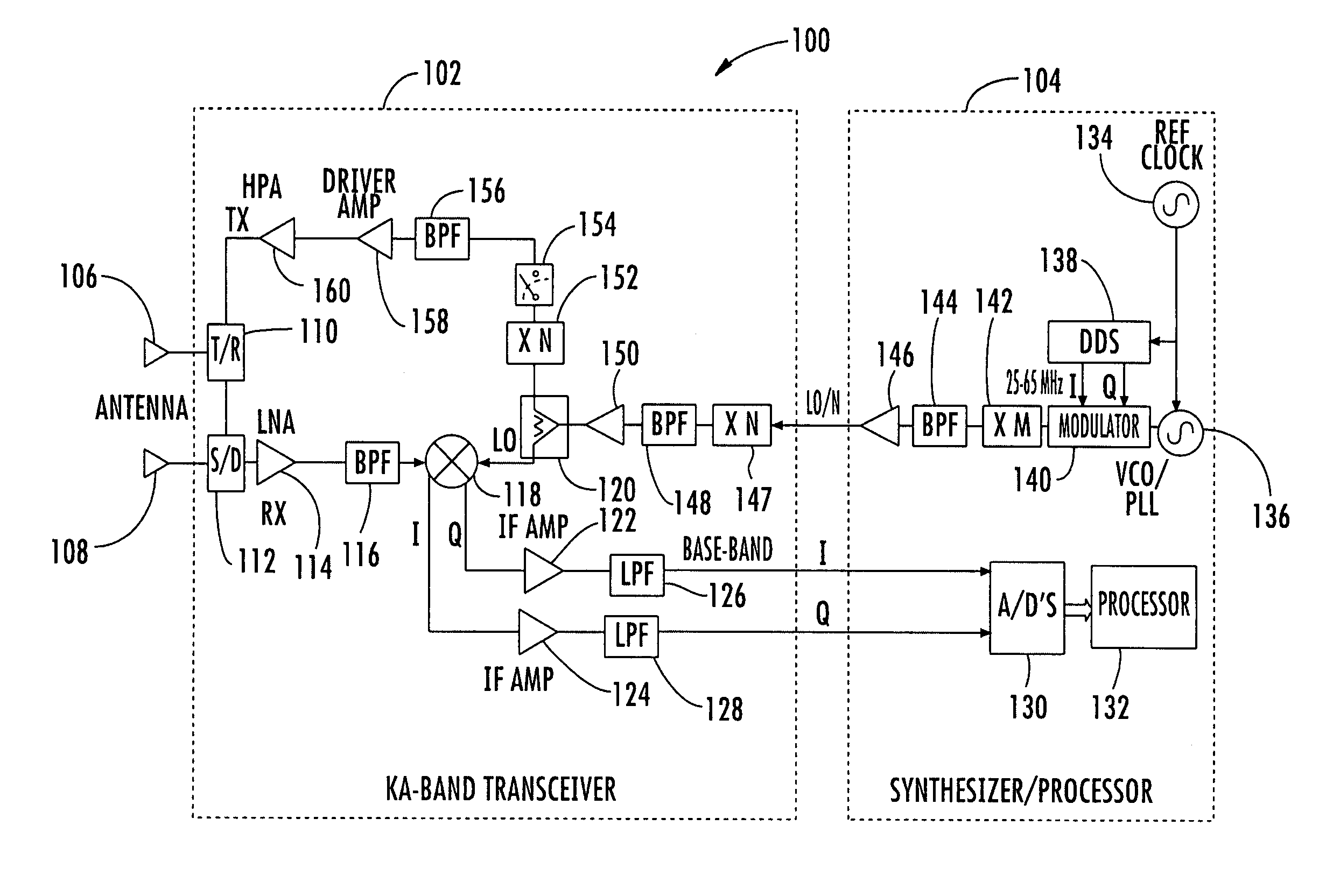
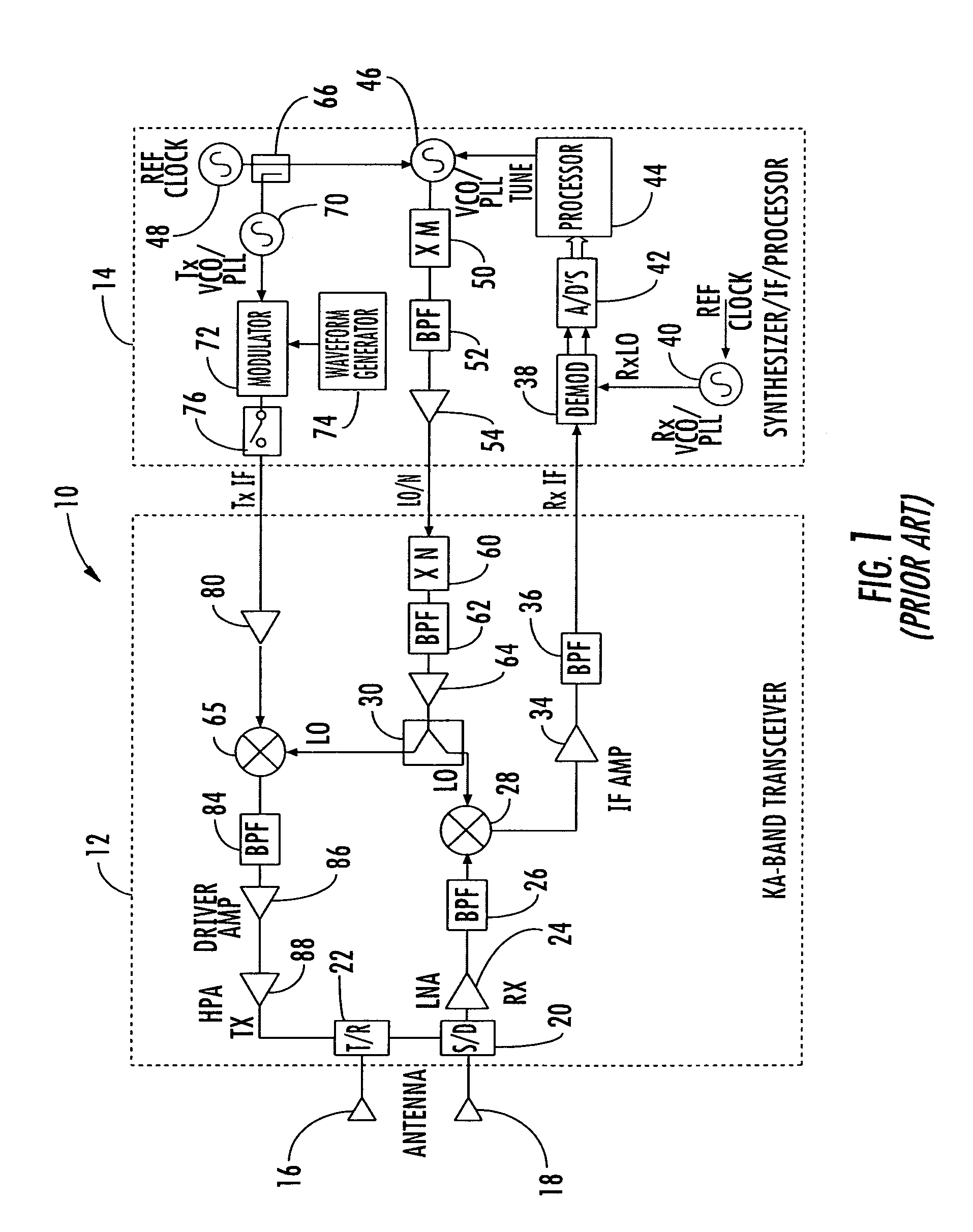
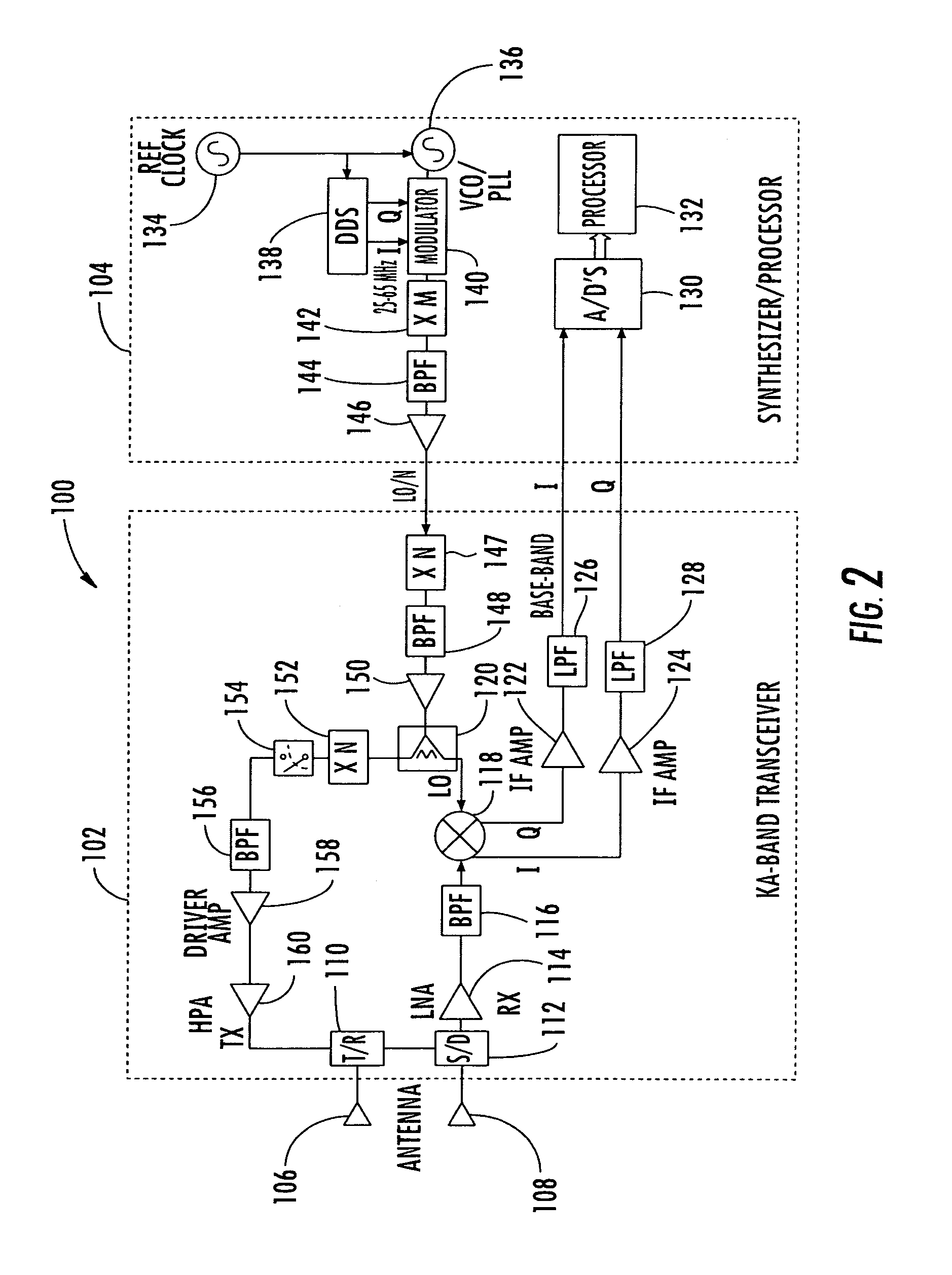
A millimeter wave pulsed radar system includes a radar synthesizer having a voltage controlled oscillator / phase locked loop (VCO / PLL) circuit, direct digital synthesizer (DDS) circuit and quadrature modulator circuit that are operative to generate an intermediate frequency local oscillator signal (IF / LO signal). A radar transceiver is operative with the radar synthesizer for receiving the IF / LO signal. A transmitter section has a frequency multiplier that multiplies the IF / LO signal up to a millimeter wave (MMW) radar signal and a receiver section and includes a direct conversion mixer that receives a MMW radar signal and the IF / LO signal to produce I / Q baseband signals that are later digitized and processed.
Owner:REVEAL IMAGING
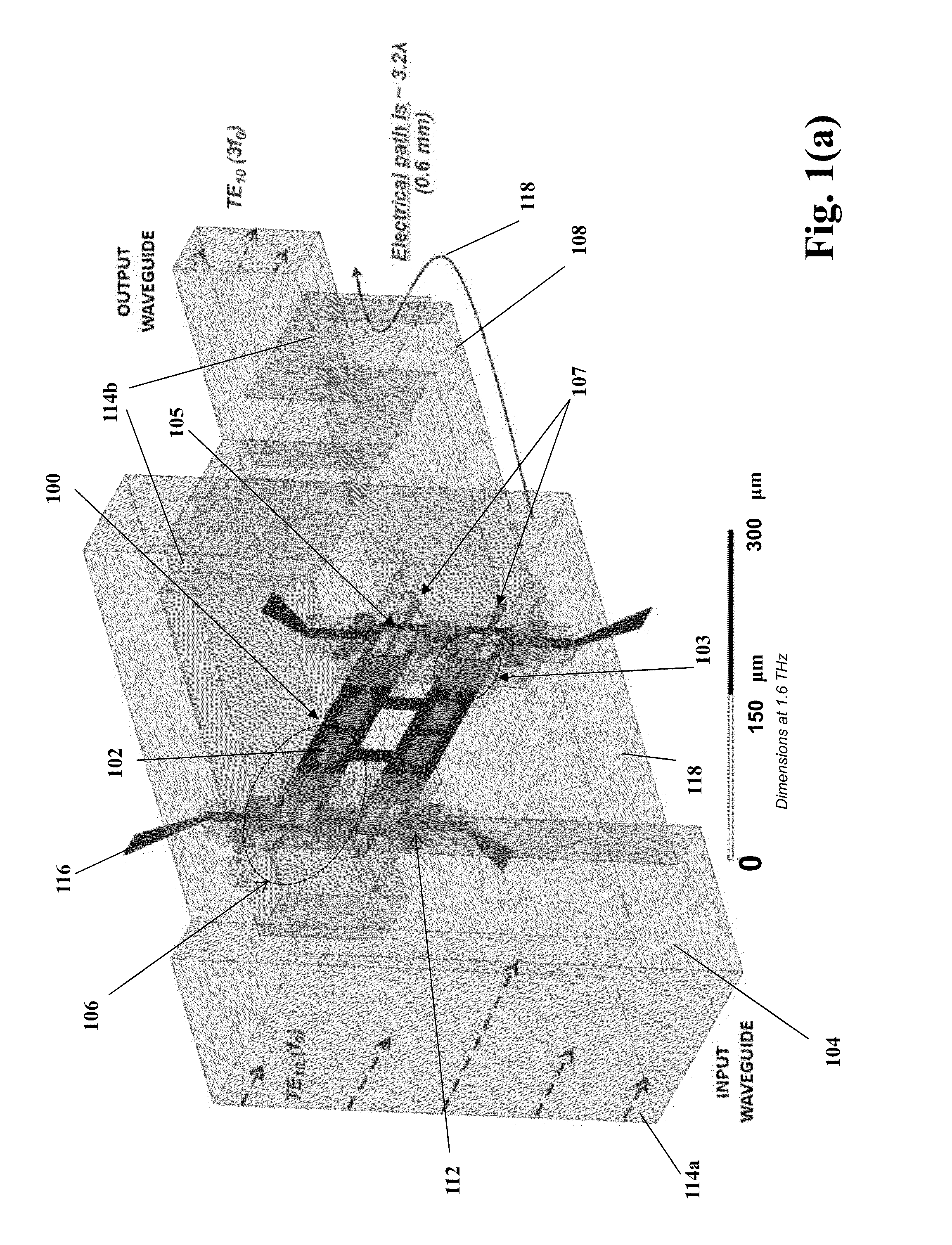
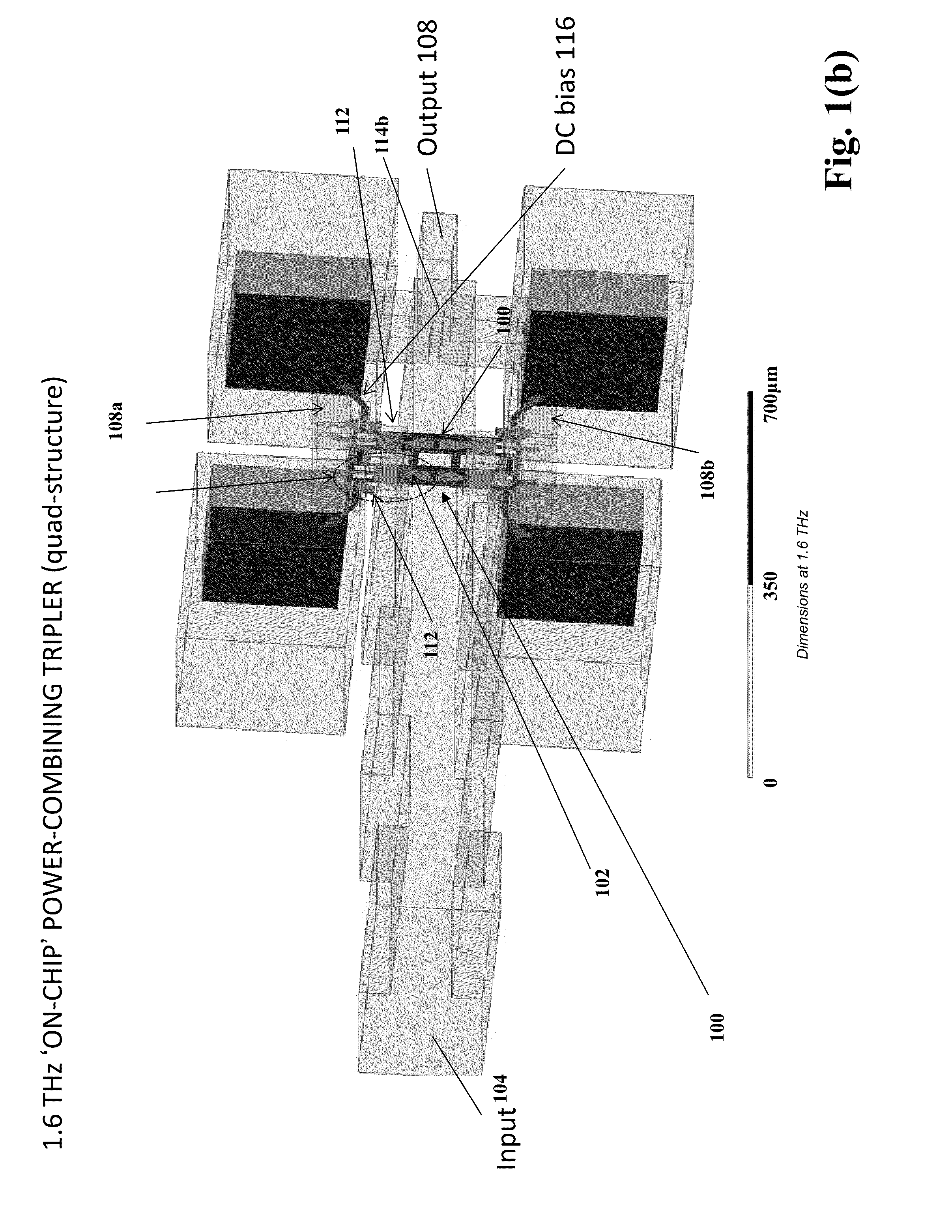
On-chip power-combining for high-power schottky diode based frequency multipliers
ActiveUS9143084B2Split evenlySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHarmonicFrequency multiplier
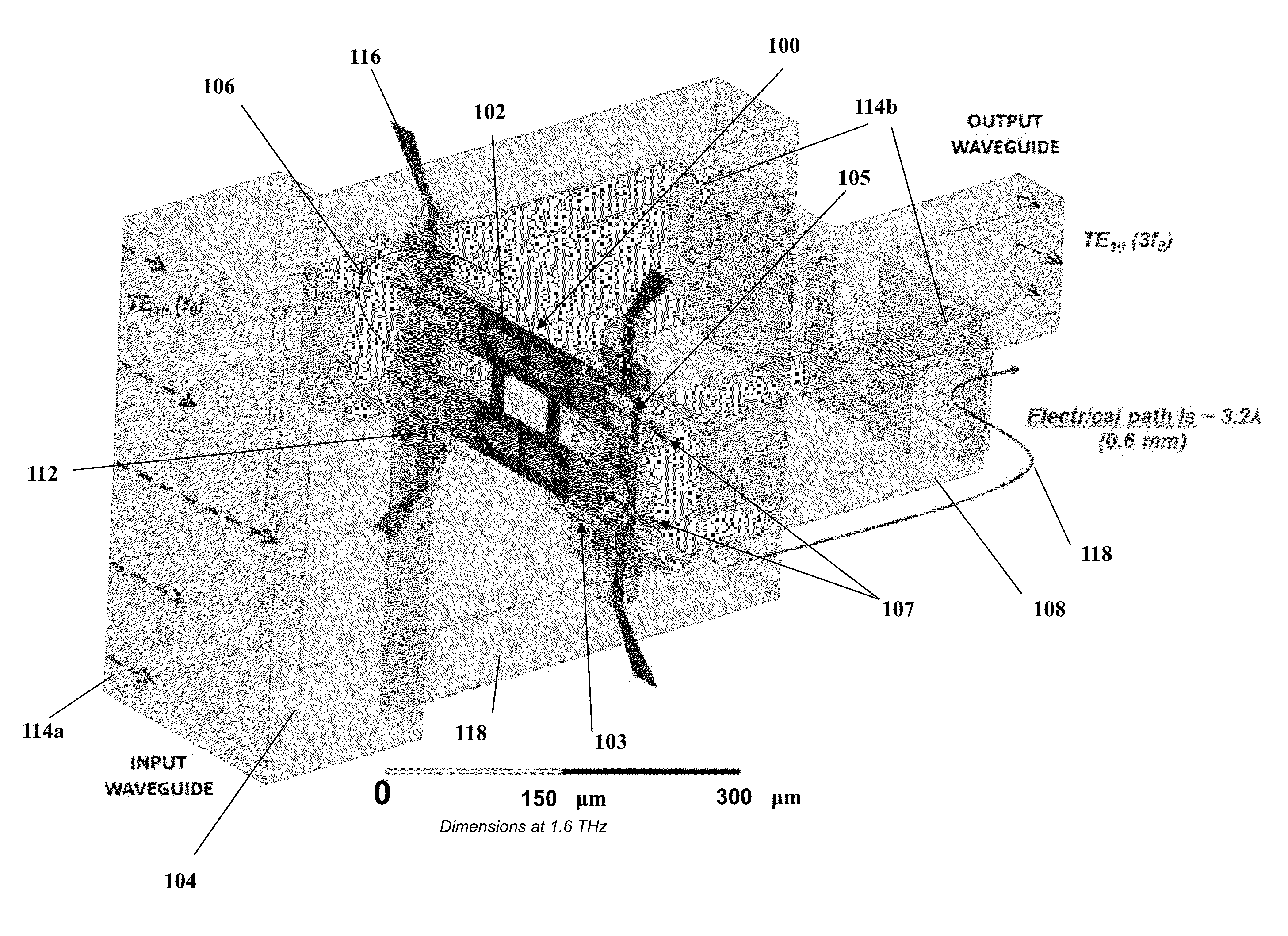
A novel MMIC on-chip power-combined frequency multiplier device and a method of fabricating the same, comprising two or more multiplying structures integrated on a single chip, wherein each of the integrated multiplying structures are electrically identical and each of the multiplying structures include one input antenna (E-probe) for receiving an input signal in the millimeter-wave, submillimeter-wave or terahertz frequency range inputted on the chip, a stripline based input matching network electrically connecting the input antennas to two or more Schottky diodes in a balanced configuration, two or more Schottky diodes that are used as nonlinear semiconductor devices to generate harmonics out of the input signal and produce the multiplied output signal, stripline based output matching networks for transmitting the output signal from the Schottky diodes to an output antenna, and an output antenna (E-probe) for transmitting the output signal off the chip into the output waveguide transmission line.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
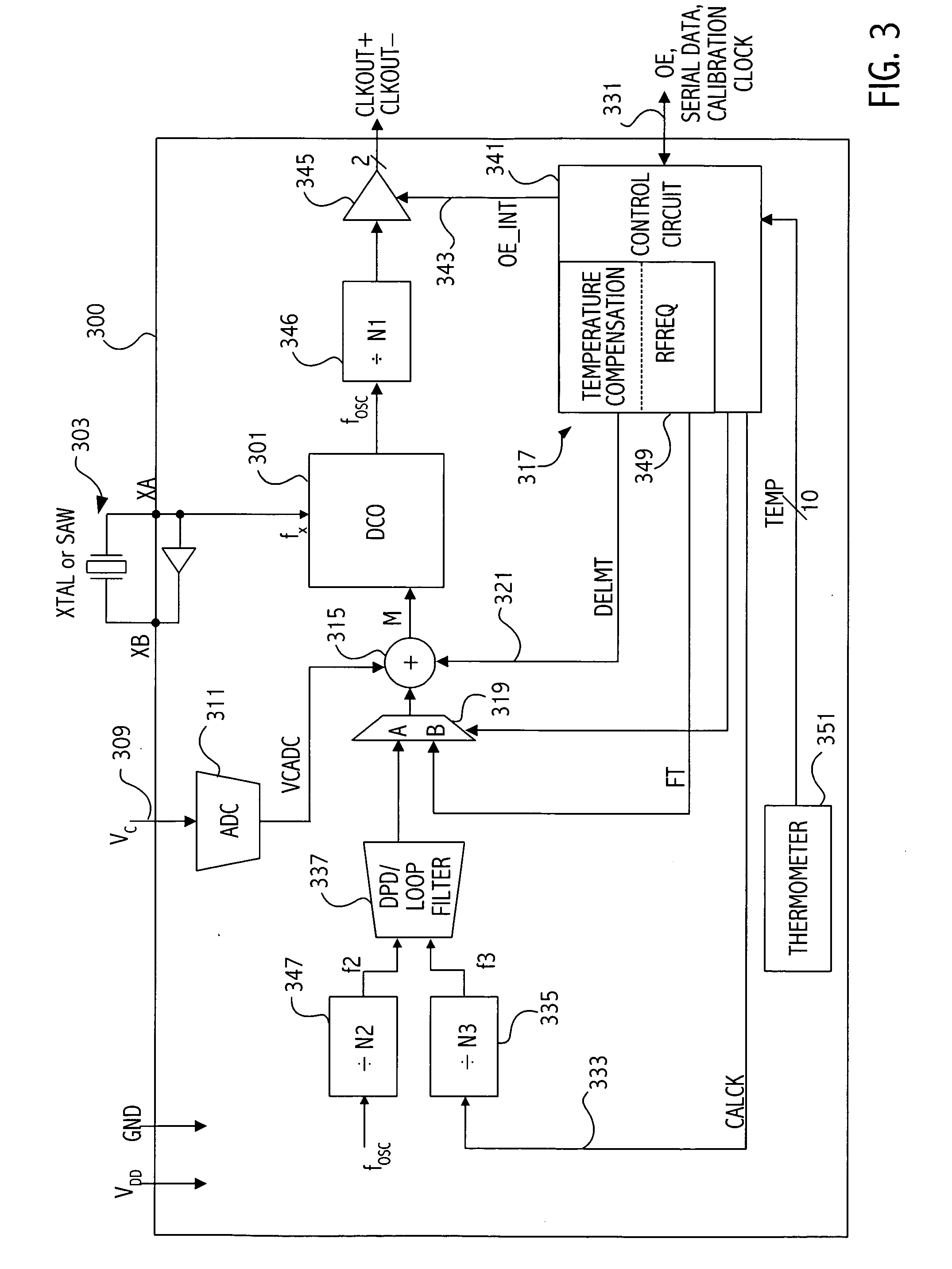
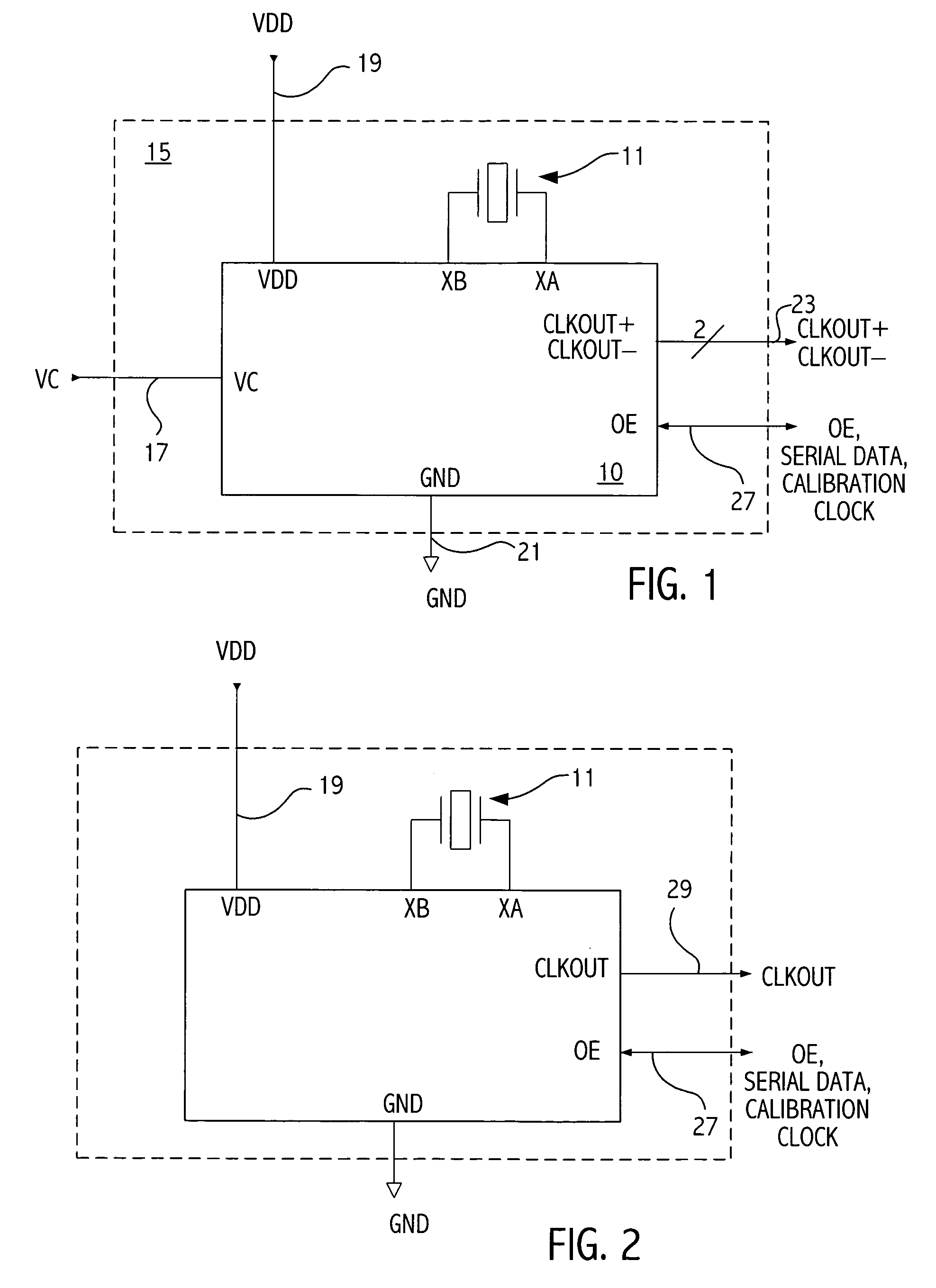
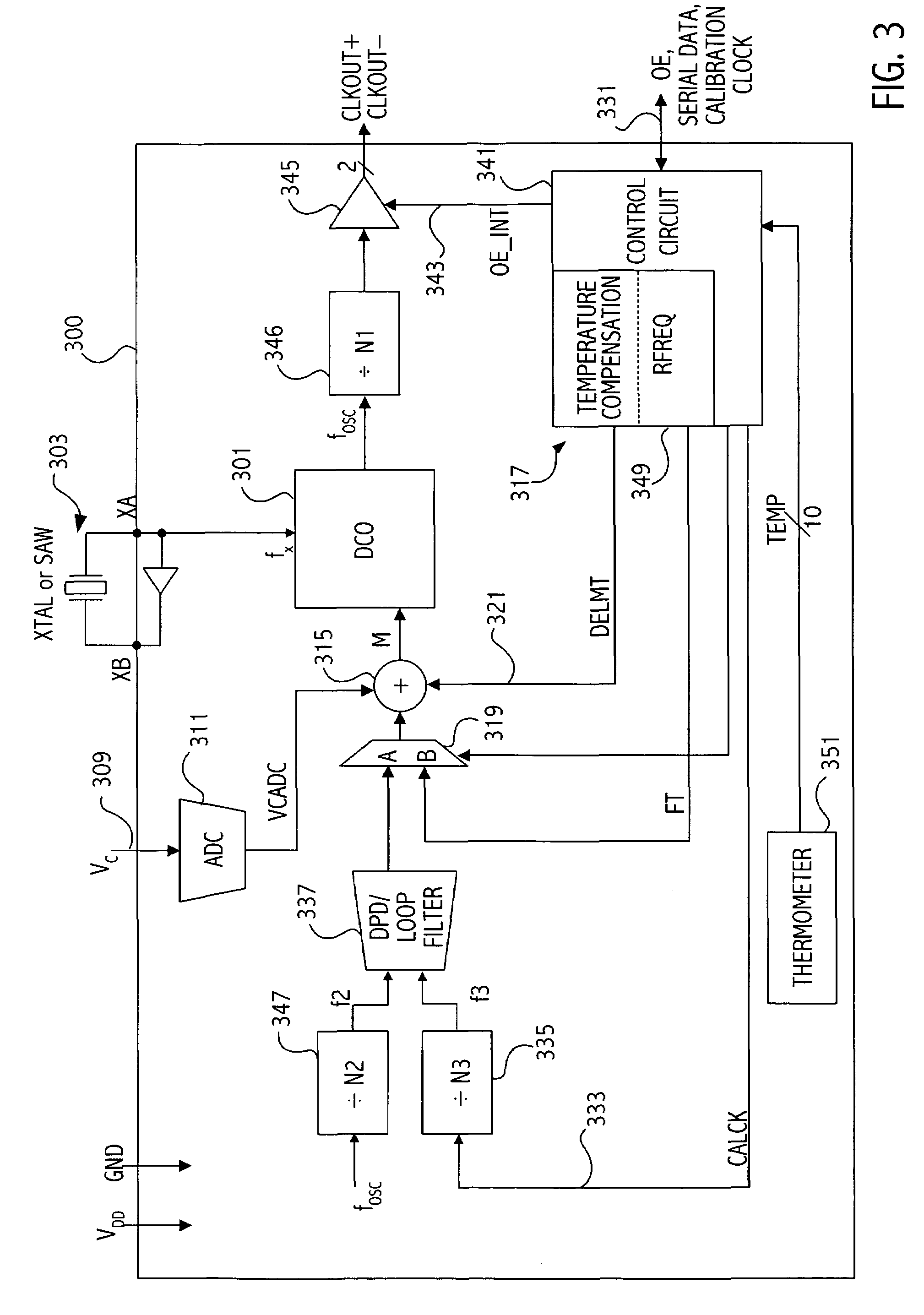
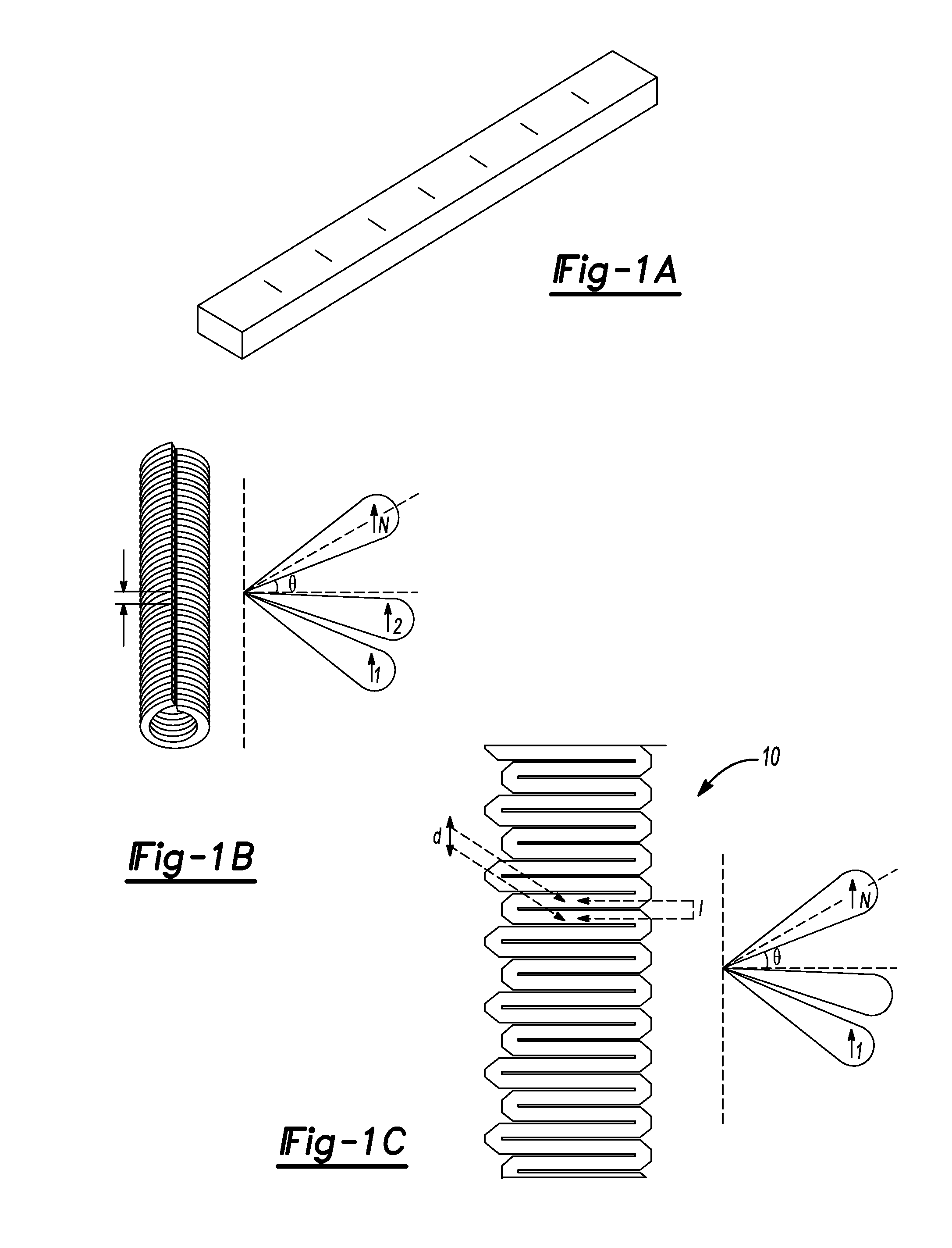
Frequency and/or phase compensated microelectromechanical oscillator
ActiveUS20050151592A1Reduce the gap widthIncreasing available voltage to applyRadiation pyrometryPulse automatic controlFrequency synthesizerFrequency multiplier
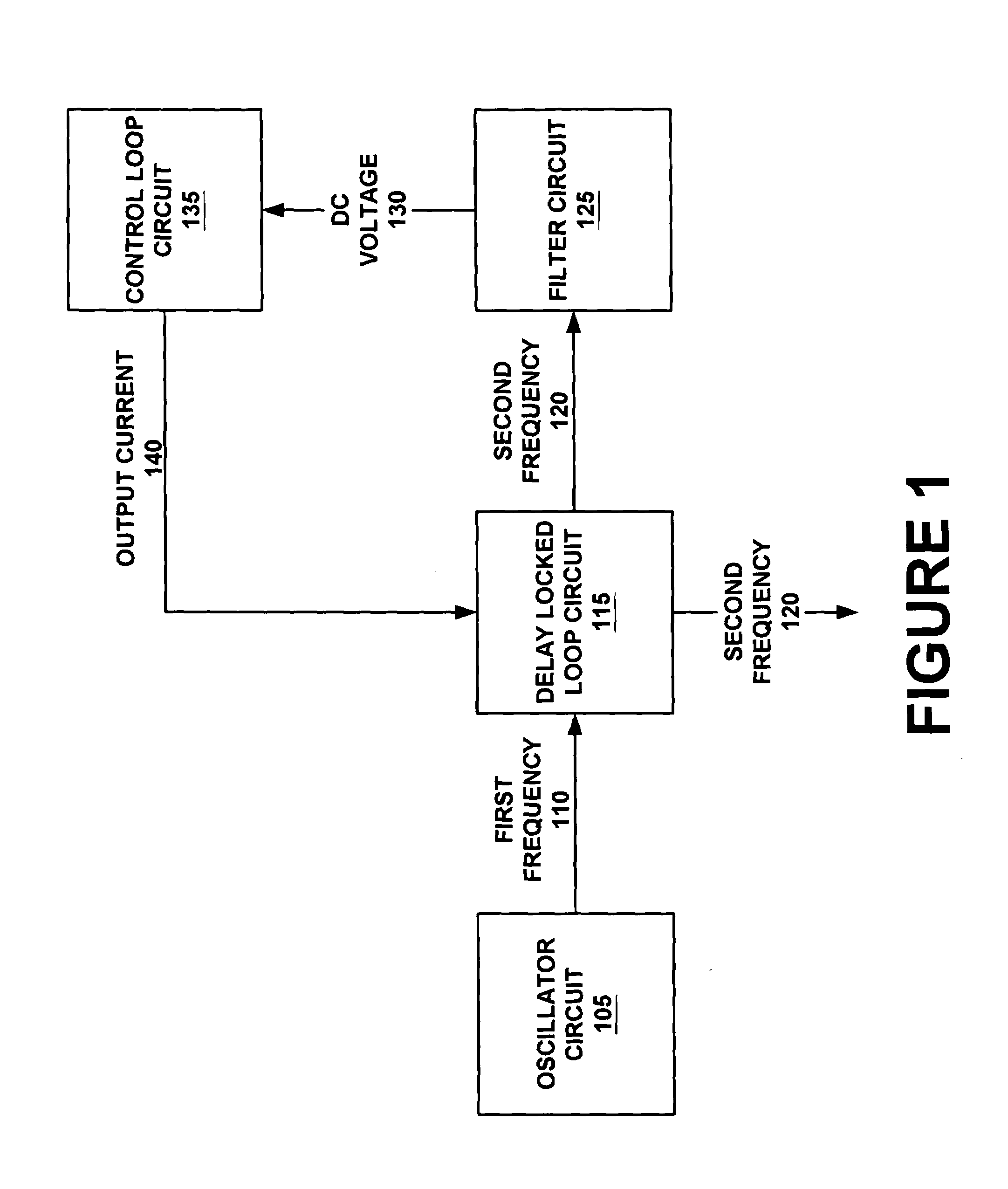
There are many inventions described and illustrated herein. In one aspect, the present invention is directed to a compensated microelectromechanical oscillator, having a microelectromechanical resonator that generates an output signal and frequency adjustment circuitry, coupled to the microelectromechanical resonator to receive the output signal of the microelectromechanical resonator and, in response to a set of values, to generate an output signal having second frequency. In one embodiment, the values may be determined using the frequency of the output signal of the microelectromechanical resonator, which depends on the operating temperature of the microelectromechanical resonator and / or manufacturing variations of the microelectromechanical resonator. In one embodiment, the frequency adjustment circuitry may include frequency multiplier circuitry, for example, PLLs, DLLs, digital / frequency synthesizers and / or FLLs, as well as any combinations and permutations thereof. The frequency adjustment circuitry, in addition or in lieu thereof, may include frequency divider circuitry, for example, DLLS, digital / frequency synthesizers (for example, DDS) and / or FLLs, as well as any combinations and permutations thereof.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
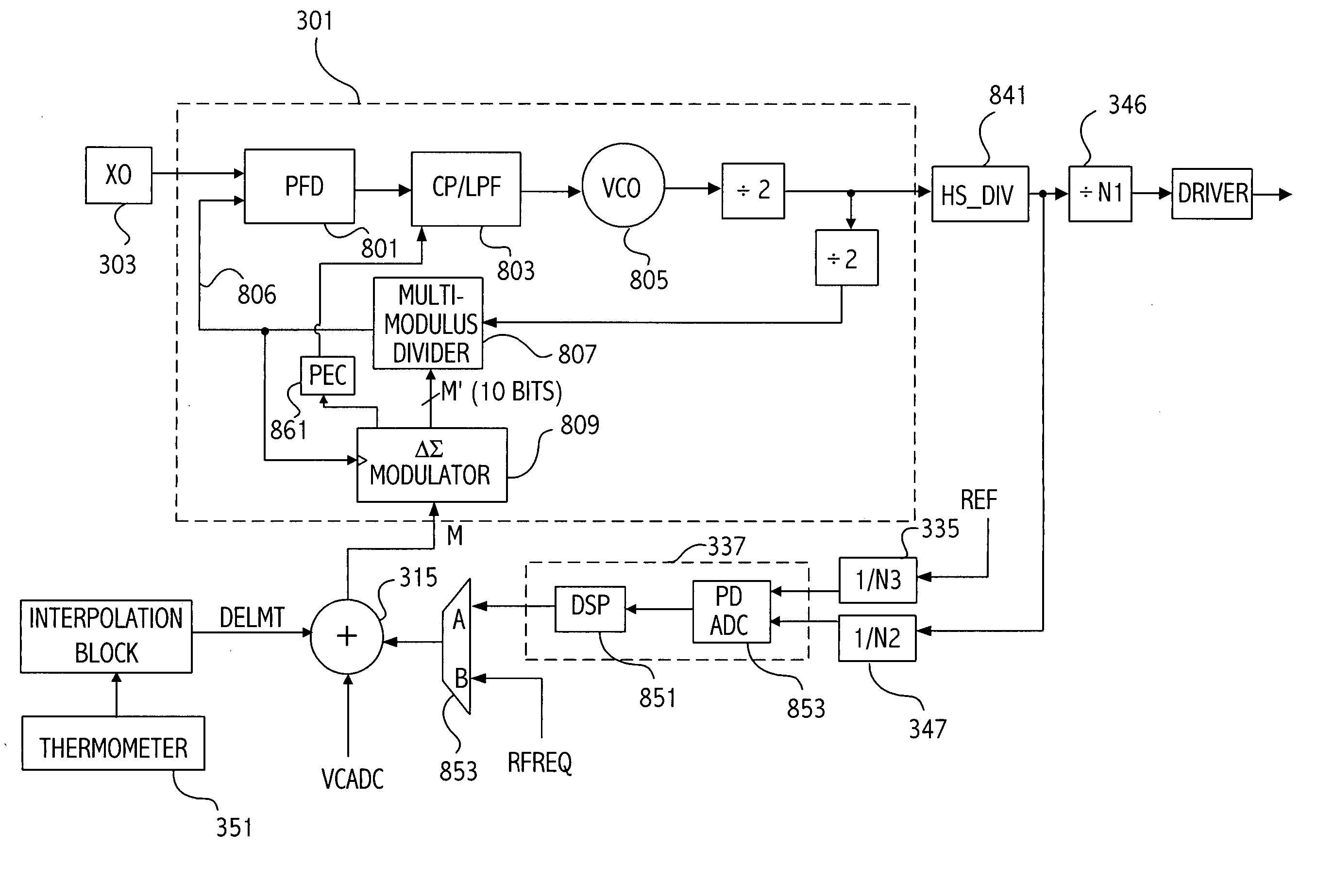
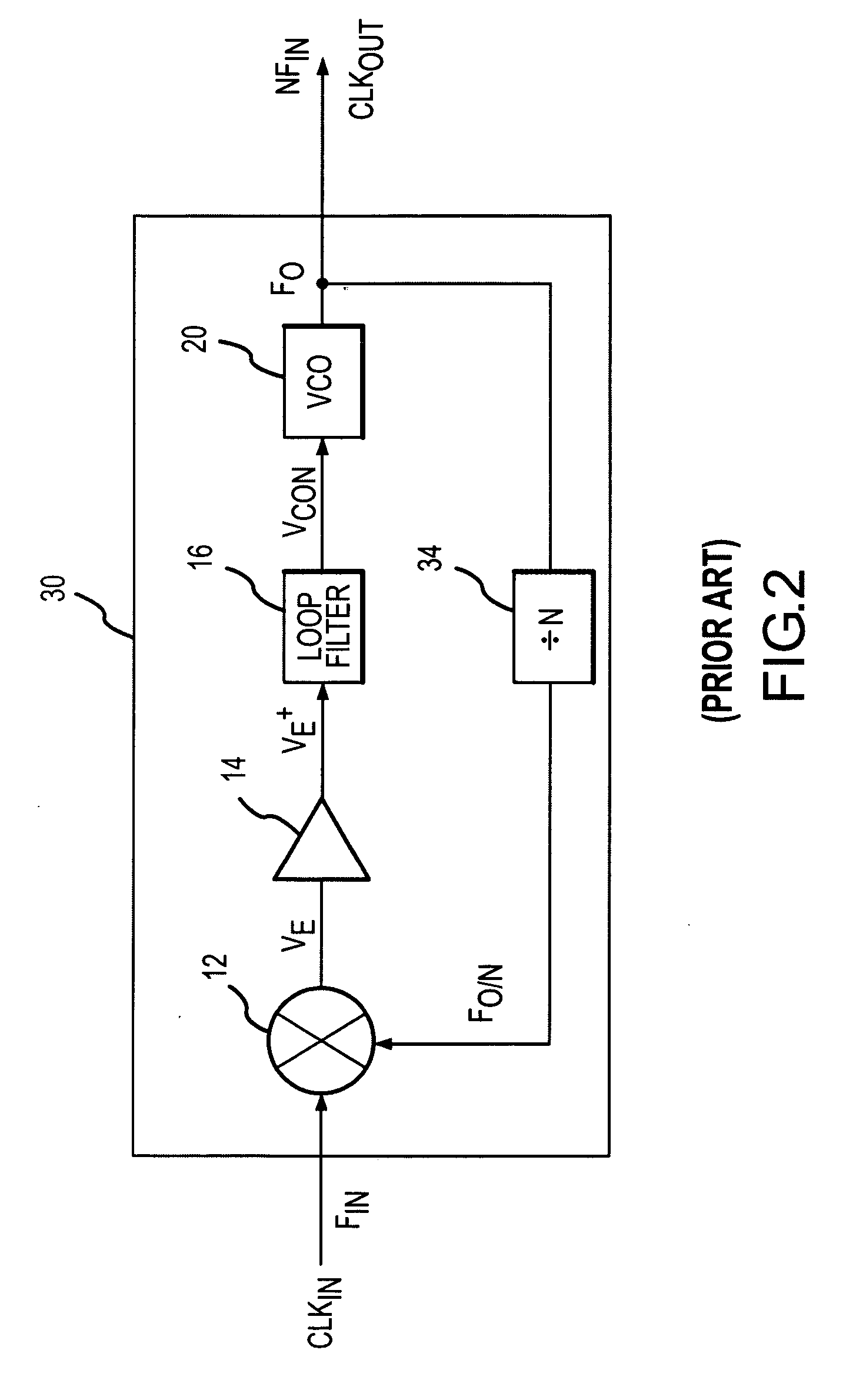
Dual loop architecture useful for a programmable clock source and clock multiplier applications
InactiveUS20040232995A1Pulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationFrequency multiplierDigital control
A first phase-locked loop (PLL) circuit includes an input for receiving a timing reference signal from an oscillator, a controllable oscillator circuit supplying an oscillator output signal, and a multi-modulus feedback divider circuit. A second control loop circuit is selectably coupled through a select circuit to supply a digital control value (M) to the multi-modulus feedback divider circuit of the first loop circuit to thereby control the oscillator output signal. While the second control loop is coupled to supply the control value to the feedback divider circuit, the control value is determined according to a detected difference between the oscillator output signal and a reference signal coupled to the second control loop circuit at a divider circuit. While the second control loop circuit is not coupled to control the first PLL circuit, the first PLL circuit receives a digital control value to control a divide ratio of the feedback divider, the digital control value is determined at least in part according to a stored control value stored in nonvolatile storage, the stored control value corresponding to a desired frequency of the oscillator output signal.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
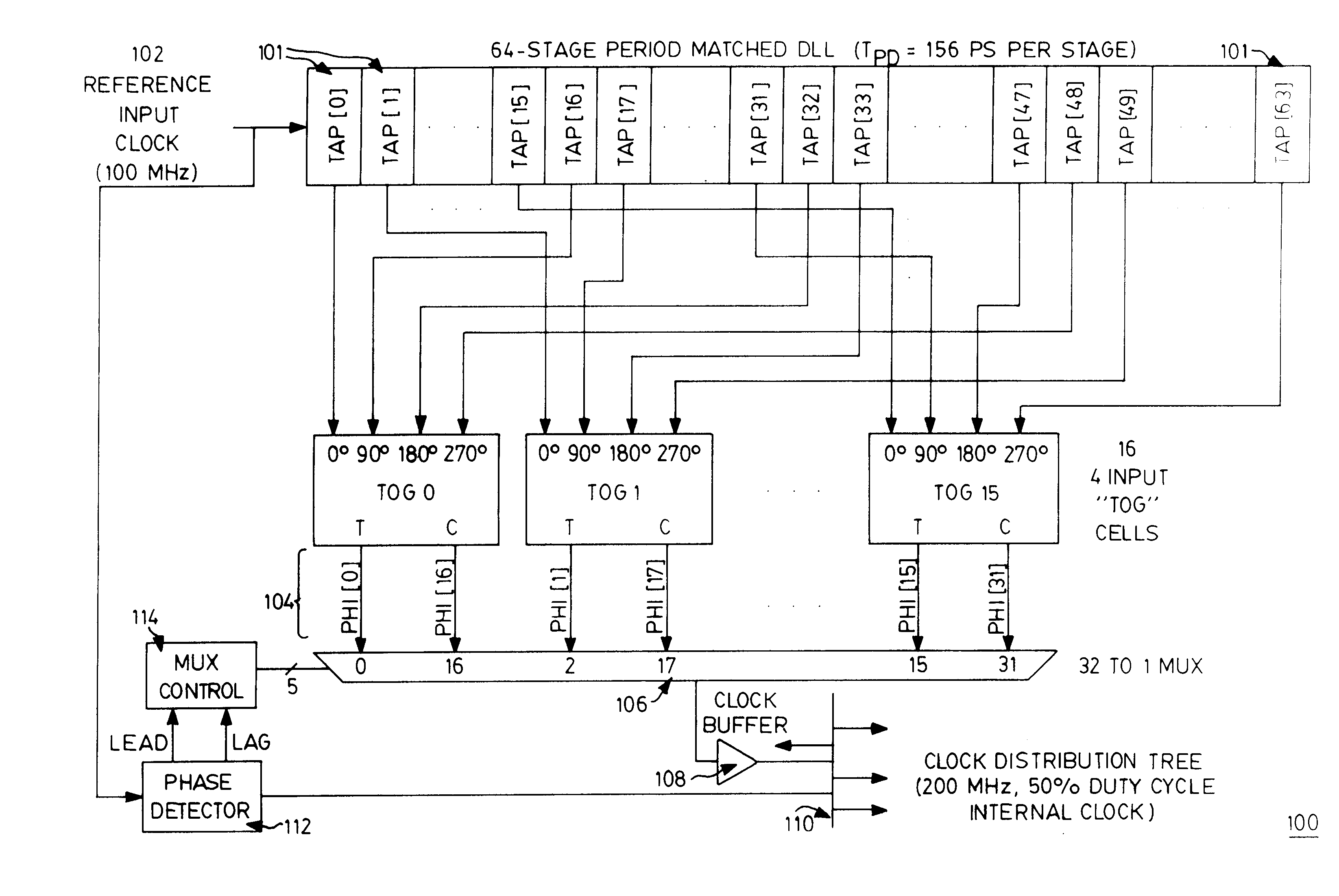
Frequency-doubling delay locked loop
A frequency multiplier circuit comprising a delay line receiving at one end thereof a reference clock for generating clock tap outputs from respective ones of a plurality of period matched delay elements; a clock combining circuit responsive to pairs of tap outputs for generating a rising and falling edge of an output clock pulse from respective ones of the pairs whereby the output clock period is less than the input clock period.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Systems and methods for synchronizing time stamps
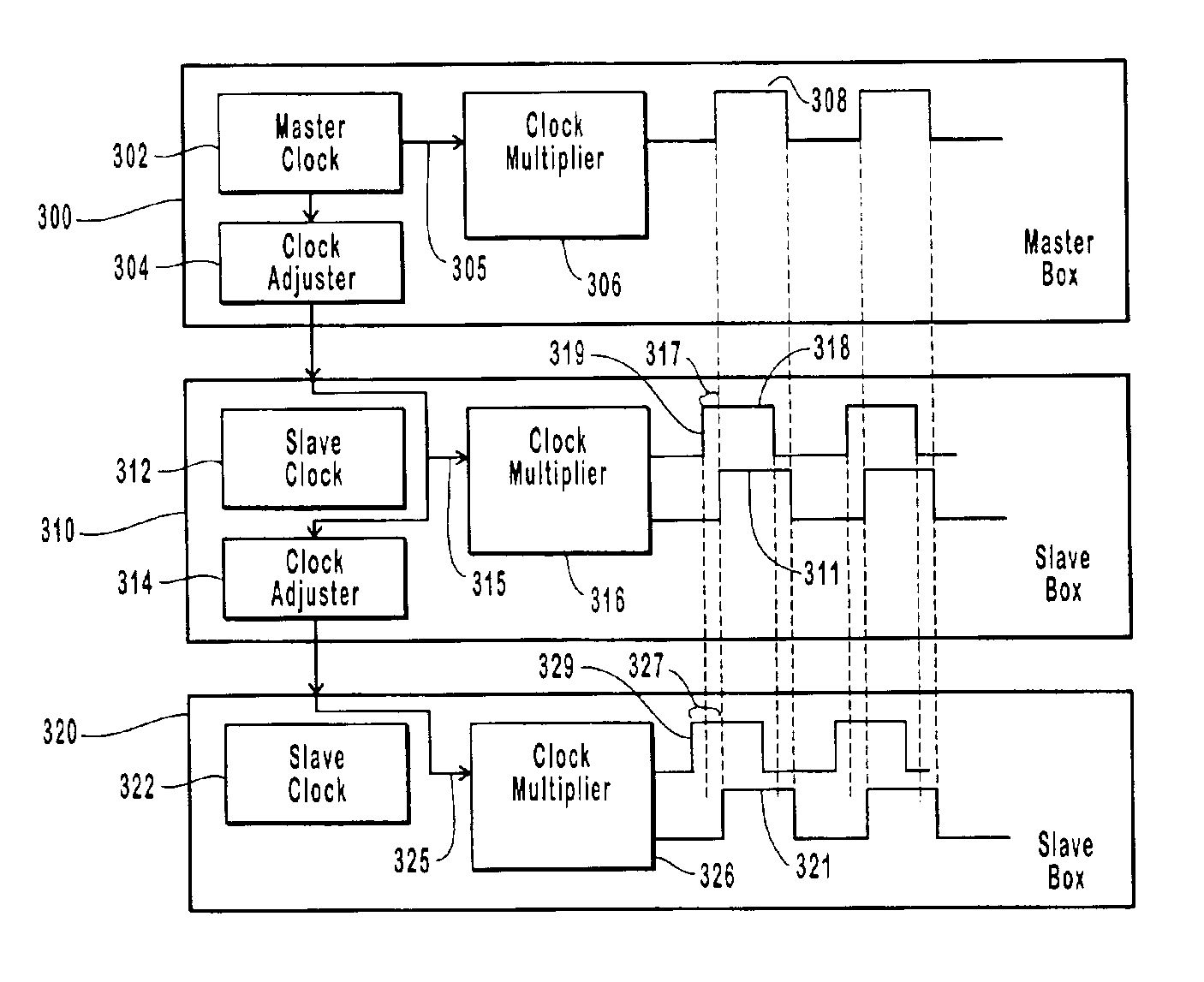
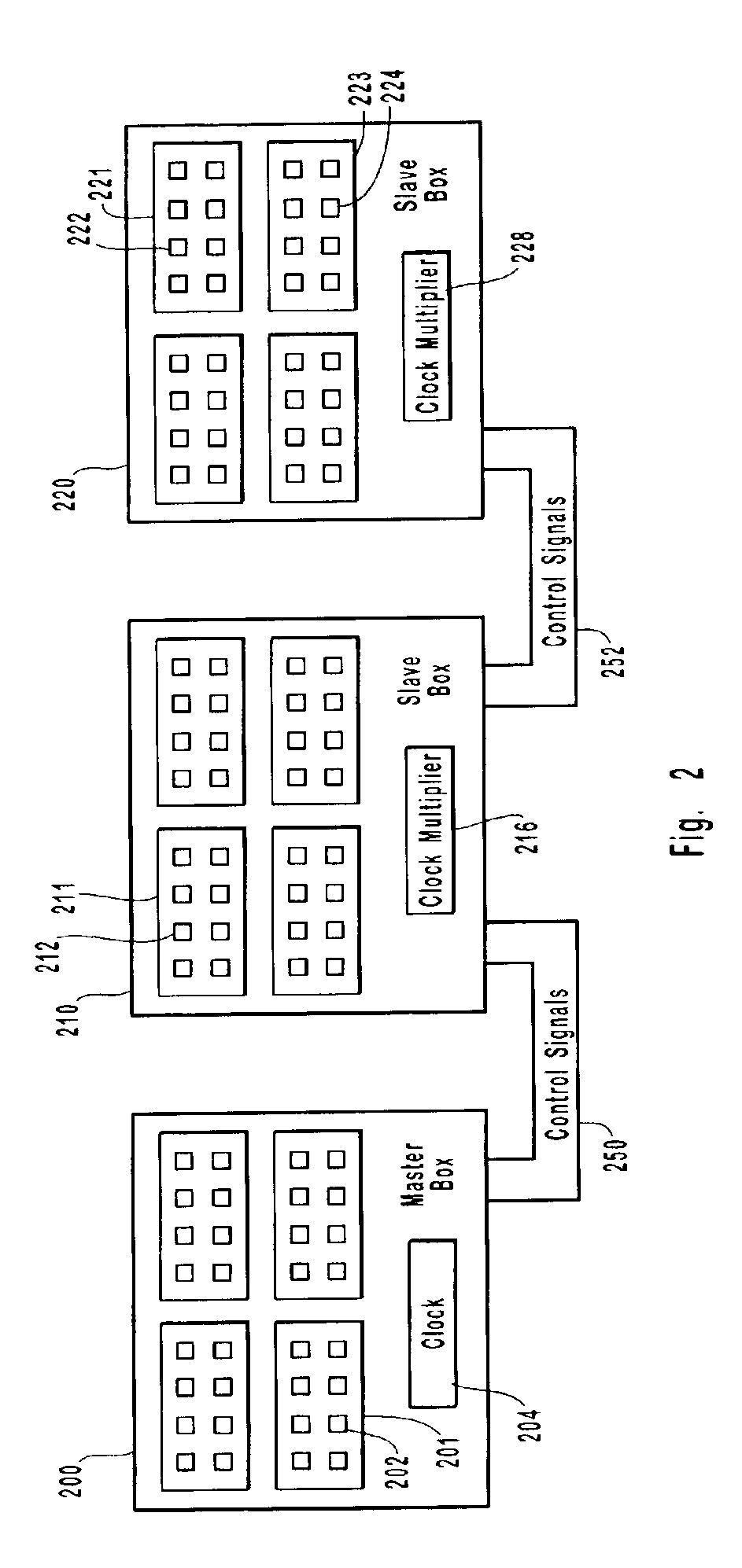
ActiveUS6941482B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsControl signalFrequency multiplier
Systems and methods for synchronizing time stamp counters of ports in a domain and for starting, stopping and triggering the ports in the domain at substantially the same time. A master box is connected with at least one slave box and the ports on the connected boxes are logically grouped in domains. The master box generates a clock signal that is adjusted and distributed to the slave boxes. The clock signal thus received by the slave boxes drives a clock multiplier that in turn drives the time stamp counters of the ports in the domains across the respective boxes. The time stamps of ports within a domain are synchronized because they are driven by the clock signal from the master box. The ports in a particular domain can be started, stopped and triggered using control signals that are similarly distributed from the master box to the slave boxes.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Clock generator and clock generating method capable of varying clock frequency without increasing the number of delay elements
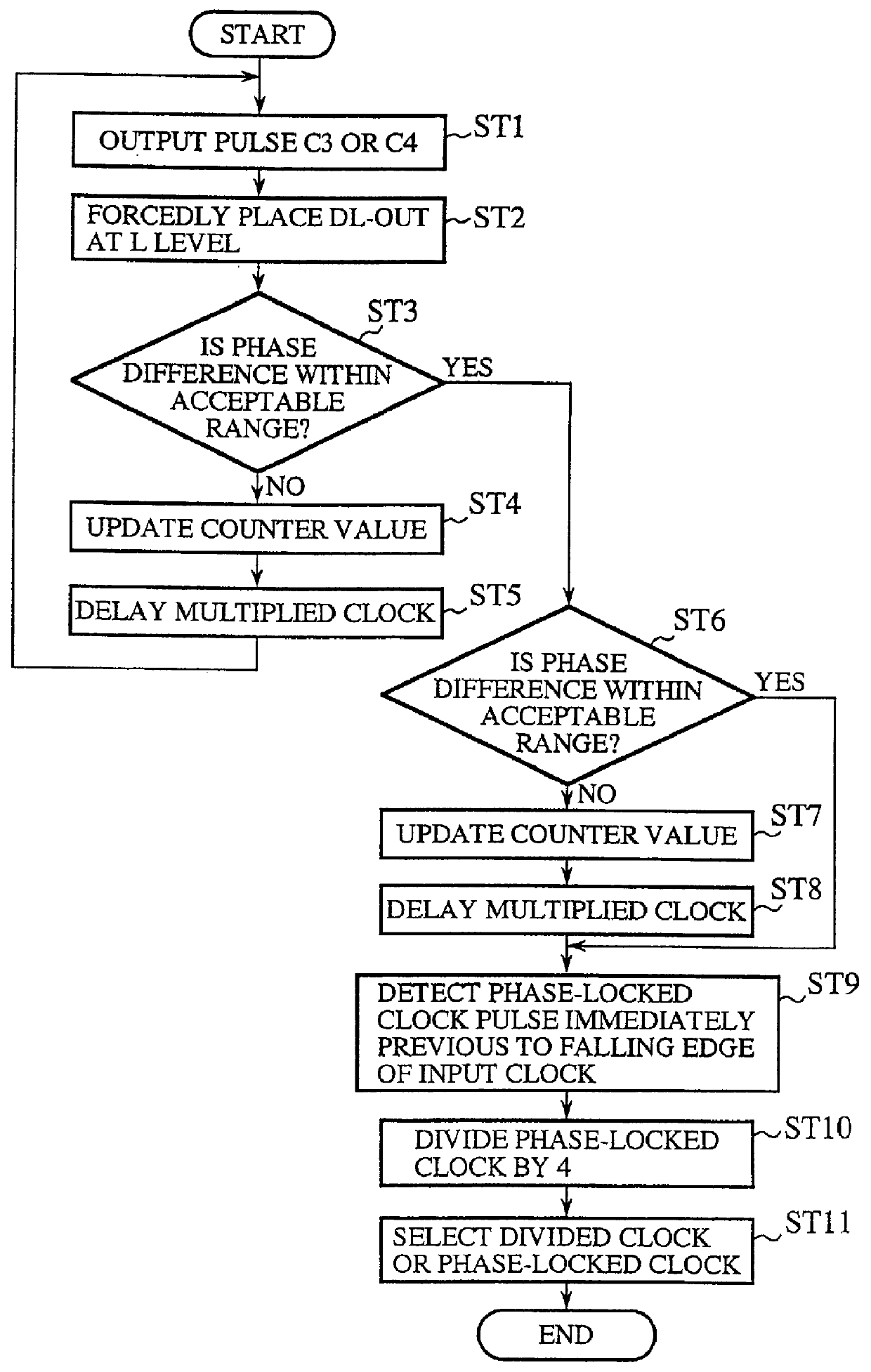
InactiveUS6049238AReduce frequencyDelay lines pulse generationPulse automatic controlPhase differenceDelayed time
A clock generator including a frequency multiplier, a phase lock circuit and a frequency divider. The frequency multiplier generates a frequency multiplied clock by multiplying the frequency of an input clock. The phase lock circuit detects a phase difference between the input clock and a frequency divided clock, and generates, by delaying the frequency multiplied clock by an amount corresponding to the phase difference, a phase-locked clock with its phase locked with the input clock. The frequency divider detects in every fixed cycle a particular pulse of the phase-locked clock, and generates the frequency divided clock by dividing the phase-locked clock with reference to the particular pulse of the phase-locked clock. In particular, the frequency divider detects the particular pulse immediately previous to a falling edge of the input clock. This can reduce the phase difference between the input clock and the phase-locked clock, and hence to solve a problem of a conventional clock generator in that a delay time of a digital delay line in a phase lock circuit must be lengthened with a reduction in the multiplication number of the frequency multiplied clock, which requires a greater number of delay elements because of a large occupying area of the delay elements and a decoder, thereby increasing the circuit scale and cost of a chip to reduce the multiplication number of the frequency multiplied clock.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Frequency doubler circuit with trimmable current control
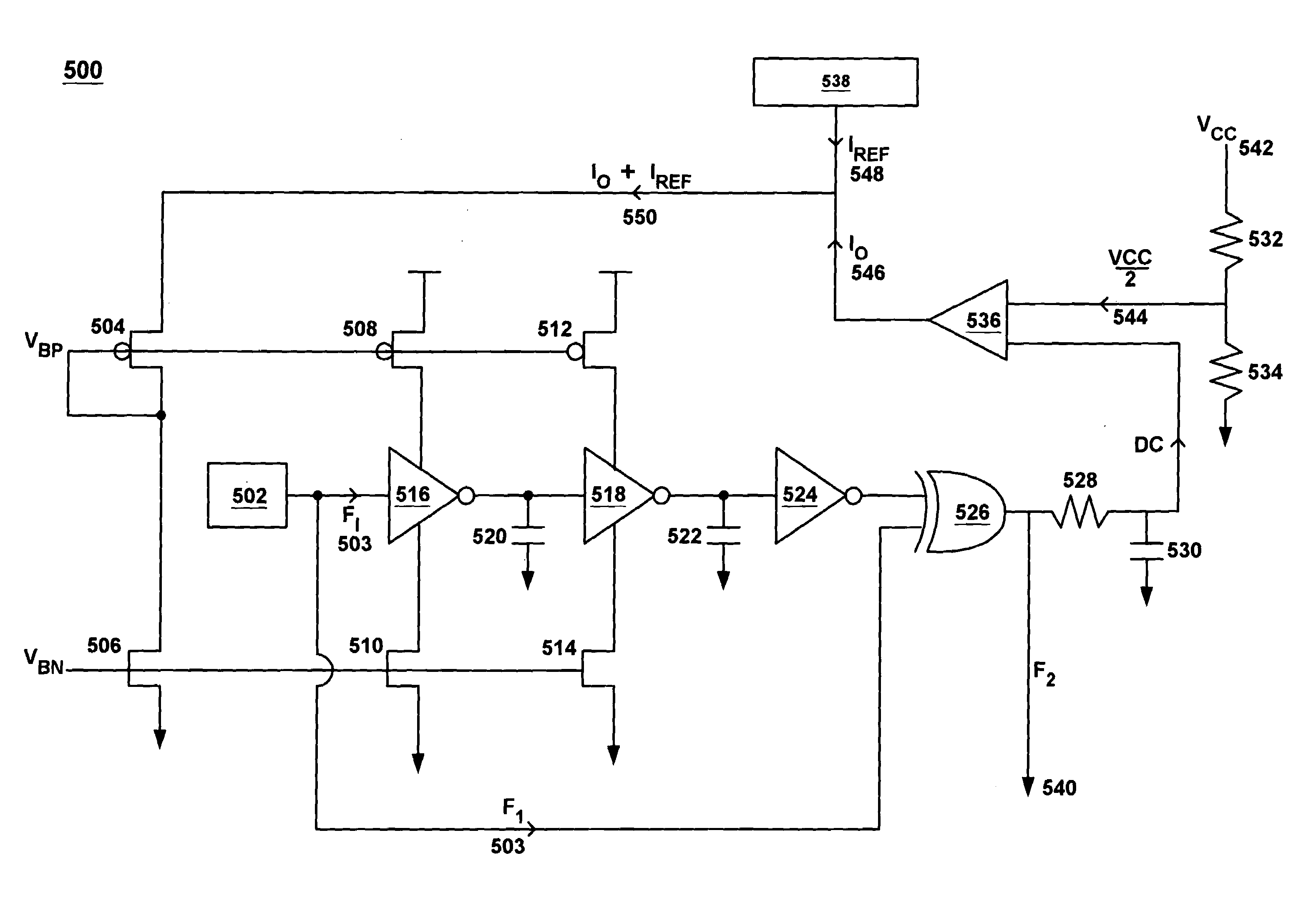
ActiveUS7180342B1Accurate duty cycleLess expensiveOscillations generatorsCapacitanceReference current
A frequency doubler circuit with trimmable current control. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a circuit comprising an oscillator with a current source and a frequency doubler circuit coupled to the current source. In one embodiment, the current source is for generating a reference current. In one embodiment, the frequency doubler circuit is operable to receive a first frequency signal for generating a second frequency signal and also receiving the reference current. The frequency doubler circuit, using the reference current, operates to compensate for process variation of capacitance of the frequency doubler circuit and uses the reference current to maintain a known duty cycle. In one embodiment, the circuit further comprises a control loop for generating an output current, wherein the output current, operating in conjunction with the reference current, operates to compensate for process variation of capacitance of the frequency doubler circuit and uses the reference current to maintain a known duty cycle. In one embodiment, the current source comprises a trimmable current control.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
True random number generator and entropy calculation device and method
InactiveUS6862605B2Random number generatorsDigital function generatorsFrequency multiplierNumber generator
Owner:QUANTUM WORLD
Apparatus and method for testing high speed components using low speed test apparatus
A system for testing a high speed integrated circuit includes a test device having a test clock with a first maximum frequency for performing level sensitive scan design (LSSD) testing of the integrated circuit device under test, a frequency multiplier circuit for multiplying the test clock signal to a higher second frequency capable of operating the device under test, and a finite state machine for generating a first internal clock for testing the device under test. In a practical embodiment, the internal clock speed may be running at a frequency many multiples of the test clock. Alternatively, a method of testing a device under test (DUT) at design speed includes running a predetermined group of tests with a test device operating at a lower speed than the design speed; incorporating LSSD or boundary scan test techniques in the device under test, together with a frequency multiplying device; generating a global clock for the device under test from the frequency multiplying circuit and using a finite state machine as a synchronizer and pulse generator to control a capture clock with respect to the global clock.
Owner:IBM CORP
Small scale clock multiplier circuit for fixed speed testing
InactiveUS20080224742A1Counting chain pulse countersComputations using pulse rate multipliers/dividersRolloverClock rate
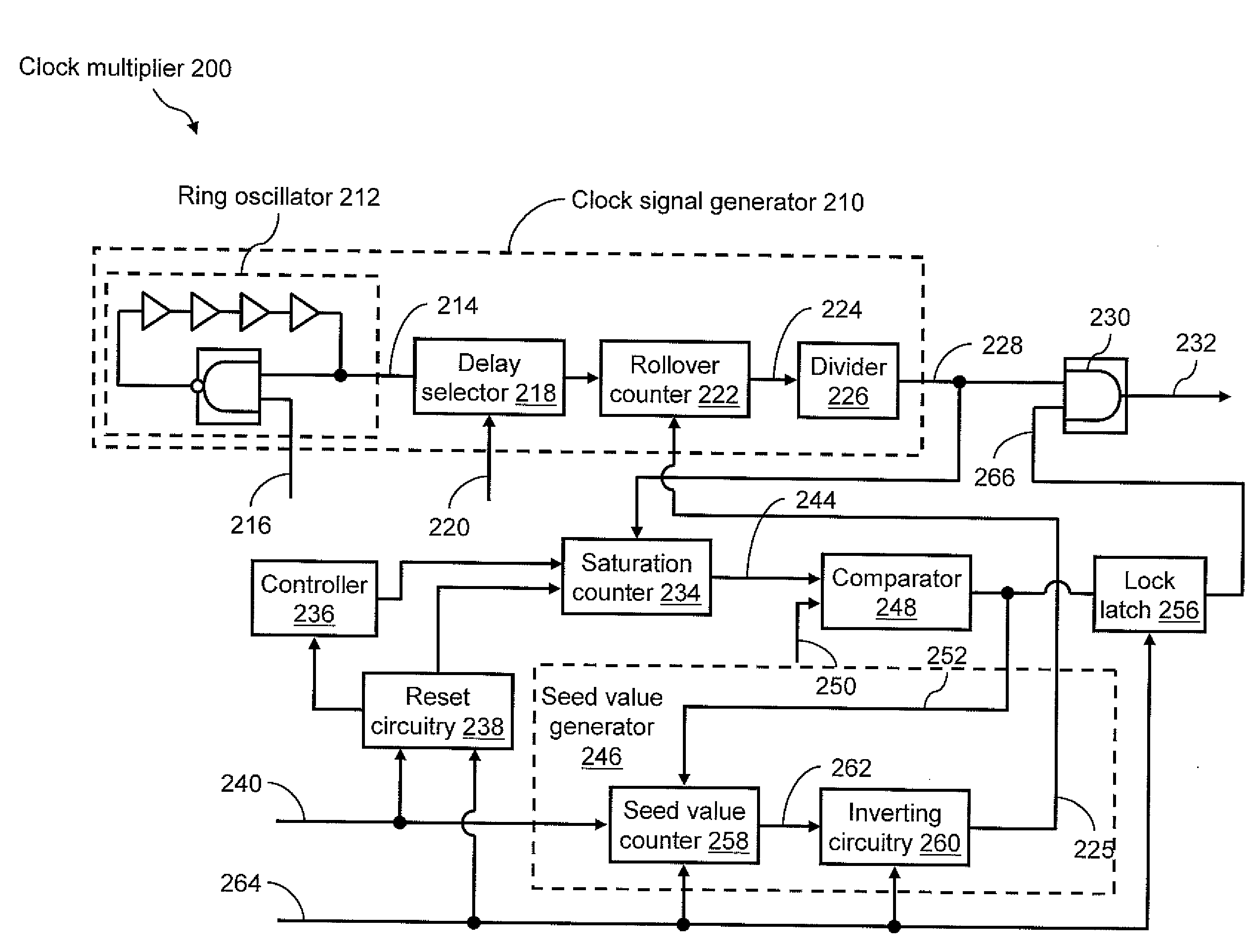
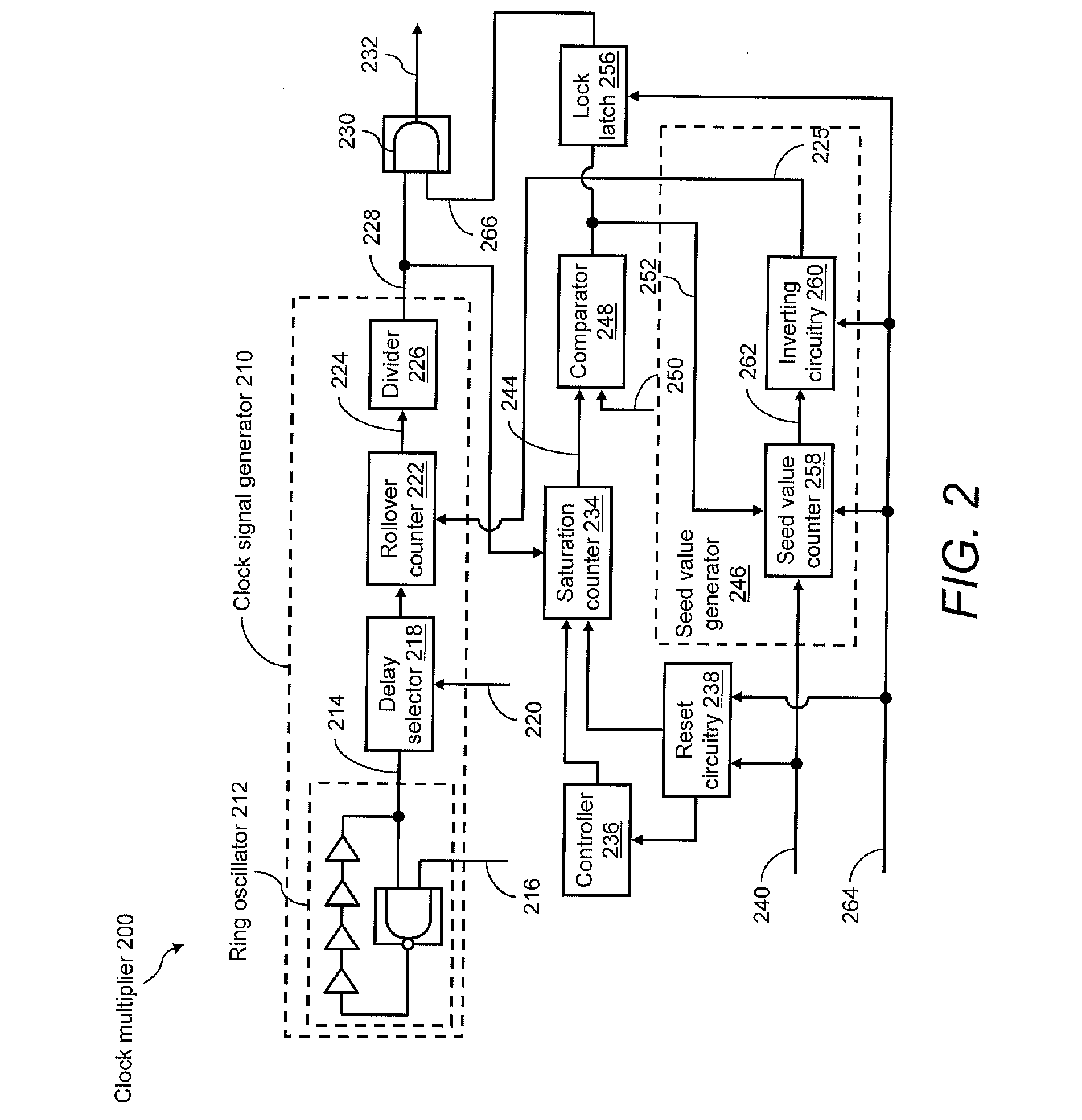
An on-chip clock multiplier for outputting a fast clock that is approximately a predetermined multiple n of a slow clock. The multiplier utilizing a high-speed oscillator to generate a high-frequency base signal. A lower frequency signal is generated using the high-frequency base signal as a function of the output of a rollover counter that counts from a seed value to a terminal value. A saturation counter is used to determine whether no more than n pulses of the lower frequency signal occur within a single cycle of the slow clock. If not, the lower frequency signal is iteratively slowed by changing the seed value until no more than n pulses of the lower frequency signal occur within a single cycle of the slow clock. When this iteration is done, the fast clock having a frequency that is approximately n times the frequency of the slow clock is output.
Owner:IBM CORP
Millimeter wave marine frequency modulation multichannel anti-collision radar
InactiveCN101373217AImprove anti-interference abilityImprove reliabilityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency multiplierAcousto-optics
The invention relates to the radio-positioning technical field, particularly a millimeter-wave marine frequency modulation multi-channel anti-collision radar, which is realized through the following steps: adopting the full-phase parameters to receive / transmit reference signals; asynchronously controlling the time division and the time sequence; watching the targets which are prone to collision on the water surface in an omni-directional manner through DSP cyclic scanning wave beams by a quasi-optical dielectric lens antenna circular array; controlling the time division SAW multi-channel passive frequency modulation through a plurality of water surface waterway cameras, an own ship speed sensor, a satellite positioning sensor GPS data MCU; sending to antenna array to transmit through an up-converter, T / R3, a frequency multiplier and a power amplifier, a circulator and T / R2; extracting the SAW multi-channel signals from the returning wave through the antenna array, a wave beam switch, T / R1, the circulator, a high amplifier, a down-converter and a medium amplifier; detecting a plurality of barrier target DSPs so as to confirm the position, the distance and the relative speed; displaying the three-dimensional image on a CRT, wherein the closer the ship gets to the target, the higher the resolution power is; controlling the false-alarm identification and tracing the nearest targets; giving an alarm when the distance is smaller than the safety distance; and intelligently avoiding the barriers or reducing if the distance is close to a risk distance, wherein the control is determined based on the actual condition of the water surface environment combined with the own ship speed and the GPS data, thereby improving the shipping safety.
Owner:阮树成
Single chip GSM/EDGE transceiver architecture with closed loop power control
InactiveUS7483678B2Resonant long antennasNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsClosed loopFrequency multiplier
Owner:INTEL CORP
True random number generator and entropy calculation device and method
InactiveUS20030037079A1Random number generatorsDigital function generatorsSoftware engineeringFrequency multiplier
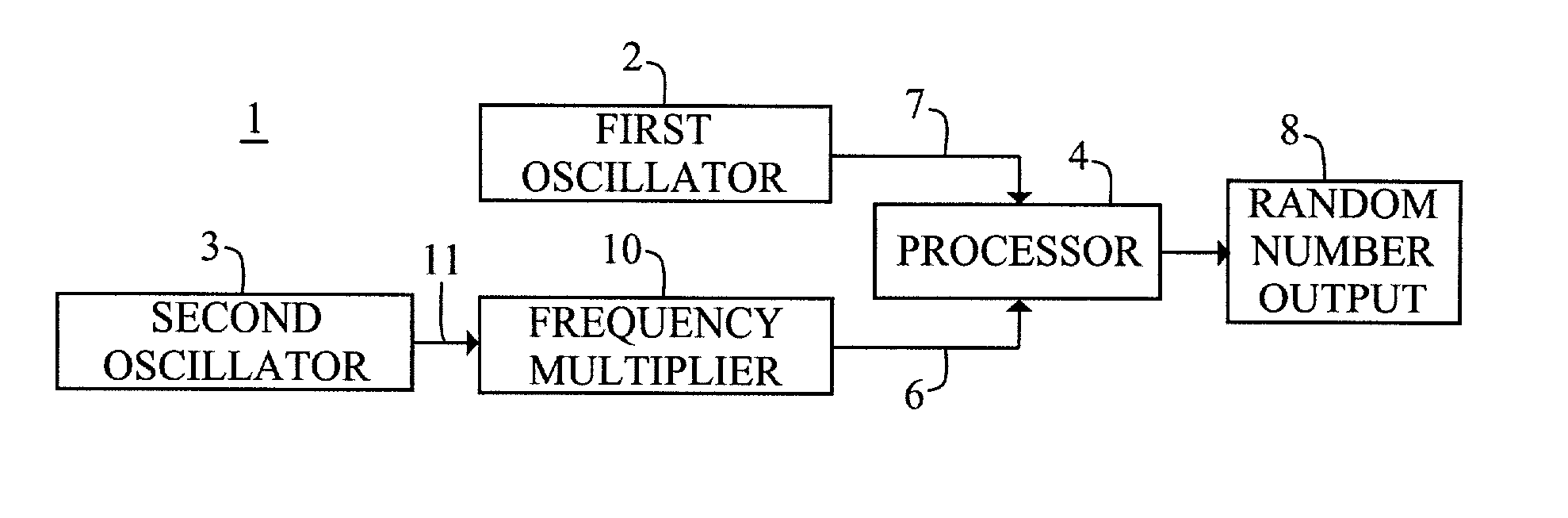
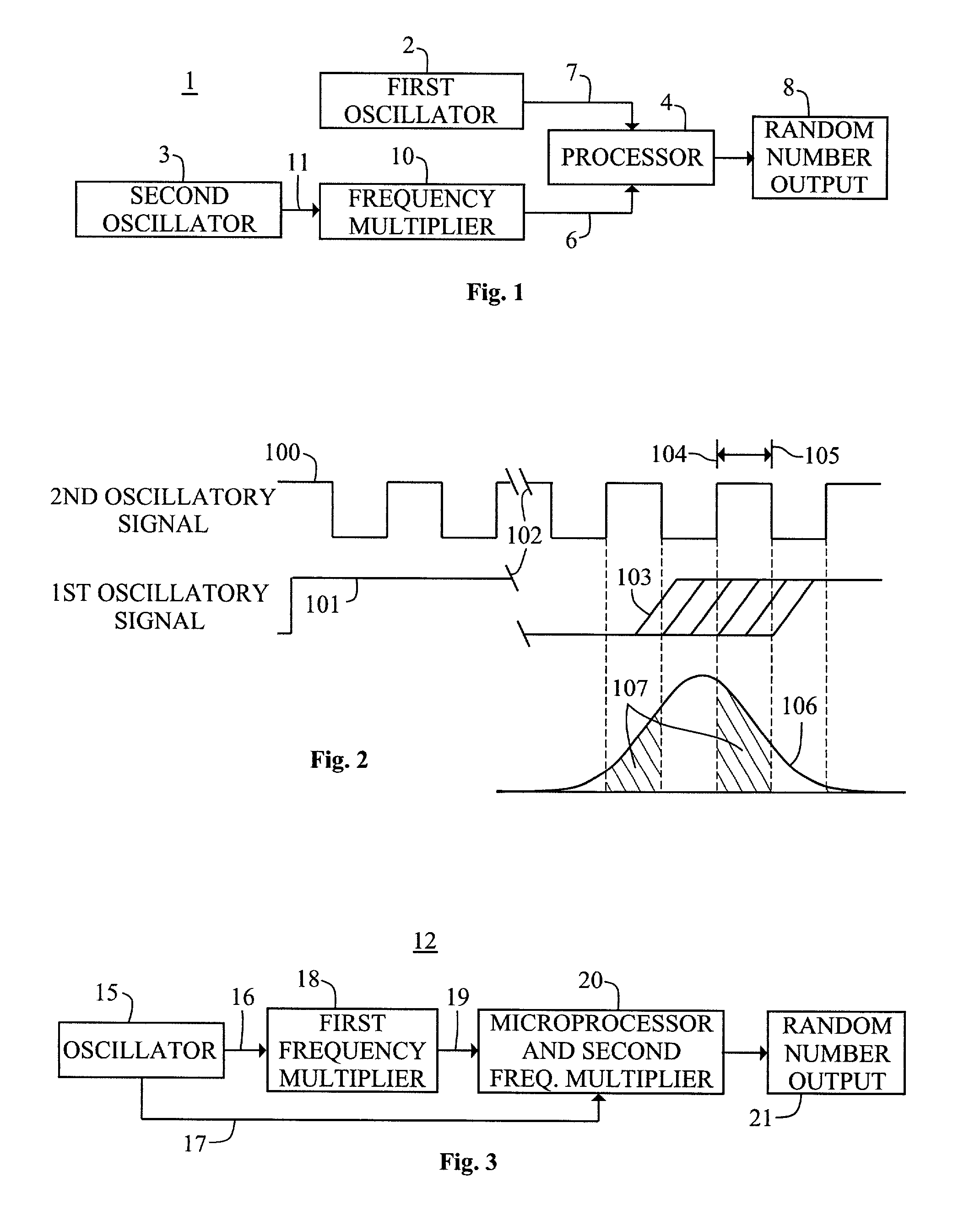
A random number generator includes a first oscillator that provides a first oscillatory signal to a processor, and a second oscillator that provides a signal to a frequency multiplier, which in turn provides a second oscillatory signal to the processor. The relative jitter between the two oscillatory signals contains a calculable amount of entropy that is extracted by the processor to produce a sequence of true random numbers.
Owner:QUANTUM WORLD
Dual loop architecture useful for a programmable clock source and clock multiplier applications
A first phase-locked loop (PLL) circuit includes an input for receiving a timing reference signal from an oscillator, a controllable oscillator circuit supplying an oscillator output signal, and a multi-modulus feedback divider circuit. A second control loop circuit is selectably coupled through a select circuit to supply a digital control value (M) to the multi-modulus feedback divider circuit of the first loop circuit to thereby control the oscillator output signal. While the second control loop is coupled to supply the control value to the feedback divider circuit, the control value is determined according to a detected difference between the oscillator output signal and a reference signal coupled to the second control loop circuit at a divider circuit. While the second control loop circuit is not coupled to control the first PLL circuit, the first PLL circuit receives a digital control value to control a divide ratio of the feedback divider, the digital control value is determined at least in part according to a stored control value stored in nonvolatile storage, the stored control value corresponding to a desired frequency of the oscillator output signal.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Micromachined millimeter-wave frequency scanning array
ActiveUS20150263429A1Available bandwidthIncrease rangeRadiating elements structural formsLinear waveguide fed arraysPatch arrayFrequency multiplier
A frequency scanning traveling wave antenna array is presented for Y-band application. This antenna is a fast wave leaky structure based on rectangular waveguides in which slots cut on the broad wall of the waveguide serve as radiating elements. A series of aperture-coupled patch arrays are fed by these slots. This antenna offers 2° and 30° beam widths in azimuth and elevation direction, respectively, and is capable of ±25° beam scanning with frequency around the broadside direction. The waveguide can be fed through a membrane-supported cavity-backed CPW which is the output of a frequency multiplier providing 230˜245 GHz FMCW signal. This structure can be planar and compatible with micromachining application and can be fabricated using DRIE of silicon.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Superconductor semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS7129869B2Timing design is facilitatedReduce frequencyElectric signal transmission systemsDigital storageQuantum circuitFrequency multiplier
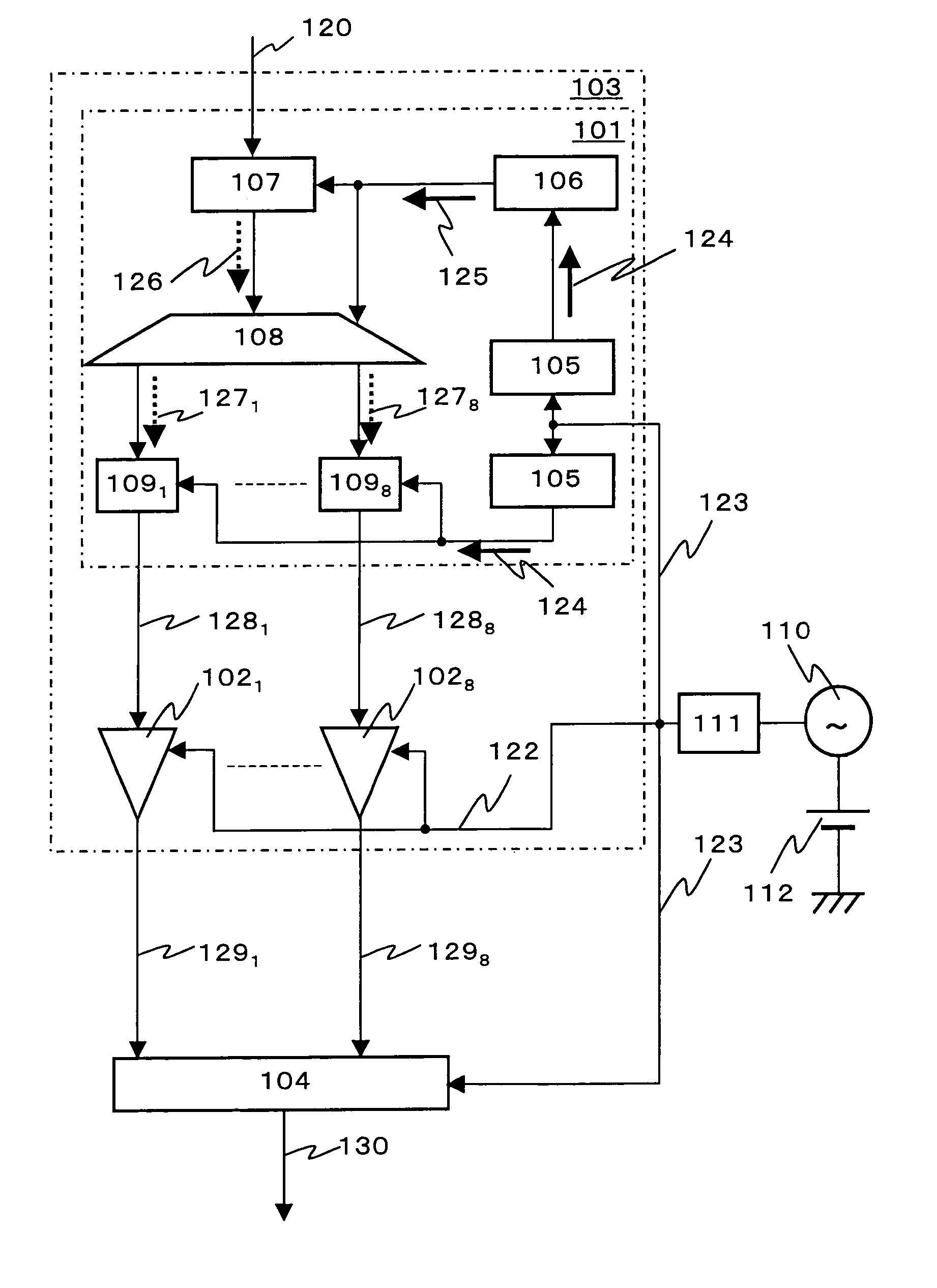
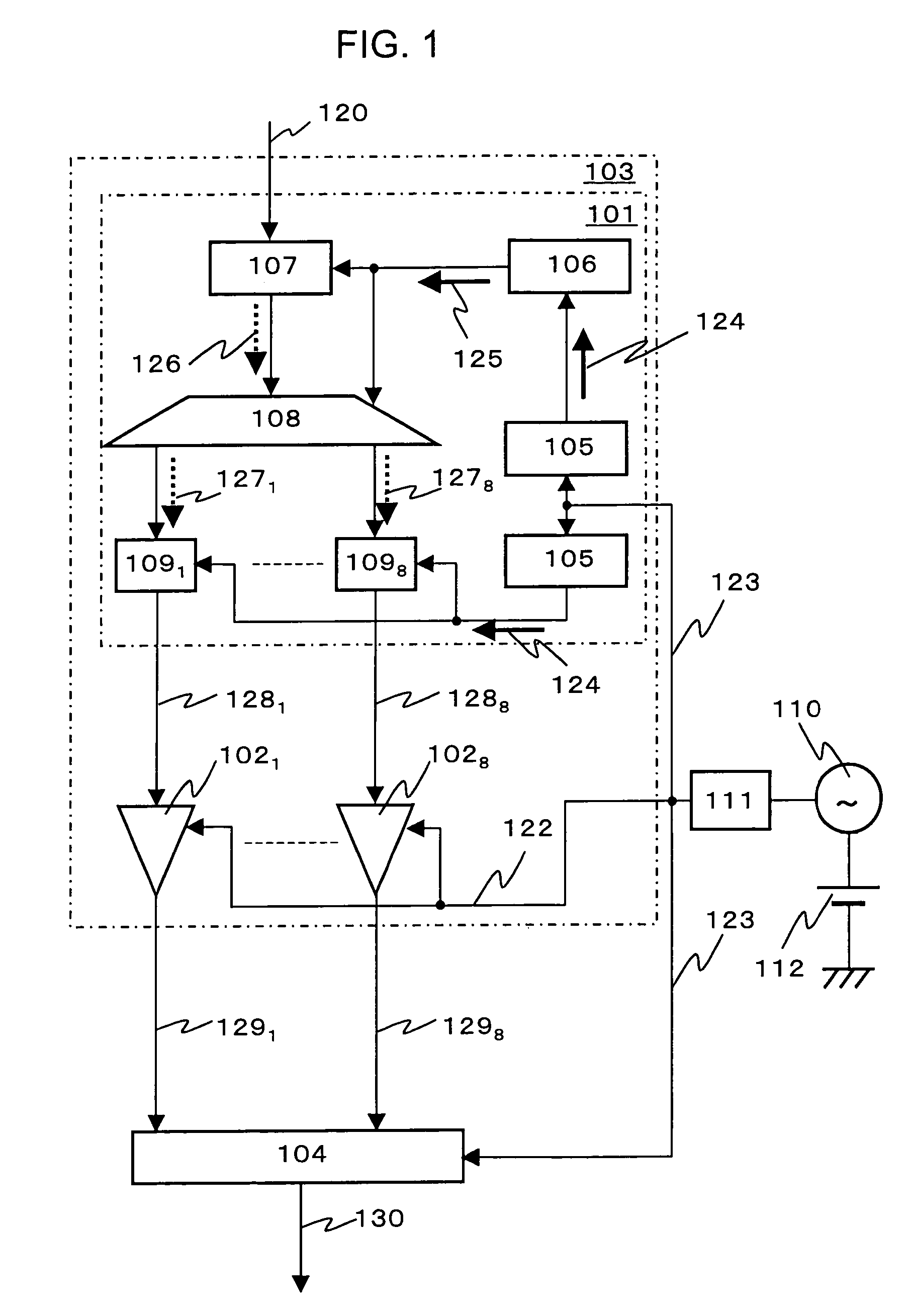
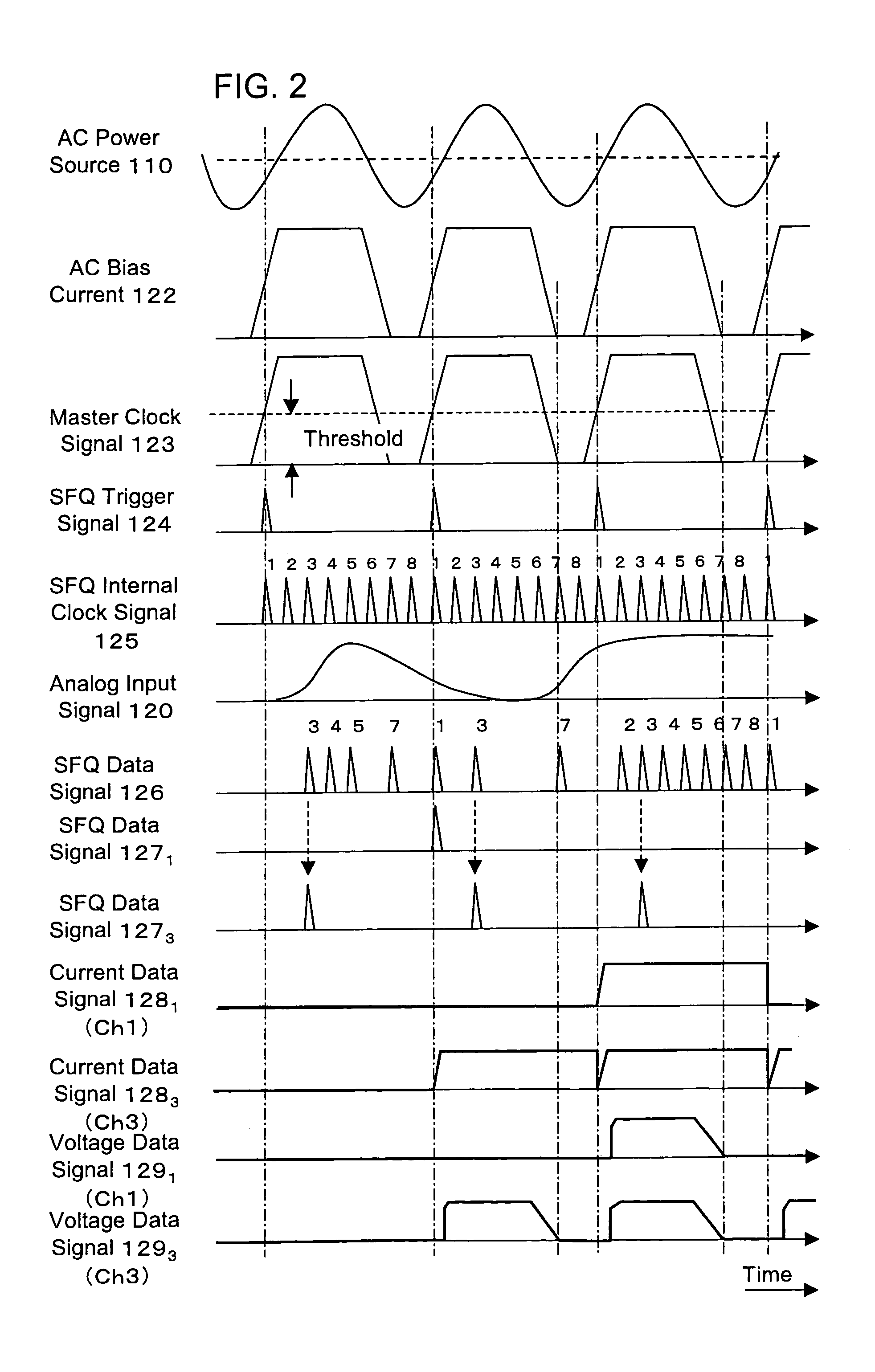
In an A / D converter having a single flux quantum circuit having a flux quantum as an information carrier, a superconducting amplifier circuit driven by an AC current, and a semiconductor circuit, the operations of the circuits are synchronized with each other and a data signal from the single flux quantum circuit is transmitted to the semiconductor circuit.An AC current as the power source of a superconducting amplifier circuit is inputted as a master clock signal to the single flux quantum circuit and the semiconductor circuit to synchronize the operations of the circuits with the master clock signal. The single flux quantum circuit has a clock signal frequency multiplier circuit, a demultiplexing circuit and a memory circuit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
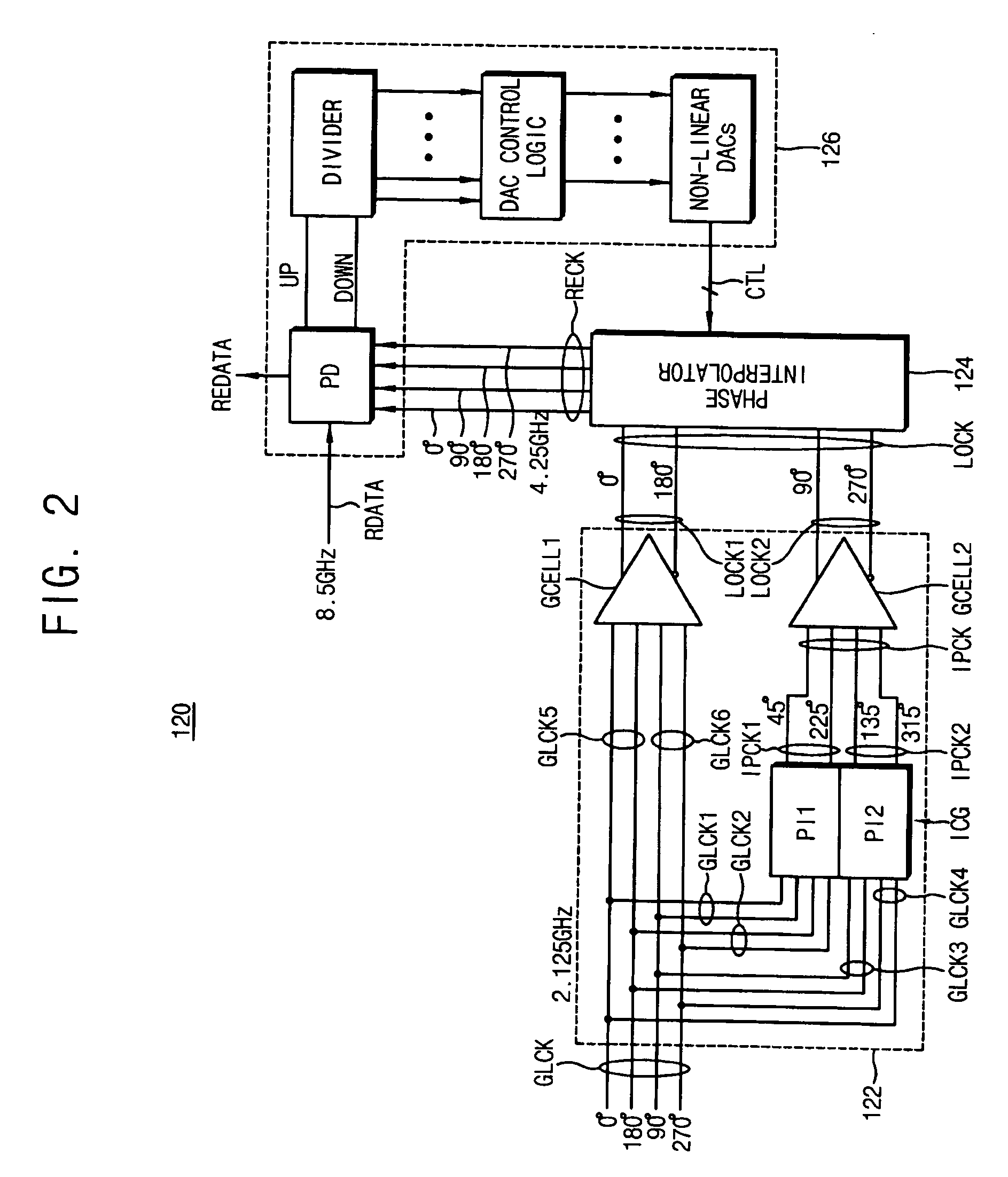
Circuits and methods for recovering a clock signal
ActiveUS20060008041A1Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionFrequency multiplierClock signal
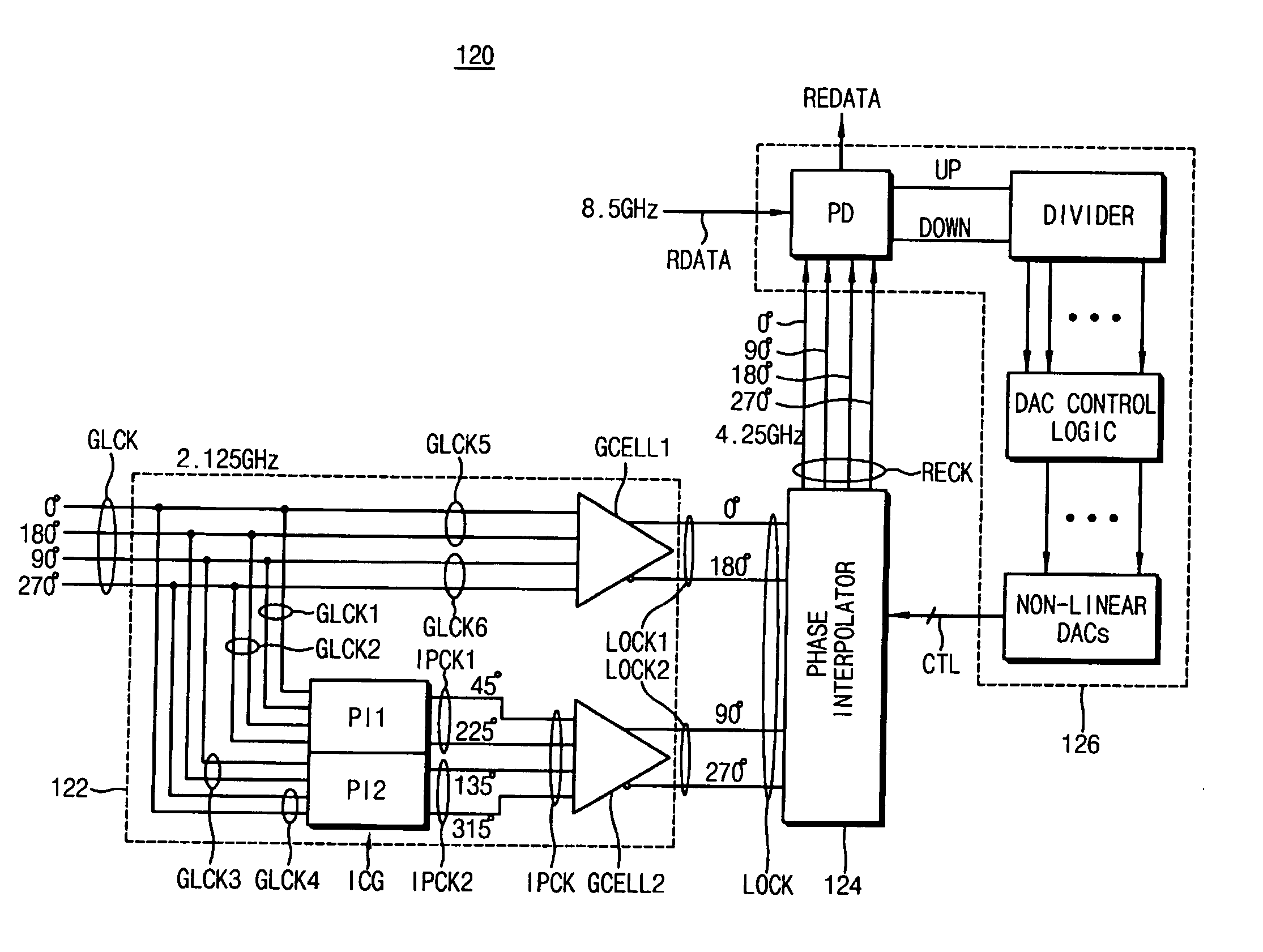
A circuit for recovering a clock signal may include a frequency multiplier configured to generate a plurality of local clock signals, each having a different phase, based on a plurality of received global clock signals at a first frequency and each having a different phase. The local clock signals may be generated at a second frequency higher than the first frequency. The circuit may include a phase interpolator configured to generate a recovered clock signal at a given phase and at a third frequency, based on the generated local clock signals, and a phase shifter configured to adjust the phase of the recovered clock signal so as to synchronize the phase of the recovered clock signal with a phrase of input data that is input to the phase shifter.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
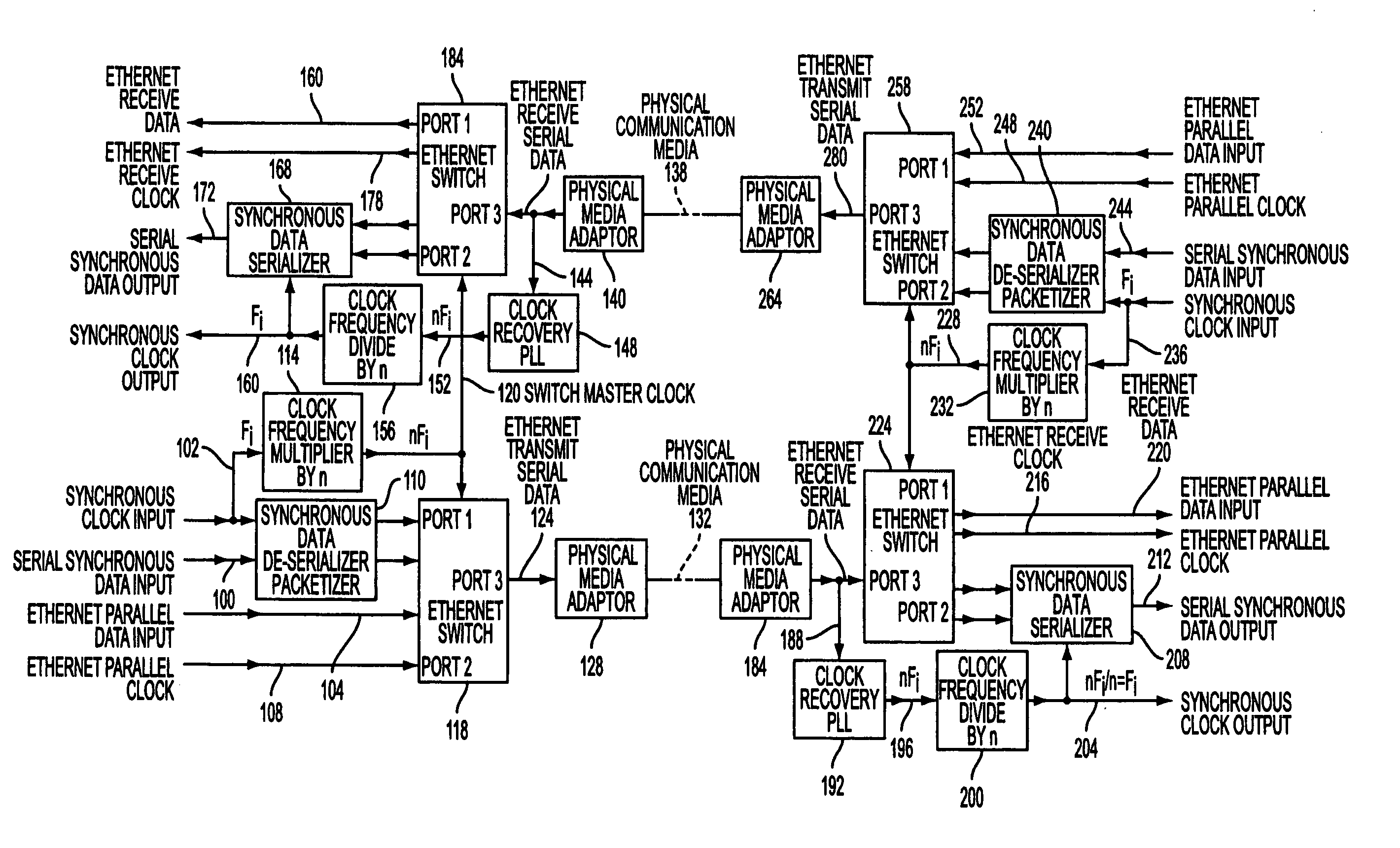
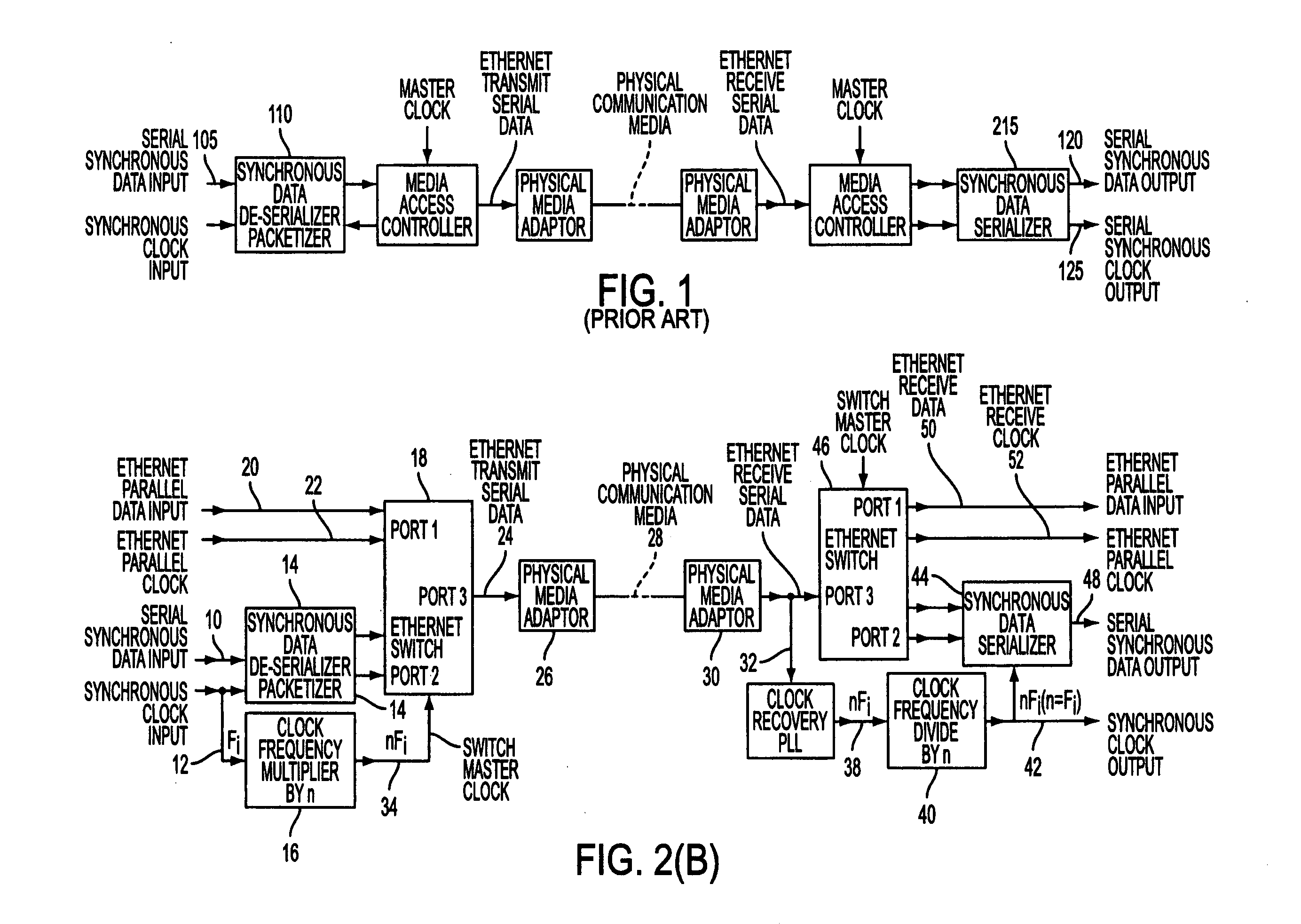
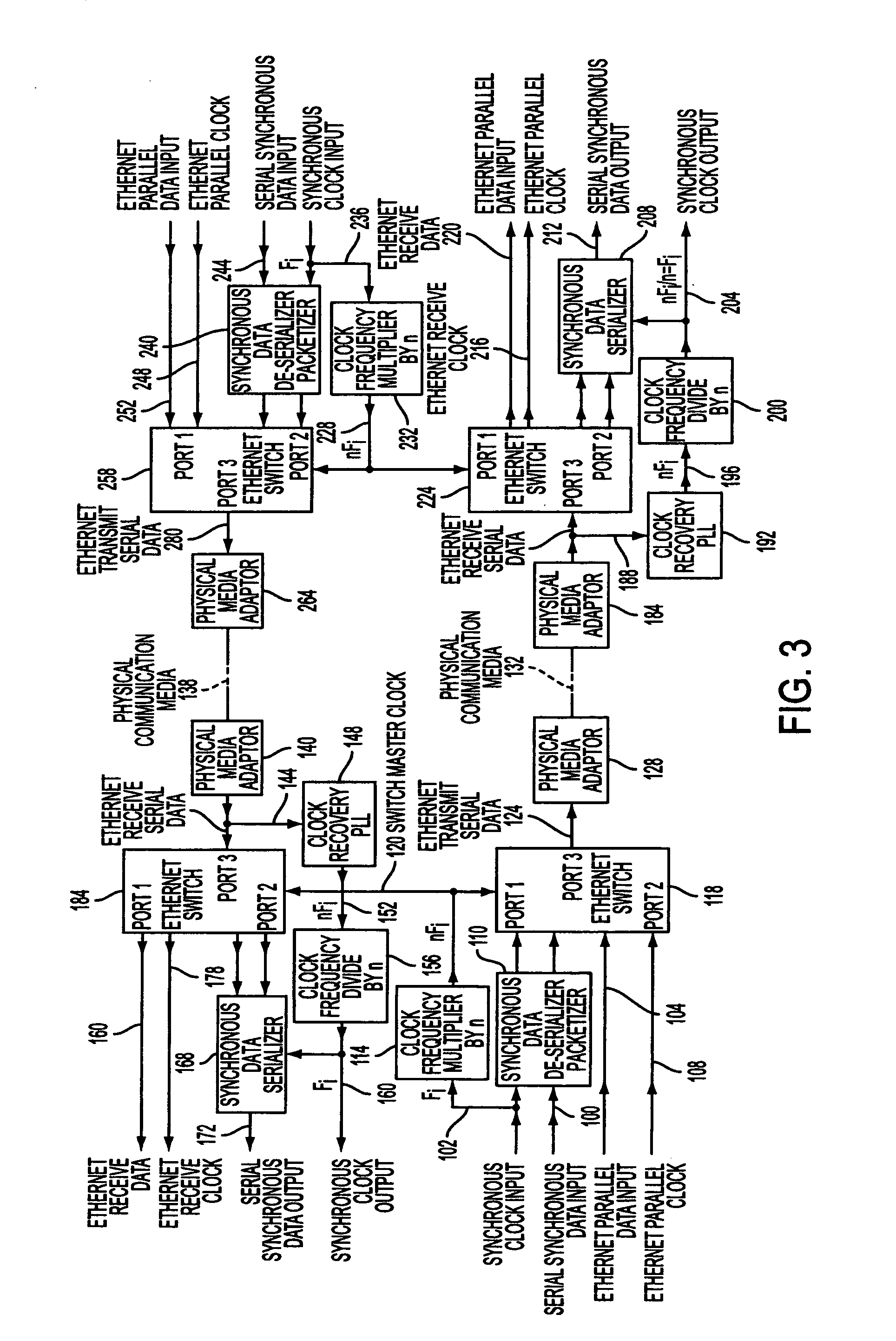
Apparatus and methods for providing synchronous digital data transfer over an ethernet
InactiveUS20050041691A1Pulse automatic controlTime-division multiplexFrequency multiplierDigital data
Systems, means and methods for reliably transporting Time Domain Multiplexing (TDM) data over one or more Ethernet installations or networks are provided. The present systems, means and methods provide coordinated frequency multipliers and dividers that are adapted and arranged with phase locked loops such that the respective clock functions of data can be recovered to the extent necessary to assure dependable communication of TDM data over one or more Ethernet networks. Advantageously, the original TDM clock frequency is restored.
Owner:LAUFER ELI +1
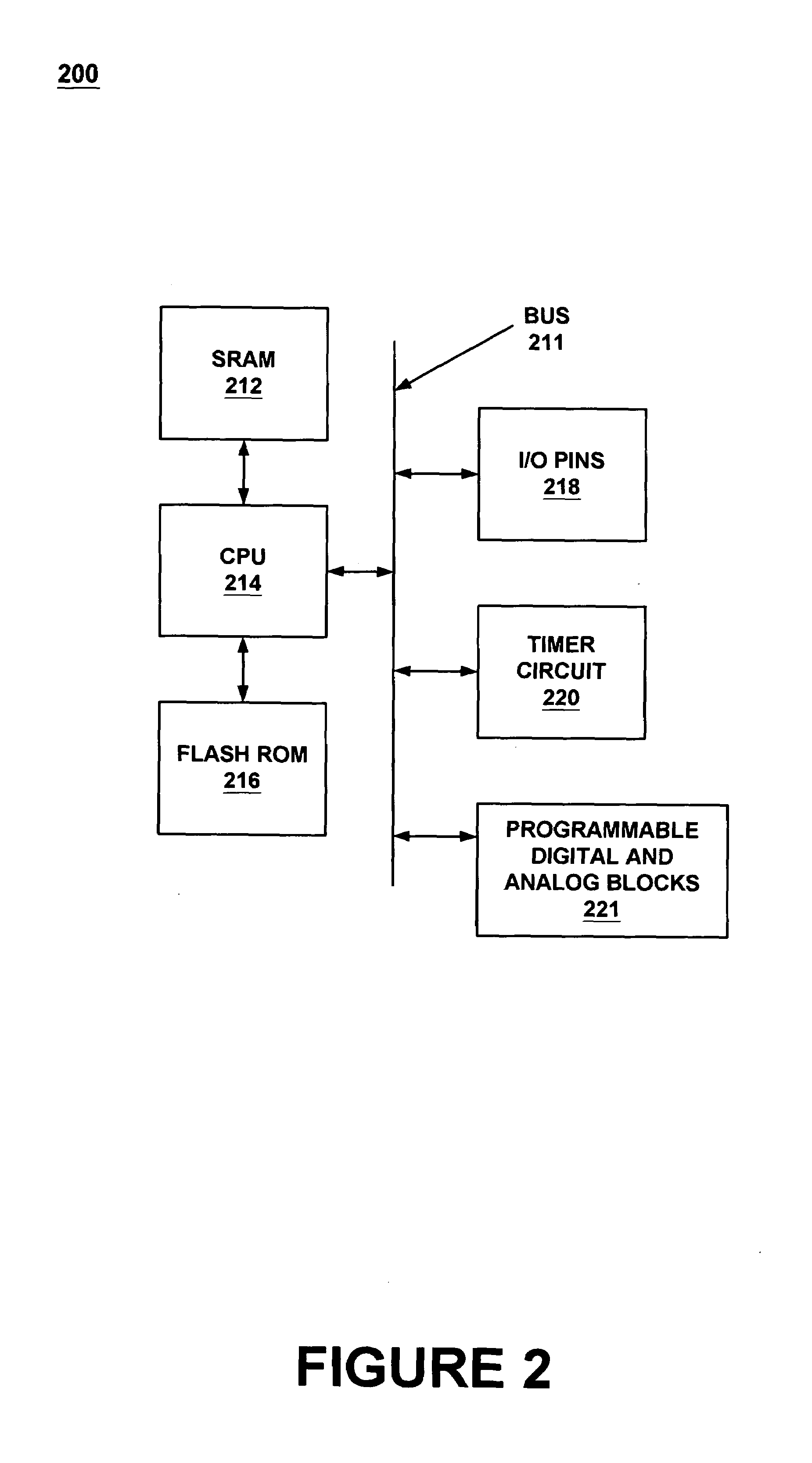
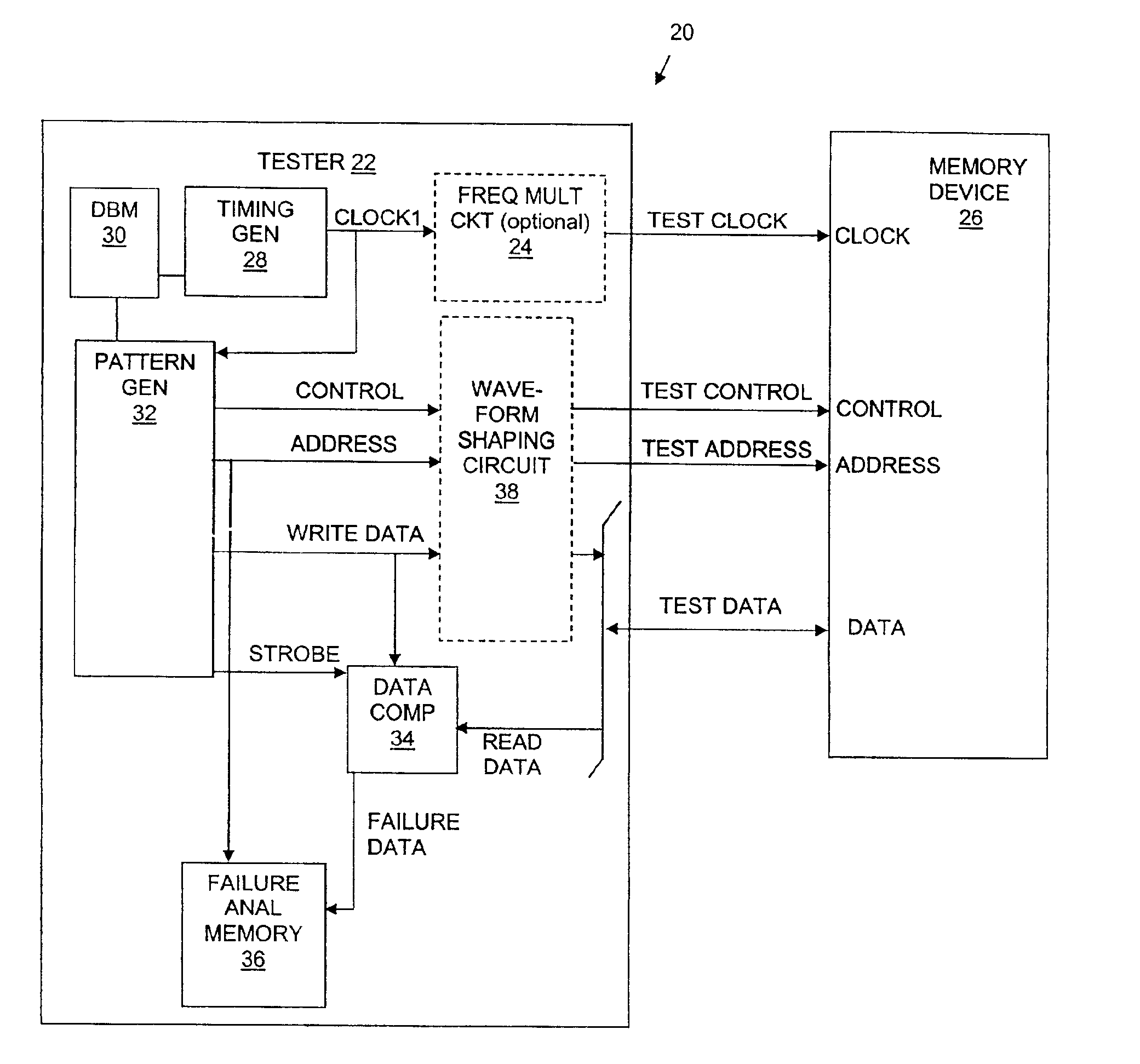
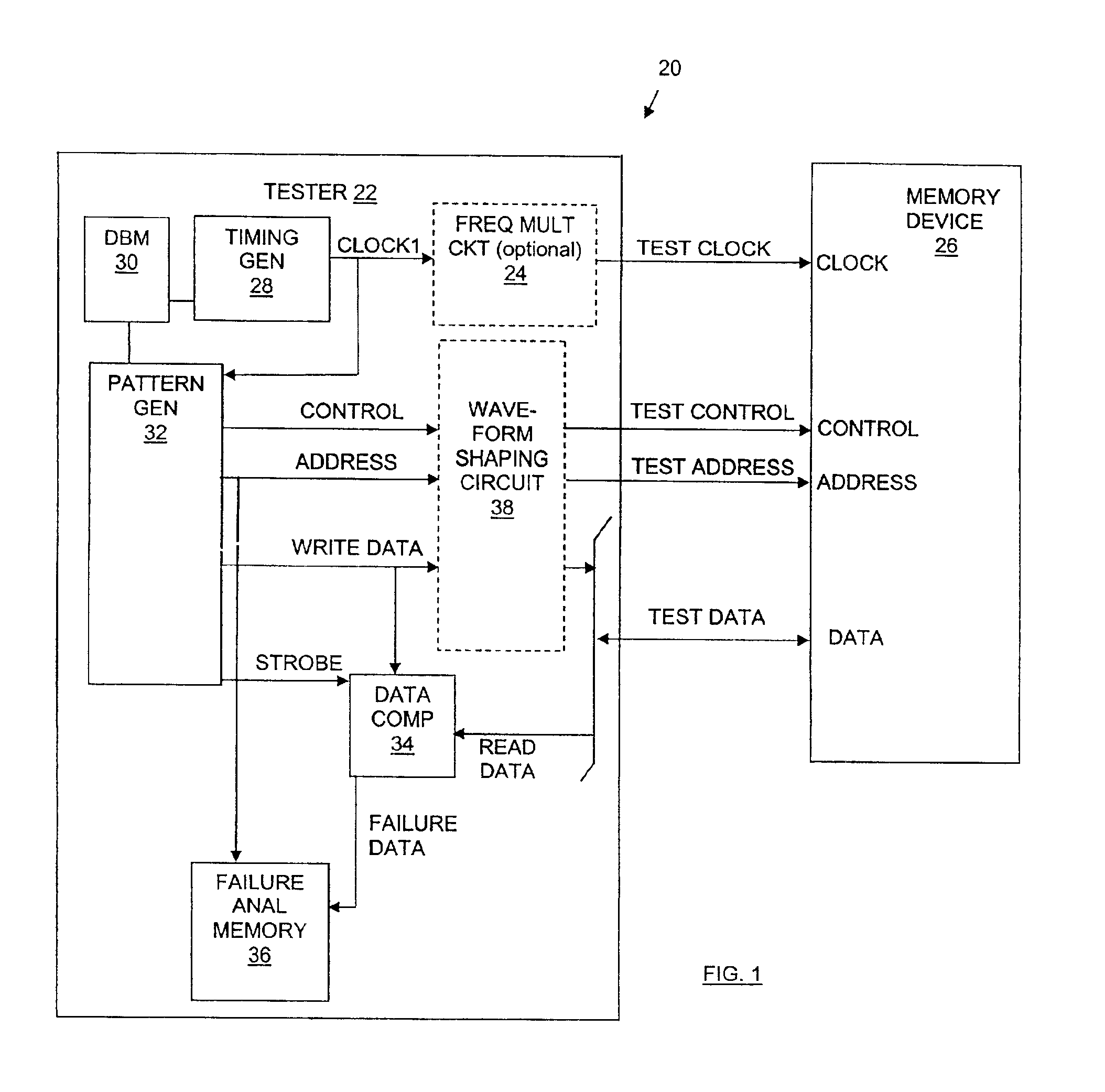
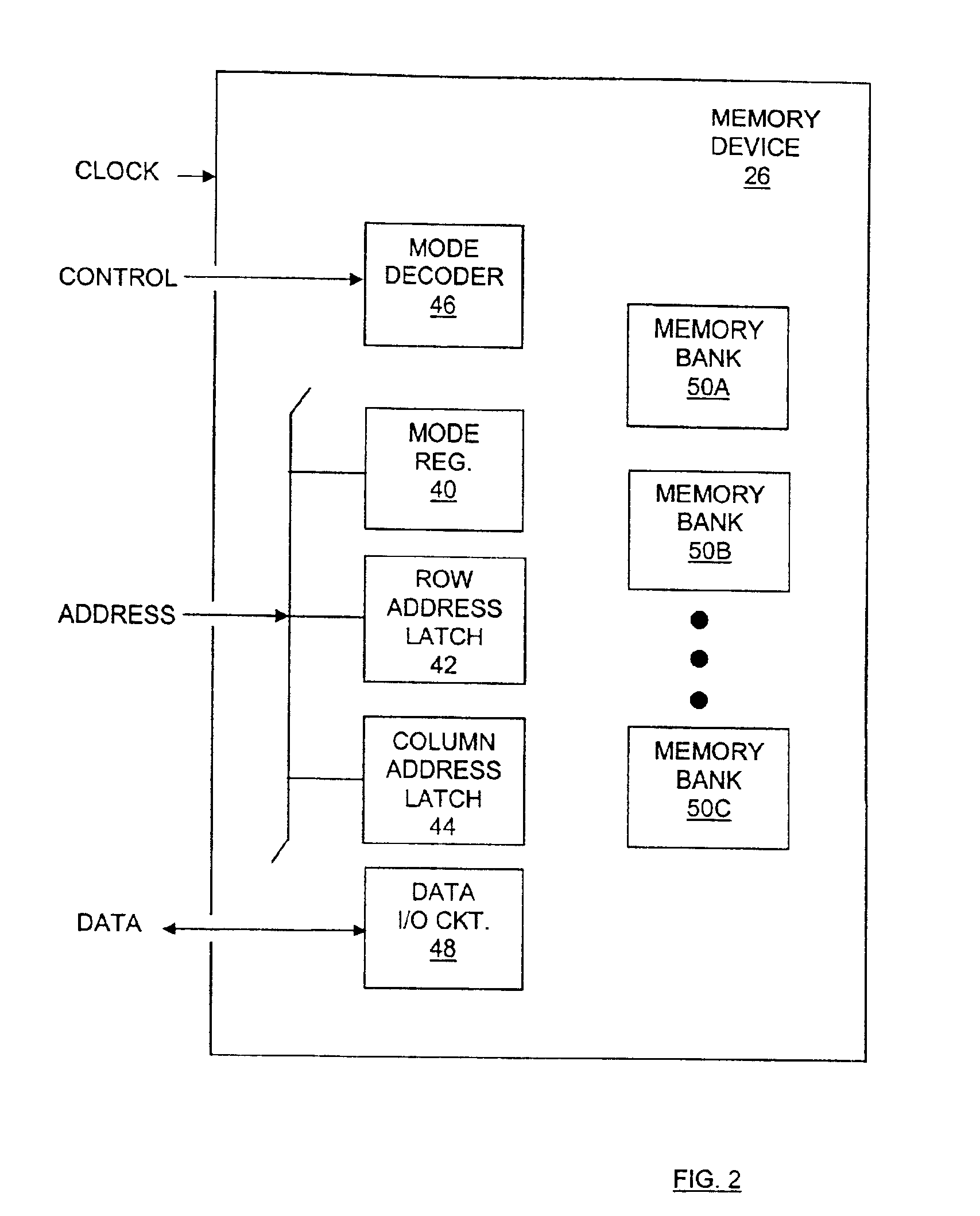
Memory device test system and method
InactiveUS6880117B2Shorten test timeStatic storageSpecial data processing applicationsTiming generatorWaveform shaping
A testing system is described for testing a memory device. The testing system includes a timing generator, an optional frequency multiplier circuit, a pattern generator, and a waveform shaping circuit. The timing generator generates a first clock signal. The frequency multiplier circuit receives the first clock signal, and uses the first clock signal to produce a second clock signal. In general, the second clock signal has a frequency greater than a frequency of the first clock signal. The frequency of the second clock signal may twice the frequency of the first clock signal. The testing system provides the second clock signal to the memory device such that operations within the memory device are synchronized to the second clock signal. The waveform shaping circuit produces an address signal synchronized to the first clock signal, and provides the address signal to the memory device when reading data from the memory device. In another embodiment, the first clock signal is not used and the address signals are synchronized to every two cycles of the second clock signal. A method for testing a memory device, which may be embodied in the testing system, is also described.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Receiver system and method for receiver testing
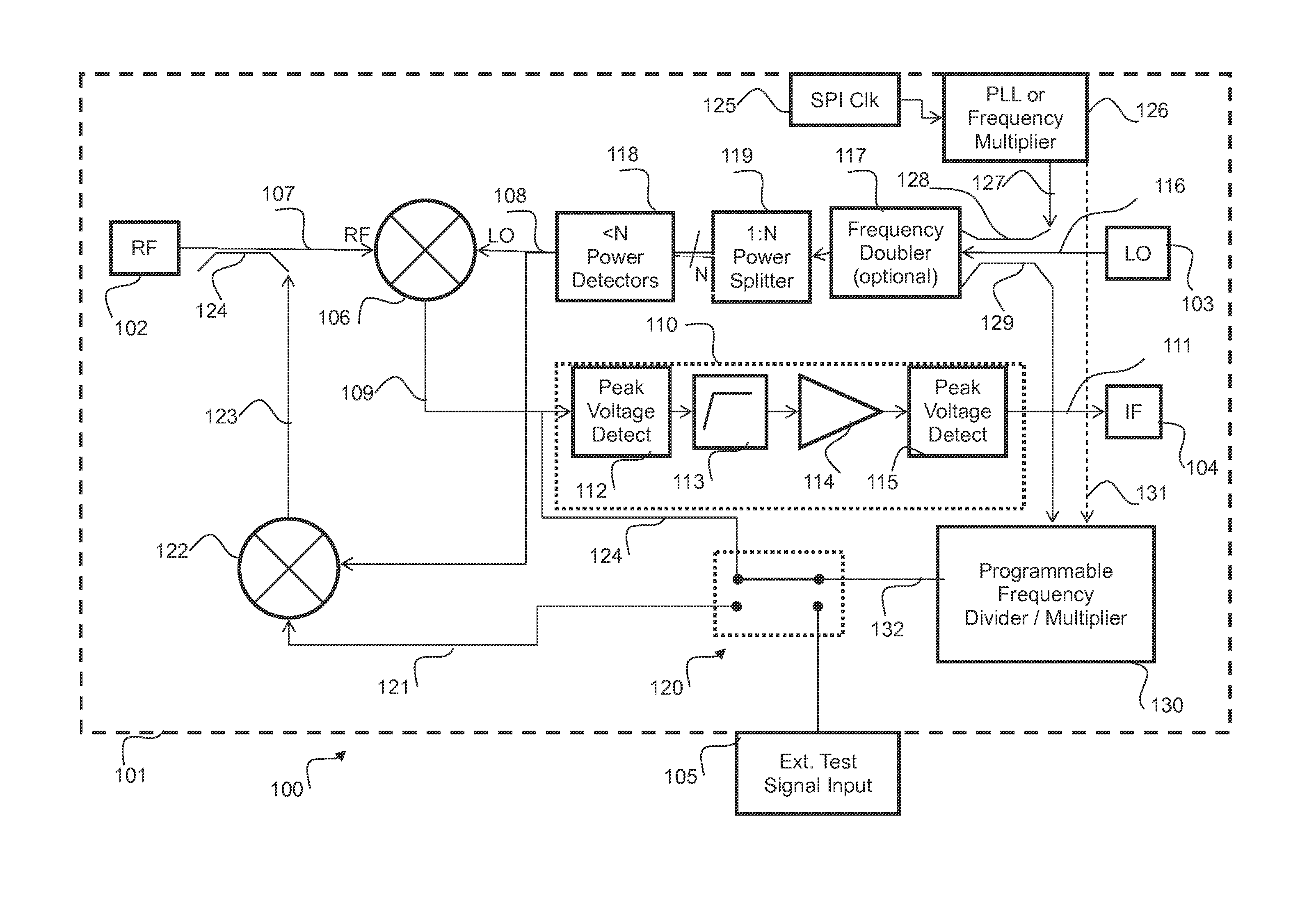
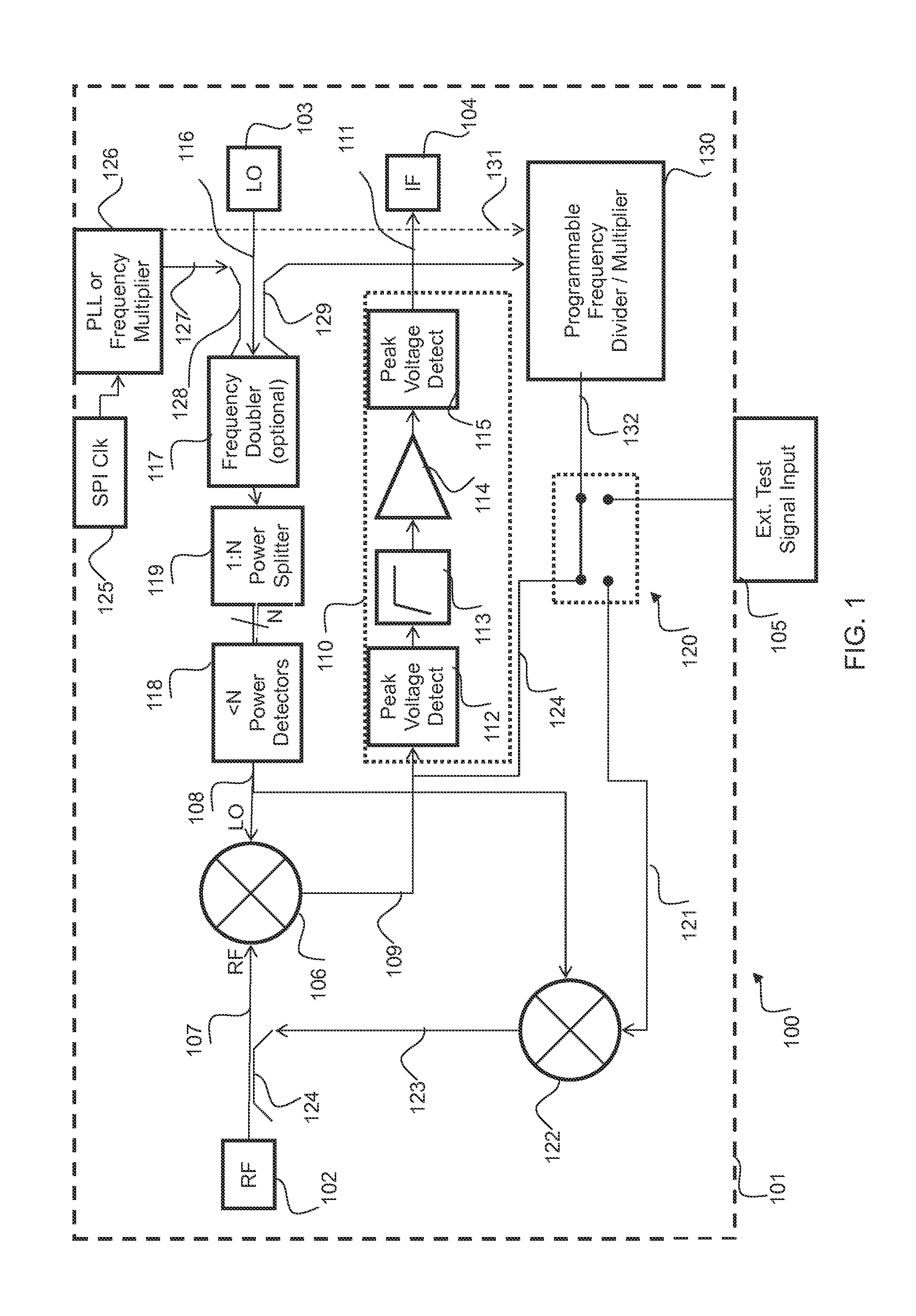
InactiveUS20160077196A1Receivers monitoringRadiofrequency circuit testingOn boardDown conversion mixer
A receiver system which may be implemented in an integrated circuit device and suitable for use in automotive radar systems such as collision avoidance systems, includes self test circuitry whereby a local oscillator test signal is generated by an on-board frequency multiplier and mixed in a down-conversion mixer with an RF test signal. The RF test signal is generated on the device by up-conversion of an externally generated low-frequency test signal with the local oscillator test signal. Baseband components may also be checked using test signals of suitable frequency divided down from the local oscillator test signal by a programmable frequency divider. This self test arrangement obviates any need for applying externally generated RF test signals to the IC device.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS7106294B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayFrequency multiplier
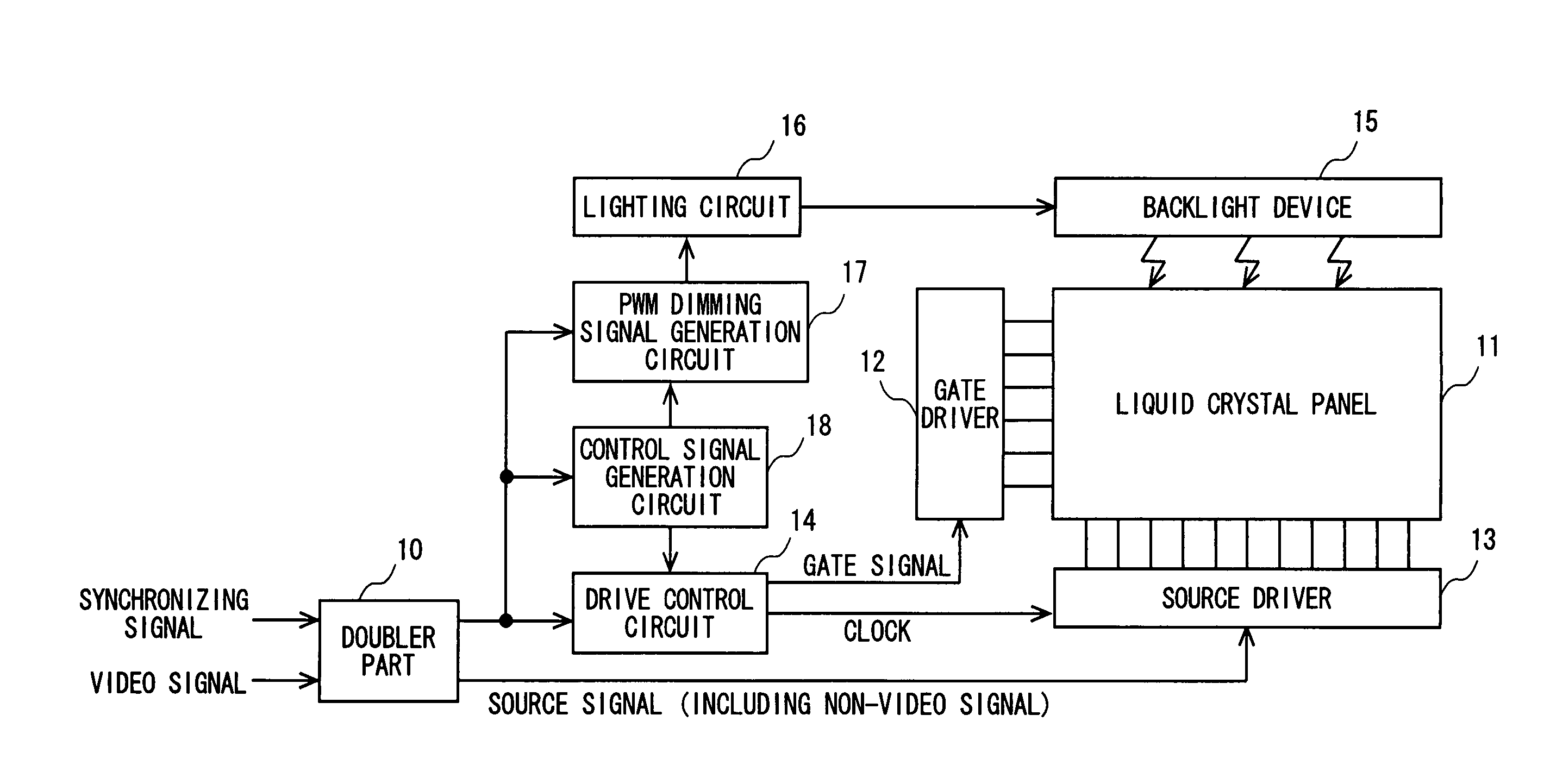
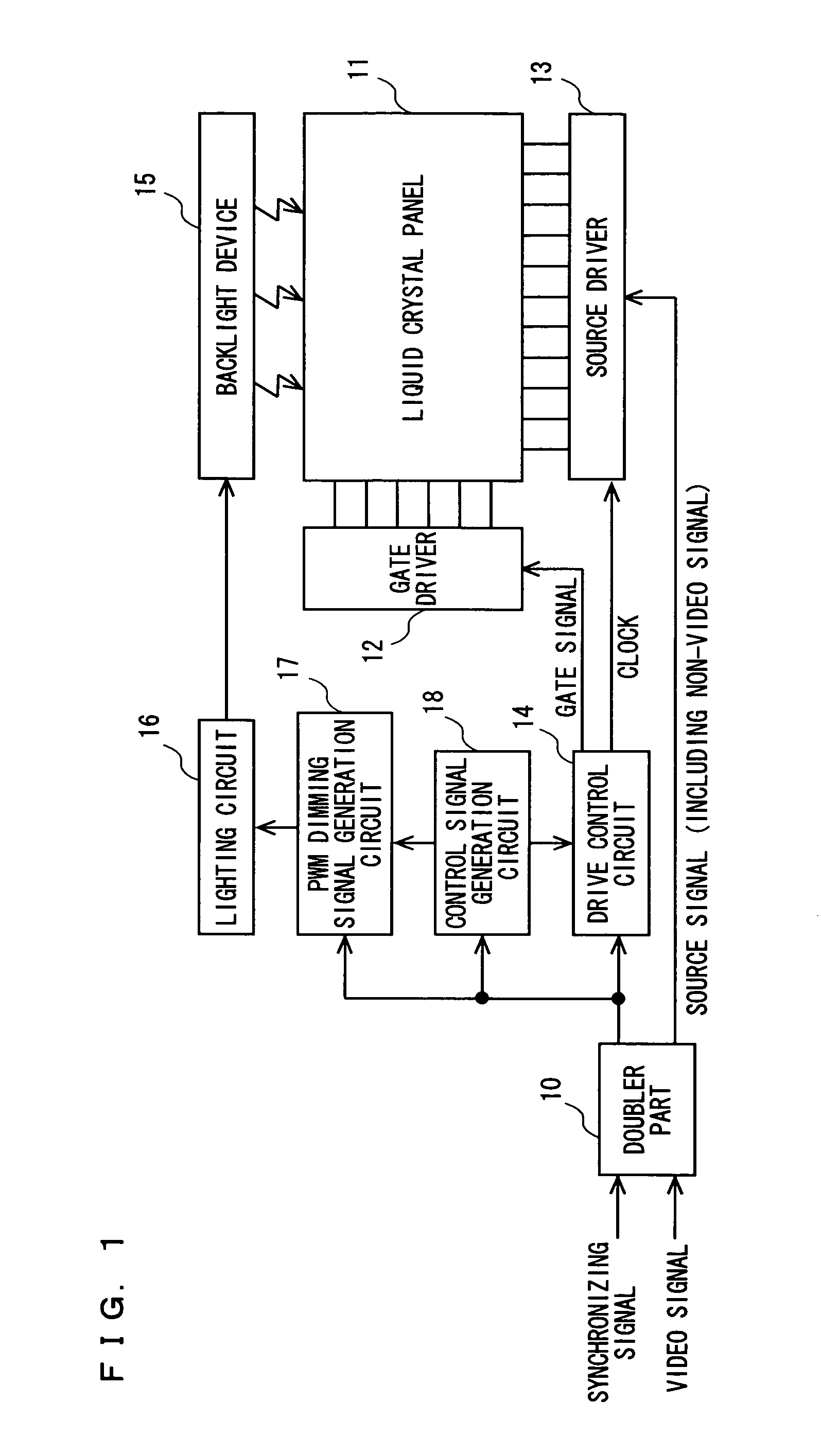
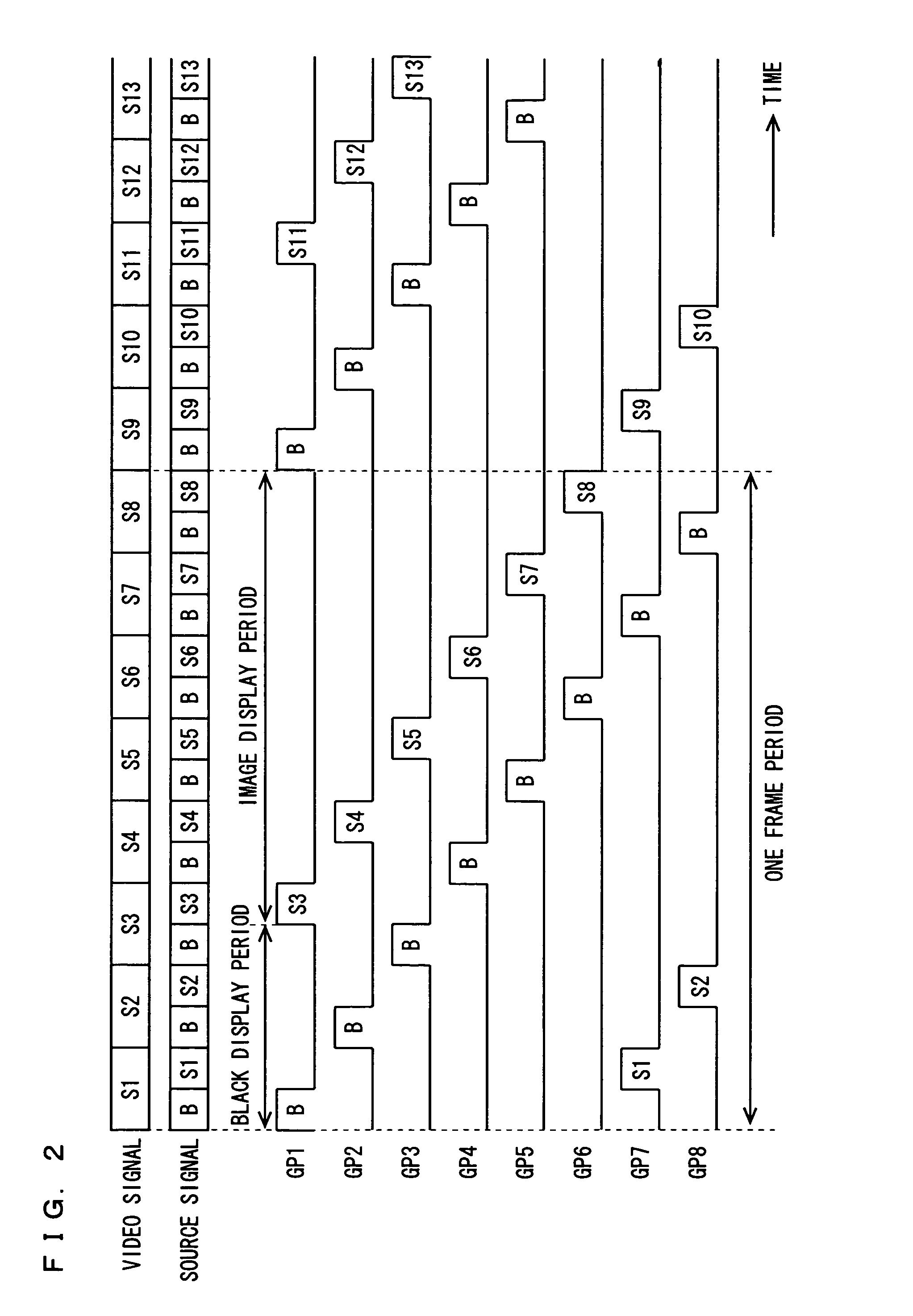
A doubler part doubles frequencies of video signals. A drive control circuit generates, in response to a synchronizing signal outputted from the doubler part, PWM dimming frequency information such that a PWM dimming frequency f and a black display ratio B satisfy the relationships f≧25B+250 and B>10, and provides such information to a PWM dimming signal generation circuit. In addition, the drive control circuit drives a gate driver and a source driver such that one frame period is divided into an image display period and a black display period. The PWM dimming signal generation circuit generates, in response to a synchronizing signal and the PWM dimming frequency information, a PWM dimming signal and provides the PWM dimming signal to a lighting circuit. The lighting circuit activates a backlight device with dimming, in response to the PWM dimming signal. This configuration reduces colored interference fringes in a liquid crystal display device resulting from the combination of a black insertion drive technique and a PWM dimming technique.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Tera-hertz silica-based quadrupler and frequency multiplier
InactiveCN102104363AIncrease the output frequencyHigh multiplierOscillations generatorsFrequency spectrumRFIC
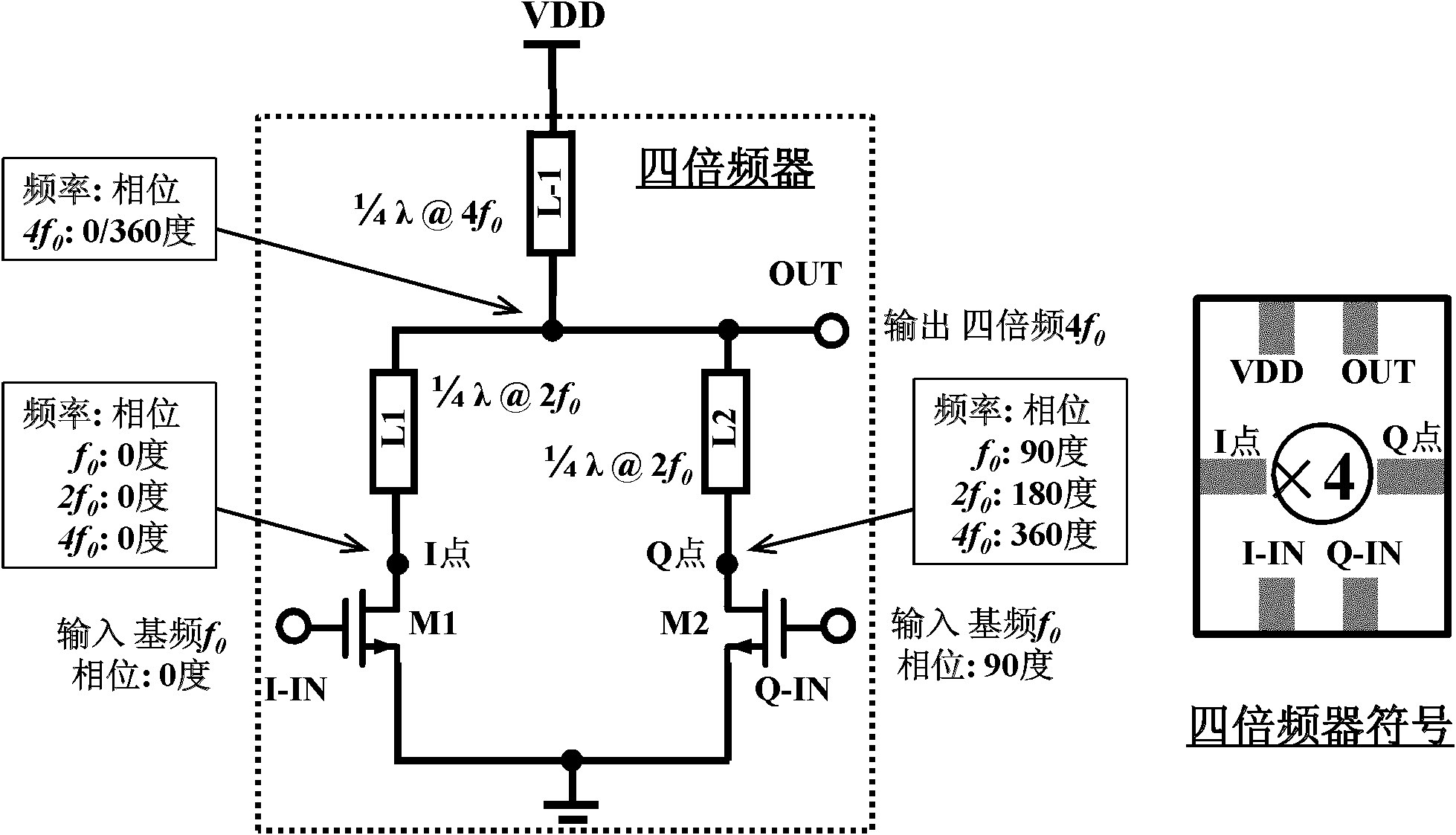
The invention discloses a tera-hertz silica-based quadrupler and a frequency multiplier, belonging to the field of RFIC (Radio Frequency Integrated Circuit). The quadrupler comprises transistors (M1 and M2) and transmission lines (L1, L2 and L-1), wherein the drain ends of the transistors (M1 and M2) are respectively connected to an output port through the transmission lines (L1 and L2), source ends are connected with a ground line, grid ends are respectively connected with the signal input ends of an path (I) and the path (Q) of a baseband signal (f0); the transmission line (L-1) is connected between the output port and a power supply; and the length of the transmission lines (L1 and L2) are 1 / 4 of that of the corresponding wavelength of a signal (2f0), the length of the transmission line (L-1) is 1 / 4 of that of the corresponding wavelength of a signal (4f0). The multi-frequency multiplier comprises a 2n frequency multiplier (1), a 2n frequency multiplier (2) and a transmission line (L), wherein the output ports of the 2n frequency multiplier (1) and the 2n frequency multiplier (2) are connected to be used as the output port of a 2n+1 frequency multiplier, the transmission line (L) is connected between the output port of the 2n+1 frequency multiplier and the power supply, and the length of the transmission line (L) is 1 / 4 of that of the corresponding wavelength of a signal (2n+1f0). The tera-hertz silica-based quadrupler and the multi-frequency multiplier, provided by invention, have the advantages of high output frequency, pure frequency spectrum, low power consumption and easiness for integration.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
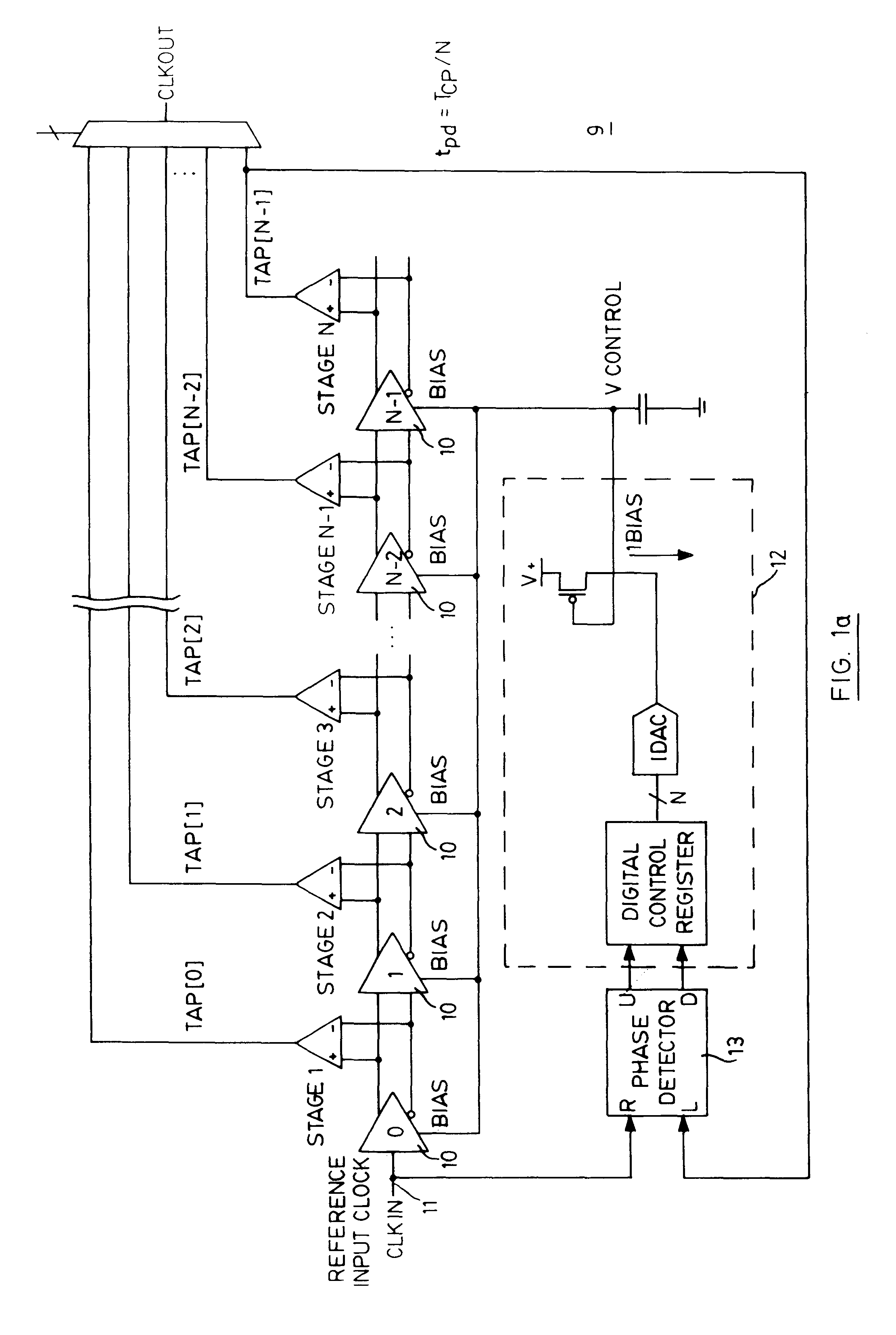
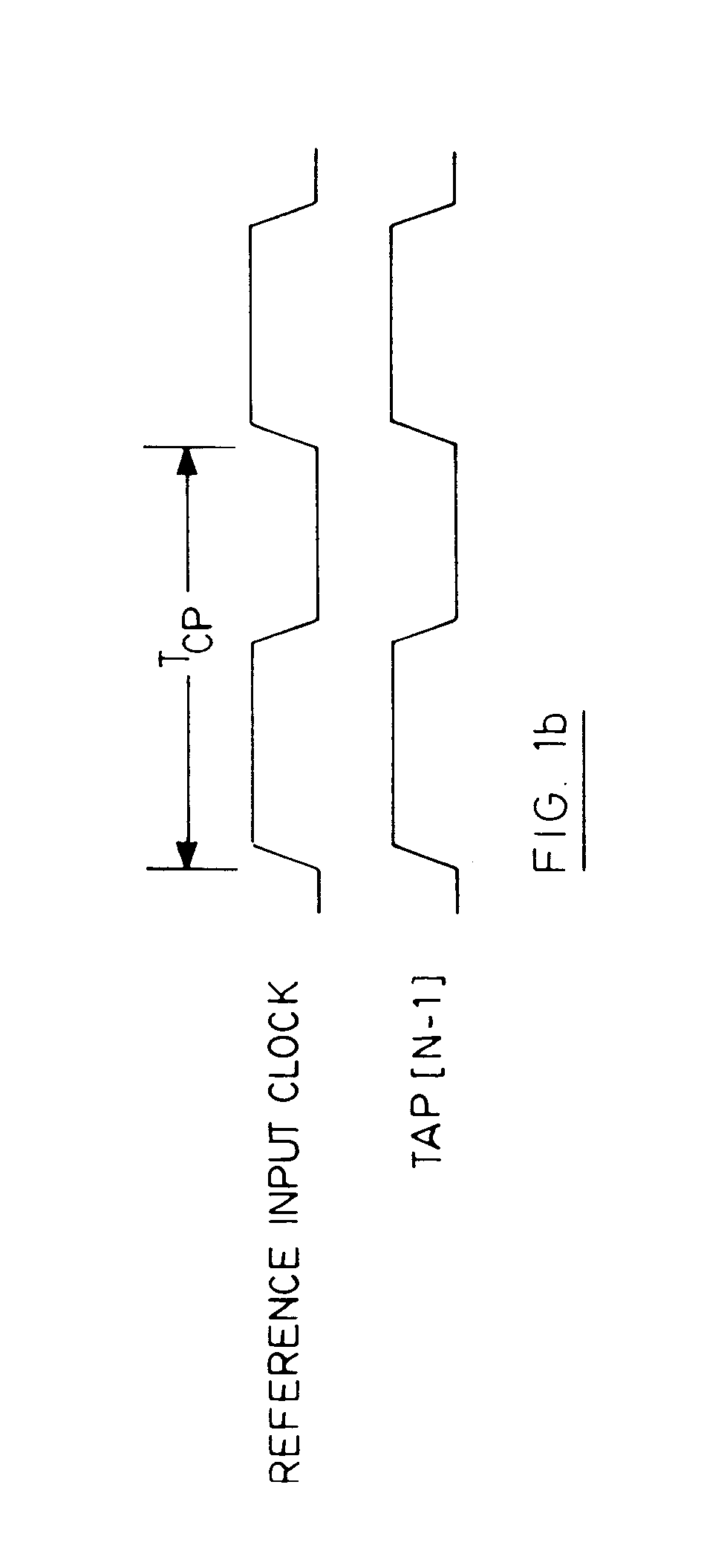
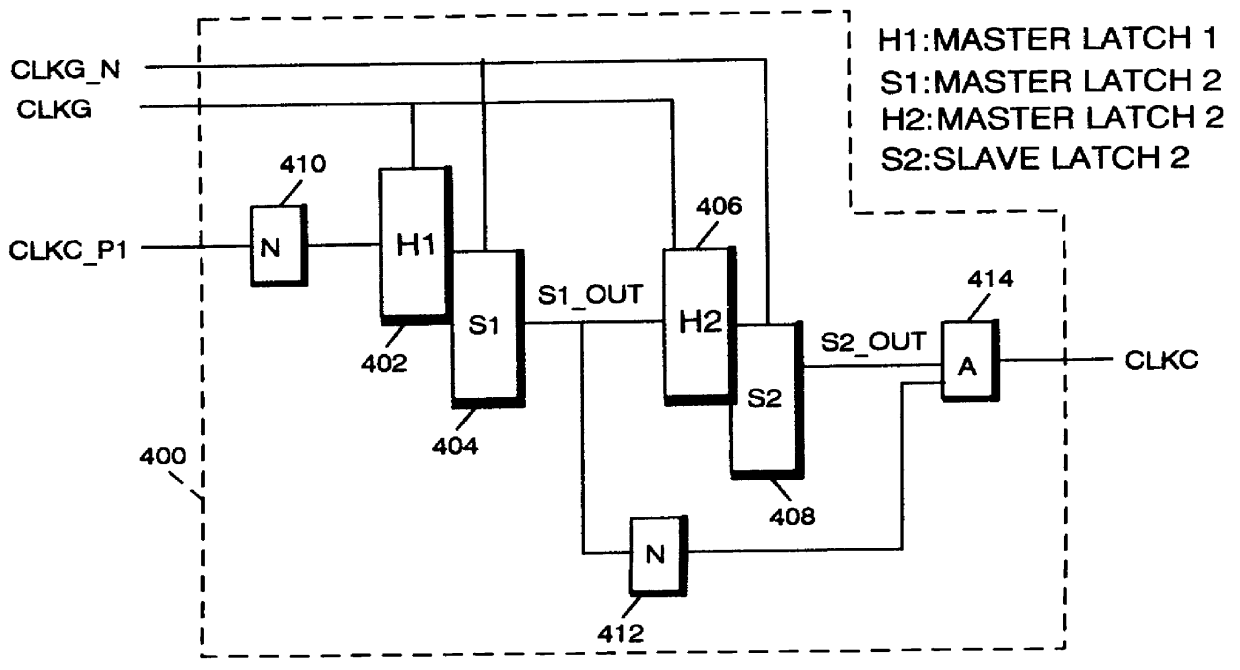
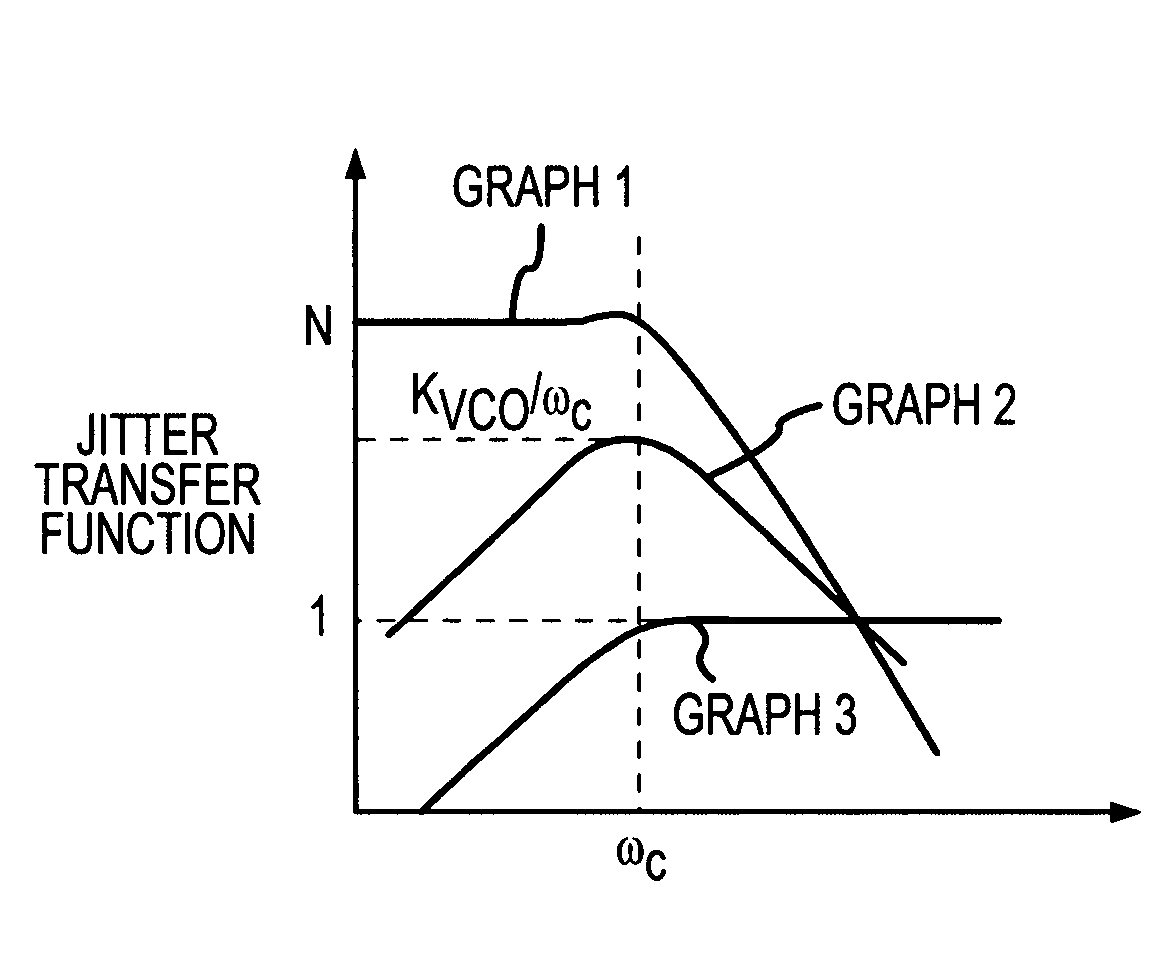
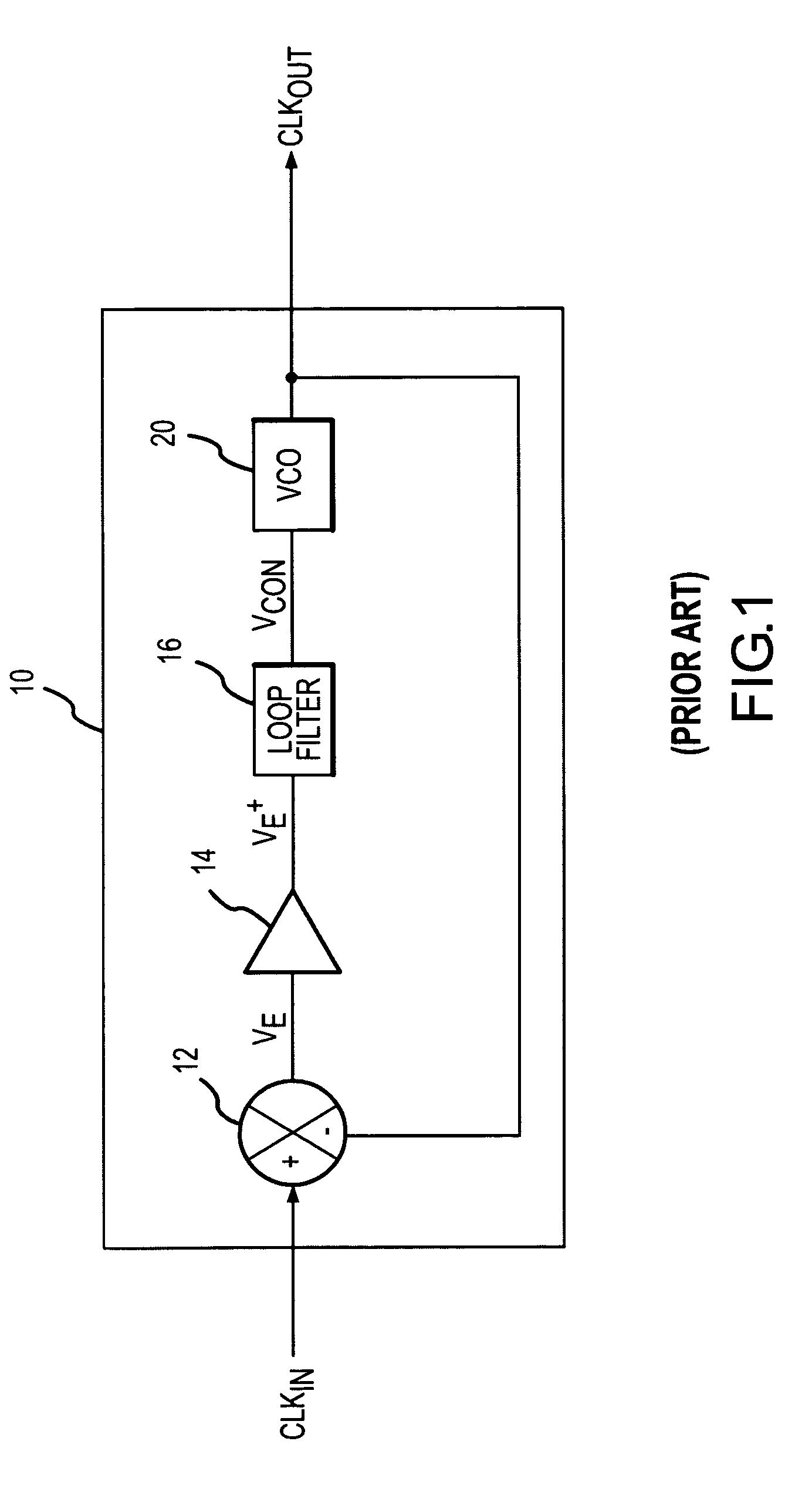
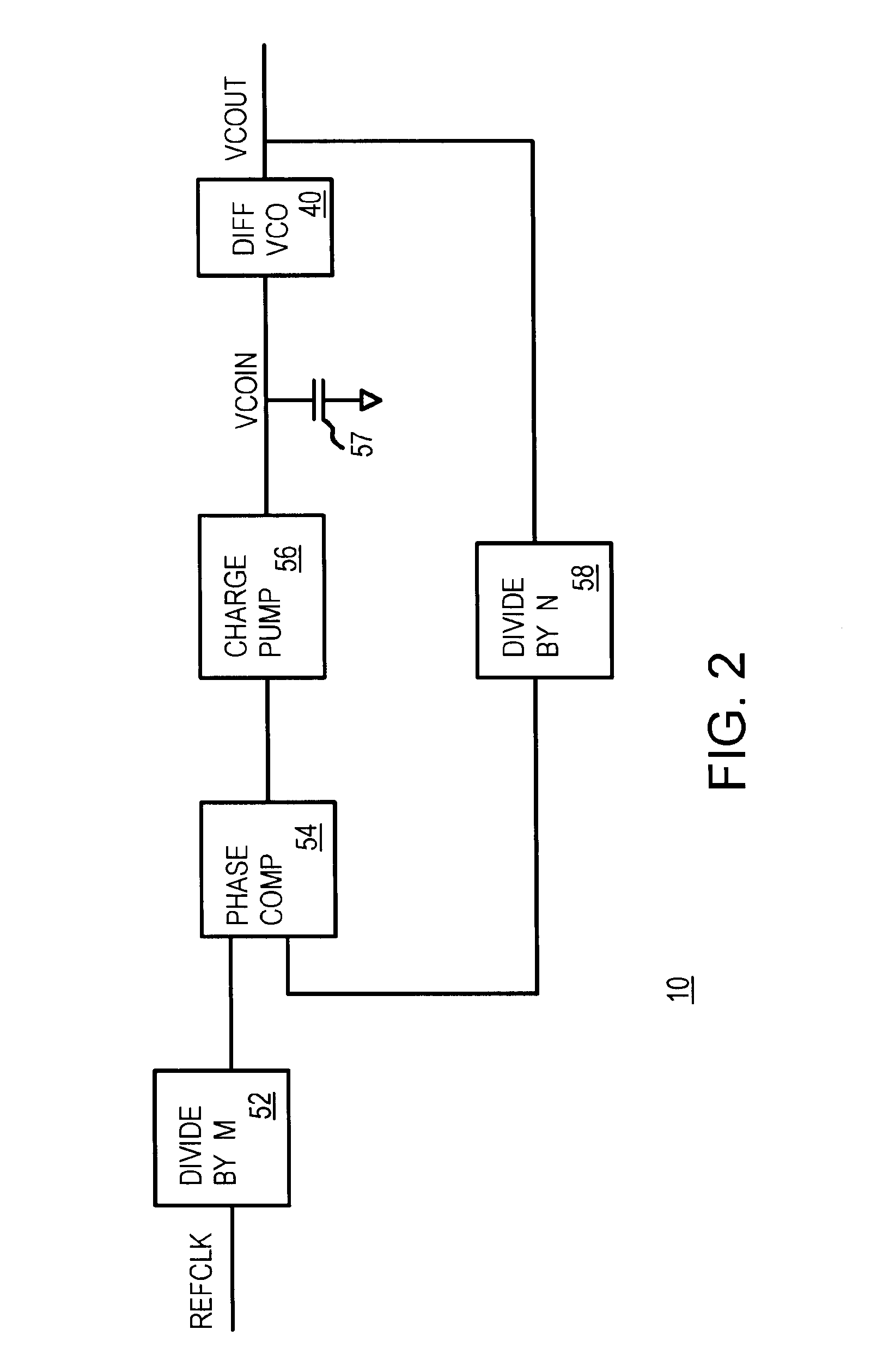
Low power and low timing jitter phase-lock loop and method
A phase-lock loop generates an output clock signal from an input clock signal. The output clock signal is coupled through a clock tree and is fed back to a phase detector, which compares the phase of the output clock signal to the phase of the input clock signal. The output clock signal is generated by a voltage controlled oscillator having a control input coupled to receive an output from the phase detector, and a frequency multiplier coupled to the output of the voltage controlled oscillator. As a result, the CLKOUT signal generated by the frequency multiplier has a relatively high frequency while the voltage controlled oscillator, by operating at a relatively low frequency, uses relatively little power.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
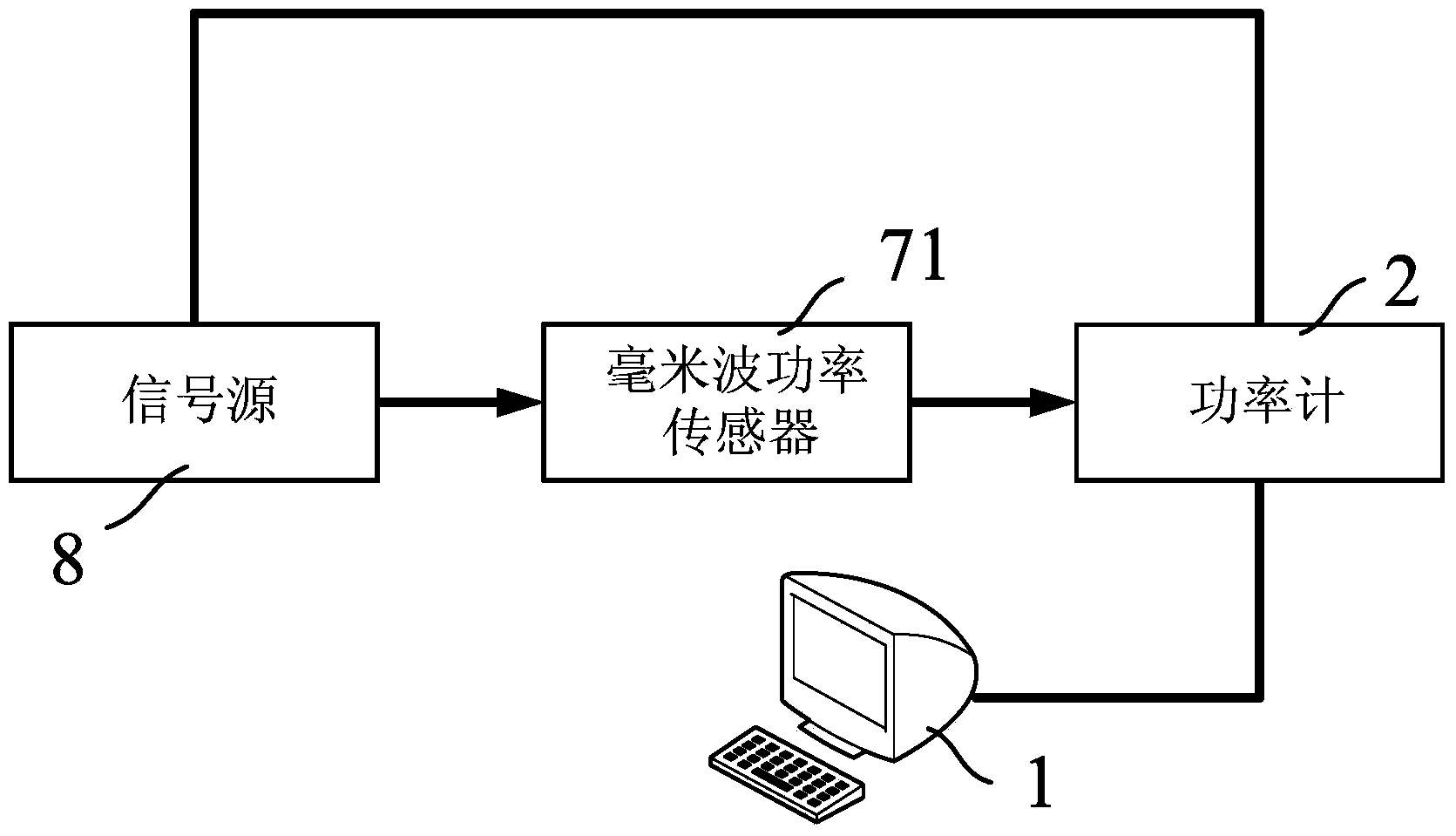
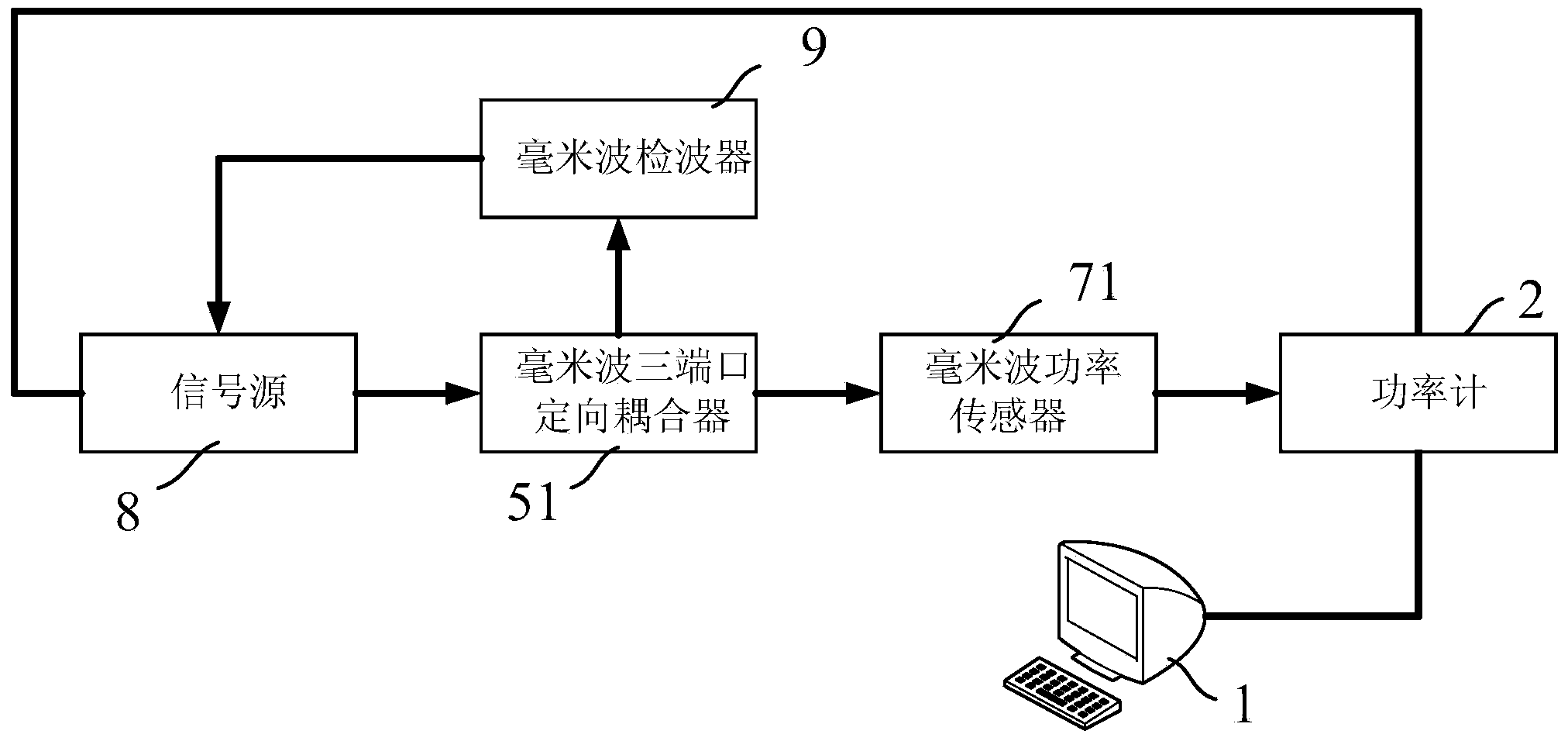
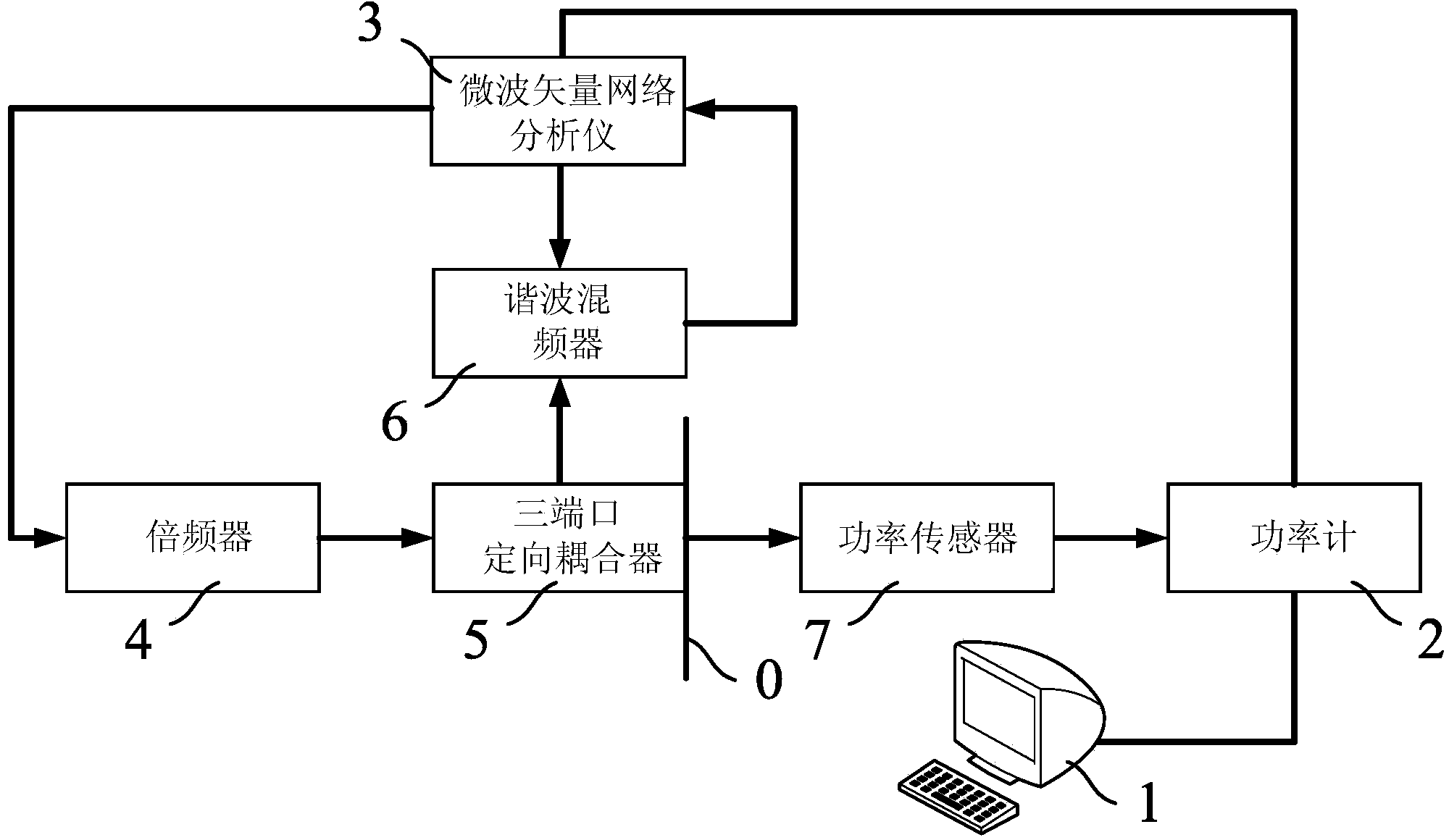
Power calibration test system and power calibration measurement method
ActiveCN104062620ARealize monitoringRealize regulationElectrical measurementsPower sensorClosed loop feedback
The invention provides a power calibration test system. The power calibration test system comprises a system setting device for setting target power and a target frequency band, a power meter connected with the system setting device and used for measuring output power in cooperation with a power sensor, a microwave vector network analyzer connected with the power meter and used for generating microwave signals, a frequency multiplier connected with the microwave vector network analyzer, a three-port directional coupler connected with the frequency multiplier, and a harmonic mixer connected with the microwave vector network analyzer and the three-port directional coupler. By means of a closed loop feedback loop, real-time closed loop monitoring and adjustment on input power of the reference plane of an input port of a component to be tested are achieved, real-time closed loop calibration on power within any frequency band and accurate measurement on circuits and devices can be achieved, and the universality, effectiveness, consistency and accuracy of the power calibration test system are largely improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
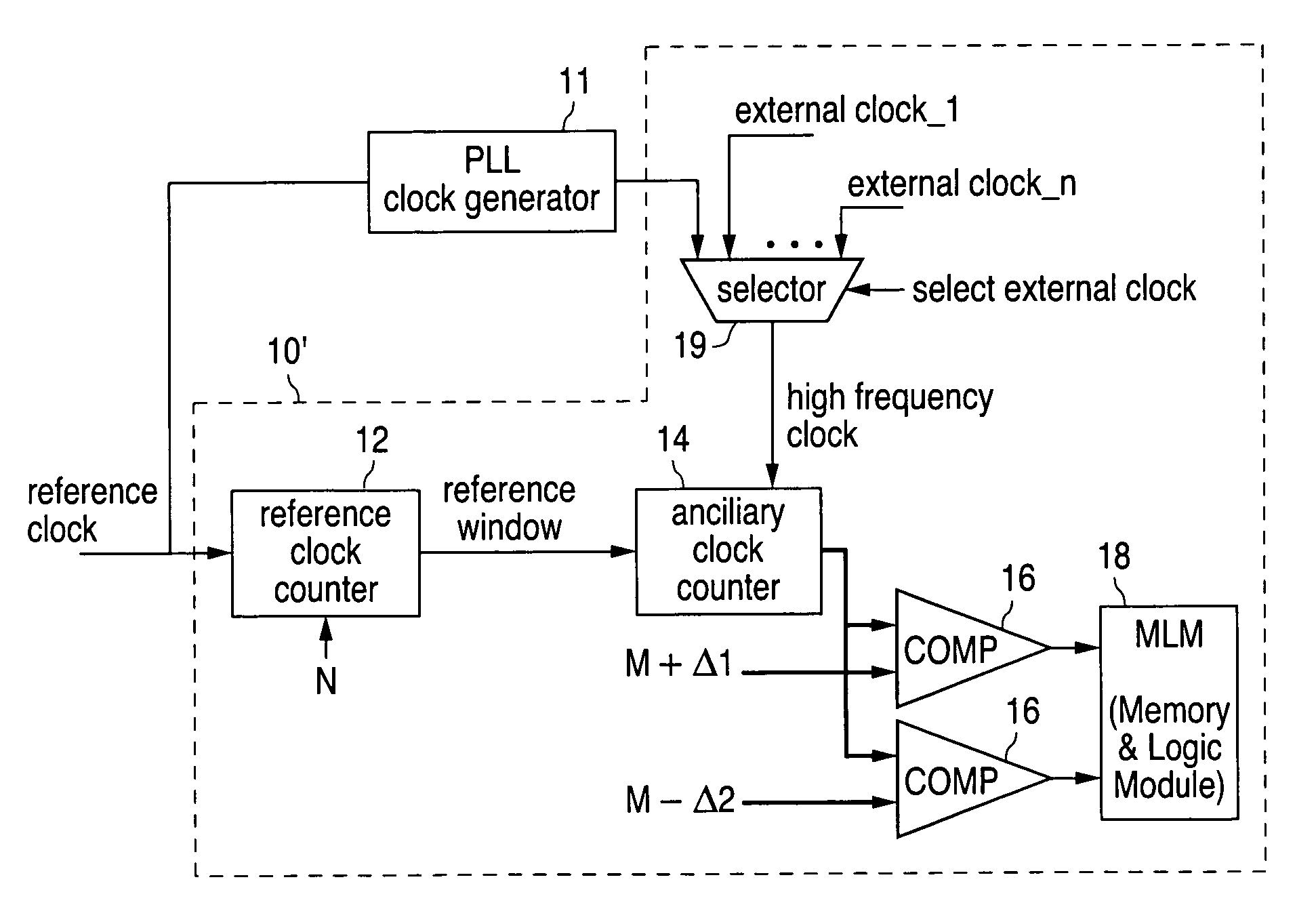
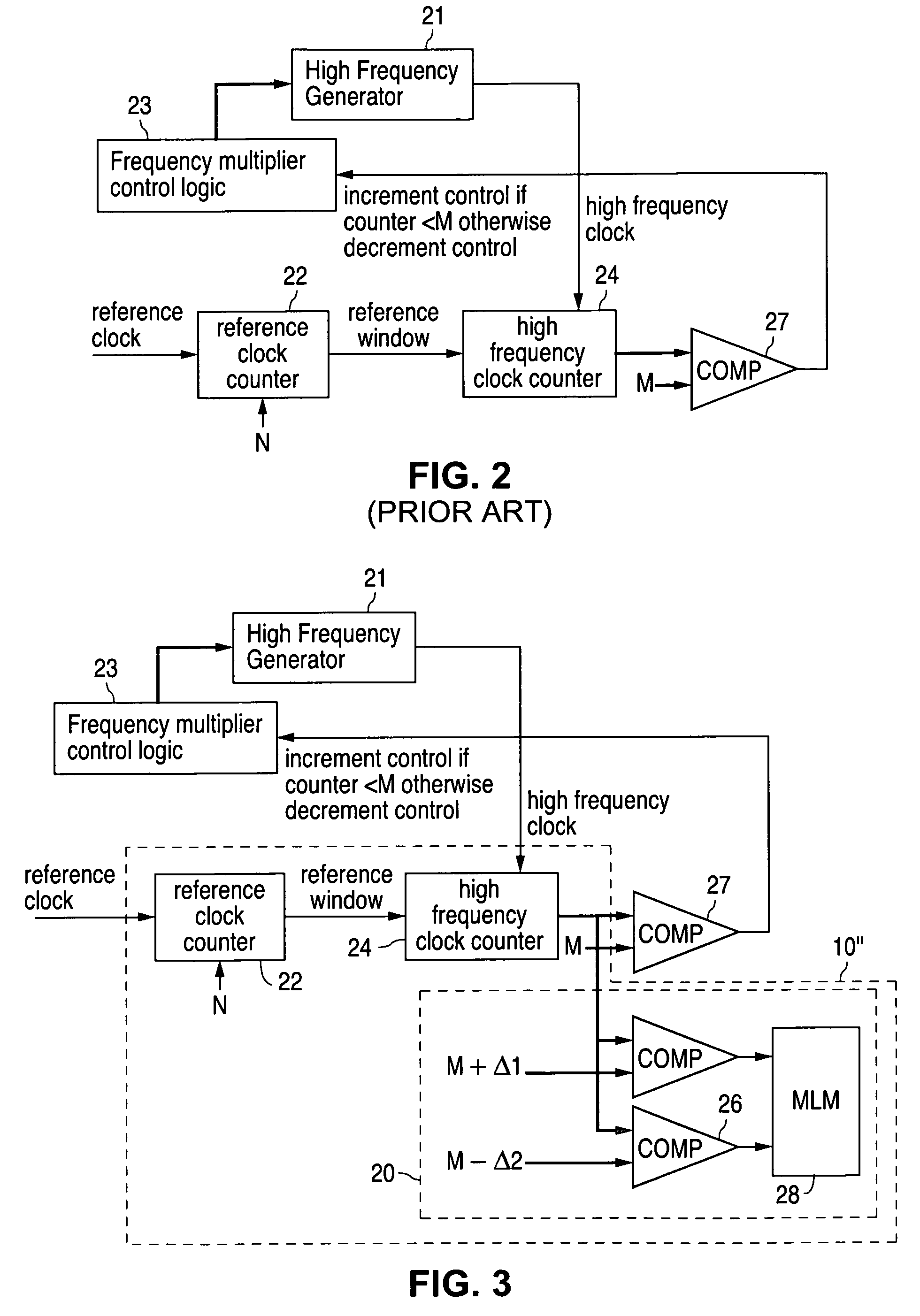
Clock frequency monitor
ActiveUS7242223B1Frequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationFrequency measurement arrangementClock rateReference window
A frequency monitor circuit (FMC) that is part of an integrated circuit chip for monitoring the frequency of one or more clocks present on the chip is disclosed. The FMC includes a reference window generator, operative to output a reference window signal of a given duration, and a clock counter, operative to count all pulses, in any one of the clocks, that occur within the duration of the reference window and to output a corresponding pulse count. The FMC further includes two or more comparators, each operative to compare the pulse count with a respective given threshold value and to output a corresponding indication of frequency deviation. In one configuration, in which the clock is generated on the chip by a frequency multiplier, the reference window generator and the clock counter are shared between the frequency monitor circuit and the frequency multiplier.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Planar laser induced fluorescence (PLIF) imaging device and method for acquiring hydroxyl (OH) concentration spatial distribution through device
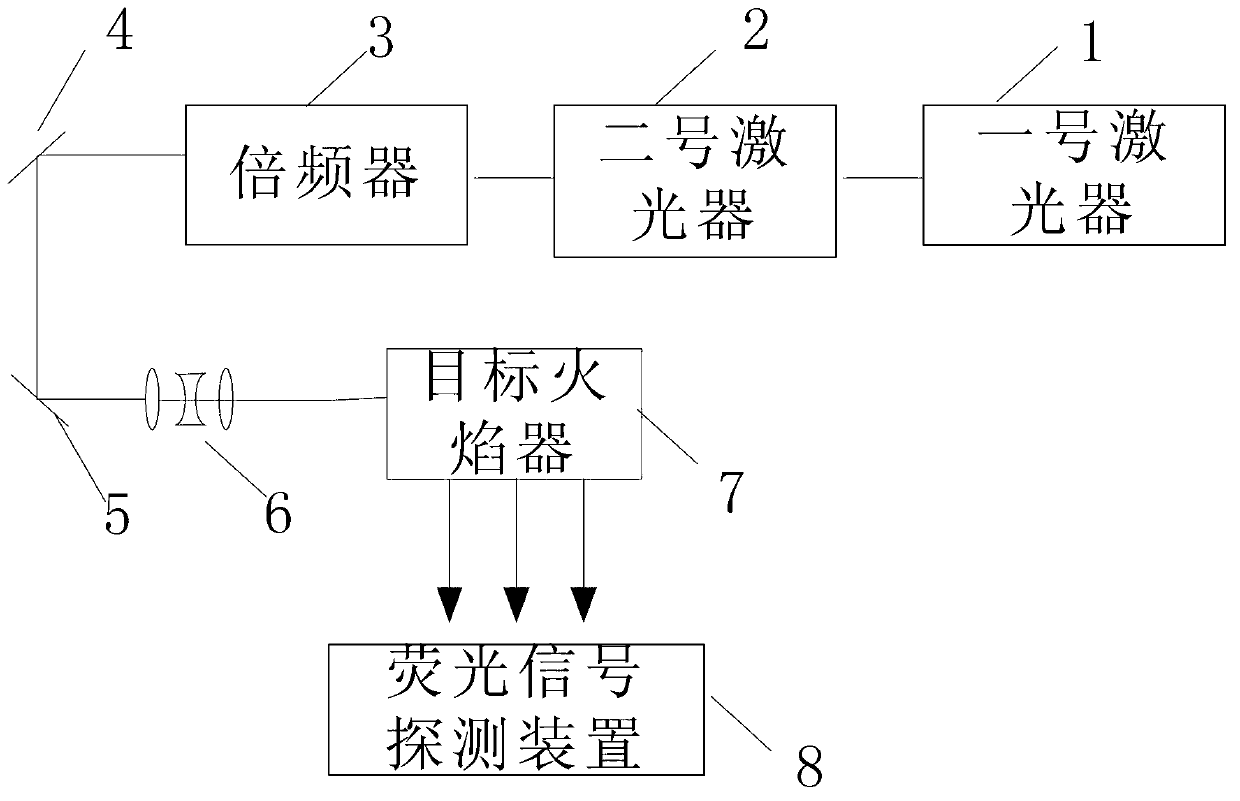
InactiveCN103344619ASimple processHigh precisionFluorescence/phosphorescencePlanar laser-induced fluorescenceFluorescence
The invention discloses a planar laser induced fluorescence (PLIF) imaging device and a method for acquiring hydroxyl (OH) concentration spatial distribution through the device, and relates to a method for determining the OH-radical concentration spatial distribution. According to the device and the method, the problem that the average concentration of components on a certain line can be only determined and the spatial distribution of the concentration cannot be determined through a PLIF imaging technology is solved. A laser generates a laser signal, the laser signal is subjected to frequency multiplication through a frequency multiplier, and a sheet pulse signal is obtained through a sheet beam reshaping system; a target flame device excites an OH-radical fluorescence signal; a fluorescence signal detection device detects the OH-radical fluorescence signal to obtain an OH-radical fluorescence image; n to-be-measured points and n auxiliary points are selected from the OH-radical fluorescence image, the gray value and light intensity of the OH-radical fluorescence image of each to-be-measured point and each auxiliary point are calculated; the average molar concentration of each to-be-measured point is obtained according to a Lambert-Bill absorption law so as to obtain the OH-radical concentration spatial distribution. The invention is applied to the method for determining the OH-radical concentration spatial distribution.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
On-chip power-combining for high-power schottky diode based frequency multipliers
ActiveUS20130229210A1Split evenlySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialHarmonic
A novel MMIC on-chip power-combined frequency multiplier device and a method of fabricating the same, comprising two or more multiplying structures integrated on a single chip, wherein each of the integrated multiplying structures are electrically identical and each of the multiplying structures include one input antenna (E-probe) for receiving an input signal in the millimeter-wave, submillimeter-wave or terahertz frequency range inputted on the chip, a stripline based input matching network electrically connecting the input antennas to two or more Schottky diodes in a balanced configuration, two or more Schottky diodes that are used as nonlinear semiconductor devices to generate harmonics out of the input signal and produce the multiplied output signal, stripline based output matching networks for transmitting the output signal from the Schottky diodes to an output antenna, and an output antenna (E-probe) for transmitting the output signal off the chip into the output waveguide transmission line.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Single chip GSM/EDGE transceiver architecture with closed loop power control
InactiveUS20070072577A1Resonant long antennasNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsClosed loopFrequency multiplier
A single chip GSM / EDGE transceiver comprises a fully differential receive chain, a subharmonic mixer in the receive chain, the subharmonic mixer configured to receive a radio frequency (RF) input signal and a local oscillator (LO) signal that is phase-shifted by a nominal 45 degrees, and a synthesizer having a voltage controlled oscillator and having at least one frequency divider to generate desired transmit and receive LO signals. The transceiver also comprises a transmitter having a closed power control loop, and a harmonic rejection modulator, the use thereof made possible by a frequency plan designed to allow the synthesizer to develop the transmit and receive LO signals without a frequency multiplier.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Divide-by-X.5 circuit with frequency doubler and differential oscillator
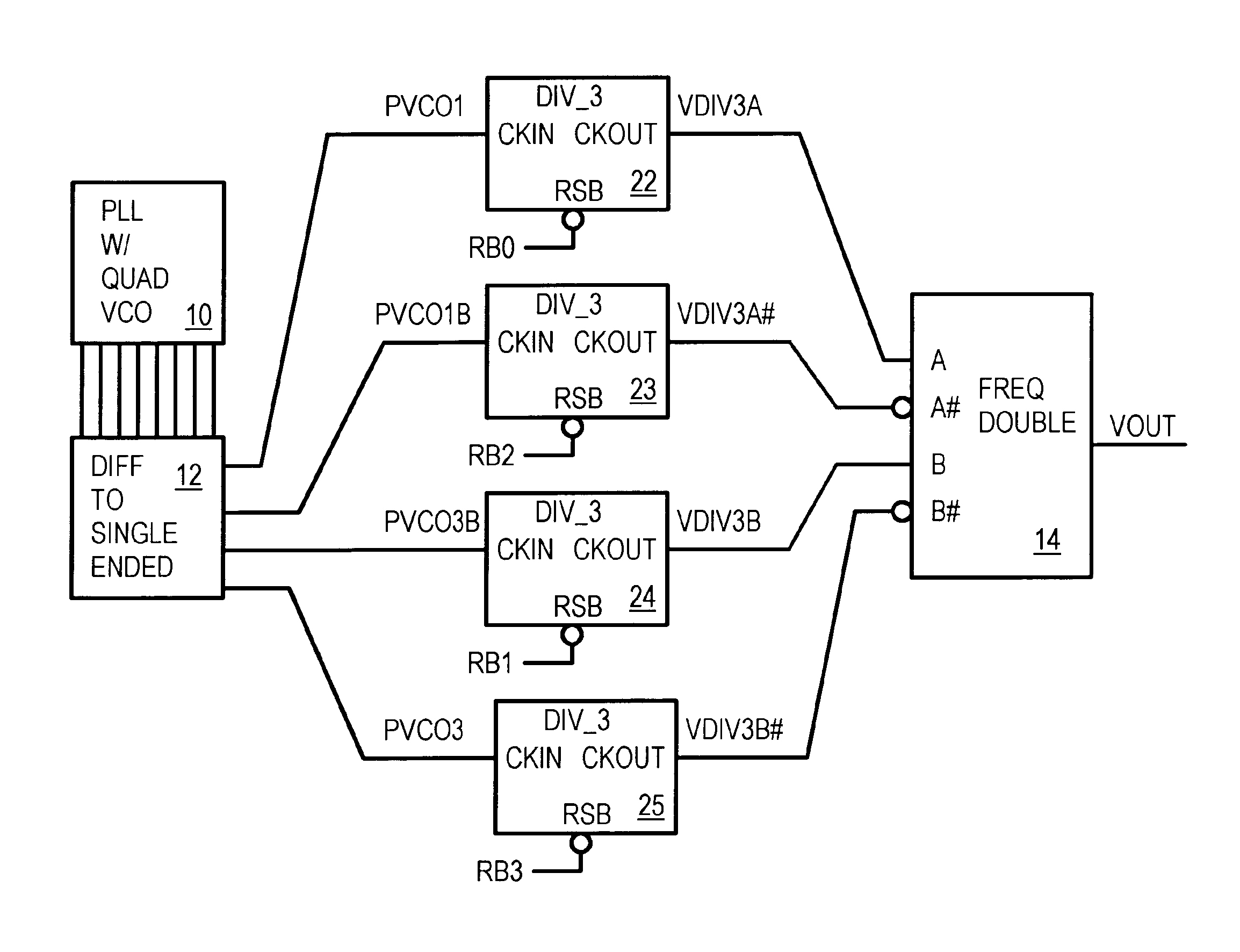
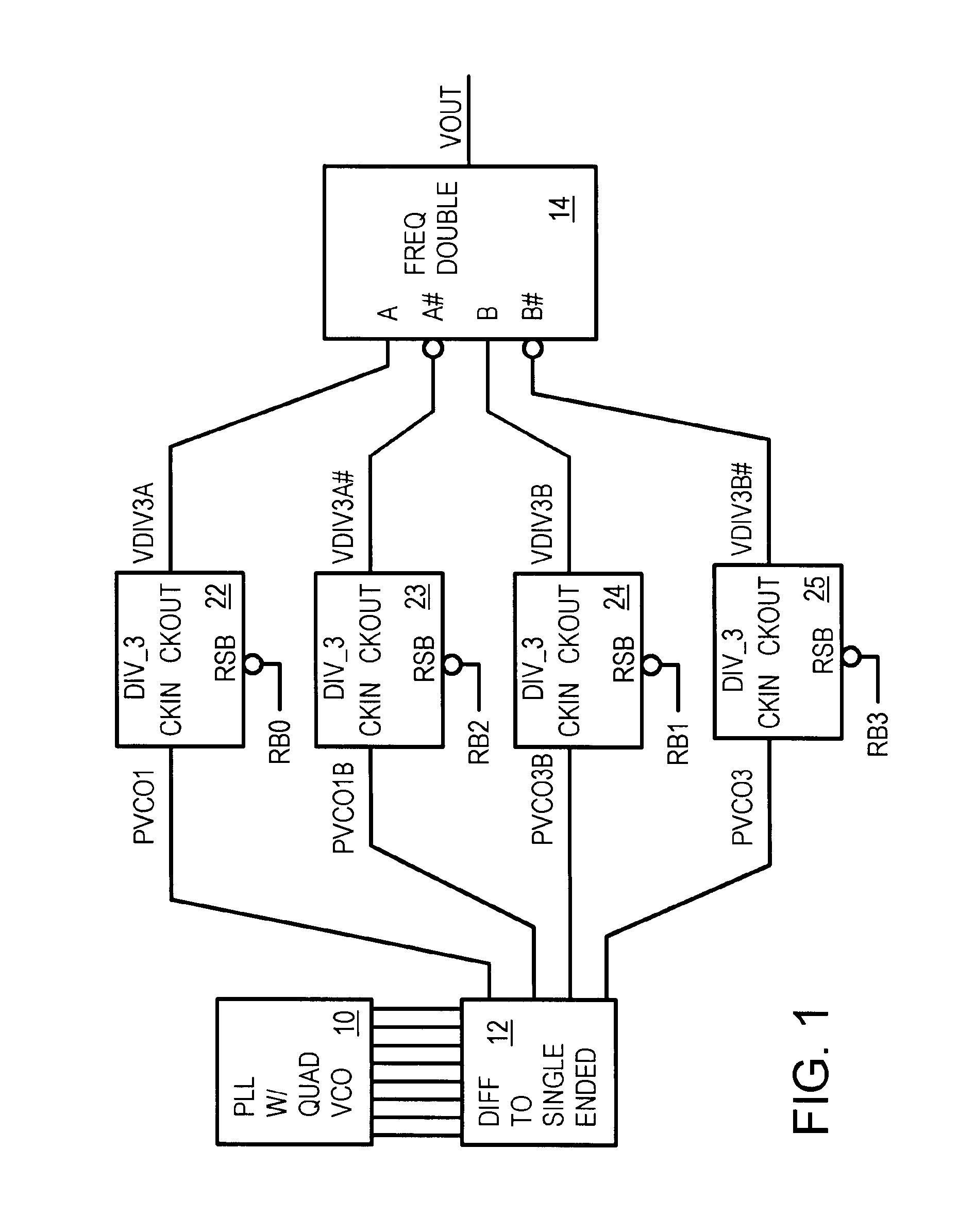
InactiveUS6882229B1Pulse automatic controlCounting chain synchronous pulse countersFrequency multiplierQuadrature voltage controlled oscillator
A divide by X.5 circuit can be implemented as a divided by 1.5 circuit. A phase-locked loop (PLL) has a quadrature voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) that generates four phases offset at 0, 90, 180, and 270 degrees. Differential signals from the VCO are converted to single-ended VCO clocks that drive four divide-by-3 circuits, each clocked by one of the four phases of the VCO clocks. Resets to the divide-by-3 circuits are staggered to activate each divide-by-3 circuit synchronously with its phase clock. Outputs from the divide-by-3 circuits are applied to a frequency doubler that generates the final clock that is 1.5 times slower than the VCO clocks. The final clock has a near 50%-50% duty cycle.
Owner:DIODES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com