Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
813 results about "Master clock" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A master clock is a precision clock that provides timing signals to synchronise slave clocks as part of a clock network. Networks of electric clocks connected by wires to a precision master pendulum clock began to be used in institutions like factories, offices, and schools around 1900. Today, many radio clocks are synchronised by radio signals or Internet connections to a worldwide time system called Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), which is governed by master atomic clocks in many countries.
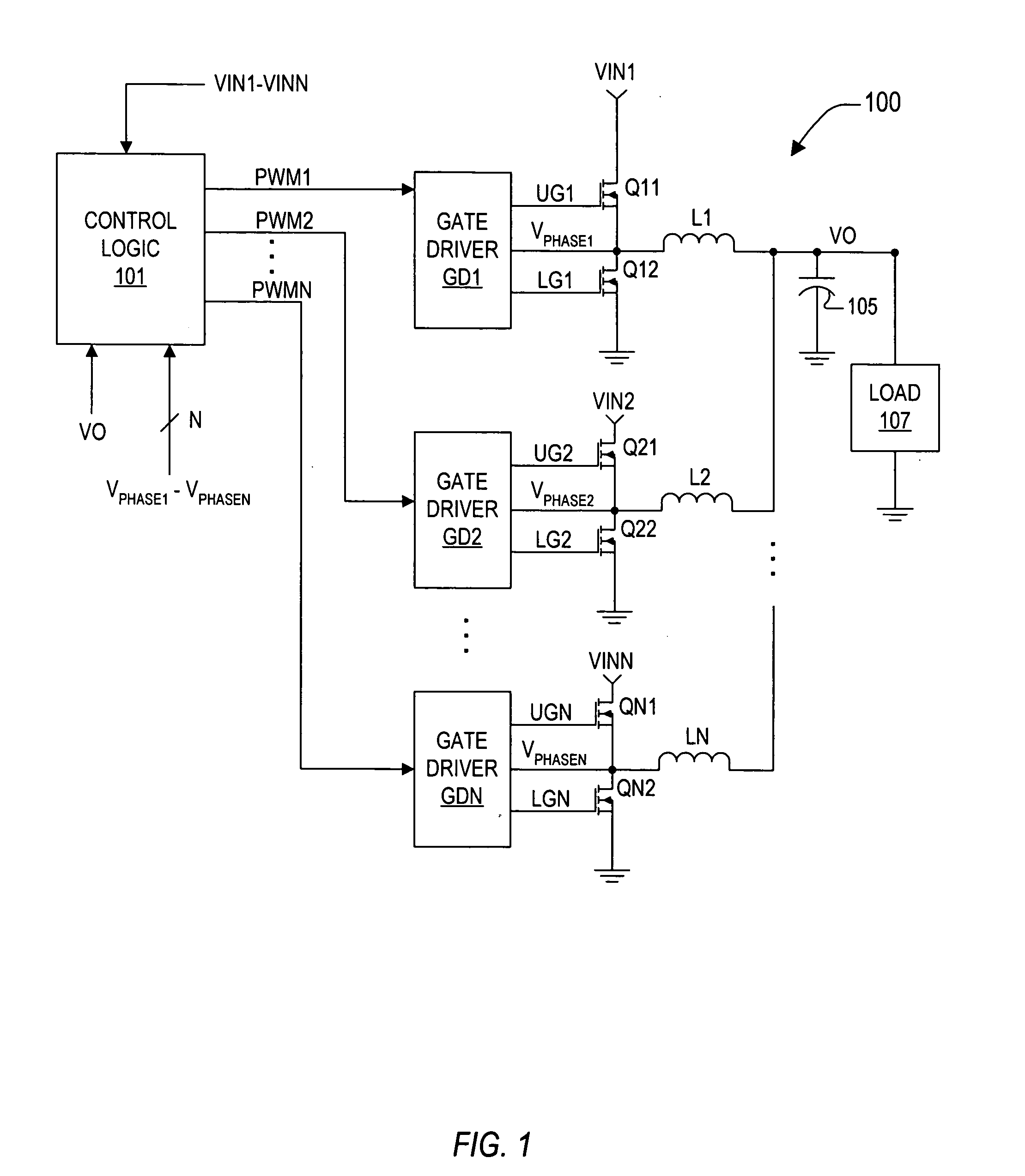
System and method for acquiring data
InactiveUS6839659B2Easy to carryImprove clarityAngiographyData acquisition and loggingData connectionHigh rate
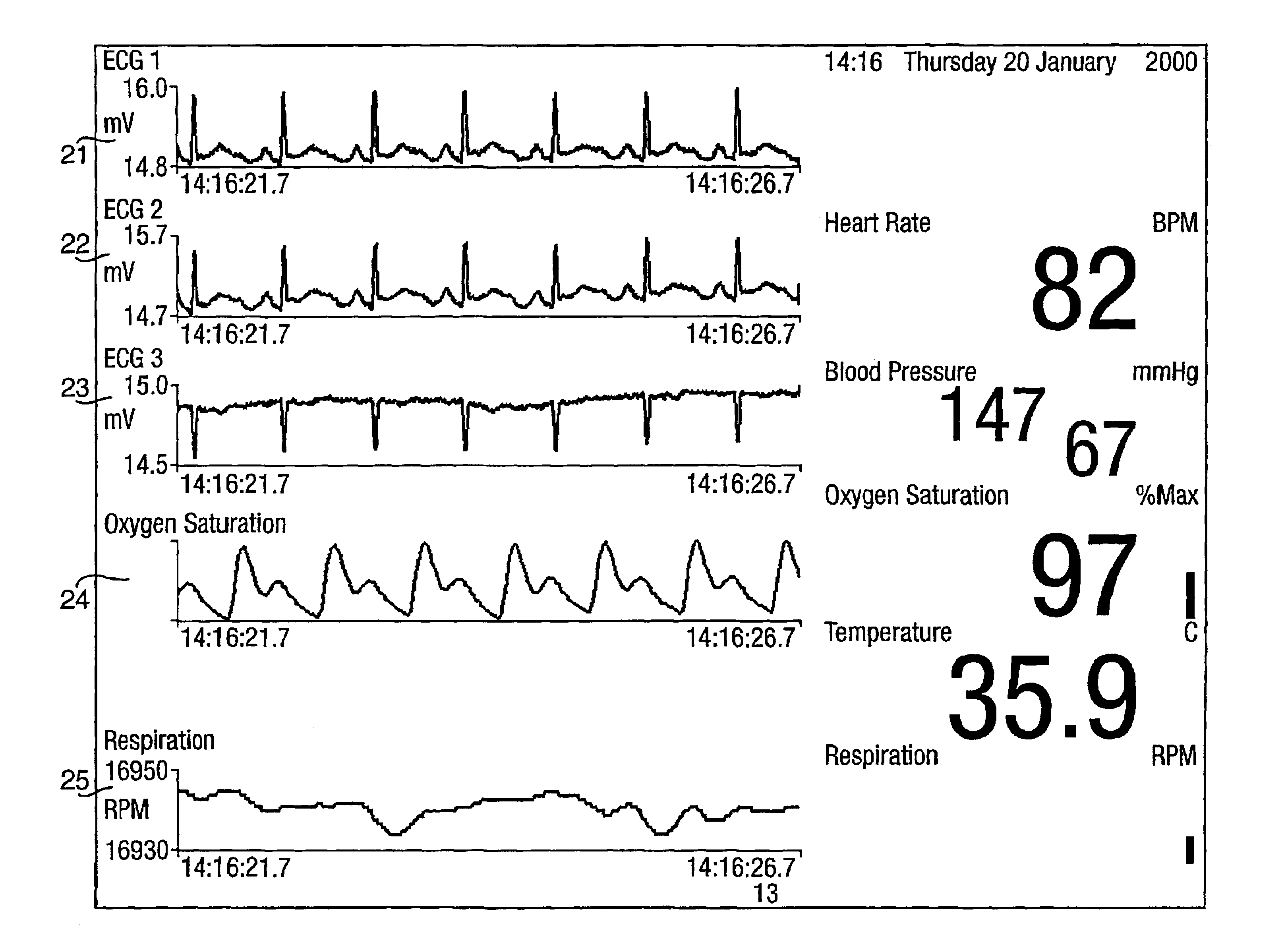
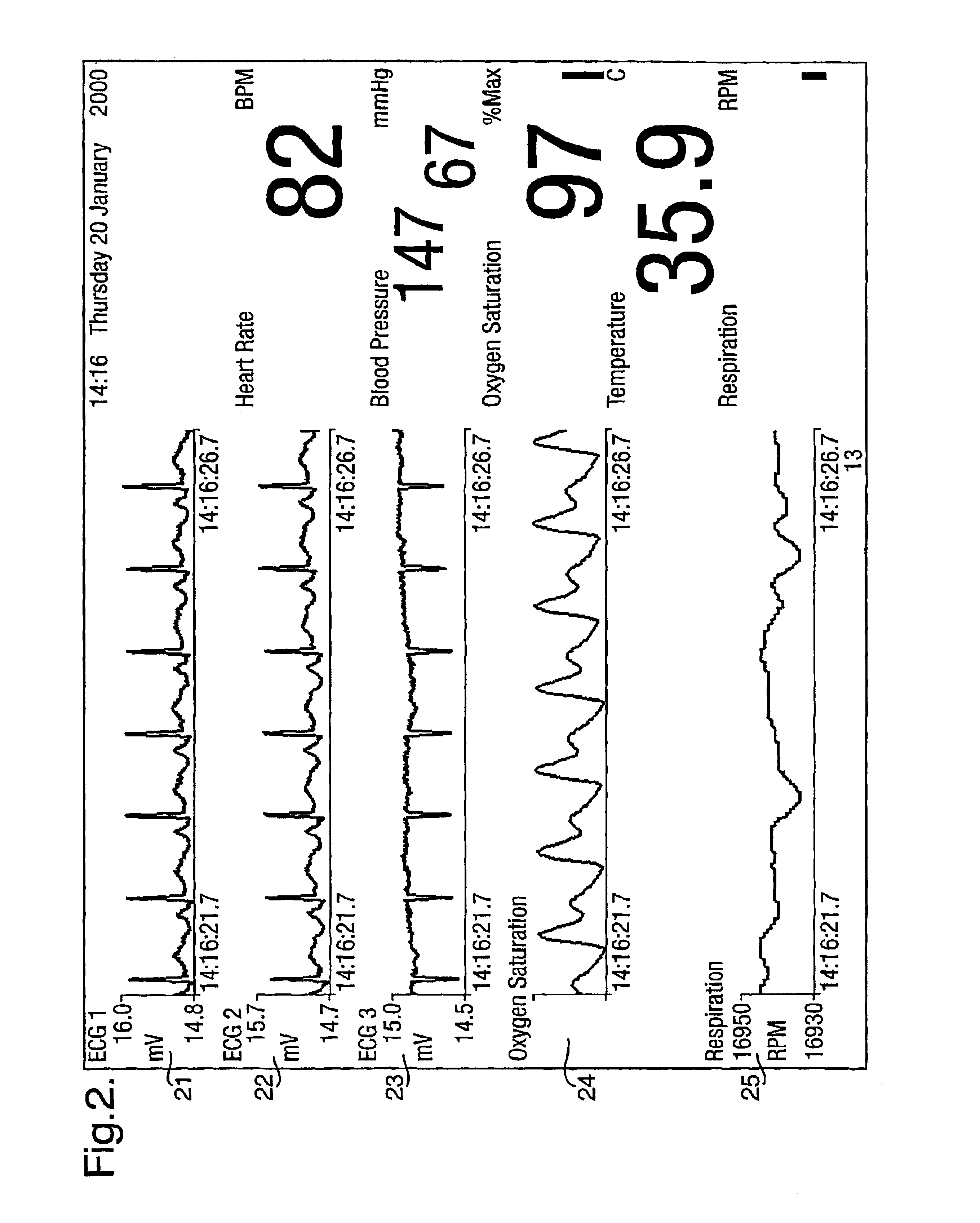
A system for acquiring, and displaying, data such as physiological data, from a plurality of data connection devices, each of which monitor one or more different parameters and output data at different sampling frequencies based on their own system clocks. The system receives the data signals at different sampling frequencies and associates each sample of each signal with a time stamp derived from a single master clock. Low rate and high rate data are treated differently. Low rate data is associated with the current value of the master clock, where as high rate data is time stamped by giving the first sample a time stamp equal to the current value of the current master clock, subsequent samples being given an estimated time stamp based on the expected interval between samples derived from the sampling frequency of the data collection device, and the timescale given to the first example. The estimated time stamp may be periodically corrected, and the estimation calculation can be improved by correcting the value used for the interval between samples. The different signals can be displayed together on a display aligned with respect to a time axis. The system can display, the data in two different timescales, one showing a few seconds of data and one showing a few hours of data. The data traces are scrolled across the time axis, new data being added to one end of the trace.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
Method and apparatus for time synchronization in a communication system
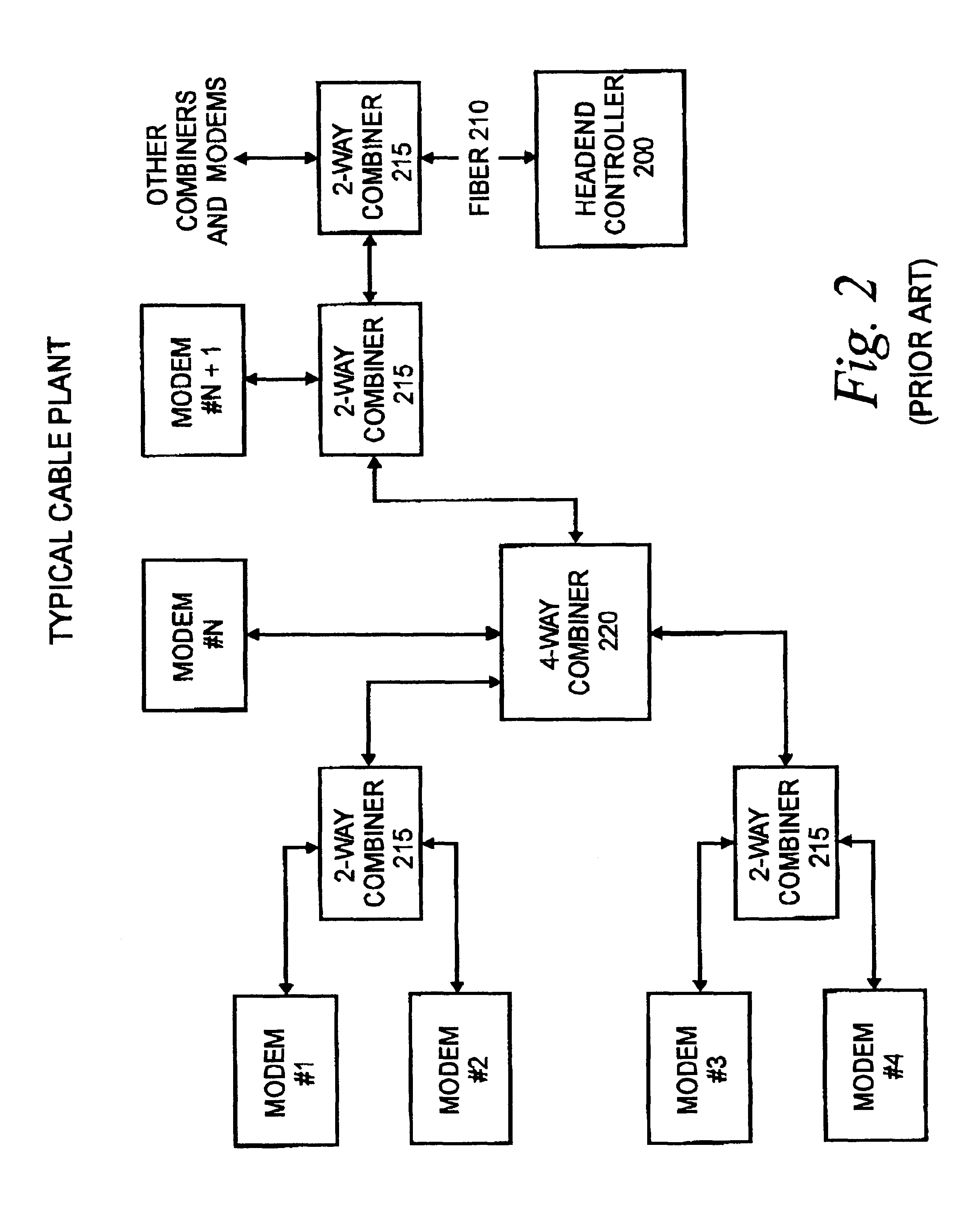
InactiveUS6449291B1Avoid problemsBroadband local area networksTime-division multiplexTimestampModem device
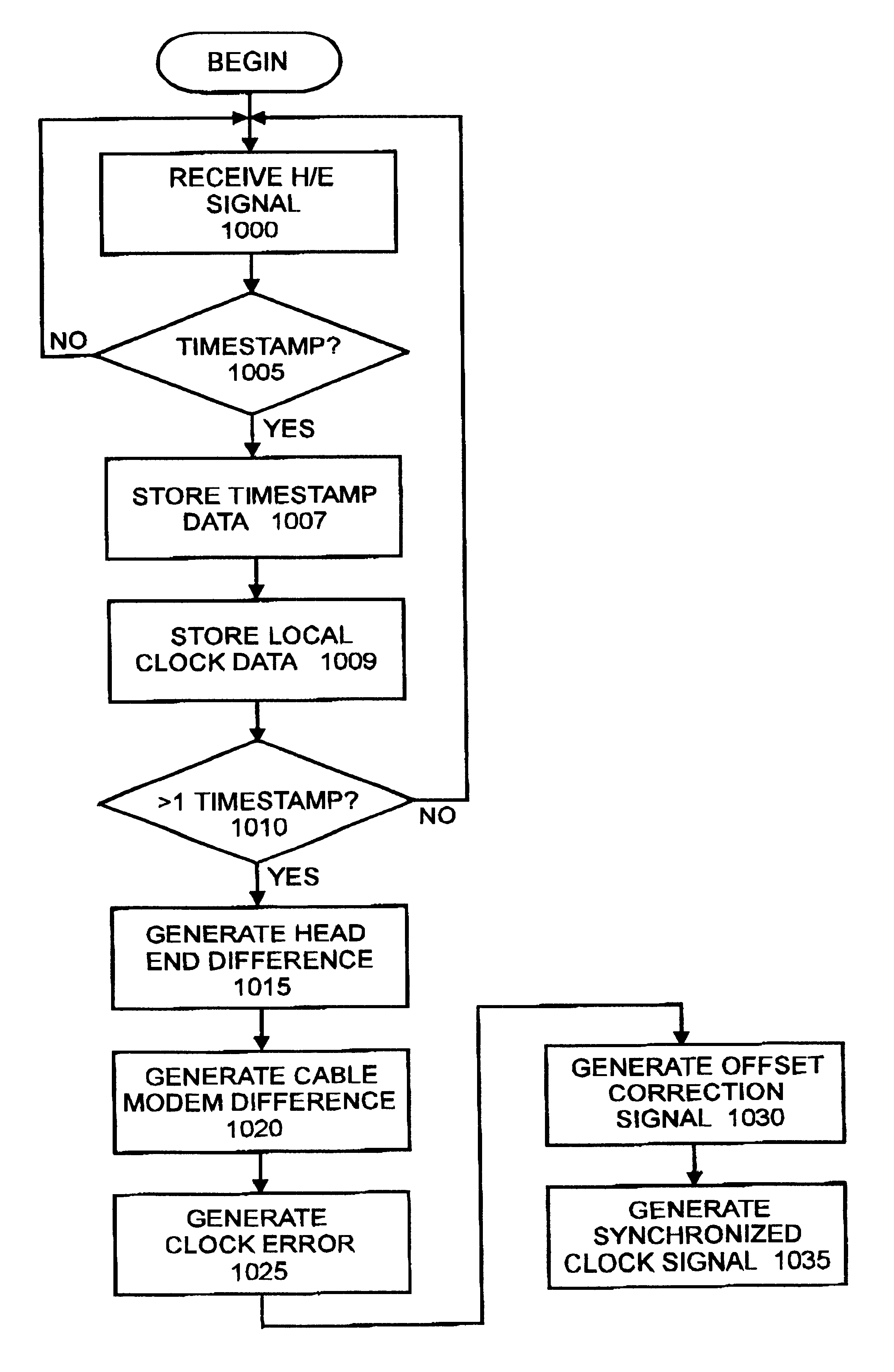
A method and apparatus for time synchronization in a communications system such as a system including cable modems is provided. The synchronization method comprises the steps of receiving a first timestamp from a headend unit with the cable modem, and generating a first cable modem time reference with the cable modem in response to the receipt of the first timestamp. The cable modem then receives a second timestamp from the headend unit and generates a second cable modem time reference in response to the receipt of the second timestamp. A headend difference time comprising the difference of the first and second timestamps is then generated as is a cable modem difference time comprising the difference of the first and second cable modem time references. A clock error time that comprises the difference of the headend difference time and the cable modem difference time is then generated as well as a correction factor in response to the clock error time. The local clock of the cable modem is then synchronized with the master clock of the headend unit through the adjusting of the output of the local clock output in response to the correction factor. The correction factor in one instance comprises an offset value representative of the amount of clock error per local clock pulse. This offset value is added to an accumulator on each local clock pulse, and the local clock output is adjusted when the accumulator rolls over. The synchronized clock signal can then be utilized to determine a time slot in which the cable modem can transmit an upstream signal to the headend without colliding the upstream signal with upstream signals from other modems in the system.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Method for transporting digital media
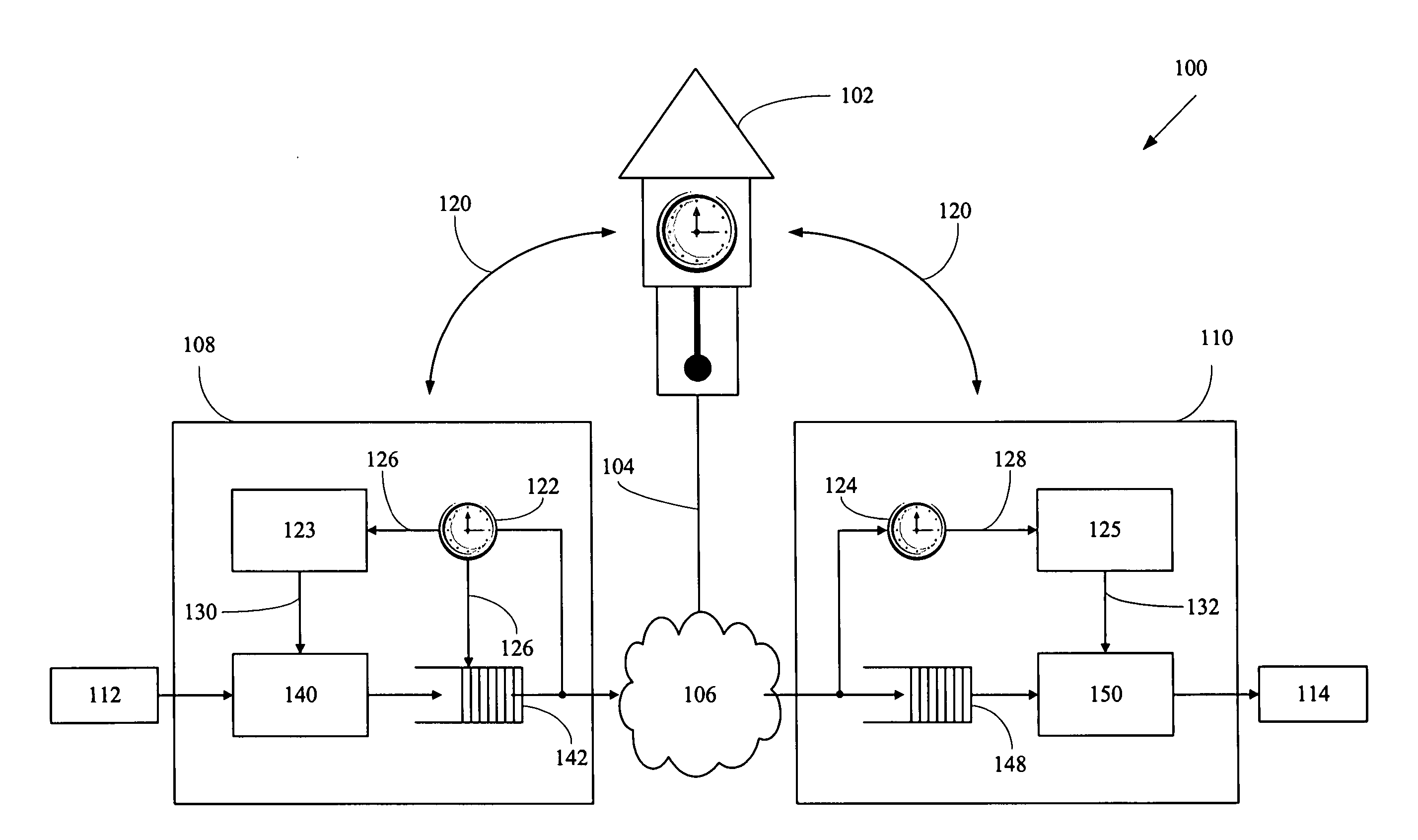
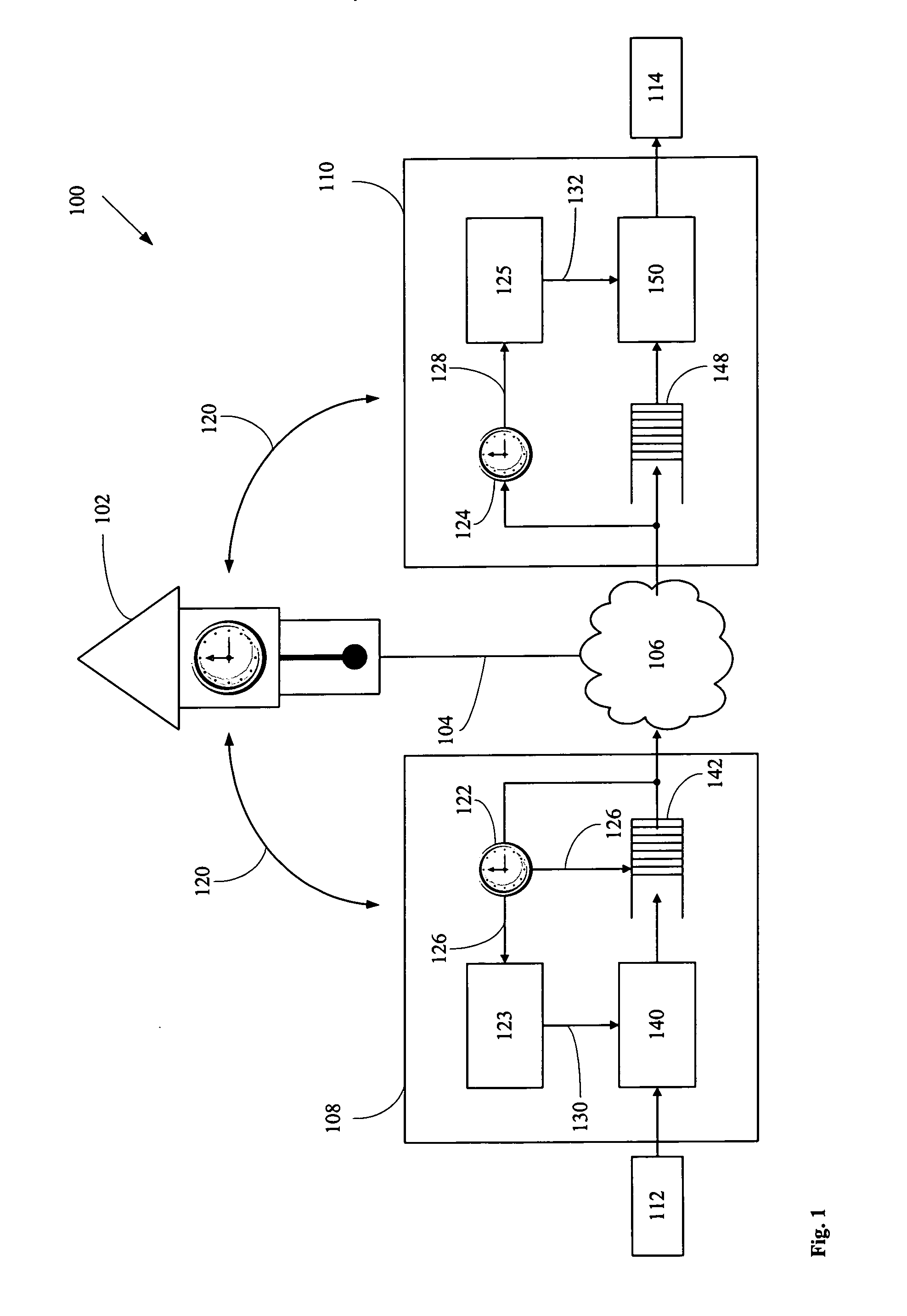
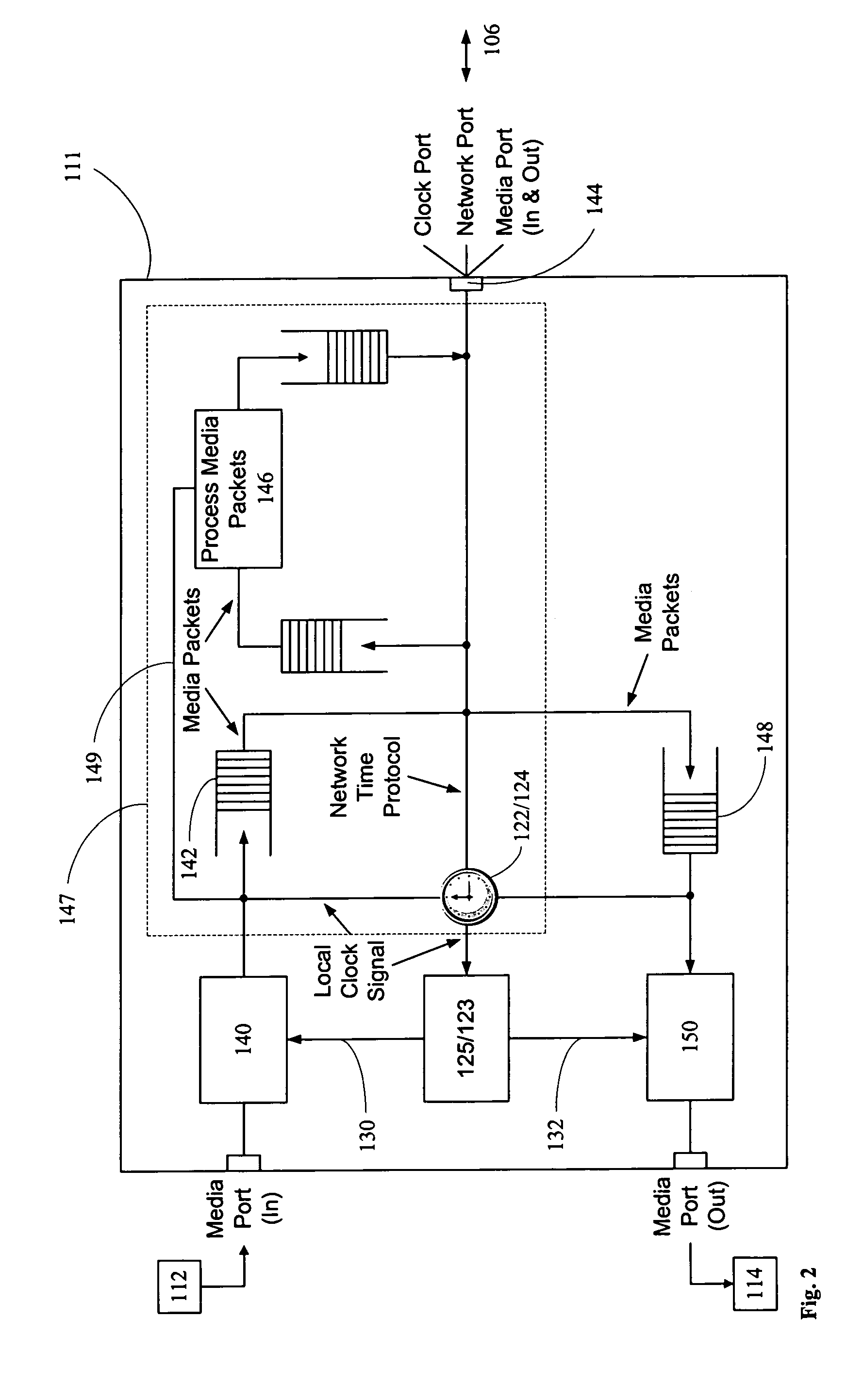
ActiveUS20060280182A1Low costSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesTime-division multiplexTime ProtocolNetworked system
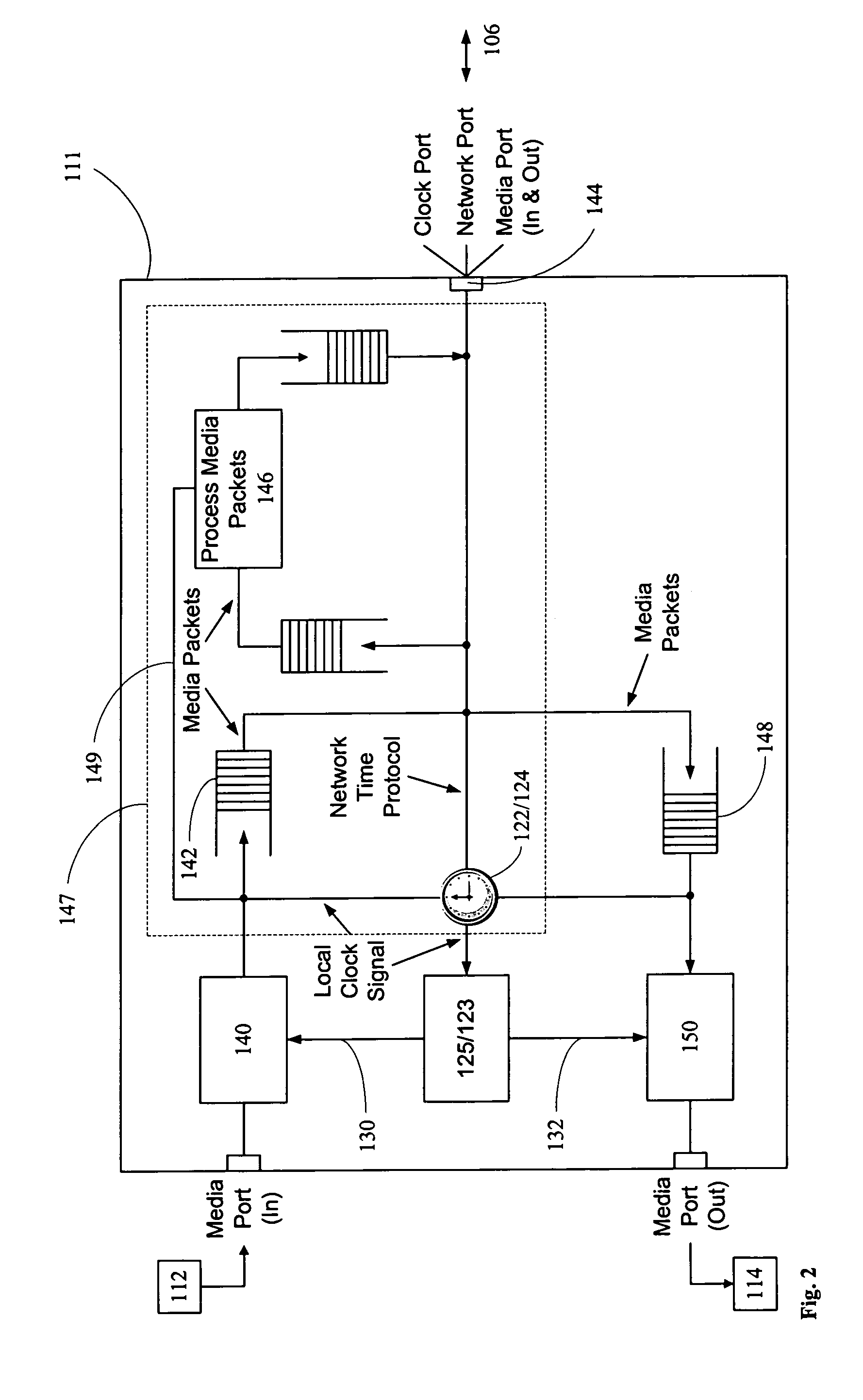
A networked system is provided for transporting digital media packets, such as audio and video. The network includes network devices interconnected to send and receive packets. Each network device can receive and transmit media signals from media devices. A master clock generates a system time signal that the network devices use, together with a network time protocol to generate a local clock signal synchronised to the system time signal for both rate and offset. The local clock signal governs both the rate and offset of the received or transmitted media signals. The system, which can be implemented using conventional network equipment enables media signals to be transported to meet quality and timing requirements for high quality audio and video reproduction.
Owner:AUDINATE HLDG PTY LTD
Step time change compensation in an industrial automation network
ActiveUS7447931B1Easy to handleEfficient transferSynchronous motors for clocksTime-division multiplexTime changesComputer science
One or more embodiments provide Common Industrial Protocol (CIP) based time synchronization systems and methods. The CIP Sync solution can be part of Ethernet / IP and can be based on standard UDP (User Datagram Protocol) and / or IEEE 1588 (Time Synchronization) Ethernet technology. According to an embodiment is a system that compensates for step changes in a master clock.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
System for accomplishing bi-directional audio data and control communications
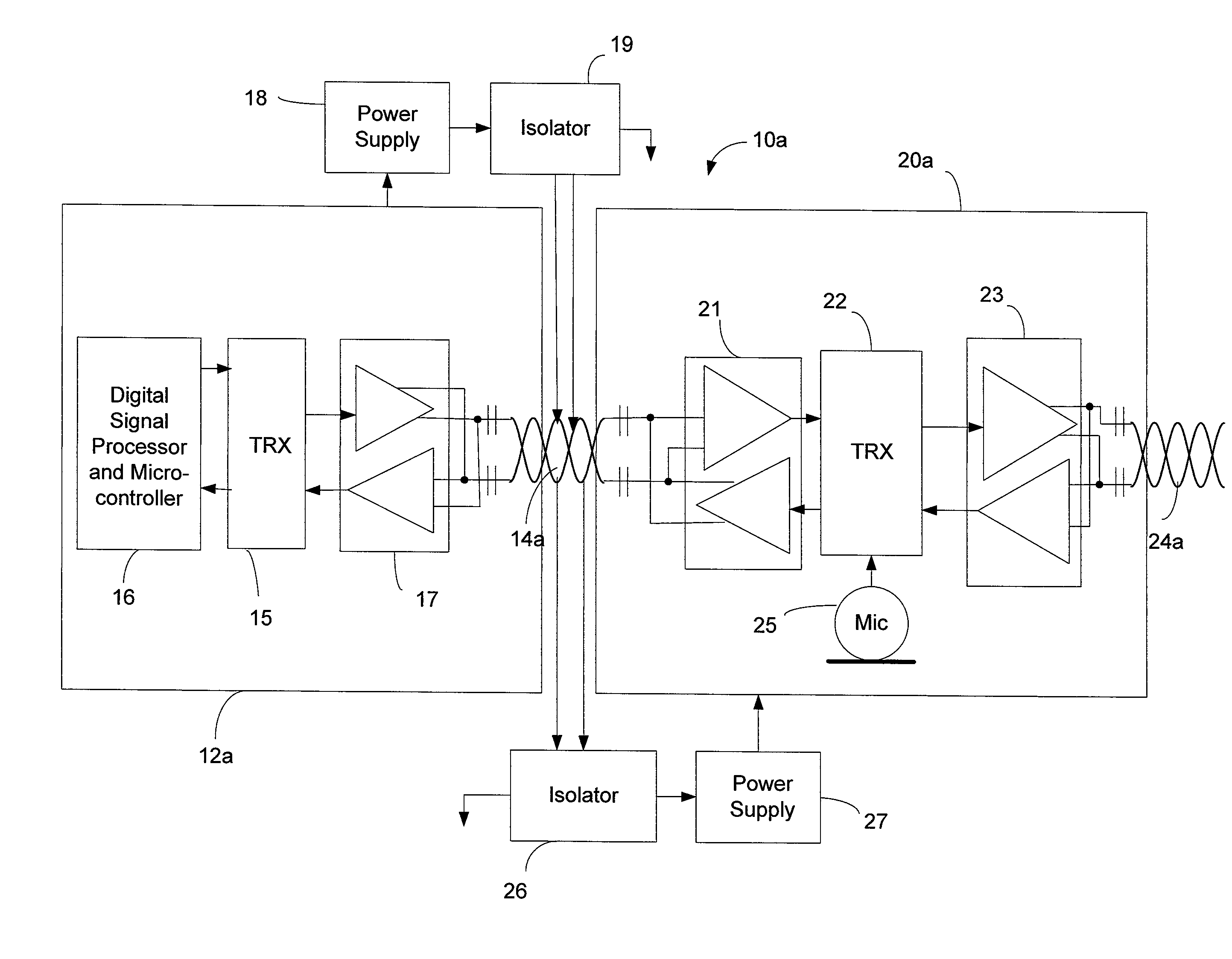
ActiveUS8615091B2Synchronisation information channelsAudio data retrievalTransceiverControl communications
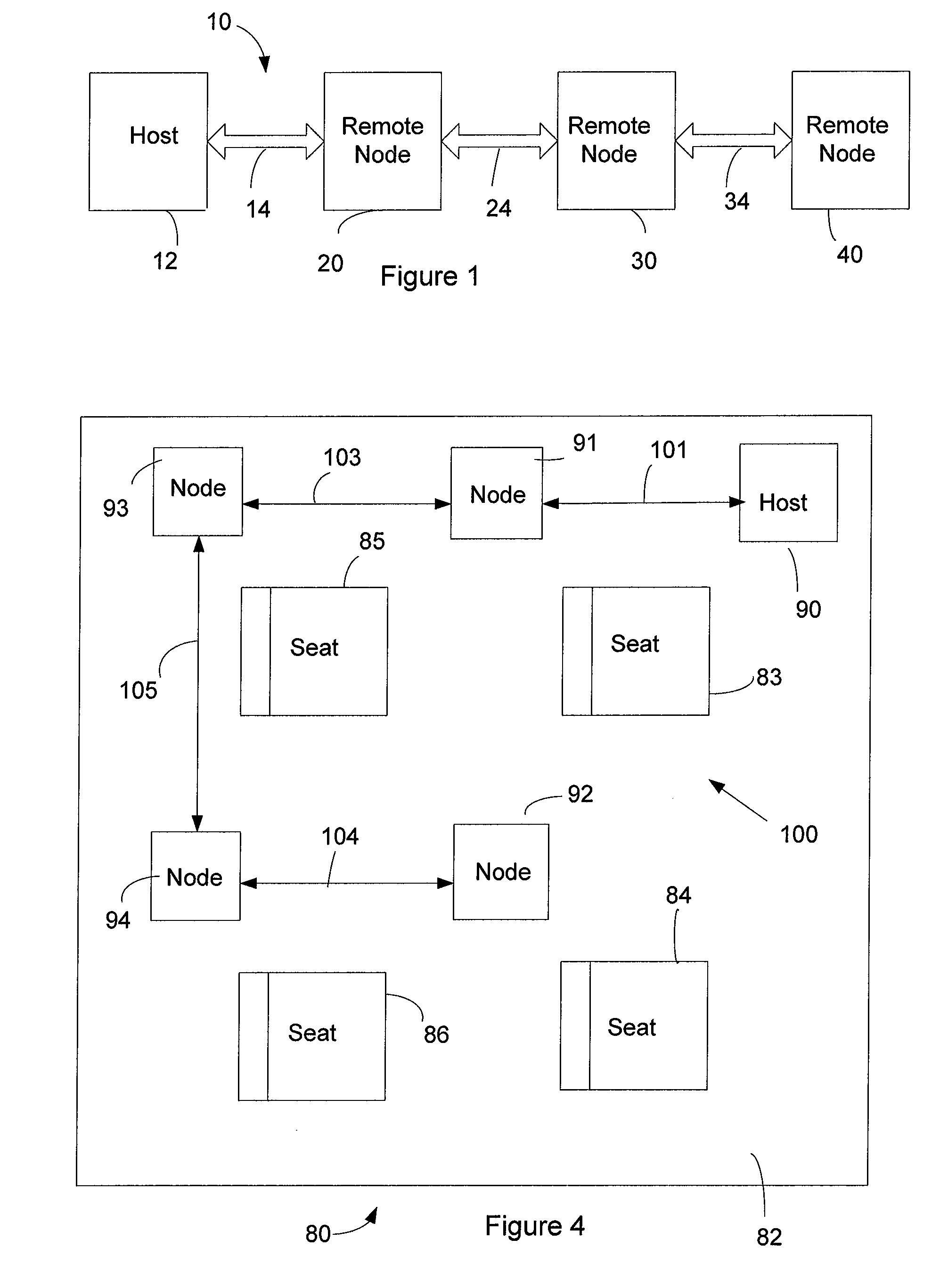
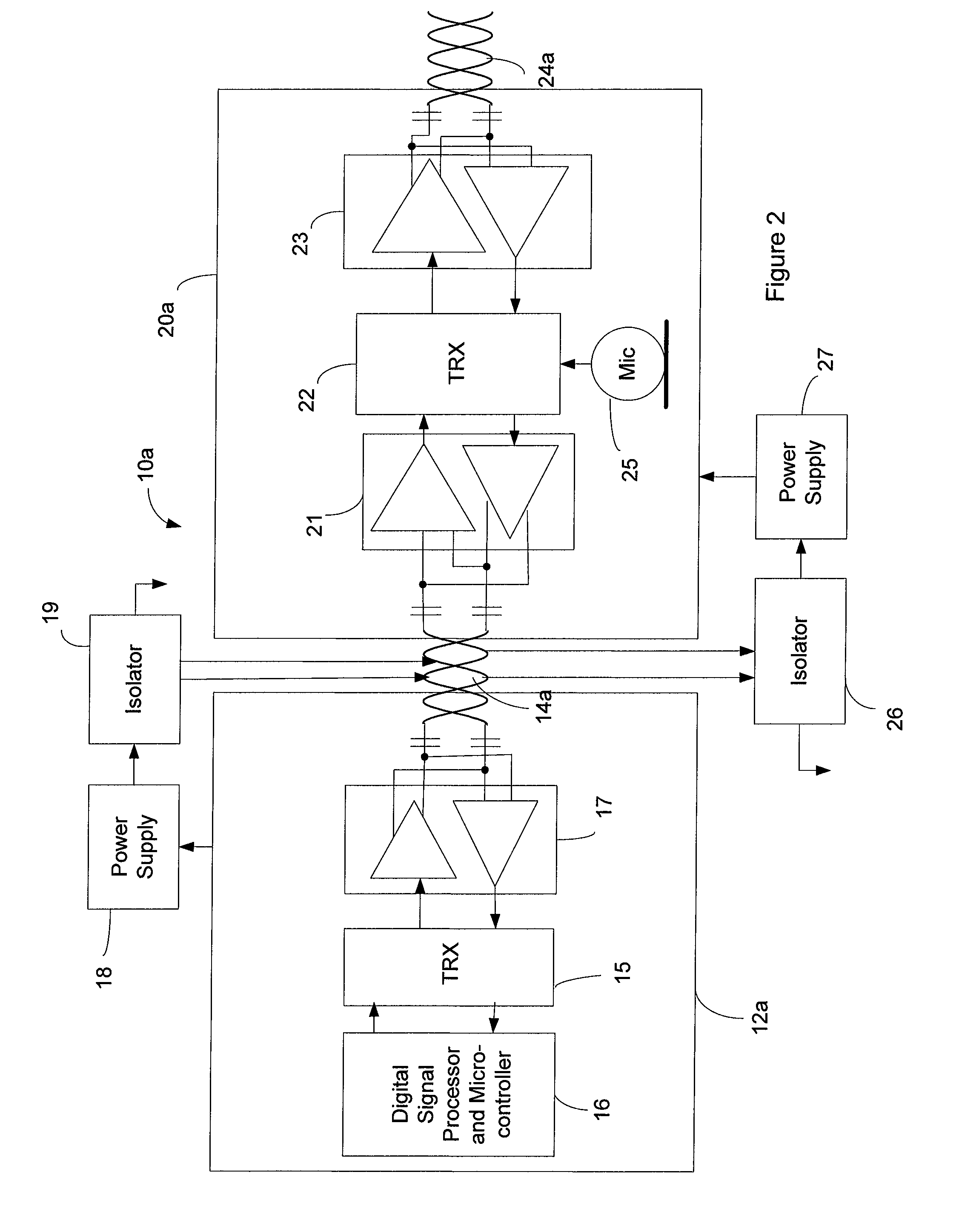
A system for accomplishing bi-directional digital audio data and control communications. There is a host end that includes a host transceiver, a host digital signal processor that outputs a master clock signal and audio data, and a source of low-voltage power for the host components. There are a number of remote nodes connected together serially. Each remote node includes a transceiver and a low-voltage power supply that provides power to the other remote node components. A shielded two-wire communication network connects the host node to one of the remote nodes, and connects each remote node to either one or two other remote nodes in a daisy-chain configuration. The host end is enabled to transmit and receive over the communication network digital audio data and digital control signals. The remote nodes are each enabled to receive over the communication network digital audio data and digital control signals, and are each enabled to transmit over the communication network digital control signals. The source of low-voltage power at the host end is coupled to the communication network. The remote power supplies each have an input coupled to the communication network to derive the power for the remote nodes from the power coupled to the network by the host end.
Owner:BOSE CORP
Synchronization and positioning of seismic data acquisition systems
InactiveUS20050047275A1Good synchronizationLess transmission delaySeismic signal receiversSeismic signal transmissionData acquisitionGlobal positioning system receiver
A network distributed seismic data acquisition system comprises seismic receivers, connected to remote acquisition modules, receiver lines, line tap units, base lines, central recording system and a seismic source event generation unit. Global positioning system receivers of full or partial capability are combined with some of these modules and units and a master global positioning receiver aids the distributed receivers. The global positioning receivers may be used to synchronize high precision clocks as well as to provide positioning information. A master clock is designated and one or more high precision clocks is added to the network to correct for timing uncertainty associated with propagation of commands through the network. Seismic receivers and seismic sources are thereby synchronized with greater accuracy than otherwise possible, thus enabling an improvement in subsurface geologic imaging.
Owner:GEO X SYST
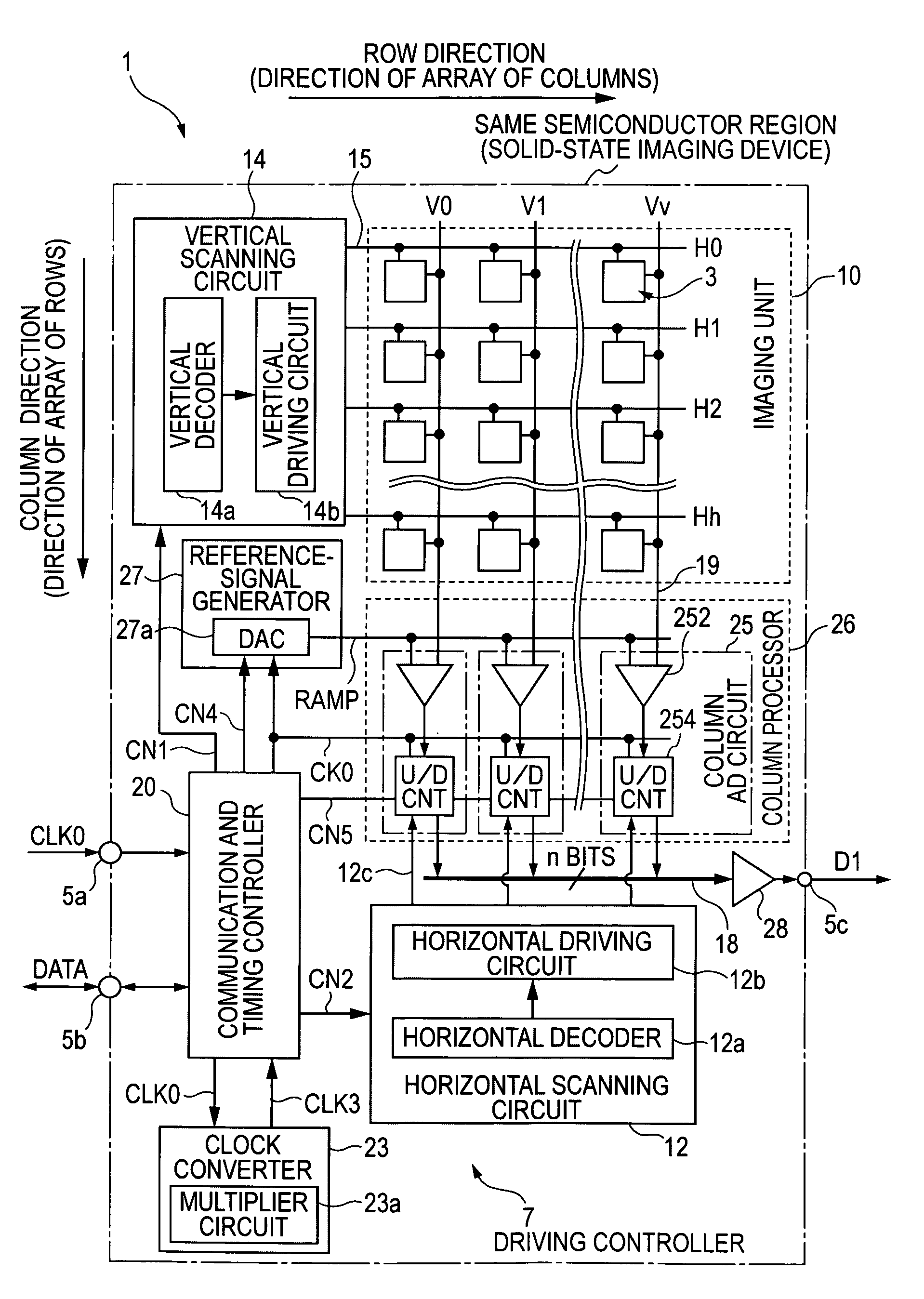
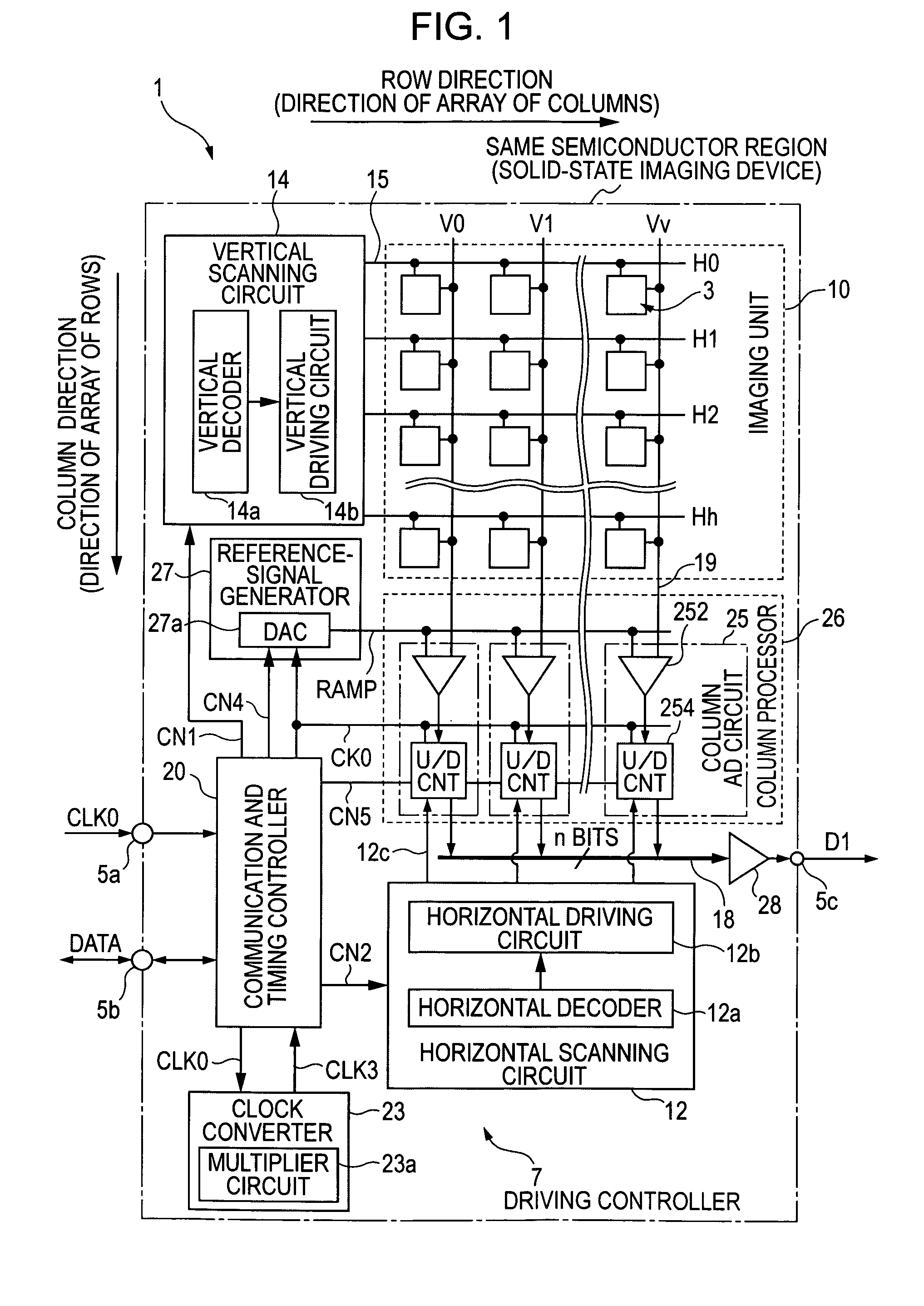
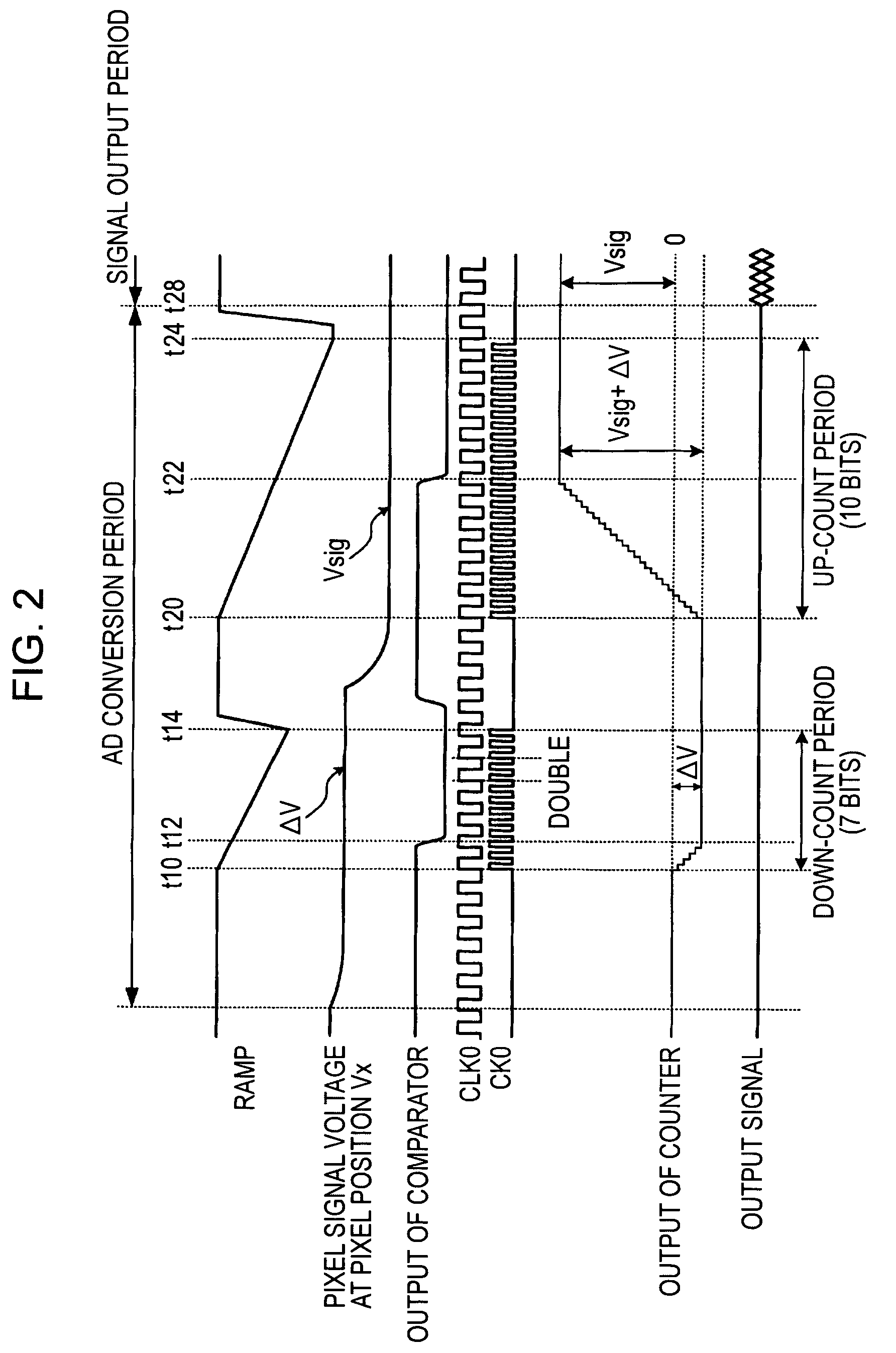
AD conversion method, AD converter, semiconductor device for detecting distribution of physical quantities, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS7088279B2Television system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsControl lineĆuk converter
In a solid-state imaging device including an analog-to-digital converter, a clock converter that generates a high-speed clock that is faster than a master clock is provided. A voltage comparator compares a pixel signal input from a vertical signal line for each row control line with a reference voltage, generating pulses having magnitudes corresponding to a reset component or a signal component in a temporal direction. A counter counts the width of pulse signals until completion of the comparison in the voltage comparator based on a clock that is generated based on the high-speed clock, holding a count value at a time of completion of the comparison. A communication and timing controller exercises control so that the voltage comparator performs comparison for the reset component and the counter performs down-counting in a first processing iteration and so that the voltage comparator performs comparison for the signal component and the counter performs up-counting in a second processing iteration.
Owner:SONY CORP
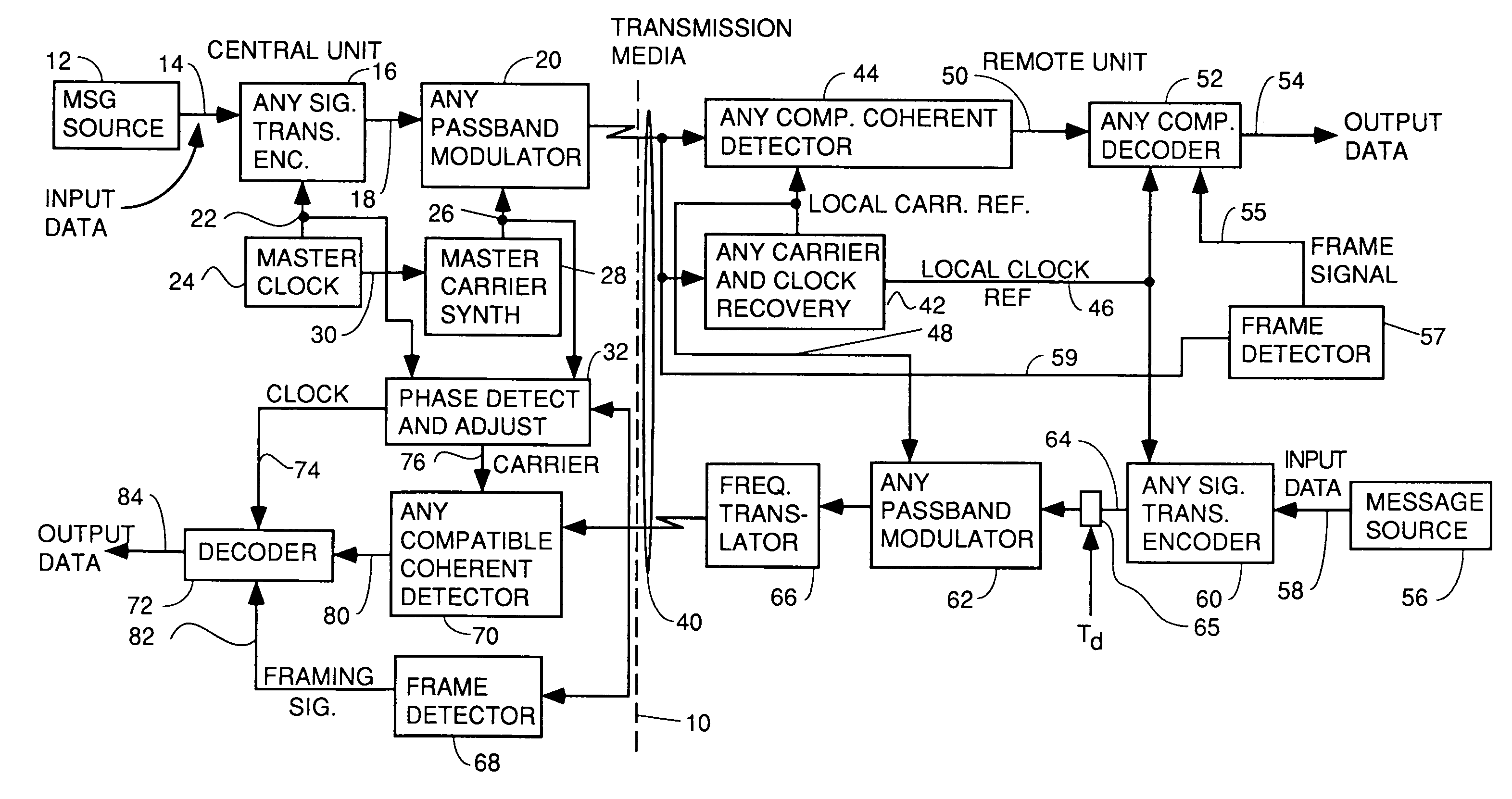
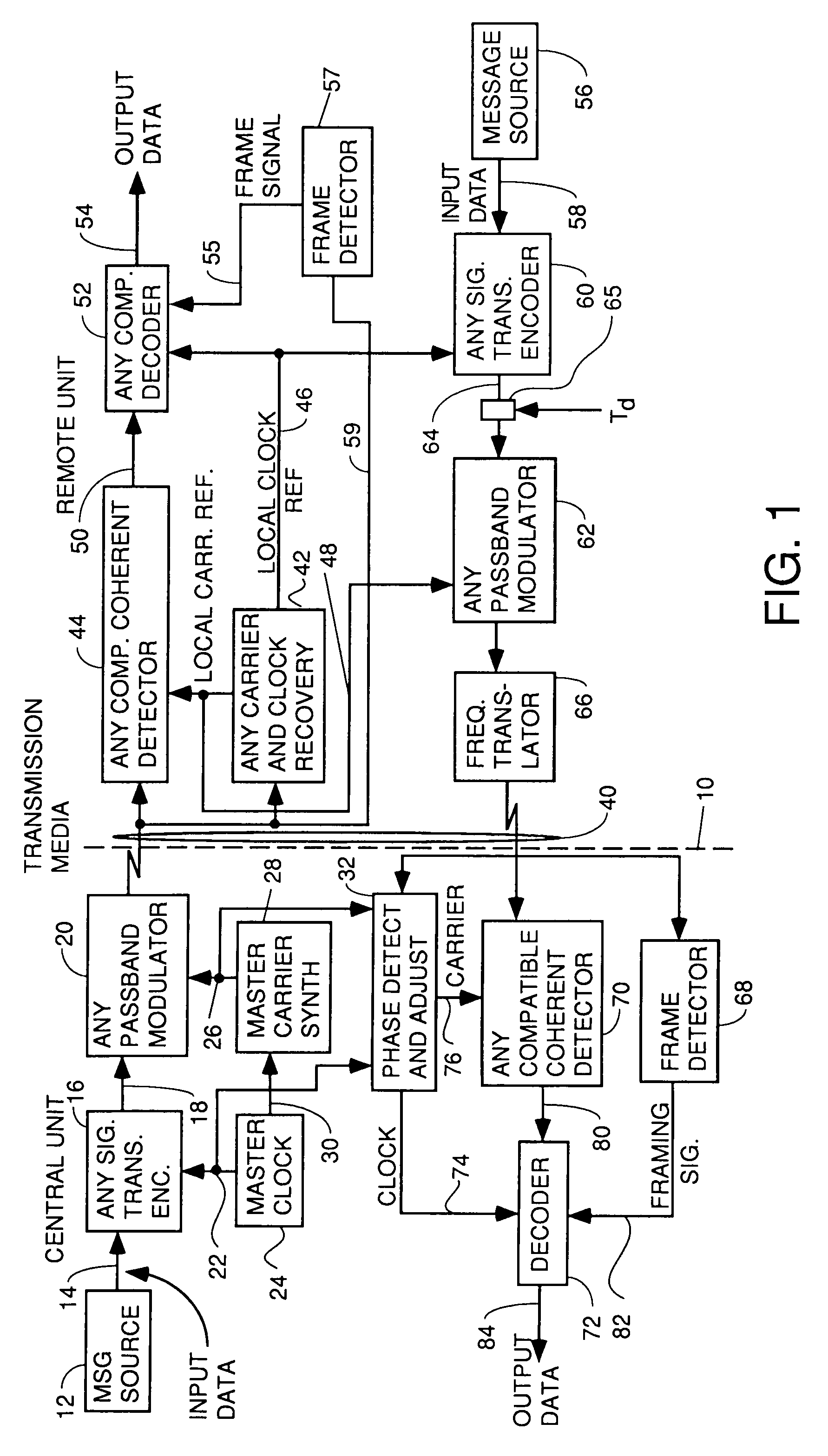
Apparatus and method for trellis encoding data for transmission in digital data transmission systems
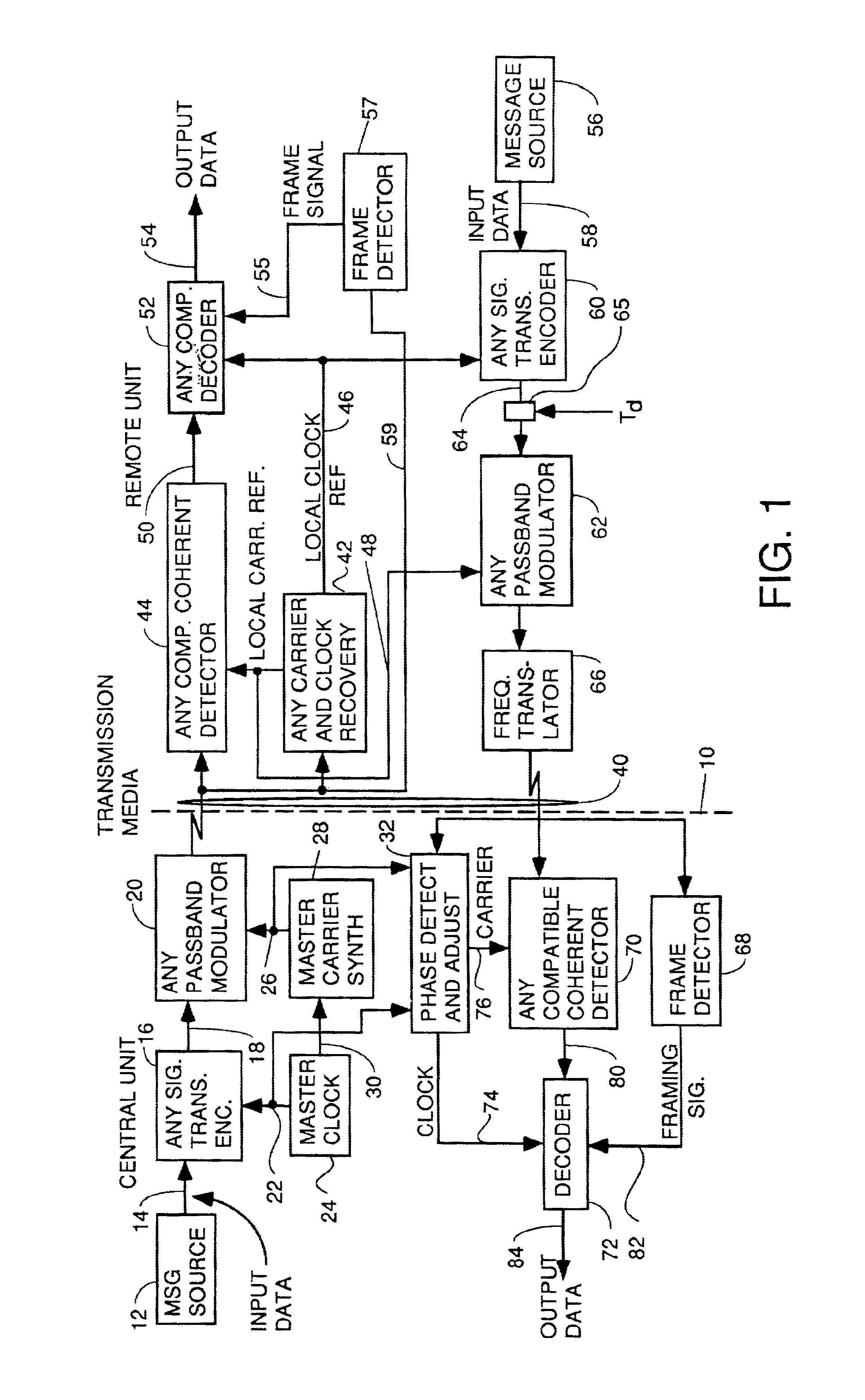
InactiveUS6937617B2Sufficient redundancyIncorrect determinationPulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionDigital dataPhase difference
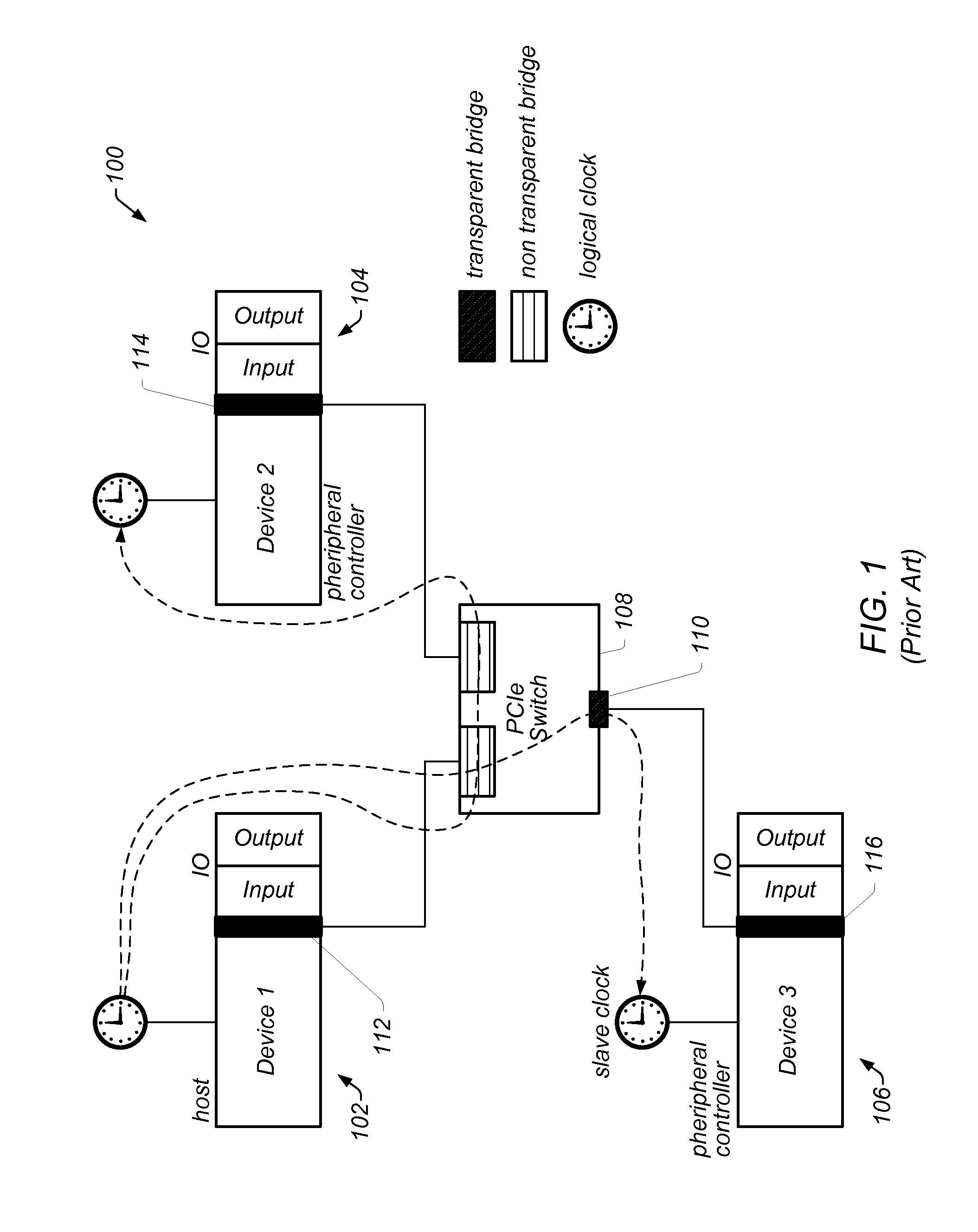
A system for bidirectional communication of digital data between a central unit and a remote unit wherein the need for tracking loops in the central unit has been eliminated. The central unit transmitter generates a master carrier and a master clock signal which are used to transmit downstream data to the remote units. The remote units recover the master carrier and master clock and synchronize local oscillators in each remote unit to these master carrier and master clock signals to generate reference carrier and clock signals for use by the remote unit receiver. These reference carrier and clock signals are also used by the remote unit transmitters to transmit upstream data to the central unit. The central unit receiver detects the phase difference between the reference carrier and clock signals from the remote units periodically and adjusts the phase of the master carrier and master clock signals for use by the central unit receiver to receive the upstream data.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Memory system with dynamic timing correction
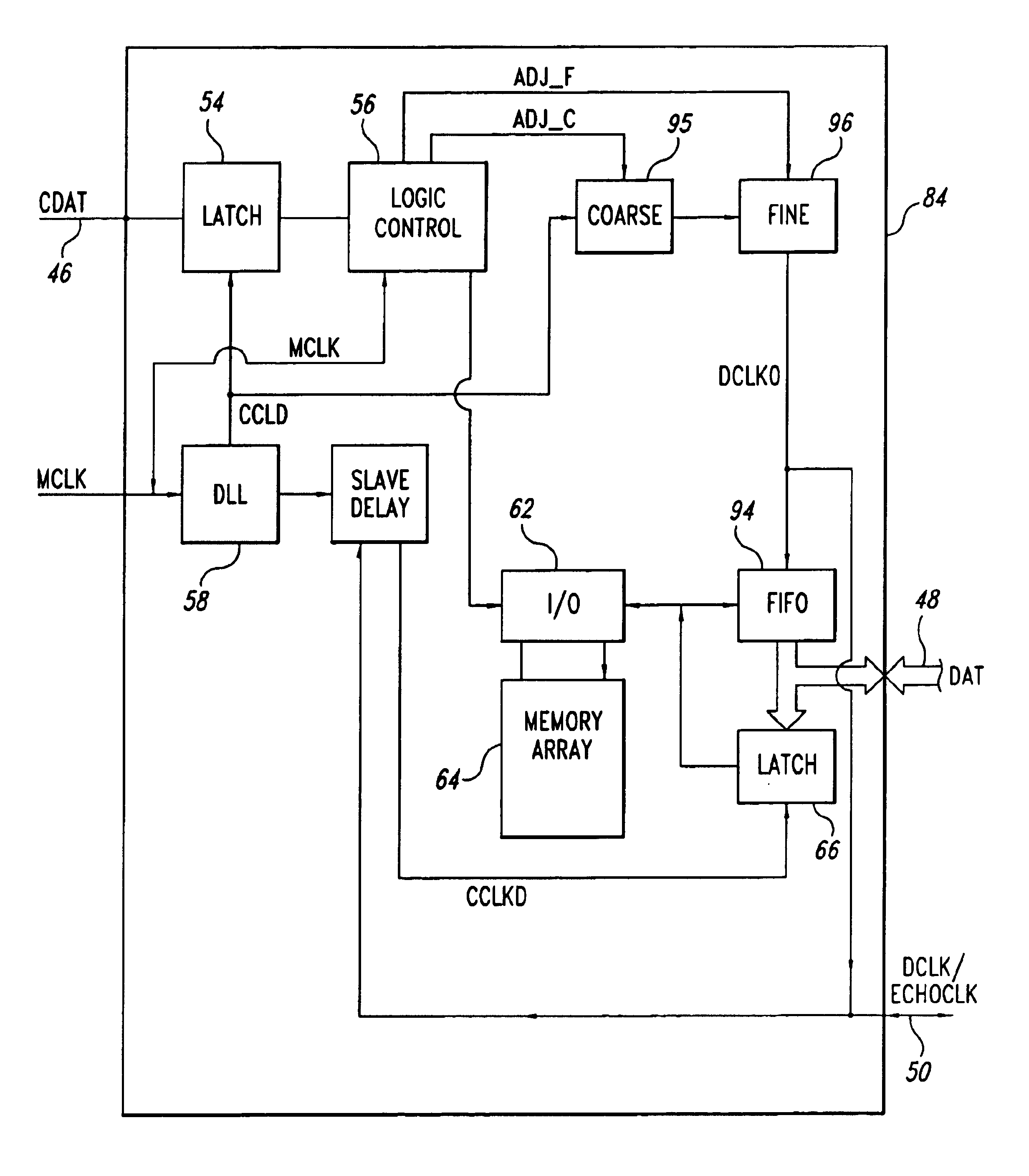
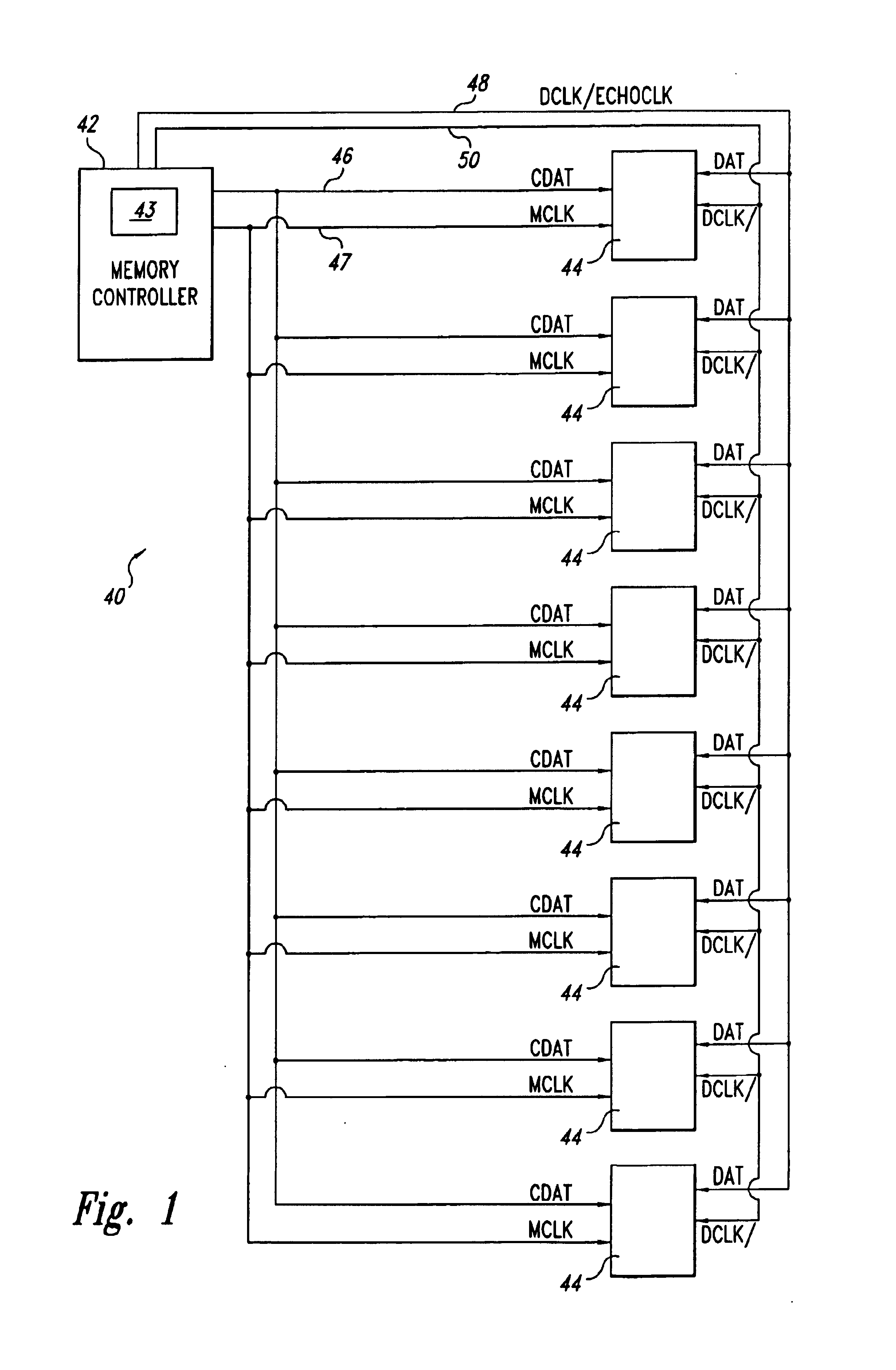
InactiveUS6912680B1Reducing the phase shiftElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionNetwork packetControl data
A memory system includes a memory controller and a bank of memory devices. The memory controller controls the memory devices through packets of control data and a master clock signal. Each of the memory devices includes an adjustable output timing vernier that can be adjusted in response to commands from the memory controller. The vernier output controls timing of output data relative to the master clock signal. As each memory device transmits data to the memory controller, the memory device also transmits an echo clock signal coincident with the data. The memory controller receives the echo clock signal and compares the echo clock signal to the master clock signal to identify shifts in timing of the echo clock signal. If the echo clock signal shifts by more than one vernier increment from the master clock signal, the master controller issues a command to the memory device to adjust the output vernier to correct the timing drift of the echo clock signal. By correcting the timing drift of the echo clock signal, the memory controller also corrects timing drift of the output data, thereby assuring that the data arrive at the memory controller coincident with edges of the master clock signal.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
System and method for synchronizing playback of audio and video
ActiveUS20080187282A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer hardwareVideo player
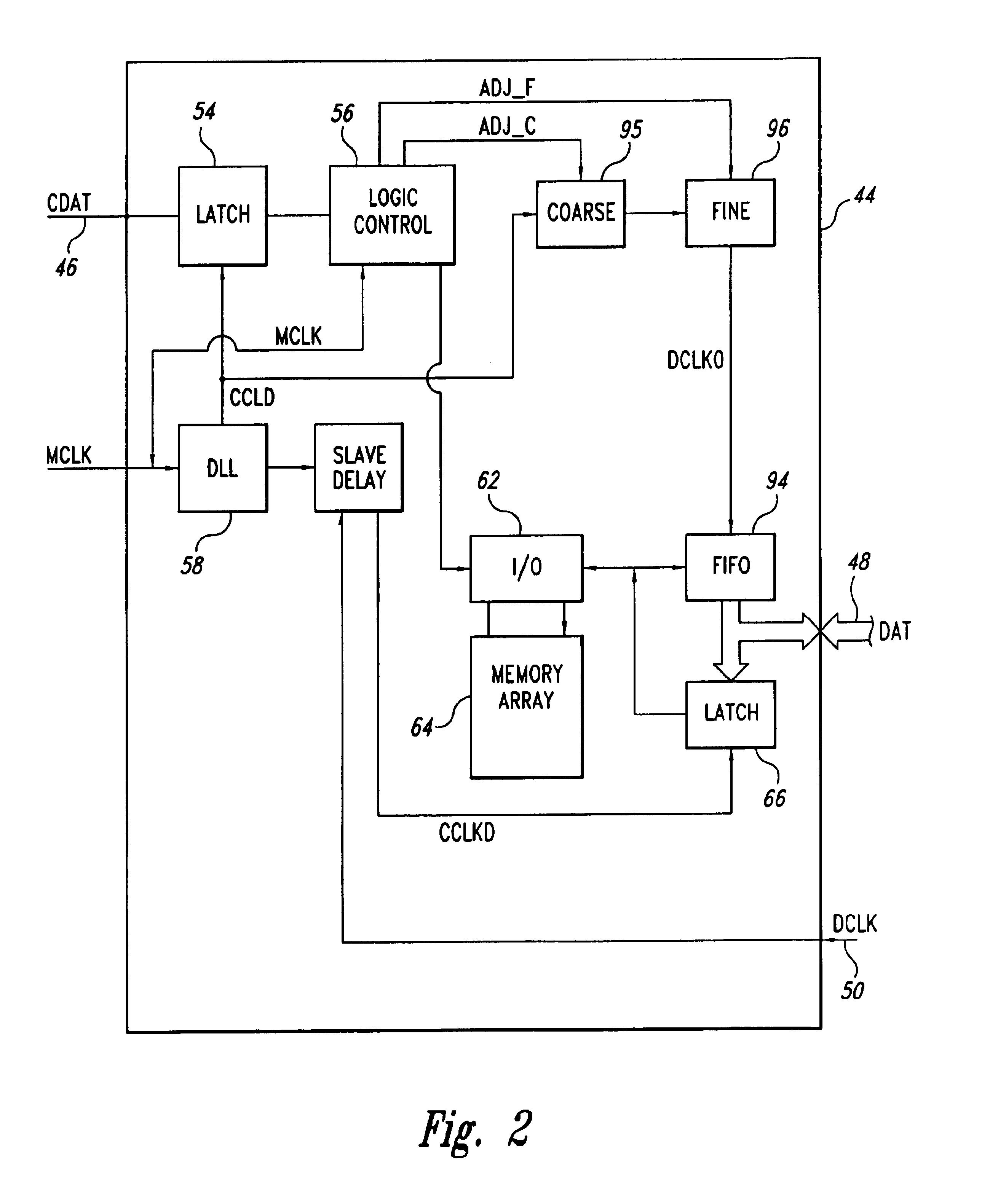
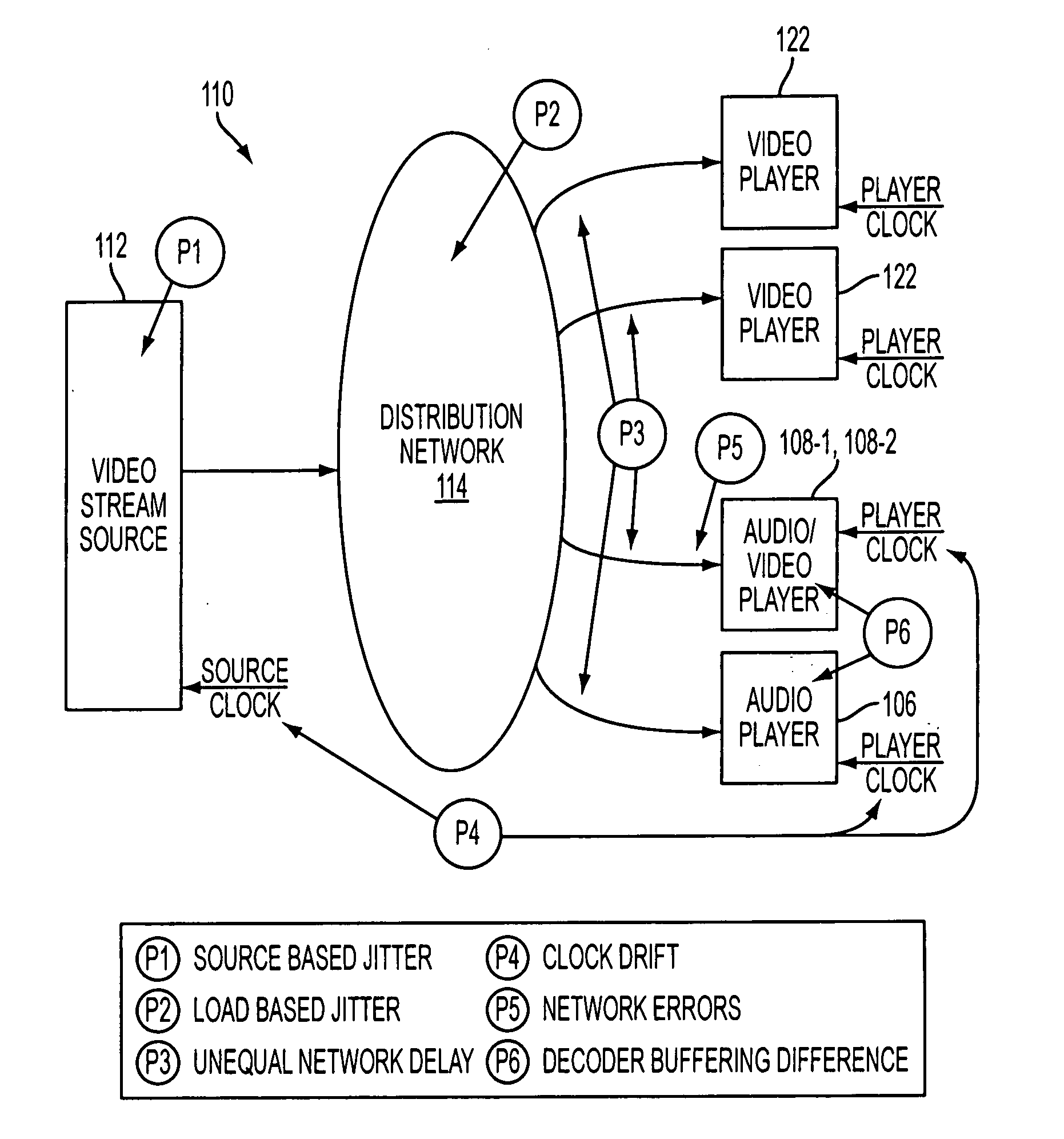
A system and method for providing a digital In-Flight Entertainment (IFE) system in a vehicle, such as an aircraft, that is capable of presenting a video program and associated audio in a synchronized manner to a large number of individual video monitors and speakers. The system and method employ processing operations in at least one decoder of the IFE system, to perform operations such as adjusting a local clock based on a master clock, setting a delay time in relation to a master clock, and adjusting video and audio playback based on the delay, to substantially synchronize playback of the audio and video data by the audio and video players, to thus eliminate or at least minimize the negative effects of source and load based jitter, network delays, clock drifts, network errors and decoder buffering differences, on synchronizing video and audio playback.
Owner:THALES AVIONICS INC
Automatic synthesis of clock distribution networks
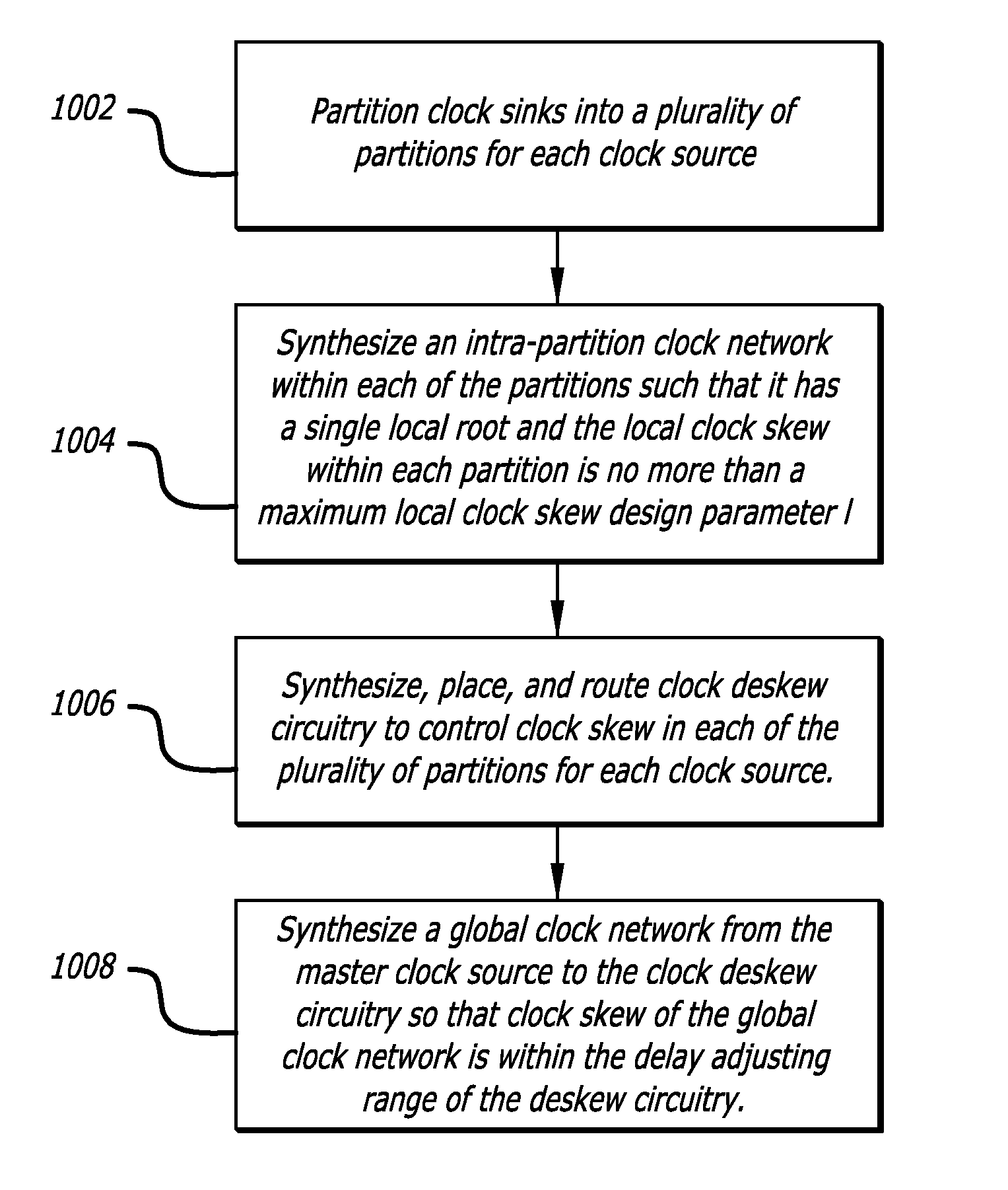
ActiveUS8205182B1Minimize and control clock skewMinimize controlCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationClock treeDistribution networks
In one embodiment of the invention, a method for designing an integrated circuit is disclosed. The method includes automatically partitioning clock sinks of an integrated circuit design into a plurality of partitions; automatically synthesizing a clock tree from a master clock generator into the plurality of partitions to minimize local clock skew within each of the plurality of partitions; and automatically synthesizing clock de-skew circuitry into each of the plurality of partitions to control clock skew between neighboring partitions.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
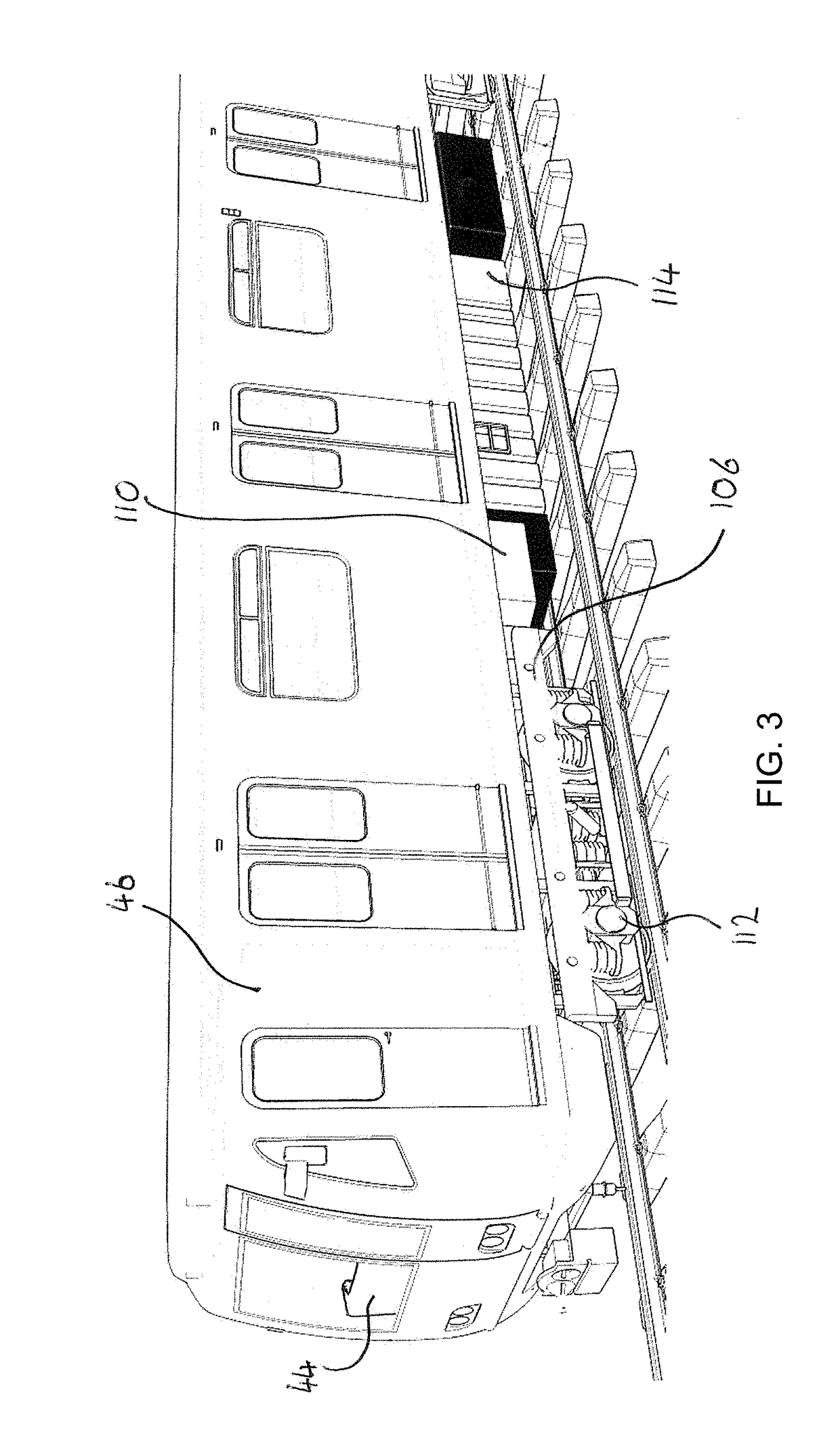
Integrated rail and track condition monitoring system with imaging and internal sensors
ActiveUS20180339720A1Improve accuracyOptimize data processingImage enhancementImage analysisData memoryData storing
A railroad track inspection system has multiple track scanning sensors, a data store, and a scan data processor. The scan data processor provides automatic analysis of the track scan data to detect track components within the scan data from a predetermined list of component types according to features identified in said scan data. The track scanning sensors, data store and scan data processor are attached to a common support structure for mounting the system to a railway vehicle in use. An inertia sensor and common master clock are used to make corrections to the output of the track scanning sensors to accommodate dynamic forces in use. The inspection system may be provided in a single housing for mounting to a conventional passenger / freight rail vehicles and may operate automatically in an unattended mode. The location of track components and / or defects may be logged.
Owner:SINGH SAMEER
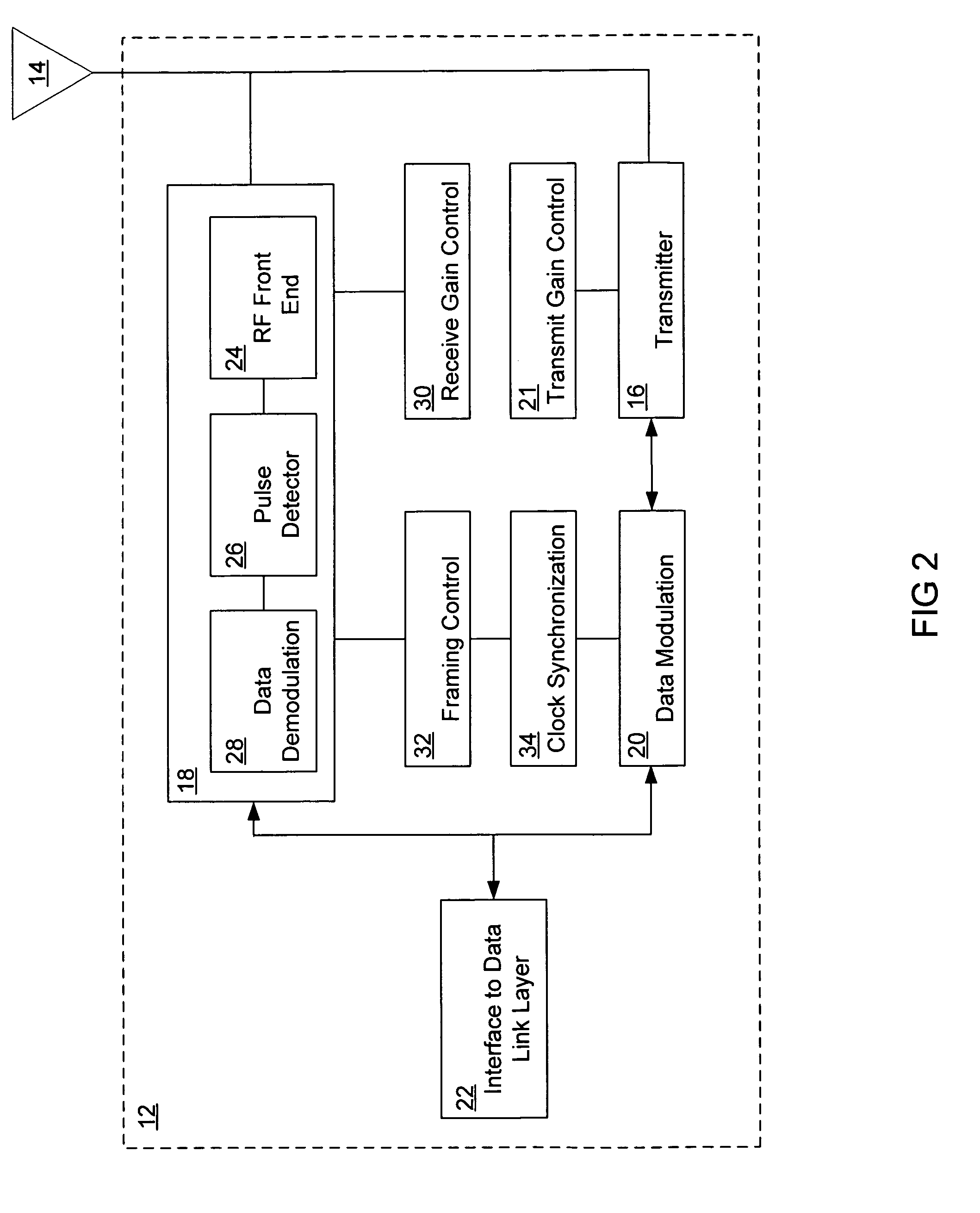
Ultra wide band transmitter
InactiveUS6952456B1Reduced clock speedMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsAngle to amplitude modulation conversionMultiplexerSubject matter
A transmitter system is provided. In one embodiment, the transmitter system includes a data modulation unit, which generates a stream of data that is synchronized with a master clock. The transmitter system additionally includes a transmitter that transmits the stream of synchronized data by way of an attached antenna. In another embodiment the transmitter system includes a Medium Access Control (MAC) layer that includes a clock synchronization device, a frequency divider, a slot allocation unit, and a multiplexer / demultiplexer. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HLDG 73
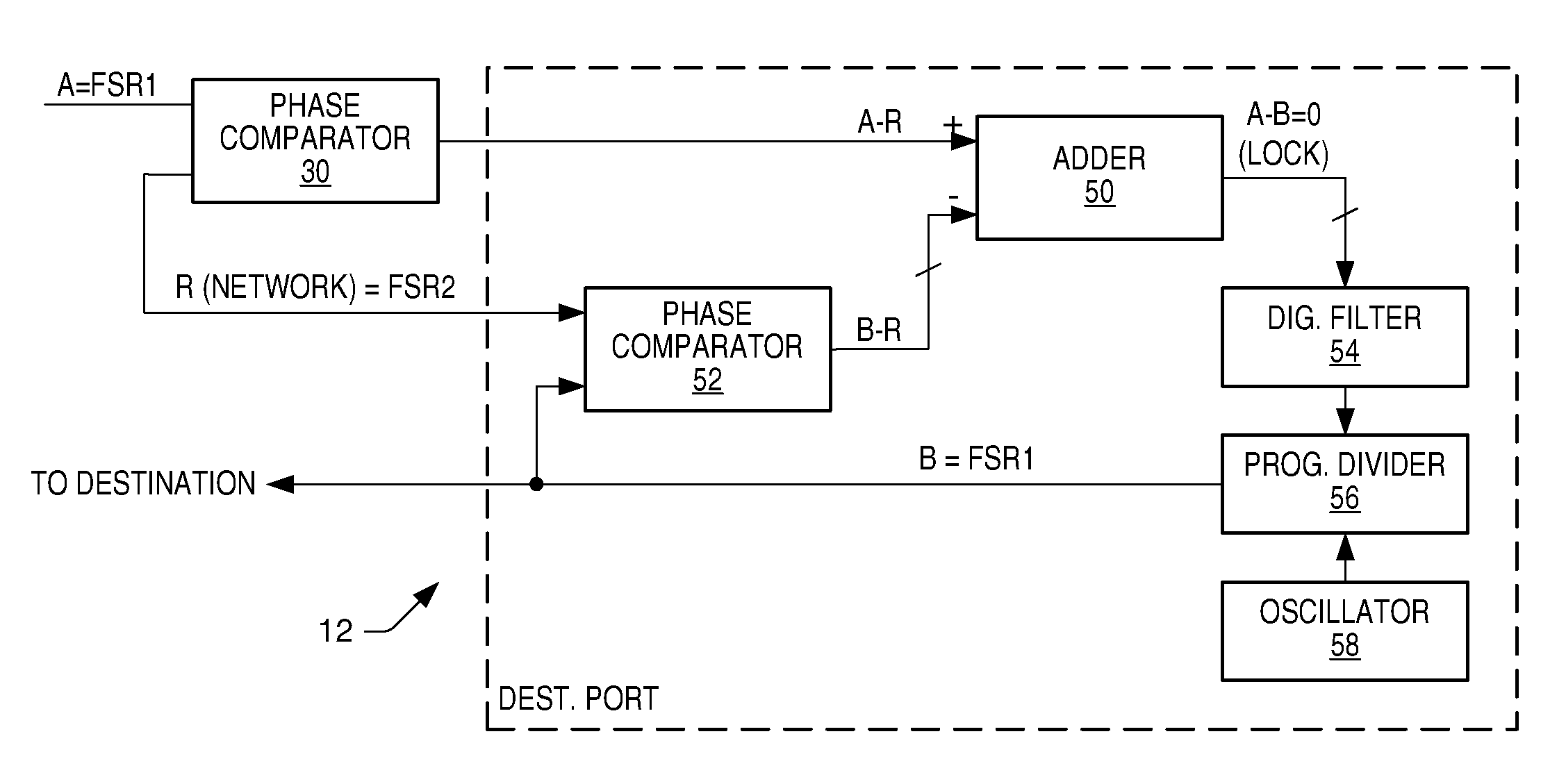
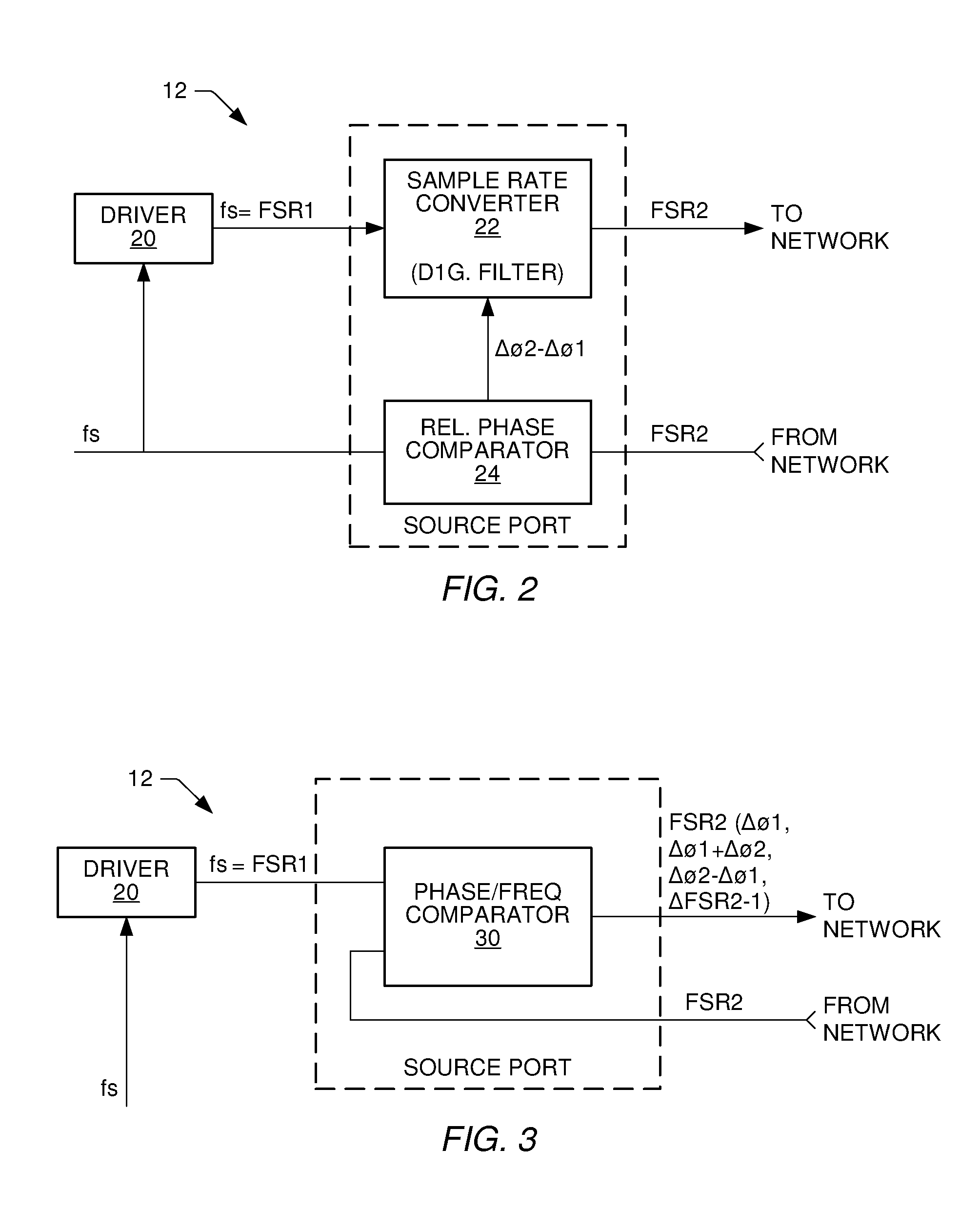
Communication system and method for sample rate converting data onto or from a network using a high speed frequency comparison technique
ActiveUS7106224B2High resolutionImprove accuracyTime-division multiplexIndividual digits conversionSample rate conversionPhase difference
A communication system, source and destination ports of the communication system, and methodology is provided for transporting data in one of possibly three different ways. Data is transported across the network at a frame sample rate that can be the same as or different from the sample rate or master clock within the source port or the destination port. If the sample rate of the source port is known, the sample rate of the destination port can be created using a PLL within the destination port and simply employing a phase comparator in the source port. The phase comparator forwards the phase or frequency difference of the network transfer rate and the source sample rate to the destination port, which then generates a local clock equivalent to the source which then compiles audio data being played at the same rate in which it was sampled at the source. Where economically feasible, sample rate conversion can be used at the source. However, sample rate conversion at the destination is preferred if the source sample rate is forwarded across the network relative to the frame transfer rate of the synchronous network. The sample rate converter simply produces a play rate from the transmitted information at the destination. Again, however, sample rate conversion compares relative phase difference changes similar to the phase difference compared in the digital PLL mode. As a further alternative, sample rates within the source and destination ports can be derived from the network frame rate using fractional dividers in the source and destination ports.
Owner:STANDRD MICROSYSTEMS CORPORATION
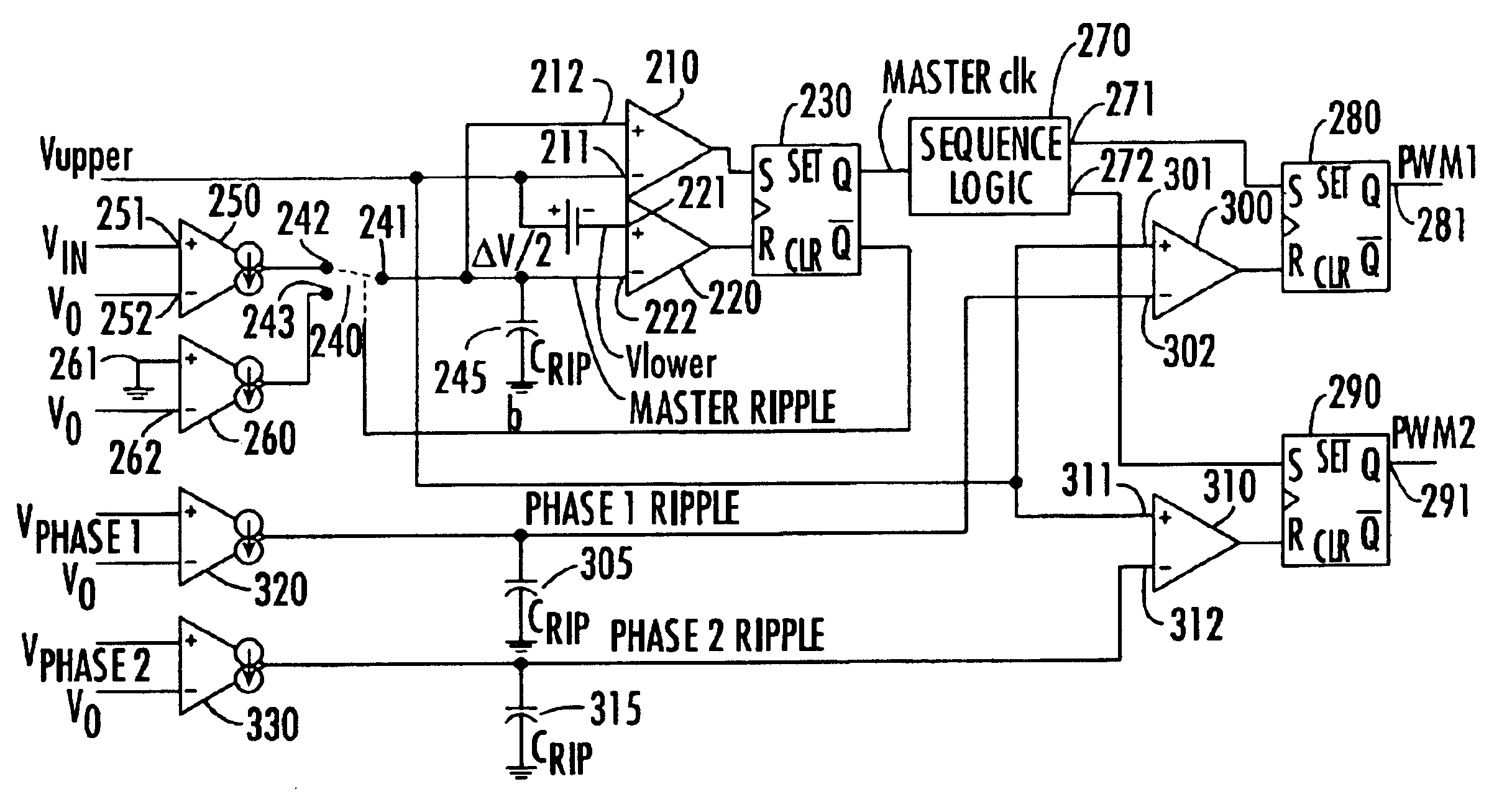
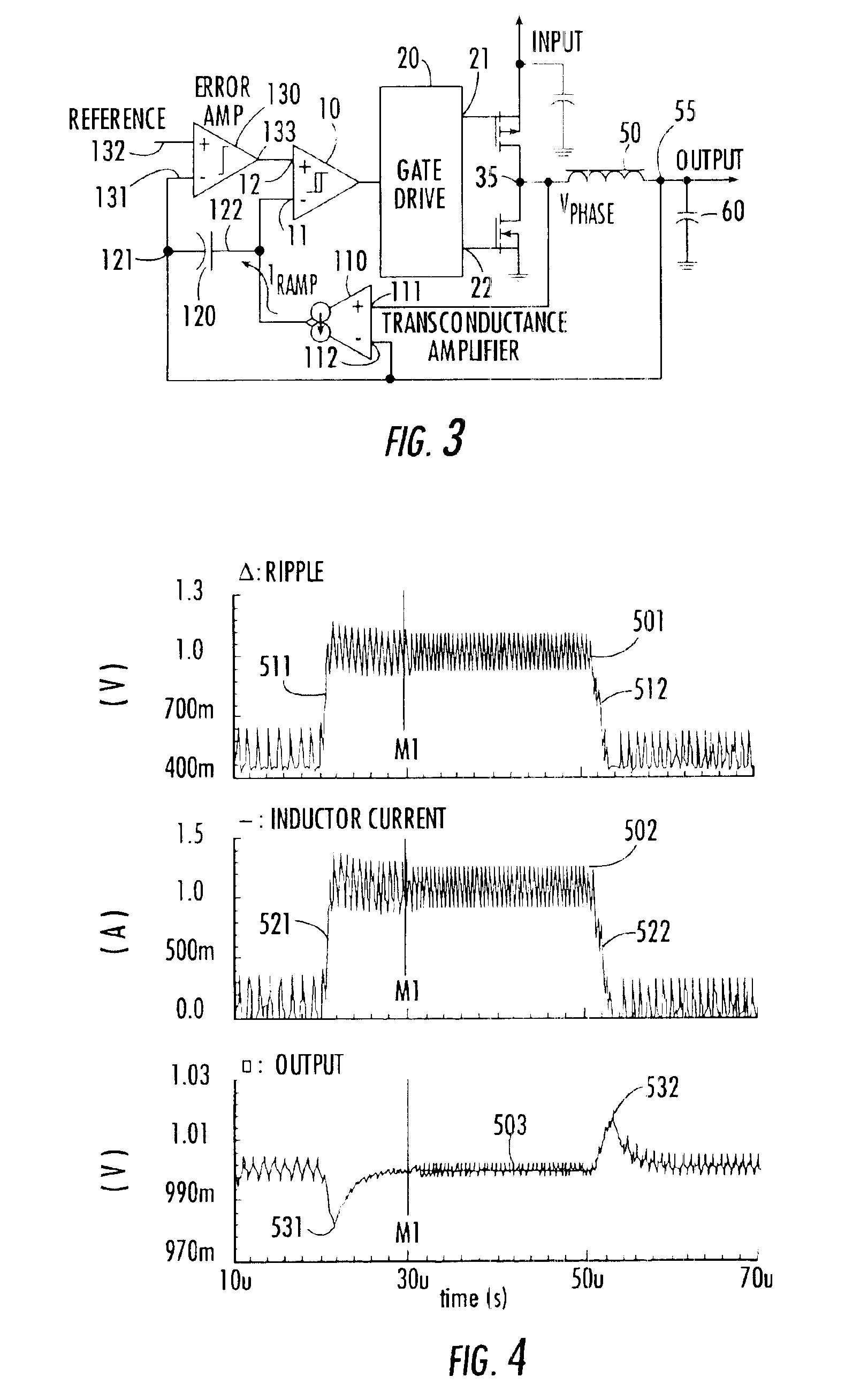
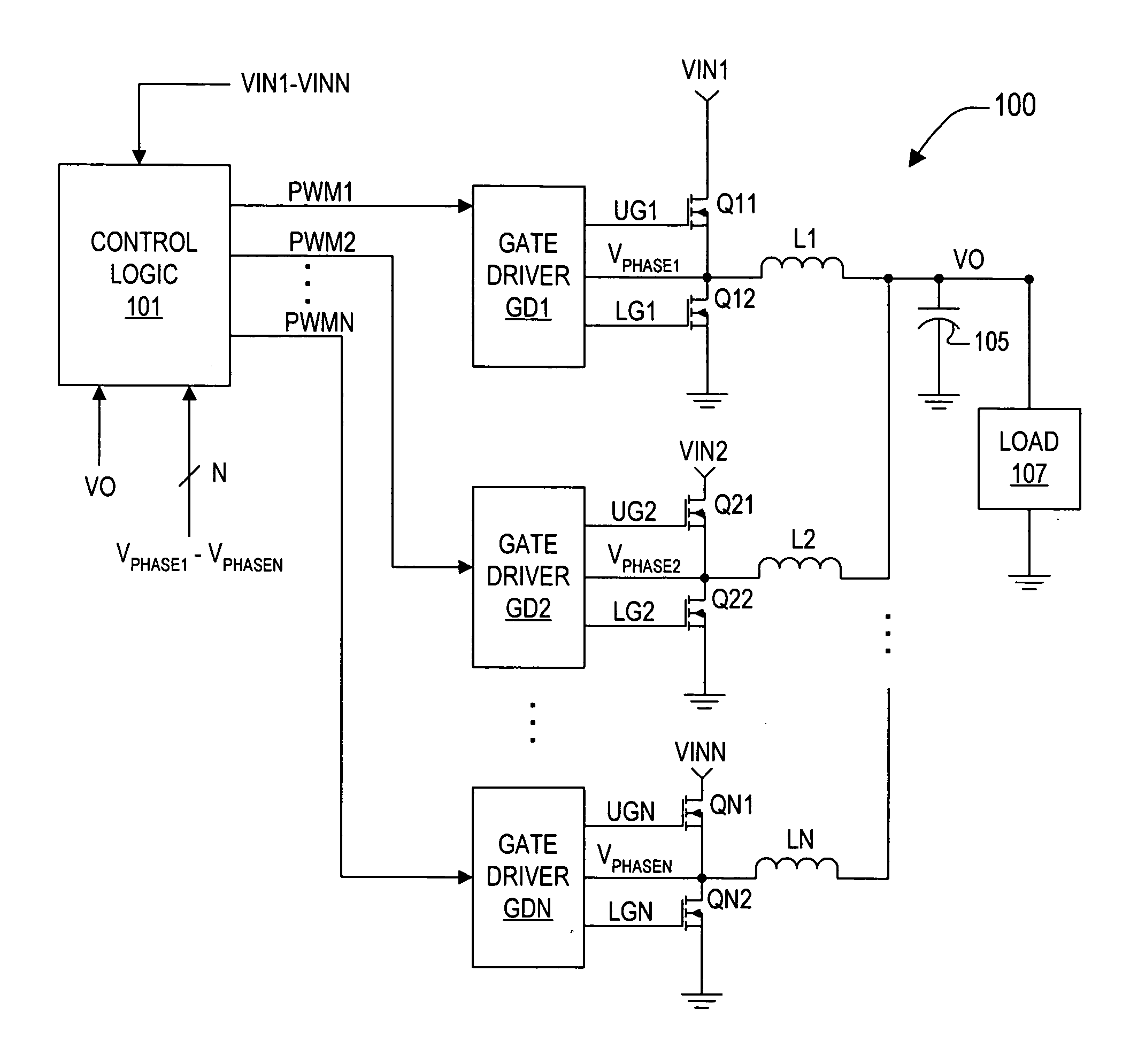
Synchronization of multiphase synthetic ripple voltage regulator
InactiveUS6922044B2Apparatus without intermediate ac conversionDc source parallel operationLow voltageVoltage regulation
A multiphase ripple voltage regulator generator employs a hysteretic comparator referenced to upper and lower voltage thresholds. The hysteretic comparator monitors a master ripple voltage waveform developed across a capacitor supplied with a current proportional to the difference between the output voltage and either the input voltage or ground. The output of the hysteretic comparator generates a master clock signal that is sequentially coupled to PWM latches, the states of which define the durations of respective components of the synthesized ripple voltage. A respective PWM latch has a first state initiated by a selected master clock signal and terminated by an associated phase voltage comparator that monitors a respective phase node voltage.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Synchronization of seismic data acquisition systems
ActiveUS7269095B2Good synchronizationLess transmission delaySeismic signal transmissionSeismic signal recordingTime errorData acquisition
A network distributed seismic data acquisition system comprises seismic receivers connected to remote acquisition modules, receiver lines, line tap units, base lines, a central recording system and a seismic source event generation unit synchronized to a master clock. One or more high precision clocks is added to the network to correct for timing uncertainty associated with propagation of commands through the network. Seismic receivers and seismic sources are thereby synchronized with greater accuracy than otherwise possible. Timing errors that interfere with the processing of the seismic recordings are greatly reduced, thus enabling an improvement in subsurface geologic imaging.
Owner:INOVA SYST CORP
Method and system for network synchronization via a femtocell
ActiveUS20100220692A1Synchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexFemtocellCommunication device
Aspects of a method and system for communication are provided. In this regard, a femtocell may receive messages from a plurality of different sources comprising one or more other femtocells, one or more cellular enabled communication devices, and one or more non-cellular network nodes. The femtocell may select, based on the received messages, a master clock within one of the plurality of different sources as a master clock for synchronization of the plurality of different sources. A femtocell clock, a global navigational satellite signal (GNSS) clock, a cellular base station clock, or a cellular enabled communication device clock may be selected as the master clock. The femtocell may transmit and / or receive synchronization messages to and / or from the one or more cellular enabled communication devices and the one or more non-cellular network nodes.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
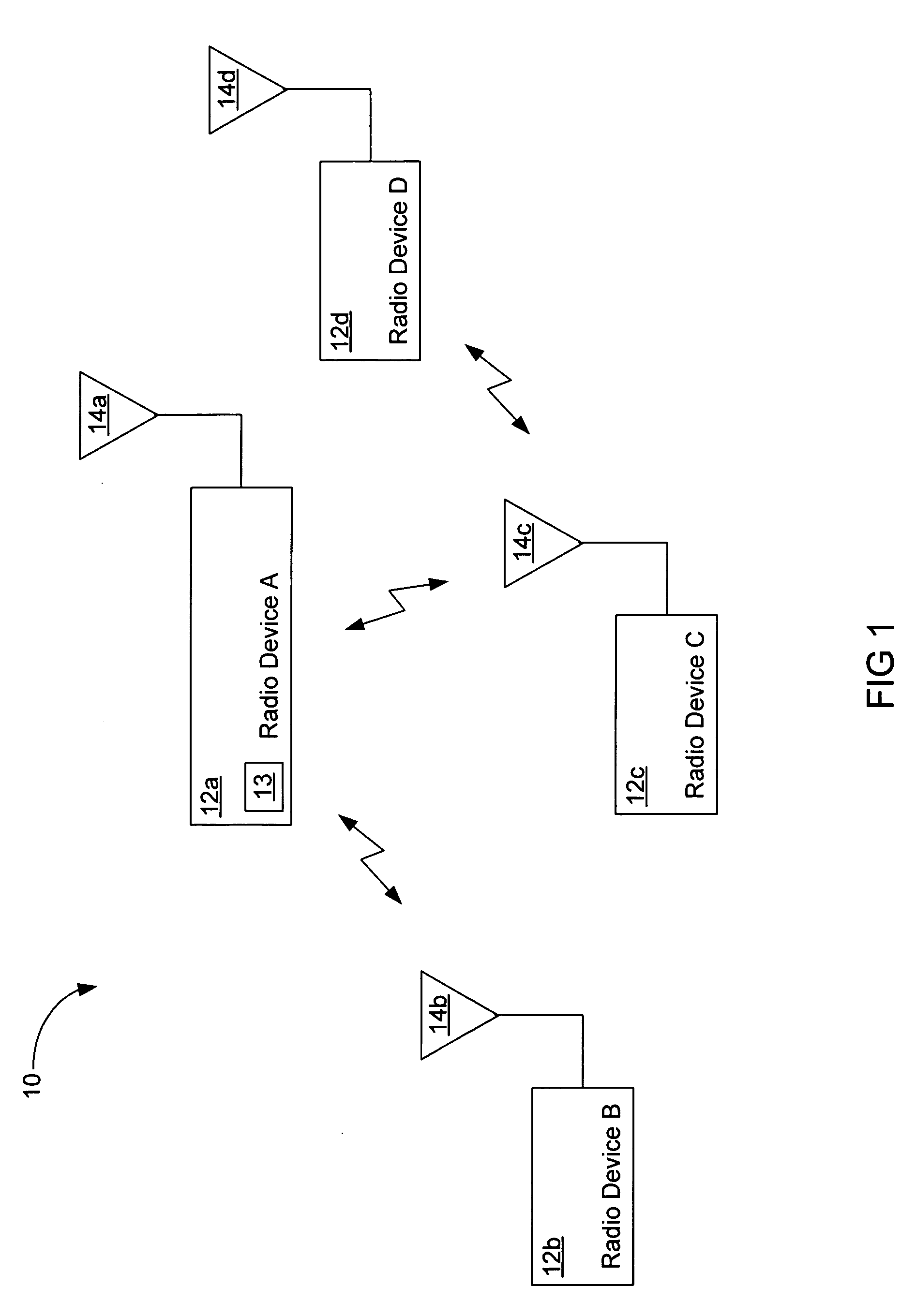
Synchronization and access of the nodes in a communications network
A wireless network is provided with a method to eliminate the commonly encountered problems associated with the development of the master timing in a network. According to the provided method, the master network timing is completely eliminated. Accordingly, in an exemplary implementation of the present invention, each node of a network has its own master clock used for transmissions that is free running and not adjusted in any way. Each node has also a receiver equipped with a mechanism to acquire and track the timing of all the network nodes that are within the communications range and that are permitted the access. In essence there is no master network timing and each transmitter hops and transmits according to its master clock. Furthermore, it is the responsibility of each receiver to track multiple timing separately for each hopping transmitter. The provided method is suitable for a wide range of applications including wireless networks and in particular for networks using frequency hopping.
Owner:PARTYKA ANDRZEJ
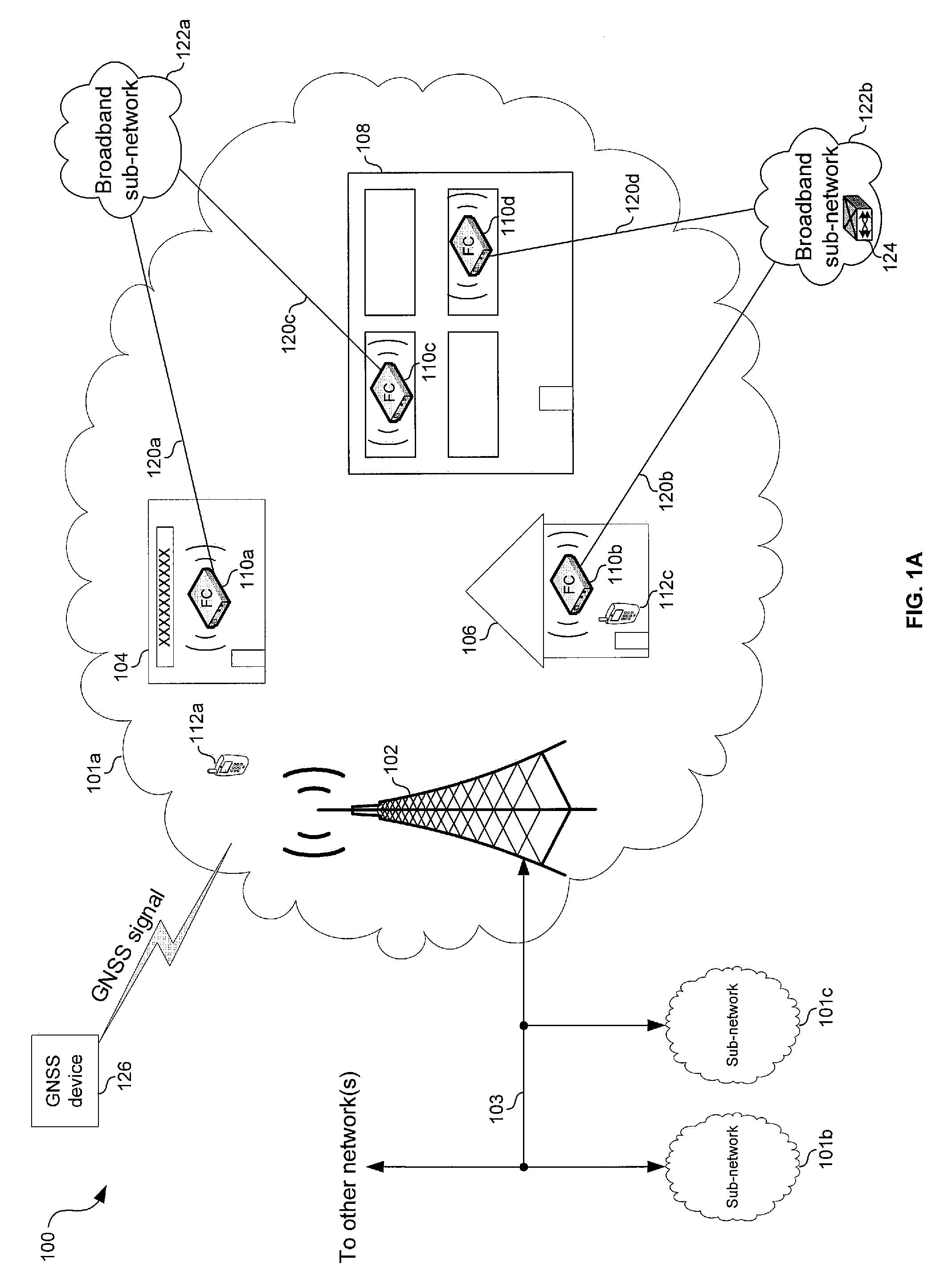
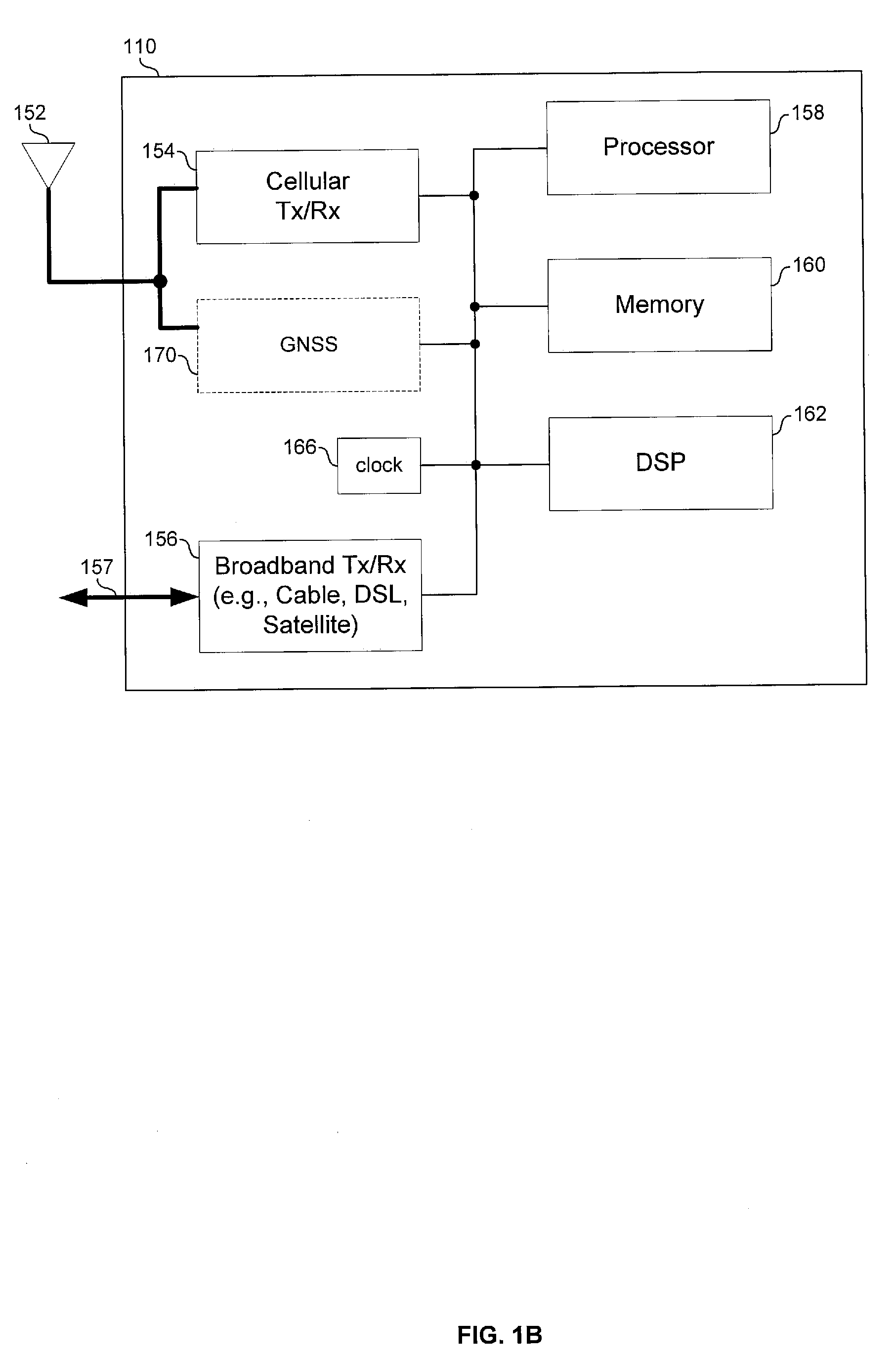
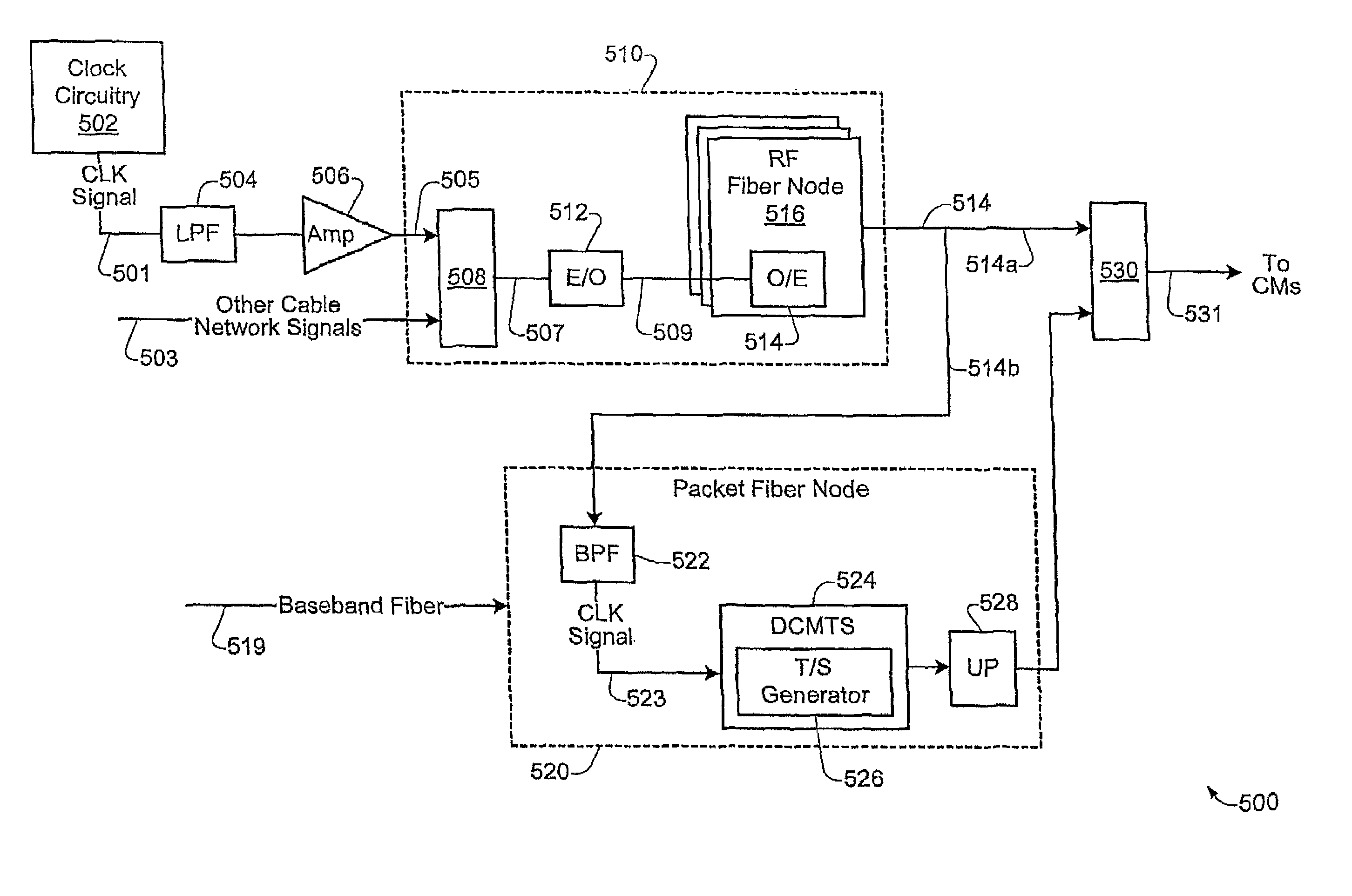
Technique for synchronizing network devices in an access data network
A master clock reference signal may be provided to selected packet fiber nodes in order to synchronize the local clock reference signals generated at selected devices in a cable network. In this way, selected portions of the cable network may be synchronized to a common timing reference signal. Additionally, synchronized timestamp information may also be provided to selected network devices in order to achieve synchronization of timestamps across a selected portion of the cable network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for transporting digital media
ActiveUS7747725B2Low costSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesTime-division multiplexComputer networkTelecommunications
A networked system is provided for transporting digital media packets, such as audio and video. The network includes network devices interconnected to send and receive packets. Each network device can receive and transmit media signals from media devices. A master clock generates a system time signal that the network devices use, together with a network time protocol to generate a local clock signal synchronized to the system time signal for both rate and offset. The local clock signal governs both the rate and offset of the received or transmitted media signals. The system, which can be implemented using conventional network equipment enables media signals to be transported to meet quality and timing requirements for high quality audio and video reproduction.
Owner:AUDINATE HLDG PTY LTD
Clock Distribution in a Distributed System with Multiple Clock Domains Over a Switched Fabric
ActiveUS20120030495A1Compensation differenceGenerating/distributing signalsTransmission path multiple useReal-time computingSwitched fabric
System and method for synchronizing devices. A device reads a first counter coupled to and associated with a master clock and a second counter coupled to and associated with the device, where the device is one of one or more devices coupled to the master clock and each other via a switched fabric, where each device includes a respective clock, and is coupled to and associated with a respective second counter. Each of the first counter and the second counters is accessible by each of the one or more devices. The device determines a difference between the device's associated second counter and the first counter, and determines and stores a time reference for the device relative to the master clock based on the determined difference, where the time reference is useable to timestamp events or synchronize future events.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Apparatus and method for trellis encoding data for transmission in digital data transmission systems
InactiveUS7020165B2Improve throughputReduce error ratePulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionDigital dataPhase difference
A system for bidirectional communication of digital data between a central unit and a remote unit wherein the need for tracking loops in the central unit has been eliminated. The central unit transmitter generates a master carrier and a master clock signal which are used to transmit downstream data to the remote units. The remote units recover the master carrier and master clock and synchronize local oscillators in each remote unit to these master carrier and master clock signals to generate reference carrier and clock signals for use by the remote unit receiver. These reference carrier and clock signals are also used by the remote unit transmitters to transmit upstream data to the central unit. The central unit receiver detects the phase difference between the reference carrier and clock signals from the remote units periodically and adjusts the phase of the master carrier and master clock signals for use by the central unit receiver to receive the upstream data.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
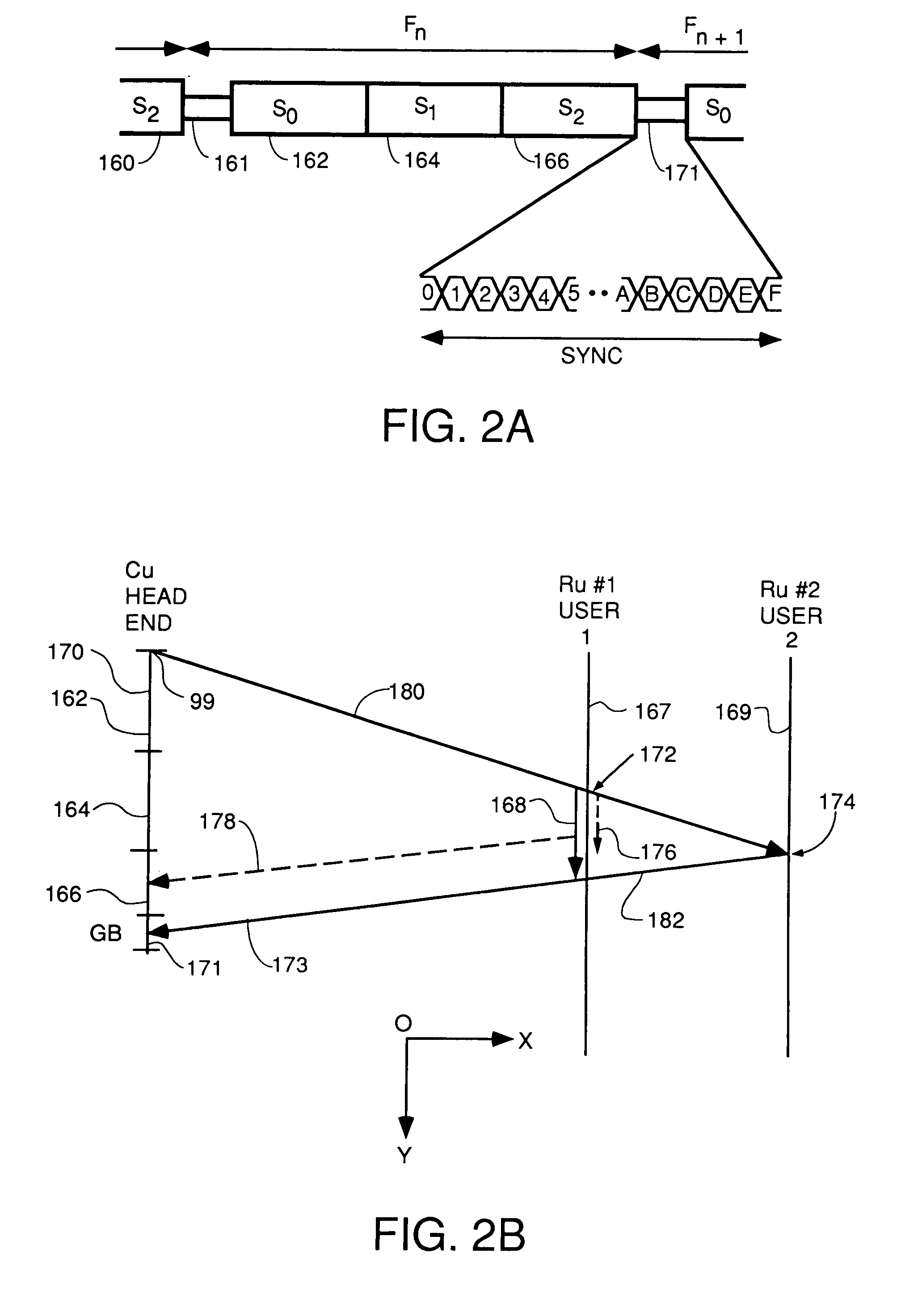
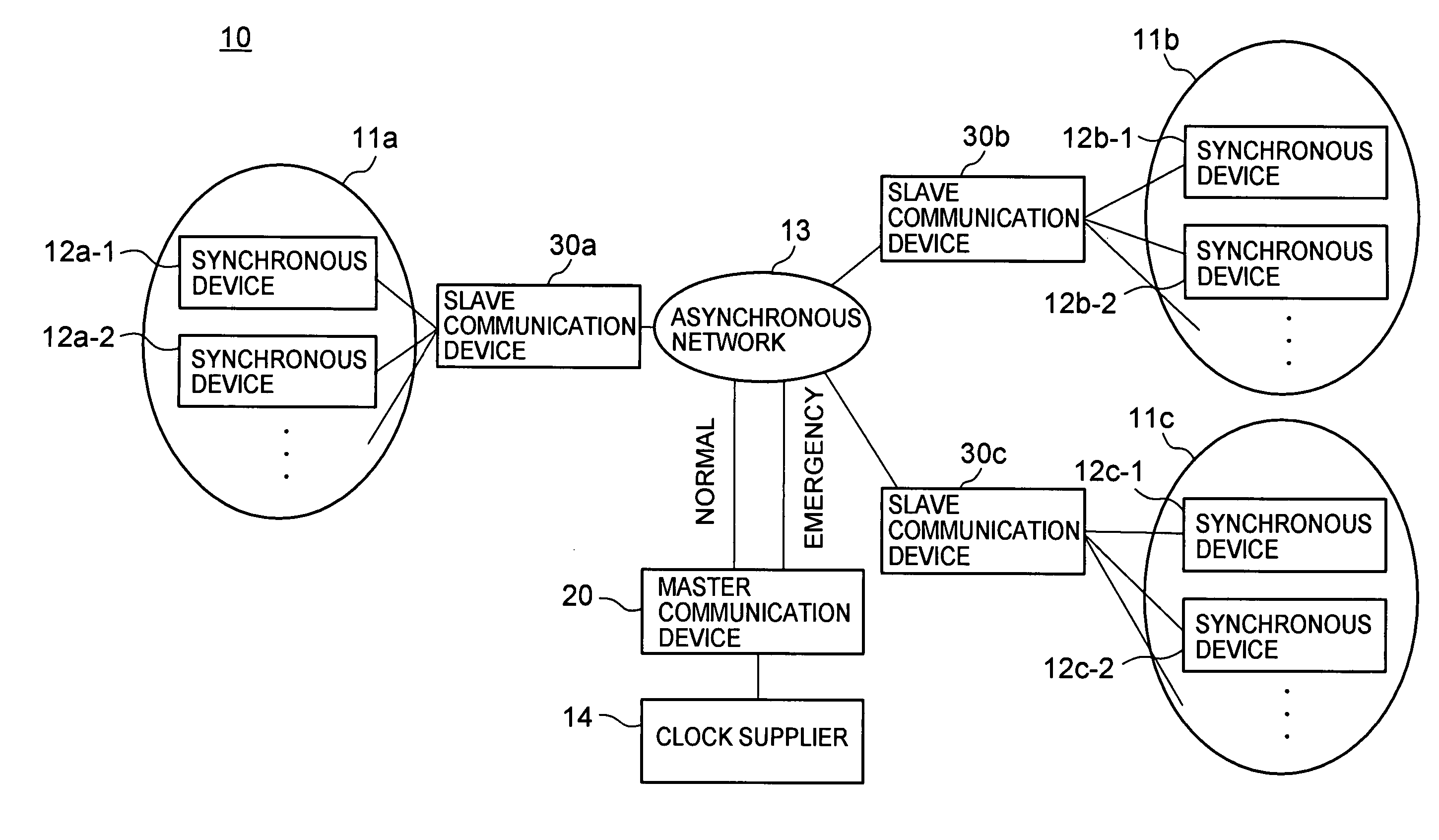
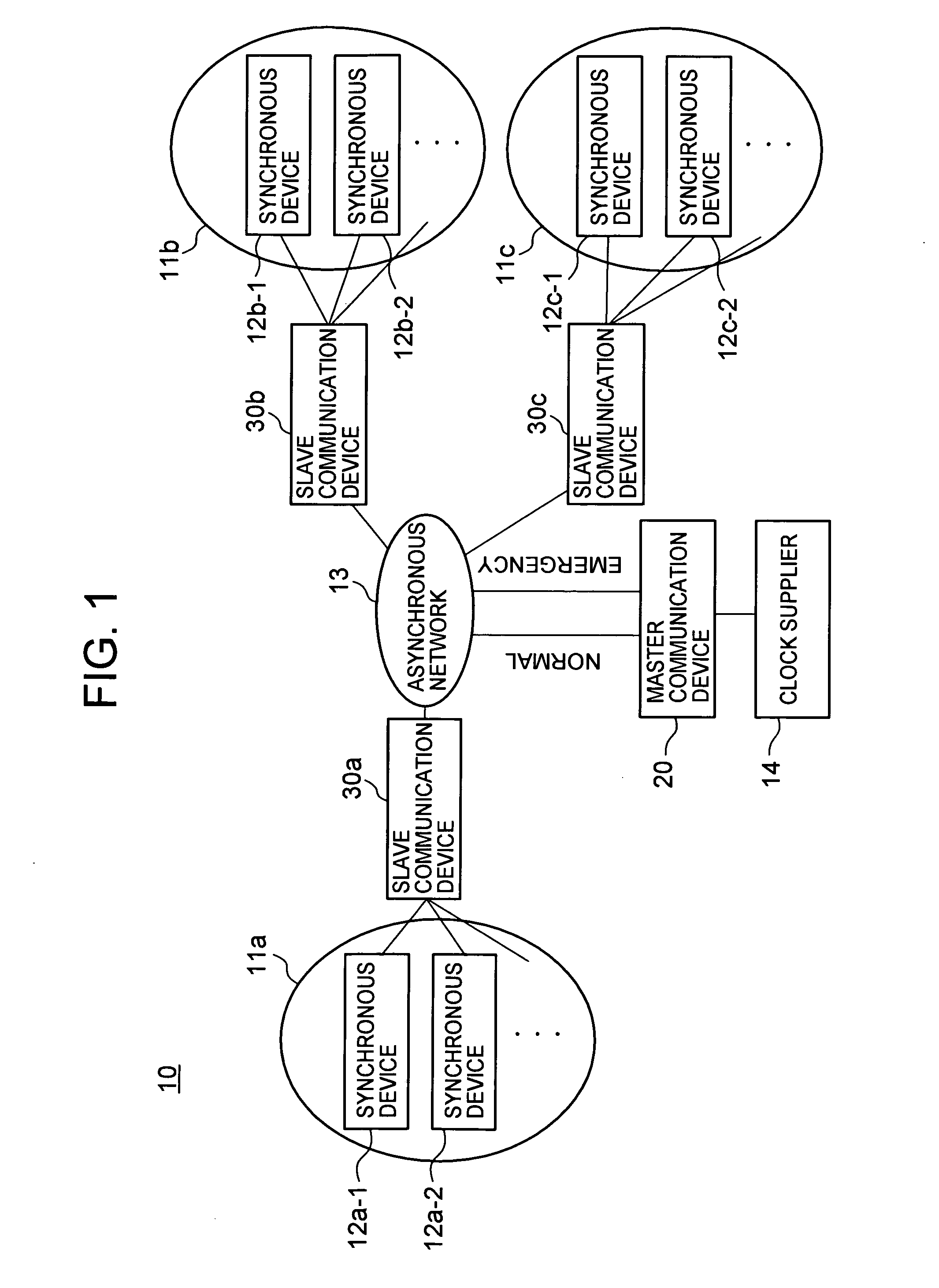
Communication system, master communication device, and slave communication device
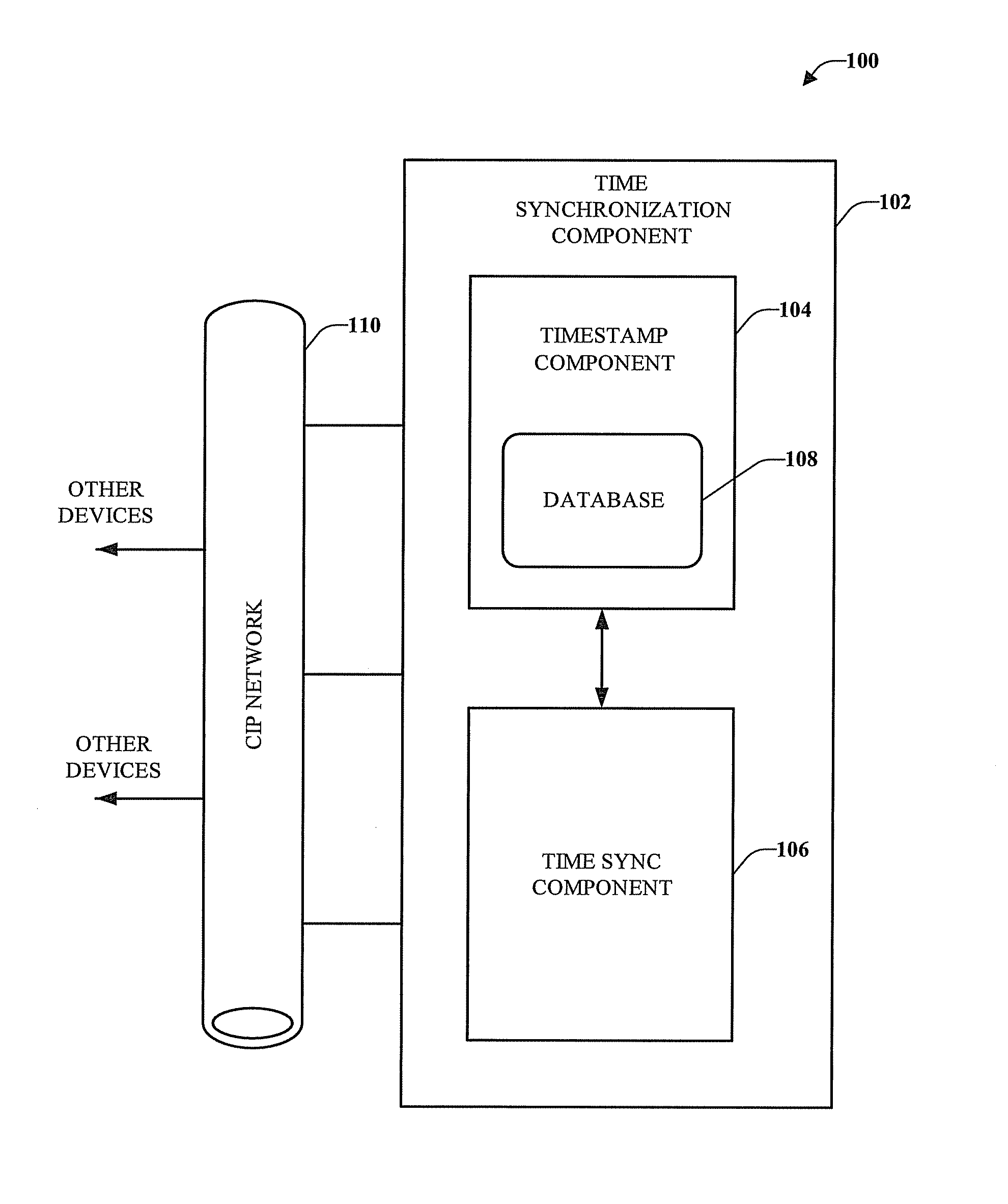
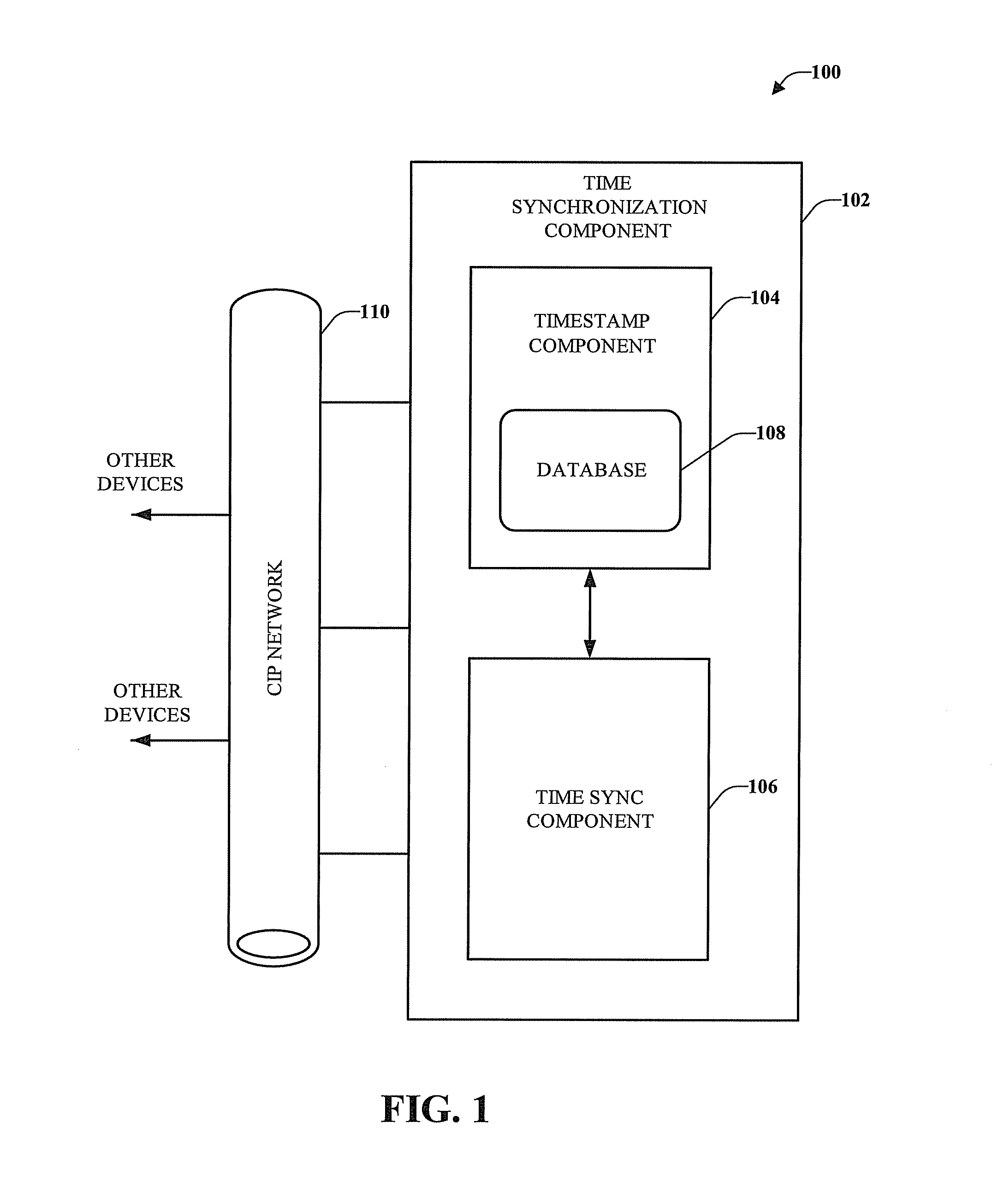
InactiveUS20070086487A1Time-division multiplexData switching networksComputer hardwareAsynchronous communication
A communication system is provided which allows synchronous devices in different synchronous communication networks to have synchronous communications with one another via an asynchronous communication network. In the communication system of the present invention, a master communication device generates a master clock based on a reference clock which is provided by a clock supplier. The master communication device sends a synchronization information frame, which contains information about the generated master clock, to plural slave communication devices via the asynchronous communication network. The slave communication devices each reproduce the master clock from the received synchronization information frame.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Synchronization of multiphase synthetic ripple voltage regulator
InactiveUS20050001597A1Dc-dc conversionDc source parallel operationVoltage generatorAudio power amplifier
A multiphase synthetic ripple voltage generator for a multiphase DC-DC regulator including a master clock circuit that generates a master clock signal, sequence logic and a ripple regulator for each phase. The DC-DC regulator includes multiple switching circuits, each responsive to a corresponding PWM signal to switch input voltages via a phase node through an output inductor to develop an output voltage. The sequence logic sets each PWM signal in sequential order based on the master clock signal. Each ripple generator includes a transconductance amplifier, a ripple capacitor and a comparator. The transconductance amplifier has an input coupled to a corresponding output inductor and an output coupled to a corresponding ripple capacitor. The comparator has a first input coupled to the ripple capacitor, a second input receiving an error voltage, and an output coupled to the sequence logic for resetting a corresponding PWM signal.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
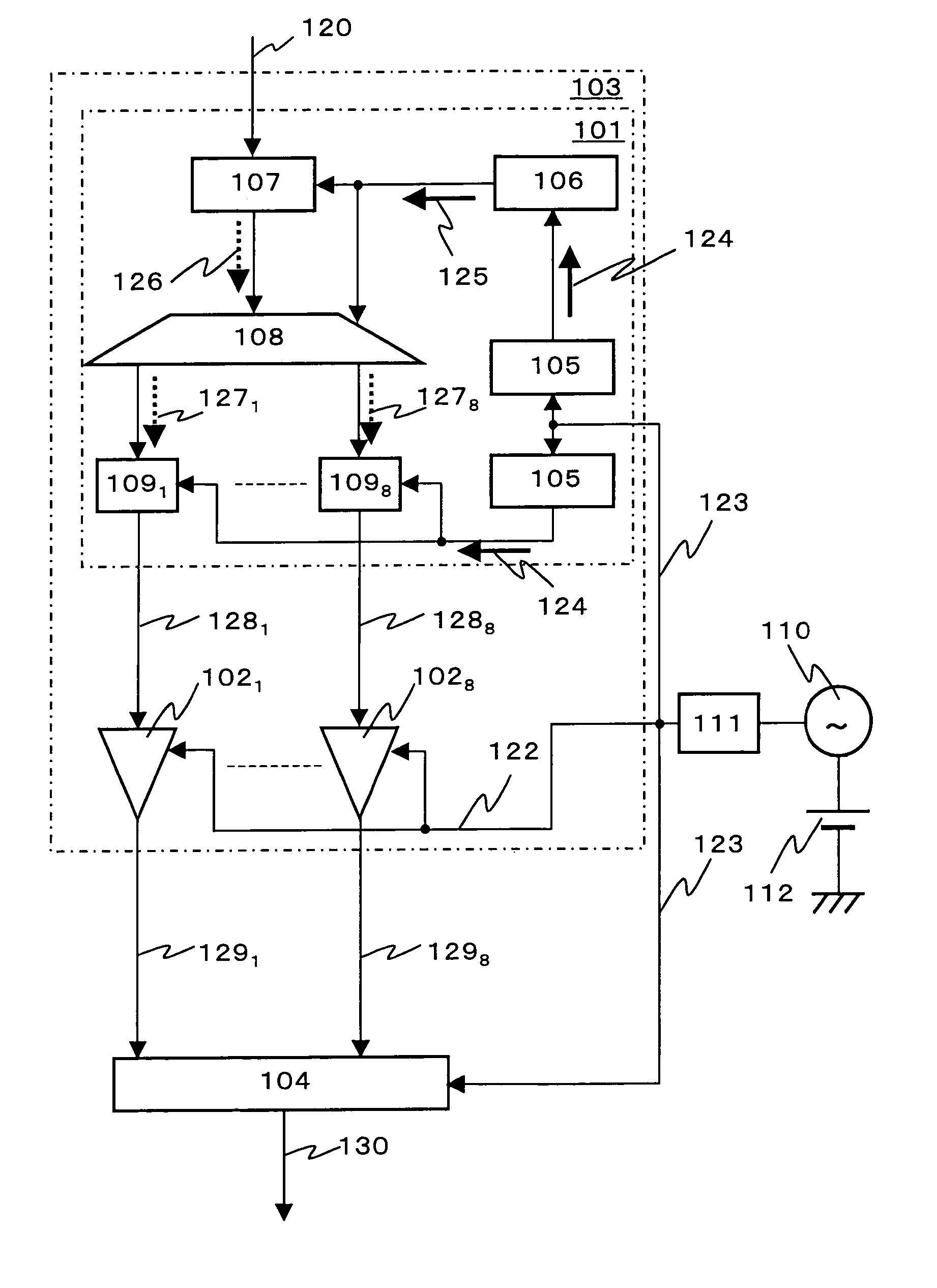
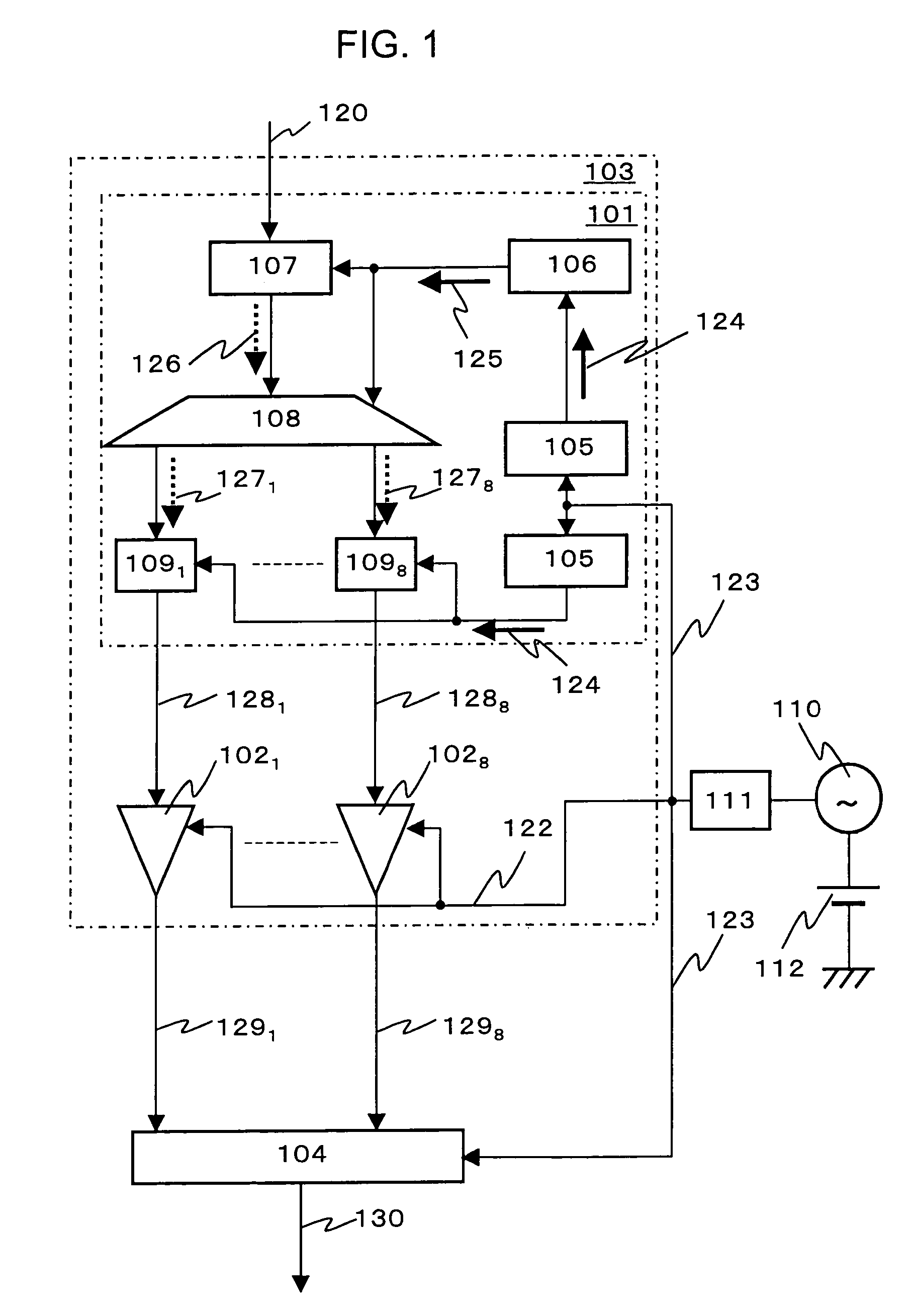
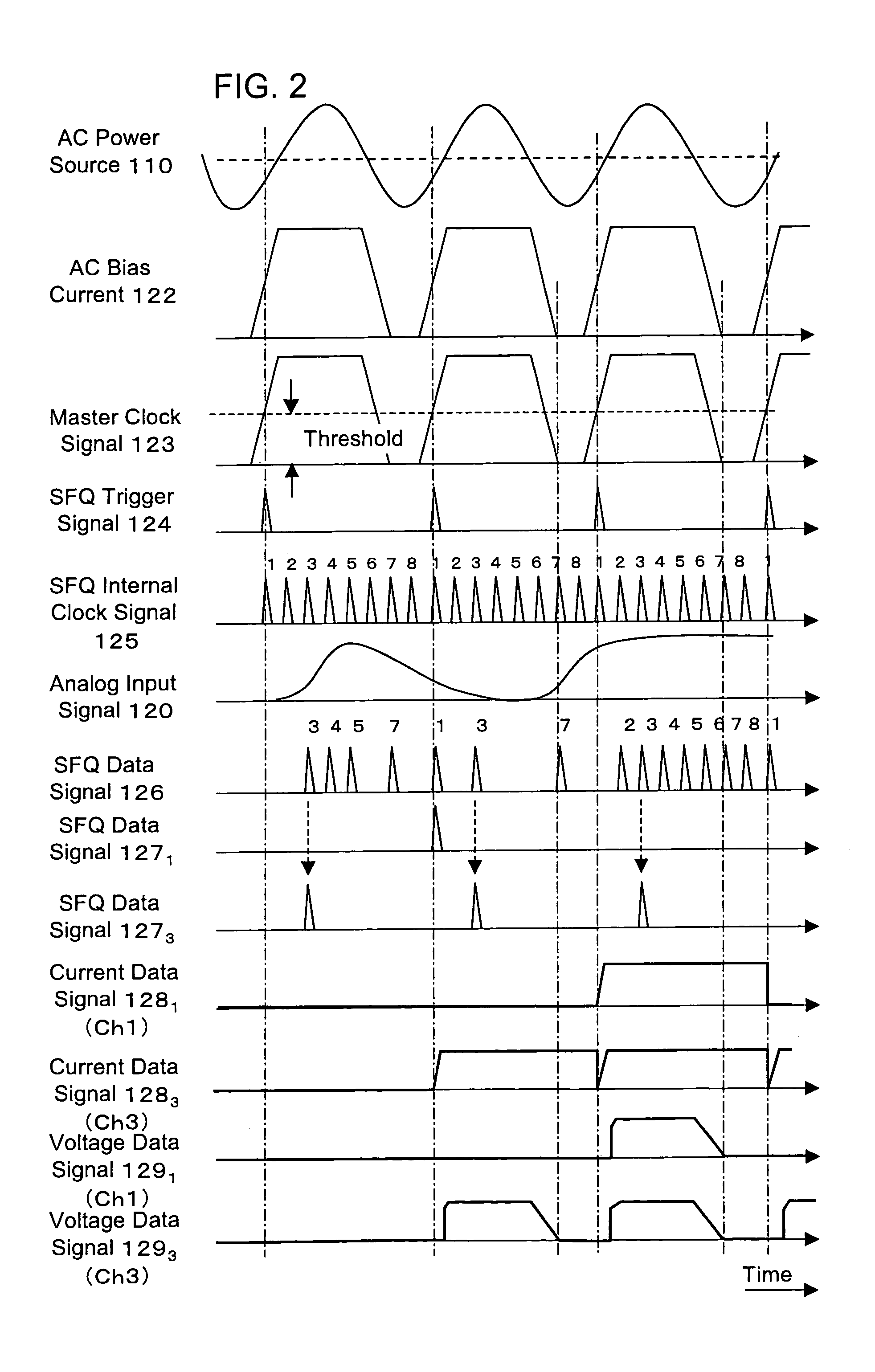
Superconductor semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS7129869B2Timing design is facilitatedReduce frequencyElectric signal transmission systemsDigital storageQuantum circuitFrequency multiplier
In an A / D converter having a single flux quantum circuit having a flux quantum as an information carrier, a superconducting amplifier circuit driven by an AC current, and a semiconductor circuit, the operations of the circuits are synchronized with each other and a data signal from the single flux quantum circuit is transmitted to the semiconductor circuit.An AC current as the power source of a superconducting amplifier circuit is inputted as a master clock signal to the single flux quantum circuit and the semiconductor circuit to synchronize the operations of the circuits with the master clock signal. The single flux quantum circuit has a clock signal frequency multiplier circuit, a demultiplexing circuit and a memory circuit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Superscale processor performance enhancement through reliable dynamic clock frequency tuning
InactiveUS7671627B1Easy to optimizeGuaranteed uptimeElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionPhase shiftedPerformance enhancement
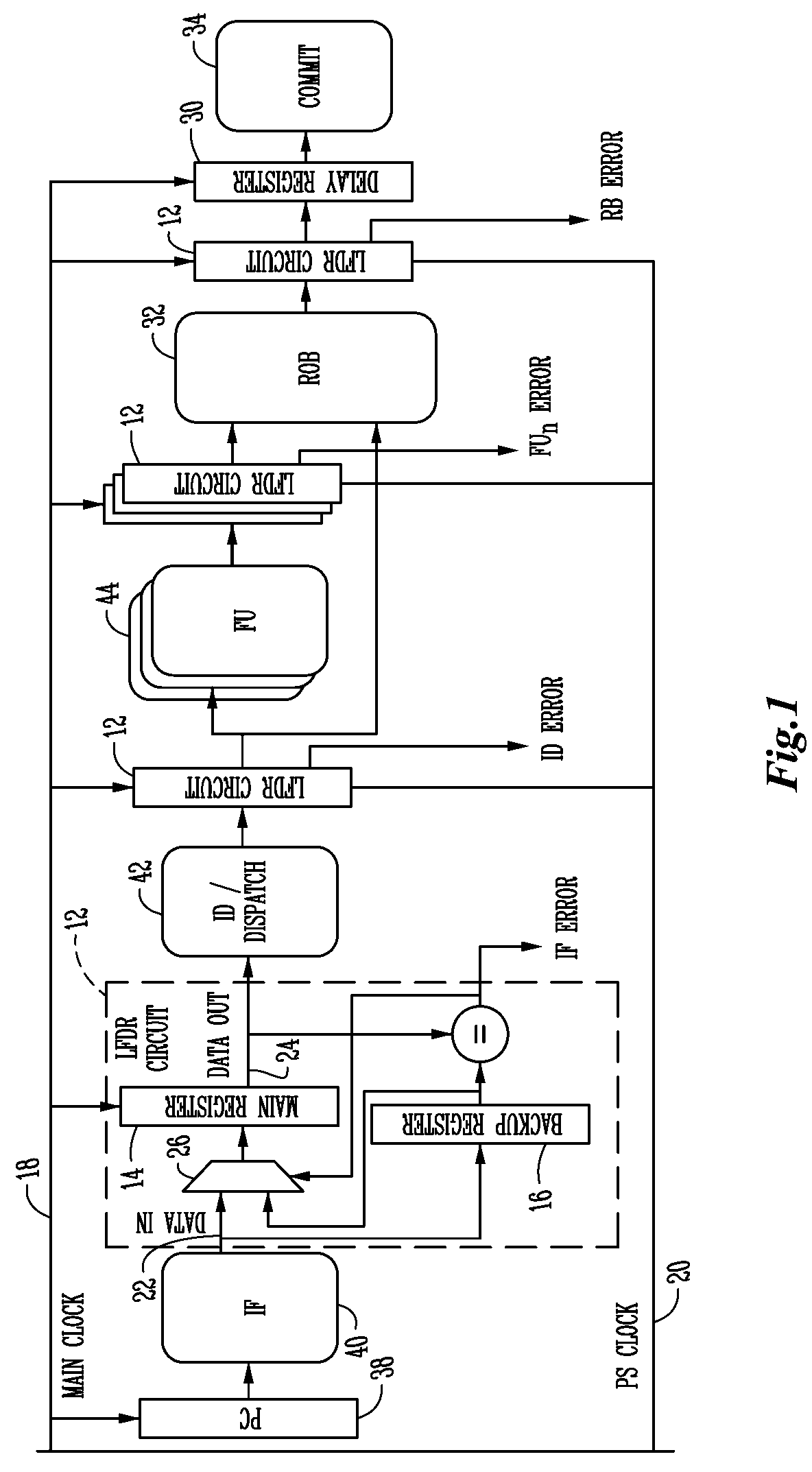
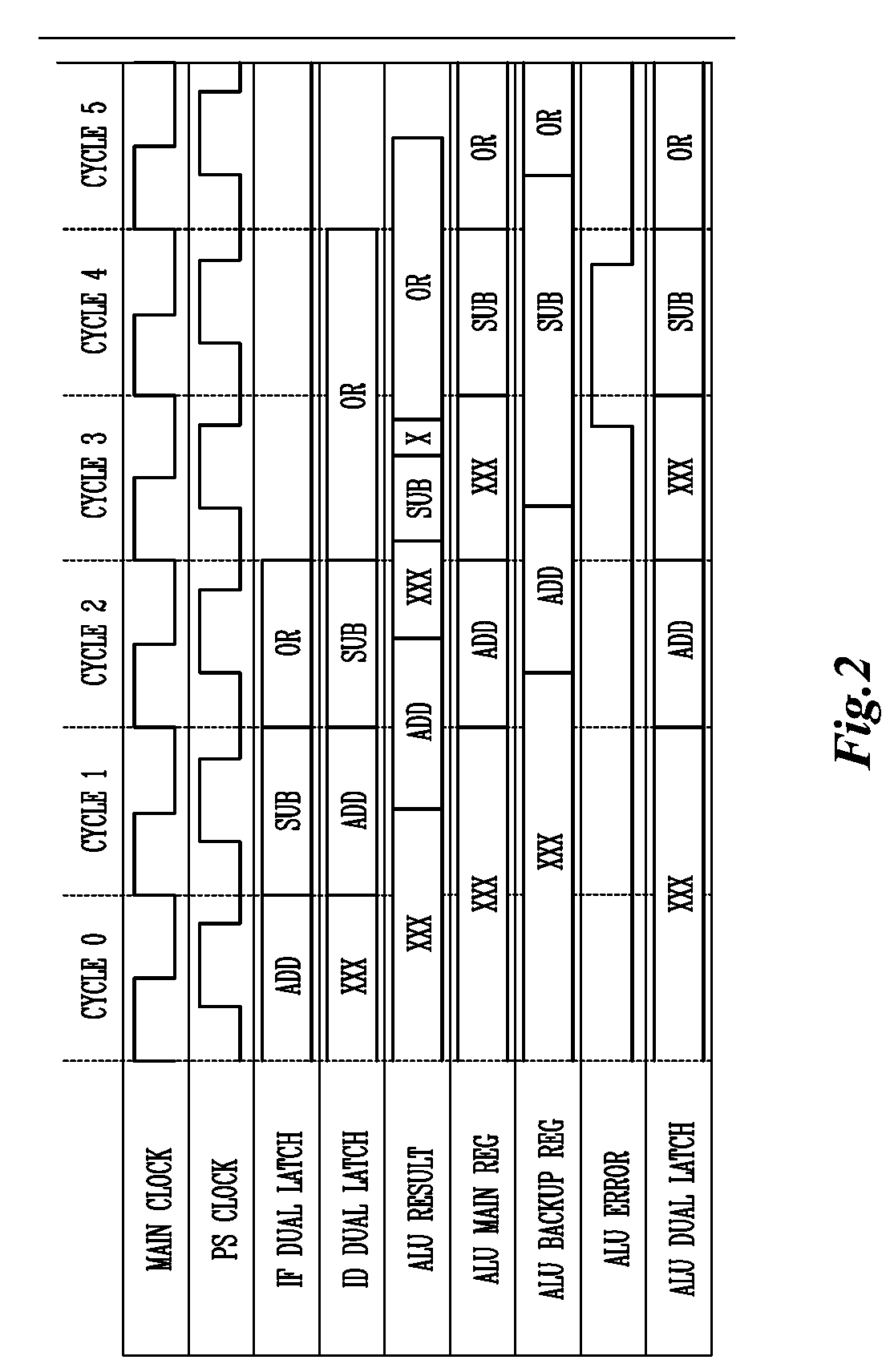
In the case of a pipelined processor, a performance gain is achievable through dynamically generating a main clock signal associated with a synchronous logic circuit and generating at least one backup register clock signal, the backup register clock signal at the same frequency as the main clock signal and phase shifted from the main clock signal to thereby provide additional time for one or more of the logic stages to execute. Error detection or error recovery may be performed using the backup registers. The methodology can further be extended, to design a system with cheaper technology and simple design tools that initially operates at slower speed, and then dynamically overclocks itself to achieve improved performance, while guaranteeing reliable execution.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Method and apparatus for presentation of media content
ActiveUS20160034240A1Television system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer moduleDisplay device
Aspects of the subject disclosure may include, for example, a method including receiving, by a system comprising a processor, a multicast video stream directed to an array of a plurality of display modules movably attached to a modular display, extracting, by the system, video display data from the multicast video stream according to a location within the array of a first display module of the plurality of display modules, and updating, by the system, a video display of the first display module according to the video display data that is extracted from the multicast video stream, wherein the updating is synchronized to a master clock of the modular display. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Wideband active phased array antenna system
ActiveUS20070194986A1Particular array feeding systemsRadio transmissionAudio power amplifierControl signal
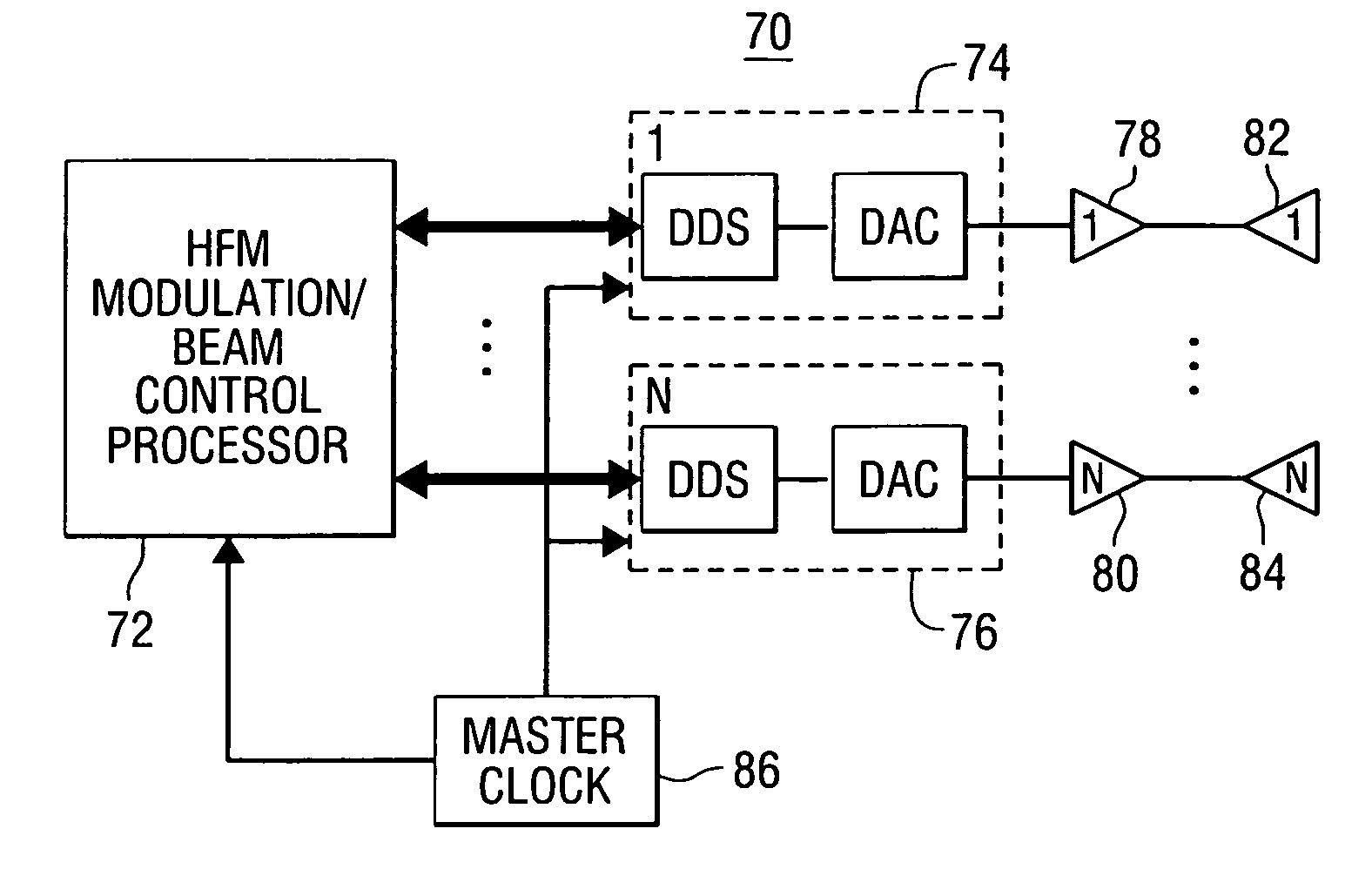
A transmission system comprises a plurality of antenna elements; a plurality of power amplifiers, each of power amplifiers being connected to one of the antenna elements; a plurality of waveform / beam synthesizer assemblies, each of the waveform / beam synthesizer assemblies being connected to one of the power amplifiers; a processor for controlling modulation and beam forming / steering functions of the waveform / beam synthesizer assemblies; and a master clock for synchronizing operation of the processor and waveform / beam synthesizer assemblies, wherein each of the waveform / beam synthesizer assemblies generates a transmit element signal with embedded phase offset and amplitude adjustments in response to control signals from the processor, and each of the plurality of antenna elements radiates one of the transmit element signals. A method of producing one or more beams using an array of antenna elements is also provided.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Real Time Sensor and Method for Synchronizing Real Time Sensor Data Streams
A Holocam Orb system uses multiple Holocam Orbs (Orbs) within a real-life environment to generate an artificial reality representation of the real-life environment in real time. Each Orb is an electronic and software unit that includes a local logic module, a local CPU and multiple synchronous and asynchronous sensors, include stereo cameras, time-of-flight sensors, inertial measurement units and a microphone array. Each Orb synchronizes itself to a common master clock, and packages its asynchrony data into data bundles whose timings are matched to frame timing of synchronous sensors, and all gathered data bundles and data frames are given a time stamp using a reference clock common to all Orbs. The overlapping sensor data from all the Orbs is combined to create the artificial reality representation.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
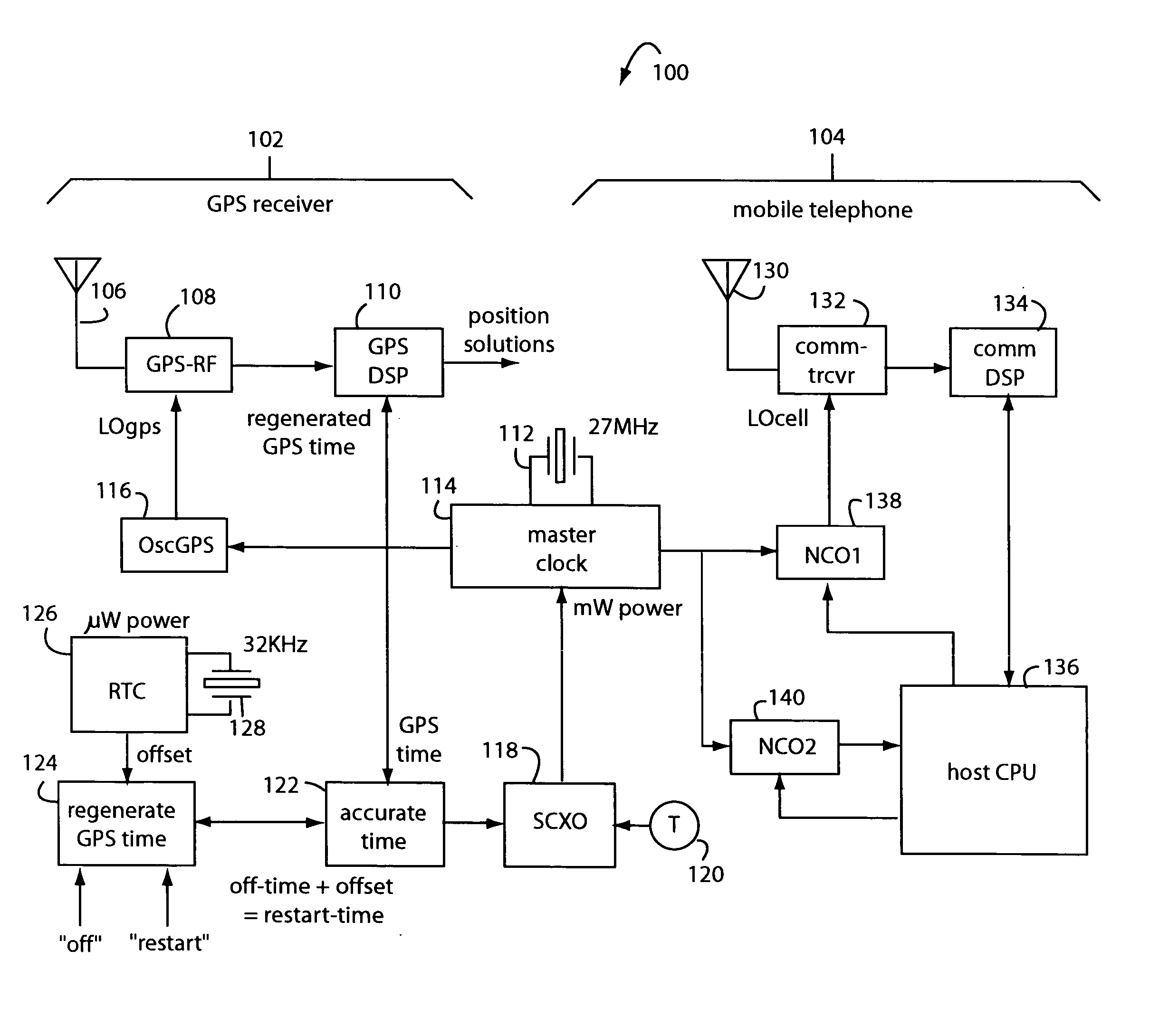
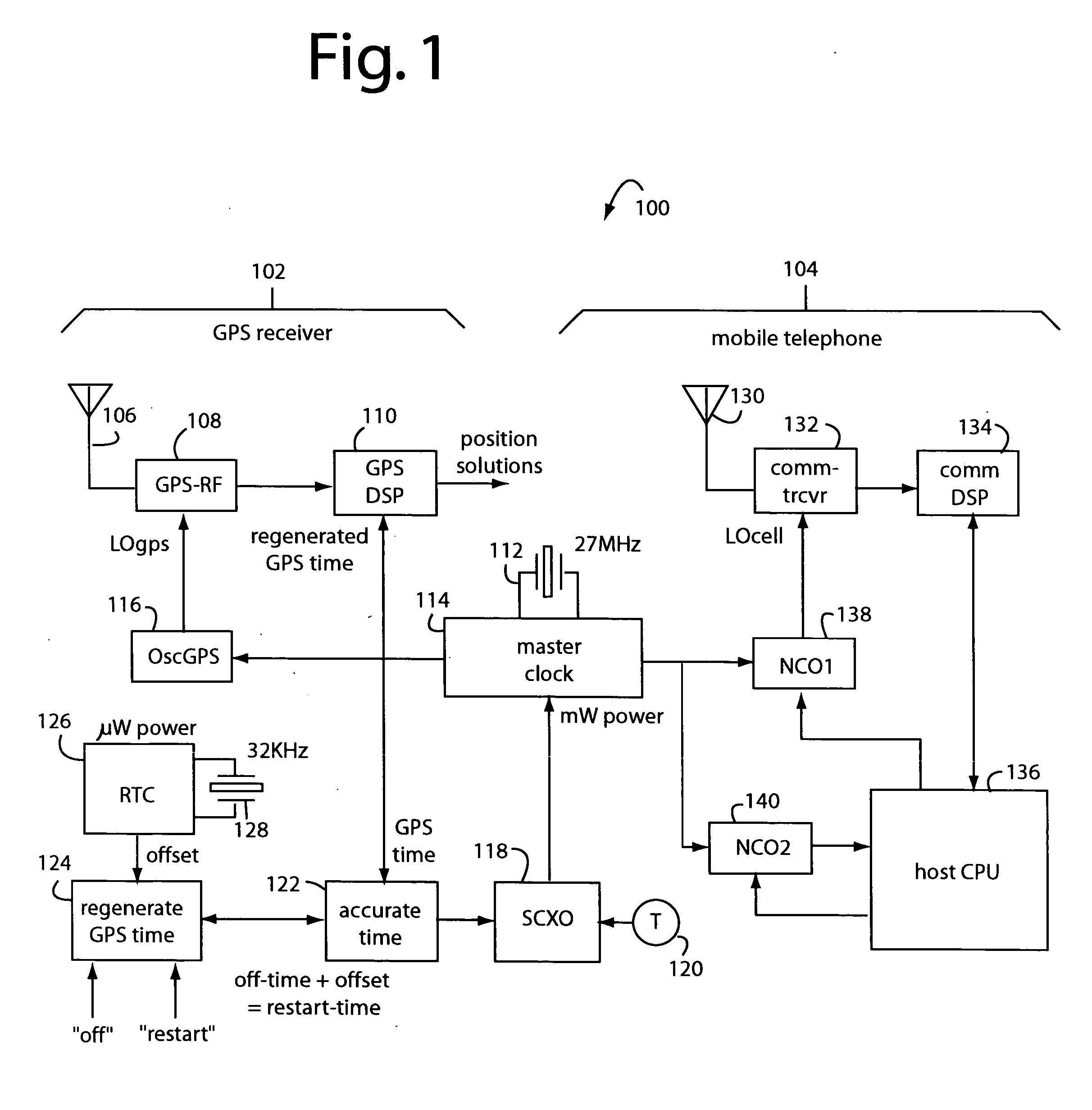
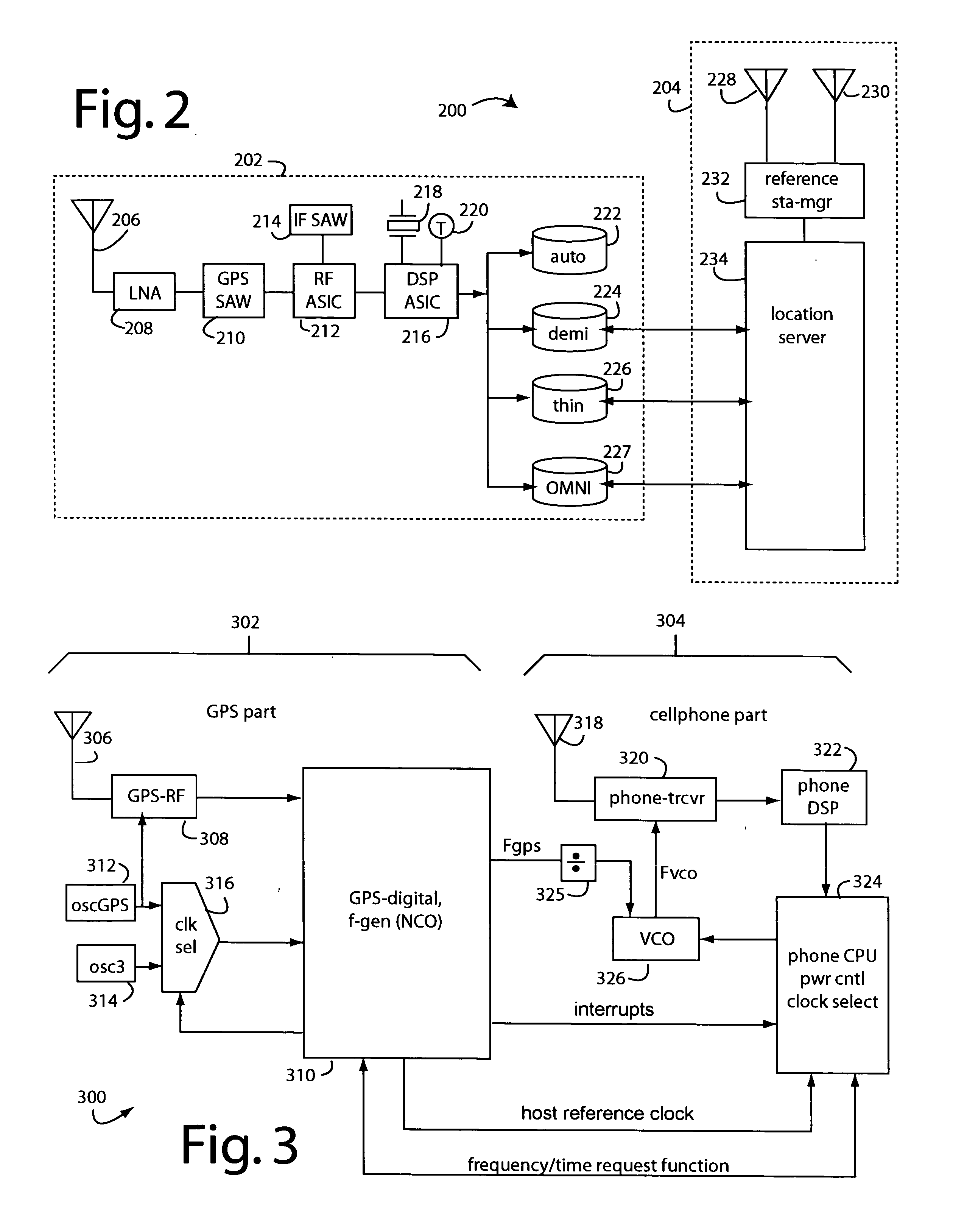
Keeping accurate time for a hybrid GPS receiver and mobile phone when powered off
ActiveUS20050195105A1Quick initializationPower managementSynchronisation arrangementReal-time clockGps receiver
A hybrid navigation satellite receiver and mobile telephone uses only two crystal oscillators. One that operates a master clock around 27-MHz and that consumes milliwatts of power. The other oscillator consumes only microwatts of power and operates continuously on battery power at about 32-KHz. Only the second, low frequency oscillator is kept running during power “off”. On power “restart”, a real-time-clock counter is consulted to cause an estimate of the GPS system time to be regenerated and supplied to the GPS-DSP to quicken its initialization. The master clock is GPS-calibrated, and the accurate clock is used to drive NCO's for the mobile telephone part and host CPU.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com