Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1026 results about "User Datagram Protocol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
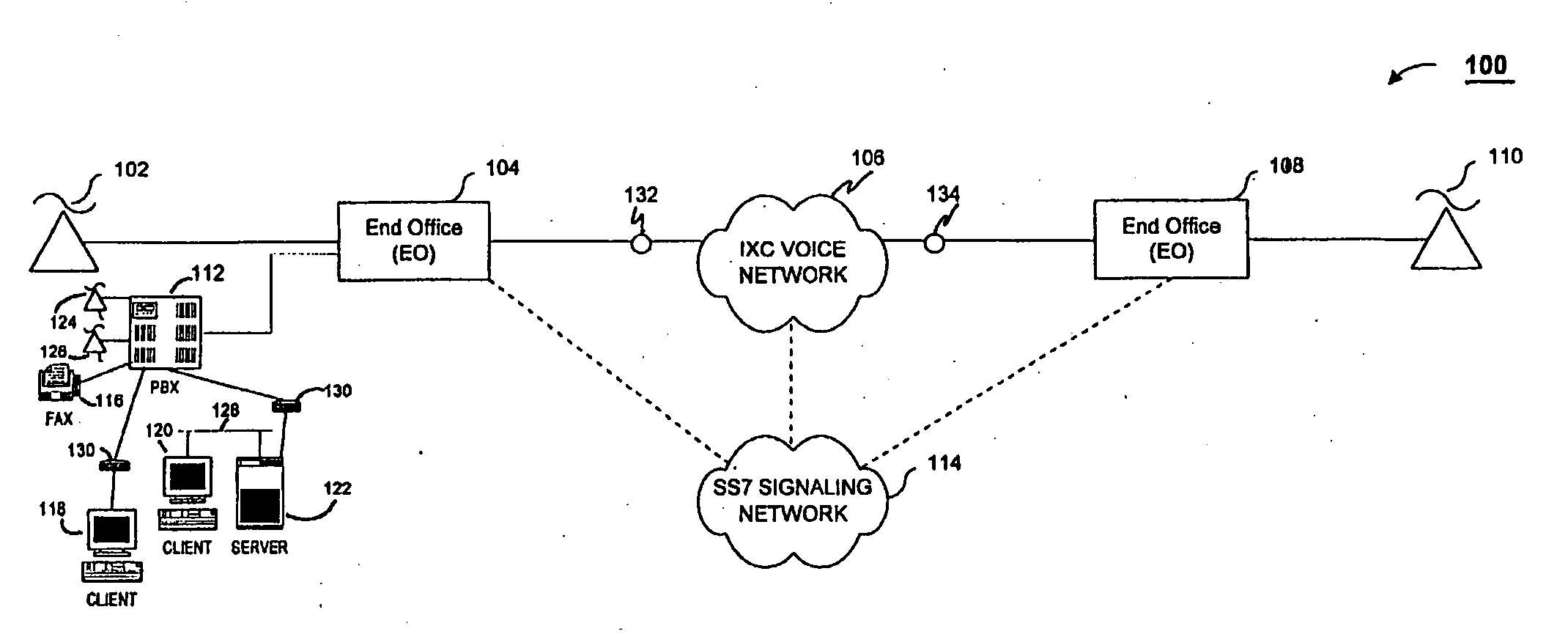
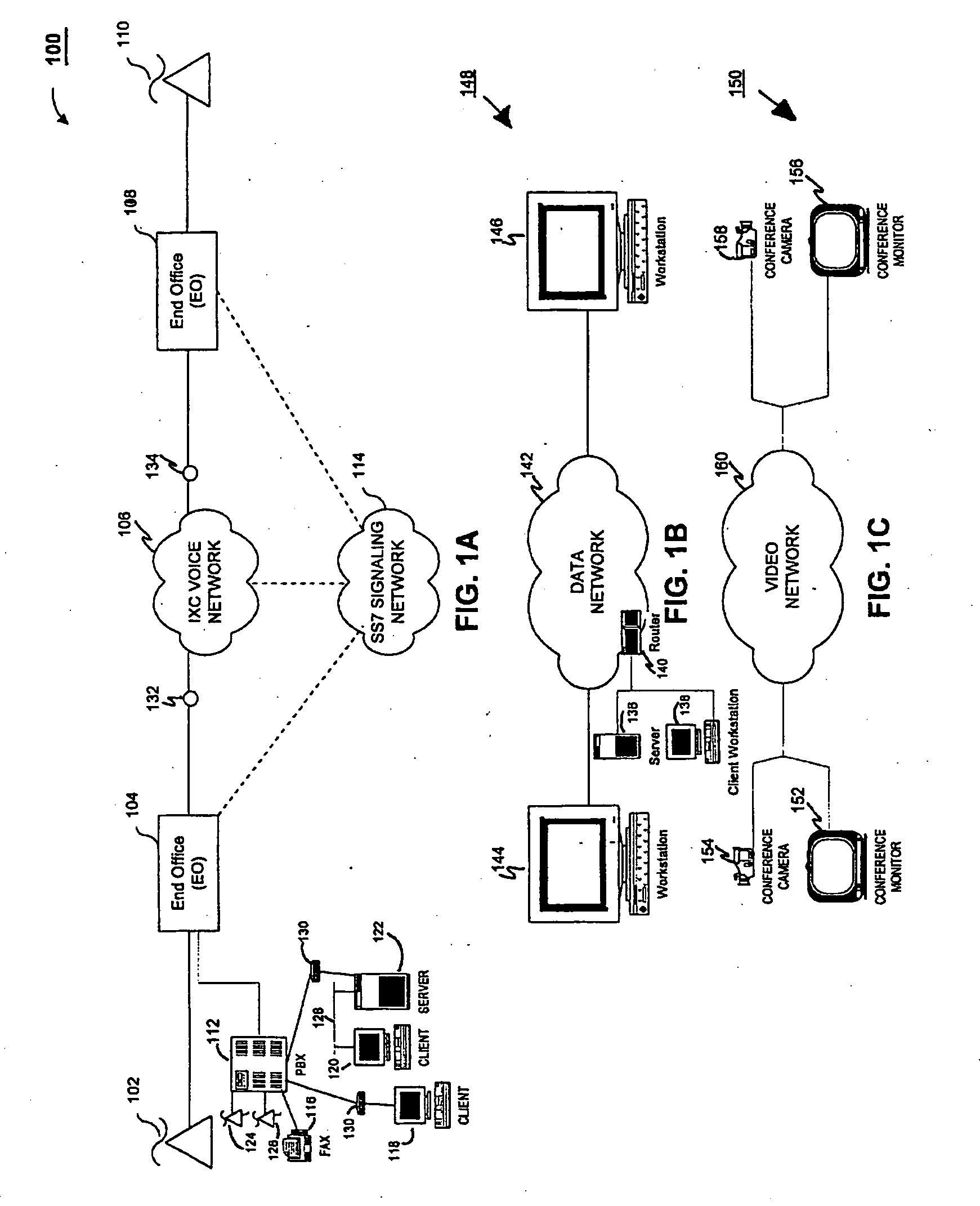
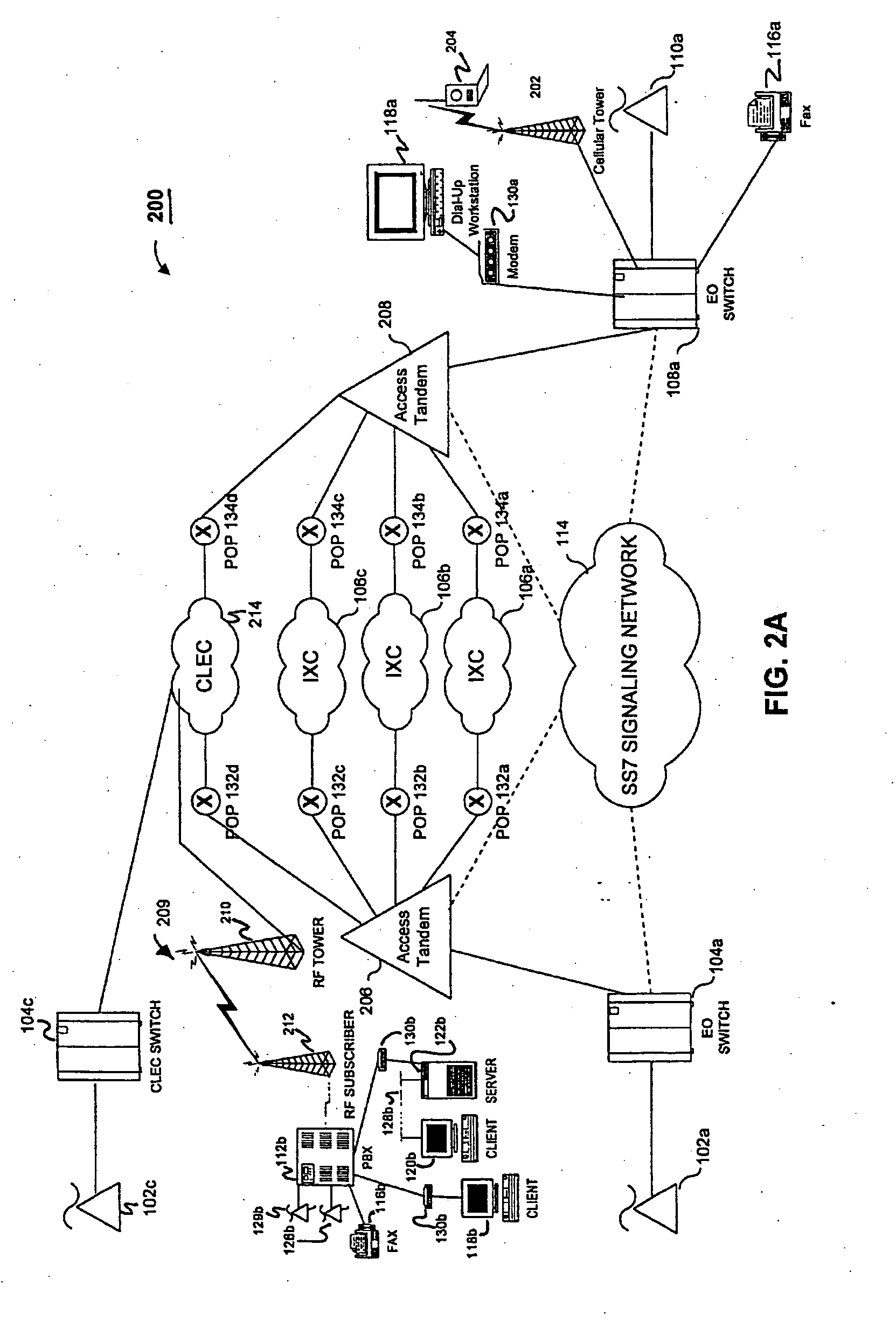
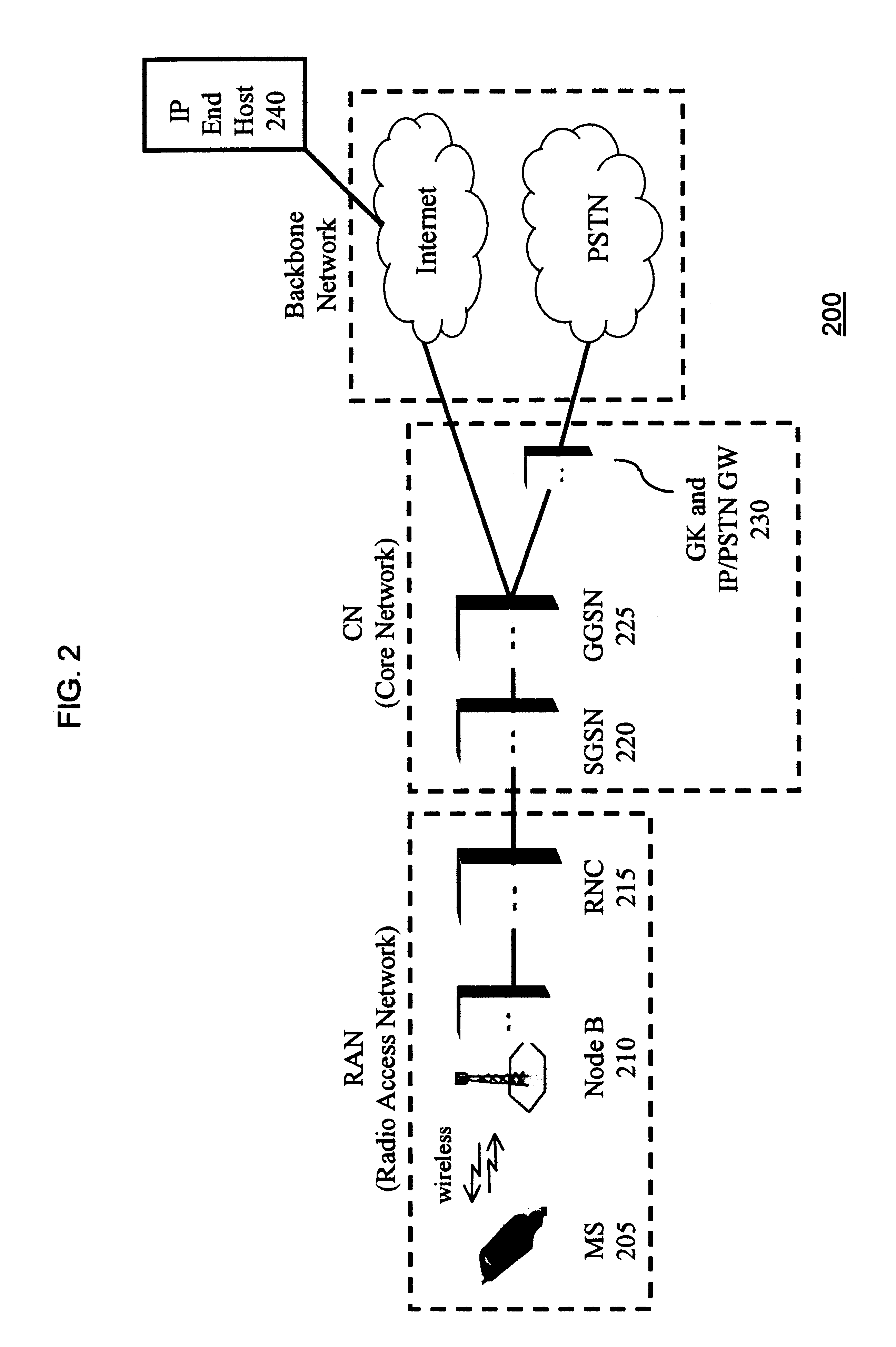
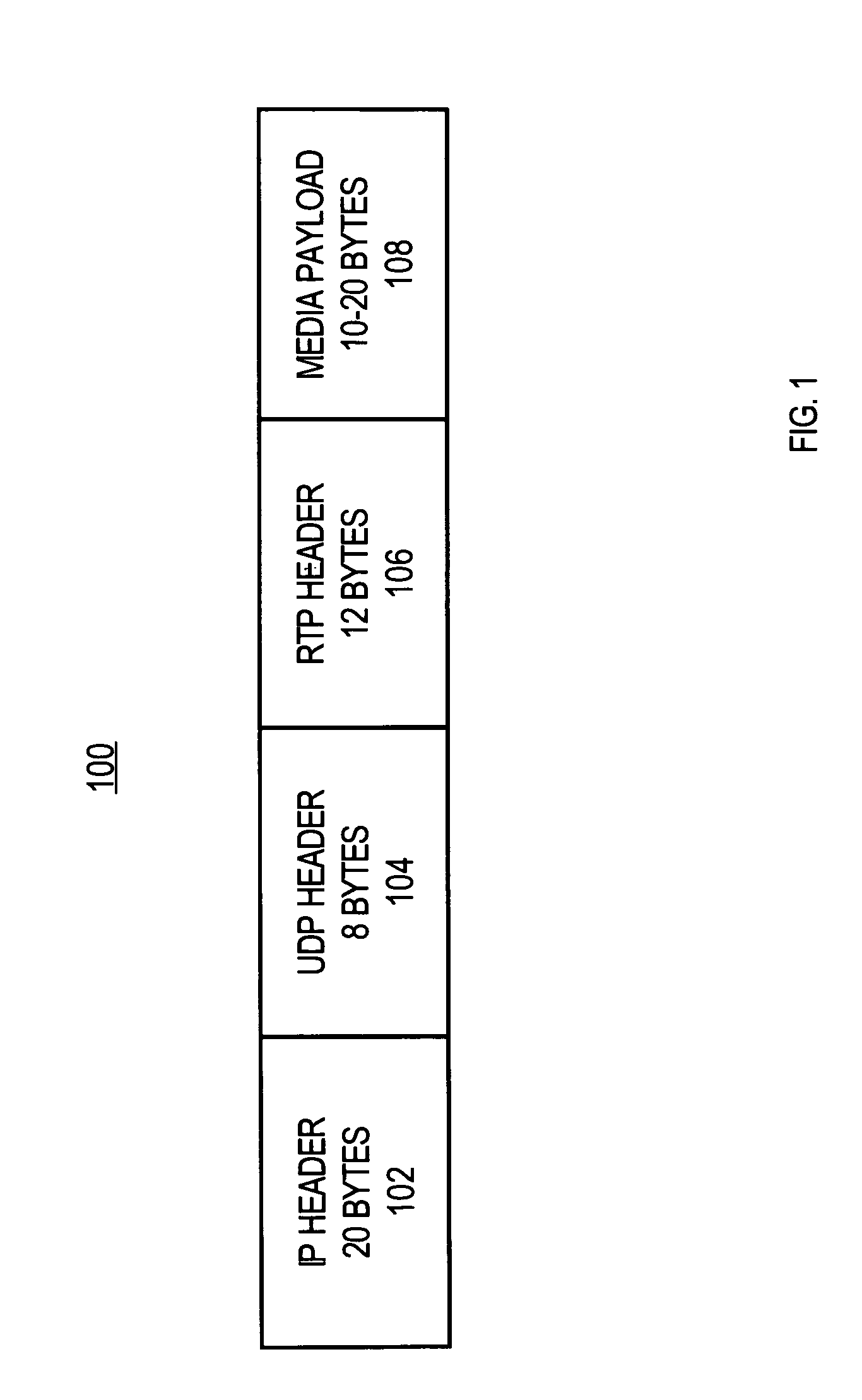
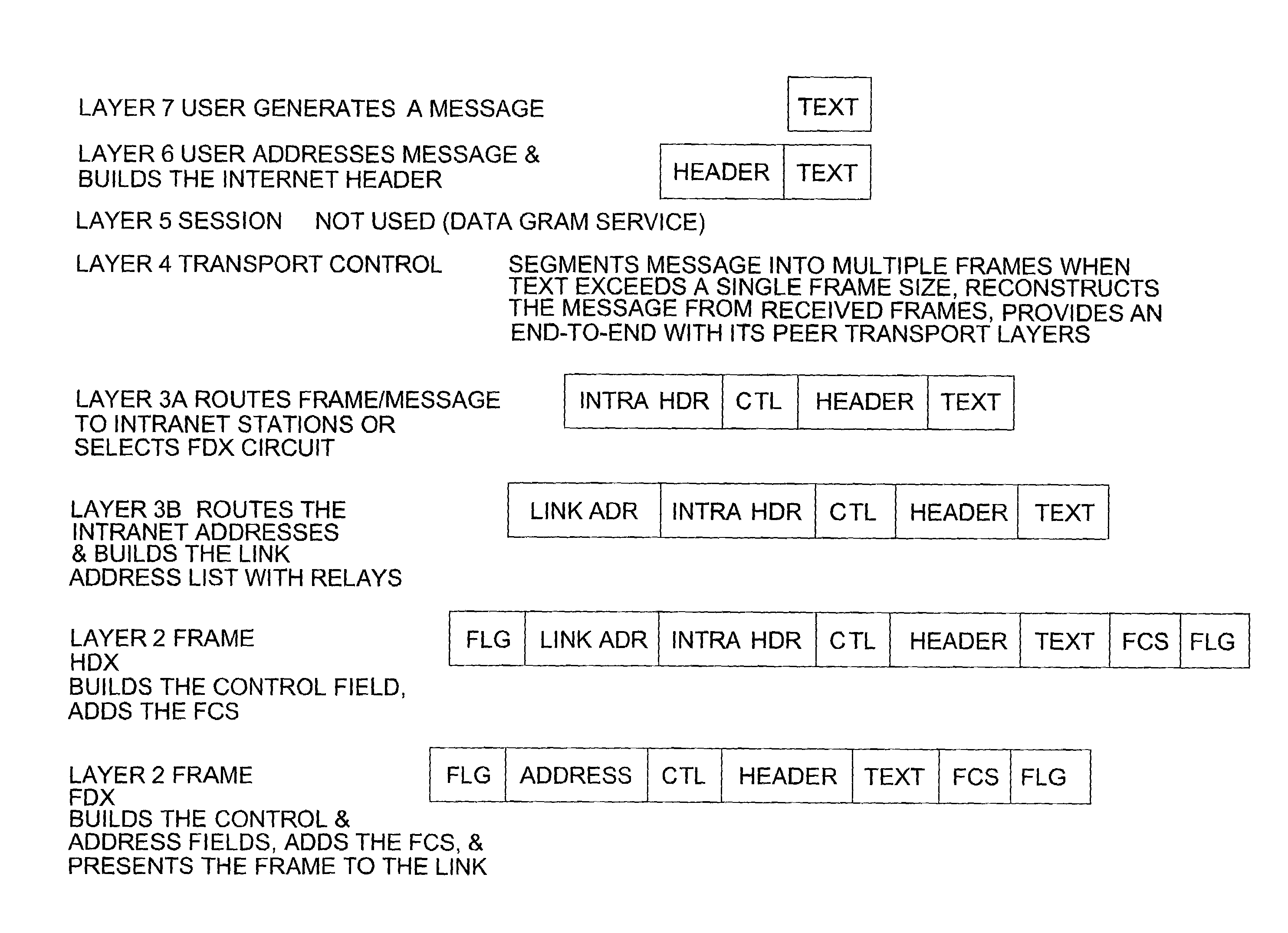
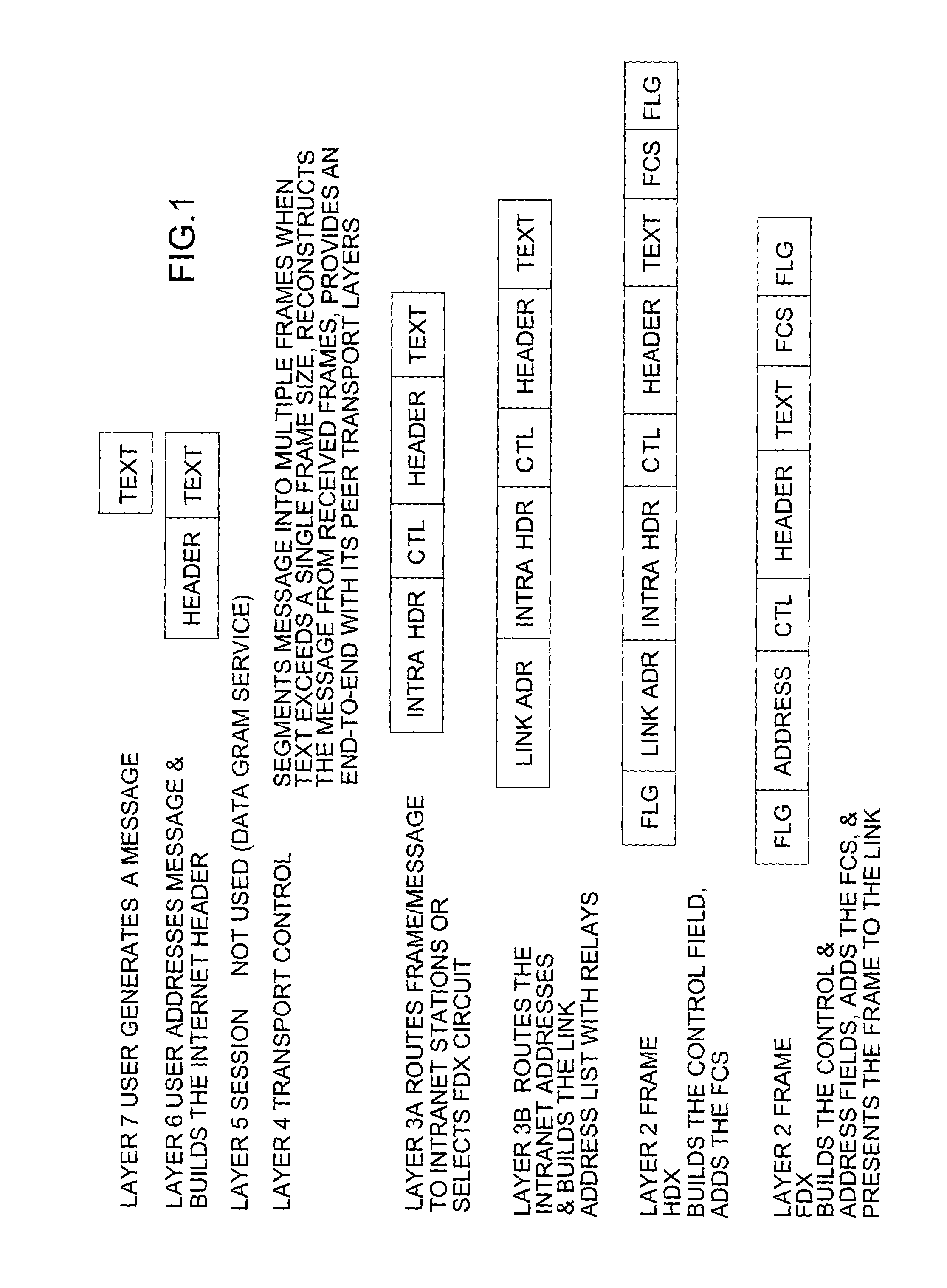
In computer networking, the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is one of the core members of the Internet protocol suite. The protocol was designed by David P. Reed in 1980 and formally defined in RFC 768. With UDP, computer applications can send messages, in this case referred to as datagrams, to other hosts on an Internet Protocol (IP) network. Prior communications are not required in order to set up communication channels or data paths.
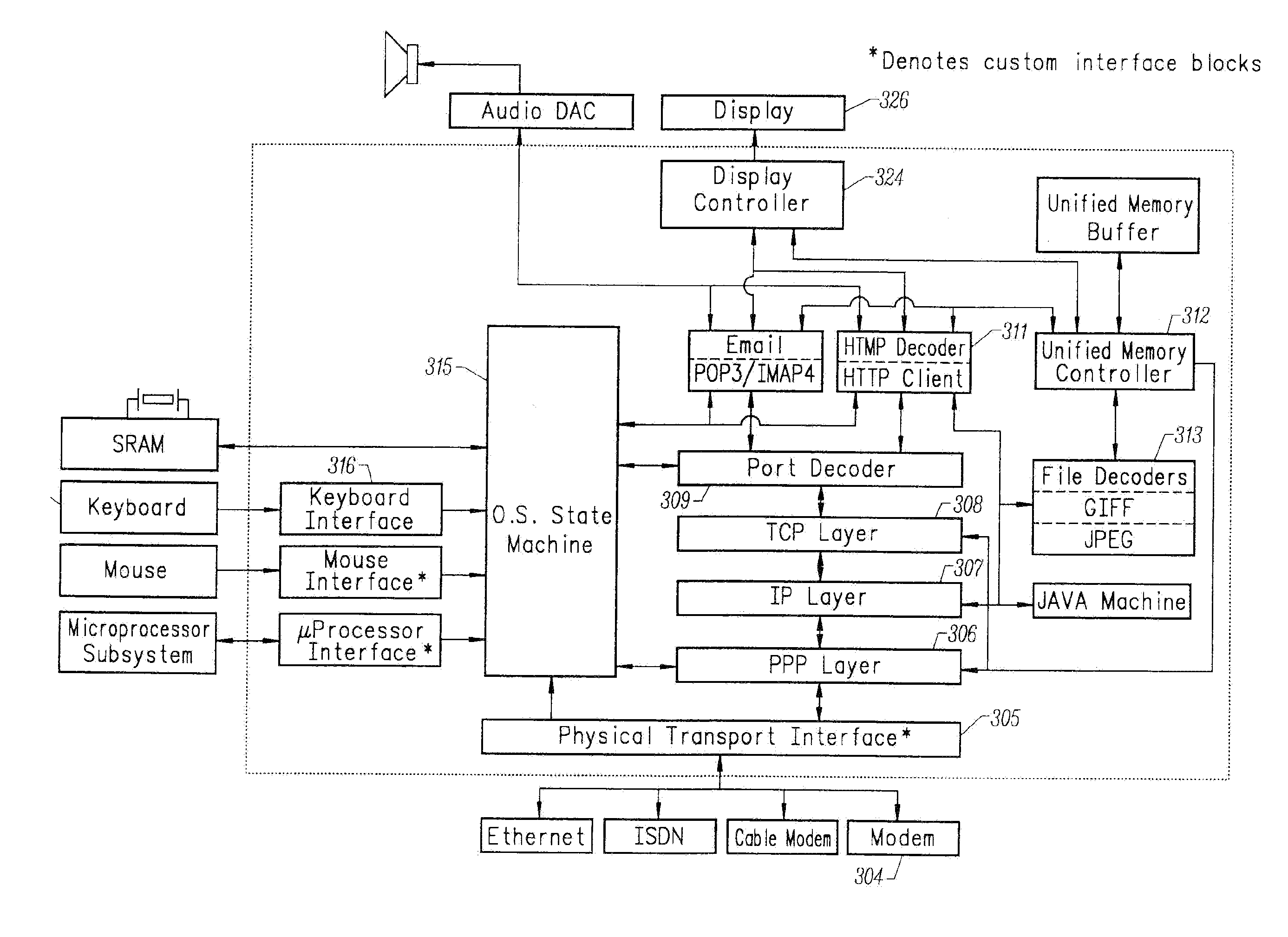
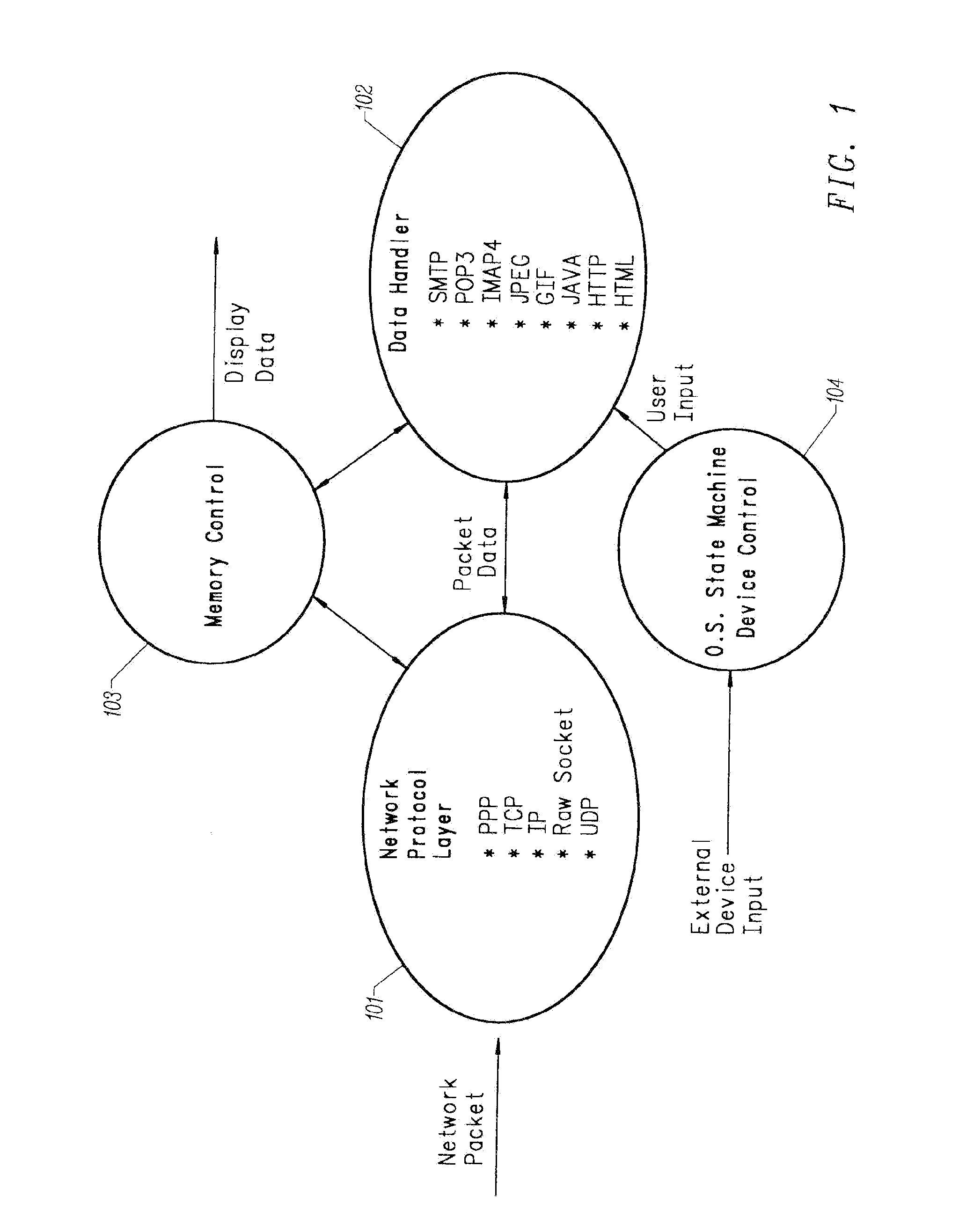
Multiple network protocol encoder/decoder and data processor
InactiveUS6034963AReduce system costLow costTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationRaw socketByte
A multiple network protocol encoder / decoder comprising a network protocol layer, data handler, O.S. State machine, and memory manager state machines implemented at a hardware gate level. Network packets are received from a physical transport level mechanism by the network protocol layer state machine which decodes network protocols such as TCP, IP, User Datagram Protocol (UDP), PPP, and Raw Socket concurrently as each byte is received. Each protocol handler parses and strips header information immediately from the packet, requiring no intermediate memory. The resulting data are passed to the data handler which consists of data state machines that decode data formats such as email, graphics, Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), Java, and Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). Each data state machine reacts accordingly to the pertinent data, and any data that are required by more than one data state machine is provided to each state machine concurrently, and any data required more than once by a specific data state machine, are placed in a specific memory location with a pointer designating such data (thereby ensuring minimal memory usage). Resulting display data are immediately passed to a display controller. Any outgoing network packets are created by the data state machines and passed through the network protocol state machine which adds header information and forwards the resulting network packet via a transport level mechanism.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
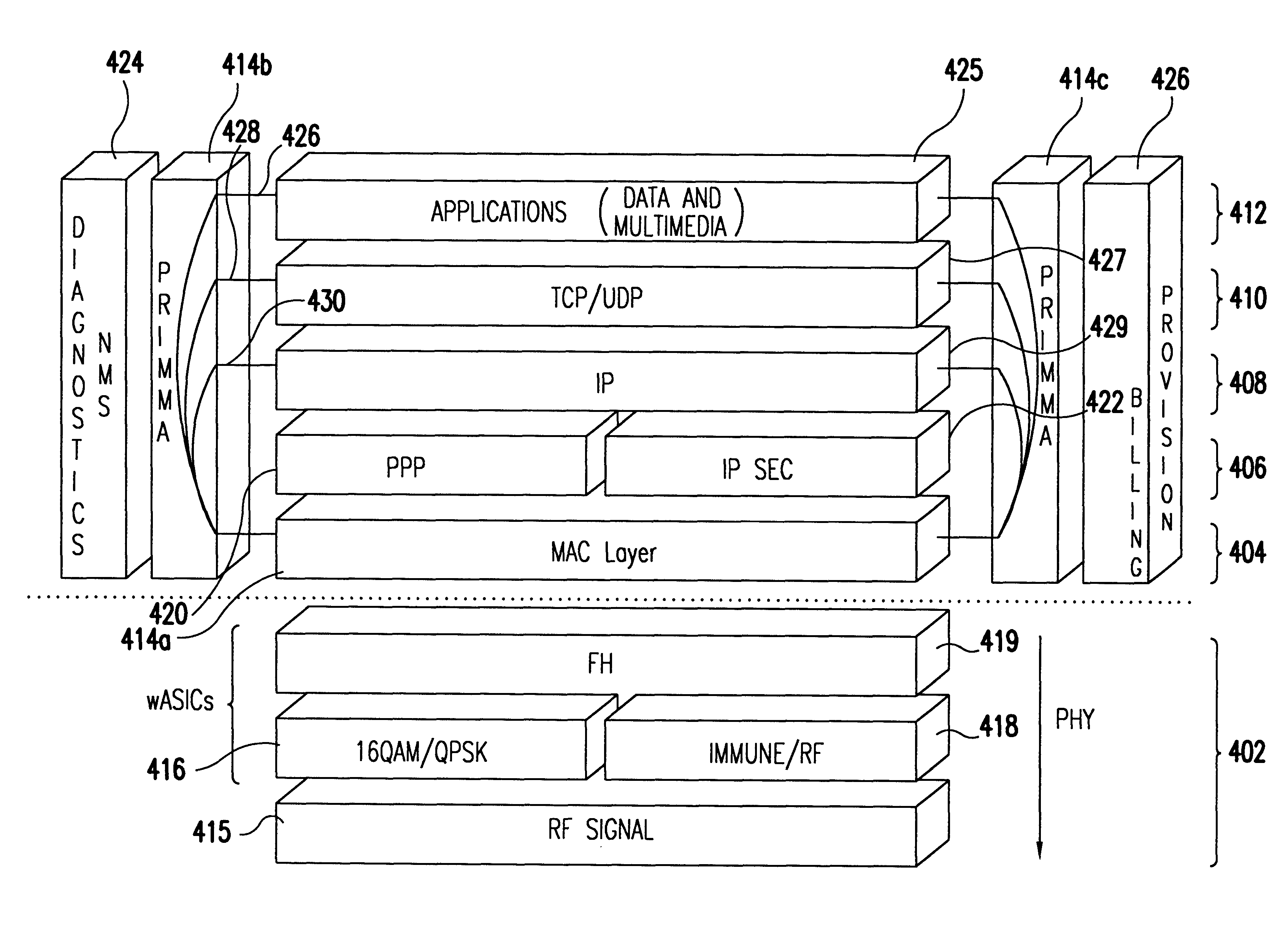
Transmission control protocol/internet protocol (TCP/IP) packet-centric wireless point to multi-point (PTMP) transmission system architecture
InactiveUS6862622B2Special service provision for substationError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransport systemWorkstation
A packet-centric wireless point to multi-point telecommunications system includes: a wireless base station communicating via a packet-centric protocol to a first data network; one or more host workstations communicating via the packet-centric protocol to the first data network; one or more subscriber customer premise equipment (CPE) stations coupled with the wireless base station over a shared bandwidth via the packet-centric protocol over a wireless medium; and one or more subscriber workstations coupled via the packet-centric protocol to each of the subscriber CPE stations over a second network. The packet-centric protocol can be transmission control protocol / internet protocol (TCP / IP). The packet-centric protocol can be a user datagram protocol / internet protocol (UDP / IP). The system can include a resource allocation means for allocating shared bandwidth among the subscriber CPE stations. The resource allocation is performed to optimize end-user quality of service (QoS). The wireless communication medium can include at least one of: a radio frequency (RF) communications medium; a cable communications medium; and a satellite communications medium. The wireless communication medium can further include a telecommunications access method including at least one of: a time division multiple access (TDMA) access method; a time division multiple access / time division duplex (TDMA / TDD) access method; a code division multiple access (CDMA) access method; and a frequency division multiple access (FDMA) access method.The first data network includes at least one of: a wireline network; a wireless network; a local area network (LAN); and a wide area network (WAN). The second network includes at least one of: a wireline network; a wireless network; a local area network (LAN); and a wide area network (WAN).
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
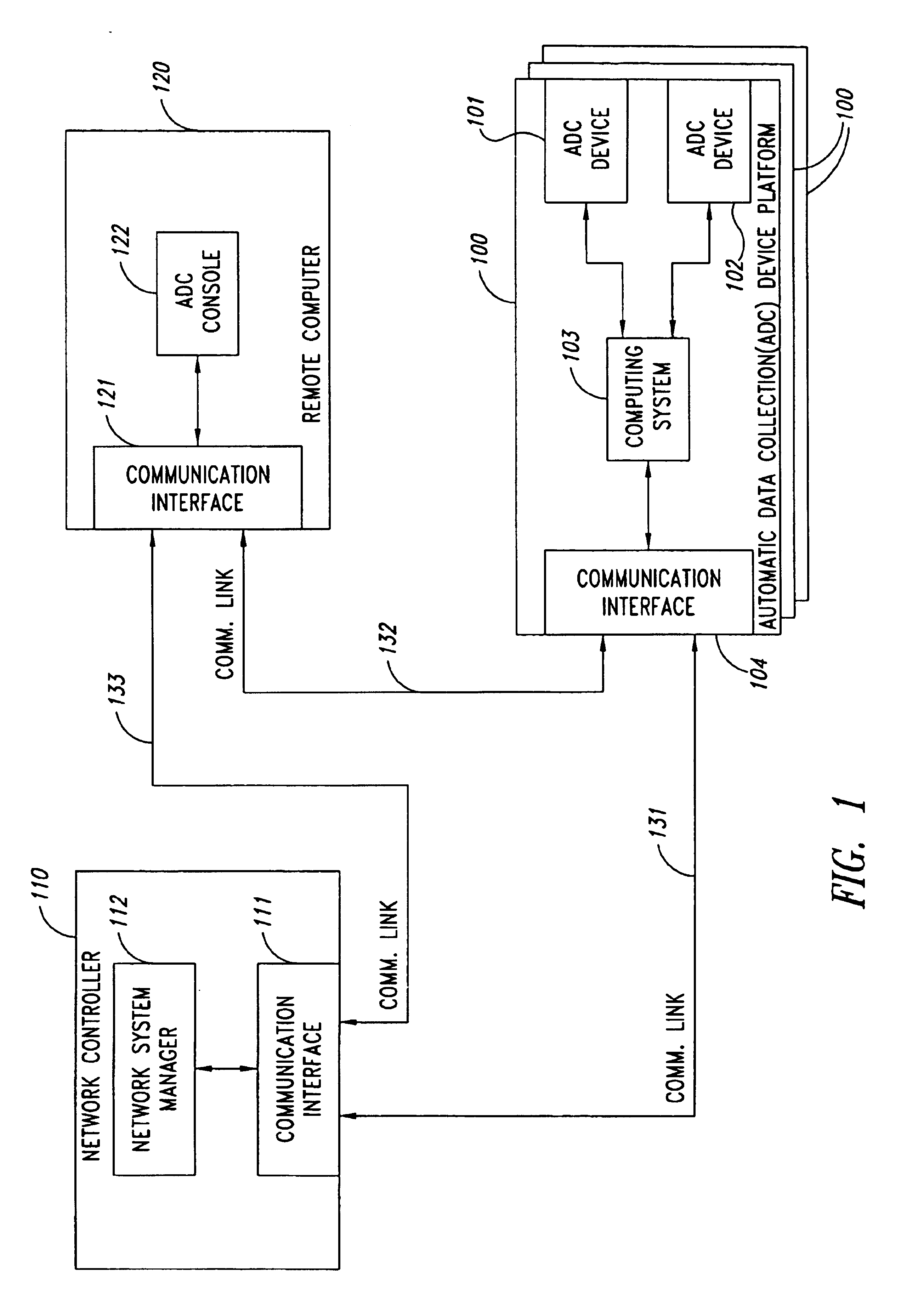
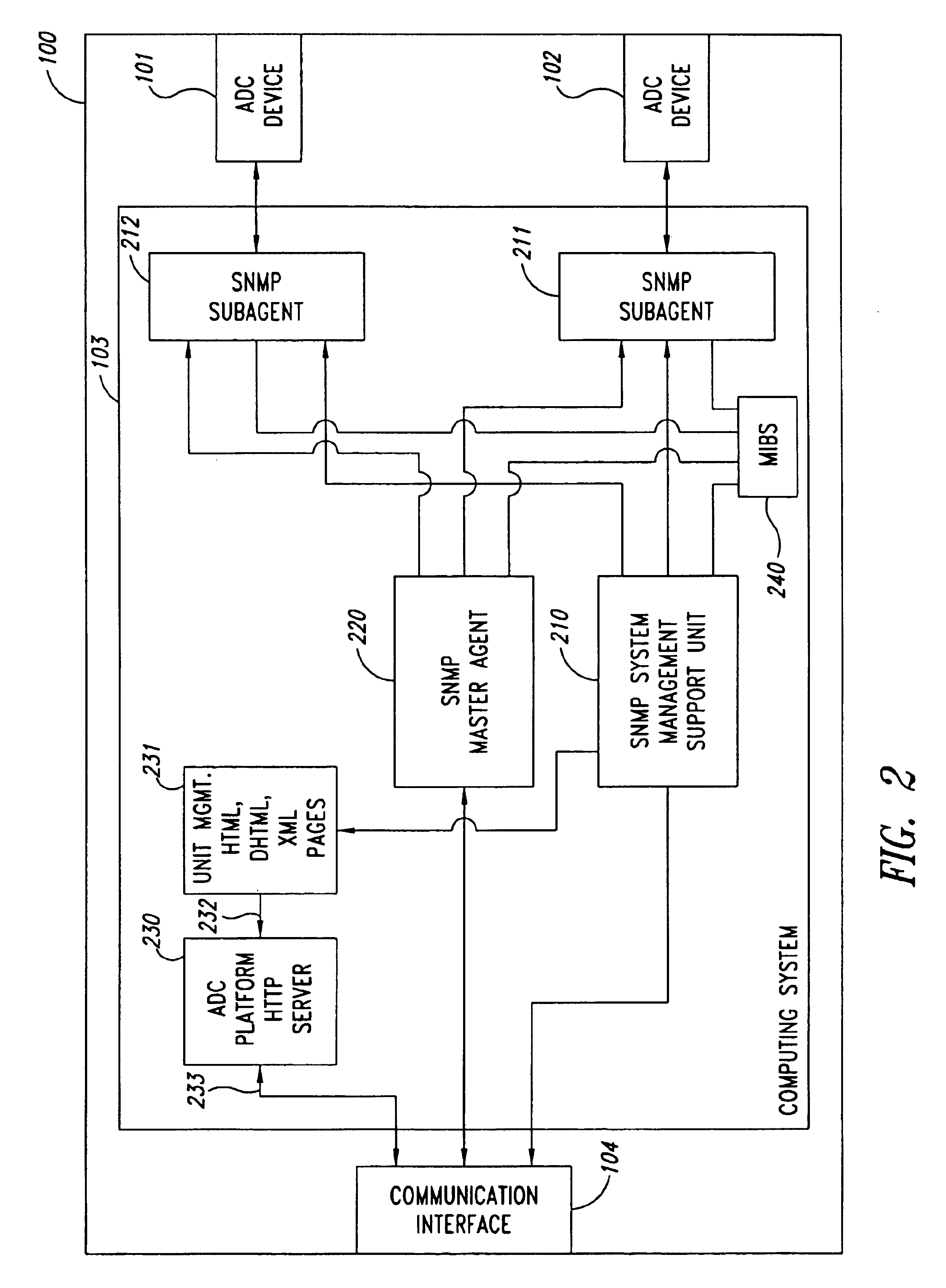
Remote anomaly diagnosis and reconfiguration of an automatic data collection device platform over a telecommunications network
InactiveUS6857013B2Detecting faulty hardware by remote testDigital computer detailsTelecommunications linkExtensible markup
Owner:INTERMEC IP CORP
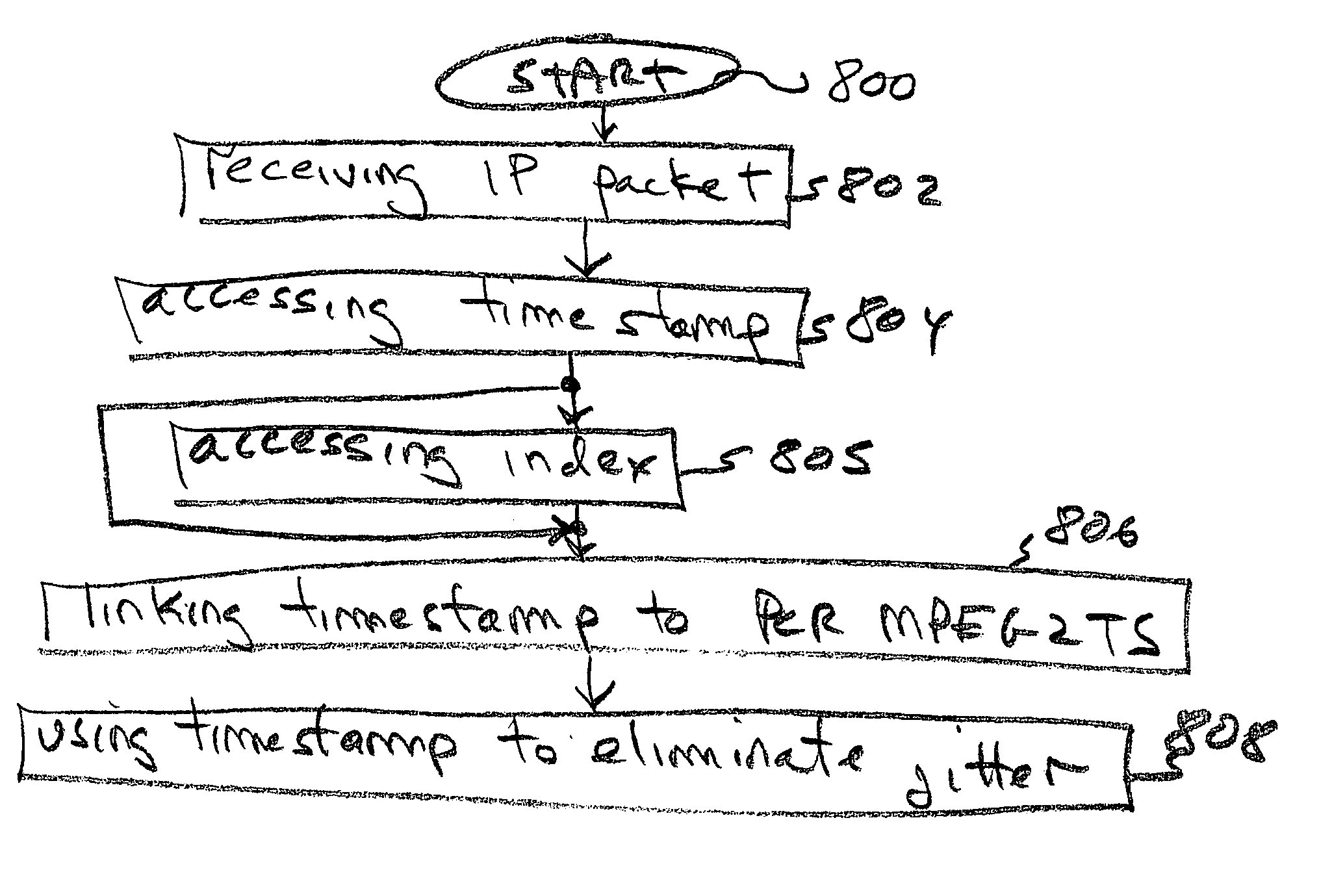
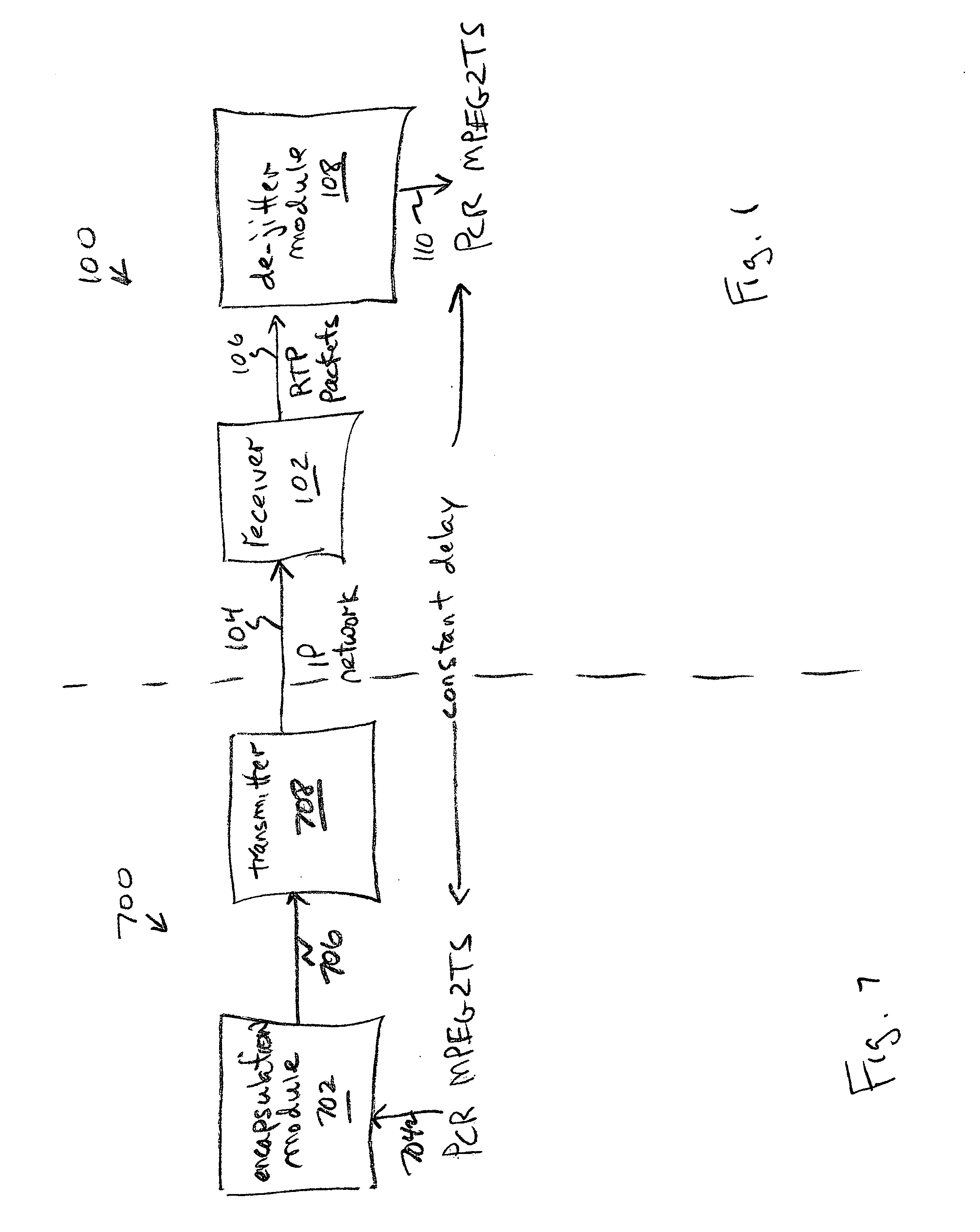
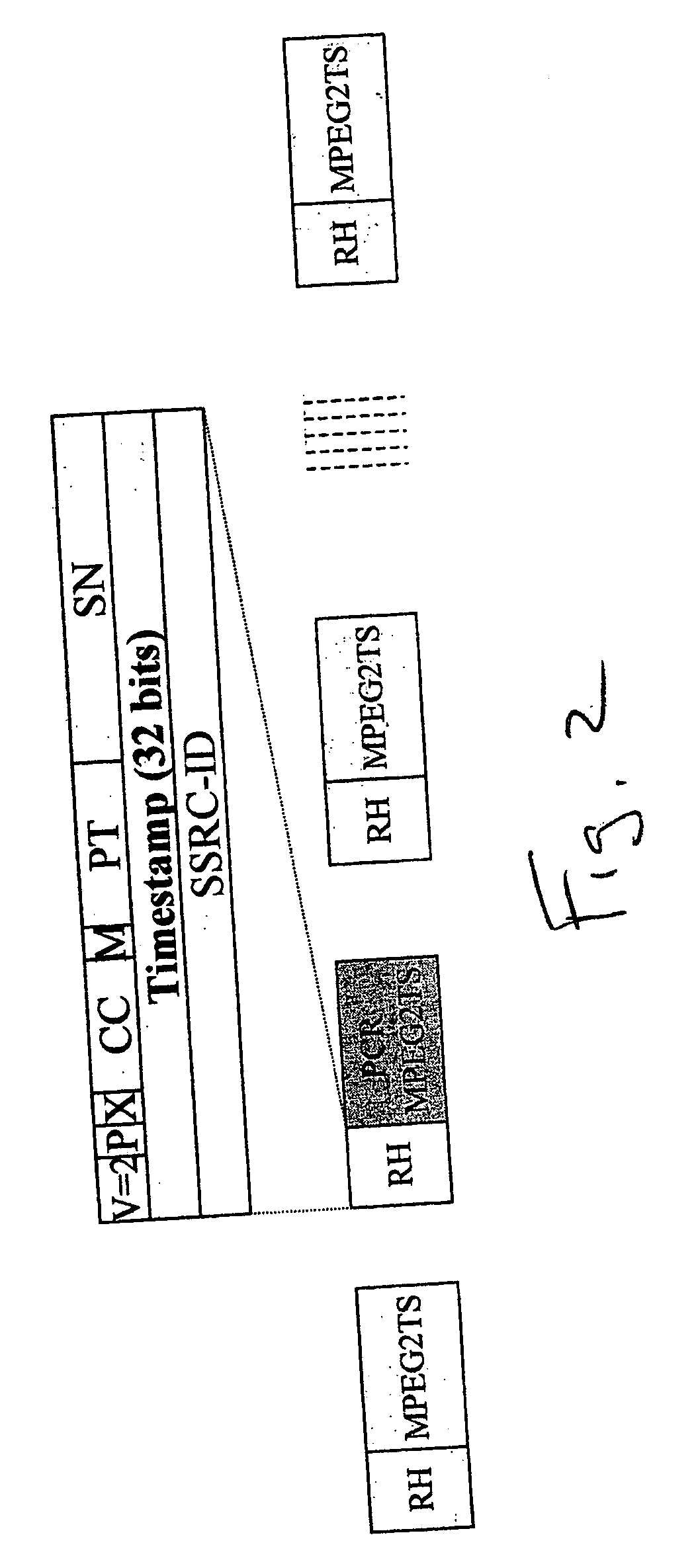
System and method for transporting MPEG2TS in RTP/UDP/IP
InactiveUS20050177643A1Eliminate variable transmission delay jitterError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsProgram clock referenceNanosecond
Systems and methods are provided for receiving and transmitting an MPEG2 transport stream (TS) in a real-time protocol (RTP) / user datagram protocol (UDP) / Internet protocol (IP) packet. The receiving method comprises: receiving an IP packet via an IP network, having a variable transmission delay; accessing a timestamp carried in a RTP packet; linking the timestamp with a program clock reference (PCR) MPEG2TS carried in the RTP packet payload; and, using the timestamp to eliminate variable transmission delay jitter, associated with the PCR MPEG2TS. In one aspect of the method, the timestamp has a resolution of greater than 500 nanoseconds (ns), so that the variable transmission delay jitter, associated with the PCR MPEG2TS can be reduced to a jitter of less than 500 ns.
Owner:SHARP KK
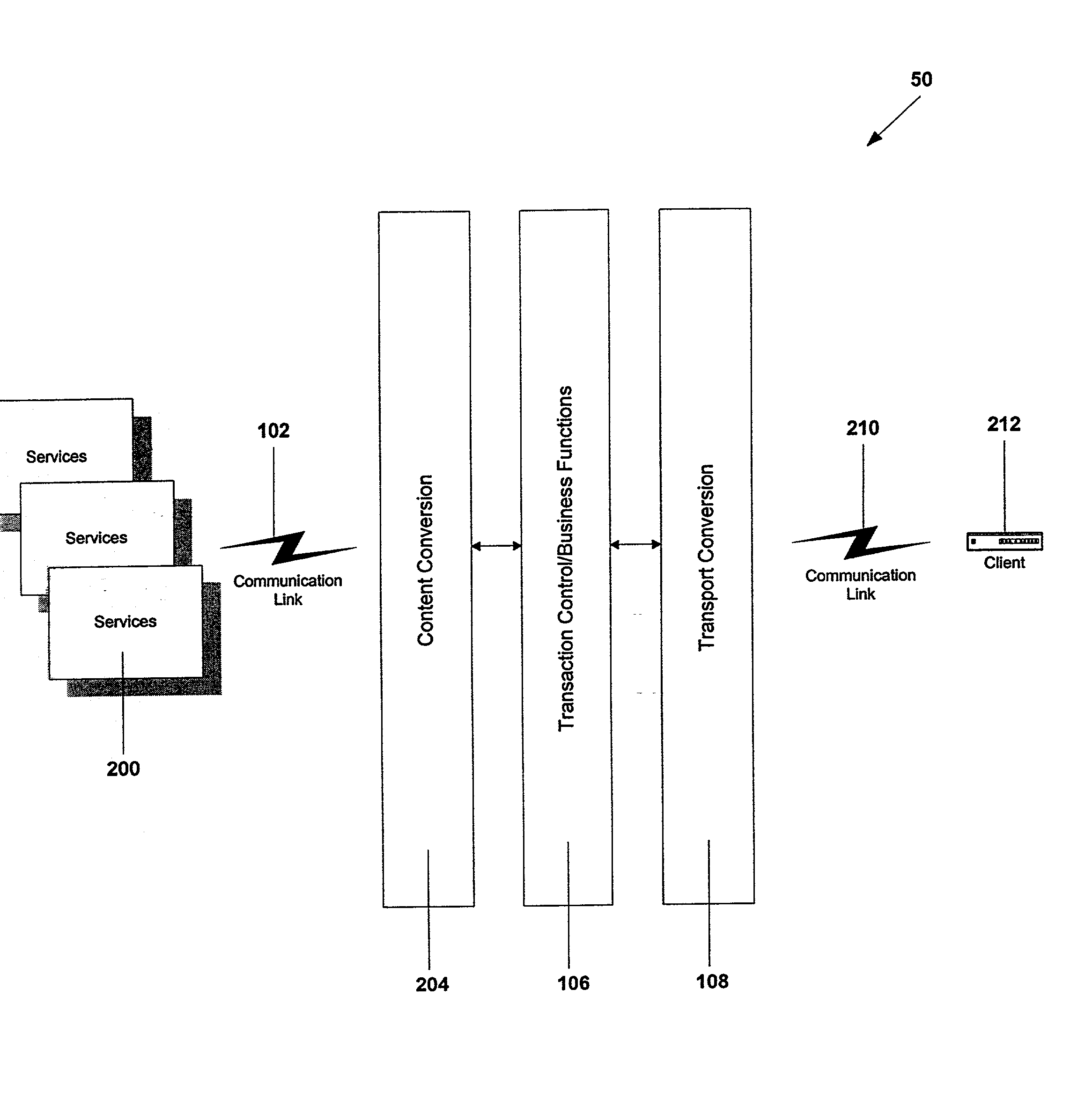
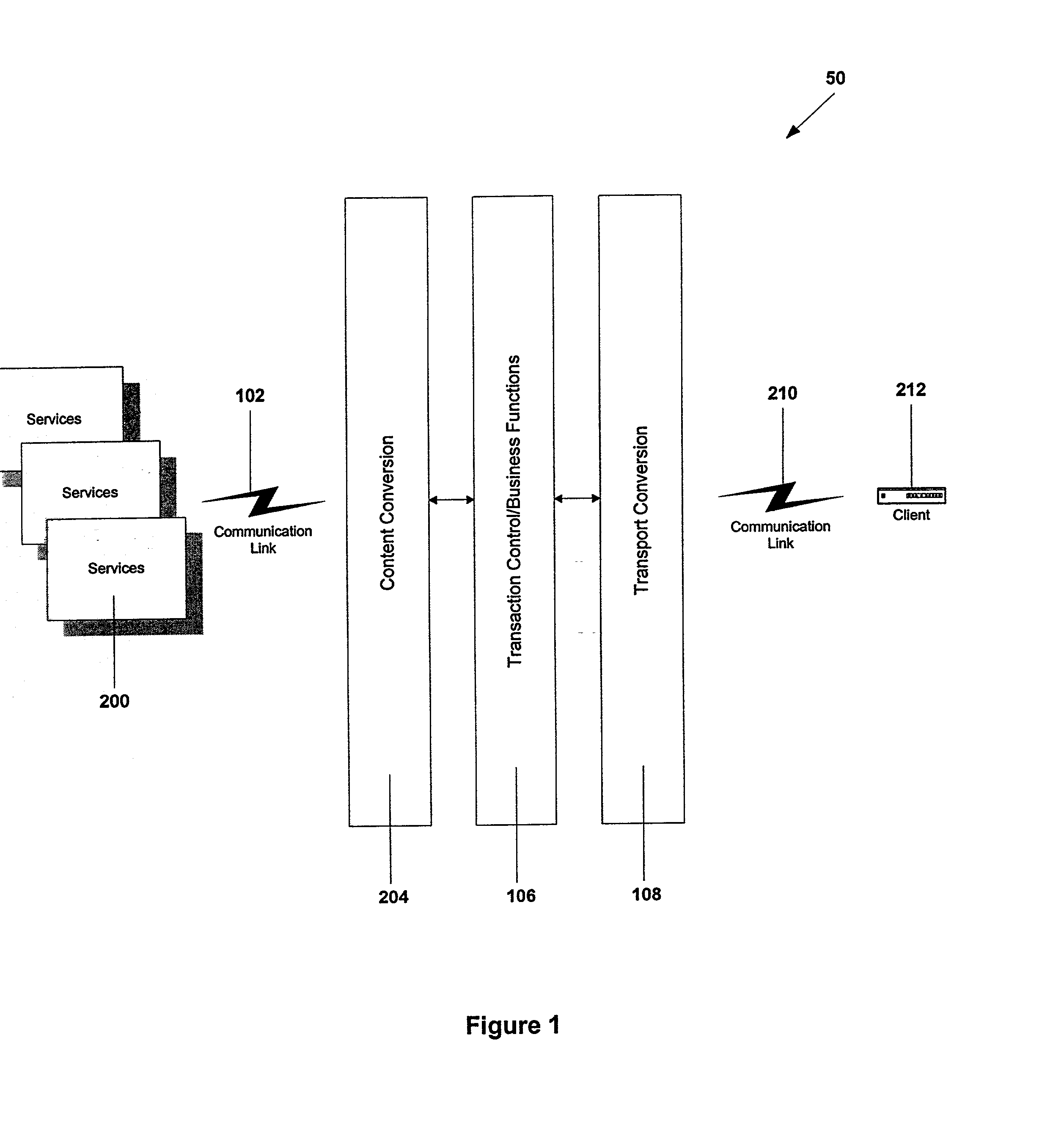
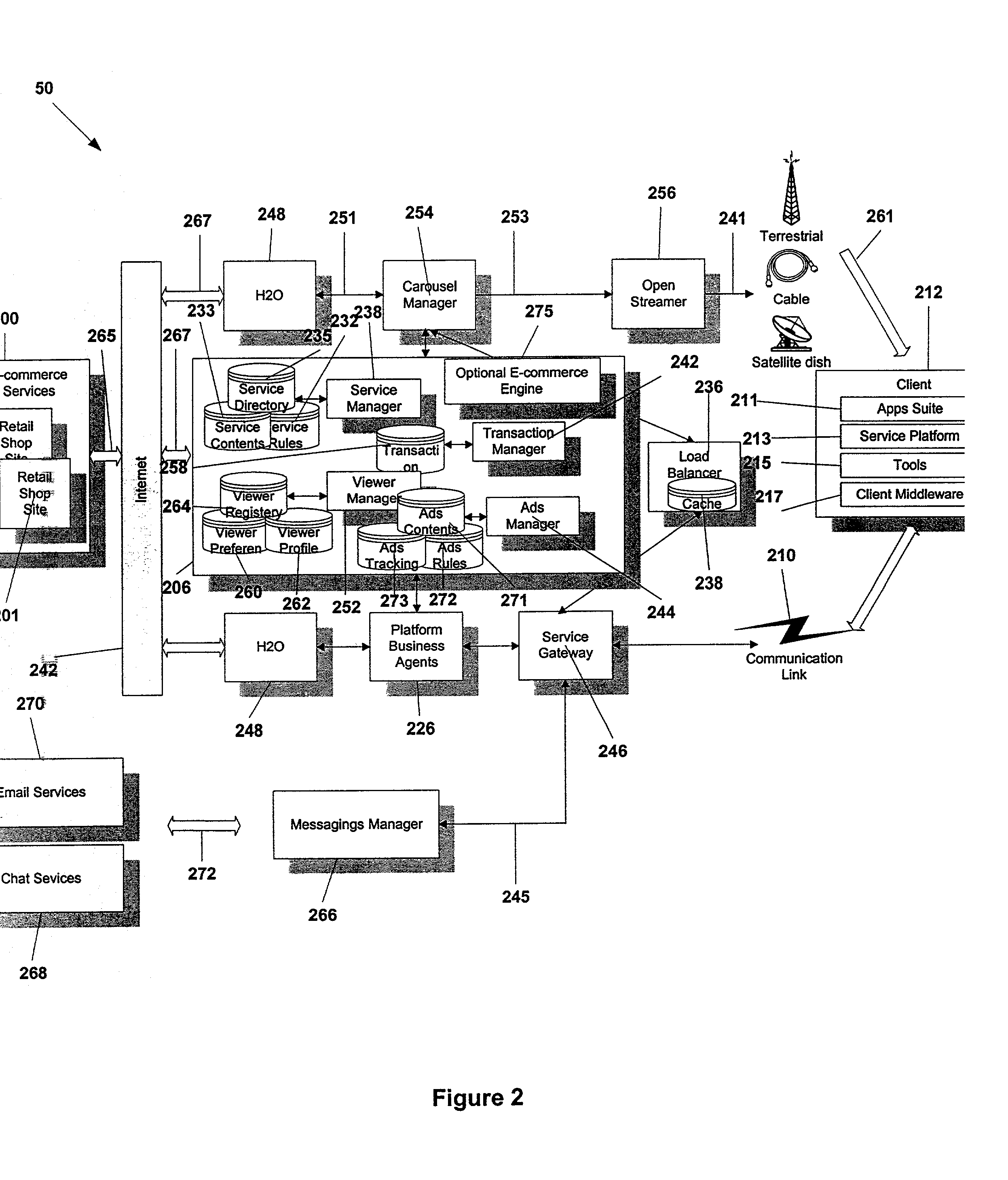
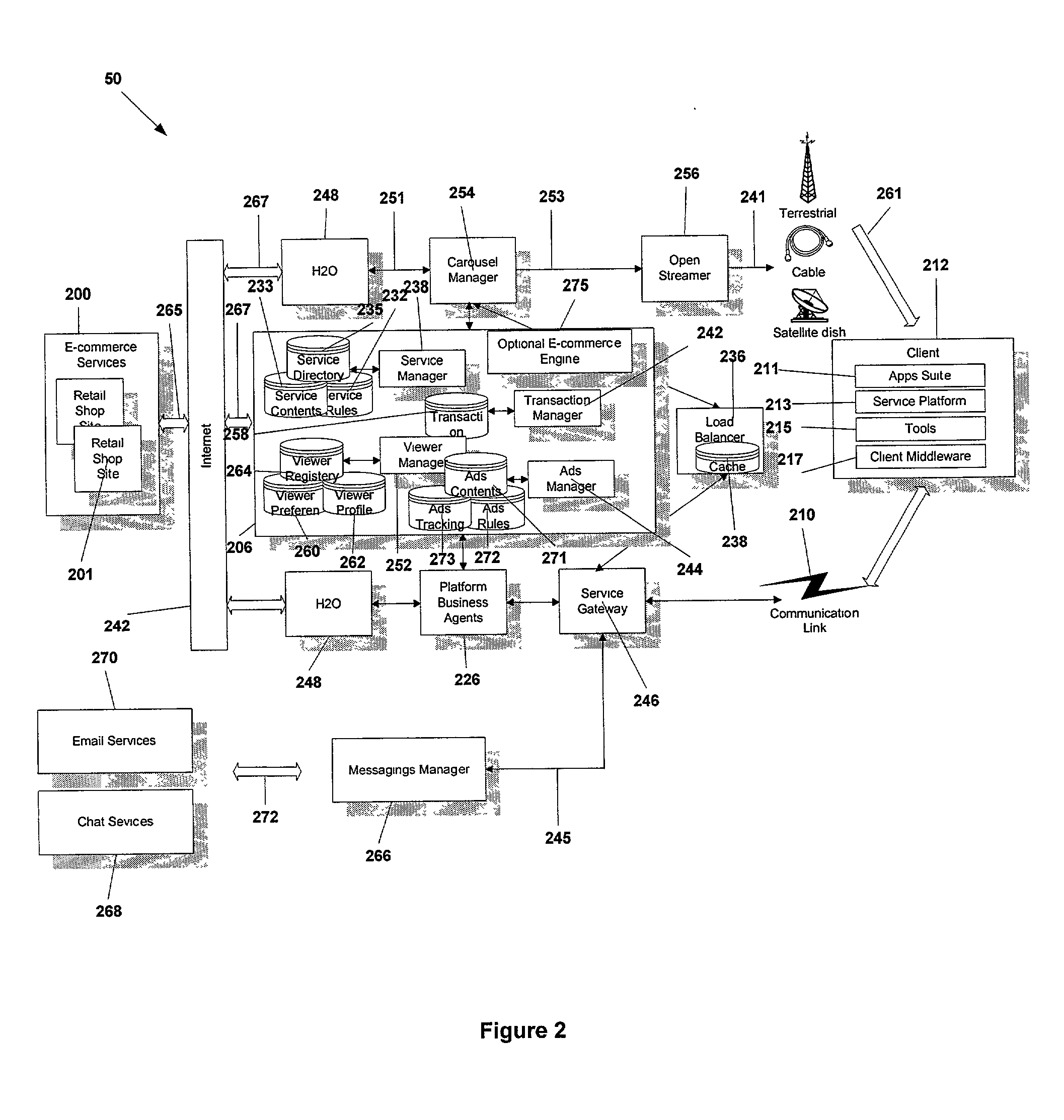
Service gateway for interactive television
ActiveUS20020108121A1Easy to handleSimplify communicationAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsMultiple digital computer combinationsData compressionTelecommunications link
A service gateway provides a proxy between a client protocol and a plurality of standard communication protocols. The service gateway provides asymmetrical routing, data compression and encryption to optimize client processing power and communication link bandwidth. The service gateway enables content translation between clients and service providers. The service gateway keeps track of client available memory and sequence numbers in messages to generate error codes when applicable. A store and forward message capability is provided along with abstract session identifiers. The service gateway supports user datagram protocol.
Owner:OPEN TV INC
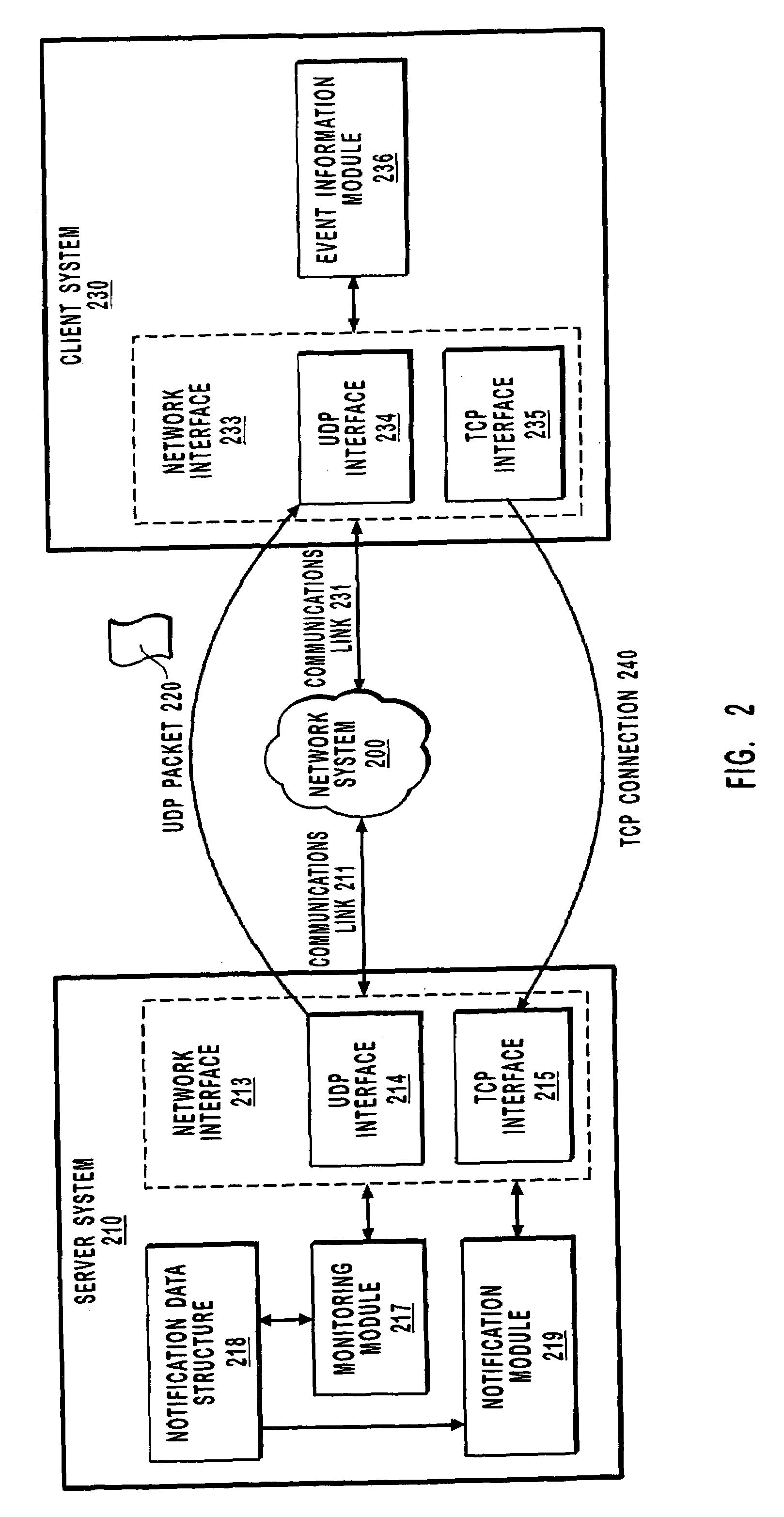
Efficiently sending event notifications over a computer network
InactiveUS6999992B1Reduce data volumeEliminate overheadMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionApplication softwareClient-side
A method for efficiently sending notifications over a network. A client system requests to be notified when an event occurs. A server system receives the requests and monitors for the occurrence of the event. When the event occurs a single packet using a connectionless protocol (such as User Datagram Protocol) is sent to the client to notify the client of the occurrence of the event. Using a connectionless protocol to send notification reduces the overall amount of data on the network and thus reduces network congestion and the processing capacity of the server and client. When the client system receives notification an attempt to establish a connection using as connection-oriented protocol is executed. Additional data associated with the occurrence of the event is transferred over the connection. The server may repeatedly send notification using a connectionless protocol until a connection using a connection-oriented protocol is established. The server may send notification that notifies the client of the occurrence of multiple events simultaneously within a single packet. The server may also notify multiple applications of the occurrence of an event using a single notification.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Service gateway for interactive television
ActiveUS20020138848A1Easy to handleSimplify communicationAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsMultiple digital computer combinationsData compressionTelecommunications link
A service gateway provides a proxy between a client protocol and a plurality of standard communication protocols. The service gateway provides asymmetrical routing, data compression and encryption to optimize client processing power and communication link bandwidth. The service gateway enables content translation between clients and service providers. The service gateway keeps track of client available memory and sequence numbers in messages to generate error codes when applicable. A store and forward message capability is provided along with abstract session identifiers. The service gateway supports user datagram protocol.
Owner:OPEN TV INC
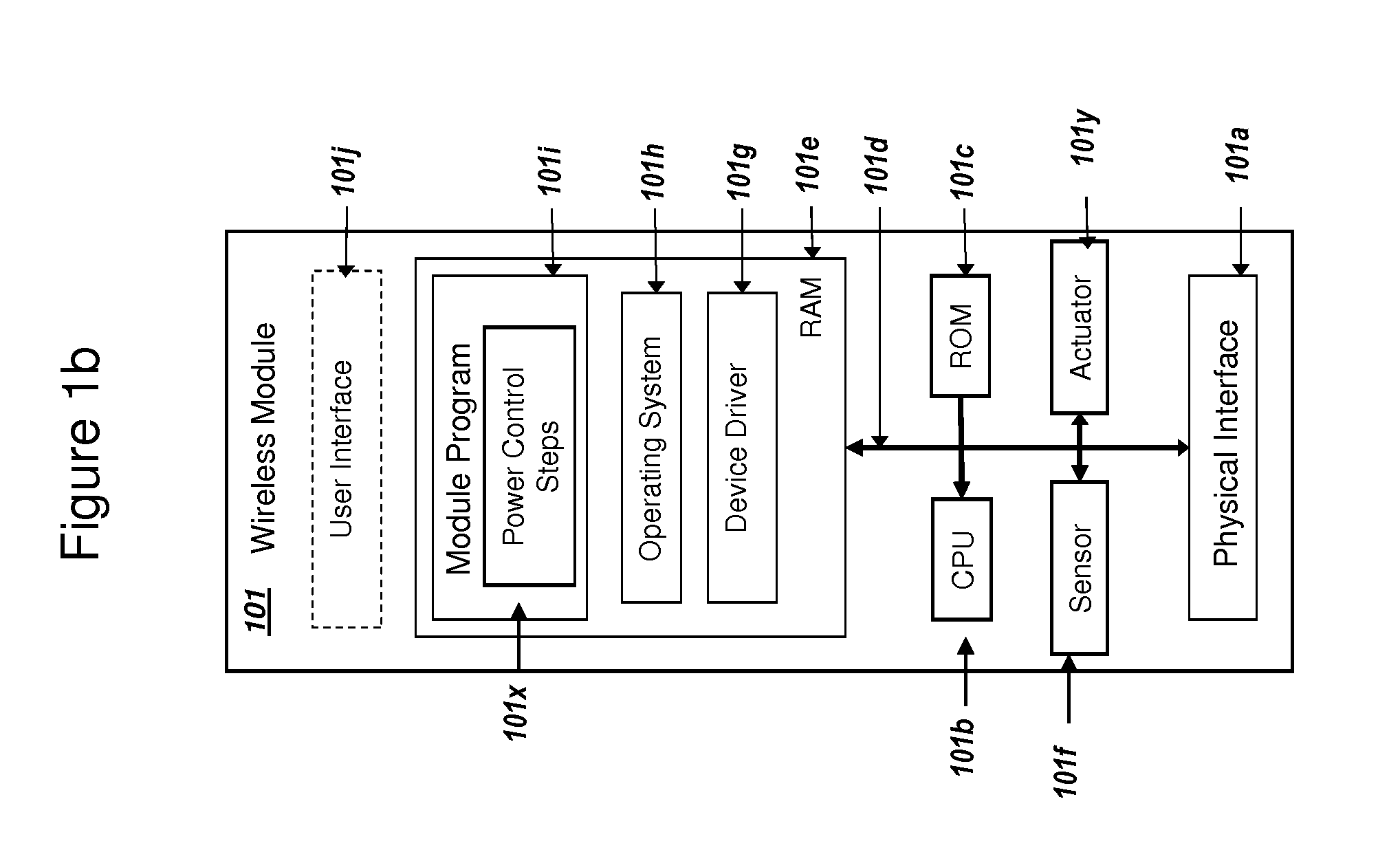
Power Management and Security for Wireless Modules in "Machine-to-Machine" Communications
ActiveUS20150071139A1Efficient power controlExtend battery lifeMultiple keys/algorithms usagePublic key for secure communicationPublic land mobile networkThe Internet
Methods and systems are provided for power management and security for wireless modules in “Machine-to-Machine” communications. A wireless module operating in a wireless network and with access to the Internet can efficiently and securely communicate with a server. The wireless network can be a public land mobile network (PLMN) or a wireless local area network (LAN). The wireless module may include a sensor and may be installed next to a monitored unit. The wireless module may utilize active states for collecting and sending data, and sleep states at other times to conserve a battery and / or energy usage. The wireless module minimize the time spent in a radio resource control (RRC) connected state. Messages between the wireless module and server can be transmitted according to a user datagram protocol (UDP). The wireless module and server can utilize public key infrastructure (PKI) for encryption and digital signatures.
Owner:NIX JOHN A +1
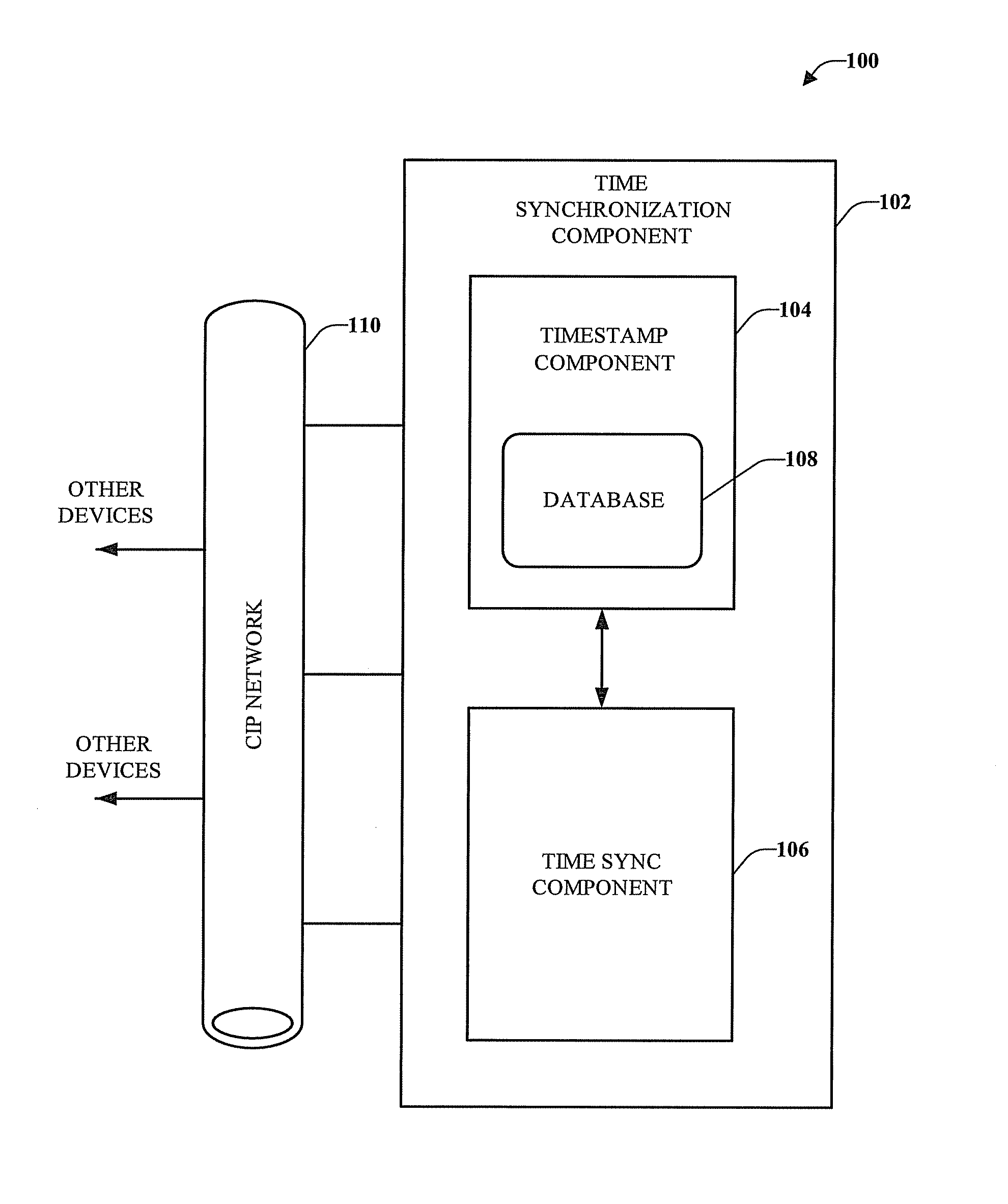
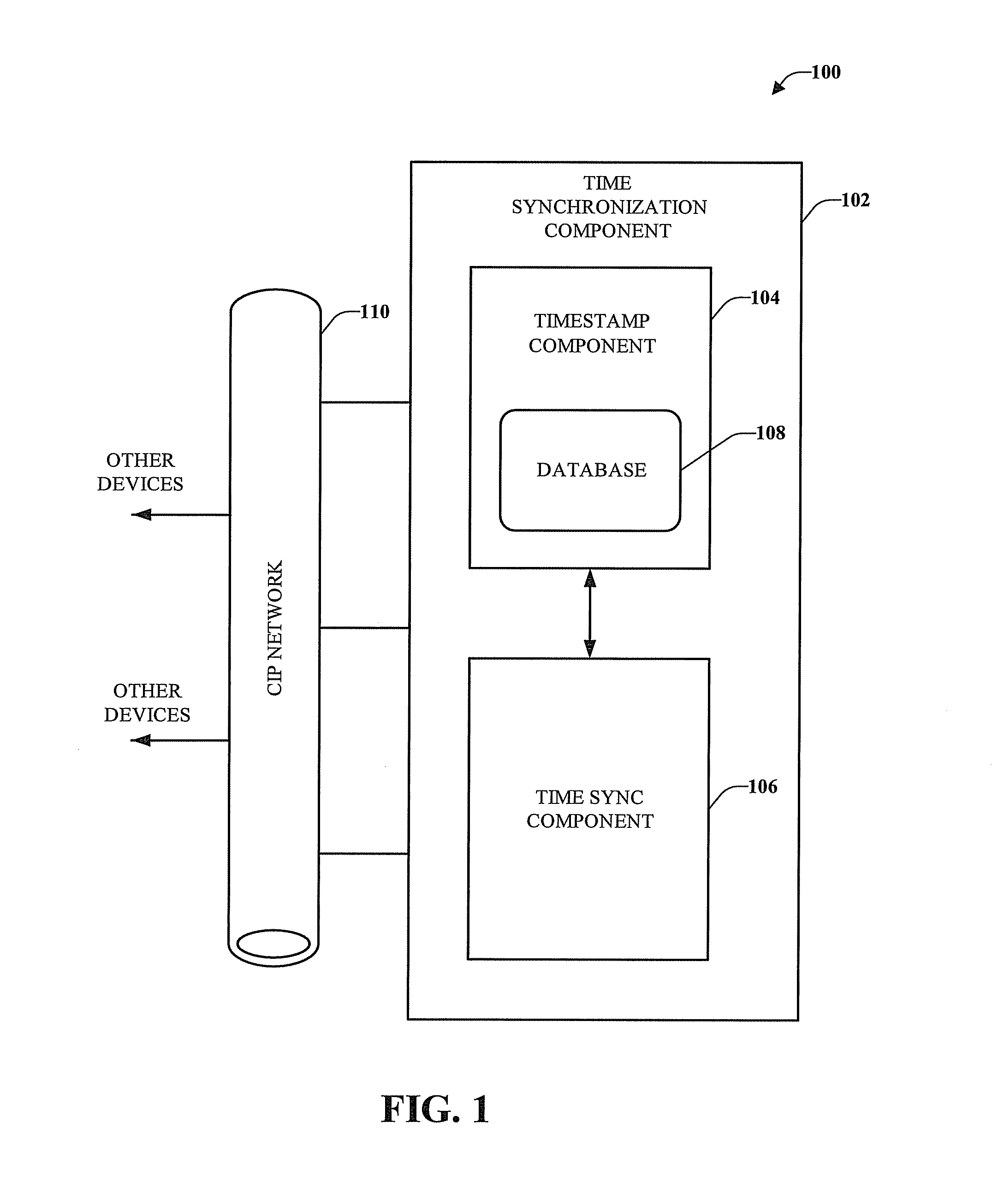
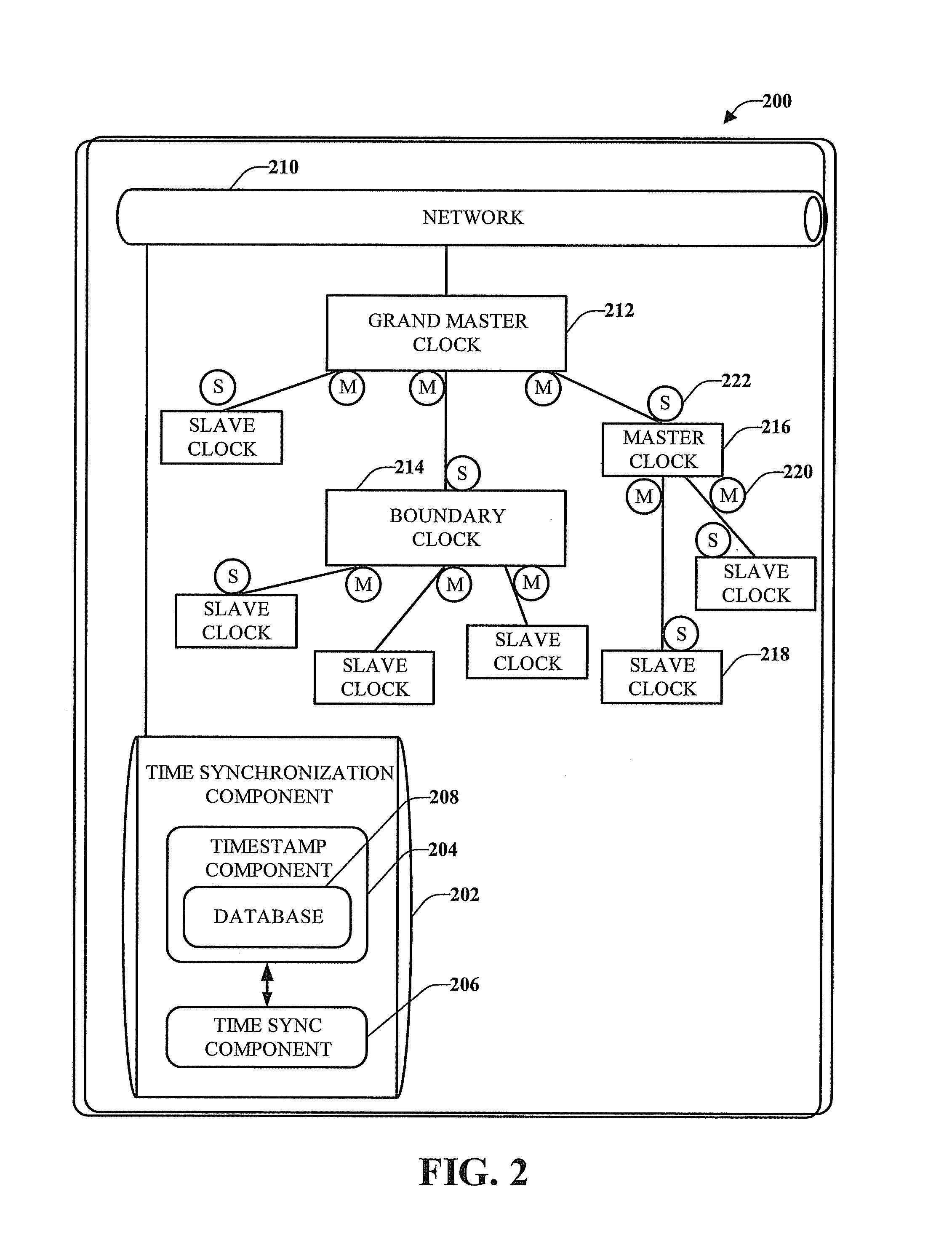
Step time change compensation in an industrial automation network
ActiveUS7447931B1Easy to handleEfficient transferSynchronous motors for clocksTime-division multiplexTime changesComputer science
One or more embodiments provide Common Industrial Protocol (CIP) based time synchronization systems and methods. The CIP Sync solution can be part of Ethernet / IP and can be based on standard UDP (User Datagram Protocol) and / or IEEE 1588 (Time Synchronization) Ethernet technology. According to an embodiment is a system that compensates for step changes in a master clock.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Transmission control protocol/internet protocol (TCP/IP) packet-centric wireless point to multi-point (PtMP) transmission system architecture
InactiveUS20050232193A1Special service provision for substationError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorQuality of serviceCode division multiple access
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Method of preserving data packet sequencing
InactiveUS6738379B1Augments UDPTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTelecommunications networkNetwork packet
A method of preserving data packet sequencing between nodes in a radio telecommunications network in which the User Datagram Protocol / Internet Protocol (UDP / IP) is utilized to communicate between the nodes of the network. Sequencing numbers are added to the headers of a plurality of data packets which are transmitted over a plurality of data transmission paths. The UDP / IP protocol is adapted with a resequencing layer which is utilized at the receiving node to resequence the packets.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
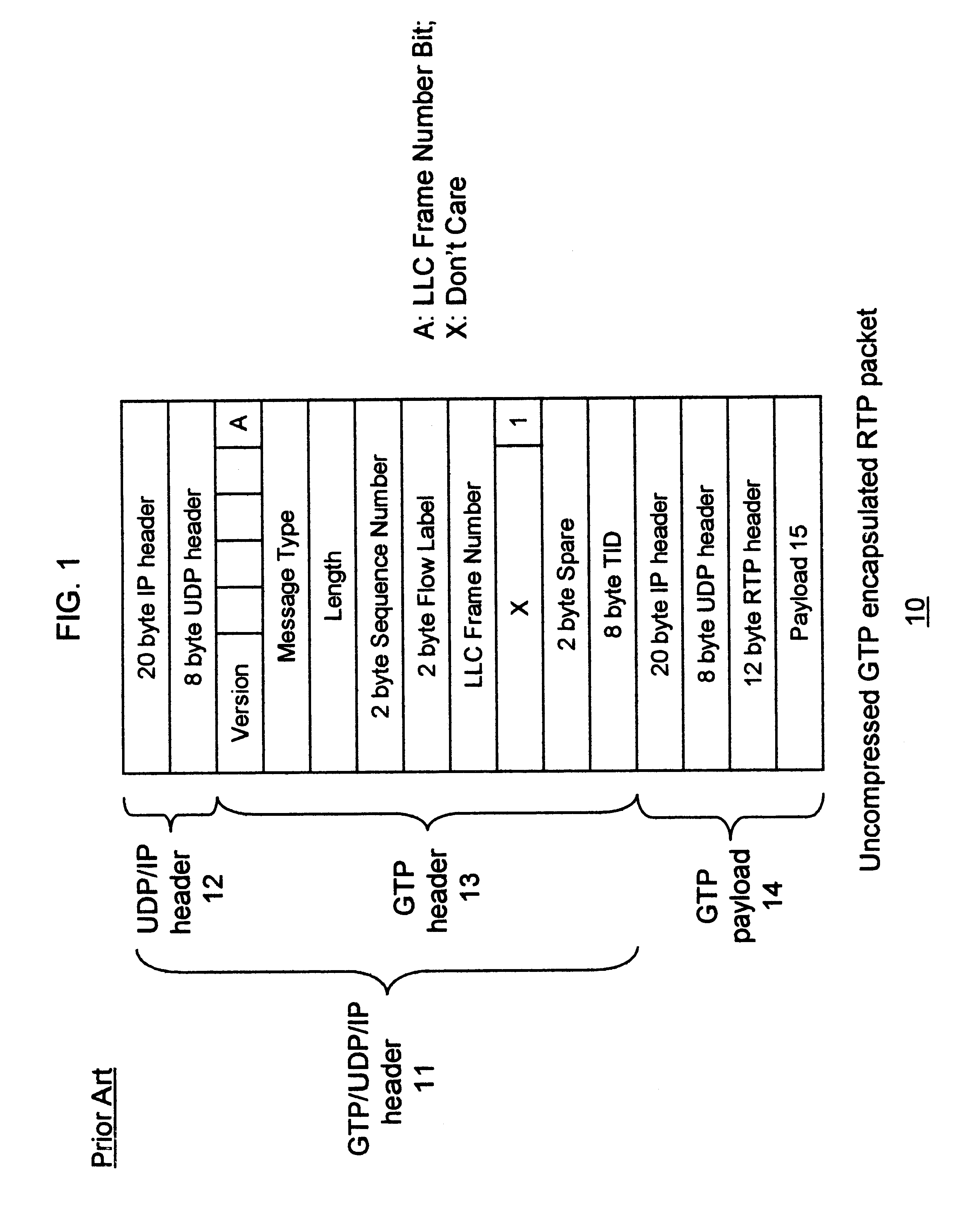
Header compression for general packet radio service tunneling protocol (GTP)-encapsulated packets
InactiveUS6839339B1Efficient transportNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesGeneral Packet Radio ServiceTime Protocol
A UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) core network supports a compression framework that provides for header compression of General Packet Radio Service Tunneling Protocol (GTP)-Encapsulated Packets. In particular; the GTP / UDP(User Datagram Protocol) / IP(Internet Protocol) header is compressed. In addition, the UMTS core network also supports RTP(Real Time Protocol) / UDP / IP header compression independent of the GTP / UDP / IP header compression.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
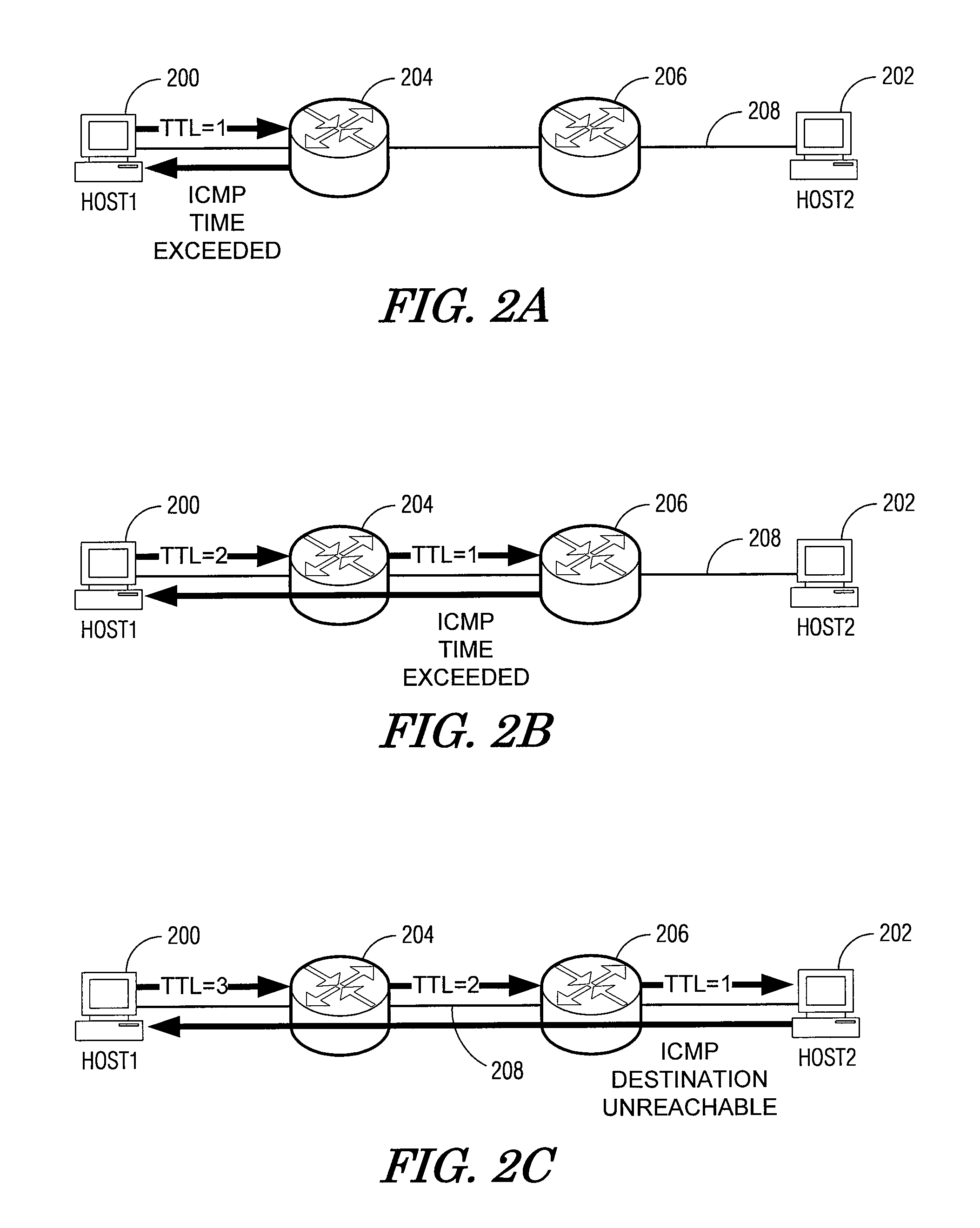
User datagram protocol traceroute probe extension
The embodiments described herein provide methods and apparatuses for implementing a User Datagram Protocol traceroute probe extension. In an example embodiment, a request to transmit a User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packet to a remote destination is received. A probe header and a probe data element is then stored in a data field of the UDP packet. The UDP packet is then transmitted toward the remote destination. In an example embodiment, a User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packet is received and it is determined whether the UDP packet includes a probe data structure. When the determination is affirmative, the probe data structure is processed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Gigabit Ethernet Adapter
InactiveUS20070253430A1Fast communication speedCompact solutionWide area networksRaw socketSmall form factor
A gigabit Ethernet adapter provides a provides a low-cost, low-power, easily manufacturable, small form-factor network access module which has a low memory demand and provides a highly efficient protocol decode. The invention comprises a hardware-integrated system that both decodes multiple network protocols byte-streaming manner concurrently and processes packet data in one pass, thereby reducing system memory and form factor requirements, while also eliminating software CPU overhead. A preferred embodiment of the invention comprises a plurality of protocol state machines that decode network protocols such as TCP, IP, User Datagram Protocol (UDP), PPP, Raw Socket, RARP, ICMP, IGMP, iSCSI, RDMA, and FCIP concurrently as each byte is received. Each protocol handler parses, interprets, and strips header information immediately from the packet, requiring no intermediate memory. The invention provides an internet tuner core, peripherals, and external interfaces. A network stack processes, generates and receives network packets. An internal programmable processor controls the network stack and handles any other types of ICMP packets, IGMP packets, or packets corresponding to other protocols not supported directly by dedicated hardware. A virtual memory manager is implemented in optimized, hardwired logic. The virtual memory manager allows the use of a virtual number of network connections which is limited only by the amount of internal and external memory available.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
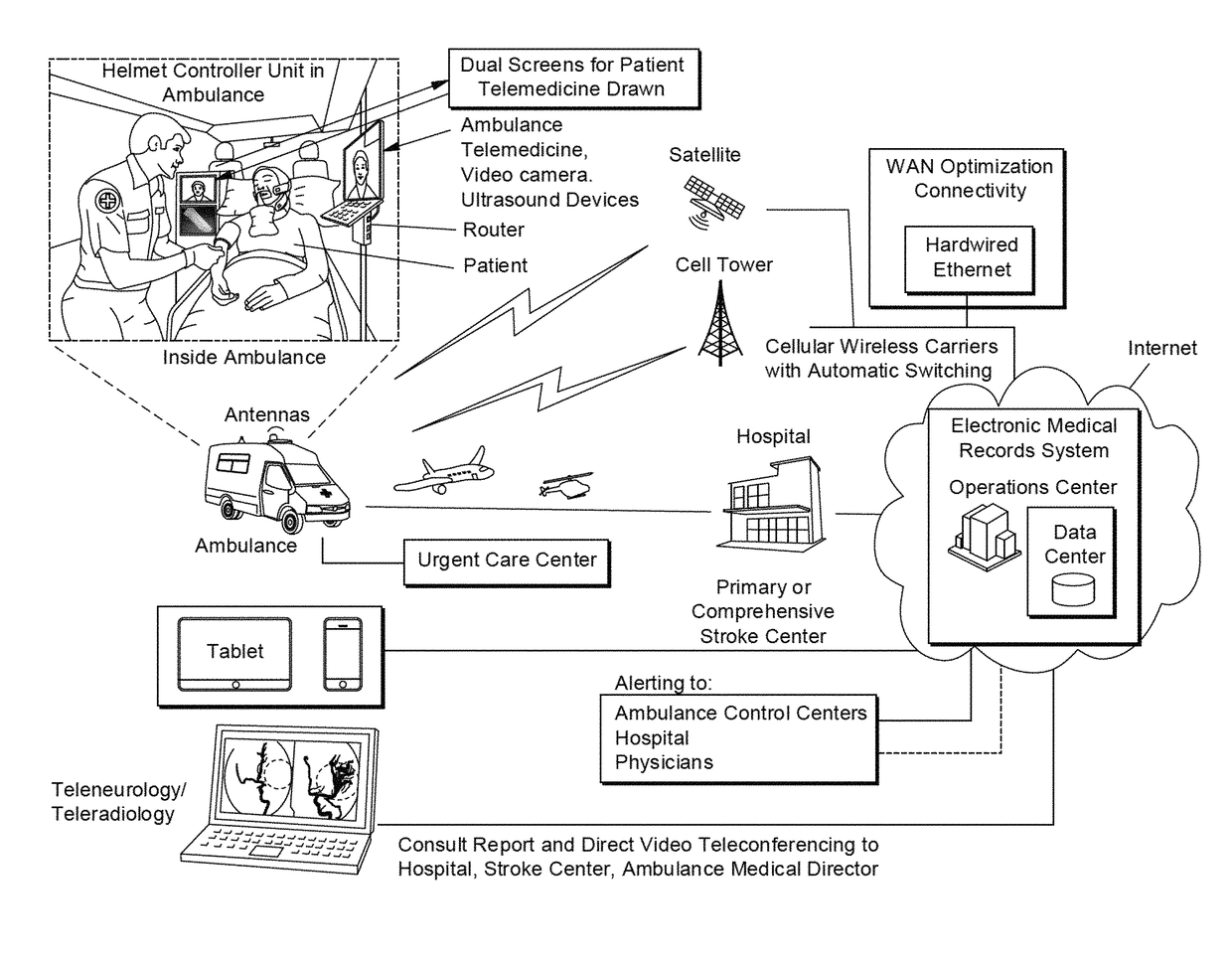
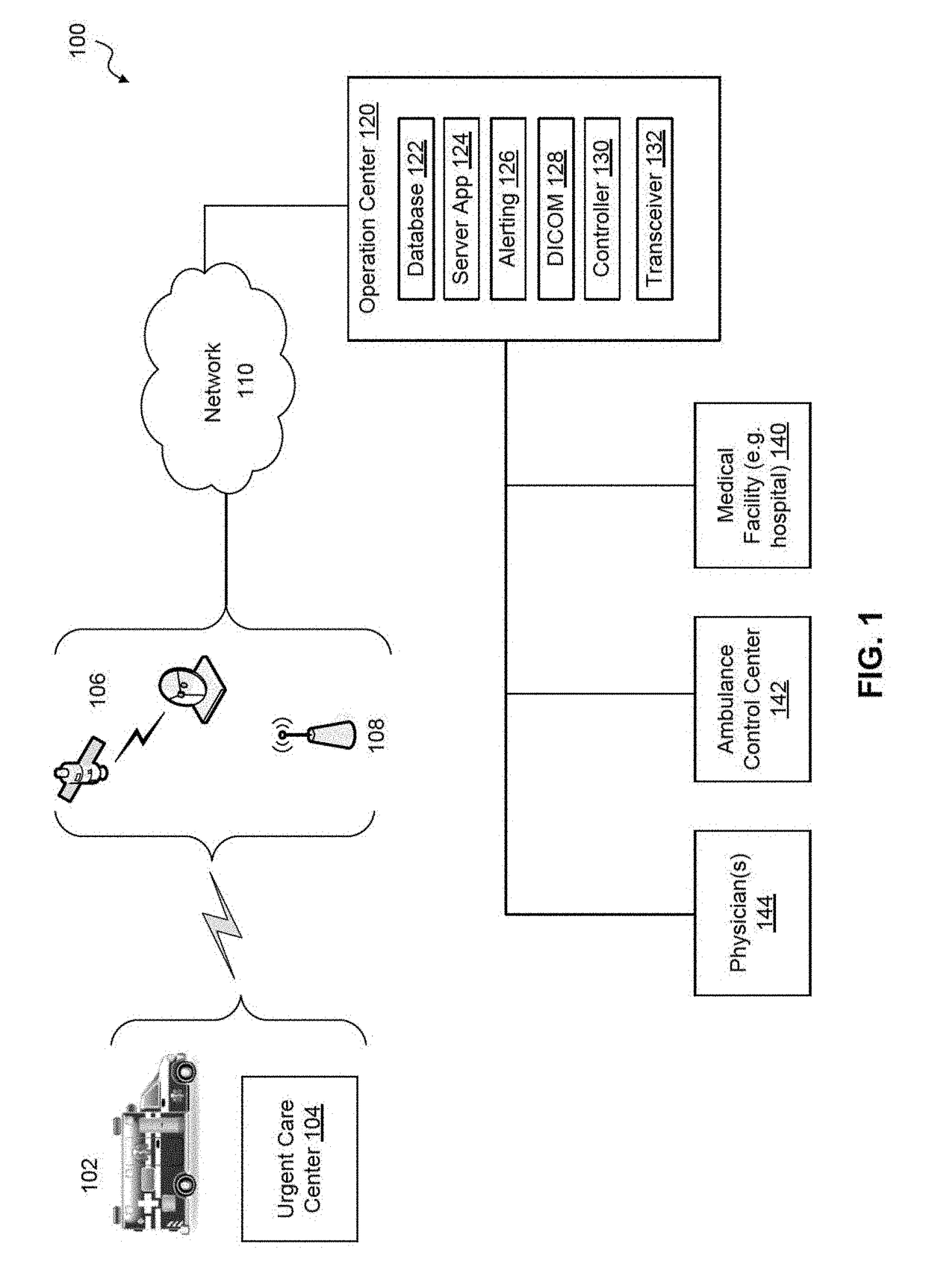
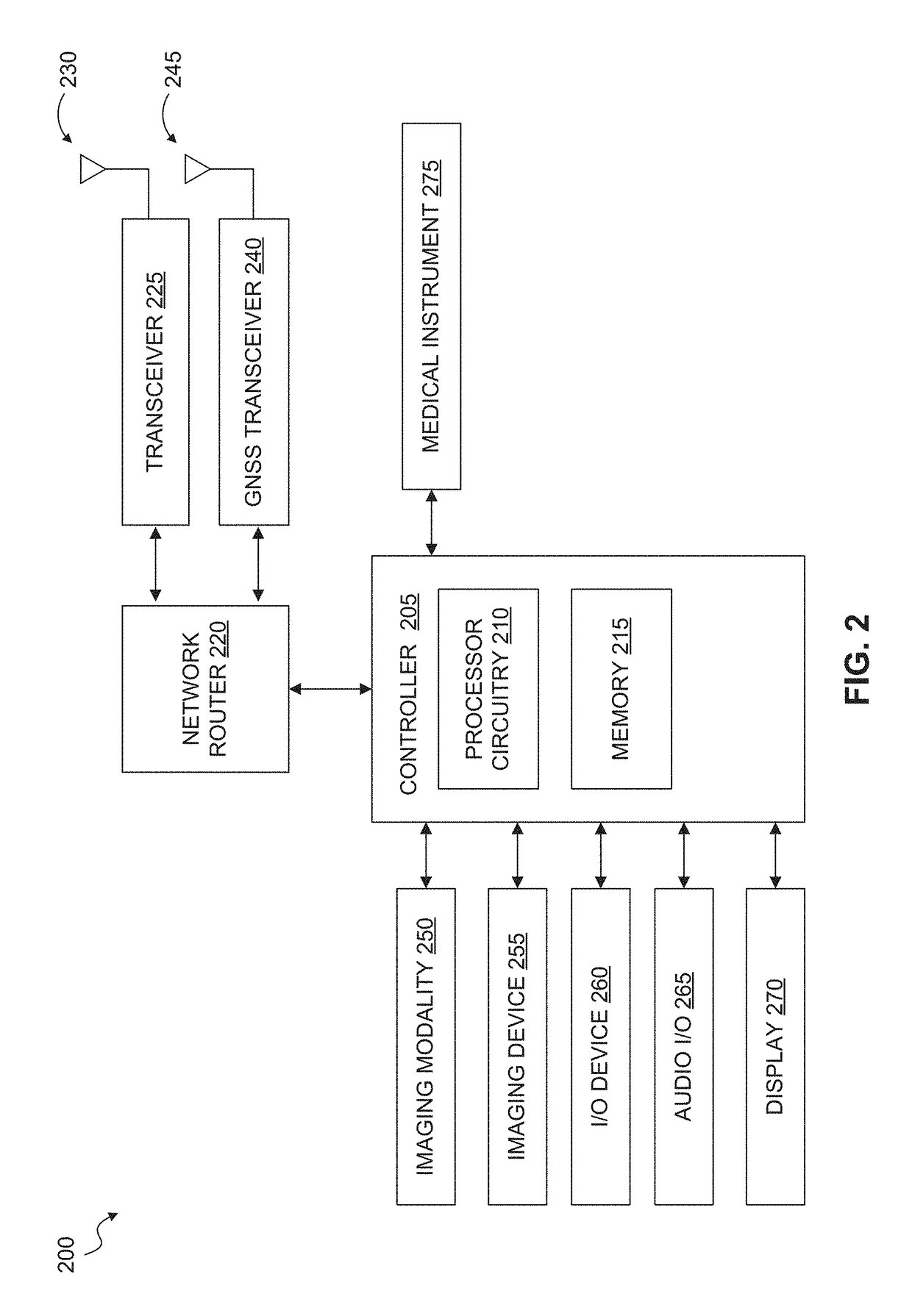
Mobile medicine communication platform and methods and uses thereof
ActiveUS20170300654A1Increase elasticityReduce packet lossError preventionSimultaneous aerial operationsComputer networkTransceiver
Telemedicine systems and methods are described. In a telemedicine system operable to communicate with a remote operations center, communications can be transmitted / received using a transceiver having an antenna. The antenna can include first and second di-pole antenna elements, the first di-pole antenna element being vertically polarized and the second di-pole antenna element being horizontally polarized. A controller of the system can establish, using the transceiver, a telemedicine session with the operations center using a Transport Morphing Protocol (TMP), the TMP being an acknowledgement-based user datagram protocol. The controller can also mask one or more transient network degradations to increase resiliency of the telemedicine session. The telemedicine system can include a 2D and 3D carotid Doppler and transcranial Doppler and / or other diagnostic devices, and provides for real-time connectivity and communication between medical personnel in an emergency vehicle and a receiving hospital for immediate diagnosis and treatment to a patient in need.
Owner:BR INVENTION HLDG LLC
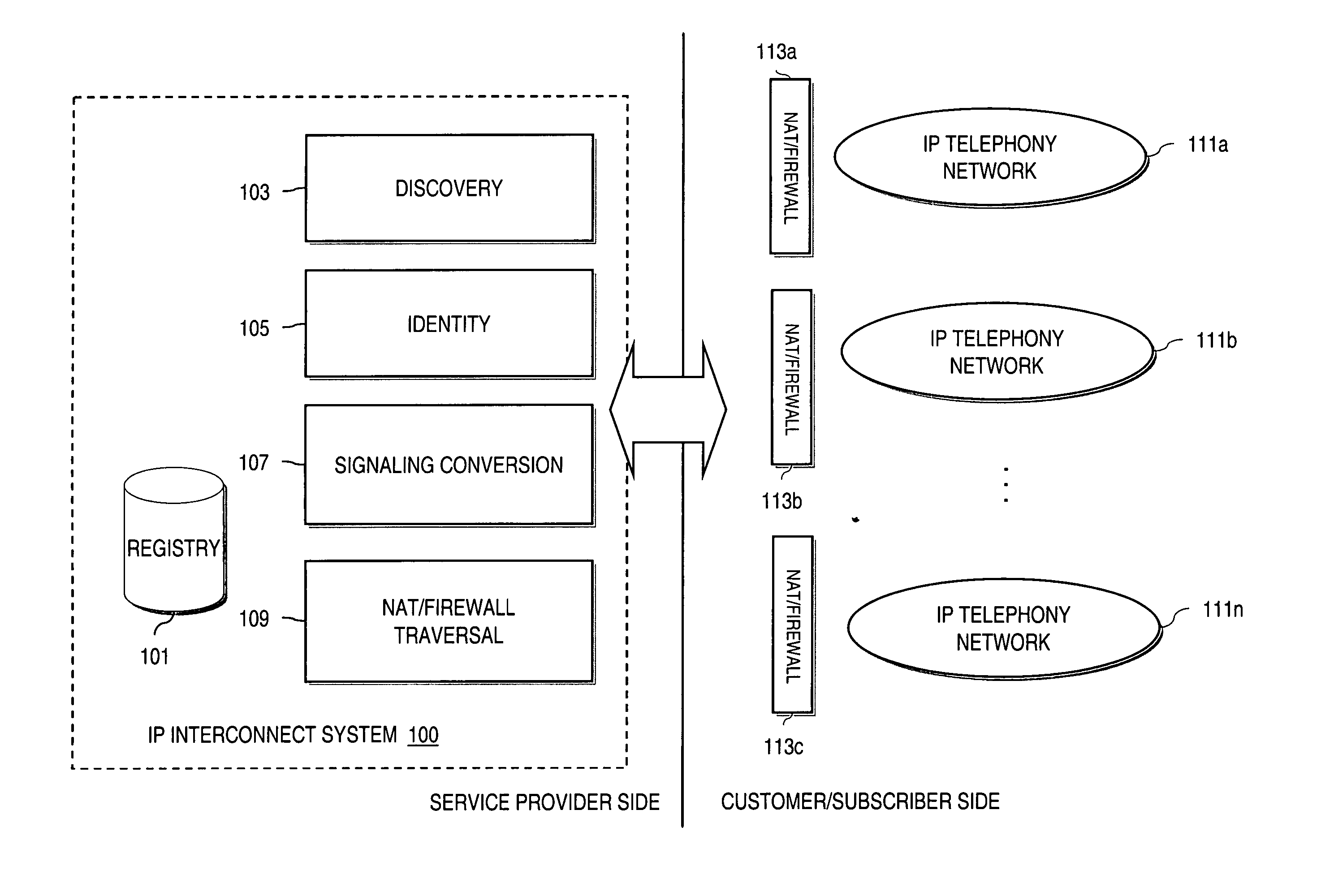
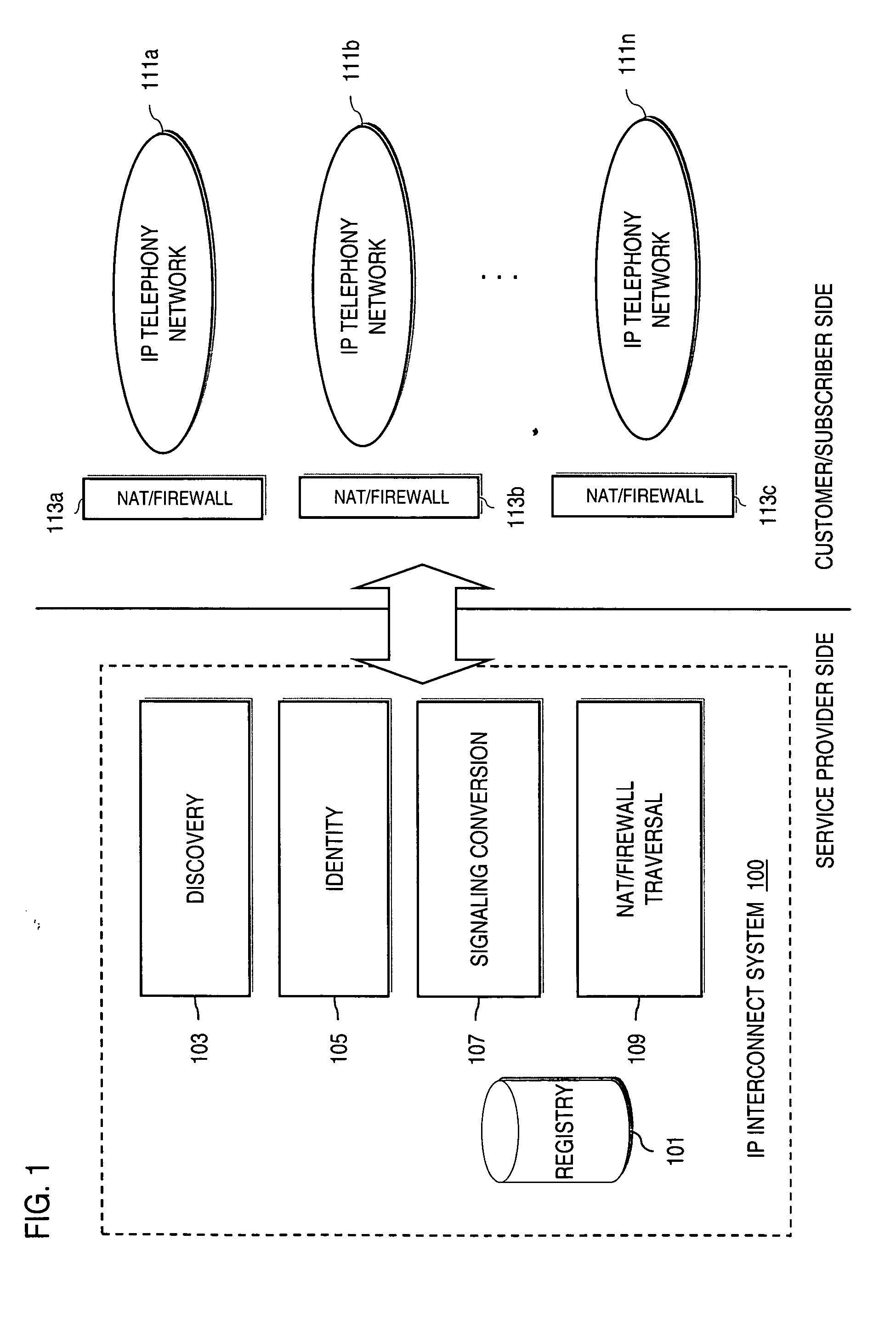
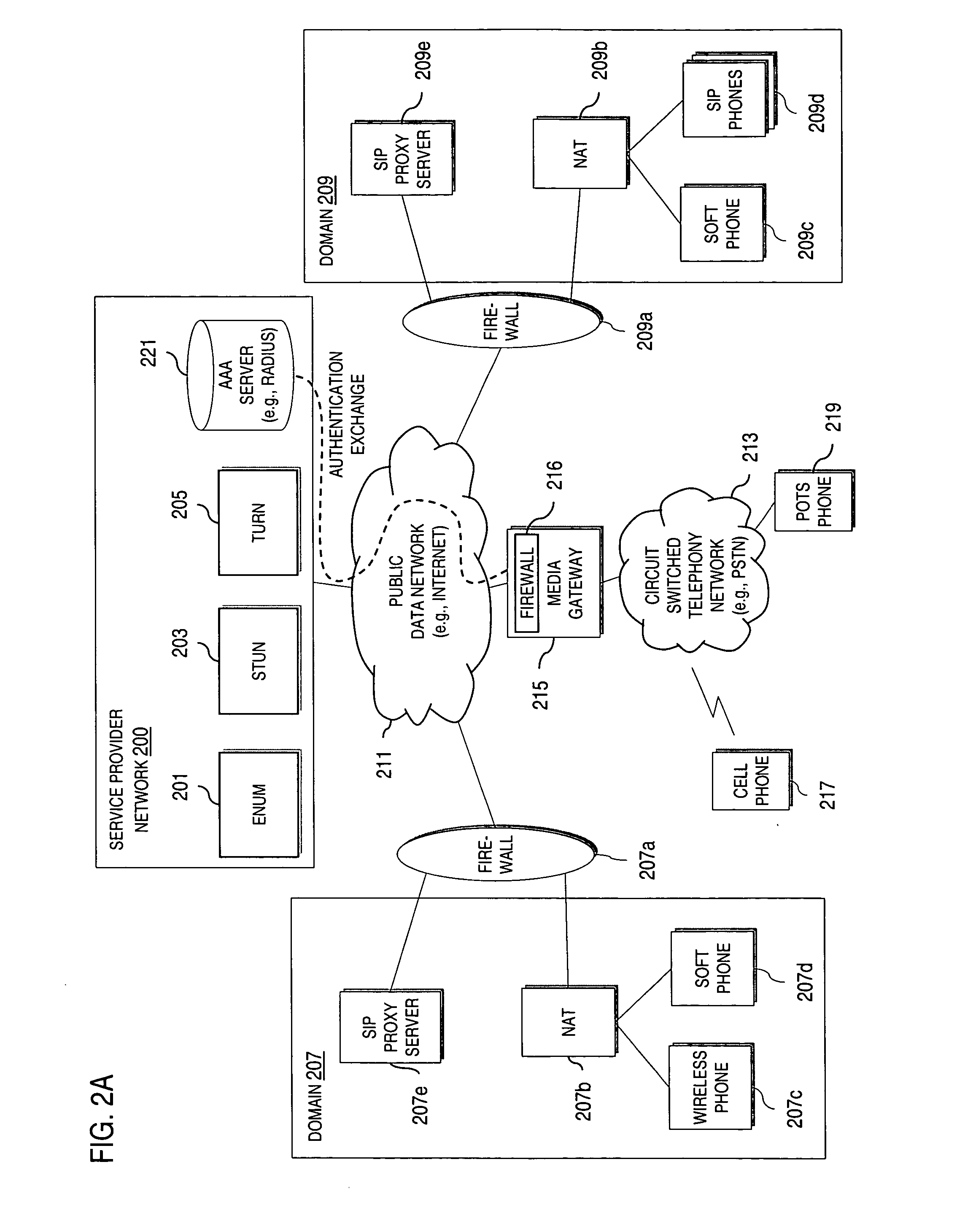
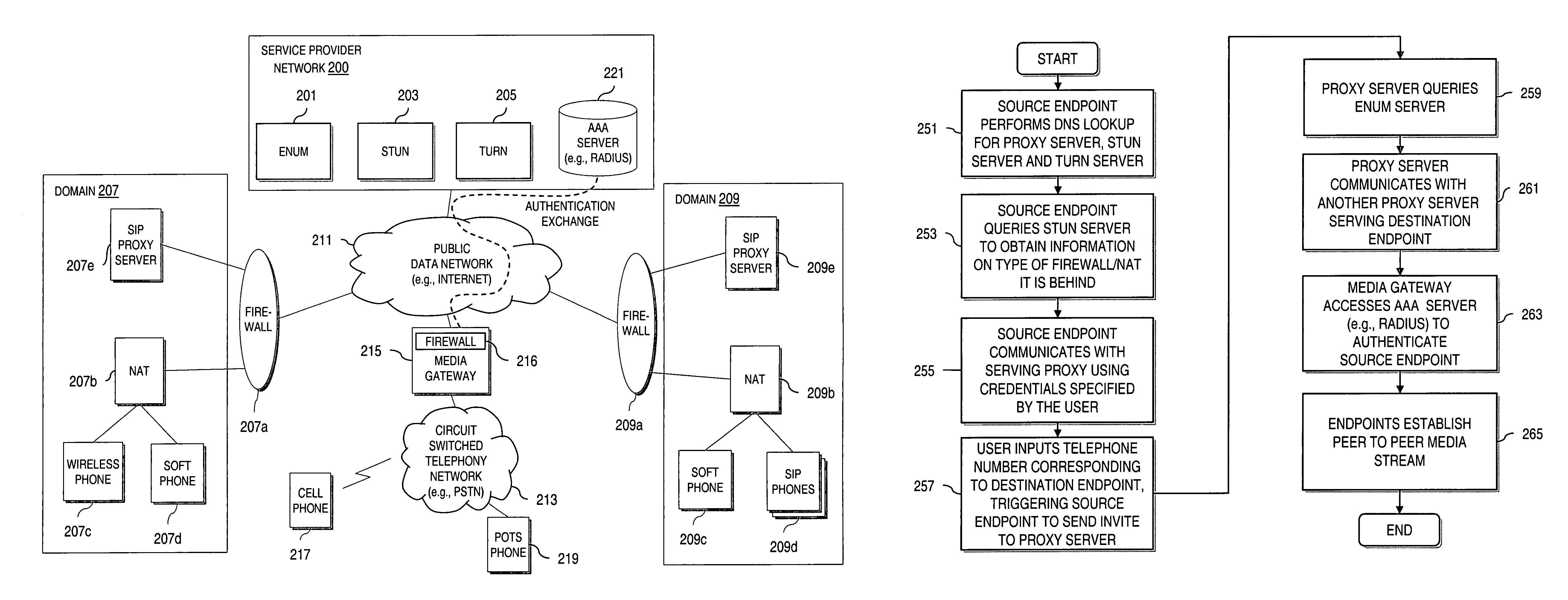
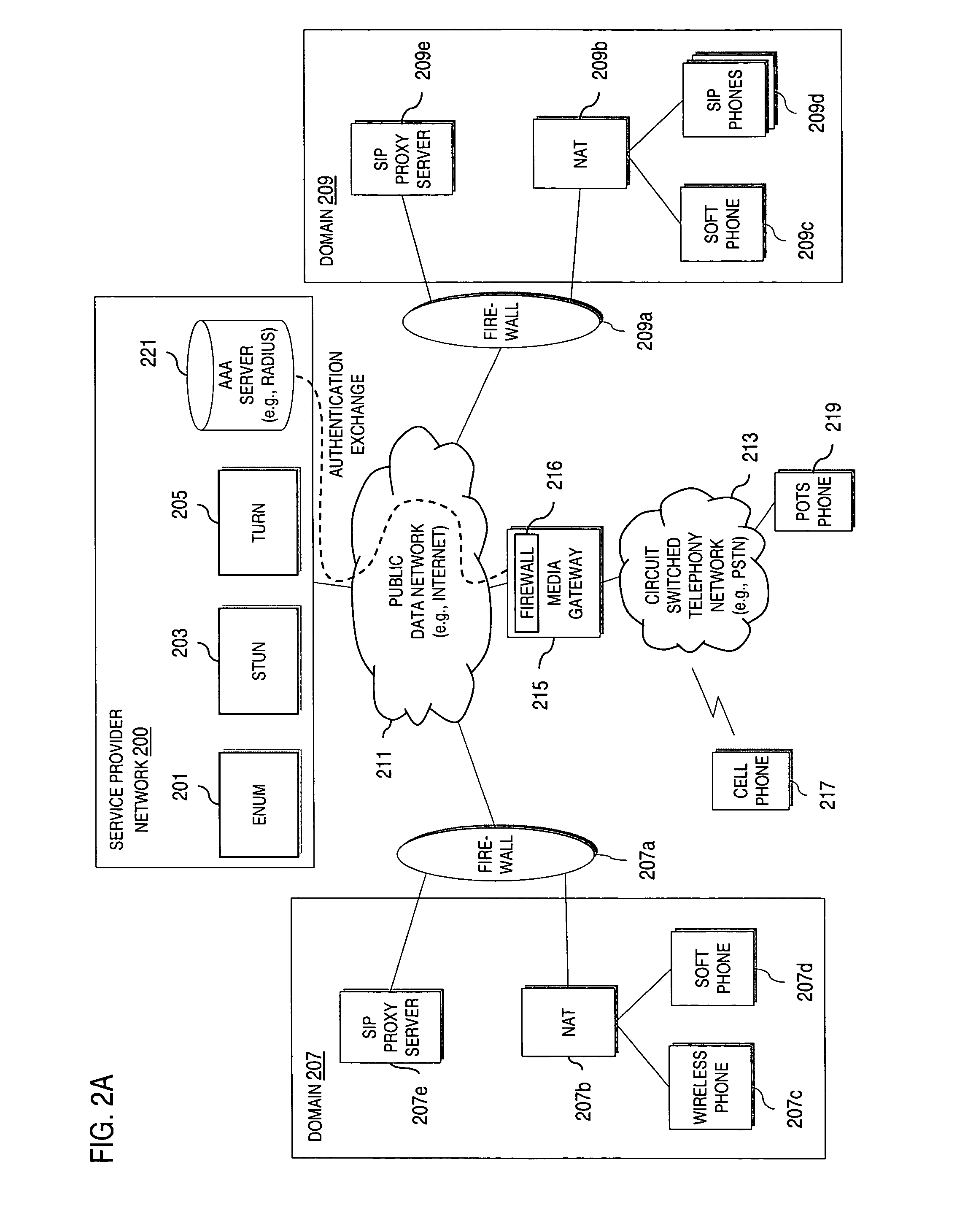
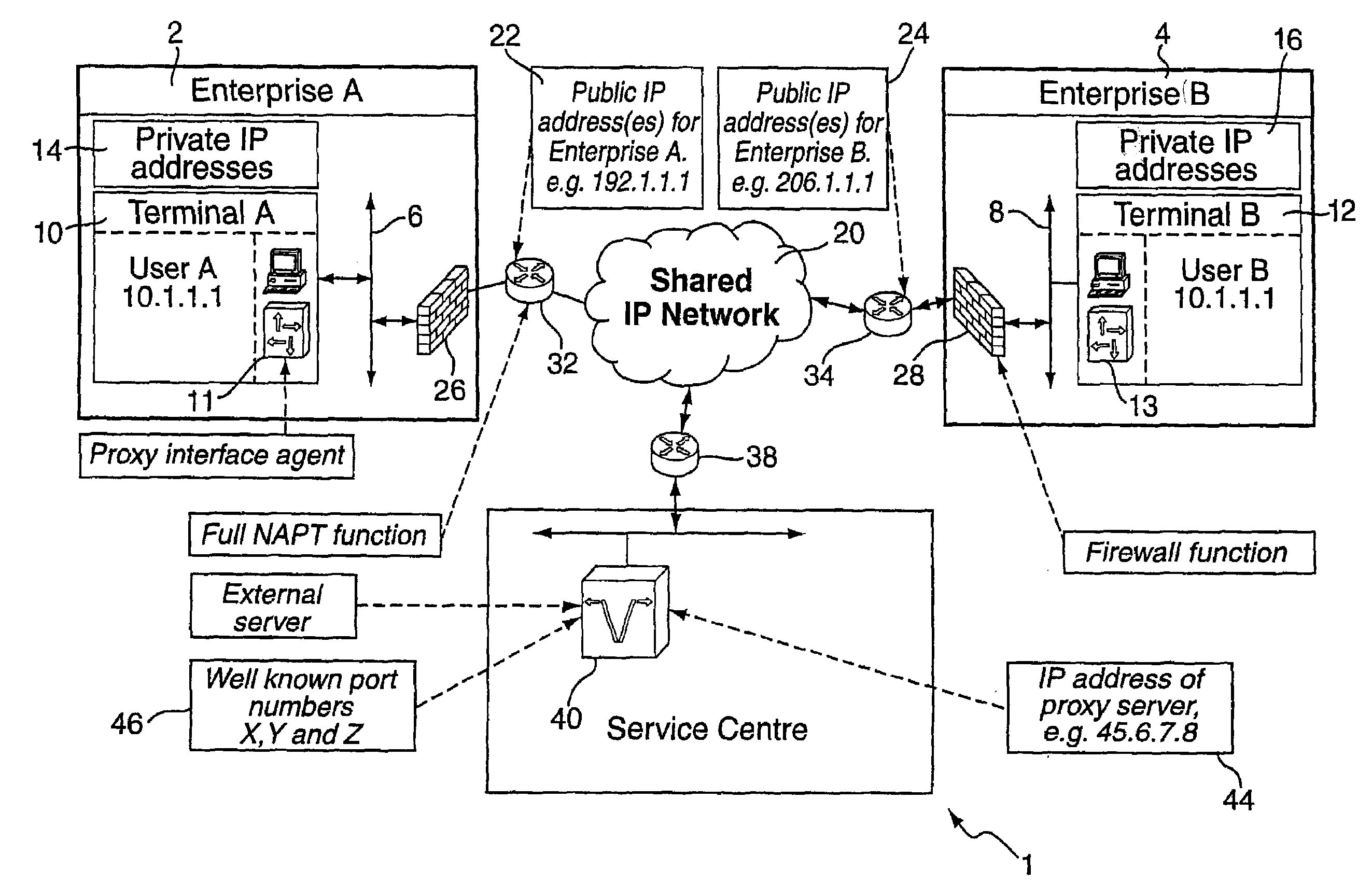
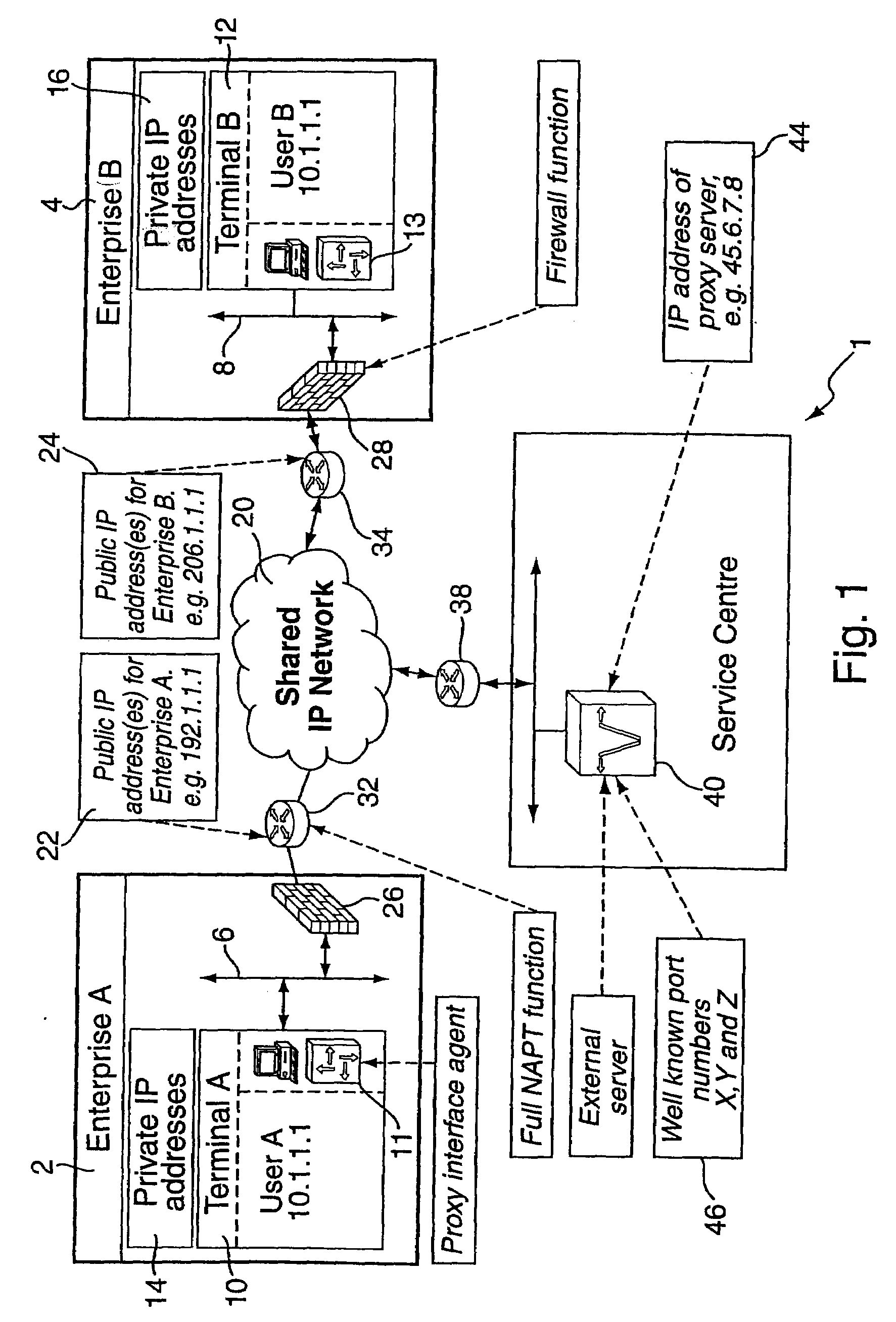
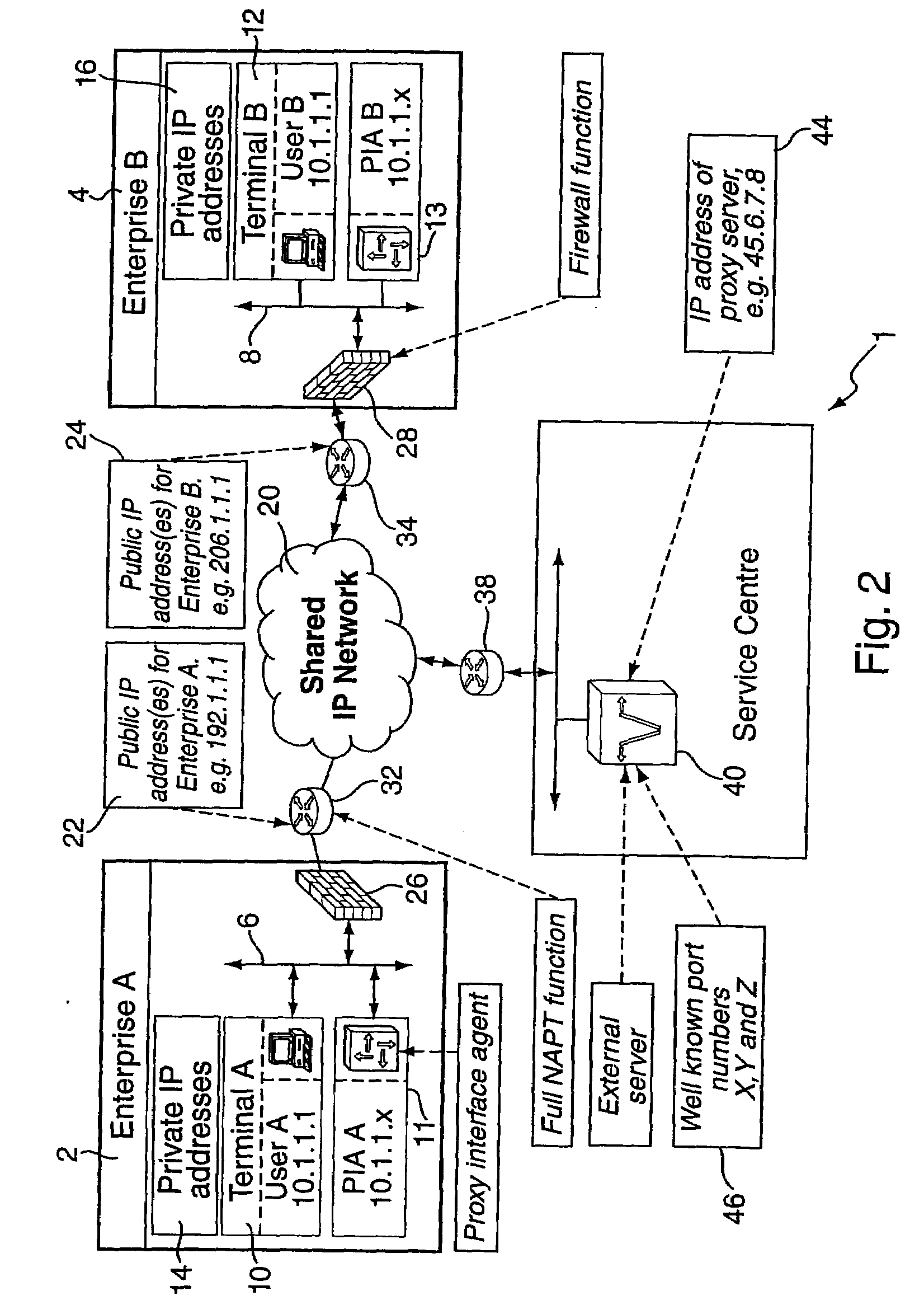
Method and system for providing secure media gateways to support interdomain traversal
ActiveUS20070019623A1Special service for subscribersData switching by path configurationNetwork addressNetwork address translation
An approach provides interdomain traversal to support packetized voice transmissions. A signaling message is received for establishing a voice call from a first endpoint associated with a first domain to a second endpoint associated with a second domain. The first endpoint queries a STUN (Simple Traversal of UDP (User Datagram Protocol)) server to determine information relating to a firewall and network address translator that the first endpoint is behind, and to log into a TURN (Traversal Using Relay NAT (Network Address Translation)) server configured to establish a media path between the first endpoint and the second endpoint. A first proxy server serving the first endpoint communicates with an ENUM (Electronic Number) server to convert a directory number corresponding to the second endpoint to a network address. The first proxy server communicates with a second proxy server serving the second endpoint to establish the voice call. The STUN server, the TURN server and the ENUM server are maintained by service provider. The first endpoint is authenticated to permit exchange of a media stream over the media path. The media stream is relayed, if the first endpoint is successfully authenticated.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
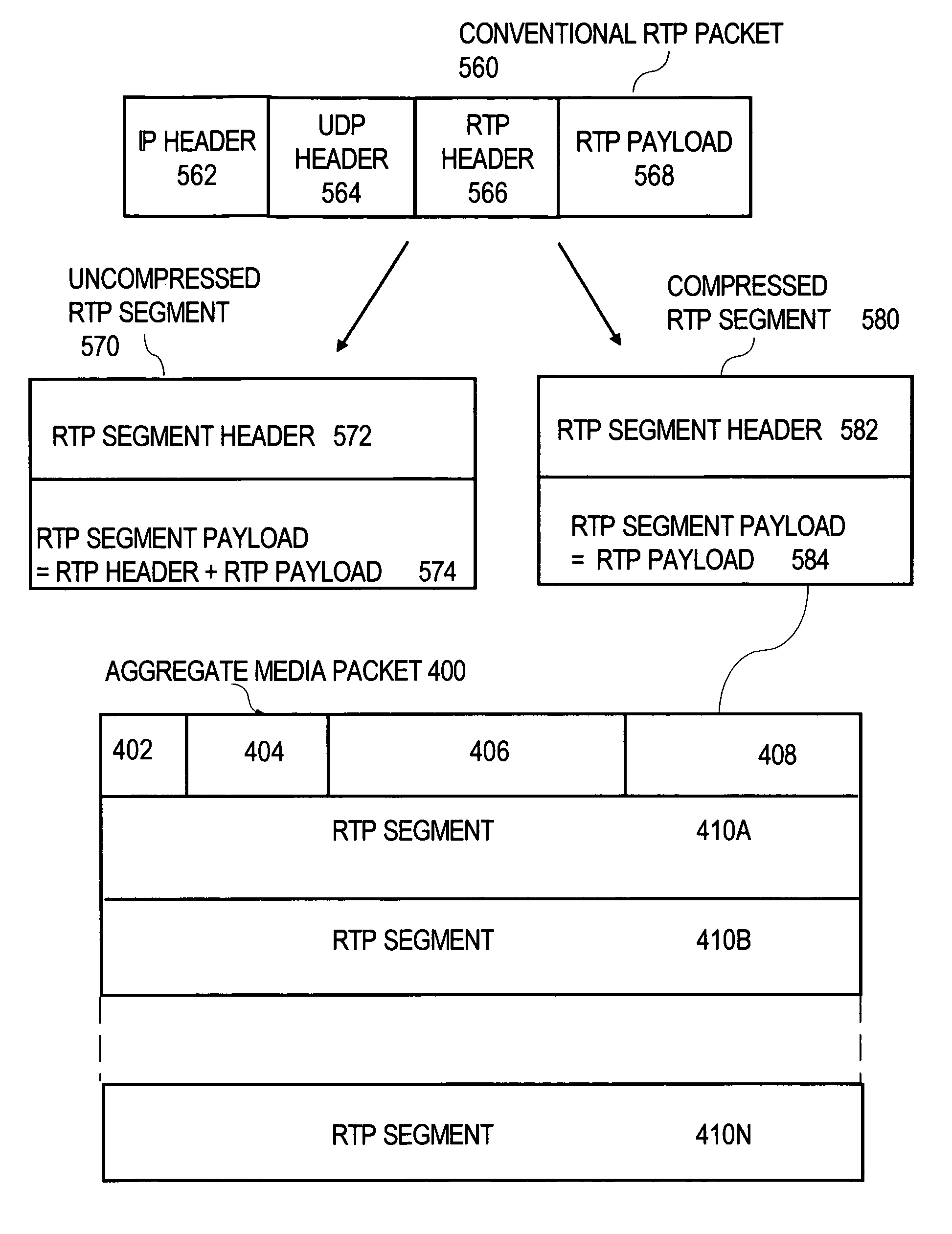
Method and apparatus providing media aggregation in a packet-switched network
Techniques are described for aggregating multiple media packets to improve end-to-end bandwidth efficiency. The techniques include using an RTP aggregation protocol that is not sensitive to packet loss to aggregate multiple media packets under a single header. According to the RTP aggregation protocol, the single header for an aggregated media packet comprises a version field, a zero field, a sequence number field and a trunk ID field. The single header encapsulates the aggregated payload, which is an aggregation of Real-Time Protocol (RTP) segments. An RTP segment either has a compressed format or an uncompressed format. The uncompressed RTP segment includes the complete uncompressed RTP packet copied from the original User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packet. The compressed RTP segment includes the payload of the original RTP rather than the complete original RTP packet.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Method and system for providing secure media gateways to support interdomain traversal
ActiveUS7920549B2Special service for subscribersData switching by path configurationNetwork addressNetwork address translation
An approach provides interdomain traversal to support packetized voice transmissions. A signaling message is received for establishing a voice call from a first endpoint associated with a first domain to a second endpoint associated with a second domain. The first endpoint queries a STUN (Simple Traversal of UDP (User Datagram Protocol)) server to determine information relating to a firewall and network address translator that the first endpoint is behind, and to log into a TURN (Traversal Using Relay NAT (Network Address Translation)) server configured to establish a media path between the first endpoint and the second endpoint. A first proxy server serving the first endpoint communicates with an ENUM (Electronic Number) server to convert a directory number corresponding to the second endpoint to a network address. The first proxy server communicates with a second proxy server serving the second endpoint to establish the voice call. The STUN server, the TURN server and the ENUM server are maintained by service provider. The first endpoint is authenticated to permit exchange of a media stream over the media path. The media stream is relayed, if the first endpoint is successfully authenticated.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
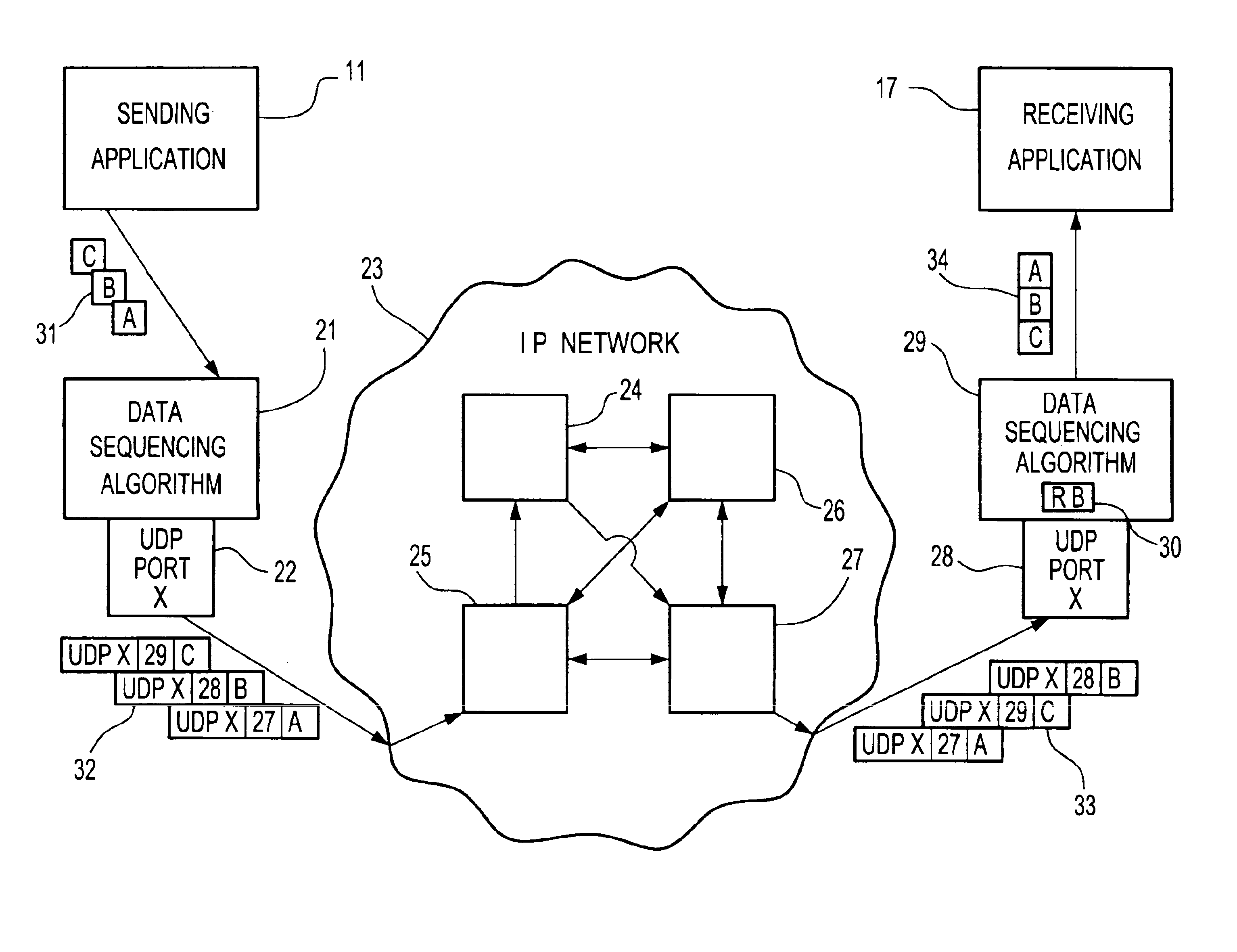
User data protocol for internet data communications
InactiveUS7031309B1Reduce consumptionData augmentationSpecial service provision for substationData switching by path configurationTTEthernetThe Internet
An improved user data protocol involves a multi-addressing capability that allows a user at a source node to address a single message to many users at respective destination nodes within a communication network. The multi-address messages that are provided to the network are inserted once at the source node, and messages routed between network nodes going to the same next node travel once across each interconnecting communication channel, thereby minimizing the communication bandwidth consumed.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Data communication system, data transmission apparatus, data reception apparatus, data communication method, and computer program
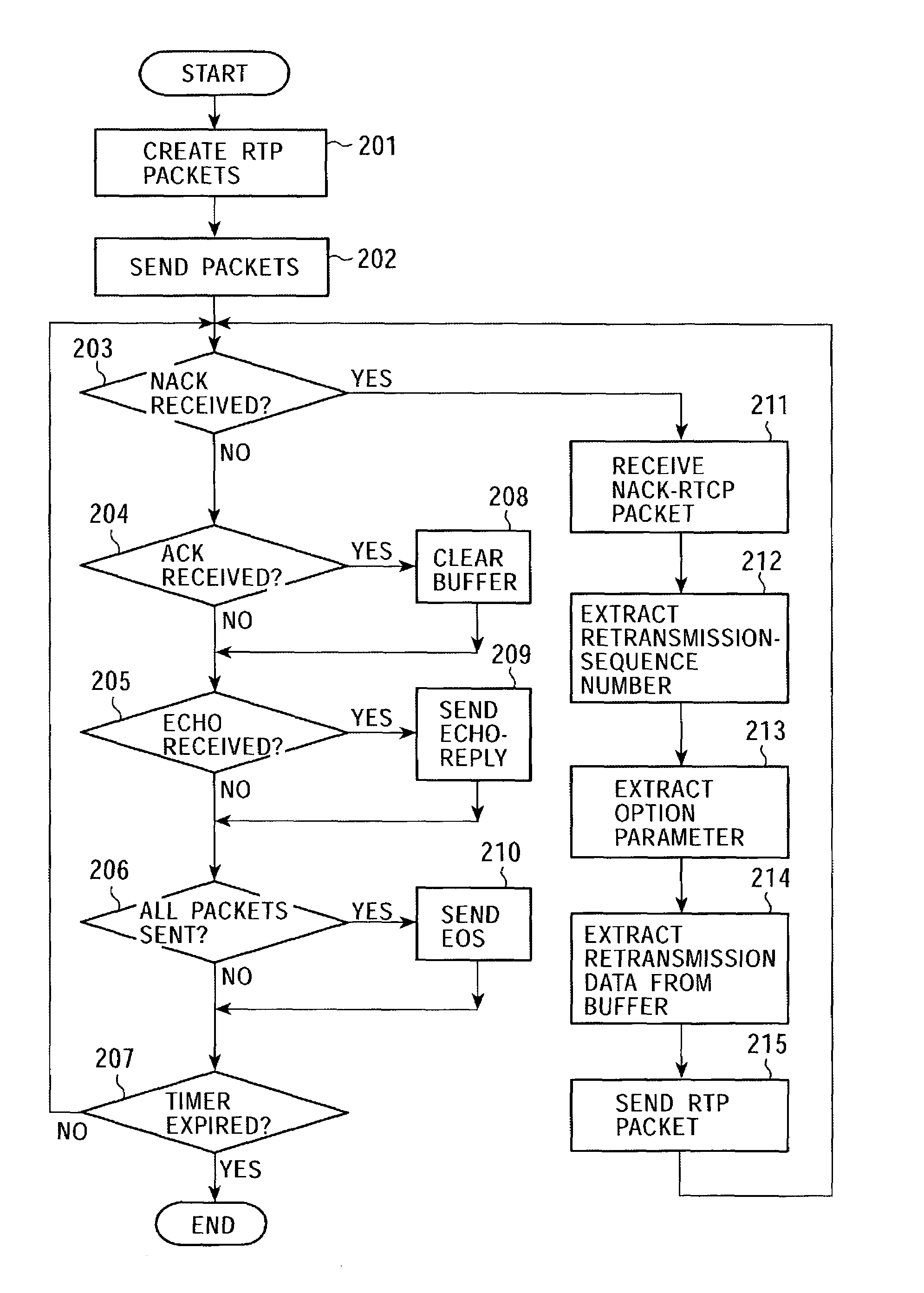
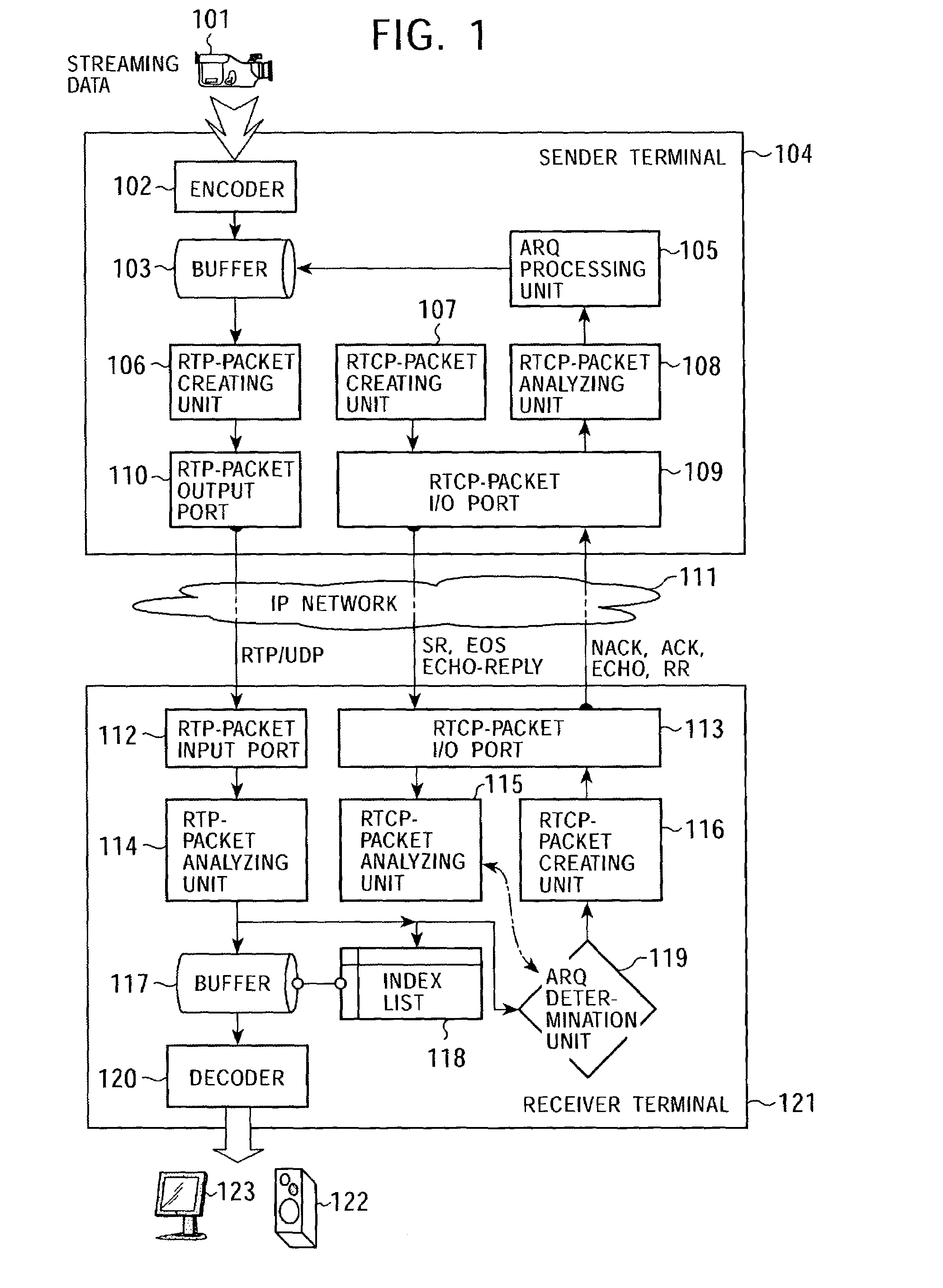
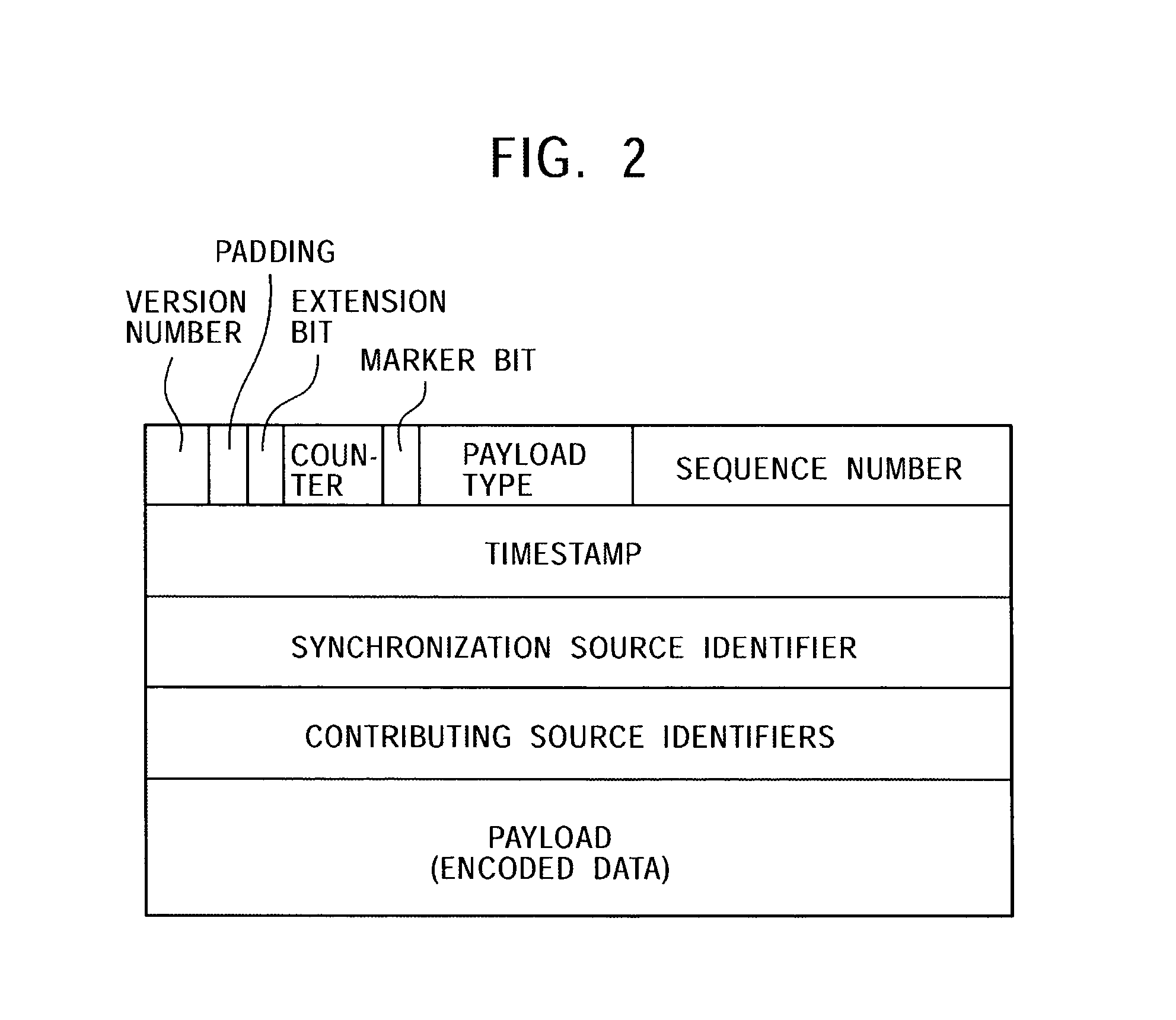
ActiveUS7315898B2Quality improvementEfficient transferError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemAutomatic repeat request
In a data communication system, the function of automatic repeat request is provided for transmission of packets based on a data communication protocol such as the Real-Time Transport Protocol or the User Datagram Protocol. Lost packets are detected at various timings, for example, when the beginning packet of each frame is received, the final frame of each frame is received, at a time limit of processing, and at a regular interval, and retransmission requests are issued accordingly. A data reception terminal does not issue a retransmission request if associated retransmission data will not be in time for playing with consideration of processing time and roundtrip time, thereby avoiding the transmission of useless retransmission request packets and retransmission packets.
Owner:SONY CORP
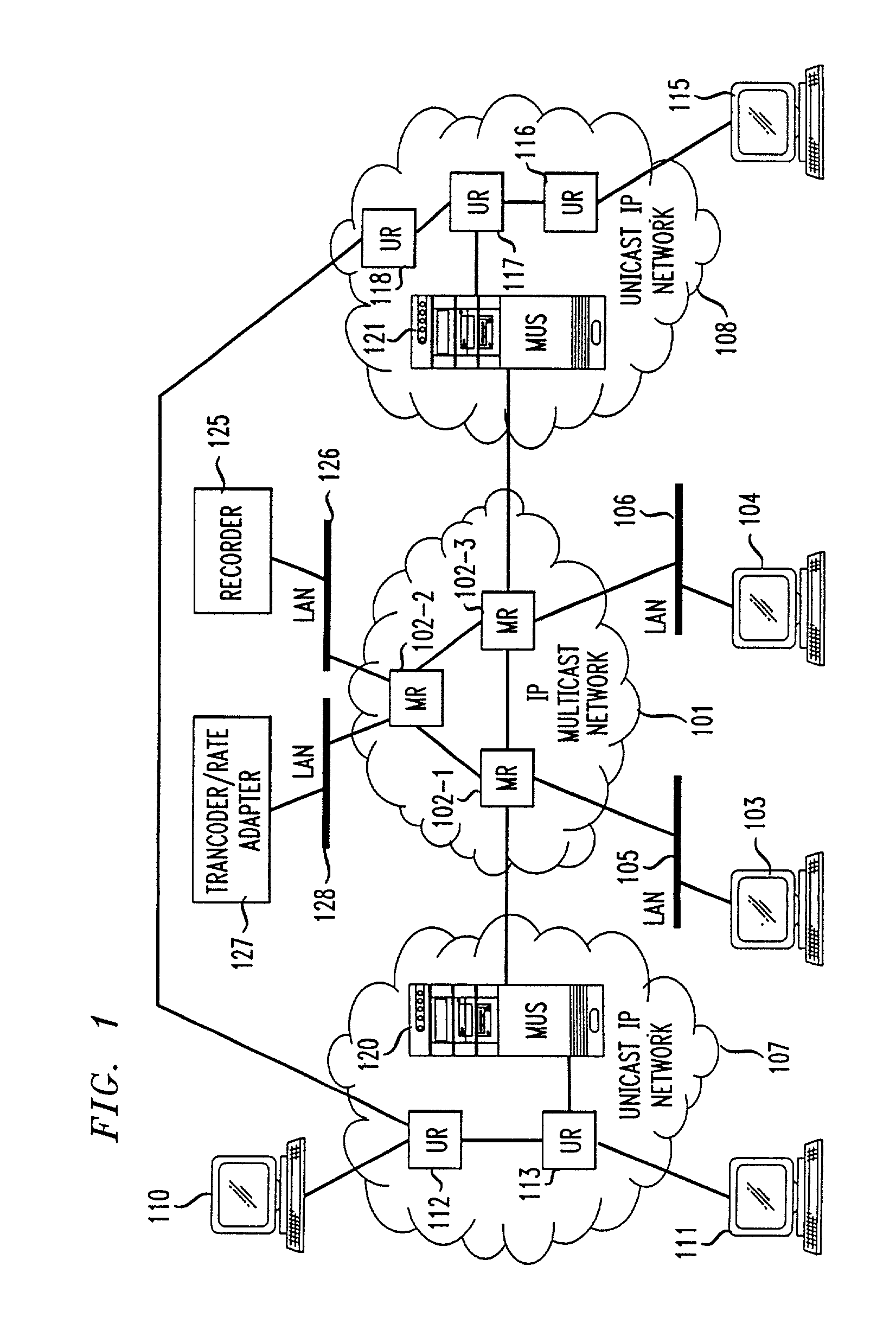
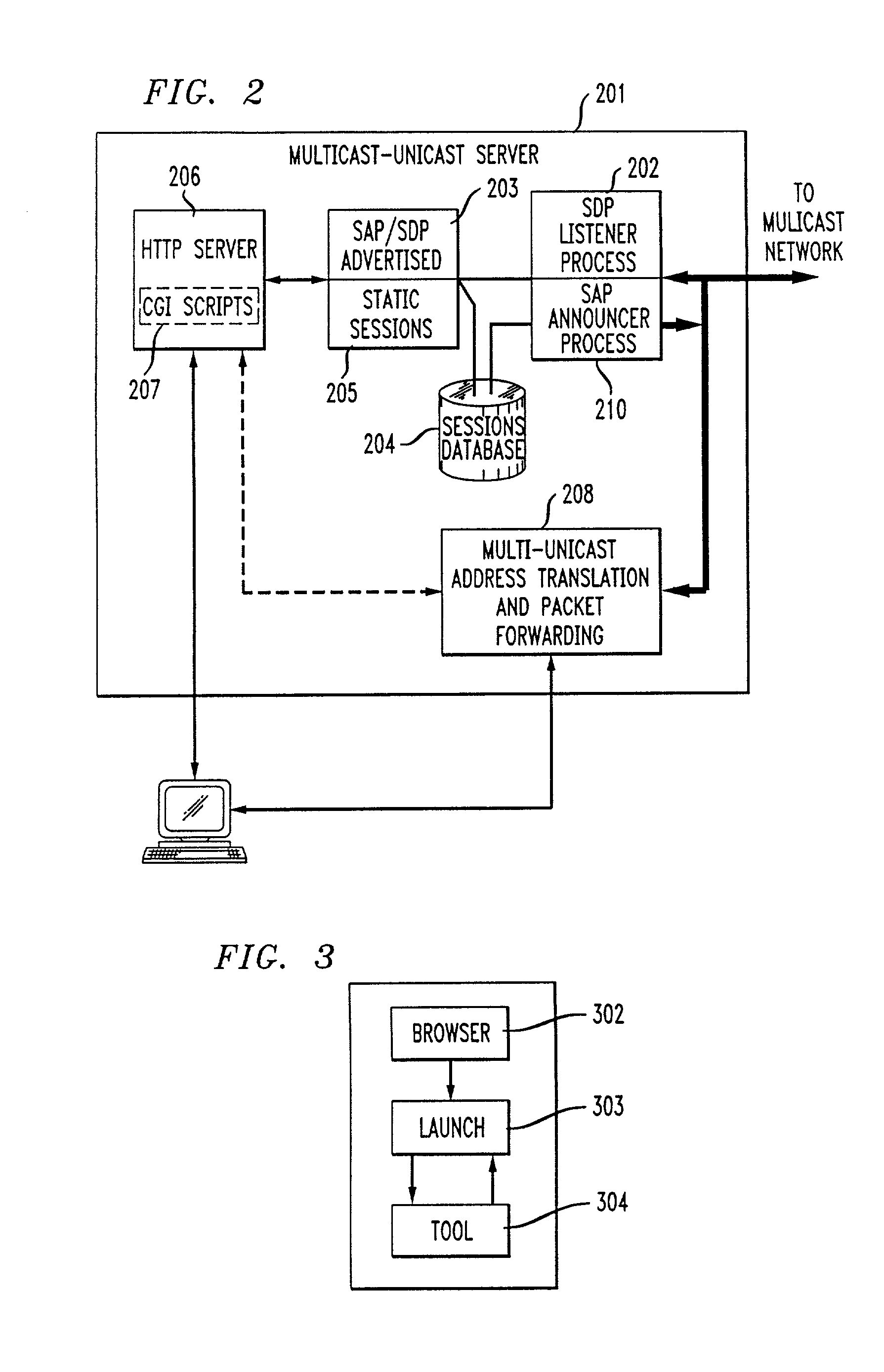
Method and system for a Unicast endpoint client to access a multicast internet protocol (IP) session
InactiveUS7031326B1Information obtainTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationMedia typeNetwork packet
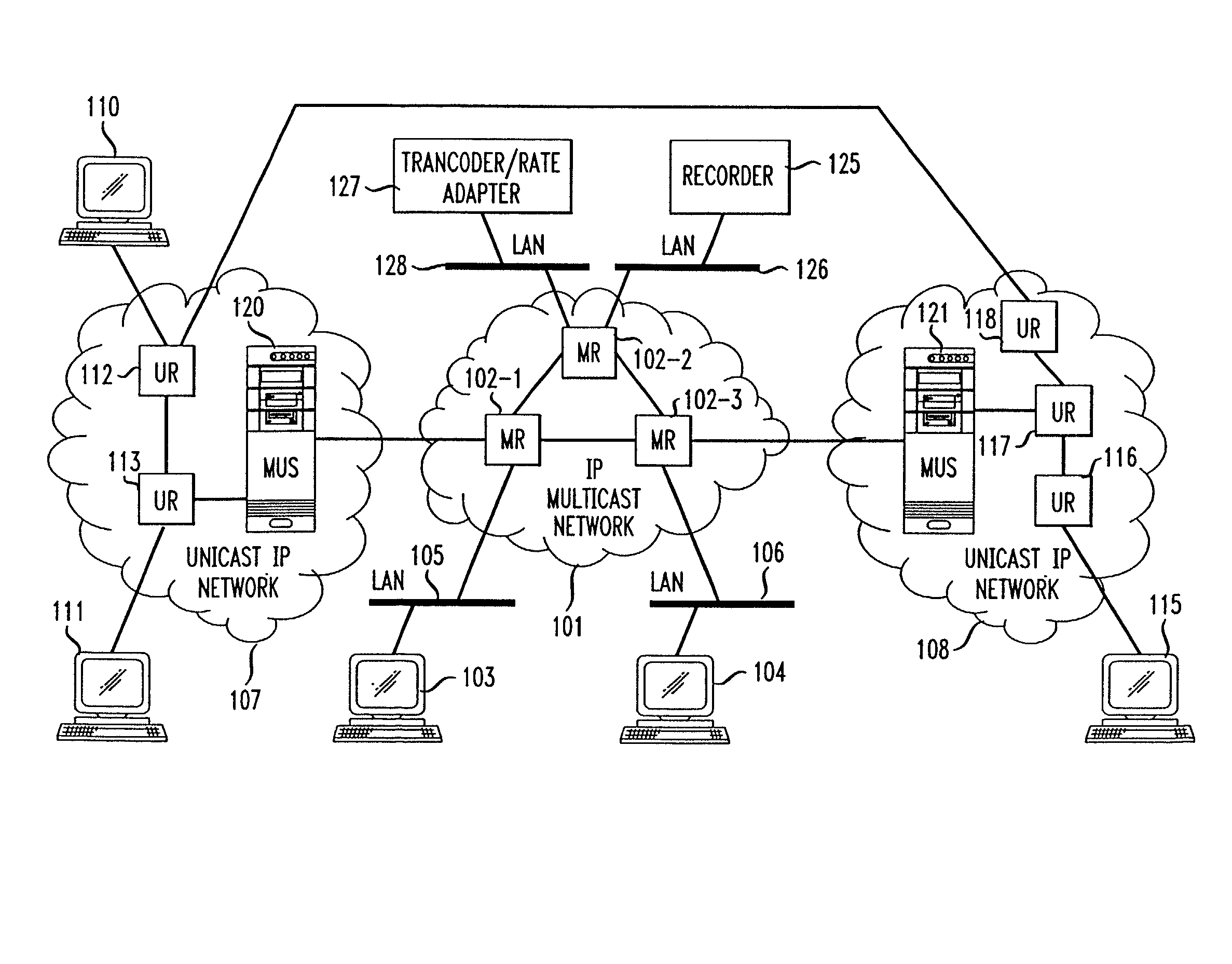
Unicast endpoint clients (110, 111, 115) on an IP Unicast network (107, 108) are provided access to Multicast sessions on an IP Multicast network (101) through a Multicast-Unicast gateway server (120, 121). The server obtains information about sessions on the Multicast network and makes such information available to a Unicast client on the Unicast network upon request by the client. Upon being presented with a list describing the subject matter of each session, the user at the Unicast client selects the session to which he or she wants to join, which causes the Multicast-Unicast server to join the appropriate session on behalf of the requesting client for each media type in which the joining client wants to be a participant. The server then sets a bi-directional Unicast User Datagram Protocol (UDP) stream between itself and the client. All packets then received by the server from the Unicast client are address-translated to the appropriate Multicast session address. In addition, all packets received by the server on the Multicast session address are address-translated and sent to the Unicast client. The Unicast client is then able to participate in the Multicast session as both a sender and a receiver of packets to and from other Unicast and Multicast clients which are active during the session. Further, the Unicast client is capable of creating a new session, recording a session in the network for later retrieval and playback, and creating and accessing low bandwidth versions of existing sessions.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
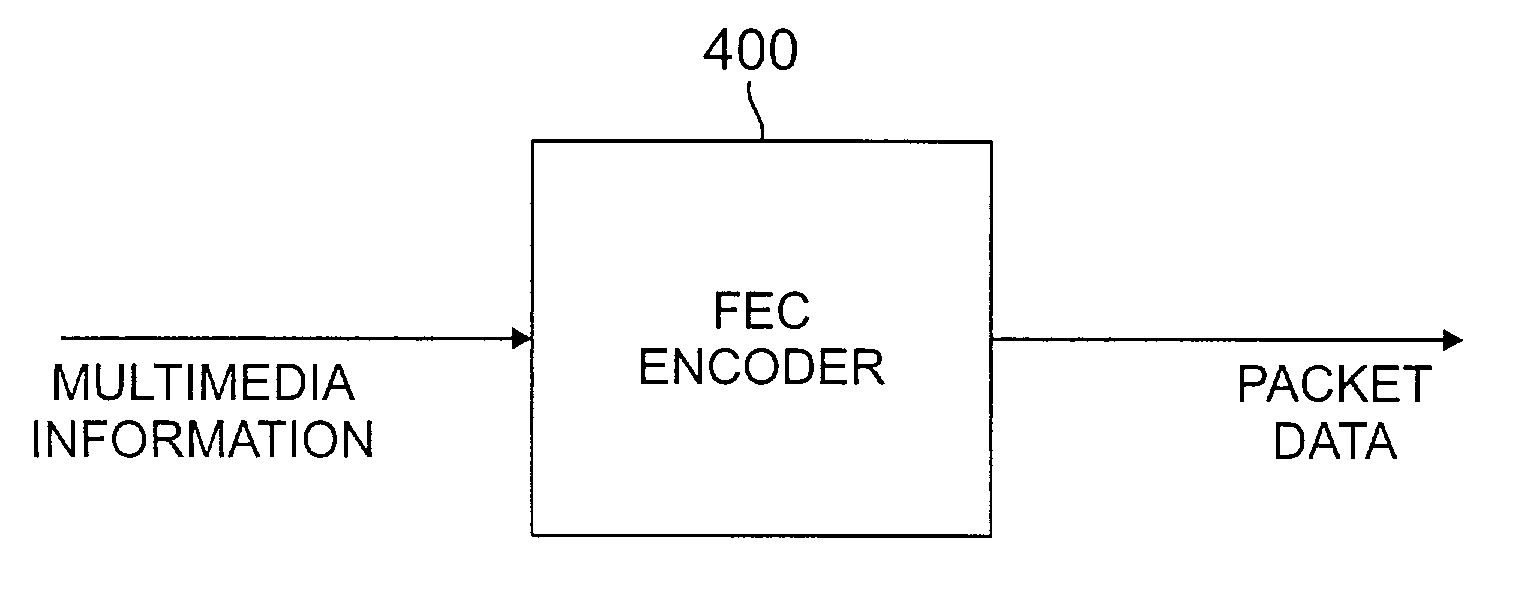
Complete user datagram protocol (CUDP) for wireless multimedia packet networks using improved packet level forward error correction (FEC) coding
InactiveUS7151754B1Reduces unnecessary packet discardingReduce information lossTransmission systemsCode conversionPacket lossForward error correction
A complete User Datagram Protocol (CUDP) is disclosed that reduces packet loss. Channel frame error information is used with a packet level forward error correction (FEC) coding technique to accommodate wireless multimedia traffic. Each packet, as well as the channel frame error information, is forwarded to a given application. The CUDP protocol further assists the FEC decoding process by forwarding the locations of corrupted frames to the FEC decoder. Maximal Distance Separable (MDS) codes can be applied to a group of packets, to achieve additional robustness. An MDS decoder utilizes the frame error information to recognize the erasures within each packet. The error information can be represented as a set of LTU error indicators associated with each packet (for FEC decoders requiring an erasure indicator). The error indicators point to the starting and ending location of the erroneous data. The error information can also be represented as a reformatted packet (for FEC decoders Recognizing Erasures). The frame (LTU) error information from the lower layers is incorporated in the packet payload. An FEC encoder is also disclosed that encodes multimedia packets utilizing a packet-coding scheme, such as a Vertical Packet Coding (VPC) scheme or a Long Vertical Packet Coding (LVPC) scheme.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Classification for media stream packets in a media gateway
InactiveUS20070121580A1Commmunication supplementary servicesData switching by path configurationField-programmable gate arrayUser Datagram Protocol
A method in Field Programmable Gate Array for processing packets received at a media gateway is provided. The method includes ascertaining whether a received packet is a UDP (User Datagram Protocol) packet. The method also includes comparing first portion of UDP destination port number from UDP packet header with first portion with UDP port base that has been set up in media gateway. If a match exist, employing second portion of UDP destination port number as a key to UDP port table to ascertain whether packets associated with media stream ID are to be discarded, and discarding received packet if packet associated with media stream ID is to be discarded. If not, obtaining media processing CPU ID associated with media stream ID, formulating destination MAC address, and updating packet with destination MAC address, thereby enabling packet to be switched to media processing CPU associated with media processing CPU ID.
Owner:DIVITAS NETWORKS INC
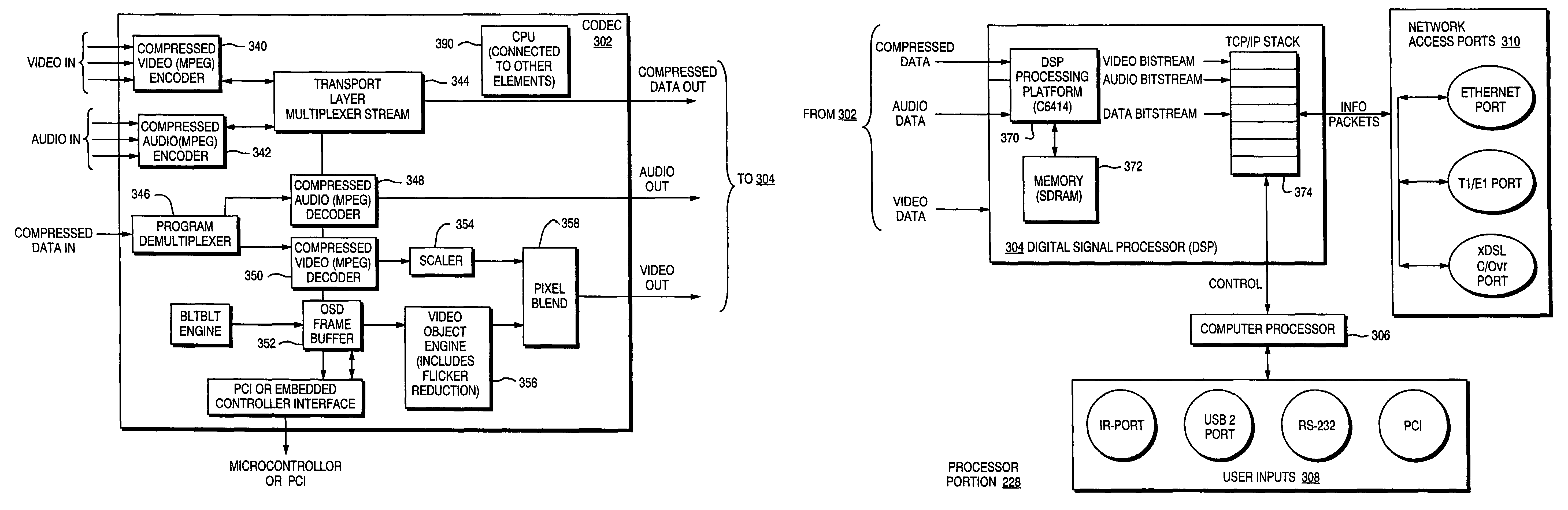
Broadband network system configured to transport audio or video at the transport layer, and associated method
InactiveUS7124195B2Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionTransceiverUser Datagram Protocol
A broadband network system configured to transfer user datagram protocol with value-added (UDPVA) packet from to a broadband interface unit (BIntU) transceiver. The broadband network system may comprise a data distribution center and the BIntU transceiver. The BIntU transceiver is configured to generate the UDPVA packet. The BIntU transceiver includes an encoder / decoder (codec) configured to alternatively code or decode UDP frame information and a digital signal processor (DSP) portion. The DSP portion is coupled to the codec. In one aspect, the DSP portion includes a stack that temporarily stores the UDPVA packet within the stack. In one aspect, the UDPVA packet is in a form to be transmitted directly to a network destination address device. In another aspect, the UDPVA packet is available to delivery to a network destination address or storage located on a local area network or a wide area network. In certain aspects, the BIntU transceiver is configured to transmit the UDPVA packet to the data distribution center.
Owner:VELCERO BROADBAND APPL
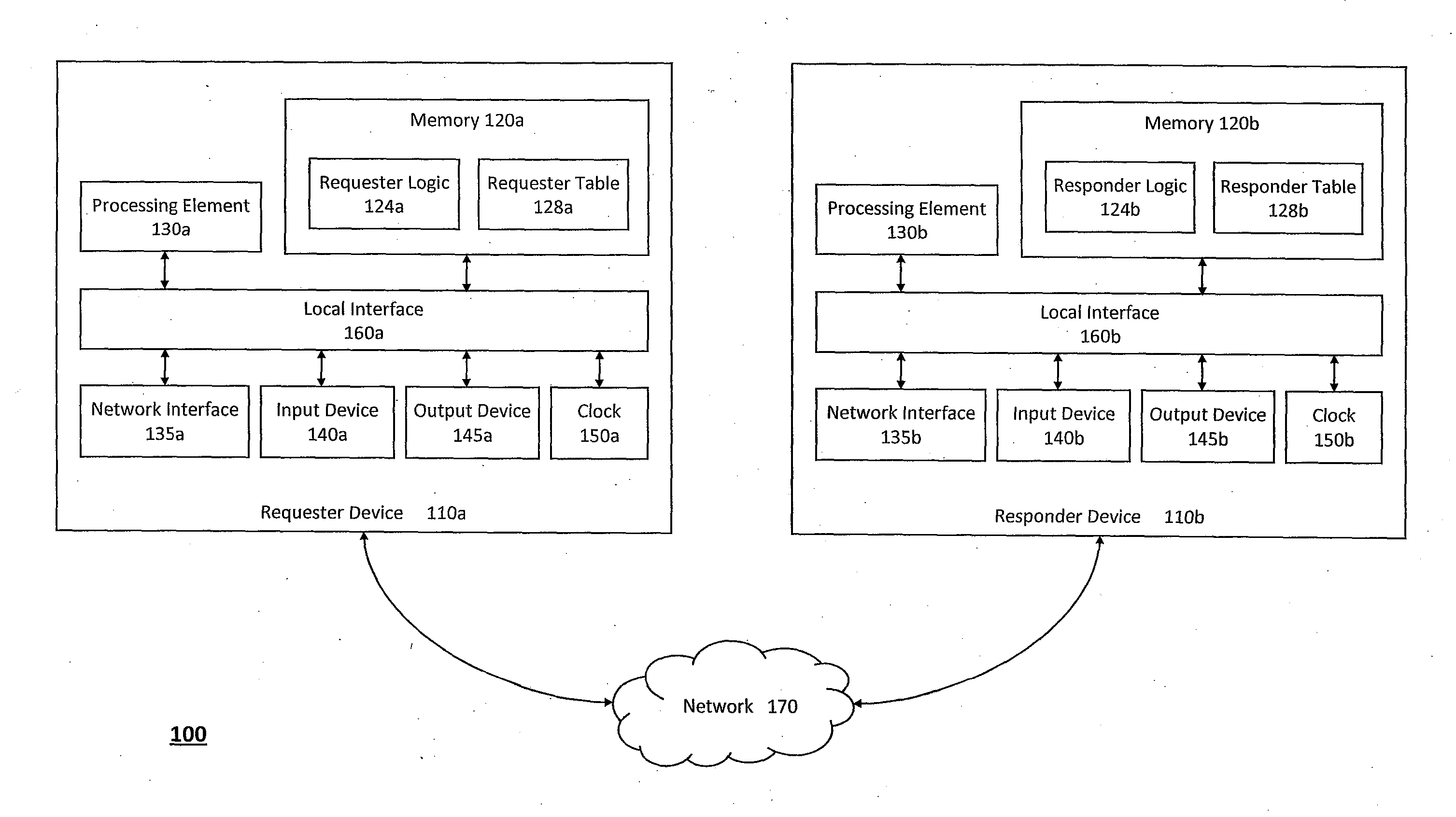
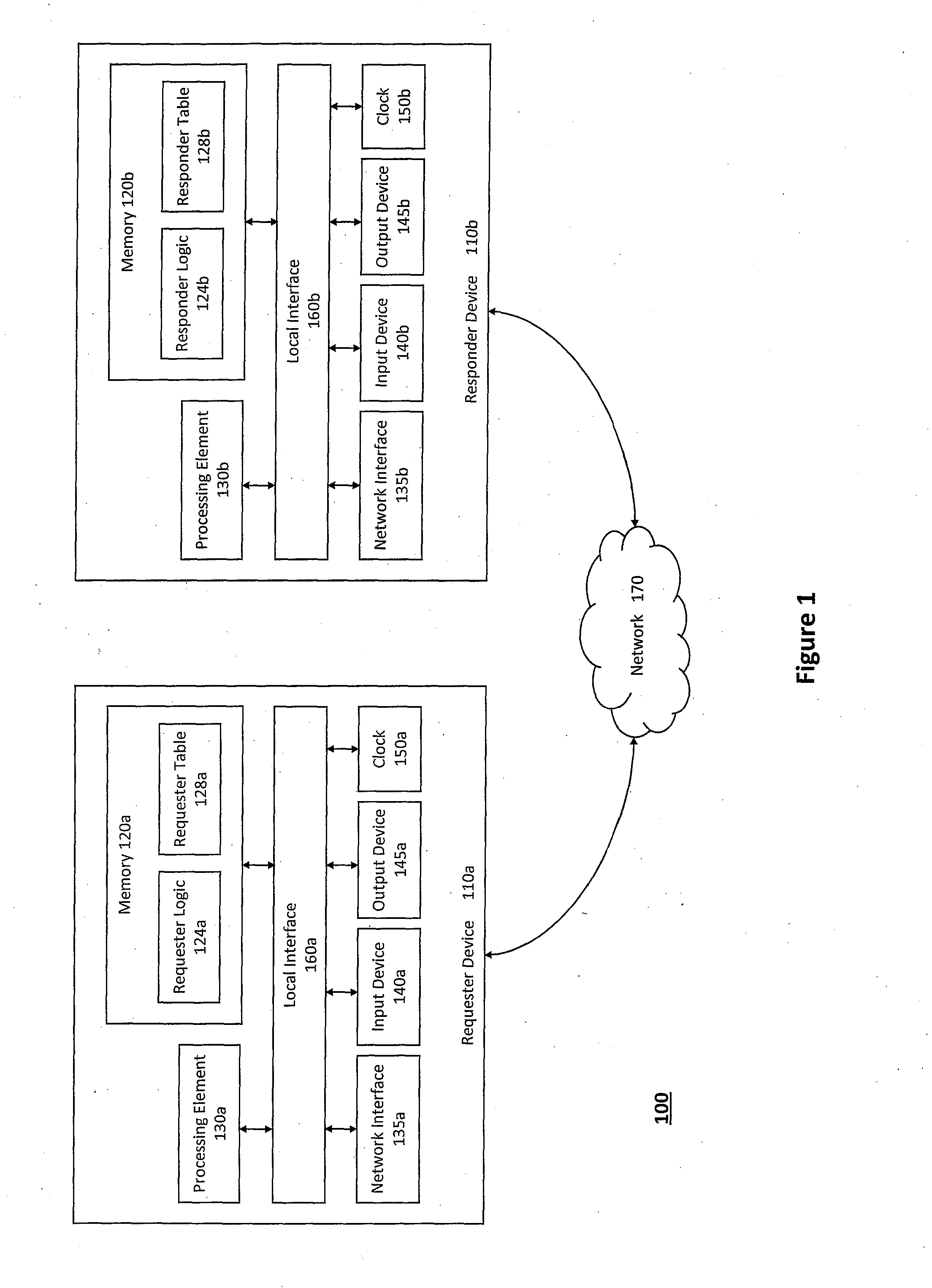
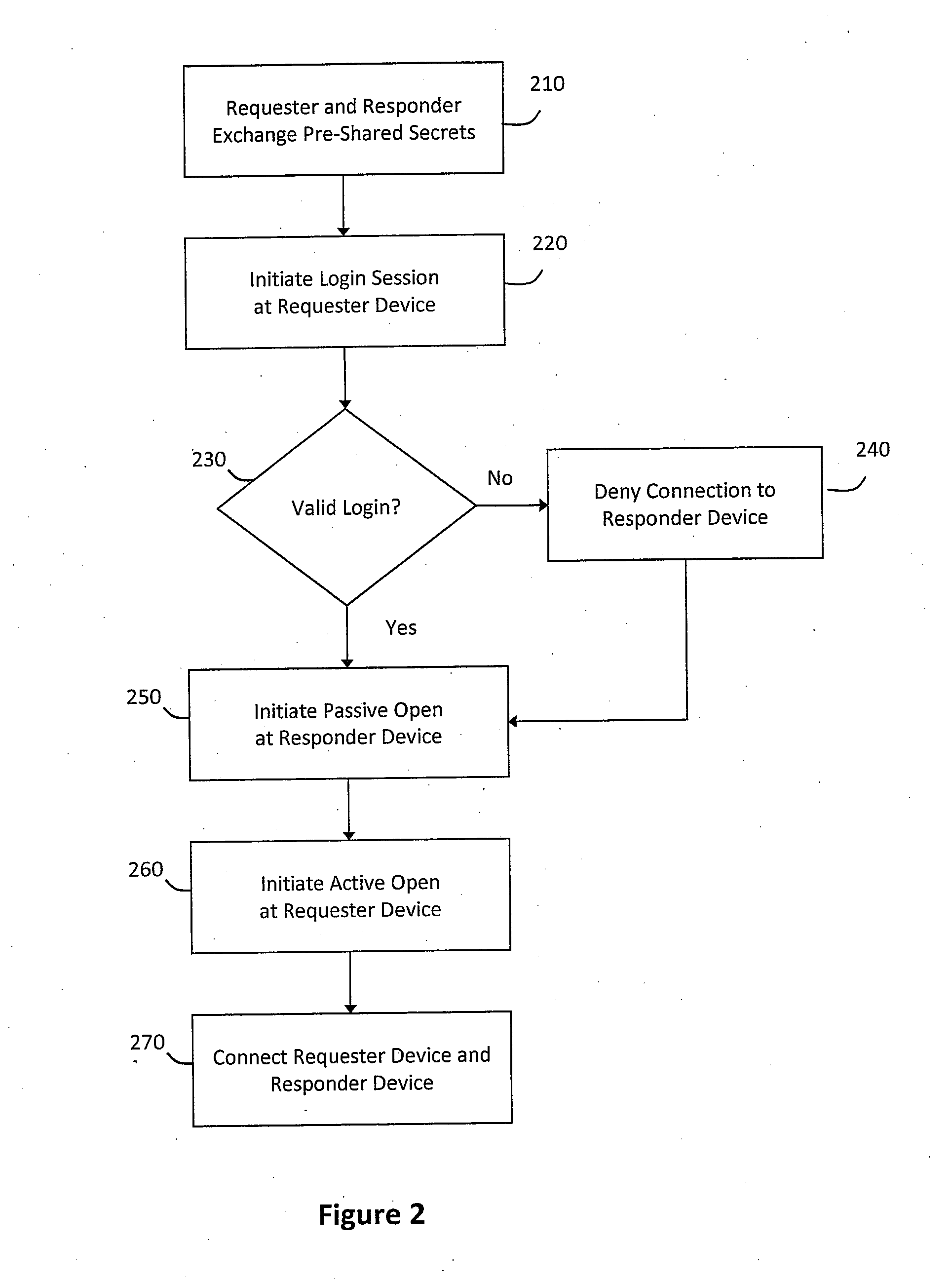
System and method for providing unified transport and security protocols
InactiveUS20110099623A1Minimize delayFast and efficientMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionPacket lossMessage frame
The system and method described herein may provide unified transport and security protocols. In particular, the unified transport and security protocols may include a Secure Frame Layer transport and security protocol that includes stages for initially configuring a requester device and a responder device, identifying the requester device and the responder device to one another, and authenticating message frames communicated between the requester device and the responder device. Additionally, the unified transport and security protocols may further include a Secure Persistent User Datagram Protocol that includes modes for processing message frames received at the requester device and the responder device, recovering the requester device in response to packet loss, retransmitting lost packets sent between the requester device and the responder device, and updating location information for the requester device to restore a communications session between the requester device and the responder device.
Owner:AUNIGMA NETWORK SECURITY CORP
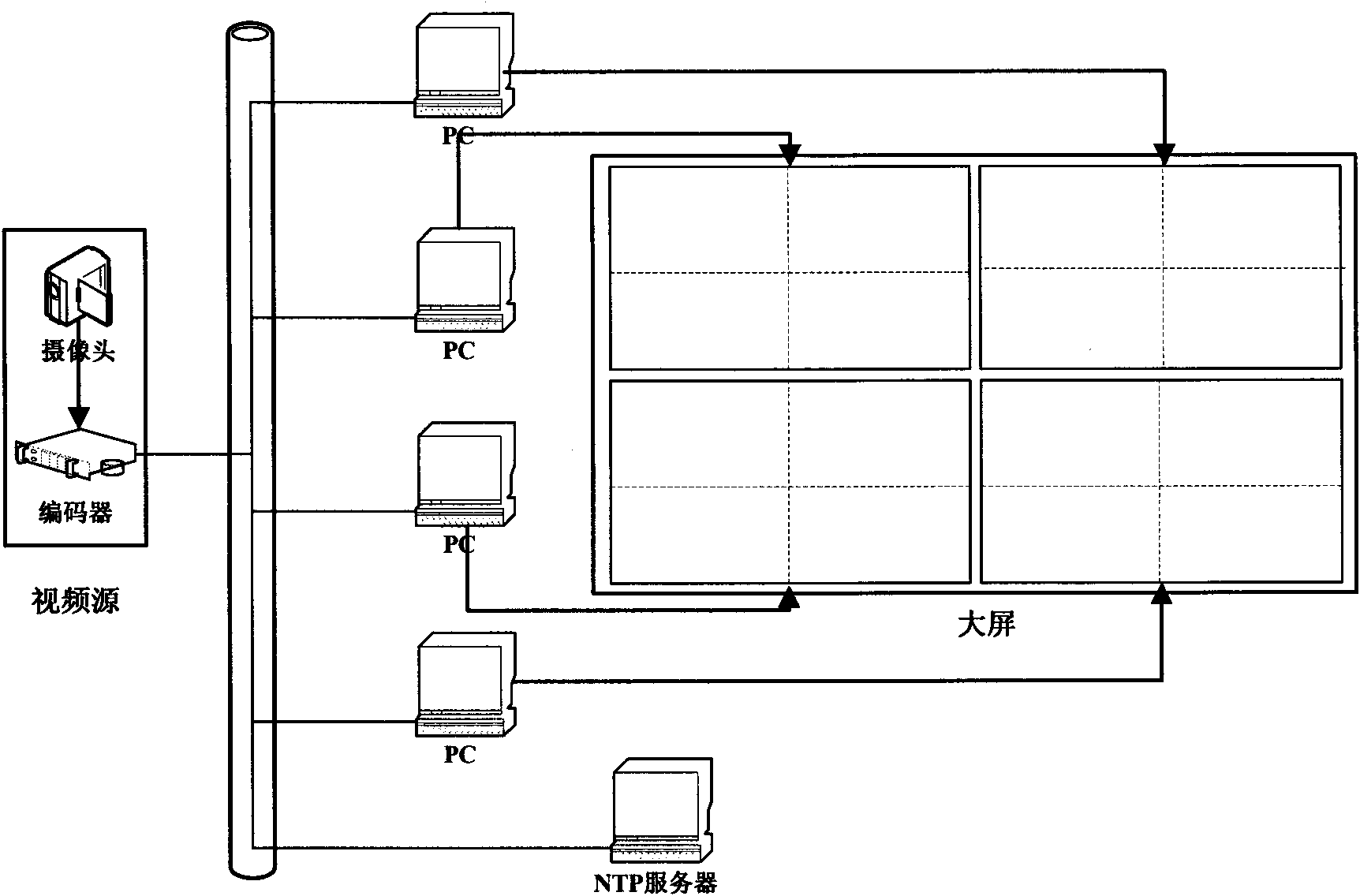
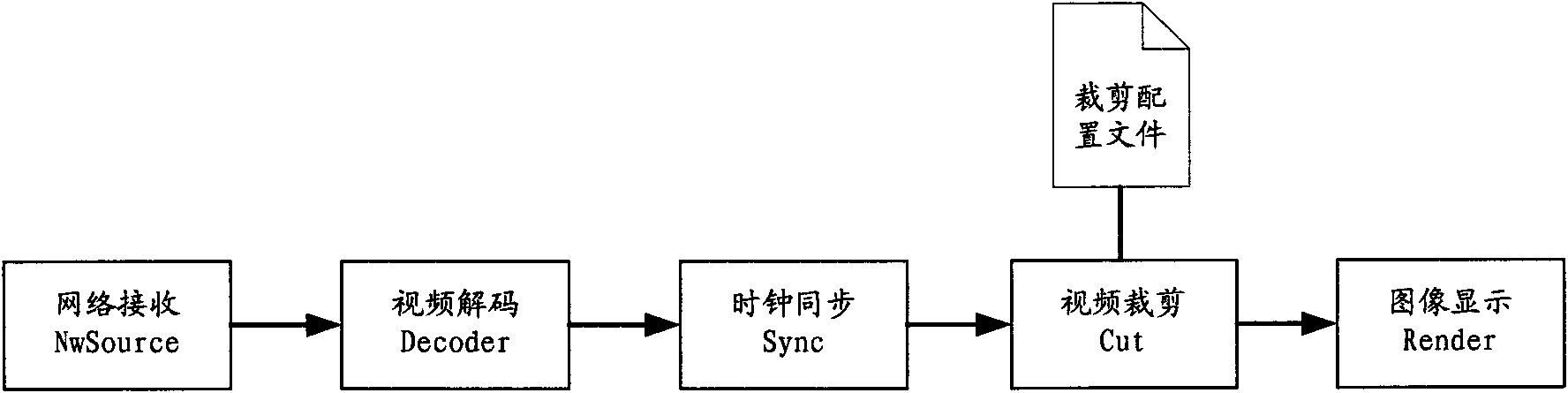
Large screen splicing method and system
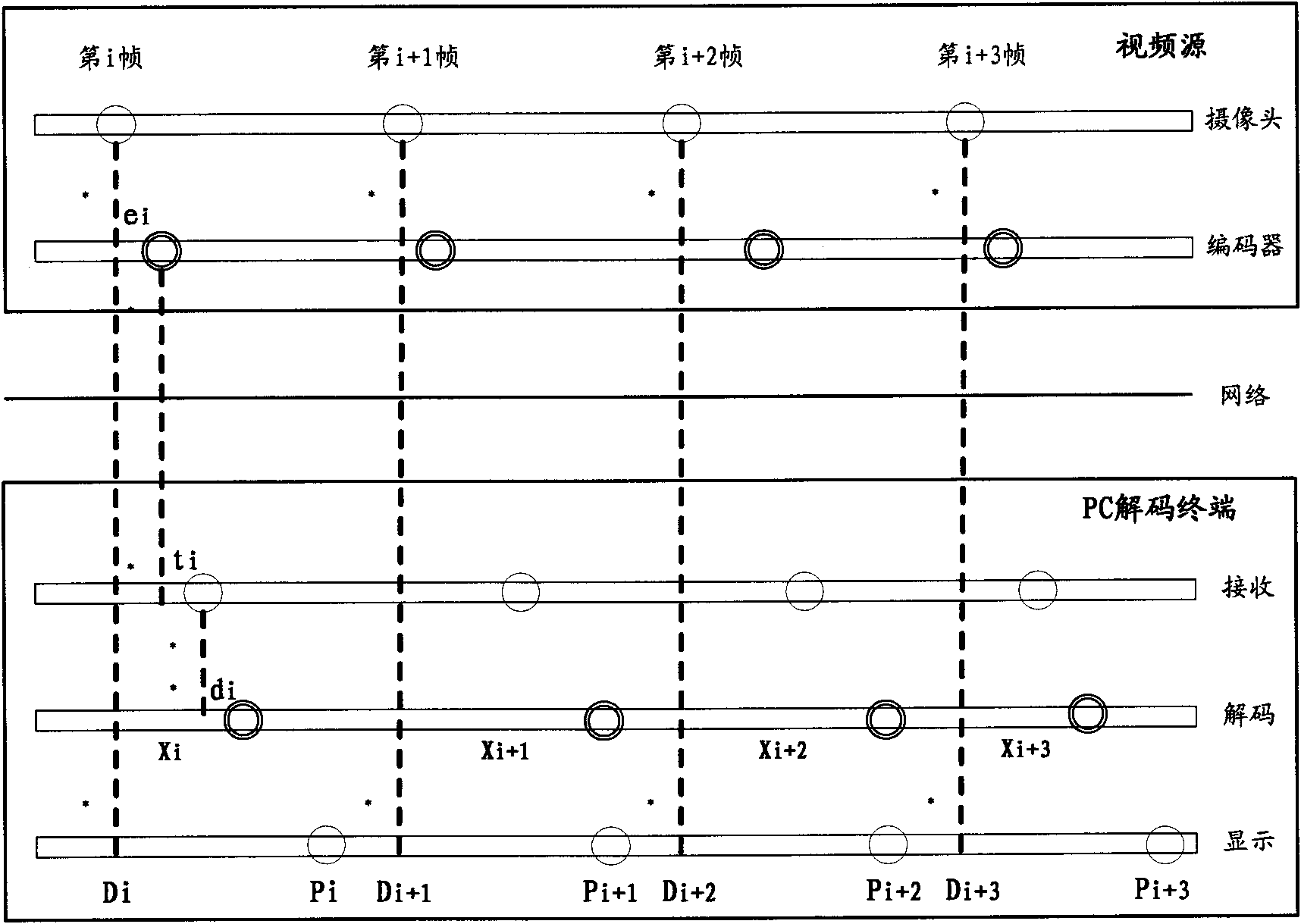
ActiveCN101807389AGuaranteed synchronizationEnsure uniform and continuousCathode-ray tube indicatorsTelevision systemsTimestampImaging quality
The invention discloses large screen splicing method and system, wherein the method comprises the following steps of: A, transmitting the same video stream to a plurality of PC (Personal Computer) decoding terminals connected through a network to ensure the synchronous transmission of data through the modes of UDP (User Datagram Protocol) multicasting transmission and the like; B, carrying out delay regulation on each PC decoding terminal through NTP (Network Time Protocol) clock synchronism and frame timestamp to ensure the image quality of a spliced large screen; and C, cutting and displaying part of the image by using each PC decoding terminal to ensure that the image of the spliced large screen is integral and non-overlapped. The invention realizes the infinite amplification on splicing the large screen through the infinite expansion of the PC terminal, realizes the flexible changes of the splicing size and the resolution ratio of the large screen through the arbitrary combination of the PC decoding terminals and ensures the synchronism of each part of the image of the spliced large screen as well as the uniformity and the continuity of the whole image through video delay regulation.
Owner:ENC DATA SERVICE CO LTD
Communications system
InactiveUS20090116487A1Acceptable performanceReduce chanceNetworks interconnectionTelecommunications linkCommunications system
A method of performing a multimedia communication session over a communication link using Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and over a communication link using User Datagram Protocol (UDP), including the acts of: receiving a request, over the TCP link, to register from a client terminal located within a private network; a probe data packet to the client terminal, over the TCP link, requesting to send a data packet over the UDP link; and receiving a data packet from the client terminal that contains information relating to an address of the client terminal and a dynamic port over which the multimedia communication session is to be established.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Systems and methods for reducing denial of service attacks against dynamically generated next secure records
ActiveUS20140344925A1Lower capability requirementsService degradationMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionData packIp address
In one aspect, the present disclosure is directed to a method for reducing denial of service (DoS) attacks against dynamically generated next secure (NSEC) records. A domain name system (DNS) proxy may prevent spoofed IP addresses by forcing clients to transmit DNS queries via transmission control protocol (TCP), by replying to a user datagram protocol (UDP) DNS request with a blank or predetermined resource record with a truncation bit set to indicate that the record is too large to fit within a single UDP packet payload. Under the DNS specification, the client must re-transmit the DNS request via TCP. Upon receipt of the retransmitted request via TCP, the DNS proxy may generate fictitious neighbor addresses and a signed NSEC record and transmit the record to the client. Accordingly, the DNS Proxy need not waste time and processor cycles generating and signing records for requests from spoofed IP addresses via UDP.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Automatic guided vehicle scheduling system and method based on global wireless precise positioning
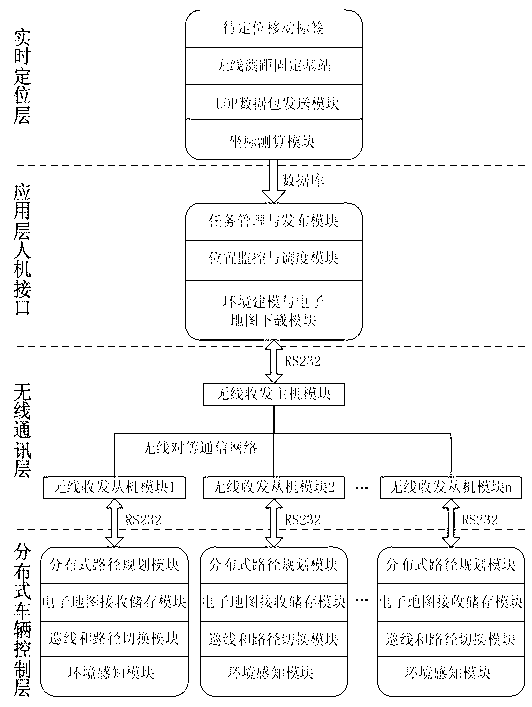
InactiveCN103309350AEnsure safetyReduce communication burdenElectric/hybrid propulsionTotal factory controlWireless transceiverEnvironmental perception
The invention provides an automatic guided vehicle scheduling system based on global wireless precise positioning. The system comprises a real-time positioning layer, an application layer man-machine interface, a distributive vehicle control layer and a wireless communication layer; the real-time positioning layer comprises a to-be-positioning mobile tag, a wireless ranging fixed base station, a UDP (user datagram protocol) datagram transmission module and a coordinate calculation module; the application layer man-machine interface comprises a task management and publishing module, a position monitoring and scheduling module and an environmental modeling and electronic map downloading module; the distributive vehicle control layer comprises a distributive route planning module, an electronic map receiving and storing module, a line patrol and route switching module and an environmental perception module; and the wireless communication layer comprises a wireless transceiver host module, a wireless transceiver slave module and a wireless peer-to-peer communication network. According to the system and the method provided by the invention, as the global real-time wireless accurate timing technology is introduced, the positions of all AGVs (automated guided vehicles) in the system are monitored in real time, and are fed back to a centralized main control computer, so that the computer can perform uniform scheduling on all equipment in the system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
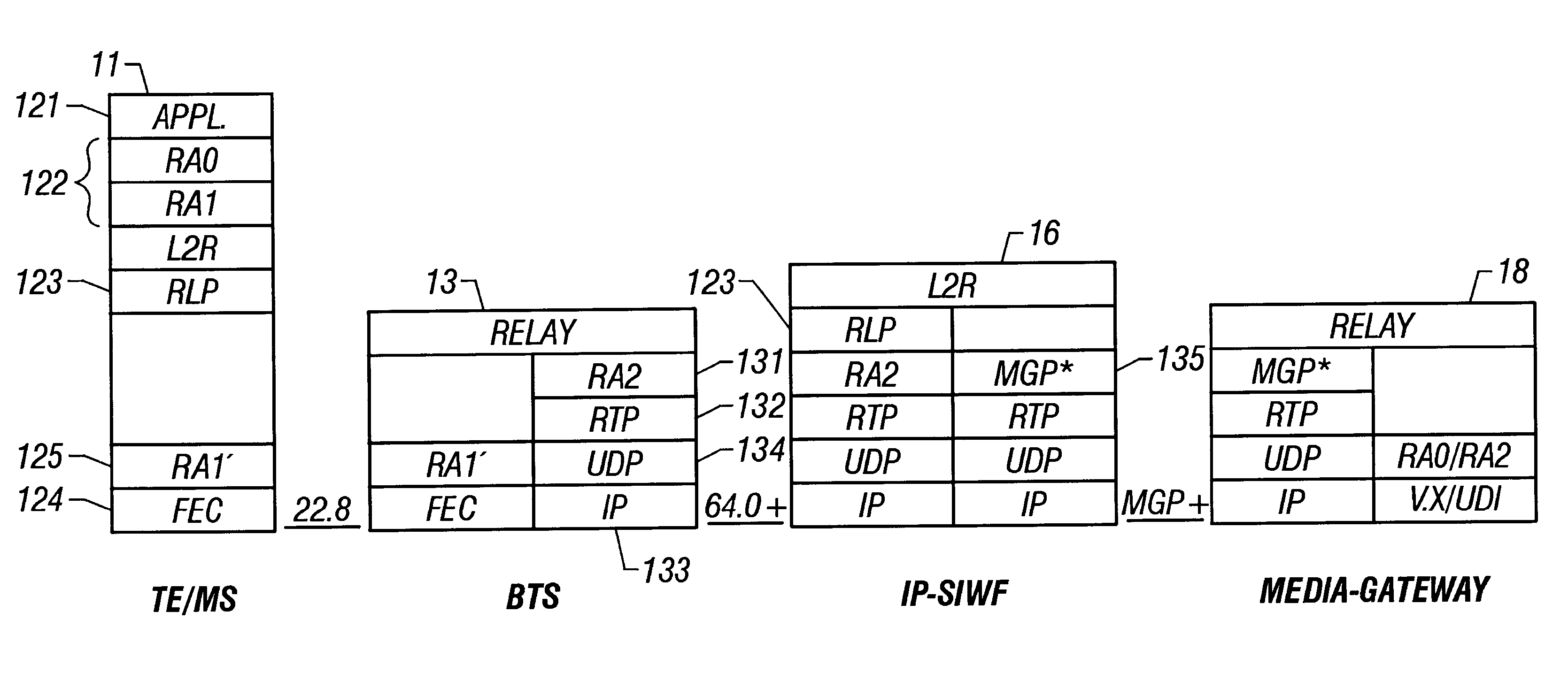
Interworking function in an internet protocol (IP)-based radio telecommunications network
InactiveUS6377799B1Time-division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsInternet protocol suiteTTEthernet
An Internet Protocol (IP)-based radio telecommunications network and method of providing data services to a mobile terminal. An Internet Protocol Shared Interworking Function (IP-SIWF) is implemented in the network, and is controlled from a Mobile Switching Center (MSC) utilizing the Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) device control protocol. When a data call carrying a data payload is originated by a mobile terminal, the data call is transported utilizing radio access and radio link protocols to the IP-SIWF. The radio access and radio link protocols are terminated in the IP-SIWF, and the data payload is transported thereafter utilizing a real time protocol over a User Datagram Protocol (UDP) and an IP protocol layer.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com