Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
123 results about "Traceroute" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
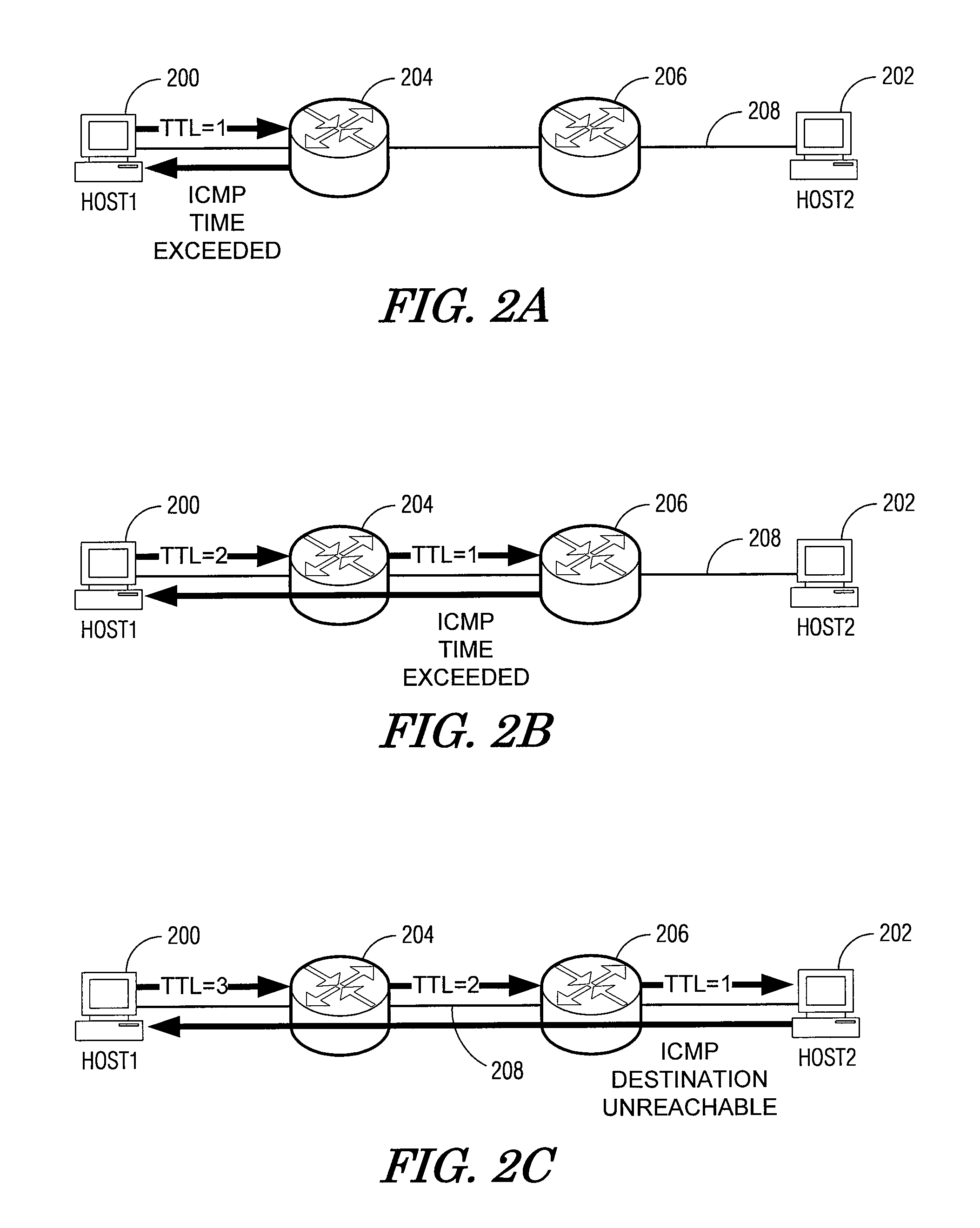
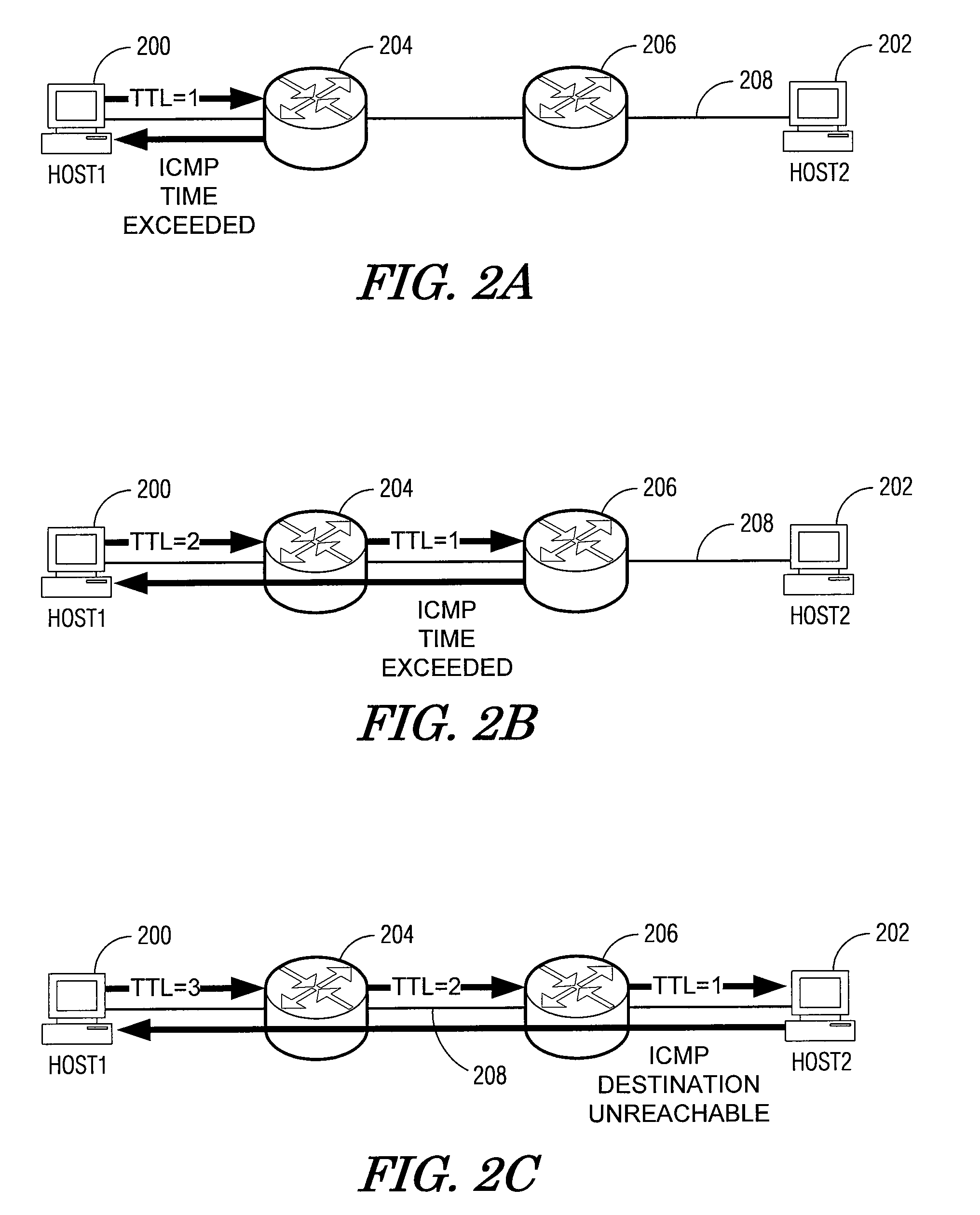
In computing, traceroute and tracert are computer network diagnostic commands for displaying the route (path) and measuring transit delays of packets across an Internet Protocol (IP) network. The history of the route is recorded as the round-trip times of the packets received from each successive host (remote node) in the route (path); the sum of the mean times in each hop is a measure of the total time spent to establish the connection. Traceroute proceeds unless all (three) sent packets are lost more than twice; then the connection is lost and the route cannot be evaluated. Ping, on the other hand, only computes the final round-trip times from the destination point.
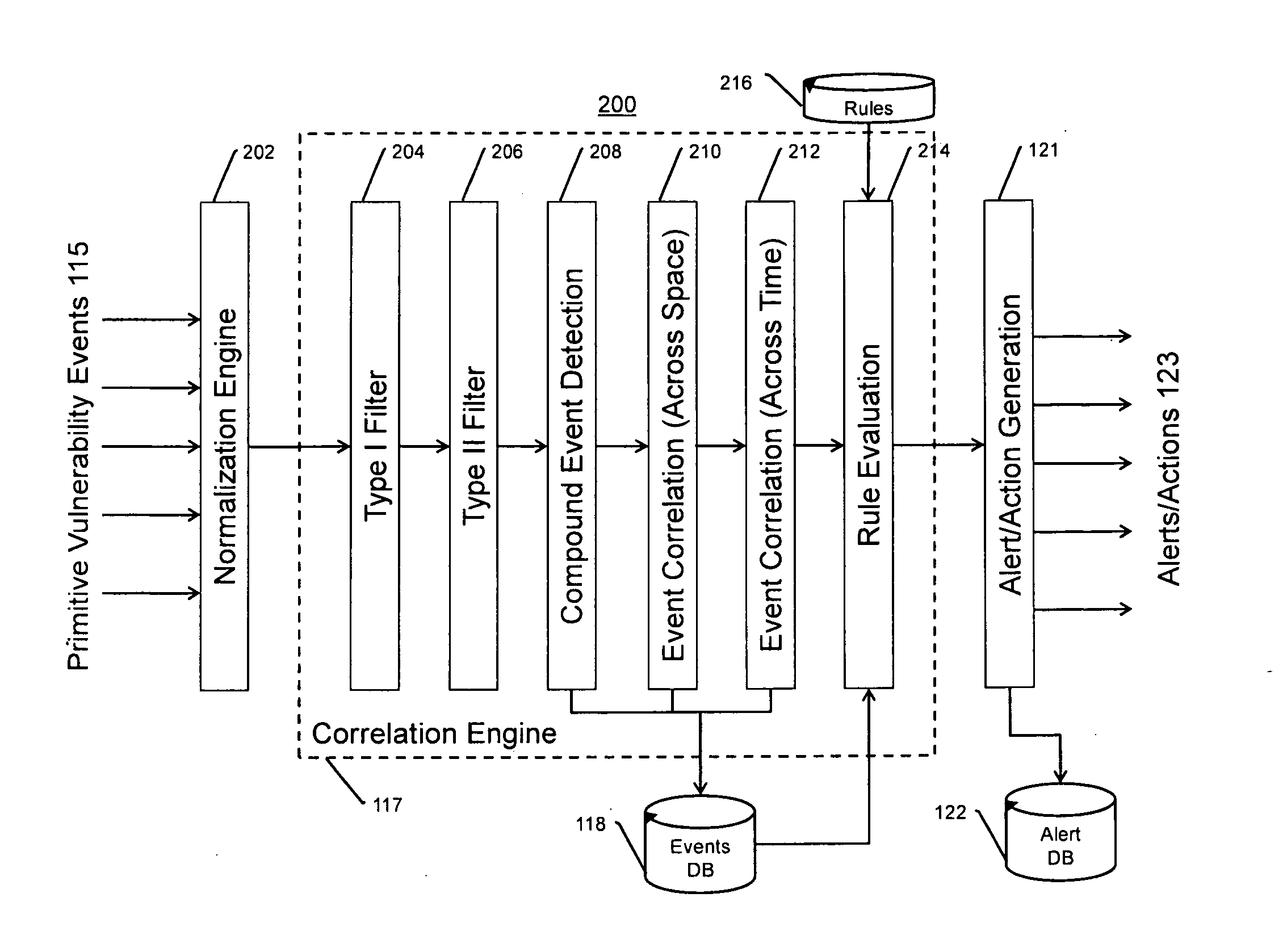
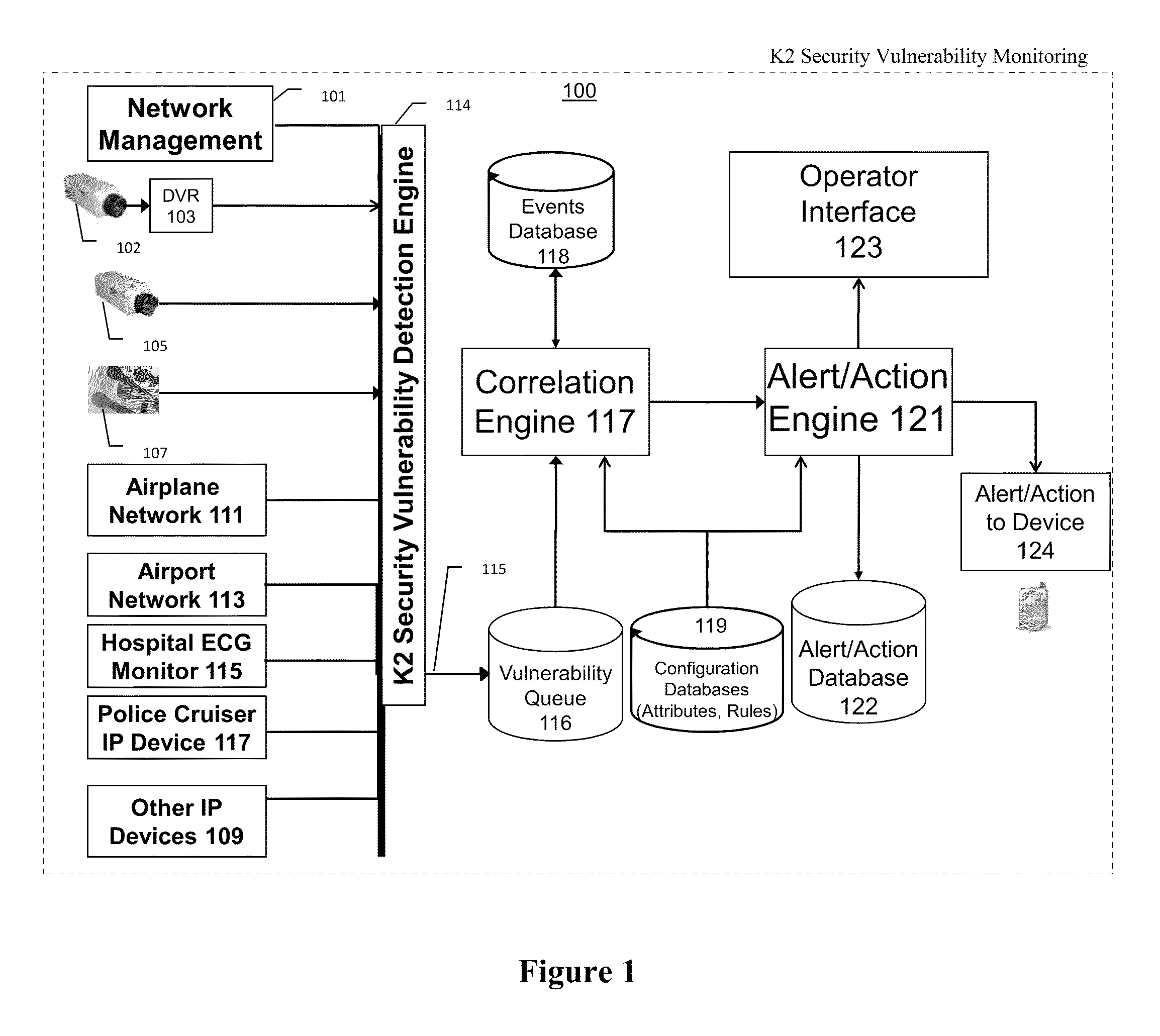
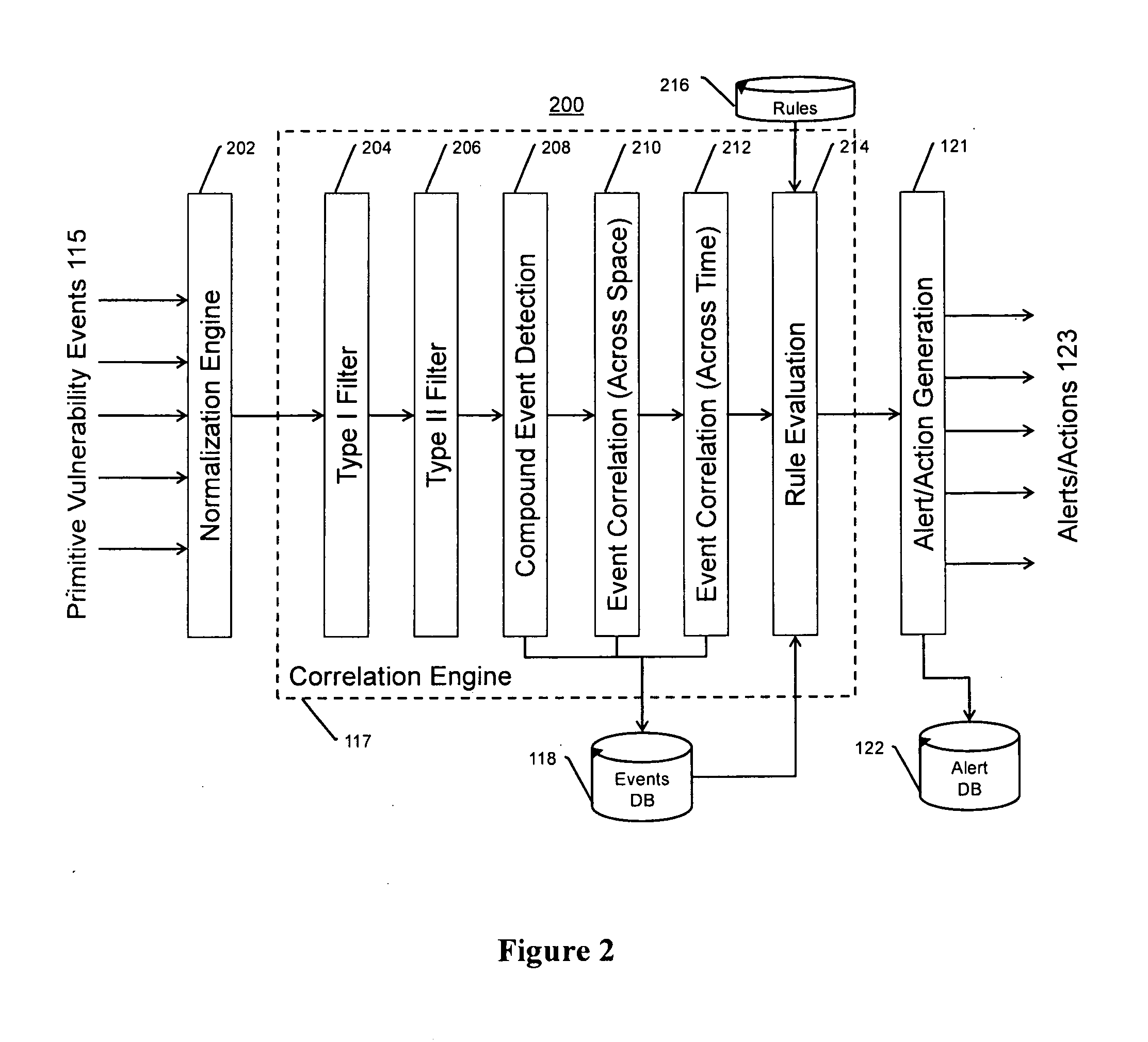
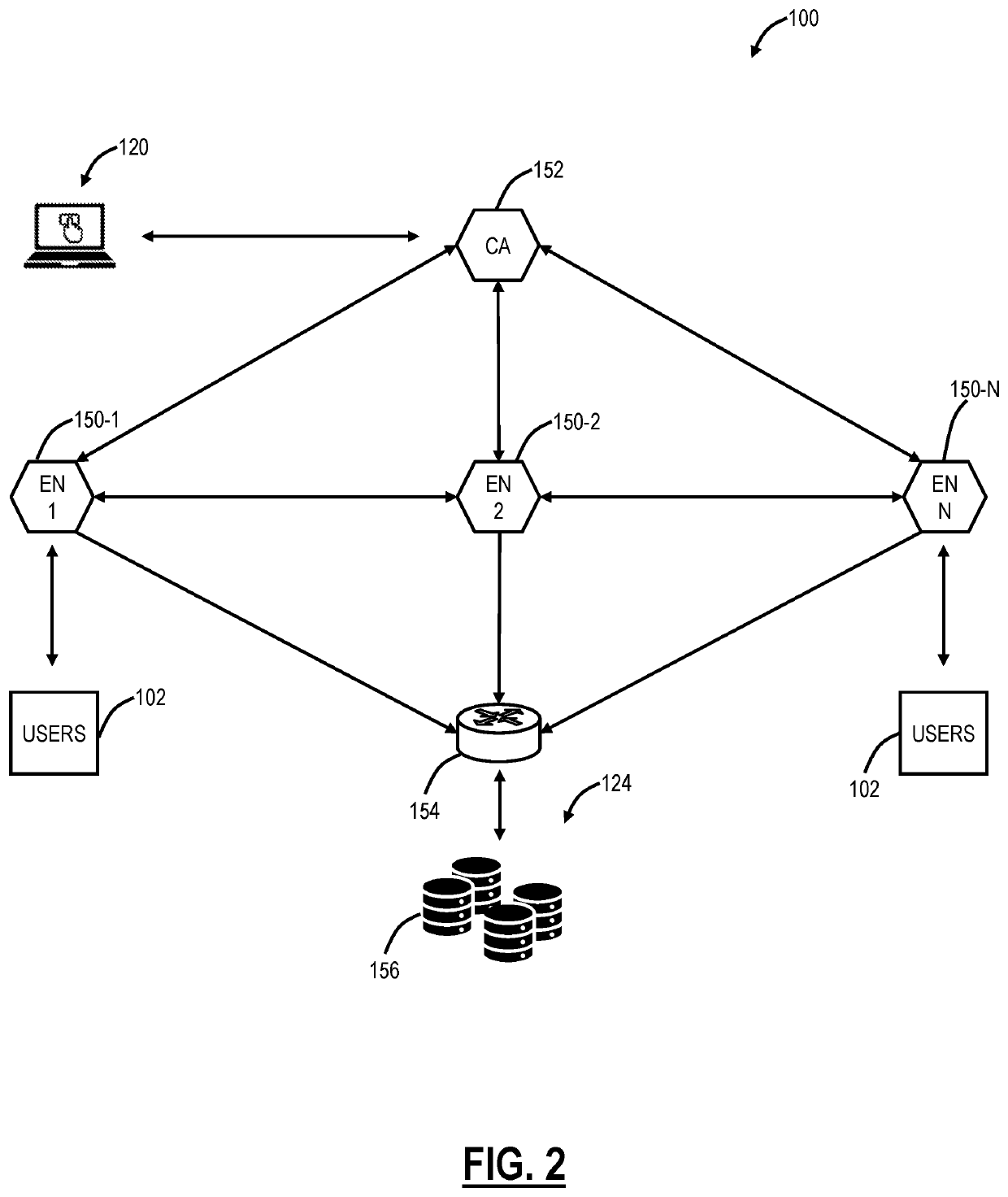
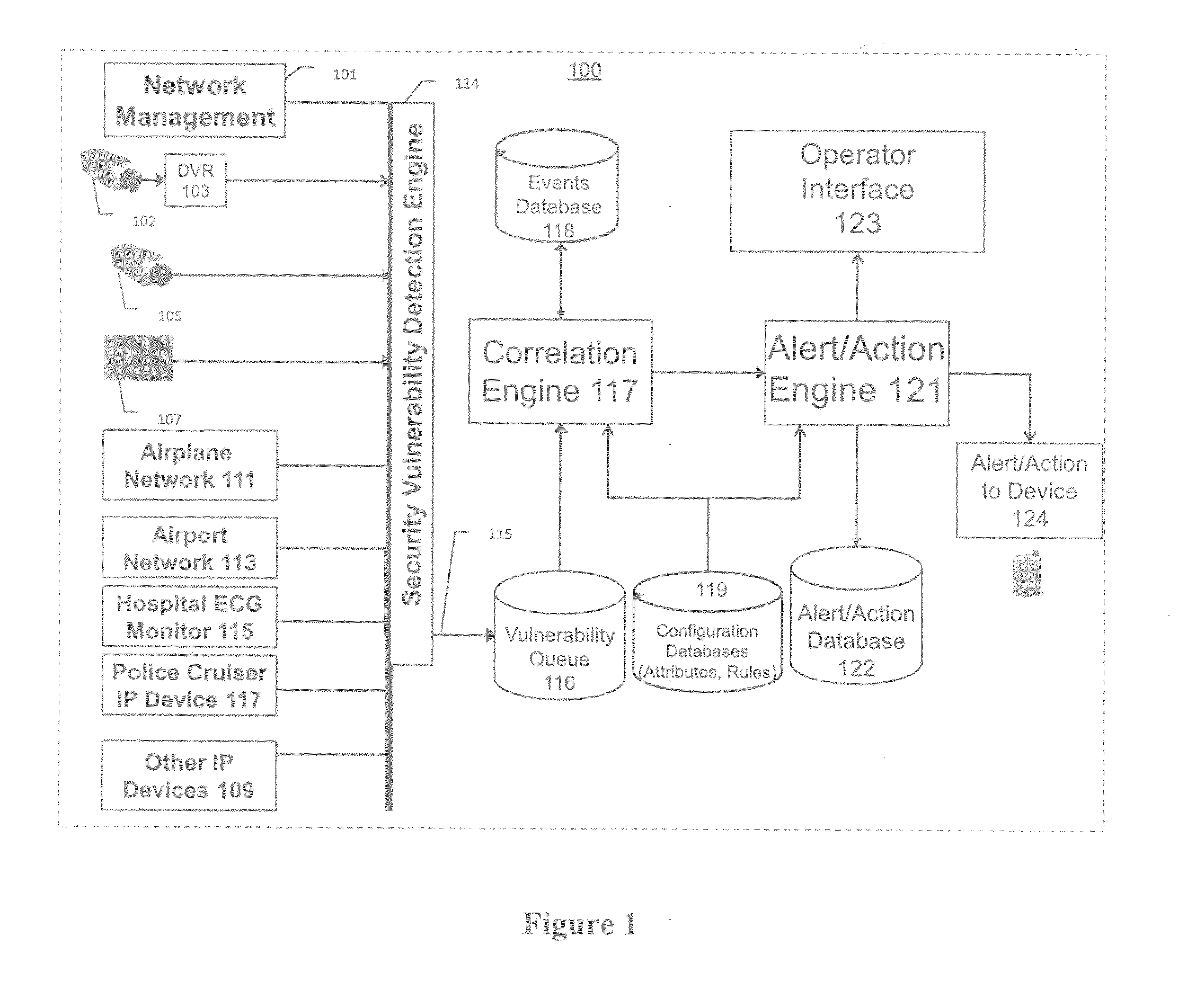
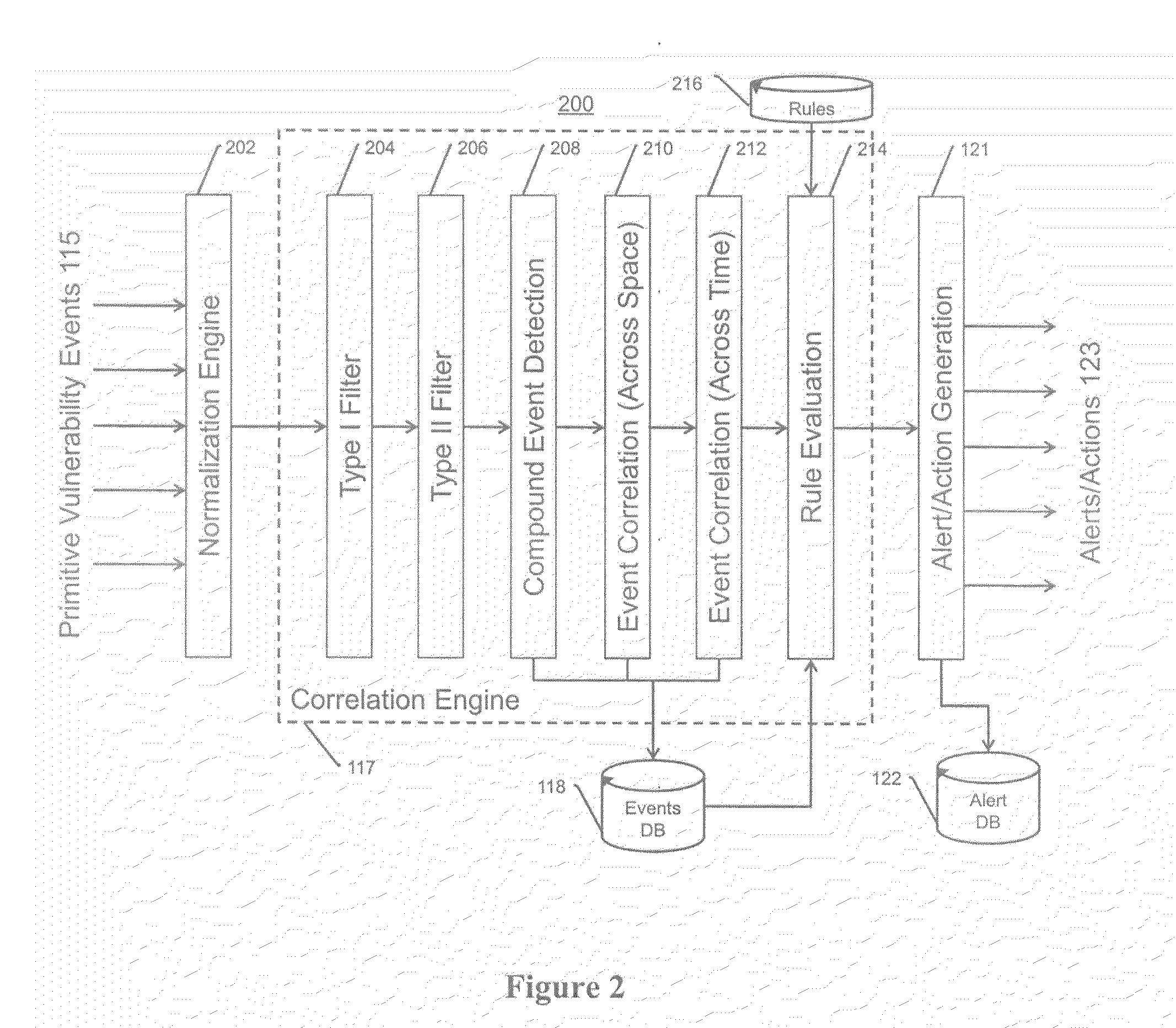
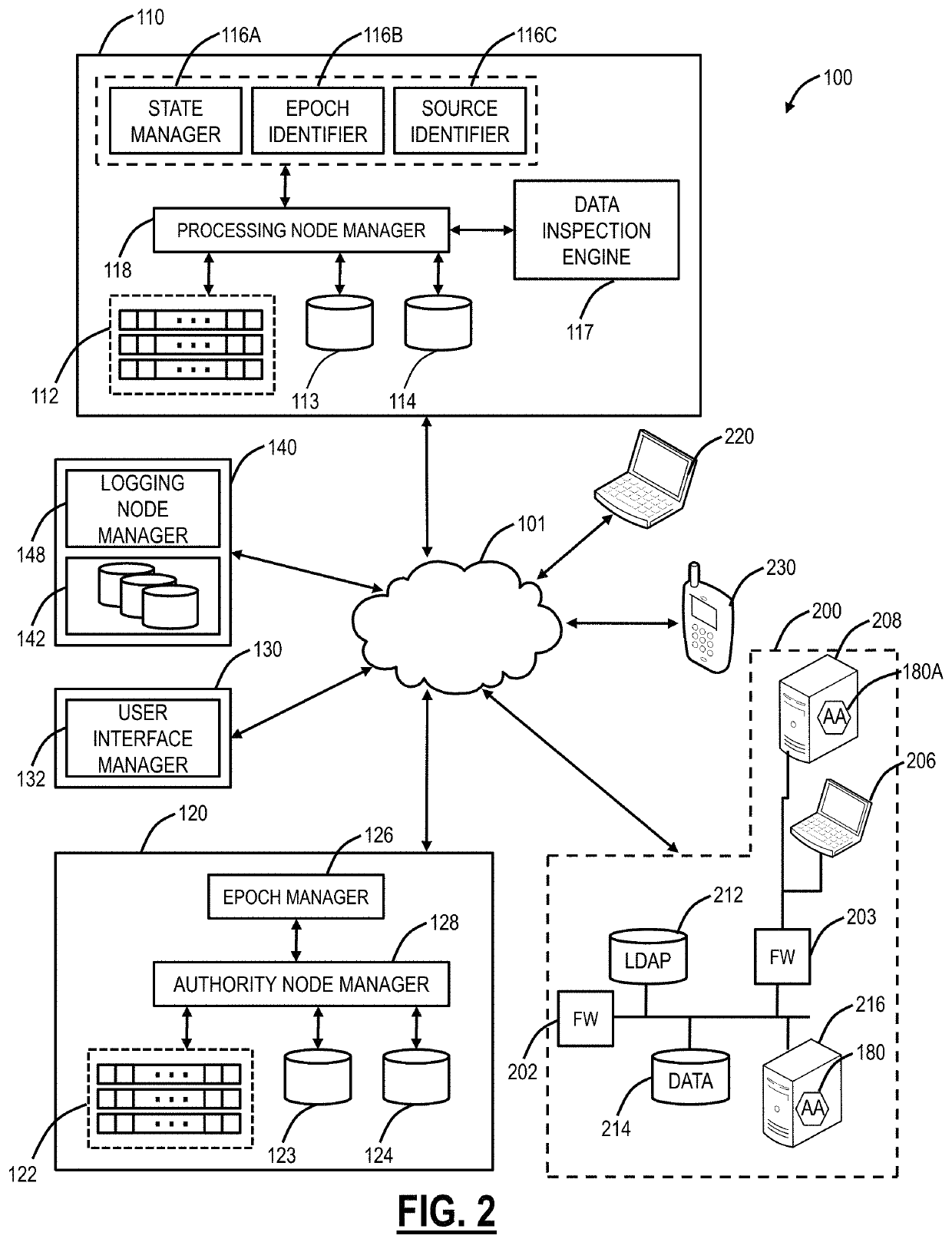
Systems, methods, and devices for detecting security vulnerabilities in IP networks
InactiveUS20100262688A1Detect and prevent spoofingEasy to addMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsBaseline dataData stream
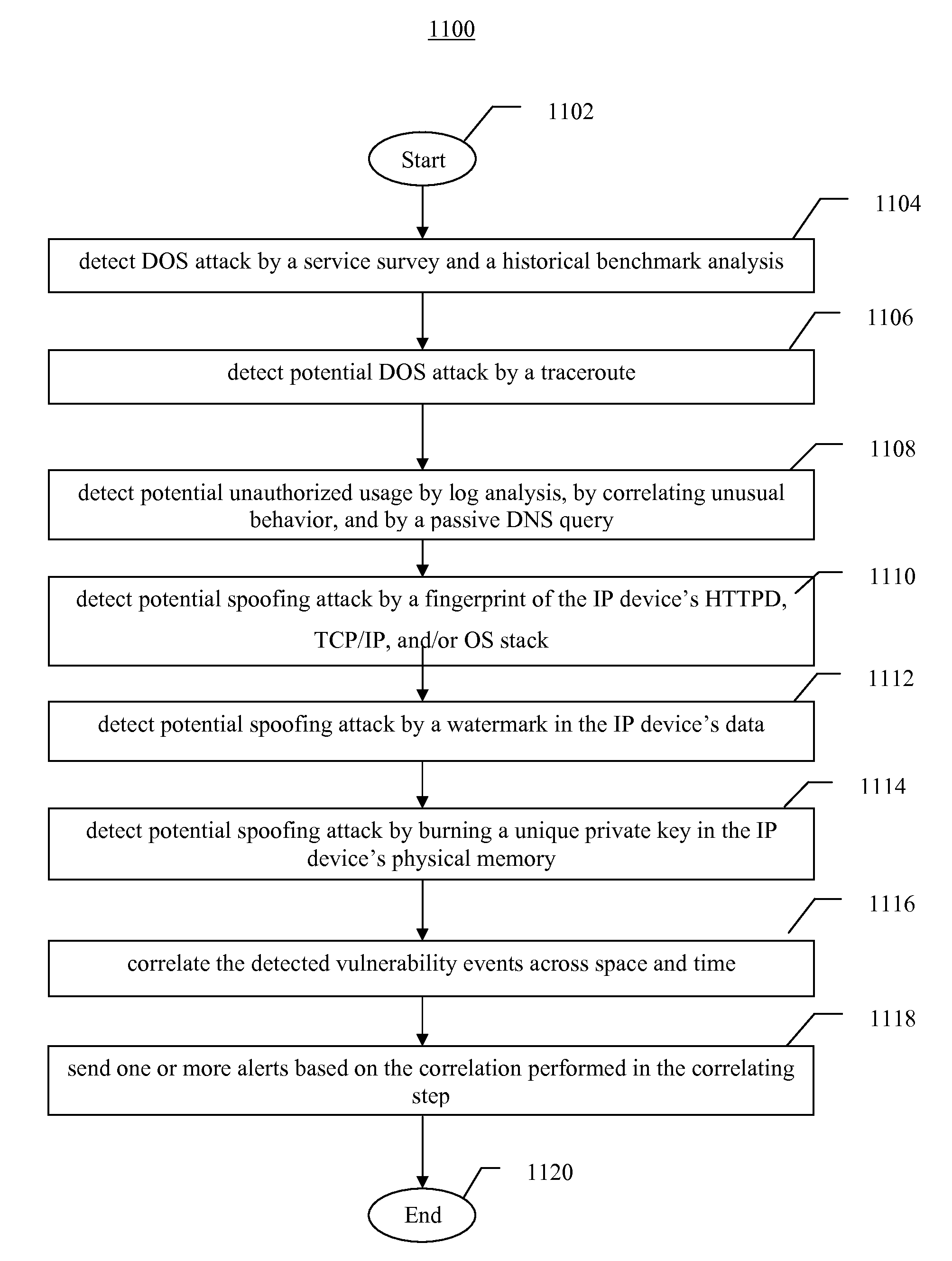
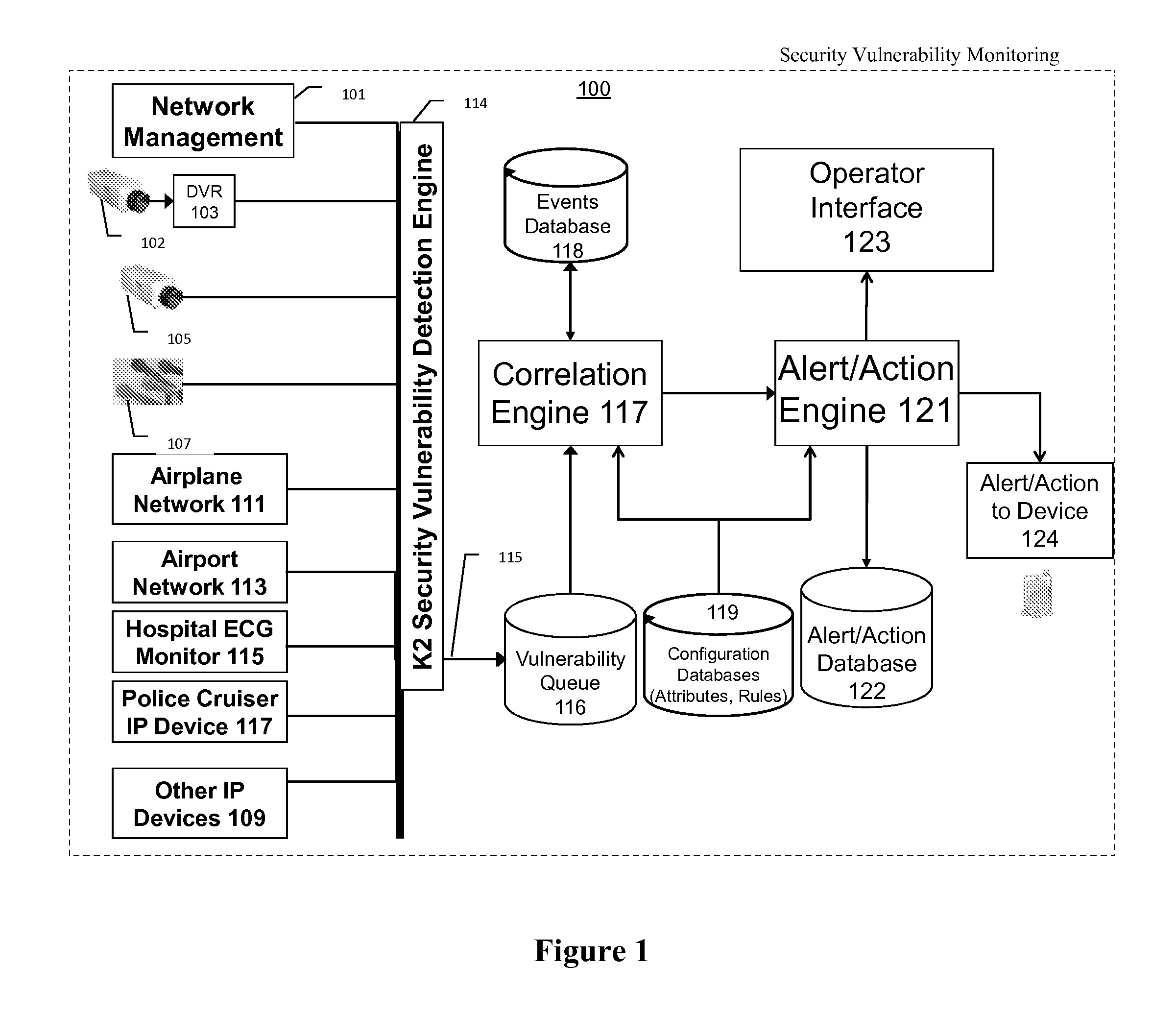
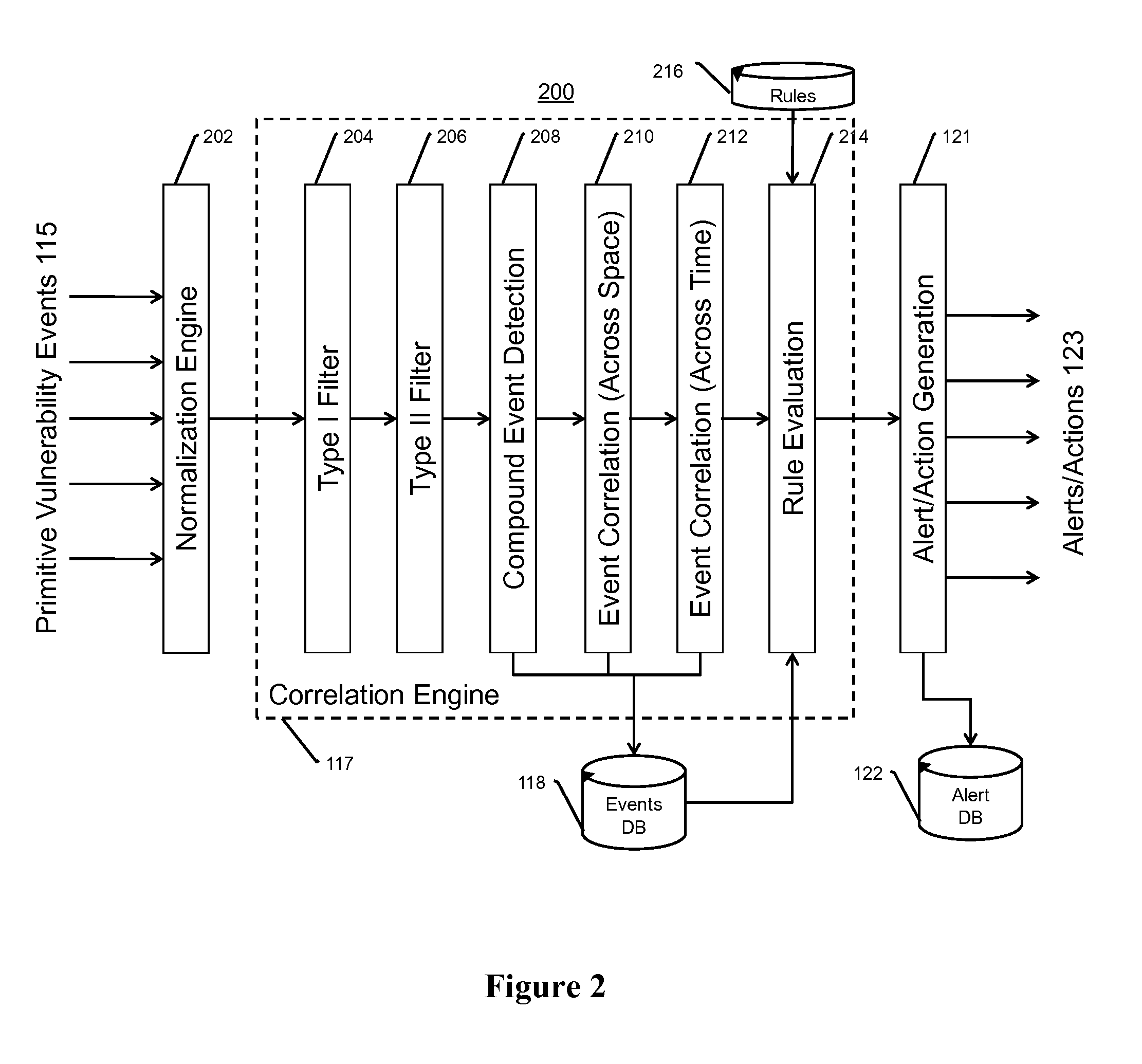
This invention is a system, method, and apparatus for detecting compromise of IP devices that make up an IP-based network. One embodiment is a method for detecting and alerting on the following conditions: (1) Denial of Service Attack; (2) Unauthorized Usage Attack; and (3) Spoofing Attack. A survey of services running on the IP device, historical benchmark data, and traceroute information may be used to detect a possible Denial of Service Attack. A detailed log analysis and a passive DNS compromise system may be used to detect a possible unauthorized usage. Finally, a fingerprint of the IP device or its configuration settings, a watermark inserted in the data-stream, and a private key burned into the IP devices' physical memory may be used to detect a possible spoofing attack. The present invention may be used to help mitigate intrusions and vulnerabilities in IP networks.
Owner:HUSSAIN DANIAR +1
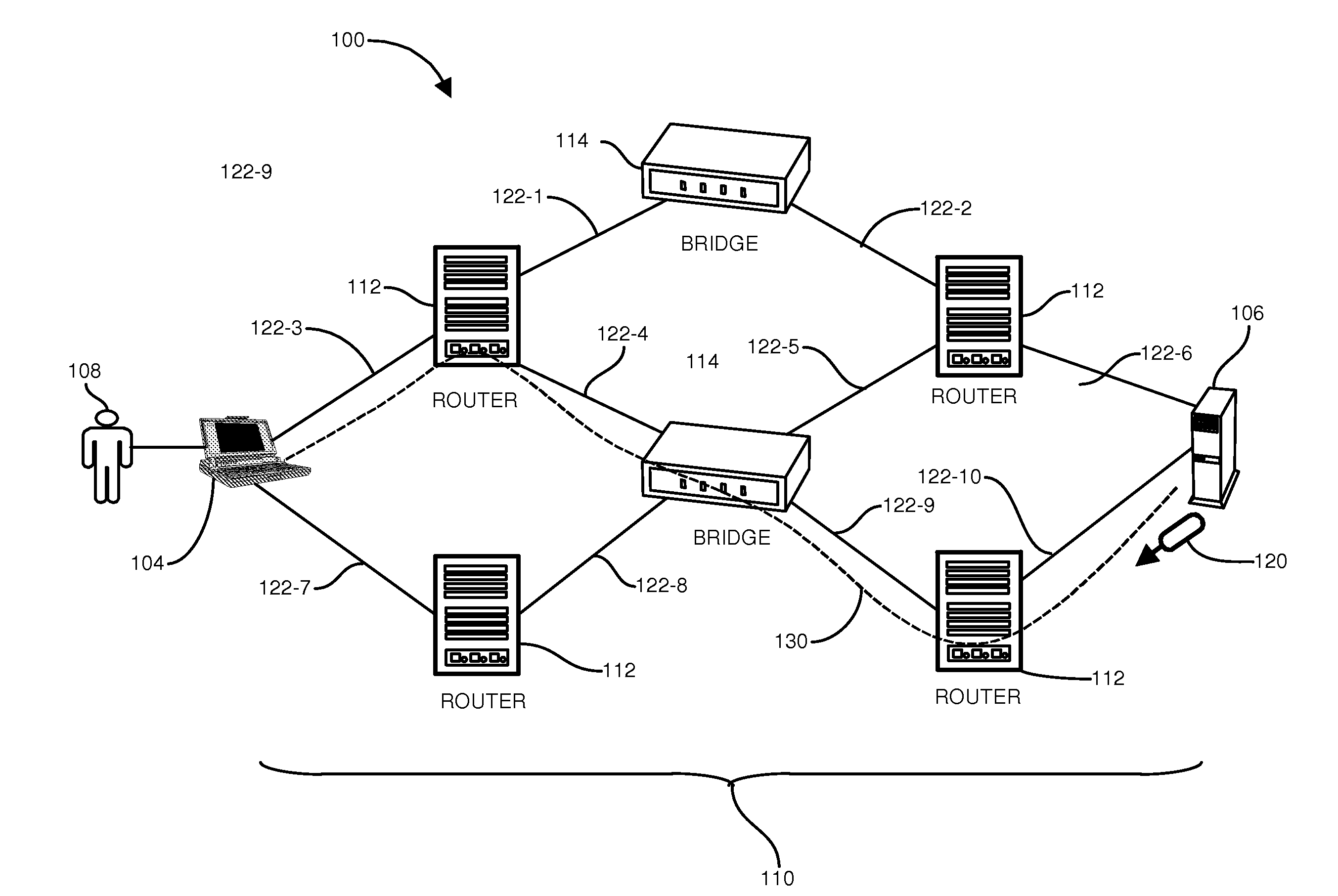
Network geo-location system
ActiveUS20050021738A1Prevent address spoofing (forging)Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionTracerouteIp address
A method for accurately determining the geographic location of a PC or other networked device on the Internet. Client software furnished by a service provider performs trace-route or other network analysis commands to known servers (e.g., eBay, Yahoo, Amazon) or even servers at random locations. The client collects an array of IP address and other network information as a result of the trace-routes, and the trace-route IP information is then transmitted to the service provider that is trying to identify the geographic location of the client. Using the array of IP addresses thus generated, the Internet server software can analyze location information of each Internet hop within each trace-route. For example, the server might look at the first five hops from the client to the server. If four of the five routers have addresses within the geographic area of interest, the server can conclude that the client is probably within the geographic area.
Owner:BLOCKBUSTER LLC
LSP ping and traceroute for bypass tunnels
ActiveUS7937492B1Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationTracerouteLabel switching
A method performed by a network device may include assembling a multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) echo request, the echo request including an instruction for a transit node to forward the echo request via a bypass path associated with the transit node, and an instruction for an egress node to send an echo reply indicating that the echo request was received on the bypass path. The method may also include sending the MPLS echo request over a functioning label switched path (LSP).
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
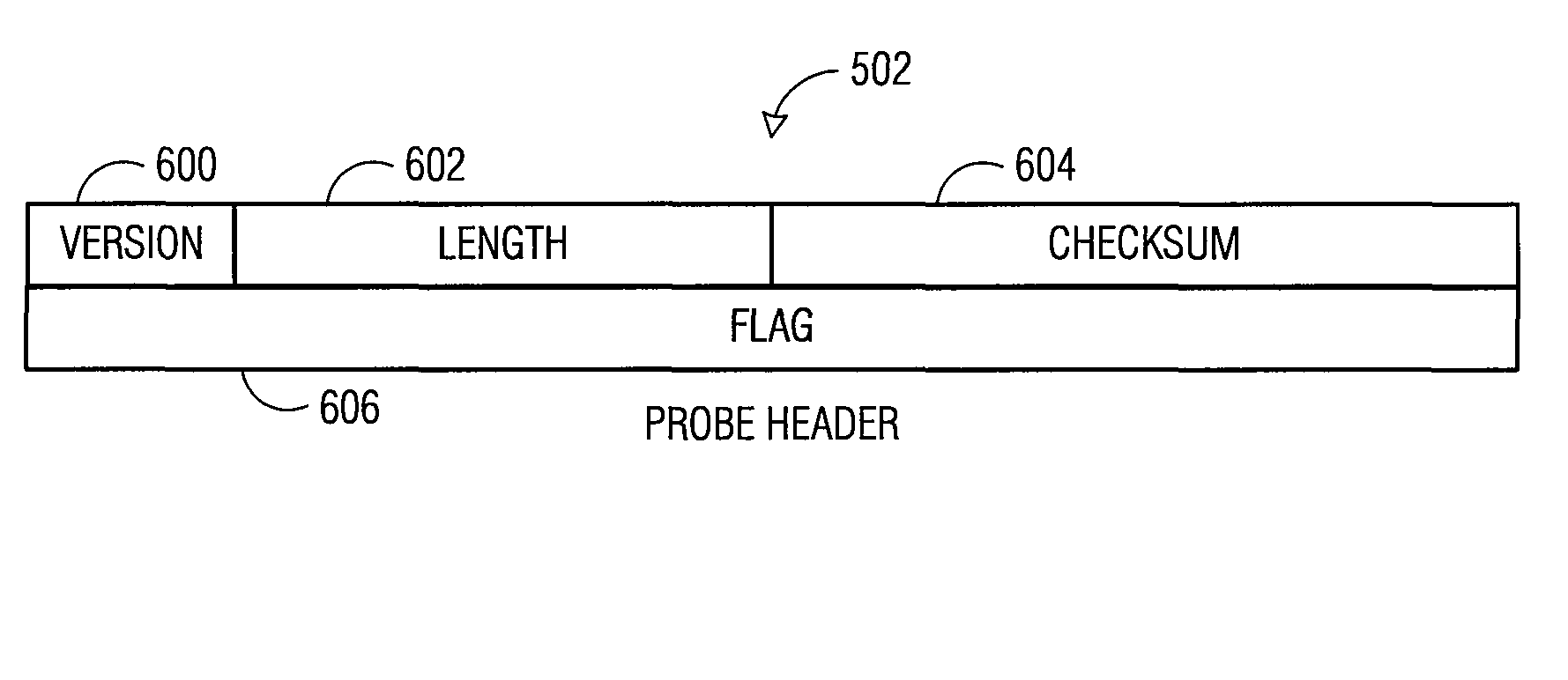
User datagram protocol traceroute probe extension
The embodiments described herein provide methods and apparatuses for implementing a User Datagram Protocol traceroute probe extension. In an example embodiment, a request to transmit a User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packet to a remote destination is received. A probe header and a probe data element is then stored in a data field of the UDP packet. The UDP packet is then transmitted toward the remote destination. In an example embodiment, a User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packet is received and it is determined whether the UDP packet includes a probe data structure. When the determination is affirmative, the probe data structure is processed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
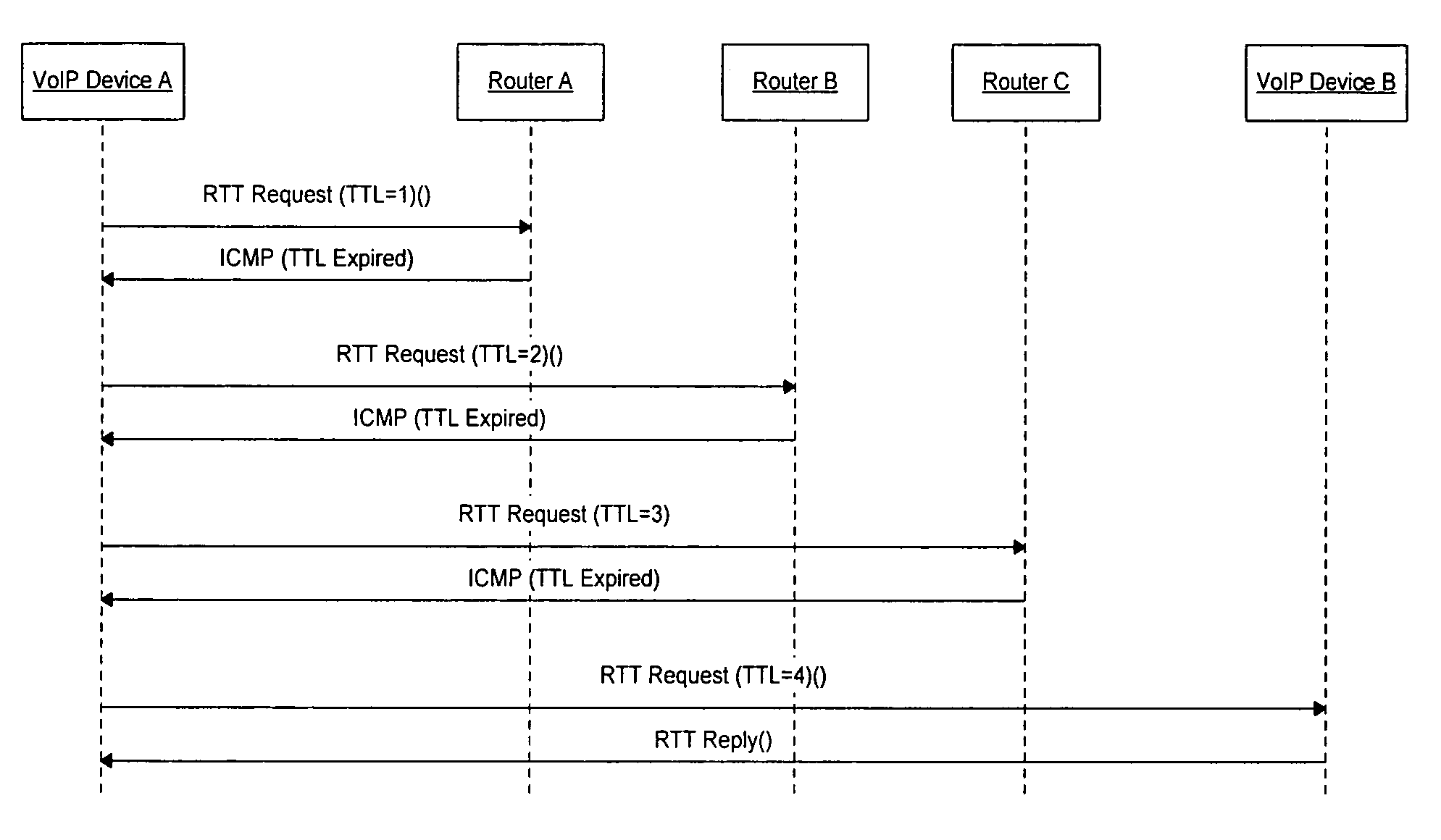
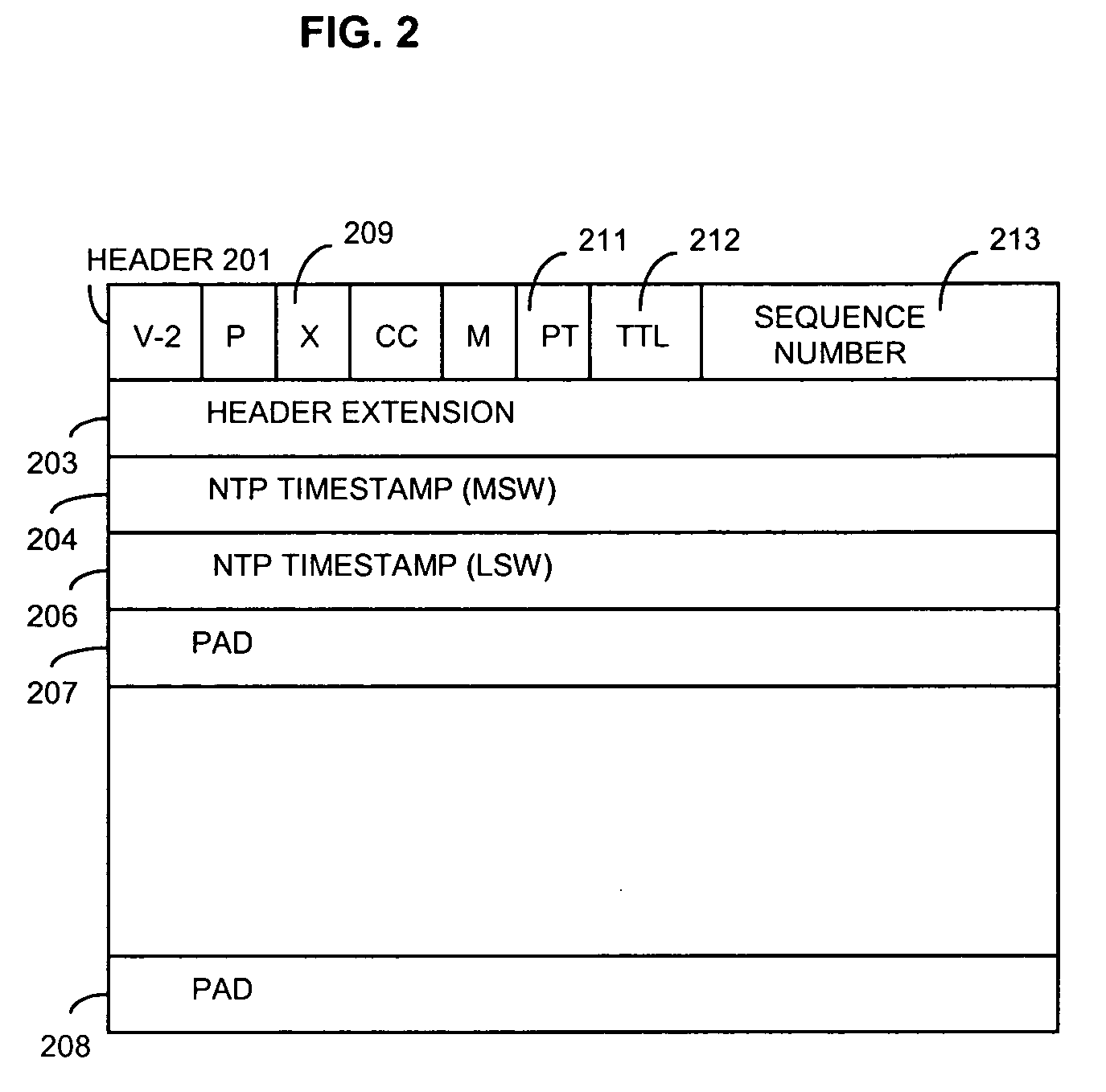
Method and apparatus for providing trace route and timing information for media streams
An apparatus and method that use RTP packets with a specially define profile to determine the traceroute and round-trip-time information.
Owner:AVAYA INC
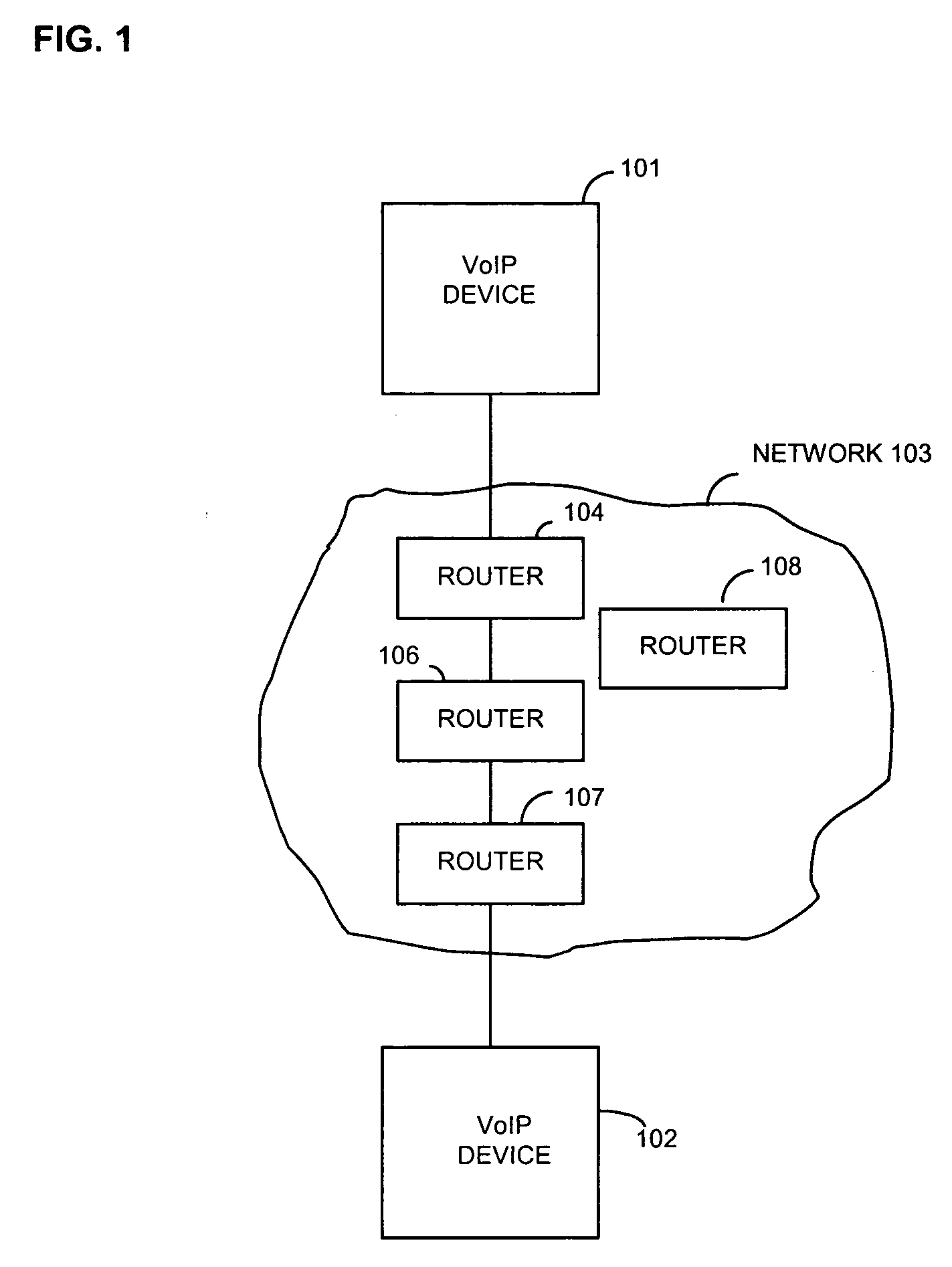
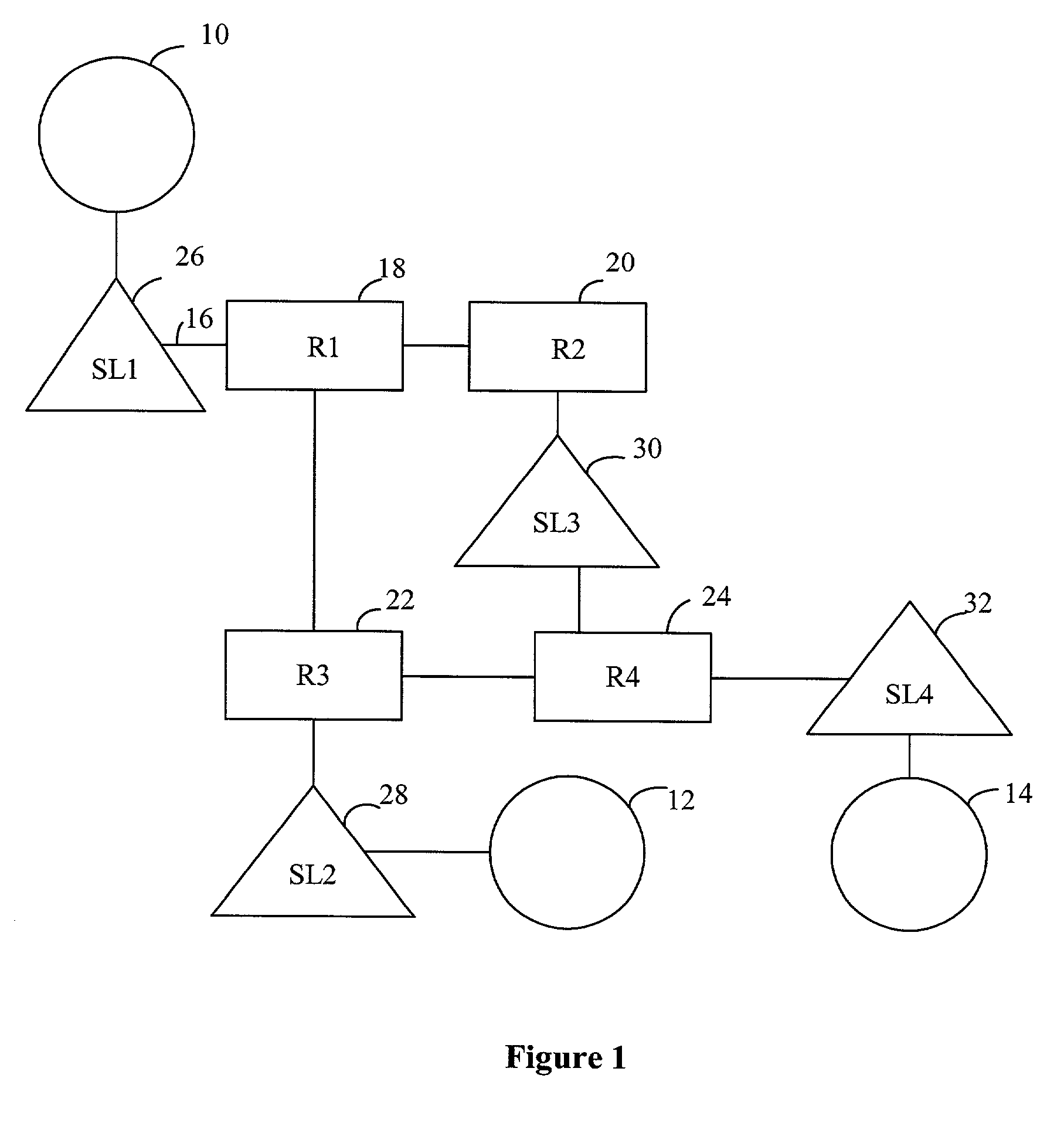
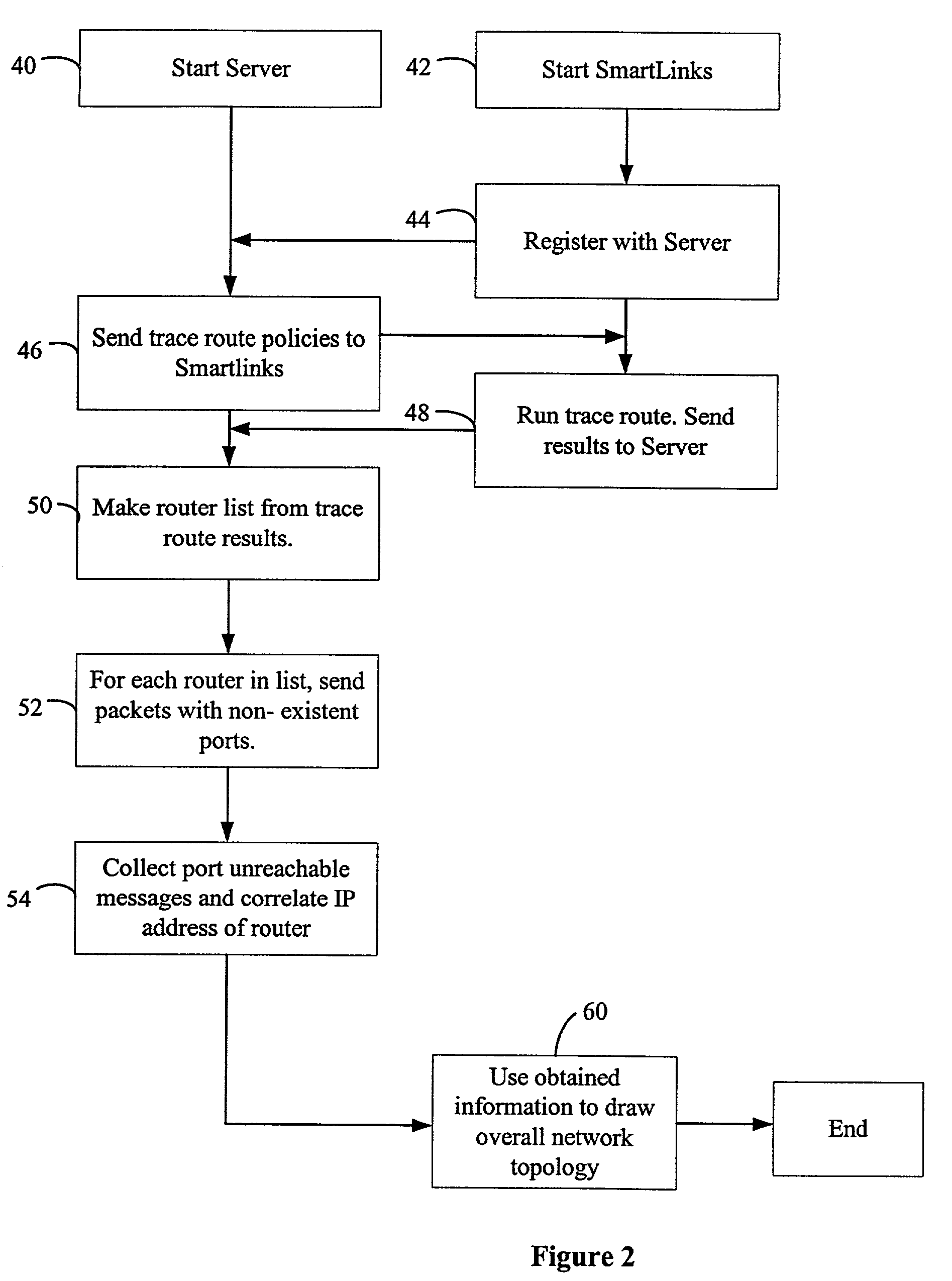
Method and apparatus for discovering network topology
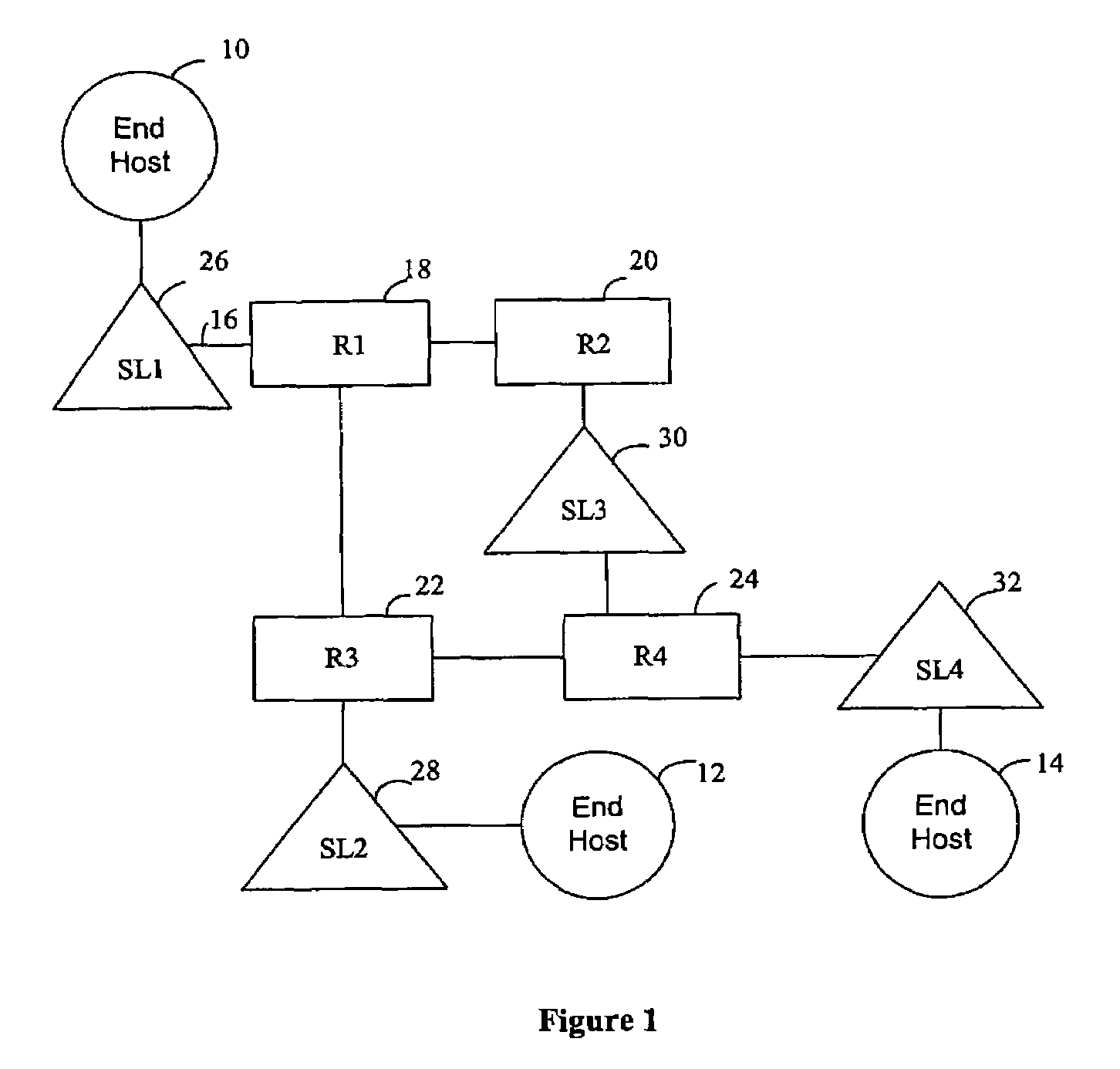
A method and apparatus are provided that allow the automatic discovery of the topology of a network. In one embodiment, the invention includes identifying a second network device at a first network device, sending a message from the first network device to the second network device, the message establishing the identity of any network device between the first network device and the second network device, and compiling the established identities to determine the topology of the network. The invention can use PING and Traceroute utilities to find nodes and identify network devices.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Network multi-path discovery
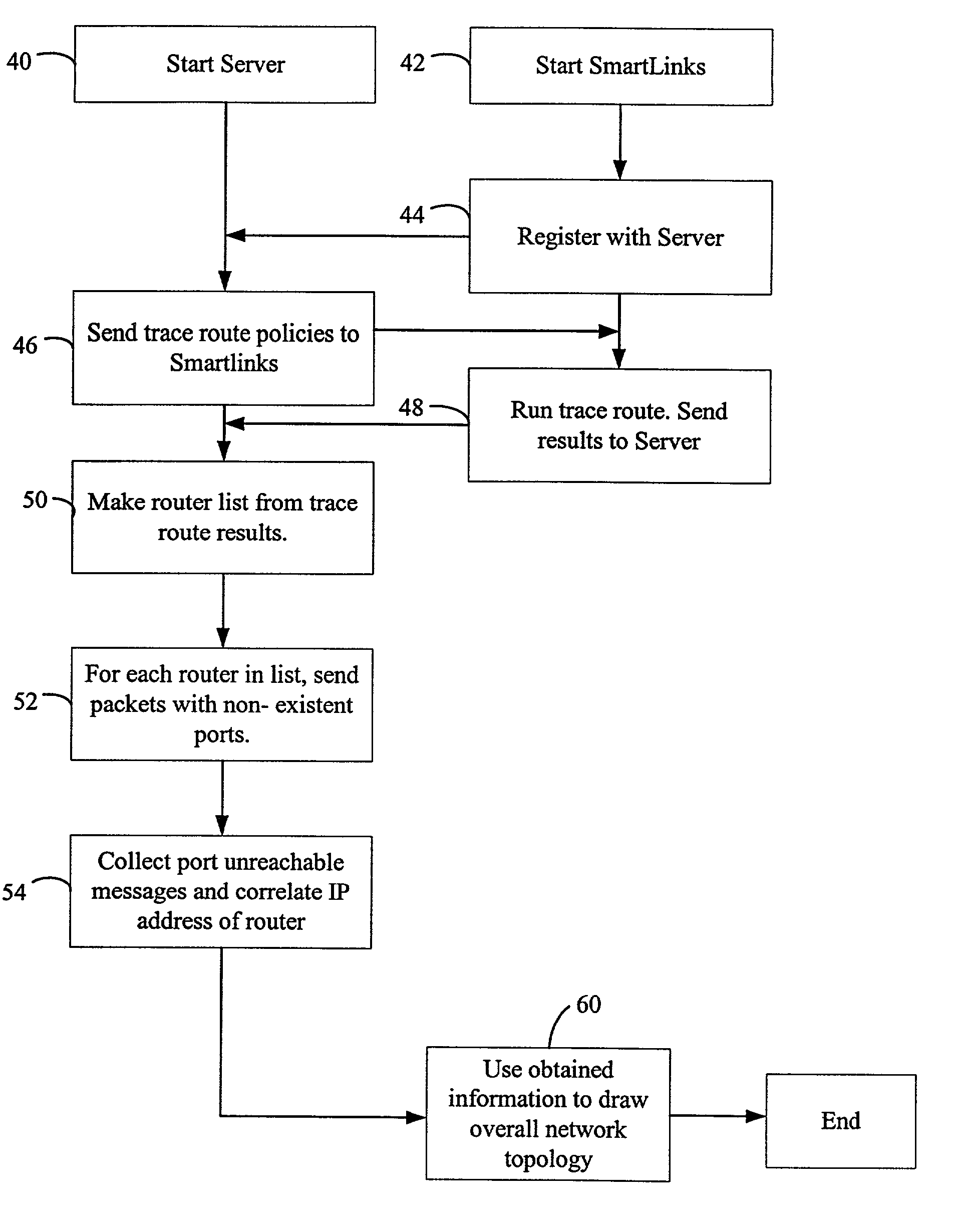
Potential paths between a source and destination of a network are identified based on trace-route information, then filtered to eliminate paths or links that are not supported by ancillary information associated with the network so as to identify feasible / actual paths between the source and destination. The ancillary information includes, for example, routing tables and ARP tables. If a feasible path cannot be identified based on the ancillary information, supplemental information regarding nodes further along the potential path is assessed to provide a basis for inferring the nodes that may provide a feasible path. The determined feasible paths are displayed for review, and provided to serve as filters for subsequent path-analysis tools.
Owner:RIVERBED TECH LLC
Real-time services network quality control
Owner:TITUS TIMOTHY G
Systems, methods, and devices for detecting security vulnerabilities in IP networks
InactiveUS20100125663A1Easy to addMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionBaseline dataCamera image
This invention is a system, method, and apparatus for detecting compromise of IP devices that make up an IP-based network. One embodiment is a method for detecting and alerting on the following conditions: (1) Denial of Service Attack; (2) Unauthorized Usage Attack (for an IP camera, unauthorized person seeing a camera image); and (3) Spoofing Attack (for an IP camera, unauthorized person seeing substitute images). A survey of services running on the IP device, historical benchmark data, and traceroute information may be used to detect a possible Denial of Service Attack. A detailed log analysis and a passive DNS compromise system may be used to detect a possible unauthorized usage. Finally, a fingerprint (a hash of device configuration data) may be used as a private key to detect a possible spoofing attack. The present invention may be used to help mitigate intrusions and vulnerabilities in IP networks.
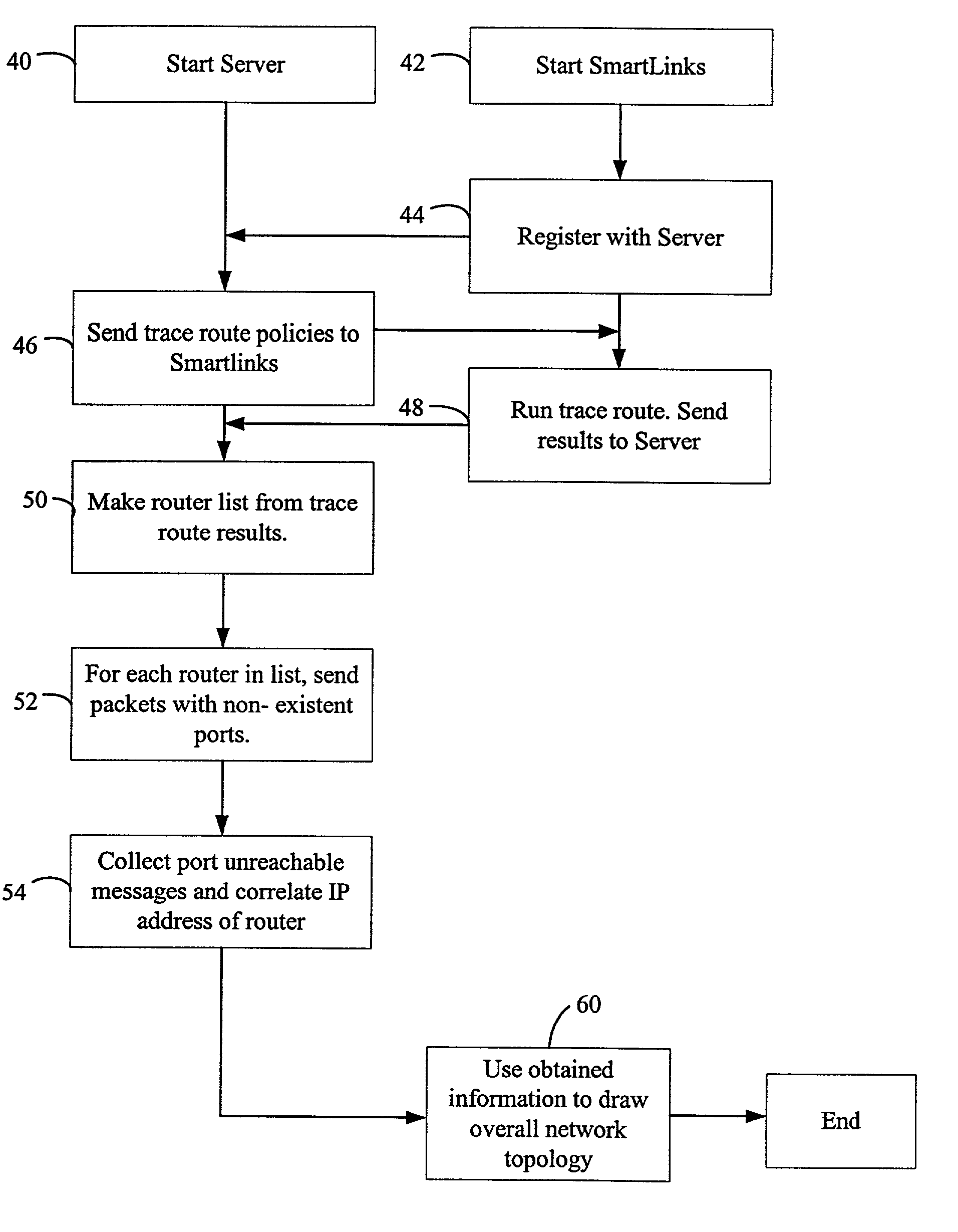
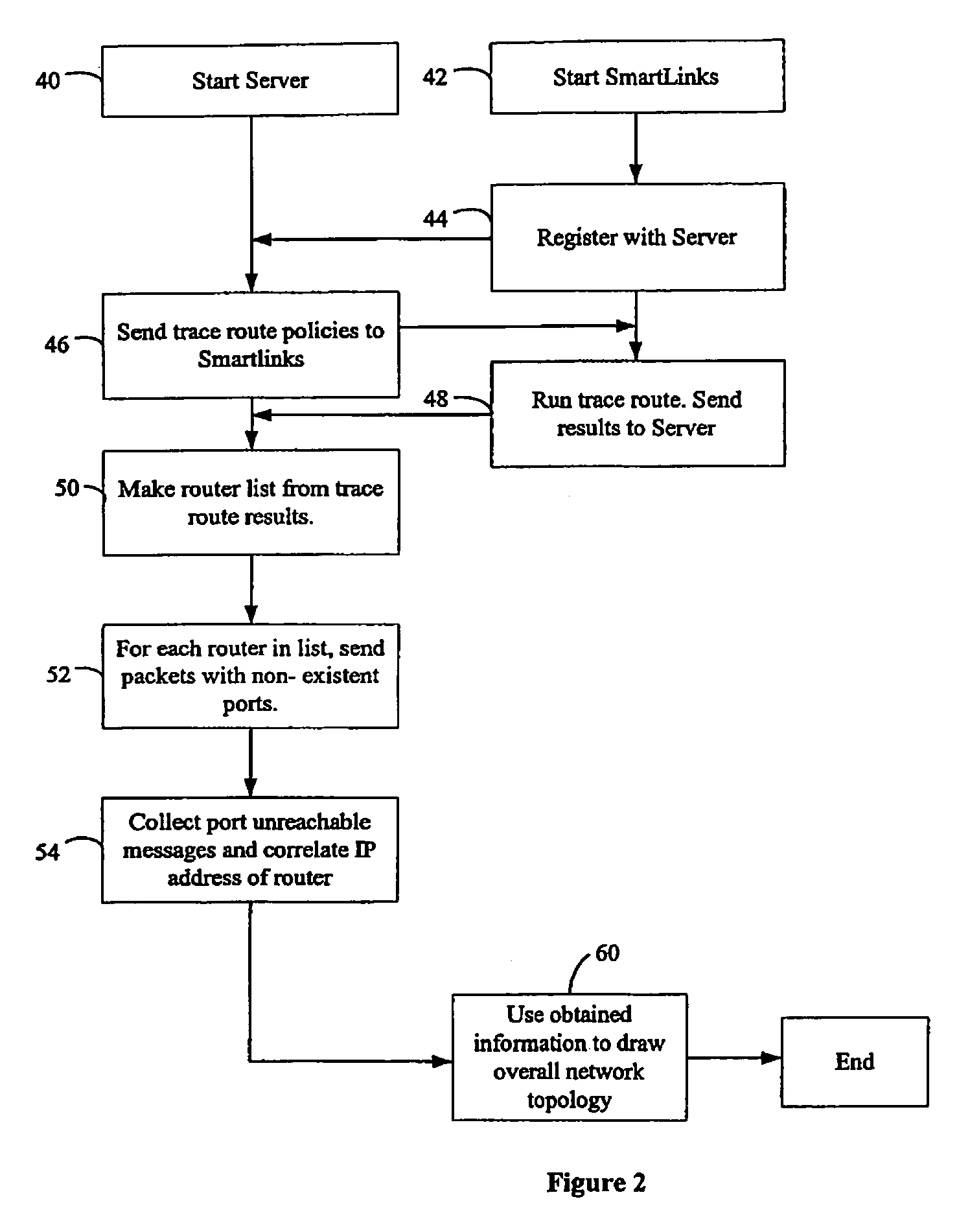
Owner:DNSSTUFF
Multi-layer network diagnostic tracing
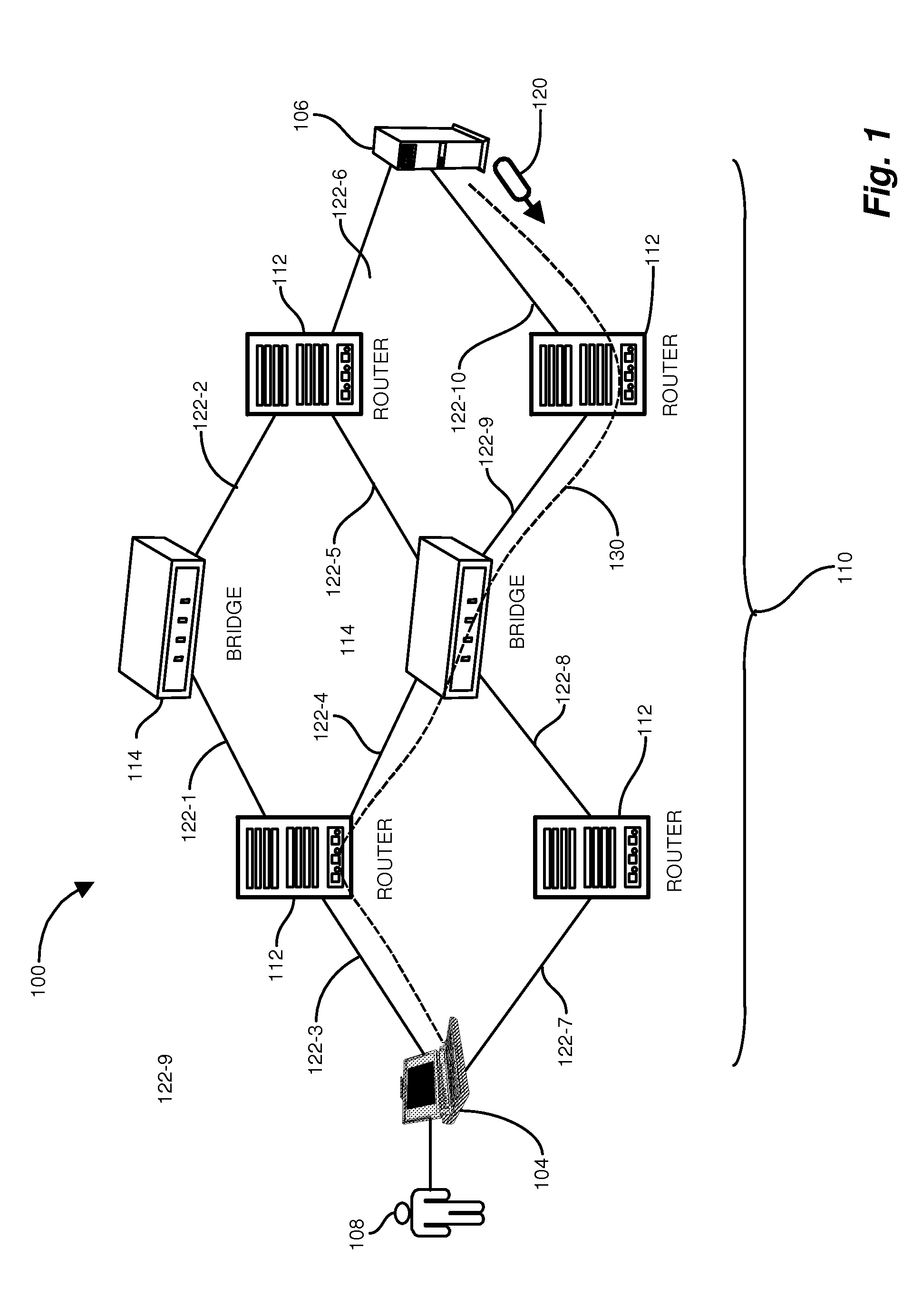
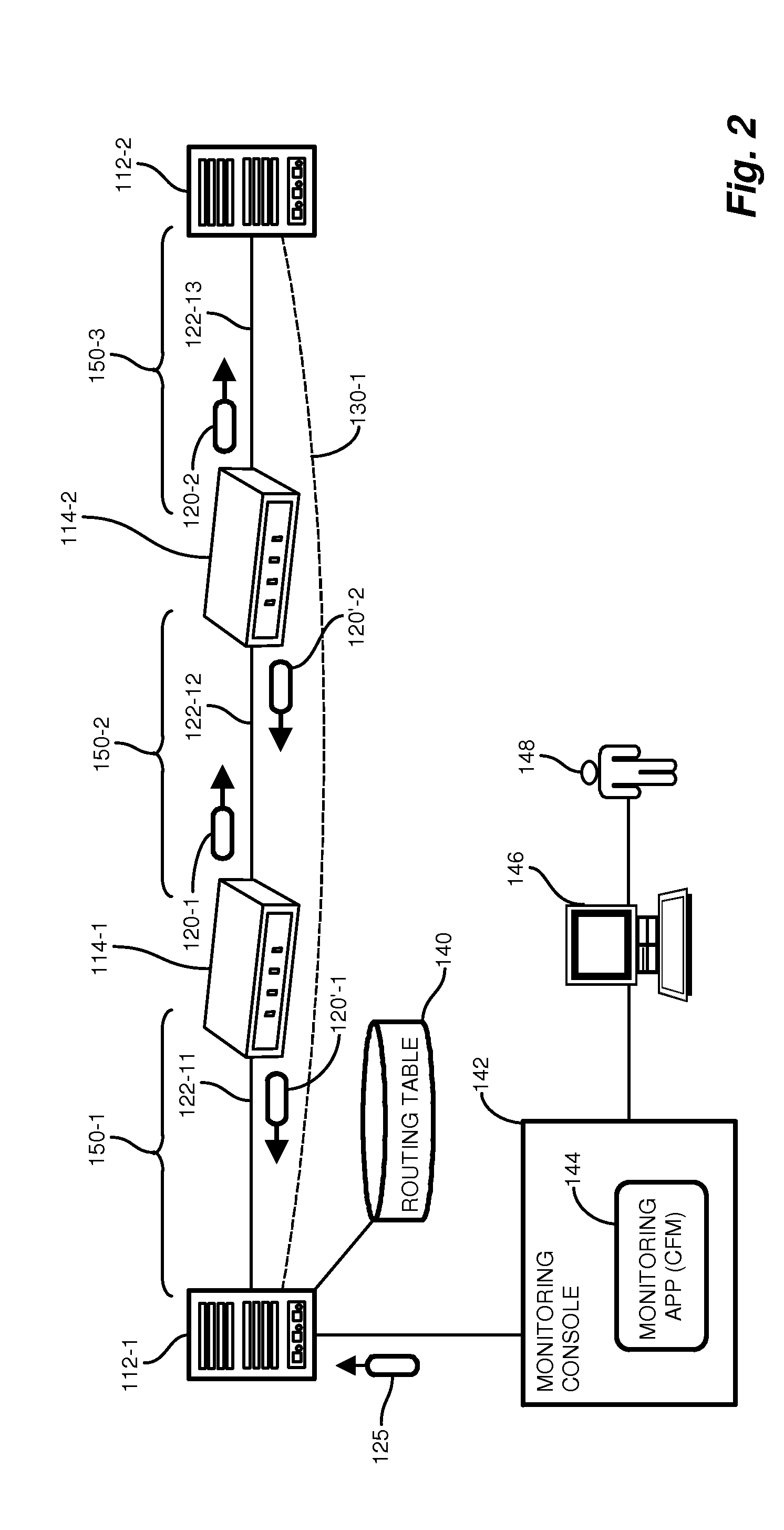
A network management and monitoring application employs diagnostic messages for confirming network path connectivity and identifying and locating connectivity faults. Diagnostic messages similar to conventional “ping” and “traceroute” messages traverse the network along a prescribed path for which diagnostic feedback is desired. The application receives and analyzes return messages sent from network entities along the path to ascertain connectivity issues on the path. The application receives layer 3 identifiers such as IP addresses, however performs diagnostic operations such as continuity checks based on layer 2 identifiers such as MAC (Media Access Control) identifiers because certain network entities operate on L2 identifiers and would otherwise evade a continuity check based on layer 3 identifiers. The monitoring application therefore performs continuity diagnostics such as ping and traceroute operations using L2 identifiers, therefore pinpointing problems with an L2 network forwarding entity such as a bridge that lies between L3 entities such as routers.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
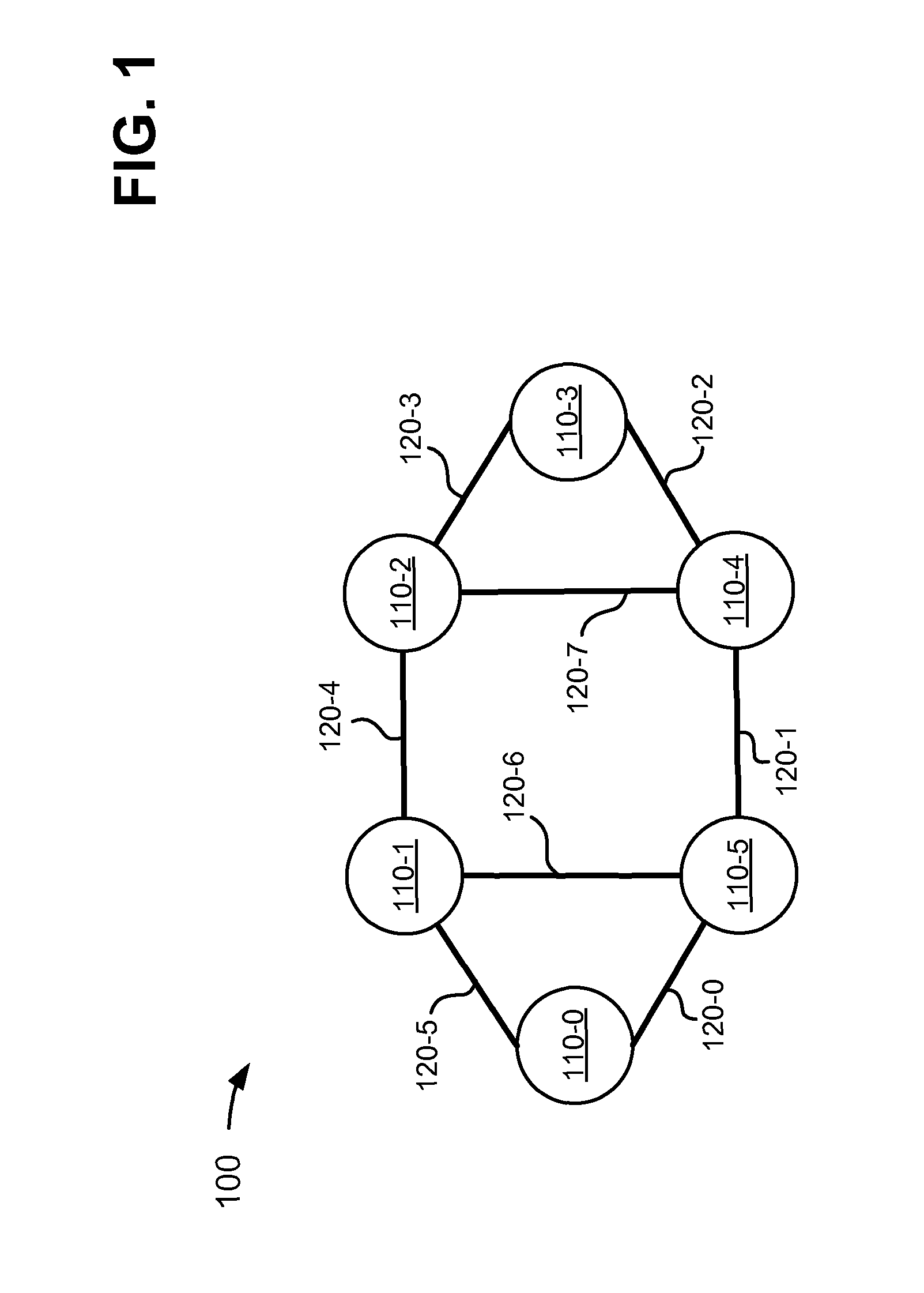
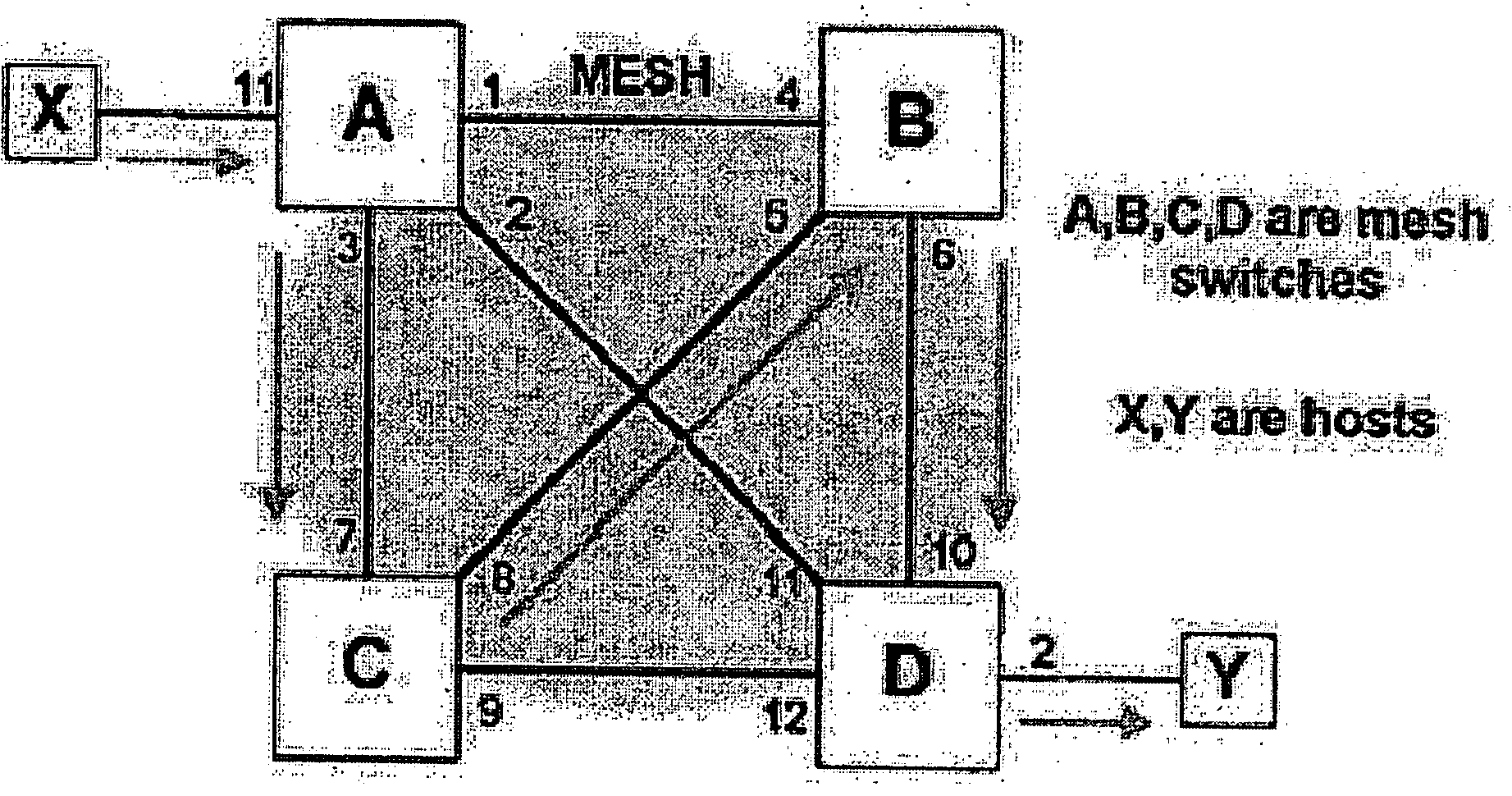
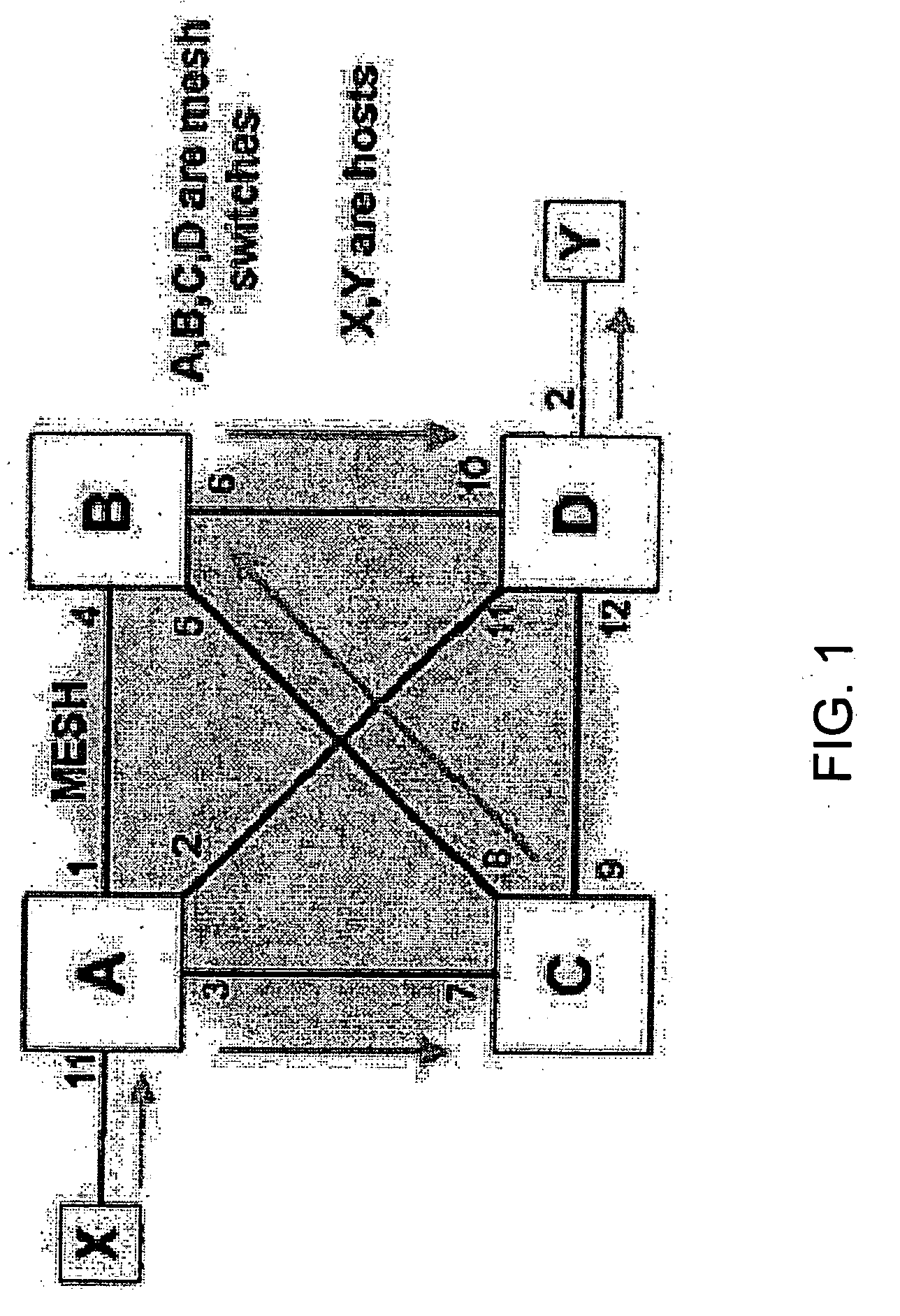
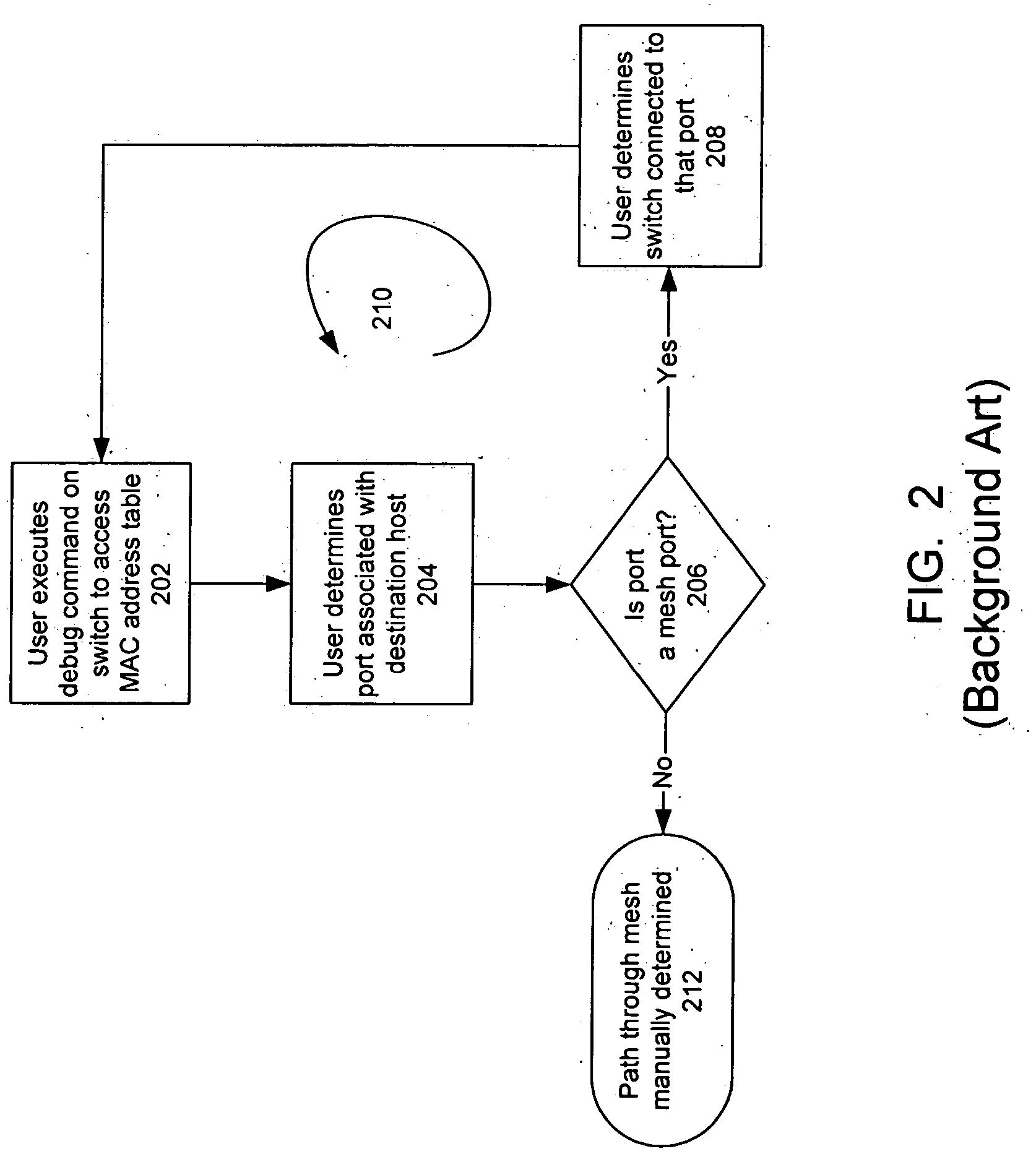
Automated path tracing through switching mesh
One embodiment disclosed relates to a method of automated path tracing from an original mesh switch through a switching mesh to a specified destination. A mesh traceroute packet to the specified destination is built. The mesh traceroute packet is transmitted via an exit port associated with the specified destination and the returned packet is received. Another embodiment disclosed relates to a method of responding to receipt of a mesh traceroute packet during an automated path tracing. The mesh traceroute packet is received at a switch. A hop entry is appended to the mesh traceroute packet by the switch.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
User datagram protocol traceroute probe extension
The embodiments described herein provide methods and apparatuses for implementing a User Datagram Protocol traceroute probe extension. In an example embodiment, a request to transmit a User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packet to a remote destination is received. A probe header and a probe data element is then stored in a data field of the UDP packet. The UDP packet is then transmitted toward the remote destination. In an example embodiment, a User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packet is received and it is determined whether the UDP packet includes a probe data structure. When the determination is affirmative, the probe data structure is processed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for discovering network topology
InactiveUS7263552B2Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationTracerouteNetwork topology
A method and apparatus are provided that allow the automatic discovery of the topology of a network. In one embodiment, the invention includes identifying a second network device at a first network device, sending a message from the first network device to the second network device, the message establishing the identity of any network device between the first network device and the second network device, and compiling the established identities to determine the topology of the network. The invention can use PING and Traceroute utilities to find nodes and identify network devices.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Traceroute implementing method and equipment
InactiveCN101335689AImprove operational deployabilityReduce in quantityStar/tree networksDistributed computingTraceroute
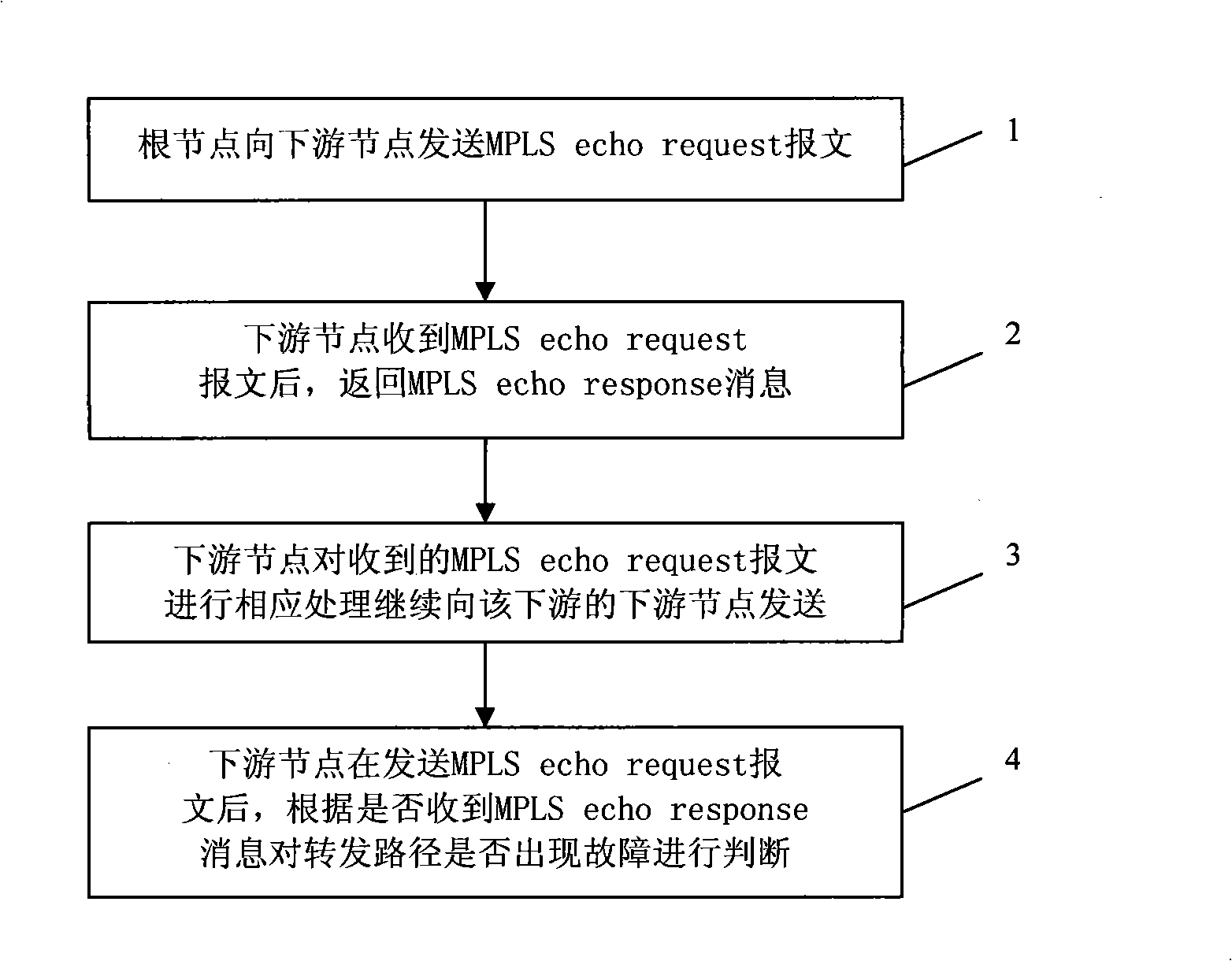
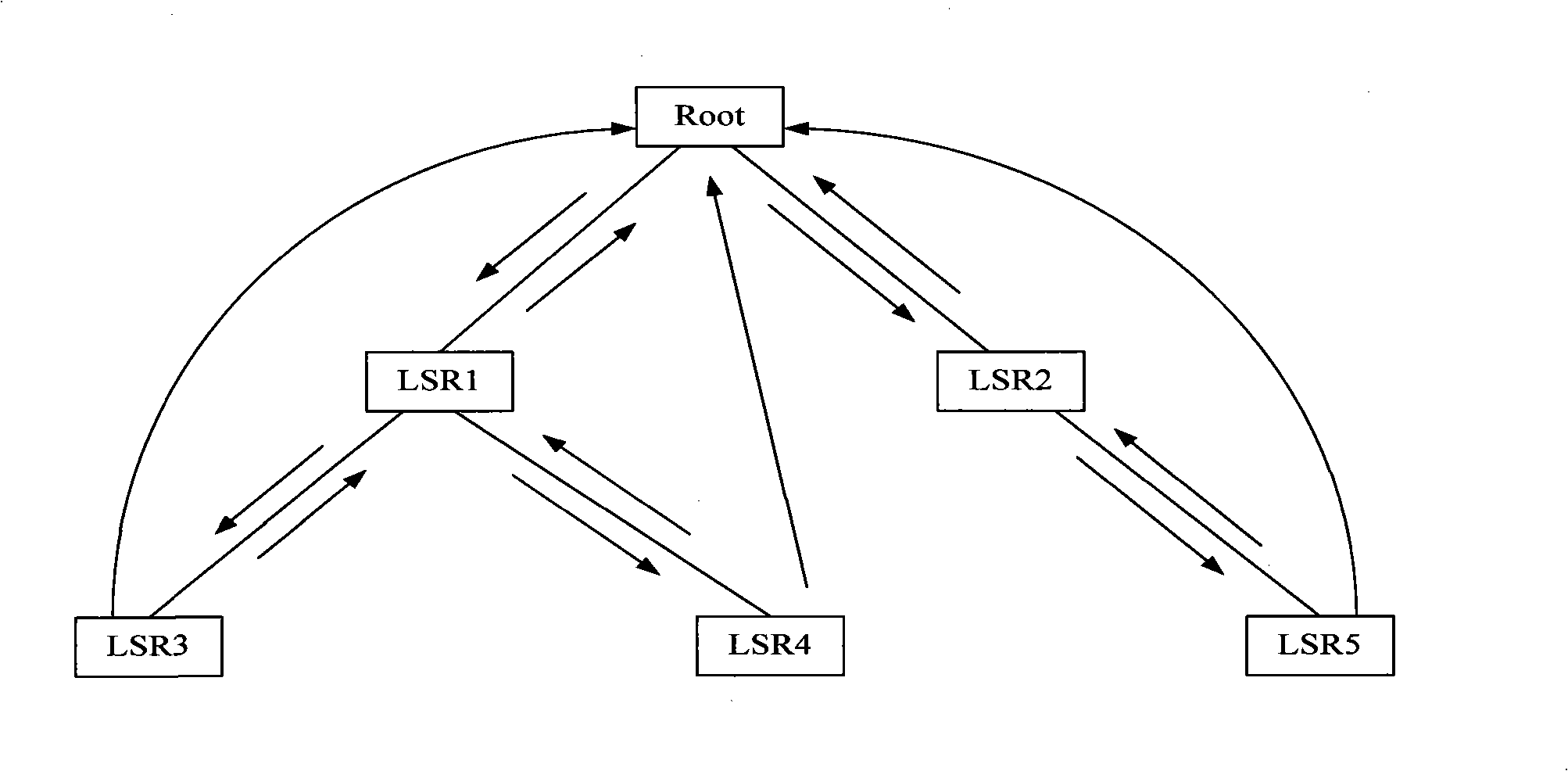
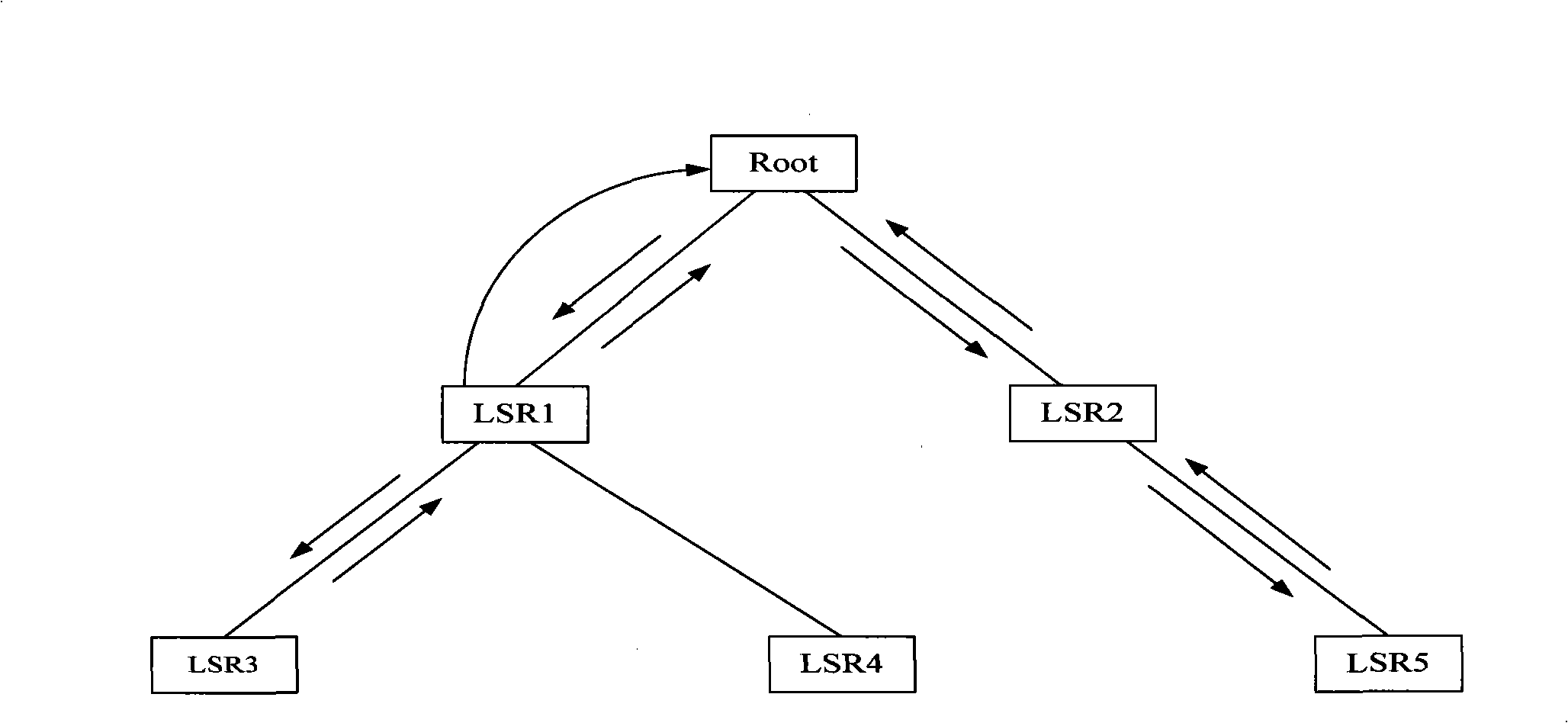
The invention relates to a realizing method for route tracing and equipment. The method concretely comprises the steps that: first, an initial node sends a request message for route tracing; then, after receiving the request message, an intermediate node returns a response message to a node of a higher level and transmits the request message to a node of a lower level until the request message reaches a leaf node; finally, the node of a higher level realizes the operation of route tracing according to the condition of the received response message. The realization proposal for route tracing provided by the embodiment of the invention can effectively reduce the number of response messages received by the initial node such as a root node, etc., solve the problem that the burden of processing the response messages of the initial node such as the root node, etc., in a multicast tree during the process of route tracing, improve the operation deployability of route tracing and can reduce bandwidth resources occupied by the whole tree during the operating process of route tracing.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
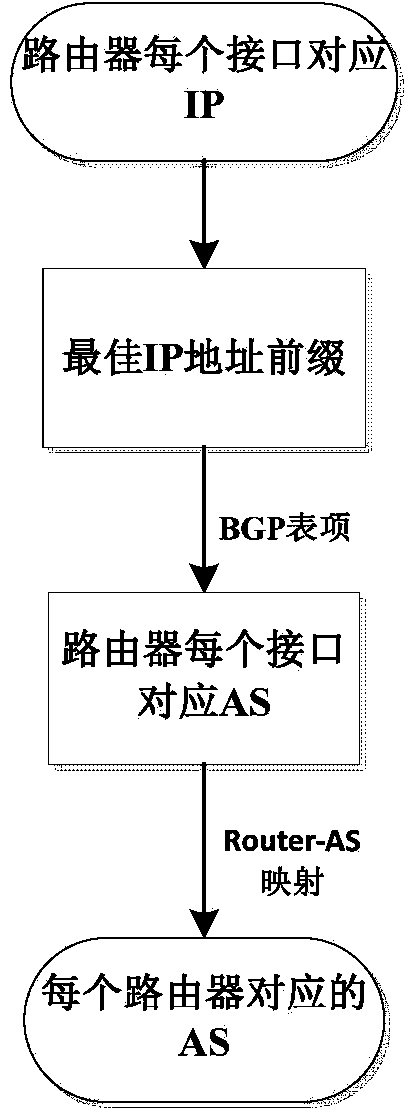
Autonomous system level network topology identification method combining active and passive measurement
ActiveCN104202211AImprove accuracyImprove integrityData switching networksBorder Gateway ProtocolRouting table
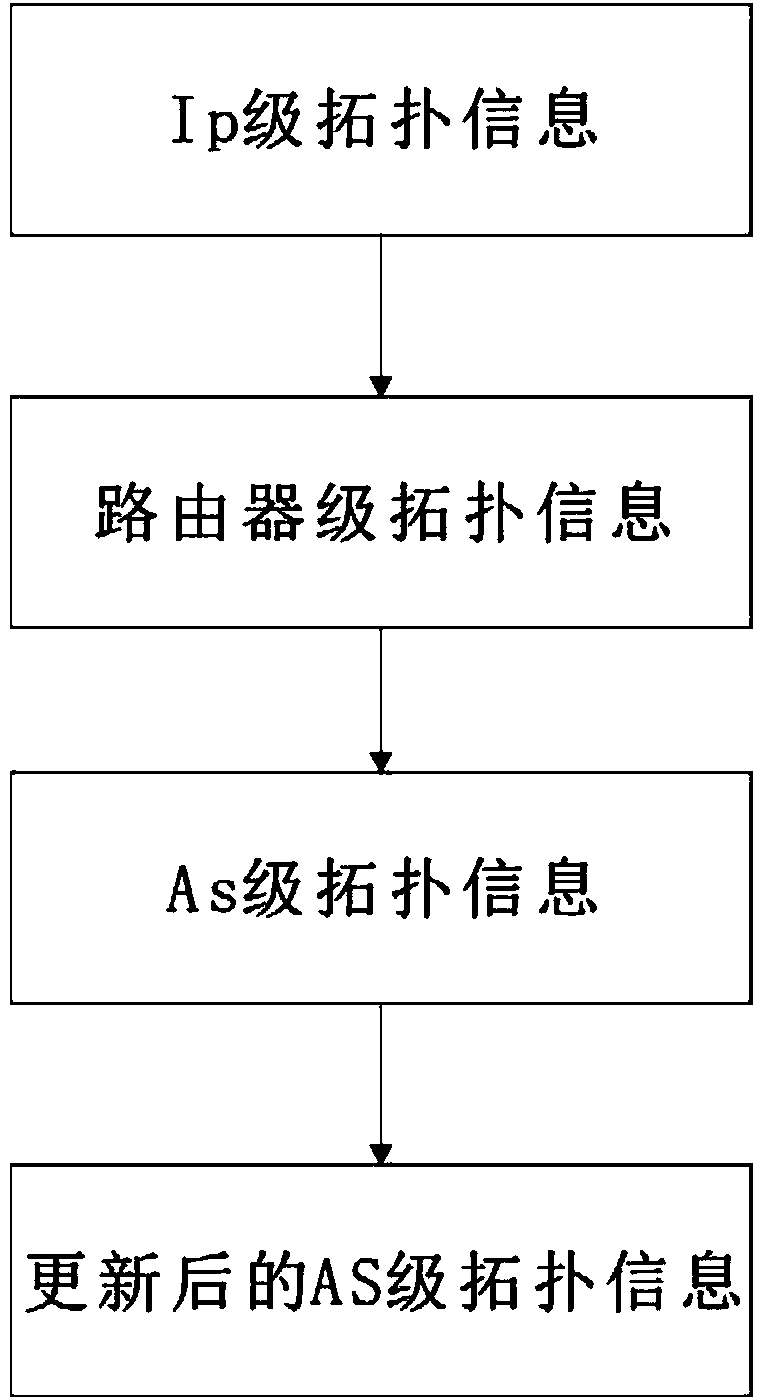
The invention discloses an autonomous system level network topology identification method combining active and passive measurement. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring IP (Internet Protocol) level topology information; acquiring router level topology information; acquiring AS level topology information; acquiring updated level topology information. The autonomous system level network topology identification method combining active and passive measurement has the beneficial effects that the IP level topology information obtained by a Traceroute data source is mapped onto router level topology, the router level topology is mapped onto AS level topology, and the AS level topology information obtained by Traceroute is supplemented and corrected before a BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) routing table is monitored in order to obtain complete AS level topology information, thereby realizing high-accuracy and complete AS level topology recovery.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
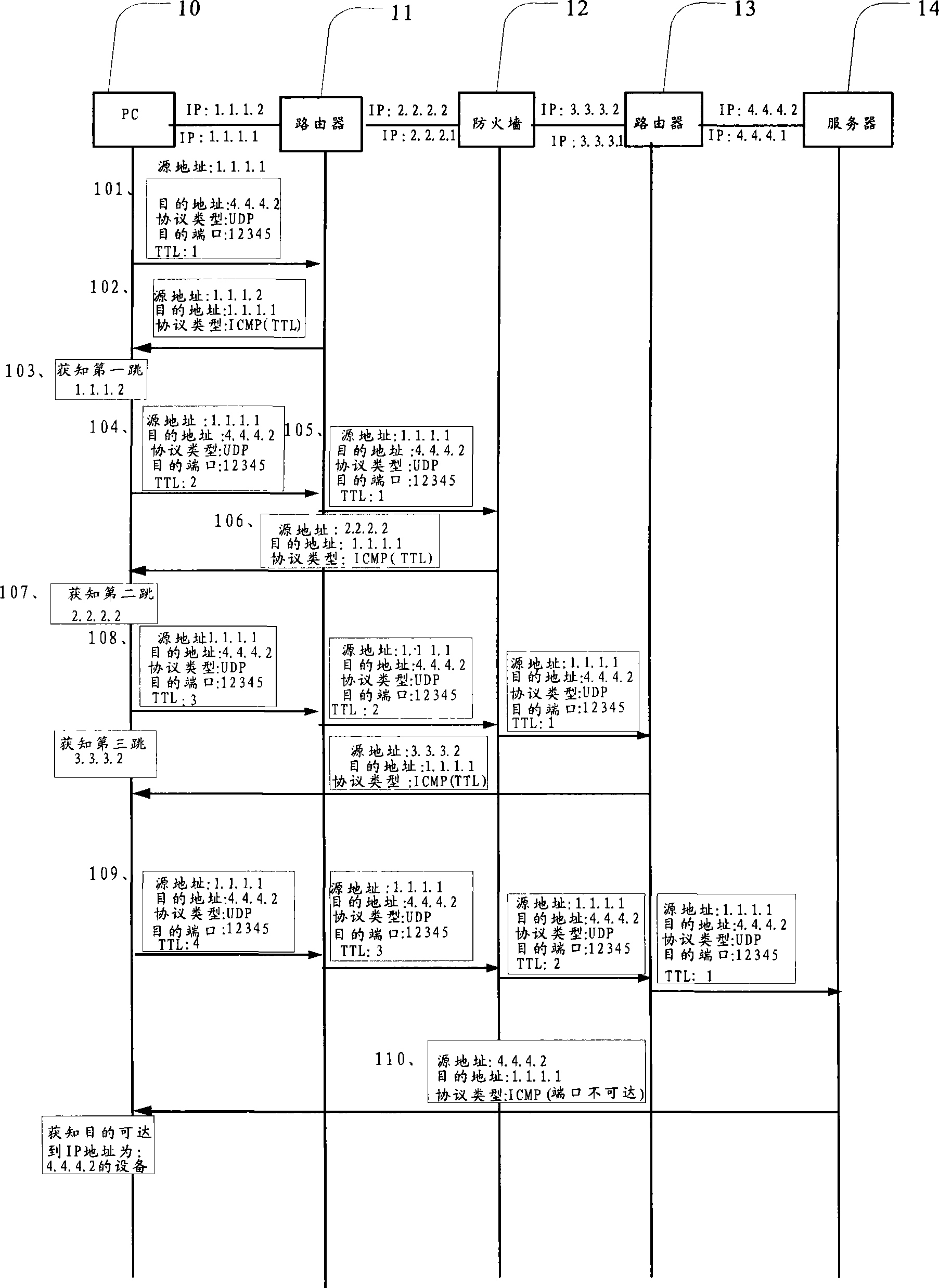
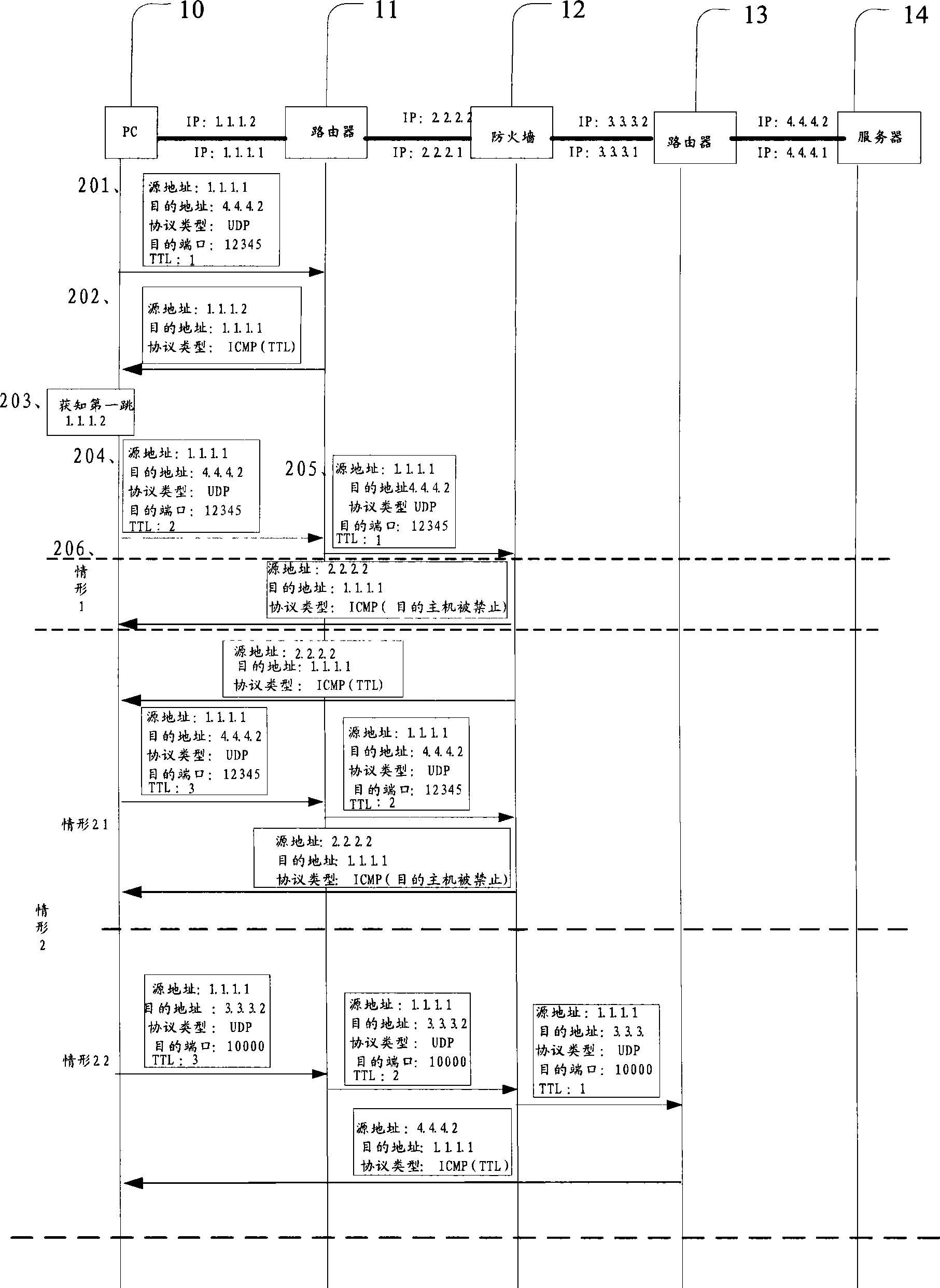
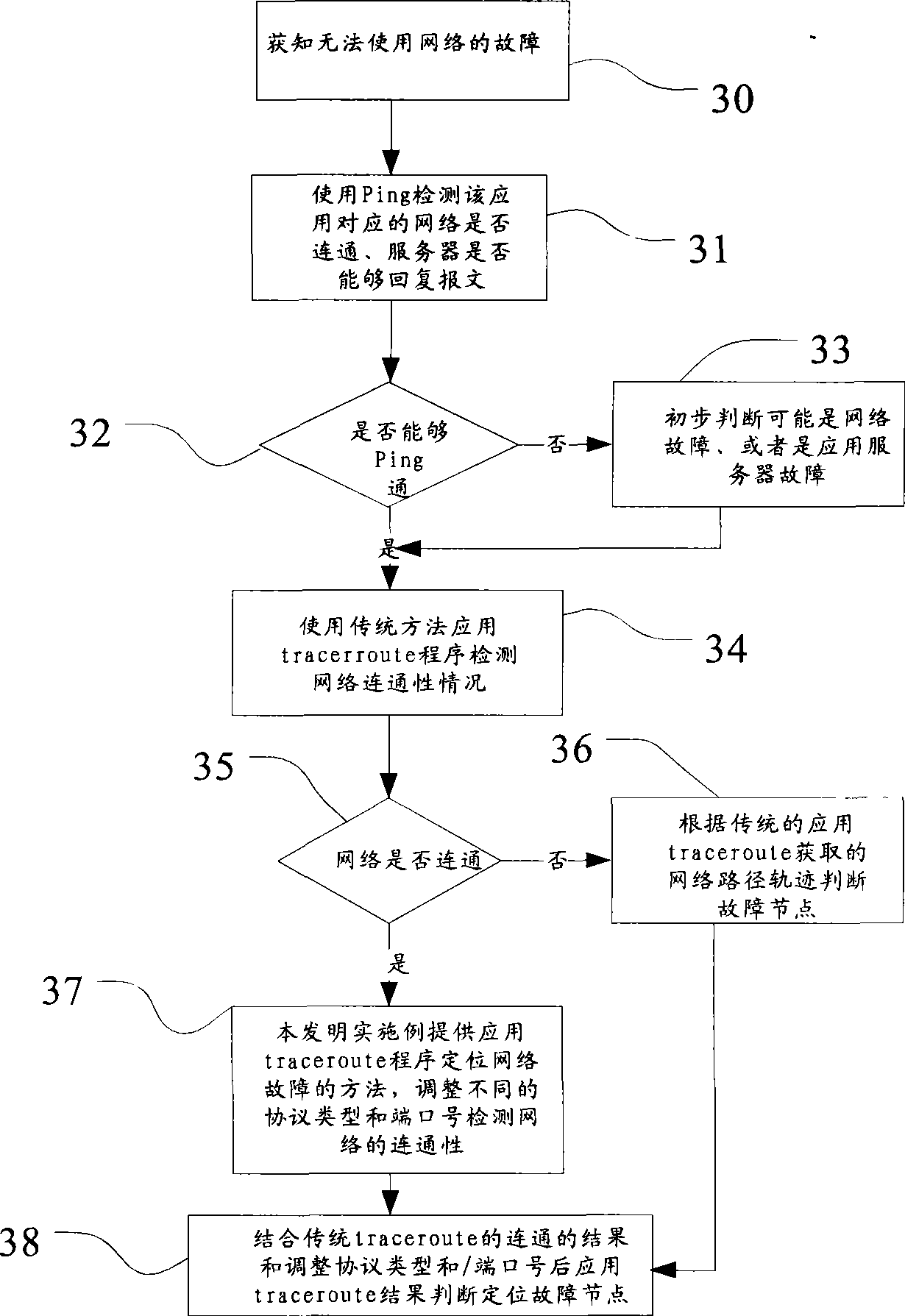
Method and system for locating network fault
InactiveCN101471822ASolve the problem of correctly locating network faultsData switching networksTracerouteProtocol Application
The invention relates to the field of communication and provides a method for locating a network fault. The method comprises the following steps: dynamically adjusting the protocol type and the port number of a detection message when applying traceroute program and sending an adjusted detection message for detection; and determining the position of a network fault according to the communication status in a network, which is detected by applying the traceroute program. The invention further provides a system for locating a network fault, which comprises an information acquisition unit, a detection message sending unit and a network fault positioning unit. The invention provides a method for detecting and locating a network fault in a specified network, which solves the problem that the prior traceroute program can not detect a specified network and an application layer of the network and locate the position of a fault by using fixed port number and protocol type.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Systems, methods, and devices for detecting security vulnerabilities in IP networks
ActiveUS8806632B2Easy to addMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionBaseline dataCamera image
This invention is a system, method, and apparatus for detecting compromise of IP devices that make up an IP-based network. One embodiment is a method for detecting and alerting on the following conditions: (1) Denial of Service Attack; (2) Unauthorized Usage Attack (for an IP camera, unauthorized person seeing a camera image); and (3) Spoofing Attack (for an IP camera, unauthorized person seeing substitute images). A survey of services running on the IP device, historical benchmark data, and traceroute information may be used to detect a possible Denial of Service Attack. A detailed log analysis and a passive DNS compromise system may be used to detect a possible unauthorized usage. Finally, a fingerprint (a hash of device configuration data) may be used as a private key to detect a possible spoofing attack. The present invention may be used to help mitigate intrusions and vulnerabilities in IP networks.
Owner:SECURENET SOLUTIONS GRP
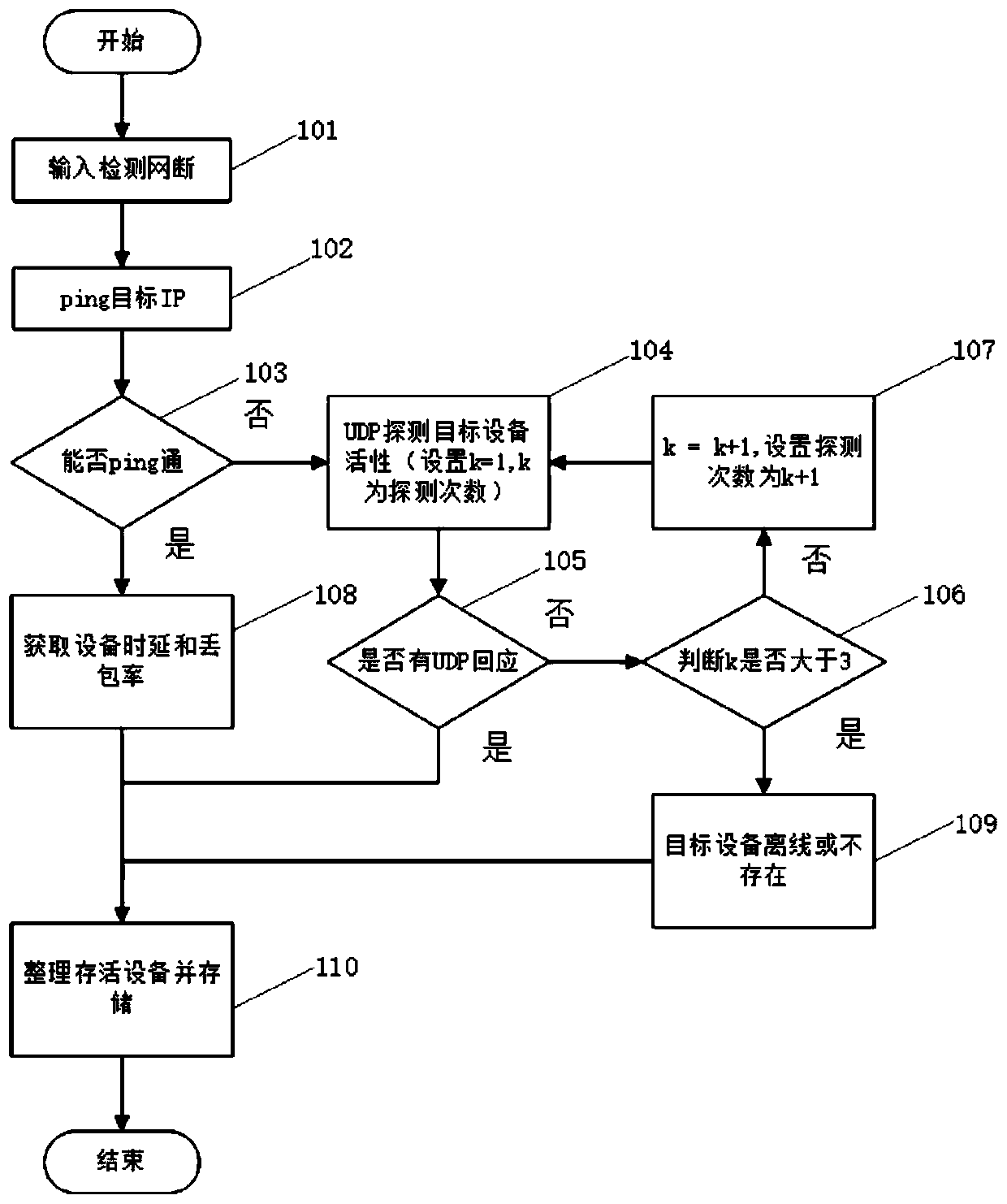
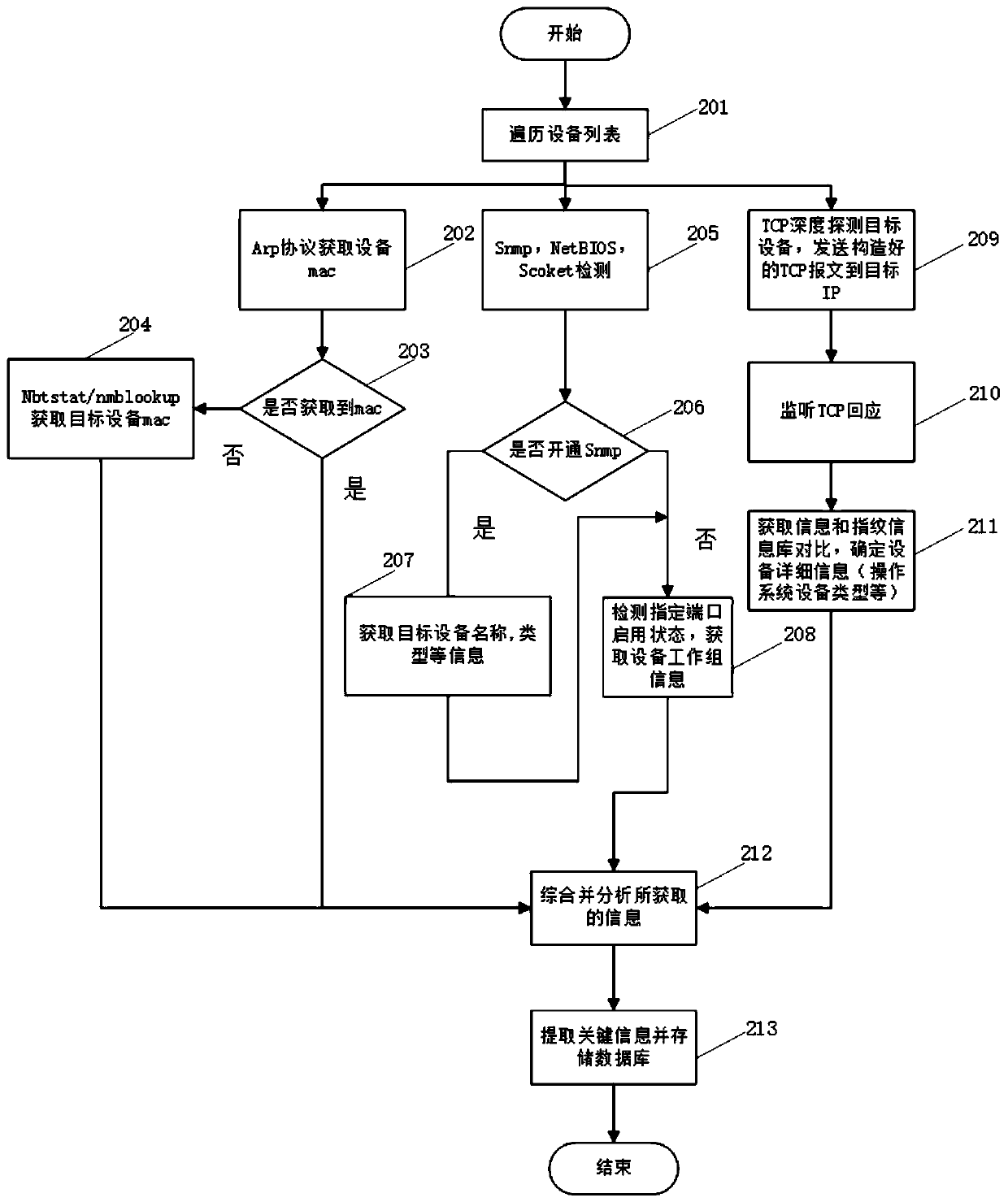
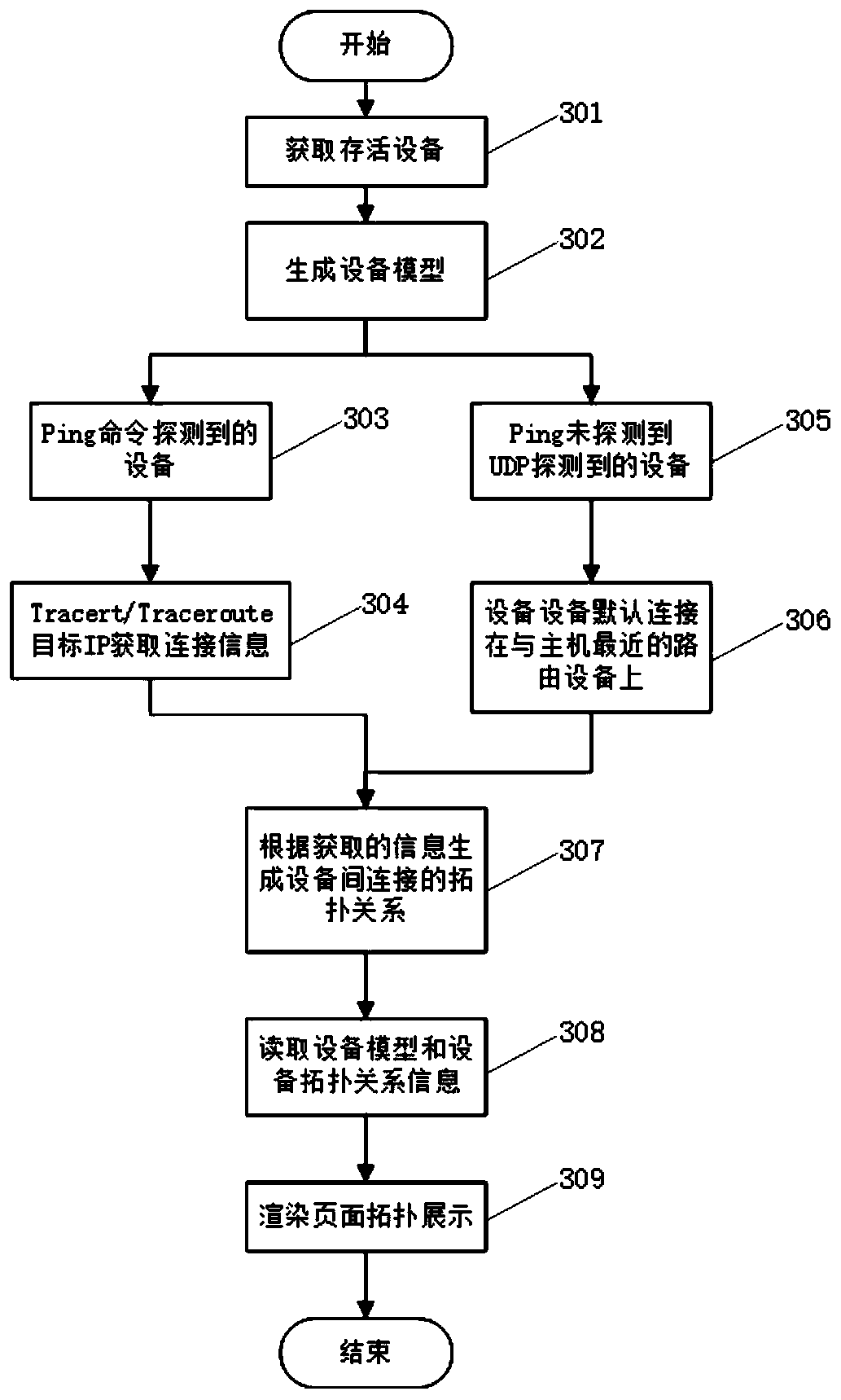
Network topology automatic discovery method of network equipment based on ICMP, TCP and UDP protocols
The invention discloses a network topology automatic discovery method of network equipment based on ICMP, TCP and UDP protocols. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: detecting a target network through ICMP and UDP protocols; confirming target device survivability, detecting a link connection condition of survival equipment by using tracert / traceroute (windows / linux platform), and acquiring basic equipment information by using a simple network management protocol, an ARP protocol and a NetBIOS protocol according to a target equipment activity list; and finally, based on the acquired information, performing deep scanning on the survival equipment by using a TCP protocol to acquire more detailed fingerprint information, comparing the acquired information with a fingerprint library to determine detailed information of the target equipment, drawing a complete topological graph by integrating all the acquired information, and displaying the acquired equipment information. According to the invention, the topological structure of the network and the detailed information of the equipment can be accurately, comprehensively and quickly obtained.
Owner:云南电网有限责任公司德宏供电局
Metric computation for traceroute probes using cached data to prevent a surge on destination servers
Techniques for using traceroute with tunnels and cloud-based systems for determining measures of network performance are presented. Systems and methods include receiving a request, from a client, for one or more of a first trace of a tunnel and a second trace to a destination; checking a cache at the node for results from previous traces of the first trace and the second trace; responsive to the results not being in the cache, performing one or more of the first trace and the second trace; and providing the results to the client so that the client aggregates the results with details from one or more additional legs to provide an overall view of a service path between the client and the destination.
Owner:ZSCALER INC
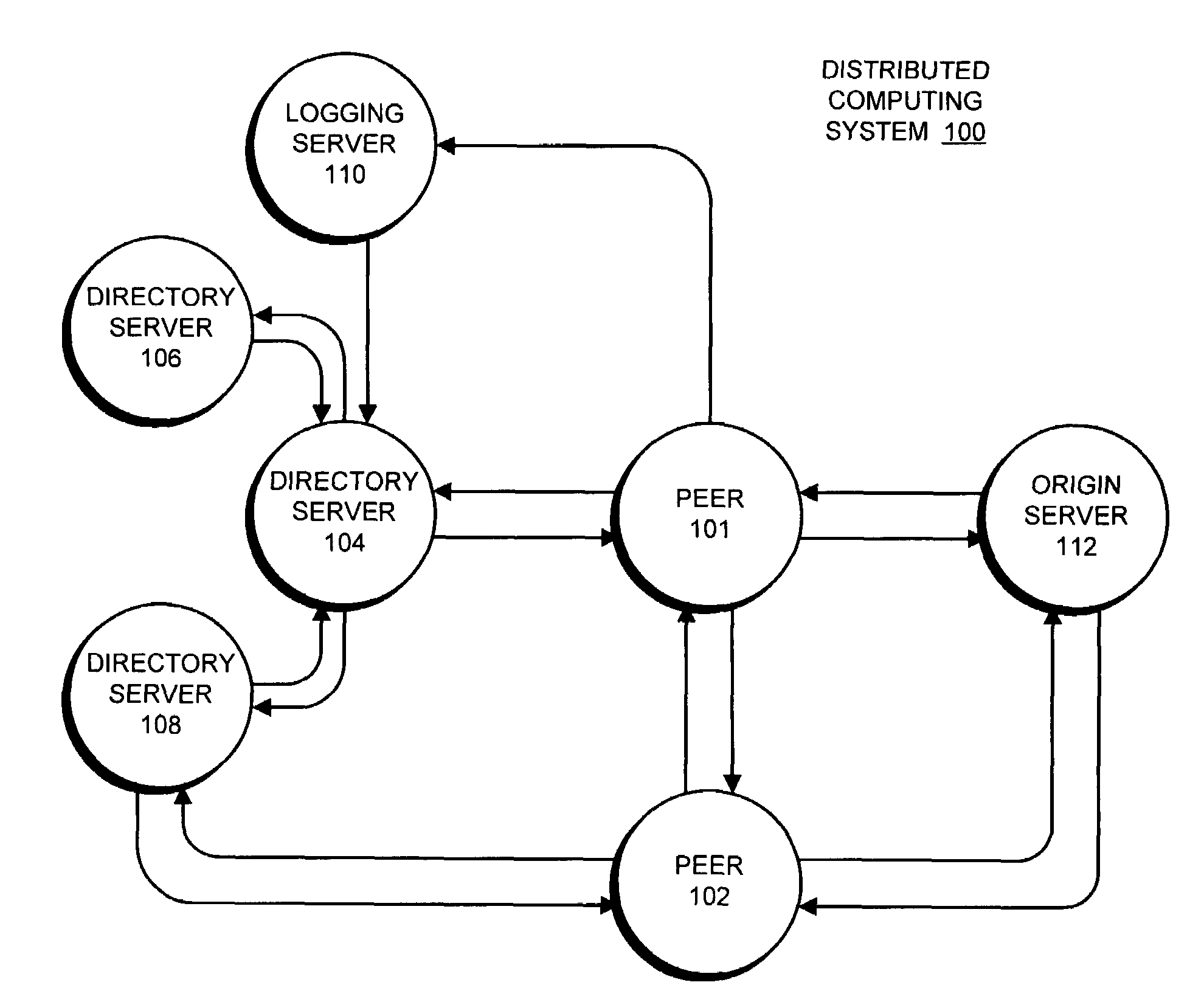
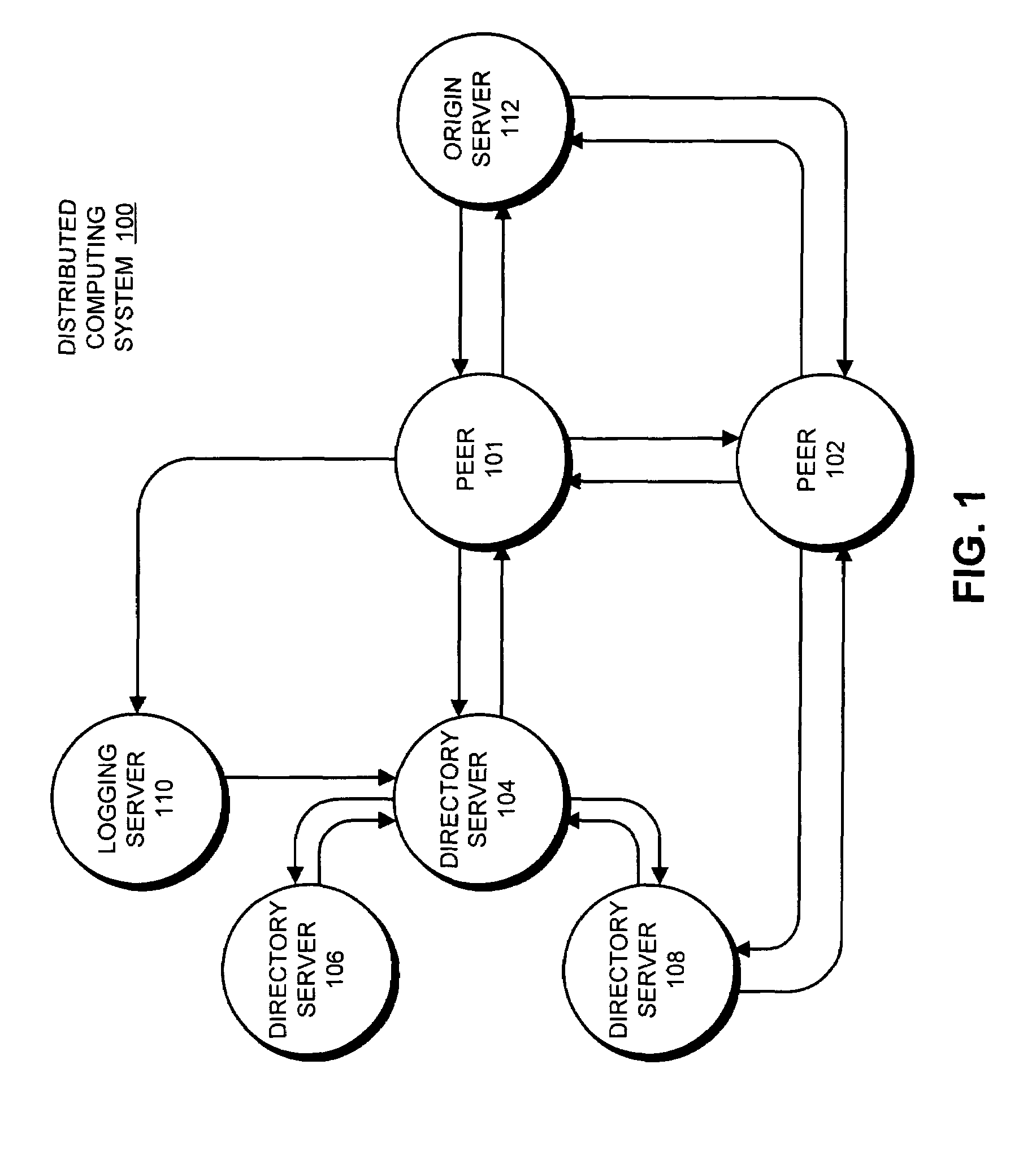
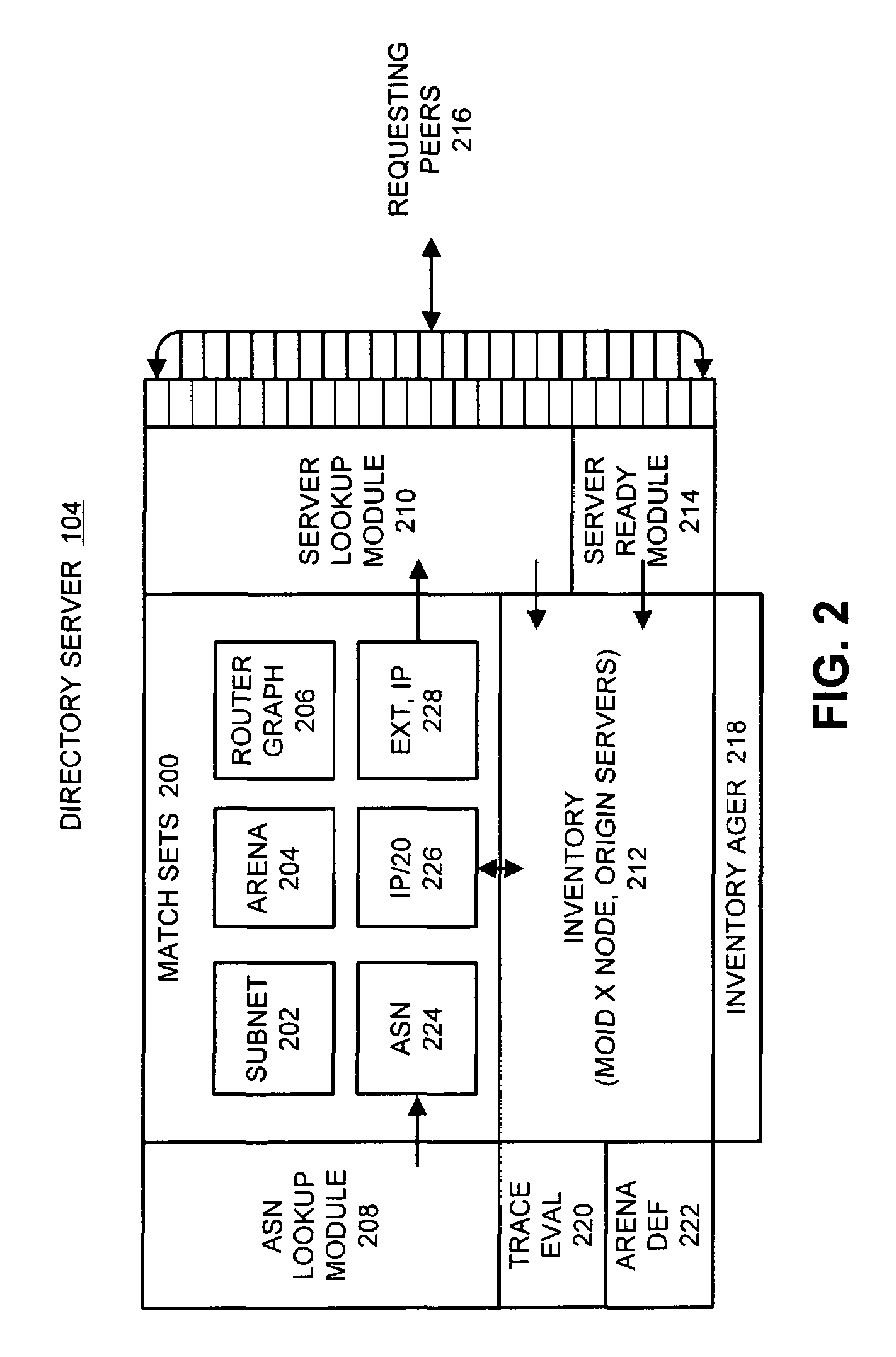
Method and apparatus for determining network topology in a peer-to-peer network
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that facilitates determining the network topology in a peer-to-peer network. The system operates by performing a tracerouting operation to obtain a traceroute from a first client to a directory server, wherein a traceroute describes a path through which a packet travels between the first client and the directory server, including addresses of the routers through which the packet travels. Next, the system sends the traceroute to the directory server from the first client. The directory server then uses the traceroute to build a router graph that represents the topology of the peer-to-peer network.
Owner:KOLLECTIVE TECH
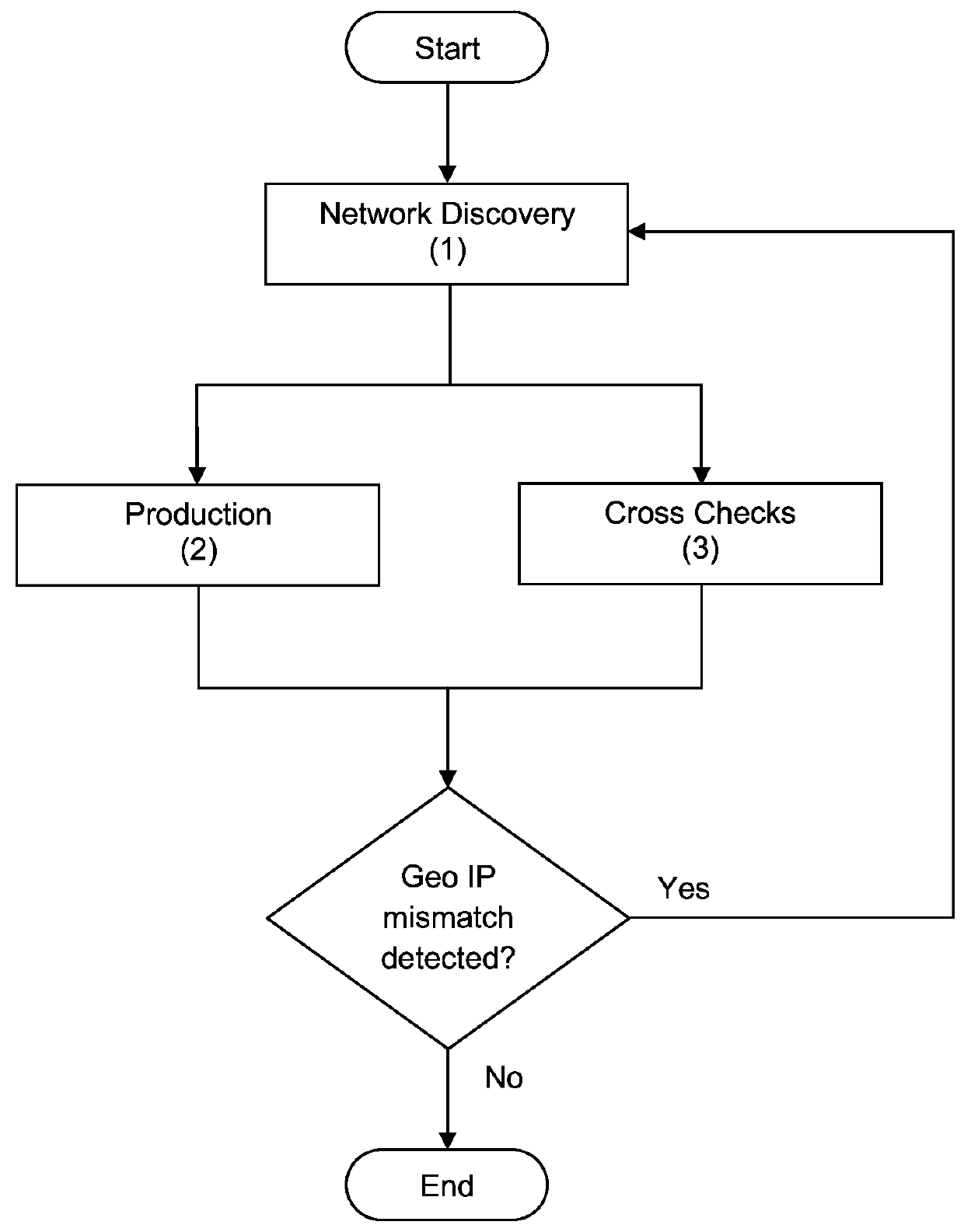
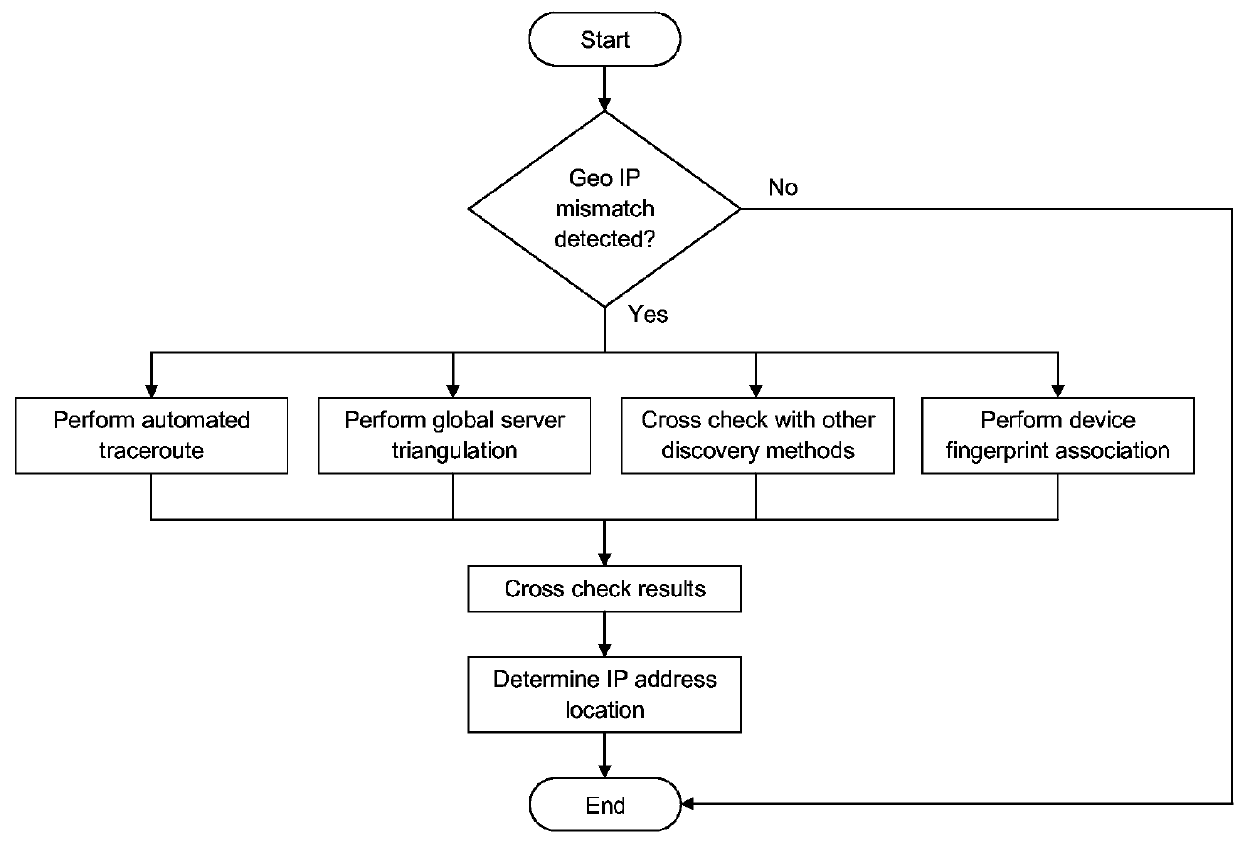
Method Of Near Real-Time Automated Global Geographical IP Address Discovery and Lookup by Executing Computer-Executable Instructions Stored On a Non-Transitory Computer-Readable Medium
ActiveUS20160036777A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksGeographic siteTraceroute
A method of near real-time global geographical IP address automated lookup utilizes an automated system continually performing a plurality of IP address location discovery techniques including traceroute automation, global server triangulation other geo IP discovery techniques and rolling cross checks across the system to build and maintain a global geo IP database with known geo locations of IP addresses. The geo IP database may be utilized to request the geo location of a specific IP address, and if the geo location of the specific IP address is unknown the system attempts to acquire the geo location of the specific IP address using the IP address location discovery techniques.
Owner:AAA INTERNET PUBLISHING
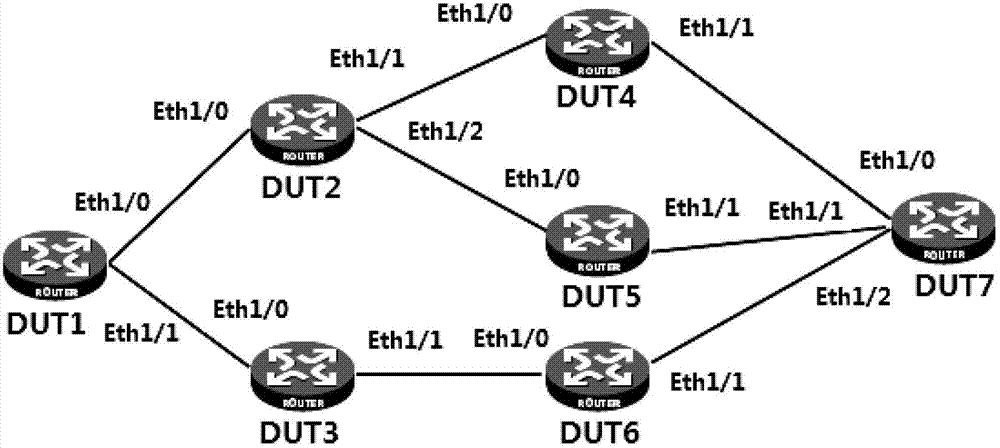
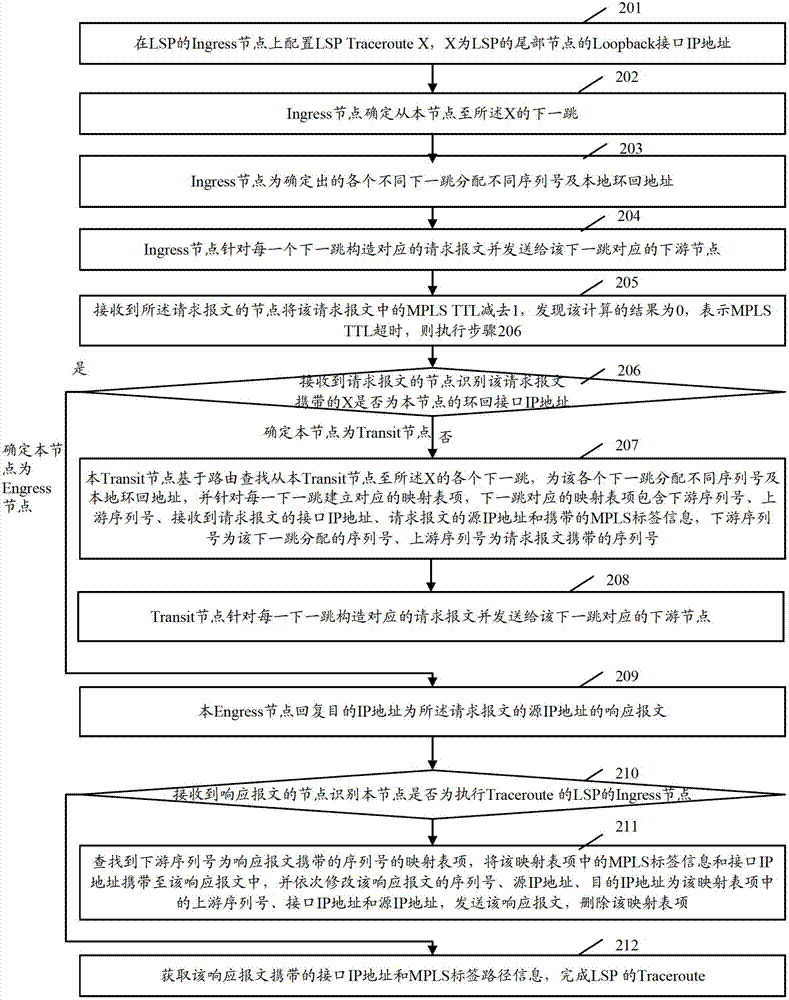
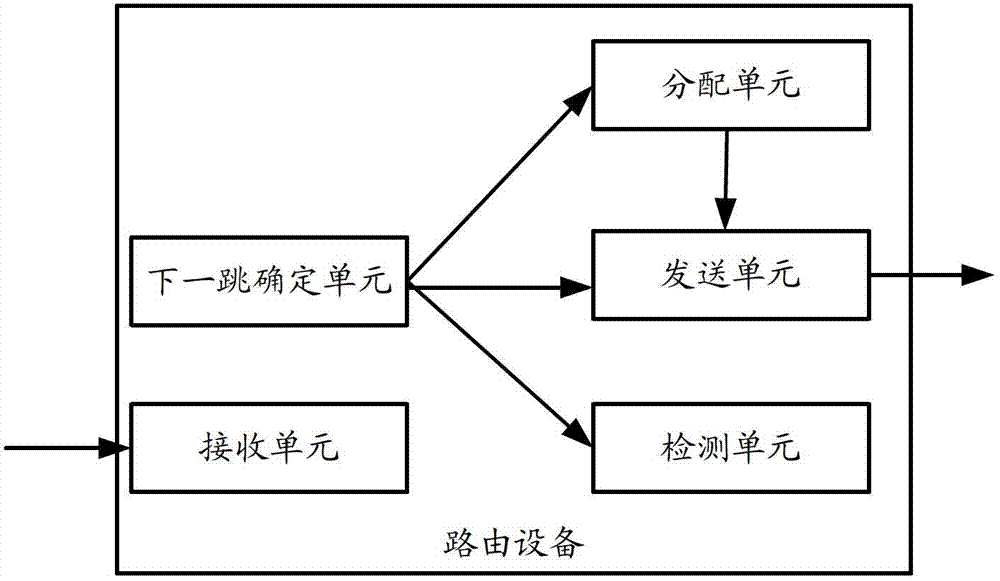
Traceroute method for label switched paths (LSP) in multi-protocol label switching (MPLS) network and routing equipment
The invention provides a traceroute method for label switched paths (LSP) in a multi-protocol label switching (MPLS) network and routing equipment. When the LSP of a load sharing path exist in the MPLS, connectivity that each path can be traced at low load and high accuracy rate can be achieved by technological means that a transit node acts as an ingress node in a traceroute process, so that the condition that a large amount of messages in the whole traceroute process are transmitted can be avoided.
Owner:XINHUASAN INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Systems, methods, and devices for detecting security vulnerabilities in IP networks
ActiveUS20100169975A1Easy to addMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionBaseline dataCamera image
This invention is a system, method, and apparatus for detecting compromise of IP devices that make up an IP-based network. One embodiment is a method for detecting and alerting on the following conditions: (1) Denial of Service Attack; (2) Unauthorized Usage Attack (for an IP camera, unauthorized person seeing a camera image); and (3) Spoofing Attack (for an IP camera, unauthorized person seeing substitute images). A survey of services running on the IP device, historical benchmark data, and traceroute information may be used to detect a possible Denial of Service Attack. A detailed log analysis and a passive DNS compromise system may be used to detect a possible unauthorized usage. Finally, a fingerprint (a hash of device configuration data) may be used as a private key to detect a possible spoofing attack. The present invention may be used to help mitigate intrusions and vulnerabilities in IP networks.
Owner:SECURENET SOLUTIONS GRP
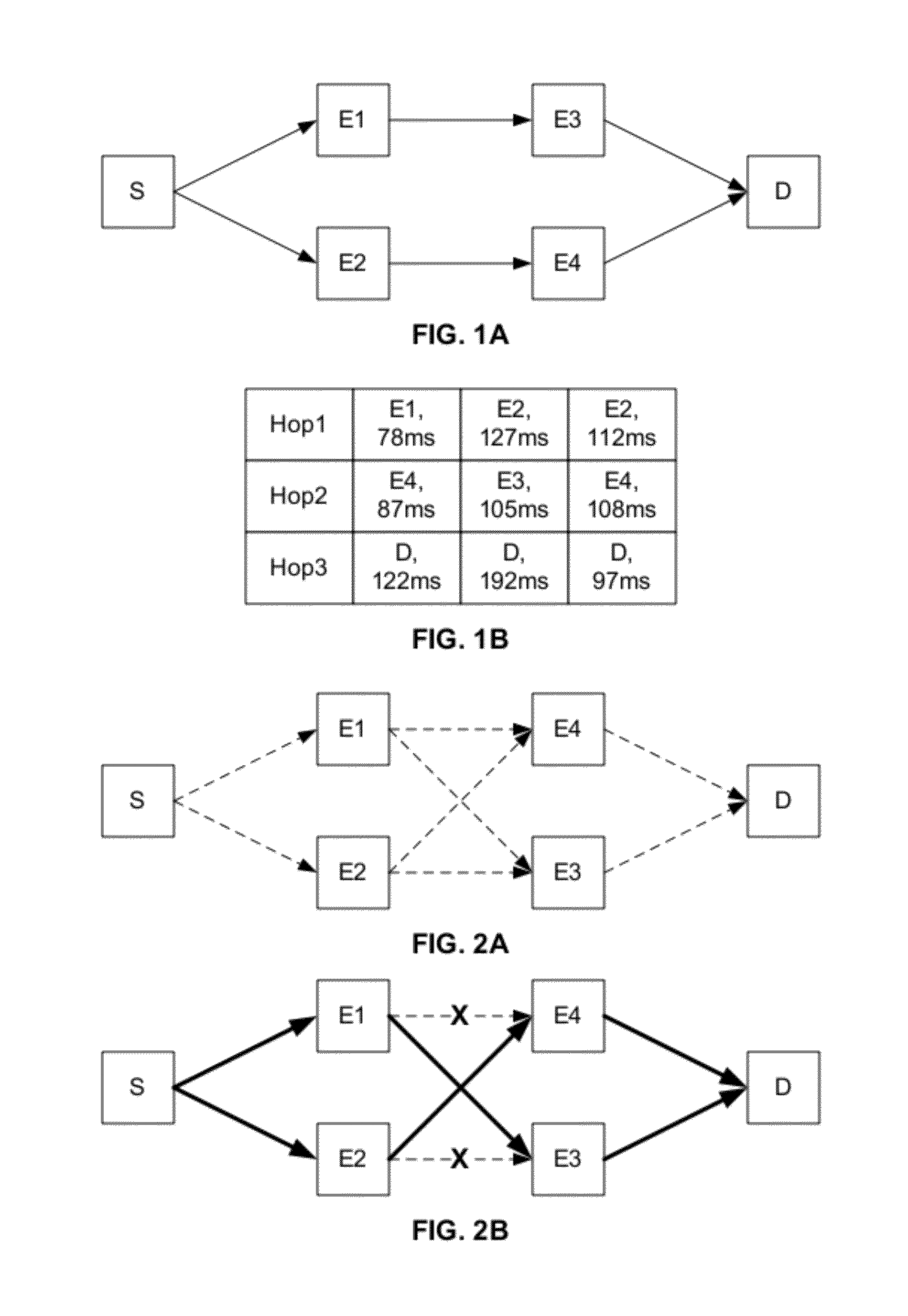
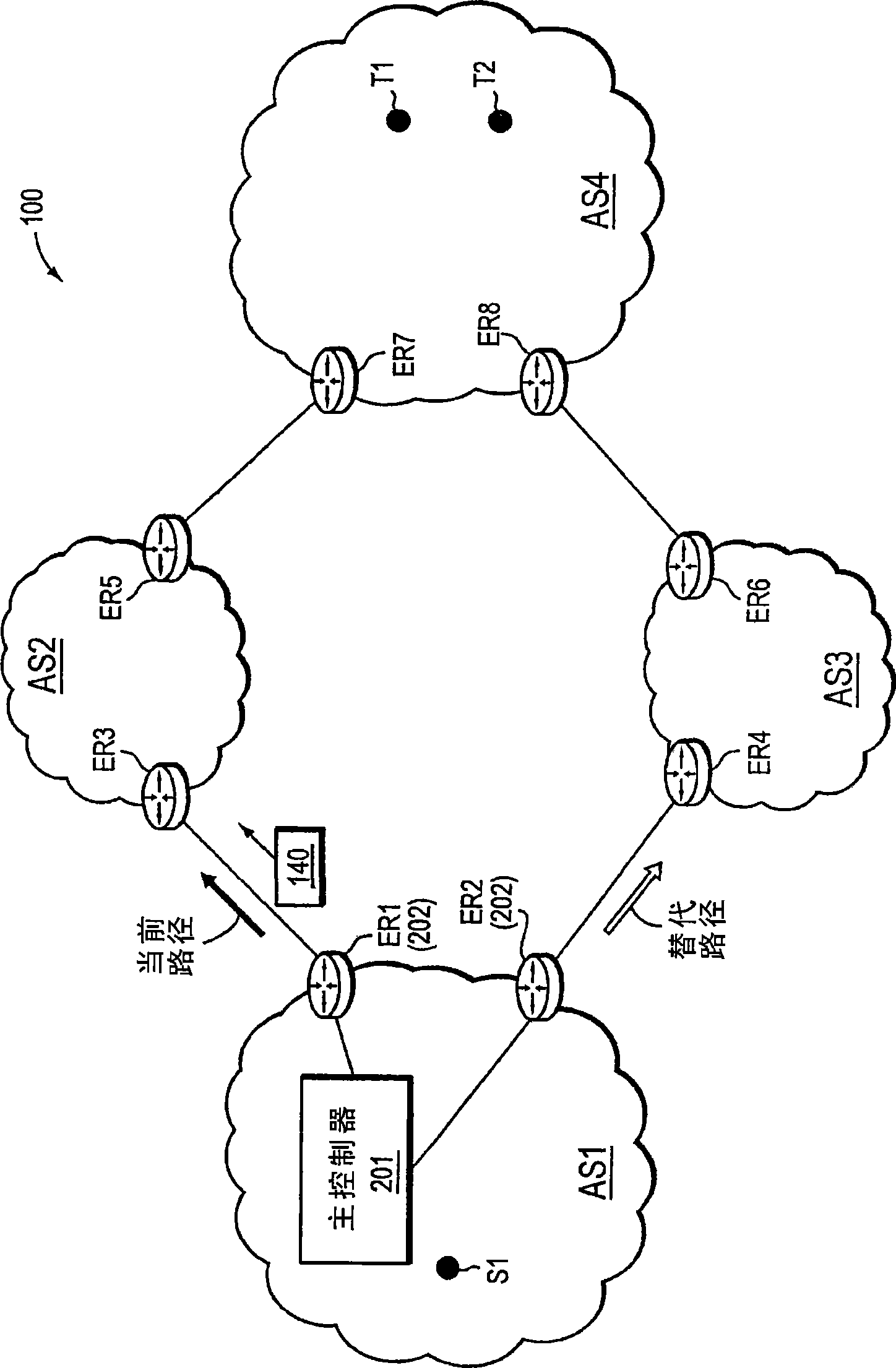
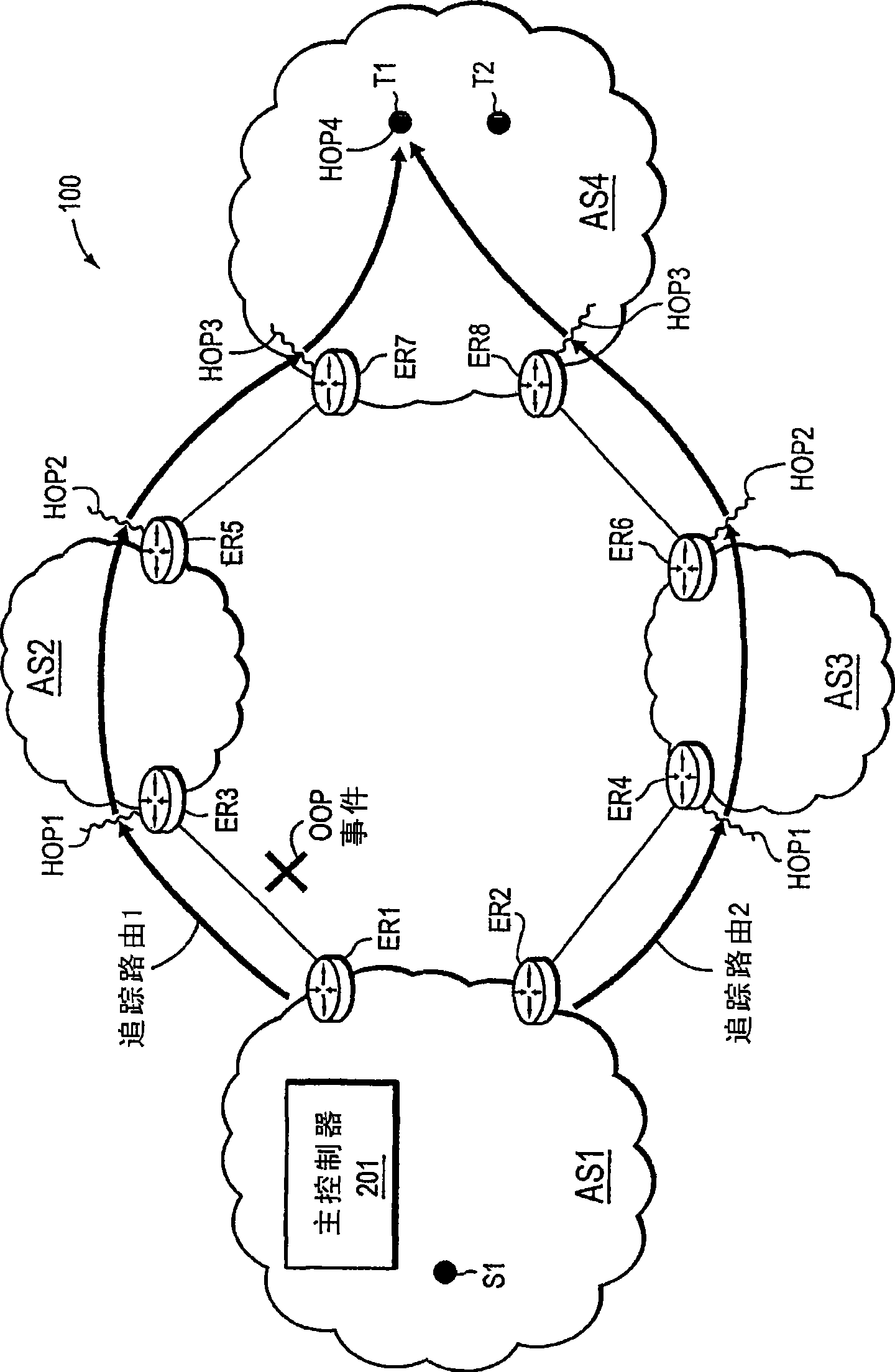
Event triggered traceroute for optimized routing in a computer network
In one embodiment, a network device (e.g., a master controller) may detect an event on a current path in a computer network from a local network domain to a destination address prefix of a remote domain. In response, the device may dynamically (e.g., intelligently) determine a trace target destination address within the destination address prefix, and may perform (or request performance of) a Traceroute of the current path and a selection of alternate paths in the network from the local network domain to the trace target, where the Traceroute is adapted to obtain per-hop measurements along the respective traced path. The measurements may then be stored, for example, to be used for optimal path selection, fault identification reporting, etc.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for providing detection of internet protocol address hijacking
A method and apparatus for detecting an address hijacking in a network are disclosed. For example, the method sends one or more traceroute packets to a target prefix, wherein the target prefix comprises one or more destination Internet Protocol (IP) addresses, and records traceroute data received for the one or more traceroute packets sent to the target prefix. The method then determines one or more hop count distance measurements for the target prefix, and determines if there are one or more changes in the one or more hop count distance measurements for the target prefix.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
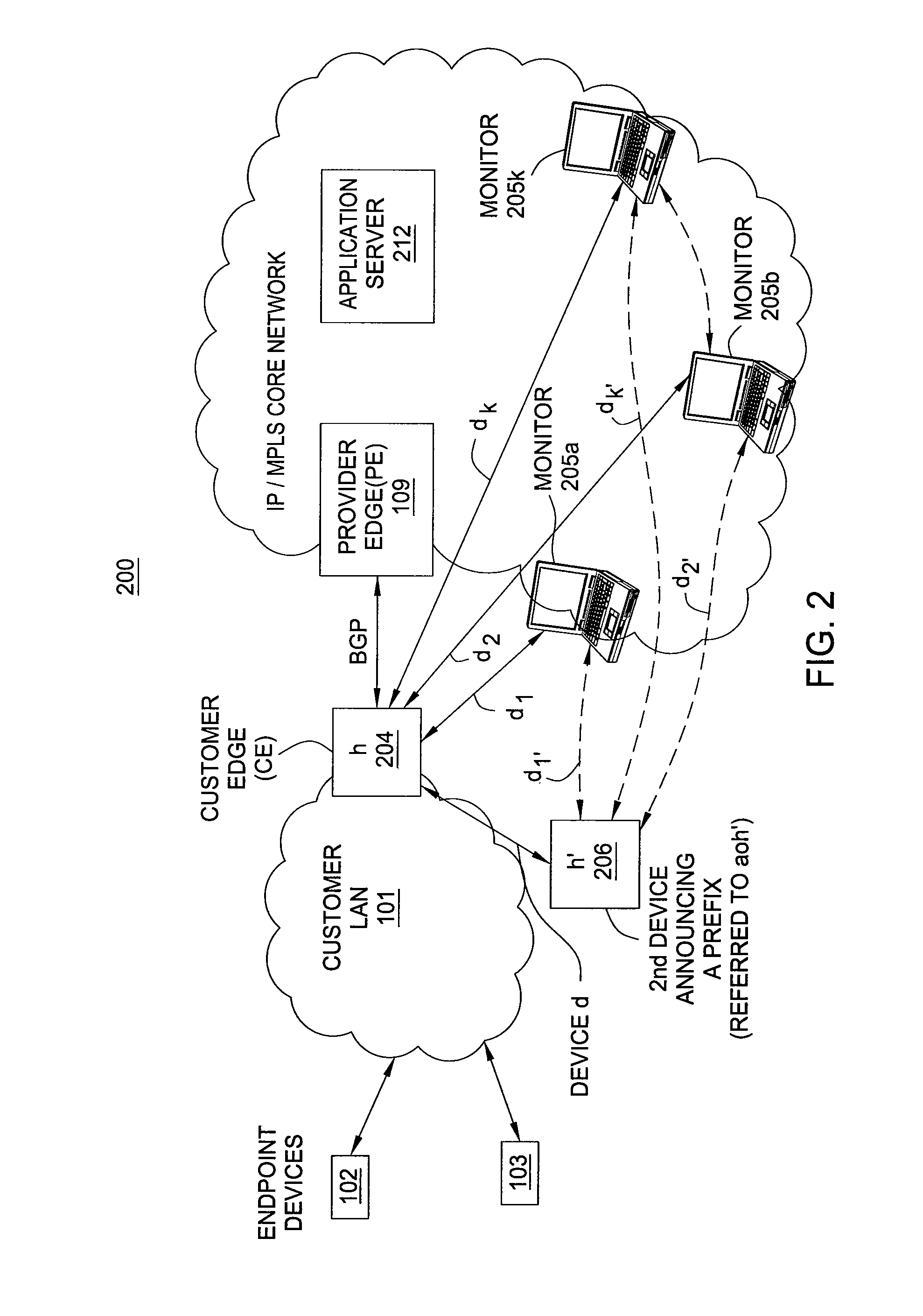
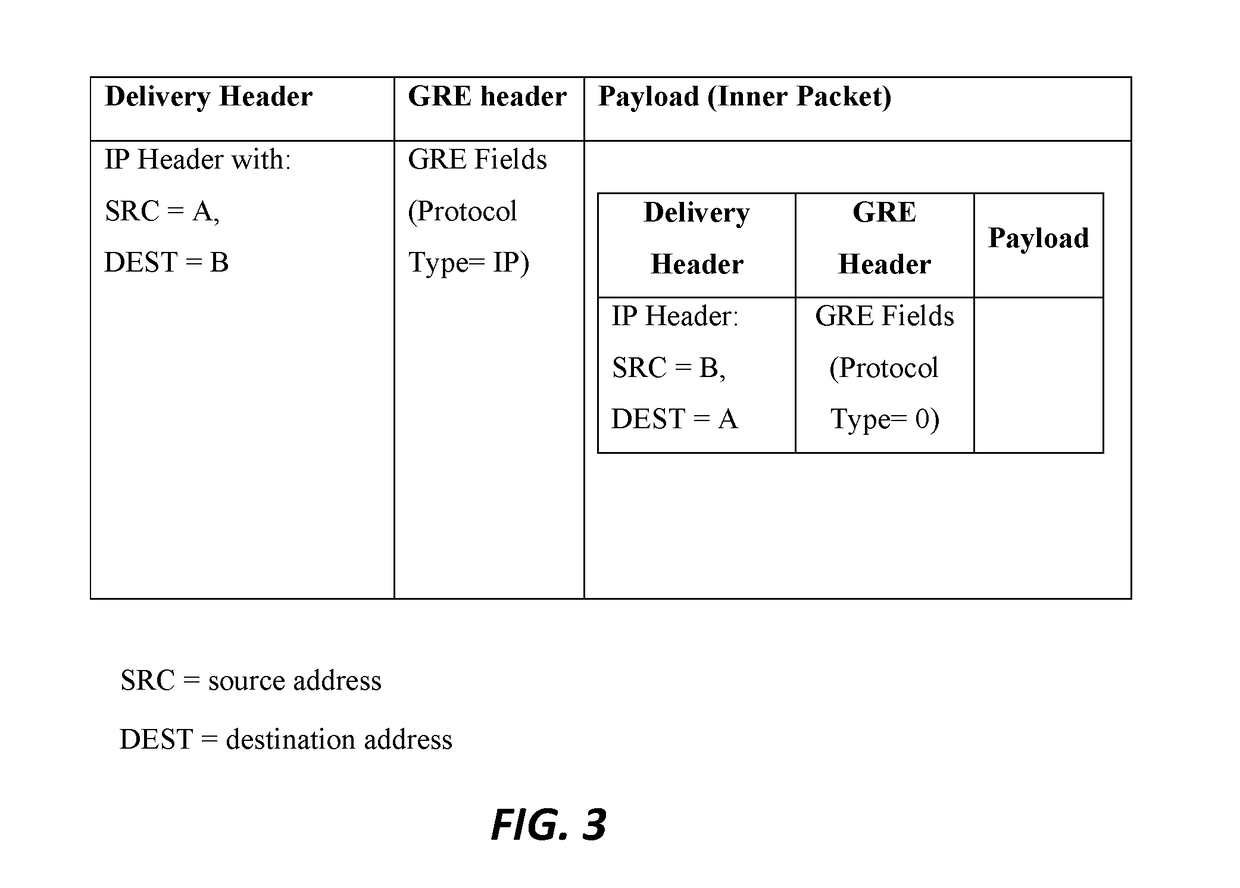
Traceroutes for discovering the network path of inbound packets transmitted from a specified network node
Disclosed herein are systems, methods, and apparatus for performing a new kind of traceroute. This traceroute is referred to herein as a “reverse” traceroute, as it enables a given network node to determine the path of packets sent to it from another node. Preferably, an encapsulating tunnel between the two nodes is leveraged. Preferably, a given network node (“first node”) performs the reverse traceroute by sending encapsulated inner packets in the tunnel to another network node (“second node”). The second node reflects the inner packets back to the first node. Preferably, the inner packets are configured such that their IP header TTLs expire at intermediate nodes (such as routers), and such that the resulting error messages are reported to the first node. In this way, the first node obtains information about the topology of the network and the path taken by inbound packets.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
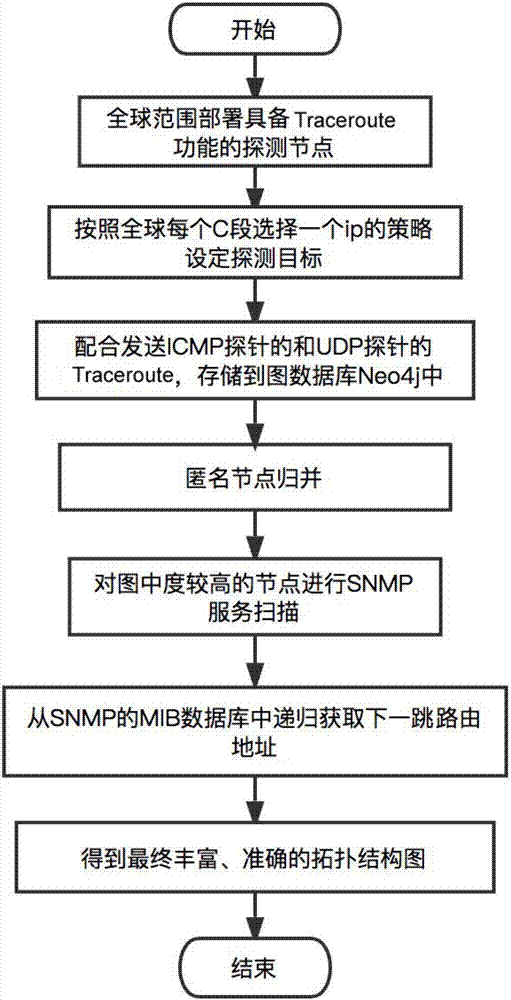
IP level global internet topological mapping method based on Traceroute and SNMP
ActiveCN108011746AReduce in quantityReduce redundancyData switching networksInternet networkTraceroute
The invention relates to an IP level global internet topological mapping method based on Traceroute and SNMP. The method comprises the steps that 1) detection nodes having the Traceroute function aredeployed in the global cyberspace; 2) routing node detection is performed in the routable space around the world by using the Traceroute tool with cooperative use of an ICMP probe and a UDP probe; 3)a topological map is generated according to the detection result obtained in the step 2); 4) the anonymous nodes in the topological map are merged; and 5) the information of the anonymous nodes is speculated by using the SNMP and updated to the topological map so as to obtain the global internet topological map. The number of the anonymous nodes can be effectively reduced and the real informationof certain anonymous nodes can be identified, and the topological map can be further expanded and enhanced so that the topological map is enabled to be closer to the actual situation.
Owner:北京知道未来信息技术有限公司
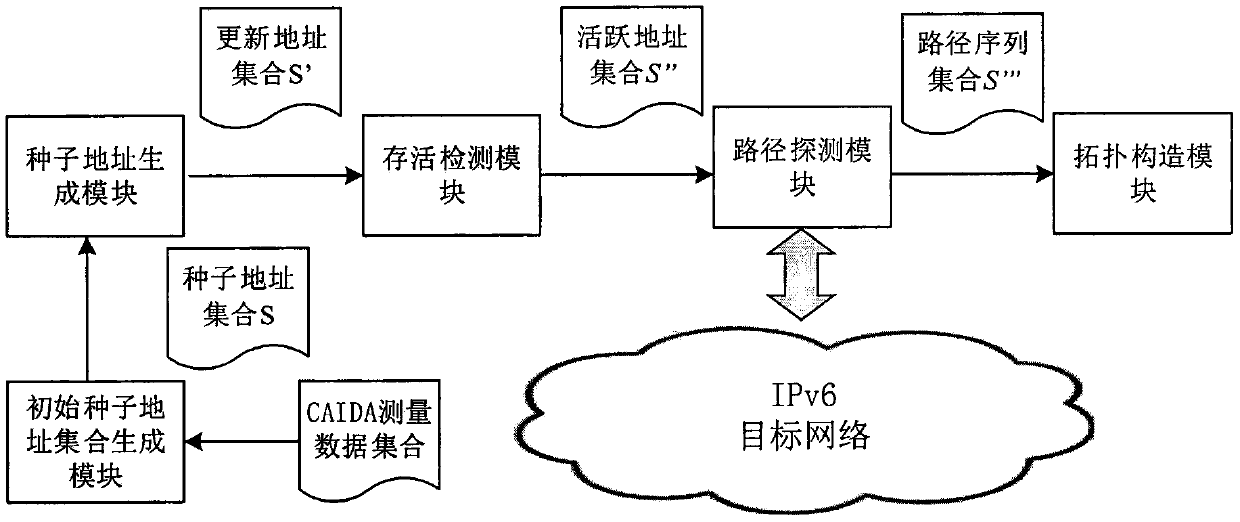
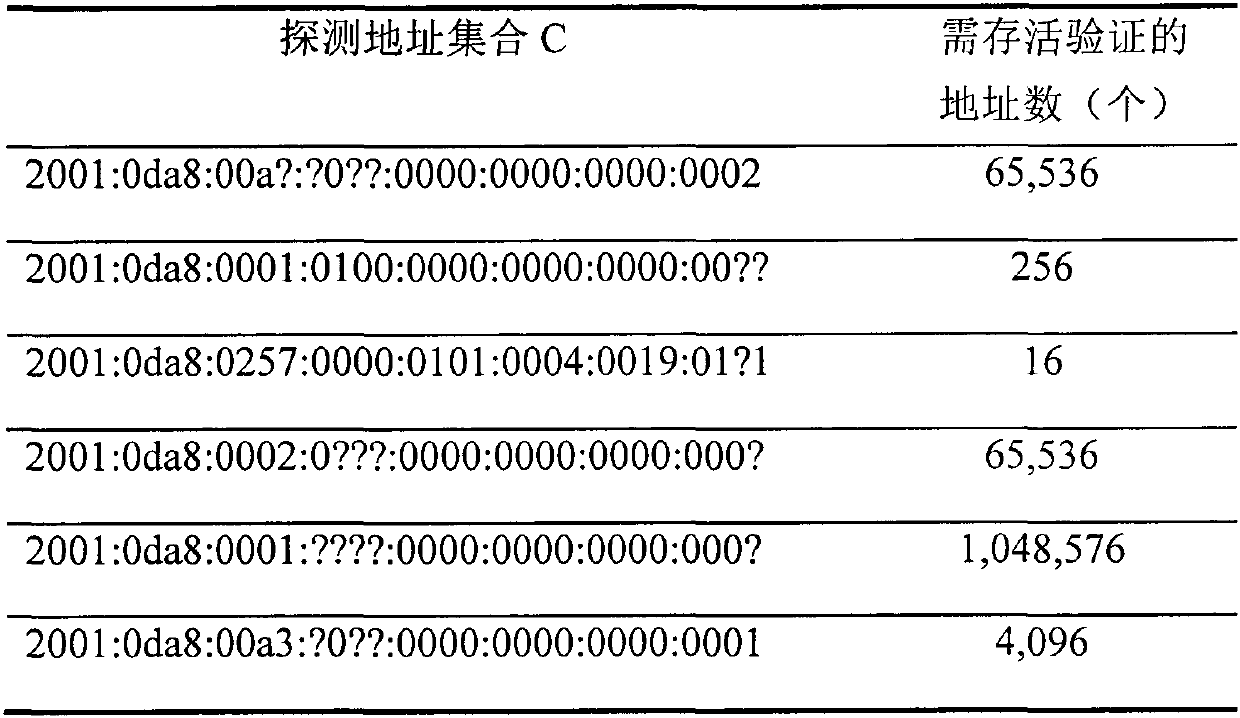
Method for effectively measuring and constructing IPv6 network topology
The invention provides a method for effectively measuring and constructing an IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6) network in order to solve the problem that the network topology cannot be measured by using a Trace tool due to the sparse number of seed addresses in the IPv6 network. The is characterized by comprising the following steps: filtering out an initial seed address set from an open Internet topology measurement data set; and expanding the initial seed address set into an updated address set, performing survival detection on the updated address set to obtain an active address set, and measuring the active address set by adopting a Traceroute method and constructing the topology of the target IPv6 network. The method has the advantages of being capable of effectively measuring the IPv6 network topology and high in robustness.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
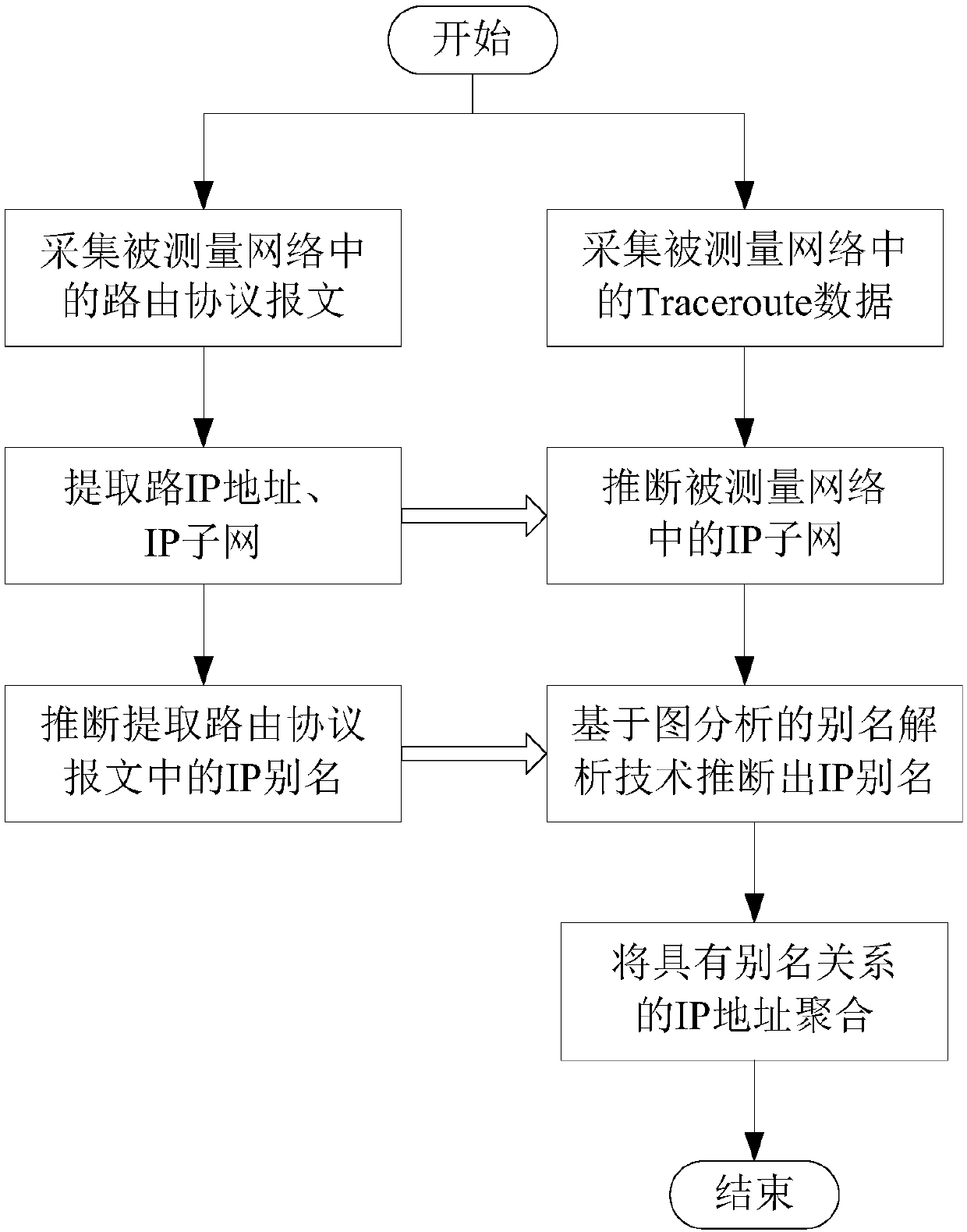
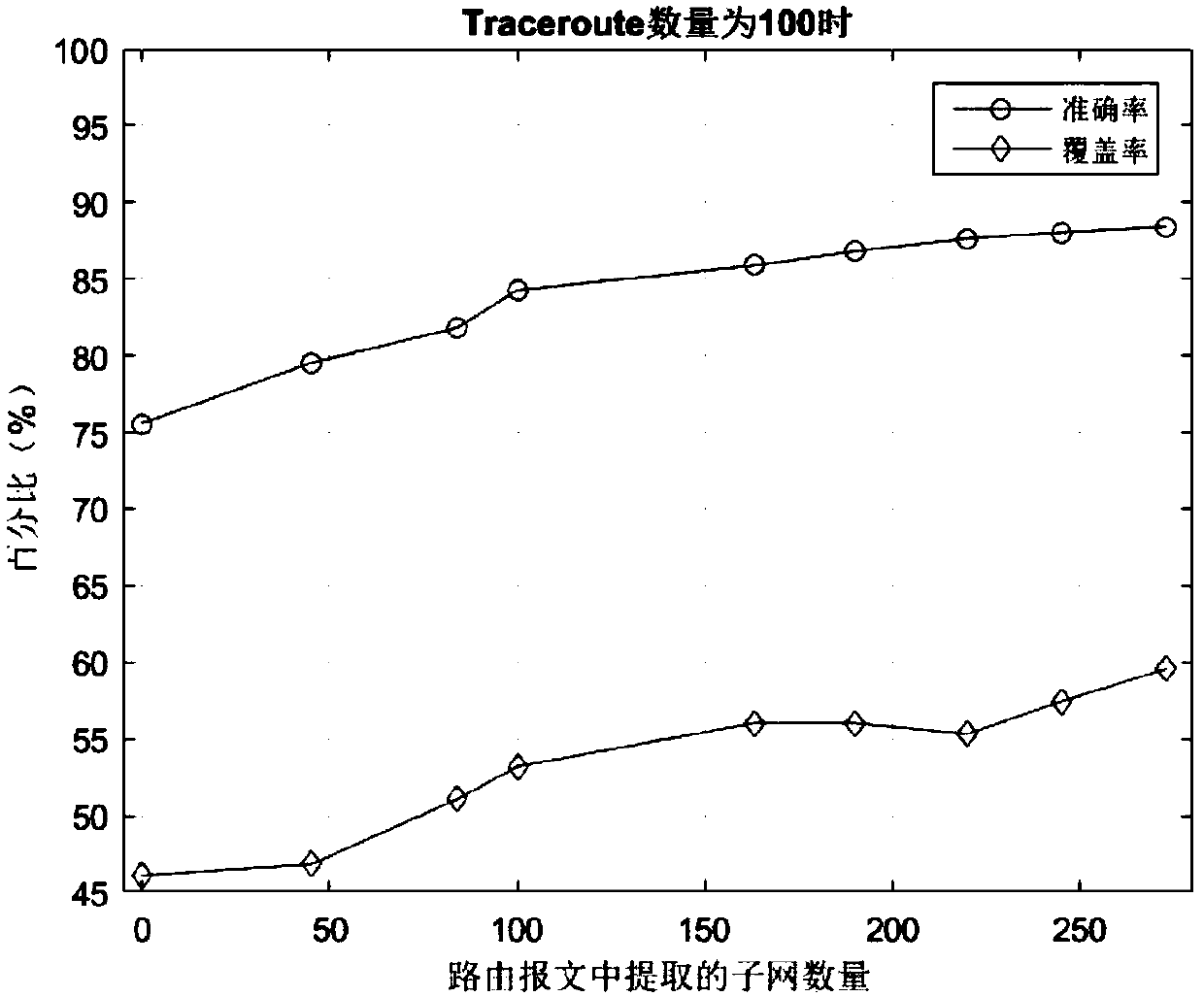
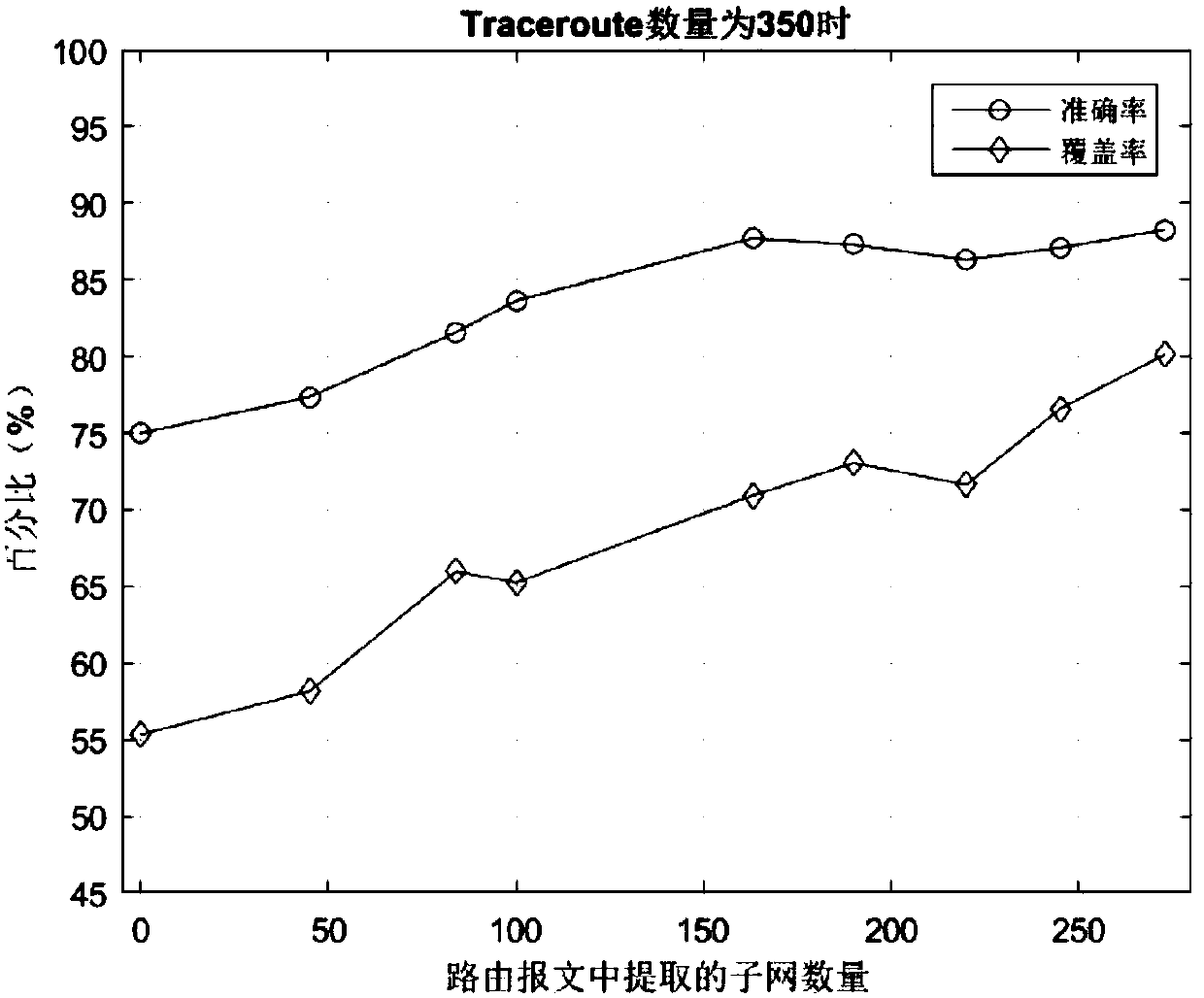
Analysis method for alias of router based on routing information and Traceroute information
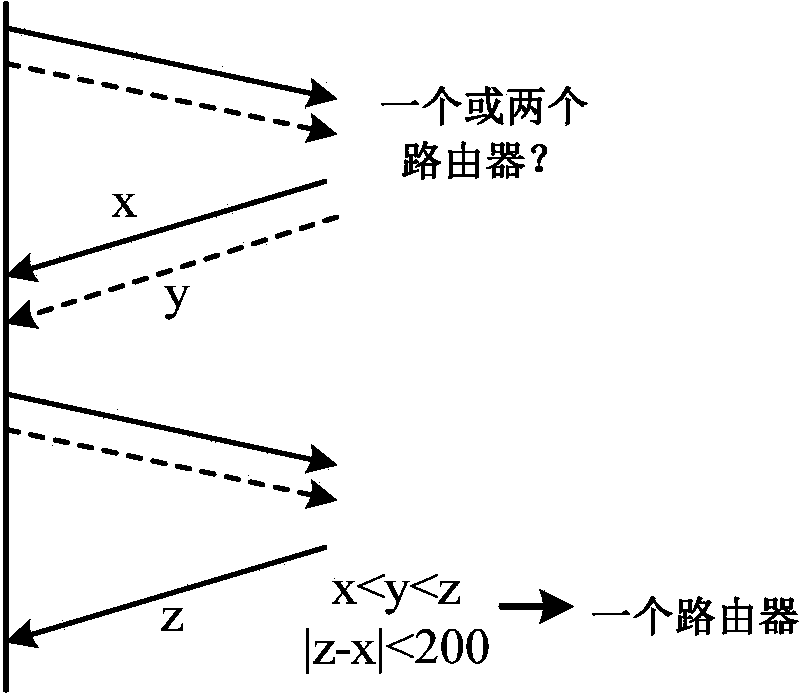
ActiveCN107566279AMake up for incomplete defectsIncrease coverageData switching networksIP aliasingTraceroute
The invention discloses an analysis method for alias of a router based on routing information and Traceroute information. The method comprises the following steps of S1, collecting a routing message and Traceroute data in a measured network; S2, extracting an IP address and an IP subnet in the routing message, and inferring an IP alias; S3, analyzing the Traceroute information, and the IP addressand the IP subnet extracted in the step S2 according to an IP address distribution strategy, and inferring the IP subnet in the measured network; S4, inferring the IP alias by using an alias analysistechnology based on graph analysis; and S5, integrating the IP addresses with alias relations to acquire an actual node of the measured network. According to the method provided by the invention, therouting information is integrated into a traditional graph analysis method, the IP address, the IP subnet and the IP alias are extracted by using the routing information, and the extracted informationis used for inferring the IP subnet and recognizing the IP alias, so that the defect that the information acquired by only depending on Traceroute is incomplete is made up, accuracy and coverage of alias analysis are greatly improved, and the alias analysis efficiency is also improved.
Owner:四川易诚智讯科技有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com