Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4594 results about "Multicast" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
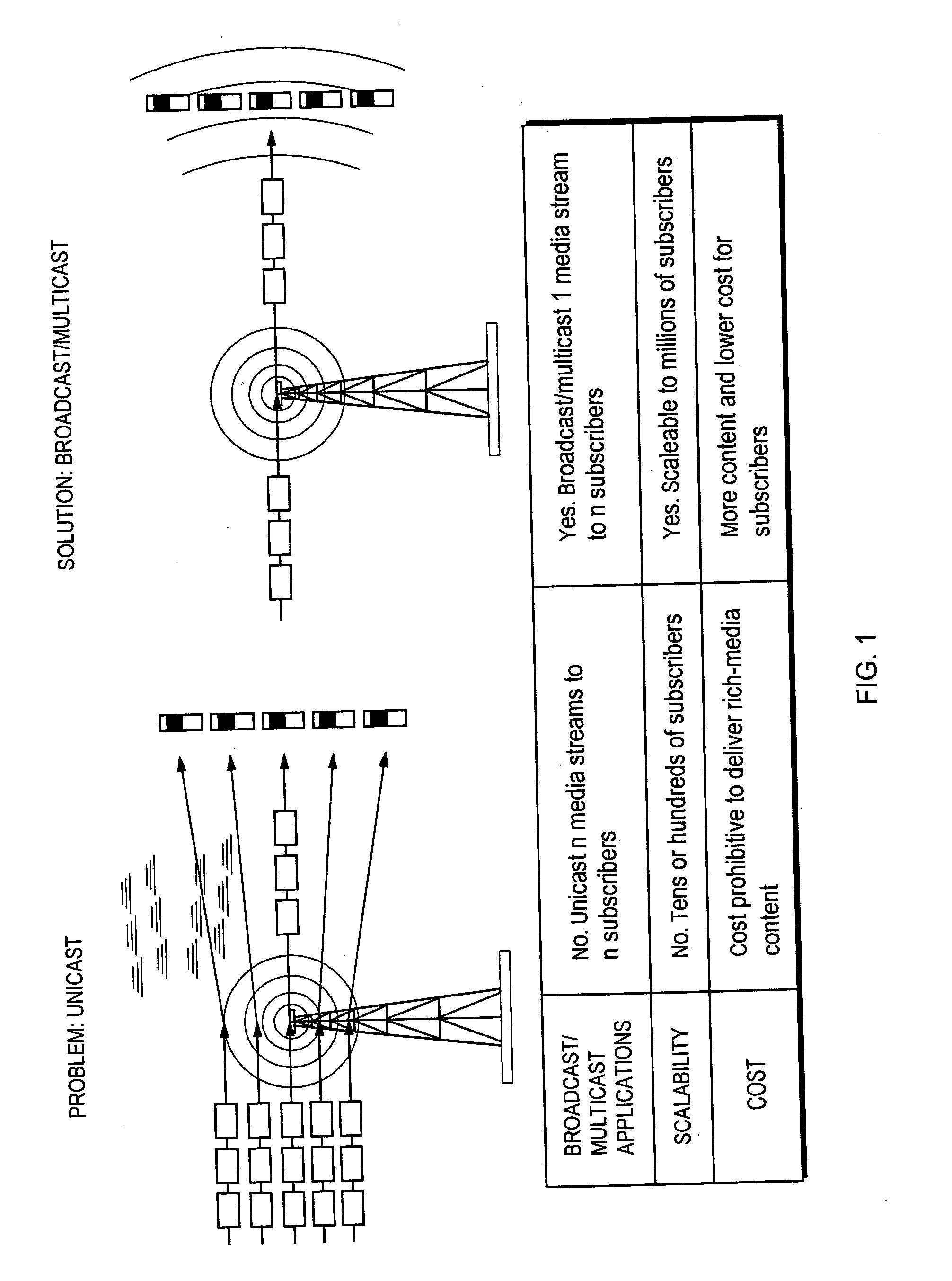
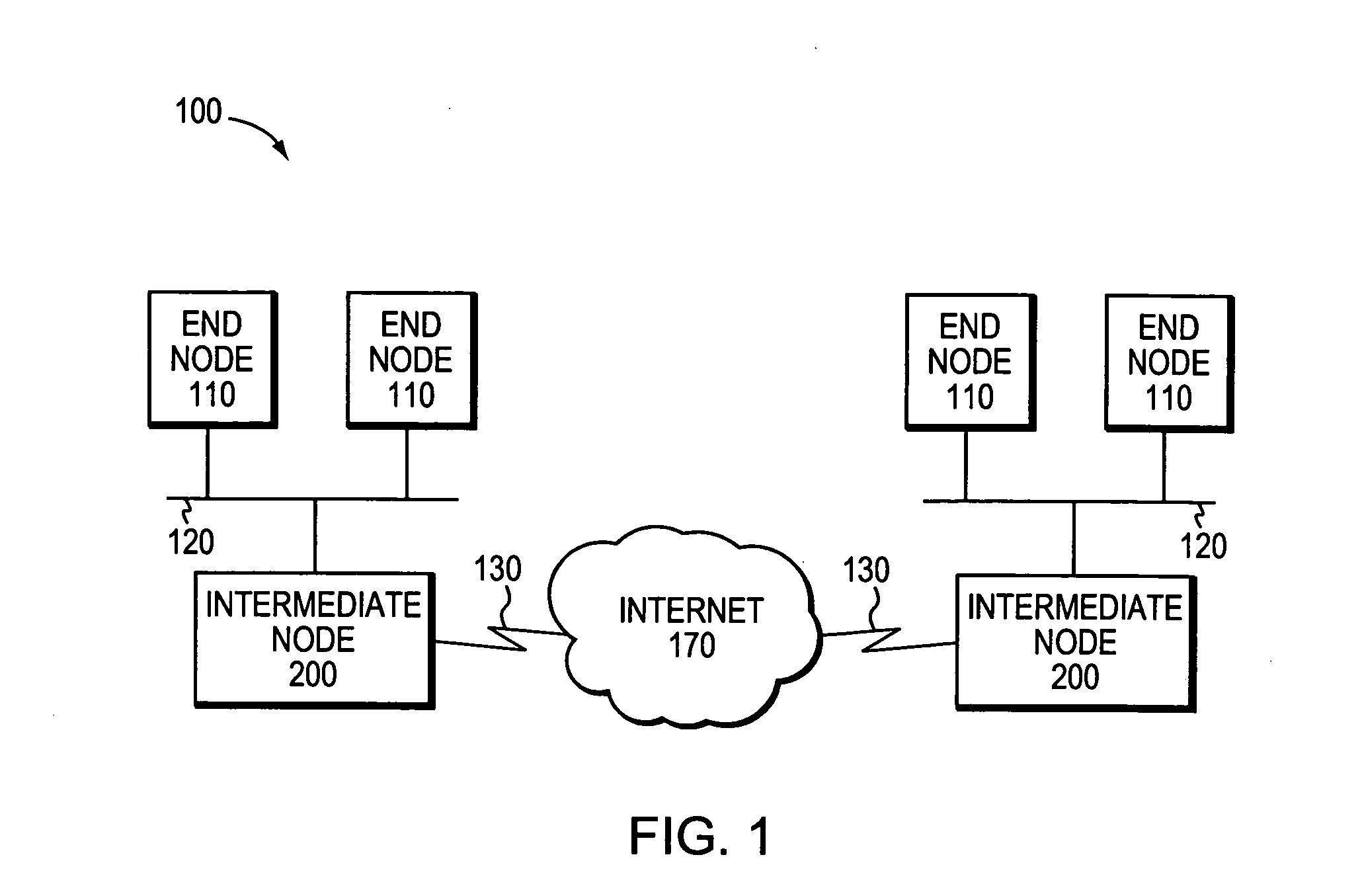
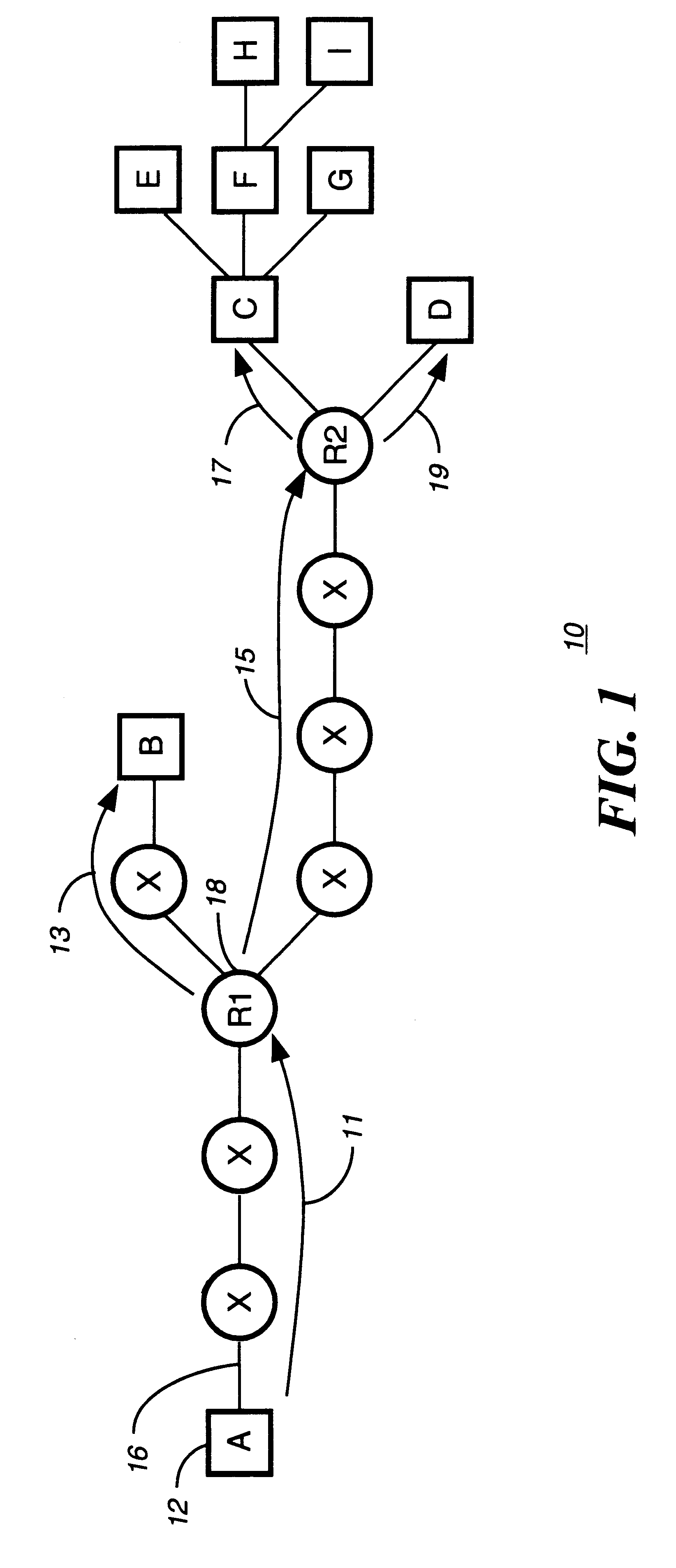
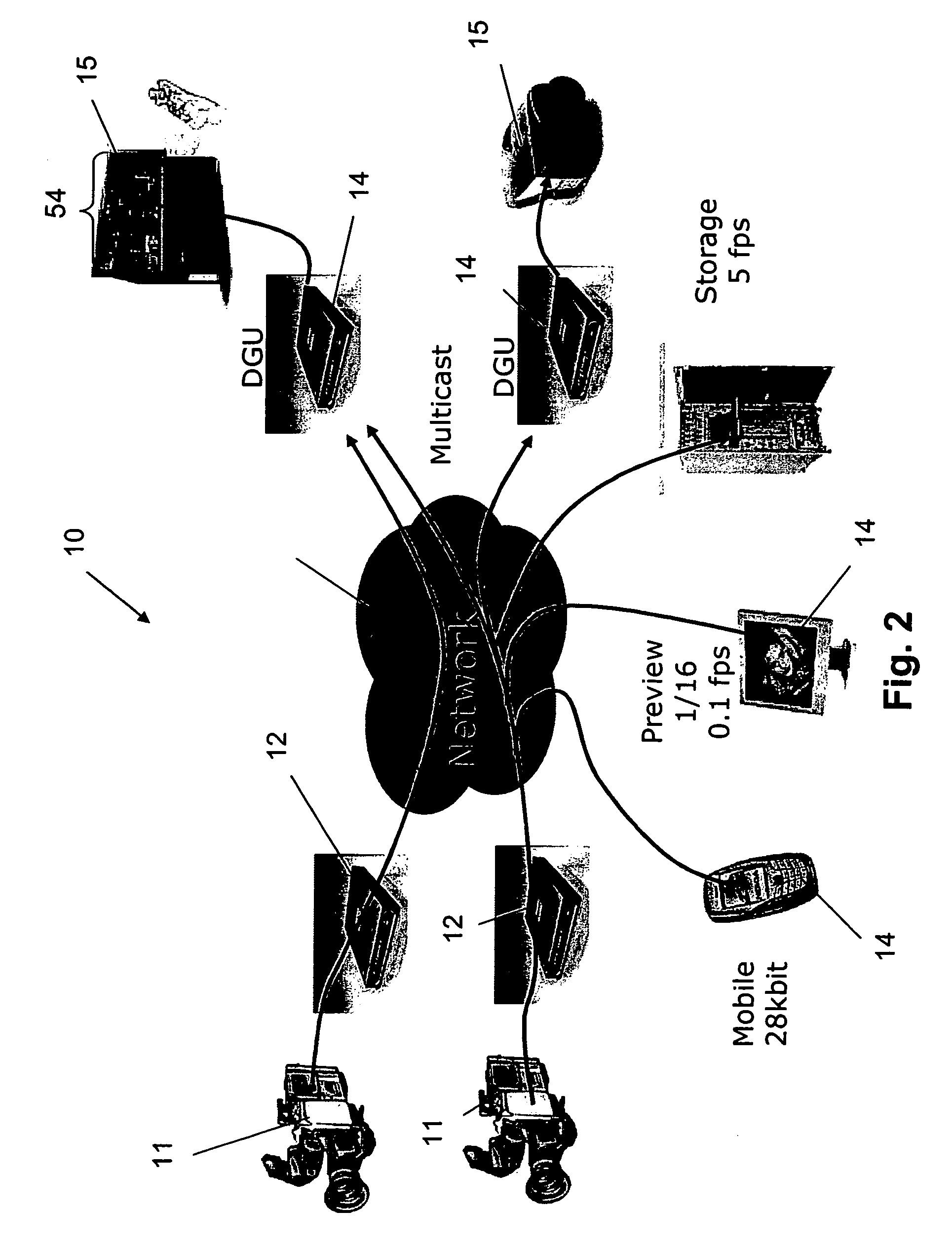
In computer networking, multicast is group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast should not be confused with physical layer point-to-multipoint communication.
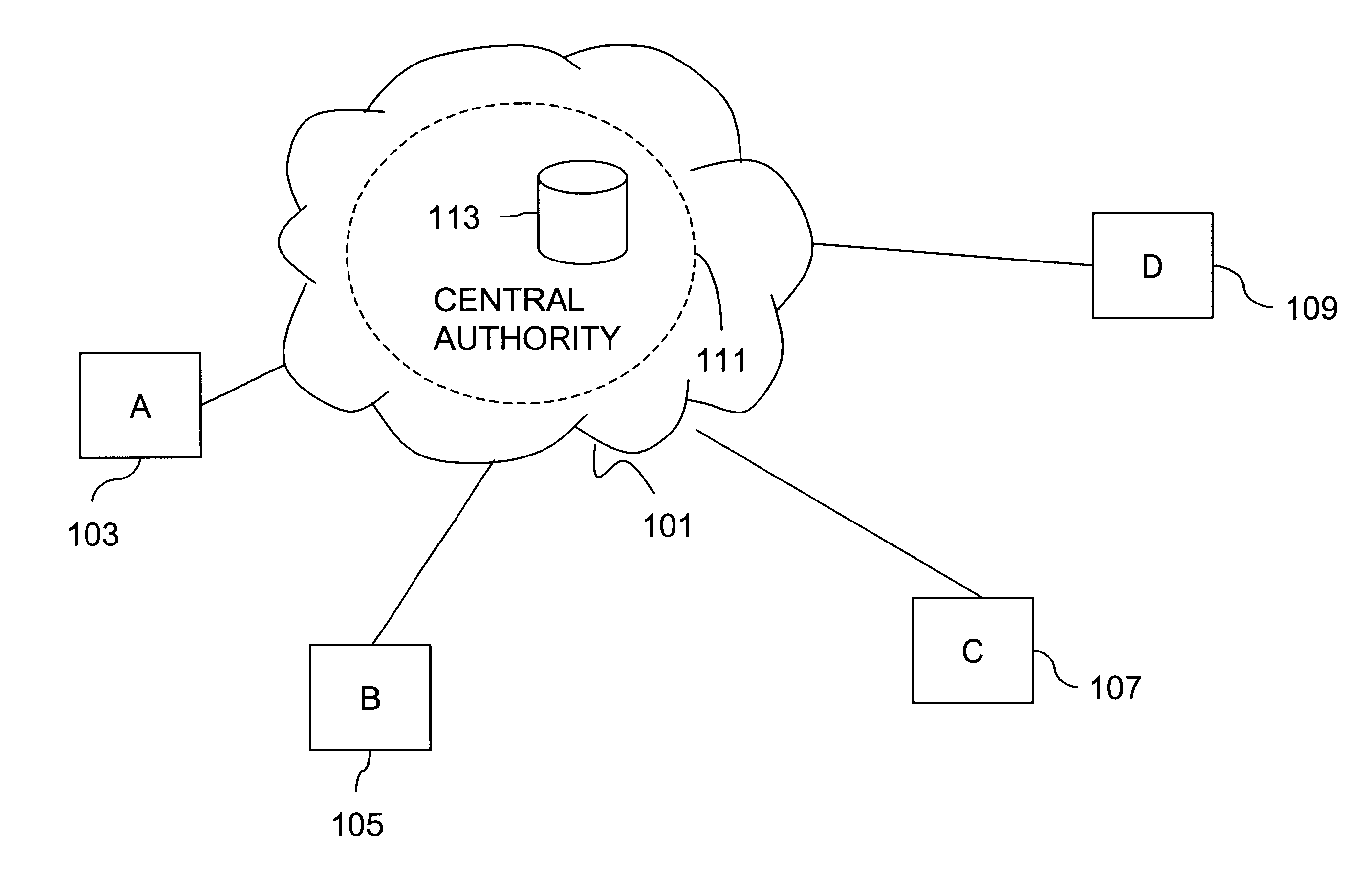
Method and apparatus for creating a secure communication channel among multiple event service nodes
InactiveUS7013389B1Easy to scaleUser identity/authority verificationSecure communicationGroup session
An approach for establishing secure multicast communication among multiple event service nodes is disclosed. The event service nodes, which can be distributed throughout an enterprise domain, are organized in a logical tree that mimics the logical tree arrangement of domains in a directory server system. The attributes of the event service nodes include the group session key and the private keys of the event service nodes that are members of the multicast or broadcast groups. The private keys provide unique identification values for the event service nodes, thereby facilitating distribution of such keys. Because keys as well as key version information are housed in the directory, multicast security can readily be achieved over any number of network domains across the entire enterprise. Key information is stored in, and the logical tree is supported by, a directory service. Replication of the directory accomplishes distribution of keys. Event service nodes may obtain current key information from a local copy of the replicated directory.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
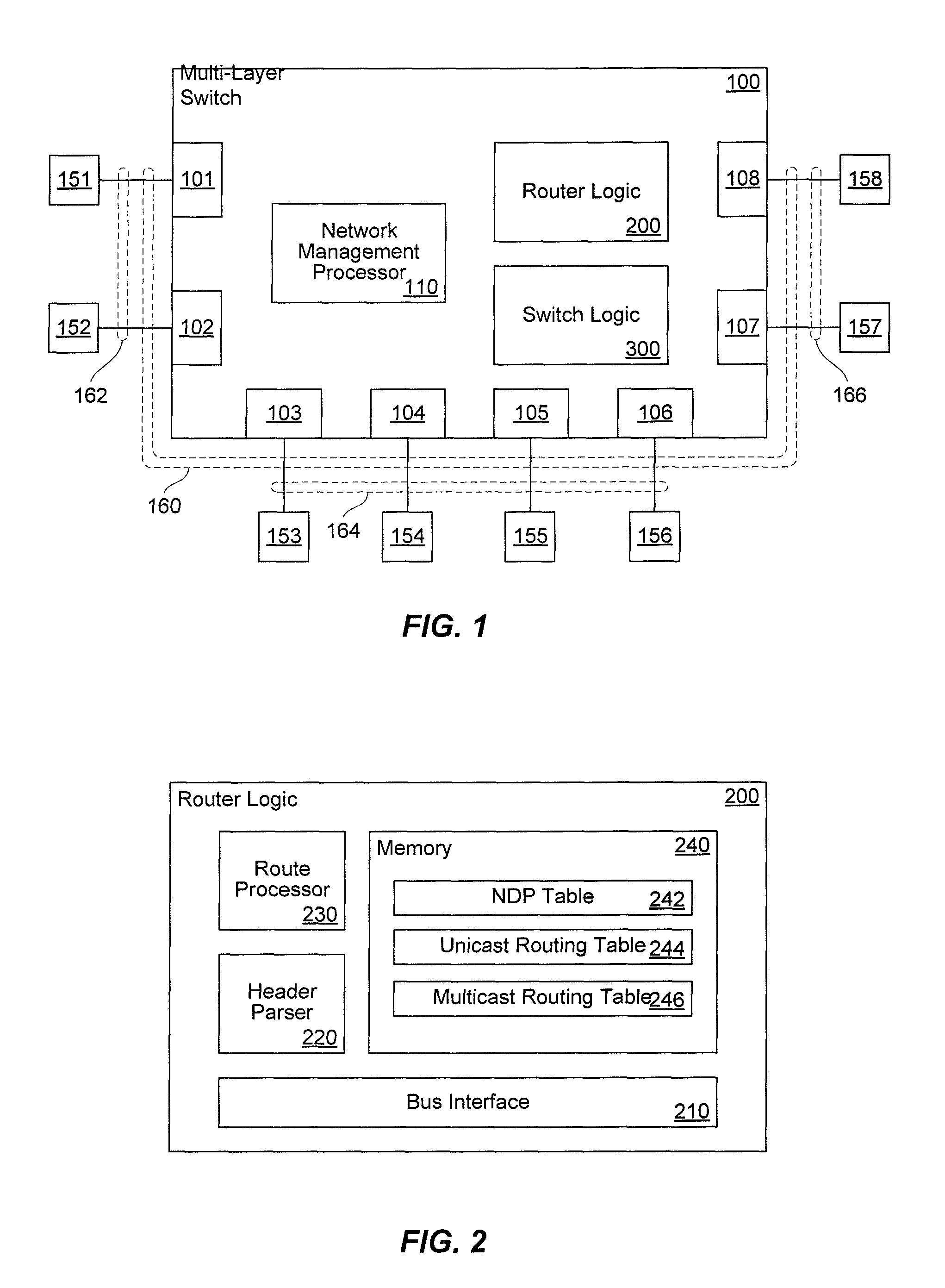
Router, frame forwarding method, and lower layer frame virtual forwarding system
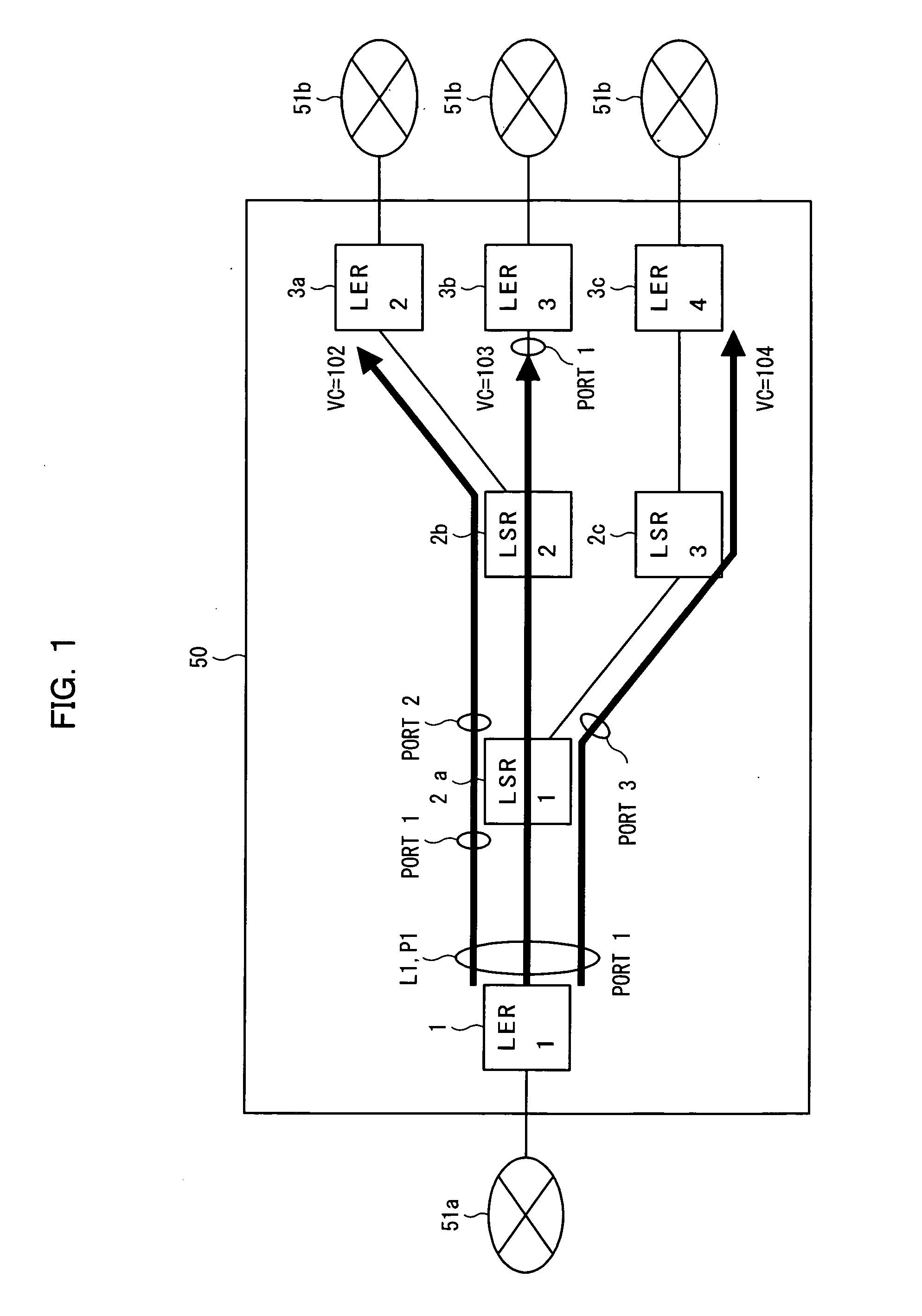
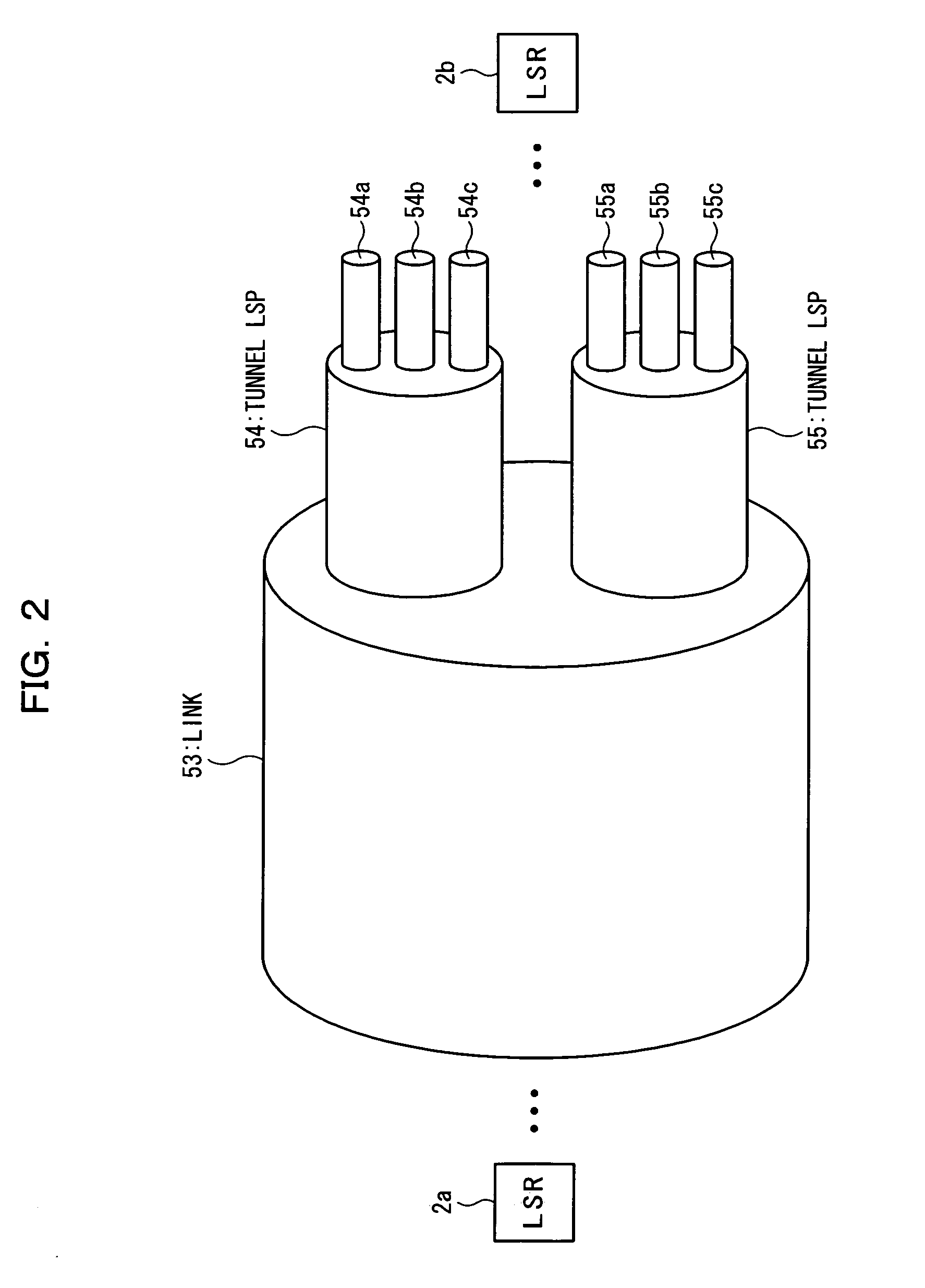
InactiveUS20050169270A1Avoid loadEasy to useTime-division multiplexNetworks interconnectionPhysical addressLabel switching
In an MPLS network, multicast, broadcast and address learning belonging to the layer 2 functions are realized. An ingress router comprises a frame receiving unit, a determining unit, a first frame transmitting unit, a physical address table for multicast, a label switching unit, a tunnel label table, a VCID giving unit, a L2 header creating unit and a second frame transmitting unit. The load on the network is suppressed, the band is efficiently used, and wasteful frame duplication and frame forwarding between edge routers are avoided.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Real-time multicast peer-to-peer video streaming platform
InactiveUS20080133767A1Reduce bandwidth requirementsMinimal costMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionThe InternetPeer-to-peer
A peer-to-peer platform makes use of a streaming agent running at each peer. The streaming agent causes a peer to receive chunks of content from different neighboring peers, store some of the chunks in a local cache, and distribute those cached chunks to neighboring peers. Delivering next generation broadcasts (e.g., as streams of live audio and digital media) of any size utilizing the Internet is achieved. Users can view a live or prerecorded stream of a broadcast through an integrated media player, or can replay a broadcast through an integrated, intelligent archiving service. Use of the platform reduces bandwidth demands on live streaming and archiving services to a level where it is sustainable within a profitable business model to offer the services for at most a negligible fee.
Owner:METIS ENTERPRISE TECH
Multicast routing in ad-hoc networks
InactiveUS7310335B1Special service provision for substationTime-division multiplexMulticast packetsManet routing
Multicast routing in ad-hoc networks by exchange of multicast group update information and routing tree information among neighboring routers is disclosed. A router propagates multicast group update information based on the update information and the routing tree information. A router also determines whether to forward multicast data packets based on control information in the multicast data packets and the routing tree information.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
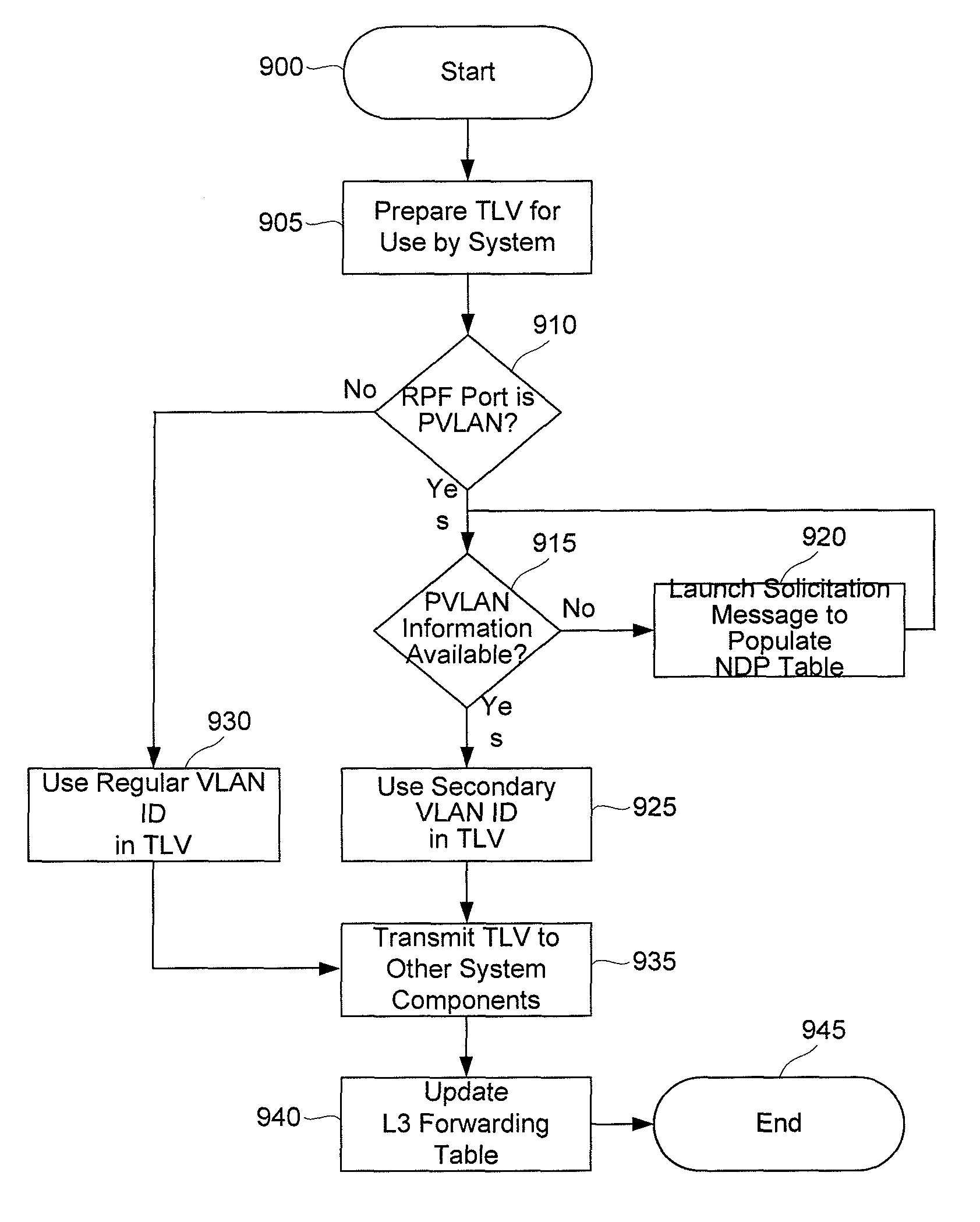
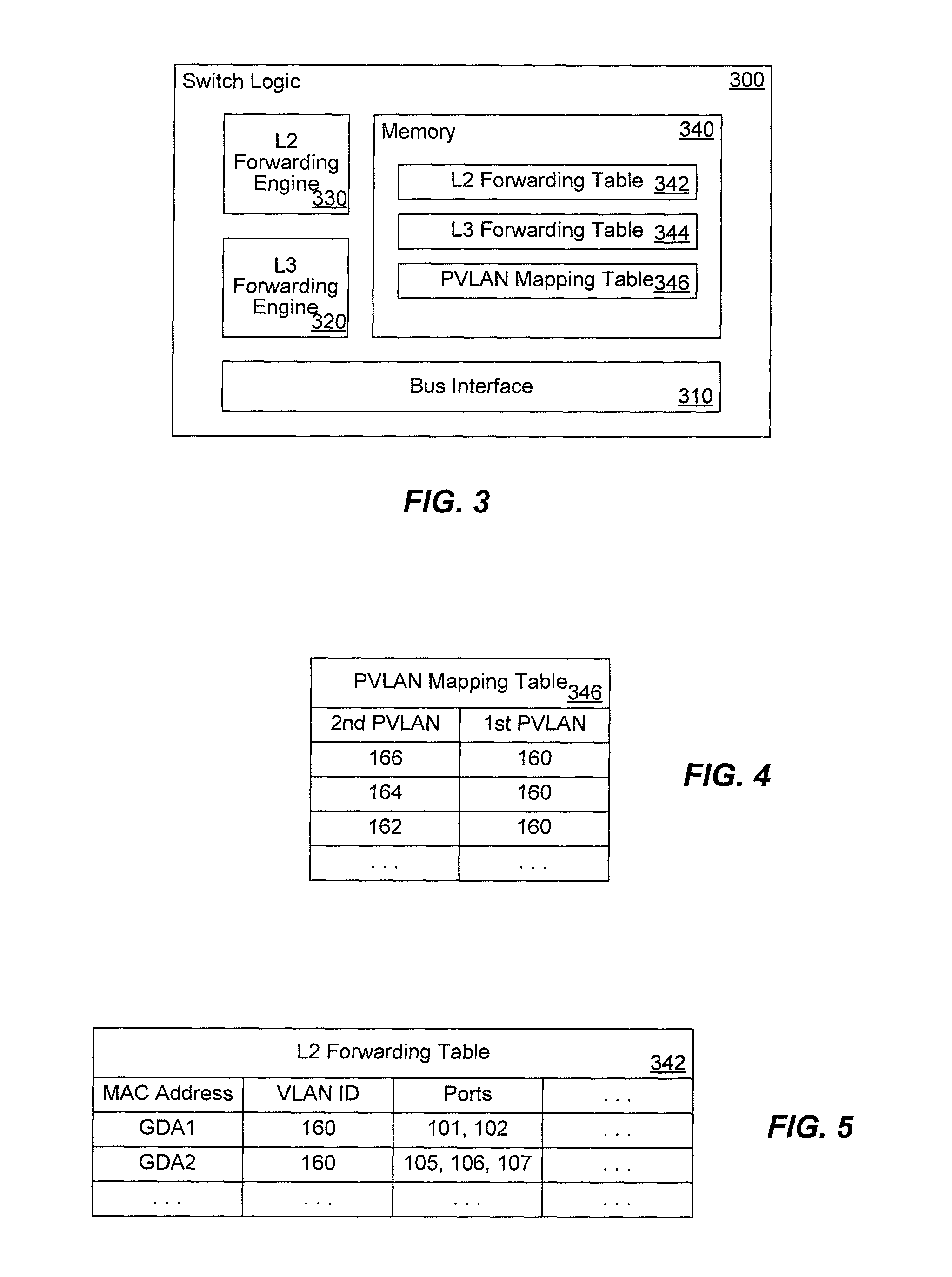
Systems and methods for multicast switching in a private VLAN
ActiveUS8625603B1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsReverse path forwardingPrivate VLAN
A Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) protocol query and / or report snooping process is modified to appropriately map secondary PVLAN identifiers to corresponding primary PVLAN identifiers, thereby accommodating other system elements that are otherwise unaware of primary / secondary PVLAN distinctions. Special cases are also accommodated where reverse path forwarding (RPF) checks in support of multicast operation might otherwise fail due to primary / secondary PVLAN distinctions. Additional steps are taken to ensure that PVLAN information properly accounts for changes in configuration and / or location of various network hosts.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Handling broadcast and multicast traffic as unicast traffic in a wireless network
An access point is to handle received broadcast or multicast traffic as multiple instances of unicast traffic, where each instance is destined for a corresponding wireless client device associated with the access point. A client device may adjust its listen interval parameter according to predefined considerations, for example a charge level of a battery to power the client device and an expected usage model for the device. A client device may initiate a reassociation request to inform the access point of its adjusted listen interval parameter.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
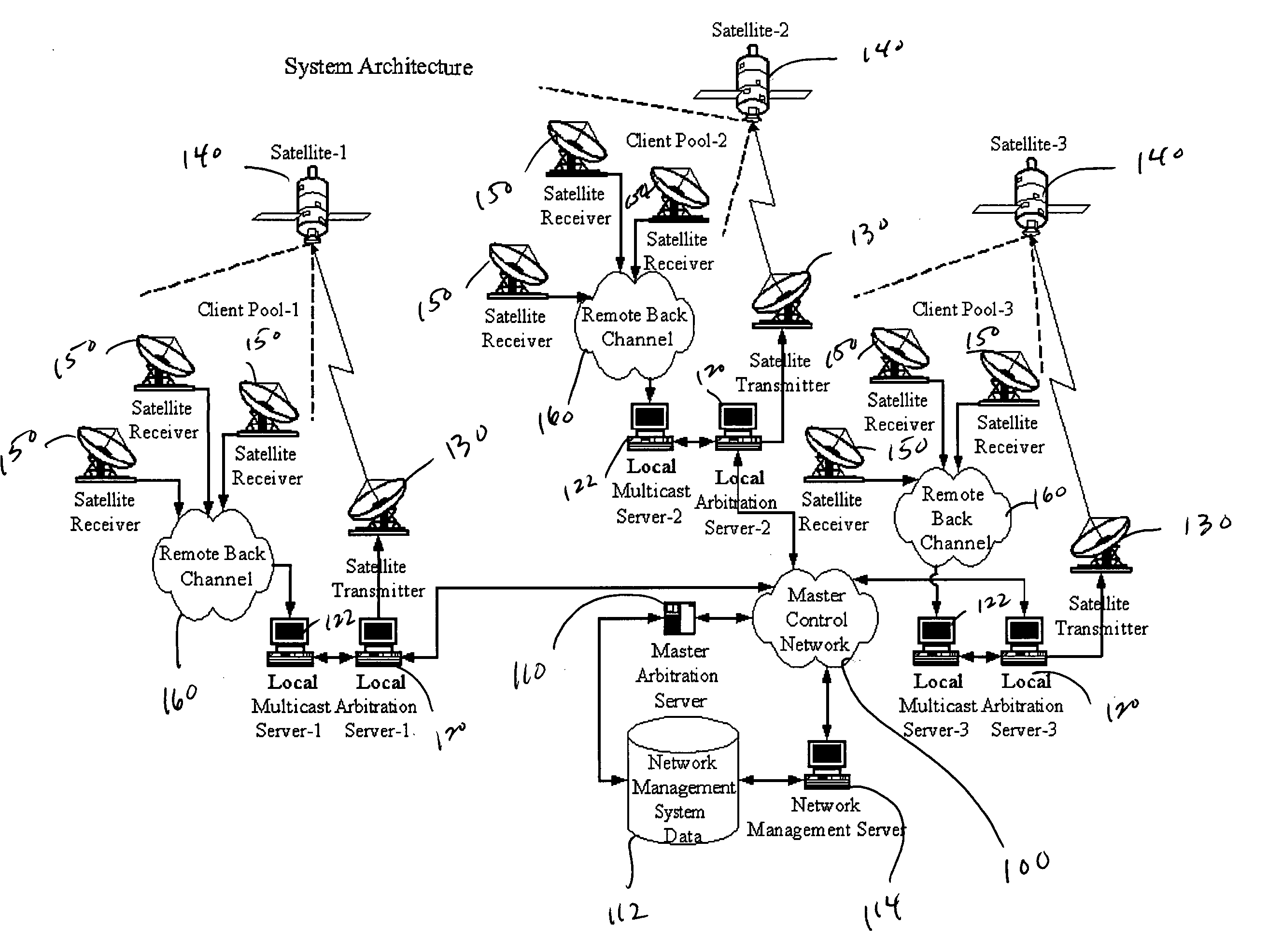
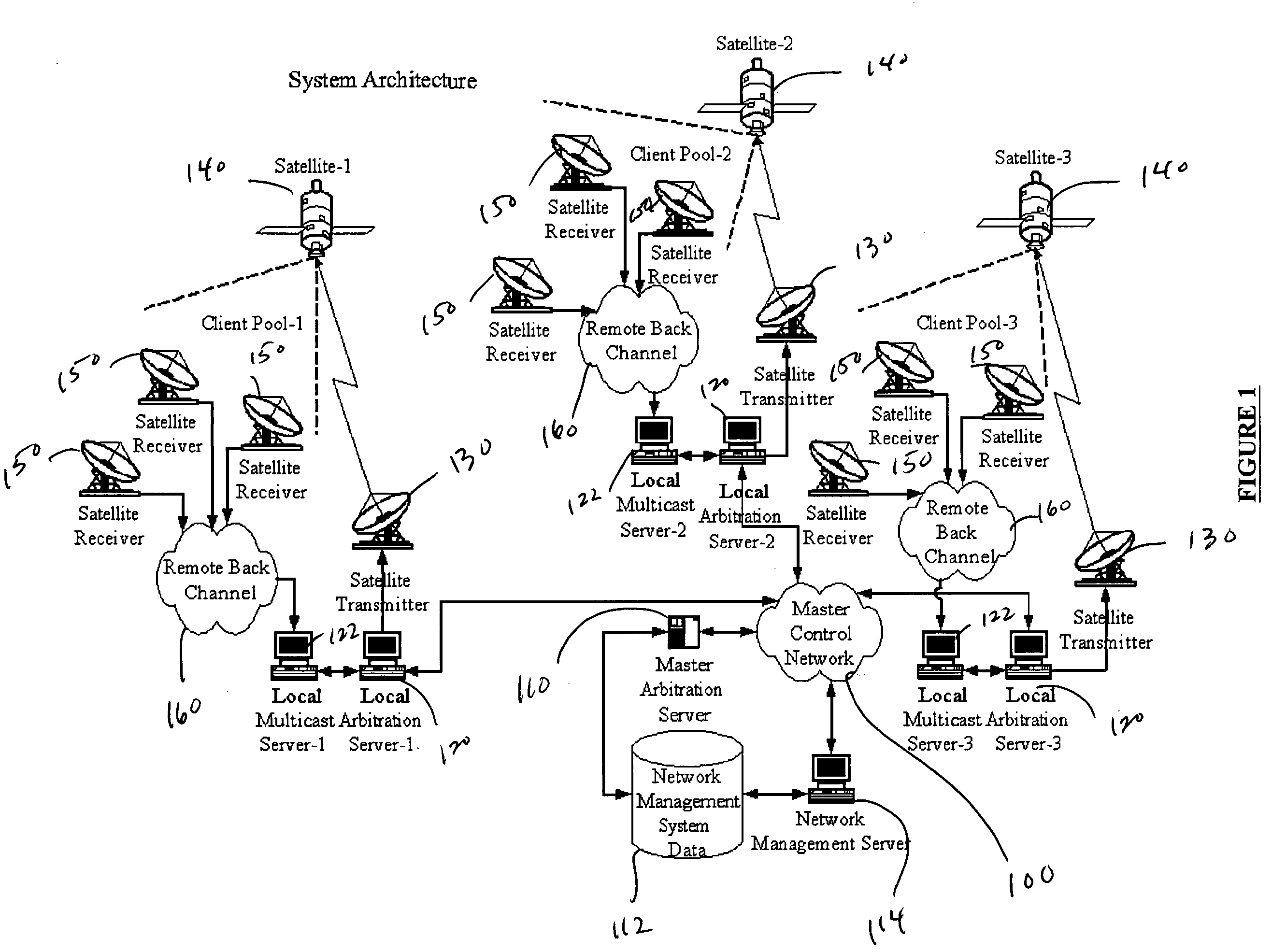
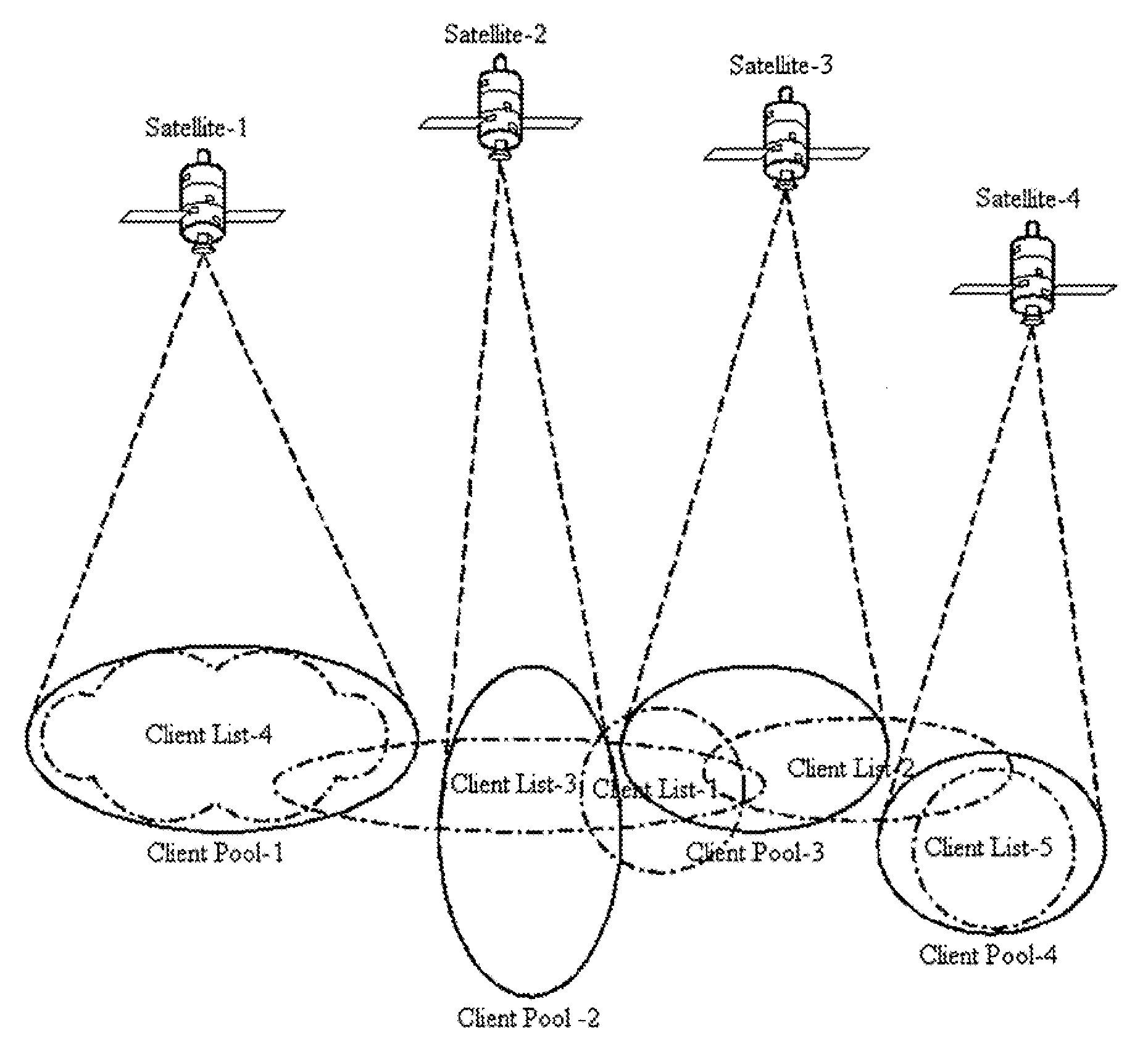
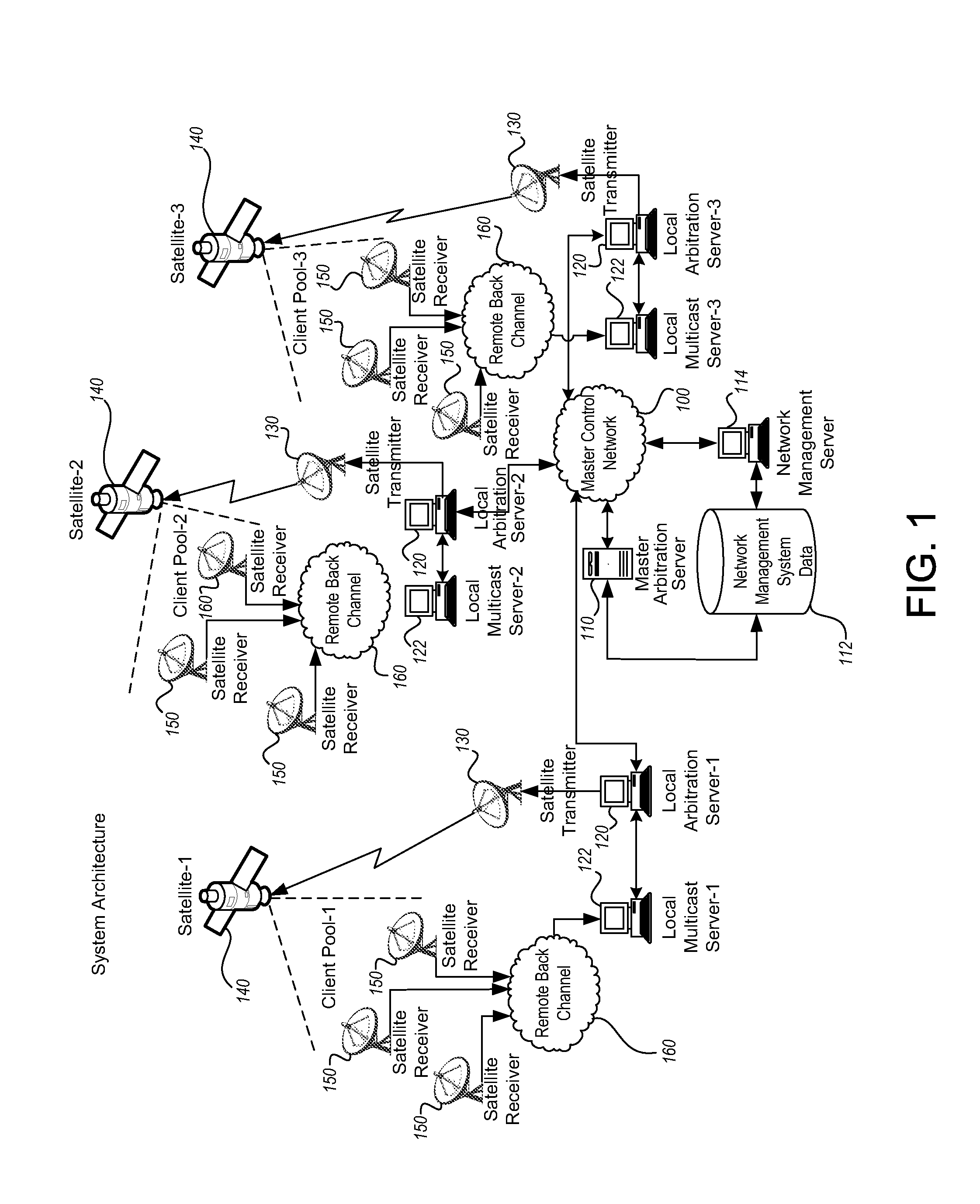
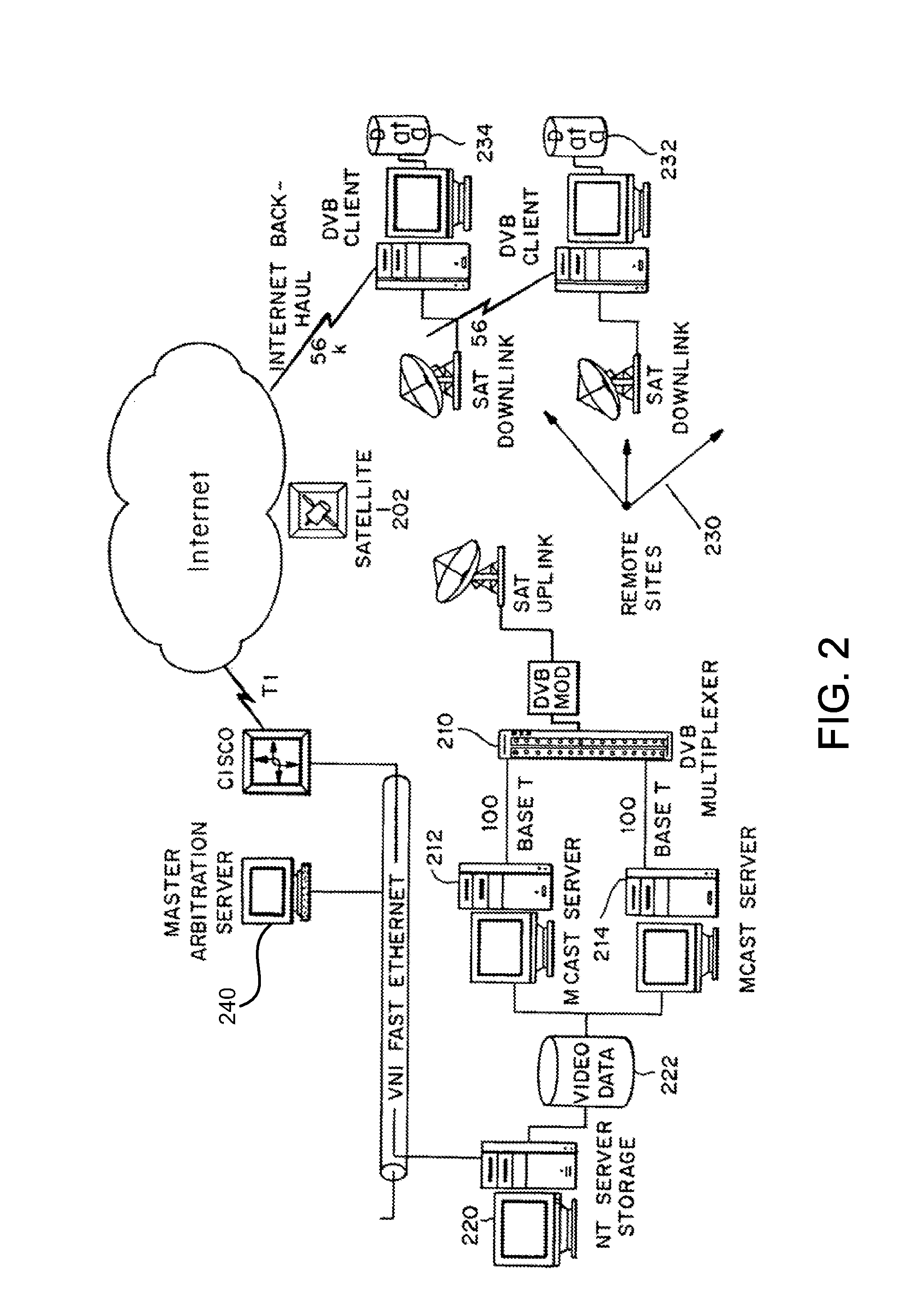
Multicast control systems and methods for dynamic, adaptive time, bandwidth,frequency, and satellite allocations
InactiveUS20050037706A1Improve transmission performanceMaximizing numberBroadcast with distributionNetwork traffic/resource managementControl systemThe Internet
Methods and systems to efficiently share multiple satellites and associated transponders or links among a network of uplinking earth stations are disclosed. An embodiment of this invention uses a terrestrial communications link, such as the Internet, to control access to the transponder or satellite links. Communications over this link may employ a TCP / IP protocol to connect the requesting uplinking earth stations with a centralized controller. This control system creates more efficient use of satellite resources and reduces the overall amount of time needed for transmitting data through the satellite. By reducing the overall amount of time needed for transmitting data, the control system may reduce the cost of using the satellite transponder capacity.
Owner:EXTREME REACH INC +1
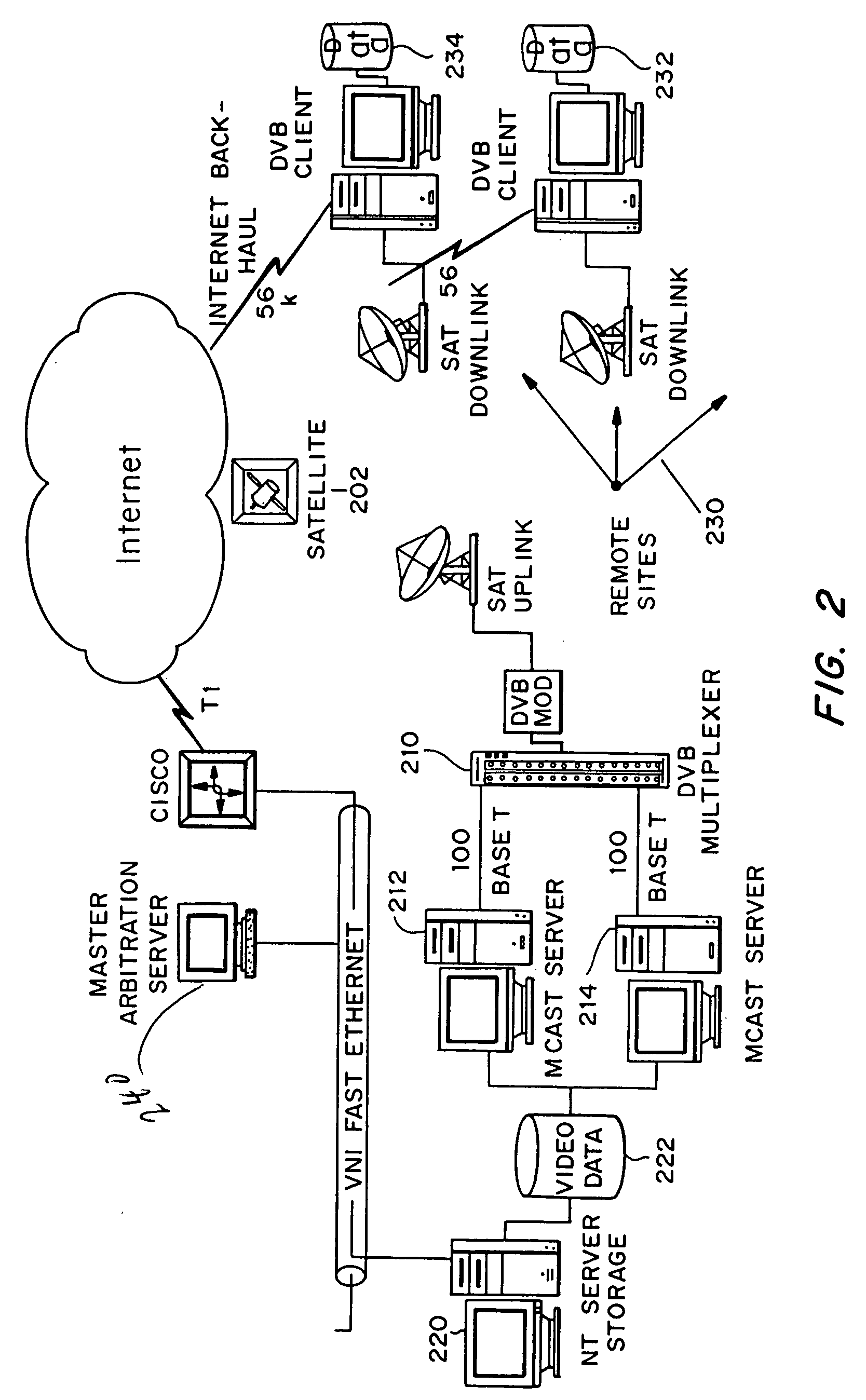
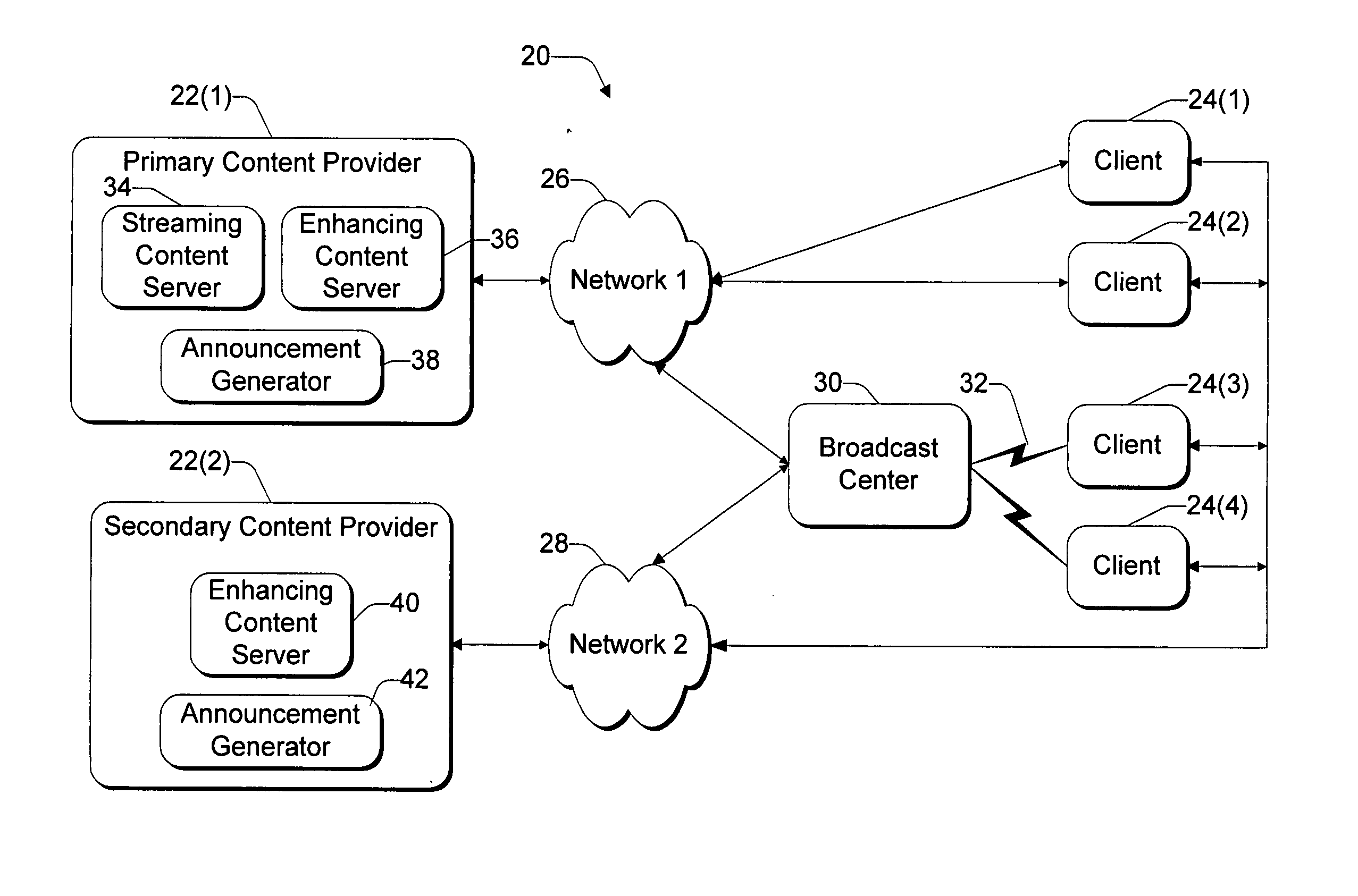
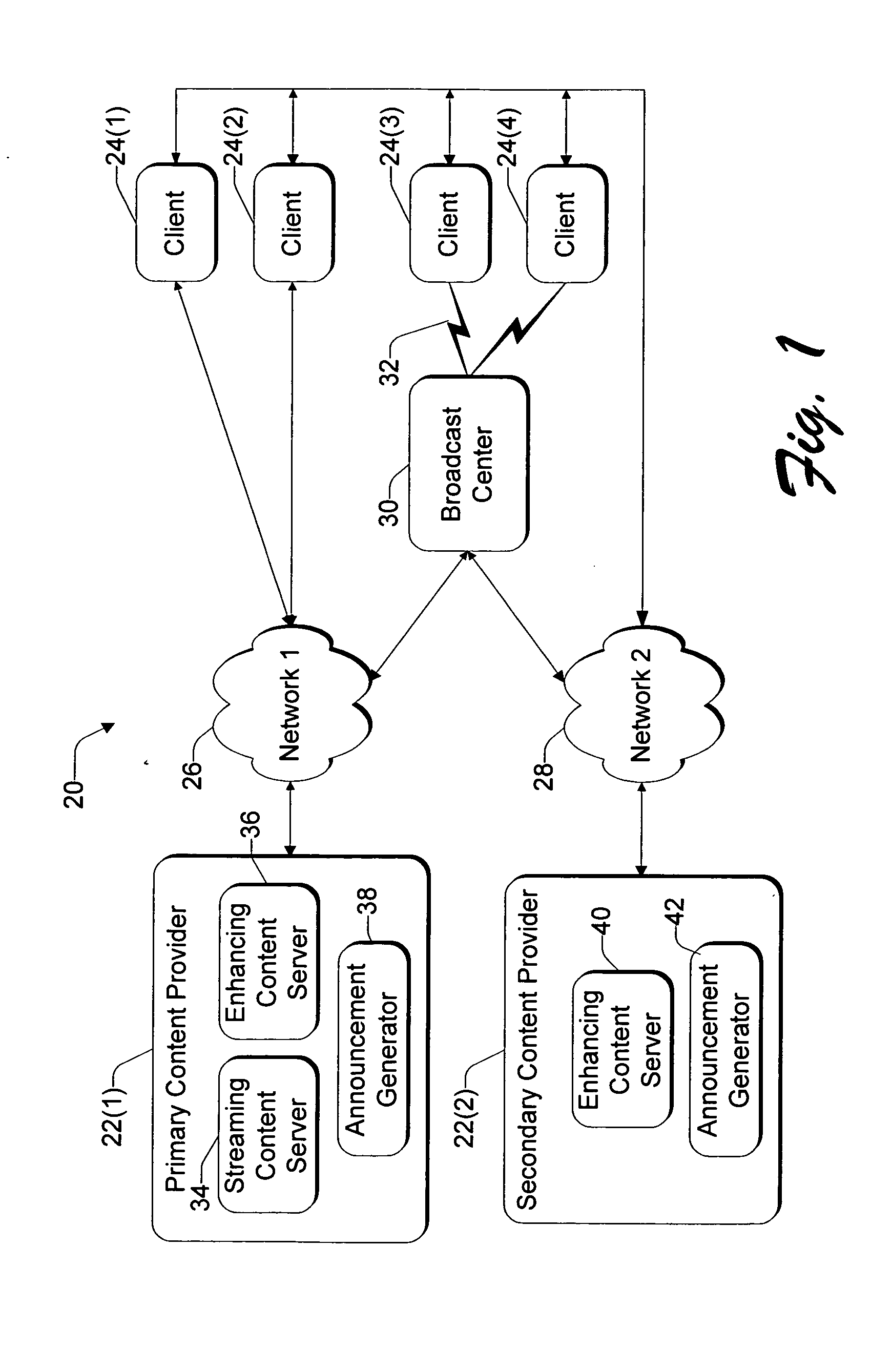
System and method for synchronizing streaming content with enhancing content using pre-announced triggers
ActiveUS20050028195A1Increase contentTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsIp addressClient-side
A client-server architecture synchronizes streaming content with enhancing content via pre-announced triggers. The architecture includes server-based components to generate announcements containing information specifying how and when to receive upcoming triggers that will be transmitted at a later time. The server transmits the announcements to a general broadcast or multicast IP address. Client-based components monitor the IP address to receive and filter the announcements. Selected announcements are stored in a guide database in correlation with the streaming content programs to indicate that the programs are interactive. When a user tunes to an interactive program, the client opens a container HTML page that contains controls to receive the streaming content program and to extract the announcements from the guide database. The latter control monitors the IP address at the times specified in the selected announcements to receive the triggers corresponding to the interactive program. The server delivers the triggers at times synchronized to the streaming content. When triggers arrive, the client control processes the triggers to coordinate presentation of the enhancing content with the streaming content program. The triggers may further be used to carry items that fill a ticker being displayed with the program.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
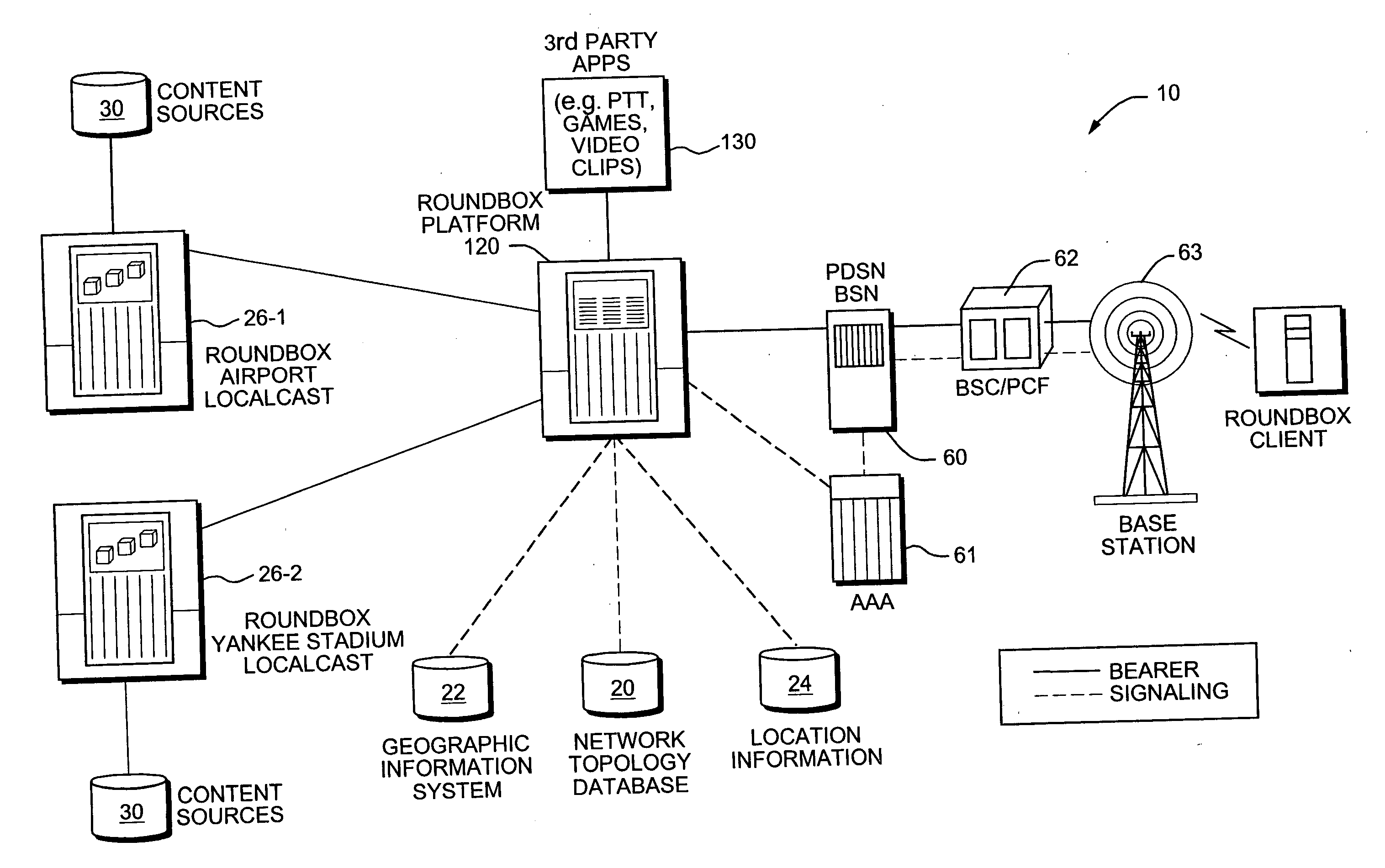
Territory mapping for efficient content distribution in wireless networks using broadcast/multicast
InactiveUS20060126556A1Special service provision for substationTime-division multiplexContent distributionData set
A technique for content delivery in wireless networks which associates a desired broadcast / multicast (BCMC) territory with the content, estimates cell sector coverage area from a subscriber location data set, and then identifies a set of cell sectors to be sent the content using a BCMC protocol. The method involves first receiving a description of a designated broadcast / multicast (BCMC) territory in terms of a physical area. Next, a content indicator associated with the BCMC territory is identified. The content indicator identifies content, such as text or image data, that is to be supplied to subscribers located in the territory. A cell sector coverage area is then estimated from a subscriber location data set wherein the data set includes at least a geographic location and a cell sector identifier for multiple subscribers. The BCMC territory description and the estimated cell sector coverage areas are then compared against the subscriber location data set to identify a set of targeted cell sectors. Finally, the content indicator is then sent to the set of targeted cell sectors using a BCMC protocol.
Owner:ROUNDBOX
Method for retransmitting a radio resource control connection request message in mobile communication system capable of providing a multimedia broadcast/multicast service
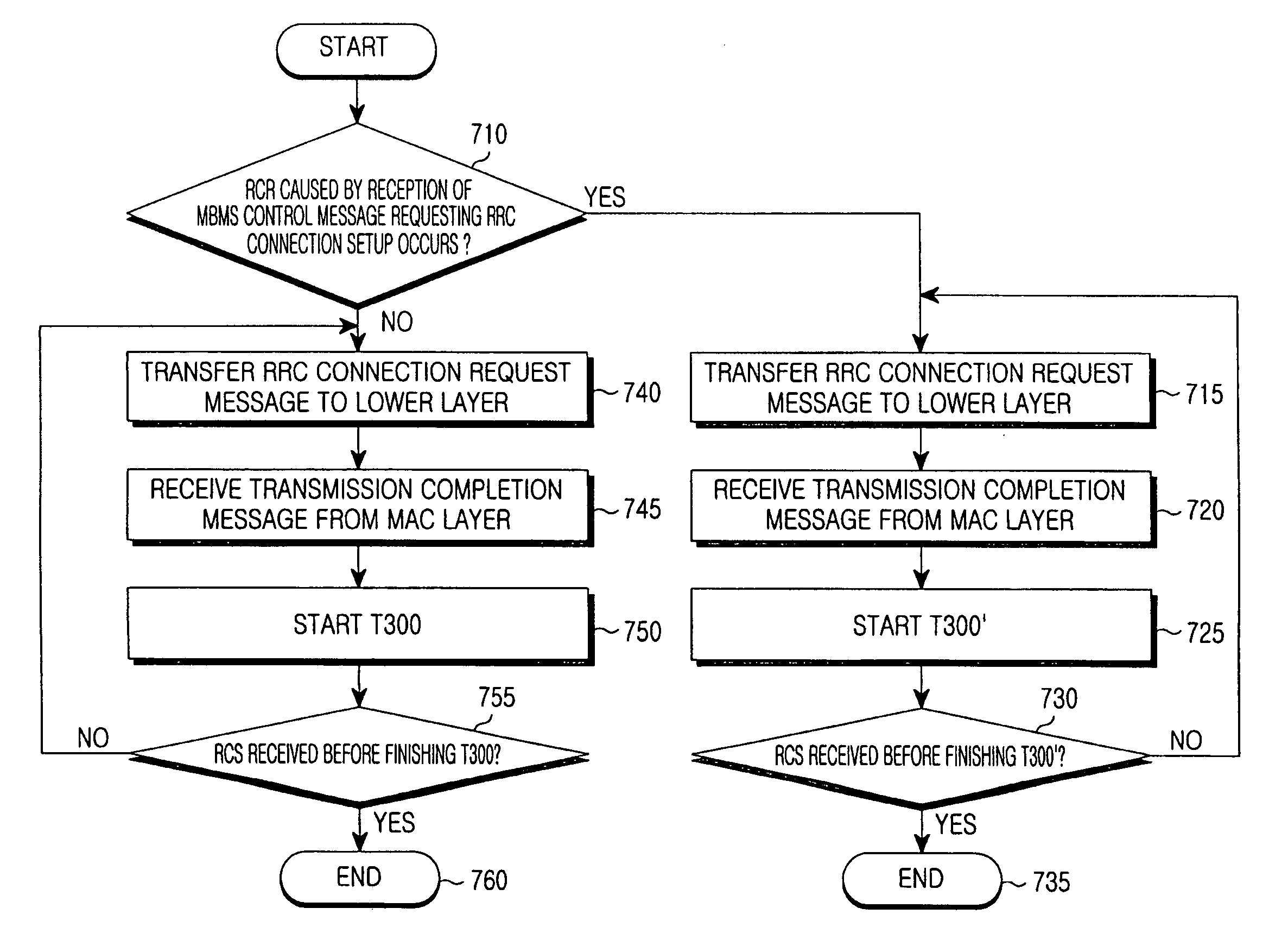
InactiveUS20050026597A1Special service provision for substationAssess restrictionTelecommunicationsMobile communication systems
A method for controlling a UE (User Equipment) to retransmit an RRC (Radio Resource Control) connection request message in a mobile communication system capable of providing an MBMS (Multimedia Broadcast / Multicast Service). The method includes the steps of determining, by an RRC layer of the UE, if a control message including a timer value corresponding to a cell having the UE is received from a RNC (Radio Access Controller); transmitting the RRC connection request message to the BSC over an uplink common channel when the control message is equal to an MBMS control message; and repeatedly transmitting the RRC connection request message in response to the timer value until receiving a response message from the BSC.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transparent, look-up-free packet forwarding method for optimizing global network throughput based on real-time route status
ActiveUS20040032856A1Fast protection re-routingEfficient multicastingData switching by path configurationPrivate networkOSI model
A packet forwarding method for optimizing packet traffic flow across communications networks and simplifying network management. The invention provides look-up-free and packet-layer-protocol transparent forwarding of multi-protocol packet traffic among Layer-N (N=2 or upper in the ISO OSI model) nodes. The invention enables flexible and efficient packet multicast and anycast capabilities along with real-time dynamic load balancing and fast packet-level traffic protection rerouting. Applications include fast and efficient packet traffic forwarding across administrative domains of Internet, such as an ISP's backbone or an enterprise virtual private network, as well as passing packet traffic over a neutral Internet exchange facility between different administrative domains.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
Secure network-routed voice multicast dissemination
InactiveUS20040095900A1Efficient processTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationVoice communicationMobile communication systems
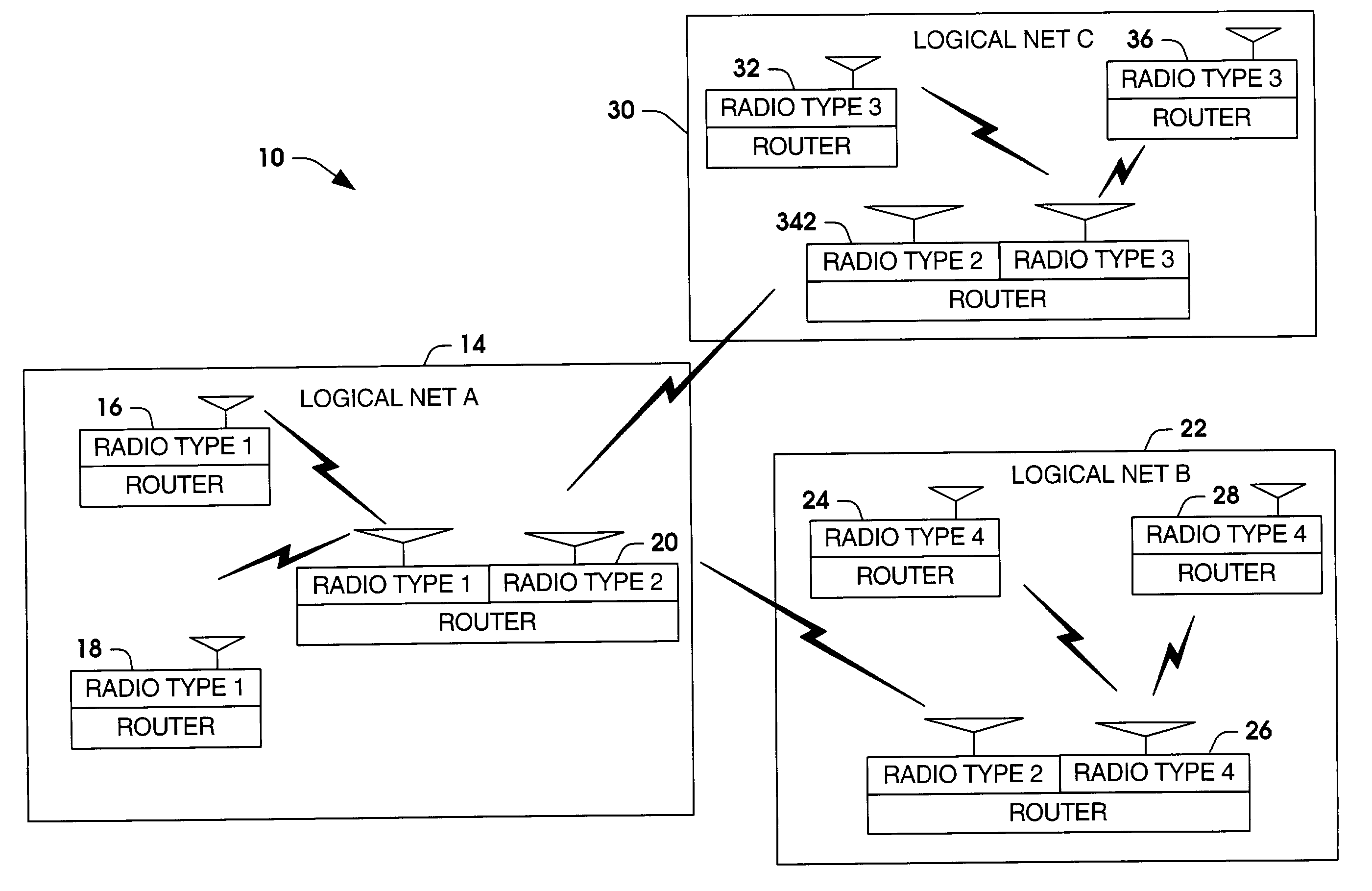
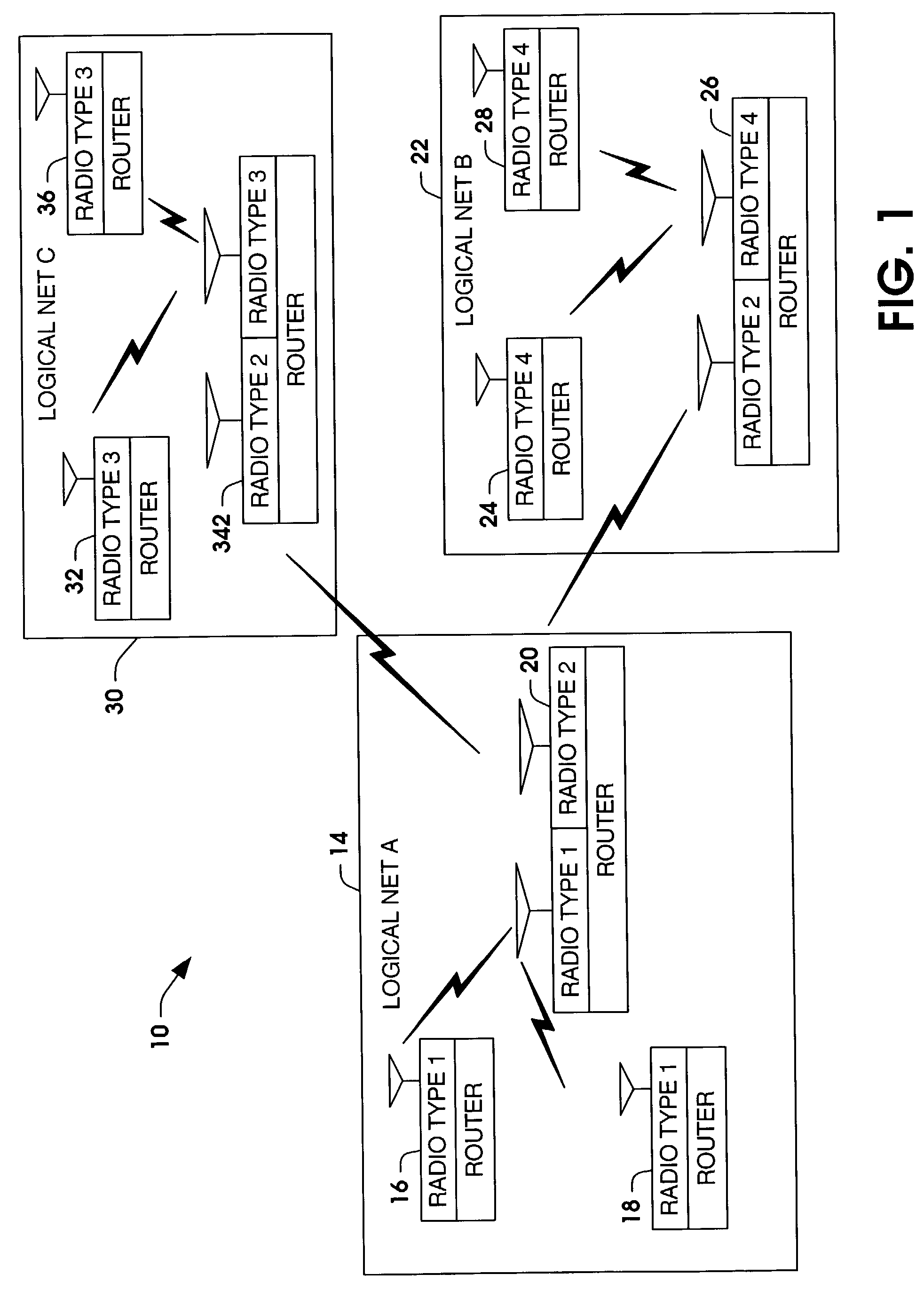
Systems and methods are provided for routing voice communications to groups in a voice communication system. The voice communication system can be a mobile communication system having a plurality of members grouped as logical networks and / or unit task organizations. One or more routers are provided in the system. The one or more routers extract routing information from received voice messages. The routing information is used with a router database to determine which identified group to route the digitized voice packets. The one or more routers can be adapted to receive and route voice communications to different radio types across different logical networks.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
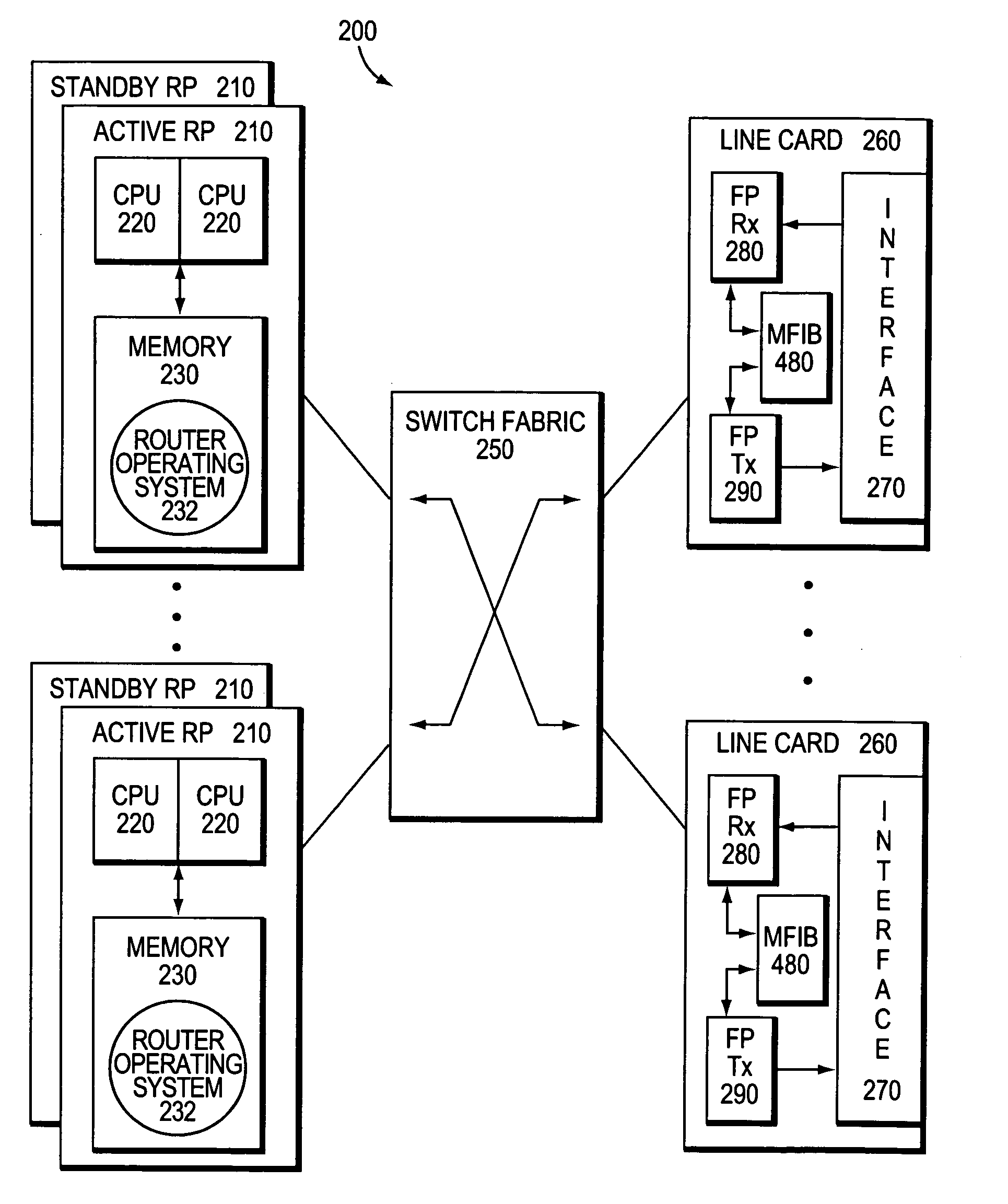
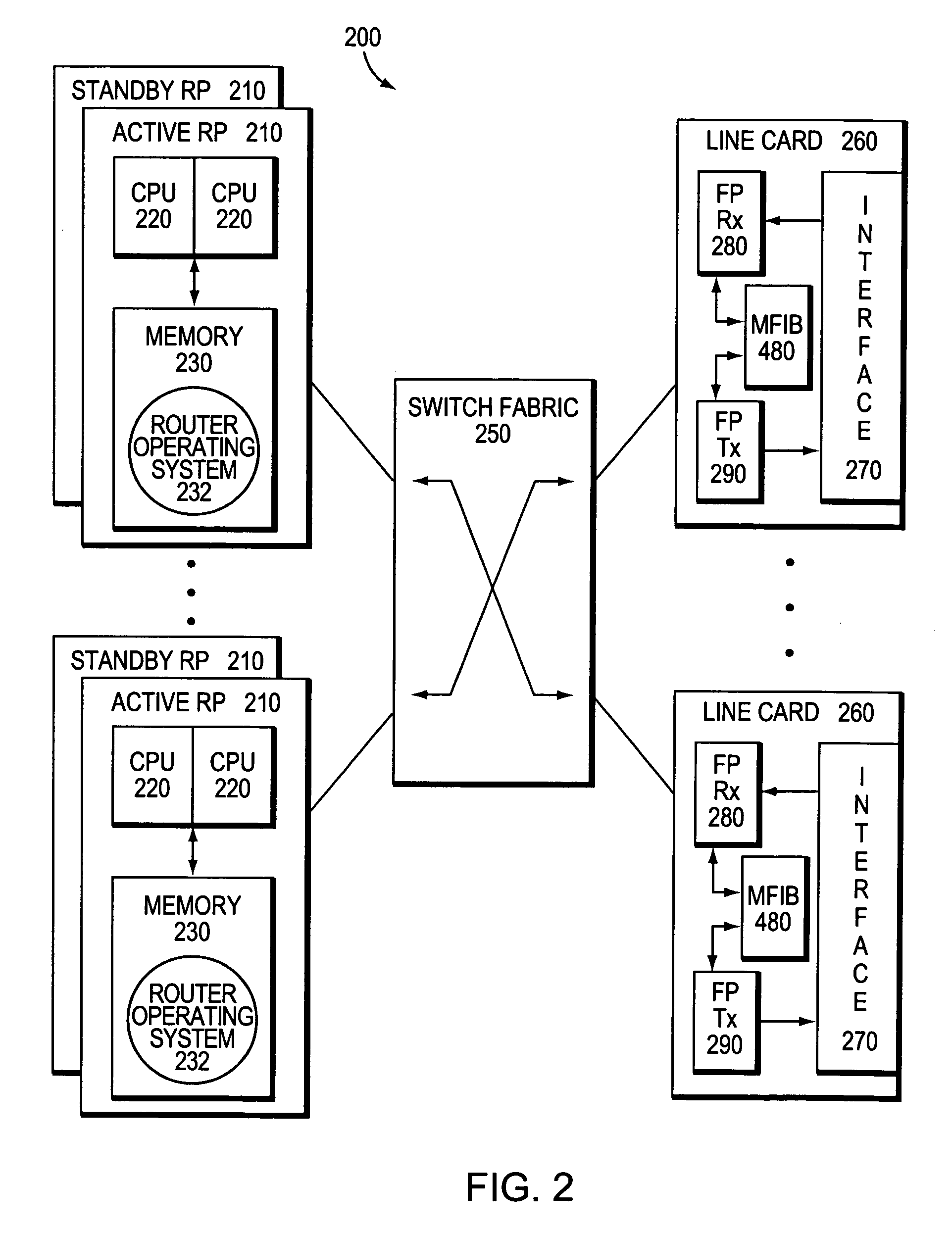
System and method for preserving multicast data forwarding during control failures in a router
ActiveUS20060018253A1Eliminate needImprove usabilityError preventionTransmission systemsData connectionHigh availability
A multicast non-stop forwarding (NSF) router architecture enhances high availability of a multicast router in a computer network. The router architecture further preserves multicast data forwarding through a data plane during NSF recovery of one or more failures in a control plane of the router. Various multicast components of the router cooperate to provide a checkpointing and recovery technique of the multicast NSF architecture that enables efficient restart and recovery of the control plane failures without loss of data connectivity.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
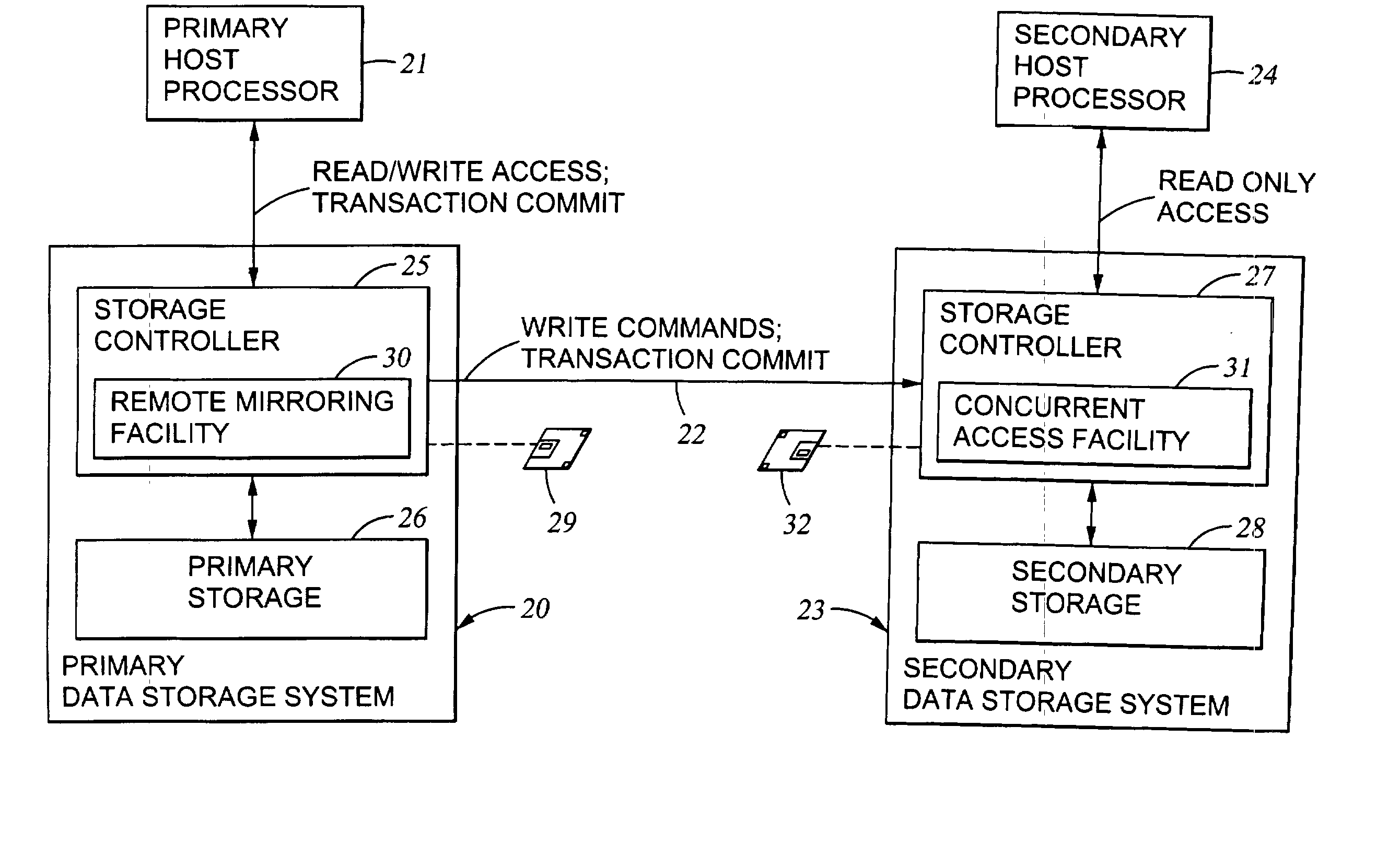
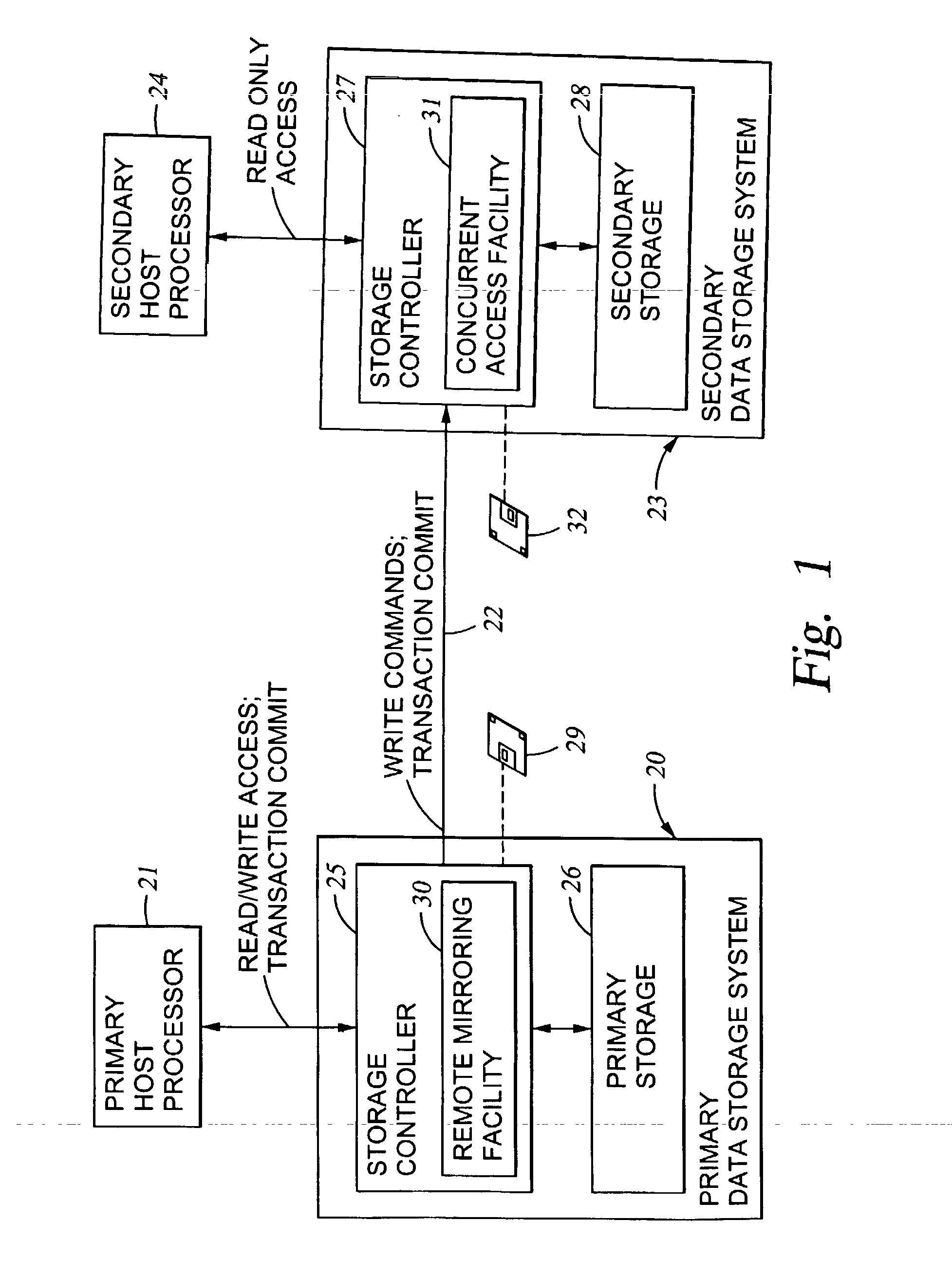
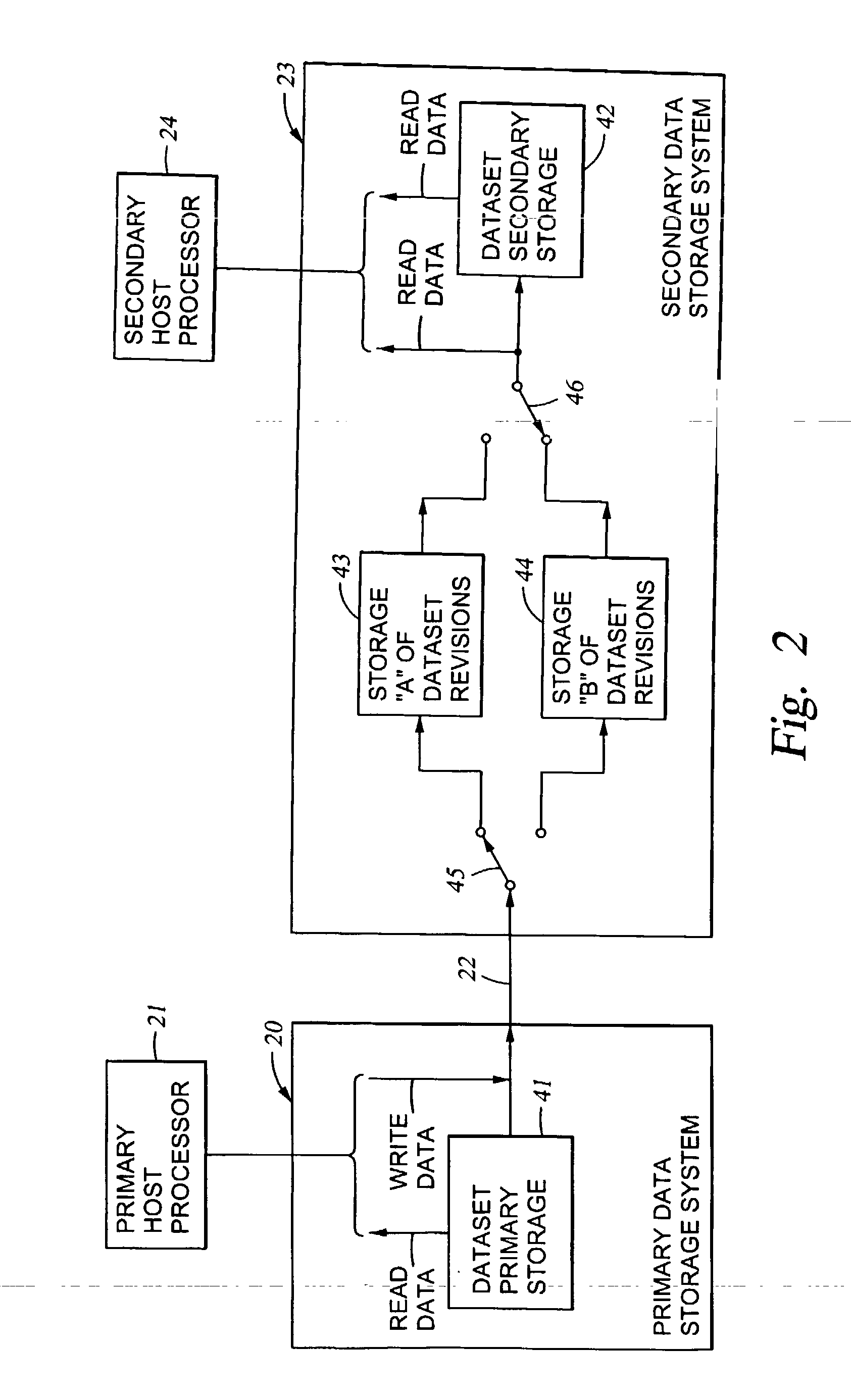
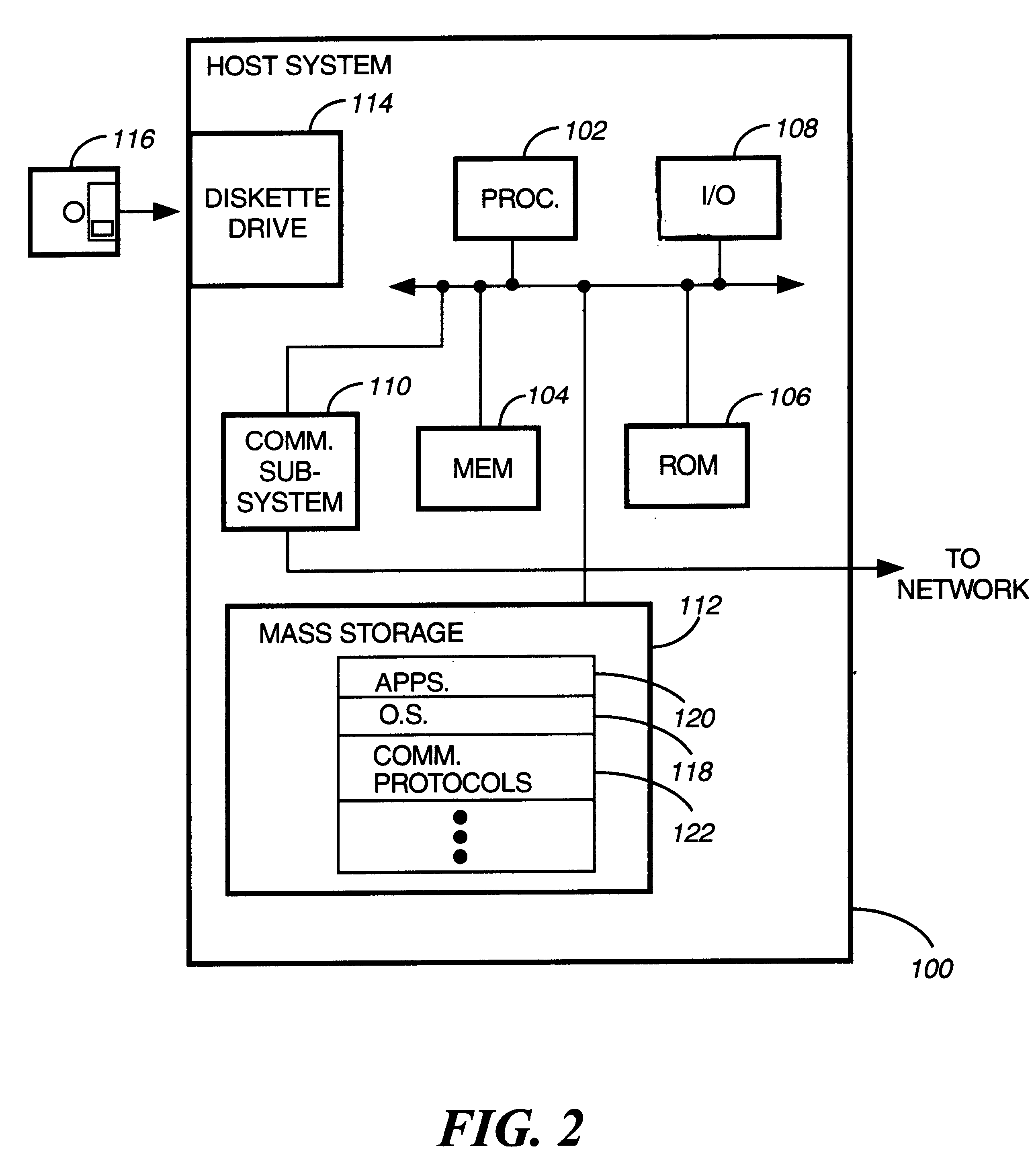
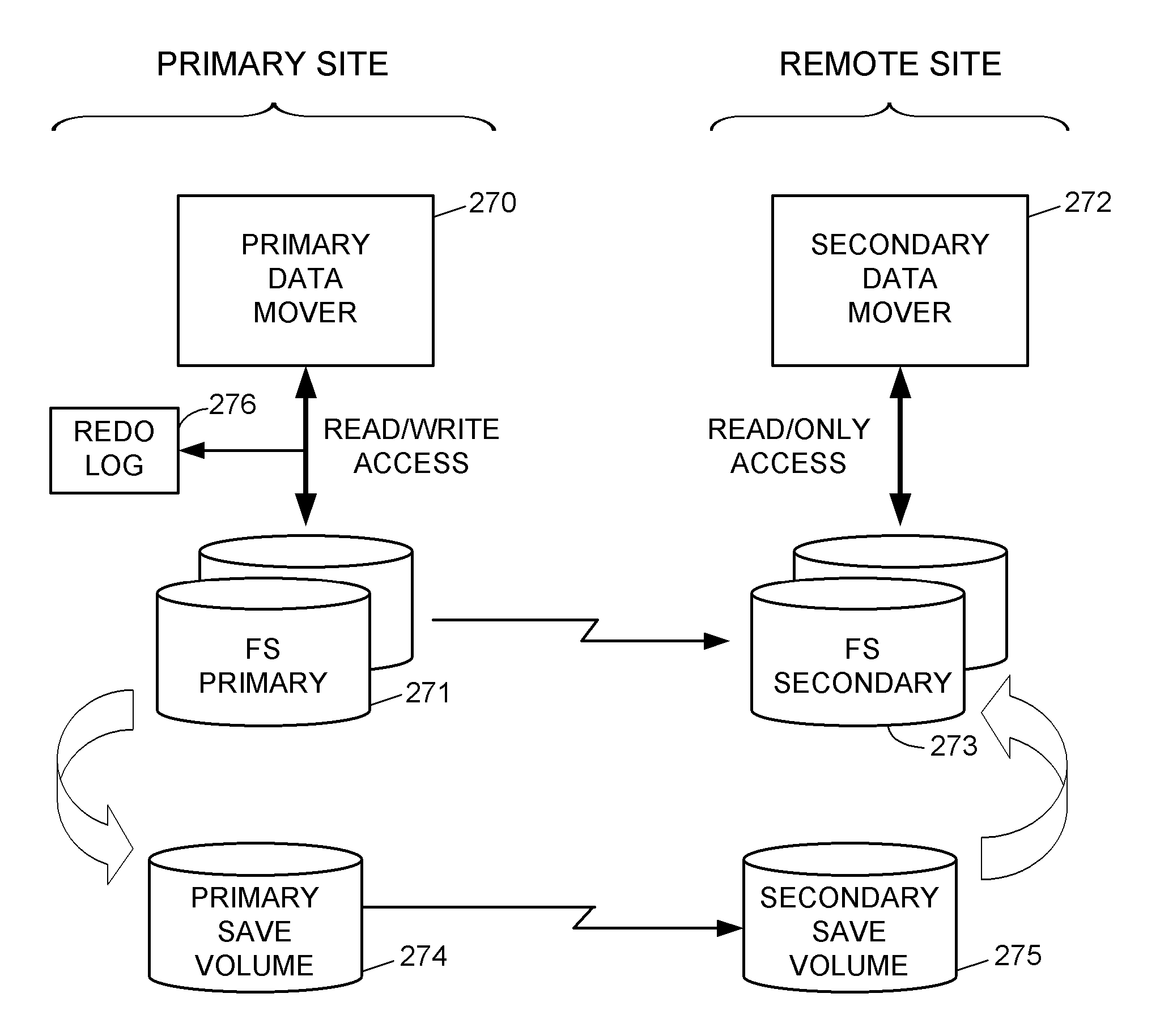
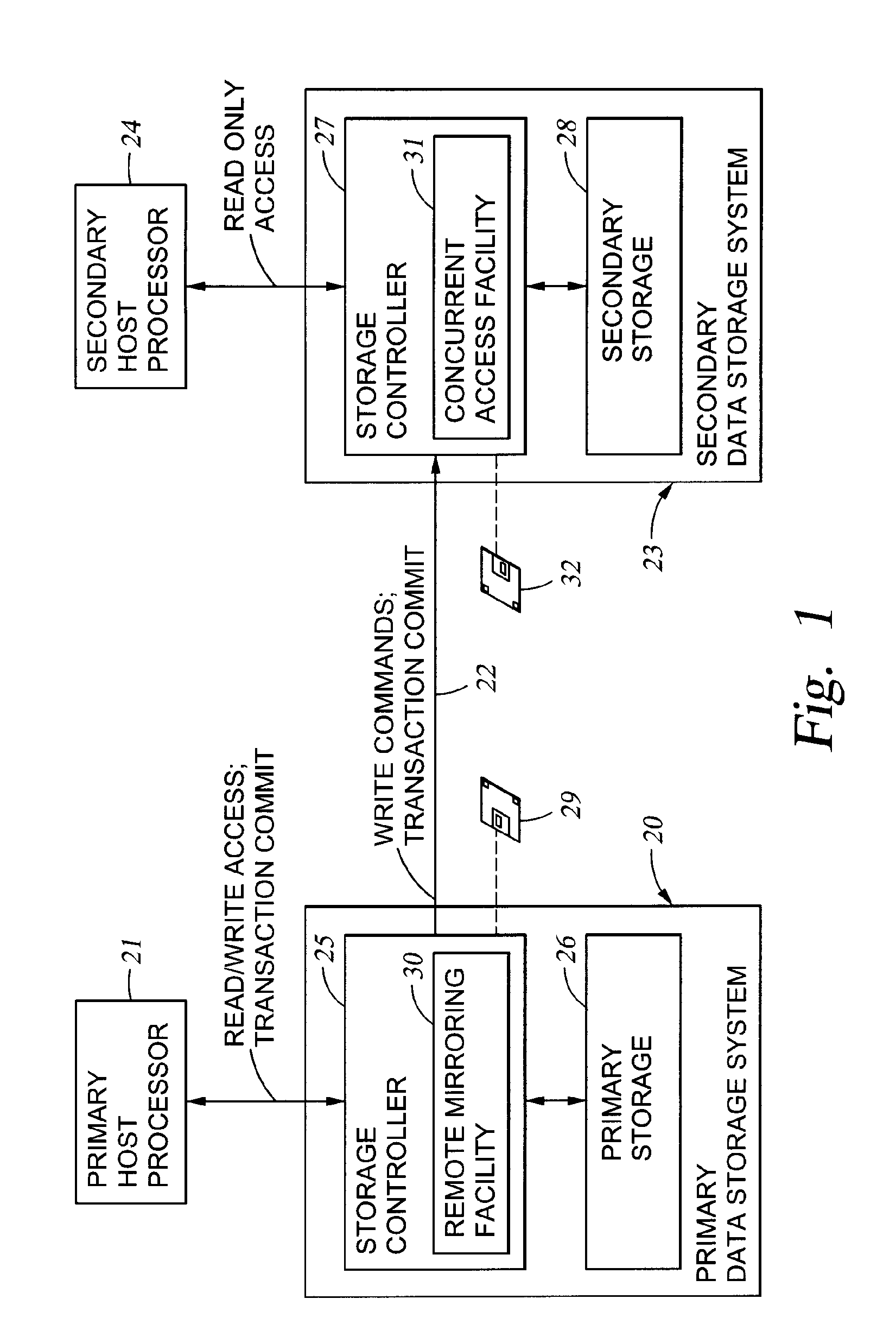
Replication of remote copy data for internet protocol (IP) transmission
ActiveUS20030217119A1Special service provision for substationError detection/correctionInternet protocol suiteRouting table
Consistent updates are made automatically over a wide-area IP network, concurrently with read-only access to the remote copies. A replication control protocol (RCP) is layered over TCP / IP providing the capability for a remote site to replicate and rebroadcast blocks of the remote copy data to specified groups of destinations, as configured in a routing table. A volume multicast layer over RCP provides for multicasting to specified volume extents of the blocks. The blocks are copied at the logical level, so that it does not matter what physical structure is used for storing the remote copies. Save volumes buffer the remote copy data transmitted between the primary or secondary file system volume and the IP network, in order to ensure independence between the replication process, the IP transport method, and the primary file system being replicated.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Multicast control systems and methods for dynamic, adaptive time, bandwidth,frequency, and satellite allocations
InactiveUS7236738B2Additional satellite capacityOptimize resource allocationNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesControl systemThe Internet
Methods and systems to efficiently share multiple satellites and associated transponders or links among a network of uplinking earth stations are disclosed. An embodiment of this invention uses a terrestrial communications link, such as the Internet, to control access to the transponder or satellite links. Communications over this link may employ a TCP / IP protocol to connect the requesting uplinking earth stations with a centralized controller. This control system creates more efficient use of satellite resources and reduces the overall amount of time needed for transmitting data through the satellite. By reducing the overall amount of time needed for transmitting data, the control system may reduce the cost of using the satellite transponder capacity.
Owner:EXTREME REACH INC +1
Collaborative multicast for dissemination of information in vehicular ad-hoc networks
InactiveUS20070001869A1Anti-collision systemsOptical signallingInter vehicle communicationDissemination
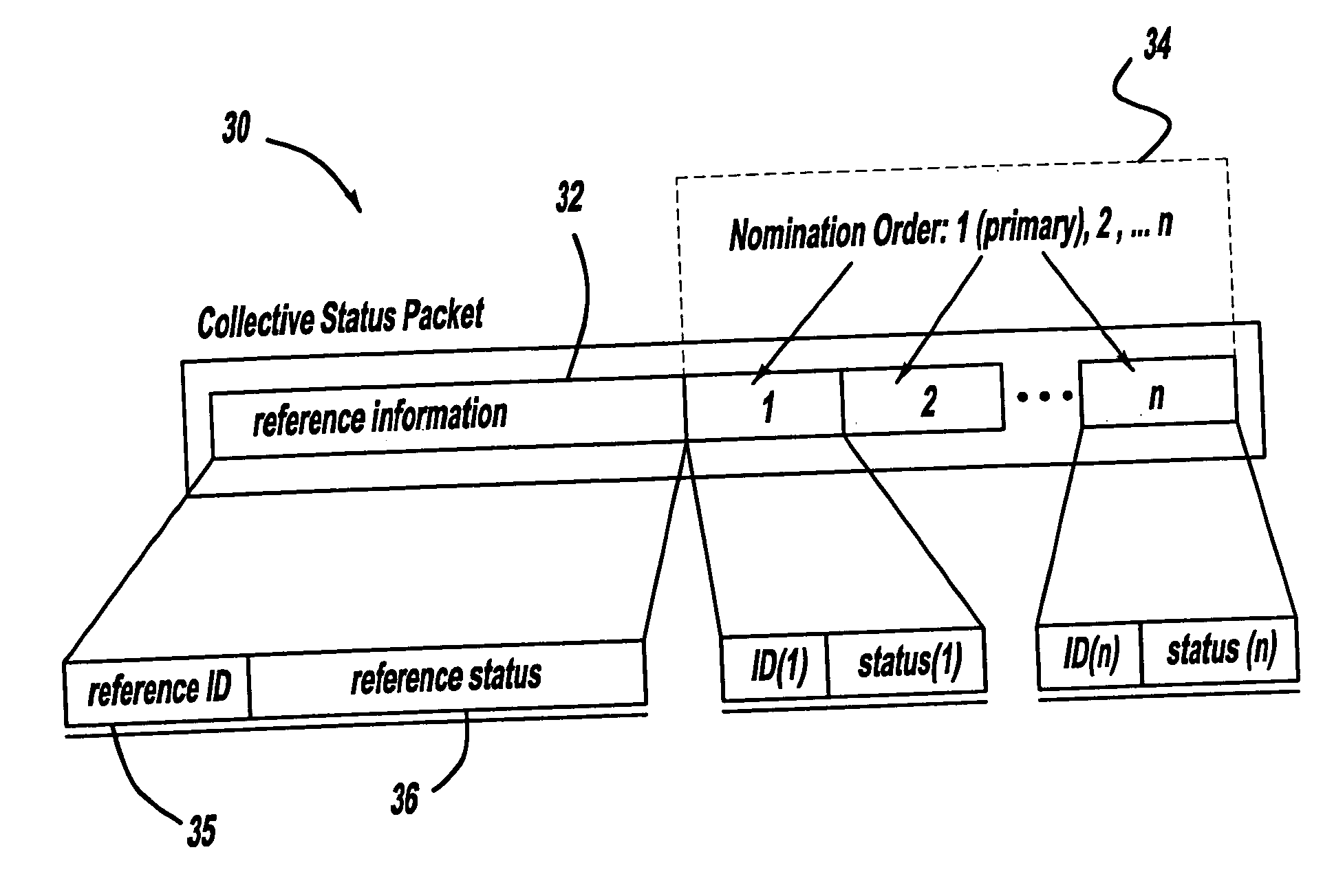
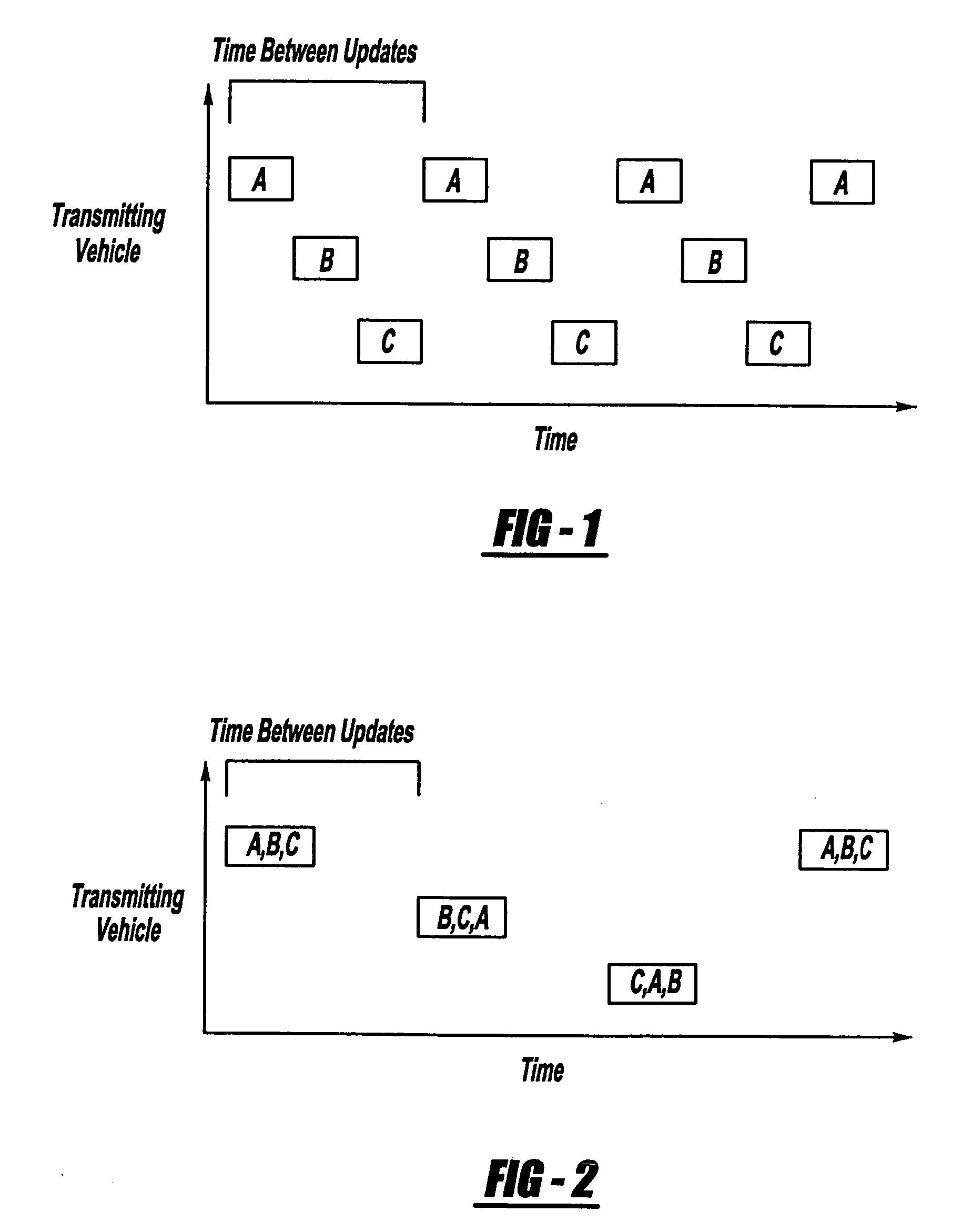
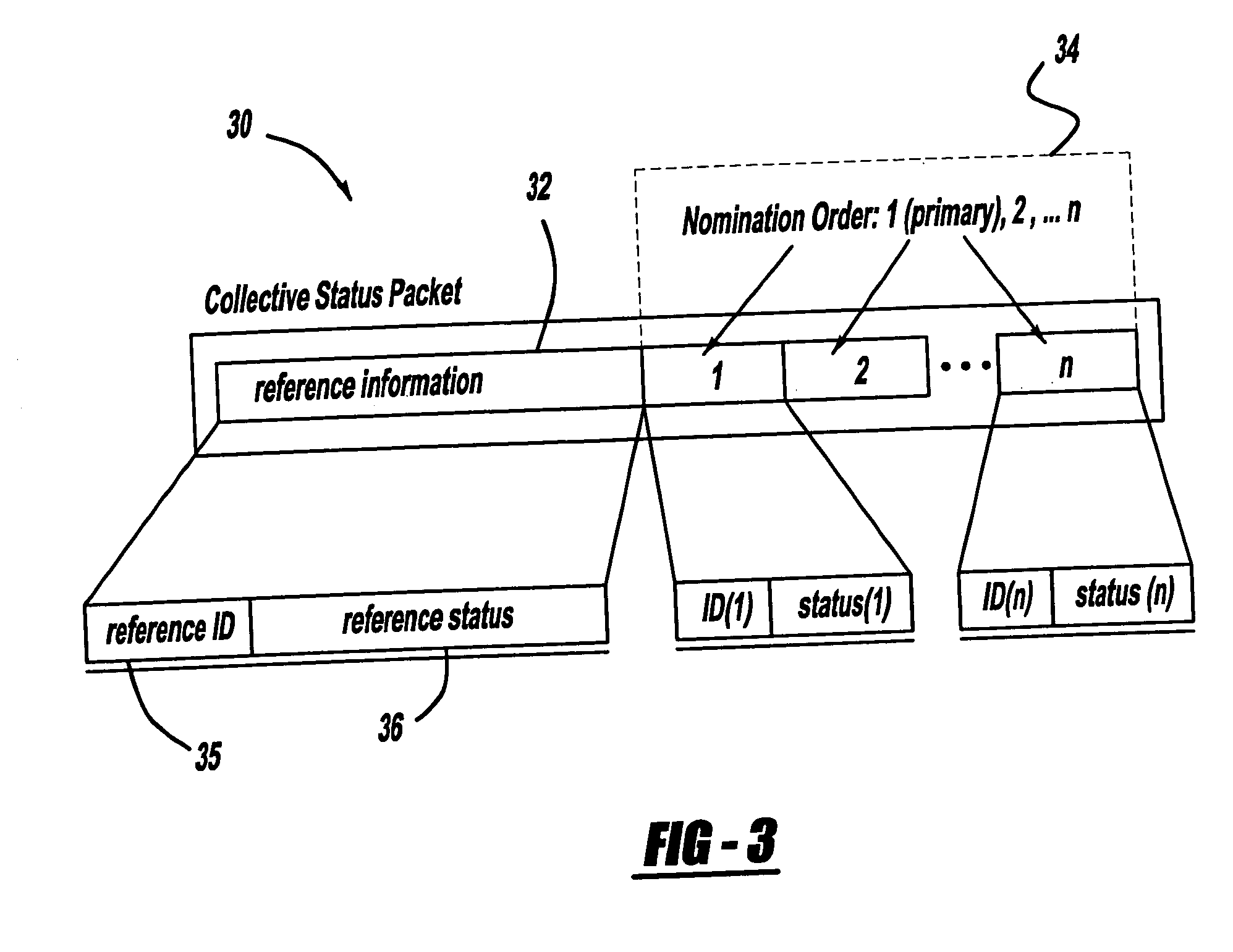
A collaborative nomination algorithm is provided for disseminating information amongst a plurality of collaborating vehicles in an inter-vehicle communication network. The method includes: receiving an incoming vehicle communication message at a recipient vehicle from one of the collaborating vehicles; nominating one of the collaborating vehicles identified in the incoming vehicle communication message to broadcast a subsequent vehicle communication message; and transmitting an outgoing vehicle communication message from the recipient vehicle, where the outgoing vehicle communication message identifies the vehicle nominated to broadcast the subsequent vehicle communication message.
Owner:DENSO CORP
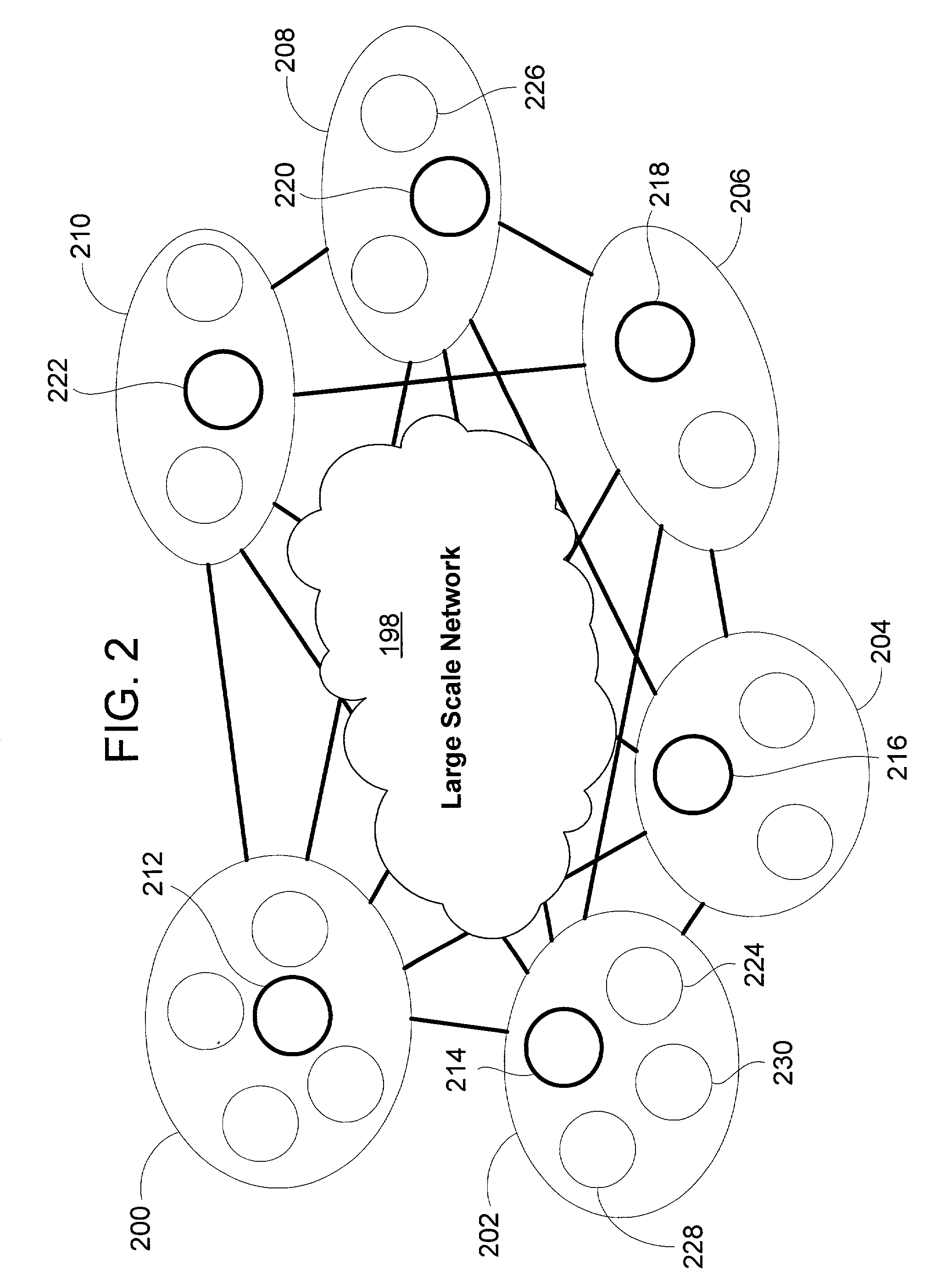
Peer-to-peer based network performance measurement and analysis system and method for large scale networks
ActiveUS7194002B2Improve balanceSlowed network performanceSpecial service provision for substationDigital computer detailsSelf formingGroup method
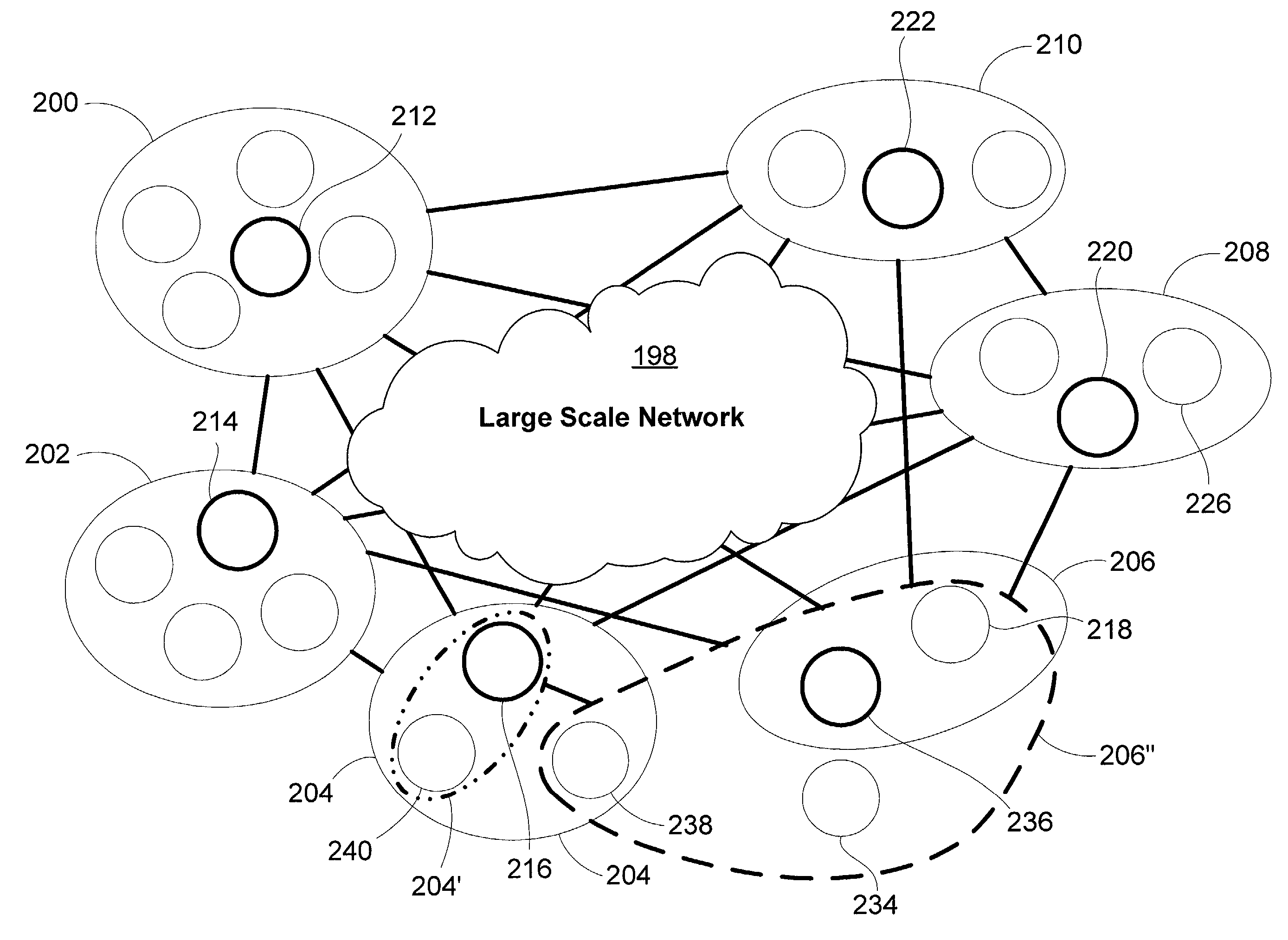
A network performance (e.g., latency and bandwidth) measurement infrastructure for large scale networks based on self-organized probing groups of devices. Each group of devices has a lead device that measures network characteristics, and then shares the measurement information with other devices. This grouping method reduces the amount of network bandwidth needed for adequate measurements, while still providing necessary information to individual devices. The system utilizes a novel multicast-based algorithm that is adopted for both intra-group and inter-group performance measurement. The measurement groups (MeGroups) are dynamic and self-forming, and use a set of heuristic algorithms to optimize the dynamic groupings.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
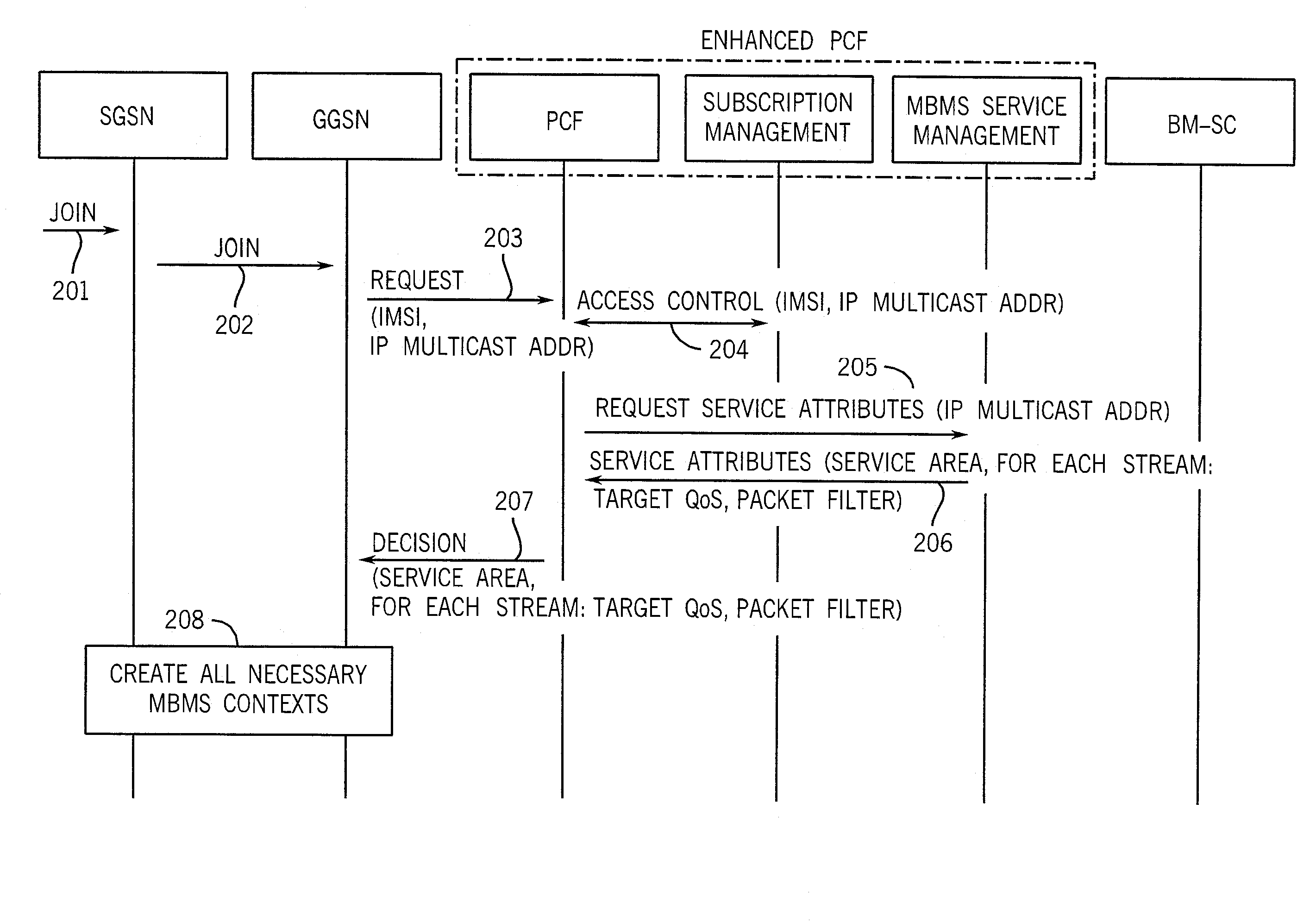
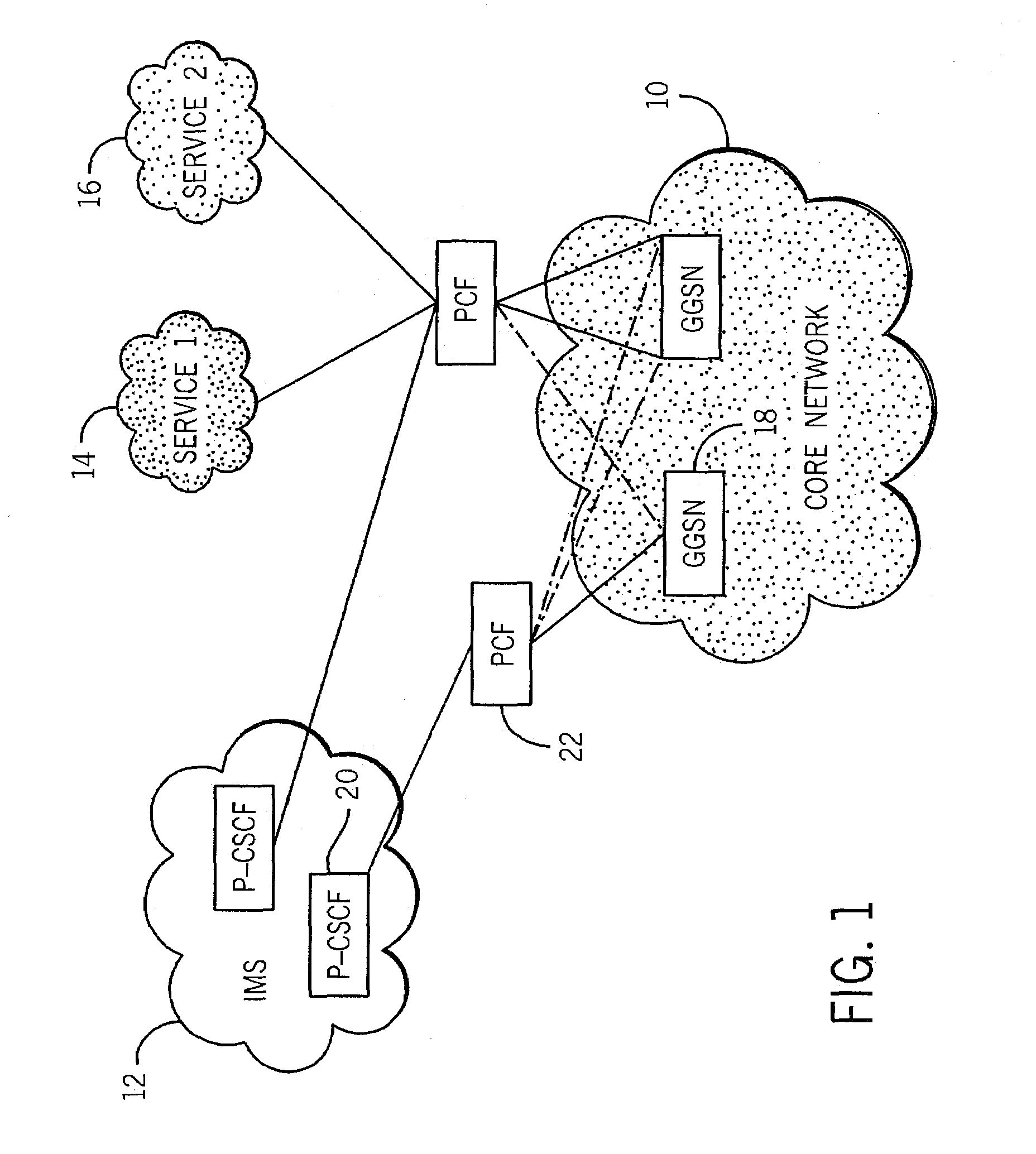
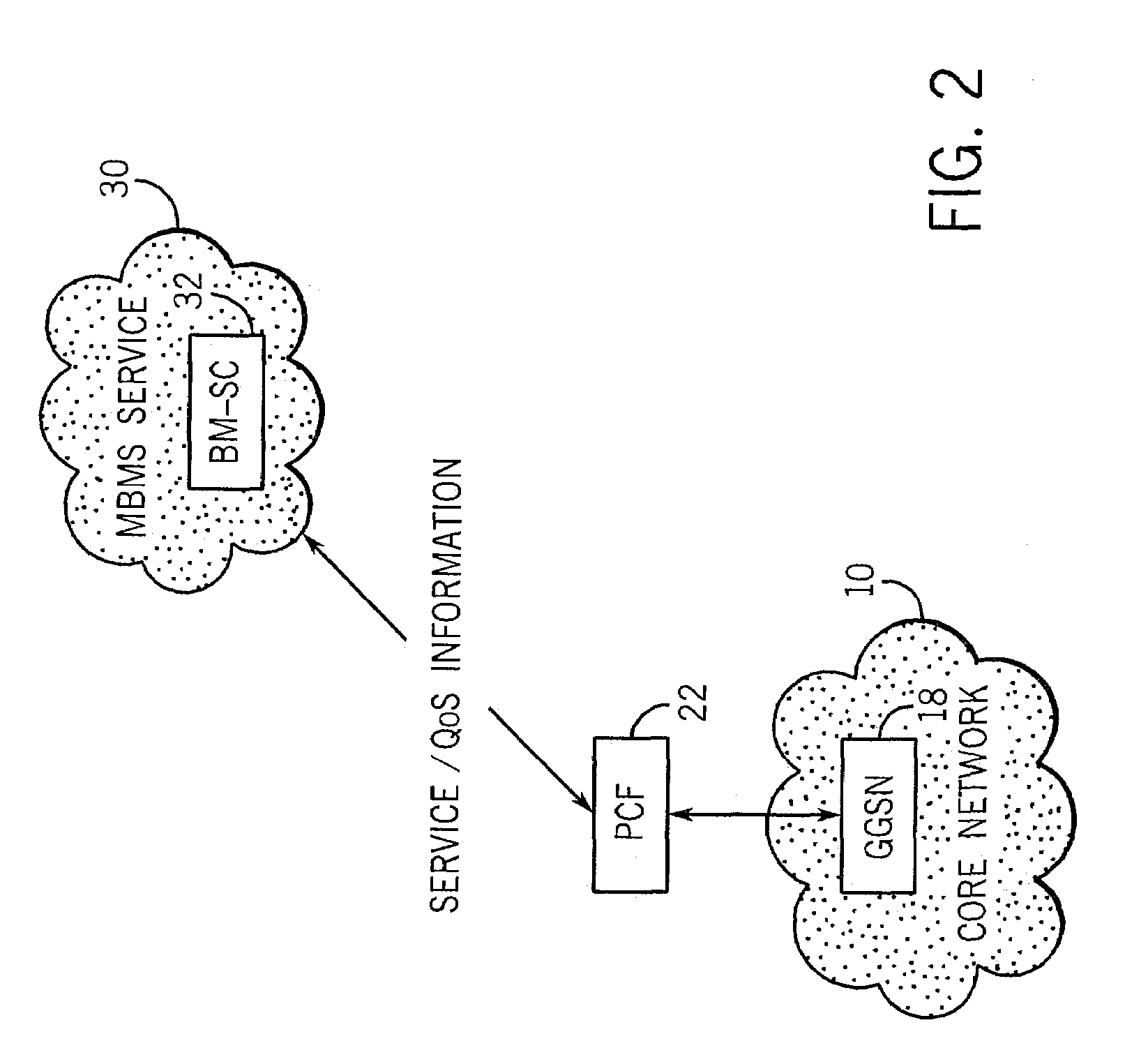
System and method with policy control function for multimedia broadcast/multicast system services
ActiveUS7391724B2Special service provision for substationError preventionApplication serverAuthorization
A system and method with policy control function (PCF) for multimedia broadcast / multicast system (MBMS) services that includes a core network, one or more application servers, and one or more policy control functions (PCF). In one embodiment, the core network includes one or more gateway GPRS support nodes (GGSN). One of the application servers provides a MBMS service. At least one policy control function is operatively connected between each GGSN and application server. MBMS session request information is sent from the MBMS service server to the policy control function. The policy control function provides authorization information for a MBMS session to the GGSN.
Owner:CRYSTAL MOUNTAIN COMM LLC
Method and apparatus for using wireless hotspots and semantic routing to provide broadband mobile serveices
InactiveUS20050128995A1Network traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexCost effectivenessHigh bandwidth
A system and method for providing cost-effective broadband mobile services using a hybrid wireless network consisting of wide-area cellular (“3G”) supplemented by hotspot caches are provided. The proposed architecture uses opportunistic access of high-bandwidth wireless hotspot to dramatically reduce the cost per MB of media delivered to mobile end-users. The system also uses a “semantic multicast routing” approach to caching and delivering media based on individual user profiles.
Owner:OTT MAXIMILIAN A +2
Systems and methods for providing multicast routing in an overlay network
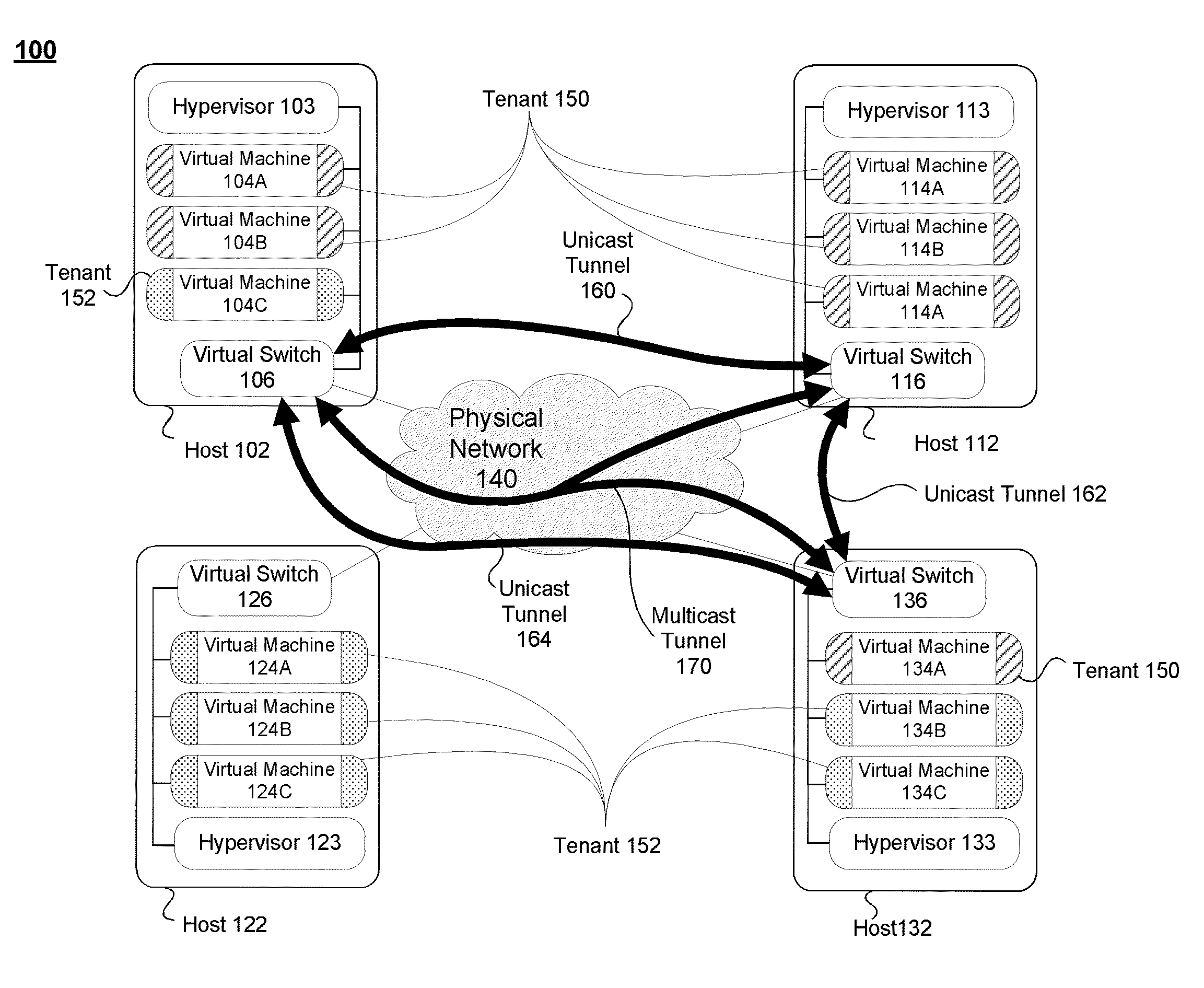
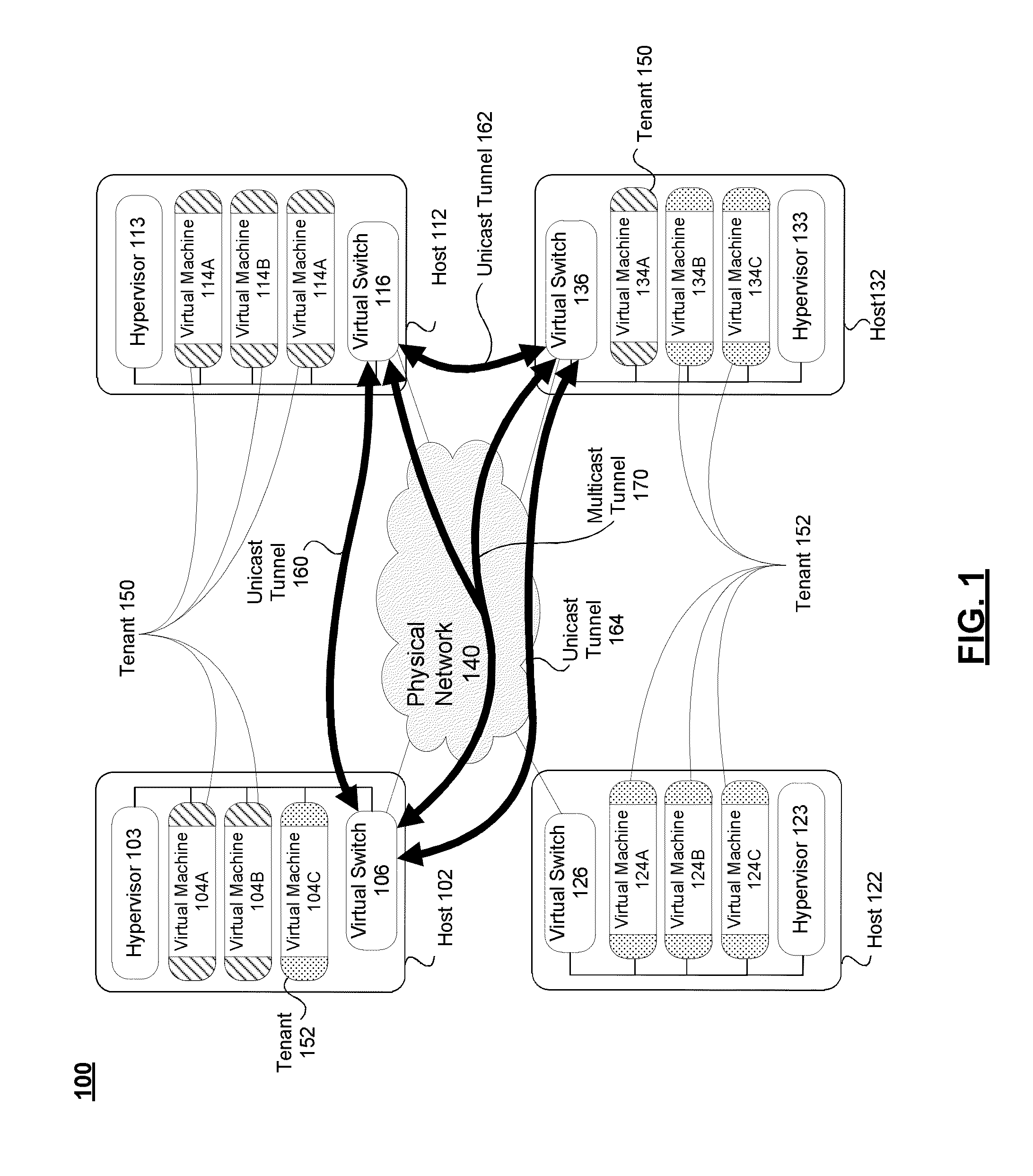
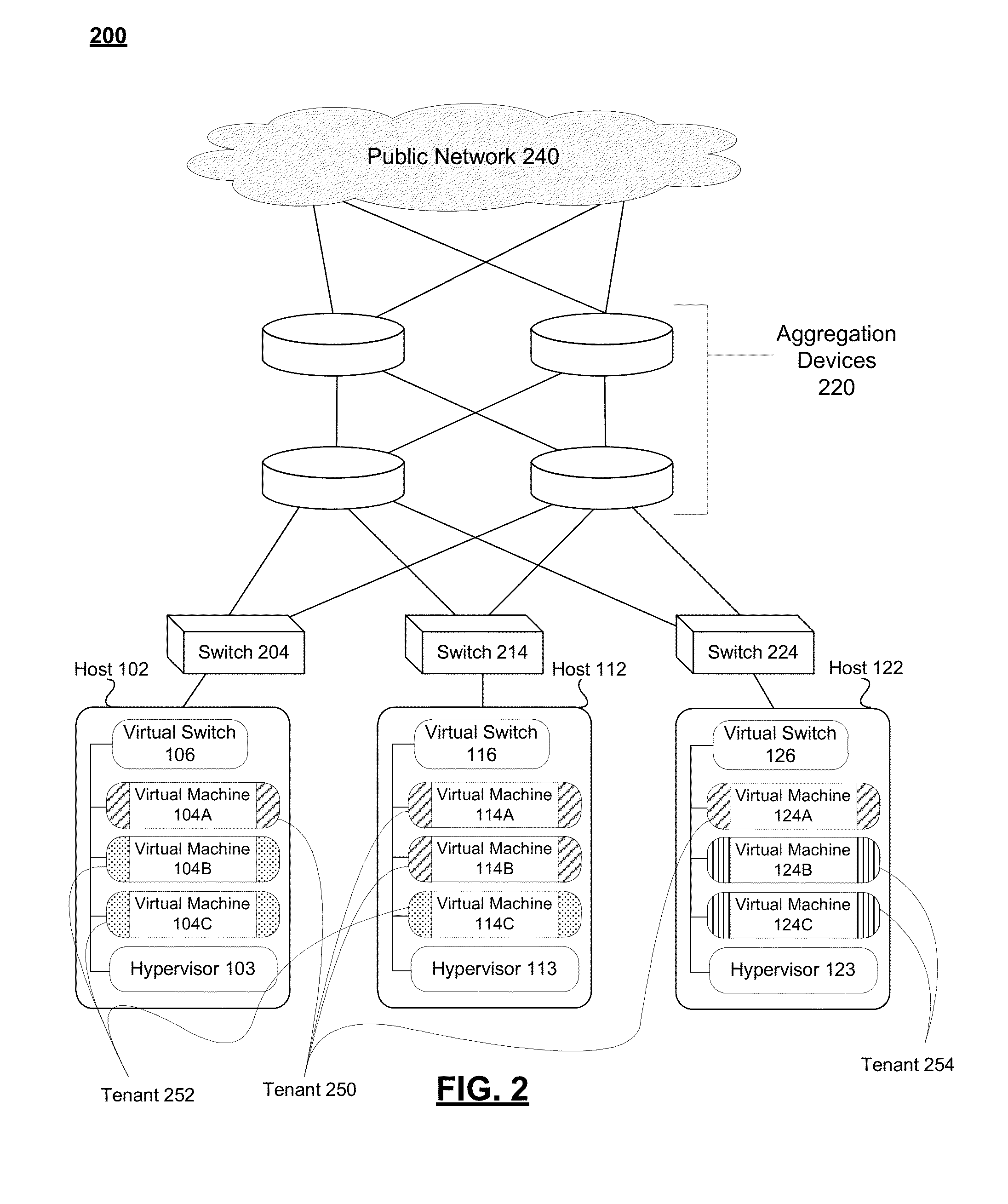
ActiveUS20140192804A1Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationIp addressMulticast address
An information handling system is provided. The information handling system includes a first hypervisor running on a first host and a second hypervisor running on a second host. The first hypervisor managing a first virtual switch, and the second hypervisor managing a second virtual switch. The information handling system also includes a plurality of virtual machines (VMs), including a first VM, which is part of a first tenant, running on the first host, and a second VM, part of a second tenant, running on the second host. The first virtual switch has a mapping in memory that maps a customer-specific multicast IP address, used by the plurality of VMs to indicate a multicast group that includes VMs on the first and second tenants, to a global multicast IP address used by the first and second hosts.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Reliable multicast for small groups
InactiveUS6415312B1Special service provision for substationError prevention/detection by using return channelReliable multicastPayload
A system for reliable multicast transmission [multicasting data packets] in a packet-based data network includes mechanisms for performing the following: (1) preparing at least one packet comprising a payload portion and multicast route information, an error detection mechanism; (2) transmitting the packet to at least one intermediate node for delivery to at least two destination nodes; (3) waiting for a period of time for at least one acknowledgment signal indicating receipt of the at least one packet by at least one destination node; and (4) retransmitting a packet to a set of destination nodes from which no positive acknowledgment has been received. The multicast routing information includes information for use by the at least one intermediate node to forward the packet to at least two destination nodes.
Owner:IBM CORP
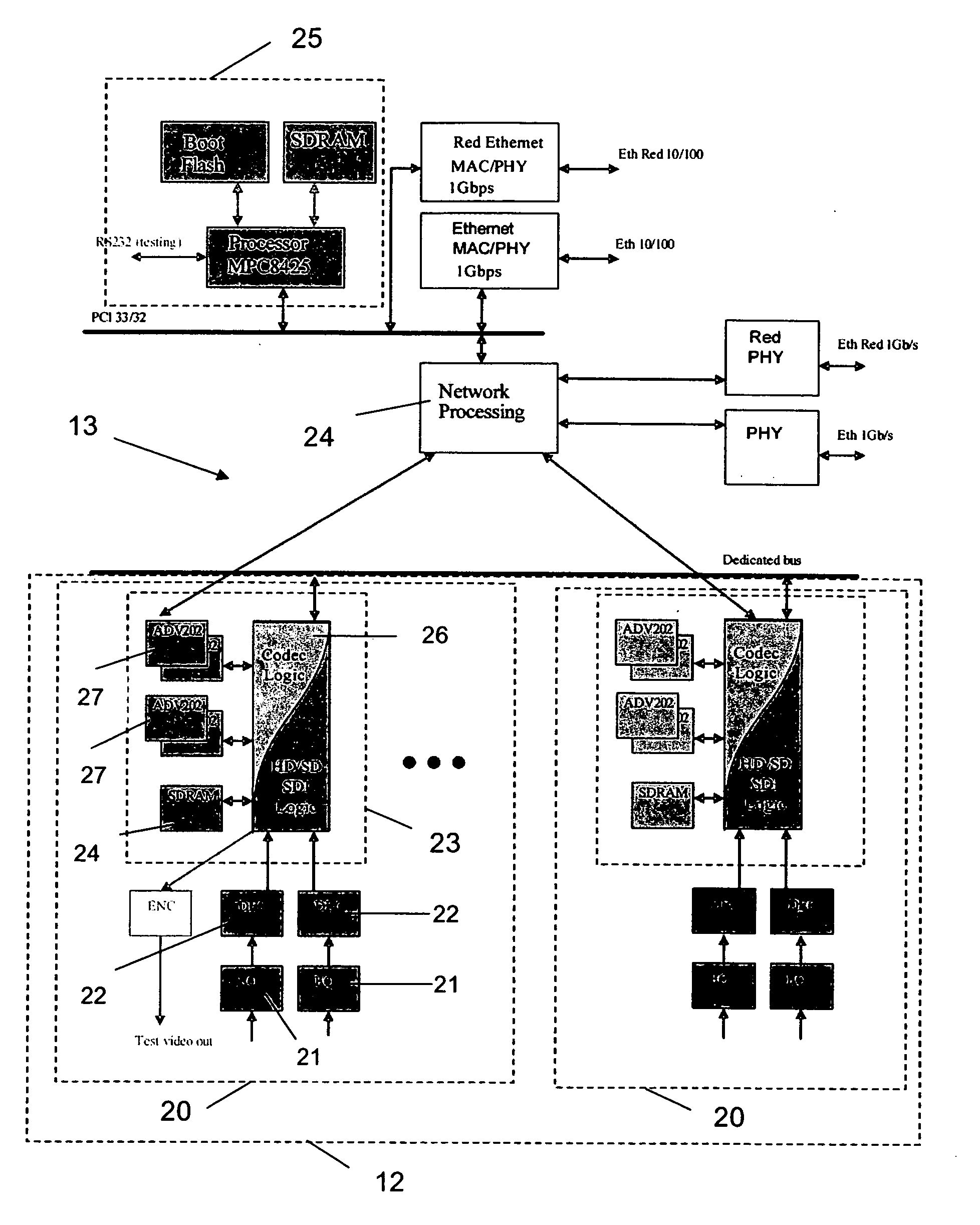
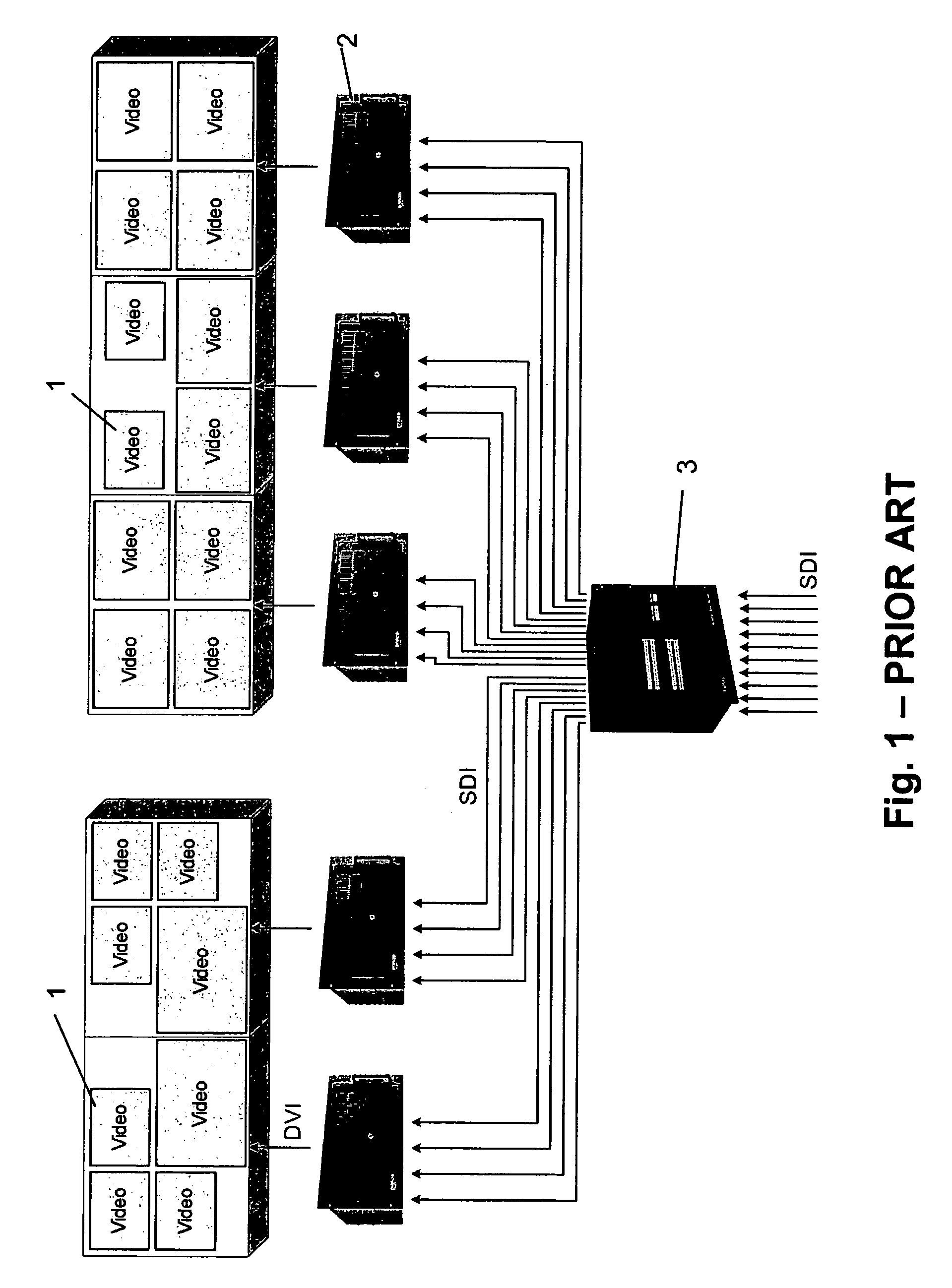
Network displays and method of their operation
ActiveUS20070033289A1Static indicating devicesMultiple digital computer combinationsGraphicsOff the shelf
A digital networked studio and the needed software services to allow the use of the system for monitoring the creation and distribution processes of real-time created content is described. Distribution problems are solved using an off-the-shelf network, e.g. using an IP based or similar data protocol, such as an IP network based distributed system architecture to bring the display controller functionality closer to the source and to replace proprietary busses used for transporting video, audio, RGB, graphical information and / or metadata with building blocks based on standard IP and compression technologies. A characteristic of such a network is to use unicast, multicast and / or broadcast technologies (based on network addresses) and to route data from one address to another. The network provides redundancy in case any of the digital generation units.
Owner:BARCO NV
Transparent, look-up-free packet forwarding method for optimizing global network throughput based on real-time route status
ActiveUS7254138B2Improve performanceFast and efficient packet-level traffic protection re-routingError preventionTransmission systemsPrivate networkOSI model
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
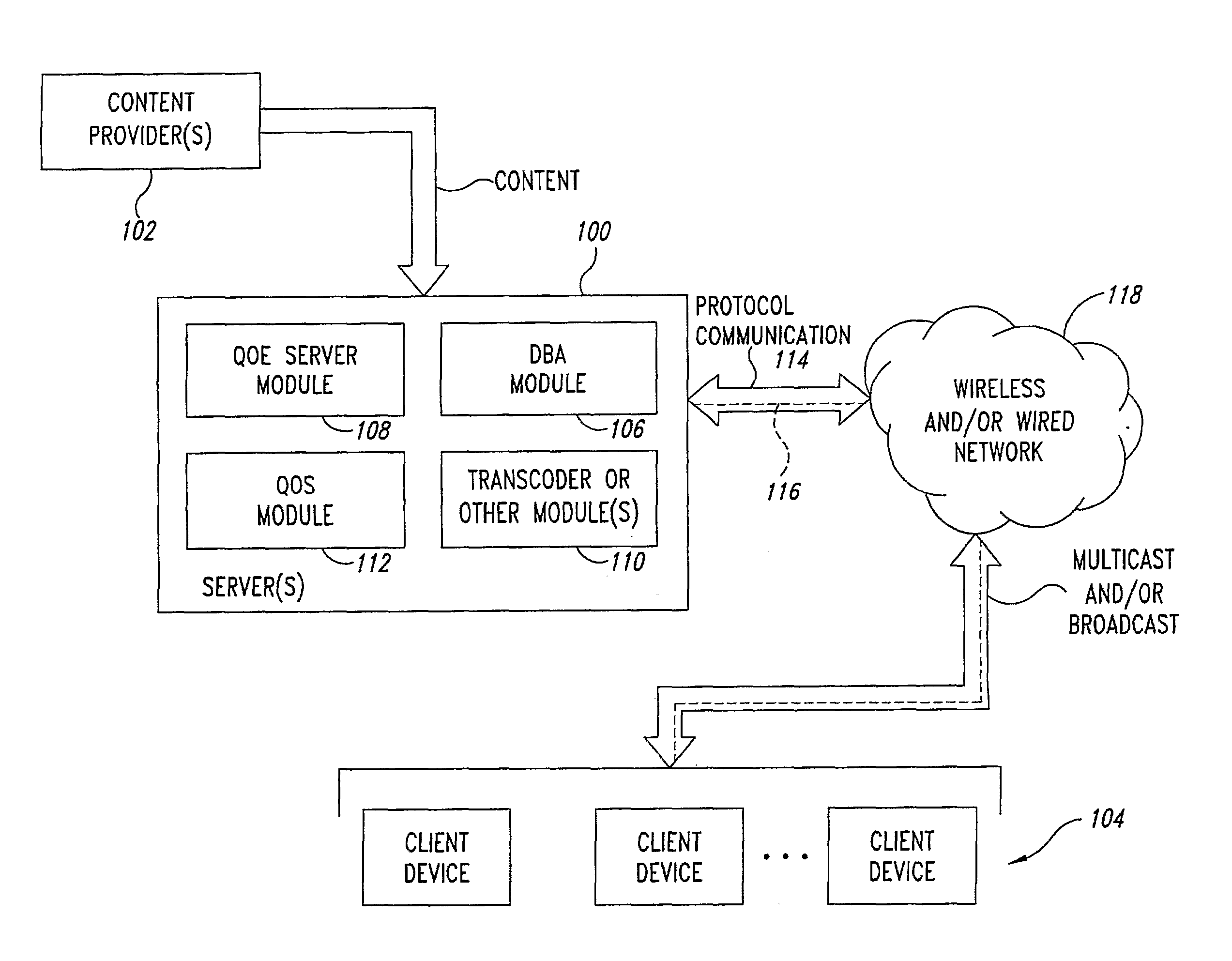
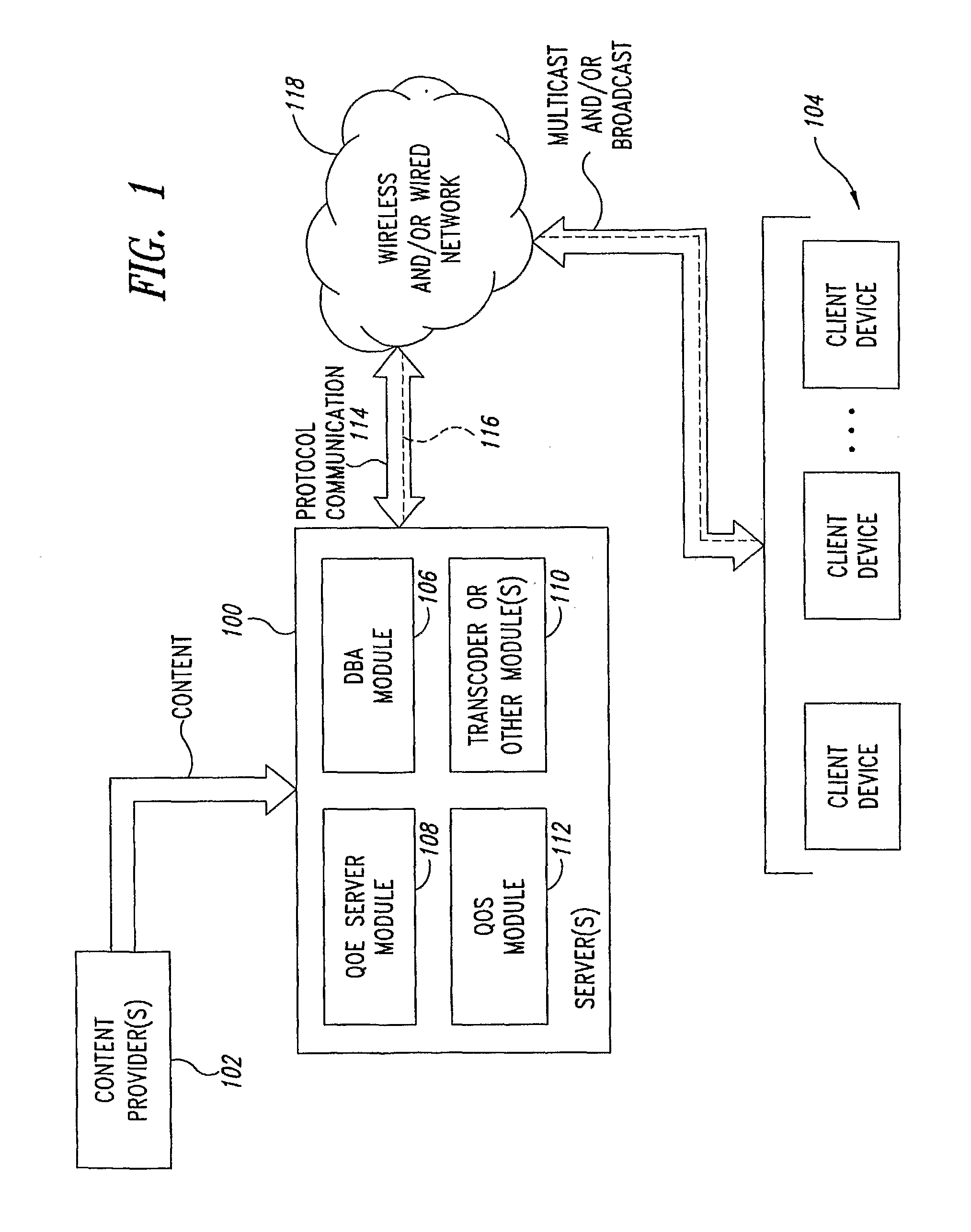
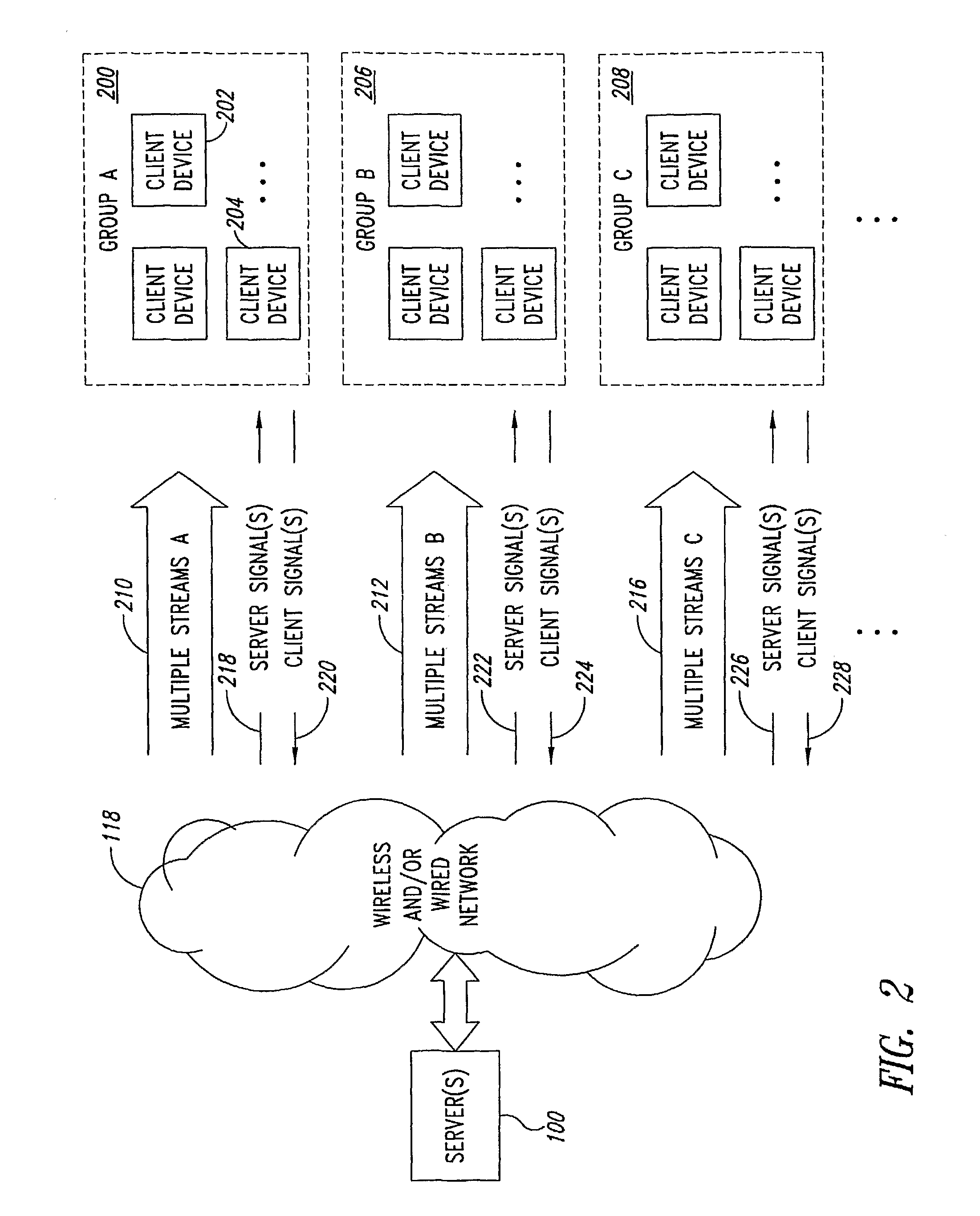
Multicast and Broadcast Streaming Method and System
InactiveUS20080098446A1Two-way working systemsData switching networksClient-sideQuality of experience
In a multicast and / or broadcast streaming environment over wired and / or wireless networks, a server provides a plurality of different streams to each group (such as multicast groups) of client devices. Each of the client devices in the respective groups tune in to one of the plurality of streams that is most optimum. Quality of Experience (QoE) metric data or other data pertaining to dynamically changing client device characteristics or channel conditions are collected and evaluated by the server. If results of the evaluated metric data recommend a change to a different stream for a particular one or more client devices, the server switches the client device(s) to a different stream in the same group, or switches the client device(s) to a different stream in a different group if that stream is not available in the current group.
Owner:VIDIATOR ENTERPRISES INC
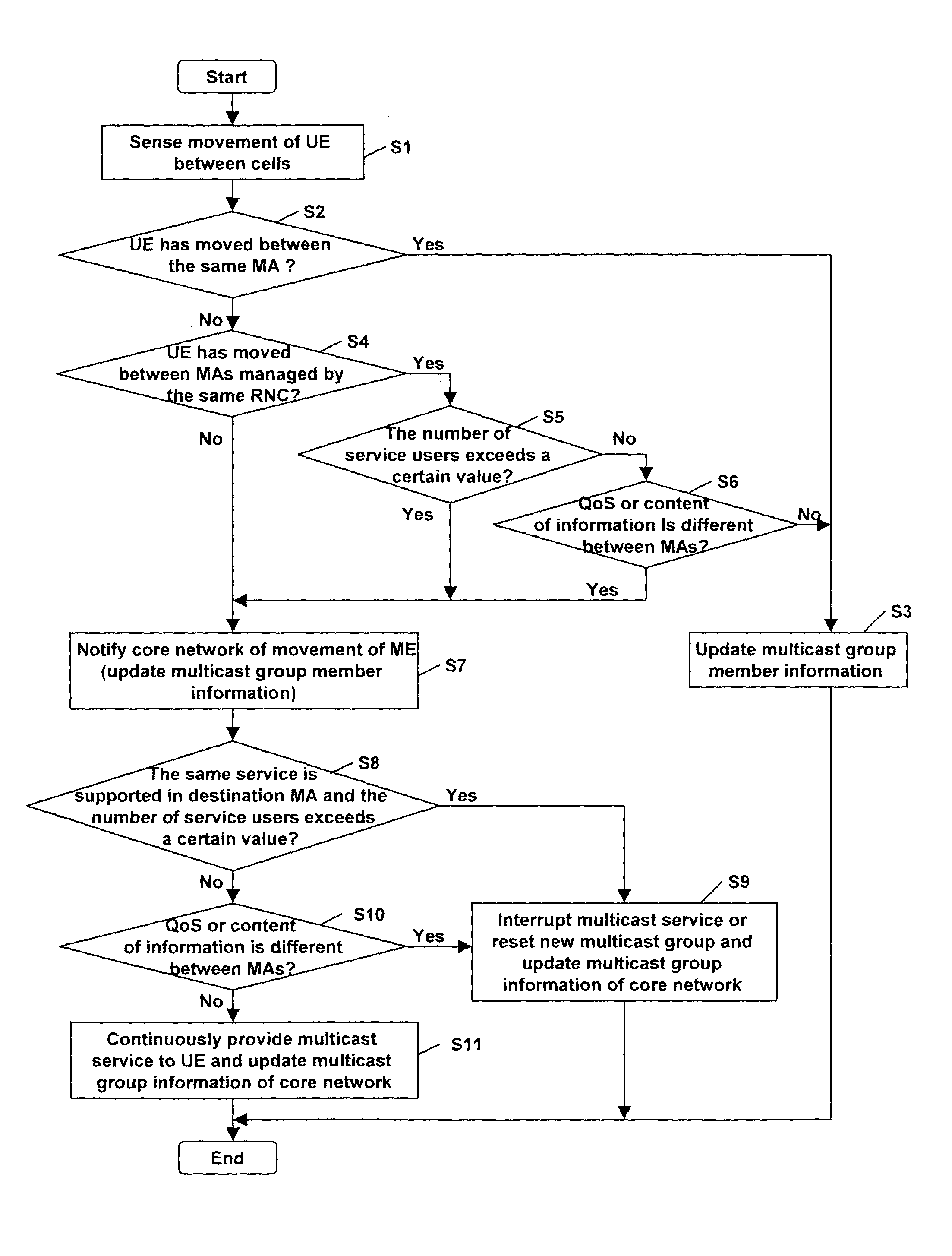
Method for managing multicast group in mobile communication system
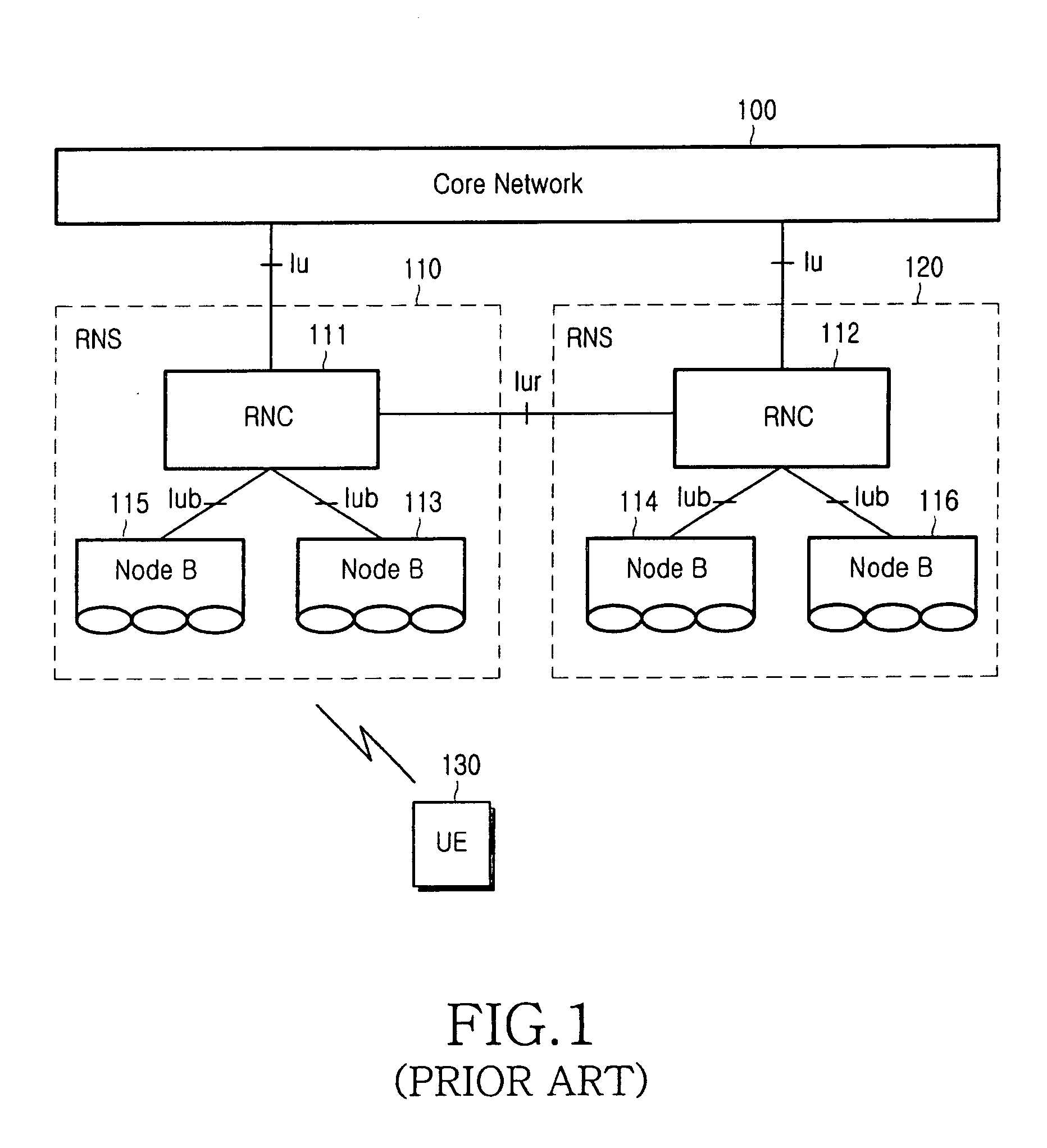
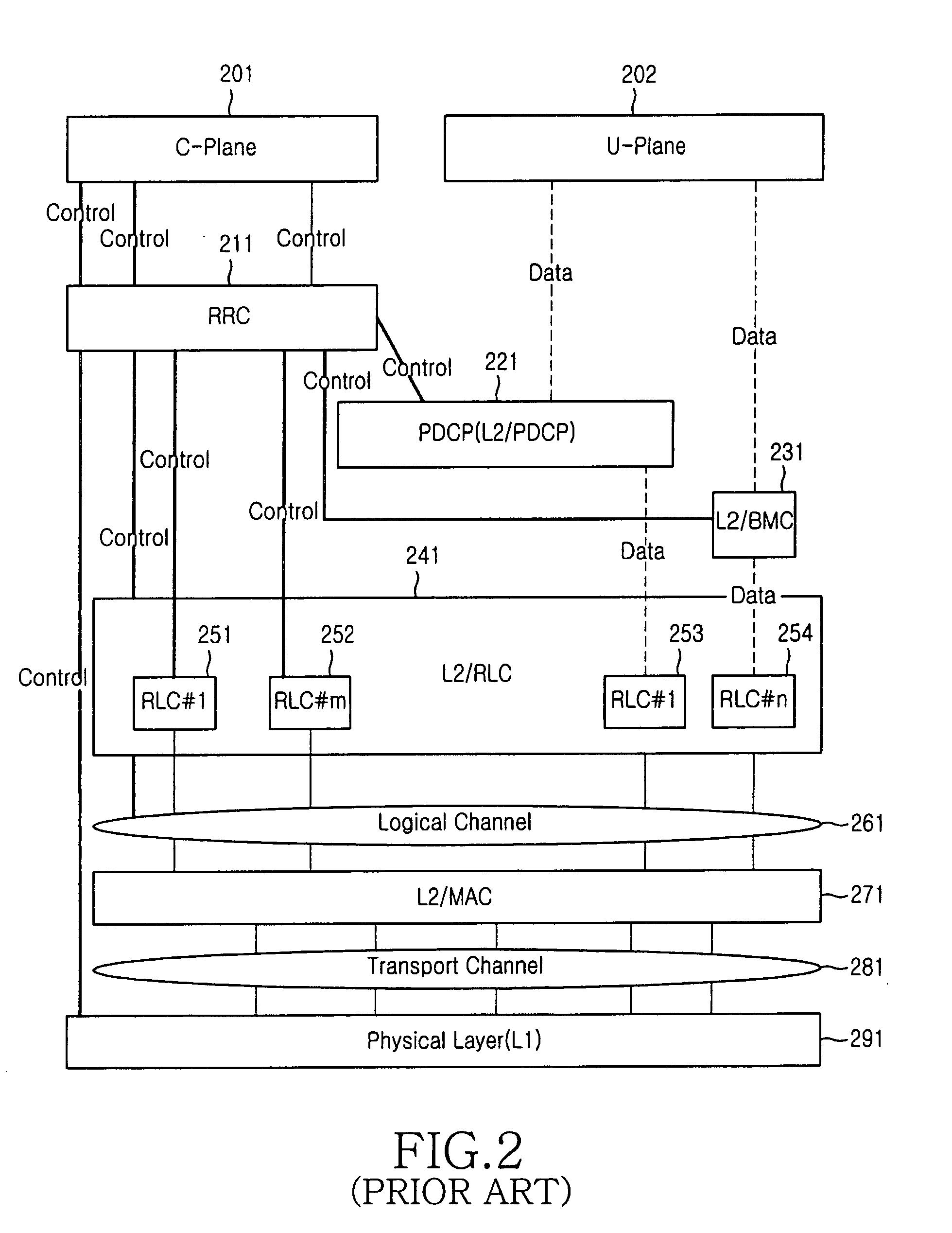
InactiveUS7162241B2Avoid transmissionSpecial service provision for substationError prevention/detection by using return channelMobile communication systemsCore network
A multicast service of a 3GPP Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is disclosed. By allowing an RNC to manage multicast group member information by multicast services on multicast areas, when a user terminal being currently provided with an MBMS service moves, the RNC sends information on the movement of the terminal to a core network. Since the RNC notifies the core network of the terminal's movement selectively on the basis of the multicast group member information by multicast services on the multicast area, the network resource can be effectively used, and especially, unnecessary transmission of terminal's movement information from the RNC to the multicast group managing entity of the core network can be prevented.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Fast rerouting apparatus and method for MPLS multicast
InactiveUS20060159009A1Fast reroutingSpecial service provision for substationError preventionMulticast packetsReal-time computing
Disclosed is a fast rerouting apparatus and method for multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) multicast. The fast rerouting apparatus and method is to rapidly cope with a failure occurring on an MPLS network. The fast rerouting method of redirecting a packet to be transmitted at the nearest location from a location where the failure occurs is applied to the MPLS multicast, so that it is possible to rapidly cope with the failure generated when an MPLS multicast packet is transmitted.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
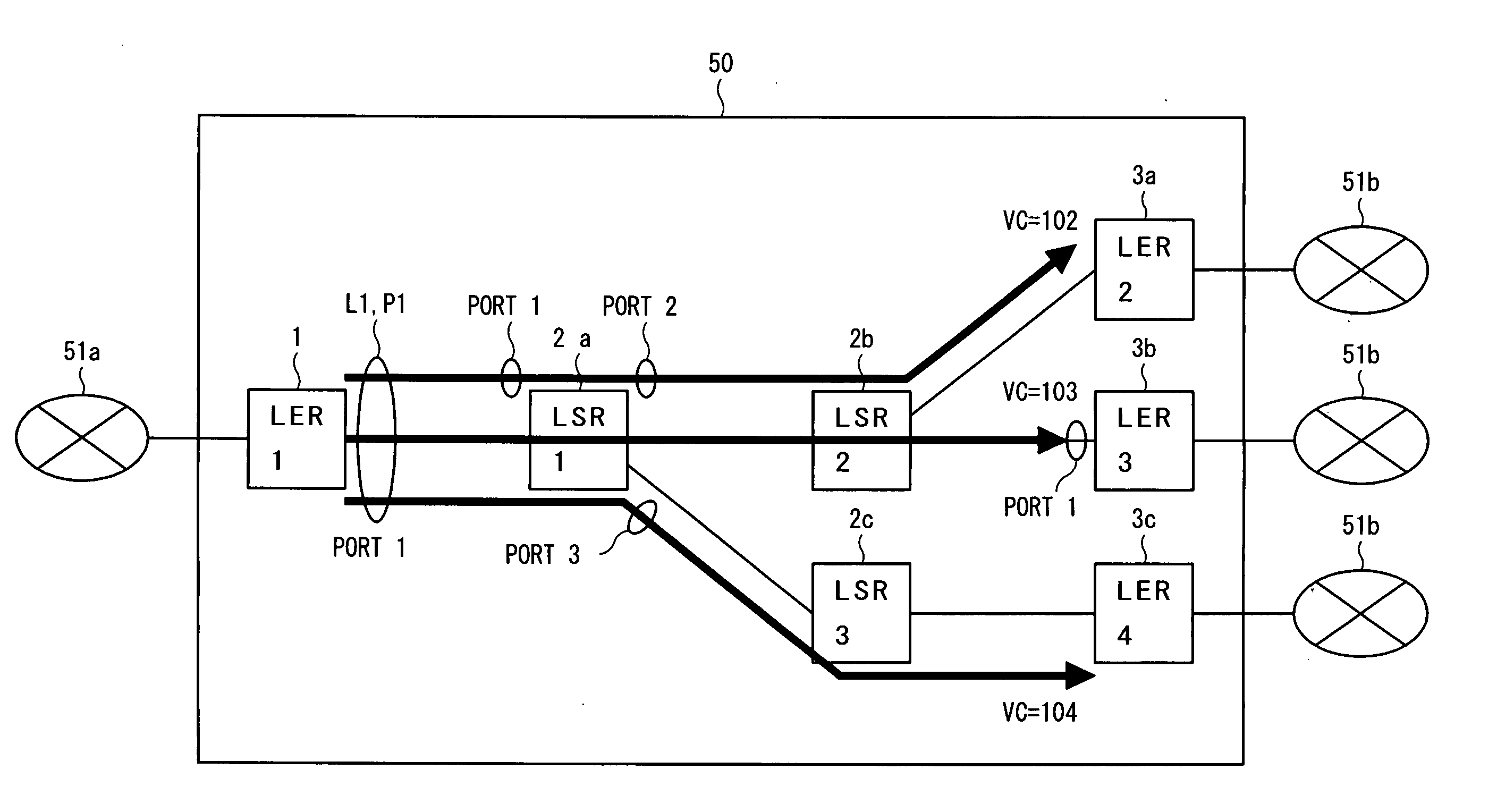
Source routed multicast LSP
Source routed multicast LSP is described herein. In one embodiment, when a first node receives a first packet having a label stack including a plurality of labels compatible with MPLS (multi-protocol label switching), in response to a first label on a top of the label stack, the first packet is duplicated into a second packet. In addition, at least two labels are popped from the top of the label stack of the second packet forming a third packet. Thereafter, the first and third packets are processed based on a label on the top of the label stack of the first and third packets respectively. Other methods and apparatuses are also described.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
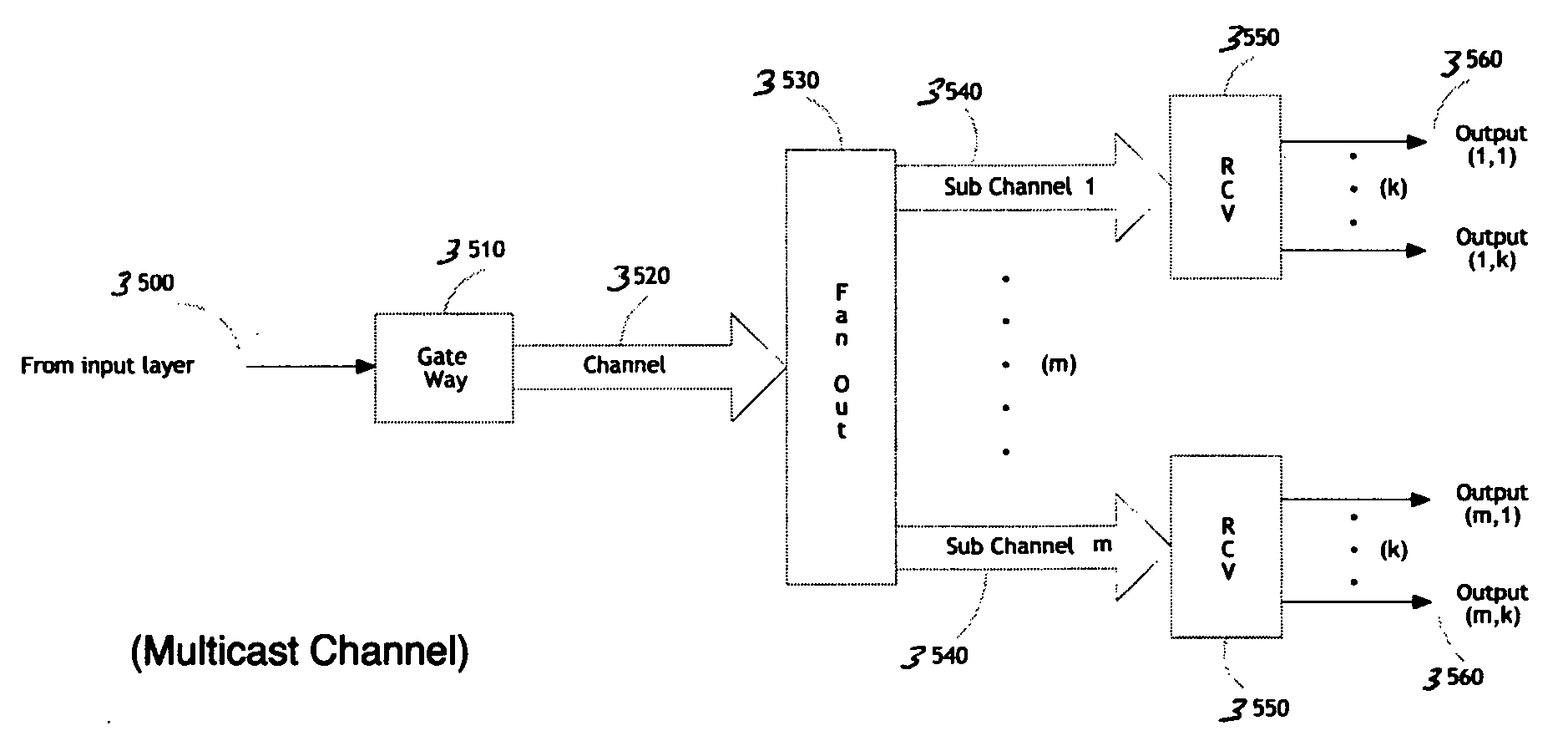
N-way serial-channel interconnect
Methods and apparatus are described for an n-Way, Serial-Channel interconnect. An apparatus includes a communications network interconnect including an input layer including a plurality of input channels; a multicast channel branching fabric coupled to the input layer; and a modular output layer coupled to the multicast channel branching fabric layer, the modular output layer including a plurality of individual serial data channels; and a plurality of sets of endpoints, each set of endpoints coupled to one of the plurality of individual serial data channels.
Owner:LIGHTFLEET CORP
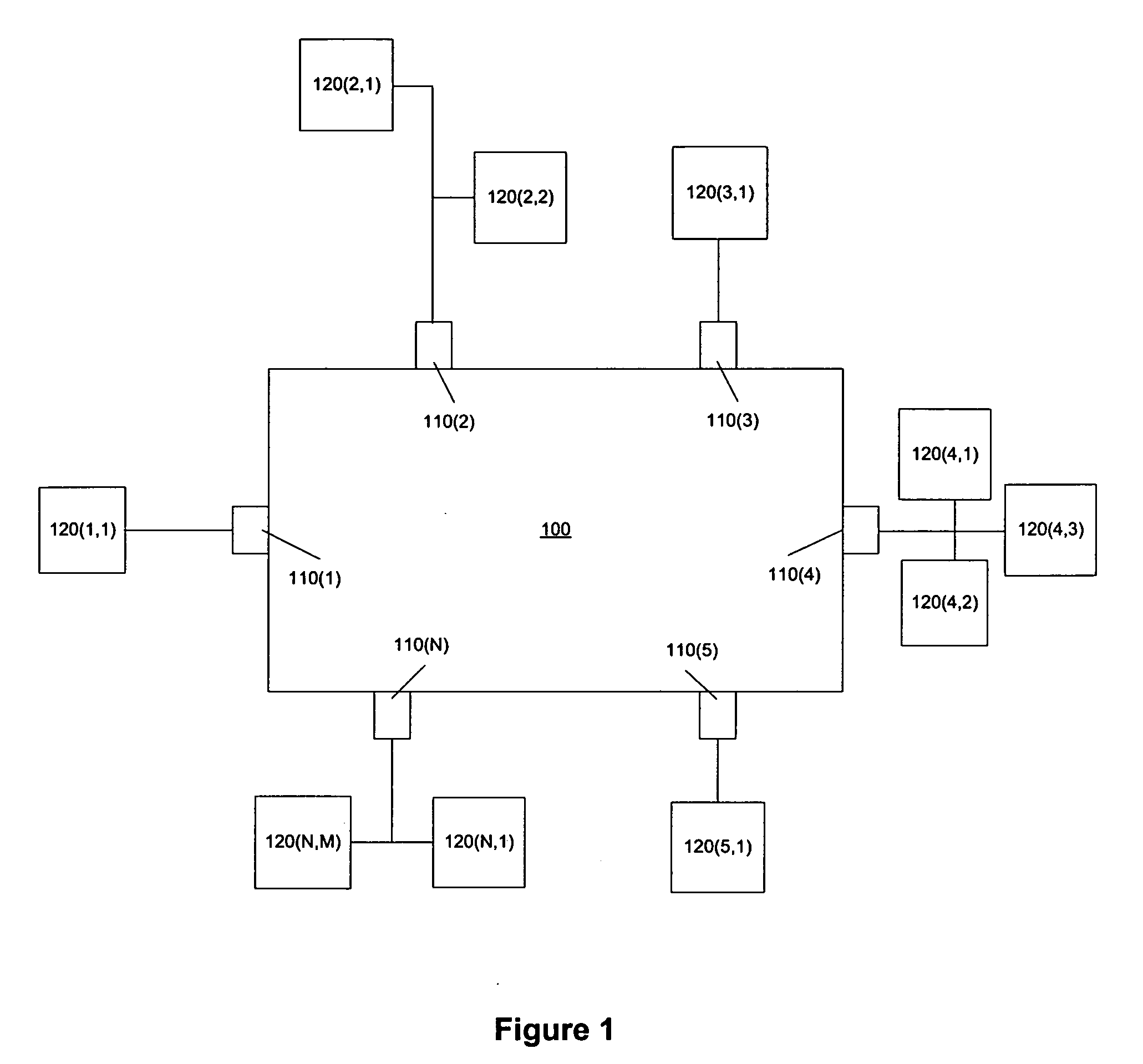
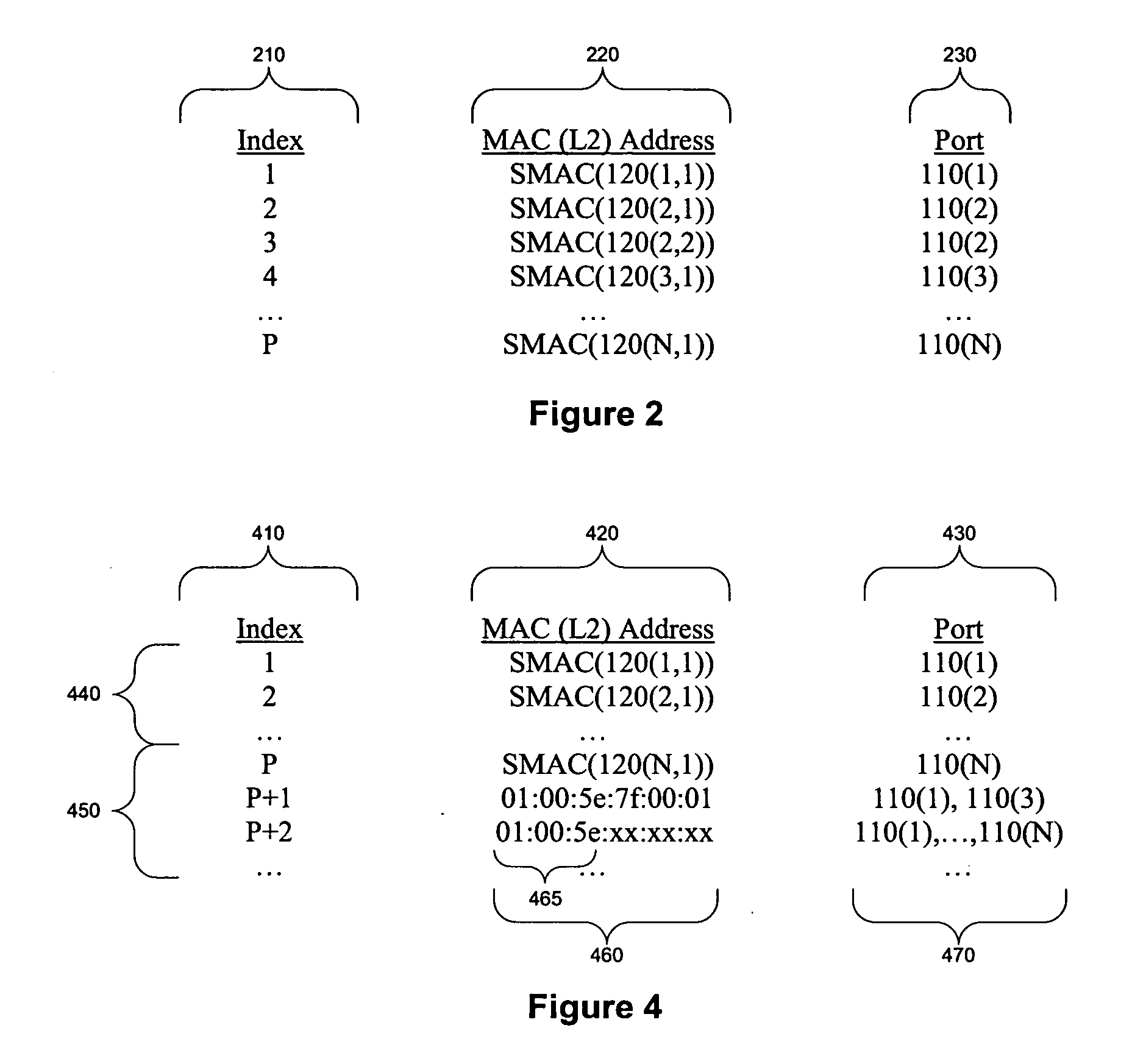
Performing extended lookups on mac-based tables
ActiveUS20060221960A1Special service provision for substationTime-division multiplexInternet trafficIp address
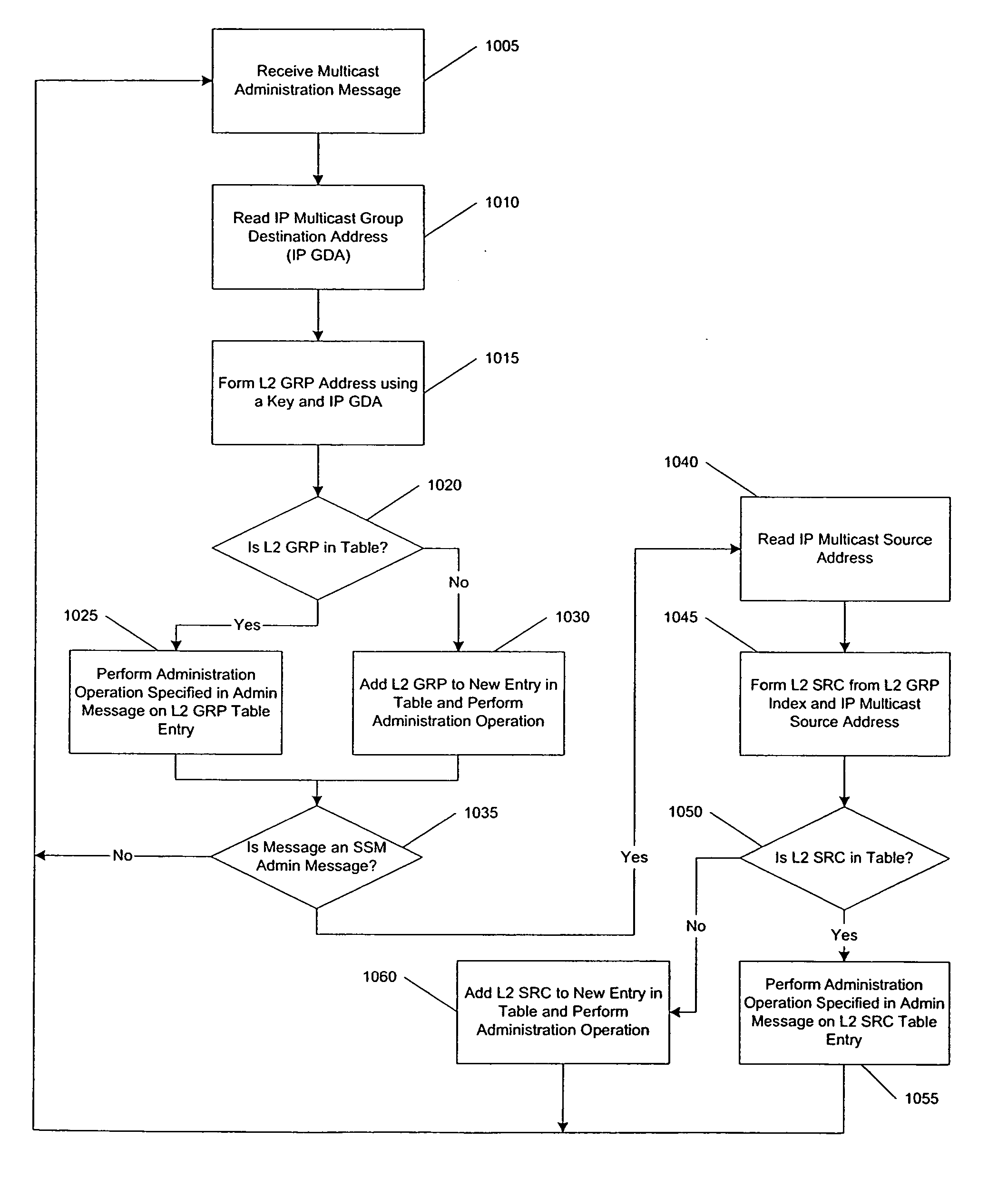
A method, system, and computer program product are presented to optimize OSI Level 2 switch forwarding of frames comprising IP addresses, 802.1 QinQ VLAN identifiers, multi-protocol label switching labels, and any other usable information meaningful to derive an L2 forwarding result on frames. In one embodiment, a 16-bit key is included as a prefix to a 48-bit OSI Level 2 address entry, thereby allowing the inclusion of a 32-bit OSI Level 3 address in the lookup table (e.g., a complete IP version 4 address). Implementations of such a solution are presented to resolve address aliasing issues experienced with multicast group destination addresses, including single source multicast. Solutions to optimizing forwarding of frames in an IEEE 802.1 QinQ environment are also presented. A result of these implementations can be reduction of the amount of unnecessary network traffic generated by a network switch incorporating such an OSI Level 2 address lookup table.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com