Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
296 results about "Inter vehicle communication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
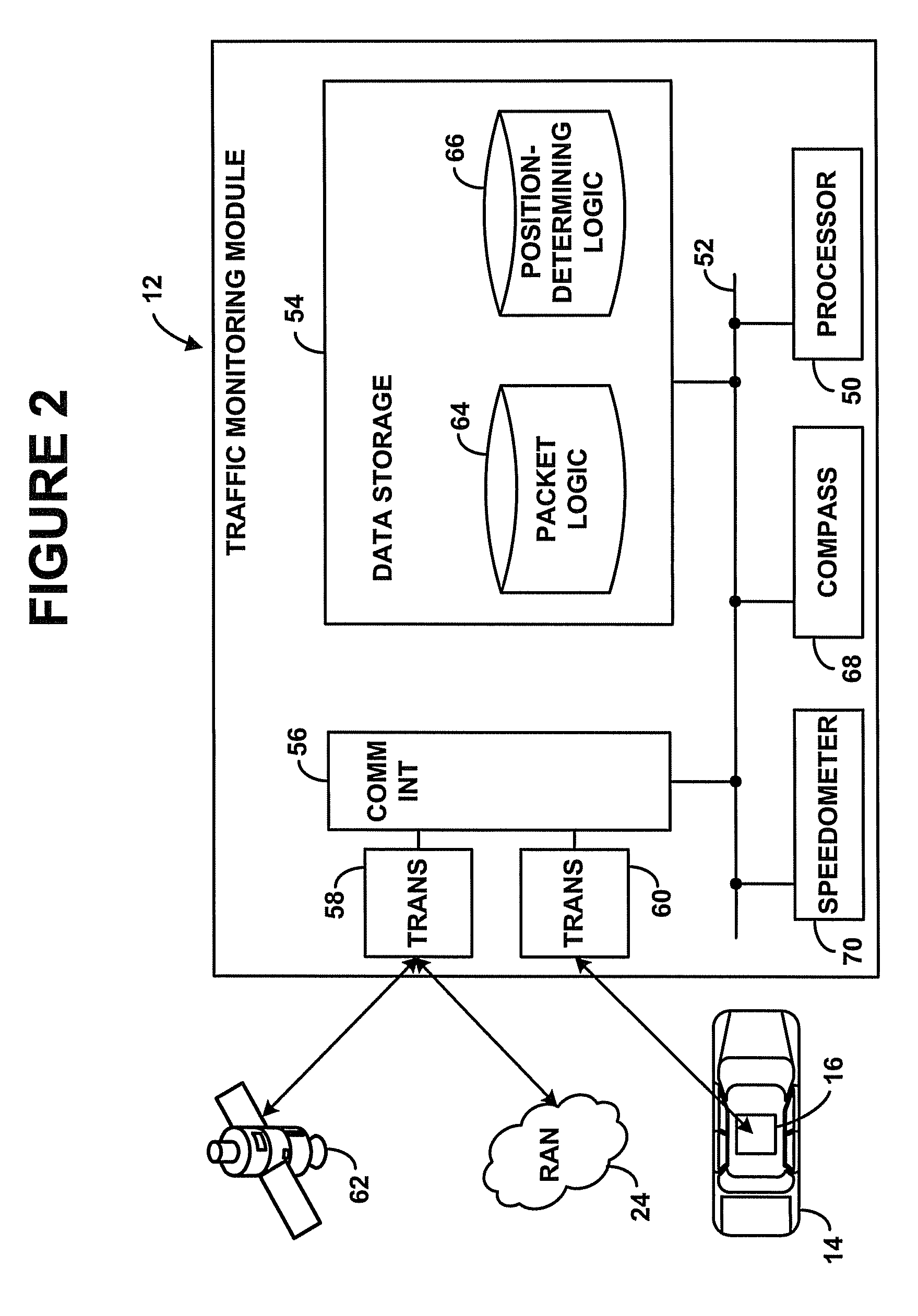
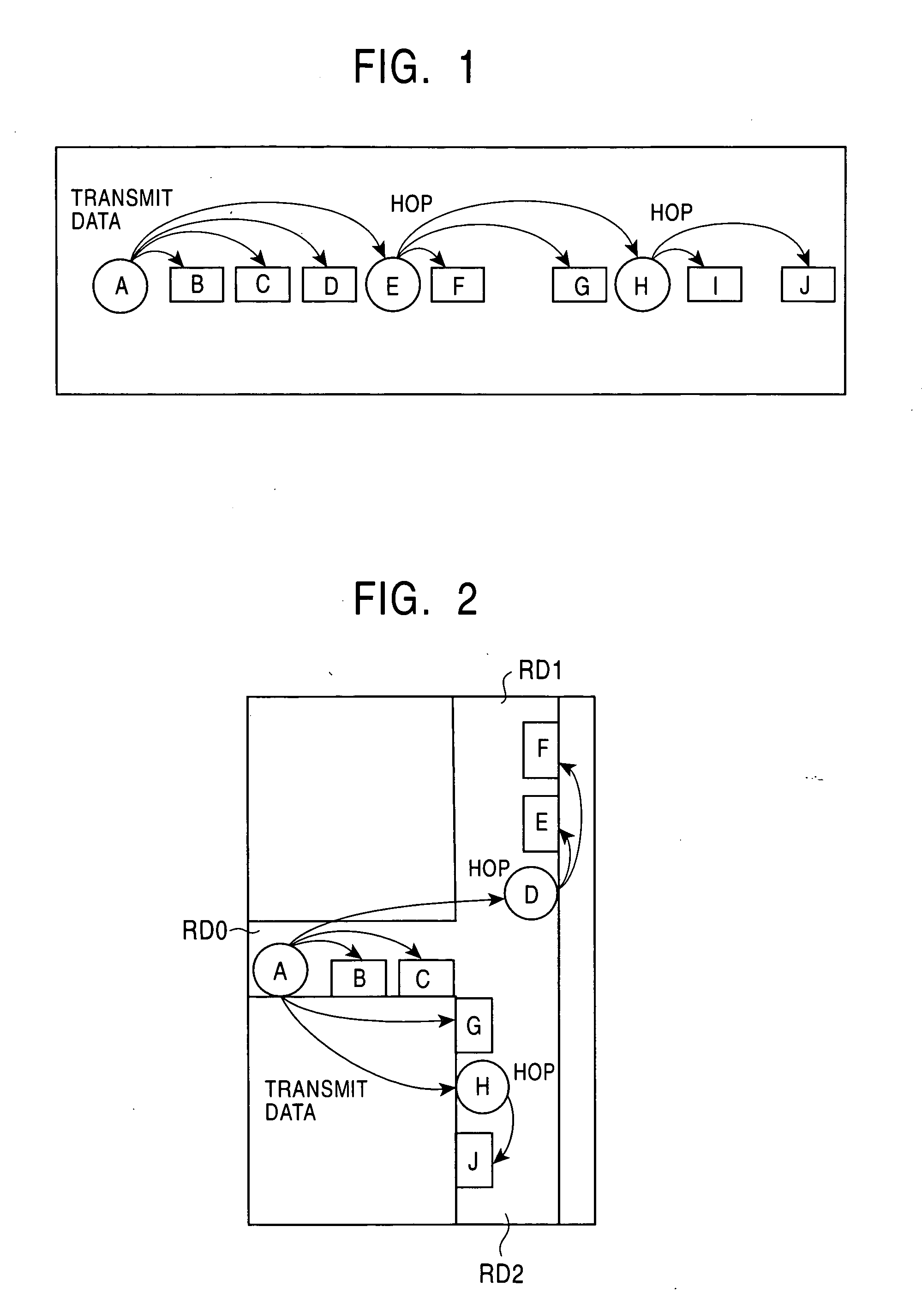
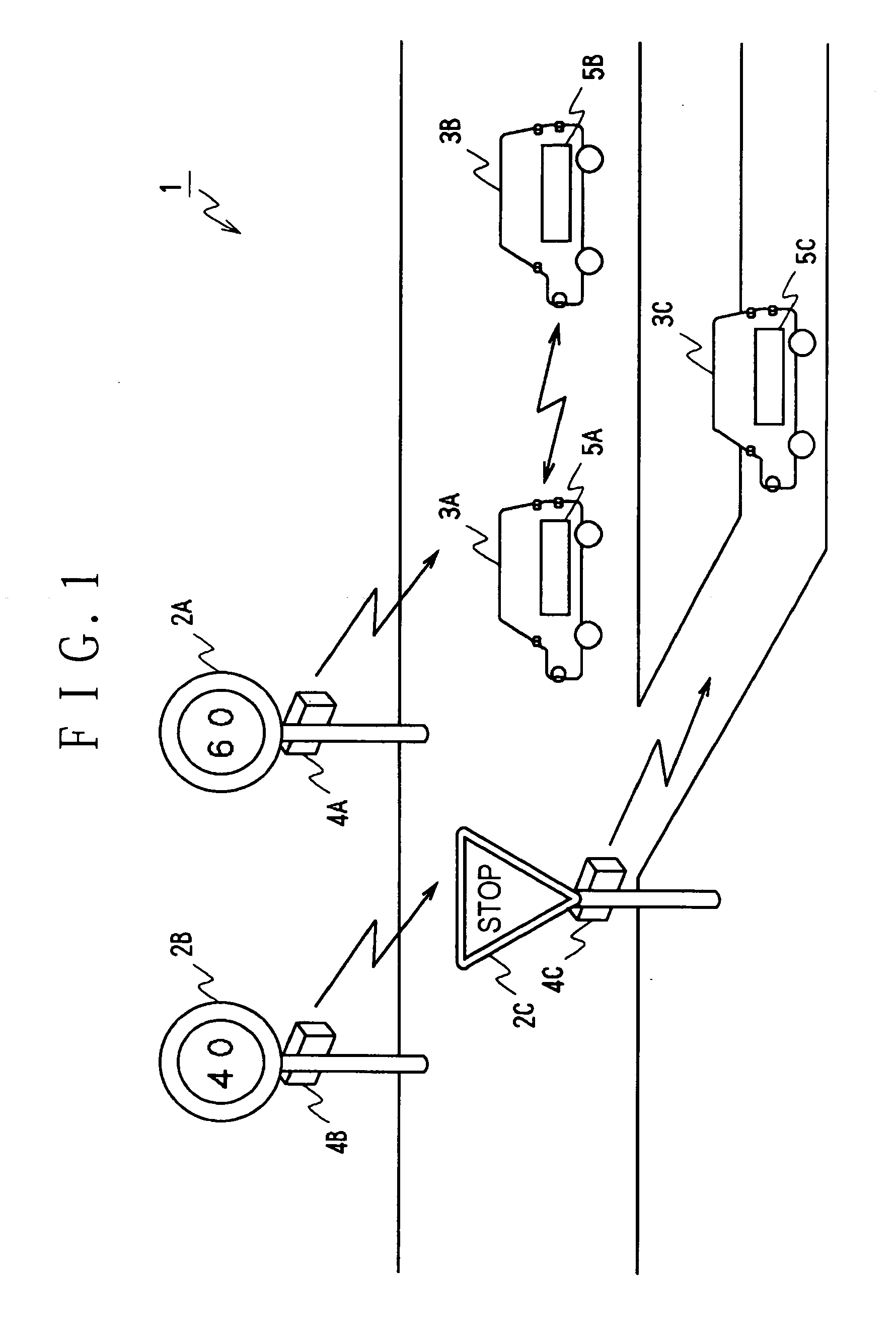
Inter vehicle communication INTRODUCTION Vehicular communication systems are a type of network in which vehicles and roadside units are the communicating nodes, providing each other with information, such as safety warnings and traffic information.
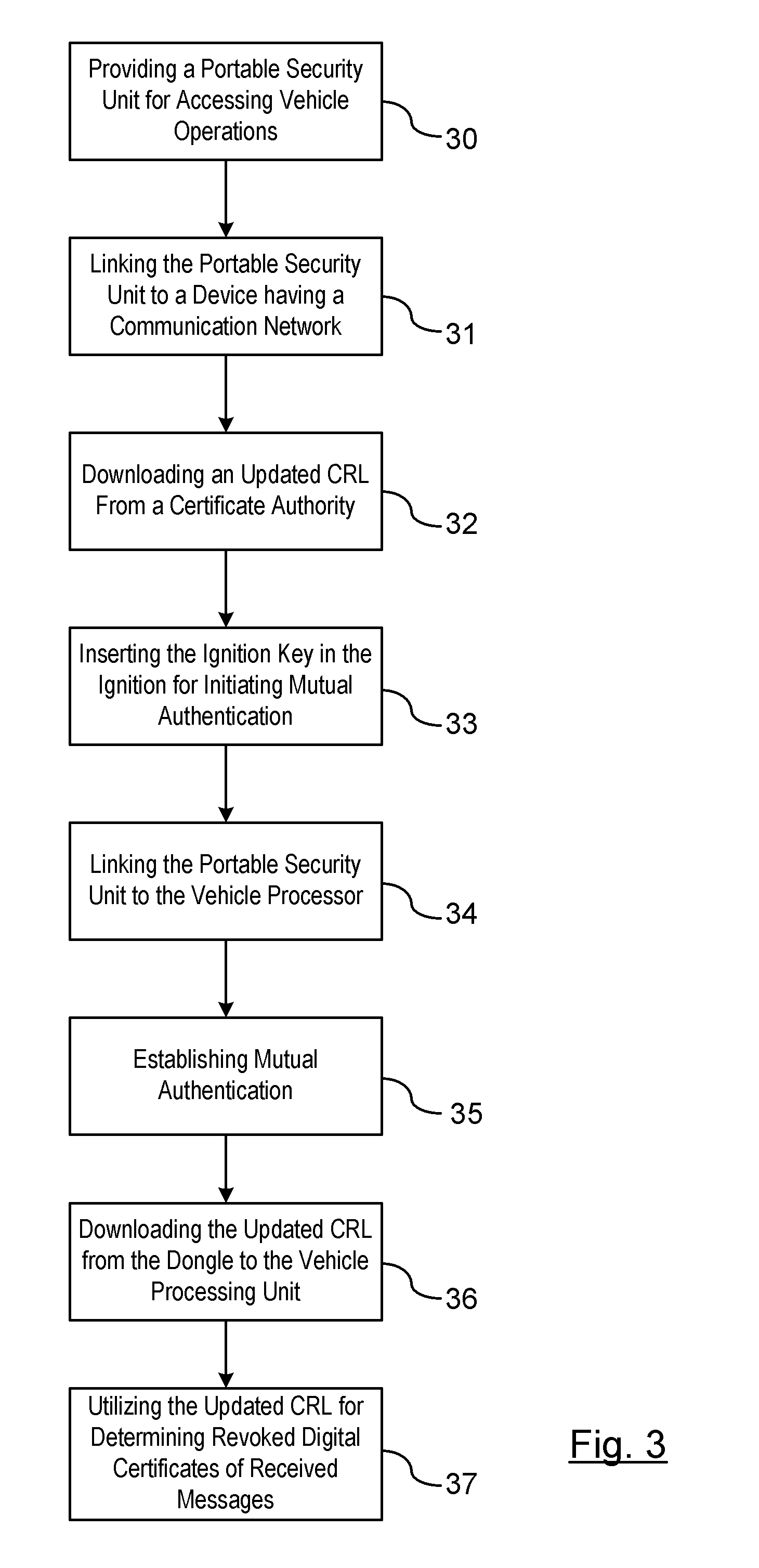
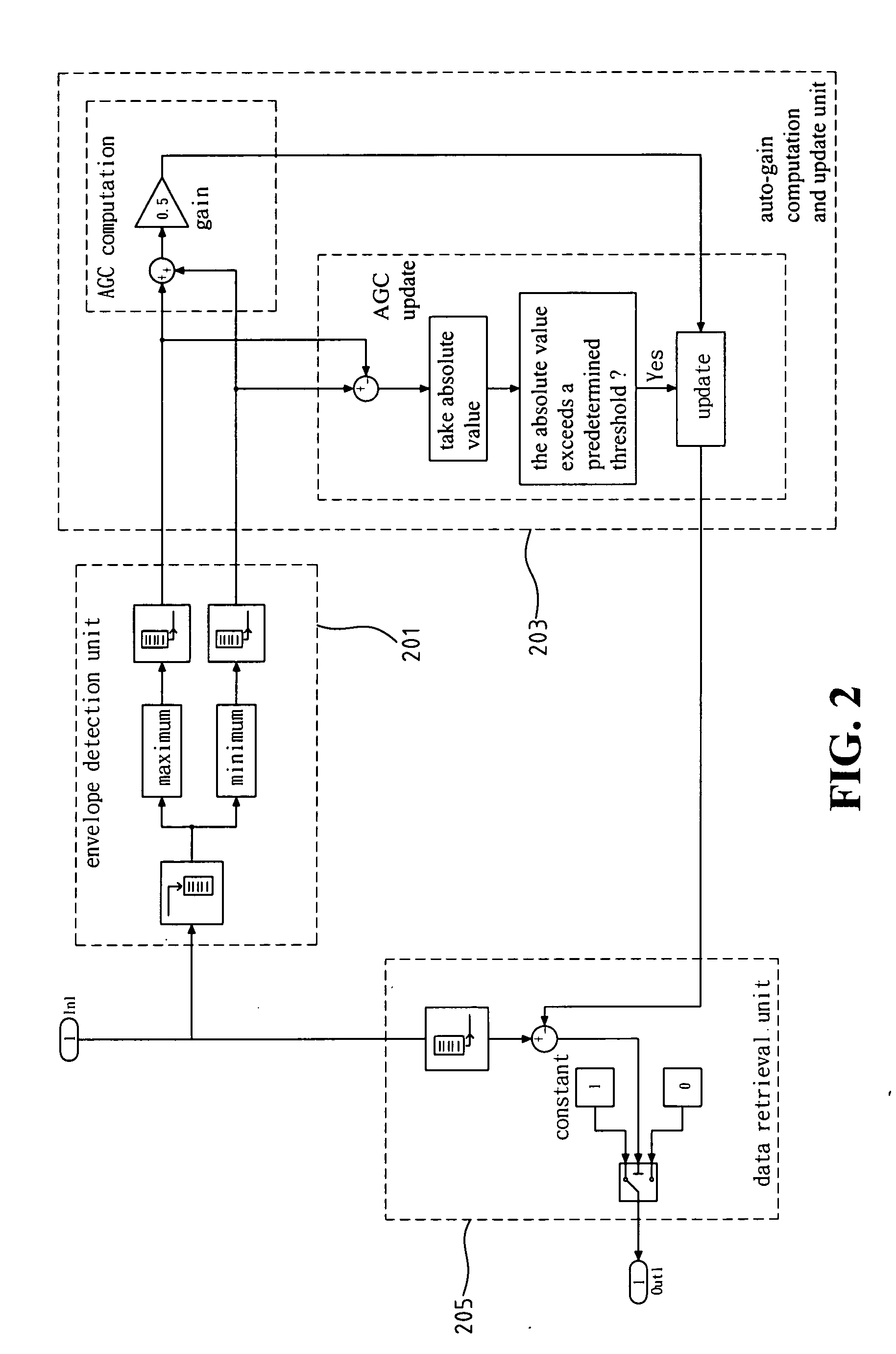
Time-slot-based system and method of inter-vehicle communication
ActiveUS8520695B1Efficient communicationEfficient codingInstruments for road network navigationArrangements for variable traffic instructionsWireless transmissionCommunications system
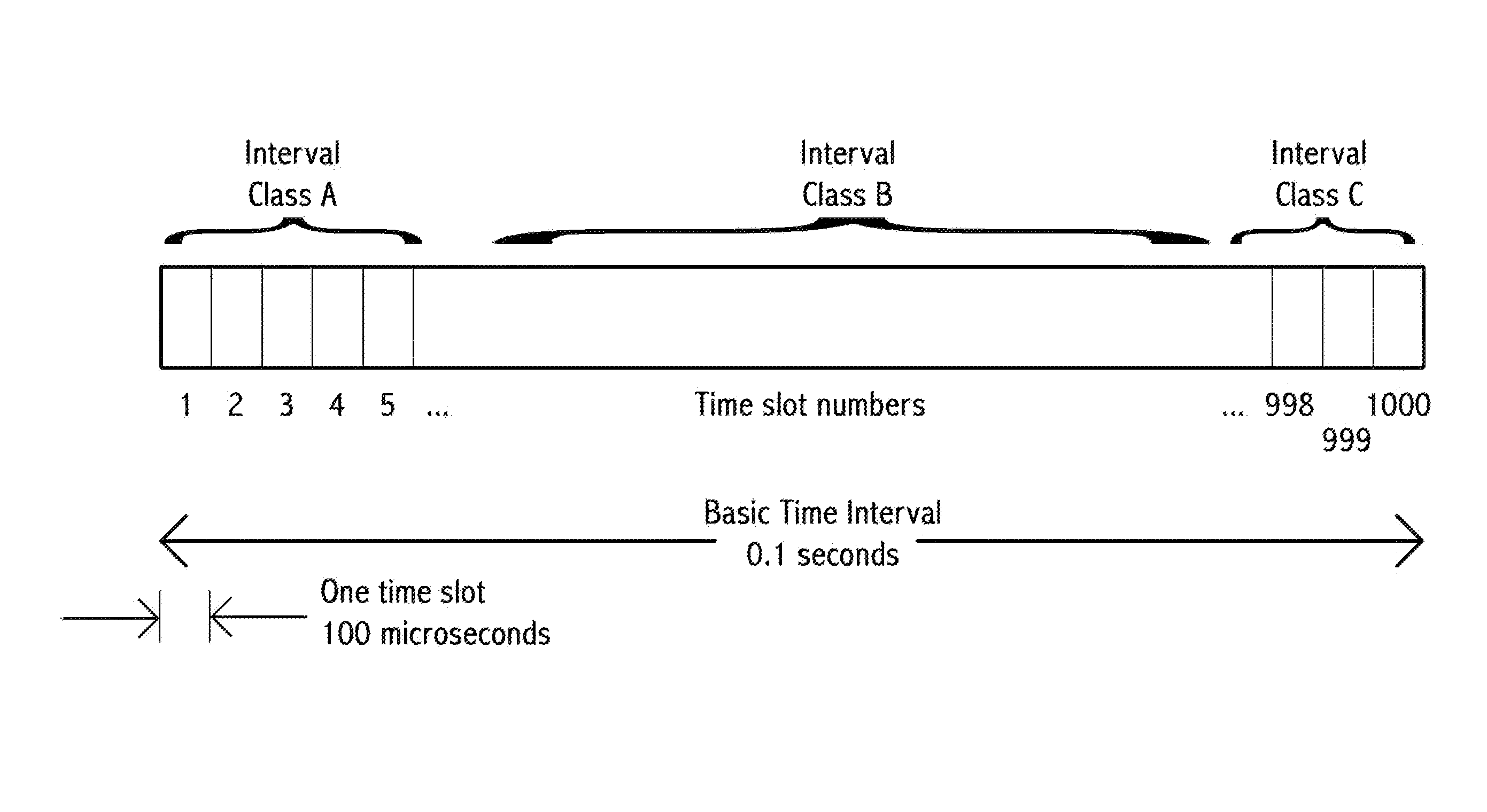
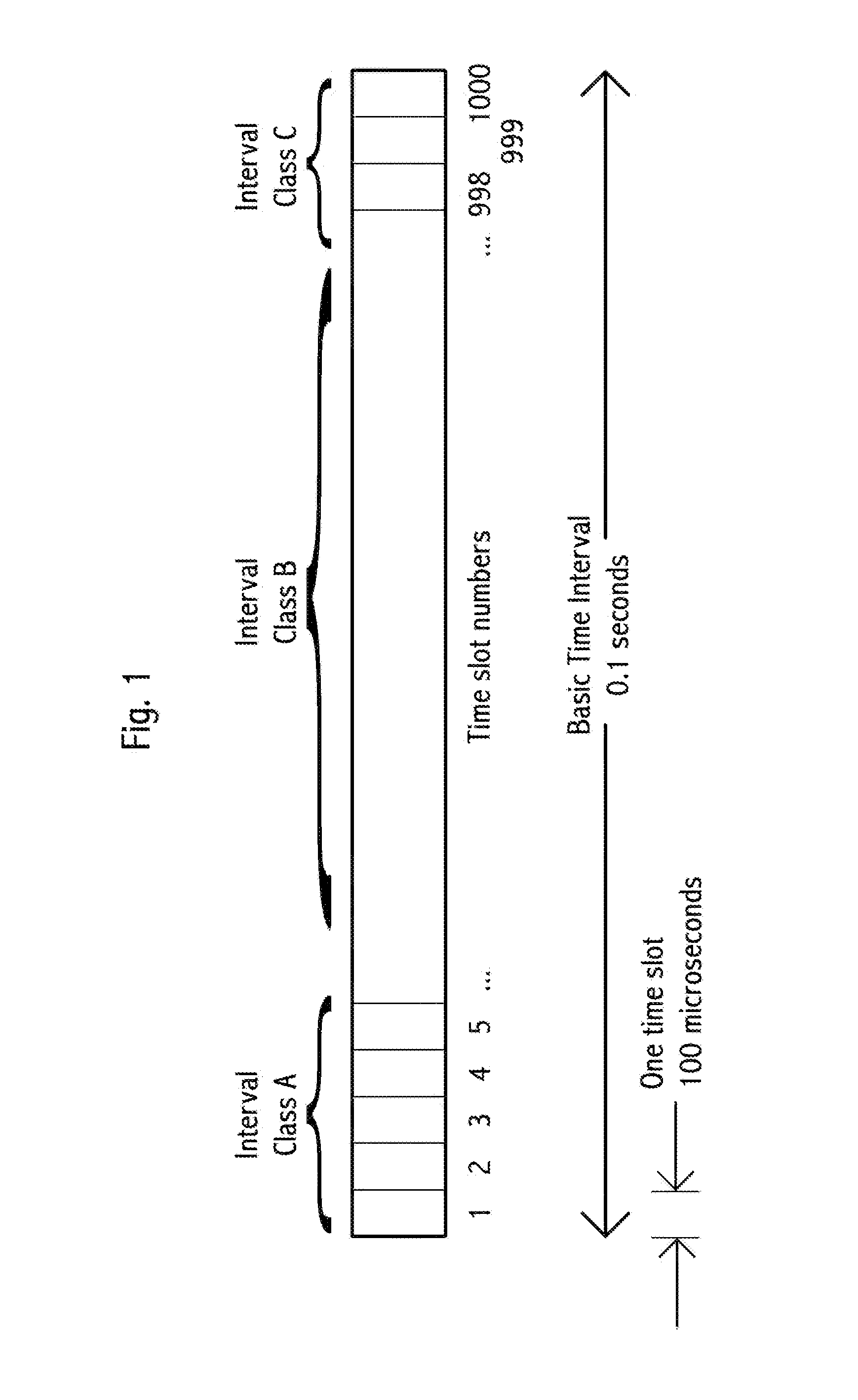
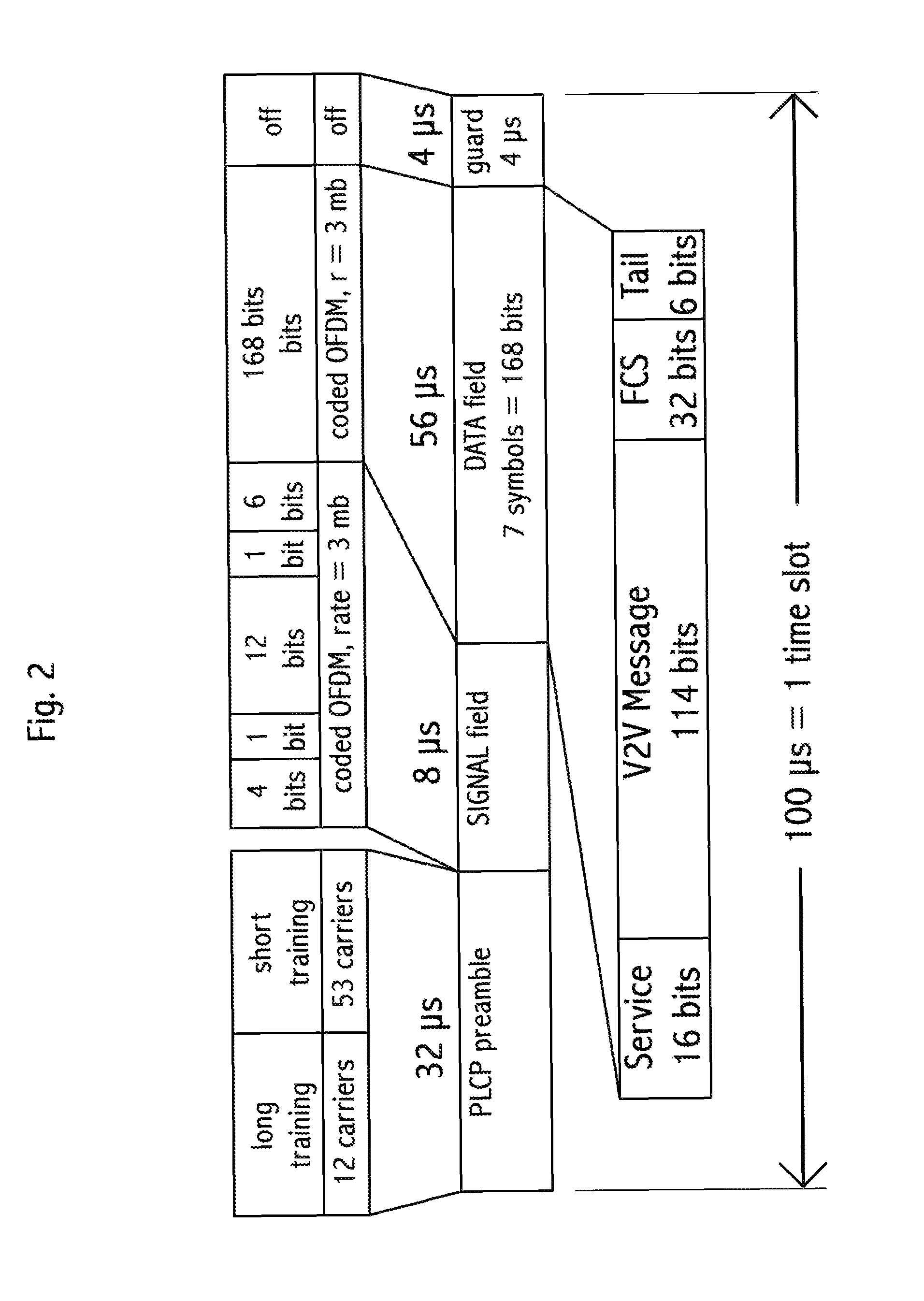
Device, system and method, in a vehicle communication system, to transmit wirelessly a message comprising the position, heading and speed of a vehicle or other moving object, wherein the transmission is repeated at regular intervals in a temporarily fixed time slot within a predetermined basic time interval. In a key embodiment the message duration is equal to or less than a predetermined time slot duration. Embodiments use generally the same time slot in a contiguous sequence of basic time intervals. Algorithms are described to resolve wireless interference within a time slot. Embodiments divide the basic time interval in multiple durations, “class regions,” for different message classes. Embodiments use different wireless bandwidth allocation algorithms for the class regions.
Owner:ZETTA RES & DEV - FORC SERIES
Collaborative multicast for dissemination of information in vehicular ad-hoc networks
InactiveUS20070001869A1Anti-collision systemsOptical signallingInter vehicle communicationDissemination
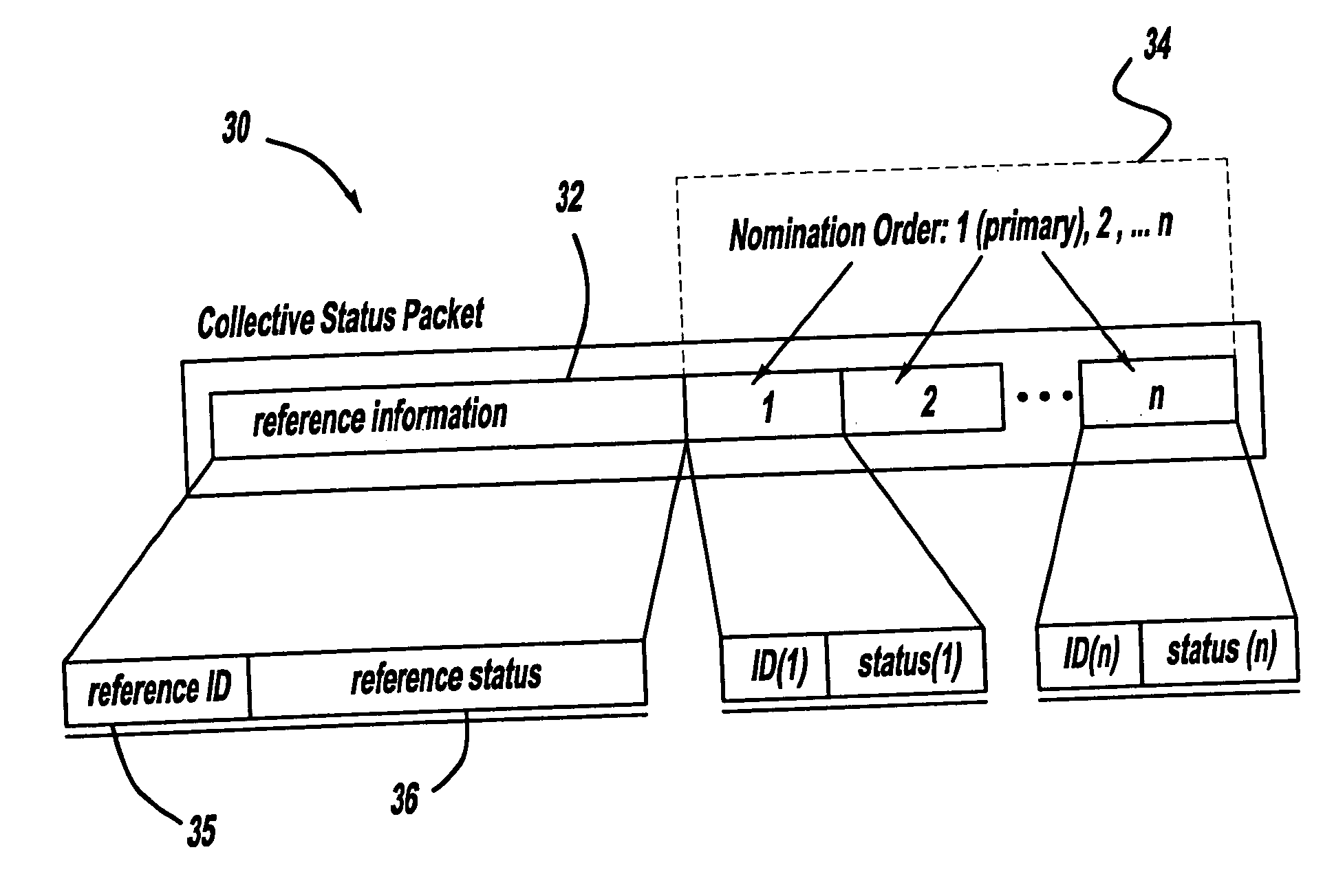
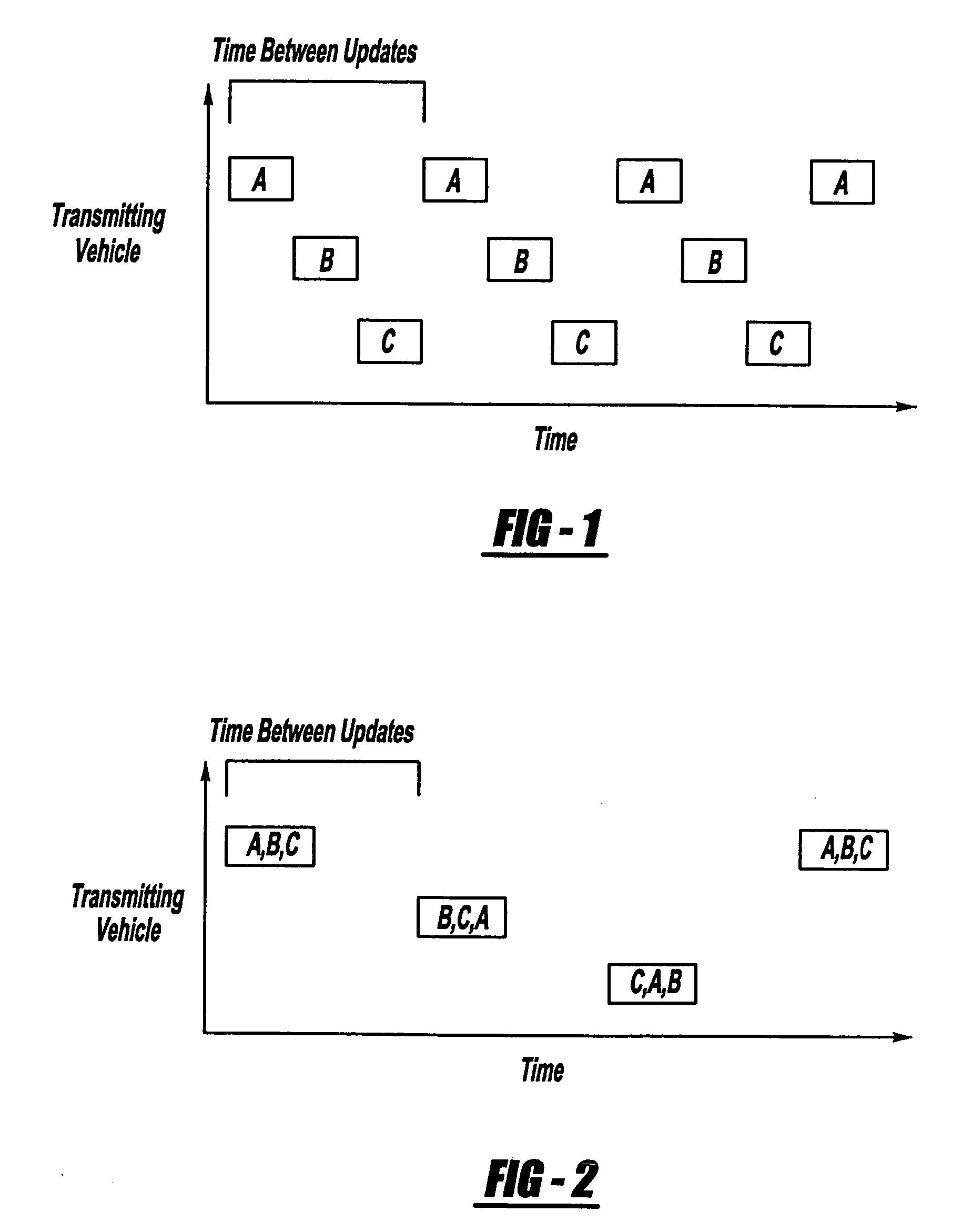
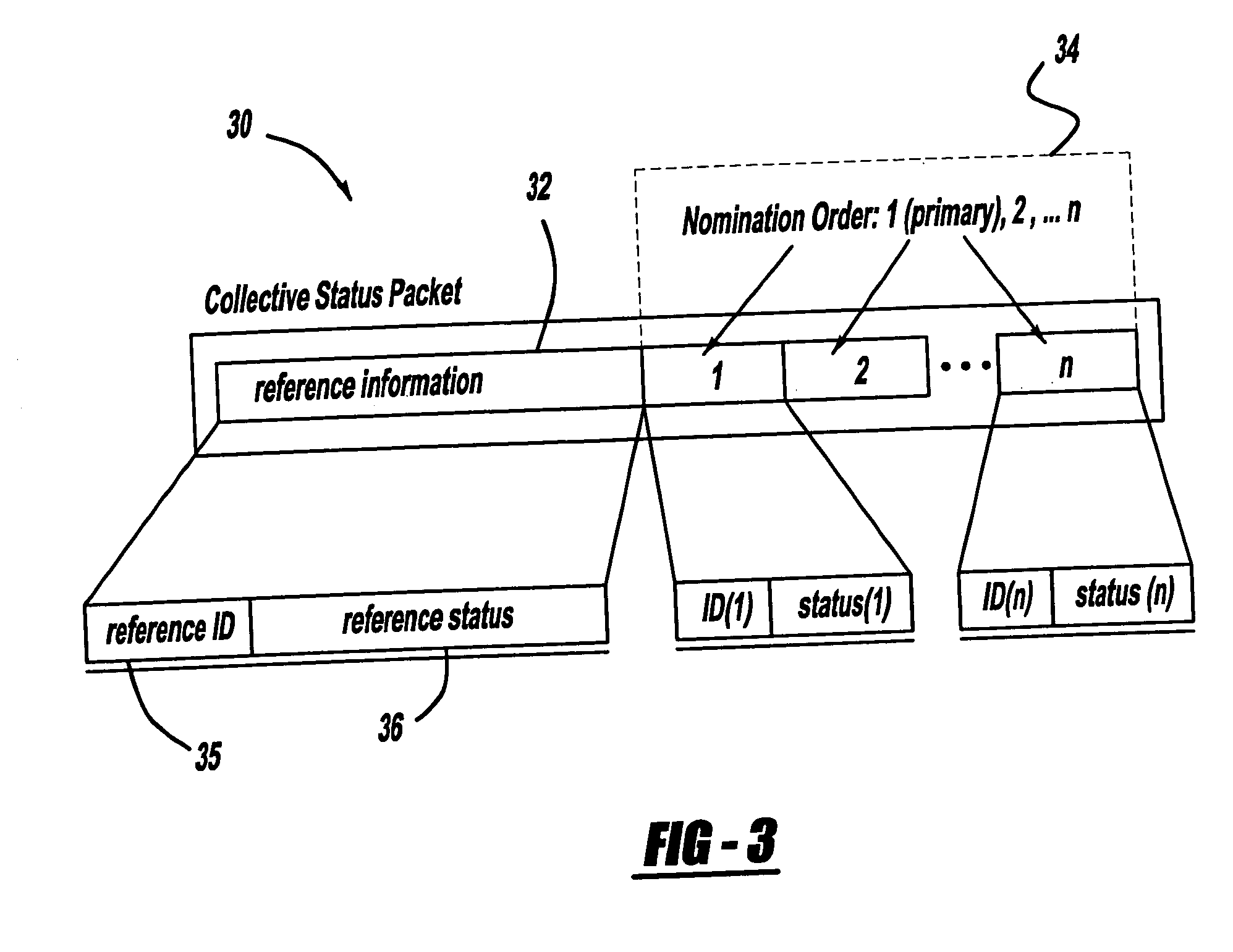
A collaborative nomination algorithm is provided for disseminating information amongst a plurality of collaborating vehicles in an inter-vehicle communication network. The method includes: receiving an incoming vehicle communication message at a recipient vehicle from one of the collaborating vehicles; nominating one of the collaborating vehicles identified in the incoming vehicle communication message to broadcast a subsequent vehicle communication message; and transmitting an outgoing vehicle communication message from the recipient vehicle, where the outgoing vehicle communication message identifies the vehicle nominated to broadcast the subsequent vehicle communication message.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Wireless communication system and method
InactiveUS20100202346A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesCommunications systemInter vehicle communication
Provided in some embodiments is a method of wireless inter-vehicle communication. The method includes storing a message packet in a shared memory location of a first communication device. The shared memory location is wirelessly accessible by one or more other communication devices. The method also includes assessing, at a second communication device, whether or not the message packet stored in the shared memory location of the first communication device is intended to be received at the second communication device and assessing, at the second communication device, whether or not to accept the message packet from the shared memory location of the first communication device. Further, the method includes receiving at least a portion of the message packet at the second communication device if it is determined that the message packet should be accepted from the shared memory location of the first communication device.
Owner:GRAVITY TECH
Vehicular traffic congestion monitoring through inter-vehicle communication and traffic chain counter
InactiveUS7979198B1Analogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficNetwork packetTraffic congestion
Methods and systems are disclosed for monitoring vehicular traffic congestion through the use of inter-vehicle communication and traffic chain counters. Data packets including counter, vehicle identification, direction, location, and speed information are transmitted between vehicles via short-range wireless communications. A receiving vehicle edits a data packet if the data packet reflects that the receiving vehicle has not yet edited the packet and is traveling in substantially the same direction as the vehicle which transmitted the packet to the receiving vehicle. If a receiving vehicle is the last vehicle to edit a packet, the receiving vehicle transmits a reporting packet to a traffic monitoring server via long-range wireless communications.
Owner:SPRING SPECTRUM LP
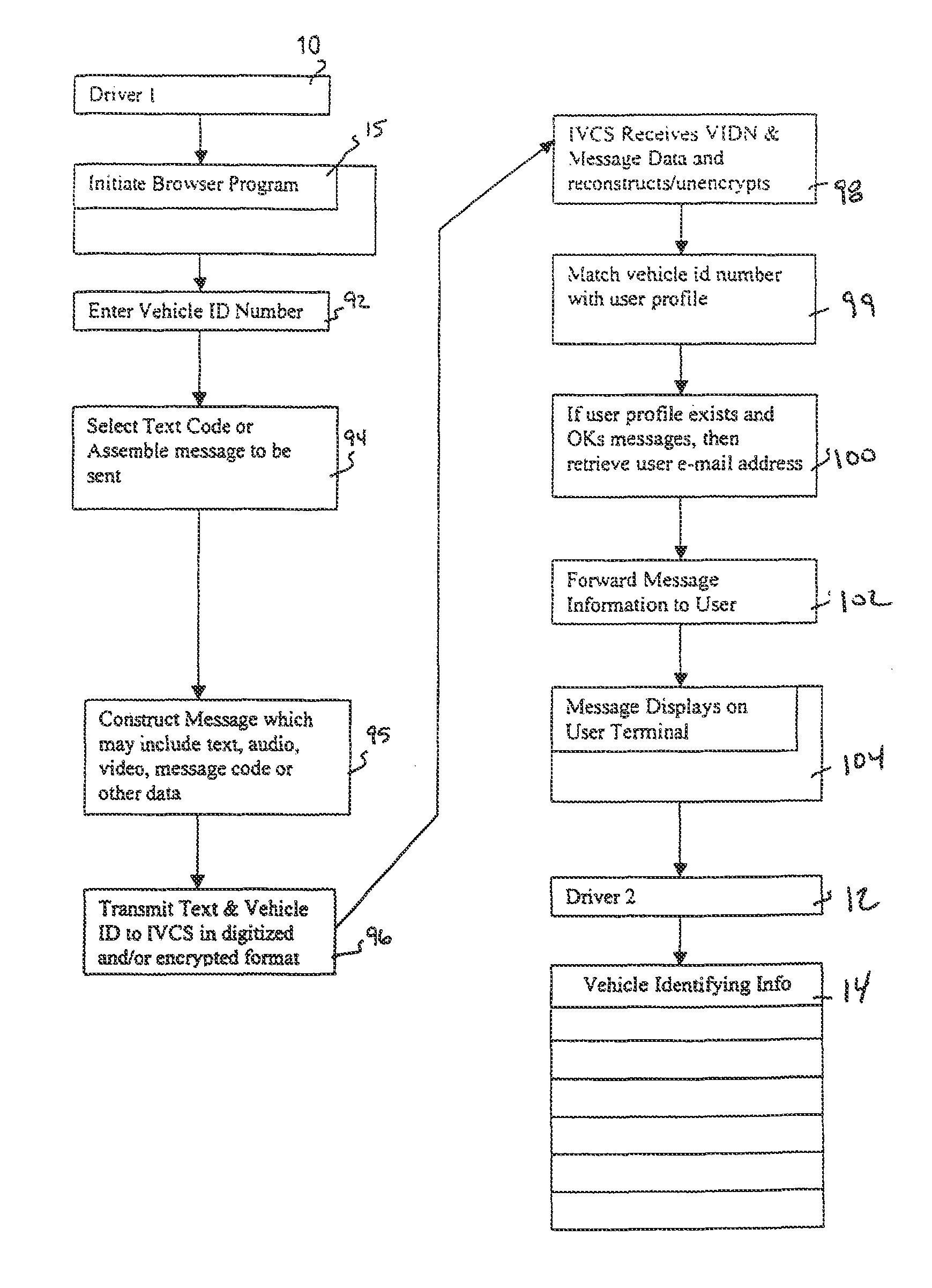
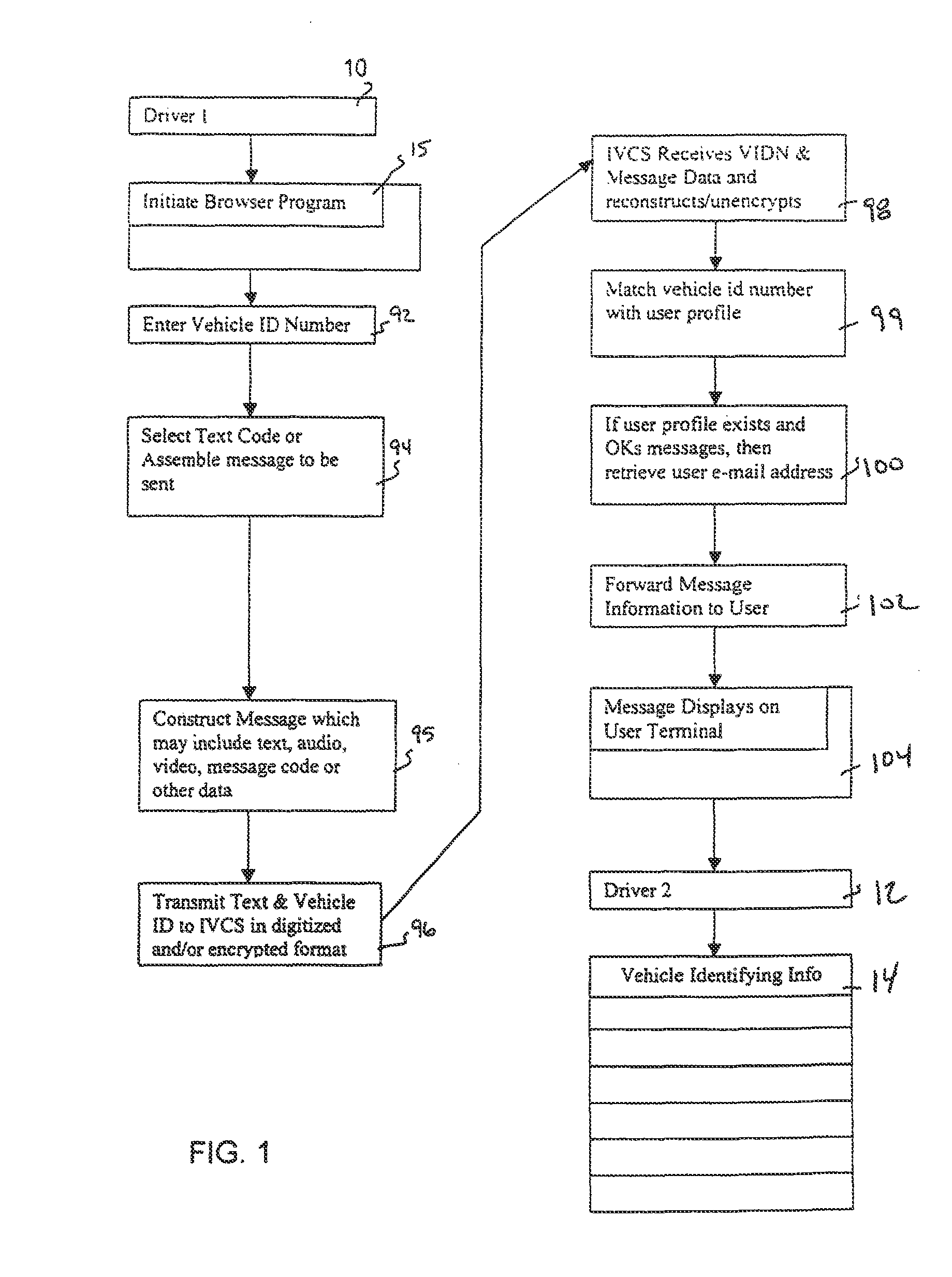
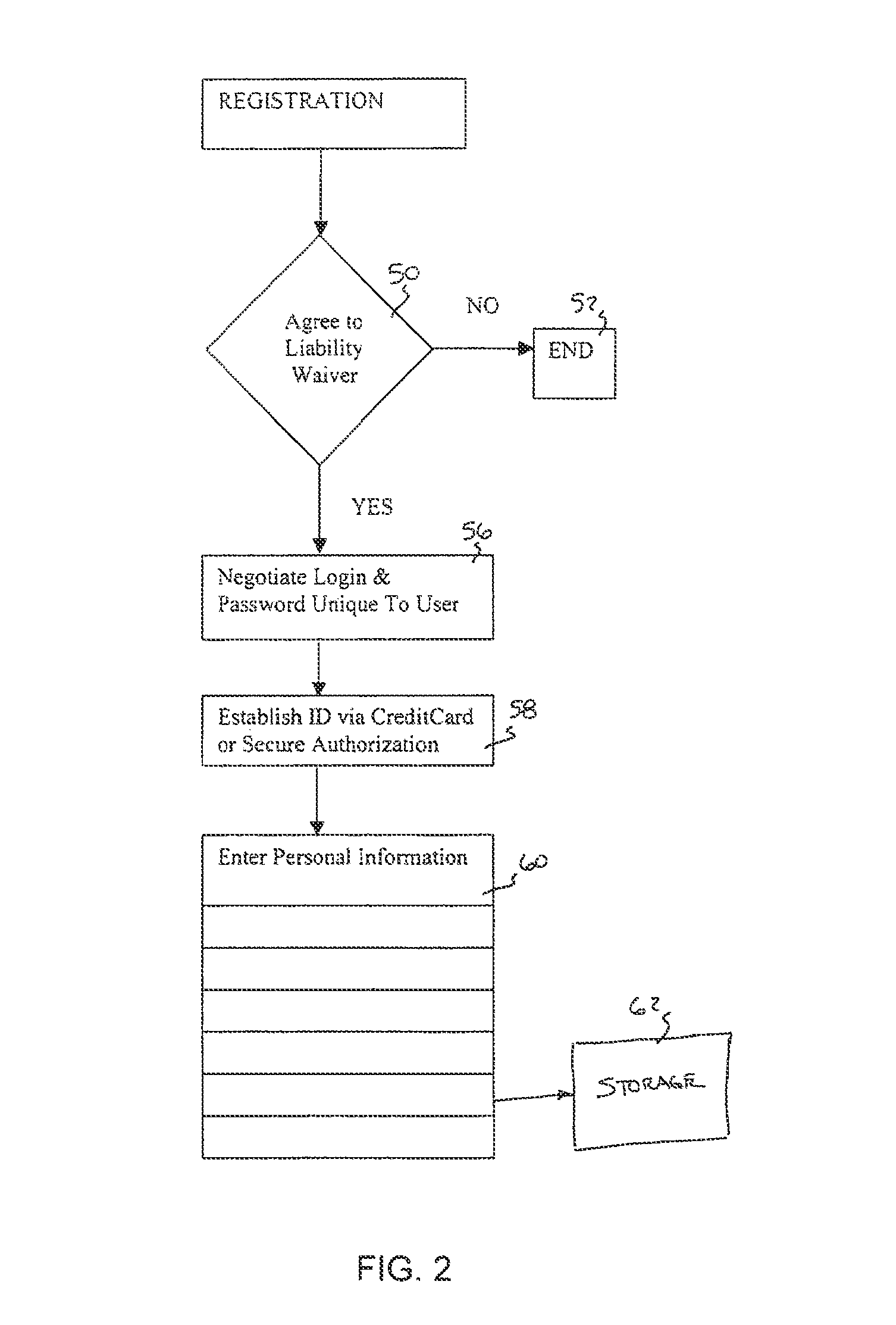
Inter vehicle communication system
InactiveUS8713121B1Instruments for road network navigationData processing applicationsDatabase servicesInter-process communication
A method and network for transmitting a message from a sender to a recipient wherein the sender has no previous knowledge of the recipient's identity. A method is provided for registering a user with a web-enabled database service by providing correlating data on the user's identity and vehicle license plate number and / or other vehicle identifying information. A sender observing a vehicle can send a message to the recipient by logging onto the service and sending a message including the license plate number of the vehicle or other vehicle identifying information. The service will forward the message to the recipient by looking up the vehicle information, discerning the most appropriate communications method(s), and causing the message to be transmitted to the recipient or stored for later delivery.
Owner:EVENTS COM INC
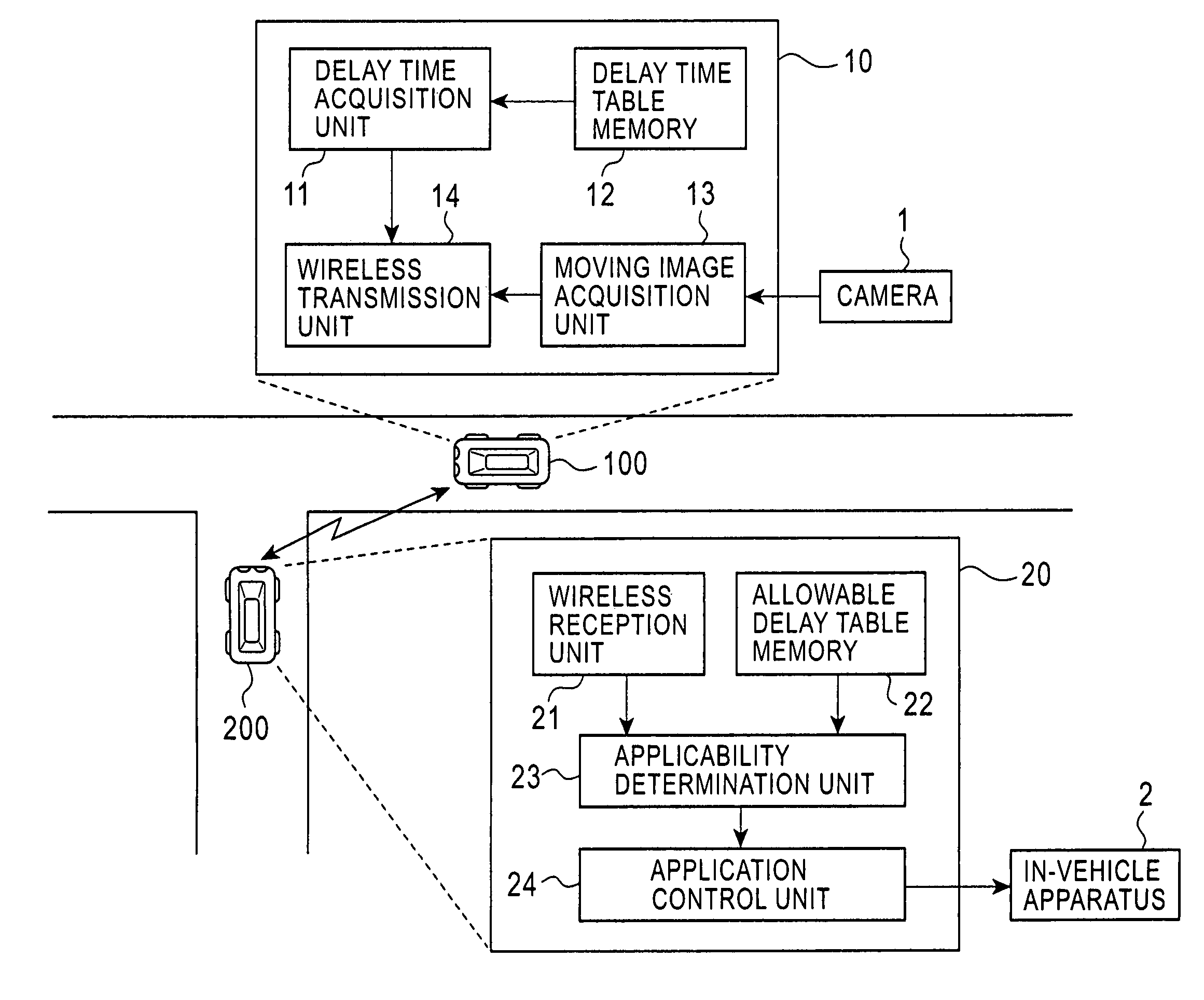
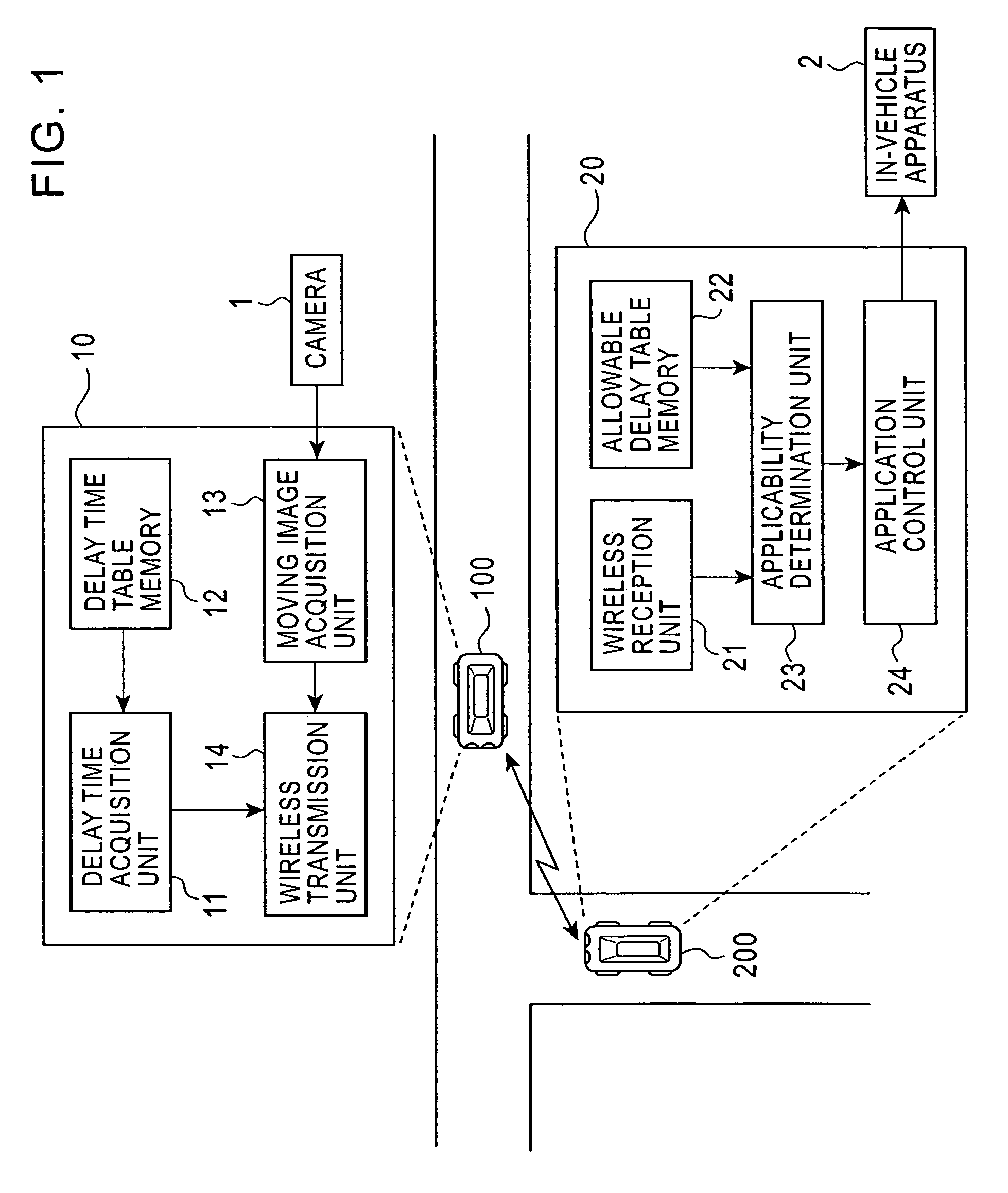
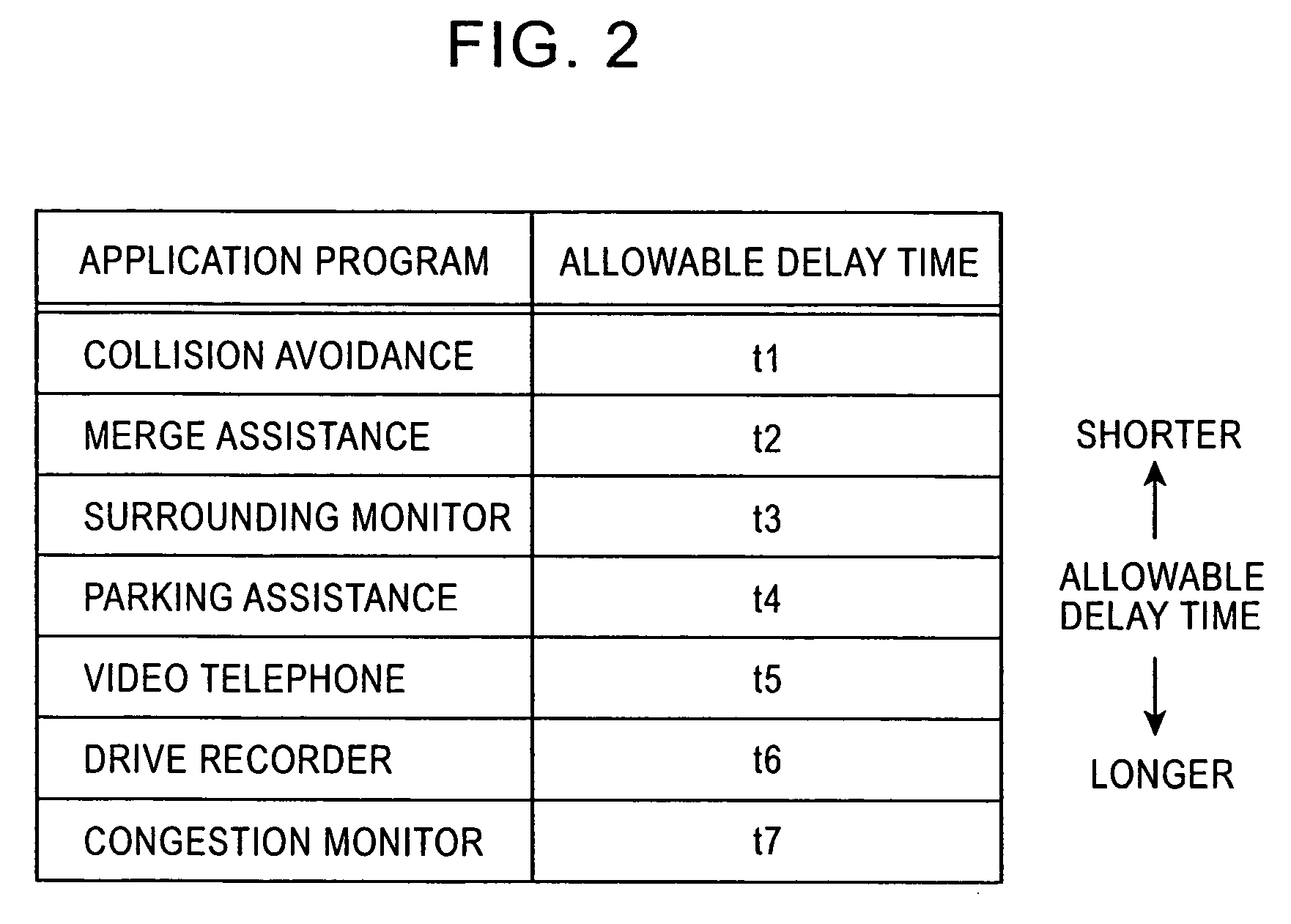
Vehicle-to-vehicle communication apparatus, vehicle-to-vehicle communication system, and method of determining applicability of moving image information to an application program
ActiveUS7751945B2Television system detailsArrangements for variable traffic instructionsCommunications systemIn vehicle
In a vehicle-to-vehicle communication system, when moving image information is transmitted between vehicles, a delay time acquisition unit determines a delay time that occurs when the moving image information is transmitted from a first vehicle to a second vehicle, and an applicability determination unit determines whether the moving image information transmitted with such a delay time is applicable to an application program running on an in-vehicle apparatus installed in the second vehicle. This makes it possible to transmit only moving image information which is usable by the in-vehicle apparatus.
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
Inter vehicle communication system
InactiveUS20060059229A1Instruments for road network navigationMultiple digital computer combinationsDatabase servicesInter-process communication
A method and network for transmitting a message from a sender to a recipient wherein the sender has no previous knowledge of the recipient's identity. A method is provided for registering a user with a web-enabled database service by providing correlating data on the user's identity and vehicle license plate number and / or other vehicle identifying information. A sender observing a vehicle can send a message to the recipient by logging onto the service and sending a message including the license plate number of the vehicle or other vehicle identifying information. The service will forward the message to the recipient by looking up the vehicle information, discerning the most appropriate communications method(s), and causing the message to be transmitted to the recipient or stored for later delivery.
Owner:EVENTS COM INC
Method for communication among mobile units and vehicular communication apparatus
ActiveUS7286825B2Arrangements for variable traffic instructionsUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionLogic networkInter vehicle communication
A method for communication among mobile units and vehicular communication apparatus make it possible to automatically establish connection with a party who can provide required information on the basis of an environment or condition change of a driver or a vehicle or in response to a driver's request so as to permit communication with the party. An inter-vehicle communication apparatus of a vehicle acquires information from other mobile units through physical networks while it is moving or stopped, and registers, in a member table, mobile units satisfying predetermined conditions on the basis of the acquired information as the members of different virtual logic networks according to the conditions. In such a state, the inter-vehicle communication apparatus selects one virtual logic network from among a plurality of virtual logic networks on the basis of an environment or condition change of a driver or a vehicle or in response to a driver's request so as to permit communication with the party. The selected virtual logic network is set as an active network to establish connection with a predetermined mobile unit in the active network thereby to request or provide required information from or to the mobile unit.
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
Threat mitigation in a vehicle-to-vehicle communication network
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
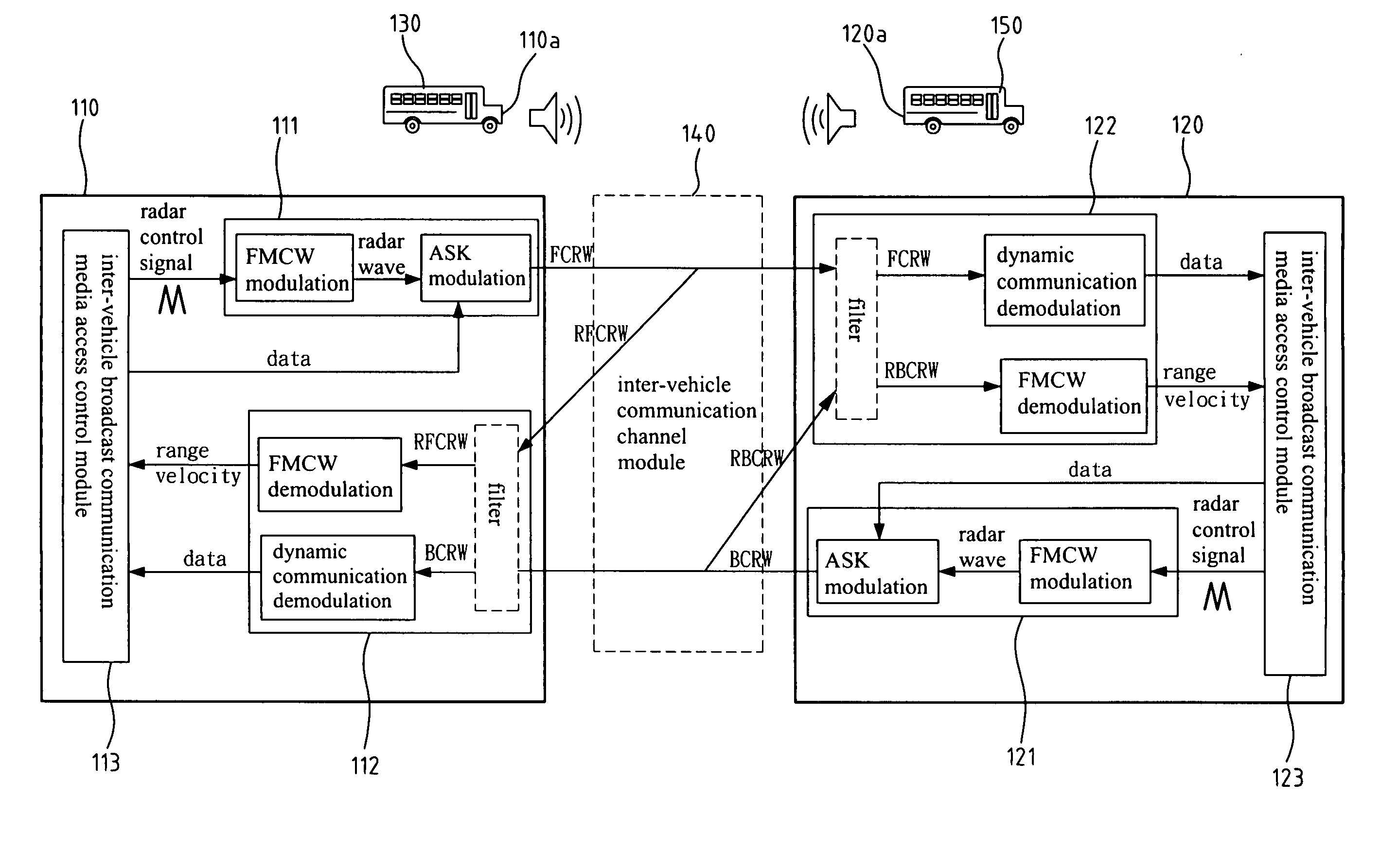
Inter-vehicle communication and warning apparatus
InactiveUS20070096885A1Enhance traffic transportation safetyEasy to transportDigital data processing detailsDetection of traffic movementRadarEngineering
A short-range inter-vehicle communication and warning apparatus comprises a forward radar and a backward radar. The apparatus uses the radars to generate Frequency Modulation / Continuous Wave (FMCW) signals, uses amplitude shift keying for data modulation and arranges a special packet format, to realize such a low cost and fast response device of collision avoidance for vehicles. The invention has the dual capabilities of detecting and communicating simultaneously. It can also measure the relative speed of a preceding / rear vehicles and the relative inter-vehicle distance. The invention also exchanges the real-time traffic information with the preceding / rear vehicles at the same time. It is applicable to a one-to-one or one-to-many inter-vehicle channel model.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
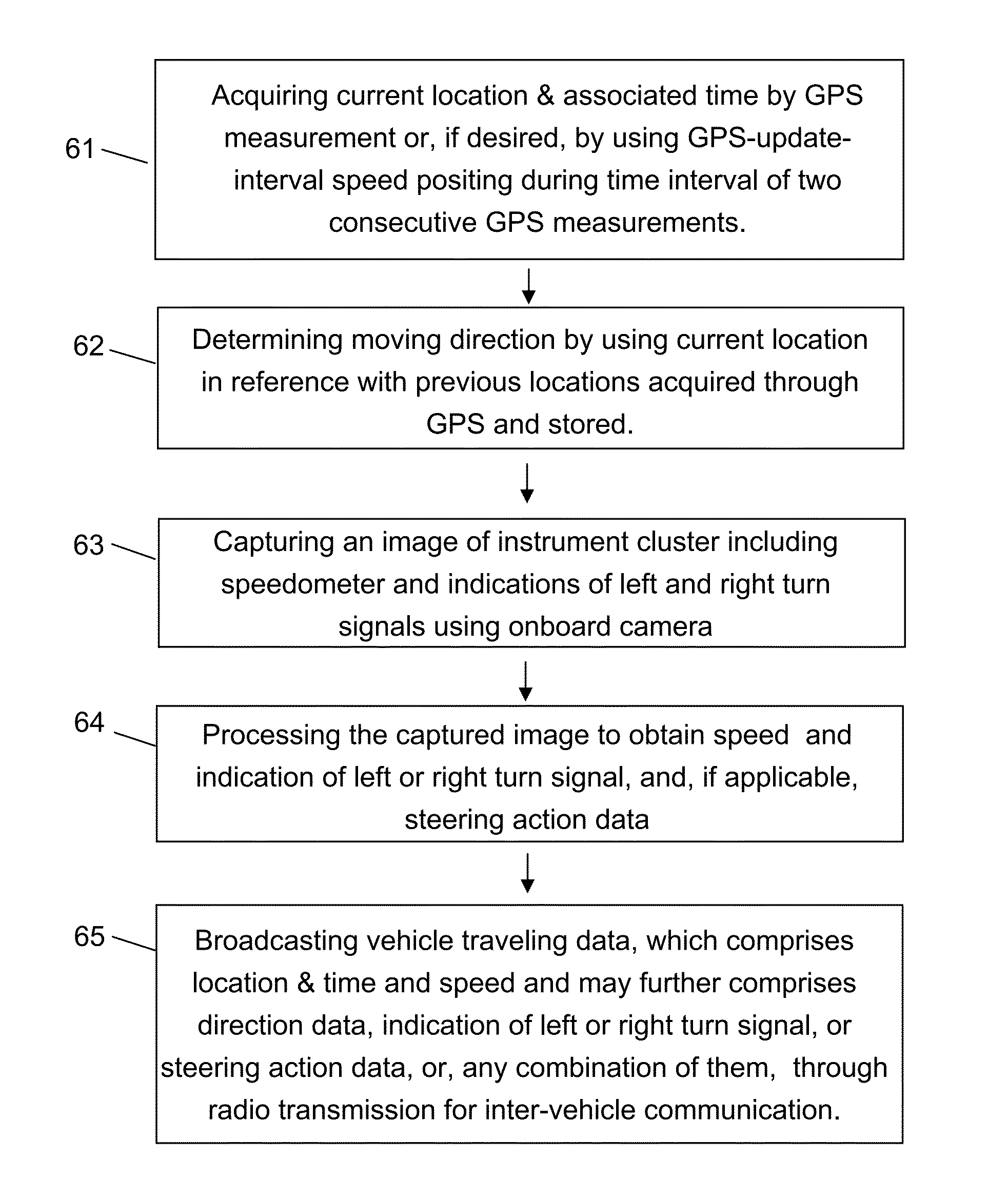
Methods for road safety enhancement using mobile communication device
InactiveUS20130082874A1Sufficiently accurateQuick responseRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDetection of traffic movementKinematic couplingSimulation
Methods for road safety enhancement use mobile communication device (MCD) onboard vehicle to share traveling data through inter-vehicle communication broadcasting, perform road hazard warning, enhance road navigation, and provide autonomous road assistance. The methods have a variety of vehicle status data, such as moving data, steering data, or indicator data, obtained through GPS or image capturing and recognition of instrument cluster of vehicle. The image capturing and recognition allows to get speed data from indication of speedometer, indication of left or right turn signal, steering action data corresponding to steering wheel rotation, and light-on indication of system status indicators. To facilitate that, the MCD may be placed in front of steering wheel, and, if applicable, also in coupling with movement of steering wheel. The MCD may perform relative positioning map-matching lane correlation and GPS-update-interval speed positioning to improve data quality regarding vehicle moving status.
Owner:ZHANG WEI
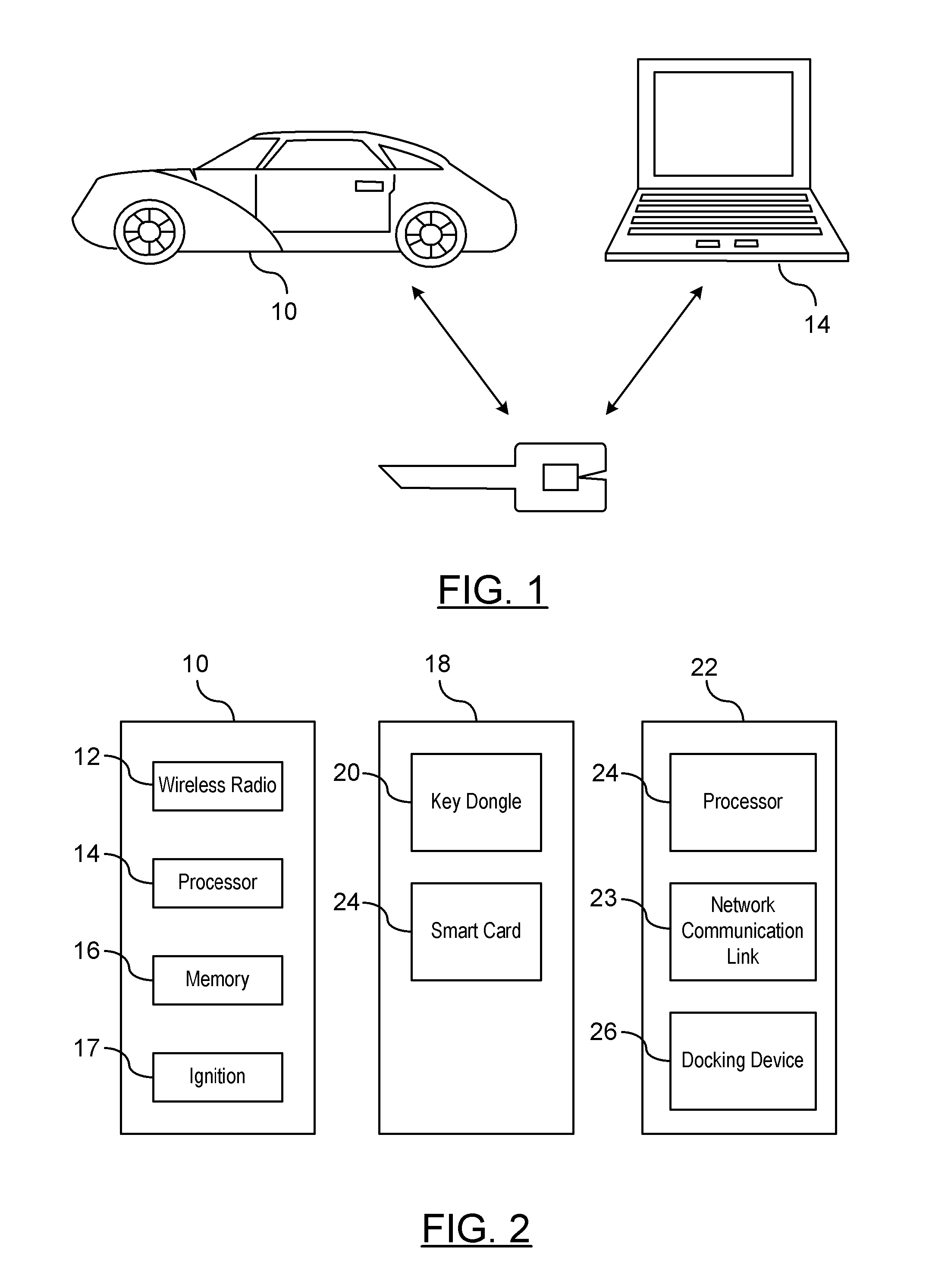
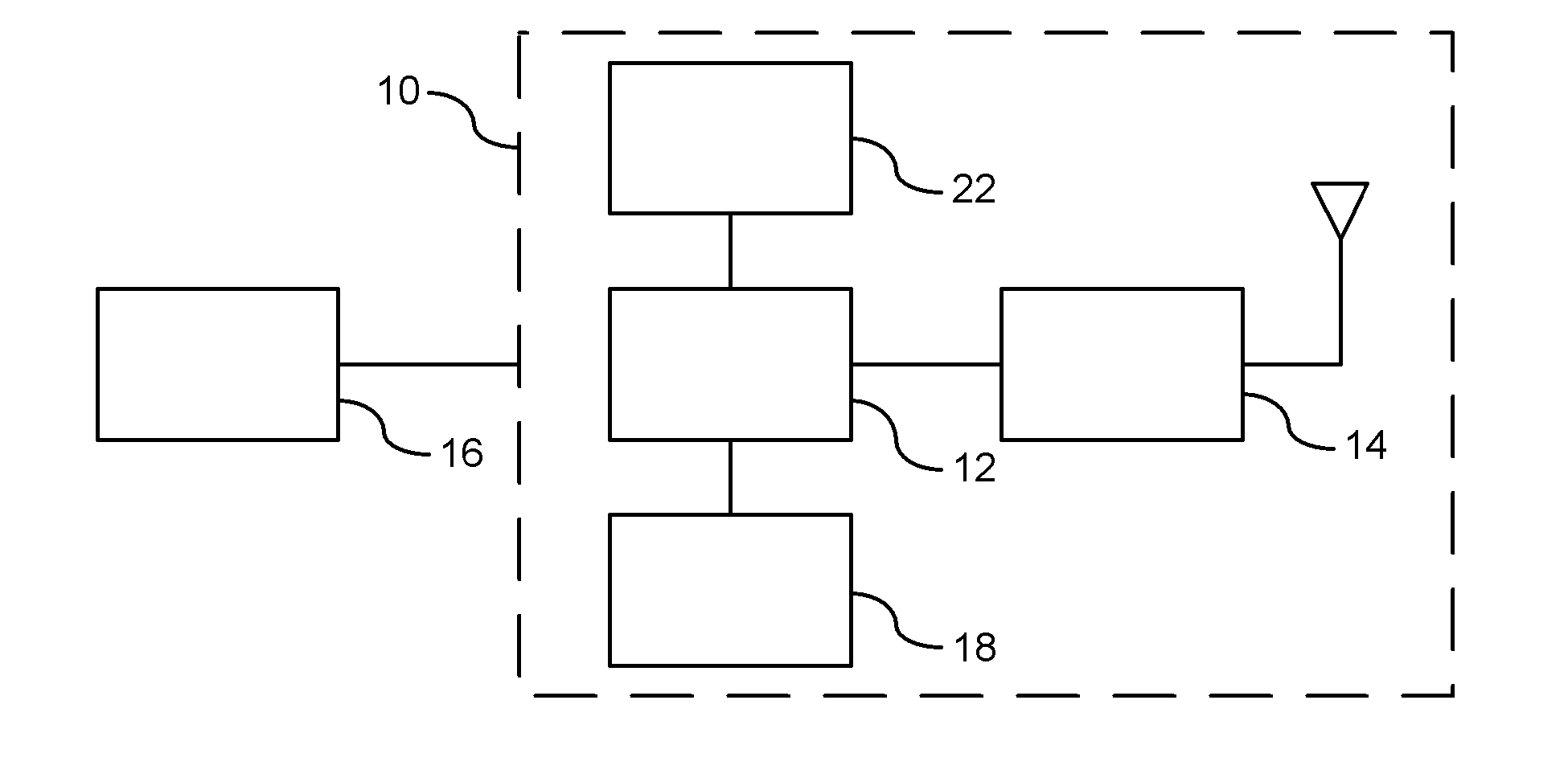
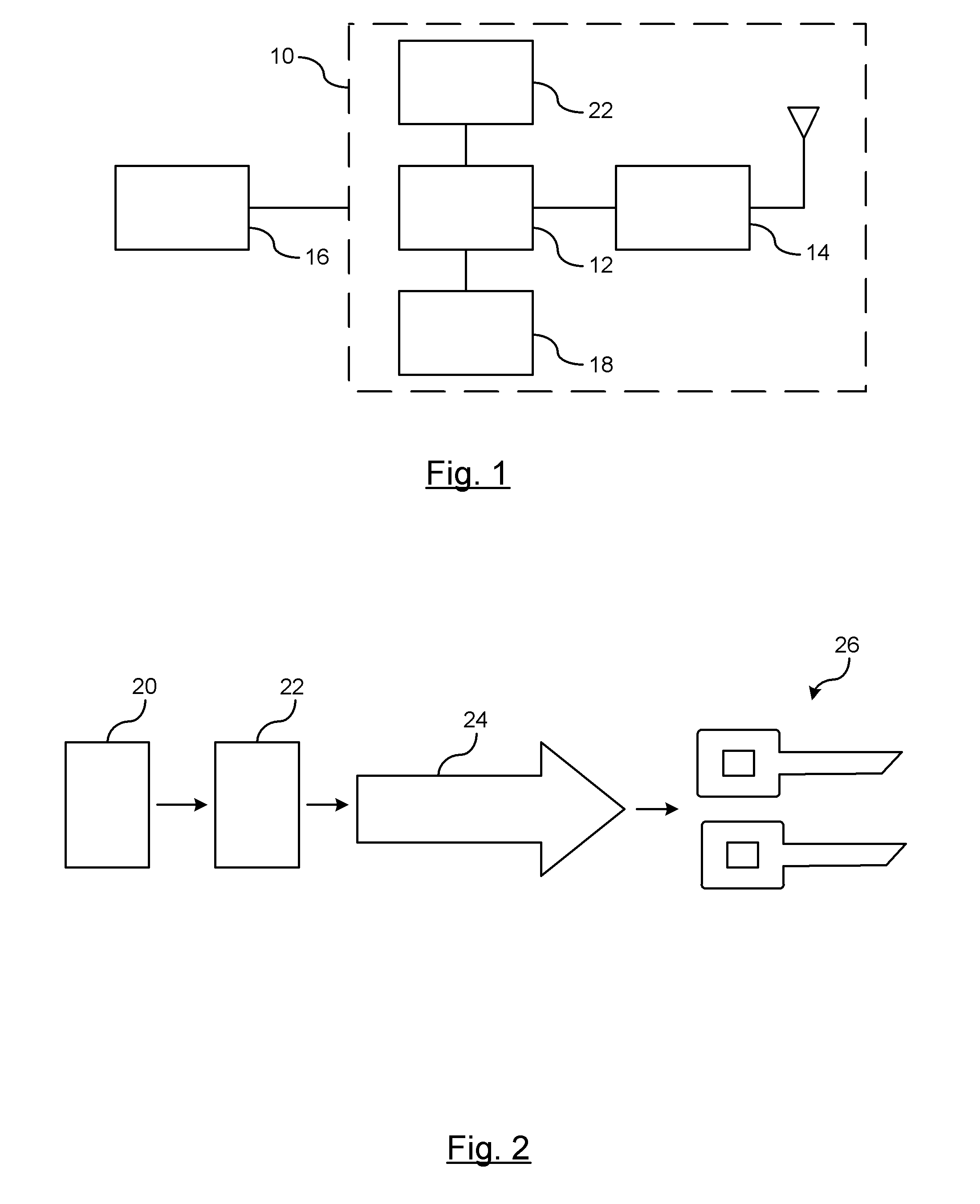
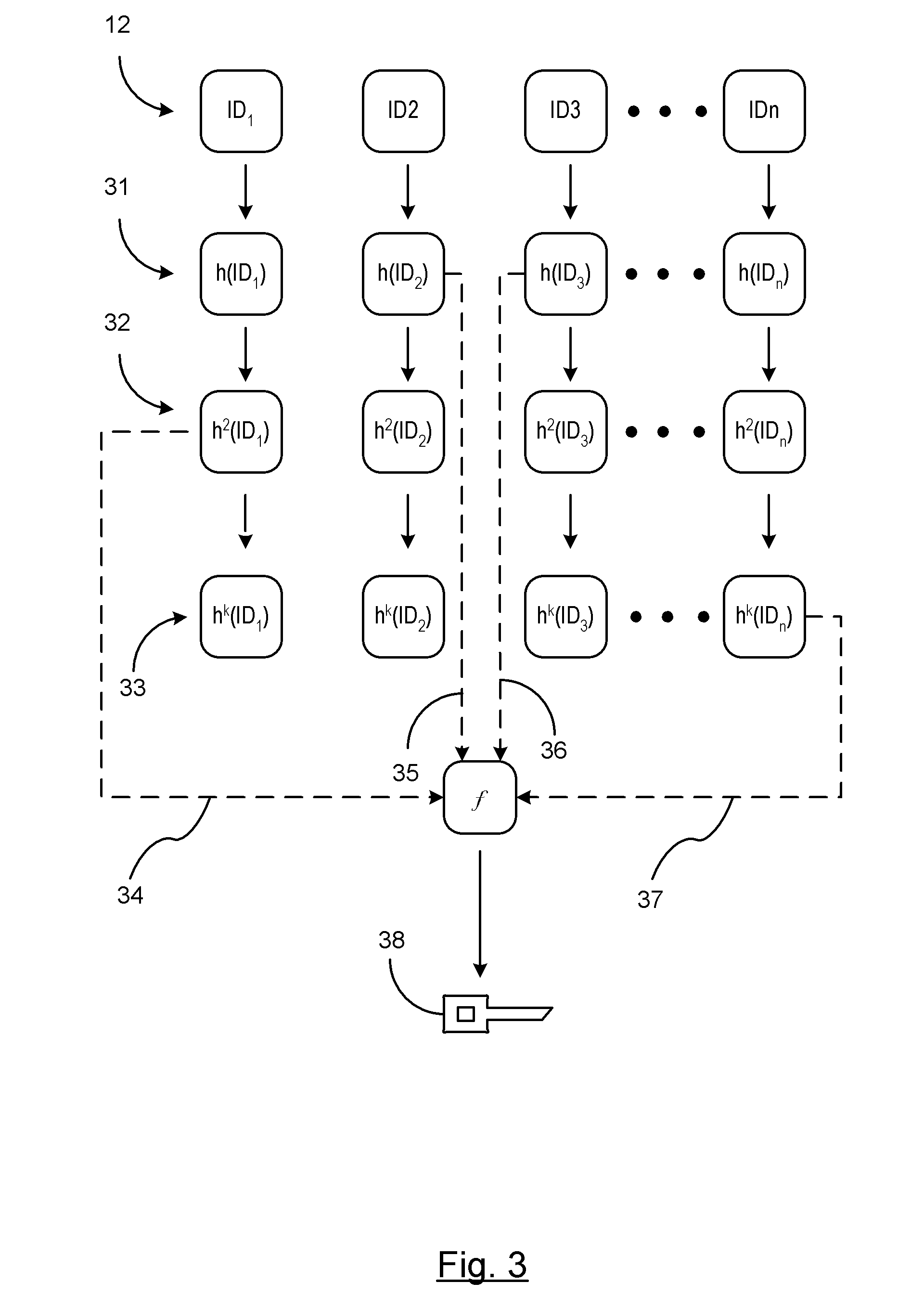
On-Demand Secure Key Generation
ActiveUS20120155636A1Secret communicationSecuring communicationComputer hardwareCommunications system
A method is provided for generating on-demand cryptographic keys in a vehicle-to-vehicle communication system. At least one unique identifier is obtained relating to a user of the vehicle. The host vehicle generates cryptographic keys for encrypting, decrypting, and authenticating secured messages between the host vehicle and at least one remote vehicle in the vehicle-to-vehicle communication system. The cryptographic keys are generated as a function of the at least one unique identifier. A respective cryptographic key used to decrypt or encrypt messages communicated between the host vehicle and the at least one remote entity is temporarily stored in a memory device of the host vehicle. The host vehicle utilizes the respective cryptographic key to decrypt or encrypt a secure message transmitted between the host vehicle and the remote vehicle. The respective cryptographic key temporarily stored in the memory device of the host vehicle is deleted after the vehicle-to-vehicle communications of the host vehicle is disabled.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Navigation apparatus and intersection guidance method
InactiveUS20050209776A1Instruments for road network navigationArrangements for variable traffic instructionsEngineeringInter vehicle communication
A navigation apparatus and an intersection guidance method are provided for guiding a user through a guidance intersection located on a guidance route in an easy-to-understand manner even when no facility serving as a landmark is located near the guidance intersection, or when facility located near the guidance intersection is difficult to observe. When a user's vehicle is approaching within a specified distance of a guidance intersection on a guidance route, a navigation apparatus mounted in the vehicle obtains information about a traveling position and a traveling direction of another vehicle located near the user's vehicle and characteristics information about the other vehicle through inter-vehicle communication between the vehicles. Then, based on the information, the apparatus provides a guidance message indicating a travel direction of the user's vehicle in relation to the information about the other vehicle. Accordingly, the use of the other vehicle as a landmark can show the user the direction of travel in which the user's vehicle is to travel at the guidance intersection in an easy-to-understand manner.
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
Inter-vehicle communication apparatus and method with restrictions on size of network
InactiveUS7272357B2Avoid interferenceRestrict formArrangements for variable traffic instructionsAssess restrictionArea networkInter vehicle communication
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
Display apparatus and display method
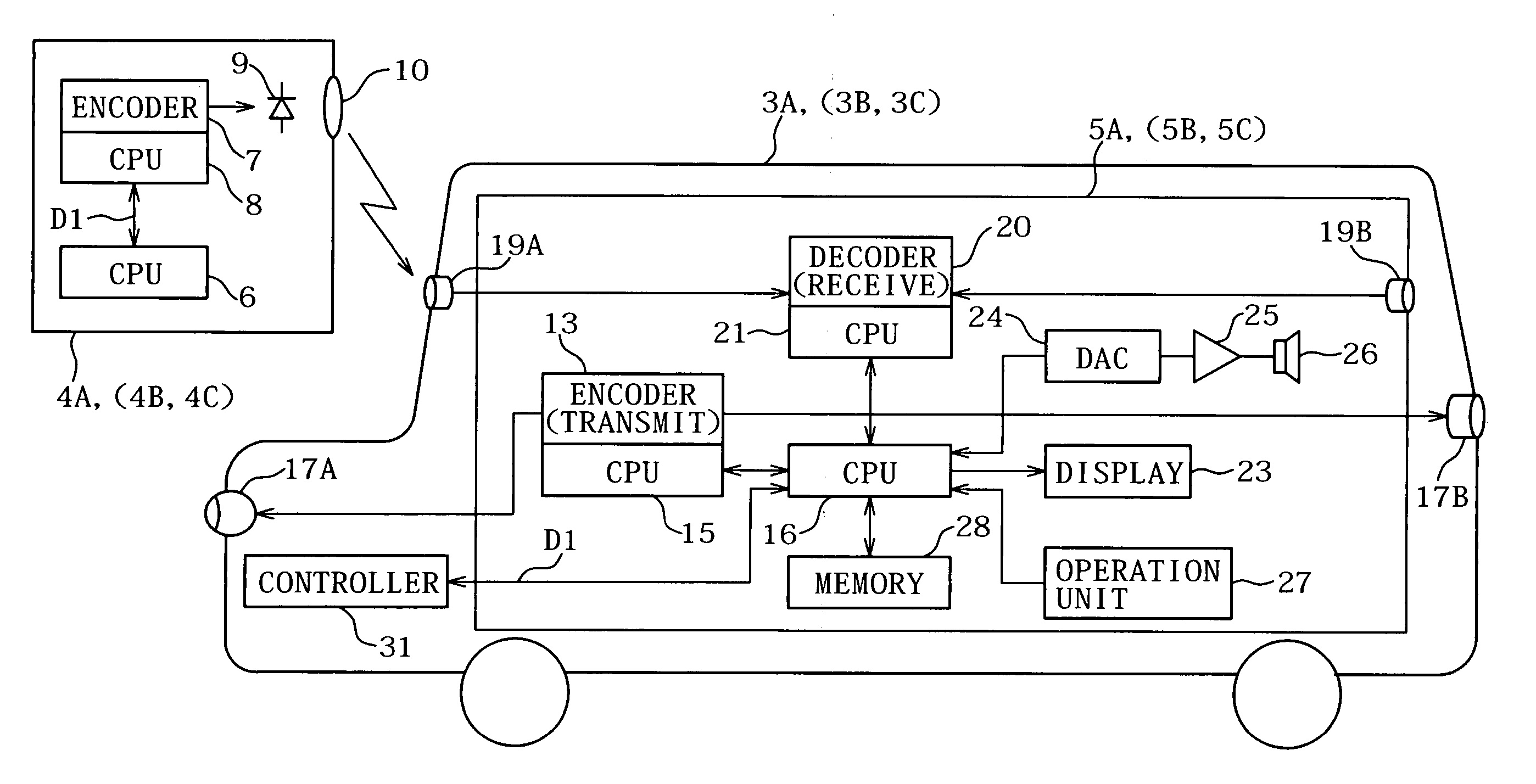
A DSRC in-vehicle communication apparatus (1) operates as a base station based on the DSRC communication standard when a base station function section (3) is selected by an operation function selection section (2), and operates as a mobile station based on the DSRC communication standard when a mobile station function section (4) is selected. After a plurality of vehicles equipped with a DSRC in-vehicle communication apparatus (1) have been disposed, an inter-vehicle communication system is constructed by the function of each DSRC in-vehicle communication apparatus (1) being selected, and vehicles whose function has been selected as base station or mobile station performing DSRC communication.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Inter-vehicle communication method and device
ActiveUS20050030202A1Reduce in quantityAnalogue computers for vehiclesArrangements for variable traffic instructionsInter vehicle communicationReal-time computing
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
Vehicle interference prevention device
InactiveUS20010044697A1Instruments for road network navigationAnti-collision systemsEngineeringInter vehicle communication
There is provided a vehicle interference prevention device that, by computing a range of possible locations of a vehicle taking into consideration the time at which the location of the vehicle is measured, can safely predict the location of the vehicle, even with minimal frequency of radio contact, and prevent interference among unmanned vehicles or manned vehicles over the entirety of large work site, An unmanned vehicle uses the latest position data for a manned vehicle acquired (received) via an inter-vehicle communication device to determine a position (position at a certain point in time) as the basis for computing a circle having this position as its center and having a radius equal to the distance traveled at maximum speed from this point to a predetermined future point in time, and designates the area within this circle on a prearranged travel route as a range of possible locations for the manned vehicle. The unmanned vehicle then decides whether its own vehicle position interferes with this circle.
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
System and method for controlling vehicular traffic flow
InactiveUS20070135989A1Minimizes distributionImprove securityAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficModem deviceControl communications
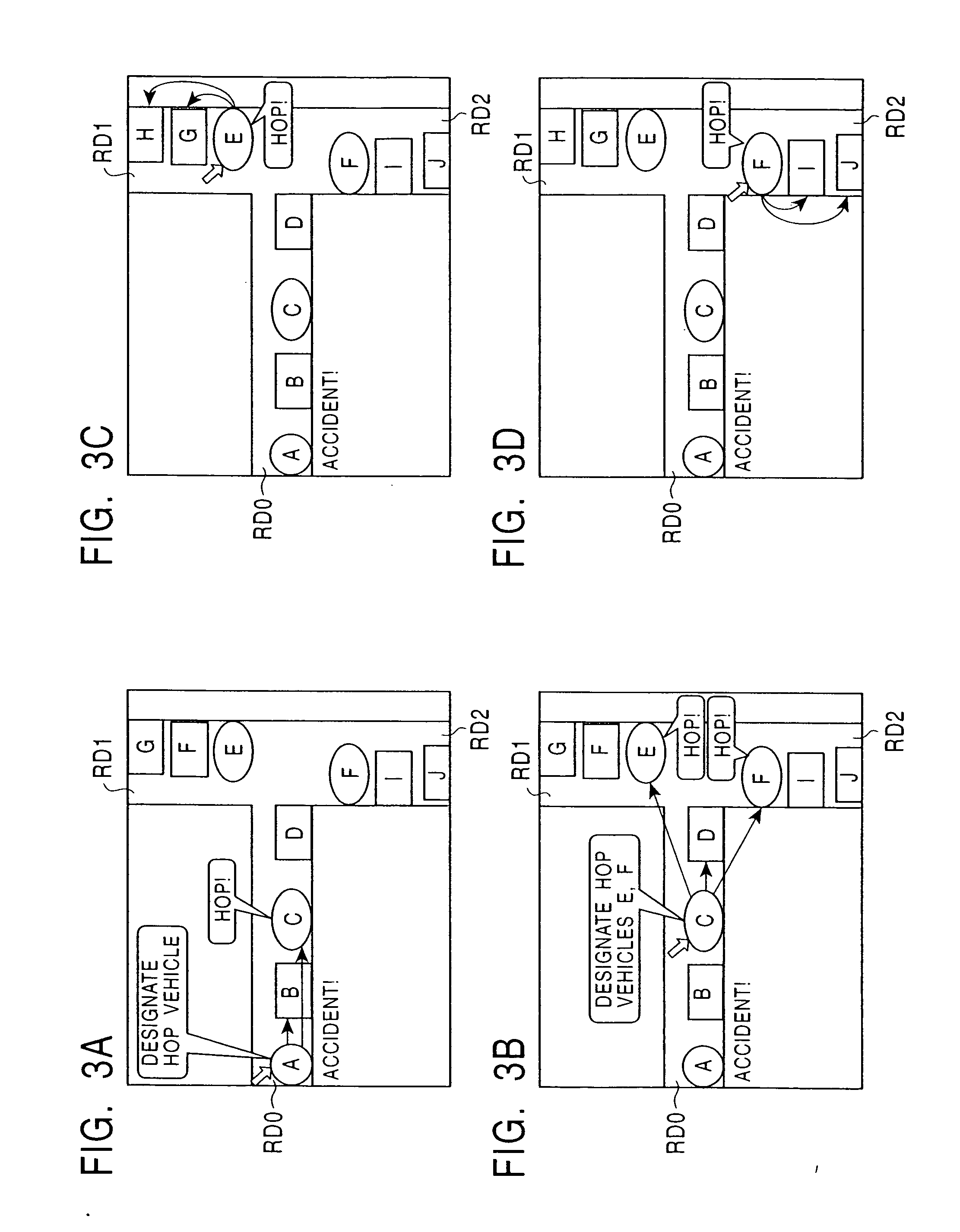
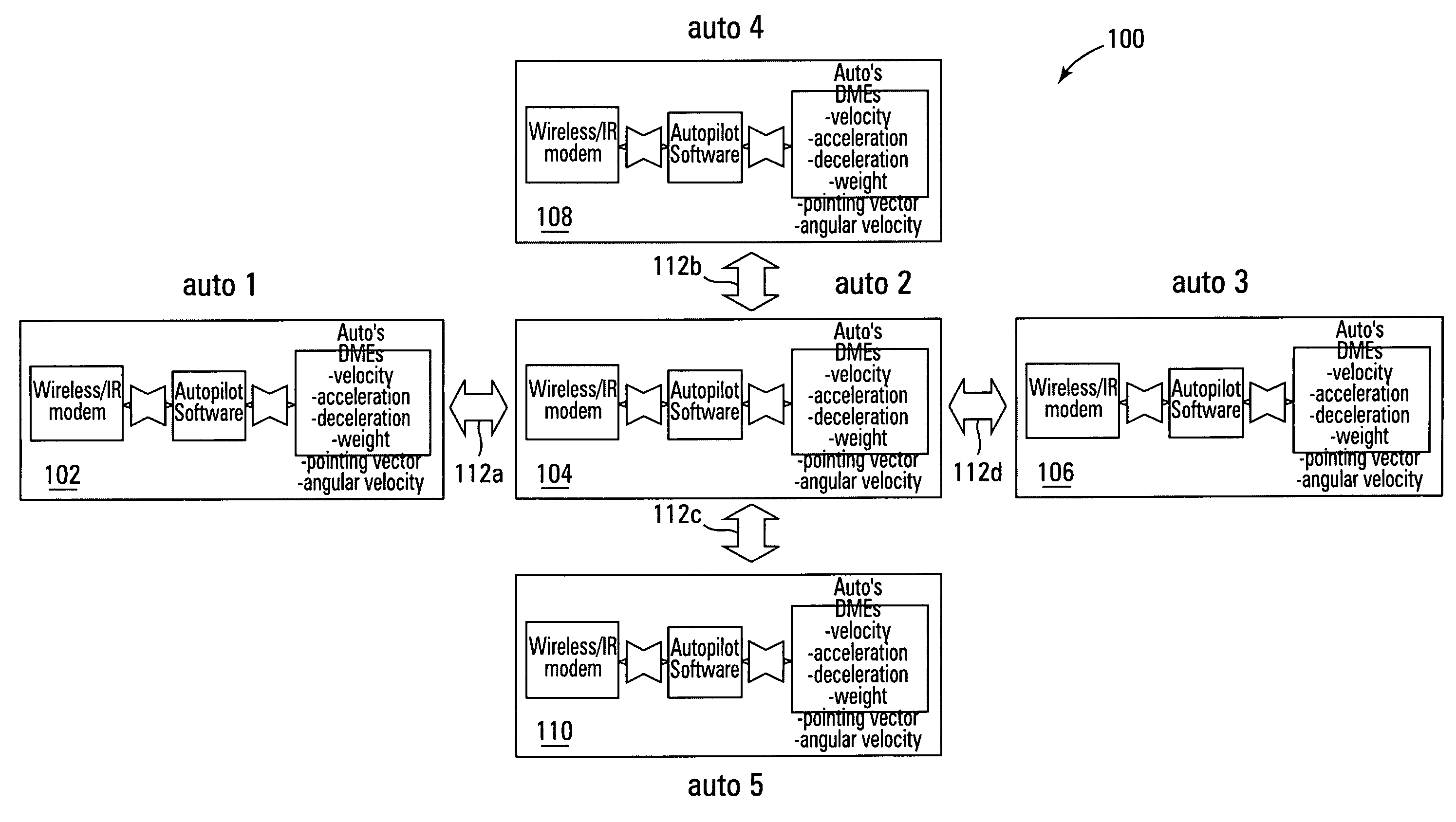
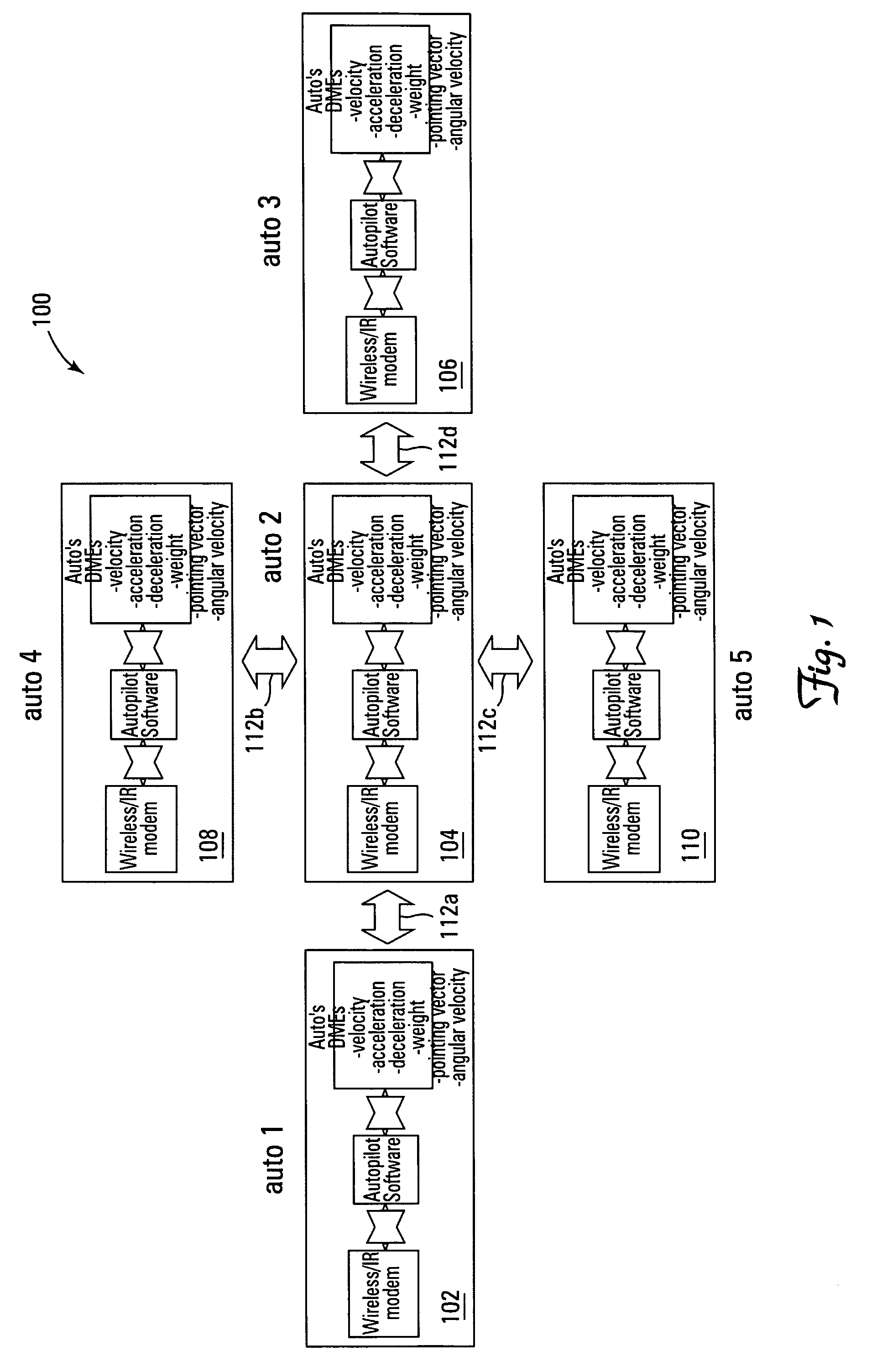
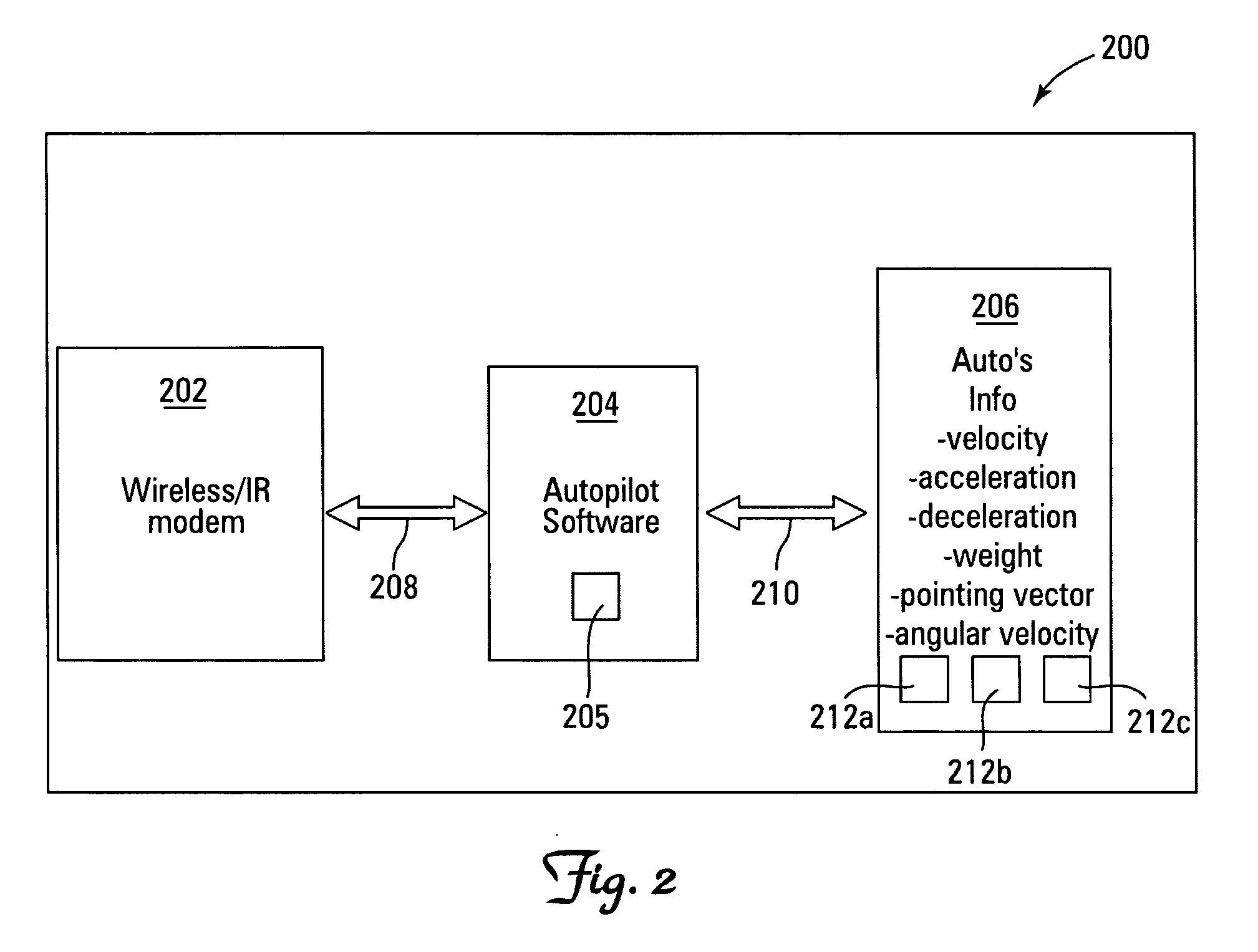
A system and method for controlling vehicular traffic flow is disclosed, which creates a communication system between vehicles that allows the vehicles to share their respective velocities and acceleration or deceleration rates. Thus, each vehicle within the system can respond immediately to any acceleration or deceleration rate changes of the surrounding vehicles (e.g., the vehicle directly in front, directly in back, and in the adjacent lane). Essentially, the system functions similar to a wireless vehicular train, with a queue of cars linked together by a stiff, wireless communications “chain”. Notably, the term “vehicle” is not limited only to land-based vehicles (e.g., motor vehicles), and the system can include airborne vehicles (e.g., multiple aircraft flying in close formation, military aircraft flying in drone formation, etc.). For example, a system for controlling vehicular traffic flow is disclosed, which includes in each vehicle of a plurality of vehicles, a wireless or infrared (IR) modem for inter-vehicular communications, a range finder for determining the distance and closing rate between vehicles, a processing unit for retrieving vehicular operational data (e.g., velocity, angular velocity, acceleration rate, deceleration rate, braking pressure, weight, pointing vector, etc.) and executing flow control system software instructions, and a vehicular flow control communications protocol that enables the communication of various flow control parameters between vehicles via the wireless or IR modem. Thus, each vehicle in the system “knows” what the surrounding vehicles are doing and can respond immediately to changes in the traffic flow. As such, the system minimizes the distribution of vehicles' velocities in the queue, and increases traffic throughput and safety as a result.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
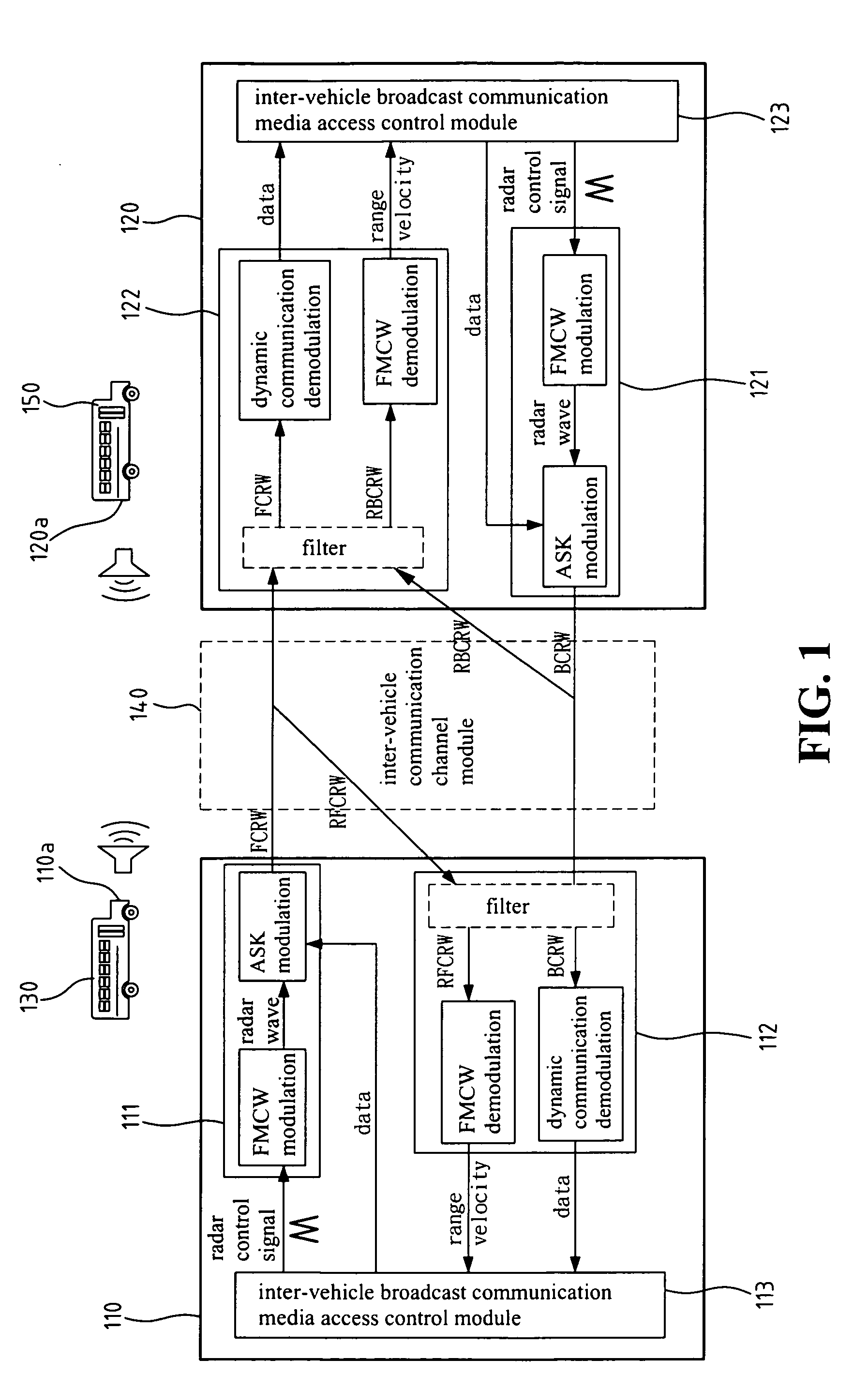
Inter-vehicle communication and warning apparatus
InactiveUS7315239B2Easy to transportInterference minimizationDigital data processing detailsDetection of traffic movementNetwork packetRadar
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
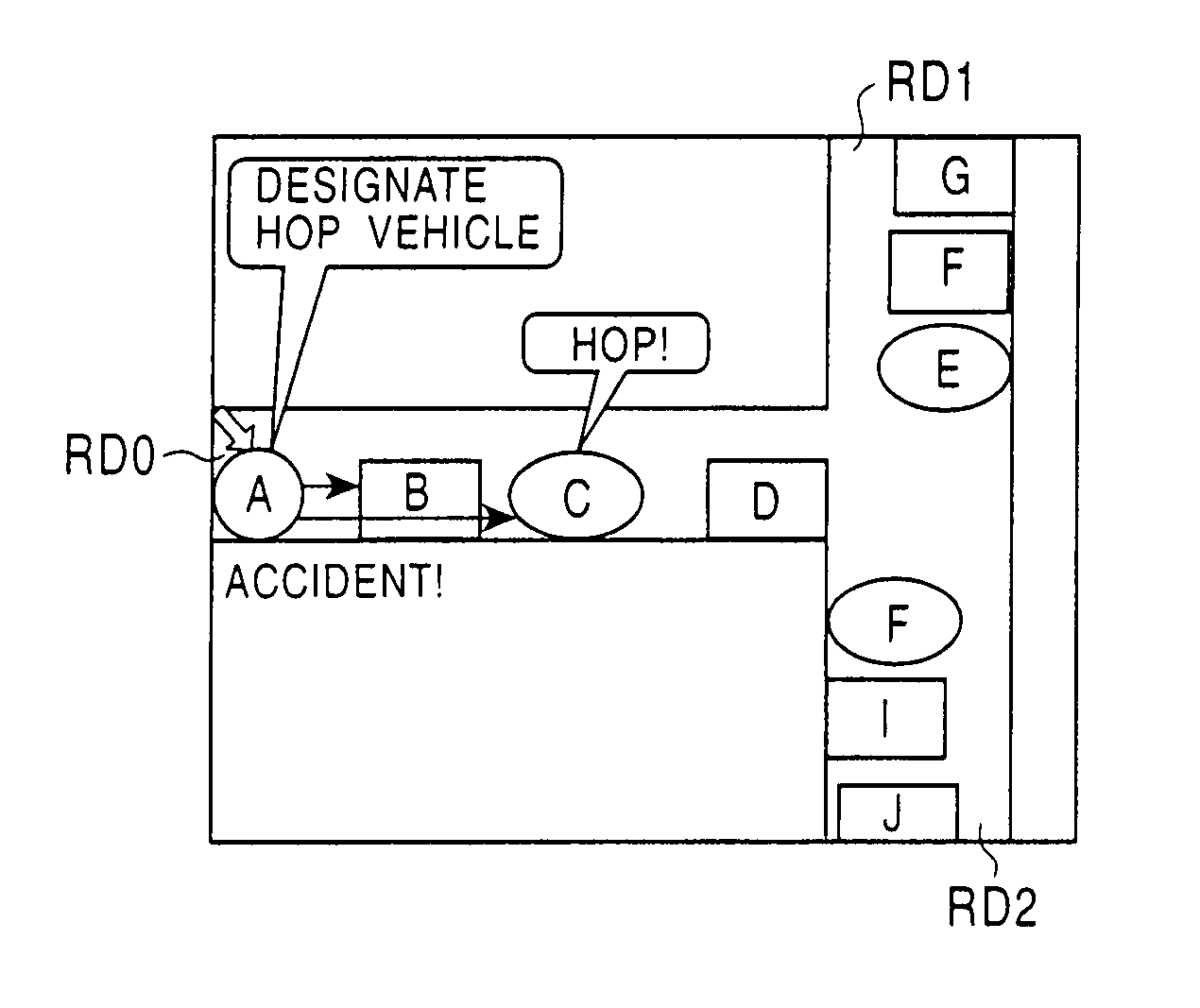
Lane changing and overtaking assisting method and system based on inter-vehicle communication
InactiveCN103359013AGood behavior for changing lanes and overtakingImprove scalabilityElectric/fluid circuitInformation processingInformation support
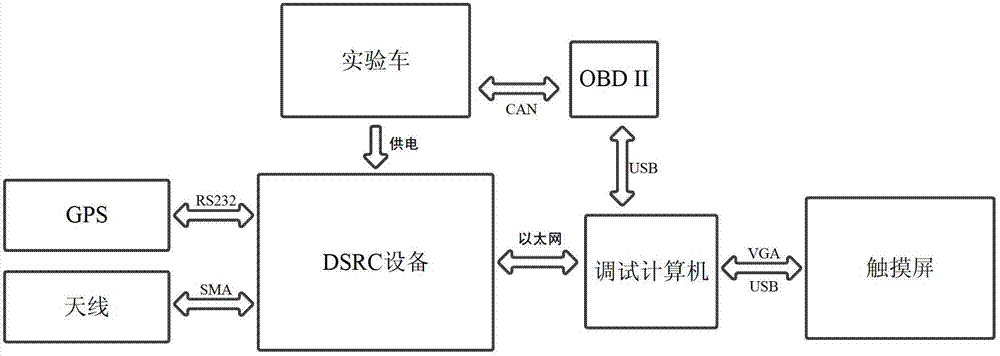
Disclosed is a lane changing and overtaking assisting method and system based on inter-vehicle communication. The method is characterized in that inter-vehicle communication is built among different vehicles, information support is provided for lane changing and overtaking is provided for drivers of the vehicles through information interaction, the inter-vehicle communication is achieved through short-range communication protocols, when a driver triggers a lane changing and overtaking event, a system identify and process the event and transmits the same to a specified vehicle, and the vehicle received the event restores the event and displays the same as prompt information which can be identified by the driver of the specific vehicle. The system comprises an event identifying module, an event processing module, a wireless communication transceiving module, an event restoring module, a user interface module, and a hardware system formed by a wireless communication device, a positioning device, an antenna, an information processing system and a touch screen. By the method and the system which can be normally used under conditions of bad weather and bad vision, driving safety can be increased effectively.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Inter vehicle communication system
InactiveUS20010034768A1Instruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsEmail addressInter-process communication
A method and network for transmitting a message from a sender to a recipient wherein the sender has no previous knowledge of the recipient's address. A network is provided for registering a user with an internet service by providing correlating data on the user's e-mail address and vehicle license plate number and other vehicle identifying information. A sender observing a recipient's can send a message to the recipient by logging onto the service and sending a message including the license plate number of the vehicle or other vehicle identifying information. The service will forward the message to the recipient by looking up the vehicle information and providing the corresponding e-mail address to the message and sending to the recipient.
Owner:BUMP NETWORK
Inter-vehicle communication feature awareness and diagnosis system
InactiveUS20100019891A1Environmental AwarenessAssesses an uncertainty affecting an accuracy of the sensor informationAnti-collision systemsOptical signallingInformation accuracyInter vehicle communication
A method is provided for sharing data between a host vehicle and remote entity in an inter-vehicle communication system. Wireless messages are transmitted between the remote entity and the host vehicle. The wireless messages include data relating to sensor information used to enhance environmental awareness of surrounding conditions of the host vehicle. A received wireless message includes sensor information transmitted from the remote entity to the host vehicle. The wireless message further includes an uncertainty indicator relating to the remote vehicle's assessment of an uncertainty of the sensor information transmitted by the remote vehicle. The uncertainty affecting an accuracy of the sensor information is assessed for determining a degree for which the sensor information is to be used in evaluating environmental awareness conditions affecting the host vehicle. Environmental awareness features of the host vehicle are selectively activated in response to assessing the uncertainty affecting the accuracy of sensor information.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Resource allocation method and road side unit
ActiveCN105657842AReduce the frequency of assignmentsQuality improvementParticular environment based servicesVehicle-to-vehicle communicationThe InternetCommunication link
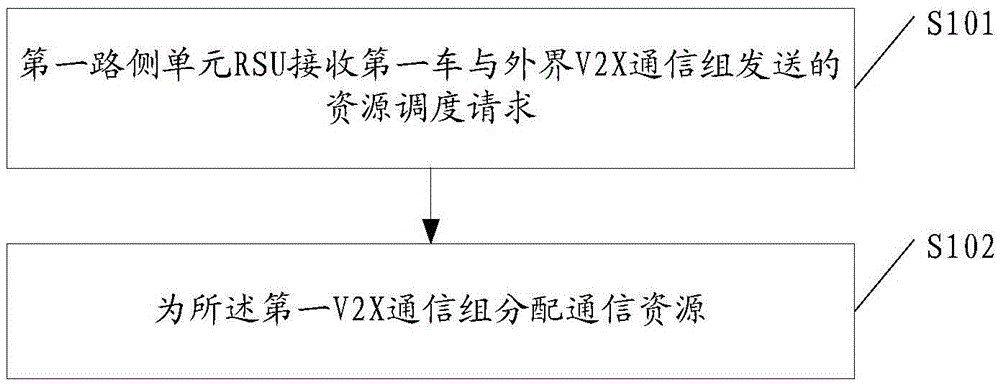
Embodiments of the invention disclose a resource allocation method. The resource allocation method comprises: a first road side unit (RSU) receives a resource scheduling request transmitted by a first vehicle-to-X (V2X) communication group; a communication resource is allocated to the first V2X communication group, wherein the driving directions of vehicles included in the first V2X communication group are same. The embodiments of the invention further disclose a road side unit. By adopting the resource allocation method and the road side unit, the reasonability of resource allocation can be improved, communication links among vehicles and chancel quality are more stable, and performances of internet of vehicles are fully utilized.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Optical communication equipment and vehicle control method
InactiveUS20050137782A1Simple configurationReliable supplyAnalogue computers for vehiclesNon-electrical signal transmission systemsRoad traffic controlEngineering
The present invention relates to optical communication equipment and a vehicle control method, and in particular, the present invention is applied to a system utilizing inter-vehicle communication equipment via optical communication to notify information of traffic regulation utilizing optical communication according to an inter-vehicle communication system so that traveling of a vehicle can be controlled easily and reliably even in such a complicated place where a plurality of roads intersect as in urban cities or the like.
Owner:SONY CORP
Inter-vehicle communication device
ActiveUS20160232791A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce congestionWireless commuication servicesNetwork traffic/resource managementData transmissionInter vehicle communication
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method for handling case of detecting unauthorized frame transmitted over onboard network
ActiveUS20160373449A1Prevent effectEliminate the effects ofParticular environment based servicesVehicle-to-vehicle communicationAnomaly detectionSecure state
An anomaly handling method that suitably handles a case where the possibility of a vehicle being unauthorizedly controlled so as to suppress the effects thereof is provided. In an anomaly handling method used in one or a plurality of electronic control units installed in one vehicle, an inter-vehicle communication message transmitted from a device installed in the other vehicle is received as an anomaly detection notification, the anomaly detection notification being issued when an unauthorized frame is detected on an onboard network installed in another vehicle, and an anomaly handling processing is selected from a plurality of predetermined anomaly handling processing in accordance with the received content to transition to a safe state for example, and the selected anomaly handling processing is executed.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Communication apparatus and method for performing inter-vehicular communication
ActiveUS20150156662A1Blocking in networkSatisfies requirementError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsChannel state informationInter vehicle communication
A communication apparatus for inter-vehicular communication according to the present invention includes: a network state estimating unit configured to estimate network state information indicating a current network state based on driving information and channel state information of neighboring vehicles; a network access controller configured to control whether to transmit a message based on the network state information; a transmission scheduler configured to control a transmission time point of the message based on the network state information; and a transmission buffer unit configured to delay transmission of the message according to the control of the transmission time point of the transmission scheduler.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOBIS CO LTD
Cooperative autonomous driving for traffic congestion avoidance
ActiveUS20190051159A1Shorten speedAutonomous decision making processDetection of traffic movementTraffic congestionProgram planning
Systems and methods for traffic congestion avoidance may use cooperative autonomous driving based on vehicle-to-vehicle communication to resolve deadlock conditions. The method may include automatically detecting, by a given autonomous vehicle, that the given vehicle is deadlocked, initiating, by the given vehicle, formation of a coordination group including the given vehicle, a front vehicle traveling in the same driving lane as the given vehicle, and an assistant autonomous vehicle traveling in a lane adjacent to the lane in which the given vehicle and the front vehicle are traveling, and sending, by the given vehicle using vehicle-to-vehicle communication, a cooperative driving task request to initiate actions by the autonomous vehicles in the coordination group to resolve the deadlock condition. The actions may include modifying a driving plan of an autonomous vehicle in the coordination group and initiating a speed negotiation with an autonomous vehicle in the coordination group.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Control device and control method for vehicle
ActiveUS20130131949A1Appropriate follow-up runningAppropriate runningVehicle fittingsDigital data processing detailsEngineeringInter vehicle communication
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
On-demand secure key generation in a vehicle-to-vehicle communication network
A method is provided for generating on-demand cryptographic keys in a vehicle-to-vehicle communication system. At least one unique identifier is obtained relating to a user of the vehicle. The host vehicle generates cryptographic keys for encrypting, decrypting, and authenticating secured messages between the host vehicle and at least one remote vehicle in the vehicle-to-vehicle communication system. The cryptographic keys are generated as a function of the at least one unique identifier. A respective cryptographic key used to decrypt or encrypt messages communicated between the host vehicle and the at least one remote entity is temporarily stored in a memory device of the host vehicle. The host vehicle utilizes the respective cryptographic key to decrypt or encrypt a secure message transmitted between the host vehicle and the remote vehicle. The respective cryptographic key temporarily stored in the memory device of the host vehicle is deleted after the vehicle-to-vehicle communications of the host vehicle is disabled.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com