Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1433results about How to "Reduce bandwidth requirements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
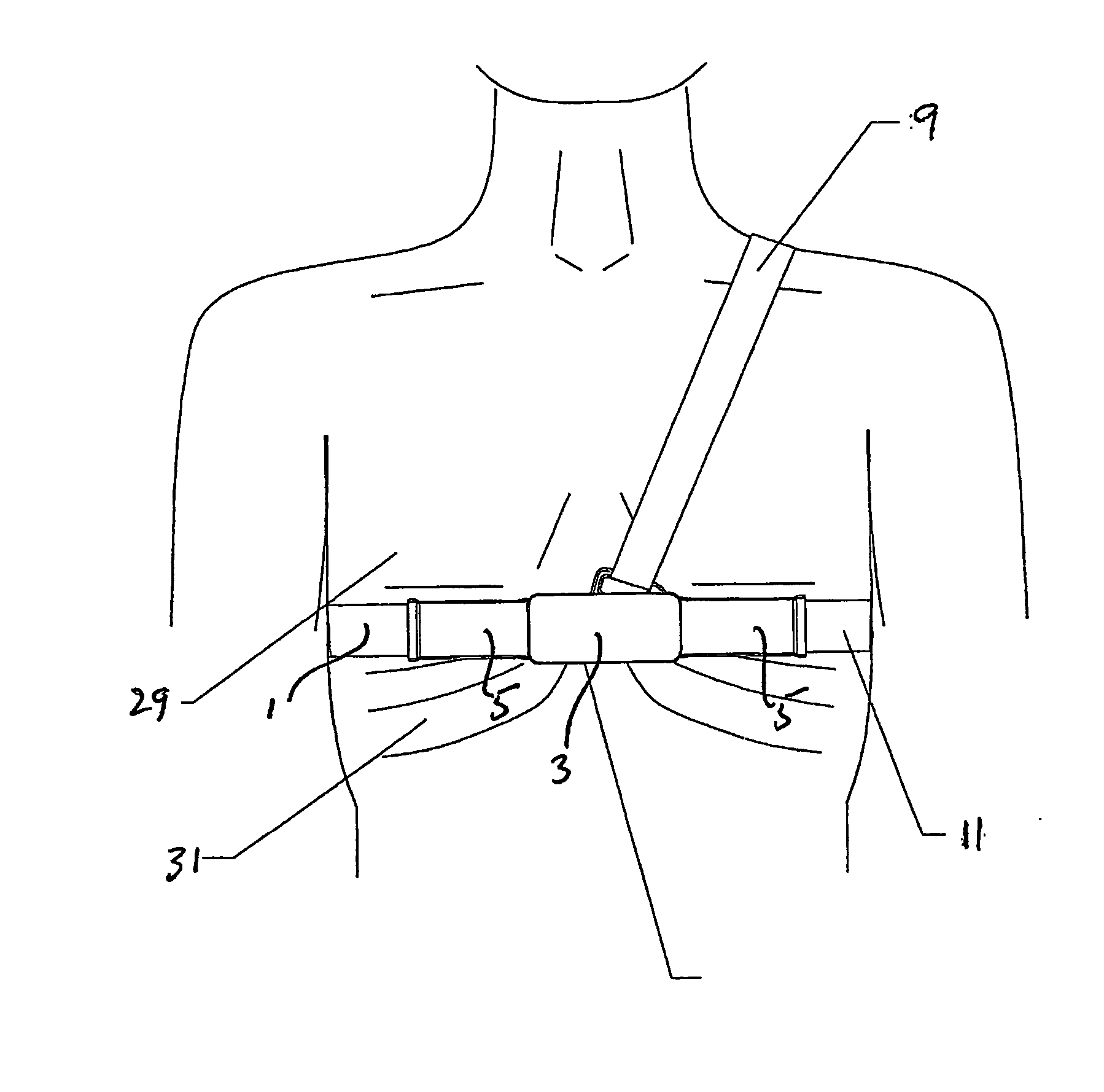
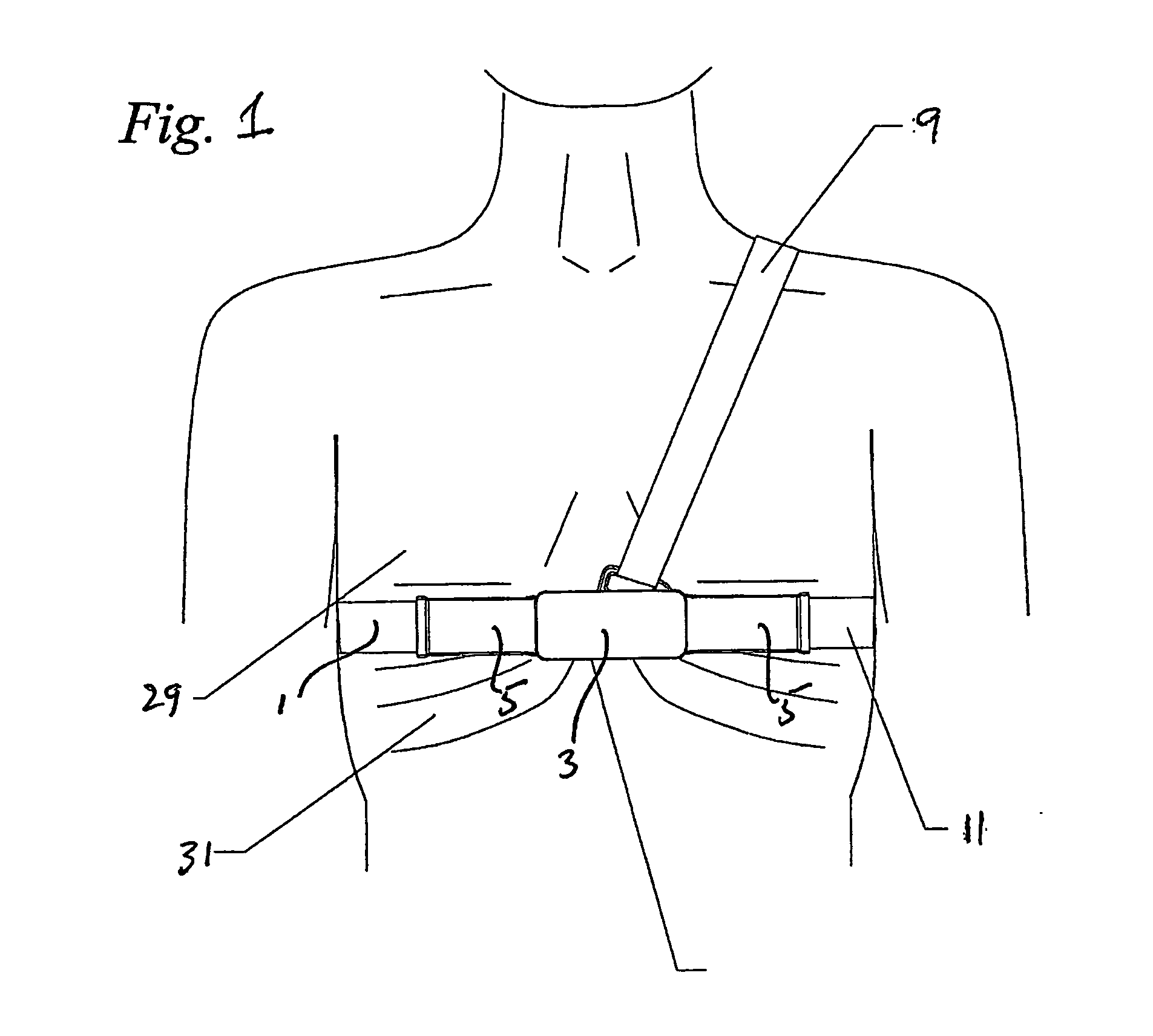
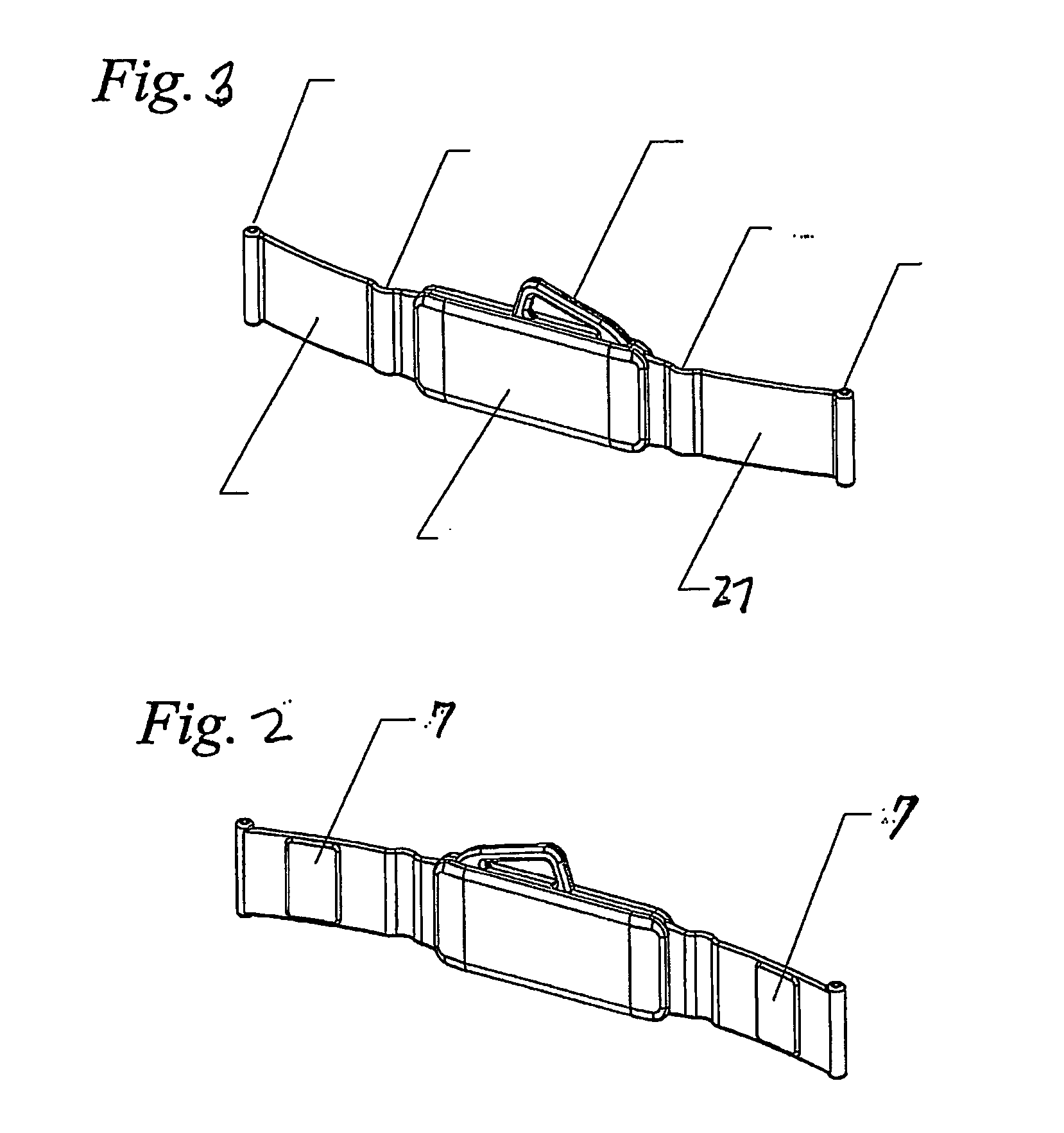
Respiration Motion Detection and Health State Assesment System
InactiveUS20070293781A1Guaranteed normal transmissionReduce bandwidth requirementsDiagnostic signal processingHealth-index calculationBody shapeAccelerometer
A wearable platform embodied in a belt or flattened patch-like central body shaped to conform to the abdomen provides physiological monitoring of soldiers during field operations or trauma victims at accident sites and makes health state assessments. The platform includes sensors for heart rate, body motion, respiration rate and intensity, and temperature and further contains a microprocessor and short range transmitter. The respiration sensor uses conductive ink in a novel manner. A small square of the ink is coated on an arched structure so that flexing of the arch either to increase or decrease its radius of curvature modifies the resistance of the structure. This is utilized to set the unstressed resistance of the arch structure and to allow a greater range of resistance values capable of measuring distortions in different deformations of the arch. The respiration sensor supplements the motion information provided by an accelerometer sensor.
Owner:SIMS NATHANIEL +4
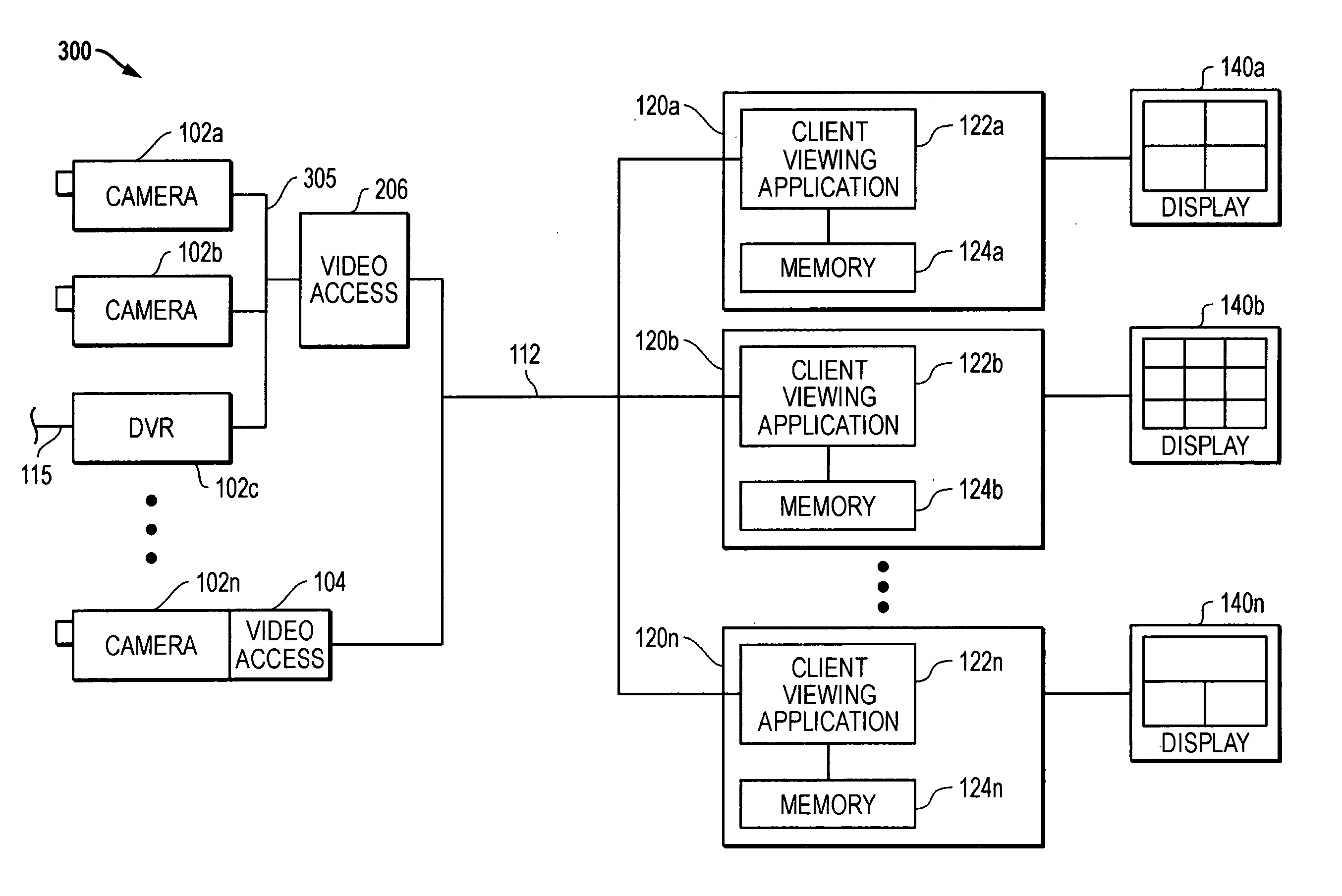
Systems and methods for providing high-resolution regions-of-interest
InactiveUS20070024706A1Less video compressionEnhanced color formatColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsRegion of interestHigh resolution
Systems and methods for providing high-quality region of interest (HQ-ROI) viewing within an overall scene by enabling one or more HQ-ROIs to be viewed in a controllable fashion, as higher quality ‘windows-within-a-window’ of regions (spatial subsets) of a scene.
Owner:UTC FIRE & SECURITY AMERICAS CORPORATION INC
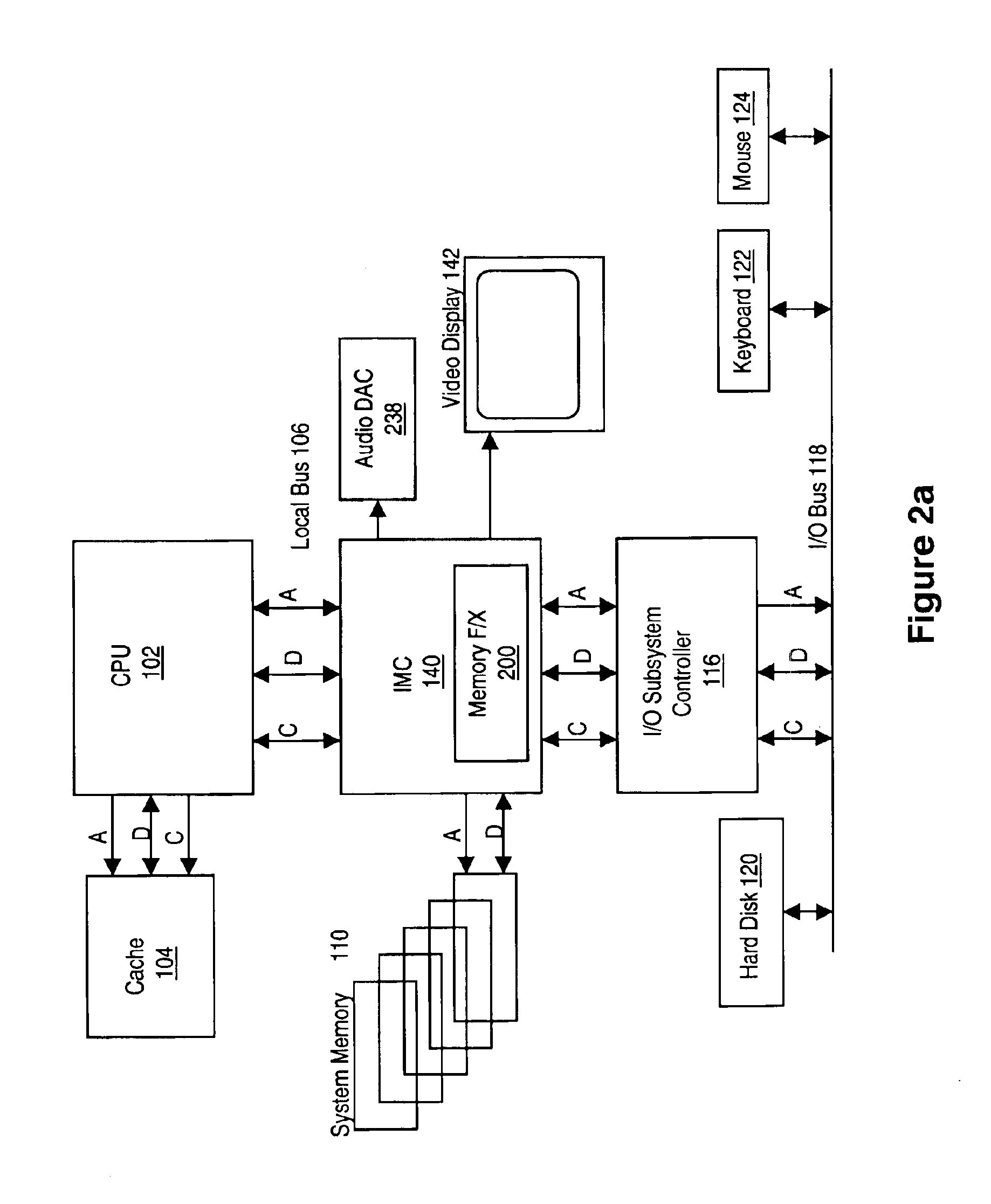
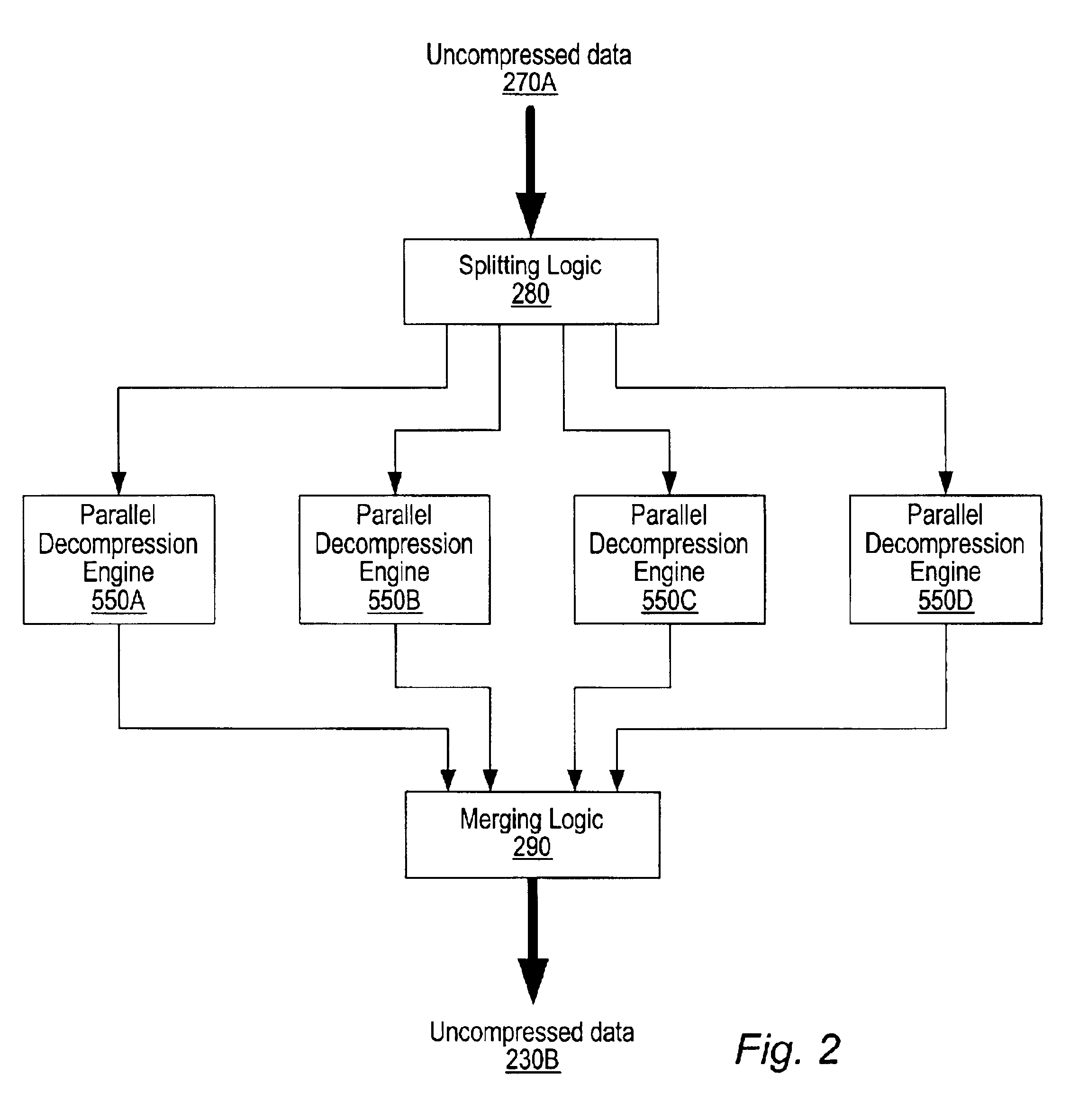
Memory module including scalable embedded parallel data compression and decompression engines
InactiveUS6879266B1Low costSmall data storage requirementMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTParallel compressionParallel computing
An memory module including parallel data compression and decompression engines for improved performance. The memory module includes MemoryF / X Technology. To improve latency and reduce performance degradations normally associated with compression and decompression techniques, the MemoryF / X Technology encompasses multiple novel techniques such as: 1) parallel lossless compression / decompression; 2) selectable compression modes such as lossless, lossy or no compression; 3) priority compression mode; 4) data cache techniques; 5) variable compression block sizes; 6) compression reordering; and 7) unique address translation, attribute, and address caches. The parallel compression and decompression algorithm allows high-speed parallel compression and high-speed parallel decompression operation. The memory module-integrated data compression and decompression capabilities remove system bottlenecks and increase performance. This allows lower cost systems due to smaller data storage, reduced bandwidth requirements, reduced power and noise.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
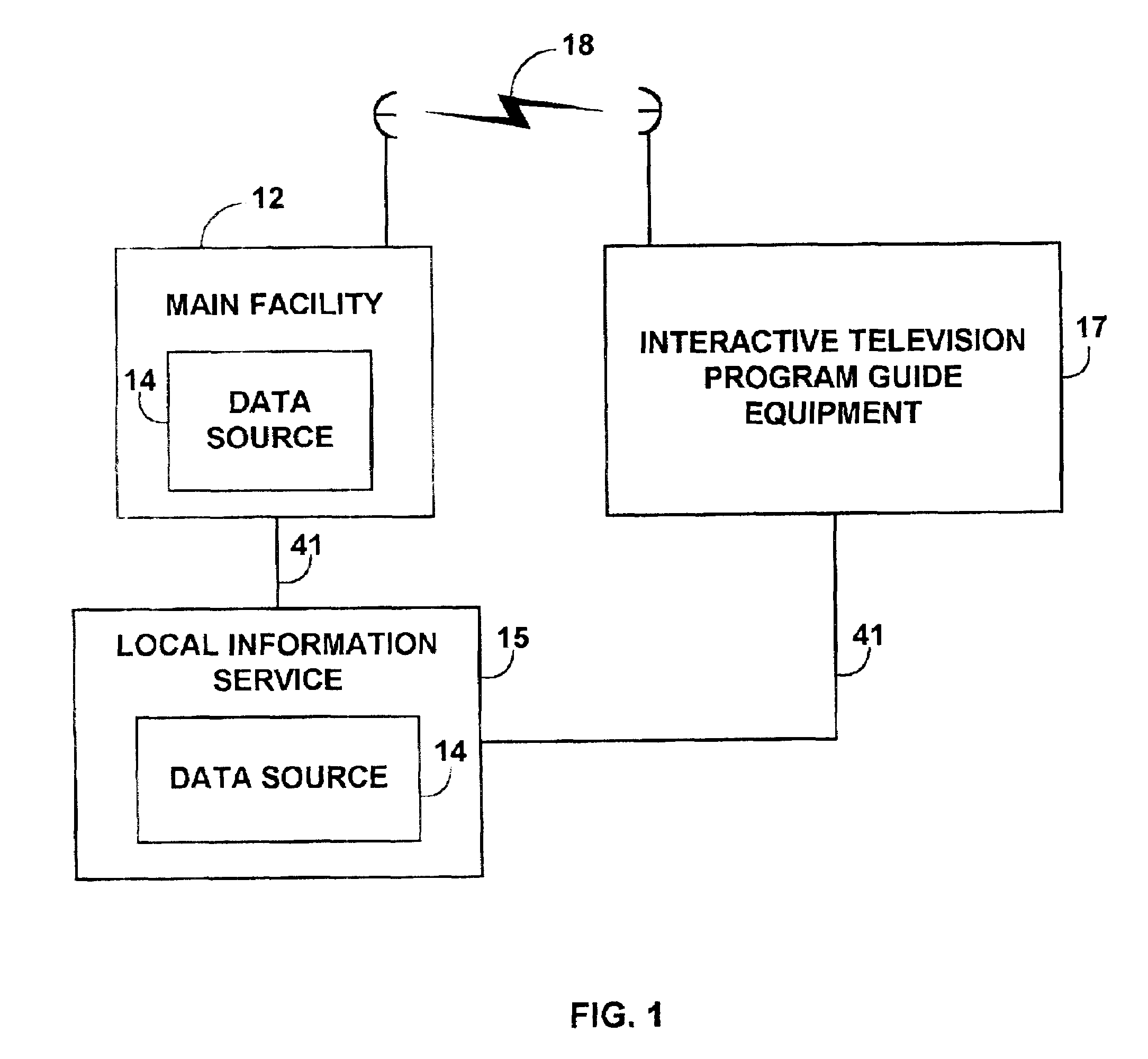
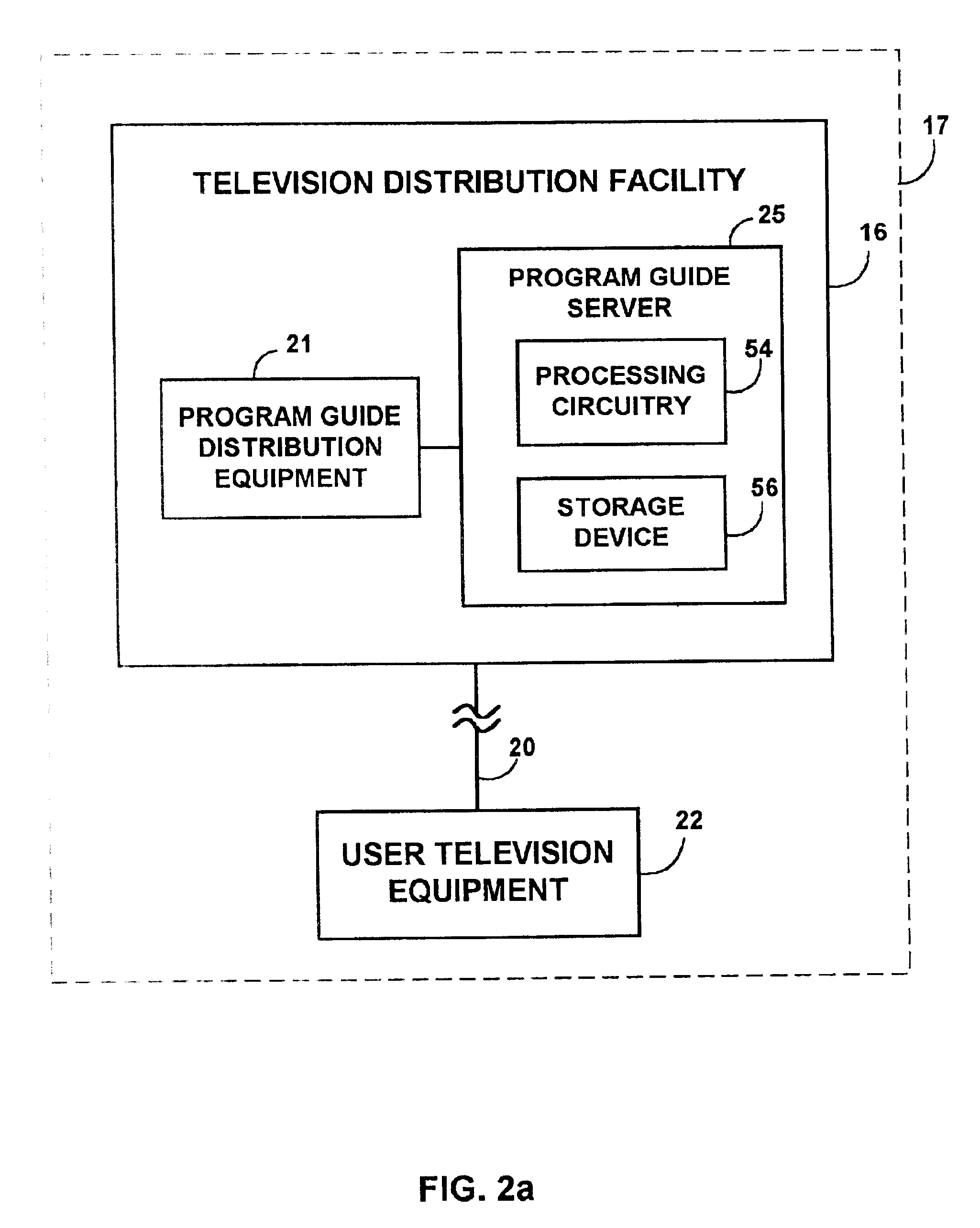
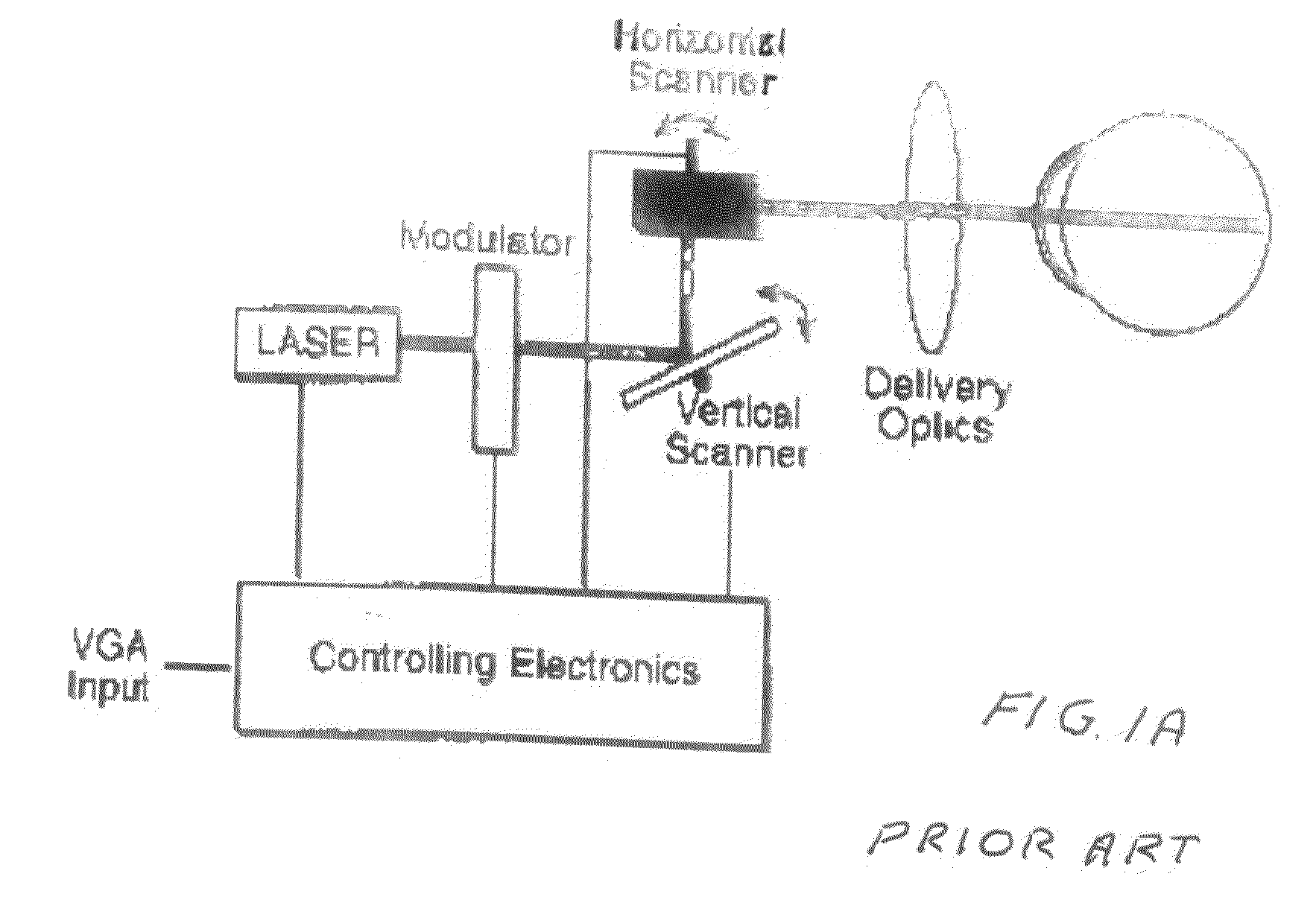
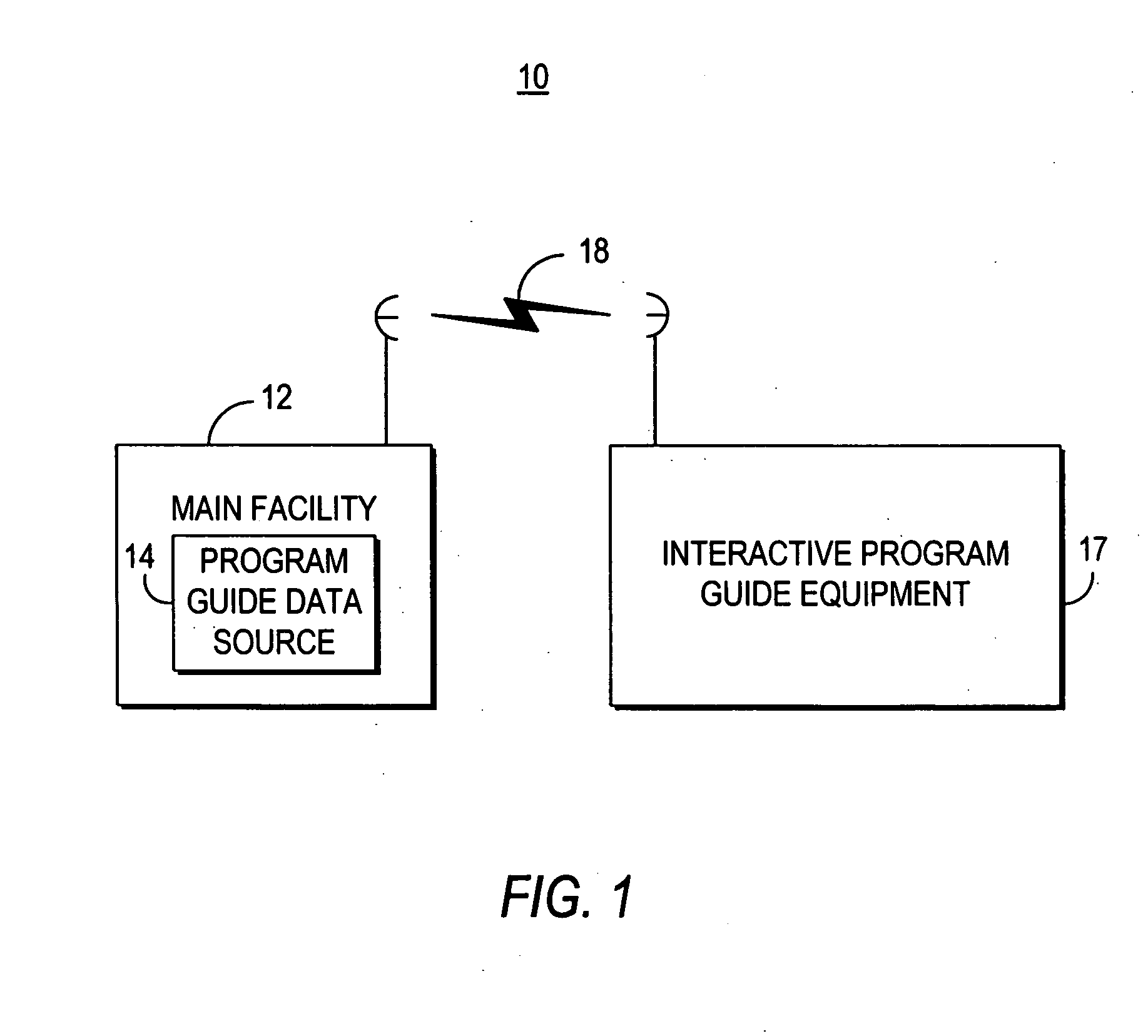
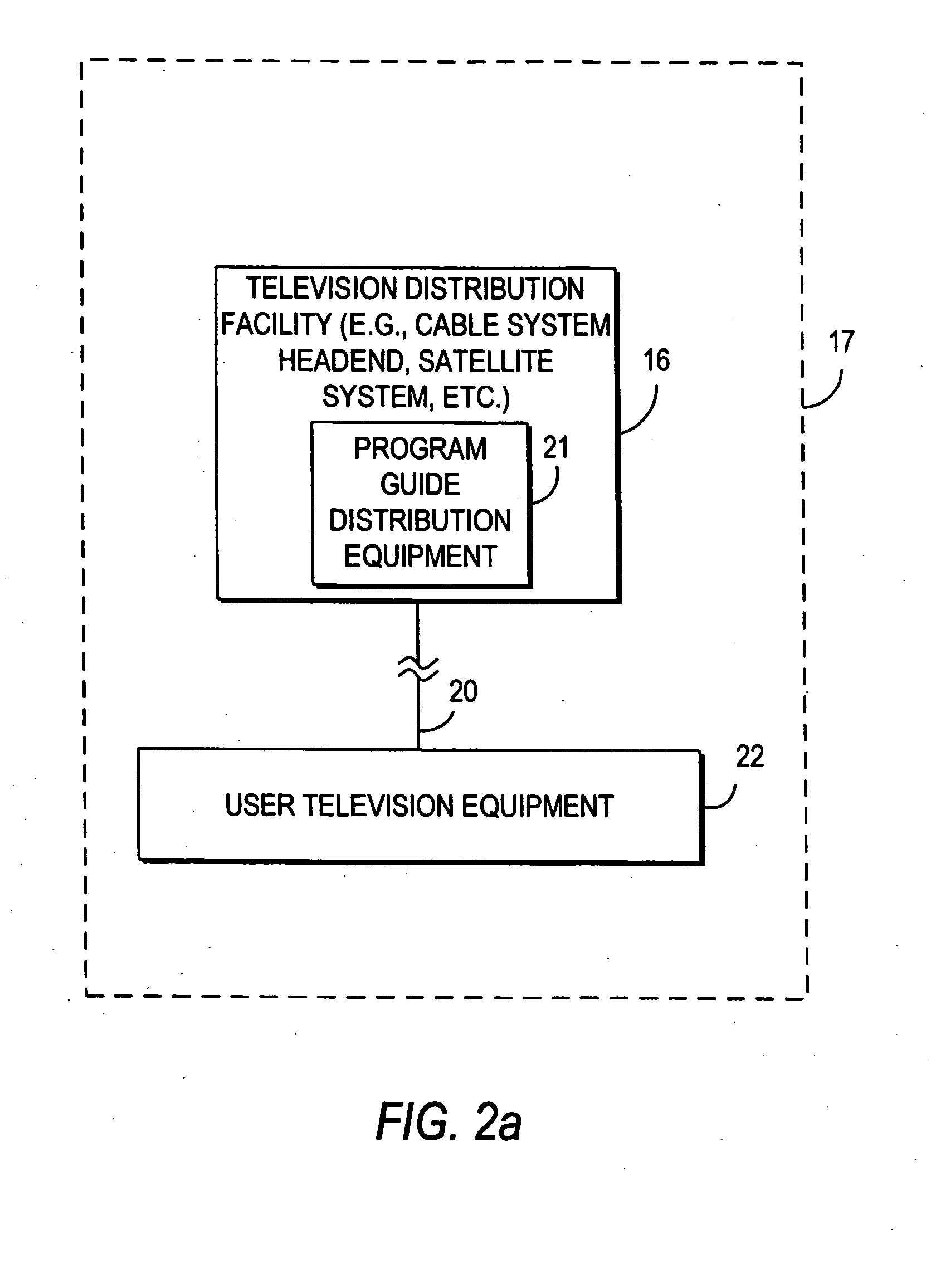
Client-server electronic program guide
InactiveUS7065709B2Improve experienceMinimize memory requirementTelevision system detailsVideo data queryingInteractive televisionTelevision equipment
A client-server interactive television program guide system is provided. An interactive television program guide client is implemented on user television equipment. The interactive television program guide provides users with an opportunity to define expressions that are processed by the program guide server. The program guide server may provide program guide data, schedules reminders, schedules program recordings, and parentally locks programs based on the expressions. Users' viewing histories may be tracked. The program guide server may analyze the viewing histories and generates viewing recommendations, targets advertising, and collects program ratings information based on the viewing histories.
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
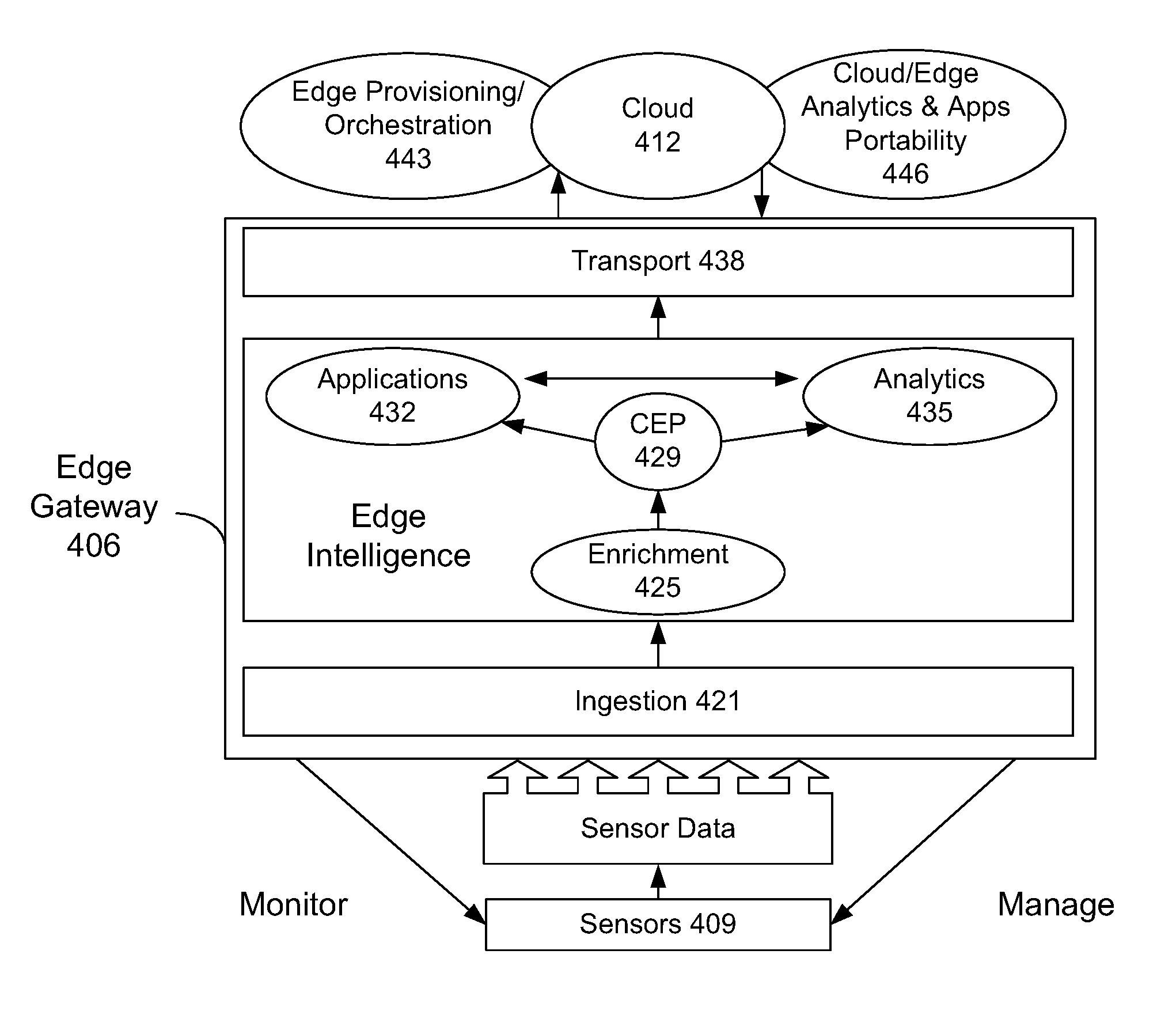
Edge Intelligence Platform, and Internet of Things Sensor Streams System
ActiveUS20170060574A1Delay minimizationMaximum performanceDigital data information retrievalParticular environment based servicesAnalytical expressionsApplication software
A method for enabling intelligence at the edge. Features include: triggering by sensor data in a software layer hosted on either a gateway device or an embedded system. Software layer is connected to a local-area network. A repository of services, applications, and data processing engines is made accessible by the software layer. Matching the sensor data with semantic descriptions of occurrence of specific conditions through an expression language made available by the software layer. Automatic discovery of pattern events by continuously executing expressions. Intelligently composing services and applications across the gateway device and embedded systems across the network managed by the software layer for chaining applications and analytics expressions. Optimizing the layout of the applications and analytics based on resource availability. Monitoring the health of the software layer. Storing of raw sensor data or results of expressions in a local time-series database or cloud storage. Services and components can be containerized to ensure smooth running in any gateway environment.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TYCO IP HLDG LLP
Real-time multicast peer-to-peer video streaming platform
InactiveUS20080133767A1Reduce bandwidth requirementsMinimal costMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionThe InternetPeer-to-peer
A peer-to-peer platform makes use of a streaming agent running at each peer. The streaming agent causes a peer to receive chunks of content from different neighboring peers, store some of the chunks in a local cache, and distribute those cached chunks to neighboring peers. Delivering next generation broadcasts (e.g., as streams of live audio and digital media) of any size utilizing the Internet is achieved. Users can view a live or prerecorded stream of a broadcast through an integrated media player, or can replay a broadcast through an integrated, intelligent archiving service. Use of the platform reduces bandwidth demands on live streaming and archiving services to a level where it is sustainable within a profitable business model to offer the services for at most a negligible fee.
Owner:METIS ENTERPRISE TECH
System for redirecting requests for data to servers having sufficient processing power to transcast streams of data in a desired format
InactiveUS6981045B1Attenuation bandwidthReduce deliveryMultiple digital computer combinationsTwo-way working systemsBandwidth requirementDistributed computing
A method includes polling a first plurality of one-hop gateway serves for available bandwidth and available number of CPU cycles for each respective one-hop gateway server, receiving a request to provide data to a media sink in a desired format, determining a bandwidth requirement and an estimated number of CPU cycles required for servicing the media sink, determining a second plurality of one-hop gateway servers having an available bandwidth greater or equal to the bandwidth requirement and an available number of CPU cycles greater or equal to the estimated number of CPU cycles, determining a one-hop gateway server from the second plurality of one-hop gateway servers appropriate for providing the data to the media sink and configured to receive data in a second format, and transcoding the data from a first format to the second format. An example gateway server and a computer program product usable therewith are also provided.
Owner:ADAPTIVE STREAMING INC
Selective lossless, lossy, or no compression of data based on address range, data type, and/or requesting agent
InactiveUS7190284B1Increase performanceIncrease system bandwidthMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTMemory controllerData transmission
An integrated memory controller (IMC) including MemoryF / X Technology which includes data compression and decompression engines for improved performance. The memory controller (IMC) of the present invention preferably selectively uses a combination of lossless, lossy, and no compression modes. Data transfers to and from the integrated memory controller of the present invention can thus be in a plurality of formats, these being compressed or normal (non-compressed), compressed lossy or lossless, or compressed with a combination of lossy and lossless. The invention also indicates preferred methods for specific compression and decompression of particular data formats such as digital video, 3D textures and image data using a combination of novel lossy and lossless compression algorithms in block or span addressable formats. To improve latency and reduce performance degradations normally associated with compression and decompression techniques, the MemoryF / X Technology encompasses multiple novel techniques such as: 1) parallel lossless compression / decompression; 2) selectable compression modes such as lossless, lossy or no compression; 3) priority compression mode; 4) data cache techniques; 5) variable compression block sizes; 6) compression reordering; and 7) unique address translation, attribute, and address caches. The parallel compression and decompression algorithm allows high-speed parallel compression and high speed parallel decompression operation. The IMC also preferably uses a special memory allocation and directory technique for reduction of table size and low latency operation. The integrated data compression and decompression capabilities of the IMC remove system bottle-necks and increase performance. This allows lower cost systems due to smaller data storage, reduced bandwidth requirements, reduced power and noise.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Mobile terminal with a text-to-speech converter
InactiveUS6931255B2Reduce bandwidth requirementReduce bandwidth requirementsInformation formatContent conversionVoice transformationSpeech sound
A mobile terminal includes a receiver for receiving text messages over an RF channel. The mobile terminal also includes a text-to-speech (TTS) converter that converts the transmitted text messages to an audible form. In this way, the present invention takes advantage of the reduced bandwidth required for transmitting text messages to provide an audible message to subscribers that use the mobile terminals. In an exemplary embodiment, the mobile terminal operates in a GSM communication system and receives text messages that are defined under short message service (SMS) protocol. Also, the TTS converter in the mobile terminal can be used to output the text menus of the mobile terminal's interface in speech (voice) format.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
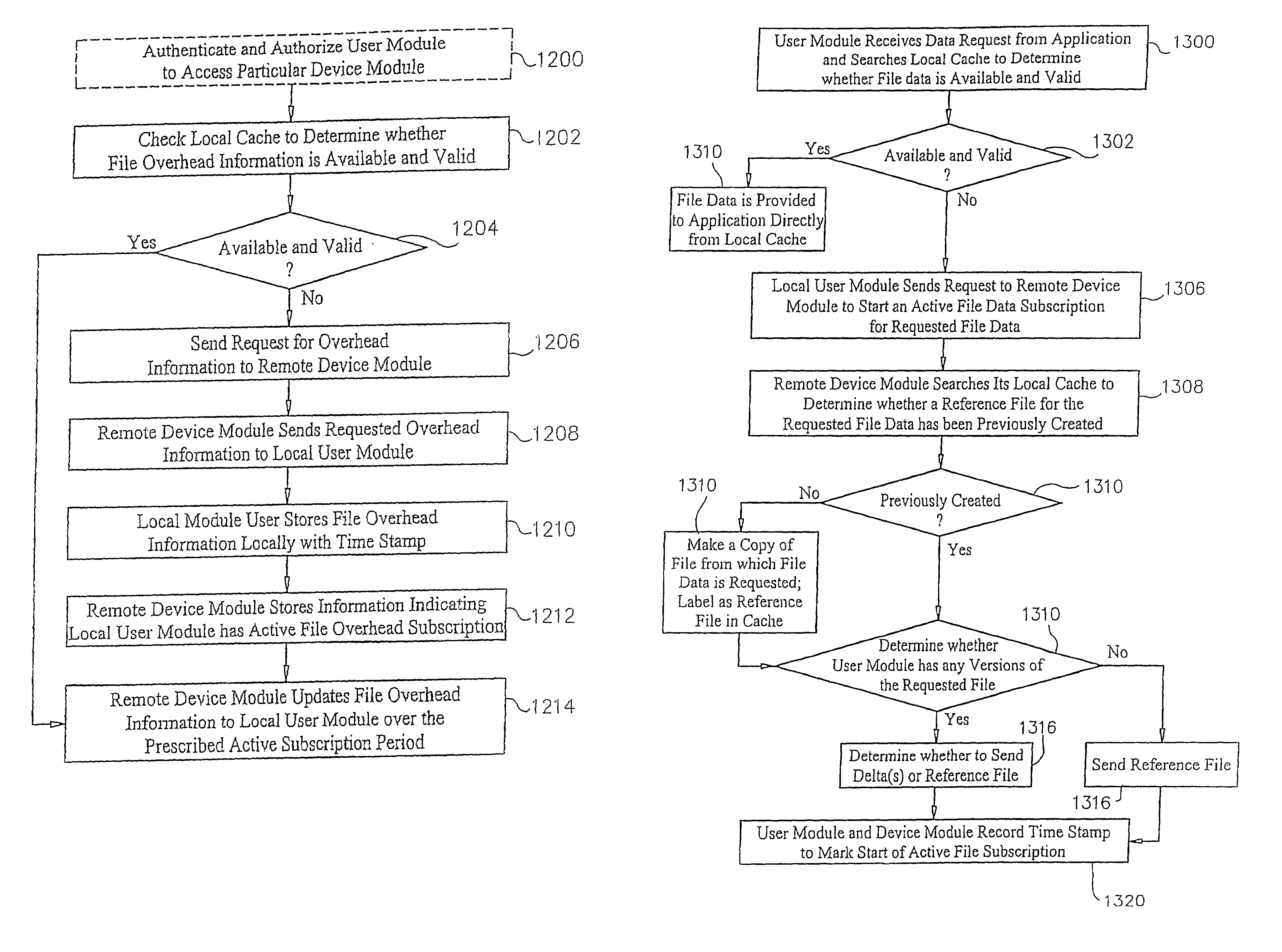
Managed peer-to-peer applications, systems and methods for distributed data access and storage
InactiveUS7546353B2Reduce bandwidth requirementsLimited dataDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationNetwork connectionData access
Applications, systems and methods for efficiently accessing data and controlling storage devices among multiple computers connected by a network. Upon receiving a request for access to data originally stored in a remote storage device, determining whether the data is already available and valid in a local storage device. Accessing the data from the local storage device if the data is available and valid. Authenticating a request for a secure connection between a local computer associated with the local storage device and a remote computer associated with the remote storage device. Securely connecting the local computer with the remote computer. Requesting the data from the remote storage device, over the network, if the data is not locally available and valid. Receiving data over the network from the remote storage device, and storing the data in the local storage device for direct local access thereto.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
System and method for transmitting wireless digital service signals via power transmission lines
ActiveUS7929940B1Reduce bandwidth requirementLow costInterconnection arrangementsWireless systems/telephoneElectric power transmissionBase transceiver station
A system and method of transmitting and receiving RF service signals between a base transceiver station (BTS) of a wireless communication system and subscriber units within a structure. In the forward link, the system demodulates the RF service signal from a BTS to recover a digital service signal; conditions the digital service signal for transmission via the powerline of a structure; and modulates an RF carrier with the digital service signal to generate the RF service signal for wireless transmission to subscriber units within the structure. In the reverse link, the system demodulates the RF service signal from subscriber unit(s) to generate a digital service signal; conditions the digital service signal for transmission via the powerline; and modulates an RF carrier with the digital service signal to generate the RF service signal for transmission to the BTS. Another embodiment eliminates the modulation of an RF carrier with the digital service signal to generate an RF service and vice-versa at the BTS.
Owner:NEXTEL COMMUNICATIONS
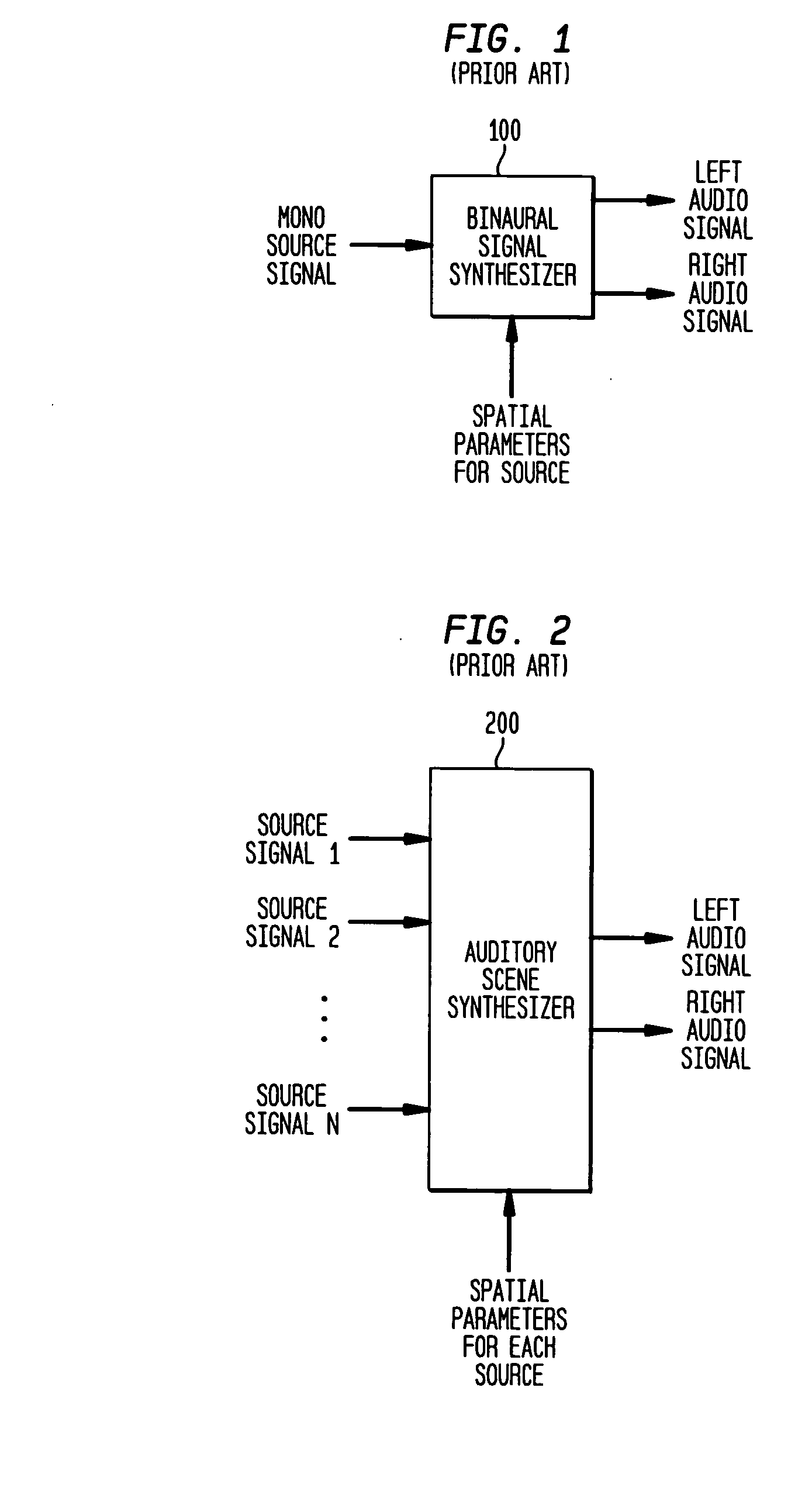
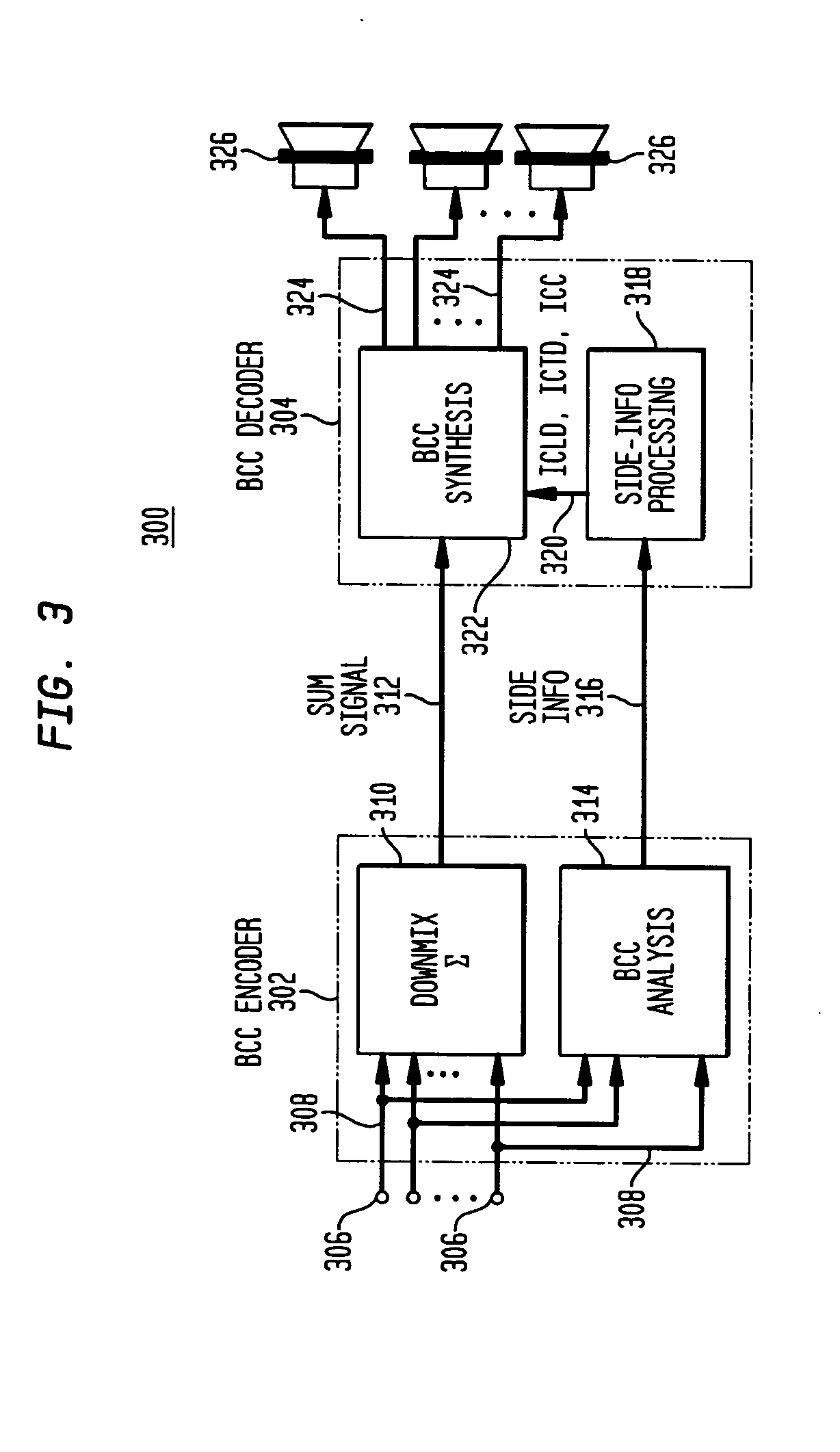
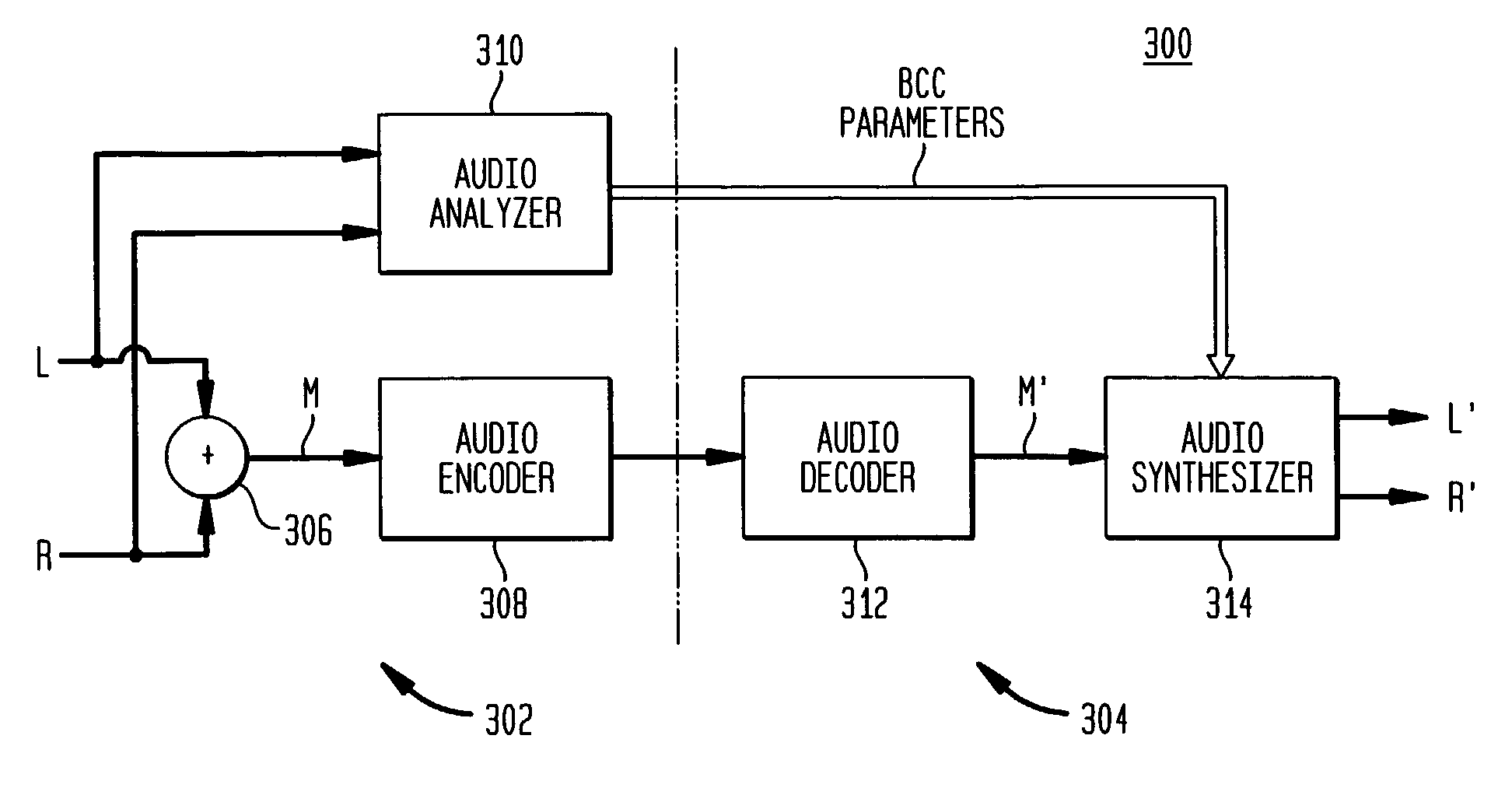
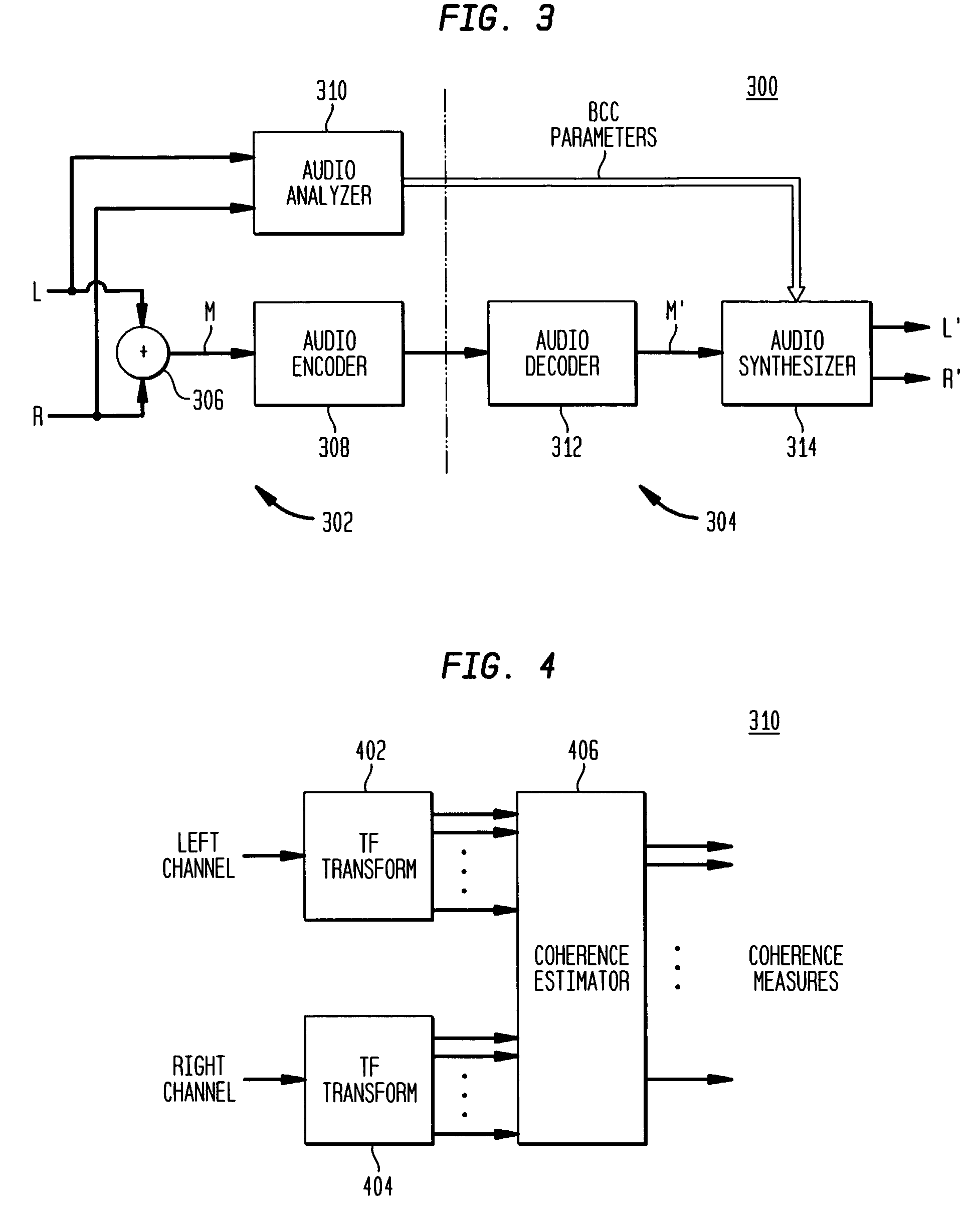
Late reverberation-based synthesis of auditory scenes
ActiveUS20050180579A1Reduce transmission bandwidth requirementsReduce bandwidth requirementsGain controlSpeech analysisComputation complexityChannel correlation
A scheme for stereo and multi-channel synthesis of inter-channel correlation (ICC) (normalized cross-correlation) cues for parametric stereo and multi-channel coding. The scheme synthesizes ICC cues such that they approximate those of the original. For that purpose, diffuse audio channels are generated and mixed with the transmitted combined (e.g., sum) signal(s). The diffuse audio channels are preferably generated using relatively long filters with exponentially decaying Gaussian impulse responses. Such impulse responses generate diffuse sound similar to late reverberation. An alternative implementation for reduced computational complexity is proposed, where inter-channel level difference (ICLD), inter-channel time difference (ICTD), and ICC synthesis are all carried out in the domain of a single short-time Fourier transform (STFT), including the filtering for diffuse sound generation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
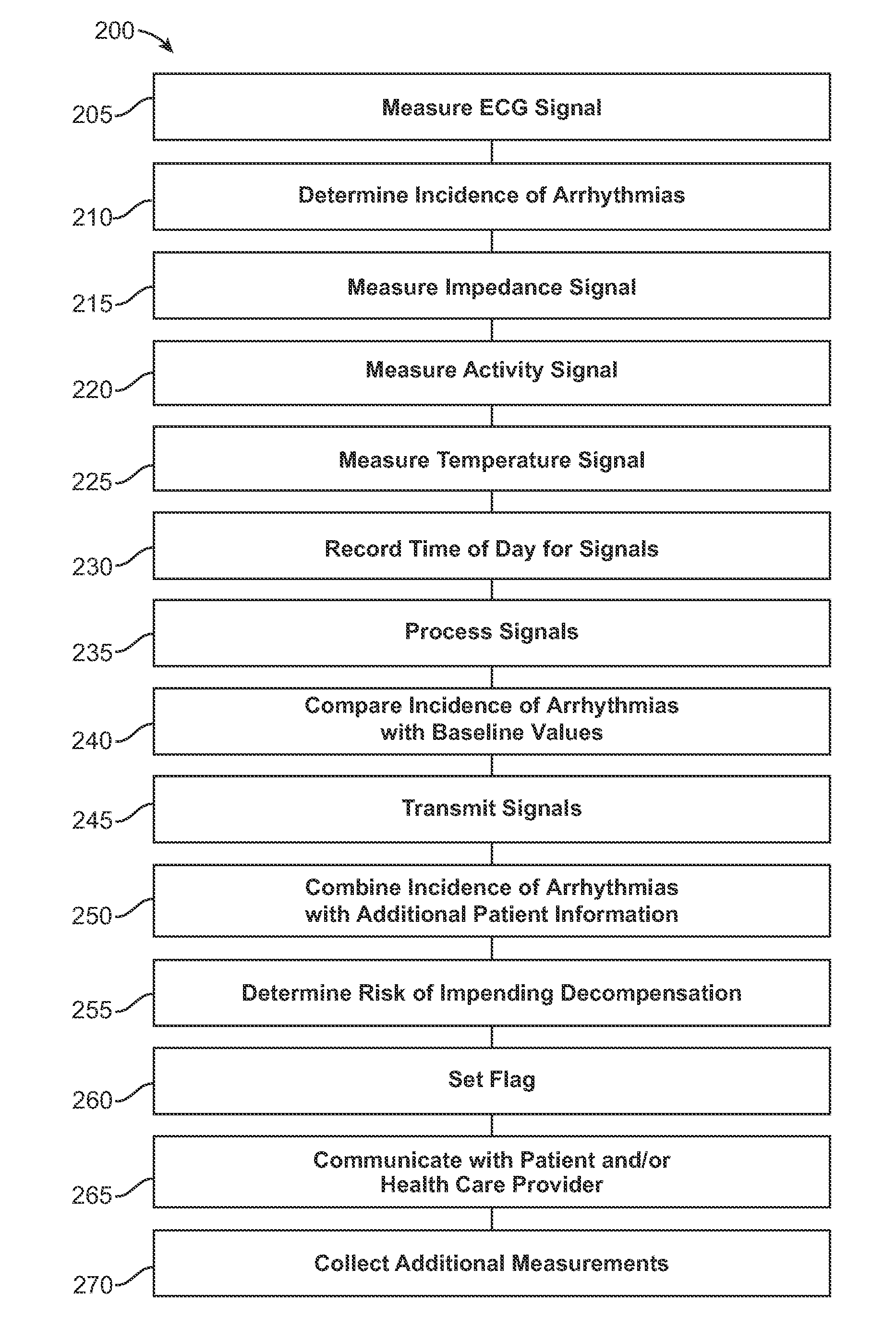
Heart Failure Decompensation Prediction Based on Cardiac Rhythm
ActiveUS20090234410A1Reduce traumaSave livesElectrocardiographyHealth-index calculationPhysiological monitoringSystems approaches
Systems and methods of detecting an impending cardiac decompensation of a patient measure an electrocardiogram signal of the patient. An incidence of cardiac arrhythmias is determined from the electrocardiogram signal. A risk of impending decompensation is determined in response to the incidence of cardiac arrhythmias. In many embodiments, the impending decompensation can be detected early enough to avoid, or at least delay, the impending decompensation, such that patient trauma and / or expensive ICU care can be avoided. Although embodiments make specific reference to monitoring electrocardiogram and other physiological signals with an adherent patch, the system methods and devices are applicable to many applications in which physiological monitoring is used, for example wireless physiological monitoring with implanted sensors for extended periods.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MONITORING
Heart failure decompensation prediction based on cardiac rhythm
ActiveUS8718752B2Reduce traumaSave livesElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyPhysiological monitoringSystems approaches
Systems and methods of detecting an impending cardiac decompensation of a patient measure an electrocardiogram signal of the patient. An incidence of cardiac arrhythmias is determined from the electrocardiogram signal. A risk of impending decompensation is determined in response to the incidence of cardiac arrhythmias. In many embodiments, the impending decompensation can be detected early enough to avoid, or at least delay, the impending decompensation, such that patient trauma and / or expensive ICU care can be avoided. Although embodiments make specific reference to monitoring electrocardiogram and other physiological signals with an adherent patch, the system methods and devices are applicable to many applications in which physiological monitoring is used, for example wireless physiological monitoring with implanted sensors for extended periods.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MONITORING
Dynamic foveal vision display
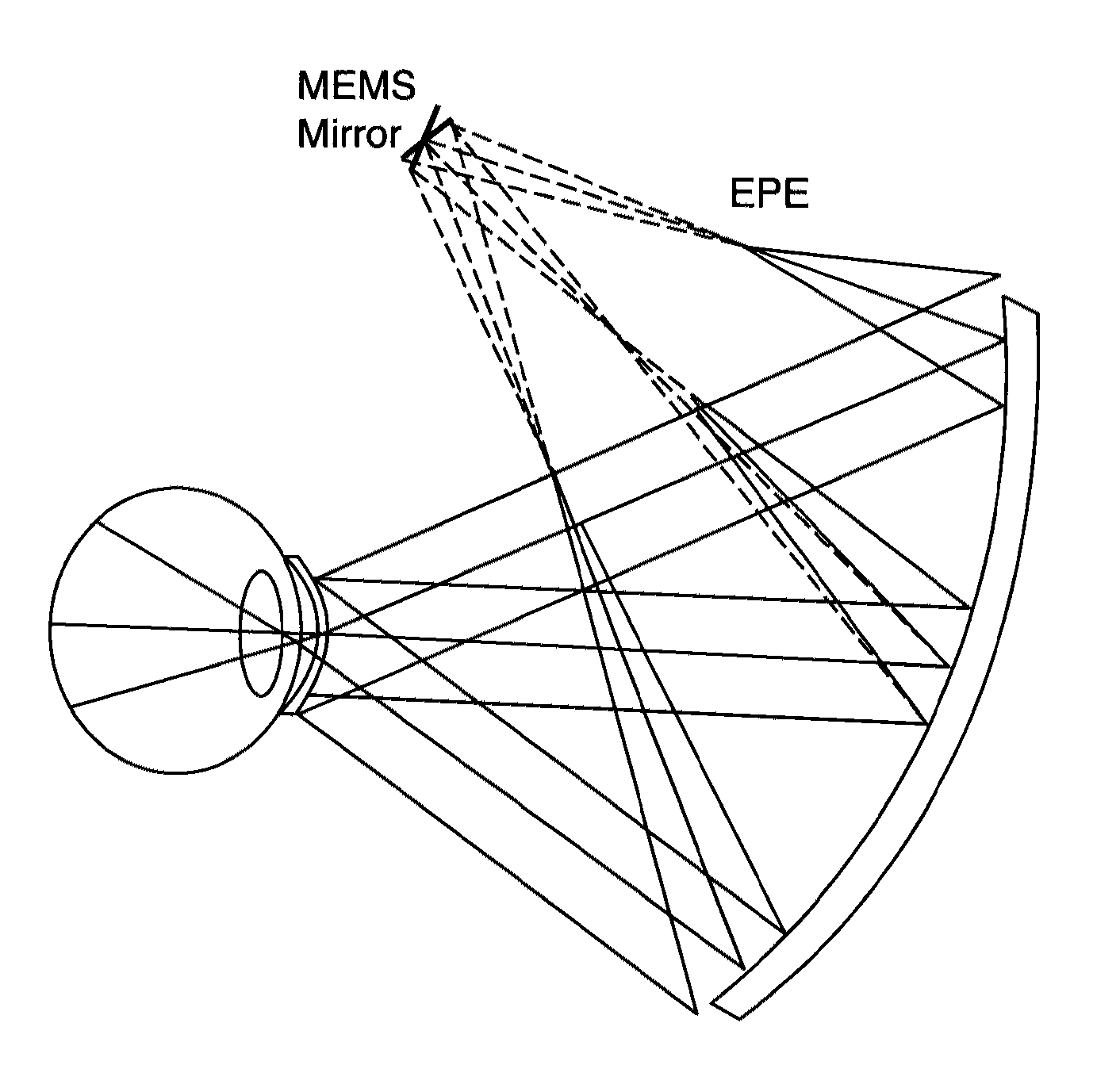
InactiveUS20120105310A1Reduce bandwidth requirementsOvercome limitationsCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical elementsRetinaInfrared laser beam
A head mounted display system with at least one retinal display unit having a curved reflector positioned in front of one eye or both eyes of a wearer. The unit includes a first set of three modulated visible-light lasers co-aligned and adapted to provide a laser beam with selectable color and a first scanner unit providing both horizontal and vertical scanning of the laser beam across a portion of the curved reflector in directions so as to produce a reflection of the color laser beam through the pupil of the eye onto a portion of the retina large enough to encompass the fovea. The unit also includes a second set three modulated visible-light lasers plus an infrared laser, all lasers being co-aligned and adapted to provide a color and infrared peripheral view laser beam, and a second scanner unit providing both horizontal and vertical scanning of the visible light and infrared laser beams across a portion of the curved reflector in directions so as to produce a reflection of the scanned color and infrared laser beams through the pupil of the eye onto a portion of retina corresponding to a field of view of at least 30 degrees×30 degrees.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Interactive television program guide with selectable languages
InactiveUS20060143655A1Reduce bandwidth requirementsTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesRelevant informationInteractive television
An interactive television program guide is provided. The interactive television program guide provides a user with the opportunity to select a language for playing television programming and displaying program guide text. Television program audio in the desired language may be obtained from a SAP or digital audio track and played in the selected language. Television related information in the desired language may be obtained from a digital track. If television program audio or related information is not provided in the selected language, the program guide may use a default language. The program guide may coordinate program guide display screen text with languages available for television programs when the programs are broadcast to users.
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
System and Method for Managing Multimedia Communications Across Convergent Networks
InactiveUS20120321058A1Reduce bandwidth requirementsOptimizing bandwidth usageTelephonic communicationTransmissionTelecommunications
A method and device that interrogates the availability of a called party before placing a communication from the calling party to the called party. A callback may be initiated so that both communications are completed simultaneously. The routing of communication may take place through any one of a number of different networks and at another time of the day, even if the caller does not otherwise have access to those networks.
Owner:AIP ACQUISITION
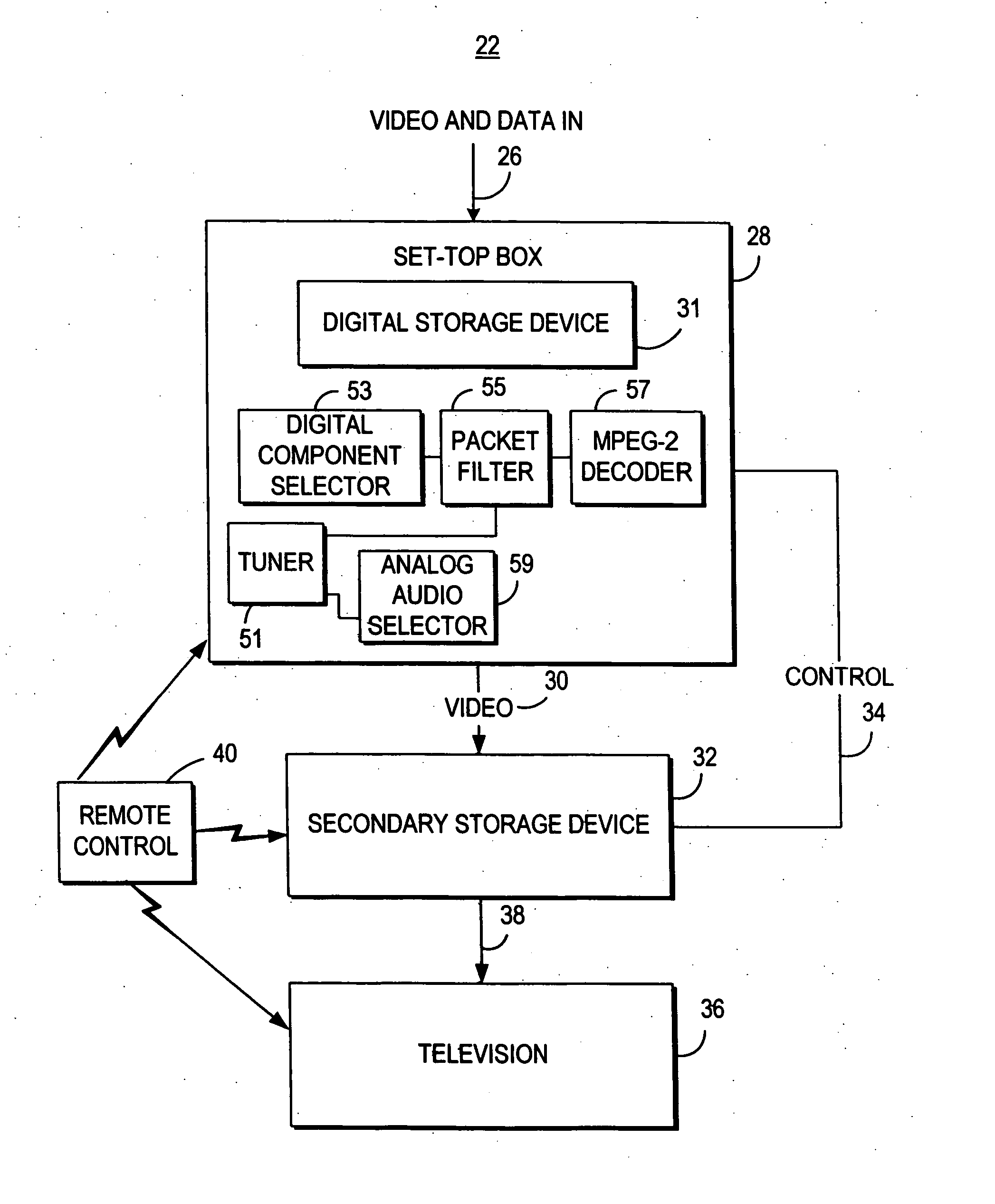
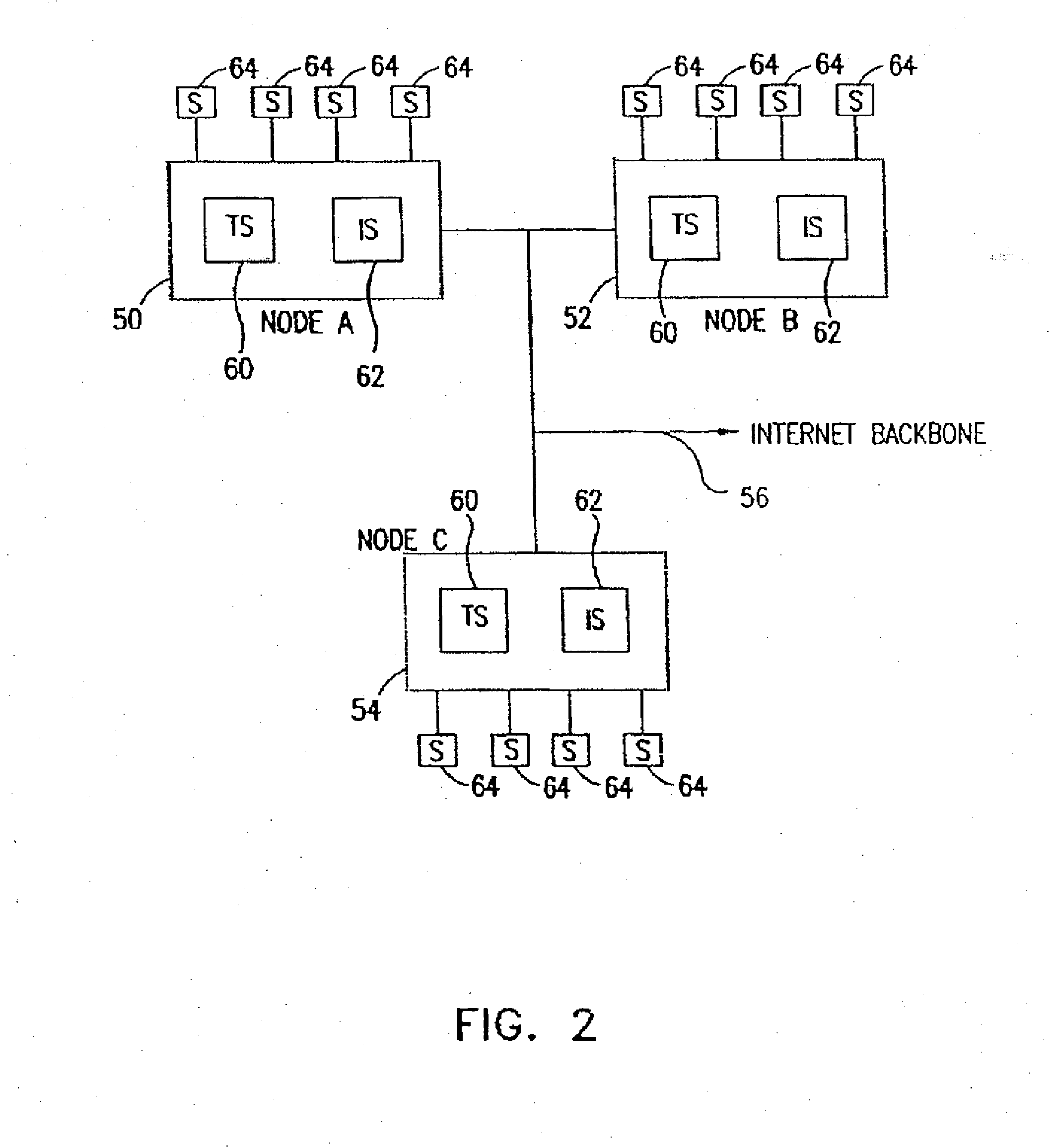
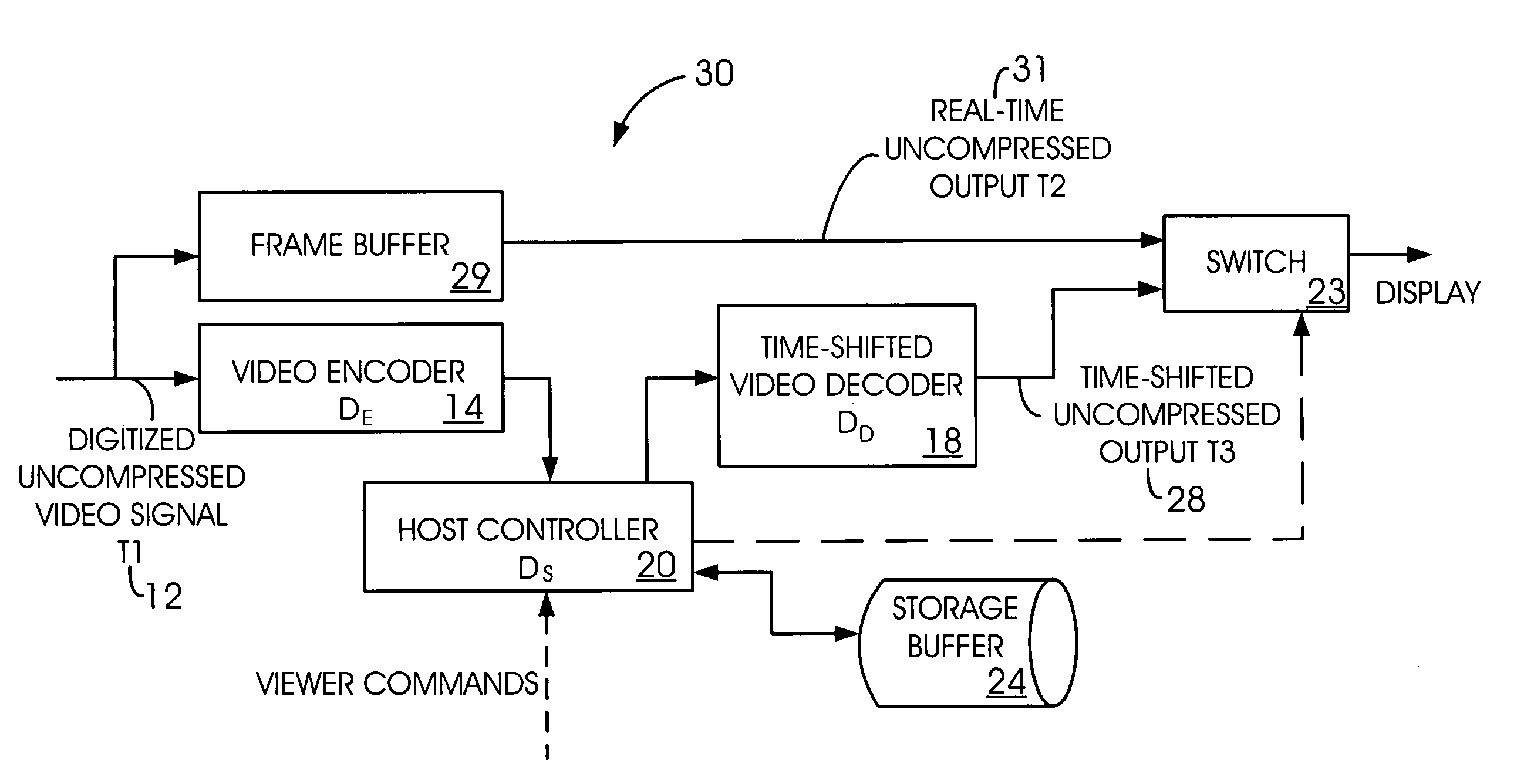
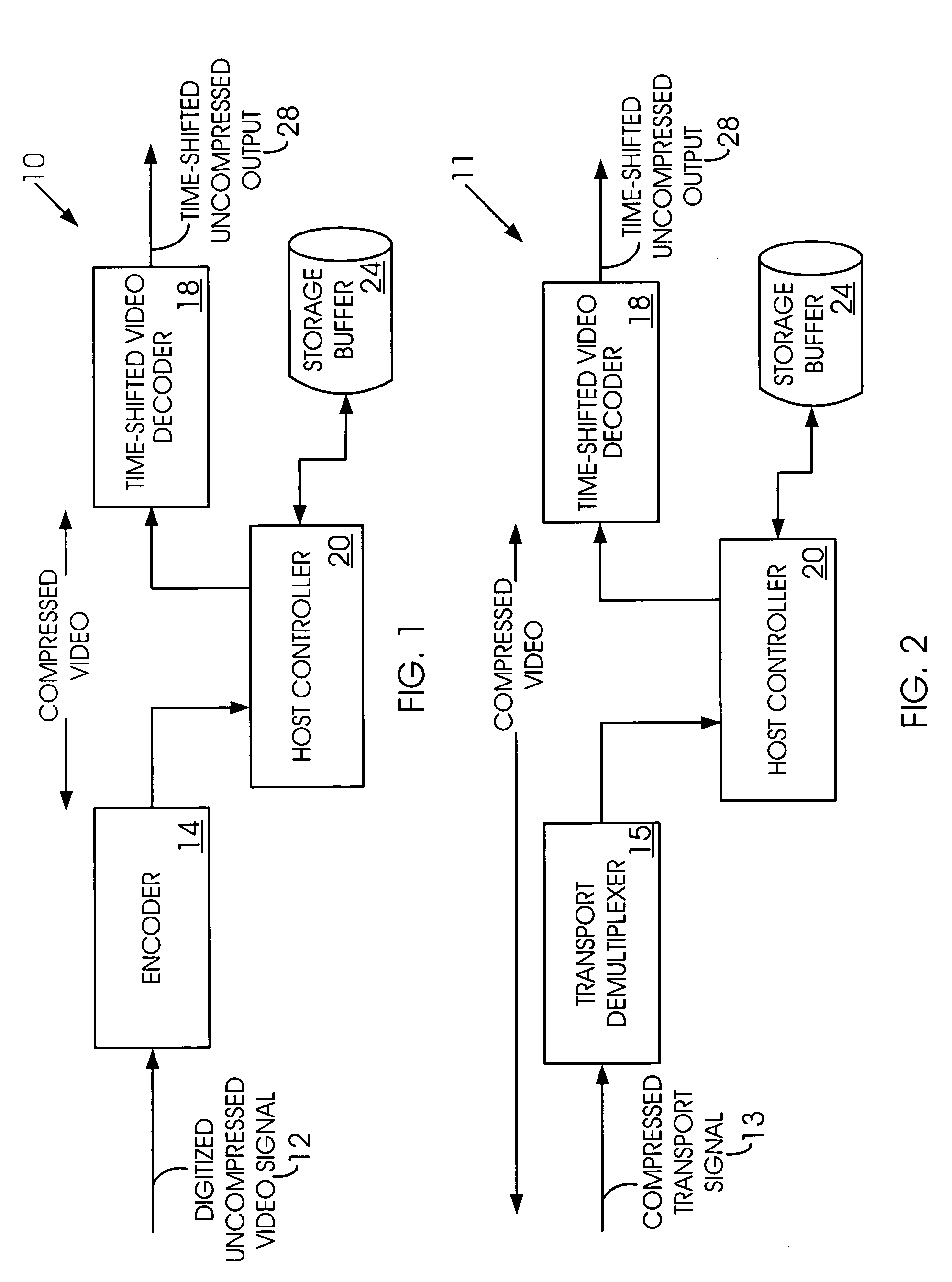
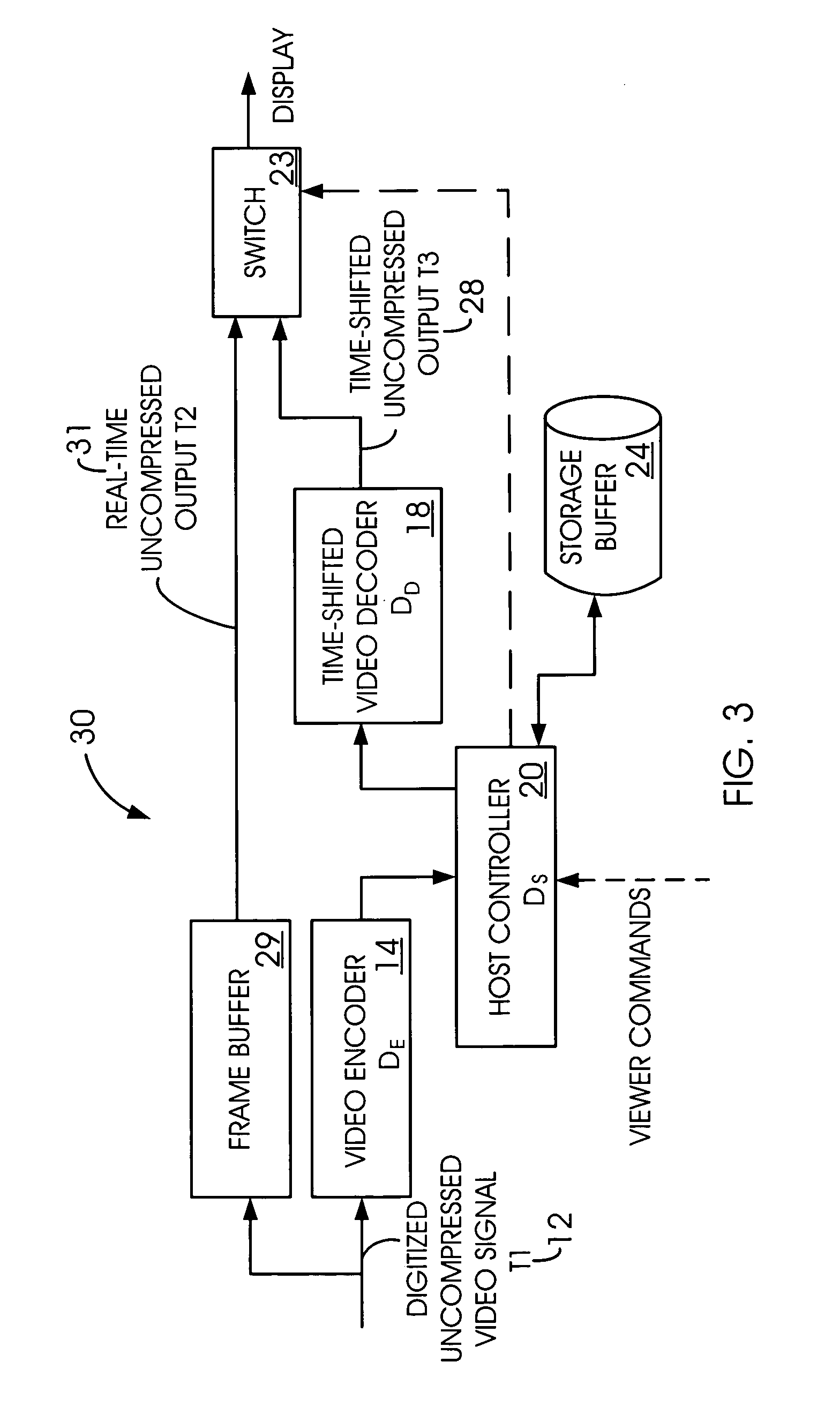
Time-shifted video signal processing
InactiveUS7020892B2Reduce bandwidth requirementsHard disc life span increasedTelevision system detailsColor television signals processingTime frameSignal processing
A time-shifted video method has a real-time mode during which real-time video frames are delivered for display. In a time-shifted mode, time-shifted video frames are delivered for display. The time-shifted video frames are delayed relative to the real-time video frames. A real-time frame is paused during a transition from the real-time mode to the time-shifted mode.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and device for inserting and authenticating a digital signature in digital data
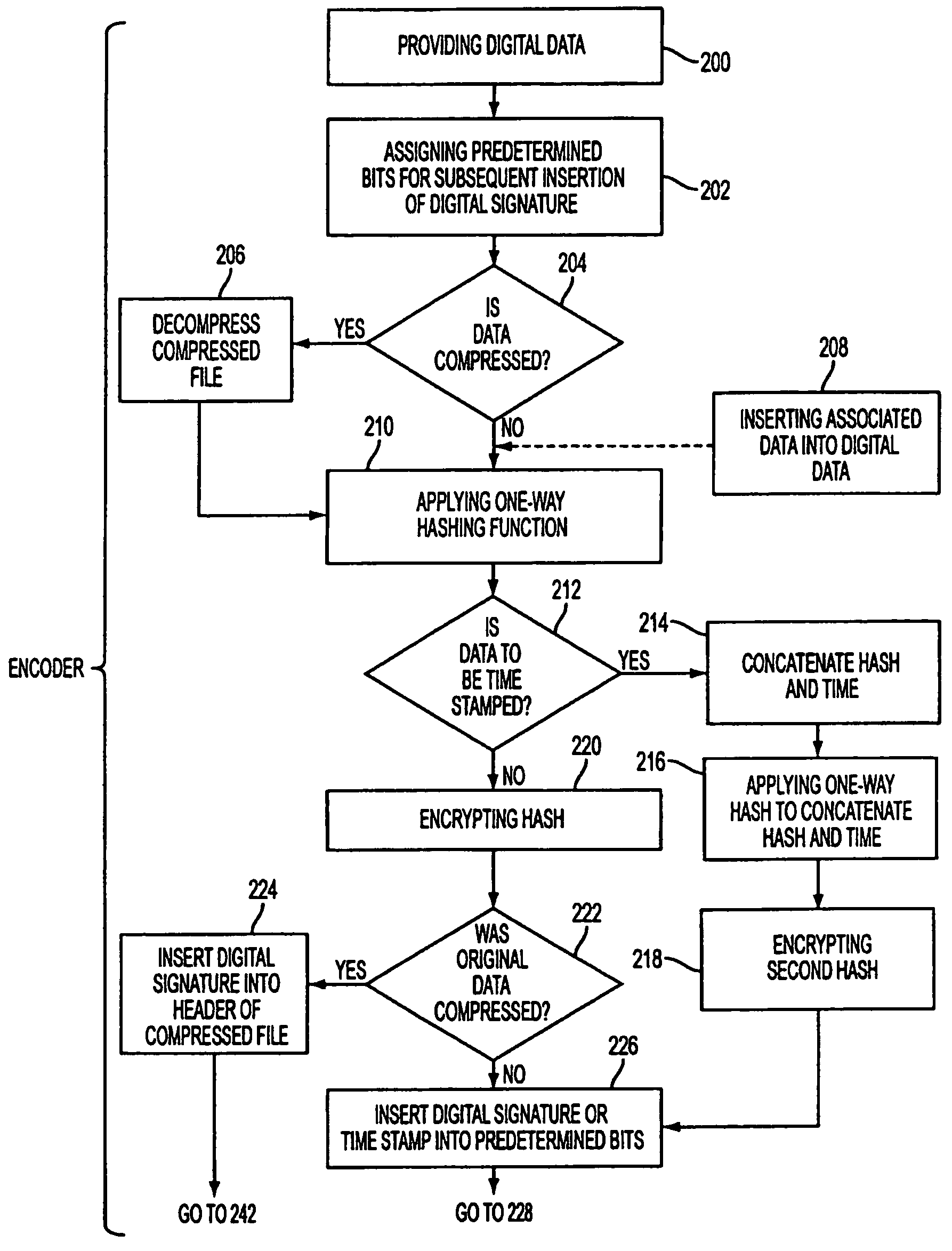
InactiveUS7216232B1Reduce storageReduce bandwidth requirementsUser identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionDigital dataHash function
A method for inserting a digital signature into digital data is provided. The digital data has bits and the method includes the steps of: assigning predetermined bits of the digital data for receiving the digital signature; signing the digital data excluding the predetermined bits resulting in the digital signature; and inserting the digital signature into the predetermined bits of the digital data for subsequent authentication of the digital data. Also provided is a method for authenticating digital data having the embedded digital signature in the predetermined bits of the digital data including the steps of: extracting the digital signature from the predetermined bits; decrypting the digital signature from the digital data resulting in a first hash; applying a known one-way hashing function used by an encoder of the digital data to the digital data excluding the predetermined bits resulting in a second hash; and comparing the first hash to the second hash wherein if the first hash matches the second hash the digital data is authentic. In a preferred version of the methods of the present invention, the method further includes the step of inserting associated data into the digital data prior to the signing step such that the digital signature authenticates both the associated data as well as the digital data. Preferably, the associated data is inserted into the bits of the digital data excluding the predetermined bits.
Owner:NEC CORPOATION OF AMERICA
Real time video game uses emulation of streaming over the internet in a broadcast event
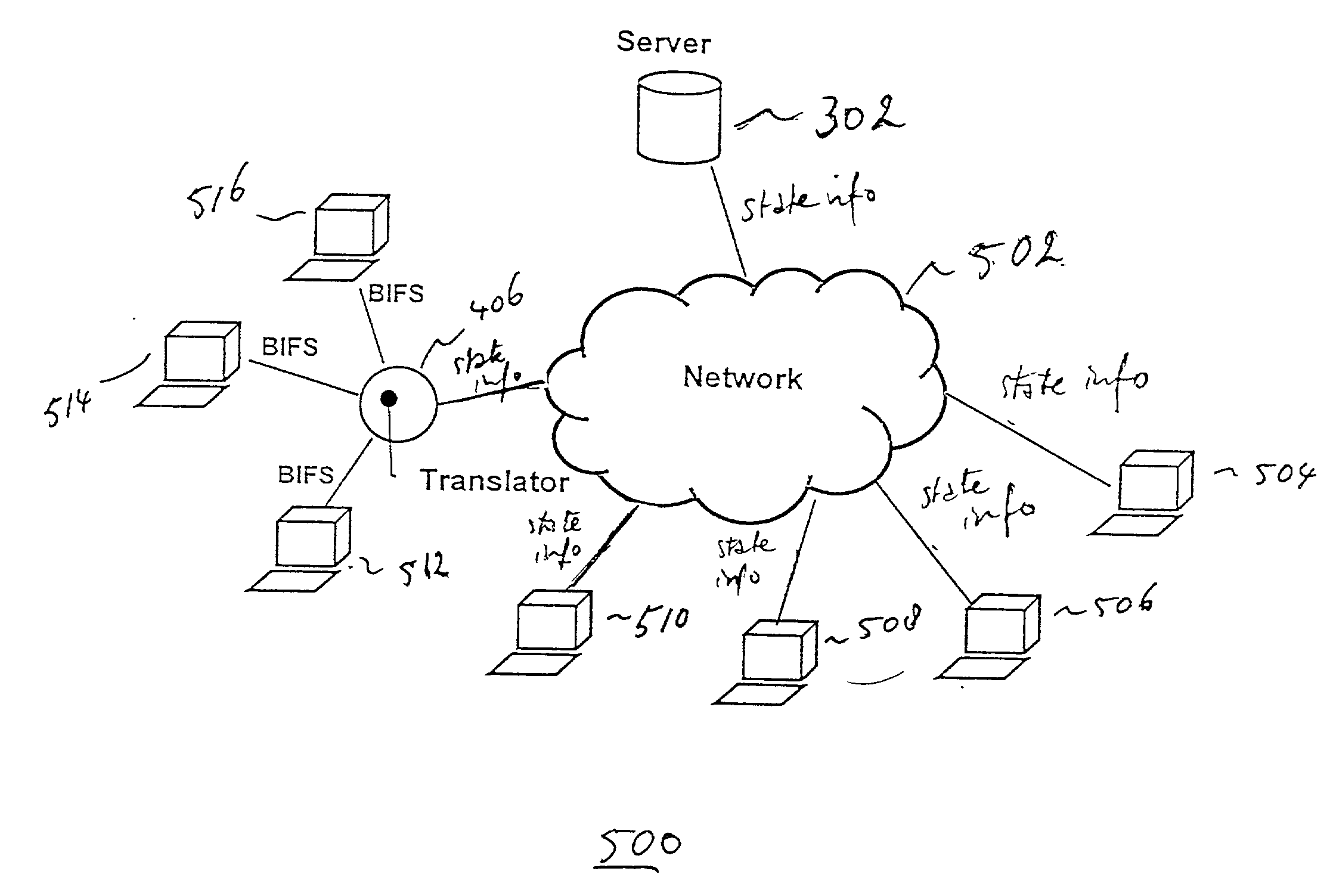
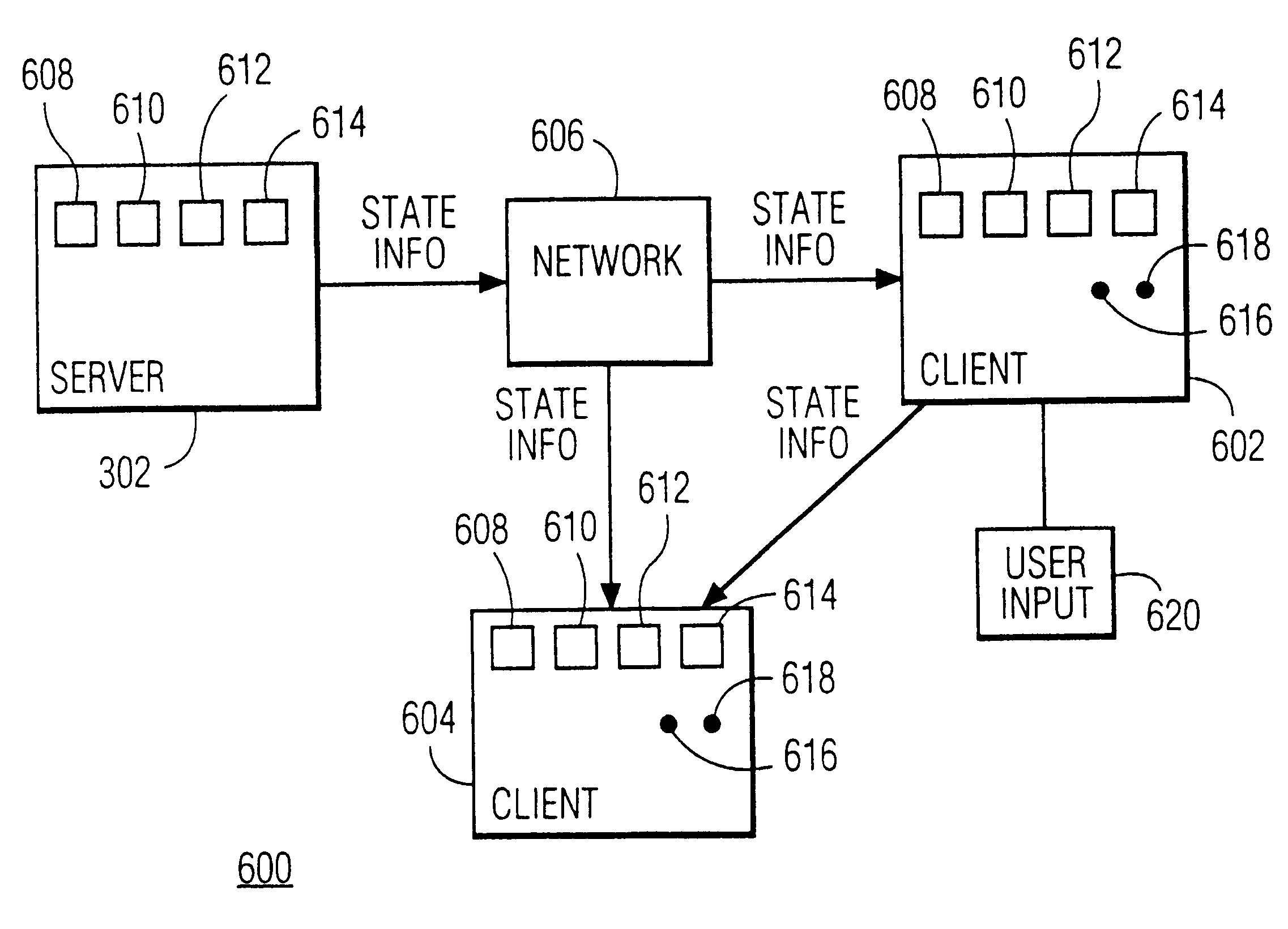
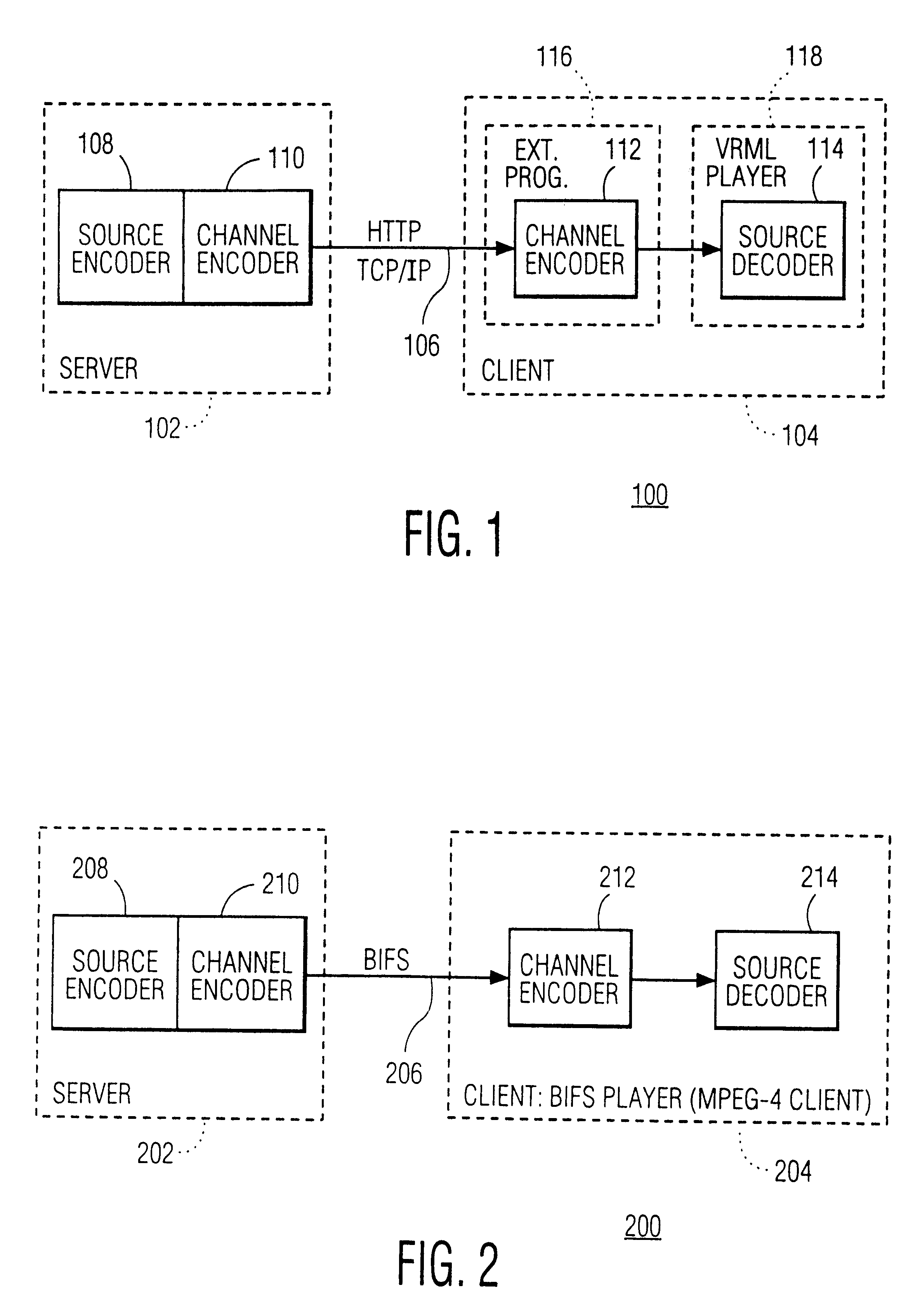
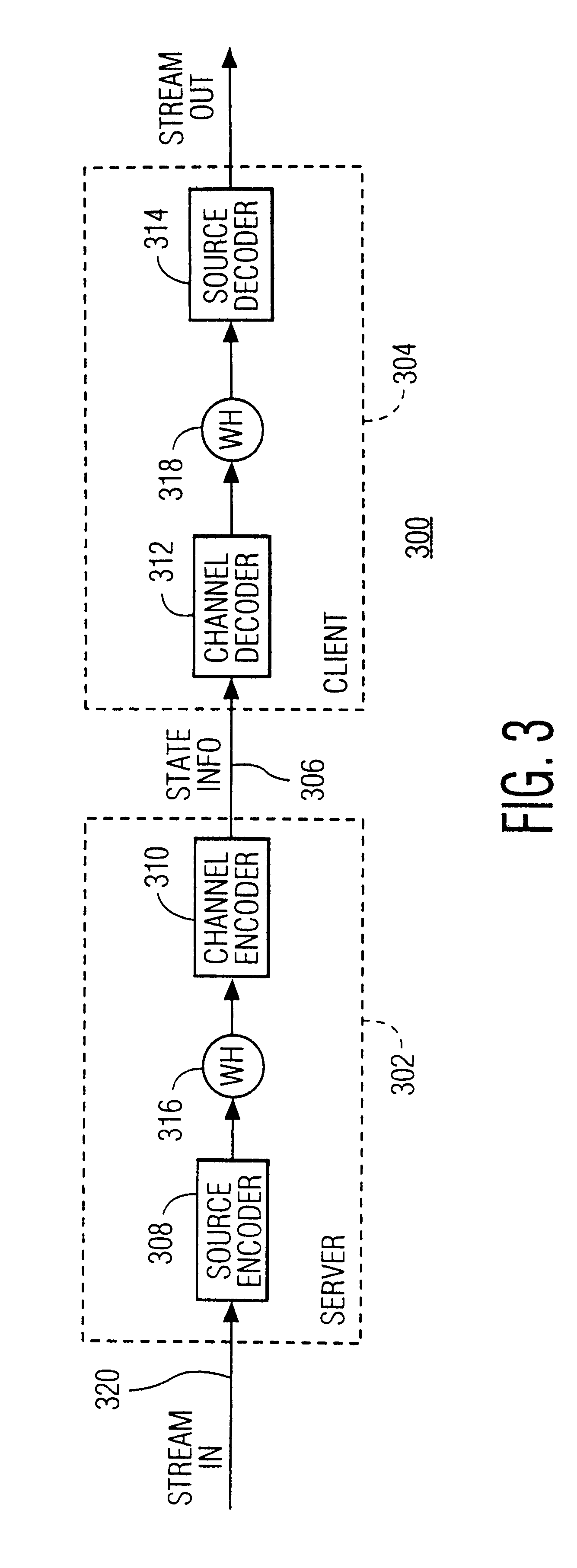
InactiveUS20030037156A1Easy programmingLow bandwidthSpecial service provision for substationPulse modulation television signal transmissionGraphicsAnimation
In a broadcast application on a client-server network the streaming is emulated of animation data over the Internet to a large number of clients. The animation is considered a sequence of states. State information is sent to the clients instead of the graphics data itself. The clients generate the animation data itself under control of the state information. The server and clients communicate using a shared object protocol. Thus, streaming is accomplished as well as a broadcast without running into severe network bandwidth problems. This approach is used to map a real life event, e.g., a motor race, onto a virtual environment in order to let the user participate in a virtual race against the real life professionals, the dynamics of the virtual environment being determined by the state changes sent to the user.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Real time video game uses emulation of streaming over the internet in a broadcast event
InactiveUS6557041B2Easy programmingLow bandwidthSpecial service provision for substationPulse modulation television signal transmissionGraphicsState variation
In a broadcast application on a client-server network the streaming is emulated of animation data over the Internet to a large number of clients. The animation is considered a sequence of states. State information is sent to the clients instead of the graphics data itself. The clients generate the animation data itself under control of the state information. The server and clients communicate using a shared object protocol. Thus, streaming is accomplished as well as a broadcast without running into severe network bandwidth problems. This approach is used to map a real life event, e.g., a motor race, onto a virtual environment in order to let the user participate in a virtual race against the real life professionals, the dynamics of the virtual environment being determined by the state changes sent to the user.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
System and method of procedural visibility for interactive and broadcast streaming of entertainment, advertising, and tactical 3D graphical information using a visibility event codec
ActiveUS20120256915A1Eliminate frequent interruptionReduced bandwidthDetails involving image processing hardware3D-image renderingComputer generationComputer device
A system includes a server and a client computer device. The server determines a graphical object visible from a view region and determines one or more parameters defining the graphical object visible from the view region. The server further transmits the determined one or more parameters to a client computing device. The client computing device includes a processor to generate the graphical object using the determined one or more parameters received from the server. The client computing device further includes a display device to display the generated graphical object within a computer generated modeled environment.
Owner:PRIMAL SPACE SYST
Systems and methods for integrating graphic animation technologies in fantasy sports contest applications
ActiveUS7548242B1Way of increaseReduce bandwidth requirementsMultiple digital computer combinationsApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingGraphicsAnimation
Systems and methods for integrating graphic animation technologies with fantasy sports contest applications are provided. This invention enables a fantasy sports contest application to depict plays in various sporting events using graphic animation. The fantasy sports contest application may combine graphical representation of real-life elements such as, for example, player facial features, with default elements such as, for example, a generic player body, to create realistic graphic video. The fantasy sports contest application may provide links to animated videos for depicting plays on contest screens in which information associated with the plays may be displayed. The fantasy sports contest application may play the animated video for a user in response to the user selecting such a link. In some embodiment of the present invention, the fantasy sports contest application may also customize animated video based on user-supplied setup information. For example, the fantasy sports contest application may provide play information and other related data to allow a user to generate animated videos using the user's own graphics processing equipment and graphics animation program.
Owner:ROVI TECH CORP
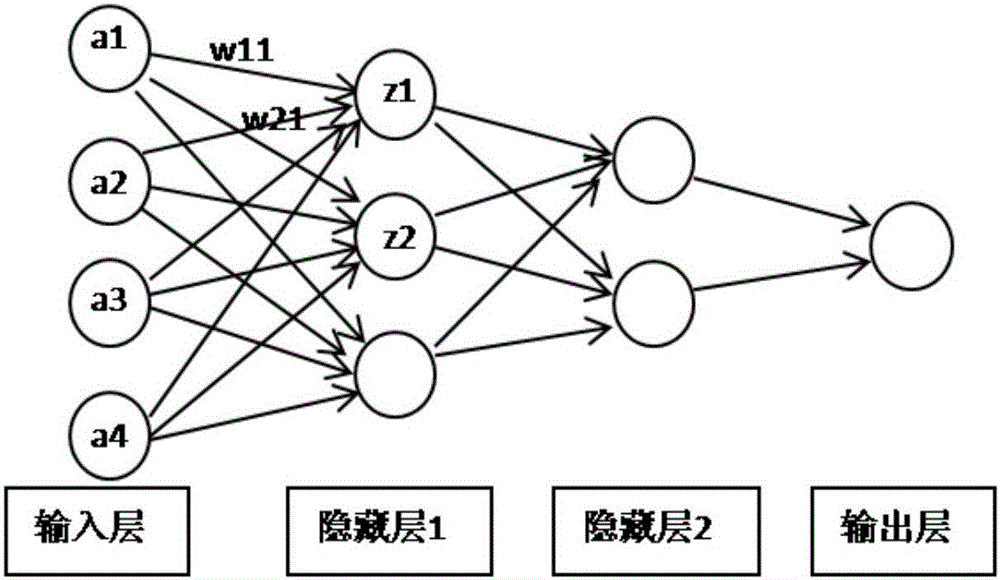
Calculation engine and electronic equipment
ActiveCN106126481AMaximize UtilizationReduce bandwidth requirementsPhysical realisationComplex mathematical operationsReal-time computingCache management
The invention relates to the technical field of calculation acceleration and discloses a calculation engine and electronic equipment to increase the utilization rate of data, reduce bandwidth requirement and improve calculation performance. The calculation engine comprises a cache management module, a matching and distributing module and at least L calculation modules, wherein the cache management module is used for reading L element values in an M-dimensional input vector and conducting caching, reading L-dimensional row vectors in submatrixes corresponding to the L element values in an M*N parameter matrix in sequence and transmitting the L-dimensional row vectors to the matching and distributing module, and the matching and distributing module is used for taking out a corresponding element value from the cache management module every time an L-dimensional row vector is received, matching the element value taken out with values in the L-dimensional row vectors, and sending matching results to the corresponding calculation modules in the at least L calculation modules; any one calculation module is used for calculating the matching results.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Managed peer-to-peer applications, systems and methods for distributed data access and storage
InactiveUS7917628B2Reduce bandwidth requirementsDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsData accessRemote computer
Applications, systems and methods for efficiently accessing and controlling data of devices among multiple computers over a network. Peer-to-peer exchanges of data between private computers is made possible while providing seamless, firewall-compliant connectivity. Such functionality is available even among private users over a public network, and even when multiple firewalls must be passed through. A firewall compliant connection may be established between a local computer and at least one remote computer; at least one file on a storage device associated with one of the computers is selected, and securely sent to at least one other computer over the secure connections. Computers may be connected over a wide area network with or without a connection server, with or without a VPN.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
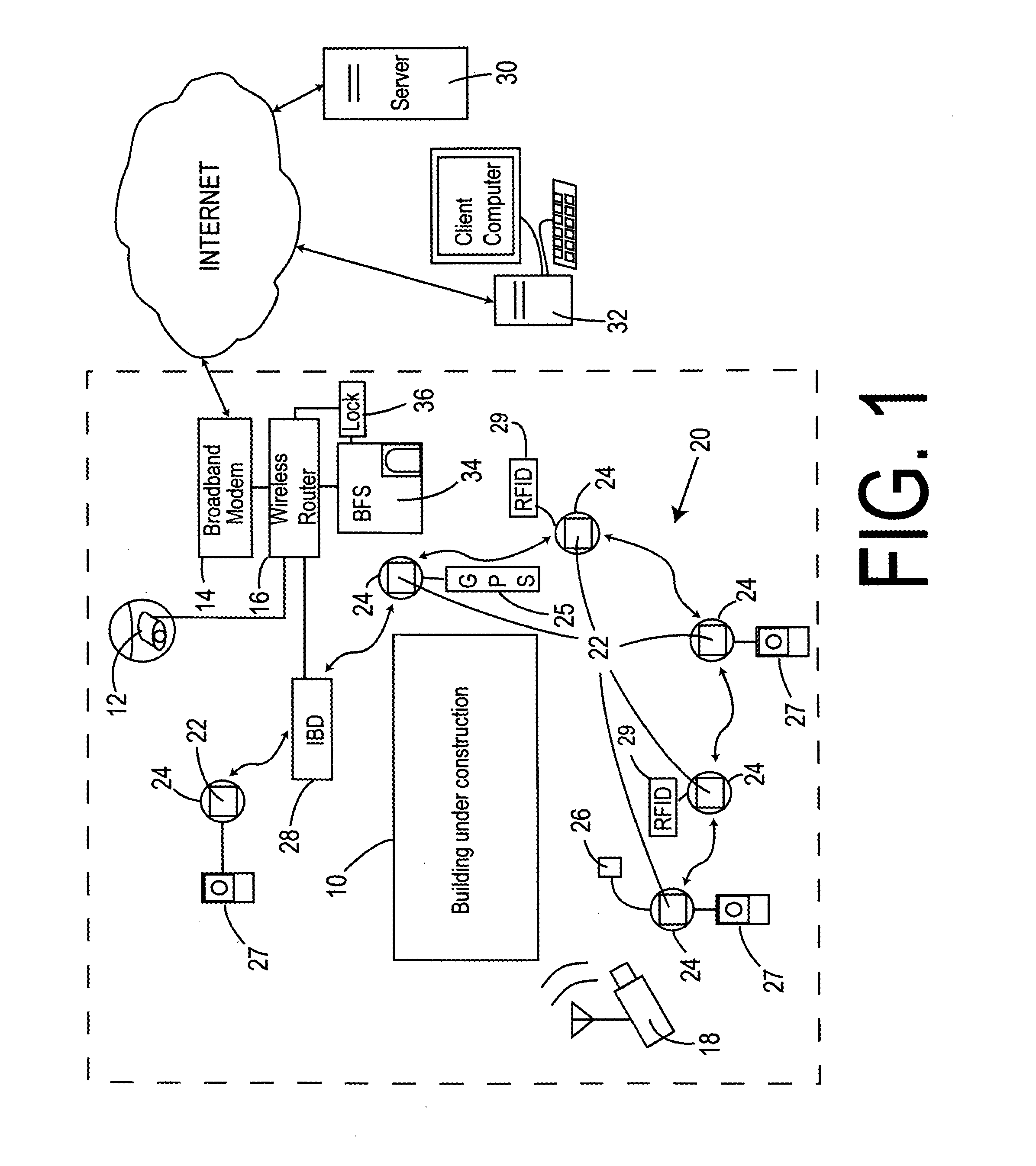
Work site remote monitoring and employee time tracking system and method
InactiveUS20080177646A1Security monitoring be enhanceReduce bandwidth requirementsElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisBroadbandFingerprint
A work site monitoring and employee time tracking system that includes a work site Internet connection having a broadband modem in communication with a router for transporting data to and from the work site and a work site IP camera in communication with the router for transporting images from the work site to client computers in communication with the Internet. A biometric fingerprint scanner for identifying and clocking-in and clocking-out work site workers is also included. The biometric scanner is in communication with the router for transmitting identification, clock-in and clock-out data to a server computer in communication with the Internet.
Owner:PROPERTY MONITORS
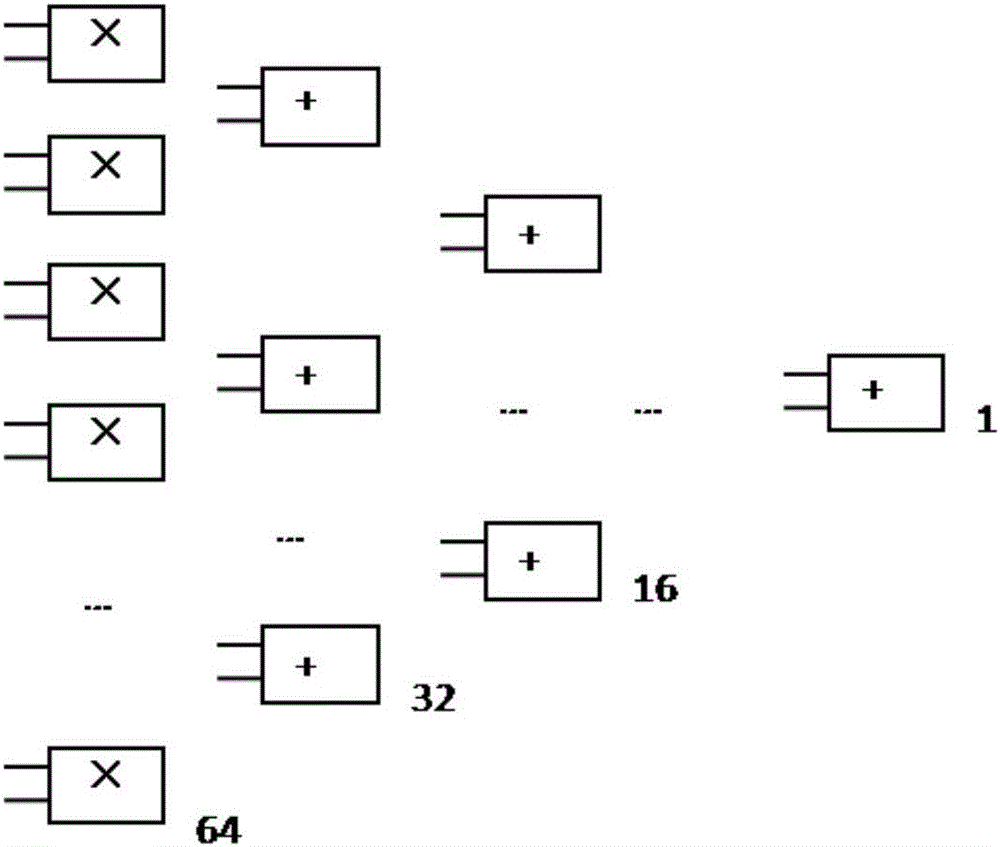
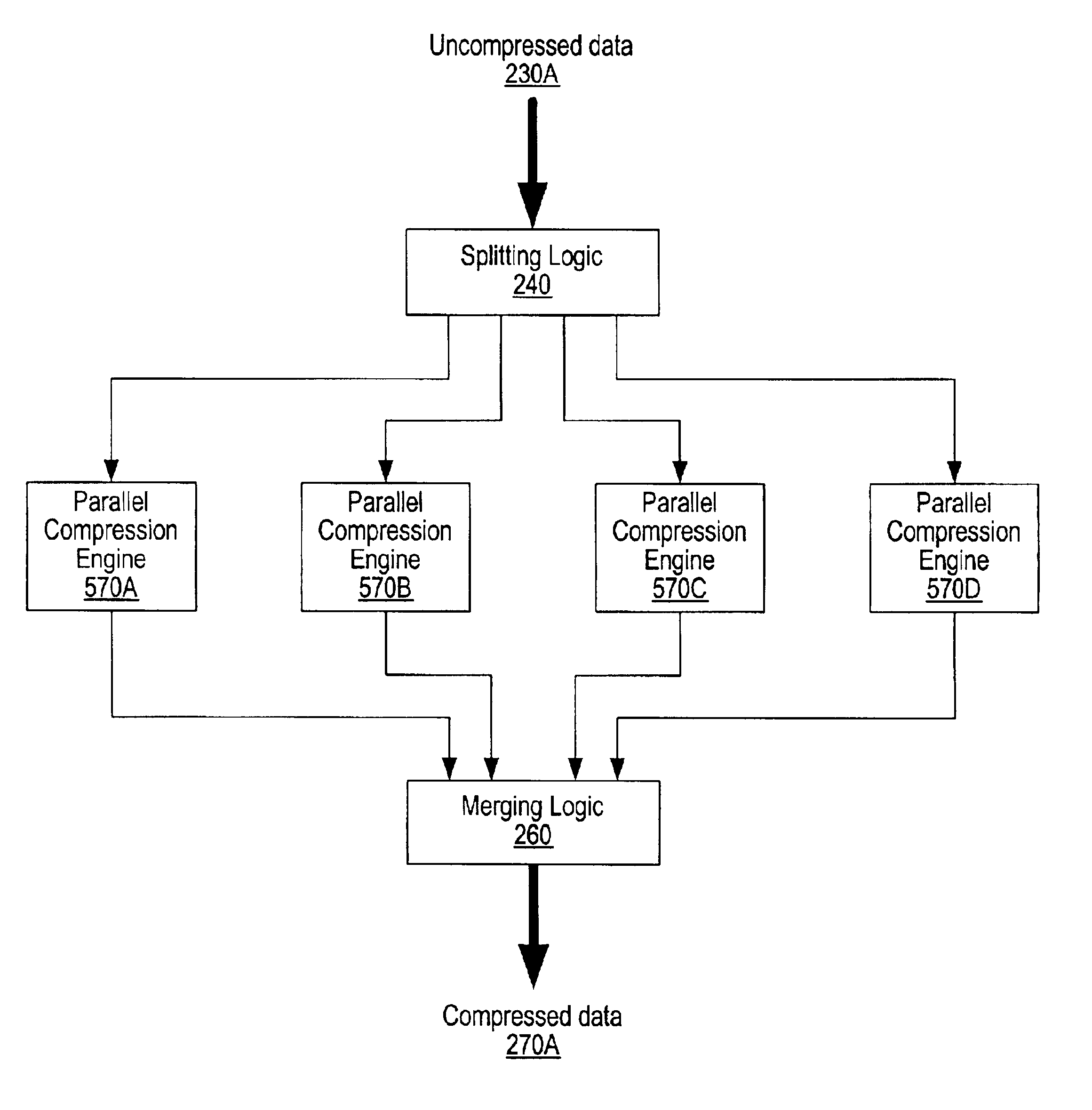
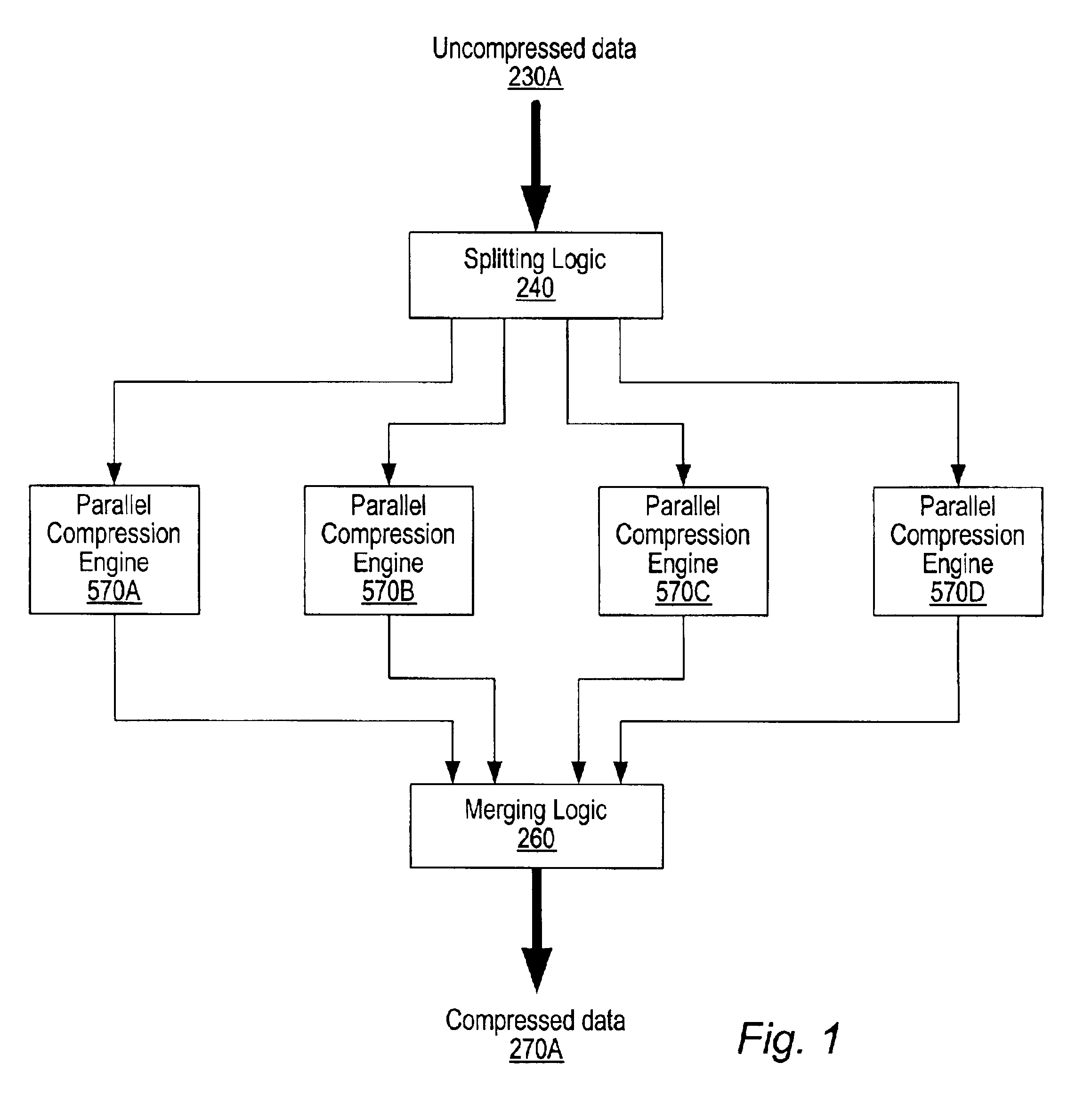
System and method for generating optimally compressed data from a plurality of data compression/decompression engines implementing different data compression algorithms
InactiveUS6885319B2Increase compression and decompression performanceIncrease performanceCode conversionImage codingMemory controllerStreaming data
Embodiments of a compression / decompression (codec) system may include a plurality of data compression engines each implementing a different data compression algorithm. A codec system may be designed for the reduction of data bandwidth and storage requirements and for compressing / decompressing data. Uncompressed data may be compressed using a plurality of compression engines in parallel, with each engine compressing the data using a different lossless data compression algorithm. At least one of the data compression engines may implement a parallel lossless data compression algorithm designed to process stream data at more than a single byte or symbol at one time. The plurality of different versions of compressed data generated by the different compression algorithms may be examined to determine an optimal version of the compressed data according to one or more predetermined criteria. A codec system may be integrated in a processor, a system memory controller or elsewhere within a system.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
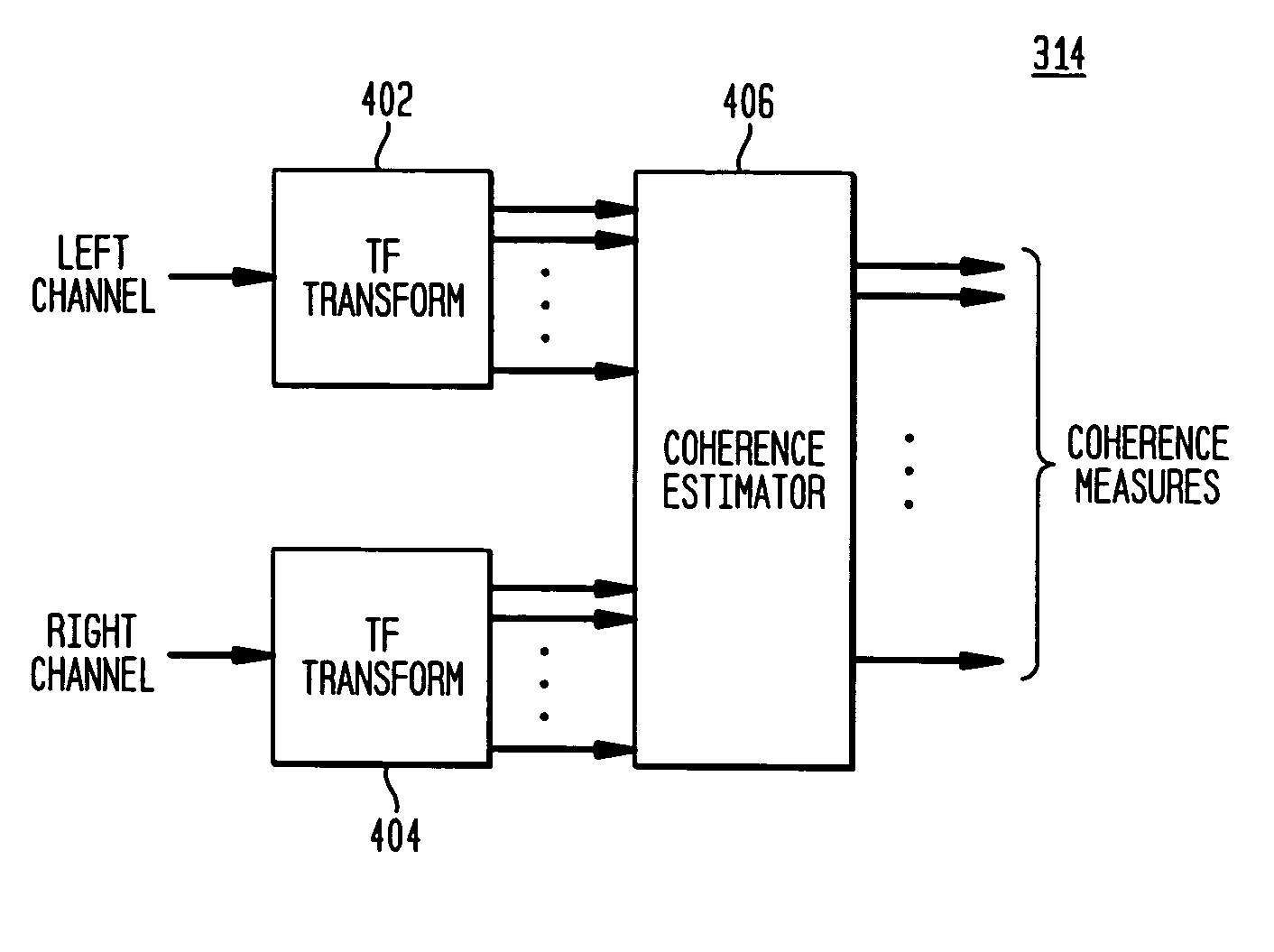
Coherence-based audio coding and synthesis
InactiveUS7006636B2Reduce transmission bandwidth requirementsReduce bandwidth requirementsSpeech analysisPseudo-stereo systemsInteraural time differenceVocal tract
An auditory scene is synthesized from a mono audio signal by modifying, for each critical band, an auditory scene parameter (e.g., an inter-aural level difference (ILD) and / or an inter-aural time difference (ITD)) for each sub-band within the critical band, where the modification is based on an average estimated coherence for the critical band. The coherence-based modification produces auditory scenes having objects whose widths more accurately match the widths of the objects in the original input auditory scene.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and method for performing compound vector operations
InactiveUS6192384B1Reduce bandwidth requirementsMinimize the numberOperational speed enhancementRegister arrangementsOperating instructionImaging processing
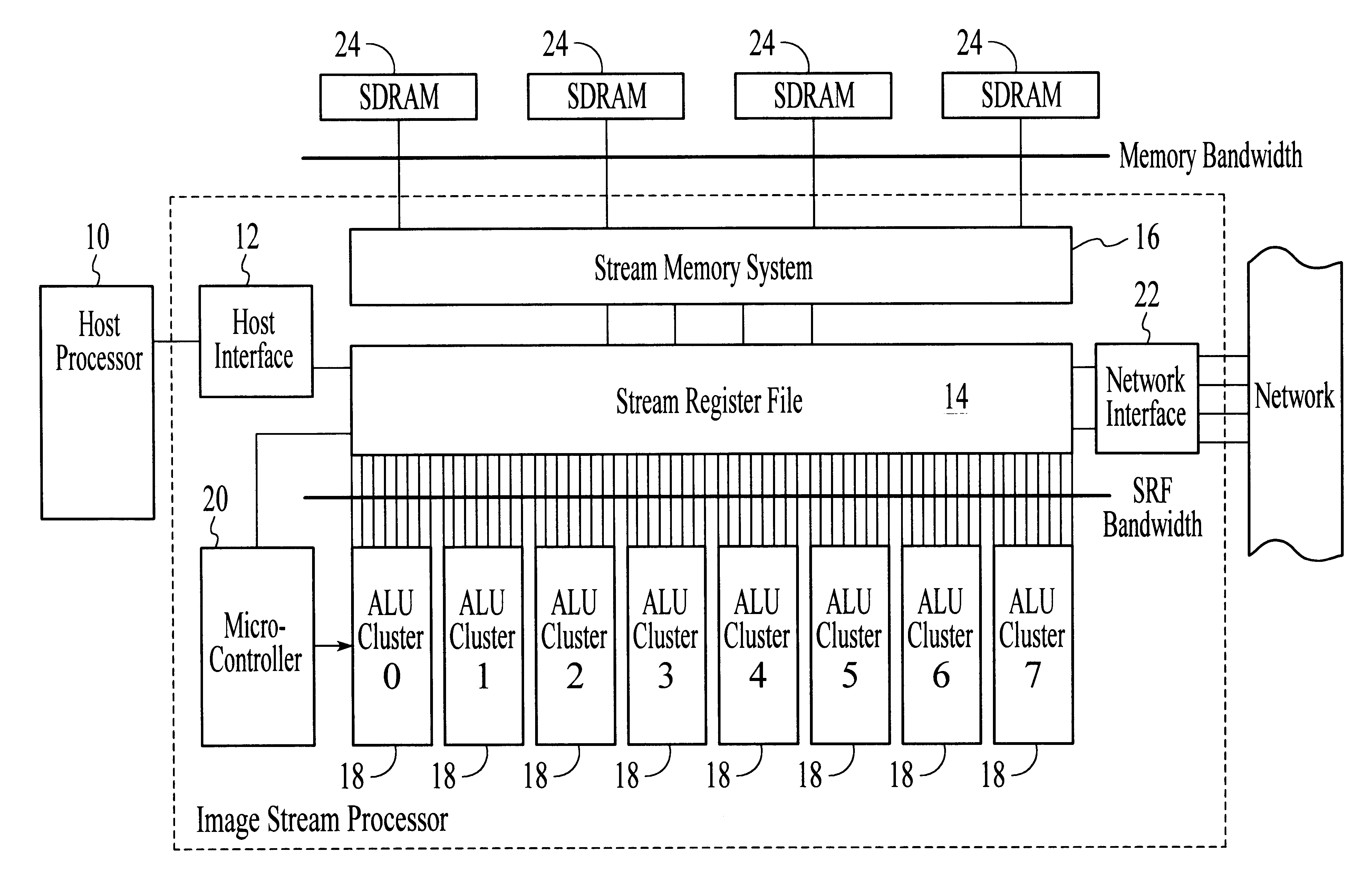
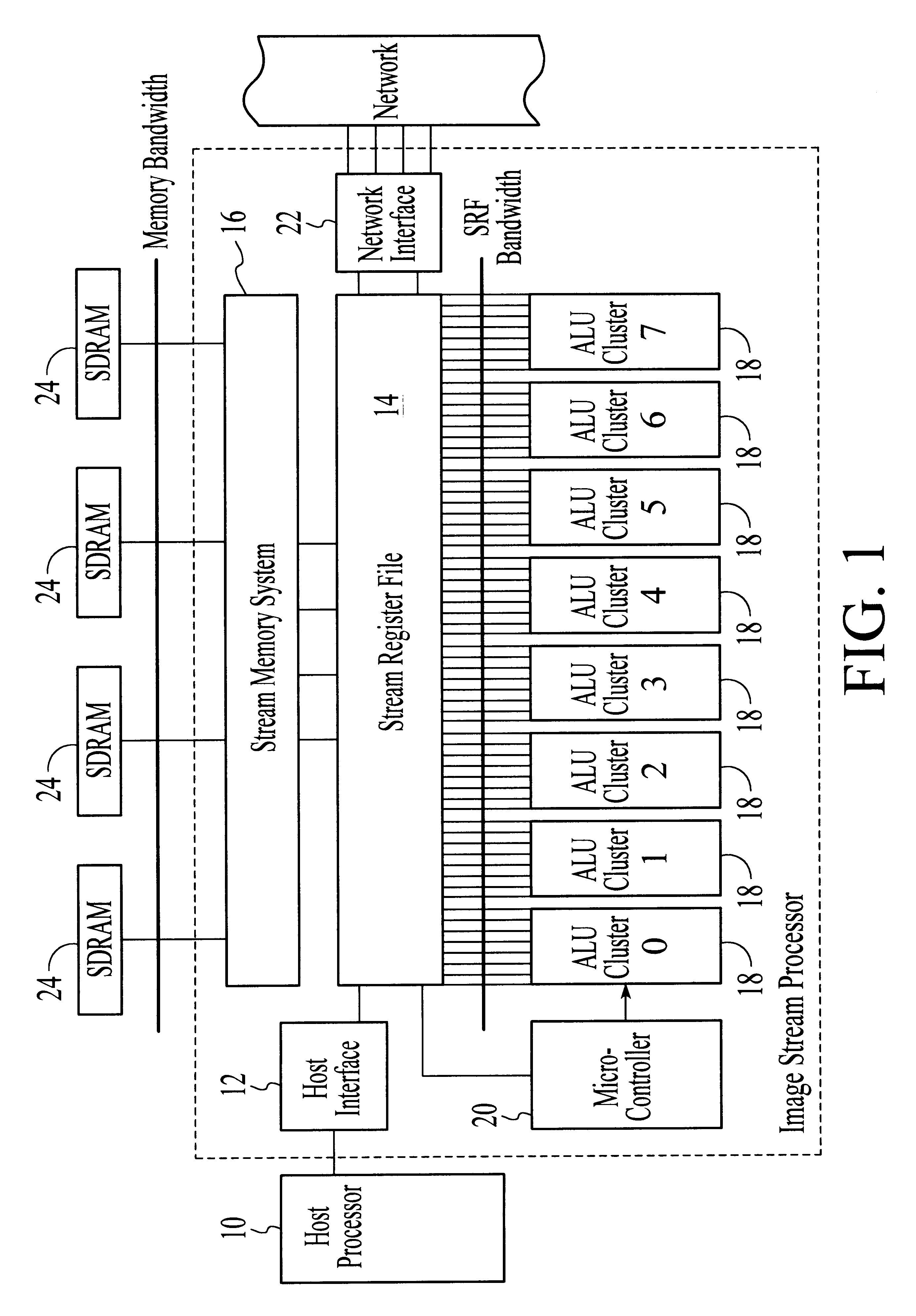
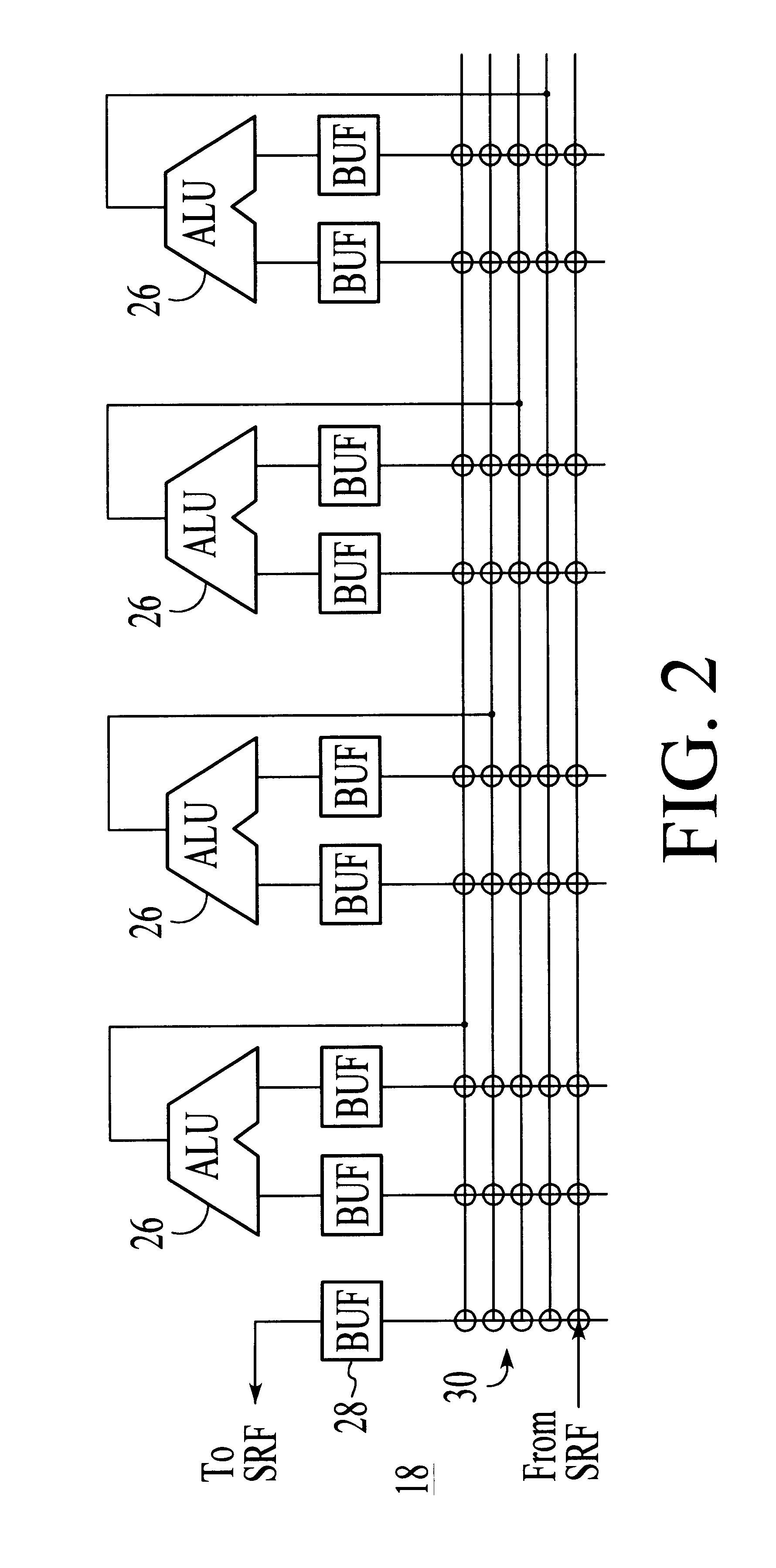
A processor particularly useful in multimedia applications such as image processing is based on a stream programming model and has a tiered storage architecture to minimize global bandwidth requirements. The processor has a stream register file through which the processor's functional units transfer streams to execute processor operations. Load and store instructions transfer streams between the stream register file and a stream memory; send and receive instructions transfer streams between stream register files of different processors; and operate instructions pass streams between the stream register file and computational kernels. Each of the computational kernels is capable of performing compound vector operations. A compound vector operation performs a sequence of arithmetic operations on data read from the stream register file, i.e., a global storage resource, and generates a result that is written back to the stream register file. Each function or compound vector operation is specified by an instruction sequence that specifies the arithmetic operations and data movements that are performed each cycle to carry out the compound operation. This sequence can, for example, be specified using microcode.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND +1
Method for generating map data
InactiveUS20130297198A1Less data-intensiveReduce bandwidth requirementsInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsGps navigationPosition dependent
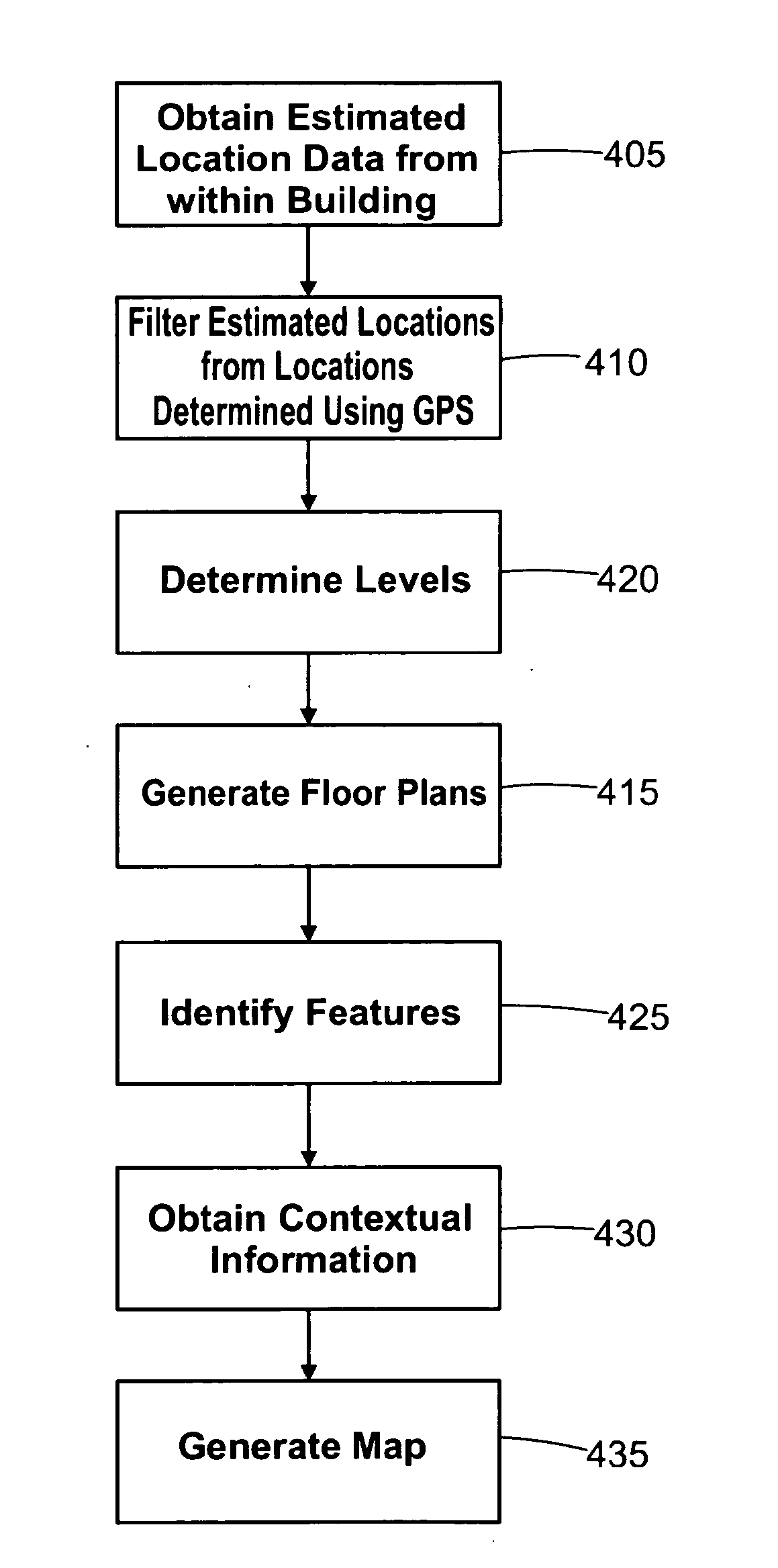
A method and system for generating map data is disclosed, wherein the map data represents the inside of a building and / or an enclosed and / or covered area. Location related data is firstly generated by a plurality of mobile devices using at least one non-GPS navigation sensor and at least one GPS sensor, preferably in each mobile device. The location related data is then aggregated and map data determined from the aggregated data.
Owner:TOMTOM BELGIUM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com