Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
453 results about "Physiological monitoring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Physiological monitoring is the direct measure of the status of an athlete—usually a one-body system or a combined set of systems. Most monitoring systems are passive, meaning they don’t require actual physical testing to capture data, thus making them popular in elite sport.
Sports health care apparatus with physiological monitoring function
InactiveUS20090247368A1Avoid injuryDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhysiologic StatesPhysiological monitoring
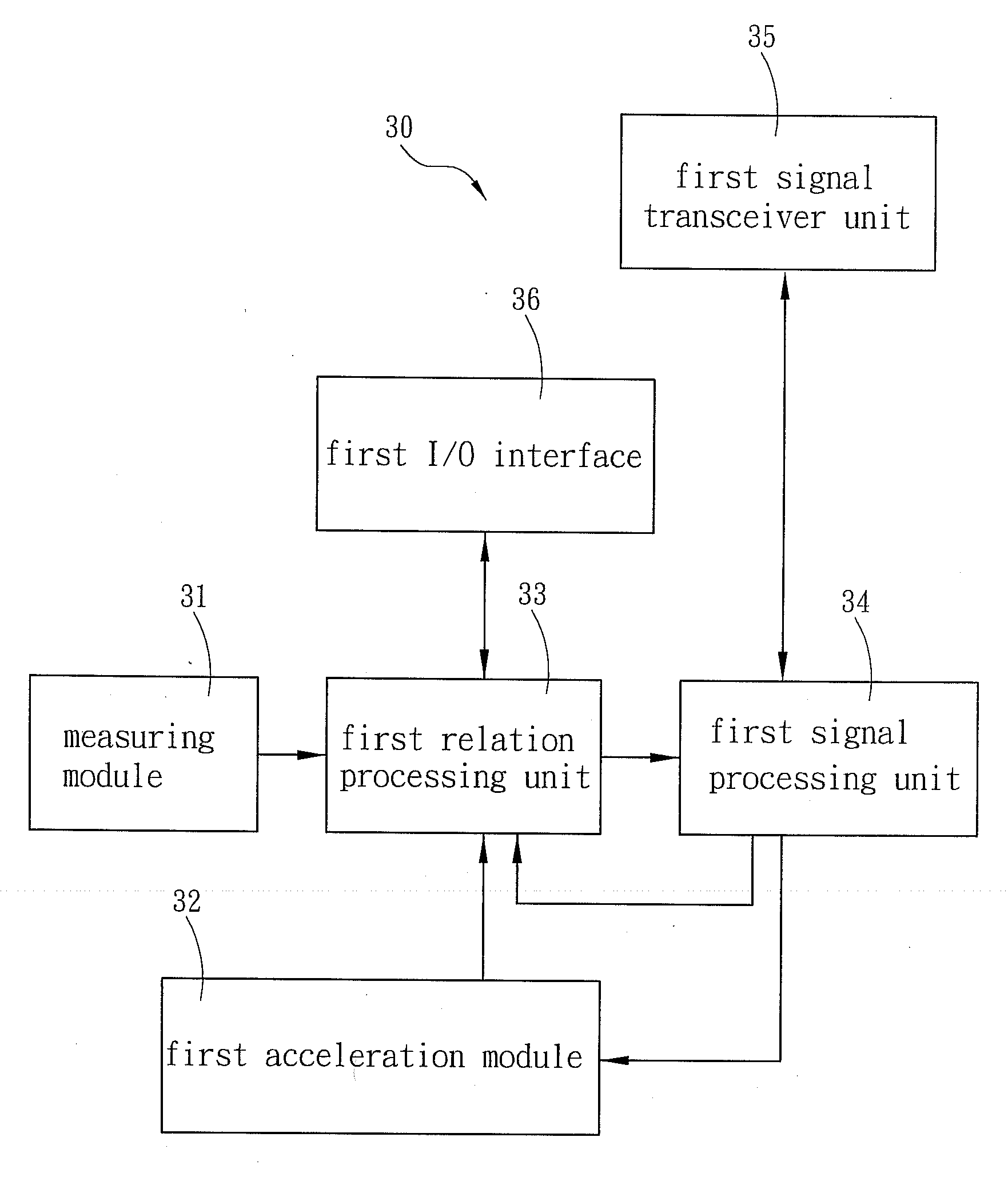
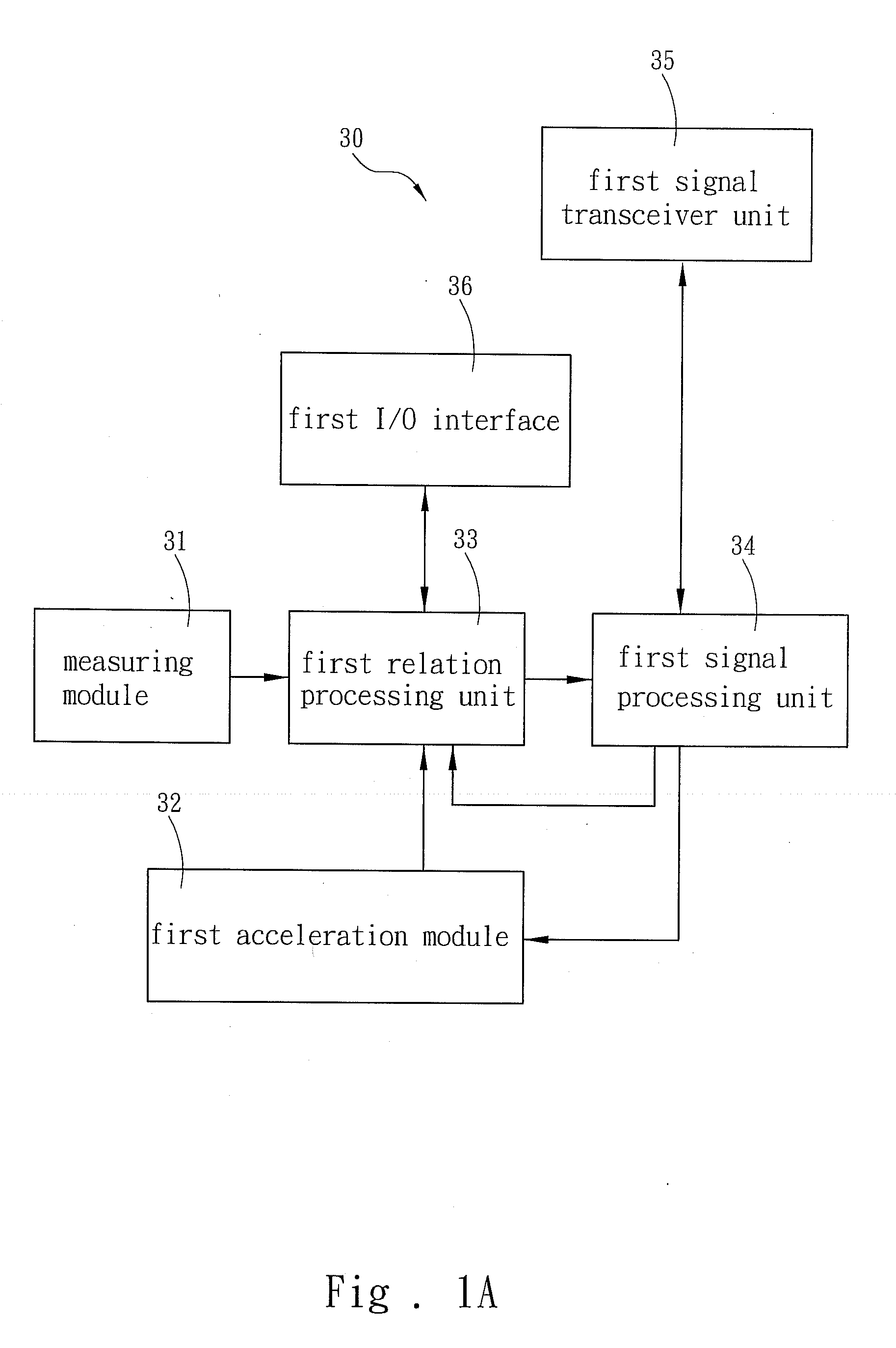
The present invention includes a handheld device and a main device, wherein the handheld device is held by an athlete and the main device is moved with the athlete. Through a measuring device acquiring a physiological condition of the athlete and a movement state of the handheld device and transmitting thereof to the main device, the main device can produce an exercise indication signal according thereto, so that the athlete can obtain an exercise direction and also can manage the physical condition during exercise.
Owner:BOSON TECH
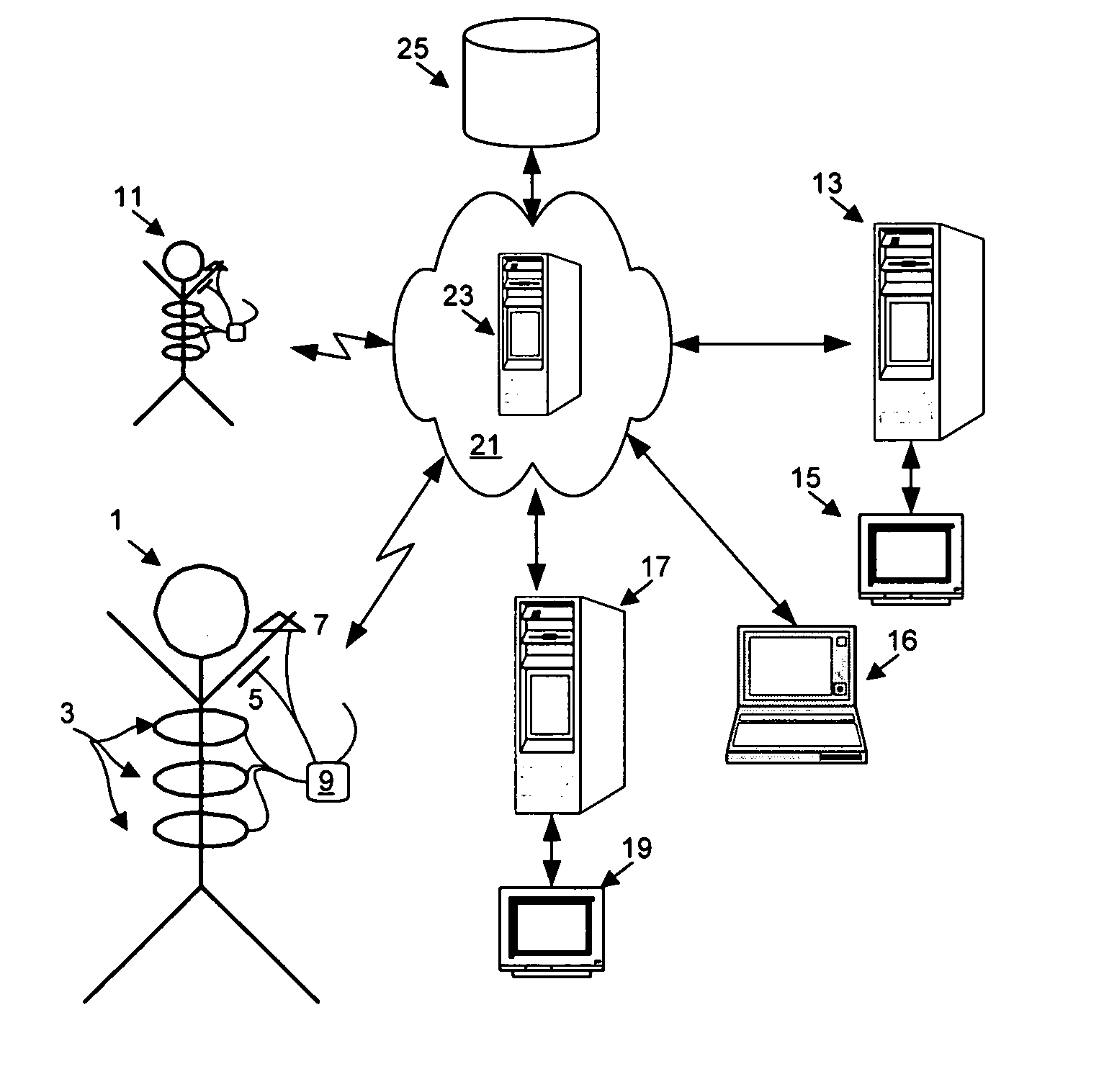
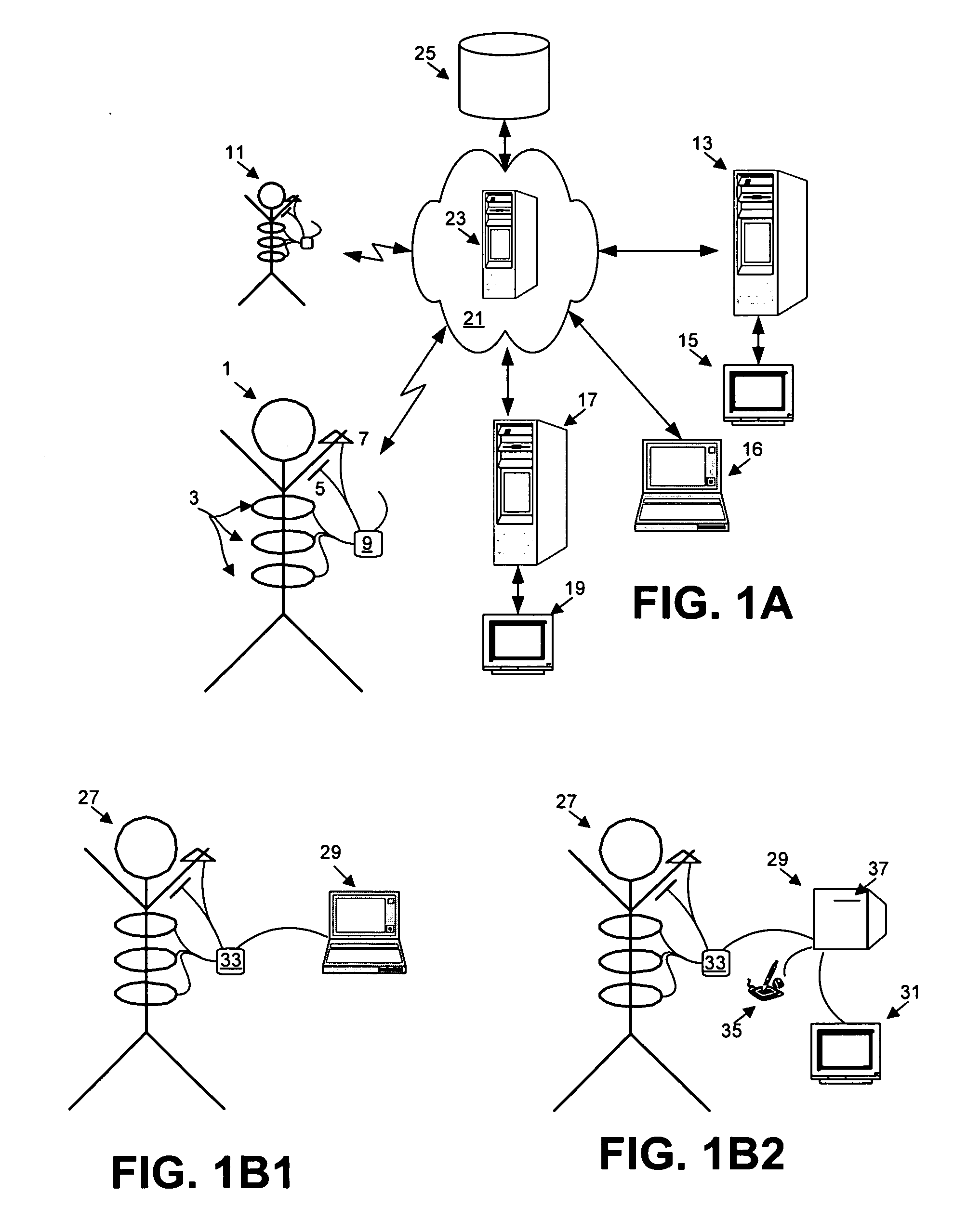
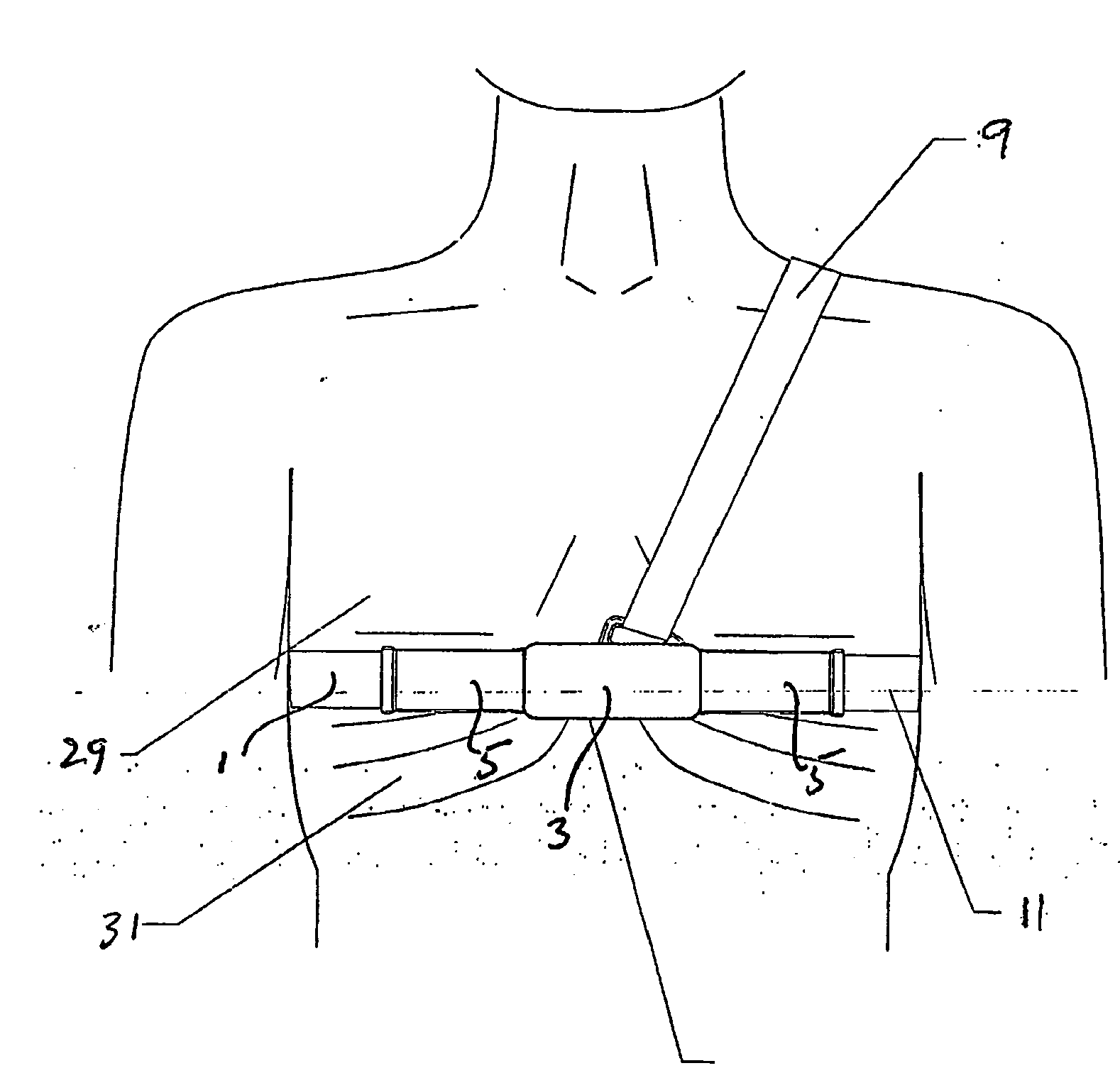
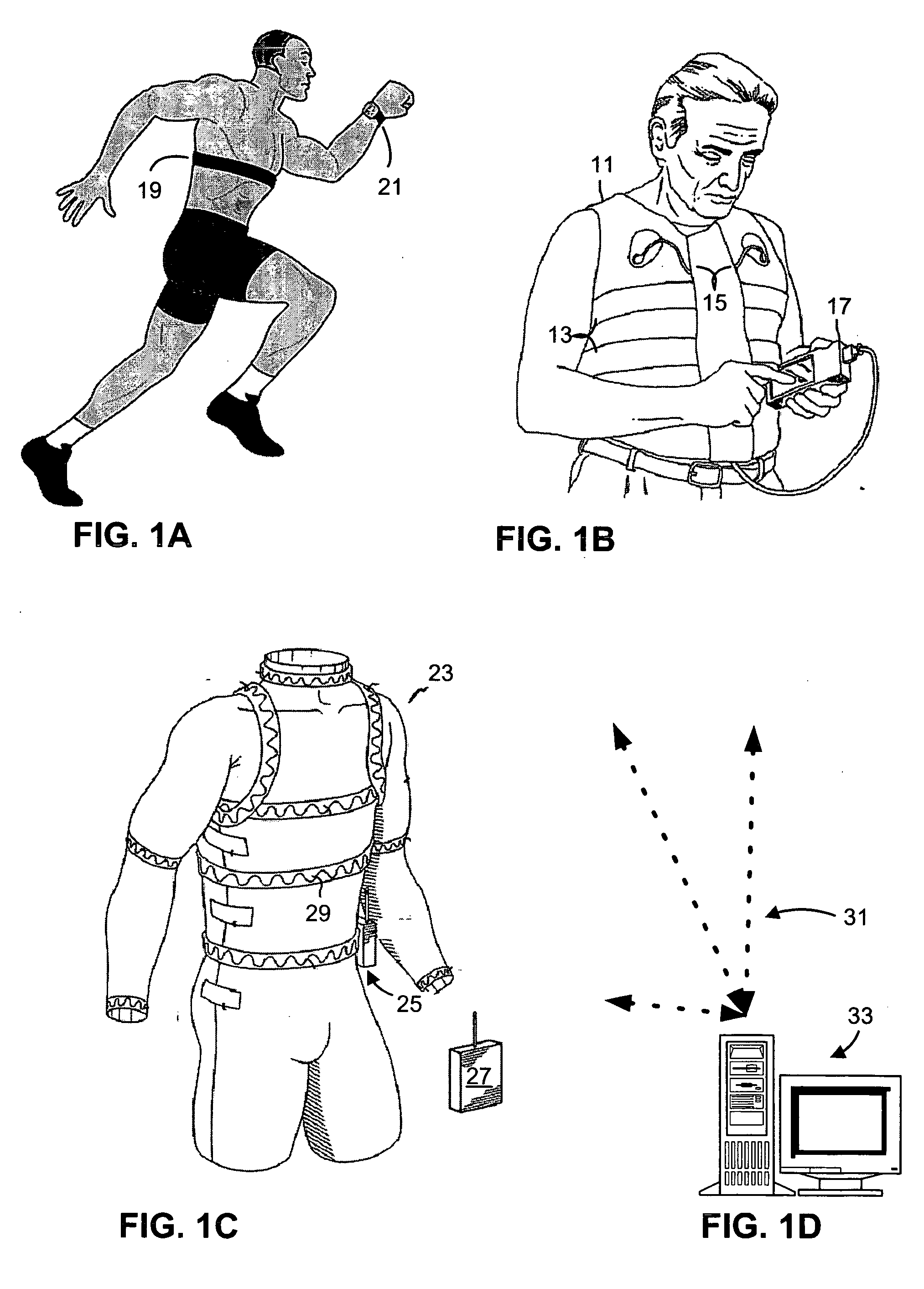
Systems and methods for ambulatory monitoring of physiological signs
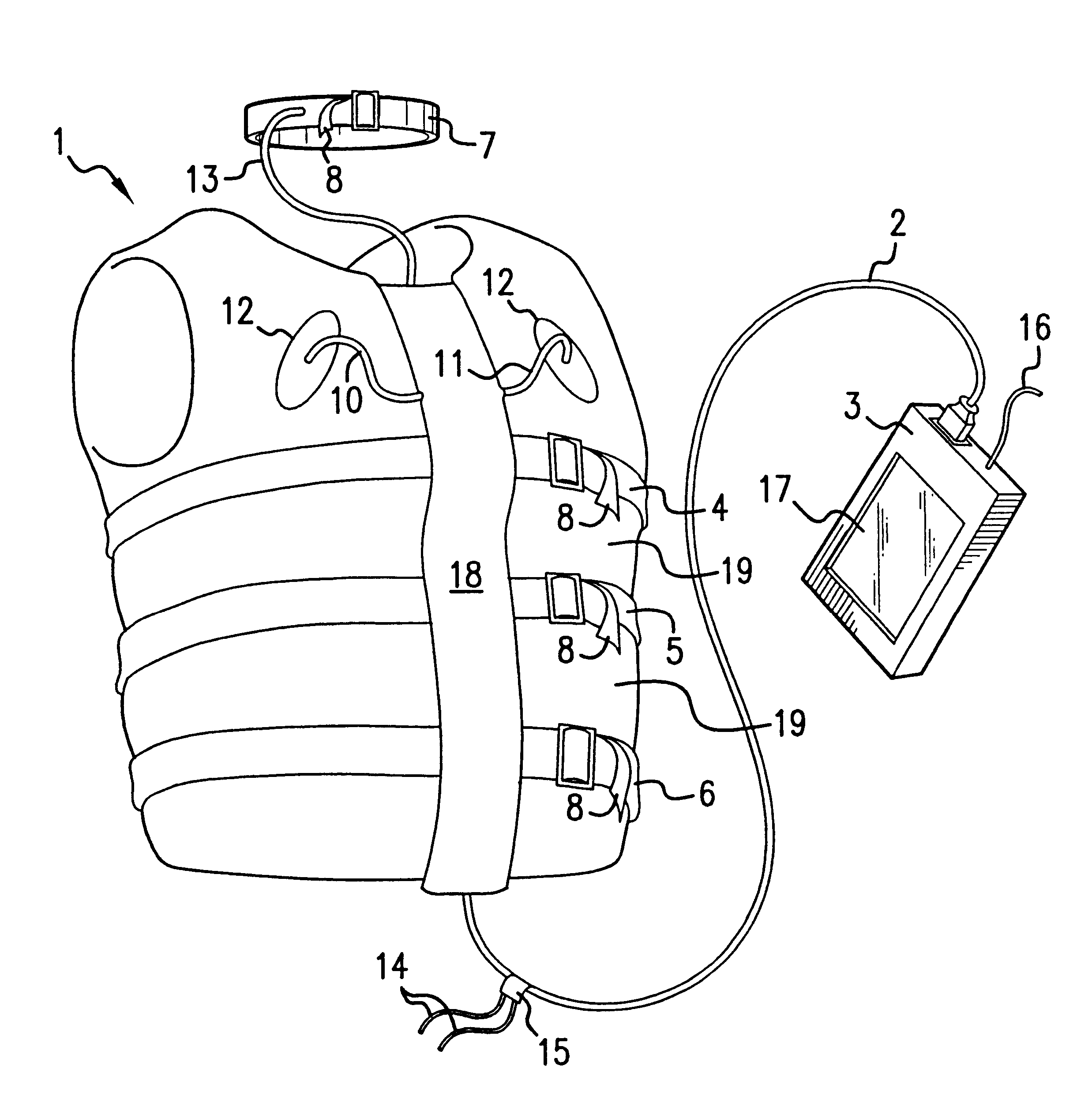
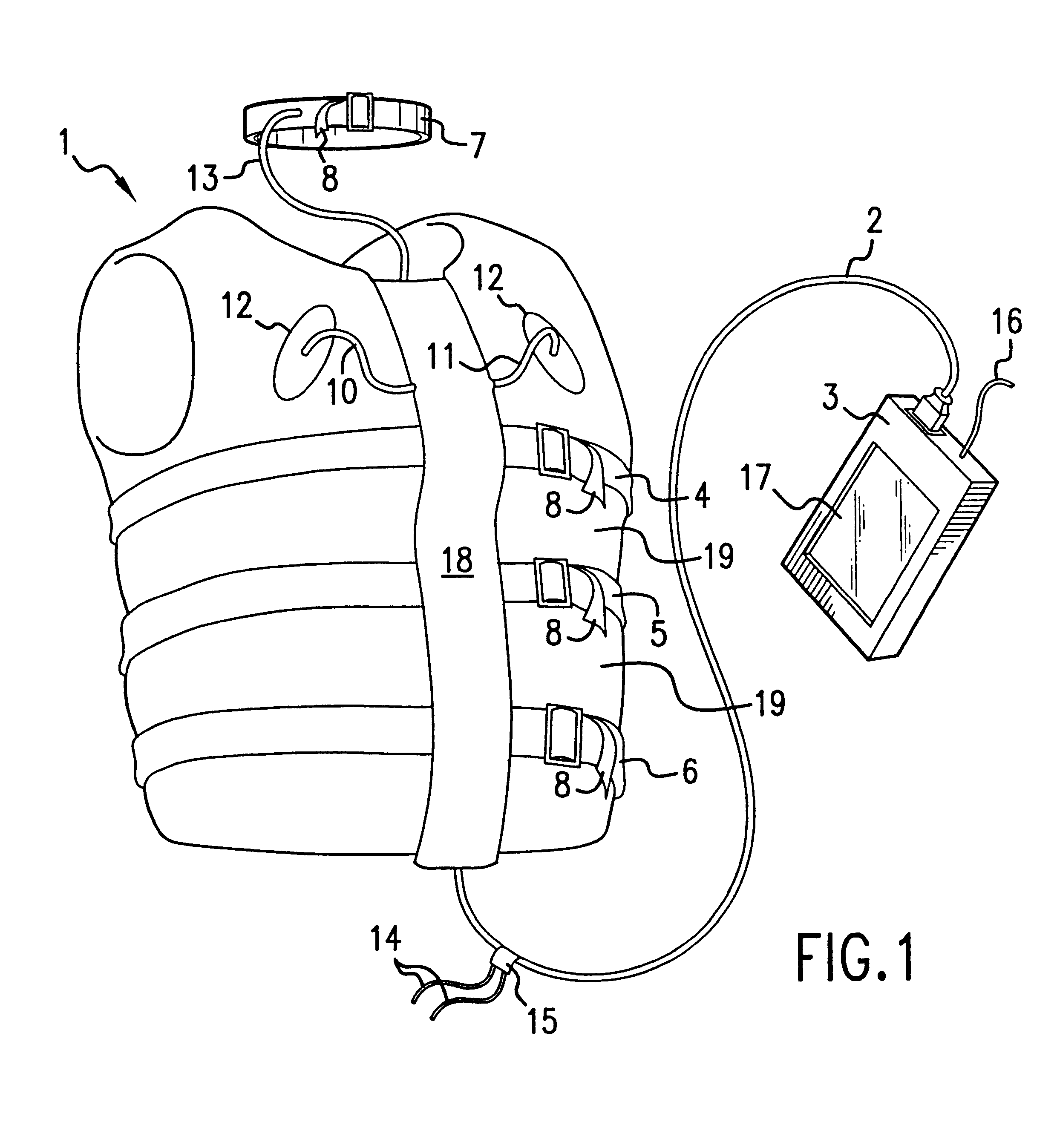
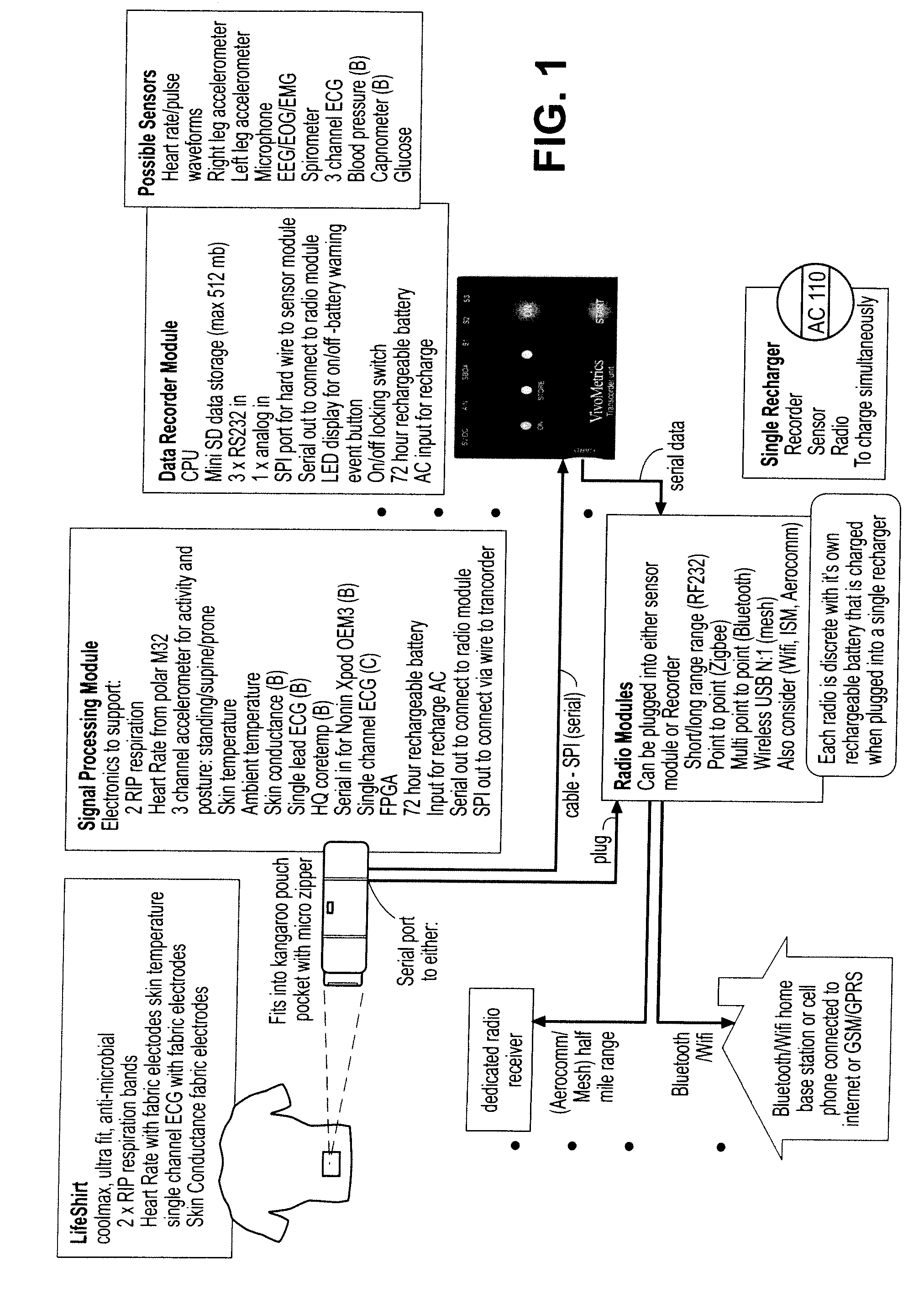
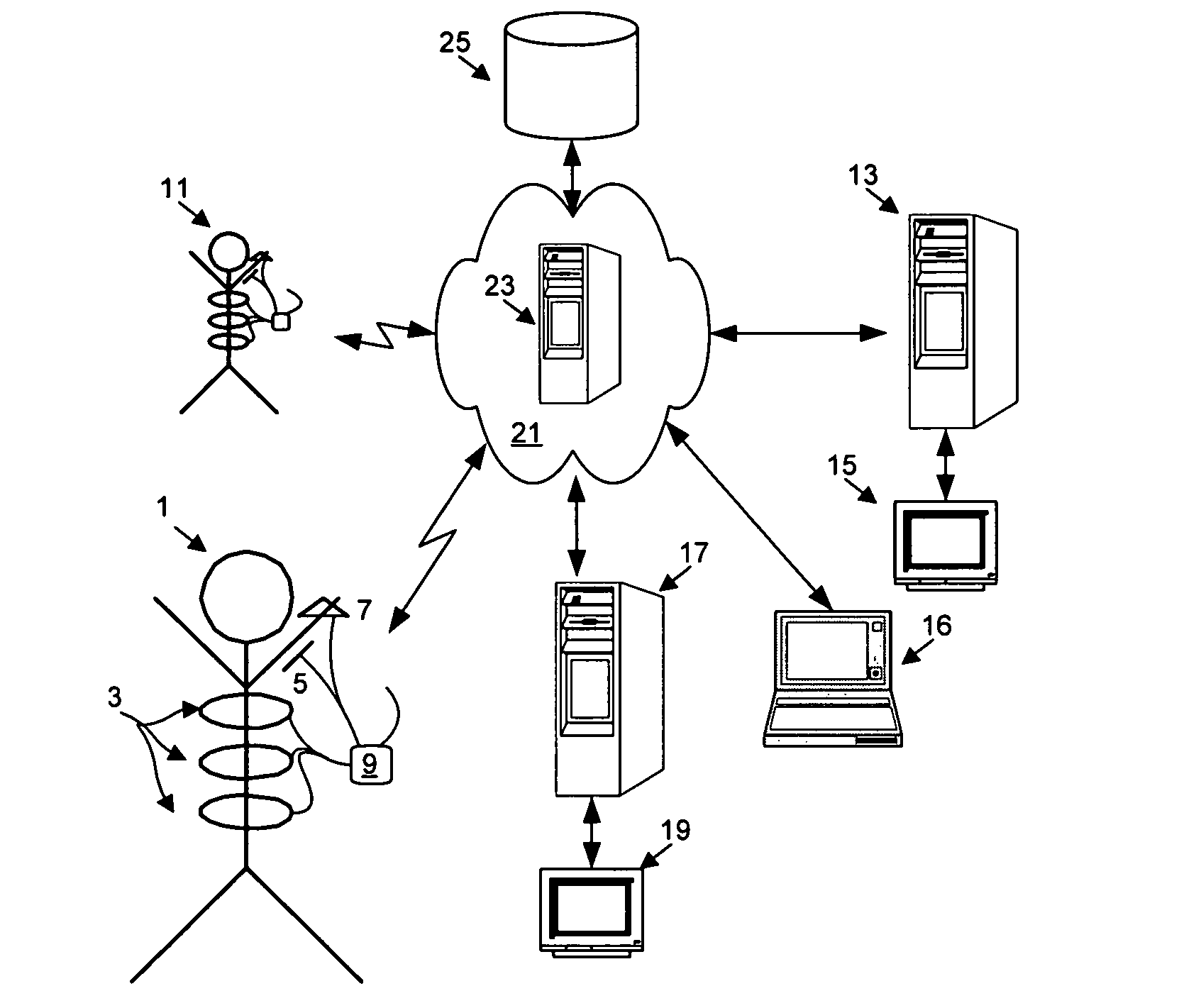
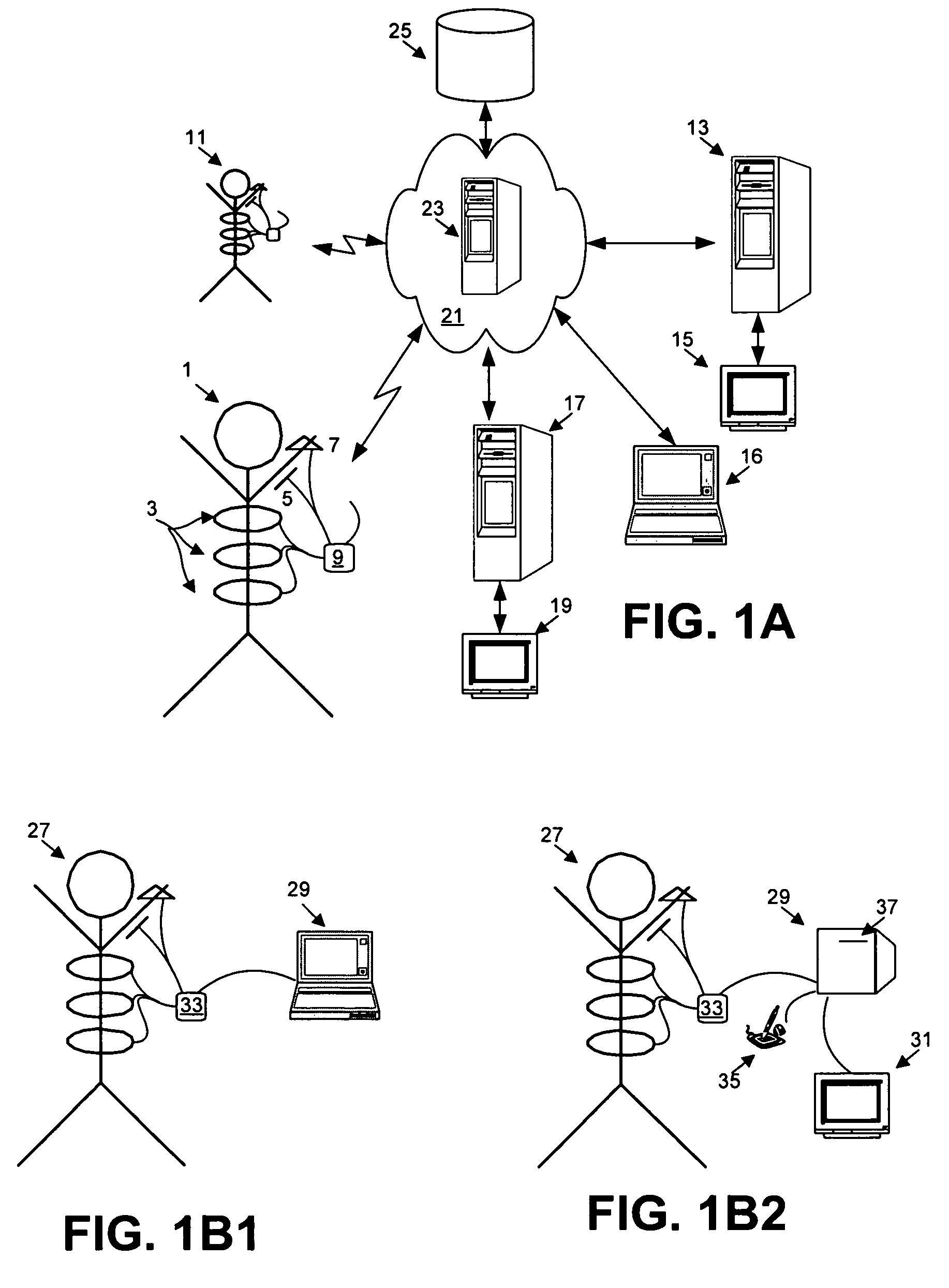
The present invention relates to the field of ambulatory and non-invasive monitoring of a plurality of physiological parameters of a monitored individual. The invention includes a physiological monitoring apparatus with an improved monitoring apparel worn by a monitored individual, the apparel having attached sensors for monitoring parameters reflecting pulmonary function, or parameters reflecting cardiac function, or parameters reflecting the function of other organ systems, and the apparel being designed and tailored to be comfortable during the individual's normal daily activities. The apparel is preferably also suitable for athletic activities. The sensors preferably include one or more ECG leads and one of more inductive plethysmographic sensor with conductive loops positioned closely to the individual to preferably monitor at least basic cardiac parameters, basic pulmonary parameters, or both. The monitoring apparatus also includes a unit for receiving data from the sensors, and for storing the data in a computer-readable medium. The invention also includes systems comprising a central data repository for receiving, storing, and processing data generated by a plurality of physiological monitored apparatus, and for making stored data available to the individual and to health care providers.
Owner:ADIDAS
Methods and Systems for Physiological and Psycho-Physiological Monitoring and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080214903A1Data processing applicationsElectrocardiographyPhysiological monitoringComputer module
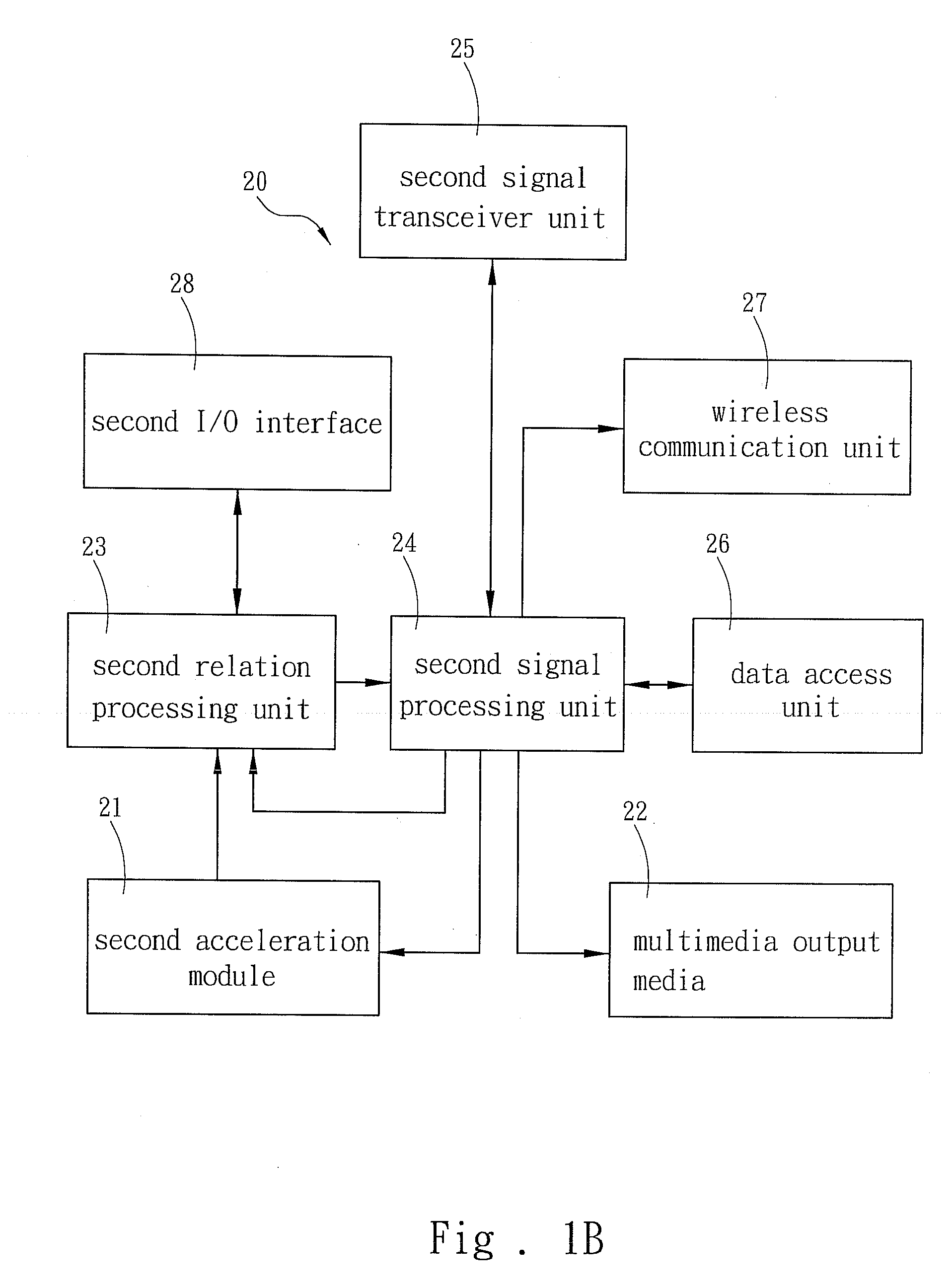
The invention provides a system and method for monitoring one or more physiological parameters of a user. The system of the invention includes one or more wearable sensor modules sensing the one or more physiological parameters. One or more transmitters wirelessly transmit signals indicative of values of the one or more physiological parameters to a mobile monitor. The mobile monitor includes a processor processing the signals received from the transmitter in real time using expert knowledge. A device provides one or more indications of results of the processing. The invention also provides wearable mobile sensors for use in the system of the invention. The method of the invention includes obtaining values of the physiological parameters of the user from one or more wearable sensor modules. Signals indicative of values of the one or more physiological parameters are wirelessly transmitted to a mobile monitor. The signals are processed in real time using expert knowledge, and one or more indications of results of the processing are provided to the mobile unit.
Owner:HEALTH SMART
Systems and methods for ambulatory monitoring of physiological signs
InactiveUS20020032386A1Improve health care outcomeReduce health case costElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsSports activityCardiac functioning
The present invention relates to the field of ambulatory and non-invasive monitoring of a plurality of physiological parameters of a monitored individual. The invention includes a physiological monitoring apparatus with an improved monitoring apparel worn by a monitored individual, the apparel having attached sensors for monitoring parameters reflecting pulmonary function, or parameters reflecting cardiac function, or parameters reflecting the function of other organ systems, and the apparel being designed and tailored to be comfortable during the individual's normal daily activities. The apparel is preferably also suitable for athletic activities. The sensors preferably include one or more ECG leads and one of more inductive plethysmographic sensor with conductive loops positioned closely to the individual to preferably monitor at least basic cardiac parameters, basic pulmonary parameters, or both. The monitoring apparatus also includes a unit for receiving data from the sensors, and for storing the data in a computer-readable medium. The invention also includes systems comprising a central data repository for receiving, storing, and processing data generated by a plurality of physiological monitored apparatus, and for making stored data available to the individual and to health care providers.
Owner:ADIDAS
Computer interfaces including physiologically guided avatars
This invention provides user interfaces that more intuitively display physiological data obtained from physiological monitoring of one or more subjects. Specifically, the user interfaces of this invention create and display one or more avatars having behaviors guided by physiological monitoring data. The monitoring data is preferably obtained when the subject is performing normal tasks without substantial restraint. This invention provides a range of implementations that accommodate user having varying processing and graphics capabilities, e.g., from handheld electronic devices to ordinary PC-type computers and to systems with enhanced graphics capabilities.
Owner:ADIDAS
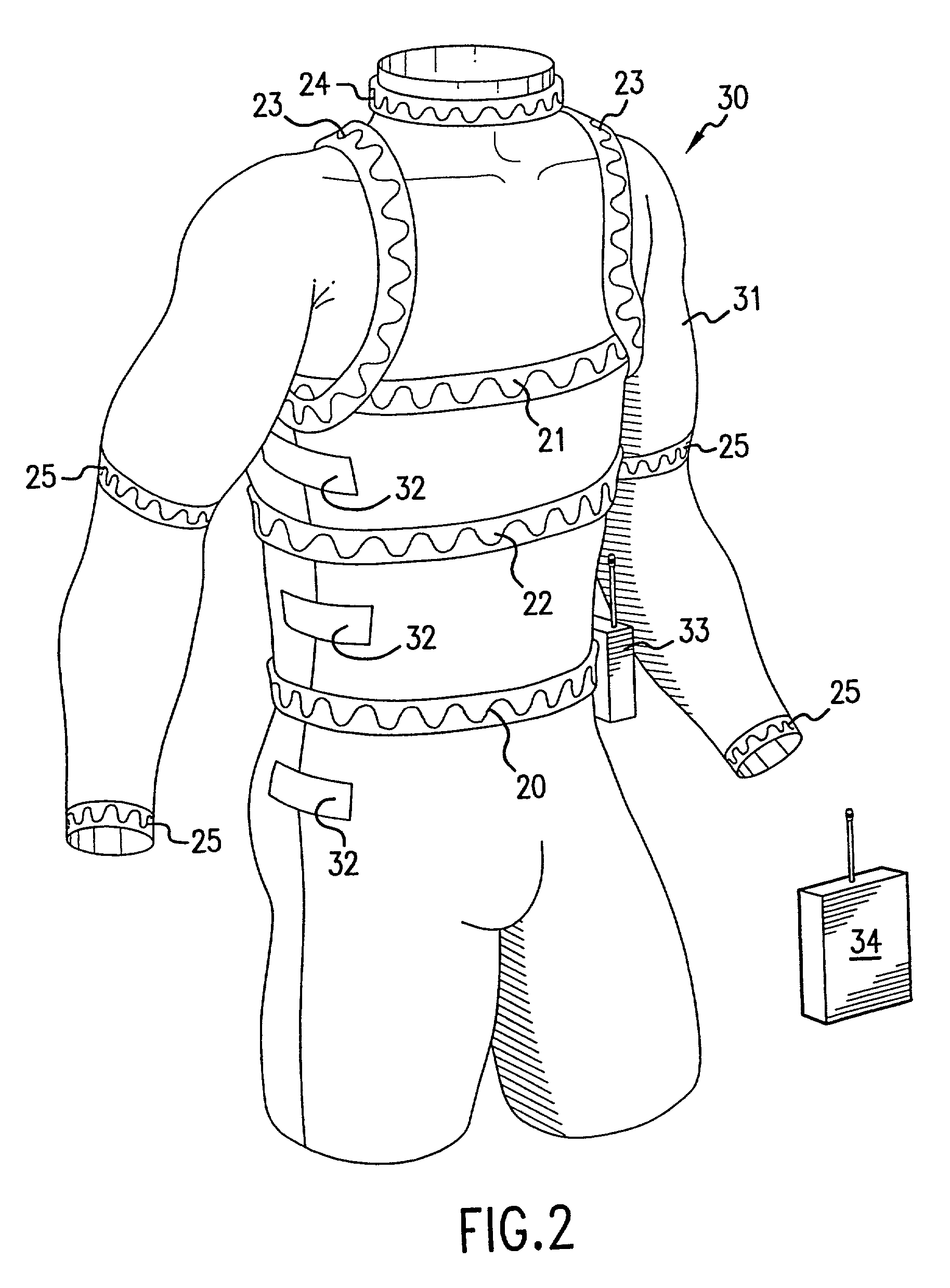
Life sign detection and health state assessment system
InactiveUS20090131759A1Sufficient confidenceGuaranteed normal transmissionDiagnostic signal processingHealth-index calculationSign detectionEngineering
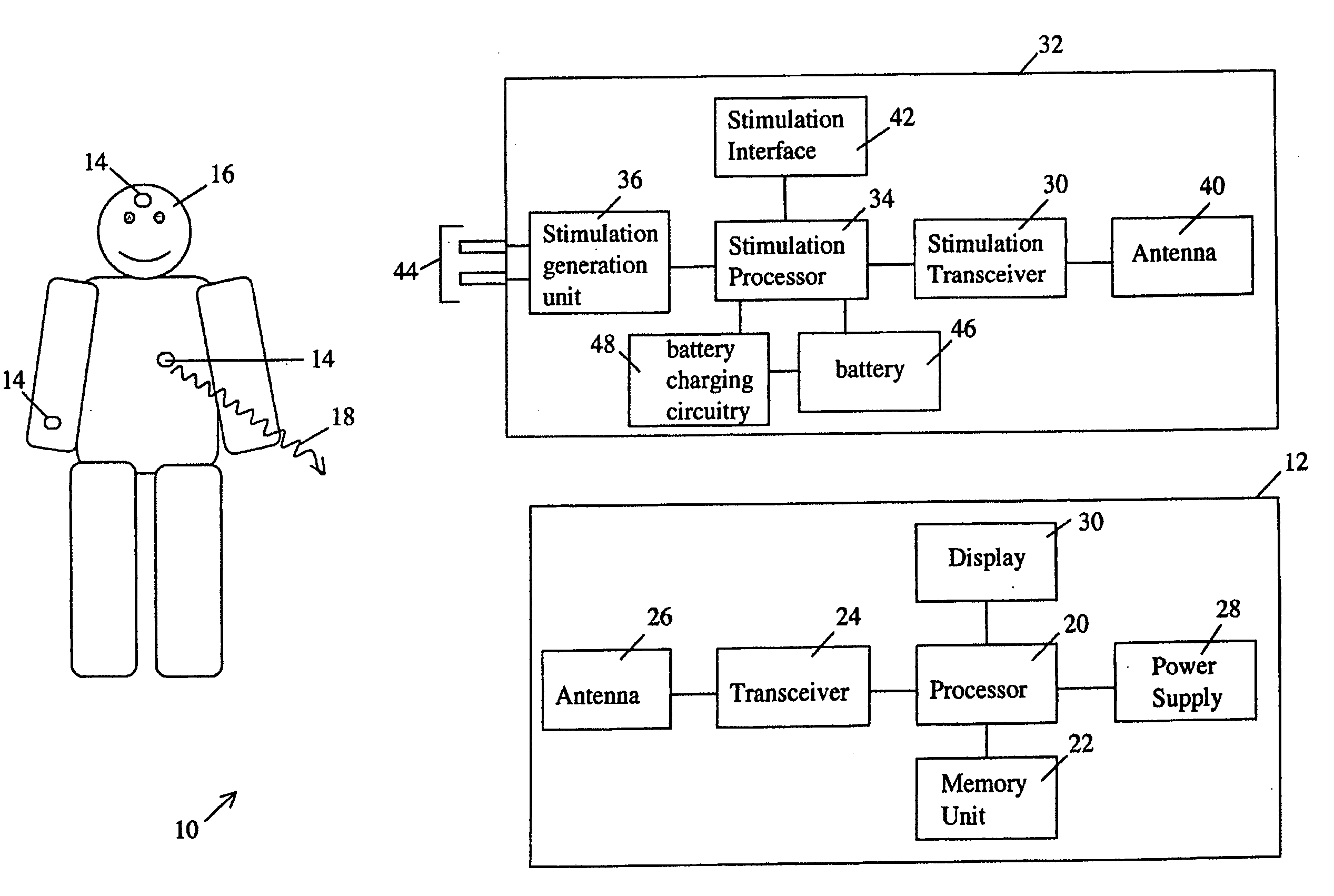
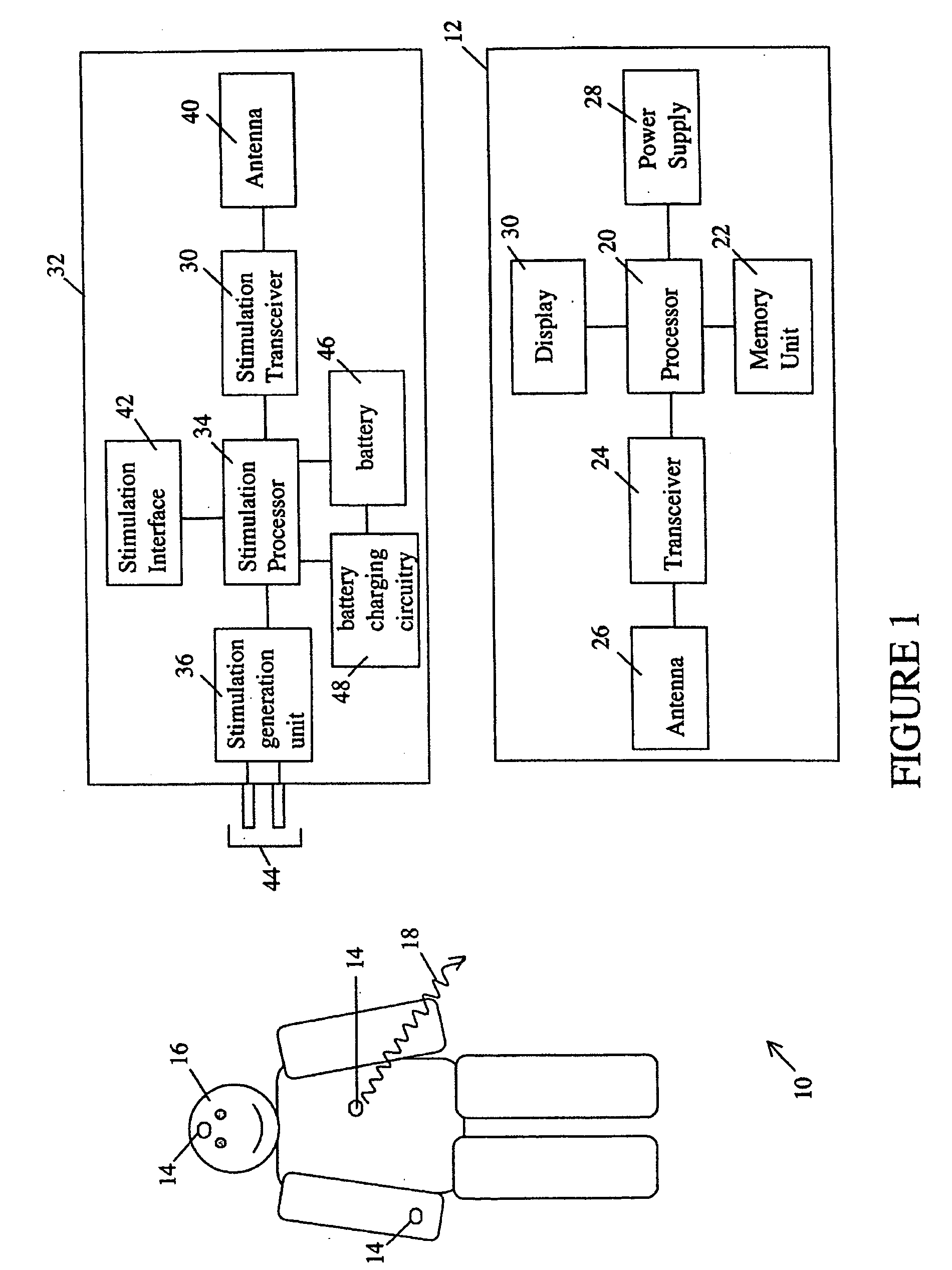
A wearable platform embodied in a belt or patch provides physiological monitoring of soldiers during field operations or trauma victims at accident sites and makes health state assessments. The platform includes sensors for heart rate, body motion, respiration rate and intensity, and temperature and further contains a microprocessor and short range transmitter. An analog circuit running an algorithm obtains the R-wave period from the EKG signal and produces electrical pulses with the period between pulses corresponding to the R-wave period. A rule based processing engine having an evaluation algorithm is capable of making a medical evaluation of subject condition and determines a confidence level for the evaluation. The rules are subject to variation depending upon the subject population. The information is communicated wirelessly to a local hub for relay to a remote monitor.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
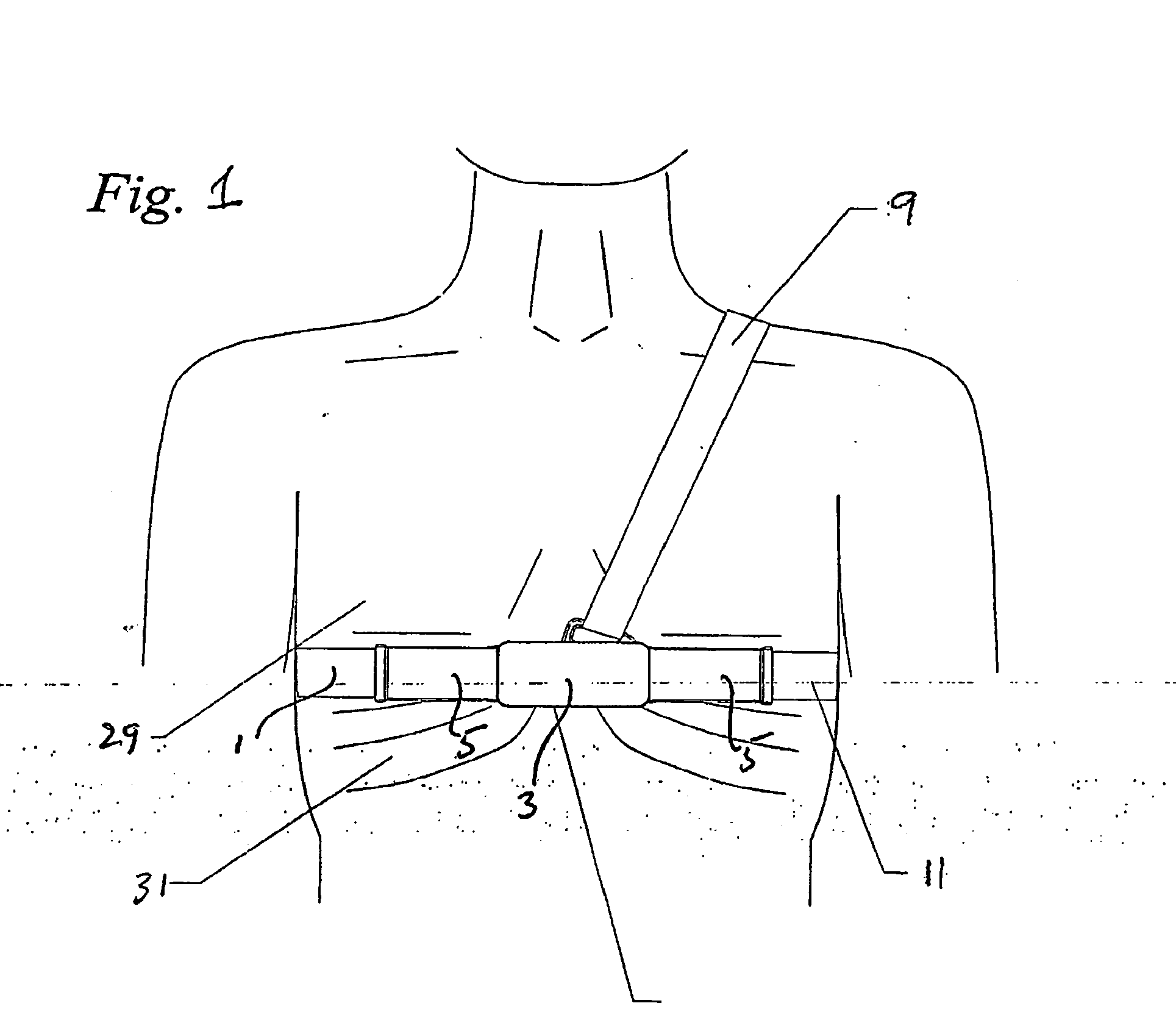
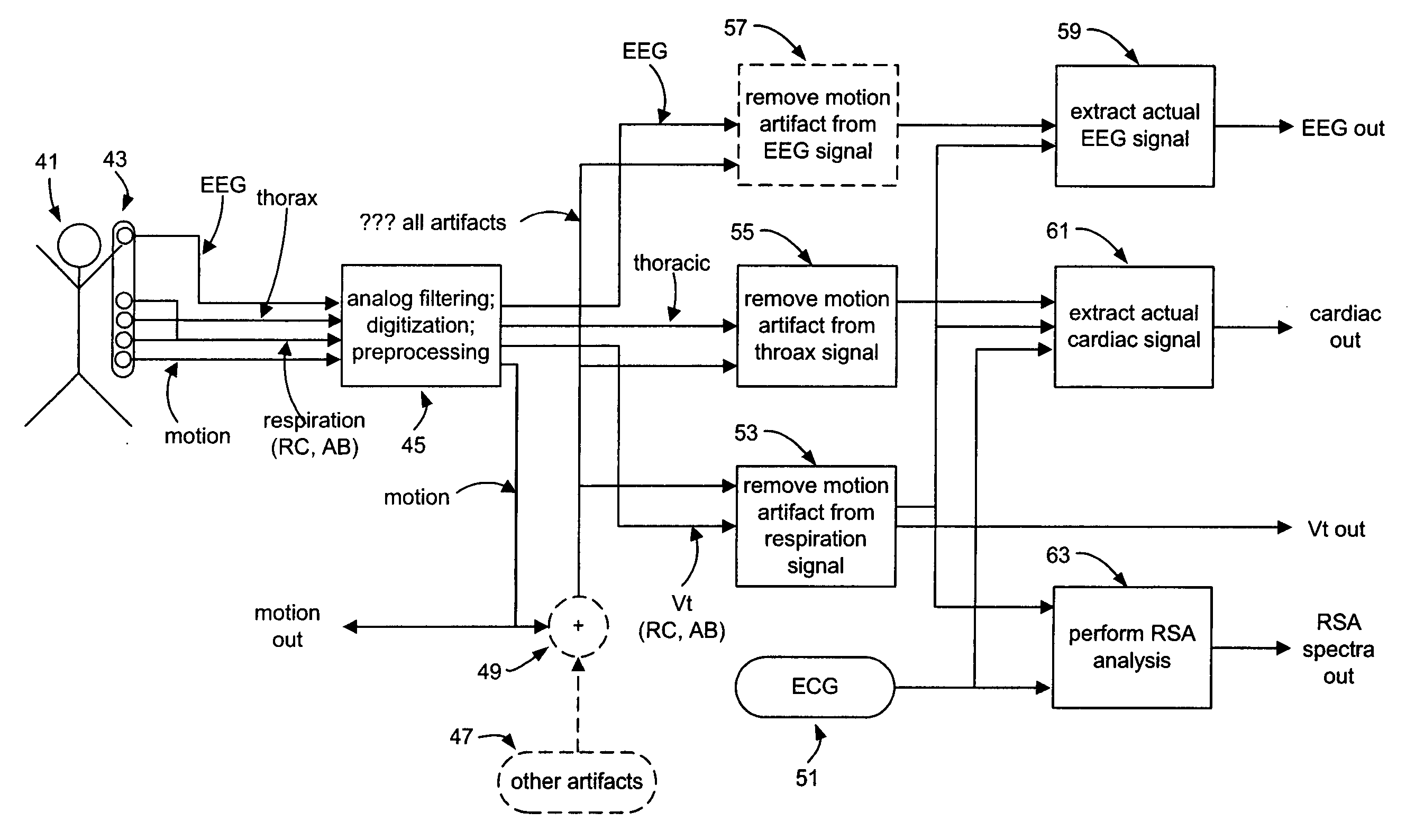
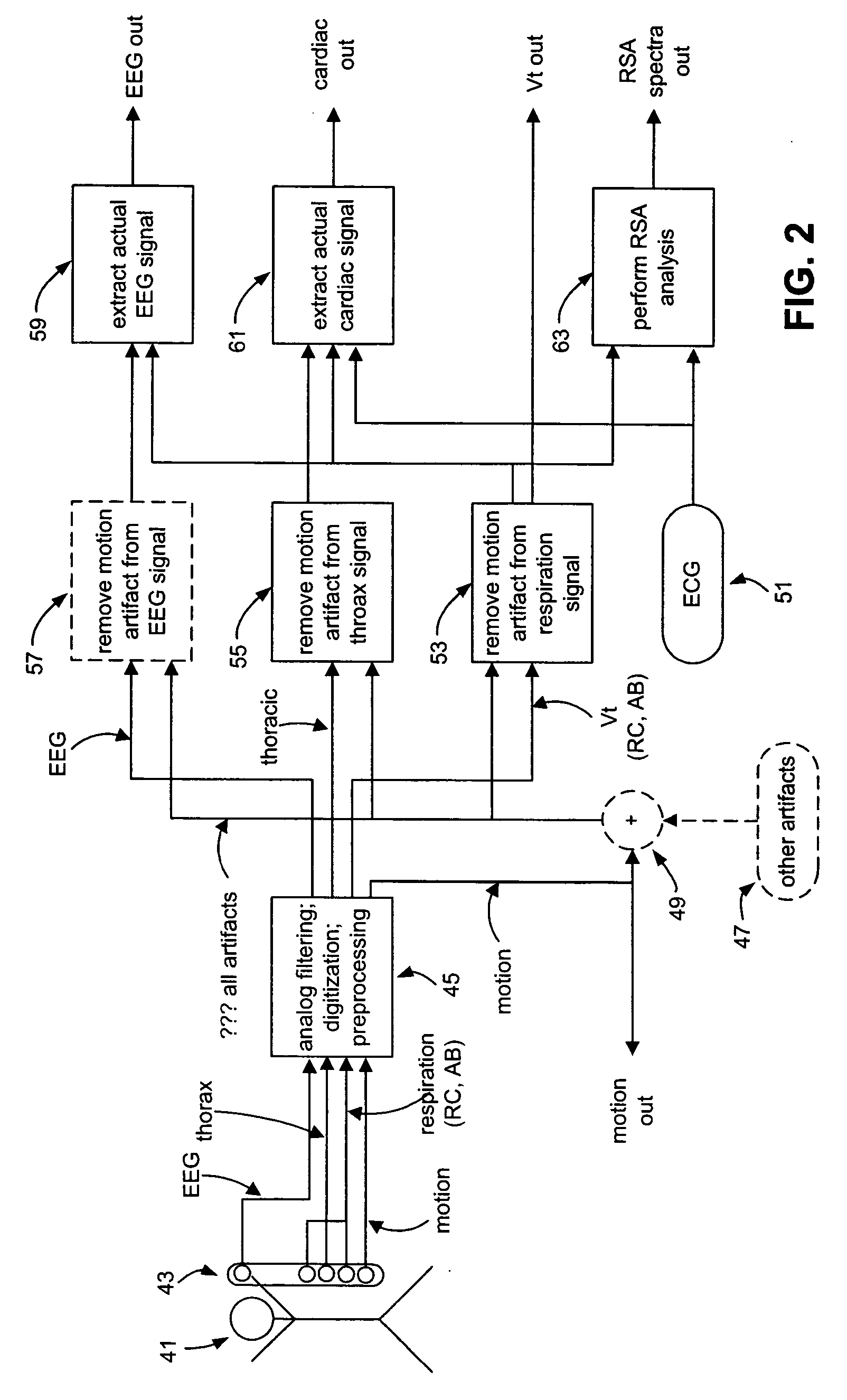
Method and system for processing data from ambulatory physiological monitoring
ActiveUS20050240087A1Improved robust and reliable extractionAvoid injuryElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyPhysiological monitoringEngineering
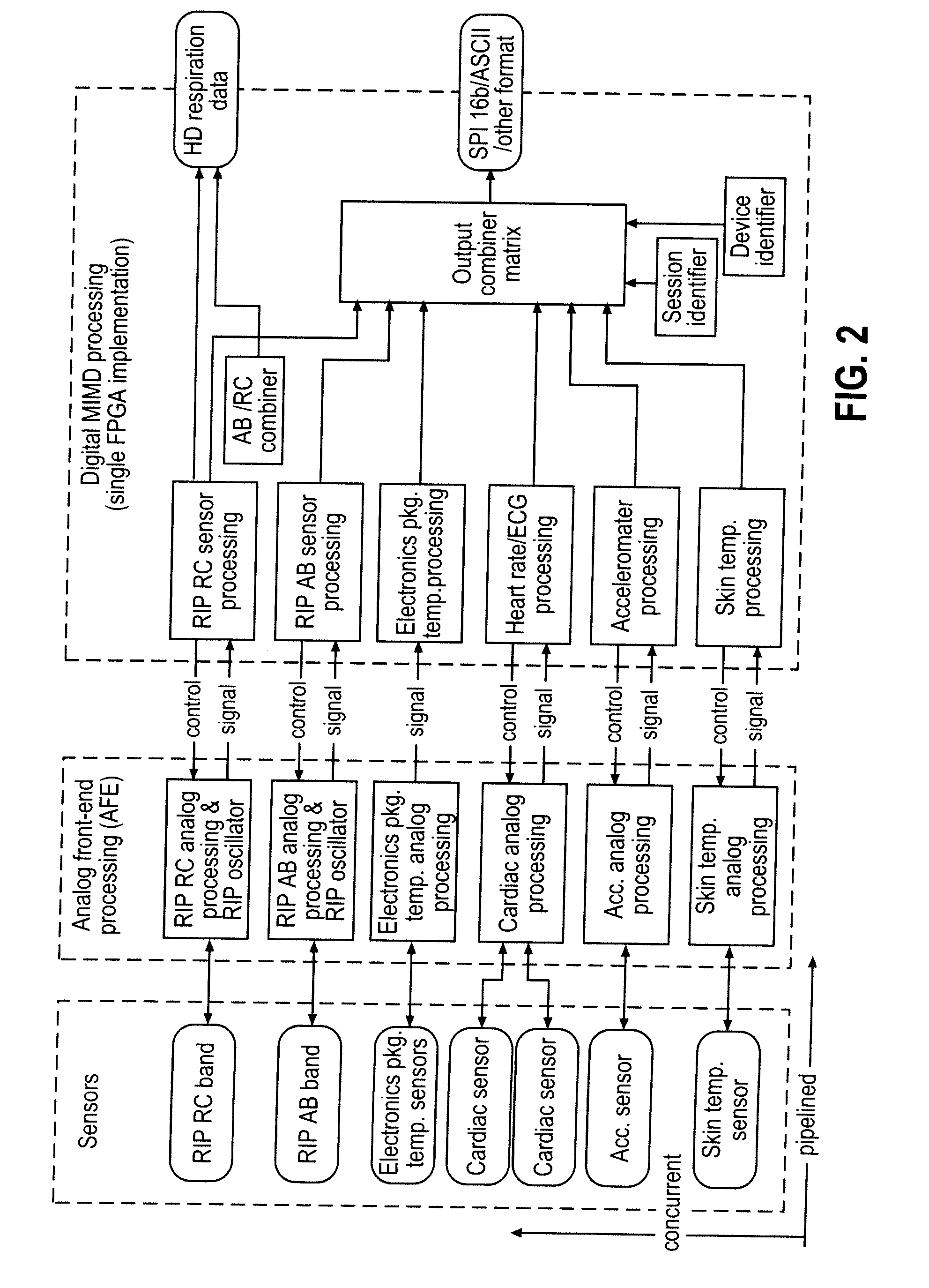
This invention provides methods and systems for the analysis of data returned from monitoring multiple physiological parameters of a subject, especially from ambulatory multiple parameter monitoring. The methods and systems remove motion artifacts from signals and separate multiple components of single signals due to two or more physiological systems or processes. Each output signal is are preferably free from motion artifacts and reflects primarily functioning of only a single physiological system or process.
Owner:ADIDAS
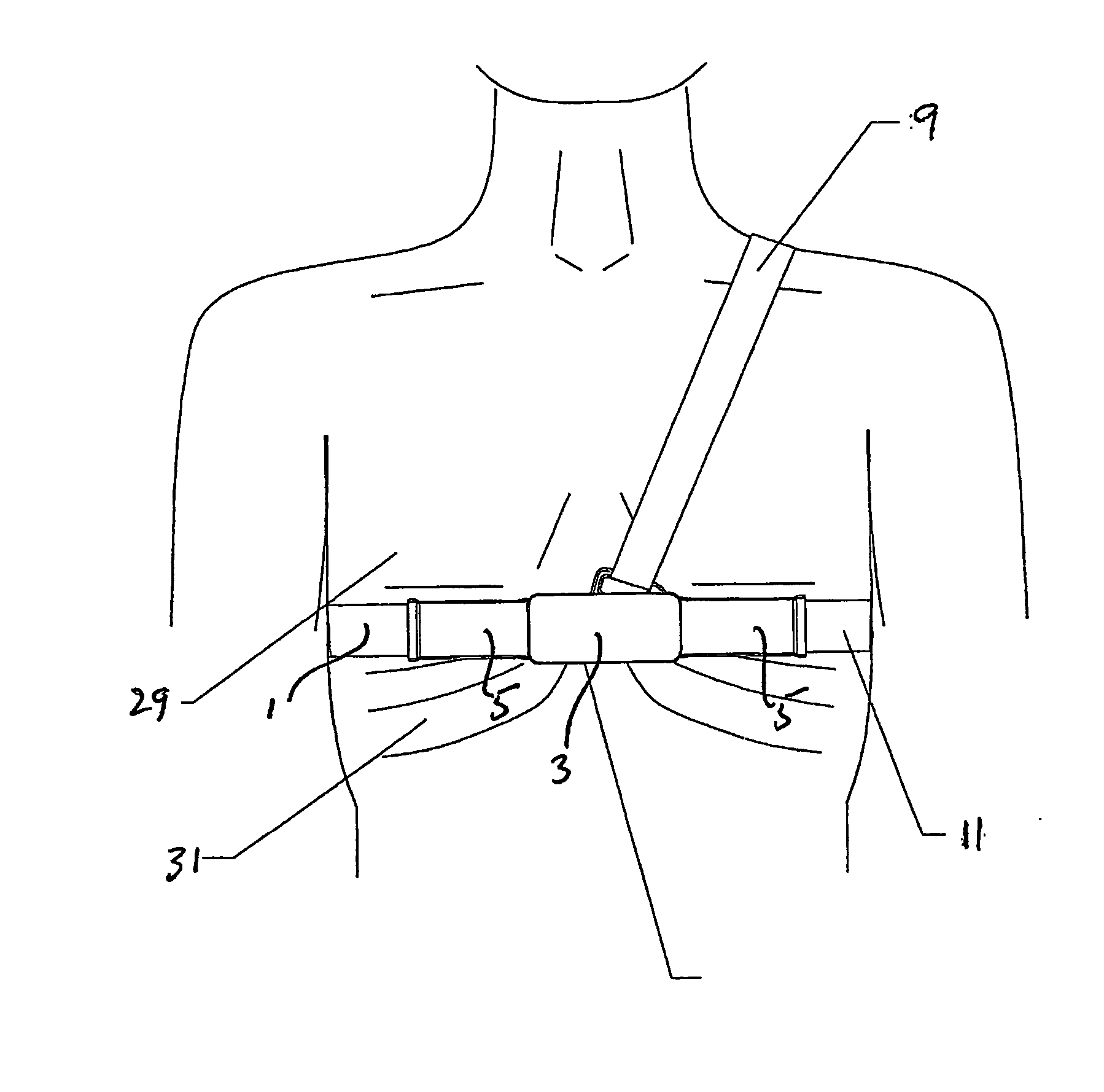
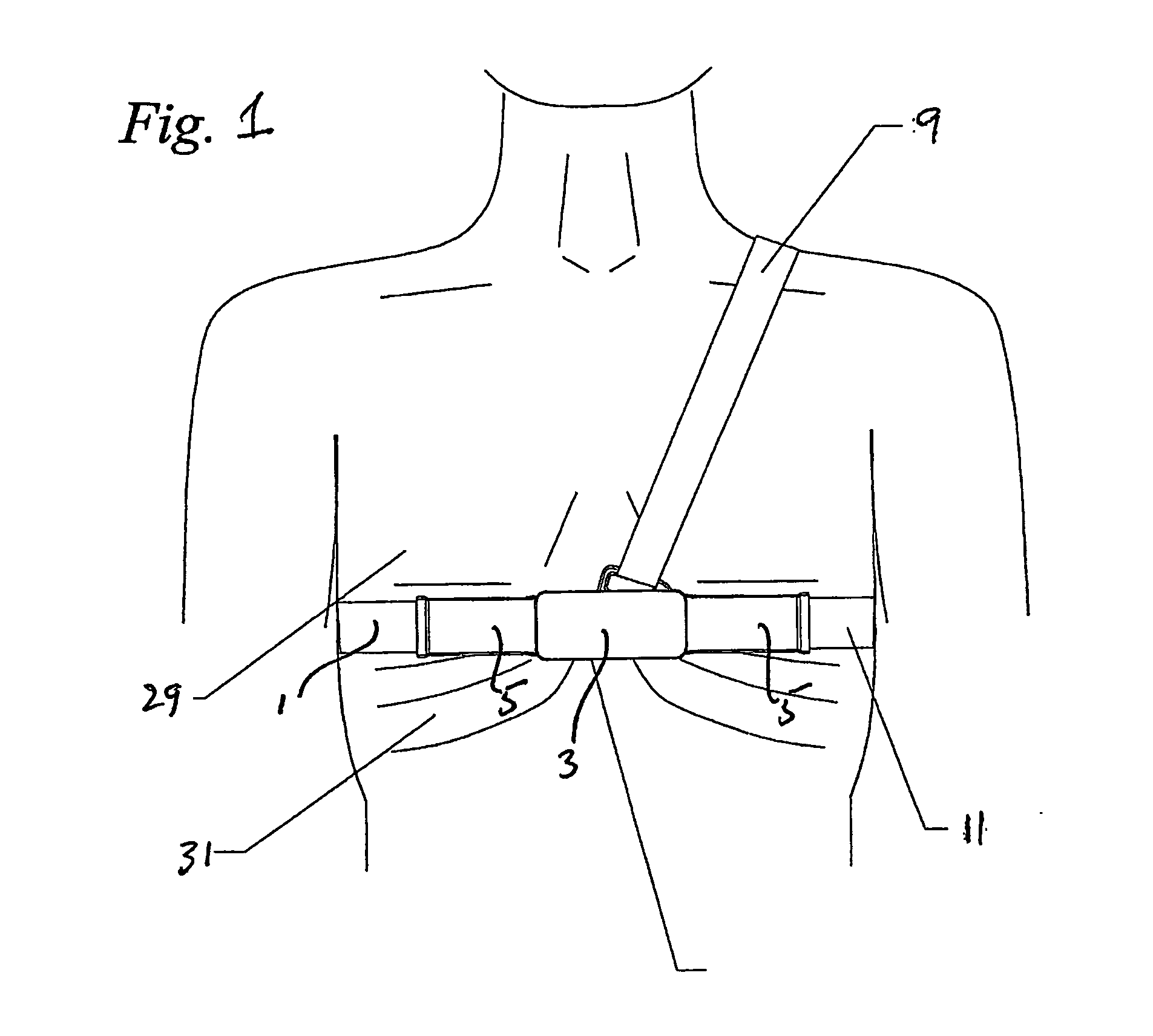
Respiration Motion Detection and Health State Assesment System
InactiveUS20070293781A1Guaranteed normal transmissionReduce bandwidth requirementsDiagnostic signal processingHealth-index calculationBody shapeAccelerometer
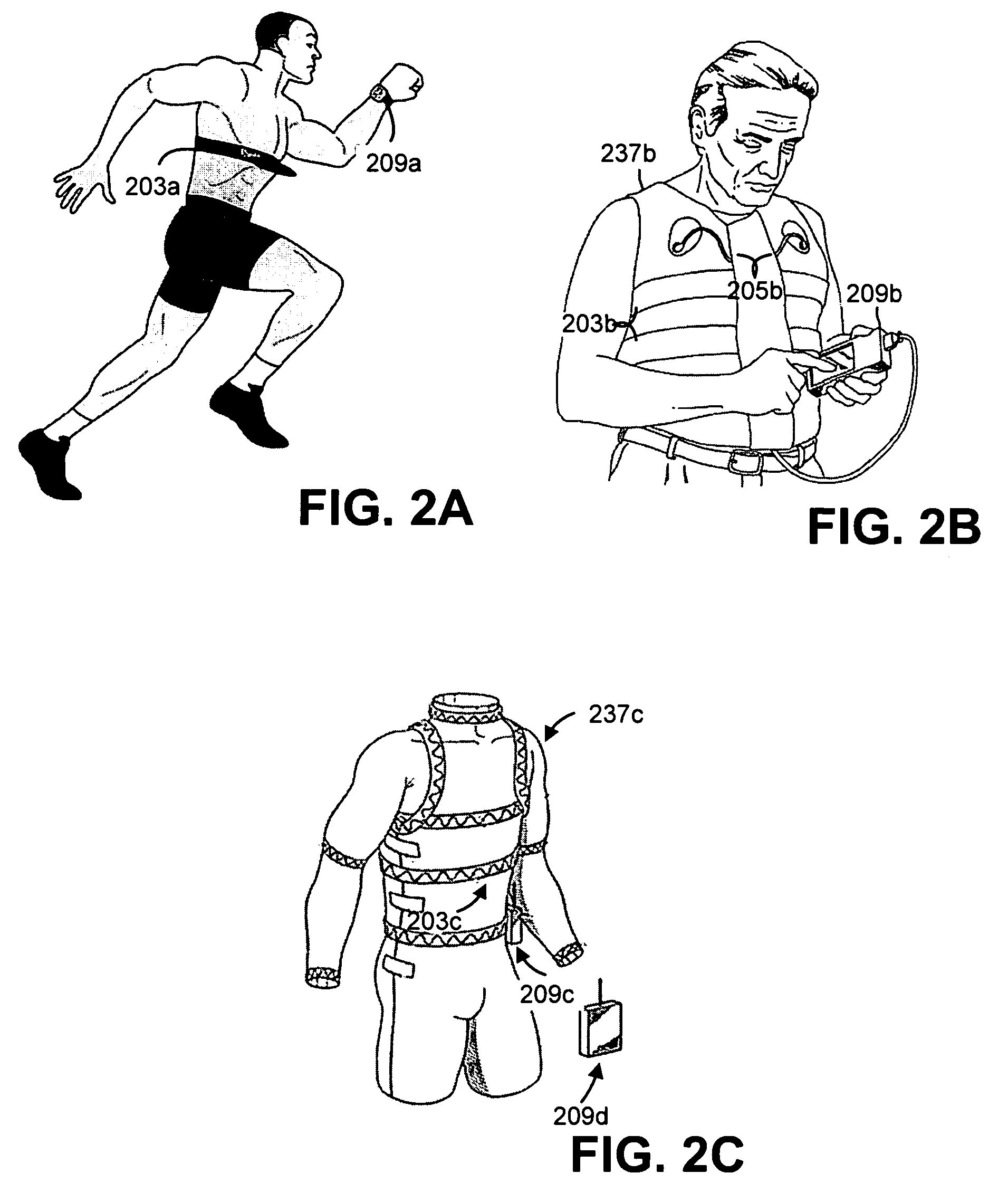
A wearable platform embodied in a belt or flattened patch-like central body shaped to conform to the abdomen provides physiological monitoring of soldiers during field operations or trauma victims at accident sites and makes health state assessments. The platform includes sensors for heart rate, body motion, respiration rate and intensity, and temperature and further contains a microprocessor and short range transmitter. The respiration sensor uses conductive ink in a novel manner. A small square of the ink is coated on an arched structure so that flexing of the arch either to increase or decrease its radius of curvature modifies the resistance of the structure. This is utilized to set the unstressed resistance of the arch structure and to allow a greater range of resistance values capable of measuring distortions in different deformations of the arch. The respiration sensor supplements the motion information provided by an accelerometer sensor.
Owner:SIMS NATHANIEL +4
Magnetic electrical connector for patient monitors
ActiveUS9775545B2Reduce the risk of contaminationImprove efficiency and benefitElectroencephalographySensorsElectricityMonitoring system
The present disclosure relates to an electrical connector for providing signal isolation between various components of a physiological monitoring system. In an embodiment, the electrical connector is placed between a sensor and associated monitoring system and includes a physical barrier and inductive components.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Physiological signal processing devices and associated processing methods
InactiveUS20070270671A1Speed up the processEasy to integrateSensorsTelemetric patient monitoringPhysiological monitoringParallel processing
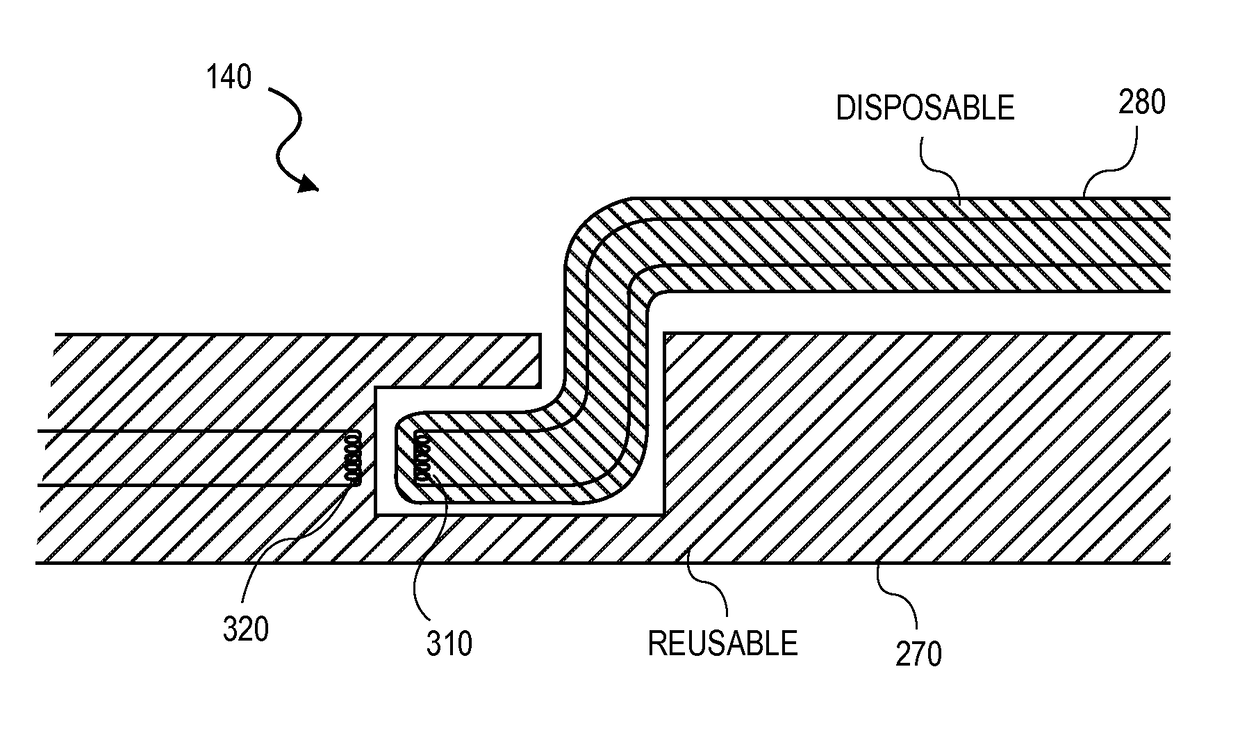
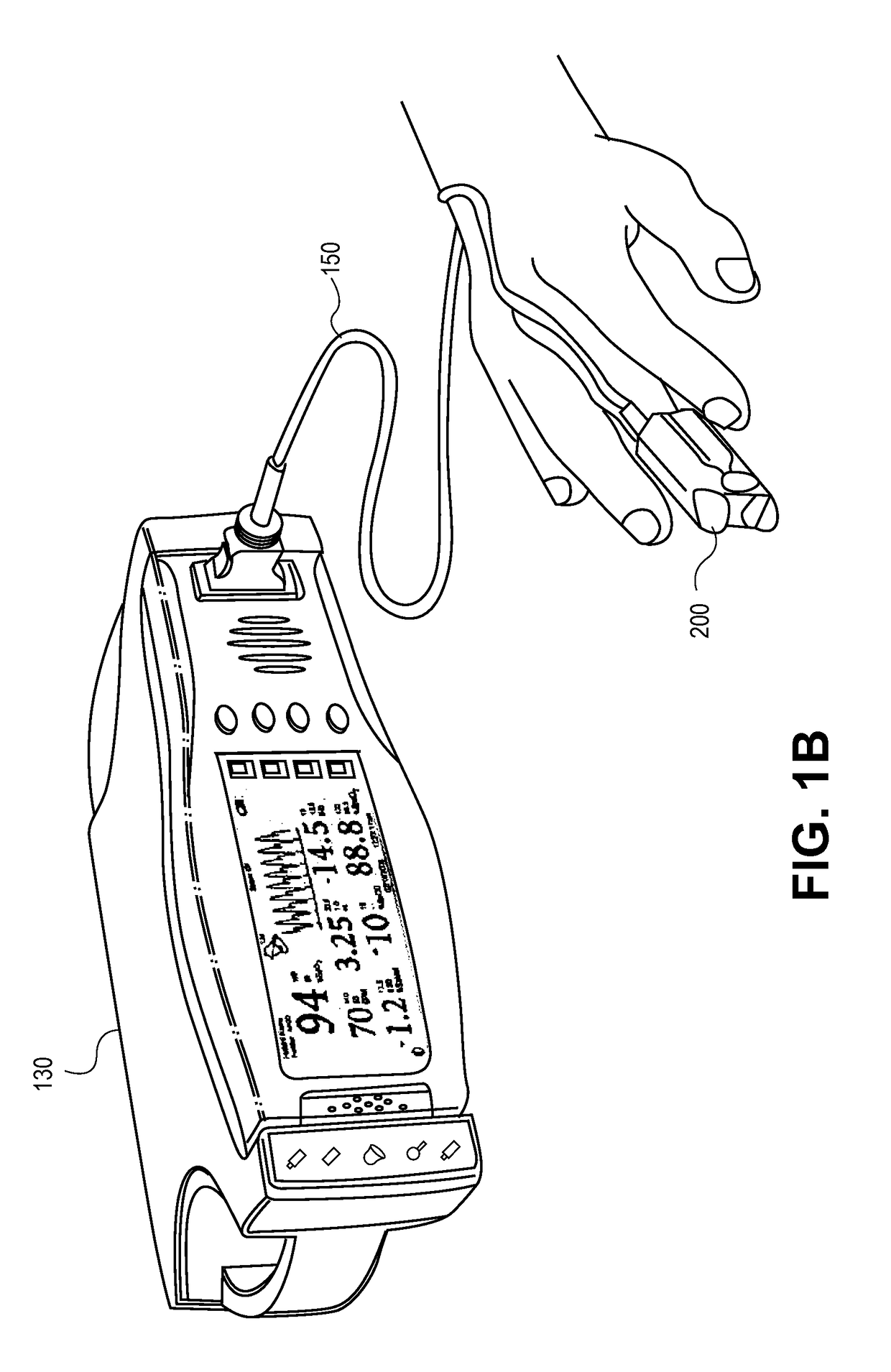
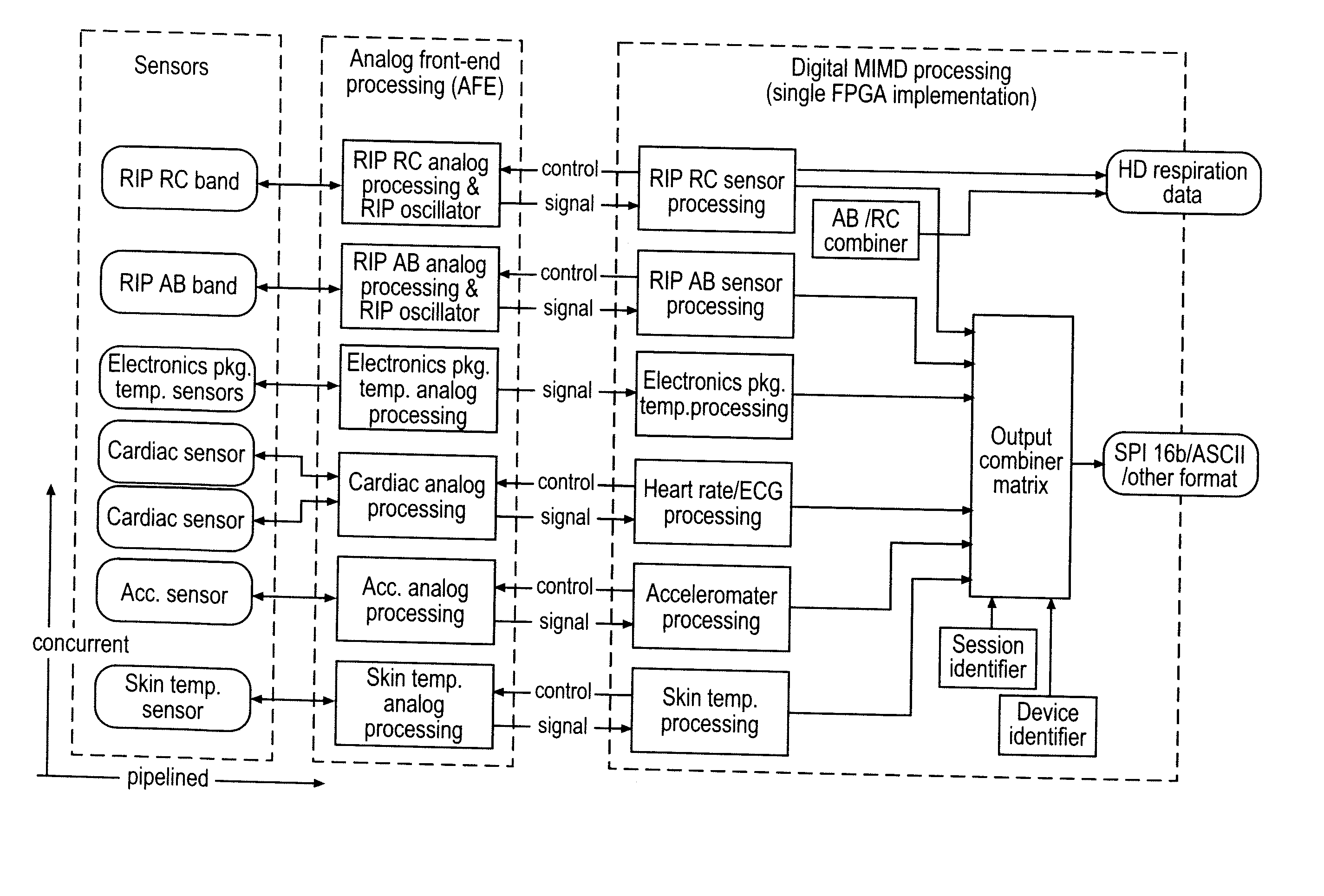
The invention provides improved devices for processing data from one or more physiological sensors based on parallel processing. The provided devices are small, low power, and readily configurable for use in most physiological monitoring applications. In a preferred embodiment, the provided devices are used for ambulatory monitoring of a subject's cardio-respiratory systems, and in particular, process data from one or more respiratory inductive plethysmographic sensors.
Owner:ADIDAS
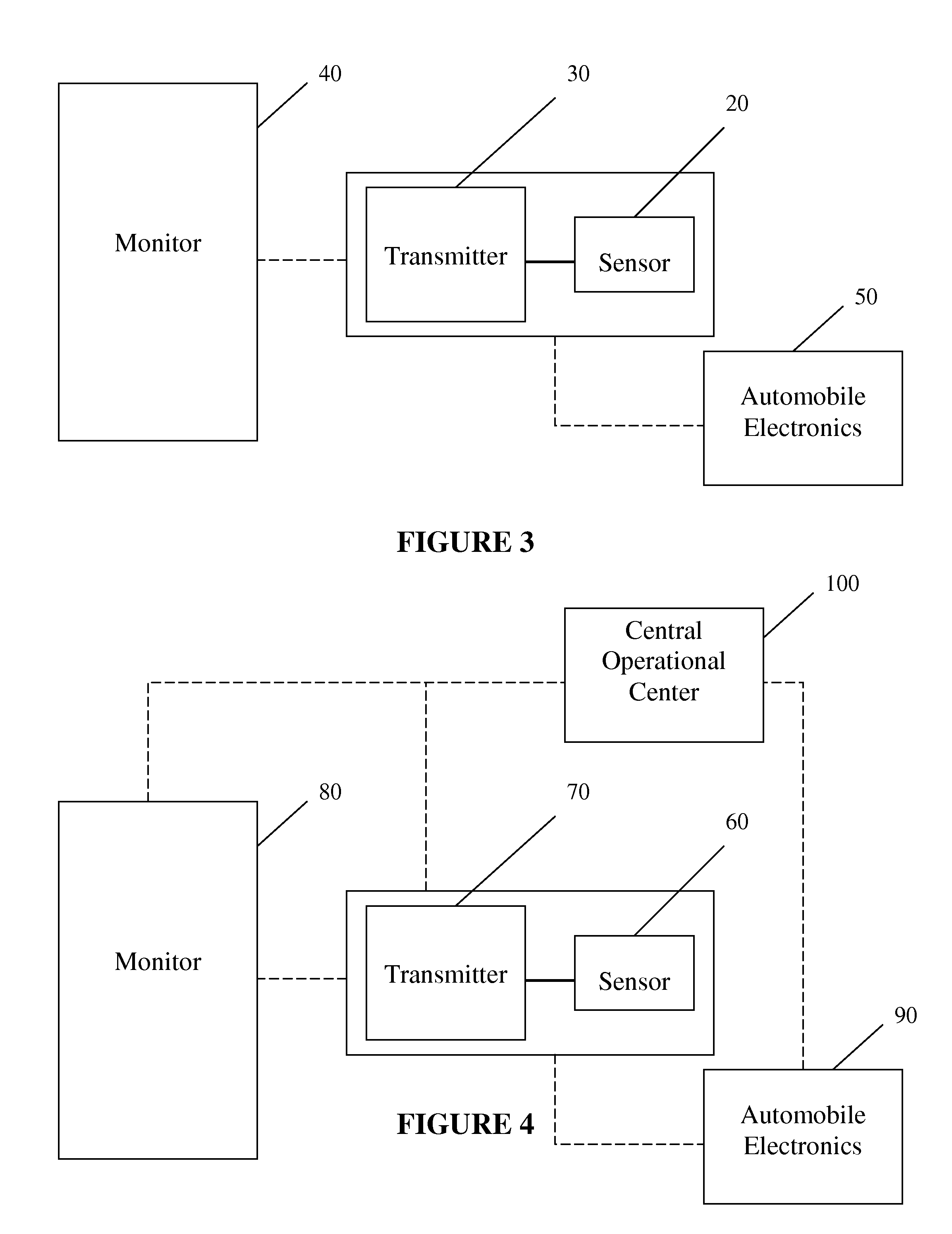
Automobile physiological monitoring system and method for using the same
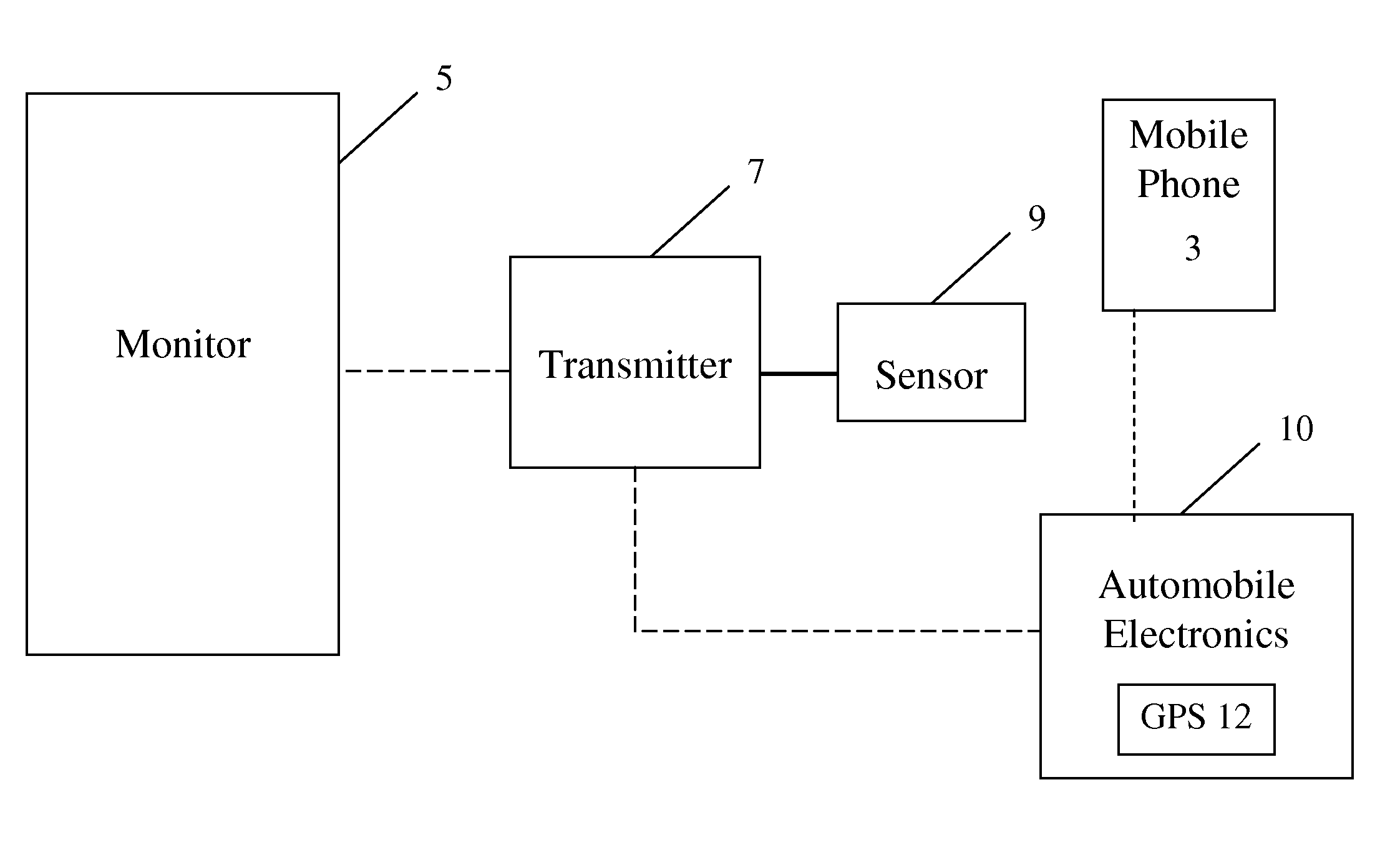
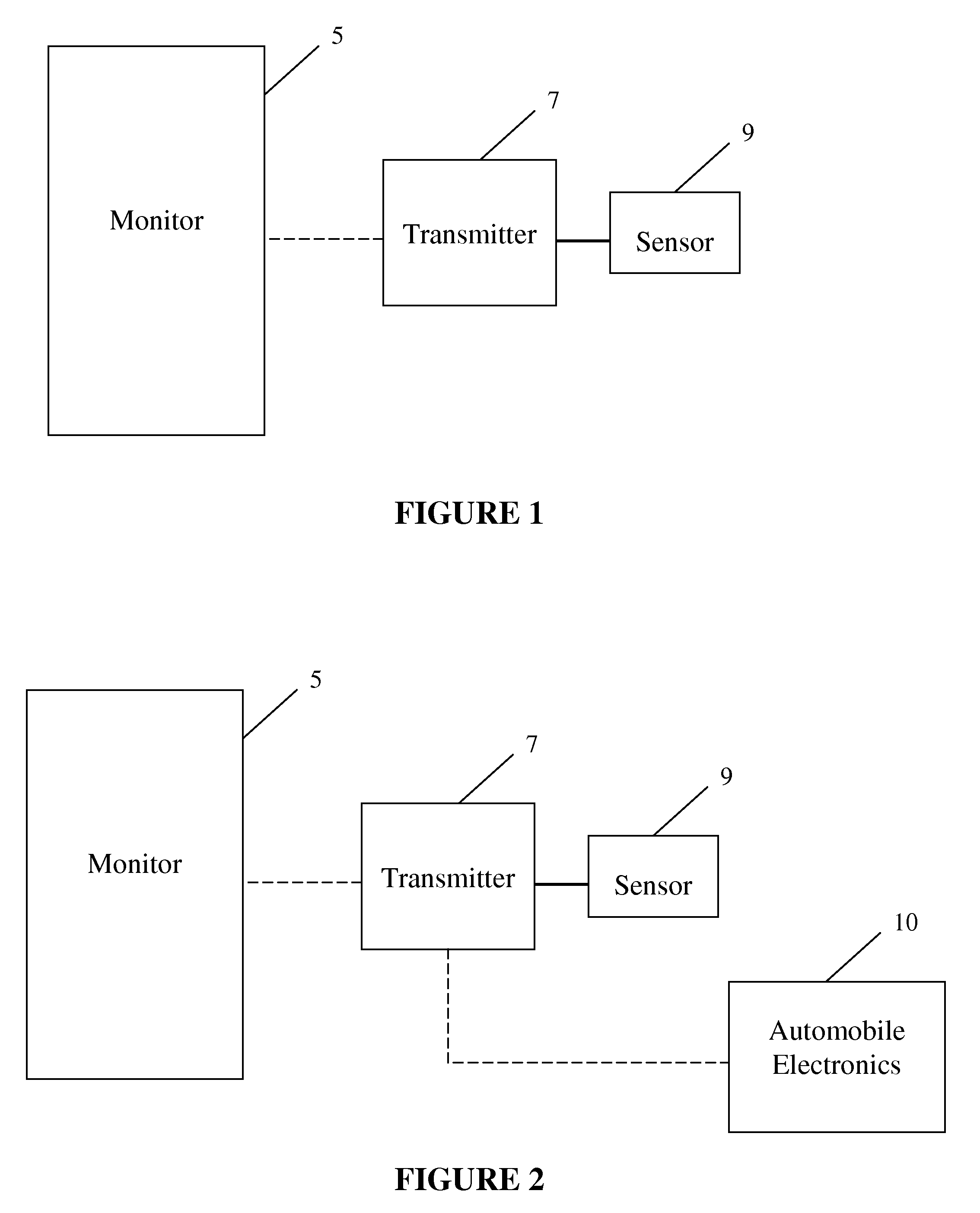
ActiveUS8207859B2Avoid ignitionElectric devicesAnti-theft devicesPhysiological monitoringMonitoring system
An automobile monitoring system to monitor user body characteristics, includes at least one sensor to monitor at least one user body characteristic. The at least one sensor is operatively coupled to a body of a user to monitor the at least one user body characteristic while the user is operating an automobile. The at least one user body characteristic is at least a glucose level of the user's body. At least one transmitter is operatively coupled to the at least one sensor to communicate sensor data obtained from the at least one sensor while the user is operating the automobile. Automobile electronics are operatively coupled to the at least one transmitter to receive sensor data from the at least one sensor while the user is operating the automobile. The automobile electronics provide the sensor data to the user while the user is operating the automobile. A mobile telephone is operatively coupled to the automobile electronics, wherein the automobile electronics initiate a communication via the mobile telephone based on the sensor data received from the at least one sensor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
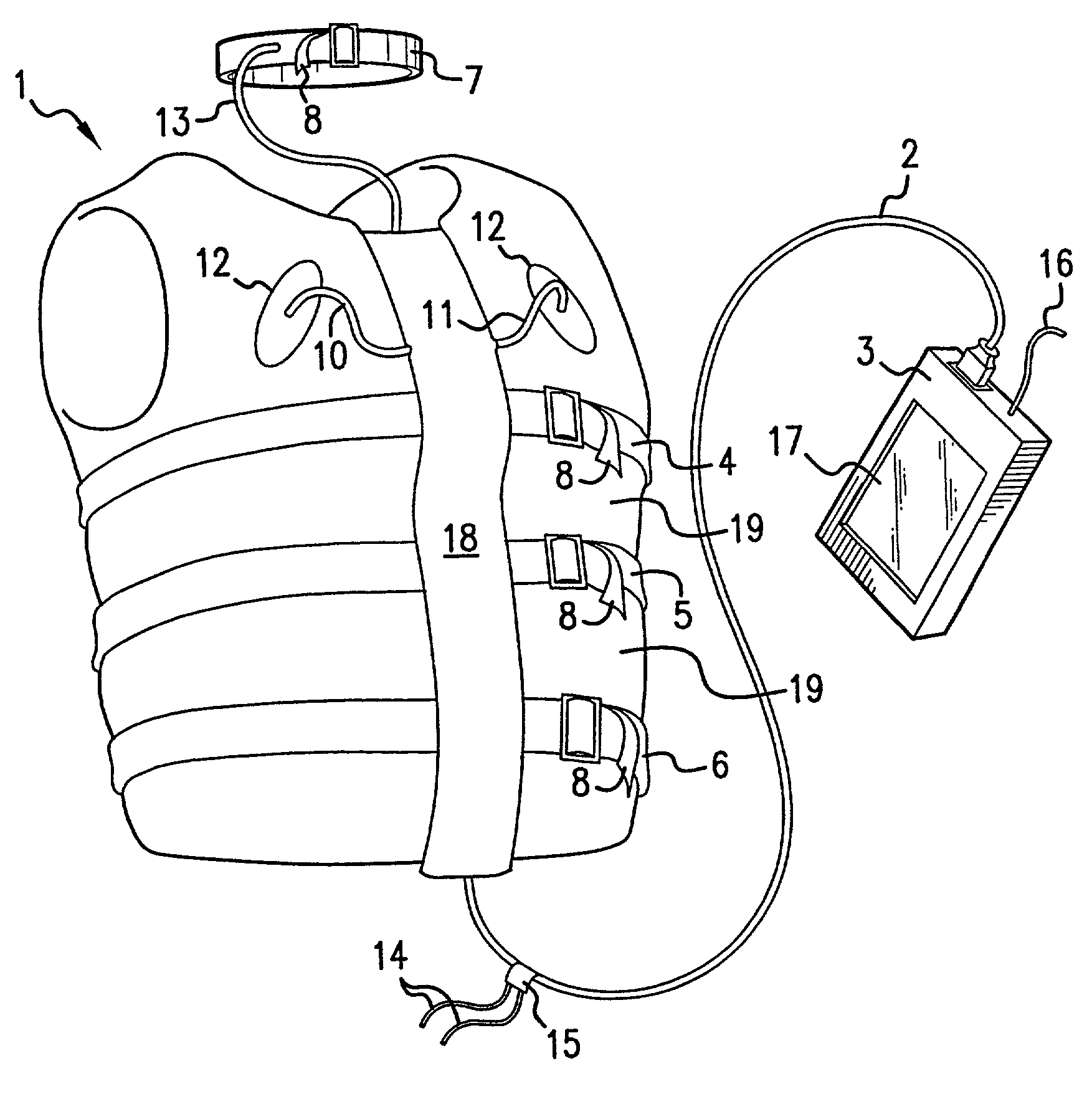
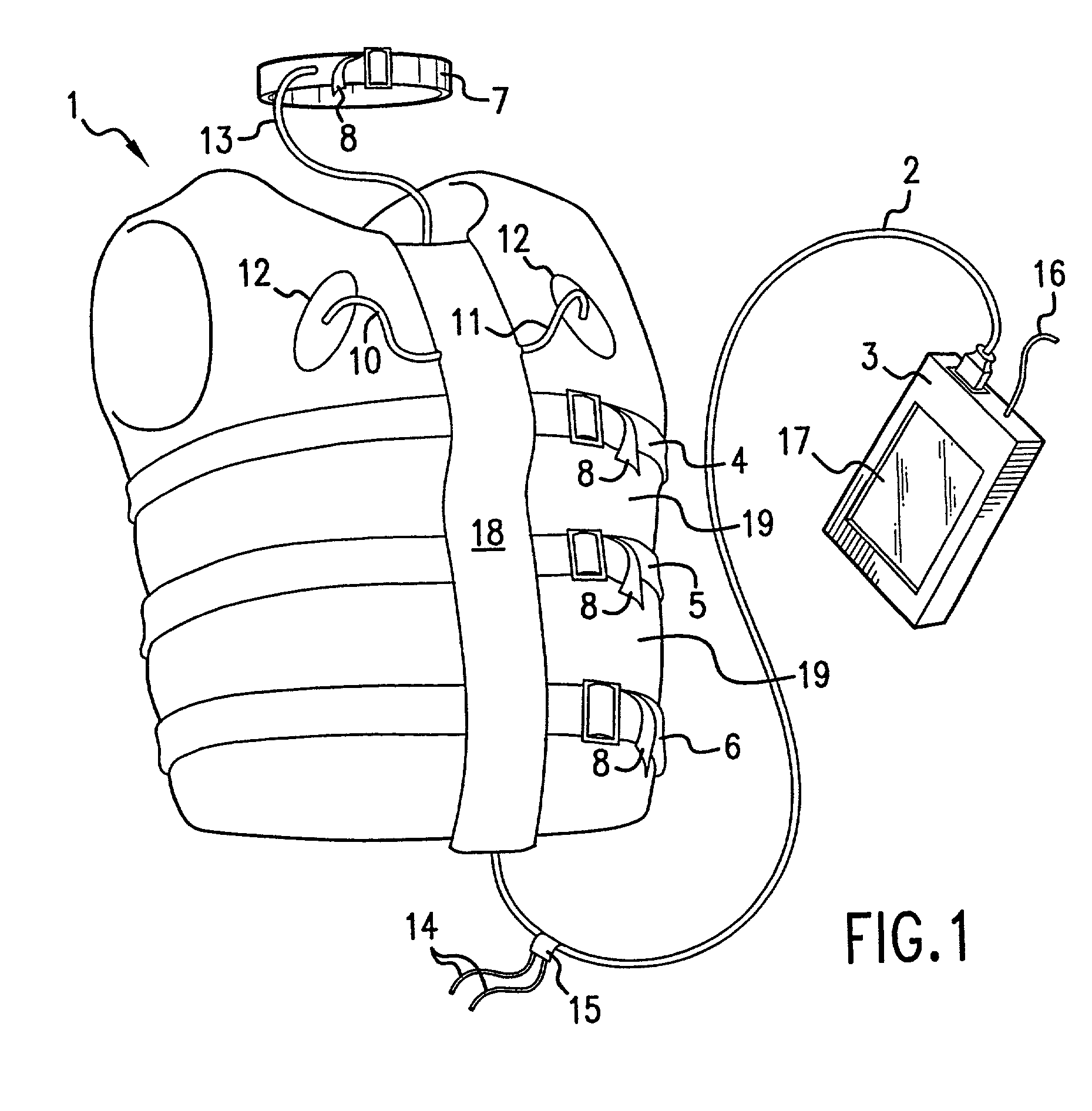
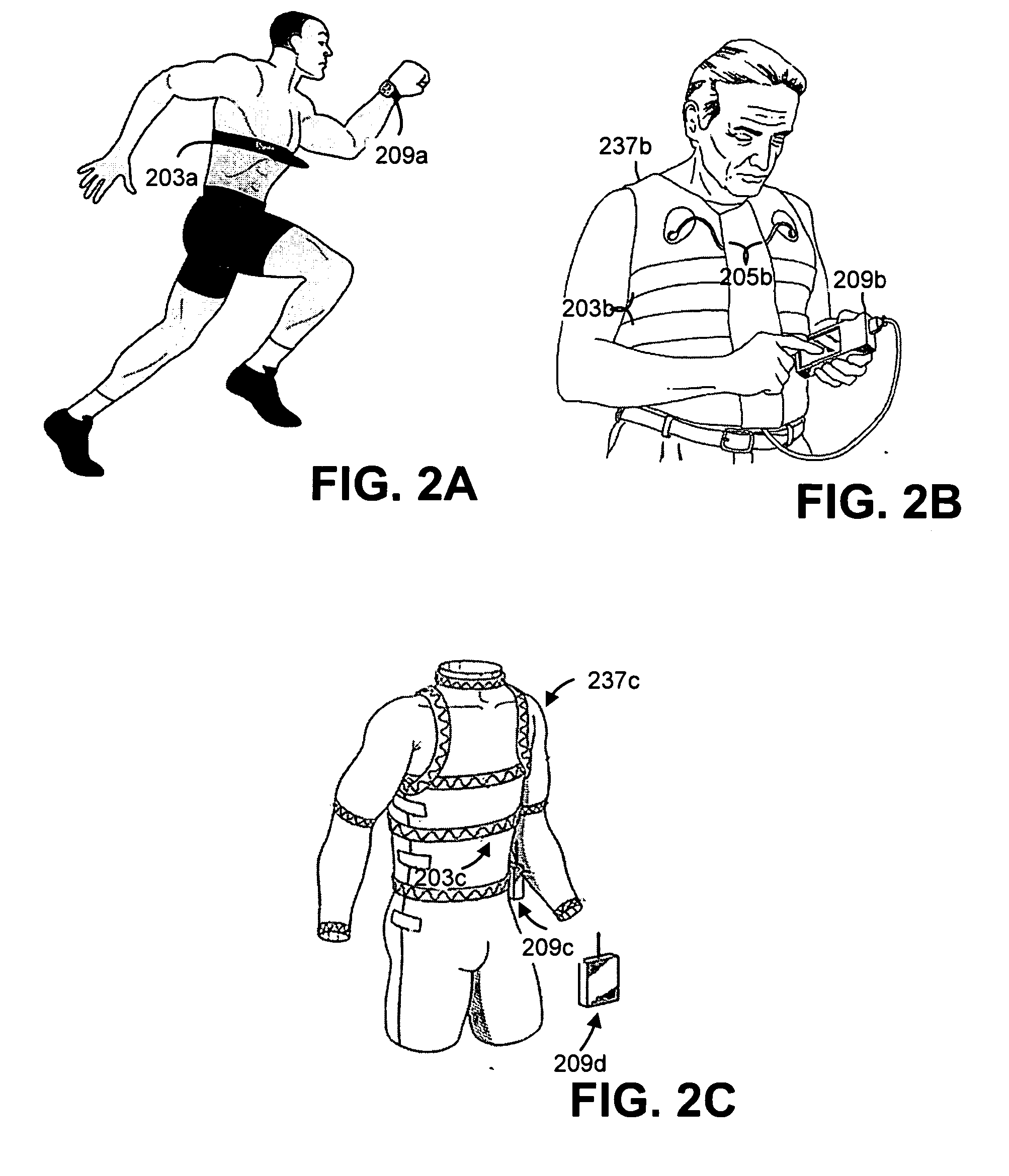
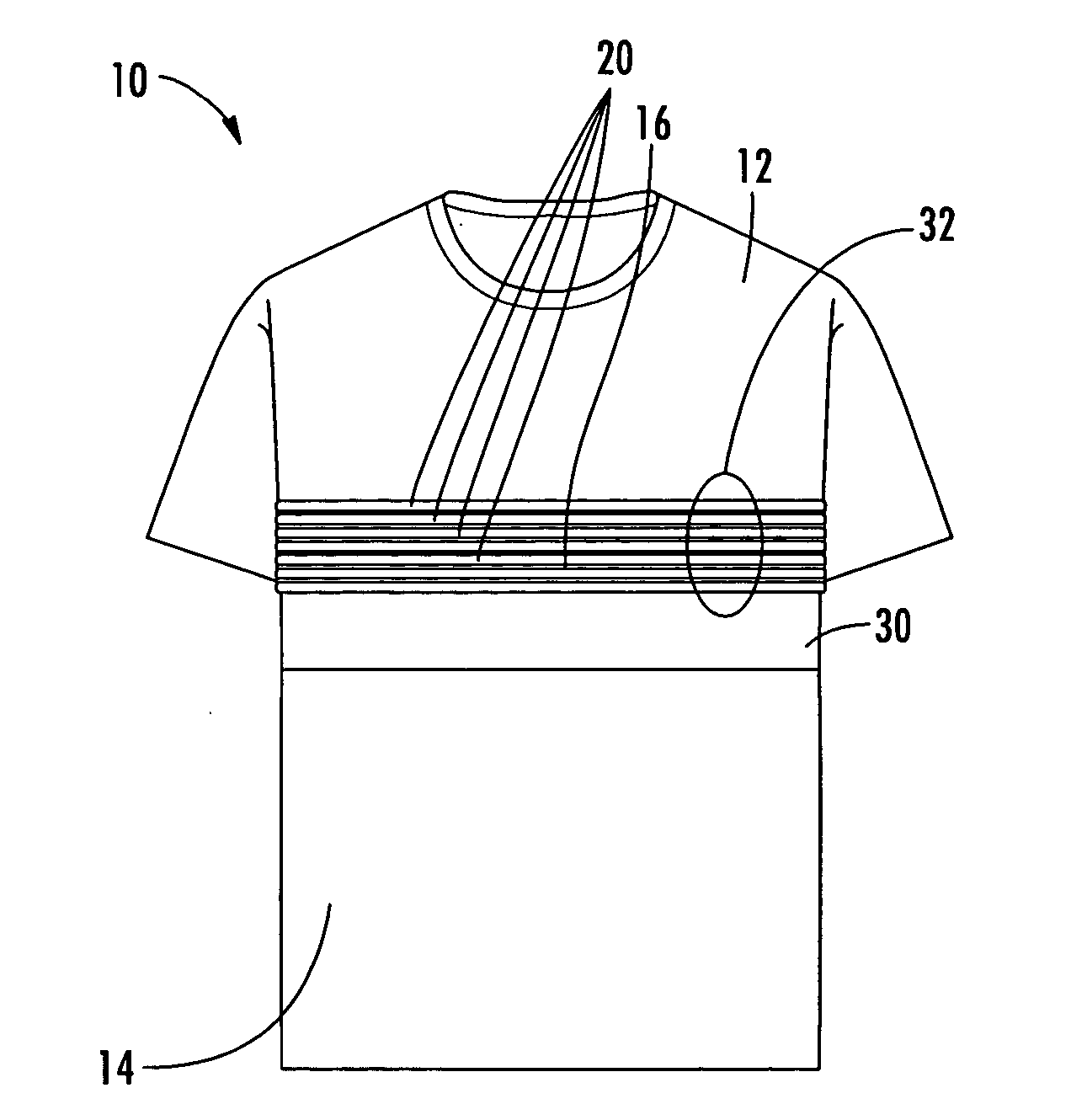
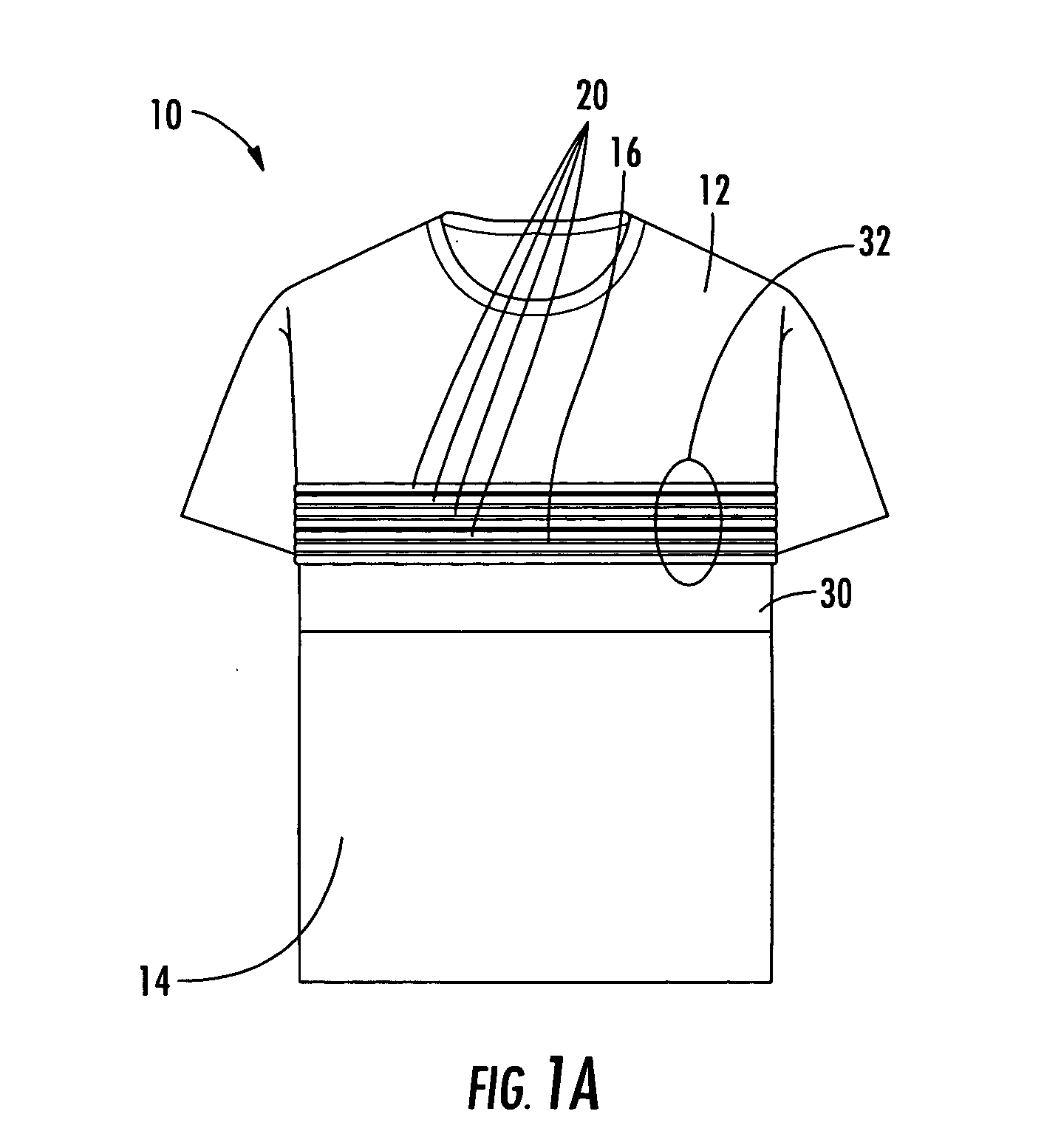
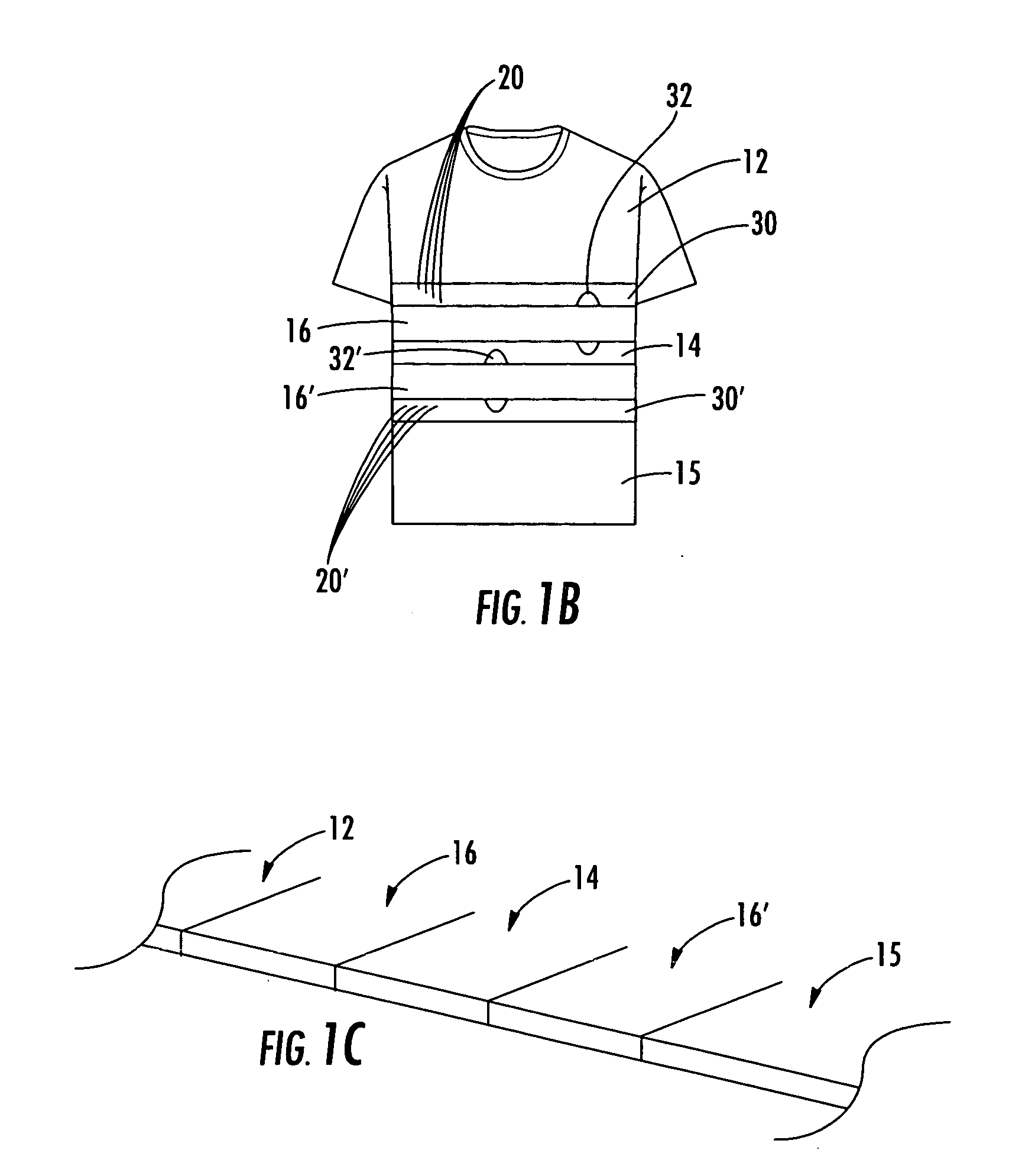
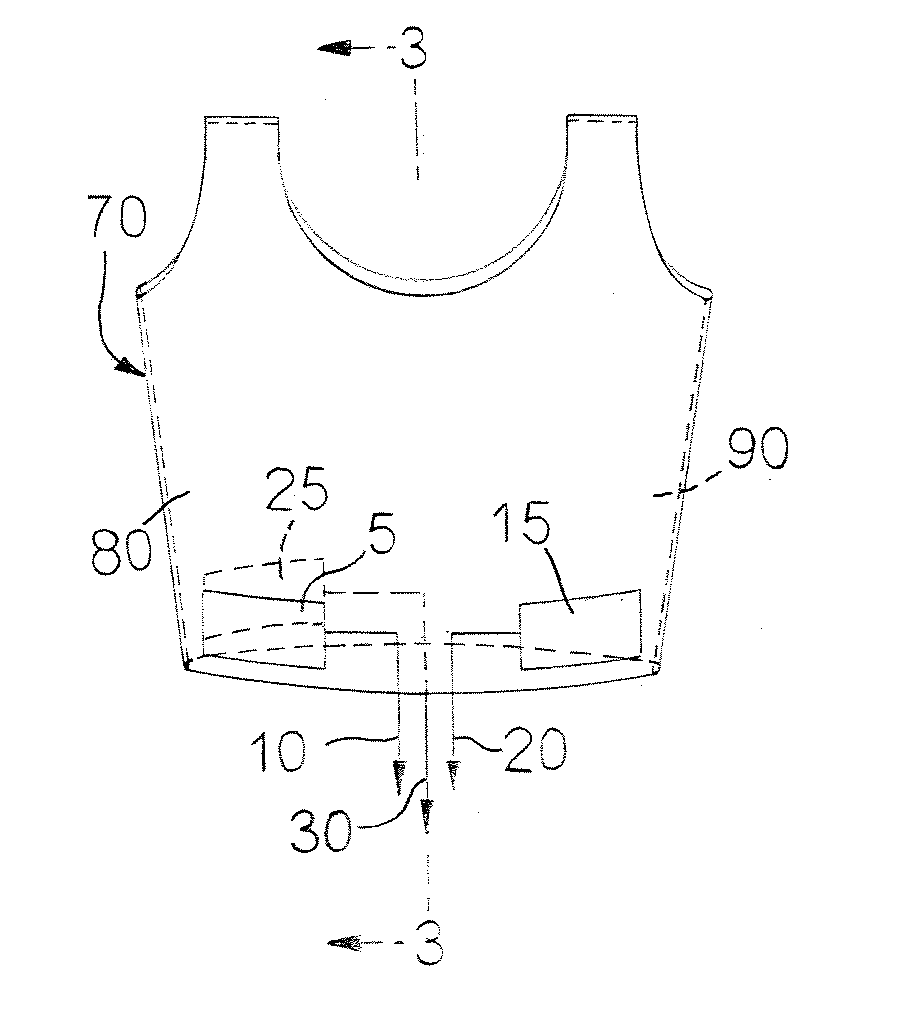
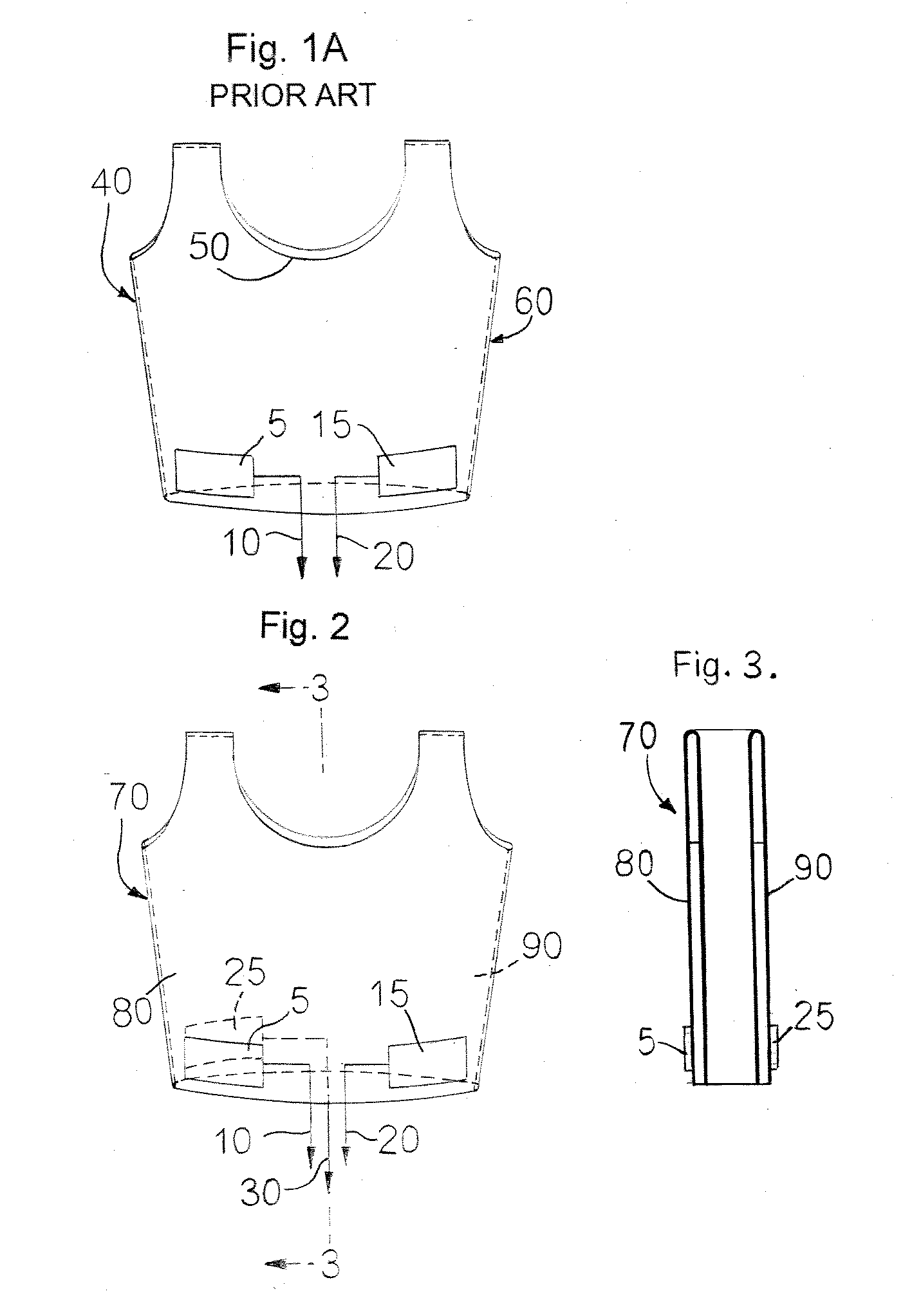
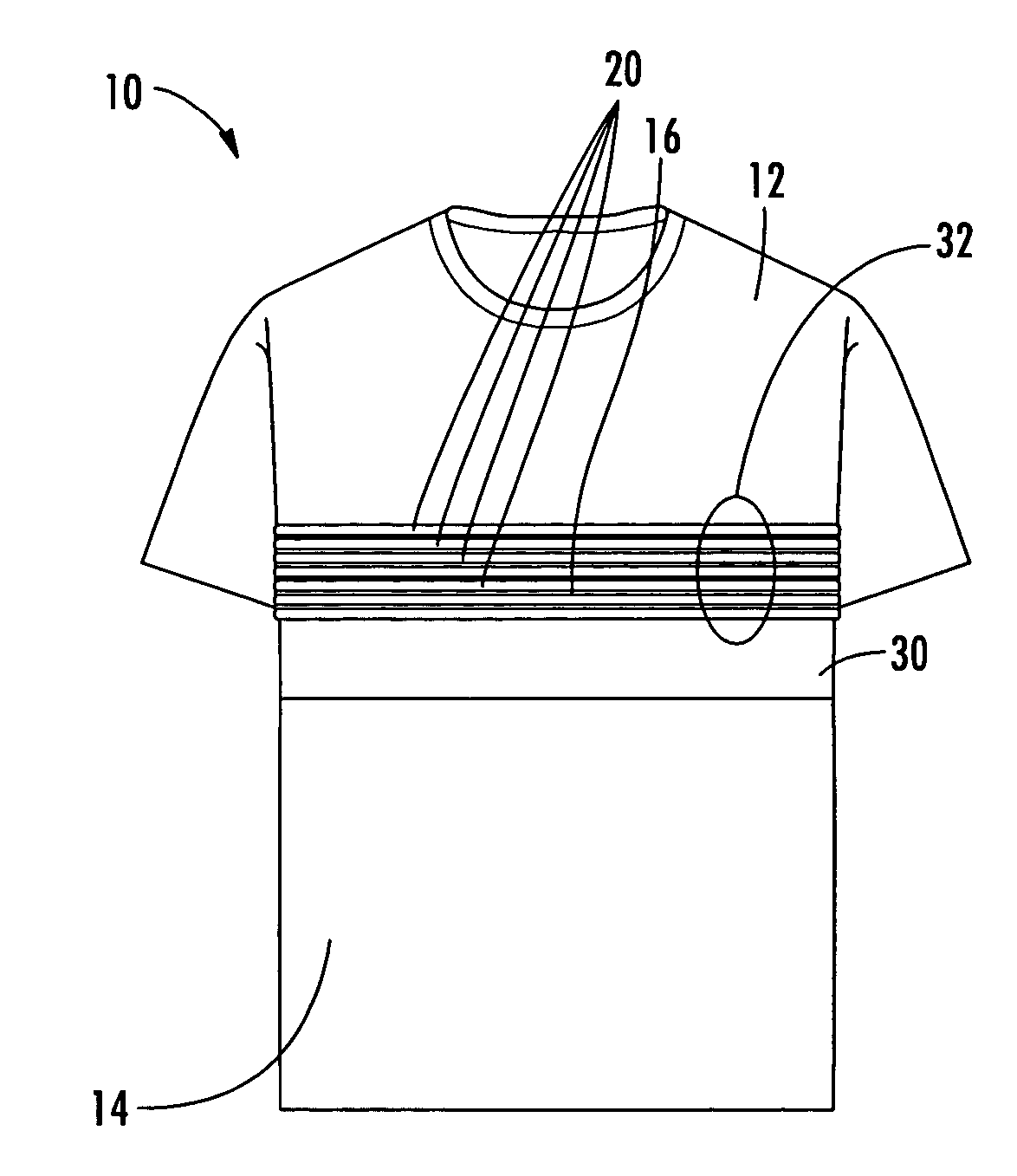
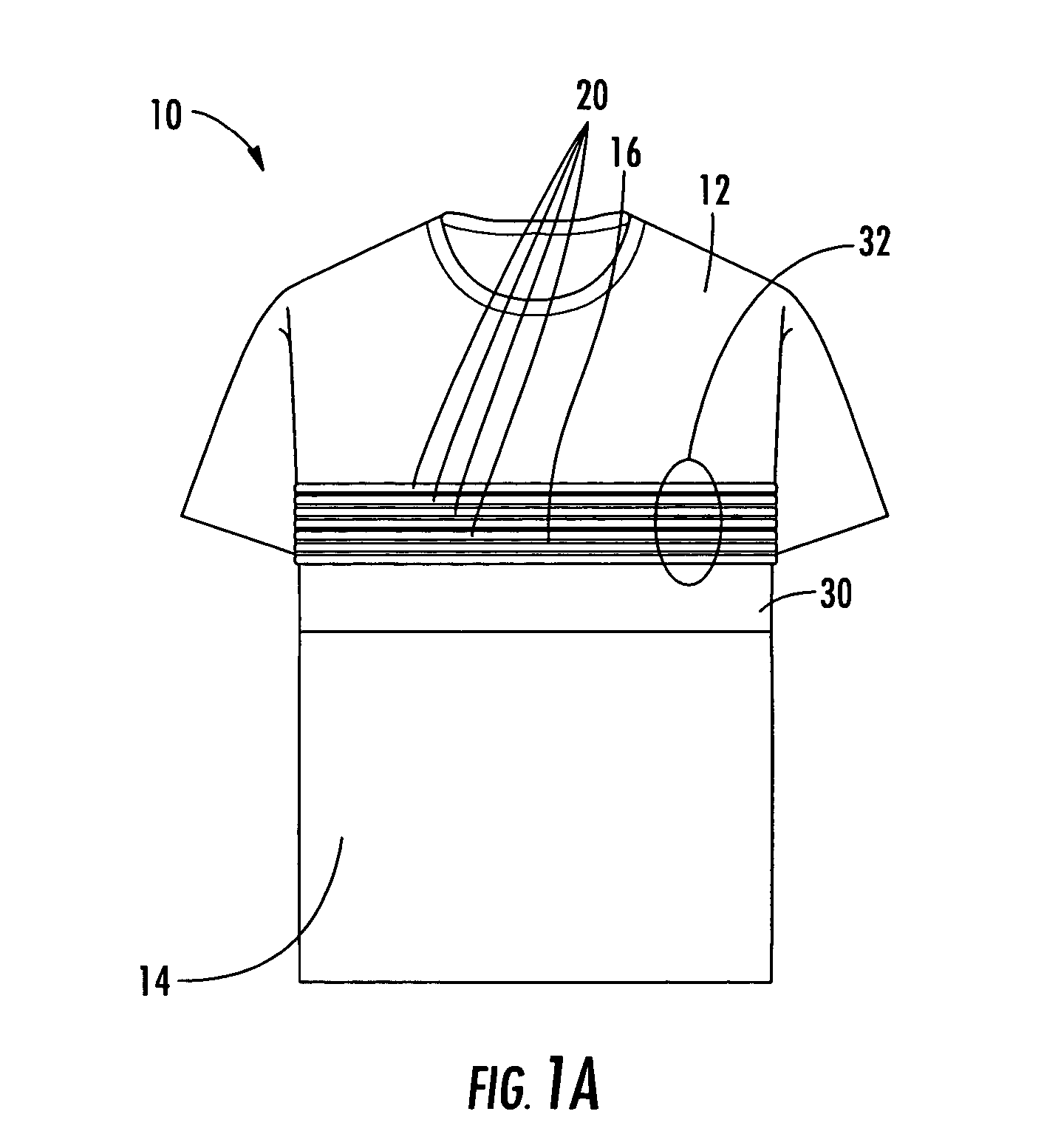
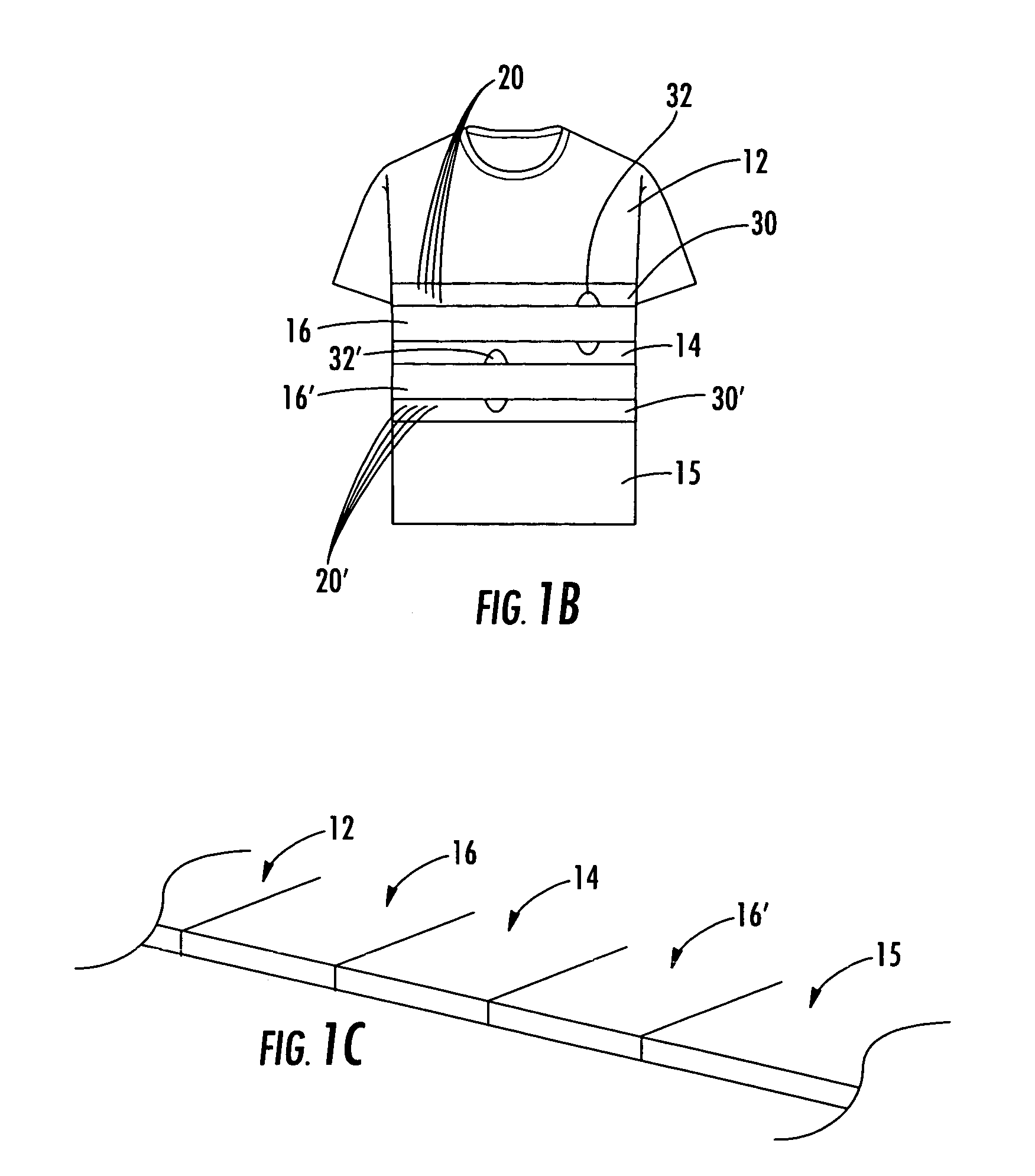
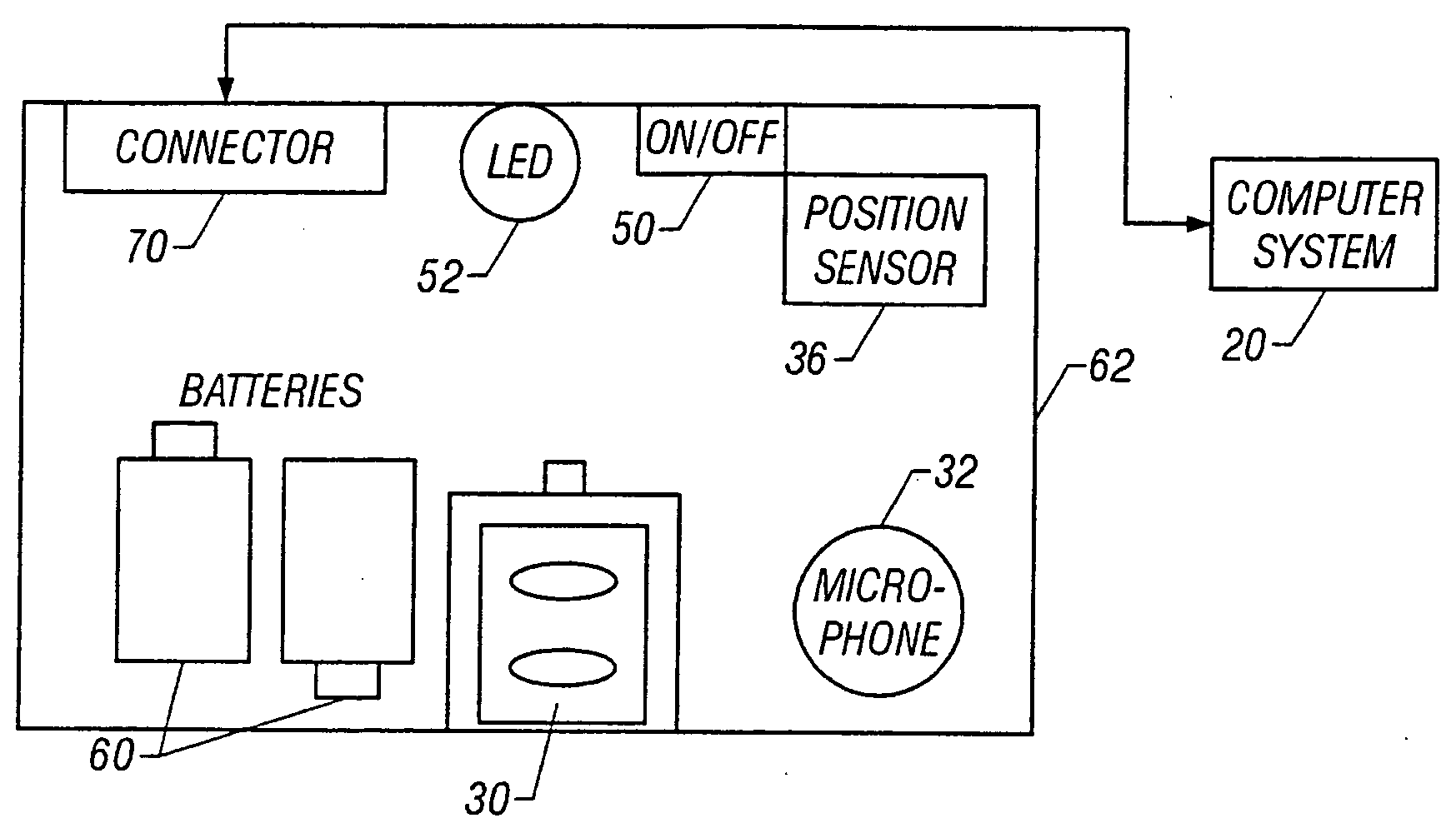
Physiological monitoring garment
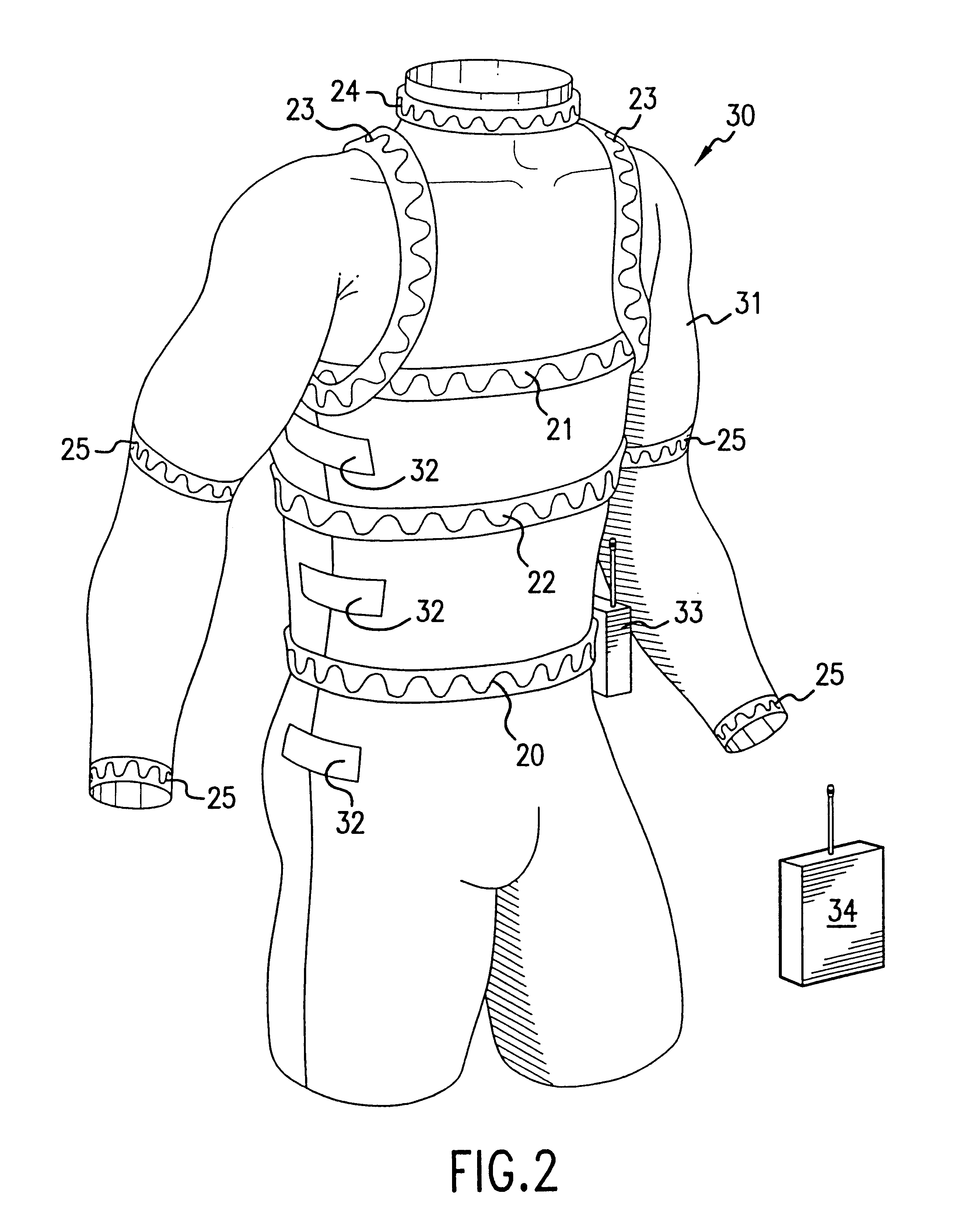
InactiveUS20050054941A1Not impede mobilityEasy to manufactureElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyElectrical conductorPhysiological monitoring
A physiological monitoring garment includes first and second elastic fabric portions. An elongate stretchable textile data / power bus is disposed between the first and second elastic fabric portions. The elongate stretchable textile data / power bus includes a plurality of integral conductors, woven, knitted, or braided along the length thereof. One or more sensors are connected to the elongate stretchable textile data / power bus.
Owner:FOSTER-MILLER
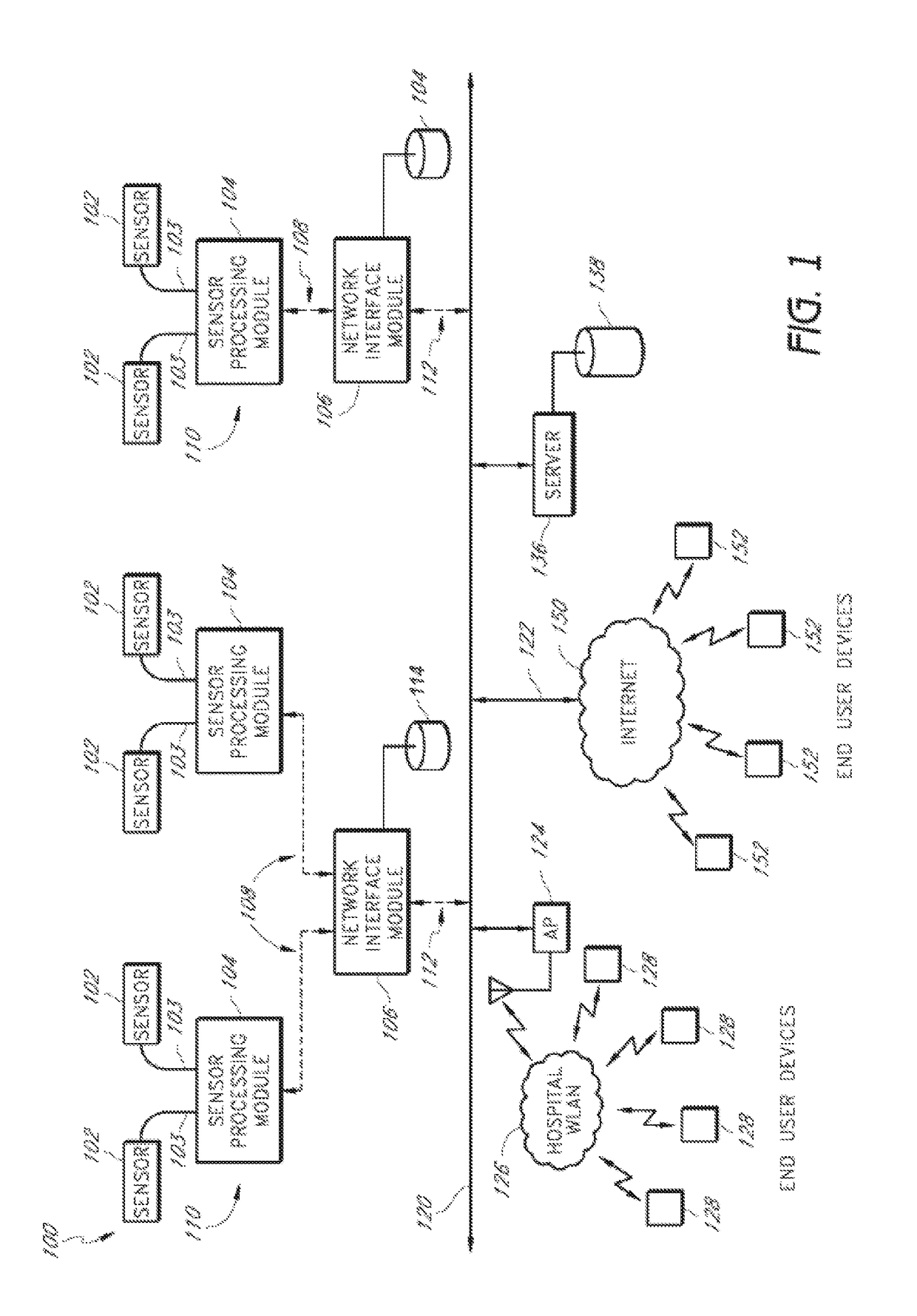
Patch-type physiological monitoring apparatus, system and network
InactiveUS20070027388A1Signal interferenceBioelectric signal measurementSensorsPatch electrodePhysiological monitoring
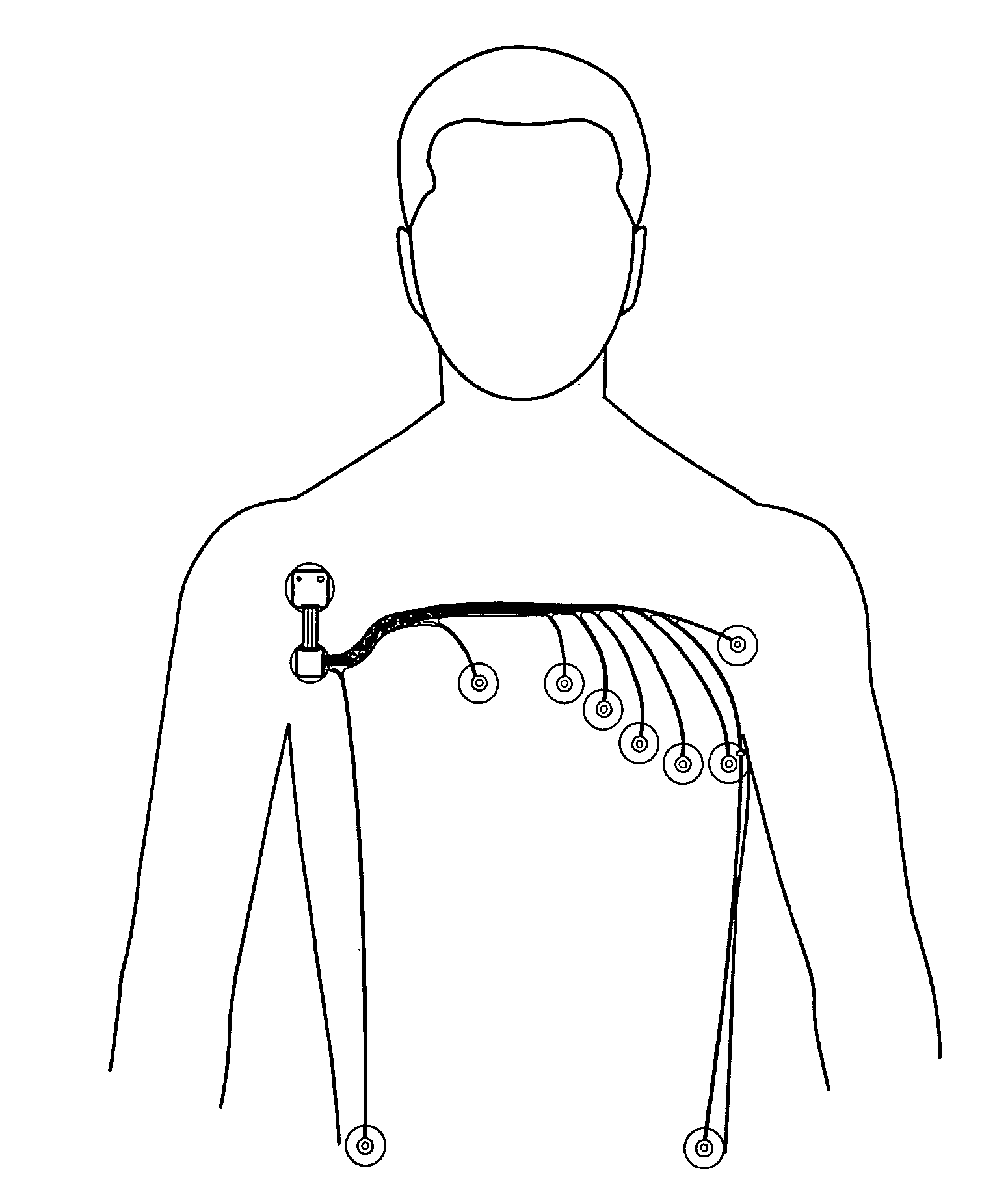
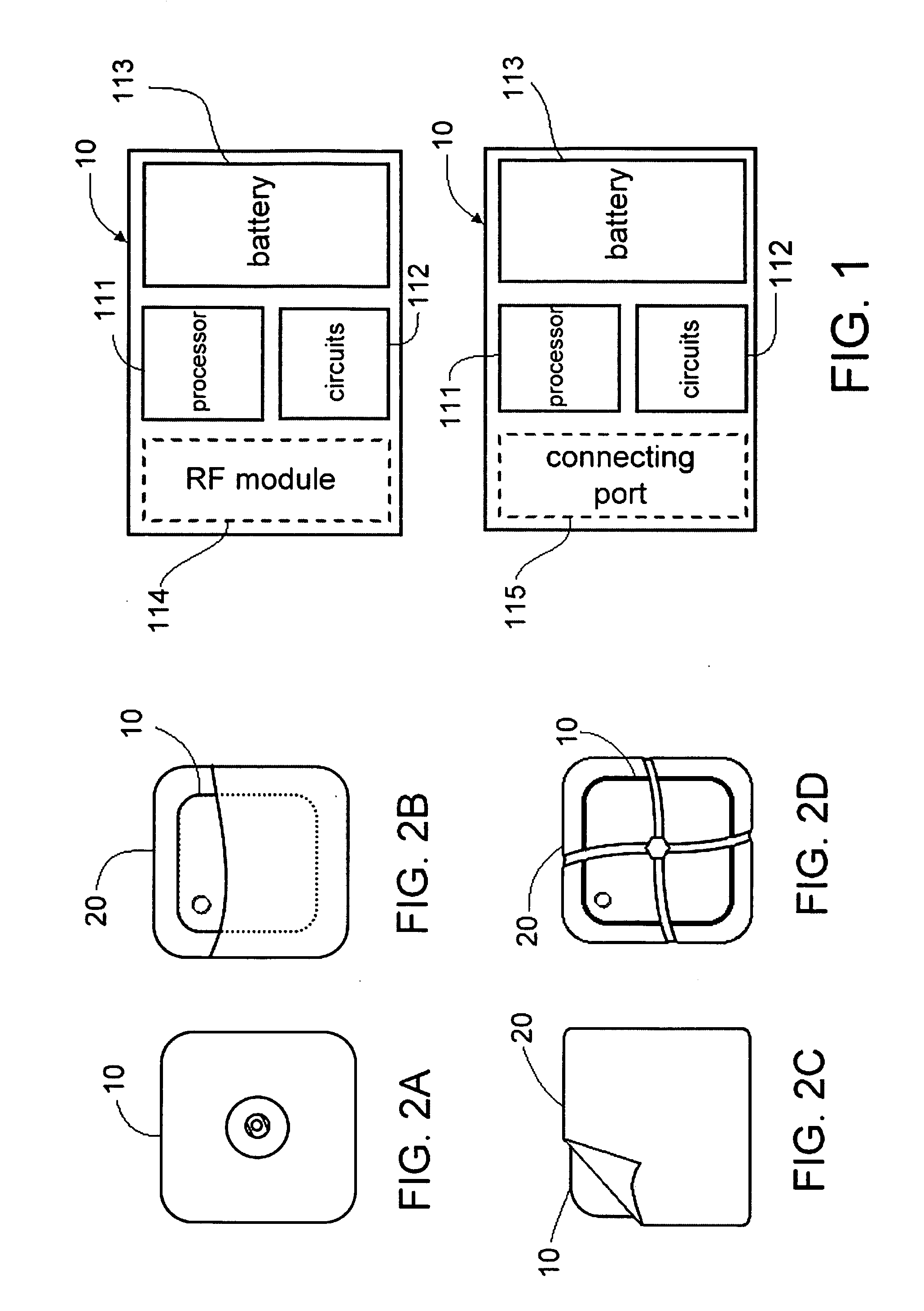
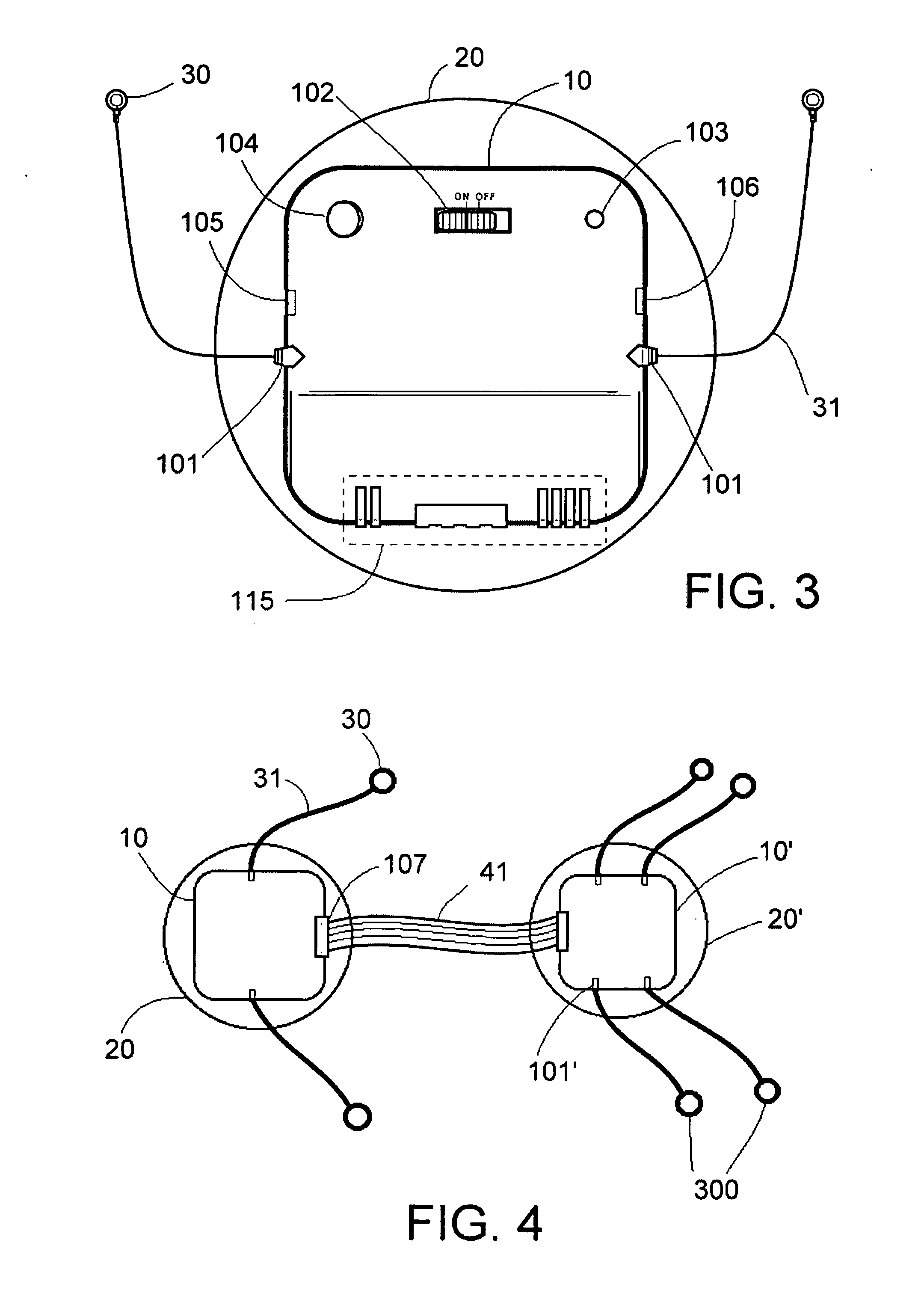
Patch-type physiological monitoring apparatus, system and network are disclosed. The patch-type physiological monitoring apparatus includes at least a node, and at least a patch for attaching to a skin surface of a user and for supporting the node on the skin surface through joining therewith, wherein the node includes at least a signal I / O port for externally connecting to at least a sensor or electrode through a connecting wire so as to acquire a physiological signal, and a RF module for transmitting and receiving signal. The apparatus according to the present invention is of light weight and compact size and easily attached to human body through adhesive patches. Through a RF module, the system can wirelessly communicate with corresponding devices without additional wiring. Further, the system can utilize conventional electrodes, patch electrodes and electrode wiring to avoid extra cost for facilities' renewal and replacement.
Owner:CHOU
Pulser with double-bearing position encoder for non-invasive physiological monitoring
ActiveUS9891079B2Insufficient stabilityImprove stabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhysiological monitoringEngineering
A double-bearing position encoder has an axle stabilized within a housing via two bearings disposed on opposite walls of the housing. The axle is in communications with a rotating cam. The cam actuates a pulser so as to generate an active pulse at a tissue site for analysis by an optical sensor. The axle rotates a slotted encoder wheel or a reflective encoder cylinder disposed within the housing so as to accurately determine the axle position and, hence, the active pulse frequency and phase.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
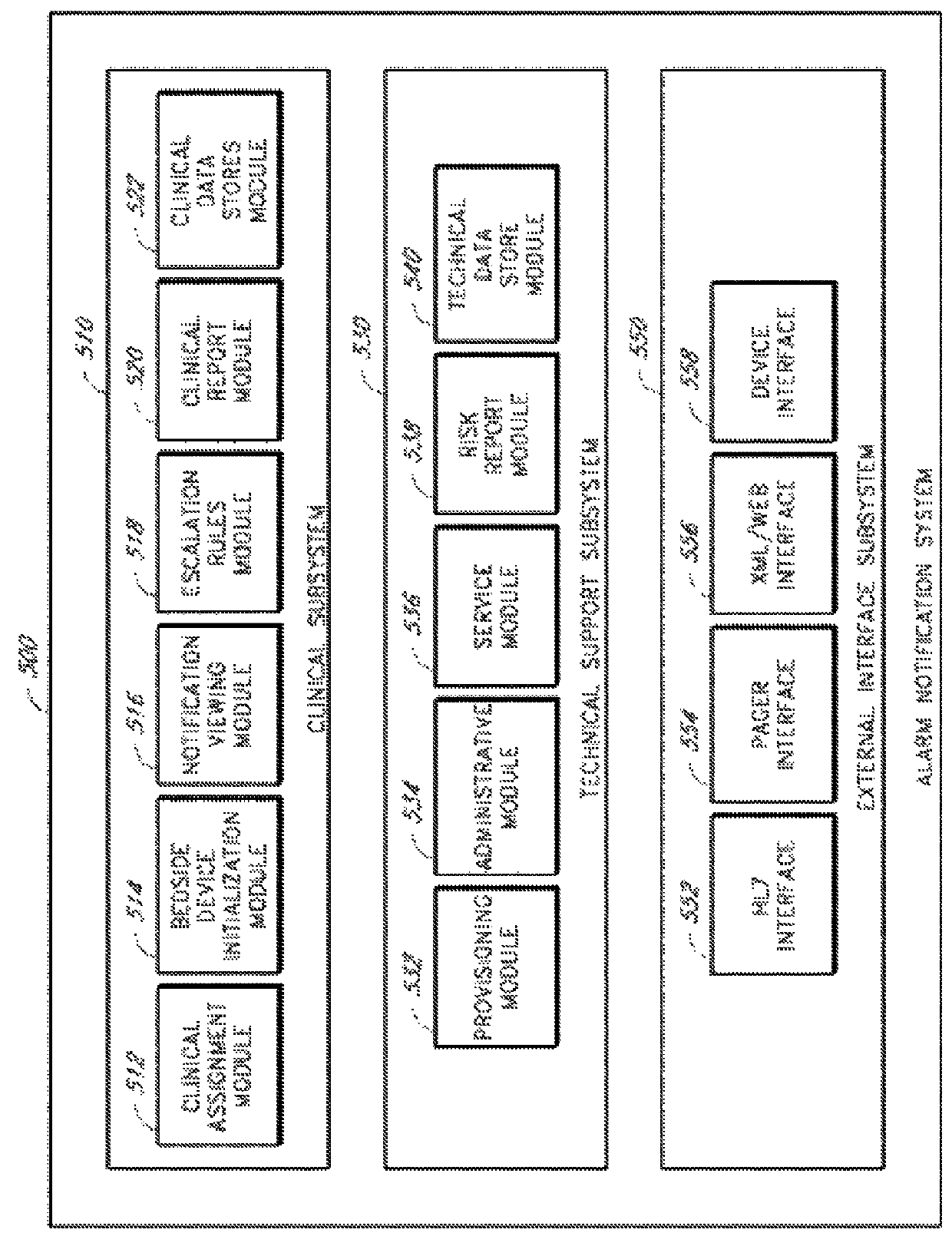
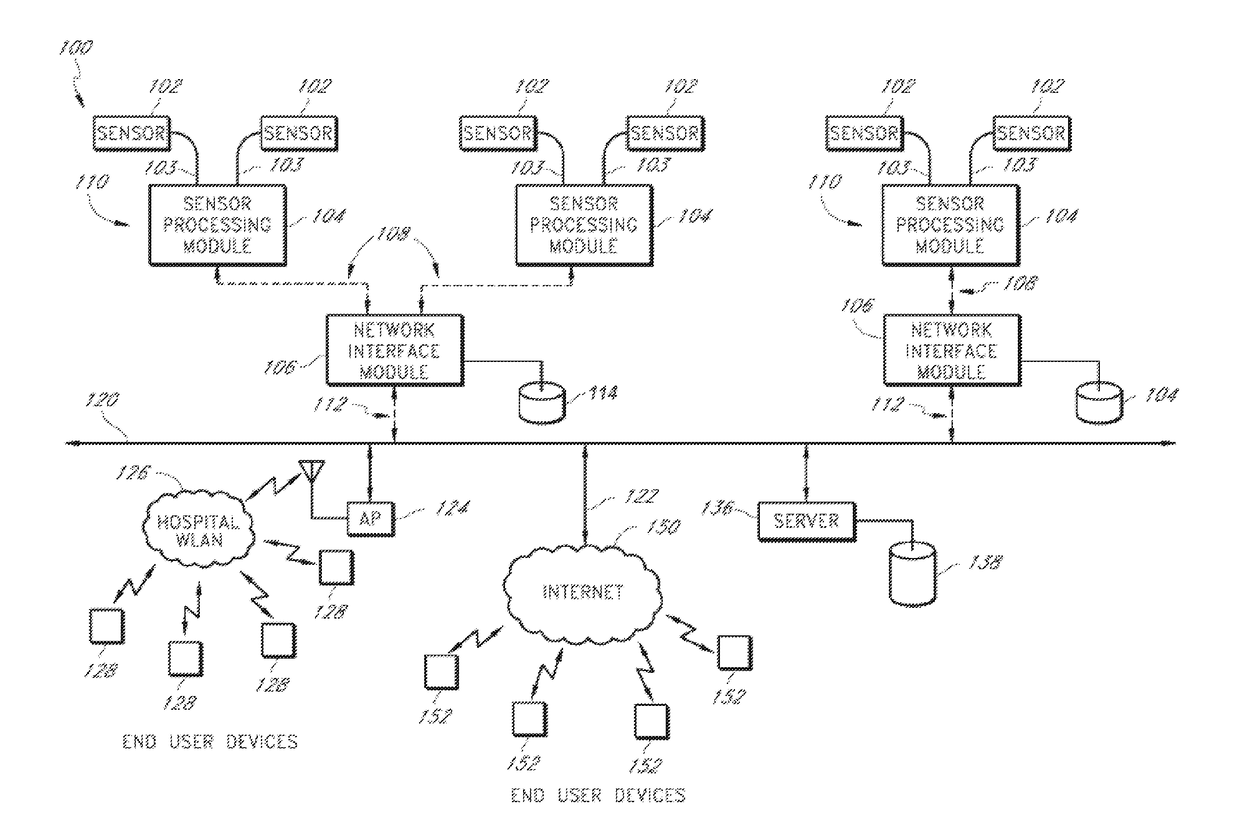
Systems and methods for monitoring a patient health network
ActiveUS9965946B2Transmission systemsTesting/monitoring control systemsCommunication interfacePhysiological monitoring
Systems and methods for monitoring physiological monitoring systems are described herein. A communication interface module can be configured to receive from a physiological monitoring system first data based on a snapshot taken of a status of the physiological monitoring system at a first time. A memory module can be configured to store the first data and a baseline associated with the physiological monitoring system. A processor module can be configured to compare the first data with the baseline and to generate a notification if the first data deviates from the baseline by a predetermined amount. A display module can be configured to display a physical location of a plurality of physiological monitoring systems and display the notification.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Physiological Monitoring Wearable Having Three Electrodes
A wearable system or garment comprises at least three conductive electrodes that may, for example, be made of stretch-recovery electrically conductive yarns integrated with non-conductive stretch-recovery yarns that make up the remaining portion of the wearable system or garment. The wearable or garment further comprises means for using three electrodes to monitor at least one physiological or biophysical event or characteristic of the wearer. One electrode is specifically used to feed back an inverted noise signal to the wearer to destructively interfere with the wearer generated noise. Specifically, the wearer's heart rate, ECG and associated electrical characteristics may be monitored in high resolution under dry electrode conditions.
Owner:TEXTRONICS
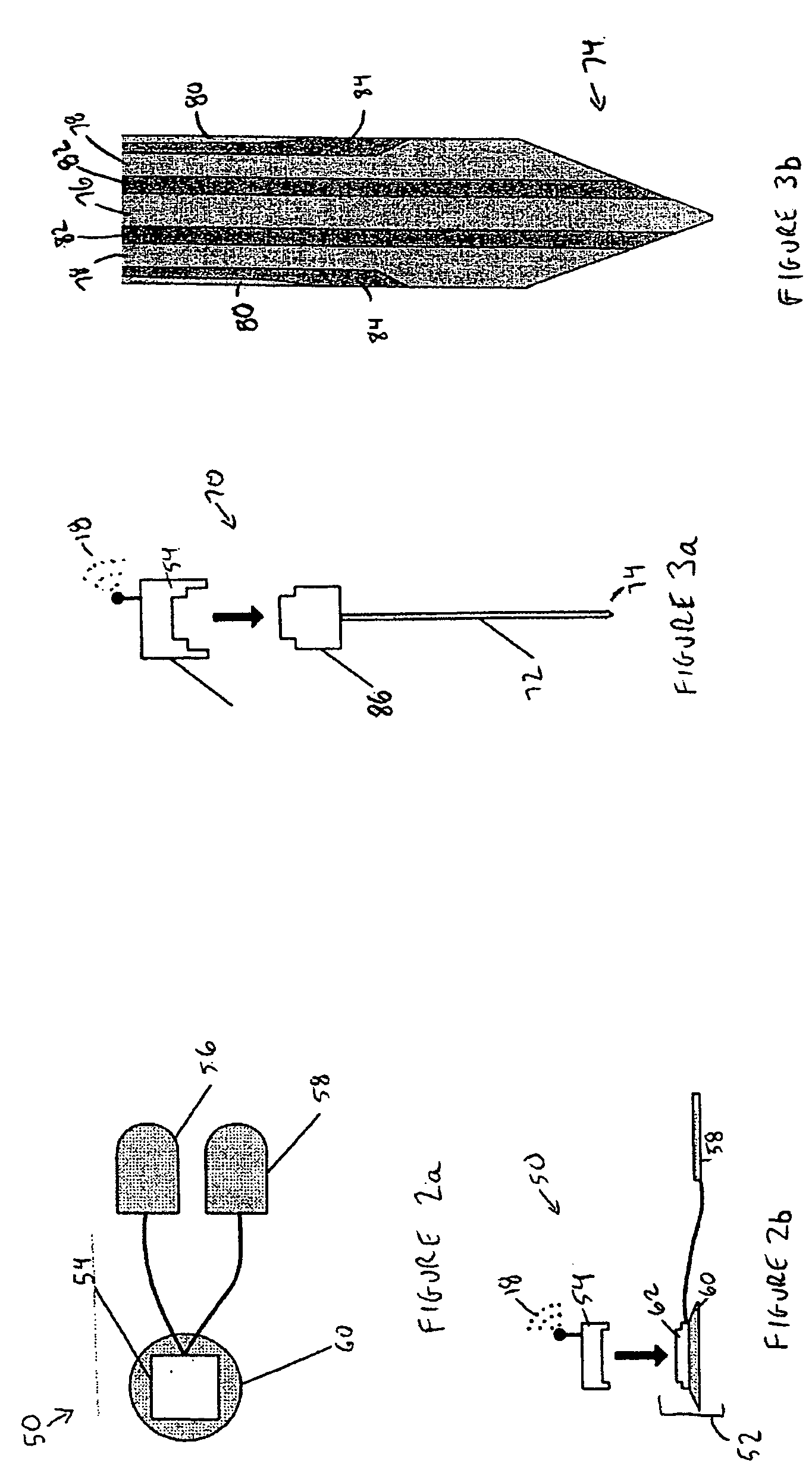
Portable integrated physiological monitoring system
InactiveUS6083156ALow costEasy to transportElectrocardiographyElectromyographyMeasurement deviceUltrasonic sensor
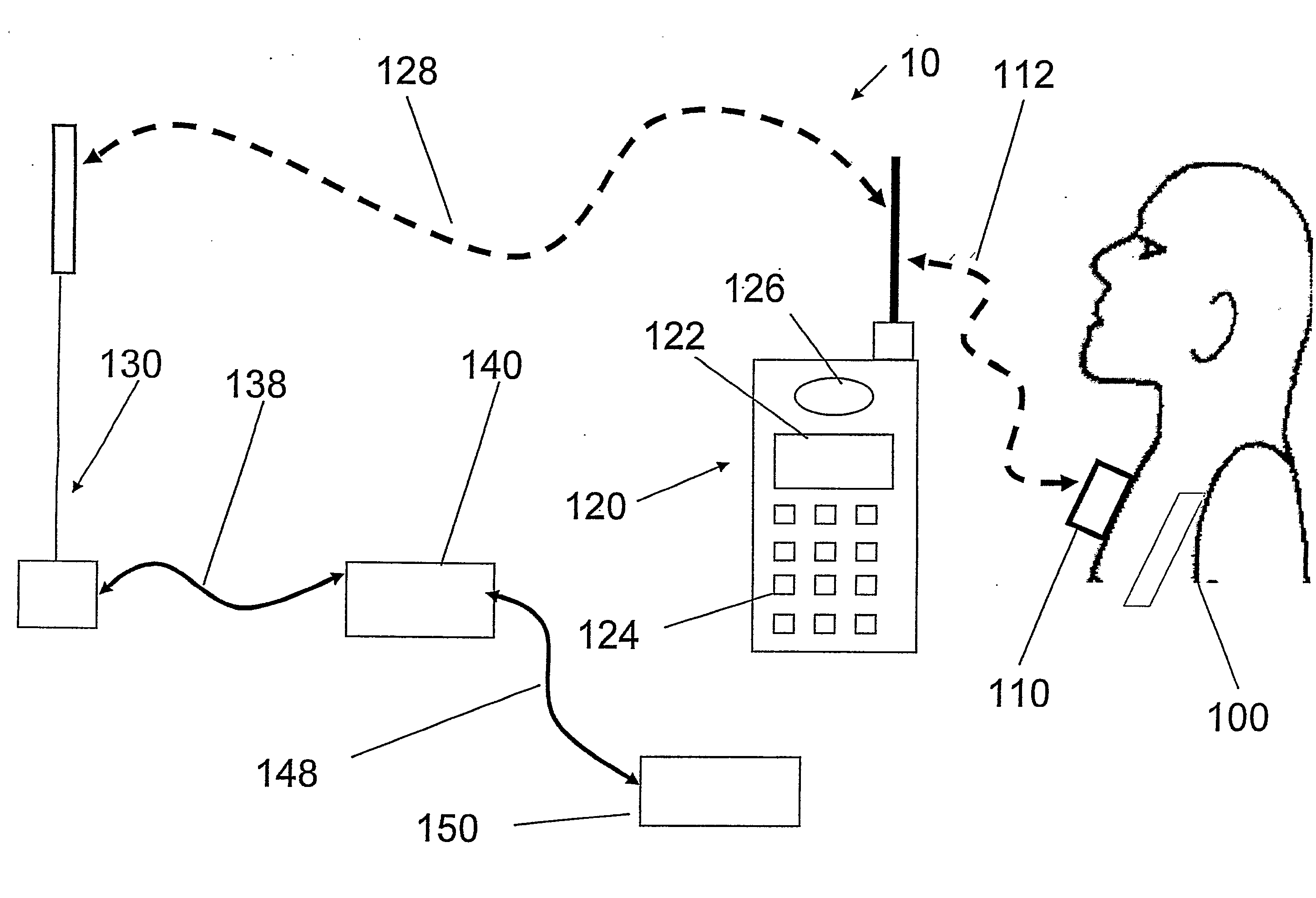
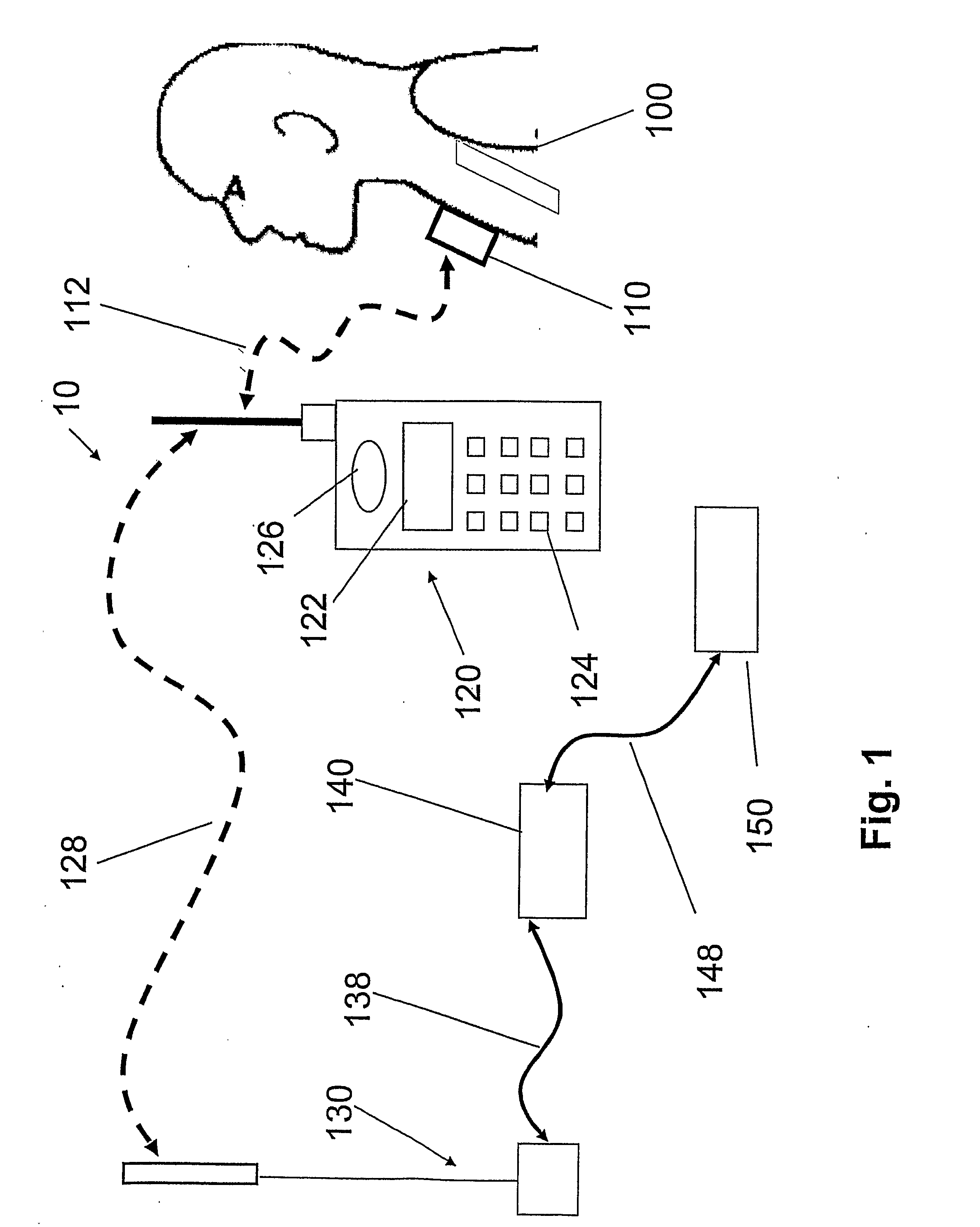
A portable, integrated physiological monitoring system is described for use in clinical outpatient environments. This systems consists of a plethora of sensors and auxiliary devices, an electronics unit (100) that interfaces to the sensors and devices, and a portable personal computer (102). Electrodes (106) are provided to acquisition electrocardiographic, electroencephalographic, and neuromuscular signals. Electrodes (108) are provided to stimulate neural and muscular tissue. A finger pulse oximeter (110), an M-mode ultrasonic transducer (112), an airflow sensor (114), a temperature probe (120), a patient event switch (116), and an electronic stethoscope (118) are provided. A portable personal computer (102) interfaces to the electronics unit (100) via a standard parallel printer port interface (258) to allow communication of commands and information to / from the electronics unit (100). Control and display of the information gathered from the electronics unit (100) is accomplished via an application program executing on the portable personal computer (102). Sharing of common data acquisition hardware along with preliminary processing of information gathered is accomplished within the electronics unit (100). The entire system is battery operated and portable. This system, because of its architecture, offers significant cost advantages as well as unique modes of operation that cannot be achieved from the individual physiological parameter measurement devices alone. The system allows for the integration of acquisitioned information from the sensors into a patient's database stored on the portable personal computer.
Owner:LISIECKI RONALD S
Physiological monitoring garment
InactiveUS7559902B2Inhibition of mobilityEasy to manufactureElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyElectrical conductorPhysiological monitoring
Owner:FOSTER-MILLER
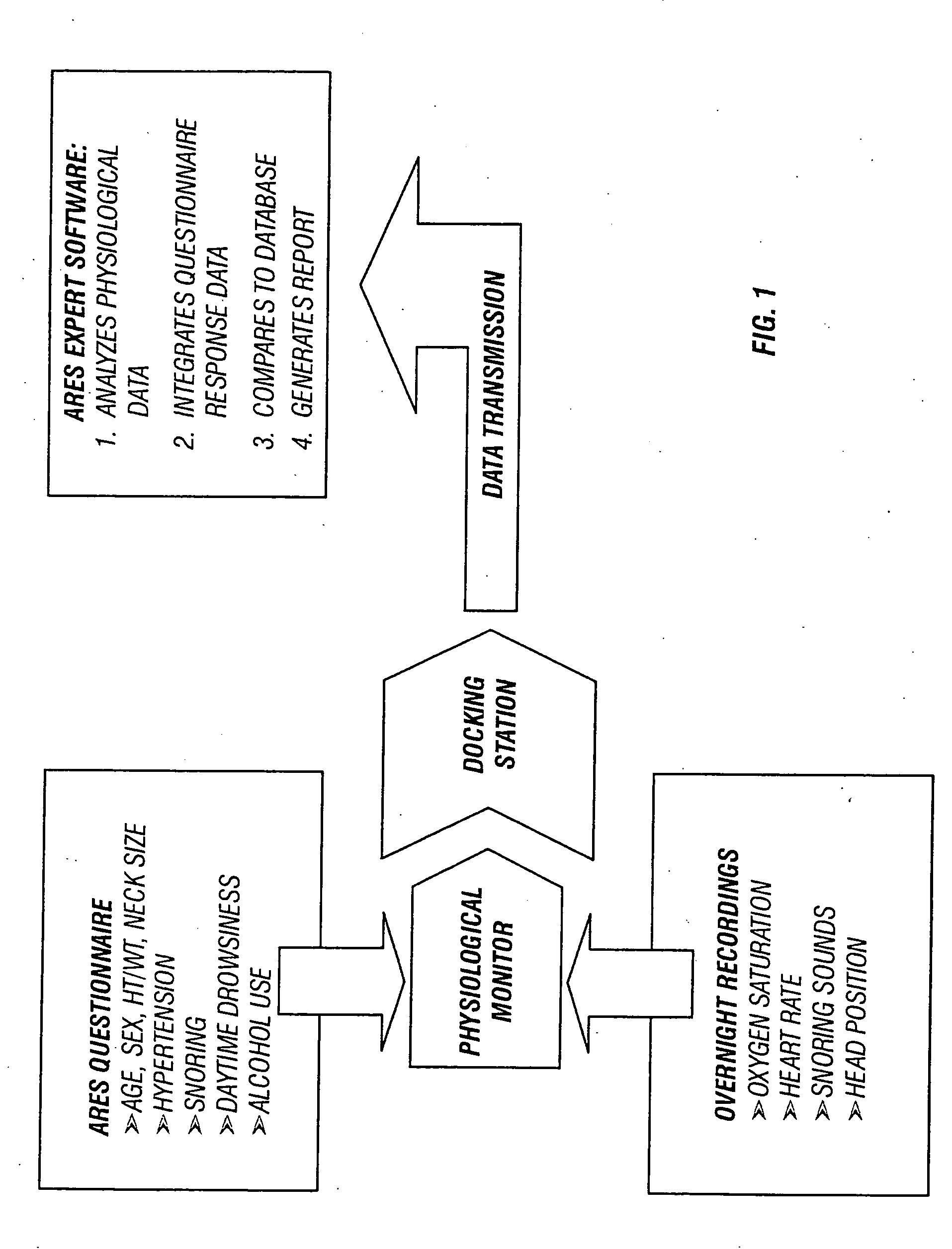
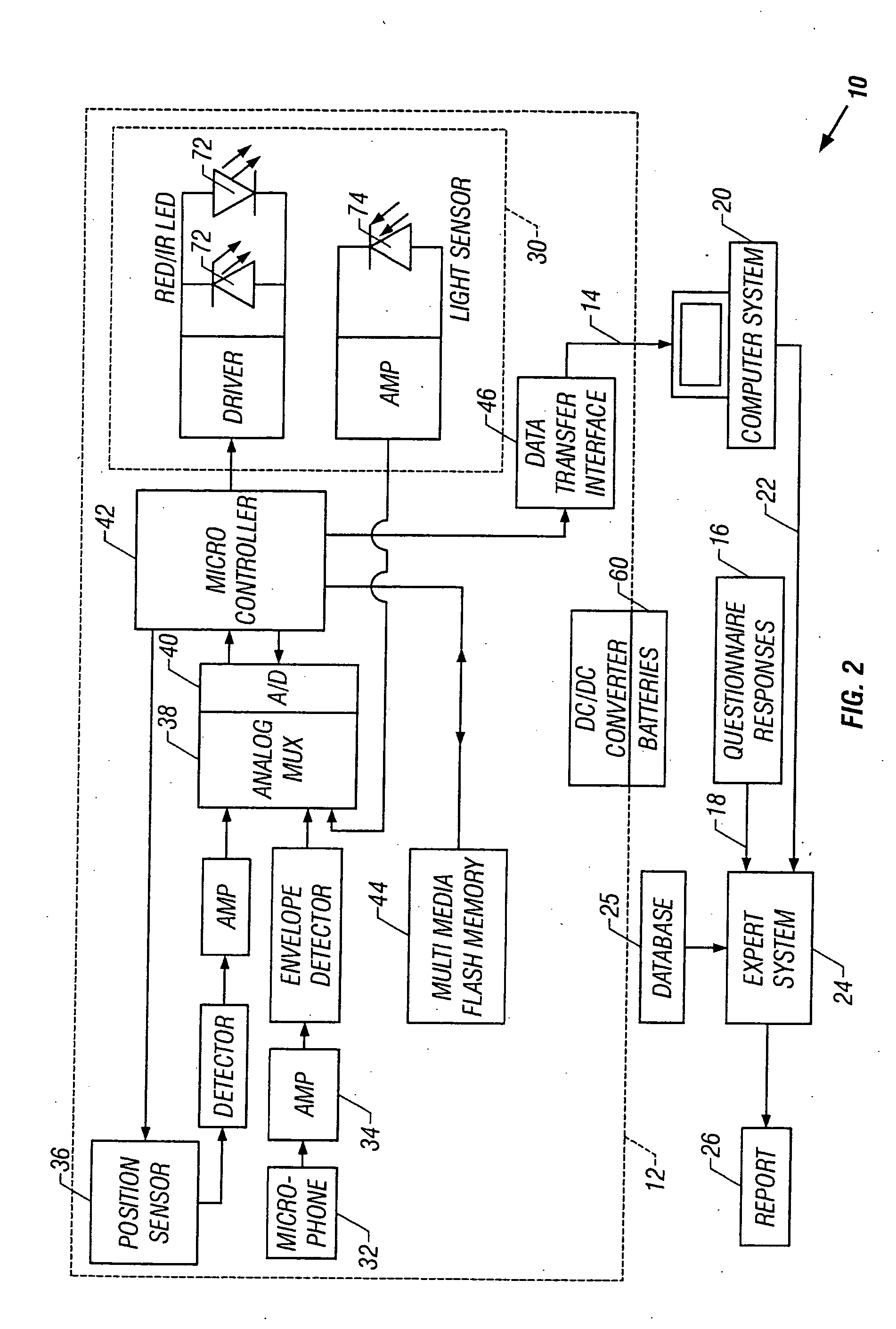
Sleep apnea risk evaluation
InactiveUS20050027207A1Improve accuracyImprove resolutionRespiratorsHealth-index calculationMedicinePulse oximeters
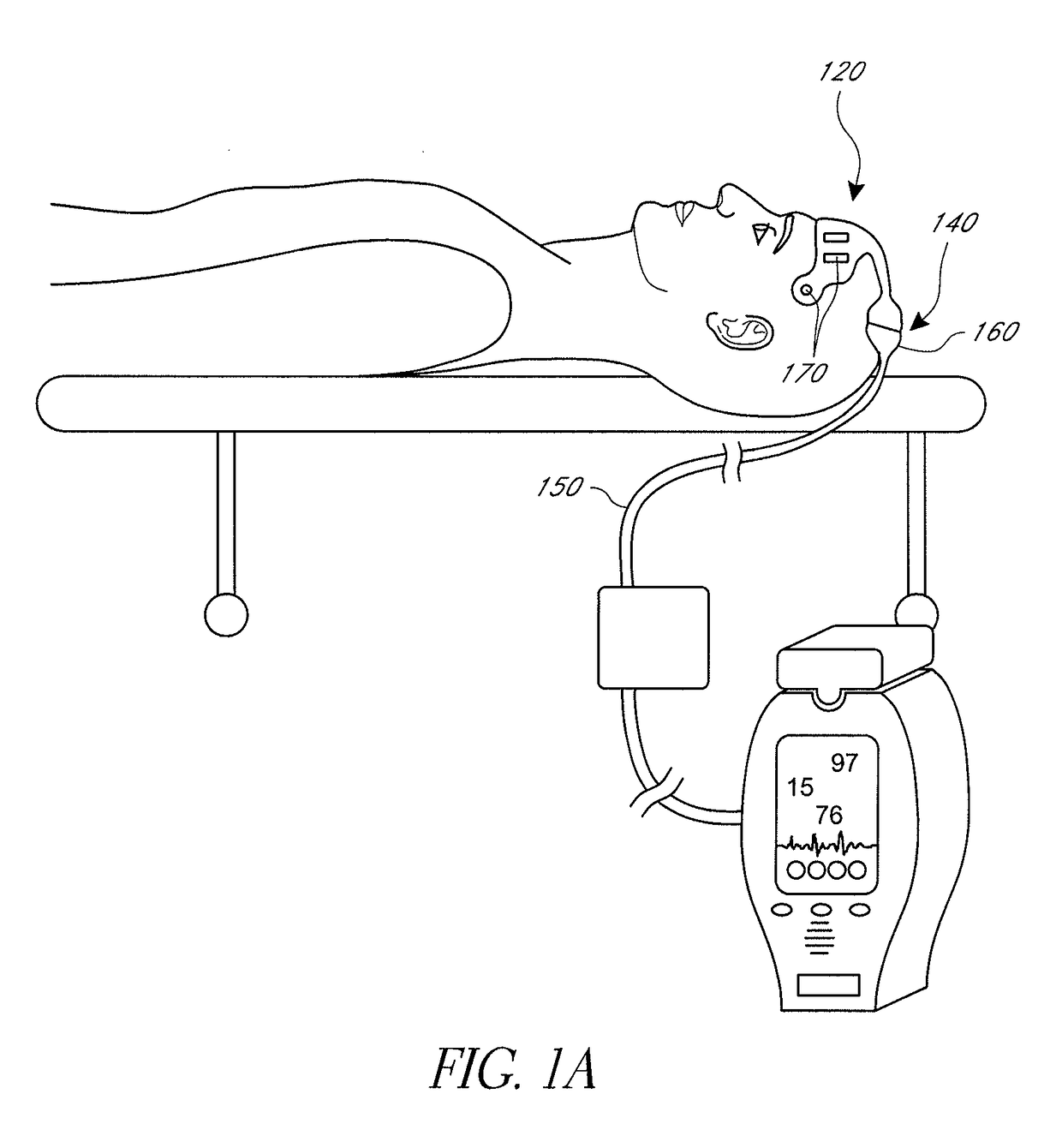
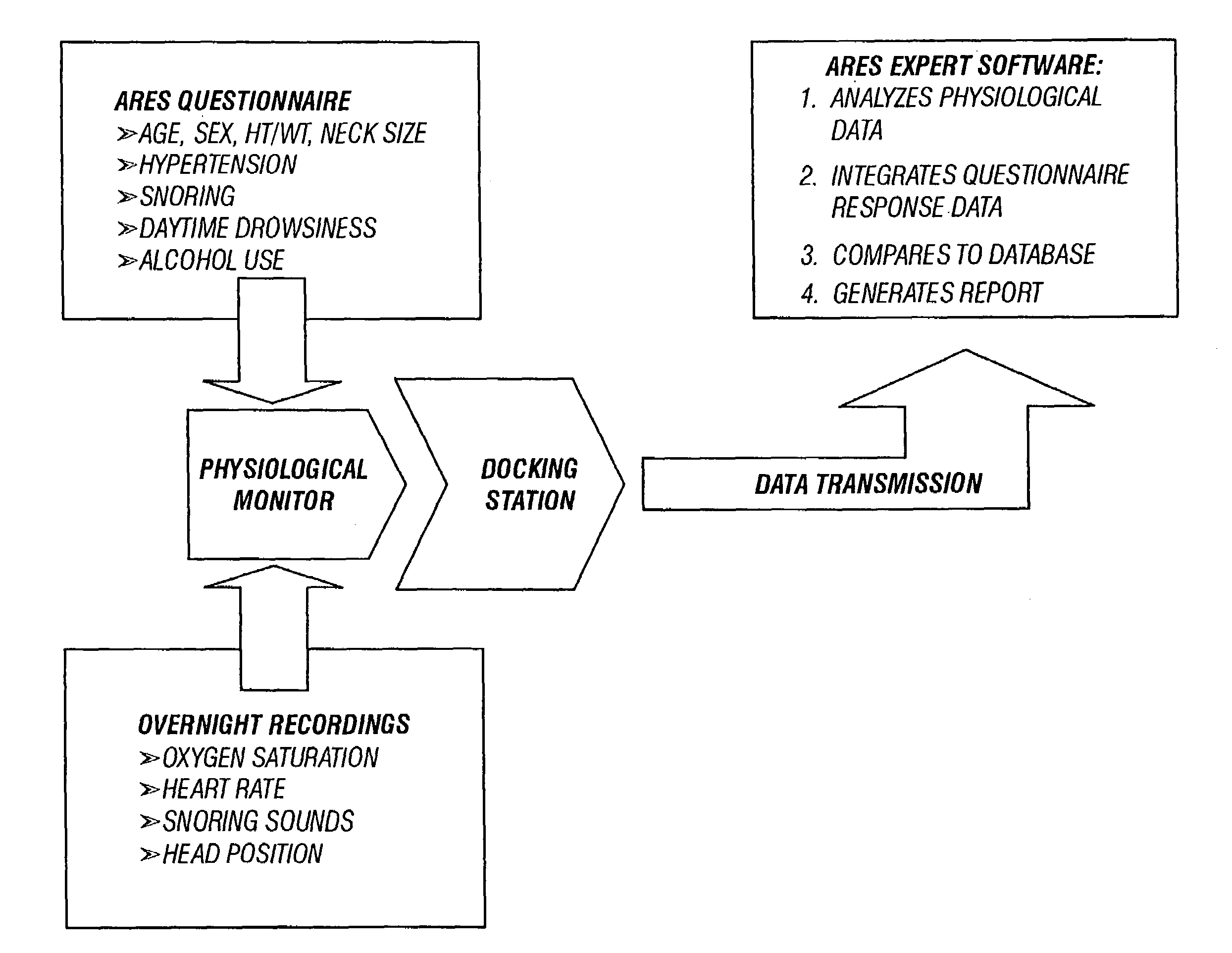
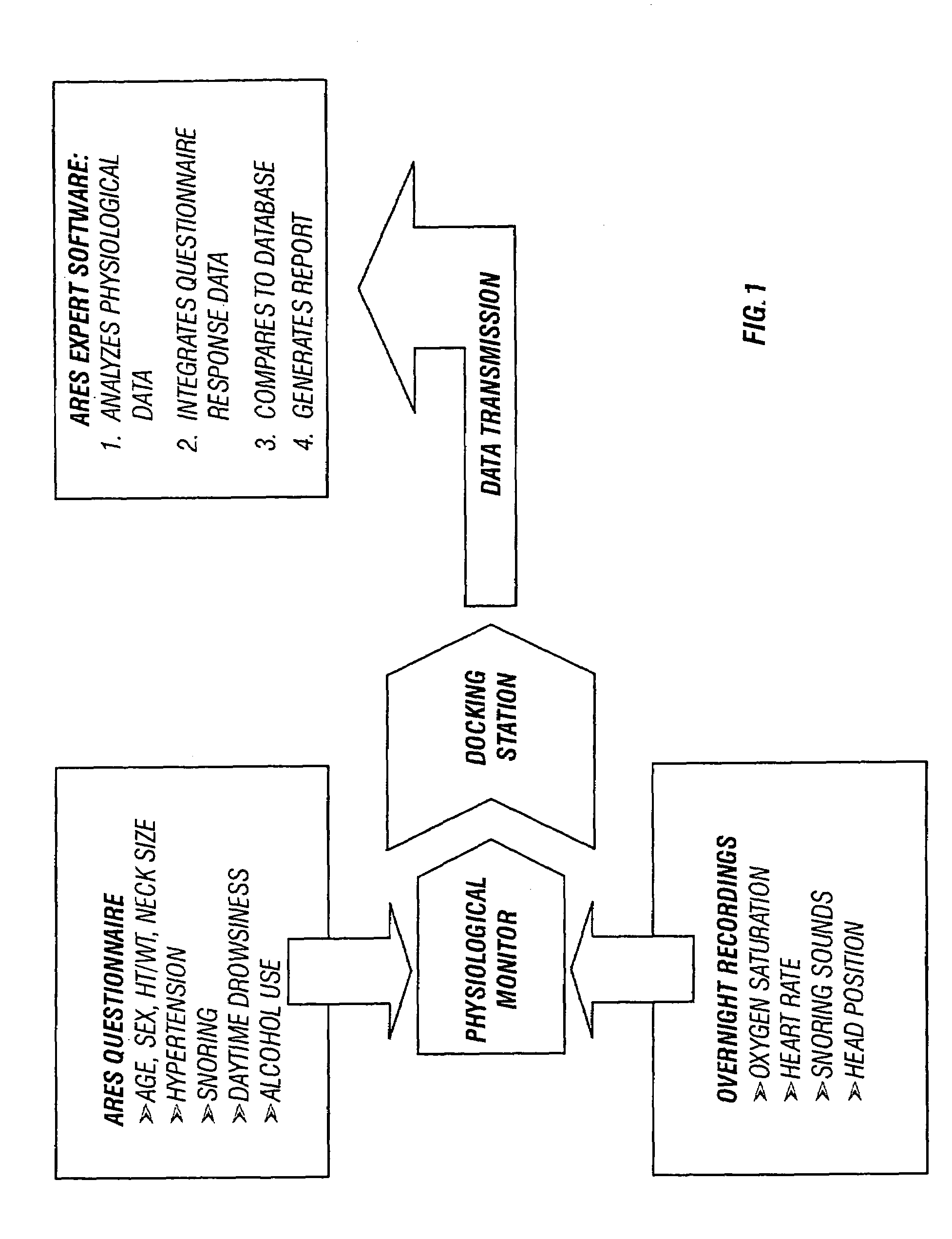
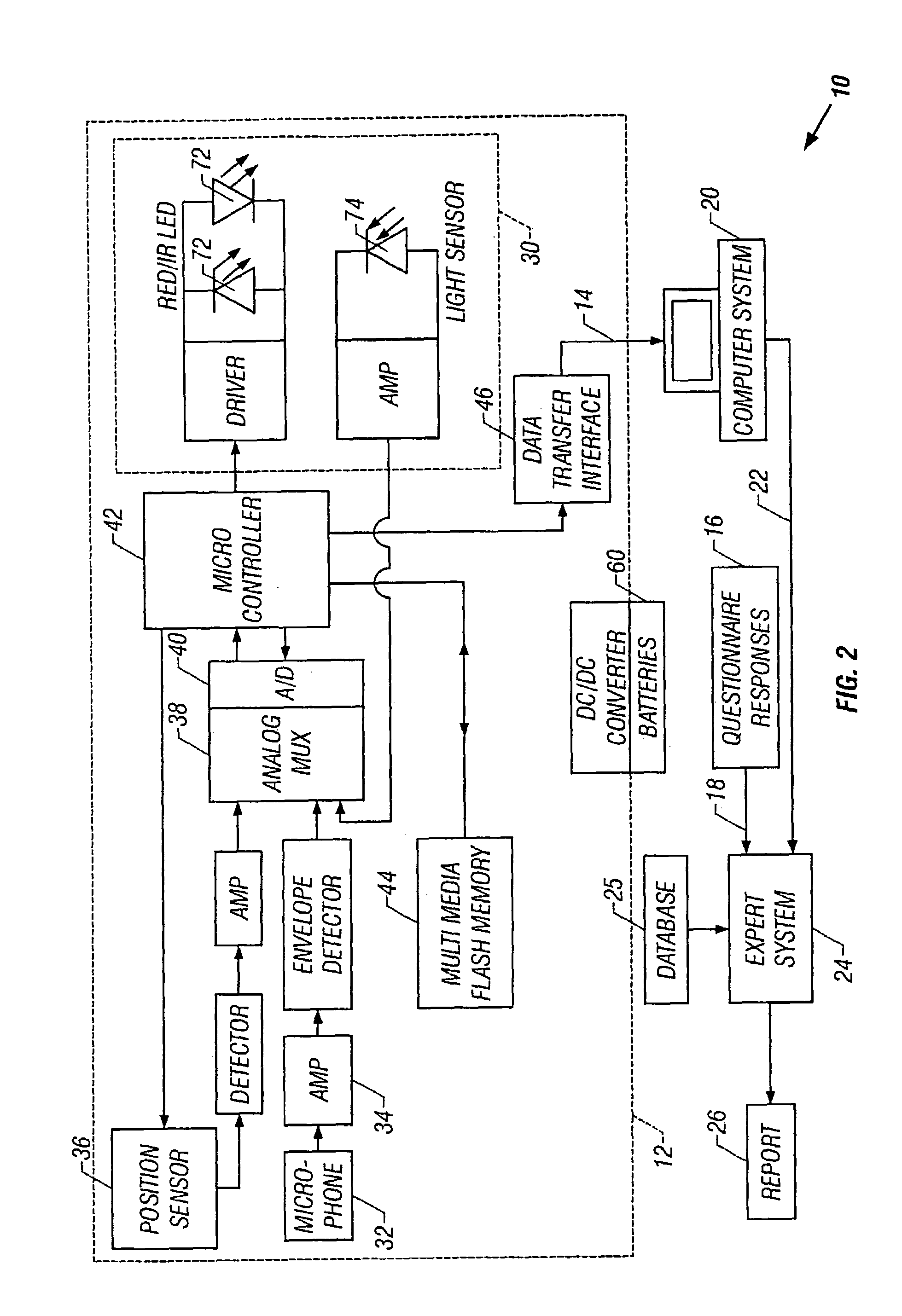
In a technique for collecting and analyzing physiological signals to detect sleep apnea, a small light-weight physiological monitoring system, affixed to a patient's forehead, detects and records the pulse, oximetry, snoring sounds, and head position of a patient to detect a respiratory event, such as sleep apnea. The physiological monitoring system may contain several sensors including a pulse oximeter to detect oximetry and pulse rate, a microphone to detect snoring sounds, and a position sensor to detect head position. The physiological monitoring system also can contain a memory to store or record the signals monitored by the mentioned sensors and a power source. The physiological monitoring system may be held in place by a single elastic strap, thereby enabling a patient to use the system without the assistance of trained technicians.
Owner:WATERMARK MEDICAL
Patient monitor for determining microcirculation state
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Capturing data for individual physiological monitoring
InactiveUS20080292151A1Character and pattern recognitionEye diagnosticsPhysiological monitoringComputer science
A method for capturing images of an individual to determine wellness for such individual, including establishing baseline physiological data for the individual, and baseline capture condition data for the individual; detecting and identifying the presence of the individual in the image capture environment; providing semantic data associated with the individual; capturing one or more images of the individual during a capture event and determining the capture conditions present during the capture event; using the event capture conditions, the baseline physiological data for the individual and the baseline capture condition data to determine the acceptability of event captured images; and using the acceptable images and the semantic data in determining the wellness of the individual.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
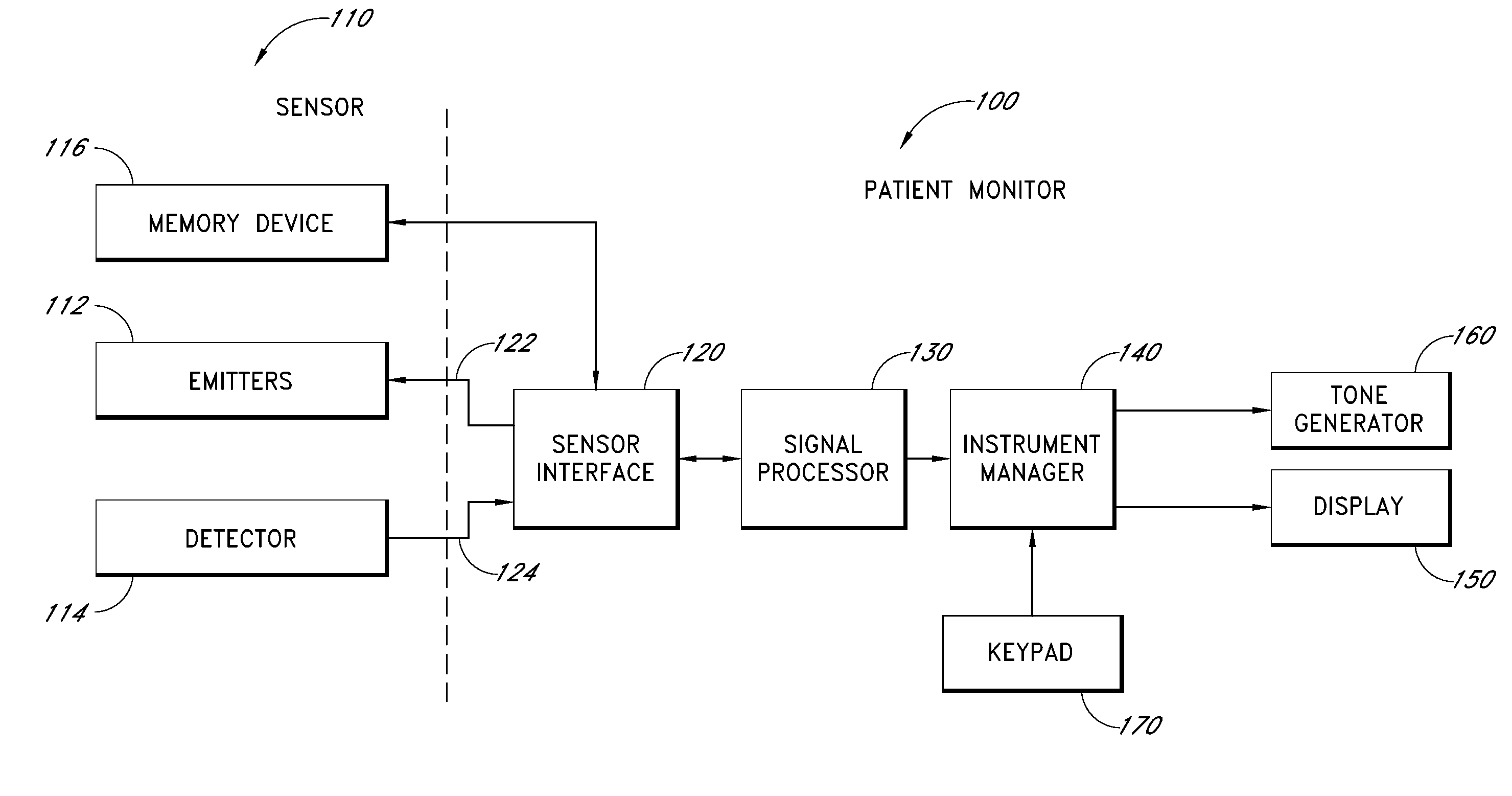
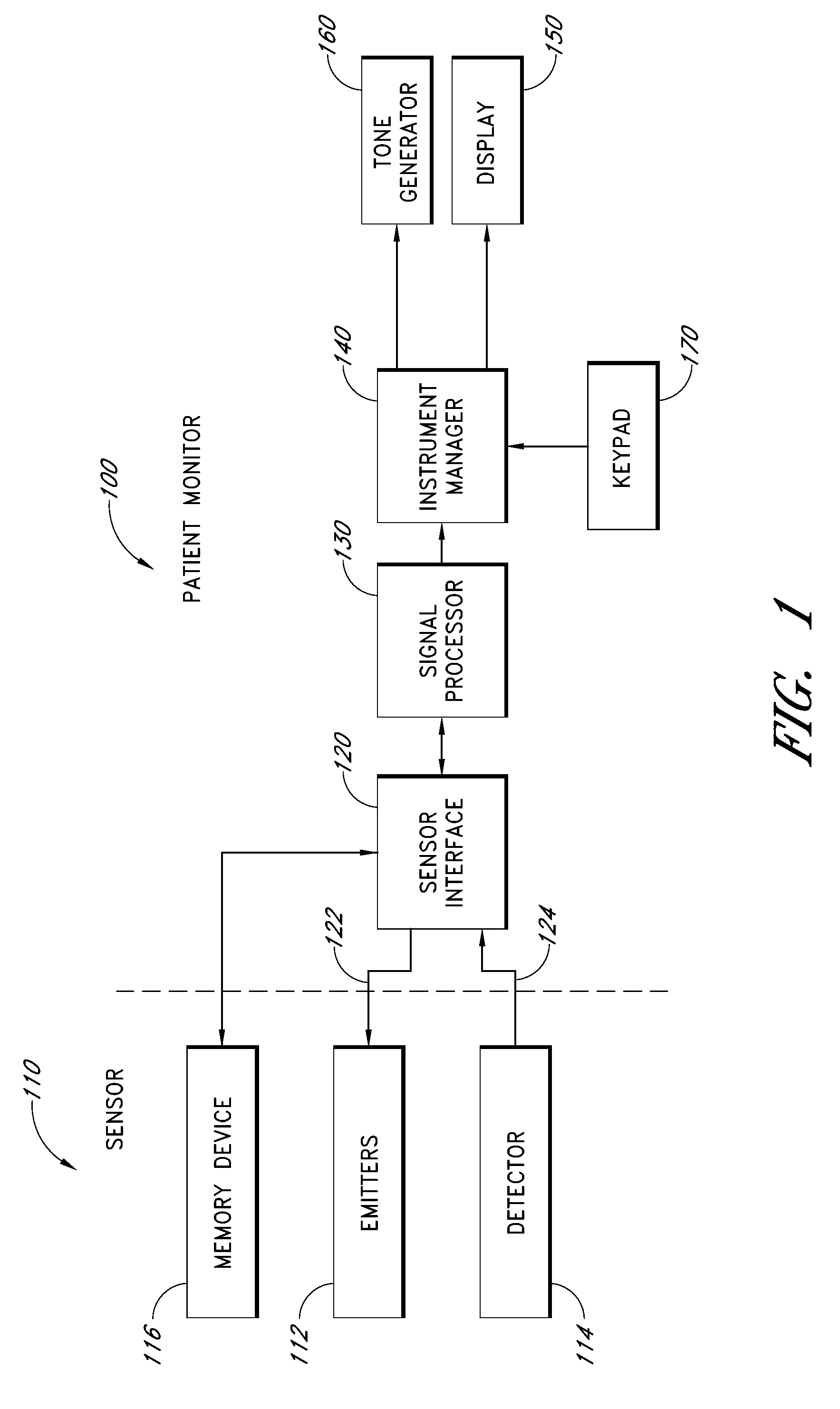
Method and circuit for indicating quality and accuracy of physiological measurements
InactiveUS20060030764A1Accurate detectionAccurate qualitySensorsColor/spectral properties measurementsPhysiological monitoringEngineering
Sensors and monitors for a physiological monitoring system having capability to indicate an accuracy of an estimated physiological condition. The sensor senses at least one physiological characteristic of a patient and is connectable to a monitor that estimates the physiological condition from signals detected by the sensor. The sensor includes a detector for detecting the signals from the patient which are indicative of the physiological characteristic. The sensor is associated with a memory configured to store data that defines at least one sensor signal specification boundary for the detected signals. The boundary is indicative of a quality of the signals and an accuracy of the physiological characteristic estimated from the signals by the monitor. The sensor further includes means for providing access to the memory to allow transmission of the data that defines the at least one sensor boundary to the monitor.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
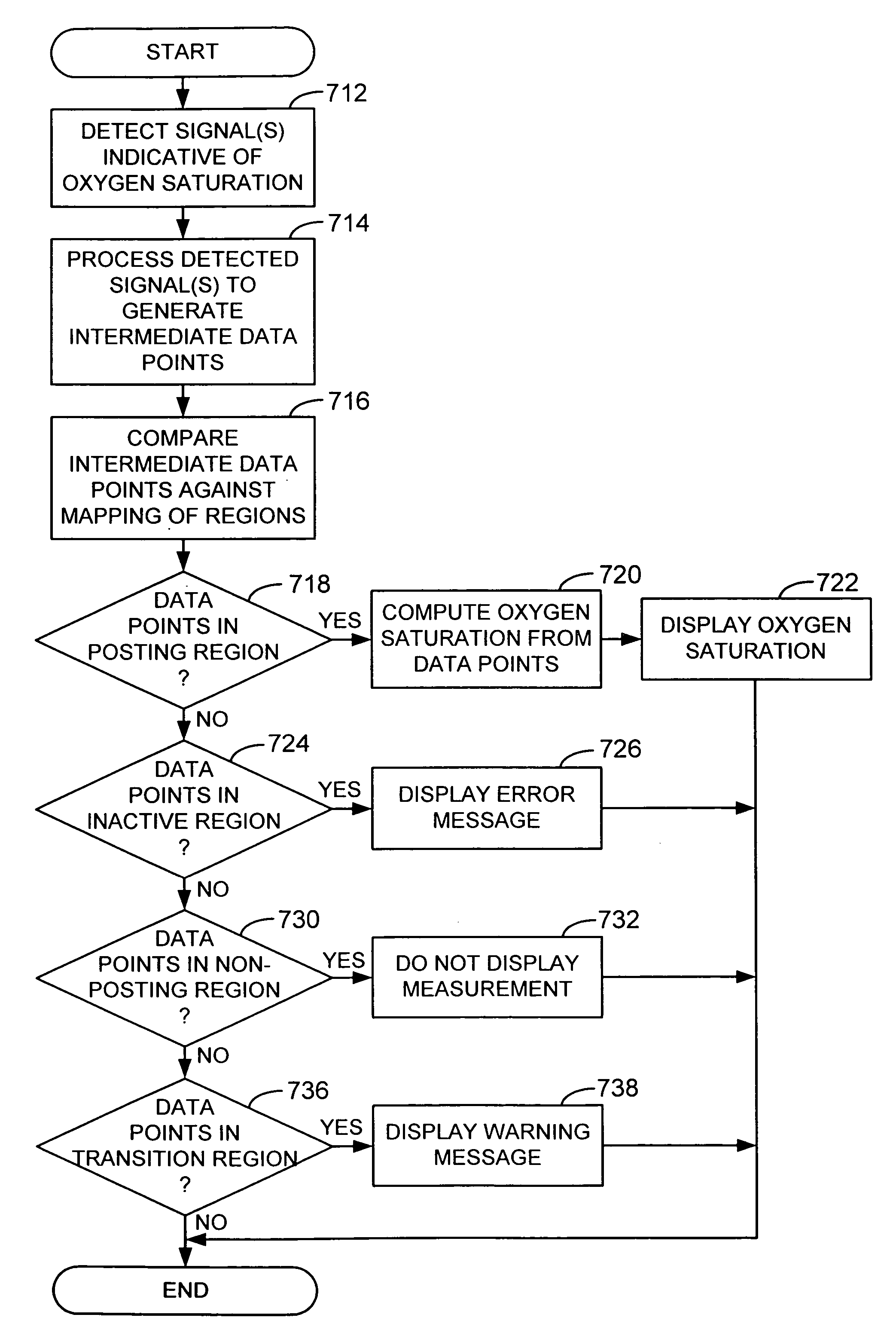
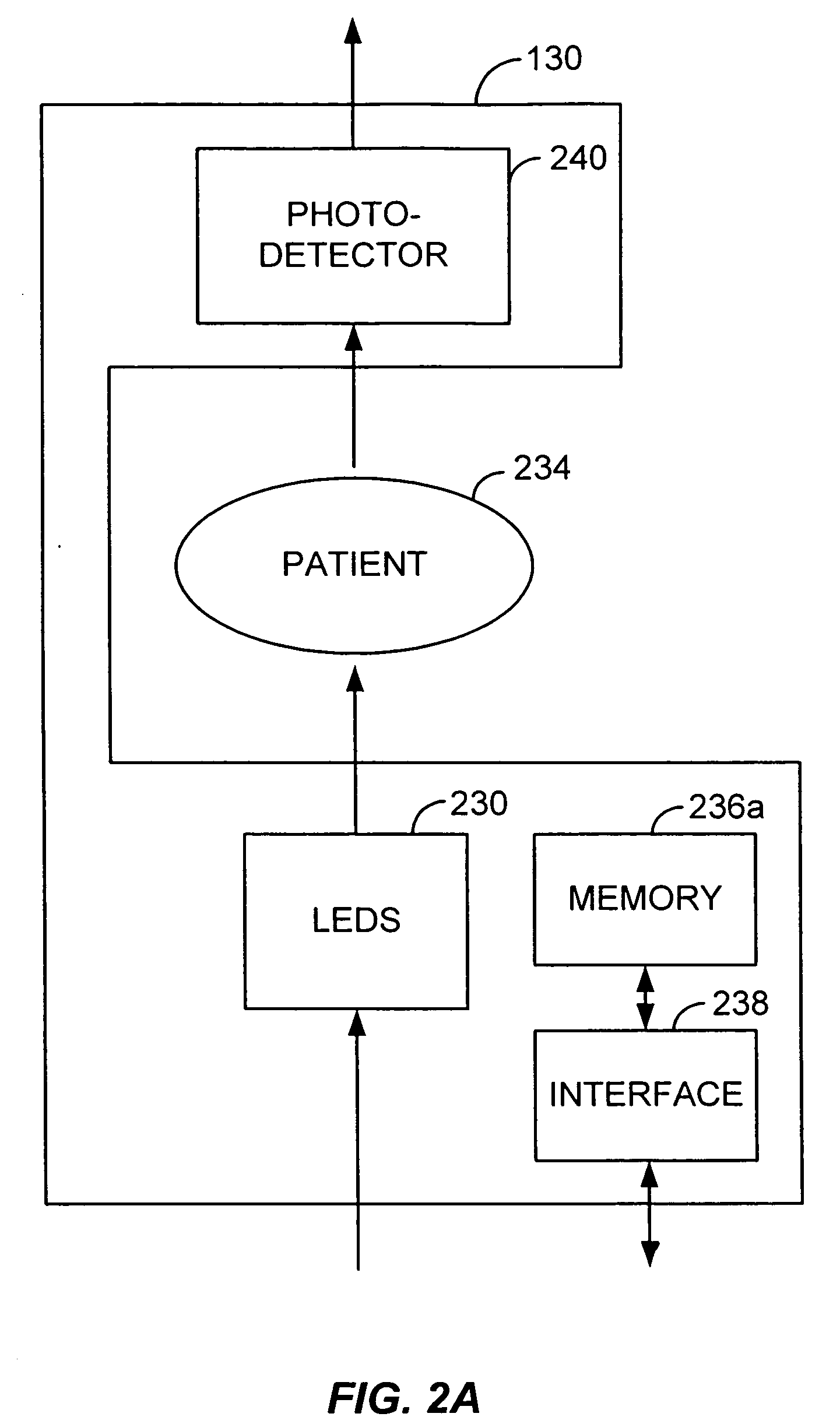
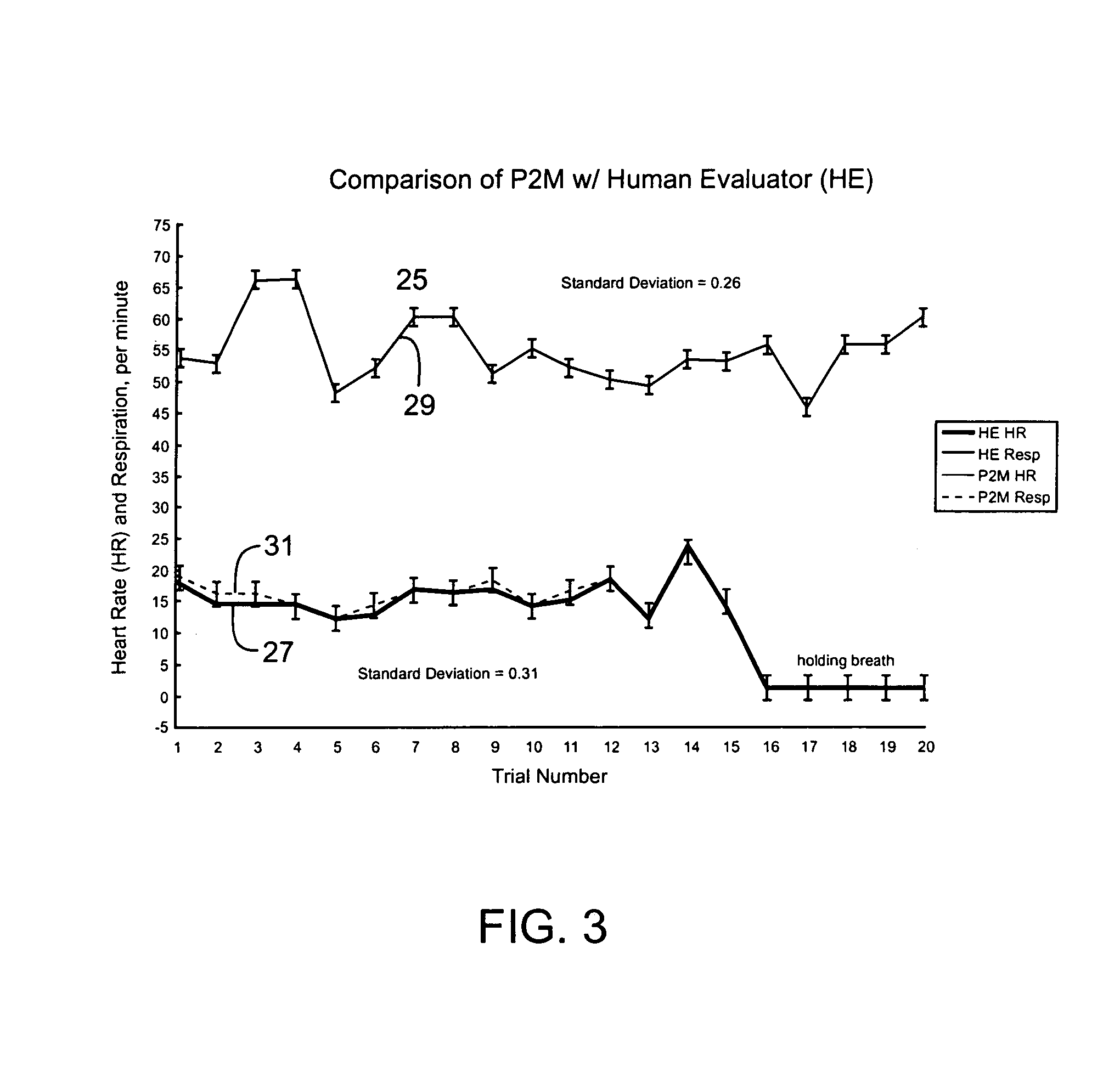
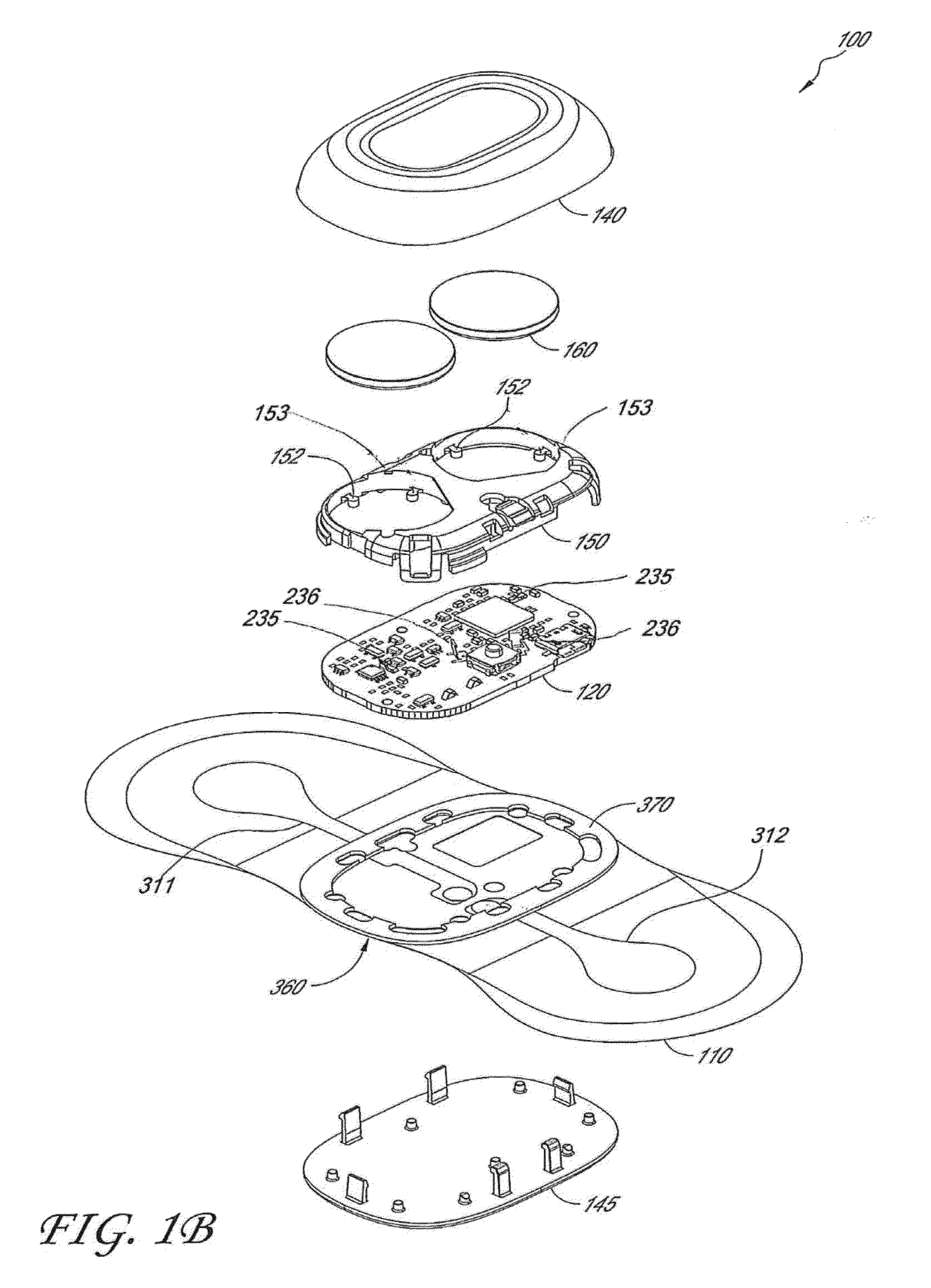
Passive physiological monitoring (P2M) system
InactiveUS6984207B1Easy to deployEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterInternal bleedingBand-pass filter
Passive Physiological monitoring apparatus and method have a sensor for sensing physiological phenomenon. A converter converts sensed data into electrical signals and a computer receives and computes the signals, and outputs computed data for real-time interactive display. The sensor is a piezoelectric film of polyvinylidene fluoride. A band-pass filter filters out noise and isolates the signals to reflect data from the body. A pre-amplifier amplifies signals. Signals detected include mechanical, thermal and acoustic signatures reflecting cardiac output, cardiac function, internal bleeding, respiratory, pulse, apnea, and temperature. A pad may incorporate the PVDF film and may be fluid-filled. The film converts mechanical energy into analog voltage signals. Analog signals are fed through the band-pass filter and the amplifier. A converter converts the analog signals to digital signals. A Fourier transform routine is used to transform into the frequency domain. A microcomputer is used for recording, analyzing and displaying data for on-line assessment and for providing realtime response. A radio-frequency filter may be connected to a cable and the film for transferring signals from the film through the cable. The sensor may be an array provided in a MEDEVAC litter or other device for measuring acoustic and hydraulic signals from the body of a patient for field monitoring, hospital monitoring, transport monitoring, home, remote monitoring.
Owner:HOANA MEDICAL
Physiological monitoring device
InactiveUS20140206977A1Avoid mechanical stressPrecise positioningElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsPhysiological monitoringLong term monitoring
The present invention relates to a physiological monitoring device. Some embodiments of the invention allow for long-term monitoring of physiological signals. Further embodiments may also allow for the monitoring of secondary signals such as motion.
Owner:IRHYTHM TECH
Systems and methods for monitoring a patient health network
ActiveUS20180225960A1Transmission systemsTesting/monitoring control systemsCommunication interfacePhysiological monitoring
Systems and methods for monitoring physiological monitoring systems are described herein. A communication interface module can be configured to receive from a physiological monitoring system first data based on a snapshot taken of a status of the physiological monitoring system at a first time. A memory module can be configured to store the first data and a baseline associated with the physiological monitoring system. A processor module can be configured to compare the first data with the baseline and to generate a notification if the first data deviates from the baseline by a predetermined amount. A display module can be configured to display a physical location of a plurality of physiological monitoring systems and display the notification.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
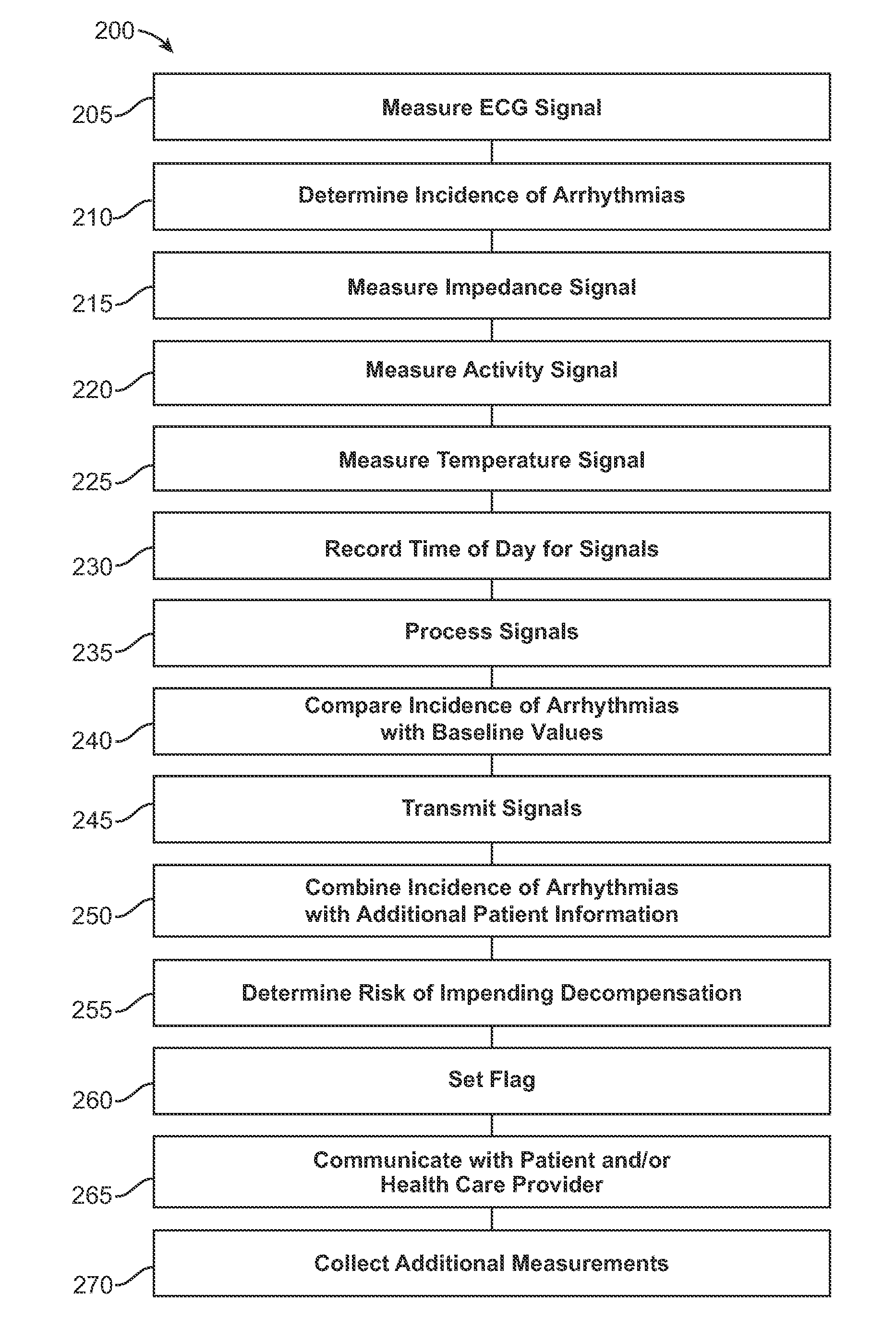
Heart Failure Decompensation Prediction Based on Cardiac Rhythm
ActiveUS20090234410A1Reduce traumaSave livesElectrocardiographyHealth-index calculationPhysiological monitoringSystems approaches
Systems and methods of detecting an impending cardiac decompensation of a patient measure an electrocardiogram signal of the patient. An incidence of cardiac arrhythmias is determined from the electrocardiogram signal. A risk of impending decompensation is determined in response to the incidence of cardiac arrhythmias. In many embodiments, the impending decompensation can be detected early enough to avoid, or at least delay, the impending decompensation, such that patient trauma and / or expensive ICU care can be avoided. Although embodiments make specific reference to monitoring electrocardiogram and other physiological signals with an adherent patch, the system methods and devices are applicable to many applications in which physiological monitoring is used, for example wireless physiological monitoring with implanted sensors for extended periods.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MONITORING
Wireless physiological monitoring system
InactiveUS20050261559A1Quick applicationQuick removalSensorsSkin piercing electrodesLine sensorElectrical conductor
Embodiments of the invention relate to a wireless physiological monitoring system. The system includes at least one wireless sensor and a monitoring device which are linked to one another of a wireless fashion for measuring physiological signals of a patient. The at least one wireless sensor is located on the patient and may comprise a wireless surface electrode assembly or a wireless needle assembly. The system may also comprise a wireless stimulator syncronized with the wireless sensor for performing certain diagnostic tests, such as nerve conduction velocity tests, for example. The wireless sensor preferably includes active, reference and common conductors. The common conductor can be used to measure the common mode voltage of the patient in the vicinity of the testing, and this voltage can then be subtracted from the measured active and reference voltages.
Owner:EXCEL TECH
Heart failure decompensation prediction based on cardiac rhythm
ActiveUS8718752B2Reduce traumaSave livesElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyPhysiological monitoringSystems approaches
Systems and methods of detecting an impending cardiac decompensation of a patient measure an electrocardiogram signal of the patient. An incidence of cardiac arrhythmias is determined from the electrocardiogram signal. A risk of impending decompensation is determined in response to the incidence of cardiac arrhythmias. In many embodiments, the impending decompensation can be detected early enough to avoid, or at least delay, the impending decompensation, such that patient trauma and / or expensive ICU care can be avoided. Although embodiments make specific reference to monitoring electrocardiogram and other physiological signals with an adherent patch, the system methods and devices are applicable to many applications in which physiological monitoring is used, for example wireless physiological monitoring with implanted sensors for extended periods.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MONITORING
Sleep apnea risk evaluation
InactiveUS7297119B2Improve accuracyImprove resolutionHealth-index calculationSurgeryPulse oximetersLate apnea
In a technique for collecting and analyzing physiological signals to detect sleep apnea, a small light-weight physiological monitoring system, affixed to a patient's forehead, detects and records the pulse, oximetry, snoring sounds, and head position of a patient to detect a respiratory event, such as sleep apnea. The physiological monitoring system may contain several sensors including a pulse oximeter to detect oximetry and pulse rate, a microphone to detect snoring sounds, and a position sensor to detect head position. The physiological monitoring system also can contain a memory to store or record the signals monitored by the mentioned sensors and a power source. The physiological monitoring system may be held in place by a single elastic strap, thereby enabling a patient to use the system without the assistance of trained technicians.
Owner:WATERMARK MEDICAL
Computer interfaces including physiologically guided avatars
This invention provides user interfaces that more intuitively display physiological data obtained from physiological monitoring of one or more subjects. Specifically, the user interfaces of this invention create and display one or more avatars having behaviors guided by physiological monitoring data. The monitoring data is preferably obtained when the subject is performing normal tasks without substantial restraint. This invention provides a range of implementations that accommodate user having varying processing and graphics capabilities, e.g., from handheld electronic devices to ordinary PC-type computers and to systems with enhanced graphics capabilities.
Owner:ADIDAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com