Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
231results about "Operational speed enhancement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
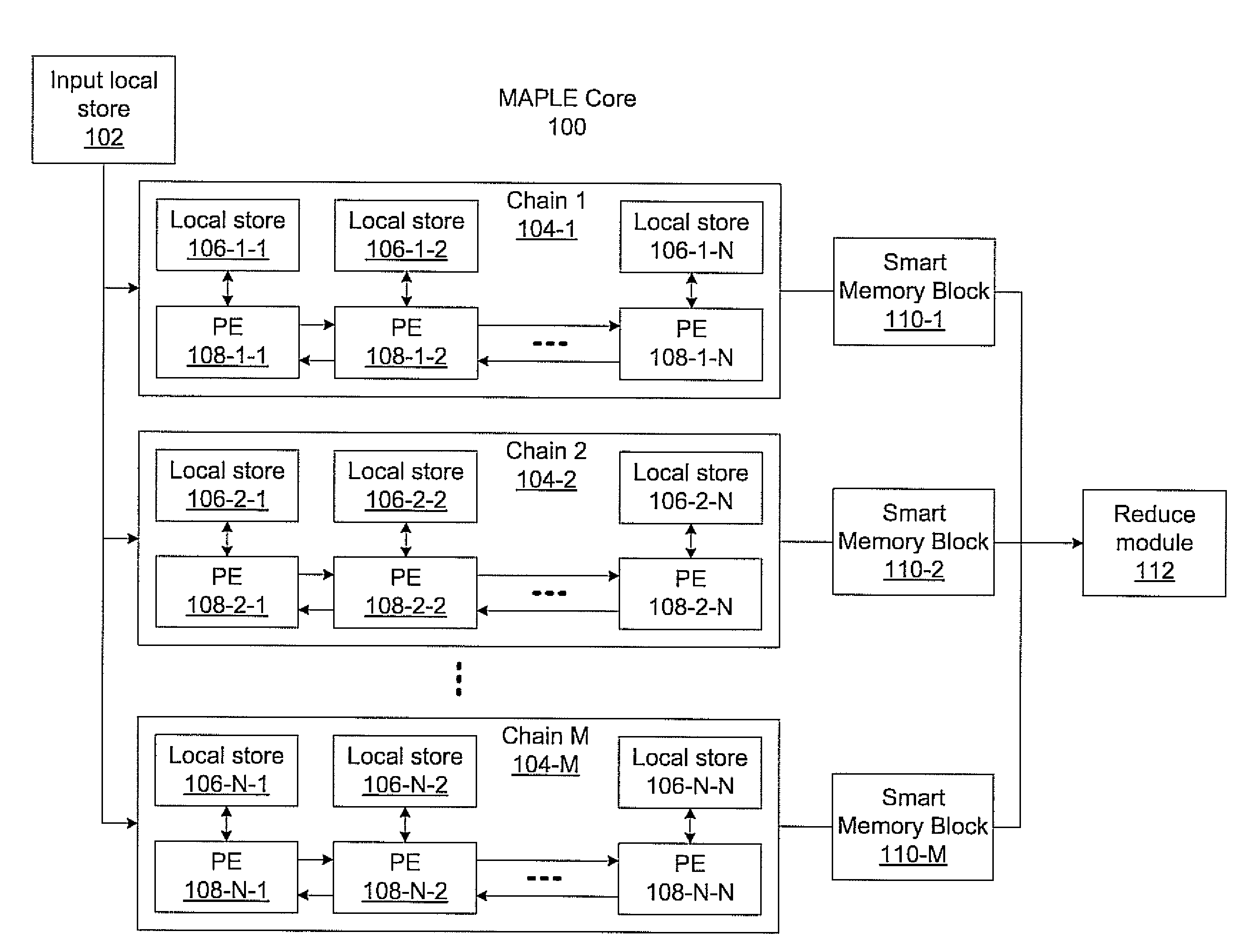
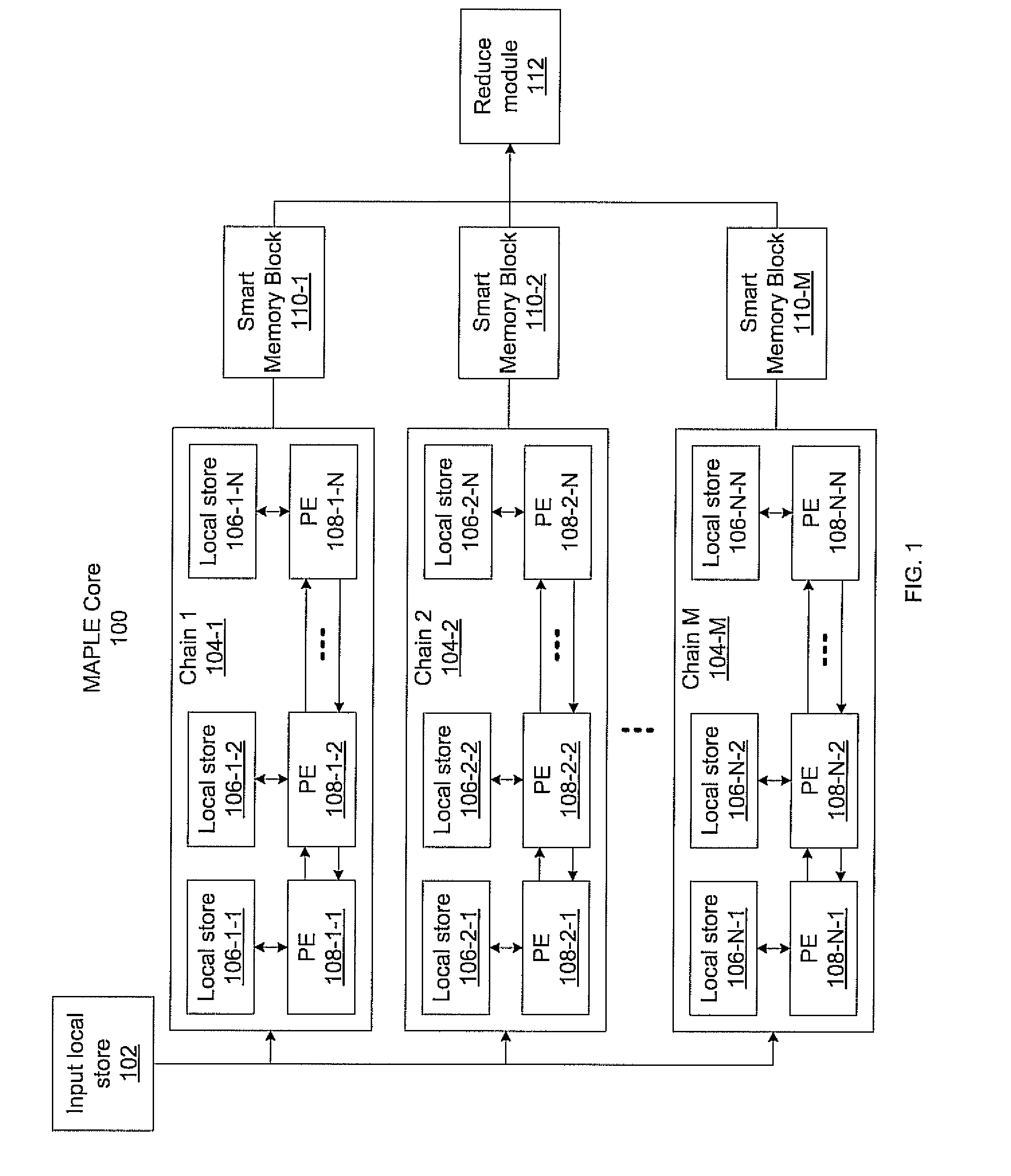
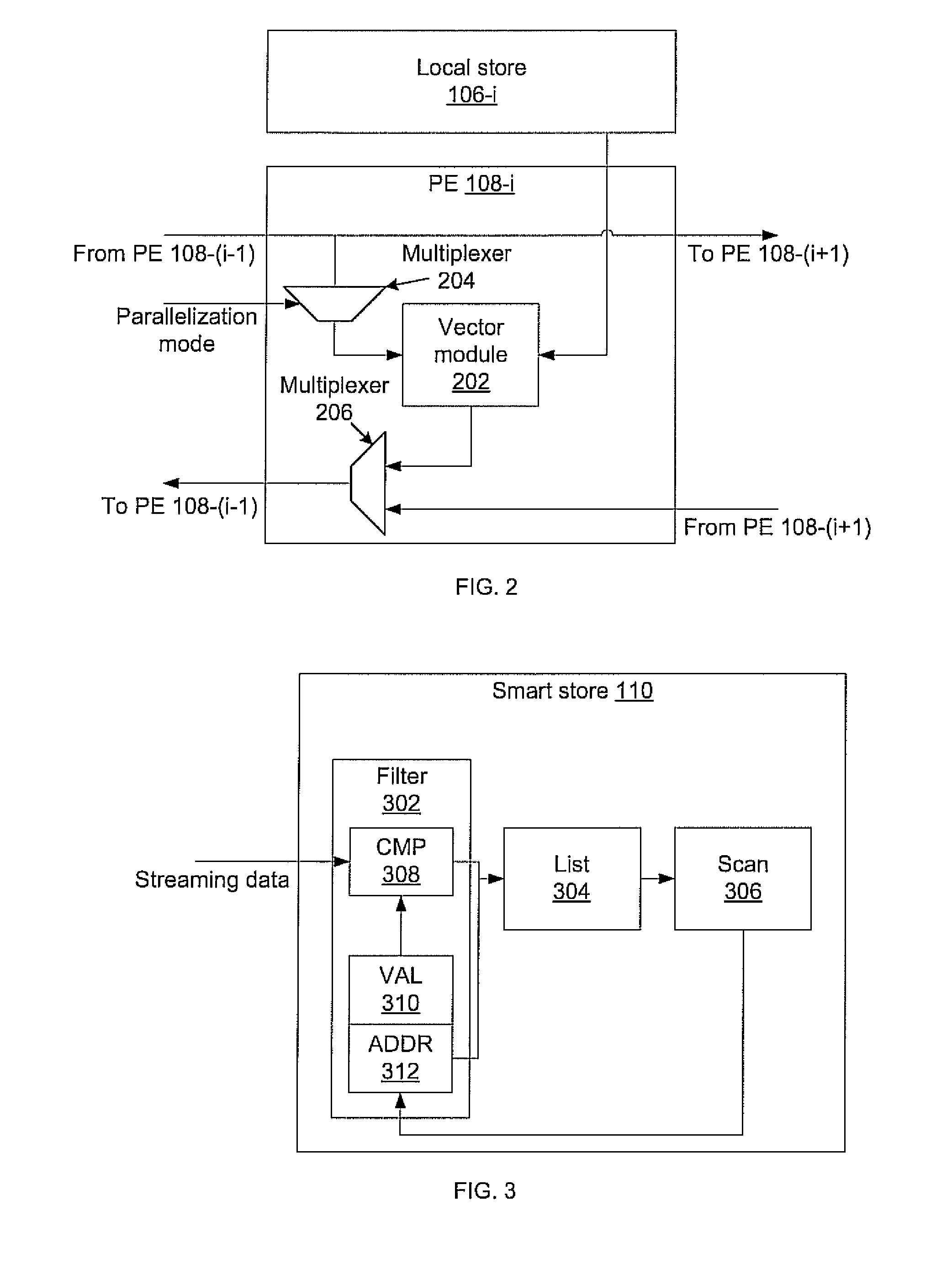
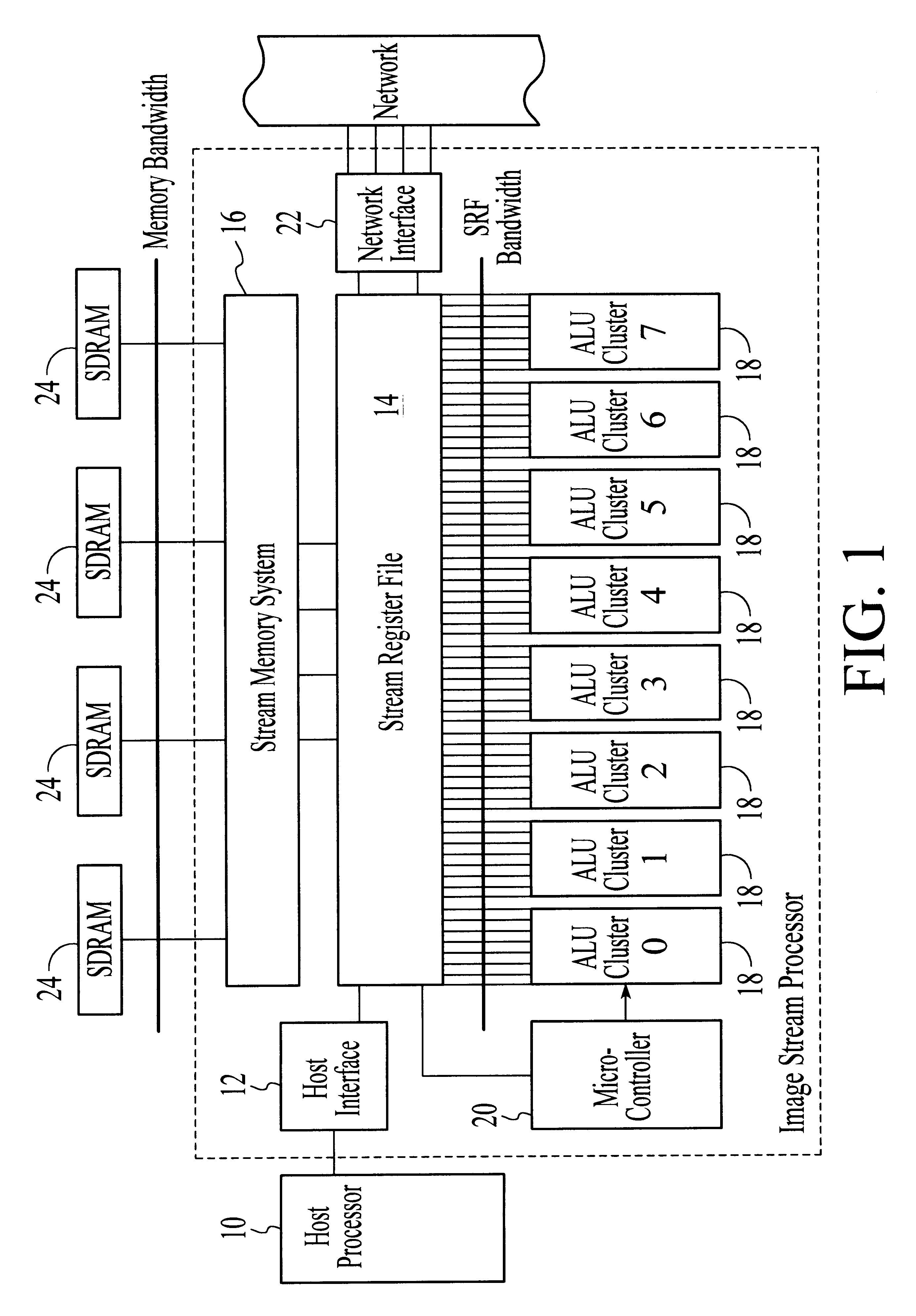
Massively parallel, smart memory based accelerator
Systems and methods for massively parallel processing on an accelerator that includes a plurality of processing cores. Each processing core includes multiple processing chains configured to perform parallel computations, each of which includes a plurality of interconnected processing elements. The cores further include multiple of smart memory blocks configured to store and process data, each memory block accepting the output of one of the plurality of processing chains. The cores communicate with at least one off-chip memory bank.
Owner:NEC CORP
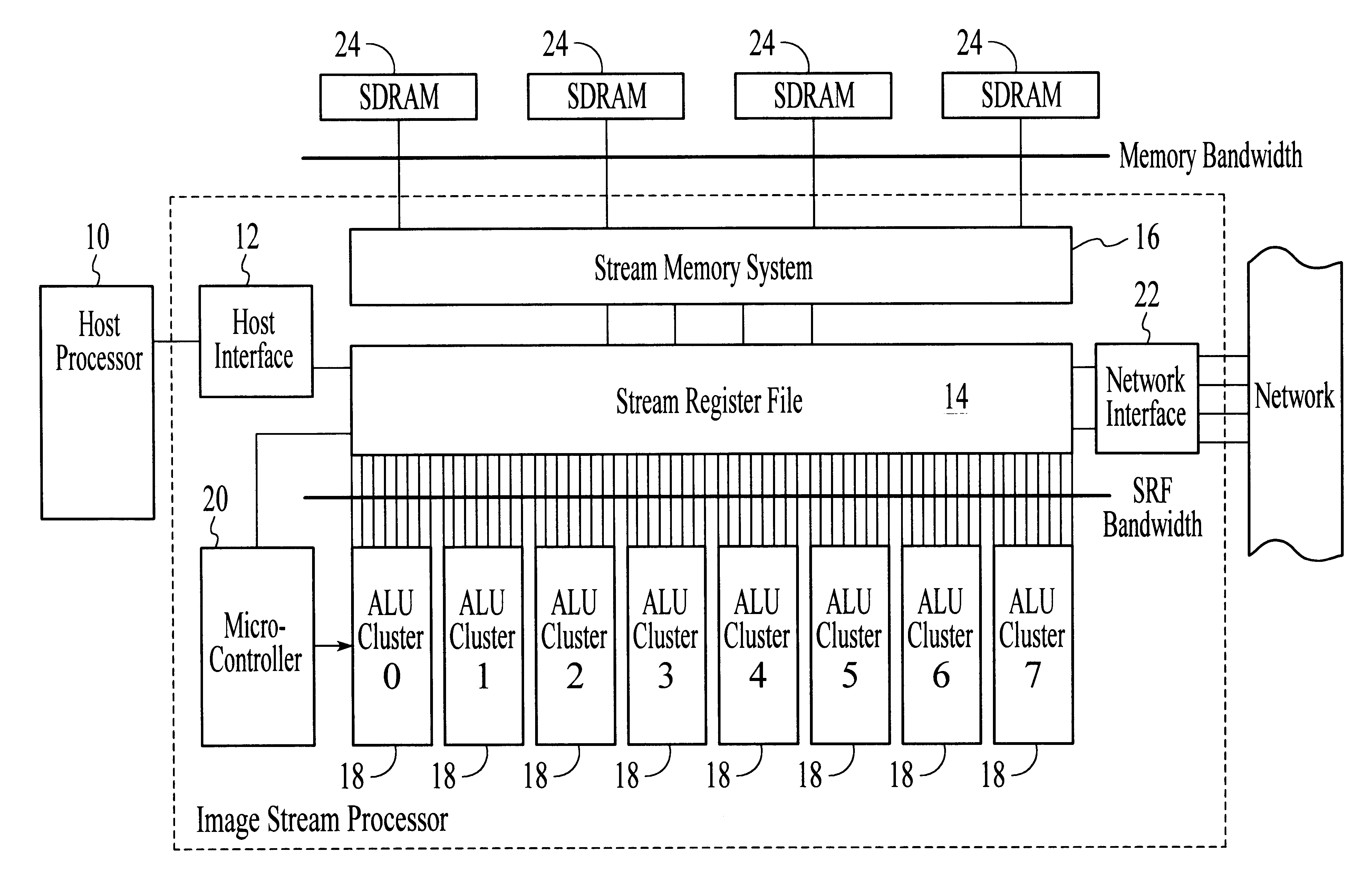
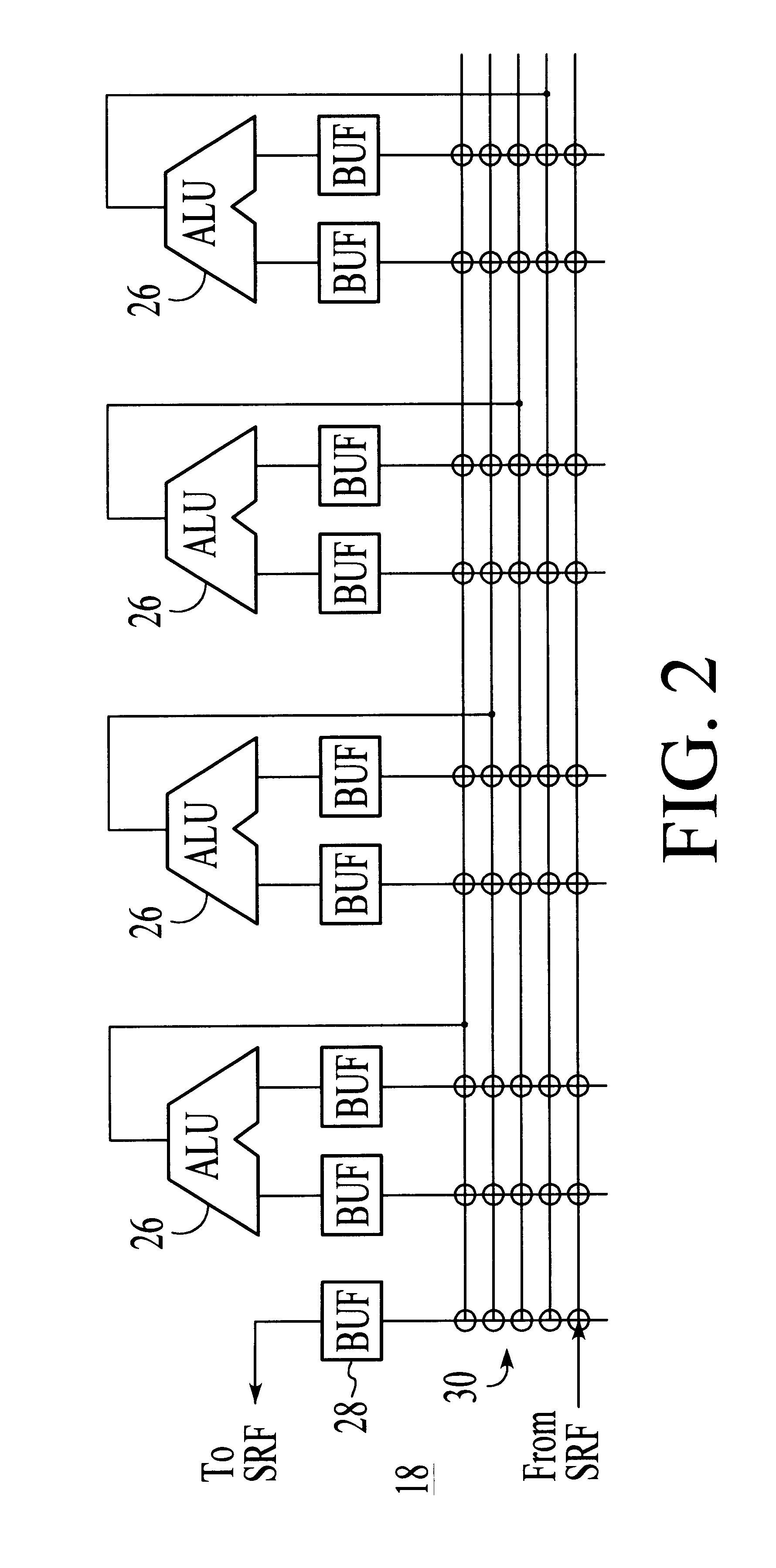
System and method for performing compound vector operations
InactiveUS6192384B1Reduce bandwidth requirementsMinimize the numberOperational speed enhancementRegister arrangementsOperating instructionImaging processing
A processor particularly useful in multimedia applications such as image processing is based on a stream programming model and has a tiered storage architecture to minimize global bandwidth requirements. The processor has a stream register file through which the processor's functional units transfer streams to execute processor operations. Load and store instructions transfer streams between the stream register file and a stream memory; send and receive instructions transfer streams between stream register files of different processors; and operate instructions pass streams between the stream register file and computational kernels. Each of the computational kernels is capable of performing compound vector operations. A compound vector operation performs a sequence of arithmetic operations on data read from the stream register file, i.e., a global storage resource, and generates a result that is written back to the stream register file. Each function or compound vector operation is specified by an instruction sequence that specifies the arithmetic operations and data movements that are performed each cycle to carry out the compound operation. This sequence can, for example, be specified using microcode.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND +1
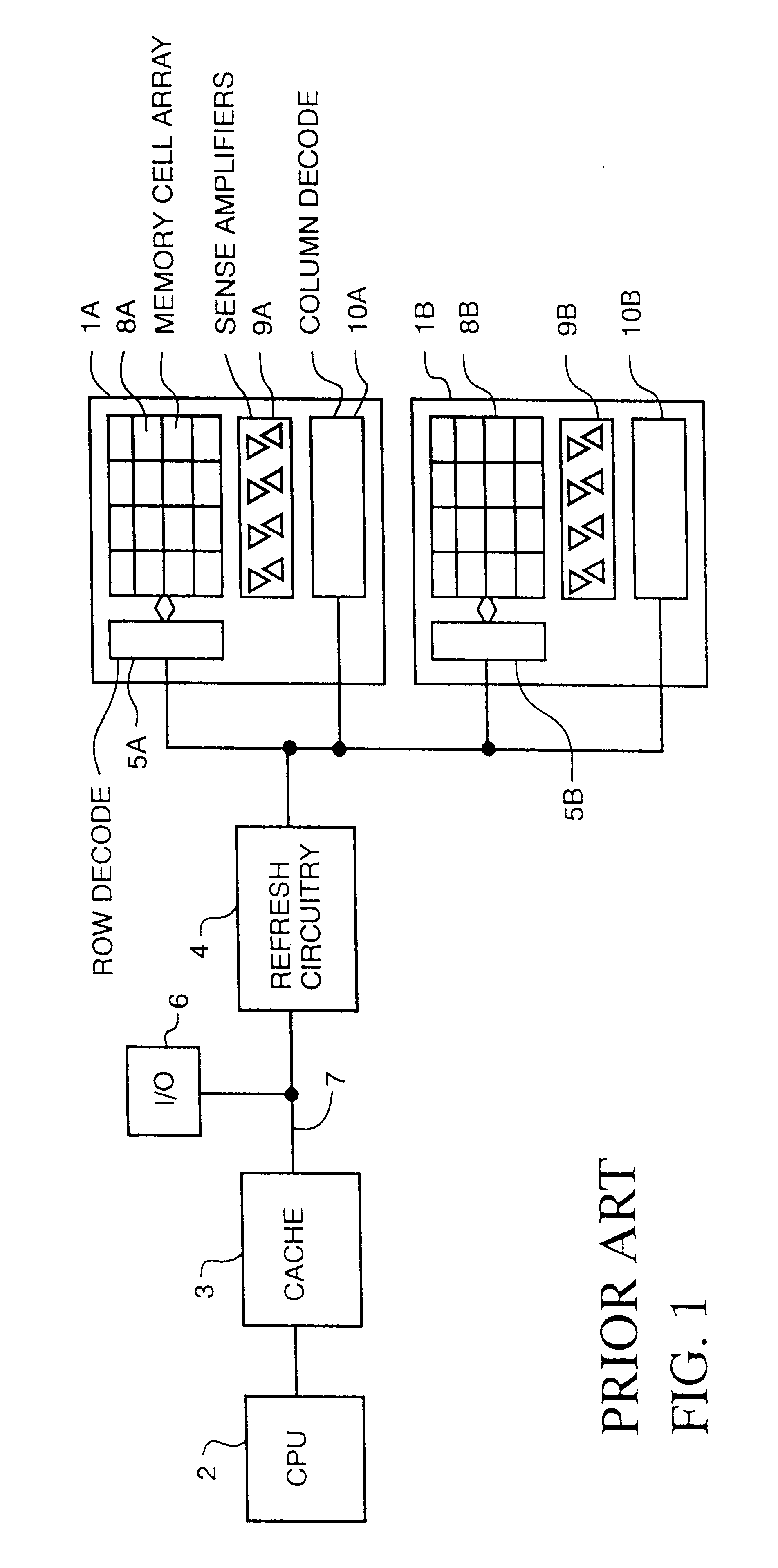
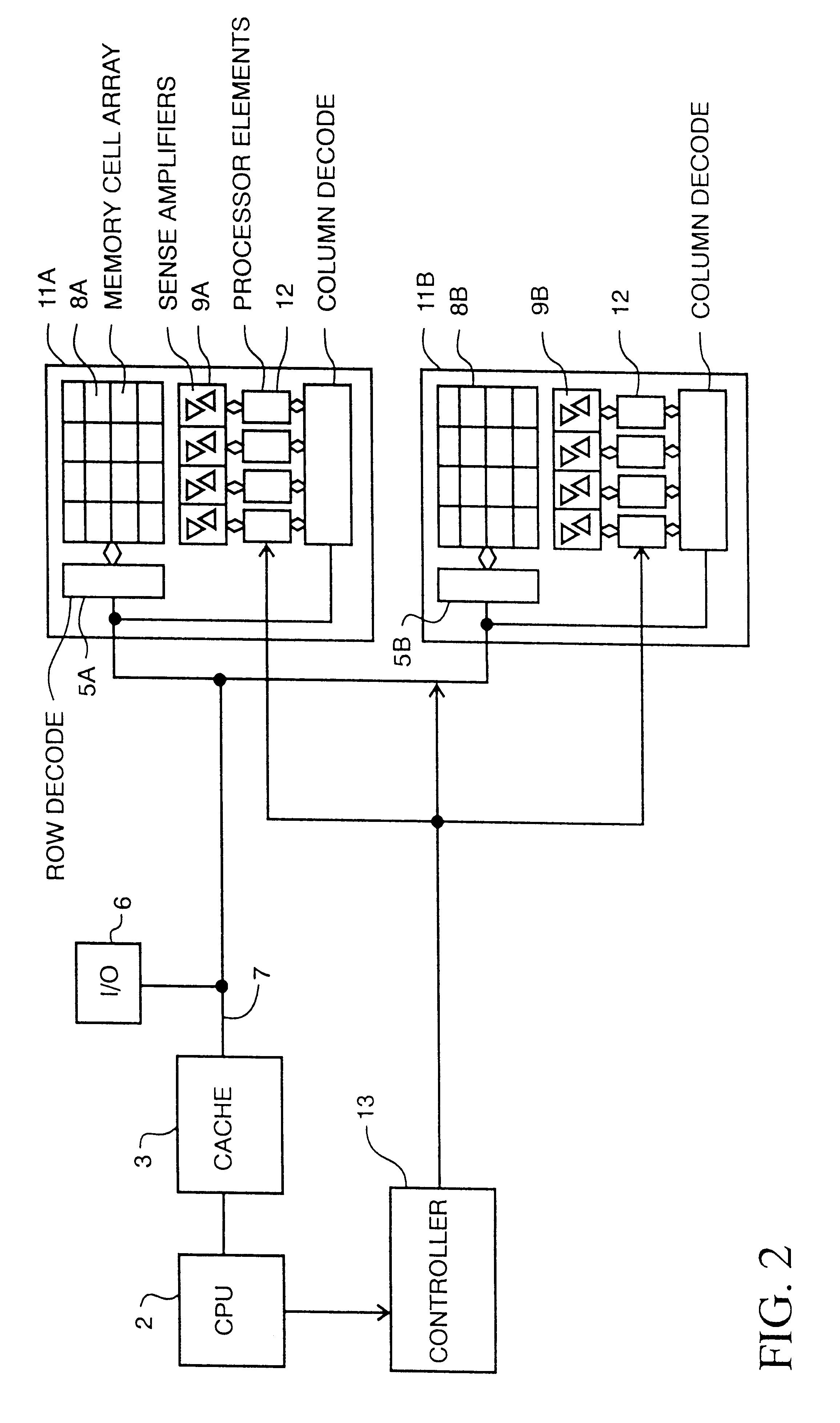
Memory device with multiple processors having parallel access to the same memory area
InactiveUS6279088B1Energy efficient ICTOperational speed enhancementArithmetic logic unitRead-modify-write
A digital computer performs read-modify-write (RMW) processing on each bit of a row of memory in parallel, in one operation cycle, comprising: (a) addressing a memory, (b) reading each bit of a row of data from the memory in parallel, (c) performing the same computational operation on each bit of the data in parallel, using an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) in a dedicated processing element, and (d) writing the result of the operation back into the original memory location for each bit in the row.
Owner:SATECH GRP A B LLC
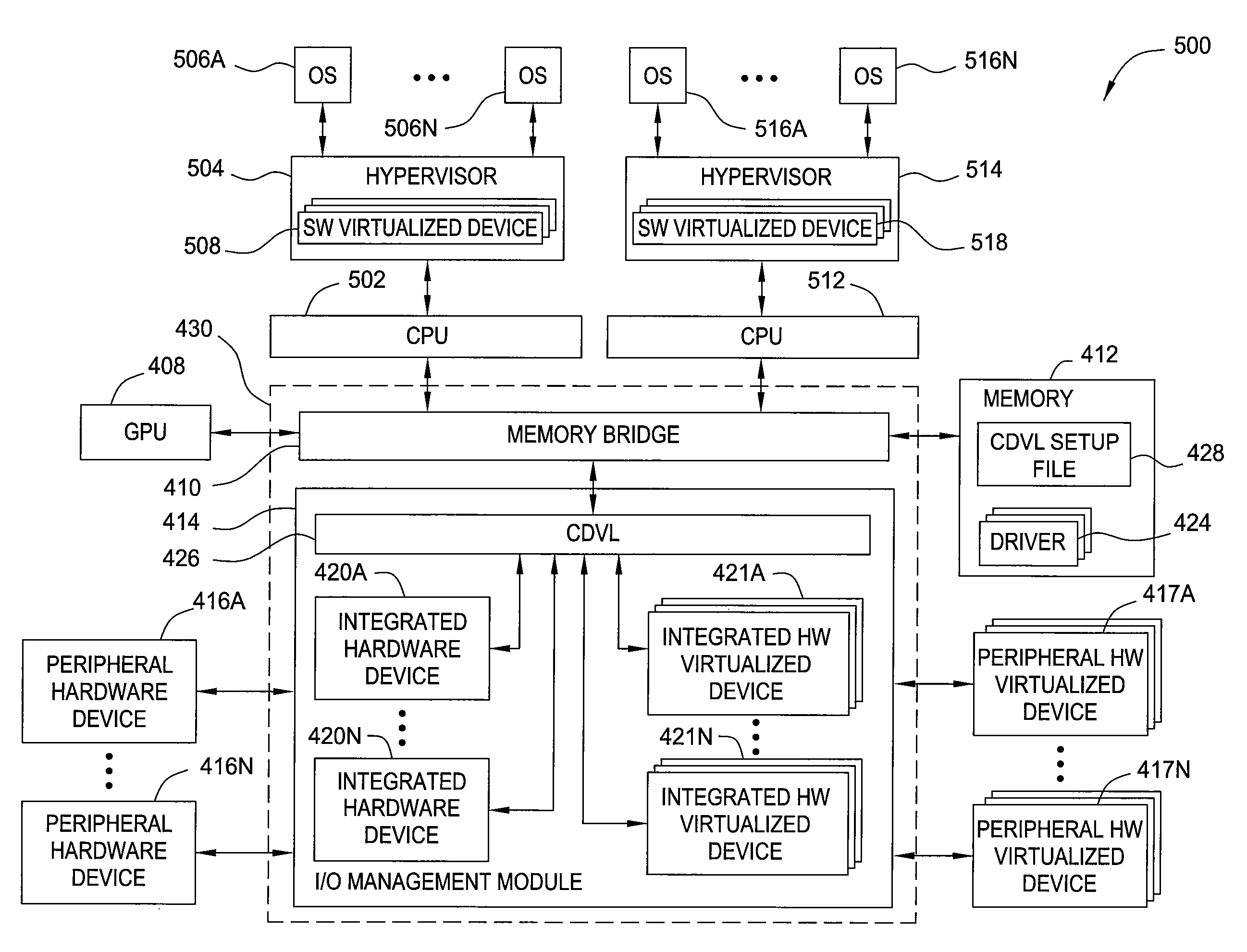
Centralized device virtualization layer for heterogeneous processing units
ActiveUS8239938B2Operational speed enhancementProgram control using stored programsVirtualizationOperational system
A method for providing an operating system access to devices, including enumerating hardware devices and virtualized devices, where resources associated with a first hardware device are divided into guest physical resources creating a software virtualized device, and multiple instances of resources associated with a second hardware device are advertised thereby creating a hardware virtualized device. First and second permission lists are generated that specify which operating systems are permitted to access the software virtualized device and the hardware virtualized device, respectively. First and second sets of virtual address maps are generated, where each set maps an address space associated with either the software virtualized device or the hardware virtualized device into an address space associated with each operating system included in the corresponding permission list. The method further includes arbitrating access requests from each of the plurality of operating systems based on the permission lists and the virtual address maps.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
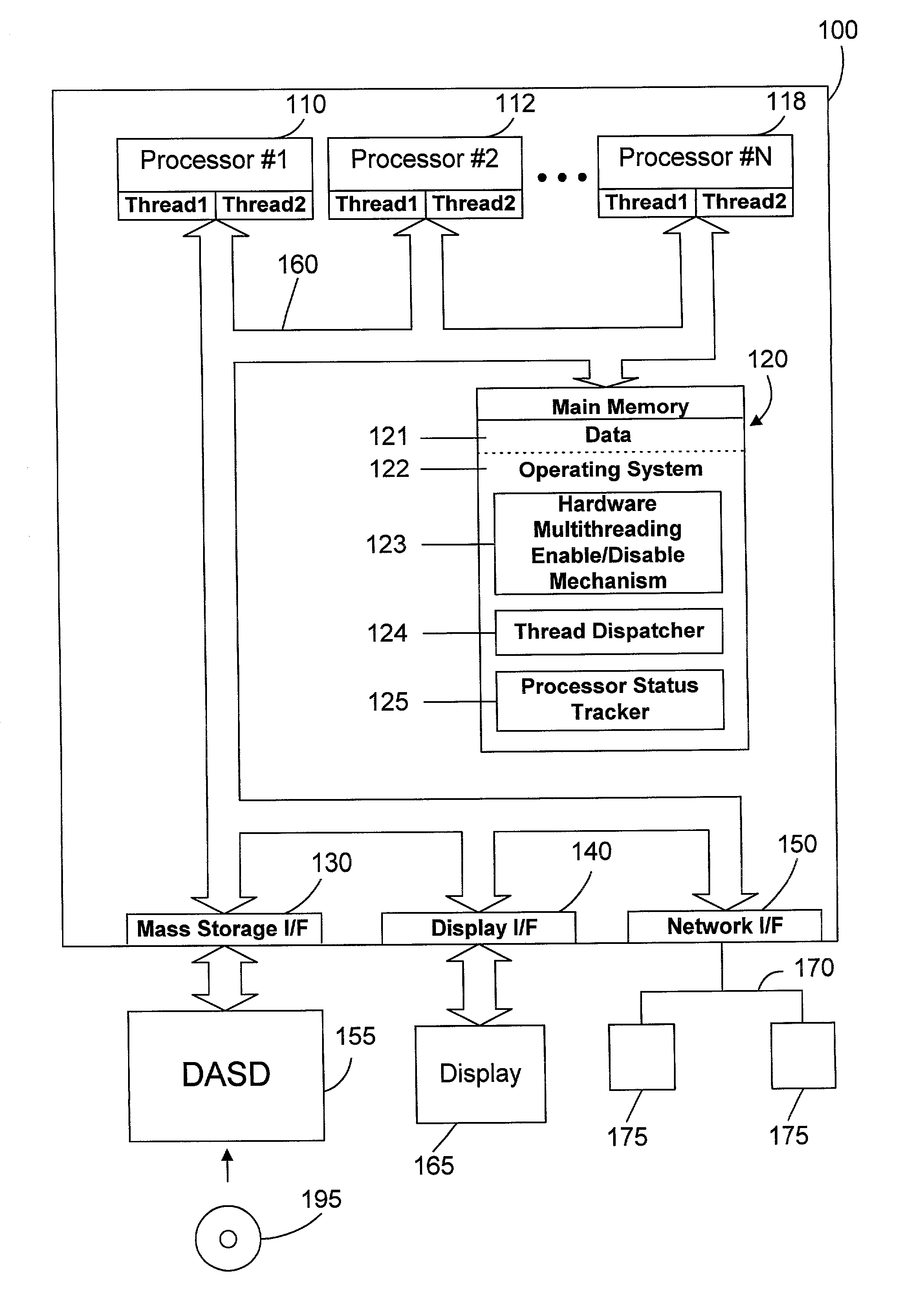
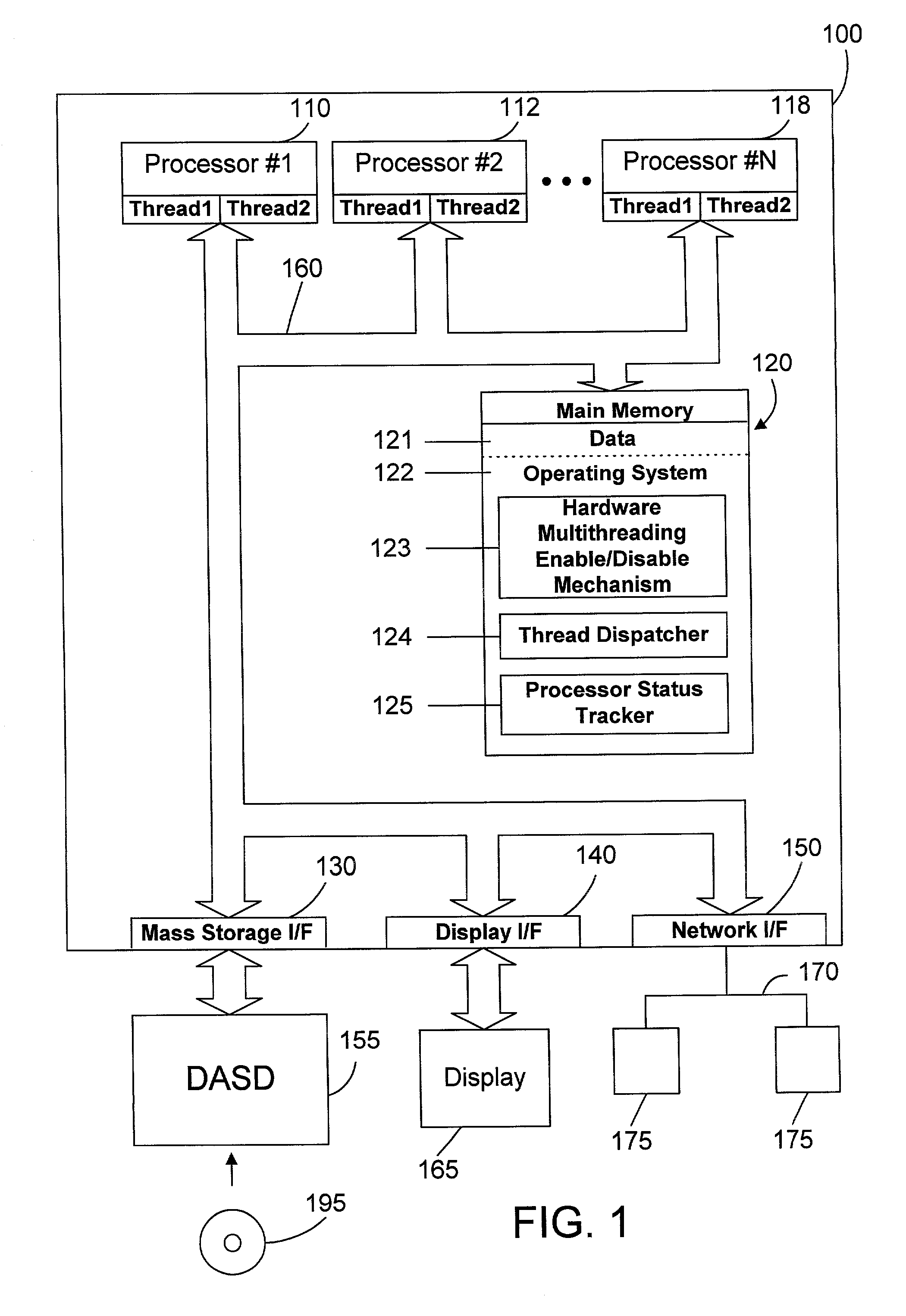
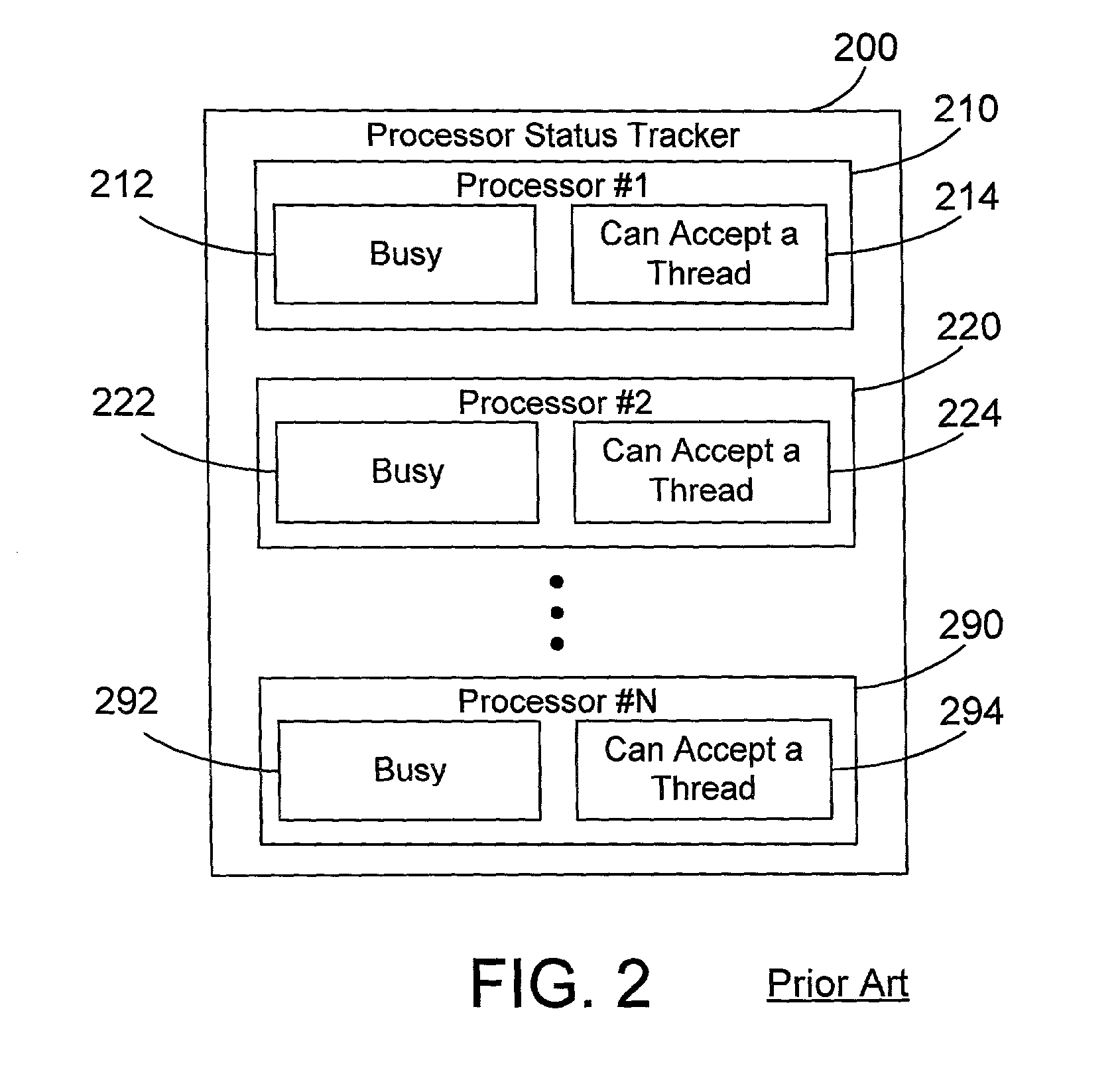
Thread dispatch mechanism and method for multiprocessor computer systems
InactiveUS20030149716A1Minimizing thread spreadHuman perceptionOperational speed enhancementResource allocationMulti processorThread scheduling
A thread dispatch mechanism dispatches threads in a multiprocessor computer system that has hardware multithreading enabled, thereby allowing each processor to execute multiple threads. The thread dispatch mechanism determines which processors are busy and cannot execute an additional thread, which processors are working on a thread but can still accept an additional thread, and which processors are idle. As threads are ready to be dispatched, each is dispatched to an idle processor instead of a processor that is already working on another thread. If there are no idle processors, the thread is dispatched to a processor working on one or more threads that can still process the new thread. In this manner the thread dispatch mechanism and method of the present invention provides greatly improved consistency in response times between threads and higher throughput compared to prior art methods of dispatching threads.
Owner:IBM CORP
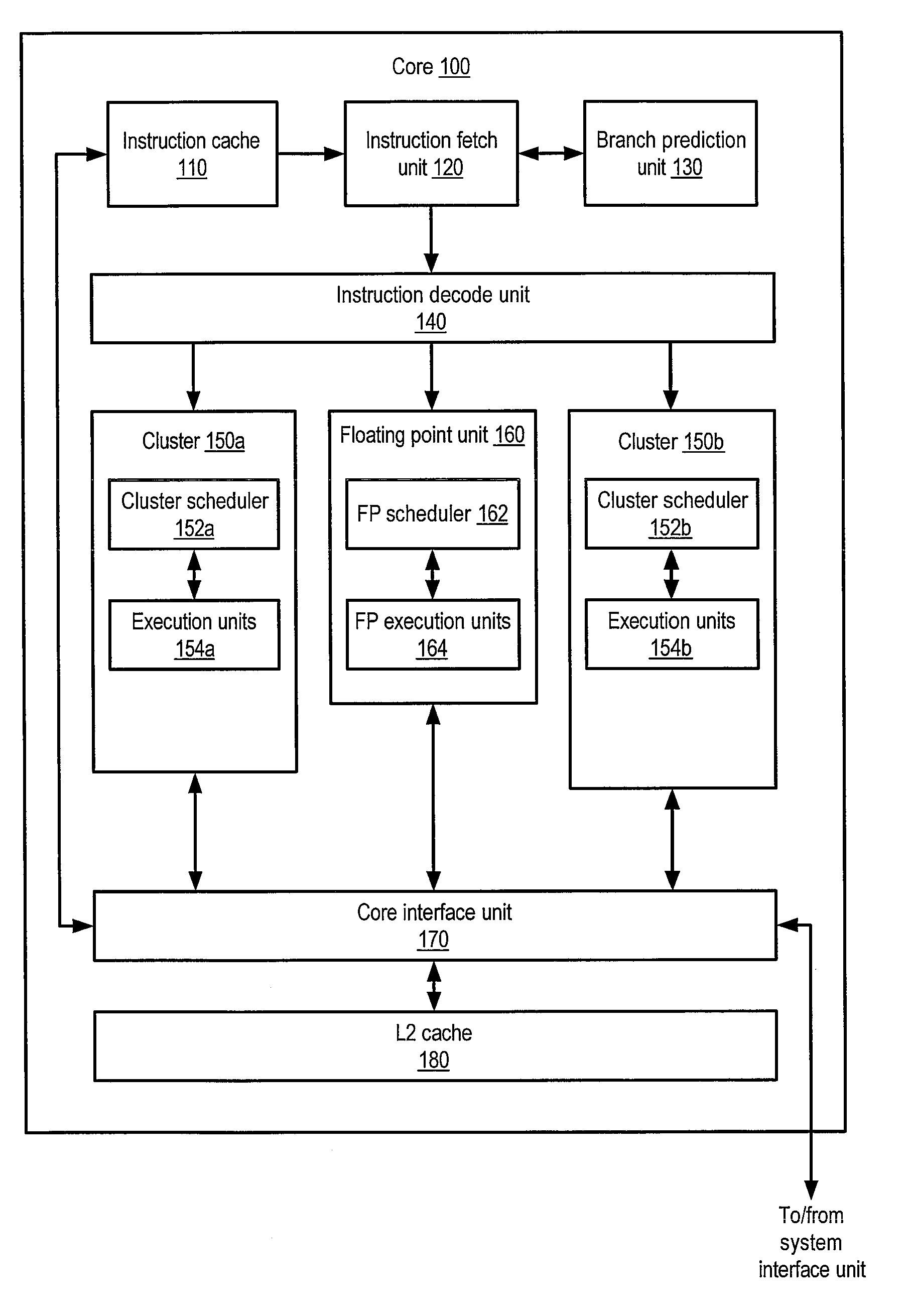
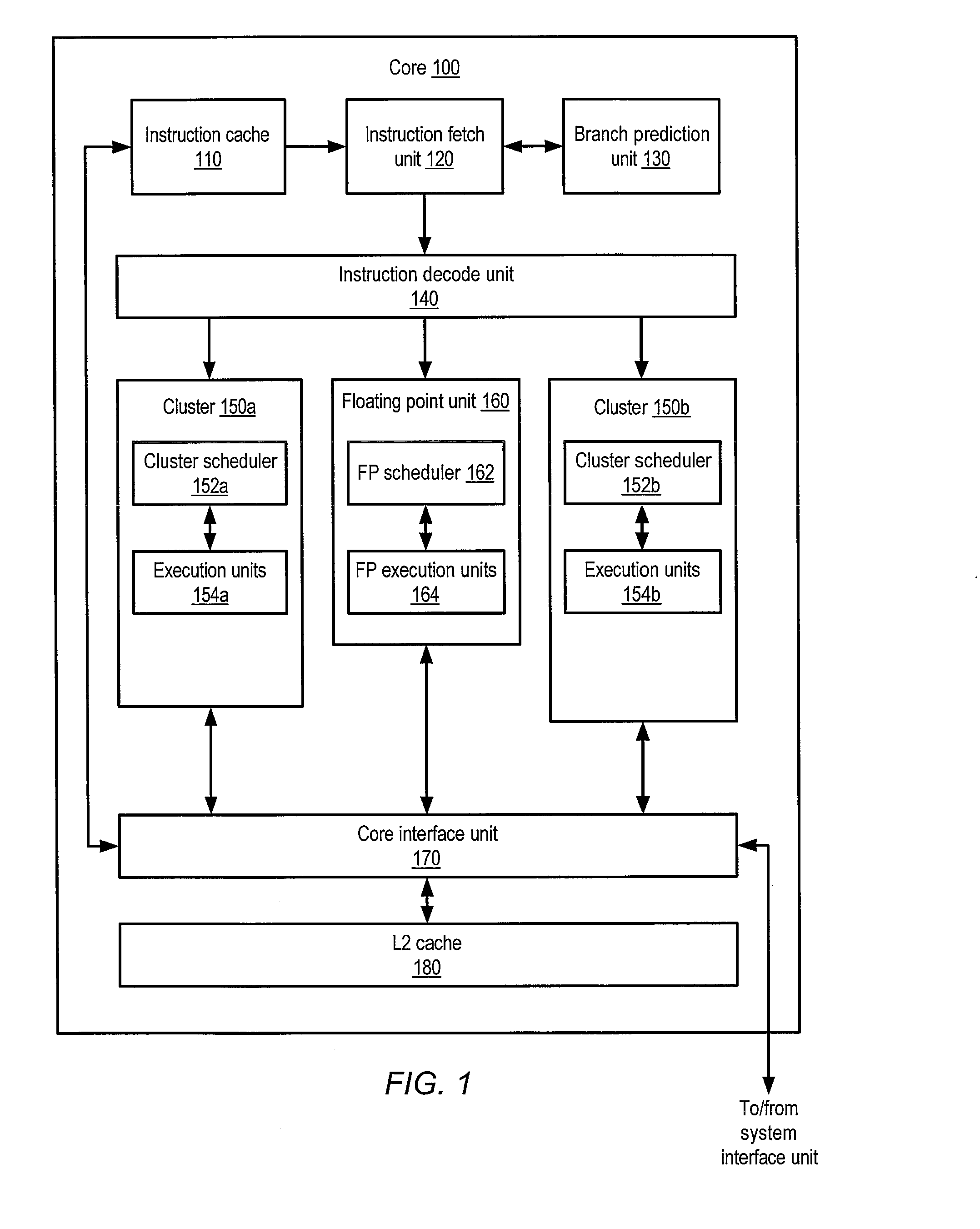
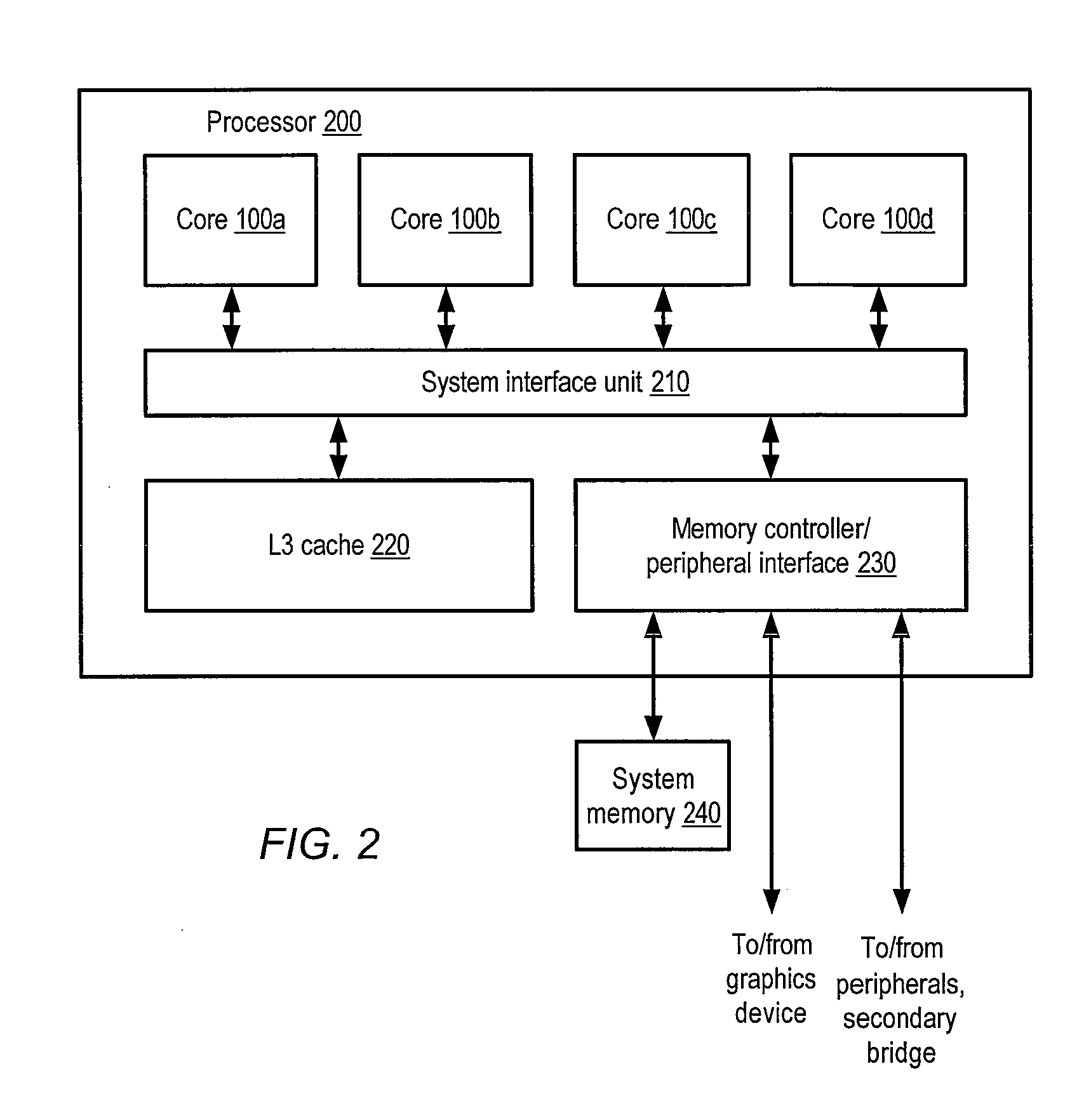
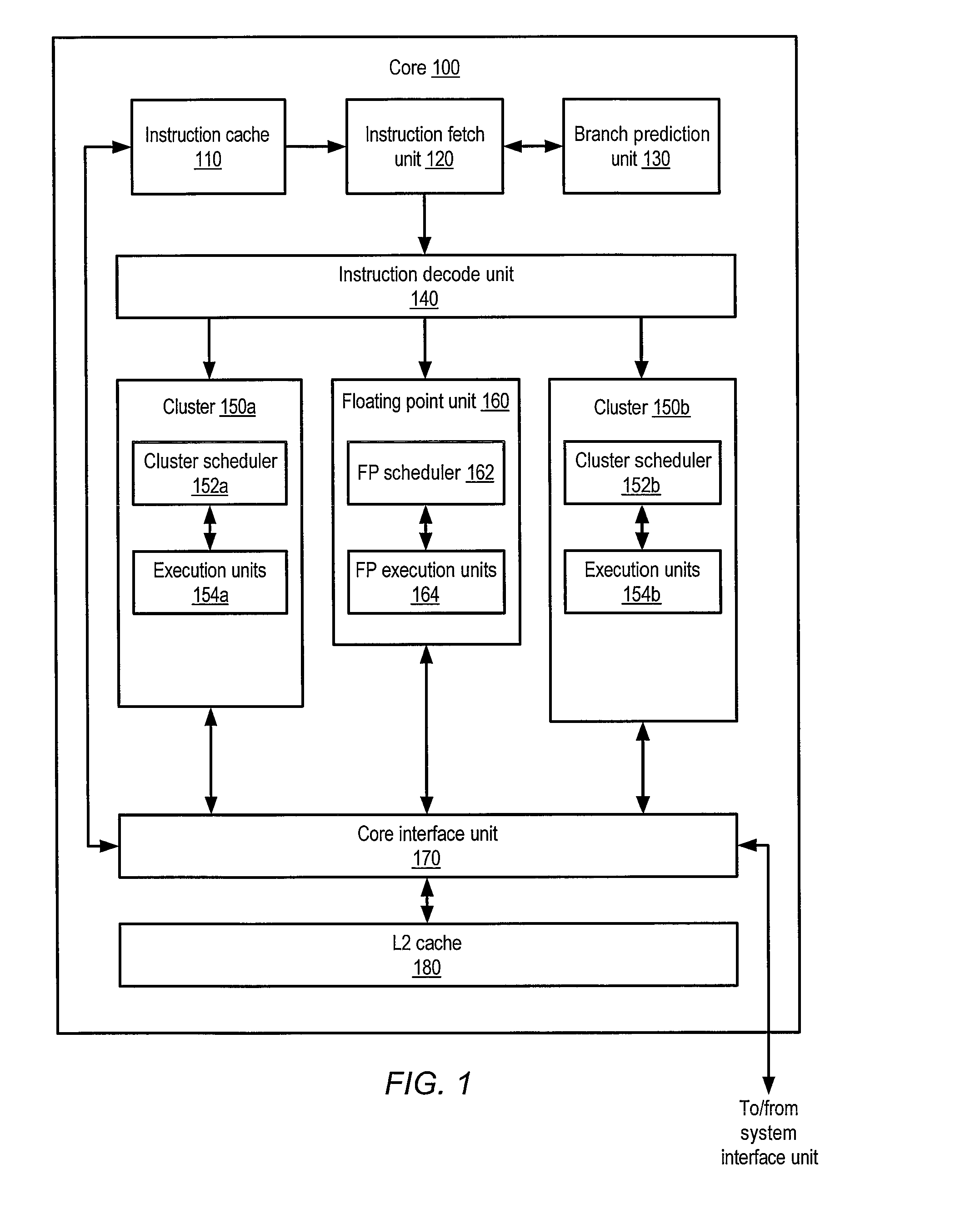
Multiple-core processor with hierarchical microcode store
ActiveUS20090024836A1Operational speed enhancementDigital computer detailsMulti-core processorInstruction set
A multiple-core processor having a hierarchical microcode store. A processor may include multiple processor cores, each configured to independently execute instructions defined according to a programmer-visible instruction set architecture (ISA). Each core may include a respective local microcode unit configured to store microcode entries. The processor may also include a remote microcode unit accessible by each of the processor cores. Any given one of the processor cores may be configured to generate a given microcode entrypoint corresponding to a particular microcode entry including one or more operations to be executed by the given processor core, and to determine whether the particular microcode entry is stored within the respective local microcode unit of the given core. In response to determining that the particular microcode entry is not stored within the respective local microcode unit, the given core may convey a request for the particular microcode entry to the remote microcode unit.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
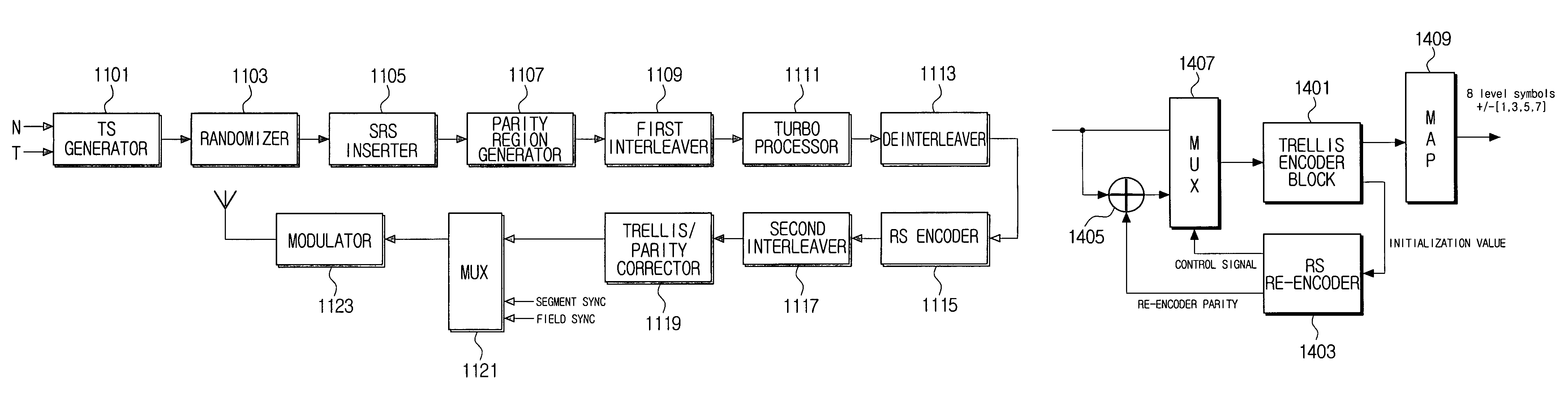
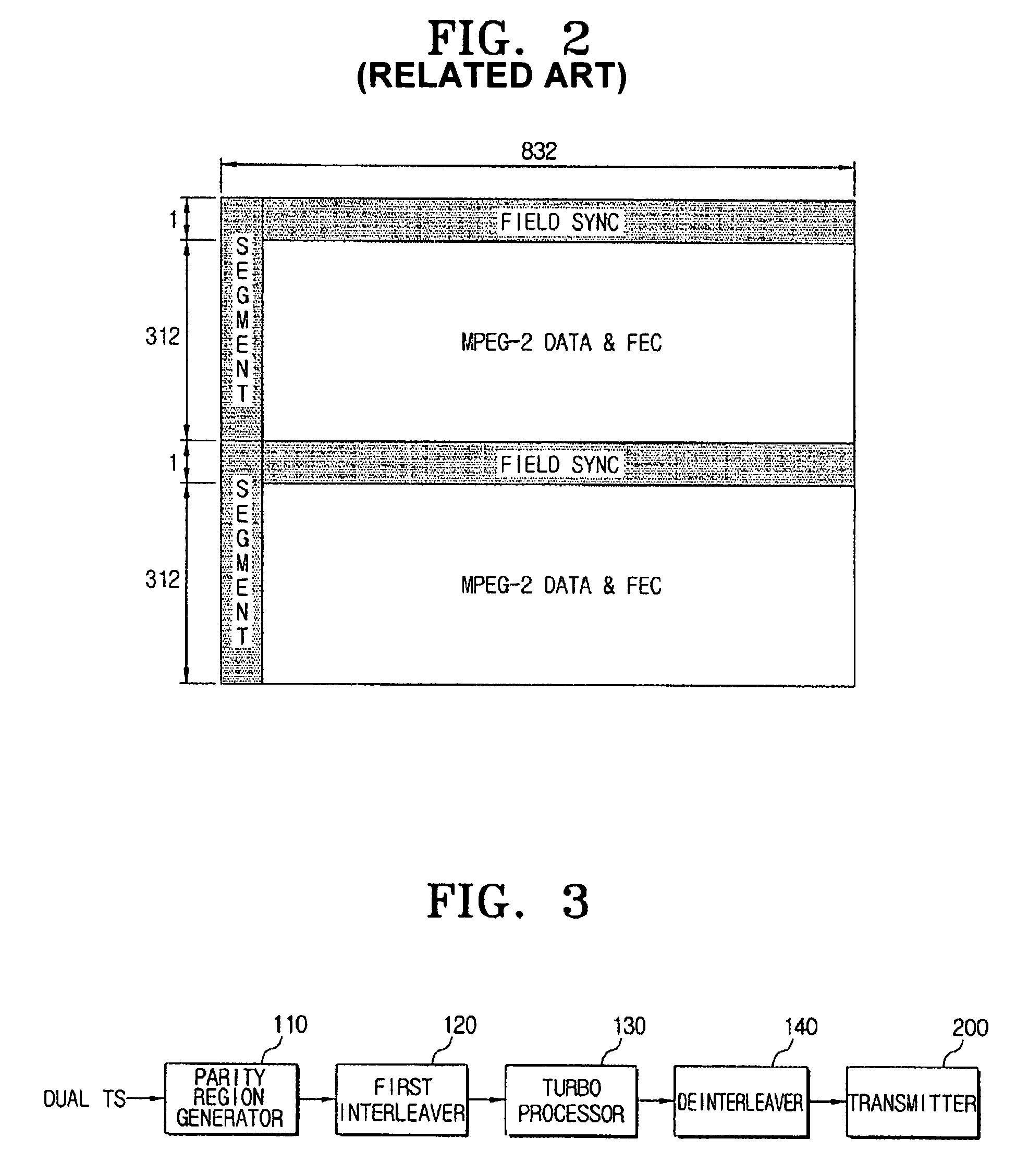
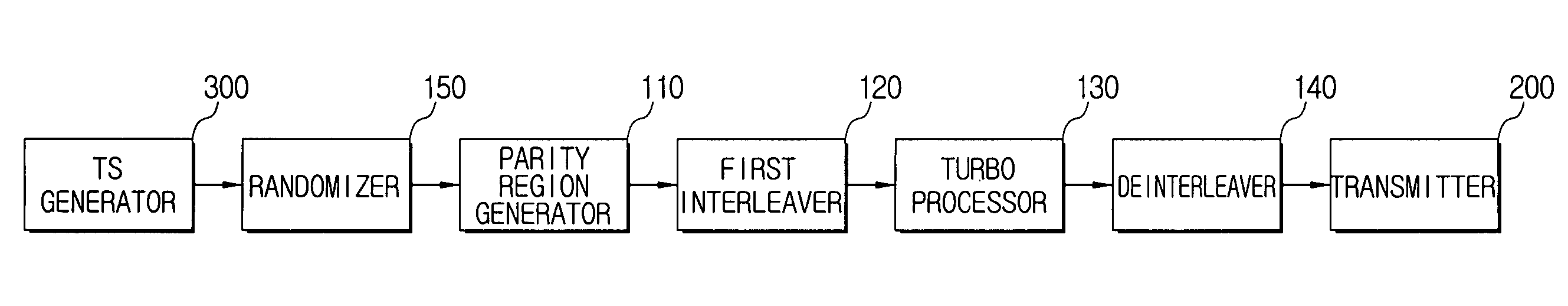
Transmitter and system for transmitting/receiving digital broadcasting stream and method thereof
ActiveUS7913152B2Improve reception performanceData representation error detection/correctionPulse modulation television signal transmissionMultiplexingComputer network
A digital broadcasting transmission system processes dual transport stream (TS) including multi turbo streams. The digital broadcasting transmission system includes a turbo processor to detect a turbo stream from a dual transport stream (TS) which includes a multiplexed normal stream and a turbo stream, encoding the detected turbo stream and stuffing the encoded turbo stream into the dual TS; and a transmitter to trellis-encode the processed dual TS, and to output the resultant stream, wherein the turbo processor encodes the turbo stream using a plurality of turbo processors. Accordingly, a plurality of turbo streams may be processed in parallel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transmitter and system for transmitting/receiving digital broadcasting stream and method thereof
ActiveUS20070168842A1Improve reception performanceData representation error detection/correctionPulse modulation television signal transmissionMultiplexingComputer network
A digital broadcasting transmission system processes dual transport stream (TS) including multi turbo streams. The digital broadcasting transmission system includes a turbo processor to detect a turbo stream from a dual transport stream (TS) which includes a multiplexed normal stream and a turbo stream, encoding the detected turbo stream and stuffing the encoded turbo stream into the dual TS; and a transmitter to trellis-encode the processed dual TS, and to output the resultant stream, wherein the turbo processor encodes the turbo stream using a plurality of turbo processors. Accordingly, a plurality of turbo streams may be processed in parallel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Data processing method, data processor and apparatus including a data processor
A method of processing data in a data processor comprising at least two data processing units. The method comprises performing different data processing steps in the data processing units concurrently during a parallel operation, and replicating performances of selected identical data processing steps in the data processing units during a non-synchronised redundant operation. The non-synchronised redundant operation comprises an initial performance of the selected identical data processing steps in one of the data processing units and a replicate performance of the data processing steps starting later than the initial performance, preferably in another of the data processing units. Initial result data representative of results from the initial performance are registered, and compared with replicate result data representative of results from the replicate performance, and an error signal is produced in case of discrepancy.
Owner:NXP USA INC
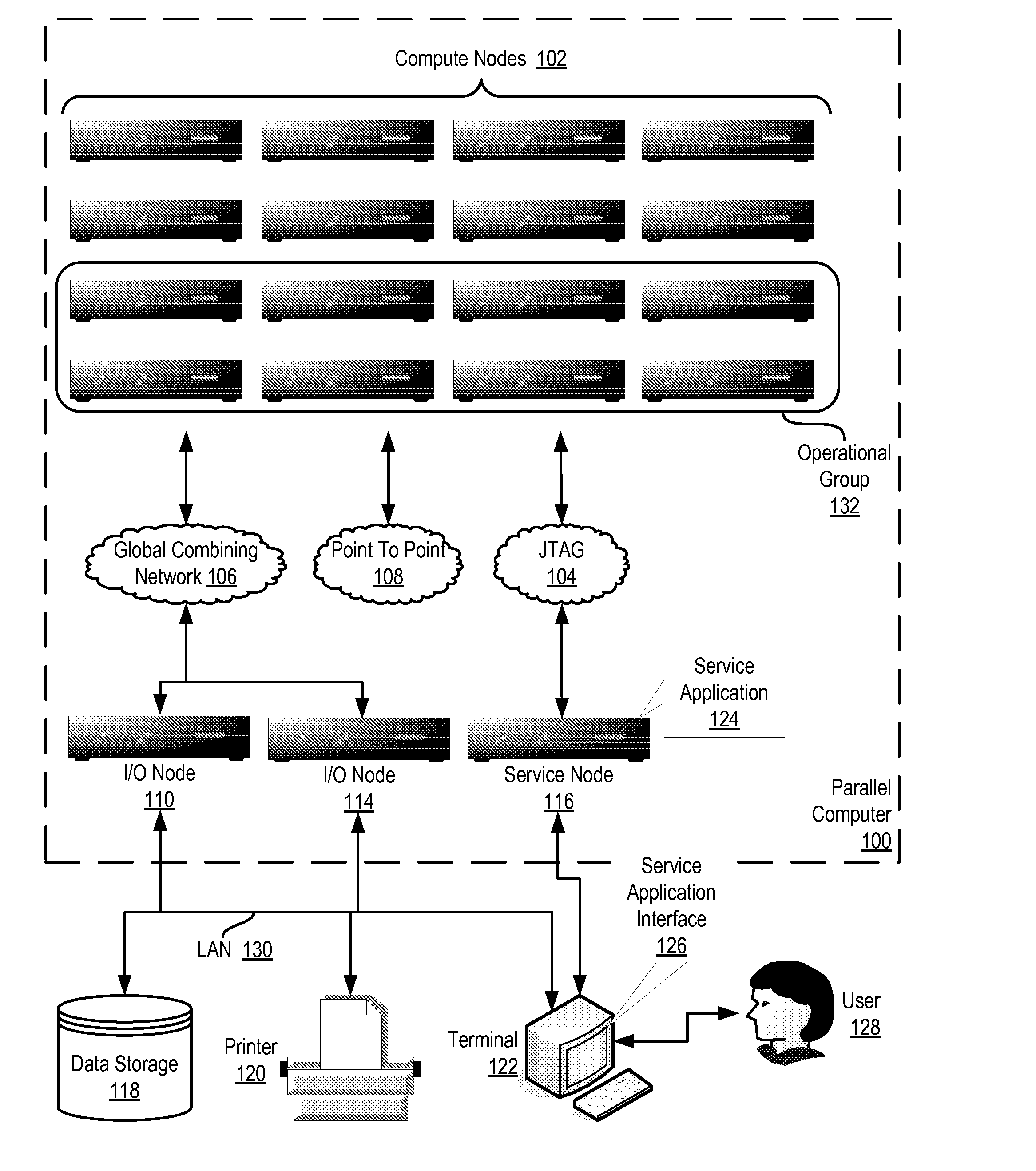
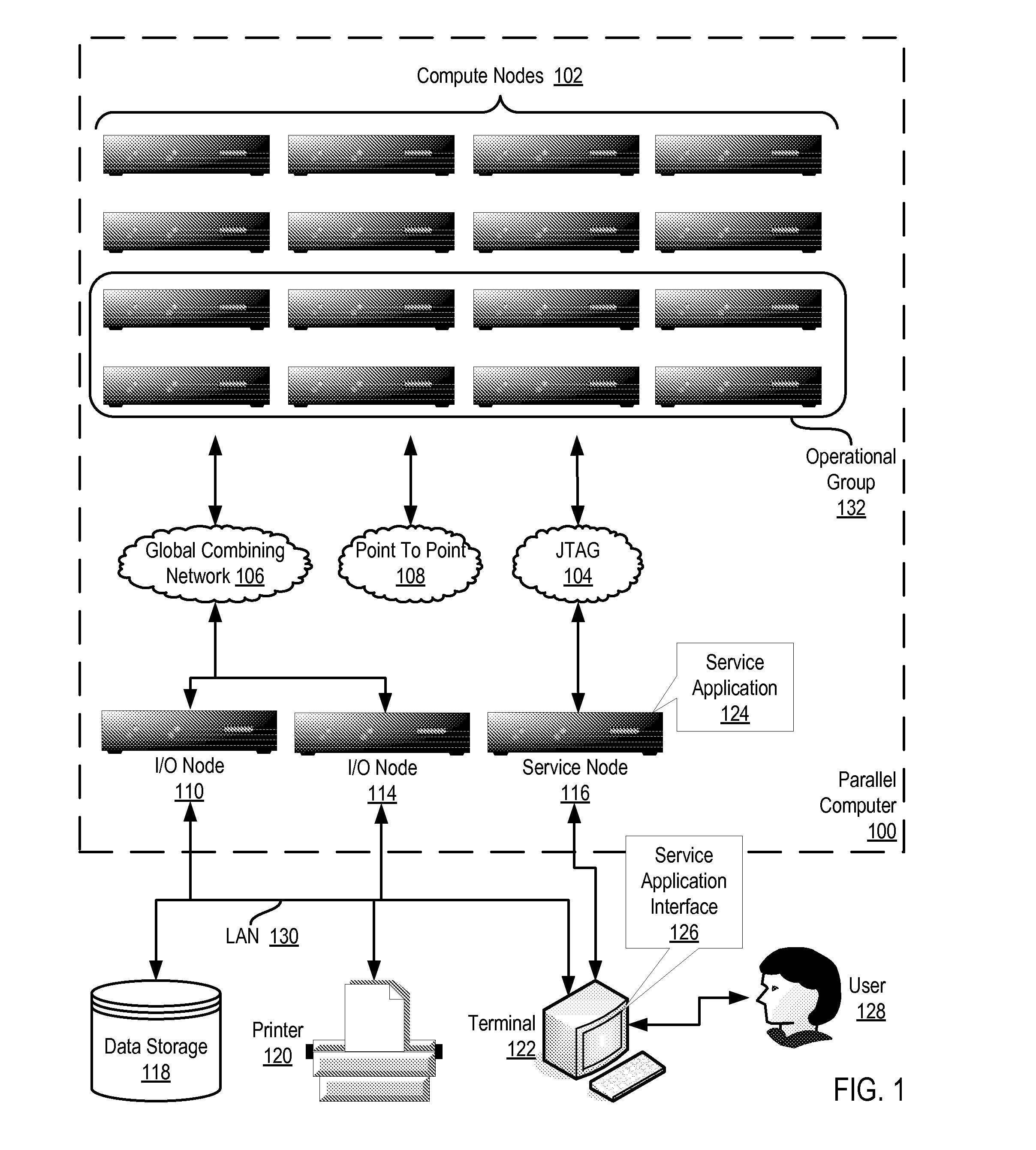
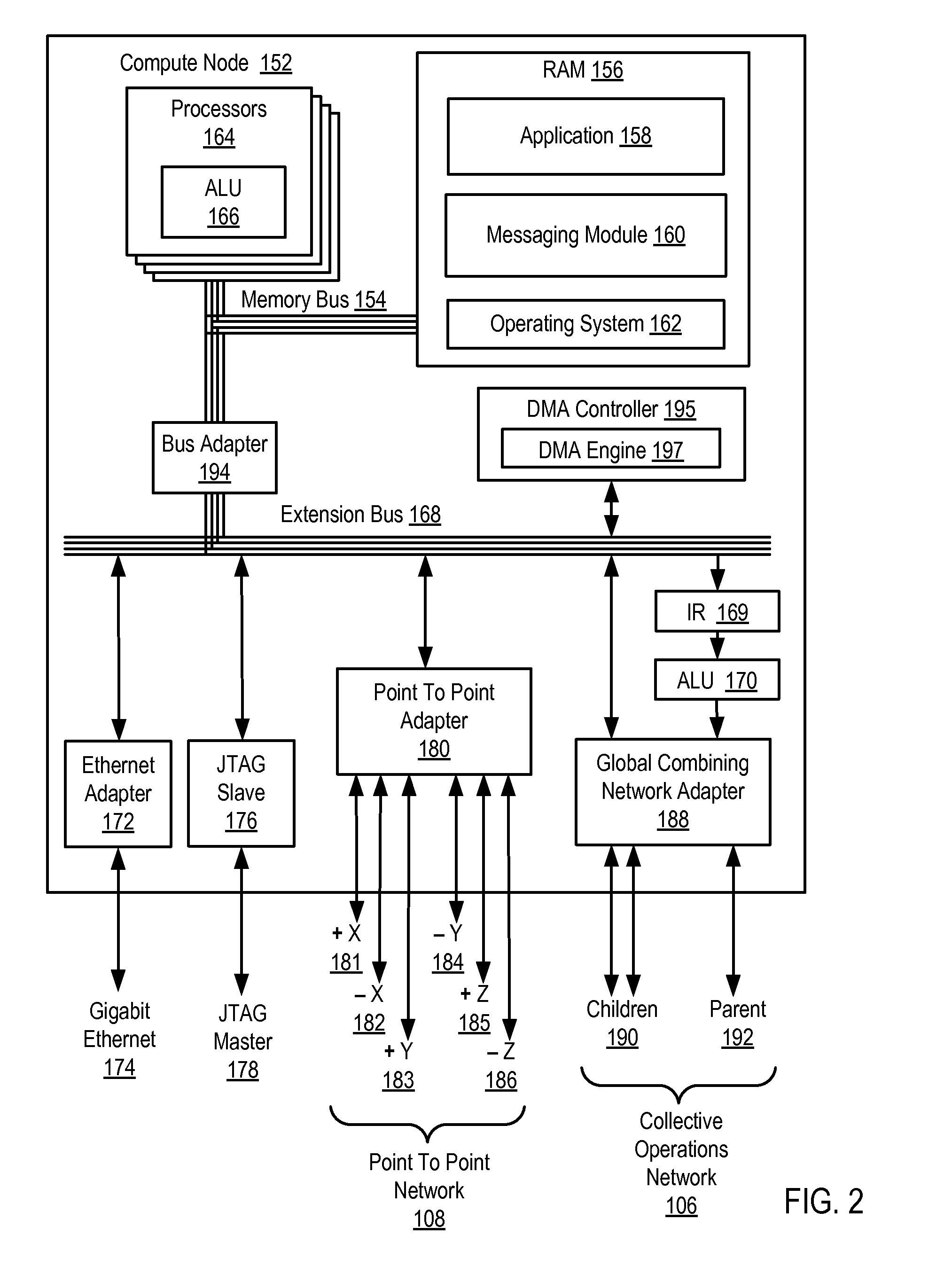
Determining When a Set of Compute Nodes Participating in a Barrier Operation on a Parallel Computer are Ready to Exit the Barrier Operation
InactiveUS20090037707A1Operational speed enhancementProgram synchronisationParallel computingBroadcasting
Methods, apparatus, and products are disclosed for determining when a set of compute nodes participating in a barrier operation on a parallel computer are ready to exit the barrier operation that includes, for each compute node in the set: initializing a barrier counter with no counter underflow interrupt; configuring, upon entering the barrier operation, the barrier counter with a value in dependence upon a number of compute nodes in the set; broadcasting, by a DMA engine on the compute node to each of the other compute nodes upon entering the barrier operation, a barrier control packet; receiving, by the DMA engine from each of the other compute nodes, a barrier control packet; modifying, by the DMA engine, the value for the barrier counter in dependence upon each of the received barrier control packets; exiting the barrier operation if the value for the barrier counter matches the exit value.
Owner:IBM CORP
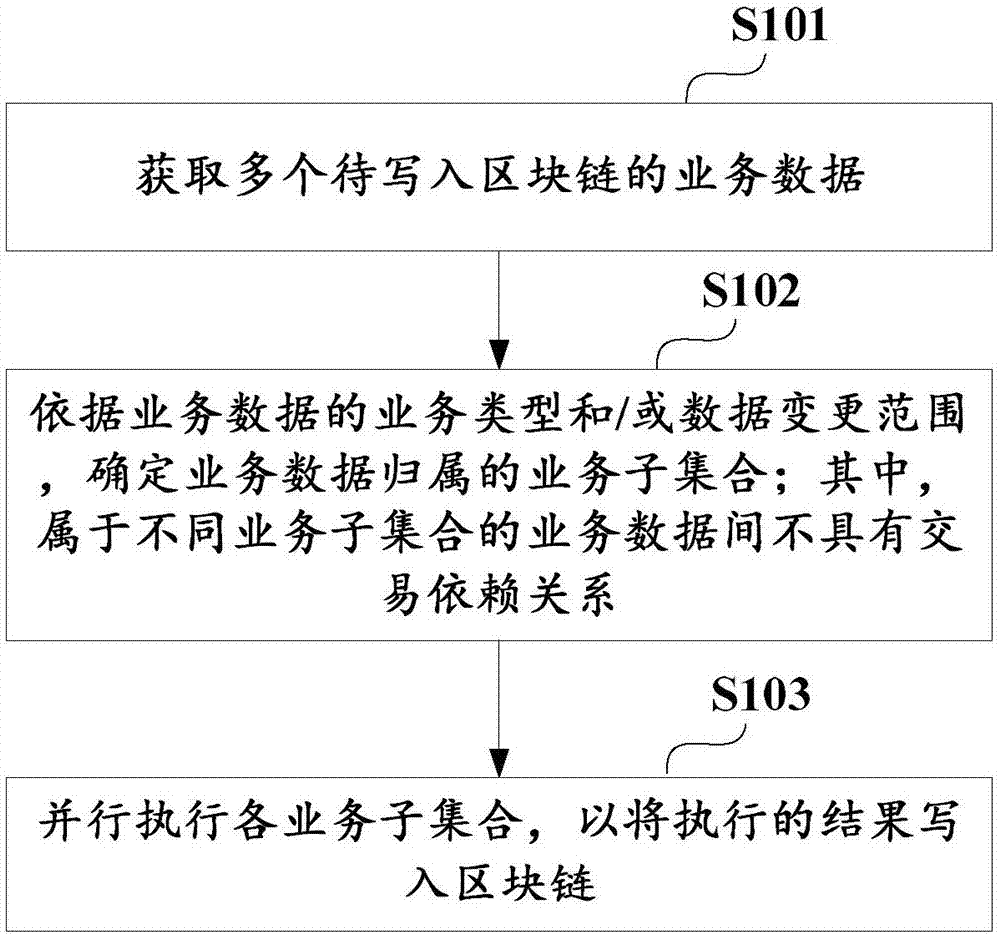
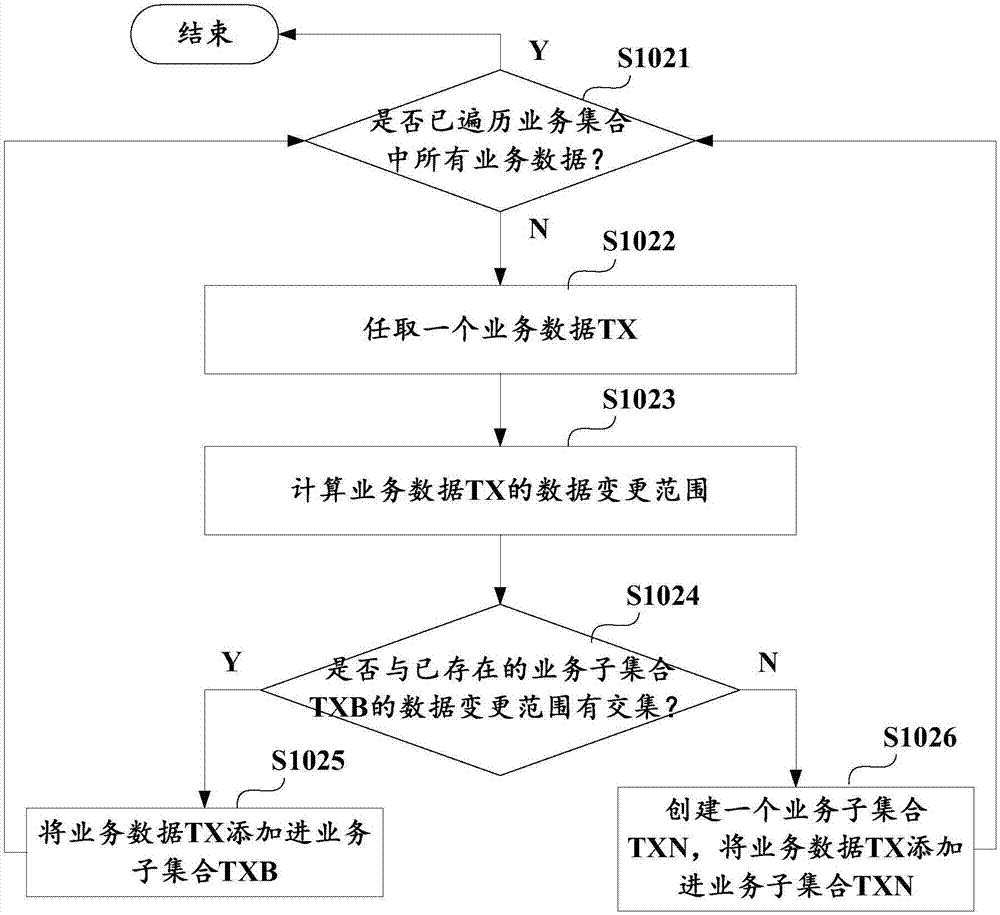
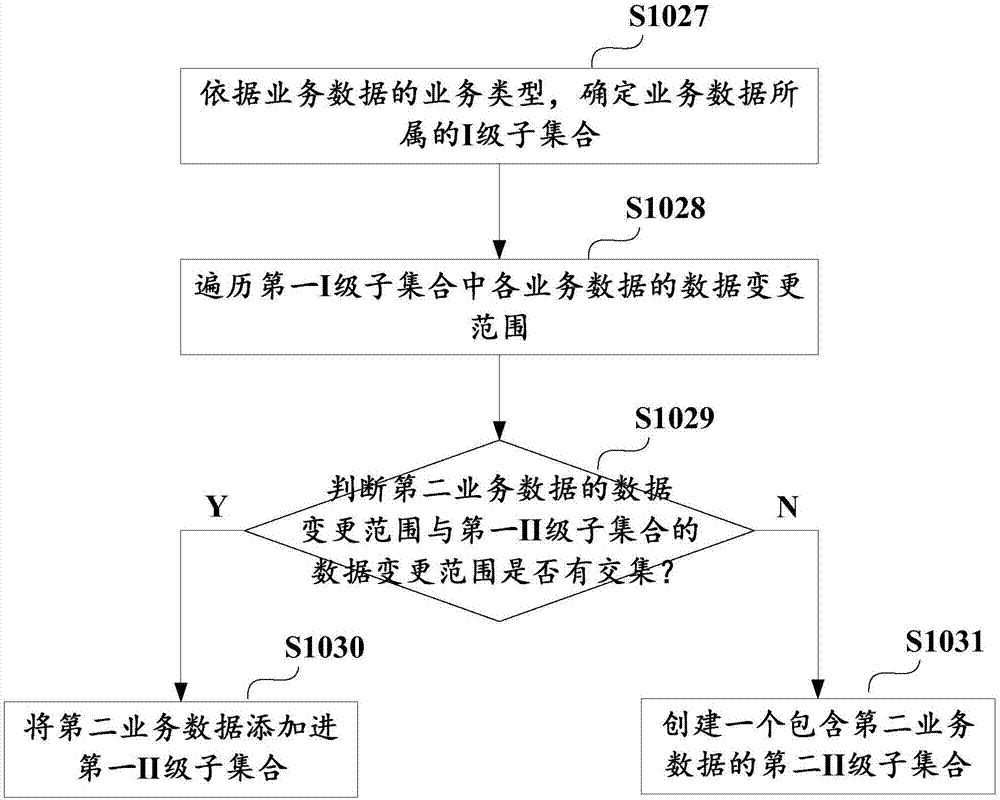
Method and apparatus for writing business data of block chain, and business subset determination method
ActiveCN106980649ADoes not affect consistencyEnsure consistencyOperational speed enhancementDatabase distribution/replicationExtensibilityBusiness data
The invention discloses a method for writing business data of a block chain. The method comprises the steps of obtaining multiple pieces of business data to be written in the block chain; according to business types and / or a data change range of the business data, determining business subsets which the business data belongs to, wherein the business data belonging to different business subsets does not have a transaction dependency relationship; and executing the business subsets in parallel, thereby writing executive results in the block chain. The invention furthermore discloses an apparatus for writing the business data of the block chain, and a business subset determination method. According to the method and the apparatus, parallel execution of the business data free of the transaction dependency relationship can be realized, so that the cost of improving data processing execution efficiency is reduced and the expandability is improved.
Owner:ADVANCED NEW TECH CO LTD
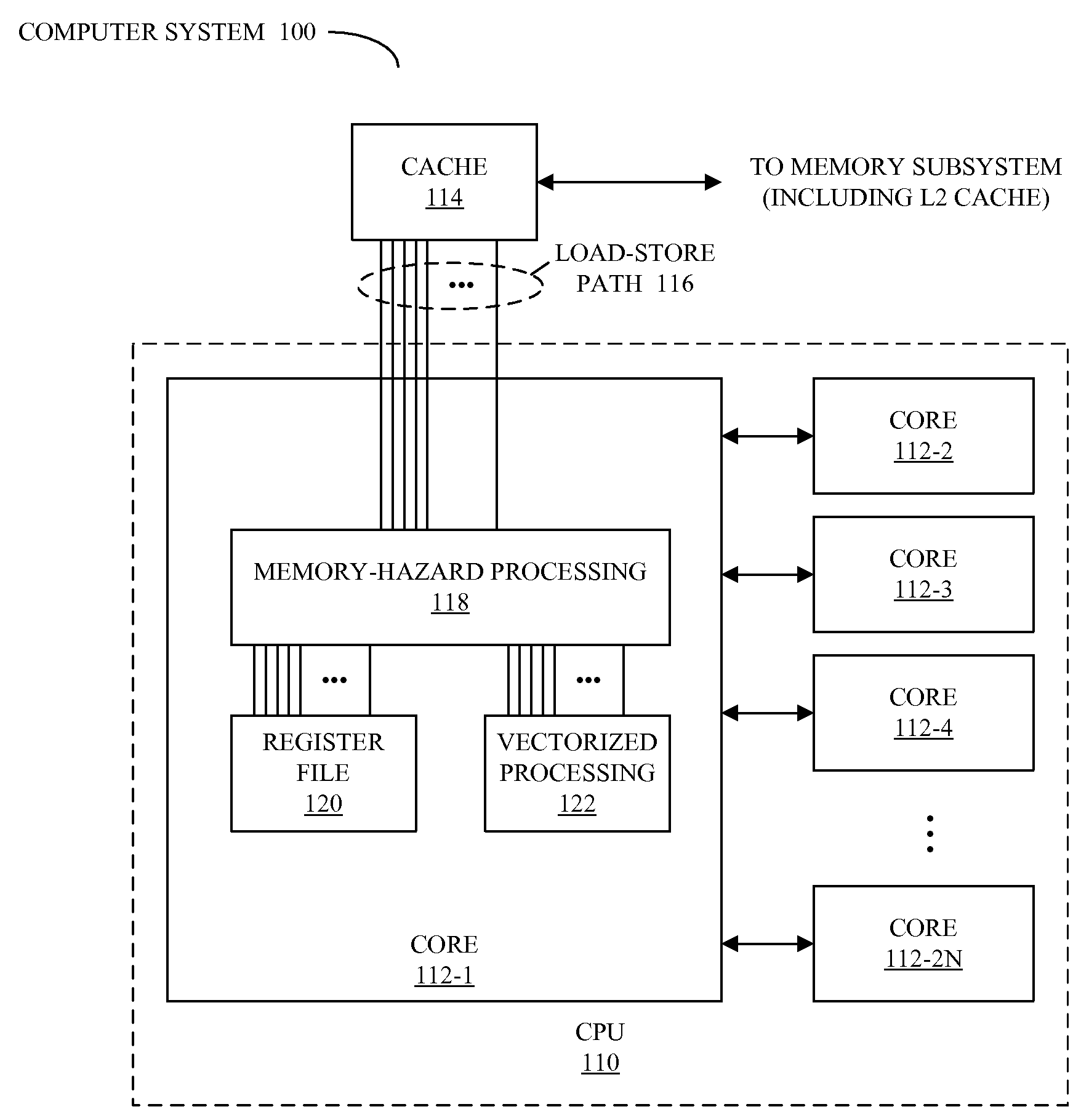
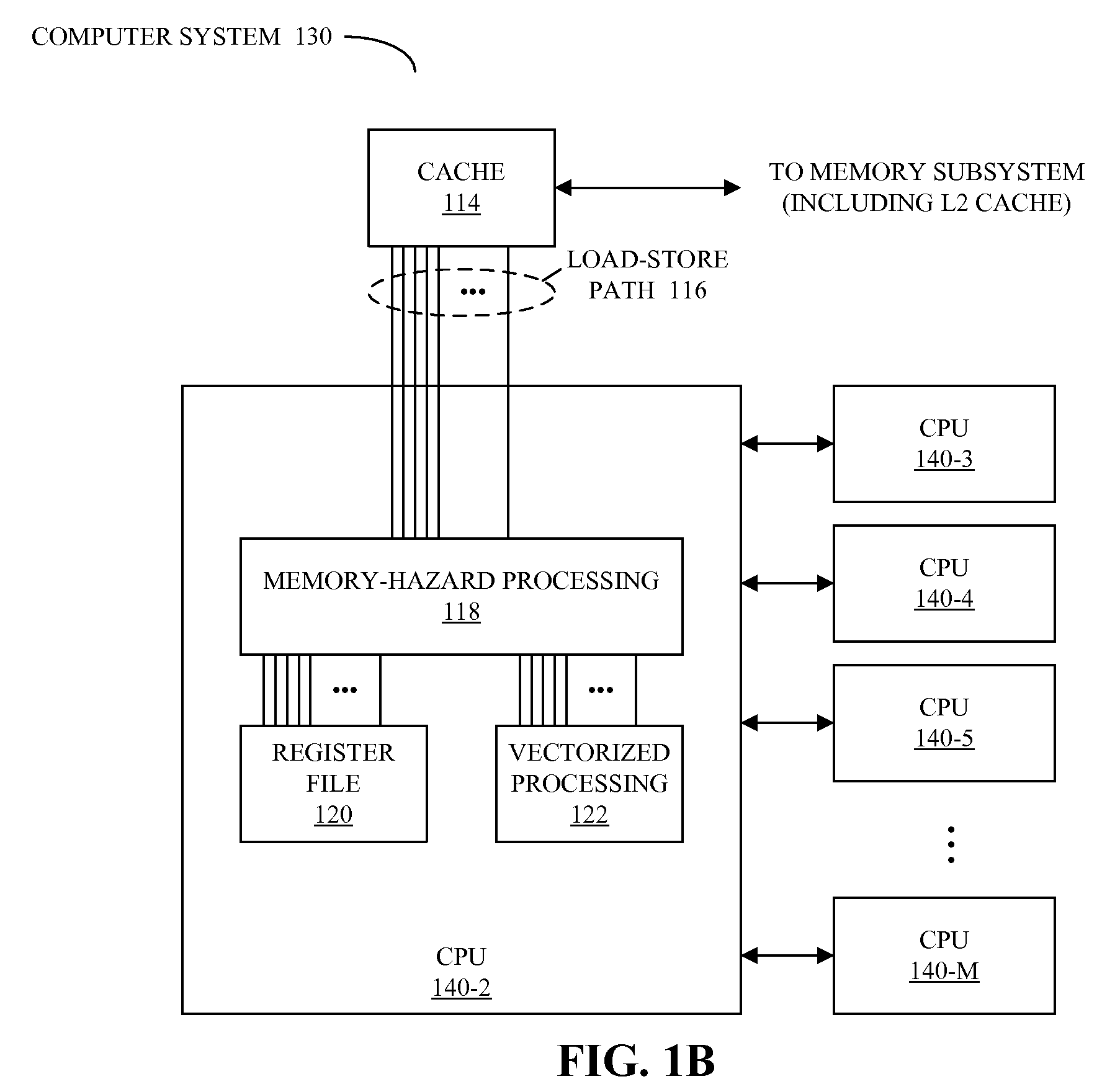
Detecting memory-hazard conflicts during vector processing
ActiveUS20080288744A1Operational speed enhancementConditional code generationMemory addressComputerized system
A method for performing parallel operations in a computer system when one or more memory hazards may be present, which may be implemented by a processor, is described. During operation, the processor receives instructions for detecting conflict between memory addresses in vectors when memory operations are performed in parallel using at least a portion of the vectors, and tracking positions in at least one of the vectors of any detected conflict between the memory addresses. Next, the processor executes the instructions for detecting the conflict between the memory addresses and tracking the positions.
Owner:APPLE INC
Acceleration processing unit based on convolutional neural network and array structure thereof
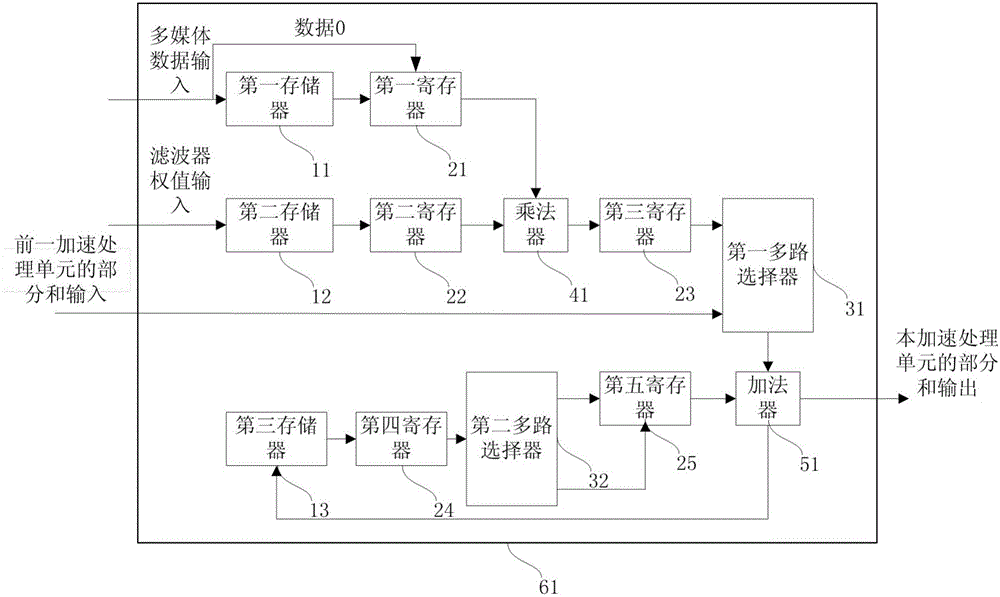
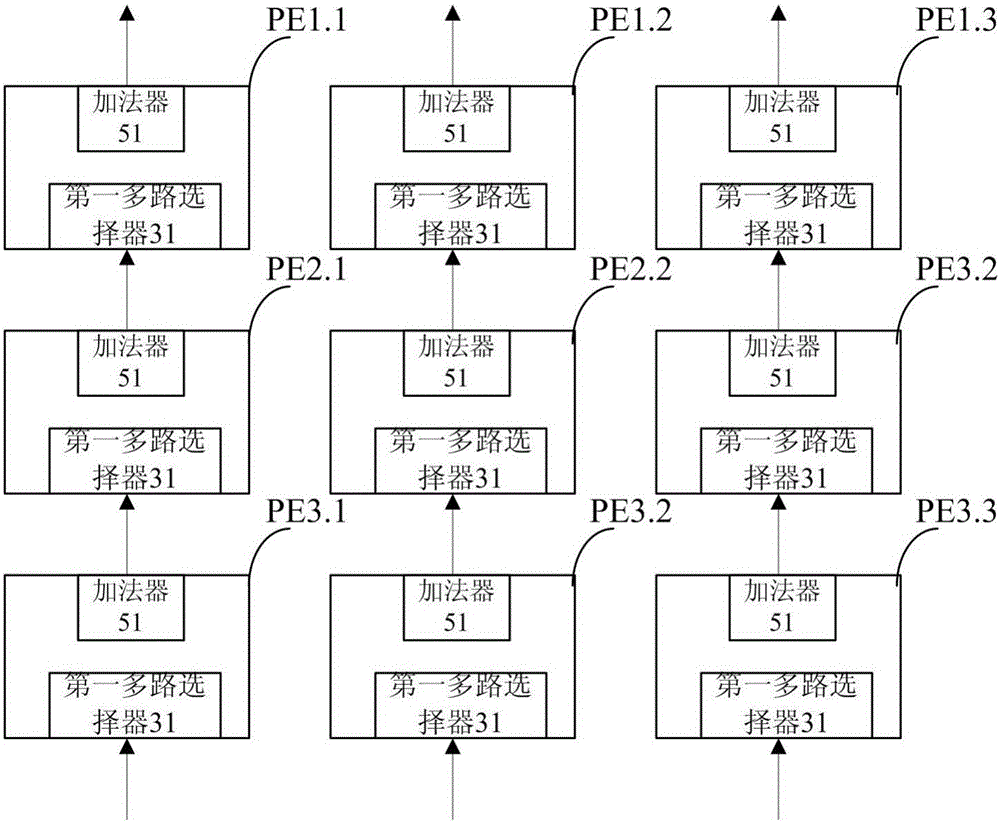
InactiveCN106203617AReduce usageReduce areaOperational speed enhancementBiological neural network modelsBinary multiplierArray data structure
The invention discloses an acceleration processing unit based on a convolutional neural network, and is used for performing convolution operation on local data. The local data include multiple multimedia data. The acceleration processing unit comprises a first register, a second register, a third register, a fourth register, a fifth register, a multiplier, an adder, a first multipath selector and a second multipath selector. The single acceleration processing unit controls the first multipath selector and the second multipath selector so that the multiplier and the adder are enabled to be repeatedly usable, one acceleration processing unit is enabled to only need one multiplier and one adder to complete convolution operation and use of the multiplier and the adder can be reduced. Processing speed can be enhanced and energy consumption can be reduced by reducing use of the multiplier and the adder in implementing the same convolution operation, and the on-chip area of the single acceleration processing unit is smaller.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL +1
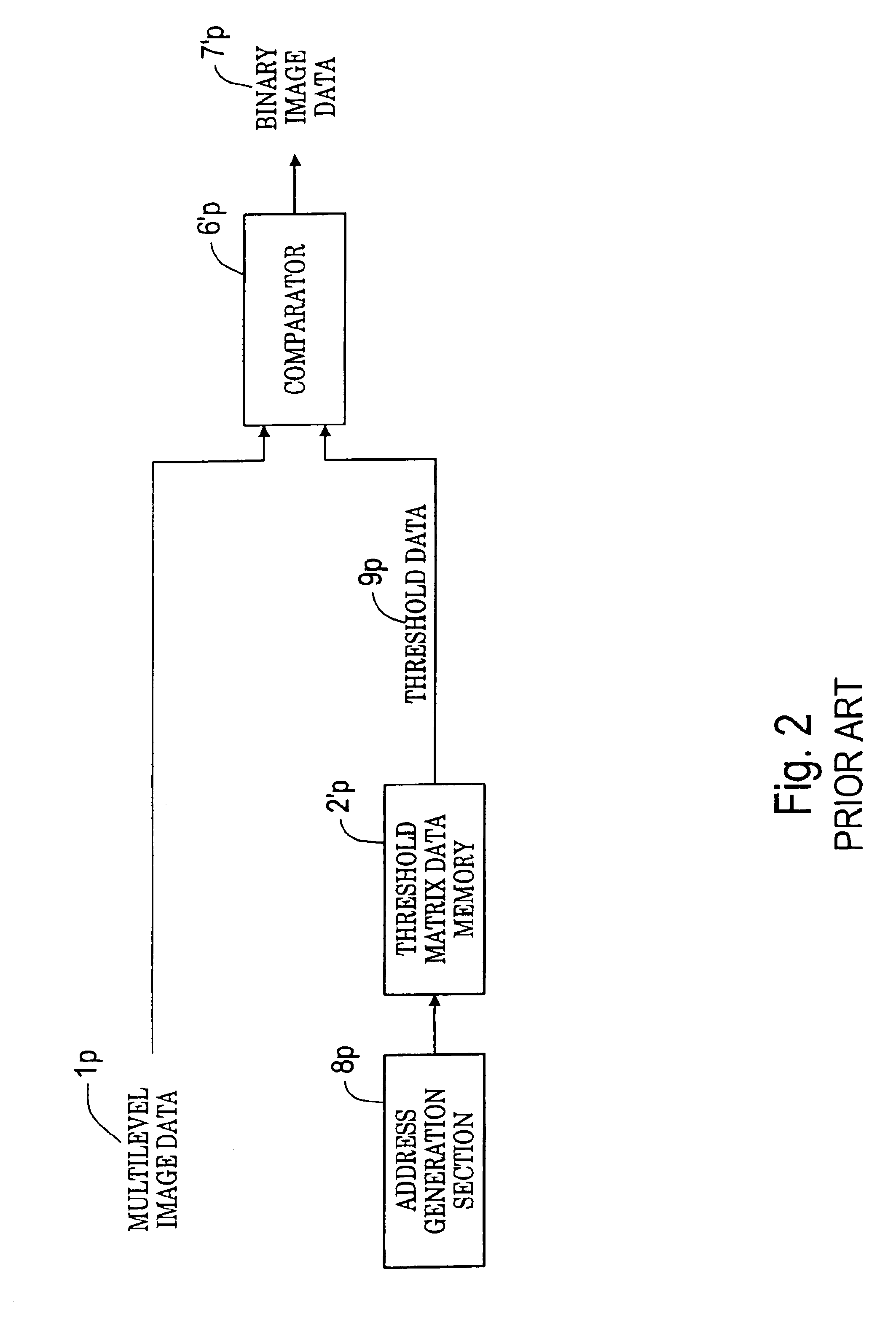
Halftone generation system and halftone generation method
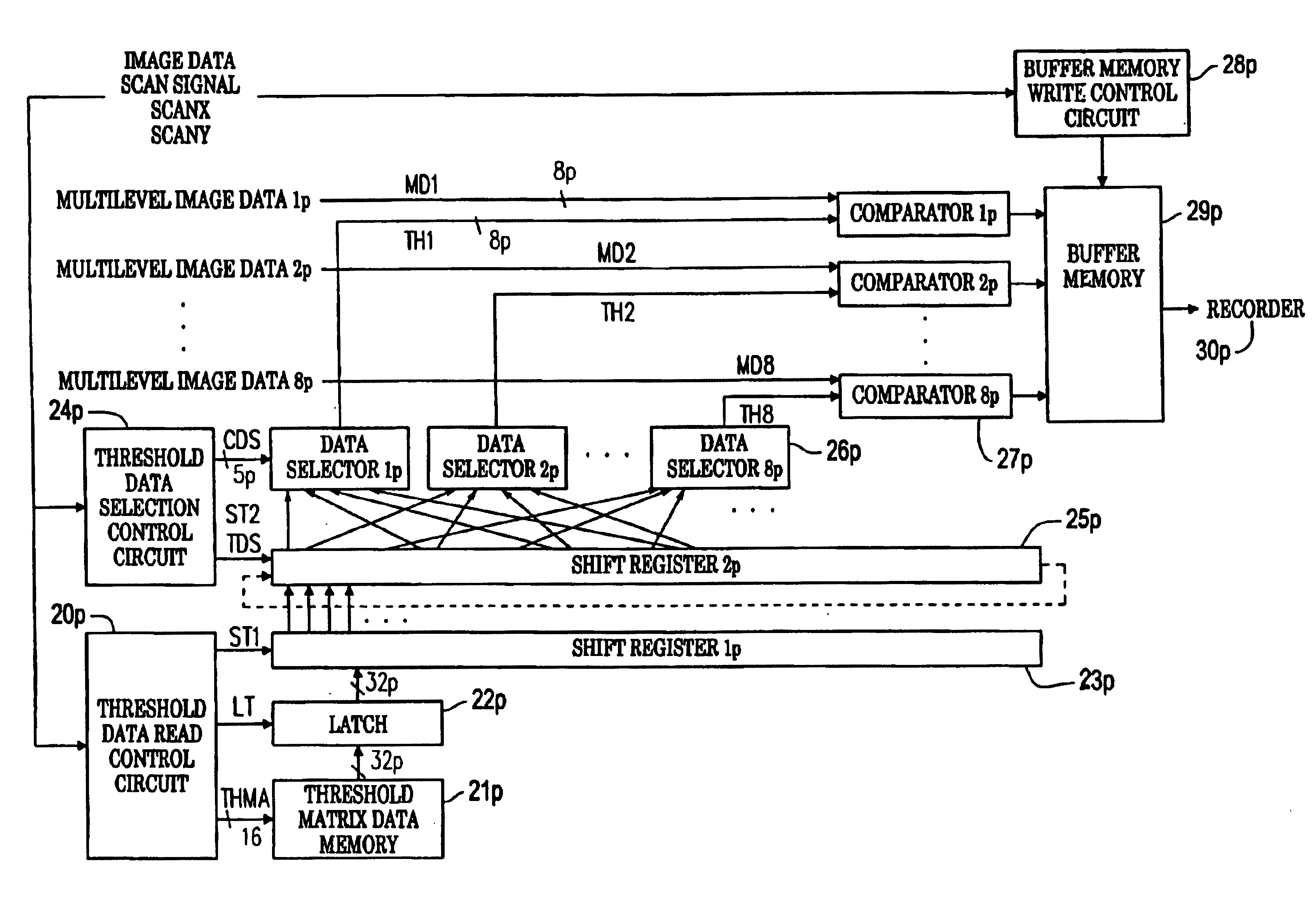
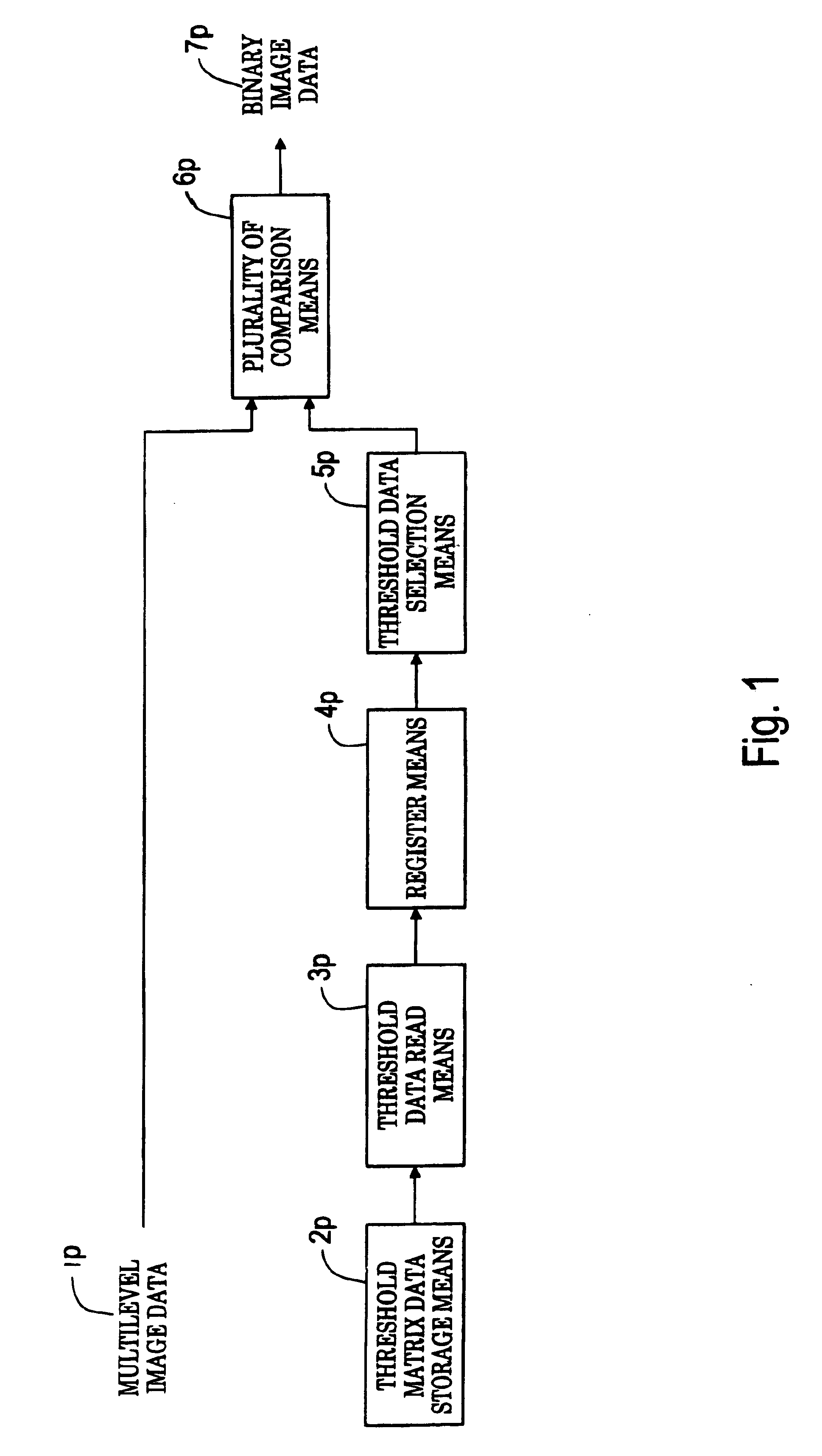
InactiveUS6930800B1Improve image qualityOperational speed enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionData setProcessor register
All threshold data applied to processing is read into a register so that threshold data read from threshold matrix memory can be recycled until the end of a scanning line for processing, and is selectively output to a plurality of comparison means for executing parallel comparison processing. The threshold data set in the register is shifted in order for repetitive use. The threshold data of the next scanning line is read into the register during the comparison processing, and upon completion of processing of one scanning line, comparison processing on the next scanning line is executed as pipeline processing. Threshold data read from the memory needs to be executed only once for each scanning line for processing, and threshold data can also be read during halftone data generation of the preceding line.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
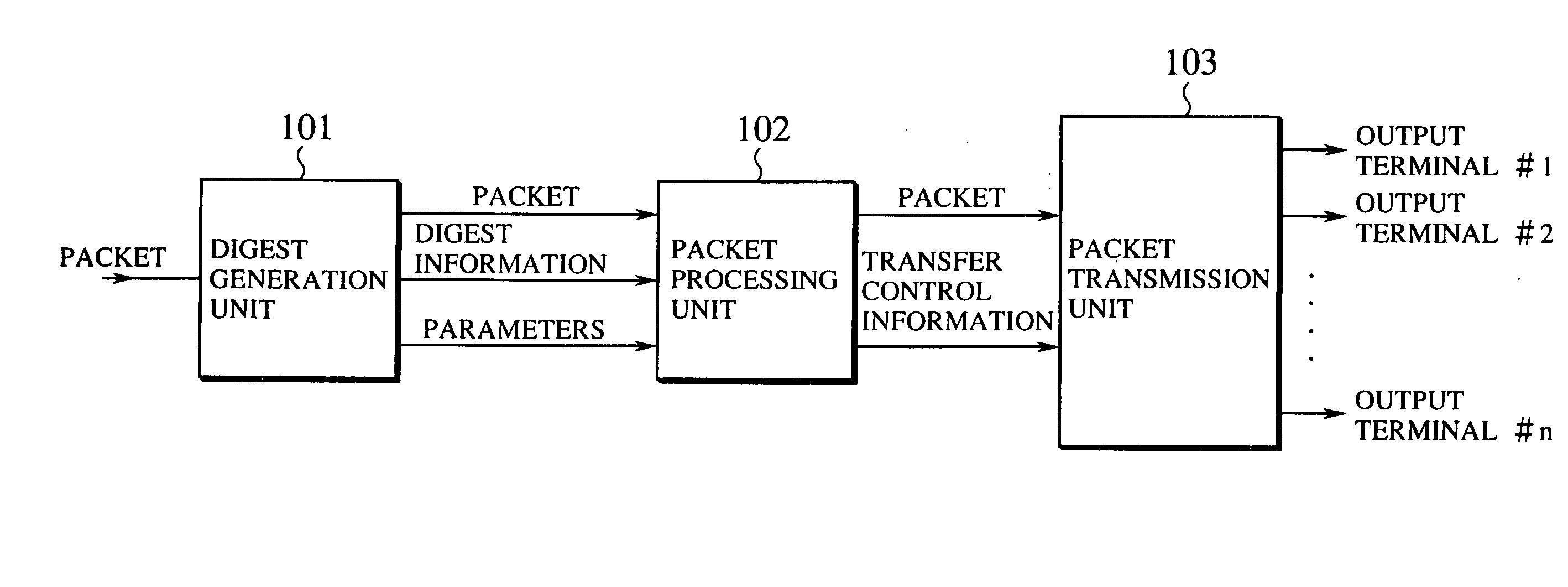
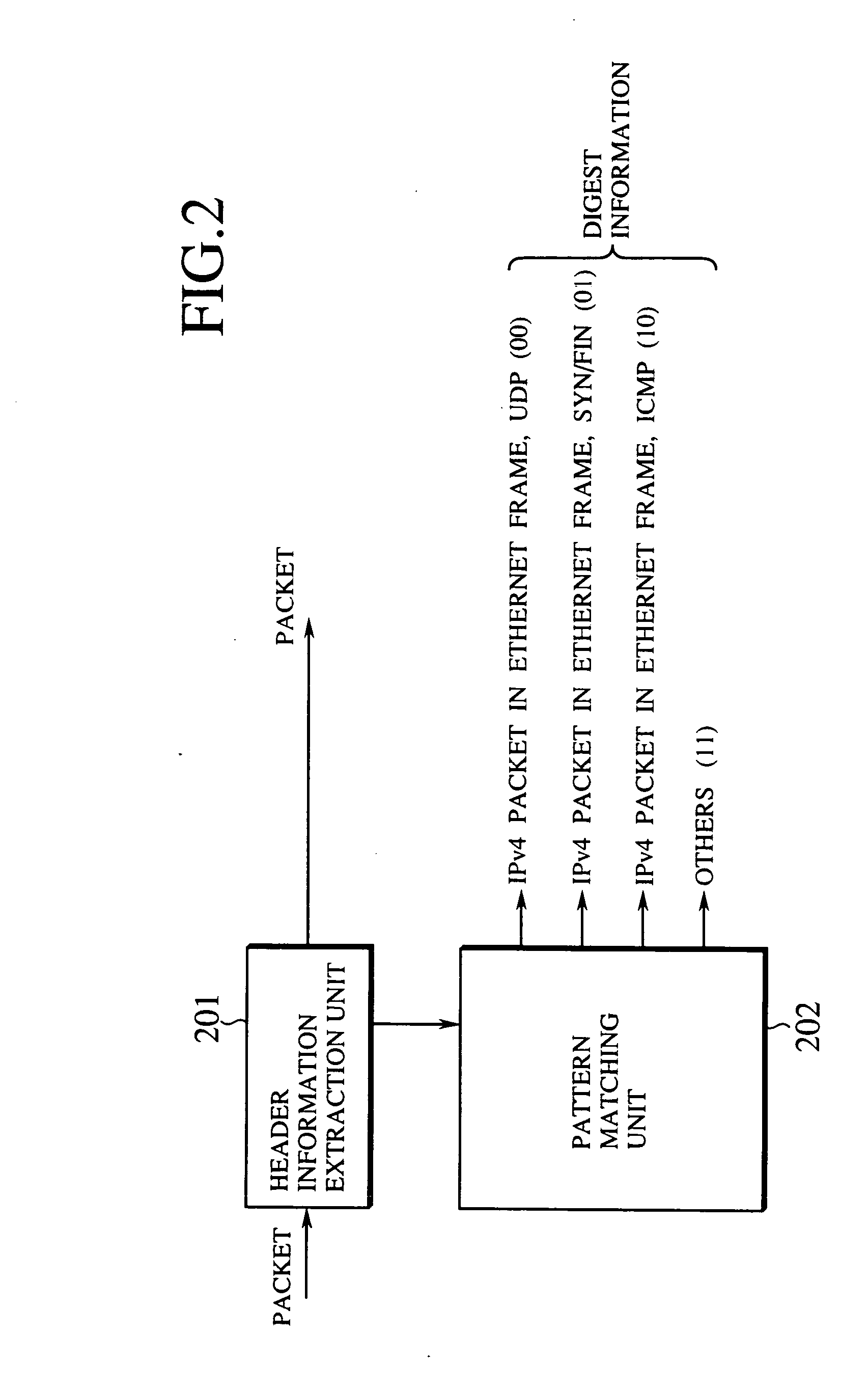
Fast and adaptive packet processing device and method using digest information of input packet
InactiveUS20050086353A1Improve adaptabilityEasy to handleOperational speed enhancementMultiple digital computer combinationsSequence processingInstruction sequence
A packet processing device is formed by a digest information generation unit configured to extract a plurality of prescribed bit sequences from an input packet, and generate a digest information capable of specifying at least a part of a processing to be applied to the input packet, according to values of the plurality of prescribed bit sequences; and a packet processing unit configured to process the input packet using an instruction sequence to be applied to the input packet that is obtained according to the digest information generated by the digest information generation unit, where the digest information generation unit generates the digest information with respect to a next input packet while the packet processing unit carries out a processing for one packet.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
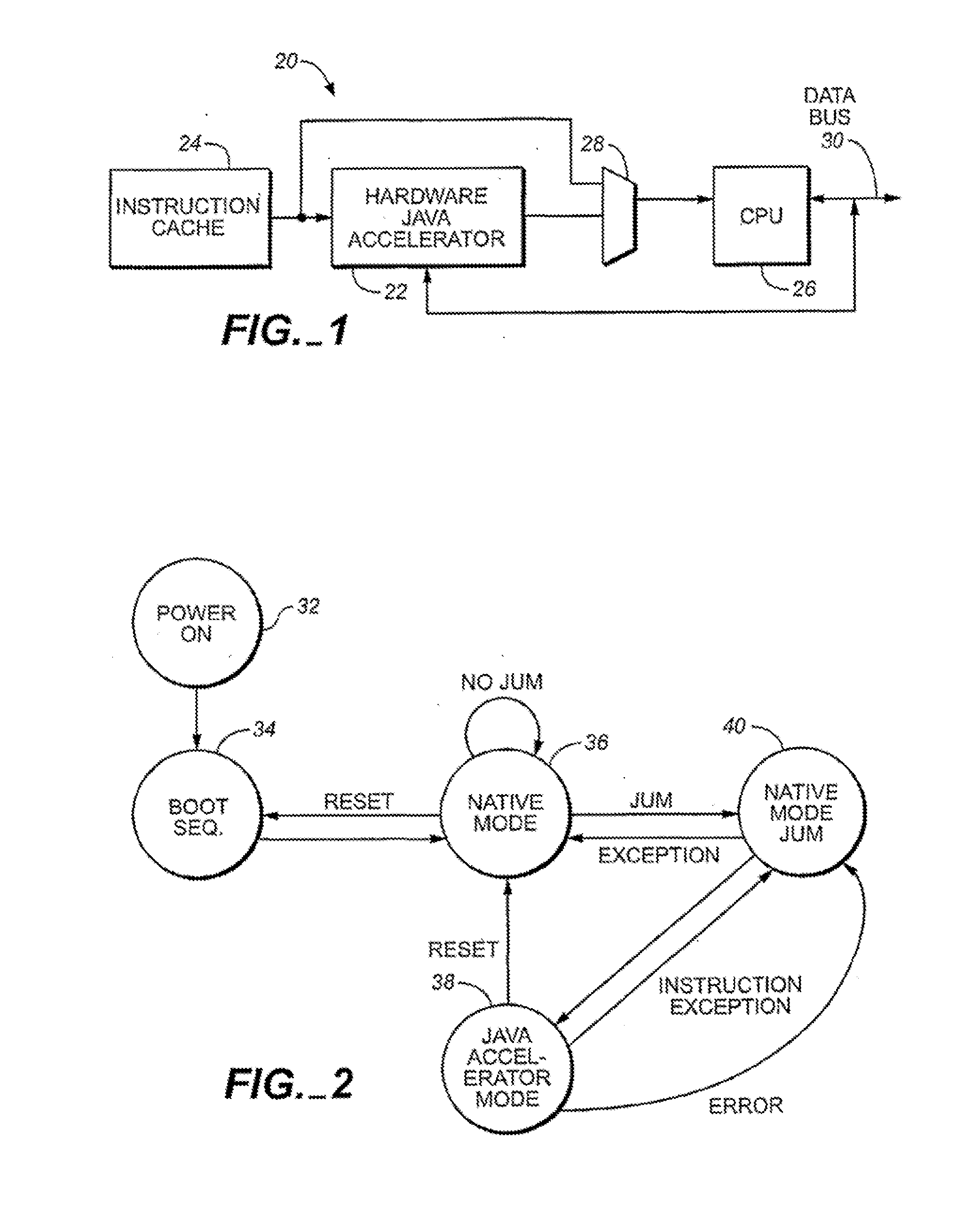
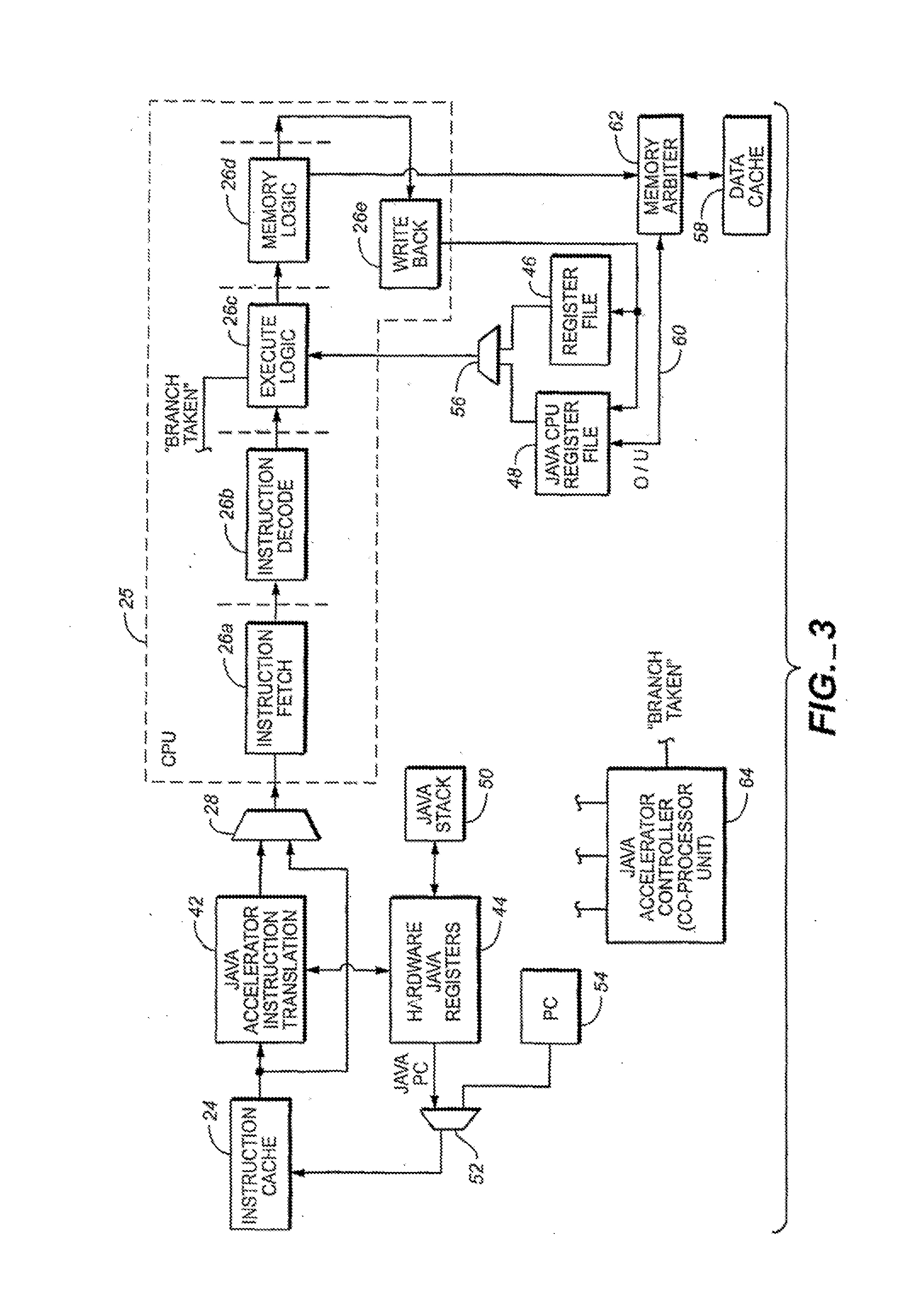
JAVA hardware accelerator using microcode engine
InactiveUS20070118724A1Easy to handleOperational speed enhancementTransformation of program codeJava bytecodeHardware acceleration
A hardware Java accelerator is comprised of a decode stage and a microcode stage. Separating into the decode and microcode stage allows the decode stage to implement instruction level parallelism while the microcode stage allows the conversion of a single Java bytecode into multiple native instructions. A reissue buffer is provided which stores the converted instructions and reissues them when the system returns from an interrupt. In this manner, the hardware accelerator need not be flushed upon an interrupt. A native PC monitor is also used. While the native PC is within a specific range, the hardware accelerator is enabled to convert the Java bytecodes into native instructions. When the native PC is outside the range, the hardware accelerator is disabled and the CPU operates on native instructions obtained from the memory.
Owner:NAZOMI COMM
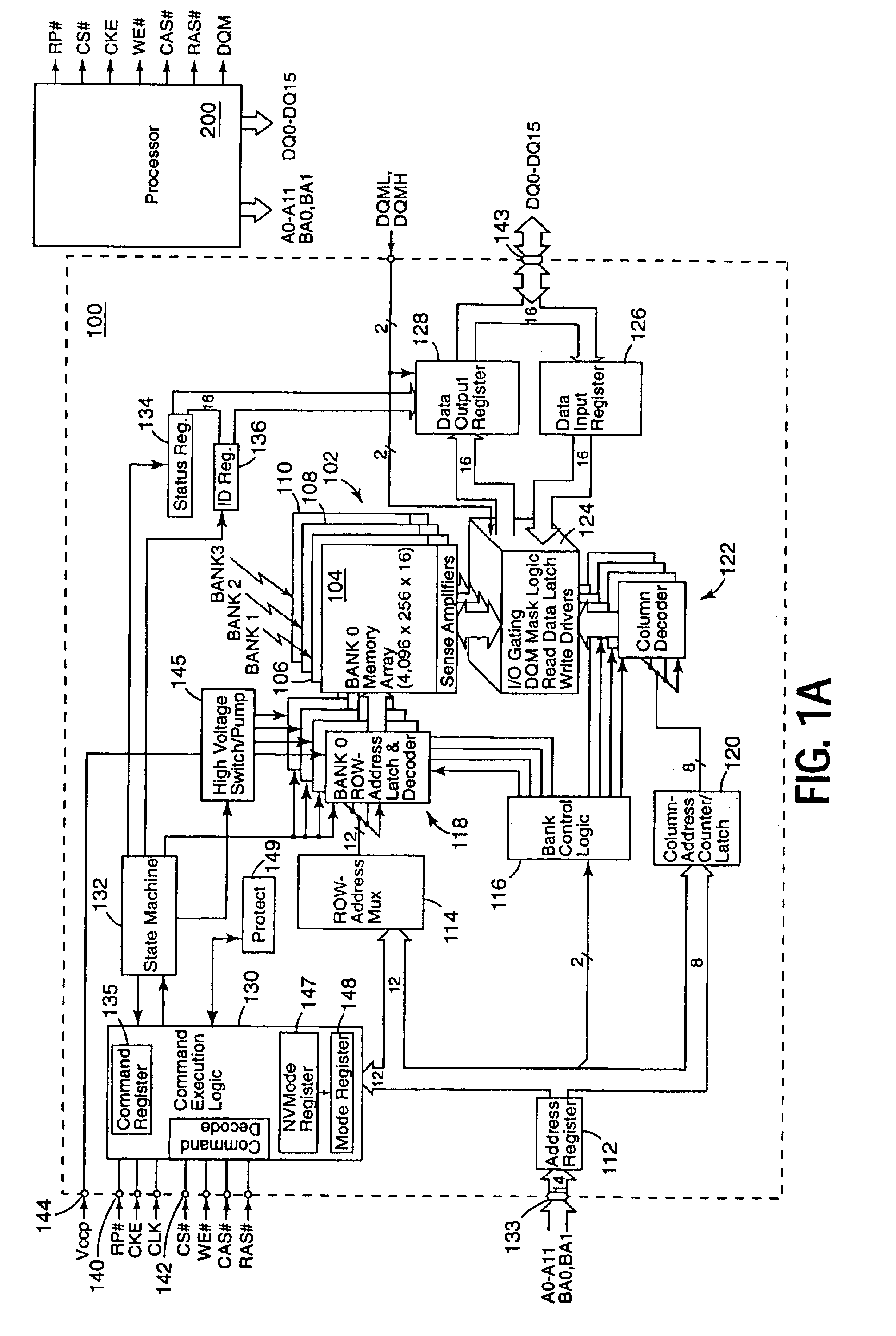
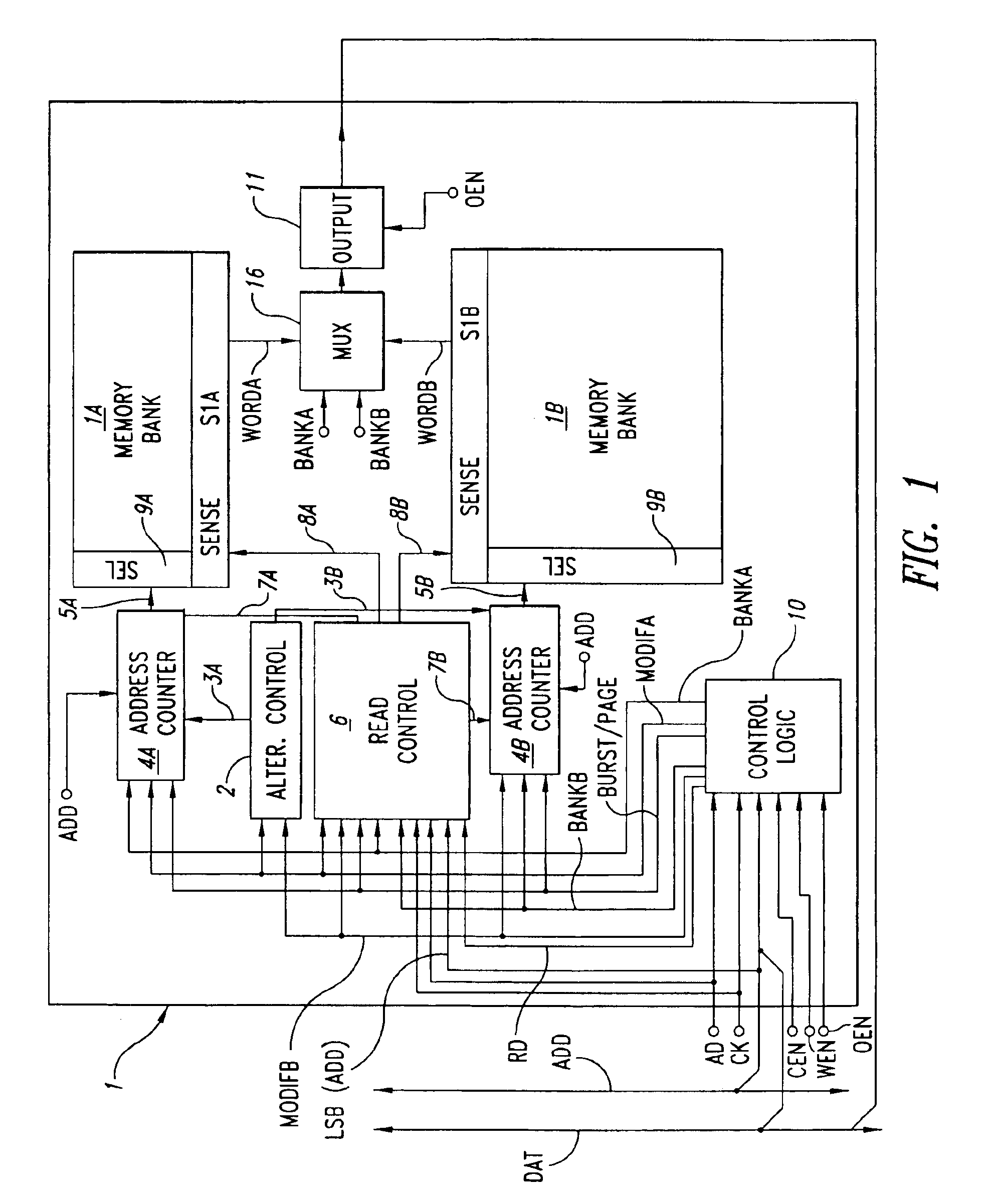
Synchronous flash memory with simultaneous access to one or more banks
InactiveUS6883044B1Operational speed enhancementMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory controllerNon-volatile memory
A synchronous flash memory includes an array of non-volatile memory cells. The memory array is arranged in rows and columns, and can be further arranged in addressable blocks. Data communication connections are used for bi-directional data communication with an external device(s), such as a processor or other memory controller. In one embodiment a non-volatile synchronous memory device includes an array of memory cells arranged in a plurality of addressable banks. A bank buffer circuit is coupled to each of the banks. Each of the buffers can store data from a row of memory cells contained in a corresponding bank. A method of operating a synchronous flash memory includes storing instruction code in each array block and copying the instruction code from a first array block to a buffer circuit, during a write operation, so that the instruction code can be read from the buffer circuit during the write operation.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Broadcasting Collective Operation Contributions Throughout A Parallel Computer
InactiveUS20090240915A1Operational speed enhancementGeneral purpose stored program computerNetwork linkCollective operation
Owner:IBM CORP
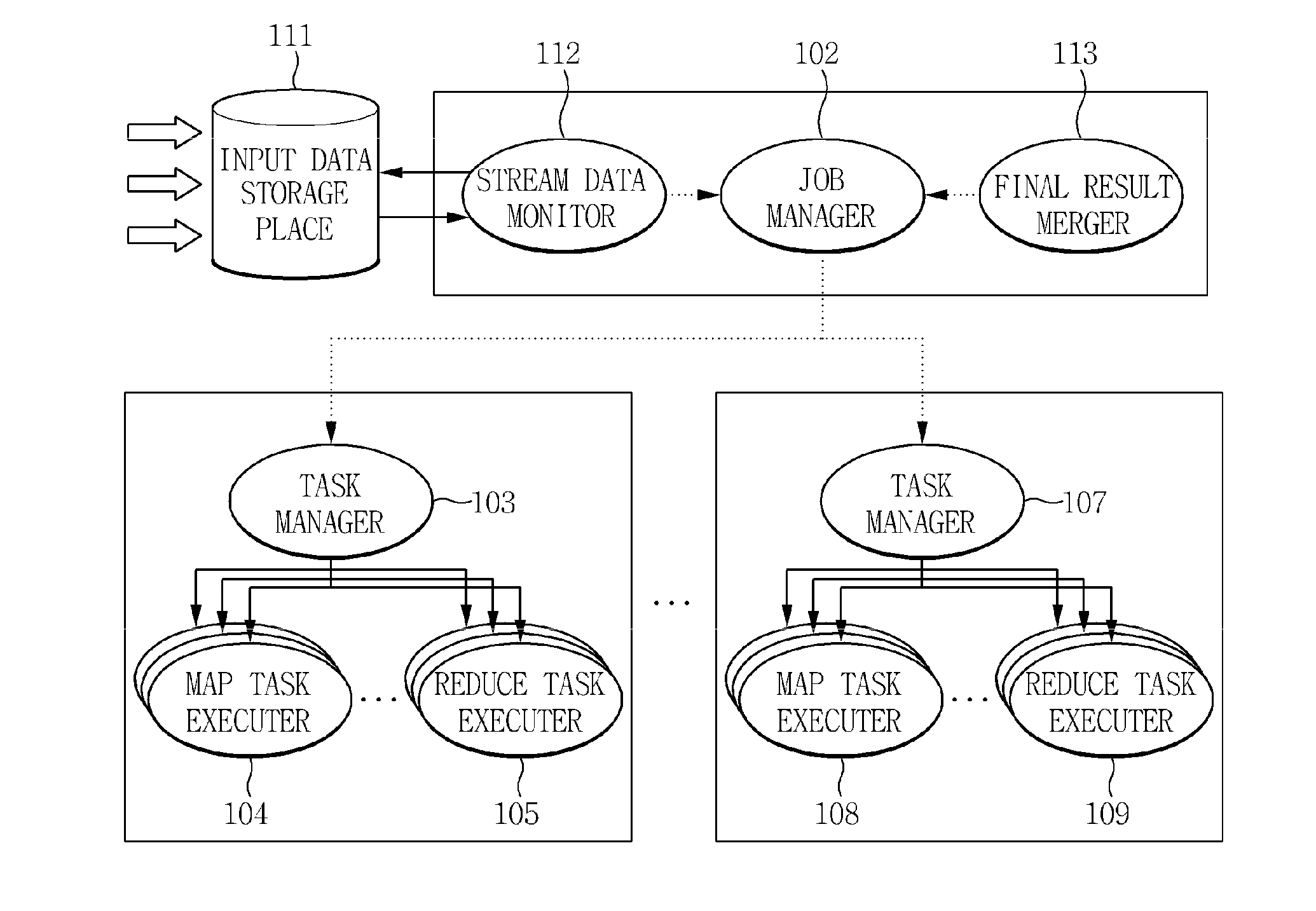
Incremental mapreduce-based distributed parallel processing system and method for processing stream data
InactiveUS20110154339A1Increase speedOperational speed enhancementGeneral purpose stored program computerMass storageStream data
Disclosed herein is a system for processing large-capacity data in a distributed parallel processing manner based on MapReduce using a plurality of computing nodes. The distributed parallel processing system is configured to provide an incremental MapReduce-based distributed parallel processing function for large-capacity stream data which is being continuously collected even during the performance of the distributed parallel processing, as well as for large-capacity stored data which has been previously collected.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
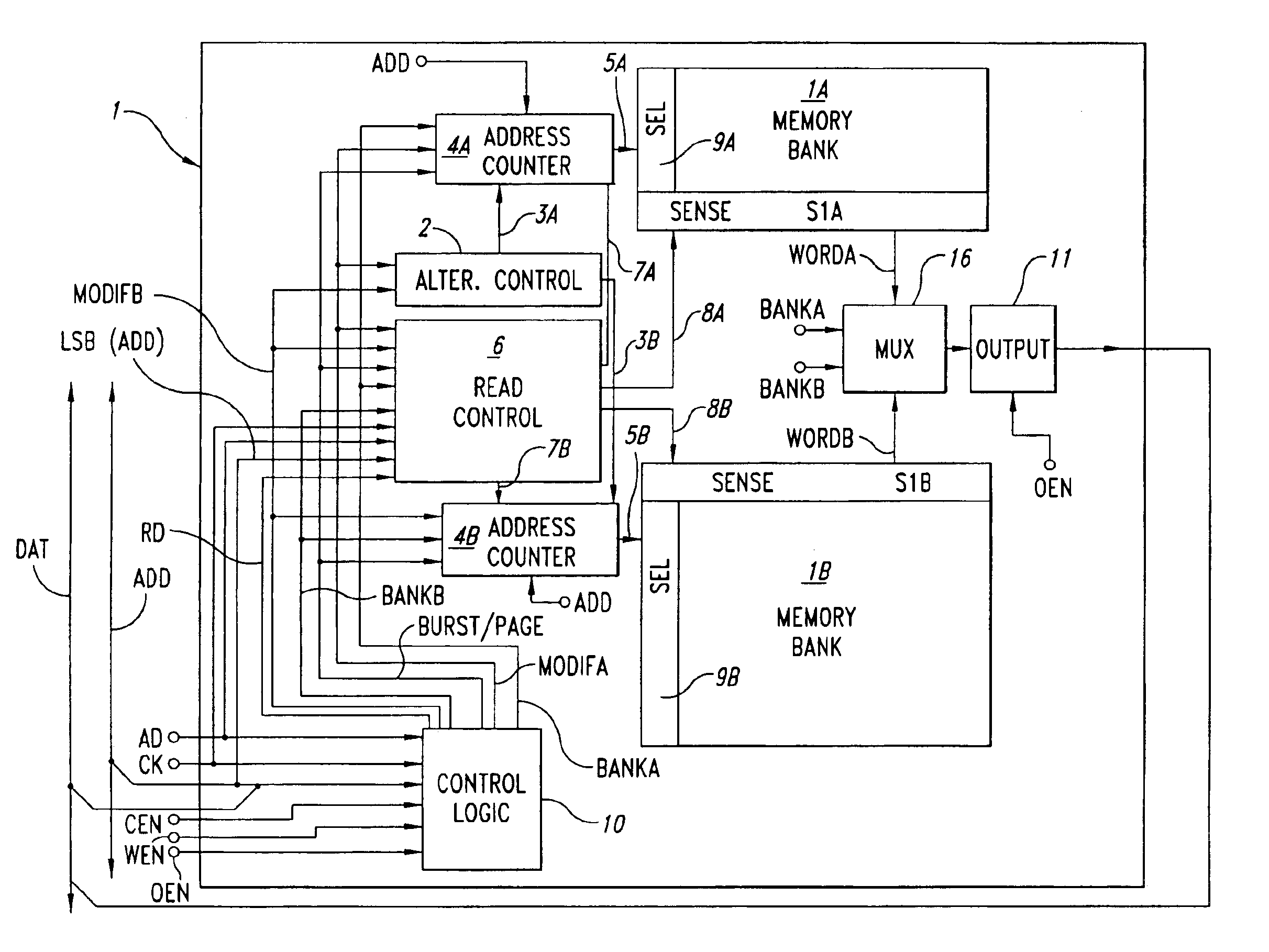
Non-volatile memory with functional capability of simultaneous modification of the content and burst mode read or page mode read
InactiveUS6912598B1Operational speed enhancementMemory adressing/allocation/relocationElectricityMemory bank
An electrically alterable semiconductor memory comprises at least two substantially independent memory banks, and a first control circuit for controlling operations of electrical alteration of the content of the memory. The first control circuit permits the selective execution of an operation of electrical alteration of the content of one of the at least two memory banks. The memory also comprises second control circuit that permits, simultaneously with said operation of electrical alteration of the content of one of the at least two memory banks, a burst mode, page mode, or standard read operation for reading the content of the other memory bank.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method and apparatus for SIMD processing using multiple queues
InactiveUS6898692B1Operational speed enhancementGeneral purpose stored program computerGraphicsMultilevel queue
A method of processing data relating to graphical primitives to be displayed on a display device using region-based SIMD multiprocessor architecture, has the shading and blending operations deferred until rasterization of the available graphical primitive data is completed. For example, the method may comprise the steps of: a) defining a data queue having a predetermined number of locations therein; b) receiving fragment information belonging to an image to be displayed by the pixel; c) determining whether the fragment information belongs to an opaque image or to a blended image; d) if the fragment information relates to a blended image, storing the fragment information on the next available location in the queue; e) if the fragment information relates to an opaque image, clearing the locations of the queue and storing the fragment information in the first location in the queue; f) repeating steps b) to e) for new fragment information until fragment information is stored in all the locations in the data queue or until no further fragment information is available; and g) processing in turn fragment information stored in the locations of the queue to produce respective pixel display values.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
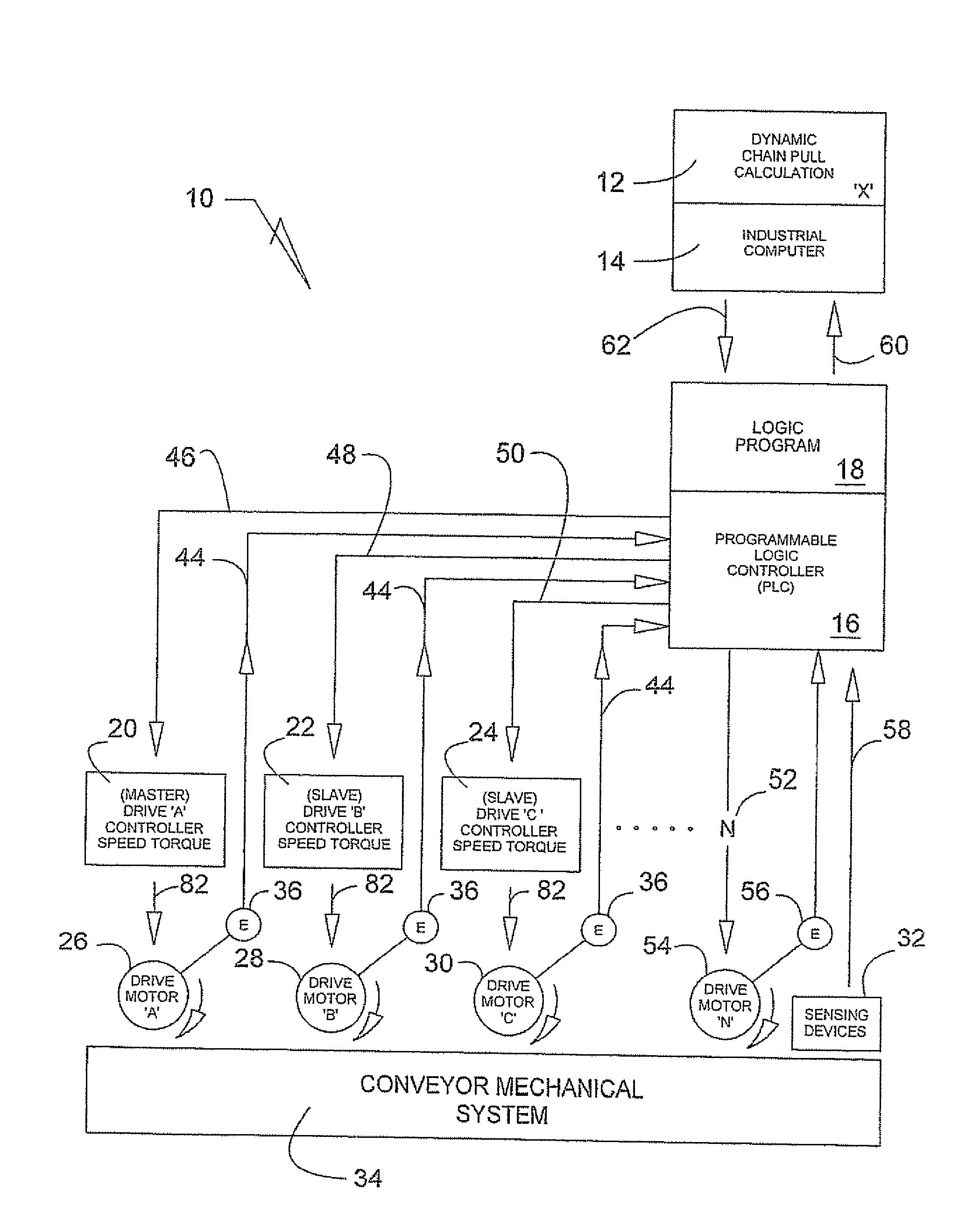
Conveyor drive control system
InactiveUS20080234858A1Raise the possibilityLong chainProgramme controlOperational speed enhancementAuto regulationControl system
A drive control system for conveyor utilizes a dynamic chain pull calculation program that is integrated with a PLC, which communicates to a plurality of controllers. The controllers in turn automatically adjust their associated drive motors so as to maximize efficiency at moving material on a conveyor system. Sensing devices provide continuous load parameters to a PLC that in turn, processes the data and adjusts the system's operation based upon desired conditions.
Owner:NEUMANN LINDA E
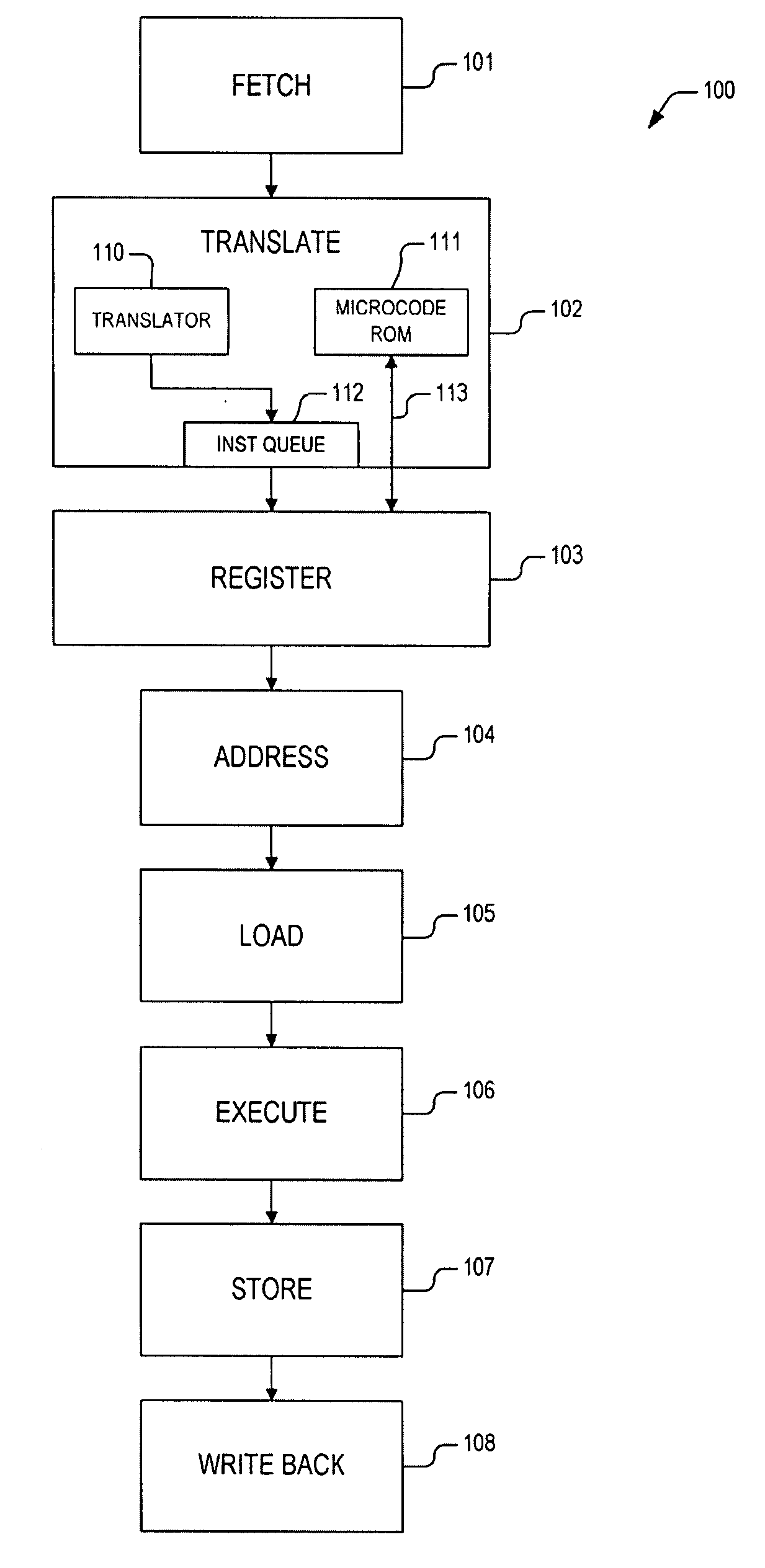
Early access to microcode ROM
An apparatus and method are provide for precluding stalls in a microprocessor pipeline due to microcode ROM access delay. The apparatus includes a micro instruction queue and early access logic. The micro instruction queue provides a plurality of queue entries to register logic. Each of tile plurality of queue entries includes first micro instructions and a microcode entry point. All of the first micro instructions correspond to an instruction. The microcode entry point is coupled to the first micro instructions. The microcode entry point is configured to point to second micro instructions stored within a microcode ROM. The early access logic is coupled to the micro instruction queue. The early access logic employs the microcode entry point to access the microcode ROM prior to when the each of the plurality of queue entries is provided to the register logic, whereby a first one of the second micro instructions is provided to the register logic when the first one of the second micro instructions is required by the register logic.
Owner:IP FIRST
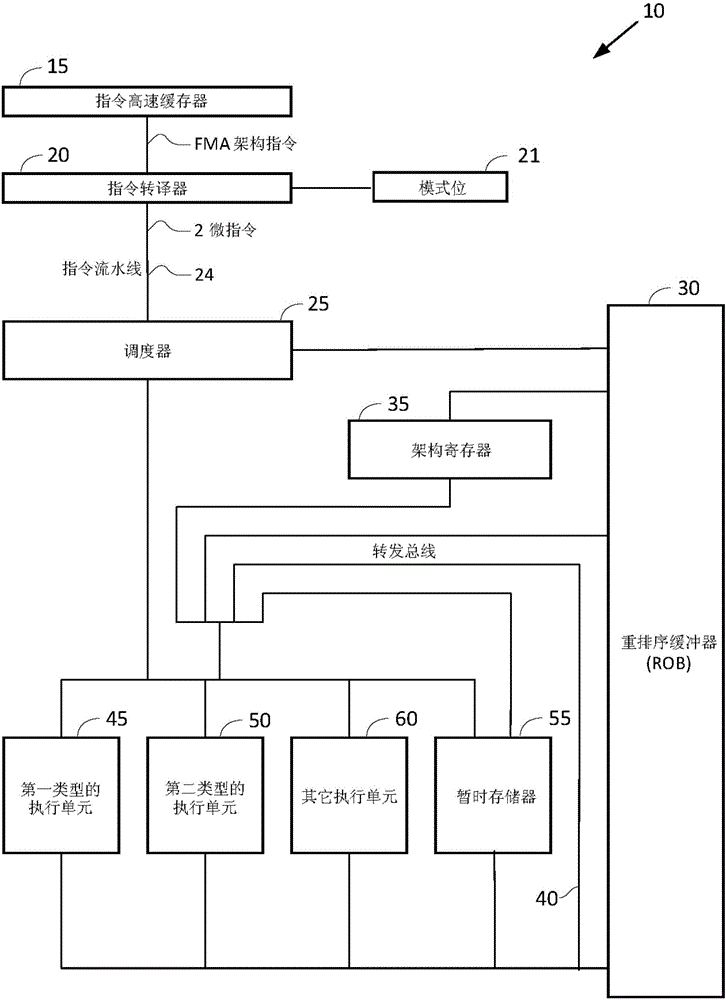
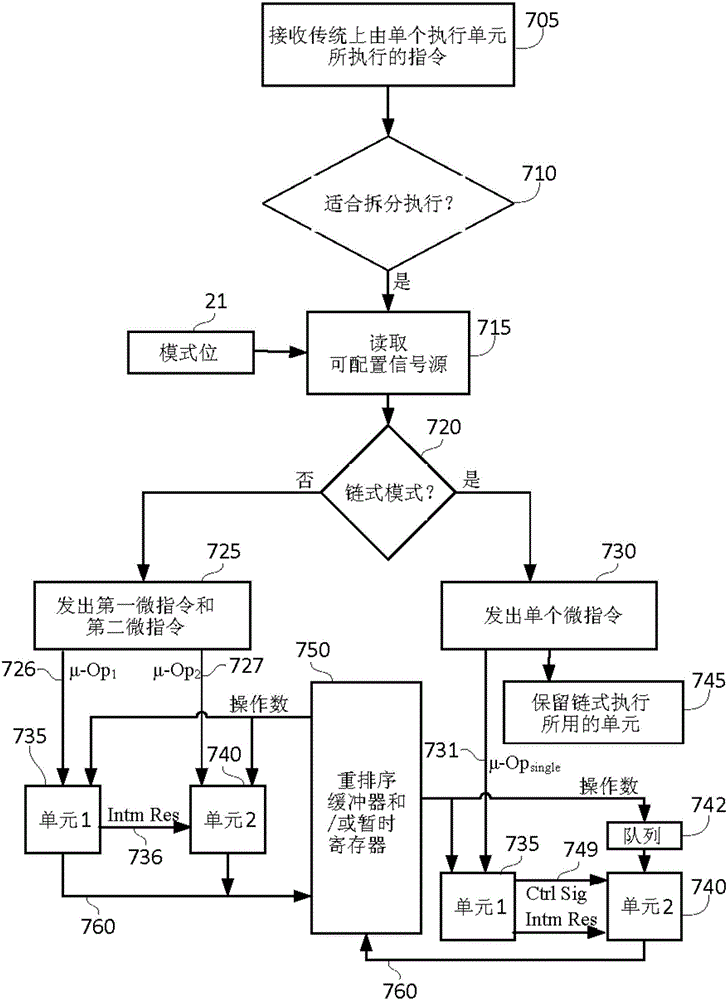
Microprocessor, and method of executing fused composite arithmetical operation therein
ActiveCN106406812AOperational speed enhancementDigital data processing detailsControl signalParallel computing
The invention relates to a microprocessor and a method of executing fused composite arithmetical operation therein. The microprocessor is configured for a non-chain mode and a chain mode of splitted execution of the composite arithmetical operation; in the two modes of hte splitted execution, a first command executing unit only executes a first part in the fused composite arithmetical operation and generates an inter-result thereof; and a second command executing unit receives the inter-result and executing a second part in the fused composite arithmetical operation so as to obtain a final result. In the non-chain mode, independent splitted execution micro-commands are distributed to the first and the second command executing units to achieve the execution. In the chain mode, single splitted execution micro-command is distributed to the first command executing unit, and a chain-type control signal or signal group is sent to the second command executing unit so that the second command executing unit, without commands, executes the second part of hte fused composite arithmetical operation, thus achieving execution.
Owner:VIA ALLIANCE SEMICON CO LTD
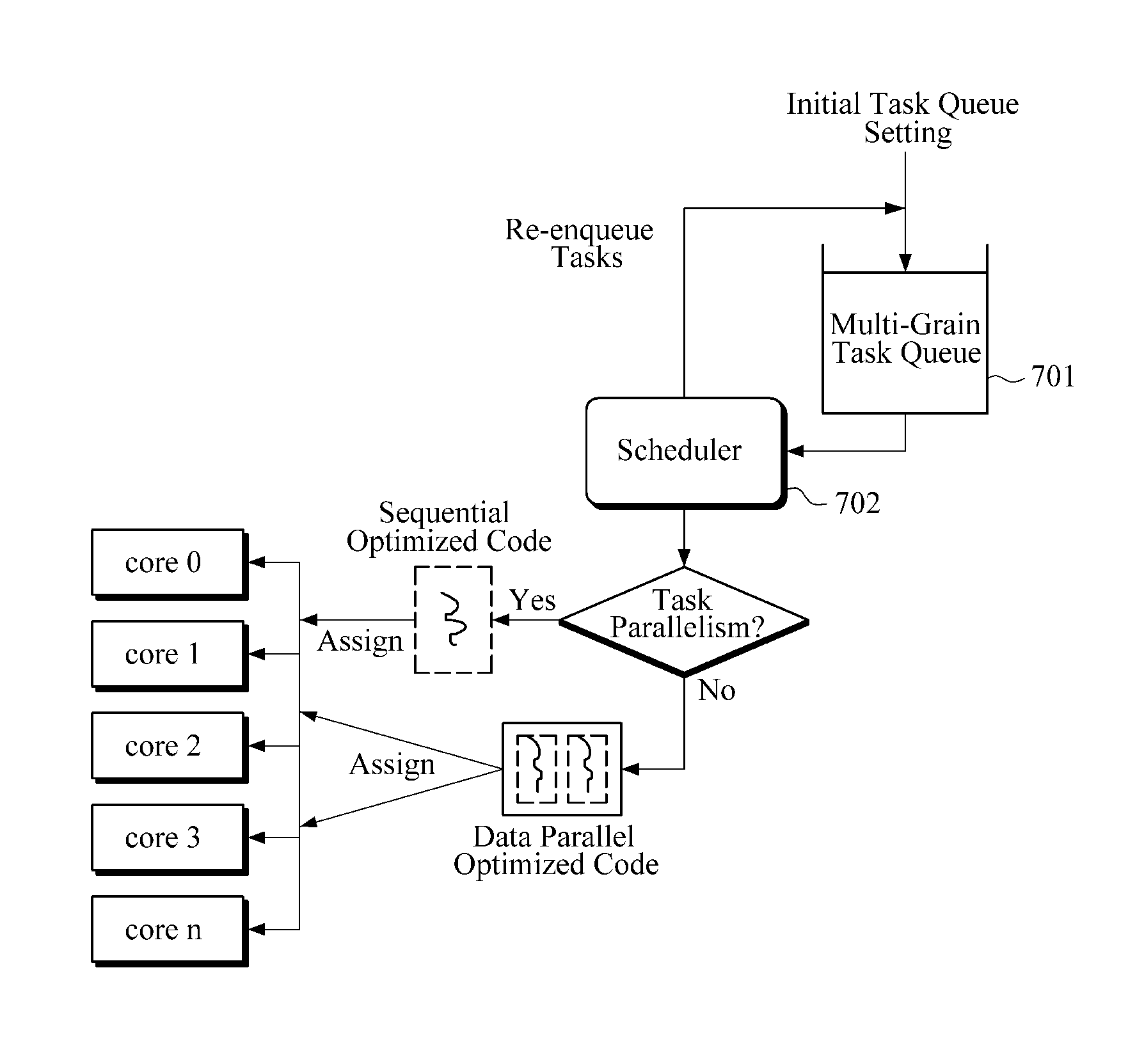
Apparatus and method for parallel processing
InactiveUS20110161637A1Operational speed enhancementDigital computer detailsParallel processingDegree of parallelism
An apparatus and method for parallel processing in consideration of degree of parallelism are provided. One of a task parallelism and a data parallelism is dynamically selected while a job is processed. In response to a task parallelism being selected, a sequential version code is allocated to a core or processor for processing a job. In response to a data parallelism being selected, a parallel version code is allocated to a core a processor for processing a job.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
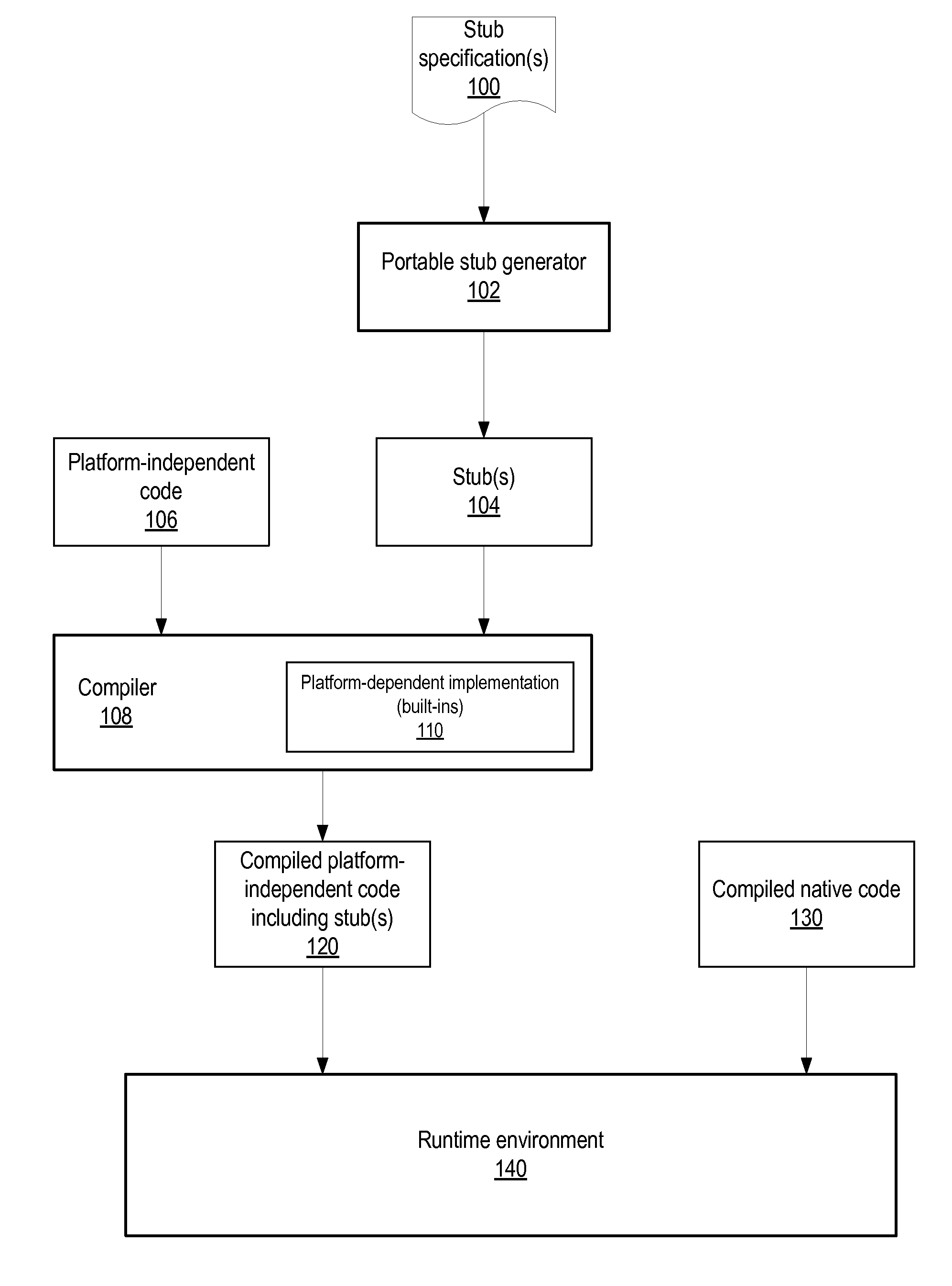
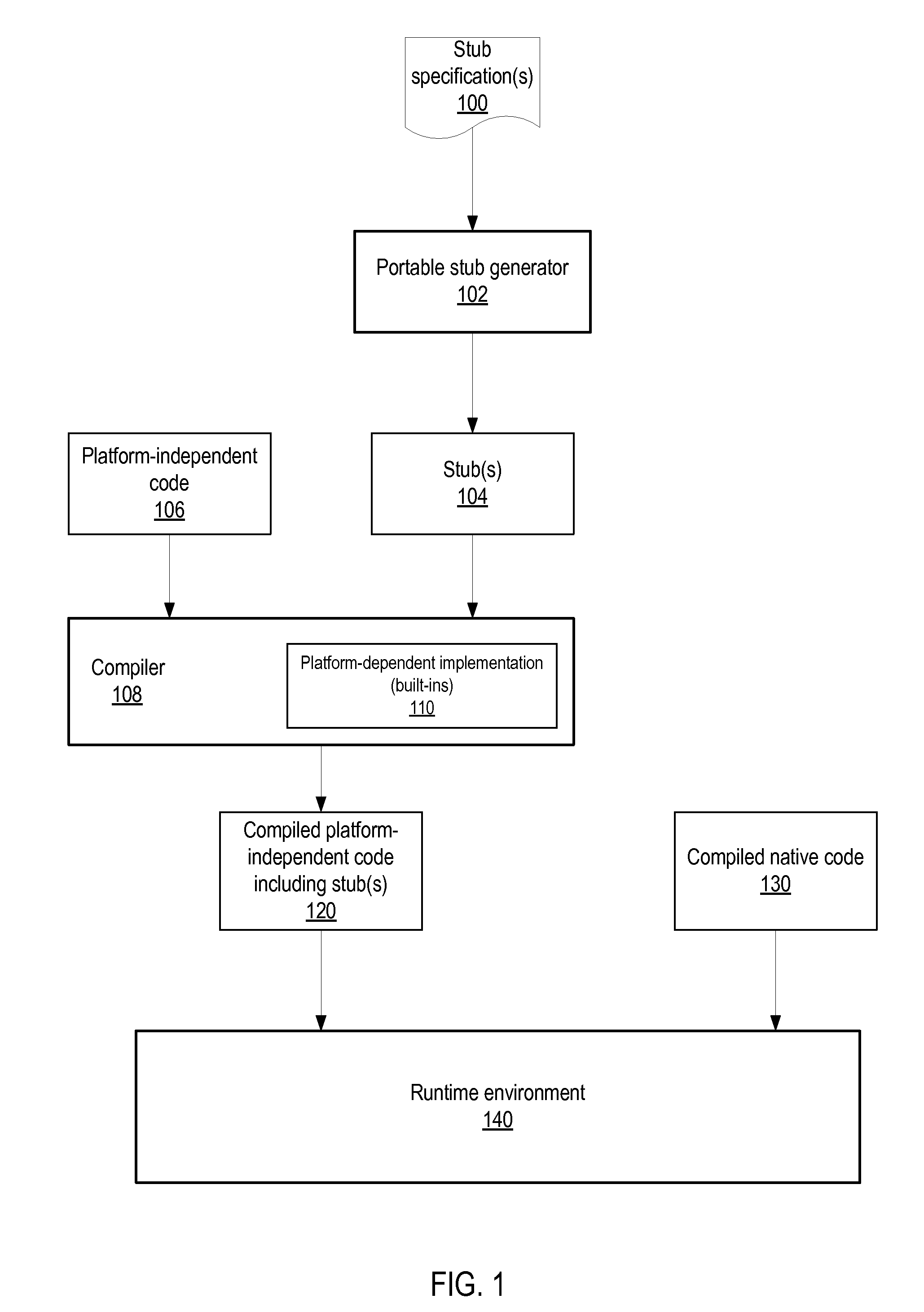
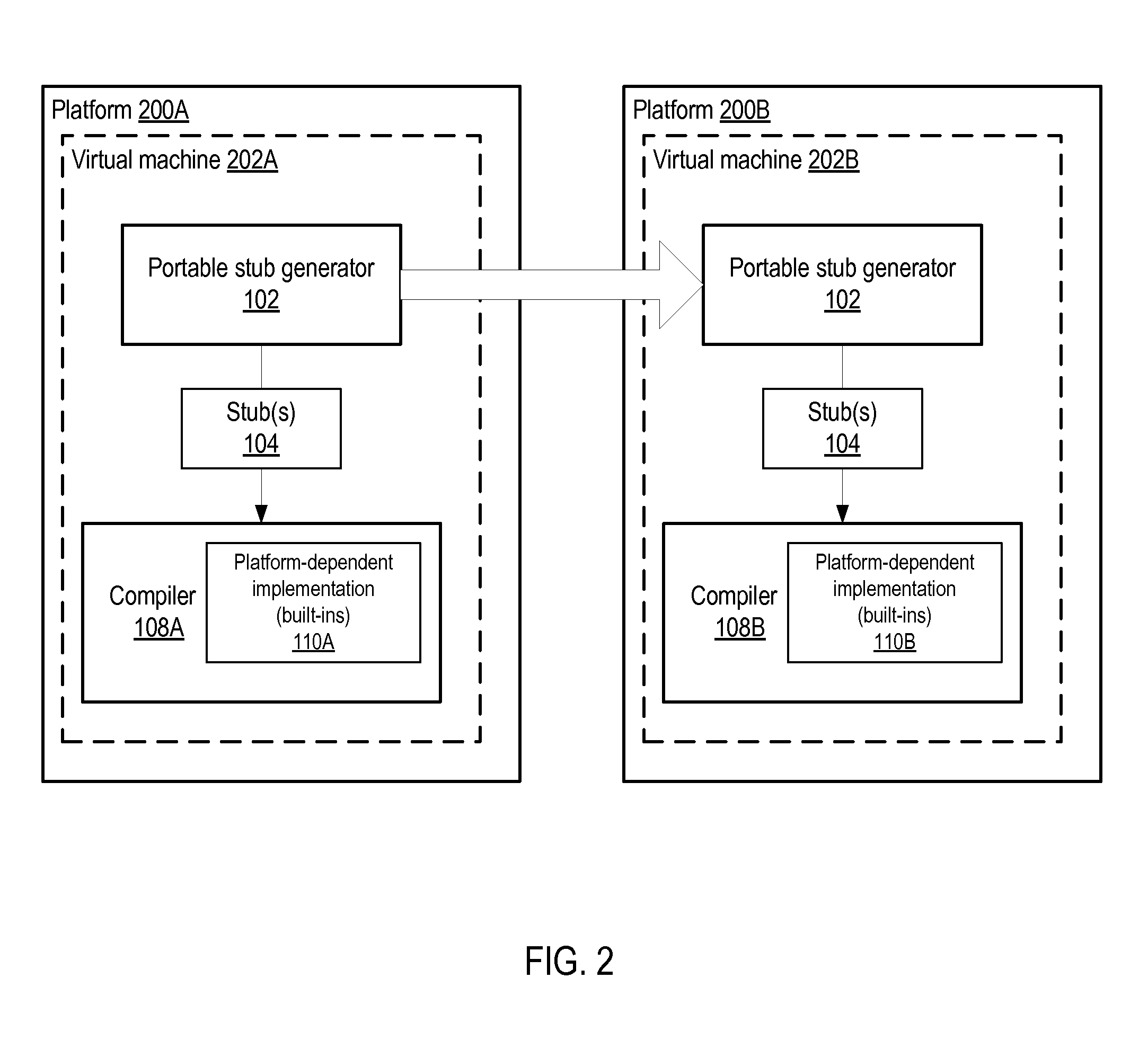
Method And Apparatus For Portable Stub Generation
Method and apparatus for automatically generating intermediate-level interfaces between program methods written in a platform-independent language and program methods written in a native language. A portable stub generator generates stubs in an intermediate, tokenized internal representation. The stub generator is portable across platforms as the stubs it generates are not platform-specific. In addition, the generated stubs are available to the compiler at intermediate compilation stages rather than at the backend compilation stage, and thus may be optimized together with the rest of the platform-independent code, and also may be inlined. The portable stub generator may be directed at virtual machine environments. An exemplary virtual machine environment in which the stub generator may be implemented is the Java™ Virtual Machine (JVM). In JVMs, Java™ is the platform-independent language, and Java™ bytecode the tokenized internal representation. In a JVM, the stubs may be generated in accordance with Java™ Native Interface (JNI).
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Multiple-core processor with hierarchical microcode store
ActiveUS7743232B2Operational speed enhancementDigital computer detailsMulti-core processorInstruction set
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
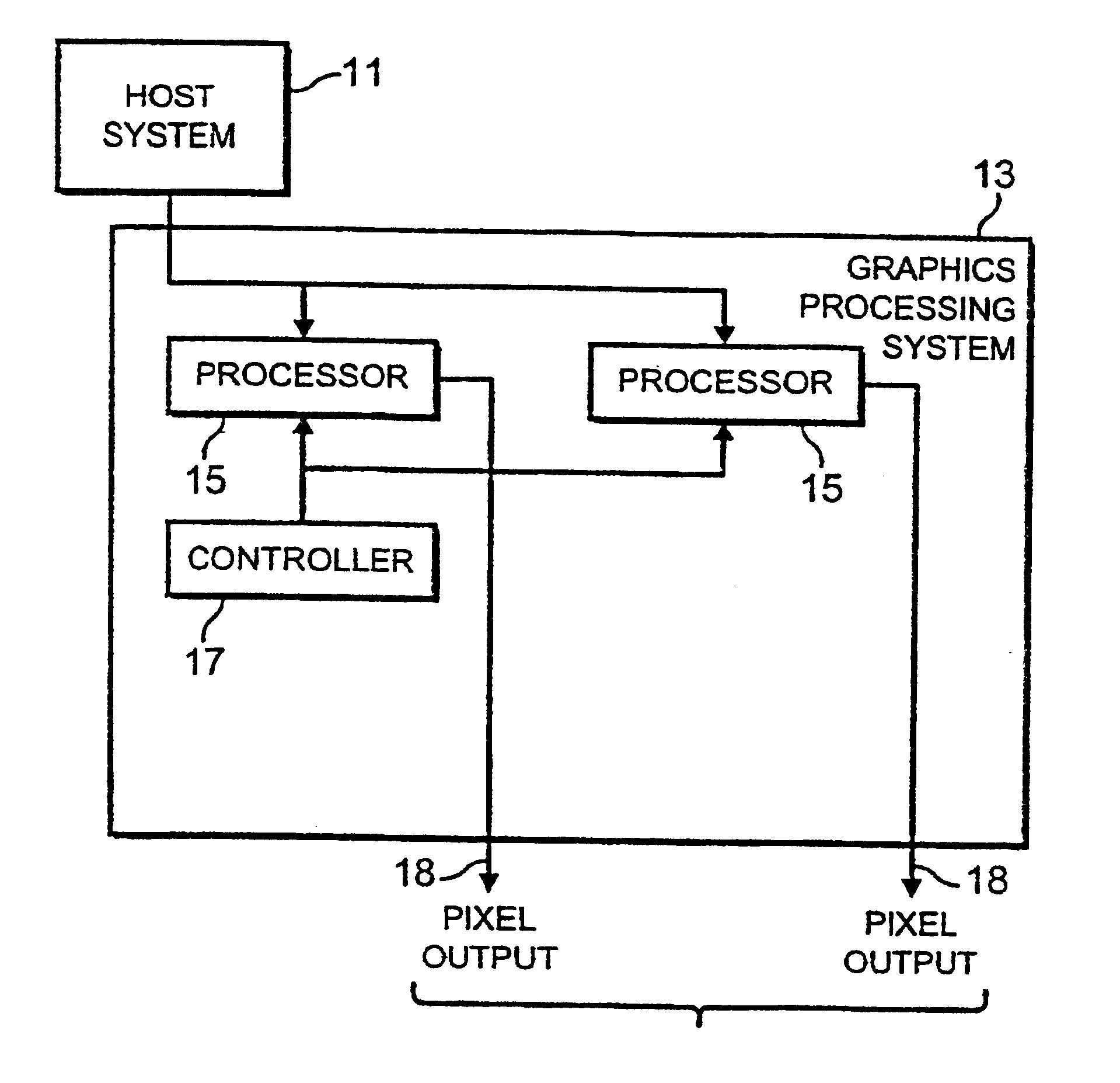
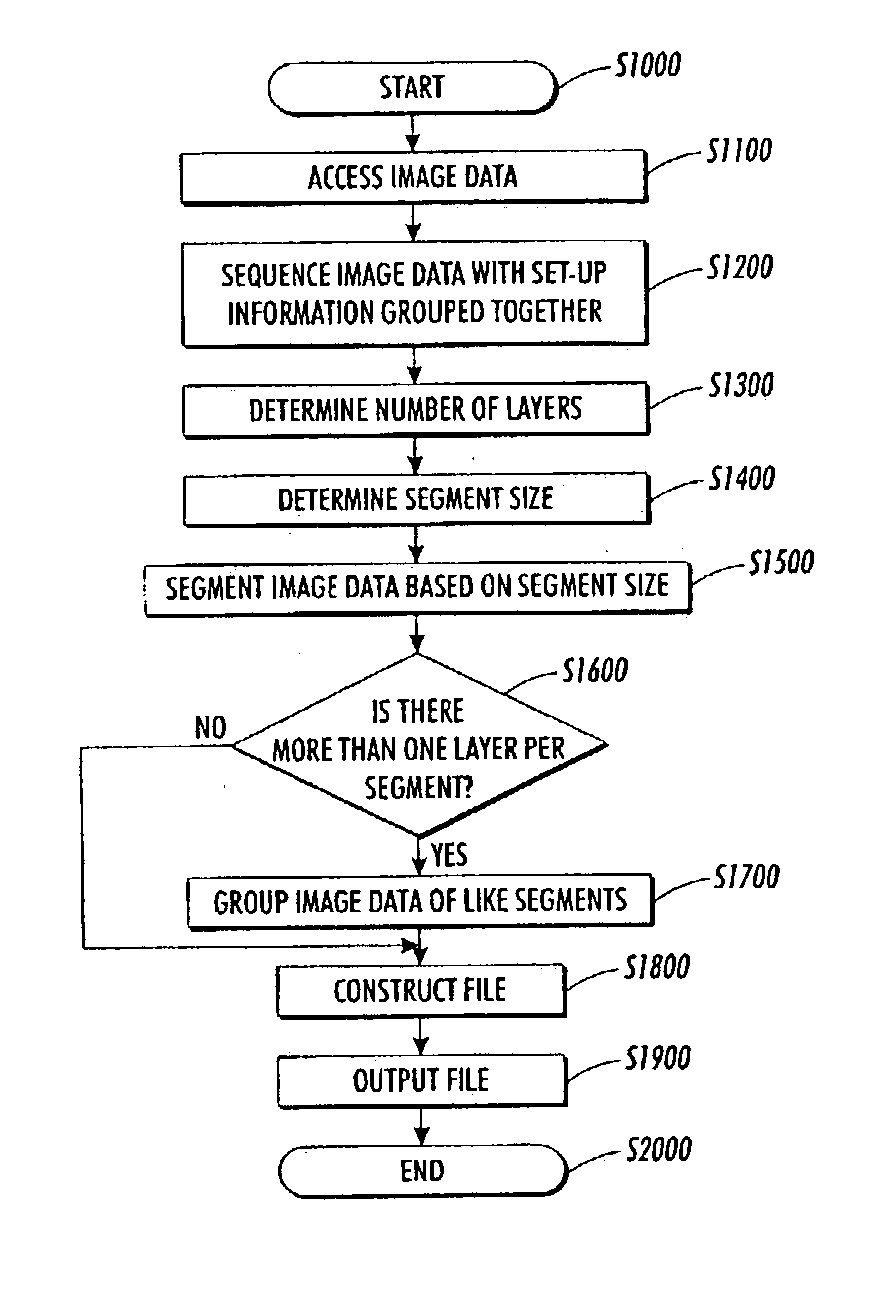
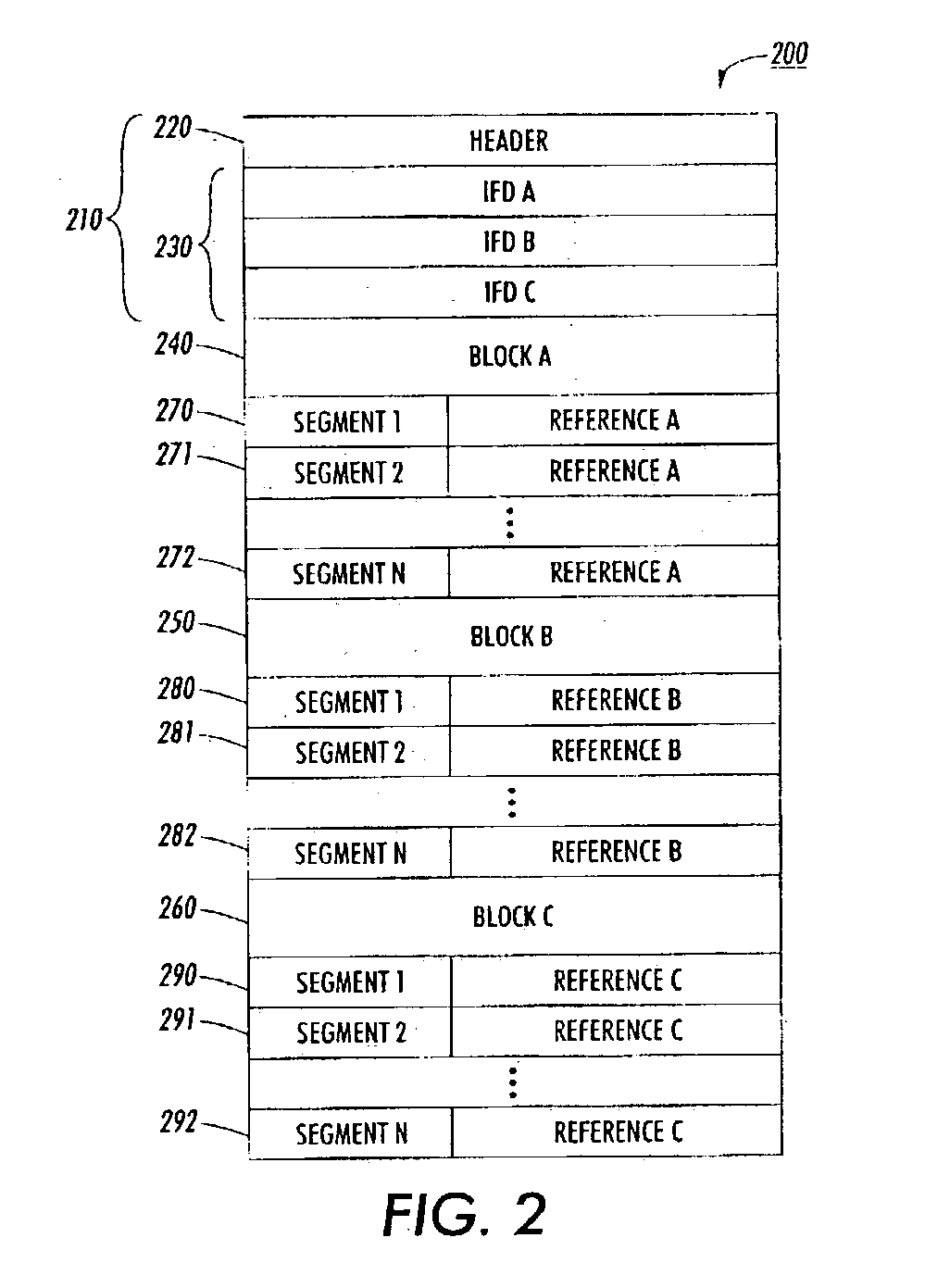
Methods and systems for structuring a raster image file for parallel streaming rendering by multiple processors
InactiveUS20040150840A1Operational speed enhancementDigitally marking record carriersGratingComputer graphics (images)
Structuring a raster image data file includes accessing image data containing set-up information and image data, determining a structure of the image data, sequencing contents of the image data file such that different parts of the set-up information are grouped together, segmenting the image data, and constructing an output image data file. The structure of image data may include one or more layers. The set-up information may be sequenced to precede the image data. Therefore, segmented image data can be distributed to more than one processor and sequentially processed and reproduced. This results in shortening the printing time.
Owner:XEROX CORP
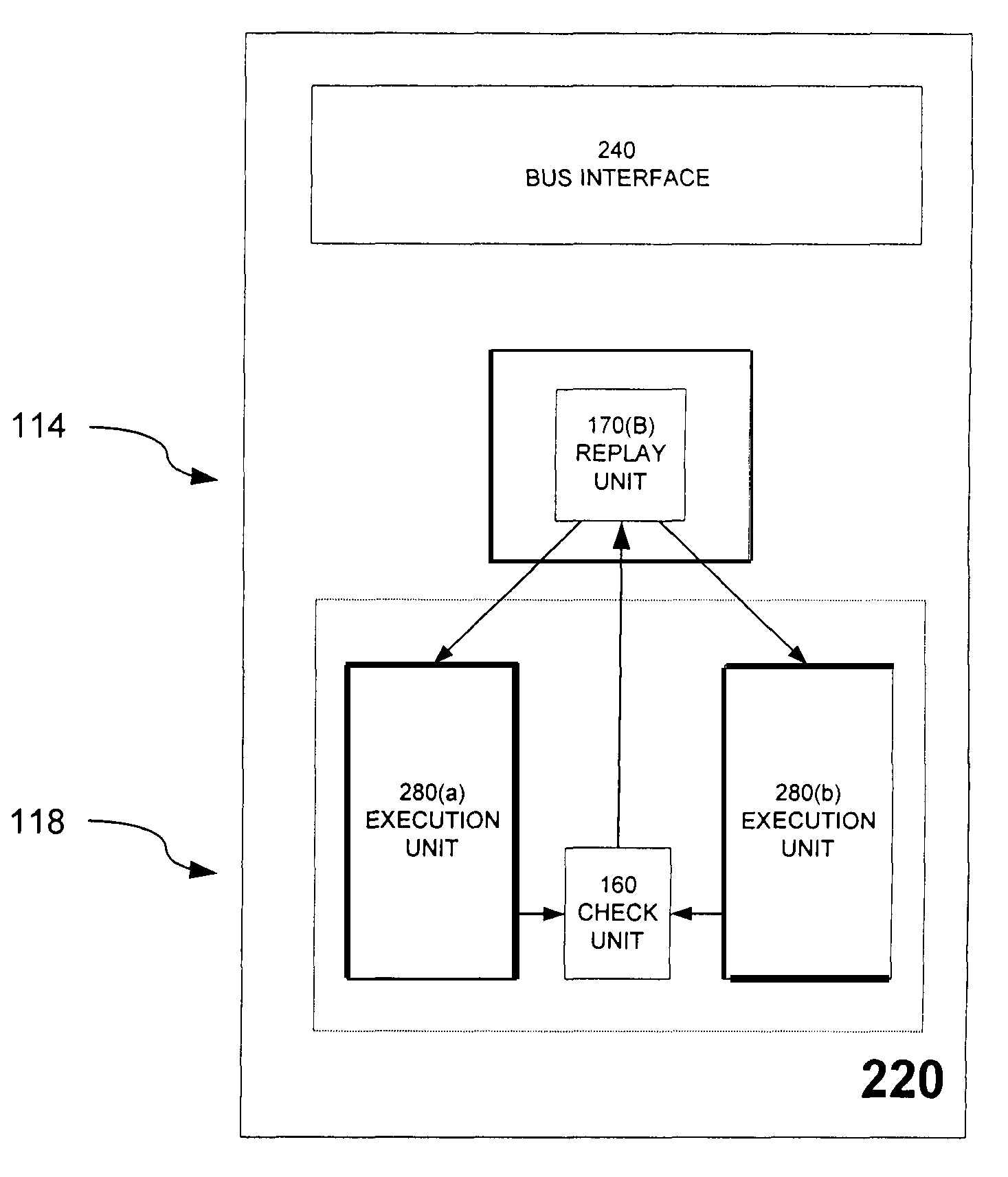
Replay mechanism for correcting soft errors
InactiveUS7340643B2Soft errorOperational speed enhancementError detection/correctionSoft errorParallel computing
A processor is provided that implements a replay mechanism to recover from soft errors. The processor includes a protected execution unit, a check unit to detect errors in results generated by the protected execution unit, and a replay unit to track selected instructions issued to the protected execution unit. When the check unit detects an error, it triggers the replay unit to reissue the selected instructions to the protected execution unit. One embodiment of the replay unit provides an instruction buffer that includes pointers to track issue and retirement status of in-flight instructions. When the check unit indicates an error, the replay unit resets a pointer to reissue the instruction for which the error was detected.
Owner:INTEL CORP
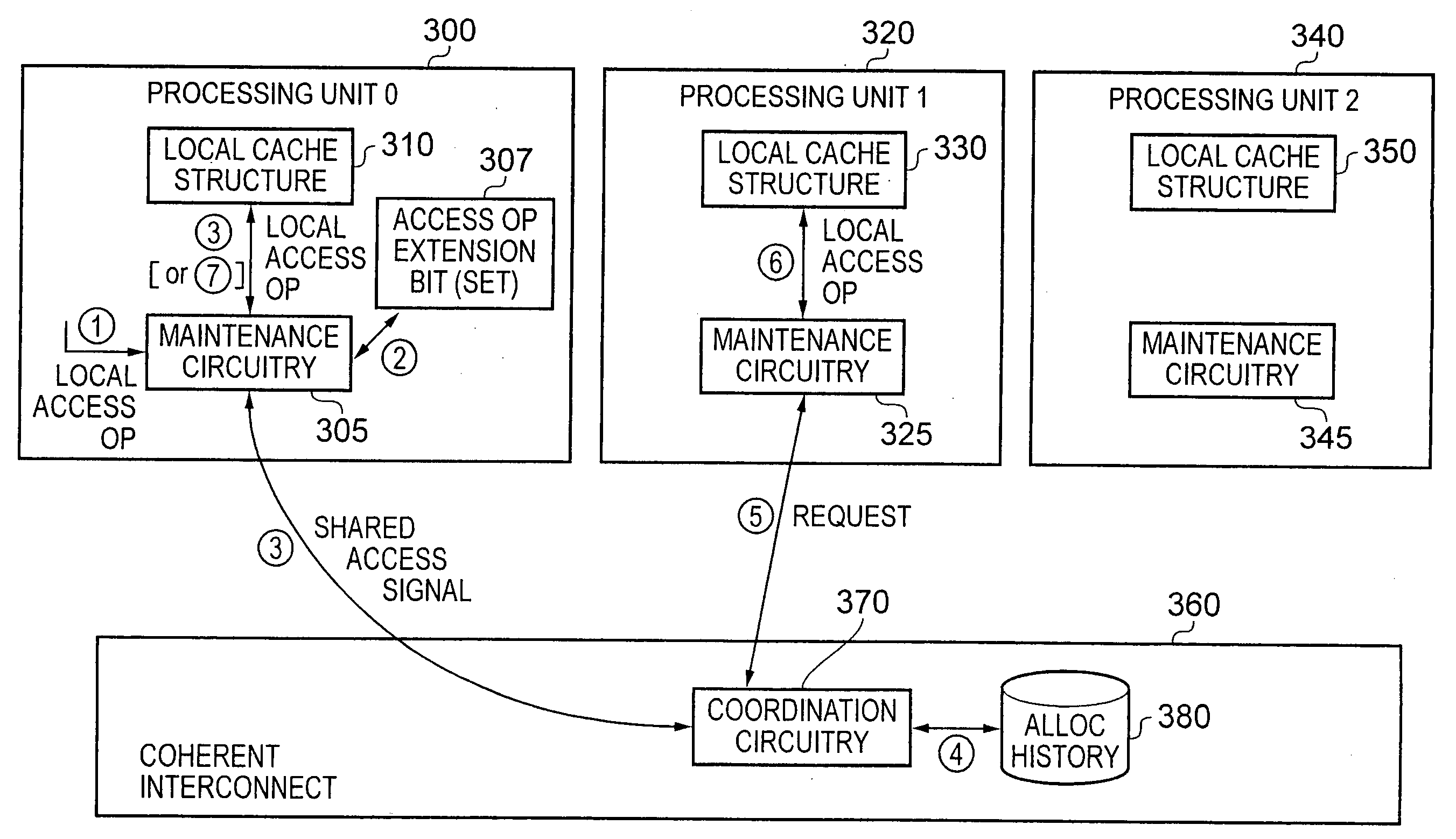
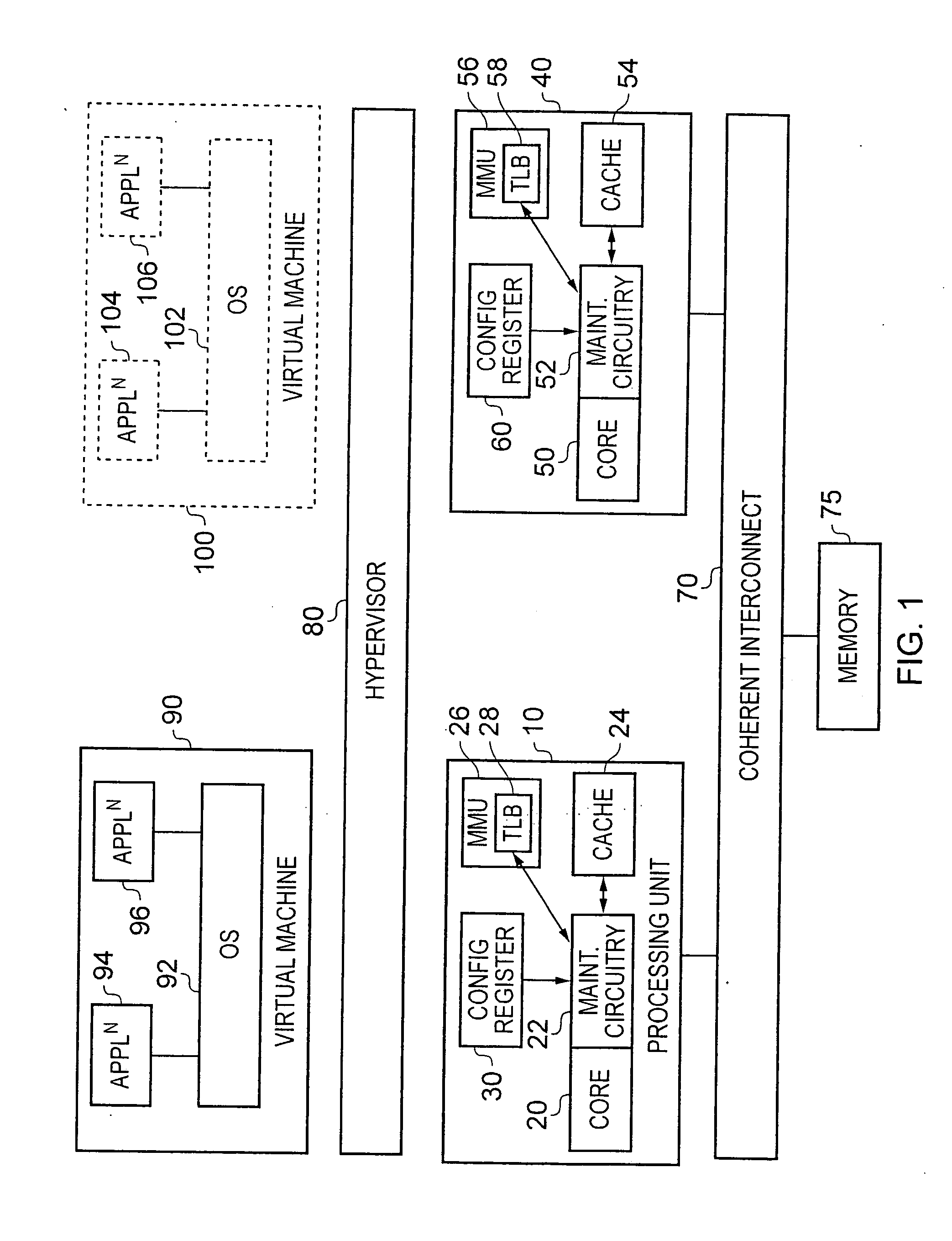
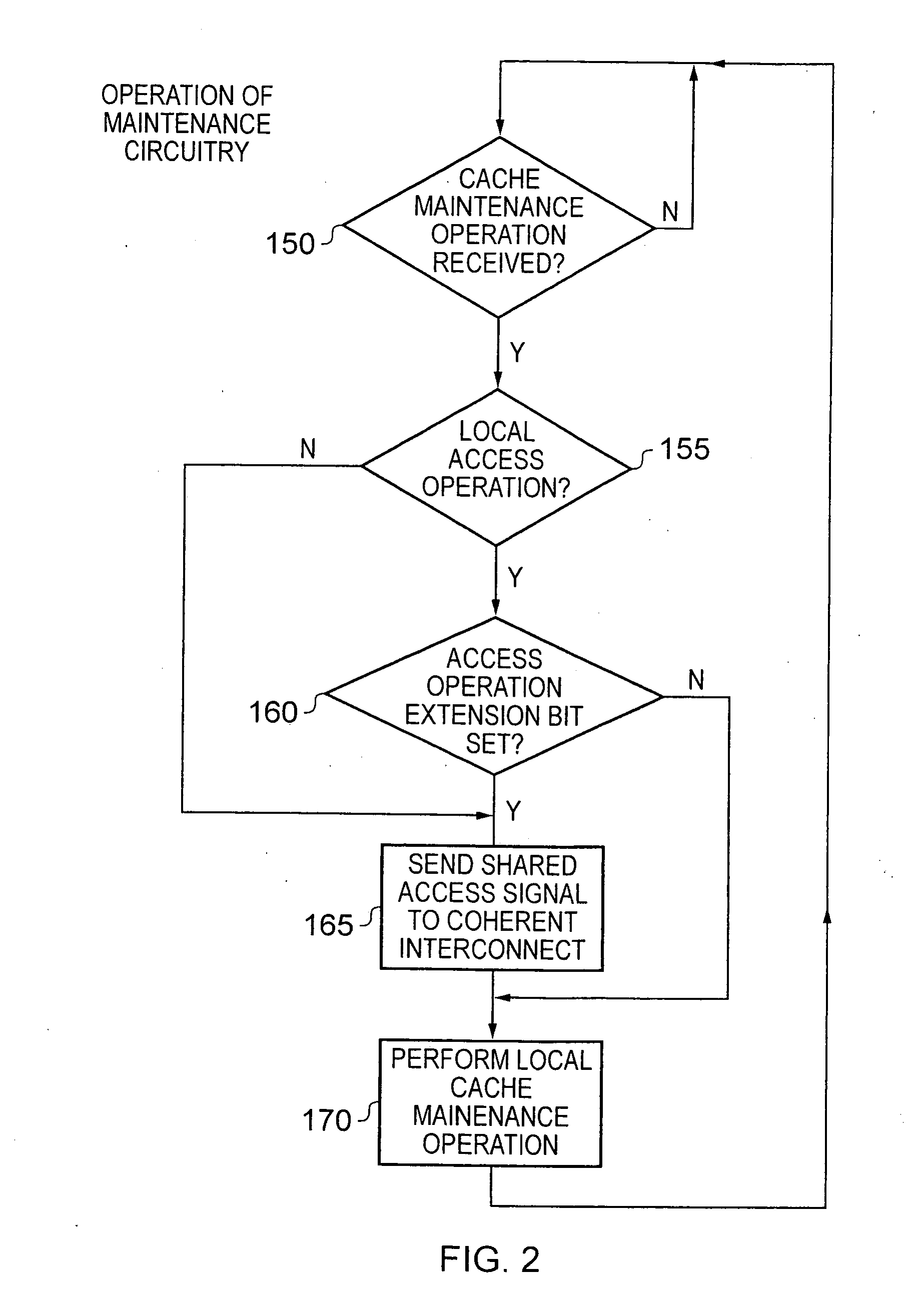
Apparatus and method for handling access operations issued to local cache structures within a data processing apparatus
ActiveUS20110314224A1Reduce decreaseImprove performanceOperational speed enhancementProgram synchronisationOperational systemLocal structure
An apparatus and method are provided for handling access operations issued to local cache structures within a data processing apparatus. The data processing apparatus comprises a plurality of processing units each having a local cache structure associated therewith. Shared access coordination circuitry is also provided for coordinating the handling of shared access operations issued to any of the local cache structures. For a shared access operation, the access control circuitry associated with the local cache structure to which that shared access operation is issued will perform a local access operation to that local cache structure, and in addition will issue a shared access signal to the shared access coordination circuitry. For a local access operation, the access control circuitry would normally perform a local access operation on the associated local cache structure, and not notify the shared access coordination circuitry. However, if an access operation extension value is set, then the access control circuitry treats such a local access operation as a shared access operation. Such an approach ensures correction operation even after an operating system and / or an application program are migrated from one processing unit to another.
Owner:ARM LTD
Popular searches
Physical realisation Concurrent instruction execution Single instruction multiple data multiprocessors Digital storage Energy efficient computing Memory systems Unauthorized memory use protection Analogue secracy/subscription systems Special data processing applications Machine execution arrangements
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com