Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
132 results about "Version code" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cache management system utilizing cascading tokens
InactiveUS6691137B1Data processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMagnetic tapeParallel computing
A data storage system, employing cache and base storage, assigns an "anywhere" token to each data object received for storage, whether the object is stored in cache or base storage. The anywhere token contains the latest metadata for the data object and includes at least a version code. If a data object is stored in base storage, the data object is assigned a "base" token with the same value as its anywhere token. These "cacading" tokens are available for use in tracking functions such as cache grooming, de-staging data to base storage, and processing cache miss events. All tokens are stored in a token database. For each data object, the token database lists its anywhere token and base token. If the storage system experiences a cache failure, normal storage operations are halted until the cache is repaired. Then, the controller implements a replacement token database. Namely, the controller accesses base storage to retrieve tokens of all data objects lost from cache. Using these base tokens, the controller populates a replacement token database, inserting the retrieved base tokens as both base and anywhere token for each data object lost from cache. Then, the replacement token database is used to the exclusion of the previous token database. With this procedure, the newly created token database accurately represents the contents of tape and cache. This avoids any danger of unknowingly recalling down-level data objects from tape, where their current counterpart data objects were stored on cache but lost in the cache failure.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method for selective software rollback
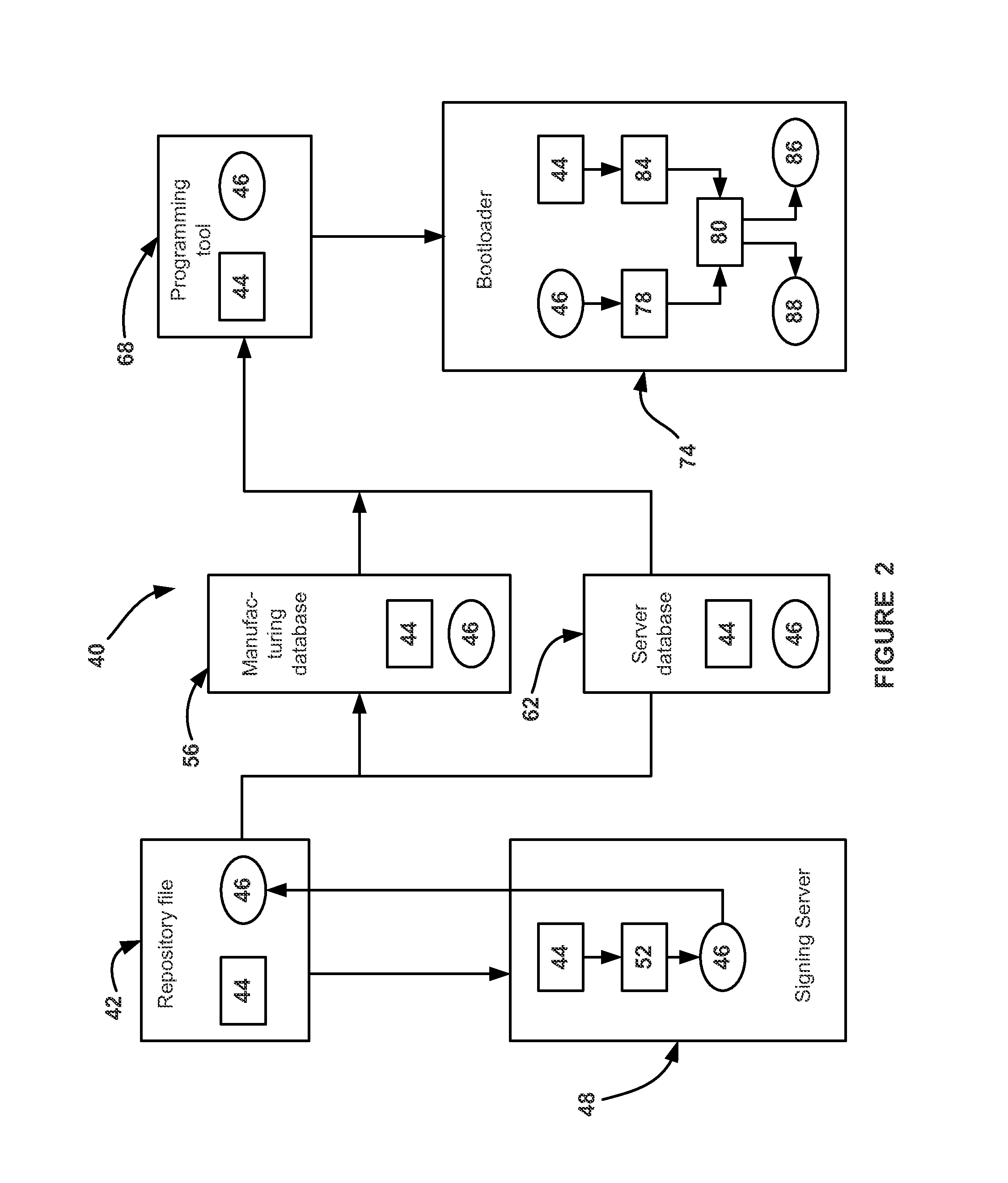
ActiveUS20140075197A1User identity/authority verificationDigital data protectionCode distributionVersion code
A system and method for validating a software file to be installed into a controller. The method includes preparing the software file including assigning a software version code to the software file, assigning a security version code to the software file, and signing the software file with the software file version code and the security version code. The signed software file is presented to the controller for installing on the controller and the controller verifies the software file signature to determine if the software file is valid and the security version code is valid. The controller allows the software file to be installed in the controller if both the signed software file is valid and the security version code is valid.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
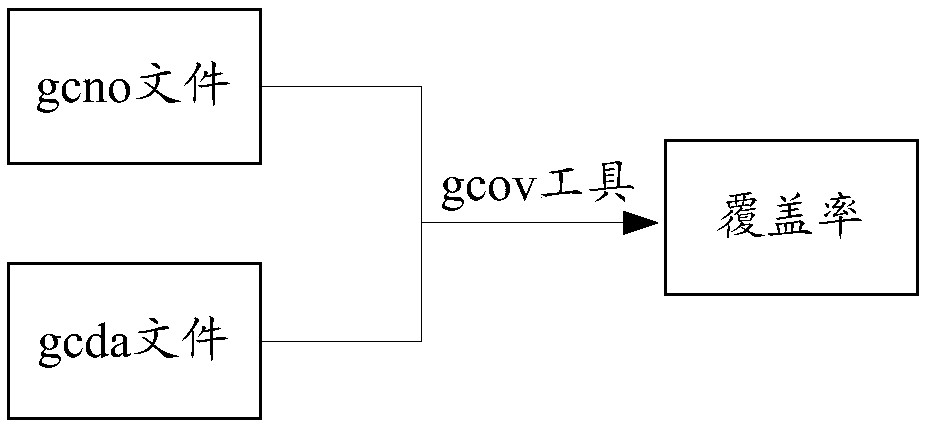
Statistical method and device for incremental coverage information
ActiveCN102722436AEasy accessImprove work efficiencySoftware testing/debuggingTest efficiencyDesign testing
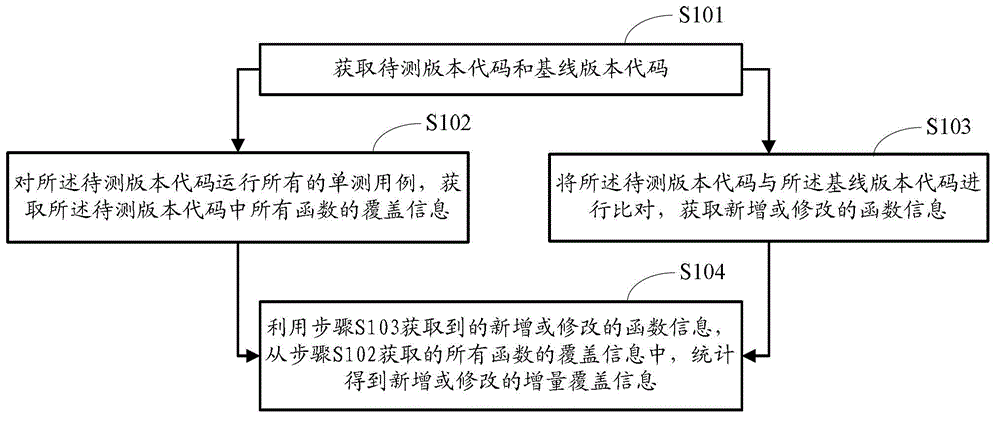
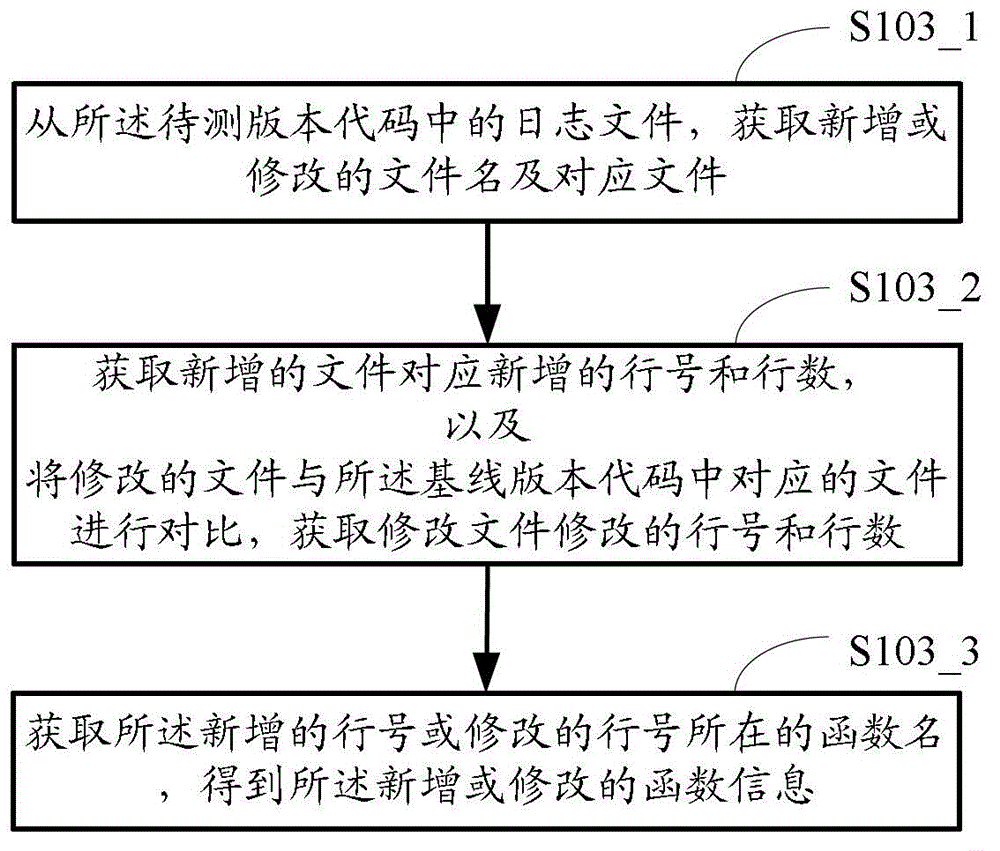
The invention provides a statistical method and a statistical device for incremental coverage information. The statistical method comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring a test version code and a baseline version code; S2, running all single test cases for the test version code, acquiring coverage information of all functions in the test version code, and comparing the test version code and the baseline version code so as to obtain newly-added or modified function information; and S3, acquiring newly-added or modified incremental coverage information from the coverage information of all the functions according to the newly-added or modified function information. Compared with the prior art, the statistical method and the statistical device can automatically count the incremental information of a test version, so that a tester can quickly acquire the incremental coverage information and pertinently design a test case according to the incremental coverage information, thus improving the test efficiency and the test accuracy and reducing the missing test.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
Apparatus and method for parallel processing
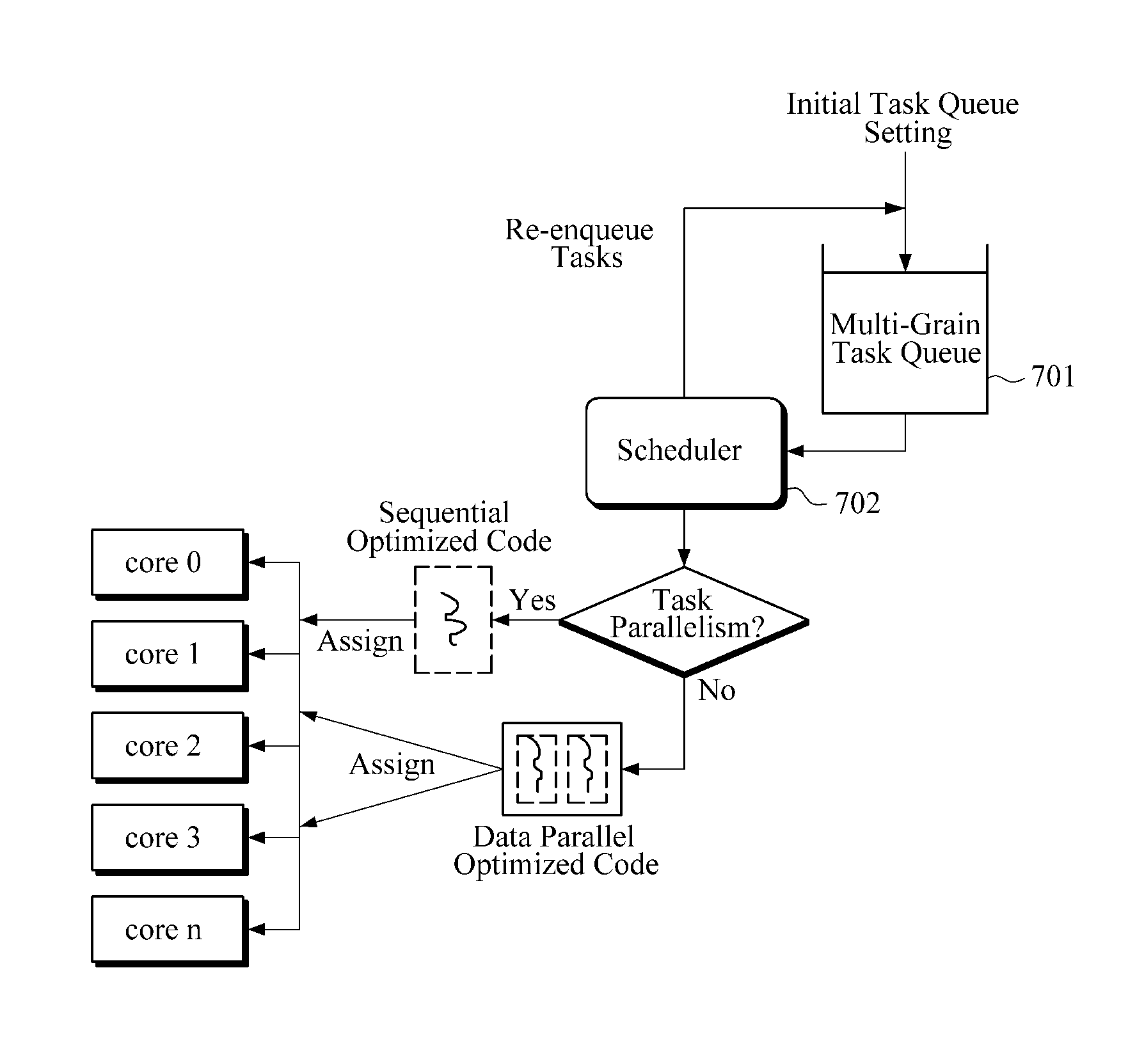
InactiveUS20110161637A1Operational speed enhancementDigital computer detailsParallel processingDegree of parallelism
An apparatus and method for parallel processing in consideration of degree of parallelism are provided. One of a task parallelism and a data parallelism is dynamically selected while a job is processed. In response to a task parallelism being selected, a sequential version code is allocated to a core or processor for processing a job. In response to a data parallelism being selected, a parallel version code is allocated to a core a processor for processing a job.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
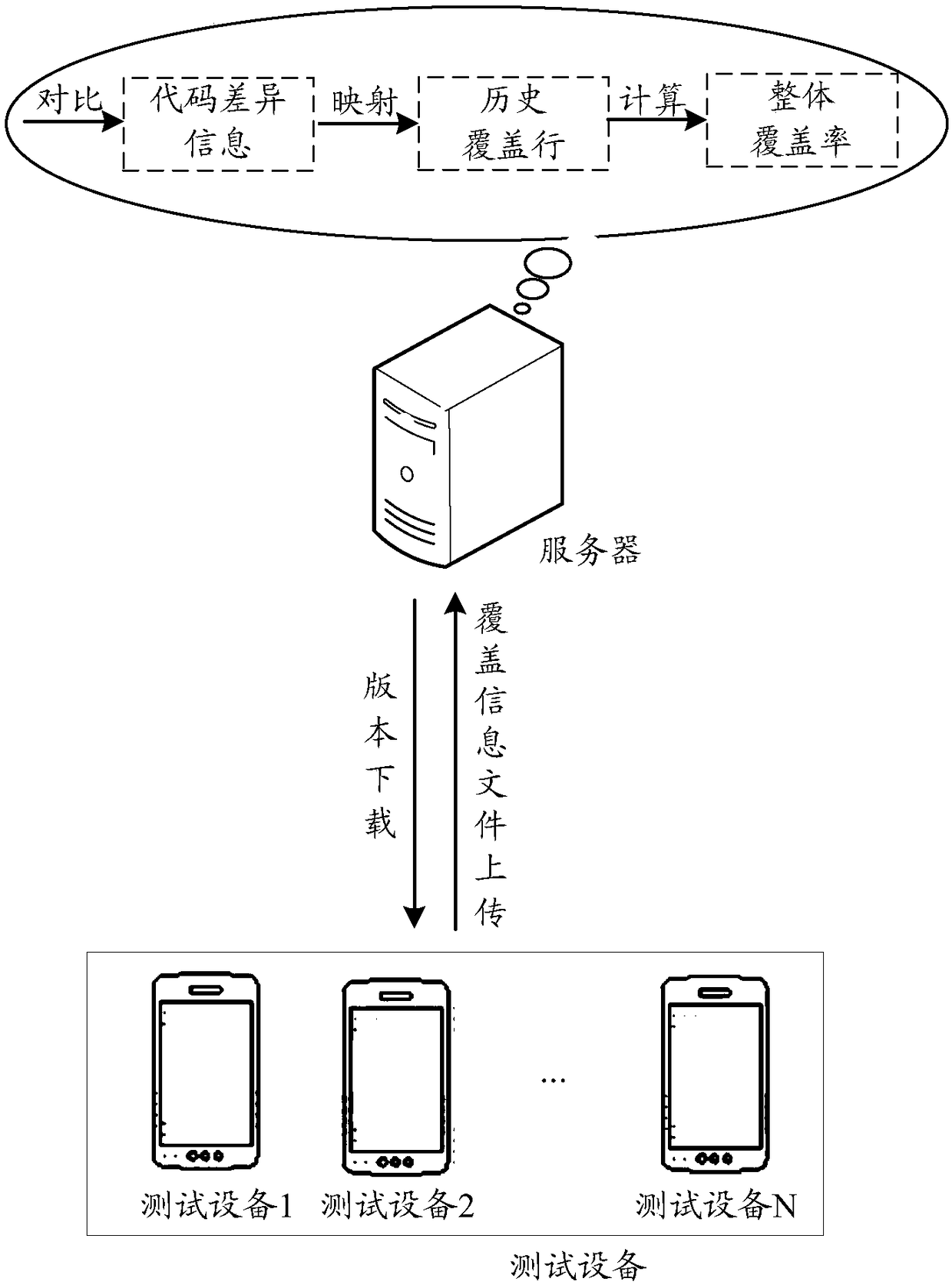
Coverage rate testing method and device and storage equipment
The embodiment of the invention discloses a coverage rate testing method and device and storage equipment. The coverage rate testing method comprises the steps of obtaining a first coverage information file obtained after a first version code of an application program is tested, and obtaining a second coverage information file obtained after a second version code of the application program is tested, wherein the first coverage information file comprises a code coverage row of the first version code, and the second coverage information file comprises a code coverage row of the second version code; comparing the first version code with the second version code to obtain code difference information of the first version code and the second version code; according to the code difference information, mapping the code coverage row of the first version code to the second version code to obtain a history coverage row of the second version code; calculating the overall coverage rate of the application program according to the history coverage row of the second version code and the code coverage row of the second version code.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
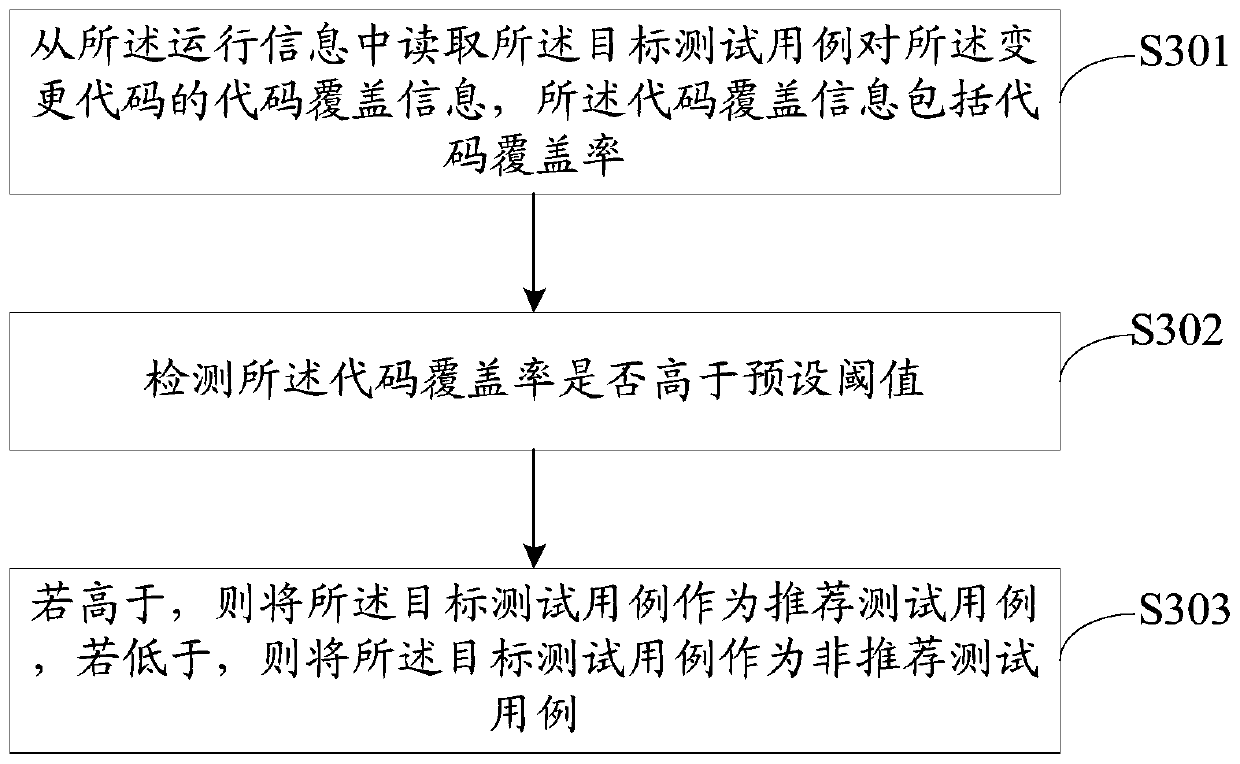
Test case recommendation method, device, equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN110413506AReduce workloadAccurate judgmentSoftware testing/debuggingParallel computingCode coverage
The invention relates to software testing, and discloses a test case recommendation method, a device, equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of reading a current version code and a previous version code corresponding to a to-be-tested application program, and obtaining a change code between the two version codes through a version comparison tool; executing the target test case and obtaining running information of a current version code in a case execution process; reading code coverage information of the target test case on the change code from the running information,judging whether the target test case is used as a recommended test case or not; because the change code is firstly determined,, and then code coverage rate detection is performed on the change code through a target test case corresponding to the previous version code; whether the target test case can be used as the recommended test case is determined according to the detection result, so that whether the currently used test case meets the actual test requirement can be accurately judged after the system source code is changed, and the workload of development testers is reduced.
Owner:PINGAN PUHUI ENTERPRISE MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Method and device for obtaining code coverage rate
PendingCN106201863AEasy to understandImprove Acquisition AccuracySoftware testing/debuggingCoverage ratioParallel computing
The invention discloses a method for obtaining a code coverage rate. The method comprises the following steps: sending the unique identification of an original version code and the unique identification of a revised version code to a server for the server to obtain the original version code and the revised version code according to the unique identification of the original version code and the unique identification of the revised version code; according to the original version code and the revised version code, obtaining total code coverage rate data and difference code information, and feeding back the total code coverage rate data and the difference code information to the client side; and receiving the total code coverage rate data and the difference code information, and obtaining difference code coverage rate data according to the total code coverage rate data and the difference code information. The invention also discloses a device for obtaining the code coverage rate. By use of the method and the device, the acquisition accuracy of the code coverage rate is improved, and convenience for development personnel to increase the test case of the code coverage rate is improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU PINWEI SOFTWARE
Code change-based mobile application test script automatic maintenance method
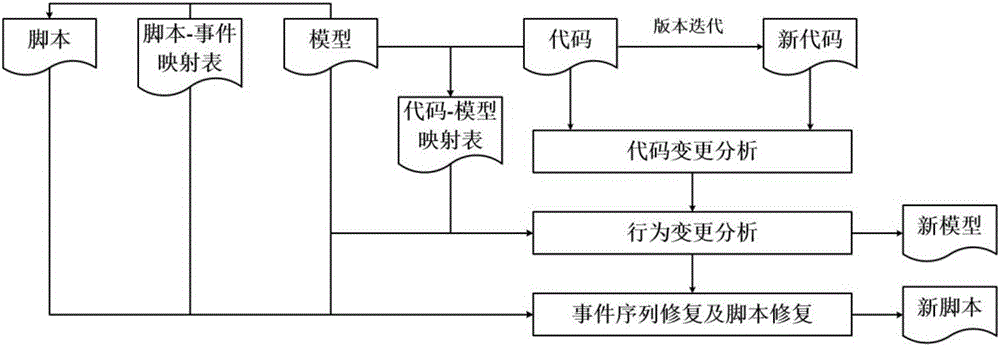
ActiveCN106021103AReduce the burden onImprove versatilitySoftware testing/debuggingTest scriptFiltration
The invention proposes a code change-based mobile application test script automatic maintenance method. The method comprises the following steps of 1, performing code change analysis: analyzing changed codes in codes with new and old versions, and performing filtration to obtain code change resulting in change of an interface behavior model; 2, performing model change analysis: performing behavior change analysis on the model by utilizing a corresponding relationship between the codes and elements in the model to obtain behavior change information and model change information, and applying the change to the model so as to obtain a new model; and 3, performing script change repair: abstracting a script statement as an event sequence, and repairing and updating the event sequence corresponding to a script according to the behavior change information and the model change information to obtain a new script that can be normally used. The event sequence in the influenced script is automatically maintained and updated to finally obtain the script that can be applied to the new version so as to reduce the script maintenance burden of test personnel.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
A method and a system for remote online upgrading of a data acquisition and transmission instrument terminal
InactiveCN109101261ASolve the problem that the remote online upgrade cannot be doneDoes not affect normal workError preventionSoftware engineeringData acquisitionComputer terminal
The invention is applicable to the technical field of software upgrading, and provides a remote on-line upgrading method and a system of a data acquisition and transmission instrument terminal. The method comprises the following steps: a server sends an upgrading command to the data acquisition and transmission instrument terminal; the server sends an upgrading command to the data acquisition andtransmission instrument terminal; the data acquisition and transmission instrument terminal judges whether the upgrade command contains the new version information; if yes, the answer server downloadsthe upgrade code file data and sets the upgrade flag bit by the data acquisition and transmission instrument terminal; otherwise, a notification message without upgrading is sent to the server; afterdownloading the upgrade code file data, the terminal of the data acquisition and transmission instrument softly starts, runs the bootloader program, reads the flag bit, and if the upgrade flag bit isread, the upgrade code file data is overwritten with the low version code file data, otherwise, the original user application program is executed. The invention solves the problem that the terminal of the data acquisition and transmission instrument cannot be upgraded remotely and online, and although the terminal is in the upgrading mode, the normal operation of the data acquisition and transmission instrument terminal is not affected.
Owner:SHENYANG WARE ENVIRONMENT TECH LTD
Device and method for determining coverage rate information of increment codes
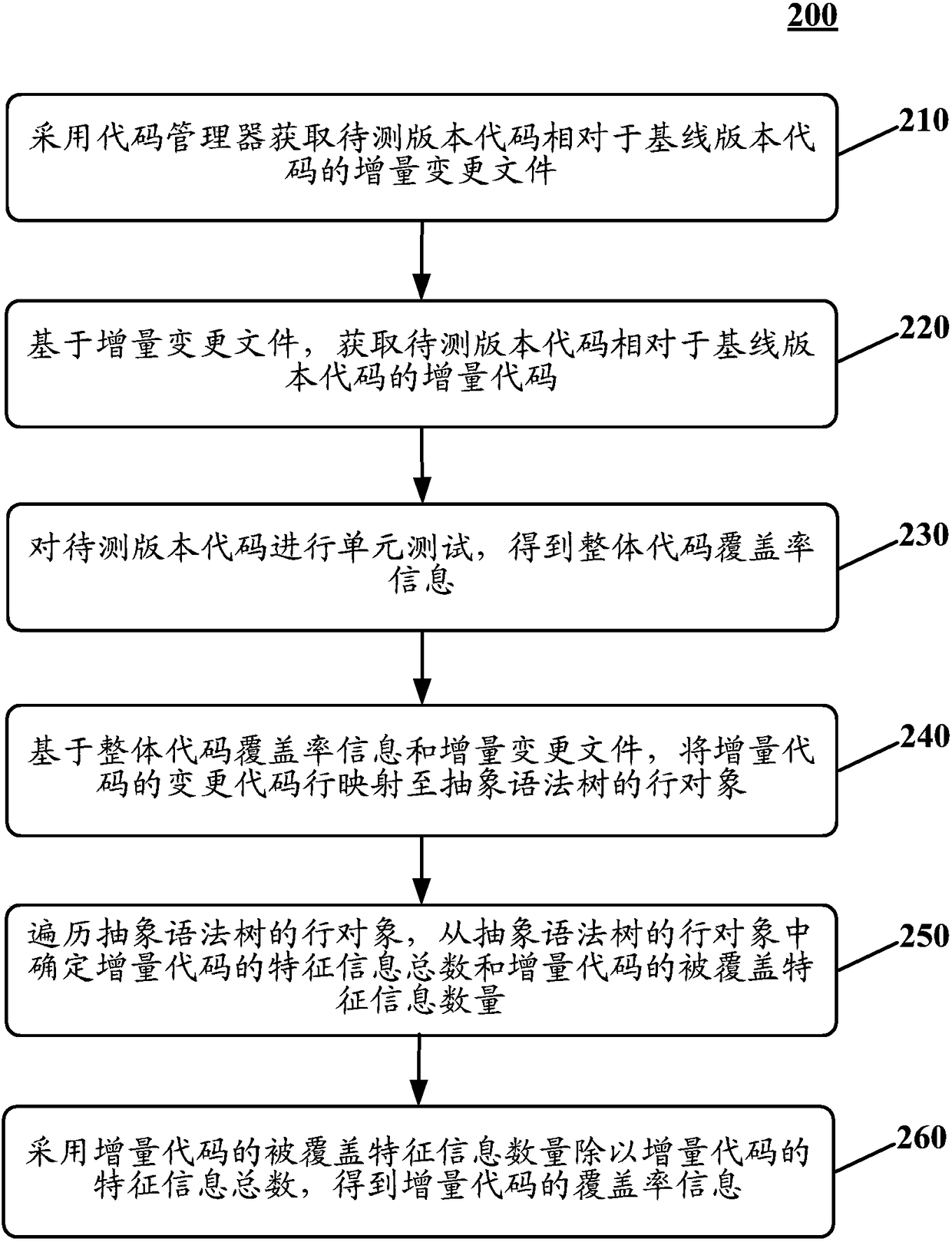
ActiveCN108197036AImprove efficiencyImprove accuracySoftware testing/debuggingInformation quantityCode coverage
The invention discloses a device and method for determining coverage rate information of increment codes. The method includes: adopting a code management device for acquiring increment change files ofto-be-tested version codes relative to base line version codes; acquiring the increment codes of the to-be-tested version codes relative to the base line version codes on the basis of the increment change files; subjecting the to-be-tested version codes to unit testing to obtain integral code coverage rate information; on the basis of the integral code coverage rate information and the incrementchange files, mapping change codes of the increment codes to row objects of an abstract syntax tree; performing traversal of the row objects of the abstract syntax tree, and determining characteristicinformation amount of the increment codes and covered characteristic information quantity of the increment codes from the row objects of the abstract syntax tree; dividing the characteristic information amount of the increment codes by the covered characteristic information quantity of the increment codes to obtain the coverage rate information of the increment codes. By adoption of the method, increment code testing efficiency and accuracy are improved.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
Data processing apparatus and control method for a data processing apparatus
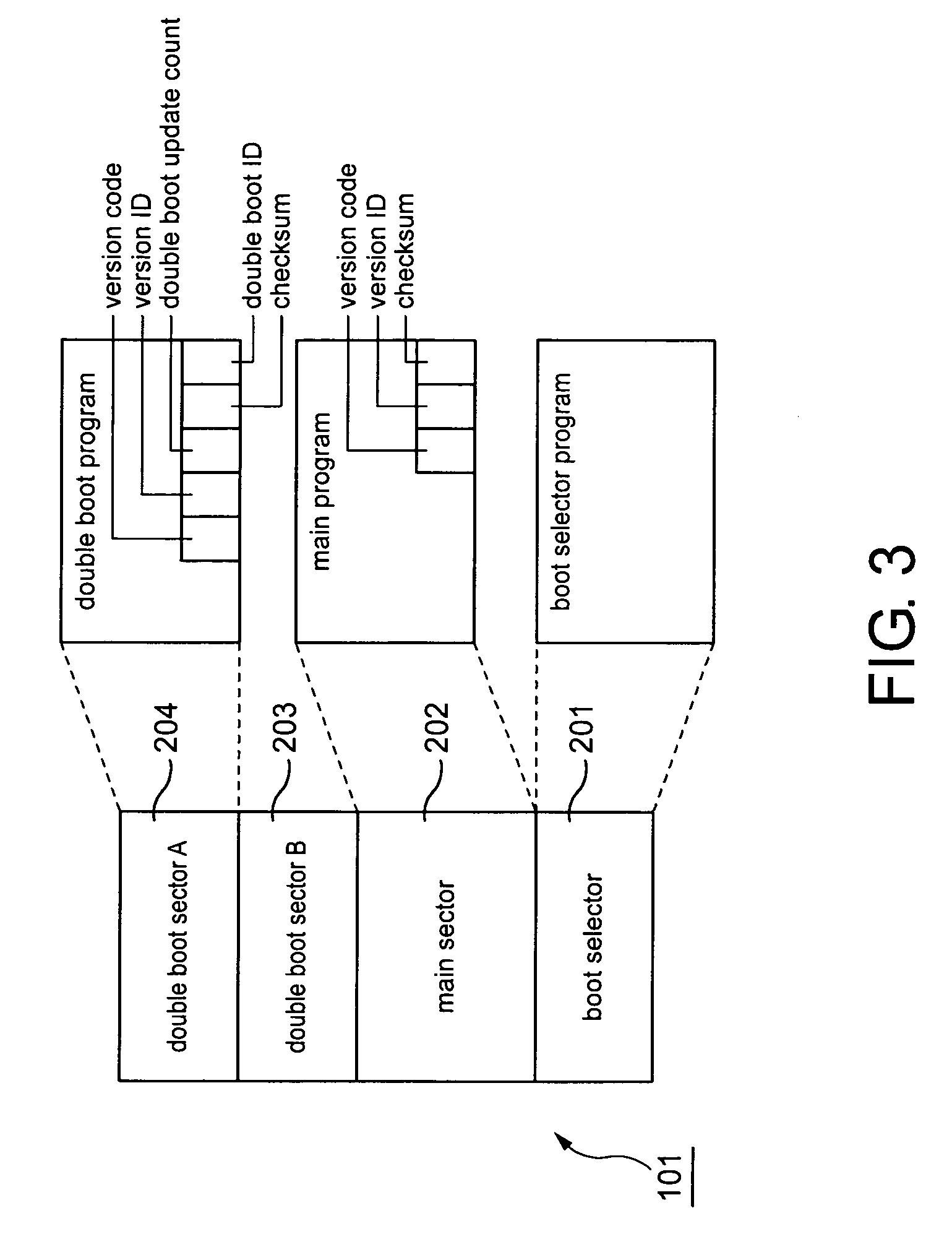
InactiveUS20060184781A1Easily and reliably verifiedDigital computer detailsMemory systemsBoot sectorVersion code
A data processing apparatus comprising: flash ROM that can communicate with a CPU, the flash ROM comprises a boot sector that stores a boot selector program, a first boot sector and a second boot sector each storing a boot program that is selectively called by the boot selector program. The CPU executes the boot selector program to select the first boot sector or the second boot sector each storing a boot program to be executed. The CPU executes the selected boot program to verify a version code stored in a main sector and the selected boot sector. The CPU executes a main program when the version code in the main sector matches the version code in the selected boot sector.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Regression test case determination method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
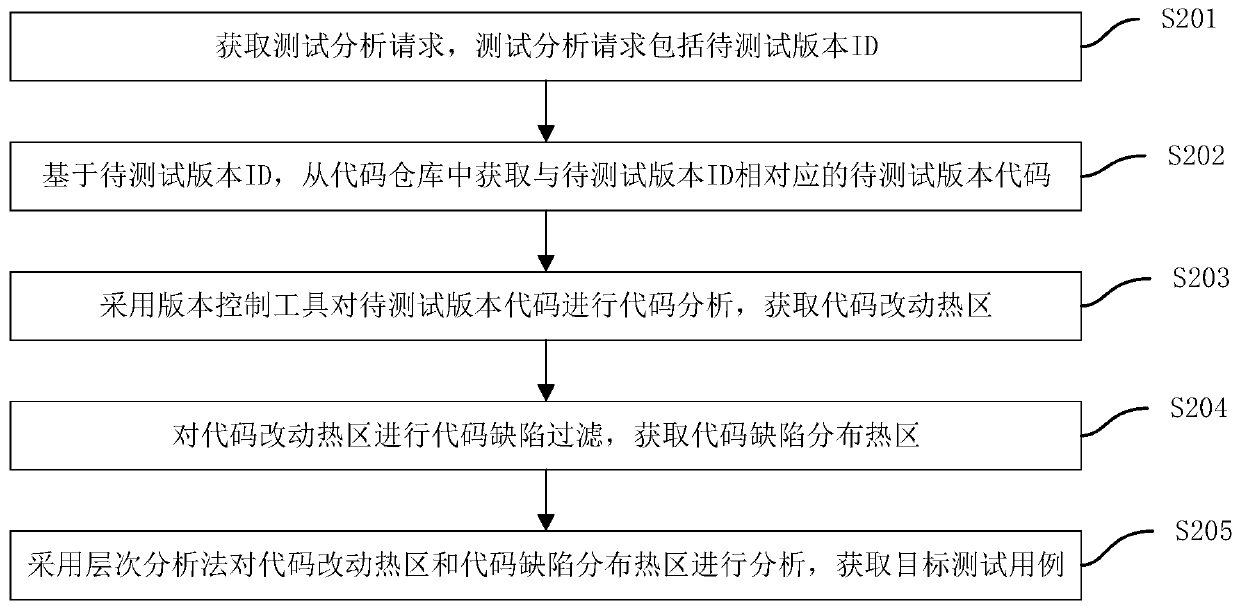
PendingCN110109820AEnsure software qualityReduce duplicationSoftware testing/debuggingRegression testingHot zone
The invention discloses a regression test case determination method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a test analysis request, wherein the test analysis request comprises a to-be-tested version ID; based on the to-be-tested version ID, obtaining a to-be-tested version code corresponding to the to-be-tested version ID from a code warehouse; carrying out code analysis on the version code to be tested by adopting a version control tool to obtain a code change hot area; performing code defect filtering on the code modificationhot area to obtain a code defect distribution hot area; and analyzing the code change hot zone and the code defect distribution hot zone by adopting an analytic hierarchy process to obtain a target test case. According to the method, when the regression test is carried out based on the target test case subsequently, the repeated redundancy of the workload can be effectively reduced, unnecessary manpower waste is also reduced, and the software quality of the regression test is guaranteed.
Owner:ONE CONNECT SMART TECH CO LTD SHENZHEN
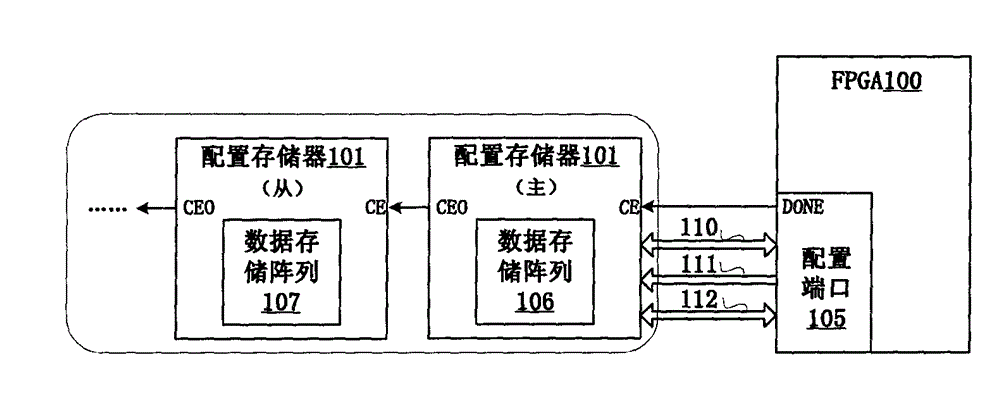
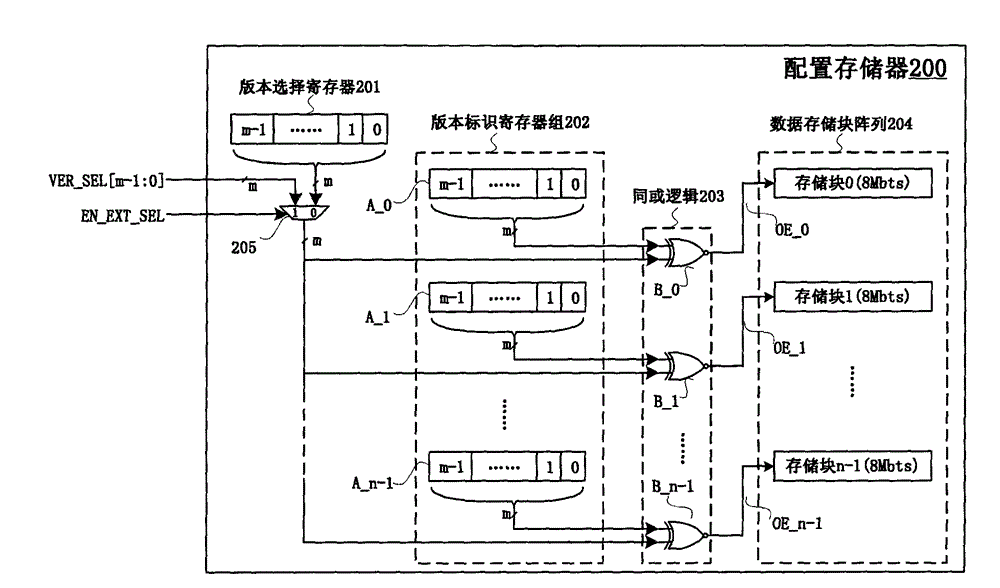
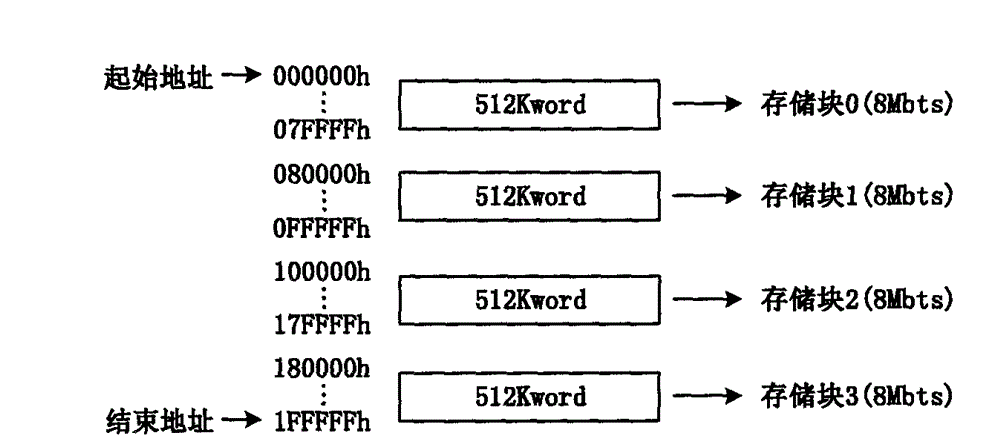
Multi-version code stream storage circuit architecture for configuration memory dedicated for FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array)
ActiveCN102866865AImprove debugging efficiencyImprove test efficiencyInput/output to record carriersProcessor registerParallel computing
The invention relates to a multi-version code stream storage circuit architecture for a configuration memory dedicated for an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array). The multi-version code stream storage circuit architecture comprises a version selecting register 201, a version identification register group 202, XNOR logic 203, a data storage block array 204 and a multi-channel selector 205. According to the multi-version code stream storage circuit architecture, a data storage block array which can only store design code streams of one version in the traditional architecture is replaced with the data storage block array which can store the design code streams of multiple versions, and the selection of the code stream version can be carried out in a manner that a port is selected by using an external version or a control bit is selected by using an internal programmable version. With the adoption of the multi-version code stream storage circuit architecture for the configuration memory dedicated for the FPGA, disclosed by the invention, a single design code stream can be stored in one data storage block, and a design code stream with larger capacity can be stored by spanning multiple data storage blocks and even can be stored by spanning multiple configuration memories which are cascaded; and the configuration memory dedicated for the FPGA, which adopts the circuit architecture, supports online system multi-version code stream storage, so that the flexibility of FPGA-oriented configuration applications is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
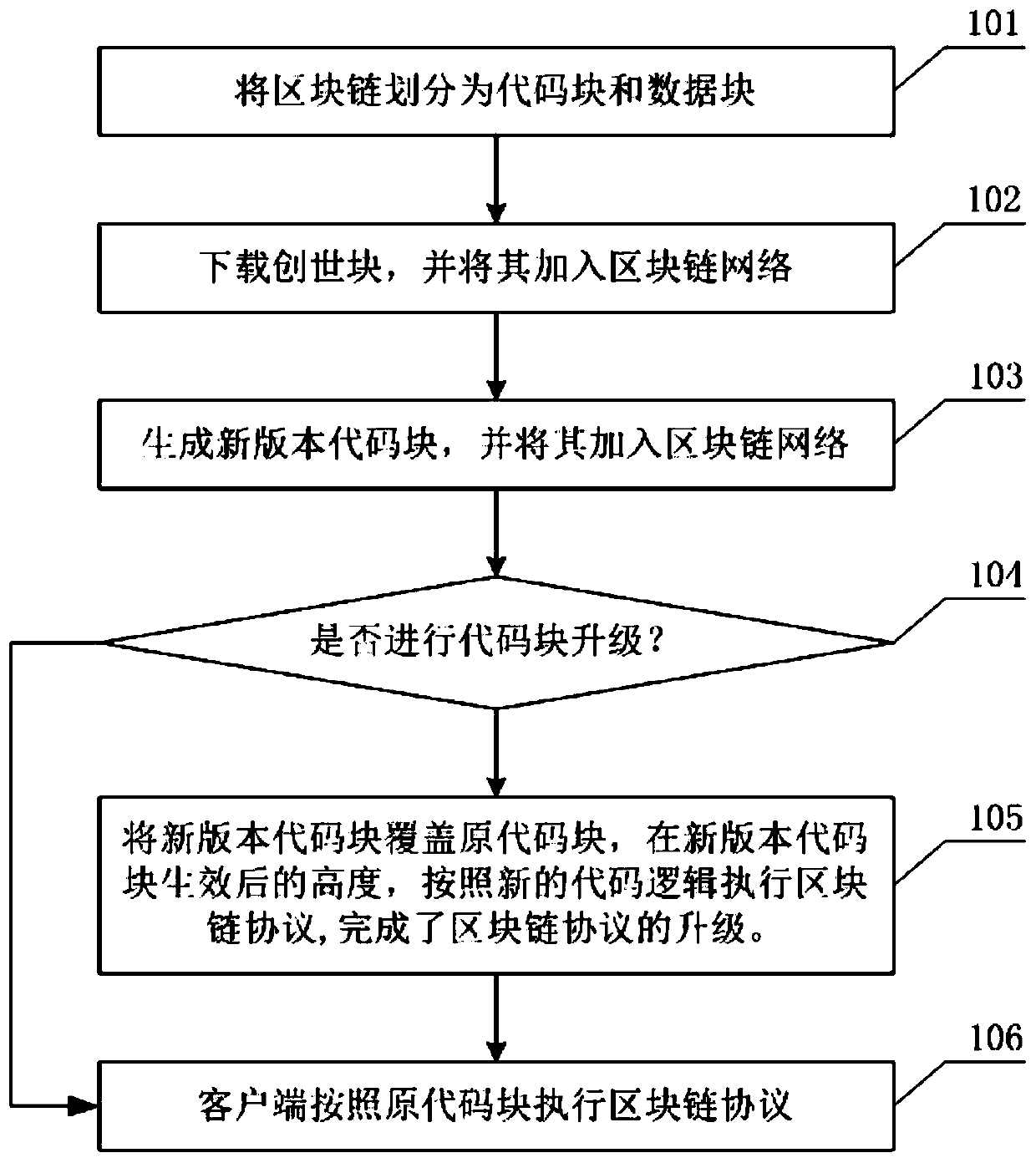
Block chain code block independent upgrading method and device and electronic equipment
ActiveCN109992285AEasy to develop and upgradeSimple designVersion controlSoftware deploymentCoding blockIndependent function
The invention relates to a blockchain code block independent upgrading method, a block on a blockchain comprises a code block and a data block, and the method comprises the following steps: writing adownloaded provenance block code into a local computing device, executing the provenance block code, and adding the provenance block code into a blockchain network; linking the new version code blockcontaining the upgrade code after a consensus process; and if the new version code block takes effect, executing the block chain protocol according to the new code logic to complete the upgrading of the block chain protocol. The invention further provides a block chain code block independent upgrading device, the code blocks with relatively independent functions on the block chain are independently upgraded, and development and upgrading of the block chain technology are facilitated; the upgrading process of the protocol is carried out on the chain, the voting process is public and transparent, and each user obtains the voting right with the equal proportion of rights and interests held by the user and is very fair for each user; the new version code does not need to consider and process the old version code logic, the design is simple, the logic is clear, maintenance is convenient, and testing is convenient.
Owner:杭州秘猿科技有限公司
Software code fragment history tracing method
ActiveCN110532019AEfficient miningEfficient analysisSoftware maintainance/managementCode snippetControl system
The invention discloses a software code fragment history tracing method, which comprises the following steps of: 1) for each target software project, acquiring code submission information of each version of the project from a Git version control system to obtain a Git library of the project, and acquiring Issue data of the project from a Jira defect tracing system; 2) for a to-be-queried code snippet, firstly scanning the Git library of the corresponding project, positioning the class file of the version to which the code snippet belongs, and then obtaining all versions of the class file; secondly, constructing an abstract syntax tree AST for each version of code, and matching nodes of AST of adjacent versions to obtain related code fragments in the adjacent versions; and 3) comparing whether the code snippets are the same or not, if so, filtering out the code snippets of the next version, and finally, retaining the changed code snippets through filtering, and displaying the code submission information of the corresponding version and the related Issue information in a time axis manner.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Coverage rate testing method and device and storage equipment
ActiveCN110209568AGrasp the progress of the testGrasp the quality of the testSoftware testing/debuggingProgramming languageCode coverage
The embodiment of the invention discloses a coverage rate testing method and device and storage equipment. The coverage rate testing method comprises the steps of acquiring code difference informationand a mapping relation between a new version code and an adjacent historical version code; modifying the mapping relation according to the code difference information; mapping the code coverage lineidentifier of the historical version code into a code coverage line identifier in a new version code according to the modified mapping relationship to obtain a mapped code coverage line identifier ofthe historical version code; when a coverage rate acquisition instruction is received, integrating the code coverage line identifier of the new version code and the mapped code coverage line identifier of the historical version code; and obtaining the overall coverage rate of the code according to the integrated code coverage line identifier. According to the scheme, the overall coverage rate testof multi-version service codes can be supported.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Code detection method, device and electronic equipment
ActiveCN107368313AImprove detection efficiencyShorten the development cycleVersion controlSoftware testing/debuggingTerminal equipmentComputer terminal
The invention discloses a code detection method, a code detection device and electronic equipment. The code detection method is applied to terminal equipment. The method comprises the steps of detecting a triggering operation submitted for a new-version code file; generating code change information according to the detected triggering operation, wherein the code change information indicates a difference between the new-version code file and an old-version code file; carrying out format conversion on source code information of the new-version code file according to the format of the code change information to obtain code detection information, wherein the source code information is generated when a code in the new-version code file is executed; judging whether the code detection information includes the code change information; and if not, adopting uncontained code change information as to-be-detected information corresponding to the new-version code file. By use of the code detection method, the code detection device and the electronic equipment, the code development cost is effectively reduced and the code quality is beneficially improved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Method And System For Version Control In A Reprogrammable Security System
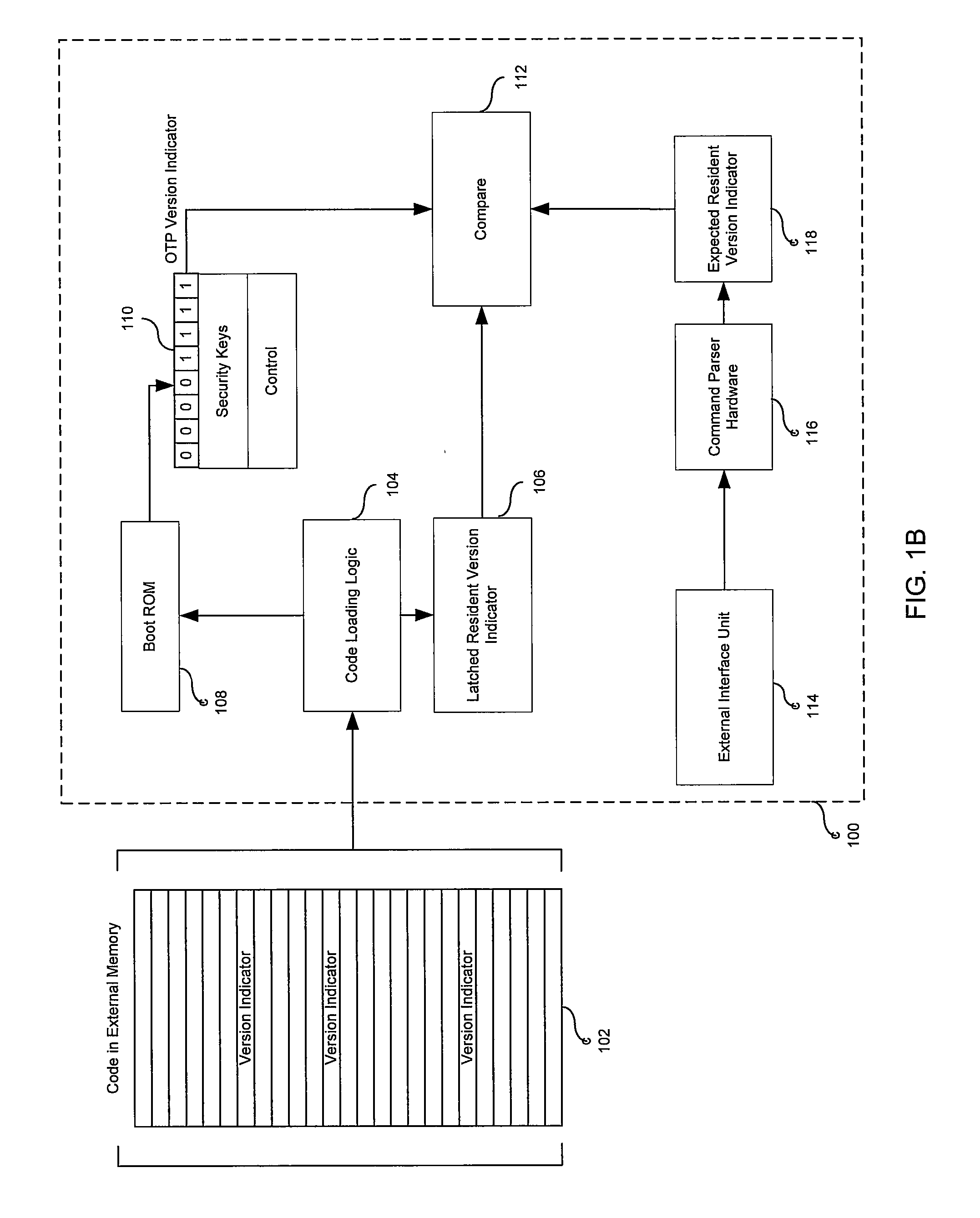
ActiveUS20080086517A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionOne time programmableSecurity system
Methods and systems for securing code in a reprogrammable security system are provided and may comprise detecting when a prior version of code is copied over a subsequent version of code. Operations within the system may be controlled based upon detection of the prior version of code. A unique version identifier may be associated with each successive version of code. The system may compare instances of unique version identifier from varied storage mechanisms on a device which may include flash memory, latch memory and one time programmable memory. The same instances of unique version identifier may be compared with a unique version identifier instance independently received from an external entity. When a comparison reveals a prior version of code copied over a subsequent version of code the system may conduct operations specified for a security breach.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Application interface rendering method and device
PendingCN110083426AReal-time rendering newSoftware engineeringExecution for user interfacesSoftware engineeringClient-side
The invention relates to an application interface rendering method and device. The method comprises the steps of obtaining interface data of a preset data structure specification; traversing interfaceelements in the interface data, and performing analyzing to obtain first identifiers and first parameters of the interface elements; converting the first identifier and the first parameter into a second identifier and a second parameter corresponding to the current client according to a preset conversion rule; and according to the second identifier and the second parameter, rendering the interface element on the current client to obtain an application interface. According to the technical scheme, a developer does not need to develop a plurality of client version codes, and real-time renderingand updating of the multi-terminal application interface can be achieved only by developing a set of UI data based on specifications. The user can experience the change of the interface without updating the version of the client.
Owner:无线生活(杭州)信息科技有限公司
Code comparison method, device and system during continuous integration
ActiveCN106919431AAccurate judgmentEasy to findSoftware engineeringProgram controlContinuous integrationDevelopment team
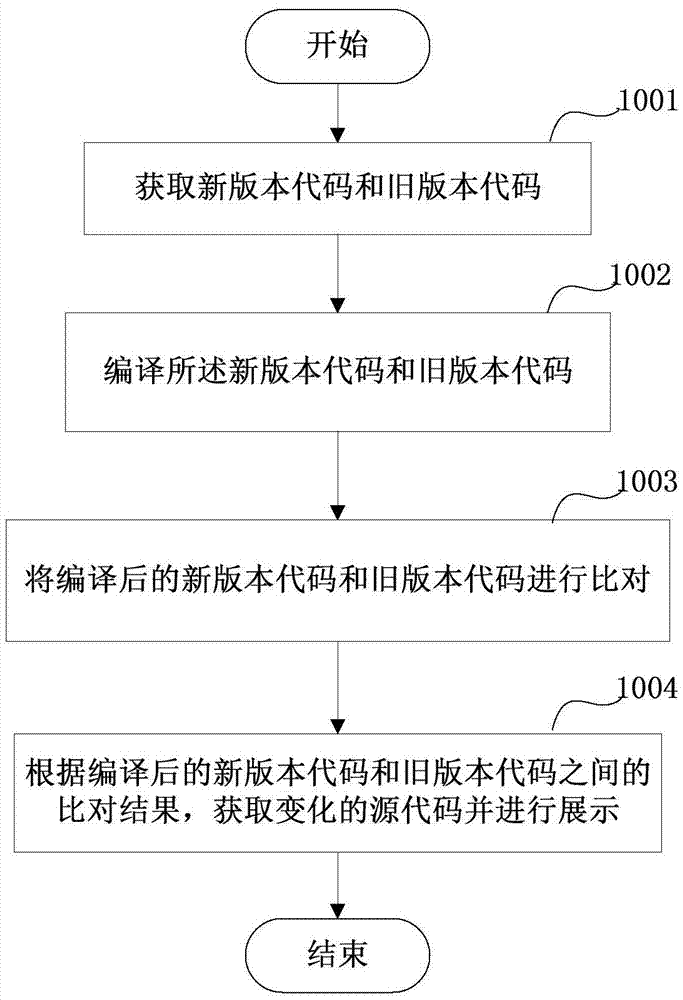
The invention relates to the field of information technology and discloses a code comparison method, device and system during continuous integration. The method comprises the steps that a new version code and an old version code are acquired; the new version code and the old version code are compiled; the new version code and the old version code obtained after compilation are compared; and a varying source code is acquired and displayed according to the comparison result of the new version code and the old version code obtained after compilation. Through the code comparison method, device and system, comparison of the new version code and the old version code can be realized in a true sense, changes of the code is precisely determined, a development team can find the difference between the new version code and the old version code conveniently, quickly and effectively, and more efficient development is realized.
Owner:AEROSPACE INFORMATION
Method for many-core circulation partitioning based on multi-version code generation
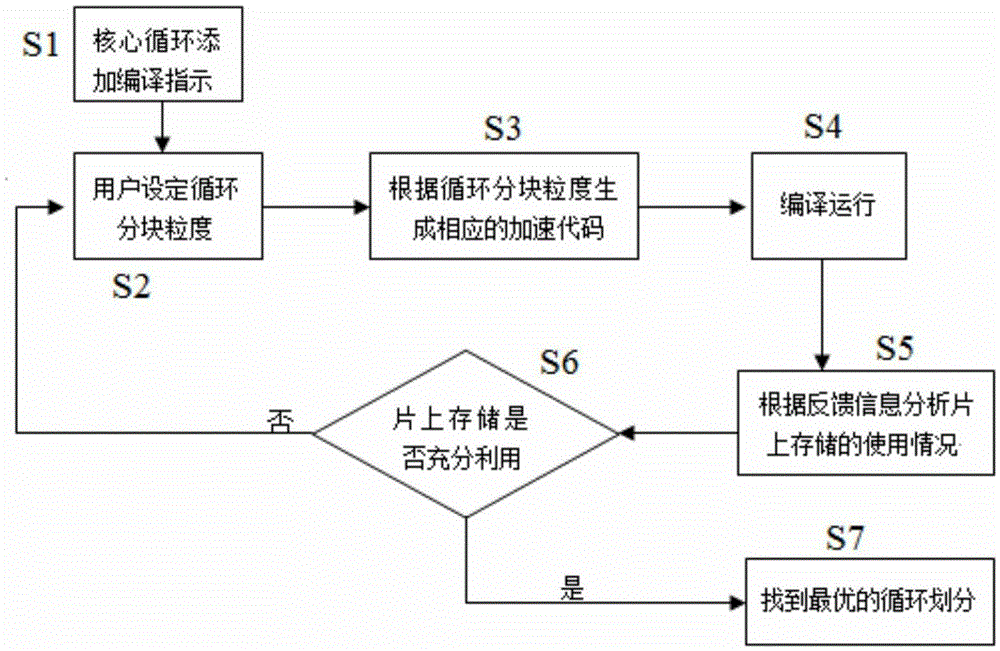
The invention provides a method for many-core circulation partitioning based on multi-version code generation. A many-core processor is composed of control cores and a calculation core array. Each calculation core is provided with a cache, and the cache which each calculation core is provided with serves as an on-chip memory to perform data transmission with a main memory in a memory direct access mode. The method is characterized in that when a compiler performs parallel transformation on many-core circulation, the particle size of circulation partitioning is determined according to the value indicated by the compiler, so that parallel codes of different versions are generated, the compiler performs feedback of use information stored on a chip during running in a code plug-in mounting mode so that the value indicated by the compiler can be correspondingly adjusted according to the use information fed back, and the utilization rate of the on-chip memory is maximized.
Owner:JIANGNAN INST OF COMPUTING TECH
Method for selective software rollback
ActiveUS8978160B2Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsSoftwareVersion code
A system and method for validating a software file to be installed into a controller. The method includes preparing the software file including assigning a software version code to the software file, assigning a security version code to the software file, and signing the software file with the software file version code and the security version code. The signed software file is presented to the controller for installing on the controller and the controller verifies the software file signature to determine if the software file is valid and the security version code is valid. The controller allows the software file to be installed in the controller if both the signed software file is valid and the security version code is valid.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Smart contract version management method and device, and readable storage medium
The invention provides a smart contract version management method and device and a readable storage medium. The management method comprises the steps of receiving a first transaction which is createdaccording to a contract code and a deployment parameter and is used for deploying an intelligent contract, generating a contract address of the intelligent contract according to the first transaction,and storing a contract code table and a condition rule table in a storage space corresponding to the contract address, wherein the contract code table comprises a plurality of contract codes and version codes in a mapping relationship, the condition rule table comprises a plurality of condition rules, each condition rule comprises a version code, a condition combination mode and a condition listwhich are in a mapping relationship, and each inspection condition is recorded in the condition list; receiving a second transaction which is created according to the contract address and the callingparameter and is used for calling the intelligent contract, and obtaining a corresponding condition rule table according to the contract address; and determining a version code according to the condition rule table so as to execute a second transaction according to the contract code corresponding to the version code. The smart contract version management method and device have the beneficial effect that the multi-contract code version is managed based on the single contract address.
Owner:HANGZHOU QULIAN TECH CO LTD
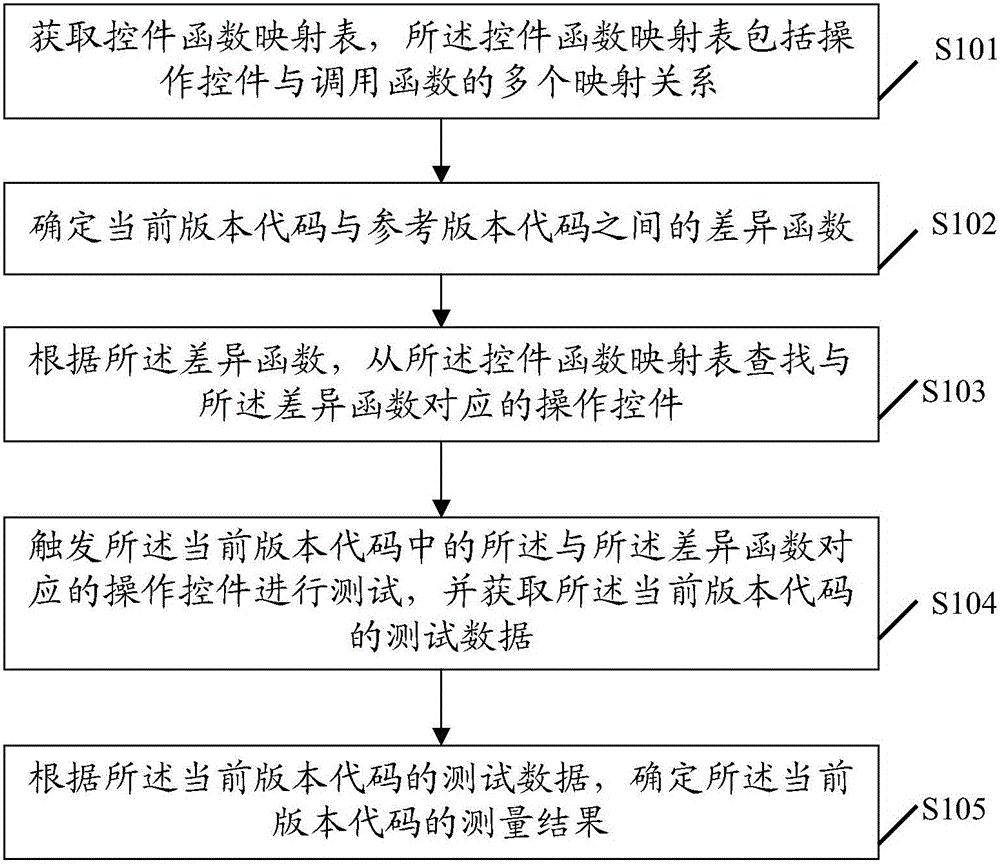
Performance test method and device
ActiveCN105912467AReduce the test input setReduce complexitySoftware testing/debuggingTest inputSoftware engineering
The embodiment of the invention discloses a performance test method. The performance test method includes: acquiring a control function mapping table, wherein the control function mapping table includes a plurality of mapping relationships between an operation control and a call function; determining a difference function between a current version code and a reference version code; searching an operation control corresponding to the difference function from the control function mapping table according to the difference function; triggering the operation control corresponding to the difference function in the current version code, and performing test to acquire test data of the current version code; and determining a test result of the current version code according to the test data of the current version code. The embodiment of the invention also discloses a performance test device. The performance test method and device can decrease test input sets, lower the complexity of test, and improve the efficiency of test.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
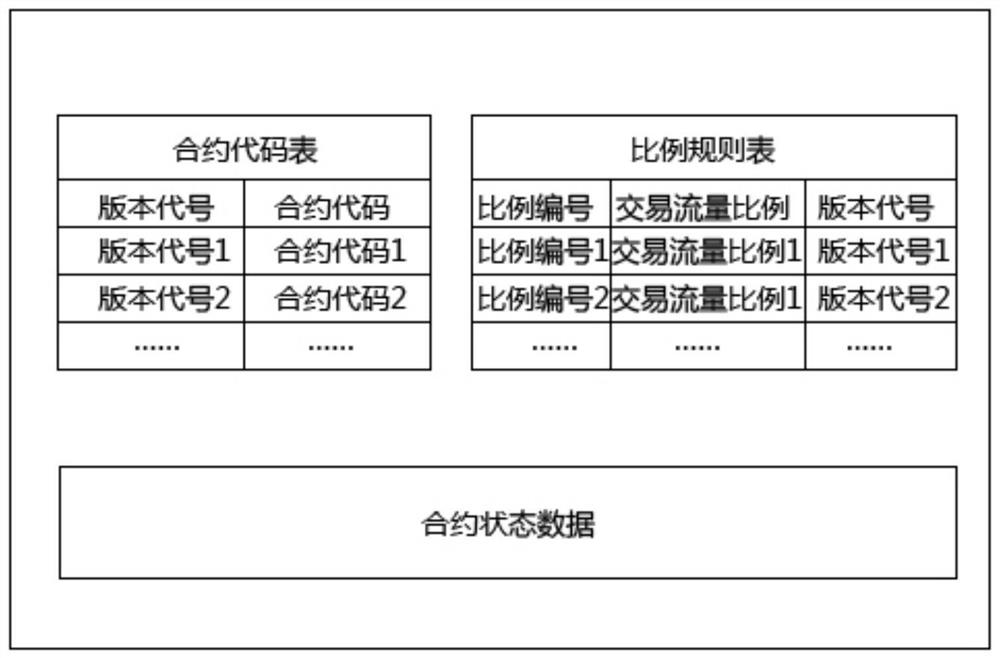
Smart contract version management method and device, and readable storage medium
The invention provides an intelligent contract version management method and device and a readable storage medium. The management method comprises the steps of receiving a first transaction which is created according to a contract code and a deployment parameter and is used for deploying an intelligent contract, generating a contract address of the intelligent contract according to the first transaction, and storing a contract code table and a proportion rule table in a storage space corresponding to the contract address, wherein the contract code table comprises a contract code and a versioncode name which are in a mapping relationship, and the proportion rule table comprises a proportion number, a version code and a transaction flow proportion which are in a mapping relationship; receiving a second transaction created according to the contract address and the calling parameter, and obtaining a corresponding proportion rule table according to the contract address; and determining a version code according to the proportion rule table so as to execute a second transaction according to the contract code corresponding to the version code. The beneficial effect of the invention is that the method achieves the multi-contract code version management based on a single contract address.
Owner:HANGZHOU QULIAN TECH CO LTD
Data processing apparatus and control method for verifying that version codes in selected boot sector and main sector match
A data processing apparatus comprising: flash ROM that can communicate with a CPU, the flash ROM comprises a boot sector that stores a boot selector program, a first boot sector and a second boot sector each storing a boot program that is selectively called by the boot selector program. The CPU executes the boot selector program to select the first boot sector or the second boot sector each storing a boot program to be executed. The CPU executes the selected boot program to verify a version code stored in a main sector and the selected boot sector. The CPU executes a main program when the version code in the main sector matches the version code in the selected boot sector.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Code release method and apparatus
The invention discloses a code release method and apparatus, relates to the technical field of data processing, and solves the problem that a large amount of Geriit server resources are occupied in an existing code release process. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a code review number of an application product personalized function code, wherein the application product personalized function code is a modification code of performing modification for a universal version code of an application product for a personalized function demand of the application product; obtaining the application product personalized function code corresponding to the code review number from a code review server according to the code review number; performing local integration on the application product personalized function code and the universal version code to obtain an application product code with a personalized function; and compiling and releasing the application product with the personalized function. The code release method and apparatus is applied to the code release process.
Owner:NEUSOFT CORP
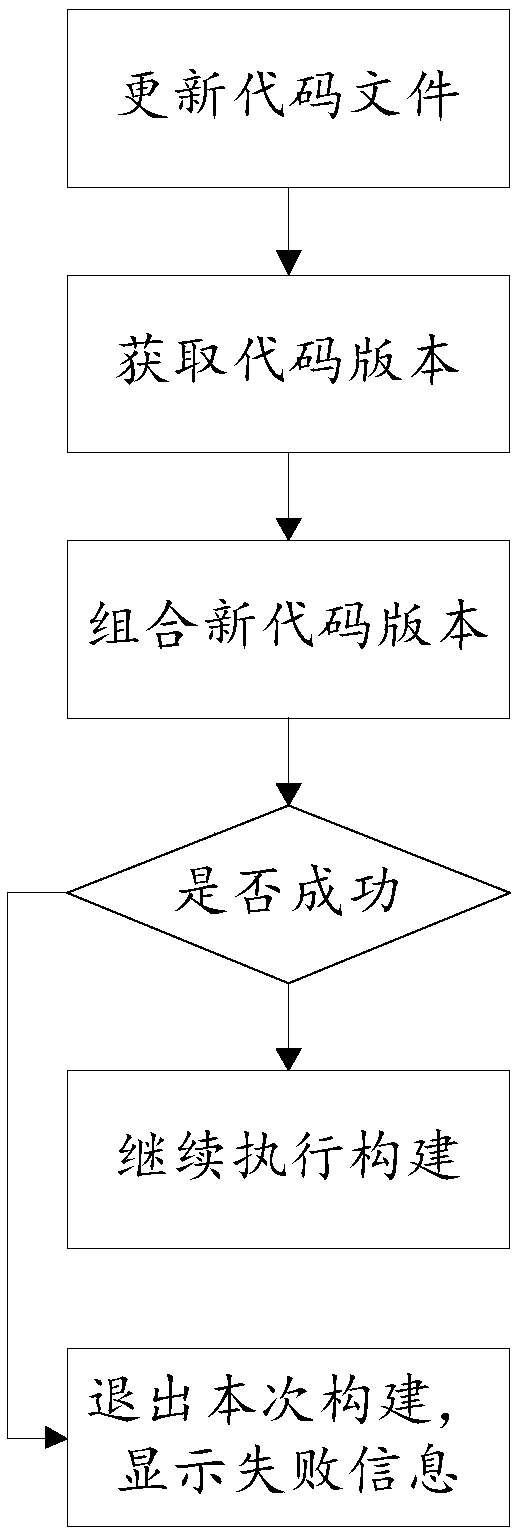
Code version information updating method and system, readable medium and storage controller
InactiveCN107656734AEasy to trace backNo manual operation requiredVersion controlCode compilationTime efficientControl store
The invention discloses a method, a system, a readable medium and a storage controller for updating code version information. The method for updating code version information includes: acquiring an updated code file from a code warehouse; acquiring the updated code file in the code warehouse A specific code version; combine the above specific code version and the internal code version of the update code file itself into a new code version. The present invention combines the basic service provided by the CI tool to automatically obtain the updated code version and modify the code file to obtain a new code version in each construction process, and then compiles, thereby realizing the purpose of automatically updating the binary version information, and the whole process does not require manual operation , to avoid mistakes, save time, and at the same time, it is convenient for the version to trace back the code when an error occurs, and ultimately improve the overall development efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING VRV SOFTWARE CO LTD
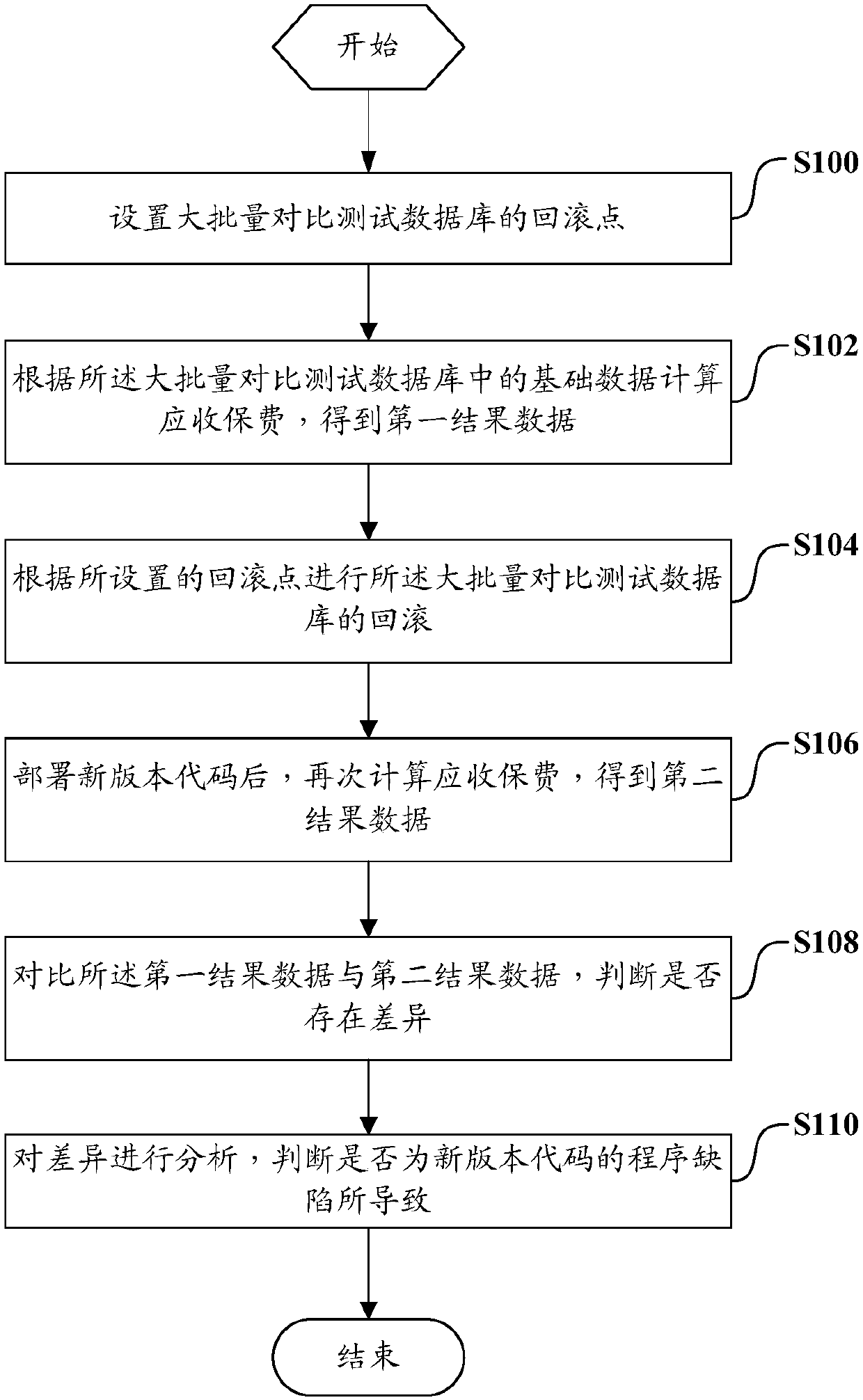
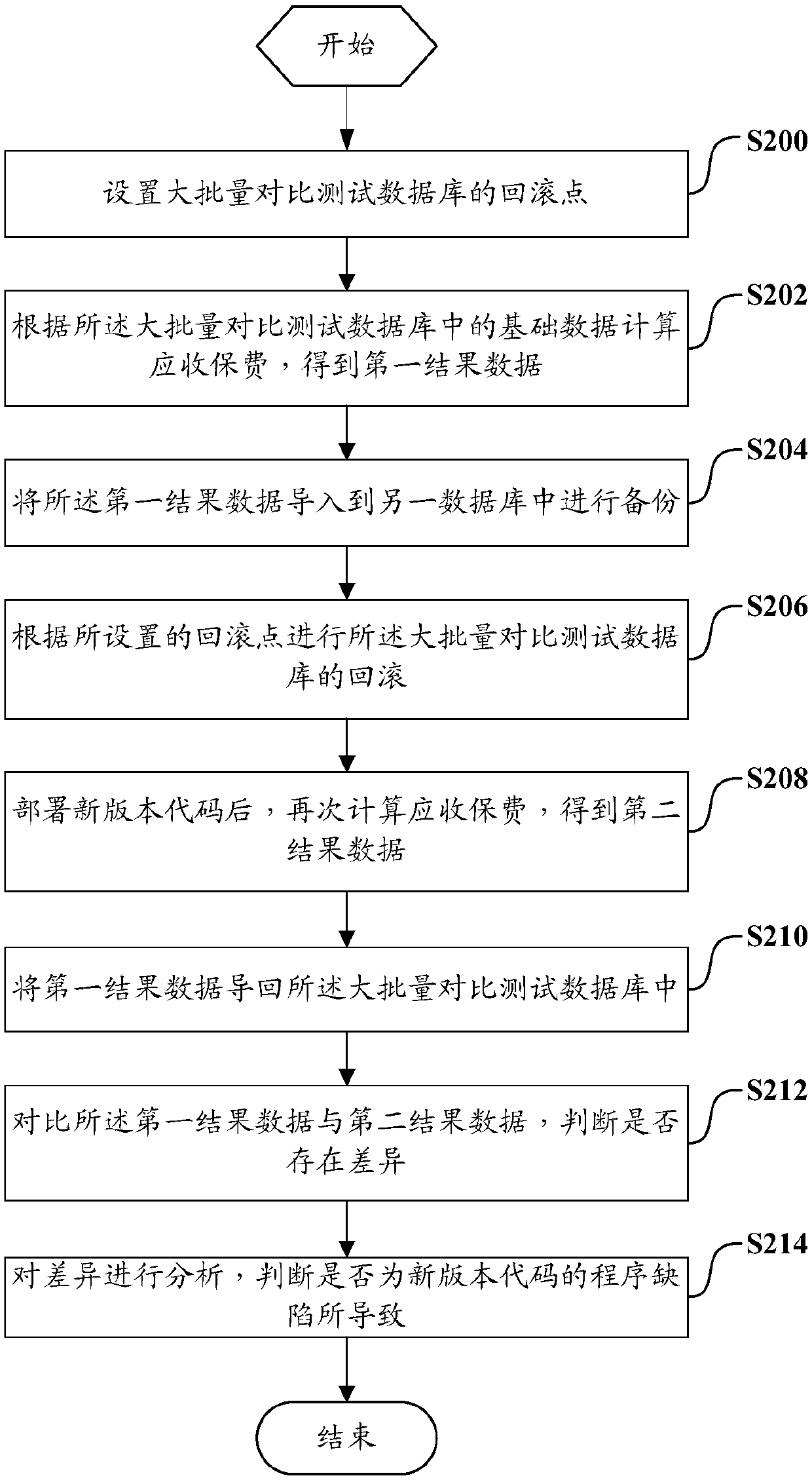
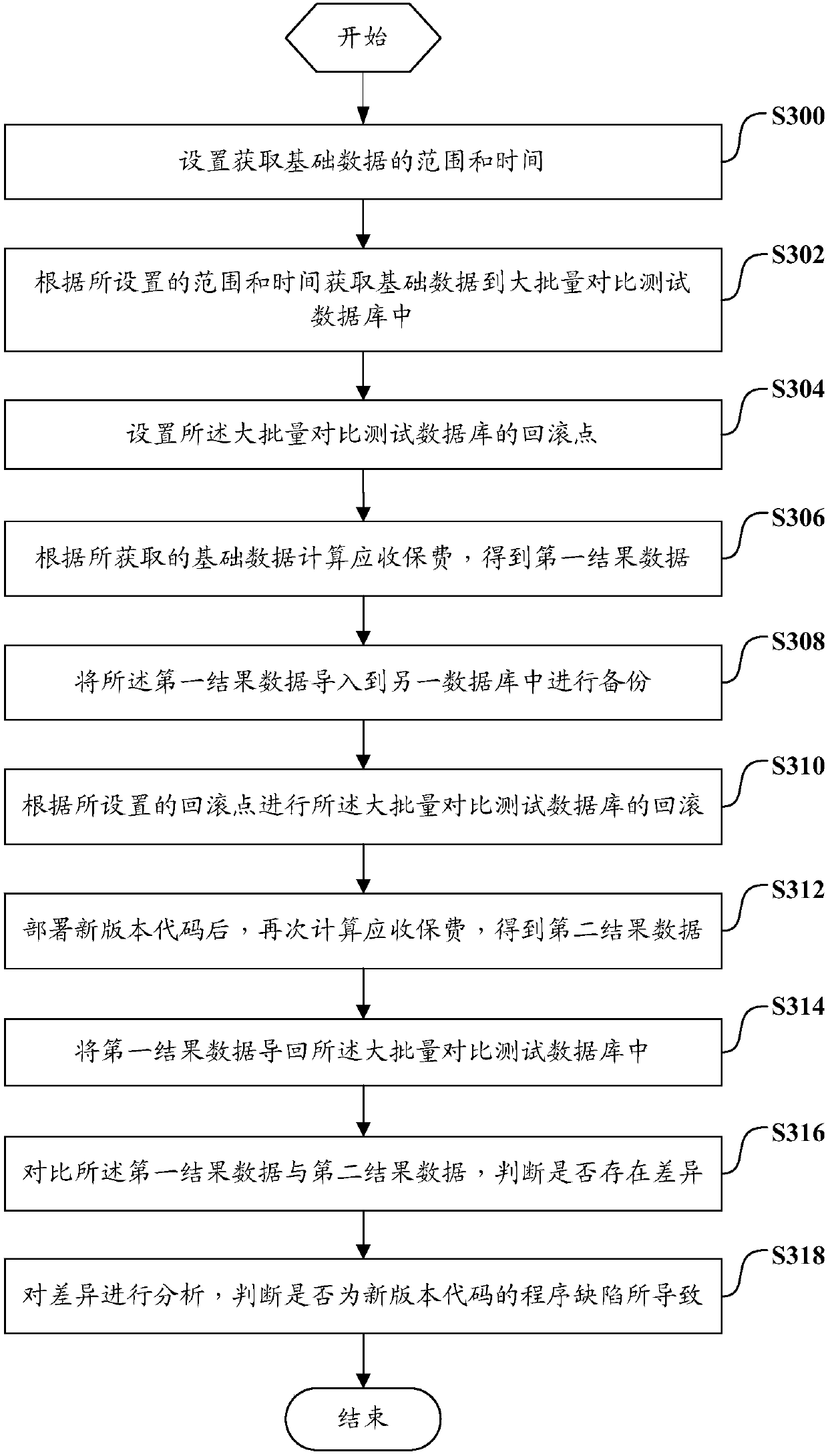
Mass comparison testing method and system
ActiveCN107870859AGuaranteed validitySave manpower for testingSoftware testing/debuggingComputer scienceVersion code
The invention discloses a mass comparison testing method and system. The method comprises the following steps that: setting the roll-back point of a mass comparison testing database; according to basic data in the mass comparison testing database, calculating insurance premiums receivable, obtaining first result data; according to the arranged roll-back point, carrying out the roll-back of the mass comparison testing database; after a new version code is deployed, calculating the insurance premiums receivable again, and obtaining second result data; comparing the first result data with the second result data, and judging whether differences are in the presence or not; and analyzing the differences, and judging whether the differences are caused by the program defects of the new version code. Therefore, the old version and new version comparison testing of the system of the insurance premiums receivable can be carried out in a full-coverage way.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
General database backup method and system
ActiveCN110928899AImprove compatibilitySave disk spaceDigital data information retrievalDigital data protectionTable (database)Database backup
The invention provides a general database backup method and system. According to the method, the corresponding system tables are inquired according to the database types, the table names needing to bebacked up are read, all the field types and the field values are read according to the table names and spliced into the corresponding statements, the statements are combined, optimized, compressed into character strings and encrypted, and data backup of different database types is achieved. The method does not depend on a database installation environment, does not depend on specific database types and versions, is high in code compatibility, can encrypt database backup file contents and ensure the security of backup data, and in addition, the file contents are compressed by adopting a GZIP compression technology, so that the compression ratio is relatively high, and the disk space of a server can be greatly saved.
Owner:中孚安全技术有限公司 +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com