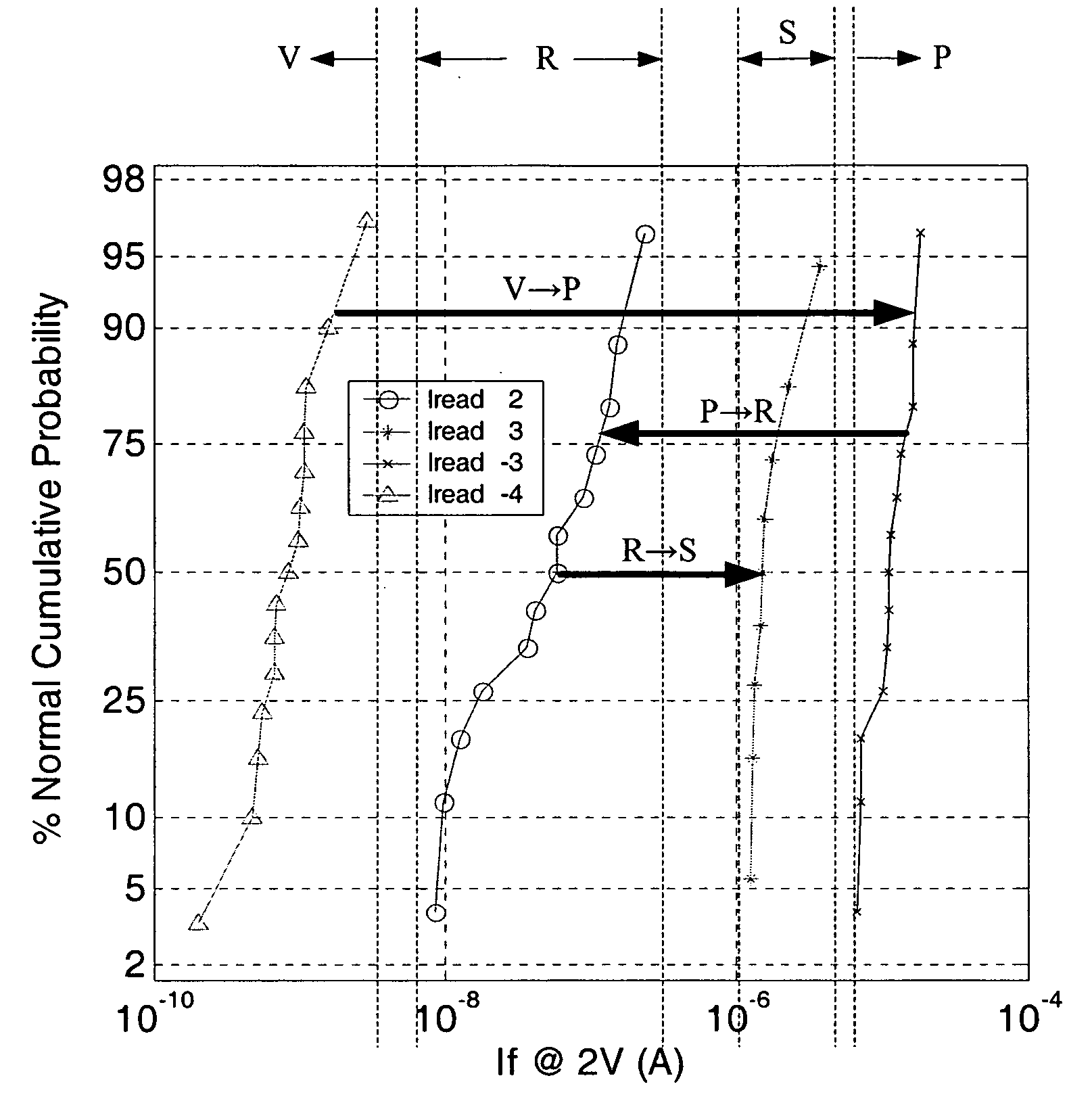
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
819 results about "One time programmable" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
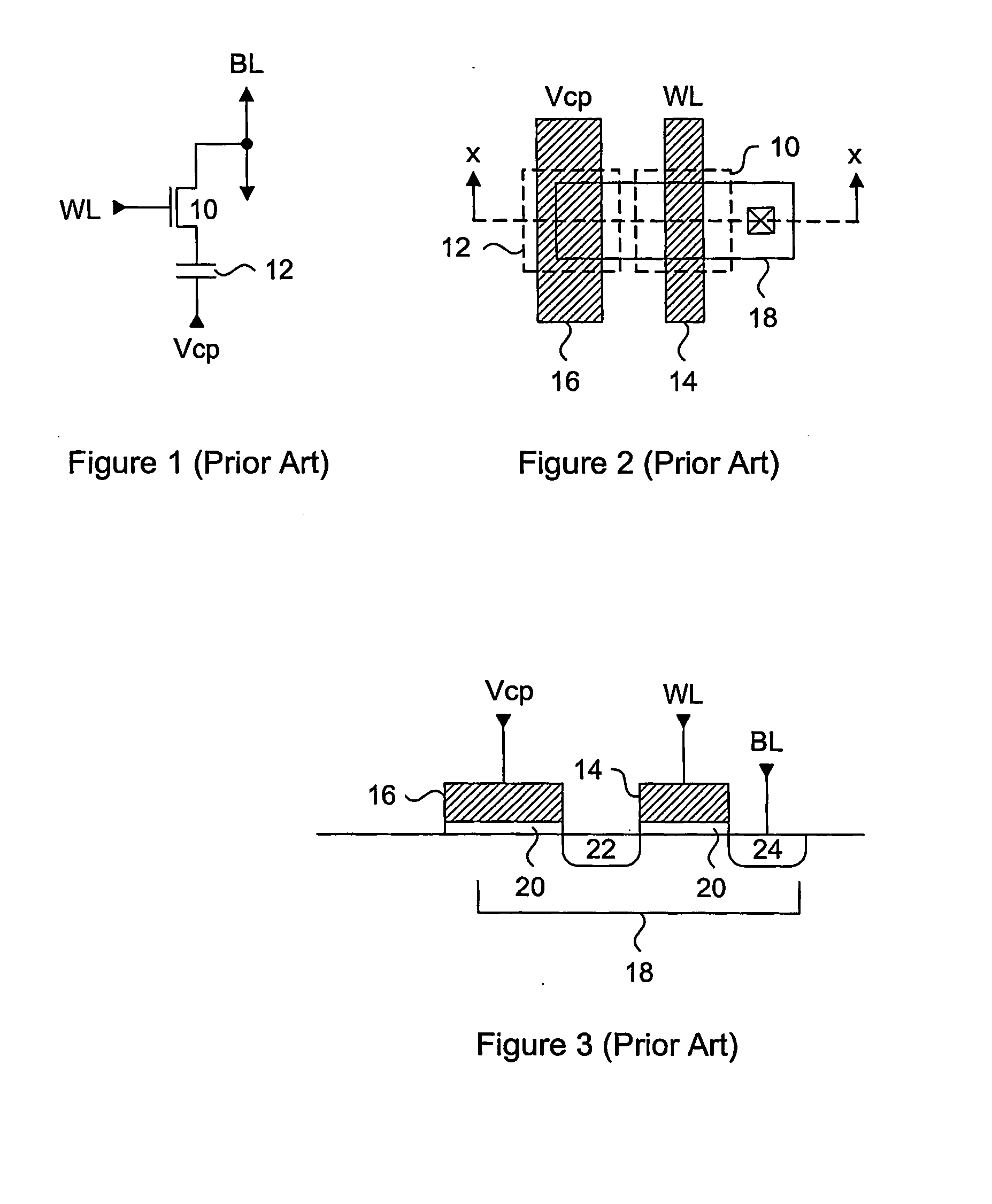
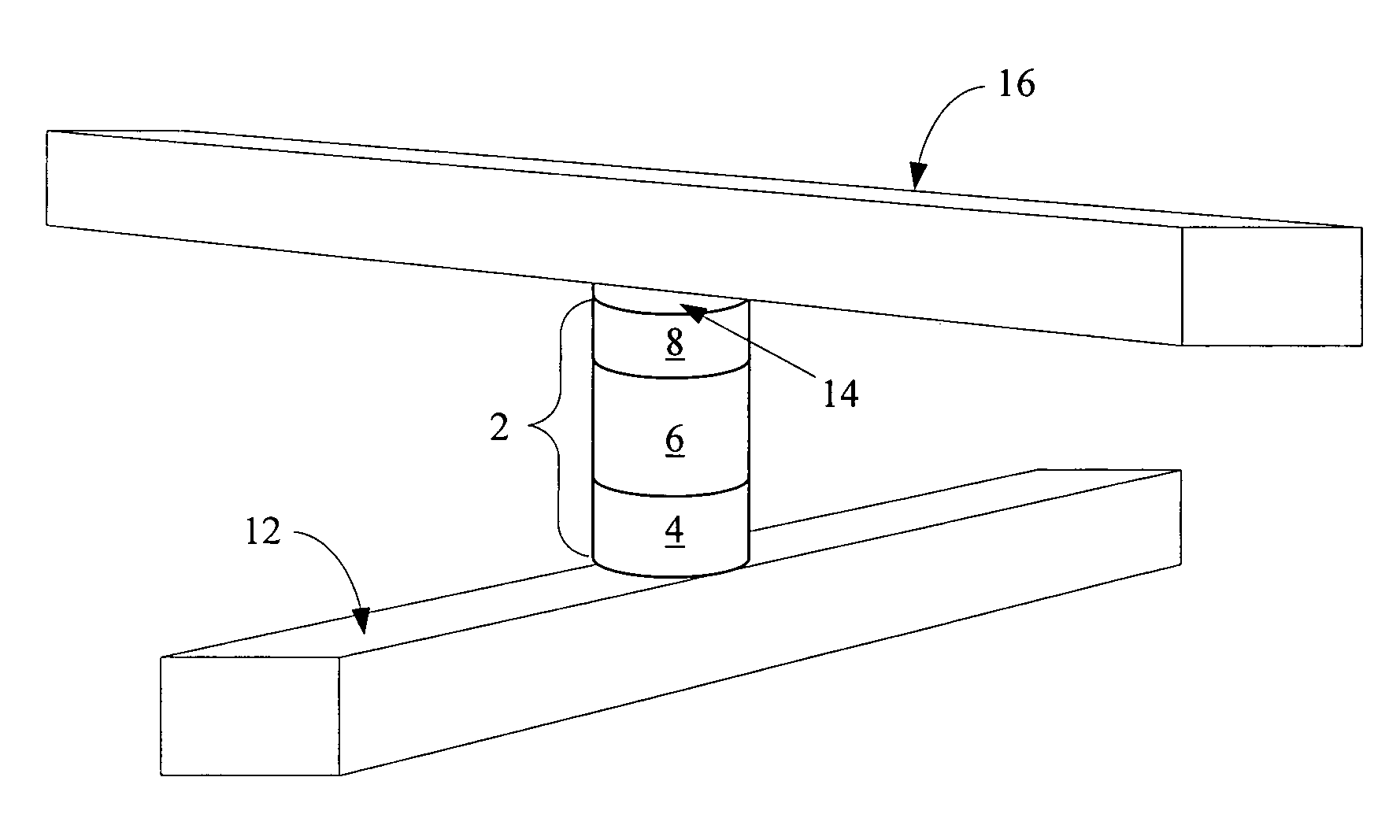
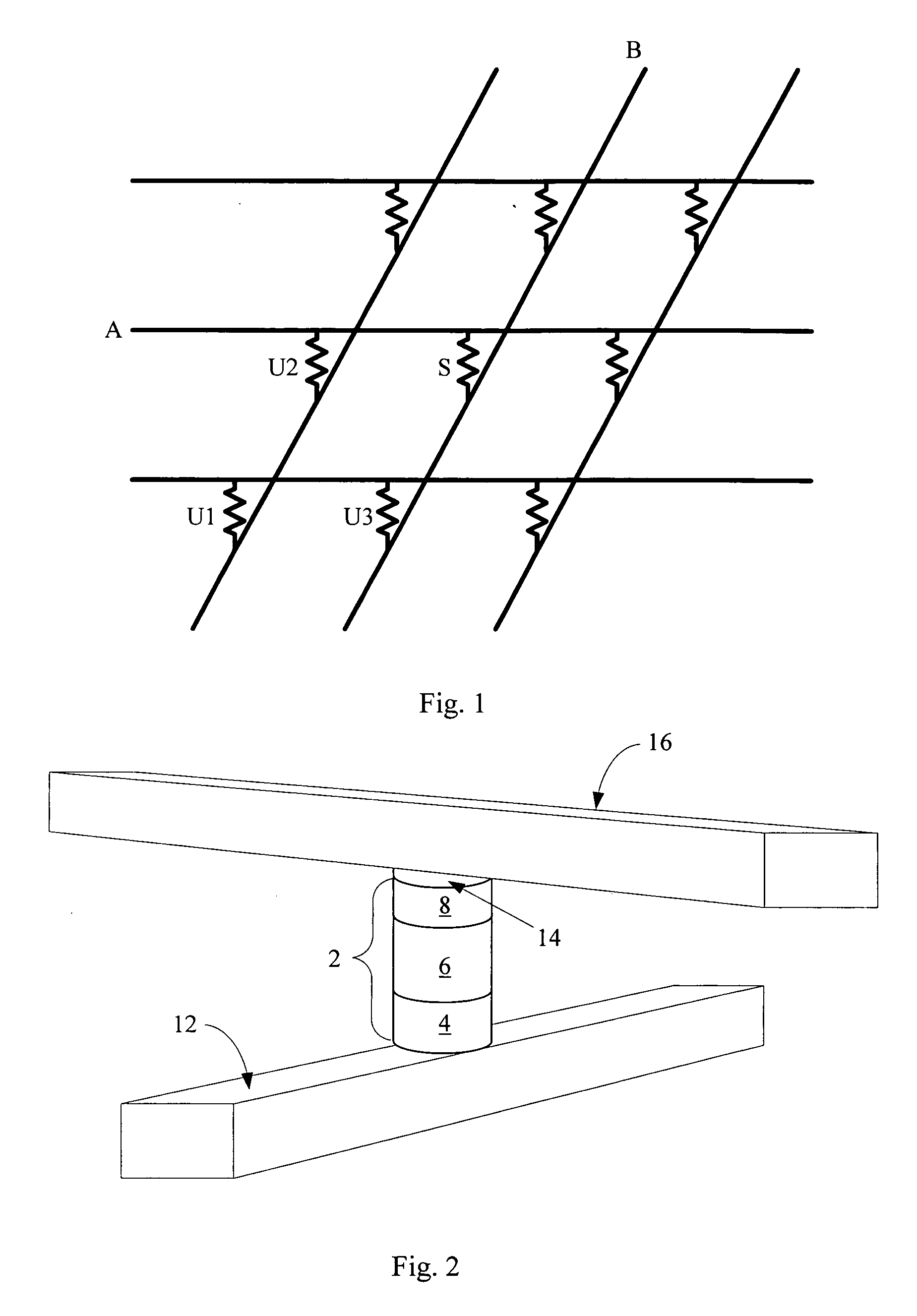
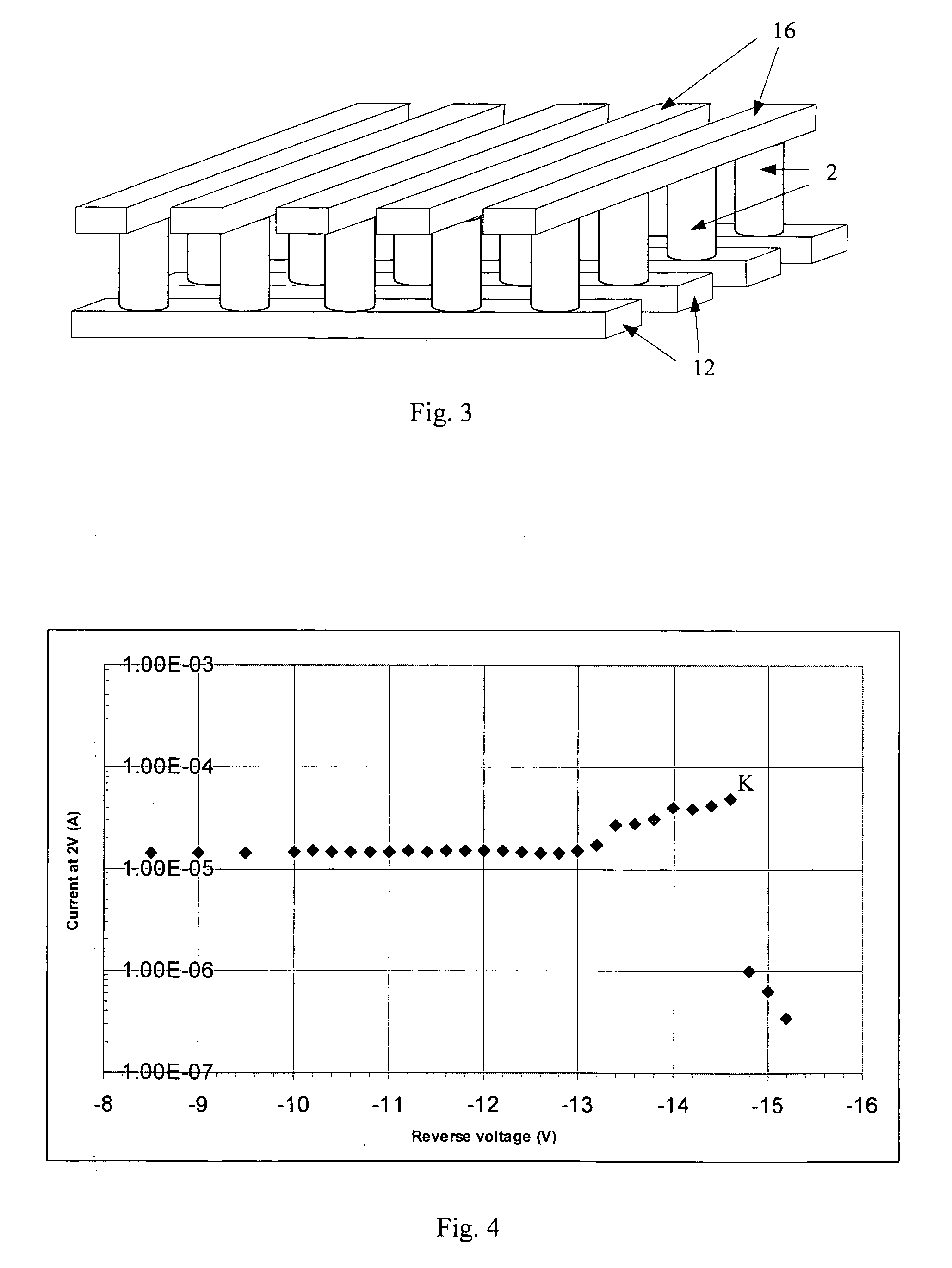
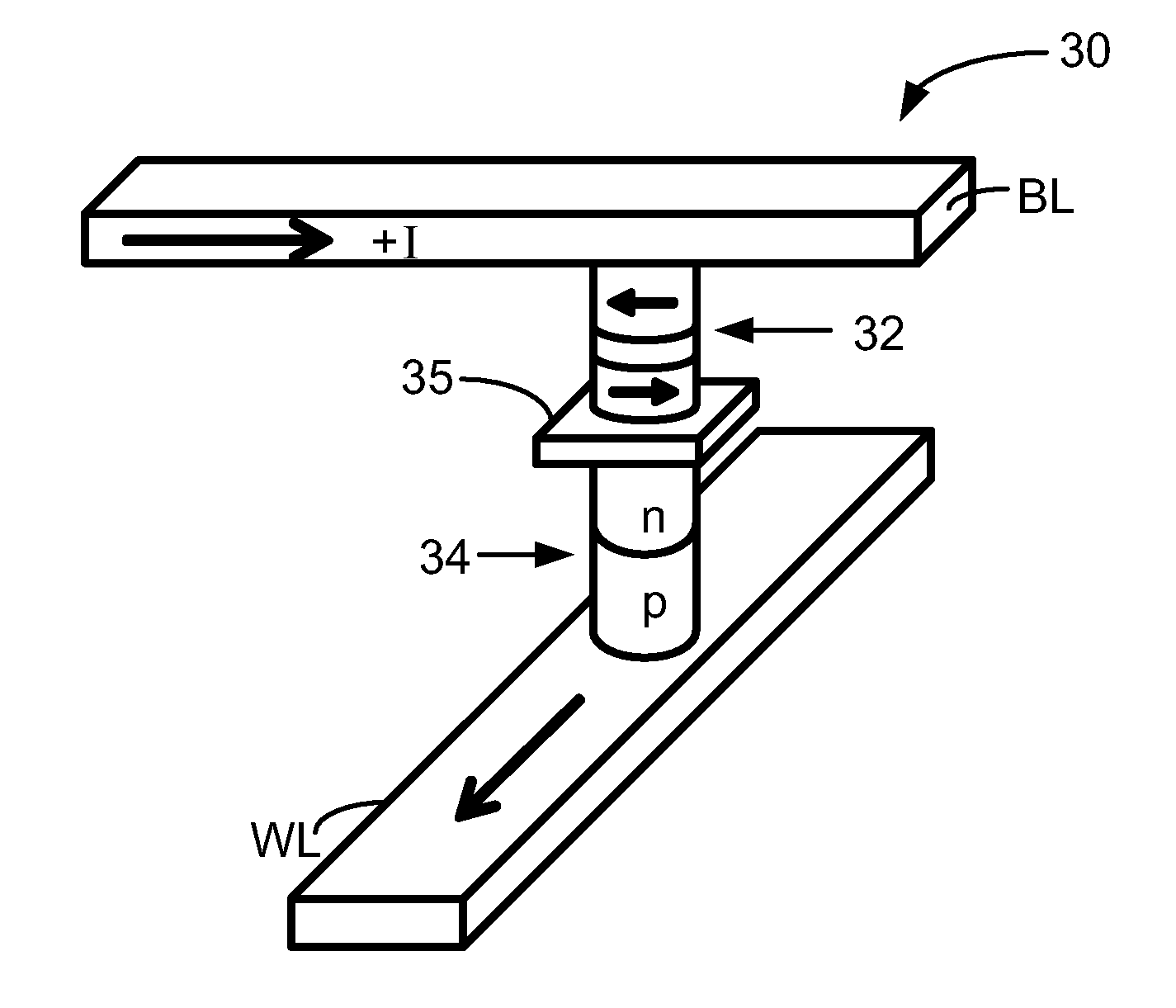
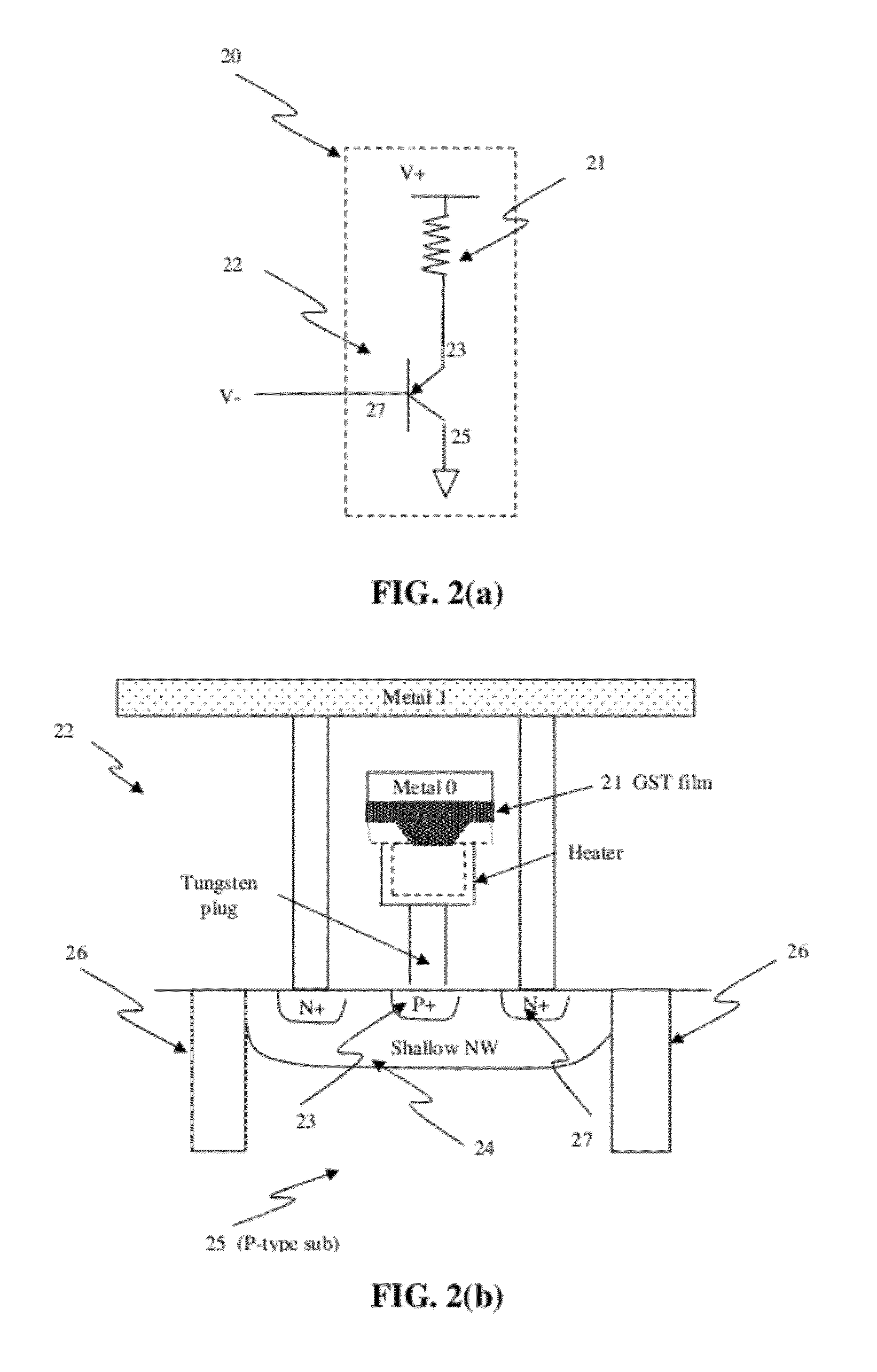
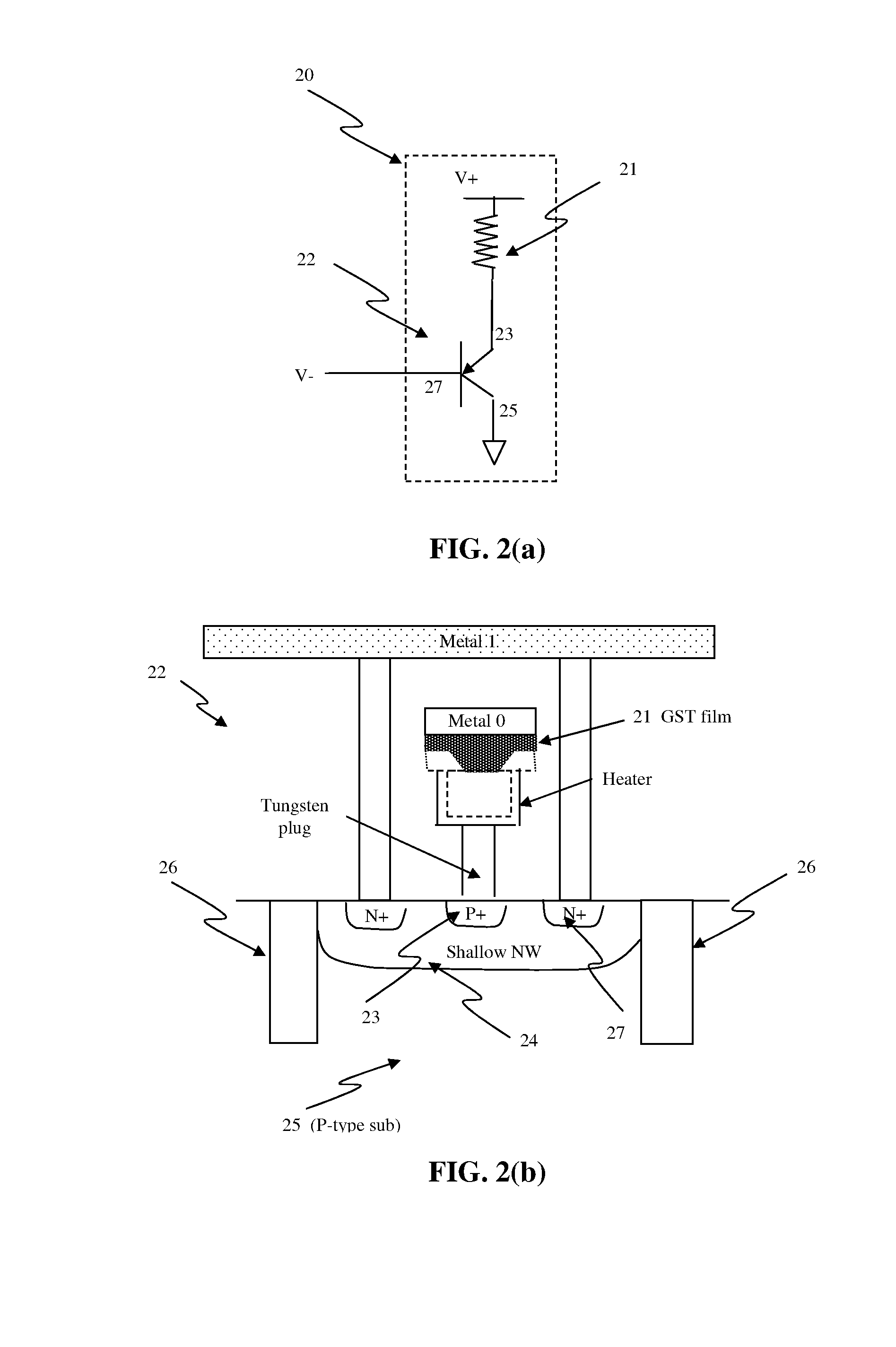
Nonvolatile memory cell comprising a diode and a resistance-switching material
In a novel nonvolatile memory cell formed above a substrate, a diode is paired with a reversible resistance-switching material, preferably a metal oxide or nitride such as, for example, NixOy, NbxOy, TixOy, HFxOy, AlxOy, MgxOy, CoxOy, CrxOy, VxOy, ZnxOy, ZrxOy, BxNy, and AlxNy. In preferred embodiments, the diode is formed as a vertical pillar disposed between conductors. Multiple memory levels can be stacked to form a monolithic three dimensional memory array. In some embodiments, the diode comprises germanium or a germanium alloy, which can be deposited and crystallized at relatively low temperatures, allowing use of aluminum or copper in the conductors. The memory cell of the present invention can be used as a rewriteable memory cell or a one-time-programmable memory cell, and can store two or more data states.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
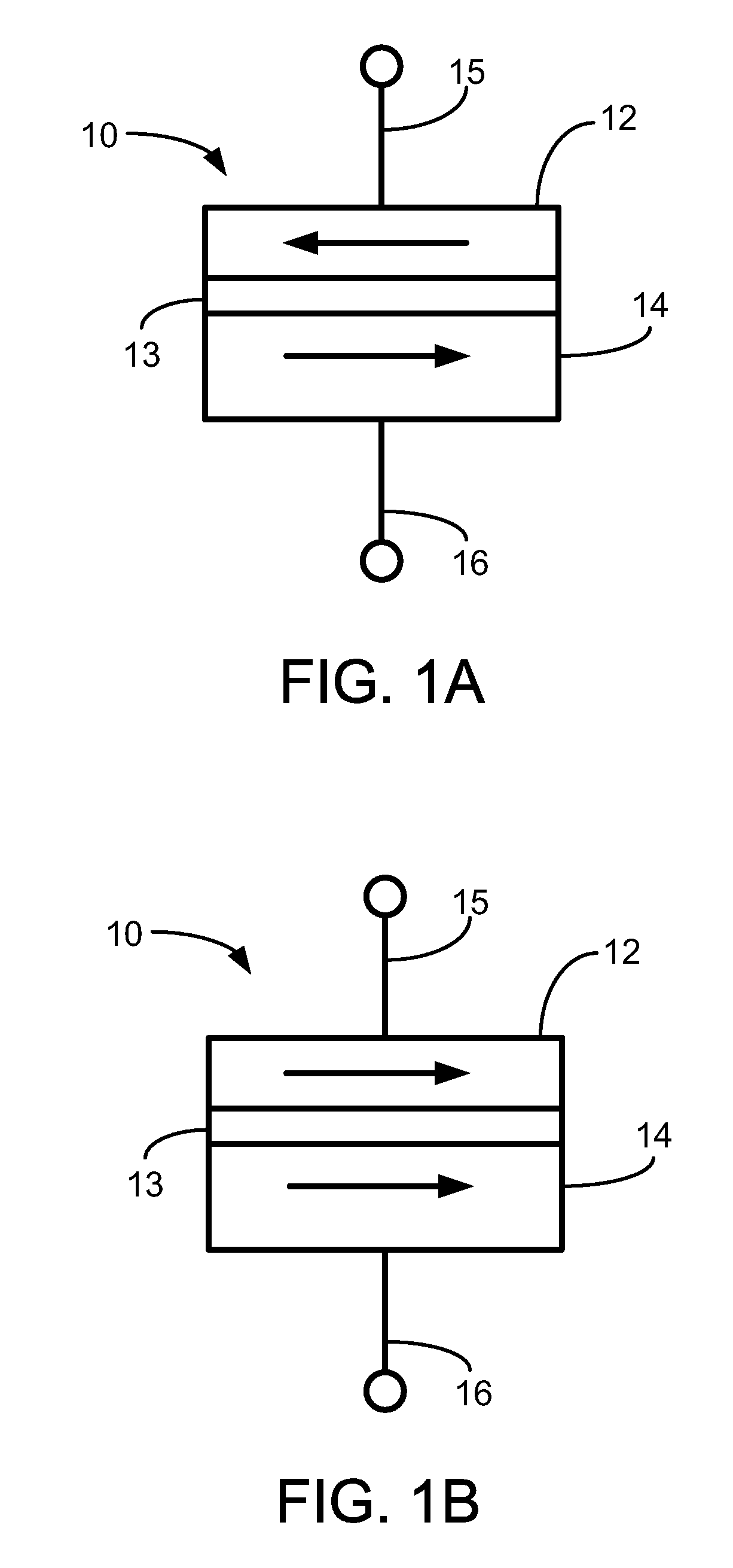
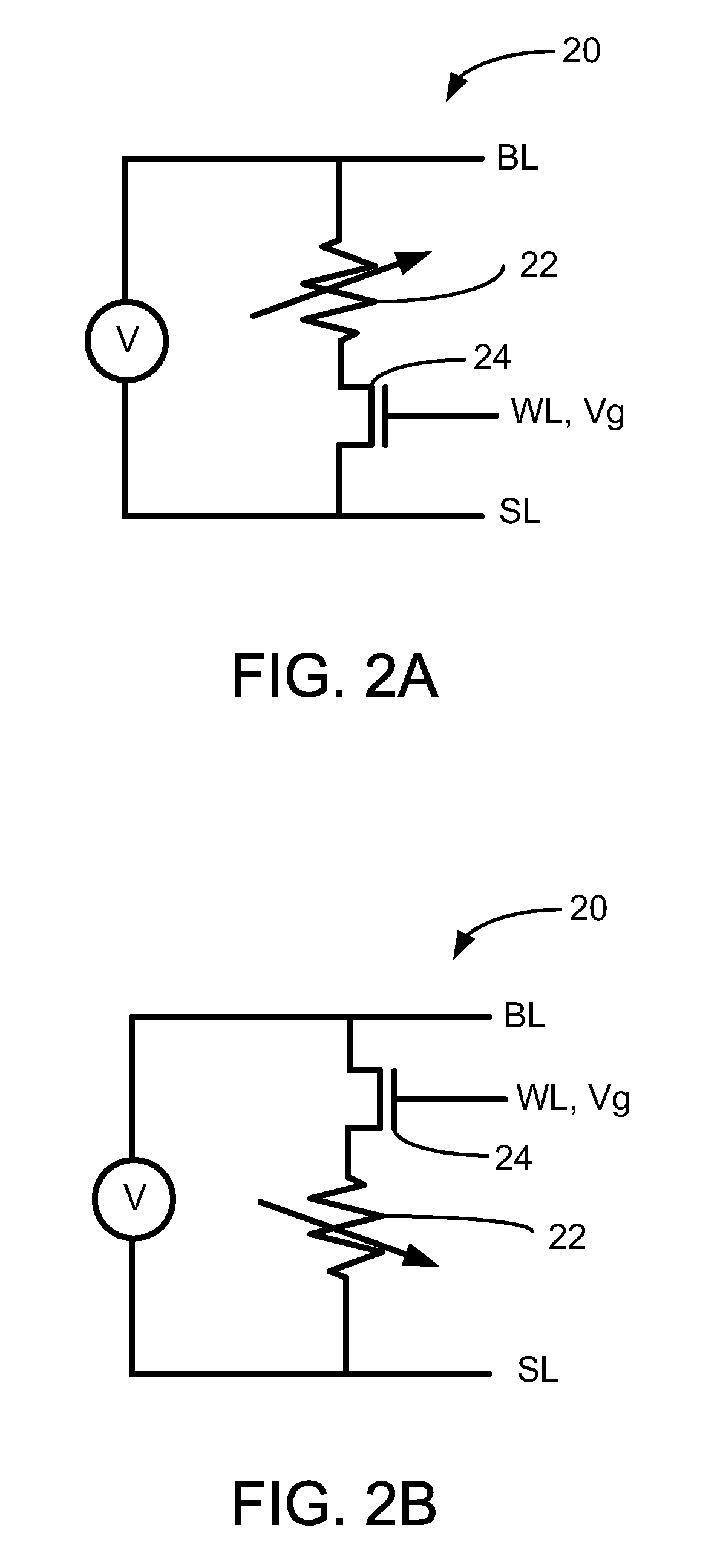
Method for using a memory cell comprising switchable semiconductor memory element with trimmable resistance
ActiveUS20070072360A1Solid-state devicesRead-only memoriesElectrical resistance and conductanceSemiconductor materials
A nonvolatile memory cell comprising a diode formed of semiconductor material can store memory states by changing the resistance of the semiconductor material by application of a set pulse (decreasing resistance) or a reset pulse (increasing resistance.) In preferred embodiments, set pulses are applied with the diode under forward bias, while reset pulses are applied with the diode in reverse bias. By switching resistivity of the semiconductor material of the diode, a memory cell can be either one-time programmable or rewriteable, and can achieve two, three, four, or more distinct data states.
Owner:WODEN TECH INC
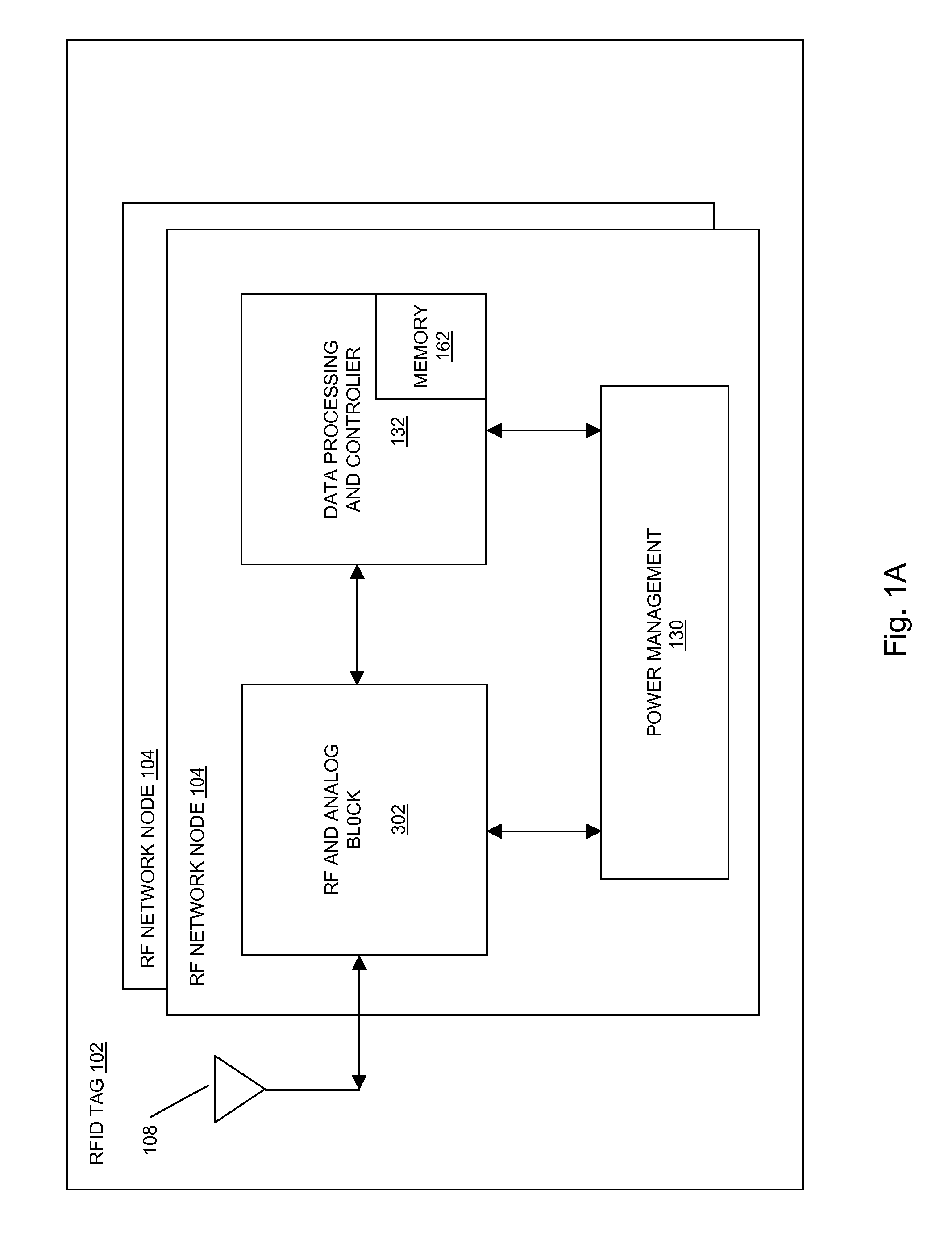
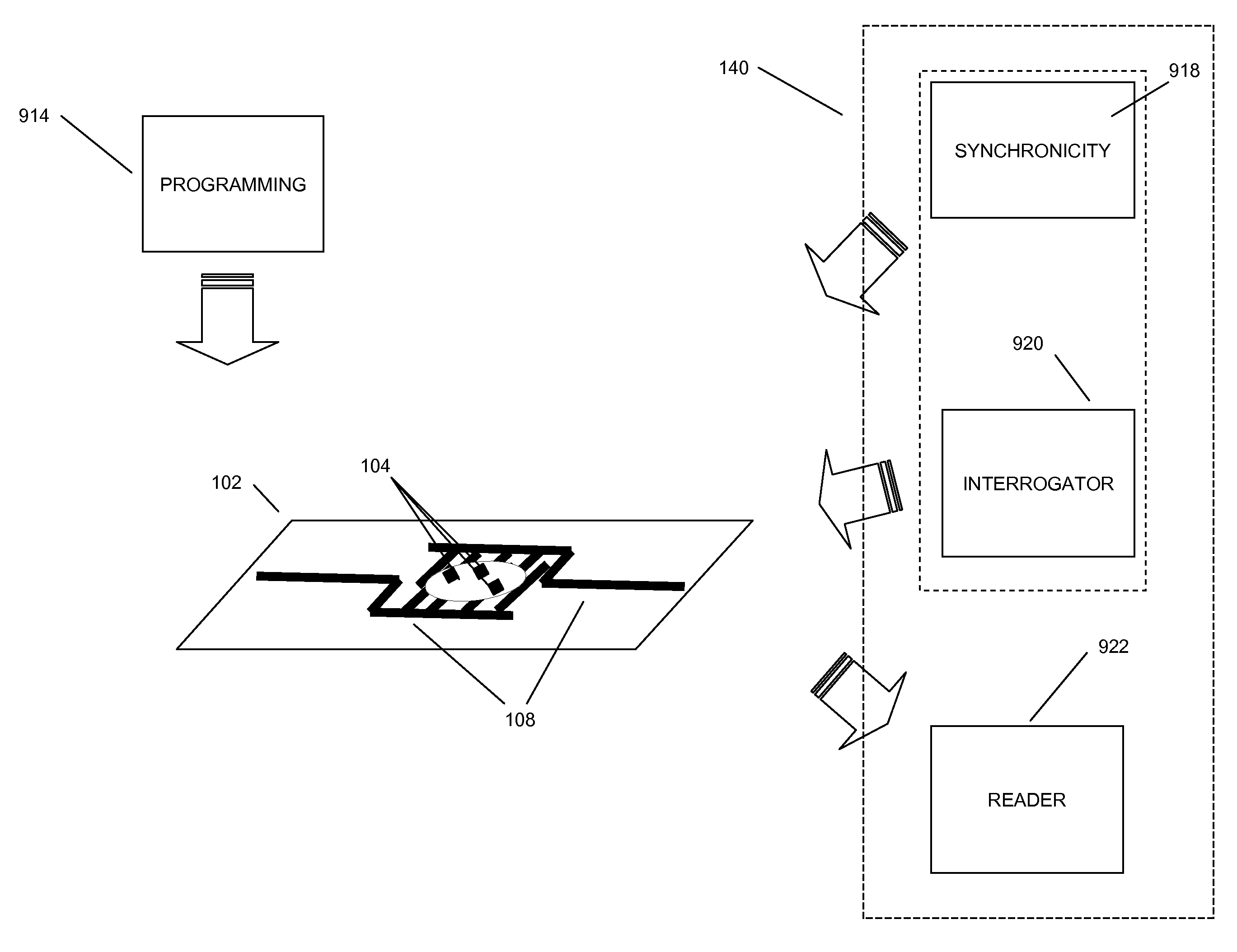
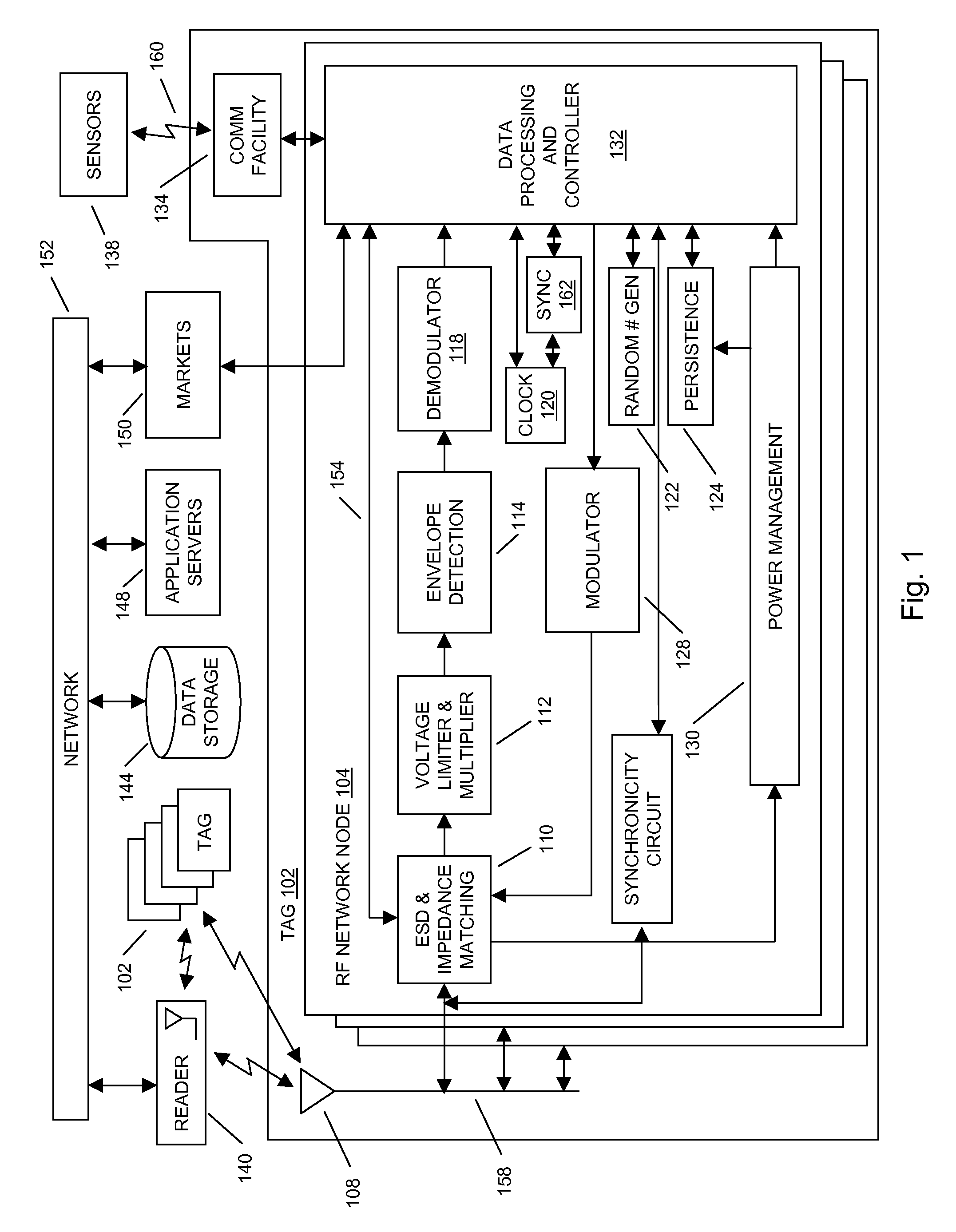
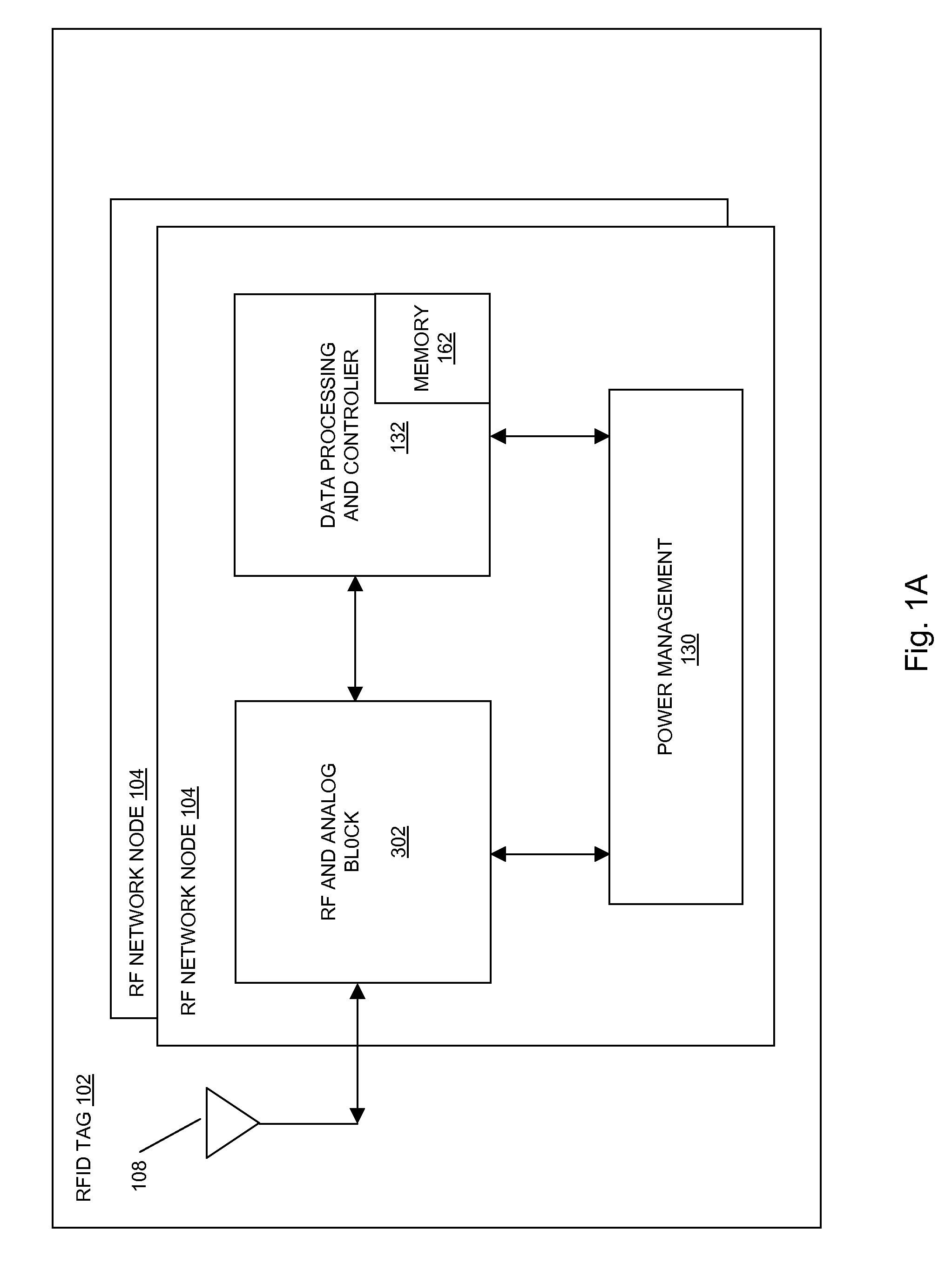
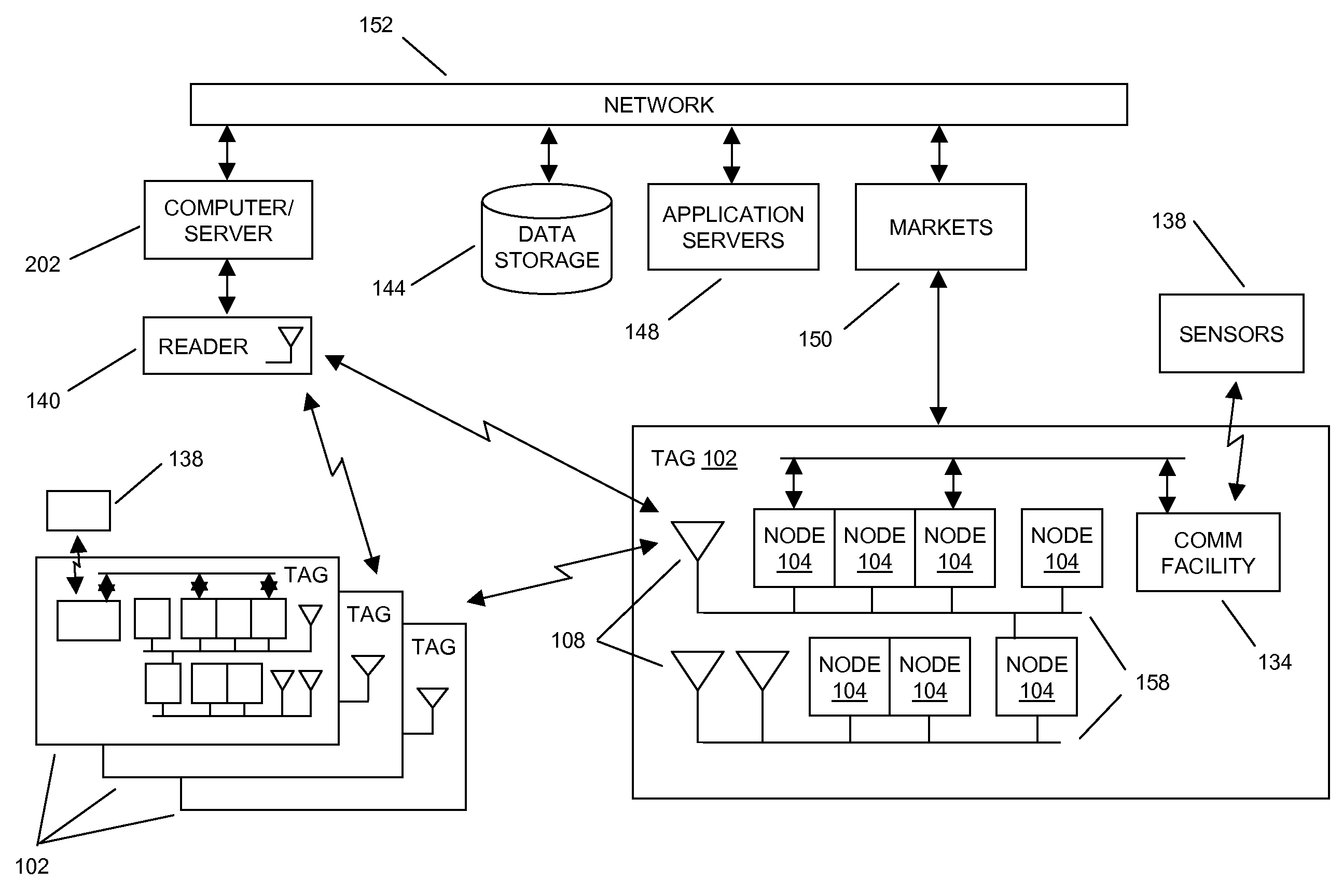
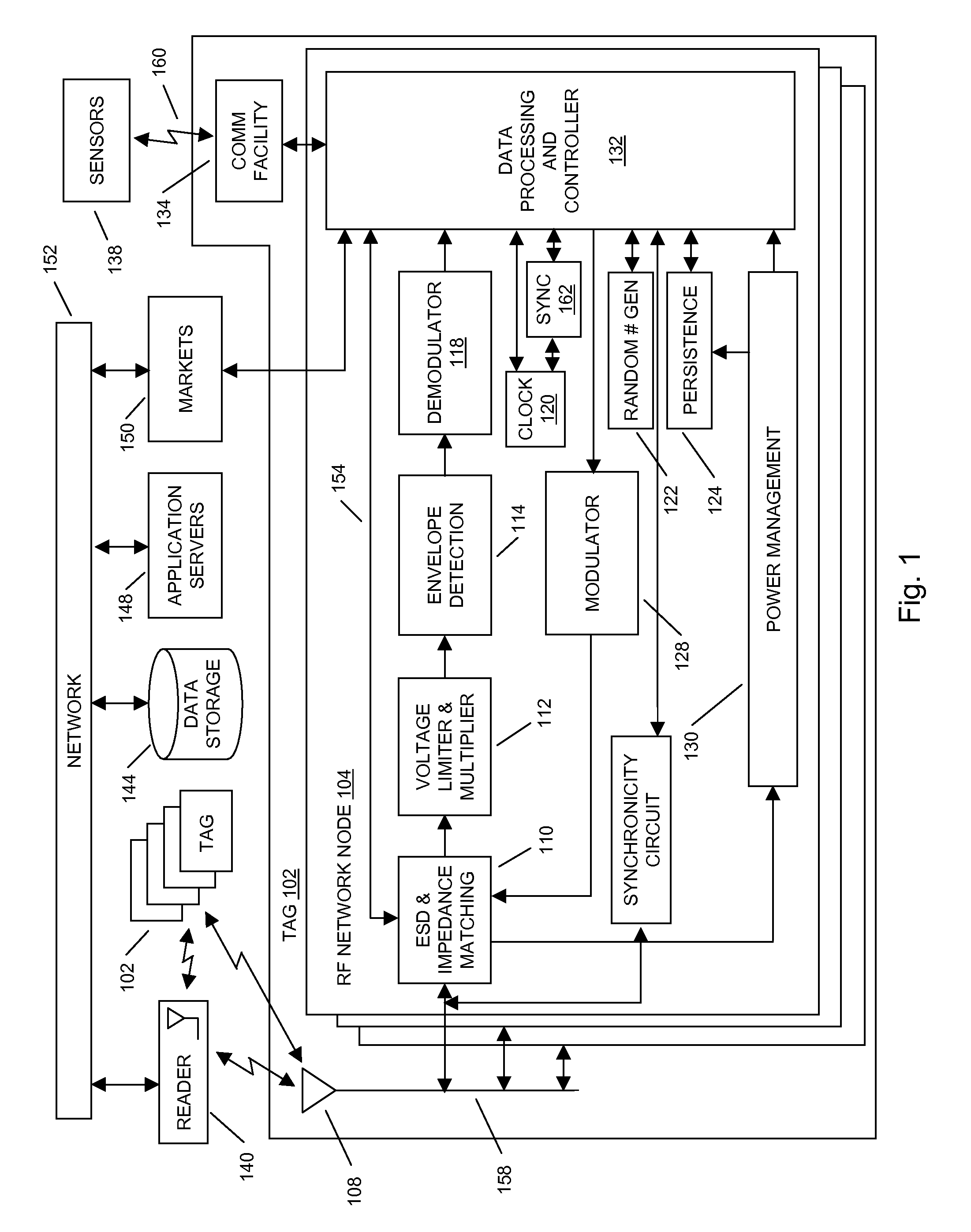
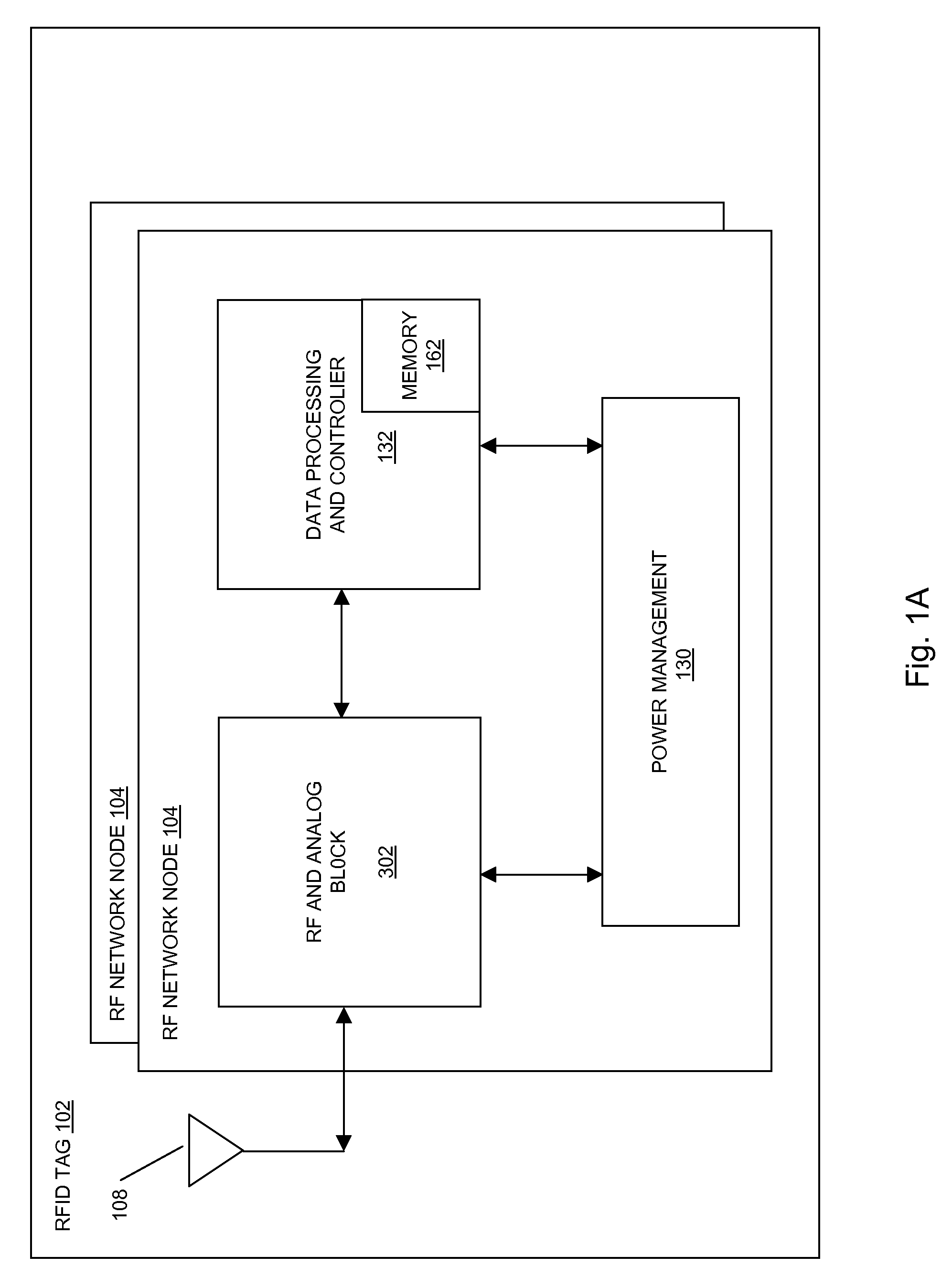
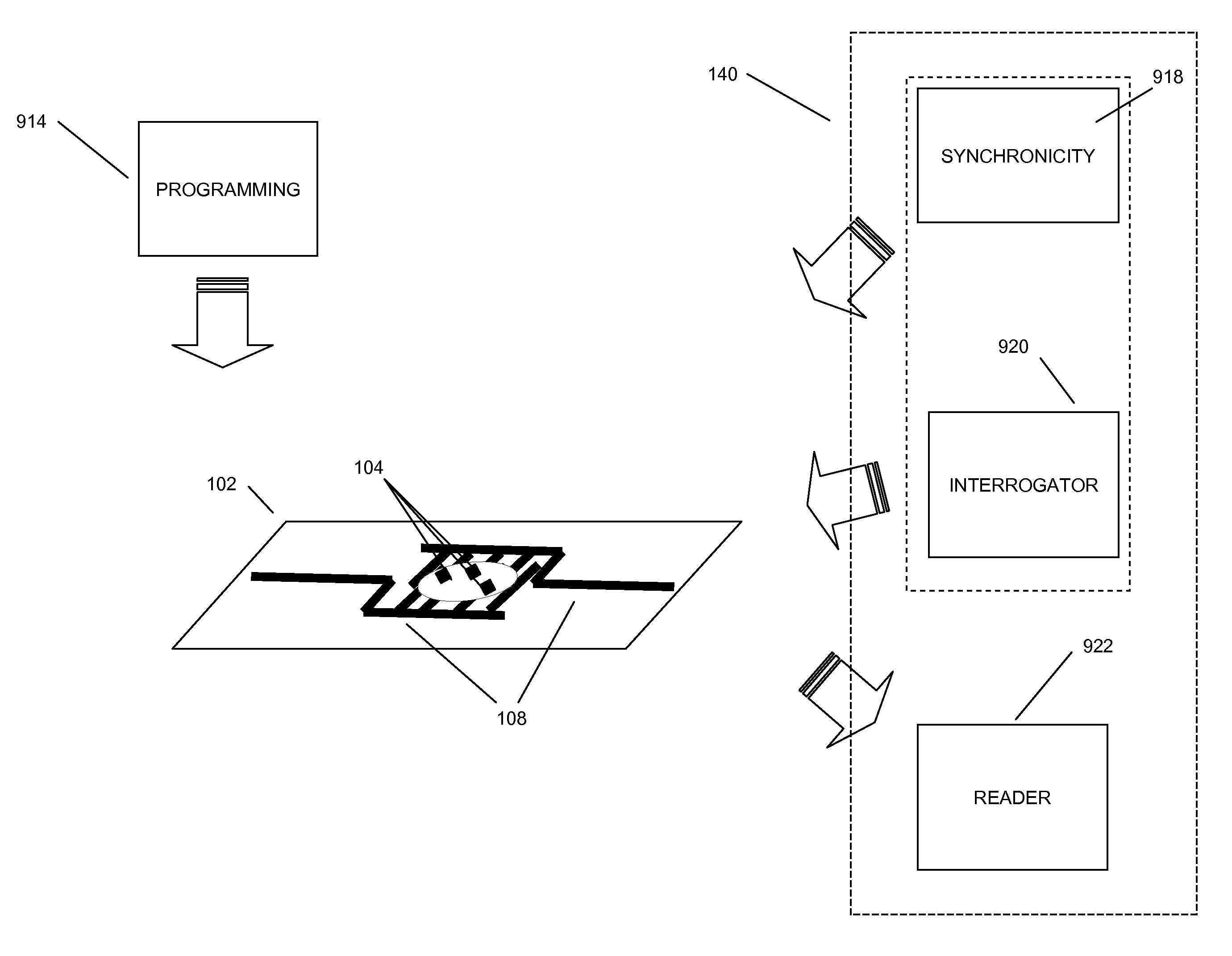
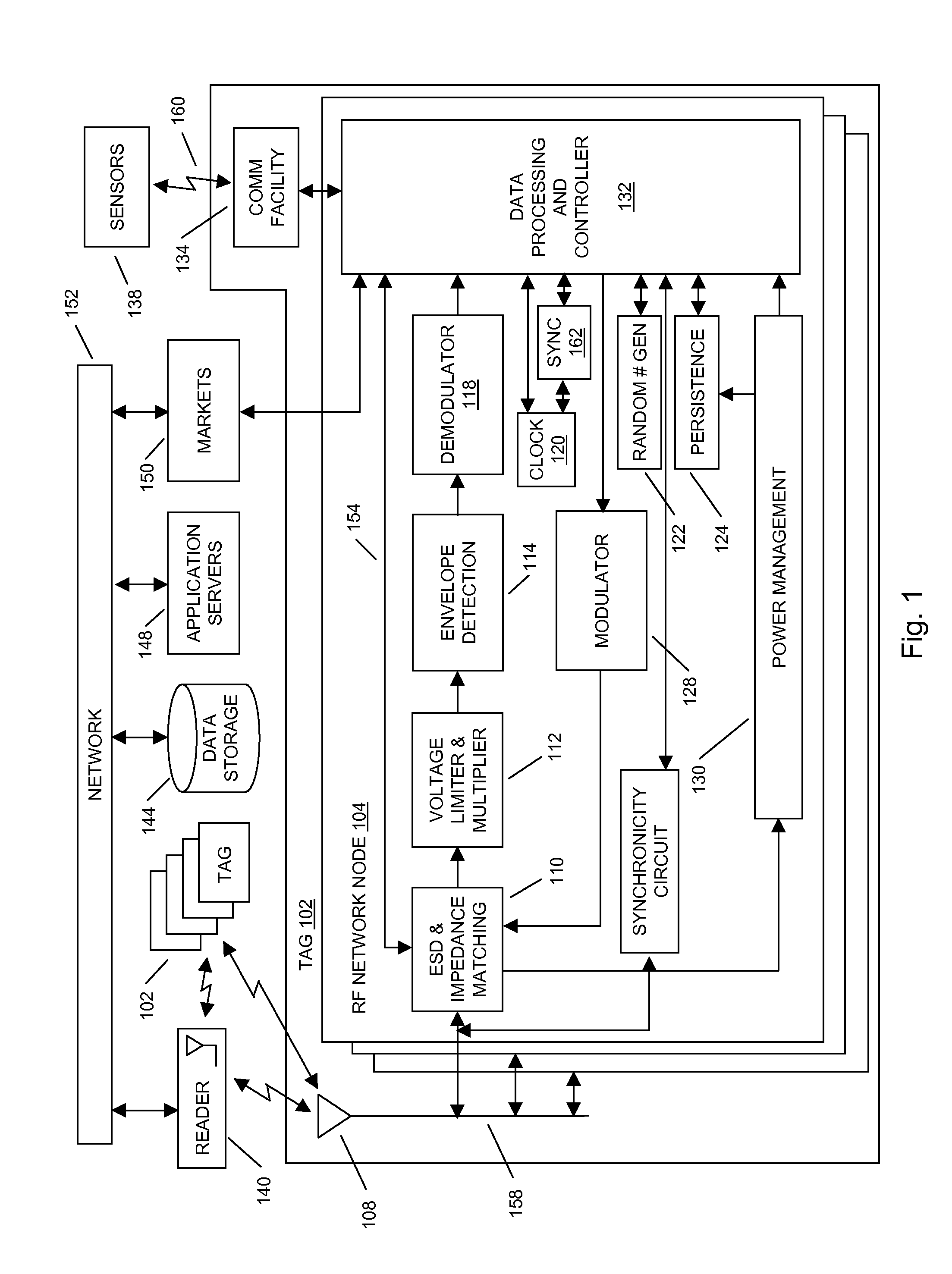
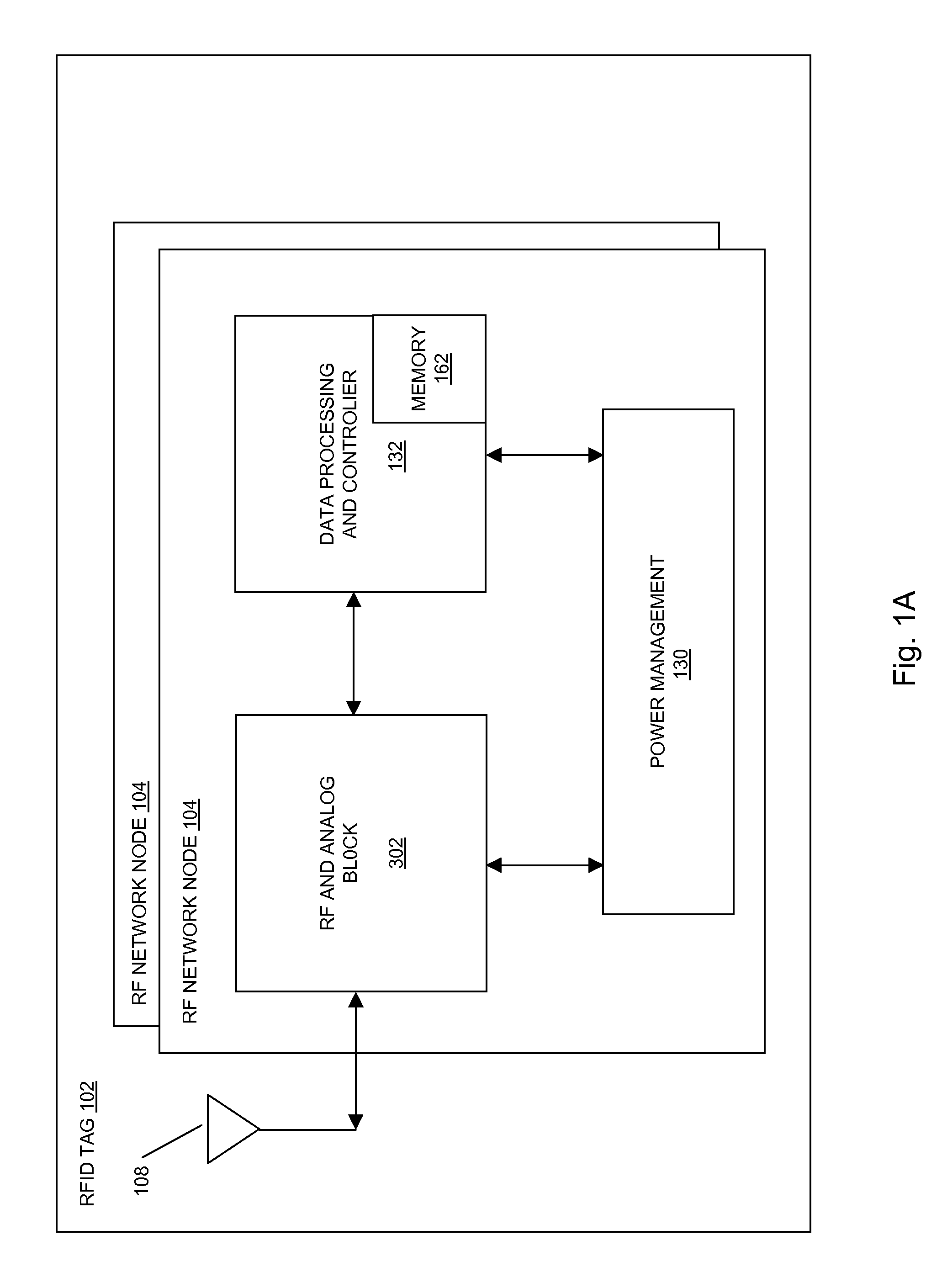
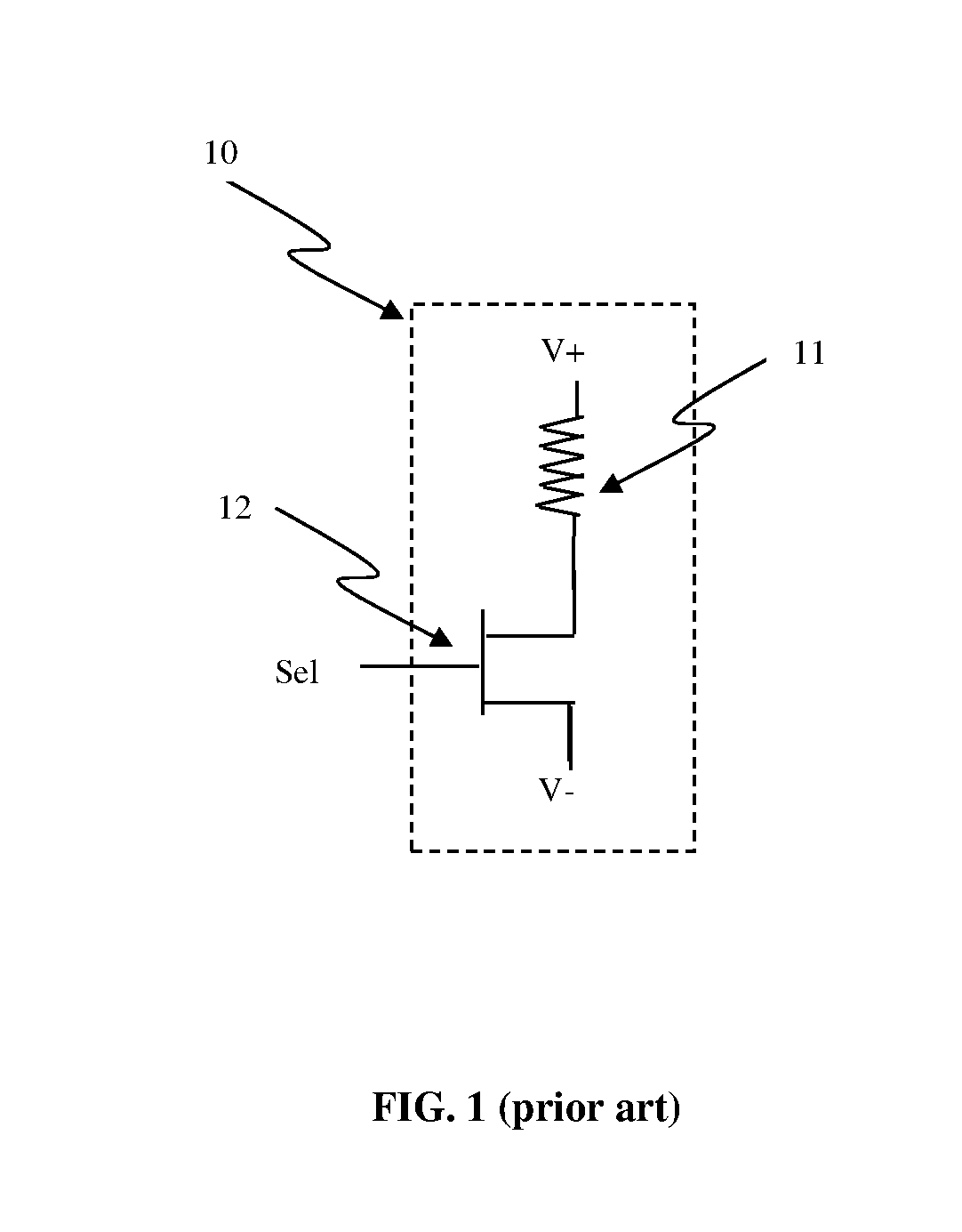
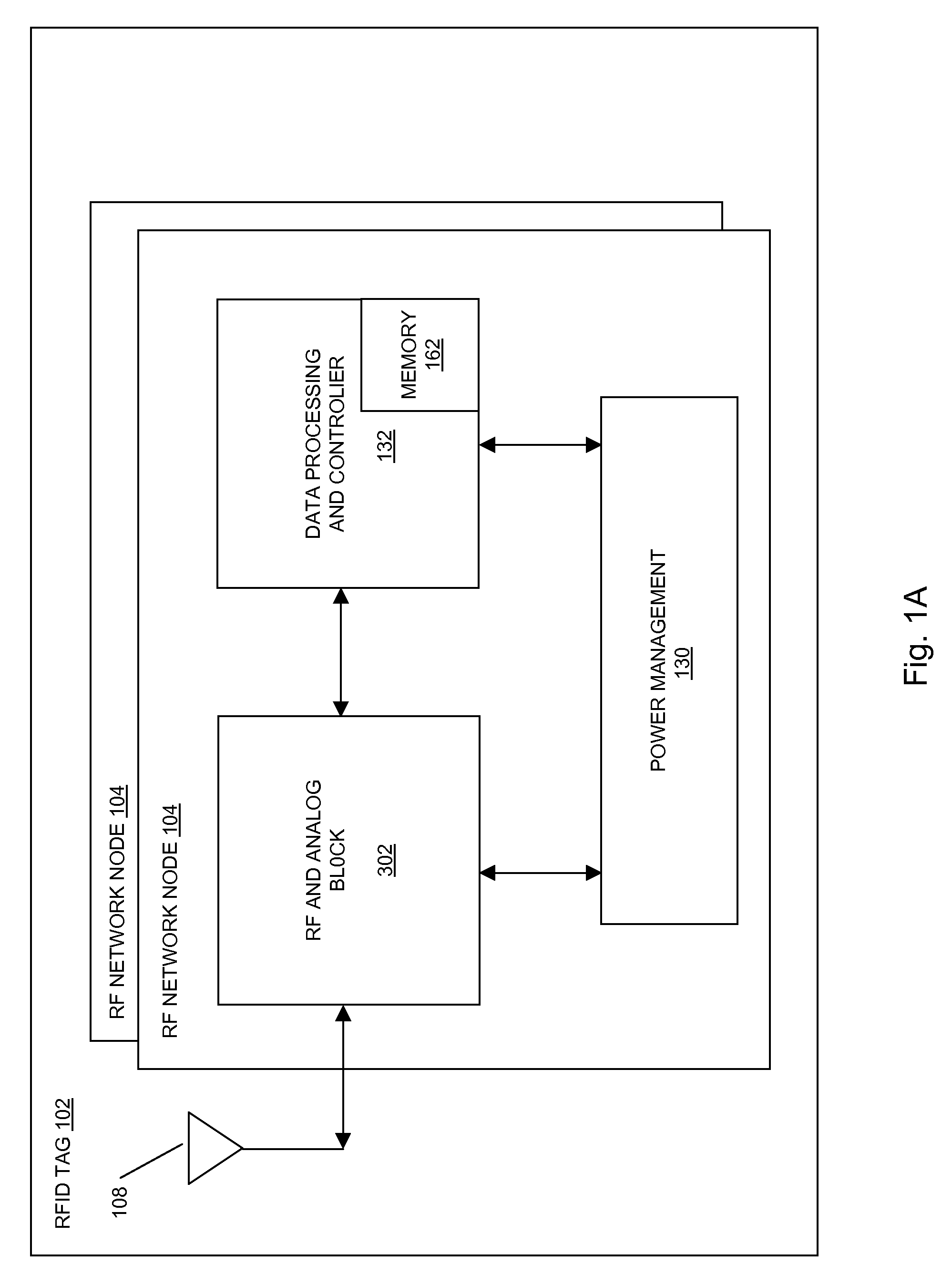
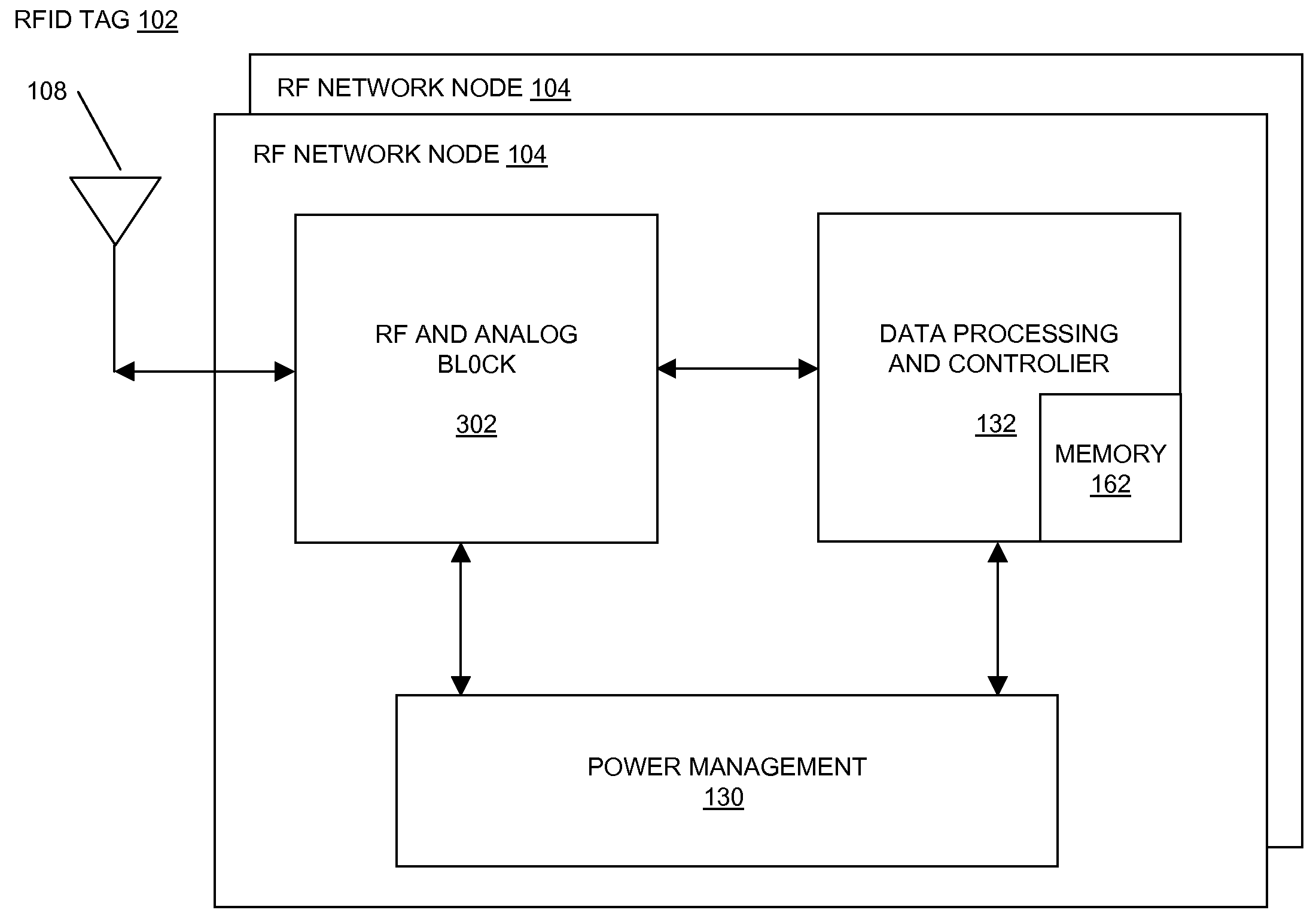
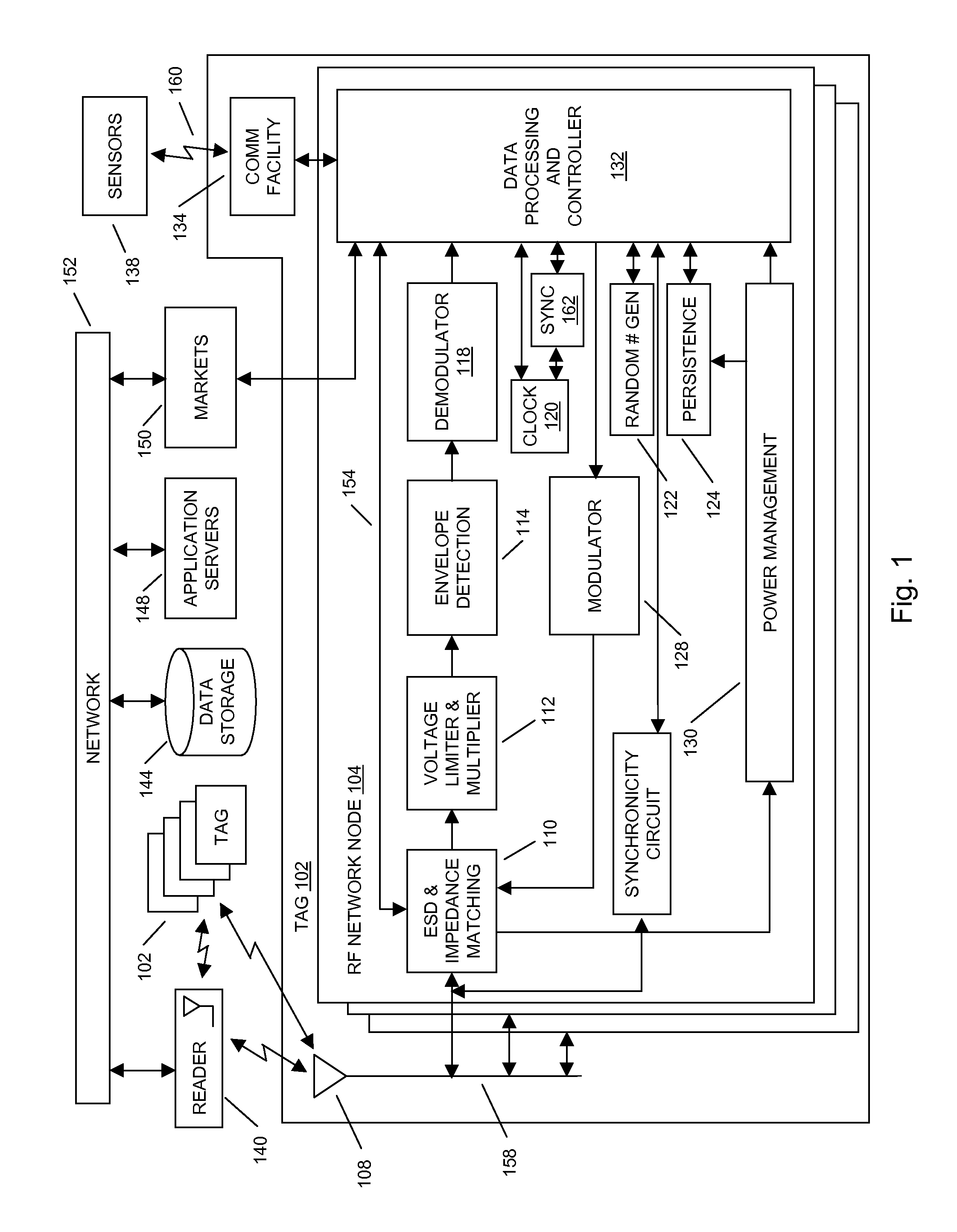
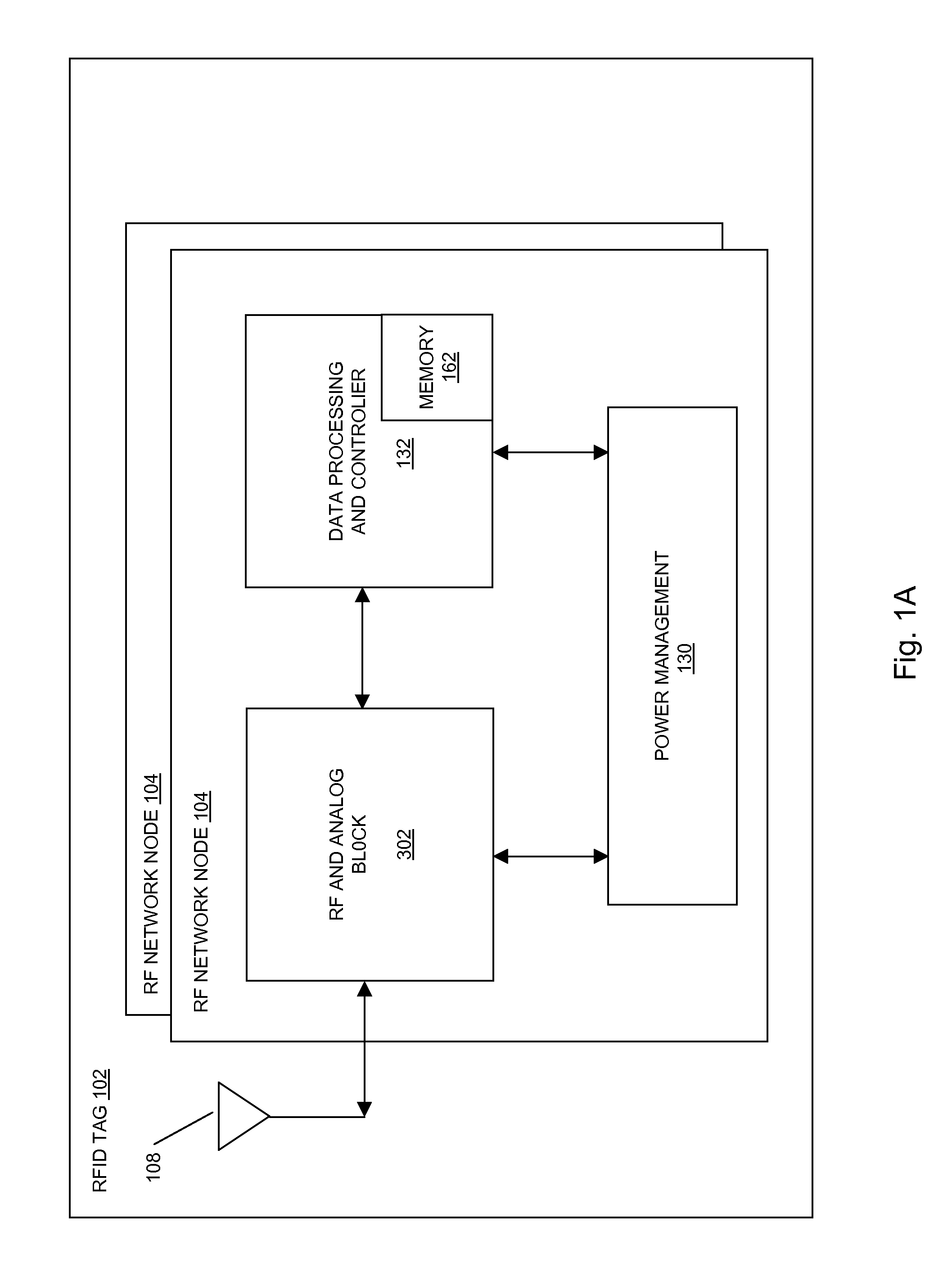
Methods and systems of a multiple radio frequency network node RFID tag
ActiveUS20080252459A1Increase redundancyFacilitates data encryptionMemory record carrier reading problemsTransmissionRadio frequencyOne time programmable
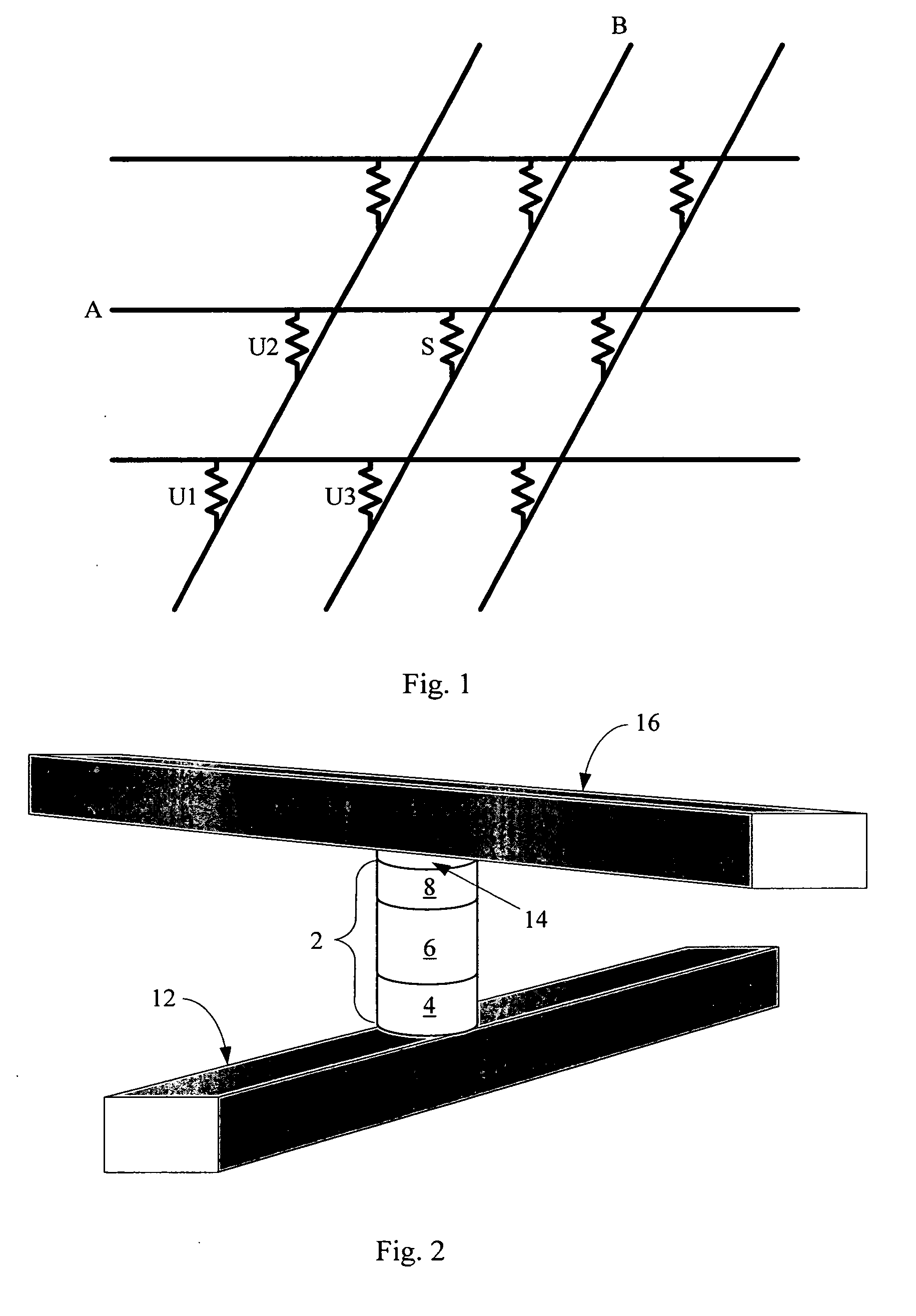
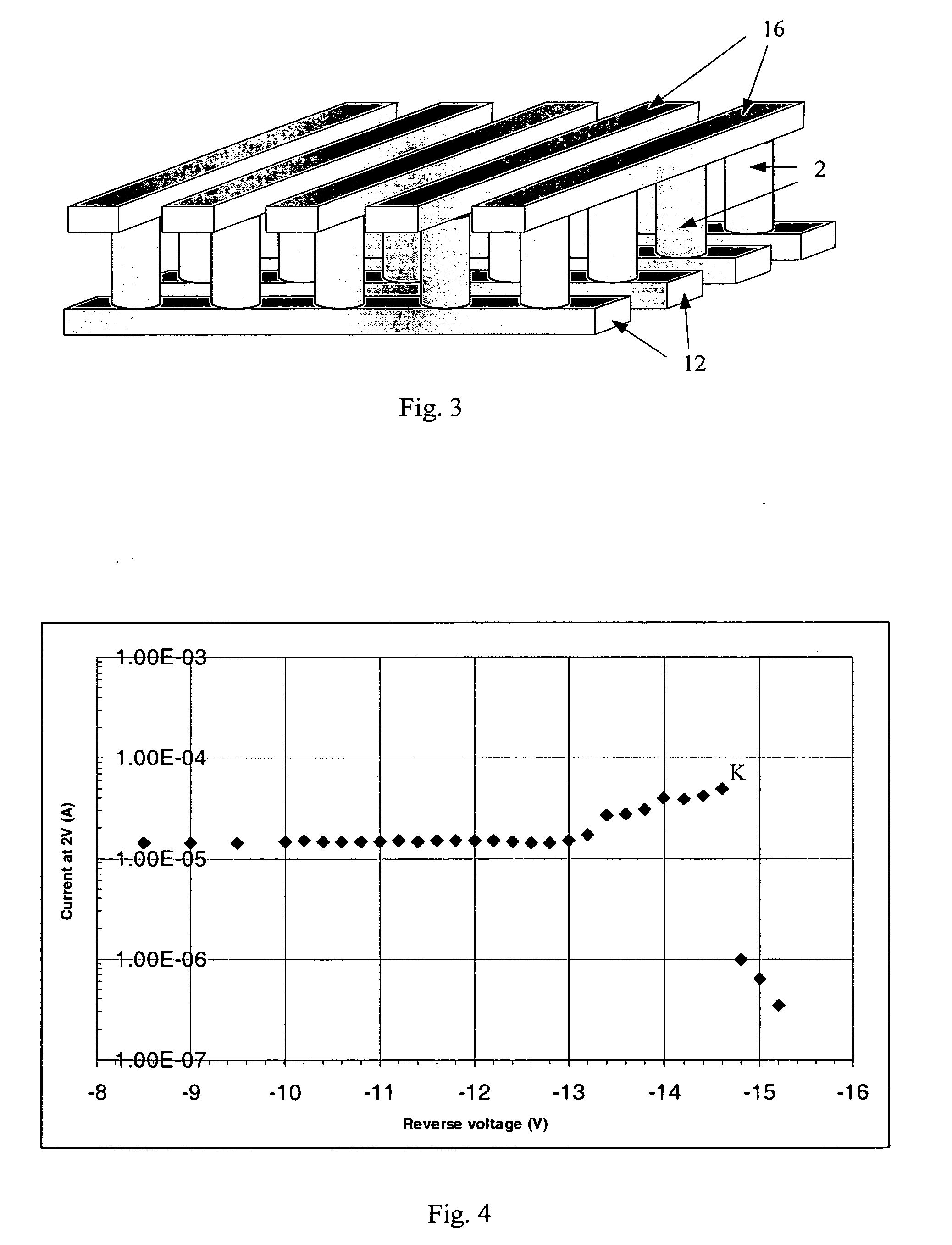
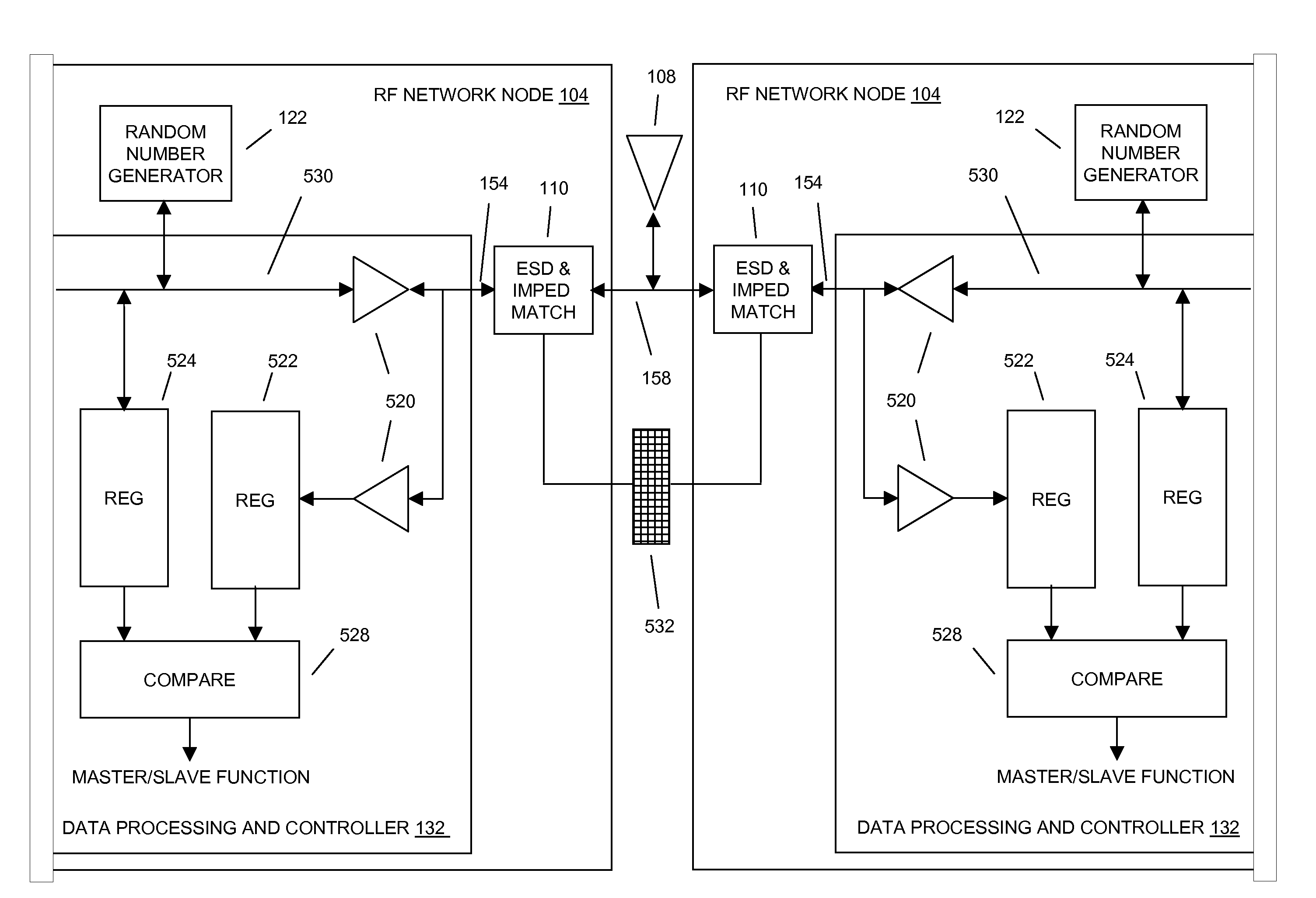
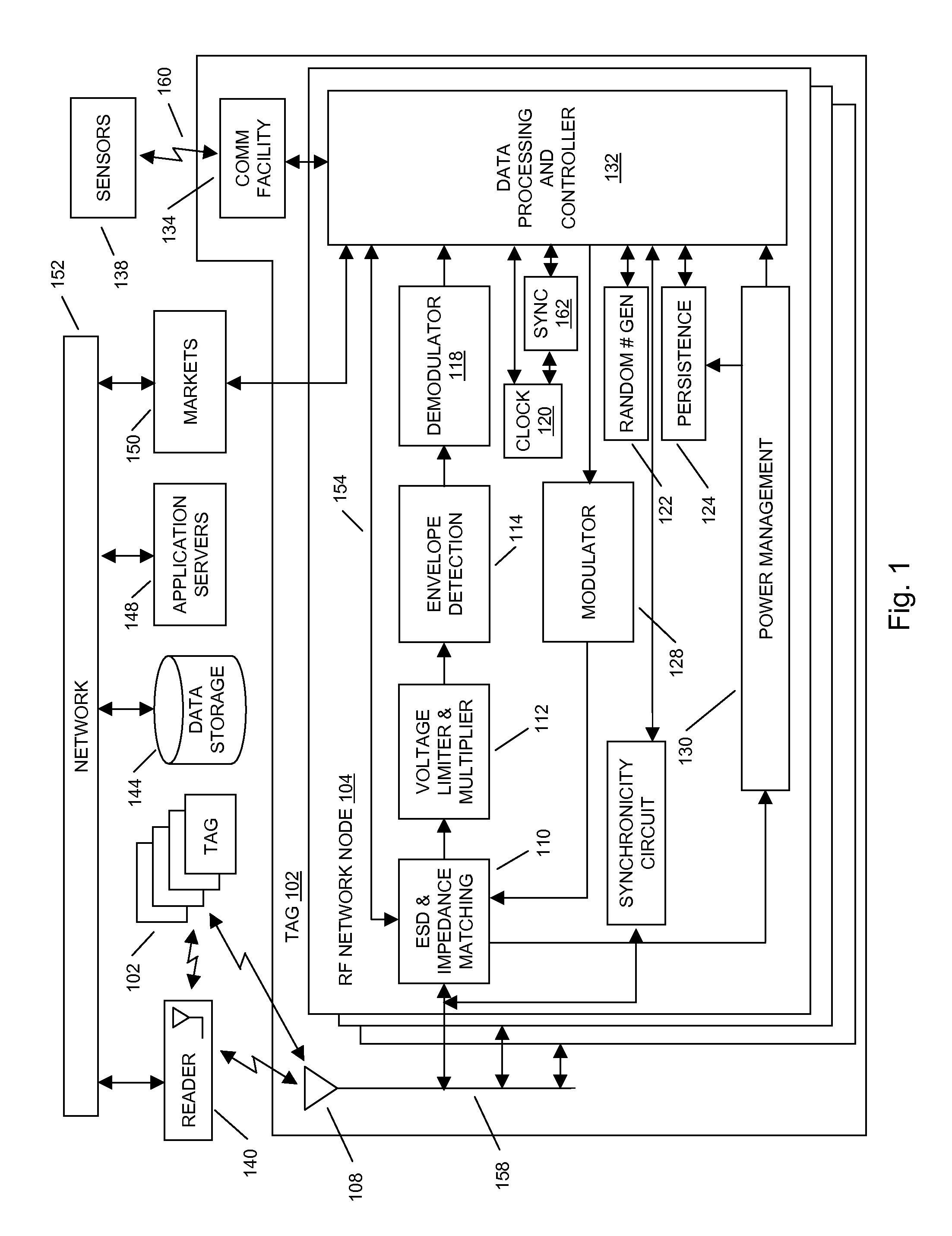
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for a Radio Frequency ID (RFID) tag that contains multiple Radio Frequency (RF) network nodes that may include memory storage for the RFID tag, the memory storage may include one time programmable (OTP) memory and many time programmable (MTP) memory and the storage of the information may be within the OTP and MTP memory.
Owner:TEGO INC
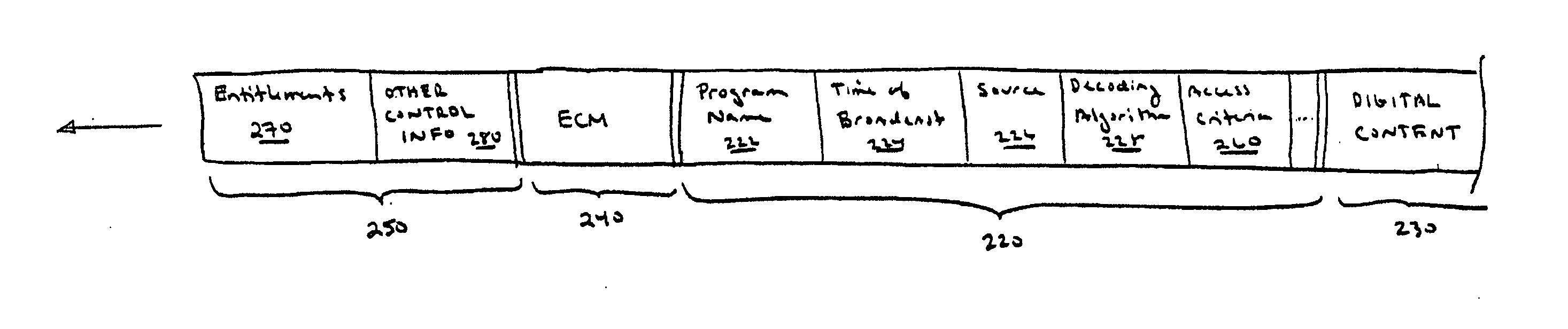
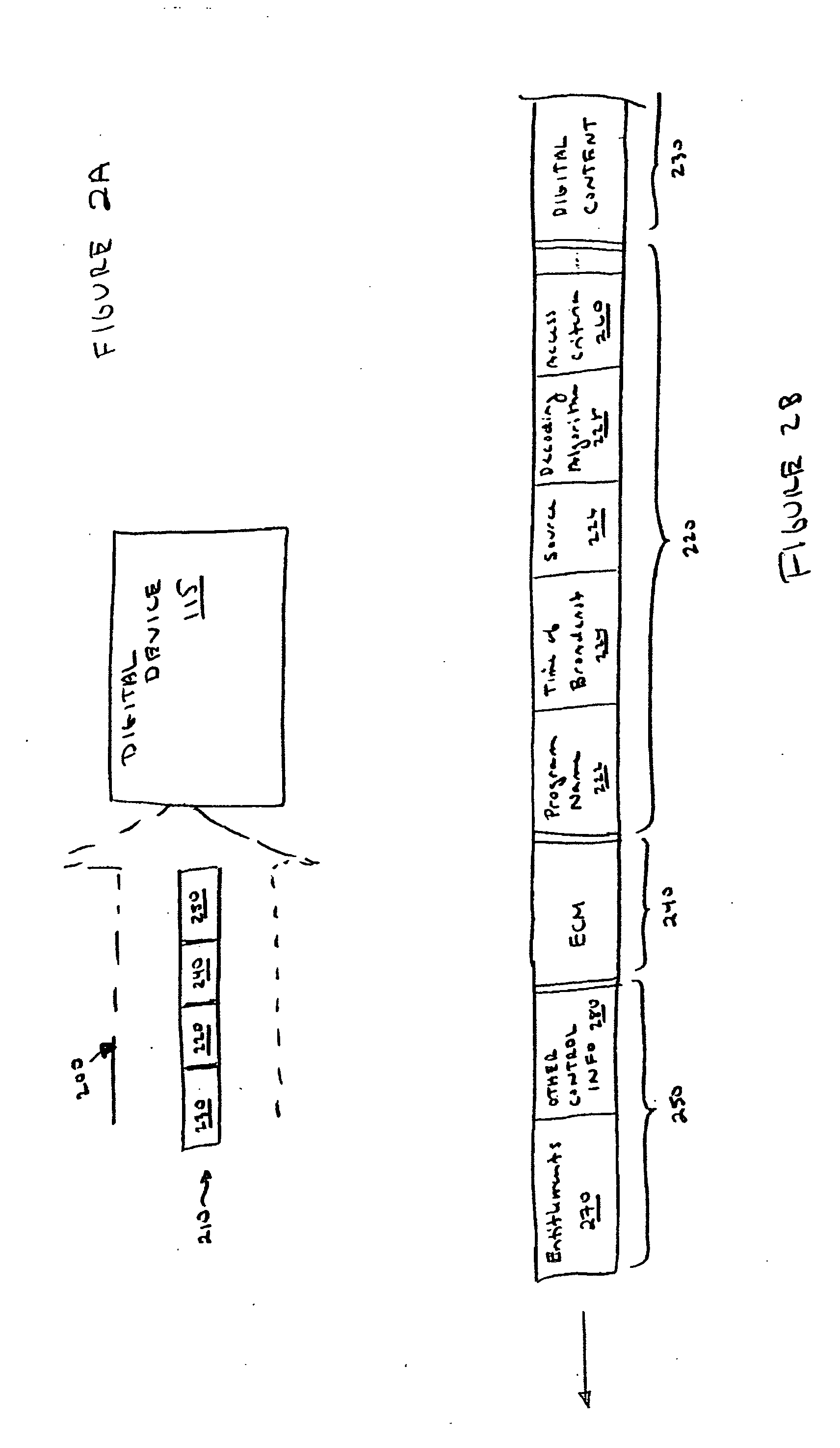
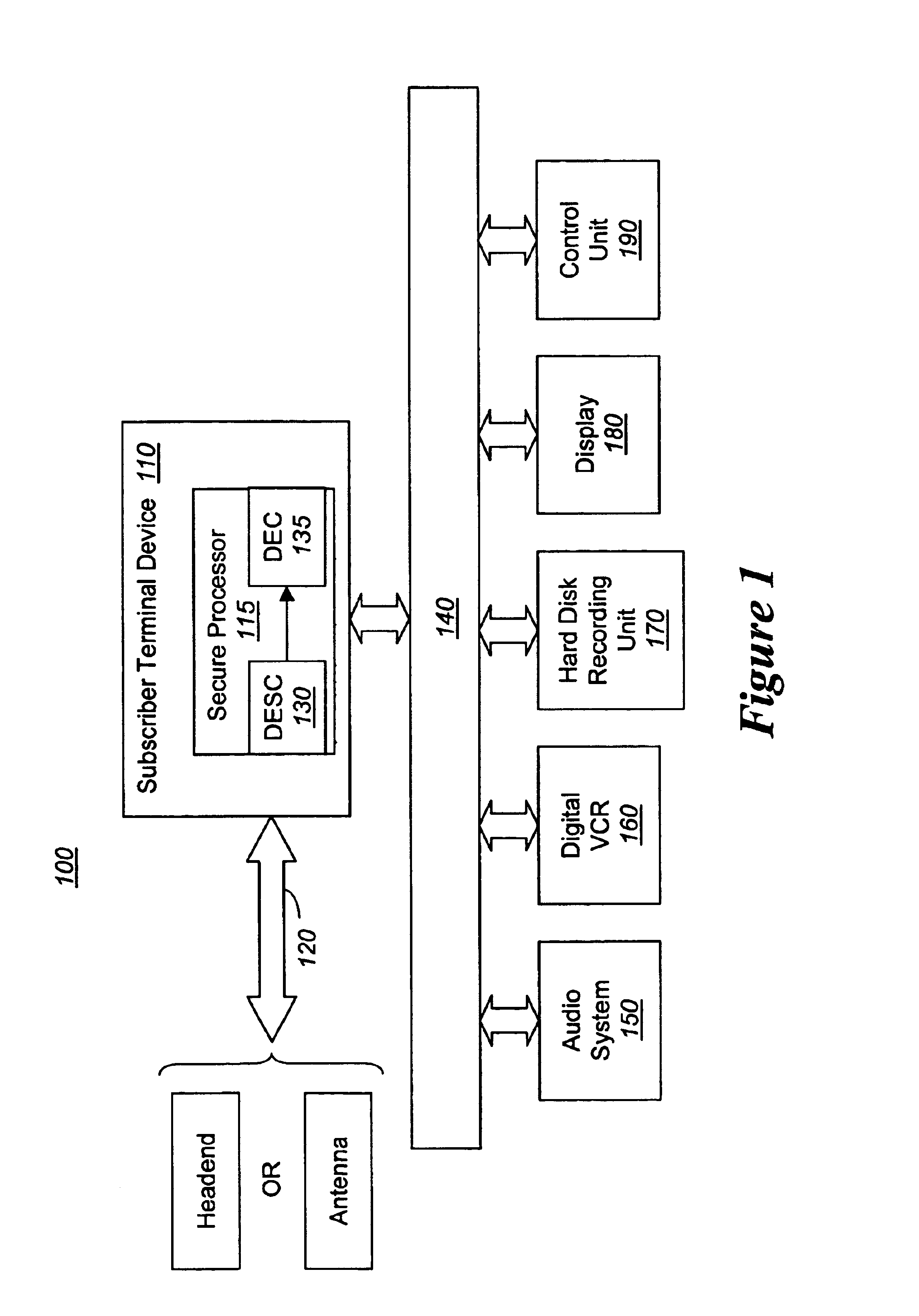
Digital rights management of a digital device
ActiveUS20050063541A1Television system detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionDigital contentRights management
According to one embodiment, an apparatus involves the descrambling of scrambled digital content using a one-time programmable key and digital rights management. The apparatus comprises a processor and a descrambler. The processor is adapted to execute a Digital Rights Management (DRM) function in order to determine whether each entitlement needed to access the digital content is pre-stored. The descrambler is adapted to decrypt encrypted information using a Unique Key stored within the one-time programmable memory. After determining that each entitlement needed to access the digital content is pre-stored, the decrypted information is used to generate a key, which is used to decrypt at least one service key for descrambling the scrambled digital content.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Non-volatile memory and method with multi-stream updating
ActiveUS20060155920A1Improve performanceWrite efficientlyMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesMulti streamData recording
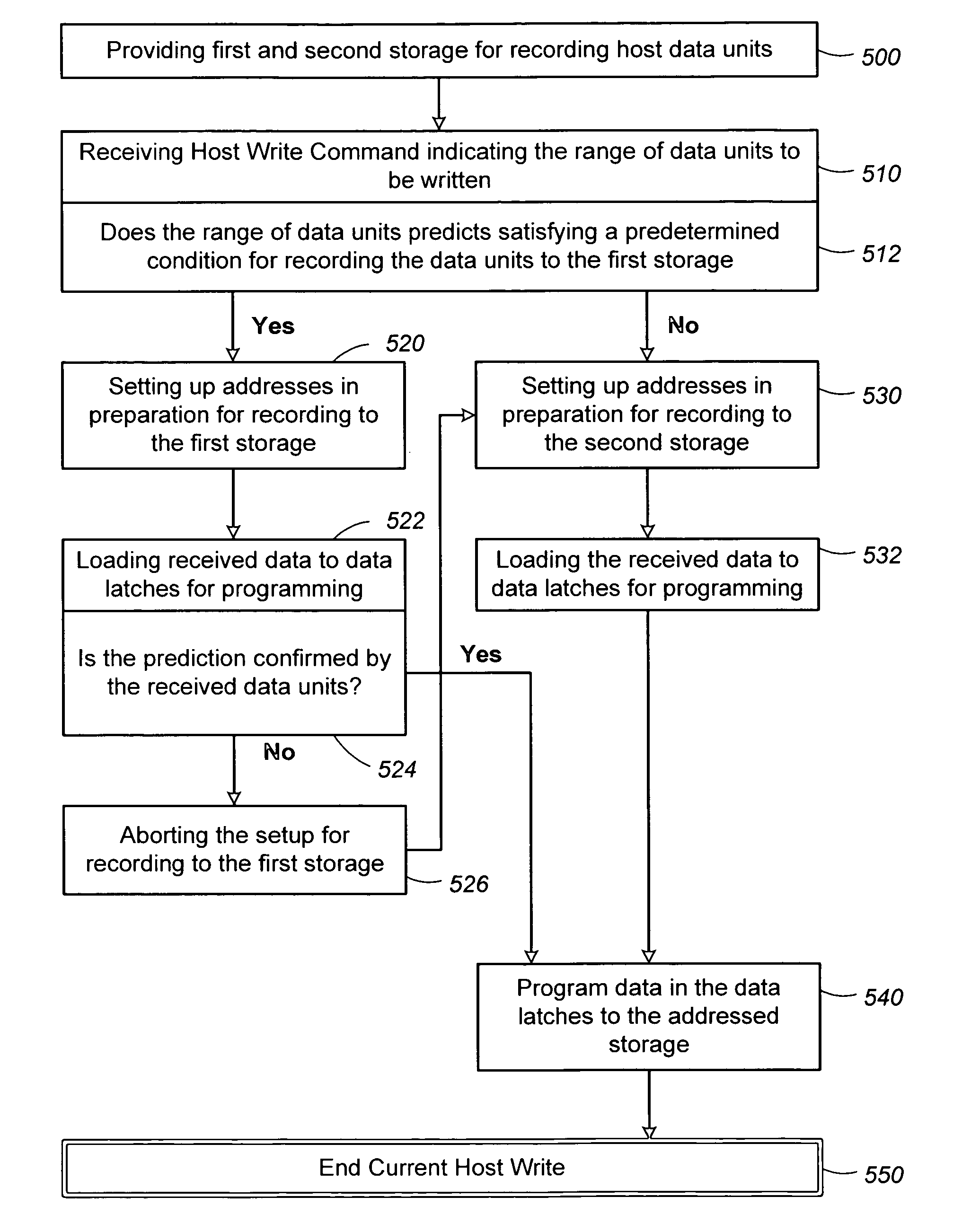
In a memory that is programmable page by page and each page having multiple sectors that are once-programmable, even if successive writes are sequential, the data recorded to an update block may be fragmented and non-sequential. Instead of recording update data to an update block, the data is being recorded in at least two interleaving streams. When a full page of data is available, it is recorded to the update block. Otherwise, it is temporarily recorded to the scratch pad block until a full page of data becomes available to be transferred to the update block. Preferably, a pipeline operation allows the recording to the update block to be set up as soon as the host write command indicates a full page could be written. If the actual write data is incomplete due to interruptions, the setup will be canceled and recording is made to the scratch pad block instead.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Split-channel antifuse array architecture
InactiveUS20060244099A1Limited over-voltage exposureSimplify and improve and accessTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCMOSEngineering
Generally, the present invention provides a variable thickness gate oxide anti-fuse transistor device that can be employed in a non-volatile, one-time-programmable (OTP) memory array application. The anti-fuse transistor can be fabricated with standard CMOS technology, and is configured as a standard transistor element having a source diffusion, gate oxide, polysilicon gate and optional drain diffusion. The variable gate oxide underneath the polysilicon gate consists of a thick gate oxide region and a thin gate oxide region, where the thin gate oxide region acts as a localized breakdown voltage zone. A conductive channel between the polysilicon gate and the channel region can be formed in the localized breakdown voltage zone during a programming operation. In a memory array application, a wordline read current applied to the polysilicon gate can be sensed through a bitline connected to the source diffusion, via the channel of the anti-fuse transistor. More specifically, the present invention provides an effective method for utilizing split channel MOS structures as an anti-fuse cell suitable for OTP memories.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
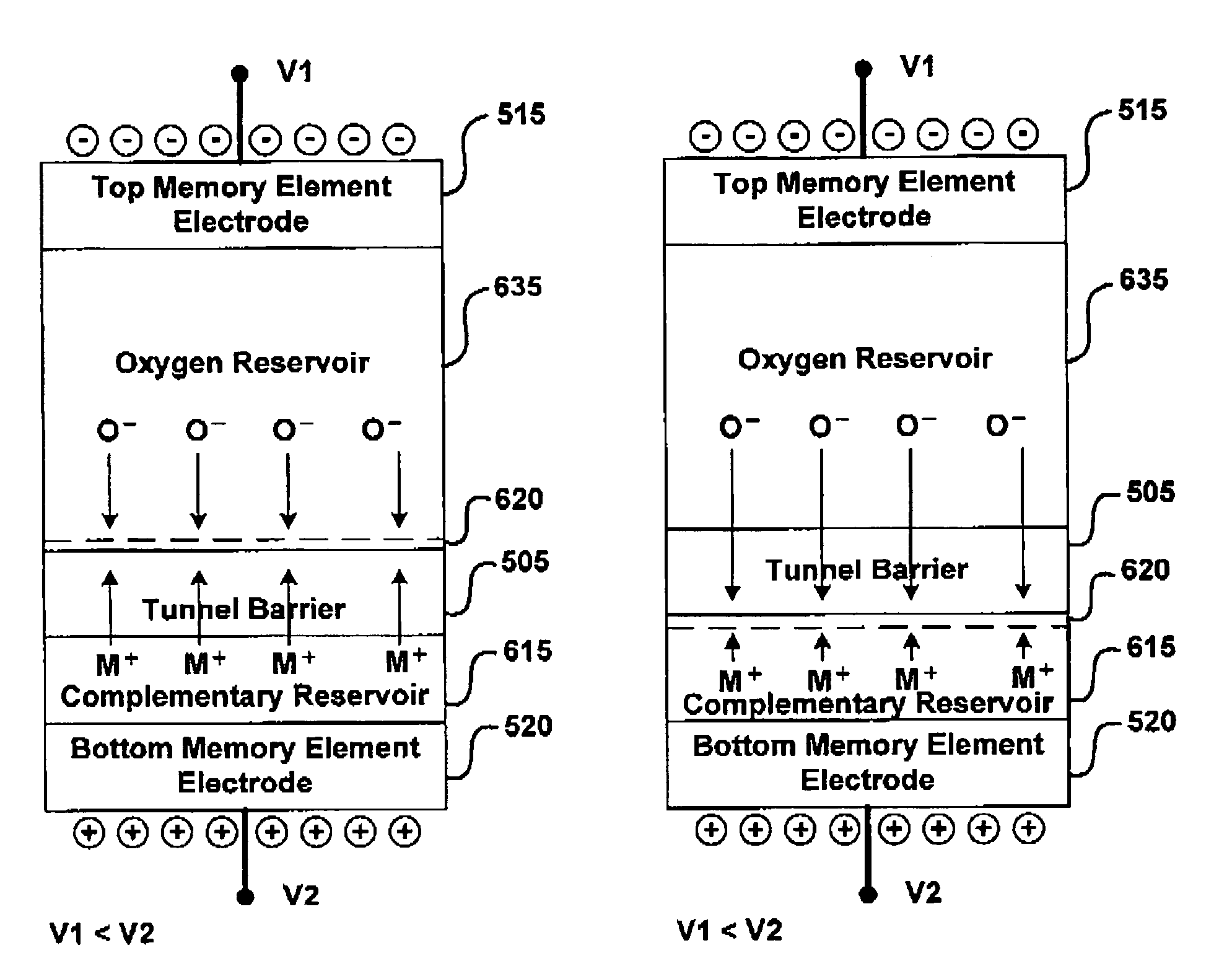
Memory using variable tunnel barrier widths
A memory using a tunnel barrier is disclosed. A memory element includes a tunneling barrier and two conductive materials. The conductive material typically has mobile ions that either move towards or away from the tunneling barrier in response to a voltage across the memory element. A low conductivity region is irreversibly formed for one time programmable memory. The tunneling barrier can be formed by mobile ions combining with complementary ions. The low conductivity region increases the effective width of the tunnel barrier, making electrons tunnel a greater distance, which reduces the memory element's conductivity. By varying conductivity, multiple states can be created in the memory cell.
Owner:HEFEI RELIANCE MEMORY LTD
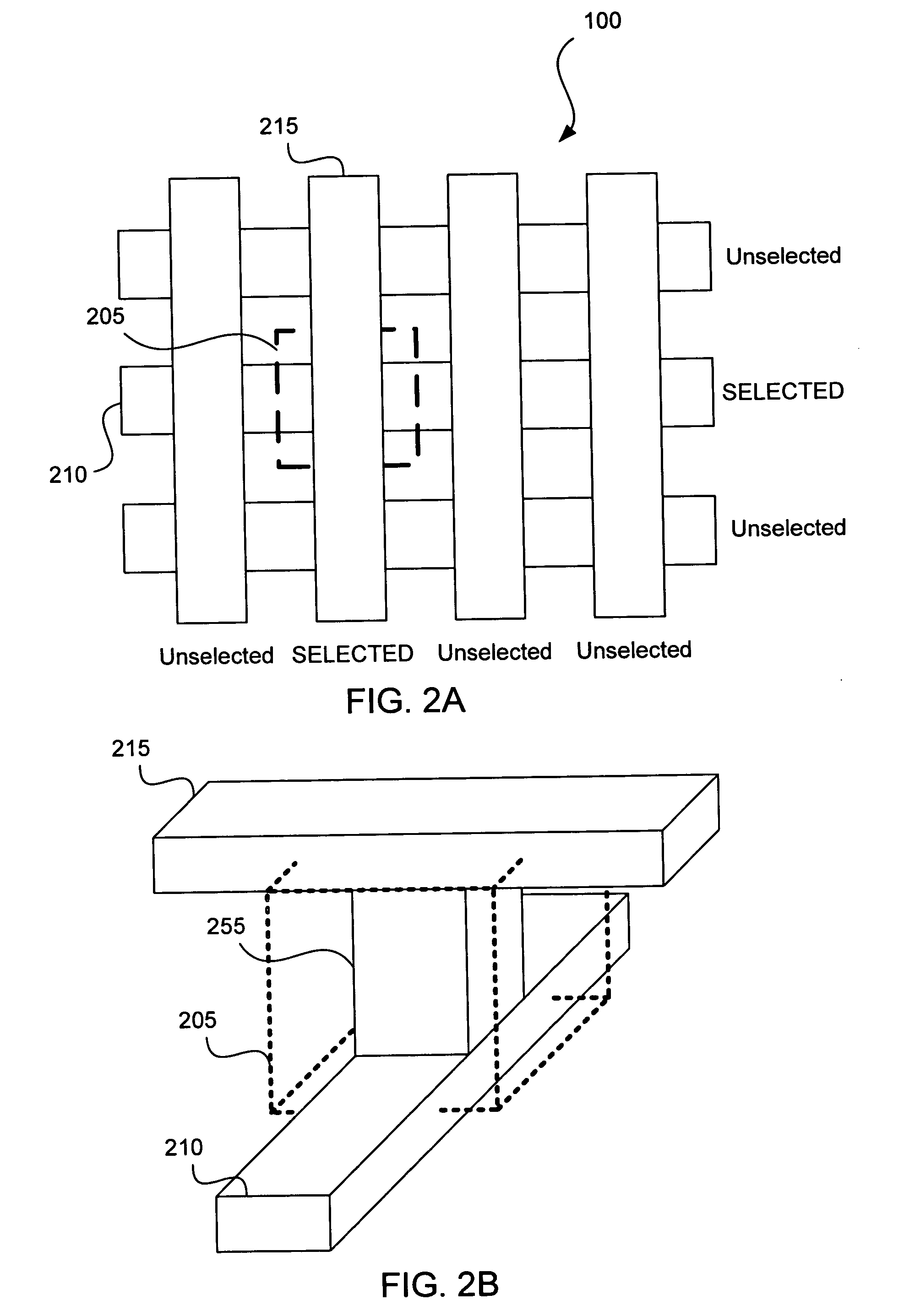
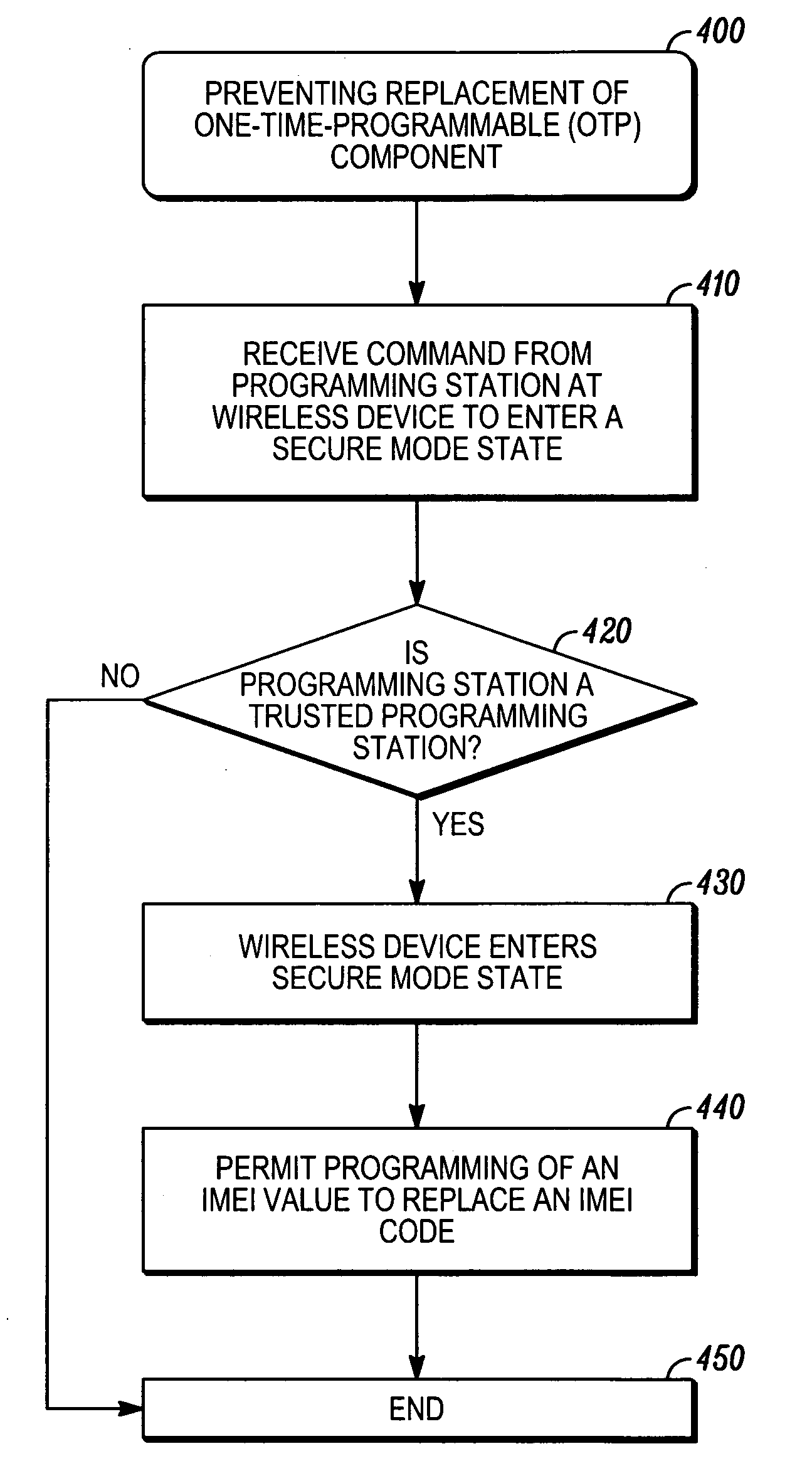
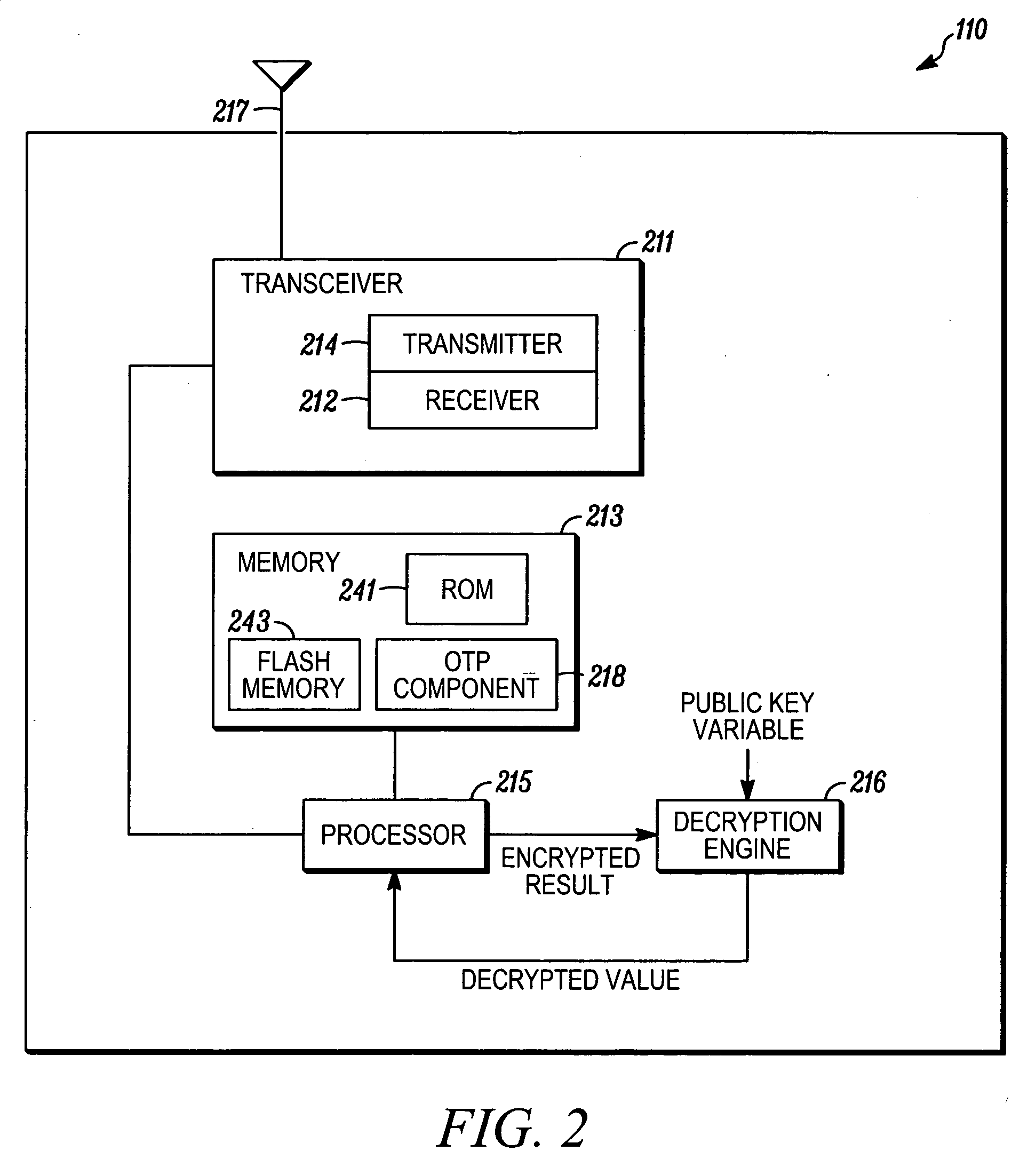
Method, system and apparatus for prevention of flash IC replacement hacking attack
InactiveUS20070050622A1User identity/authority verificationComputer security arrangementsChallenge responseOne time programmable
Techniques are provided for preventing replacement of a one-time-programmable (OTP) component. The OTP component can be part of a wireless device. The wireless device is configured such that programming of a new IMEI code into the OTP component is permitted only when the wireless device is in a secure-mode state. A challenge-response protocol is used to place the wireless device in this secure-mode state.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
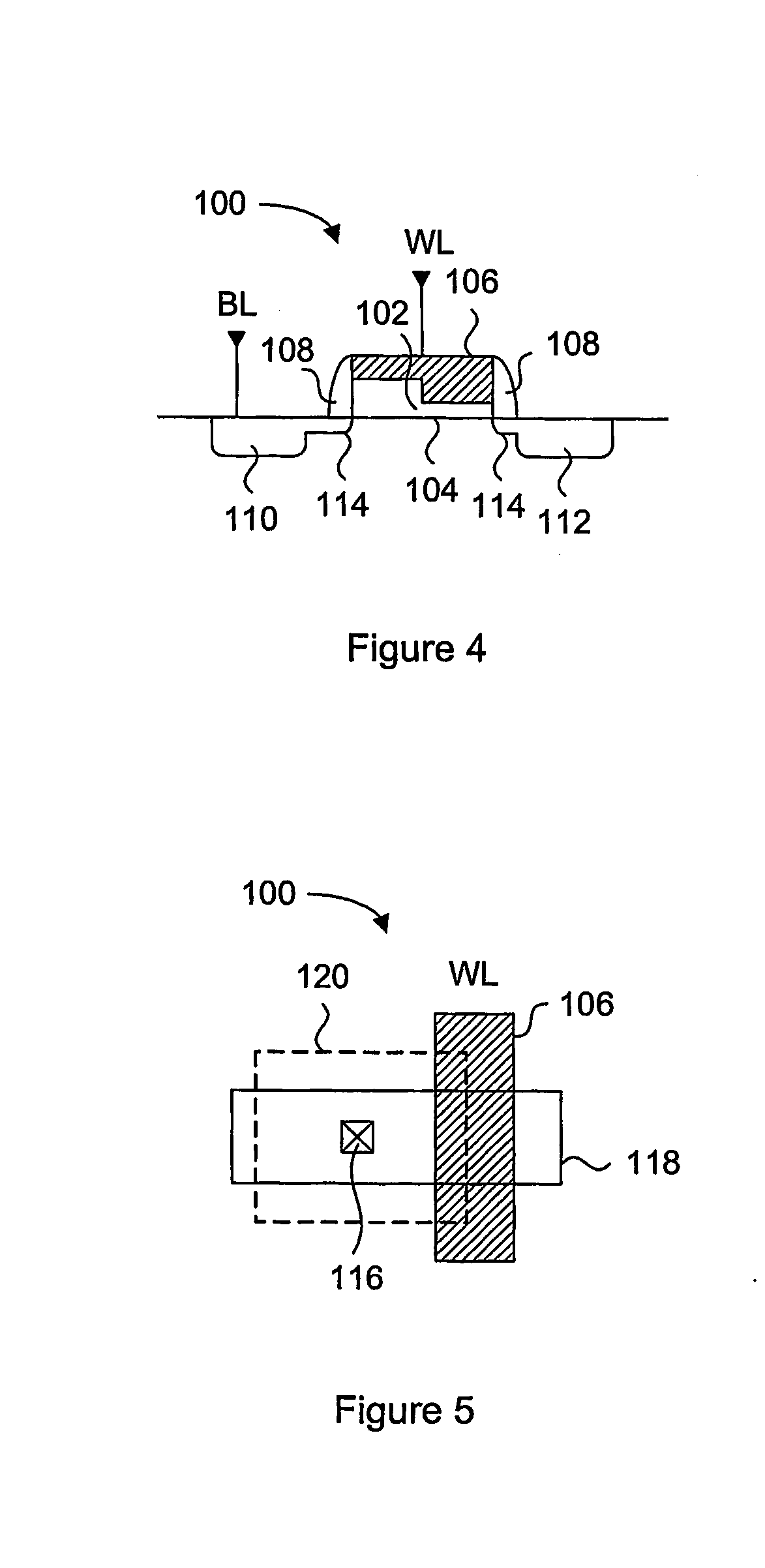
Multi-use memory cell and memory array
InactiveUS20070069276A1Solid-state devicesRead-only memoriesComputer architectureSemiconductor materials
A multi-use memory cell and memory array are disclosed. In one preferred embodiment, a memory cell is operable as a one-time programmable memory cell or a rewritable memory cell. The memory cell comprises a memory element comprising a semiconductor material configurable to one of at least three resistivity states, wherein a first resistivity state is used to represent a data state of the memory cell when the memory cell operates as a one-time programmable memory cell but not when the memory cell operates as a rewritable memory cell. A memory array with such memory cells is also disclosed. In another preferred embodiment, a memory cell is provided comprising a switchable resistance material, wherein the memory cell is operable in a first mode in which the memory cell is programmed with a forward bias and a second mode in which the memory cell is programmed with a reverse bias.
Owner:WODEN TECH INC
High density reconfigurable spin torque non-volatile memory
One time programmable memory units include a magnetic tunnel junction cell electrically coupled to a bit line and a word line. The magnetic tunnel junction cell is pre-programmed to a first resistance state, and is configured to switch only from the first resistance state to a second resistance state by passing a voltage across the magnetic tunnel junction cell. In some embodiments, a transistor is electrically coupled between the magnetic tunnel junction cell and the word line or the bit line. In other embodiments, a device having a rectifying switching characteristic, such as a diode or other non-ohmic device, is electrically coupled between the magnetic tunnel junction cell and the word line or the bit line. Methods of pre-programming the one time programmable memory units and reading and writing to the units are also disclosed.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Methods and systems of a multiple radio frequency network node RFID tag
ActiveUS20080186139A1Increase redundancyFacilitates data encryptionElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsRadio frequencyOne time programmable
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for a Radio Frequency ID (RFID) tag that contains multiple Radio Frequency (RF) network nodes that may include memory storage for the RFID tag, the memory storage may include one time programmable (OTP) memory and many time programmable (MTP) memory and the storage of the information may be within the OTP and MTP memory.
Owner:TEGO INC
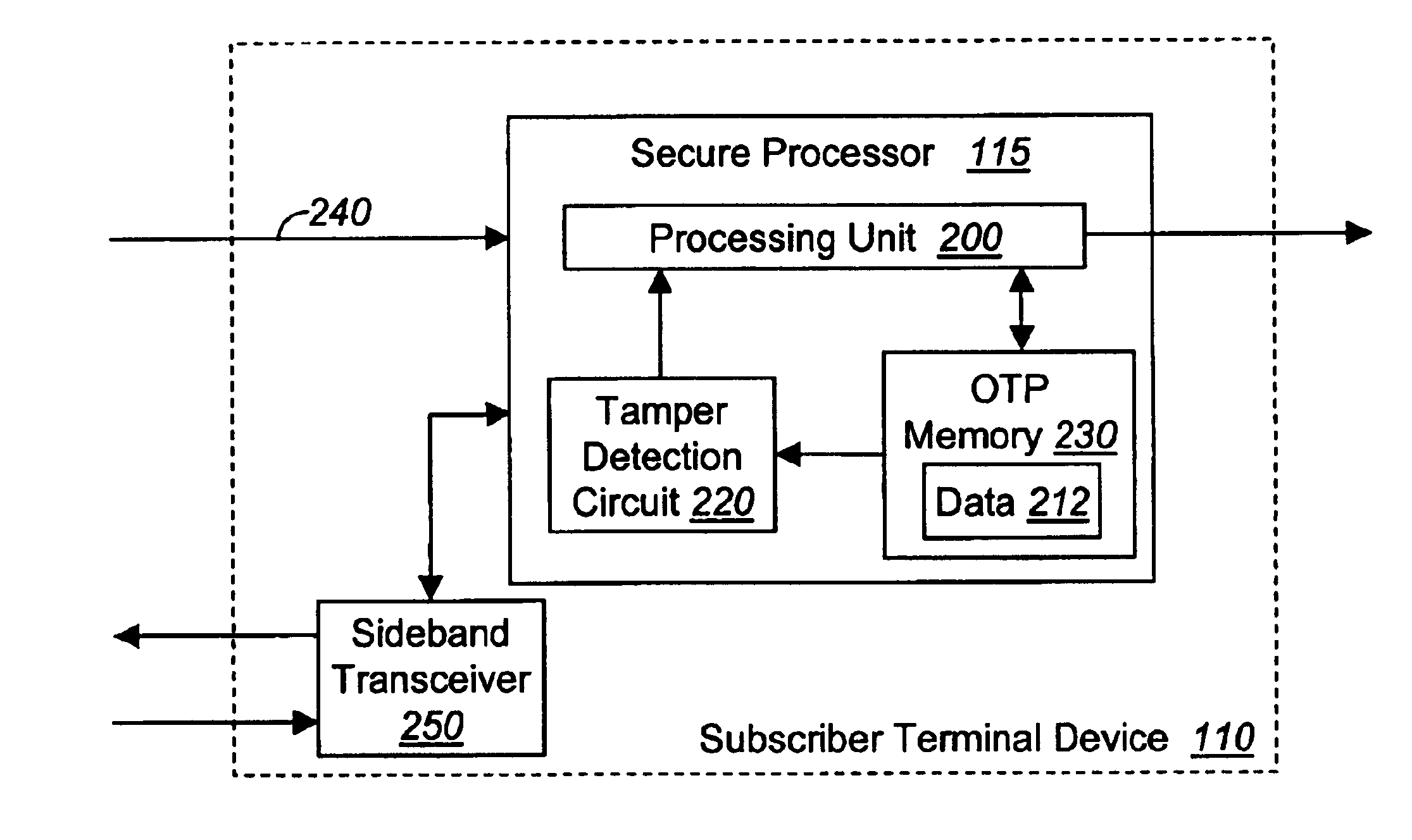
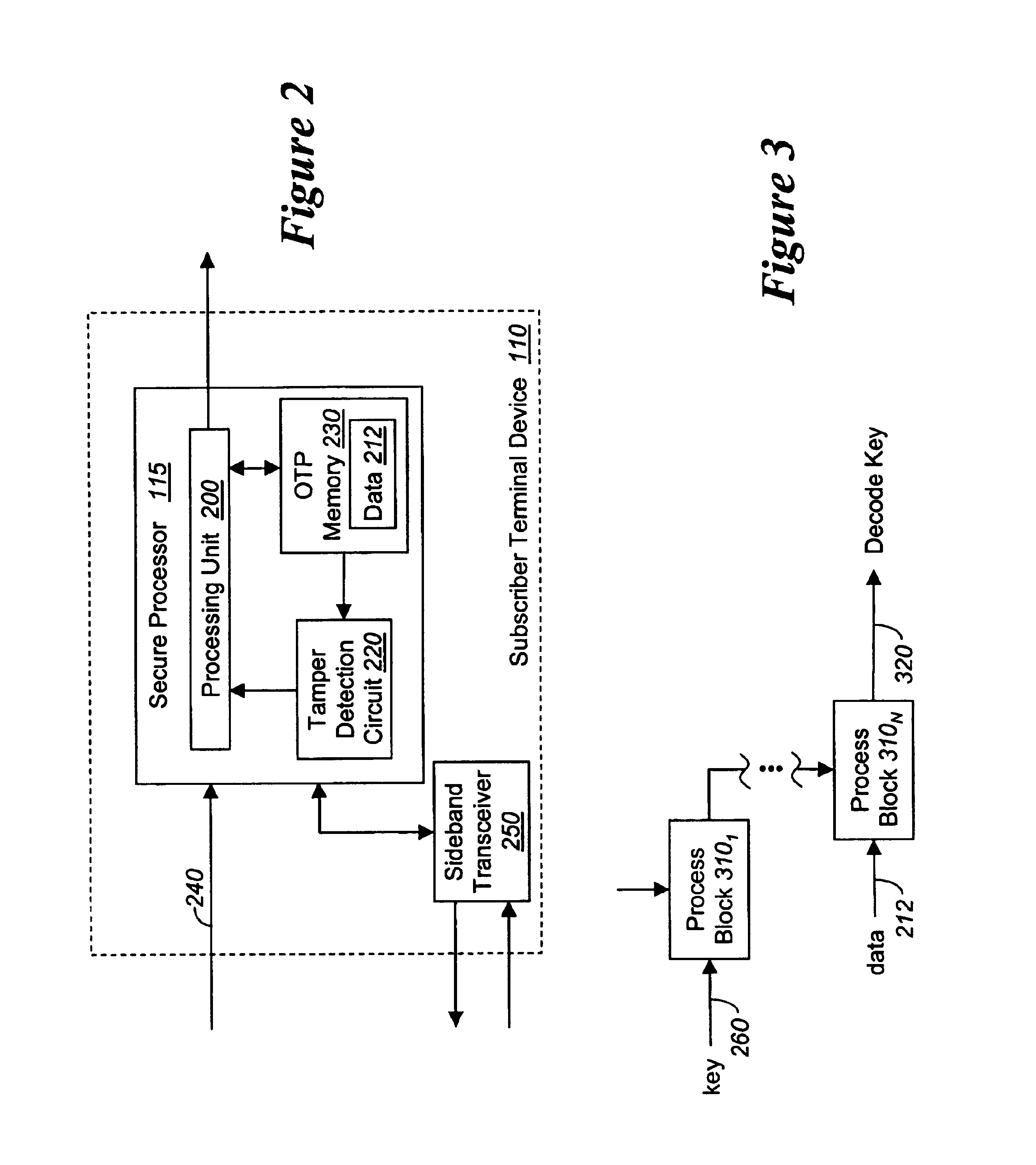
Method for detecting and preventing tampering with one-time programmable digital devices
According to one embodiment, an apparatus for detecting and preventing tampering with a programmable digital device. The apparatus comprises a one-time programmable (OTP) memory that includes a plurality of memory cells to store data. The plurality of memory cells may be programmed to a default state or a state opposite the default state. A tamper detection circuit is coupled to these memory cells in order to sense a condition when each bit associated with the plurality of memory cells is programmed to the state opposite the default state. In response to detecting this condition, it is considered that the programmable digital device implemented with the apparatus has been tampered with and operations are performed to combat the tampering of the digital device.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Method and System of Using One-Time Programmable Memory as Multi-Time Programmable in Code Memory of Processors
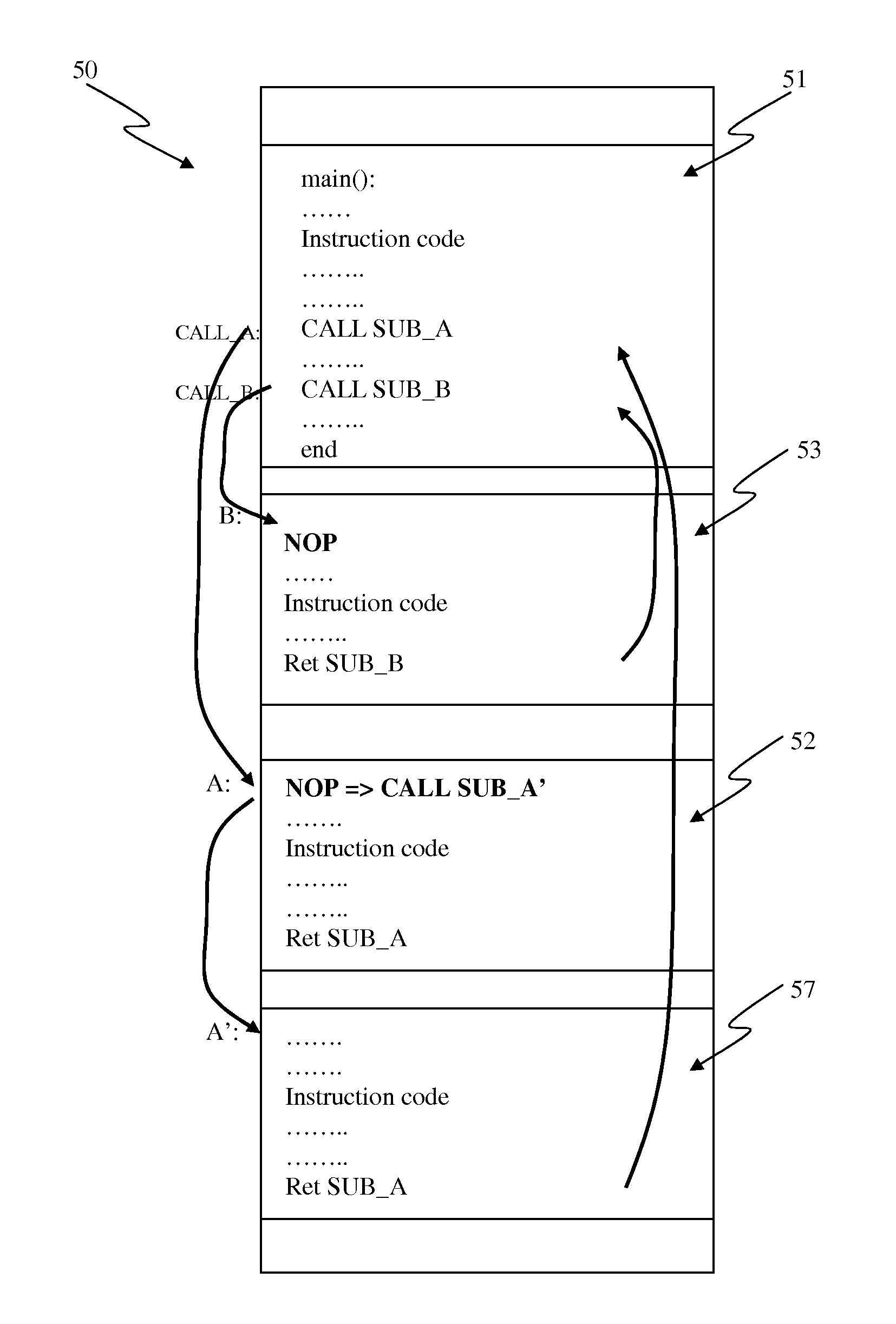
A method, device and system of using an One-Time-Programmable (OTP) memory as an Multiple-Time Programming (MTP) memory equivalent is disclosed. The use of OTP memory in this manner allows code to be updated one or more times and yet remain small in size and relatively easy to process (fabricate). The code can be program code for a processor, such as boot code, boot code kernel or other instruction code. According to one aspect, an OTP memory is able to functionally operate as if it were a MTP memory through intelligent use of NOPs, which are no operations. Subsequently, if a particular subroutine or function in the program code needs to be modified, an instruction (e.g., JUMP instruction) can be programmed into the NOP so that certain existing instructions can be bypassed and the execution of instructions of a new module can be performed.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Secure key access with one-time programmable memory and applications thereof
ActiveUS20100189262A1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesInternal/peripheral component protectionComputer moduleOne time programmable
Owner:PIXELWORKS
One-time programmable, non-volatile field effect devices and methods of making same
InactiveUS20050062062A1Small sizeReduce the required powerTransistorDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectrical stimulationsOne time programmable
One-time programmable, non-volatile field effect devices and methods of making same. Under one embodiment, a one-time-programmable, non-volatile field effect device includes a source, drain and gate with a field-modulatable channel between the source and drain. Each of the source, drain, and gate has a corresponding terminal. An electromechanically-deflectable, nanotube switching element is electrically coupled to one of the source, drain and gate and has an electromechanically-deflectable nanotube element that is positioned to be deflectable in response to electrical stimulation to form a non-volatile closed electrical state between the one of the source, drain and gate and its corresponding terminal.
Owner:NANTERO
Methods and systems of a multiple radio frequency network node RFID tag
InactiveUS20080186180A1Increase redundancyFacilitates data encryptionTransmissionRecord carriers used with machinesRadio frequencyOne time programmable
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for a Radio Frequency ID (RFID) tag that contains multiple Radio Frequency (RF) network nodes that may include memory storage for the RFID tag, the memory storage may include one time programmable (OTP) memory and many time programmable (MTP) memory and the storage of the information may be within the OTP and MTP memory.
Owner:TEGO INC
Methods and systems of a multiple radio frequency network node RFID tag
ActiveUS20080186137A1Increase redundancyFacilitates data encryptionDigital storageSubscribers indirect connectionRadio frequencyOne time programmable
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for a Radio Frequency ID (RFID) tag that contains multiple Radio Frequency (RF) network nodes that may include memory storage for the RFID tag, the memory storage may include one time programmable (OTP) memory and many time programmable (MTP) memory and the storage of the information may be within the OTP and MTP memory.
Owner:TEGO INC
Multiple-State One-Time Programmable (OTP) Memory to Function as Multi-Time Programmable (MTP) Memory
ActiveUS20120314473A1Small cell sizeLow costRead-only memoriesDigital storageOne time programmableComputer science
A circuit, method, and system for using multiple-state One-Time Programmable (OTP) memory to function as a multiple-bit programmable (MTP) memory are disclosed. The OTP memory can have N(N>2) distinct resistance states, that can be differentiated by at least N−1 reference resistances, can be functionally equivalent programmed N−1 times. The multiple-state OTP memory can have a plural of multiple-state OTP cells that can be selectively programmed to a resistance state. The reference resistance can be set to determine a state of the from the programmed multiple-state OTP cells.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Methods and systems of a multiple radio frequency network node RFID tag
InactiveUS20080186138A1Increase redundancyFacilitates data encryptionSubscribers indirect connectionTransmissionRadio frequencyOne time programmable
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for a Radio Frequency ID (RFID) tag that contains multiple Radio Frequency (RF) network nodes that may include memory storage for the RFID tag, the memory storage may include one time programmable (OTP) memory and many time programmable (MTP) memory and the storage of the information may be within the OTP and MTP memory.
Owner:TEGO INC
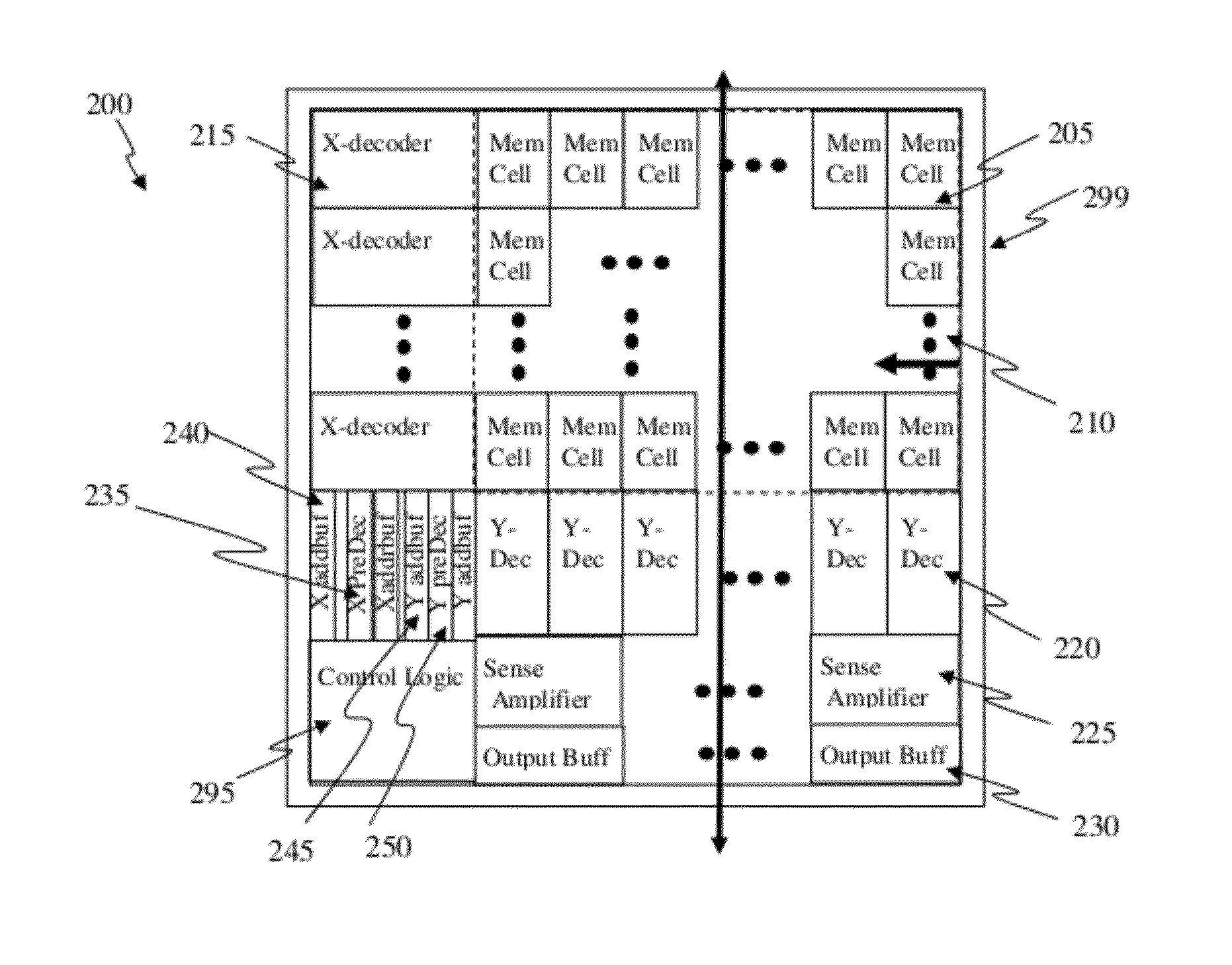
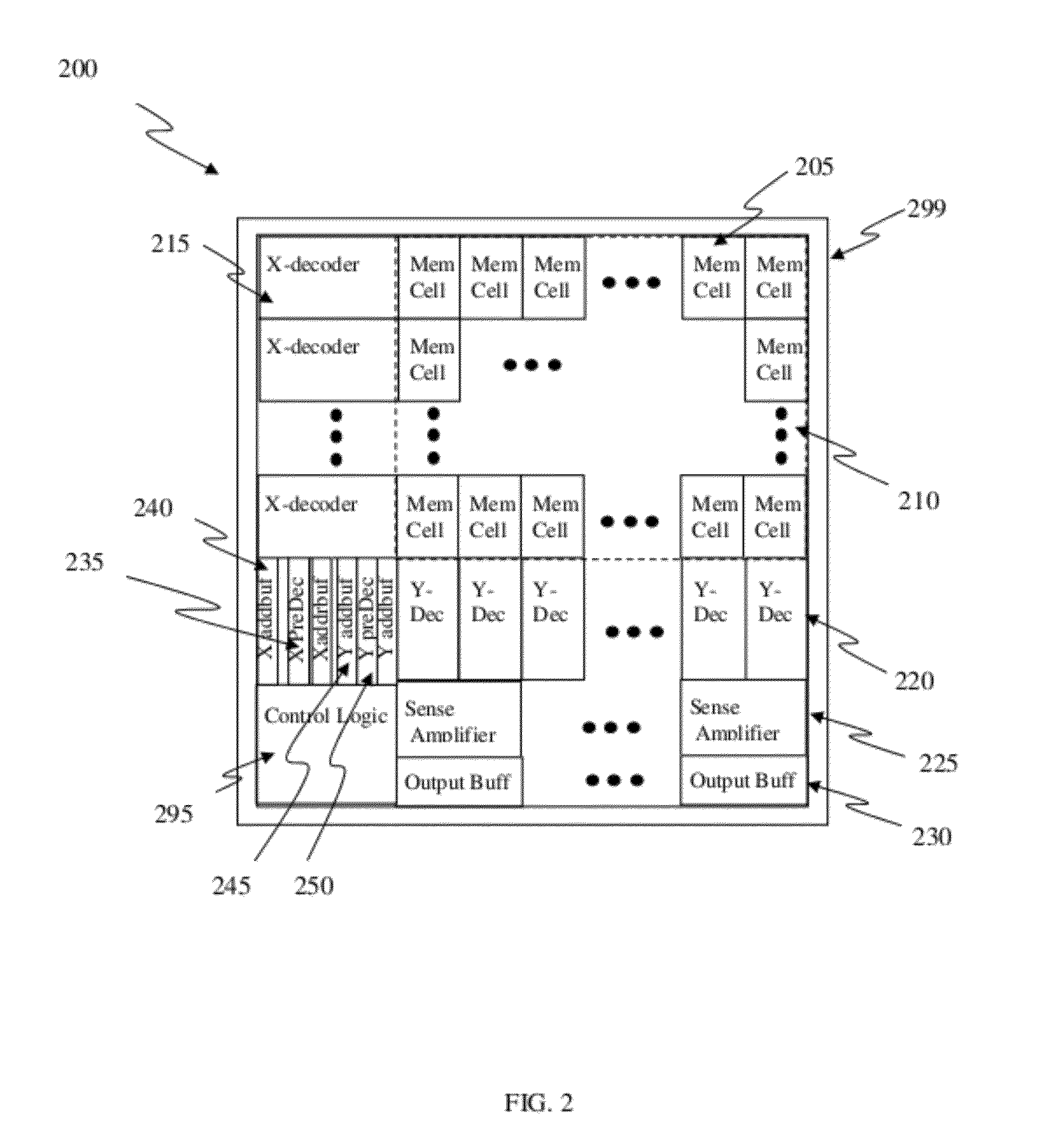
Circuit and Method of a Memory Compiler Based on Subtraction Approach
ActiveUS20120209888A1Digital data processing detailsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDatasheetParallel computing
A memory compiler to generate a set of memories is based on a subtraction approach from a set of templates (memory templates), including at least one layout database and auxiliary design databases, by software. The software can be based on general-purpose programming language or a layout-specific language. The compiled memories can be generated by reducing the memory array sizes in row and / or column directions by moving, deleting, adding, sizing, or stretching the layout objects, and disabling the high order addresses, etc. from the memory template by software. The new auxiliary design databases, such as layout phantom, behavior model, synthesis view, placement-and-routing view or datasheet, can also be generated by modifying some parameters from the memory template by software. One-time programmable memory using junction diode, polysilicon diode, or isolated active-region diode as program selector in a cell can be generated accordingly.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
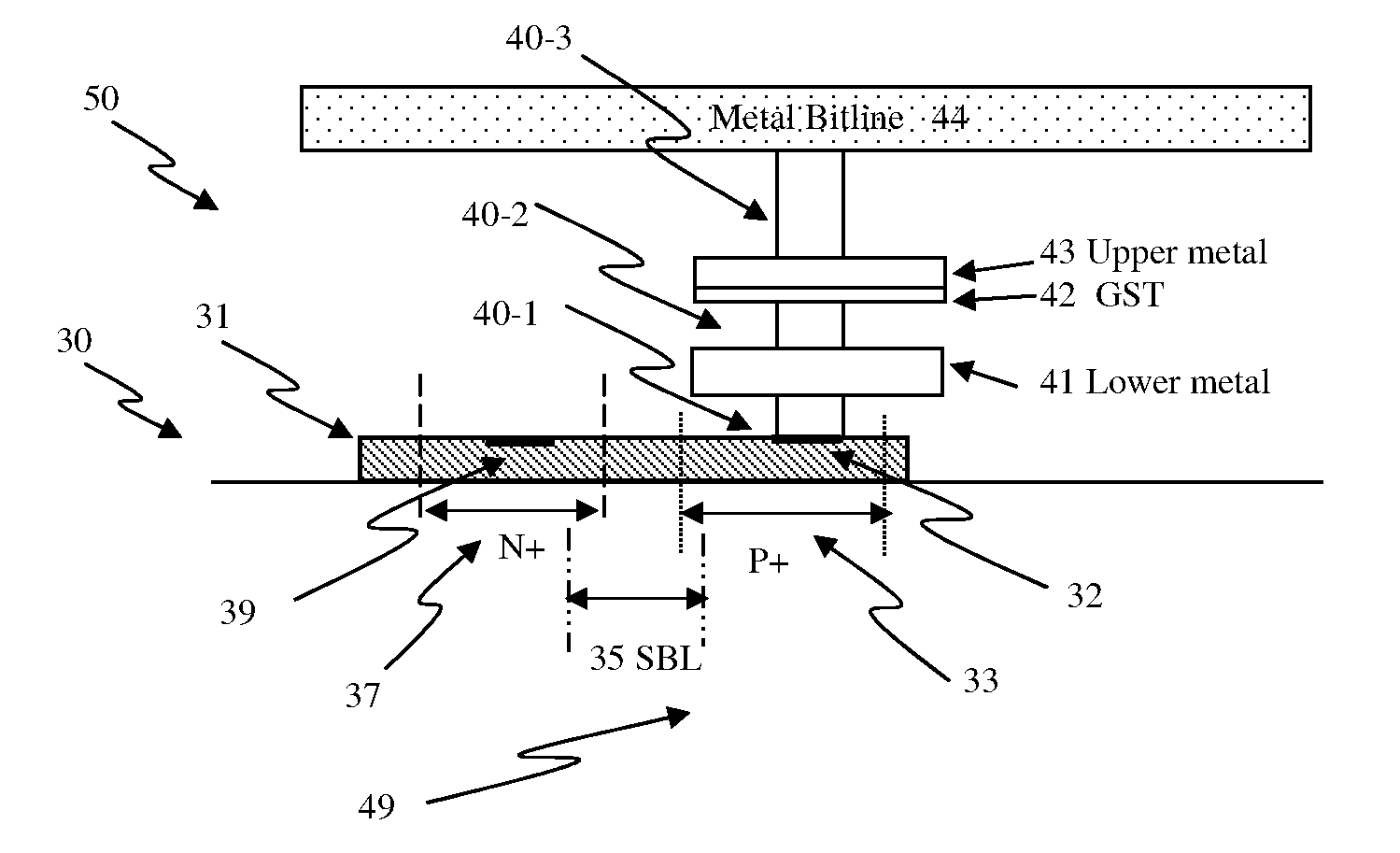
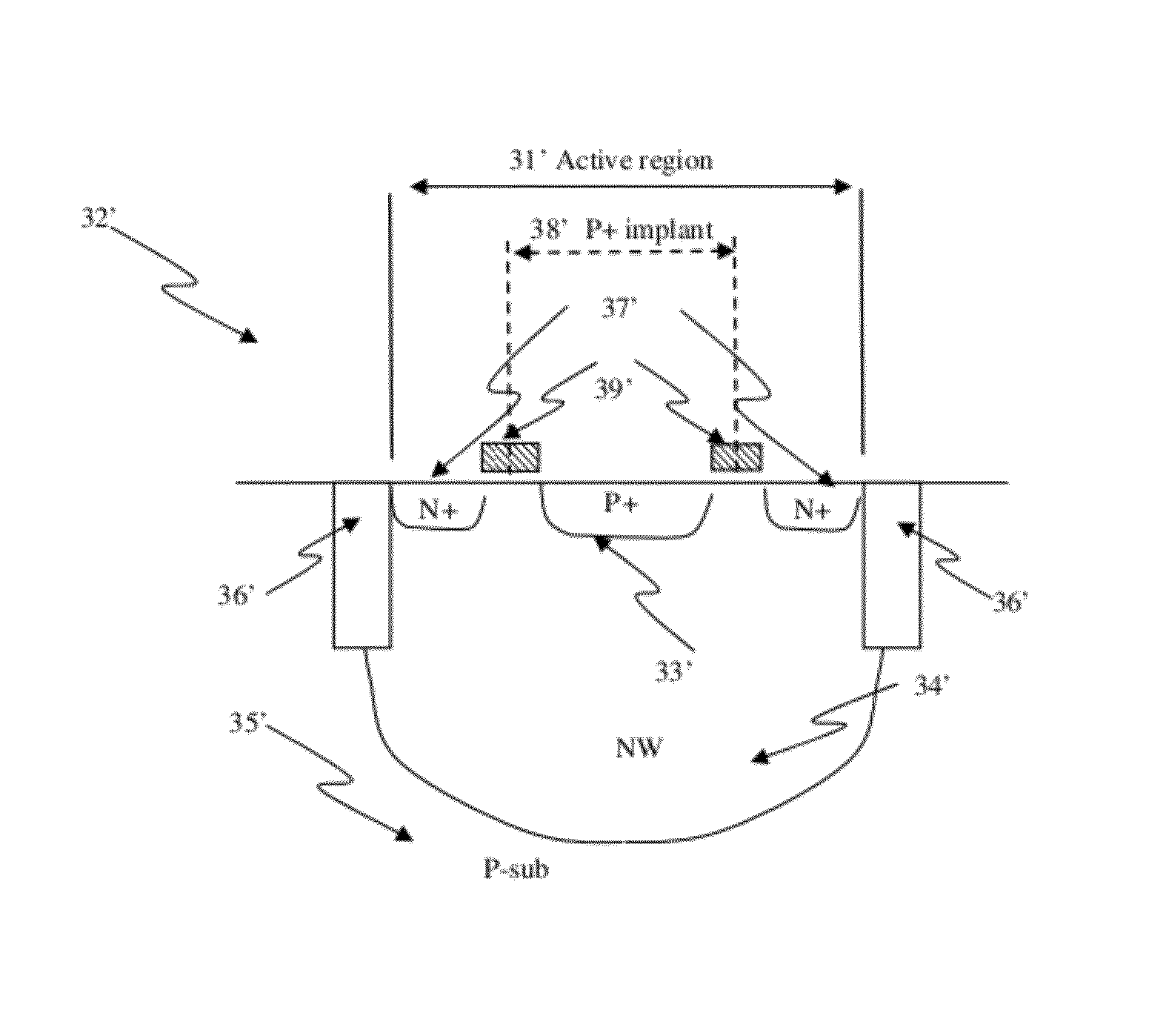
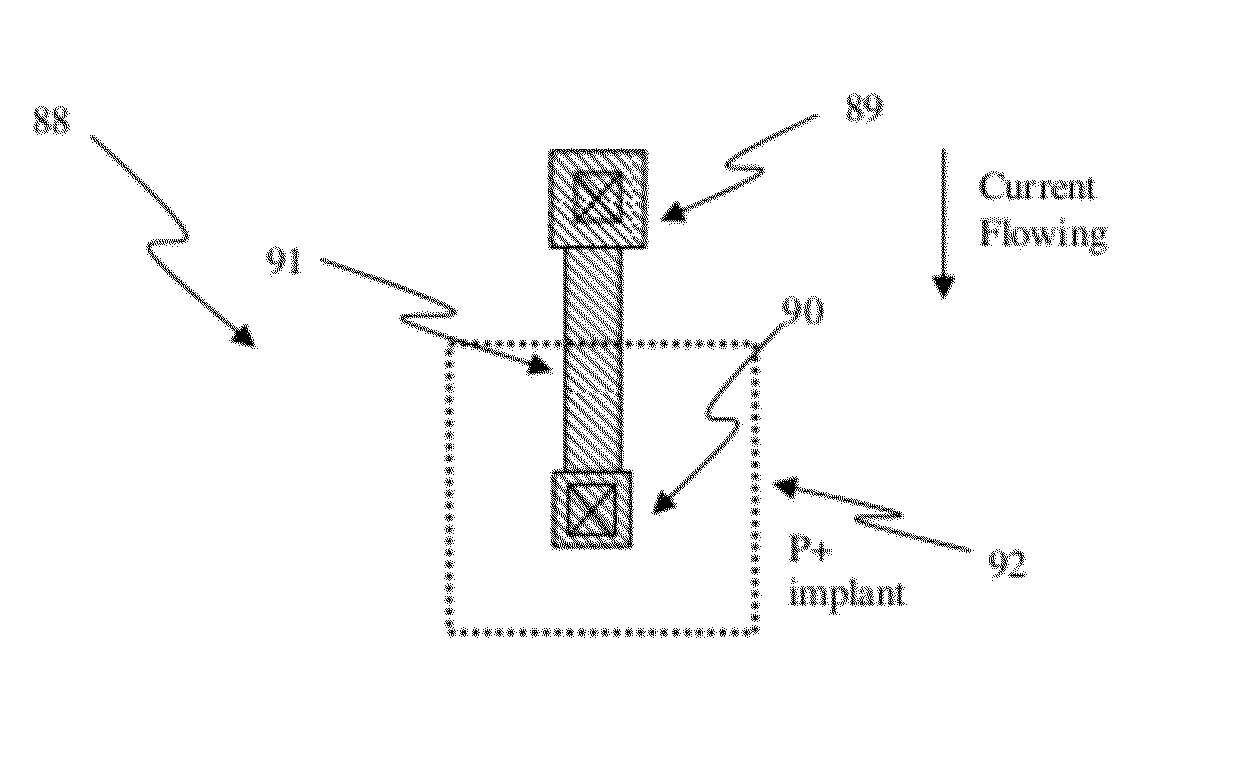
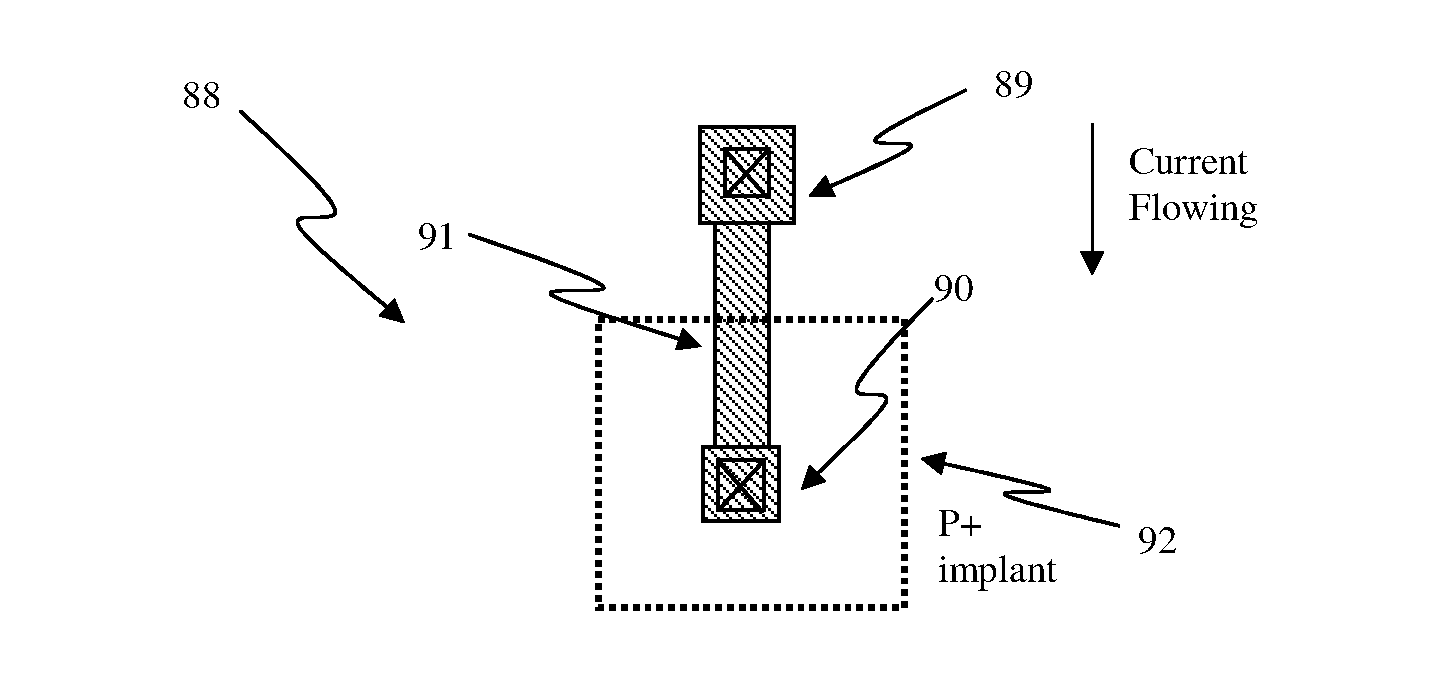
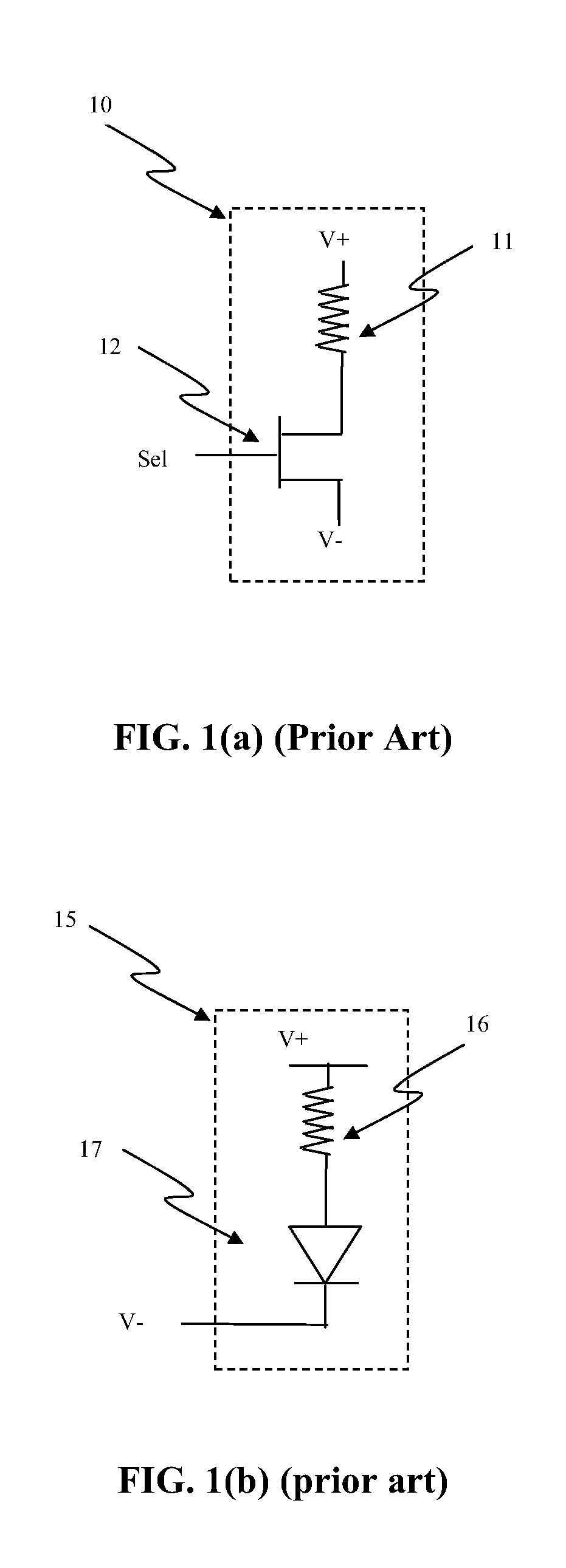
Circuit and system of using junction diode as program selector for one-time programmable devices
ActiveUS8488359B2Low costSmall sizeMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesCMOSMetal alloy
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, contact / via anti-fuse, or gate-oxide breakdown anti-fuse, etc. The OTP device has at least one OTP element coupled to at least one diode in a memory cell. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions in a CMOS N well, or on an isolated active region as the P and N terminals of the diode. The isolation between P+ and the N+ active regions of the diode in a cell or between cells can be provided by dummy MOS gate, SBL, or STI / LOCOS isolations. The OTP element can be polysilicon, silicided polysilicon, silicide, metal, metal alloy, local interconnect, thermally isolated active region, CMOS gate, or combination thereof.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
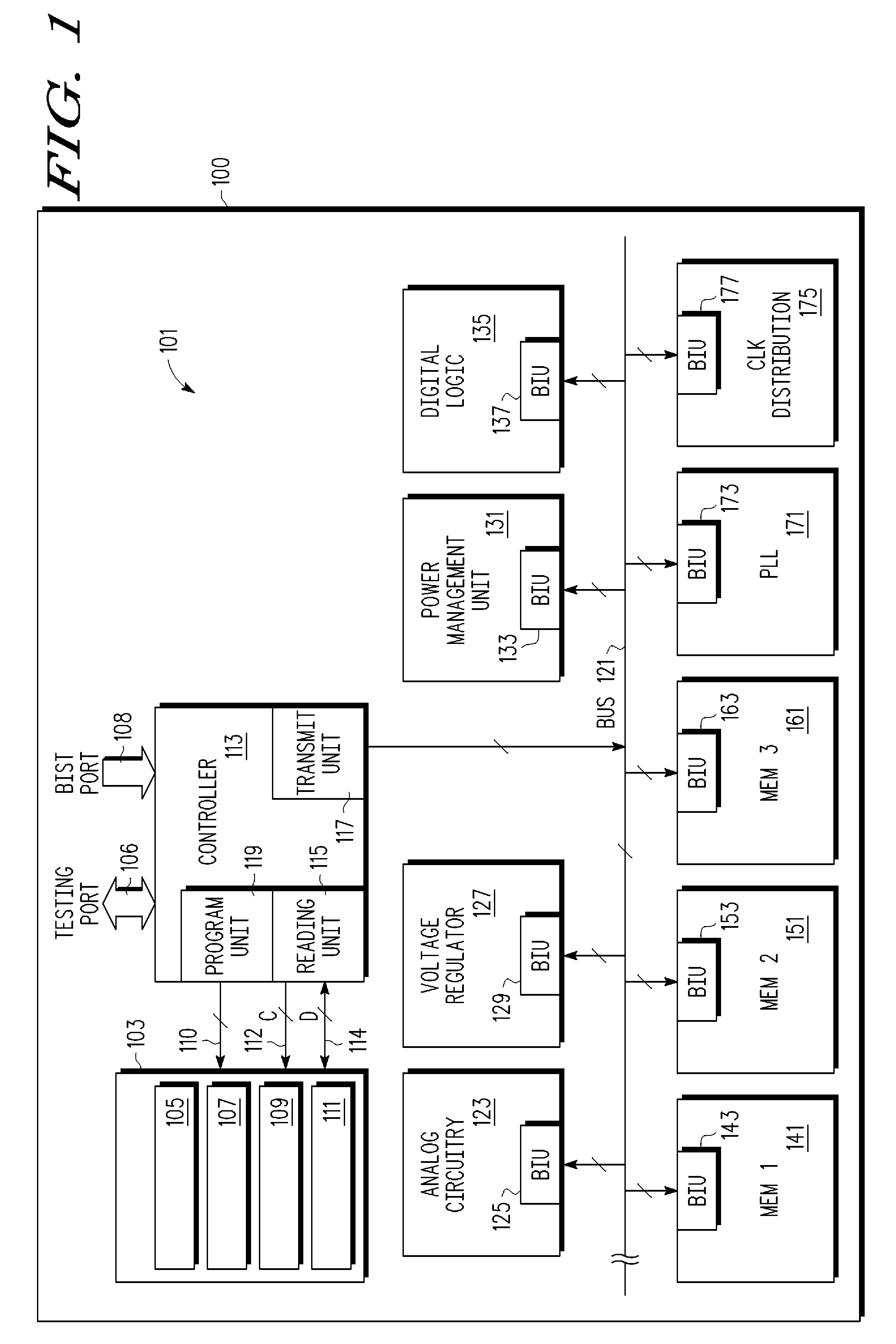
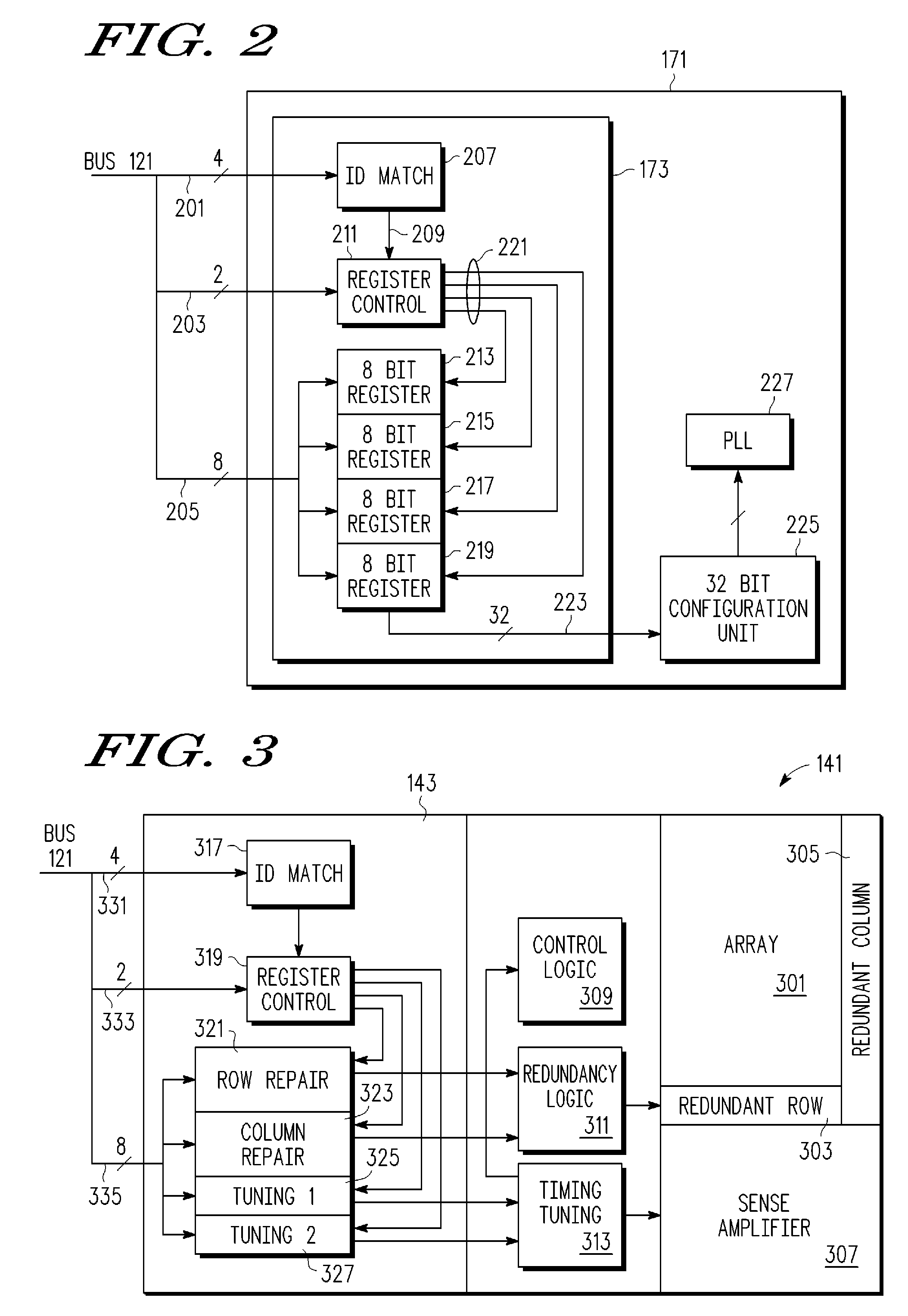
One time programmable element system in an integrated circuit
A system with a repairable memory array having redundant memory cells to replace one or more defective memory cells that are detected after fabrication. The system also includes non memory array circuits having circuitry that may adjust one or more operating parameters such as operating current, operating voltage, resistance, capacitance, timing characteristics and an operating mode. A set of one time programmable elements can be used to selectively store information for modifying operating parameters and replacing the defective memory cells with redundant memory cells.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Methods and systems of a multiple radio frequency network node RFID tag
ActiveUS20120206243A1Increase redundancyFacilitates data encryptionDigital data processing detailsRead-only memoriesRadio frequencyOne time programmable
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for a Radio Frequency ID (RFID) tag that contains multiple Radio Frequency (RF) network nodes that may include memory storage for the RFID tag, the memory storage may include one time programmable (OTP) memory and many time programmable (MTP) memory and the storage of the information may be within the OTP and MTP memory.
Owner:TEGO INC
Circuit and system for testing a one-time programmable (OTP) memory
Circuits, systems and techniques for testing a One-Time Programmable (OTP) memory are disclosed. An extra OTP bit can be provided as a test sample to be programmed. The programmed extra OTP bit can be read with any virgin cells in the OTP memory alternatively to generate a stream of logic 0 and logic 1 data so that every row or column path can be tested and the outcome can be observed in a pseudo-checkerboard pattern or other predetermined pattern. By carefully setting control signals, checkerboard-like pattern can be generated without actual programming any OTP cells in the memory array.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
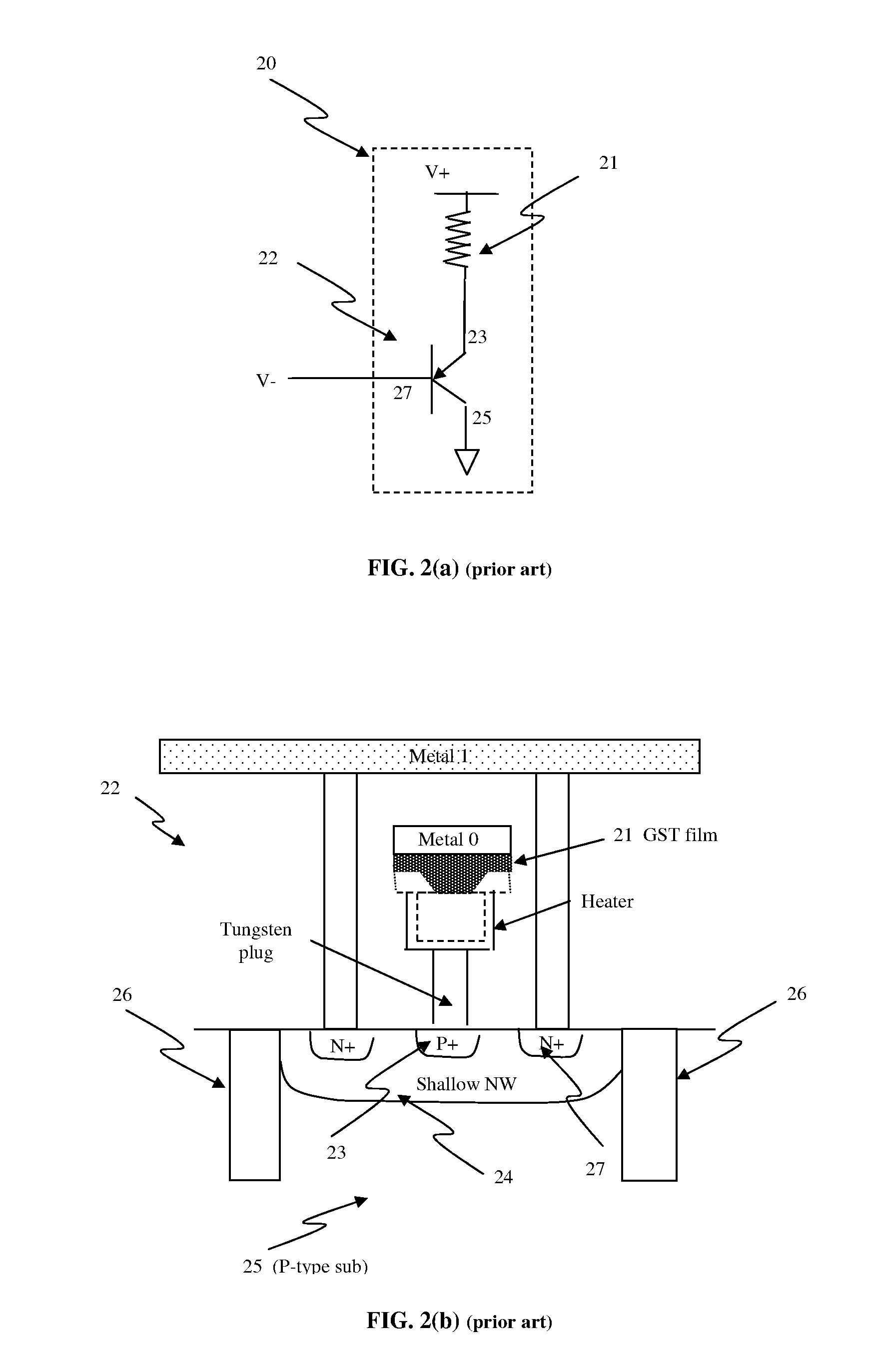
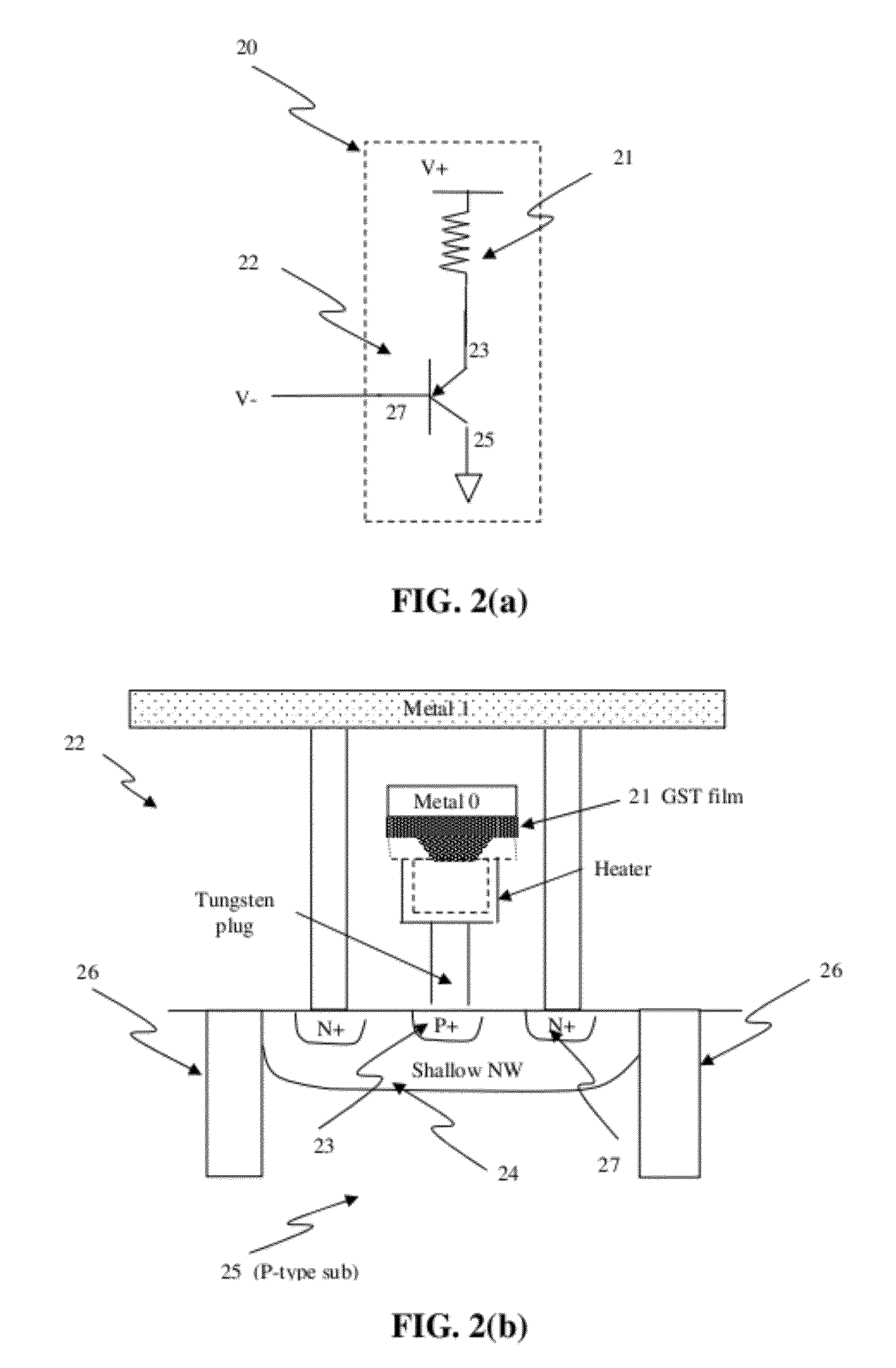
Large capacity one-time programmable memory cell using metal oxides
A method of programming a nonvolatile memory device includes (i) providing a nonvolatile memory cell comprising a diode in series with at least one metal oxide, (ii) applying a first forward bias to change a resistivity state of the metal oxide from a first state to a second state; (iii) applying a second forward bias to change a resistivity state of the metal oxide from a second state to a third state; and (iv) applying a third forward bias to change a resistivity state of the metal oxide from a third state to a fourth state. The fourth resistivity state is higher than the third resistivity state, the third resistivity state is lower than the second resistivity state, and the second resistivity state is lower than the first resistivity state.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Circuit and system of using junction diode as program selector for one-time programmable devices
ActiveUS20120044739A1Small cell sizeLow costSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesElectrical resistance and conductanceCMOS
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, contact / via anti-fuse, or gate-oxide breakdown anti-fuse, etc. The OTP device has an OTP element coupled to a diode in a memory cell. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions on an N well as the P and N terminals of the diode. By applying a high voltage to the P terminal of a diode and switching the N terminal of a diode to a low voltage for suitable duration of time, a current flows through an OTP element in series with the program selector may change the resistance state. The P+ active region of the diode can be isolated from the N+ active region in the N well by using dummy MOS gate, SBL, or STI / LOCOS isolations. If the resistive element is an interconnect fuse based on CMOS gate material, the resistive element can be coupled to the P+ active region by an abutted contact such that the element, active region, and metal are connected in a single rectangular contact.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Circuit and system of using polysilicon diode as program selector for one-time programmable devices
ActiveUS20120044737A1Avoid shortingSave extra spaceSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesLow voltageHemt circuits
Polysilicon diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, contact / via anti-fuse, or gate-oxide breakdown anti-fuse, etc. The OTP device has an OTP element coupled to a diode in a memory cell. The diode can be constructed by P+ / N+ implants on a polysilicon as a program selector. By applying a high voltage to an OTP element coupled to the P-terminal of a diode and switching the N-terminal of a diode to a low voltage for suitable duration of time, a current flows through the OTP element may change the resistance state. On the polysilicon diode, the spacing and doping level of a gap between the P- and N-implants can be controlled for different breakdown voltages and leakage currents. The Silicide Block Layer (SBL) can be used to block silicide formation on the top of polysilicon to prevent shorting. If the OTP element is a polysilicon electrical fuse, the fuse element can be merged with the polysilicon diode in one piece to save area.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
One-time programmable memories using junction diodes as program selectors
ActiveUS20120044740A1Small cell sizeLow costSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices, such as electrical fuse, contact / via fuse, contact / via anti-fuse, or gate-oxide breakdown anti-fuse, etc. The diode can be constructed by P+ and N+ active regions on an N well as the P and N terminals of the diode. The OTP device has an OTP element coupled to the diode. The OTP device can be used to construct a two-dimensional OTP memory with the N terminals of the diodes in a row connected as a wordline and the OTP elements in a column connected as a bitline. By applying a high voltage between a selected bitline and a selected wordline to turn on a diode in a selected cell for suitable duration of time, a current flows through an OTP element in series with the program selector may change the resistance state. The cell data in the OTP memory can also be read by turning on a selected wordline and to couple a selected bitline to a sense amplifier. The wordlines may have high-resistivity local wordlines coupled to low-resistivity global wordlines through conductive contact(s) or via(s).
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
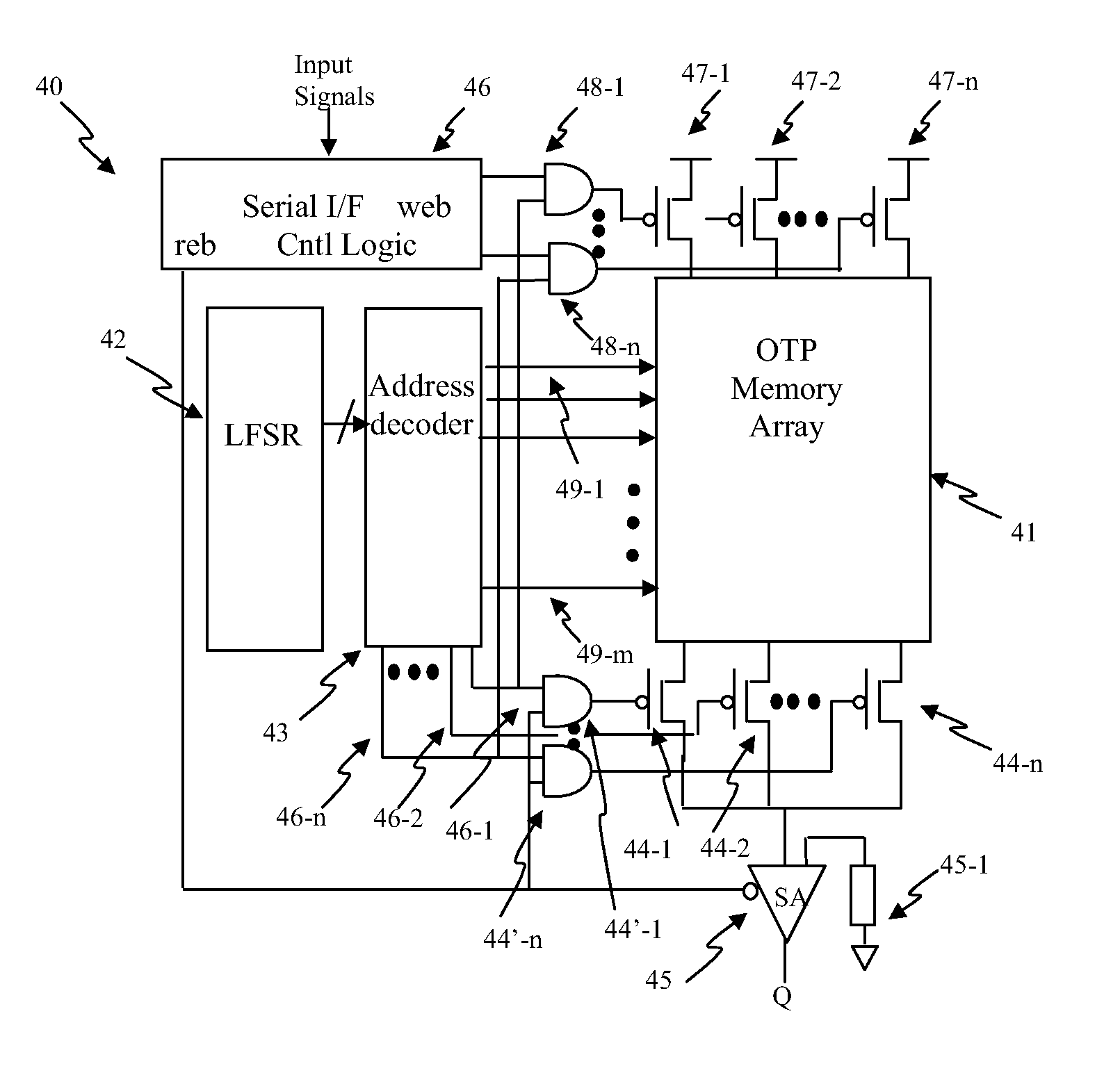
Circuit and System of a Low Density One-Time Programmable Memory
InactiveUS20130201745A1Low density OTPsReduce memory sizeElectric analogue storesRead-only memoriesAddress generatorHemt circuits
A low density One-Time Programmable (OTP) memory is disclosed to achieve low gate count and low overhead in the peripheral circuits to save the cost. A maximum-length Linear Feedback Shift Register (LFSR) can be used to generate 2n−1 address spaces from an n-bit address. The registers used in the address generator can have two latches. Each latch has two cross-coupled inverters with two outputs coupled to the drains of two MOS input devices, respectively. The inputs of the latch are coupled to the gates of the MOS input devices, respectively. The sources of the MOS input devices are coupled to the drains of at least one MOS device(s), whose gate(s) are coupled to a clock signal and whose source(s) are coupled to a supply voltage. The two latches can be constructed in serial with the outputs of the first latch coupled to the inputs of the second latch.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
Vehicle black box
InactiveUS20120109447A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesRecording durationReal-time data
A vehicle black box includes a memory device for receiving and storing real-time data associated with the vehicle during a recording time window. Upon determining that an accident has occurred, circuitry freezes the recording time window and stores the real-time data within the frozen recording time window within a one-time programmable (OTP) memory.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com