Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
95results about How to "Write efficiently" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
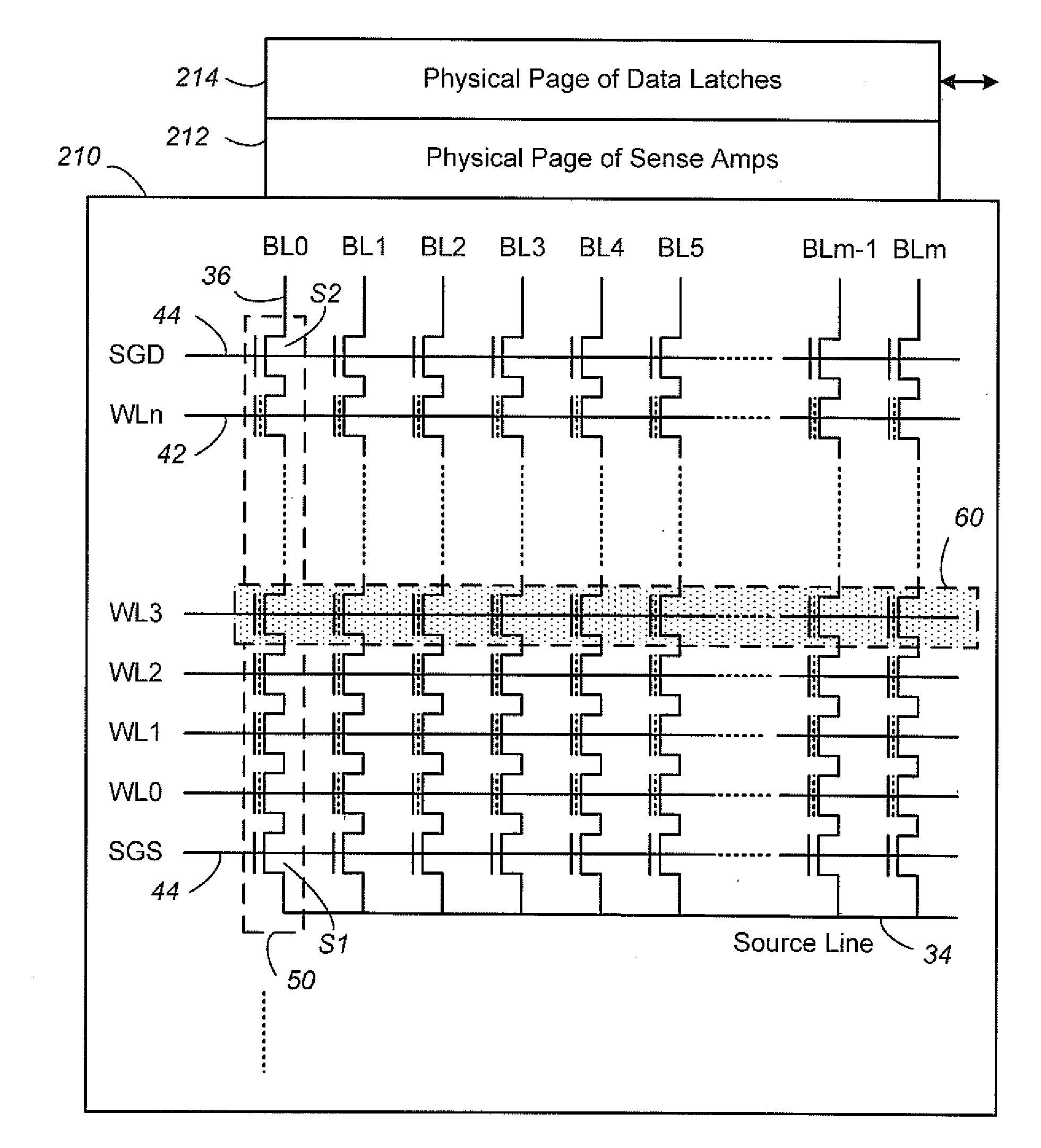
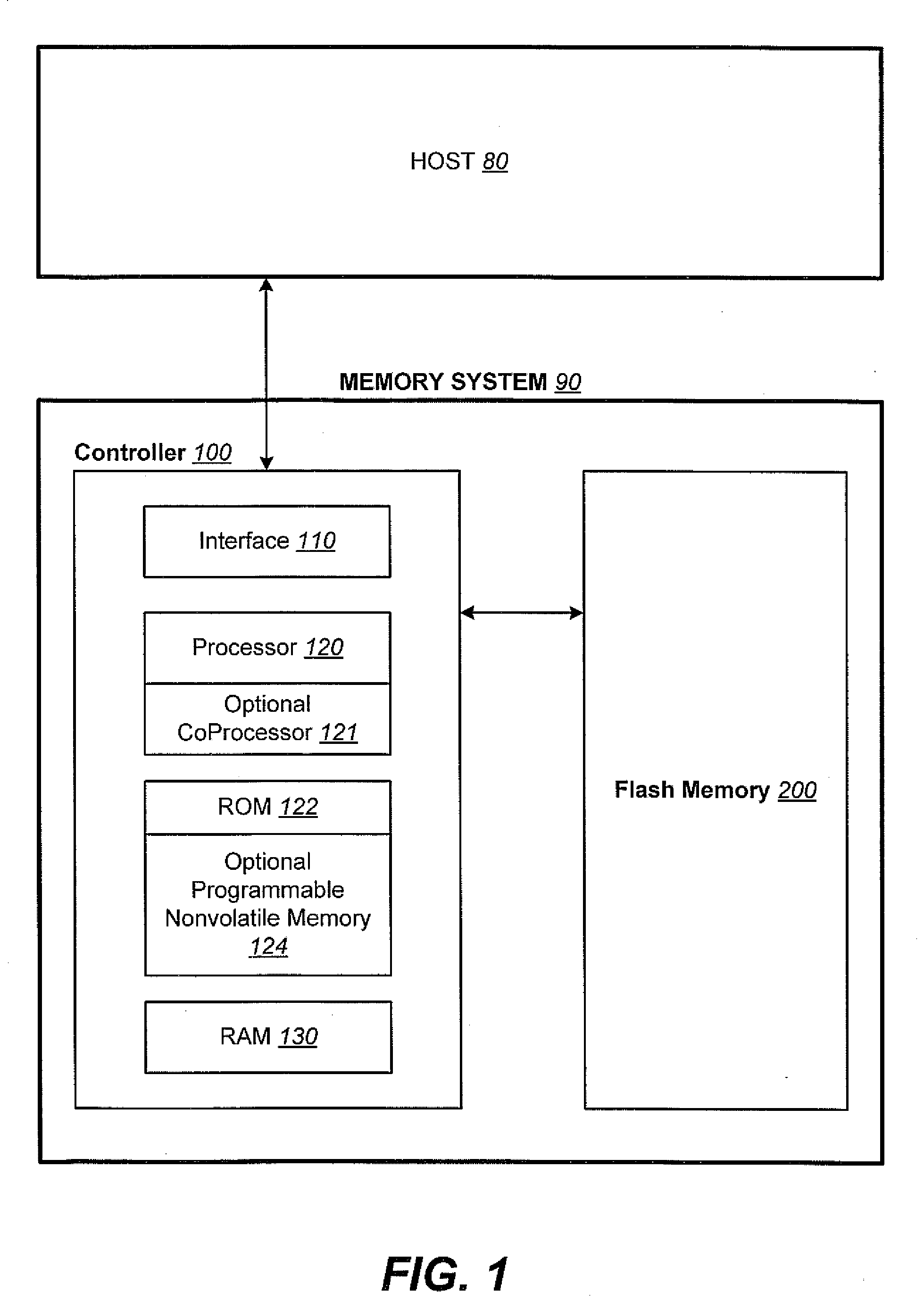
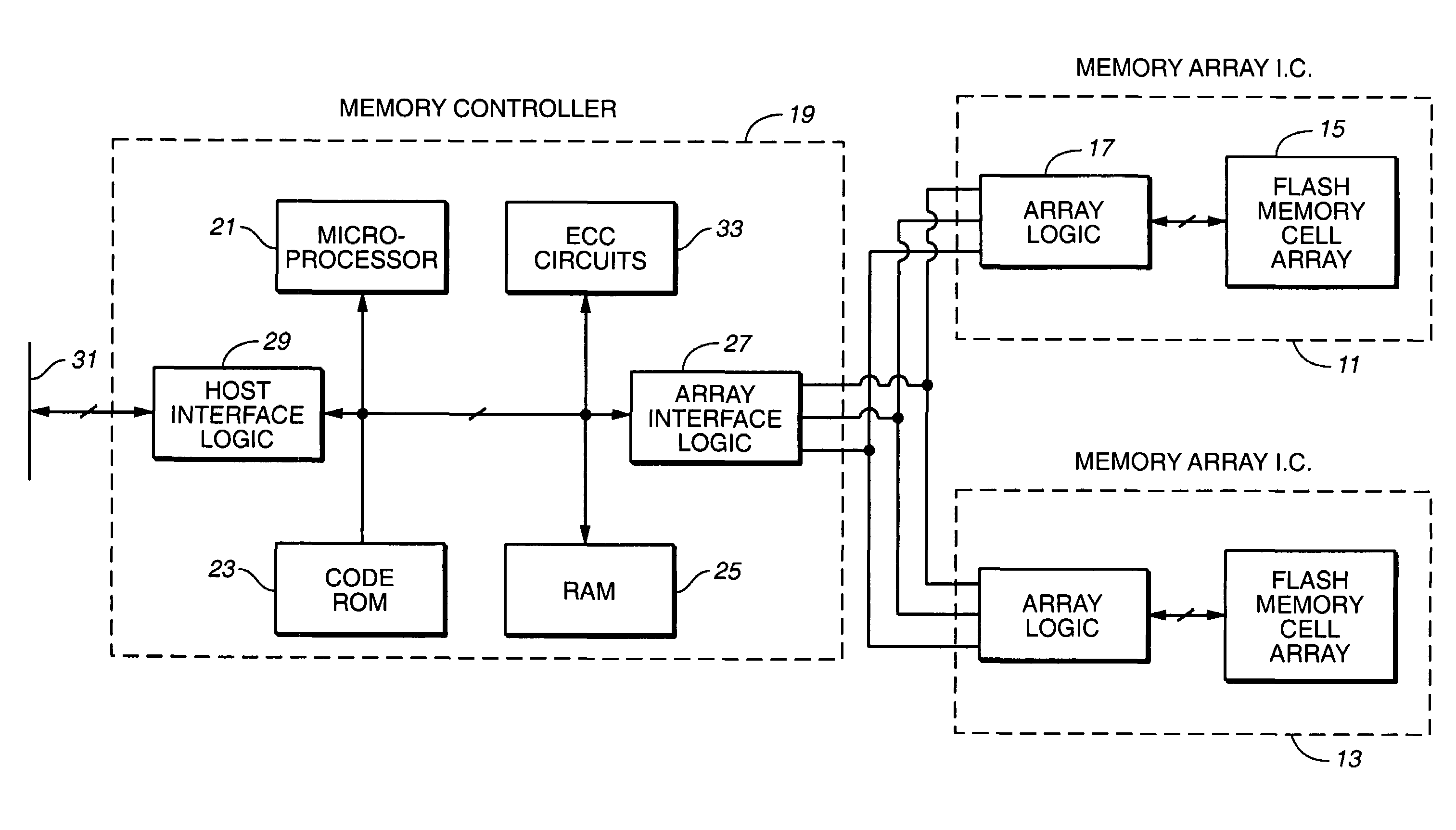
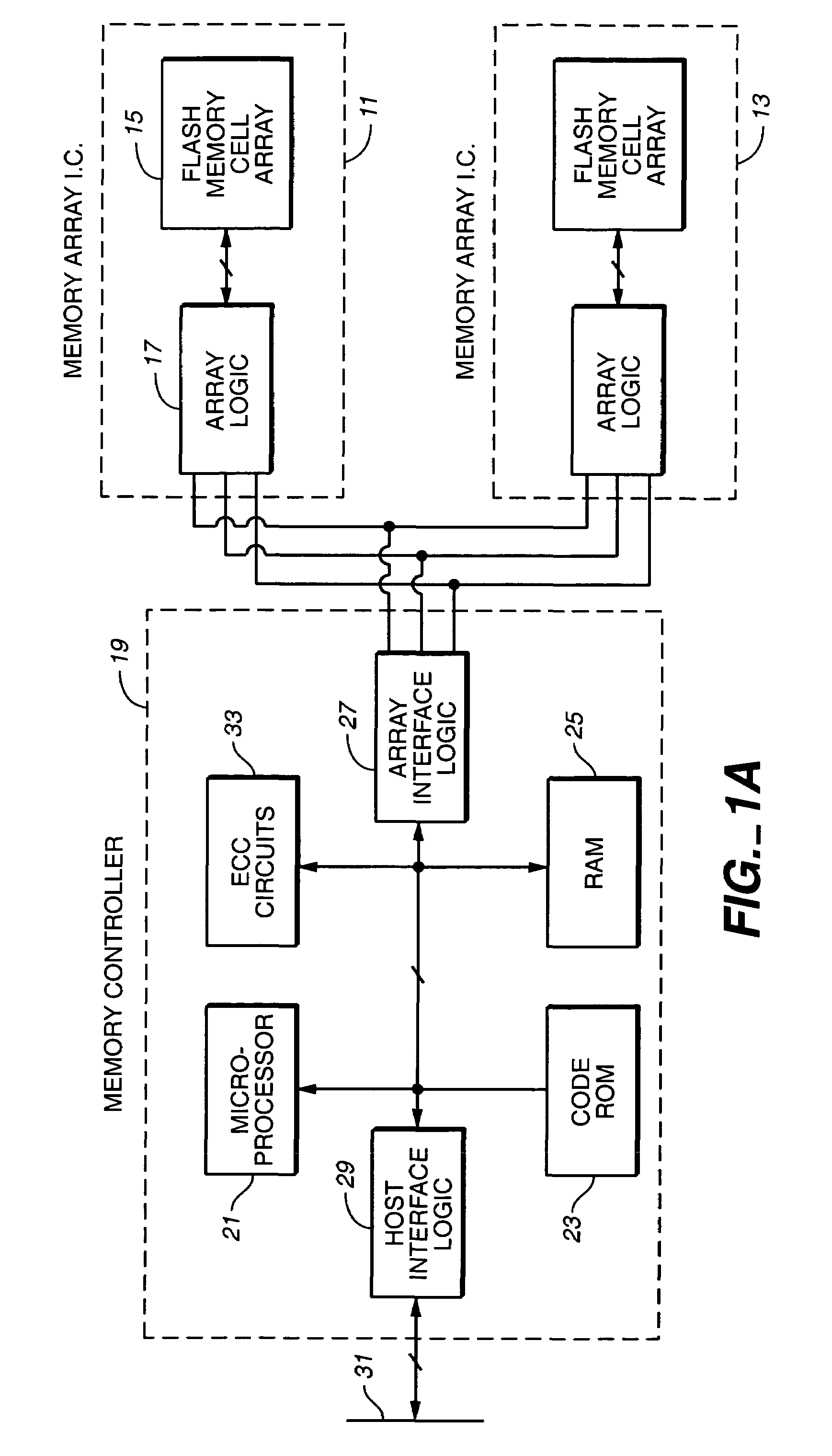
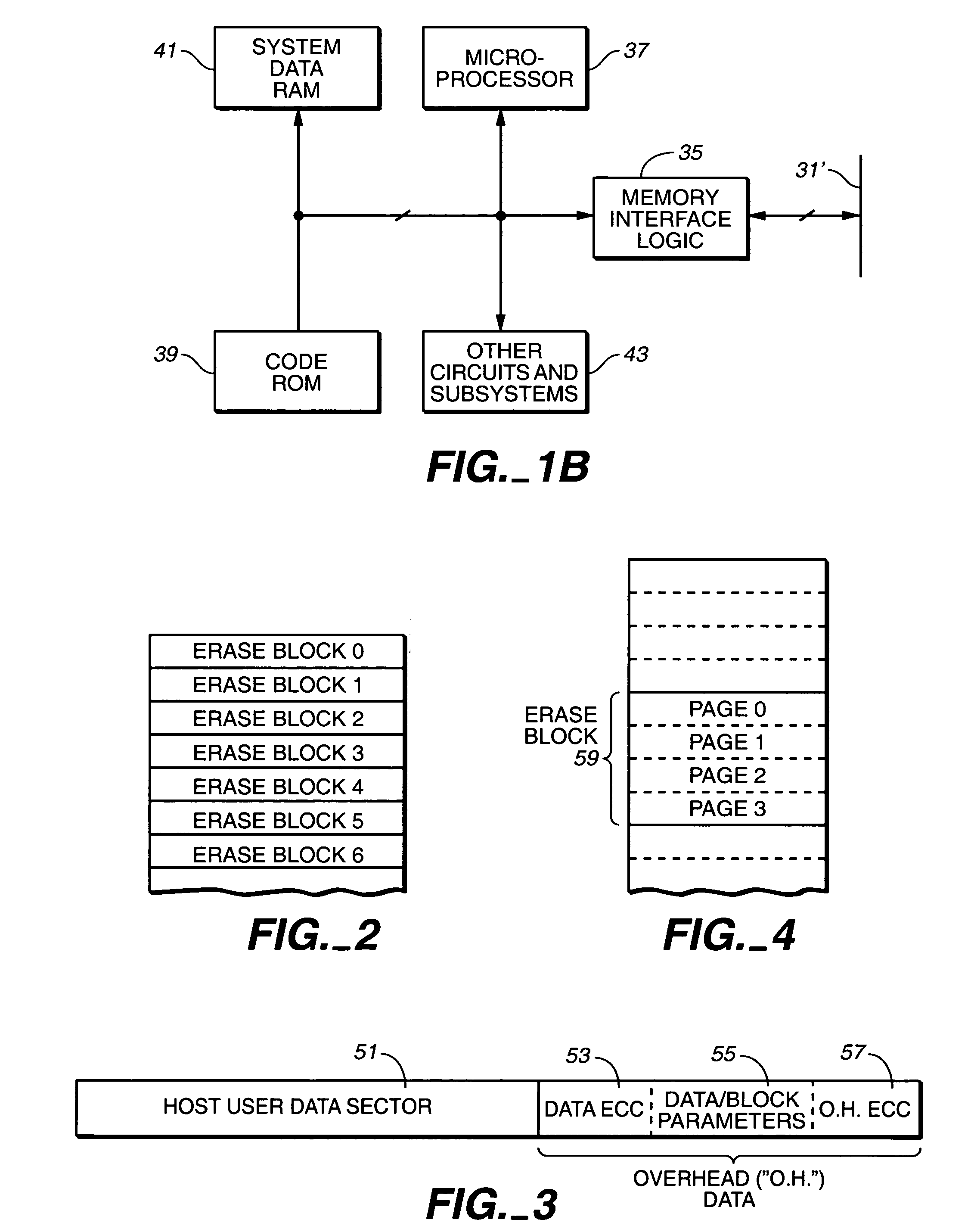
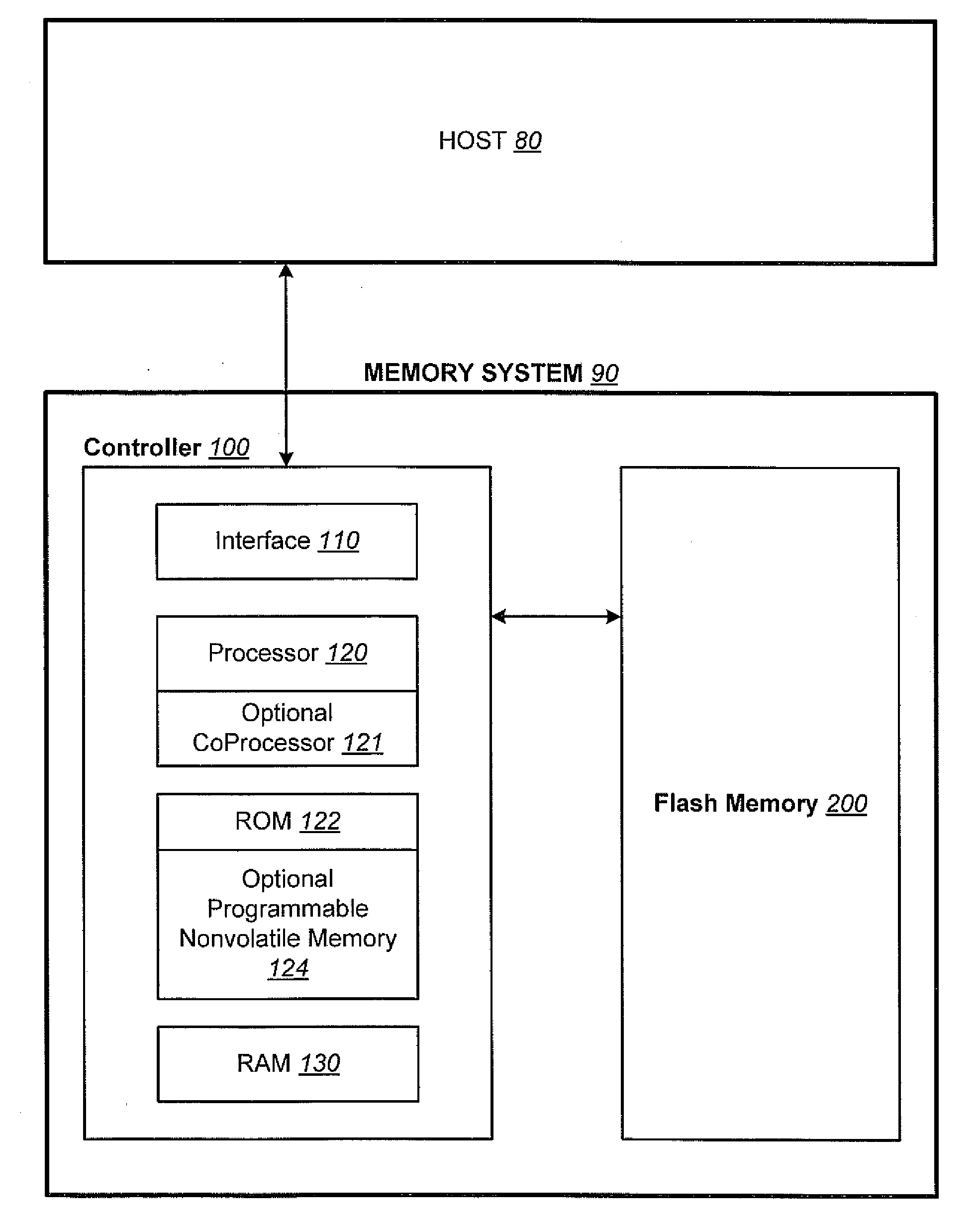
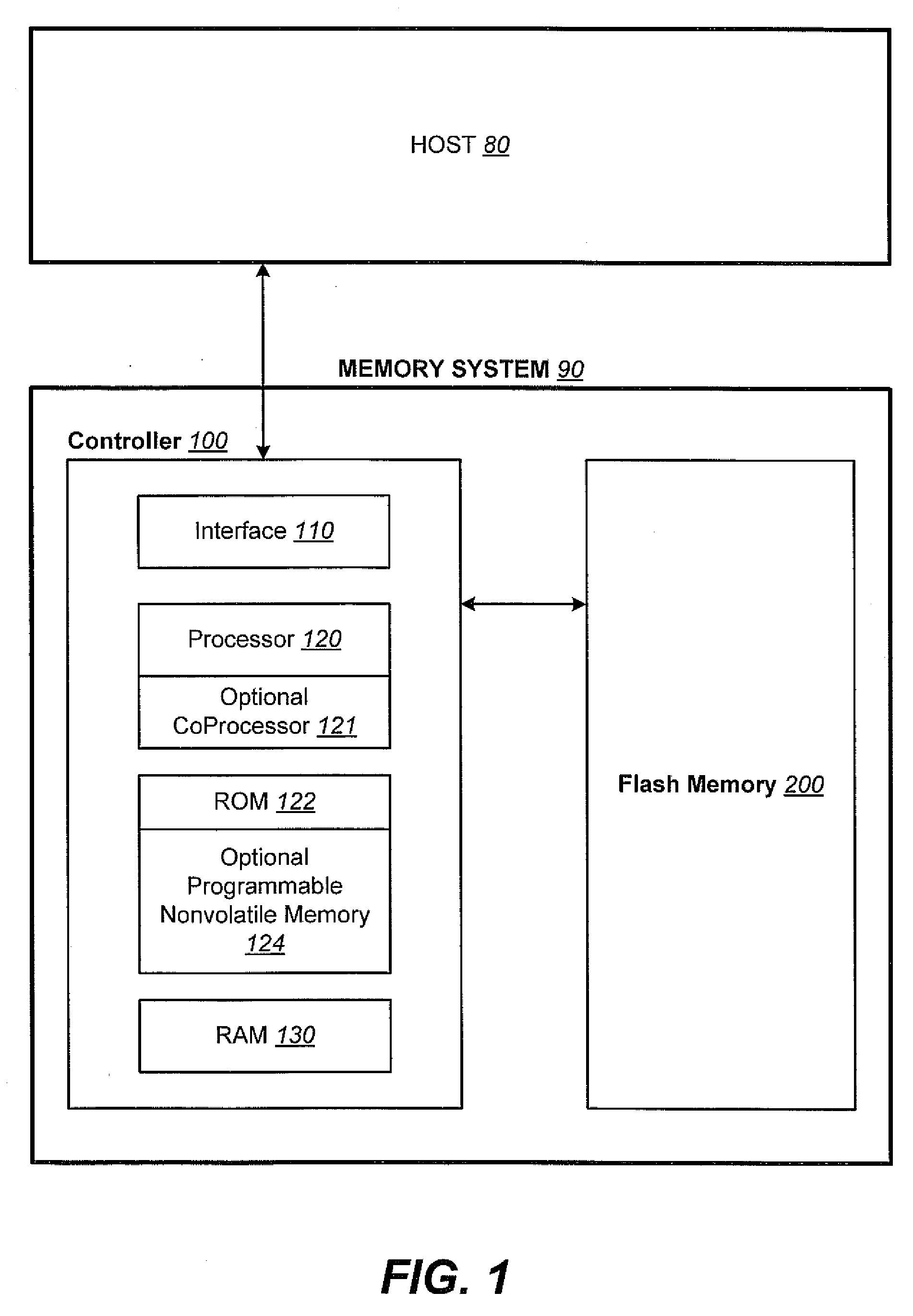
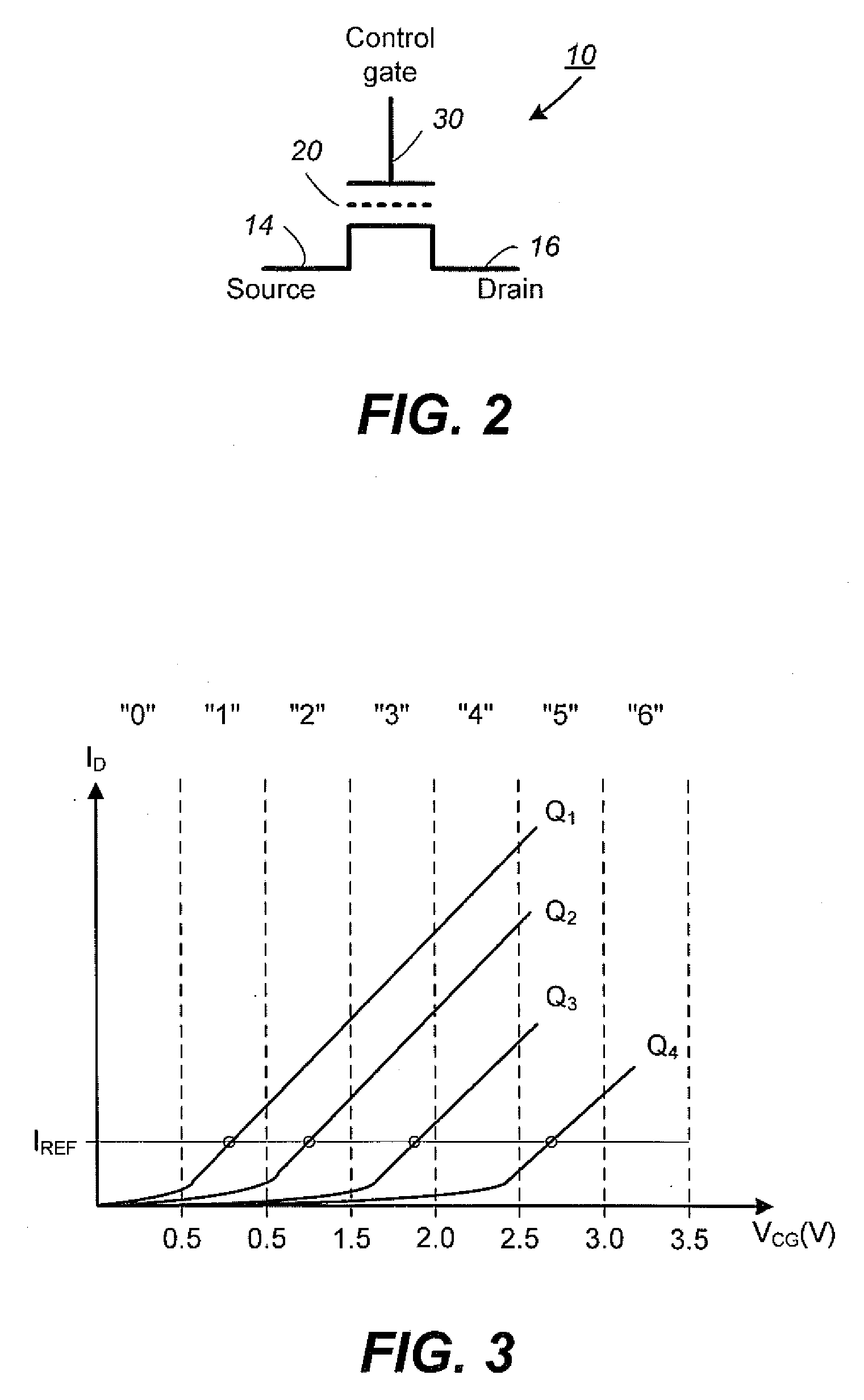
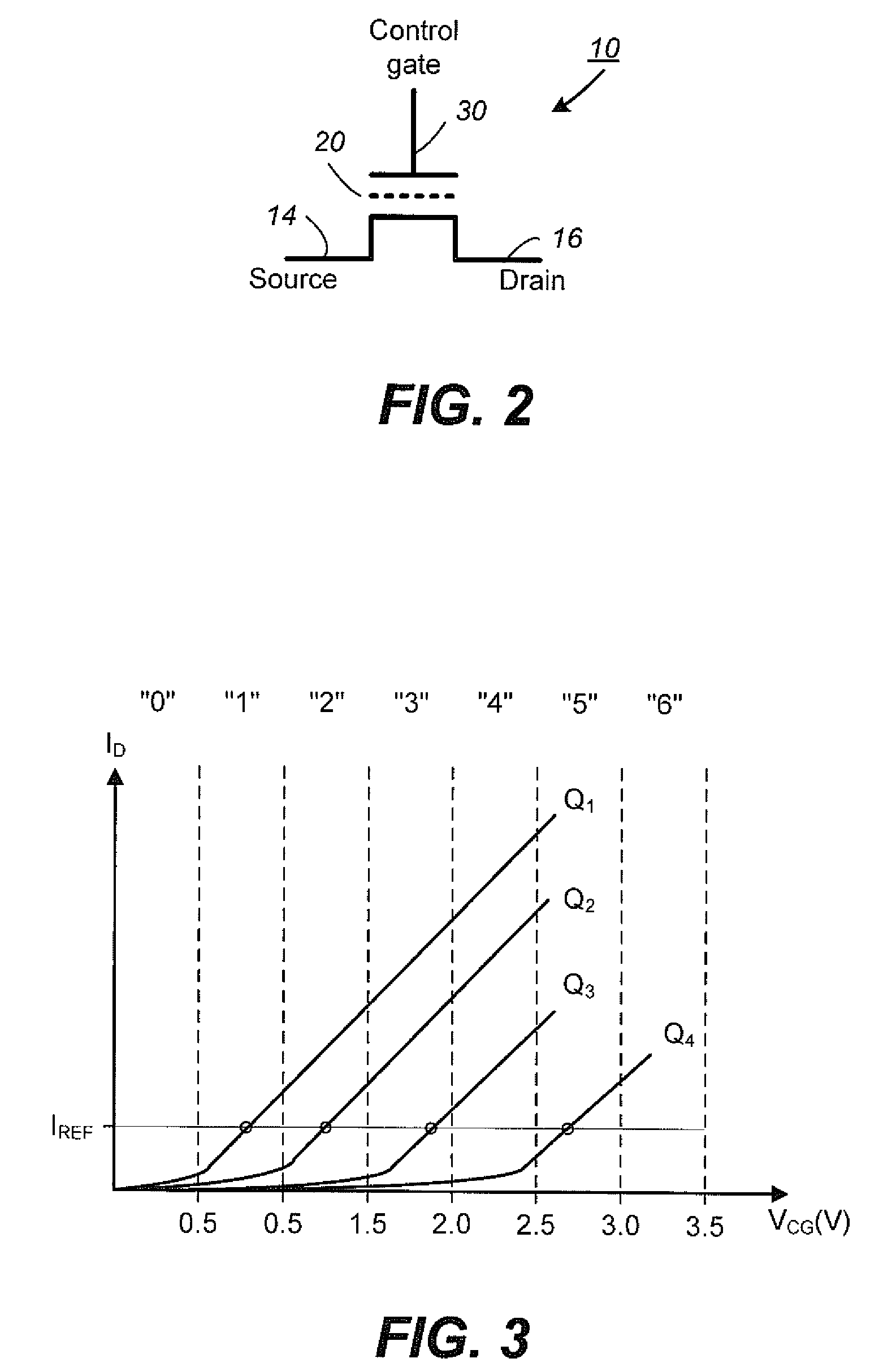
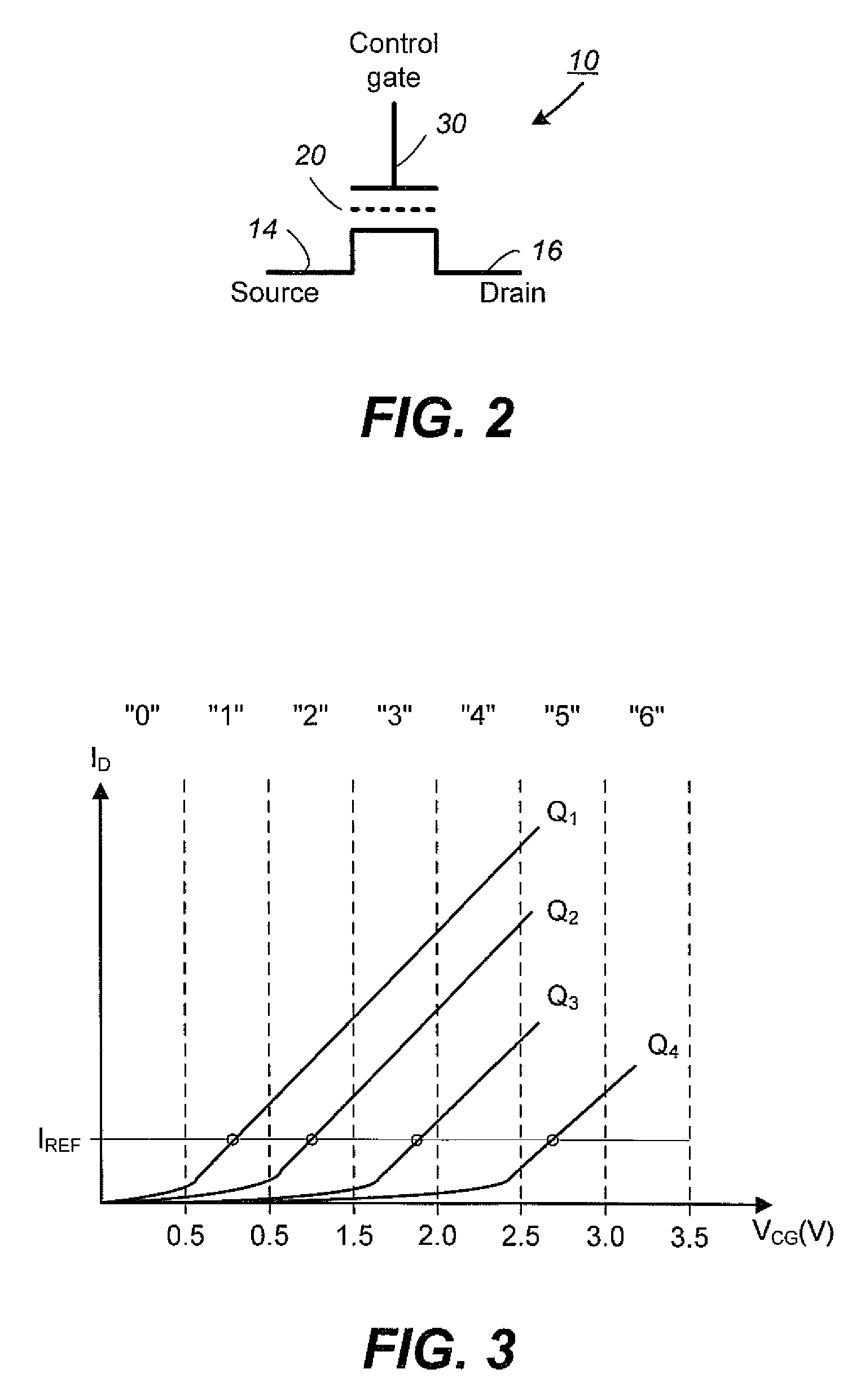
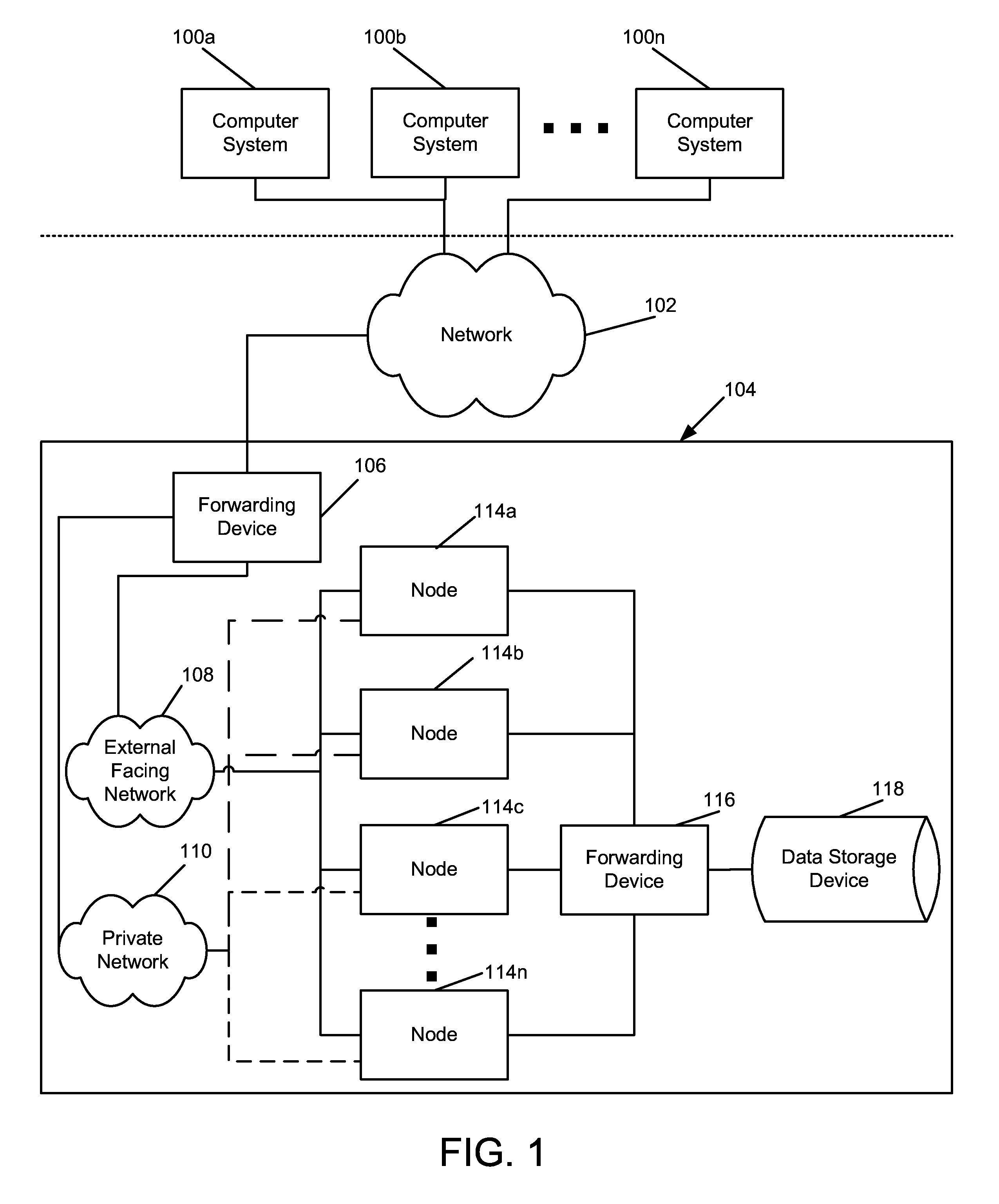
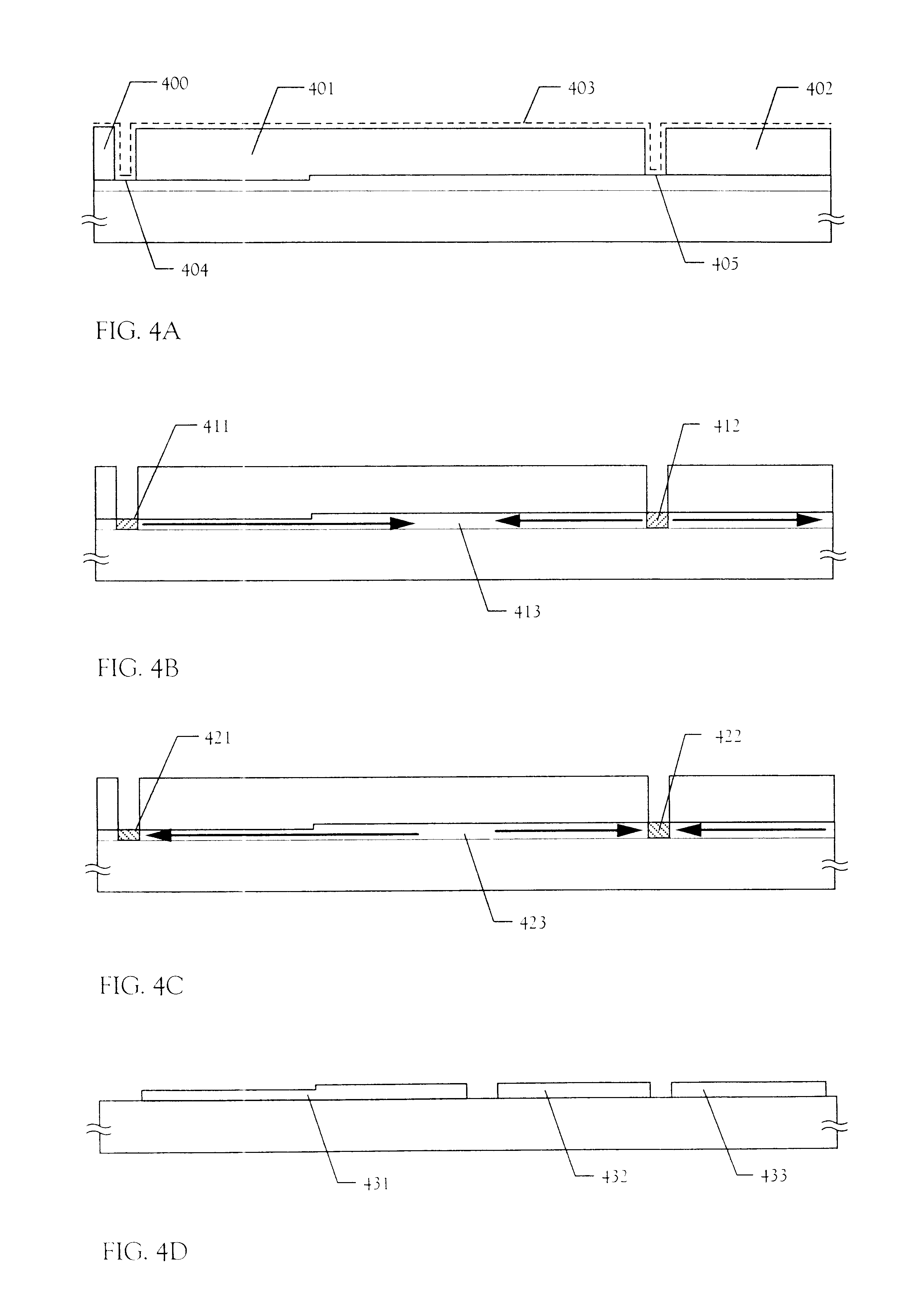
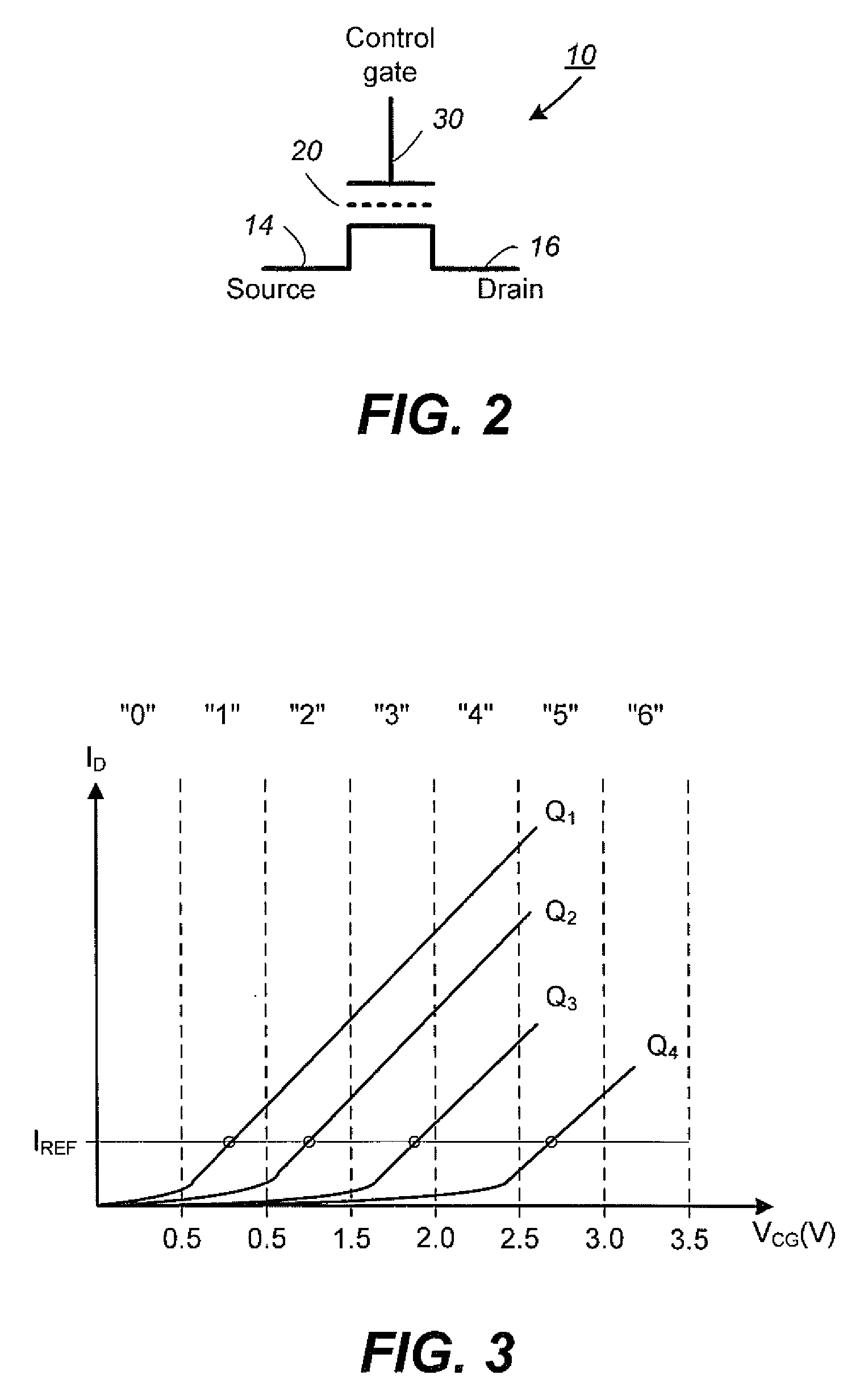
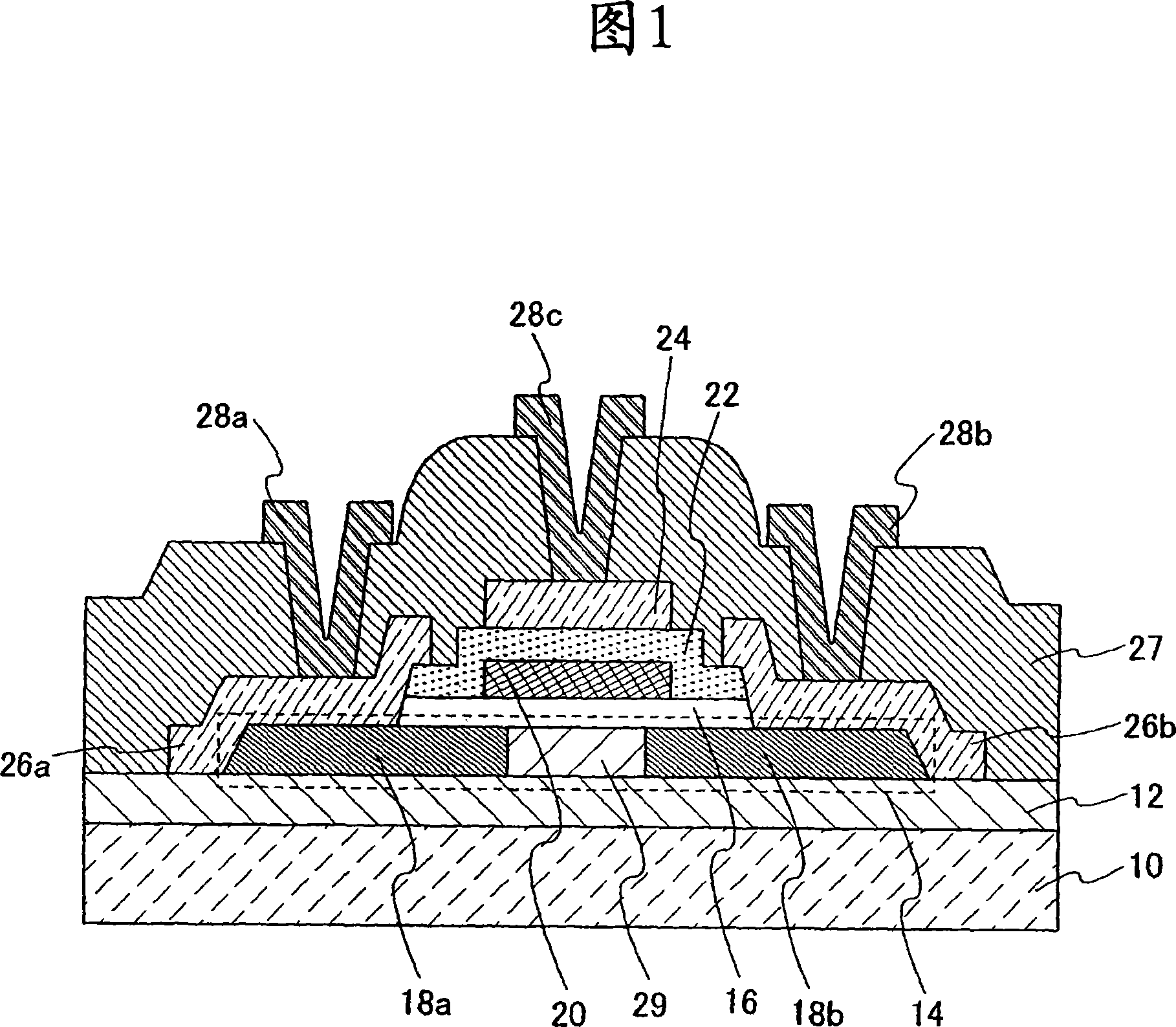
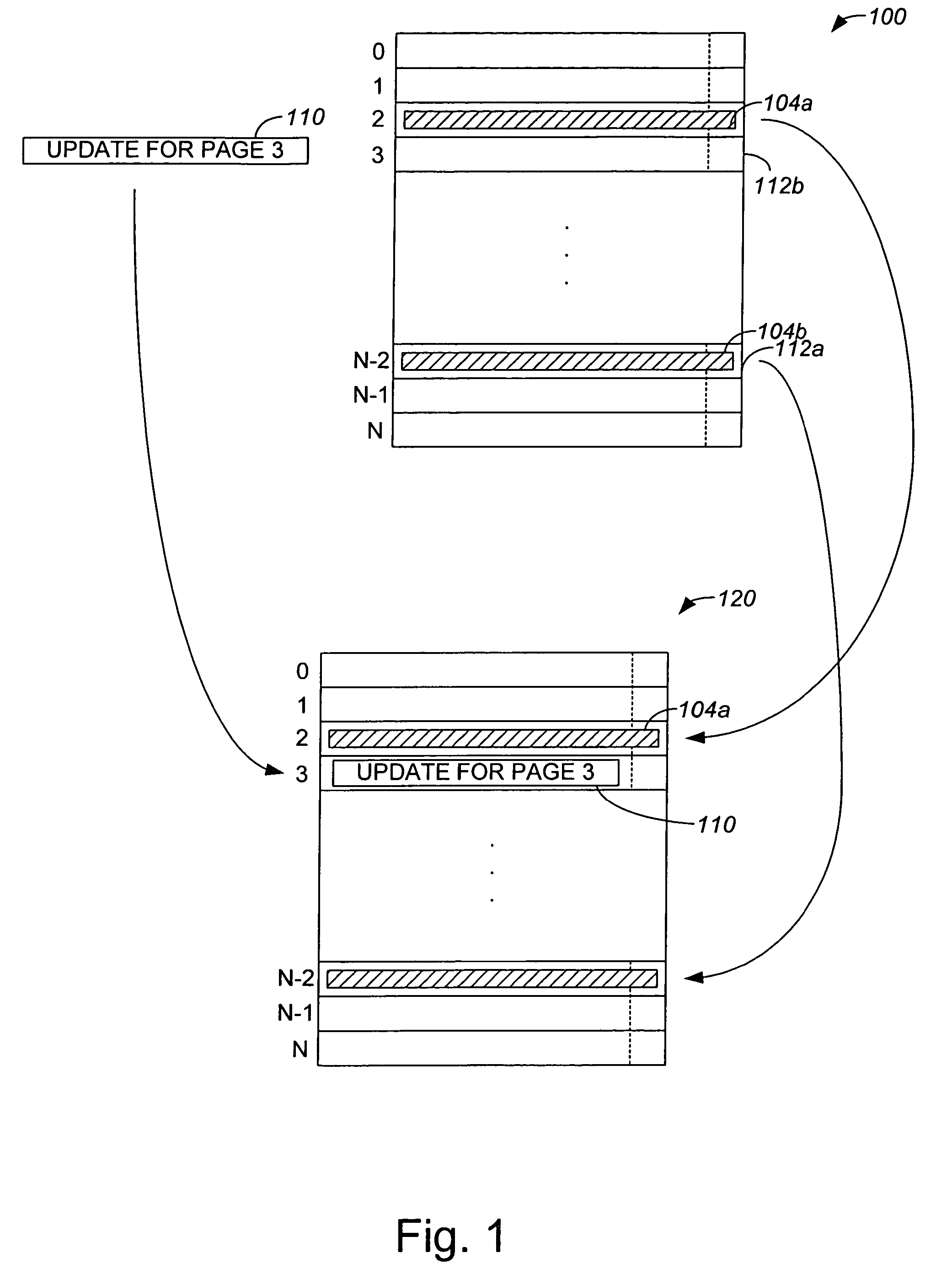
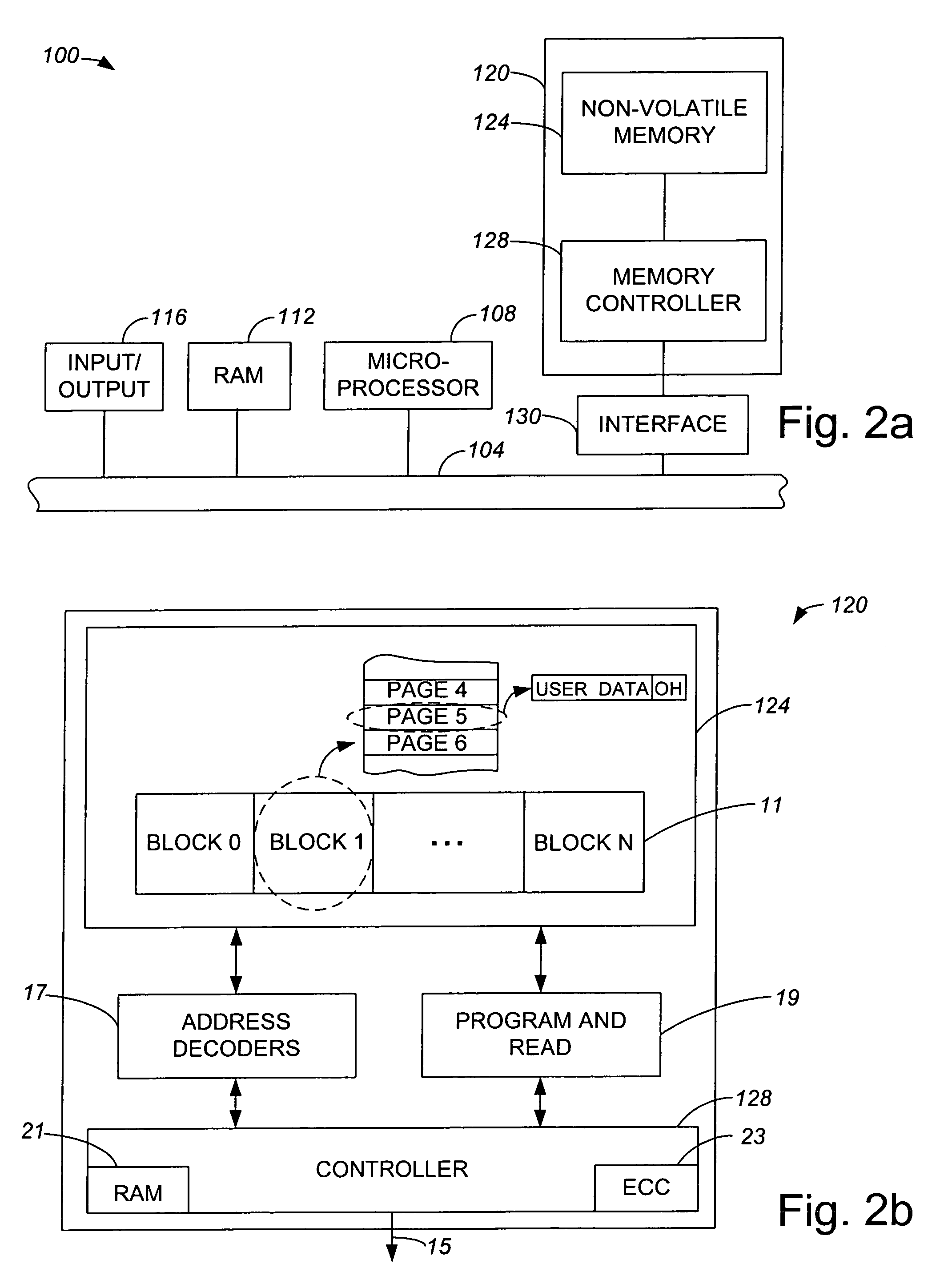
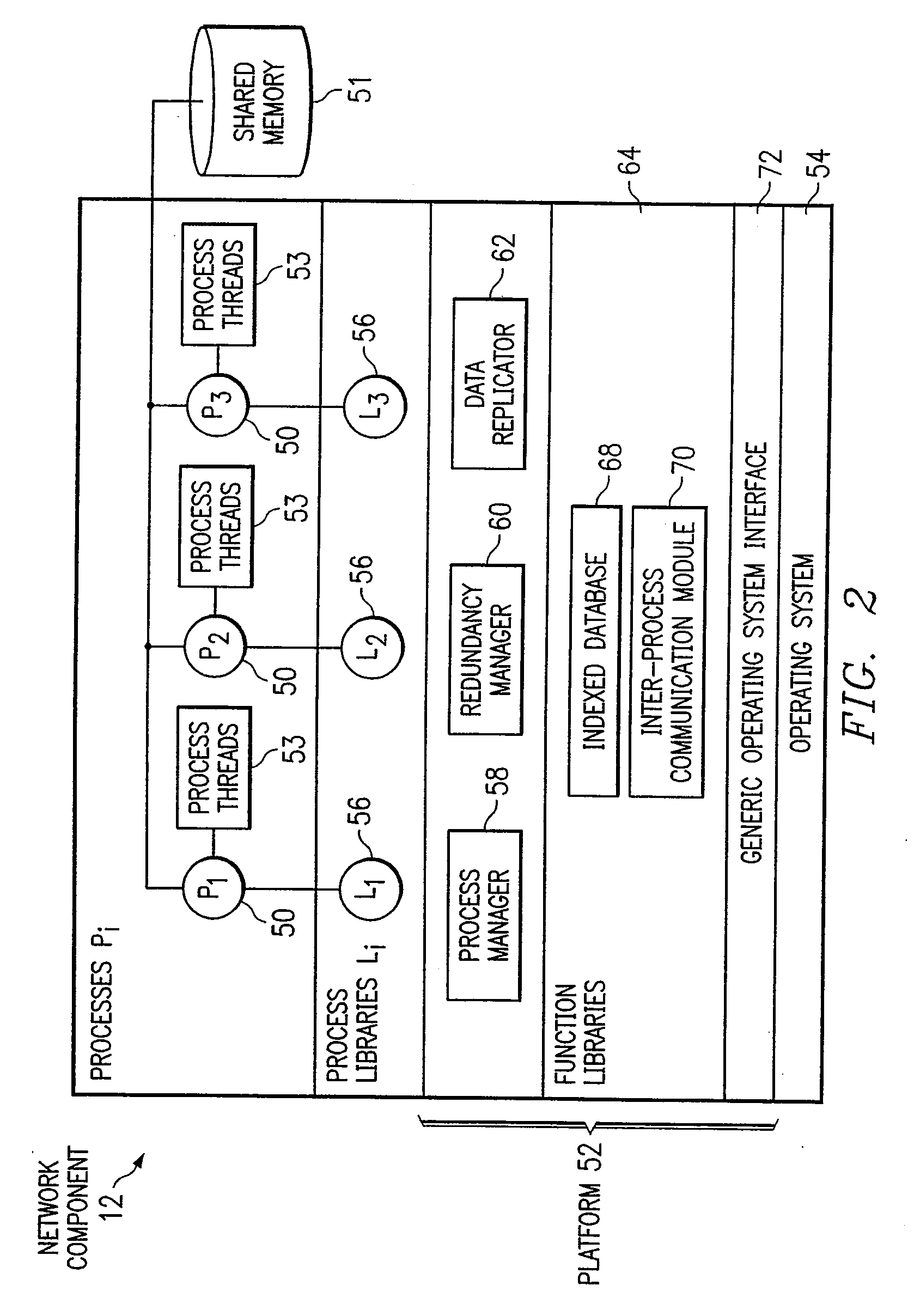
Non-Volatile Memory and Method With Write Cache Partitioning
ActiveUS20100172180A1Faster and robust write and read performanceIncrease burst write speedMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesMultilevel memoryGranularity
A portion of a nonvolatile memory is partitioned from a main multi-level memory array to operate as a cache. The cache memory is configured to store at less capacity per memory cell and finer granularity of write units compared to the main memory. In a block-oriented memory architecture, the cache has multiple functions, not merely to improve access speed, but is an integral part of a sequential update block system. Decisions to write data to the cache memory or directly to the main memory depend on the attributes and characteristics of the data to be written, the state of the blocks in the main memory portion and the state of the blocks in the cache portion.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Non-Volatile Memory and Method With Write Cache Partition Management Methods
InactiveUS20100174847A1Faster and robust write and read performanceIncrease burst write speedMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationGranularityMultilevel memory
A portion of a nonvolatile memory is partitioned from a main multi-level memory array to operate as a cache. The cache memory is configured to store at less capacity per memory cell and finer granularity of write units compared to the main memory. In a block-oriented memory architecture, the cache has multiple functions, not merely to improve access speed, but is an integral part of a sequential update block system. The cache memory has a capacity dynamically increased by allocation of blocks from the main memory in response to a demand to increase the capacity. Preferably, a block with an endurance count higher than average is allocated. The logical addresses of data are partitioned into zones to limit the size of the indices for the cache.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
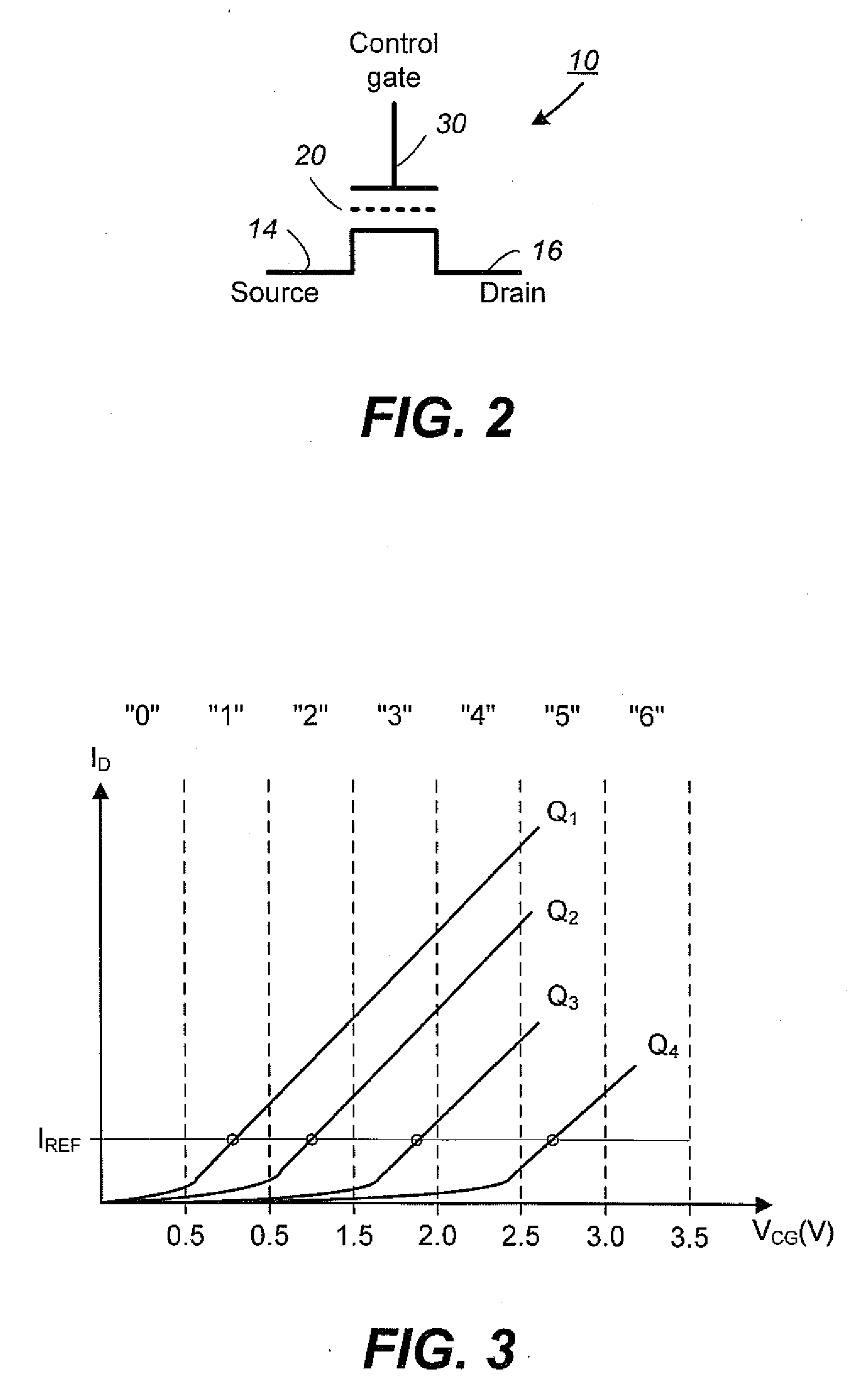
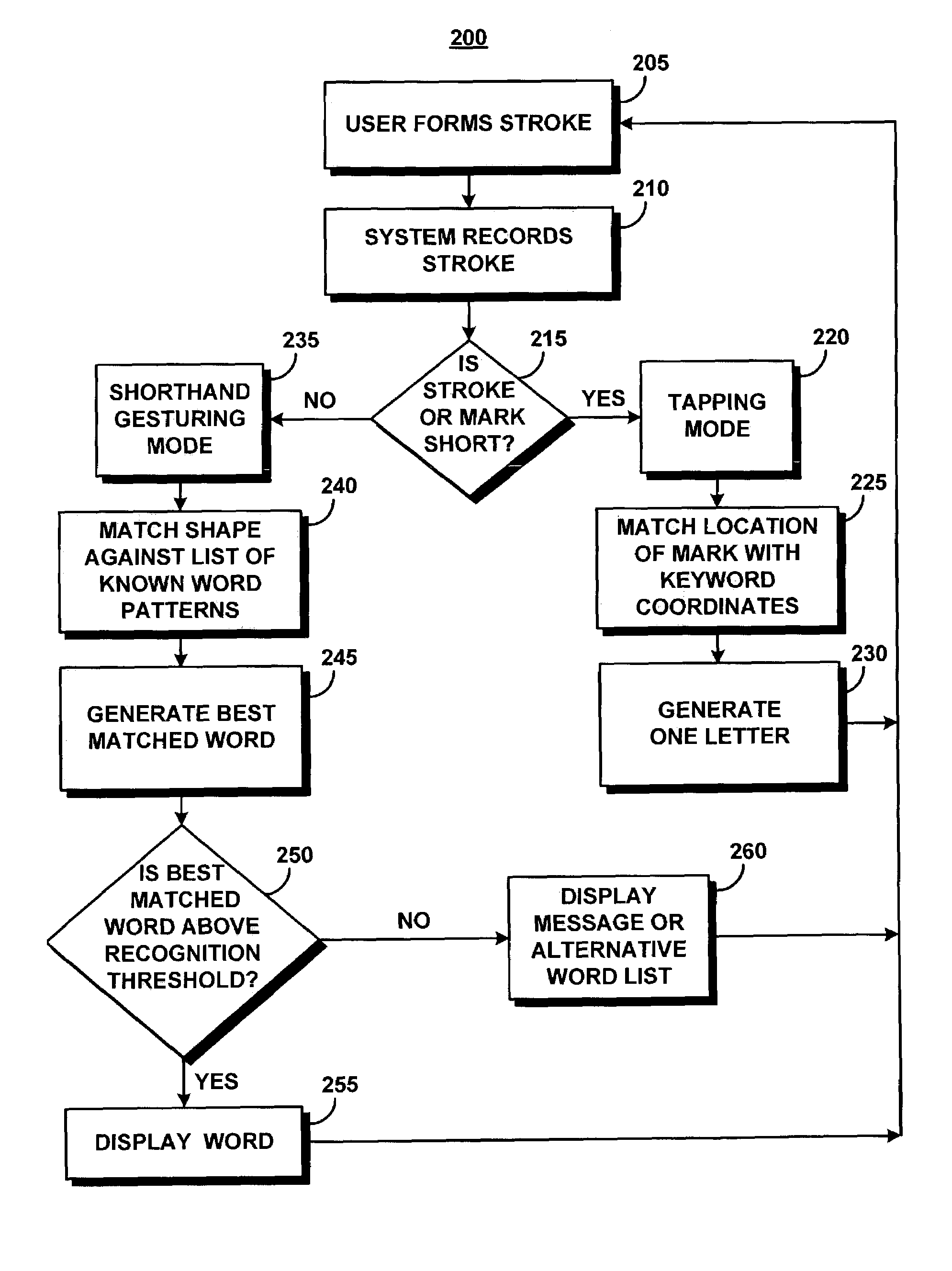
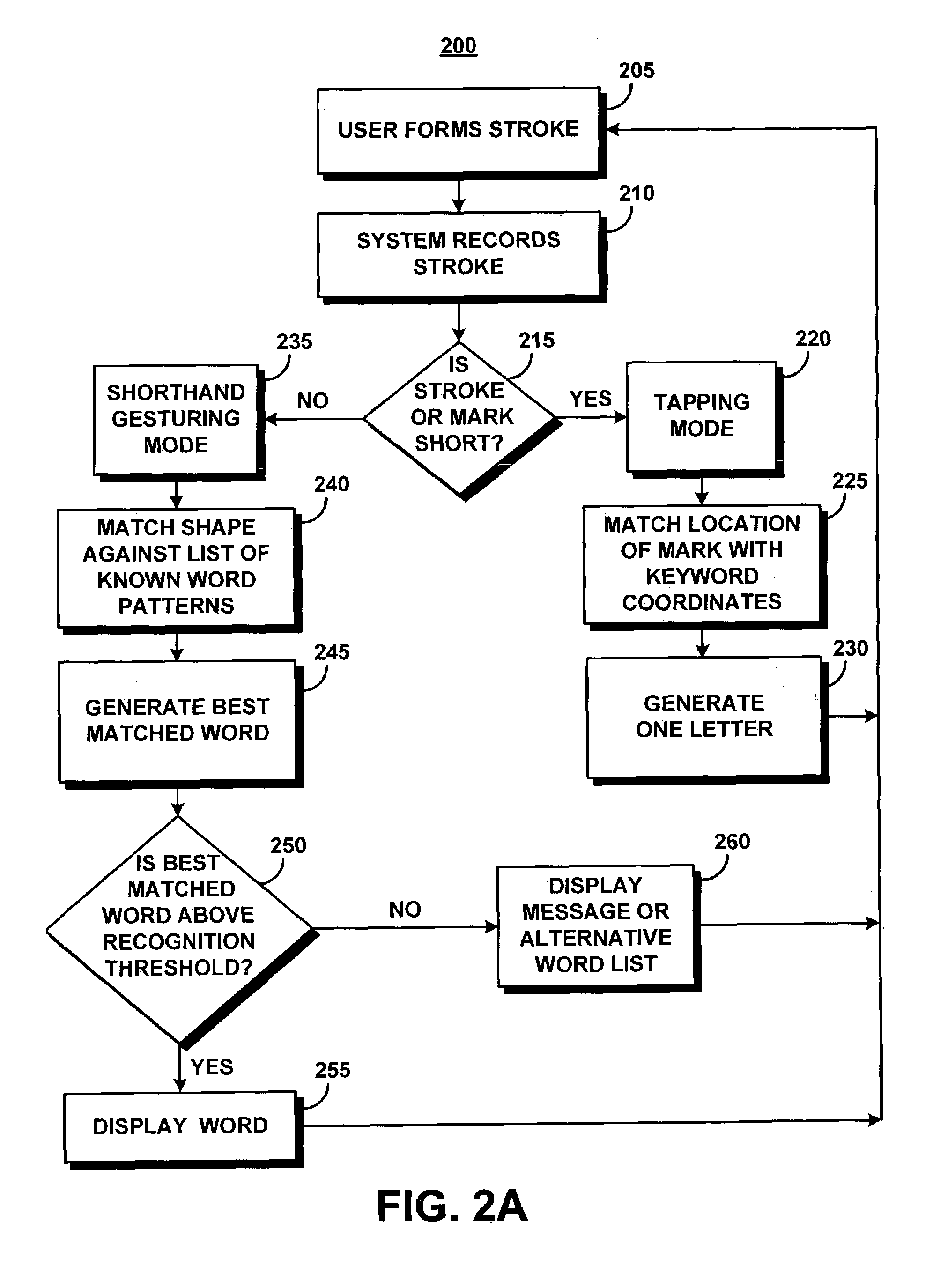
System and method for recognizing word patterns based on a virtual keyboard layout
ActiveUS7251367B2Reduce usageFast inputCharacter and pattern recognitionSystem usageShorthand secretary
A system augments stylus keyboarding with shorthand gesturing. The system defines a shorthand symbol for each word according to its movement pattern on an optimized stylus keyboard. The system recognizes word patterns by identifying an input as a stroke, and then matching the stroke to a stored list of word patterns. The system then generates and displays the matched word to the user.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
Scratch pad block
ActiveUS7315916B2Improve performanceWrite efficientlyMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesHigh densityHigh velocity
In a memory array having a minimum unit of erase of a block, a scratch pad block is used to store data that is later written to another block. The data may be written to the scratch pad block with a low degree of parallelism and later written to another location with a high degree of parallelism so that it is stored with high density. Data may be temporarily stored in the scratch pad block until it can be more efficiently stored elsewhere. This may be when some other data is received. Unrelated data may be stored in the same page of a scratch pad block.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Nonvolatile Memory With Write Cache Having Flush/Eviction Methods
ActiveUS20100174846A1Faster and robust write and read performanceIncrease burst write speedMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTGranularityMultilevel memory
A portion of a nonvolatile memory is partitioned from a main multi-level memory array to operate as a cache. The cache memory is configured to store at less capacity per memory cell and finer granularity of write units compared to the main memory. In a block-oriented memory architecture, the cache has multiple functions, not merely to improve access speed, but is an integral part of a sequential update block system. Decisions to archive data from the cache memory to the main memory depend on the attributes of the data to be archived, the state of the blocks in the main memory portion and the state of the blocks in the cache portion.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
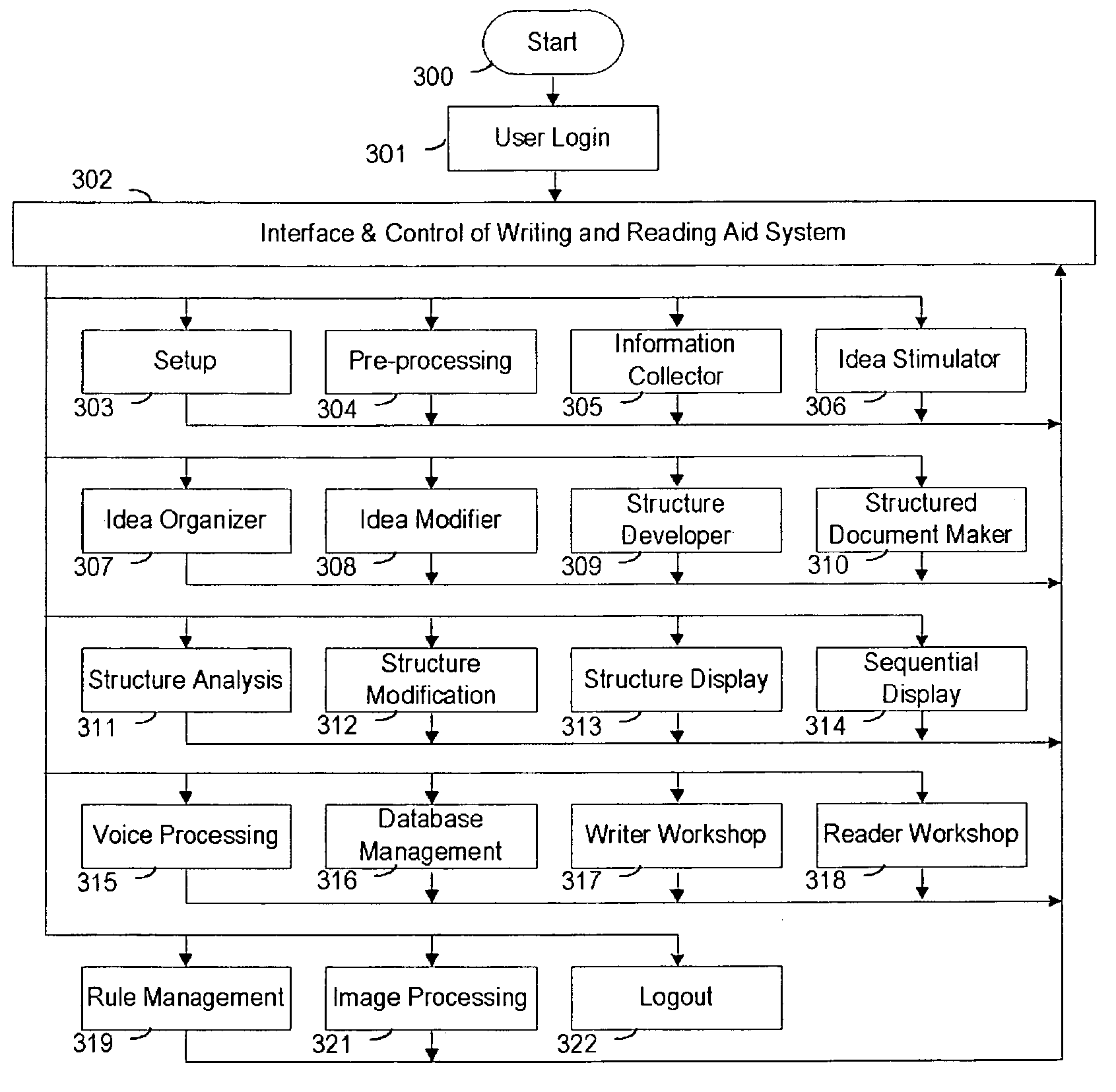
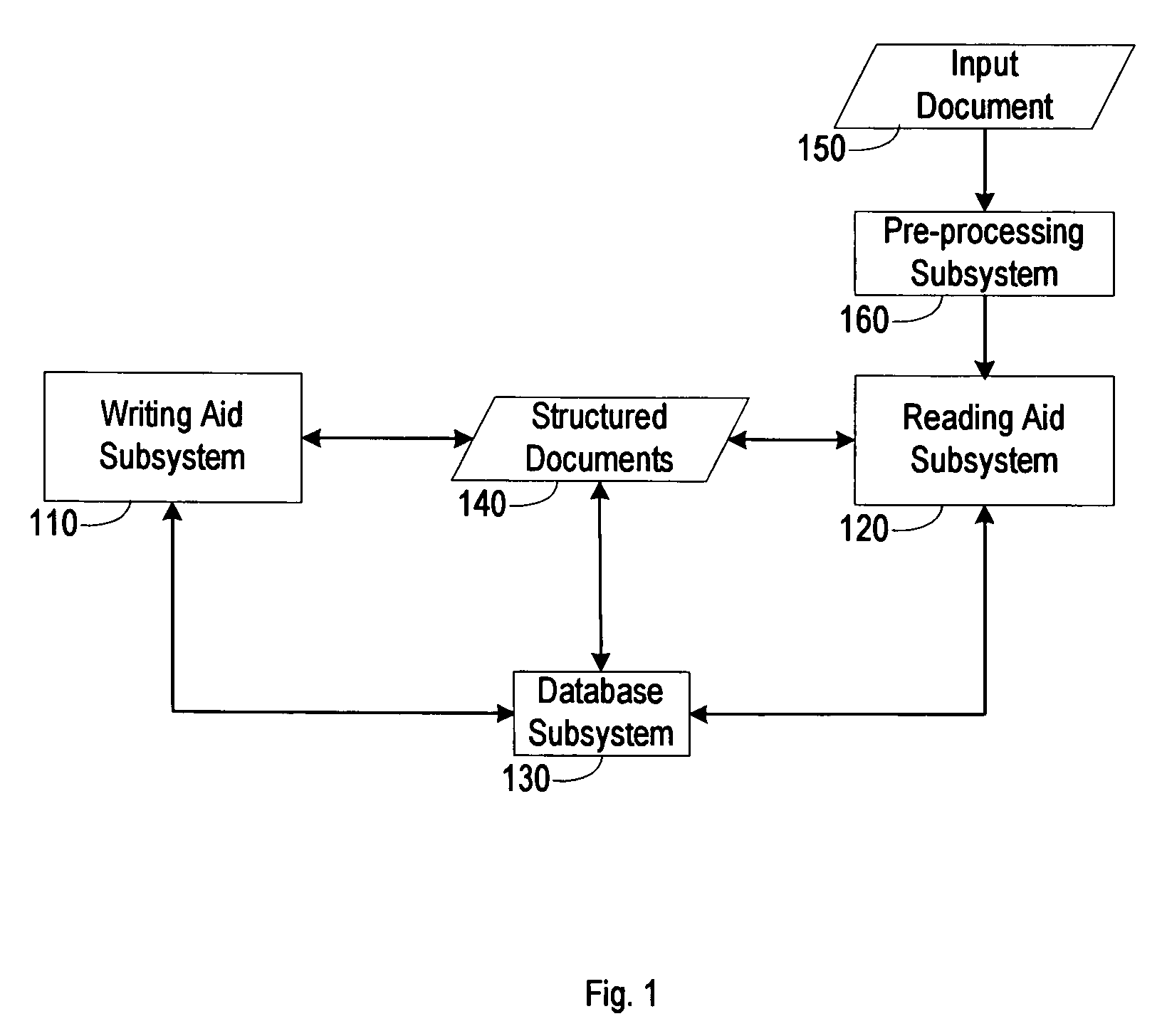
Writing and reading aid system
InactiveUS7555713B2Access informationPresent information flexiblyReadingNatural language data processingDocumentation procedureAccess method
A writing and reading assistant system helps a user to create a structured document and read a document. A structured document contains not only information as an ordinary document does but also properties and rules for holding, organizing and processing corresponding portions of information. The system helps the user as an author to search for information, generate, organize, examine, and modify ideas, to supply details, to examine one's writing from various aspects, to revise the writing, to specify information and access methods suitable for different audience, and to create a structured document. Further, the system helps the user as a reader to create and modify structures, define and modify properties and rules, and define and specify display forms, to associate text blocks with corresponding properties and rules, to extract information from an input document, to fill structures with corresponding information, to build various links among structures and display forms, and to display structures.
Owner:YANG GEORGE LIANG
Non-volatile memory and method with write cache partitioning
ActiveUS8094500B2Faster and robust write and read performanceIncrease burst write speedMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesGranularityMultilevel memory
A portion of a nonvolatile memory is partitioned from a main multi-level memory array to operate as a cache. The cache memory is configured to store at less capacity per memory cell and finer granularity of write units compared to the main memory. In a block-oriented memory architecture, the cache has multiple functions, not merely to improve access speed, but is an integral part of a sequential update block system. Decisions to write data to the cache memory or directly to the main memory depend on the attributes and characteristics of the data to be written, the state of the blocks in the main memory portion and the state of the blocks in the cache portion.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Non-volatile memory and method with write cache partition management methods
InactiveUS8244960B2Faster and robust write and read performanceIncrease burst write speedMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsGranularityMultilevel memory
A portion of a nonvolatile memory is partitioned from a main multi-level memory array to operate as a cache. The cache memory is configured to store at less capacity per memory cell and finer granularity of write units compared to the main memory. In a block-oriented memory architecture, the cache has multiple functions, not merely to improve access speed, but is an integral part of a sequential update block system. The cache memory has a capacity dynamically increased by allocation of blocks from the main memory in response to a demand to increase the capacity. Preferably, a block with an endurance count higher than average is allocated. The logical addresses of data are partitioned into zones to limit the size of the indices for the cache.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
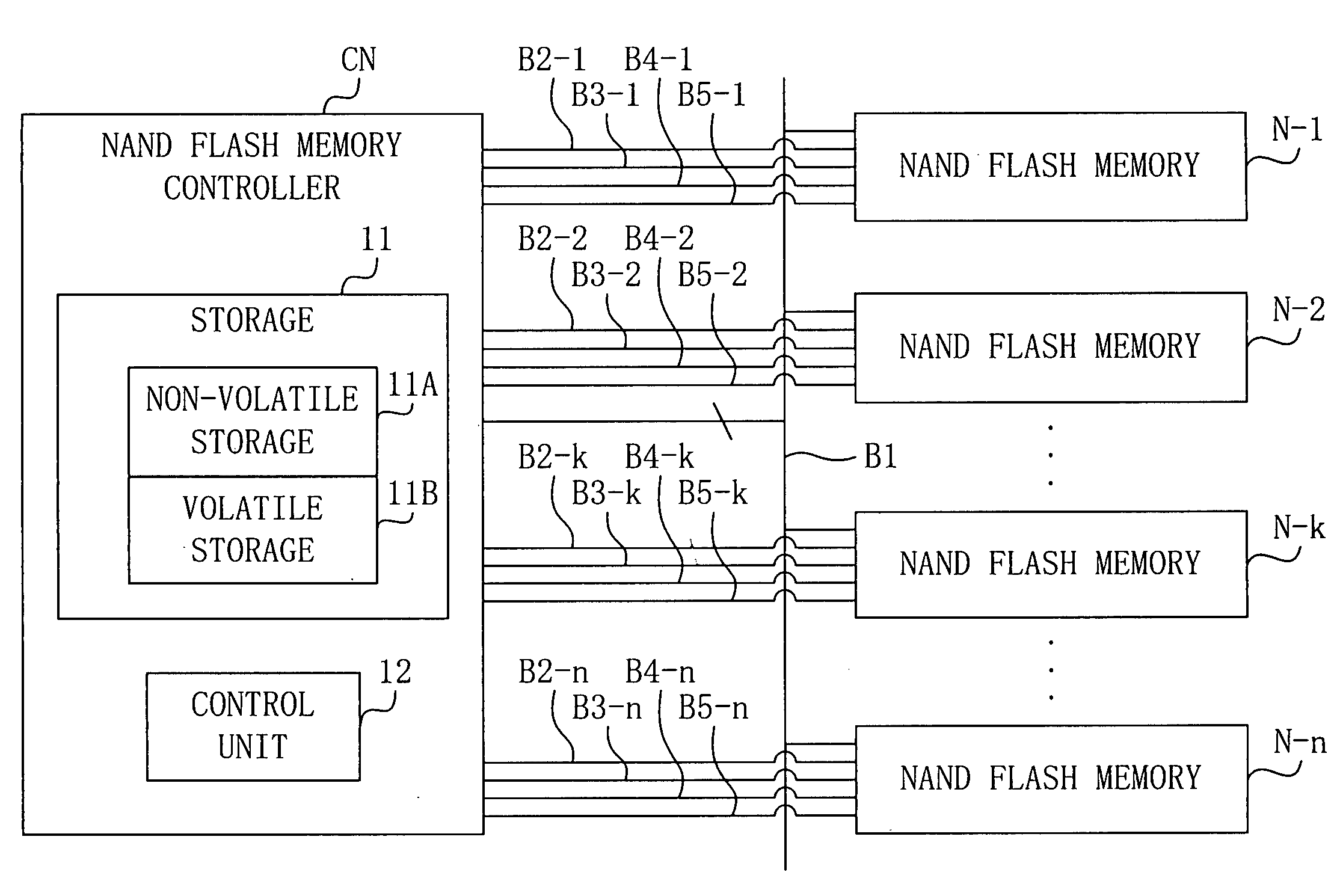
Data writing apparatus, data writing method, and program
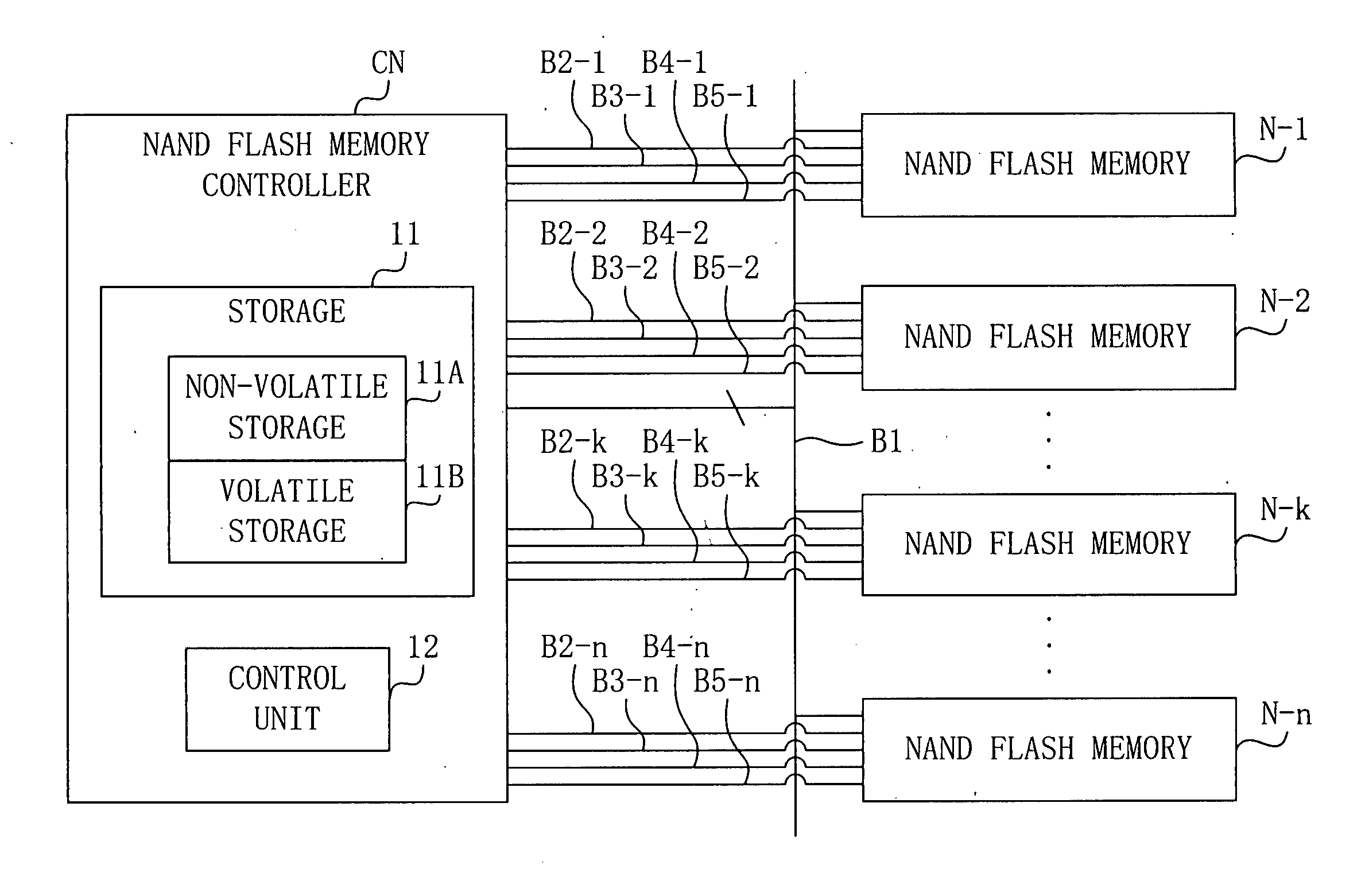
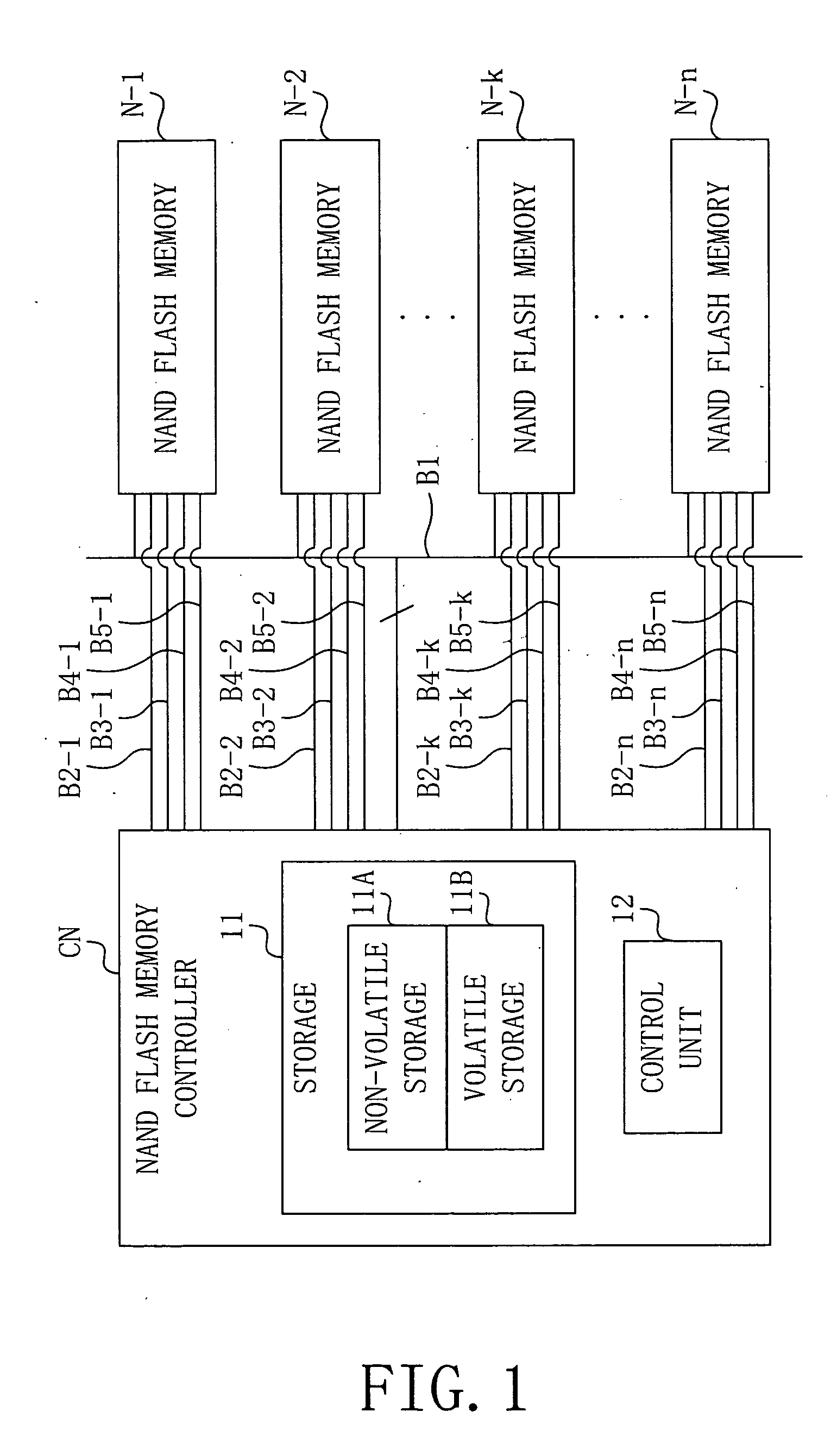
InactiveUS20040172576A1Write efficientlySame data efficientlyError preventionMemory loss protectionMemory block
Each of a plurality of storage devices (N-1 to N-n) has a plurality of memory blocks for storing data. A data writing apparatus obtains error information which represents good blocks which can store data correctly, from the plurality of storage devices (N-1 to N-n). The data writing apparatus determines a memory block in which data is to be written, in each of the plurality of storage devices (N-1 to N-n), based on the obtained error information. The data writing apparatus controls the plurality of storage devices (N-1 to N-n), and writes predetermined data in the determined memory blocks.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON DEVICE
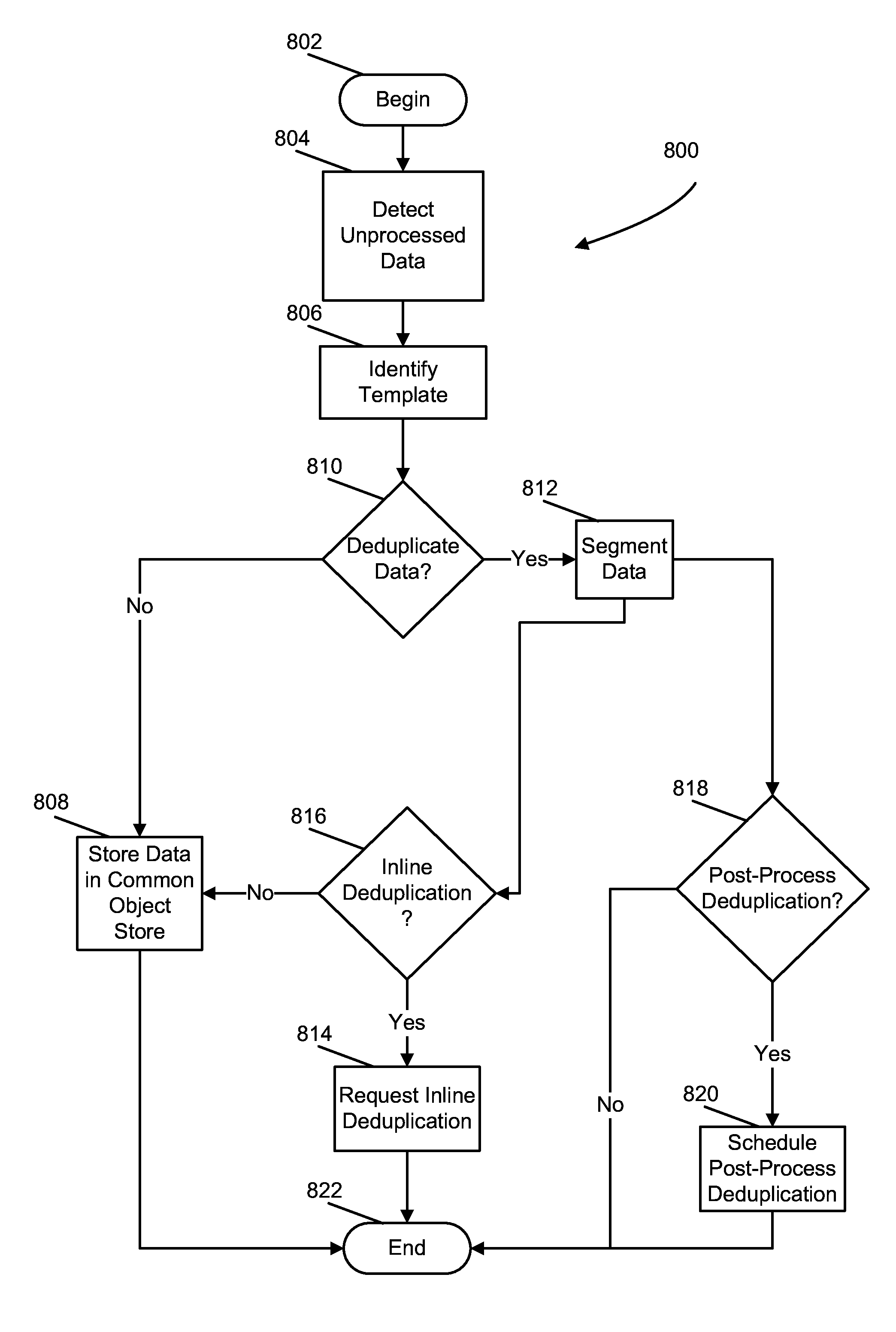
Multi-node hybrid deduplication
ActiveUS20150106345A1Easy to decoupleScalable architectureDigital data processing detailsFile access structuresAnalysis dataData storing
According to at least one embodiment, a data storage system is provided. The data storage system includes memory, at least one processor in data communication with the memory, and a deduplication director component executable by the at least one processor. The deduplication director component is configured to receive data for storage on the data storage system, analyze the data to determine whether the data is suitable for at least one of summary-based deduplication, content-based deduplication, and no deduplication, and store, in a common object store, at least one of the data and a reference to duplicate data stored in the common object store.
Owner:HITACHI VANTARA LLC
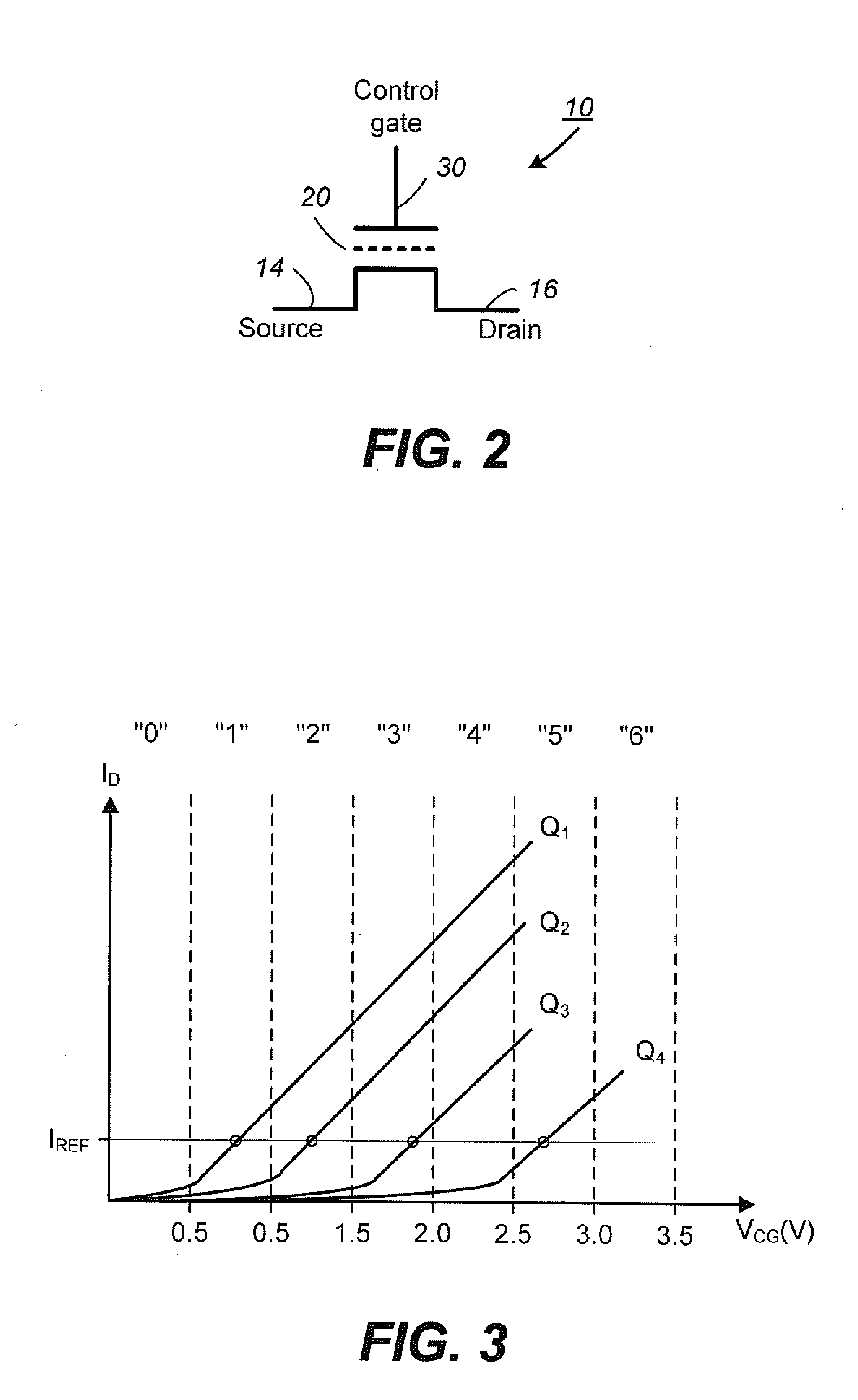
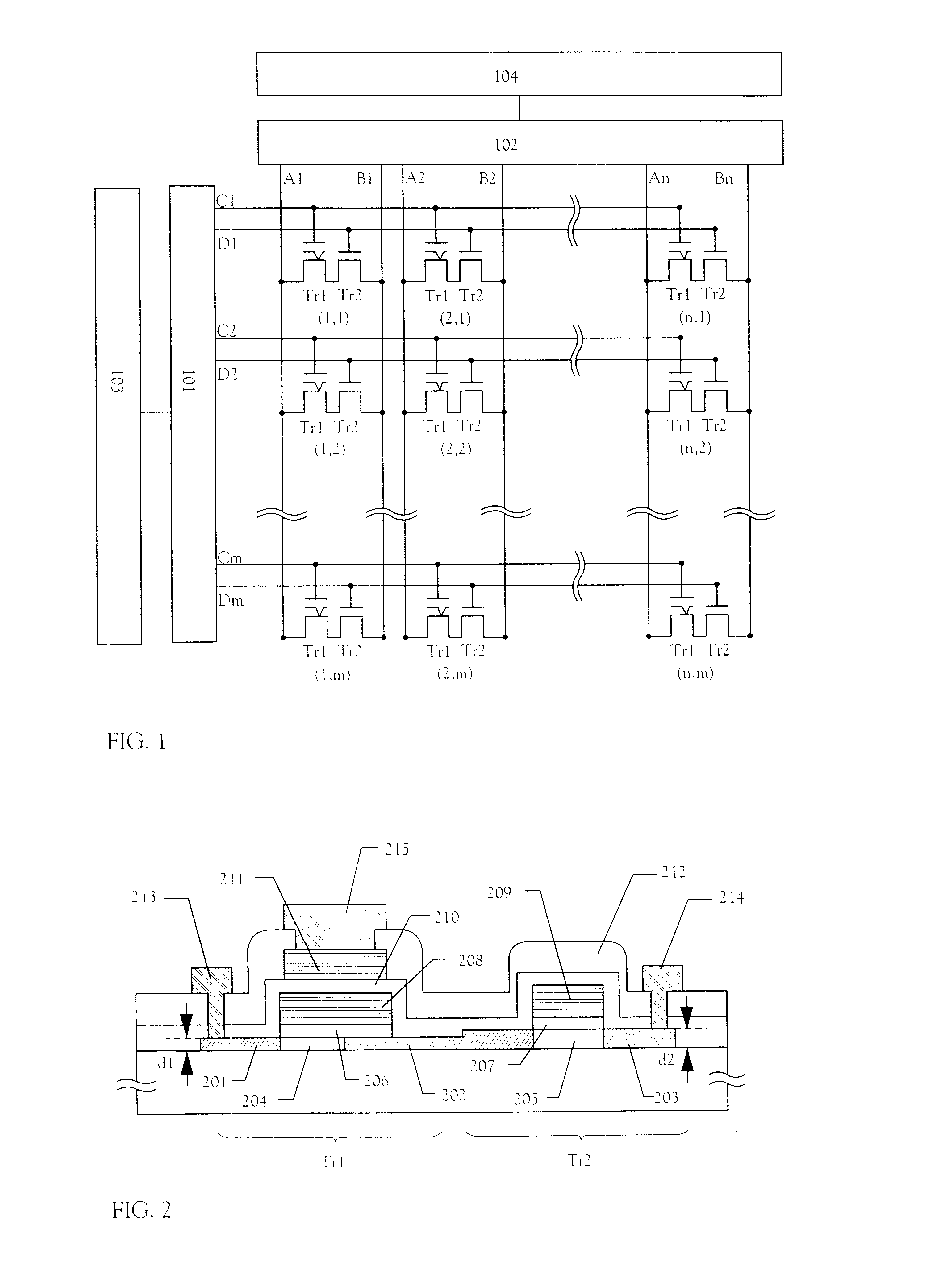
Nonvolatile memory, semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20020113268A1Small sizeIncrease the number ofTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLow voltageActive layer
The present invention provides a nonvolatile memory that can be integrally formed with other semiconductor devices and can be reduced in size. A memory TFT, a switching TFT and other peripheral circuits constituting a nonvolatile memory are integrally formed on a substrate by TFTs. The memory TFT and the switching TFT are formed on the same semiconductor active layer, and a semiconductor active layer of the memory TFT is formed thinner than semiconductor active layers of the other TFTs. As a result, a nonvolatile memory that is hardly deteriorated and that can be reduced in size is provided, in which writing / erasing for the memory TFT can be realized at a low voltage.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
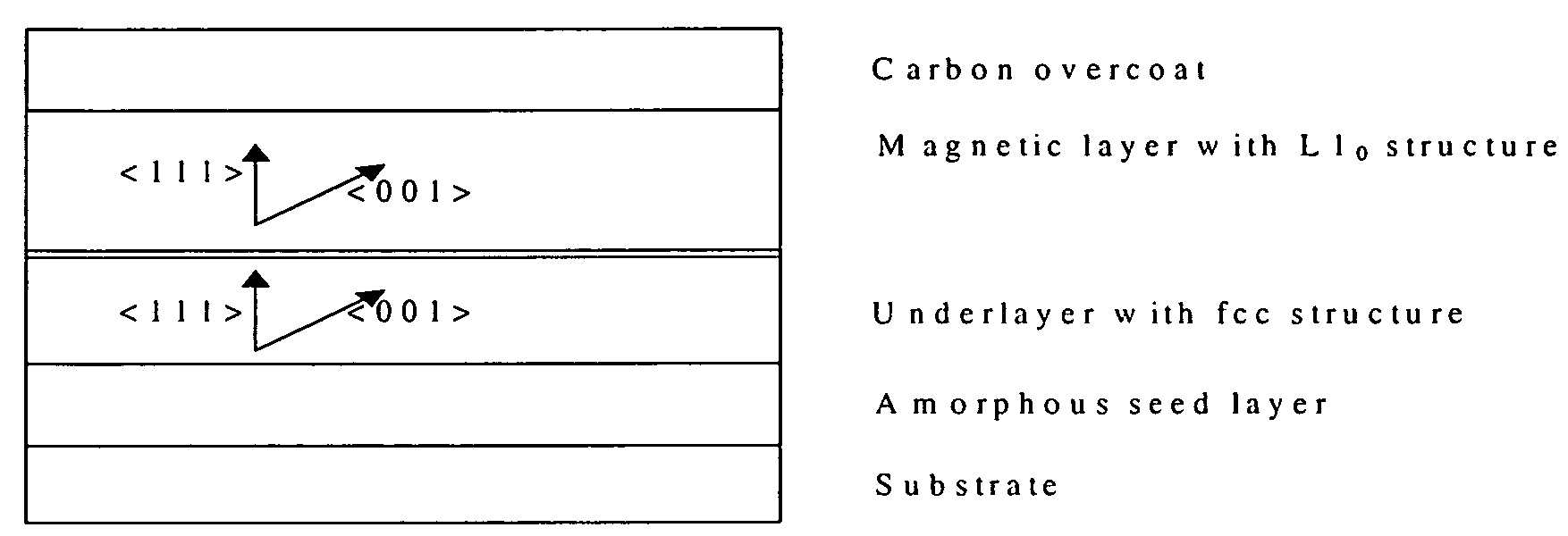
Tilted recording media with L10 magnetic layer
InactiveUS7282278B1Easily magnetizedWrite efficientlyRecord information storageDisk carriersHeat stabilityMagnetization
A magnetic recording medium having a magnetic layer with an L10 structure and an easy magnetization axis lying about 35° out-of-plane of the magnetic layer is disclosed. This medium has very high coercivity (Hc) and anisotropy field (Hk), giving rise to improved thermal stability. Combined with improved writability of the canted magnetic easy axis, this media enables improved recording signal-to-noise ratio (SNR).
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Database writing system and database writing method
InactiveCN102622426AWrite in orderWrite efficientlySpecial data processing applicationsThread poolRelease time
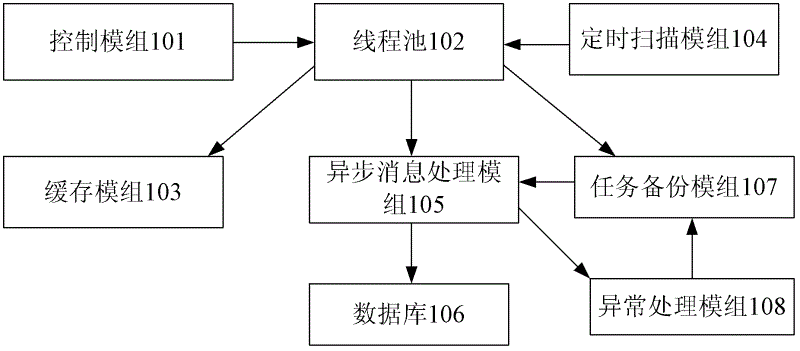
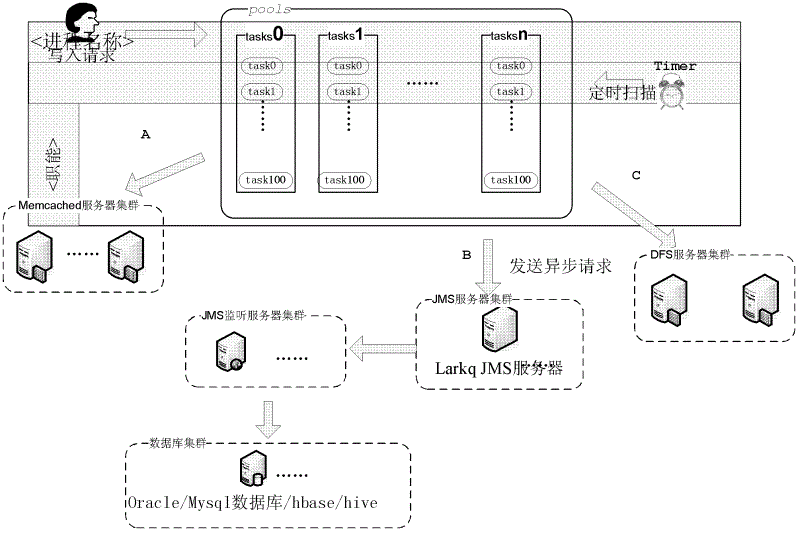
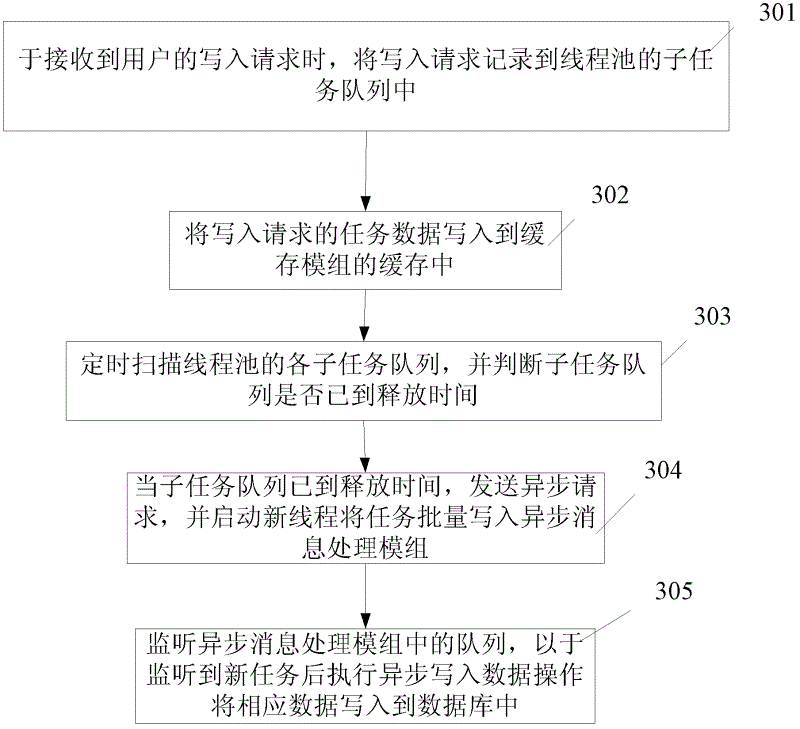
The invention discloses a database writing system and a database writing method. The system at least comprises a control module, a thread pool, a buffer memory module, a timing scanning module and an asynchronous information processing module. The control module is used for recording writing requests into subtask queues of the tread pool when receiving the writing requests, writing task data into the buffer memory module and transmitting asynchronous requests according to scanning results of the timing scanning module. The thread pool comprises a plurality of subtask queues, and each subtask queue saves a plurality of tasks. The buffer memory module is used for saving the task data. The timing scanning module timely scans the subtask queues in the thread pool to judge whether releasing time comes, judge whether one subtask queue meets the releasing time or not and conduct grouping on data in the subtask queue. The asynchronous information processing module processes the asynchronous requests, receives parameter information of the subtask queues in the releasing process, records the queue tasks and writes corresponding data into a database after monitoring new tasks. By means of the database writing system and database writing method, orderly, efficient and blocking type database writing can be achieved.
Owner:杭州闪亮科技有限公司
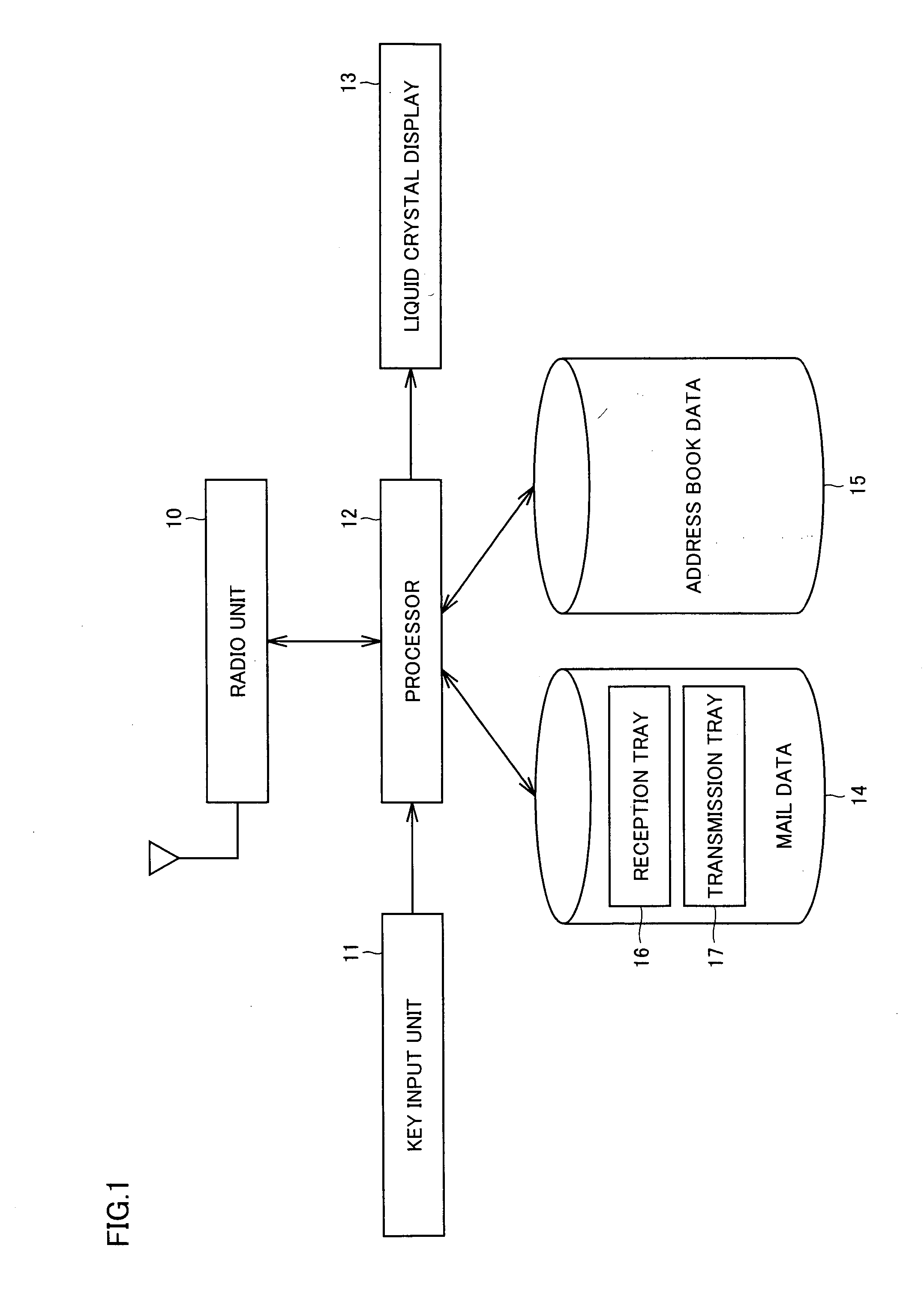
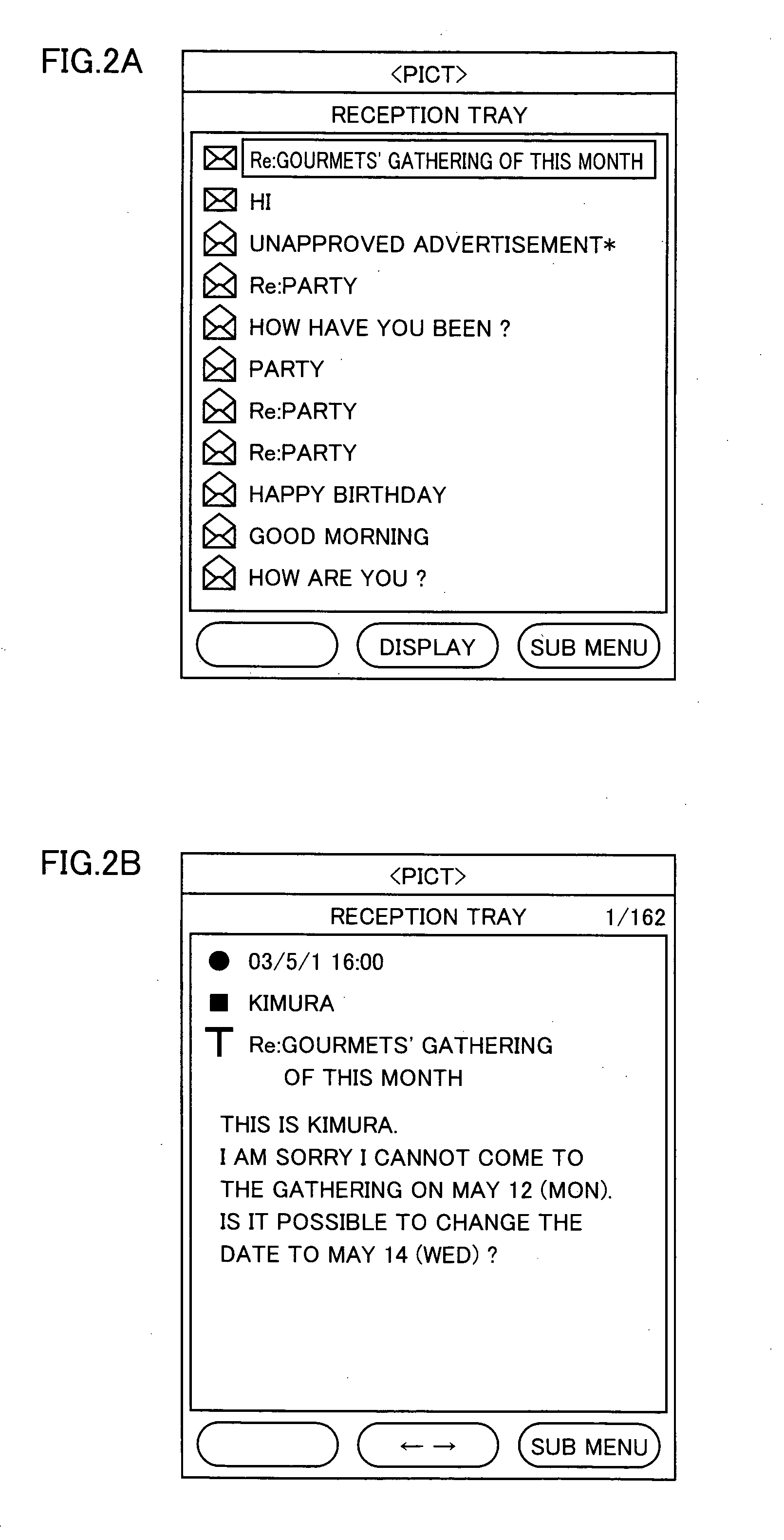
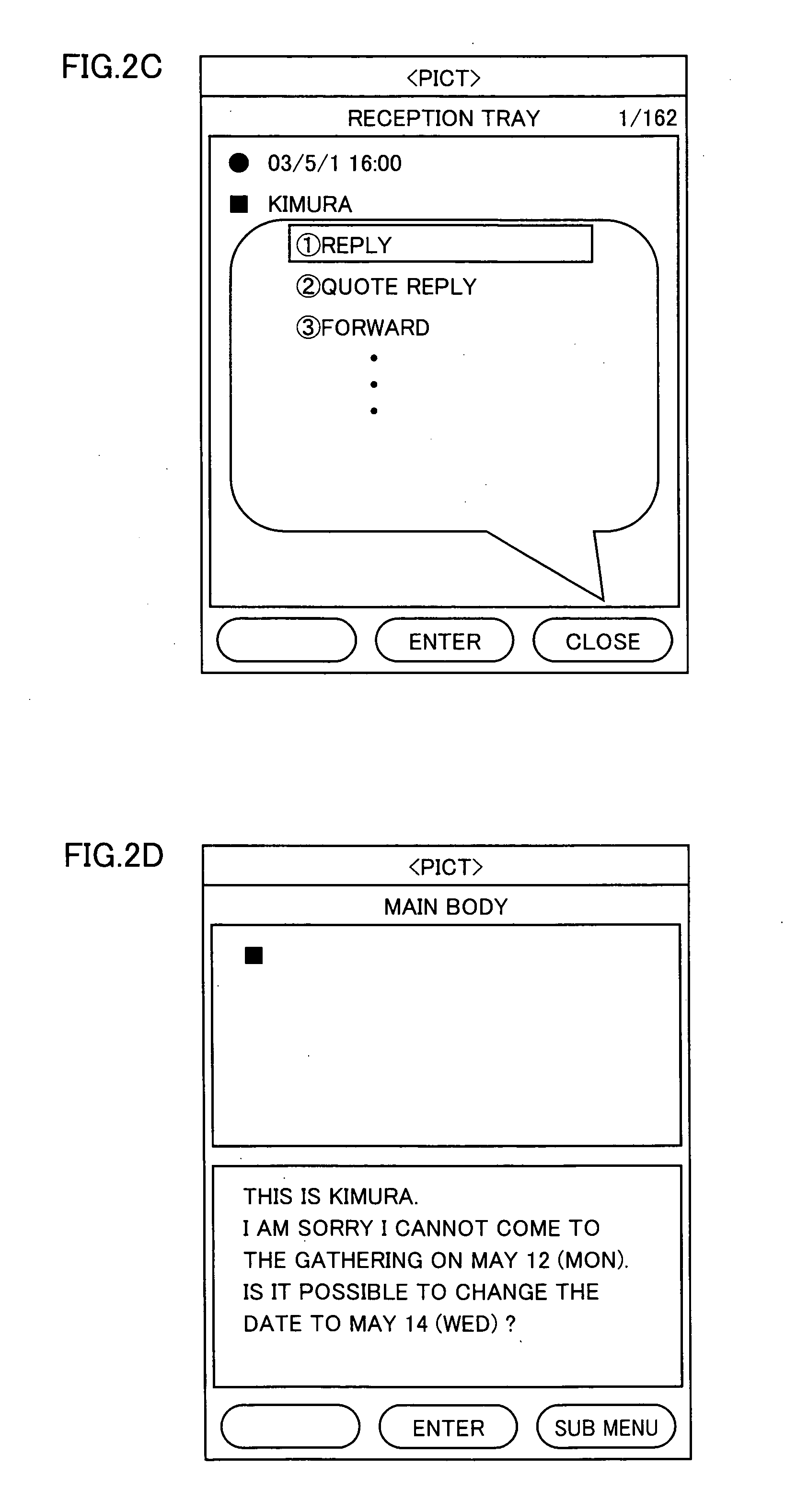
Electronic mail viewing device and electronic mail editing device
InactiveUS20050210146A1Write efficientlyEasy to operateDigital computer detailsSubstation equipmentObject copyingComputer graphics (images)
An object of the present invention is to provide an e-mail editing device having excellent operability, in particular, an e-mail editing device capable of switching and displaying related e-mails. A display processor simultaneously displays a message editing screen for displaying an edition mail and a mail reference screen for displaying a reference mail for reference. A reference processor copies an object in the reference mail to a temporary storage. An editor pastes the object to an edition mail. A mail search portion searches for an e-mail in a memory on the basis of the reference mail. When a user performs a mail switching operation, the reference mail is switched to a searched e-mail for display.
Owner:SHARP KK
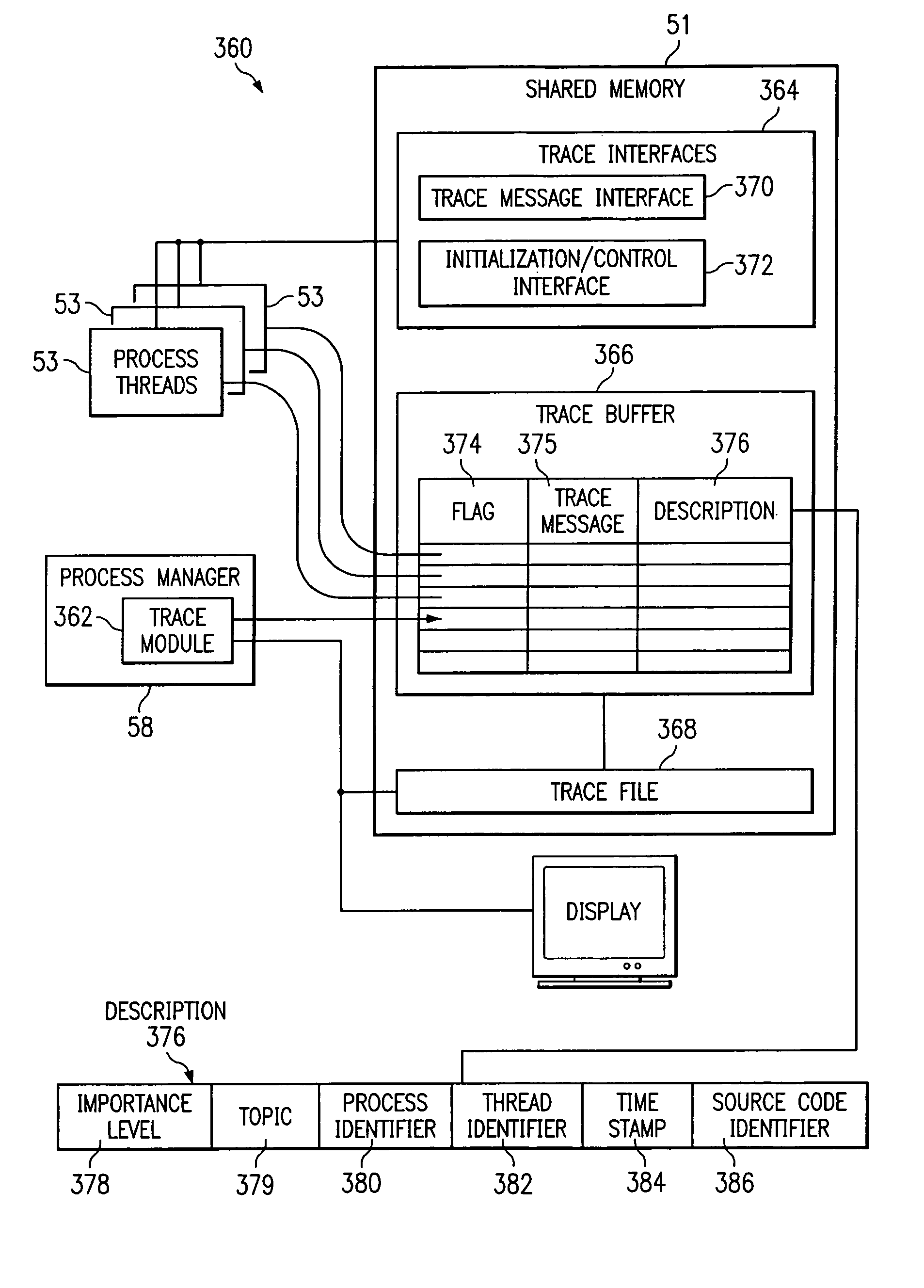
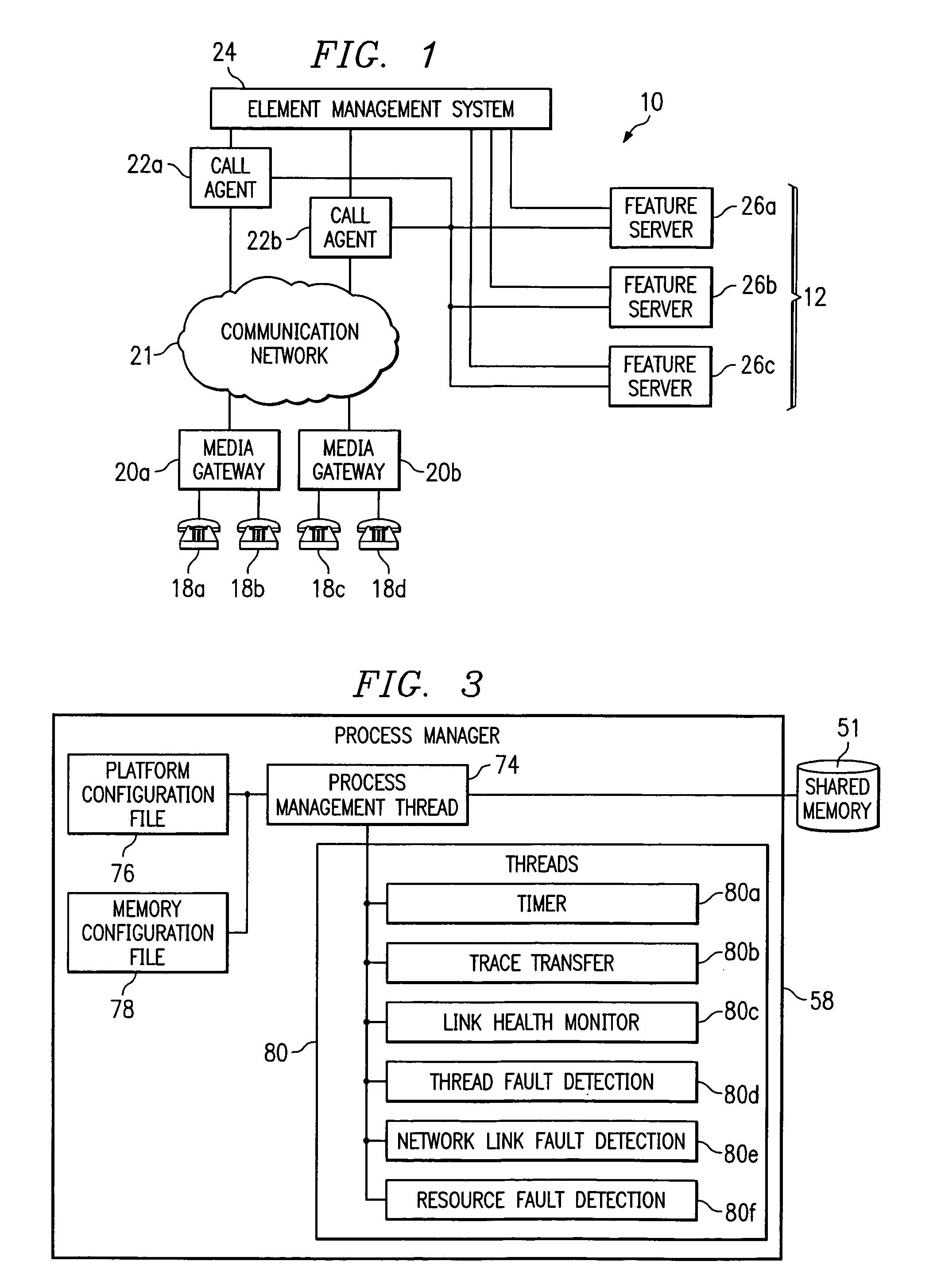
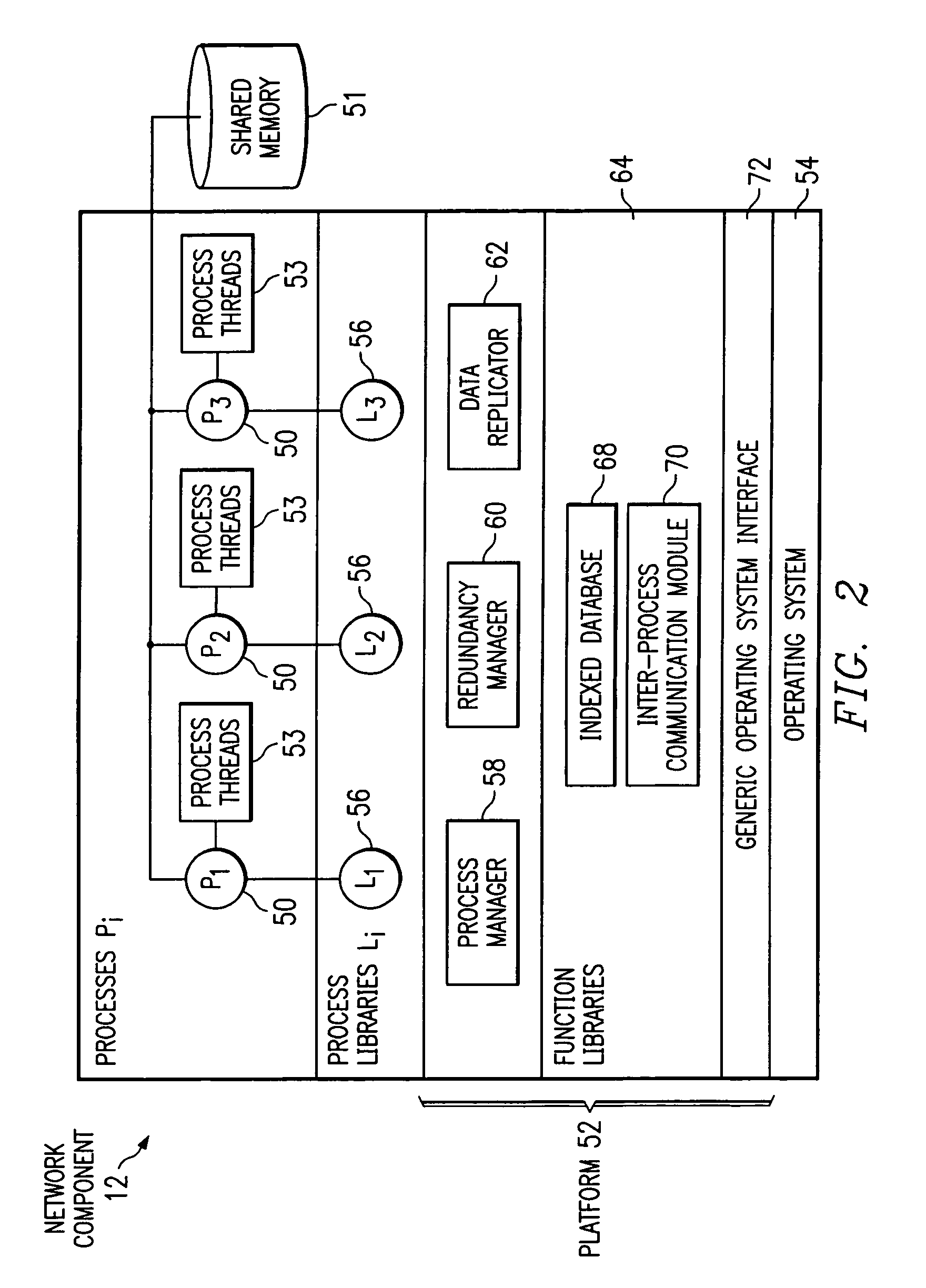
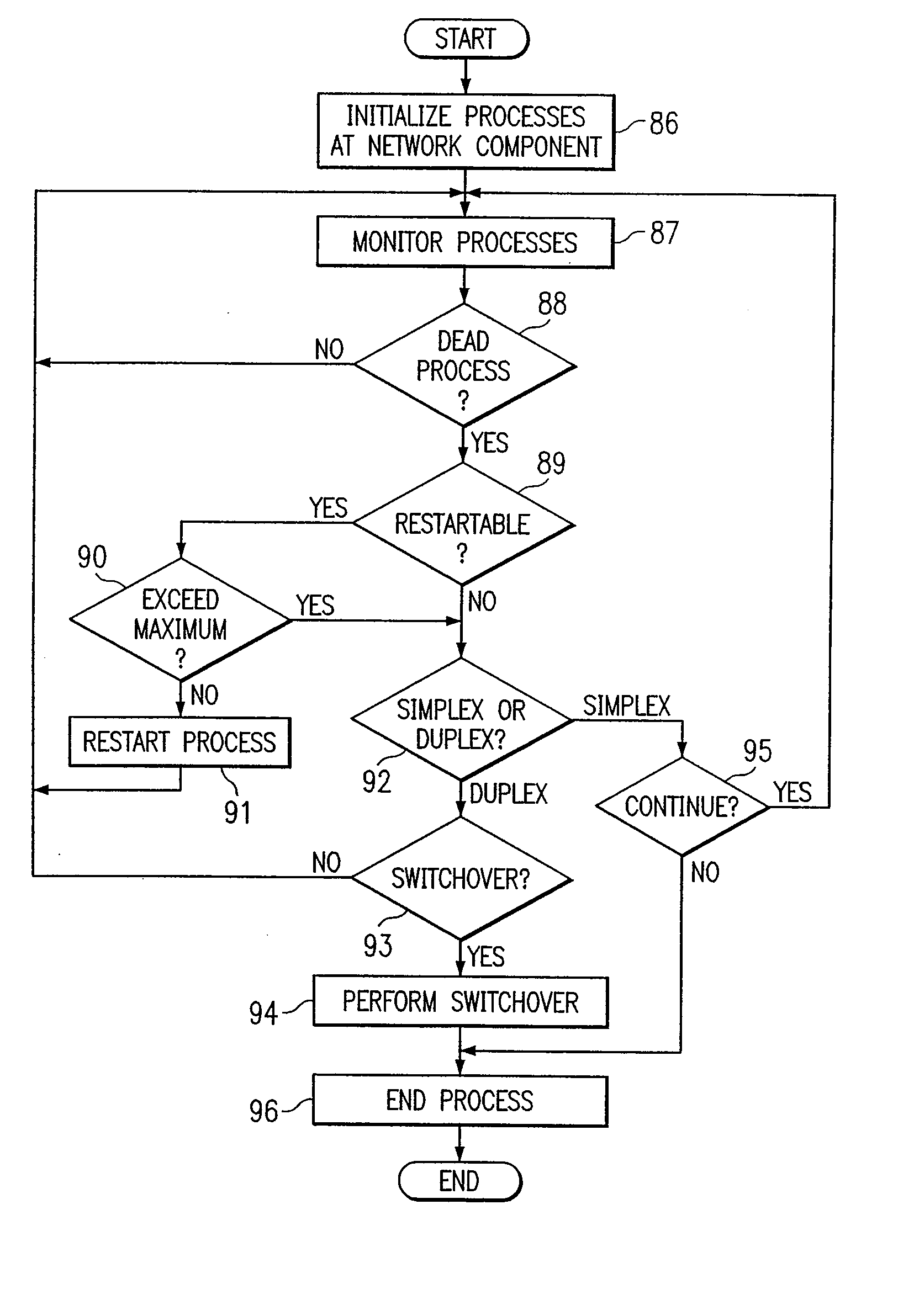
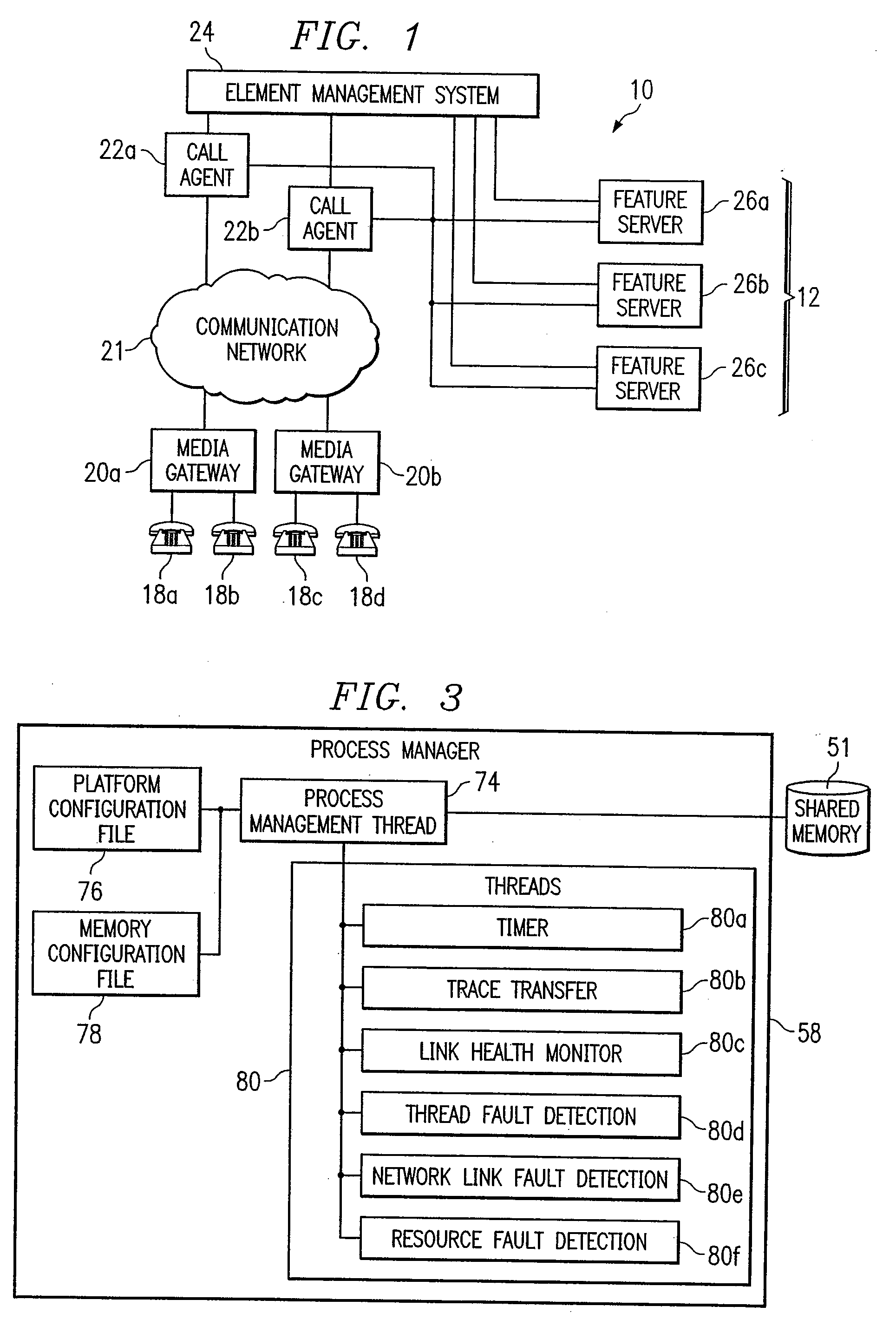
Recording trace messages of processes of a network component
ActiveUS7185061B1Disadvantages and reduced eliminatedProcess reduced eliminatedMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksData bufferTime sequence
A method for tracking a process is disclosed. Requests are received from process threads according to a time order. A request requests a buffer entry operable to record a trace message from a process thread of a process. A first buffer entry is assigned to a first process thread associated with a trace message according to the time order. A second buffer entry is assigned to a second process thread according to the time order subsequent to the assignment of the first buffer entry. The trace message associated with the first process thread is written to the first buffer entry in response to the assignment of the first buffer entry.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
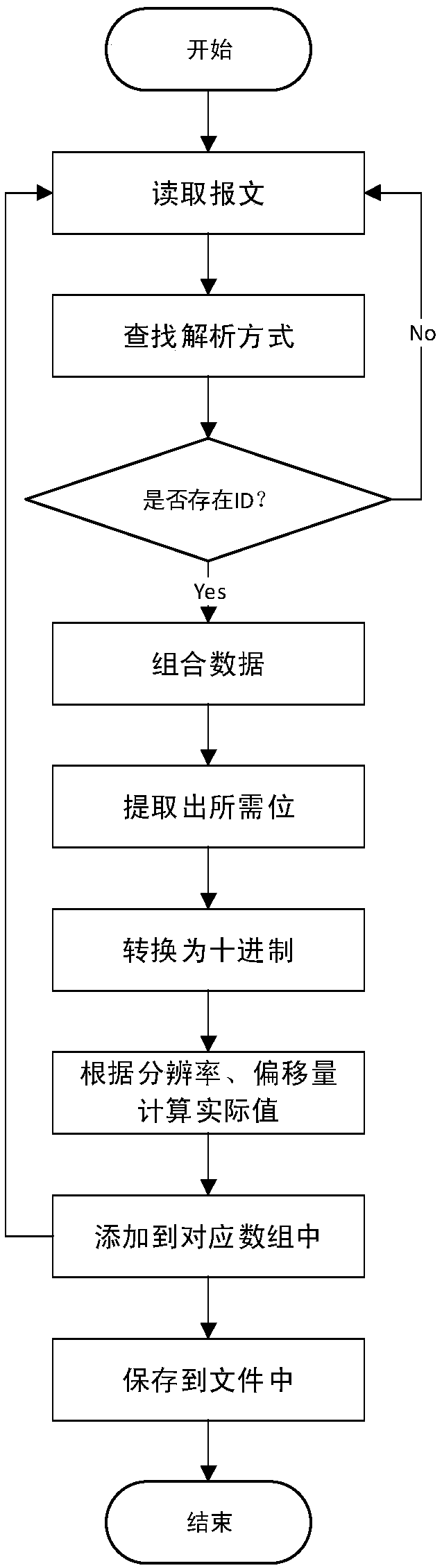
DBC file parsing and message analyzing method based on regular expression
ActiveCN108600192AReduce the probability of misdefinitionQuick port useBus networksDBcAnalysis method
The invention discloses a DBC file parsing and message analyzing method based on a regular expression. In the method, a content of a DBC file is parsed through a processing method of matching and substituting of the regular expression, the parsed DBC data is used for analyzing a CAN message acquired from a finished automobile, a corresponding CAN network message block in the DBC file and signals contained in the CAN network message block are found according to a message ID, actual data is obtained through data type, start bit, bit length, offset, proportionality coefficient and parsing type ofthe CAN network message block, and the data is stored in a corresponding file. The method provided by the invention has excellent effects of being simple and highly expandable, not only being capableof performing CAN message parsing, but also being capable of performing acquisition and calibration of use completed data of protocols of XCP and CCP.
Owner:NANJING YUEBOO POWER SYST CO LTD
Nonvolatile memory with write cache having flush/eviction methods
ActiveUS8700840B2Faster and robust write and read performanceIncrease burst write speedMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTGranularityMultilevel memory
A portion of a nonvolatile memory is partitioned from a main multi-level memory array to operate as a cache. The cache memory is configured to store at less capacity per memory cell and finer granularity of write units compared to the main memory. In a block-oriented memory architecture, the cache has multiple functions, not merely to improve access speed, but is an integral part of a sequential update block system. Decisions to archive data from the cache memory to the main memory depend on the attributes of the data to be archived, the state of the blocks in the main memory portion and the state of the blocks in the cache portion.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Complementary resistive switching memory device having three-dimensional crossbar-point vertical multi-layer structure
InactiveUS20170330916A1Write efficientlyEfficient readingSolid-state devicesDigital storageUnit deviceSemiconductor
A complementary resistive switching (CRS) memory device having a three-dimensional crossbar-point vertical multi-layer structure is provided. The CRS memory device having a three-dimensional structure comprises: a conductive pillar; a plurality of CRS memory unit devices surrounding an outer circumferential surface of the conductive pillar and positioned to be spaced apart from each other; and a plurality of word electrode lines making contact with outer circumferential surfaces of the CRS memory unit devices and positioned so as to intersect the conductive pillar, wherein the CRS memory unit devices comprise: a first oxide semiconductor film surrounding the outer circumferential surface of the conductive pillar; a conductive film surrounding the first oxide semiconductor film; and a second oxide semiconductor film surrounding the conductive film. Therefore, a CRS memory device having a CRS-based three-dimensional crossbar-point vertical structure can be provided wherein a CRS device having a three-layer structure is applied as a unit device so as to enable efficient writing and reading without a selection device.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
Nonvolatile semiconductor storage device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveCN101047190AIncrease the contact resistance valueWrite efficientlyTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceCharge retention
It is an object to provide a nonvolatile semiconductor storage device that prevents increase in a contact resistance value due to etching of a semiconductor layer when etching an interlayer insulating film and that has superiority in a writing characteristic and an electric charge-holding characteristic, and a manufacturing method thereof. A conductive layer is provided between a source or drain region and a source or drain wiring. The conductive layer is made of the same conductive layer that forms a control gate electrode. An insulating film is provided so as to cover the conductive layer, and the insulating film has a contact hole for exposing part of the conductive layer. The source or drain wiring is formed so that the contact hole is filled.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Web development environment-oriented relational database data backtracking method
ActiveCN107145403ADoes not affect log recoveryLow costRelational databasesRedundant operation error correctionRelational databaseWeb development
The invention discloses a Web development environment-oriented relational database data backtracking method which comprises the following steps: 1, establishing a Web environment SeeLog log processing model, comprising the following procedures: 1.1, automatically acquiring a SeeLog log; 1.2, dynamically adjusting a persistent behavior of the log according to an algorithm; 1.3, performing a persistent operation by adopting a log segmentation strategy; 2, performing database recovery by adopting a TBack data backtracking mechanism, comprising the following procedures: performing data backtracking by utilizing a database event log once the database fails at a certain time point, and recovering the database to any time point before failure; and 3, immediately writing each event into a persistent layer by adopting a self-backup mechanism of a memory log, so that the memory log is not lost. According to the method disclosed by the invention, low-cost data backup can be realized, and the method can be independent of specific relational database kind or version.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
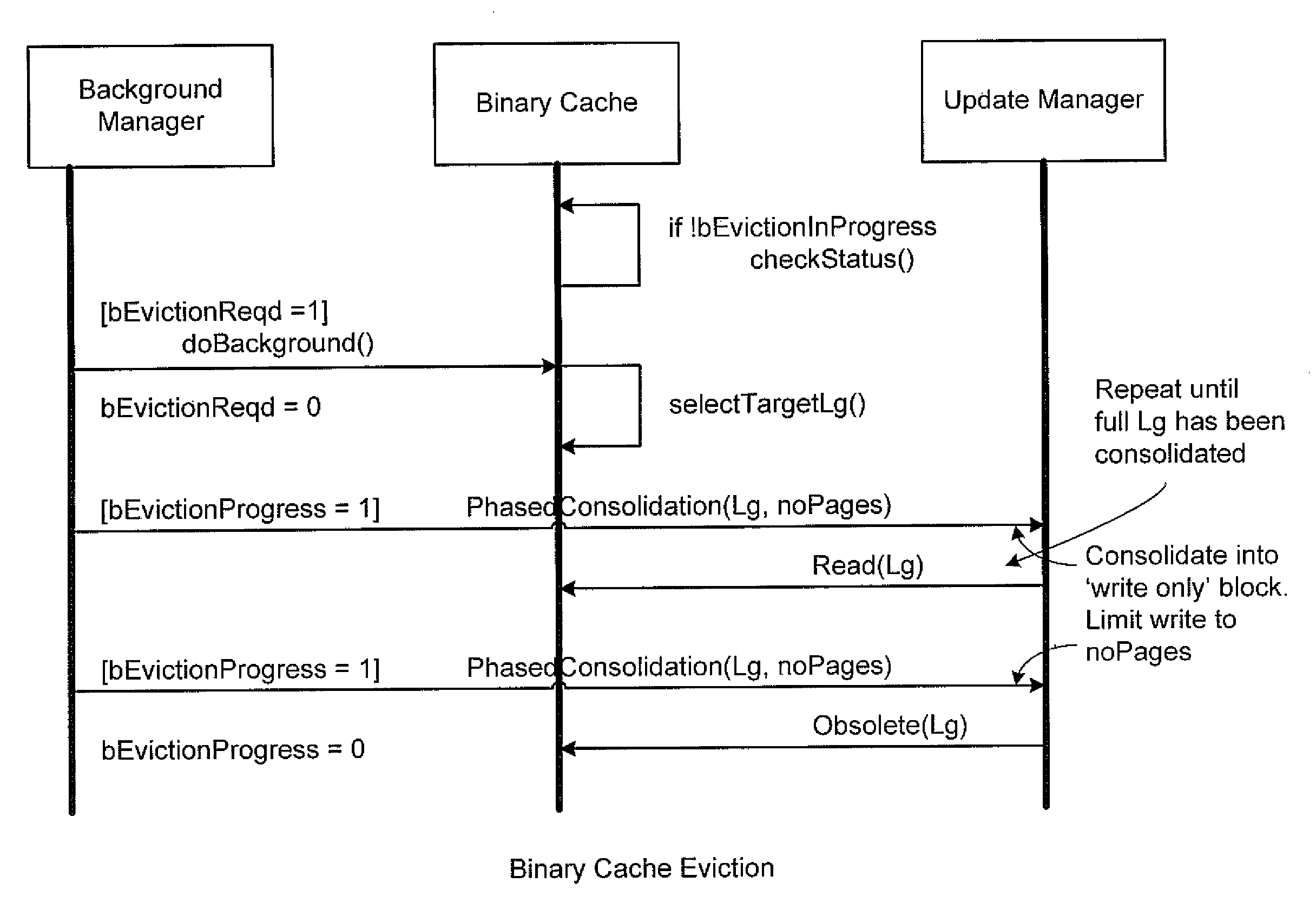
System and method for efficient updates of sequential block storage
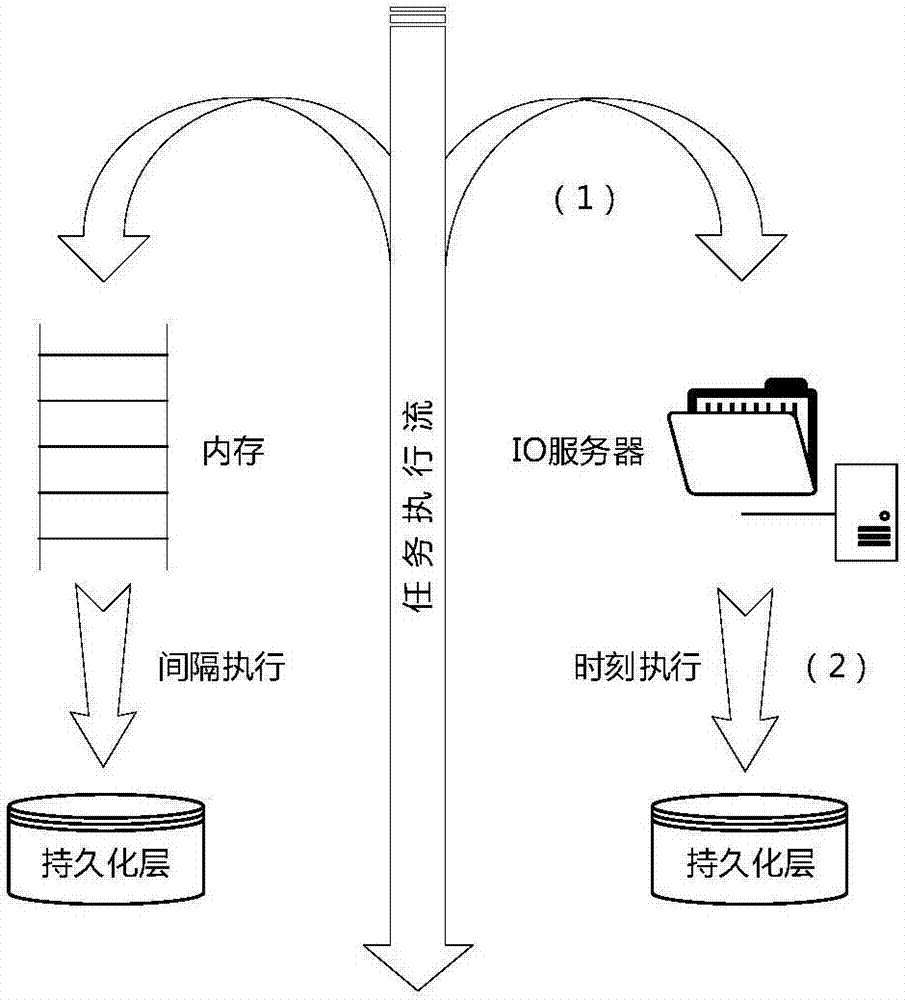
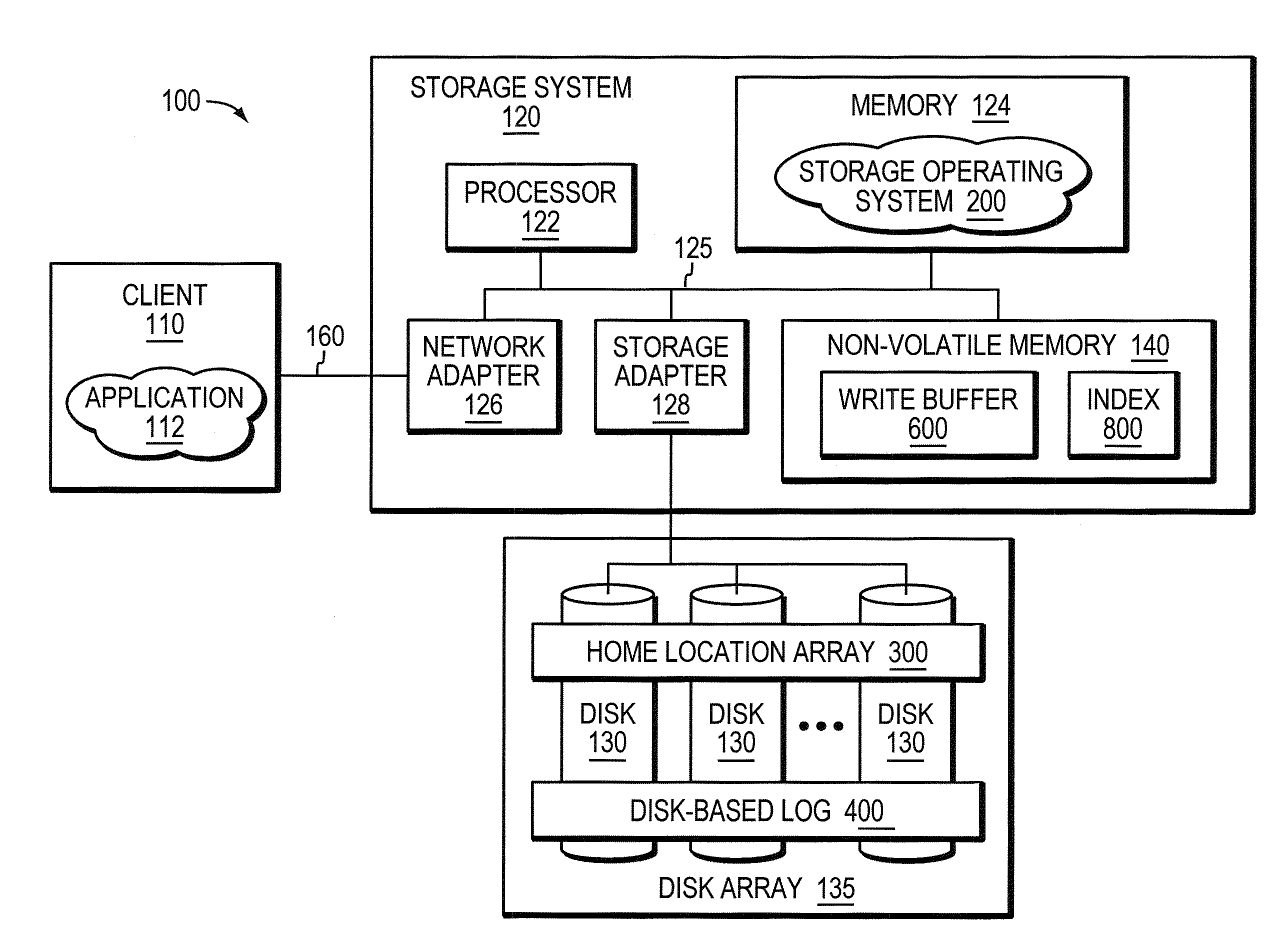
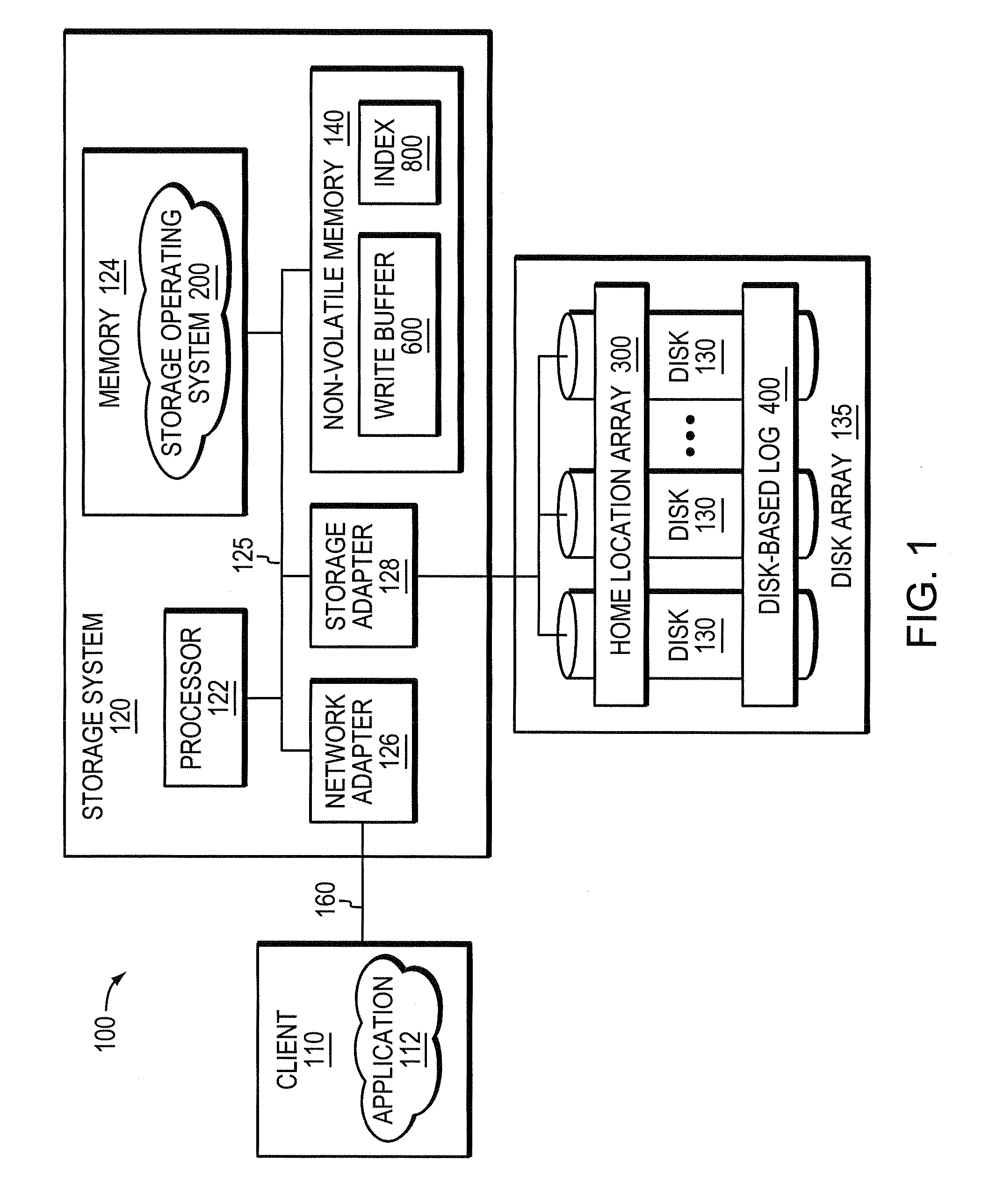
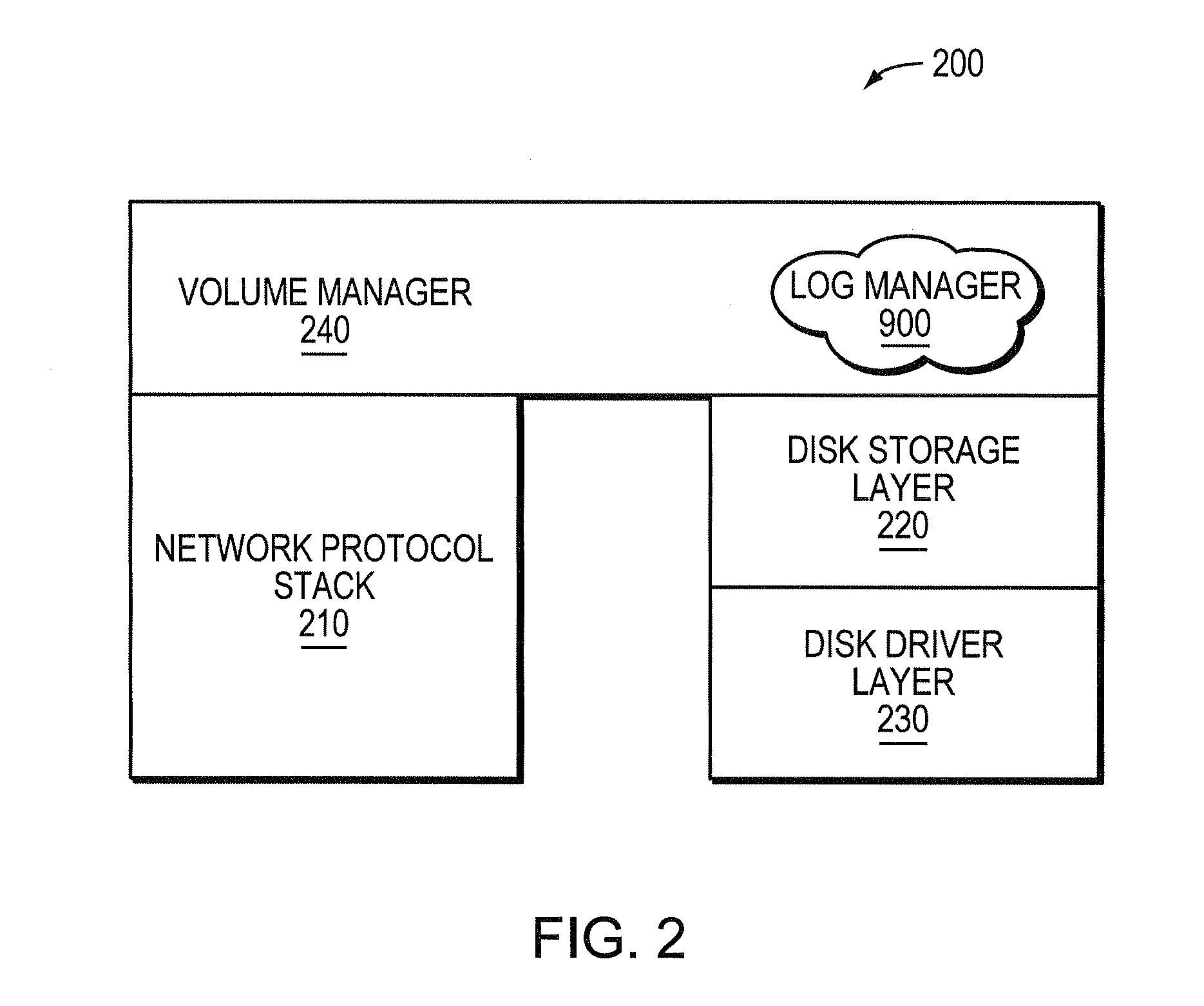
ActiveUS20080270690A1Improve update effectOvercome disadvantagesDigital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsWrite bufferDisk array
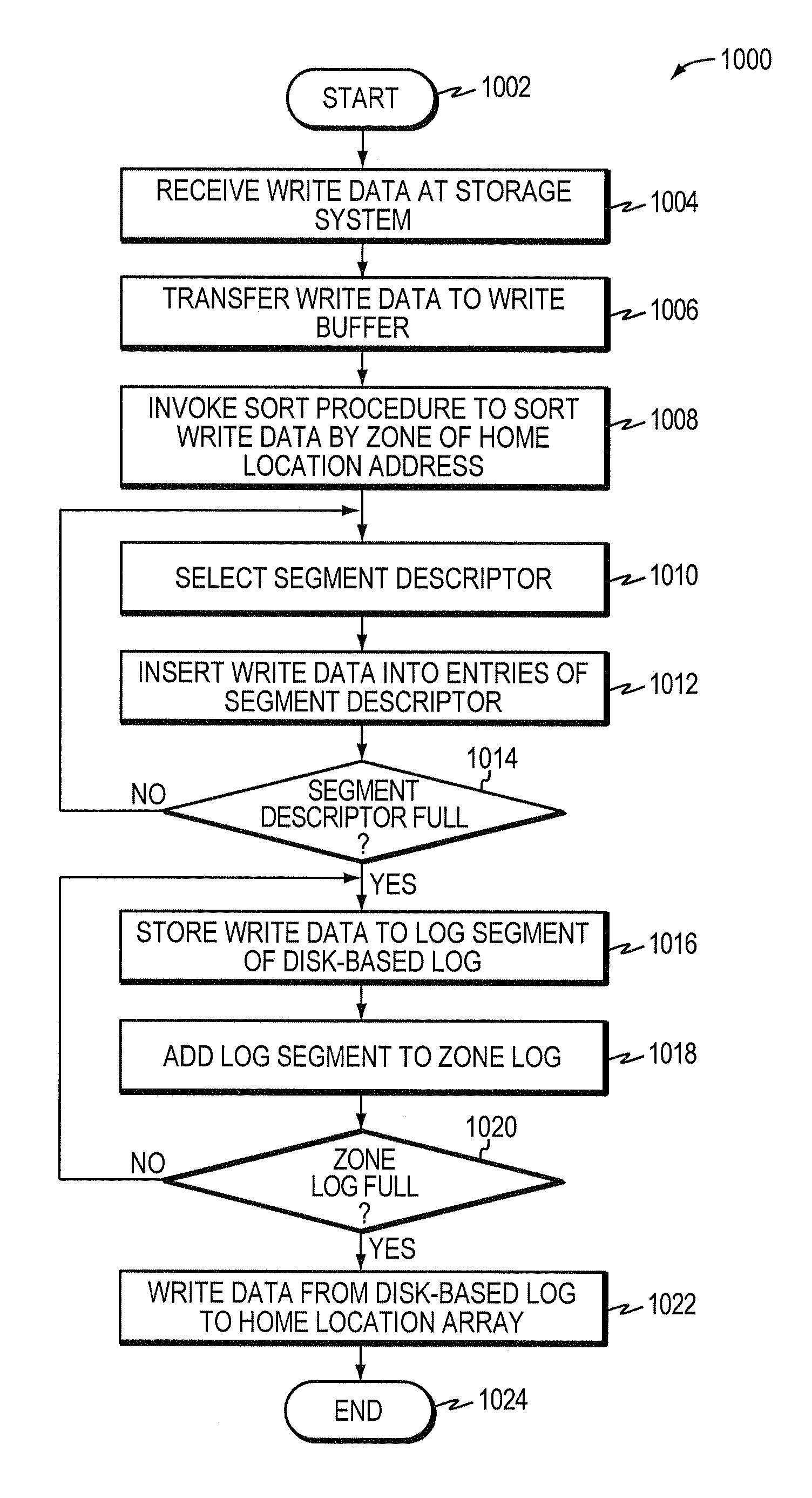
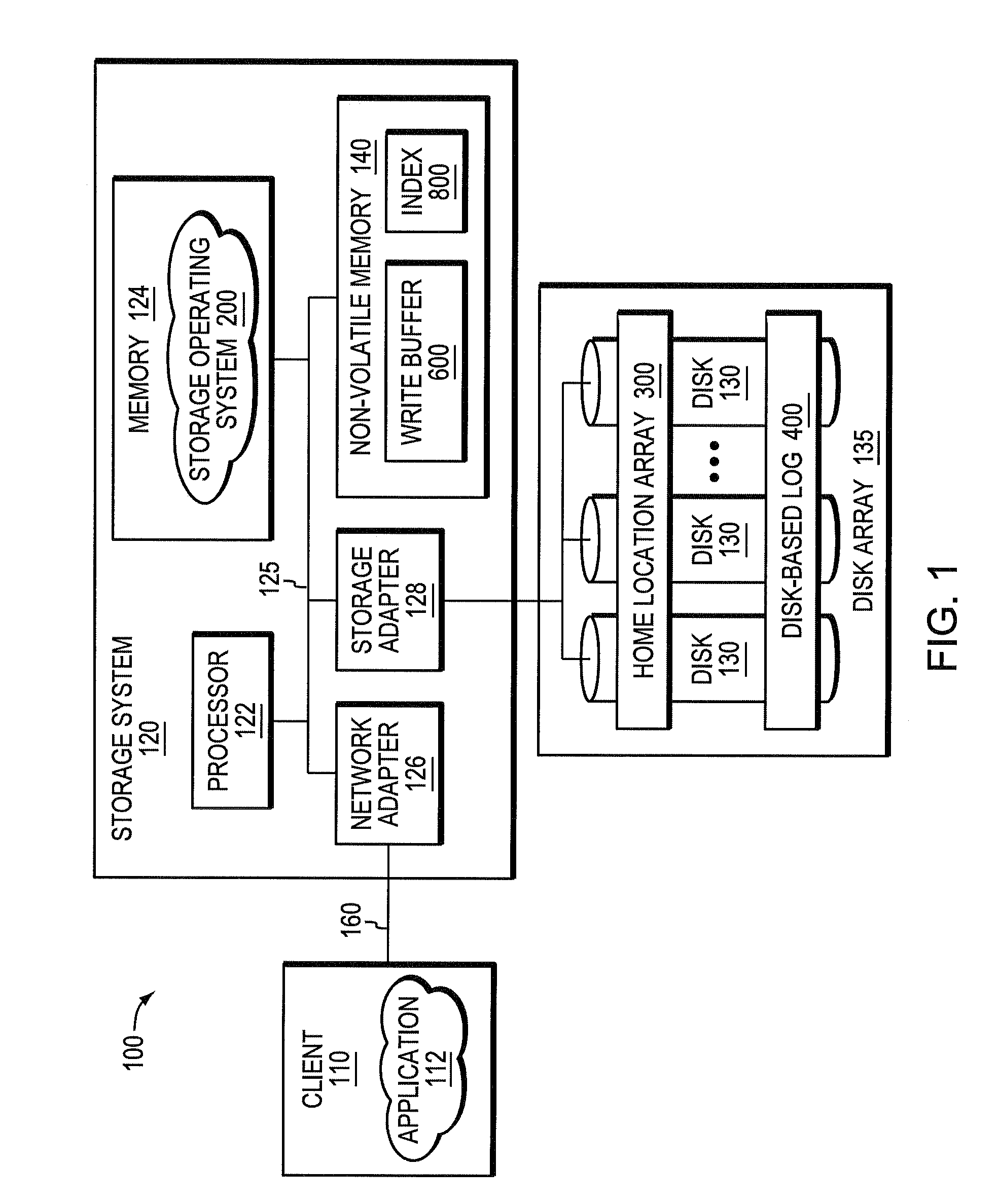
A system and method enhances performance of updates to sequential block storage of a storage system. According to an aspect of the invention, a disk array of the storage system is utilized to extend write buffers of the system, thereby rendering a portion of the disk array a disk-based log. To that end, one portion of the disk array is organized into a home location array having a set of sequential home locations for disk blocks. Another portion of the disk array is organized into the disk-based log having a set of log buffers configured to store versions of disk blocks that have yet to be returned to their home locations in the home location array. In addition, non-volatile memory of the storage system is organized as an index configured to provide efficient mappings of disk blocks not yet returned to their home locations. In accordance with another aspect of the invention, a novel disk-based multi-level sort procedure is provided to establish locality among updates (write data) held in the disk-based log, thereby enabling the write data to be efficiently written to home locations on the disk array.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Dynamic data storage method and device
ActiveCN104516912AHigh costSimple structureSpecial data processing applicationsDatabase indexingMetadataStorage structure
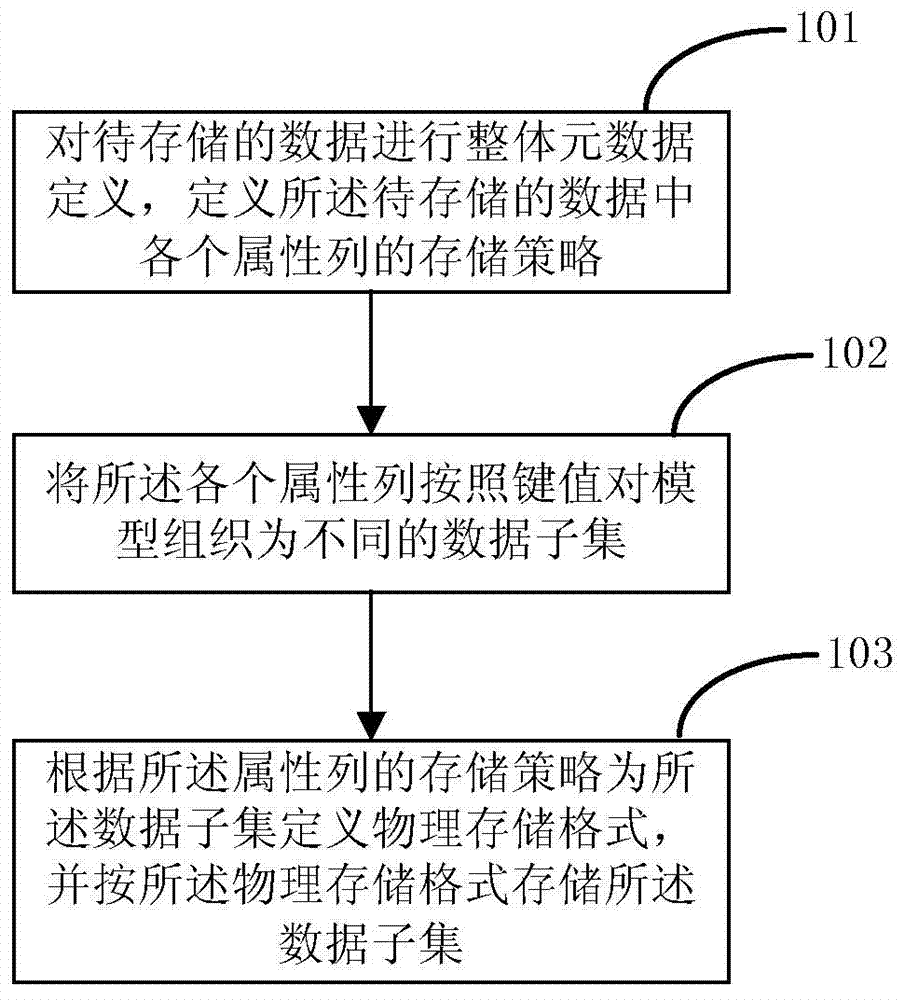
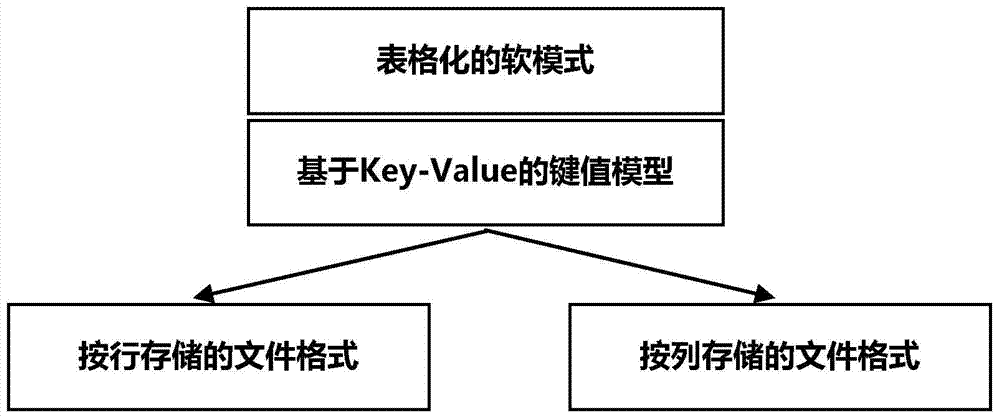
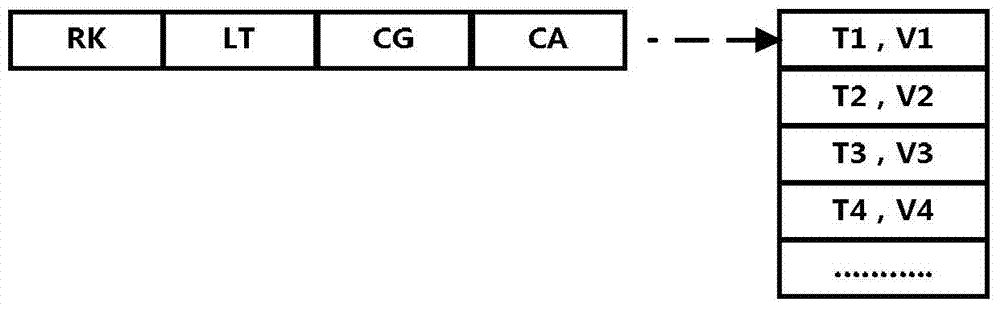
The embodiment of the invention provides a dynamic data storage method. The dynamic data storage method comprises performing integral metadata definition on data to be stored to define the storage strategy of every attribute list of the data to be stored; organizing the attribute lists into different data subsets according to a key-value pair model; according to the storage strategies of the attribute lists, defining physical storage formats for the data subsets, and storing the data subsets according to the physical storage formats. The embodiment of the invention also provides a corresponding dynamic data storage device. According to the dynamic data storage method and device, the dynamic data storage method is achieved through a layered and configurable storage structure and can meet the storage requirements of sparse data sets and dens data sets in mass data treatment simultaneously.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GRP HEILONGJIANG CO LTD +1
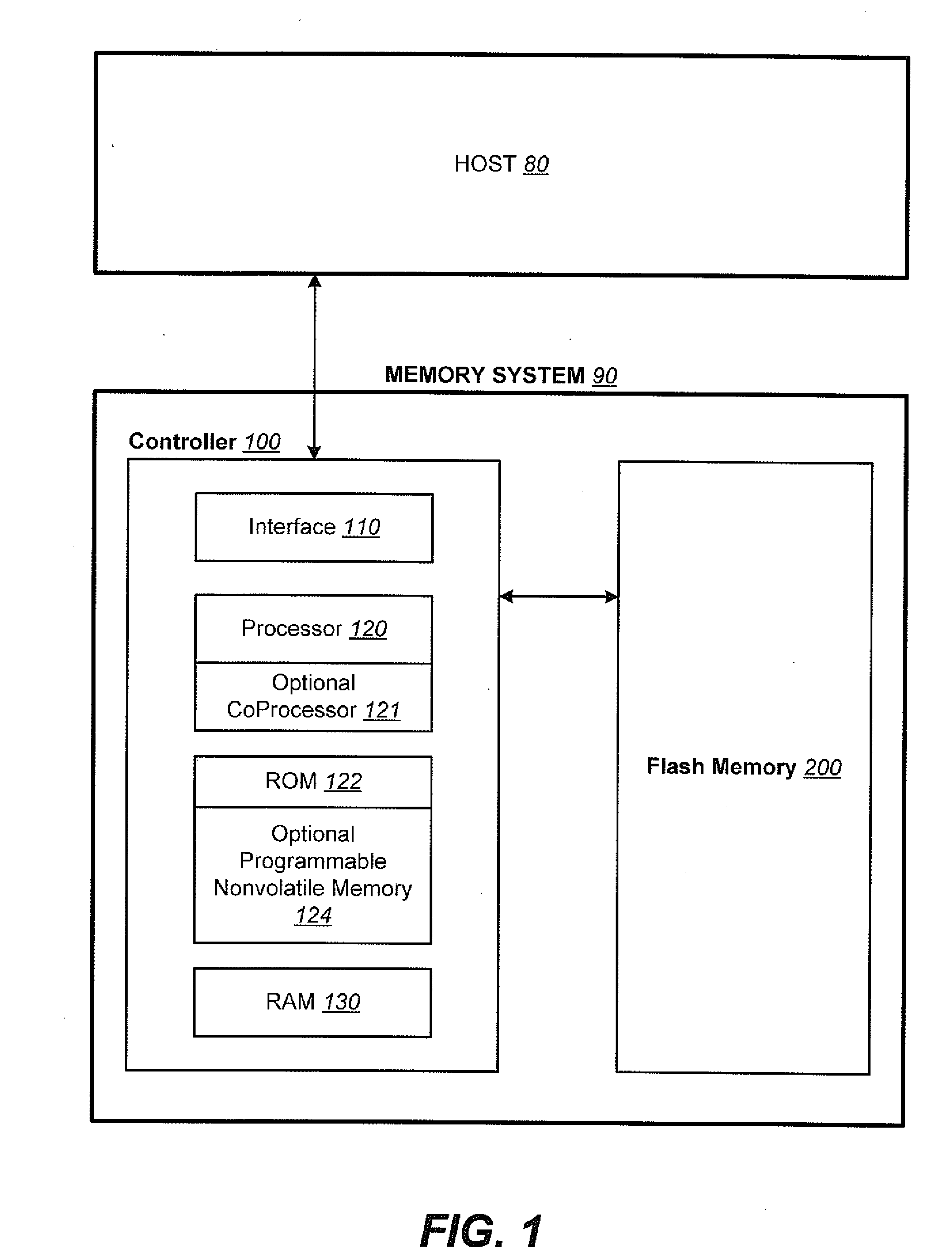
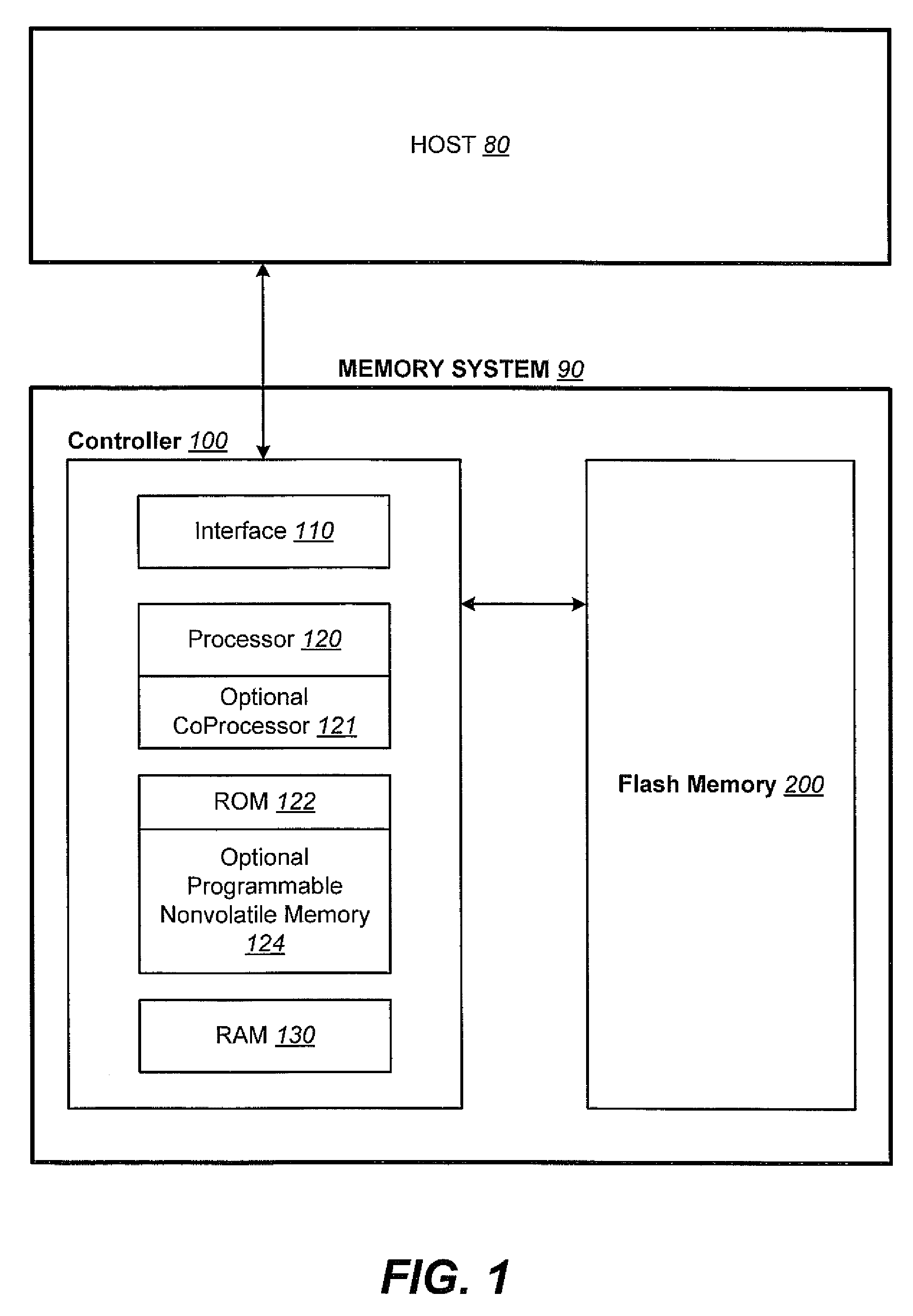
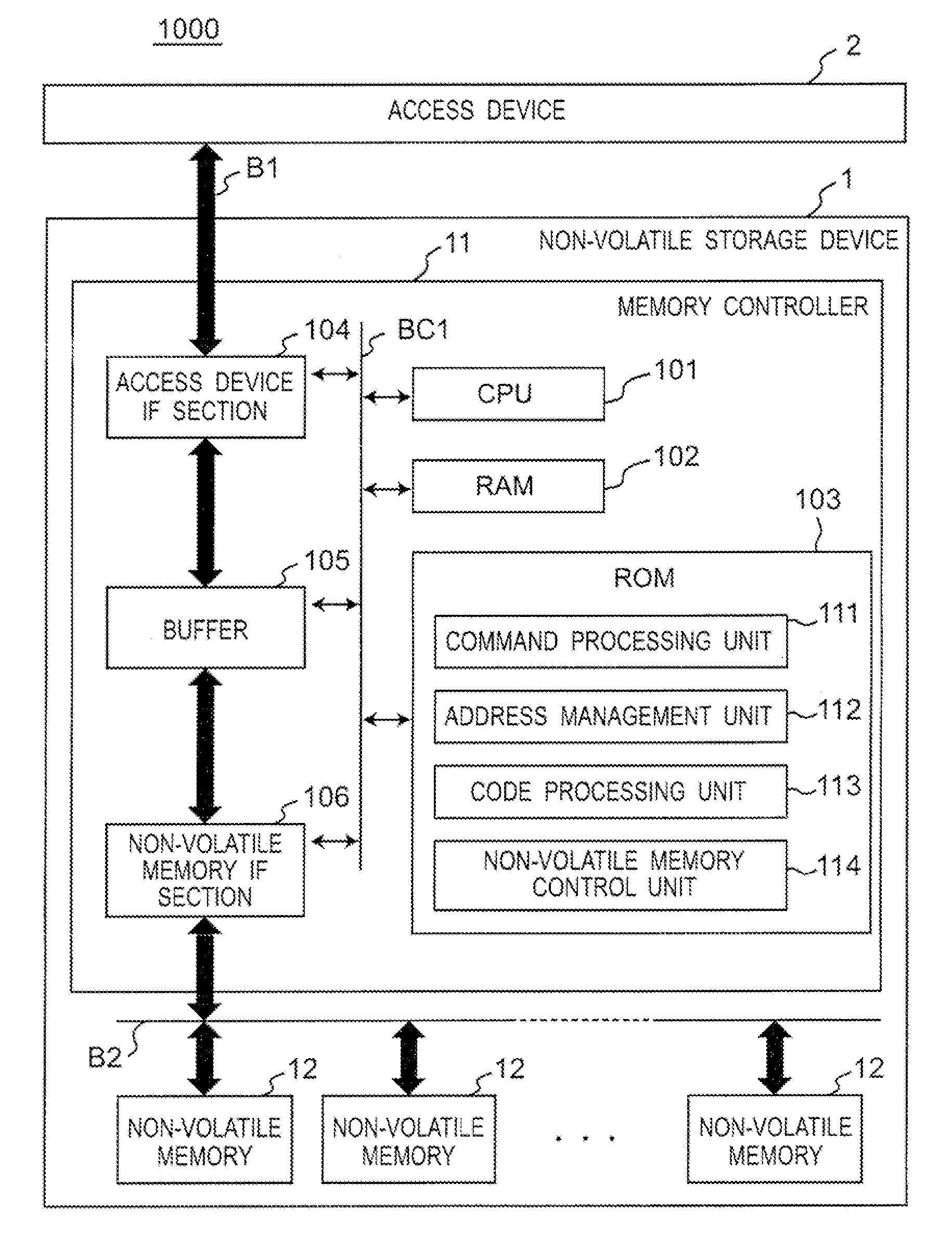
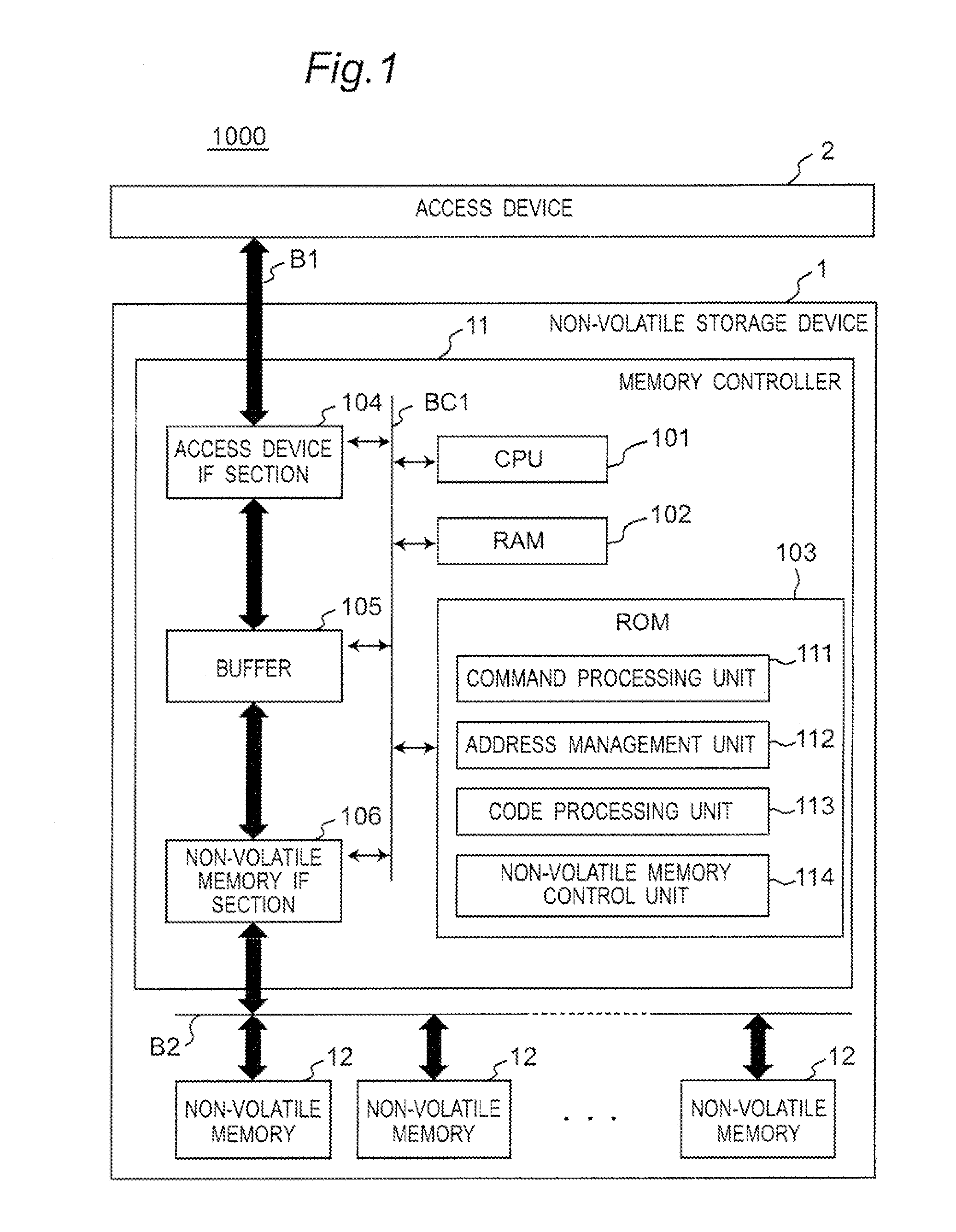
Method and apparatus for effectively enabling an out of sequence write process within a non-volatile memory system
ActiveUS7526599B2Easy to useReduce the numberMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRead-only memoriesStorage cellNon-volatile memory
Methods and apparatus for enabling contents to be efficiently stored in physical blocks of a non-volatile memory are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, a method for performing a write operation in a non-volatile memory system which has a memory unit includes writing a first set of contents into a first physical sub-unit of the memory unit and writing a second set of contents into a second physical sub-unit of the memory unit after the first set of contents is written into the first physical sub-unit. The first physical sub-unit is sequentially before the second physical sub-unit in the memory unit. The first set of contents is associated with a second logical sub-unit of a logical unit and the second set of contents is associated with a first logical sub-unit of the logical unit that is sequentially before the second logical sub-unit in the logical unit.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
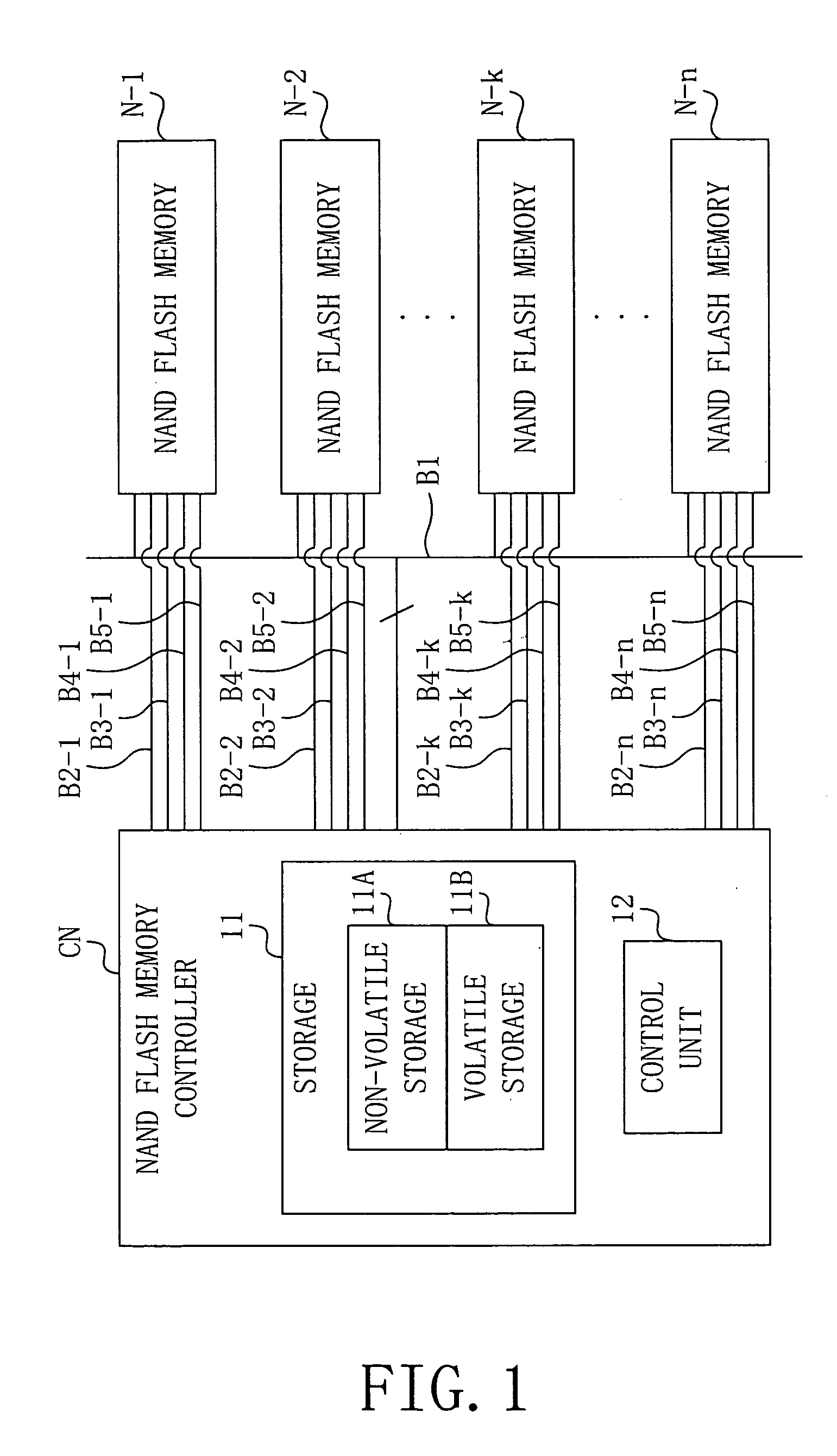
Data writing apparatus, data writing method, and program
InactiveUS7191296B2Write efficientlySame data efficientlyMemory loss protectionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory block
Each of a plurality of storage devices (N−1 to N-n) has a plurality of memory blocks for storing data. A data writing apparatus obtains error information which represents good blocks which can store data correctly, from the plurality of storage devices (N−1 to N-n). The data writing apparatus determines a memory block in which data is to be written, in each of the plurality of storage devices (N−1 to N-n), based on the obtained error information. The data writing apparatus controls the plurality of storage devices (N−1 to N-n), and writes predetermined data in the determined memory blocks.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON DEVICE
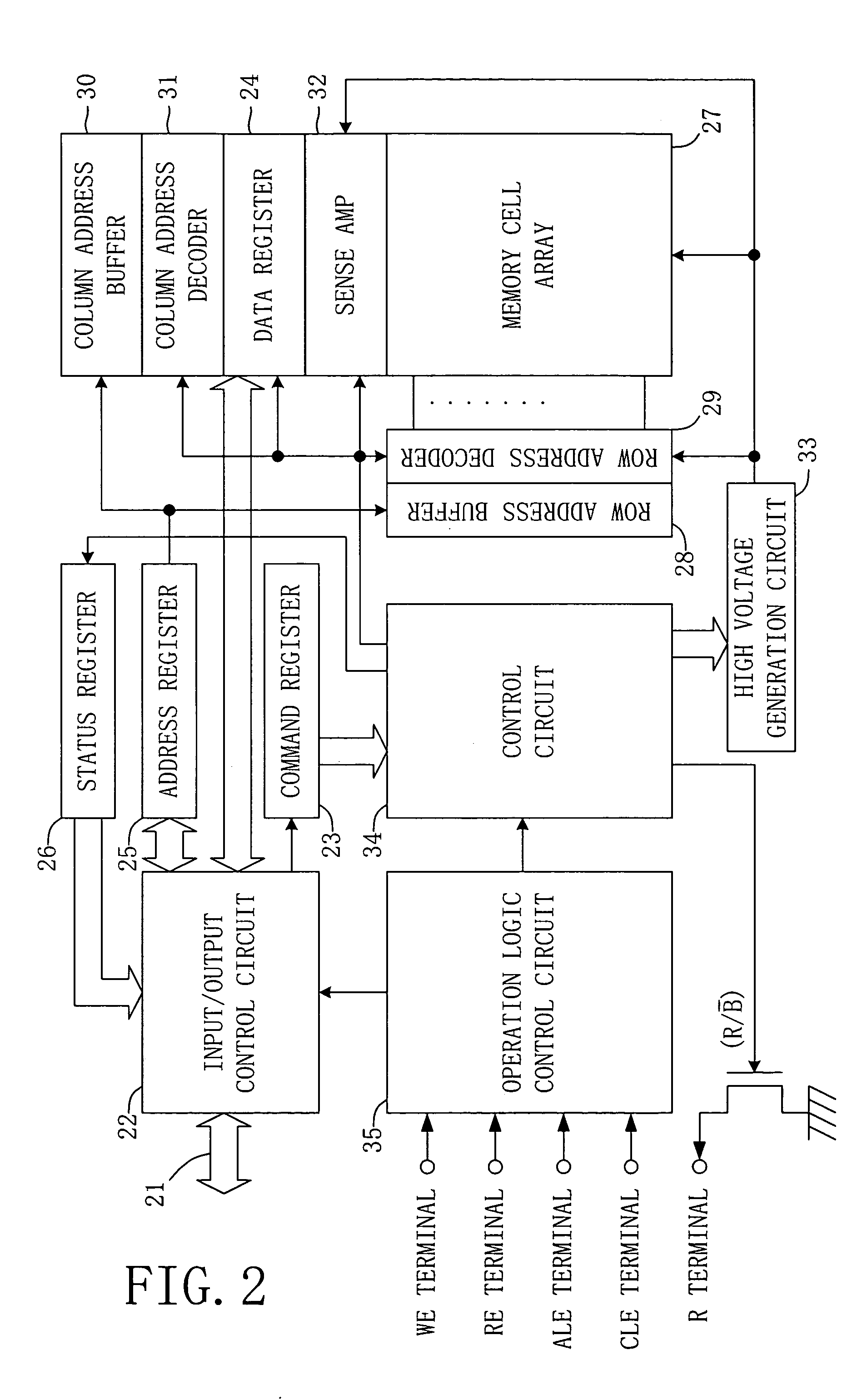
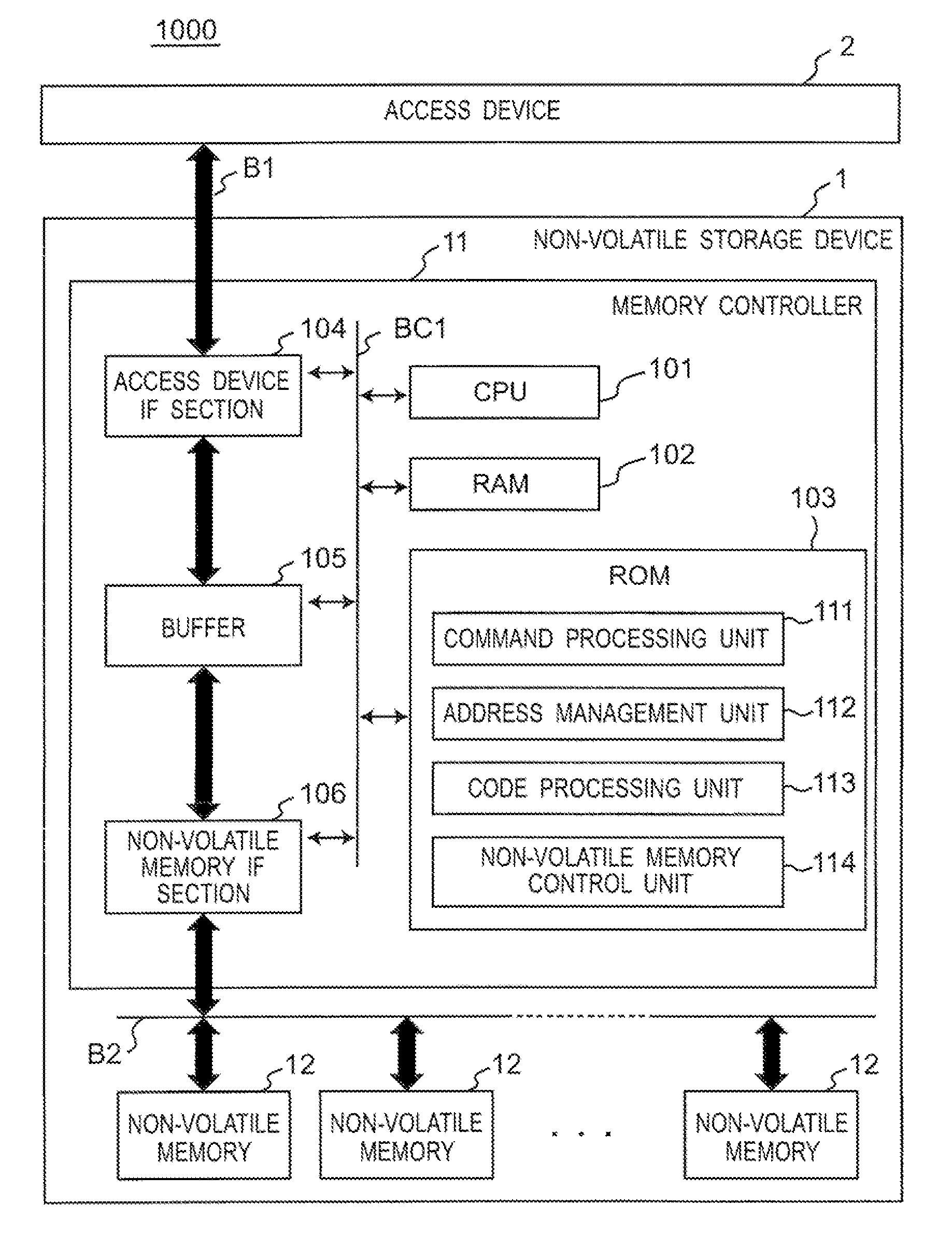
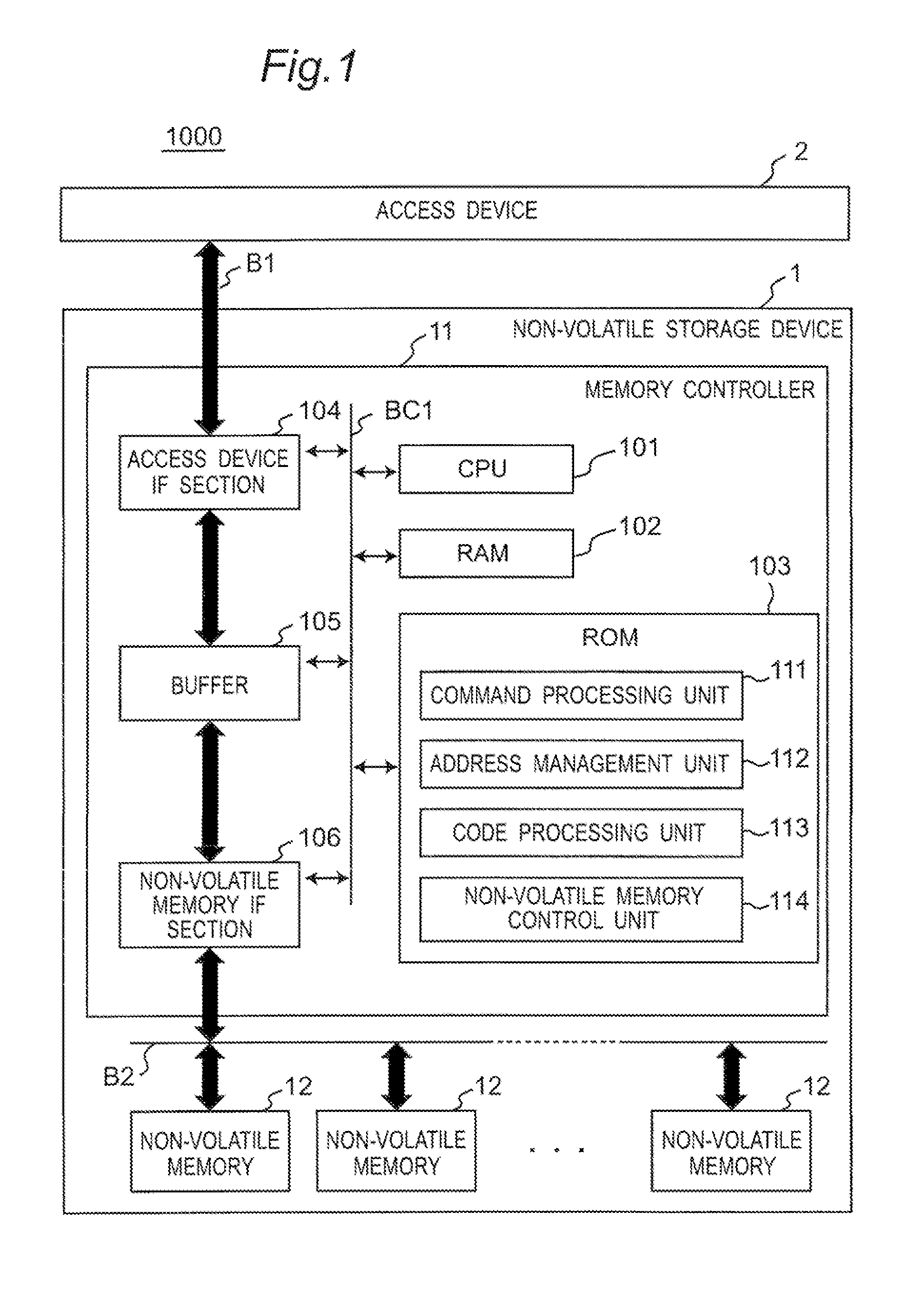
Memory controller and non-volatile storage device
InactiveUS20120317340A1Write efficientlyEfficient executionError detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData managementMemory controller
A non-volatile storage device comprises non-volatile memories for storing data; and a memory controller for carrying out control of the non-volatile memory. The memory controller stores second error correcting code as well as first error correcting code stored in the same page of the data. The memory controller, when writing data smaller than a predefined size, does not add the second error correcting code, and stores duplexed data of the data and the first correcting code in a different page. The memory controller, when reading, corrects data using the first and / or second correcting code. The valid data management table manages which logical block stores valid data with respect to an identical logical address.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
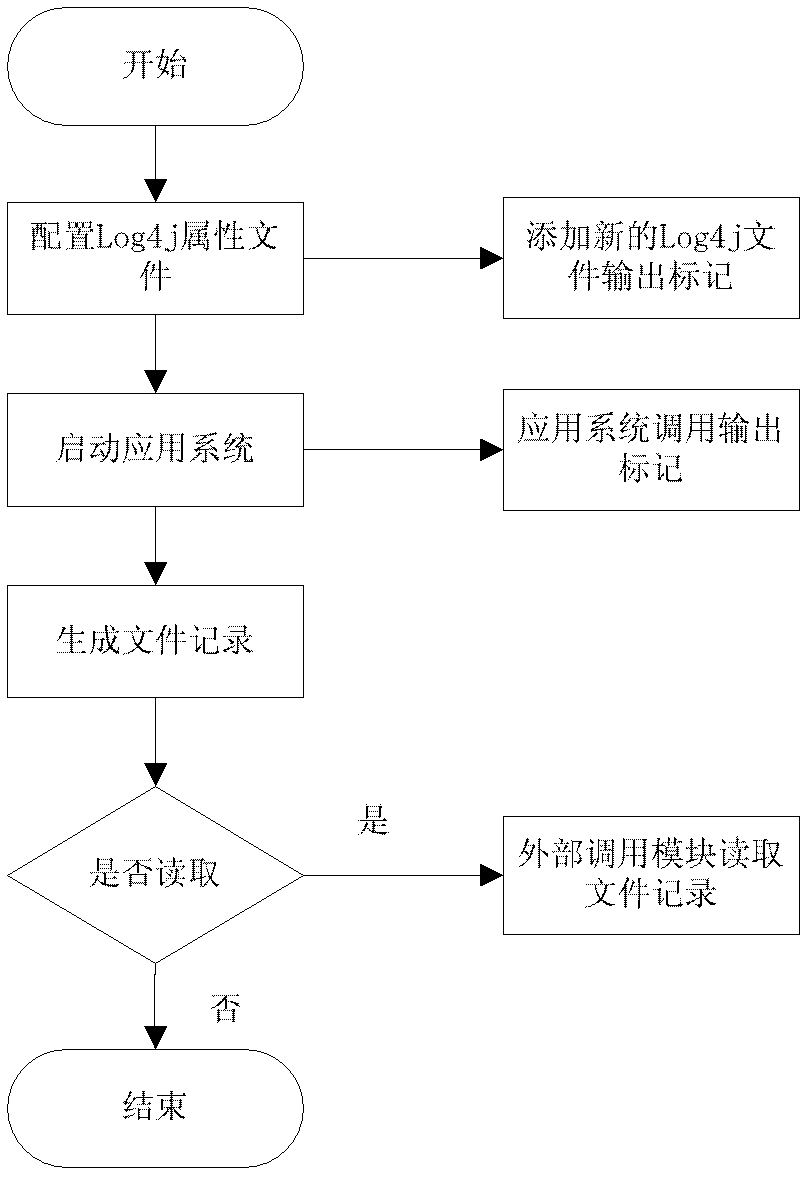
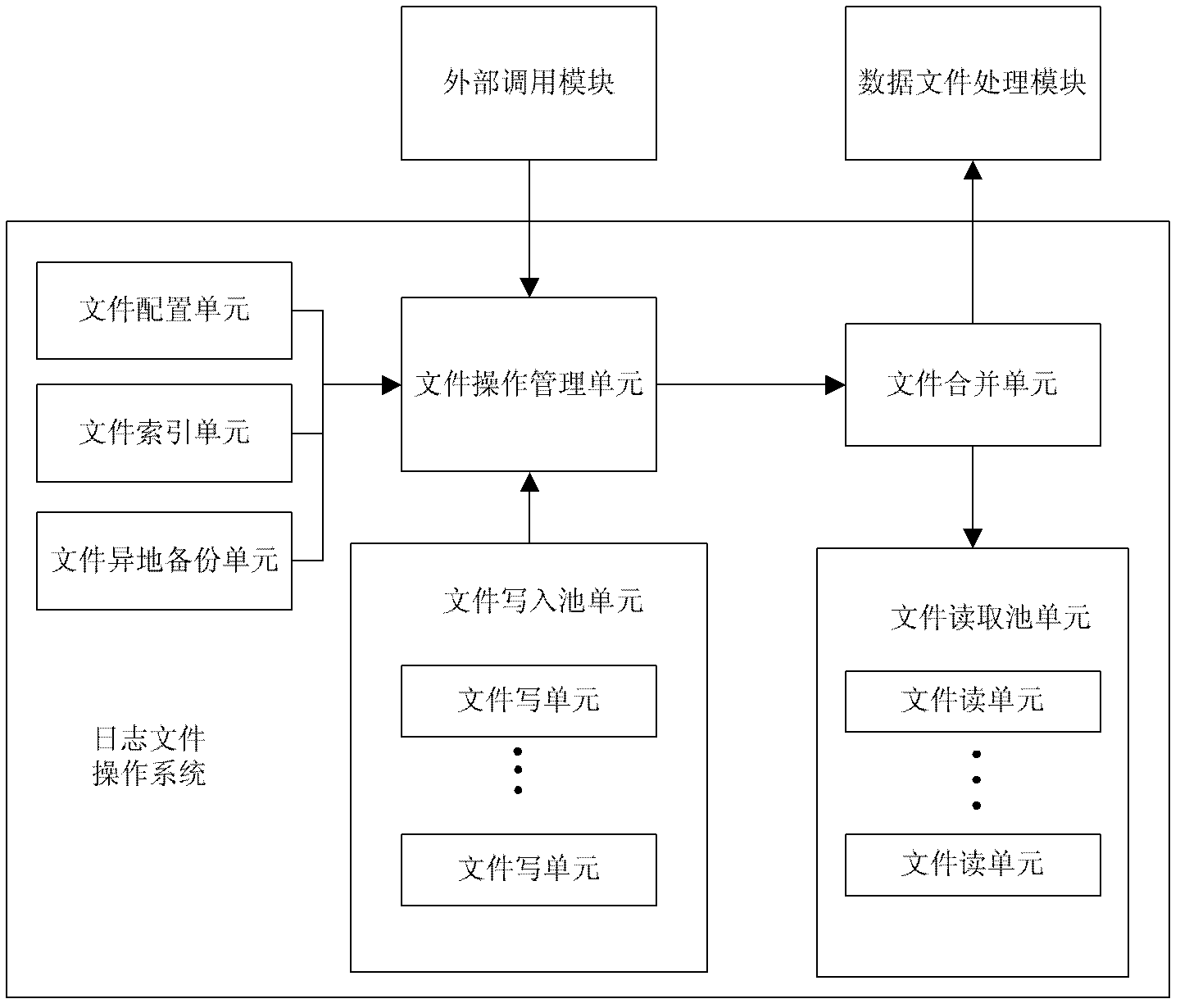
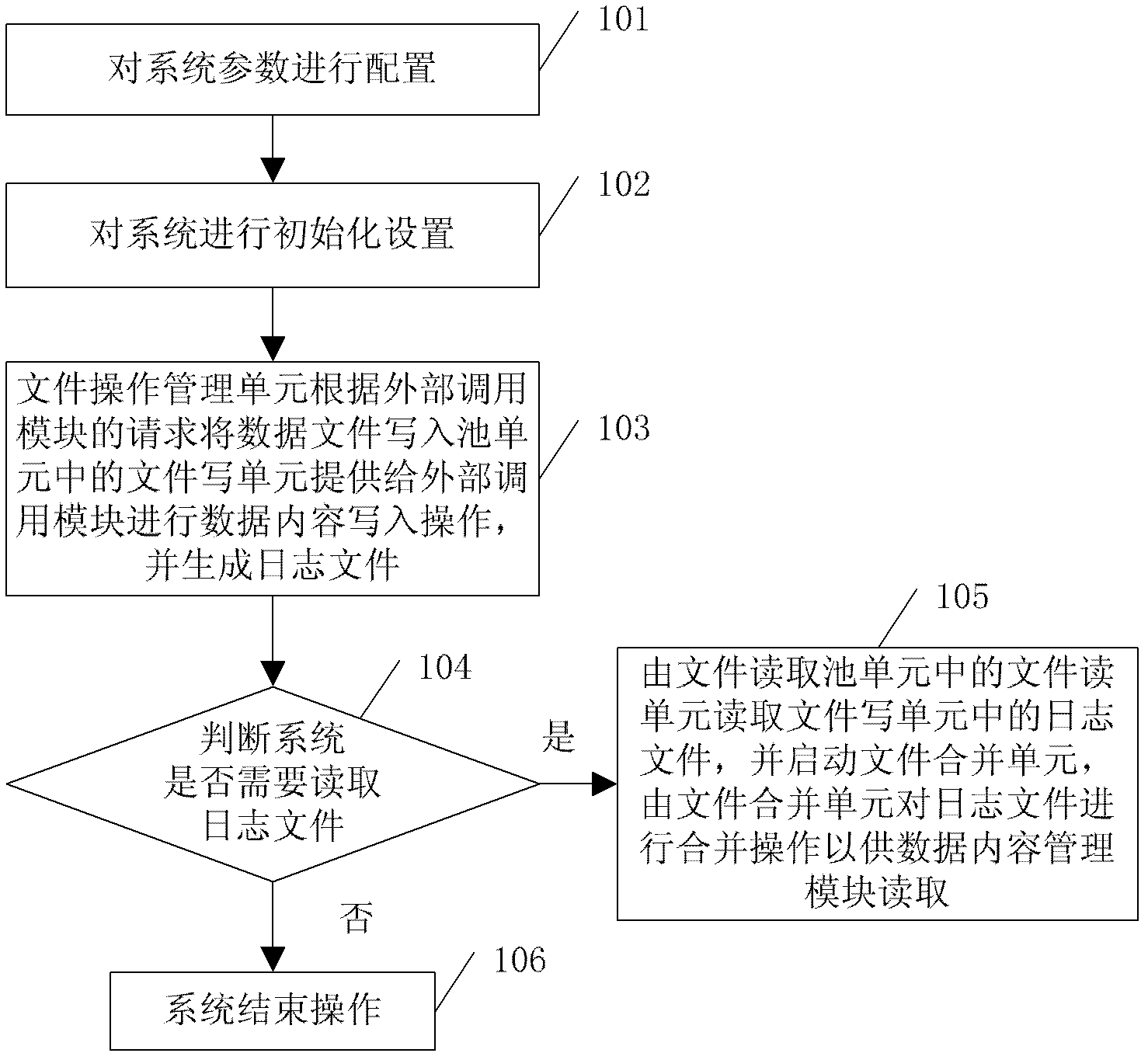
Log file operating system and log file management method
ActiveCN102622407AWrite efficientlyEasy to useSpecial data processing applicationsUser needsManagement unit
The invention discloses a log file operating system, which comprises a file write cell unit, a multi-file storage write unit, a file index unit, a file read cell unit, a multi-file storage read unit, a file merging unit, a file configuration unit and a file operation management unit. The file operation management unit is used for managing the file write cell unit, the file index unit, the file merging unit, the file read cell unit and the file configuration unit. The invention further provides a log file management method for the log file operating system, which includes: generating log files for the file write unit, allowing the file read unit to read the log files when a user needs to acquire the log files, and using the file merging unit to merge the files. Therefore, by the log file operating system and the log file management method, log files can be written efficiently and backed up, numbered and stored integrally.
Owner:广州云标局网络科技有限公司
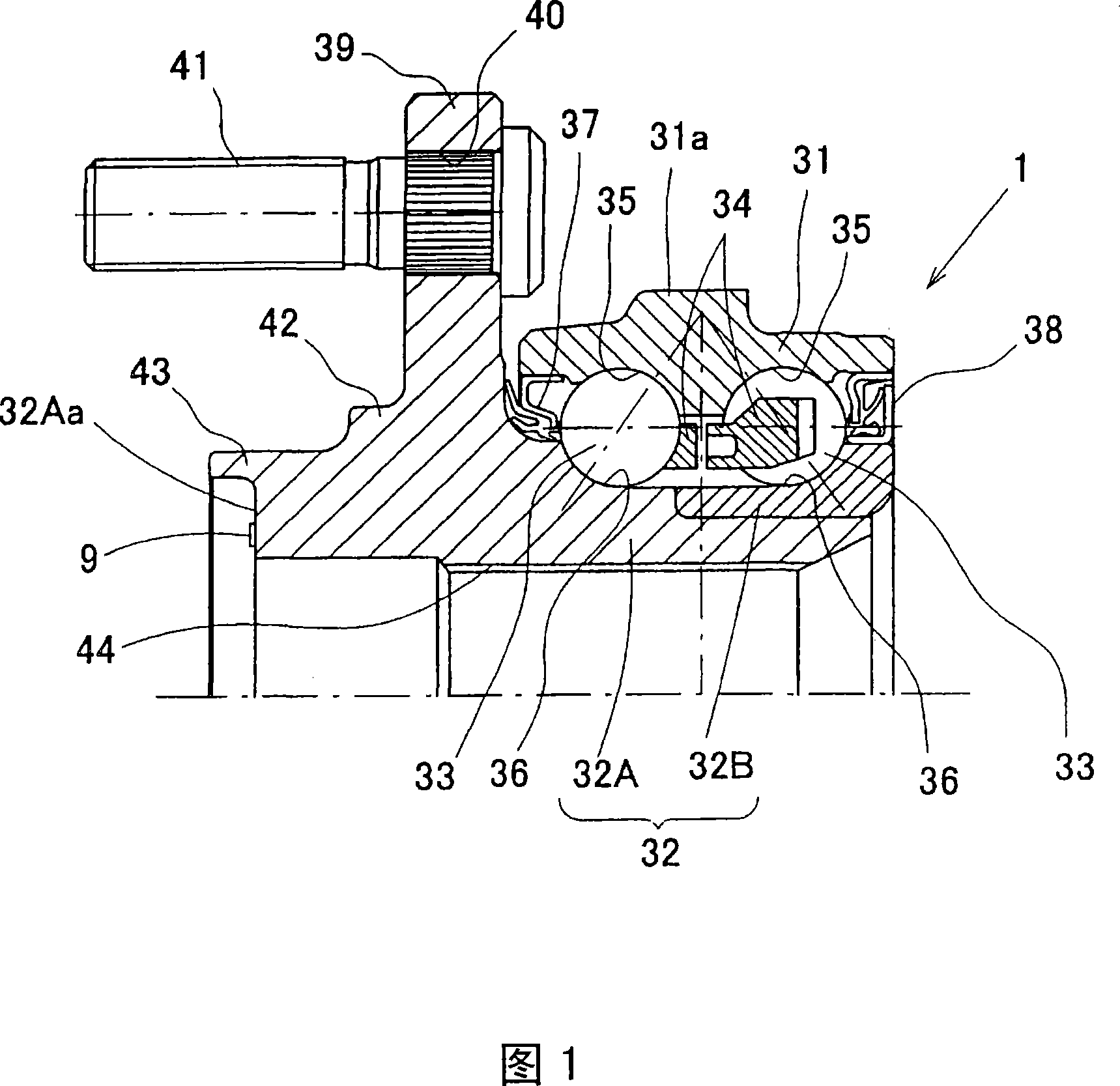
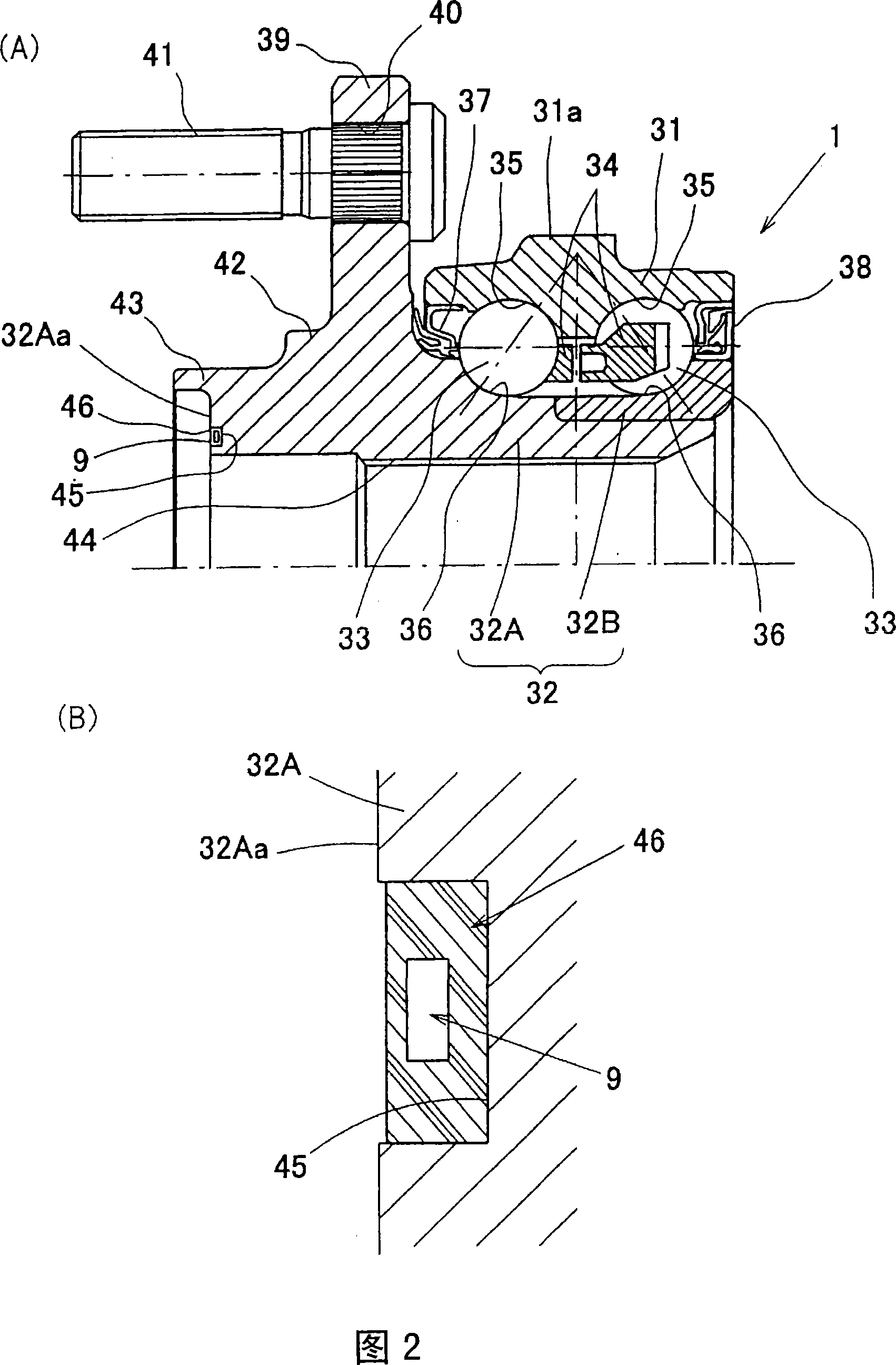
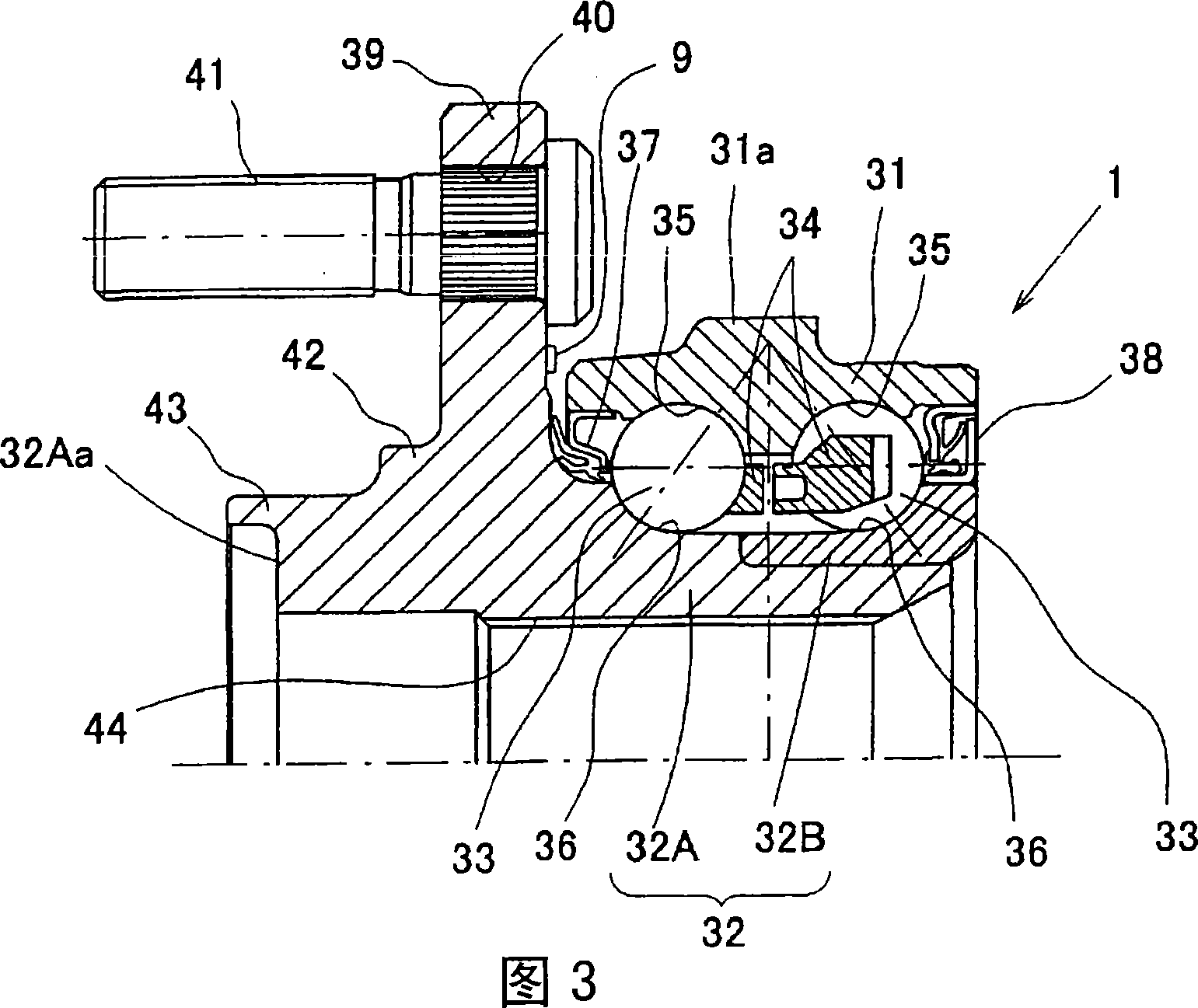
Bearing device for wheel
InactiveCN1993562AEasy to confirmWrite efficientlyRolling contact bearingsBearing assemblyEngineeringMachining
Owner:NTN CORP
Recording Trace Messages of Processes of a Network Component
InactiveUS20070168993A1Disadvantages and reduced eliminatedProcess reduced eliminatedData switching networksSpecific program execution arrangementsComputer scienceNetsniff-ng
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Memory controller and non-volatile storage device
InactiveUS20120317341A1Accurate readingWrite efficientlyError detection/correctionMemory systemsMemory controllerError correcting
A non-volatile storage device, which communicates with an access device and carries out reading and / or writing of data in accordance with a command from the access device, the device comprises one or more non-volatile memories for storing data and a memory controller for carrying out control of the non-volatile memory. The memory controller writes data to the error correcting group and writes a provisional error correcting code with respect to the data to the parity table if a data size is smaller than the first size when writing the data.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
System and method for efficient updates of sequential block storage
ActiveUS7882304B2Write efficientlyImprove data localityCarrier editingFilamentary/web record carriersLog management
An improved system and method enhances performance of updates to sequential block storage of a storage system. A disk-based sort procedure is provided to establish locality among updates (write data) held in a disk-based log, thereby enabling the write data to be efficiently written to home locations on a home location array. As the write data is received, a log manager of the storage system temporarily stores the data efficiently on the disk-based log. As more write data arrives, the log manager sorts the data in the log in accordance with the sort procedure, thus increasing the locality of data when stored on the home location array. When the log approaches capacity, the log manager writes the sorted data to their home locations on the array with high locality and performance.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com