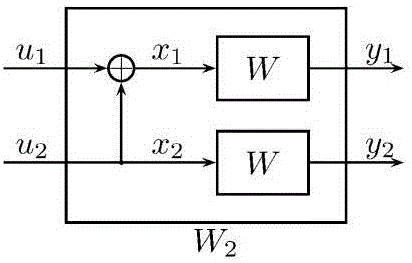
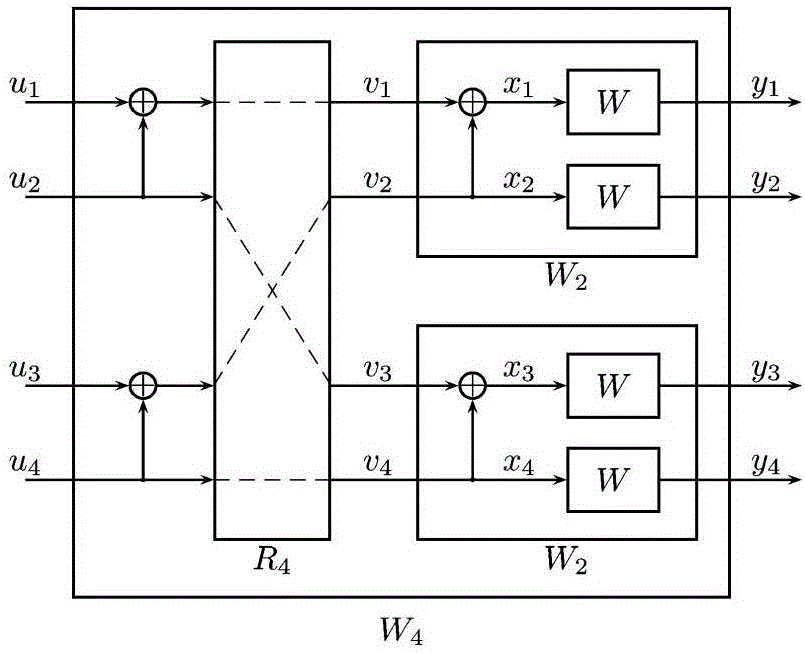
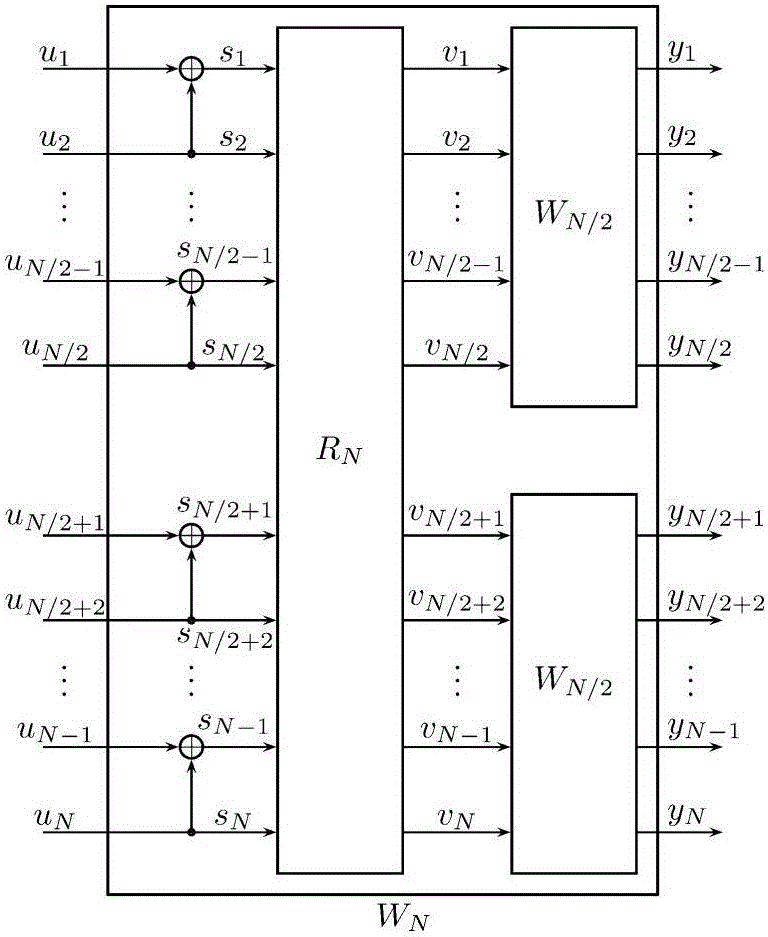
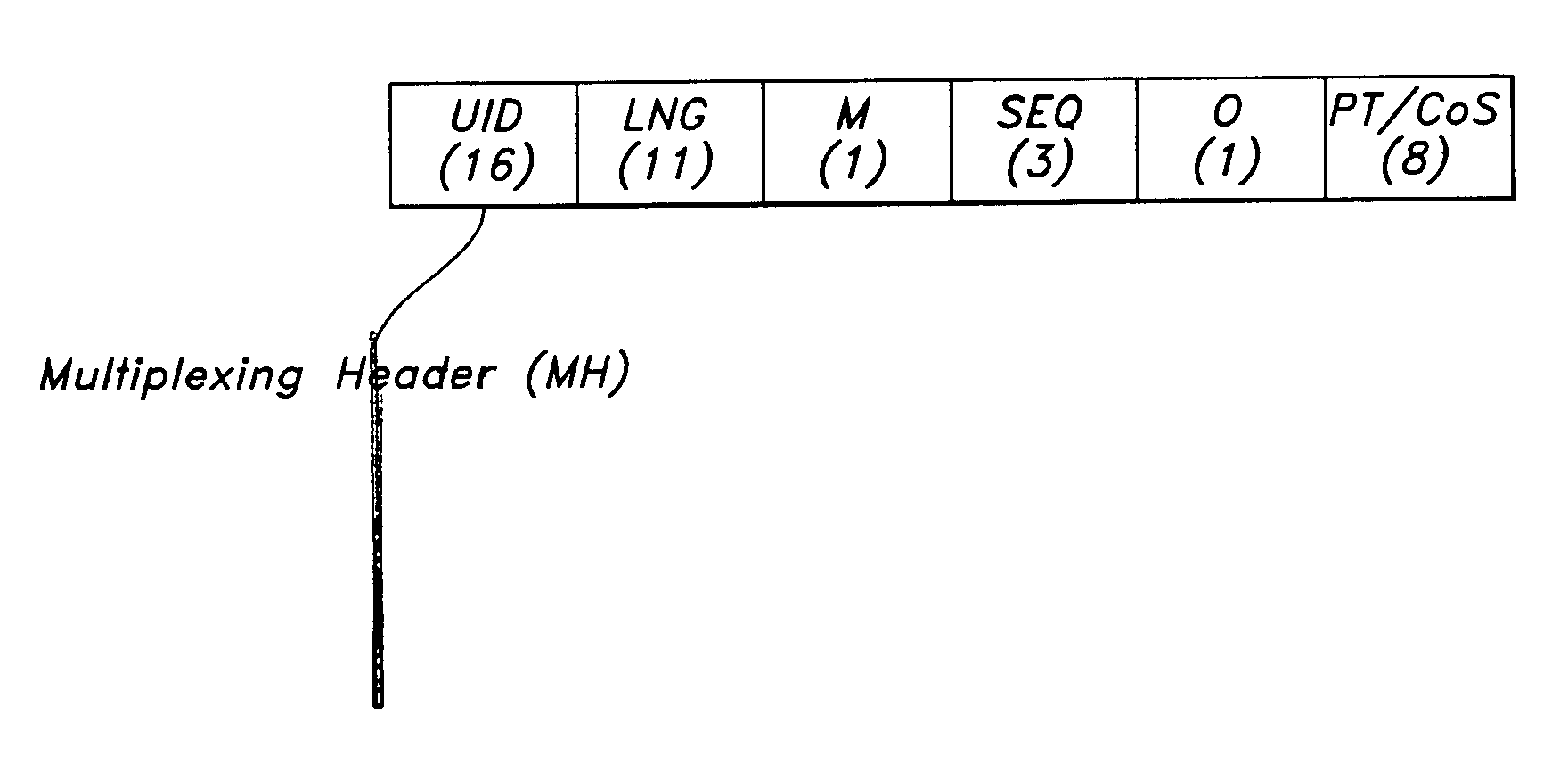
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
944 results about "Bit-length" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
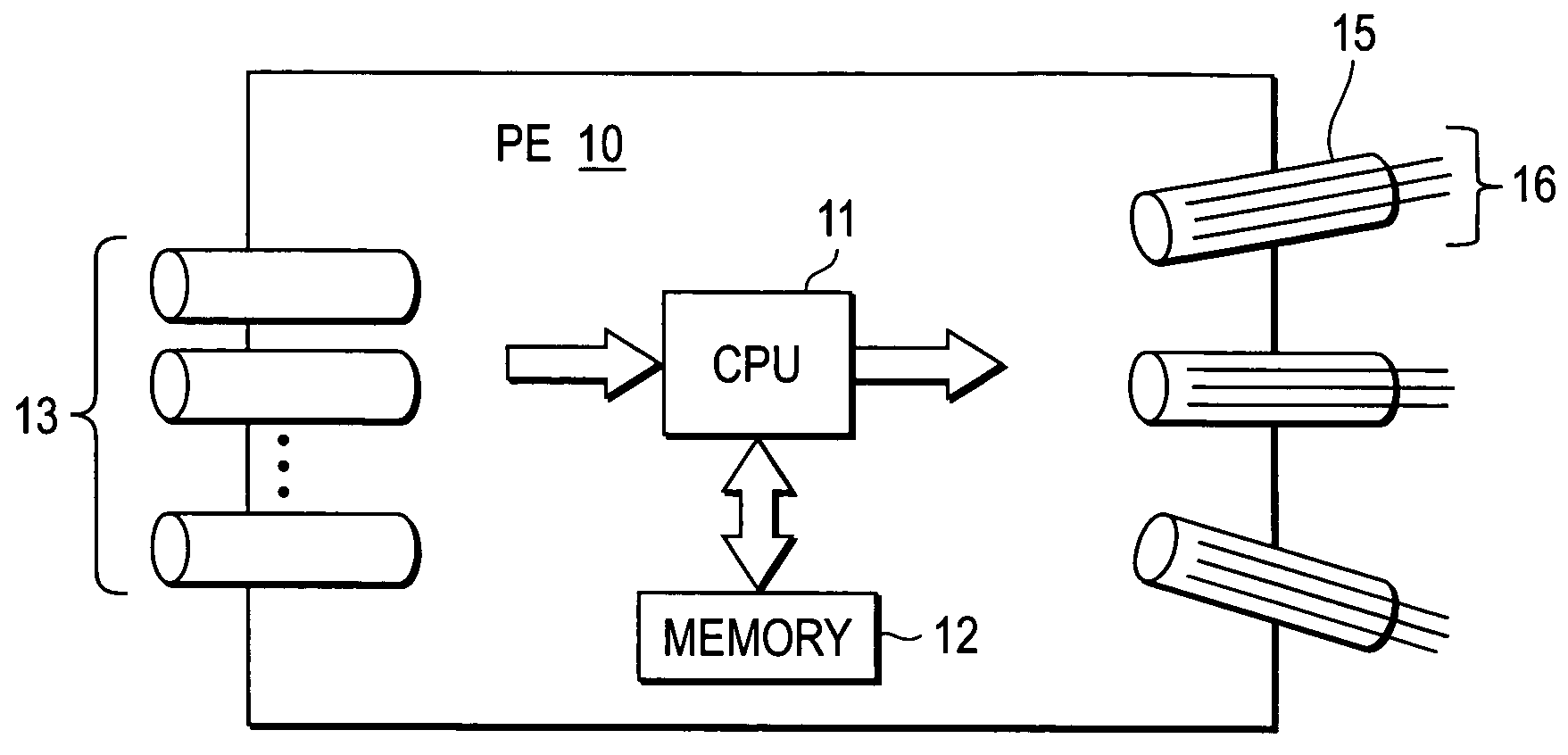
Bit-length or bit width is the number of binary digits, called bits, necessary to represent an integer as a binary number. Formally, the number of bits of zero is 1 and any other natural number n>0 is a function, bitLength(n), of the binary logarithm of n: bitLength(n)=⌊log₂(n)+1⌋=⌈log₂(n+1)⌉ At their most fundamental level, digital computers and telecommunications devices (as opposed to analog devices) can process only data that has been expressed in binary format.
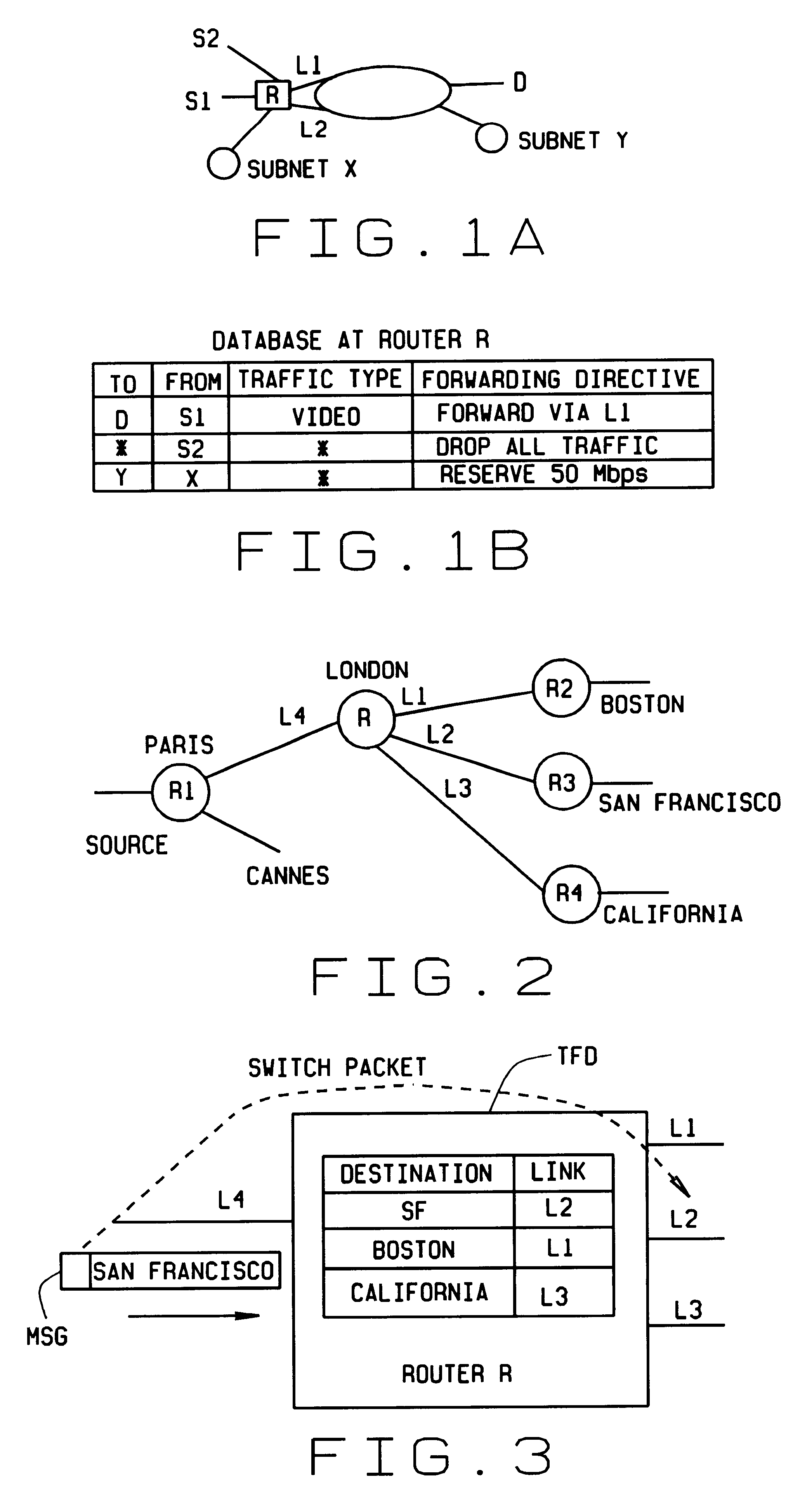
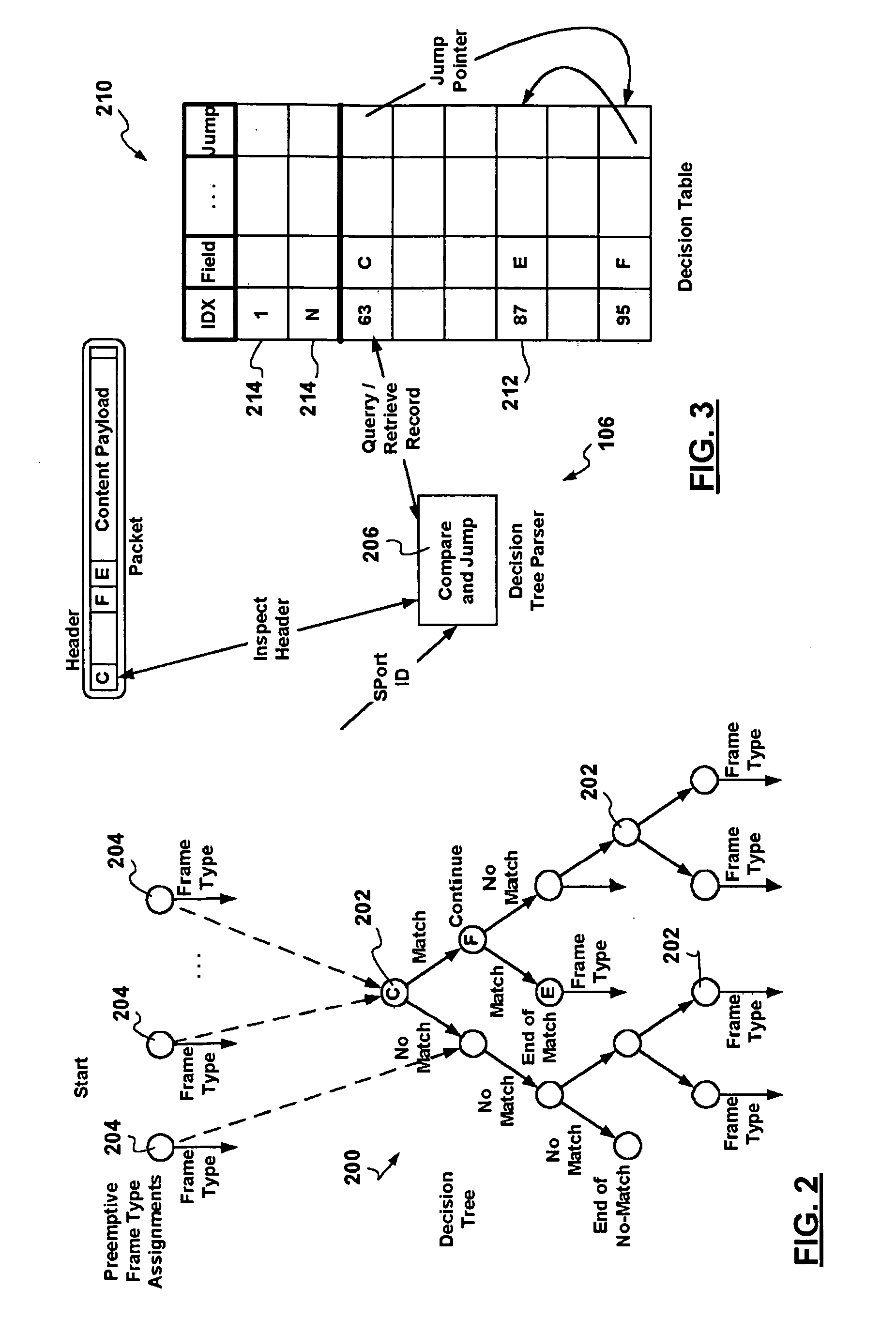
Fast scaleable methods and devices for layer four switching
InactiveUS6212184B1Enormous saving in table sizeAvoid the needError preventionTransmission systemsPrecomputationRoute filtering
Fast, scalable methods and devices are provided for layer four switching in a router as might be found in the Internet. In a first method, a grid of tries, which are binary branching trees, is constructed from the set of routing filters. The grid includes a dest-trie and a number of source tries. To avoid memory blowup, each filter is stored in exactly one trie. The tries are traversed to find the lowest cost routing. Switch pointers are used to improve the search cost. In an extension of this method, hash tables may be constructed that point to grid-of-tries structures. The hash tables may be used to handle combinations of port fields and protocol fields. Another method is based on hashing, in which searches for lowest cost matching filters take place in bit length tuple space. Rectangle searching with precomputation and markers are used to eliminate a whole column of tuple space when a match occurs, and to eliminate the rest of a row when no match is found. Various optimizations of these methods are also provided. A router incorporating memory and processors implementing these methods is capable of rapid, selective switching of data packets on various types of networks, and is particularly suited to switching on Internet Protocol networks.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
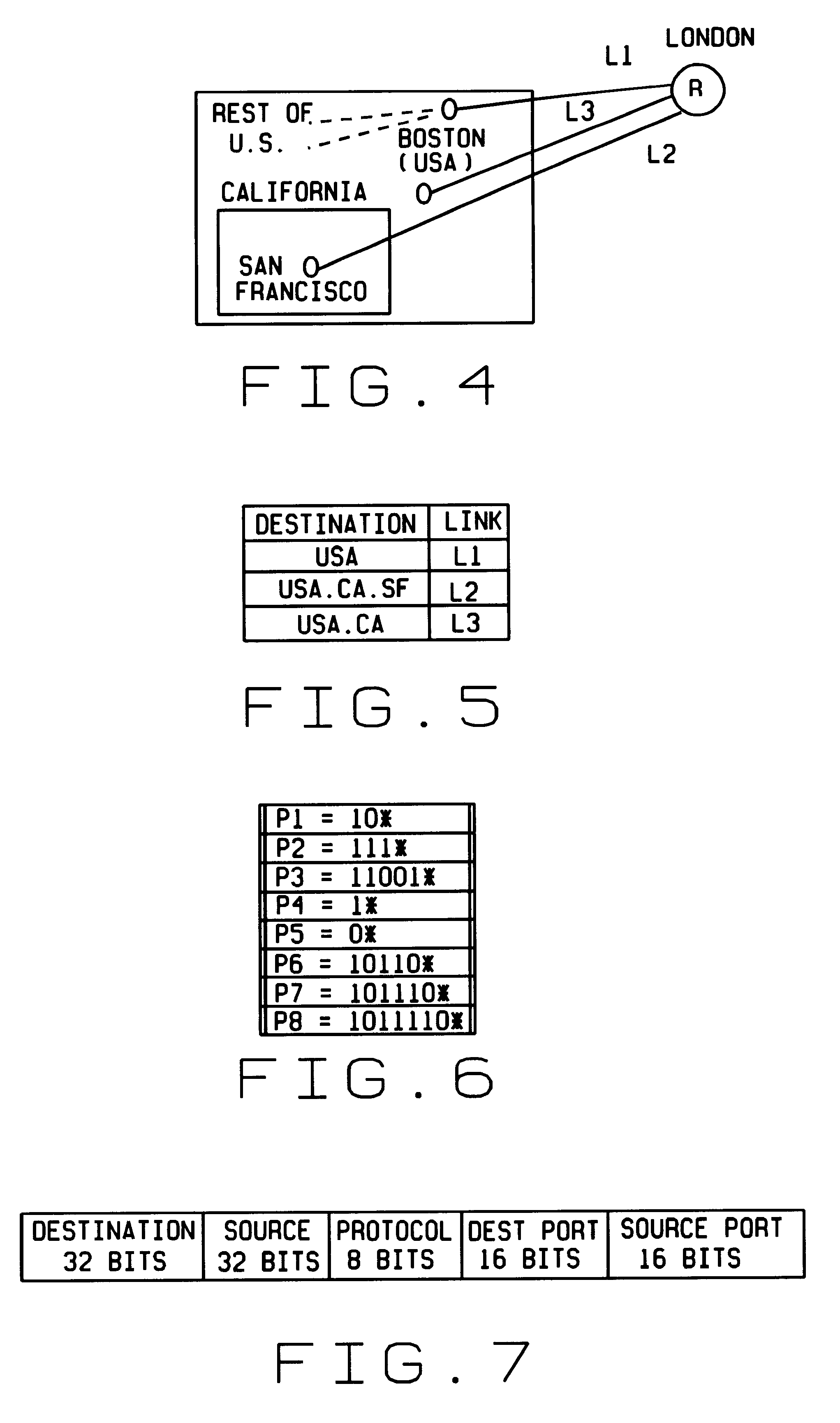
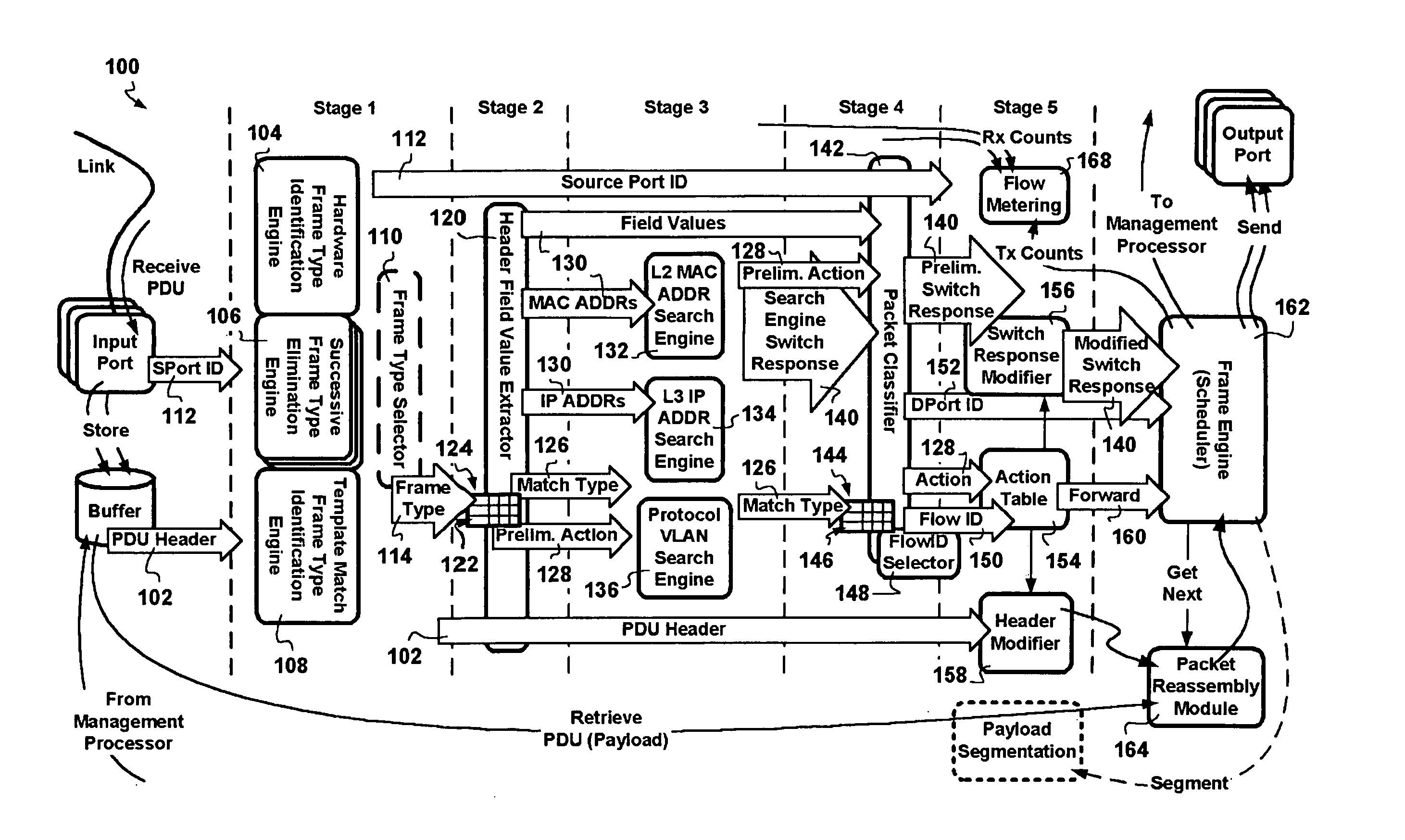
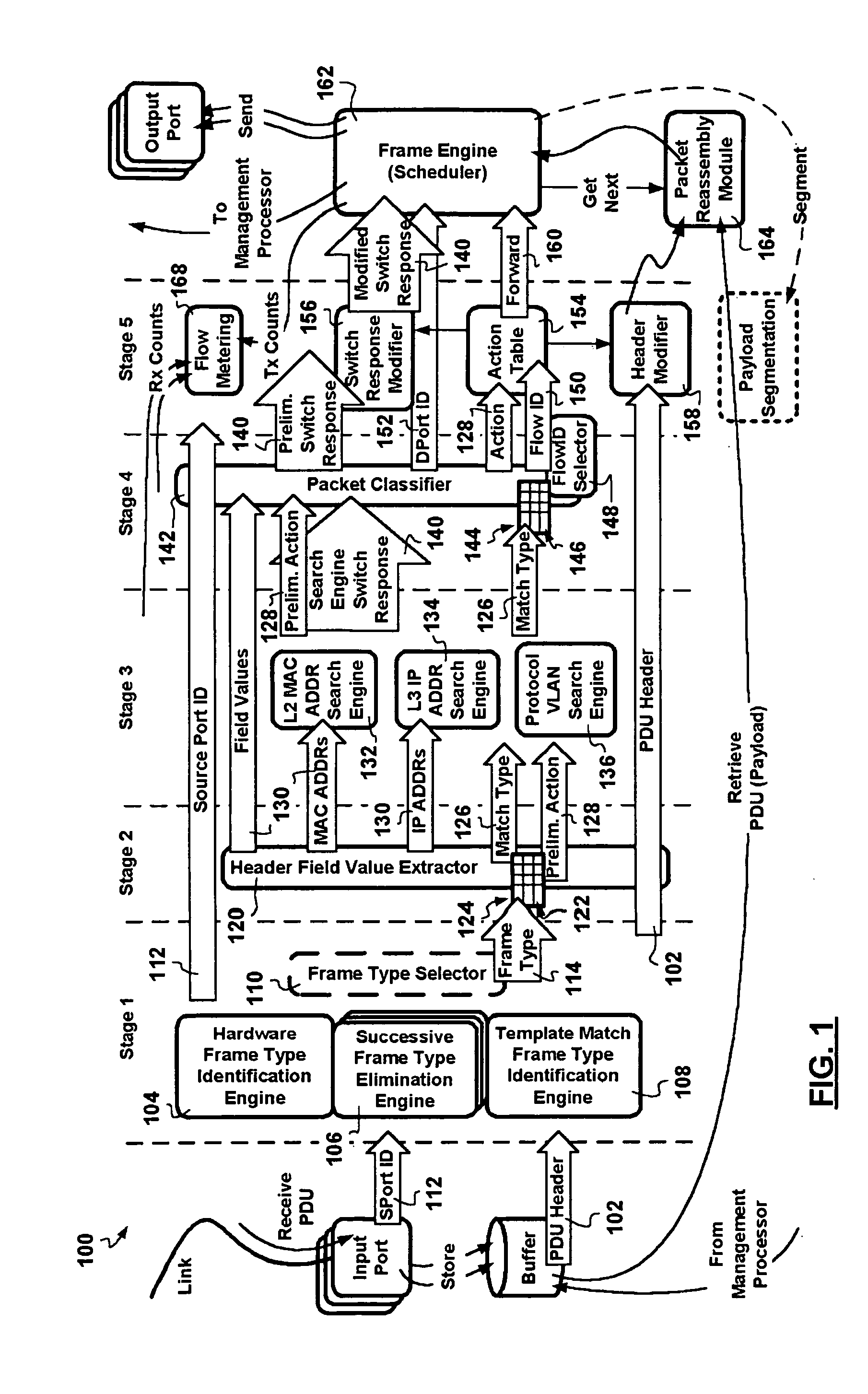
Combined pipelined classification and address search method and apparatus for switching environments
InactiveUS20060002386A1Network degradationReduce data transfer bandwidthTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork addressingObsolescence
A packet switching node having a pipelined packet processing architecture processing packets received via an input port associated with the packet switching node is presented. The method performed by the apparatus includes: determining a packet frame type of the packet received; selectively extracting packet header field values specific to a packet frame type, the extracted packet header field value including packet addressing information; ascribing to the packet a preliminary action to be performed in respect of the packet; searching packet switching information tracked by the packet switching node based on extracted packet addressing information; formulating a preliminary switch response for the packet; classifying the packet into one of a plurality of packet flows; modifying the preliminary switch response in accordance with one of the preliminary action, the packet flow into which the packet was classified, and a default port action corresponding to the input port; modifying the packet header in accordance with one of the preliminary action, the packet flow, and the default port action; and processing the packet in accordance with the switch response. Advantages are derived from: pipelined processing of packets which enables short-cutting the rest of the processing for improper packets; a flexible frame type determination which is fast for well know frame types yet flexible in support of new frame types delaying obsolescence of a particular implementation; an early determination of a processing action which is successively refined by subsequent stages; a combined Layer-2 and Layer-3 network addressing search engine operating on short bit length indexed Layer-2 and Layer-3 network addresses reducing network address table storage requirements, requiring a reduced data transfer bandwidth for network address table access, a large external hashed primary network address table, and a small internal secondary network address table; an early determination of a switch response; and packet-classification-based switch response and packet header modification.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
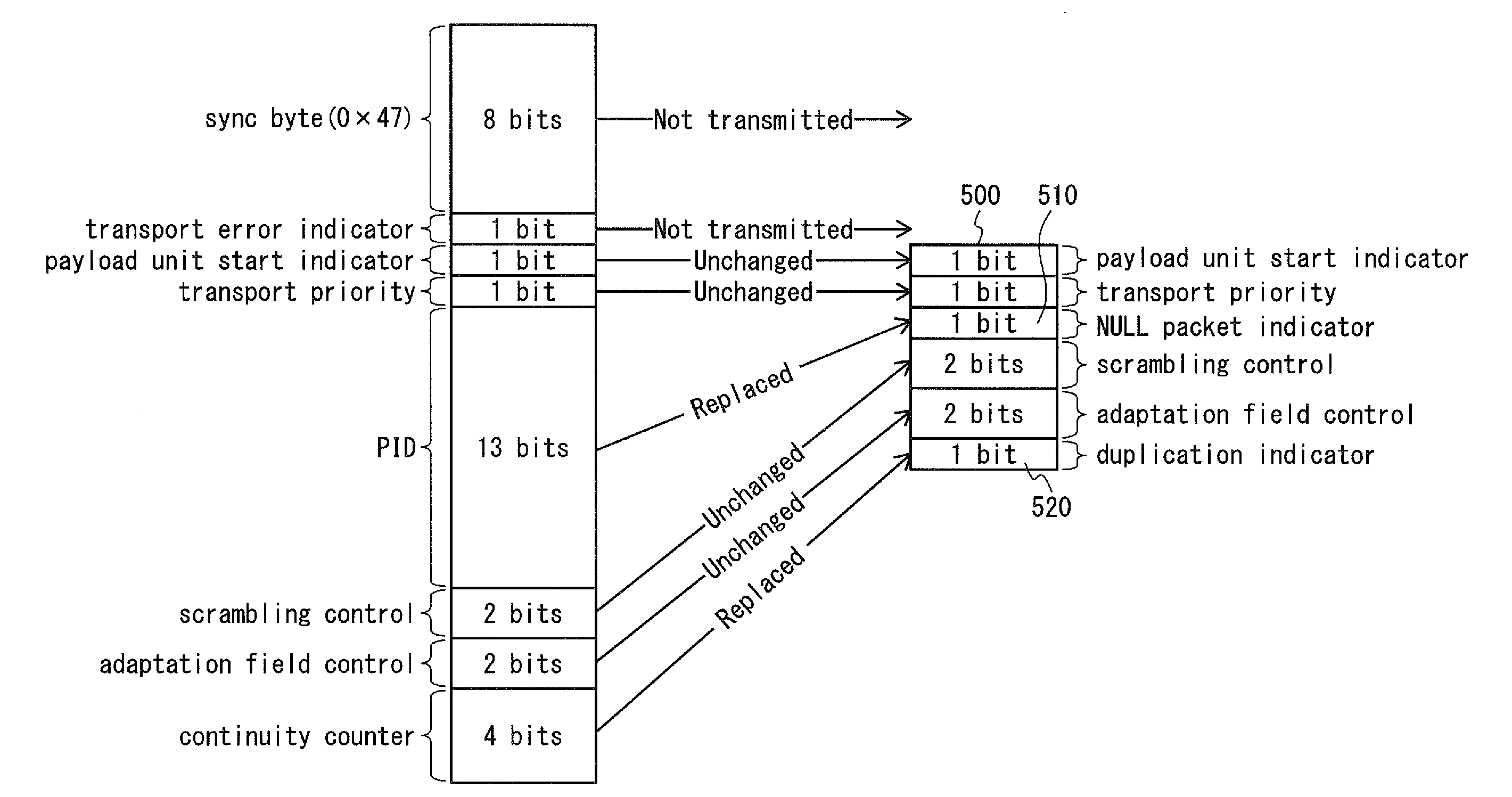
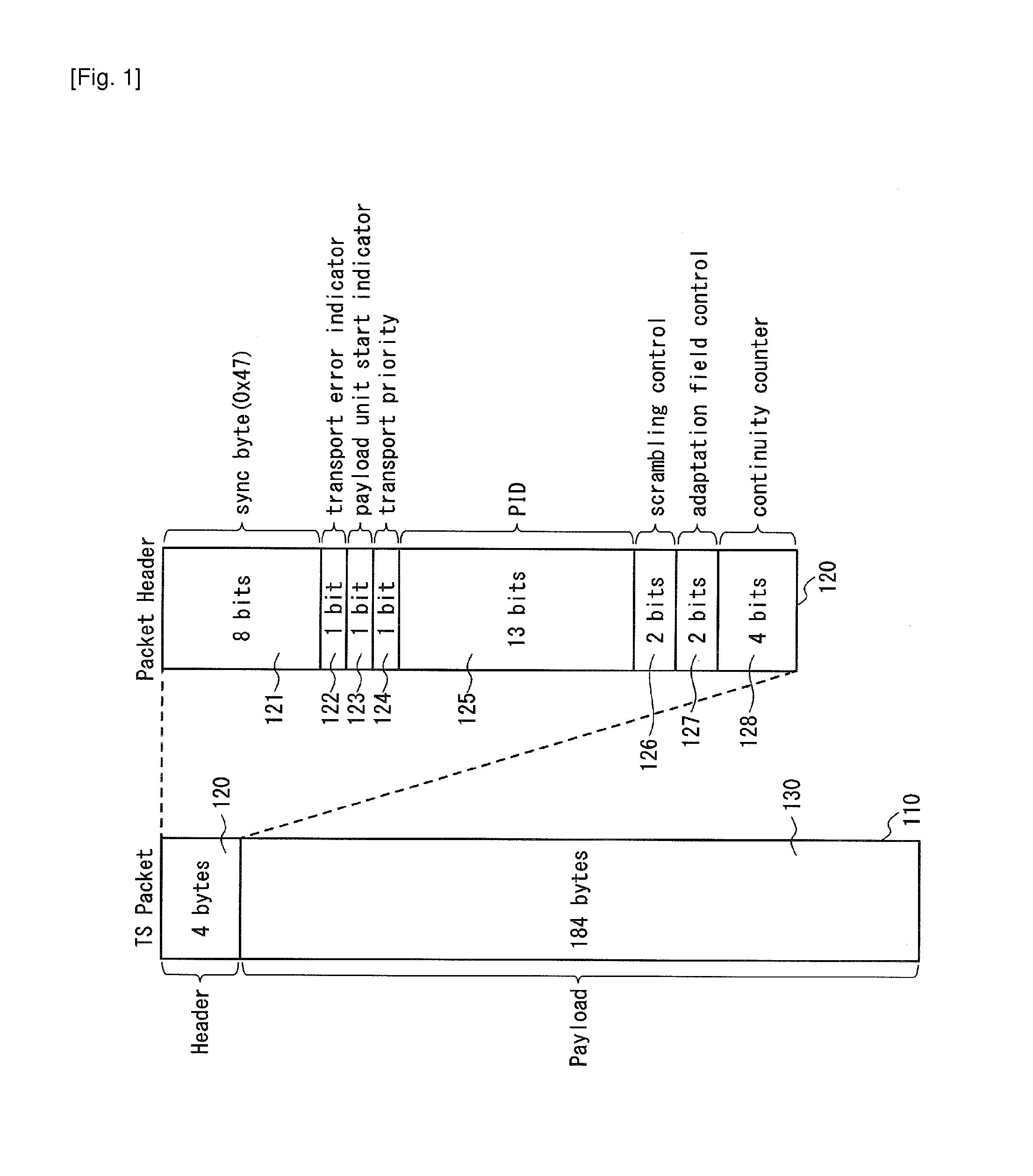
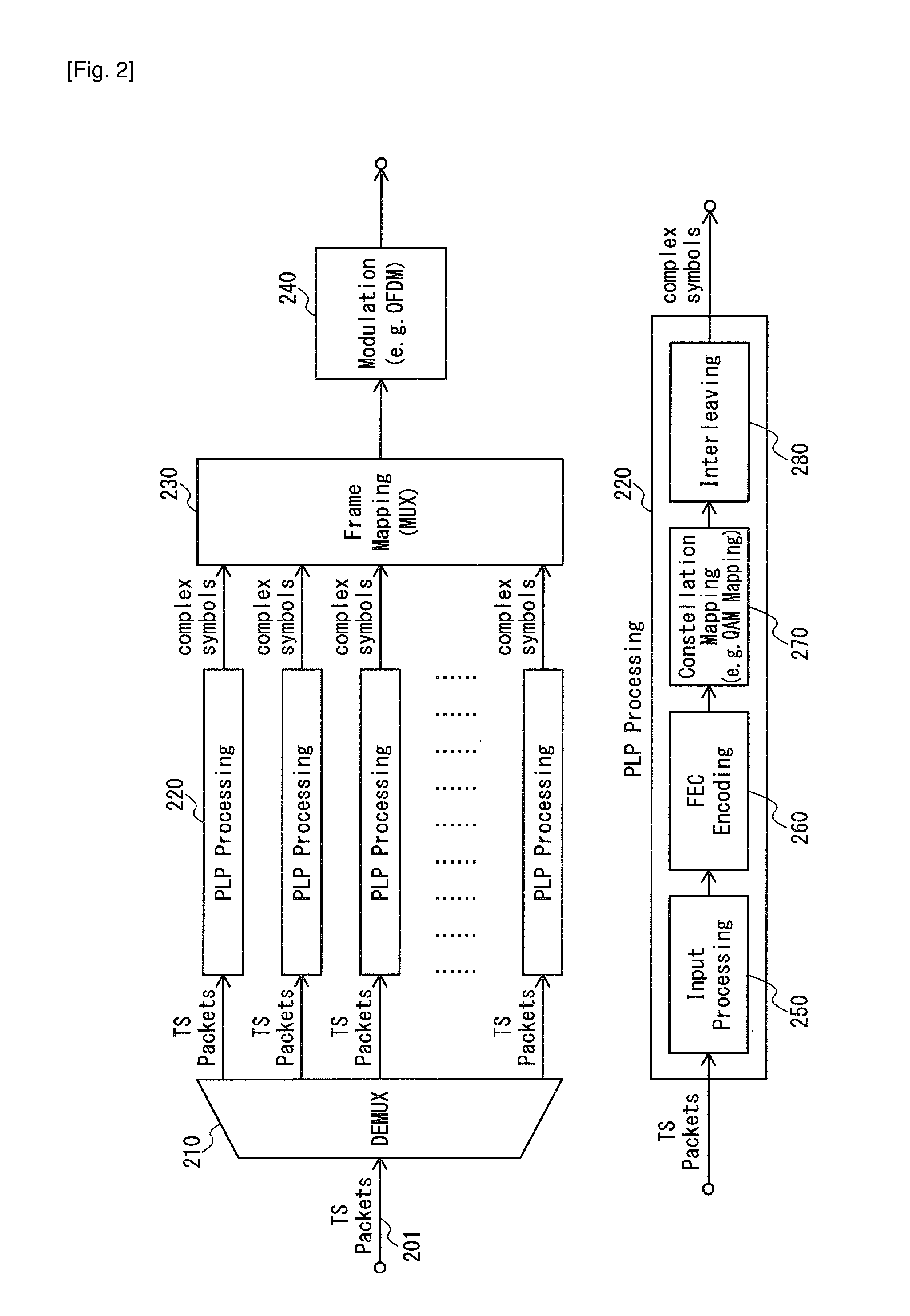
Transport stream packet header compression
ActiveUS20120307842A1Reduces packet header lengthEfficient use of resourcesPulse modulation television signal transmissionTime-division multiplexComputer networkPhysical layer
A demultiplexer 630 routes only one or more transport stream packets with a single packet identifier value to each physical layer pipe. A header compression unit 620 replaces the packet identifier of the transport stream packet with a short packet identifier of one bit length indicating at least whether the transport stream packet is a NULL packet.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
Density evolution based polarization code constructing method and polarization code coding and decoding system
ActiveCN105811998AImprove decoding performanceReduced characteristicsError correction/detection using linear codesComputation complexityDensity based
The invention discloses a density evolution based polarization code constructing method and polarization code coding and decoding system. According to the invention, the code length N and the information bit length K of an information code to be processed are obtained, an expectation value set of a log-likelihood ratio probability density function of N bit channels, K bit channels are selected as the information bit channels according to the expectation value set and information bit information index vector quantity is generated; an information bit sequence and a fixed bit sequence are mixed and the mixed bit vector quantity is multiplied by a polarization code for generating a matrix so as to output an encoding sequence; the encoding sequence is modulated and input into a transmission channel and the sequence output by the transmission channel is subjected to decoding operation by adopting a polarization code decoding algorithm, bit error probability and frame error rate of the decoded code are calculated and a design signal to noise ratio is changed, the above operation is repeated until the bit error probability and frame error rate become the minimum. The method and system provided by the invention are suitable for general binary system memoryless channels, the bit error probability and frame error rate are low, the calculation complexity is low and the communication performance of a communication system is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
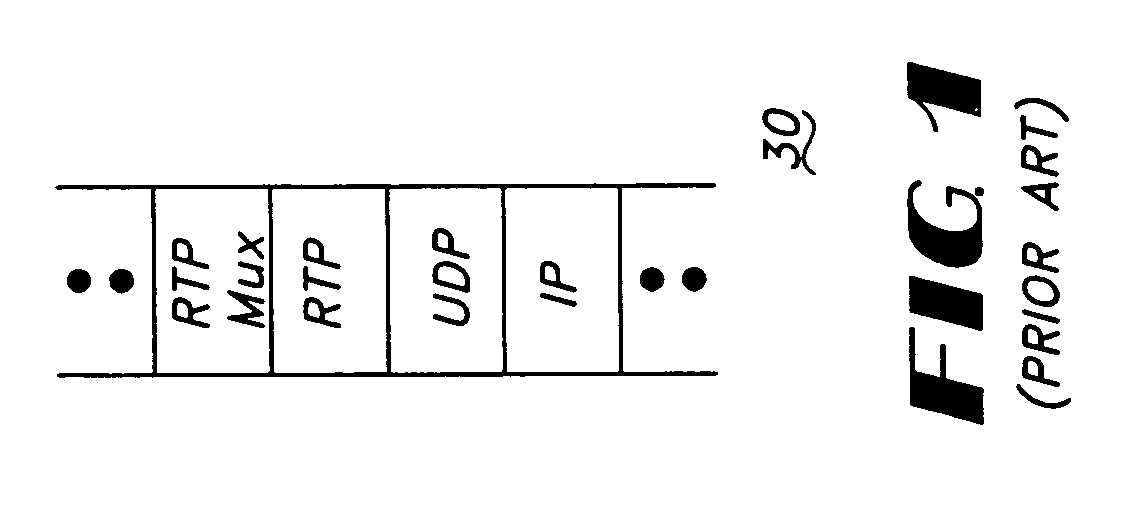
Lightweight internet protocol encapsulation (LIPE) scheme for multimedia traffic transport
InactiveUS6993021B1Increase in sizeTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityClass of service
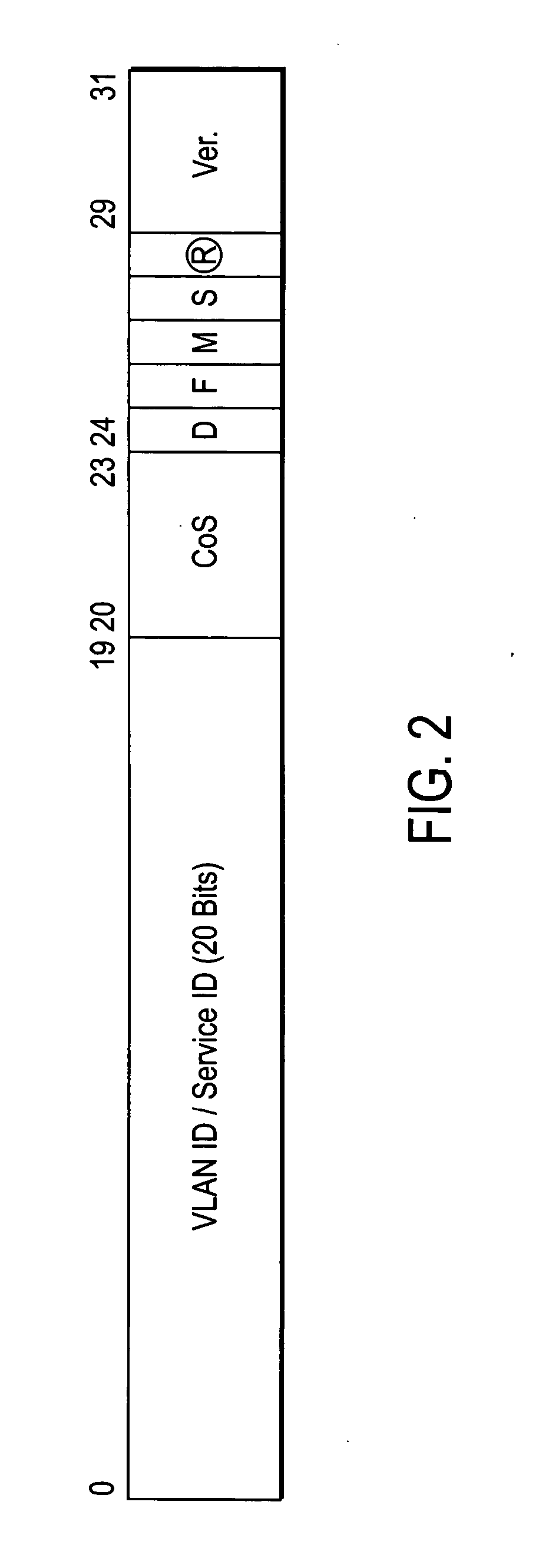
A packet encapsulation scheme for multiplexing application sessions—Lightweight IP Encapsulation (LIPE)—is described. An LIPE packet comprises at least one multiplexing header (NH) and associated multimedia data packet (MDP). The LIPE packet uses UDP / IP as transport. An MH field further comprises a 16-bit a user identifier (UID) field, an 11 bit length indicator (LNG) field, a 1 bit “more” (M) field and an optional payload type / class of service (PT / CoS) field comprising 8 bits.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
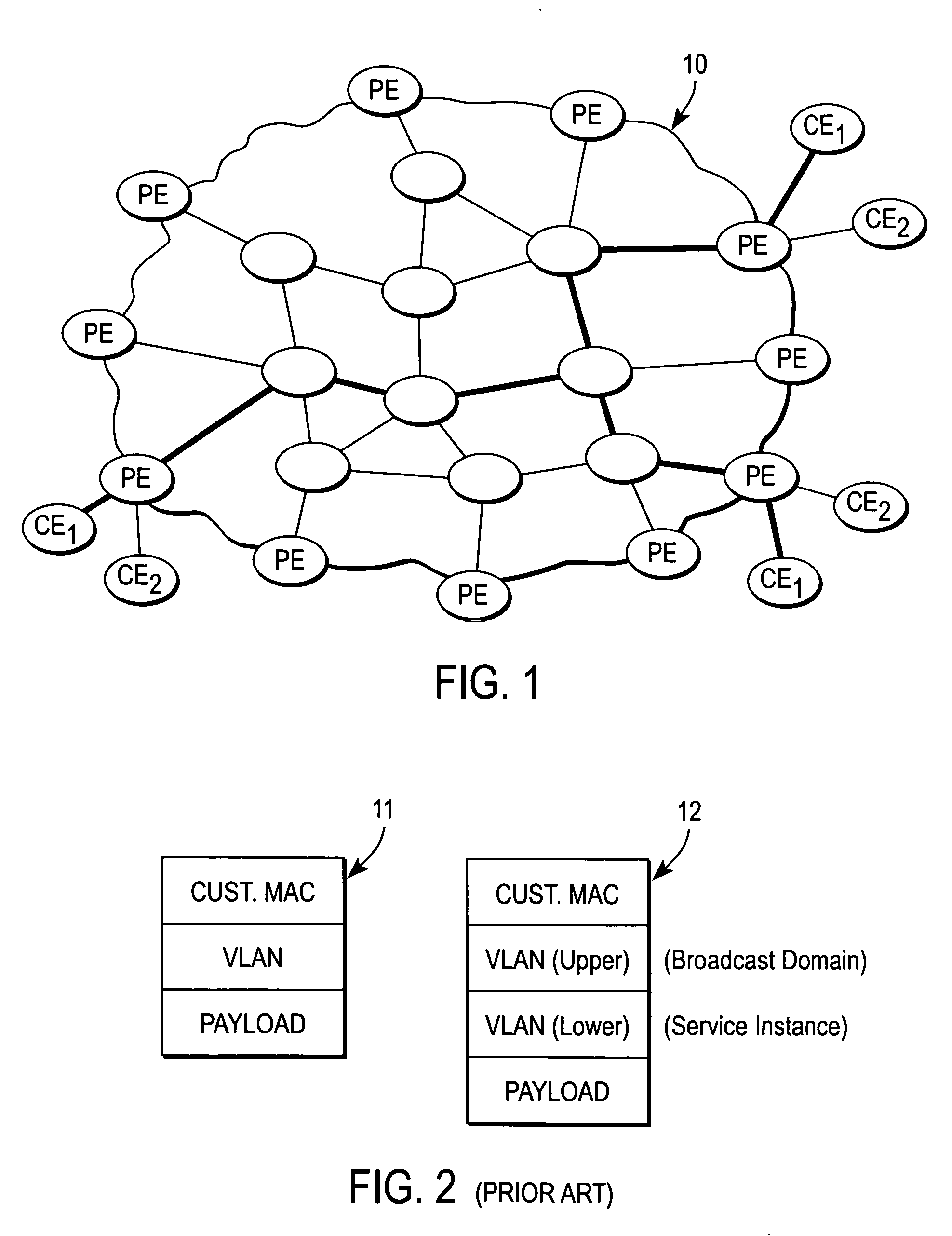
Metro ethernet network with scaled broadcast and service instance domains
ActiveUS20060245438A1Special service provision for substationMetropolitian area networksAccess networkVirtual LAN
A method of operation for a provider edge device of a core network includes receiving a customer frame from an access network; the customer frame having a first Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) tag of a first predetermined bit length. The first VLAN tag including a service instance identifier. The service instance identifier of the first VLAN tag is then mapped into a second VLAN tag of a second predetermined bit length greater than the first predetermined bit length. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. 37 CFR 1.72(b).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Identification of object on interactive display surface by identifying coded pattern
InactiveUS7204428B2Noise minimizationCharacter and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesDisplay deviceInteractive displays
A coded pattern applied to an object is identified when the object is placed on a display surface of an interactive display. The coded pattern is detected in an image of the display surface produced in response to reflected infrared (IR) light received from the coded pattern by an IR video camera disposed on an opposite side of the display surface from the object. The coded pattern can be either a circular, linear, matrix, variable bit length matrix, multi-level matrix, black / white (binary), or gray scale pattern. The coded pattern serves as an identifier of the object and includes a cue component and a code portion disposed in a predefined location relative to the cue component. A border region encompasses the cue component and the code portion and masks undesired noise that might interfere with decoding the code portion.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for decoding sync marks in a disk
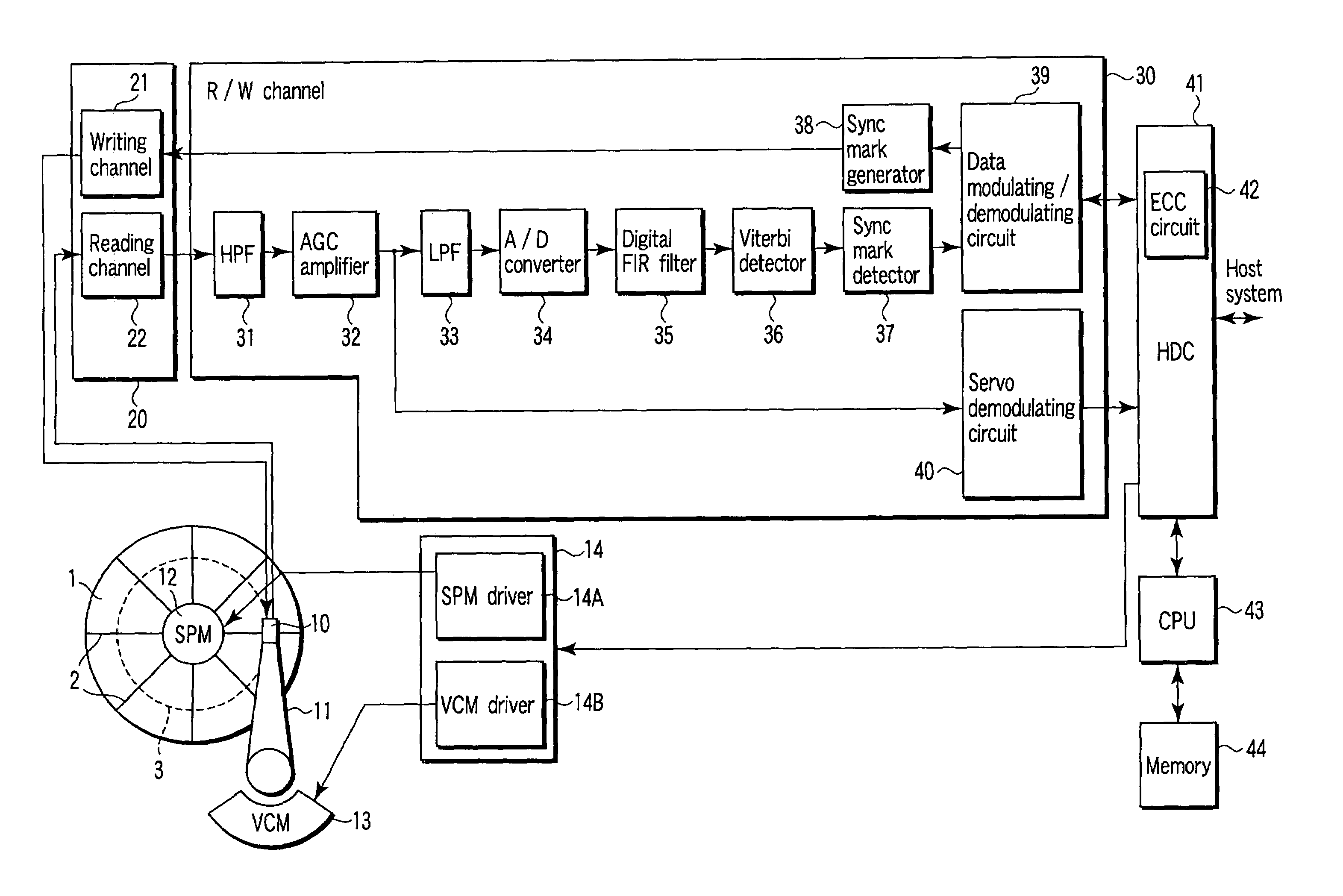
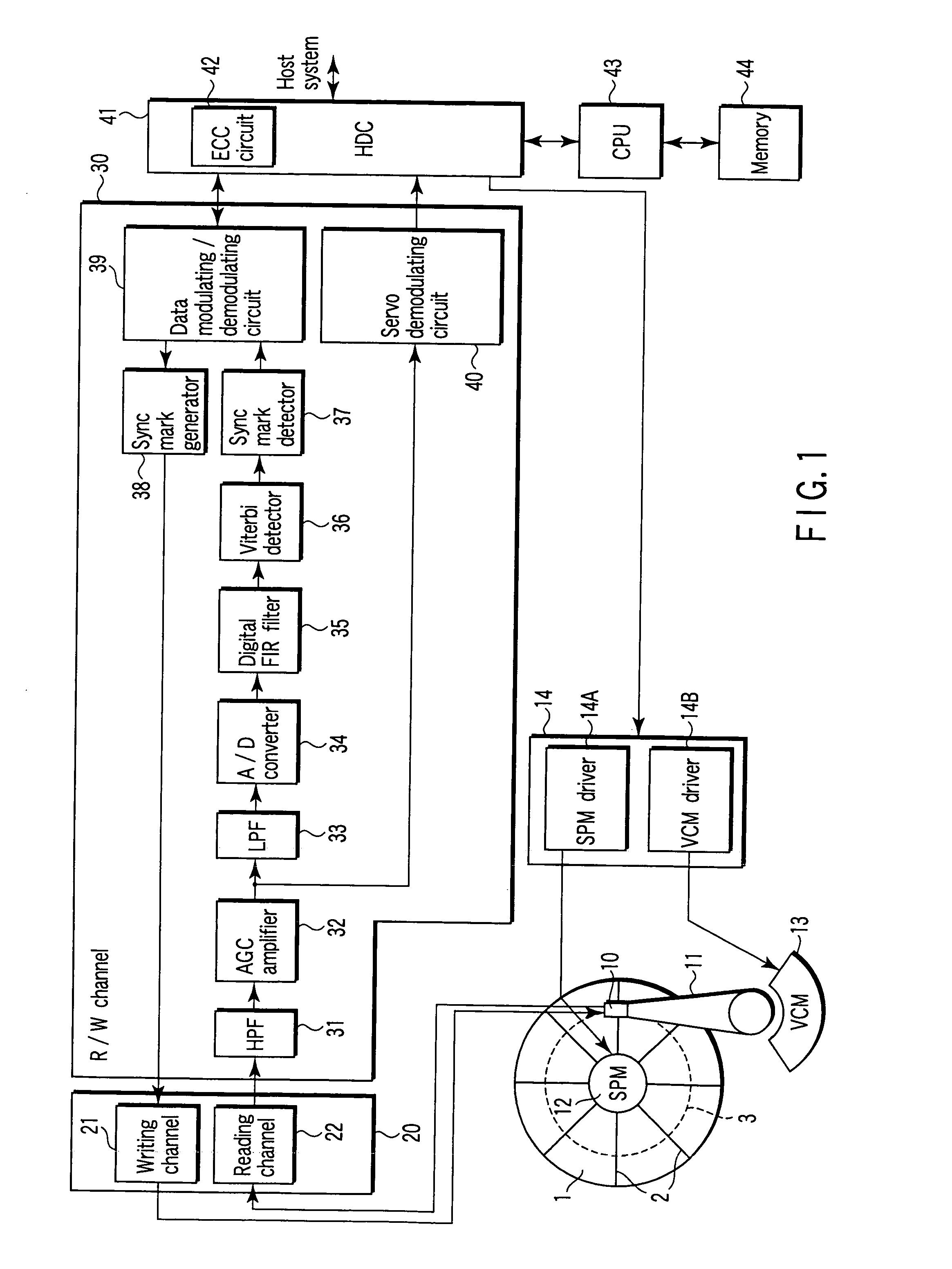
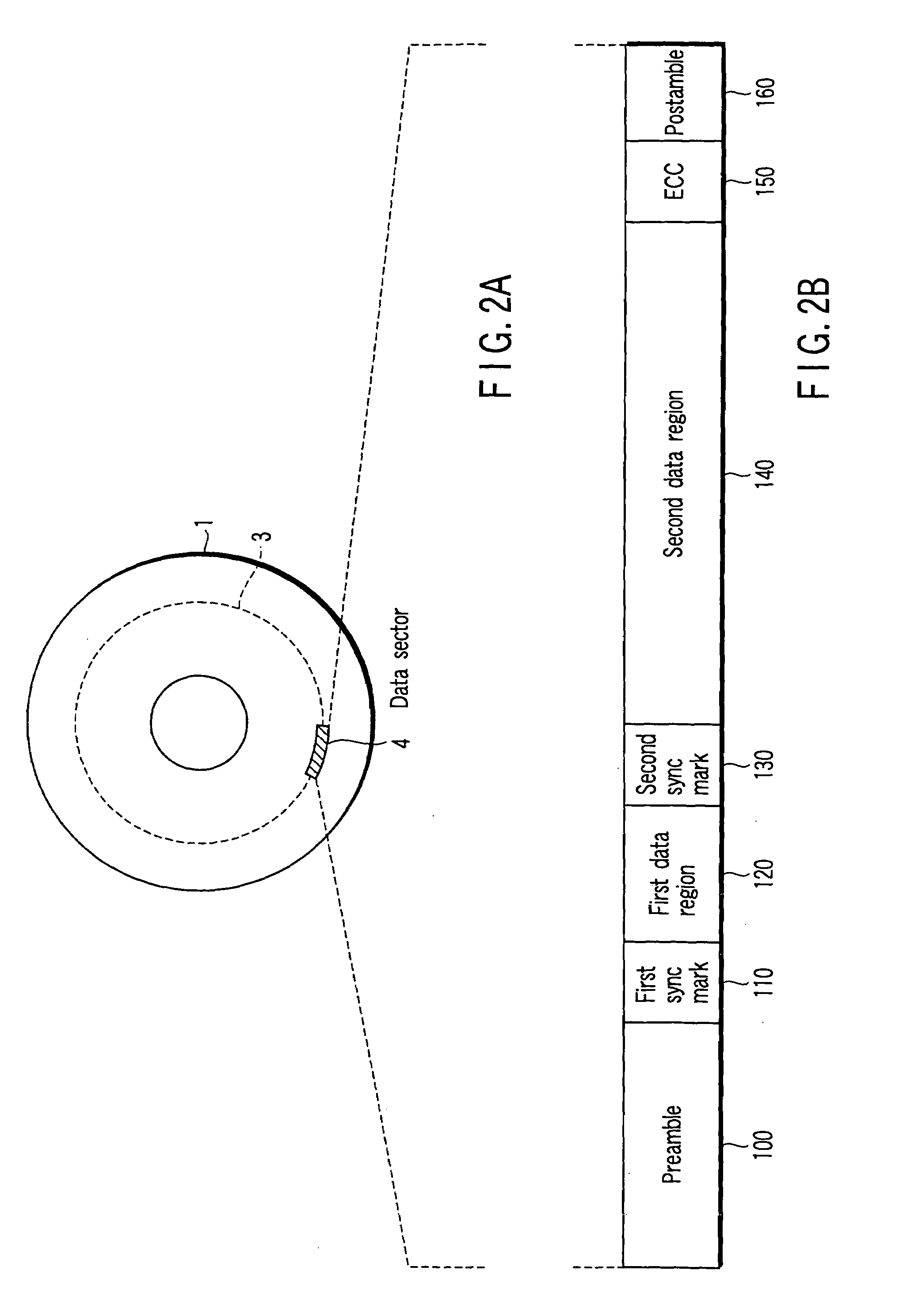
InactiveUS7203015B2High error rateIncrease probabilityModification of read/write signalsDisc-shaped record carriersComputer scienceBit-length
In a disk drive that performs perpendicular magnetic recording, the read / write channel has a sync mark generator. The sync mark generator generates a second sync mark before the read / write channel operates to write data on a disk. The second sync mark has a bit pattern including a series of bits representing positive polarity and a series of bits representing negative polarity. The series of bits, which is longer than the other, has a bit length that is at least 50% but less than 85% of the total bit length of the second sync mark.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
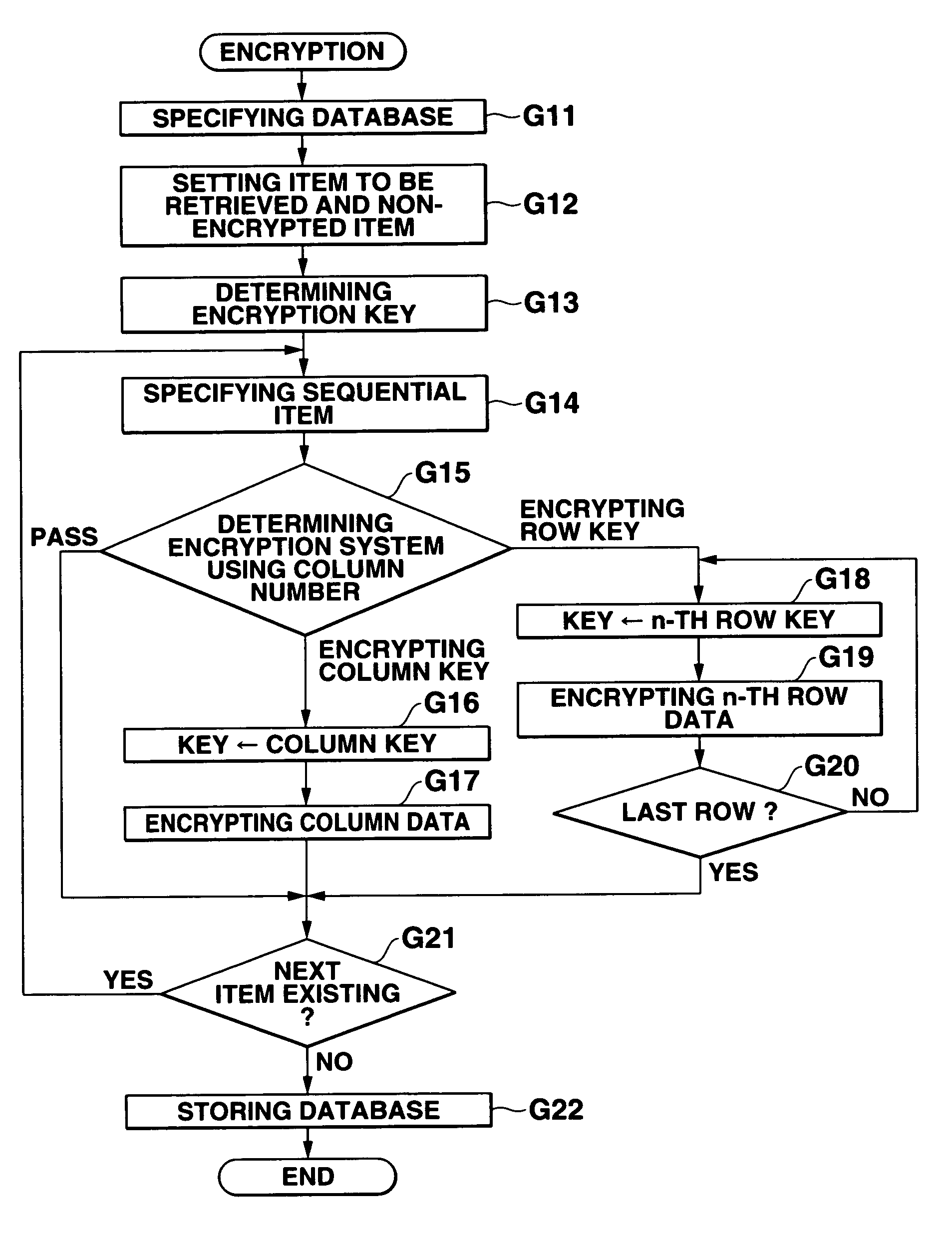
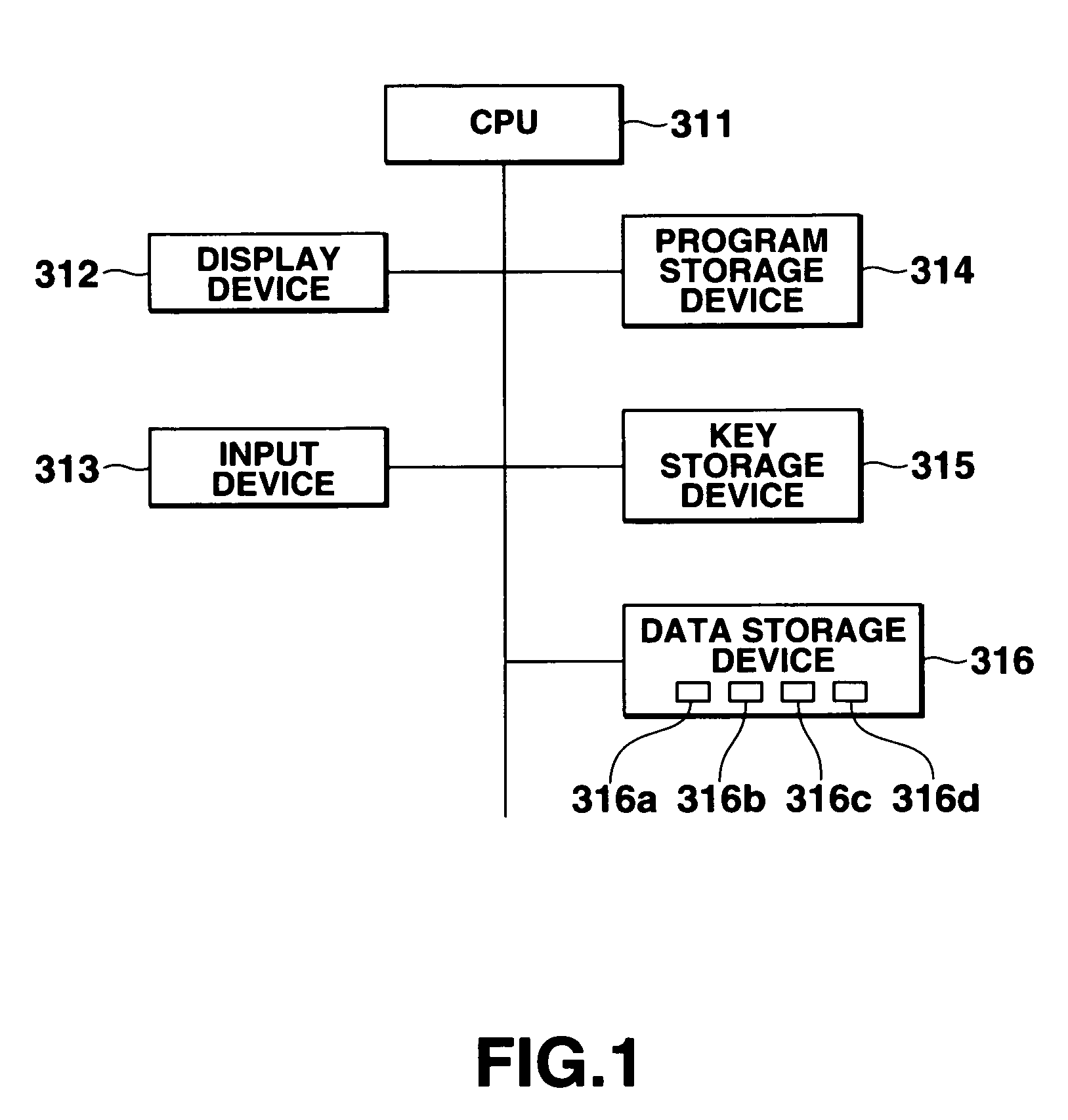
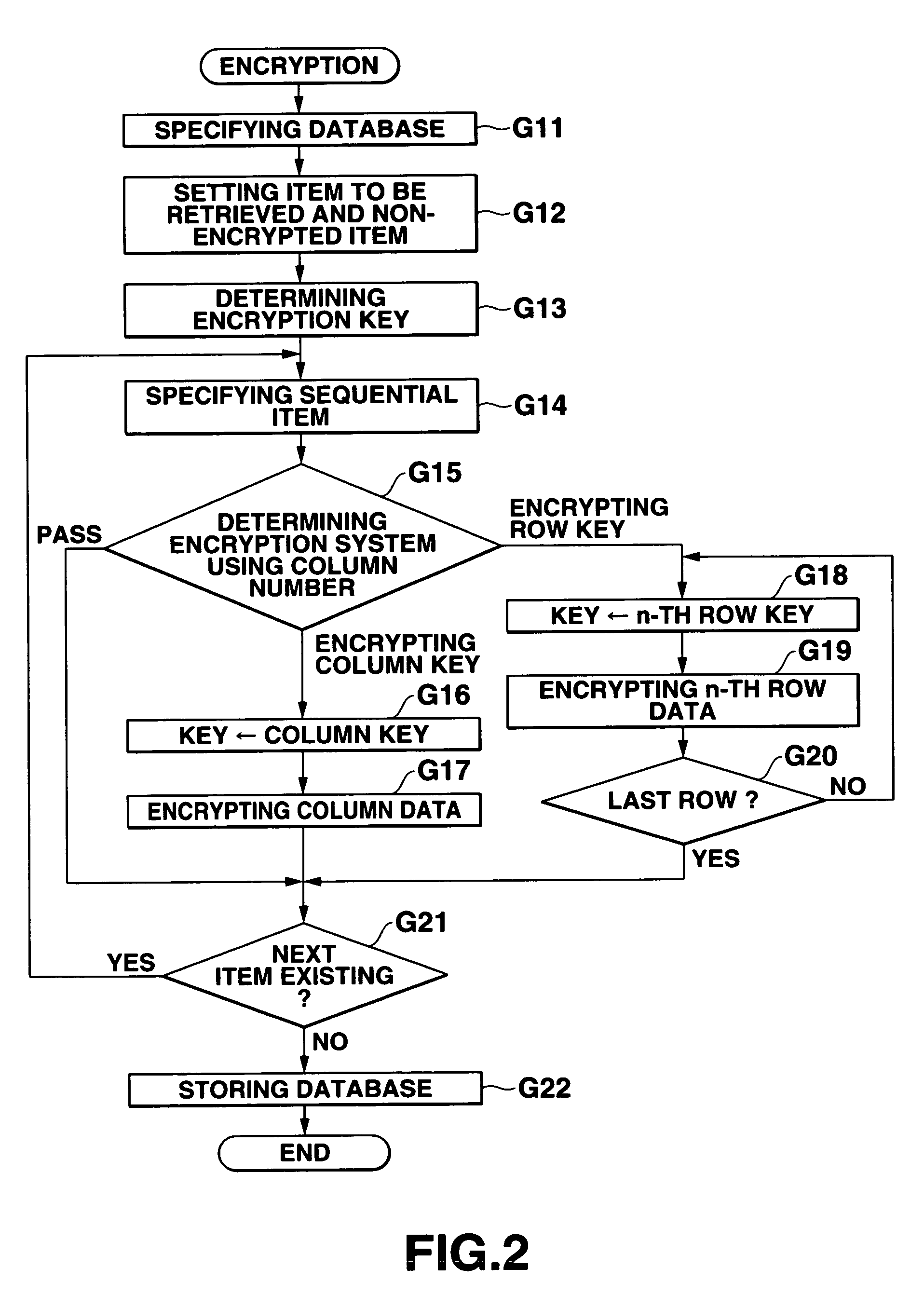
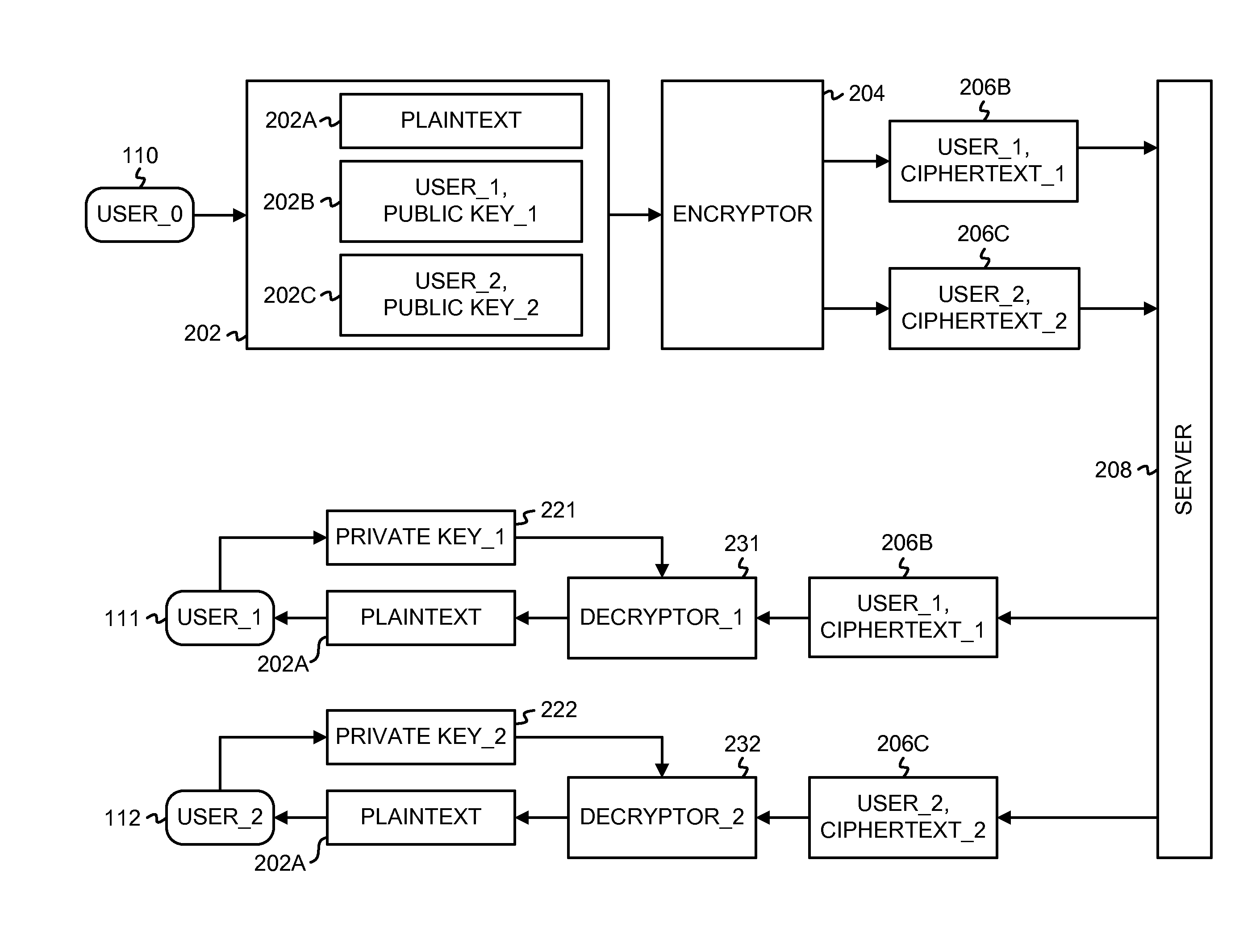
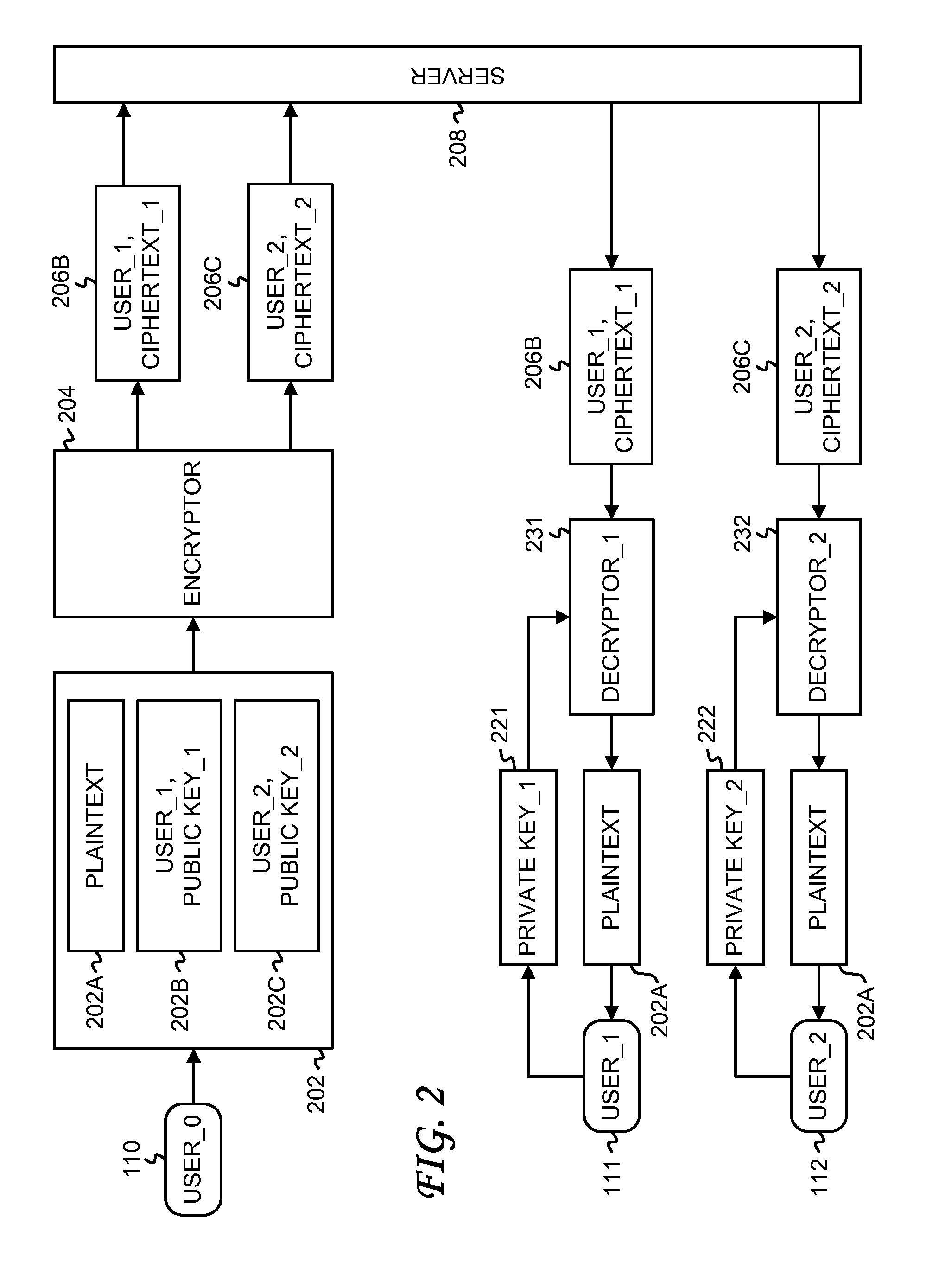
Database management apparatus and encrypting/decrypting system
InactiveUS7093137B1Easy to addEasy to changeData processing applicationsUnauthorized memory use protectionPlaintextTheoretical computer science
In a database, a frequently retrieved column is encrypted using a common key, and other columns are encrypted using a specific row key. Thus, a retrieving process can be performed at a high speed, and the security can be improved. Then, the row and column of the database are encrypted by assuming the plaintext to be encrypted as a bit string, and performing a binary operation with a random bit string. A random bit string is obtained by sequentially generating multidimensional vectors using a nonlinear function by defining a predetermined bit length as 1 word and a plurality of words as components of the multidimensional vector.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
Magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20070020490A1Excellent electromagnetic characteristic and error rate and durabilityImproved electromagnetic characteristic and error rate and durabilityBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageHigh densityMicrometer
Provided is a magnetic recording medium for high-density recording, that has excellent electromagnetic characteristics, error rates, and durability. The magnetic recording medium comprises a magnetic layer comprising a ferromagnetic powder, a binder and an abrasive on a nonmagnetic support and is employed for recording a magnetic signal on the medium and reproducing the recorded signal with a reproduction head. The abrasive has a Vickers hardness ranging from 18 to 80 GPa and a mean particle diameter ranging from 10 to 100 nm. The magnetic layer comprises the abrasive in a quantity of 5 to 60 weight parts per 100 weight parts of the ferromagnetic powder and has a thickness ranging from 10 to 100 nm. The number of abrasive present on the surface of the magnetic layer ranges from 0.01 to 1 per {(minimum bit length of the recorded signal)×(read track width of the reproduction head)} micrometer2.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Comprehensive model for VPLS
ActiveUS20060245436A1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsAccess networkVirtual LAN
A VPLS model is implemented in a network-facing provider edge (n-PE) device configured to receive a packet from an access network; the packet having a first Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) tag of a first predetermined bit length. The n-PE device mapping the service instance identifier of the first VLAN tag into a second VLAN tag of a second predetermined bit length greater than the first predetermined bit length, the second VLAN tag identifying a Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS) instance. The n-PE device then sends the packet with the second VLAN tag across a service provider (SP) core network via a pseudowire (PW) that functions as a logical link to another PE device. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. 37 CFR 1.72(b).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Outsourcing the Decryption of Functional Encryption Ciphertexts
ActiveUS20120300936A1Short bit lengthKey distribution for secure communicationFunctional encryptionAttribute-based encryption
Functional encryption (FE) ciphertext is transformed into partially-decrypted (PD) ciphertext. The PD ciphertext has a shorter bit length than the FE ciphertext, or the decryption time of the PD ciphertext is less than the decryption time of the FE ciphertext. The FE ciphertext can be an attribute-based encryption ciphertext. The transformation can be performed with a transformation key generated by an authority with a master key or by a user with a decryption key. The transformation can also be performed, without a transformation key, based on unencrypted components of the FE ciphertext and on auxiliary information associated with the unencrypted components of the FE ciphertext. The PD ciphertext can require less transmission time across a network than the FE ciphertext. The PD ciphertext can require less time to decrypt than the FE ciphertext, particularly when the computational resources performing the decryption are limited.
Owner:NTT RES INC
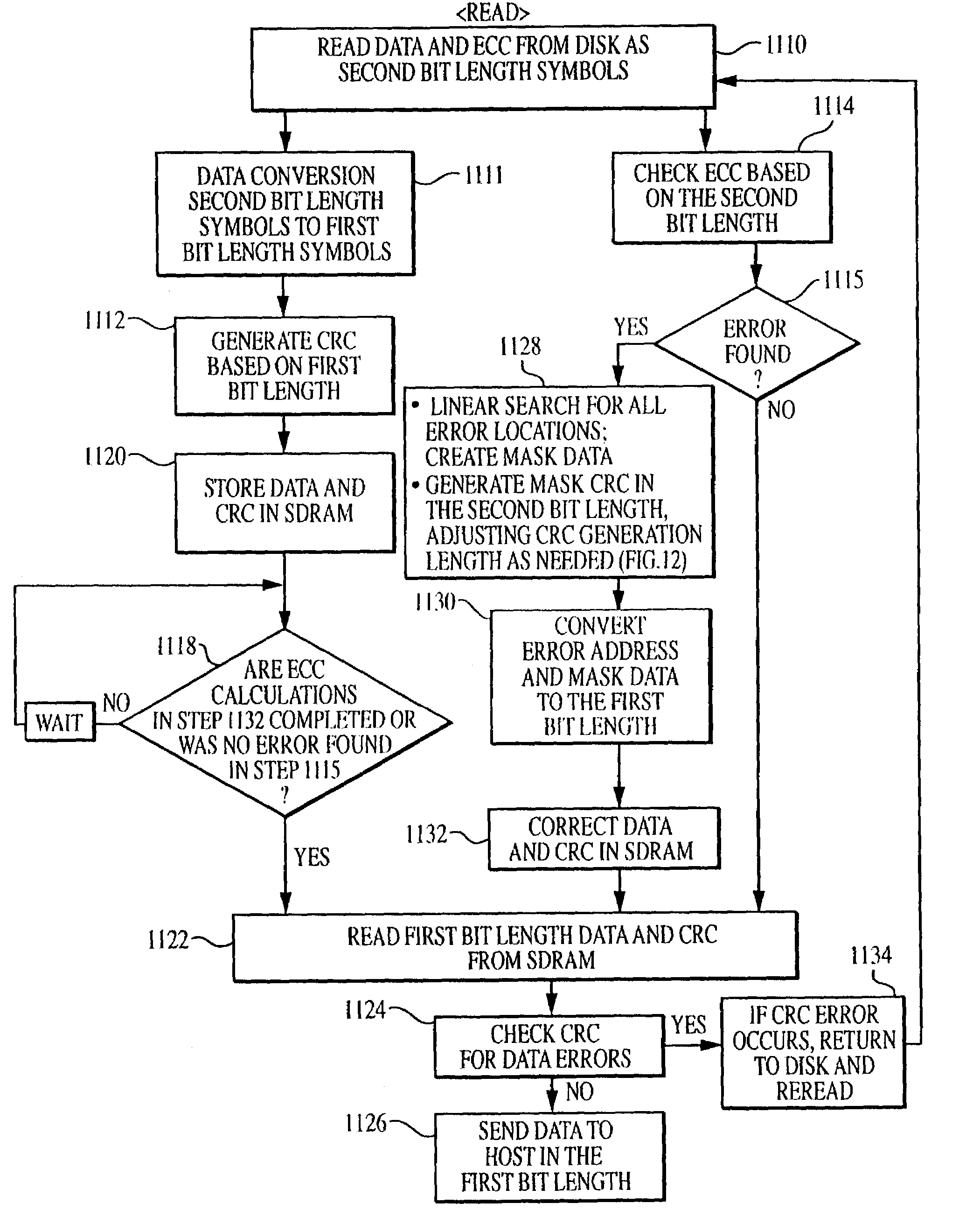
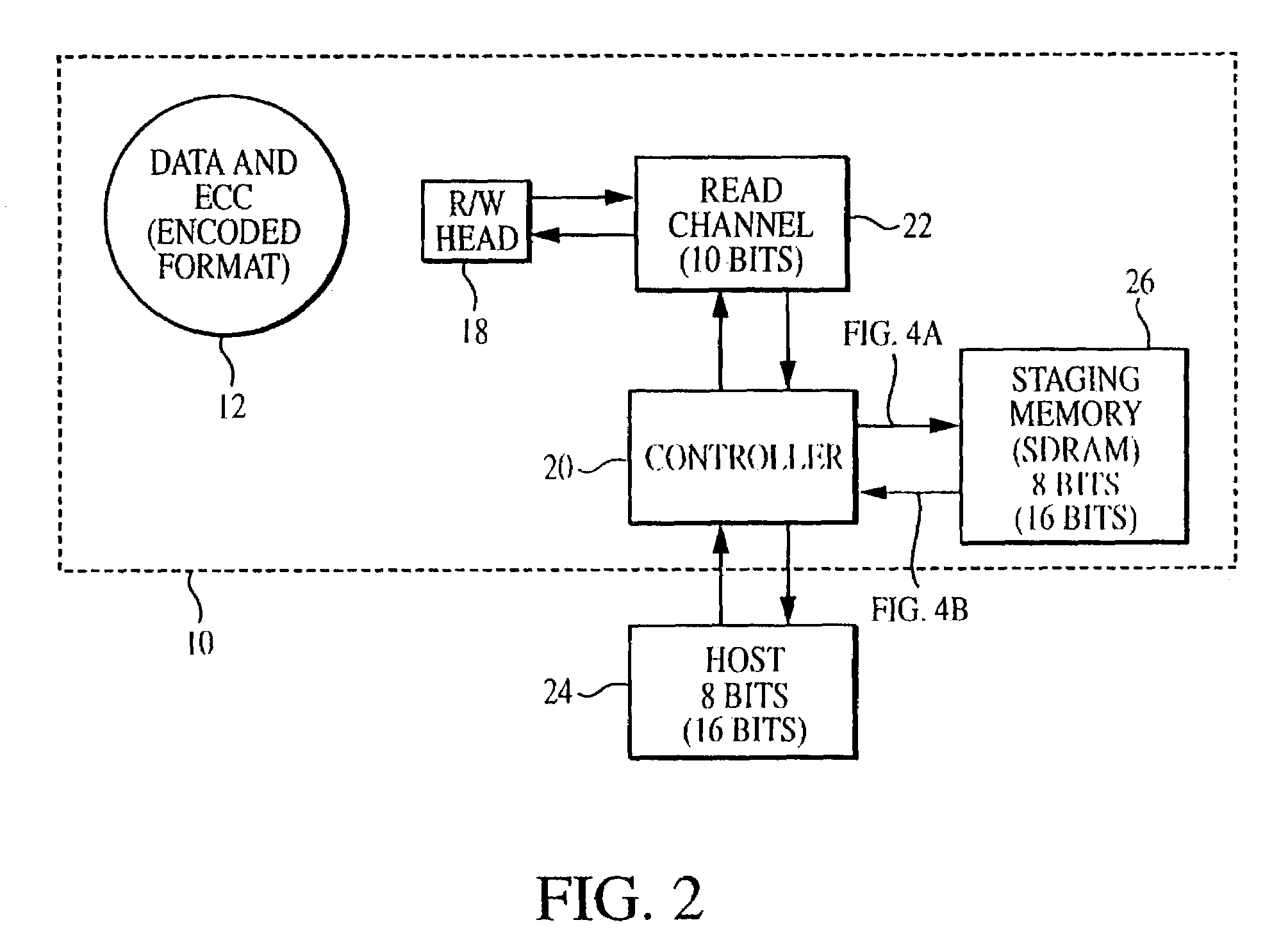
Methods and apparatus for correcting data and error detection codes on the fly
When data is read from a disk and stored in volatile memory, check bits are generated and stored in the memory using an algorithm such as cyclical redundancy check (CRC). The CRC algorithm operates on the basis of the bit length in which the data is organized, such as 8 bits. If the data has errors, an error correction code (ECC) algorithm is used to correct the data errors, but the ECC algorithm operates on the basis of symbols having a different bit length, such as 10 bits. To avoid having to re-read the data from the volatile memory to adjust the CRC value, the CRC algorithm is executed on selected mask data developed by the ECC algorithm, the CRC algorithm being executed on the basis of the second bit length to generate a CRC mask. The CRC mask corrects the stored CRC value.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
Method and device for rate matching of Polar code
ActiveCN106817195AGood coding gainCode conversionChannel coding adaptationHybrid automatic repeat requestBit-length
The invention discloses a method and device for rate matching of Polar codes. The method comprises the steps of: performing Polar code encoding on an information bit sequence with a K-bit length, and generating an encoding bit sequence with an M-bit length; selecting Nmin bits from the encoding bit sequence as the first bit to Nmin-th bit of a bit sequence to be transmitted during a hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) process; and determining each bit of (Nmin+1)th bit to Nmax-th bit of the bit sequence to be transmitted from the information bit sequence and the encoding bit sequence, wherein each bit of the (Nmin+1)th bit to the Nmax-th bit of the bit sequence to be transmitted is determined according to a frame error rate of the bit sequence to be transmitted when each bit is added into the bit sequence to be transmitted. By adopting the method of the embodiment of the invention, HARQ transmission based on Polar code encoding can be achieved, and better encoding gain can be obtained.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
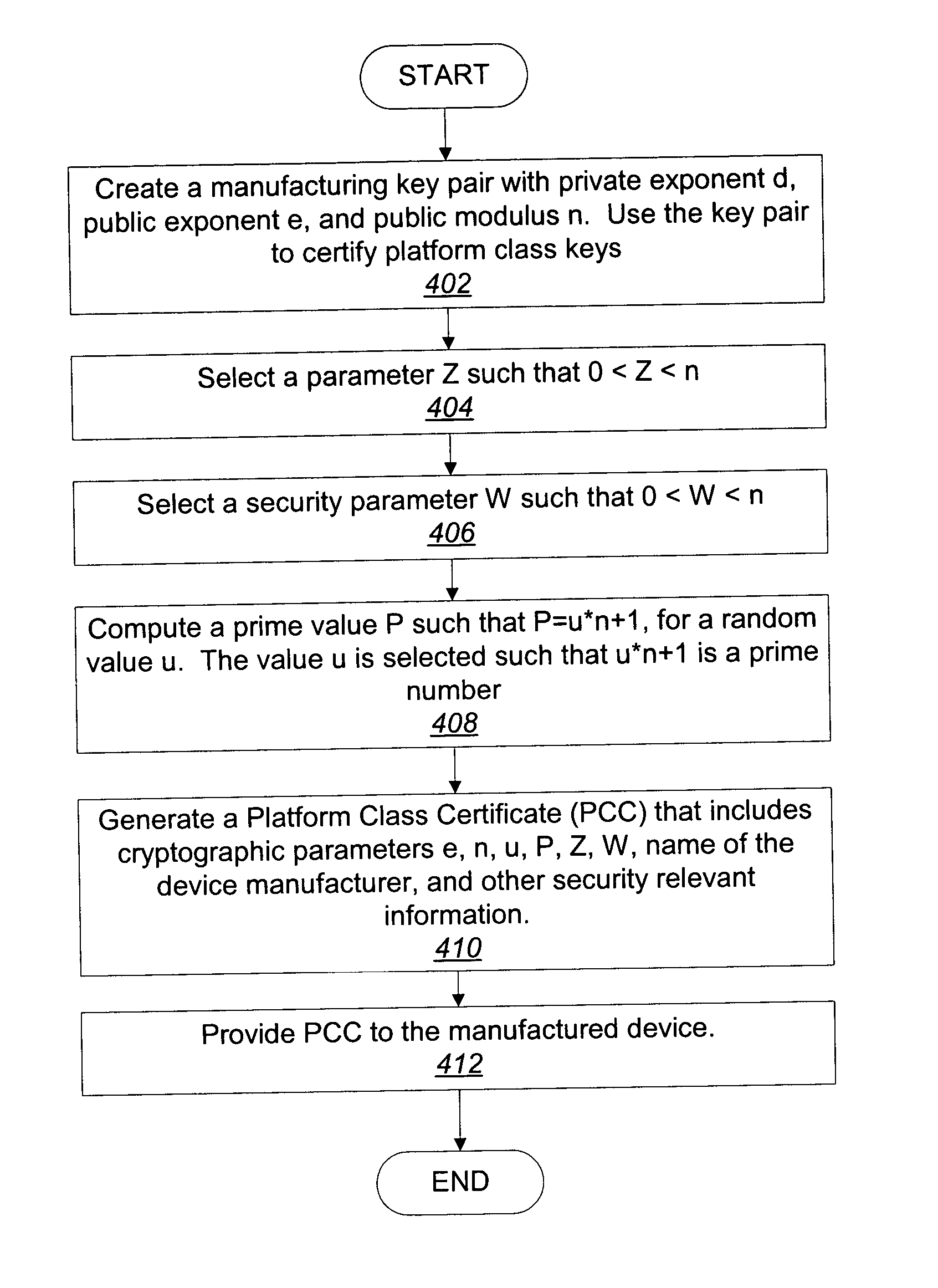
Platform and method for establishing trust without revealing identity
ActiveUS20050069135A1Public key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationOperating systemBit-length
One aspect of an embodiment of the invention provides a method and platform to prove to a challenger that a responder device possesses cryptographic information from a certifying manufacturer. This is accomplished by performing a direct proof by the responder device to prove that the responder device possesses the cryptographic information. The direct proof comprises at least one exponentiation being conducted using an exponent having a bit length no more than one-half a bit length of a modulus (n).
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
System and method to validate and authenticate digital data
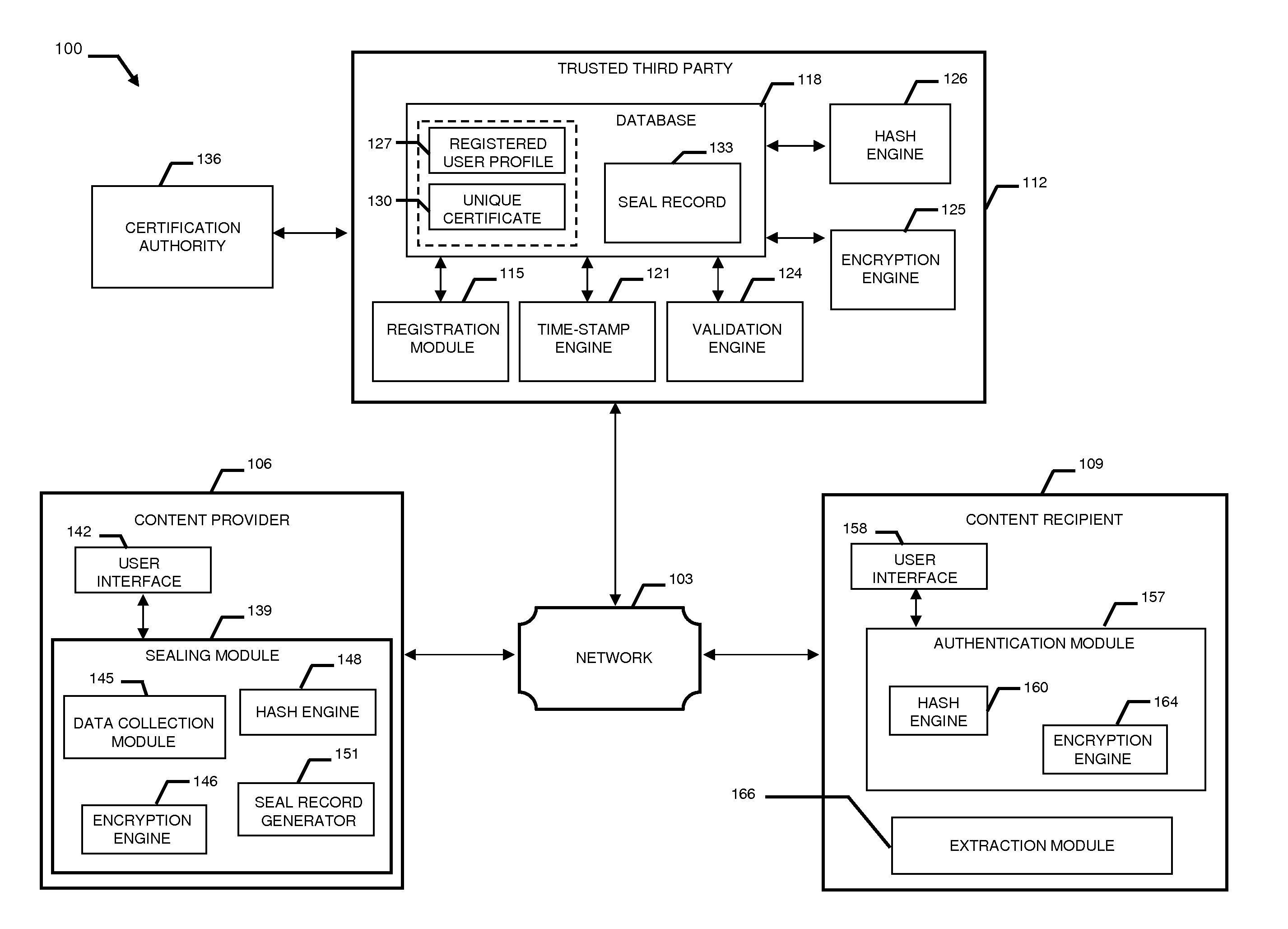
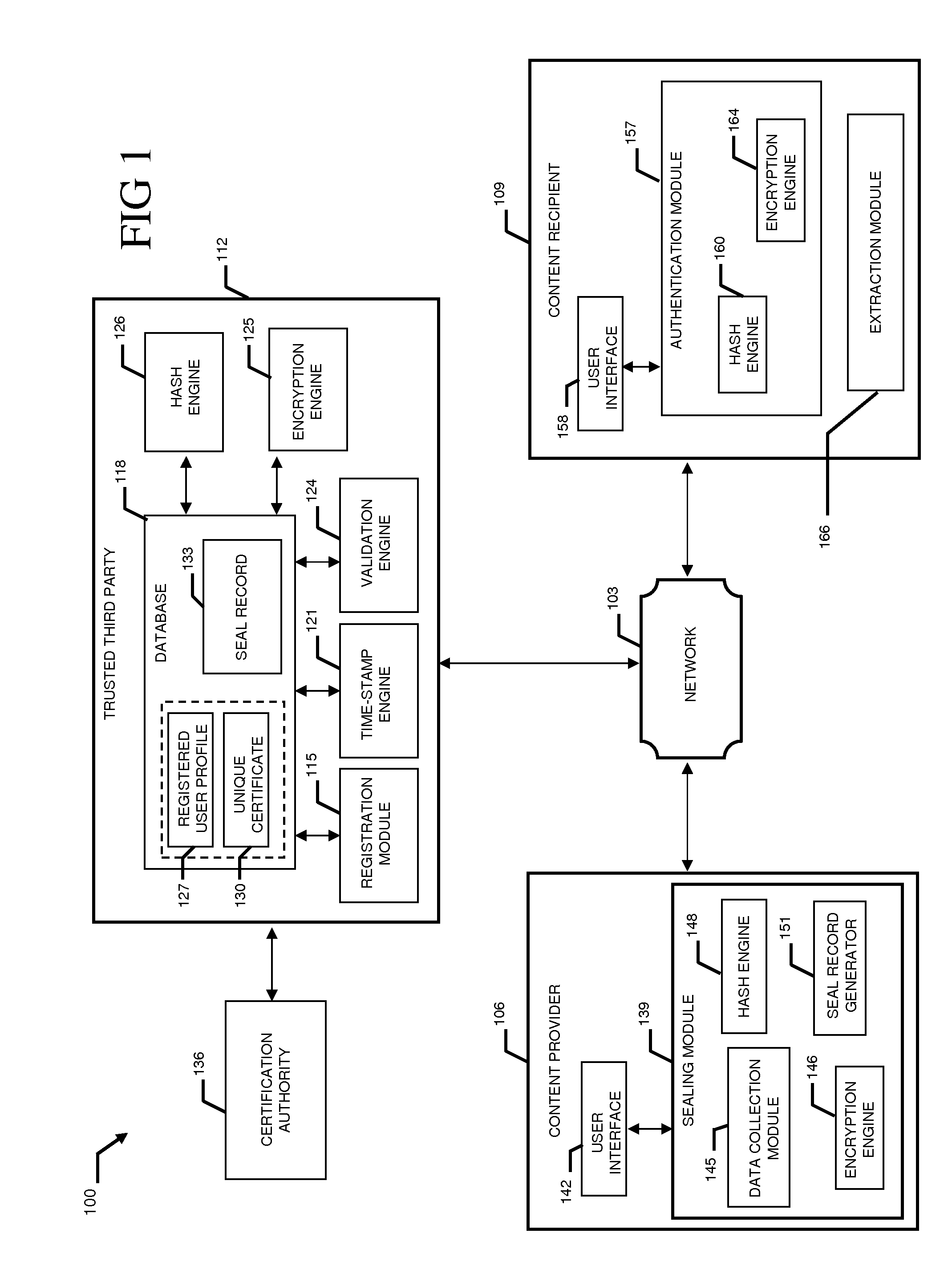
InactiveUS20110231645A1Data can be securedDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationDigital dataDocument Identifier
A system and method combining registration with a trusted third party, certificate generation, hashing, encryption, customizable file identification fields, and time-stamping technology with recognized “best practice” procedures to achieve the legal admissibility and evidential weight of any form of digital file or collection of digital files. Generally, the originator of the file (the first party) and the originator's employing organization are registered with a Trusted Third Party. The originator reduces the file, by means of a hashing algorithm, to a fixed bit length binary pattern. This provides a unique digital fingerprint of the file. The resultant hash value, the originator's identity details, the employing organization details associated and securely linked to the digital certificate, the title of the file, customizable file identification fields, and other relevant data are forwarded to a Trusted Third Party where the date and time from a known and trusted time source are added. The customizable file identification fields can provide the originator with a mechanism for configuring the seal to incorporate as much additional information as deemed necessary to prove the authenticity of the digital content and / or provide data for the purposes of adding value in functions such as source identification, sorting, analysis, investigation, and compliance. Such information could include, but would not be limited to, location / GPS coordinates, machine id, biometric information, smart-card data, reason for sealing. The original file does not leave the control of the originating party. When combined, the forwarded details and date and time create a Seal Record. The Seal Record is encrypted and hashed. The Seal Record along with all other relevant information are retained on a central secure server. The recipient of the file (the second party) can confirm the file has been received in an unaltered state with integrity retained and it is the authentic version by validating the file.
Owner:CYBERCUBE
Method Of Live Submitting A Digital Signal
InactiveUS20080205860A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionVideo transmissionAudio frequency
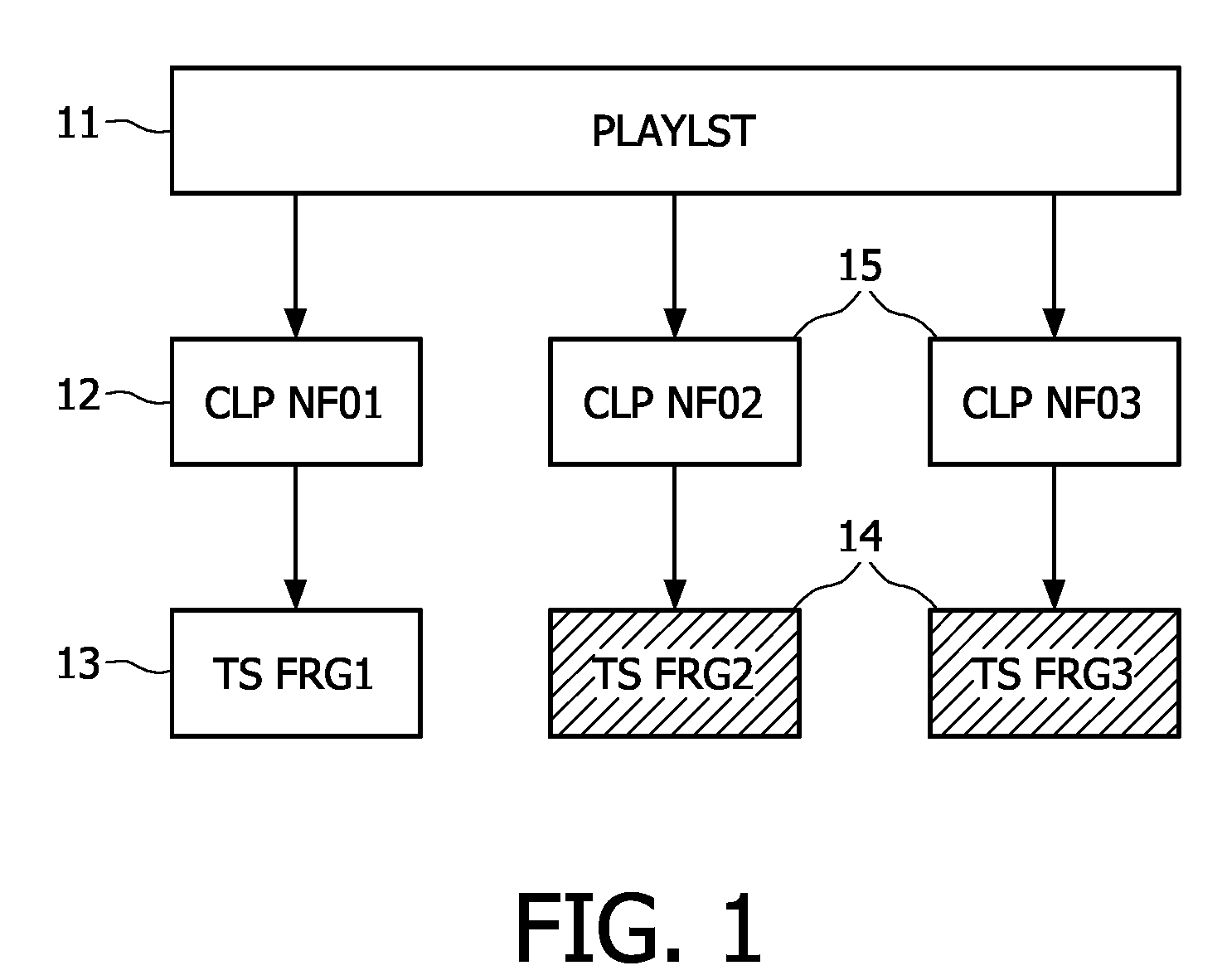
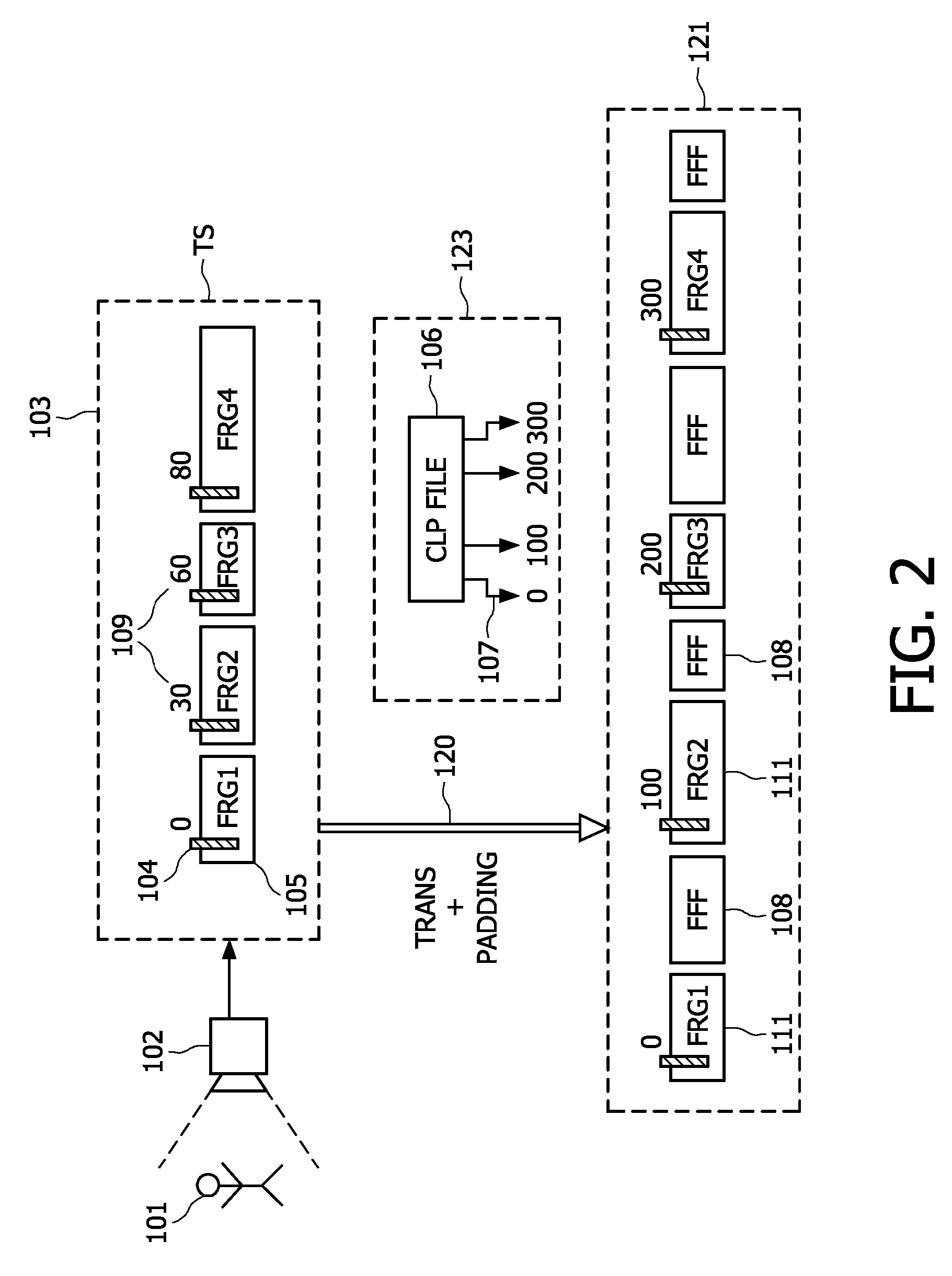
A method of generating in real-time an audio-video transport stream from a sequence of audio-video data fragments, the audio-video data fragments from the sequence having a variable bit length and a predetermined presentation time length, the method comprising steps of generating or receiving in real time the audio-video data fragments; generating the audio-video transport stream by assembling together the audio-video data fragments in the order they are generated or received; inserting padding data between subsequent parts of the audio-video transport stream corresponding to subsequent audio-video data fragments, the amount of the padding data between the subsequent parts being chosen such that a distance between locations of a start of the subsequent parts of the audio-video transport stream corresponds to a predetermined bit length.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Cryptographic key management scheme
InactiveUS6959086B2Layer is highSimple structureKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationDistributed computingBit-length
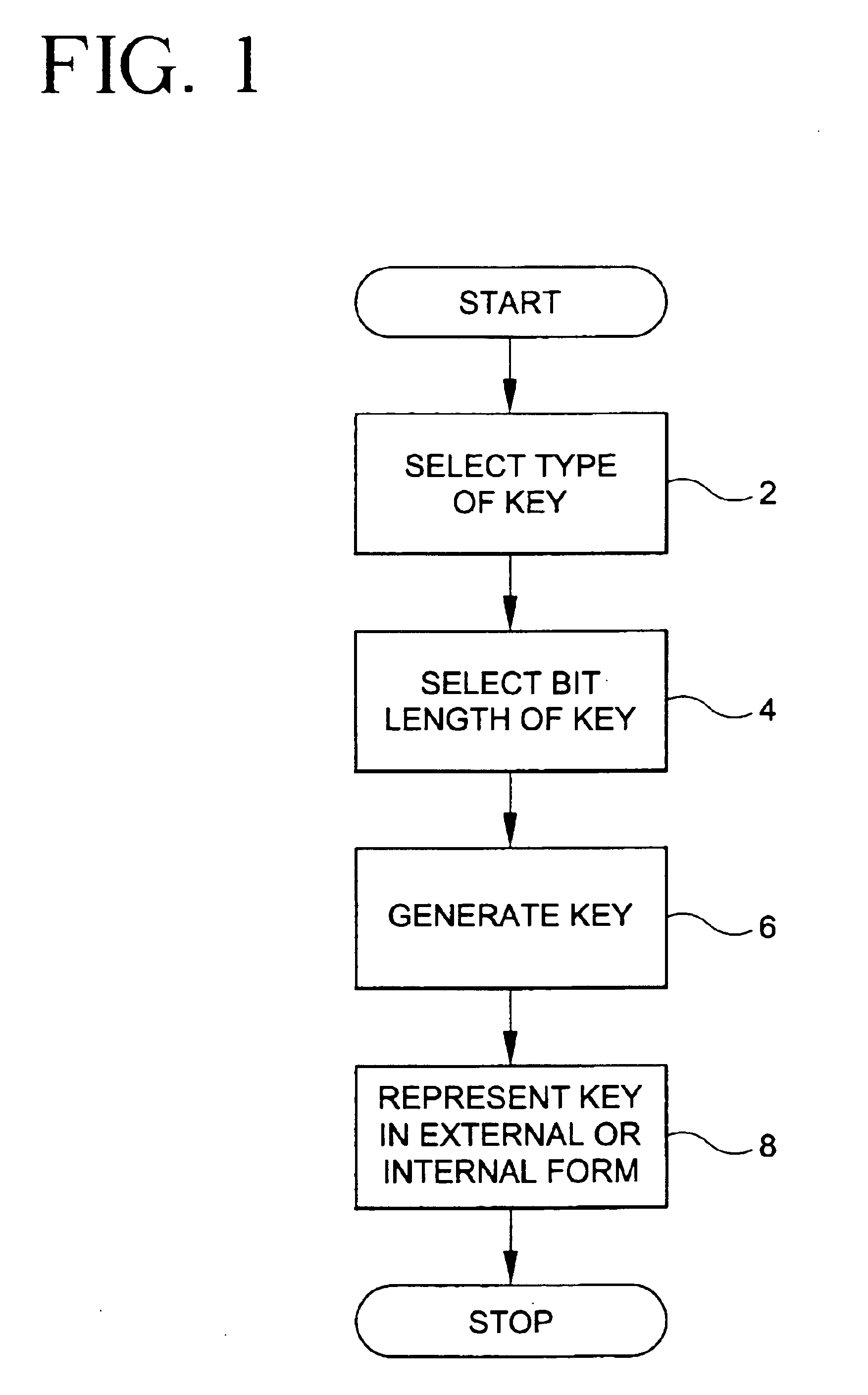
A key management scheme for managing encryption keys in a cryptographic co-processor includes the first step of selecting a key from one of a symmetrical key type and an asymmetrical key type. Then, the key bit length is selected. The key is then generated and, lastly, the key is represented in either an external form or an internal form.
Owner:SAFENET
Variable length code decoding device, digital broadcast receiving apparatus, and DVD reproducing apparatus
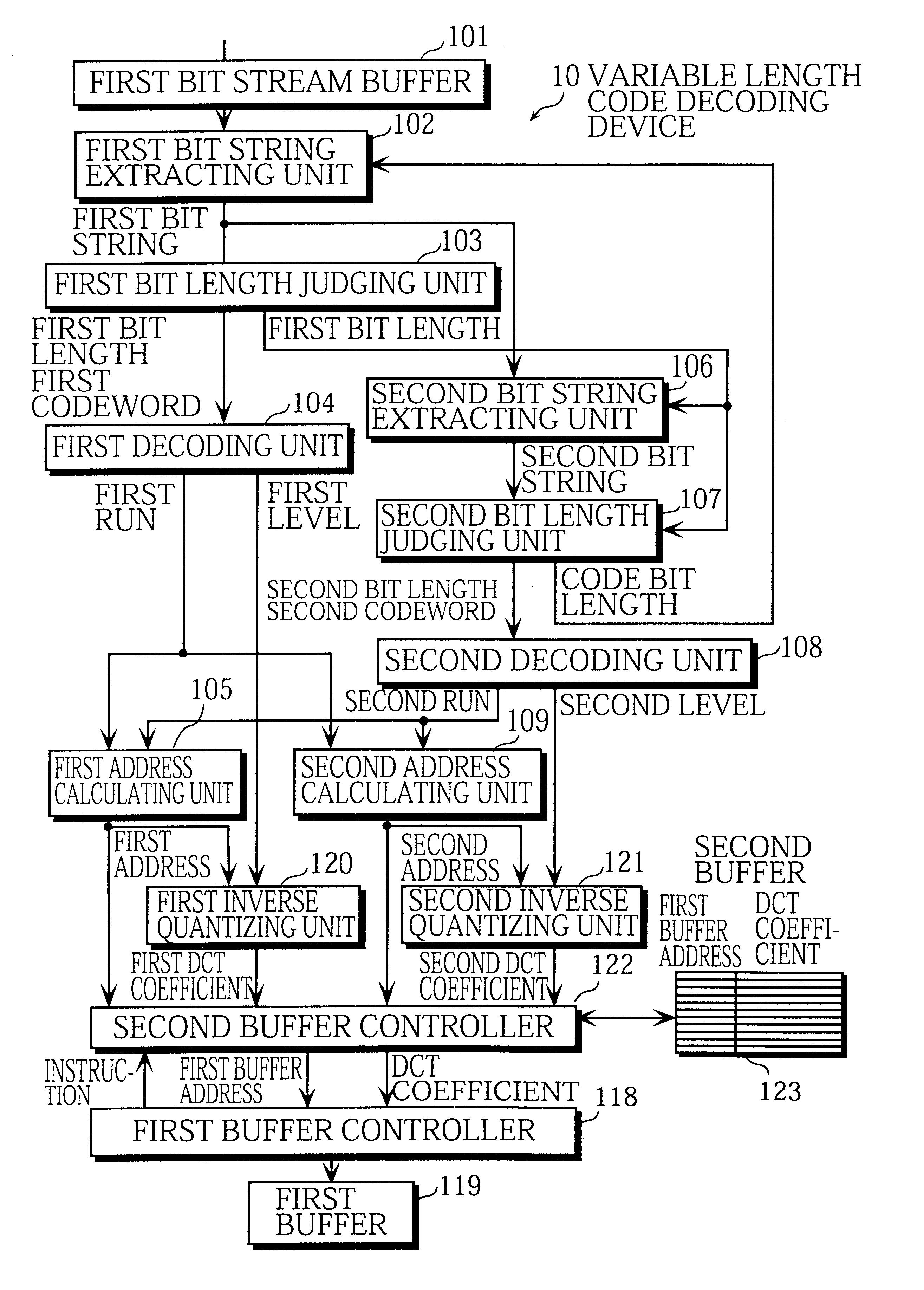
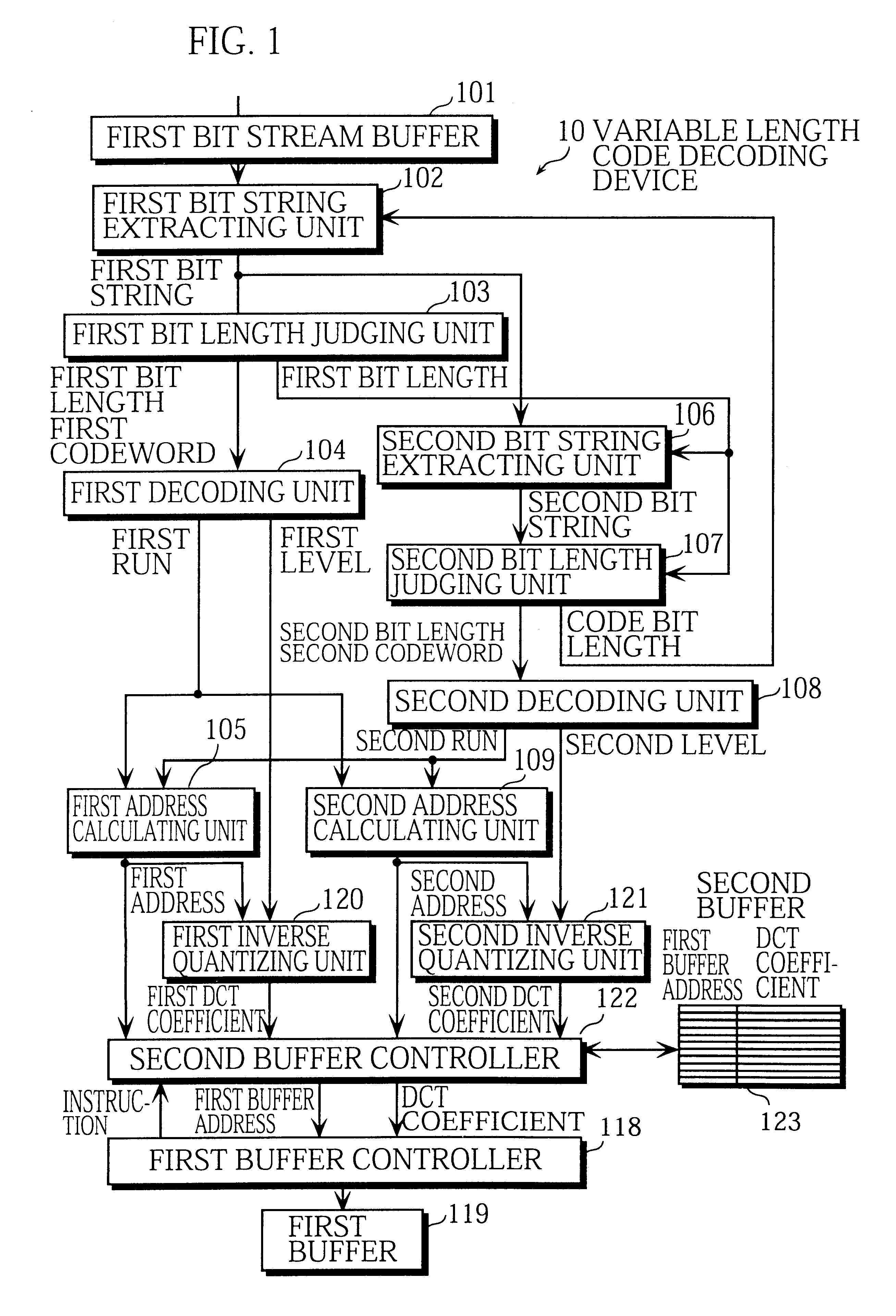
InactiveUS6414608B1Increase the number ofCode conversionTelevision systemsVariable-length codeDigital broadcasting
A first bit string extracting unit extracts a first bit string. A first bit length judging unit detects a first codeword from the first bit string. A first decoding unit generates a first run-level pair from the first codeword. A second bit string extracting unit extracts a second bit string. A second bit length judging unit detects a second codeword from the second bit string. A second decoding unit generates a second run-level pair from the second codeword. A first inverse quantizing unit inverse quantizes the first level to obtain a DCT coefficient. A second inverse quantizing unit inverse quantizes the second level to obtain a DCT coefficient. A second buffer controller writes the DCT coefficients and their first buffer addresses into a second buffer. A first buffer controller reads the DCT coefficients and the first buffer addresses from the second buffer and writes the DCT coefficients into a first buffer at the respective first buffer addresses.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
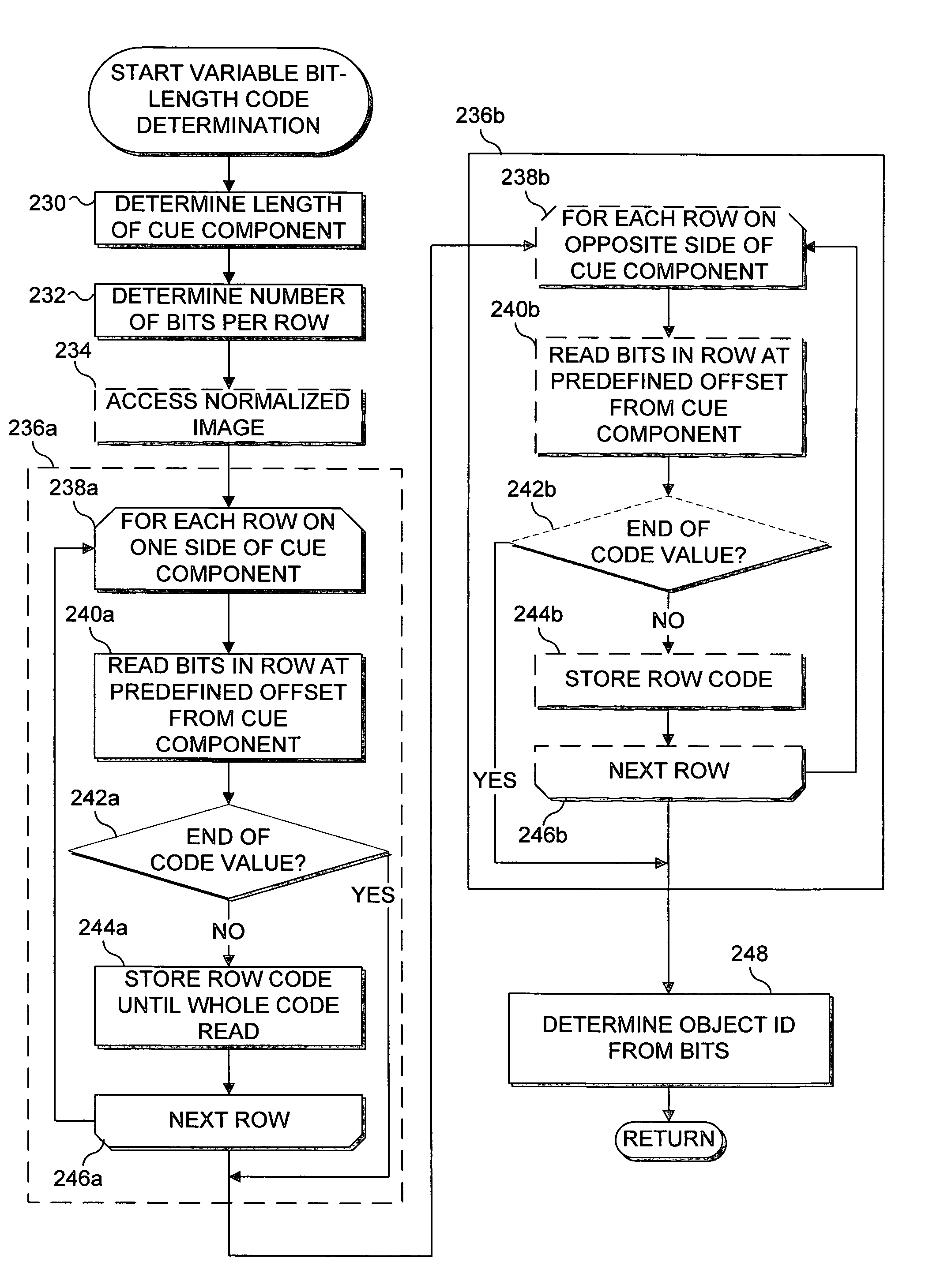
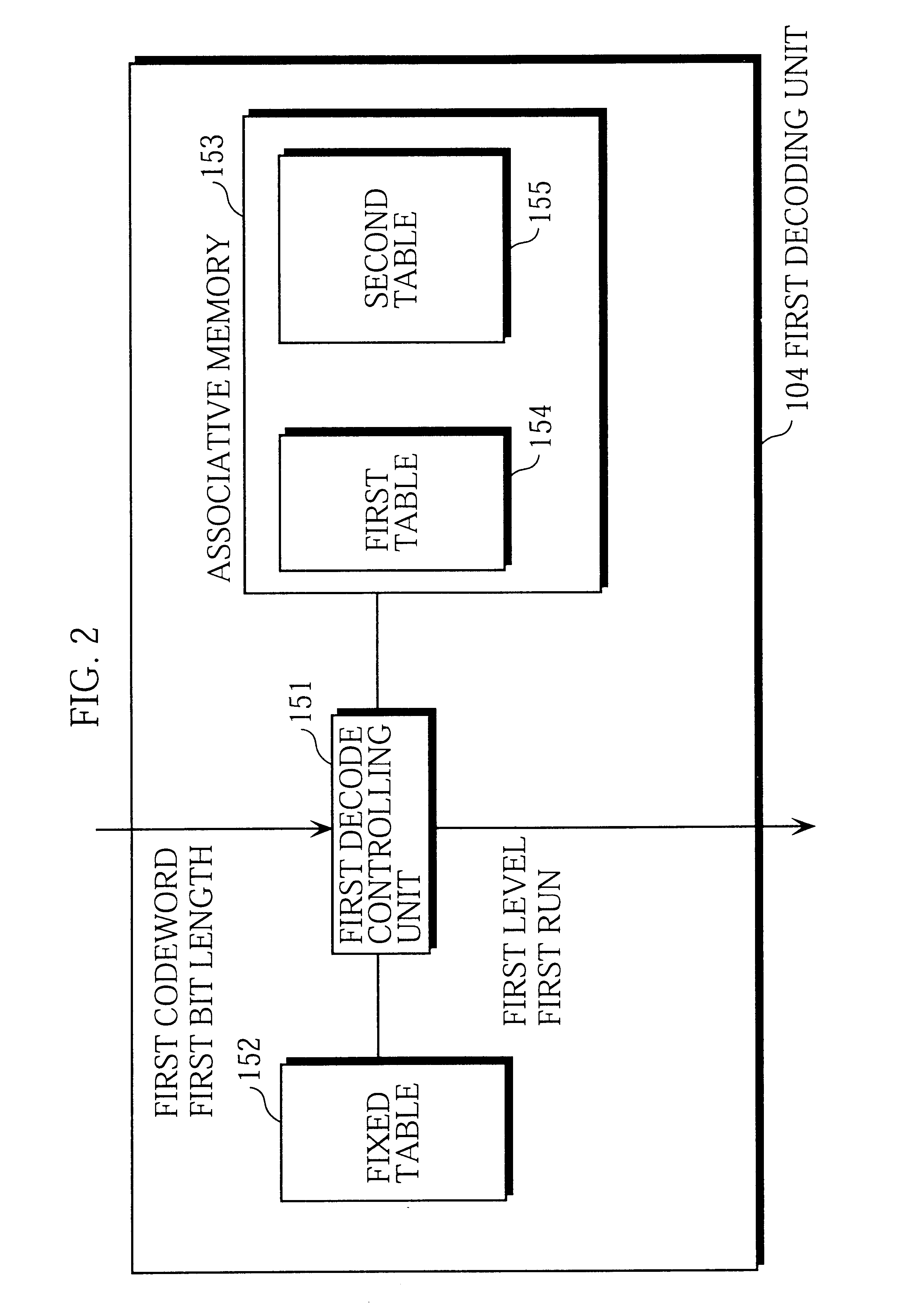
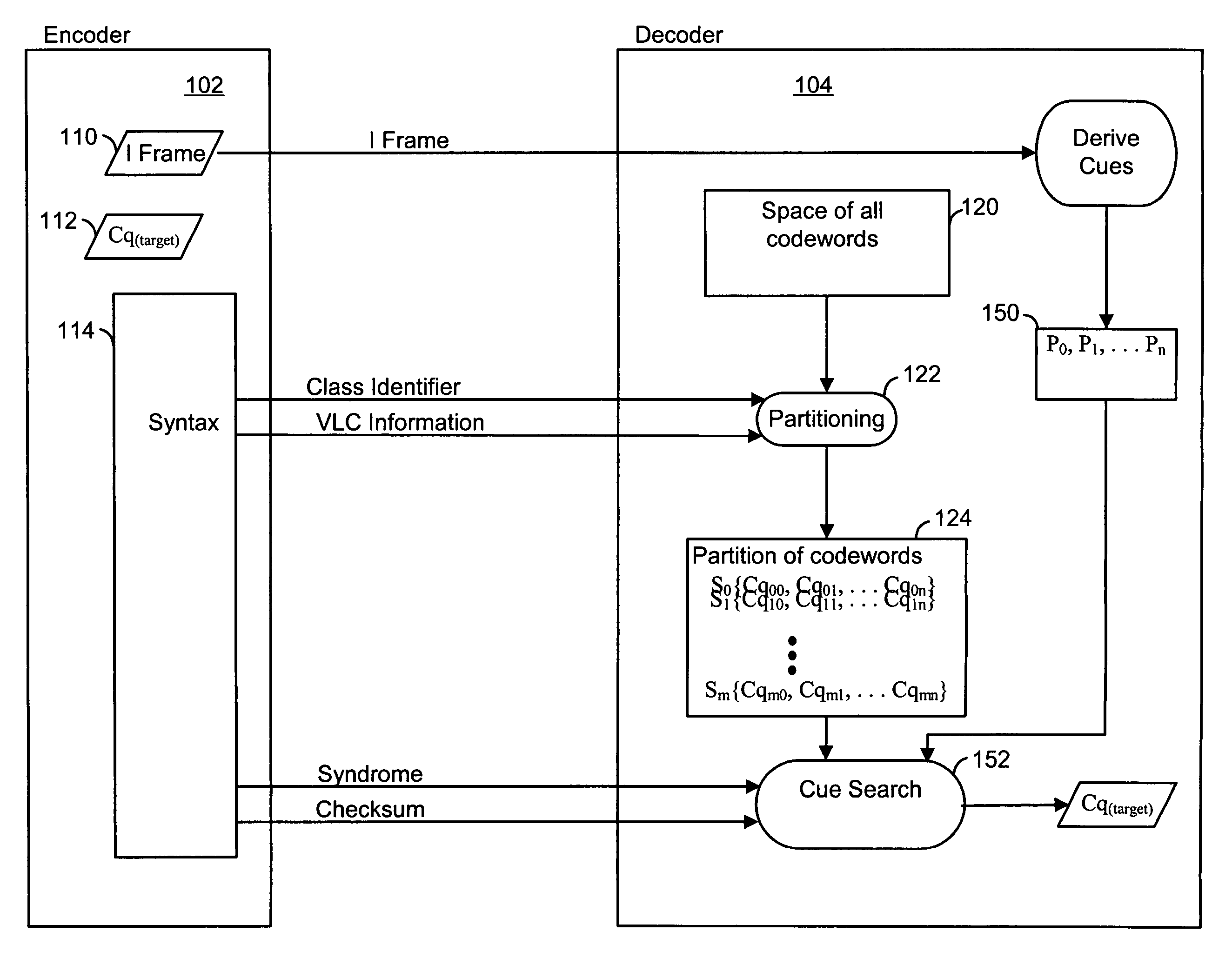
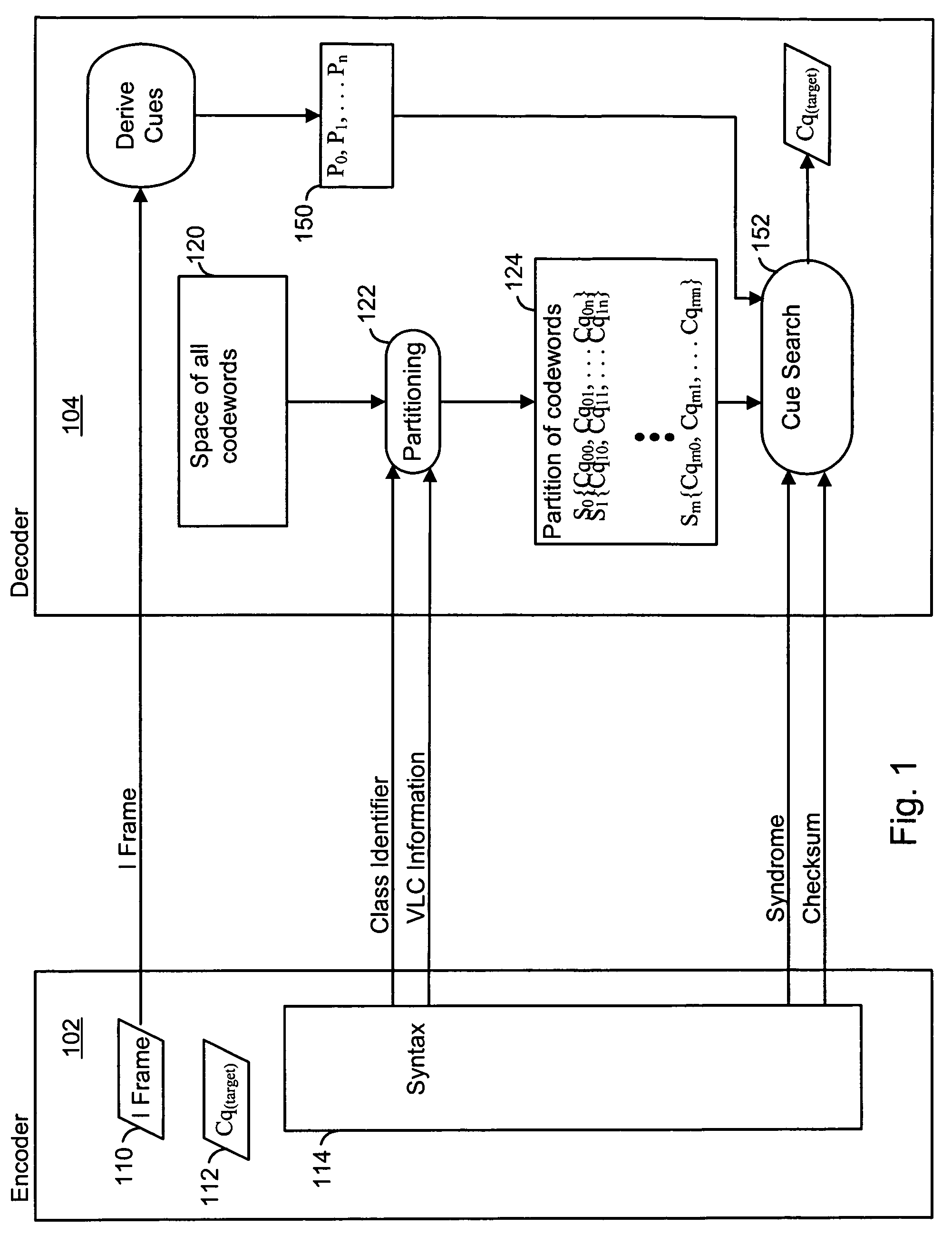
Encoding and decoding of digital data using cues derivable at a decoder
ActiveUS20050031219A1Substantial design leewayReduce complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsDigital dataEncoder decoder
Encoding digital data by using cues at a decoder. An encoder selects an index to indicate a target codeword from the complete space of all codewords to a decoder. The index identifies a group or a set of codewords that contain the target codeword. The sets are represented by a bit-length that is smaller than the code word bit-length thus achieving compression. Two or more codewords in such a set are separated by a predetermined distance and all such sets of codewords considered together form the complete space of all codewords. The encoder sends syntax information, including the index, to specify the decoding. The decoder then uses a set of candidate cues in a comparison operation to determine the target codeword from the indexed set. Processing complexity can be allocated among the encoder, decoder and other possible devices as, for example, in a digital network.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
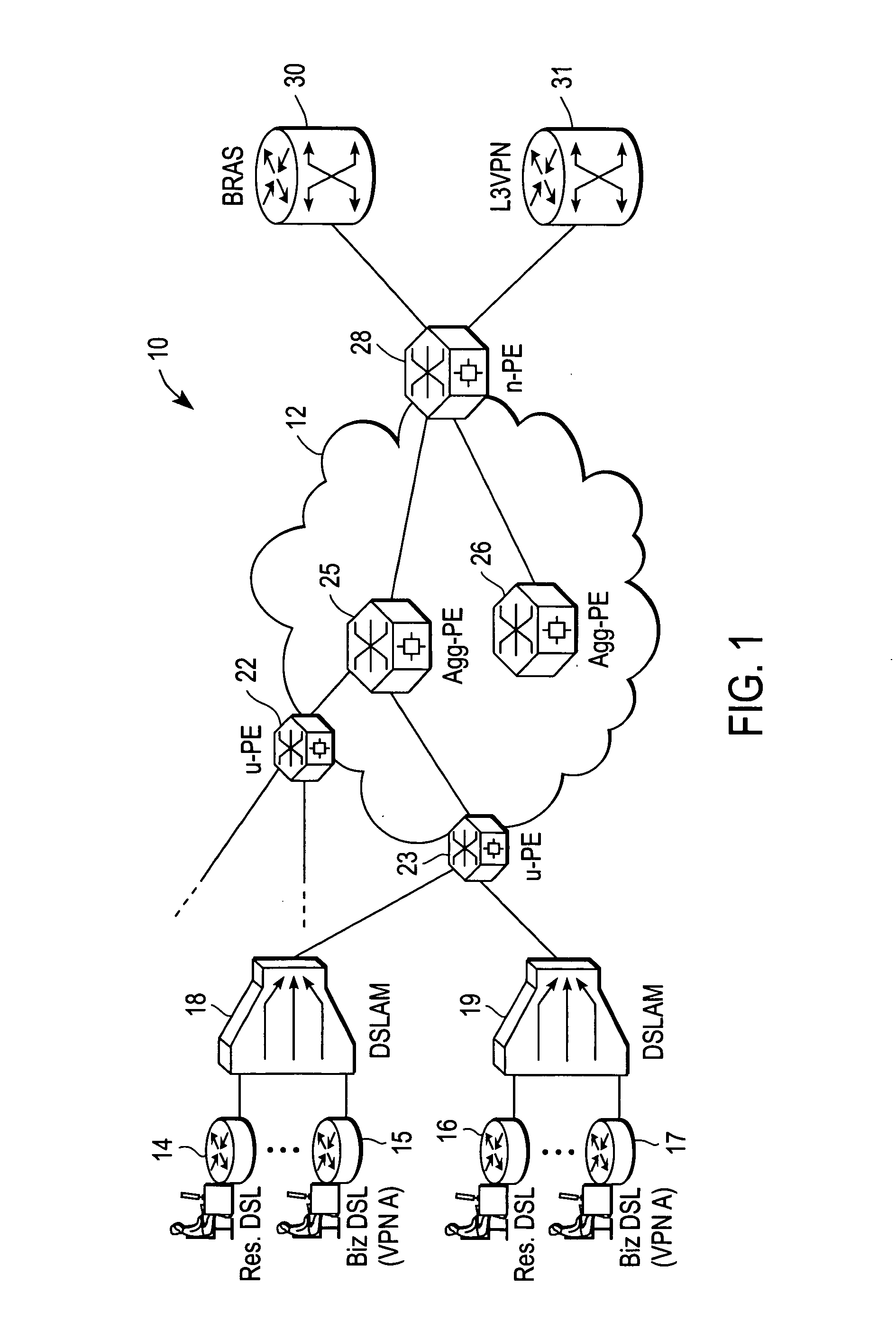
Scalable system and method for DSL subscriber traffic over an Ethernet network
ActiveUS20060245435A1Telephonic communicationData switching by path configurationBit-lengthLocal area network
A system and method for identifying and forwarding traffic to / from Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer (DSLAM) devices and feature servers without ambiguity includes a user-facing provider edge (u-PE) device that receives a customer frame from a DSLAM device, the customer frame being of a first format that includes a first Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) tag of a first bit length. The first VLAN tag identifies a Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) subscriber. The customer frame is re-formatted by the u-PE device such that the first VLAN tag is mapped to a second VLAN tag of a second bit length greater than the first bit length, the second VLAN tag identifying a service instance of the Ethernet access network. The u-PE device encapsulating the customer frame inside a provider frame, with a provider source Media Access Control (MAC) address represents a MAC address associated with the DSLAM, and a provider destination MAC address represents a MAC address of a destination device. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. 37 CFR 1.72(b).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
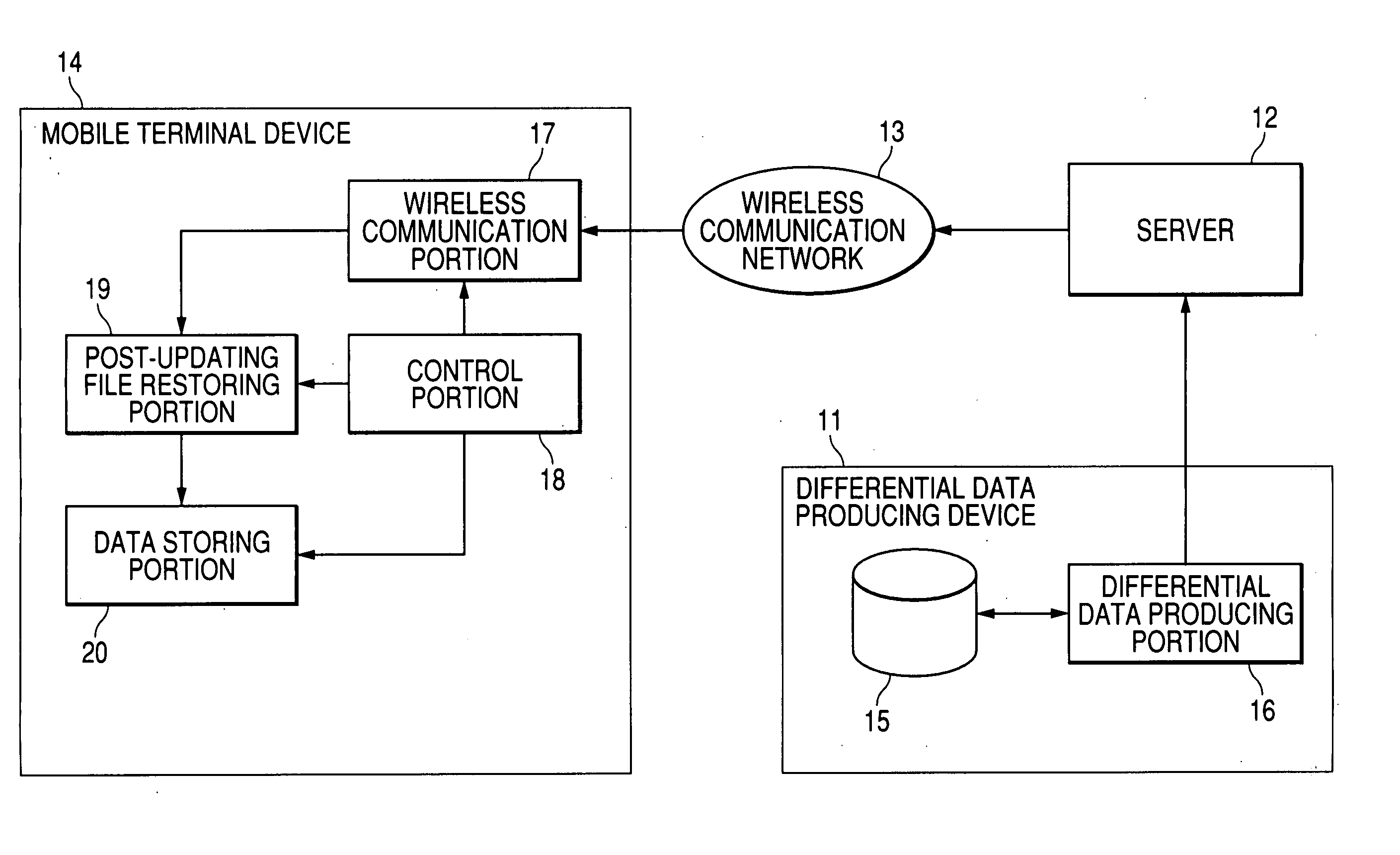
Data update system, differential data creating device and program for data update system, updated file restoring device and program
InactiveUS20060106888A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce dataSoftware engineeringNatural language data processingSystematic differenceData mining
An object of the invention is to reduce the amount of the differential data for use in data updating in a data updating system. At the time of producing differential data, a Move / Add determining unit (35) determines whether to produce Move data indicating a Move instruction to move and copy a matching data string from a pre-updating file to a post-updating file or Add data indicating an Add instruction to add and copy data. At the time, a matching data string search unit (34) searches for a matching data string between the pre-updating file and the post-updating file. If the length of the data string to be copied is not less than five bytes, the data is output from a Move data output unit (36) as Move data, and if the length is not more than four bytes, the data is output from the Add data output unit (37) as Add data. The Move data and the Add data are combined to produce differential data. The Move size and Move address of the Move data are expressed by a variable bit length. In this way, the amount of differential data can be reduced.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Digital signal encoding and decoding device and method
ActiveUS20100142811A1Improve data compression ratioEasy to operateColor television with pulse code modulationImage codingComputer scienceDecision unit
An encoding device includes: a difference generation unit for obtaining a first pixel difference value as a difference value between a first pixel value and a pixel value of a pixel having the same color as the first pixel positioned in the vicinity of the first pixel; a quantization width decision unit for deciding a quantization width in data generation by quantizing the first and the second pixel value according to the number of digits of an unsigned integer binary value of the first pixel difference value and the number of digits of an unsigned integer binary value of the second pixel difference value generated in the difference generation unit for the second pixel value of the second pixel; a quantization width information generation unit for generating quantization width information having a quantization width used for quantization / decoding of the first and the second pixel value; and a quantization unit for generating a first and a second compressed encoded pixel value of n-bit length.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
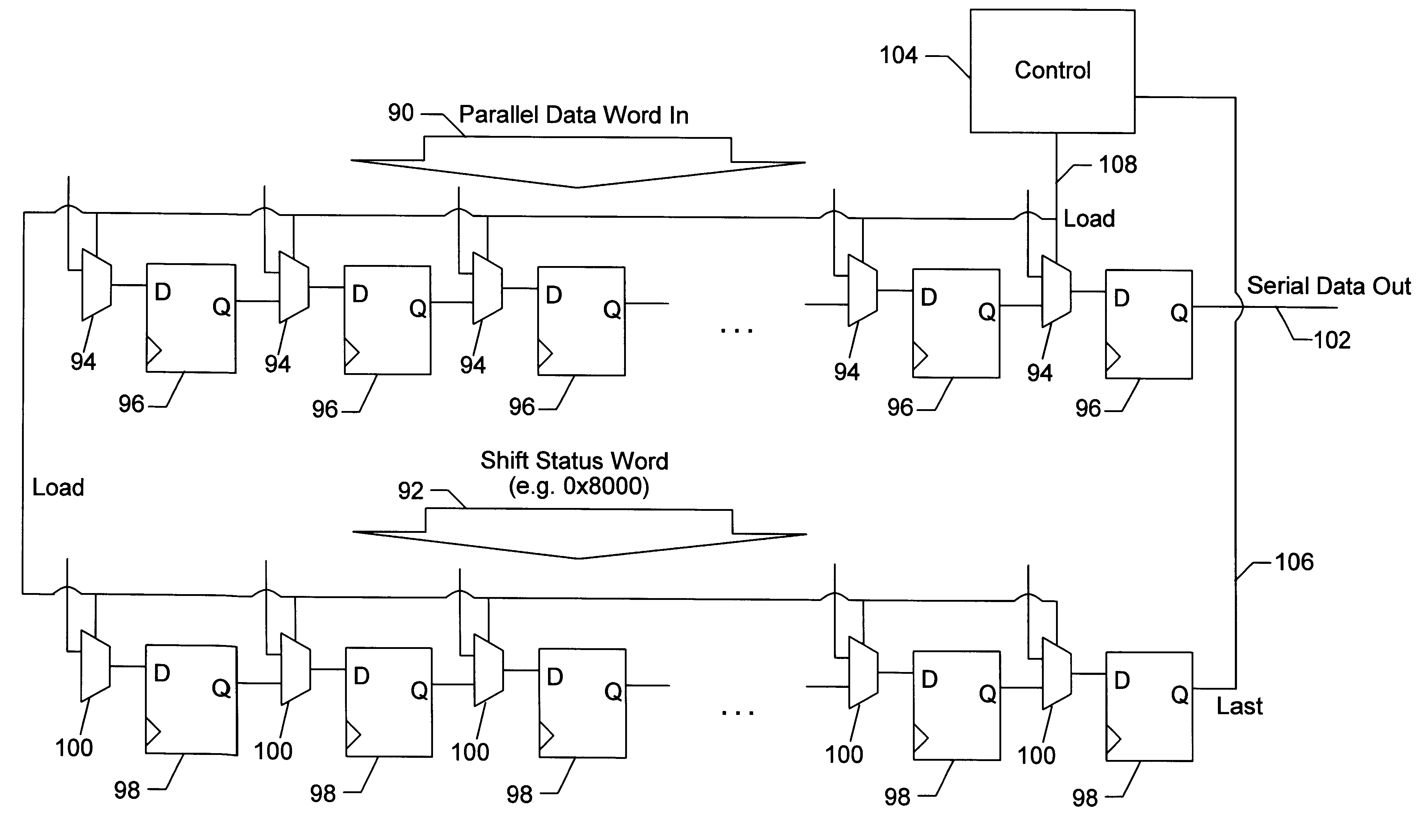
Adjustable serial-to-parallel or parallel-to-serial converter
A clock synchronizer may include two programmable counters, one which may be programmed with a bit-rate value so that it generates a signal approximately matching the bit rate of the asynchronous data signal, and the other programmed with a phase-delay value so that it generates a sample clock signal at a phase delay from the signal generated by the first counter. The phase of the sample clock may be adjusted by restarting the counters in response to a transition on the asynchronous data signal. Data may be supplied to a serial-to-parallel converter including a first shift register configured to shift a data word in serially and output the data word in parallel and a second shift register configured to track when the data word had been completely shifted into the first shift register and to cause the data word to be outputted in parallel from the first shift register so that a new word may be shifted into the first shift register. A status value may be loaded into the second shift register so that when the last bit is converted in the first shift register, the second shift register shifts out a conversion completed indication. The bit length to be converted may be changed by loading a different status value into the second shift register. This same technique may be employed in a parallel-to-serial data converter or in a general data converter that may convert from serial-to-parallel or parallel-to-serial according to a conversion-type signal.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
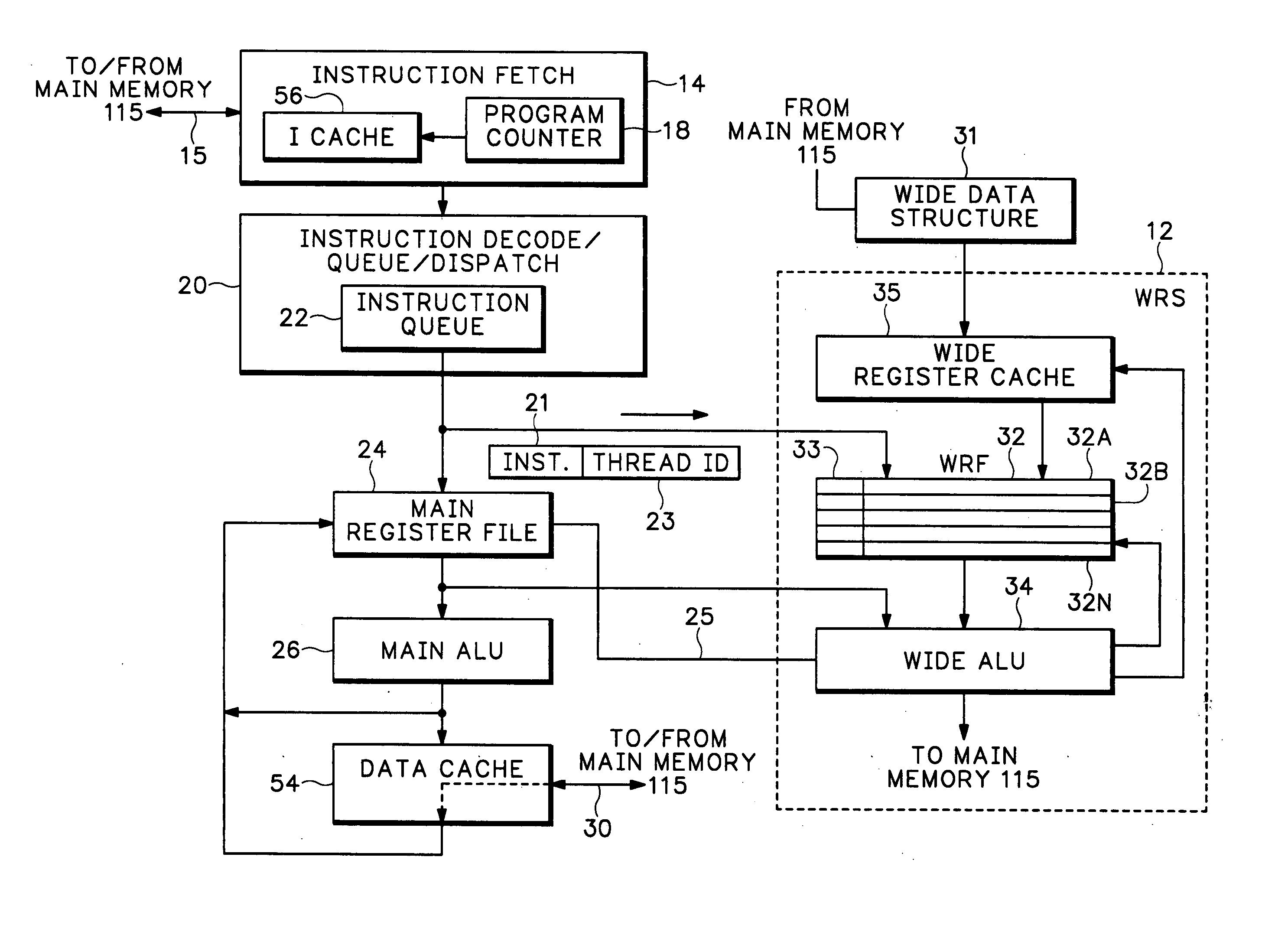
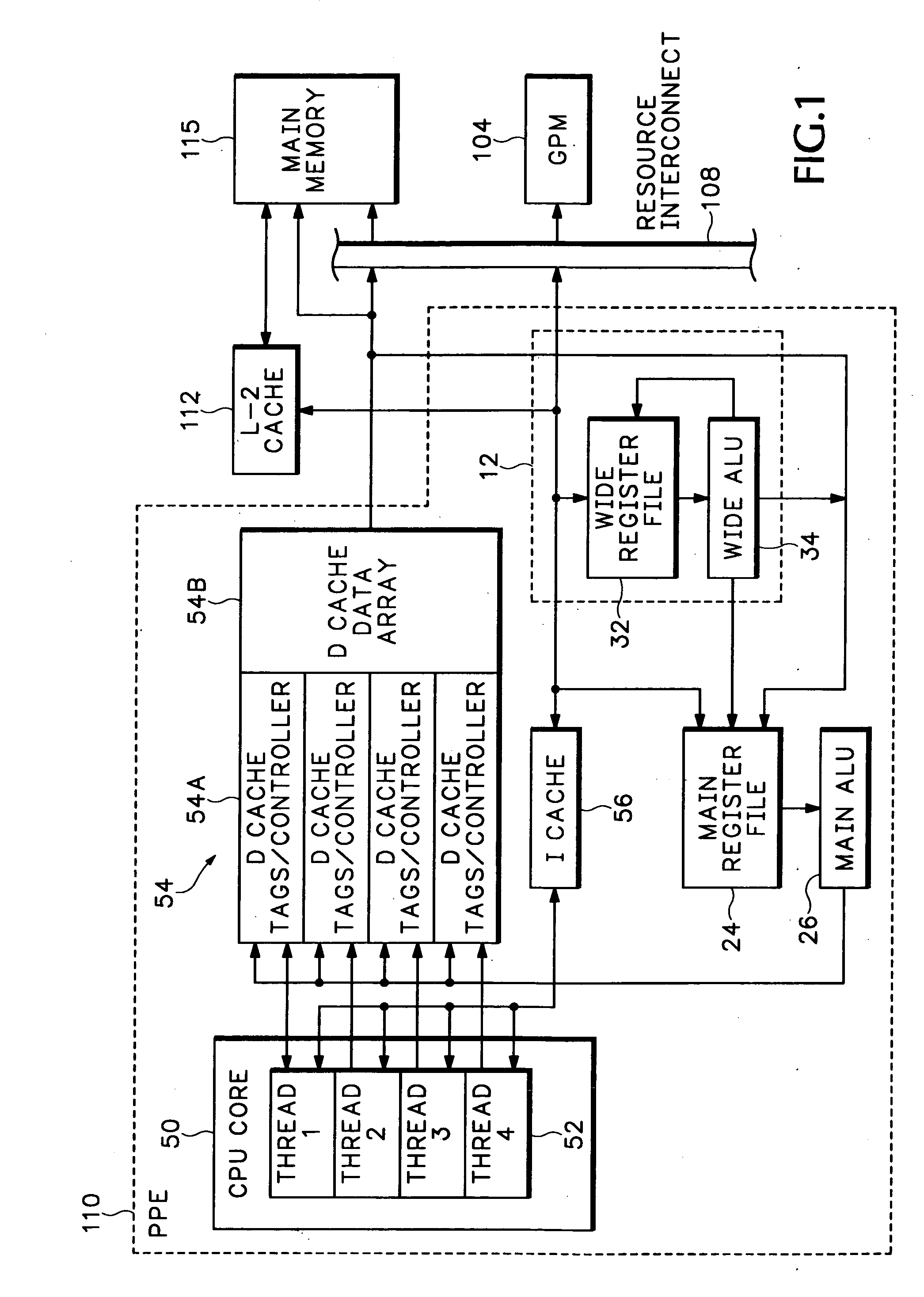
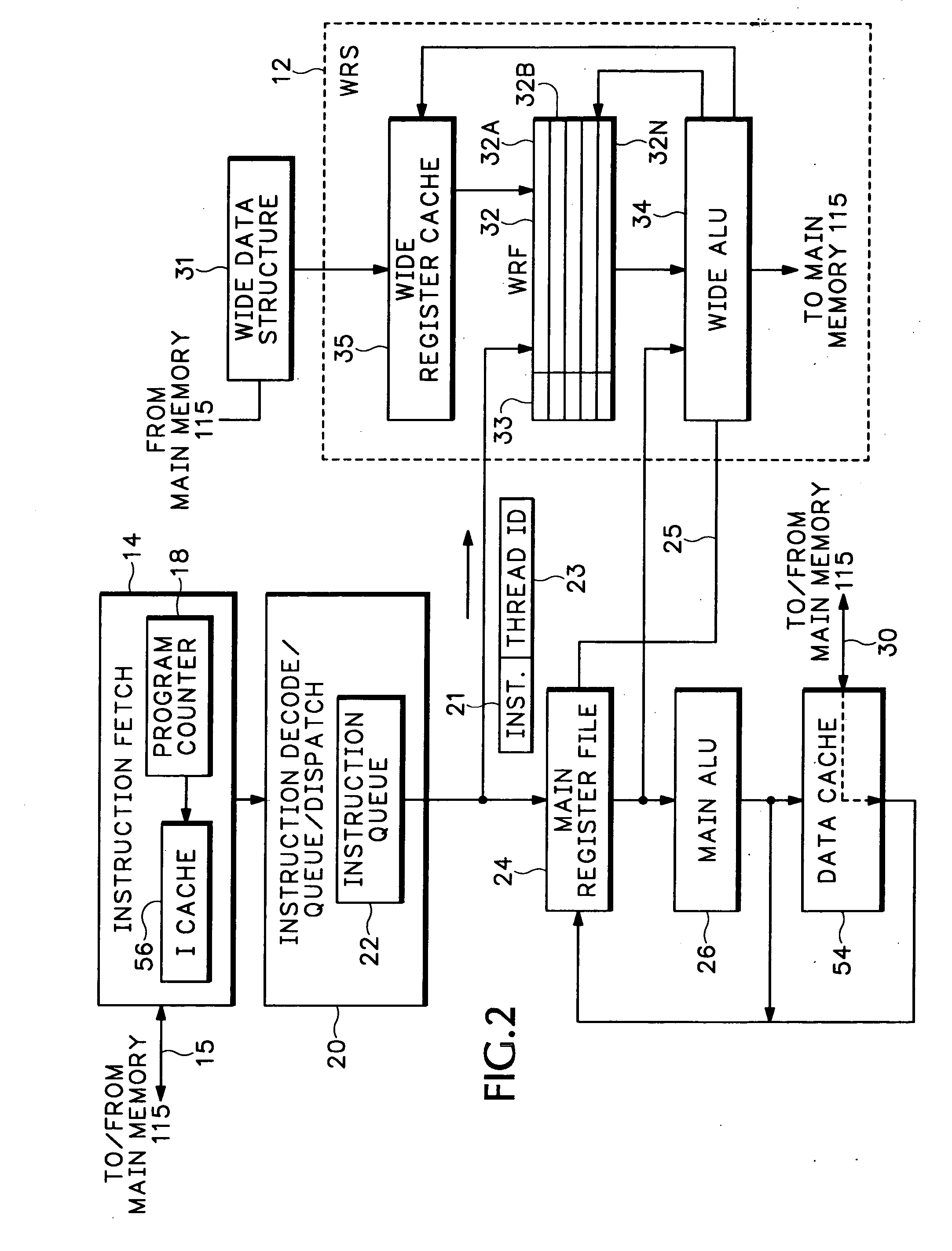
Packet processor with wide register set architecture
InactiveUS20060200647A1Improve performanceWider bitRegister arrangementsGeneral purpose stored program computerData packLogic cell
A Wide Register Set (WRS) is used in a packet processor to increase performance for certain packet processing operations. The registers in the WRS have wider bit lengths than the main registers used for primary packet processing operations. A wide logic unit is configured to conduct logic operations on the wide register set and in one implementation includes hardware primitives specifically configured for packet scheduling operations. A special interlocking mechanism is additionally used to coordinate accesses among multiple processors or threads to the same wide register address locations. The WRS produces a scheduling engine that is much cheaper than previous hardware solutions with higher performance than previous software solutions. The WRS provides a small, compact, flexible, and scalable scheduling sub-system and can tolerate long memory latencies by using cheaper memory while sharing memory with other uses. The result is a new packet processing architecture that has a wide range of cost / performance points, based on desired scheduling requirements.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Variable register and immediate field encoding in an instruction set architecture
ActiveUS20100287359A1Suppresses increase in code sizeSpecific costInstruction analysisDigital computer detailsOperation modeApplication software
A method and apparatus provide means for compressing instruction code size. An Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) encodes instructions compact, usual or extended bit lengths. Commonly used instructions are encoded having both compact and usual bit lengths, with compact or usual bit length instructions chosen based on power, performance or code size requirements. Instructions of the ISA can be used in both privileged and non-privileged operating modes of a microprocessor. The instruction encodings can be used interchangeably in software applications. Instructions from the ISA may be executed on any programmable device enabled for the ISA, including a single instruction set architecture processor or a multi-instruction set architecture processor.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
Indication method for scheduling authorization resource in long-term developing TDD system
ActiveCN101330372AReduce overheadMeet the requirements of frequency selective transmissionDuplex signal operationTime-division multiplexing usageResource blockAuthorization
The invention provides an indication method of dispatching authorized resources in a time division duplex system of long term evolution. A base station generates and sends dispatch and authorization information containing the position indication of authorized resource to a terminal. The indication method is characterized in that the position indication of authorized resource comprises resource block range and sub-frame information; and the sub-frame information comprises a sub-frame position or the initial position and the duration of the sub-frame; the total bit length of the sub-frame information is the same as the bit length of the duration in the long term evolution frequency division duplex system authorized resource position indication. The indication method utilizes a RB initial position, a RB final position and the sub-frame information to indicate the uplink or the downlink position of the dispatched and authorized resource, thereby acquiring lower authorization indication signaling overhead, enabling the authorization indication signaling forms of two systems of LET TDD and LTE FDD to be consistent, and meeting the requirement of the system for frequency selective transmission.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Pilot signals for synchronization and/or channel estimation
InactiveUS6804264B1Transmission control/equlisationBaseband system detailsMobile communication systemsComputer science
Disclosed is a method of generating pilot sequences having double lengths of slots used for frame synchronization in an up or down link of a next generation mobile communication system which adopts W-CDMA mode. Disclosed is a method of generating pilot sequences having double lengths of slots used for frame synchronization and defined by 4l+2(l=1,2,3, . . . ) while providing a mathematical method of generating code sequences of slot length. The method of generating pilot sequences having double lengths of slots used for frame synchronization includes the steps of selecting a bit length of pilot sequences used for frame synchronization, selecting a first code sequence indicative of a maximum correlation value at a specific delay point of a correlation period and indicative of a minimum correlation value at the other delay points excluding the specific delay point, selecting a second code sequence indicative of the same correlation characteristic as the selected code sequence, and combining the selected code sequences to generate pilot sequences having the selected bit length.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Digital signatures including identity-based aggregate signatures
ActiveUS20050262353A1Good security proofUser identity/authority verificationSecret communicationDigital signatureKey generator
Methods and systems are provided that allow multiple identity-based digital signatures to be merged into a single identity-based “aggregate” digital signature. This identity-based aggregate signature has a shorter bit-length than the concatenation of the original unaggregated identity-based signatures. The identity-based aggregate signature can be verified by anyone who obtains the public keys of one or more Private Key Generators (PKGs), along with a description of which signer signed which message. The verifier does not need to obtain a different public key for each signer, since the signature scheme is “identity-based”; the number of PKGs may be fewer than the number of signers. Consequently, the total information needed to verify the identity-based aggregate signature—namely, a description of who signed what, the PKGs' public keys, and the identity-based aggregate signature itself—may be less than the information needed to verify separate digital signatures—namely, a description of who signed what, the public verification keys for all of the signers, and the concatenation of the signers' signatures. In some embodiments, the identity-based aggregate signature scheme has essentially the minimum-possible Kolmogorov complexity.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Wireless communication system
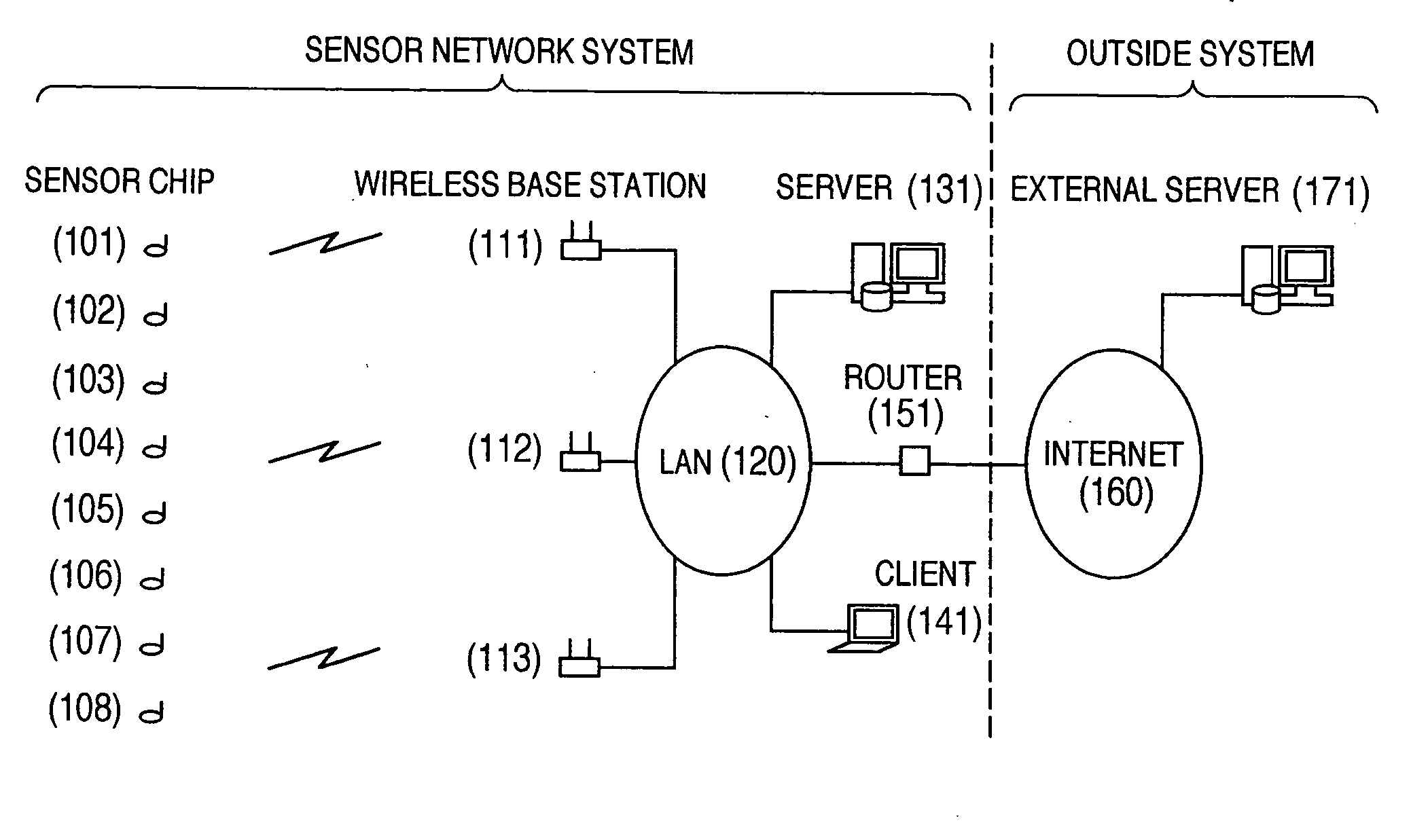
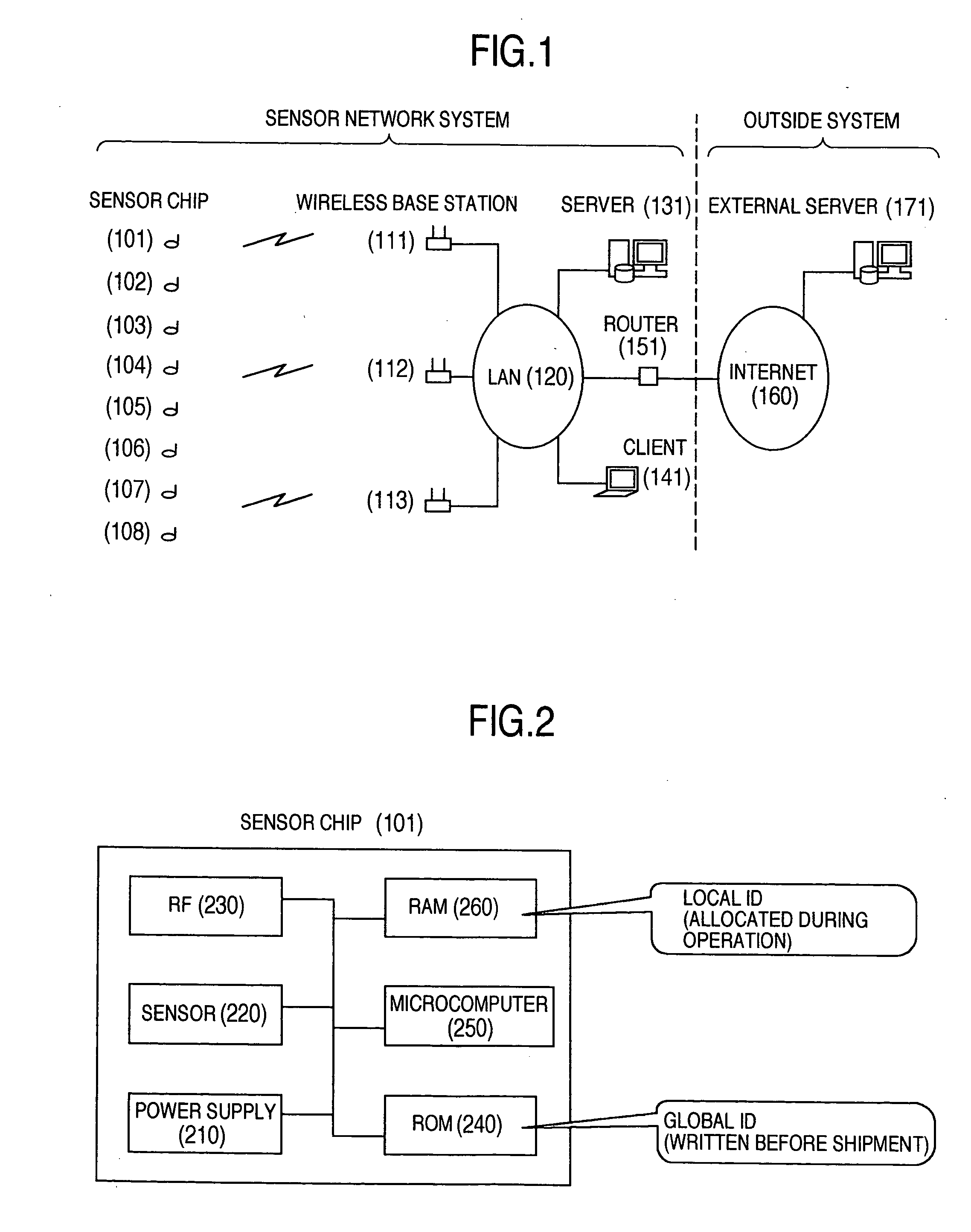
InactiveUS20060039316A1Easy to changeReduce communicationMultiplex system selection arrangementsPower managementCommunications systemBit-length
In a wireless communication system, a utilization of a global ID having a long bit length, which is useful for linking with an external system, is compatible with a reduction of a communication amount of a wireless terminal. The wireless terminal transmits the global ID only when the wireless terminal is initially registered, and after a local ID having a short bit length is allocated by a server to the wireless terminal, this wireless terminal uses one the local ID. While the server manages a corresponding relationship between the global ID and the local ID, the server uses the global ID in order to identify the wireless terminal in a communication made outside the system.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com