Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
156results about How to "Layer is high" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
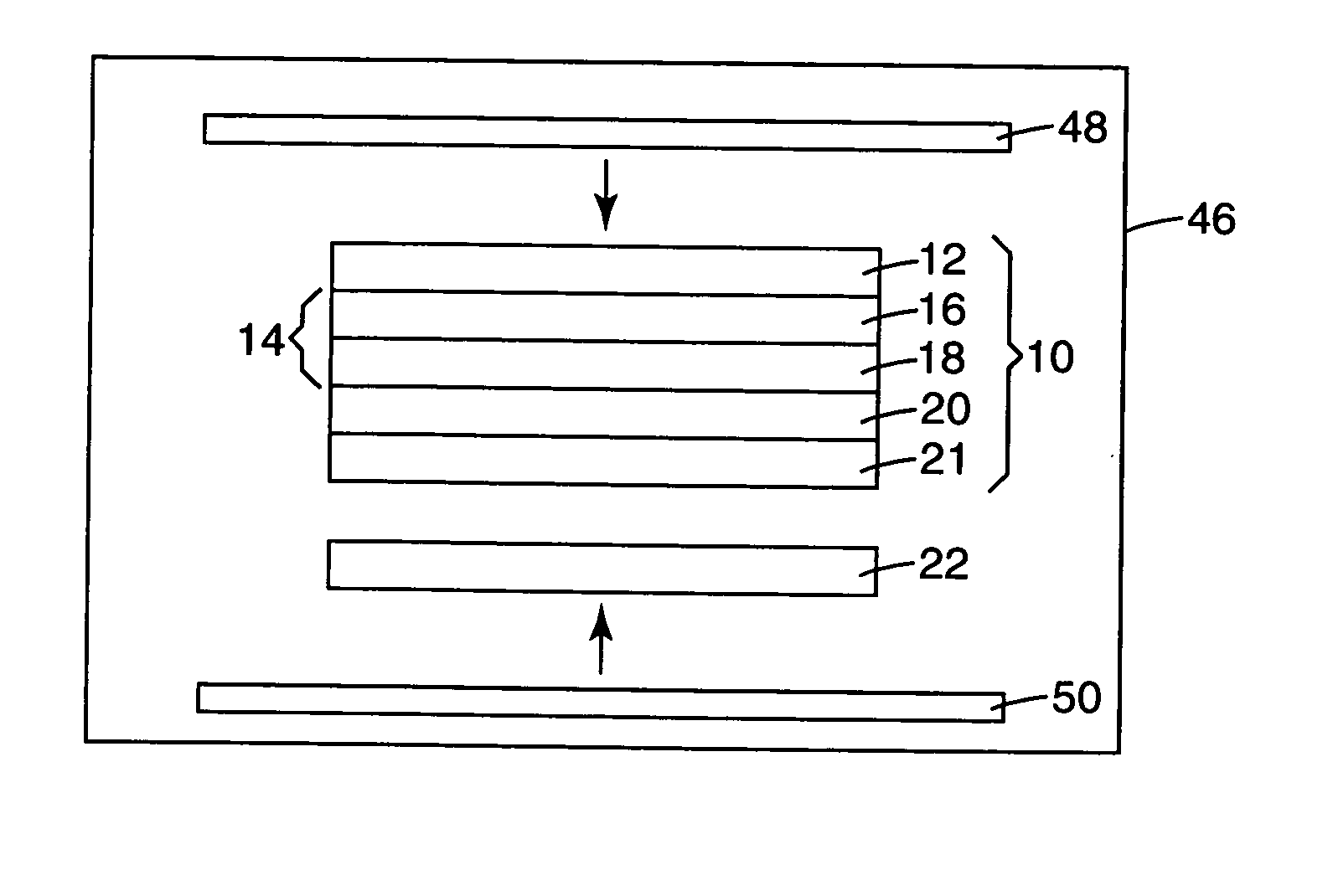
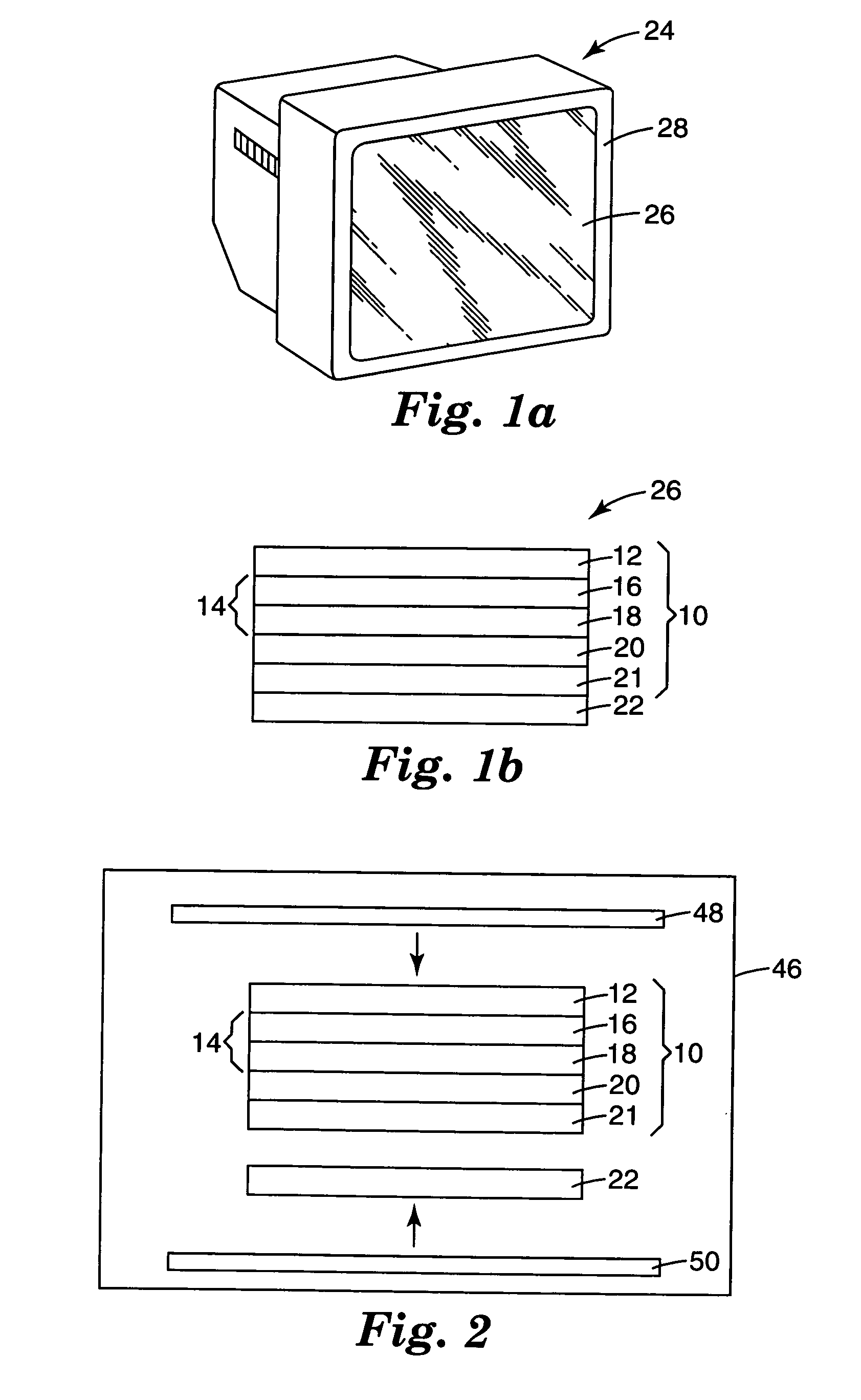
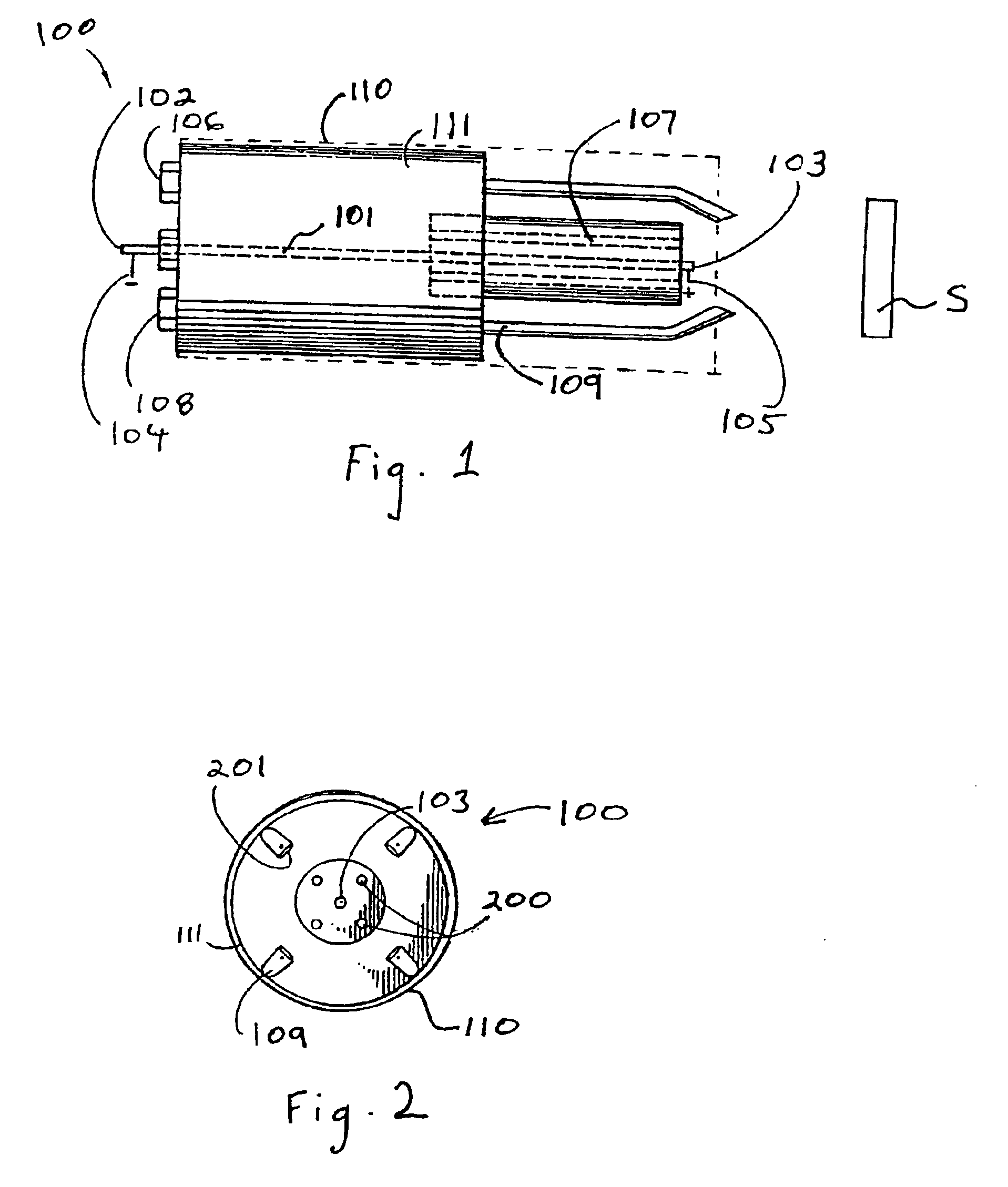
Semiconductor layer manufacturing method, semiconductor layer manufacturing apparatus, and semiconductor device manufactured using such method and apparatus
InactiveUS20100024872A1Quality improvementImprove batch productivityLiquid surface applicatorsFinal product manufactureHermetic sealManufactured apparatus
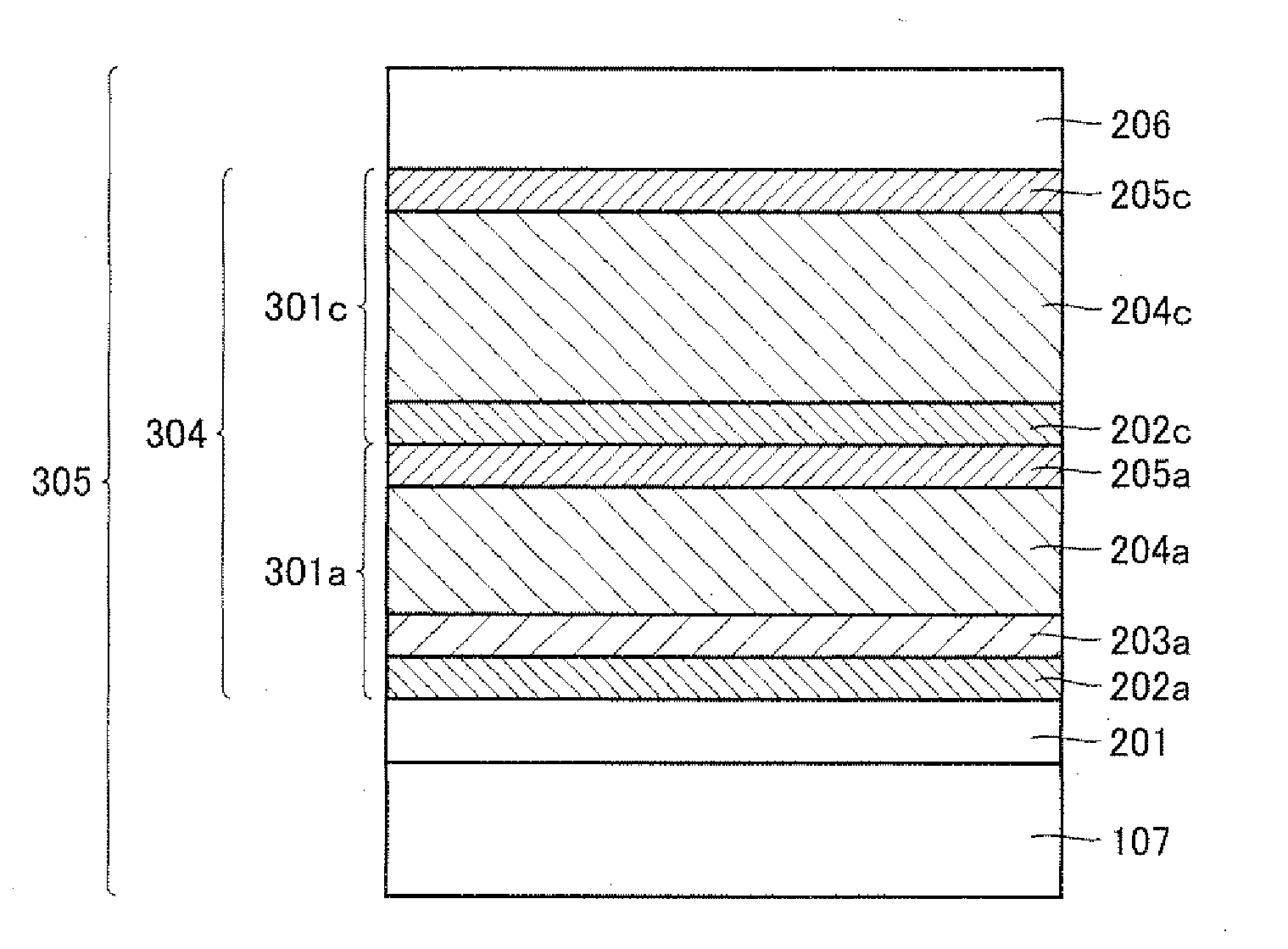
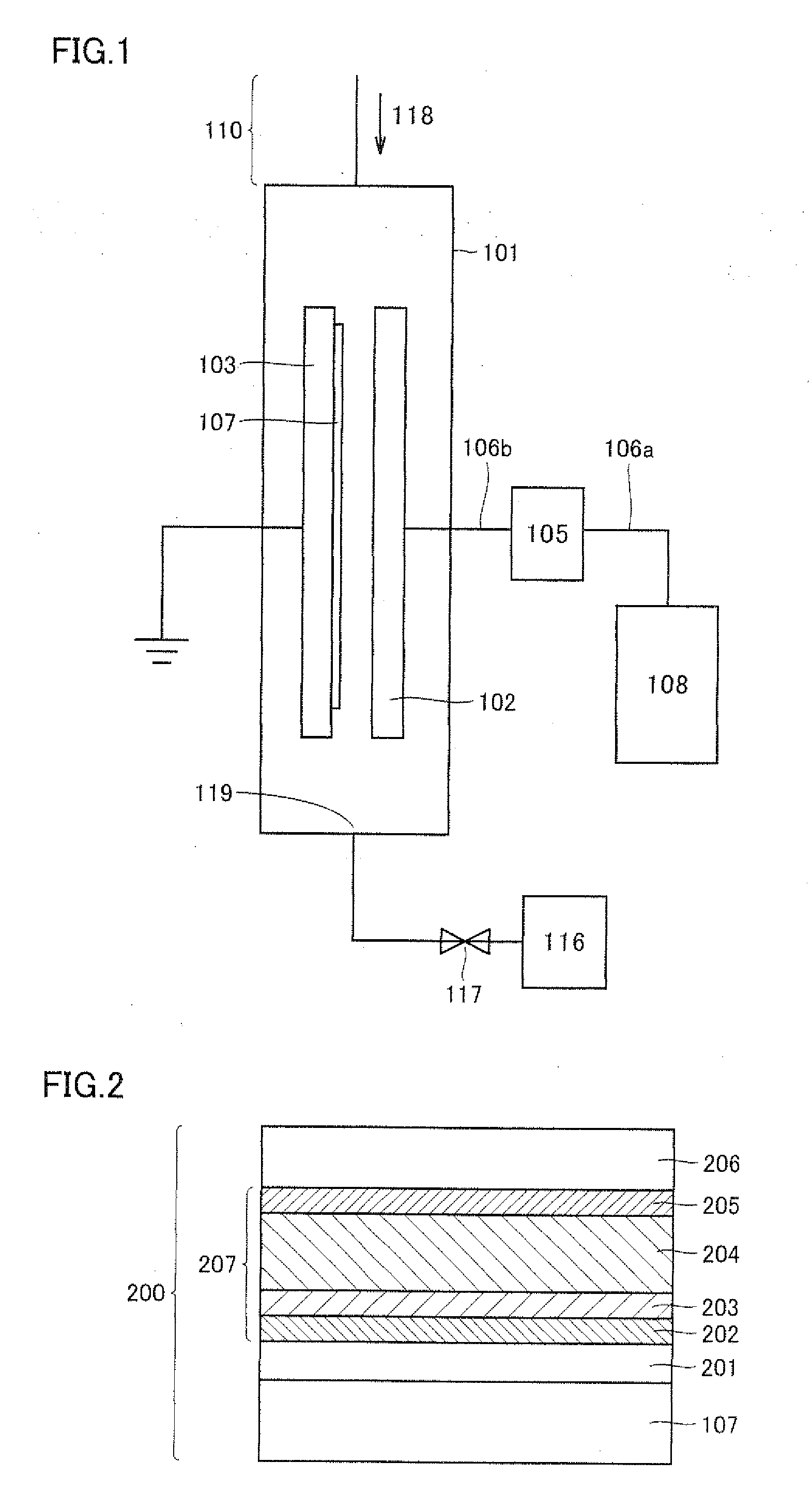
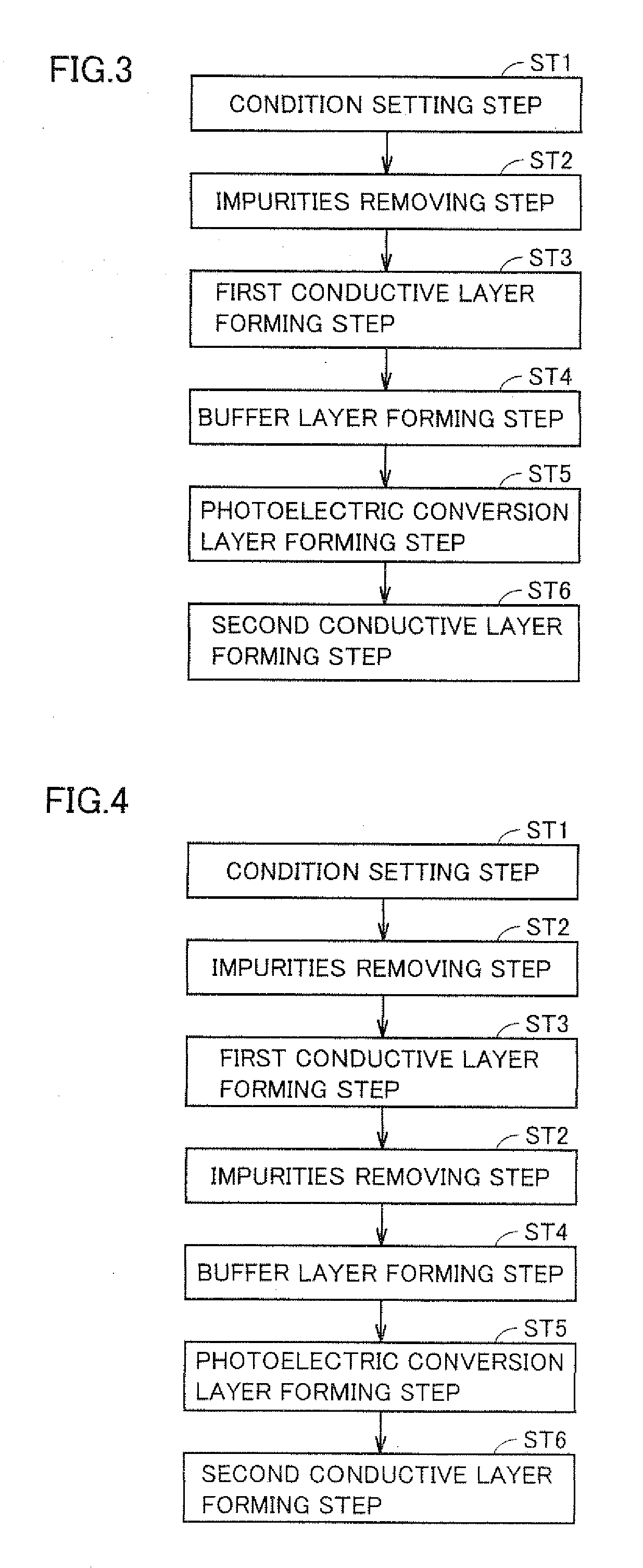
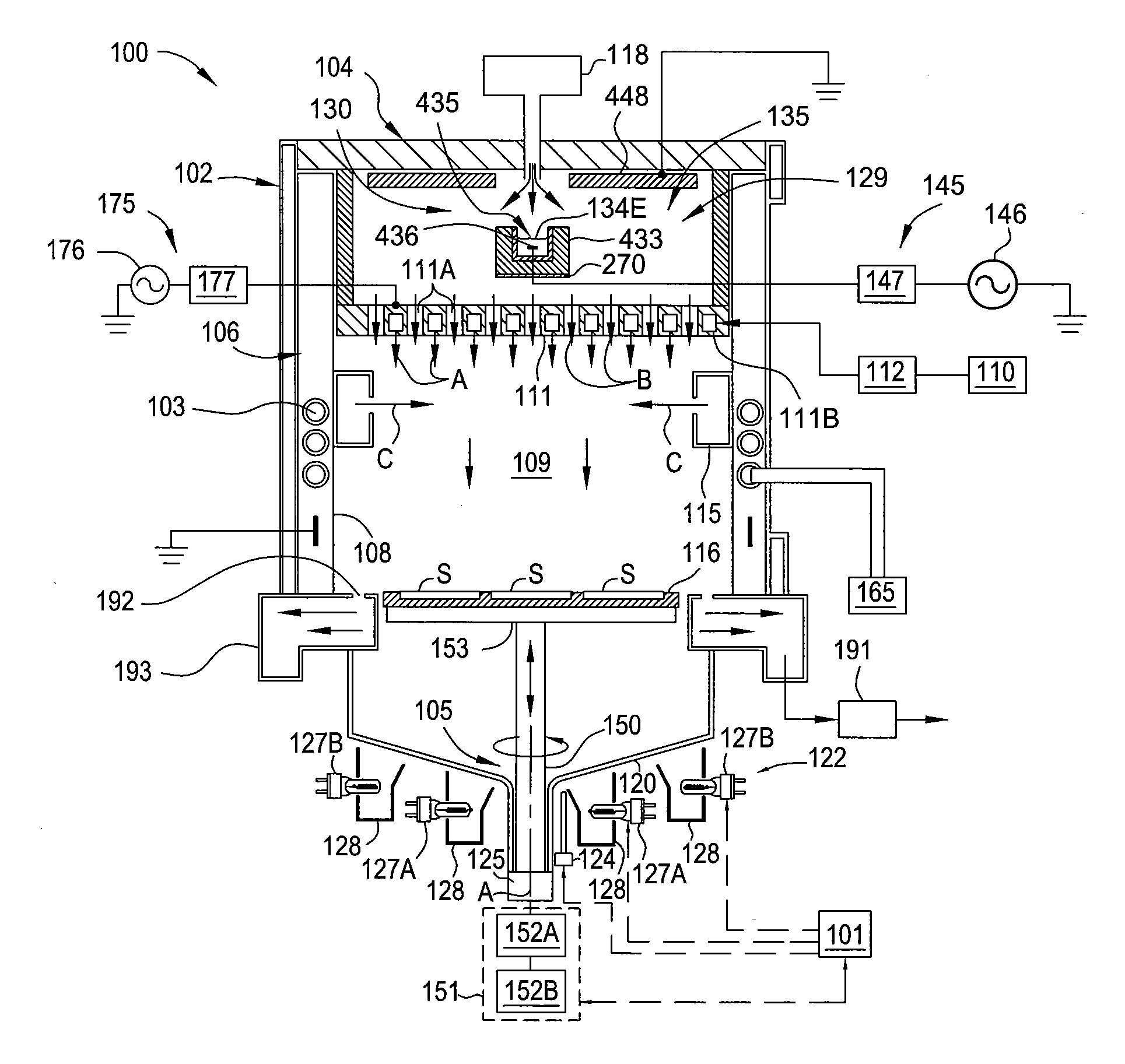
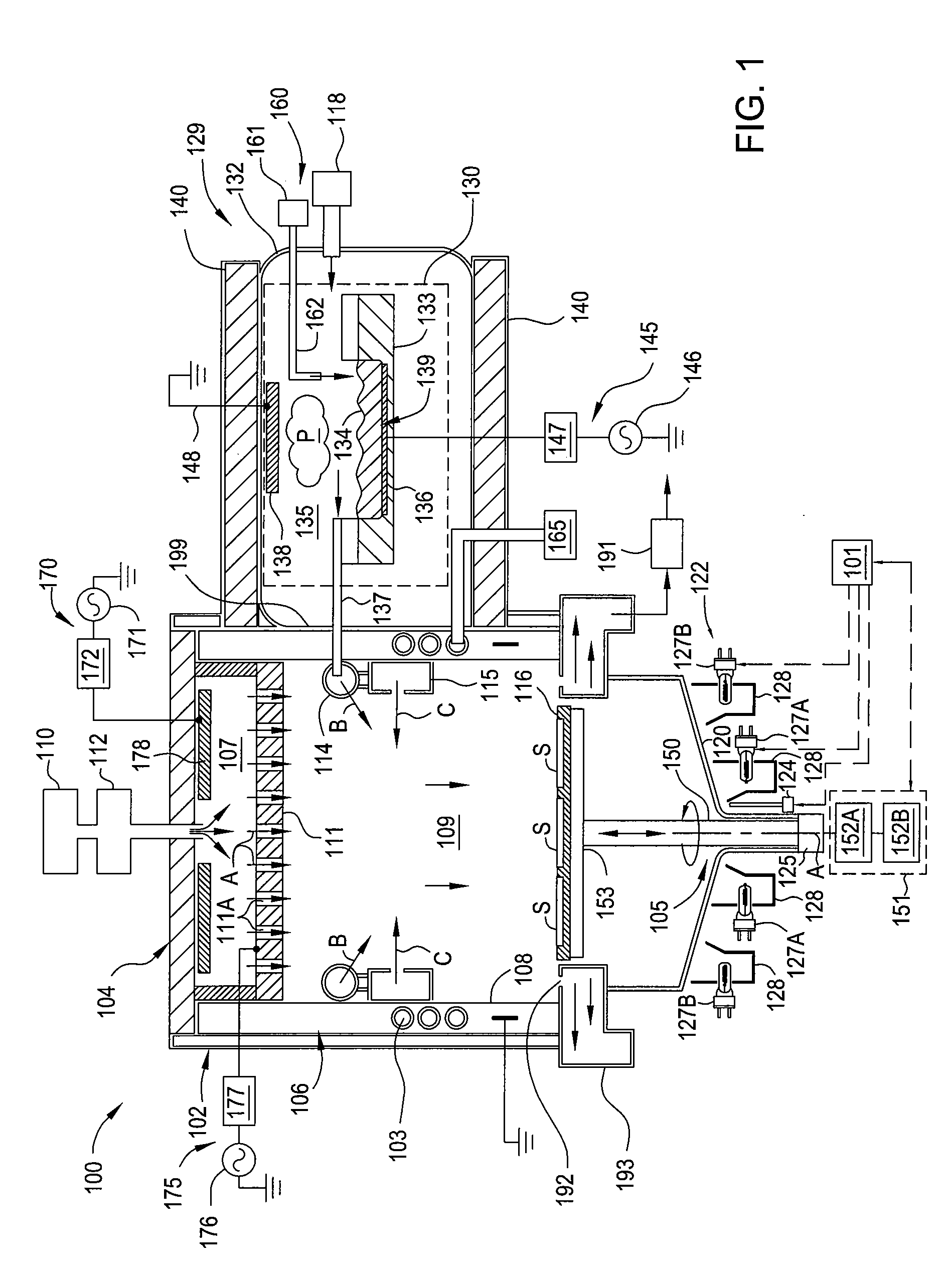
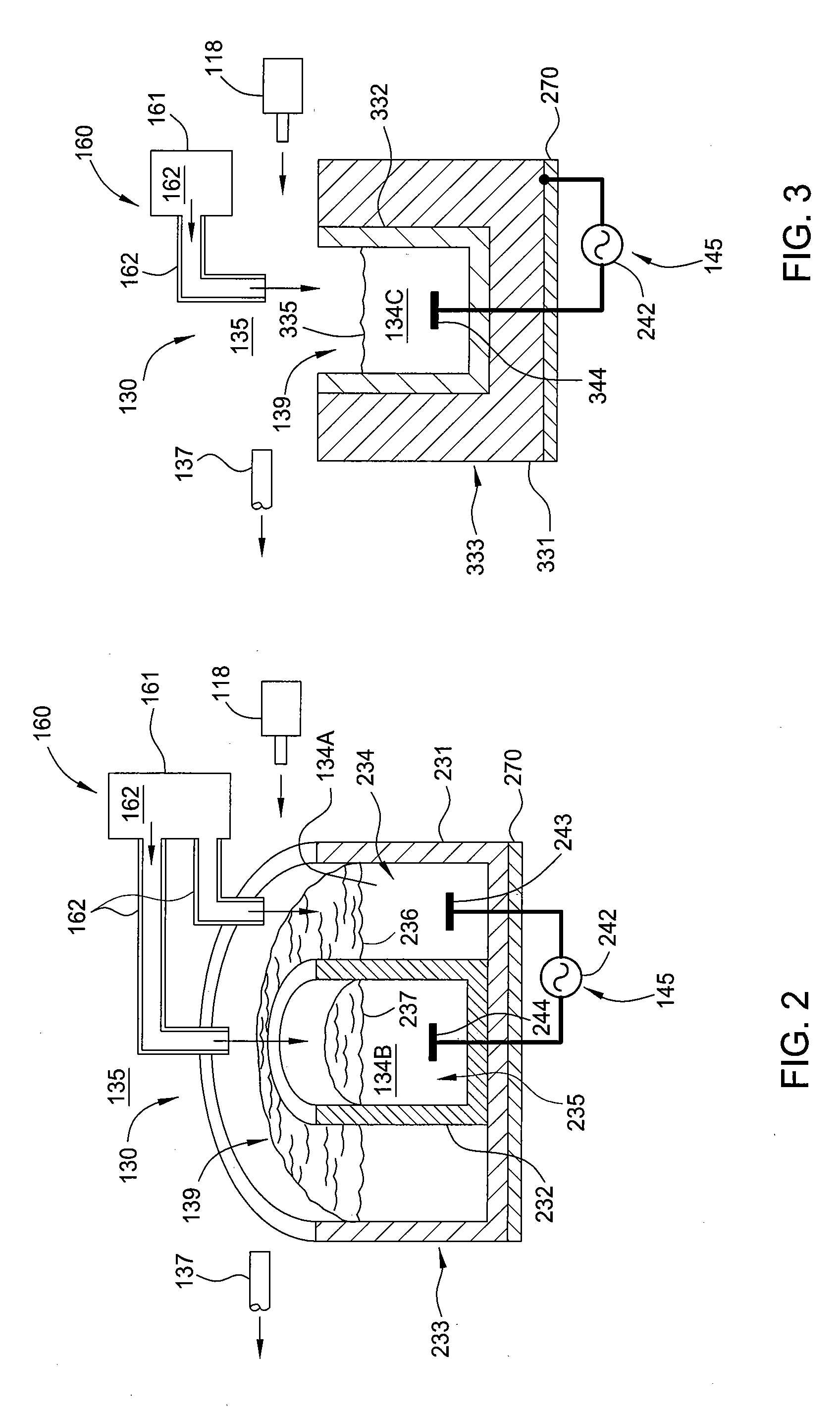
Provided are a semiconductor layer manufacturing method and a semiconductor manufacturing apparatus capable of forming a high quality semiconductor layer even by a single chamber system, with a shortened process time required for reducing a concentration of impurities that exist in a reaction chamber before forming the semiconductor layer. A semiconductor device manufactured using such a method and apparatus is also provided. The present invention relates to a semiconductor layer manufacturing method of forming a semiconductor layer inside a reaction chamber (101) capable of being hermetically sealed, including an impurities removing step of removing impurities inside the reaction chamber (101) using a replacement gas, and a semiconductor layer forming step of forming the semiconductor layer, the impurities removing step being a step in which a cycle composed of a replacement gas introducing step of introducing the replacement gas into the reaction chamber (101) and an exhausting step of exhausting the replacement gas is repeated a plurality of times, the impurities removing step being performed at least before the semiconductor layer forming step.
Owner:SHARP KK
Plasma assisted hvpe chamber design
InactiveUS20130032085A1Enhance deposition reaction kineticsReduce processing timePolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesNitrogenVapor phase
Embodiments of the invention disclosed herein generally relate to a hydride vapor phase epitaxy (HVPE) deposition chamber that utilizes a plasma generation apparatus to form an activated precursor gas that is used to rapidly form a high quality compound nitride layer on a surface of a substrate. In one embodiment, the plasma generation apparatus is used to create a desirable group-III metal halide precursor gas that can enhance the deposition reaction kinetics, and thus reduce the processing time and improve the film quality of a formed group-III metal nitride layer. In addition, the chamber may be equipped with a separate nitrogen containing precursor activated species generator to enhance the activity of the delivered nitrogen precursor gases.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Data exchange between users connected by a bus system and having separate time bases
InactiveUS6842808B2Accurate synchronizationGreat tolerance of accuracyProgramme controlError detection/correctionTime informationData exchange
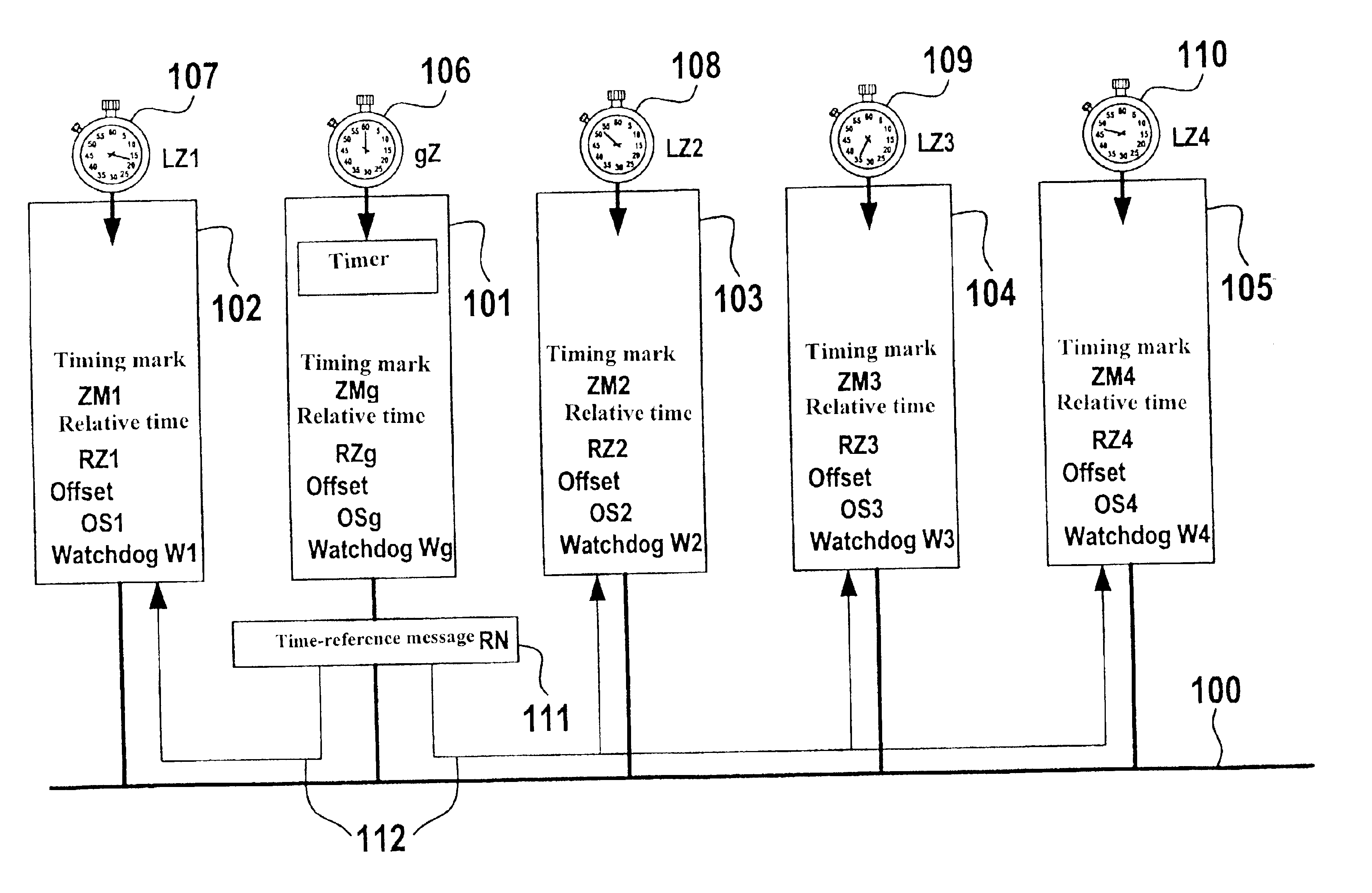
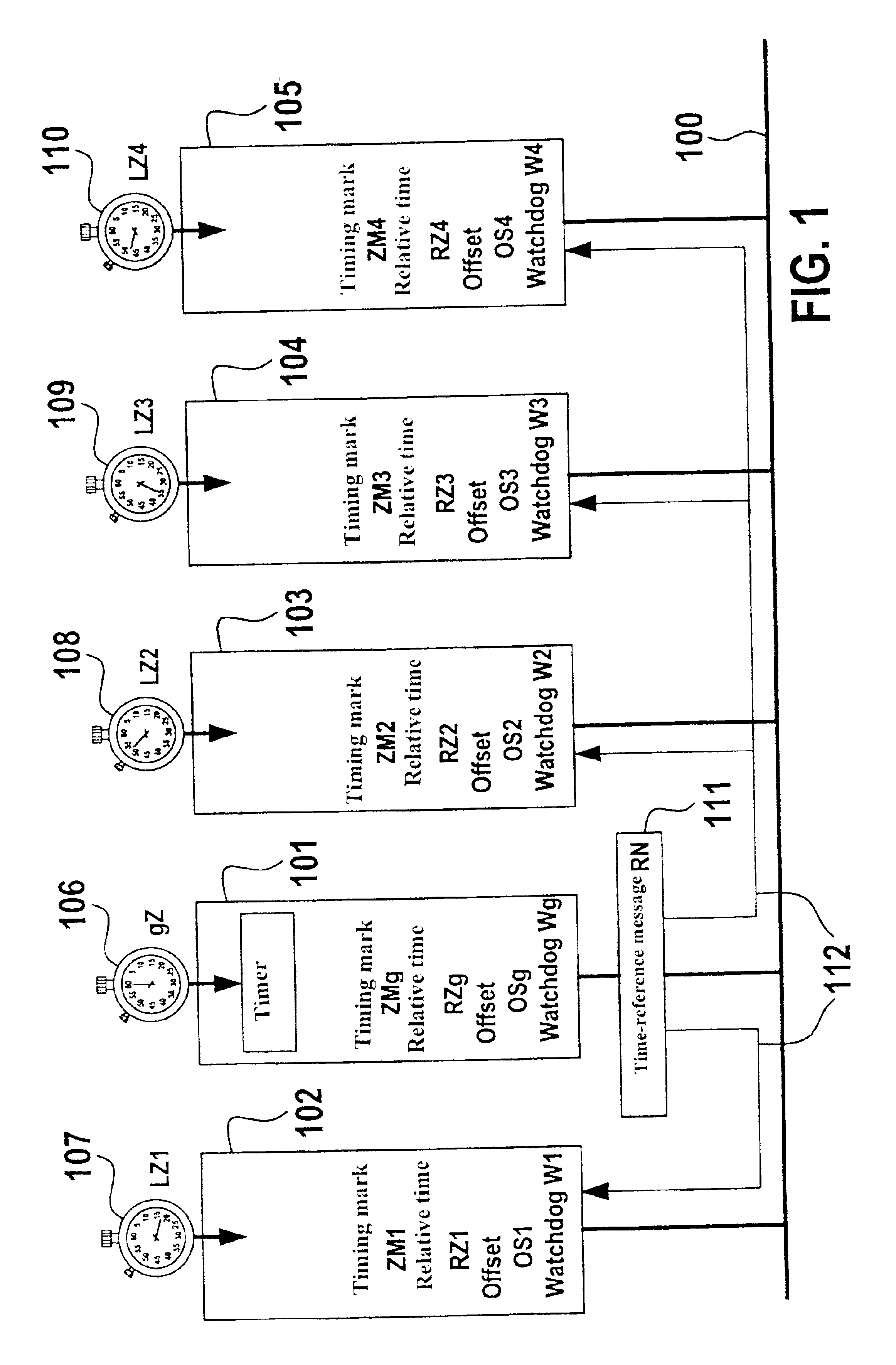
A method and device for the exchange of data in messages between at least two users which are connected by a bus system and have separate time bases, the messages containing the data being transmitted by the users via the bus system; and a first user, in a function as timer, controls the messages as a function of time in such a way that it repeatedly transmits a reference message, which contains time information regarding the time base of the first user, via the bus at a specifiable time interval; the at least second user forms its own time information, using its time base, as a function of the time information of the first user; a correction value is ascertained from the two pieces of time information; and the second user adapts its time information and / or its time base as a function of the correction value.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
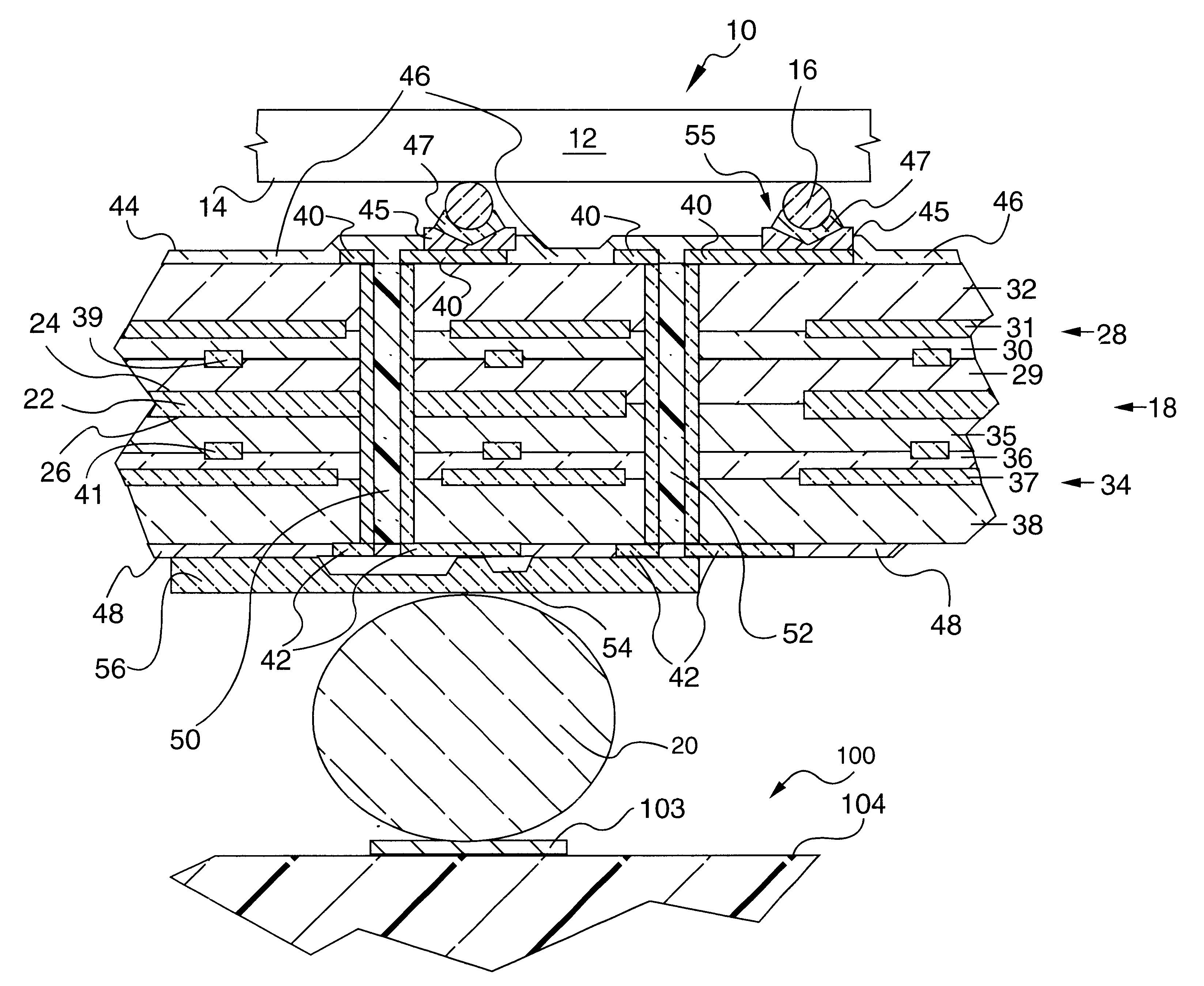
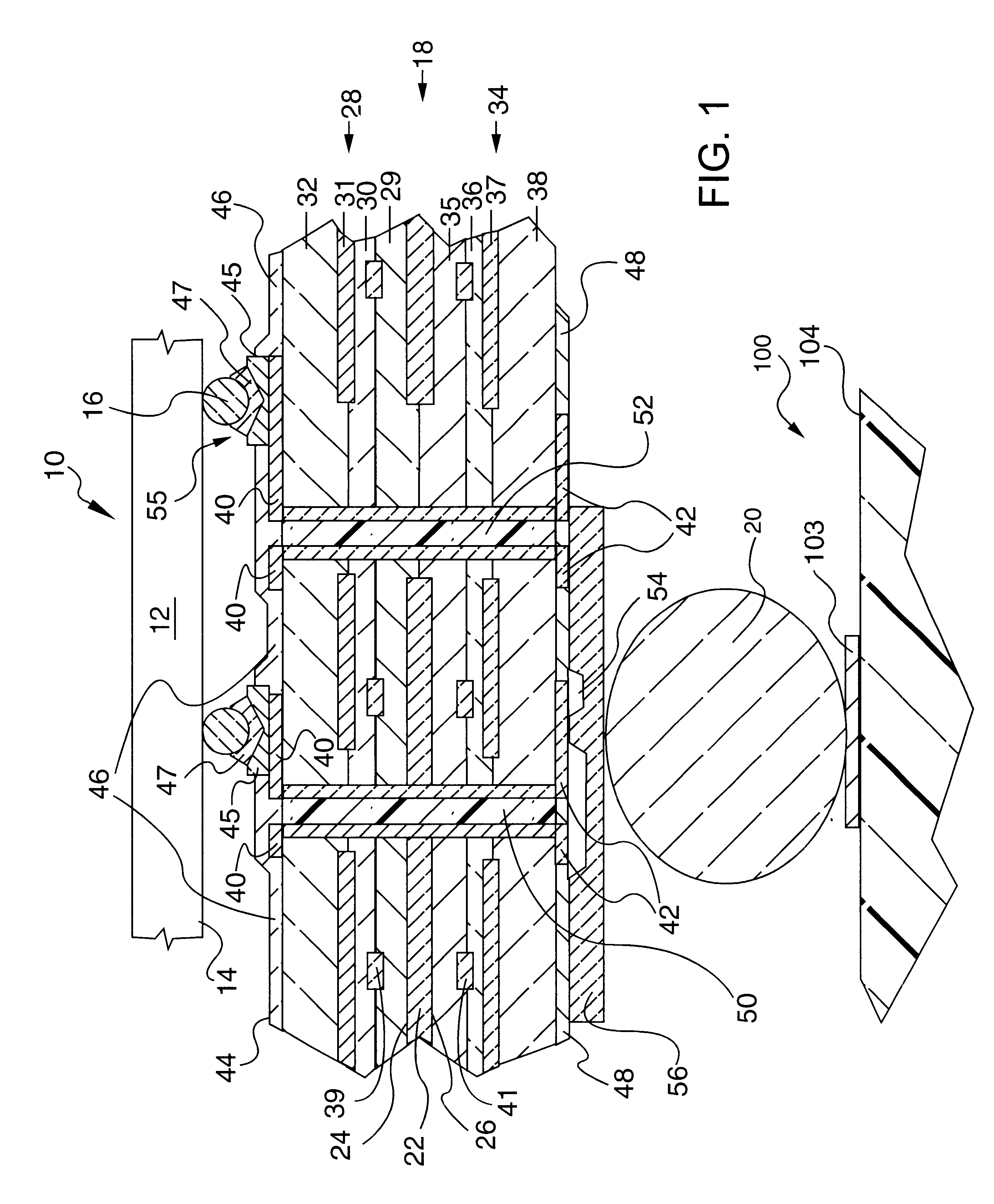
Electronic package with high density interconnect layer
InactiveUS6373717B1High densityFacilitates subsequent depositionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsHigh densitySurface layer
An electronic package, and method of making the electronic package, is provided. The package includes a semiconductor chip and an multi-layered interconnect structure having a high density interconnect layer such as an allylated surface layer. The semiconductor chip includes a plurality of contact members on one of its surfaces that are connected to the multi-layered interconnect structure by a plurality of solder connections. The multi-layered interconnect structure is adapted for electrically interconnecting the semiconductor chip to a circuitized substrate (eg., circuit board) with another plurality of solder connections and includes a thermally conductive layer being comprised of a material having a selected thickness and coefficient of thermal expansion to substantially prevent failure of the solder connections between said first plurality of electrically conductive members and the semiconductor chip. The electronic package further includes a dielectric material having an effective modulus to assure sufficient compliancy of the multi-layered interconnect structure during operation. The allylated surface layer has the property of being able to withstand thermal stresses that arise during thermal cycling operation of the electronic package.
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
High conductivity buried layer in optical waveguide
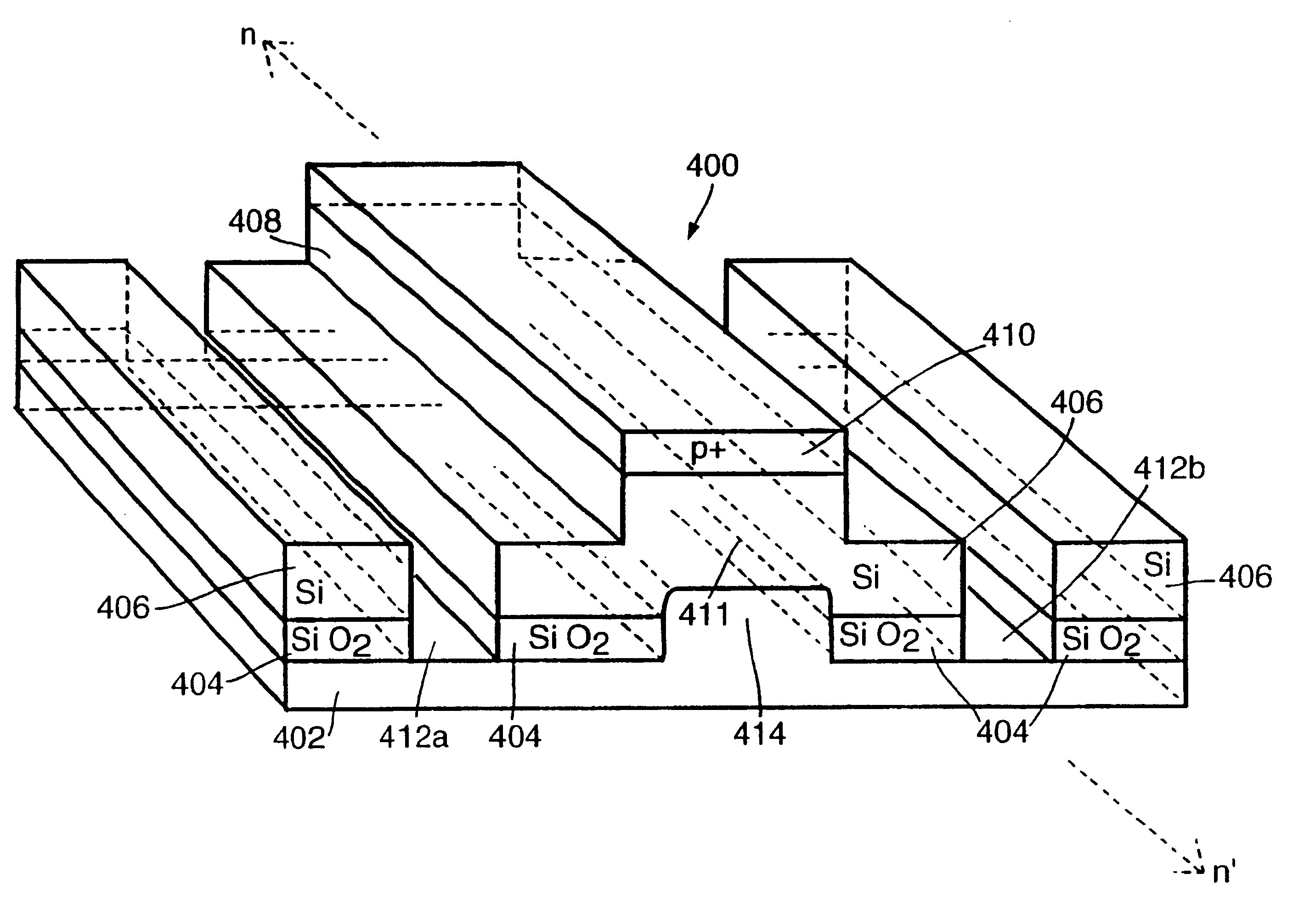
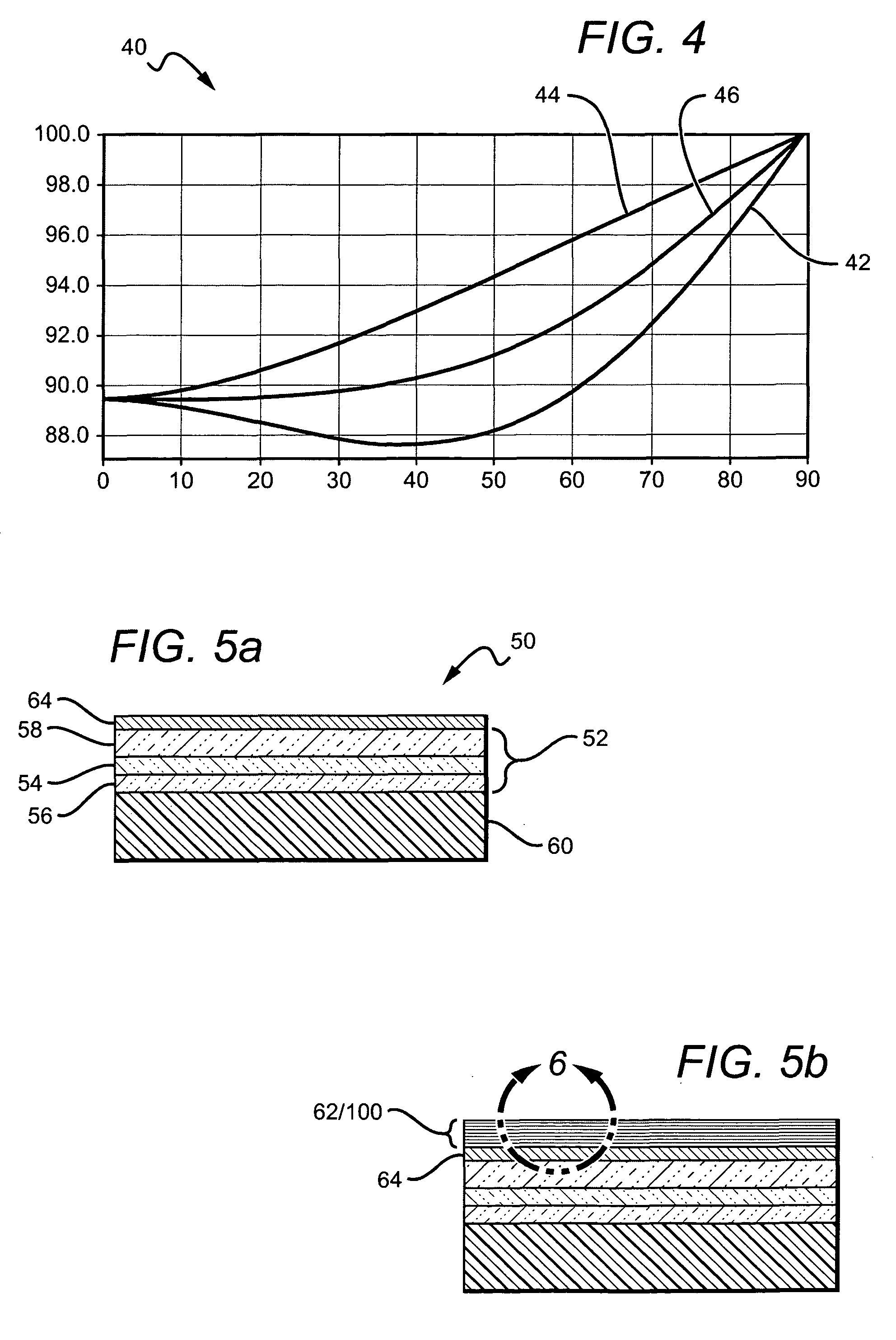
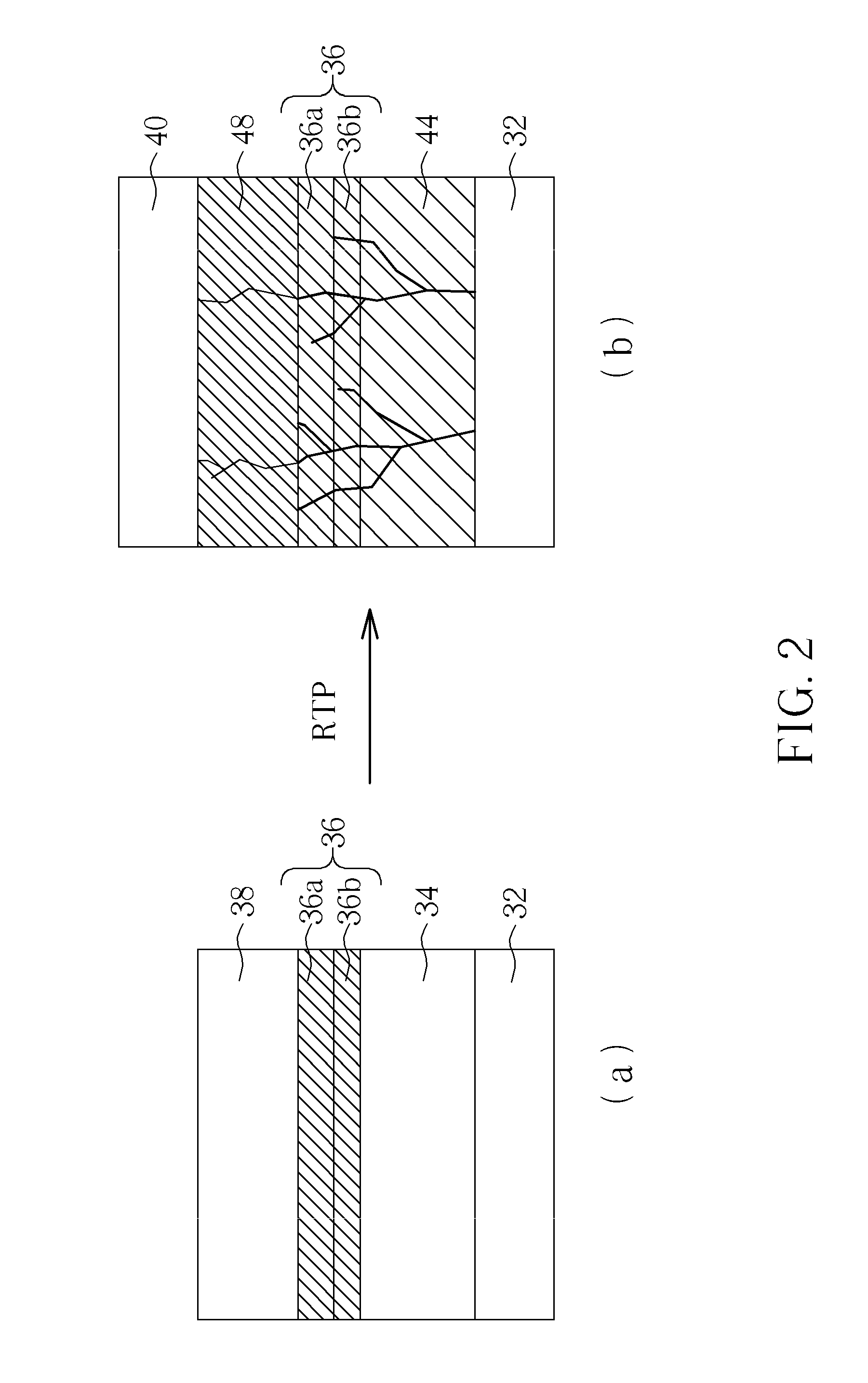
InactiveUS6374001B1Layer is highReduce dissipationCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideRefractive indexElectrical connection
An optical device (300) comprises a multilayer structure, formed by wafer bonding, incorporating in sequence a silicon dioxide layer (304), a buried silicide layer (306), a contact layer (308) and a silicon surface layer (310). The surface layer (310) is selectively etched to form an exposed rib (312). An upper surface of the rib (312) is doped to form an elongate electrode (314) therealong. The surface layer (310) is selectively etched to the contact layer (308) in regions remote from the rib (312) to form via channels (316a, 316b) for making electrical connection to the contact layer (308). The rib (312) forms a waveguide along which radiation propagates. When the electrode (314) is biased relative to the contact layer (308), charge carriers are injected into the rib (312) and induce refractive index changes in a central region (324) thereof where most of the radiation propagates along the rib (312). The silicide layer (306) provides an efficient current conduction path for injecting the carriers, thereby providing enhanced device operating bandwidth and reduced power dissipation.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
Novel universal ink jet recording medium
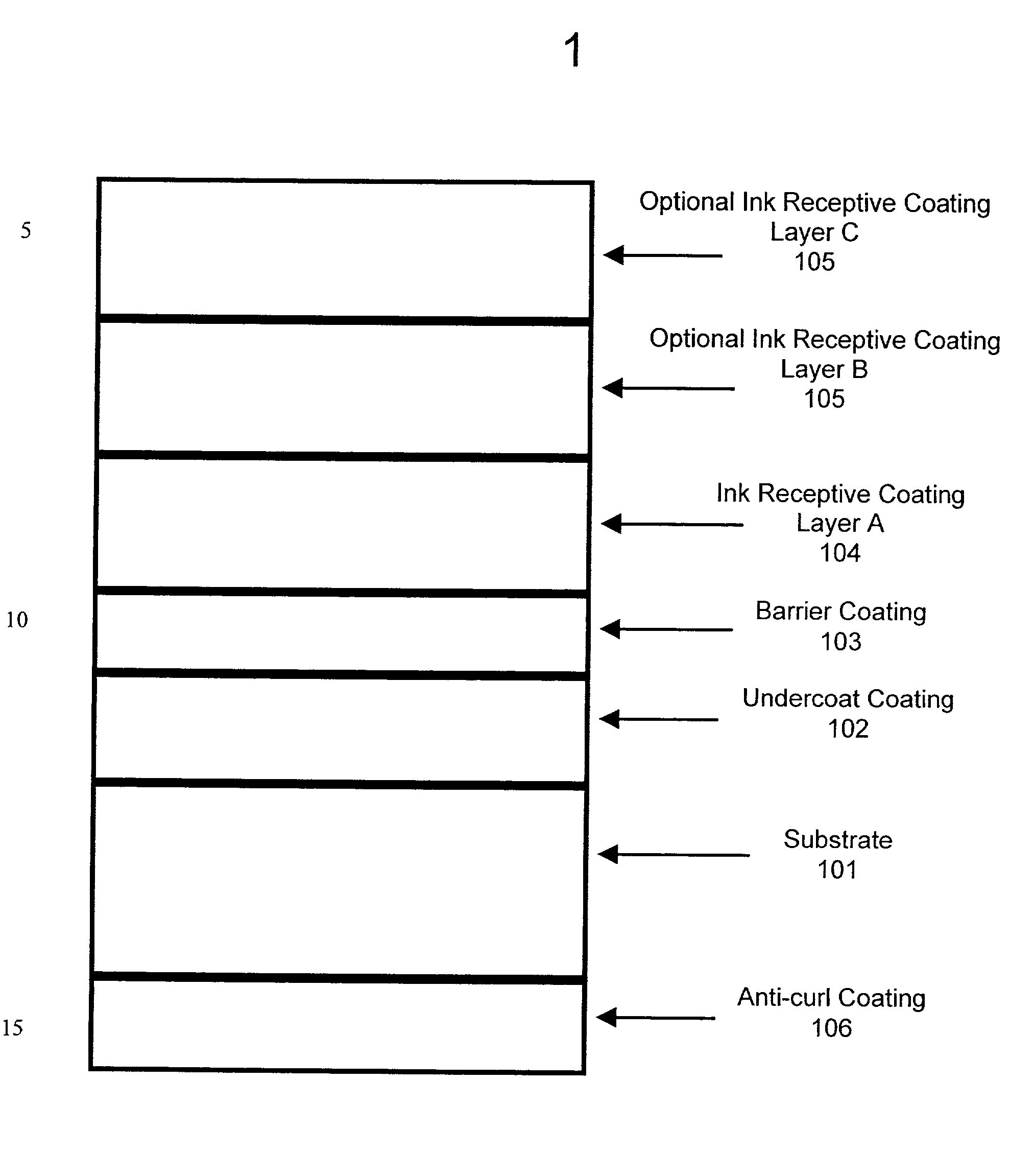
InactiveUS20020182376A1Avoid curlSmooth and high gloss surfaceDuplicating/marking methodsCoatingsCellulosePolyvinyl alcohol
The described invention is an unique universal ink jet media. The invention incorporates a unique barrier layer based upon UV or EB curable chemistry which replaces common polyethylene extruded bases. The invention also incorporates multiple ink receptive layers. The first layer is based upon gelatin and / or polyvinyl alcohol (PVOH) chemistries and gives the invention excellent ink drytime. Poor drytime is a common problem which leads to smudging and print defects, especially as ink jet printer speeds increase as technology improves. The high ink absorbency of the invention also makes this media well suited for wide format ink jet printers. The next ink receptive layer(s) are based upon pigmented, cellulose chemistry which reduces the tack of the sheet and gives the sheet good waterfastness. This is important for the end use in that the sheet may be frequently handled and exposed to dampness. Another unique property provided by the next ink receptive layer(s) is excellent print quality across a wide range of printers and ink sets (both dye and pigmented), in which other media perform poorly. A final unique property is an anti-curl coating which resists curling as the ambient conditions change from cold and dry to hot and humid.
Owner:P H GLATFELTER CO
Cryptographic key management scheme
InactiveUS6959086B2Layer is highSimple structureKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationDistributed computingBit-length
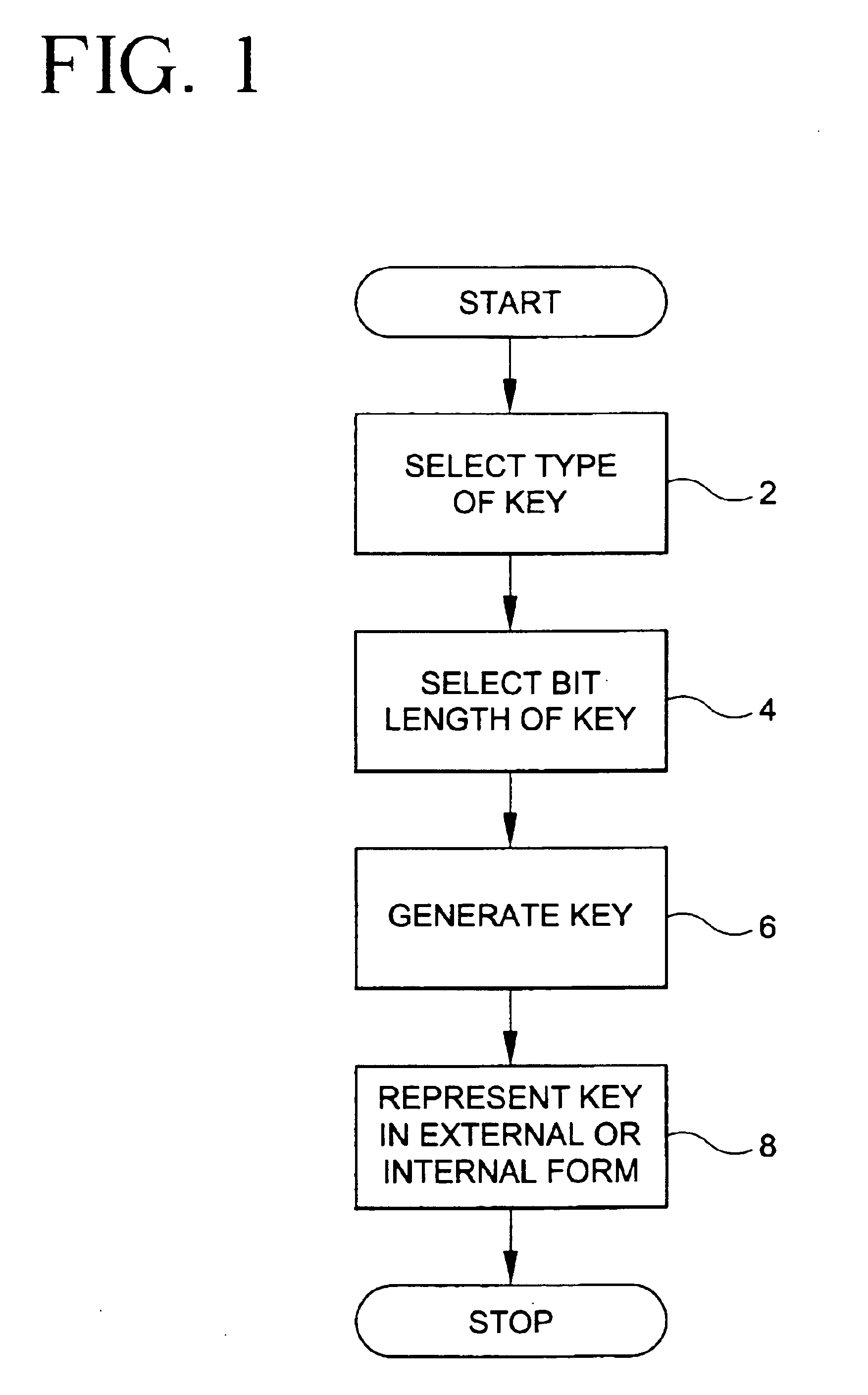
A key management scheme for managing encryption keys in a cryptographic co-processor includes the first step of selecting a key from one of a symmetrical key type and an asymmetrical key type. Then, the key bit length is selected. The key is then generated and, lastly, the key is represented in either an external form or an internal form.
Owner:SAFENET
Composite high reflectivity layer
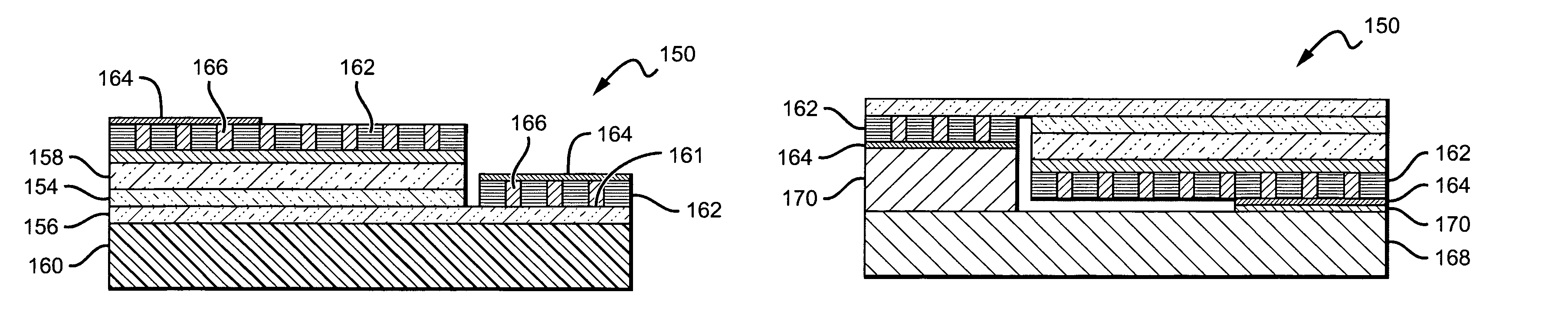
ActiveUS20100140635A1Layer is highImprove emission efficiencyMirrorsSolid-state devicesRefractive indexHigh reflectivity
A high efficiency light emitting diode with a composite high reflectivity layer integral to said LED to improve emission efficiency. One embodiment of a light emitting diode (LED) chip comprises an LED and a composite high reflectivity layer integral to the LED to reflect light emitted from the active region. The composite layer comprises a first layer, and alternating plurality of second and third layers on the first layer, and a reflective layer on the topmost of said plurality of second and third layers. The second and third layers have a different index of refraction, and the first layer is at least three times thicker than the thickest of the second and third layers. For composite layers internal to the LED chip, conductive vias can be included through the composite layer to allow an electrical signal to pass through the composite layer to the LED.
Owner:CREELED INC
Inkjet recording sheet
InactiveUS20020176970A1Improve abilitiesGood ink absorptionCoatingsThermographyPolyvinyl alcoholAcyl group
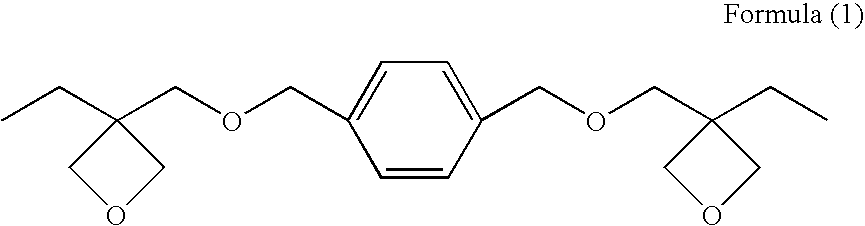
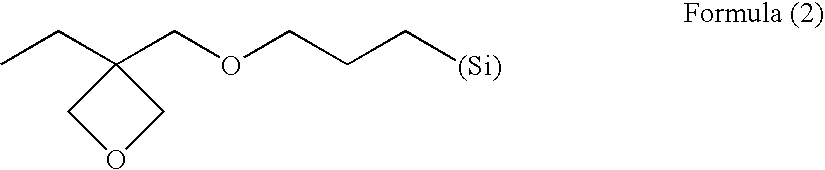
Disclosed is an inkjet recording sheet having a colorant-receiving layer on the surface of its support, in which the colorant-receiving layer contains at least one of compounds represented by the following general formula (1) and compounds represented by the following general formula (2), and contains a vapor-phase-process silica, a polyvinyl alcohol, a boron compound, and a mordant. In the formulae, R represents a saturated hydrocarbon group having from 1 to 12 carbon atoms, an unsaturated hydrocarbon group having from 1 to 12 carbon atoms, a phenyl group, or an acyl group, and n indicates an integer of 1 to 3. <paragraph lvl="0"><in-line-formula>RO(CH2CH2O)nH (1) < / in-line-formula><paragraph lvl="0"><in-line-formula>RO(CH2CH(CH3)O)nH (2) < / in-line-formula>
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Storage medium for data with improved dimensional stability
InactiveUS20030044564A1Improve dimensional stabilityHighLayered productsPhotomechanical apparatusOperating system
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Electrosurgical apparatus with low work function electrode
InactiveUS20120083782A1Enhances electrical discharge activityHigh activitySurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsMicro structureAlkaline earth metal
An electrosurgical apparatus includes an active electrode with a low-work function coating to improve ablation performance. Low-work function coatings include compounds of alkali metals and alkali earth metals. Additionally, the active electrode may include various micro-structures or asperities or nano-structures or asperities. An array of carbon nanotubes may be aligned and secured on the active electrode. A return electrode comprises a high-work function coating to suppress electrical discharge activity on the return electrode.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Filament winding apparatus
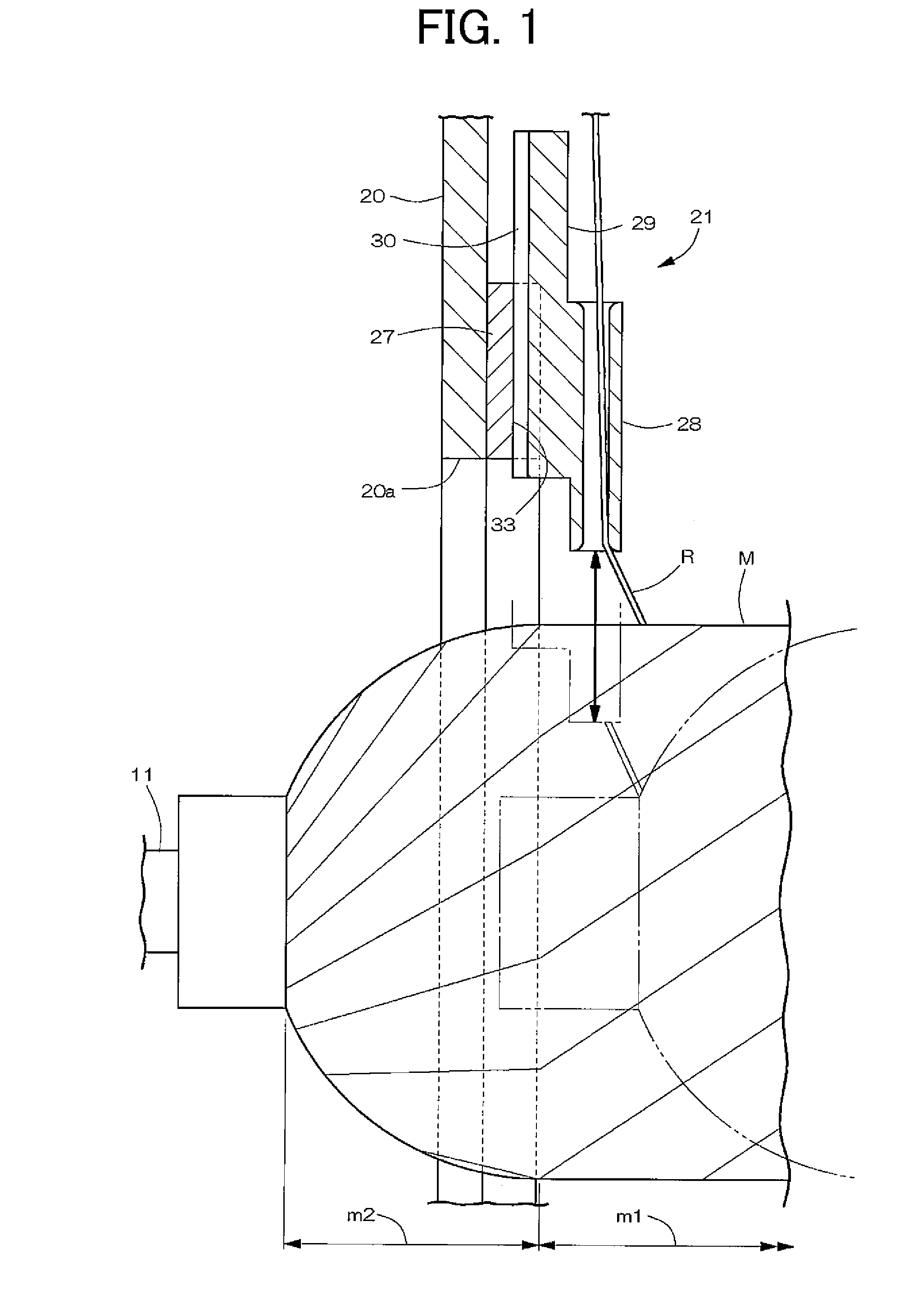
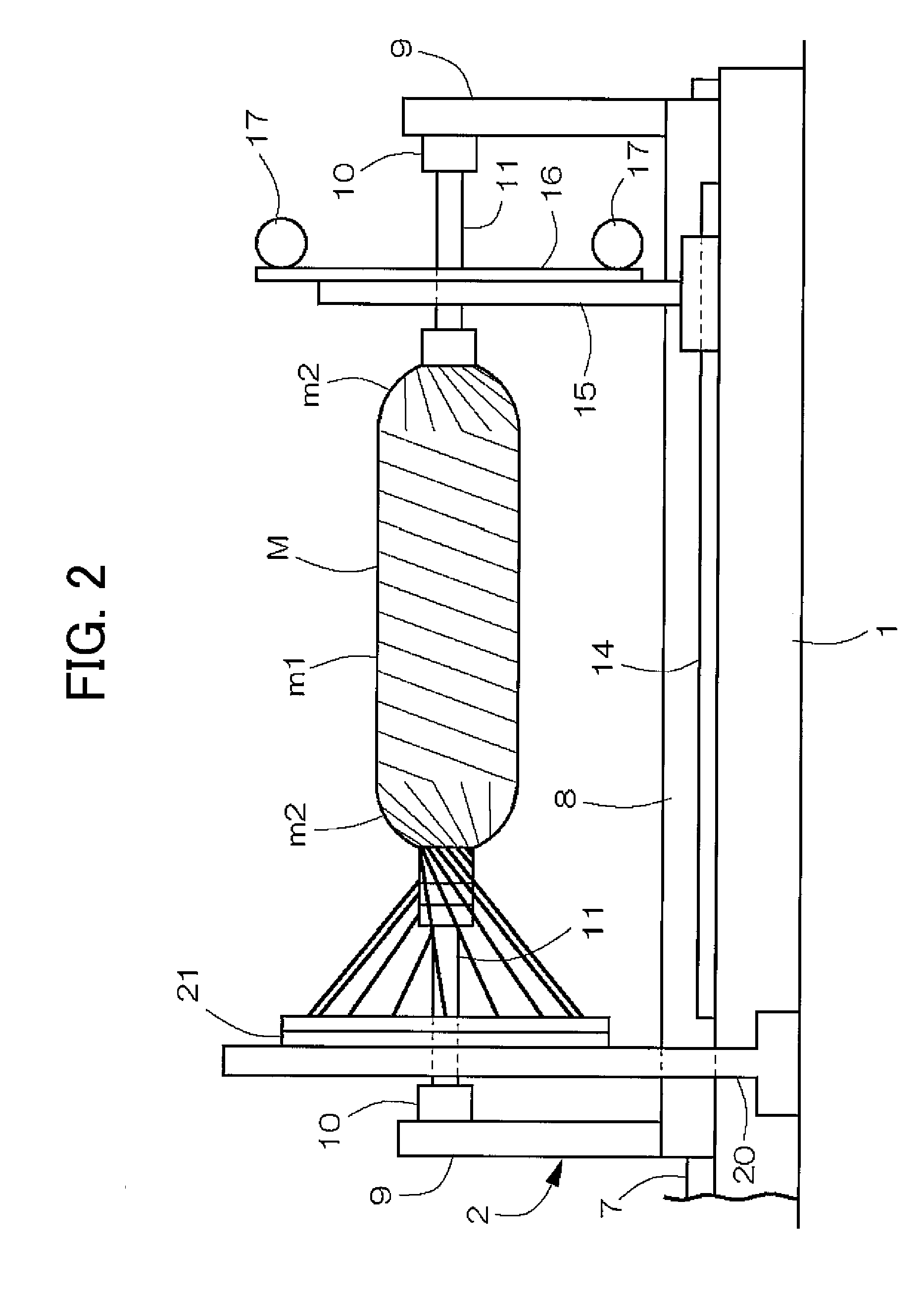
ActiveUS7815141B2Efficient executionWinding orderlyFilament handlingCoils manufactureFiber bundleReciprocating motion
A filament winding apparatus that efficiently and orderly winds a fiber bundle with respect to a mandrel in a short period of time. A supporting board supports the mandrel, and a helical winding head supplies and guides the fiber bundle towards the mandrel. The helical winding head includes a group of guide tubes radially arranged on a circumferential surface of a guide ring, and a tube operation mechanism that reciprocates the guide tube along a tube axis center direction. The guide tube is moved closer to a circumferential surface of the dome part when the guide tube is facing a dome part of the mandrel such that the distance between the winding position of the fiber bundle and the guide tube at the dome part can be reduced, and the fiber bundle is orderly wound according to an appropriate winding trajectory.
Owner:MURATA MASCH LTD
Composite high reflectivity layer
ActiveUS7915629B2Layer is highImprove emission efficiencyMirrorsSolid-state devicesRefractive indexReflective layer
A high efficiency light emitting diode with a composite high reflectivity layer integral to said LED to improve emission efficiency. One embodiment of a light emitting diode (LED) chip comprises an LED and a composite high reflectivity layer integral to the LED to reflect light emitted from the active region. The composite layer comprises a first layer, and alternating plurality of second and third layers on the first layer, and a reflective layer on the topmost of said plurality of second and third layers. The second and third layers have a different index of refraction, and the first layer is at least three times thicker than the thickest of the second and third layers. For composite layers internal to the LED chip, conductive vias can be included through the composite layer to allow an electrical signal to pass through the composite layer to the LED.
Owner:CREELED INC
Light emitting diode improved in luminous efficiency
InactiveUS20060054909A1Improve luminous efficiencyLayer is highSemiconductor devicesHigh reflectivityActive layer
The present invention relates to an LED, in which an n-doped semiconductor layer, an active layer, a p-doped semiconductor layer and a p-electrode are formed in their order on a sapphire substrate. A high reflectivity material layer containing Cu and Si is deposited on a remaining partial region of the n-doped semiconductor layer. An n-electrode is formed on the high reflectivity material layer. The high reflectivity material layer formed between the n-electrode and the partial region of the underlying n-doped semiconductor layer can reflect light toward a substrate, thereby improving the luminous efficiency of the LED.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Filament Winding Apparatus
ActiveUS20090127373A1Quality improvementReduce distanceFilament handlingCoils manufactureFiber bundleReciprocating motion
A filament winding apparatus that efficiently and orderly winds a fiber bundle with respect to a mandrel in a short period of time. A supporting board supports the mandrel, and a helical winding head supplies and guides the fiber bundle towards the mandrel. The helical winding head includes a group of guide tubes radially arranged on a circumferential surface of a guide ring, and a tube operation mechanism that reciprocates the guide tube along a tube axis center direction. The guide tube is moved closer to a circumferential surface of the dome part when the guide tube is facing a dome part of the mandrel such that the distance between the winding position of the fiber bundle and the guide tube at the dome part can be reduced, and the fiber bundle is orderly wound according to an appropriate winding trajectory.
Owner:MURATA MASCH LTD
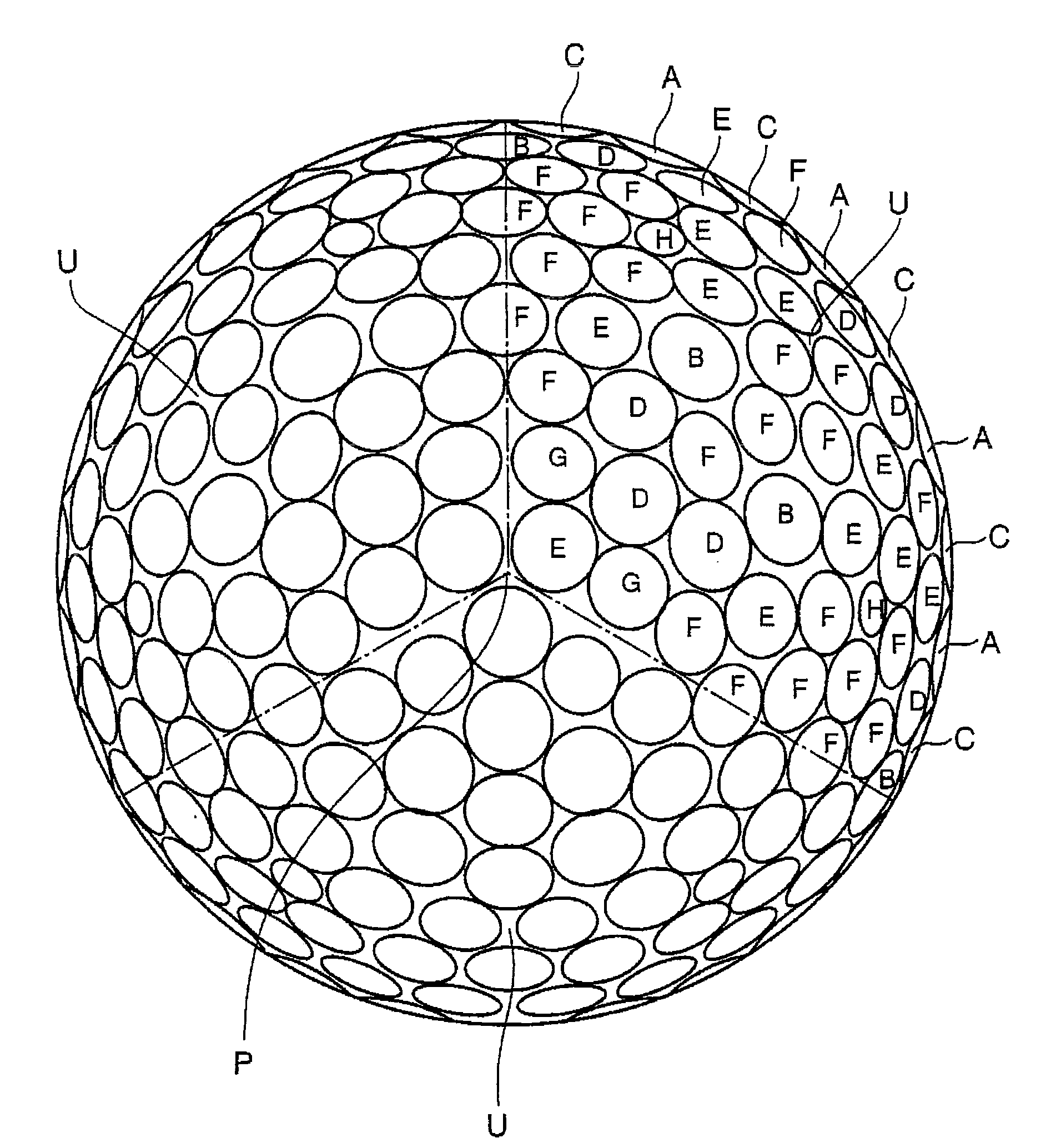
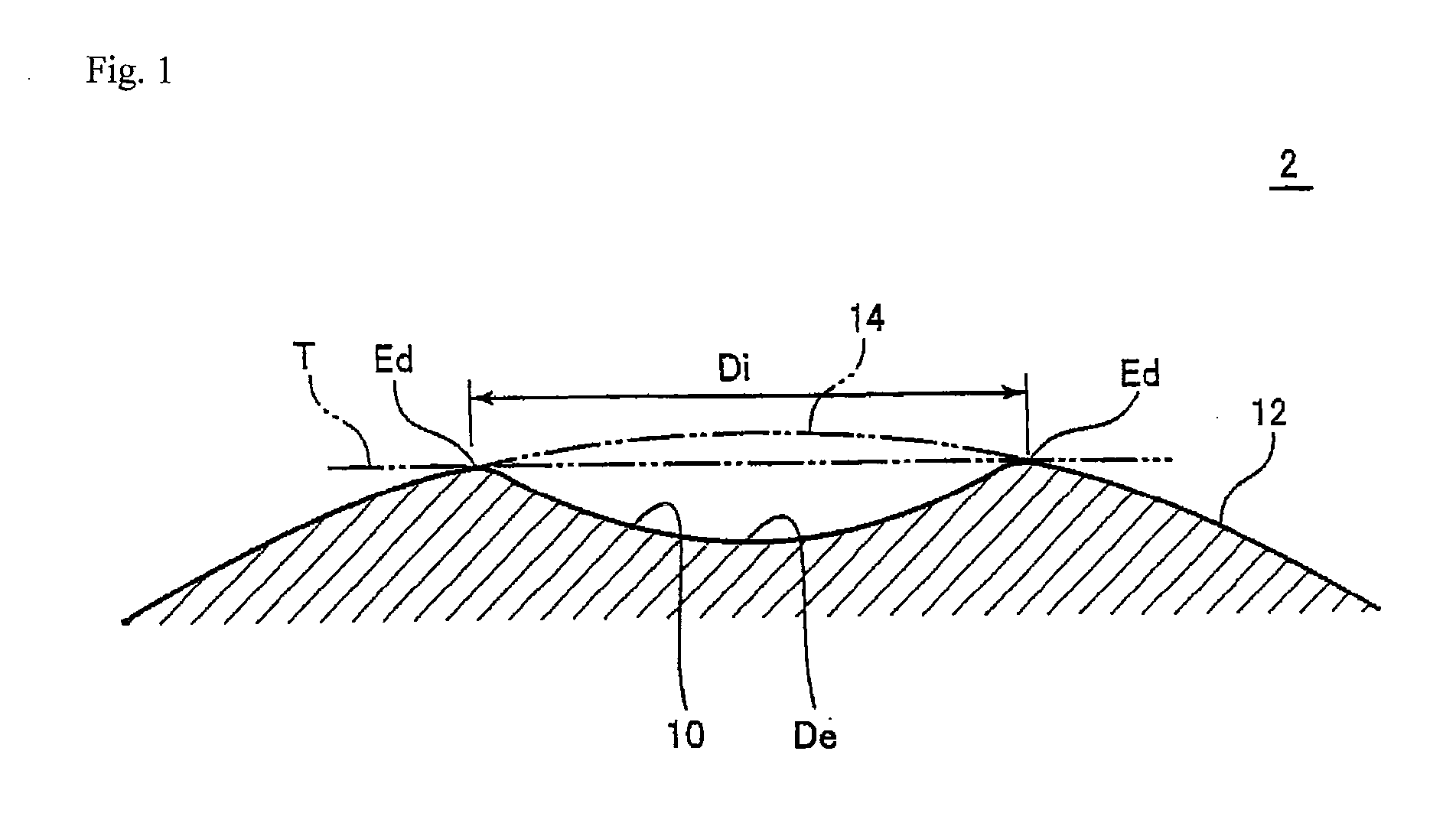
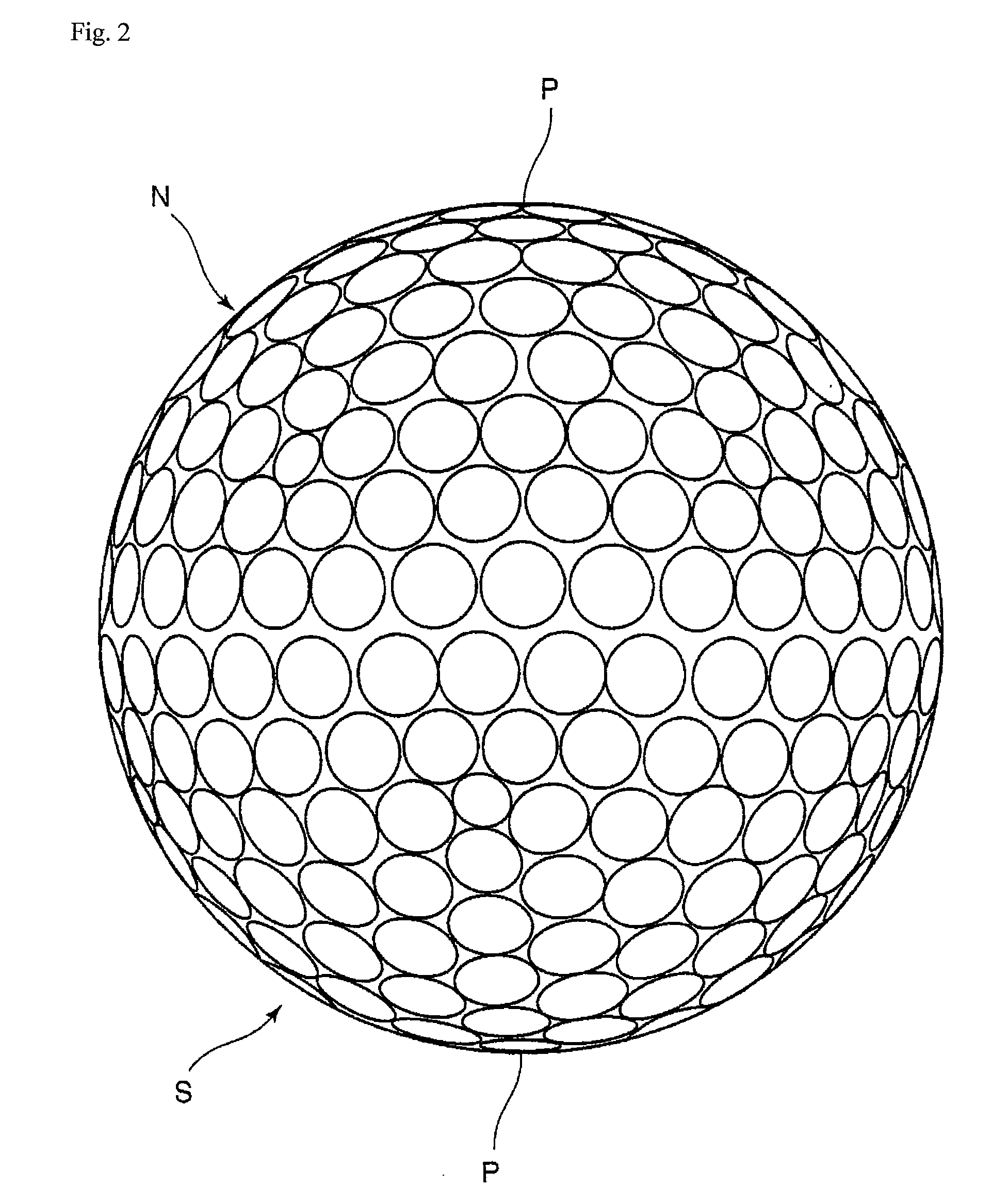
Golf ball
ActiveUS20100093466A1Increase repulsionIncrease stiffnessGolf ballsSolid ballsIonomerFlexural modulus
An objective of the present invention is to provide a golf ball striking a balance between the flight distance on the driver shots and the approach performance on the approach shots and having the excellent shot feeling and durability. The present invention provides a golf ball comprising a core consisting of a center and a surrounding layer covering the center; at least one intermediate layer covering the core; and a cover covering the intermediate layer; wherein at least one piece or one layer of the intermediate layer is formed from a highly elastic intermediate layer composition that contains (A) a highly elastic resin having a flexural modulus in a range from 700 MPa to 5,000 MPa and (B) an ionomer resin having a flexural modulus in a range from 150 MPa to 1,000 MPa in a content ratio ((A) / (B)) of (A) the highly elastic resin to (B) the ionomer resin (B) being (20 mass % to 80 mass %) / (80 mass % to 20 mass %) (the total is 100 mass %), and wherein a surface hardness (Hm) of the intermediate layer and a surface hardness (Hs) of the core satisfy the equation: Hm≧Hs, and the cover has a slab hardness (Hc) of 45 or less in Shore D hardness.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
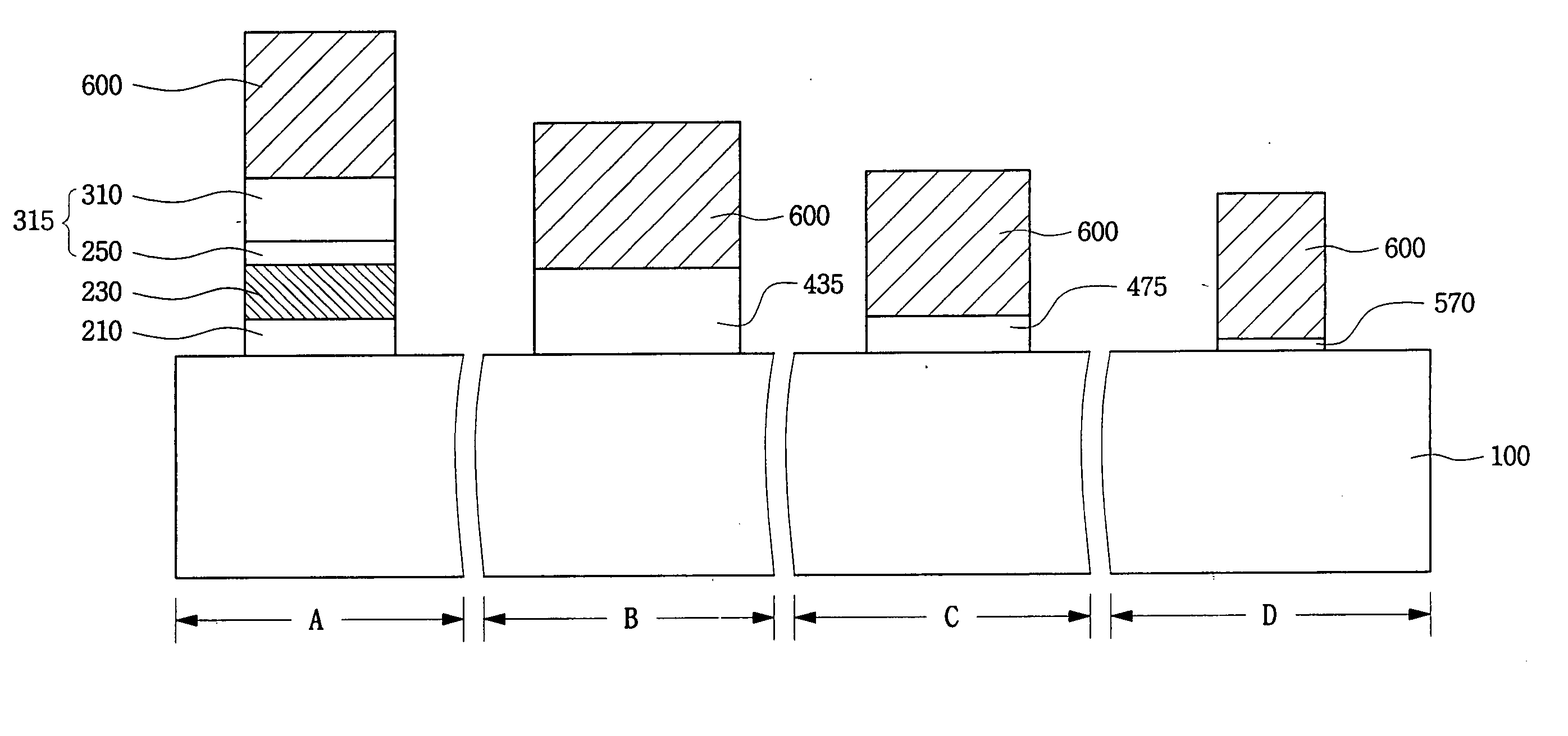
Semiconductor device with floating trap type nonvolatile memory cell and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050023604A1Reduce processing timeSlow changeTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialImpurity doping
The present invention discloses a semiconductor device having a floating trap type nonvolatile memory cell and a method for manufacturing the same. The method includes providing a semiconductor substrate having a nonvolatile memory region, a first region, and a second region. A triple layer composed of a tunnel oxide layer, a charge storing layer and a first deposited oxide layer on the semiconductor substrate is formed sequentially. The triple layer on the semiconductor substrate except the nonvolatile memory region is then removed. A second deposited oxide layer is formed on an entire surface of the semiconductor substrate including the first and second regions from which the triple layer is removed. The second deposited oxide layer on the second region is removed, and a first thermal oxide layer is formed on the entire surface of the semiconductor substrate including the second region from which the second deposited oxide layer is removed. The semiconductor device can be manufactured according to the present invention to have a reduced processing time and a reduced change of impurity doping profile. The thickness of a blocking oxide layer and a high voltage gate oxide layer can be controlled.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
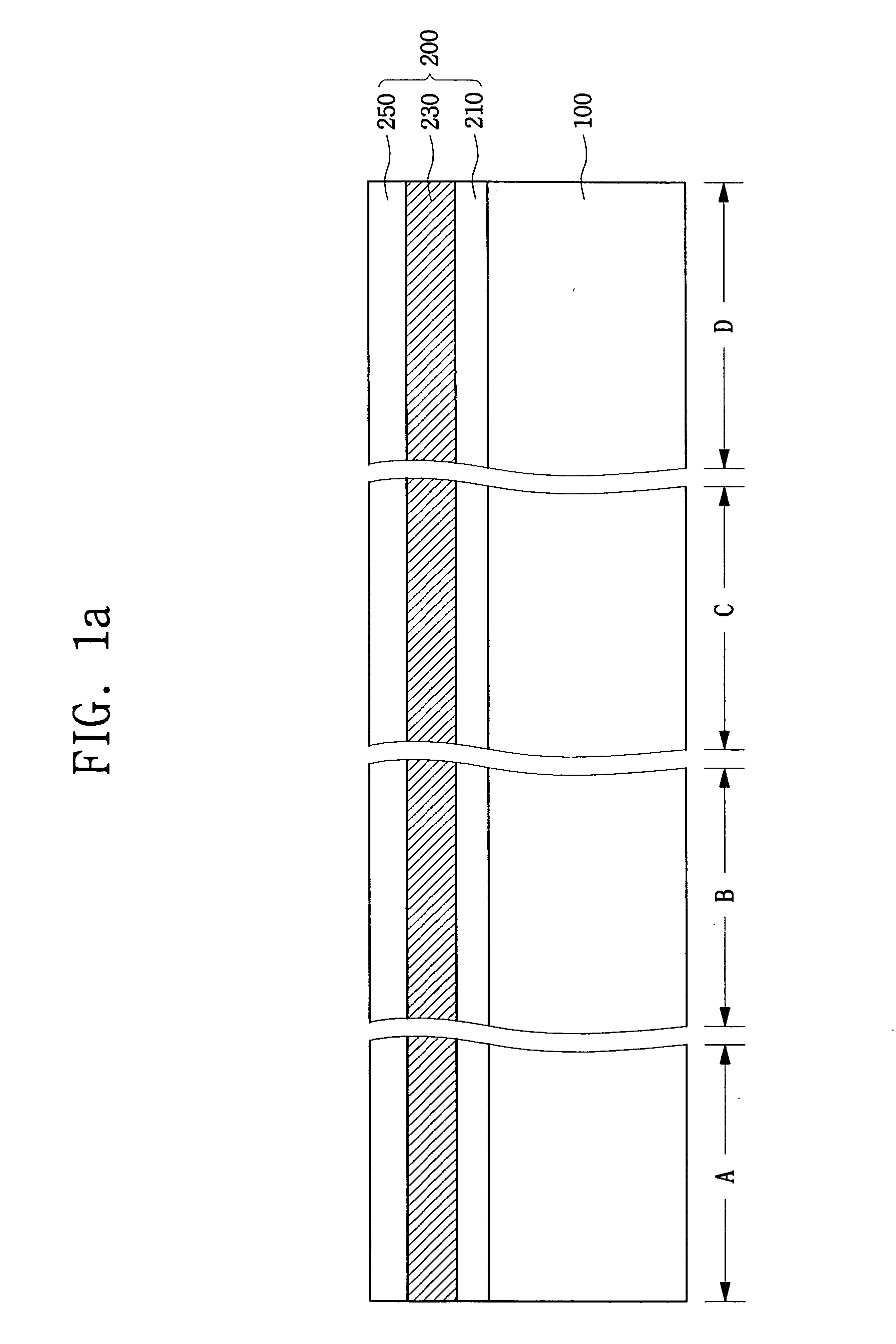
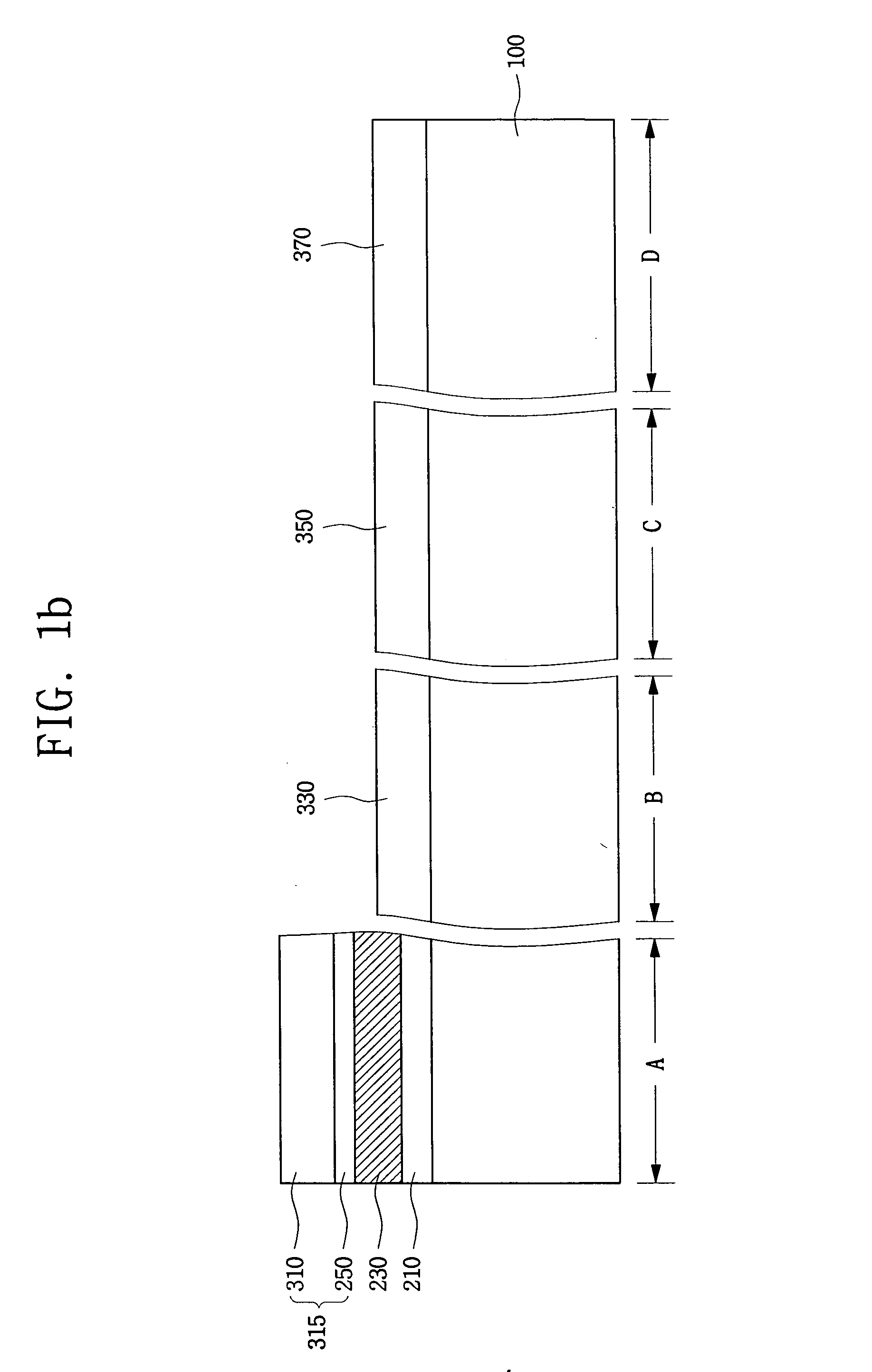
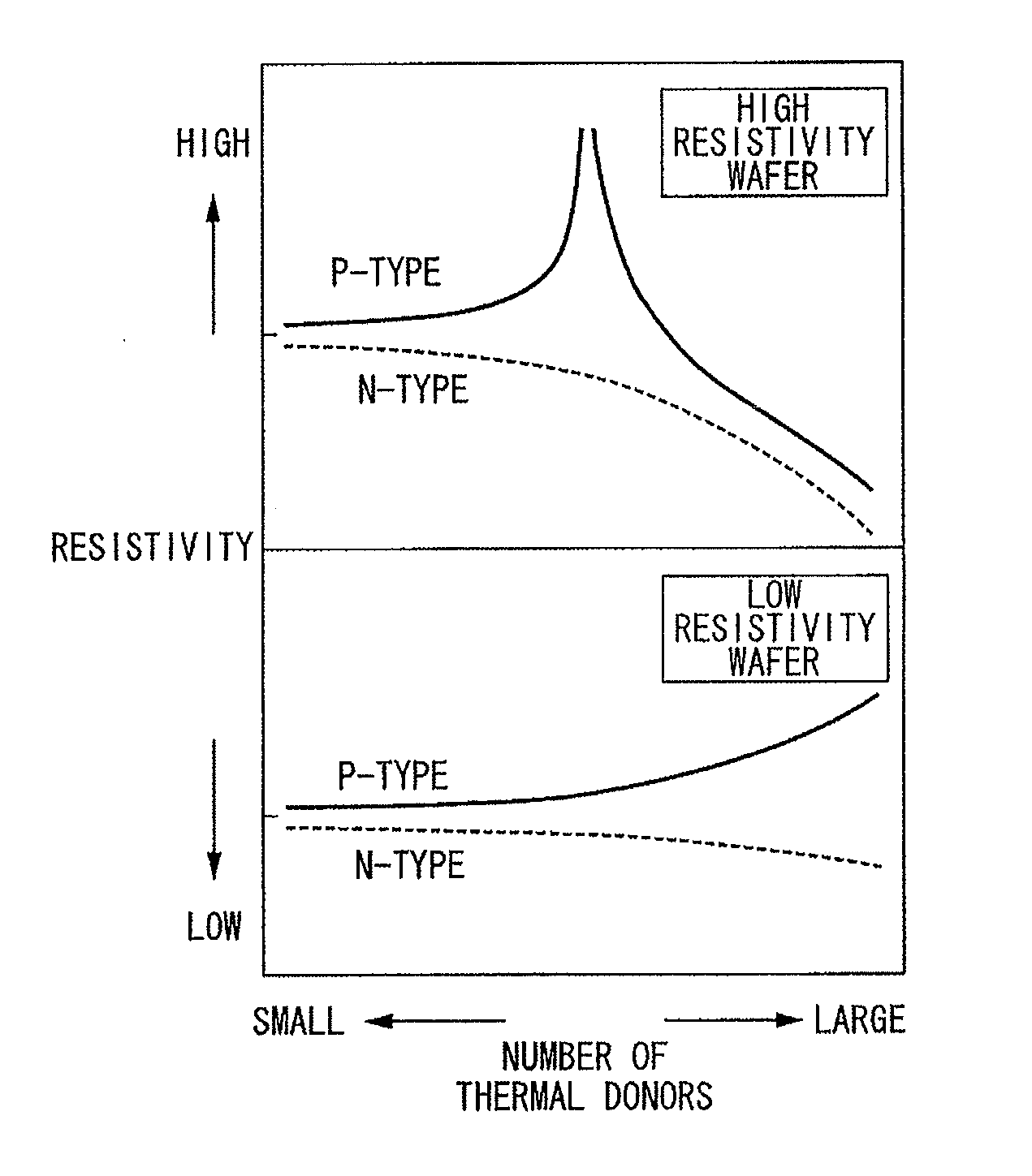
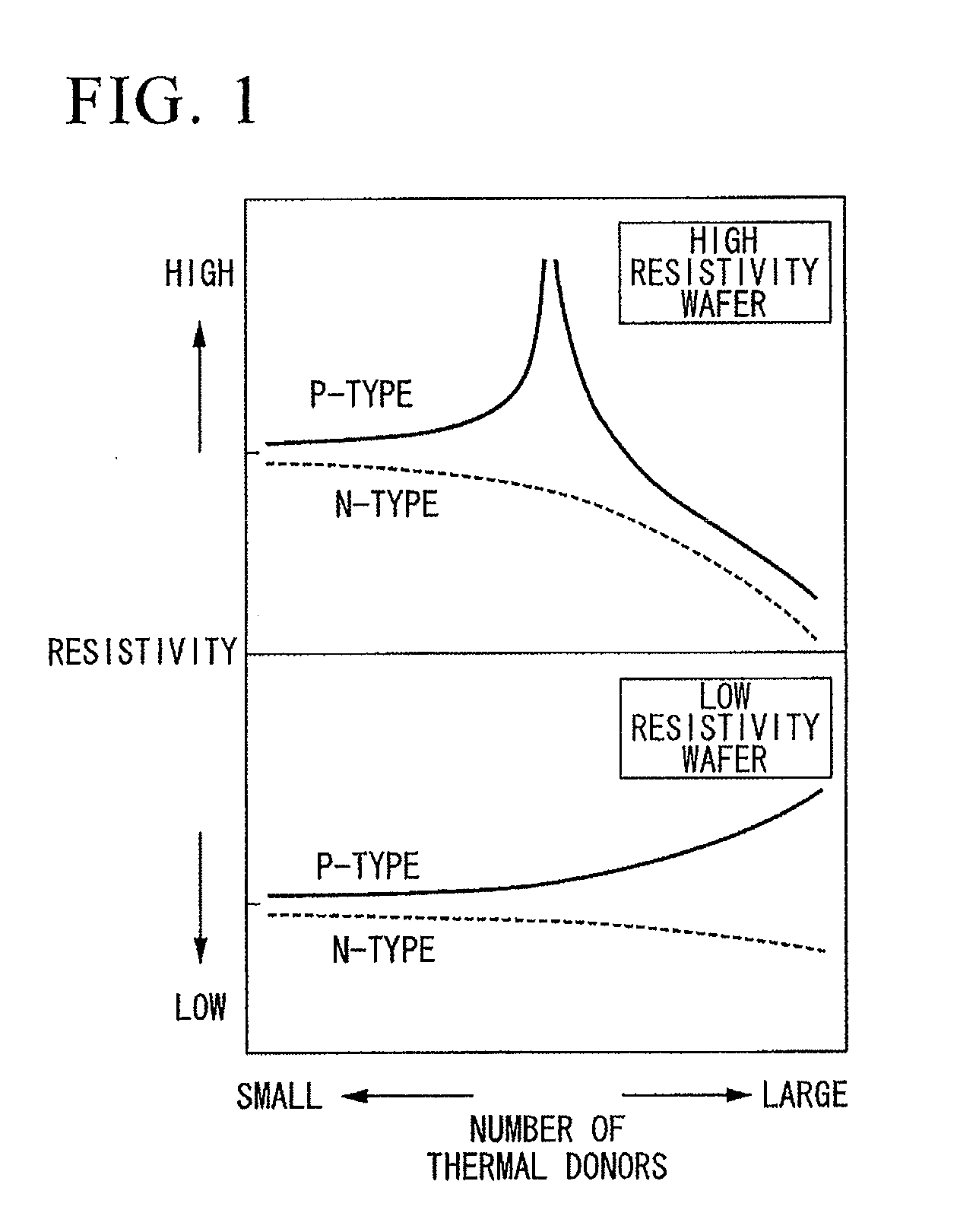
High resistivity silicon wafer and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100224968A1Avoid it happening againHigh mechanical strengthPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantCzochralski method
This method for manufacturing a high resistivity silicon wafer includes pulling a single crystal such that the single crystal has a p-type dopant concentration at which a wafer surface resistivity becomes in a range of 0.1 to 10 kΩcm, an oxygen concentration Oi of 5.0×1017 to 20×1017 atoms / cm3 (ASTM F-121, 1979), and either one of a nitrogen concentration of 1.0×1013 to 10×1013 atoms / cm3 (ASTM F-121, 1979) and a carbon concentration of 0.5×1016 to 10×1016 atoms / cm3 or 0.5×1016 to 50×1016 atoms / cm3 (ASTM F-123, 1981) by using a Czochralski method, processing the single crystal into wafers by slicing the single crystal, and subjecting the wafer to an oxygen out-diffusion heat treatment process in a non-oxidizing atmosphere. A peak position of a resistivity serving as a boundary between a p-type region of a wafer surface side and a p / n conversion region of an inner side of a thickness direction is adjusted by the nitrogen concentration or the carbon concentration such that the peak position is set to a boundary depth in a range of 10 to 70 μm from the wafer surface.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Semiconductor device and fabrication method of the semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090189188A1Improve efficiencyImprove featuresTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransition metal atomsHigh resistivity
A semiconductor device and a fabrication method of the semiconductor device, the semiconductor device including: a substrate; a nitride based compound semiconductor layer placed on the substrate and doped with a first transition metal atom; an aluminum gallium nitride layer (AlxGa1-xN) (where 0.1<=x<=1) placed on the nitride based compound semiconductor layer; a nitride based compound semiconductor layer placed on the aluminum gallium nitride layer (AlxGa1-xN) (where 0.1<=x<=1) and doped with a second transition metal atom; an aluminum gallium nitride layer (AlyGa1-yN) (where 0.1<=y<=1) placed on the nitride based compound semiconductor layer doped with the second transition metal atom; and a gate electrode, a source electrode, and a drain electrode which are placed on the aluminum gallium nitride layer (AlyGa1-yN) (where 0.1<=y<=1). Accordingly, piezo charge is inactivated, leakage current and current collapse are reduced, high frequency characteristics can be improved by obtaining a high resistivity semiconductor layer, and stable high frequency performance can be obtained.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
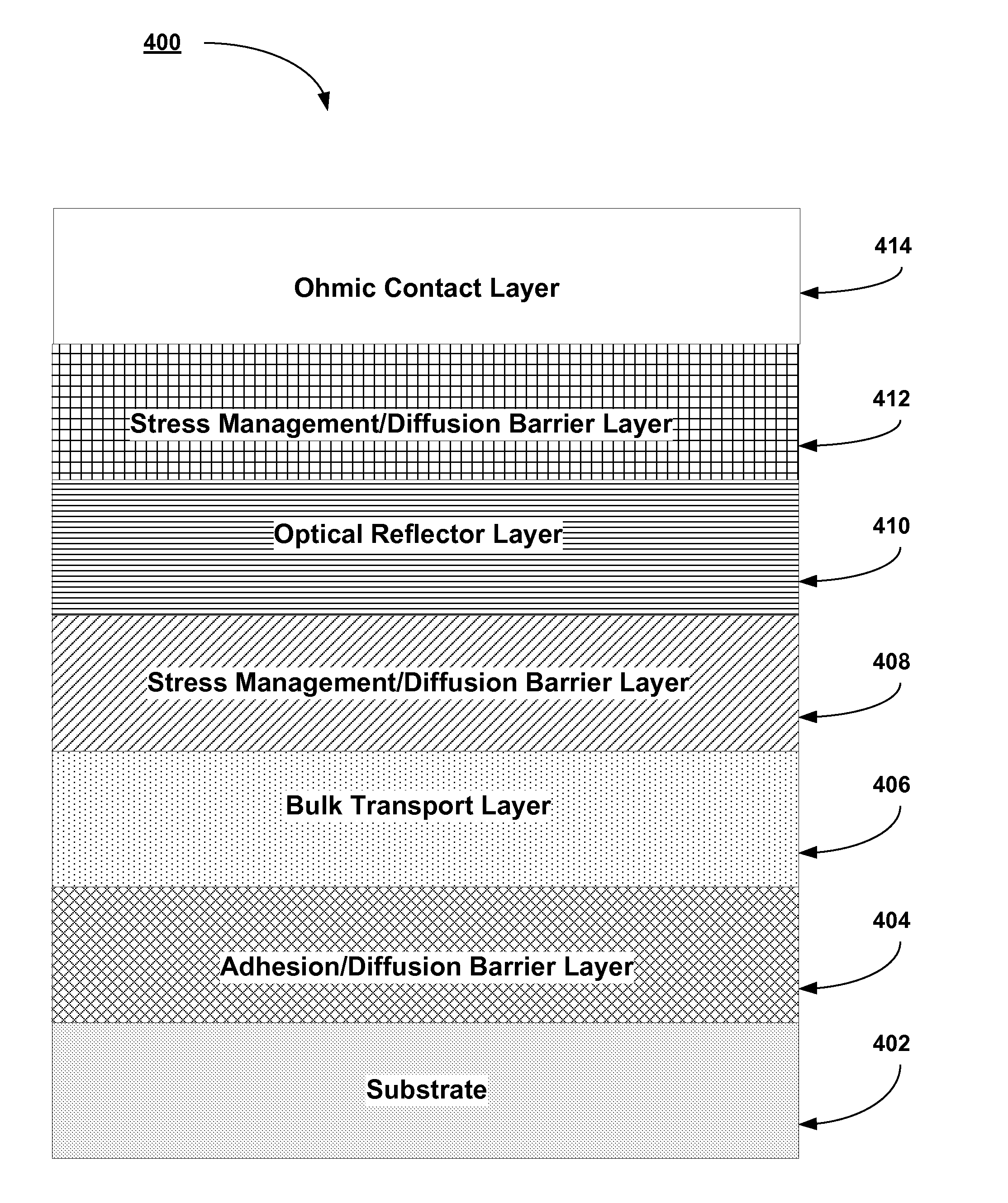
Back contacts for thin film solar cells
InactiveUS20130081688A1Enhanced light absorptionImprove adhesionFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationTransport layerOhmic contact
Method for forming back contact stacks for CIGS and CZTS TFPV solar cells are described wherein some embodiments include adhesion promoter layers, bulk current transport layers, stress management / diffusion barrier layers, optical reflector layers, and ohmic contact layers. Other back contact stacks include adhesion promoter layers, bulk current transport layers, diffusion barrier layers, and ohmic contact layers.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
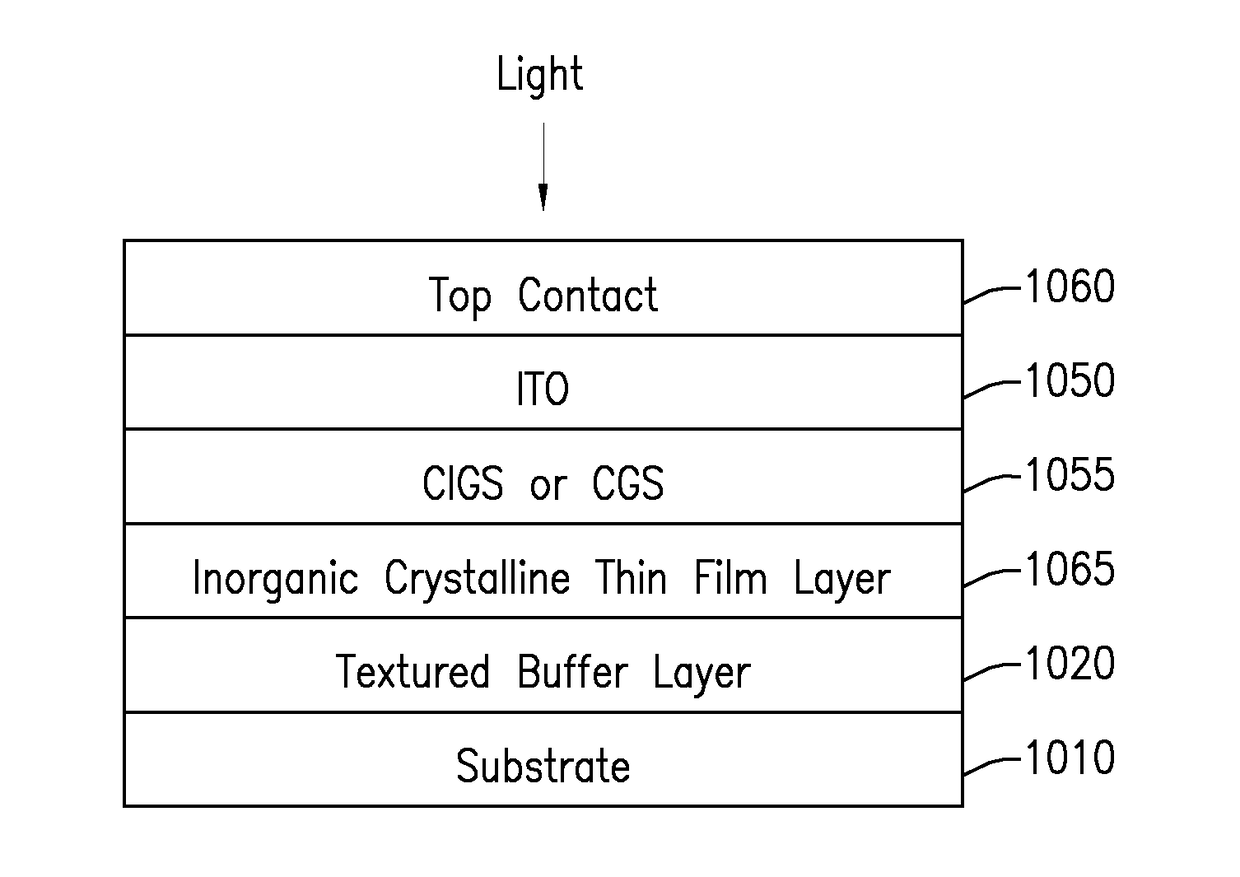
High efficiency thin film tandem solar cells and other semiconductor devices
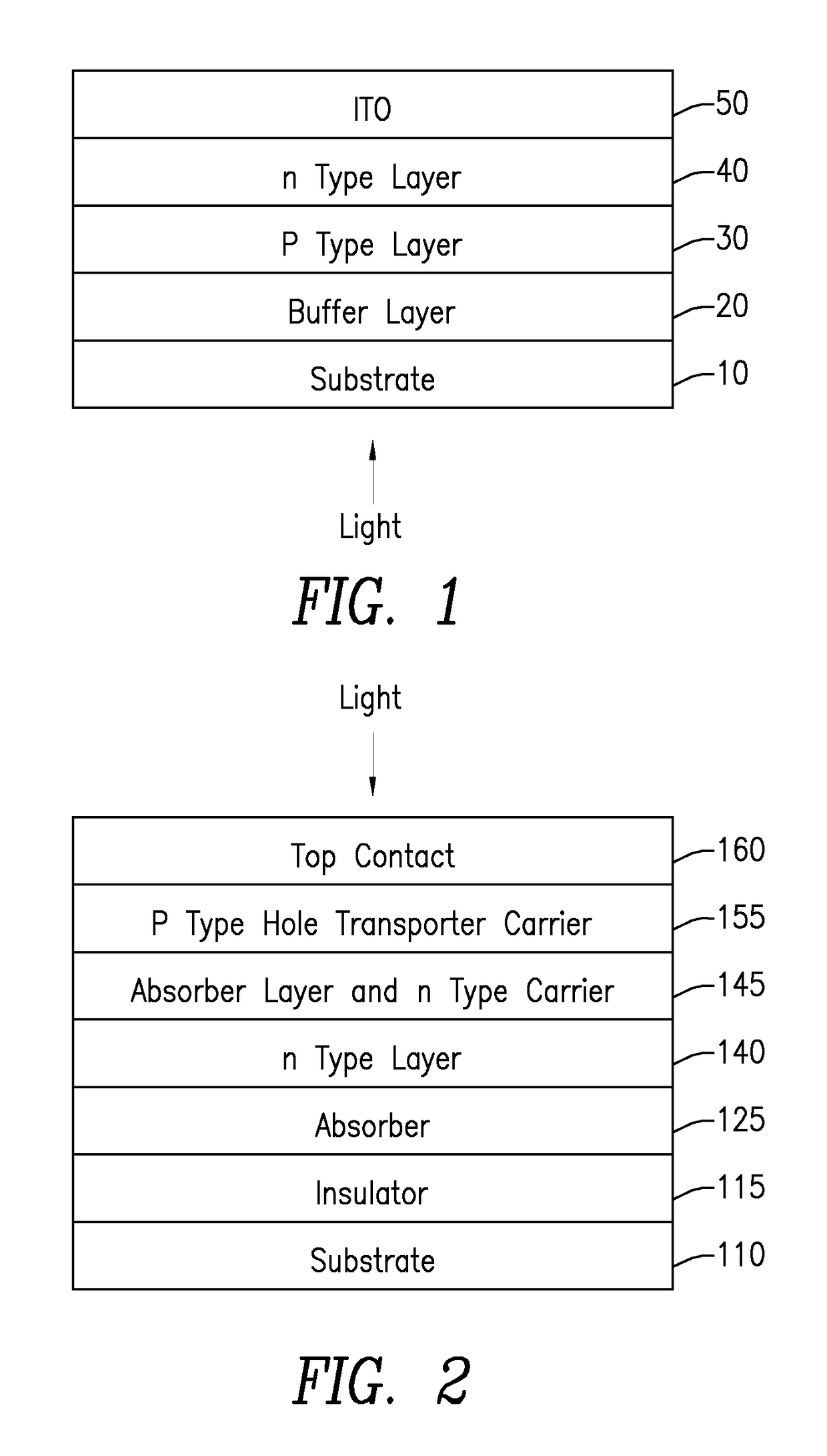
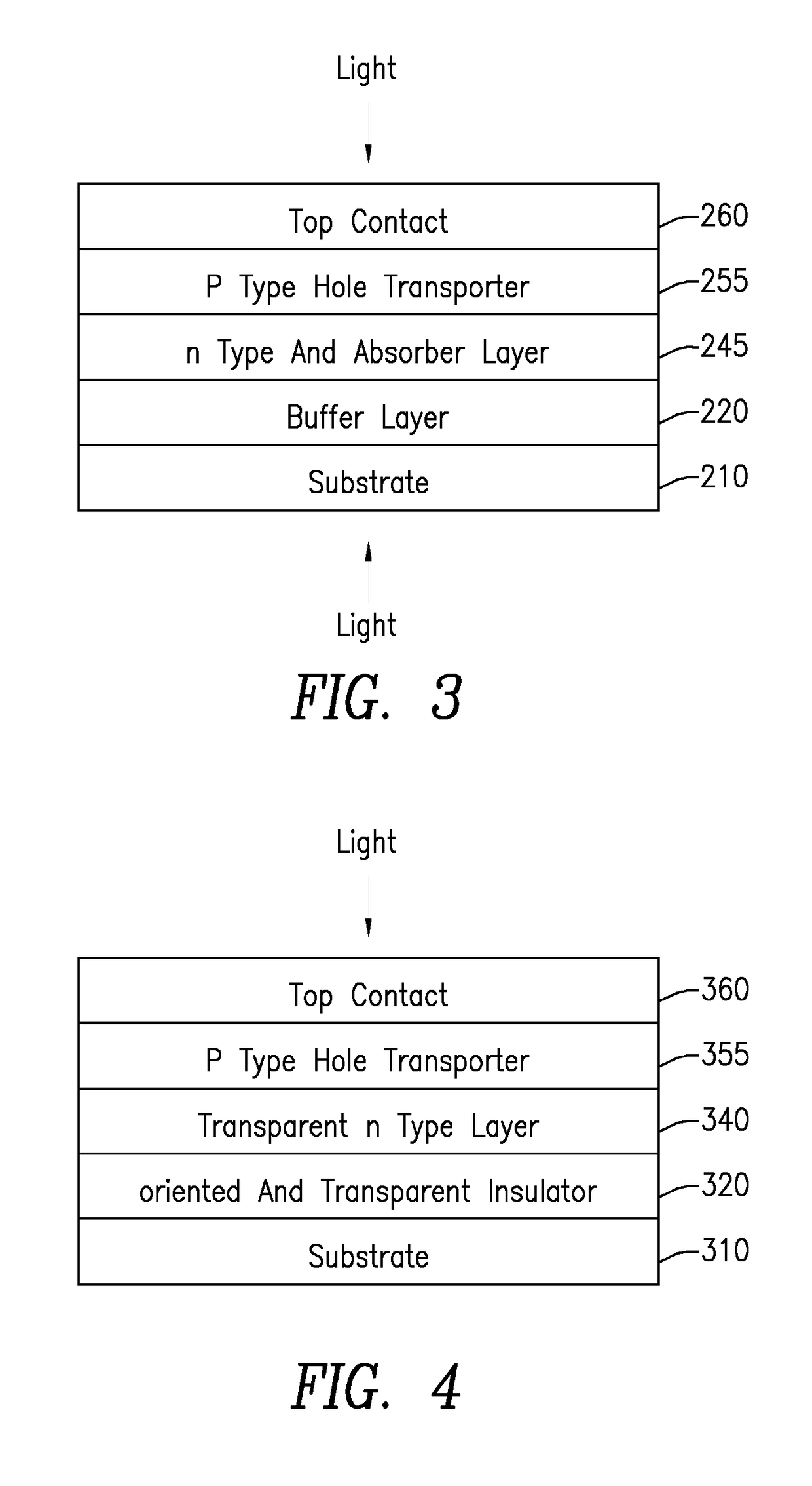
InactiveUS20170271622A1Layer is highTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorTandem solar cell
Architectures for tandem solar cell including two thin films forming a top layer and a bottom layer. Such cells can be bi-facial. Exemplary materials used for the top layer are CIGS (CGS), perovskites (Sn and Ge), amorphous silicon (a-Si), copper oxide, tin sulfide, CZTS and III-V materials. For the bottom layer an inorganic film such as either silicon or germanium may be used. In general, the architecture includes of a glass, plastic or metal substrate and a buffer layer, either an oxide insulator or nitride conductor.
Owner:SOLAR TECTIC
Method of fabricating rram
InactiveUS20100021626A1Simplify manufacturing stepsShorten production timeElectrical apparatusSpecial surfacesOxygen contentMaterials science
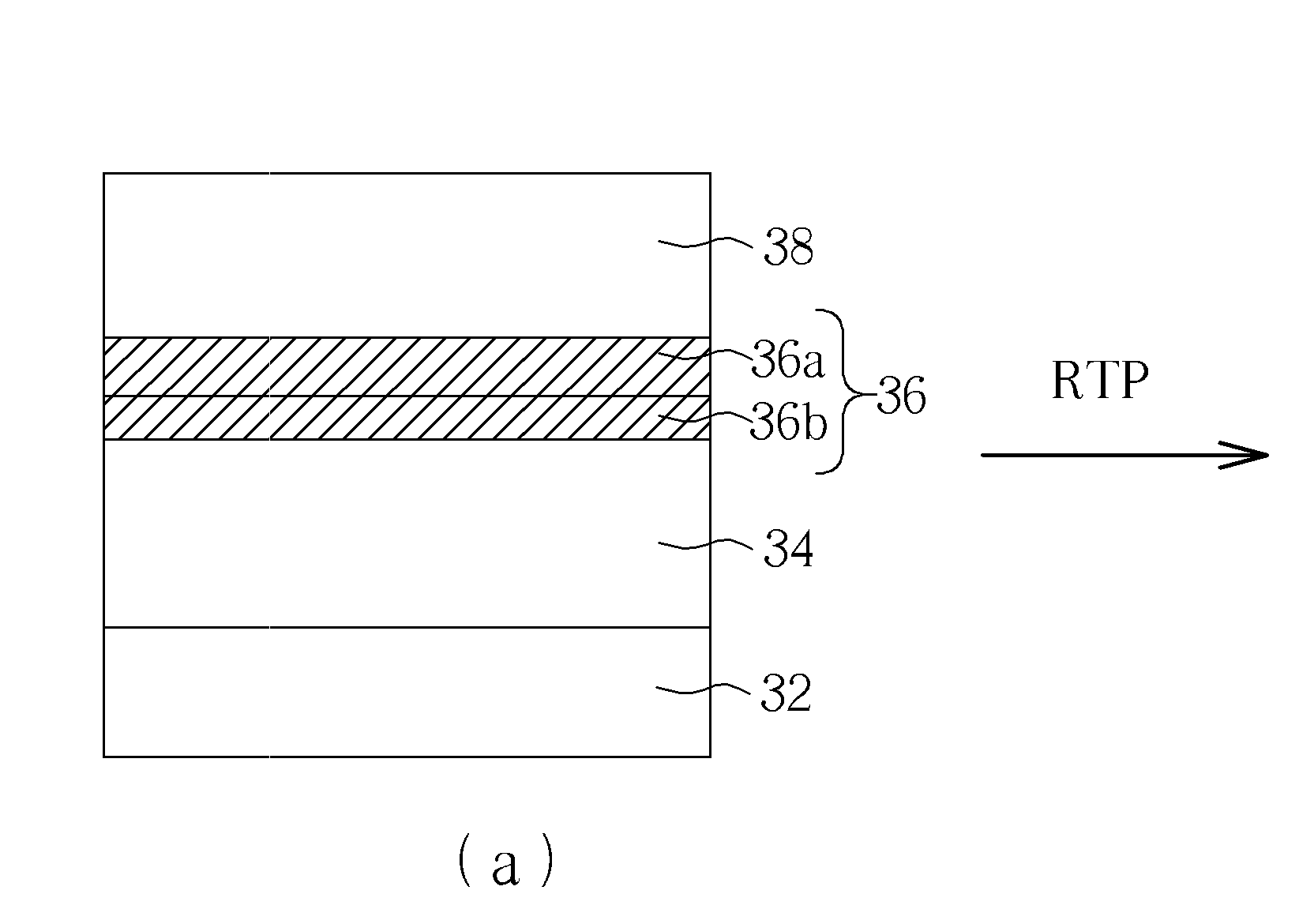
A method of fabricating a RRAM includes: forming a bottom electrode; forming a first metal layer, a first metal oxide layer, and a second metal layer on the bottom electrode in sequence; performing an RTO process followed by a top electrode formation; oxidizing the first metal layer to a second metal oxide layer comprising a second oxygen content; and oxidizing the second metal layer to a third metal oxide layer comprising a third oxygen content; wherein the first metal oxide layer has a first oxygen content after the RTO process is performed, the third oxygen content being higher than the first oxygen content and the first oxygen content being higher than the second oxygen content.
Owner:NAN YA TECH
Bag with window and method for making the same
InactiveUS20080199644A1Improve sealingLayer is highLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsAdhesiveHigh isolation
A method for making a bag with a window includes a step of making an outer surface which is composed of a first layer and a second layer glued to the first layer; a step of making a through hole through the outer surface; a step of making an inner surface which is composed of a high isolation layer and a plastic layer, and a step of connecting the second layer to the high isolation layer by way of non-liquid adhesive so as to form a bag with a window. The high isolation layer prevents air and moist from entering into the bag so as to keep freshness of the food received in the bag.
Owner:TEHN LIN ENTERPRISE
Method for manufacturing a solid electrolyte sensor element for detecting at least one property of a measuring gas in a measuring gas chamber, containing two porous ceramic layers
InactiveUS20160061767A1Increasing thermal massImprove robustnessWave amplification devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMetallurgyGas chamber
A method for manufacturing a sensor element is provided for detecting at least one property of a measuring gas in a measuring gas chamber, in particular for detecting a proportion of a gas component in the measuring gas or a temperature of the measuring gas. The method includes the following steps: providing at least one solid electrolyte which includes at least one functional element; applying, at least in sections, at least one first layer made of a ceramic material to the solid electrolyte, the first layer having a first porosity after the application; and applying, at least in sections, at least one second layer made of a ceramic material, the second layer having a second porosity after the application, and the first layer differing from the second layer with respect to at least one material property. Moreover, a sensor element which is manufacturable according to this method is provided.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Antireflection film and making method
InactiveUS7229686B2Improve the level ofImprove anti-reflection functionSynthetic resin layered productsRecord information storageRefractive indexTitanium oxide
A high refractive index layer of a cured first coating composition comprising (A) metal oxide fine particles selected from among titanium oxide, aluminum oxide, zirconium oxide, cerium oxide, iron oxide, tin oxide, and compound oxides thereof and (B) a compound having an acrylic, methacrylic, vinyl or styryl group, and a low refractive index layer of a cured second coating composition comprising (D) voided silica-base inorganic oxide fine particles and (C) a compound having at least two epoxy and / or oxetane groups are successively stacked on a substrate to form an antireflection film.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Transferable antireflection material for use on optical display
InactiveUS20060147729A1Sufficient adhesionIncreased durabilityLayered productsThin material handlingUltravioletRefractive index
An optical display, and method for forming an optical display, having improved antireflection properties and durability is formed by applying a transferable antireflection material to an optical substrate through the use of an in-mold or heat press technique or alternatively by an ultraviolet exposure technique. The transferable antireflection material is formed prior to application to the substrate and has at least a low refractive index layer and a high refractive index layer coupled to a release film. The low index reflection layer is preferably a silicon-modified fluoropolymer material having good durability, low refractivity, and appropriate adhesion to the release layer and subsequently applied high index refraction layer. The optical display is then coupled to a housing of an article for use.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Ethylenically unsaturated compound, light sensitive composition, light sensitive planographic printing plate material and printing process employing the same
InactiveUS20090263744A1High exposureExcellent developabilityCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationWater soluble polymersSolubility
The present invention provides a novel ethylenically unsaturated compound which is highly sensitive to scanning exposure due to an ultraviolet to near-infrared laser and is cured to give good physical properties; a light sensitive composition providing good developability and high sensitivity and forming a high strength layer; a planographic printing plate material having advantages that good developability, high sensitivity and high strength layer are obtained, particularly a planographic printing plate material requiring no developing machine which are mounted on a printing press without any development, followed by printing and which provides excellent developability on a printing press and printing durability; and a printing process. The ethylenically unsaturated compound has in the molecule a photo-oxidation group and a polymerizable ethylenically unsaturated bond, and has a predetermined solubility in water or an aqueous alkali solution. The planographic printing plate material is characterized in that it comprises a support and provided thereon, a light sensitive layer containing the ethylenically unsaturated compound, a polyhalogen compound as a photopolymerization initiator, a water-soluble polymer binder as a polymer binder and an infrared absorbing agent.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA MEDICAL & GRAPHICS INC
Insulated electric wire
InactiveUS20080268218A1Increase flexibilityLayer is highSynthetic resin layered productsInsulated cablesElectrical conductorPolyamide-imide
The present invention relates to an insulated electric wire. The insulated electric wire according to the present invention includes a high adhesion resin layer made of a polyamideimide resin containing a compound having a polar group in a molecular structure of an insulation material; and a high flexibility resin layer provided on the high adhesion resin layer. The present invention advantageously improves adherence between a polyamideimide resin and a conductor, and provides adhesive strength with the conductor to improve flexibility of the insulated electric wire and at the same time to improve flexibility of an insulator without deterioration of heat resistance of the insulator.
Owner:LG CABLE LTD (KR)
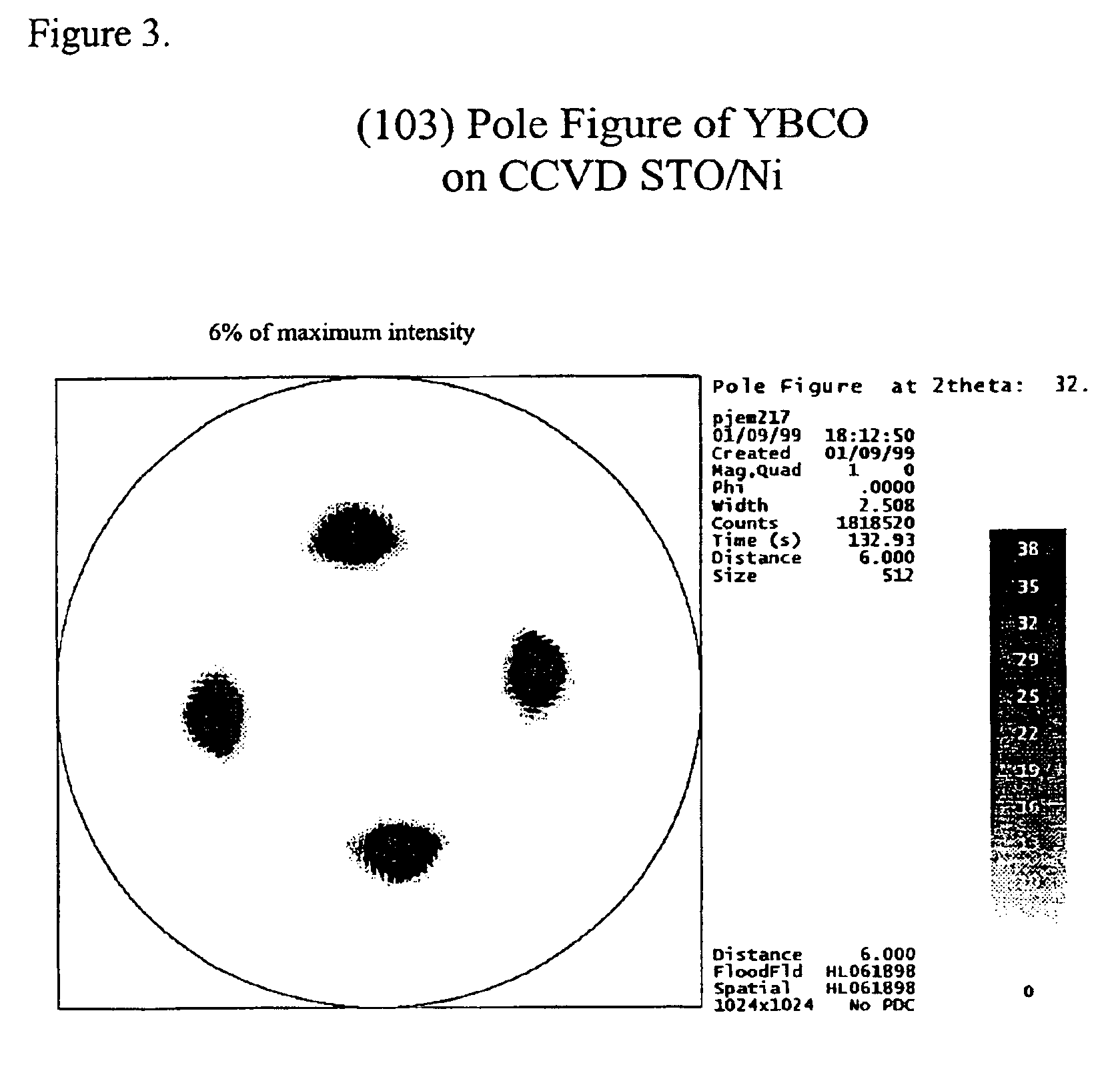
Epitaxial thin films
InactiveUS7033637B1Inhibited DiffusionReduce manufacturing costElectrolytic capacitorsFinal product manufactureCapacitanceElectrical conductor
Epitatial thin films for use as buffer layers for high temperature superconductors, electrolytes in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC), gas separation membranes or dielectric material in electronic devices, are disclosed. By using CCVD, CACVD or any other suitable deposition process, epitaxial films having pore-free, ideal grain boundaries, and dense structure can be formed. Several different types of materials are disclosed for use as buffer layers in high temperature superconductors. In addition, the use of epitaxial thin films for electrolytes and electrode formation in SOFCs results in densification for pore-free and ideal gain boundary / interface microstructure. Gas separation membranes for the production of oxygen and hydrogen are also disclosed. These semipermeable membranes are formed by high-quality, dense, gas-tight, pinhole free sub-micro scale layers of mixed-conducting oxides on porous ceramic substrates. Epitaxial thin films as dielectric material in capacitors are also taught herein. Capacitors are utilized according to their capacitance values which are dependent on their physical structure and dielectric permittivity. The epitaxial thin films of the current invention form low-loss dielectric layers with extremely high permittivity. This high permittivity allows for the formation of capacitors that can have their capacitance adjusted by applying a DC bias between their electrodes.
Owner:MICROCOATING TECH +2
Automobile use mat with a distinguished Anti-slip feature
InactiveUS20120121849A1Improve friction resistanceLayer is highLiquid surface applicatorsVehicle arrangementsEngineeringNonwoven fabric
The challenges in this invention is to provide automobile use mat that has distinguished noise absorption and anti-slip features, as well as it being light in weight for a low cost.The inventors, for their exerted investigations in resolving such challenges and as a result, as a replacement to the frequently used conventional mats with mounted resin (bump) emboss configuration, have introduced the nonwoven fabric layer from polypropylene fiber, burned on the lower surface side of the nonwoven fabric layer, deforming the fibers, forming anti-slip layer from melt bonding the fibers together, discovered the possibilities in achieving an automobile use mat that is light weight, permeable, dominant in its anti-slip effect, easy to bend as well as handle, that lead to this invention.
Owner:SUMINOE TEXTILE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com