Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
82results about How to "Suppress surface roughness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
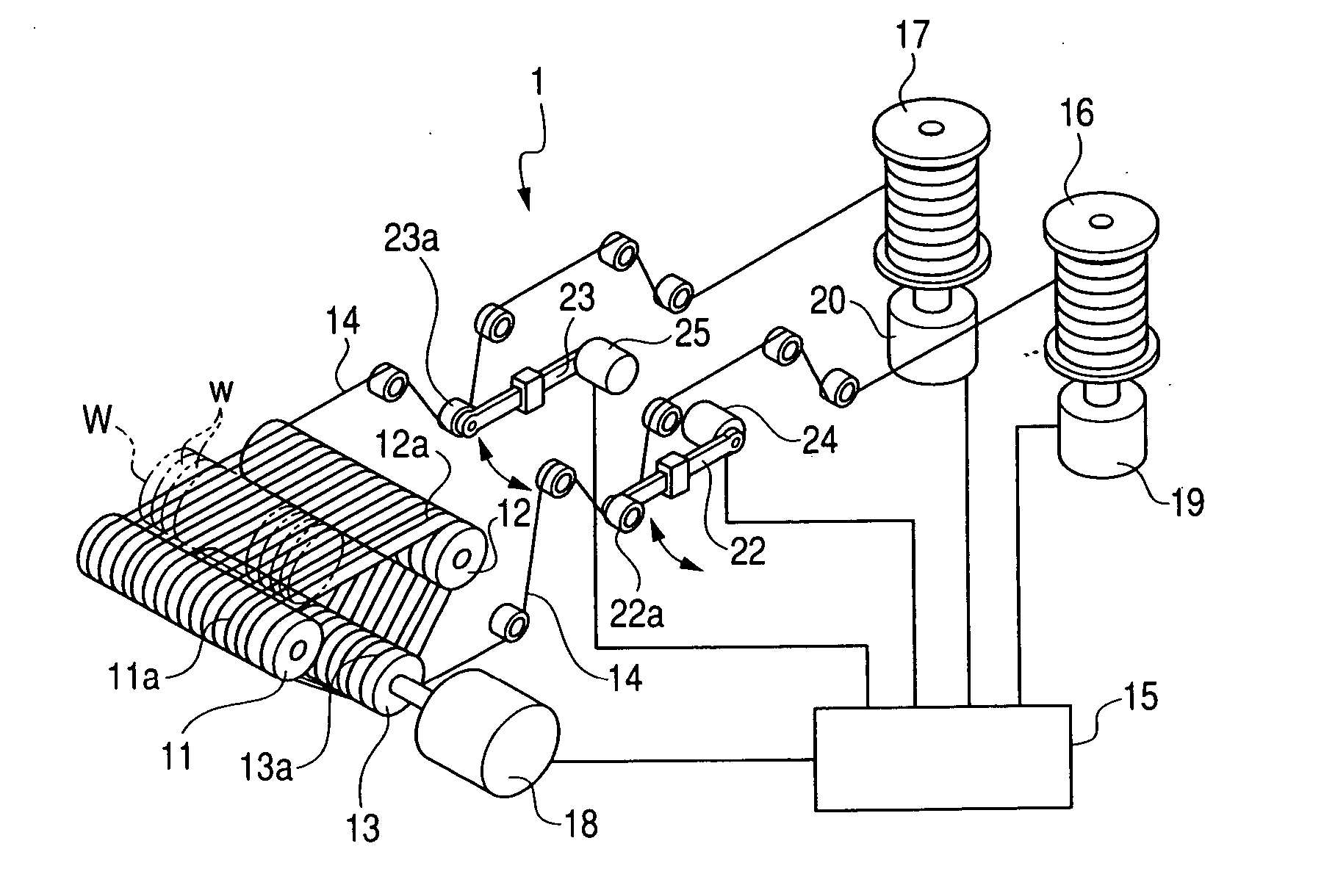
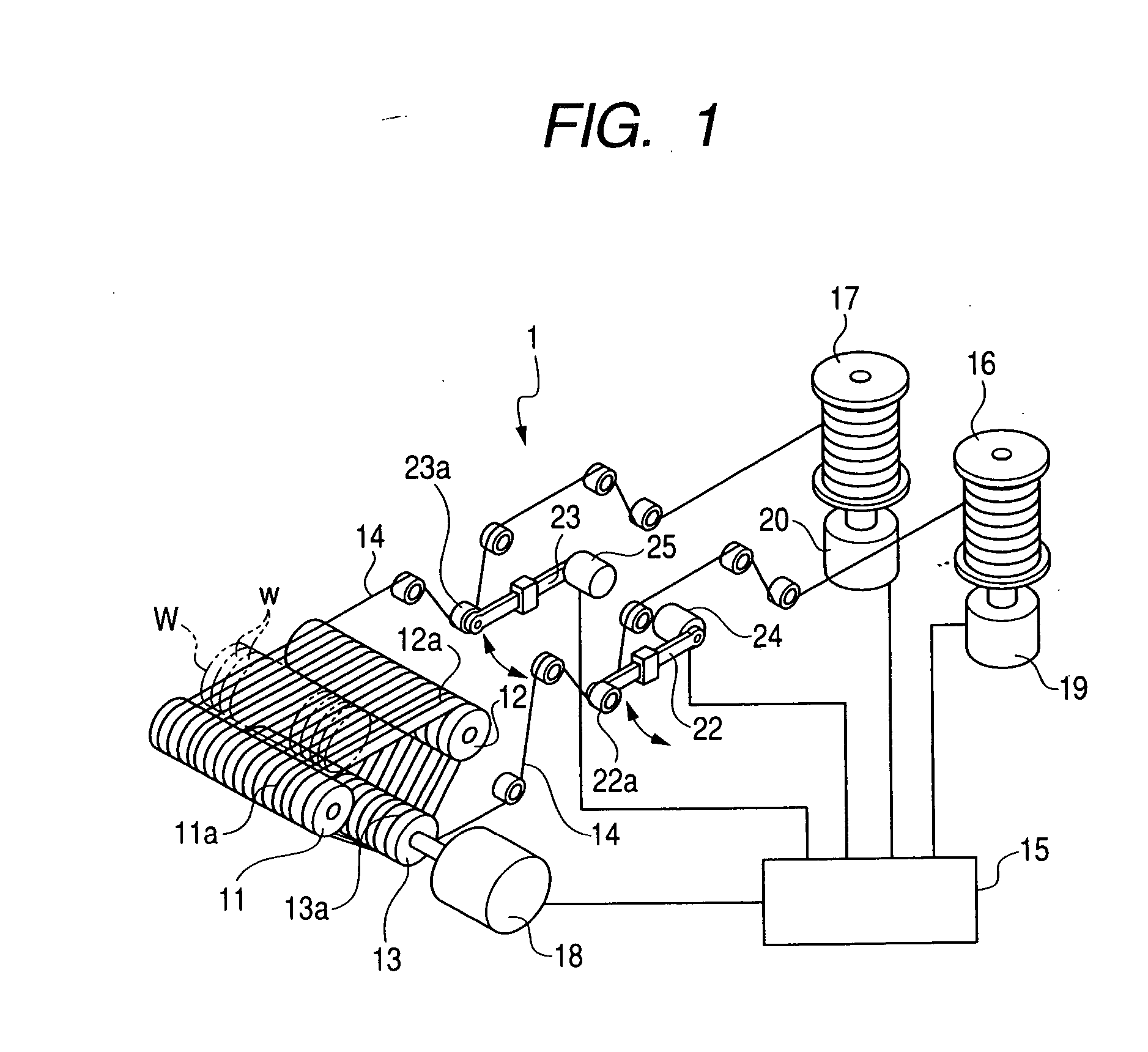
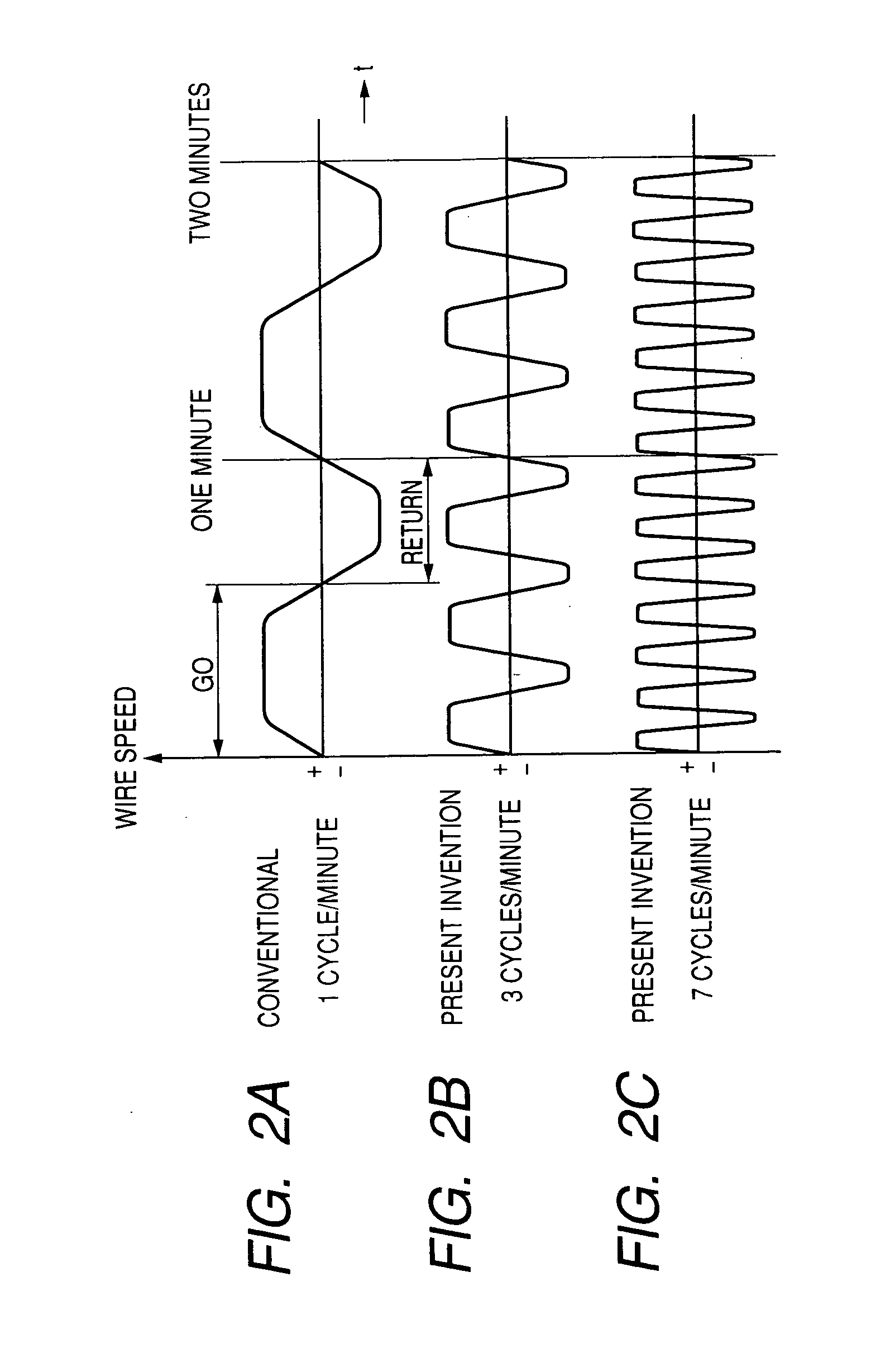
Manufacturing method for semiconductor wafers, slicing method for slicing work and wire saw used for the same
InactiveUS20060258268A1Reduce unevenness of thickness and warpReduce wavinessMetal sawing devicesEdge grinding machinesCompound (substance)Engineering
In order to omit a lapping process or a double disk grinding process by performing slicing operation so as not to generate long period waviness on the surface of the wafer in a slicing process and by completely removing short period waviness remaining in the surface of the sliced wafer during a polishing process, there is provided a manufacturing method includes a slicing process of slicing a work of the semiconductor wafer by reciprocating a wire of a wire saw at constant cycles of 3 or more and less than 8 per a minute a grinding process of grinding both sides of the sliced wafer by a grinding wheel, one-side by one-side and a polishing process of performing a chemical mechanical polishing on both sides of the ground wafer by a fixed abrasive grain polishing cloth, in which an abrasive grain is fixed, and a abrasive containing no abrasive grains.
Owner:KOMATSU NTC LTD +1
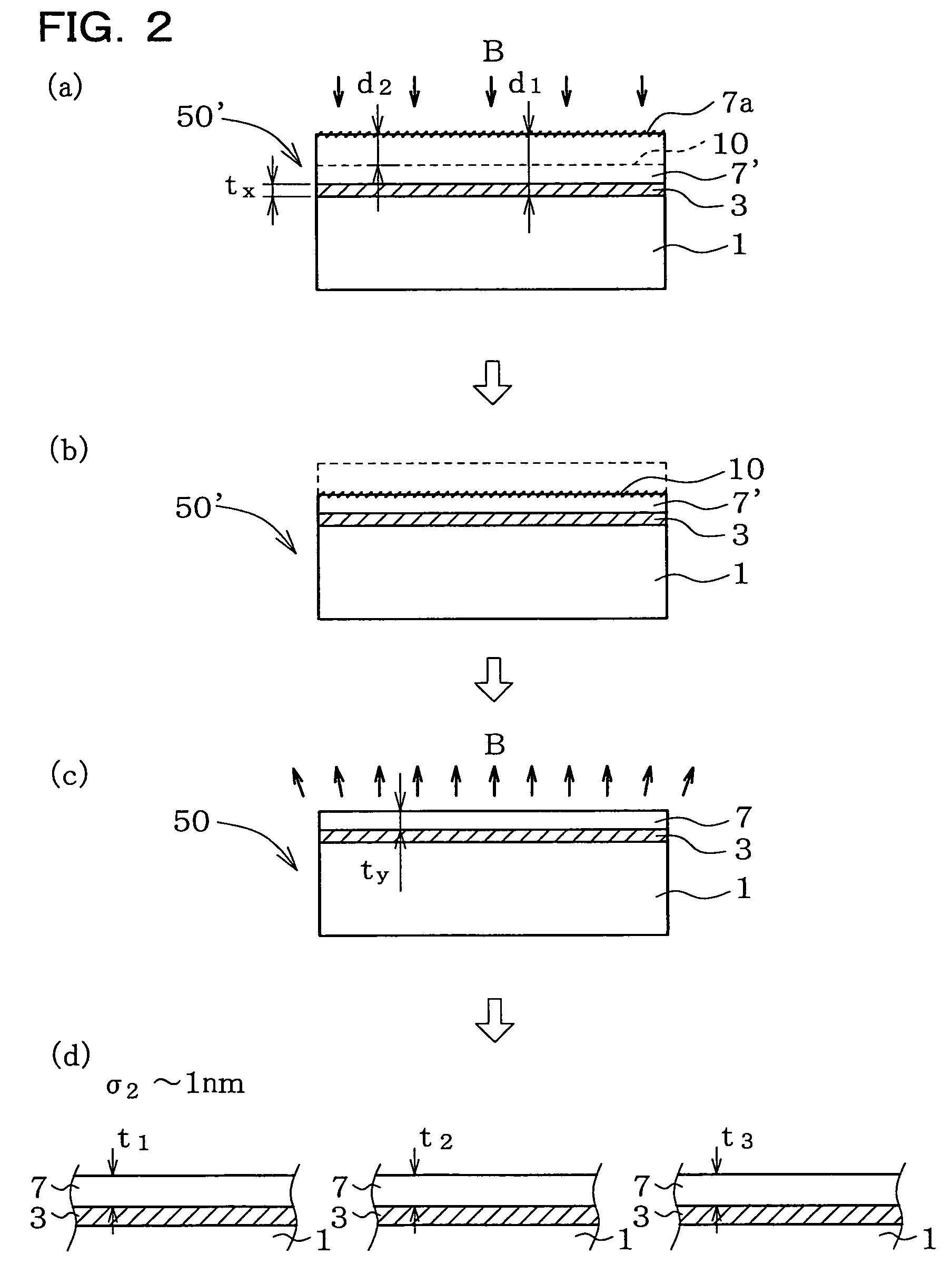
Method of fabricating SOI wafer
InactiveUS7084046B2Sharp concentration profileImprove concentrationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingThinning
After completion of annealing for bonding of the base wafer 1 and bond wafer 2, the bond wafer 2 is thinned to a first thickness suitable for ion implantation, and boron is ion-implanted to thereby form a high-boron-concentration layer 10. A second thinning step based on selective etching is then carried out while using the high-boron-concentration layer 10 as an etch stop layer. This is successful in providing a method of fabricating an SOI wafer which is suppressed both in intra-wafer uniformity of the firm thickness and in inter-wafer uniformity of the film thickness even when a required level for the thickness of the SOI layer is extremely small.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
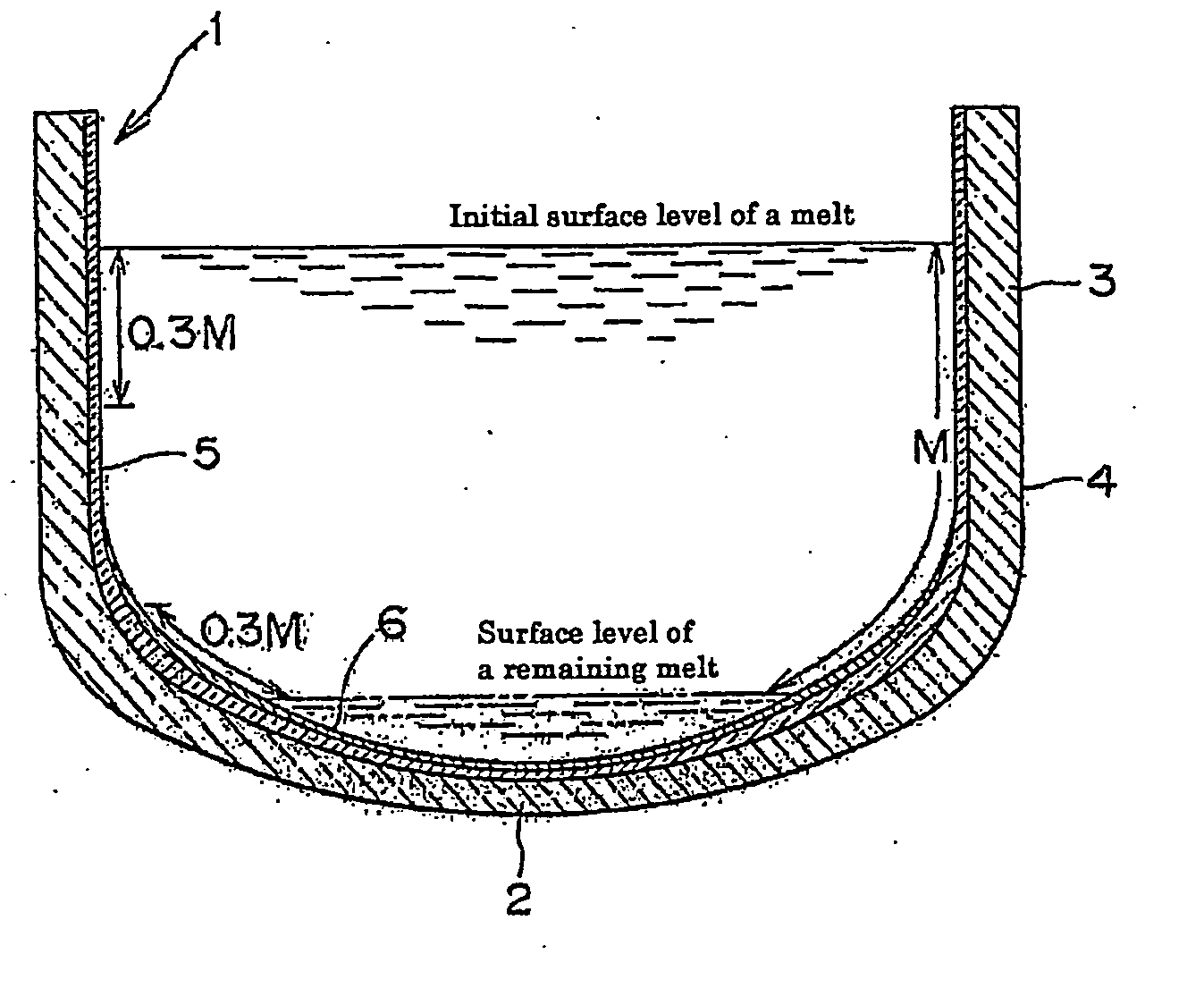
Quartz glass crucible for pulling up silicon single crystal and method for manufacture thereof
ActiveUS20060236916A1Reduce vibrationSmall sizeAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthCrucibleSingle crystal
A quartz glass crucible which has a non-transparent outer layer formed through melting a natural silica powder and a transparent layer formed in the inside of the outer layer, wherein the transparent layer comprises a natural quartz layer having a thickness of 0.4 to 5.0 mm transparent layer comprising a synthetic quarts glass is formed thereon in the inside of the crucible in the range of 0.15 to 0.55 L relative to L, which is the distance from the center of the bottom of the inner surface of the quartz glass crucible to the upper end thereof along the inner surface thereof. The quartz glass crucible can be suitably used for suppressing the occurrence of vibration and reducing the generation of roughened face in the surface of a crucible, and thus for pulling up a silicon single crystal with enhanced stability.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS +1
Transfer type inkjet recording method and transfer type inkjet recording device
InactiveUS20120113203A1Reduce workloadDecreased substancesPrintingIntermediate imageSurface roughness
The transfer type inkjet recording method has the intermediate image formation process and the transfer process defined in the specification. The transfer type inkjet recording method includes, in the intermediate image formation process, selecting an intermediate transfer body having a center line surface roughness closest to the center line surface roughness of a recording medium from a plurality of intermediate transfer bodies different from each other in the center line surface roughness, and then an intermediate image is formed on the surface of the selected intermediate transfer body. Moreover, a transfer type inkjet recording which is used for the method is provided.
Owner:CANON KK
III-V nitride semiconductor substrate and its production lot, and III-V nitride semiconductor device and its production method
ActiveUS20050139960A1Improve thermal stabilityImprove stabilityPolycrystalline material growthSolid-state devicesHydrogenHydrogen atom
A III-V nitride semiconductor substrate comprising a III-V nitride semiconductor single crystal at least in a surface portion thereof, the product of [H] and [D] being 1×1025 or less, wherein [H] represents the concentration of hydrogen atoms (the number of hydrogen atoms per cm3) in a surface portion of the single crystal, and [D] represents a dislocation density (the number of dislocations per cm2) on a single crystal surface.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
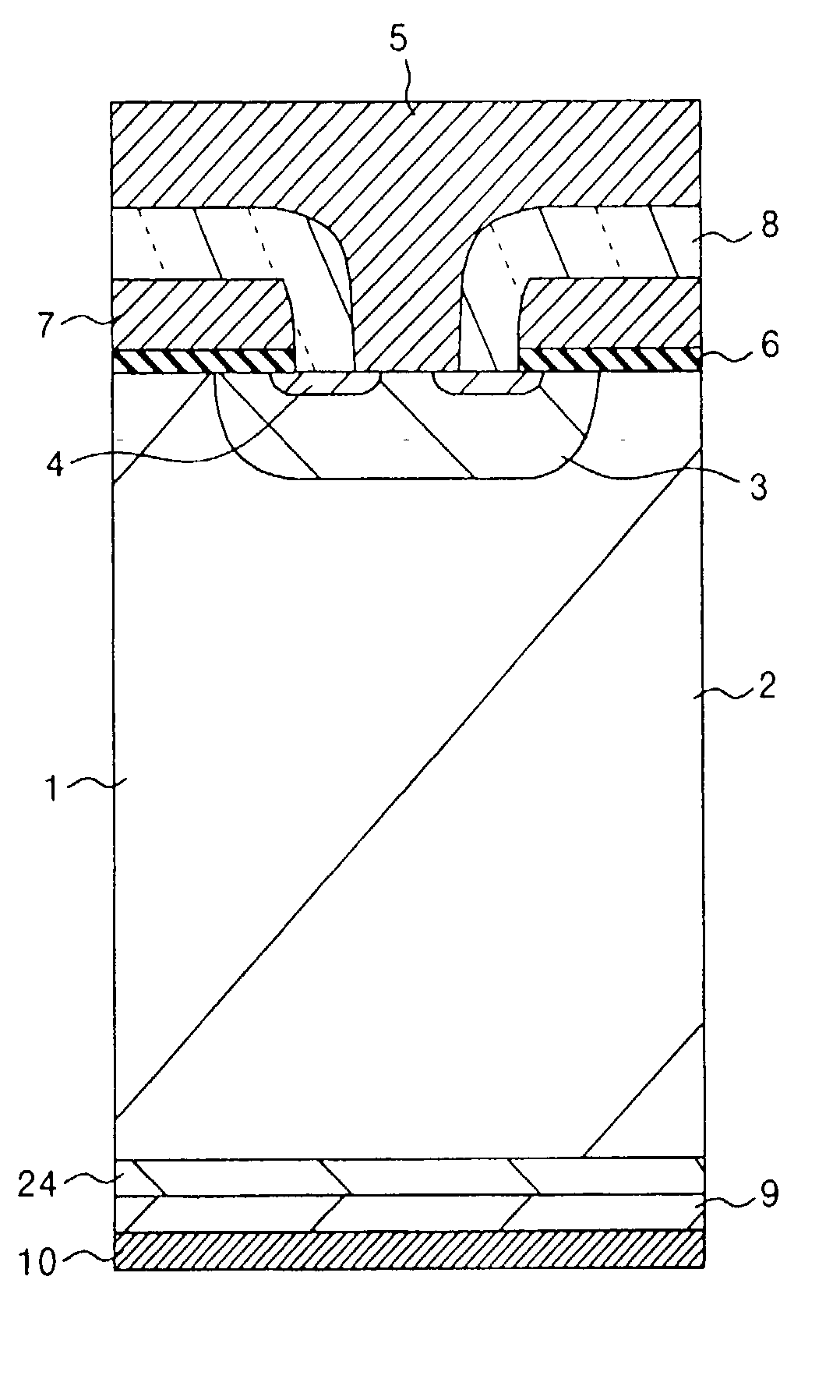
Method for manufacturing a semiconductor device
InactiveUS20020127783A1Lower resistanceIncrease concentrationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCompound (substance)Engineering
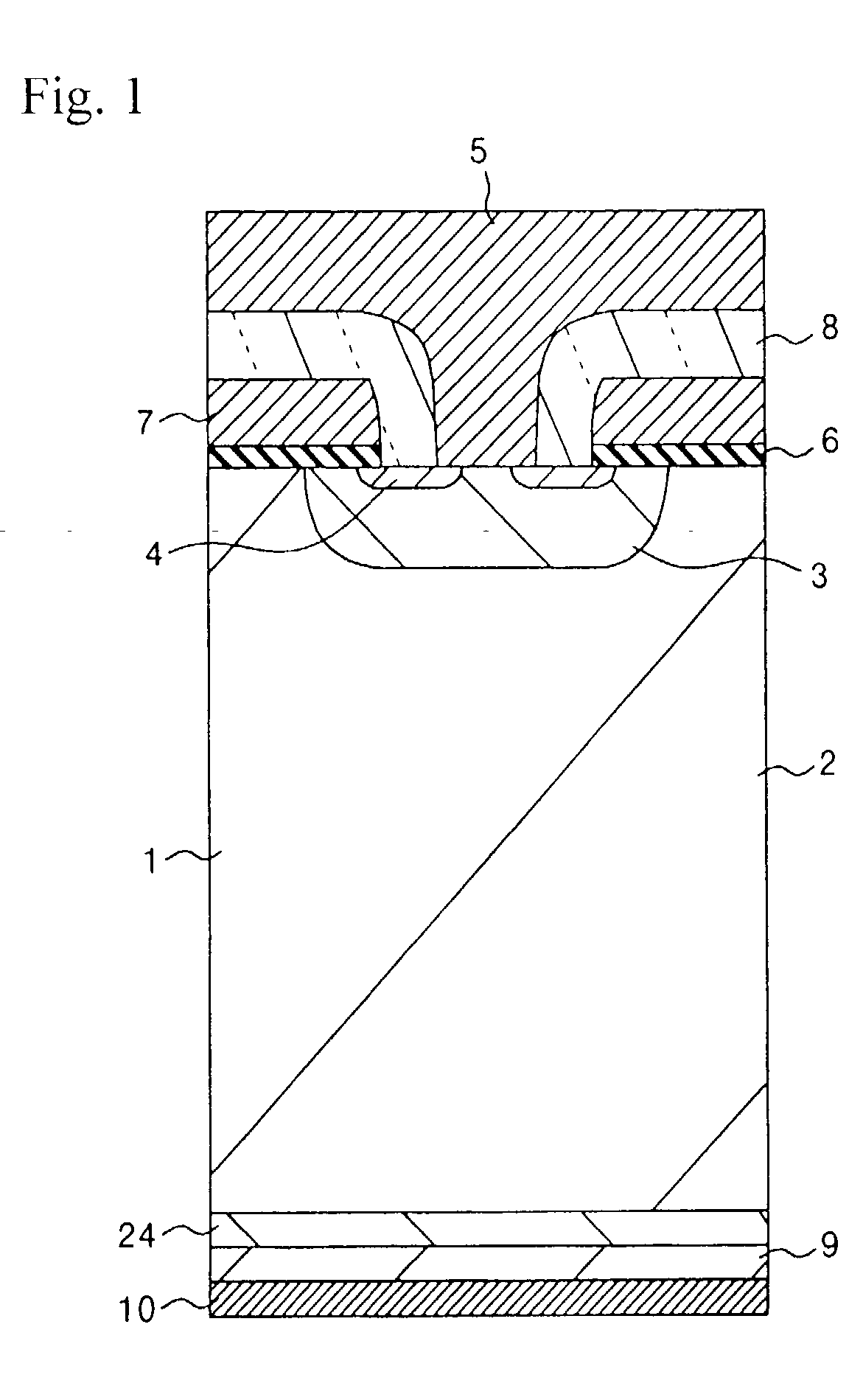
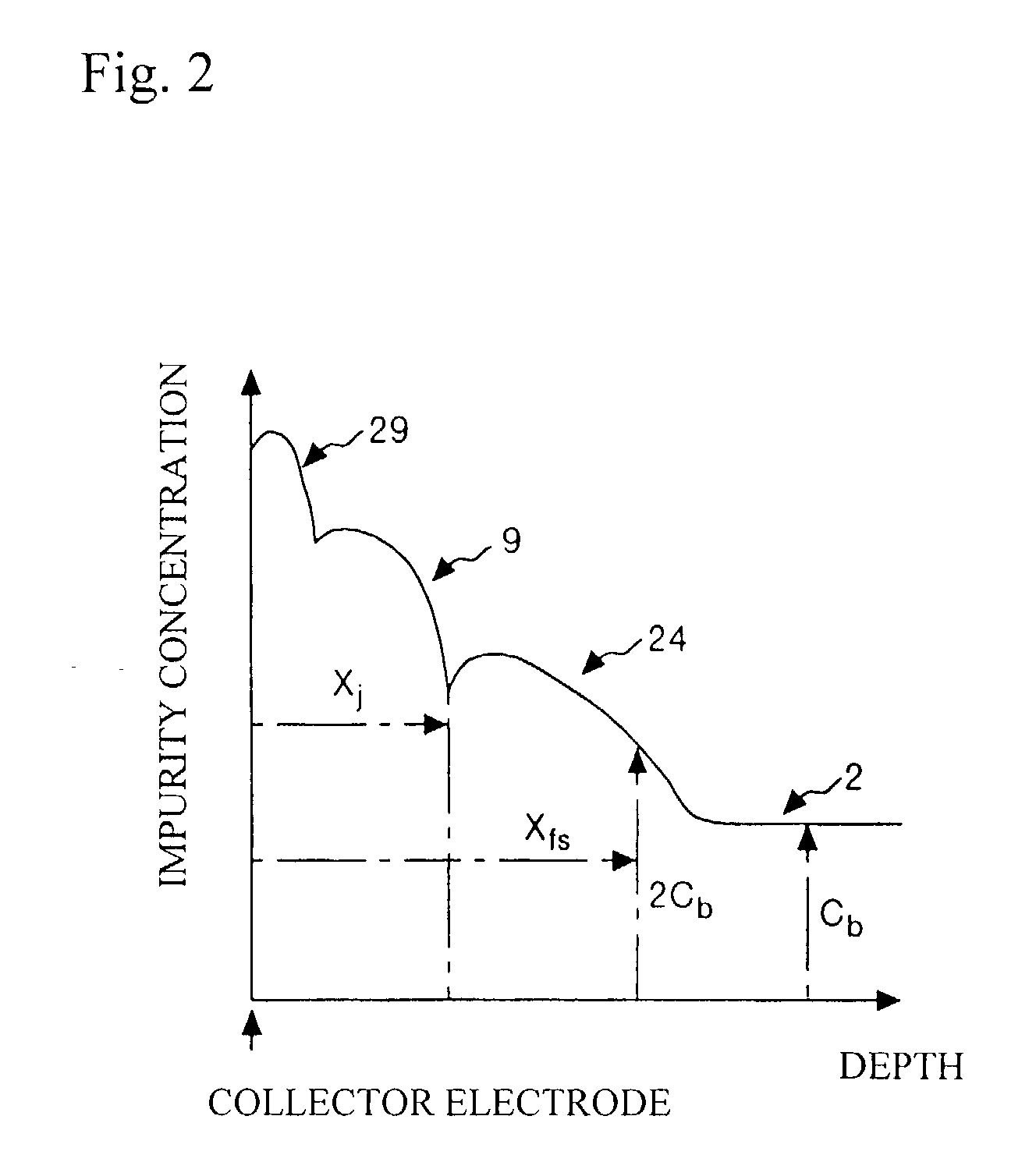
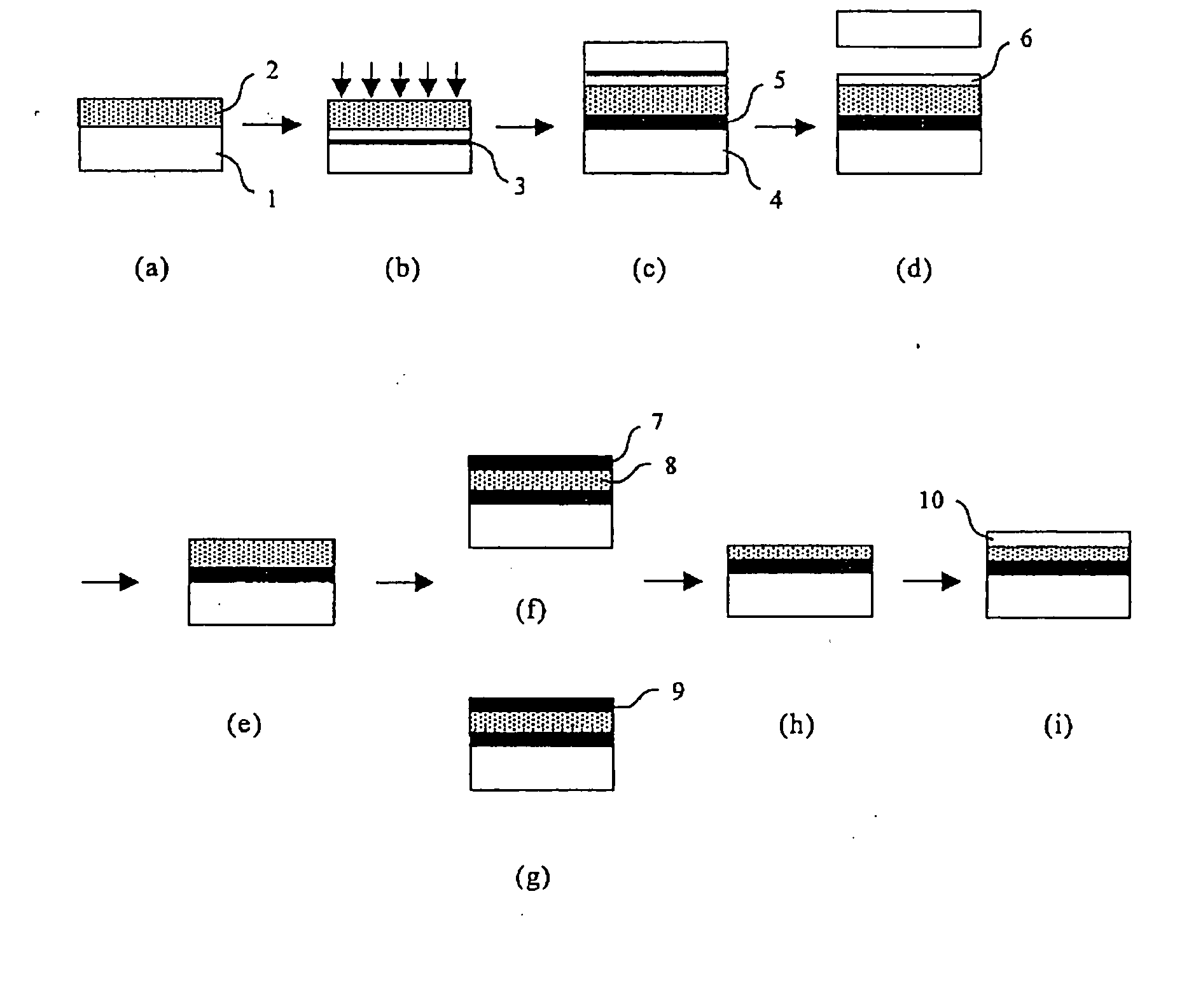
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device constituting an IGBT is provided that allows to manufacture the device using an inexpensive wafer and with high yields, and achieves low losses. Specifically, after an emitter electrode is formed, a reverse principal surface is polished to a specified thickness. The center line average height Ra of the polished surface is controlled to be not more than 1 .mu.m, and the filtered center line waviness Wca is kept within 10 .mu.m. The polished surface is selectively cleaned with chemicals-dissolved water to remove particles. To the cleaned surface, phosphorus ions are implanted for forming a field-stop layer and boron ions are implanted for forming a collector layer. The wafer is then put into a diffusion furnace and annealed at a temperature from 300.degree. C. to 550.degree. C. to form a field-stop layer and a collector layer. Finally, a collector electrode is formed.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method For Producing Semiconductor Wafer
InactiveUS20070287269A1Suppress surface roughnessHigh crystallinitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNoble gasWafering
The present invention is a method for producing a semiconductor wafer, comprising at least steps of: epitaxially growing a SiGe layer on a surface of a silicon single crystal wafer that is to be a bond wafer; implanting at least one kind of hydrogen ion and rare gas ion through the SiGe layer, so that an ion implanted layer is formed inside the bond wafer; closely contacting and bonding a surface of the SiGe layer and a surface of a base wafer through an insulator film; then performing delamination at the ion implanted layer, removing a Si layer in a delaminated layer transferred to a side of the base wafer by the delamination, so that the SiGe layer is exposed; and then subjecting the exposed SiGe layer to a heat treatment for enriching Ge under an oxidizing atmosphere and / or a heat treatment for relaxing lattice strain under a non-oxidizing atmosphere. Thereby, a method for producing a semiconductor wafer having a SiGe layer in which lattice relaxation is sufficiently performed and of which surface roughness is suppressed and of which crystallinity is good is provided.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Water-based coating composition and method for forming multilayer coating film
InactiveUS20120107619A1Prevent roughness of surfacePrevents formationSynthetic resin layered productsPretreated surfacesPolycarbonateIsocyanate
This invention relates to an aqueous coating composition comprising an acrylic or polyester resin (A); a curing agent (B); and a blocked isocyanate group-containing urethane resin emulsion (C) having a weight average molecular weight of 2,000 to 50,000, which is prepared using a polyisocyanate component and a polyol component as starting materials, the polyisocyanate component comprising an alicyclic diisocyanate, and the polyol component comprising a polycarbonate diol in an amount of 50 mass % or more, based on the total amount of the polyol component; (i) when the component (A) is an acrylic resin, the aqueous coating composition comprising the component (C) in an amount of, as solids content, 20 to 60 mass %, based on the total solids content of the components (A), (B) and (C); and (ii) when the component (A) is a polyester resin, the aqueous coating composition comprising the component (C) in an amount of, as solids content, 10 to 50 mass %, based on the total solids content of the components (A), (B) and (C).
Owner:KANSAI PAINT CO LTD
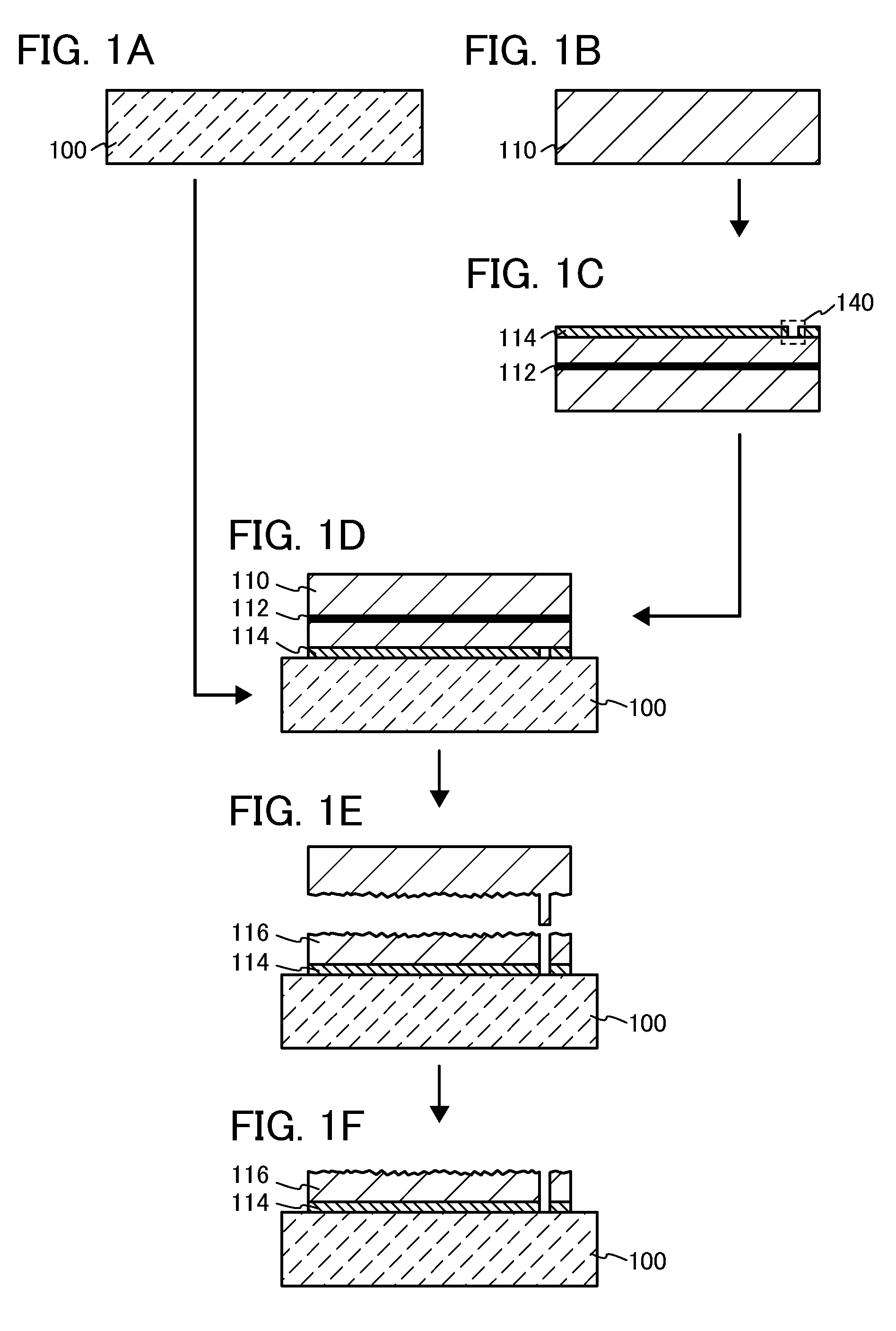
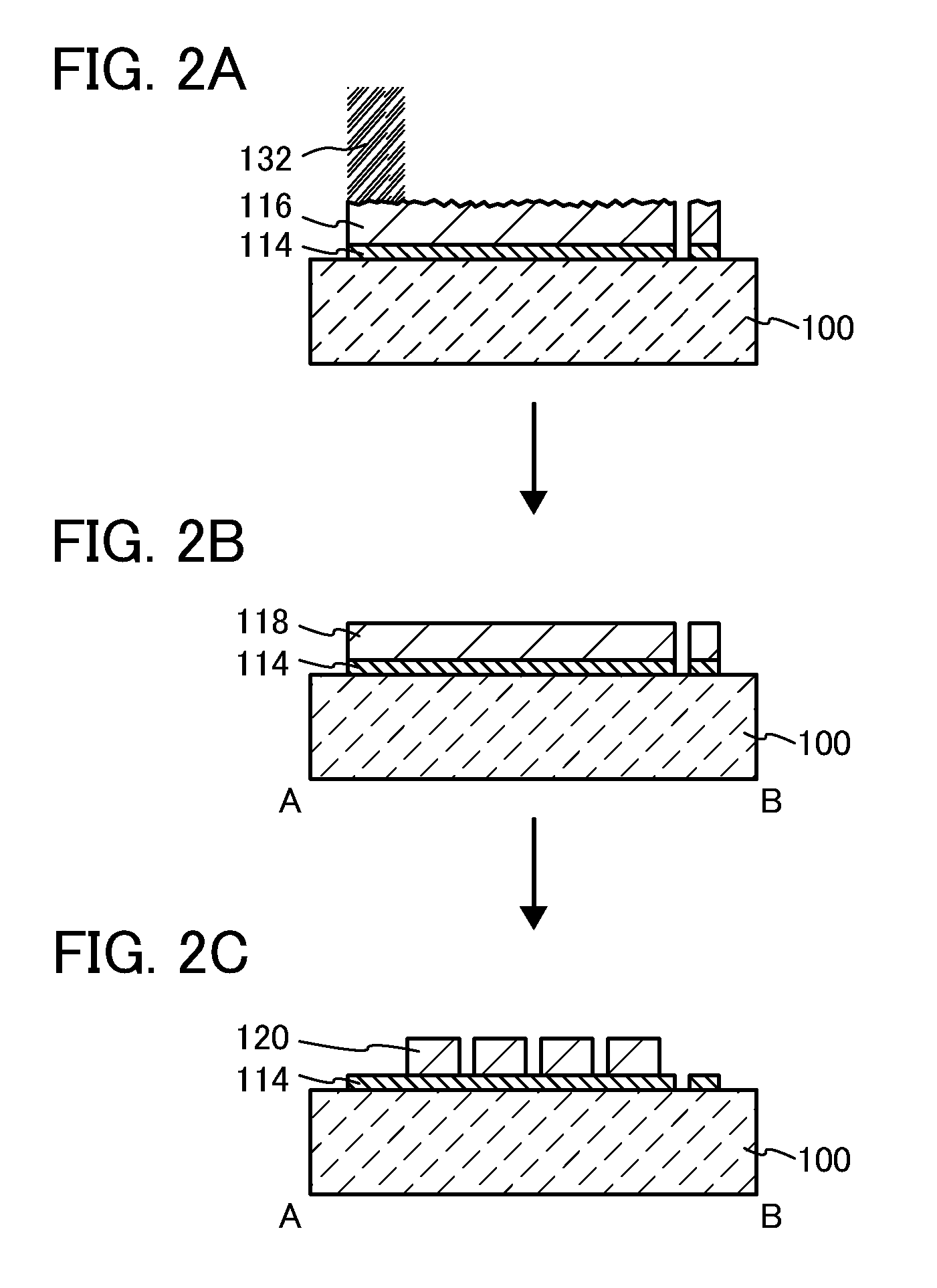
Method for manufacturing soi substrate and soi substrate
InactiveUS20100330779A1Suppress surface roughnessImprove manufacturing yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSoi substrateSemiconductor
A bond substrate is irradiated with accelerated ions to form an embrittled region in the bond substrate; an insulating layer is formed over a surface of the bond substrate or a base substrate; the bond substrate and the base substrate are bonded to each other with the insulating layer interposed therebetween; a region in which the bond substrate and the base substrate are not bonded to each other and which is closed by the bond substrate and the base substrate is formed in parts of the bond substrate and the base substrate; the bond substrate is separated at the embrittled region by heat treatment; and a semiconductor layer is formed over the base substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
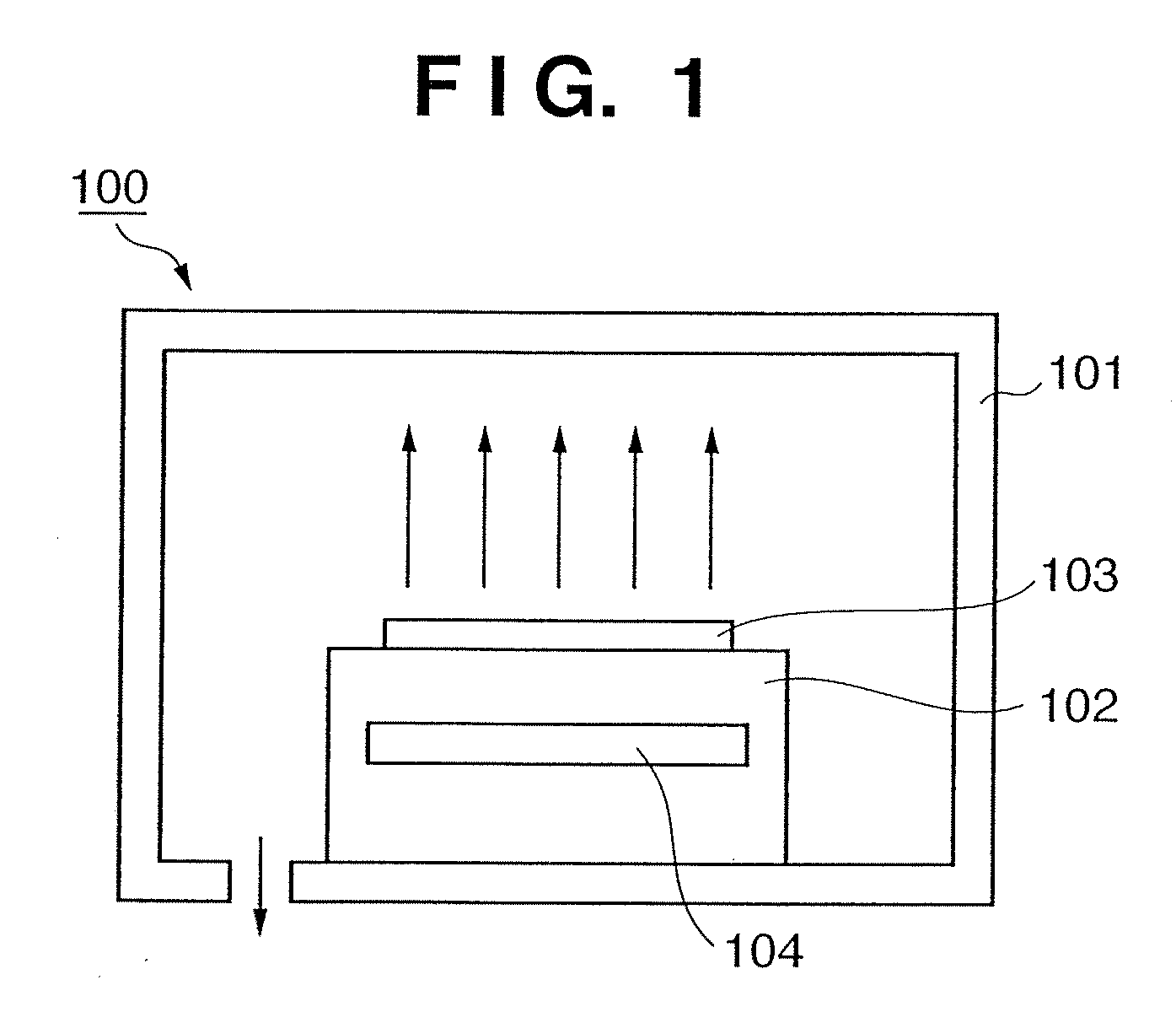
Substrate heating apparatus and semiconductor fabrication method
ActiveUS20080213988A1Suppress surface roughnessUniformity of processDrying solid materials with heatSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
Owner:CANON ANELVA CORP
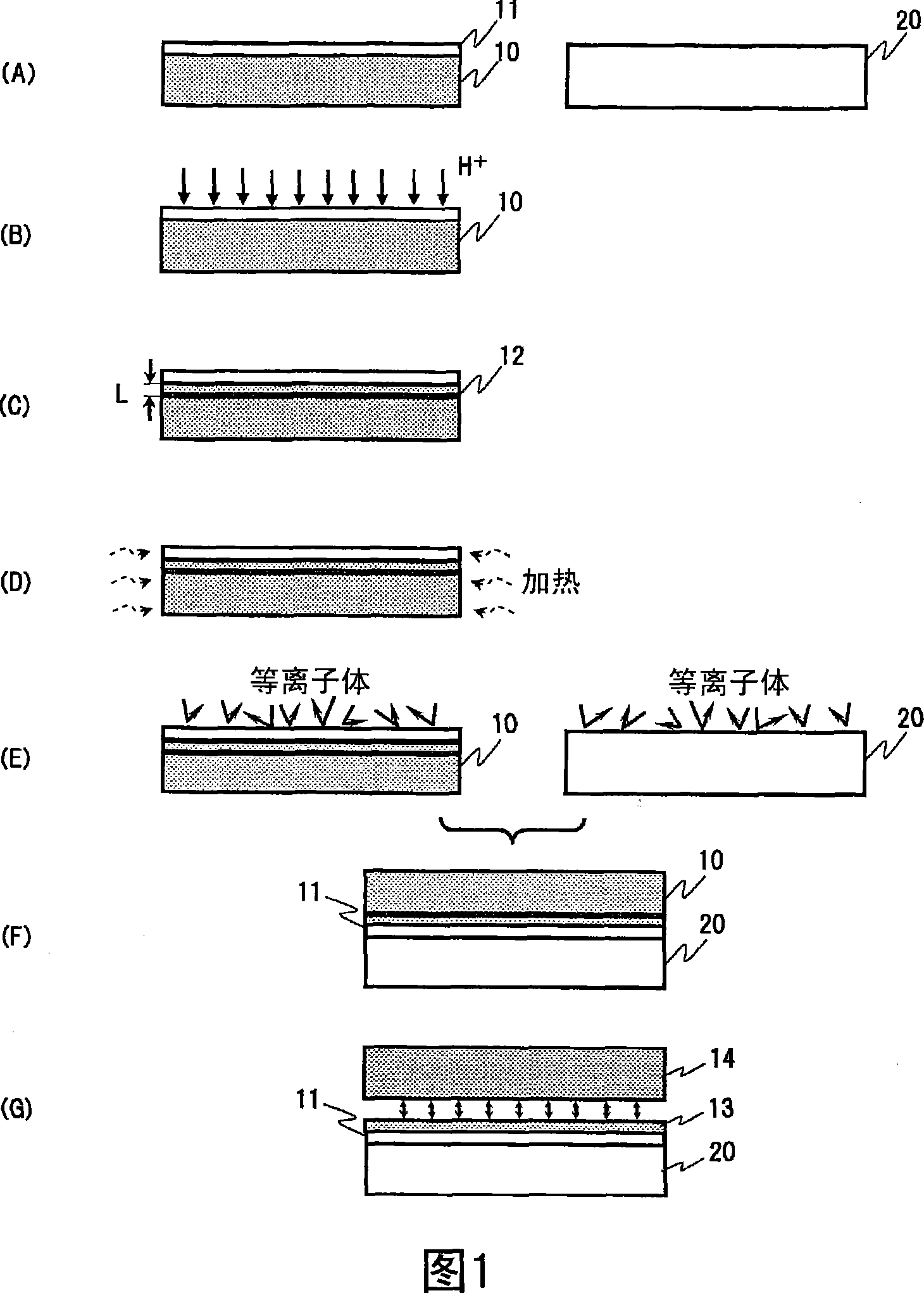
Method for manufacturing an SOI substrate
InactiveCN101207009ASuppress surface roughnessUniform thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBonding processSurface roughness
A method for manufacturing an SOI substrate, comprising: an ion implantation process, which is to form a hydrogen ion implantation layer on the main surface side of a silicon substrate; a surface treatment process, which is to at least one of the insulating substrate and the above-mentioned silicon substrate activation treatment on the main surface of the above-mentioned insulating substrate; a bonding process, which is to bond the main surface of the above-mentioned insulating substrate and the main surface of the above-mentioned silicon substrate; The silicon thin film is mechanically peeled off to form a silicon film on the main surface of the insulating substrate, and the temperature of the silicon substrate in the ion implantation process is maintained at 400° C. or lower. The method of the invention can suppress the surface roughness of the stripped SOI film, and ensure that the entire surface of the SOI substrate has a uniform thickness of the SOI film. Since all are low-temperature processes, the occurrence of transfer defects or slip dislocations can be suppressed, and high-quality SOI wafers can be obtained.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM CO LTD
Magnetic recording medium comprising a lower layer containing specific flat acicular alpha-iron oxide powder
InactiveUS6534168B2Reduce voidsSuppress surface roughnessLayered productsRecord information storageLow noiseHigh density
Provided is a magnetic recording medium exhibiting a high C / N (low noise) ratio in high-density magnetic recording. A magnetic recording medium which comprises a nonmagnetic lower layer comprising a nonmagnetic powder and a binder and a magnetic layer comprising a ferromagnetic powder and a binder provided in this order on a flexible nonmagnetic support. The nonmagnetic lower layer comprises flat acicular alpha-iron oxide powder with a major axis length ranging from 0.05 to 0.5 mum and a ratio of the major width to the minor width (major width / minor width) of the minor axis cross-section when sectioned at an angle perpendicular to the major axis is equal to or higher than 1. The granular nonmagnetic particles have a mean particle diameter equal to or less than 0.04 mum.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Roughing insert and roughing end mill
ActiveUS7993082B2Suppress surface roughnessReduce resistanceTransportation and packagingMilling cuttersWavelengthMechanical engineering
This roughing insert is provided with an insert body, and a waveform cutting edge which is formed on an intersecting ridge line portion between a rake face and a flank face of the insert body, and which undulates along this intersecting ridge line portion. The waveform cutting edges are formed such that a portion thereof has a smaller wavelength than the remaining portion thereof.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Roughing insert and roughing end mill
ActiveUS20100003089A1Cutting resistance can be reducedImprovement in chip processabilityMilling cuttersTurning toolsEngineeringRidge
This roughing insert is provided with an insert body, and a waveform cutting edge which is formed on an intersecting ridge line portion between a rake face and a flank face of the insert body, and which undulates along this intersecting ridge line portion. The waveform cutting edges are formed such that a portion thereof has a smaller wavelength than the remaining portion thereof.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
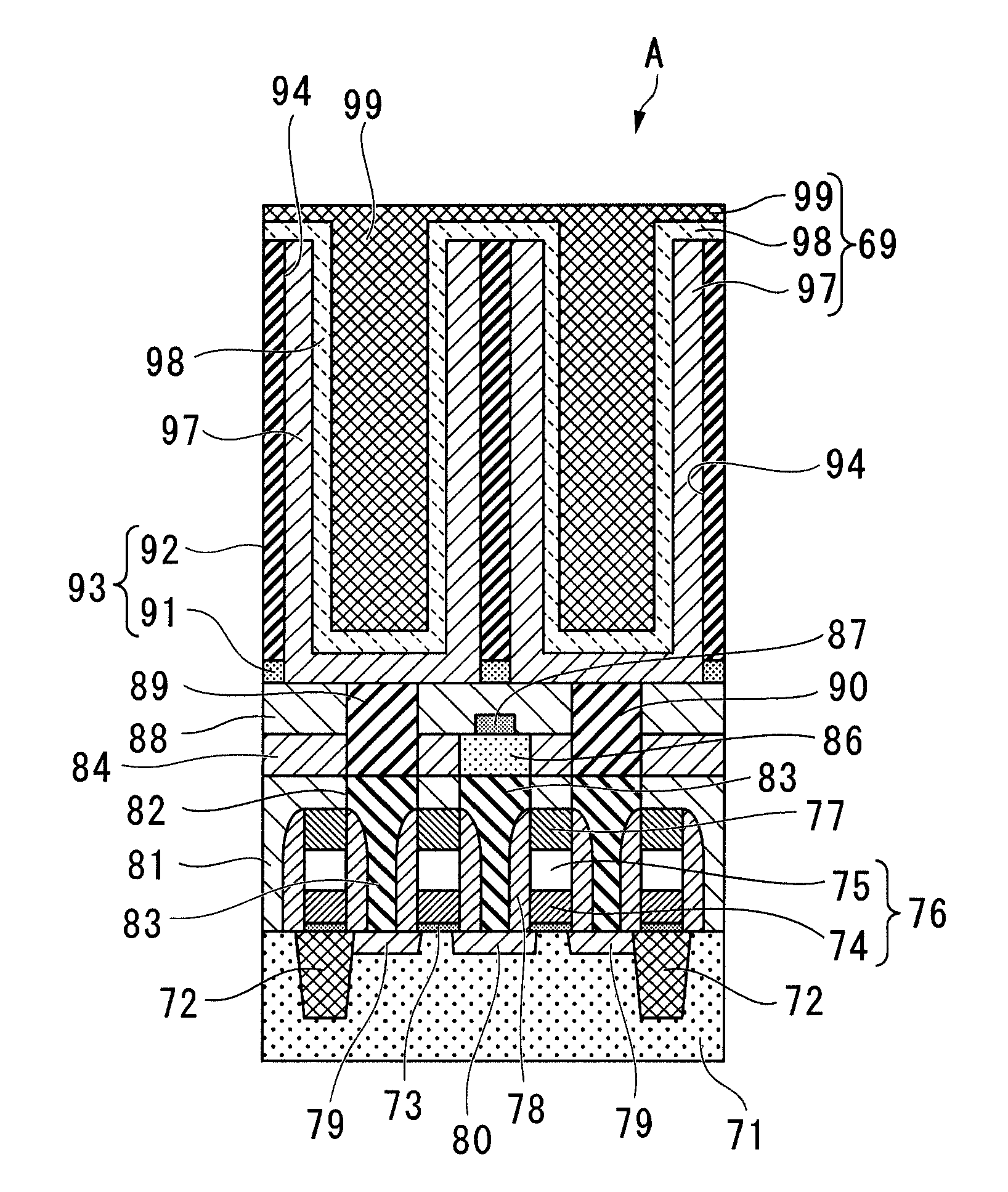
Insulator film, capacitor element, dram and semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090021889A1Easy to manufactureHigh dielectric constantThin/thick film capacitorFixed capacitor dielectricEngineeringSemiconductor
The insulator film of the present invention is suited for use as the insulator material of capacitor elements composing DRAM, is used as the insulator layer of a capacitor element provided with an insulator layer that is interposed between an upper electrode and a lower electrode, and is composed of titanium dioxide to which at least one element from among the lanthanoid elements, Hf and Y is added.
Owner:ELPIDA MEMORY INC
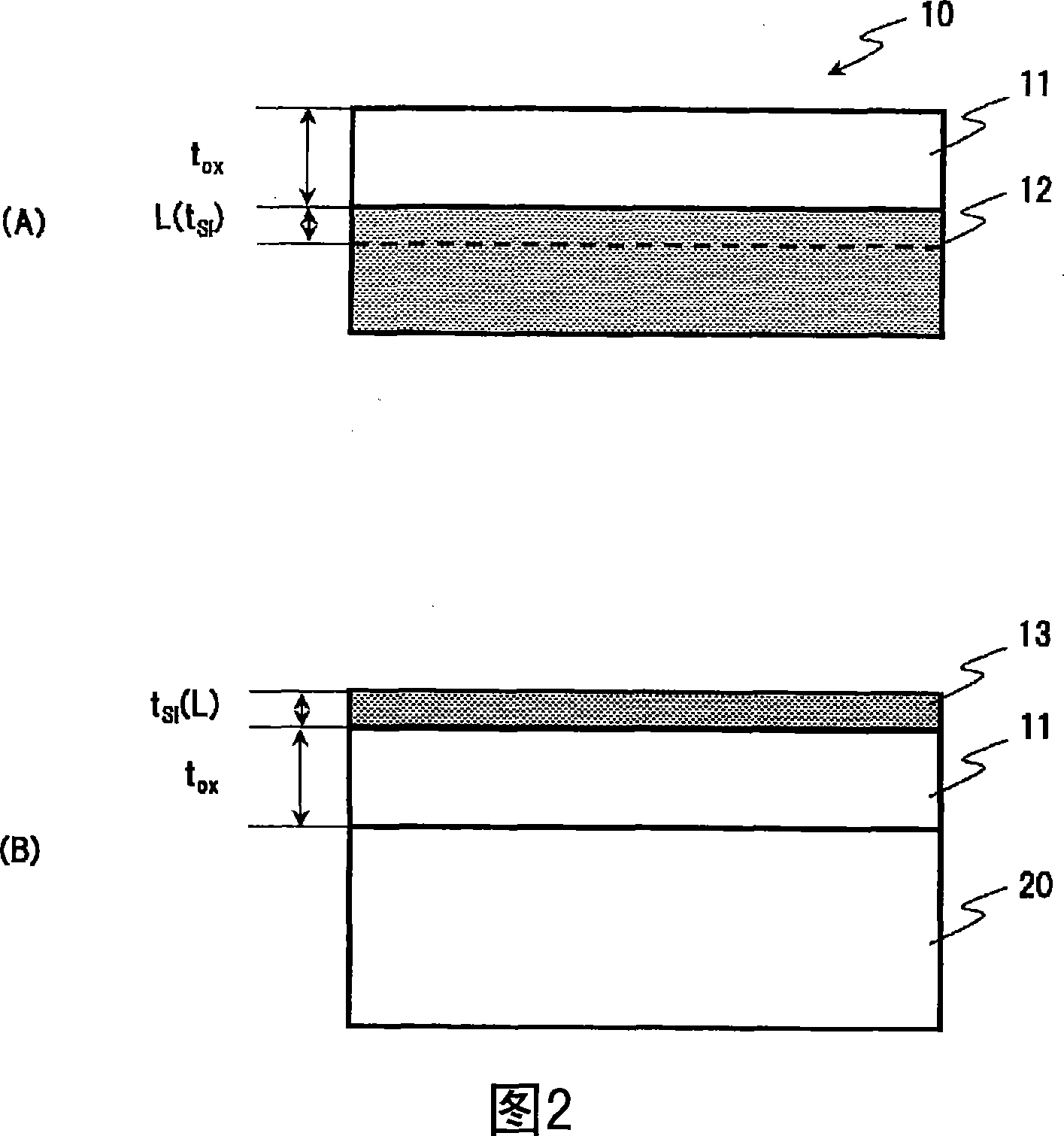
Soi substrate and method for manufacturing soi substrate
ActiveUS20100025804A1Suppression amountSuppress surface roughnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBonding processOptoelectronics
On the side of a surface (the bonding surface side) of a single crystal Si substrate, a uniform ion implantation layer is formed at a prescribed depth (L) in the vicinity of the surface. The surface of the single crystal Si substrate and a surface of a transparent insulating substrate as bonding surfaces are brought into close contact with each other, and bonding is performed by heating the substrates in this state at a temperature of 350° C. or below. After this bonding process, an Si—Si bond in the ion implantation layer is broken by applying impact from the outside, and a single crystal silicon thin film is mechanically peeled along a crystal surface at a position equivalent to the prescribed depth (L) in the vicinity of the surface of the single crystal Si substrate.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Method of crystallizing amorphous semiconductor thin film and method of fabricating poly crystalline thin film transistor using the same
InactiveUS20060121655A1Shorten heat treatment timeSuppress surface roughnessPolycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateLow leakageImpurity
A method of crystallizing an amorphous semiconductor thin film used for a thin film transistor (TFT) is provided. The method includes the steps of: forming first and second crystallization induced metal patterns locally in respective portions of a source region and a drain region of the TFT on an amorphous semiconductor thin film; and crystallizing an amorphous semiconductor via independent two-times heat treatment using the first and second crystallization induced metal patterns. In this case, the independent two-times heat treatment is executed before and after ions of impurities are injected, respectively. In this way, a metal induced lateral crystallization double heat treatment is executed before and after ions of impurities are injected, respectively. As a result, the entire crystallization heat treatment time necessary for crystallizing the amorphous semiconductor thin film can be greatly reduced, and a poly-crystalline TFT having low leakage current can be obtained.
Owner:PAIK WOON SUH
Thermal transfer sheet and ink ribbon
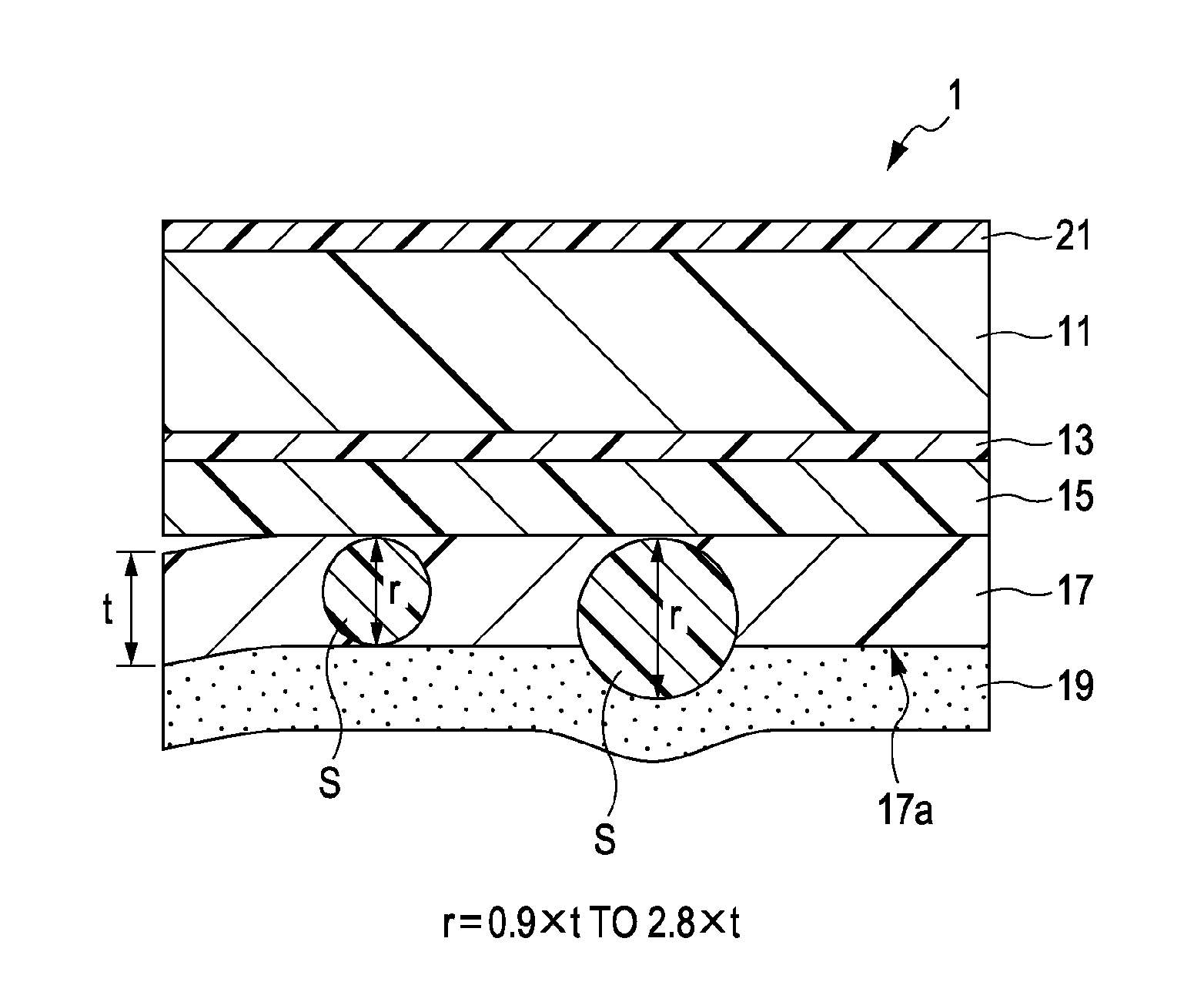
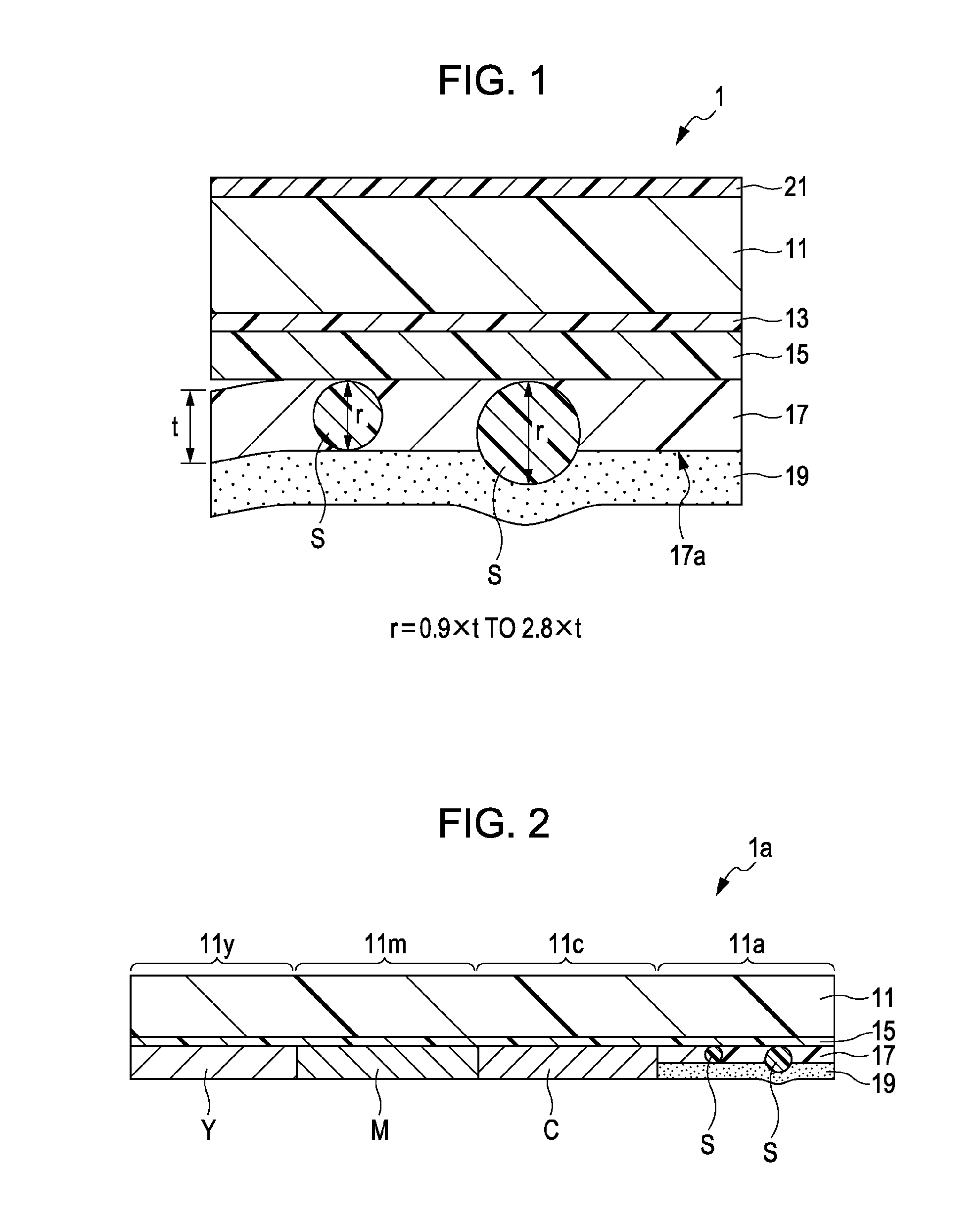
InactiveUS20100291326A1Increased durabilityIncrease resistanceThermographyOther printing apparatusProtection layerThermal transfer
A thermal transfer sheet includes a protective layer and an adhesive layer which are laminated on a sheet base material in that order, the protective layer including a binder resin containing fine particles. The particle diameter of the fine particles is 0.9 to 2.8 times the thickness of the protective layer.
Owner:SONY CORP
Film for hydraulic transfer
InactiveCN103260899ASuppress surface roughnessHigh Definition Printed ImageDecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsImaging qualitySurface roughness
Provided is a film for hydraulic transfer with which a high-resolution printed image, e.g., a photograph, can be transferred to a receiving object to obtain a transferred image having a smooth surface, without deteriorating the image quality. The film for hydraulic transfer is characterized by comprising at least two layers which are an ink-receiving layer and a base layer, the base layer having a surface roughness Ra of 0.40 [mu]m or less and a gloss of 80 or higher.
Owner:AICELLO
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS7015107B2Suppress surface roughnessImprove gate reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSurface roughnessEngineering
When a dummy sidewall and source and drain regions are once formed and then the dummy sidewall is removed to extend the source and drain regions, the removal of the dummy sidewall is performed after formation of a protective oxide film on a gate electrode and on the major surfaces of the source and drain regions. This efficiently prevents conventional surface roughness of the upper surface of the gate electrode and the impurity region due to the removal of the dummy sidewall.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Apparatus and method for the functionalisation of afm tips
InactiveUS20120096602A1Easy to implementLow costNanotechnologyMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsEngineeringCantilever
The present invention includes an apparatus that holds the probes to a solid support throughout the passages of the functionalisation process, thus avoiding user-dependent breakage or damage of the fragile AFM cantilevers. The apparatus allows the tips of the AFM probes to be placed face-down, which avoids the deposition of contaminants on their functional side. The device also allows functionalising the tips with small liquid volumes and cleaning. The present invention includes a functionalisation process preventing non-specific adsorption of molecules on the tip.
Owner:CENT DE INVESTIGACION COOP & BIOMATERIALES CIC BIOMAGUNE
Substrate heating apparatus and semiconductor fabrication method
ActiveUS7807553B2Suppress surface roughnessIncrease the exhaust conductanceDrying solid materials with heatSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
Owner:CANON ANELVA CORP
Electronic package with optimized lamination process
InactiveUS20050224961A1High densityFacilitates subsequent depositionDielectric materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectric layerMaximum temperature
An electronic package and method of formation. A thermally conductive layer having first and second opposing surfaces is provided. A first dielectric layer is laminated under pressurization to the first opposing surface of the thermally conductive layer, at a temperature between a minimum temperature T1MIN and a maximum temperature T1MAX. T1MAX constrains the ductility of the first dielectric layer to be at least D1 following the laminating. T1MAX depends on D1 and on a first dielectric material comprised by the first dielectric layer. A second dielectric layer is laminated under pressurization to the second opposing surface of the thermally conductive layer, at a temperature between a minimum temperature T2MIN and a maximum temperature T2MAX. T2MAX constrains the ductility of the second dielectric layer to be at least D2 following the laminating. T2MAX depends on D2 and on a second dielectric material comprised by the second dielectric layer.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
Glass-shaping mold and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100011815A1Guaranteed to workSuppress surface roughnessGlass transportation apparatusGlass pressing apparatusRheniumIridium
A glass-shaping mold includes a steel base member, and a crystallized, machined layer, an intermediate layer and a mold-releasing layer which are sequentially formed on the base member. The machined layer is a layer of nickel alloy containing phosphorus. The intermediate layer is a layer formed of chromium, nickel, copper or cobalt. Alternatively, the intermediate layer is a layer of an alloy layer containing at least one of these elements. The mold-releasing layer is a layer of an alloy containing iridium and rhenium.
Owner:TOSHIBA MASCH CO LTD
Method of crystallizing amorphous semiconductor thin film and method of fabricating poly crystalline thin film transistor using the same
InactiveUS7521303B2Shorten heat treatment timeSuppress surface roughnessPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsLow leakageImpurity
Owner:PAIK WOON SUH
Surface treating for micromachining and method for surface treatment
InactiveUS6797194B1Improve performanceReduce uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface treatment compositionsAutoxidationActive agent
The present invention provides a micromachining surface treatment material for and a surface treatment method that suppress widening of the diameter of contact holes when removing a natural oxidation layer arising at bottom sections of the contact holes. The micromachining surface treatment material contains less than 0.1% hydrofluoric acid, and more than 40% by weight but less than or equal to 47% by weight of ammonium fluoride. Also, a surfactant is contained therein in an amount from 0.0001 to 0.1% by weight.
Owner:STELLA CHEMIFA CORP
Heat treatment apparatus
InactiveUS20120285935A1High thermal efficiencyLow maintenanceElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsProduction ratePlanar electrode
Provided is a heat treatment apparatus in which a heat treatment apparatus in which the thermal efficiency is high, the maintenance expense is low, the throughput is high, the surface roughness of a sample can be reduced, and the discharge uniformity is excellent, although the heat treatment is performed at 1200° C. or more.A heat treatment apparatus includes: parallel planar electrodes; a radio-frequency power supply generating plasma by applying radio-frequency power between the parallel planar electrodes; a temperature measuring section measuring the temperature of a heated sample; and a control unit controlling an output of the radio-frequency power supply, wherein at least one of the parallel planar electrodes has a space where the heated sample is installed, therein, and heats the sample in the electrode by the plasma generated between the parallel planar electrodes.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Heat treatment apparatus
InactiveUS8569647B2Suppress surface roughnessReduce surface roughnessElectric discharge tubesElectric heatingProduction ratePlanar electrode
Provided is a heat treatment apparatus in which a heat treatment apparatus in which the thermal efficiency is high, the maintenance expense is low, the throughput is high, the surface roughness of a sample can be reduced, and the discharge uniformity is excellent, although the heat treatment is performed at 1200 ° C. or more.A heat treatment apparatus includes: parallel planar electrodes; a radio-frequency power supply generating plasma by applying radio-frequency power between the parallel planar electrodes; a temperature measuring section measuring the temperature of a heated sample; and a control unit controlling an output of the radio-frequency power supply, wherein at least one of the parallel planar electrodes has a space where the heated sample is installed, therein, and heats the sample in the electrode by the plasma generated between the parallel planar electrodes.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Water-based coating composition and method of forming multilayered coating film
ActiveUS8993673B2Suppress surface roughnessInhibit swellingSynthetic resin layered productsPretreated surfacesWater basedEmulsion
Owner:KANSAI PAINT CO LTD
Lubricating oil supply facility and lubricating oil supply method
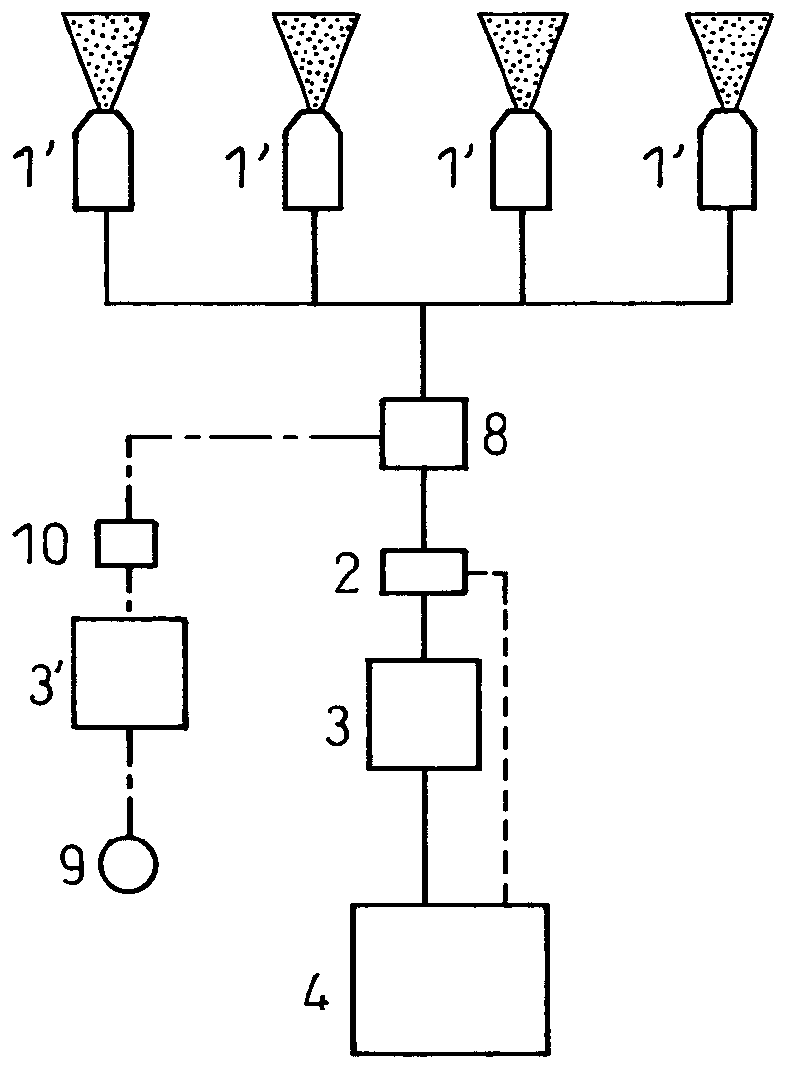
ActiveCN102844127AInhibit wearSuppress surface roughnessSpraying apparatusPretreated surfacesSpray nozzleMetallic materials
A lubricating oil supply facility for supplying lubricating oil to a mill roll (20) of a rolling mill for a plate-like metallic material (M) comprises: spray nozzles (1a, 1b) for granulating or atomizing lubricating oil together with gas and ejecting the mixture toward the mill roll; lubricating oil supply devices (2, 3, 4) for supplying the lubricating oil to the spray nozzles; and gas supply devices (5, 6) for supplying the gas to the spray nozzles. The amount of supply of the lubricating oil from side spray nozzles among the spray nozzles is set to be greater than the amount of supply of the lubricating oil from the center spray nozzle among the spray nozzles. Also, the amount of supply of the lubricating oil from the spray nozzles located between the center spray nozzle and the side spray nozzles is set to be less than or equal to the amount of supply of the lubricating oil from the side spray nozzles and greater than or equal to the amount of supply of the lubricating oil from the center spray nozzle. As a result of the configuration, the occurrence of nonuniform wear and surface roughening of the mill roll in the axial direction thereof is minimized.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com