Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4279results about How to "High dielectric constant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
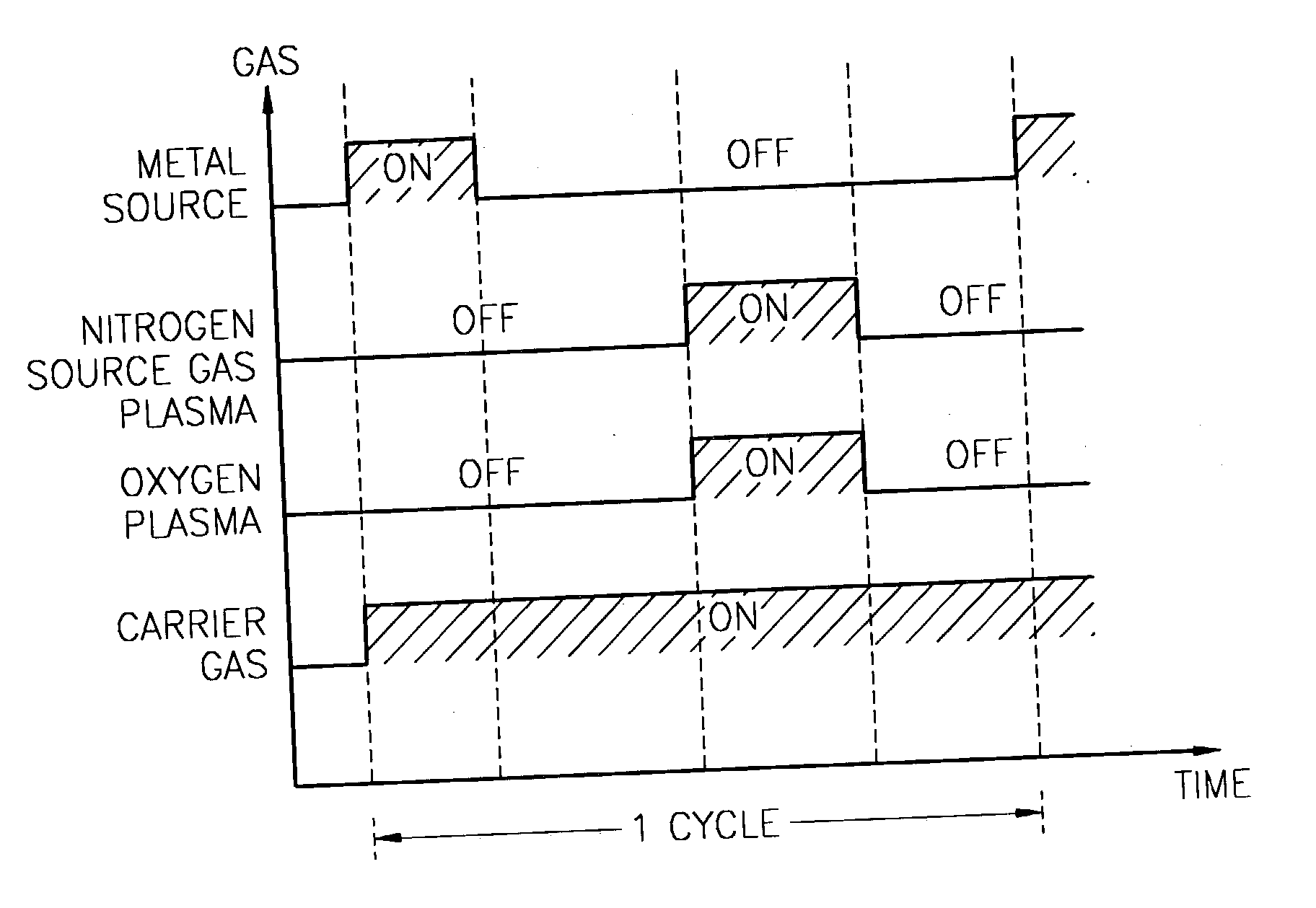
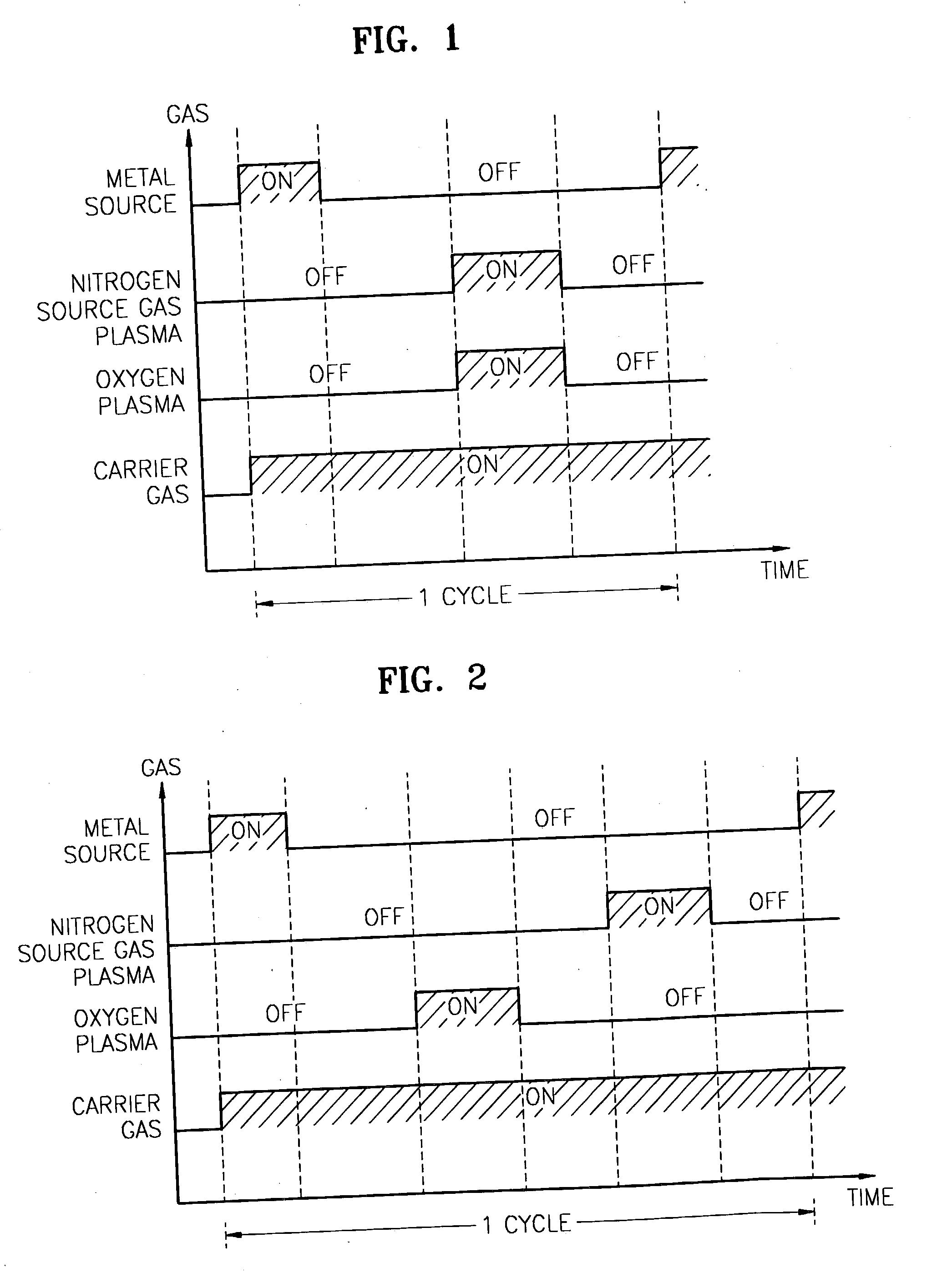
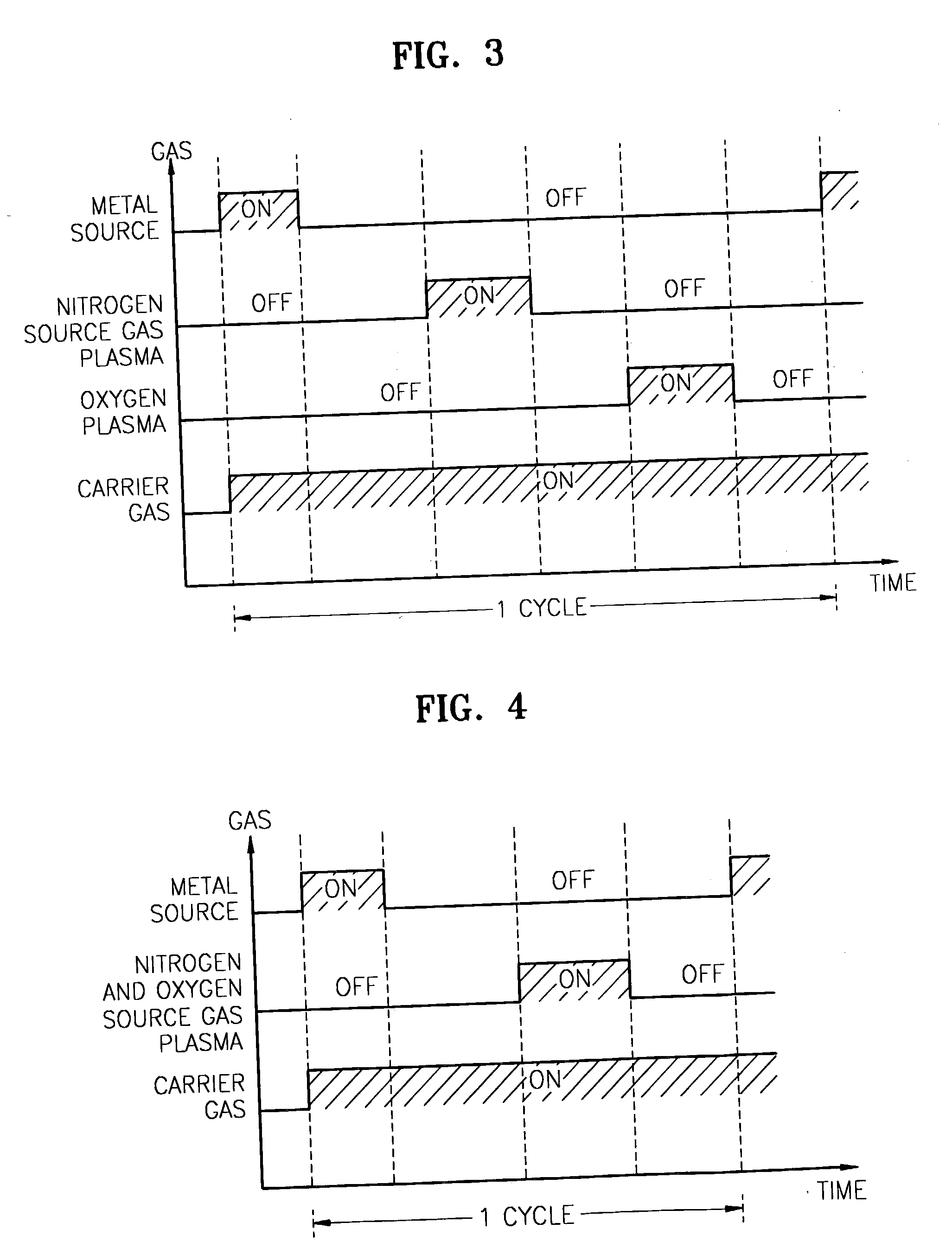
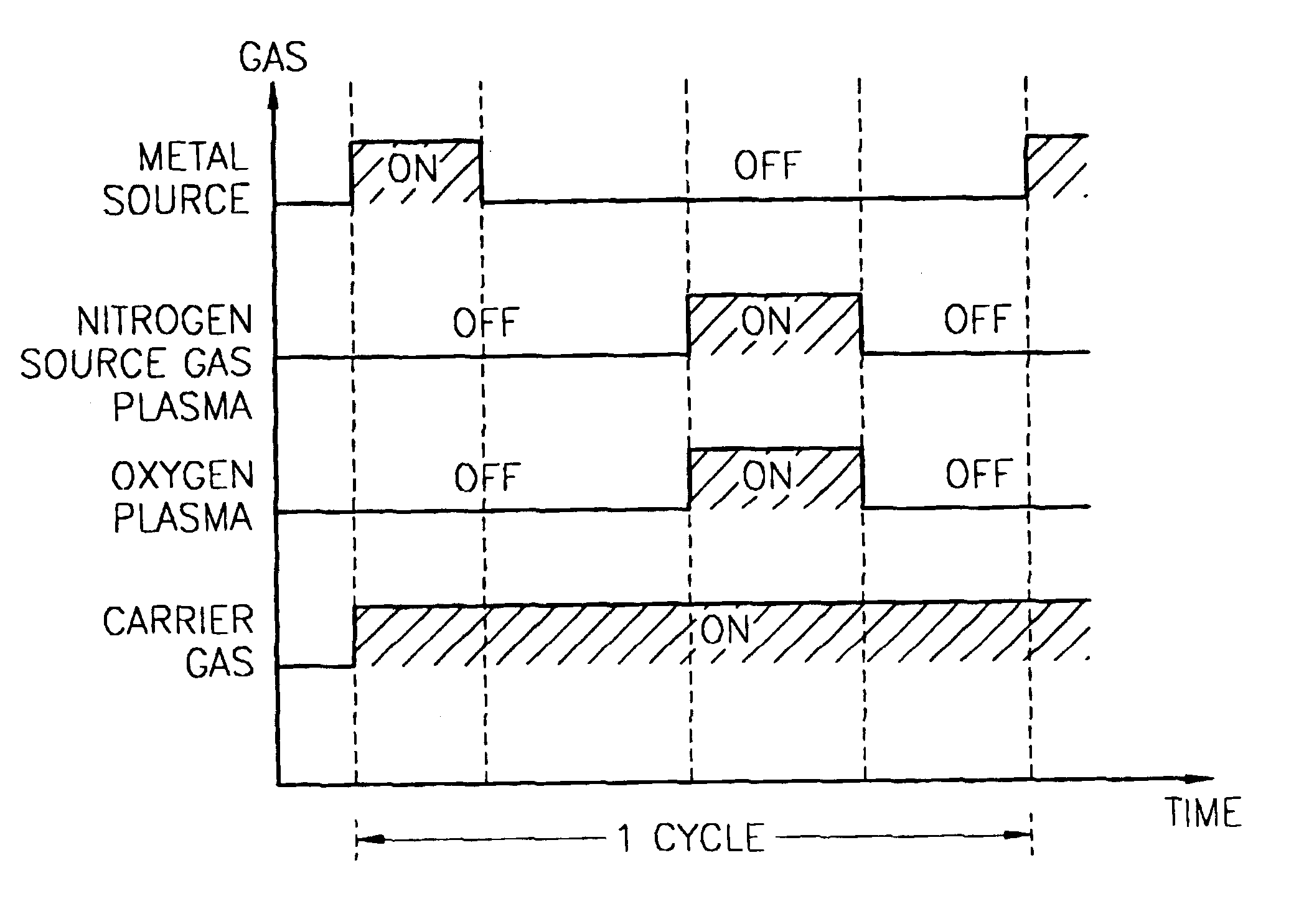
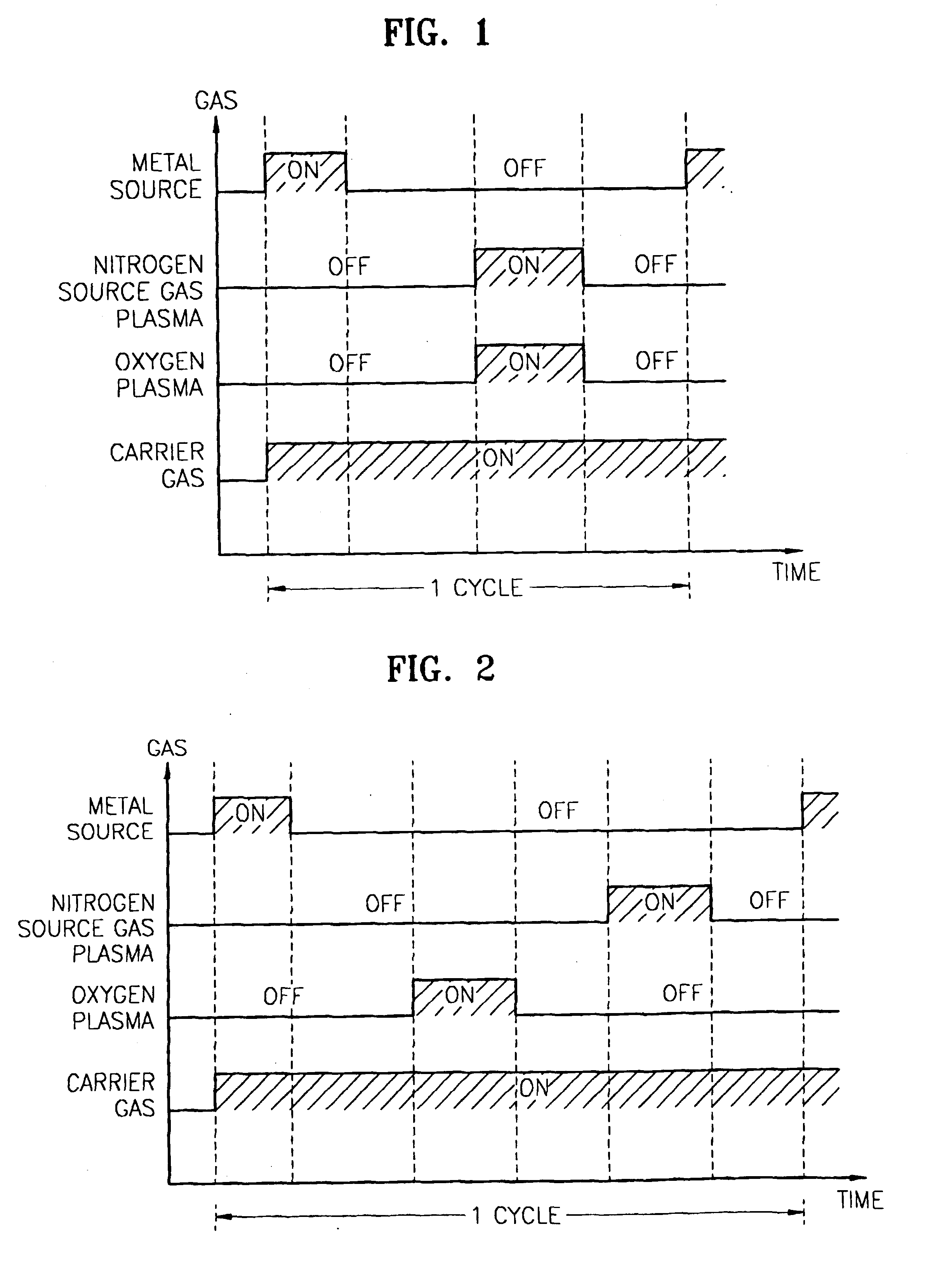
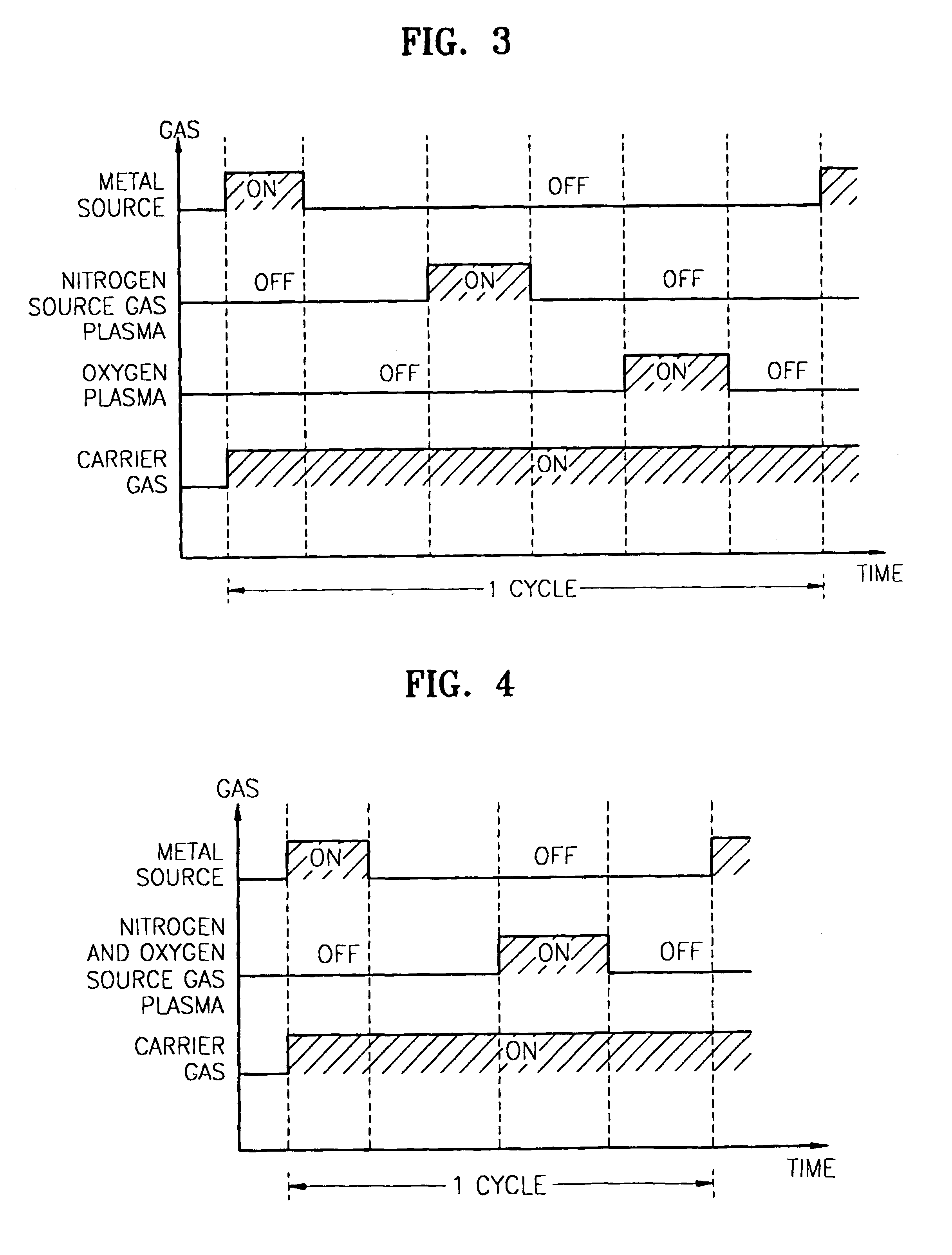
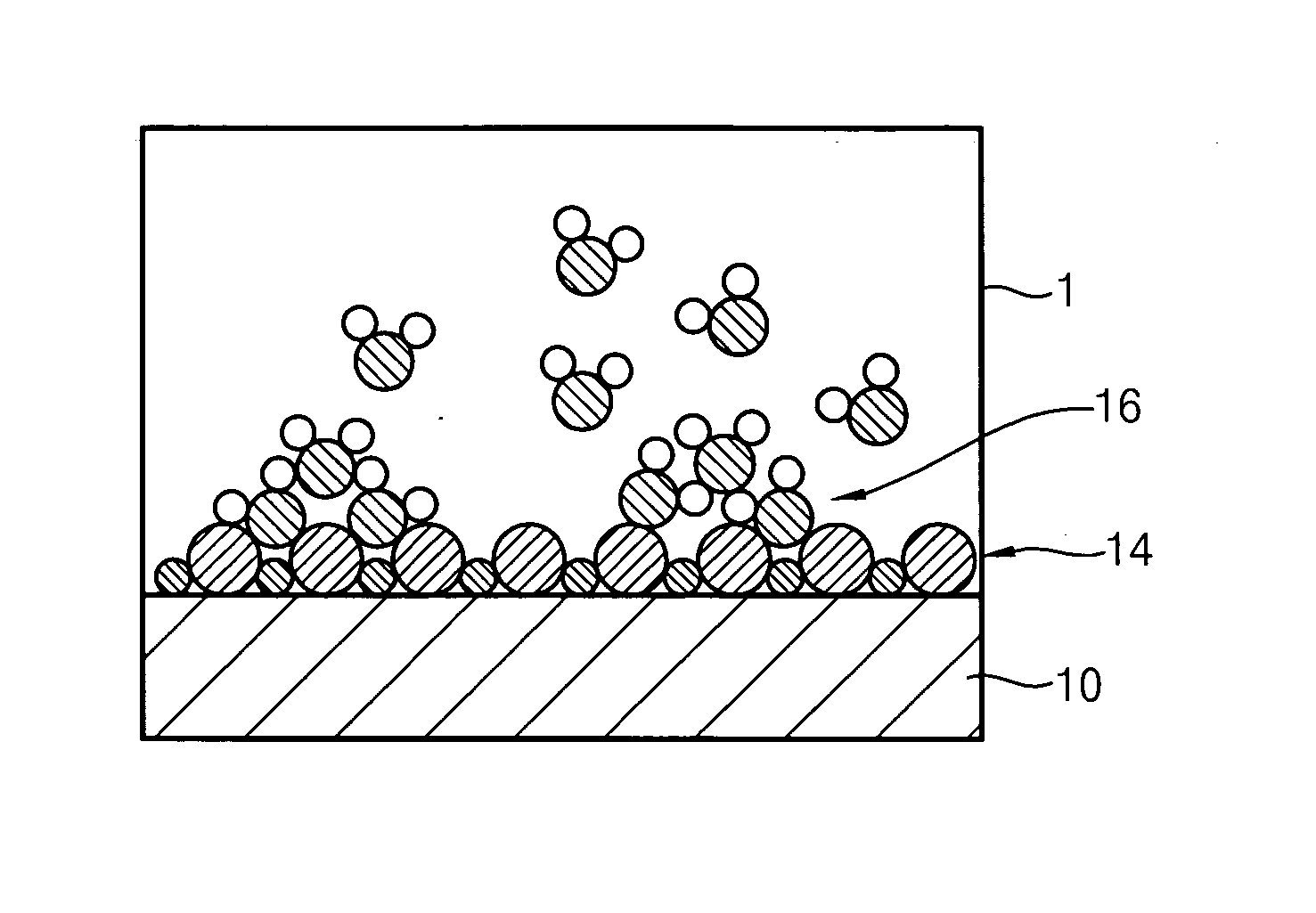
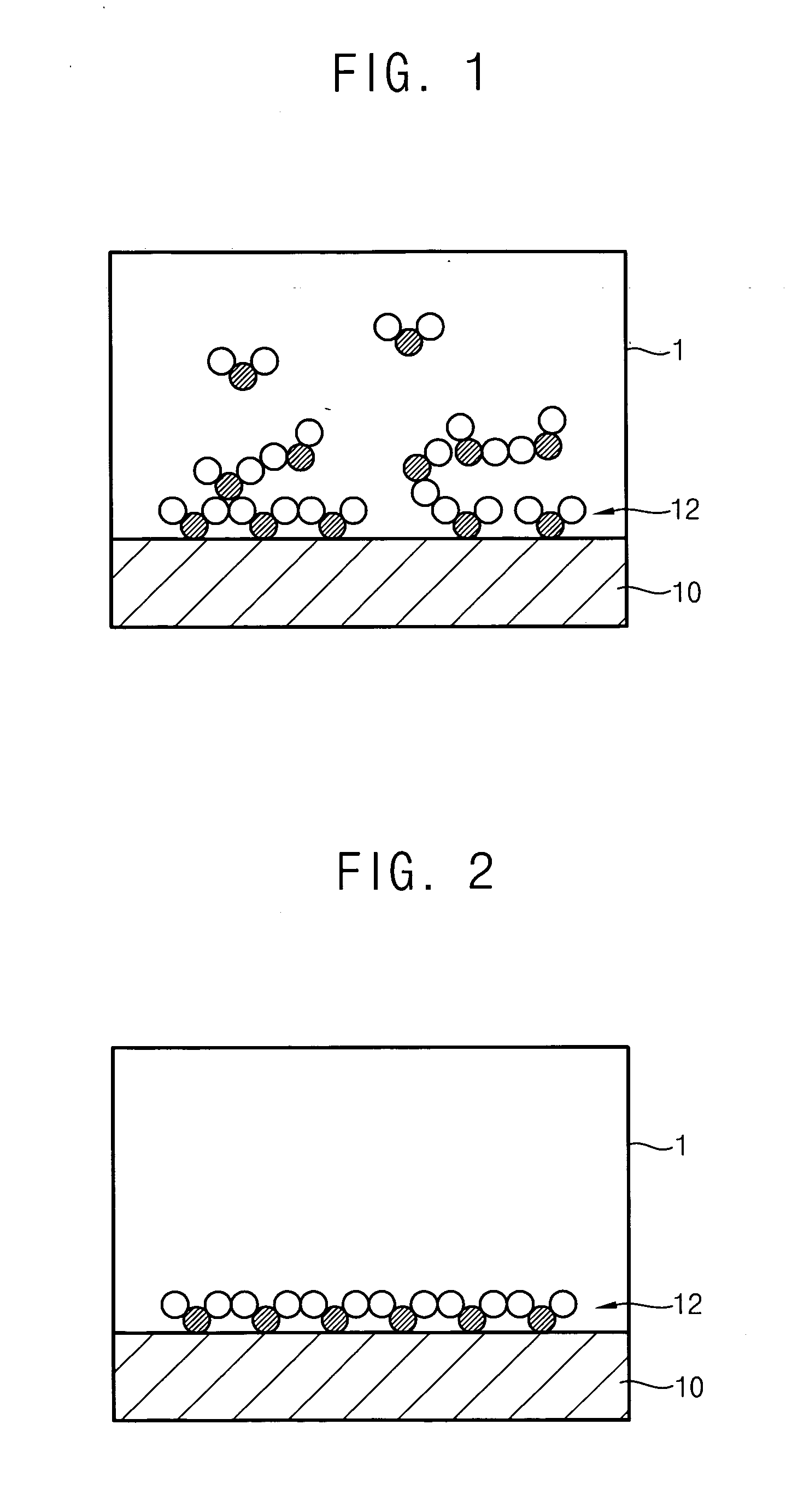
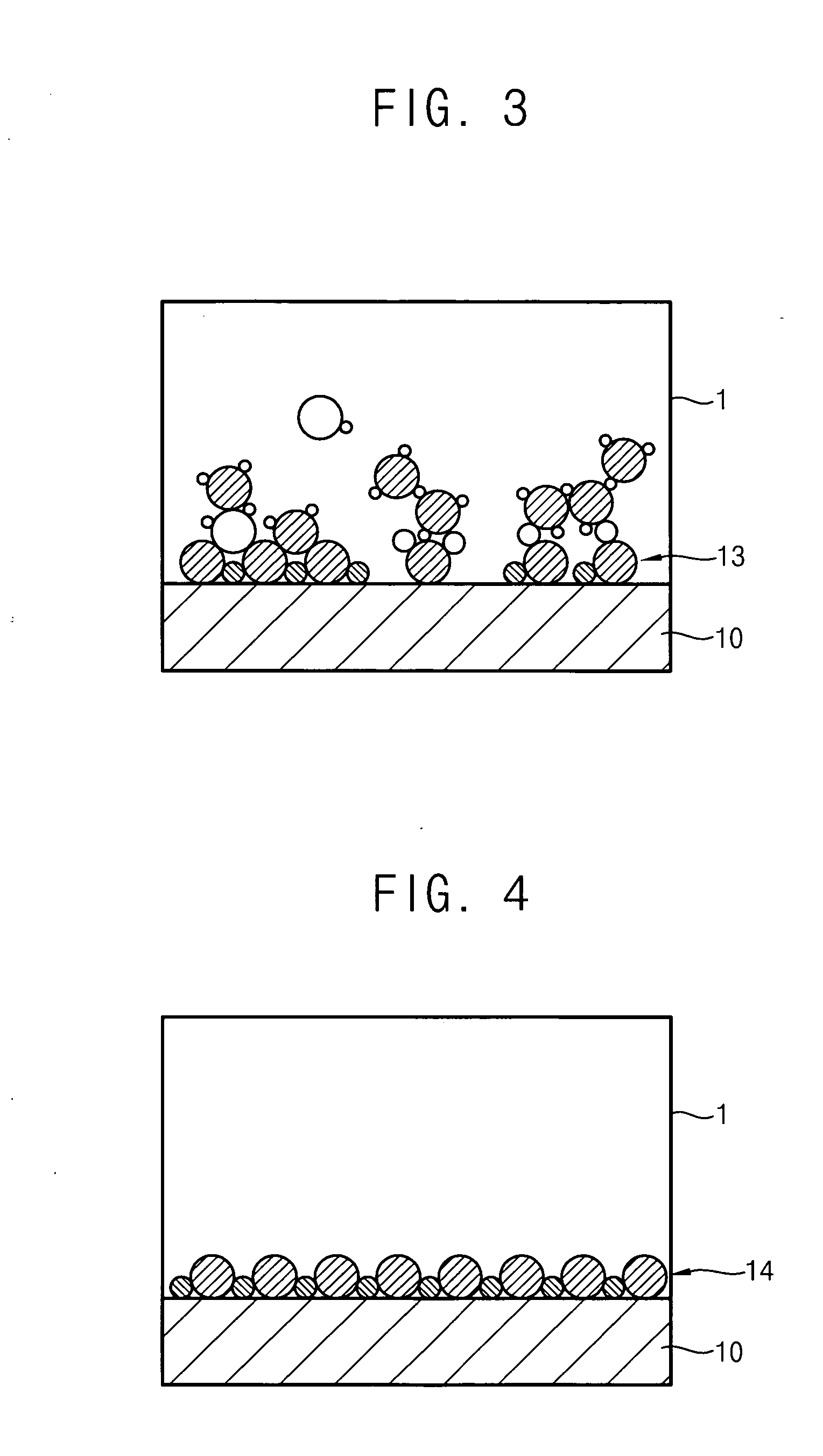
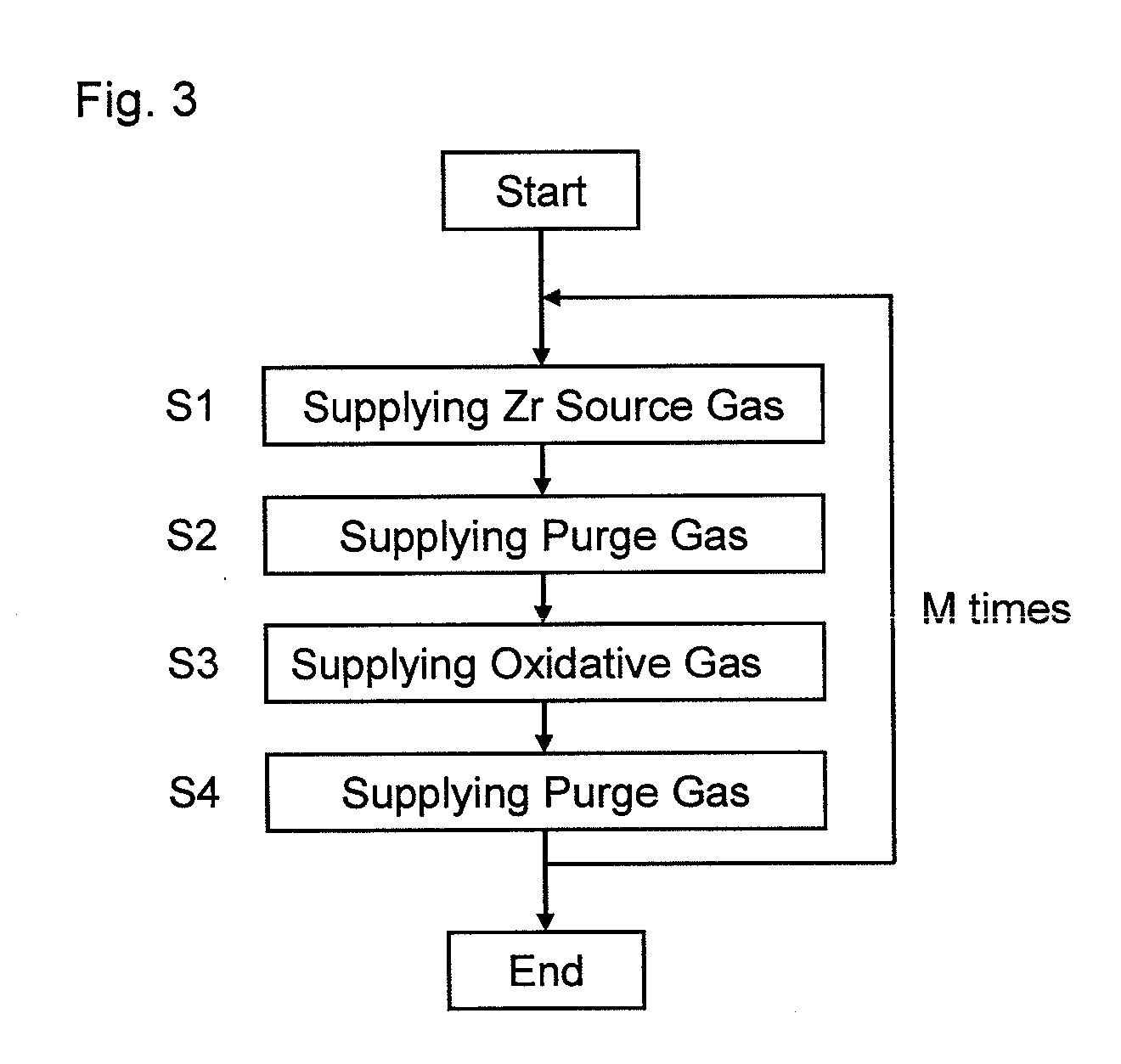
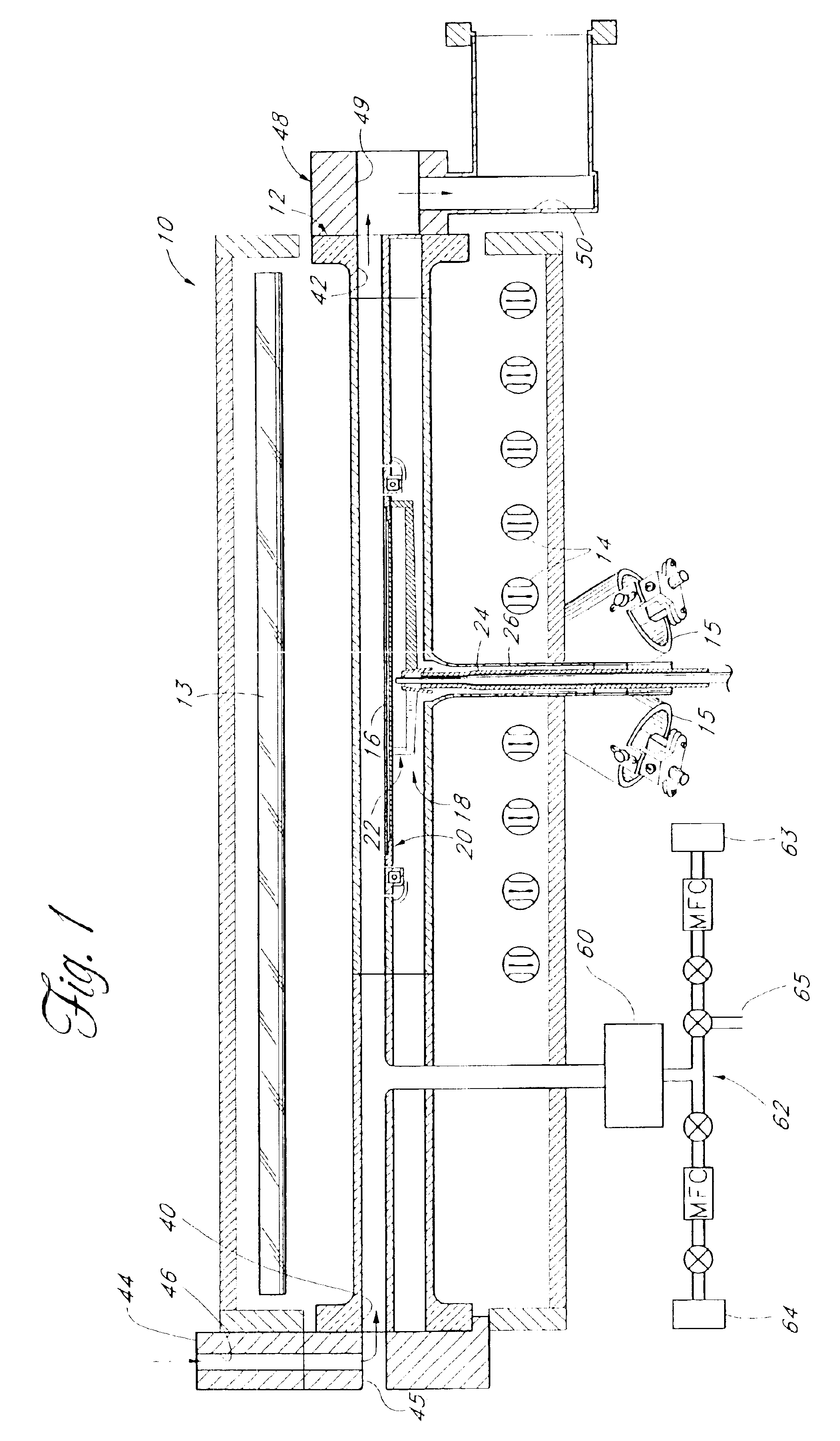
Method for forming introgen-containing oxide thin film using plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition
InactiveUS20040077182A1Density of thinThin rateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHigh rateNitrogen source
A method for forming a nitrogen-containing oxide thin film by using plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition is provided. In the method, the nitrogen-containing oxide thin film is deposited by supplying a metal source compound and oxygen gas into a reactor in a cyclic fashion with sequential alternating pulses of the metal source compound and the oxygen gas, wherein the oxygen gas is activated into plasma in synchronization of the pulsing thereof, and a nitrogen source gas is further sequentially pulsed into the reactor and activated into plasma over the substrate in synchronization with the pulsing thereof. According to the method, a dense nitrogen-containing oxide thin film can be deposited at a high rate, and a trace of nitrogen atoms can be incorporated in situ into the nitrogen-containing oxide thin film, thereby increasing the breakdown voltage of the film.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
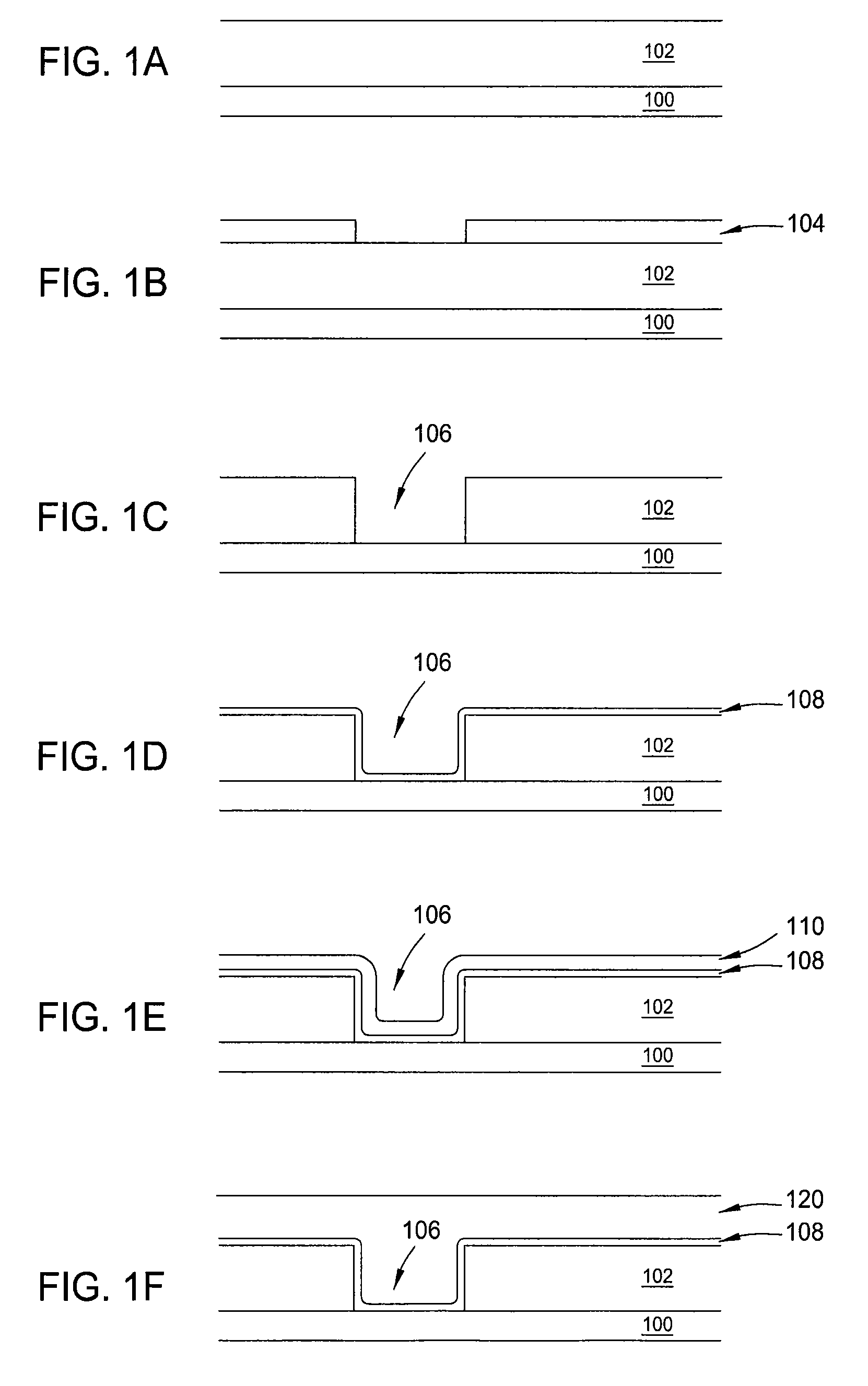
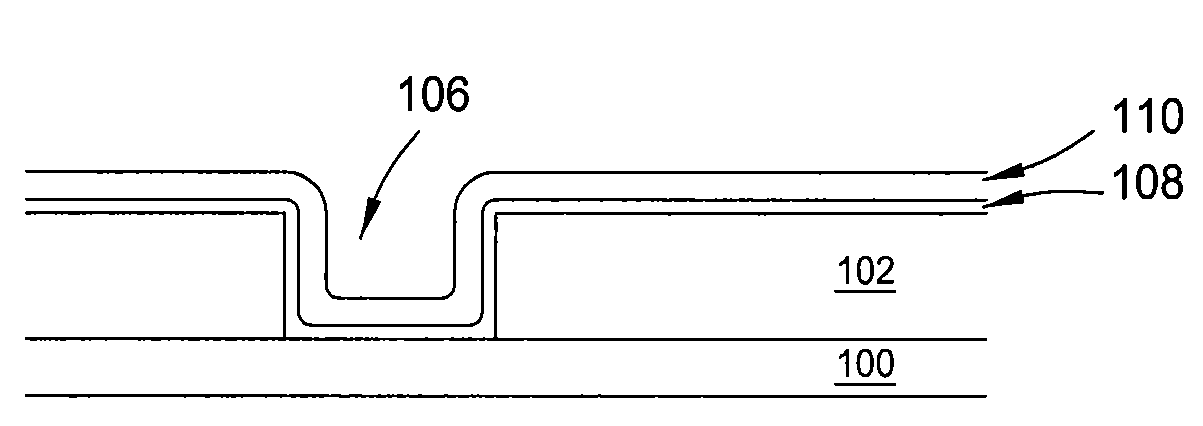
Method to minimize wet etch undercuts and provide pore sealing of extreme low k (k<2.5) dielectrics
ActiveUS8445075B2Constant ratePrevents undercuts and CD lossVacuum evaporation coatingPretreated surfacesNitrogenThin layer
Methods of processing films on substrates are provided. In one aspect, the methods comprise treating a patterned low dielectric constant film after a photoresist is removed from the film by depositing a thin layer comprising silicon, carbon, and optionally oxygen and / or nitrogen on the film. The thin layer provides a carbon-rich, hydrophobic surface for the patterned low dielectric constant film. The thin layer also protects the low dielectric constant film from subsequent wet cleaning processes and penetration by precursors for layers that are subsequently deposited on the low dielectric constant film.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for forming nitrogen-containing oxide thin film using plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition
InactiveUS6723642B1Density of thinThin rateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingNitrogen sourceNitrogen oxide
A method for forming a nitrogen-containing oxide thin film by using plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition is provided. In the method, the nitrogen-containing oxide thin film is deposited by supplying a metal source compound and oxygen gas into a reactor in a cyclic fashion with sequential alternating pulses of the metal source compound and the oxygen gas, wherein the oxygen gas is activated into plasma in synchronization of the pulsing thereof, and a nitrogen source gas is further sequentially pulsed into the reactor and activated into plasma over the substrate in synchronization with the pulsing thereof. According to the method, a dense nitrogen-containing oxide thin film can be deposited at a high rate, and a trace of nitrogen atoms can be incorporated in situ into the nitrogen-containing oxide thin film, thereby increasing the breakdown voltage of the film.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
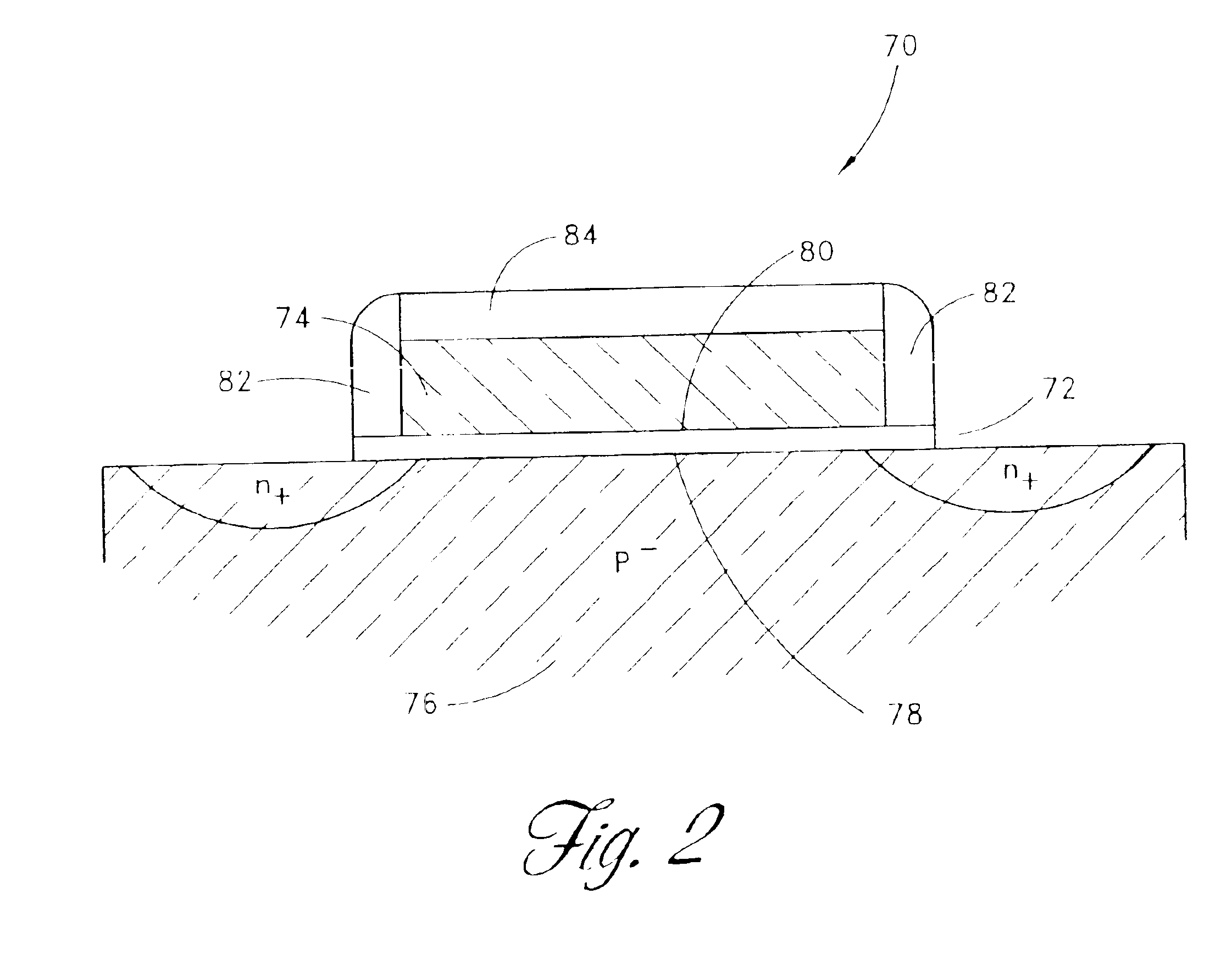
Manufacturing method of semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090011608A1Reduce hypoxiaSuppression of interface silicon oxide growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTantalum nitrideSilicon oxide
The transistor characteristics of a MIS transistor provided with a gate insulating film formed to contain oxide with a relative dielectric constant higher than that of silicon oxide are improved. After a high dielectric layer made of hafnium oxide is formed on a main surface of a semiconductor substrate, the main surface of the semiconductor substrate is heat-treated in a non-oxidation atmosphere. Next, an oxygen supplying layer made of hafnium oxide deposited by ALD and having a thickness smaller than that of the high dielectric layer is formed on the high dielectric layer, and a cap layer made of tantalum nitride is formed. Thereafter, the main surface of the semiconductor substrate is heat-treated.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Methods of forming a thin film structure, and a gate structure and a capacitor including the thin film structure
InactiveUS20060013946A1Well formedHigh dielectric constantSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial surfacesChemical reactionSilicon oxide
A thin film structure is formed that includes hafnium silicon oxide using an atomic layer deposition process. A first reactant including tetrakis ethyl methyl amino hafnium (TEMAH) is introduced onto a substrate. A first portion of the first reactant is chemisorbed to the substrate, whereas a second portion of the first reactant is physorbed to the first portion of the first reactant. A first oxidant is provided onto the substrate. A first thin film including hafnium oxide is formed on the substrate by chemically reacting the first oxidant with the first portion of the first reactant. A second reactant including amino propyl tri ethoxy silane (APTES) is introduced onto the first thin film. A first portion of the second reactant is chemisorbed to the first thin film, whereas a second portion of the second reactant is physorbed to the first portion of the second reactant. A second oxidant is provided onto the first thin film. A second thin film including silicon oxide is formed on the first thin film by chemically reacting the second oxidant with the first portion of the second reactant.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Methods of atomic layer deposition of hafnium oxide / erbium oxide bi-layer as advanced gate dielectrics
InactiveUS20130313656A1Improve electrical performanceFew defectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGate dielectricHafnium
Provided is a two-step ALD deposition process for forming a gate dielectric involving an erbium oxide layer deposition followed by a hafnium oxide layer deposition. Hafnium oxide can provide a high dielectric constant, high density, large bandgap and good thermal stability. Erbium oxide can act as a barrier against oxygen diffusion, which can lead to increasing an effective oxide thickness of the gate dielectric and preventing hafnium-silicon reactions that may lead to higher leakage current.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Methods of forming atomic layers of a material on a substrate by sequentially introducing precursors of the material
InactiveUS7201943B2Easy to integrateHigh dielectric constantVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricTitanium
A thin film is formed using an atomic layer deposition process, by introducing a first reacting material including tantalum precursors and titanium precursors onto a substrate. A portion of the first reacting material is chemisorbed onto the substrate. Then, a second reacting material including oxygen is introduced onto the substrate. A portion of the second reacting material is also chemisorbed onto the substrate, to form an atomic layer of a solid material on the substrate. The solid material may be used as a dielectric layer of the capacitor and / or a gate dielectric layer of the transistor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Recovery of hydrophobicity of low-k and ultra low-k organosilicate films used as inter metal dielectrics
InactiveUS20050106762A1Low costHigh mechanical strengthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical treatmentSilylation
Often used to reduce the RC delay in integrated circuits are dielectric films of porous organosilicates which have a silica like backbone with alkyl or aryl groups (to add hydrophobicity to the materials and create free volume) attached directly to the Si atoms in the network. Si—R bonds rarely survive an exposure to plasmas or chemical treatments commonly used in processing; this is especially the case in materials with an open cell pore structure. When Si—R bonds are broken, the materials lose hydrophobicity, due to formation of hydrophilic silanols and low dielectric constant is compromised. A method by which the hydrophobicity of the materials is recovered using a novel class of silylation agents which may have the general formula (R2N)XSiR′Y where X and Y are integers from 1 to 3 and 3 to 1 respectively, and where R and R′ are selected from the group of hydrogen, alkyl, aryl, allyl and a vinyl moiety. Mechanical strength of porous organosilicates is also improved as a result of the silylation treatment.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Metal capacitor and method of making the same
ActiveUS8114734B2Increase capacitanceAvoid delaySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceInterconnection
A method of making a metal capacitor includes the following steps. A dielectric layer having a metal interconnection and a capacitor electrode is provided. Then, a treatment is performed to increase the dielectric constant of the dielectric layer surrounding the capacitor electrode. The treatment can be UV radiation, a plasma treatment or an ion implantation. Accordingly, the metal capacitor will have a higher capacitance and RC delay between the metal interconnection and the dielectric layer can be prevented.
Owner:MARLIN SEMICON LTD
Insulating film, method of manufacturing the same, and semiconductor device
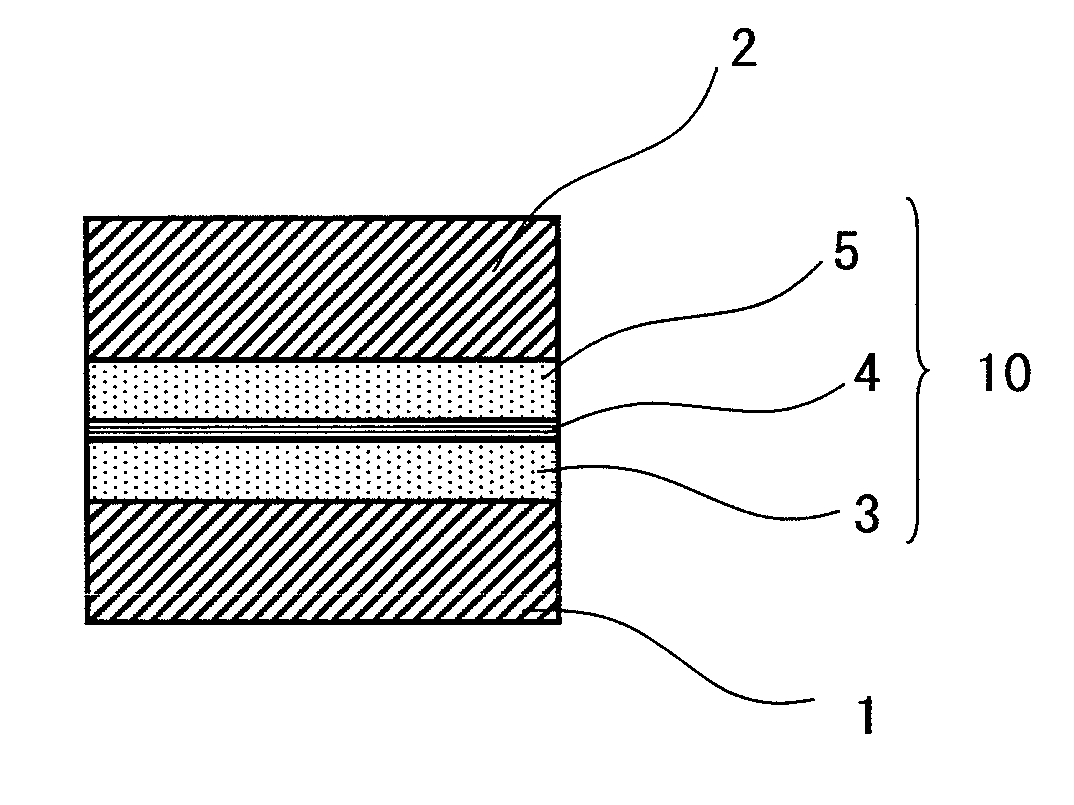
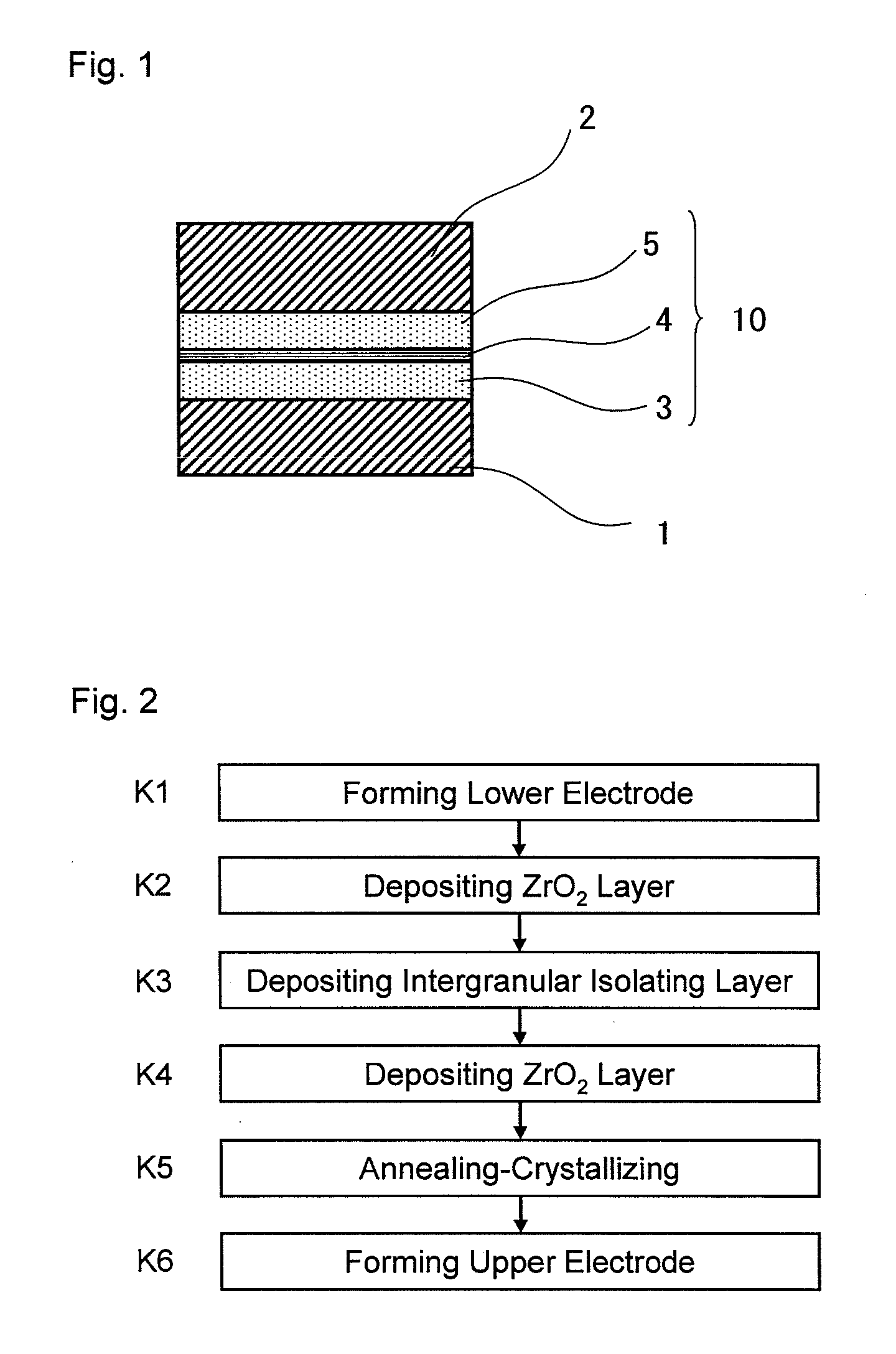
InactiveUS20110048769A1High dielectric constantSmall currentThin/thick film capacitorCeramicsCapacitanceSemiconductor
An exemplary aspect of the invention provides an insulating film which has a high dielectric constant and has small leakage current even when it is sandwiched between electrodes. The insulating film comprises two zirconium oxide layers in crystallized state; and an intergranular isolating layer composed of an amorphous material having a dielectric constant higher than that of zirconium oxide in crystallized state; wherein the intergranular isolating layer is sandwiched between the two zirconium oxide layers. The insulating film is properly used as a capacitive insulating film in a semiconductor device comprising a memory cell including a capacitor element having the capacitive insulating film between an upper electrode and a lower electrode, or as an intergate insulating film in a semiconductor device comprising a nonvolatile memory device having the intergate insulating film between a control gate electrode and a floating gate electrode.
Owner:ELPIDA MEMORY INC
Silicone hydrogel contact lens
Ophthalmically compatible contact lenses include lens bodies configured for placement on a cornea of an animal or human eye. The lens bodies are made of a hydrophilic silicon-containing polymeric material. The lens bodies have oxygen permeabilities, water content, surface wettabilities, flexibilities, and / or designs to be worn by a lens wearer even during sleep. The present lenses can be worn on a daily basis, including overnight, or can be worn for several days, such as about thirty days, without requiring removal or cleaning.
Owner:COOPERVISION INT LTD
Method to minimize wet etch undercuts and provide pore sealing of extreme low k (k<2.5) dielectrics
ActiveUS20110092077A1Constant ratePrevents undercuts and CD lossVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThin layerNitrogen
Methods of processing films on substrates are provided. In one aspect, the methods comprise treating a patterned low dielectric constant film after a photoresist is removed form the film by depositing a thin layer comprising silicon, carbon, and optionally oxygen and / or nitrogen on the film. The thin layer provides a carbon-rich, hydrophobic surface for the patterned low dielectric constant film. The thin layer also protects the low dielectric constant film from subsequent wet cleaning processes and penetration by precursors for layers that are subsequently deposited on the low dielectric constant film.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
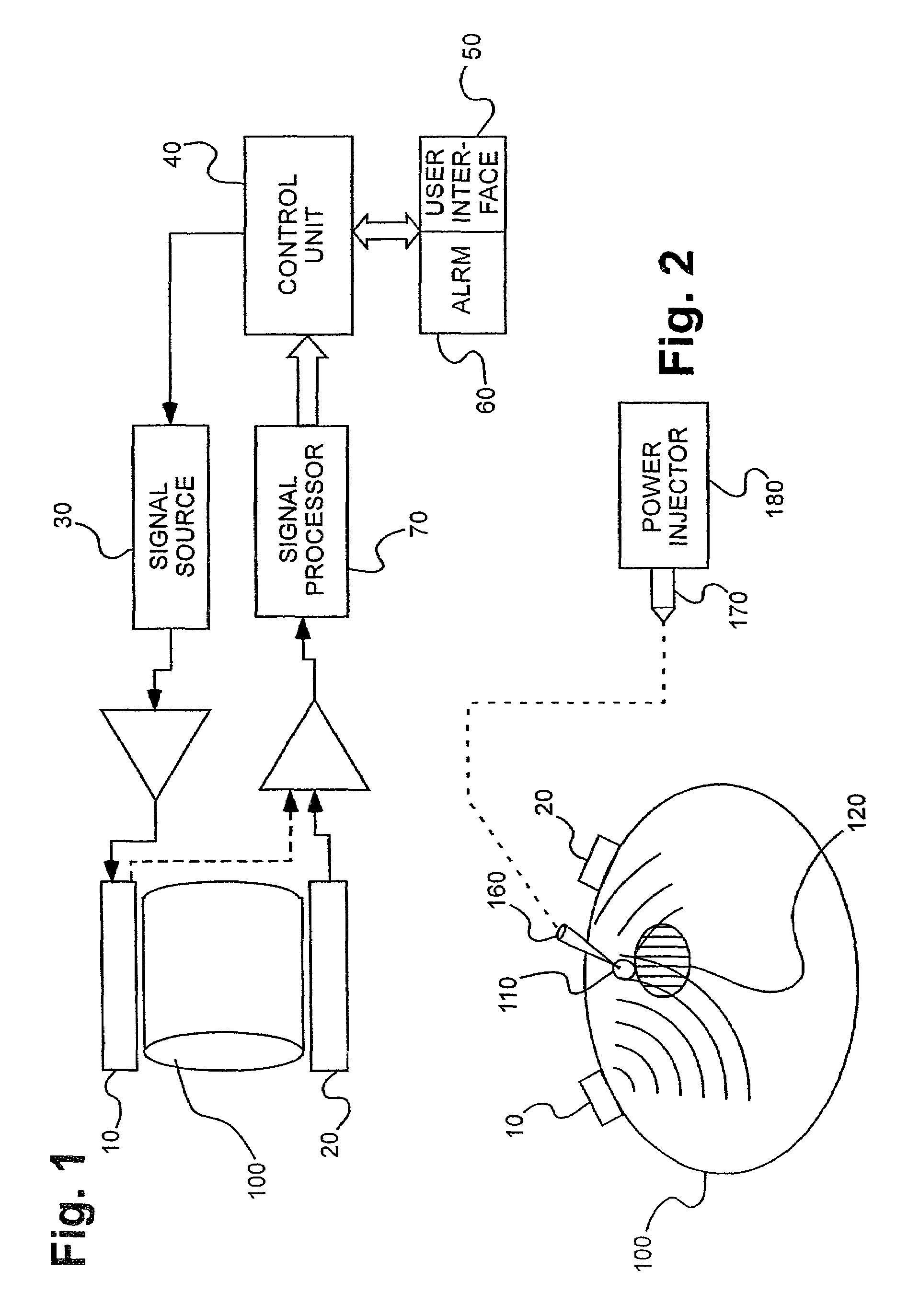
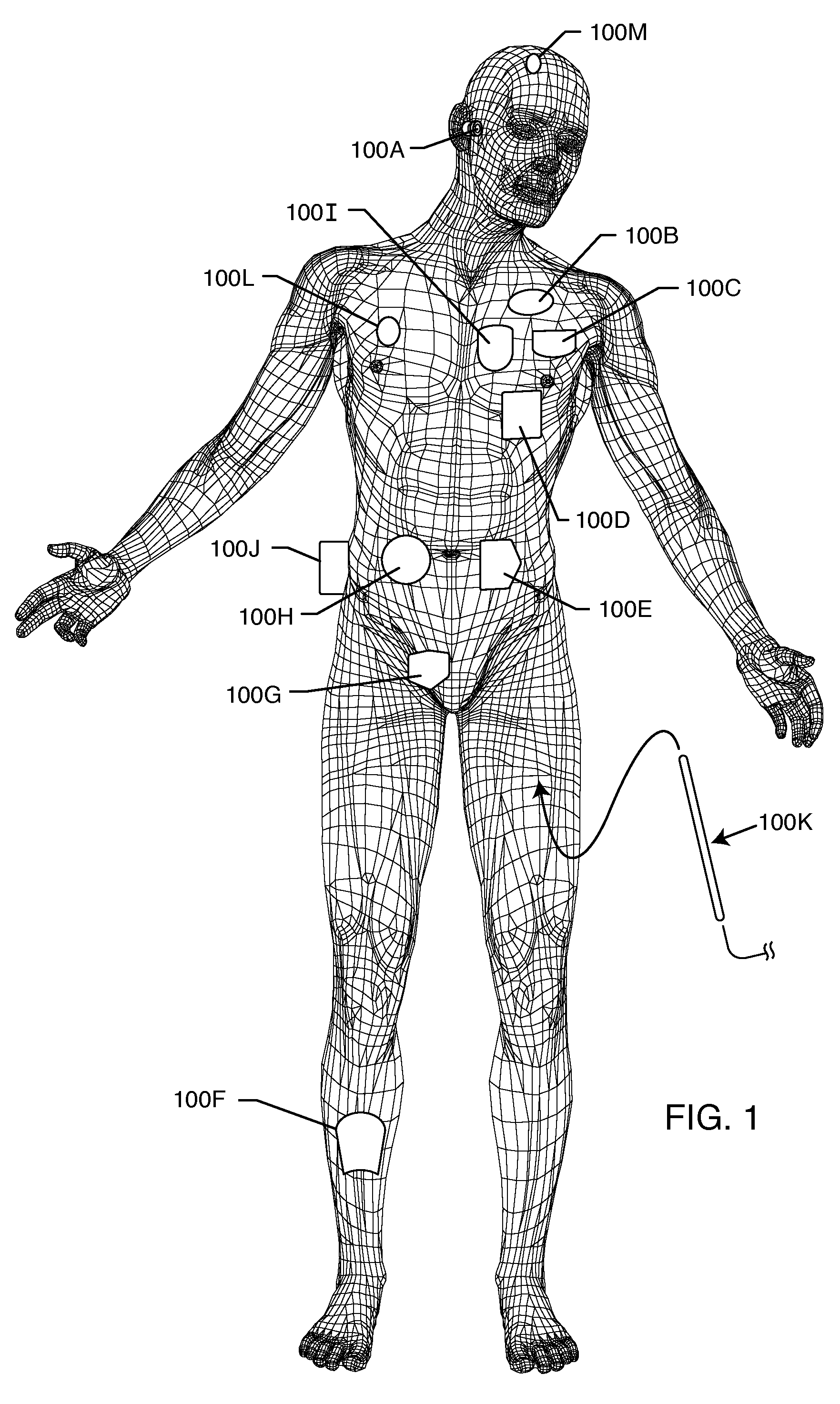
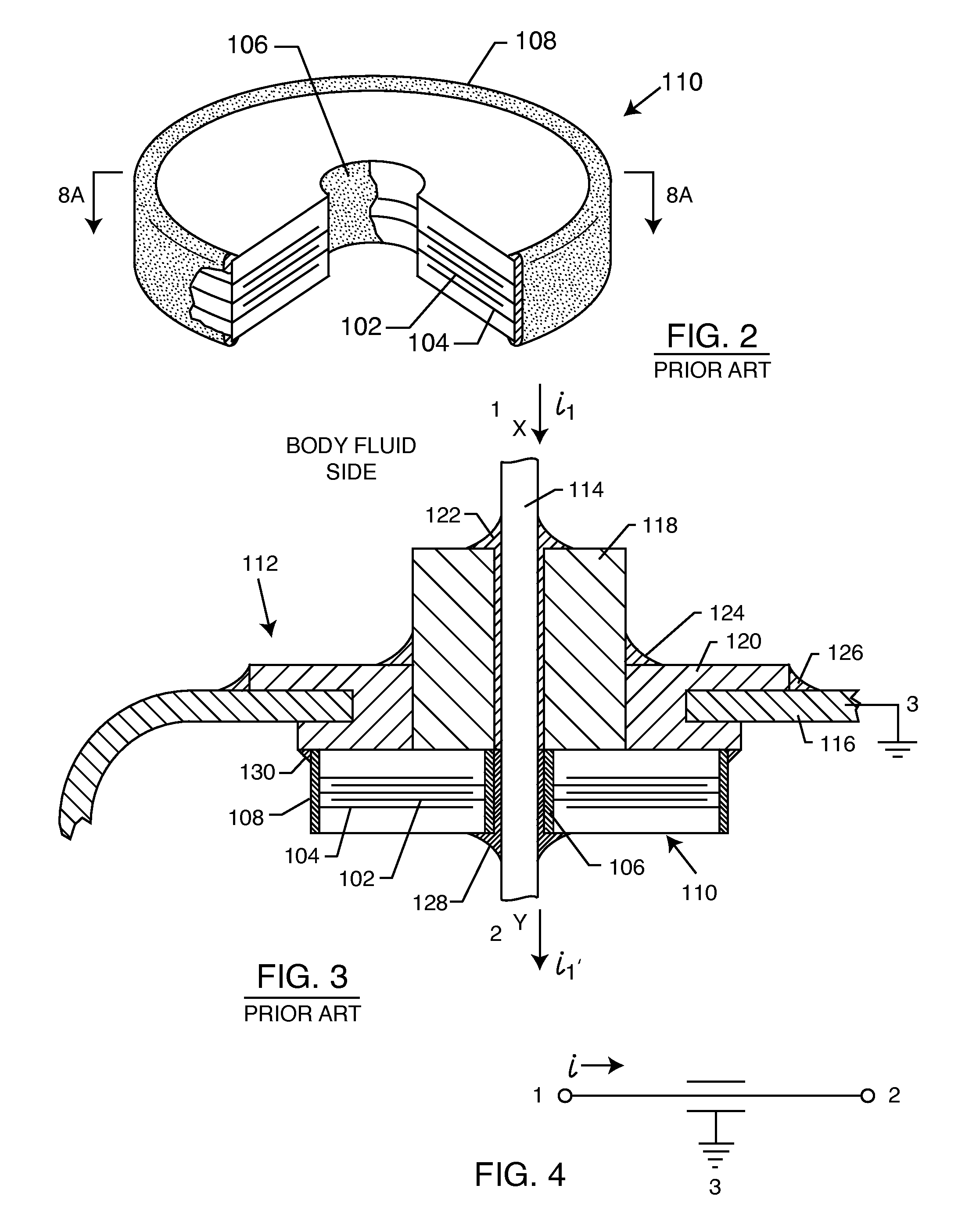
Electromagnetic sensors for biological tissue applications and methods for their use
ActiveUS7591792B2Improves signal couplingImproves resulting measurementElectrotherapyAntenna supports/mountingsMeasurement pointEngineering
Tissue sensors house one or more sensor elements. Each element has a housing mounted substrate and a superstrate with a planar antenna between. A transitional periphery (TP) of a superstrate outer surface interconnects a base to a plateau. At least some of the TP has a generally smooth transition. Plural elements are spaced by the housing. Alternately, the superstrate TP is flat, the housing extends to the outer superstrate surface and a shield surrounds the element. The housing is flush with or recessed below the superstrate and defines a TP between the housing and superstrate. A method converts a reference signal to complex form; plots it in a complex plane as a reference point (RP); converts a measurement signal to complex form; plots it in the complex plane as a measurement point (MP); determine a complex distance between the MP and the RP; and compares complex distance to a threshold.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
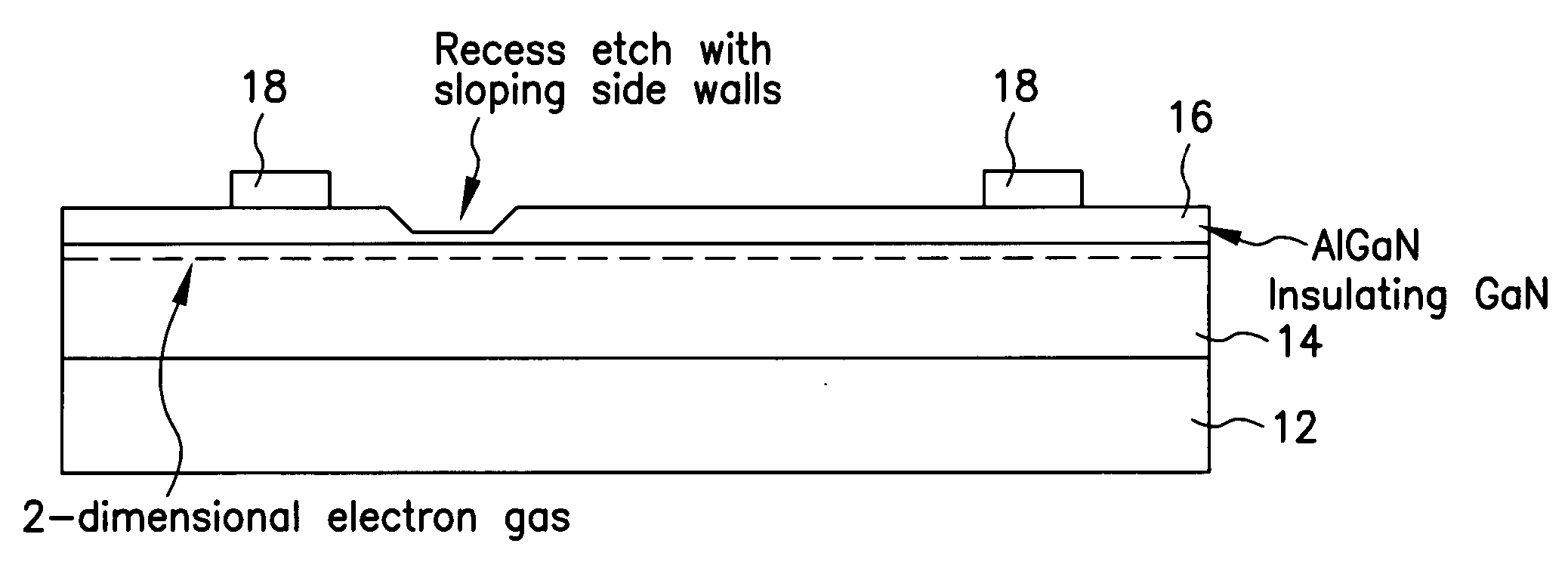
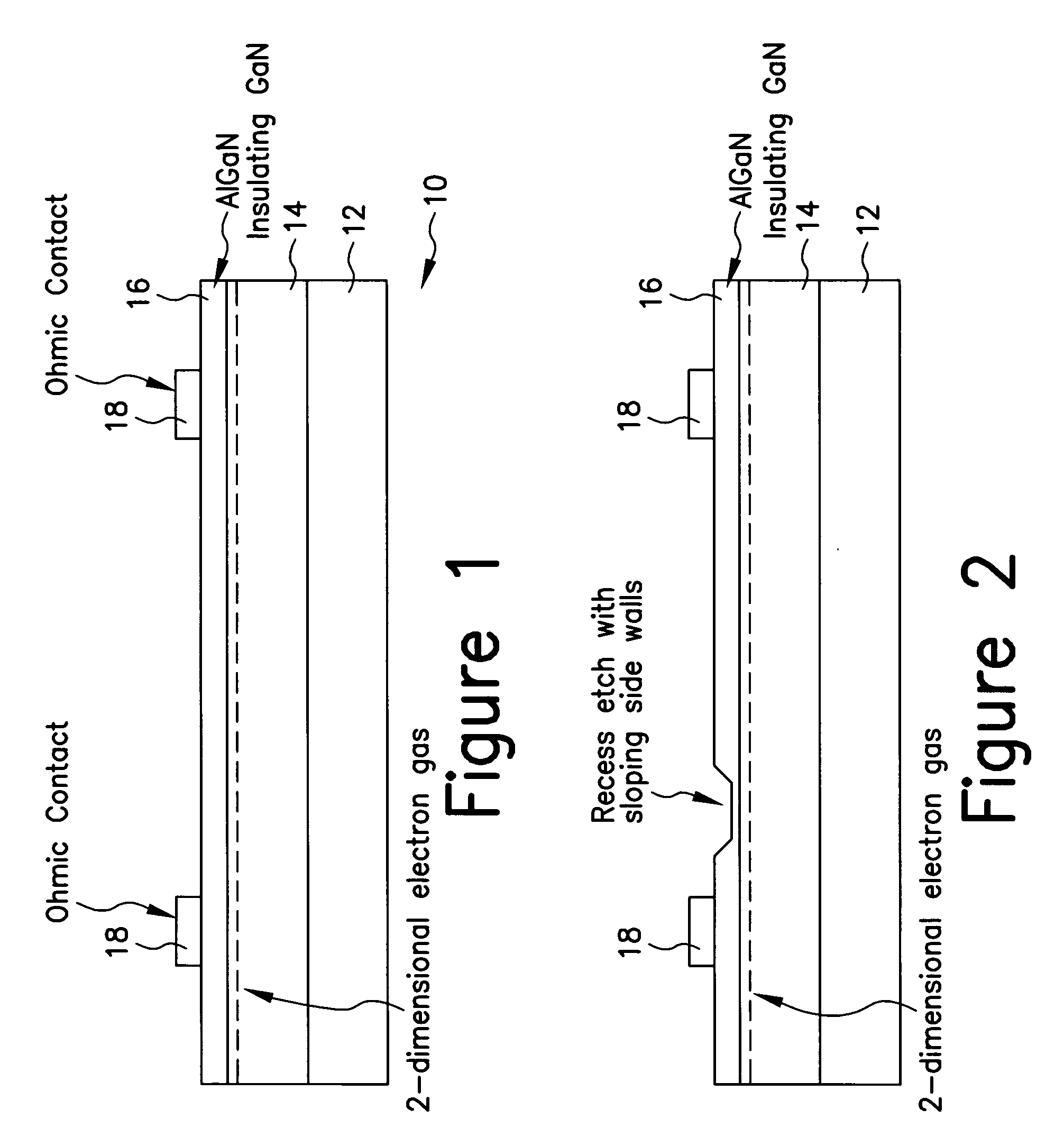
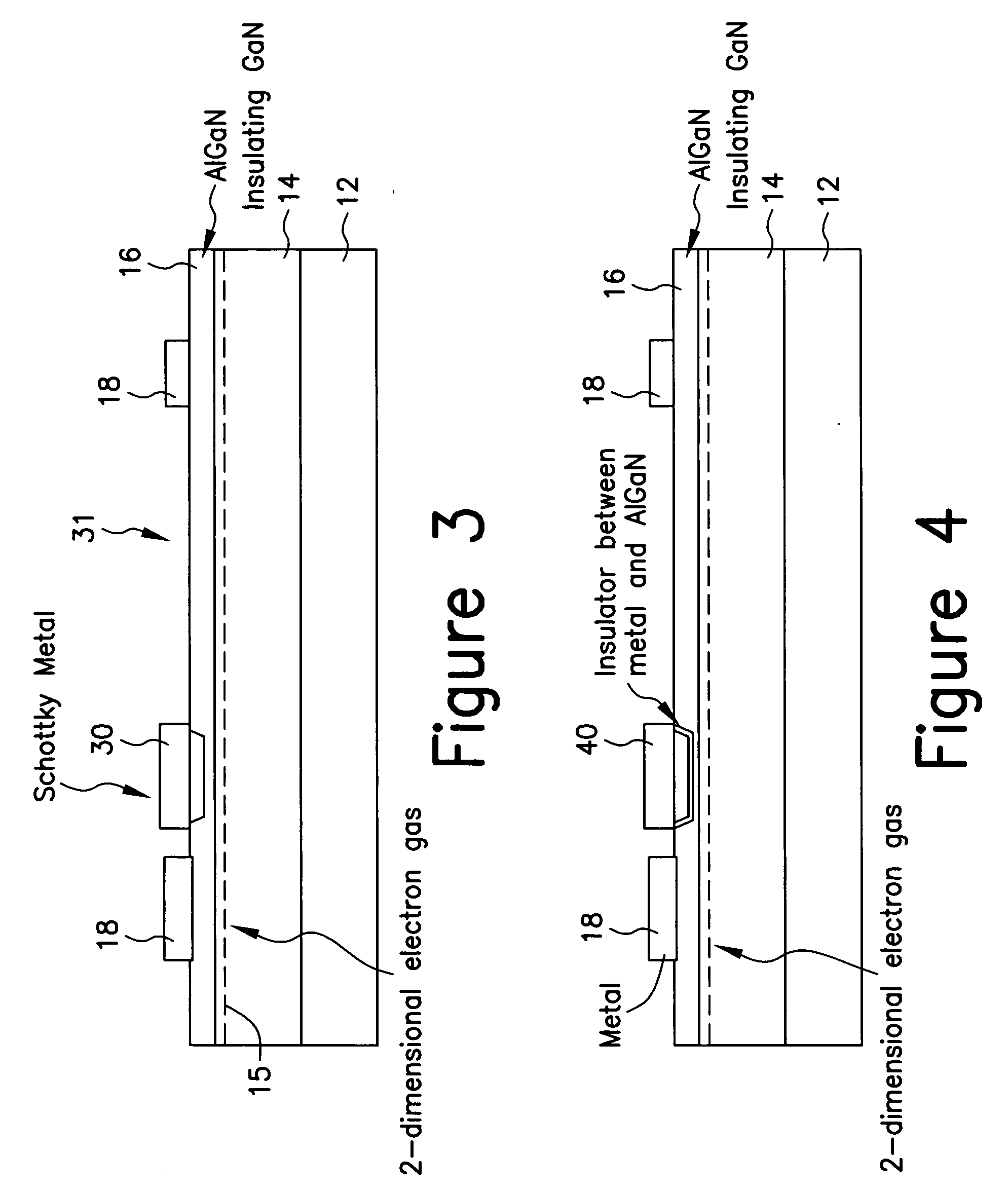
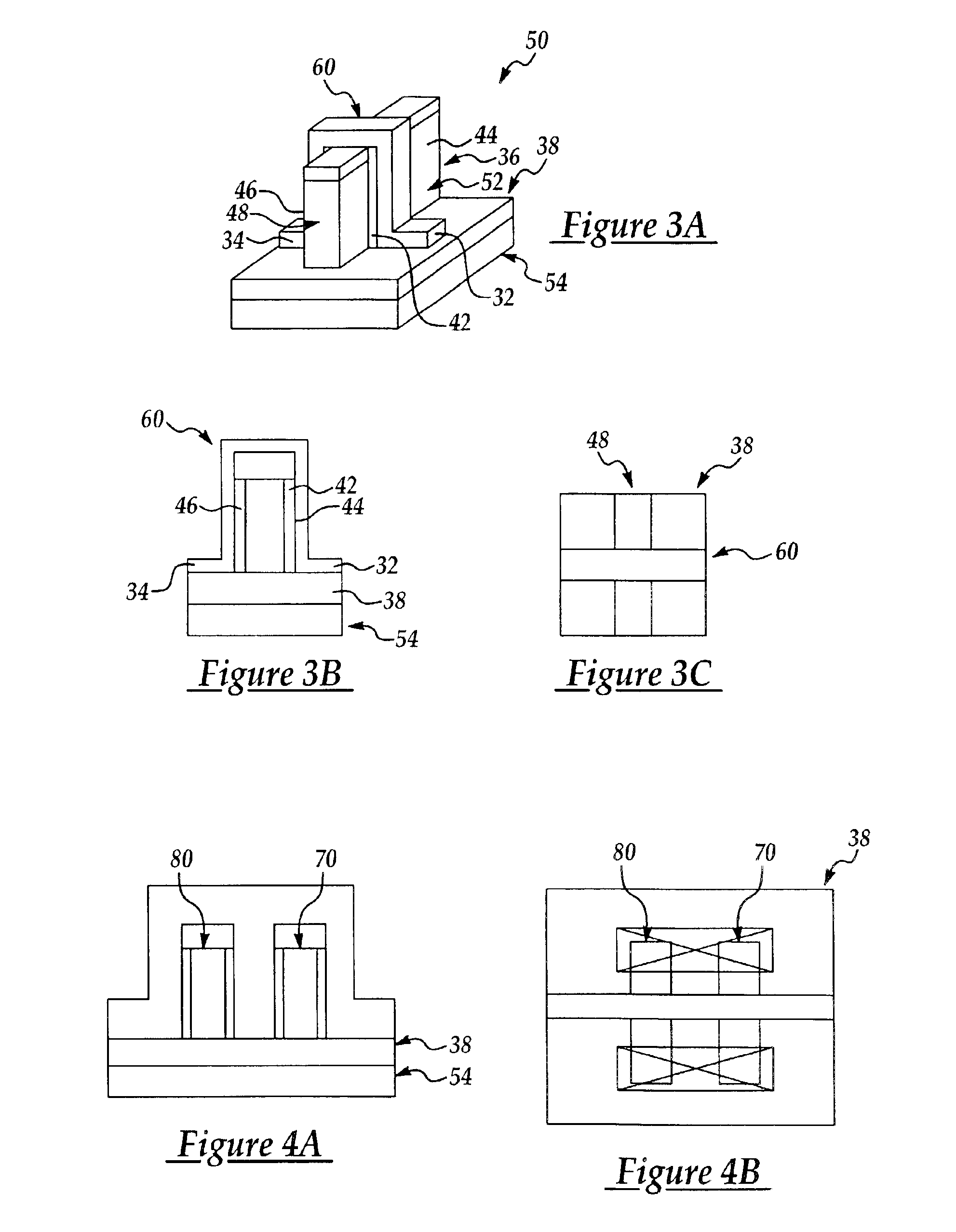
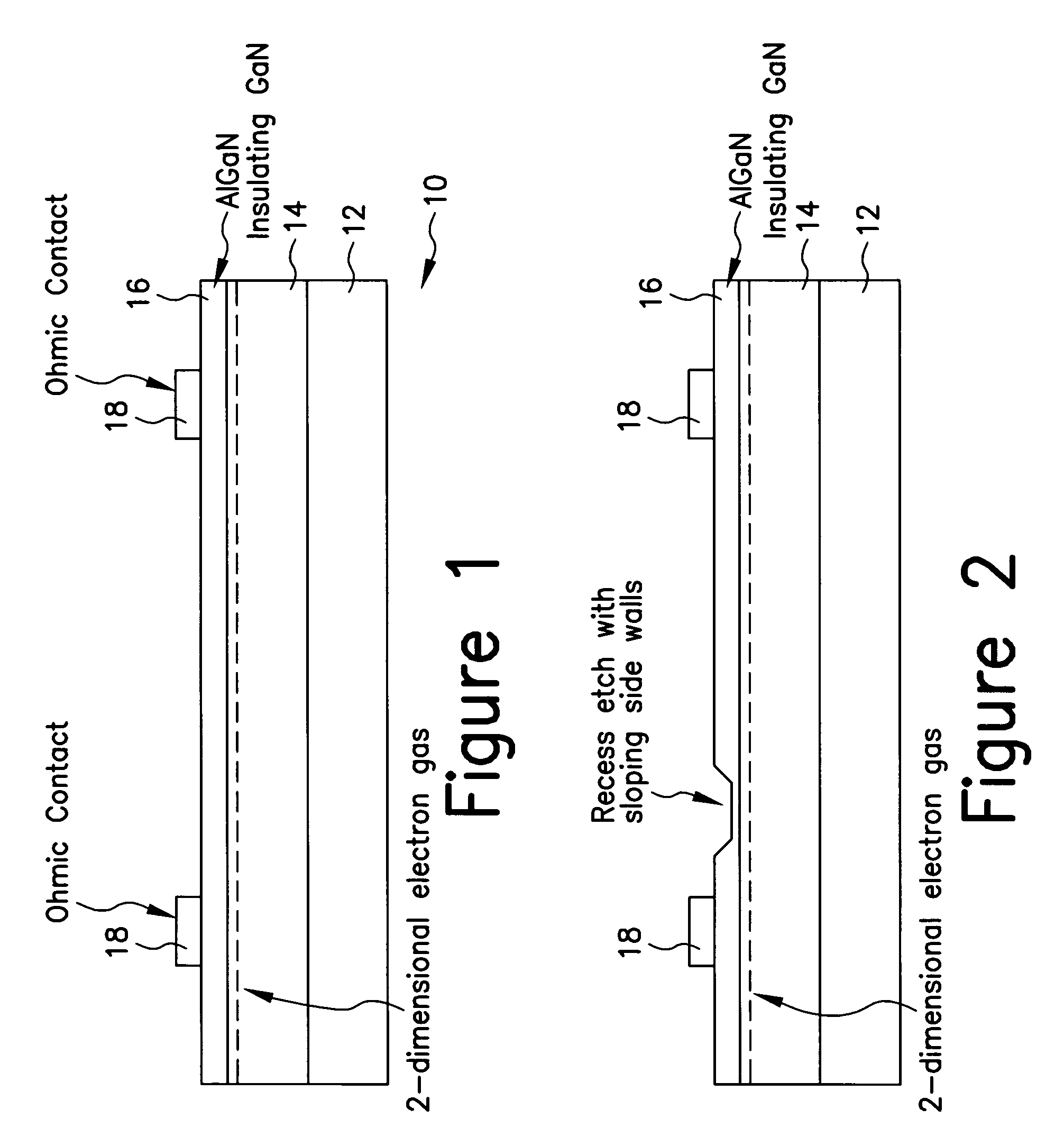
Enhancement mode III-nitride FET
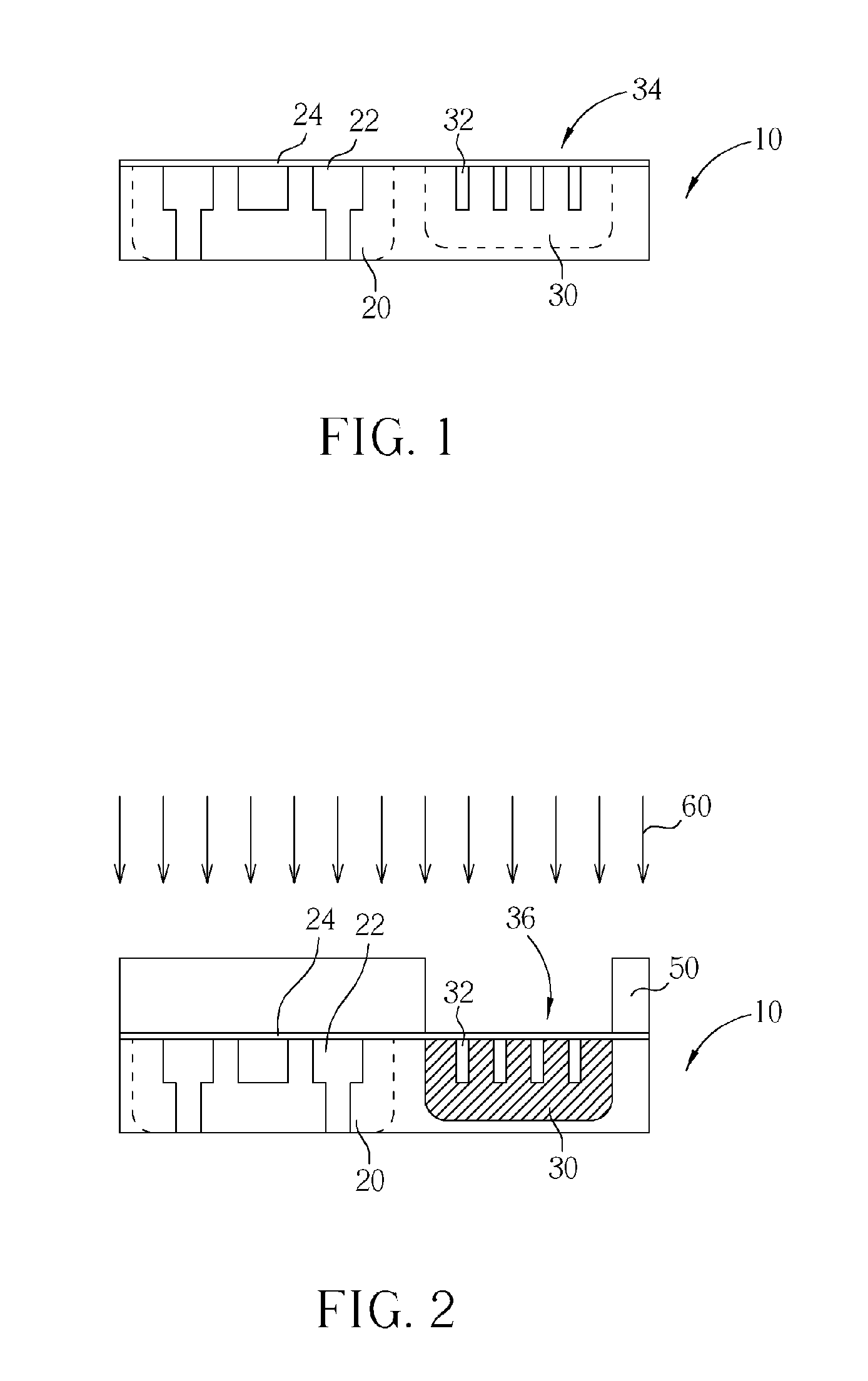
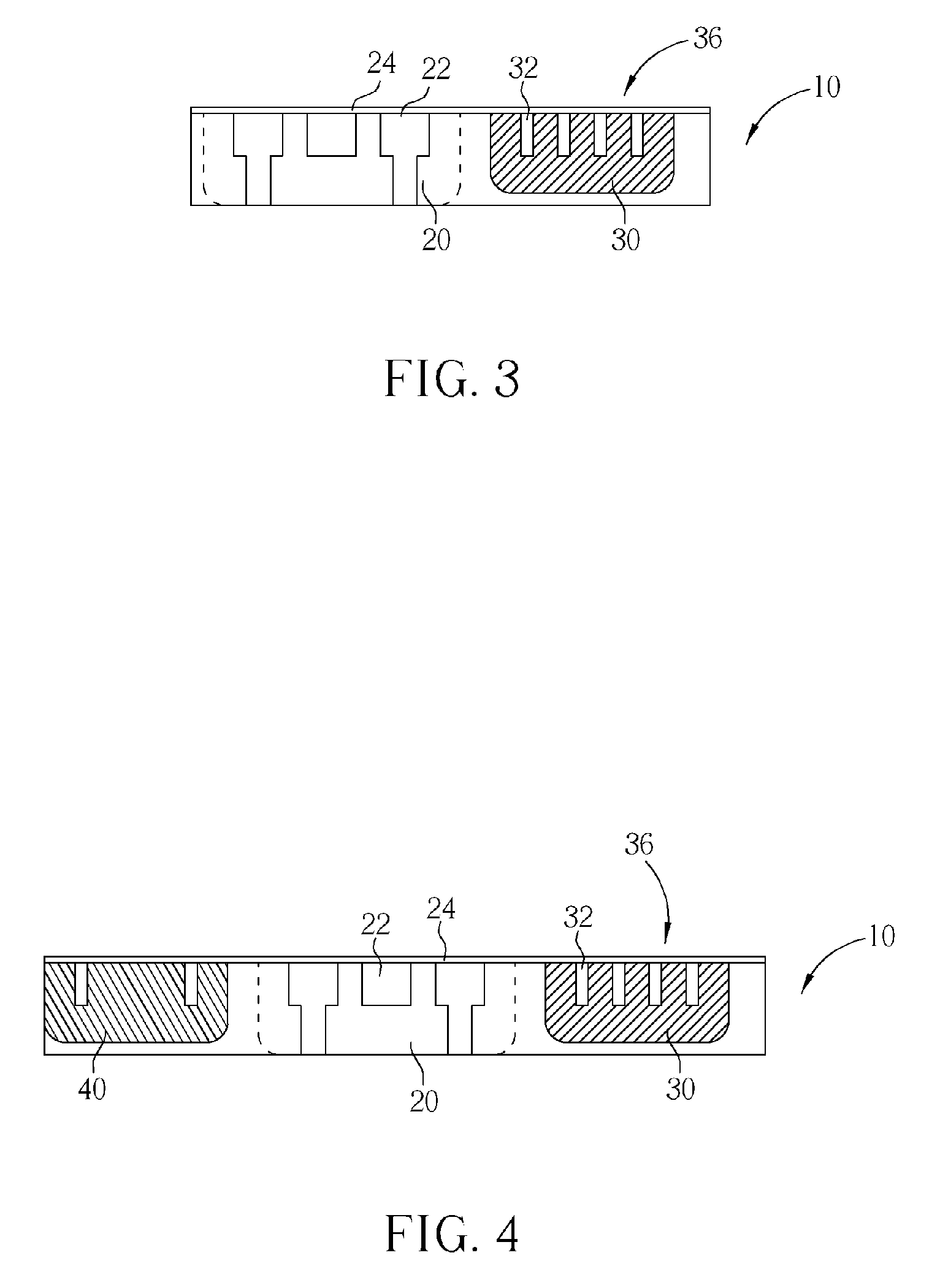
ActiveUS20060060871A1Lower resistanceReduce leakageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesNitrideConduction channel
A III-nitride switch includes a recessed gate contact to produce a nominally off, or an enhancement mode, device. By providing a recessed gate contact, a conduction channel formed at the interface of two III-nitride materials is interrupted when the gate electrode is inactive to prevent current flow in the device. The gate electrode can be a schottky contact or an insulated metal contact. Two gate electrodes can be provided to form a bi-directional switch with nominally off characteristics. The recesses formed with the gate electrode can have sloped sides. The gate electrodes can be formed in a number of geometries in conjunction with current carrying electrodes of the device.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Silicone hydrogel contact lens
ActiveUS20070066706A1Less discomfortHigh dielectric constantPharmaceutical delivery mechanismOptical partsDaily wearPolymer chemistry
Silicone hydrogel contact lenses are provided which have reduced modulus and contact angle properties, and which have acceptable wettabilities for use in daily wear and extended or continuous wear applications.
Owner:COOPERVISION INT LTD
Communication device
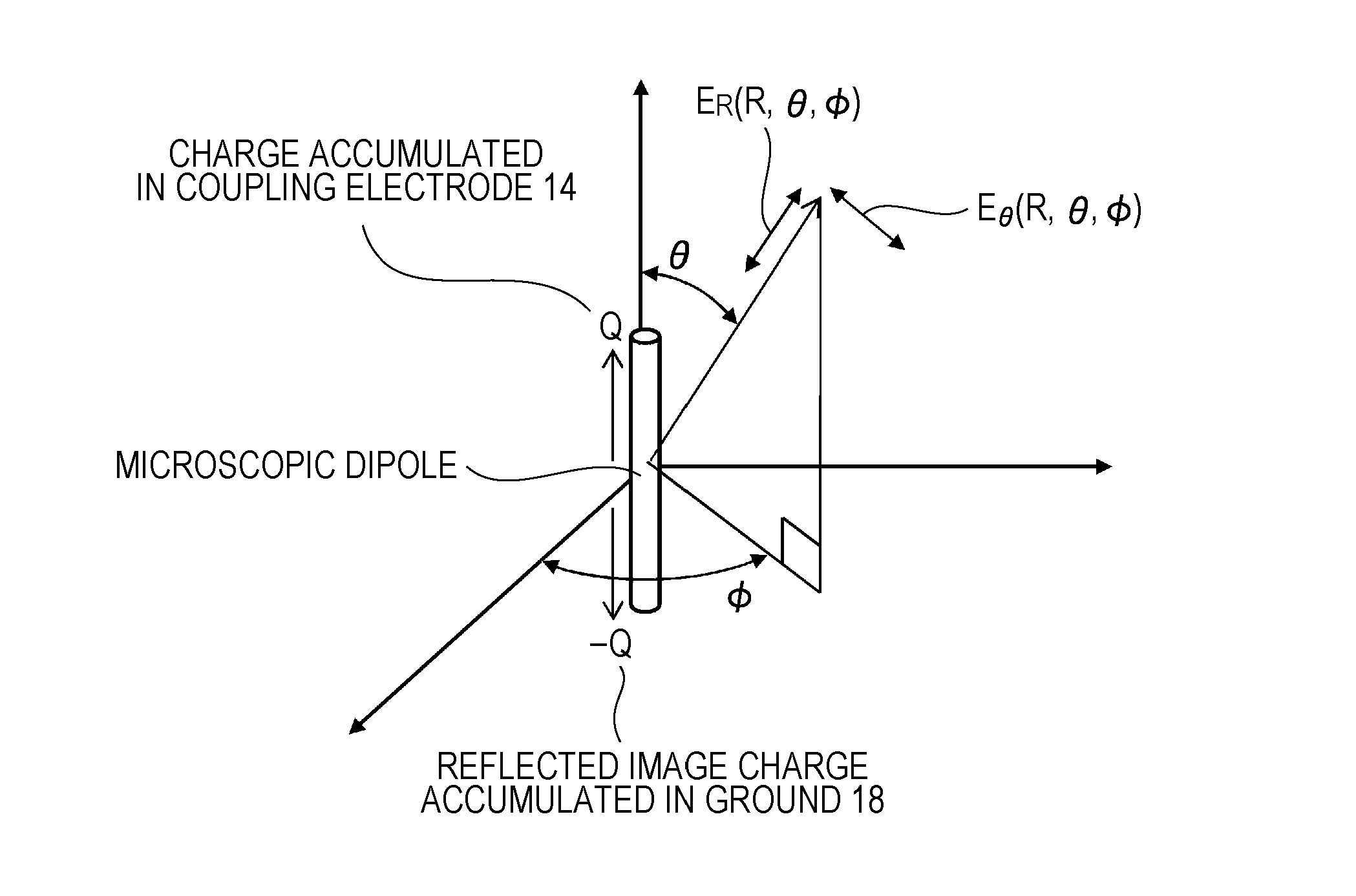
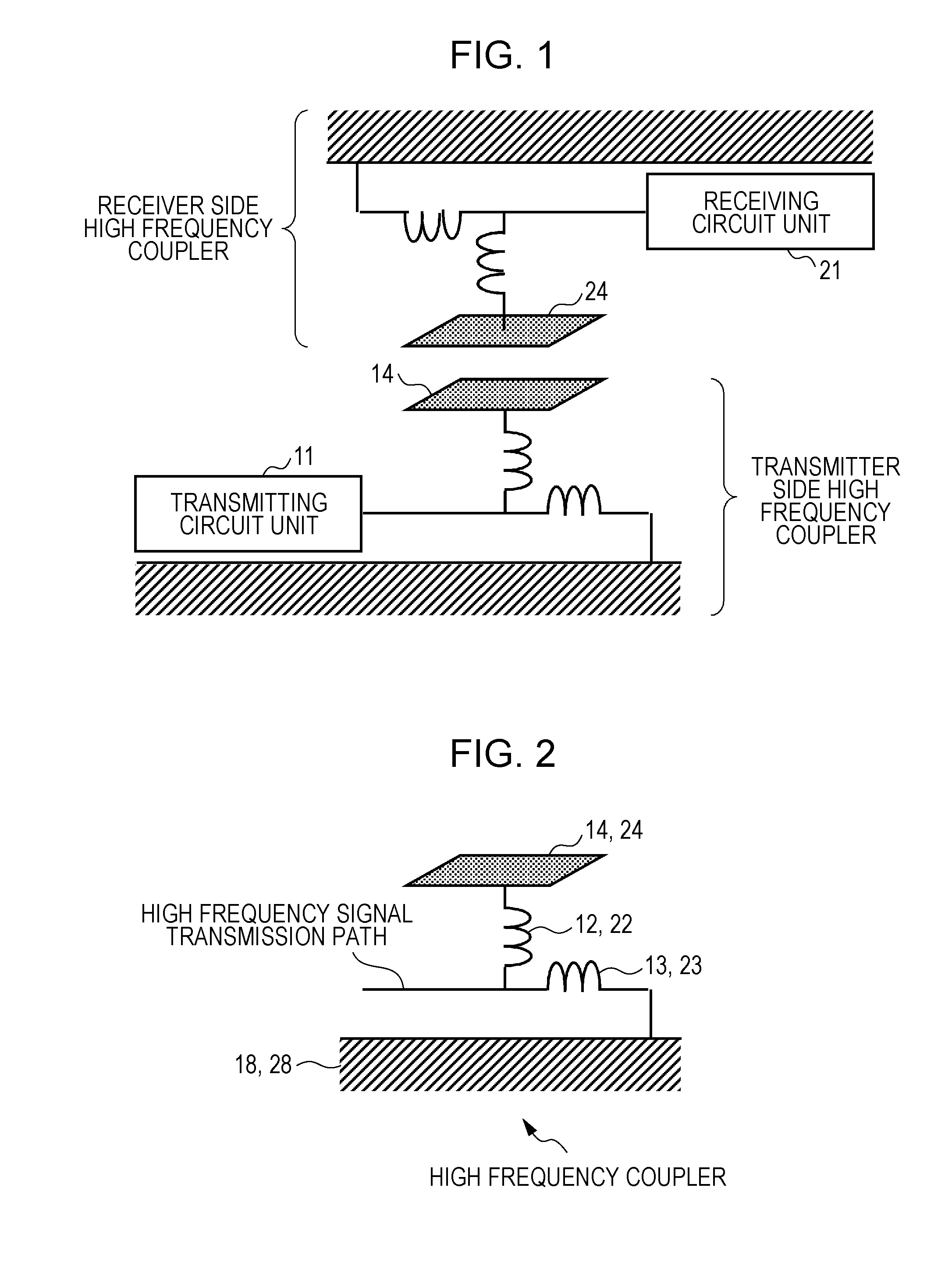
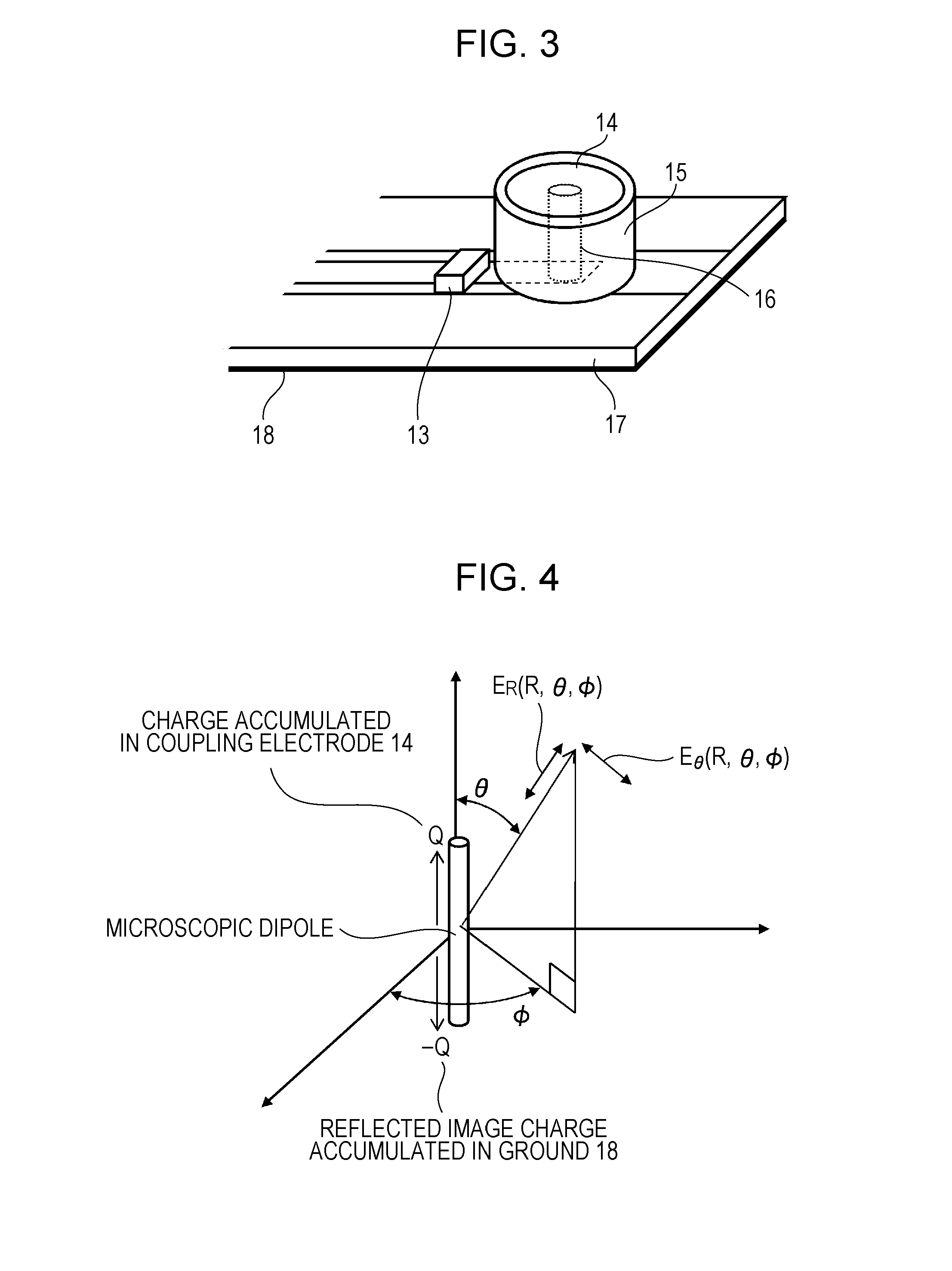
InactiveUS20110228814A1Suppress mutationHigh dielectric constantHigh level techniquesNear-field systems with capacitive couplingCommunication deviceTelecommunications equipment
A communication device includes a case, a high frequency coupler that is disposed inwards from the surface of the case so as to be spaced apart from the surface and transmits and receives a signal of an induction electric field, and a surface wave transmission path that is disposed between the radiation surface of the induction electric field of the high frequency coupler and the surface of the case.
Owner:SONY CORP
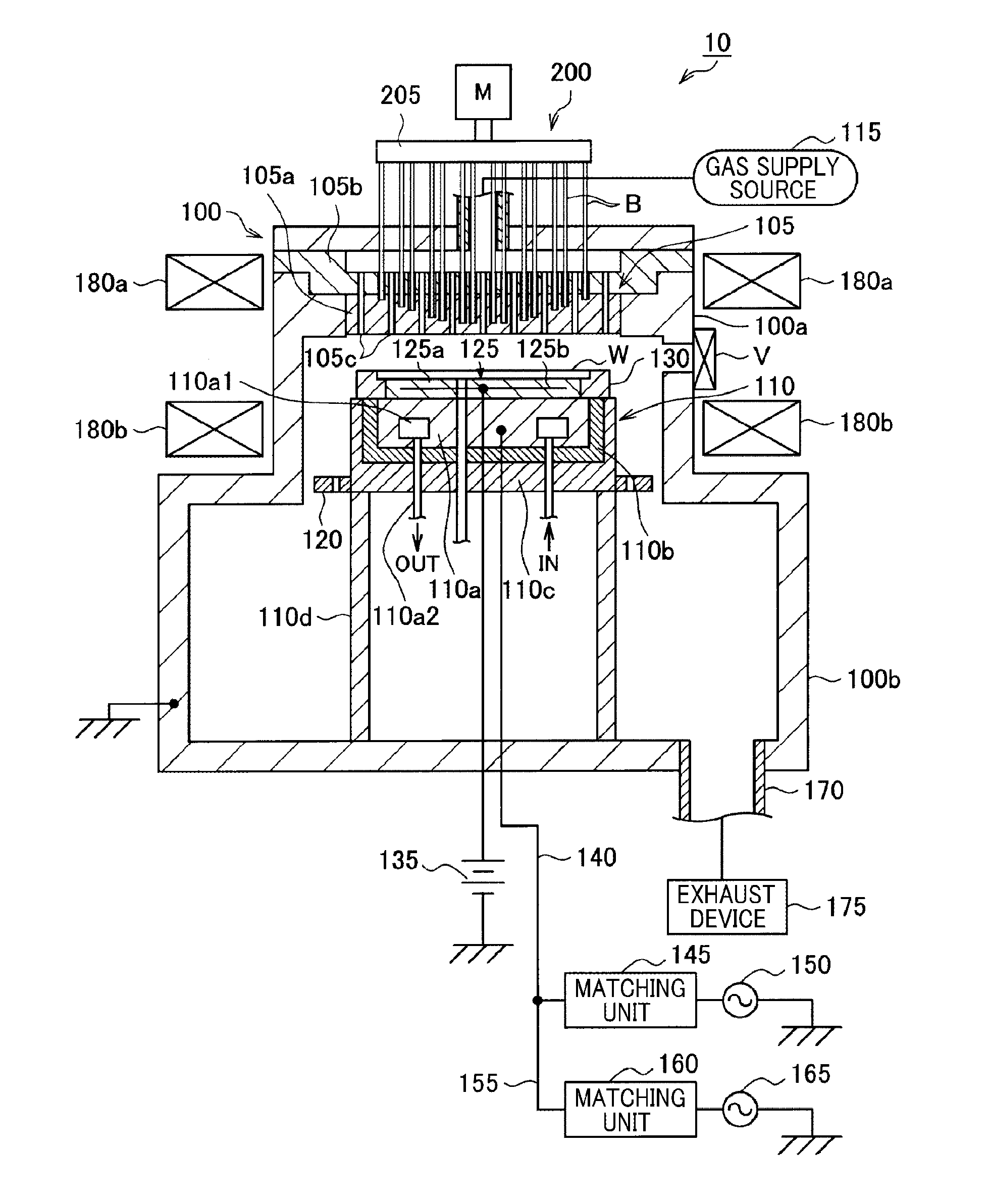
Plasma processing apparatus
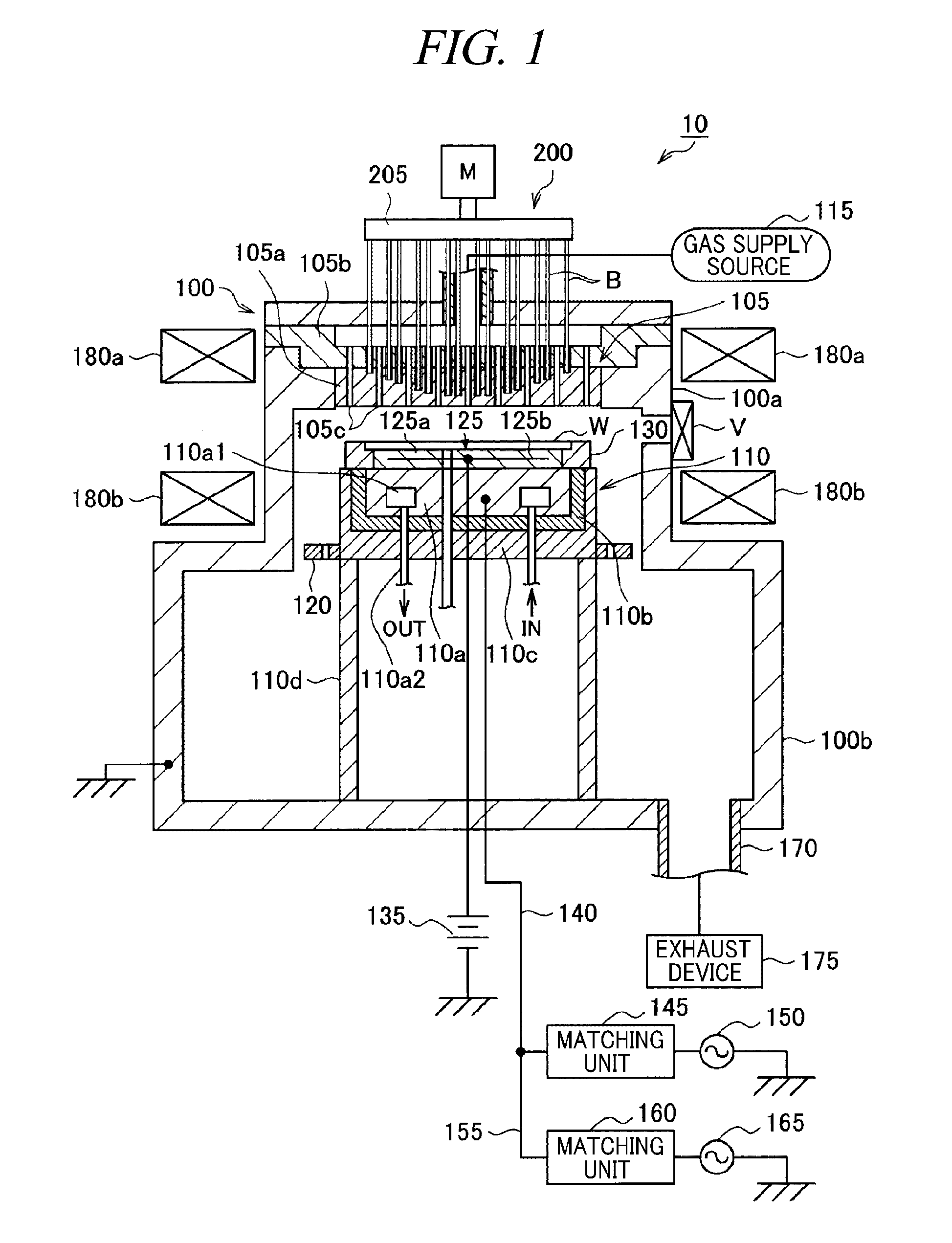
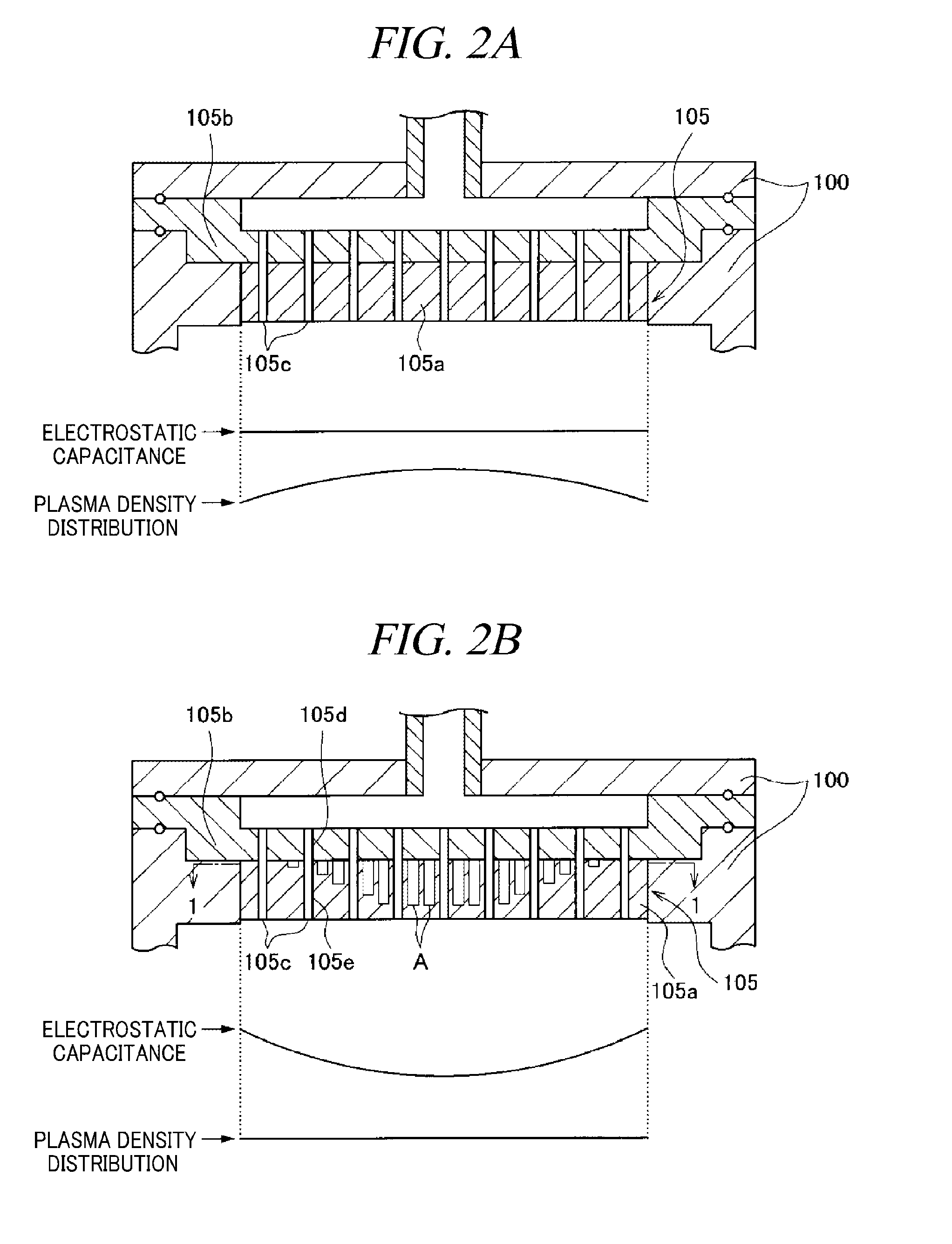
ActiveUS20110226421A1Reduce capacitanceUniform intensity distributionElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh frequency powerProduct gas
An intensity distribution of an electric field of a high frequency power used for generating plasma is controlled by using an electrode made of a homogeneous material and a moving body. There is provided a plasma processing apparatus for introducing a processing gas into an evacuable processing chamber 100 and generating plasma by a high frequency power and performing a plasma process on a wafer W by the plasma. The plasma processing apparatus includes a dielectric base 105a having a multiple number of fine holes A; a varying member 200 as the moving body provided with a multiple number of rod-shaped members B capable of being inserted into and separated from the fine holes A; and a driving mechanism 215 configured to drive the varying member 200 to allow the rod-shaped members B to be inserted into and separated from the fine holes A.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
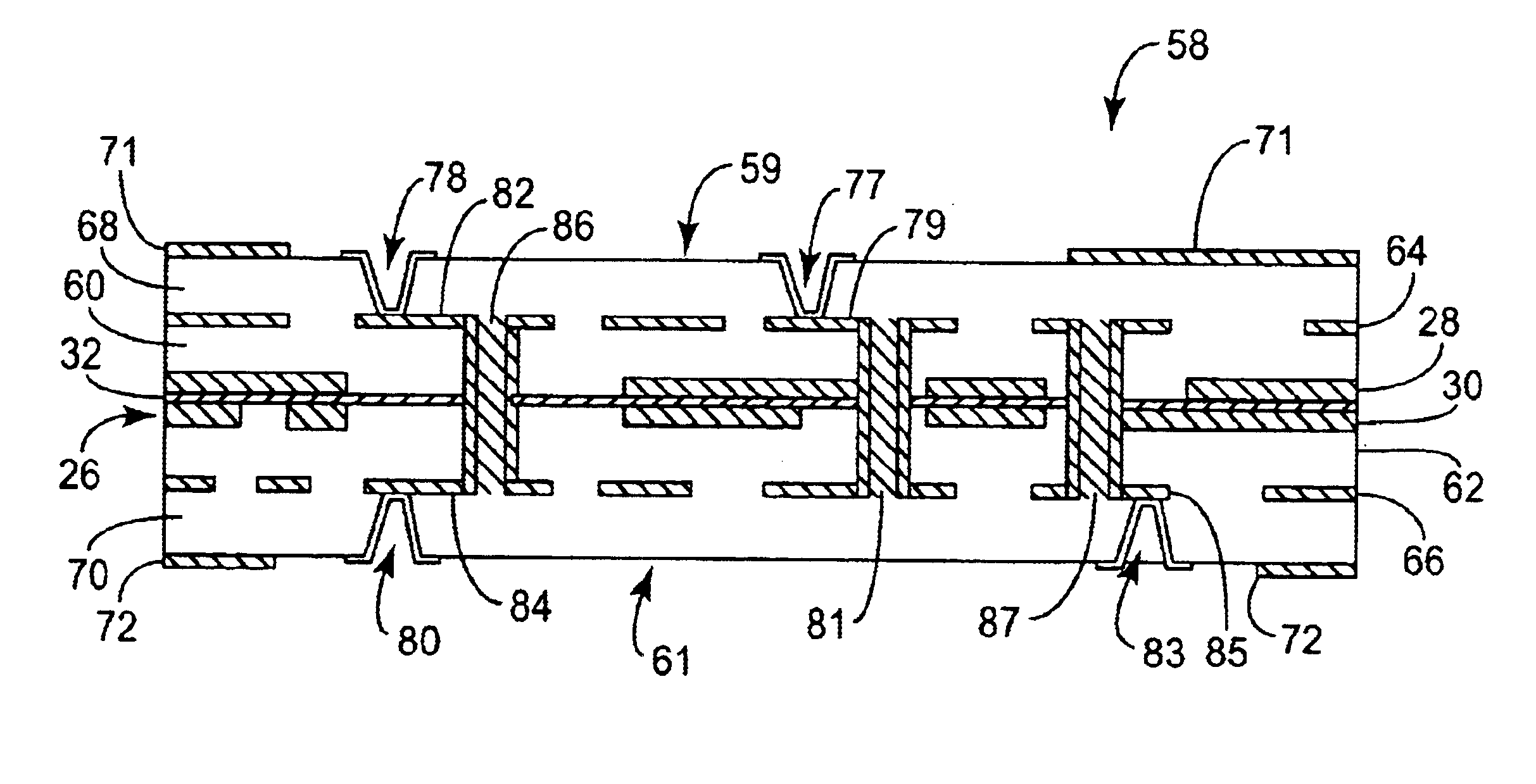
Transmission unit with reduced crosstalk signal
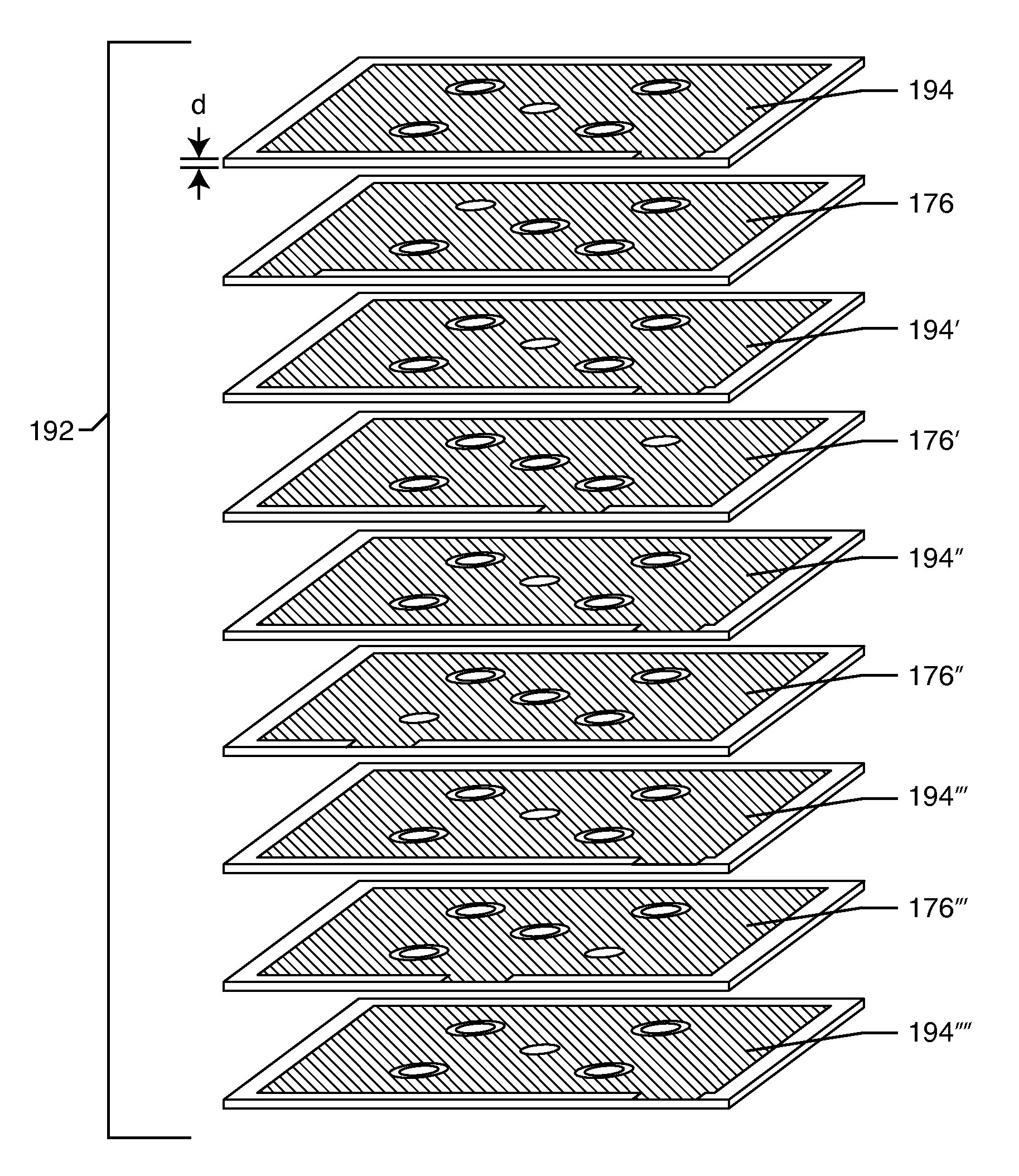
ActiveUS20130015922A1Reduce crosstalk occurredHigh dielectric constantCurrent interference reductionElectrical conductorBiomedical engineering
A transmission unit with reduced crosstalk signal includes a first conductor group having at least one first conductor surrounded by a first sheath and at least one second conductor surrounded by a second sheath. The first and the second conductor are axially arranged corresponding to one another. The first sheath has a dielectric coefficient higher than that of the second sheath, so that a difference in dielectric property exists between the first and the second conductor to enable reduction of crosstalk occurred during high-speed signal transmission over the transmission unit.
Owner:YES WAY ENTERPRISE CORP
Devices, methods, and systems for harvesting energy in the body
InactiveUS20090216292A1High dielectric constantElectrotherapyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMechanical energyAmbient pressure
In some embodiments, the power generator for converting mechanical energy to electrical energy is described may include a compressible element adapted and configured to be placed in an environment having a variable compressive force such as varying ambient pressures. The compressible element may be compressed by a force applied by the variable pressure to the compressible element. The power generator may further include a transducer that may be coupled to the compressible element and that may convert mechanical energy from the compression of the compressible element to electrical energy. In some embodiments, the power generator may be adapted to be an implantable power generator for converting mechanical energy from a patient to electrical energy, such that the compressible element adapted and configured to be placed between two adjacent tissue layers of the patient and to be compressed by a force applied from the two adjacent tissue layers to the compressible element.
Owner:AUTONOMIC TECH INC
Shielded three-terminal flat-through emi/energy dissipating filter
ActiveUS20090243756A1Maximize valueHigh surface areaMultiple-port networksAnti-noise capacitorsEngineeringFlexible cable
A shielded three-terminal flat-through EMI / energy dissipating filter includes an active electrode plate through which a circuit current passes between a first terminal and a second terminal, a first shield plate on a first side of the active electrode plate, and a second shield plate on a second side of the active electrode plate opposite the first shield plate. The first and second shield plates are conductively coupled to a grounded third terminal. In preferred embodiments, the active electrode plate and the shield plates are at least partially disposed with a hybrid flat-through substrate that may include a flex cable section, a rigid cable section, or both.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
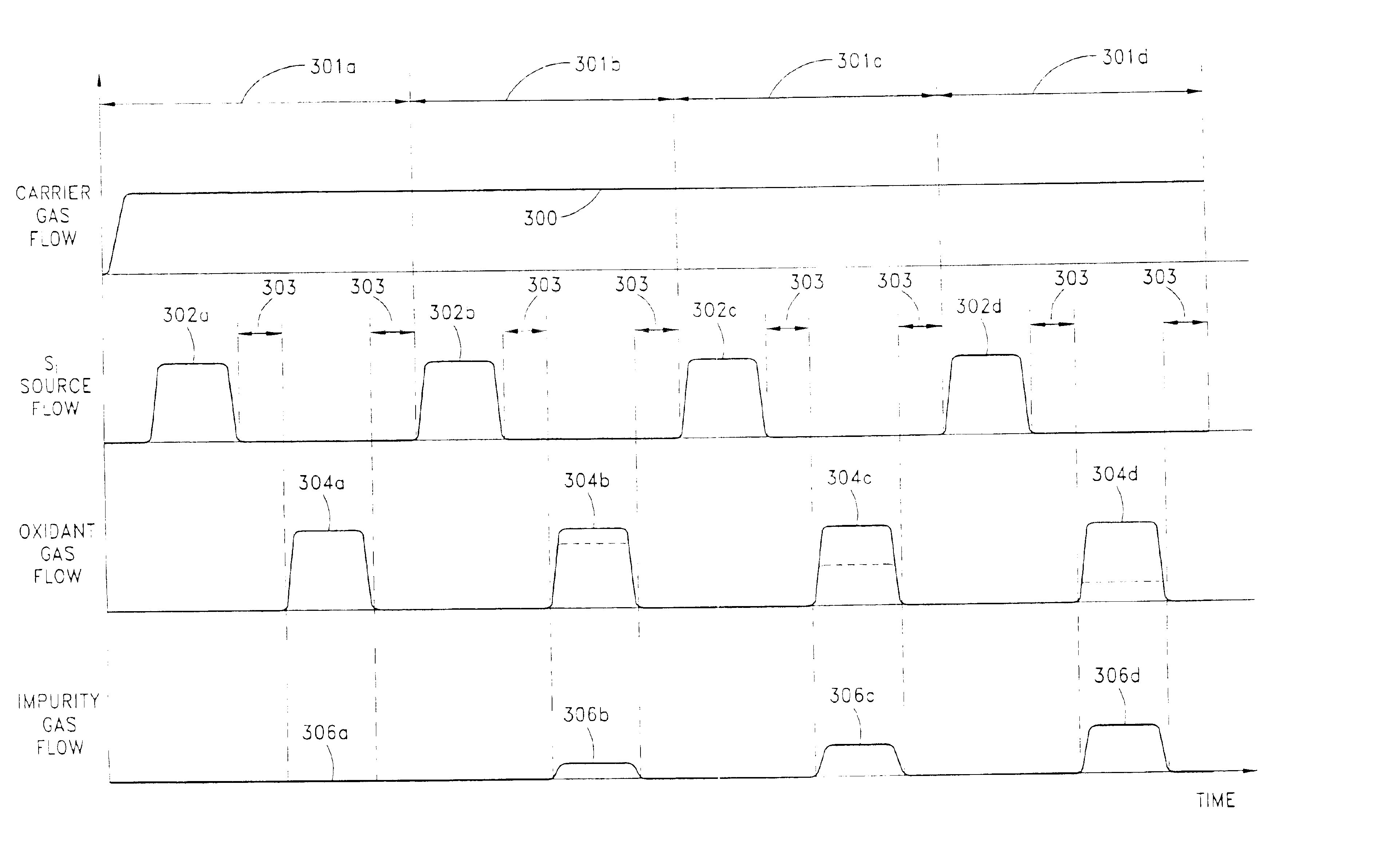
Graded thin films
InactiveUS6933225B2Reduce the temperatureDesirable interface propertySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricSilicon oxide
Thin films are formed by atomic layer deposition, whereby the composition of the film can be varied from monolayer to monolayer during cycles including alternating pulses of self-limiting chemistries. In the illustrated embodiments, varying amounts of impurity sources are introduced during the cyclical process. A graded gate dielectric is thereby provided, even for extremely thin layers. The gate dielectric as thin as 2 nm can be varied from pure silicon oxide to oxynitride to silicon nitride. Similarly, the gate dielectric can be varied from aluminum oxide to mixtures of aluminum oxide and a higher dielectric material (e.g., ZrO2) to pure high k material and back to aluminum oxide. In another embodiment, metal nitride (e.g., WN) is first formed as a barrier for lining dual damascene trenches and vias. During the alternating deposition process, copper can be introduced, e.g., in separate pulses, and the copper source pulses can gradually increase in frequency, forming a graded transition region, until pure copper is formed at the upper surface. Advantageously, graded compositions in these and a variety of other contexts help to avoid such problems as etch rate control, electromigration and non-ohmic electrical contact that can occur at sharp material interfaces.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Resin composition, cured resin, sheet-like cured resin, laminated body, prepreg, electronic parts and multilayer boards
InactiveUS20050003199A1Maintain electrical propertiesHigh dielectric constantSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsEpoxyDielectric loss
The invention provides electronic parts which comprise a composite dielectric layer composed of an organic insulating material and a dielectric ceramic powder having a larger relative dielectric constant than the organic insulating material, and which also comprise conductive element sections forming inductor elements, etc., wherein the organic insulating material comprises a cured resin obtained by curing reaction of an epoxy resin with an active ester compound obtained by reaction between a compound with two or more carboxyl groups and a compound with a phenolic hydroxyl group. The dielectric ceramic powders of the described electronic parts have larger relative dielectric constants than the organic insulating materials, and the organic insulating materials have low dielectric loss tangents. It is possible to adequately reduce time-dependent dielectric constant changes in the high-frequency range of 100 MHz and above even with prolonged use at high temperatures of 100° C. and higher, while it is also possible to satisfactorily prevent deformation and other damage to the electronic parts during their handling.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Hydrophobic Surface Coating With Low Wetting Hysteresis, Method for Depositing Same, Microcomponent and Use
ActiveUS20090142564A1Improve hydrophobicityHigh dielectric constantGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsSynthetic resin layered productsHysteresisDielectric
A hydrophobic surface coating, preferably obtained by chemical vapor deposition, comprises at least an upper thin layer formed by a compound selected from the group consisting of SiCxOy:H with x comprised between 1.4 and 2 and y comprised between 0.8 and 1.4 and SiCx′Ny′:H with x′ comprised between 1.2 and 1.4 and y′ comprised between 0.6 and 0.8, so as to obtain a free surface with a low wetting hysteresis. Such a hydrophobic surface coating can be arranged on the free surface of a microcomponent comprising at least one substrate provided with, an electrode array and particularly suitable for moving drops of liquid by electrowetting on dielectric.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
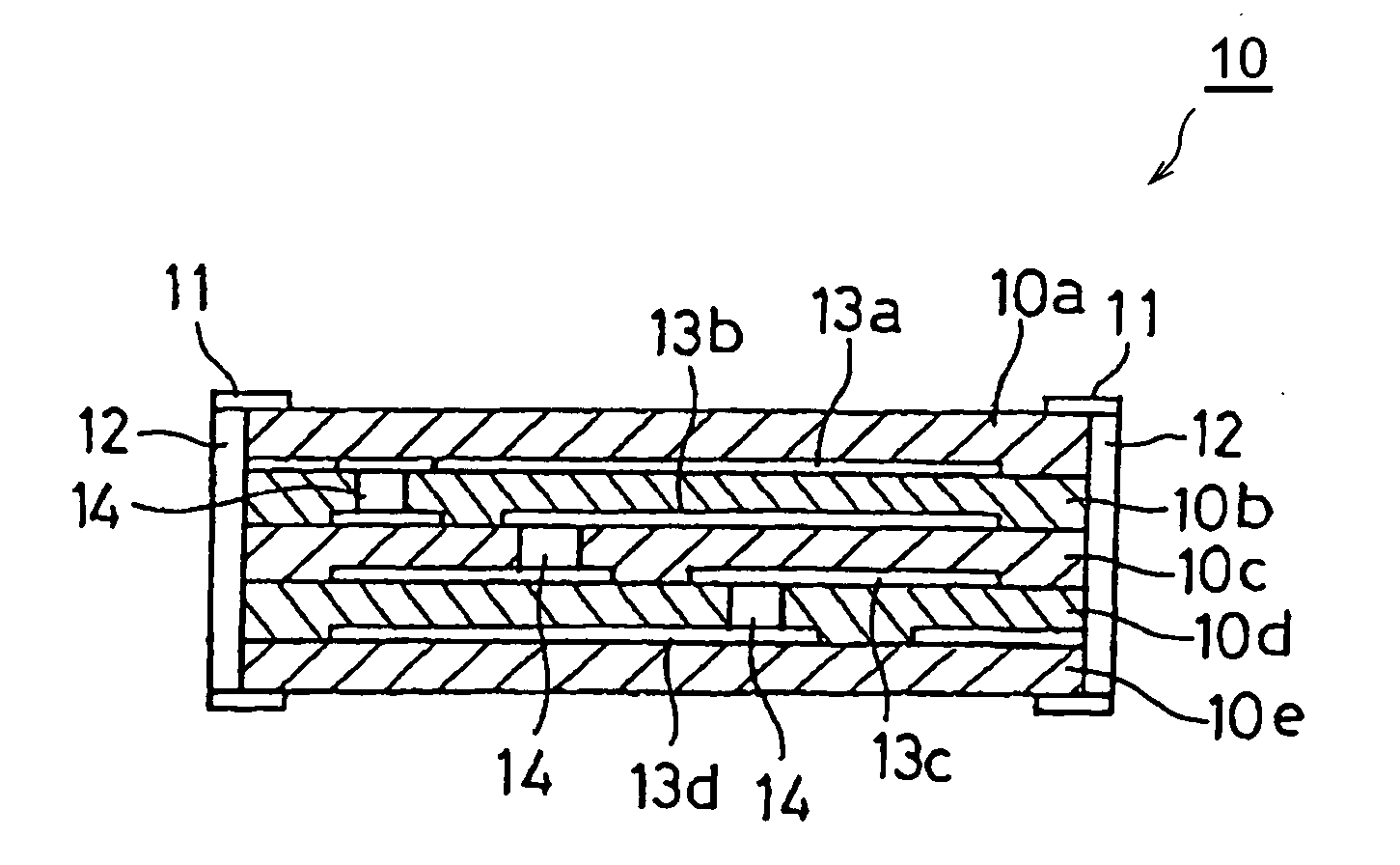
Interconnect module with reduced power distribution impedance
InactiveUS6847527B2Reduced impedance powerReduced ground distributionLight absorption dielectricsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolder ballOperating frequency
An interconnect module for an integrated circuit chip incorporates a thin, high dielectric constant embedded capacitor structure to provide reduced power distribution impedance, and thereby promote higher frequency operation. The interconnect module is capable of reliably attaching an integrated circuit chip to a printed wiring board via solder ball connections, while providing reduced power distribution impedance of less than or equal to approximately 0.60 ohms at operating frequencies in excess of 1.0 gigahertz.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
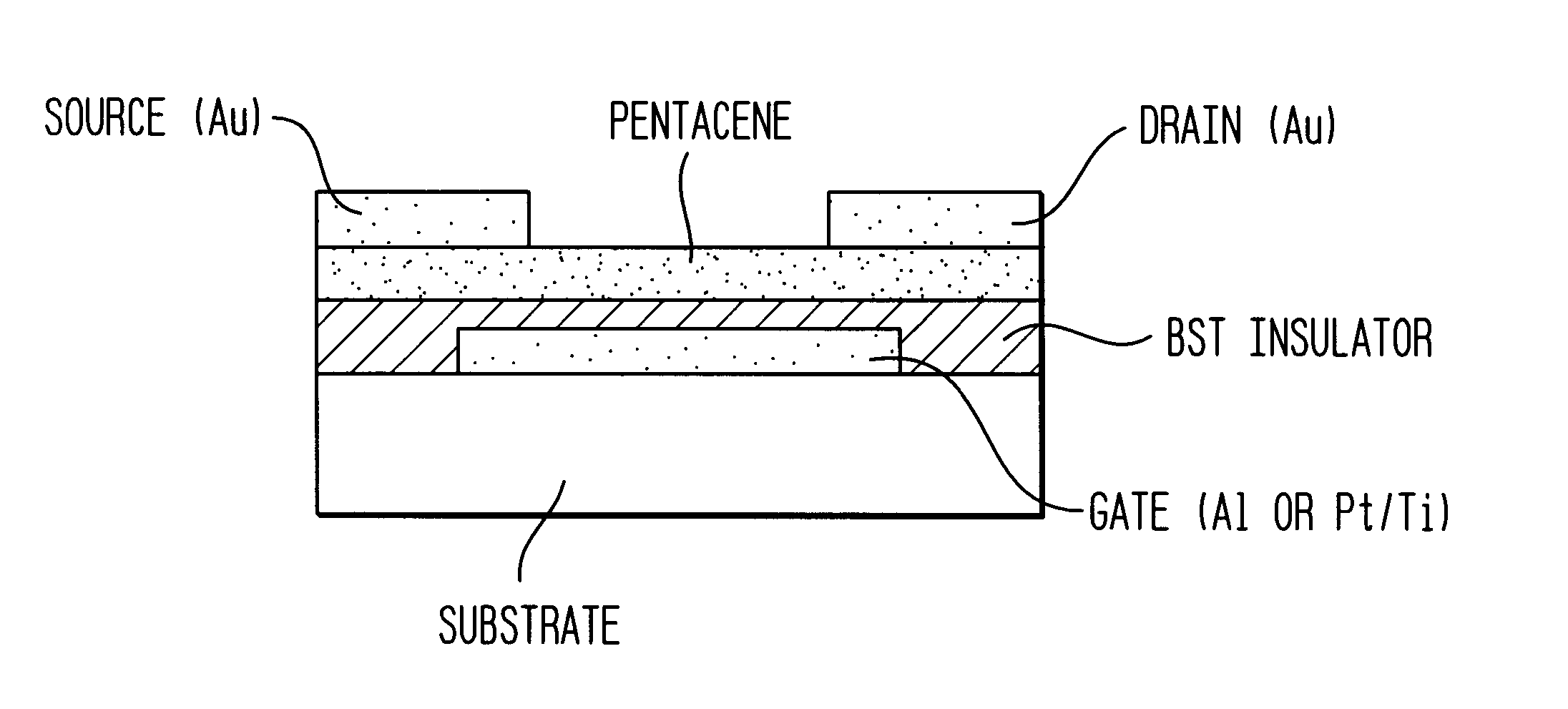
Thin-film field-effect transistor with organic semiconductor requiring low operating voltages
InactiveUS6344660B1Reduce thicknessImprove mobilityTransistorSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceFlat panel display
A thin film transistor (TFT) device structure based on an organic semiconductor material, that exhibits a high field effect mobility, high current modulation and a low sub-threshold slope at lower operating voltages than the current state of the art organic TFT devices. The structure comprises a suitable substrate disposed with he following sequence of features: a set of conducting gate electrodes covered with a high dielectric constant insulator, a layer of the organic semiconductor, sets of electrically conducting source and drain electrodes corresponding to each of the gate lines, and an optional passivation layer that can overcoat and protect the device structure. Use of high dielectric constant gate insulators exploits the unexpected gate voltage dependence of the organic semiconductor to achieve high field effect mobility levels at very low operating voltages. Judicious combinations of the choice of this insulator material and the means to integrate it into the TFT structure are taught that would enable easy fabrication on glass or plastic substrates and the use of such devices in flat panel display applications.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Deposition of hafnium oxide and/or zirconium oxide and fabrication of passivated electronic structures
InactiveUS6982230B2Stable to reducing condition necessaryImprove electrical performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic structureHydrogen
A method of fabricating hafnium oxide and / or zirconium oxide films is provided. The methods include providing a mixture of Hf and / or Zr alkoxide dissolved, emulsified or suspended in a liquid; vaporizing at least the alkoxide and depositing the vaporized component at a temperature of greater than 400° C. The resultant film is dense, microcrystalline and is capable of self-passivation when treated in a hydrogen plasma or forming gas anneal.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Inductor element and method for production thereof, and semiconductor module with inductor element
InactiveUS20070247268A1Reduce inductanceLower quality factorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAerosol depositionInductor
Owner:SONY CORP
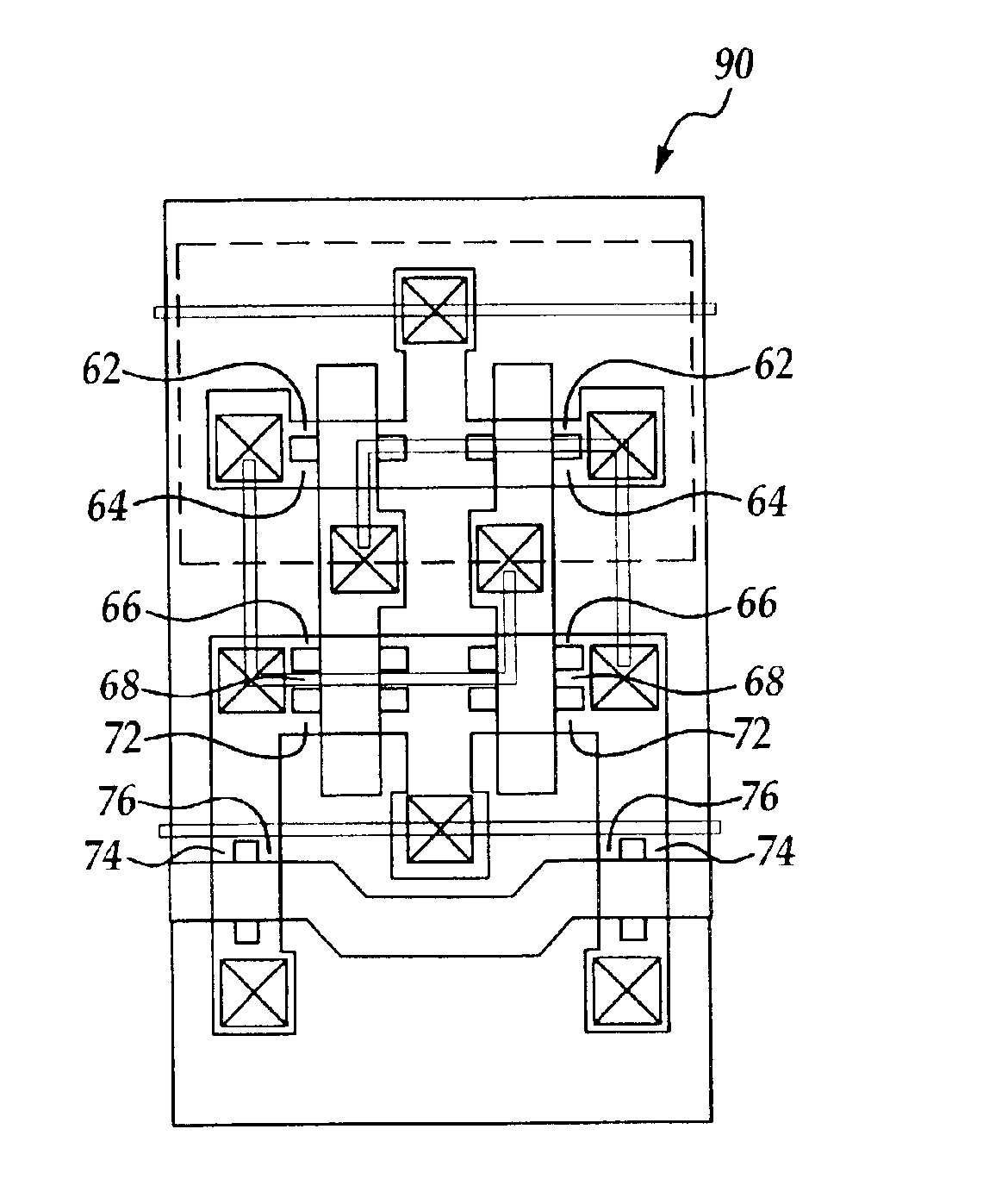
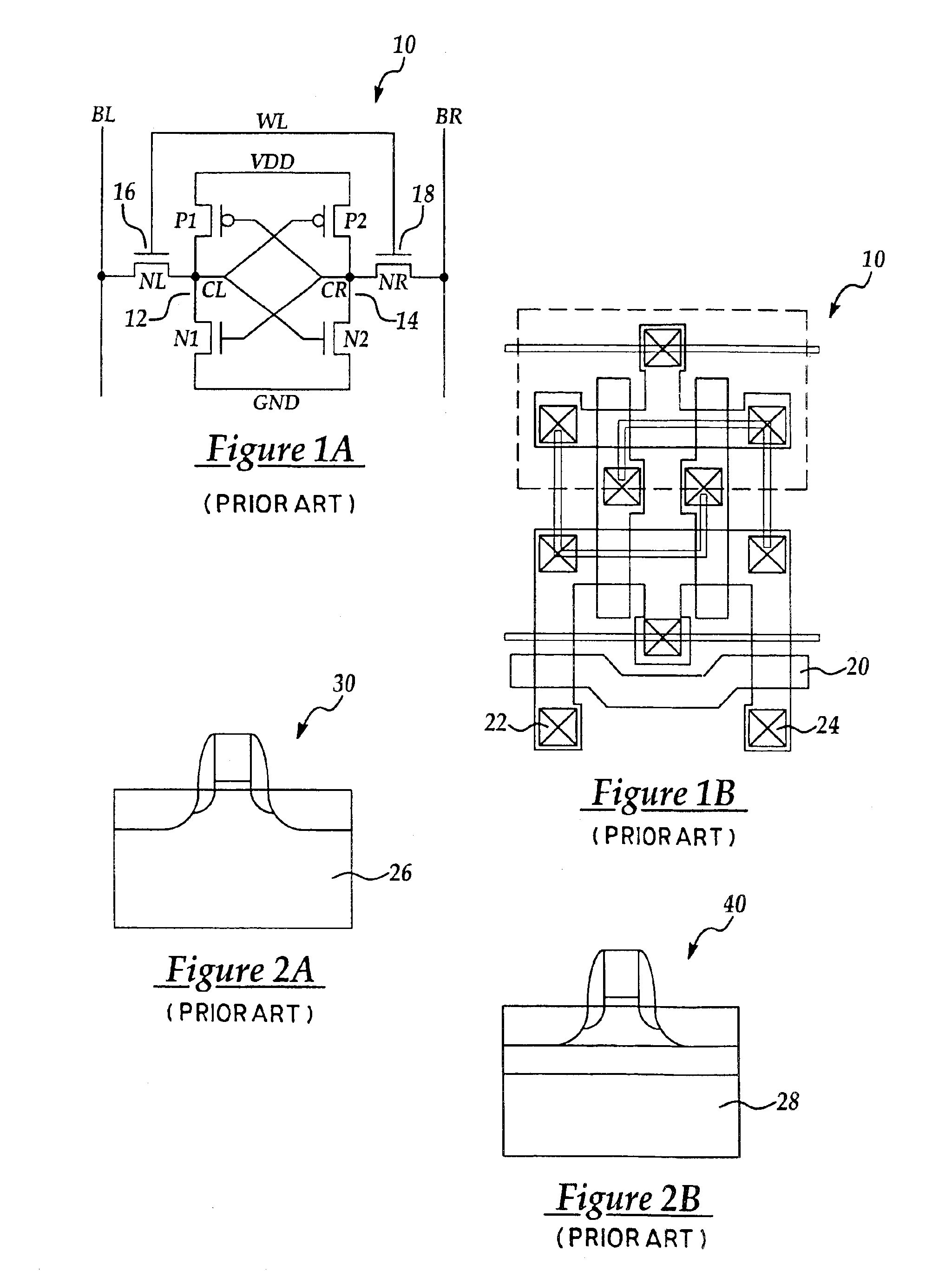
CMOS SRAM cell configured using multiple-gate transistors
InactiveUS6864519B2High dielectric constantSave layout area andTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCMOSBit line
A complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor static random access memory cell that is formed by a pair of P-channel multiple-gate field-effect transistors (P-MGFETs), a pair of N-channel multiple-gate field-effect transistors (N-MGFETs), a second pair of N-MGFETs that has a drain respectively connected to a connection linking the respective drain of the N-MGFET of the first pair of N-MGFET to the drain of the P-MGFET of the pair of P-MGFETs; a pair of complementary bit lines, each respectively connected to the source of the N-MGFET of the second pair of N-MGFETS; and a word line connected to the gates of the N-MGFETs of the second pair of N-MGFETs.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Enhancement mode III-nitride FET
ActiveUS7382001B2Lower resistanceReduce leakageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringNitride
A III-nitride switch includes a recessed gate contact to produce a nominally off, or an enhancement mode, device. By providing a recessed gate contact, a conduction channel formed at the interface of two III-nitride materials is interrupted when the gate electrode is inactive to prevent current flow in the device. The gate electrode can be a schottky contact or an insulated metal contact. Two gate electrodes can be provided to form a bi-directional switch with nominally off characteristics. The recesses formed with the gate electrode can have sloped sides. The gate electrodes can be formed in a number of geometries in conjunction with current carrying electrodes of the device.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
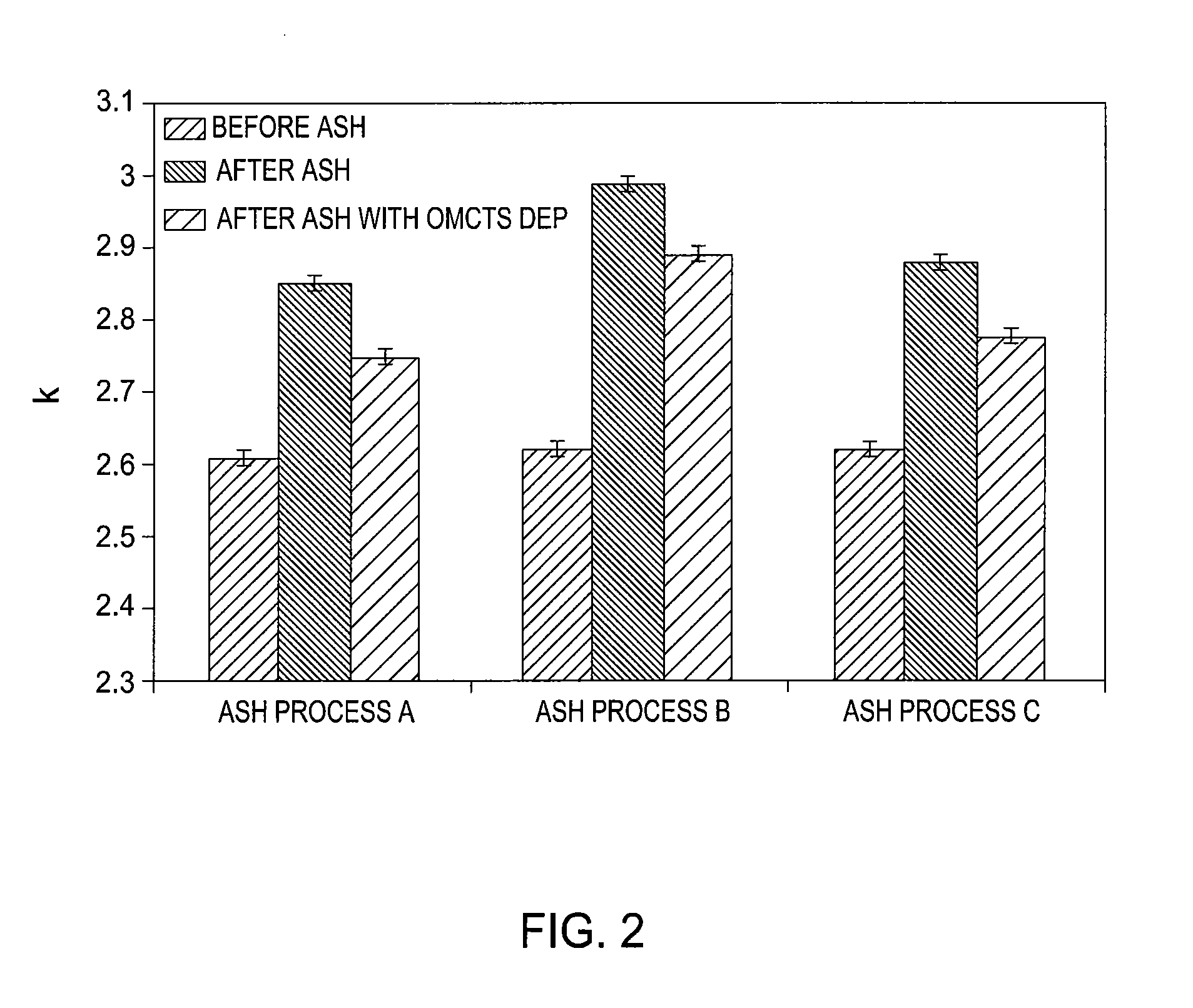
Plasma curing process for porous silica thin film
InactiveUS20010038919A1High elastic modulusLow dielectric constantSilicaPretreated surfacesSilicon dioxideMaterials science
Low dielectric constant films with improved elastic modulus. The method of making such coatings involves providing a porous network coating produced from a resin containing at least 2 Si-H groups and plasma curing the coating to convert the coating into porous silica. Plasma curing of the network coating yields a coating with improved modulus, but with a higher dielectric constant. The coating is plasma cured for between about 15 and about 120 seconds at a temperature less than about 350° C. The plasma cured coating can optionally be annealed. Rapid thermal processing (RTP) of the plasma cured coating reduces the dielectric constant of the coating while maintaining an improved elastic modulus as compared to the plasma cured porous network coating. The annealing temperature is typically less than about 475° C., and the annealing time is typically no more than about 180 seconds. The annealed, plasma cured coating has a dielectric constant in the range of from about 1.1 to about 2.4 and an improved elastic modulus.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com