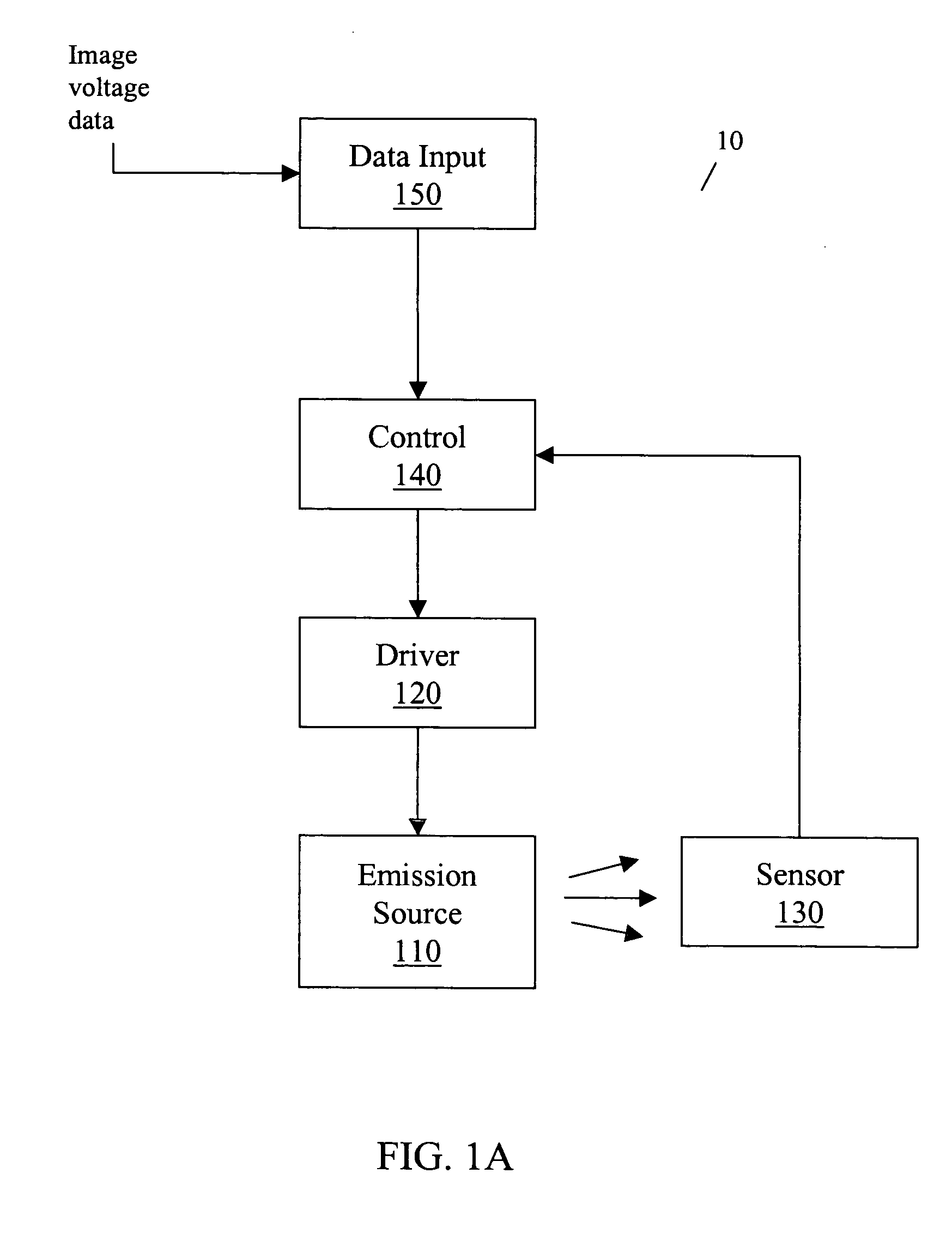
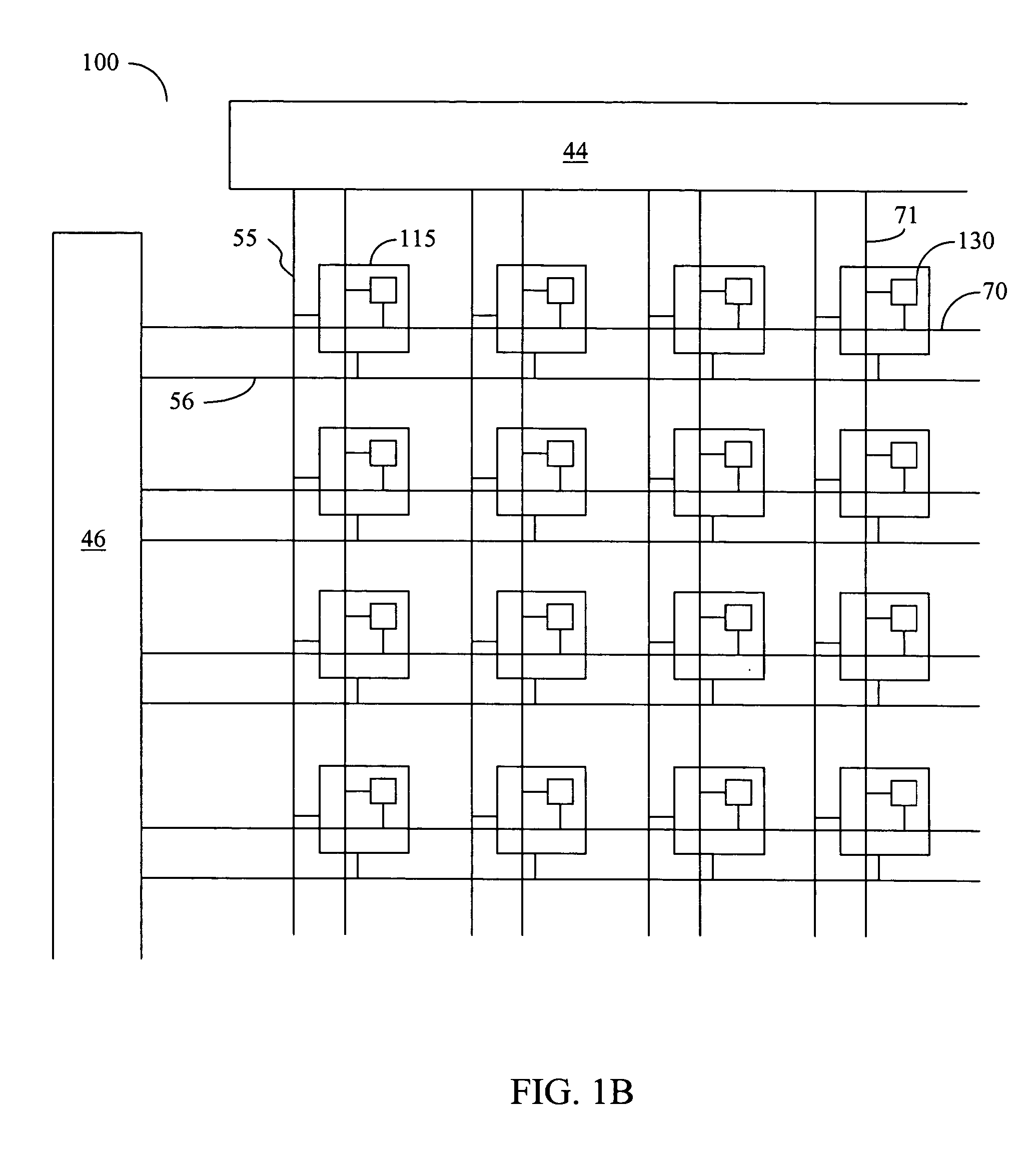
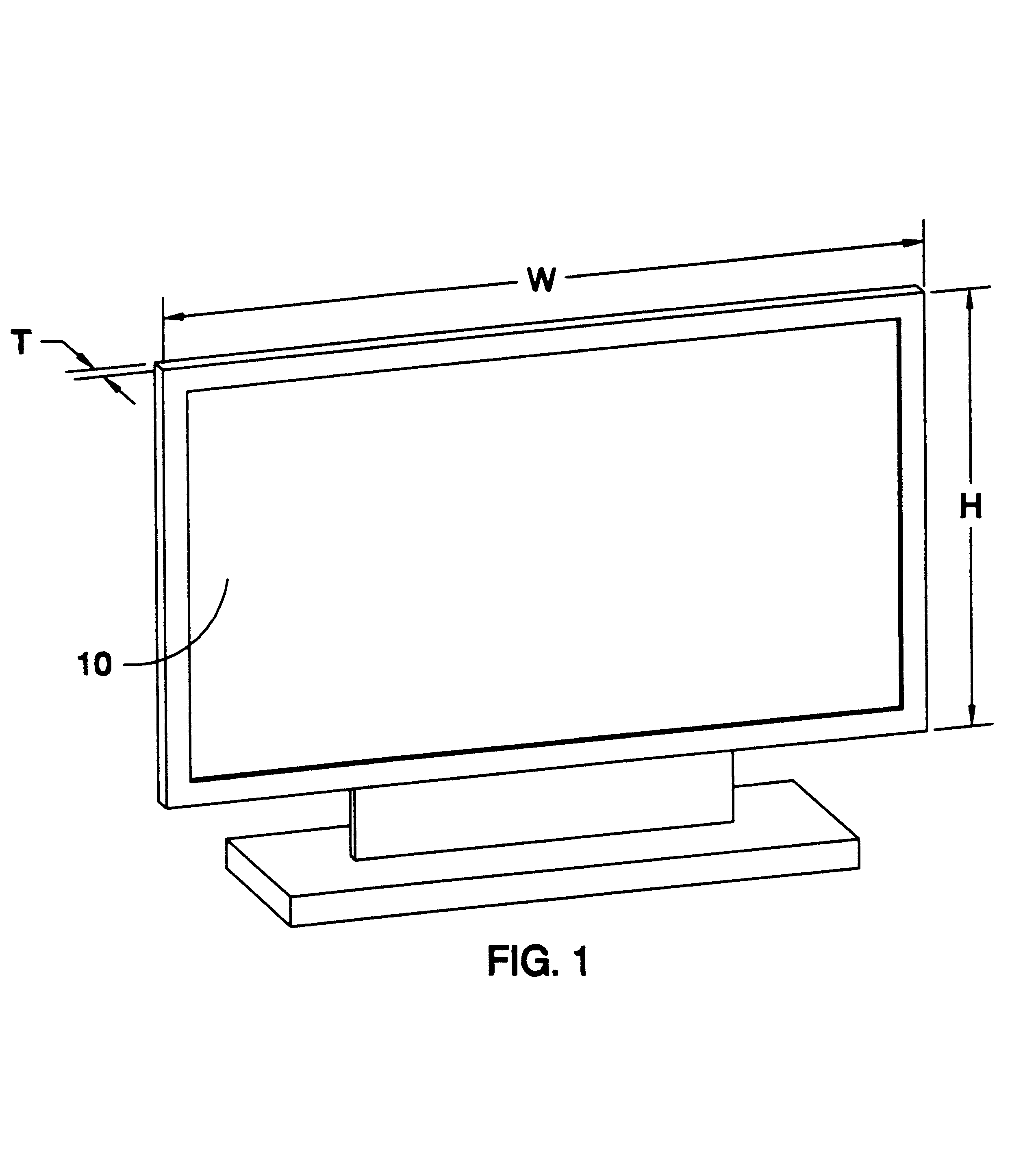
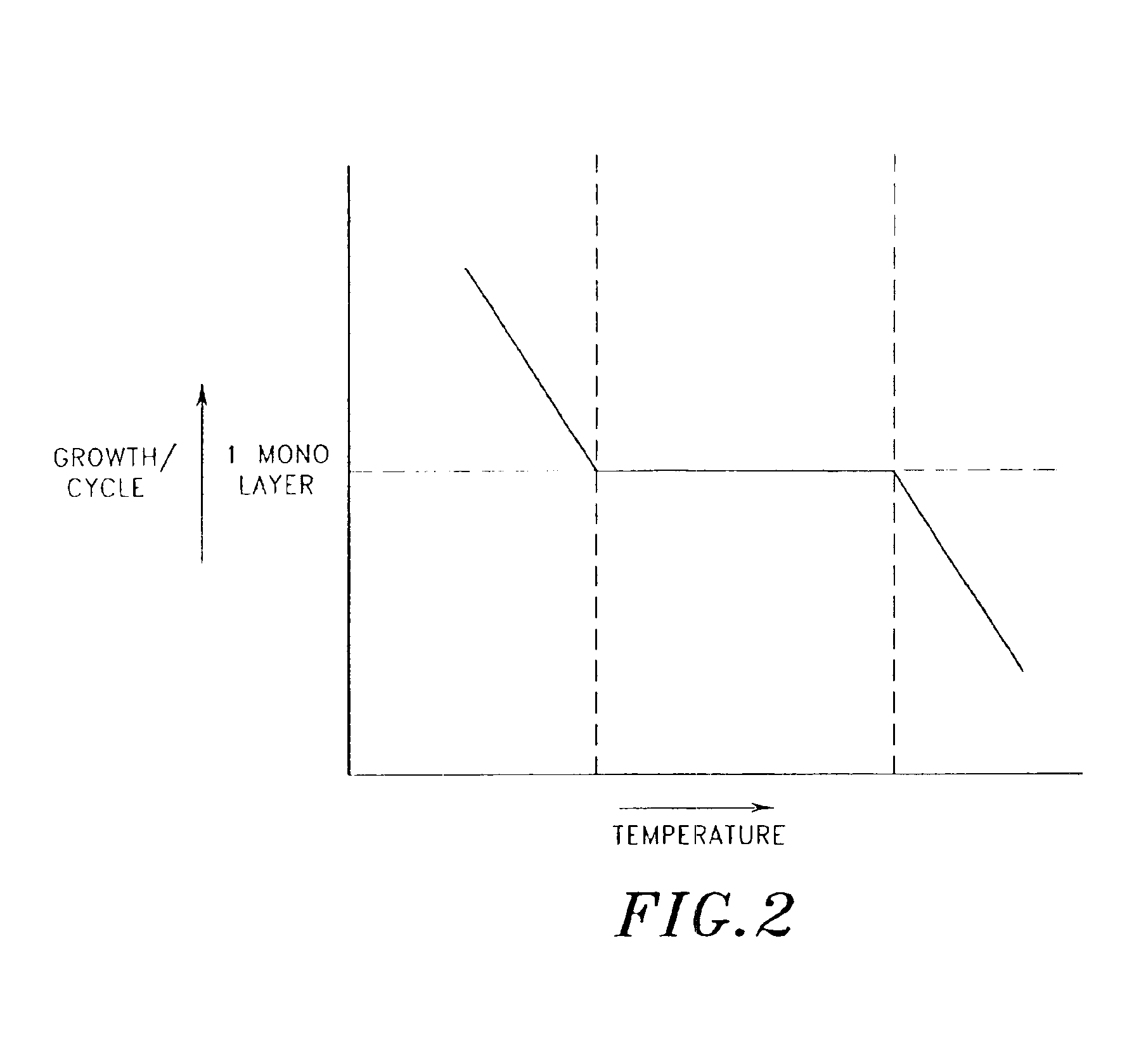Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4110 results about "Flat panel display" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
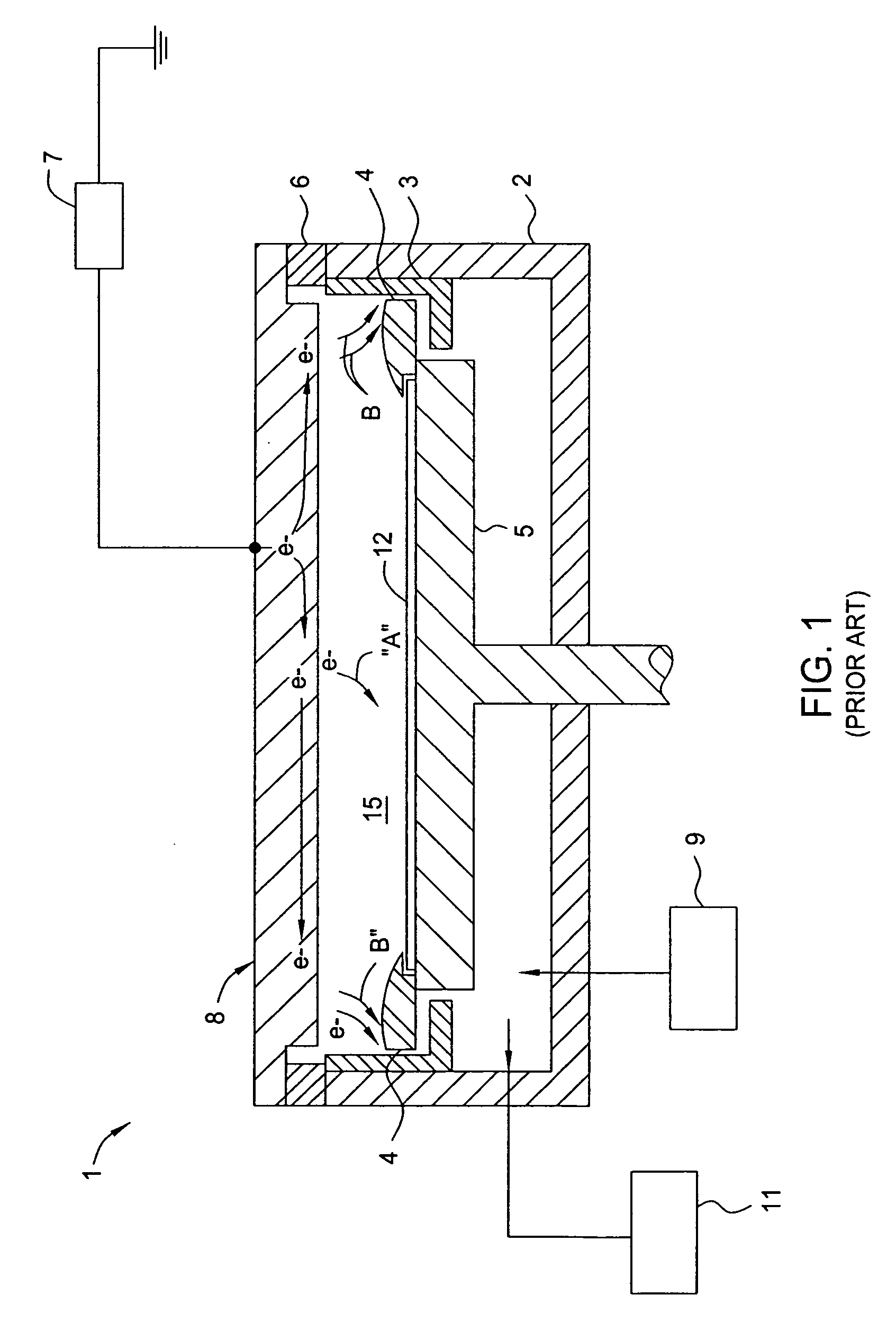
A flat-panel display (FPD) is an electronic viewing technology used to enable people to see content (still images, moving images, text, or other visual material) in a range of entertainment, consumer electronics, personal computer, and mobile devices, and many types of medical, transportation and industrial equipment. They are far lighter and thinner than traditional cathode ray tube (CRT) television sets and video displays and are usually less than 10 centimetres (3.9 in) thick. Flat-panel displays can be divided into two display device categories: volatile and static. Volatile displays require that pixels be periodically electronically refreshed to retain their state (e.g., liquid-crystal displays (LCD)). A volatile display only shows an image when it has battery or AC mains power. Static flat-panel displays rely on materials whose color states are bistable (e.g., e-book reader tablets from Sony), and as such, flat-panel displays retain the text or images on the screen even when the power is off. As of 2016, flat-panel displays have almost completely replaced old CRT displays. In many 2010-era applications, specifically small portable devices such as laptops, mobile phones, smartphones, digital cameras, camcorders, point-and-shoot cameras, and pocket video cameras, any display disadvantages of flat-panels (as compared with CRTs) are made up for by portability advantages (thinness and lightweightness).
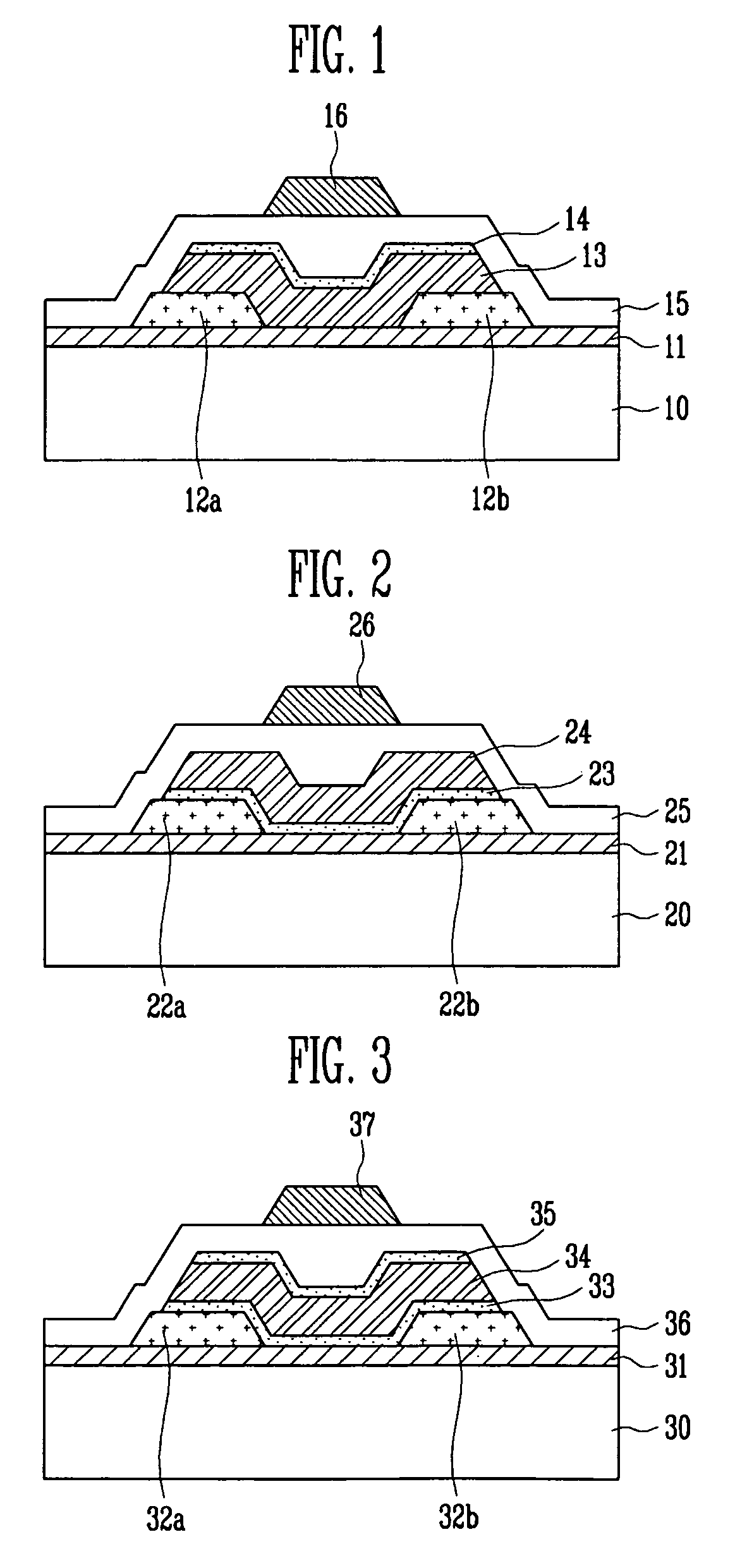
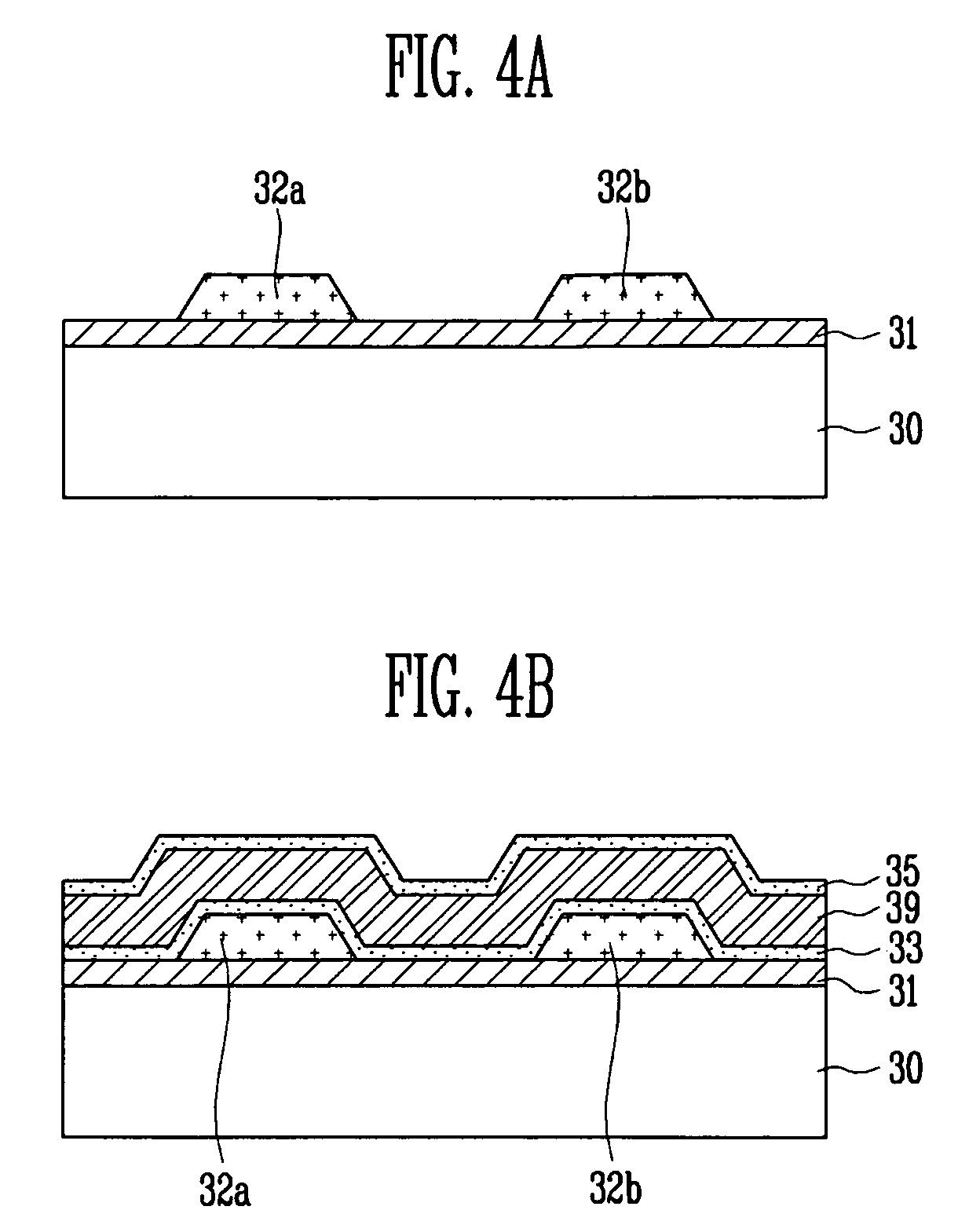
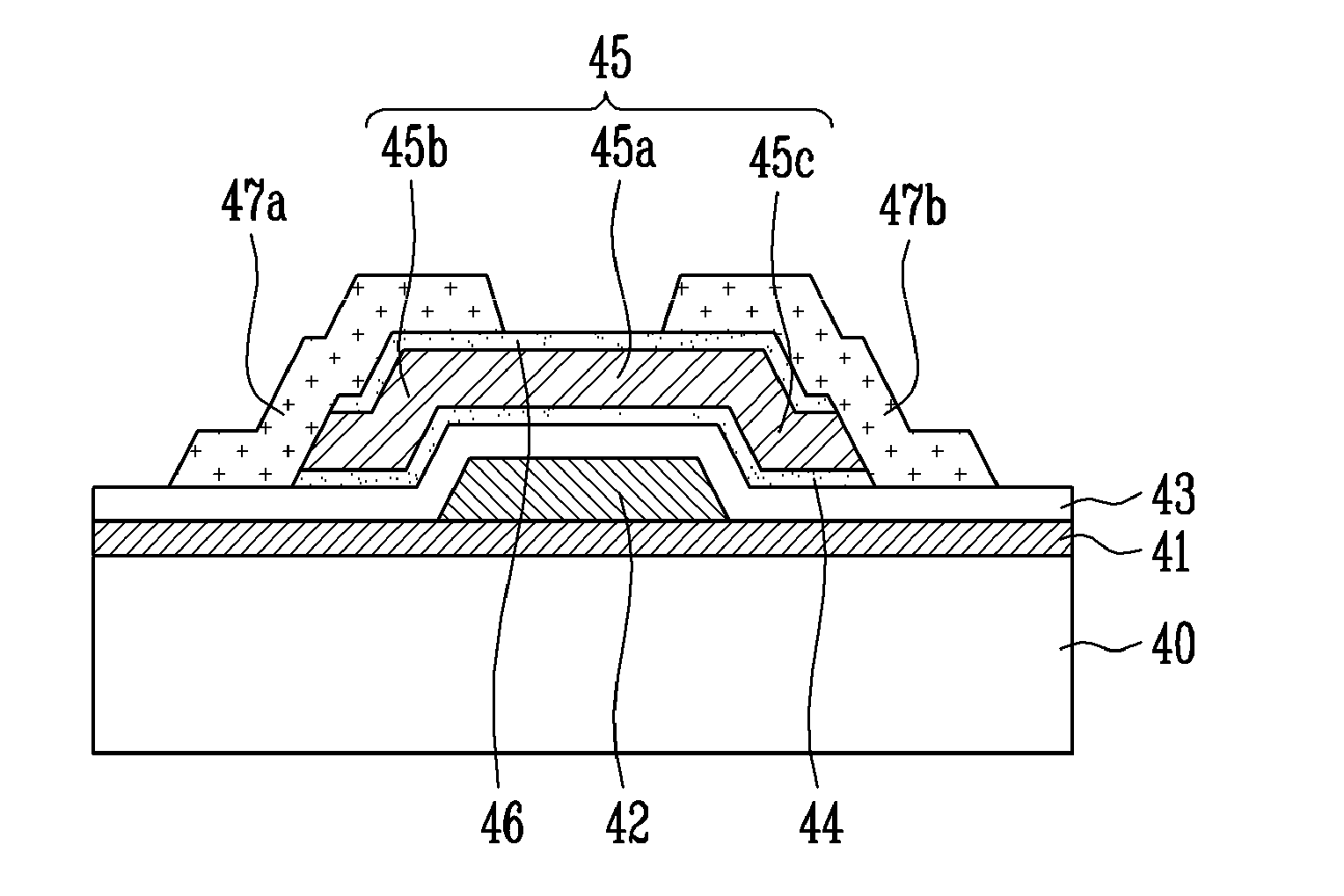
Thin film transistor, method of manufacturing the same and flat panel display device having the same
ActiveUS8148779B2Improve featuresAvoid chargingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTrappingEngineering
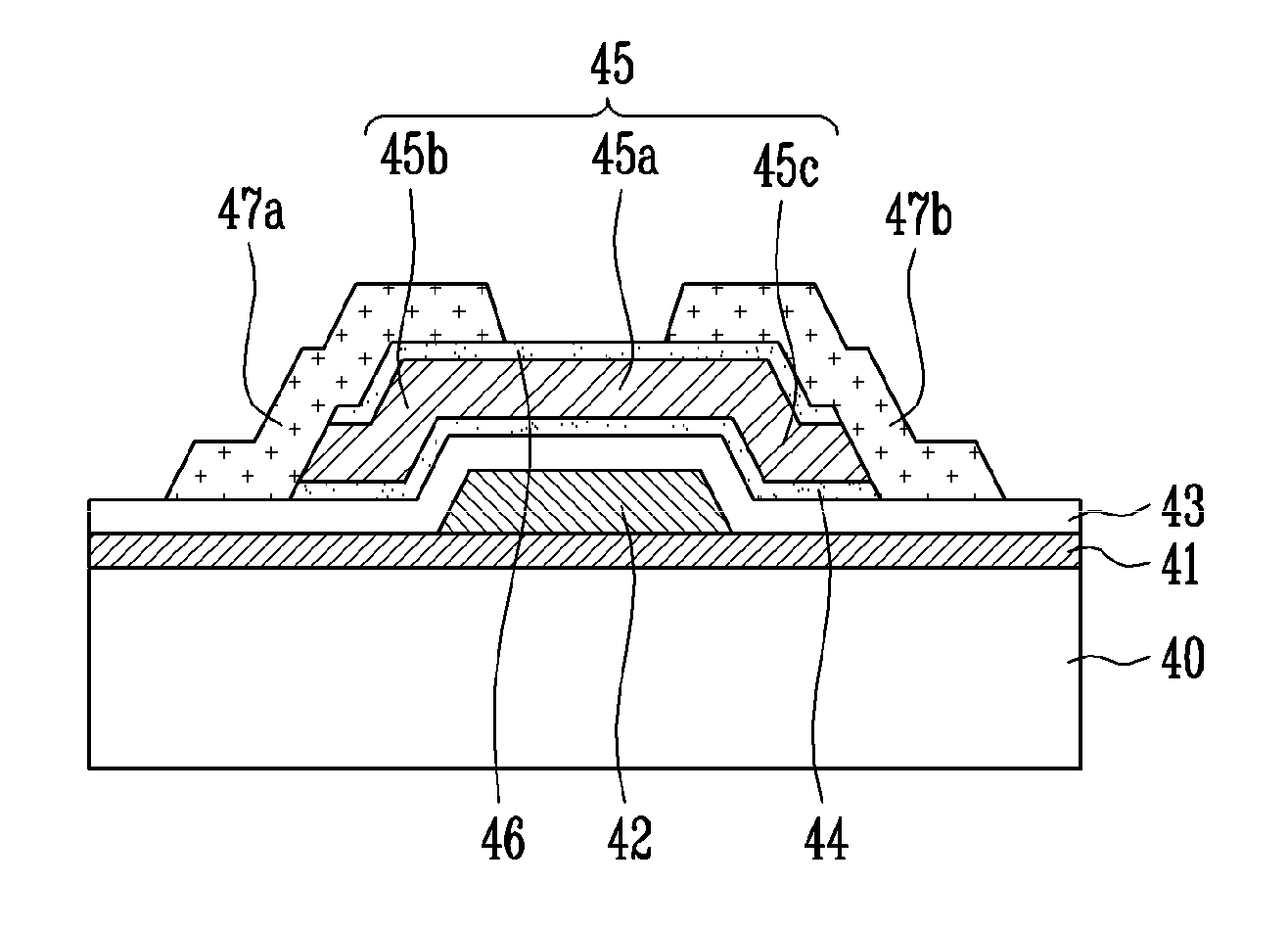
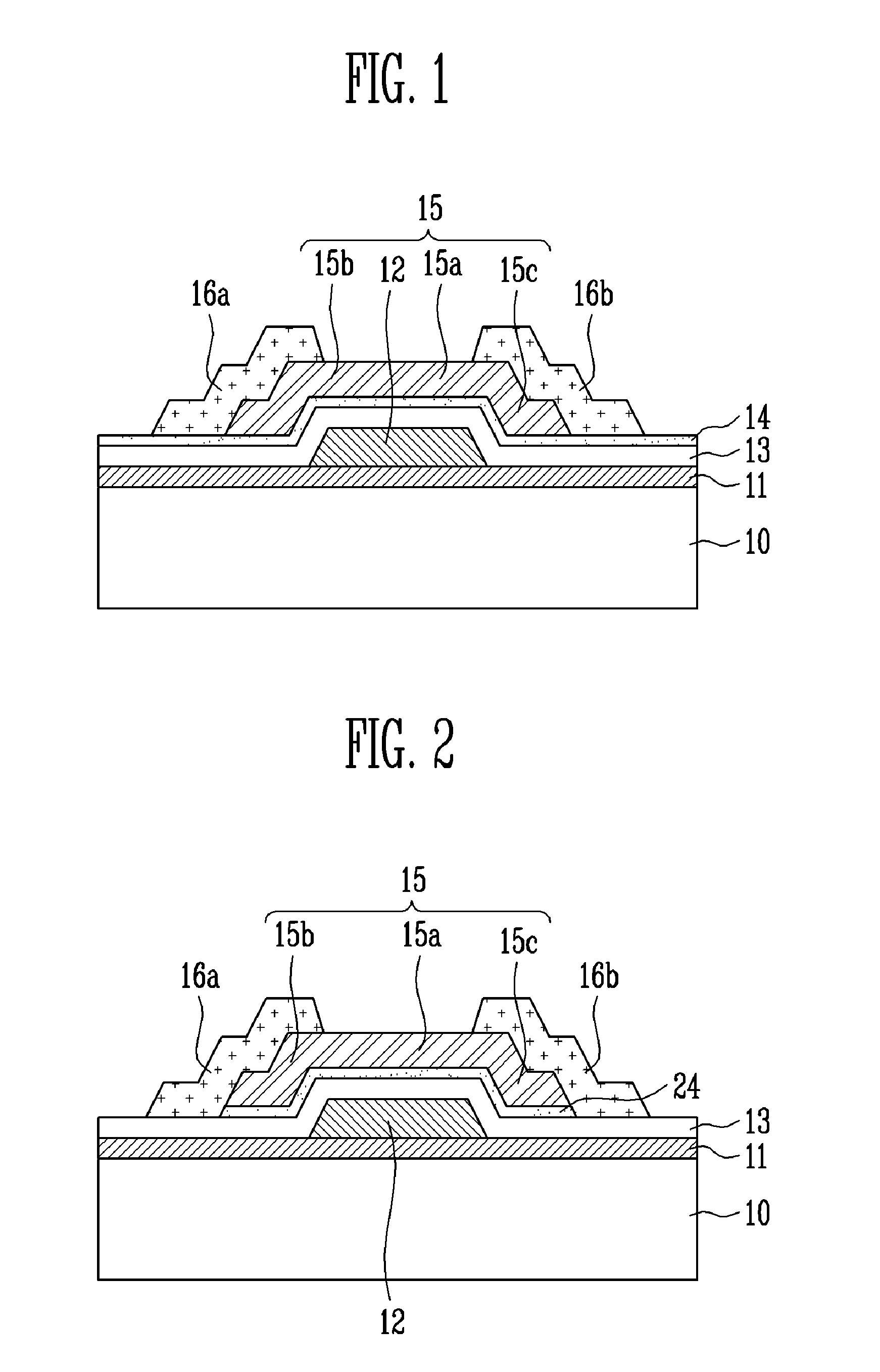
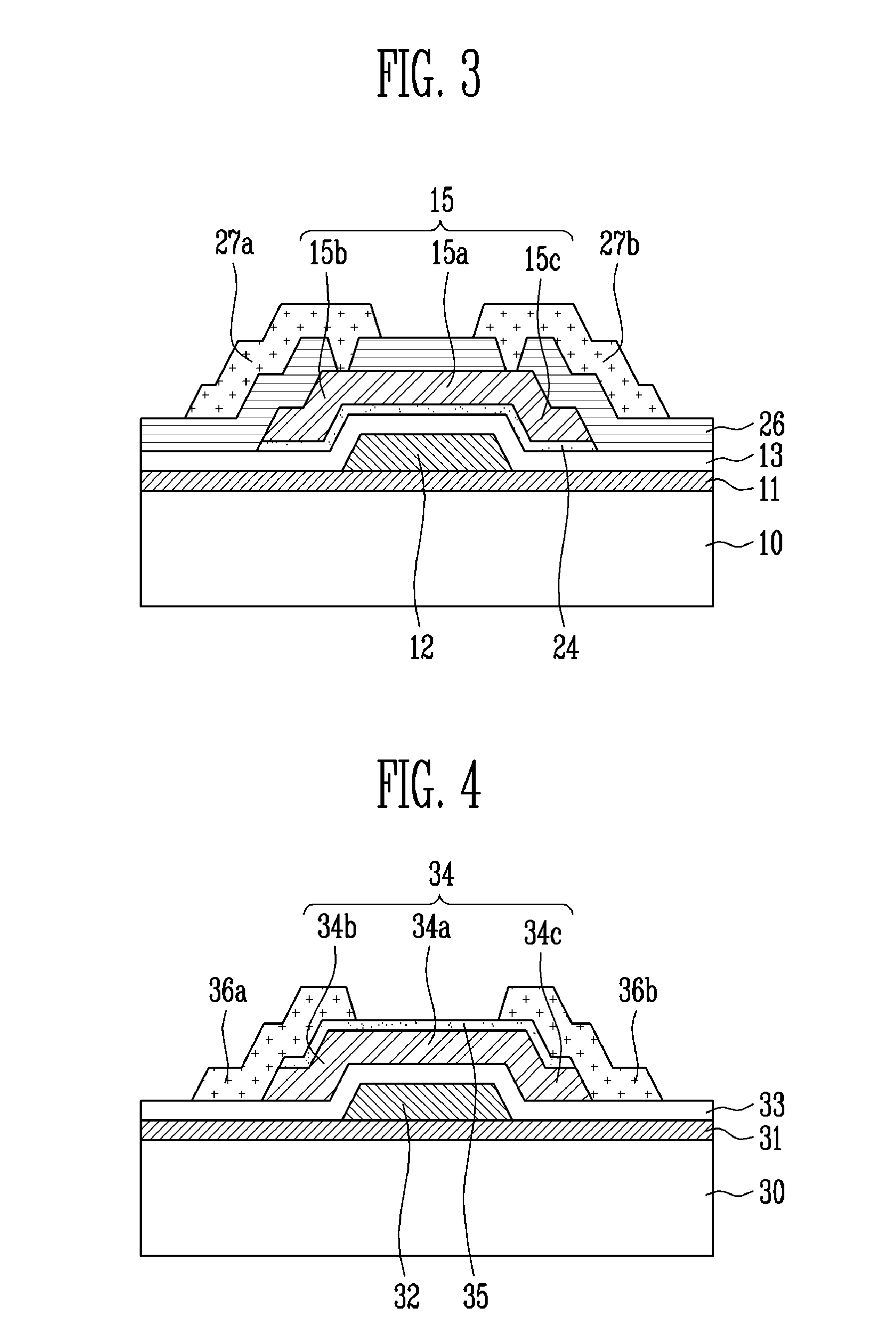
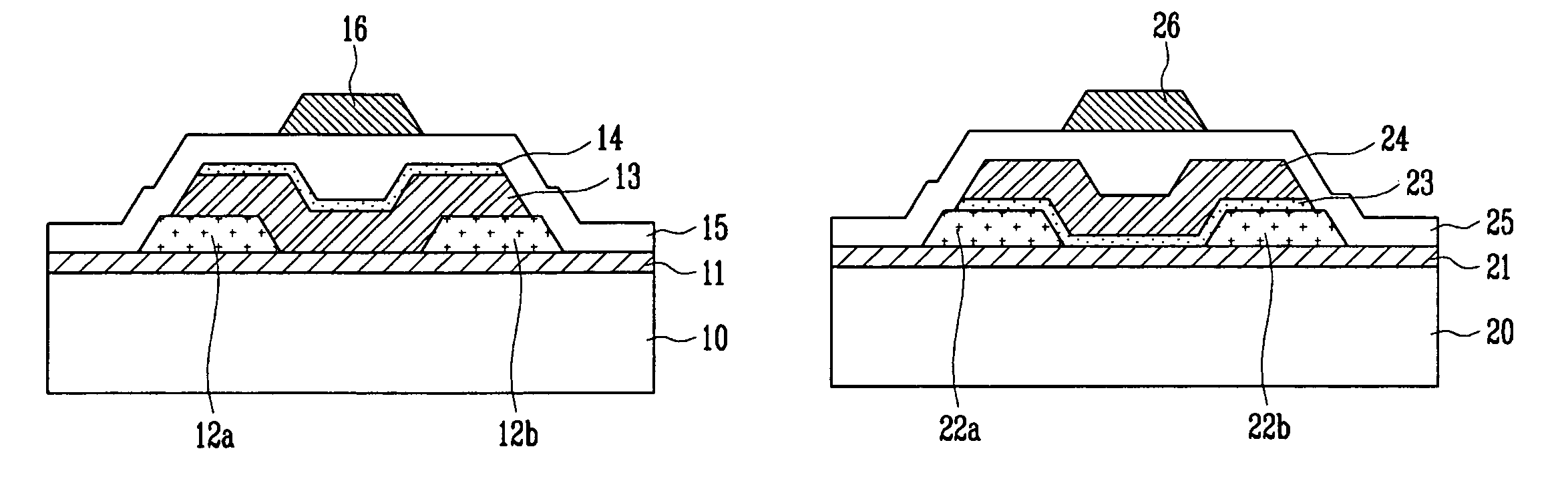
A thin film transistor (TFT) using an oxide semiconductor as an active layer, a method of manufacturing the TFT, and a flat panel display device having the TFT include a gate electrode formed on a substrate; an active layer made of an oxide semiconductor and insulated from the gate electrode by a gate insulating layer; source and drain electrodes coupled to the active layer; and an interfacial stability layer formed on one or both surfaces of the active layer. In the TFT, the interfacial stability layer is formed of an oxide having a band gap of 3.0 to 8.0 eV. Since the interfacial stability layer has the same characteristic as a gate insulating layer and a passivation layer, chemically high interface stability is maintained. Since the interfacial stability layer has a band gap equal to or greater than that of the active layer, charge trapping is physically prevented.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
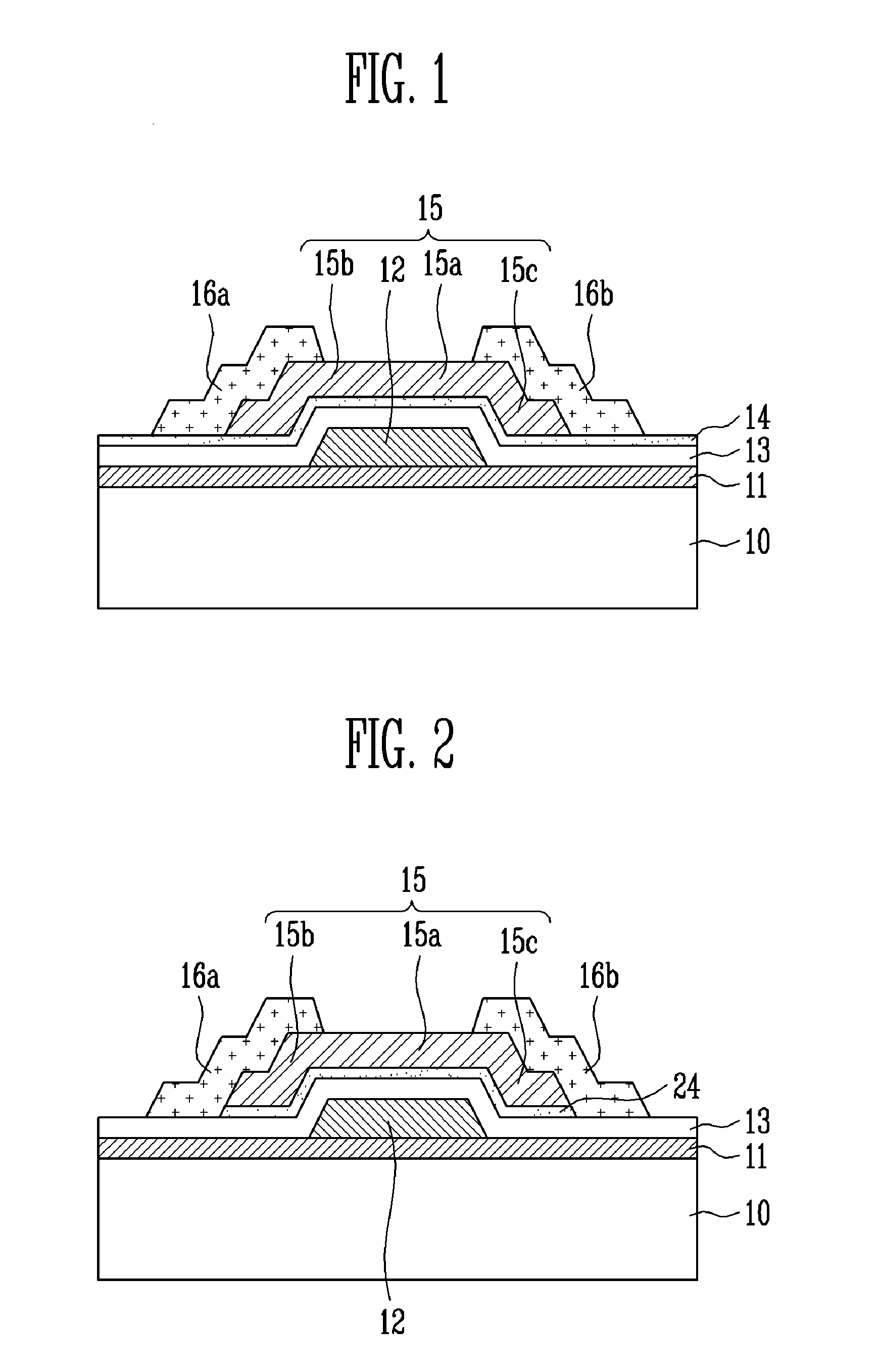
Thin film transistor, method of manufacturing the same and flat panel display device having the same
ActiveUS7994500B2Improve featuresAvoid chargingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTrappingOxide thin-film transistor
A thin film transistor (TFT) using an oxide semiconductor as an active layer, a method of manufacturing the TFT, and a flat panel display device having the TFT include source and drain electrodes formed on a substrate; an active layer formed of an oxide semiconductor disposed on the source and drain electrodes; a gate electrode; and an interfacial stability layer formed on at least one of top and bottom surfaces of the active layer. In the TFT, the interfacial stability layer is formed of an oxide having a band gap of 3.0 to 8.0 eV. Since the interfacial stability layer has the same characteristics as a gate insulating layer and a passivation layer, chemically high interface stability is maintained. Since the interfacial stability layer has a band gap equal to or greater than that of the active layer, charge trapping is physically prevented.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Method of controlling the film properties of a CVD-deposited silicon nitride film
InactiveUS20060019502A1Increase wet etch rateEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGate dielectricGas composition
We have discovered that adding H2 to a precursor gas composition including SiH4, NH3, and N2 is effective at improving the wet etch rate and the wet etch rate uniformity across the substrate surface of a-SiNx:H films which are deposited on a substrate by PECVD. Wet etch rate is an indication of film density. Typically, the lower the wet etch rate, the denser the film. The addition of H2 to the SiH4 / NH3 / N2 precursor gas composition did not significantly increase the variation in deposited film thickness across the surface of the substrate. The a-SiNx:H films described herein are particularly useful as TFT gate dielectrics in the production of flat panel displays. The uniformity of the film across the substrate enables the production of flat panel displays having surface areas of 25,000 cm2 and larger.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
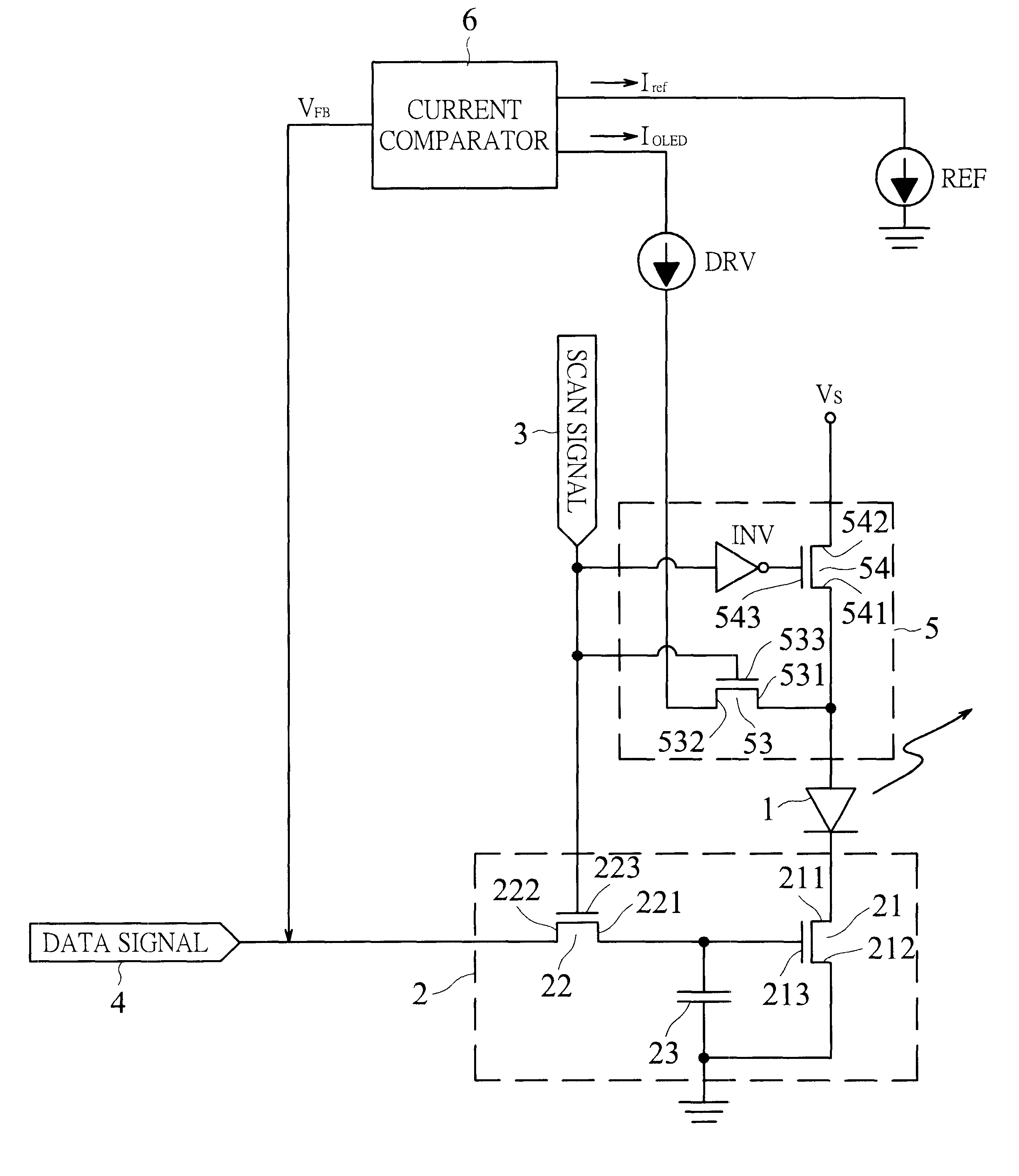
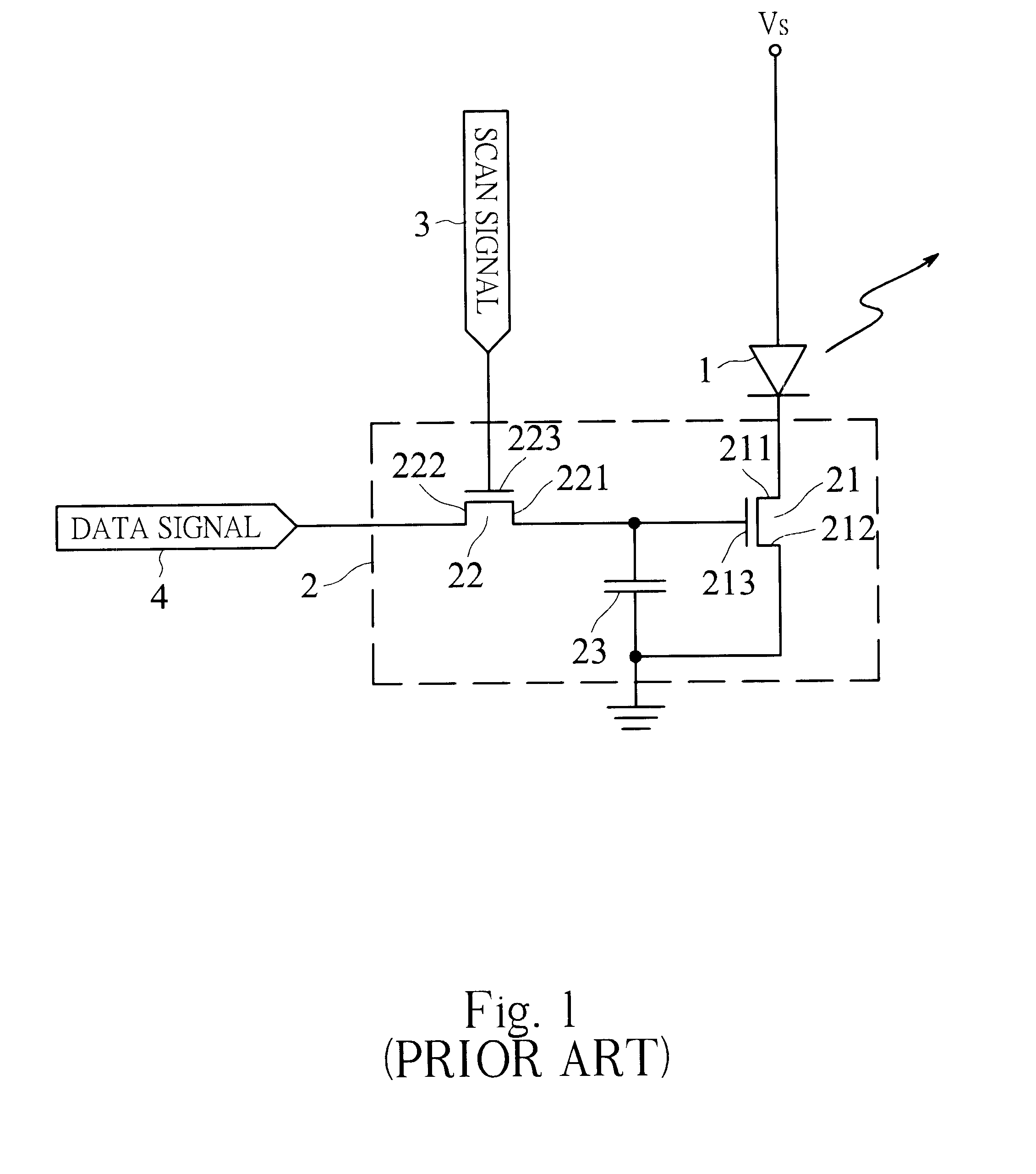
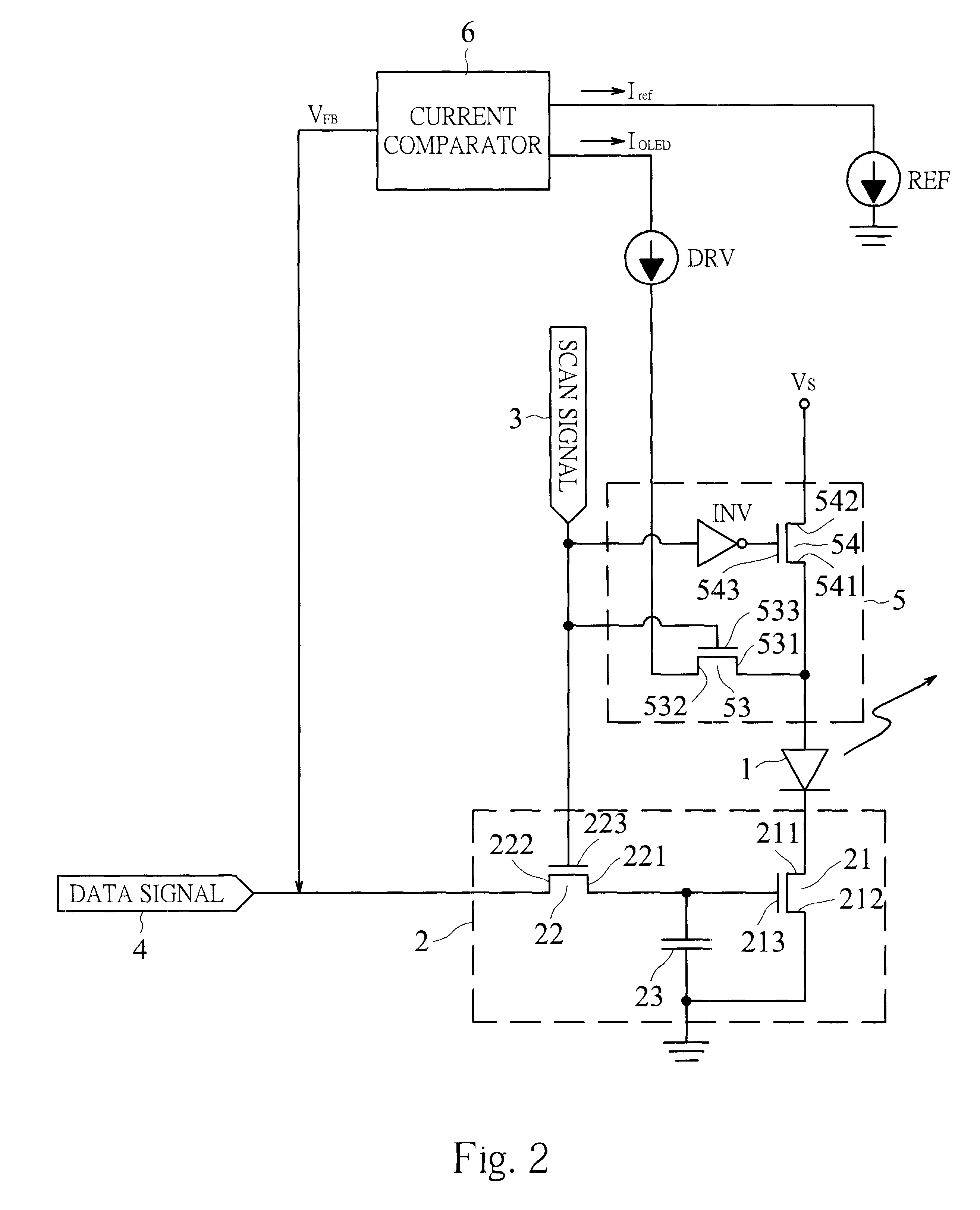
OLED active driving system with current feedback
The invention provides an organic light emitting diode active driving system with current feedback, thereby a driving current for organic light emitting diode is not affected by variation of characteristic parameters of thin film transistor under an active driving mode. The active driving system in accordance with the invention includes a transistor and a current comparator for driving an organic light emitting diode. The transistor has two current carrying electrodes respectively connected to a cathode of the organic light emitting diode and ground, and a gate controlled by a data signal. The current comparator has two input terminals respectively receive a reference current with predetermined value and a driving current flowing through the organic light emitting diode. The current comparator compares the reference current and the driving current, and then outputs a voltage to the gate of the transistor in response to the comparison result so as to make the value of the driving current equal to that of the reference current. Therefore, the active driving system for organic light emitting diode array or flat panel display in accordance with the invention can achieve a desirable light emission uniformity.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
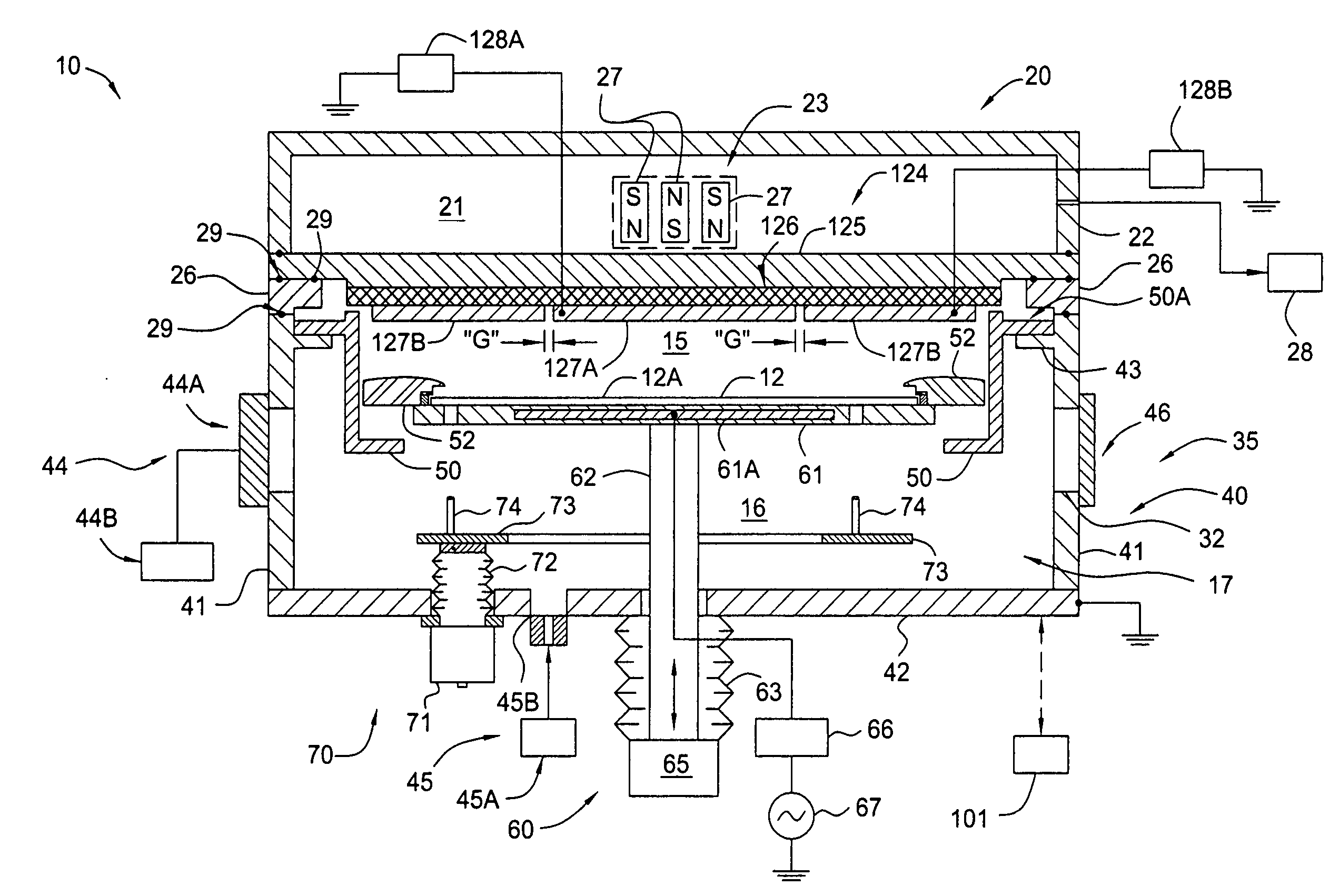
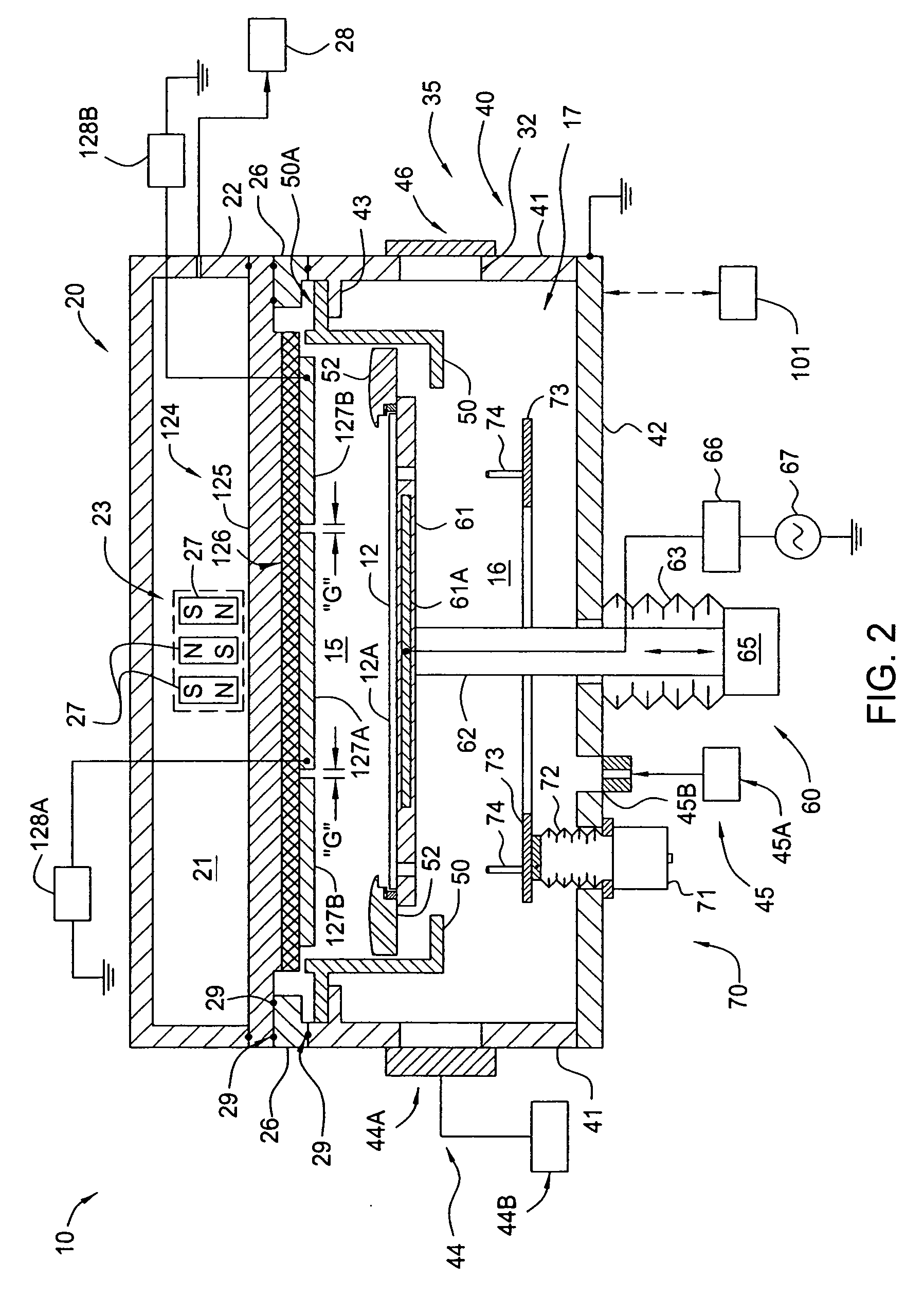
Method of processing a substrate using a large-area magnetron sputtering chamber with individually controlled sputtering zones
InactiveUS20070056843A1Vacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The present invention generally provides a method for processing a surface of a substrate in a physical vapor deposition (PVD) chamber that has a sputtering target that has separately biasable sections, regions or zones to improve the deposition uniformity. In general, aspects of the present invention can be used for flat panel display processing, semiconductor processing, solar cell processing, or any other substrate processing. In one aspect, each of the target sections of the multizone target assembly are biased at a different cathodic biases by use of one or more DC or RF power sources. In one aspect, each of the target sections of the multizone target assembly are biased at a different cathodic biases by use of one power source and one or more resistive, capacitive and / or inductive elements. In one aspect, the processing chamber contains a multizone target assembly that has one or more ports that are adapted deliver a processing gas to the processing region of the PVD chamber. In one aspect, the processing chamber contains a multizone target assembly that has one or more magnetron assemblies positioned adjacent to one or more of the target sections.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
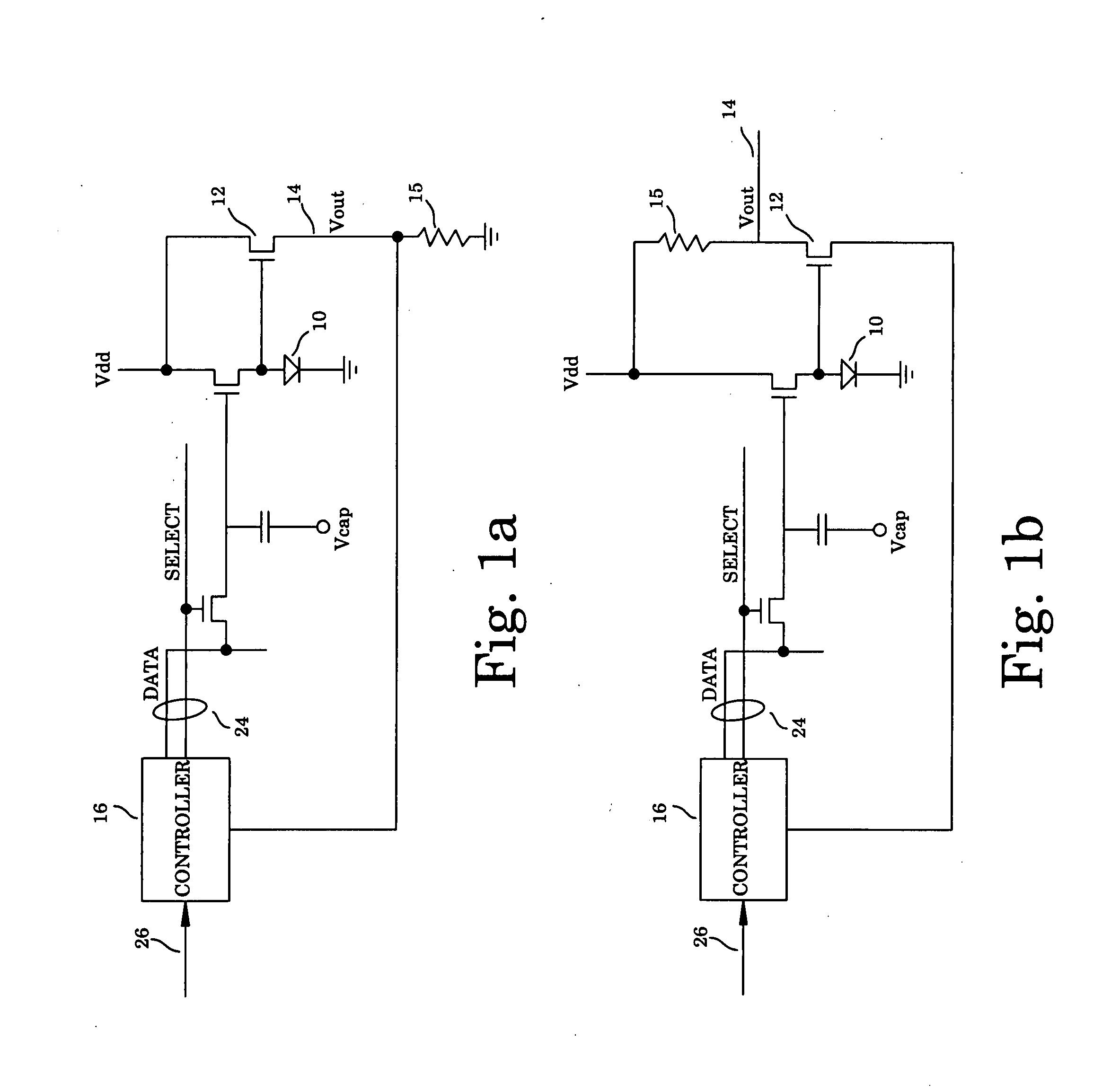
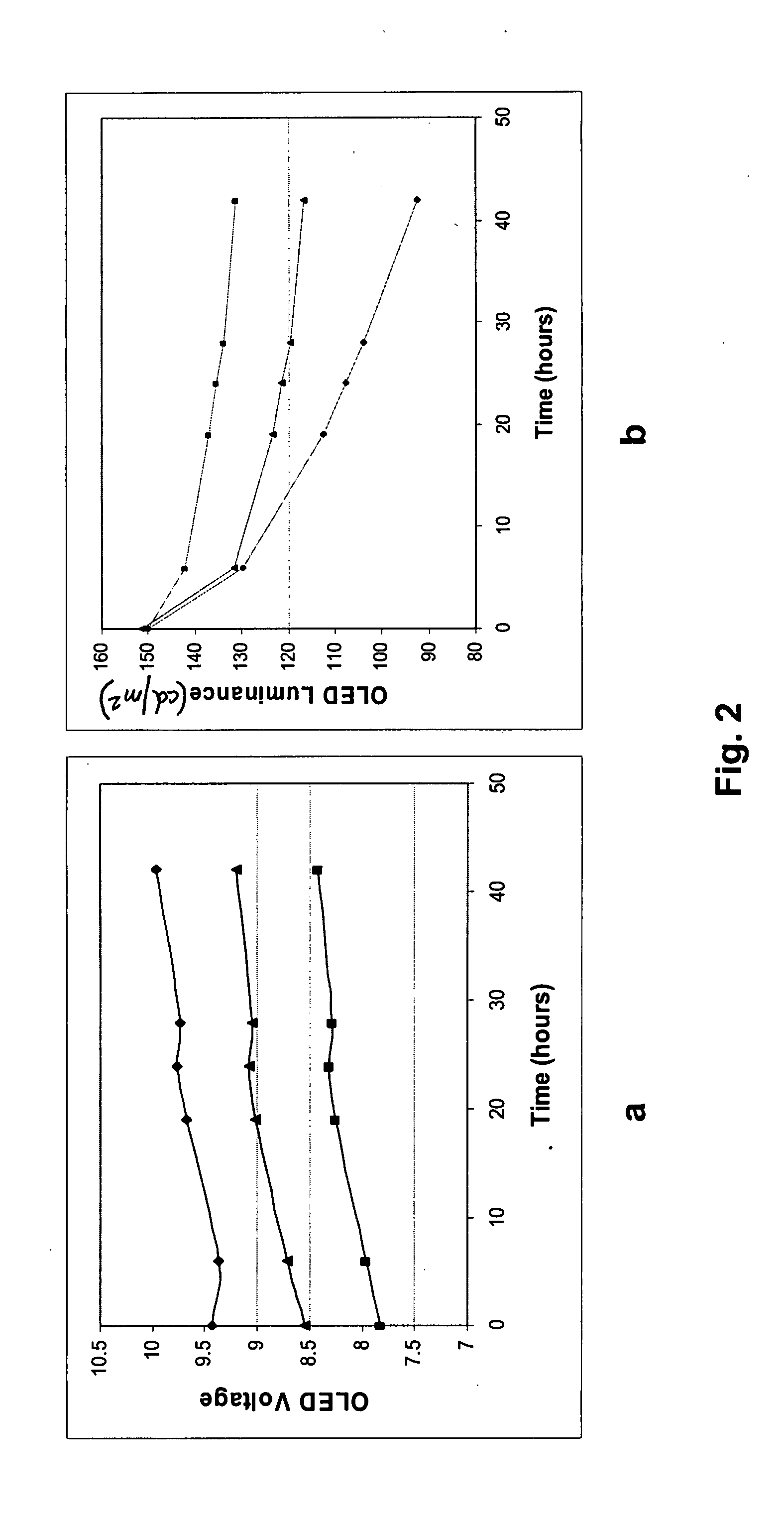
Method and apparatus for managing and uniformly maintaining pixel circuitry in a flat panel display
InactiveUS20080048951A1Accurate aging correctionStatic indicating devicesQuantum efficiencyDisplay design
The present invention describes a method and apparatus for measuring the voltage and current characteristics of the OLED pixel as it ages and correlating the measured data to the decrease in quantum efficiency and changes in OLED impedance over the life of the OLED, so that corrections can be made to the image drive system to prevent image sticking and color point drift. The method and apparatus of the present invention do not require any additional circuitry or changes in the display design. The circuitry of the present invention is implemented in the display driver integrated circuit (IC) chips. The basis of the invention is the luminance-current-voltage (LIV) curves which characterize the OLED materials over their life time. A series of these curves are stored in memory representing a OLED material at various ages. The apparatus of the present invention is used to measure driver voltages and currents for a pixel having an OLED, which measurements are then used to extract the voltage current curve for the OLED at any point in time. The extracted curve is compared to the aging curves stored in memory to determine the aging curve that best describes the measured present voltage current characteristic of the pixel. That aging curve is used to drive the pixel.
Owner:LEADIS TECH
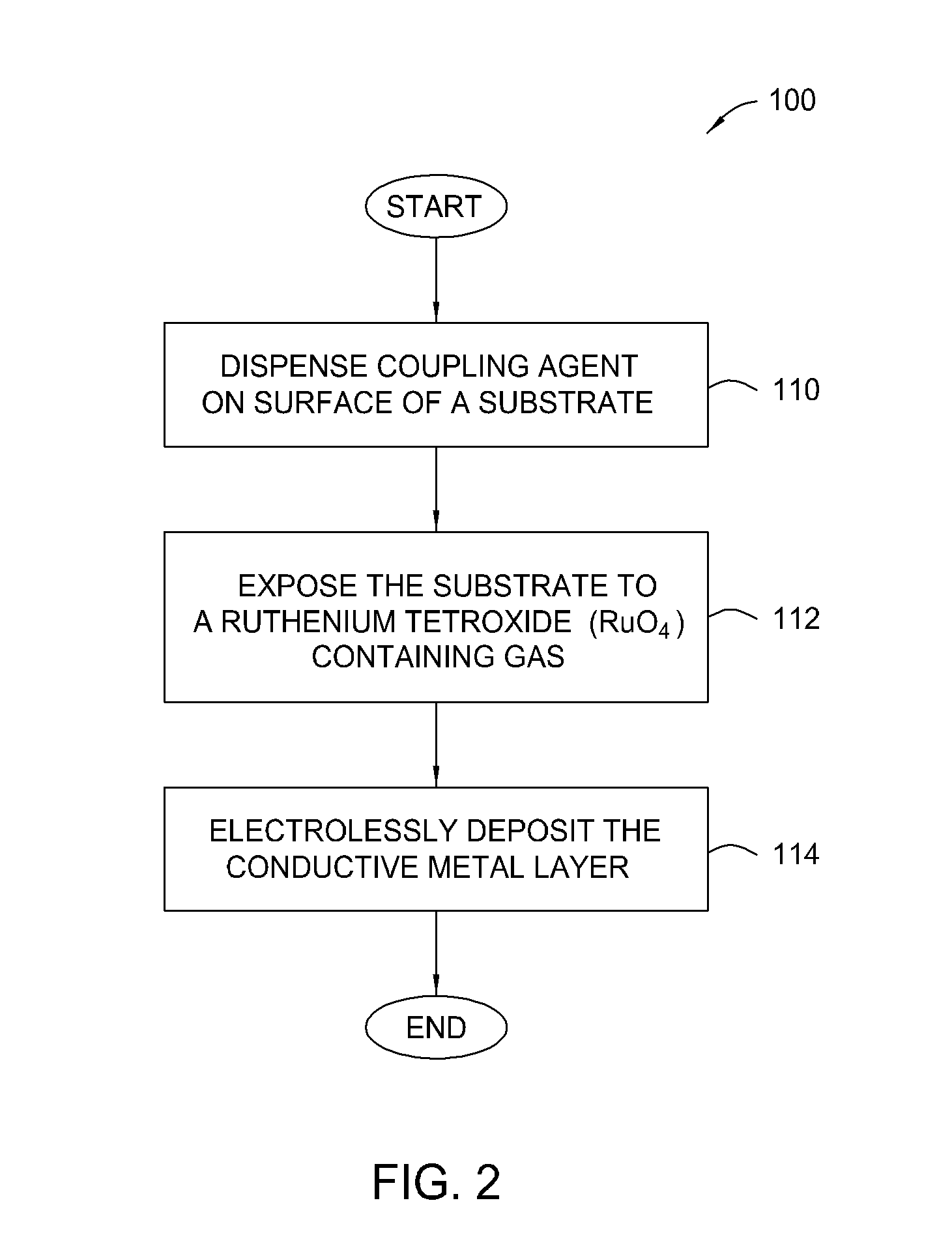
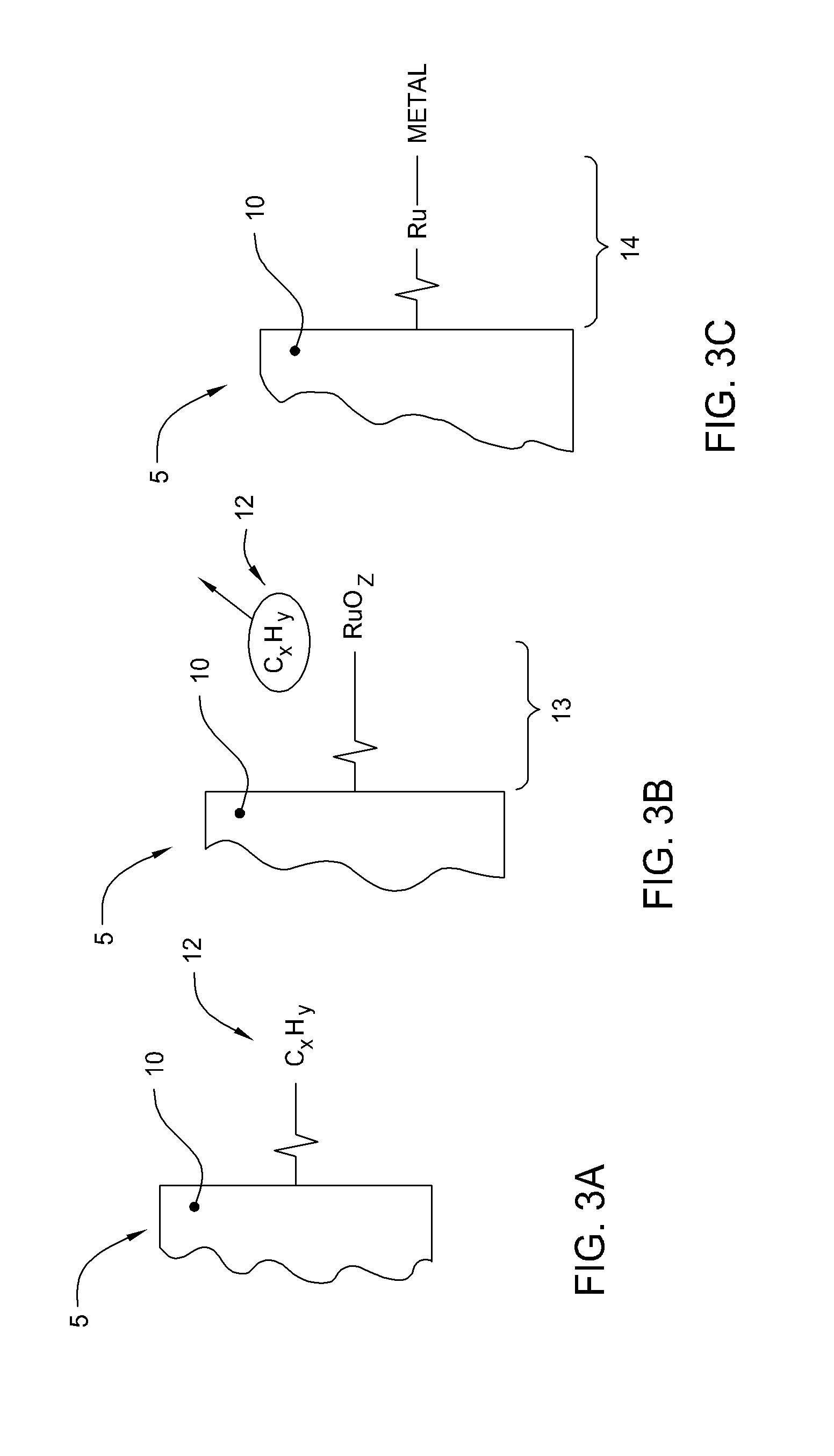
Patterned electroless metallization processes for large area electronics
The present invention generally provides an apparatus and method for selectively forming a metallized feature, such as an electrical interconnect feature, on a electrically insulating surface of a substrate. The present invention also provides a method of forming a mechanically robust, adherent, oxidation resistant conductive layer selectively over either a defined pattern or as a conformal blanket film. Embodiments of the invention also generally provide a new chemistry, process, and apparatus to provide discrete or blanket electrochemically or electrolessly platable ruthenium or ruthenium dioxide containing adhesion and initiation layers. In general, aspects of the present invention can be used for flat panel display processing, semiconductor processing, solar cell device processing, or any other substrate processing, being particularly well suited for the application of stable adherent coating on glass as well as flexible plastic substrates. This invention may be especially useful for the formation of electrical interconnects on the surface of flat panel display or solar cell type substrates where the line sizes are generally larger than semiconductor devices or where the formed feature are not generally as dense.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Electronically addressable microencapsulated ink and display thereof
InactiveUS7148128B2Inexpensive displayInking apparatusMechanical clocksSemiconductor materialsDisplay device
We describe a system of electronically active inks which may include electronically addressable contrast media, conductors, insulators, resistors, semiconductive materials, magnetic materials, spin materials, piezoelectric materials, optoelectronic, thermoelectric or radio frequency materials. We further describe a printing system capable of laying down said materials in a definite pattern. Such a system may be used for instance to: print a flat panel display complete with onboard drive logic; print a working logic circuit onto any of a large class of substrates; print an electrostatic or piezoelectric motor with onboard logic and feedback or print a working radio transmitter or receiver.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
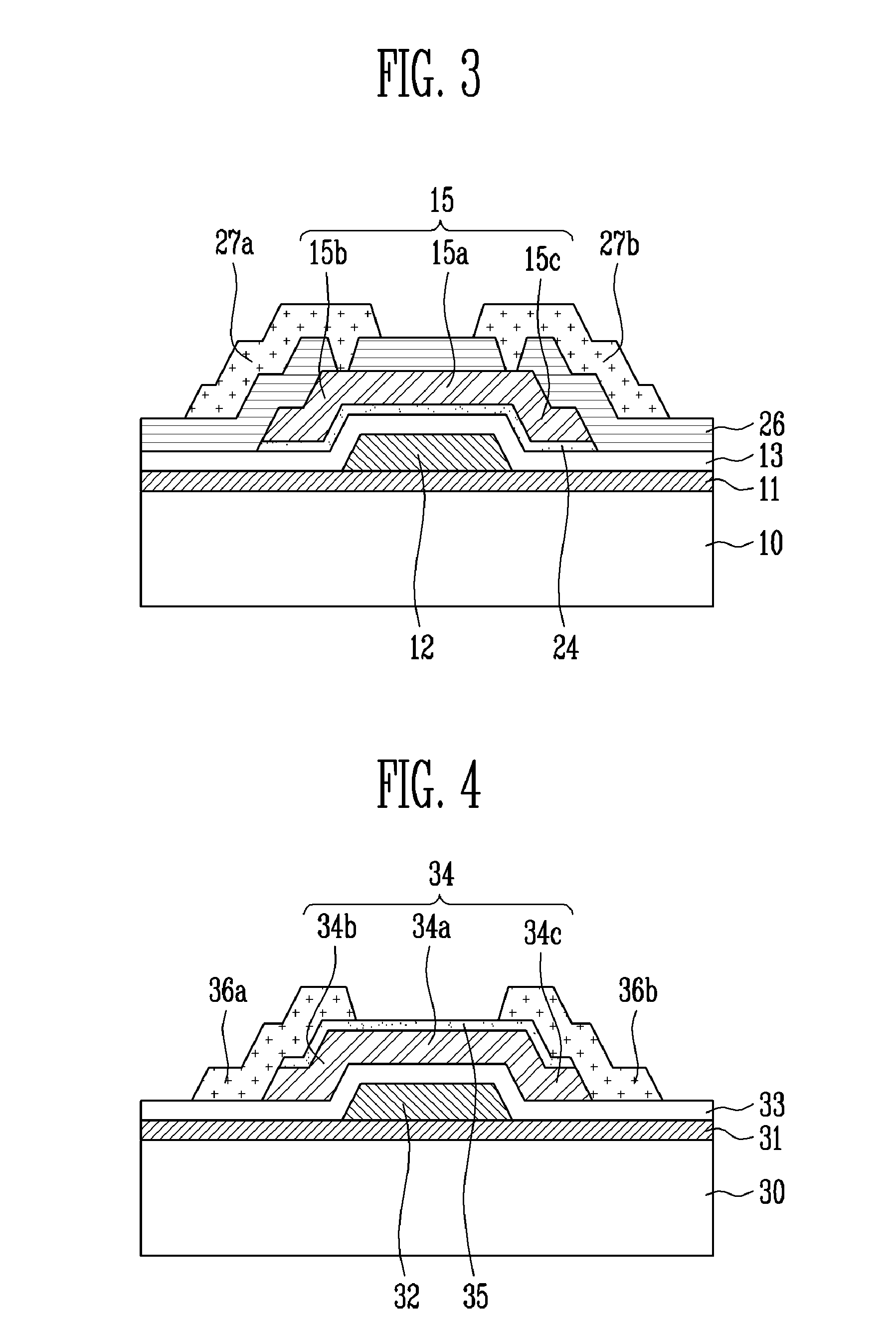
Thin film transistor, method of manufacturing the same and flat panel display device having the same
ActiveUS20090321731A1Improve featuresAvoid chargingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNon-linear opticsTrappingEngineering
A thin film transistor (TFT) using an oxide semiconductor as an active layer, a method of manufacturing the TFT, and a flat panel display device having the TFT include a gate electrode formed on a substrate; an active layer made of an oxide semiconductor and insulated from the gate electrode by a gate insulating layer; source and drain electrodes coupled to the active layer; and an interfacial stability layer formed on one or both surfaces of the active layer. In the TFT, the interfacial stability layer is formed of an oxide having a band gap of 3.0 to 8.0 eV. Since the interfacial stability layer has the same characteristic as a gate insulating layer and a passivation layer, chemically high interface stability is maintained. Since the interfacial stability layer has a band gap equal to or greater than that of the active layer, charge trapping is physically prevented.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
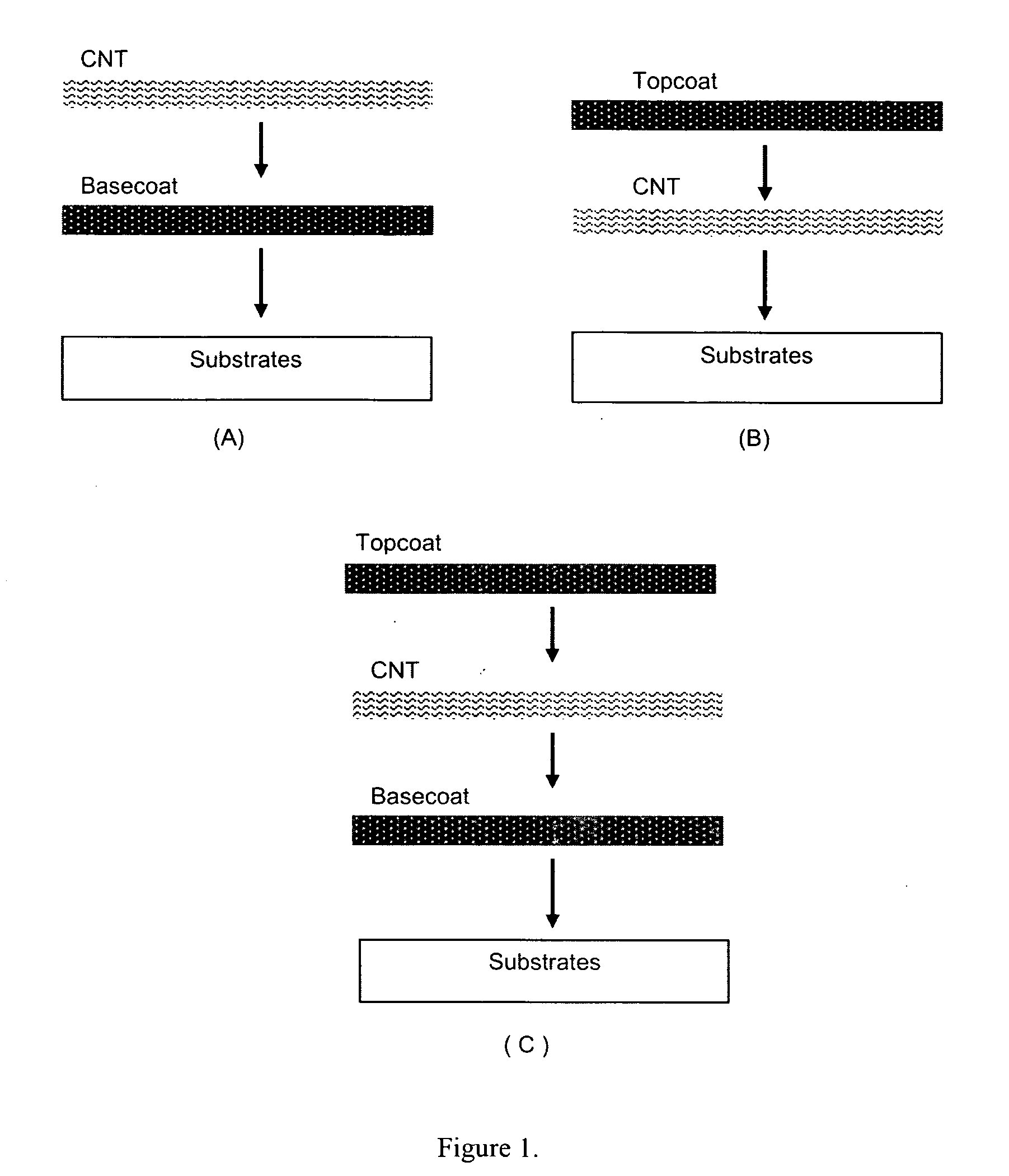
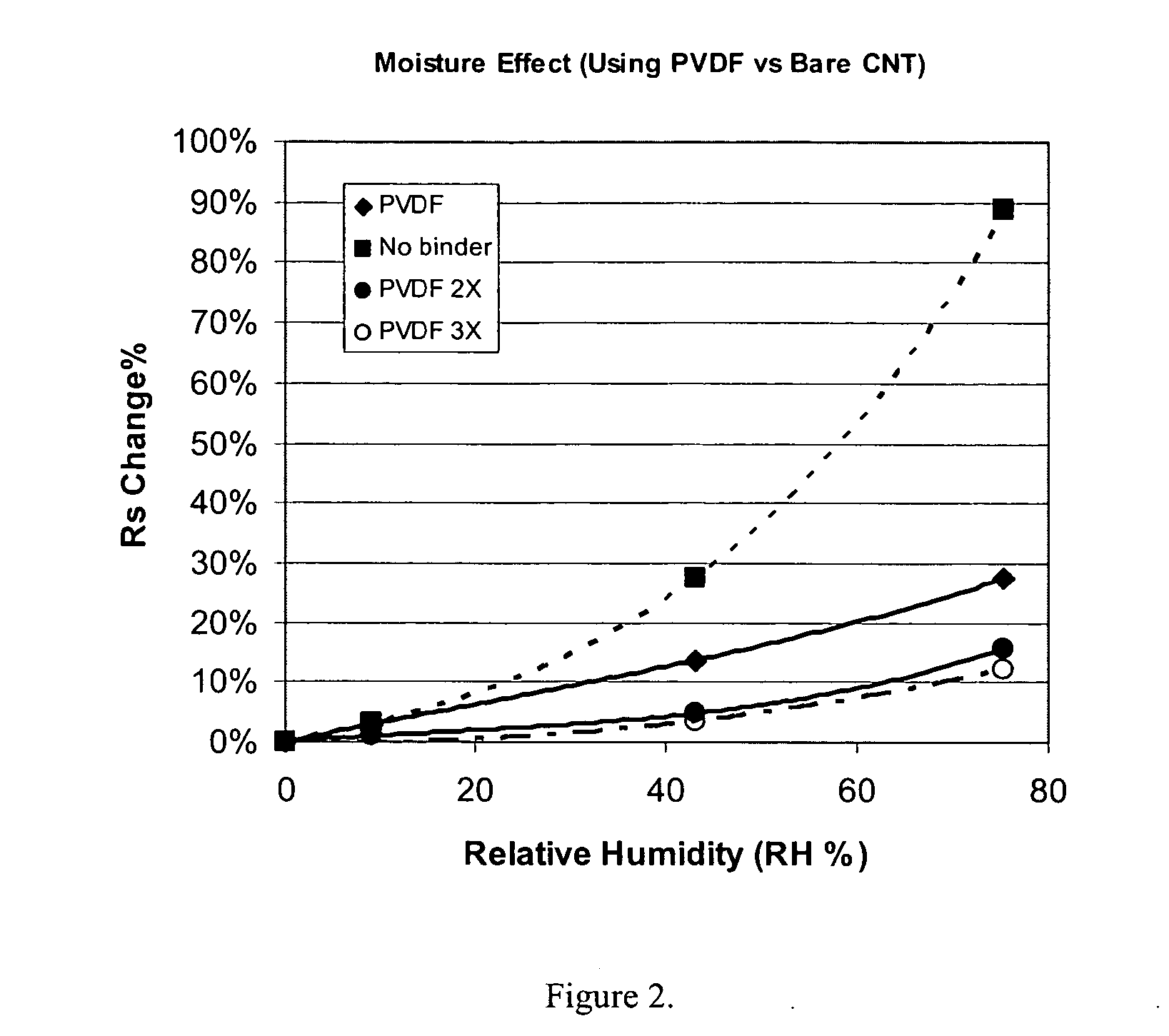
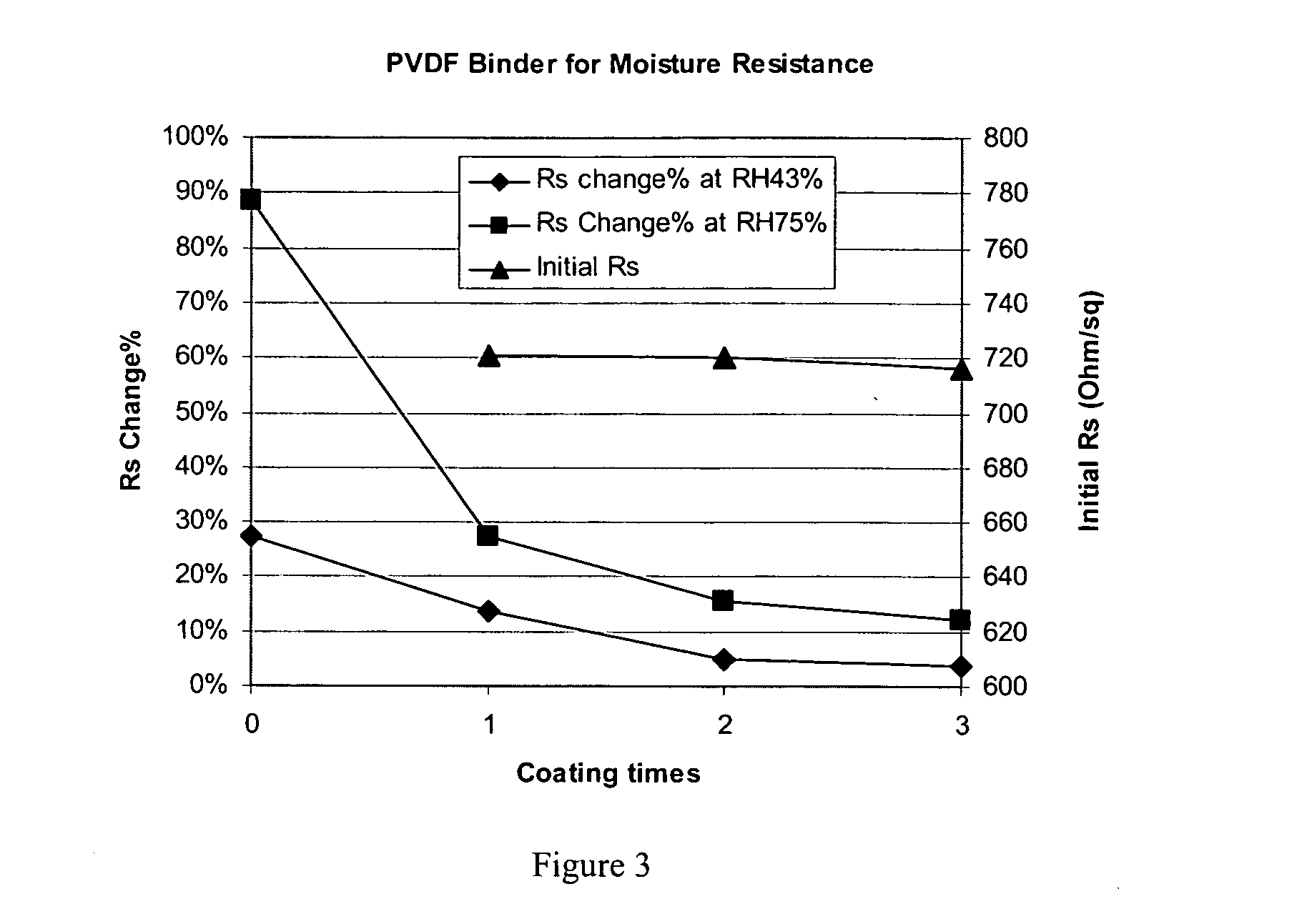
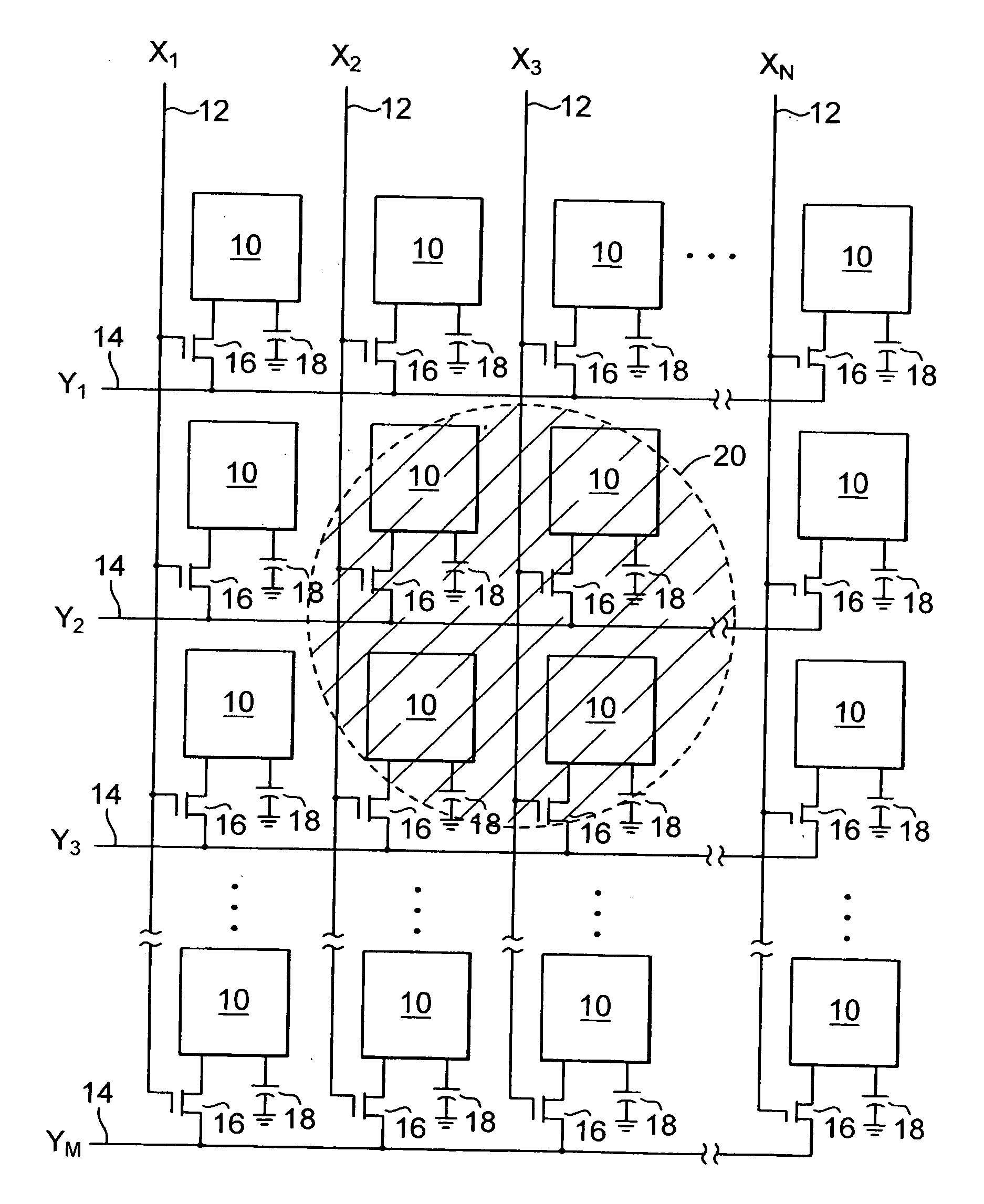
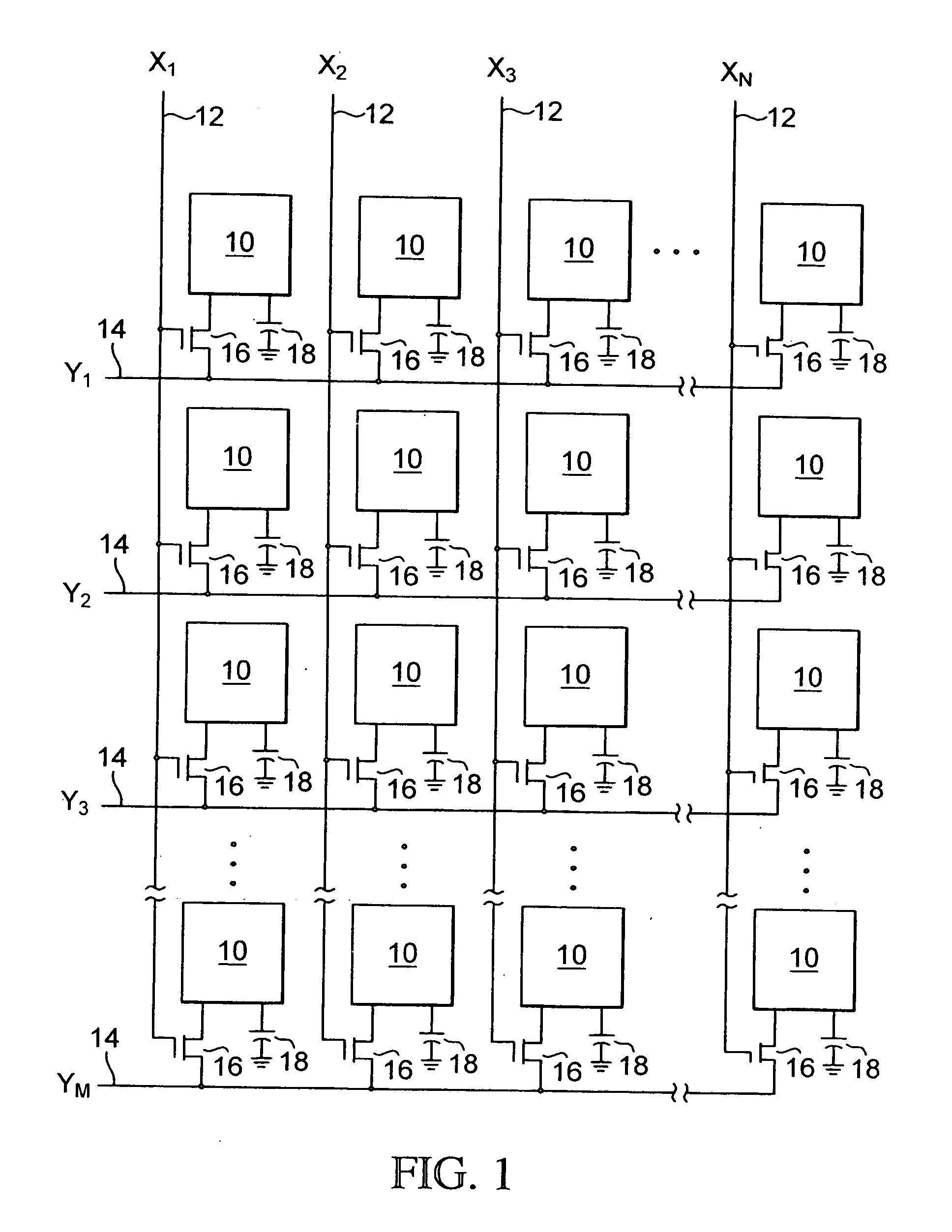
Polymer binders for flexible and transparent conductive coatings containing carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20050209392A1Decrease in optical transparencyDecrease in surface conductivityMaterial nanotechnologySpecial tyresThermoplasticCarbon nanotube
This invention relates to flexible, transparent and conductive coatings and films formed using single wall carbon nanotubes and polymer binders. Preferably, coatings and films are formed from carbon nanotubes (CNT) applied to transparent substrates forming one or multiple conductive layers at nanometer level of thickness. Polymer binders are applied to the CNT network coating having an open structure to provide protection through infiltration. This provides for the enhancement of properties such as moisture resistance, thermal resistance, abrasion resistance and interfacial adhesion. Polymers may be thermoplastics or thermosets, or any combination of both. Polymers may also be insulative or inherently electrical conductive, or any combination of both. Polymers may comprise single or multiple layers as a basecoat underneath a CNT coating, or a topcoat above a CNT coating, or combination of the basecoat and the topcoat forming a sandwich structure. Binder coating thickness can be adjusted by changing binder concentration, coating speed and / or other process conditions. Resulting films and articles can be used as transparent conductors for flat panel display, touch screen and other electronic devices.
Owner:EIKOS
Flat panel display screen operable for touch position determination system and methods
InactiveUS20070216657A1Raising pixel capacitanceQuickly and easily determineStatic indicating devicesAcquiring/reconising fingerprints/palmprintsDisplay deviceQuantum dot display
A system and method are disclosed that determines the location of an object touching a display screen. The system and method modifies already existing display technology, including using the underlying structure of many types of existing displays as the touch detecting structure. The systems and methods are applicable to virtually all LCD and LCD-like displays, including emissive displays (OLED, PLED, quantum dot displays, etc.), electronic paper, and others.
Owner:KONICEK JEFFREY C
System And Method For Camera Imaging Data Channel
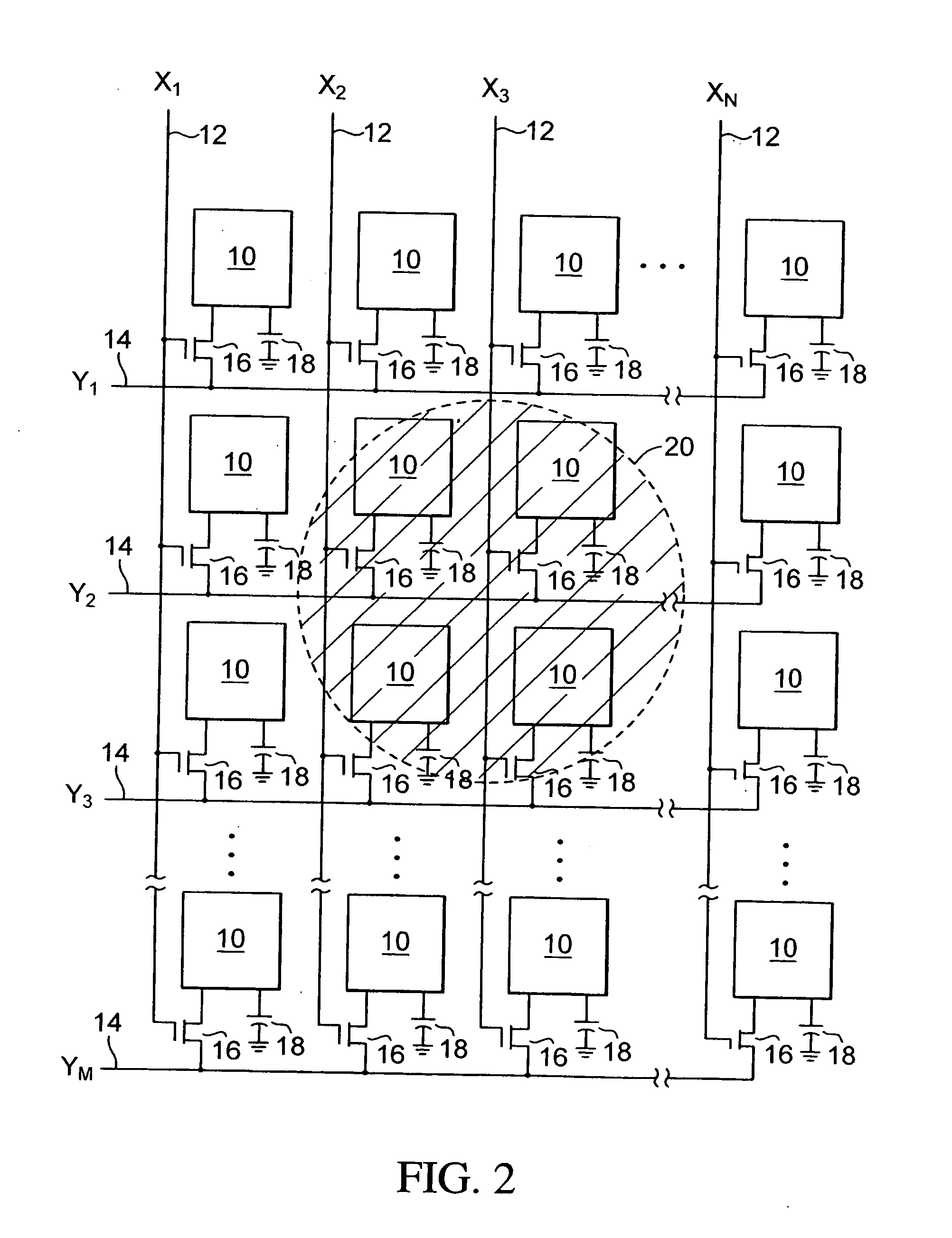
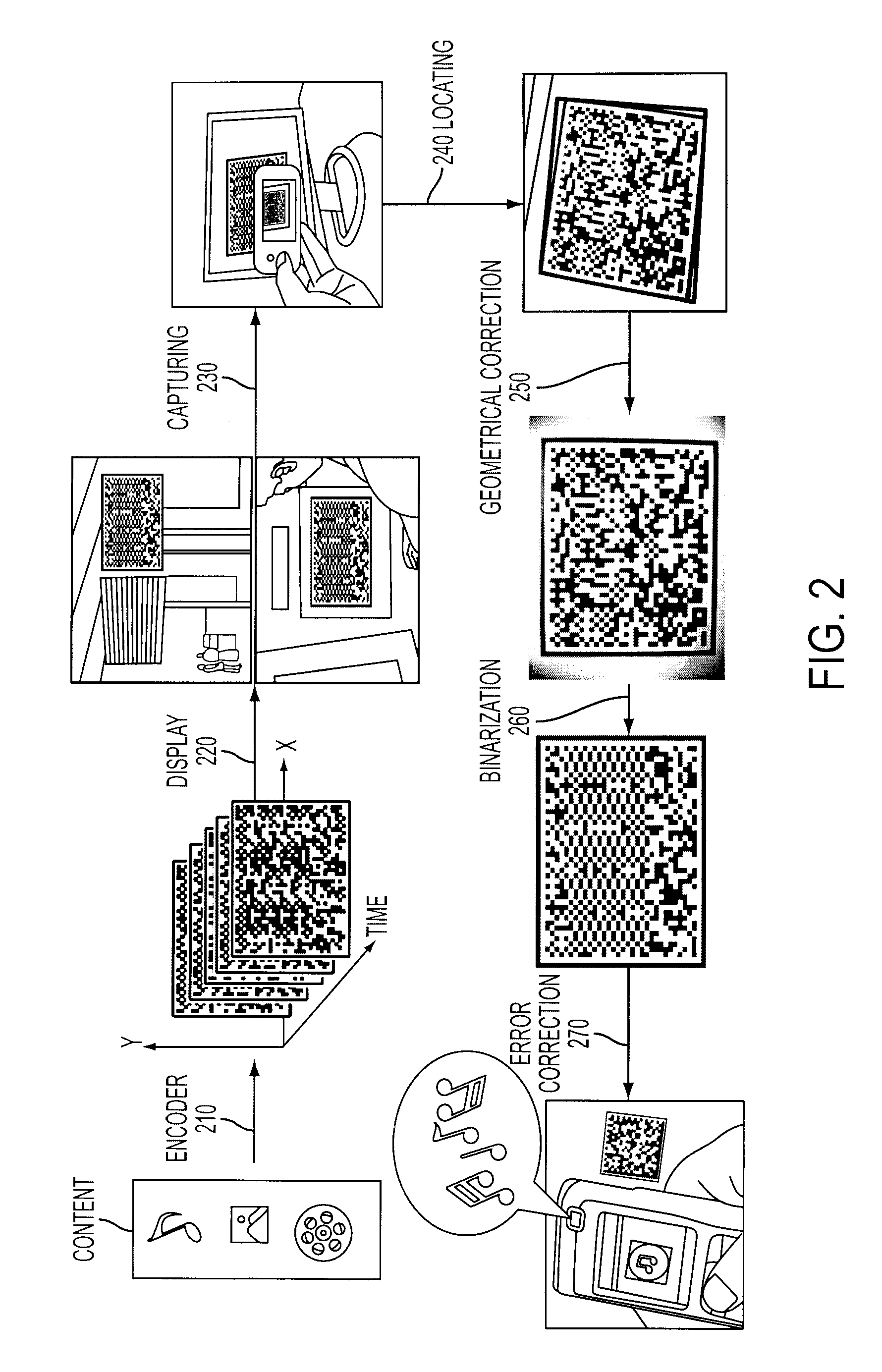
InactiveUS20100020970A1Low data costLow costCode conversionSecret communicationBarcodeDisplay device
A system and method for using cameras to download data to cell phones or other devices as an alternative to CDMA / GPRS, BlueTooth, Infrared or cable connections. The data is encoded as a sequence of images such as 2D bar codes, which can be displayed in any flat panel display, acquired by a camera, and decoded by software embedded in the device. The decoded data is written to a file. The system and method meet the following challenges: (1) To encode arbitrary data as a sequence of images. (2) To process captured images under various lighting variations and perspective distortions while maintaining real time performance. (3) To decode the processed images robustly even when partial data is lost.
Owner:LIU XU +2
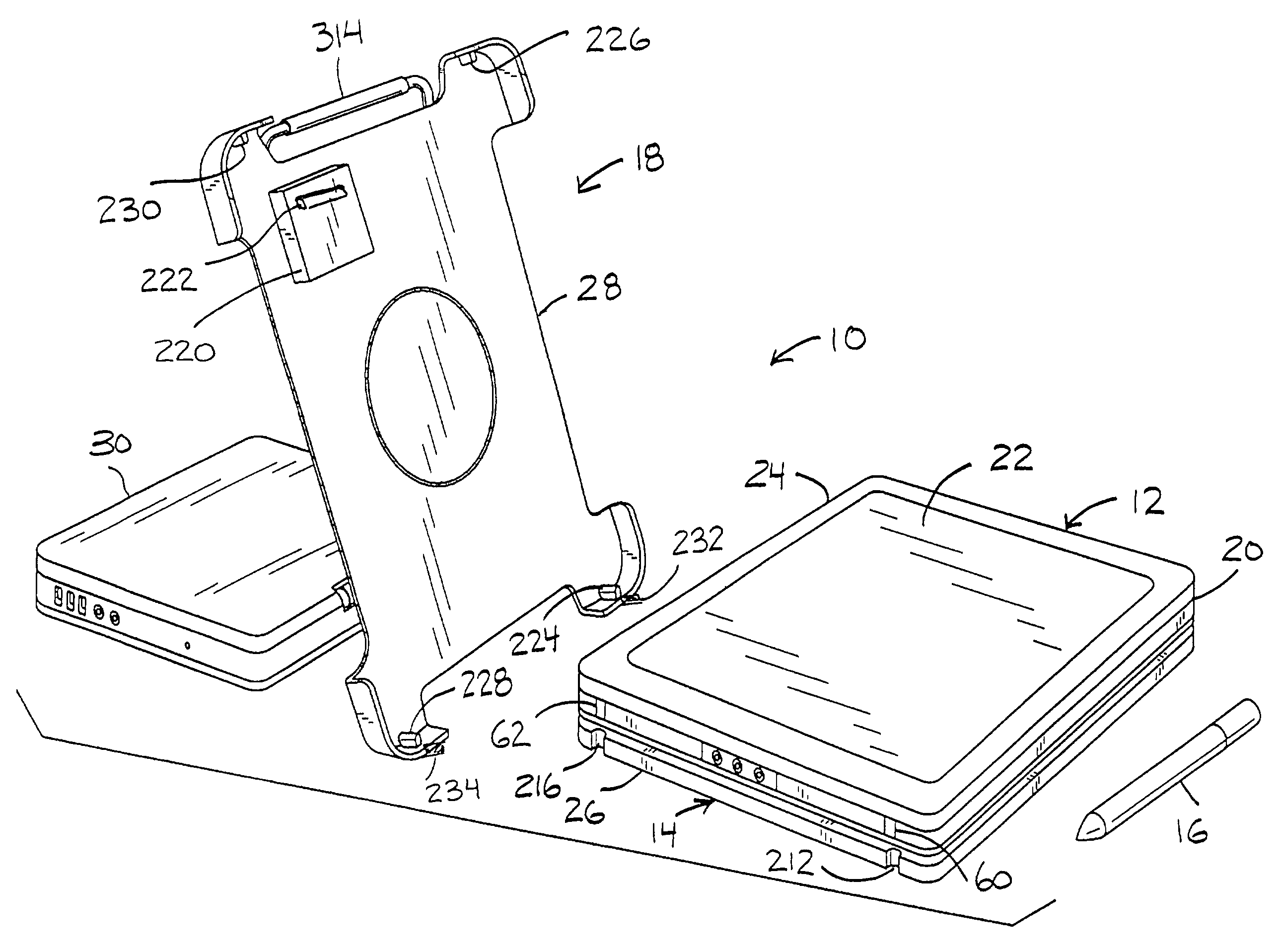
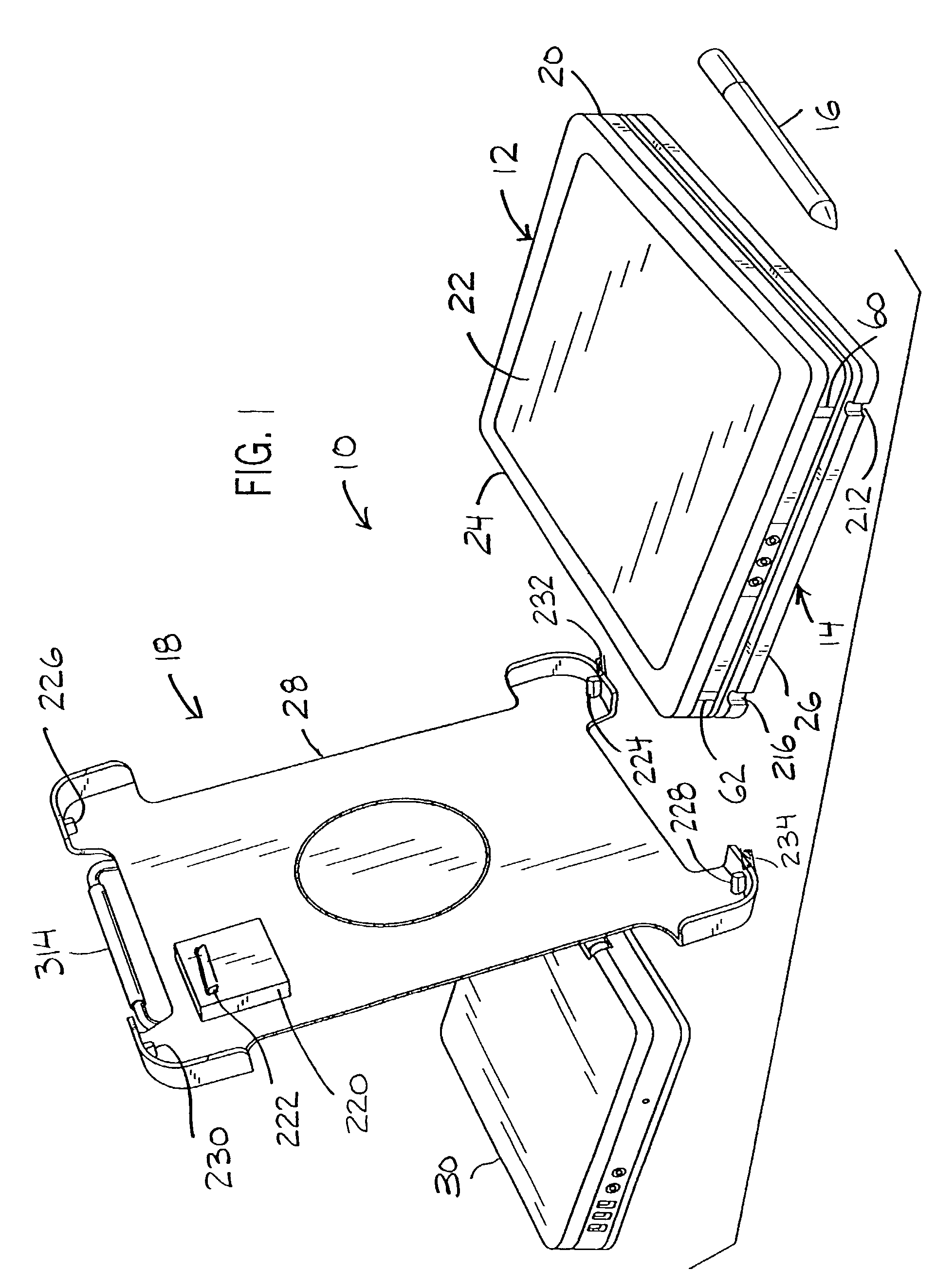
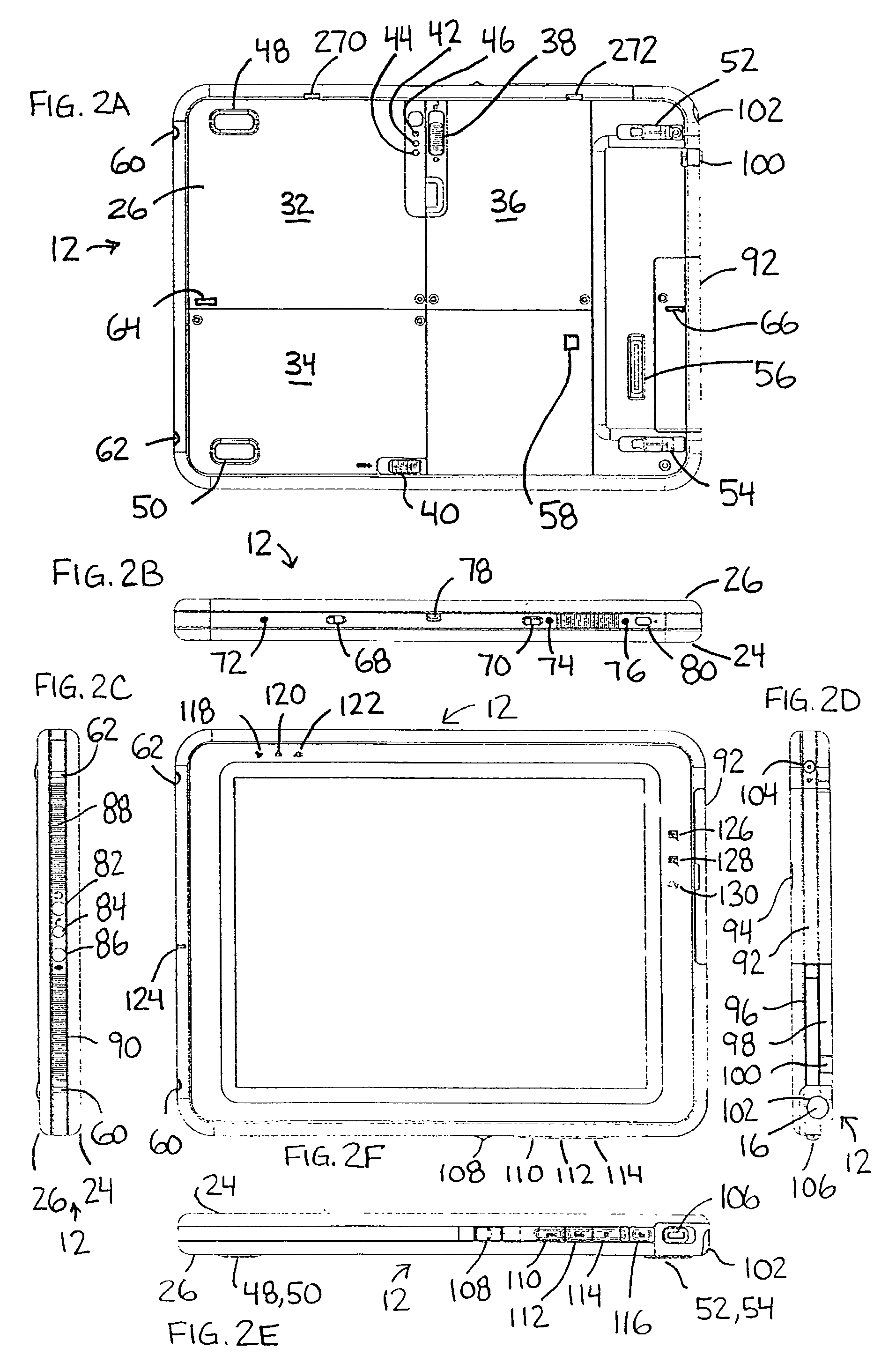
System and method of switching viewing orientations of a display
InactiveUS7542052B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsDetails for portable computersTablet computerDocking station
The present technique provides a system and method for automatically switching viewing orientations of a display in response to physical rotation of the display. The display is rotatably coupled to a base structure via a rotatable mechanism, which has one or more angular switches / sensors that sense the physical orientation of the display and trigger a change in the viewing orientation of the display. The display may be a stand-alone flat-panel display or it may be incorporated into a portable electronic / computing devices, such as a tablet computer. Moreover, the base structure may embody a display support, a port replicator, a docking station, or any other suitable structure having a rotational adjustment mechanism.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
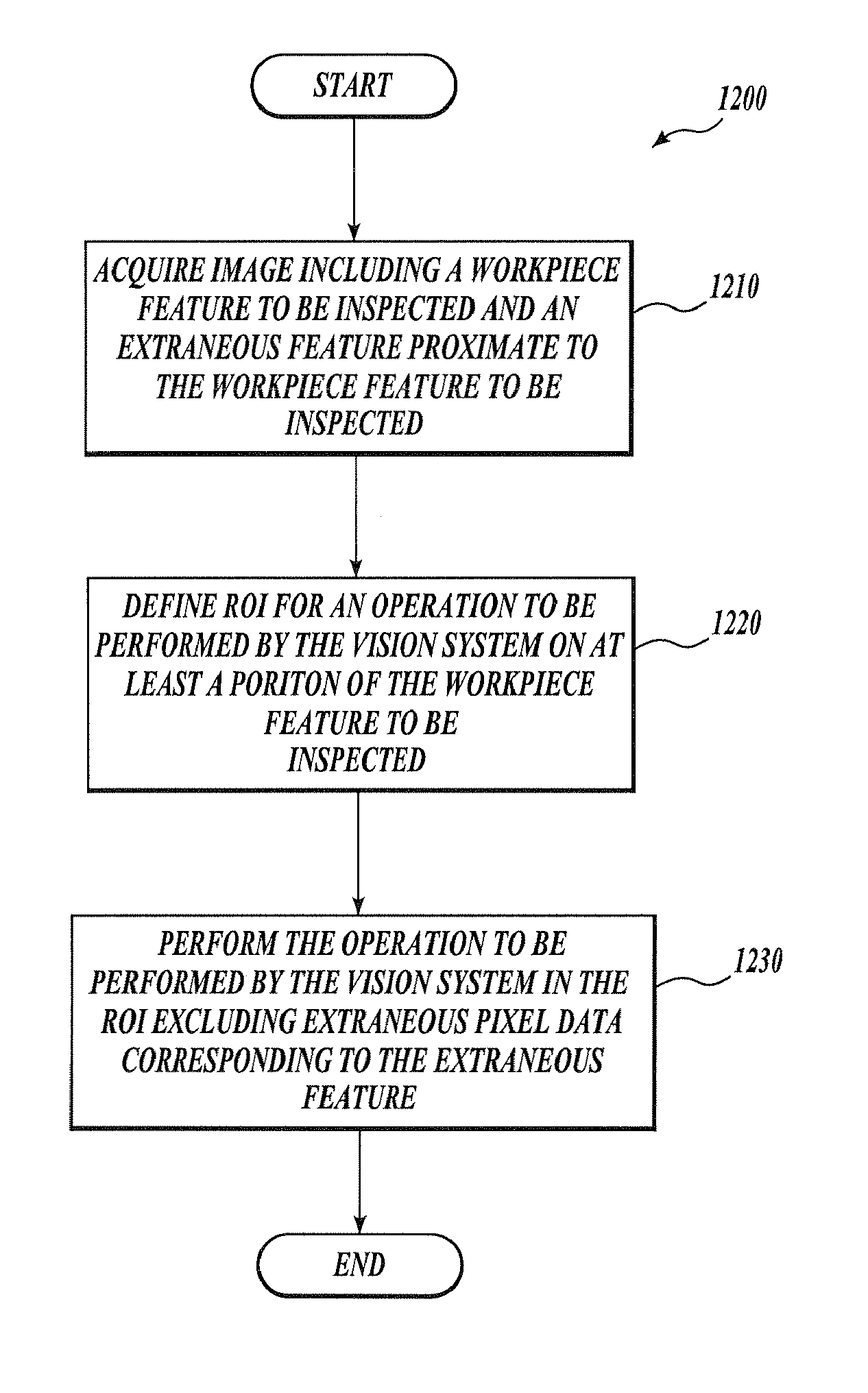
System and method for excluding extraneous features from inspection operations performed by a machine vision inspection system
ActiveUS7324682B2Easy to useVariation in spacingImage enhancementImage analysisMachine visionImaging Feature
Systems and methods are provided for excluding extraneous image features from inspection operations in a machine vision inspection system. The method identifies extraneous features that are close to image features to be inspected. No image modifications are performed on the “non-excluded” image features to be inspected. A video tool region of interest provided by a user interface of the vision system can encompass both the feature to be inspected and the extraneous features, making the video tool easy to use. The extraneous feature excluding operations are concentrated in the region of interest. The user interface for the video tool may operate similarly whether there are extraneous features in the region of interest, or not. The invention is of particular use when inspecting flat panel display screen masks having occluded features that are to be inspected.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Vertical docking and positioning apparatus for a portable computer
InactiveUS6256193B1Easy to transportIncrease profitMachine supportsBook-restsLocking mechanismEngineering
A positioning device for supporting a portable computer that includes a base member for placing on a horizontal surface, a support plate for supporting the portable computer at an inclined position relative to the base member, a hinge that rotatably connects the base member to the support plate so that the support plate can be rotated between multiple angular positions relative to the base member, and a lock mechanism for selectively fixing the angular position between the base member and the support plate. The portable computer, which includes a base housing having a front and rear end, a flat panel display rotatably attached to the rear end of the base housing, and a keyboard attached to a top surface of the base housing, can be supported in an inclined position directly by a support member that is rotatably attached to the front end of the base housing so that the support member can be rotated between multiple angular positions relative to the base housing, where a lock mechanism selectively fixes the angular position between the support member and the base housing so that the support member supports the base housing at an inclined position.
Owner:HTC CORP
Organic light emitting device and flat panel display device comprising the same
ActiveUS20070231503A1Reduce the driving voltageHigh densityLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic chemistryOrganic light emitting deviceOrganic layer
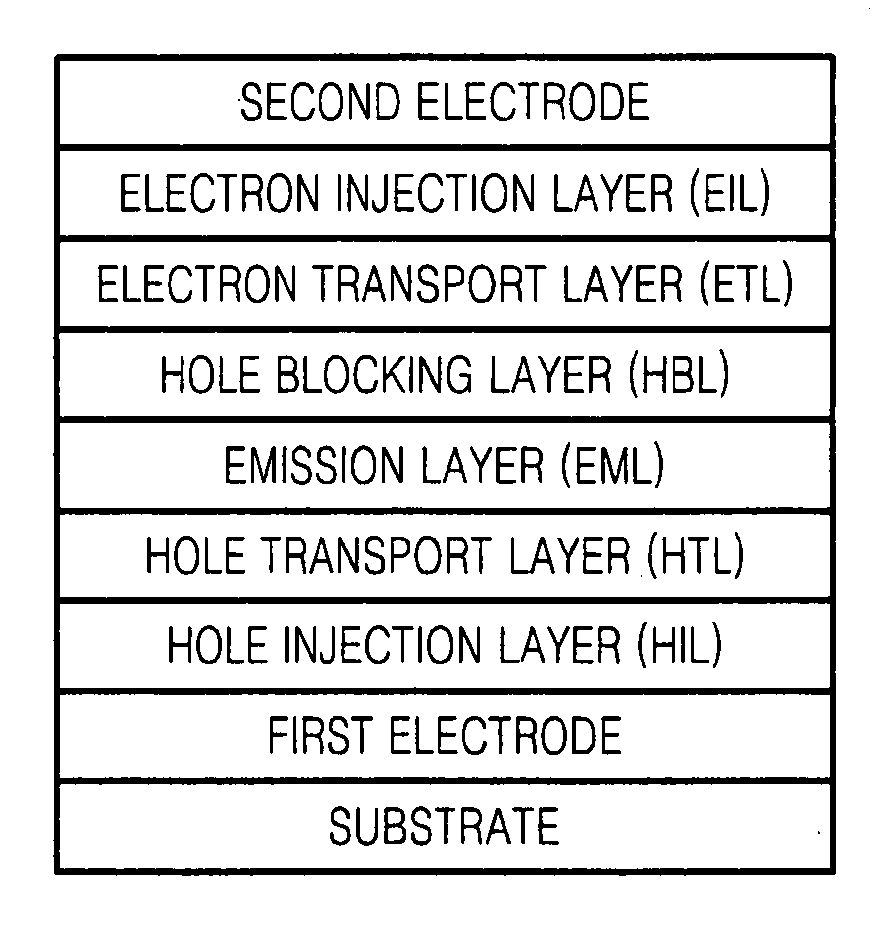
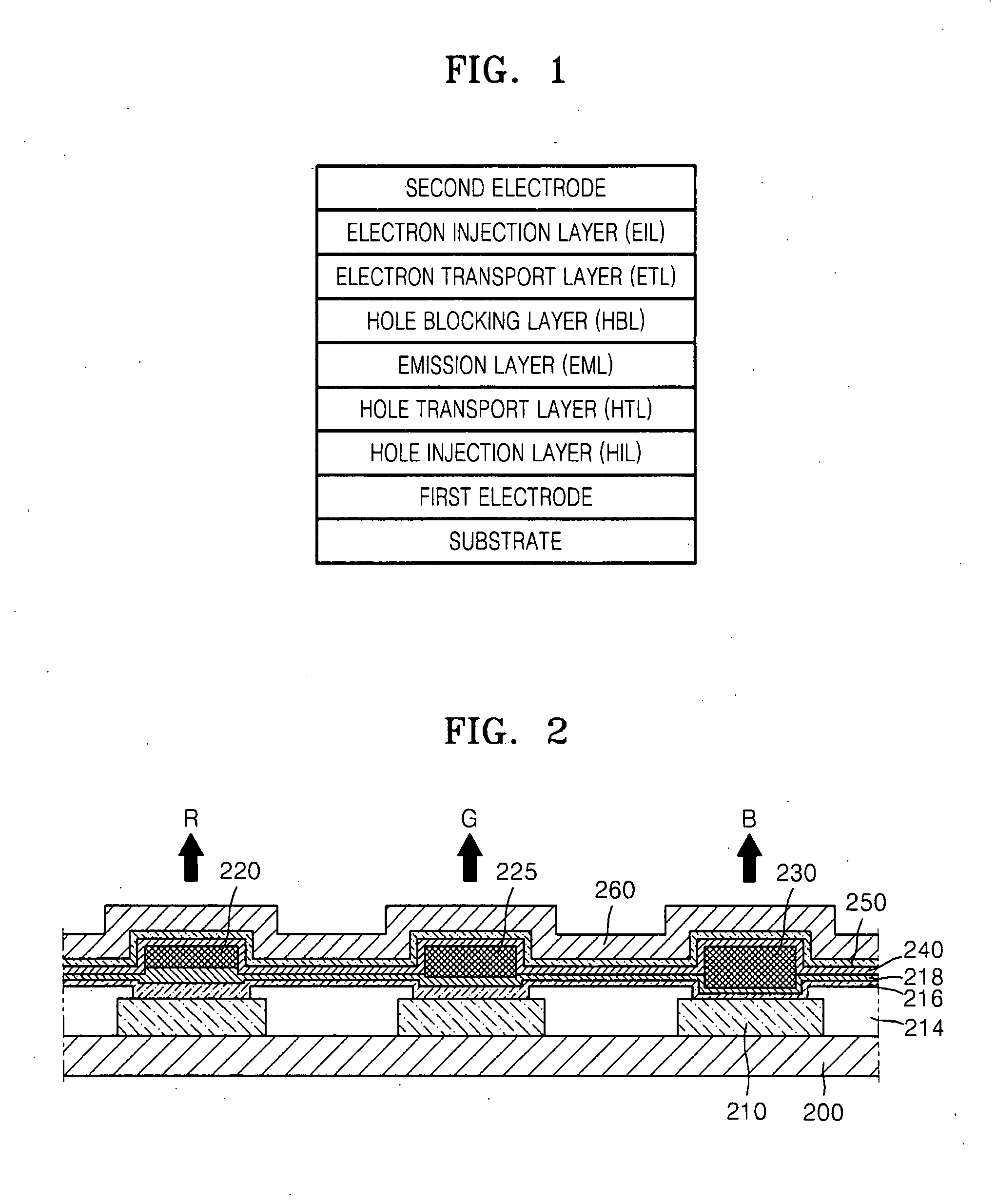
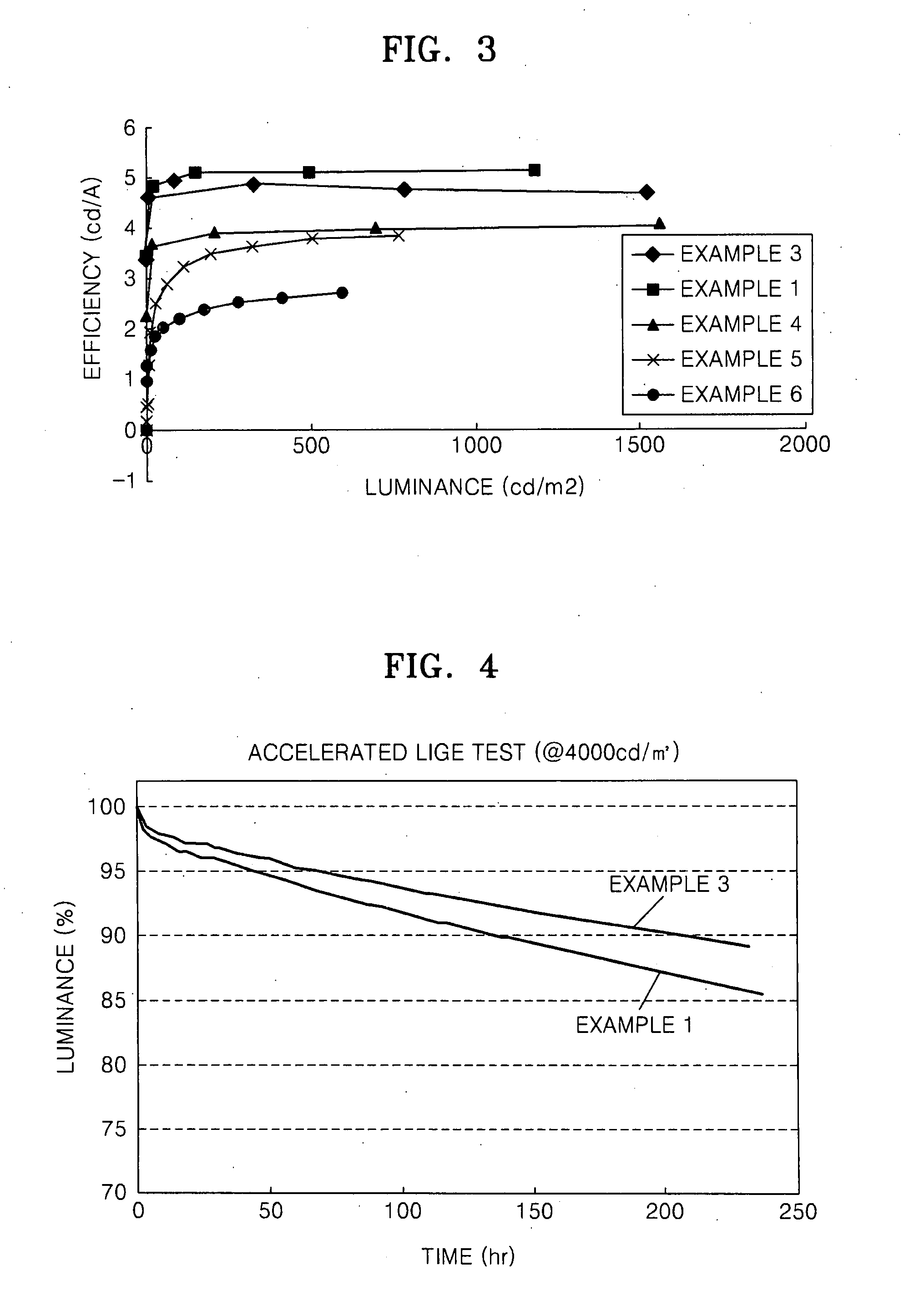
Provided are an organic light emitting device including: a substrate; a first electrode; a second electrode; and an organic layer interposed between the first electrode and the second electrode and including an emission layer, wherein one of the first electrode and the second electrode is a reflective electrode and the other is a semitransparent or transparent electrode, and wherein the organic layer includes a layer having at least one of the compounds having at least one carbazole group, and a flat panel display device including the organic light emitting device. The organic light emitting device has low driving voltage, excellent current density, high brightness, excellent color purity, high efficiency, and long lifetime.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
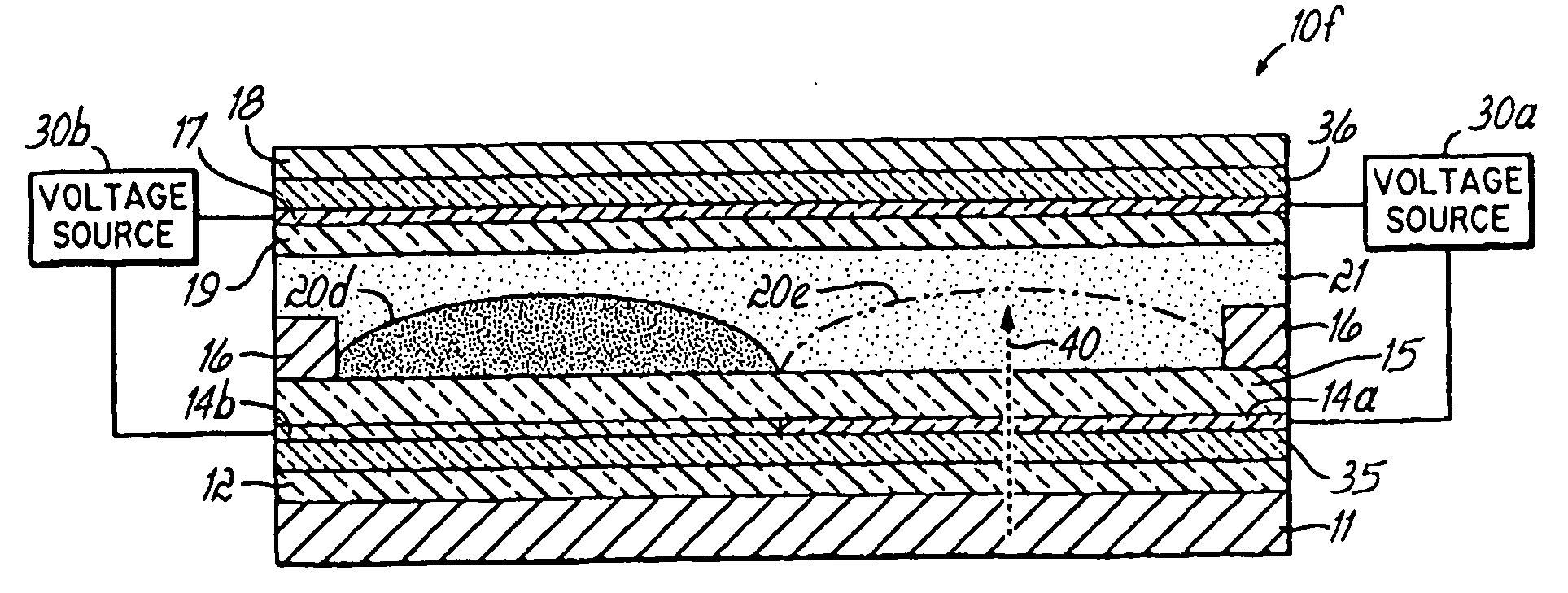
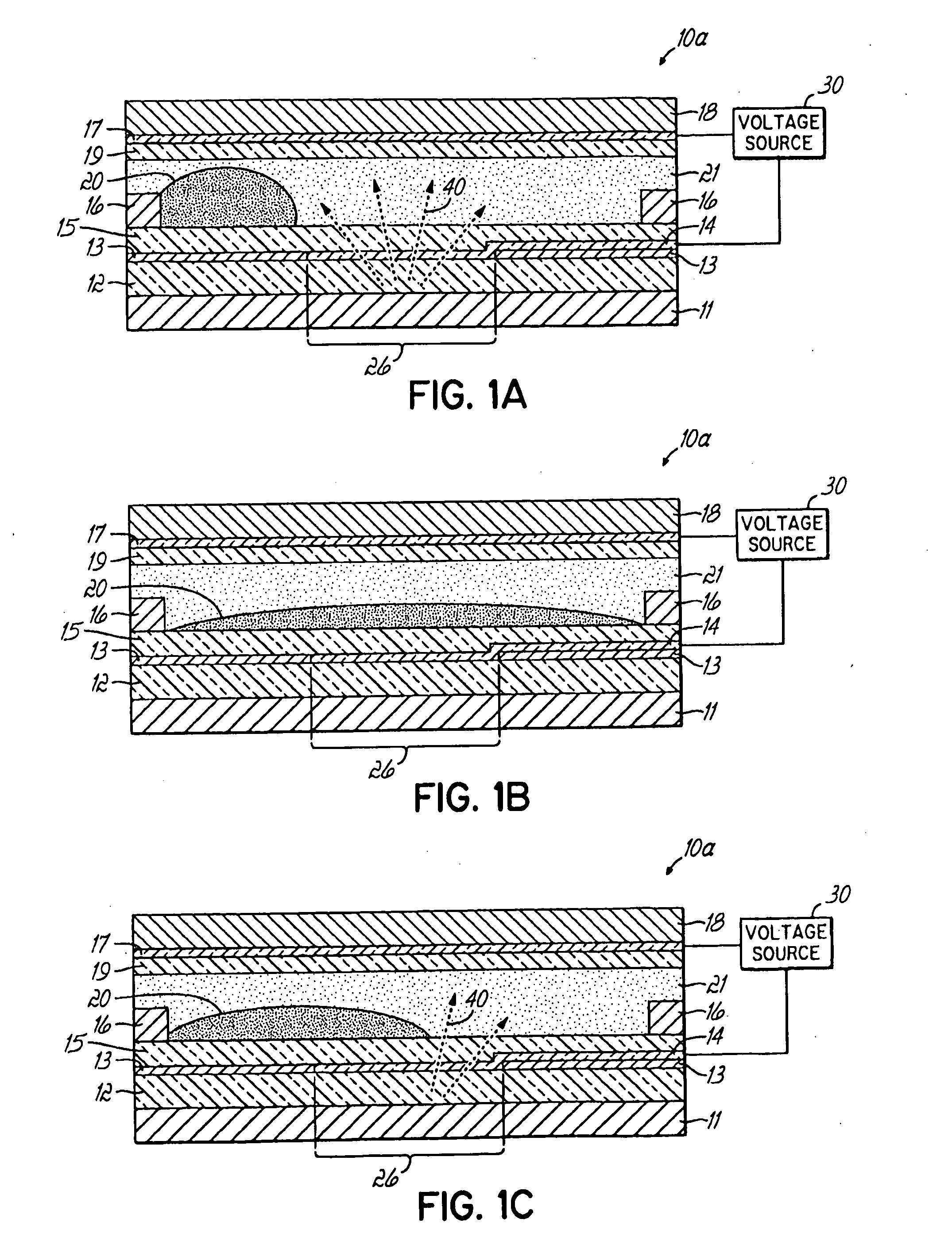
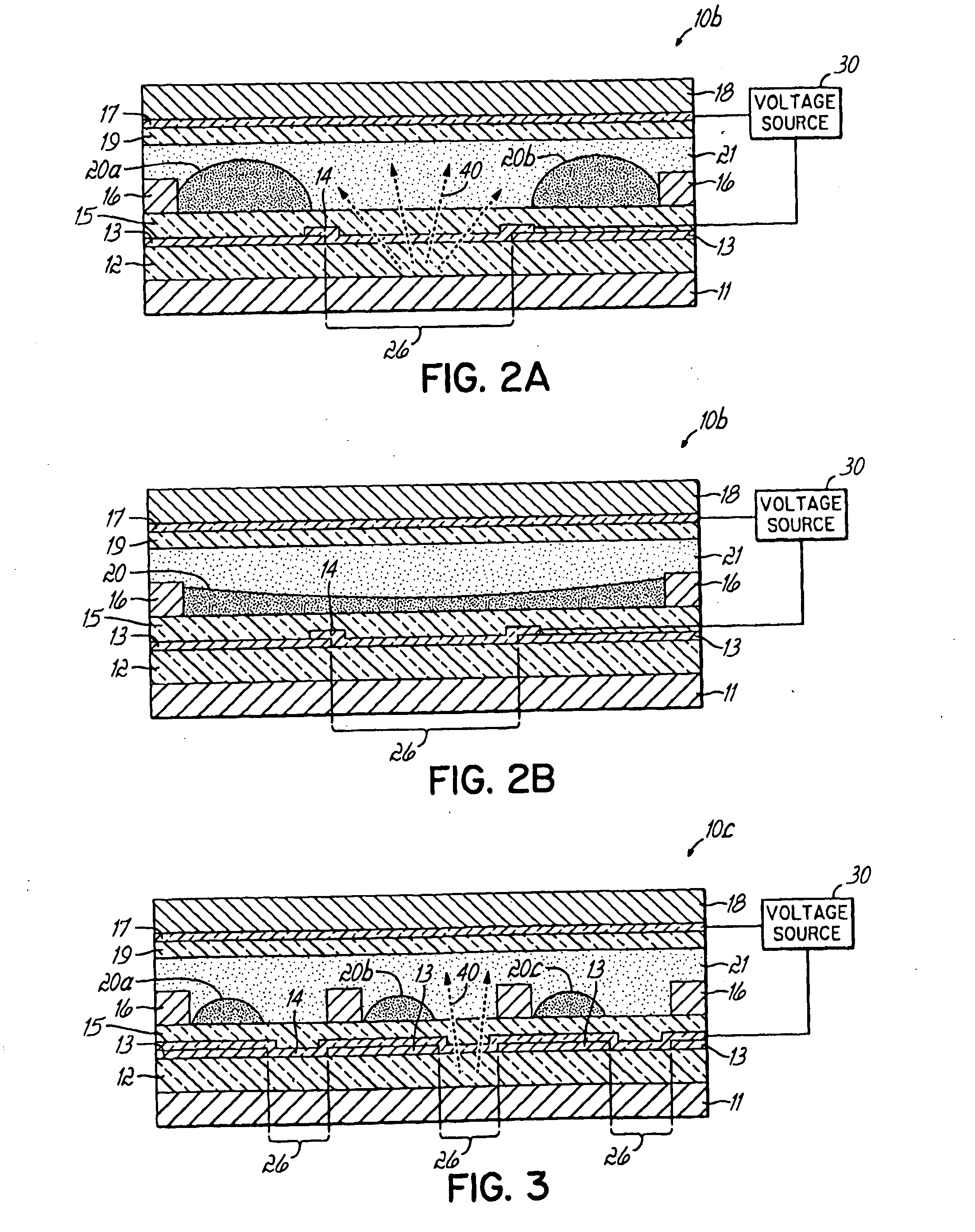
Display Capable Electrowetting Light Valve
ActiveUS20080297880A1High operating requirementsEasy constructionDiffusing elementsNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceFlat panel display
The invention relates to light transmissive, transflective, or reflective flat panel display devices and, more specifically, to light emissive flat panel displays constructed from high performance electrowetting light valve (ELV) devices (10a-g). An array of ELV devices (10a-g) is mounted on or adjacent to a backlight (11), employing a reflector (13) allowing for improved transmission. The backlight (11) may be partially diffusely reflective or translucent as to also allow for creation of a transflective display panel.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
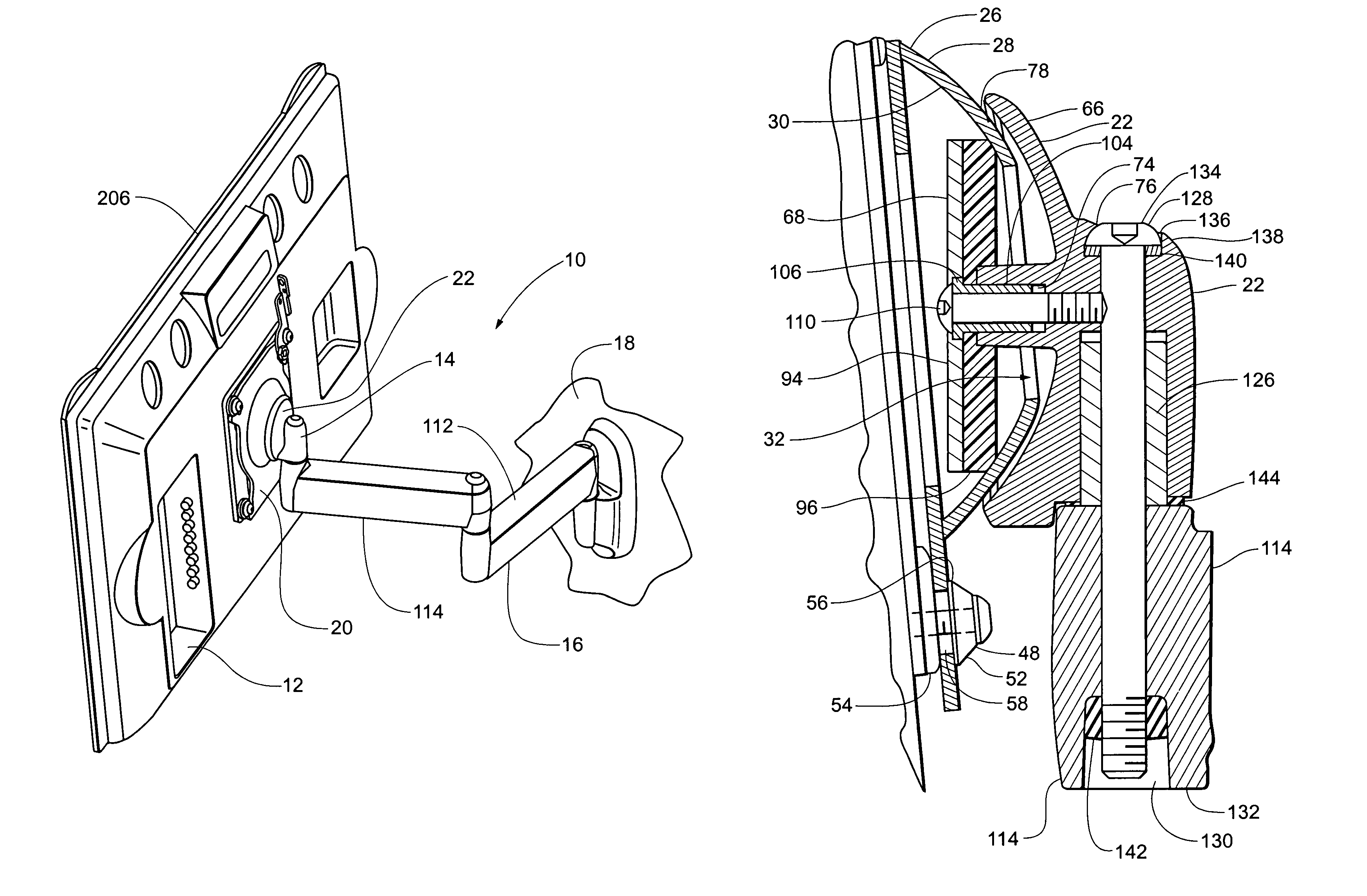
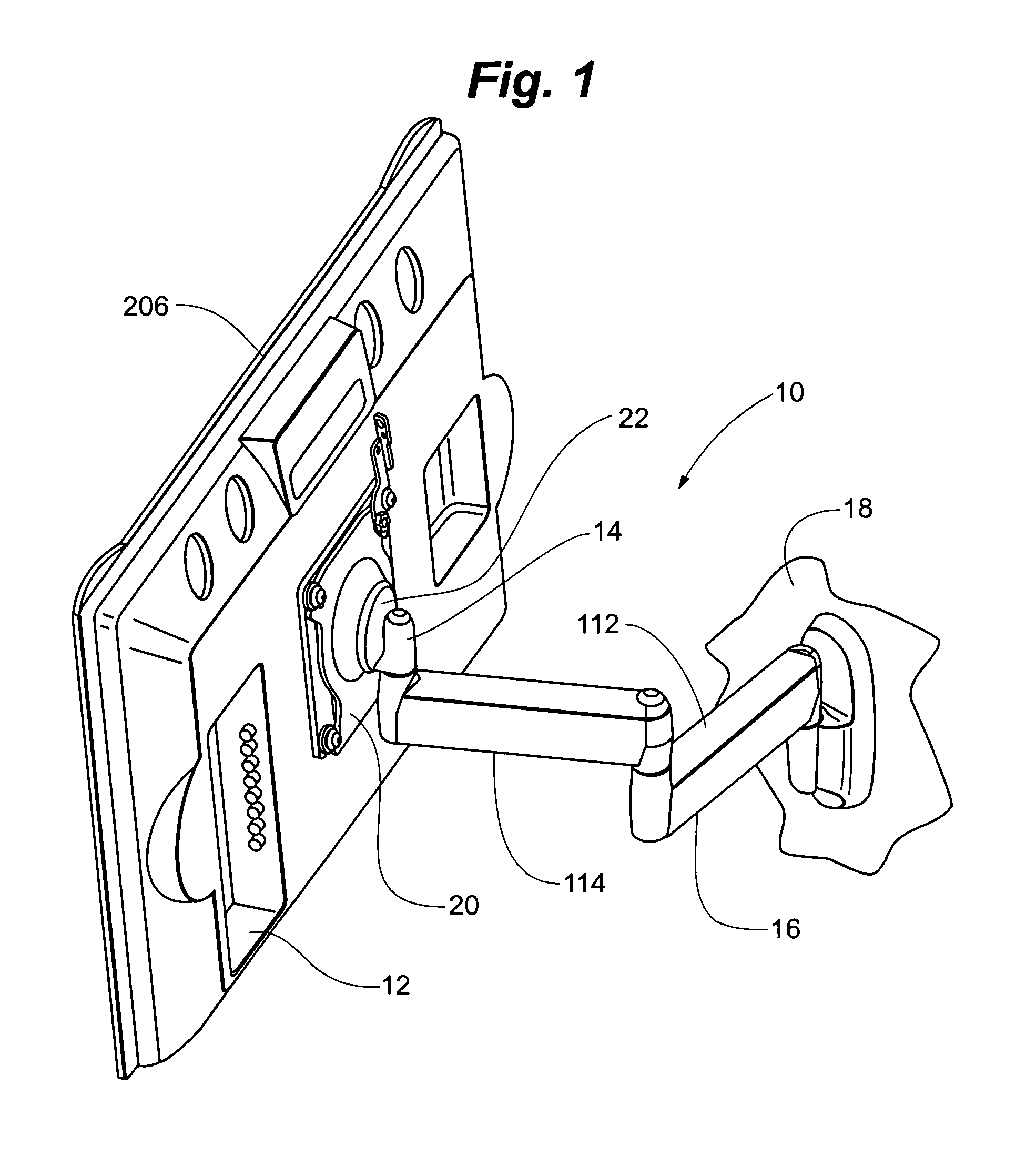
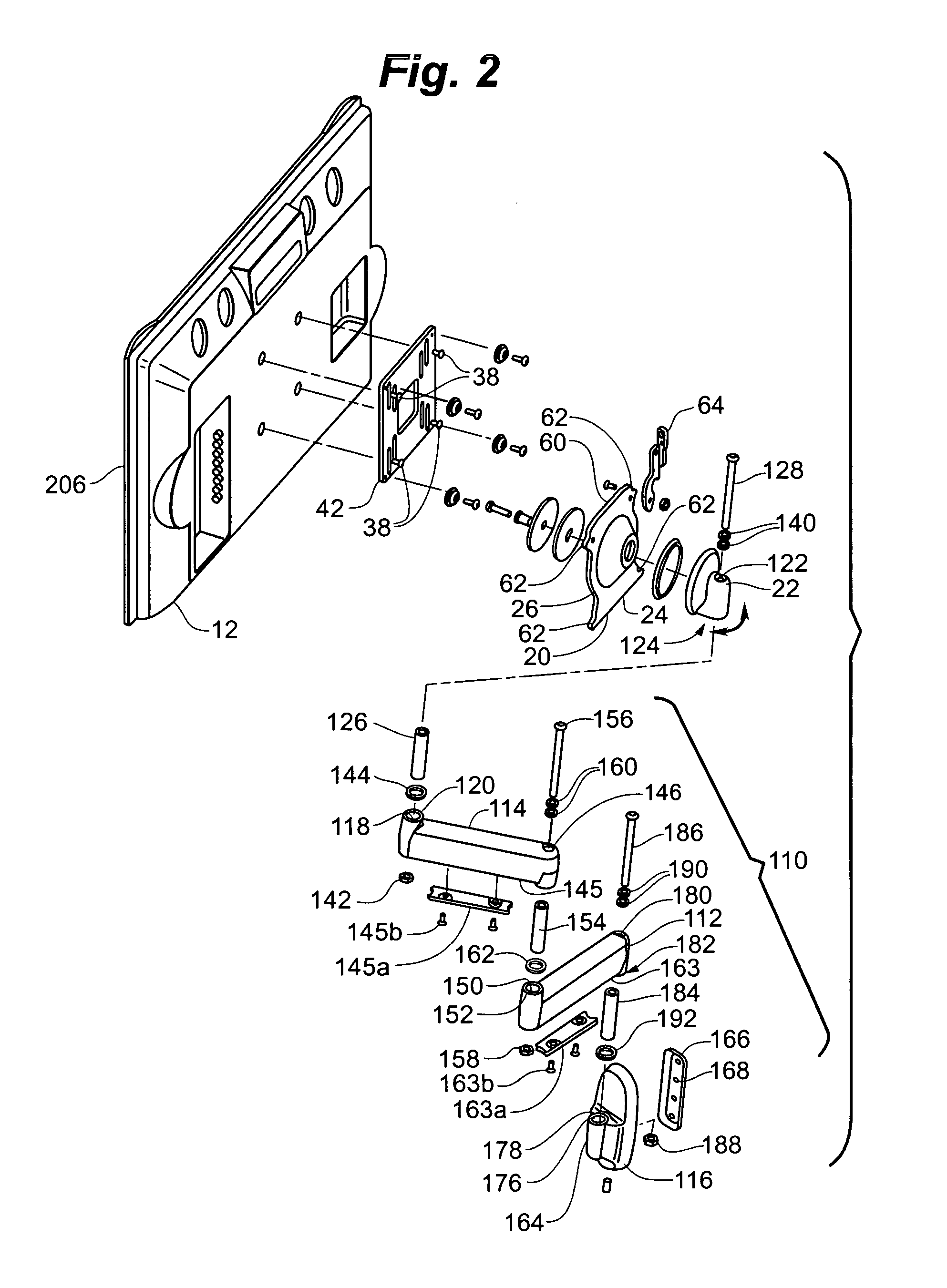
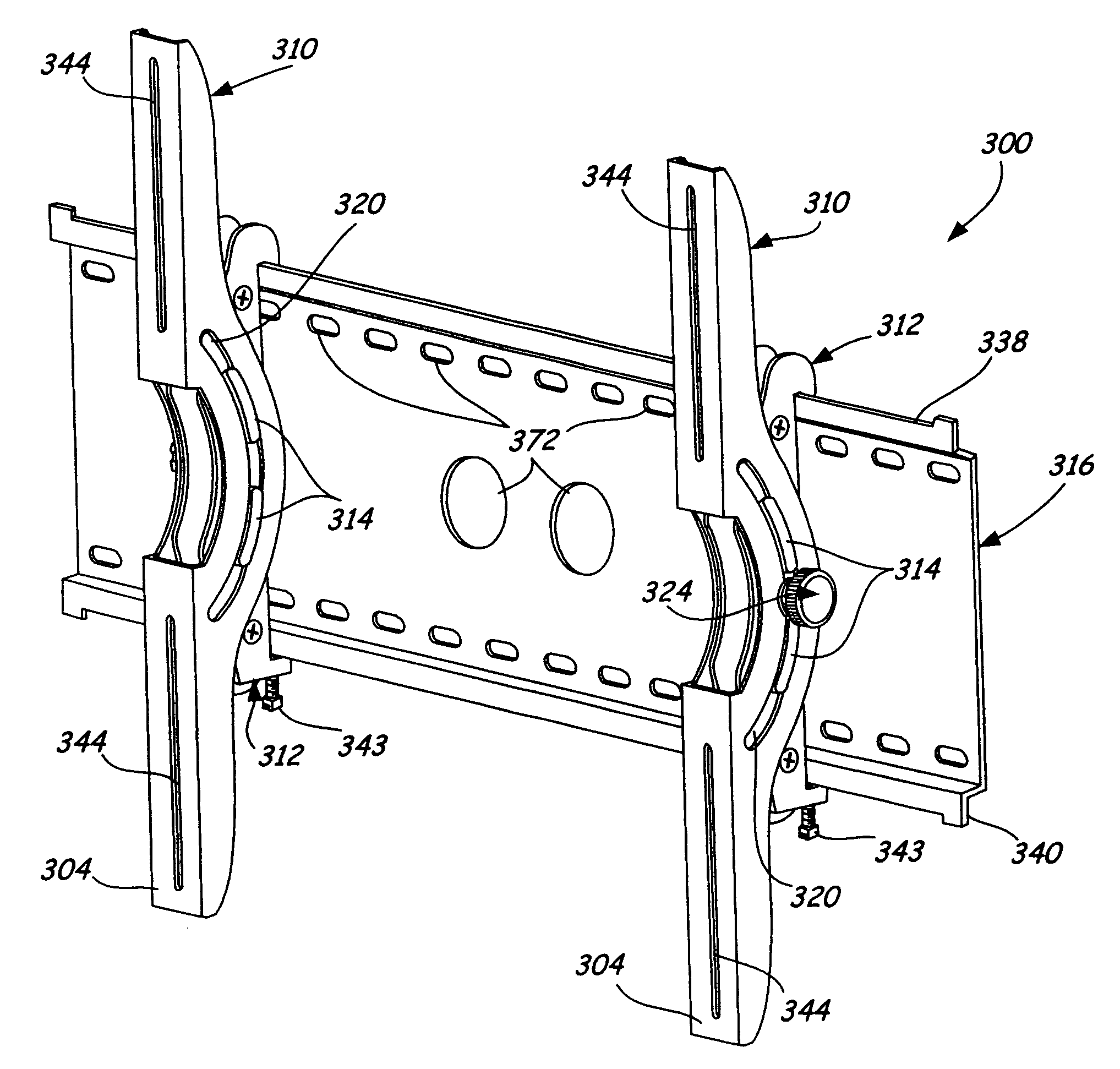
Self-balancing adjustable flat panel mounting system
A self-balanced adjustable mounting system for a flat panel display. A display interface having a hollow, semi-spherical shell portion is attached to the flat panel display. The semi-spherical shell is formed with a generally constant radius of curvature. The center of the radius of curvature is disposed proximate the center of gravity of the flat panel display with the display interface attached. The display interface is received in a guide structure that has a bearing portion engaging the outer surface of the semi-spherical shell, and a second bearing portion engaging the inner surface of the semi-spherical shell through an aperture formed in the semi-spherical shell. The semi-spherical shell is guided between the first and second bearing portions so that the flat panel display and device interface are generally rotatable about the center of the radius of curvature of the semi-spherical shell. The display is self balancing in virtually any position in the range of travel of the device due to the location of the center of rotation proximate the center of gravity.
Owner:LEGRAND AV INC
Electronically addressable microencapsulated ink and display thereof
InactiveUS20070052757A1Inexpensive displayMechanical clocksVisual indicationsElectrical conductorSemiconductor materials
A system of electronically active inks is described which may include electronically addressable contrast media, conductors, insulators, resistors, semiconductive materials, magnetic materials, spin materials, piezoelectric materials, optoelectronic, thermoelectric or radio frequency materials. We further describe a printing system capable of laying down said materials in a definite pattern. Such a system may be used for instance to: print a flat panel display complete with onboard drive logic; print a working logic circuit onto any of a large class of substrates; print an electrostatic or piezoelectric motor with onboard logic and feedback or print a working radio transmitter or receiver.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Adjustable tilt mount
Owner:LEGRAND AV INC
Multi-functional control and entertainment systems
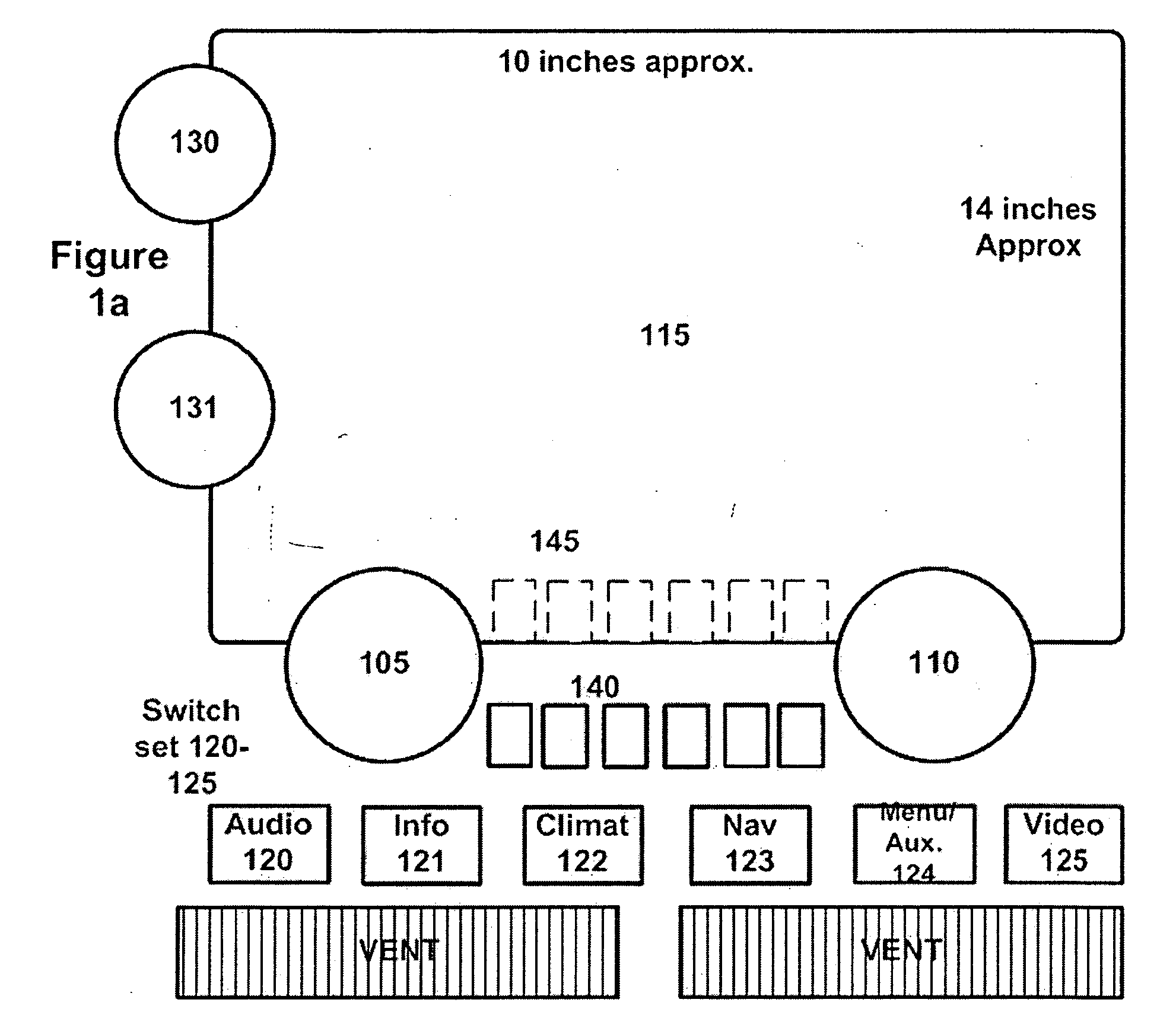
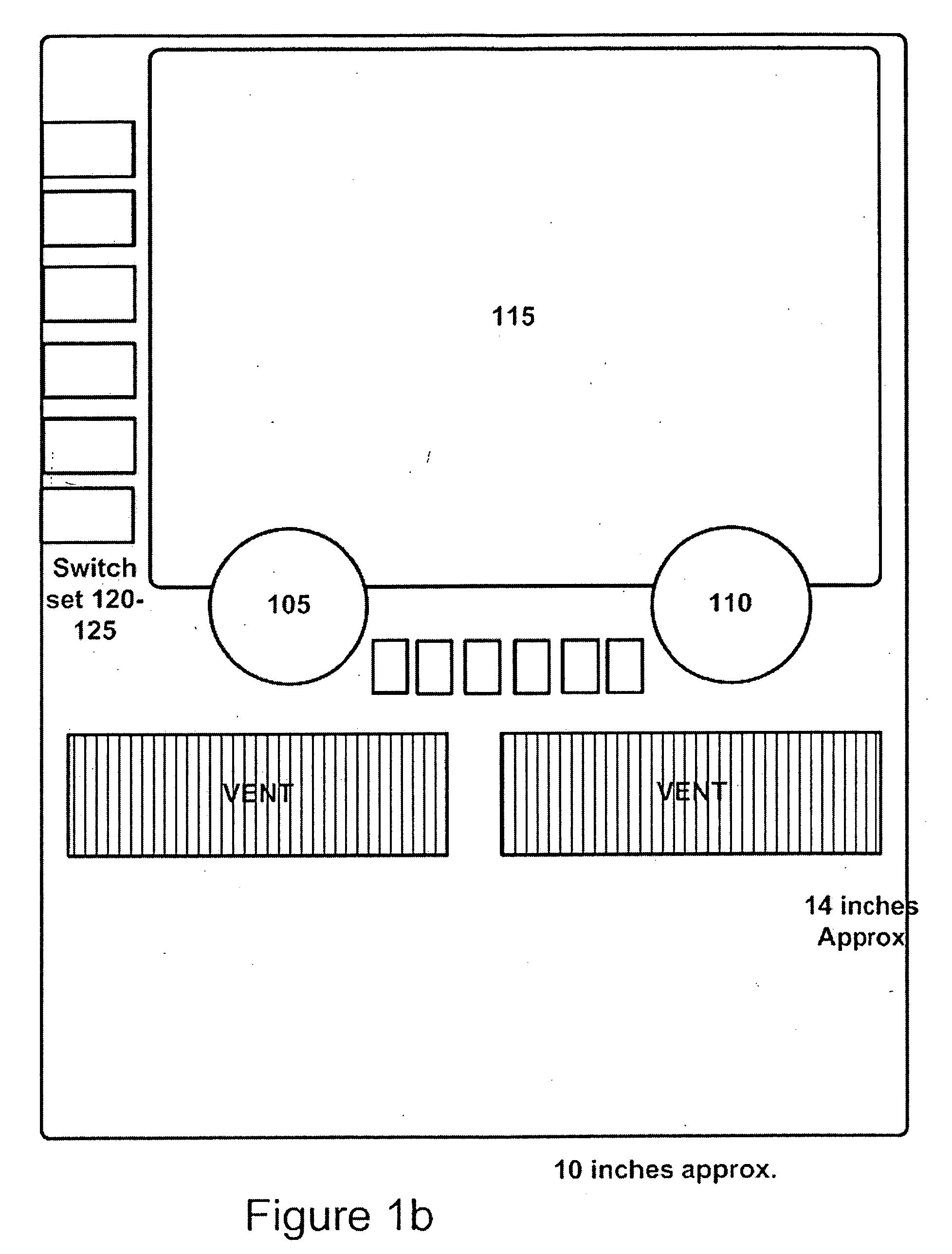
InactiveUS20050276448A1Big knobReduce in quantityDashboard fitting arrangementsInstrument arrangements/adaptationsInformation processingDriver/operator
For use in vehicles, it is desirable to have multi-functional (also known as reconfigurable) controls in the center stack portion of the instrument panel in order to best provide electronic and telematic functions to the driver. Disclosed are methods and apparatus to allow reconfiguration of classical controls such as knobs, sliders, and switches most familiar to the vast majority of the motoring public which may, if desired, utilize conventional flat panel displays (e.g., LCD based) and conventional readout electronics and switching. Also disclosed are projection based controls and new forms of rear seat entertainment controls and related apparatus for minivans and other vehicles.
Owner:TURE TECH PARTNERS
Computer-"reflected" (avatar) mirror
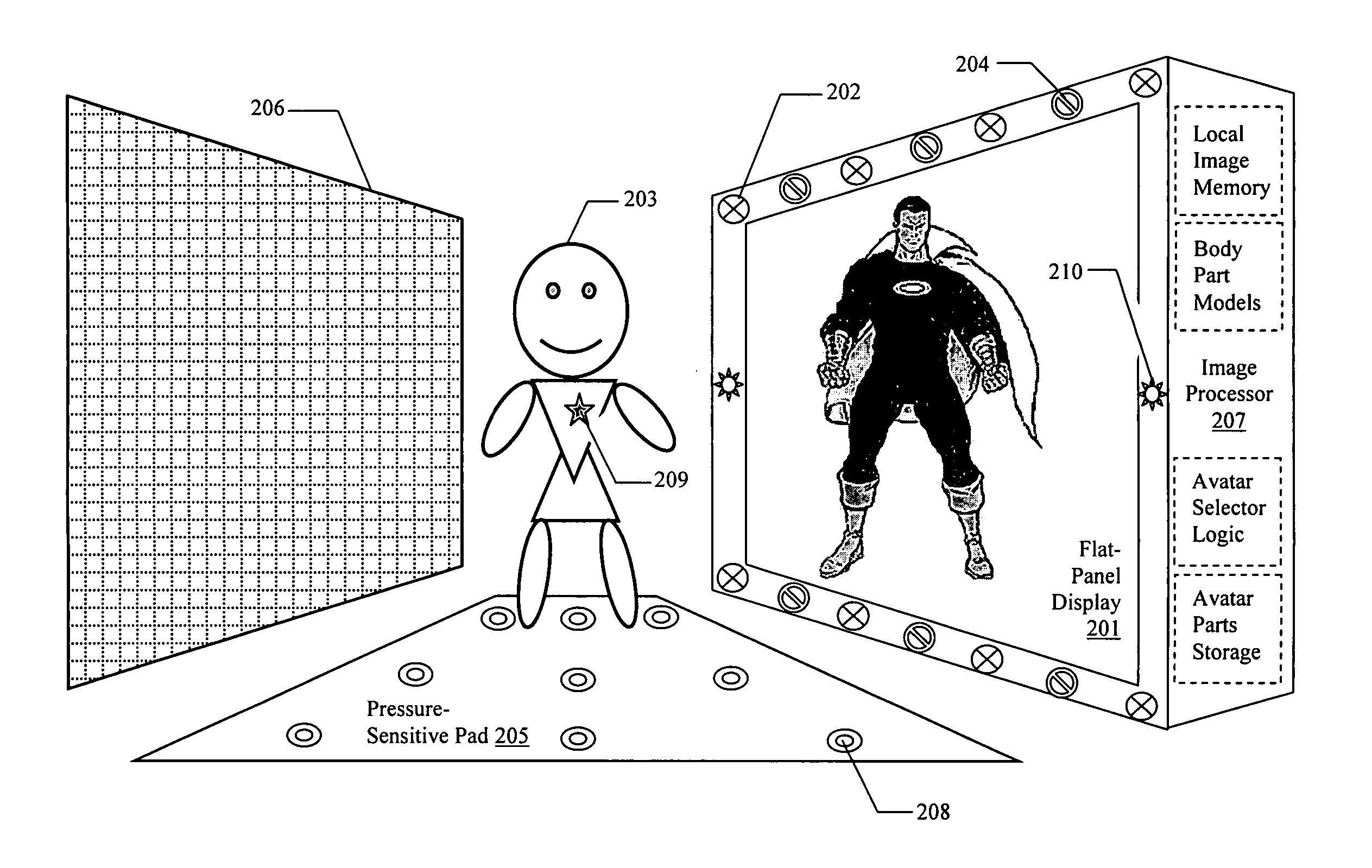
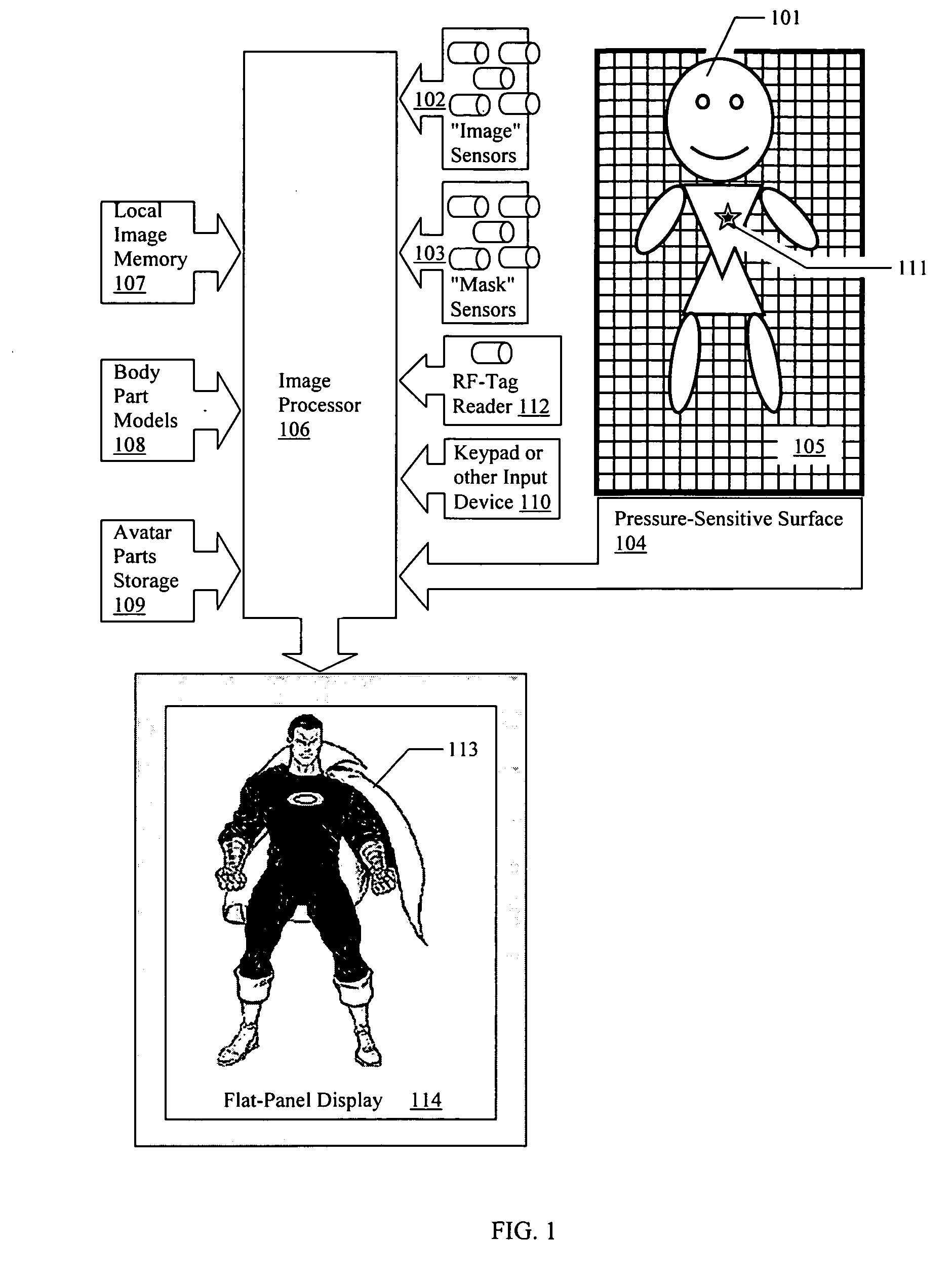
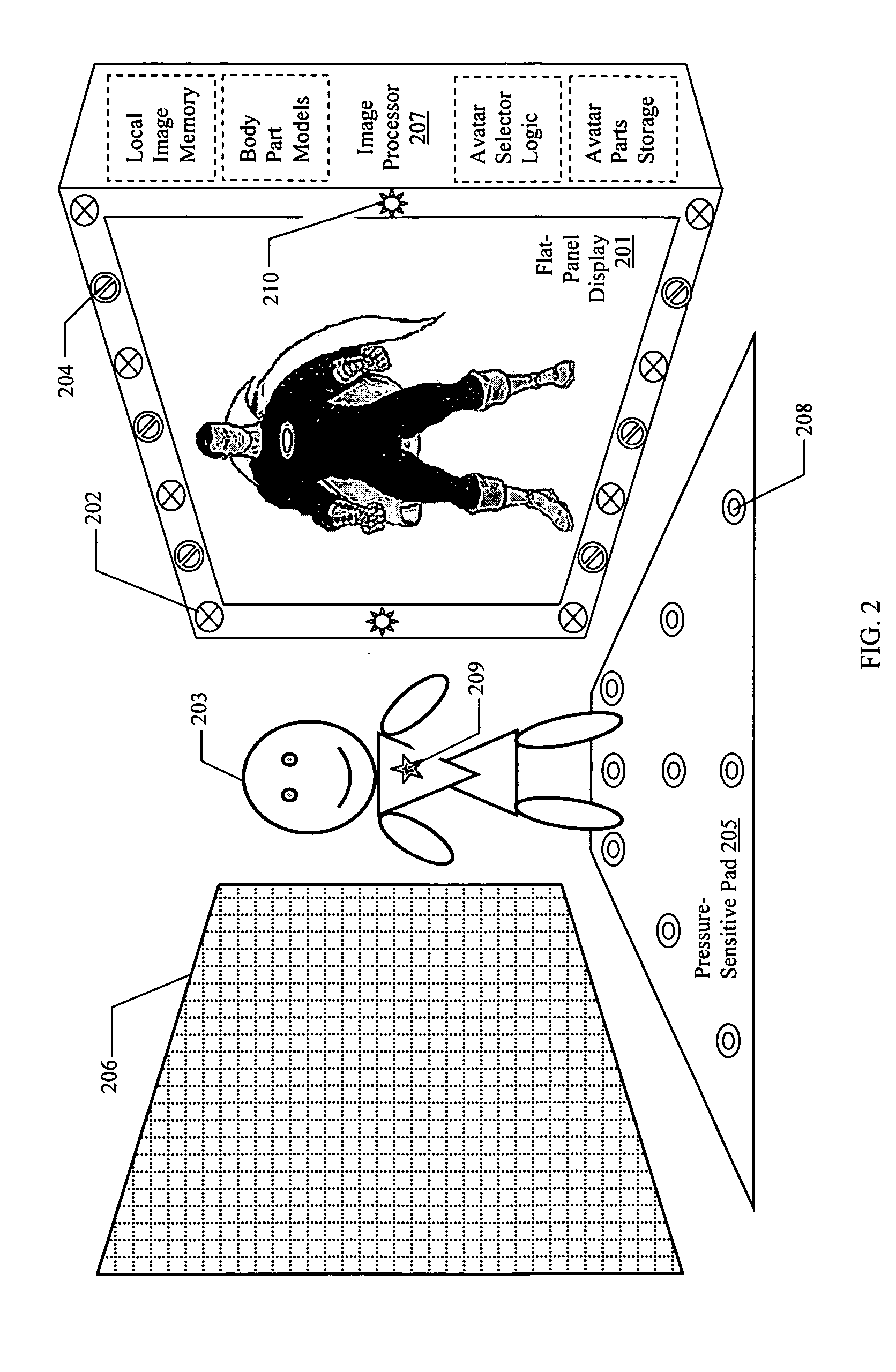
InactiveUS20050206610A1Avoid physical contactFaithfully reproducedLimiting/preventing/returning movement of partsCathode-ray tube indicatorsFlat panel displayComputer science
The mirror of the present invention provides a new device and method for generating a “reflection” of an object that may be processed before display. The invention comprises an image-capture system, an image-processor and a flat-panel display. By this combination, the invention is capable of acquiring the image of a subject in front of the display by passive means not requiring transmitters or reflectors on the subject (such means including optical, ultra-sonic, and electromagnetic sensors), processing the image in programmable ways to create an altered image of the subject and displaying the new image, which appears to mimic the movement and orientation of the original subject.
Owner:CORDELLI GARY GERARD
Digital imaging rear view mirror system
InactiveUS20030090568A1Electric devicesRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesMobile vehicleDigital imaging
The Digital Imaging Rear View Mirror System Utilizes a digital camera located low in the rear of a motor vehicle and cameras located on the sides of a vehicle all connected to a small flat panel display (e.g., LCD) located in front of the driver. The images from the cameras are to be digitally integrated so as to provide a seamless rear and side view. The Digital Imaging Rear View Mirror System incorporates a recorder that records 15 to 20 minute continuous segments while the vehicle is in operation and stops recording a few minutes after a collision. The System also incorporates a sensor that displays in real time on the LCD and on the recording the distance of objects and vehicles behind the vehicle equipped with a Digital Imaging Rear View Mirror System, the speed of the vehicle equipped with a Digital Imaging Rear View Mirror System and the time.
Owner:PICO THOMAS MICHAEL
ALD reactor and method with controlled wall temperature
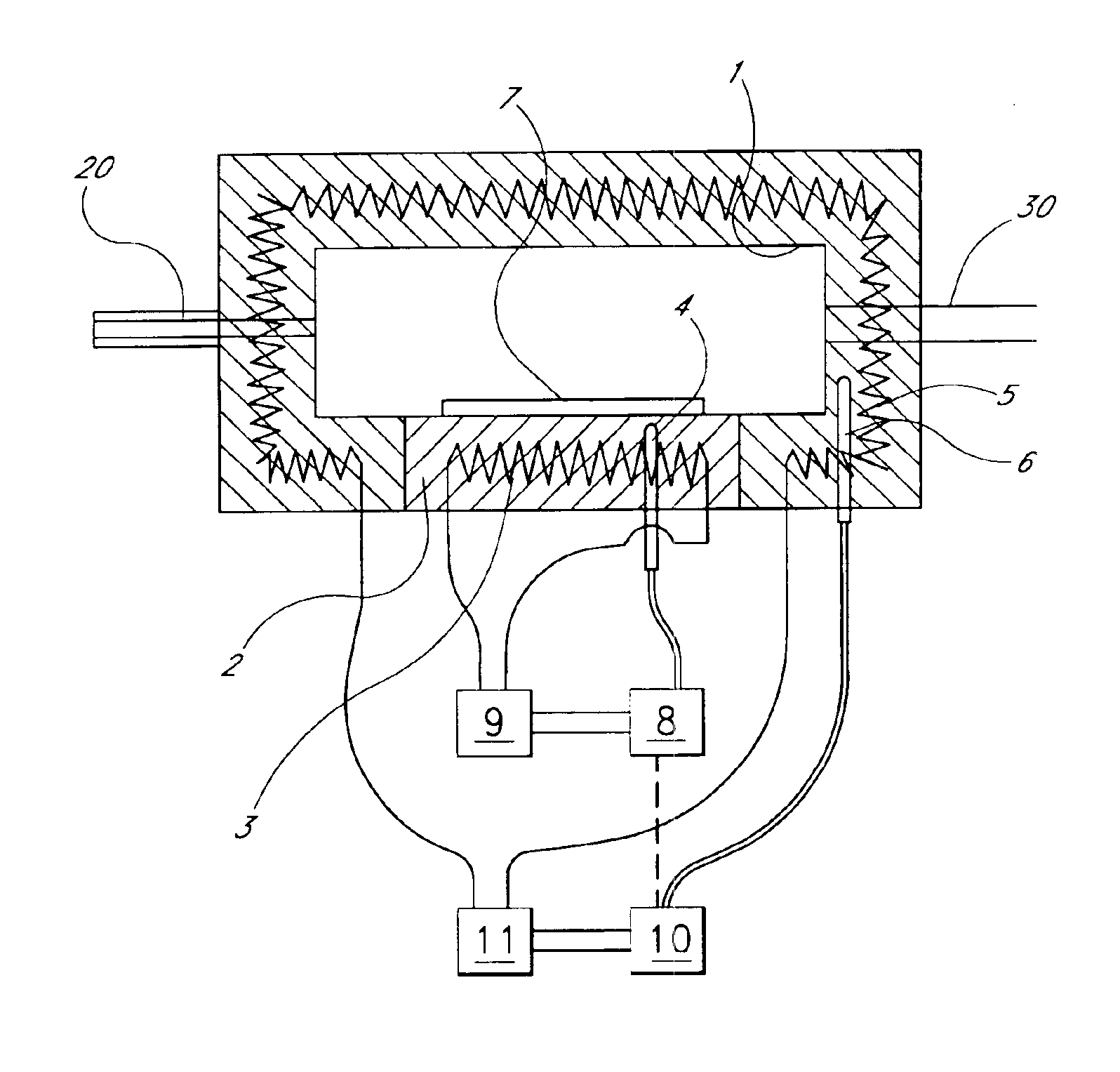
InactiveUS6939579B2Impair reactionReduce the probability of depositionFurnaces without endless corePolycrystalline material growthDisplay devicePhysisorption
The present invention relates to improved methods and apparatus for atomic layer deposition (ALD) of thin films on substrates such as wafers and flat panel displays. The invention provides an ALD reactor comprising a first temperature regulating system to control the temperature of the substrate and a second temperature regulating system to independently control the temperature of the reaction chamber walls. The invention also provides a method for ALD of a film onto a substrate in a reaction chamber, in which the temperature of the substrate is maintained to maximize ALD on the substrate while the temperature of the reaction chamber walls is set to minimize film growth thereon, whether by ALD, condensation, physisorption or thermal decomposition. The temperature of the walls may be maintained at the same temperature as the substrate, or higher or lower than the substrate temperature, depending upon the particular reaction being used.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
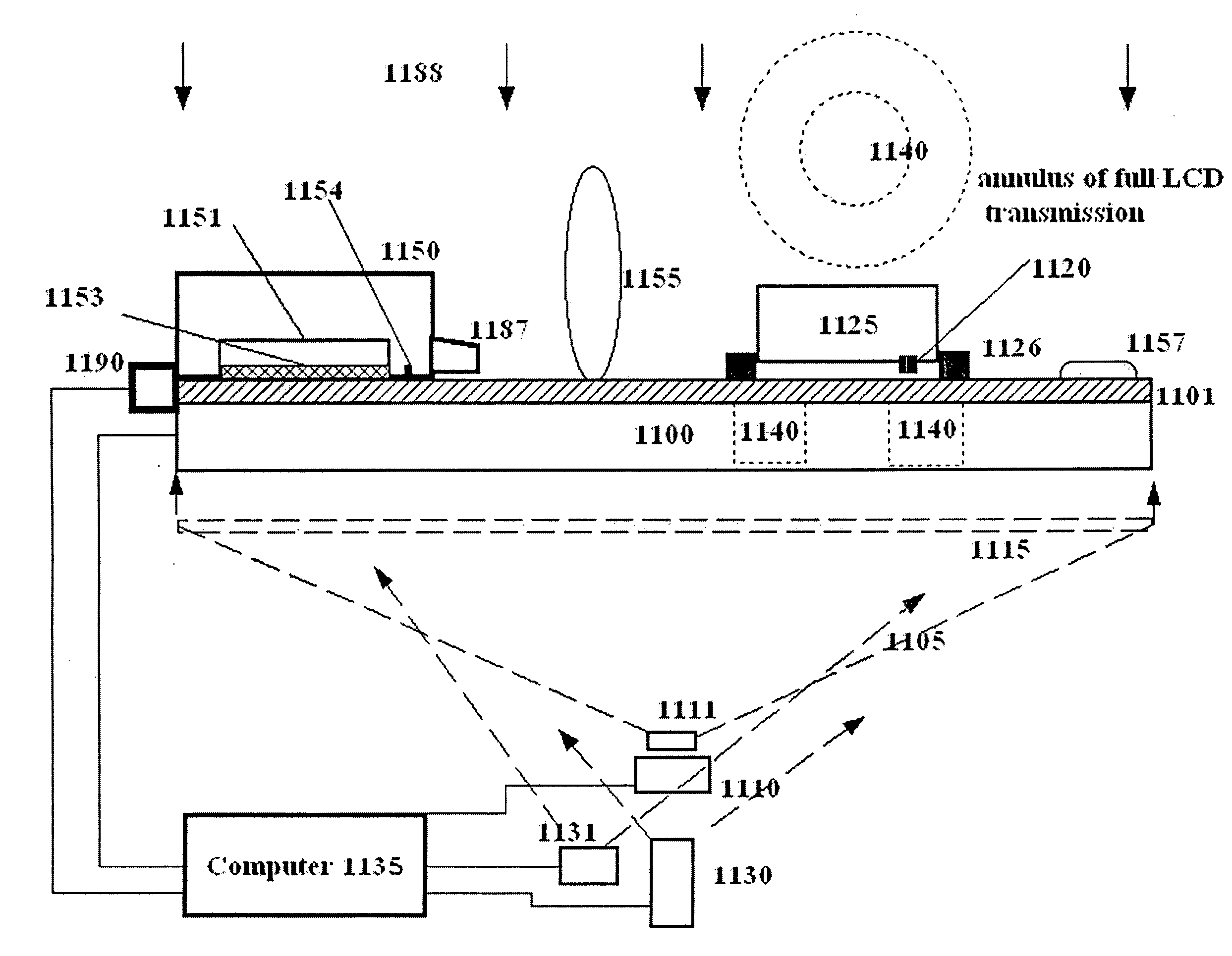
Flat-panel display using tapered waveguide
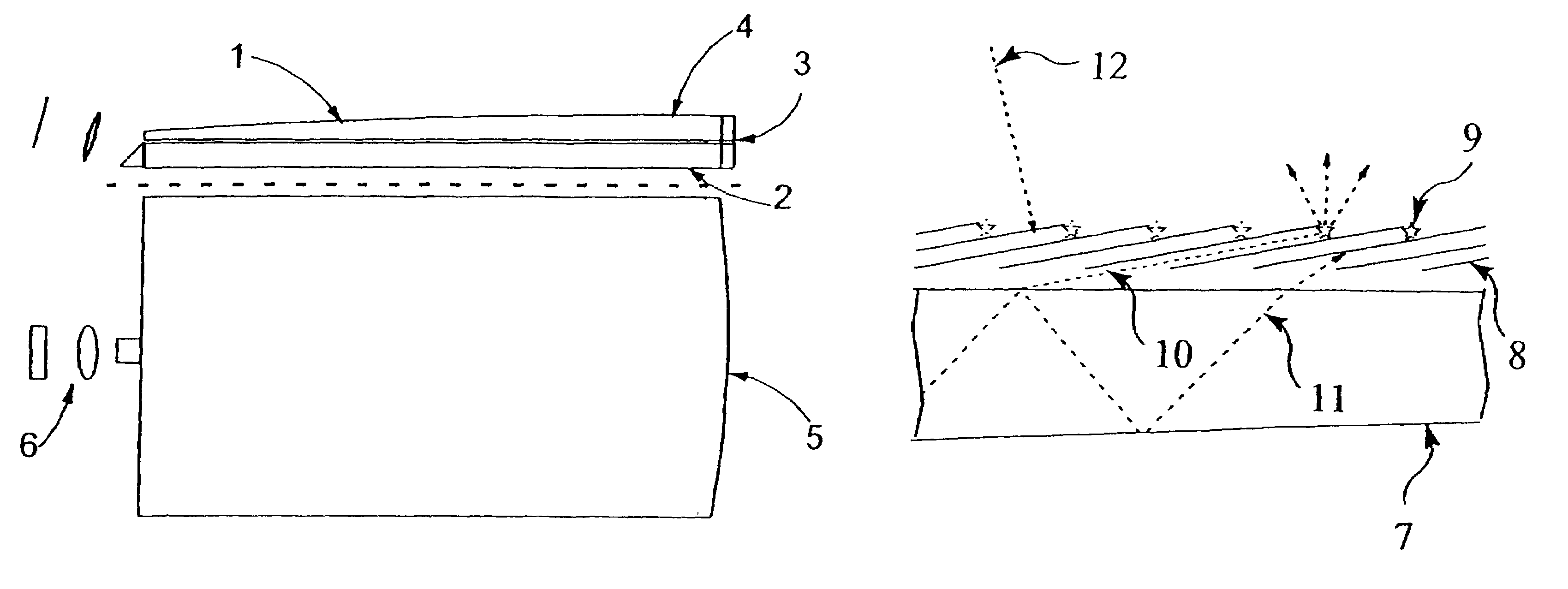
InactiveUS7410286B2Reduce blurIncrease contrastTelevision system detailsMechanical apparatusFlat panel displayWaveguide
A video display for two or three dimensions has a flat liquid-crystal screen which ejects light from the plane at a selectable line. One or, in the case of a 3-D display, several video projectors project a linear image into the plane from an edge. A complete image is written on the screen by addressing the line with appropriate images as it is scanned down the screen. To screen a three-dimensional image, the video projectors, each projecting an image as seen at a slightly different angle, combine to constitute a three-dimensional display which produces a three-dimensional image that is one line high.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
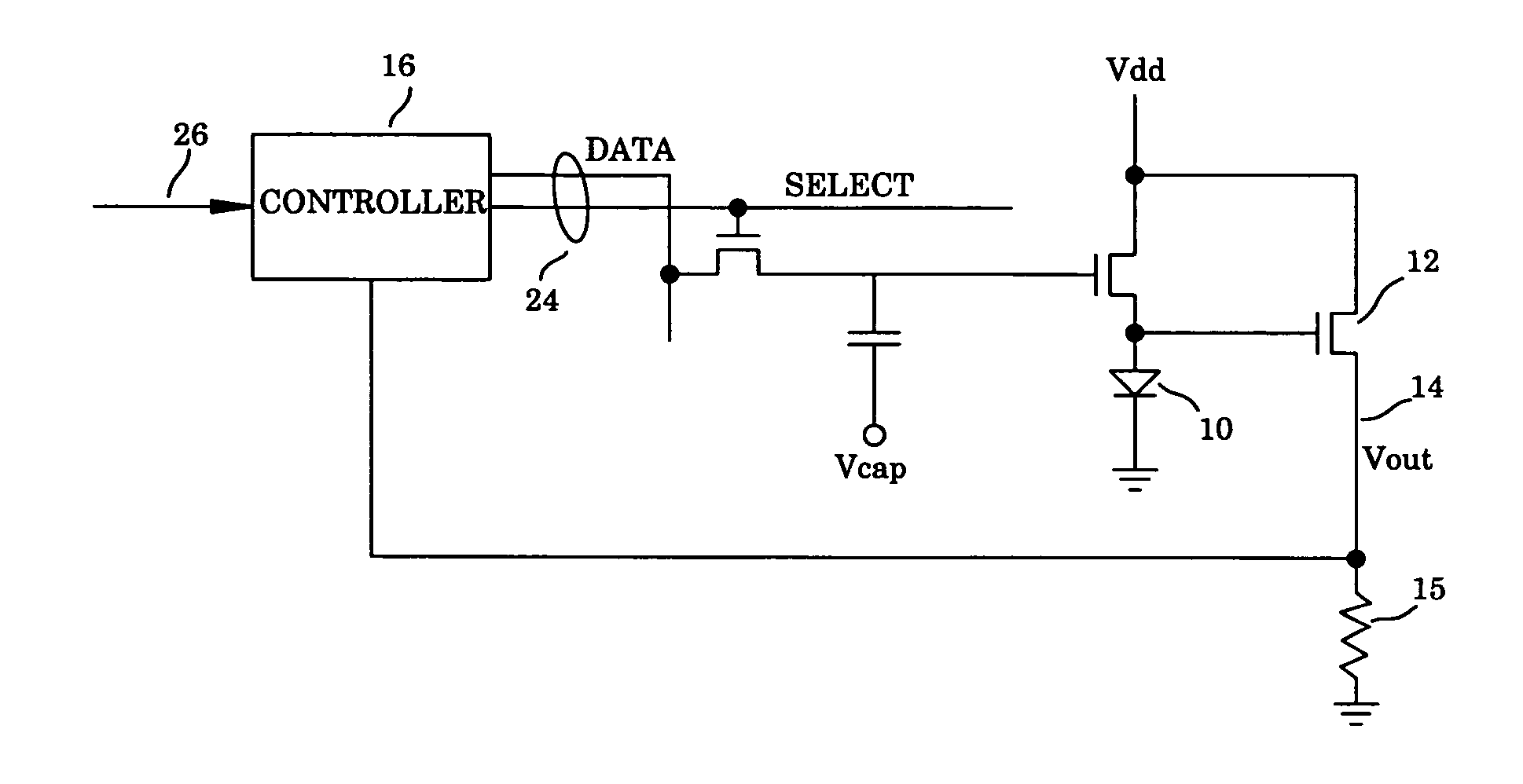
Stabilized active matrix emissive display
InactiveUS20050248515A1Eliminate needElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesActive matrixDisplay device
The embodiments of the present invention provide a flat panel display having a plurality of pixels, each comprising a light-emitting device configured to emit light in accordance with a current flowing through the light-emitting device, a transistor coupled to the light-emitting device and configured to provide the current through the light-emitting device, the current increasing with a ramp voltage applied to a control terminal of the transistor, and a switching device configured to switch off in response to the luminance of the light-emitting device having reached a specified level, thereby disconnecting the ramp voltage from the transistor and locking the brightness at the specified level. The ramp voltage is generated in each pixel instead of in peripheral circuits, thereby reducing the number of conducting lines in the display.
Owner:LEADIS TECH
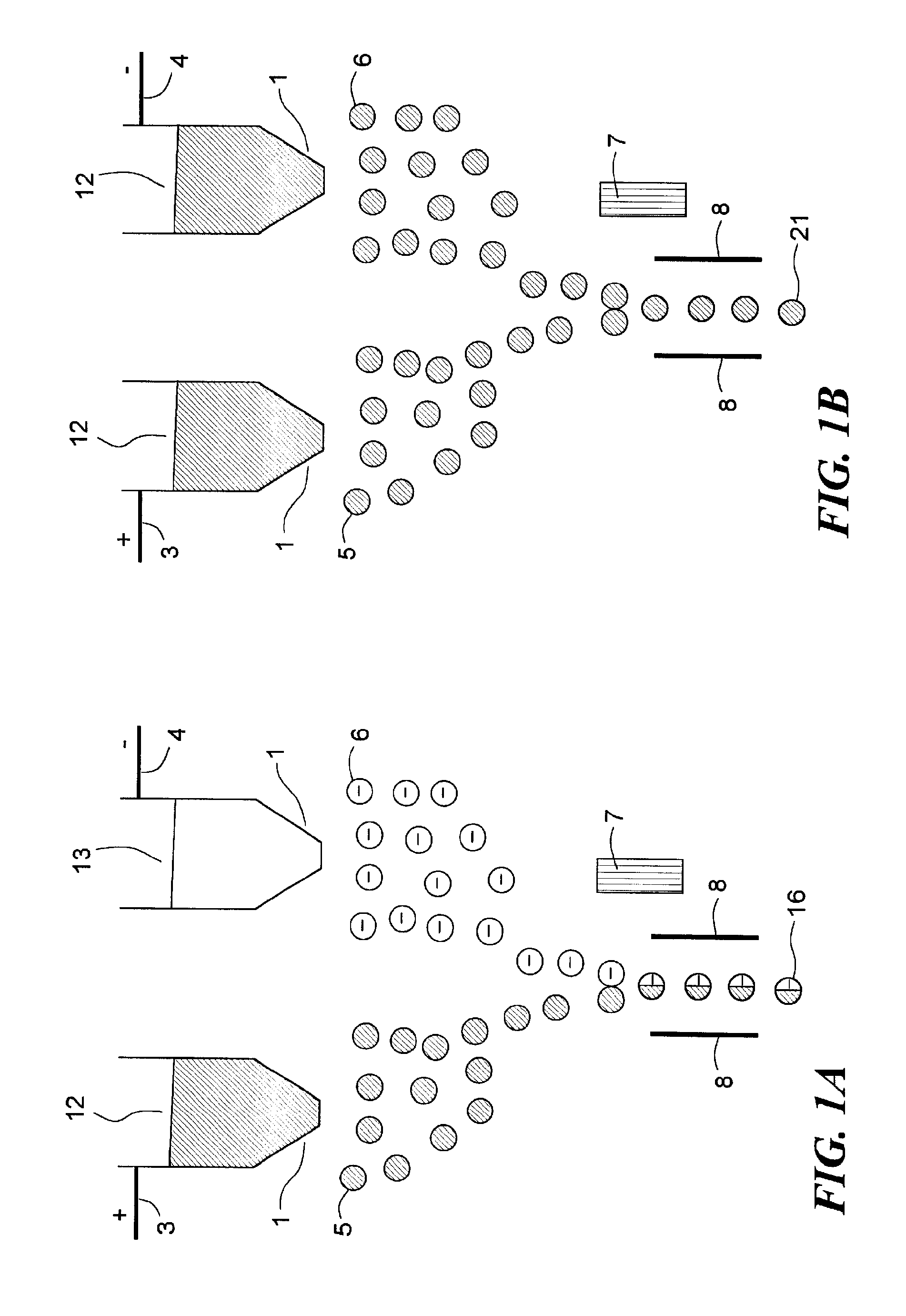
Optical device utilizing optical waveguides and mechanical light-switches
InactiveUS6650822B1High refractive indexReduction factorCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guidePhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
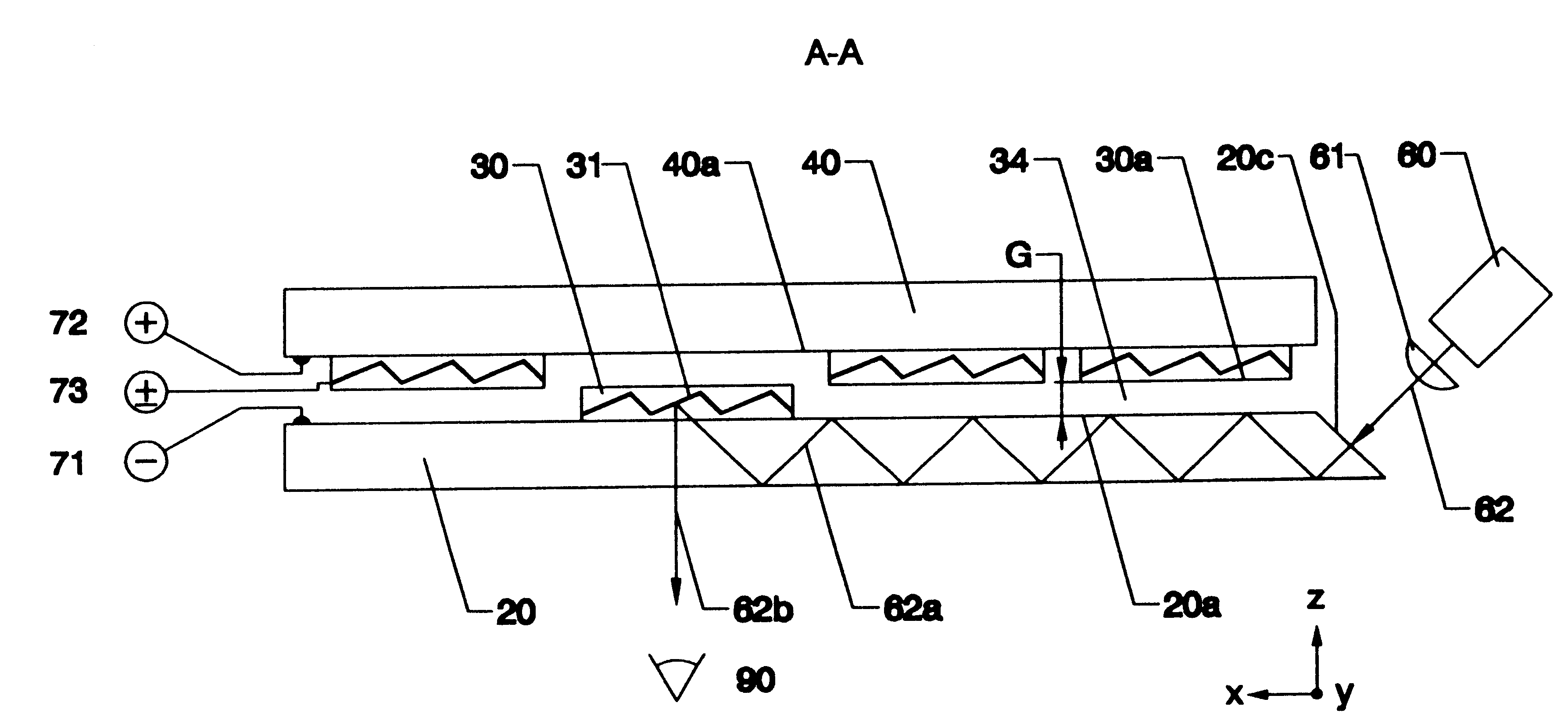
An optical device consists of one or more optical waveguides and mechanical light switches 30. When a light switch 30 is turned on, it extracts light beam 62a from a waveguide core 20 and redirect the light beam 62b into free space, it redirects an incoming light beam 80 from free space and injects the light beam 80a into the waveguide core 20, or it performs both functions at the same time, depending on specific applications. On and off states of a light switch 30 are achieved by pulling the light switch 30 into a close vicinity of the waveguide core 20 and by pushing the light switch 30 away from the waveguide core 20, respectively. An interactive fiat-panel display can be built based on this invention. A plurality of parallel channel waveguides forms a display panel. An array of light beams 62a, injected from an array light source 60, propagates along waveguide cores 20 until reaches a location where a light switch 30 is turned on. At this location, the light switch 30 redirects the light beams towards a viewer. An image is produced when the light switches 30 are turned on sequentially while the light-intensity distribution on the array light source 60 is synchronically updated. The panel display is capable of responding to an input optical signal by detecting an incoming light beam 80 from a light pen 100. An array of photodetectors 81 is used to identify the location of the incoming light beam 80 on the display panel and a computer is used to execute a corresponding action accordingly.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
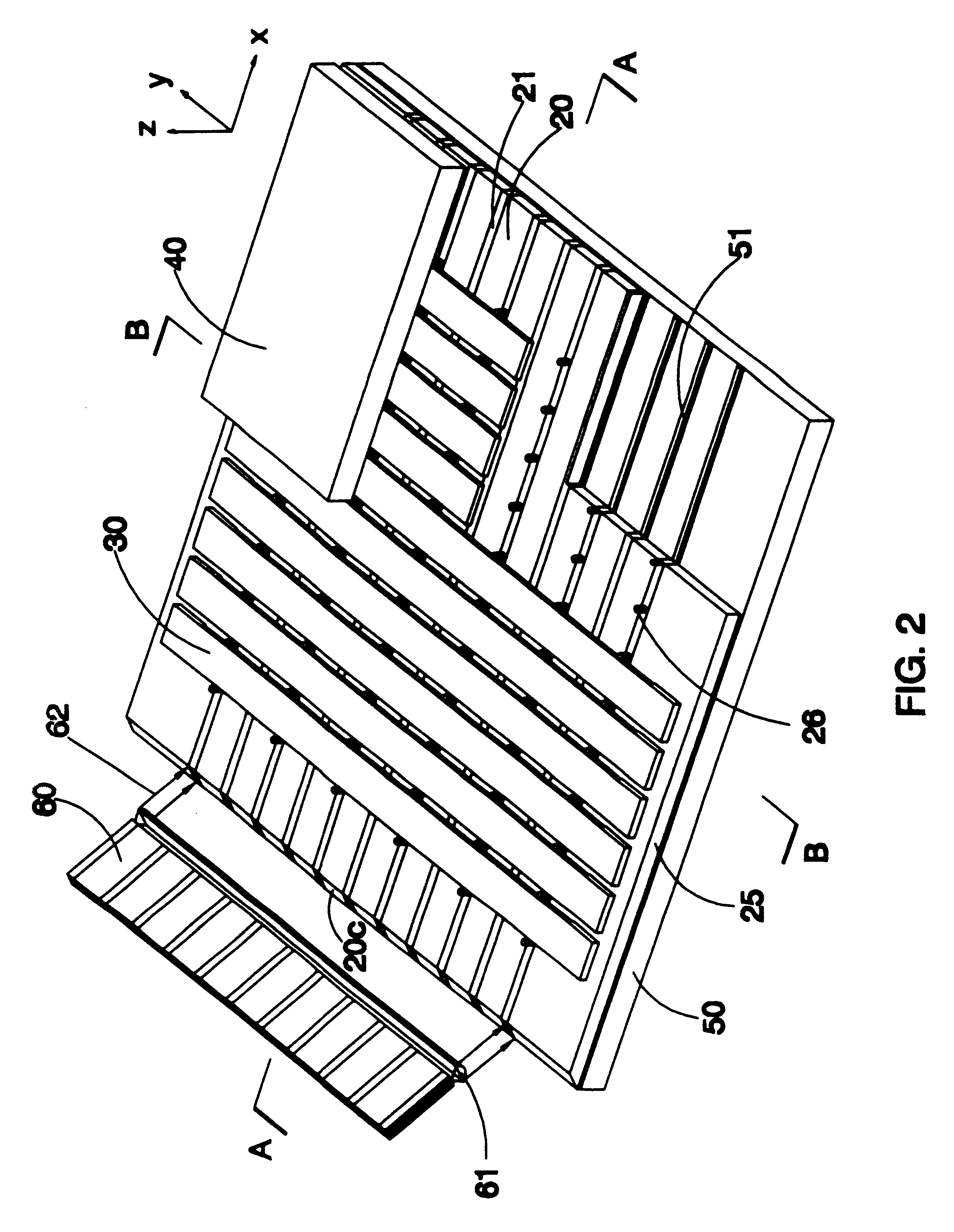
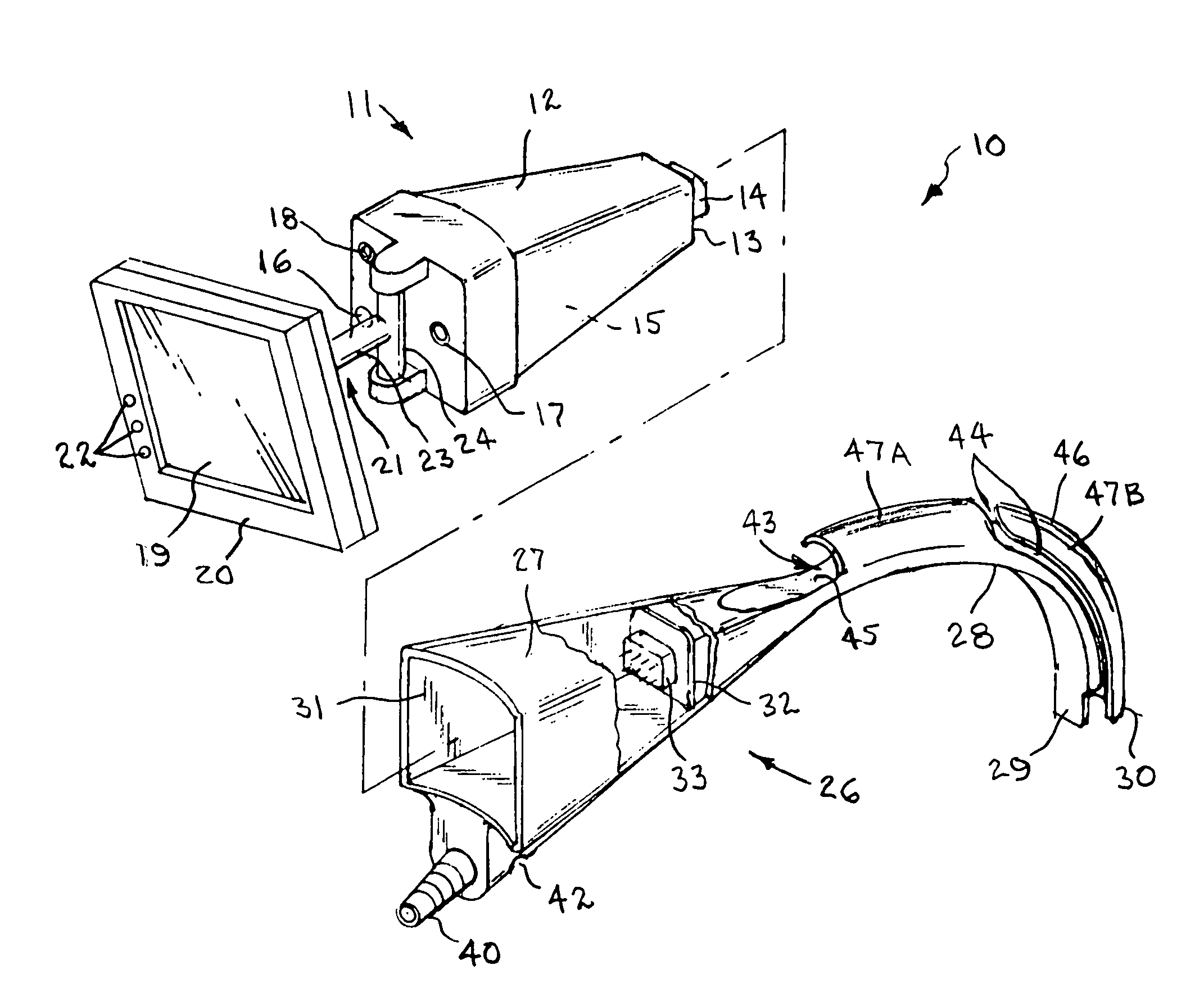
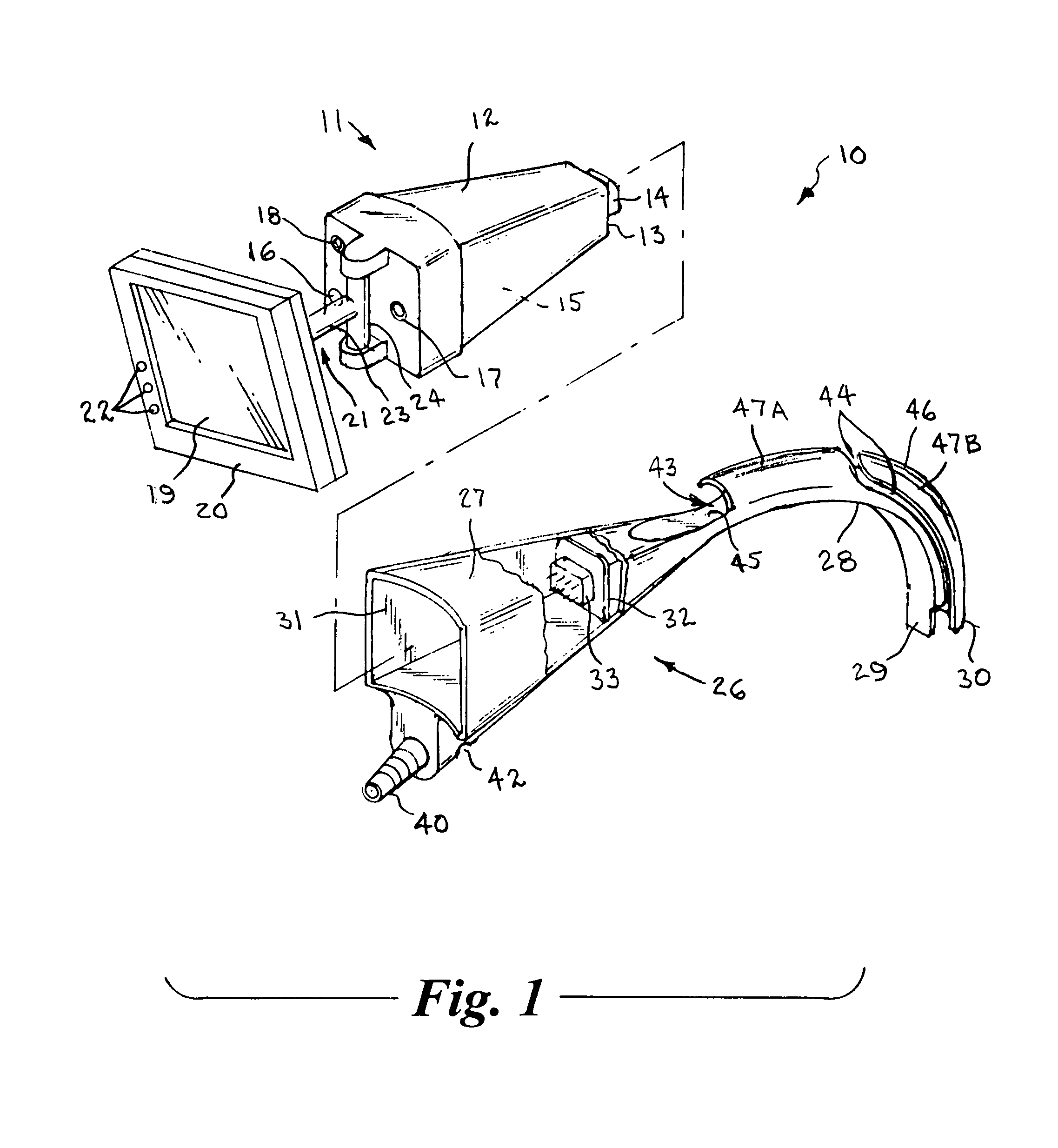
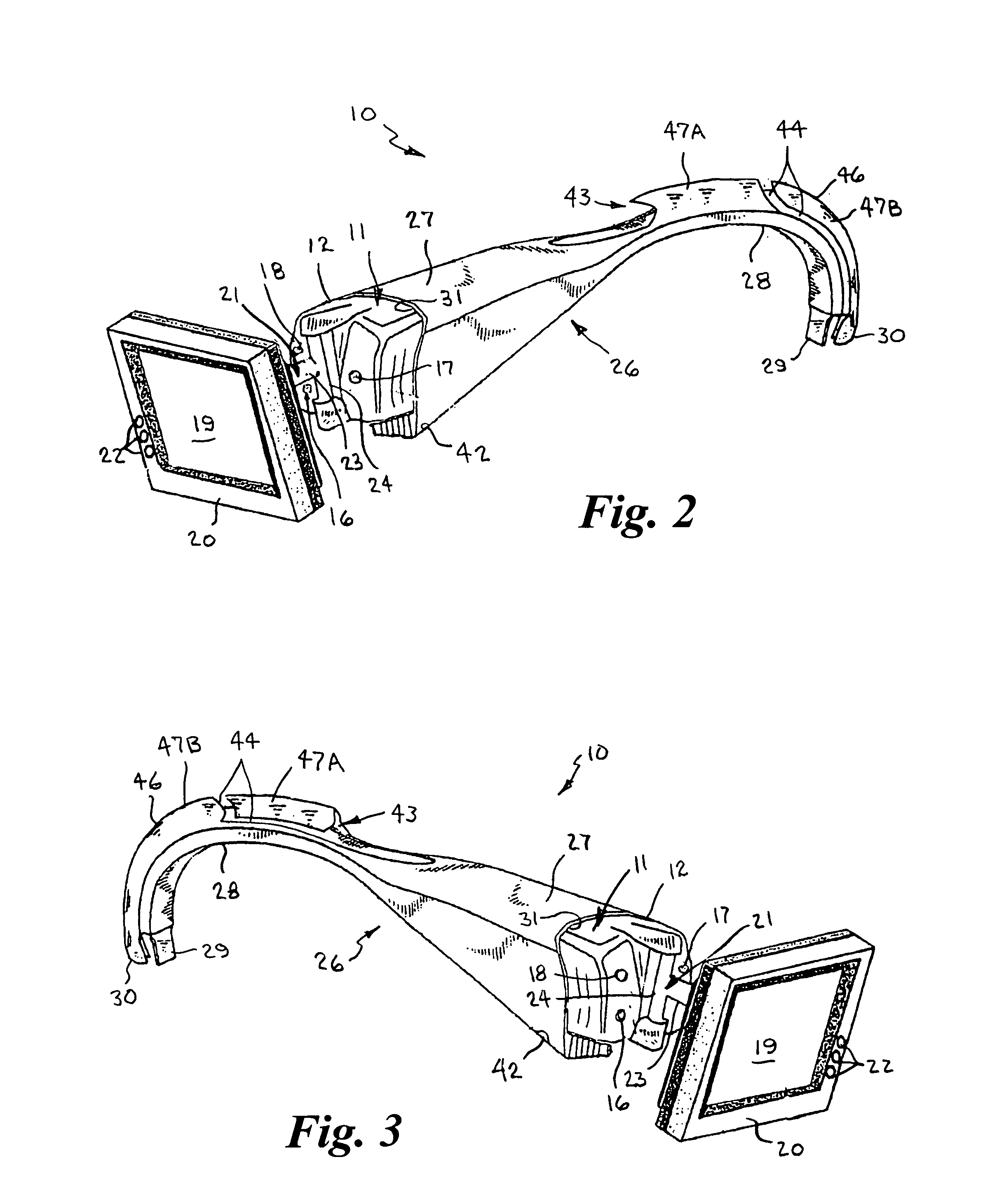
Two-piece video laryngoscope
A two-piece video laryngoscope includes a disposable handle / blade unit having a handgrip portion with a cavity at the proximal end, a curved distal end portion extending from the handgrip portion terminating in a terminal face containing a LED and a lens and digital image sensor connected with a first connector in the cavity, and a tube receptacle channel extending distally along the dorsal surface of and a vacuum / oxygen passageway extending through the curved distal end portion; and a power / video module releasably engaged in the cavity having a flat panel display pivotally mounted at the proximal end thereof and containing a rechargeable battery and electrical and video circuitry connected with a second connector. An endotracheal tube is received and releasably retained in the tube receptacle channel in a preloaded condition. When assembled, the connectors are engaged to complete the electrical and video circuits and allow viewing of insertion and intubation.
Owner:CUBB ANTHONY
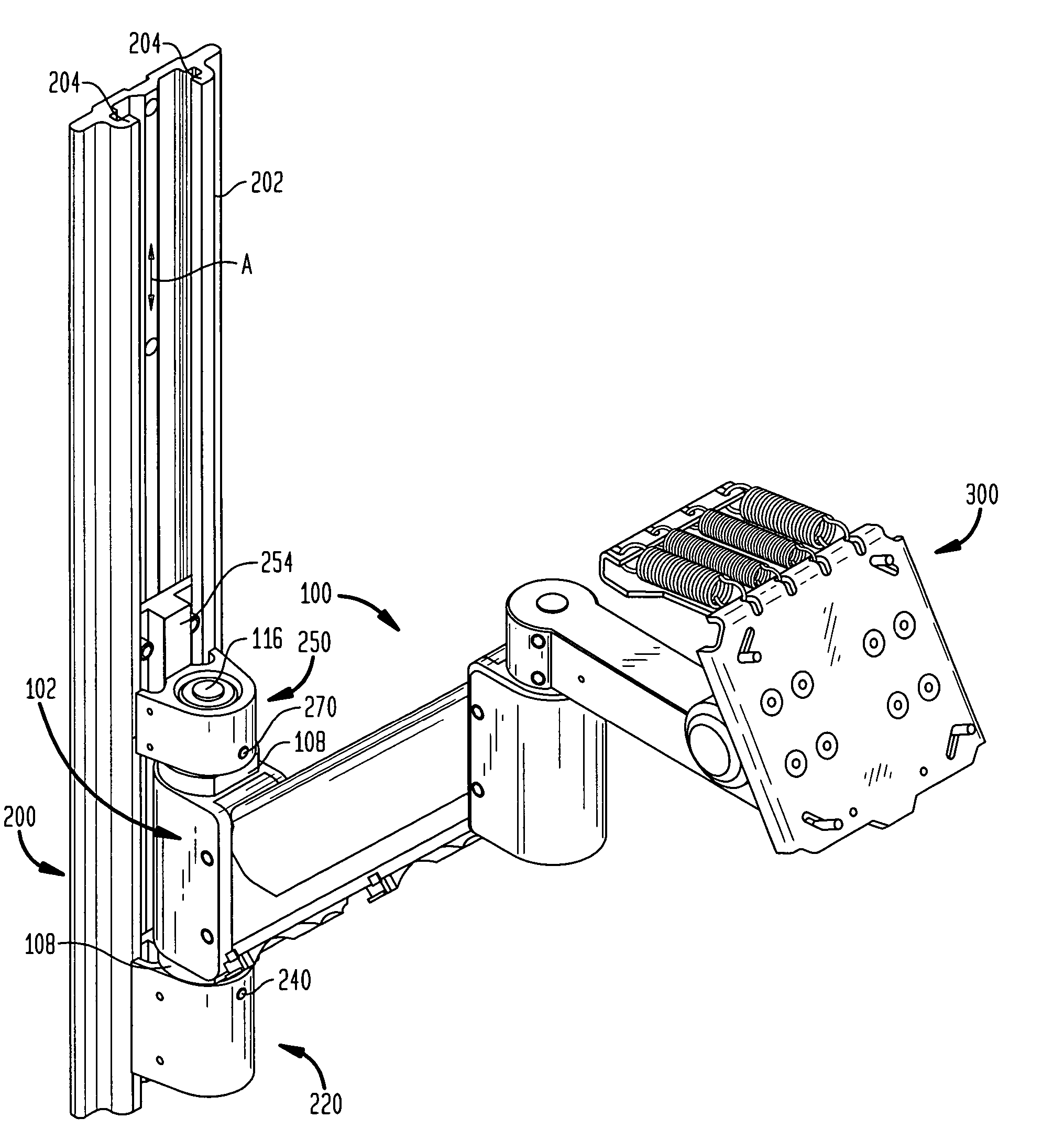
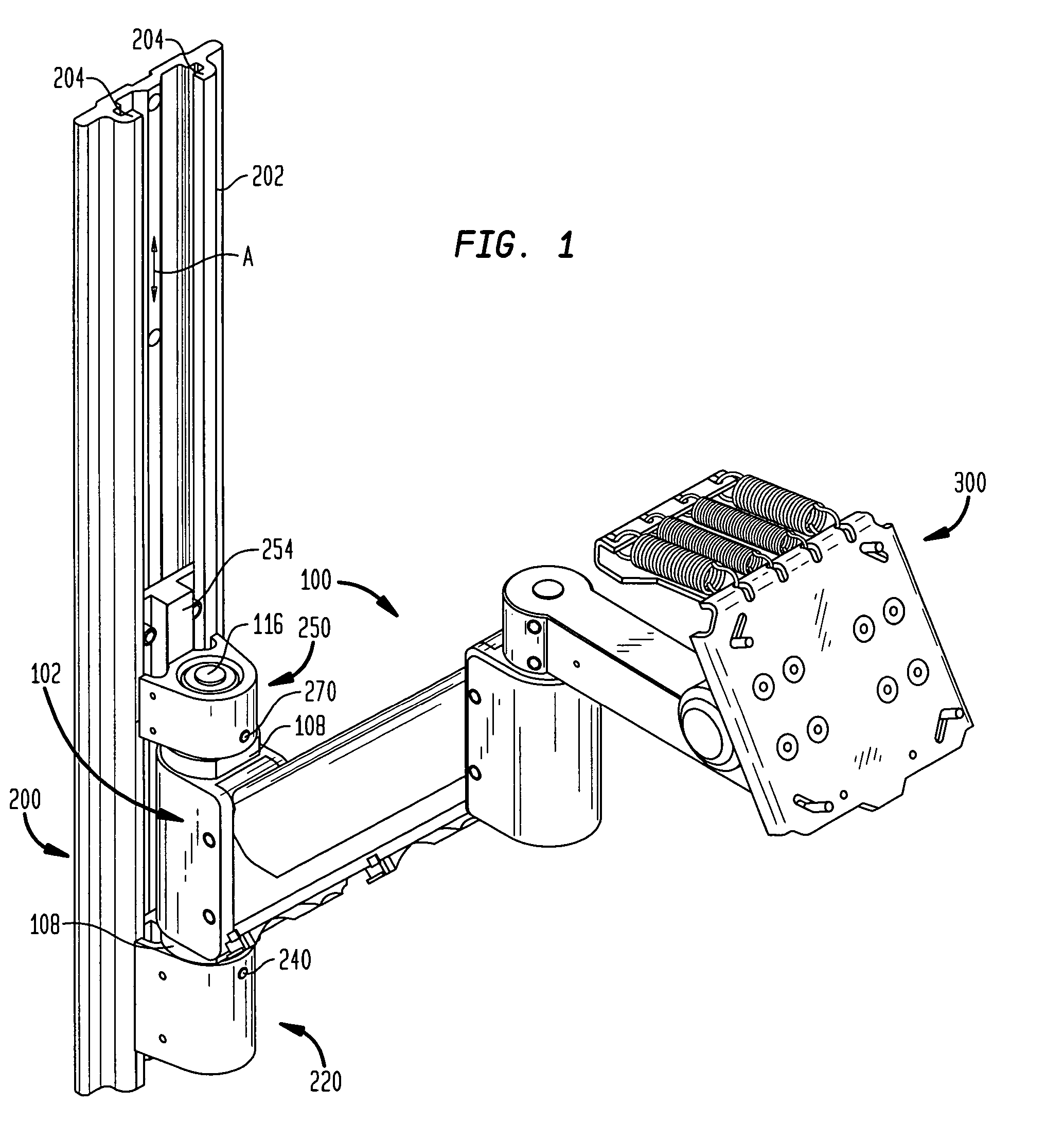
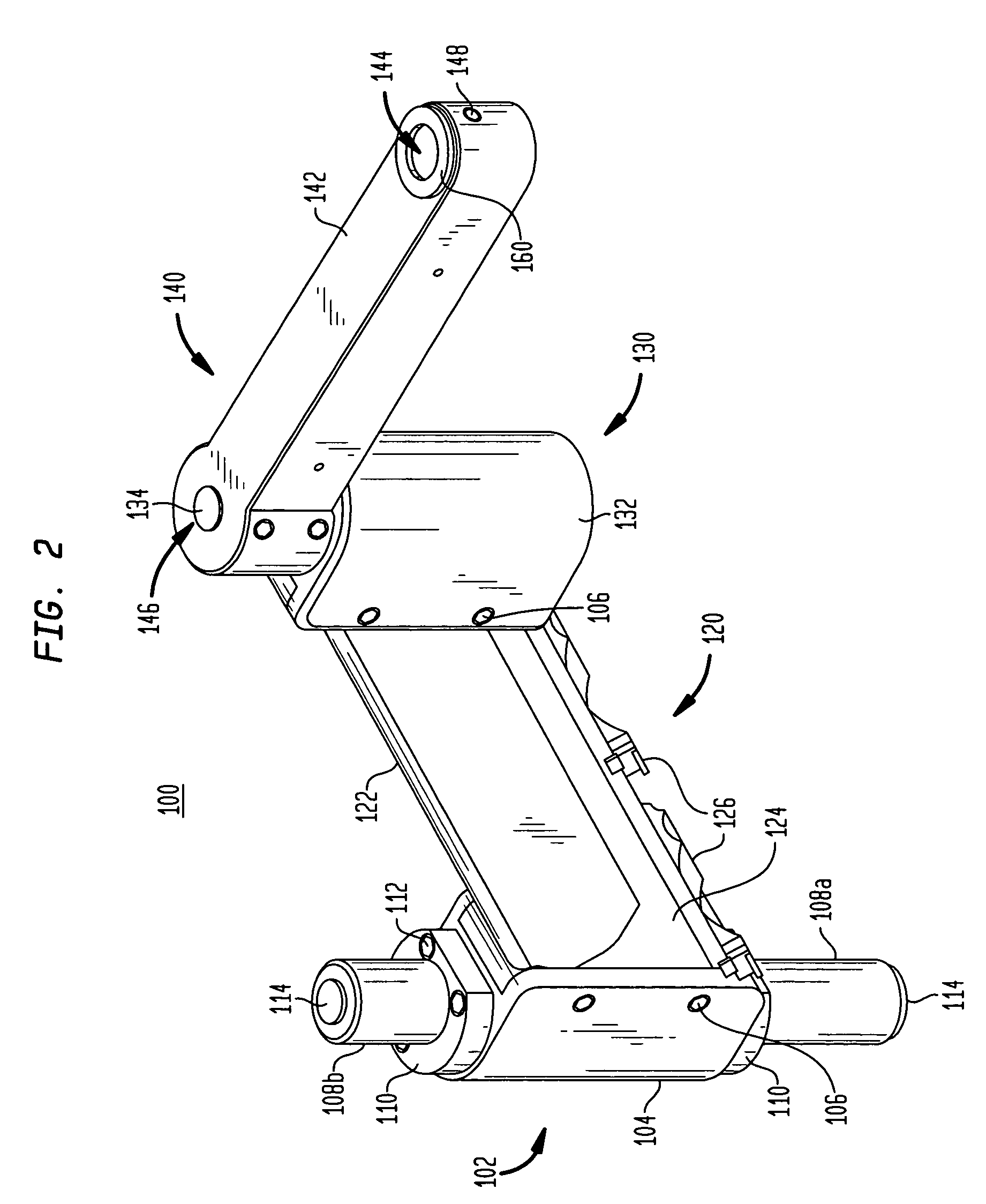
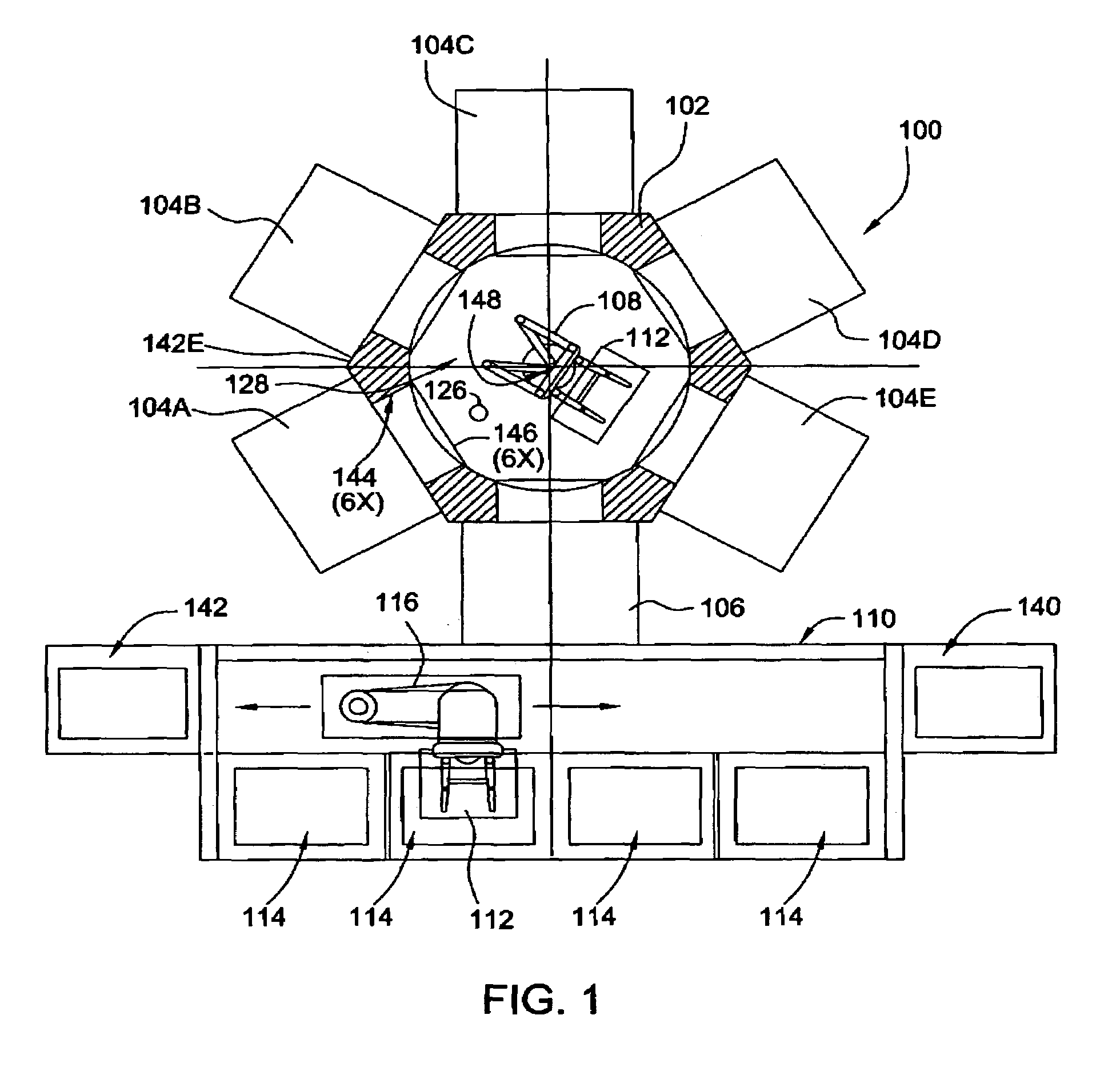
Tilter apparatus for electronic device having bias assembly
A tilter assembly is provided for positioning an electronic device such as a flat panel display. The tilter assembly includes a tilter shaft holder having an opening aligned along an axis and a shaft received within the opening. The shaft is rotatable about the axis, and may be coupled to a support. The tilter shaft holder is coupled to the electronic device. The tilter assembly also includes a torsion spring device in operative association with the shaft to provide a bias or counterbalance to the electronic device, thereby preventing undesired rotation about the axis.
Owner:HUMAN ACTIVE TECH LLC
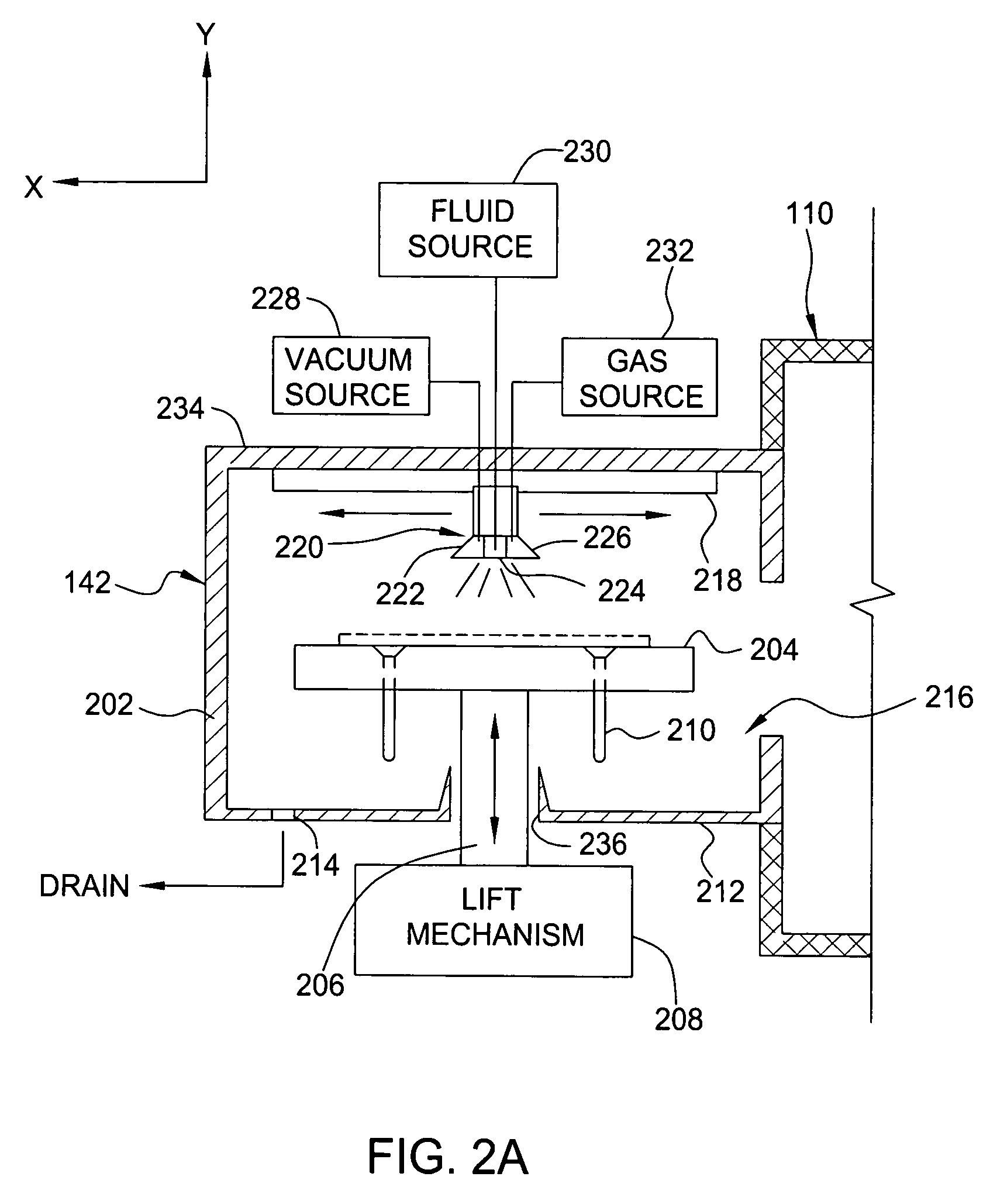
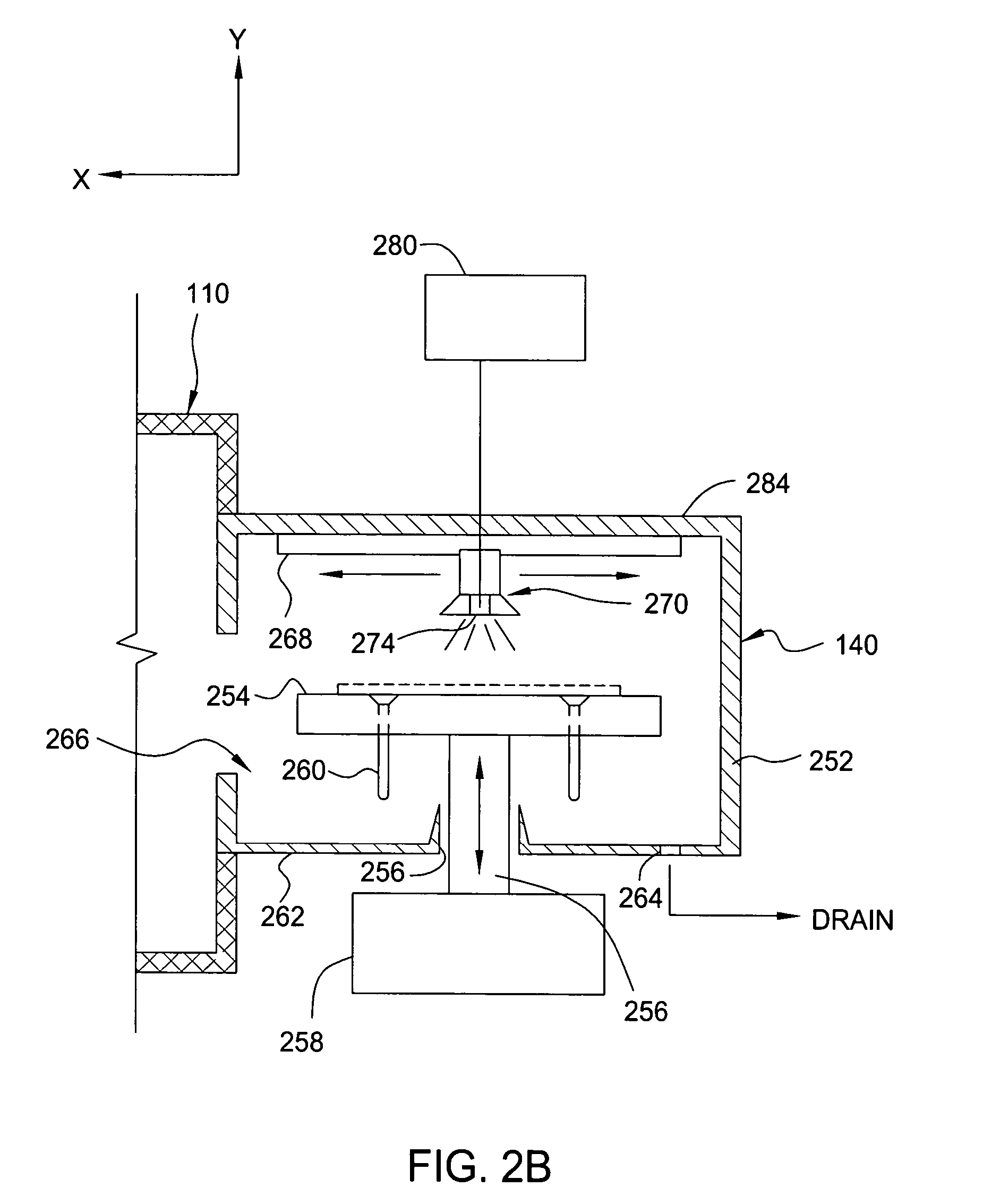
Method and apparatus for in-situ film stack processing
InactiveUS7358192B2Electric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsDisplay deviceFlat panel display
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com