Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
10040 results about "Sputtering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, sputtering is a phenomenon in which microscopic particles of a solid material are ejected from its surface, after the material is itself bombarded by energetic particles of a plasma or gas. It occurs naturally in outer space, and can be an unwelcome source of wear in precision components. However, the fact that it can be made to act on extremely fine layers of material is exploited in science and industry—there, it is used to perform precise etching, carry out analytical techniques, and deposit thin film layers in the manufacture of optical coatings, semiconductor devices and nanotechnology products.
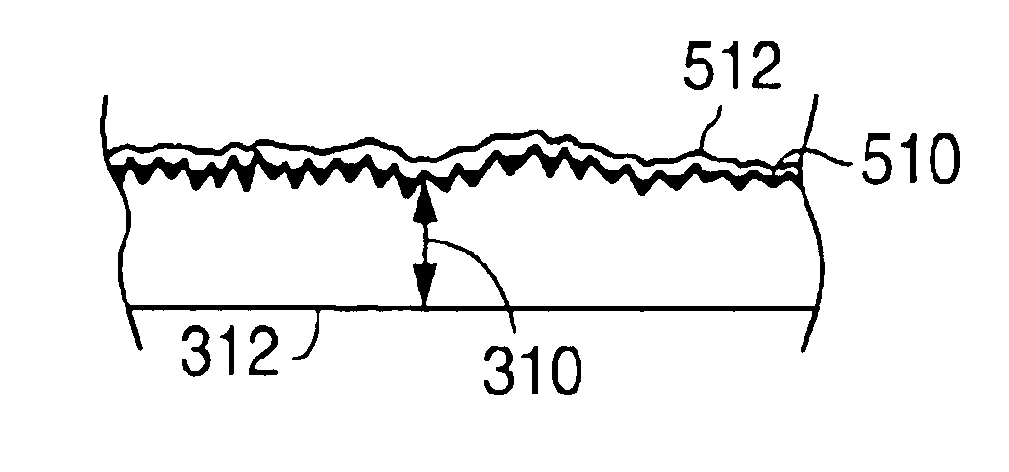
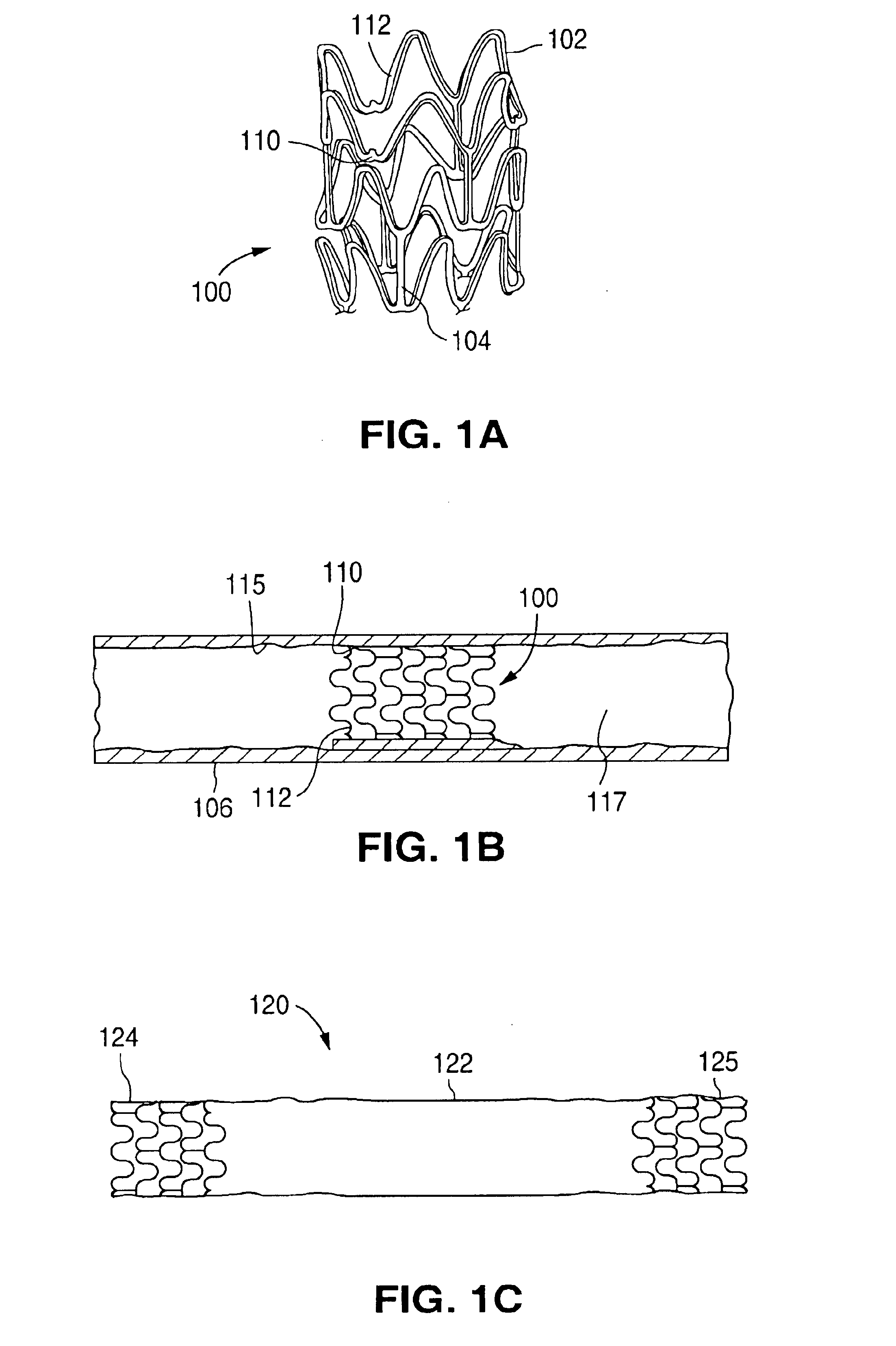
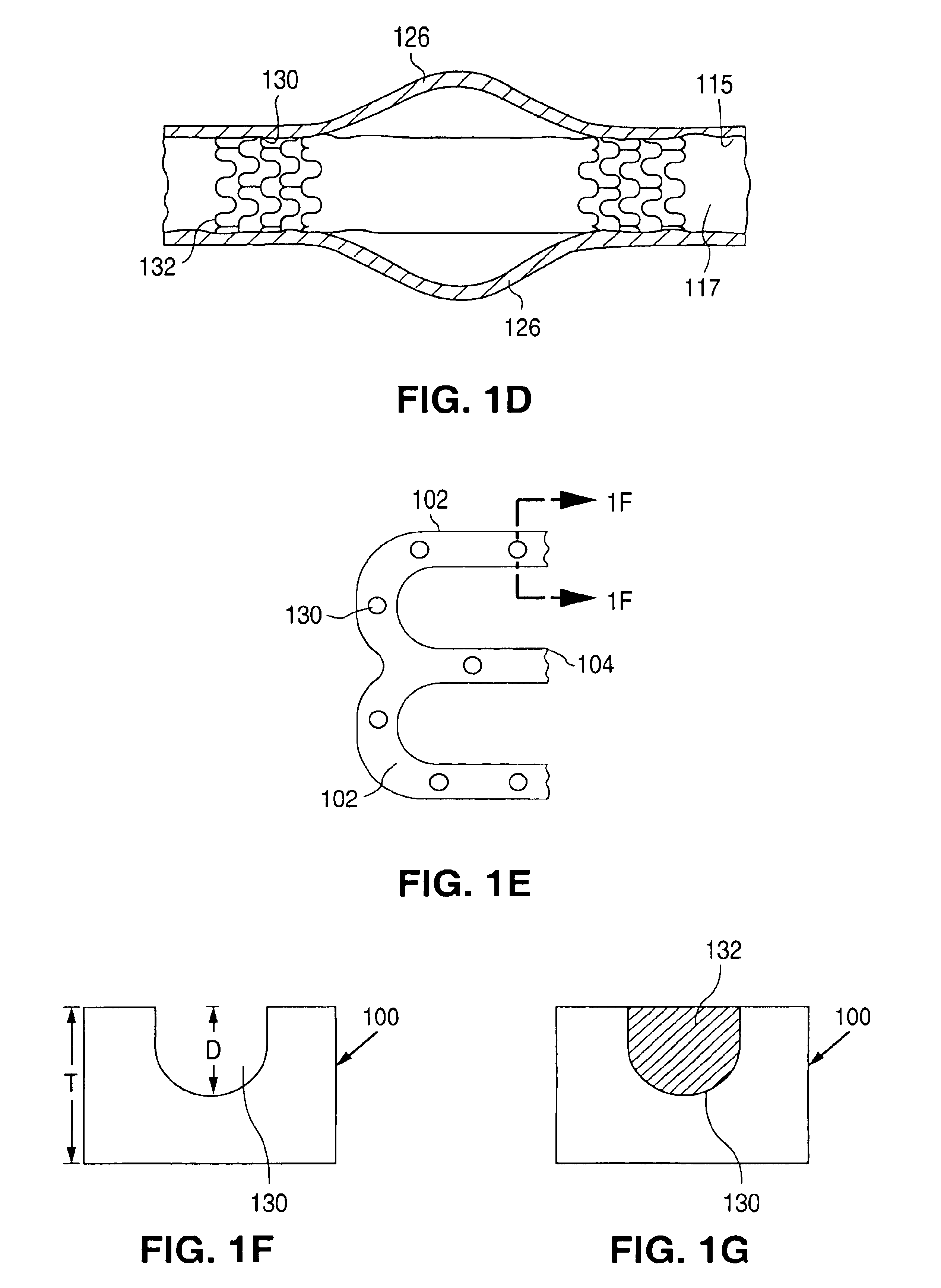
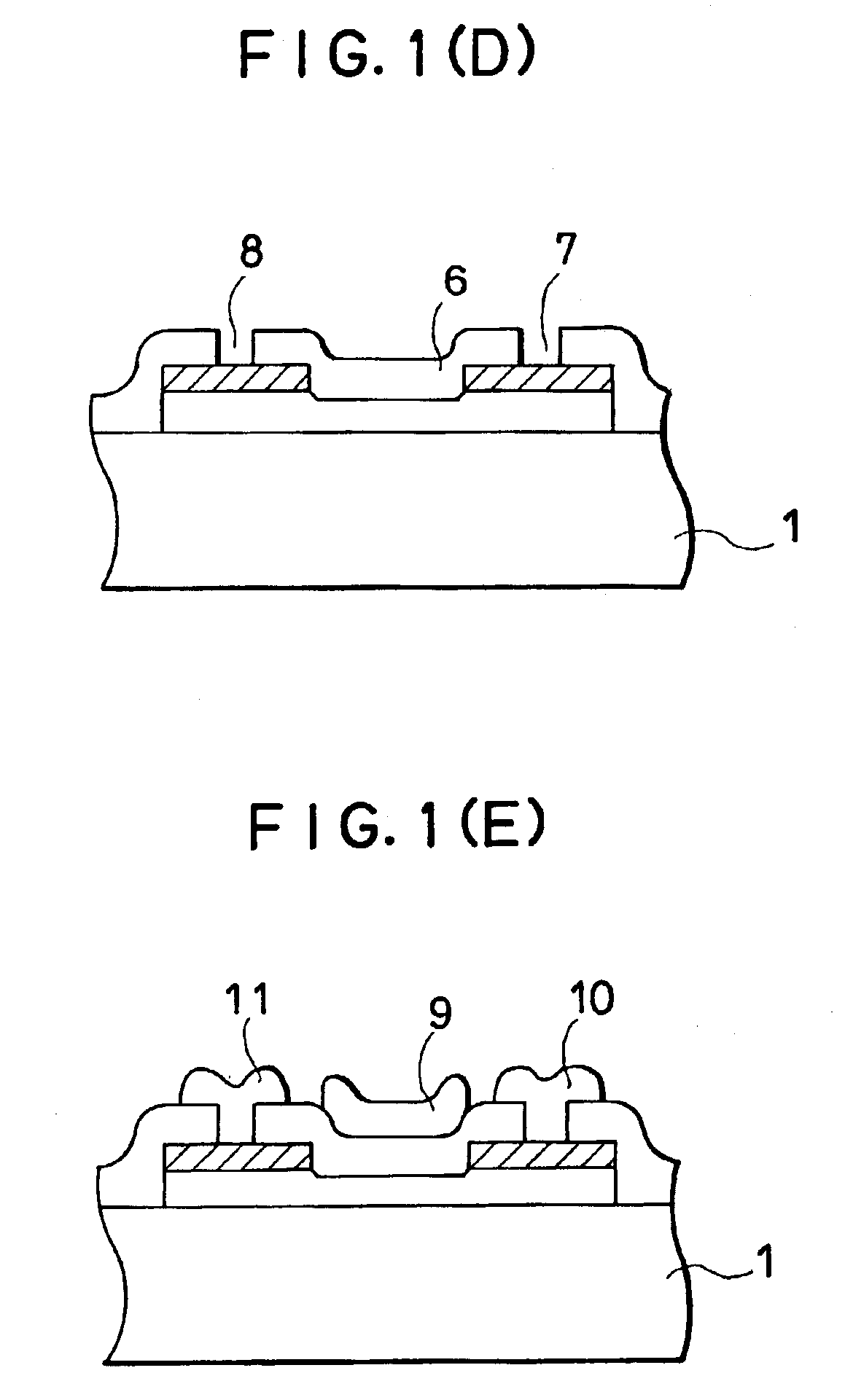
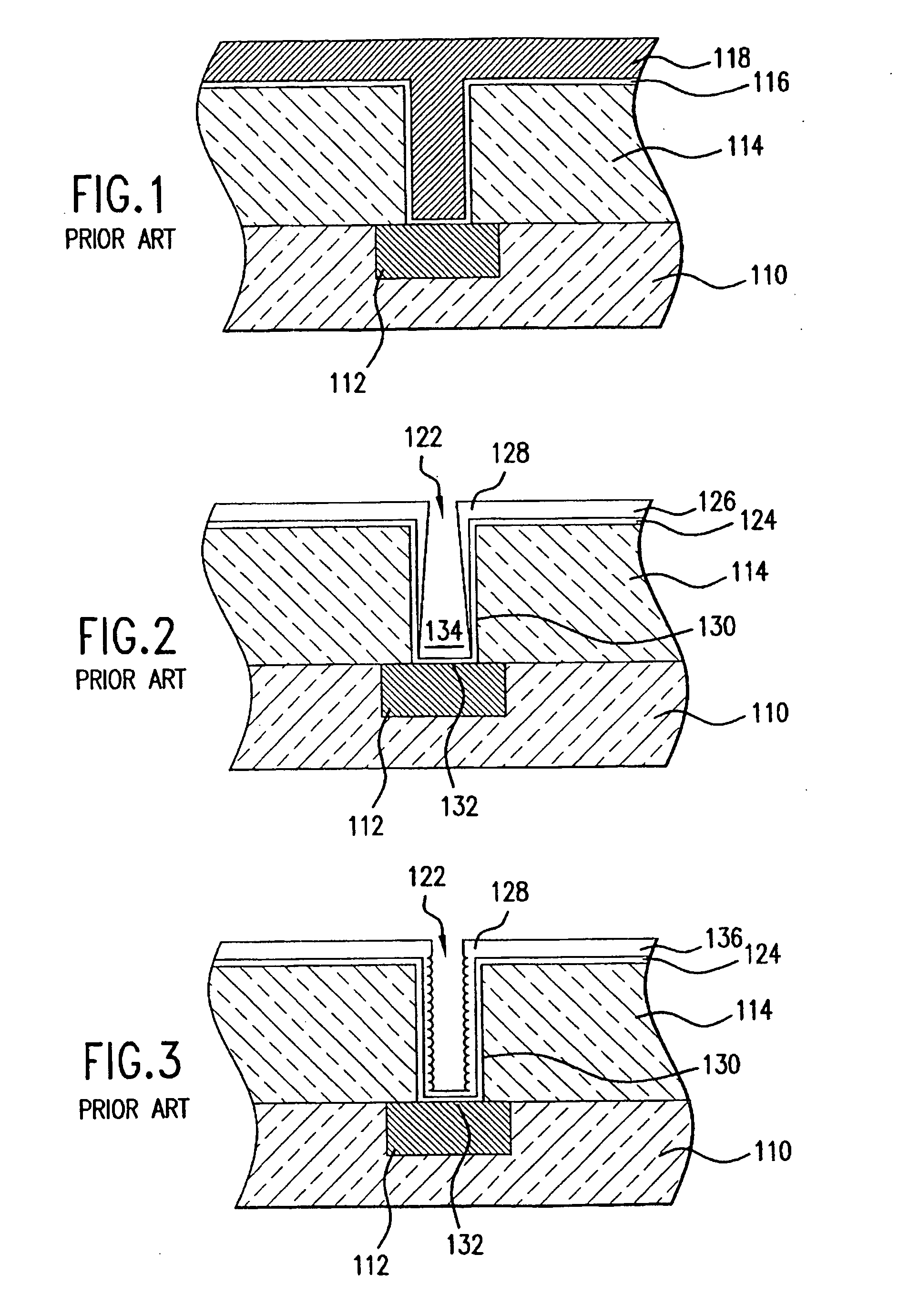
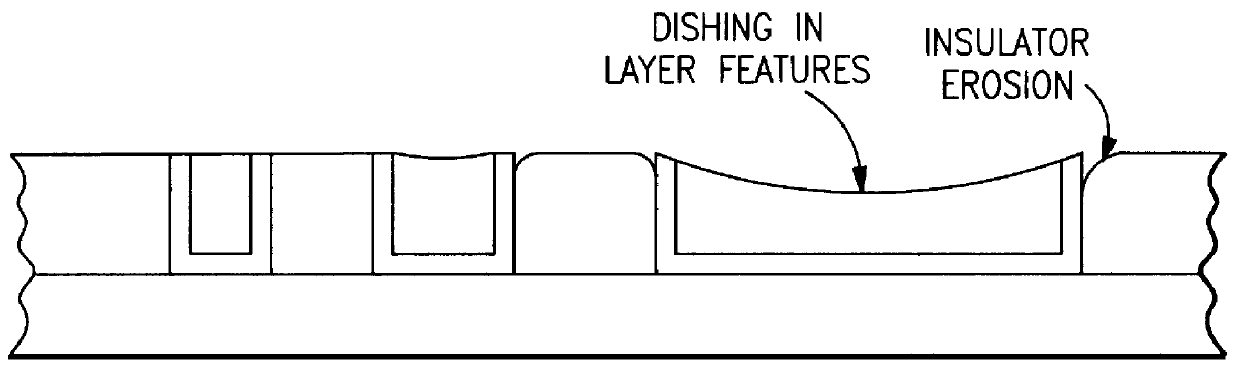
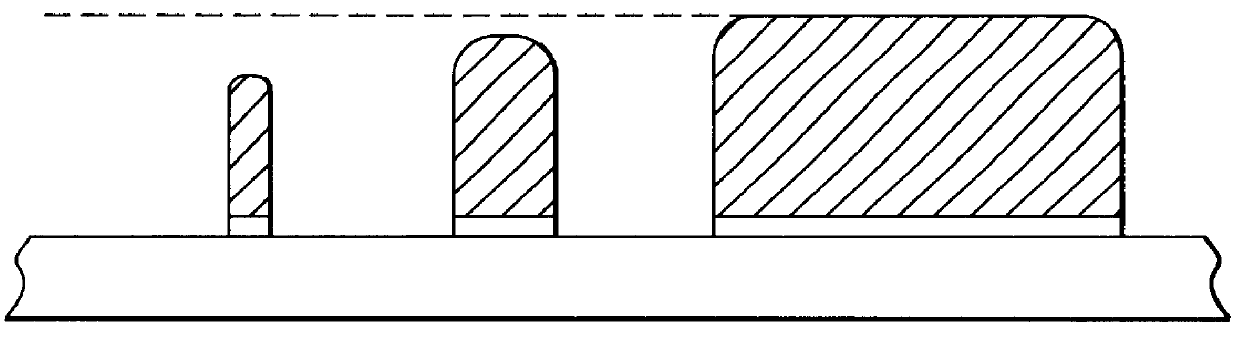
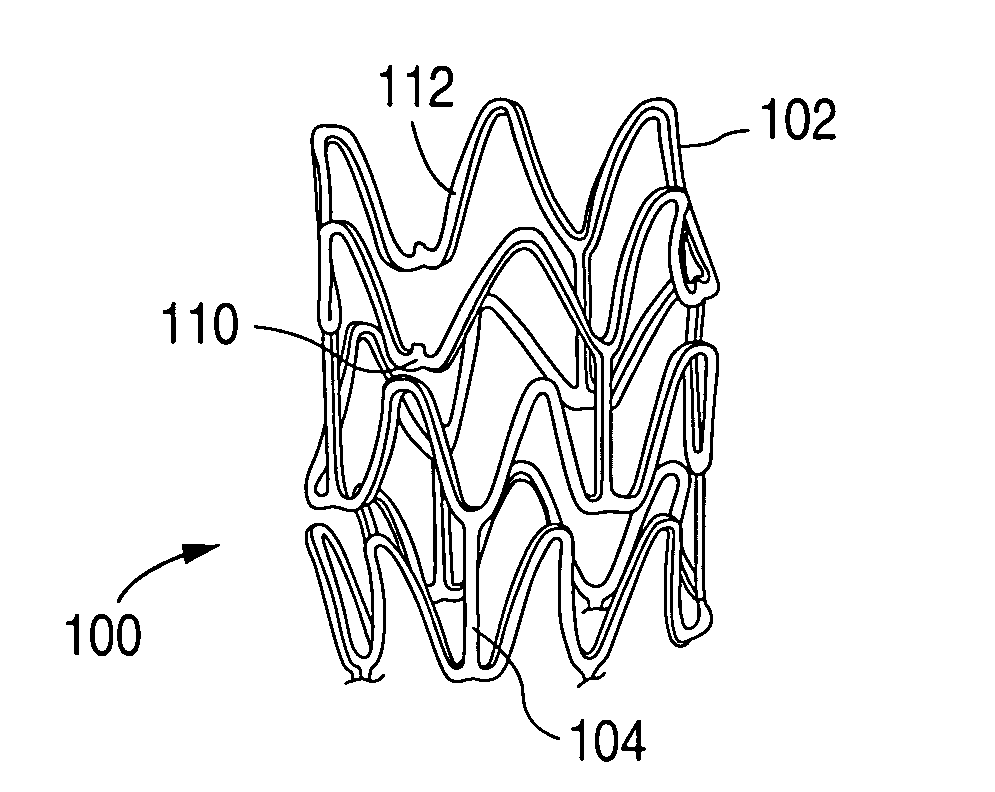
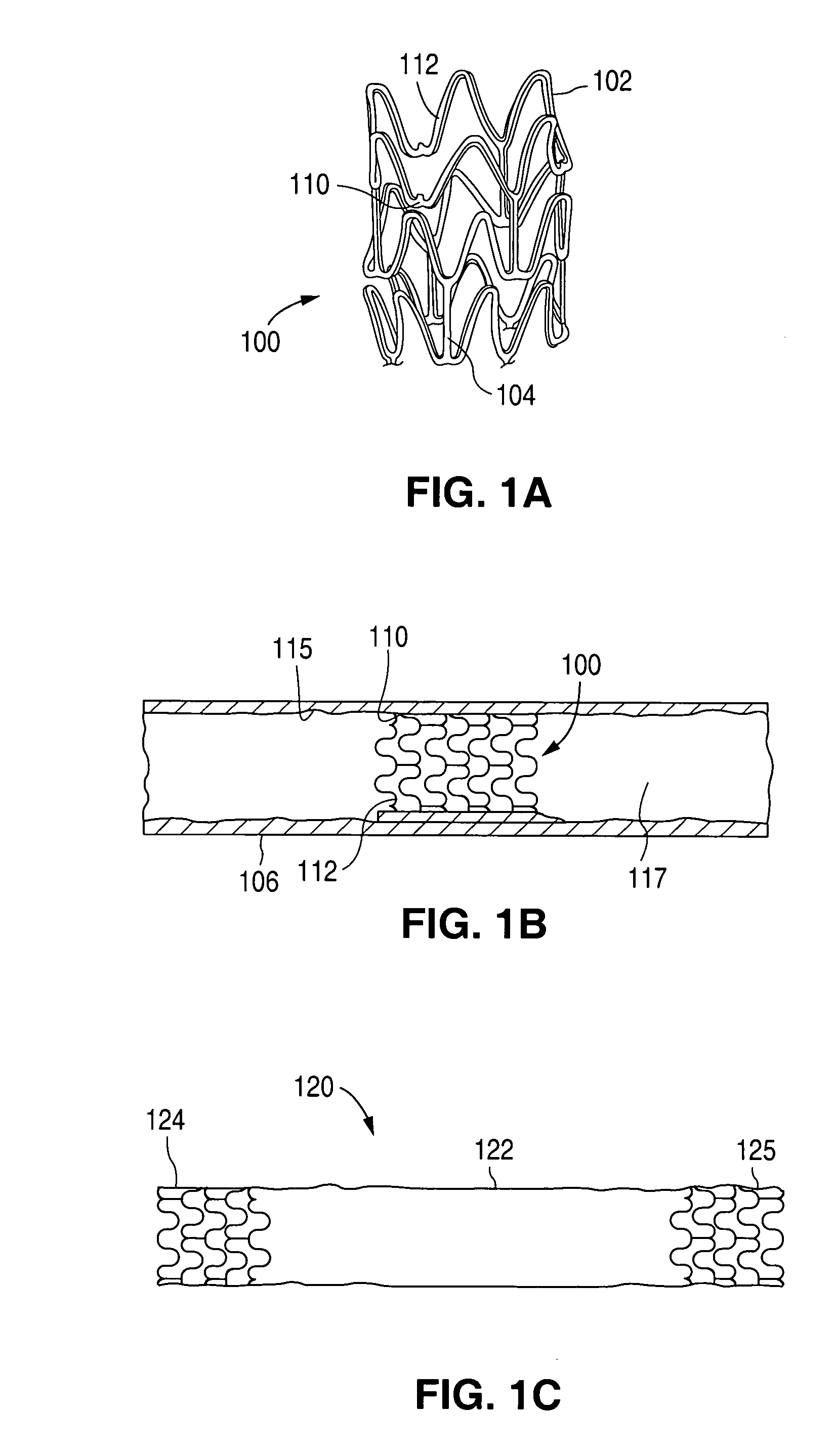
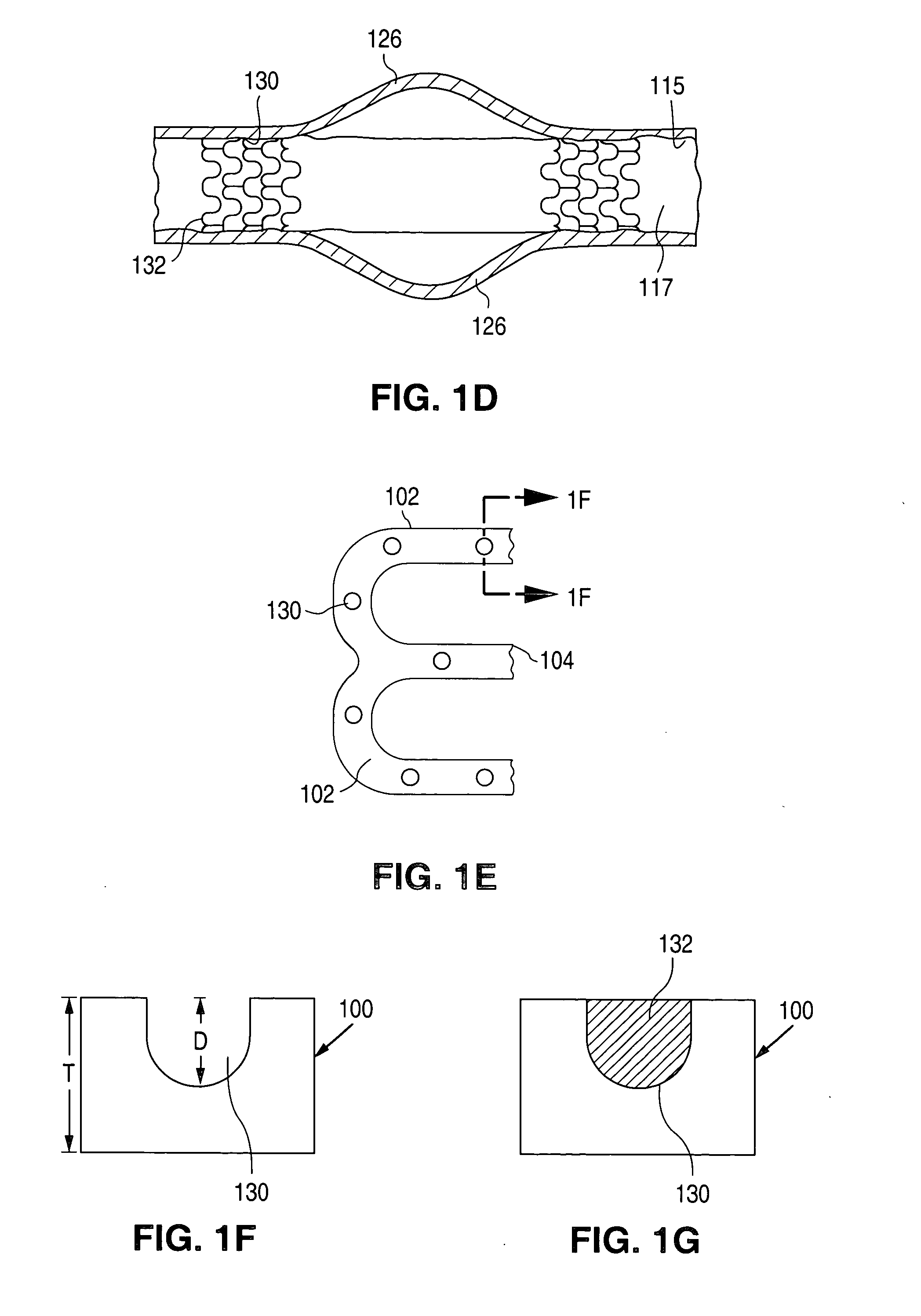
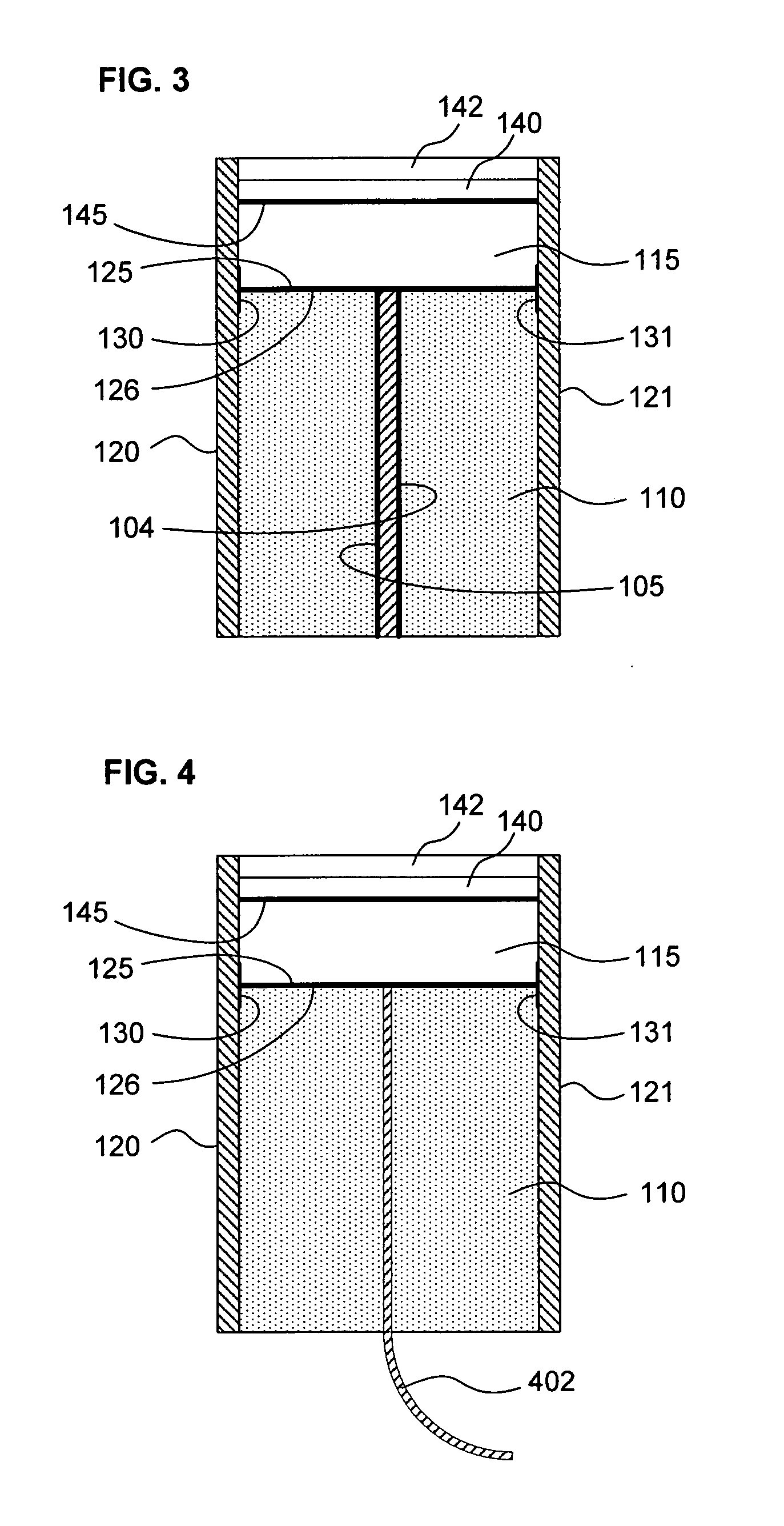
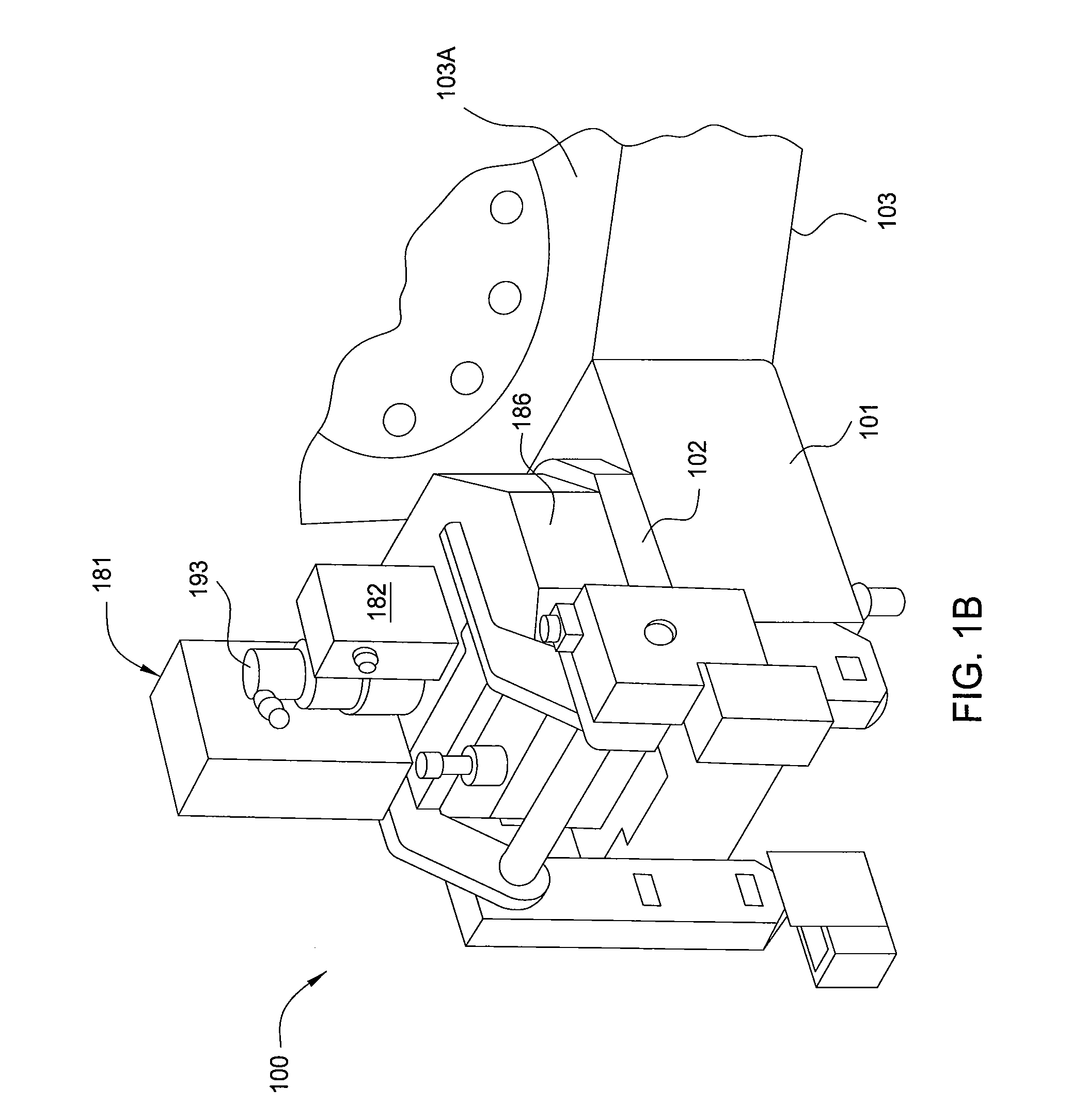
Surface features of an implantable medical device
An implantable medical device, such as a stent or graft, having asperities on a designated region of its outer surface is disclosed. The asperities can serve to improve retention of one or more layers of a coating on the device and to increase the amount of coating that can be carried by the device. The asperities can be formed by using a stream of pressurized grit to roughen the surface. The asperities can also be formed by removing material from the outer surface, for example, by chemical etching with or without a patterned mask. Alternatively, the asperities can be formed by adding material to the outer surface, for example, by welding powder particles to the outer surface or sputtering.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
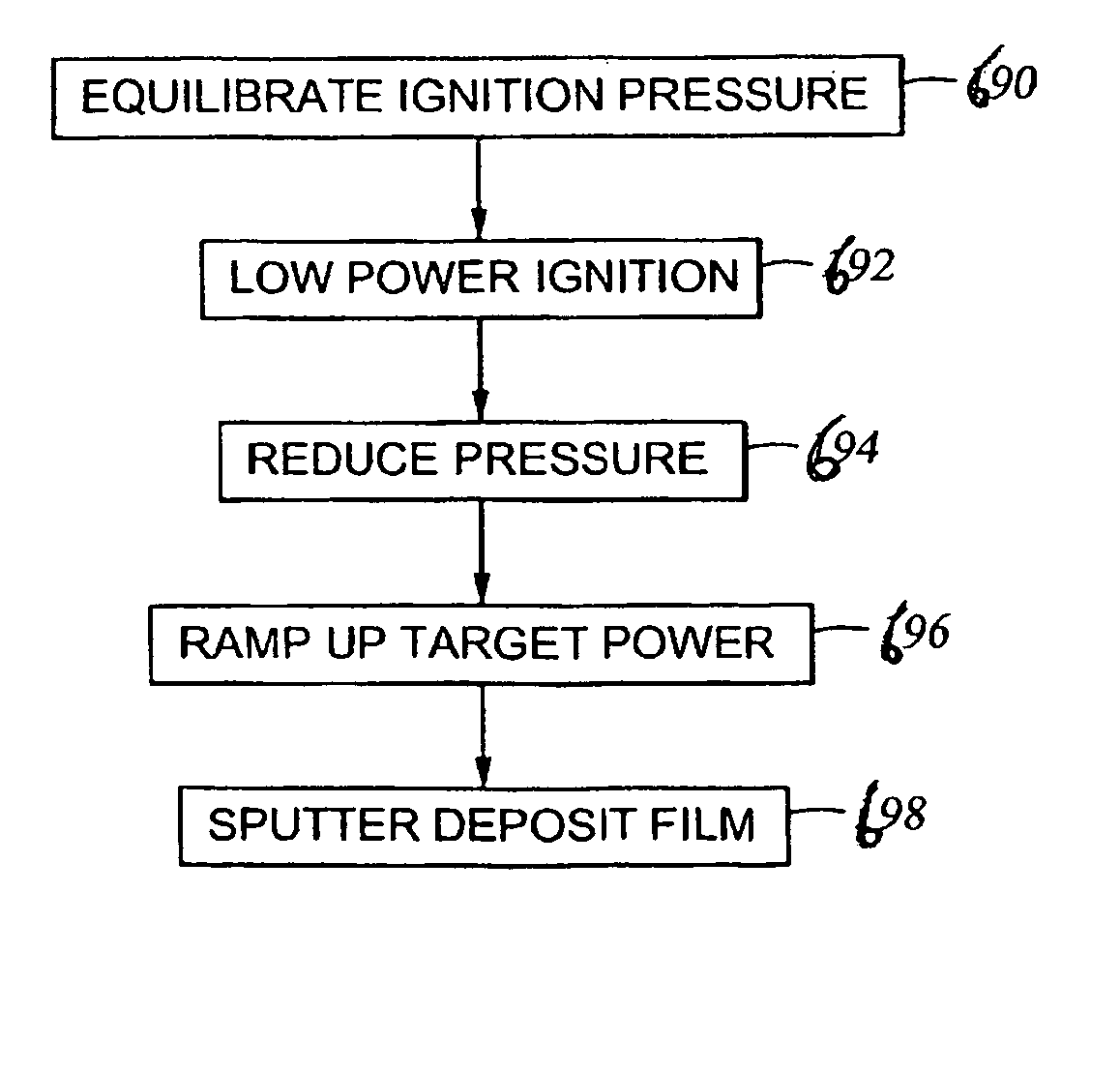
System and method for modulating power signals to control sputtering
One embodiment includes a sputtering system that includes a vacuum chamber; a substrate transport system configured to transport a substrate through the vacuum chamber; a cathode for supporting a sputtering target, the cathode at least partially inside the vacuum chamber; and a power supply configured to supply power to the cathode and the power supply configured to output a modulated power signal. Depending upon the implementation, the power supply can be configured to output an amplitude-modulated power signal; a frequency-modulated power signal; a pulse-width power signal; a pulse-position power signal; a pulse-amplitude modulated power signal; or any other type of modulated power or energy signal.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of forming an oxide film
InactiveUS6960812B2Improve performanceReduce the temperatureSolid-state devicesVacuum evaporation coatingAlkali ionsSputtering
A method of forming an oxide film and a method of manufacturing an electronic device utilizing the oxide film is disclosed. A silicon oxide film is formed on a substrate by sputtering. Therefore, the film formation is carried out at a low temperature. The sputtering atmosphere comprises an oxidizing gas and an inert gas such as argon. In order to prevent fixed electric charges from being generated in the film and to obtain an oxide film of good properties, the proportion of argon is adjusted to 20% or less. Alternatively, a gas including halogen elements such as fluorine is added to the above sputtering atmosphere at a proportion less than 20%. Hereupon, alkali ions and dangling bonds of silicon in the oxide film are neutralized by the halogen elements, whereby a fine oxide film is obtained.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Thin-film solar cells
InactiveUS6974976B2Increase reflectionInhibition formationFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingIndiumElectrical battery
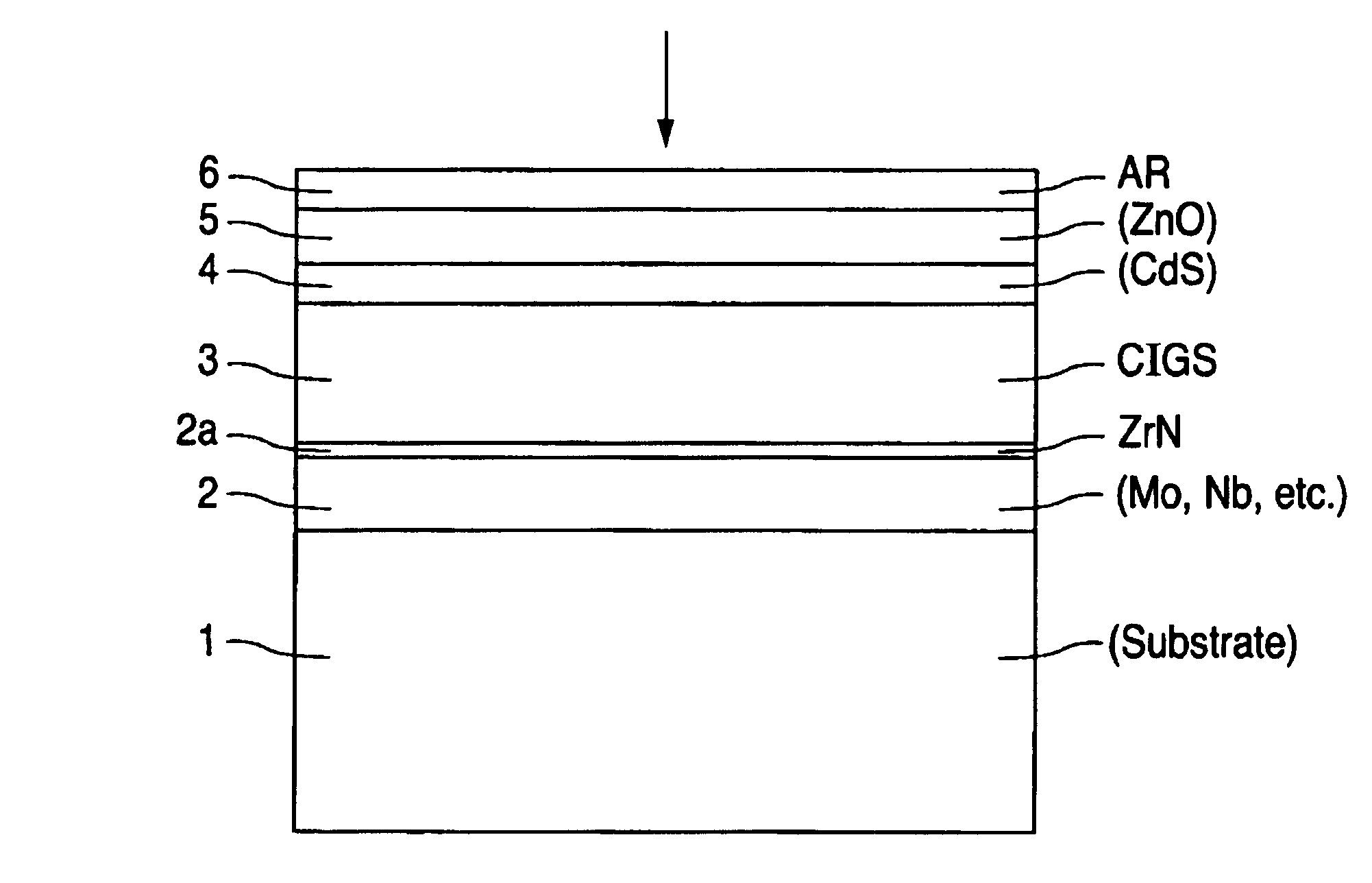
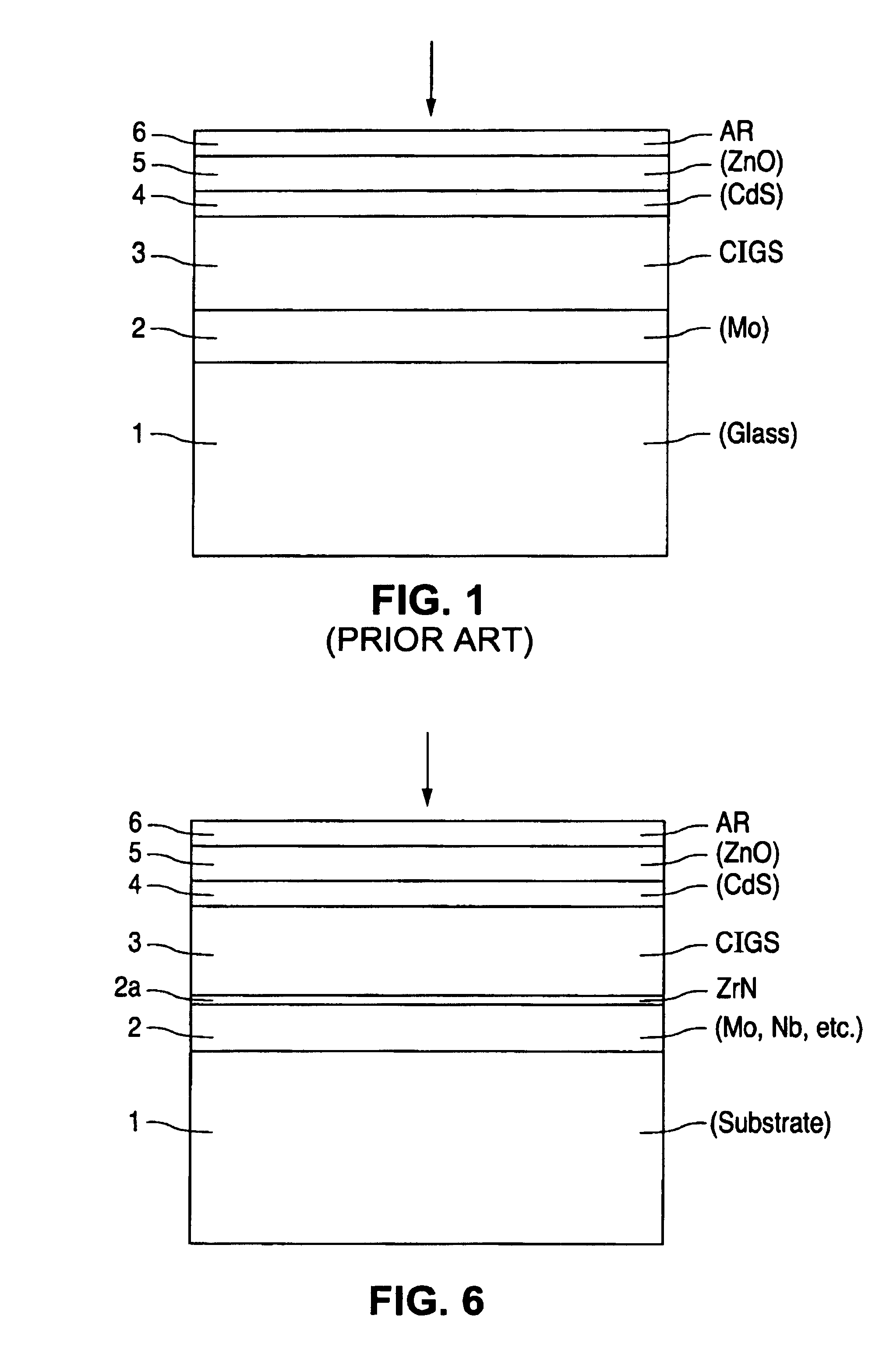
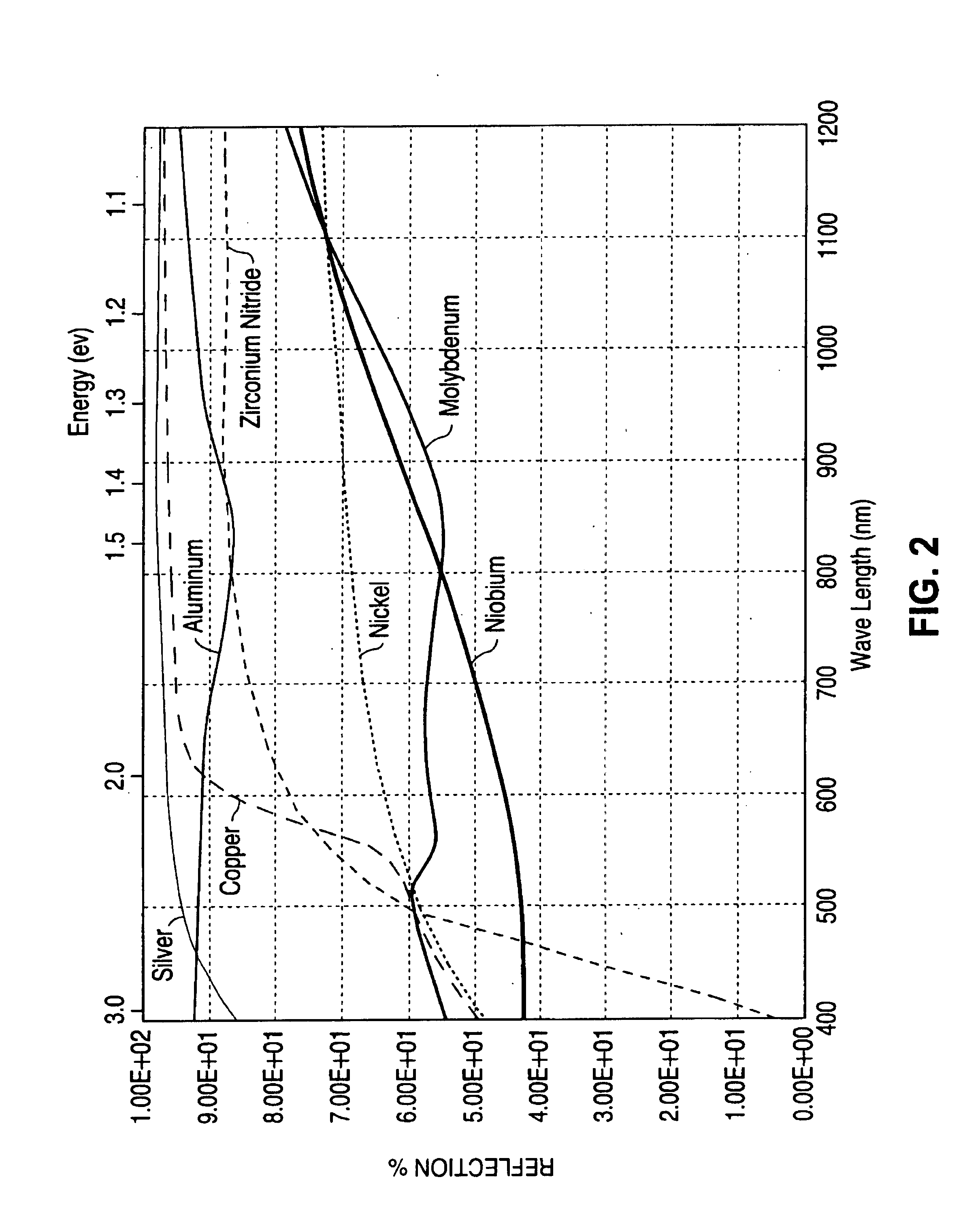
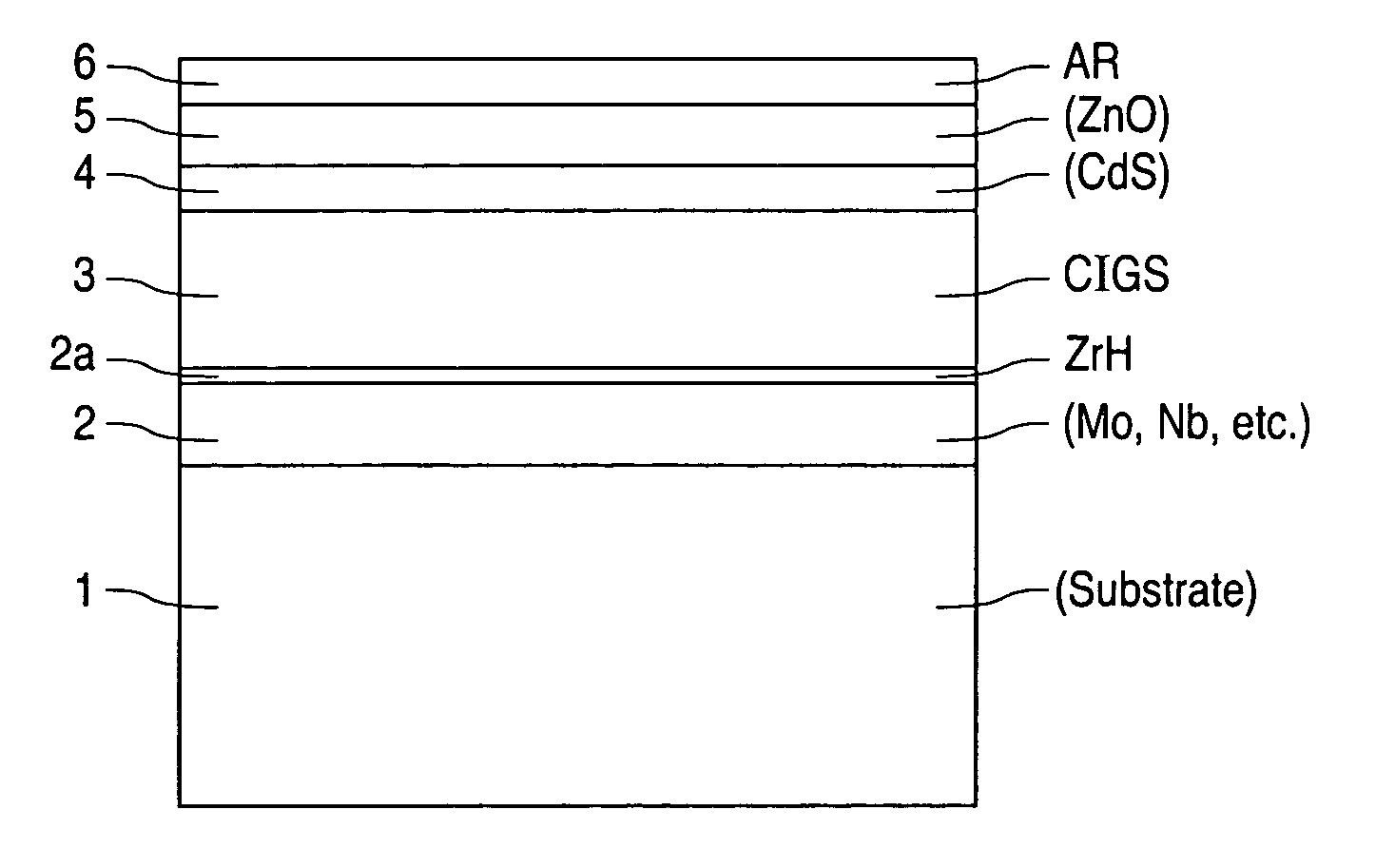
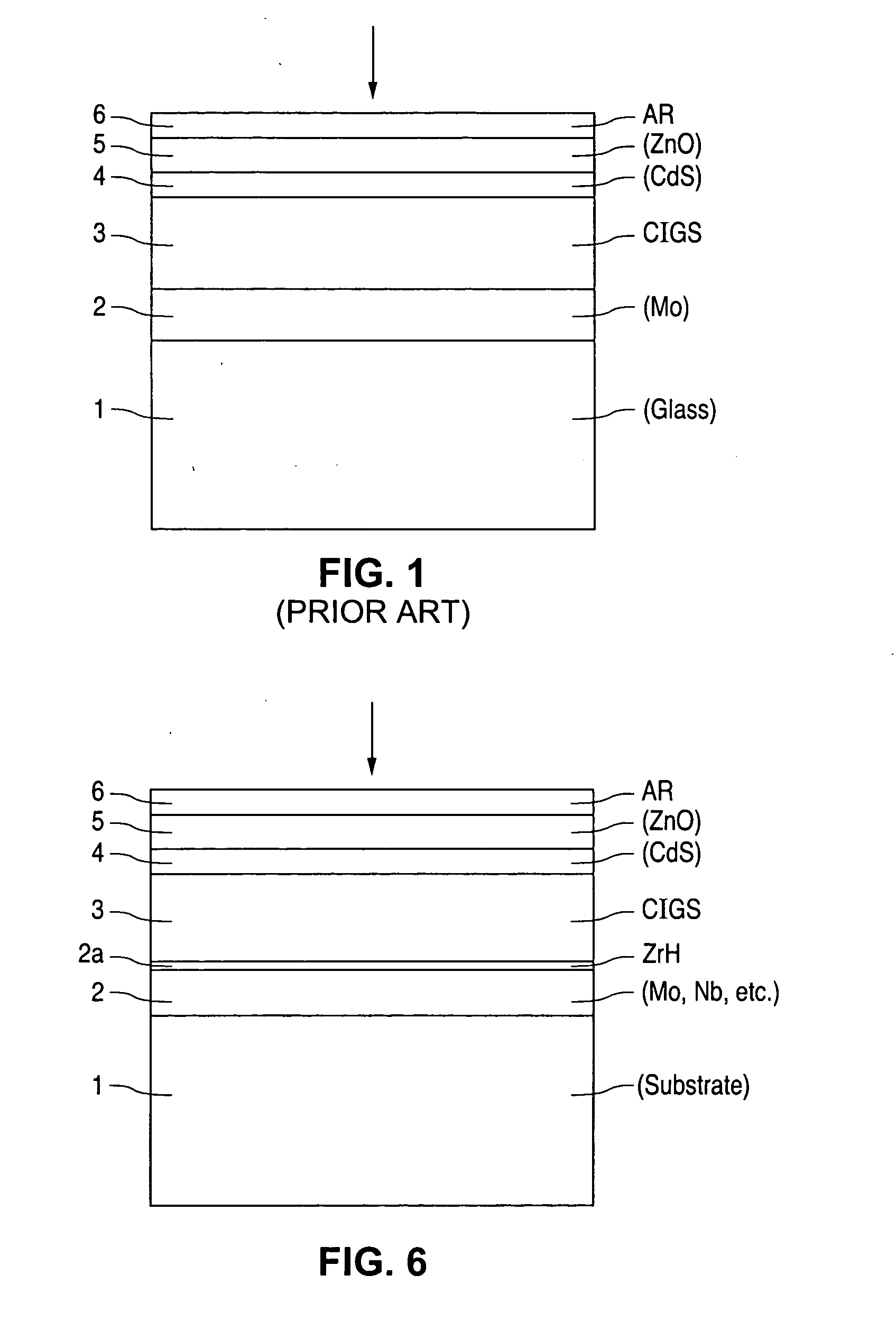
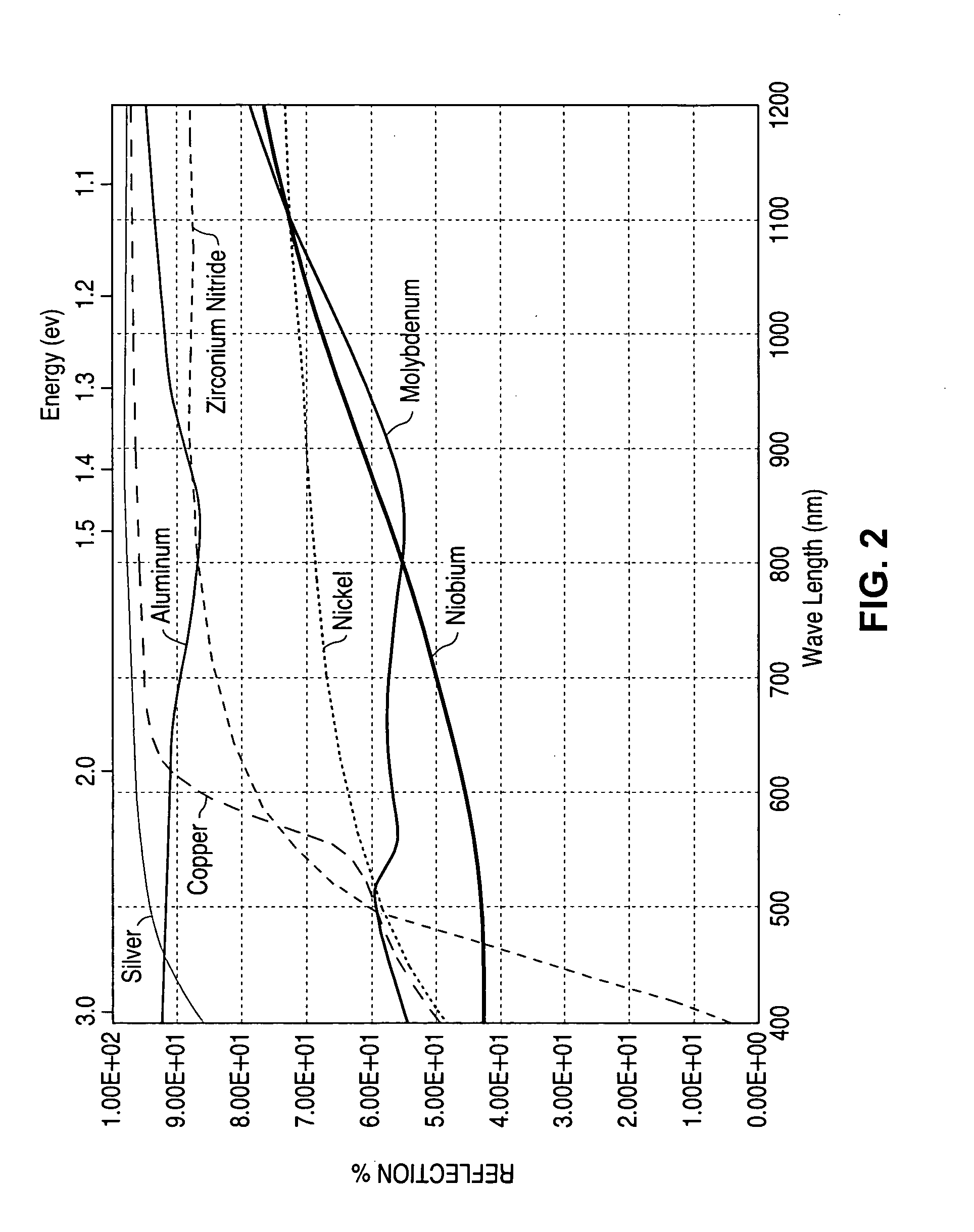
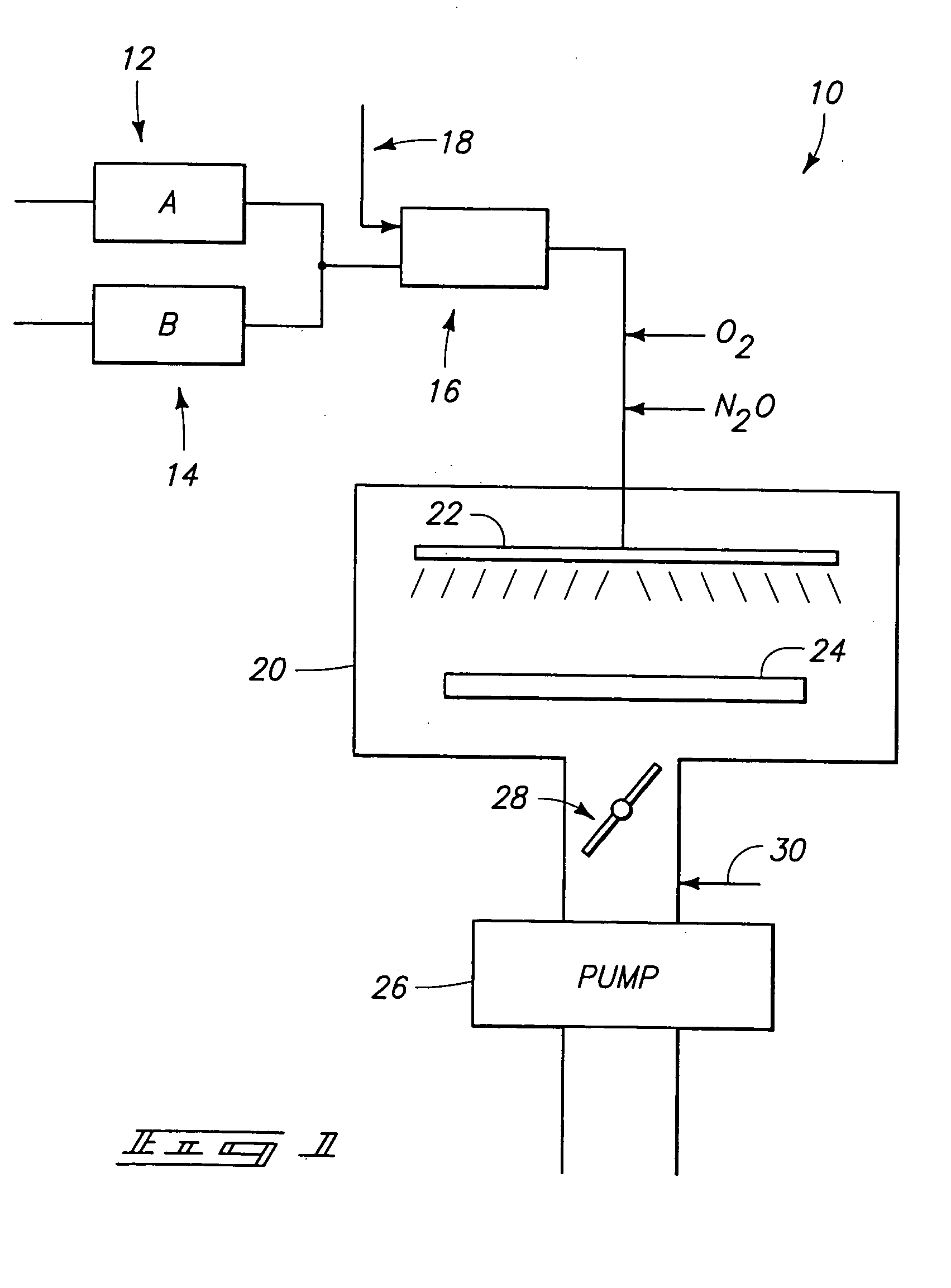
A method of manufacturing improved thin-film solar cells entirely by sputtering includes a high efficiency back contact / reflecting multi-layer containing at least one barrier layer consisting of a transition metal nitride. A copper indium gallium diselenide (Cu(InXGa1−X)Se2) absorber layer (X ranging from 1 to approximately 0.7) is co-sputtered from specially prepared electrically conductive targets using dual cylindrical rotary magnetron technology. The band gap of the absorber layer can be graded by varying the gallium content, and by replacing the gallium partially or totally with aluminum. Alternately the absorber layer is reactively sputtered from metal alloy targets in the presence of hydrogen selenide gas. RF sputtering is used to deposit a non-cadmium containing window layer of ZnS. The top transparent electrode is reactively sputtered aluminum doped ZnO. A unique modular vacuum roll-to-roll sputtering machine is described. The machine is adapted to incorporate dual cylindrical rotary magnetron technology to manufacture the improved solar cell material in a single pass.
Owner:BEIJING APOLLO DING RONG SOLAR TECH
Manufacturing apparatus and method for large-scale production of thin-film solar cells
ActiveUS20050109392A1Cheap productionLow costPV power plantsFinal product manufactureIndiumElectrical battery
A method of manufacturing improved thin-film solar cells entirely by sputtering includes a high efficiency back contact / reflecting multi-layer containing at least one barrier layer consisting of a transition metal nitride. A copper indium gallium diselenide (Cu(InXGa1-x)Se2) absorber layer (X ranging from 1 to approximately 0.7) is co-sputtered from specially prepared electrically conductive targets using dual cylindrical rotary magnetron technology. The band gap of the absorber layer can be graded by varying the gallium content, and by replacing the gallium partially or totally with aluminum. Alternately the absorber layer is reactively sputtered from metal alloy targets in the presence of hydrogen selenide gas. RF sputtering is used to deposit a non-cadmium containing window layer of ZnS. The top transparent electrode is reactively sputtered aluminum doped ZnO. A unique modular vacuum roll-to-roll sputtering machine is described. The machine is adapted to incorporate dual cylindrical rotary magnetron technology to manufacture the improved solar cell material in a single pass.
Owner:BEIJING APOLLO DING RONG SOLAR TECH
Method of forming a capacitor
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Systems and methods for reducing the influence of plasma-generated debris on the internal components of an EUV light source
ActiveUS7196342B2Prevented from reachingRadiation pyrometryLaser using scattering effectsSputteringHydrogen
Systems and methods are disclosed for reducing the influence of plasma generated debris on internal components of an EUV light source. In one aspect, an EUV meteorology monitor is provided which may have a heater to heat an internal multi-layer filtering mirror to a temperature sufficient to remove deposited debris from the mirror. In another aspect, a device is disclosed for removing plasma generated debris from an EUV light source collector mirror having a different debris deposition rate at different zones on the collector mirror. In a particular aspect, an EUV collector mirror system may comprise a source of hydrogen to combine with Li debris to create LiH on a collector surface; and a sputtering system to sputter LiH from the collector surface. In another aspect, an apparatus for etching debris from a surface of a EUV light source collector mirror with a controlled plasma etch rate is disclosed.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Chemical vapor deposition methods and physical vapor deposition methods
InactiveUS20050186688A1Vacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSputteringGas phase
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
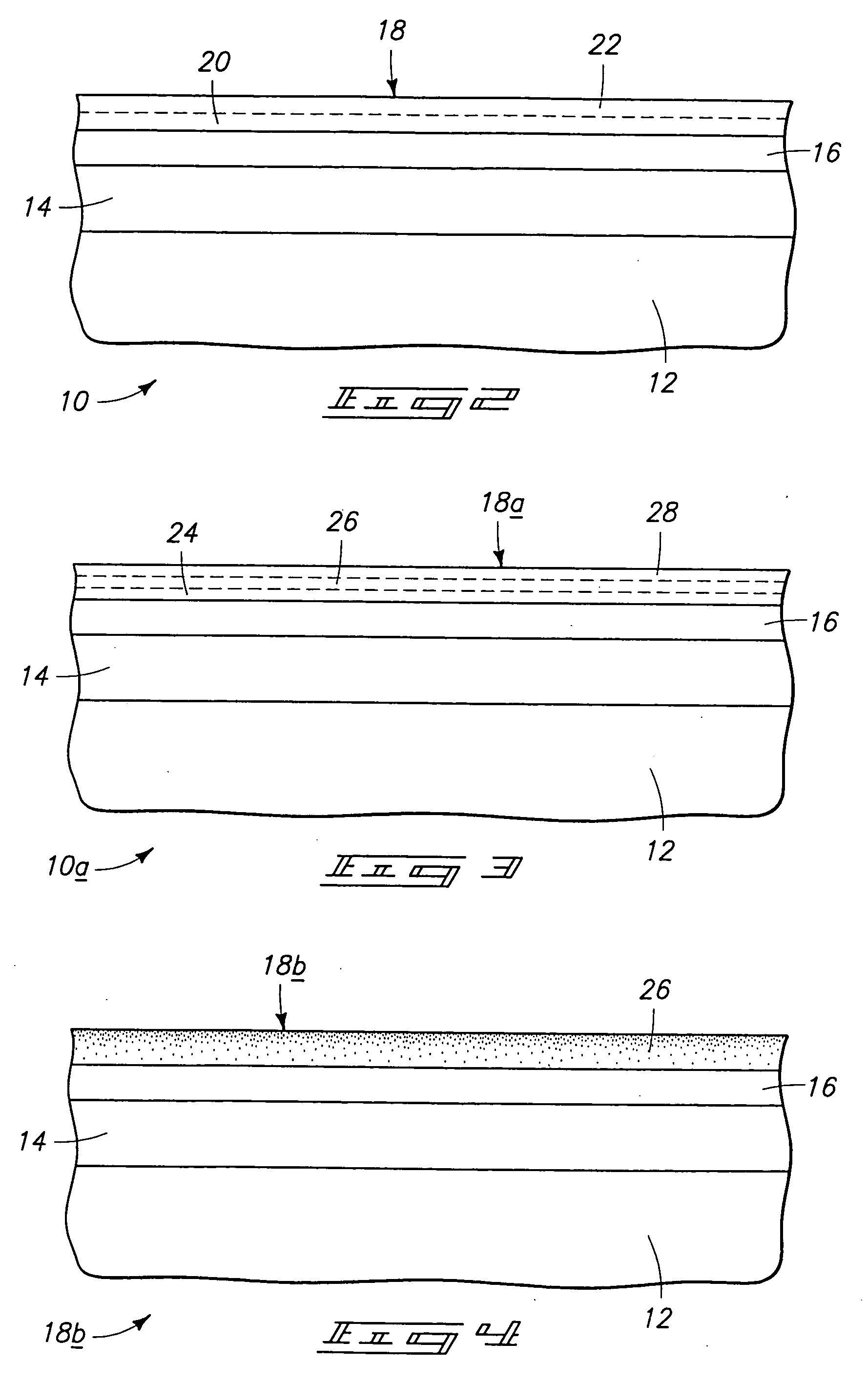
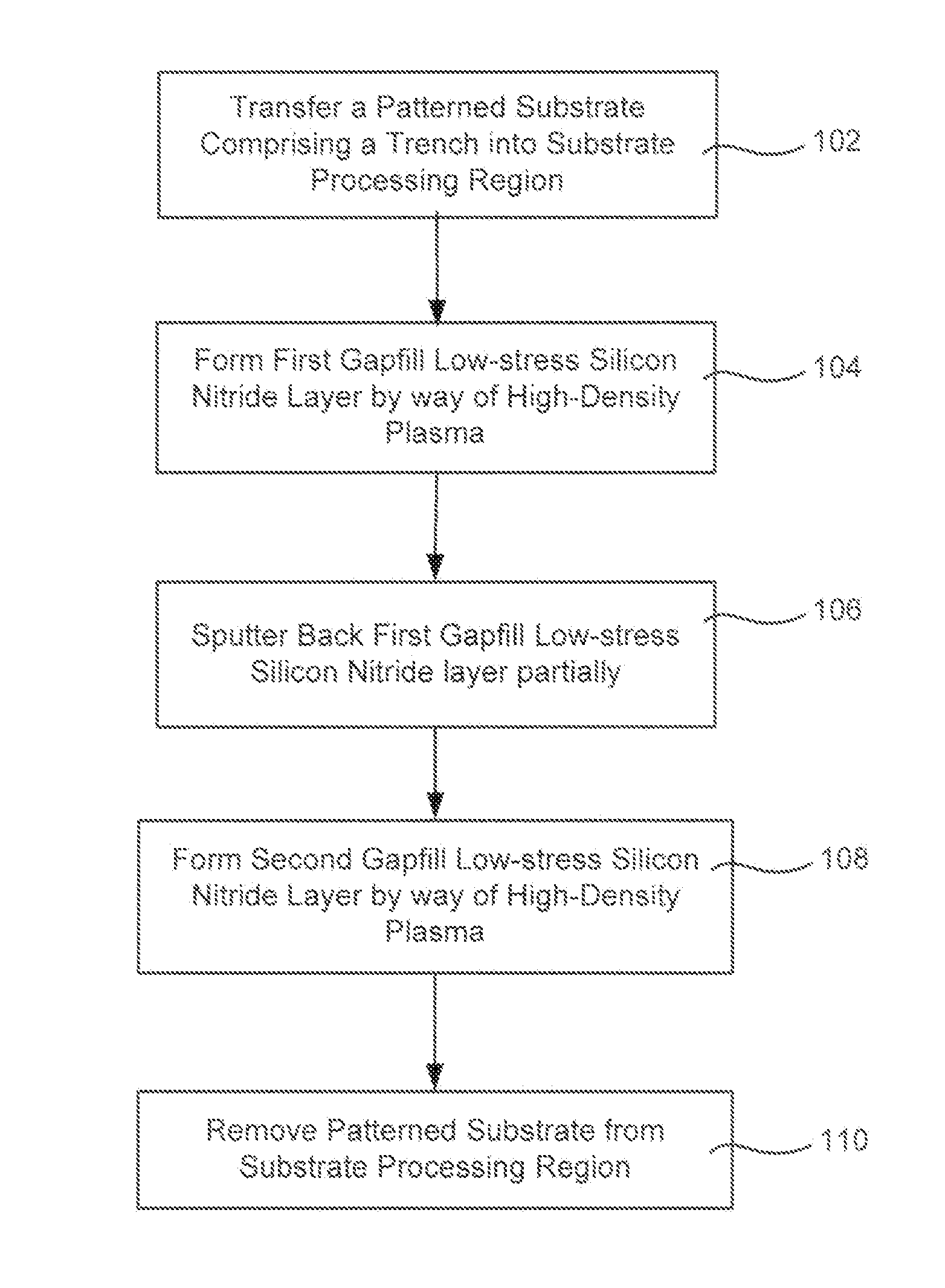
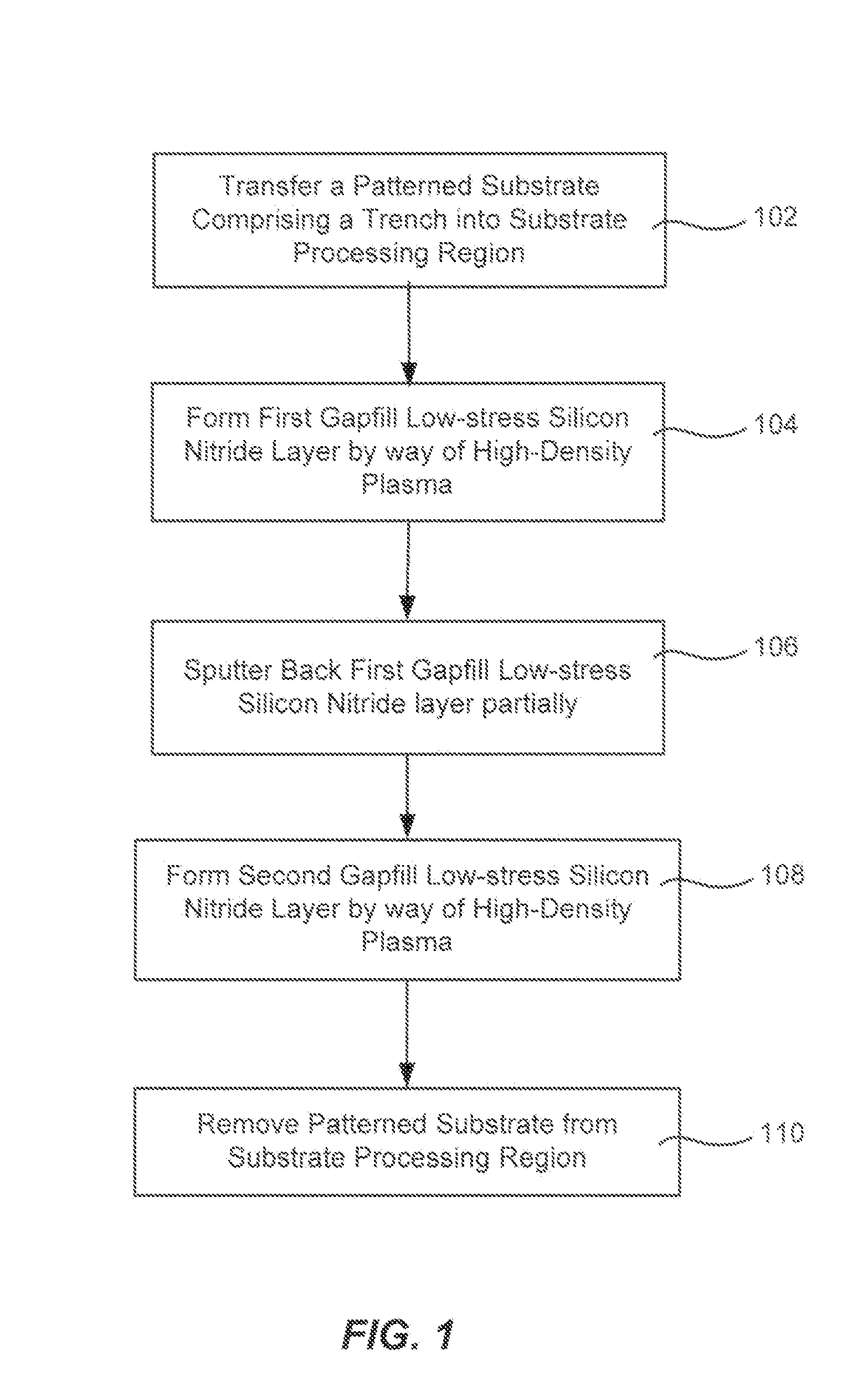
Silicon nitride gapfill implementing high density plasma
InactiveUS20140187045A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSputteringHigh density
Methods of filling features with silicon nitride using high-density plasma chemical vapor deposition are described. Narrow trenches may be filled with gapfill silicon nitride without damaging compressive stress. A low but non-zero bias power is used during deposition of the gapfill silicon nitride. An etch step is included between each pair of silicon nitride high-density plasma deposition steps in order to supply sputtering which would normally be supplied by high bias power.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Growth method for silicon nanowires and nanoparticle chains from silicon monoxide
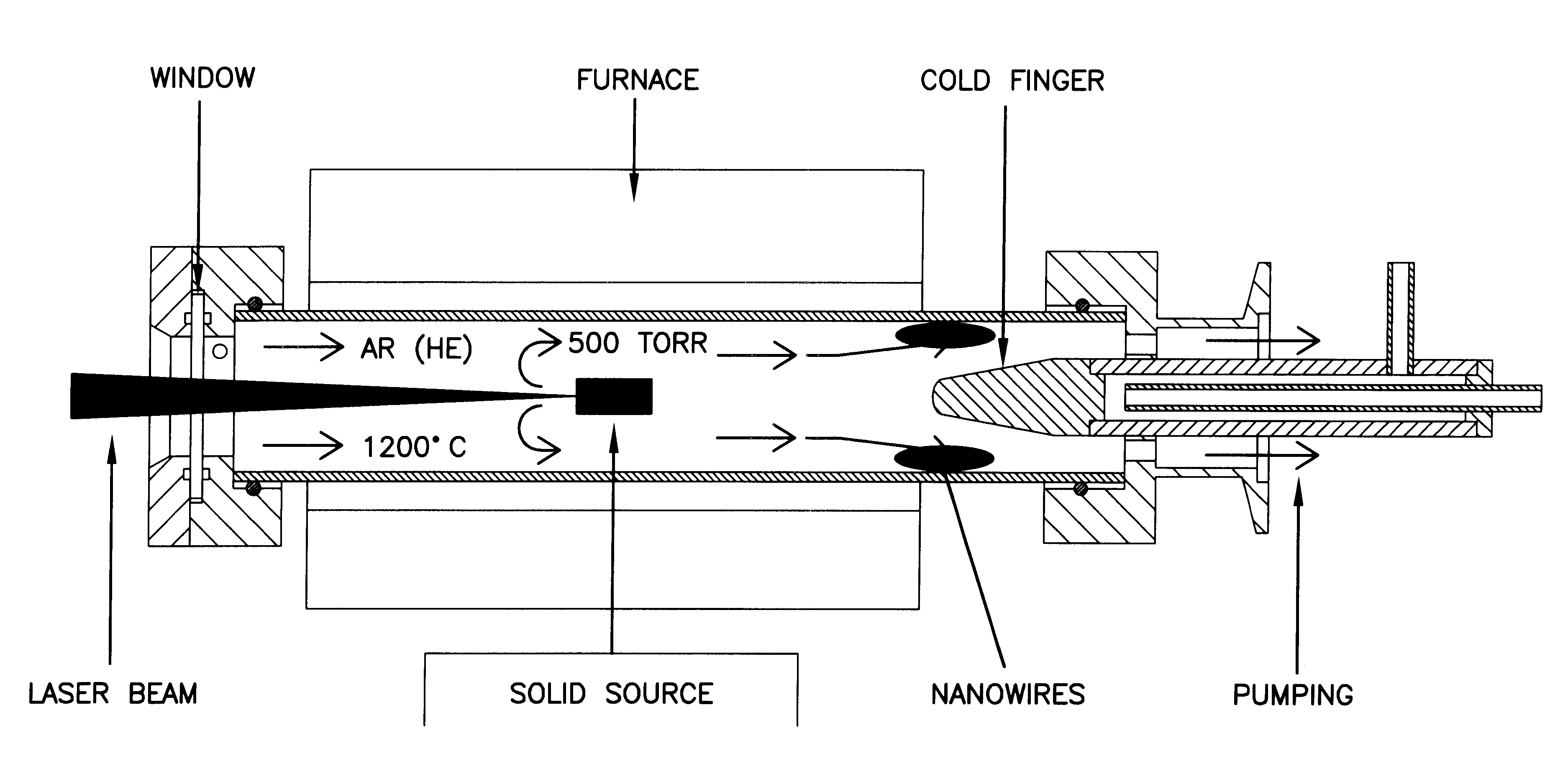
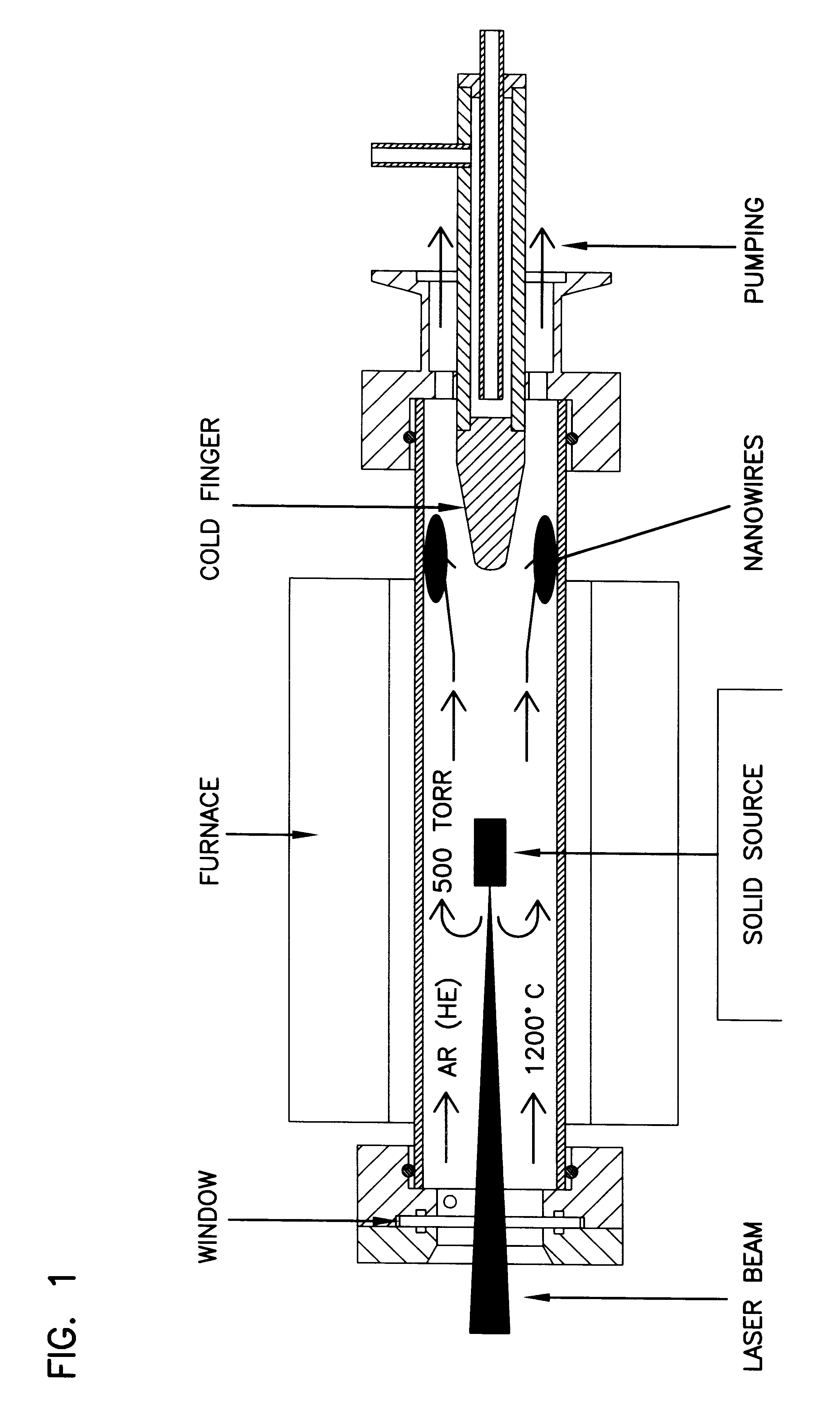
InactiveUS6313015B1Enhance one-dimensional growthLowering of total energy of systemPolycrystalline material growthNanotechSputteringSilicon monoxide
Silicon nanowires and silicon nanoparticle chains are formed by the activation of silicon monoxide in the vapor phase. The silicon monoxide source may be solid or gaseous, and the activation may be by thermal excitation, laser ablation, plasma or magnetron sputtering. The present invention produces large amounts of silicon nanowires without requiring the use of any catalysts that may cause contamination.
Owner:HONG KONG CITY UNIV OF
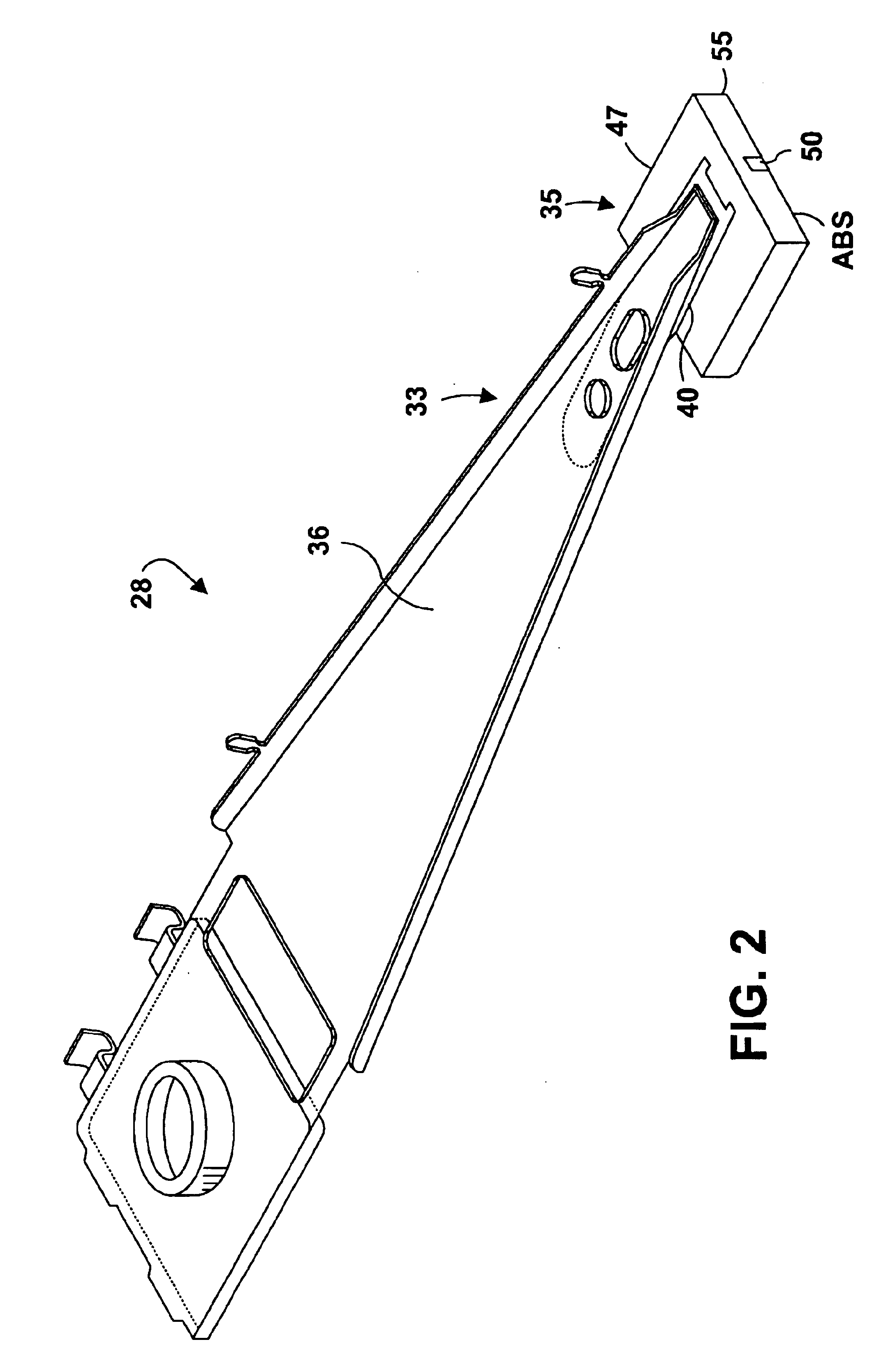
Write head having a recessed, magnetic adjunct pole formed atop a main pole, and method of making the same
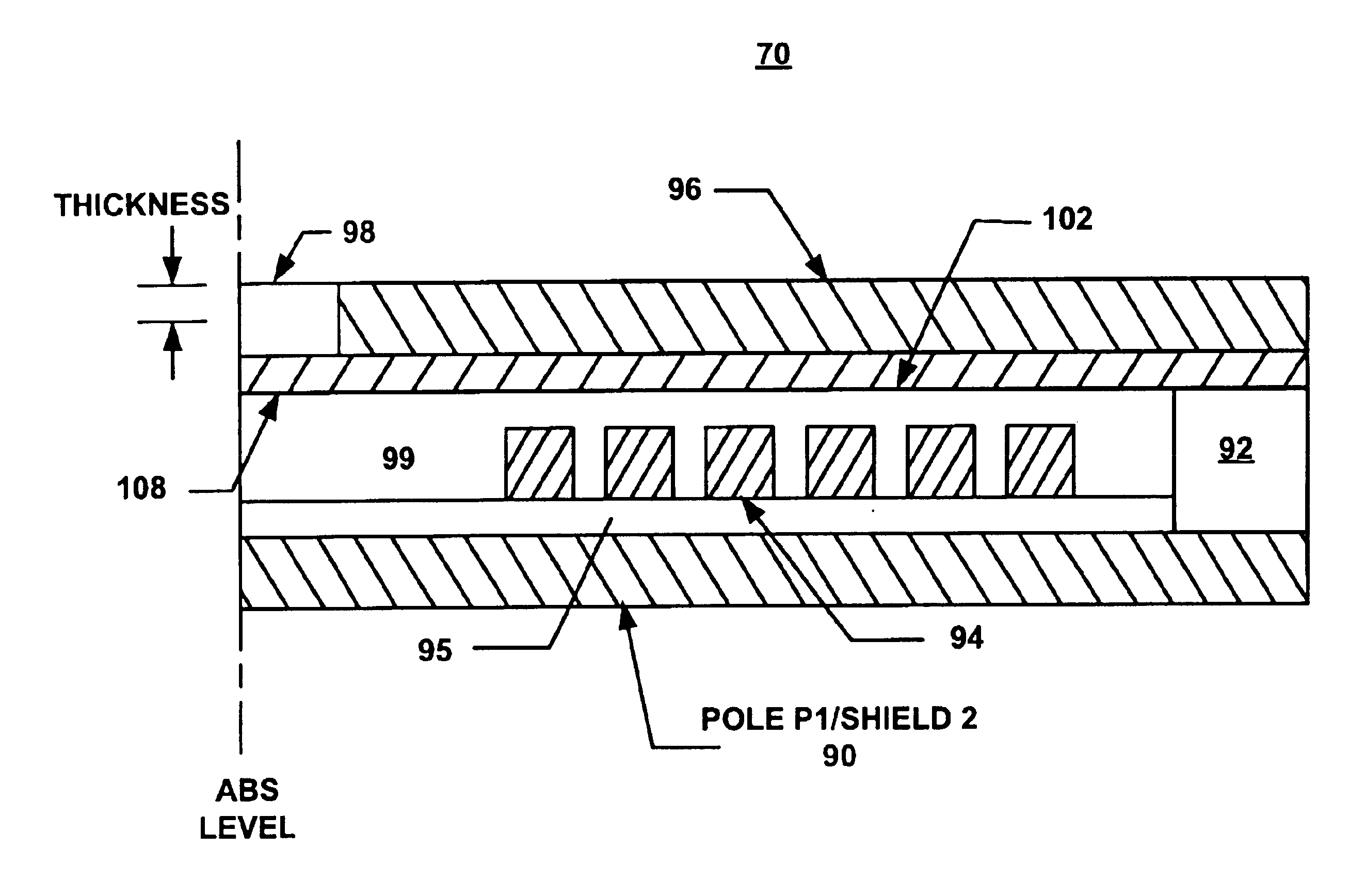
InactiveUS6906894B2Enhanced magnetic write fieldEliminate the problemConstruction of head windingsElectrical transducersSputteringEngineering
A read / write head and method of making the same are used in a data storage system, such as a disk drive, for perpendicular magnetic recording of data. The head employs a two-layer pole design with a main pole made of sputtered high moment magnetic material, and an adjunct pole made of electroplated soft magnetic film. The main pole is used to write data onto the medium, and is formed over the write coil. The adjunct pole is substantially recessed from the air bearing surface and is formed over the main pole. The present head design significantly enhances the magnetic write field, and substantially reduces side-writing that result in accidental erasure of data in adjacent tracks on the magnetic recording medium.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
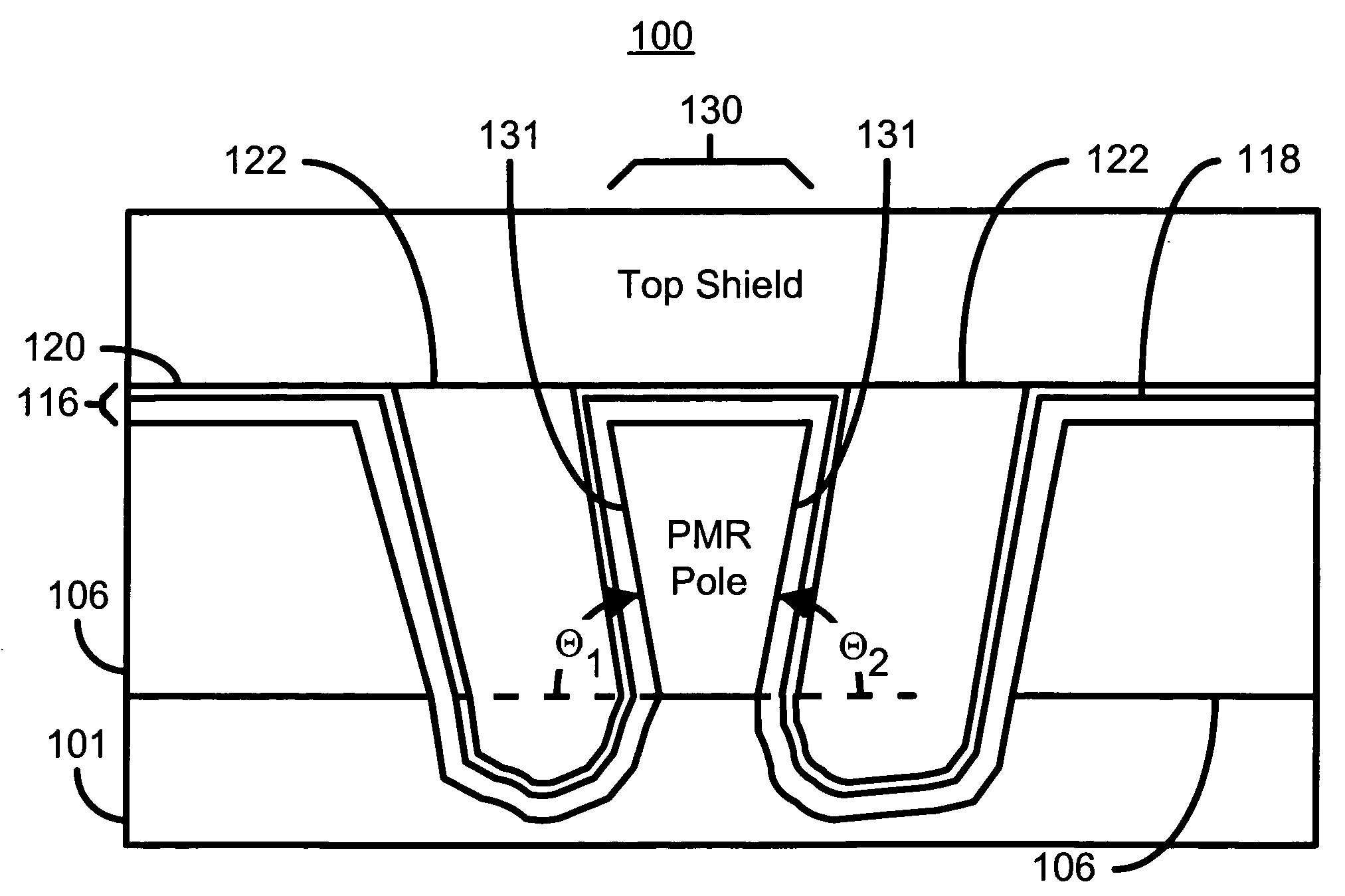
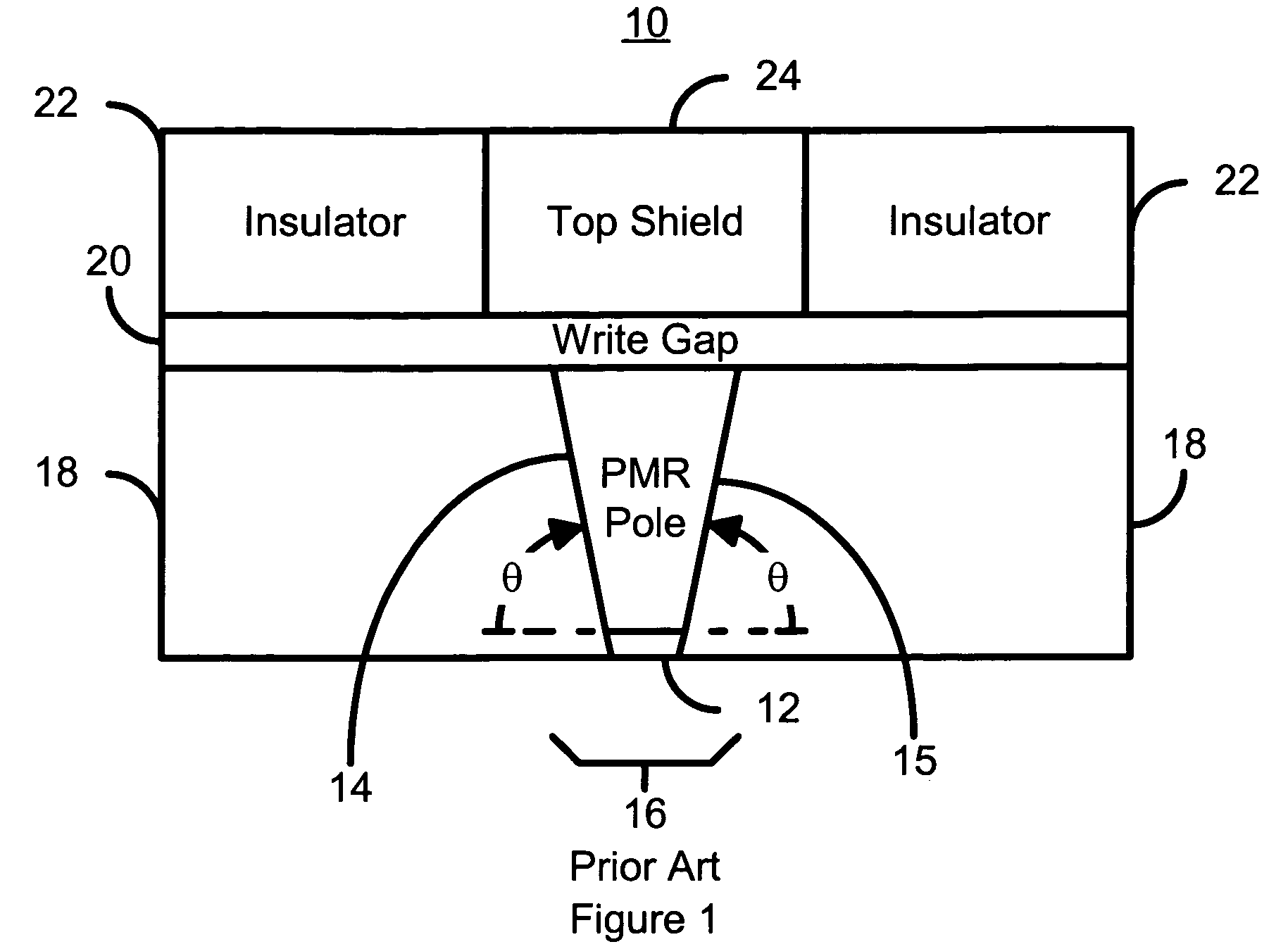
Method for manufacturing a pole for a magnetic recording head
A method and system for manufacturing a pole on a recording head is disclosed. The method and system include sputtering at least one ferromagnetic layer and fabricating a hard mask on the ferromagnetic layer. The method and system also include defining the pole and depositing a write gap on the pole. A portion of the pole is encapsulated in an insulator.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
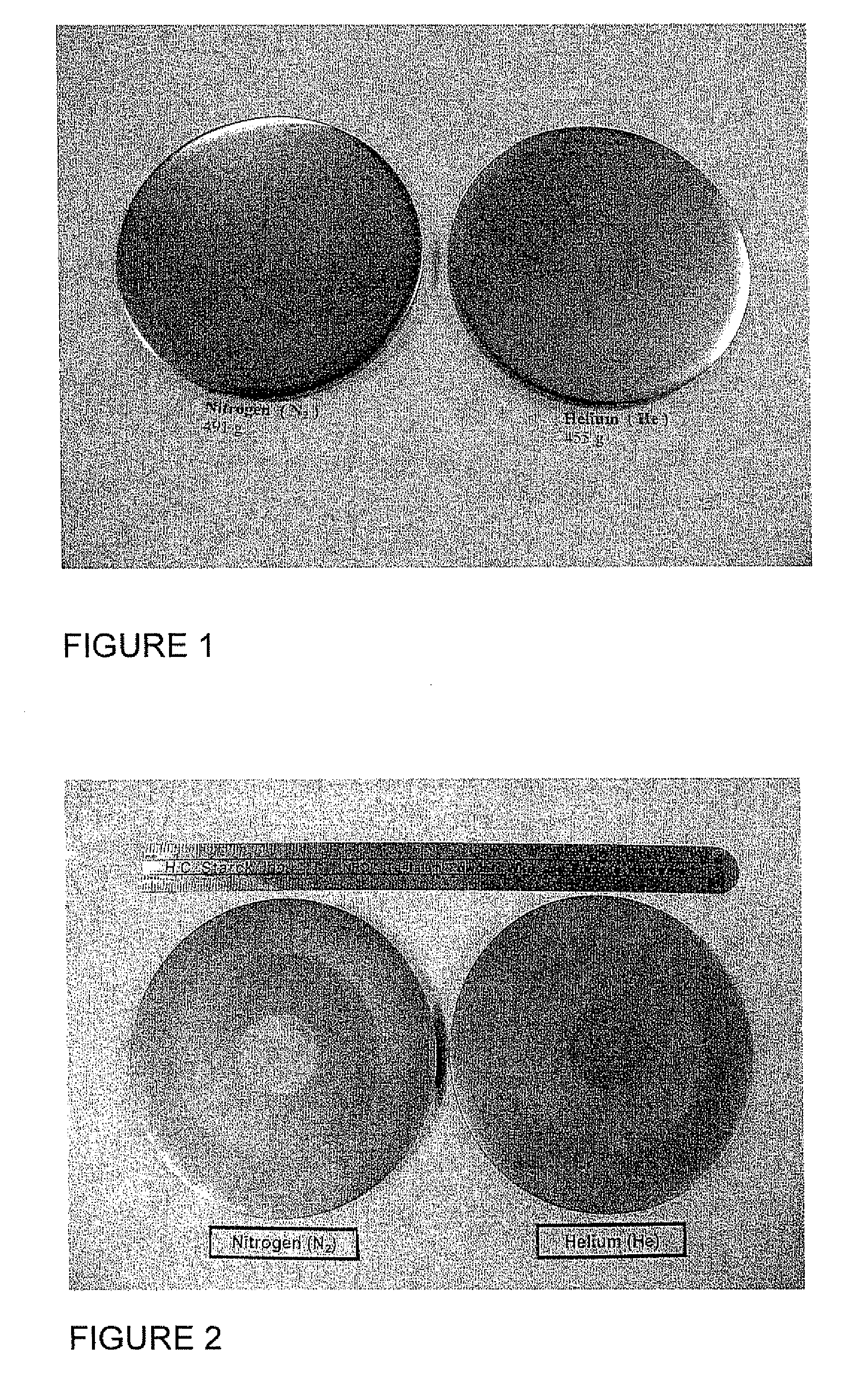
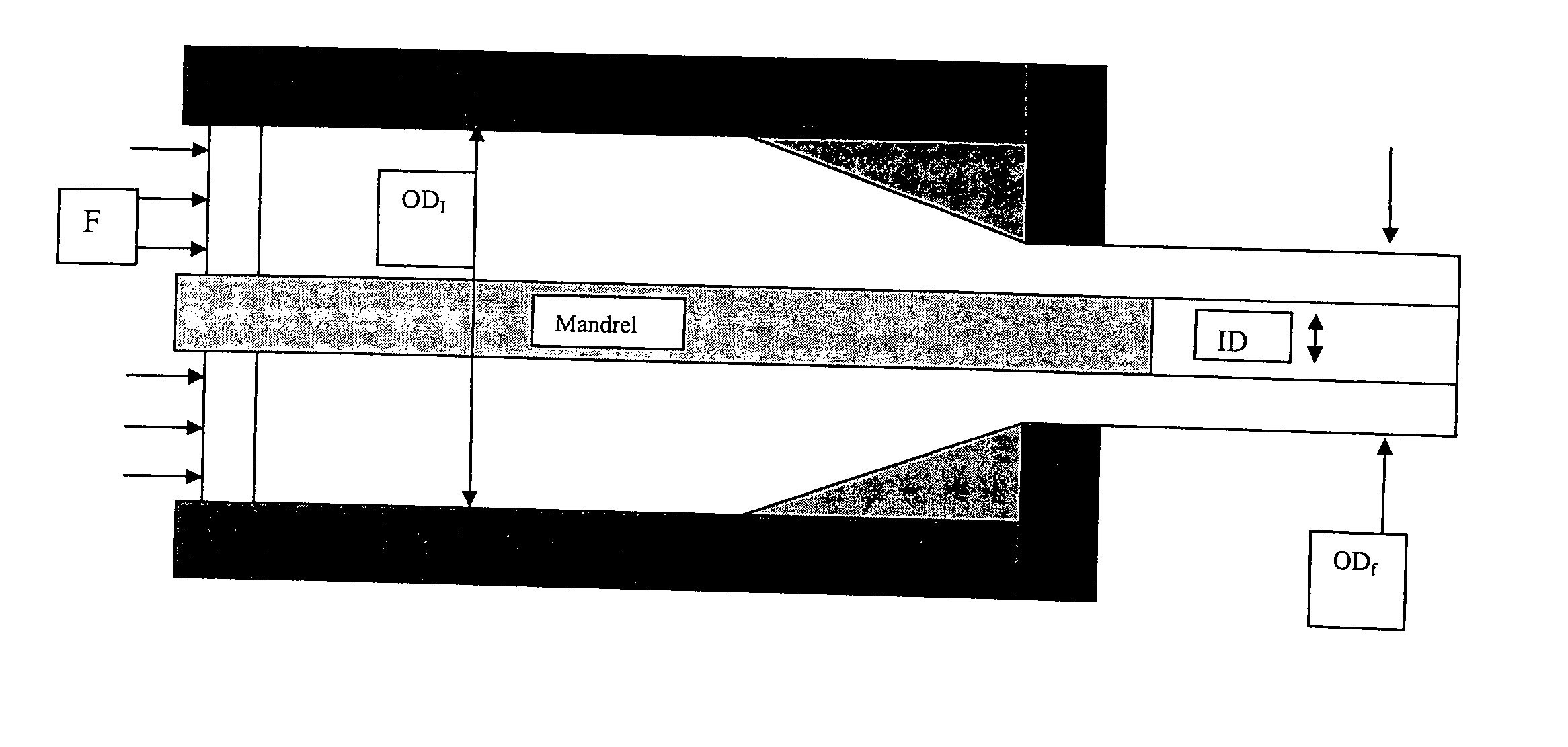
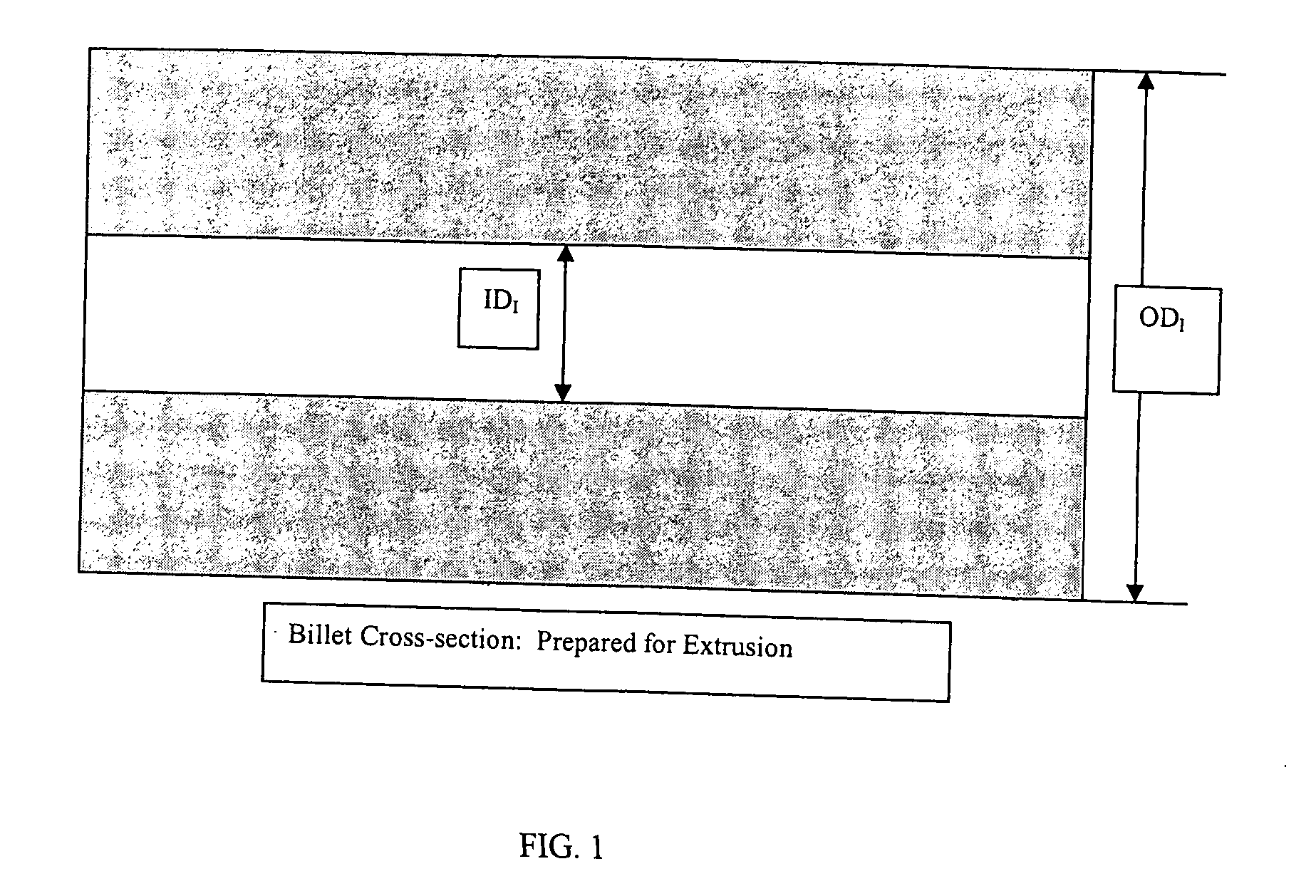
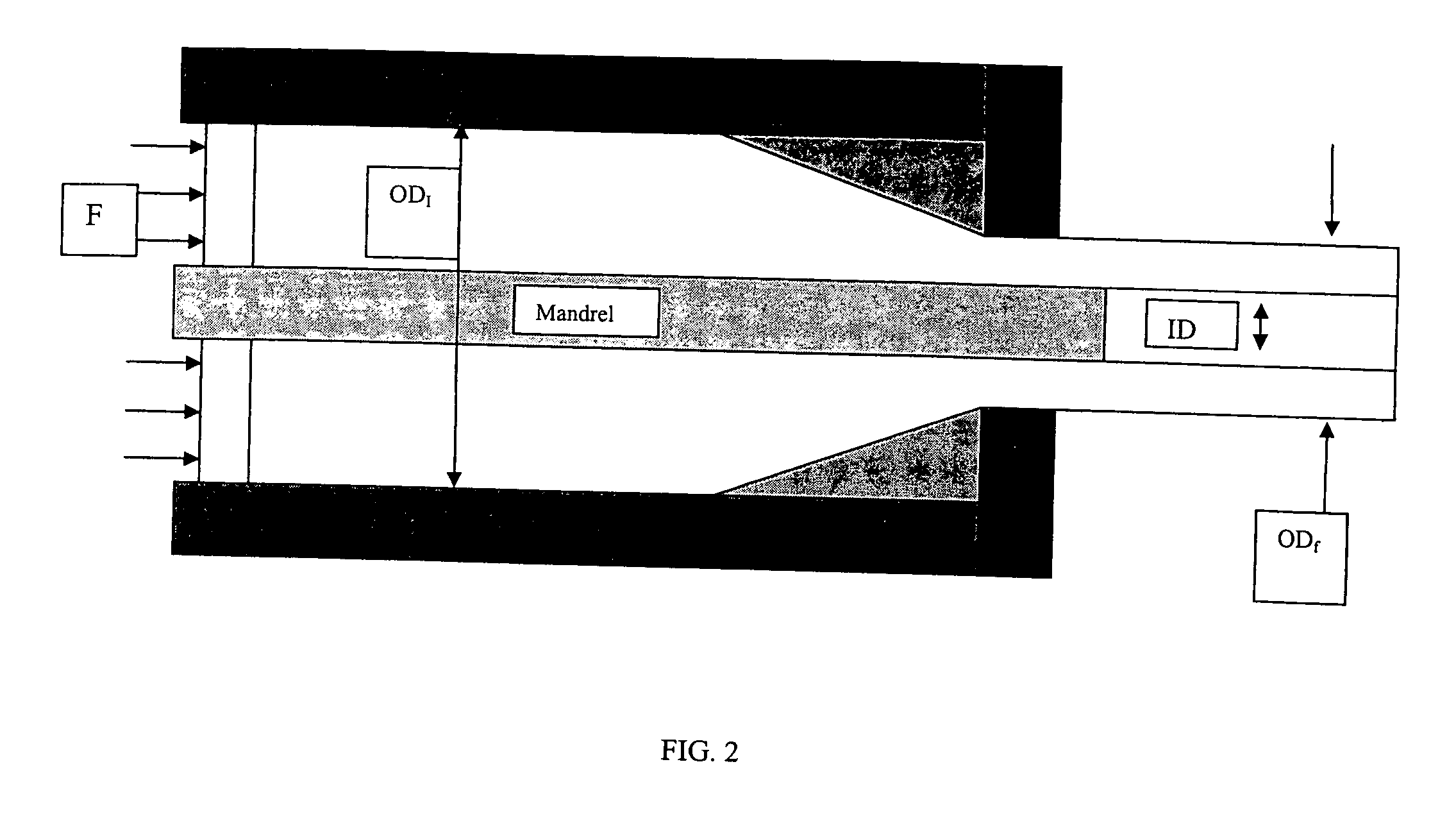
Fine Grained, Non Banded, Refractory Metal Sputtering Targets with a Uniformly Random Crystallographic Orientation, Method for Making Such Film, and Thin Film Based Devices and Products Made Therefrom
ActiveUS20080271779A1Cost-effectively createCost effectiveLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingFilm baseThermal expansion
The invention relates to a sputtering target which has a fine uniform equiaxed grain structure of less than 44 microns, no preferred texture orientation as measured by electron back scattered diffraction (“EBSD”) and that displays no grain size banding or texture banding throughout the body of the target. The invention relates a sputtering target with a lenticular or flattened grain structure, no preferred texture orientation as measured by EBSD and that displays no grain size or texture banding throughout the body of the target and where the target has a layered structure incorporating a layer of the sputtering material and at least one additional layer at the backing plate interface, said layer has a coefficient of thermal expansion (“CTE”) value between the CTE of the backing plate and the CTE of the layer of sputtering material. The invention also relates to thin films and their use of using the sputtering target and other applications, such as coatings, solar devices, semiconductor devices etc. The invention further relates to a process to repair or rejuvenate a sputtering target.
Owner:H C STARCK GMBH +1
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050215049A1Eliminate disadvantagesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsSputteringDevice material
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device having an interconnection part formed of multiple carbon nanotubes is disclosed. The method includes the steps of (a) forming a growth mode control layer controlling the growth mode of the carbon nanotubes, (b) forming a catalyst layer on the growth mode control layer, and (c) causing the carbon nanotubes to grow by heating the catalyst layer by thermal CVD so that the carbon nanotubes serve as the interconnection part. The growth mode control layer is formed by sputtering or vacuum deposition in an atmospheric gas, using a metal selected from a group of Ti, Mo, V, Nb, and W. The growth mode is controlled in accordance with a predetermined concentration of oxygen gas of the atmospheric gas.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Electroplating and electroless plating of conductive materials into openings, and structures obtained thereby
InactiveUS6897148B2Improve throughputReduce tooling costsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesResistDielectric
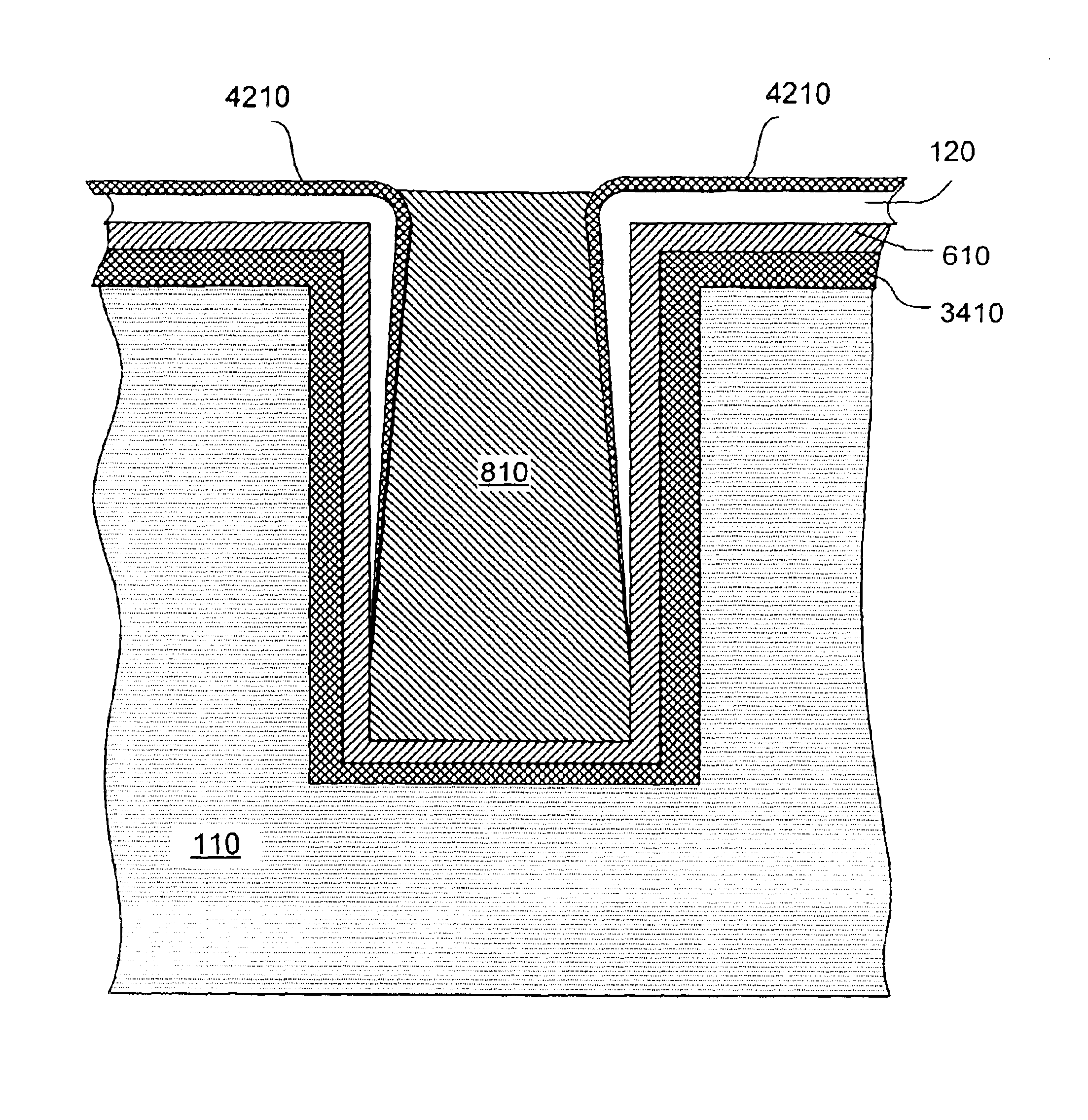
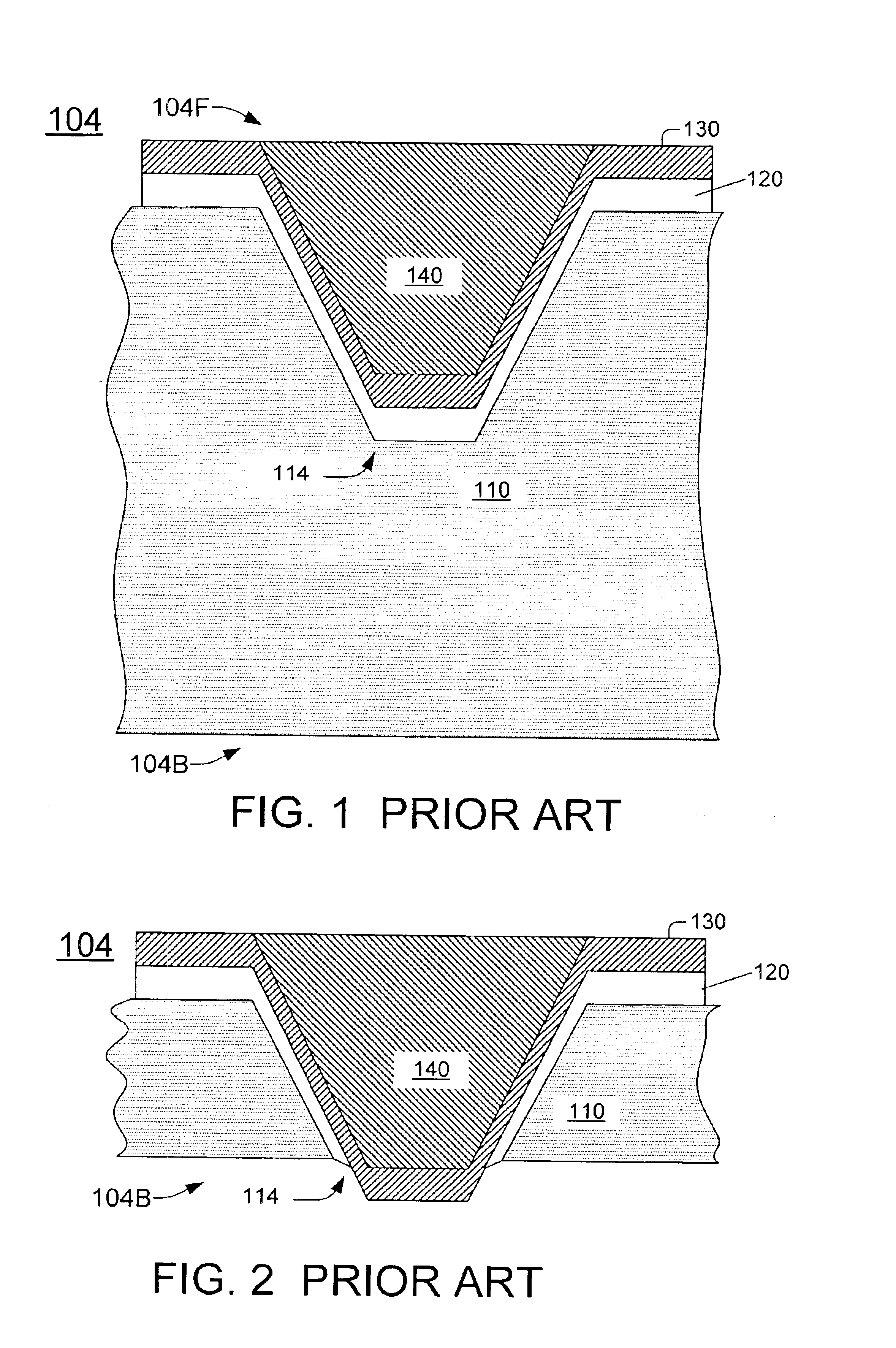
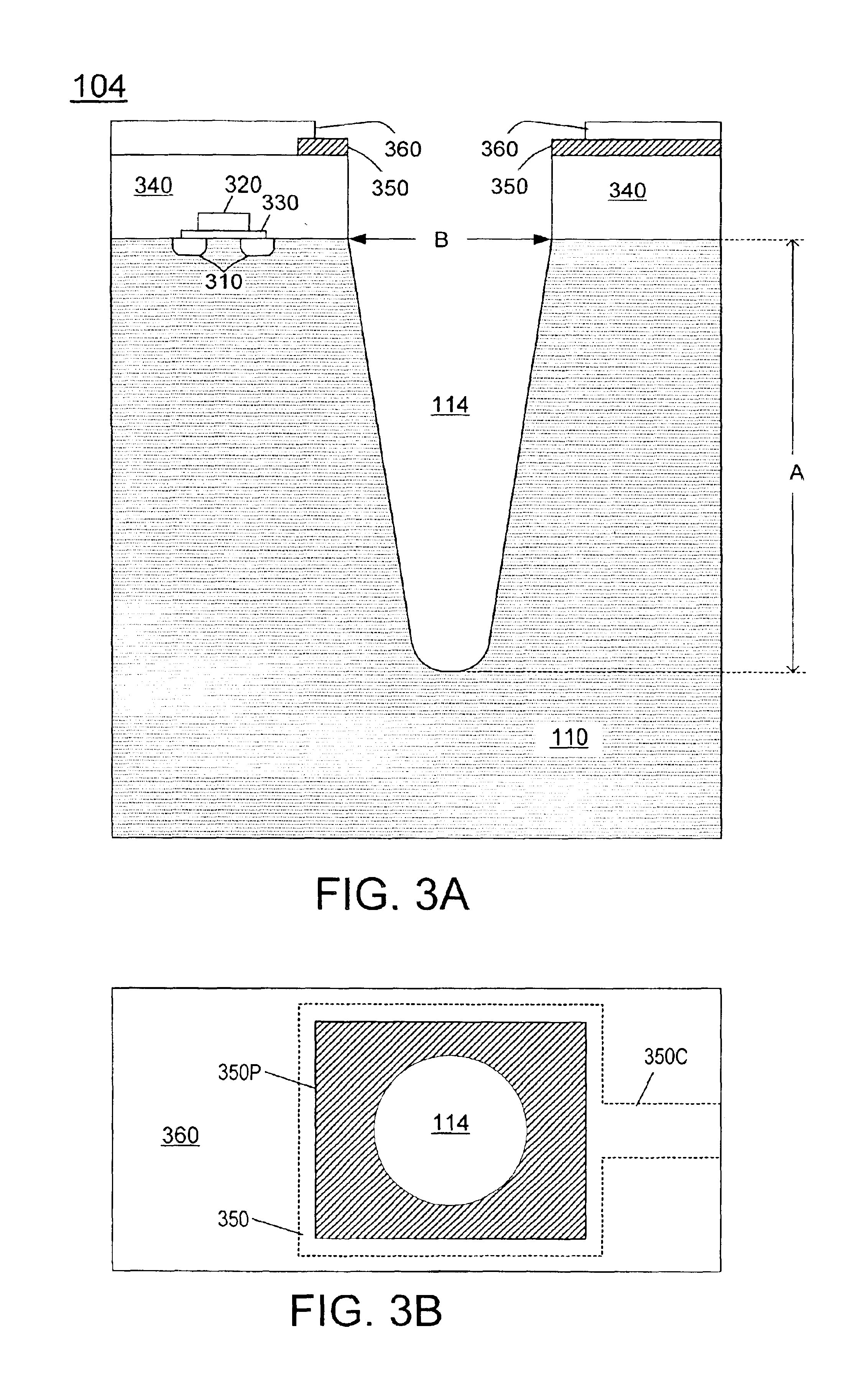
A through hole (114) is formed in a wafer (104) comprising a semiconductor substrate (110). A seed layer (610) is sputtered on the bottom surface of the wafer. The seed is not deposited over the through hole's sidewalls adjacent the top surface of the wafer. A conductor (810) is electroplated into the through hole. In another embodiment, a seed is deposited into an opening in a wafer through a dry film resist mask (1110). The dry film resist overhangs the edges of the opening, so the seed is not deposited over the opening's sidewalls adjacent the top surface of the wafer. In another embodiment, a dielectric (120) is formed in an opening in a semiconductor substrate (110) by a non-conformal physical vapor deposition (PVD) process that deposits the dielectric on the sidewalls but not the bottom of the opening. A seed (610) is formed on the bottom by electroless plating. A conductor (810) is electroplated on the seed. In another embodiment, a dielectric (2910) is formed in the opening to cover the entire surface of the opening. A non-conformal layer (120) is deposited by PVD over the sidewalls but not the bottom of the opening. The dielectric (2910) is etched off the bottom with the non-conformal layer (120) as a mask. A seed (610) is formed on the bottom by electroless plating. The non-conformal layer can be formed by electroplating. It can be tantalum deposited by electroplating, then anodized. Other embodiments are also provided.
Owner:INVENSAS CORP
Cooling plate and manufacturing method thereof, and sputtering target and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20020153130A1Improve accuracyAccurate stepElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingSputteringEngineering
The present invention is a cooling plate including a groove, which becomes a passage of a coolant, inside a body, wherein one or more fins are provided inside the groove, wherein the groove is covered with a lid having width larger than the groove, wherein the lid is joined to the body by friction stir welding, and wherein a weld bead formed by the joining is outside the passage, and the weld bead formed by the joining is formed within the body and further, is characterized by a manufacturing method of a cooling plate that has a first groove, which becomes a passage of a coolant, and a second groove, which has width larger than the first groove and receives a lid on the first groove, inside a body, receives the lid on the second groove, and is joined to the body, the manufacturing method of a cooling plate wherein, while the lid and the body are joined together by the friction stir welding owing to insertion of a rotation tool having a shoulder and a pin, the joining is performed so that a weld bead formed by the joining may become out of the passage, and furthermore, is characterized in that a target for sputtering is joined to the cooling plate.
Owner:HITACHI CABLE
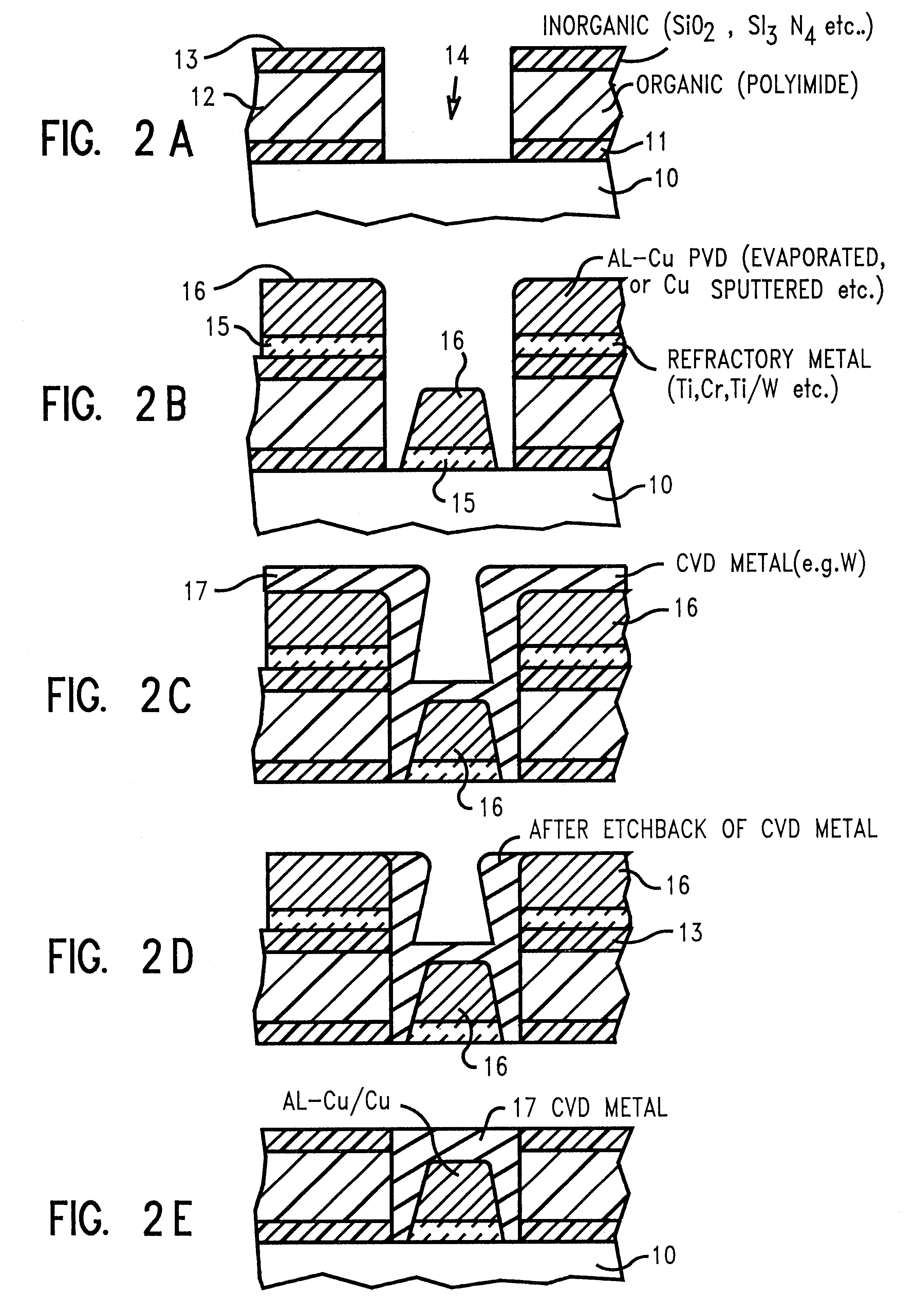
Refractory metal capped low resistivity metal conductor lines and vias formed using PVD and CVD
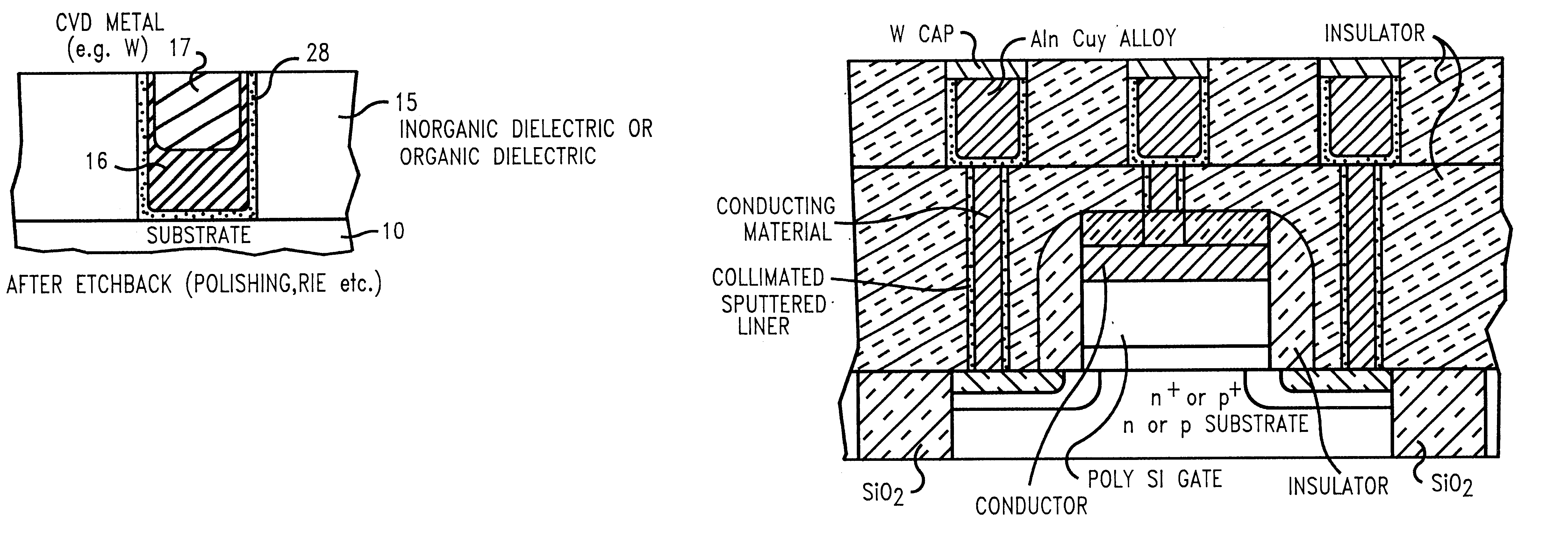
InactiveUS6323554B1High process yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricGas phase
Capping a low resistivity metal conductor line or via with a refractory metal allows for effectively using chemical-mechanical polishing techniques because the hard, reduced wear, properties of the refractory metal do not scratch, corrode, or smear during chemical-mechanical polishing. Conductive lines and vias are created using a combination of both physical vapor deposition (e.g., evaporation or collimated sputtering) of a low resistivity metal or alloy followed by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) of a refractory metal and subsequent planarization. Altering a ratio of SiH4 to WF6 during application of the refractory metal cap by CVD allows for controlled incorporation of silicon into the tungsten capping layer. Collimated sputtering allows for creating a refractory metal liner in an opening in a dielectric which is suitable as a diffusion barrier to copper based metalizations as well as CVD tungsten. Ideally, for faster diffusing metals like copper, liners are created by a two step collimated sputtering process wherein a first layer is deposited under relatively low vacuum pressure where directional deposition dominates (e.g., below 1 mTorr) and a second layer is deposited under relatively high vacuum pressure where scattering deposition dominates (e.g., above 1 mTorr). For refractory metals like CVD tungsten, the liner can be created in one step using collimated sputtering at higher vacuum pressures.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Preparation of a PH sensor, the prepared PH sensor, system comprising the same and measurement using the system
InactiveUS20070095663A1Reduce sheet resistanceImprove conductivityMaterial electrochemical variablesSputteringTitanium nitride
Preparation of a pH sensor, the prepared pH sensor, system comprising the same, and measurement using the system. The pH sensor is an extended gate field effect transistor (EGFET) structure. The preparation includes the steps of providing an extended gate ion sensitive field effect transistor comprising an extended gate region, forming a titanium nitride film on the extended gate region by RF sputtering deposition to obtain a pH sensor.
Owner:NATIONAL YUNLIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
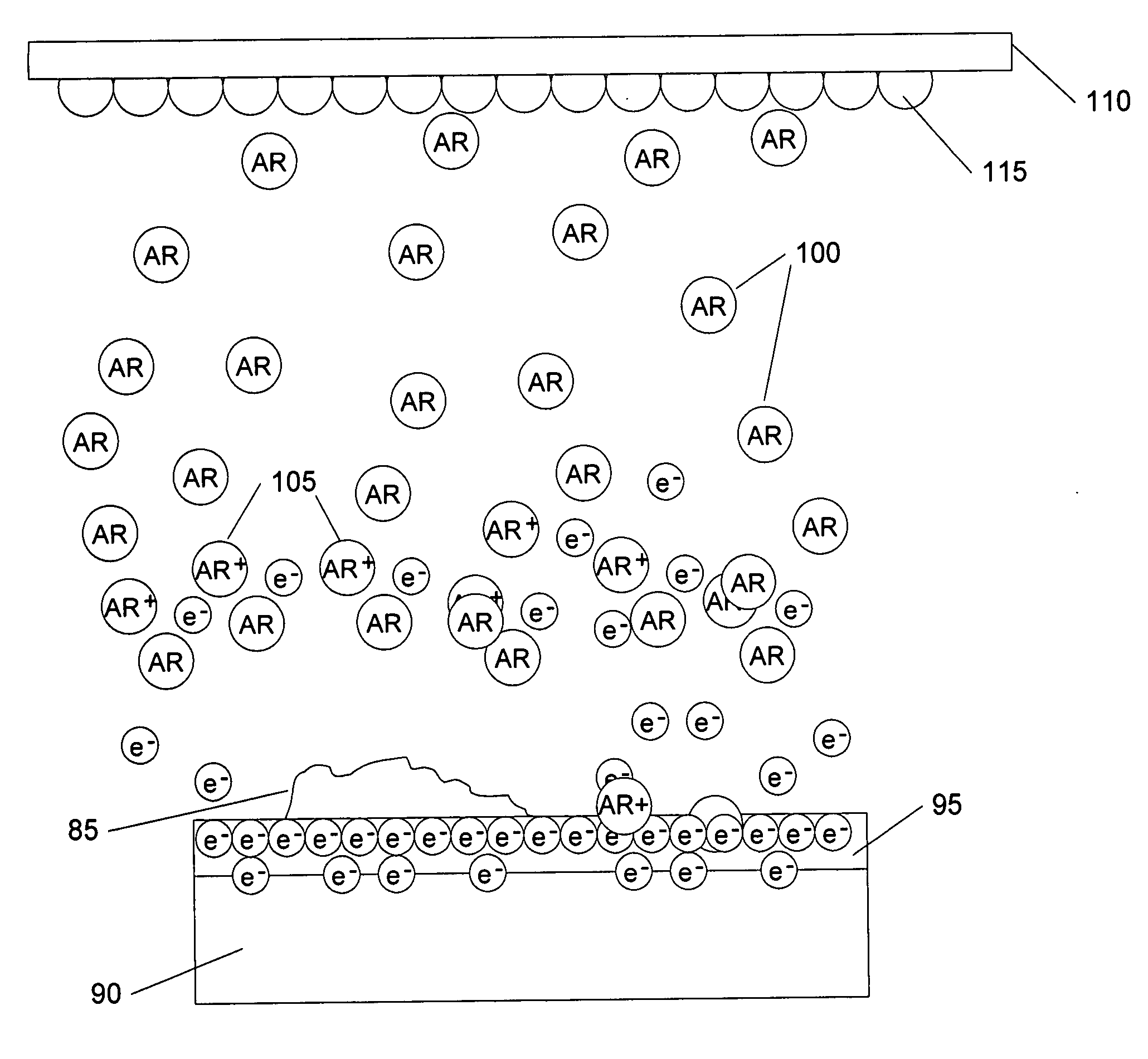
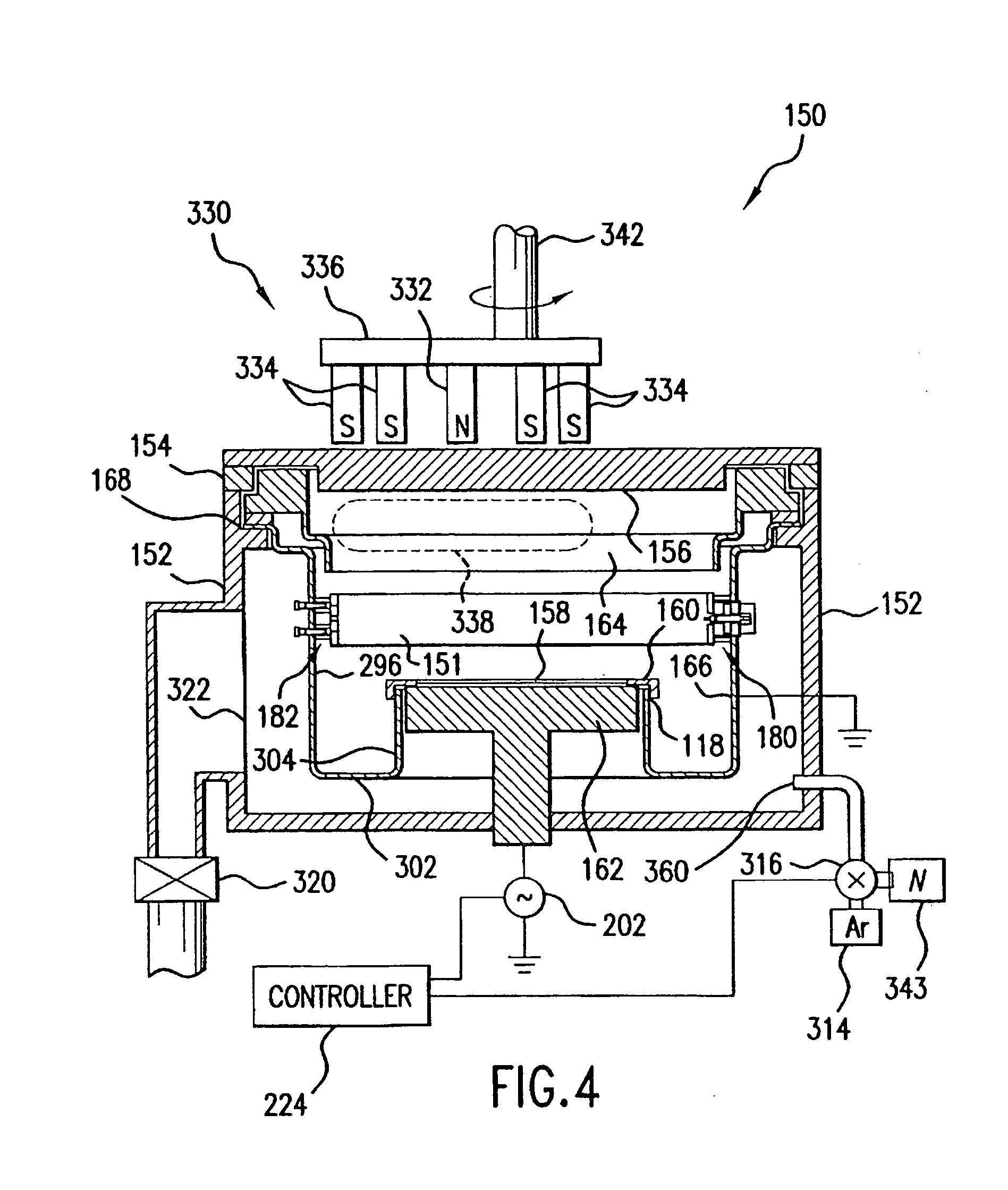
Self-ionized and inductively-coupled plasma for sputtering and resputtering
InactiveUS20050006222A1Raise the ratioReduce layer thicknessCellsElectric discharge tubesSputteringInductively coupled plasma
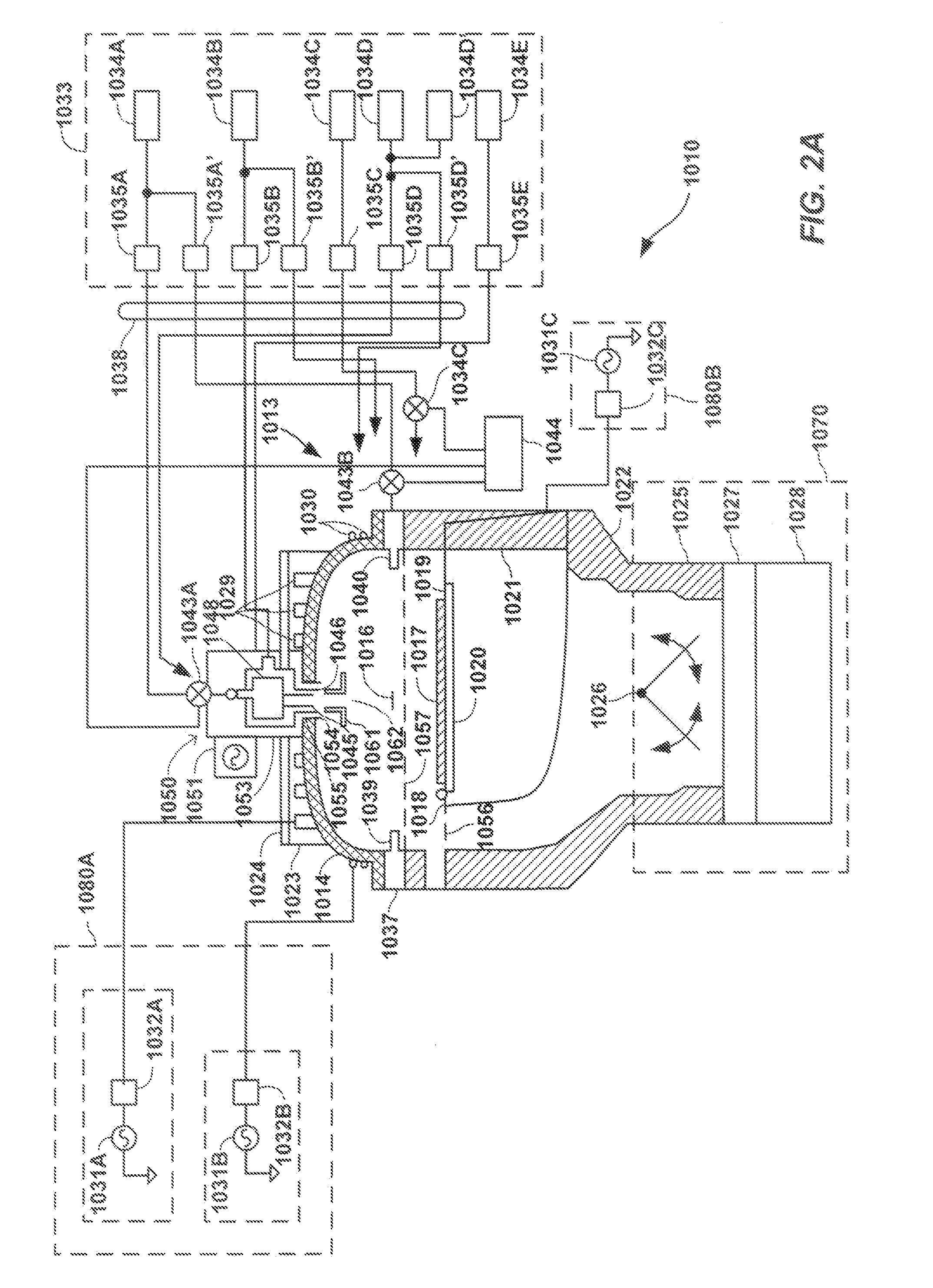
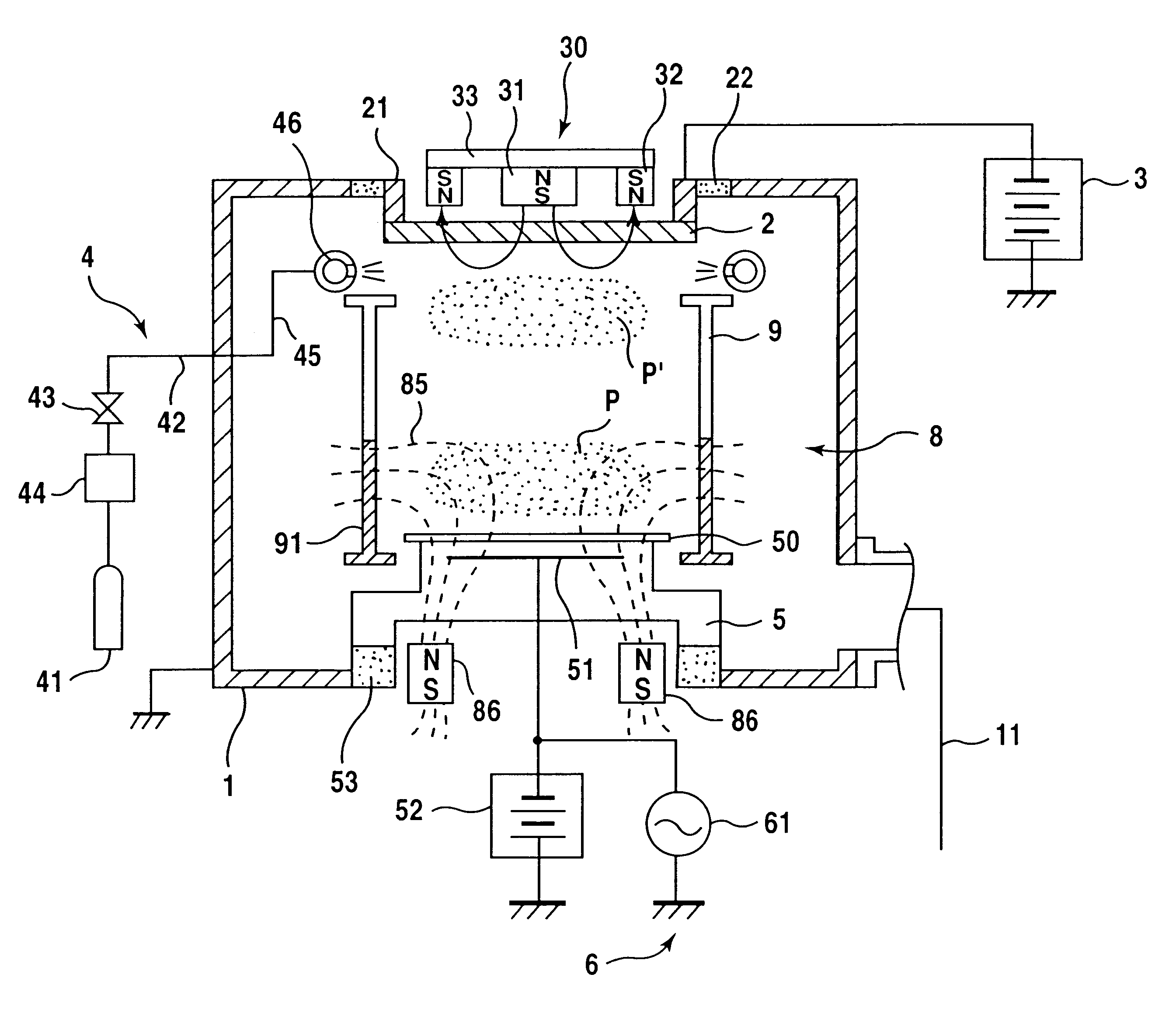
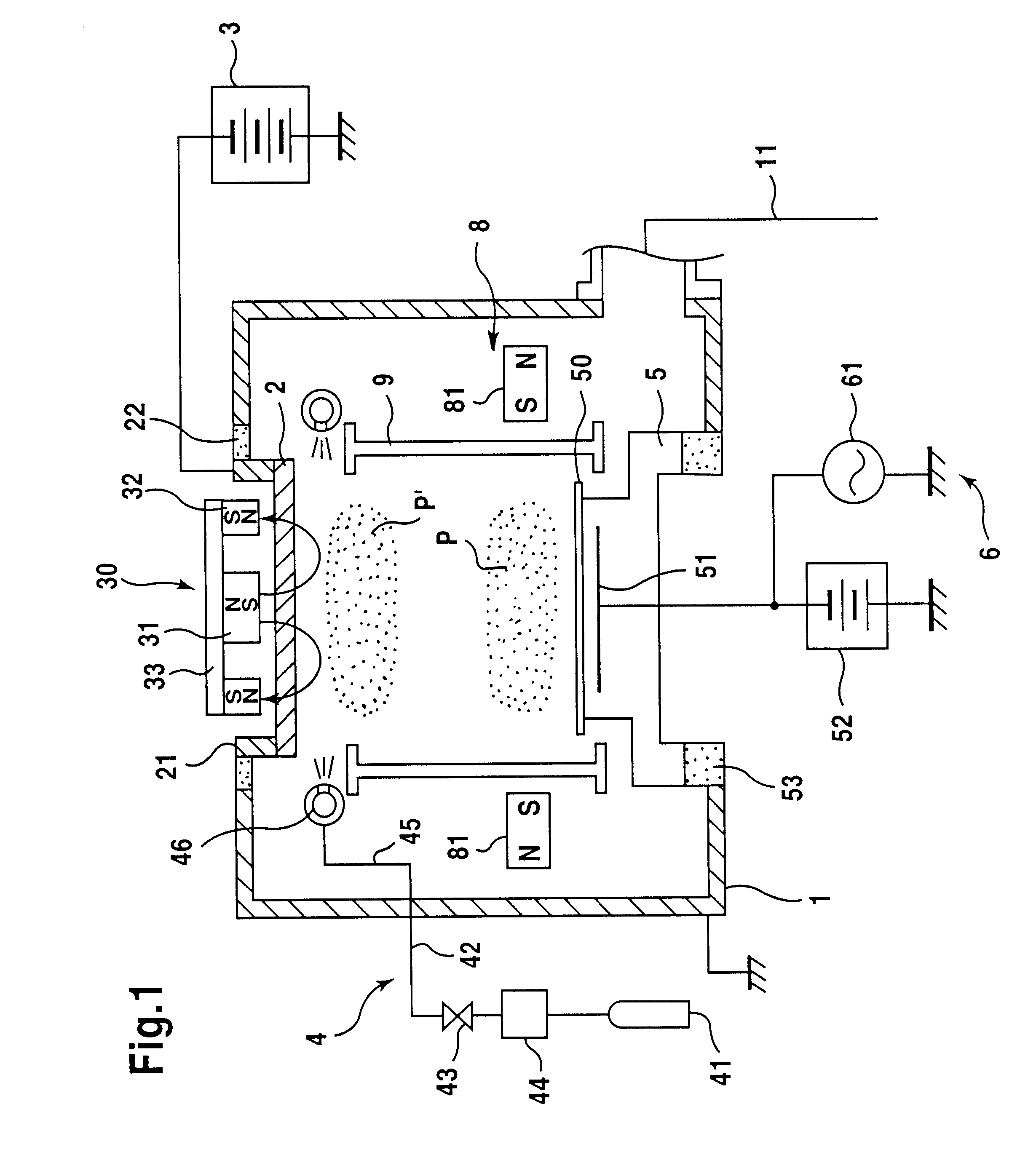
A magnetron sputter reactor (410) and its method of use, in which SIP sputtering and ICP sputtering are promoted is disclosed. In another chamber (412) an array of auxiliary magnets positioned along sidewalls (414) of a magnetron sputter reactor on a side towards the wafer from the target is disclosed. The magnetron (436) preferably is a small one having a stronger outer pole (442) of a first polarity surrounding a weaker inner pole (440) of a second polarity all on a yoke (444) and rotates about the axis (438) of the chamber using rotation means (446, 448, 450). The auxiliary magnets (462) preferably have the first polarity to draw the unbalanced magnetic field (460) towards the wafer (424), which is on a pedestal (422) supplied with power (454). Argon (426) is supplied through a valve (428). The target (416) is supplied with power (434).
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Process for integrated circuit wiring
Metal wiring is provided in an integrated circuit by sputter coating onto a semiconductor substrate a copper seed layer; depositing and patterning a photoresist; electroplating or electrolessly plating a metal within the openings of the photoresist; stripping the remaining photoresist; and etching the copper seed layer with an etchant that preferentially etches the copper seed layer at a rate higher than that for the electroplated or electrolessly plated metal.
Owner:IBM CORP
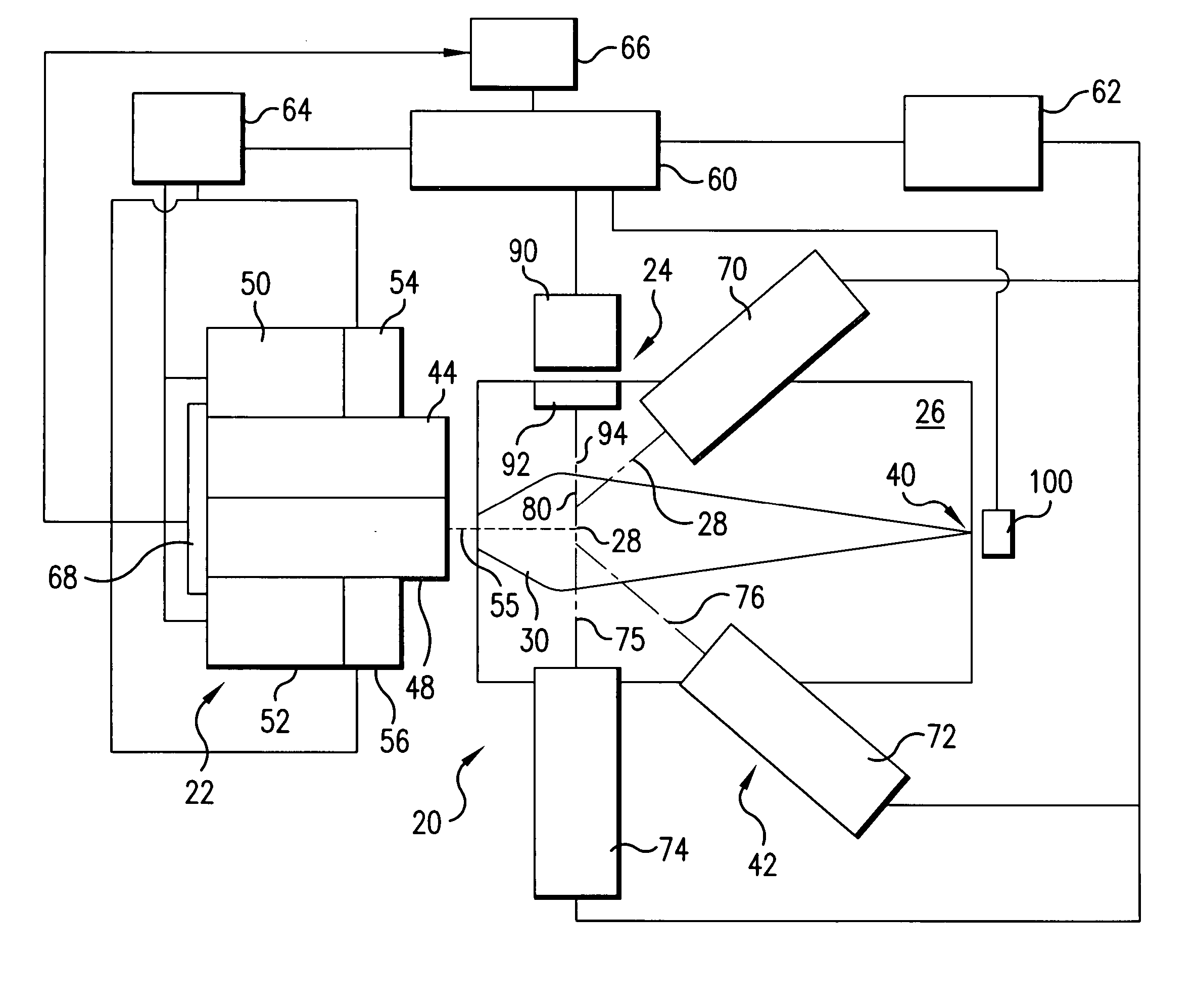
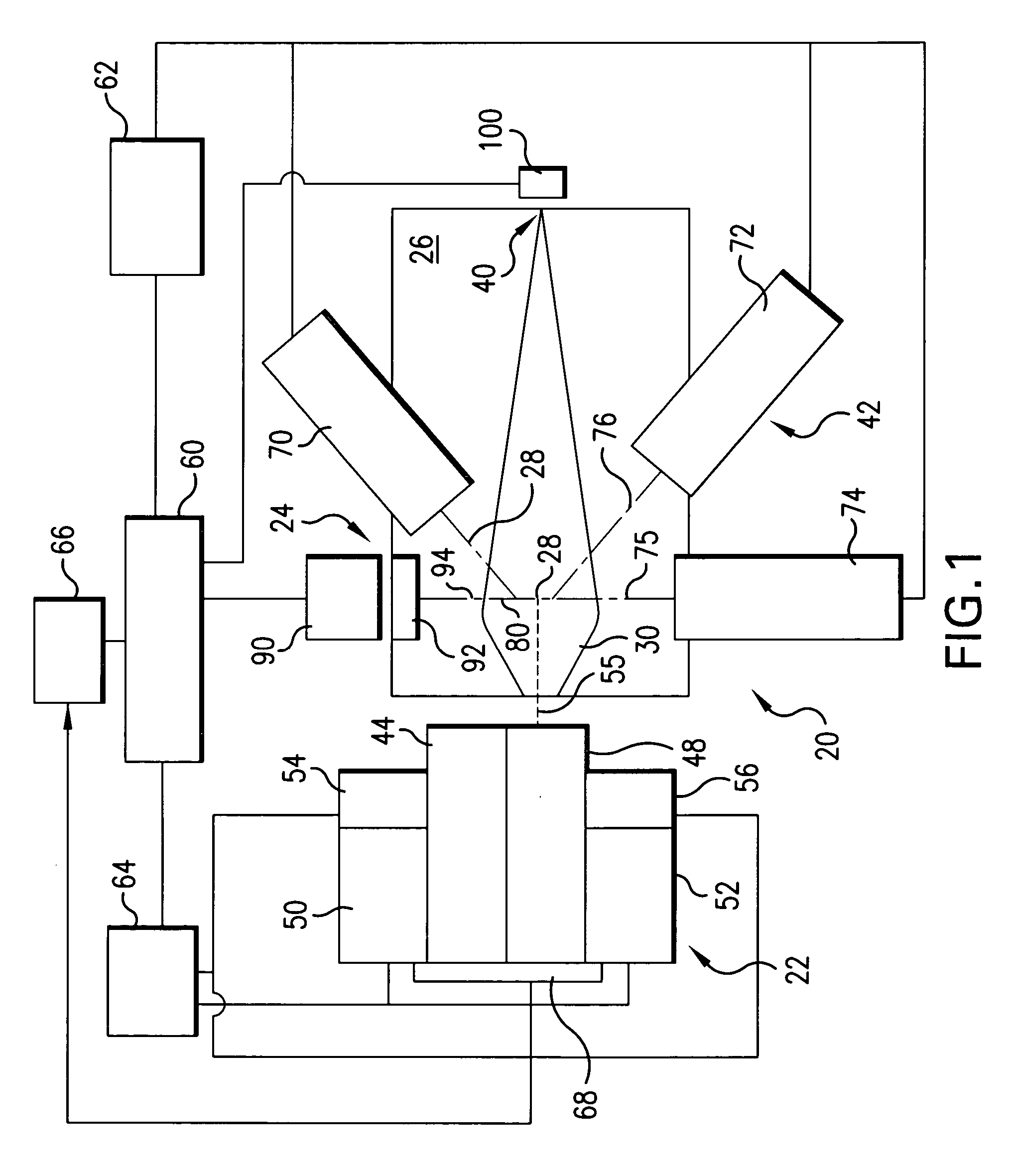
Collector for EUV light source
InactiveUS20060131515A1Increase probabilityReduce probabilityLaser detailsNanoinformaticsSputteringHigh probability
A method and apparatus for debris removal from a reflecting surface of an EUV collector in an EUV light source is disclosed which may comprise the reflecting surface comprises a first material and the debris comprises a second material and / or compounds of the second material, the system and method may comprise a controlled sputtering ion source which may comprise a gas comprising the atoms of the sputtering ion material; and a stimulating mechanism exciting the atoms of the sputtering ion material into an ionized state, the ionized state being selected to have a distribution around a selected energy peak that has a high probability of sputtering the second material and a very low probability of sputtering the first material. The stimulating mechanism may comprise an RF or microwave induction mechanism.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Ionization sputtering apparatus
This invention discloses ionization sputtering apparatuses which have a function for ionizing sputtered particles. Those apparatuses comprise an ionization means for ionizing sputtered particles from a target. The ionization means generates a plasma by applying radio frequency energy with plasma generation gas at an ionization space between the target and a holder holding a substrate. An disclosed apparatus comprises a magnetic device preventing the plasma from diffusing from the ionization space. Another disclosed apparatus comprises a magnetic device which orients the ionized sputtered particles toward the substrate.
Owner:ANELVA CORP
Method of making an implantable medical device
InactiveUS20050033412A1Improve retentionReduce deliveryStentsLayered productsSputteringMedical device
An implantable medical device, such as a stent or graft, having asperities on a designated region of its outer surface is disclosed. The asperities can serve to improve retention of one or more layers of a coating on the device and to increase the amount of coating that can be carried by the device. The asperities can be formed by using a stream of pressurized grit to roughen the surface. The asperities can also be formed by removing material from the outer surface, for example, by chemical etching with or without a patterned mask. Alternatively, the asperities can be formed by adding material to the outer surface, for example, by welding powder particles to the outer surface or sputtering.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Metal/semiconductor/metal (MSM) back-to-back Schottky diode
ActiveUS20070015330A1Inhibit currentHigh voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseEngineering
A method is provided for forming a metal / semiconductor / metal (MSM) back-to-back Schottky diode from a silicon (Si) semiconductor. The method deposits a Si semiconductor layer between a bottom electrode and a top electrode, and forms a MSM diode having a threshold voltage, breakdown voltage, and on / off current ratio. The method is able to modify the threshold voltage, breakdown voltage, and on / off current ratio of the MSM diode in response to controlling the Si semiconductor layer thickness. Generally, both the threshold and breakdown voltage are increased in response to increasing the Si thickness. With respect to the on / off current ratio, there is an optimal thickness. The method is able to form an amorphous Si (a-Si) and polycrystalline Si (polySi) semiconductor layer using either chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or DC sputtering. The Si semiconductor can be doped with a Group V donor material, which decreases the threshold voltage and increases the breakdown voltage.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS20130040167A1Suppress interferenceIncrease in ultra-high recording densityRecord information storageCoating by sputteringSputteringAlloy
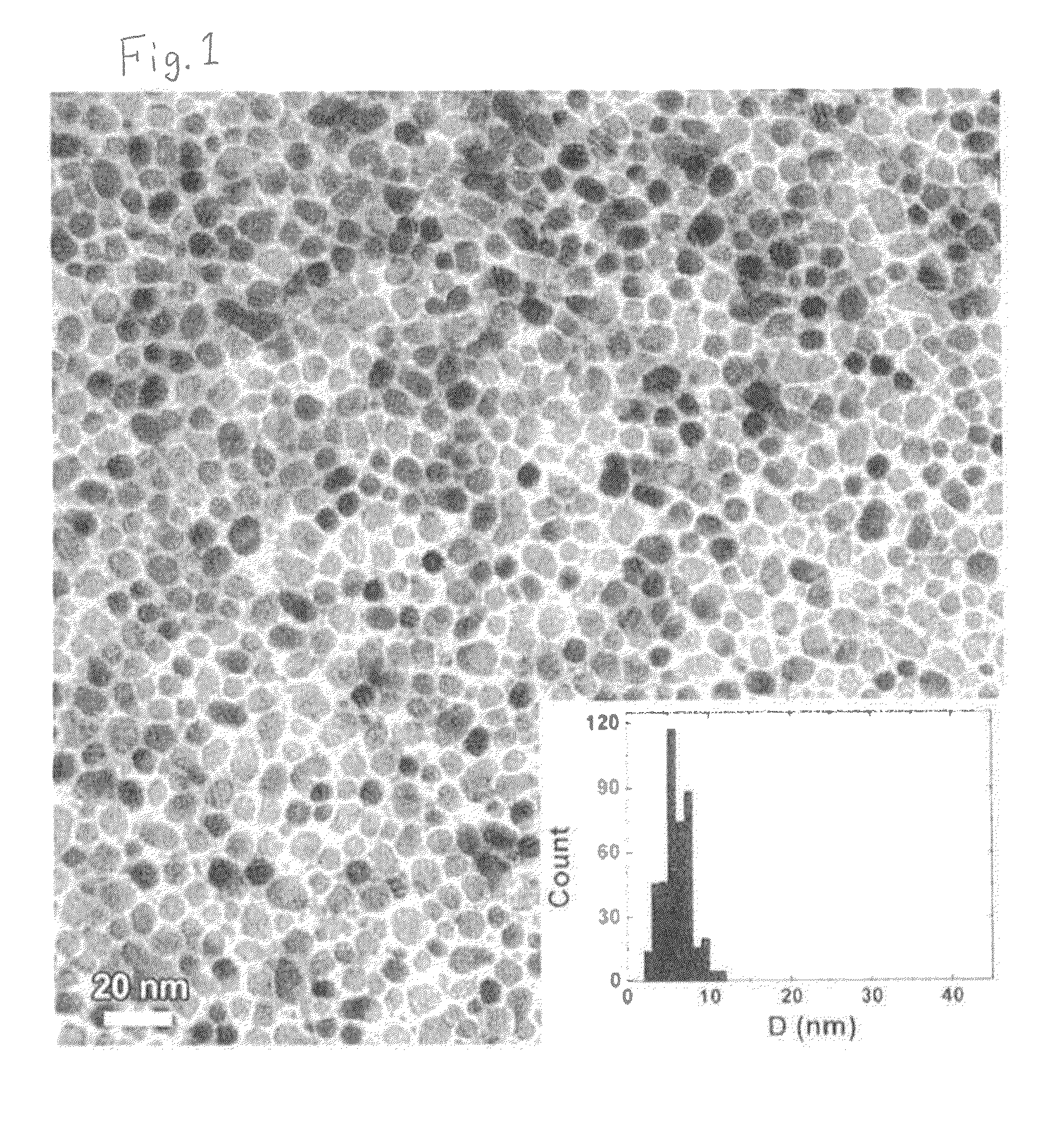
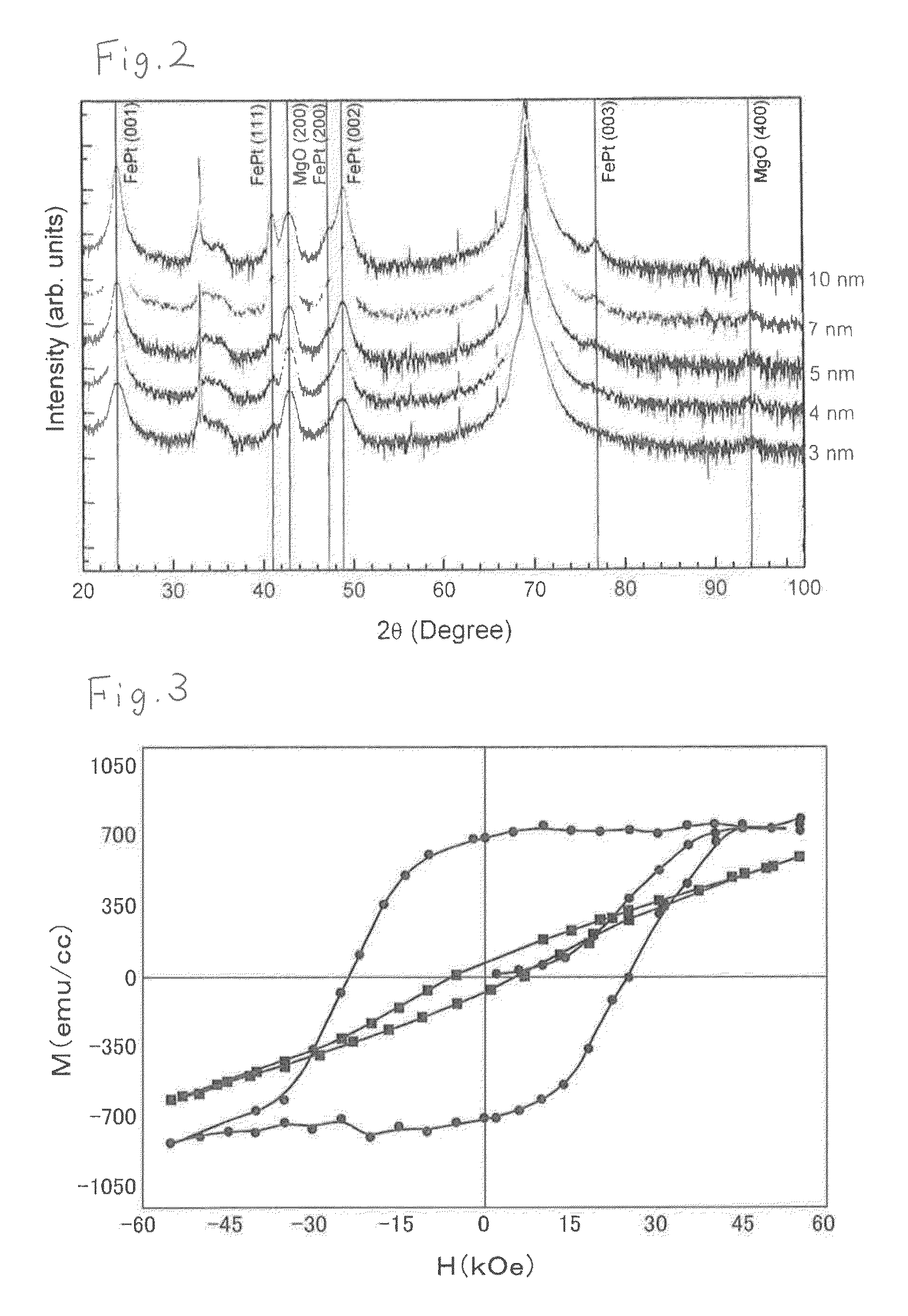
It is aimed to provide a perpendicular magnetic recording medium capable of dealing with an ultra-higher recording density than before and its manufacturing method.The present invention concerns a perpendicular magnetic recording medium including at least a seed layer made of noncrystalline ceramic, a crystalline orientation control layer and a magnetic layer made of a material mainly containing a FePt alloy in this order on a substrate. This perpendicular magnetic recording medium is suitably manufactured by forming at least the seed layer, the orientation control layer and the magnetic layer made of the material mainly containing the FePt alloy in this order on the substrate by sputtering, wherein the magnetic layer is formed at a predetermined temperature of 500° C. or less.
Owner:WD MEDIA SINGAPORE PTE +1
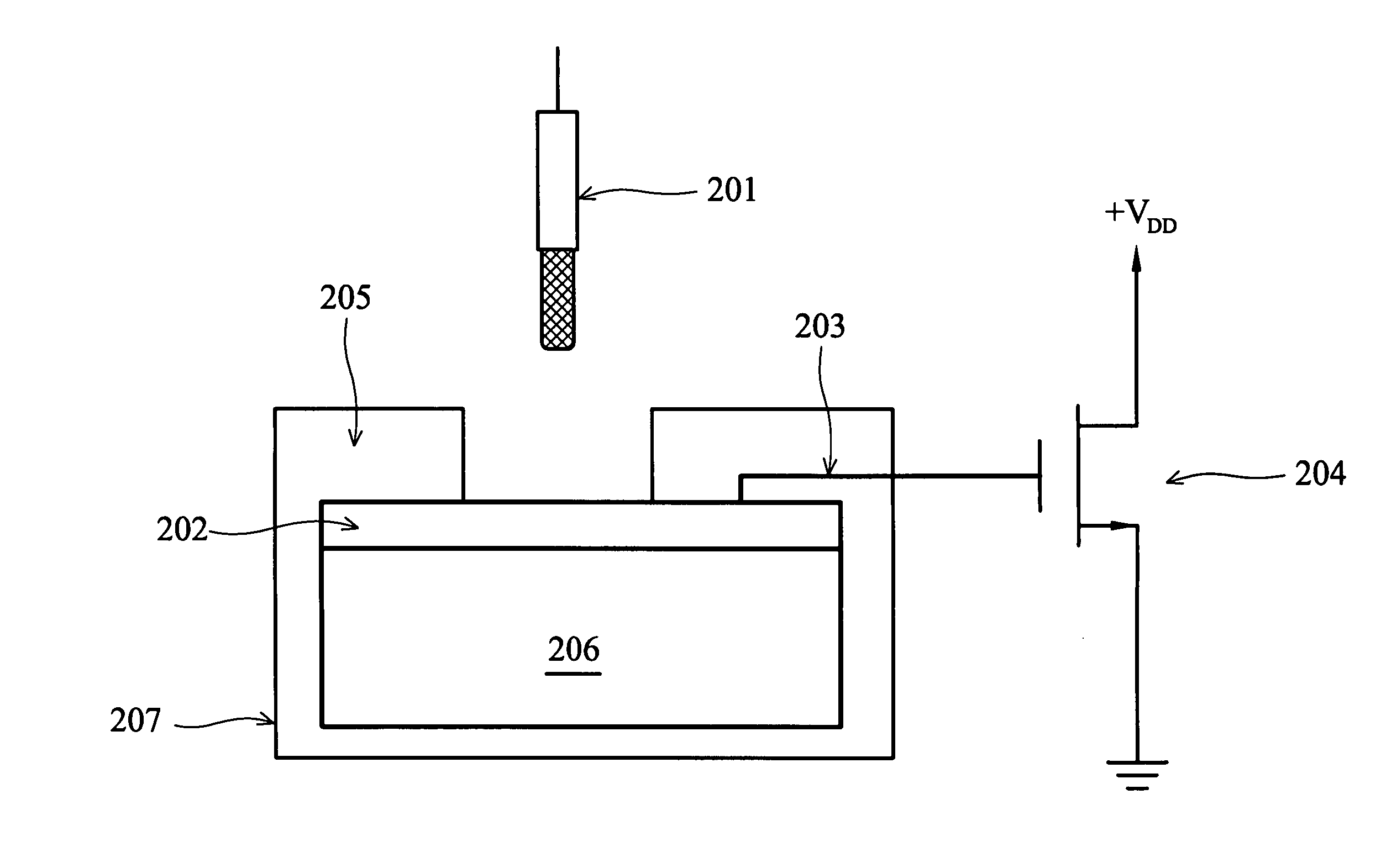
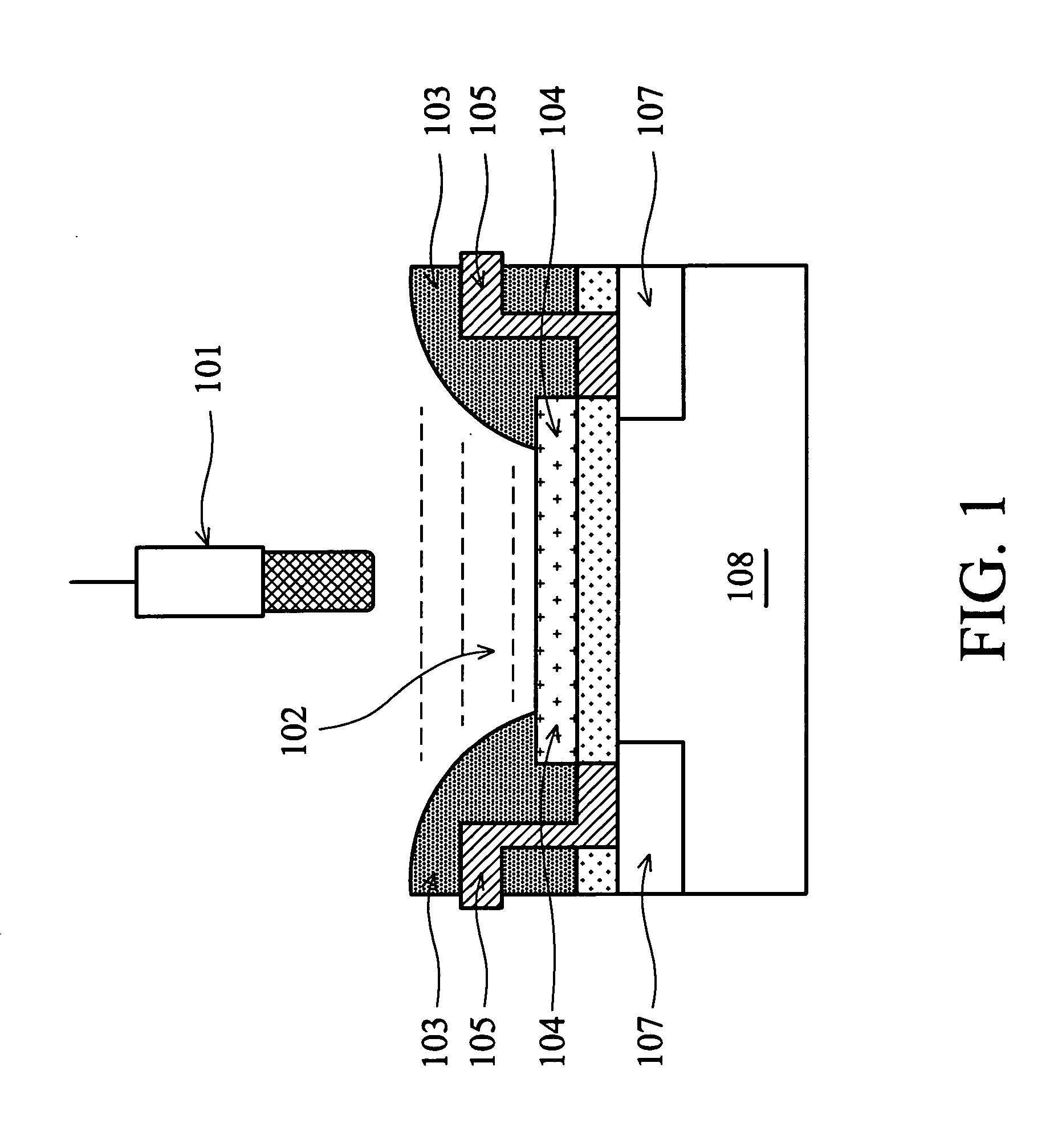
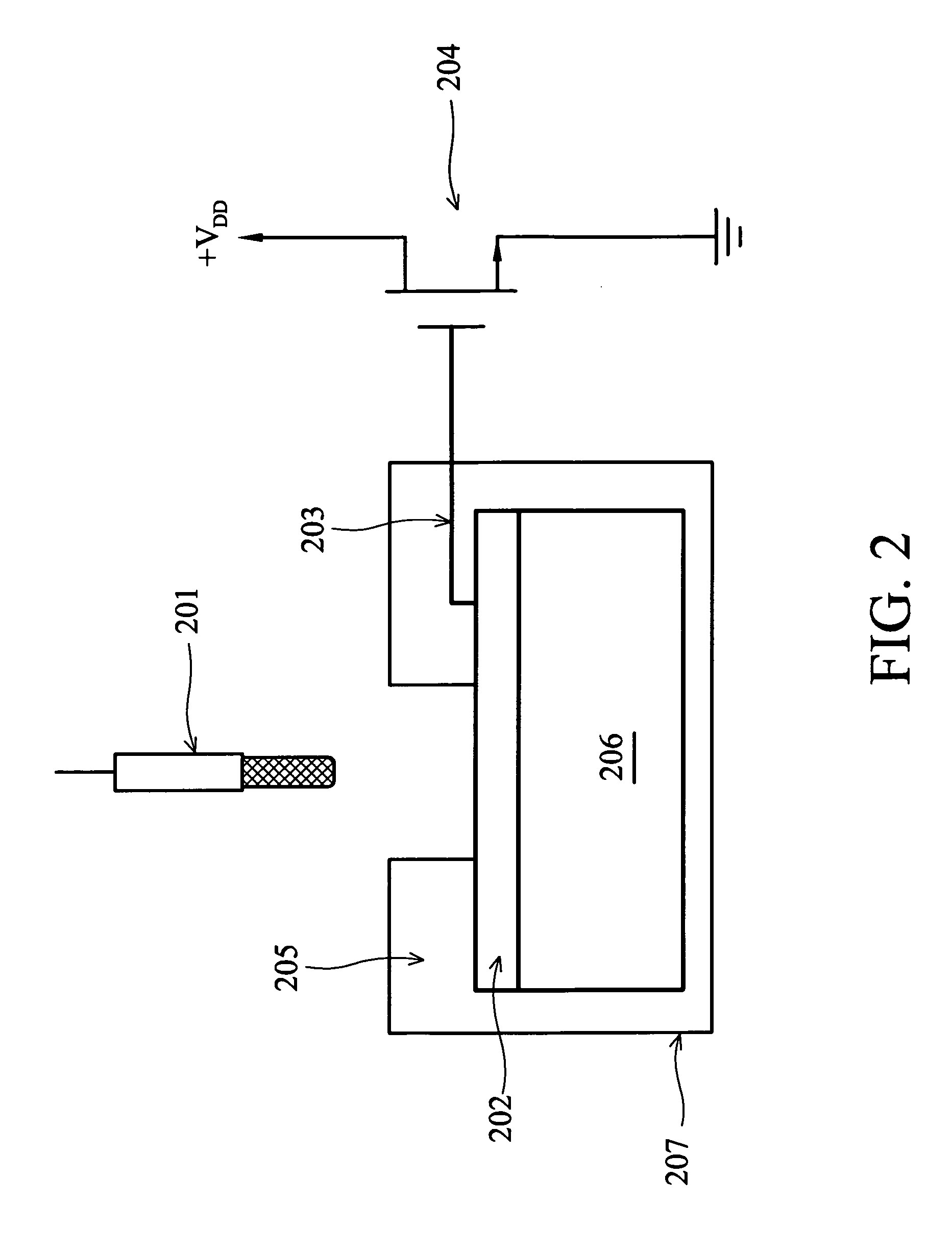
Diagnostic ultrasound transducer
ActiveUS20090034370A1Easy to guaranteeGood electrical contactUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesUltrasonic sensorEngineering
An ultrasound transducer includes an array of PZT elements mounted on a non-recessed distal surface of a backing block. Between each element and the backing block is a conductive region formed as a portion of a metallic layer sputtered onto the distal surface. Traces on a longitudinally extending circuit board—preferably, a substantially rigid printed circuit board, which may be embedded within the block—connect the conductive region, and thus the PZT element, with any conventional external ultrasound imaging system. A substantially “T” or “inverted-L” shaped electrode is thereby formed for each element, with no need for soldering. At least one longitudinally extending metallic member mounted on a respective lateral surface of the backing block forms a heat sink and a common electrical ground. A thermally and electrically conductive layer, such as of foil, transfers heat from at least one matching layer mounted on the elements to the metallic member.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY SCIENTIFIC CO LTD
Molybdenum sputtering targets
InactiveUS20060042728A1High purityImprove performanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDevice materialThin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display
Molybdenum, sputtering targets and sintering characterized as having no or minimal texture banding or through thickness gradient. The molybdenum sputtering targets having a fine, uniform grain size as well as uniform texture, are high purity and can be micro-alloyed to improved performance. The sputtering targets can be round discs, square, rectangular or tubular and can be sputtered to form thin films on substrates. By using a segment-forming method, the size of the sputtering target can be up to 6 m×5.5 m. The thin films can be used in electronic components such as Thin Film Transistor—Liquid Crystal Displays, Plasma Display Panels, Organic Light Emitting Diodes, Inorganic Light Emitting Diode Displays, Field Emission Displays, solar cells, sensors, semiconductor devices, and gate device for CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) with tunable work functions.
Owner:H C STARCK INC
High pressure rf-dc sputtering and methods to improve film uniformity and step-coverage of this process
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a processing chamber used to perform a physical vapor deposition (PVD) process and methods of depositing multi-compositional films. The processing chamber may include: an improved RF feed configuration to reduce any standing wave effects; an improved magnetron design to enhance RF plasma uniformity, deposited film composition and thickness uniformity; an improved substrate biasing configuration to improve process control; and an improved process kit design to improve RF field uniformity near the critical surfaces of the substrate. The method includes forming a plasma in a processing region of a chamber using an RF supply coupled to a multi-compositional target, translating a magnetron relative to the multi-compositional target, wherein the magnetron is positioned in a first position relative to a center point of the multi-compositional target while the magnetron is translating and the plasma is formed, and depositing a multi-compositional film on a substrate in the chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
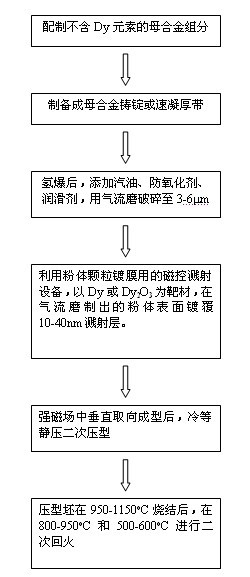
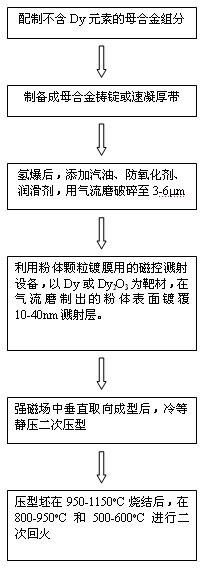
A preparation method of high-performance sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium content
The invention discloses a method for preparing sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium (Dy) content and high performance; the method comprises the following steps of: sputtering and plating the Dy element on the surface of jet mill powder by using the powder plate technology based on magnetron sputtering on the basis of preparing NdFeB powder, and then sufficiently dispersing the Dy element to micron-sized NdFeB crystal particles by dispersing the Dy element at high temperature in the sintering and tempering process, thereby achieving the effect of improving magnetic performance of the sintered NdFeB. Compared with the introduction of the Dy element in the proportioning process of the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages: the low dysprosium content and high performance is limited in the nano-size by adopting the physical gas-phase deposition, the consumption quantity of the Dy element during the production process is controlled effectively and the preparationof sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium content and high performance is realized. Compared with the sintered NdFeB of the same components prepared by the traditional casting and powder metallurgy process, both the intrinsic coercivity and the maximum magnetic energy product of the sintered NdFeB rare-earth permanent magnetic material obtained according to the invention are improved obviously; compared with the sintered NdFeB with the same performance prepared by the traditional casting and powder metallurgy process, the dosage of the dysprosium element is reduced remarkably. The method can be widely applicable to producing and manufacturing sintered NdFeB with high performance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
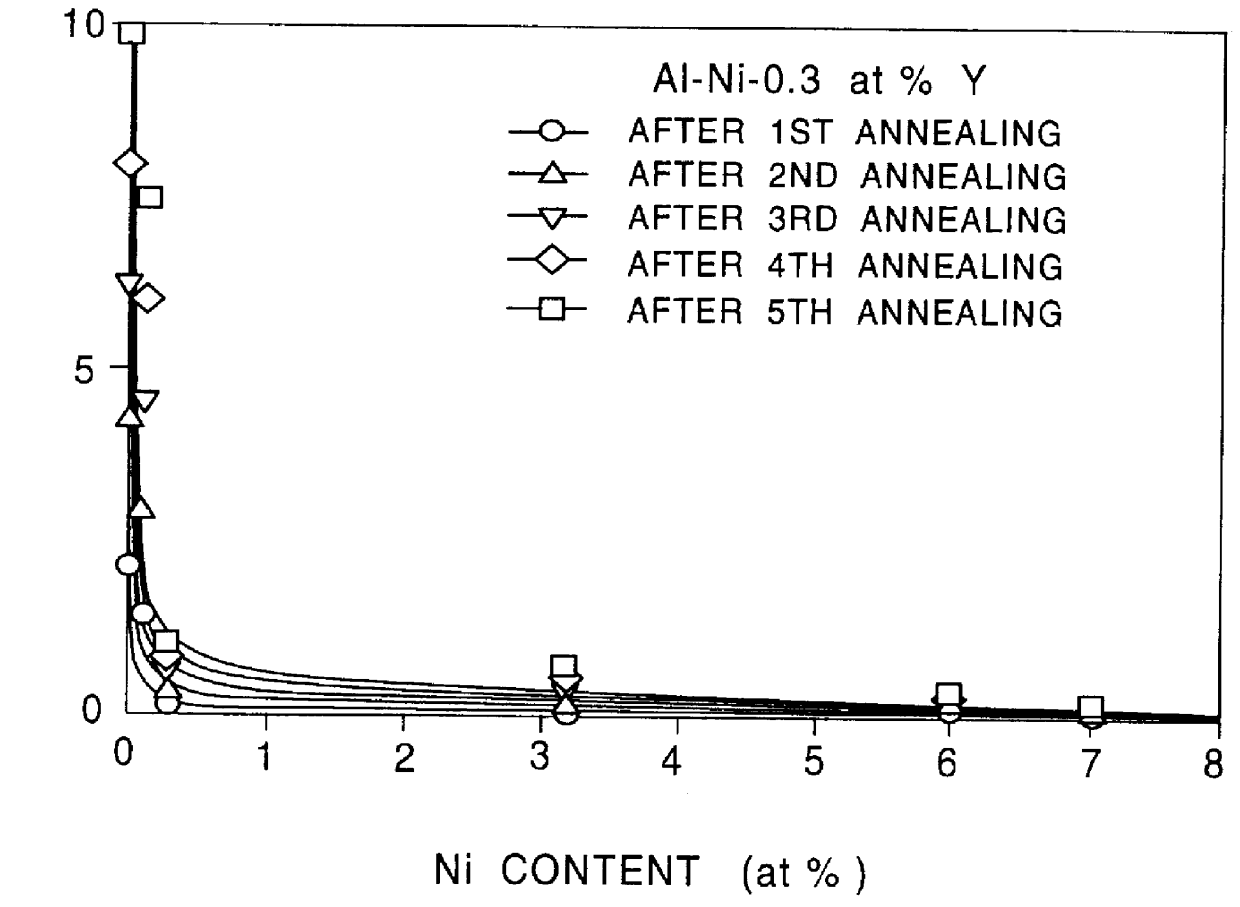
A1-N1-Y alloy films for electrodes of semiconductor devices and sputtering targets for depositing the A1-N1-Y alloy films
The invention provides an Al alloy film for use as an electrode of a semiconductor device and also provides an Al alloy sputtering target used to produce such an Al alloy film wherein the Al alloy film has not only a low resistivity equal to or less than 5 mu OMEGA cm and a high hillock resistance (property of hillock suppression) but also a high dielectric strength when it is anodized into an anodic oxide film and wherein the Al alloy film has a composition such that the Ni content is equal to or greater than 0.3 at % and the Y content is equal to or greater than 0.3 at % and such that 0.22 CNi+0.74 CY<1.6 at % where CNi denotes the Ni content (at %) and CY denotes the Y content (at %) and further wherein, in order to deposit the Al alloy film by sputtering, a spray forming Al alloy target containing Ni and Y is used.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com