Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7568 results about "Breakdown voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
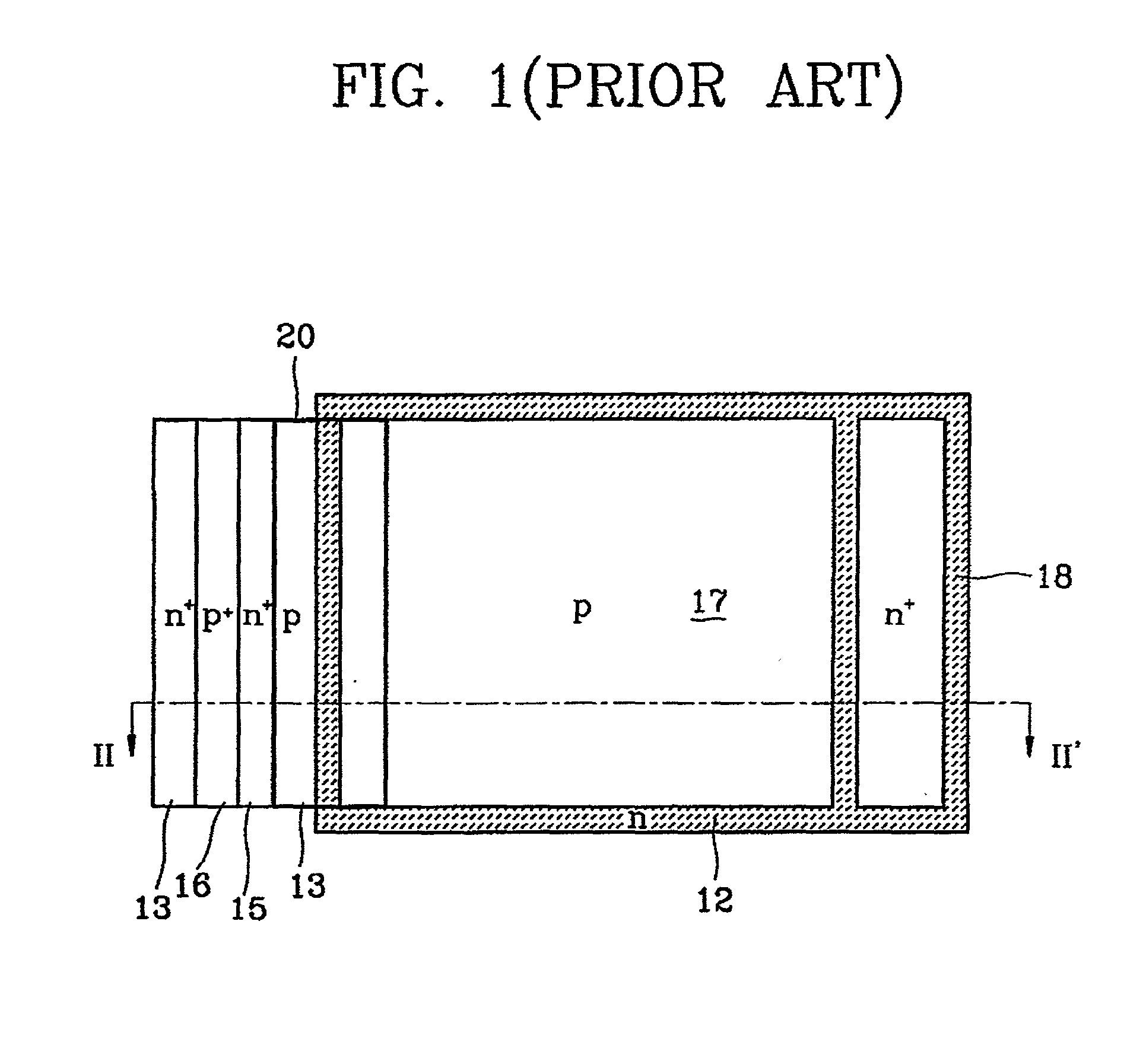
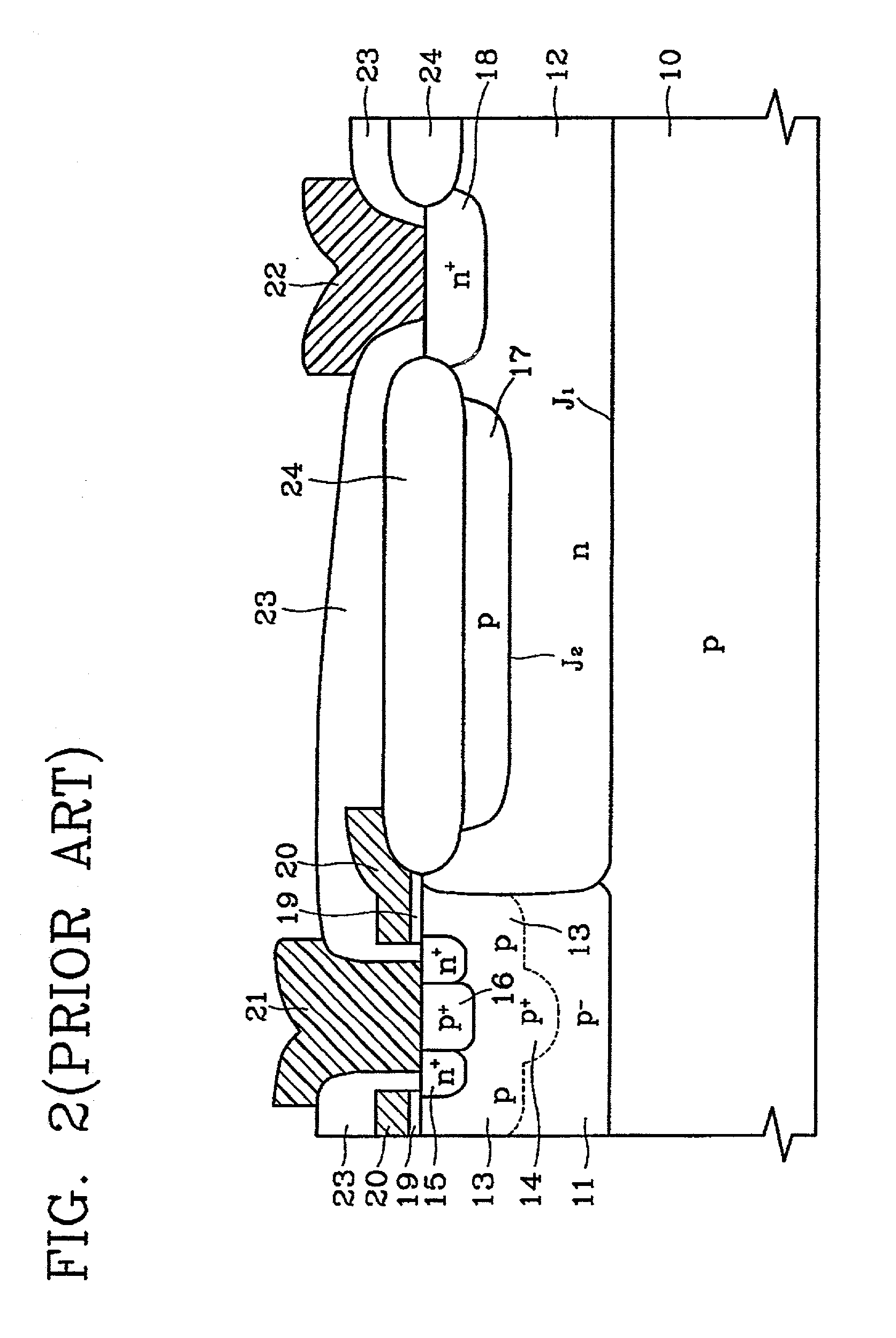
The breakdown voltage of an insulator is the minimum voltage that causes a portion of an insulator to become electrically conductive. For diodes, the breakdown voltage is the minimum reverse voltage that makes the diode conduct appreciably in reverse. Some devices (such as TRIACs) also have a forward breakdown voltage.
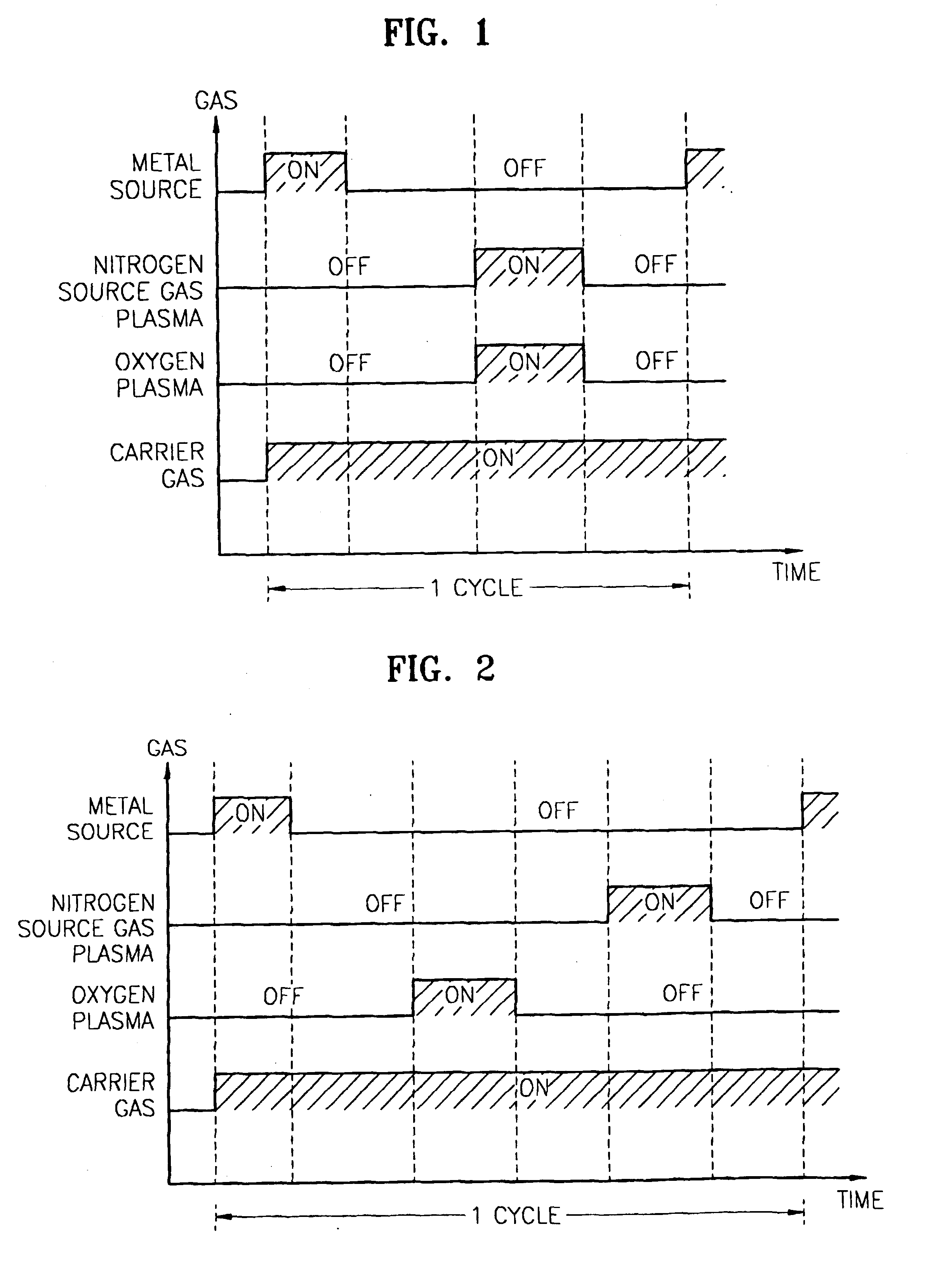
Method for forming introgen-containing oxide thin film using plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition
InactiveUS20040077182A1Density of thinThin rateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHigh rateNitrogen source
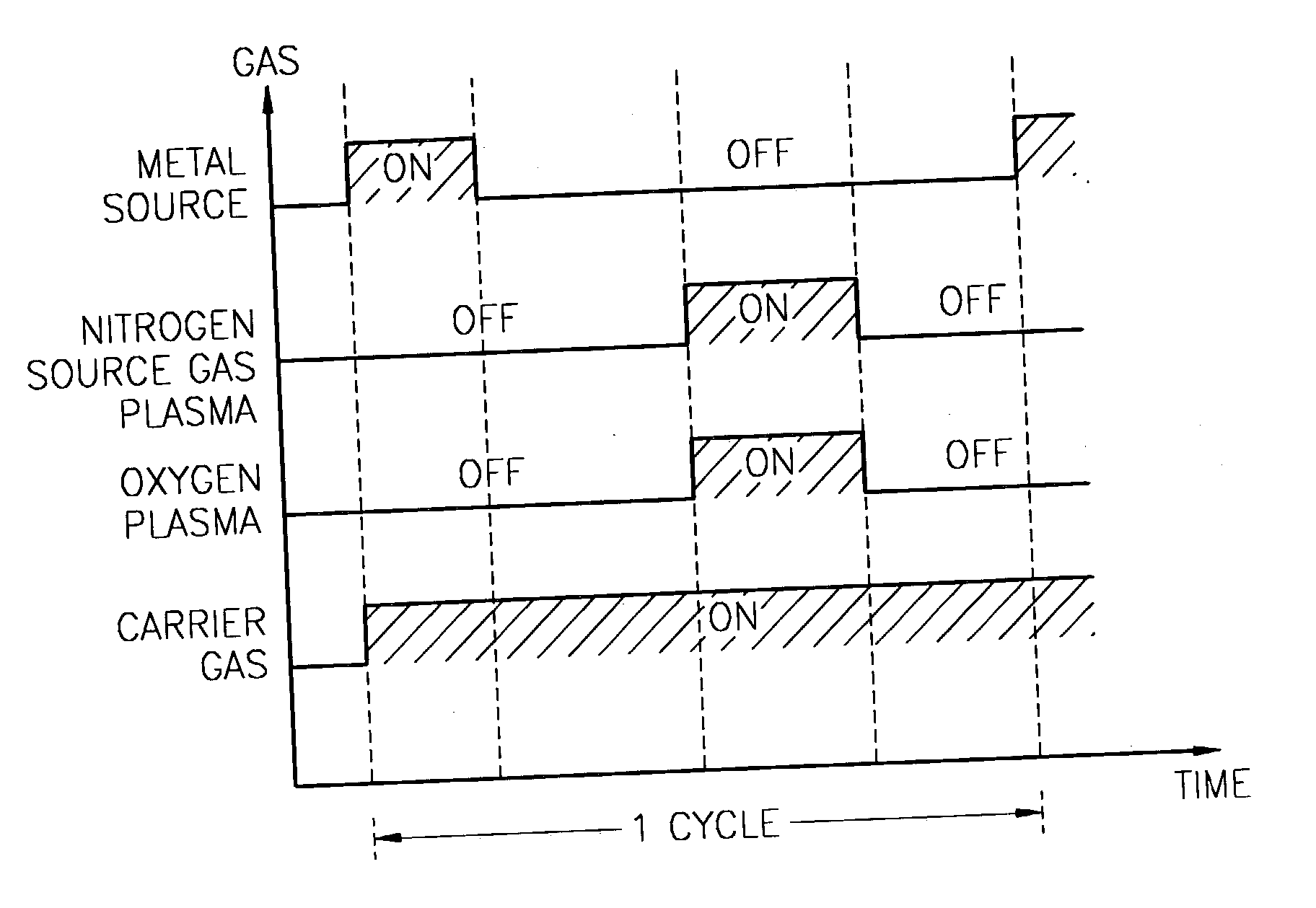
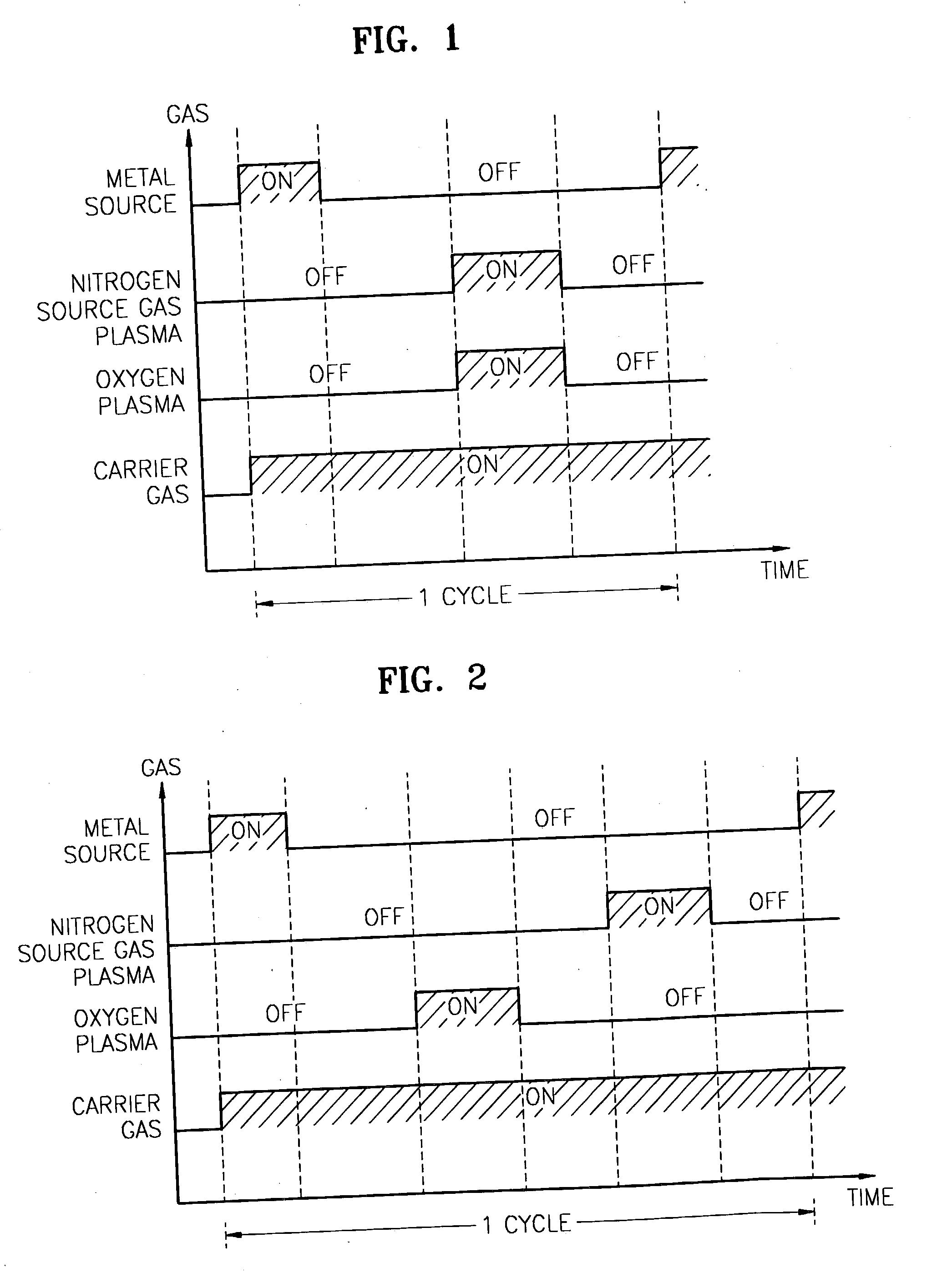
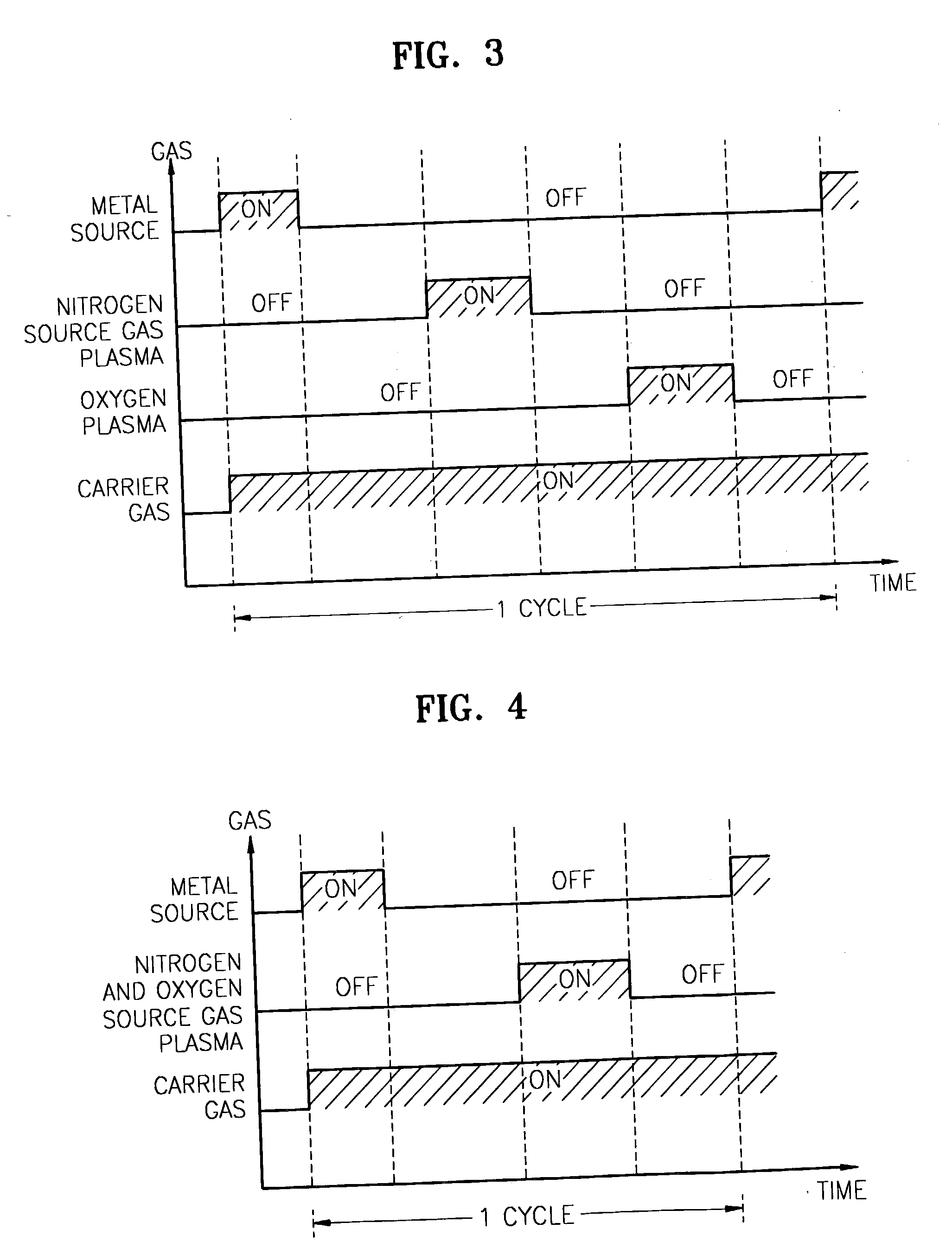
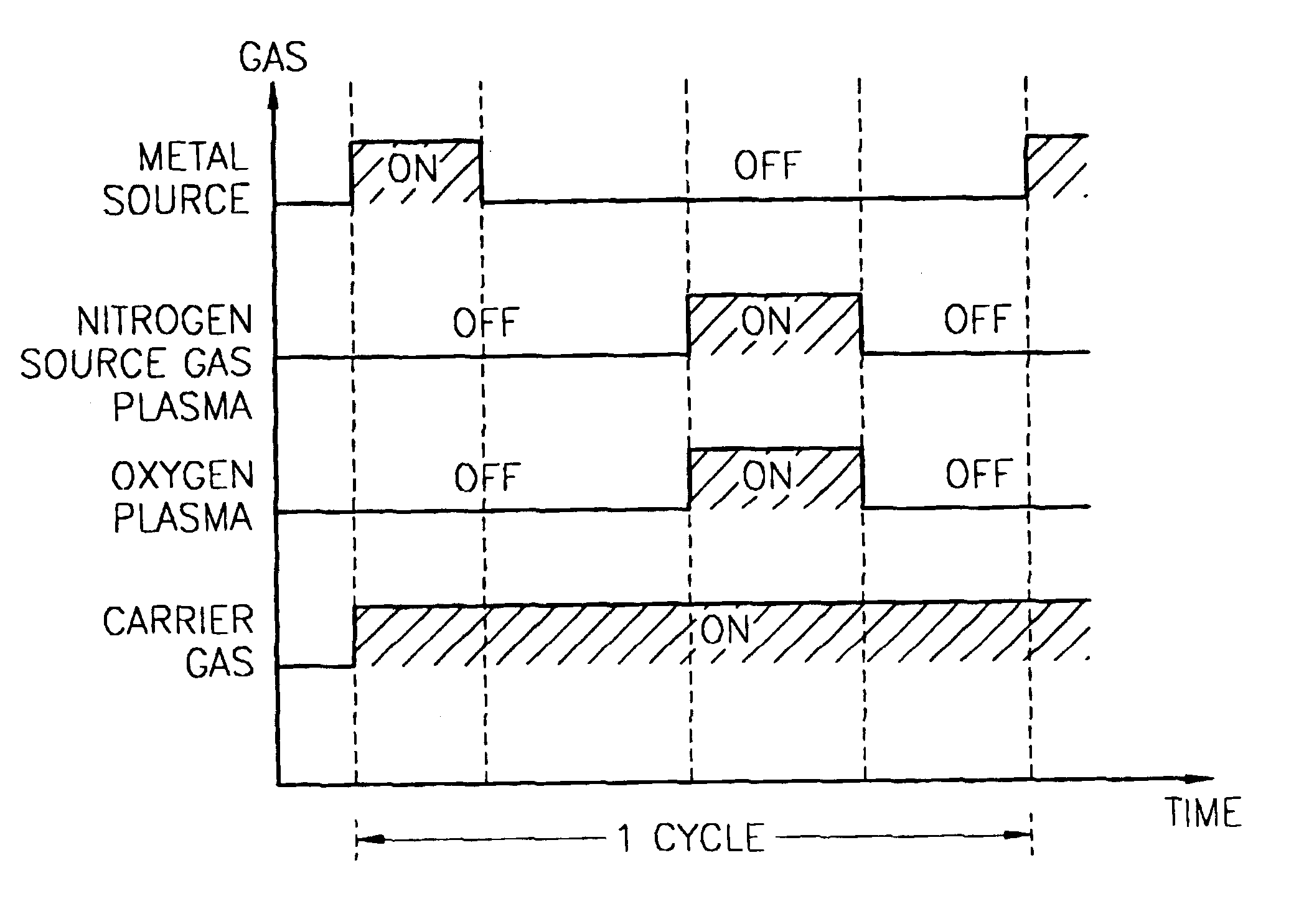
A method for forming a nitrogen-containing oxide thin film by using plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition is provided. In the method, the nitrogen-containing oxide thin film is deposited by supplying a metal source compound and oxygen gas into a reactor in a cyclic fashion with sequential alternating pulses of the metal source compound and the oxygen gas, wherein the oxygen gas is activated into plasma in synchronization of the pulsing thereof, and a nitrogen source gas is further sequentially pulsed into the reactor and activated into plasma over the substrate in synchronization with the pulsing thereof. According to the method, a dense nitrogen-containing oxide thin film can be deposited at a high rate, and a trace of nitrogen atoms can be incorporated in situ into the nitrogen-containing oxide thin film, thereby increasing the breakdown voltage of the film.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
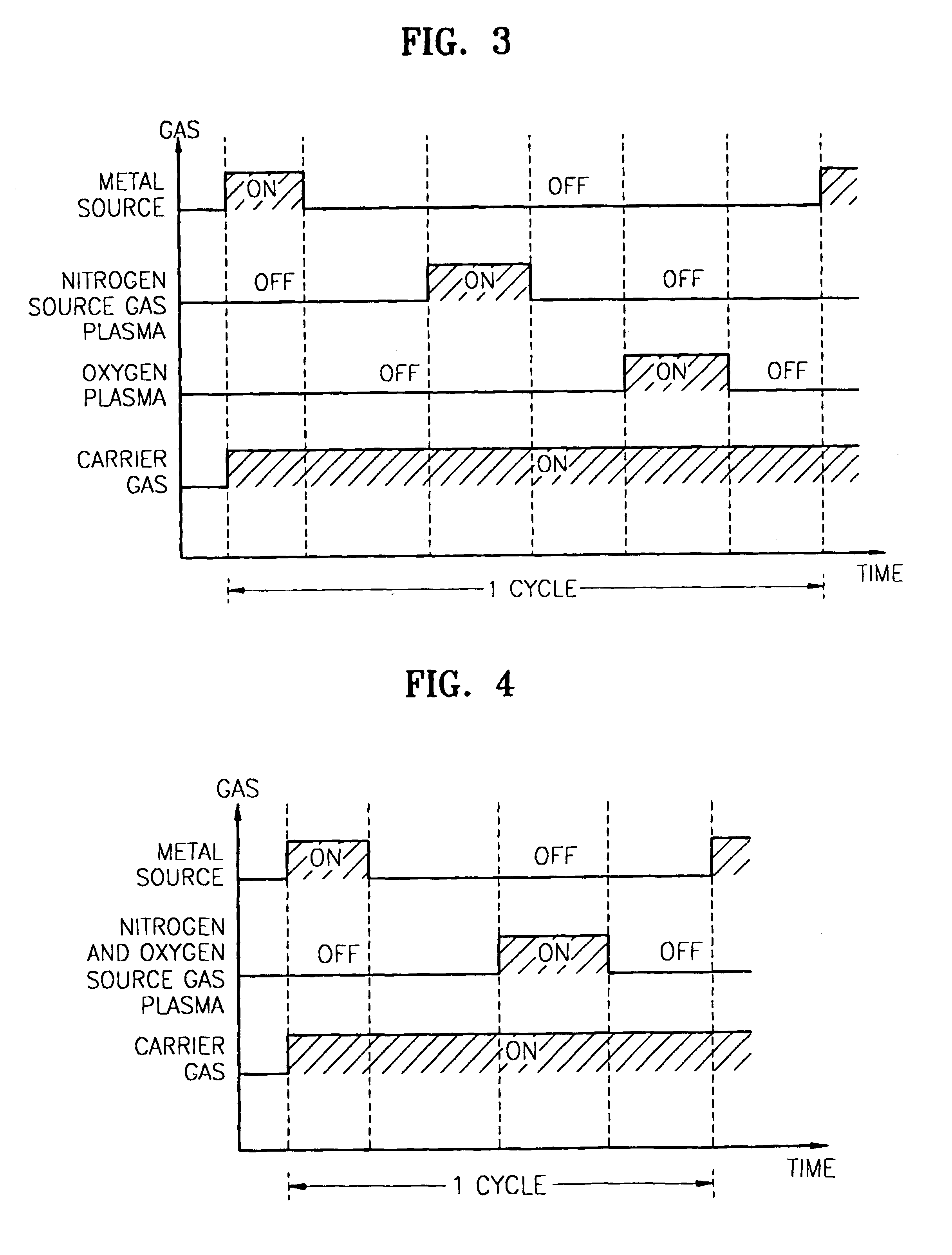
Method for forming nitrogen-containing oxide thin film using plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition
InactiveUS6723642B1Density of thinThin rateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingNitrogen sourceNitrogen oxide
A method for forming a nitrogen-containing oxide thin film by using plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition is provided. In the method, the nitrogen-containing oxide thin film is deposited by supplying a metal source compound and oxygen gas into a reactor in a cyclic fashion with sequential alternating pulses of the metal source compound and the oxygen gas, wherein the oxygen gas is activated into plasma in synchronization of the pulsing thereof, and a nitrogen source gas is further sequentially pulsed into the reactor and activated into plasma over the substrate in synchronization with the pulsing thereof. According to the method, a dense nitrogen-containing oxide thin film can be deposited at a high rate, and a trace of nitrogen atoms can be incorporated in situ into the nitrogen-containing oxide thin film, thereby increasing the breakdown voltage of the film.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
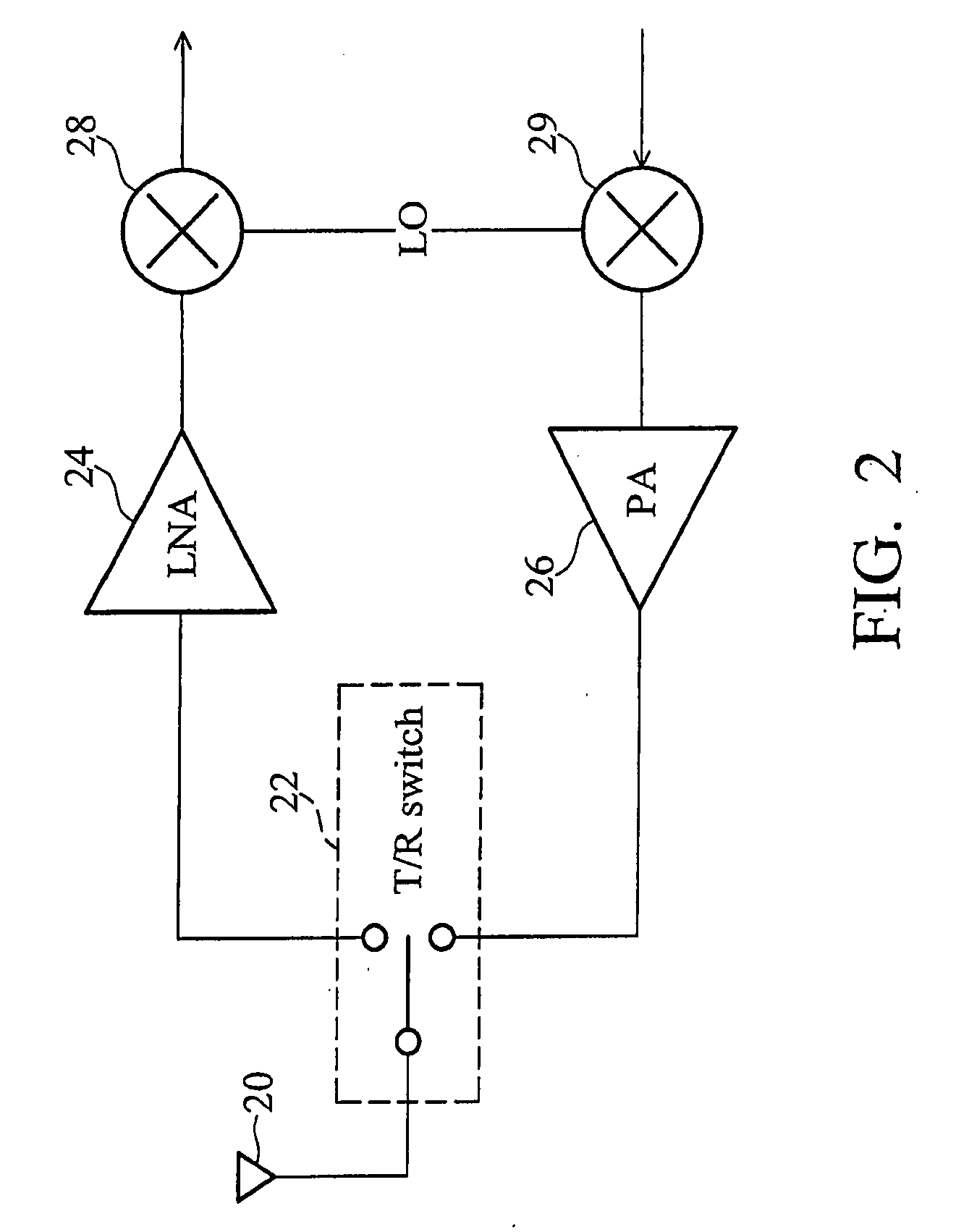
Transmit/receive switch
ActiveUS20090036065A1Reduce noiseMultiple-port networksResonant long antennasEngineeringImpedance matching
A radio frequency (RF) transmit / receive switch. The transmit / receive switch comprises an impedance matching circuit and a voltage scaling circuit. The impedance matching circuit matches an incoming RF signal to a low noise amplifier and an outgoing RF signal from a power amplifier. The voltage scaling circuit, coupled to the impedance matching circuit, the power amplifier, and the low noise amplifier, attenuates the outgoing RF signal to a scaled signal within a breakdown voltage of a transistor device in the low noise amplifier during transmission of the outgoing RF signal.
Owner:MEDIATEK USA INC
Silicon carbide semiconductor device and silicon carbide semiconductor device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20160336392A1Lower on-resistanceImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor devicesDevice materialSemiconductor
A silicon carbide semiconductor device capable of achieving a decrease in ON resistance and an increase in breakdown voltage and a method for manufacturing a silicon carbide semiconductor device. A silicon carbide semiconductor device includes a silicon carbide substrate and a drift layer. The drift layer includes a breakdown voltage holding layer extending from a point where a doping concentration has a predetermined value to a surface of the drift layer. The doping concentration in the breakdown voltage holding layer continuously decreases from the point where the doping concentration has the predetermined value to a modulation point located further toward the surface of the drift layer than a midpoint in a film thickness direction of the breakdown voltage holding layer. The doping concentration in the breakdown voltage holding layer continuously increases from the modulation point to the surface of the drift layer.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Power MOSFET having laterally three-layered structure formed among element isolation regions
A semiconductor apparatus has an NPN (or PNP) laterally three-layered pillar formed in a mesh form among a plurality of trench type element isolation regions, and having a source and gate on an upper surface of the three-layered pillar, and a drain on a lower surface thereof. A depth DT and minimum planar width WTmin of the element isolation region and a width WP of the three-layered pillar are configured to satisfy a relation of 3.75<=DT / WP<=60 or 5.5<=DT / WTmin<=14.3. The above configuration realizes a high breakdown voltage and low on-resistance are realized.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
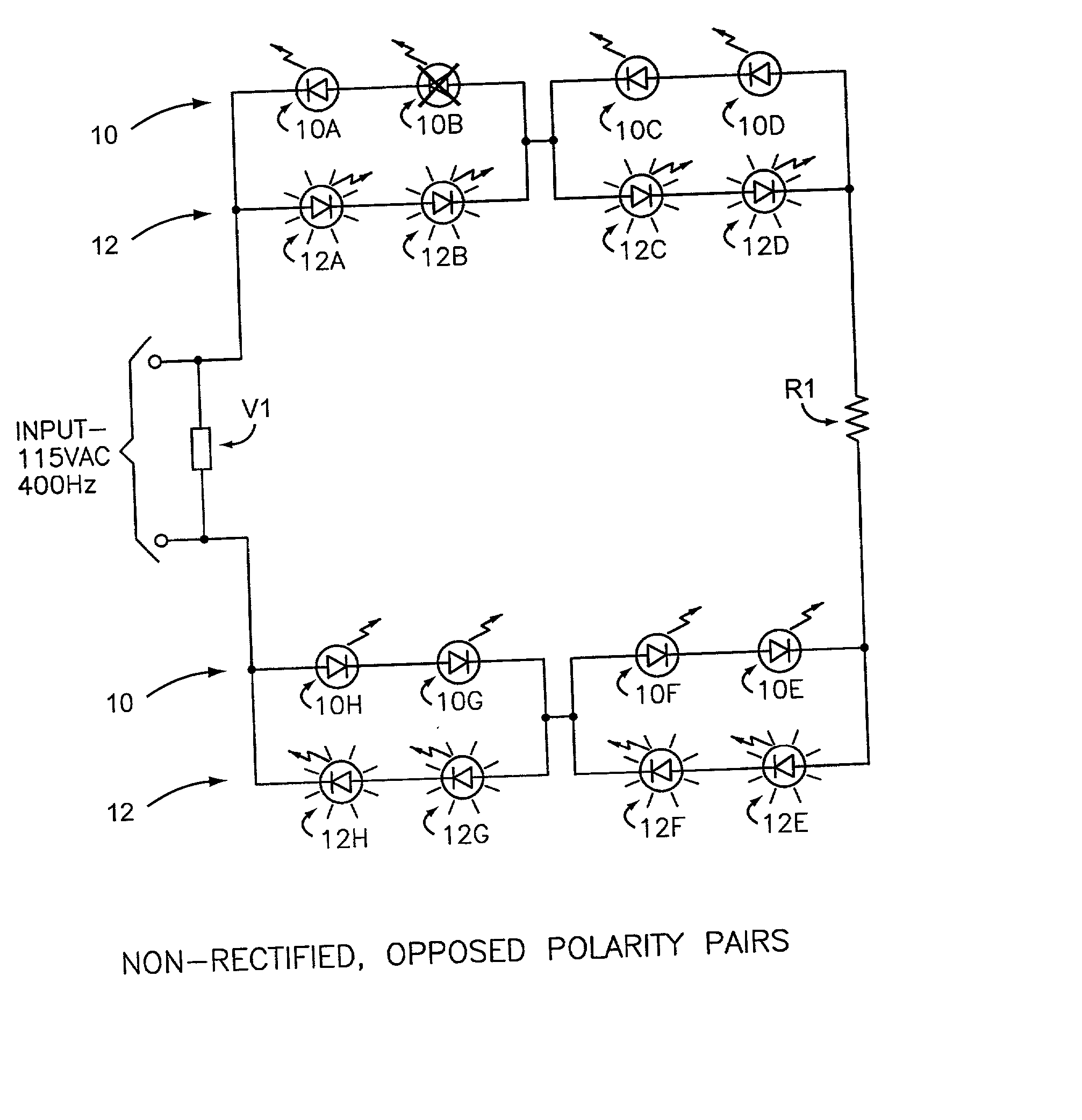
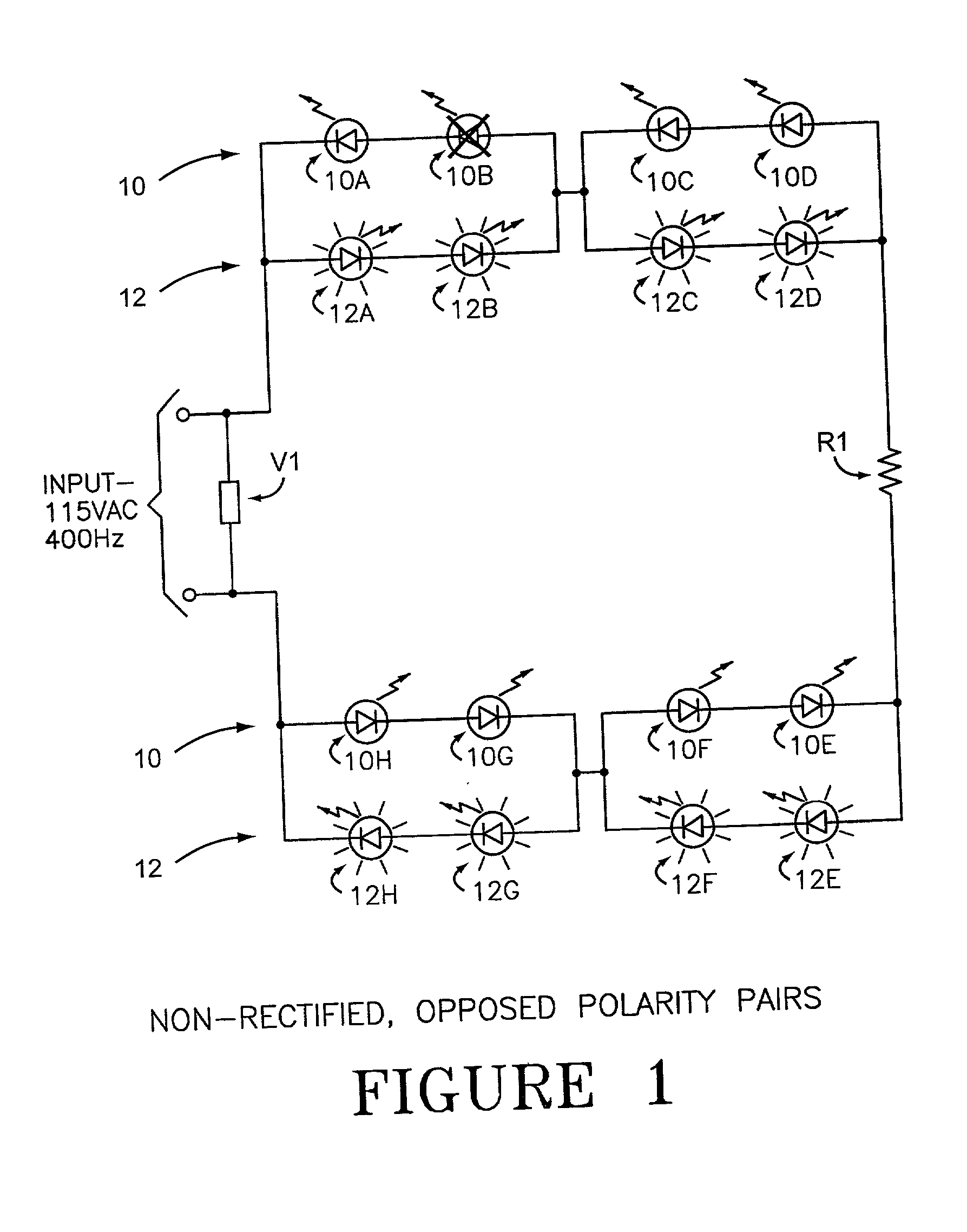
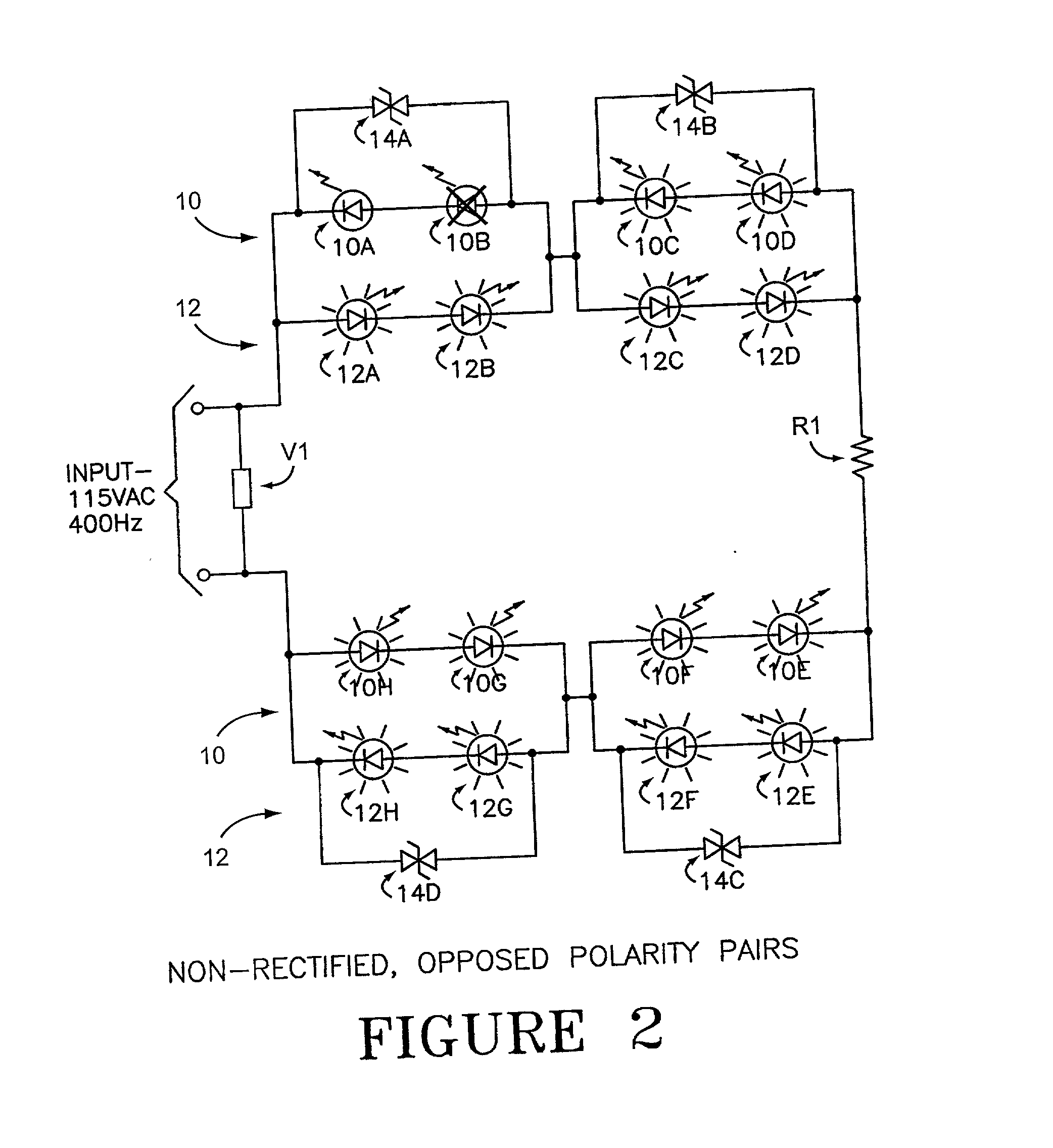
LED array primary display light sources employing dynamically switchable bypass circuitry
InactiveUS20020043943A1Reduce heat outputEasy burn-out element replacementElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesBlack outEffect light
The invention comprises use of Dynamically Switchable Bypass (DSB) elements in association with one or more Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) in arrays for illumination circuits to provide rugged, reliable lighting. The DSBs are selected from Transient Voltage Suppressors, including Silicon, Metal Oxide Varistors, and Multi Layer Varistors as well as Zener Diodes. The DSBs are not used as circuit protecting devices, but rather as alternative paths for electric current to bypass failed LEDs. Bi-directional TVSs are used as alternative electric paths for circuits using Alternating Current (AC) and parallel LED arrays that light on both phases of AC. Zener Diodes are used in parallel to, but in the opposite polarity orientation to, one or more LEDs in DC or rectified AC circuits. The inventive paired DSB / LED elements overcomes the black-out problems of prior series LED illumination systems, making possible the use of robust LEDs in illumination systems where reliability, long life, low power consumption, low heat output, resistance to shock, vibration, and humidity, and self-diagnosis are important. The DSB elements have breakdown voltages slightly higher than the LED(s) they support, so that when an LED fails, the conduction through the DSB begins. Because the conduction voltage of the DSB so nearly matches the conduction voltage of the LED(s), the remainder of the circuit continues to function as normal. The system is self-diagnostic in that any LED failure presents itself as a dark LED rather than as a whole string of dark LEDs. DSBs may be used with incandescent bulbs.
Owner:IDD AEROSPACE
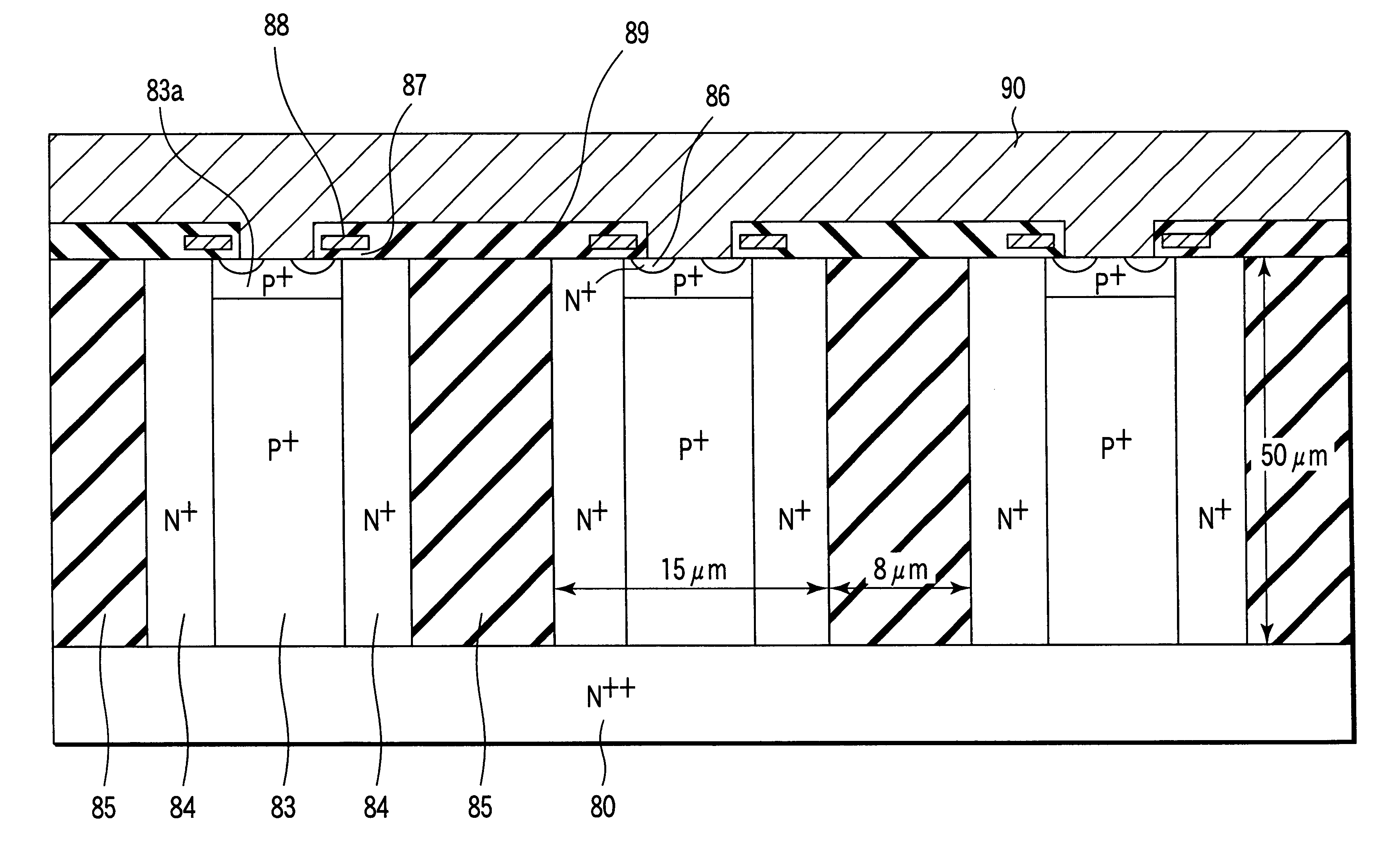
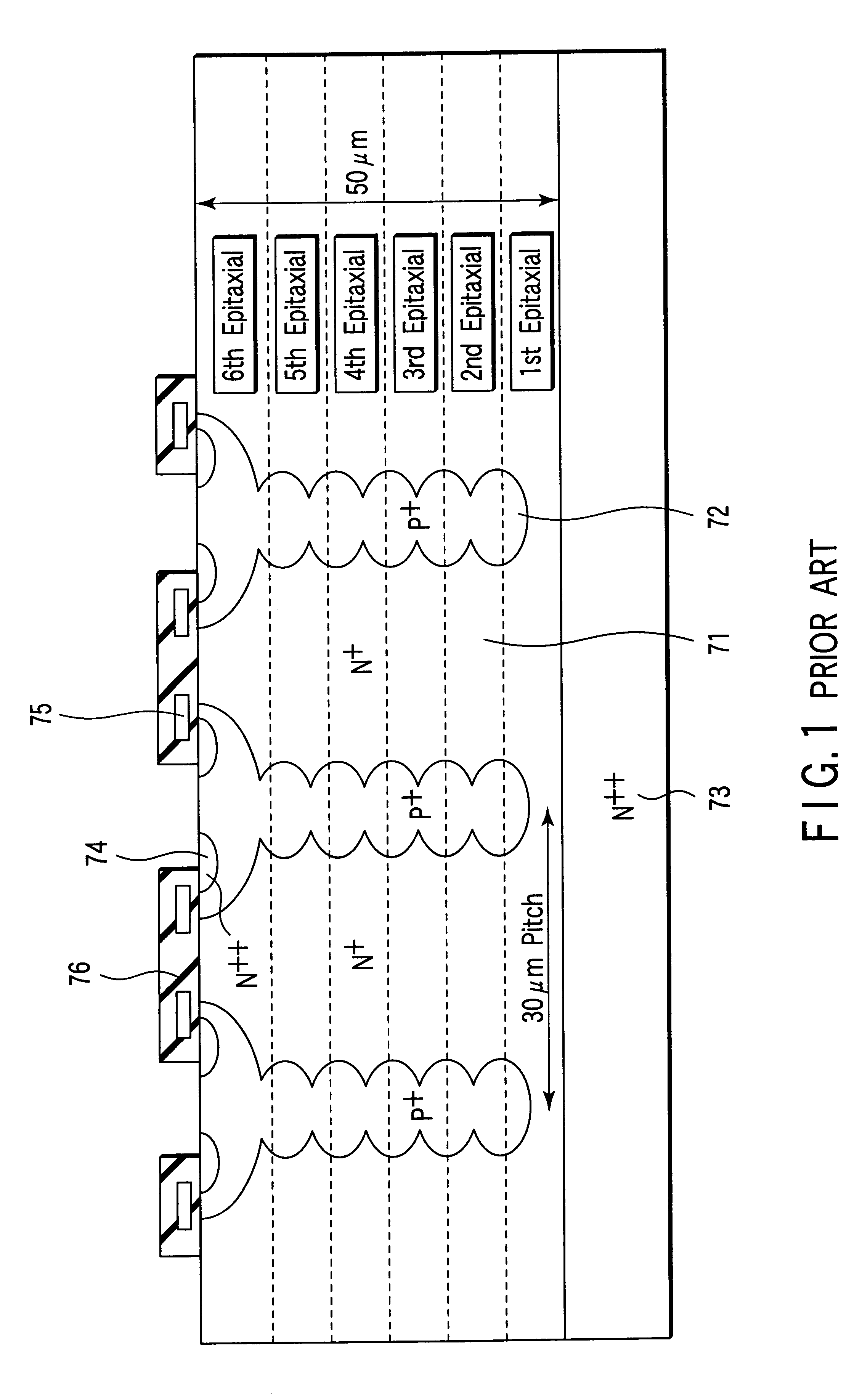
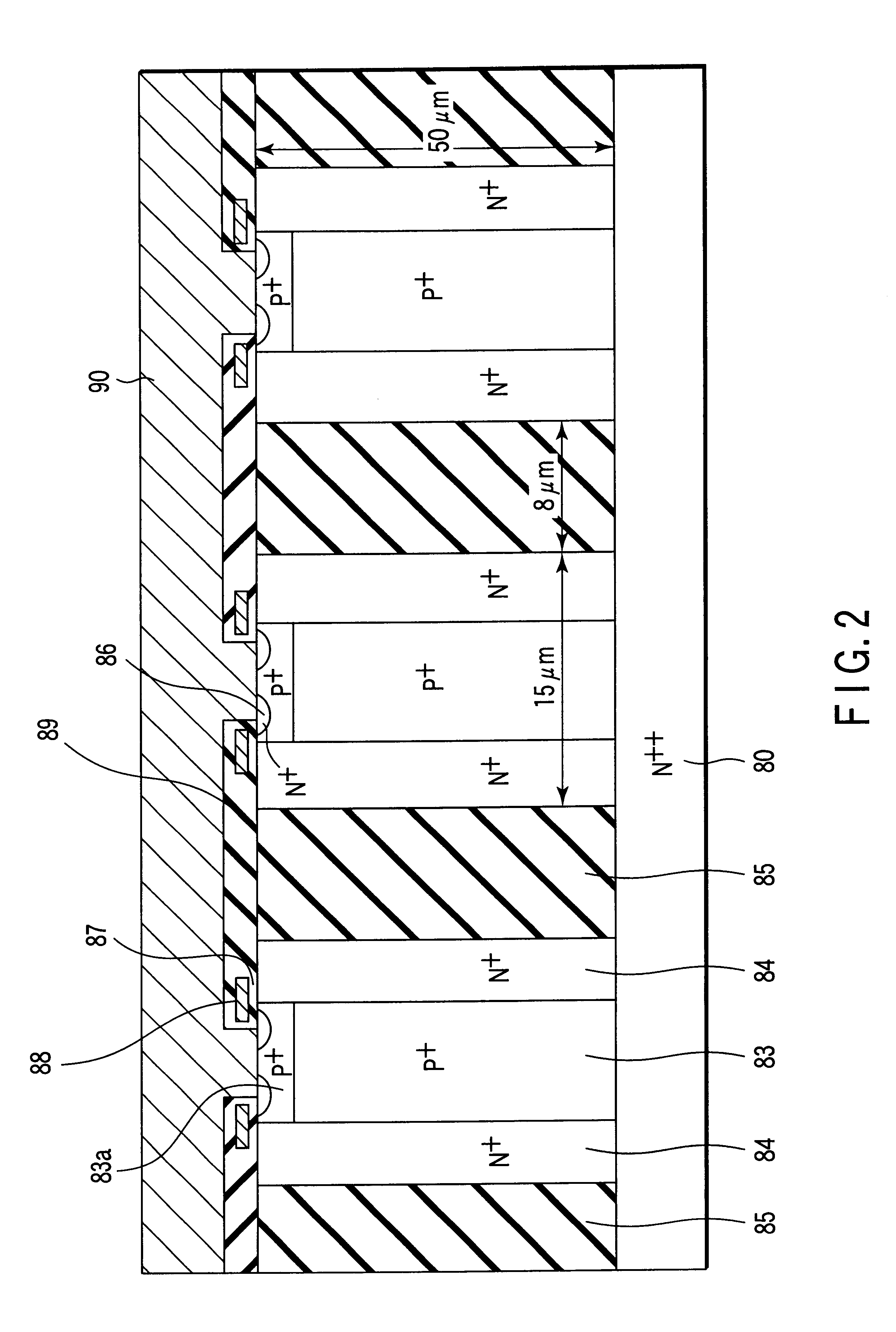
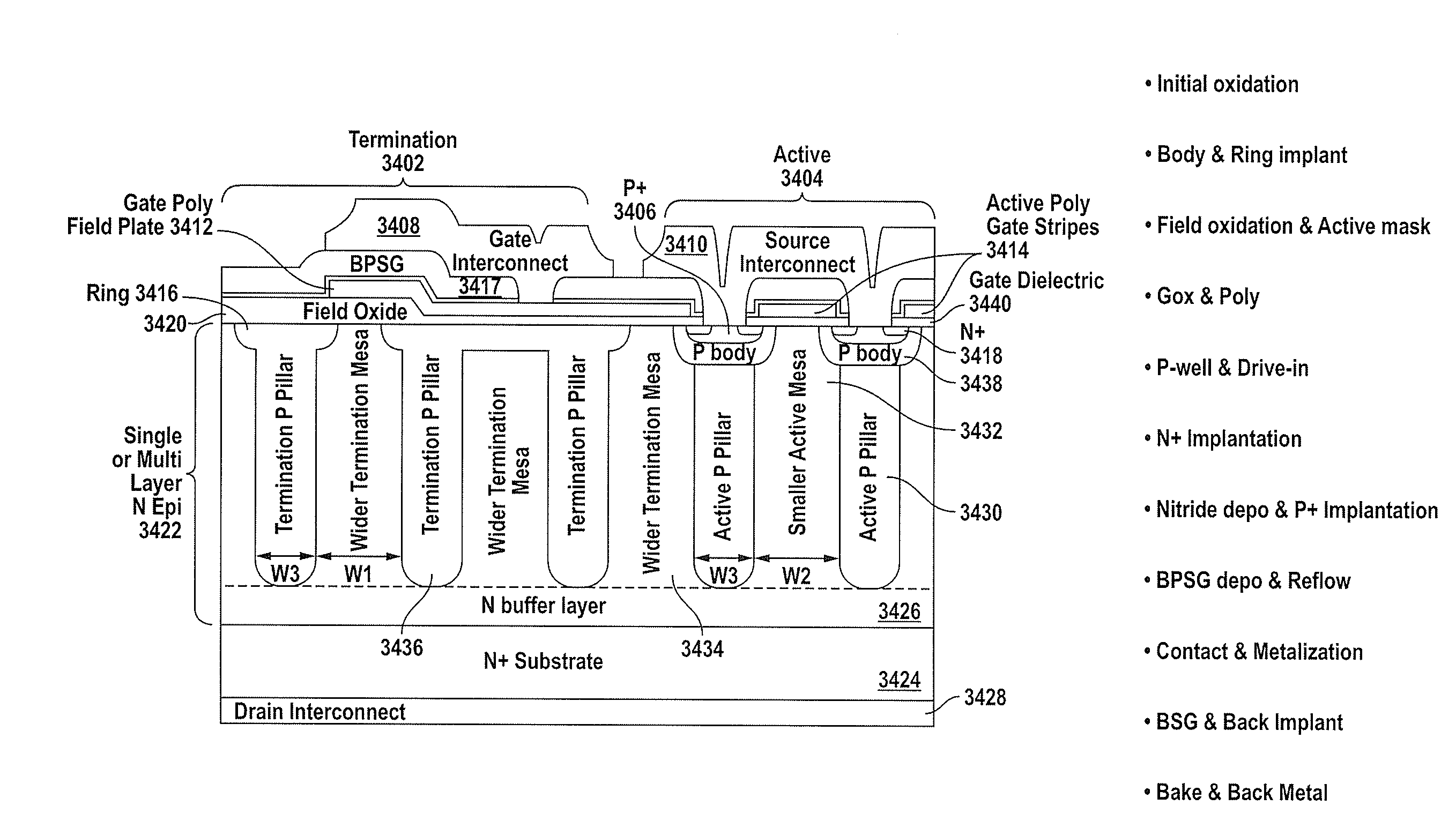
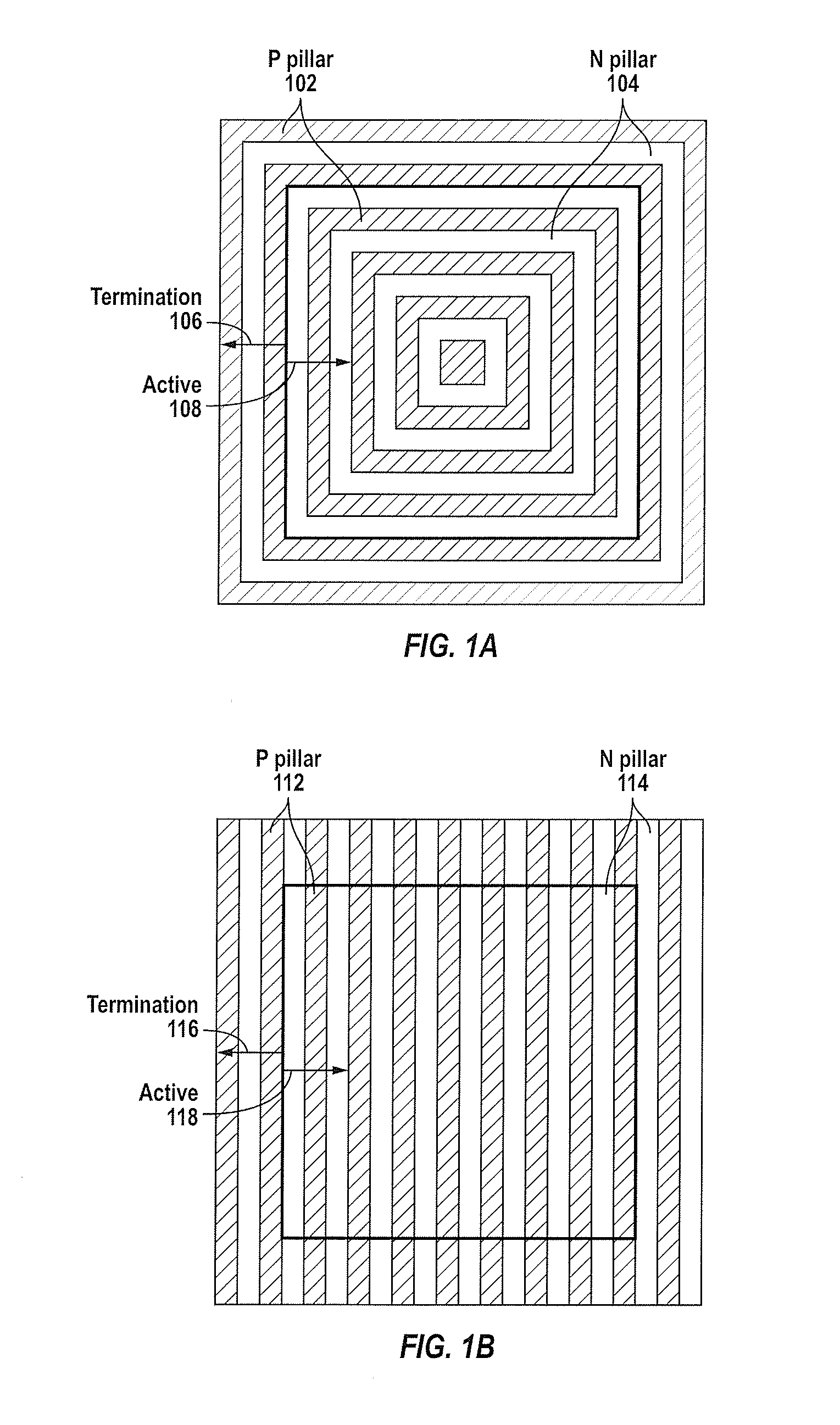
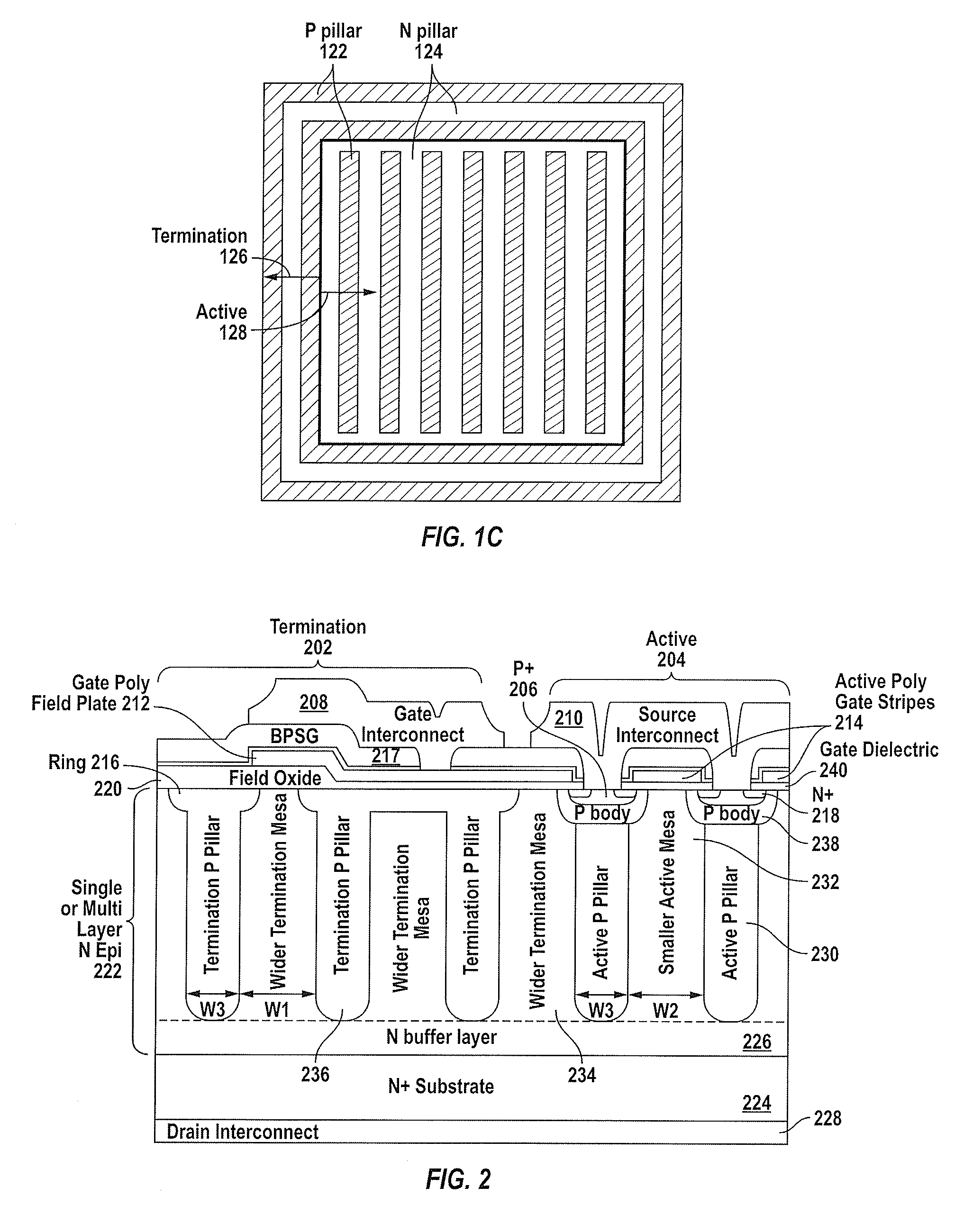
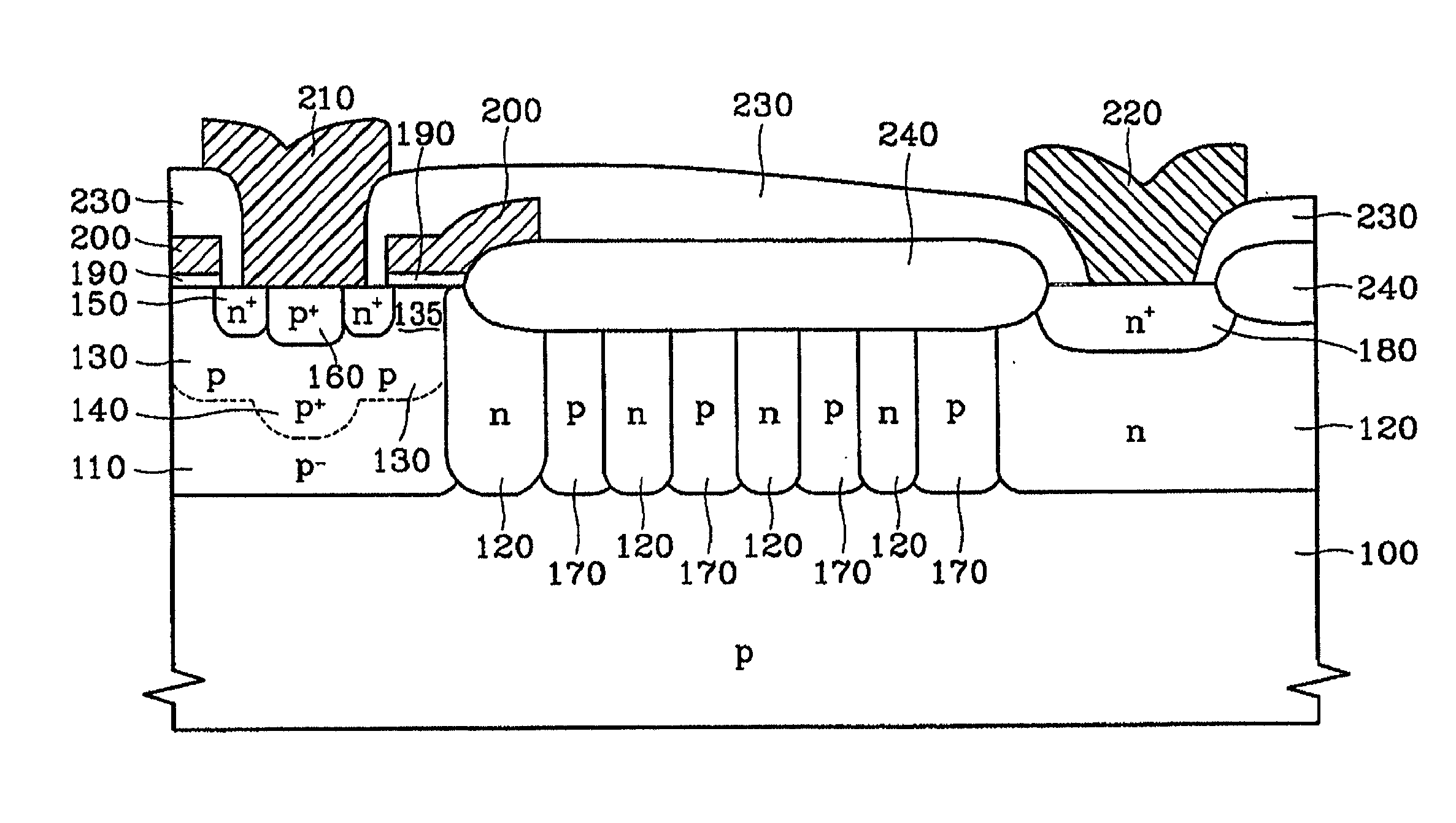
Superjunction Structures for Power Devices and Methods of Manufacture
ActiveUS20090079002A1Reduce leakageAdd depthTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringBreakdown voltage
A power device includes an active region and a termination region surrounding the active region. A plurality of pillars of first and second conductivity type are alternately arranged in each of the active and termination regions. The pillars of first conductivity type in the active and termination regions have substantially the same width, and the pillars of second conductivity type in the active region have a smaller width than the pillars of second conductivity type in the termination region so that a charge balance condition in each of the active and termination regions results in a higher breakdown voltage in the termination region than in the active region.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
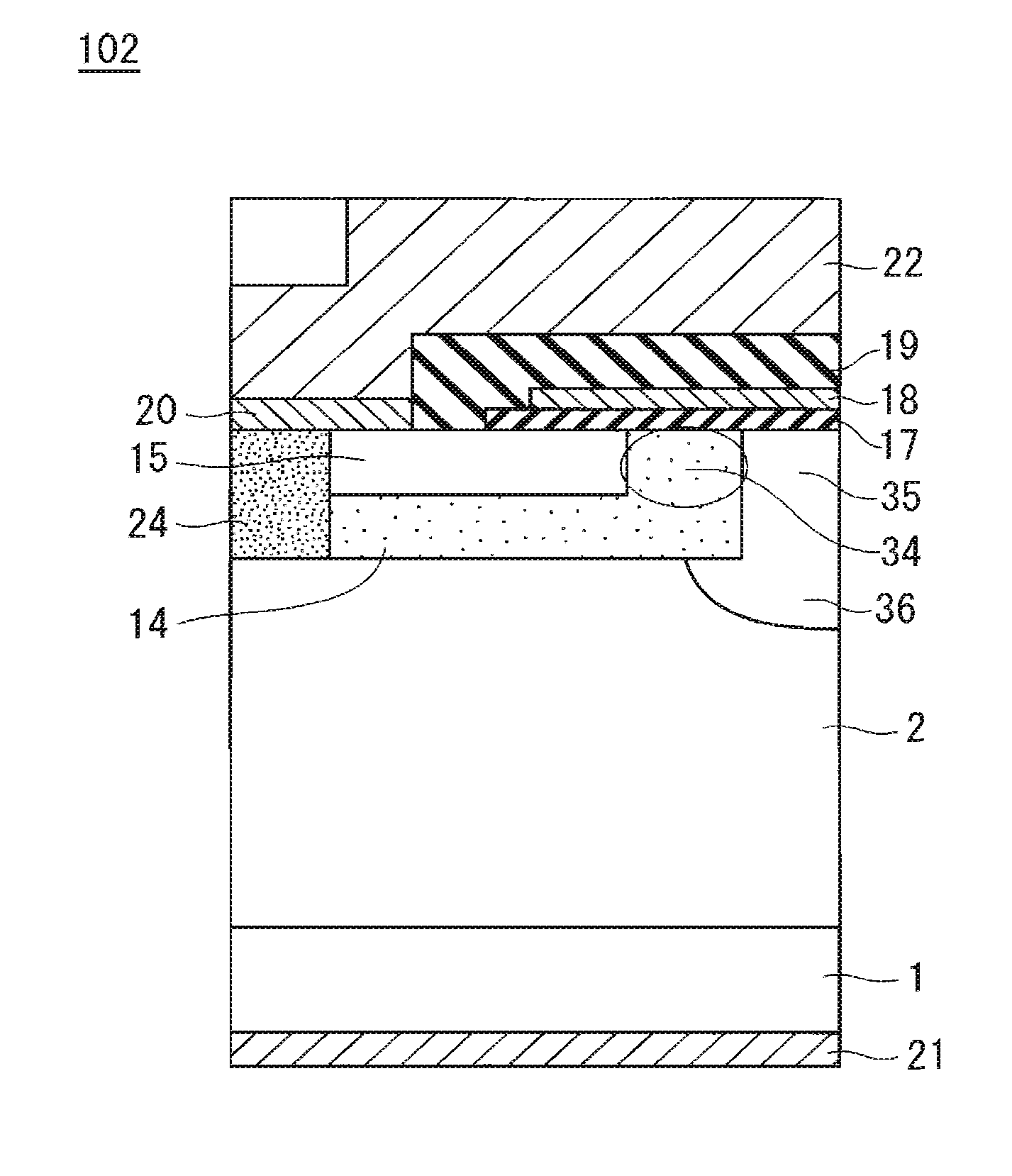
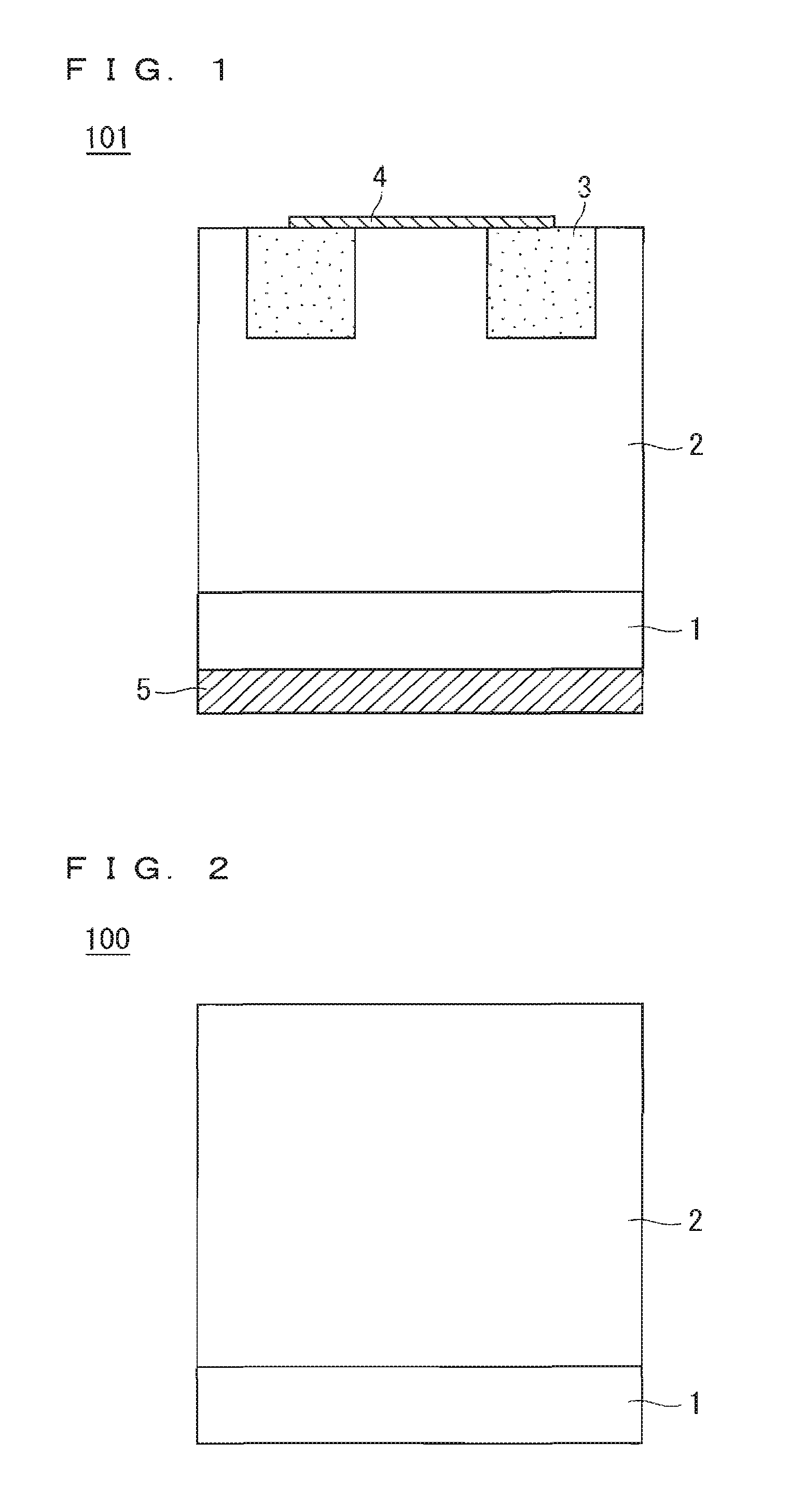
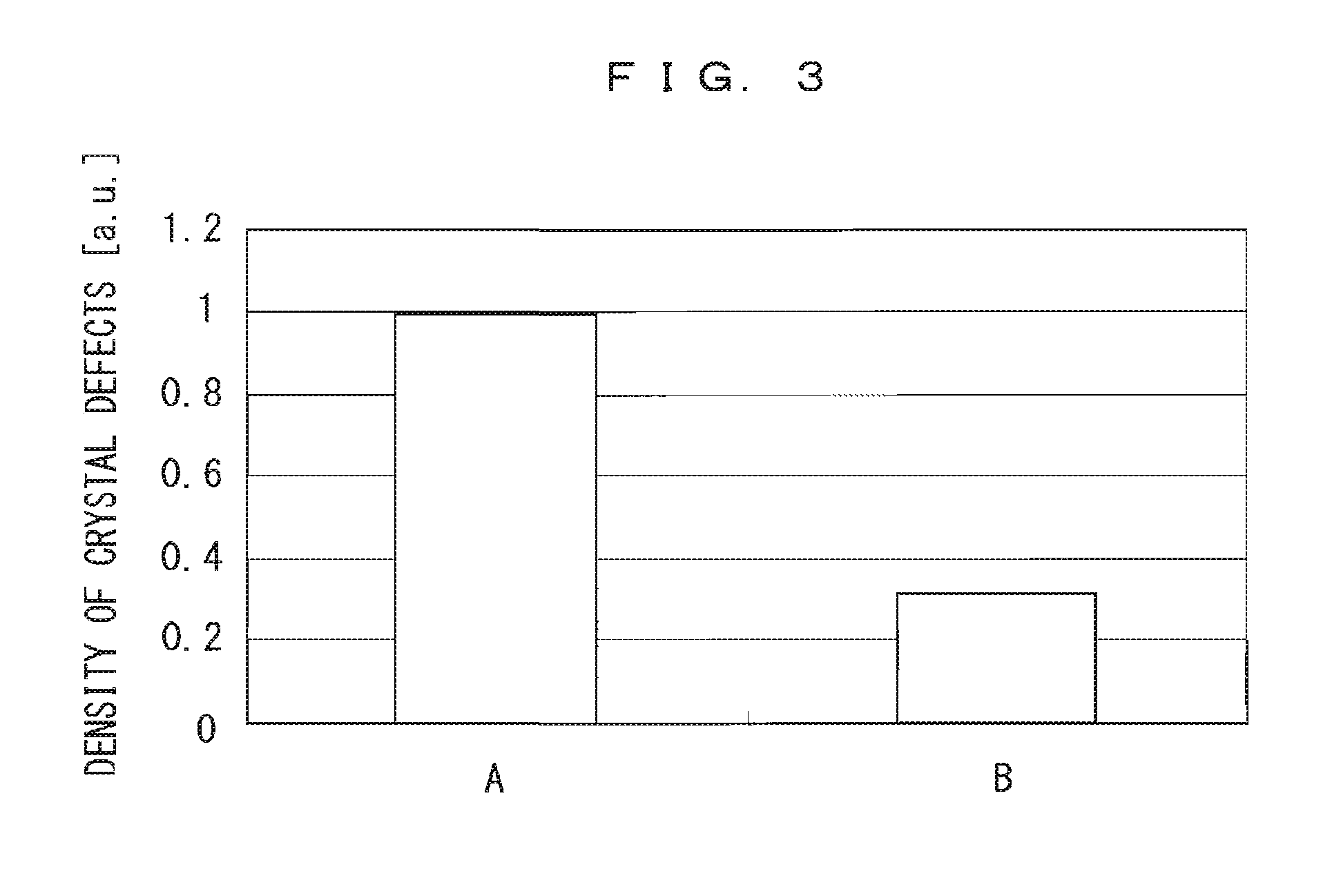
GaN field-effect transistor and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20010040246A1Reduce dislocation densityTransistorPolycrystalline material growthLateral overgrowthEngineering
There are provided a GaN field effect transistor (FET) exhibiting an excellent breakdown voltage owing to the high quality of GaN crystal in a region where the electric lines of force concentrate during operation of the same, and a method of manufacturing the same. The FET has a layer structure formed of a plurality of GaN epitaxial layers. A gate electrode and a source electrode are disposed on the surface of the layer structure, and a drain electrode is disposed on the reverse surface of the same. A region of the layer structure in which the electric lines of force concentrate during operation of the FET has a reduced dislocation density compared with the other regions in the layer structure. The GaN FET is manufactured by forming, on a crystal-growing substrate having a surface formed with a plane pattern of a material other than a GaN-based material in an identical design to a plane pattern of an electrode determining the region in which the electric lines of force concentrate, a plurality of GaN epitaxial layers, one upon another, by using the epitaxial lateral overgrowth technique, thereby forming a layer structure, and then forming operational electrodes on the surface of the layer structure.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Methods to shape the electric field in electron devices, passivate dislocations and point defects, and enhance the luminescence efficiency of optical devices
ActiveUS20070224710A1Increase output powerReduce gate leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPeak valueDislocation
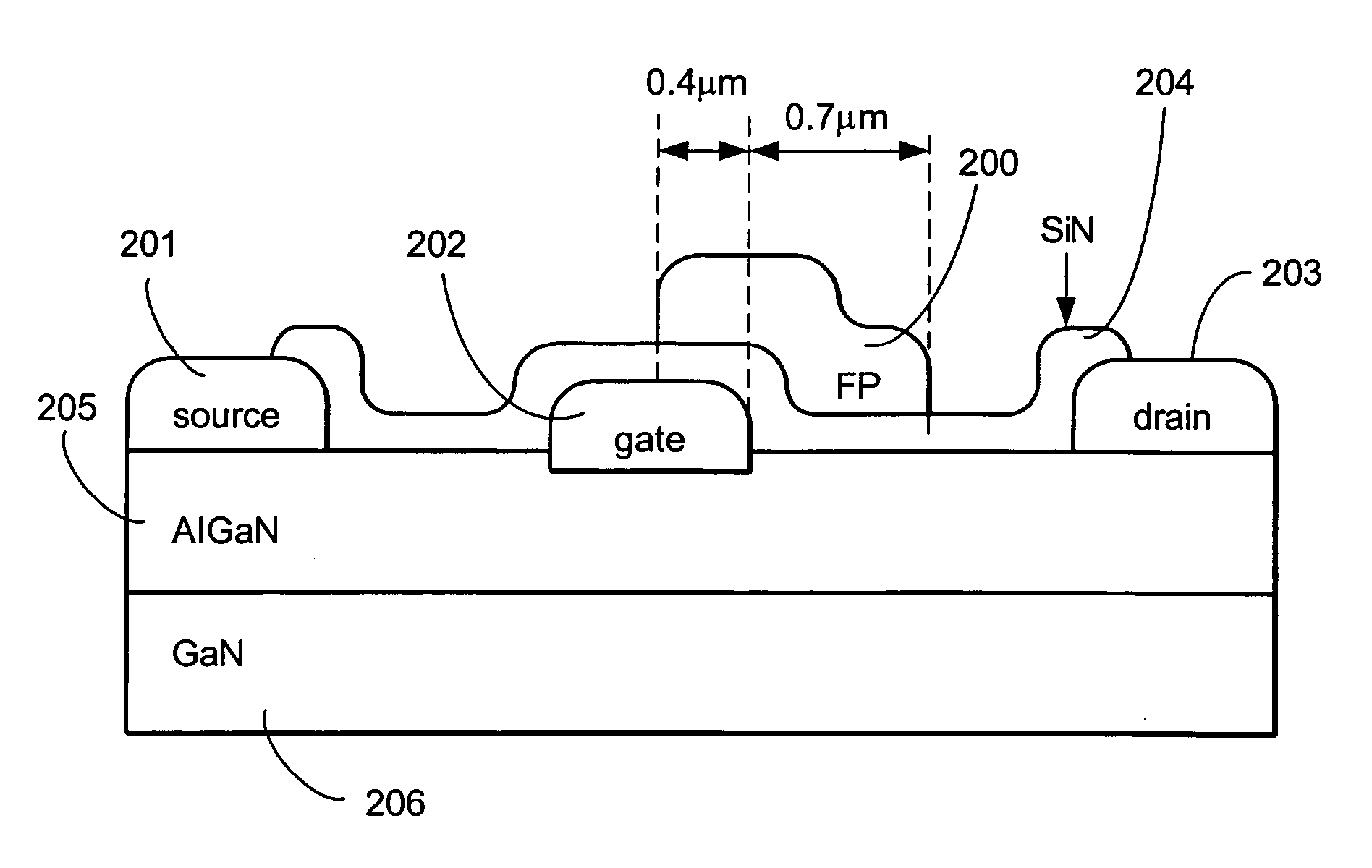
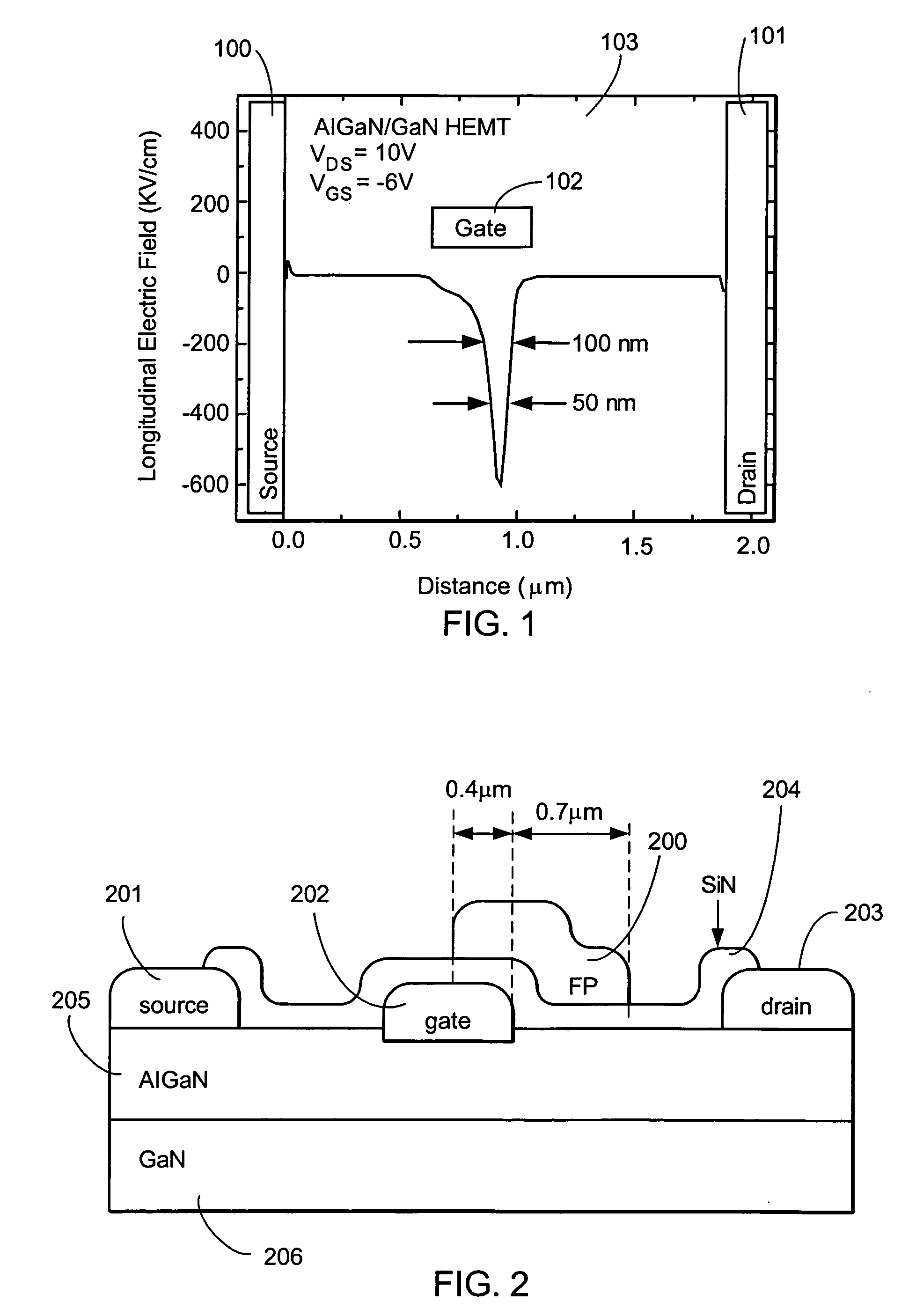
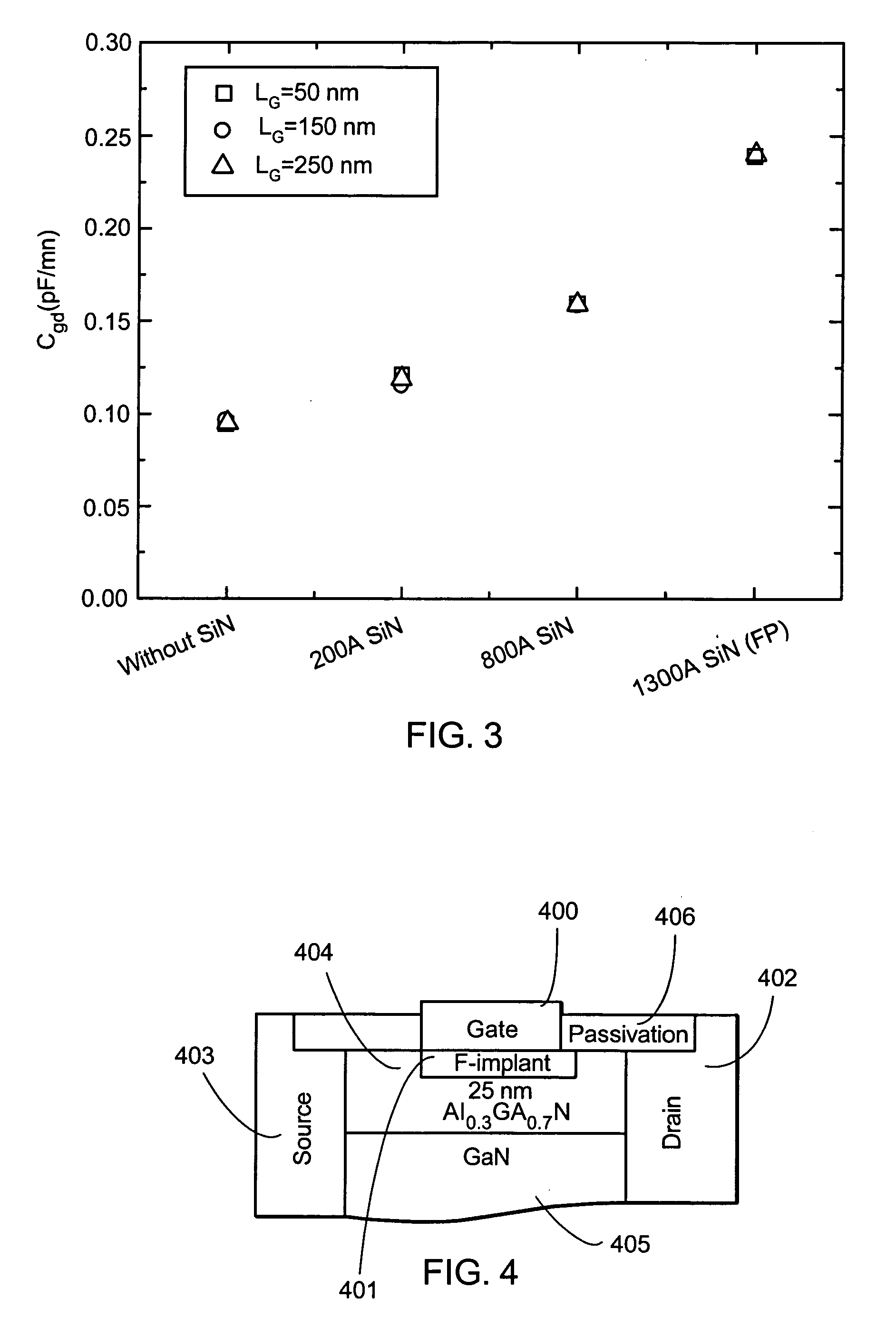
A fluorine treatment that can shape the electric field profile in electronic devices in 1, 2, or 3 dimensions is disclosed. A method to increase the breakdown voltage of AlGaN / GaN high electron mobility transistors, by the introduction of a controlled amount of dispersion into the device, is also disclosed. This dispersion is large enough to reduce the peak electric field in the channel, but low enough in order not to cause a significant decrease in the output power of the device. In this design, the whole transistor is passivated against dispersion with the exception of a small region 50 to 100 nm wide right next to the drain side of the gate. In that region, surface traps cause limited amounts of dispersion, that will spread the high electric field under the gate edge, therefore increasing the breakdown voltage. Three different methods to introduce dispersion in the 50 nm closest to the gate are described: (1) introduction of a small gap between the passivation and the gate metal, (2) gradually reducing the thickness of the passivation, and (3) gradually reducing the thickness of the AlGaN cap layer in the region close the gate.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Semiconductor device with super junction region
InactiveUS6844592B2Improve breakdown voltageEfficiently obtainedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCell regionSemiconductor
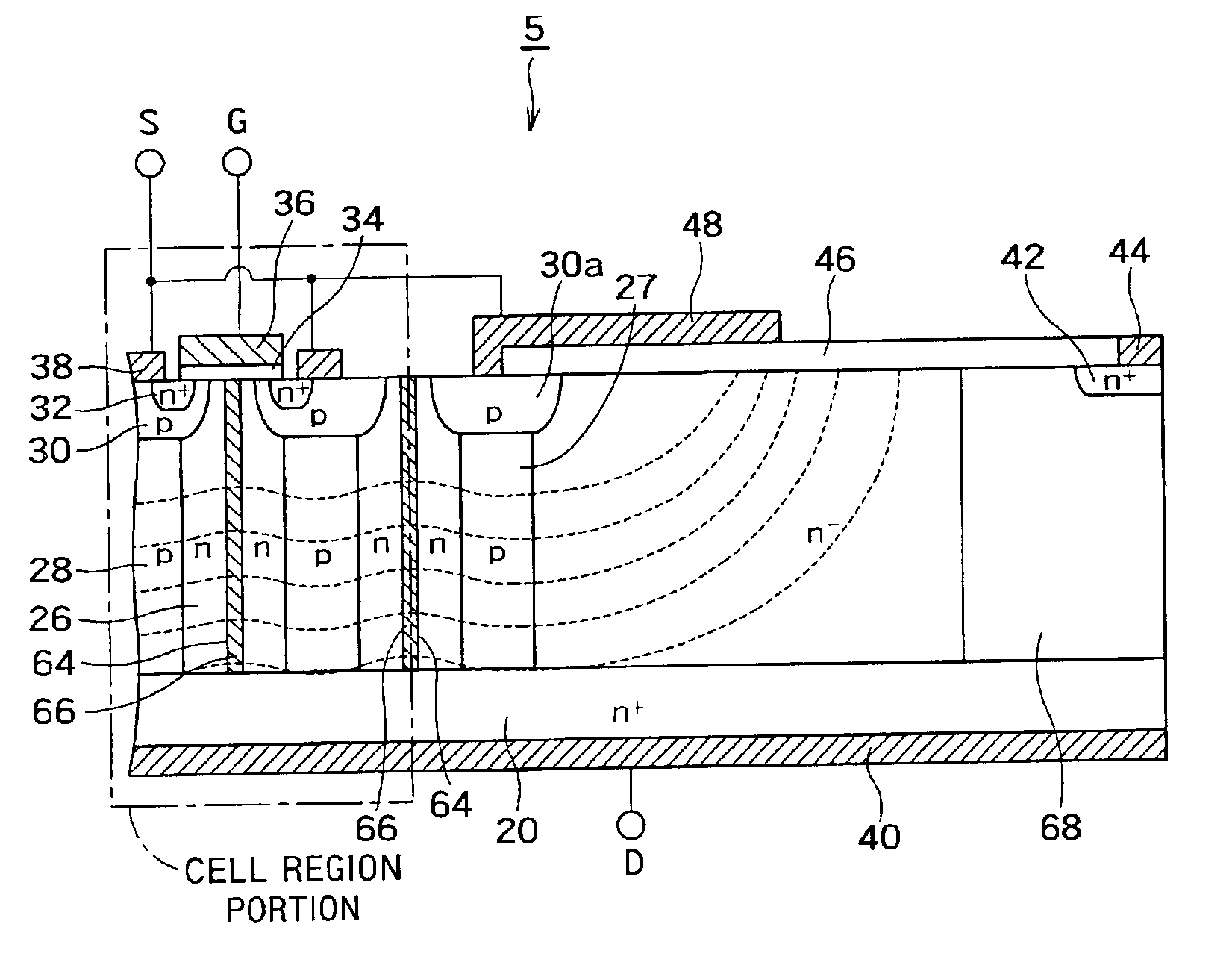
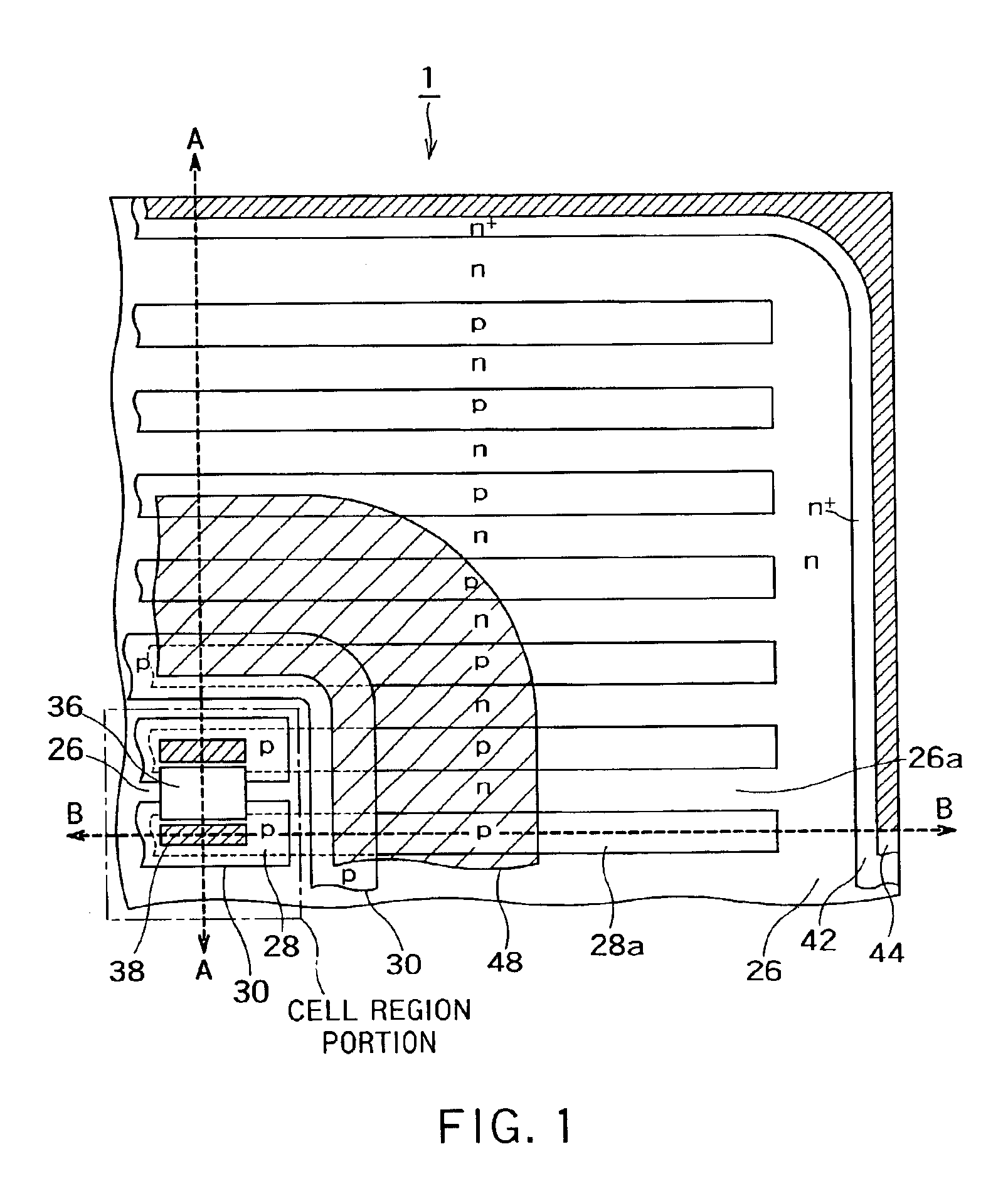
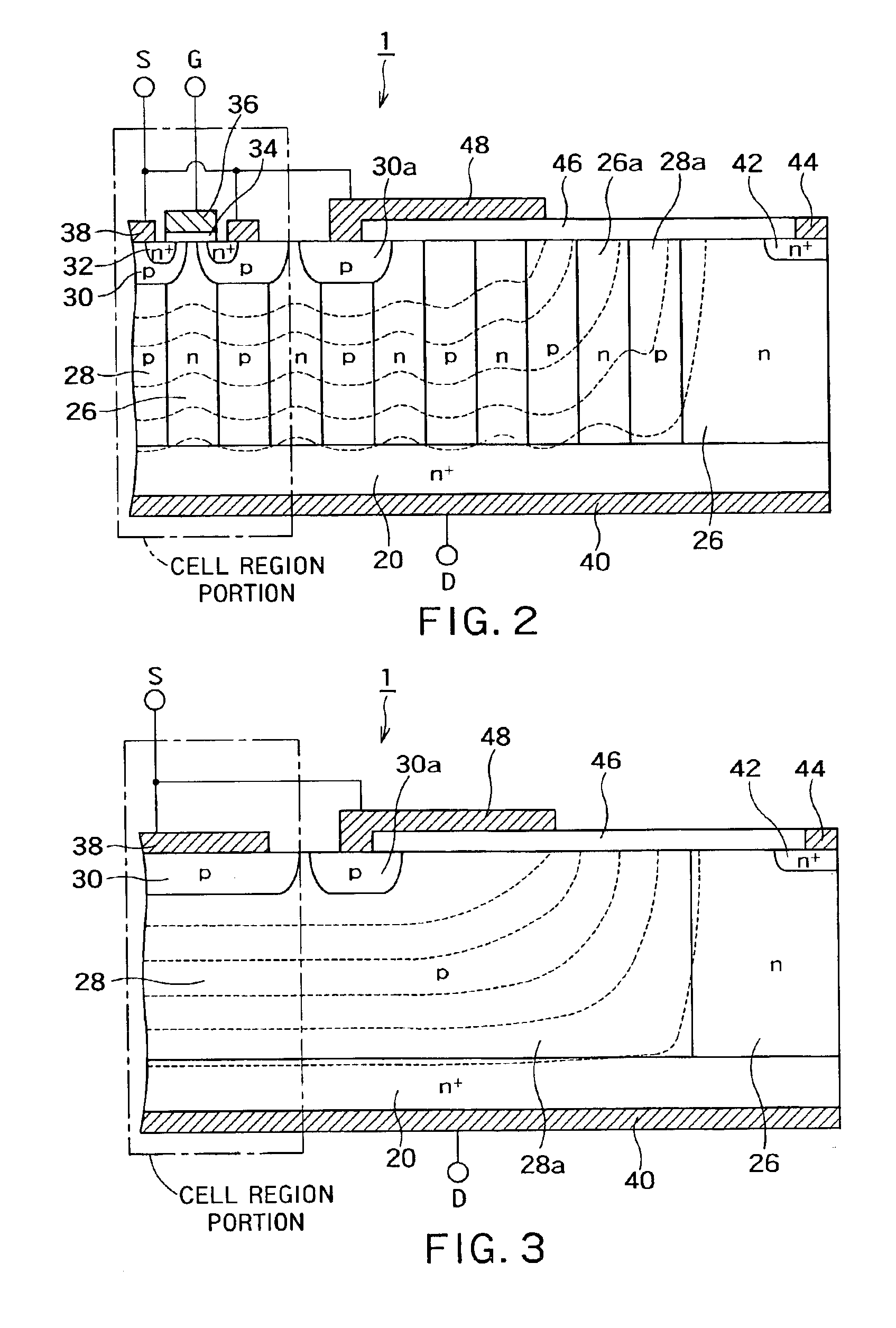
A semiconductor device includes a first-conductivity-type semiconductor layer which includes a cell region portion and a junction terminating region portion. The junction terminating region portion is a region portion which is positioned in an outer periphery of the cell region portion to maintain a breakdown voltage by extending a depletion layer to attenuate an electric field.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20030006415A1Increase flexibilityReduce in quantityTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETInductor
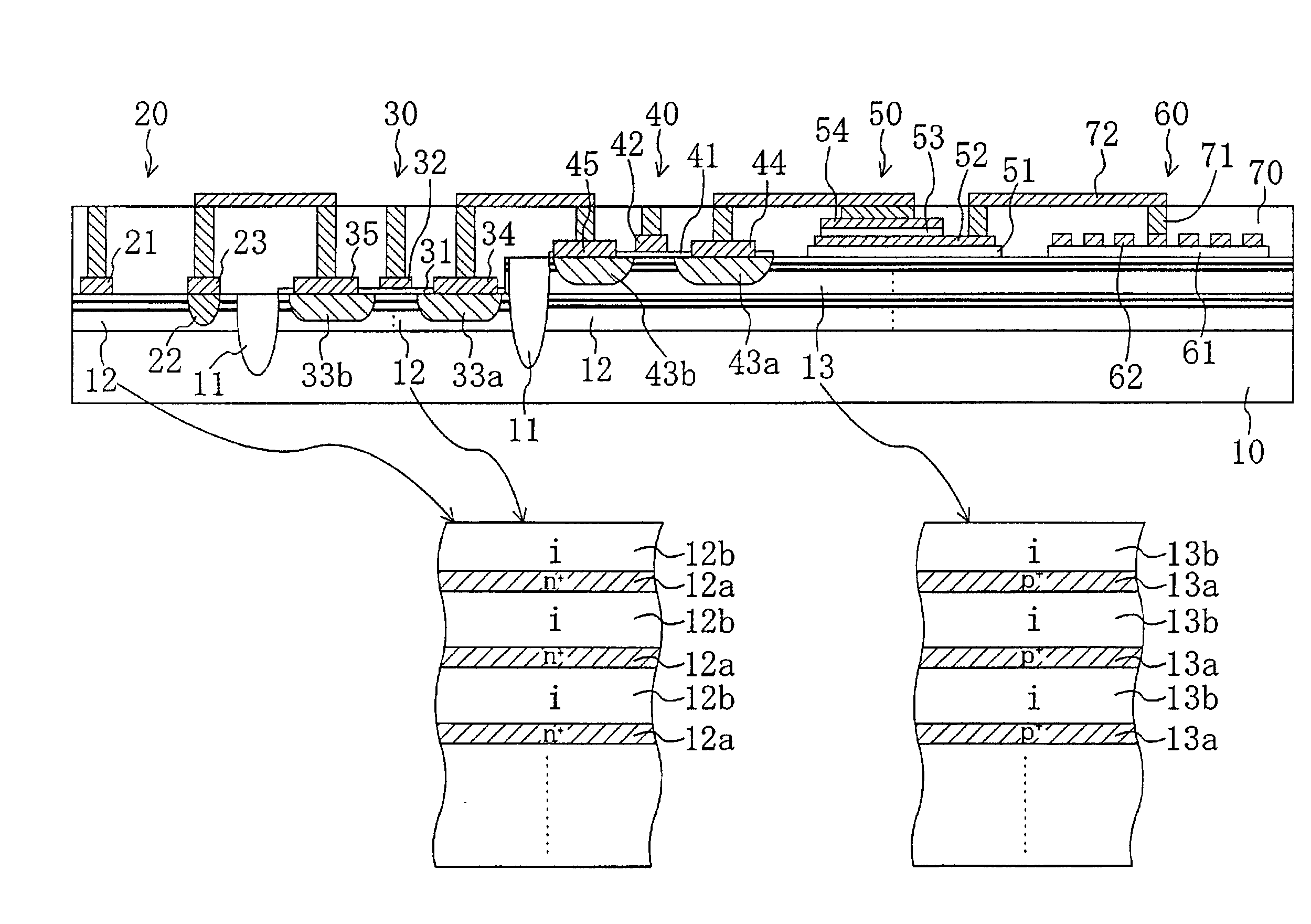
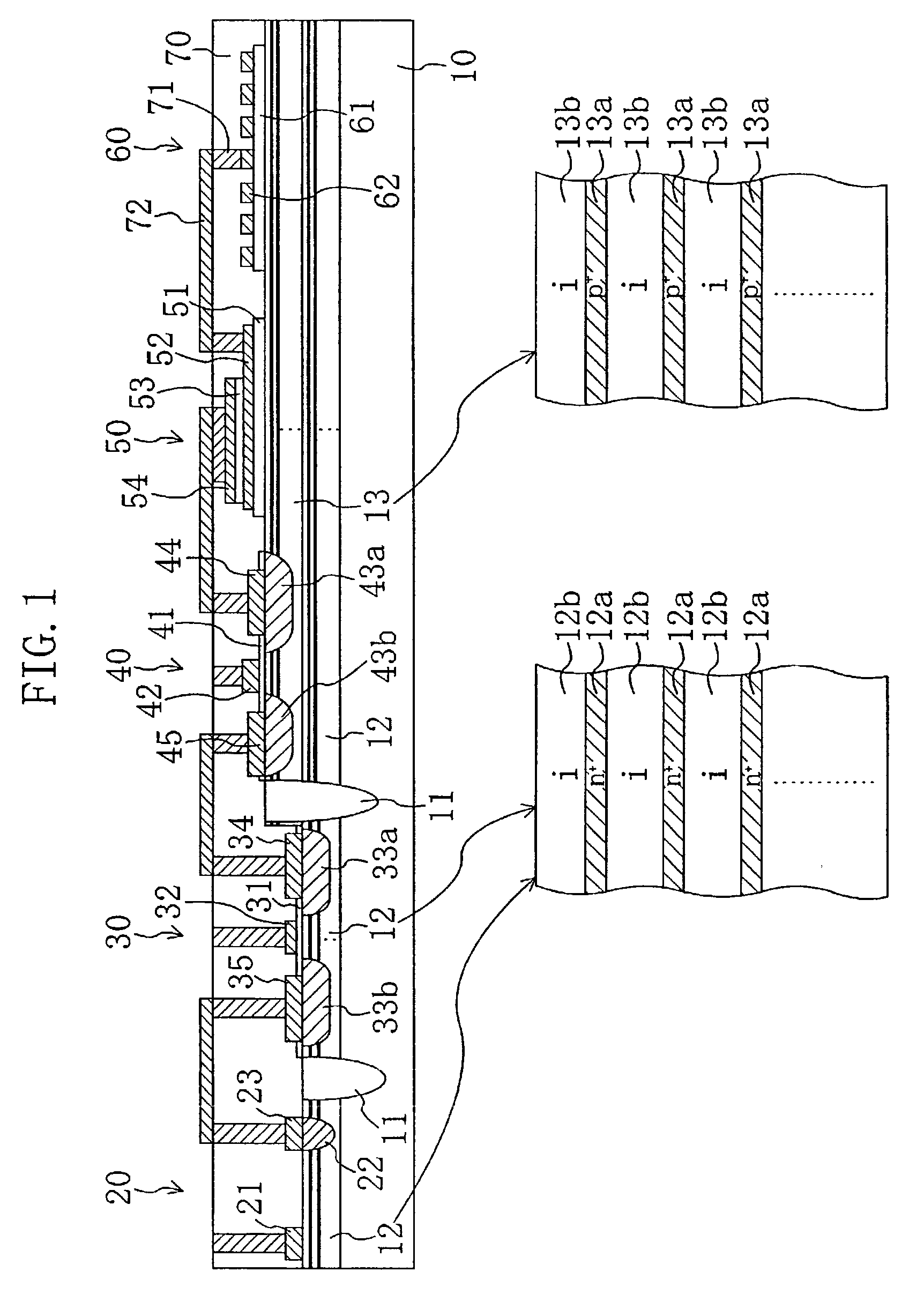
In a SiC substrate (10), a first active region (12) composed of n-type heavily doped layers (12a) and undoped layers (12b), which are alternately stacked, and a second active region (13) composed of p-type heavily doped layers (13a) and undoped layers (13b), which are alternately stacked, are provided upwardly in this order. A Schottky diode (20) and a pMOSFET (30) are provided on the first active region (12). An nMOSFET (40), a capacitor (50), and an inductor (60) are provided on the second active region (13). The Schottky diode (20) and the MOSFETs (30, 40) have a breakdown voltage characteristic and a carrier flow characteristic due to a multilayer structure composed of delta-doped layers and undoped layers and are integrated in a common substrate.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Semiconductor device, module, and electronic device including a conversion circuit having a second switch rendered conductive together with a first switch
InactiveUS7608810B2High voltageGuaranteed uptimeTransistorTelevision system detailsEngineeringSemiconductor
The breakdown voltage between the potential of a terminal and the ground potential (or power supply potential) is improved by increasing the gate width of an MOS transistor included in a switch. Accordingly, another switch and the like are protected even when surge is applied to the terminal. By increasing the gate width of the MOS transistor included in the switch, the size of the other switch does not have to be increased. Therefore, variation in the potential at a node occurring when the other switch attains a non-conductive state from a conductive state can be suppressed. Therefore, a semiconductor device having the electrostatic breakdown voltage improved without influence on processing carried out based on an input potential from an external source, a module including a plurality of such semiconductor devices, and an electronic device including such a module can be provided.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
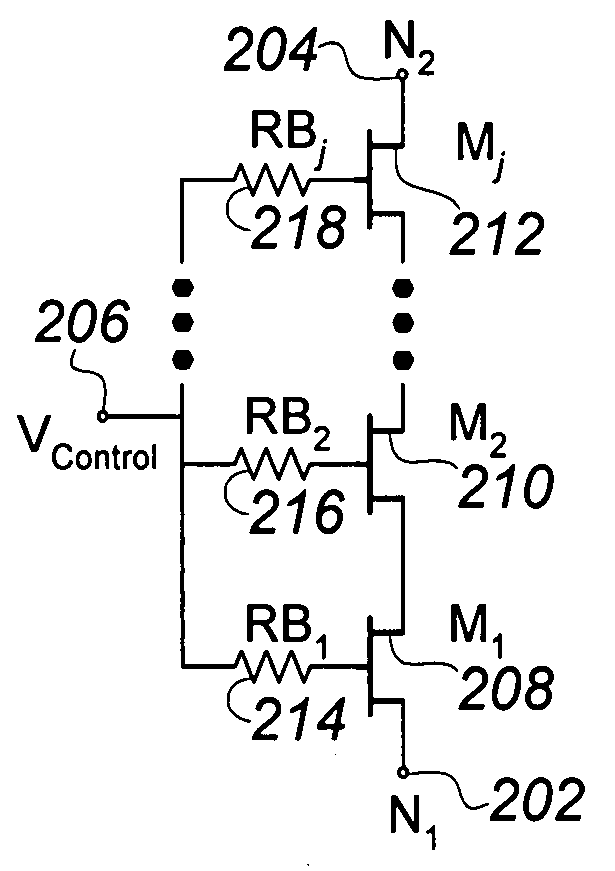
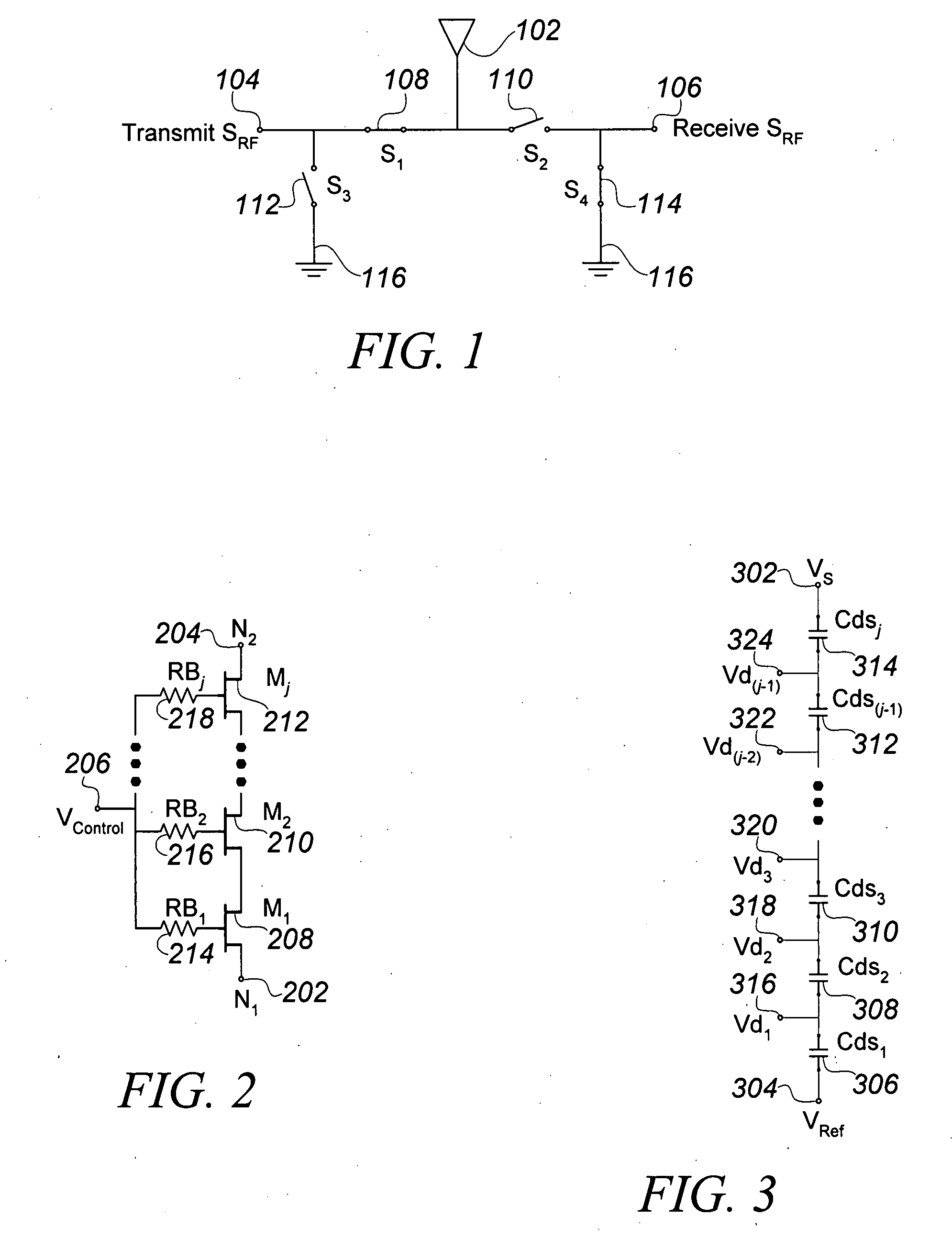
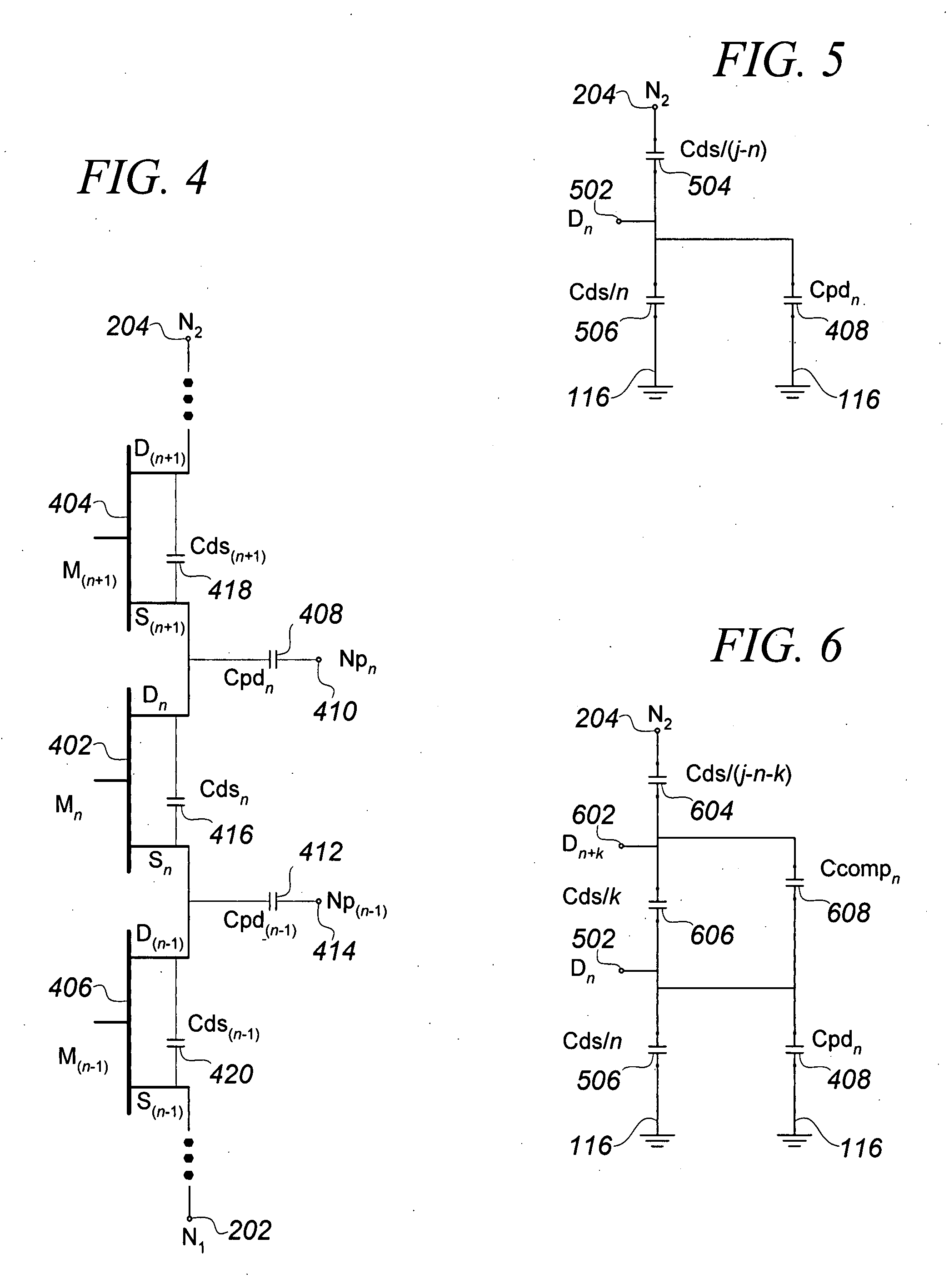
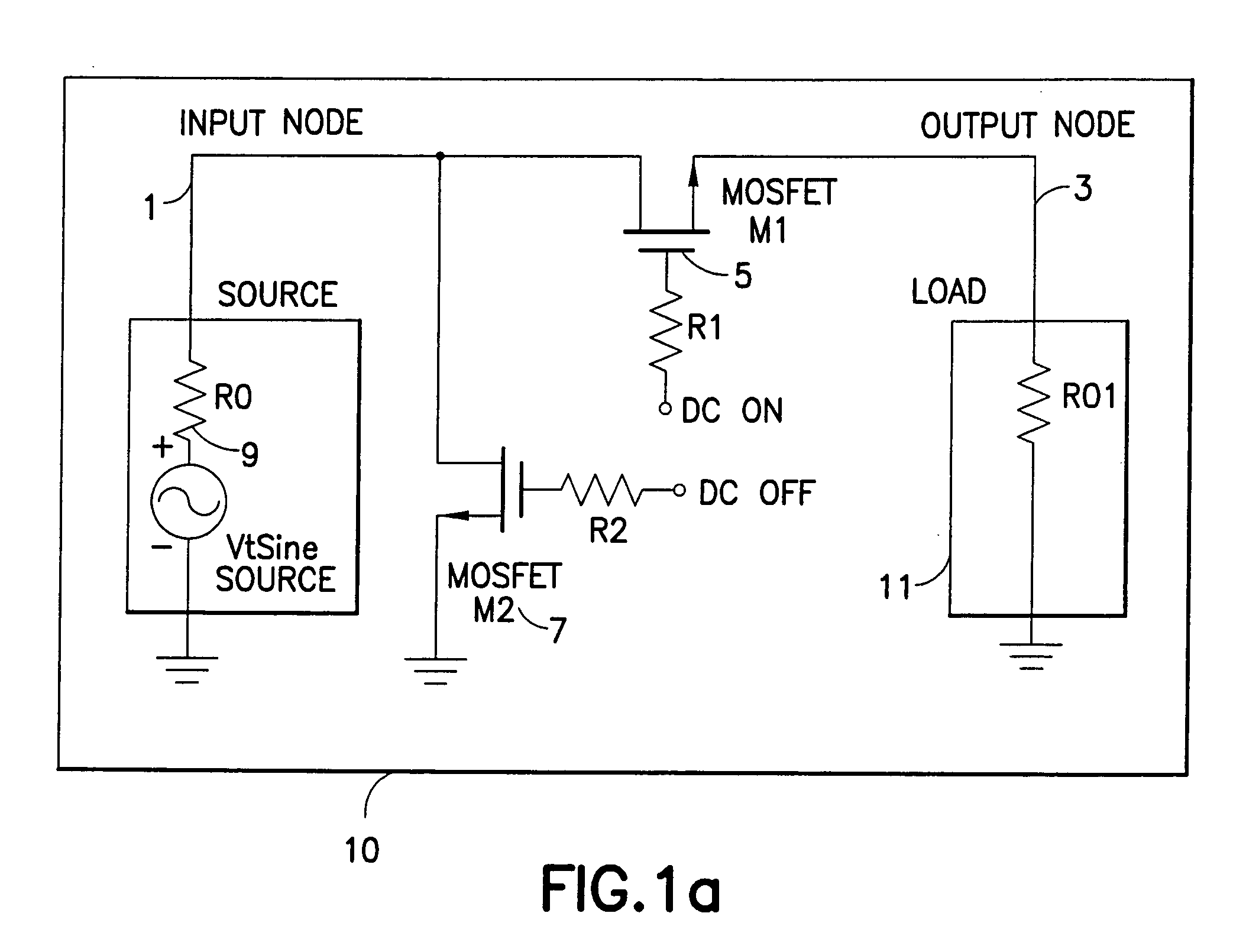
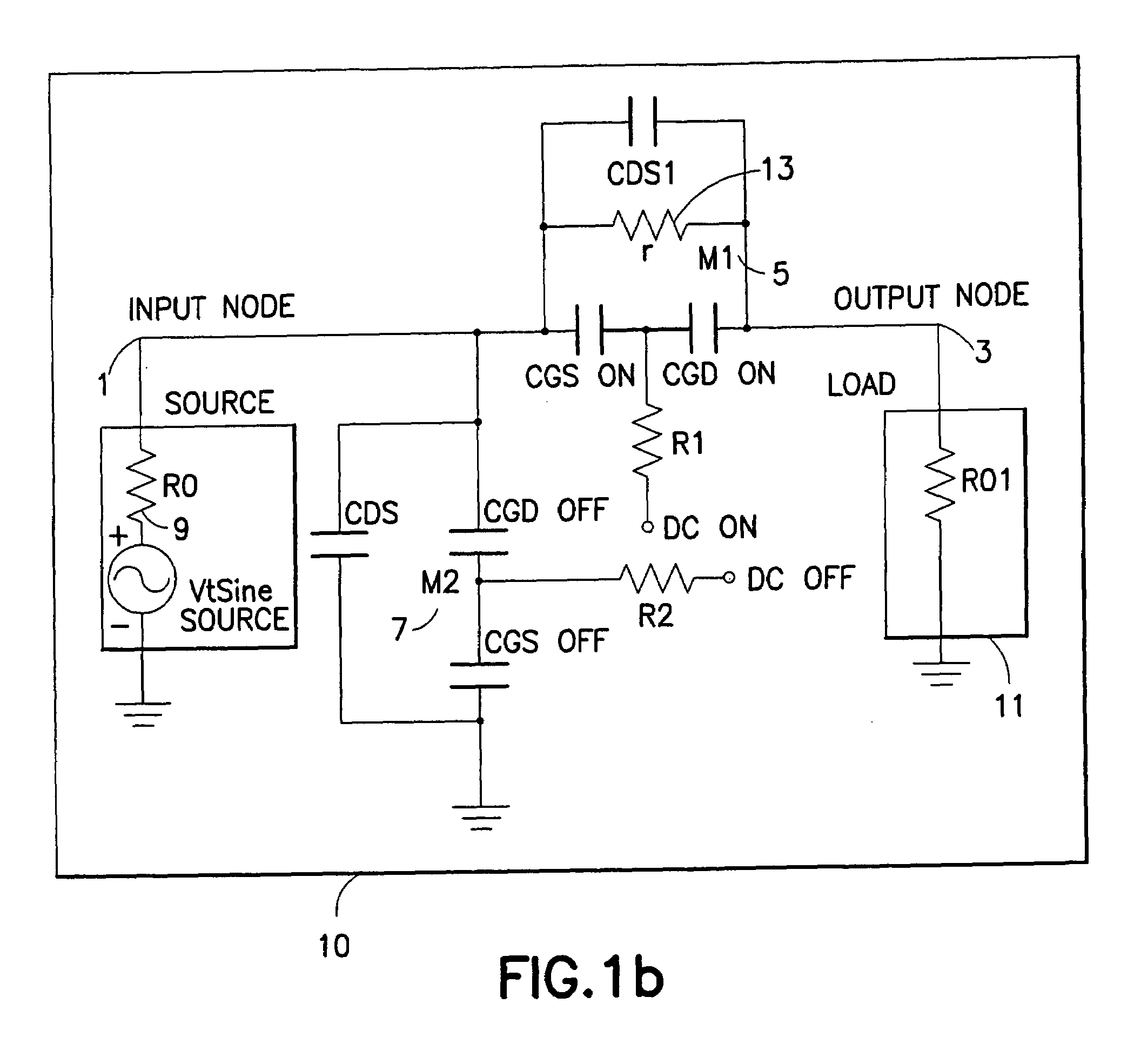
Tuning capacitance to enhance FET stack voltage withstand
An RF switch to controllably withstand an applied RF voltage Vsw, or a method of fabricating such a switch, which includes a string of series-connected constituent FETs with a node of the string between each pair of adjacent FETs. The method includes controlling capacitances between different nodes of the string to effectively tune the string capacitively, which will reduce the variance in the RF switch voltage distributed across each constituent FET, thereby enhancing switch breakdown voltage. Capacitances are controlled, for example, by disposing capacitive features between nodes of the string, and / or by varying design parameters of different constituent FETs. For each node, a sum of products of each significant capacitor by a proportion of Vsw appearing across it may be controlled to approximately zero.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Split-channel antifuse array architecture
InactiveUS20060244099A1Limited over-voltage exposureSimplify and improve and accessTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCMOSEngineering
Generally, the present invention provides a variable thickness gate oxide anti-fuse transistor device that can be employed in a non-volatile, one-time-programmable (OTP) memory array application. The anti-fuse transistor can be fabricated with standard CMOS technology, and is configured as a standard transistor element having a source diffusion, gate oxide, polysilicon gate and optional drain diffusion. The variable gate oxide underneath the polysilicon gate consists of a thick gate oxide region and a thin gate oxide region, where the thin gate oxide region acts as a localized breakdown voltage zone. A conductive channel between the polysilicon gate and the channel region can be formed in the localized breakdown voltage zone during a programming operation. In a memory array application, a wordline read current applied to the polysilicon gate can be sensed through a bitline connected to the source diffusion, via the channel of the anti-fuse transistor. More specifically, the present invention provides an effective method for utilizing split channel MOS structures as an anti-fuse cell suitable for OTP memories.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
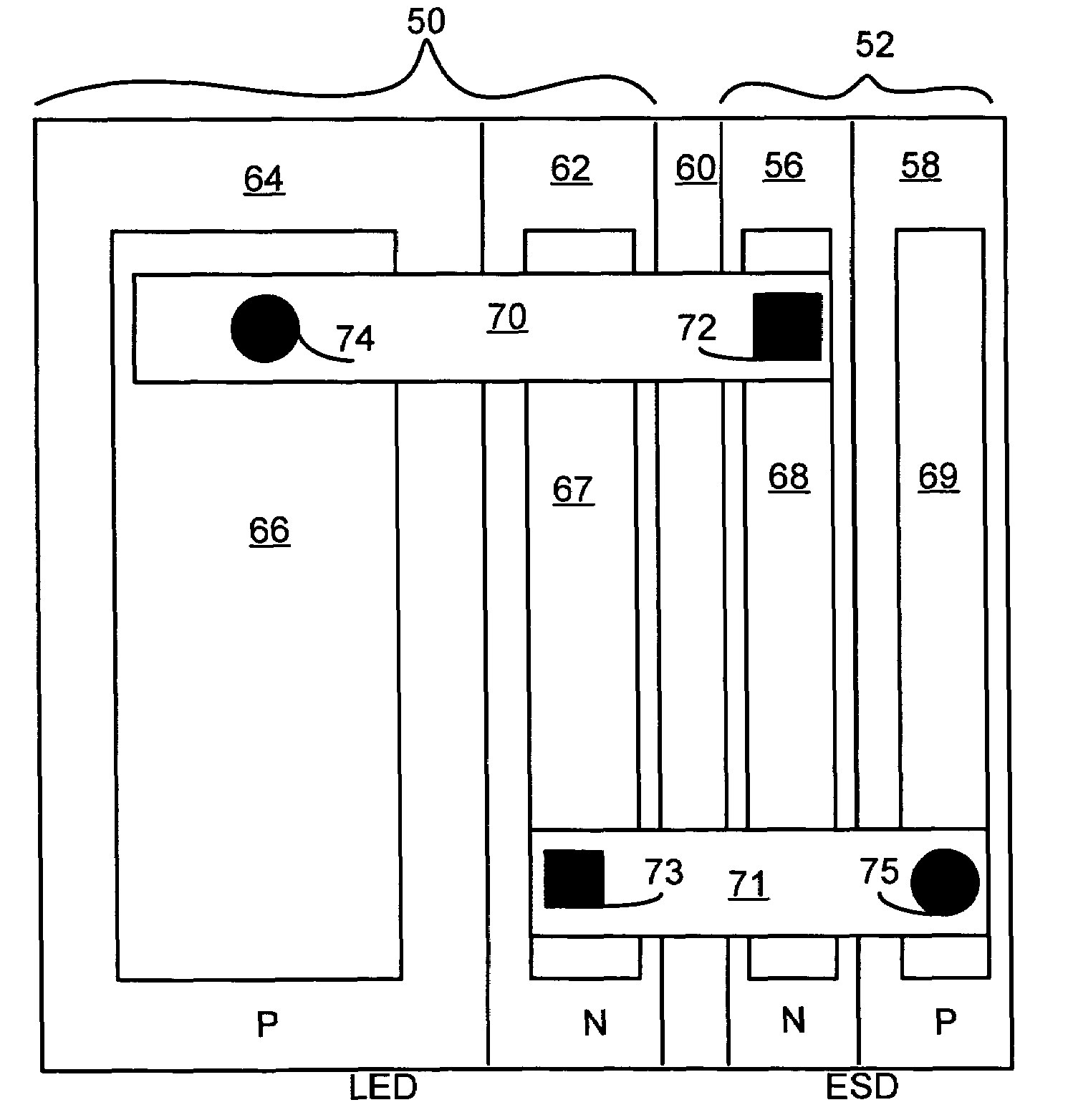
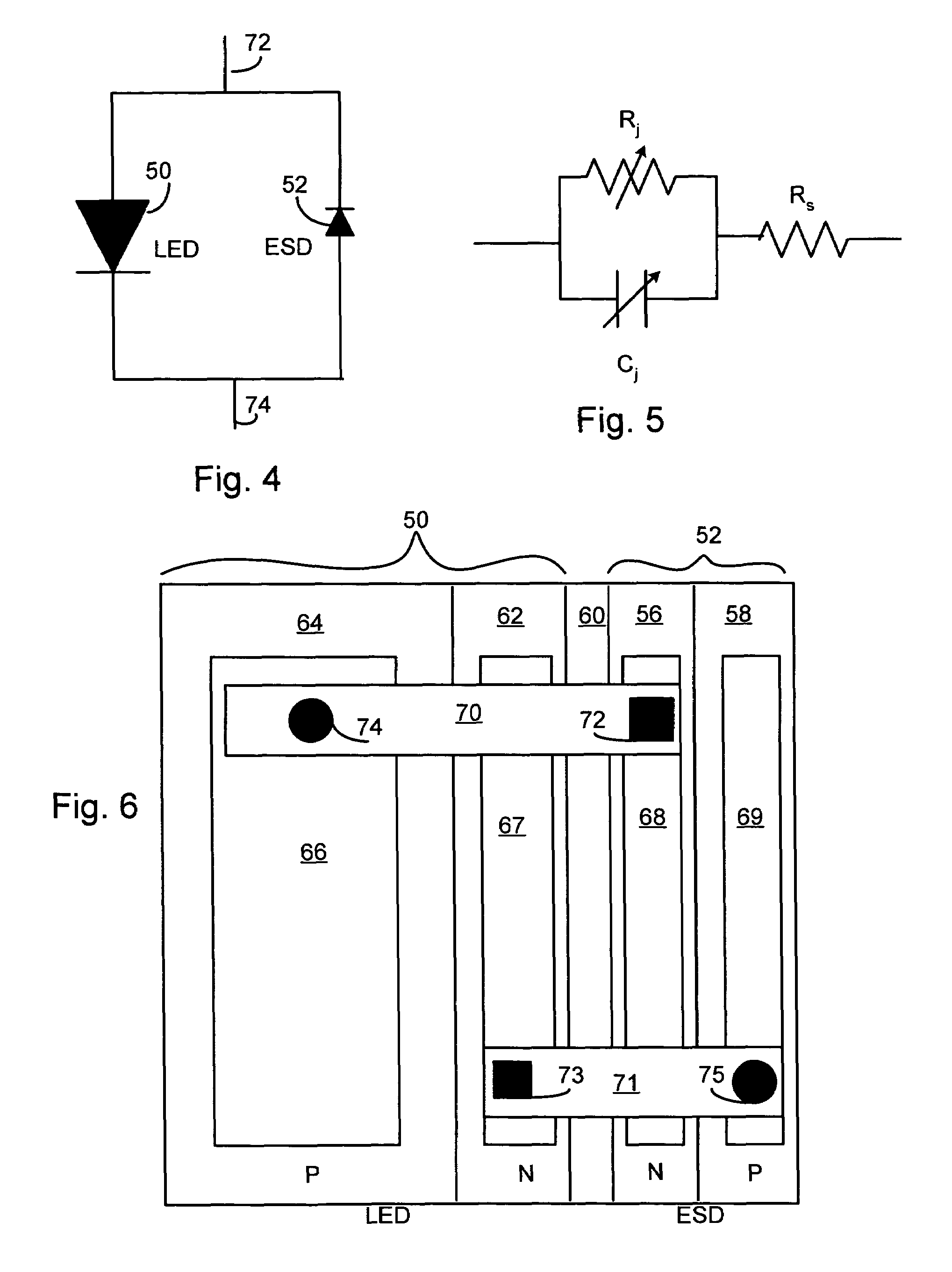
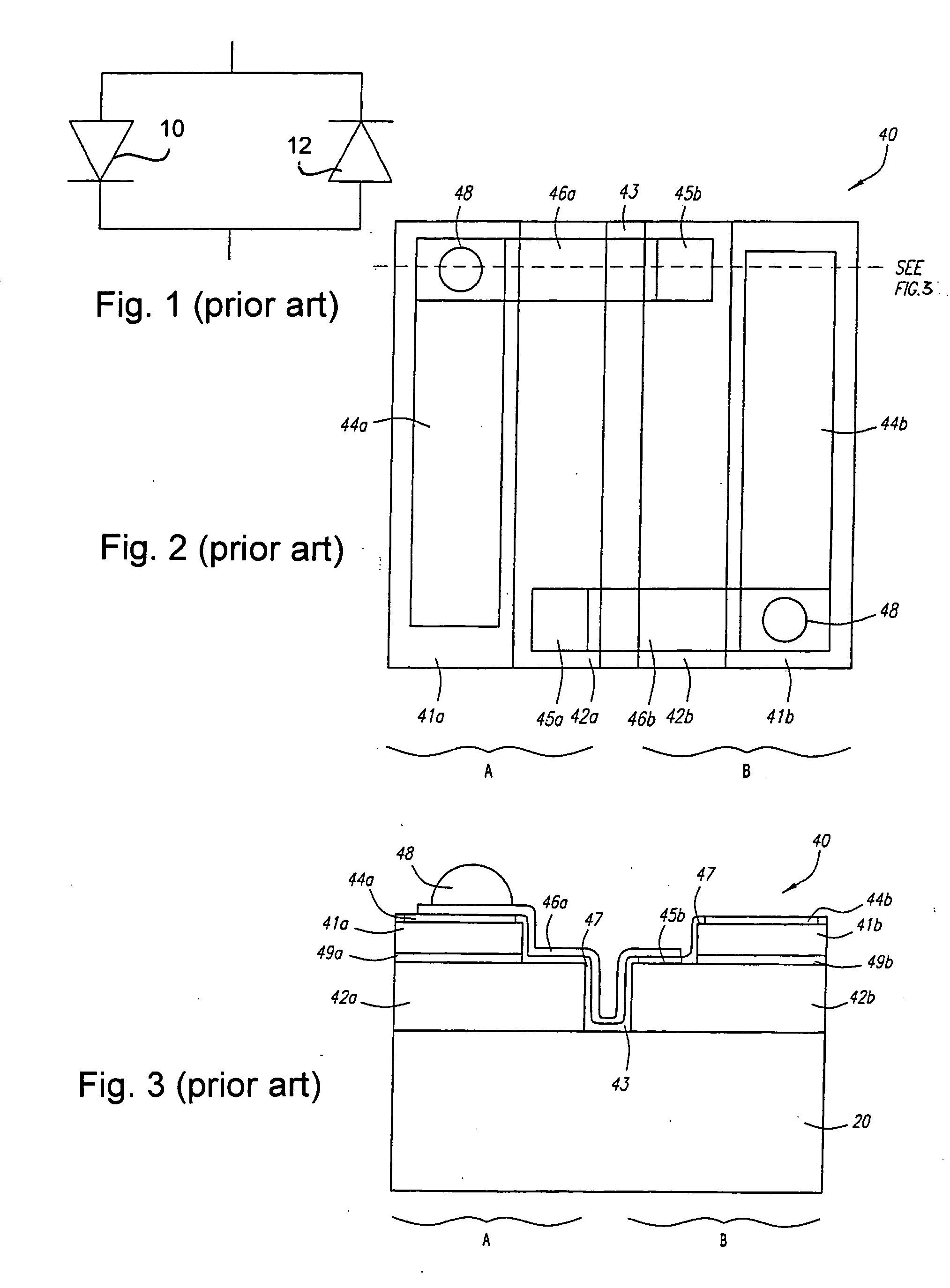
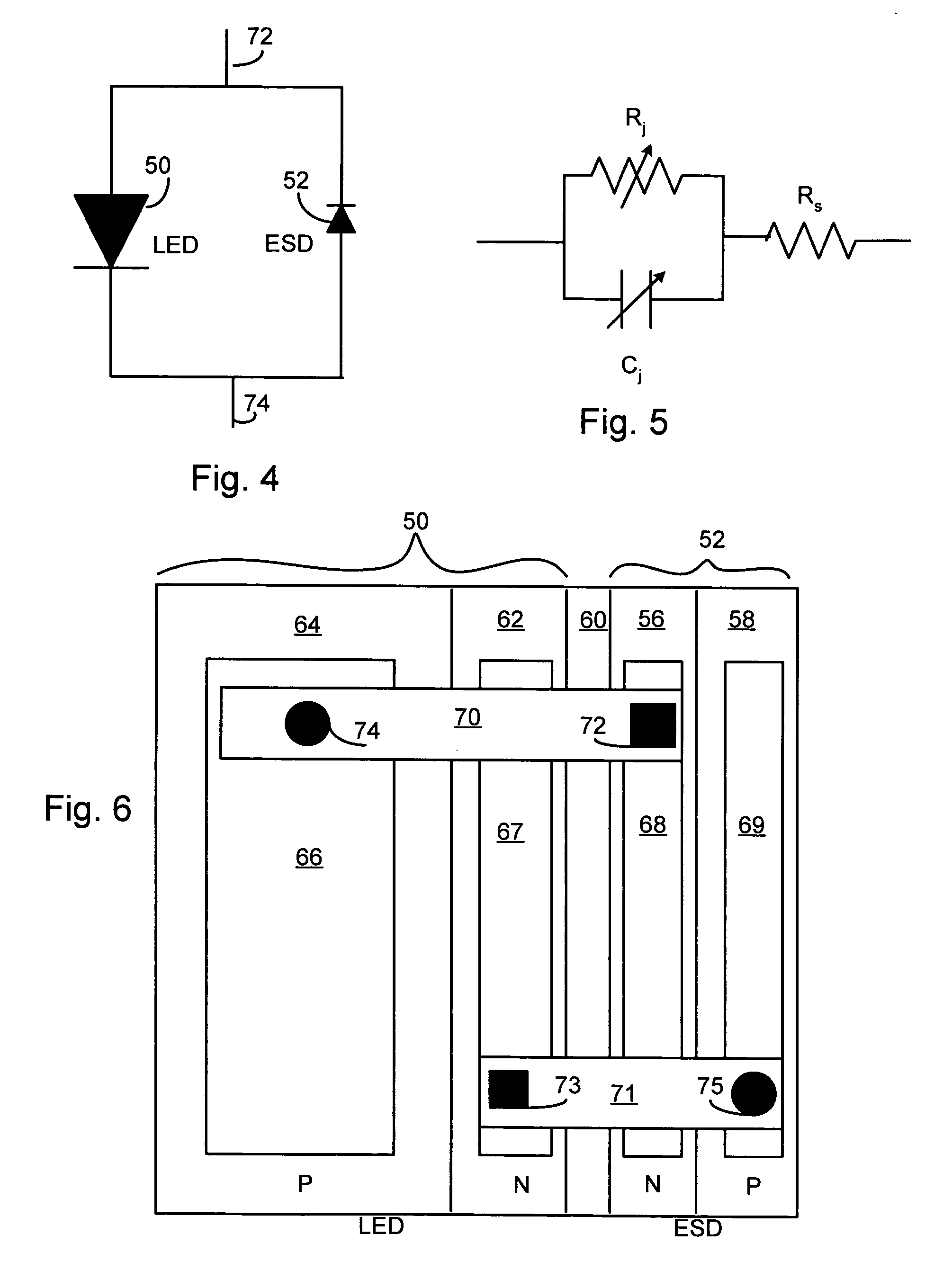
LED chip with integrated fast switching diode for ESD protection
ActiveUS7064353B2Reduced series resistanceIncrease widthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsP–n junction
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV +1
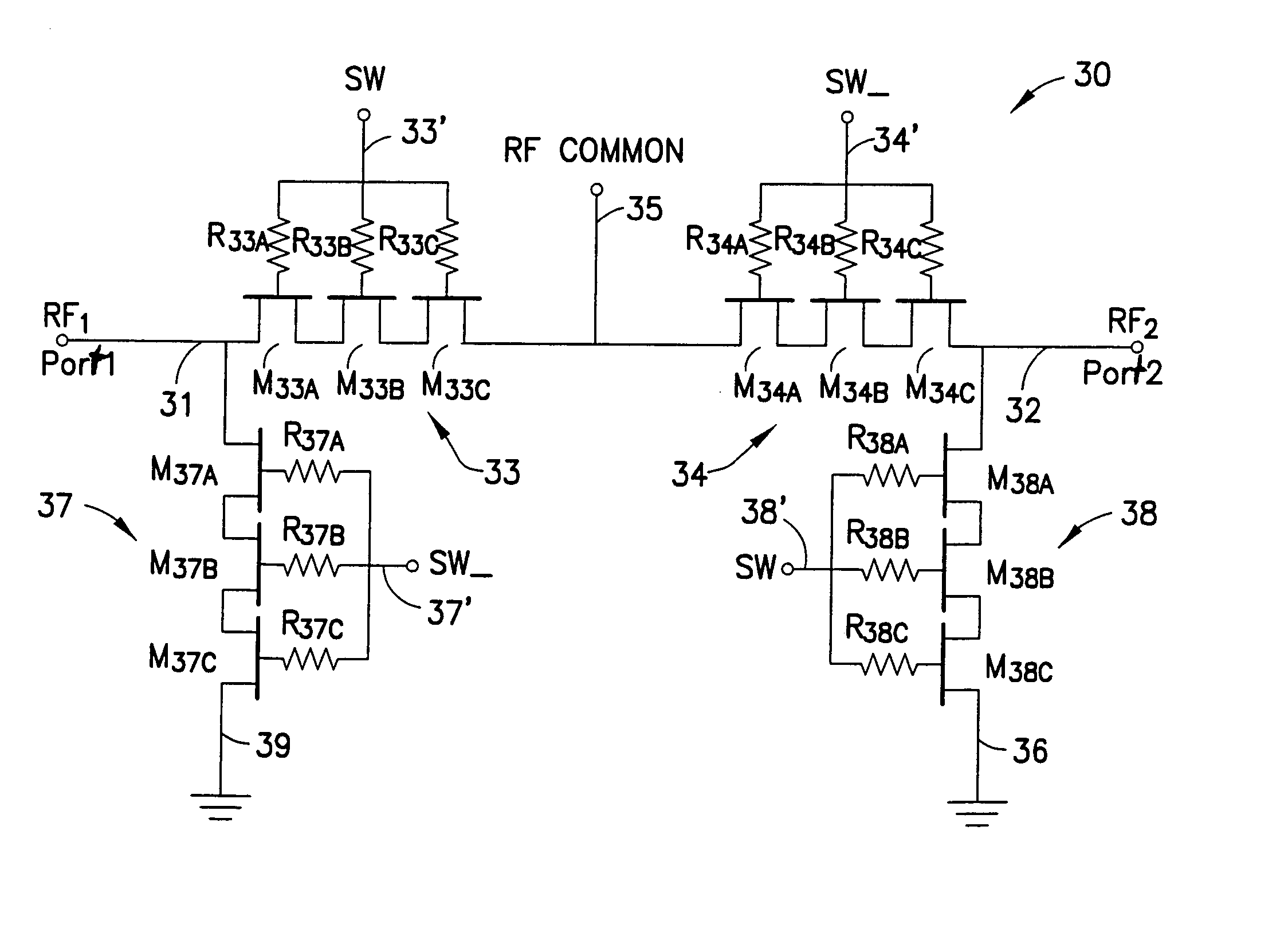
Switch circuit and method of switching radio frequency signals
InactiveUS7123898B2Easy to switchImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETDigital control
A novel RF buffer circuit adapted for use with an RF switch circuit and method for switching RF signals is described. The RF switch circuit is fabricated in a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) technology. The RF switch includes pairs of switching and shunting transistor groupings used to alternatively couple RF input signals to a common RF node. The switching and shunting transistor grouping pairs are controlled by a switching control voltage (SW) and its inverse (SW_). The switching and shunting transistor groupings comprise one or more MOSFET transistors connected together in a “stacked” or serial configuration. The stacking of transistor grouping devices, and associated gate resistors, increase the breakdown voltage across the series connected switch transistors and operate to improve RF switch compression. A fully integrated RF switch is described including digital control logic and a negative voltage generator integrated together with the RF switch elements. In one embodiment, the fully integrated RF switch includes a built-in oscillator, a charge pump circuit, CMOS logic circuitry, level-shifting and voltage divider circuits, and an RF buffer circuit. Several embodiments of the charge pump, level shifting, voltage divider, and RF buffer circuits are described. The inventive RF switch provides improvements in insertion loss, switch isolation, and switch compression.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
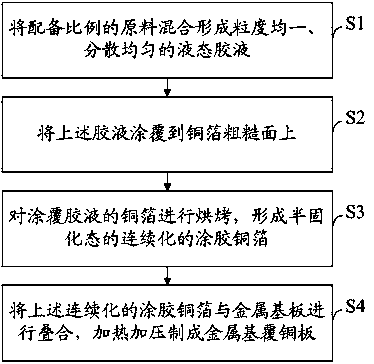
Epoxy resin composition, metal-based copper-clad plate and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103694644AHigh thermal conductivityImprove thermal conductivityFilm/foil adhesivesLaminationEpoxyOrganic solvent
The invention discloses an epoxy resin composition, a metal-based copper-clad plate and a manufacturing method thereof. The epoxy resin composition comprises the following components by mass: 90-110 parts of epoxy resin, 10-50 parts of thermoplastic resin, 1-100 parts of a curing agent, 0.05-5 parts of a curing accelerant, 1-10 parts of an additive, 20-500 parts of heat conduction filler and 0-30 parts of an organic solvent. The metal-based copper-clad plate has the characteristic that 1, the heat conductivity is high; 2, the insulation property is high as the puncture-withstand voltage is higher than 6KV; 3, the anti-bending property is high, so that the metal-based copper-clad plate can be used for manufacturing a three-dimensional aluminum substrate; 4, the thickness of the insulation layer is uniform, the coating thickness tolerance can be controlled at + / - 2 microns, and the press-fit thickness tolerance can be controlled at + / - 5 microns, so that the performance of a product can be guaranteed; 5, the production efficiency is high; 6, the cost is low and is about 1 / 4-1 / 3 of the cost of an imported product.
Owner:KINWONG ELECTRONICS TECH LONGCHUAN
High voltage lateral DMOS transistor having low on-resistance and high breakdown voltage
InactiveUS20030193067A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringHigh pressure
A high voltage lateral Double diffused Metal Oxide Semiconductor (DMOS) transistor includes a plurality of well regions of a first conductivity type formed to be spaced out within a well region of a second conductivity type between a channel region of the first conductivity type and a drain region of the second conductivity type. Most current is carried through some portions of the well region of the second conductivity type in which the well regions of the first conductivity do not appear so that the current carrying performance of the device is improved. When a bias voltage is applied to the drain region, the well region of the second conductivity type is completely depleted at other portions where the well region of the second conductivity type and the well regions of the first conductivity type alternately appear so that the breakdown voltage of the device can be increased. In addition, since the well region of the second conductivity type can be easily depleted, not only the breakdown voltage can be increased, but also the impurity concentration of the well region of the second conductivity type can be increased. Accordingly, the on-resistance of the device can be decreased.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Voltage up-conversion circuit using low voltage transistors
ActiveUS7408330B2Low costApparatus without intermediate ac conversionLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsVoltage generatorLow voltage
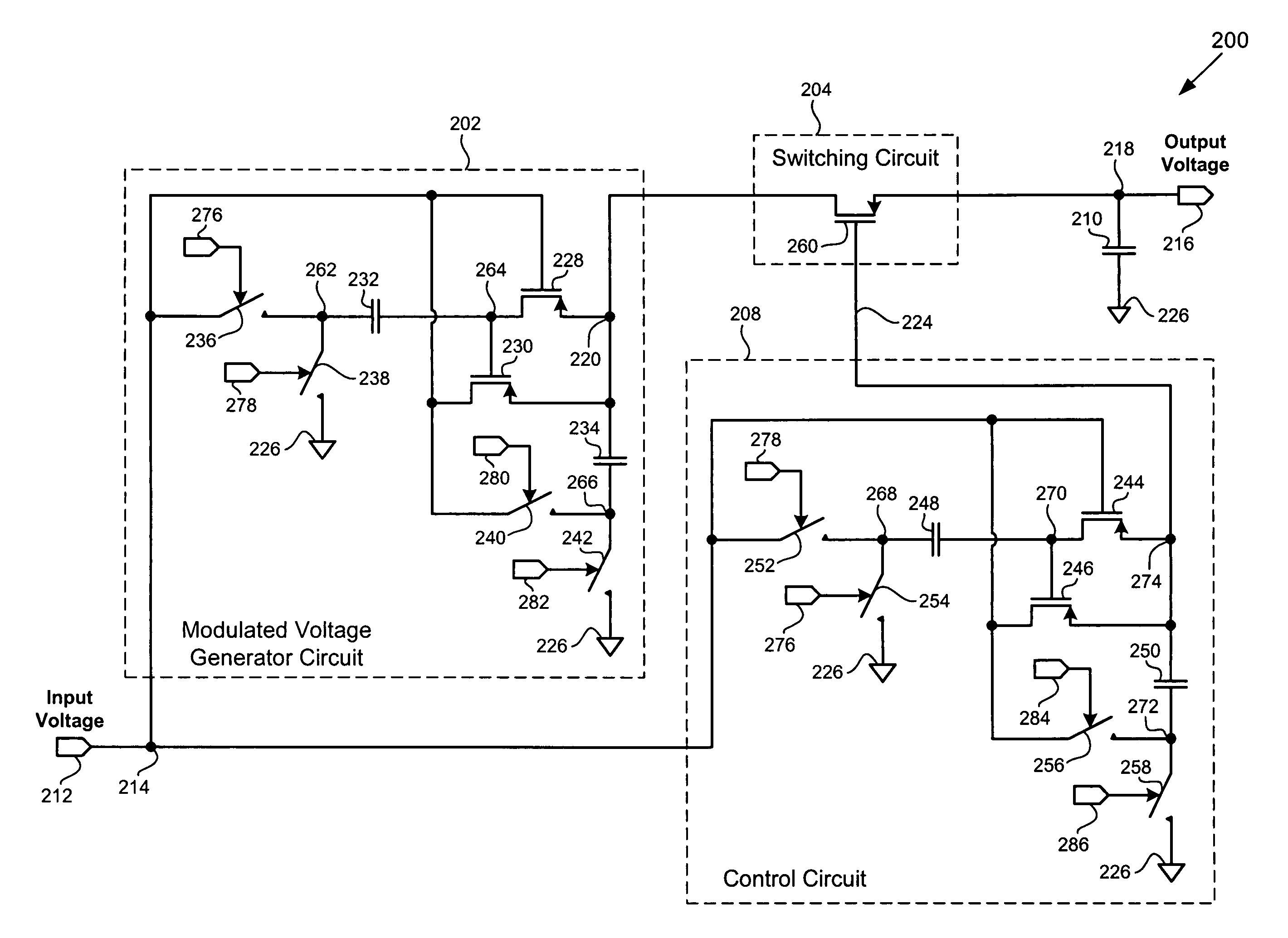
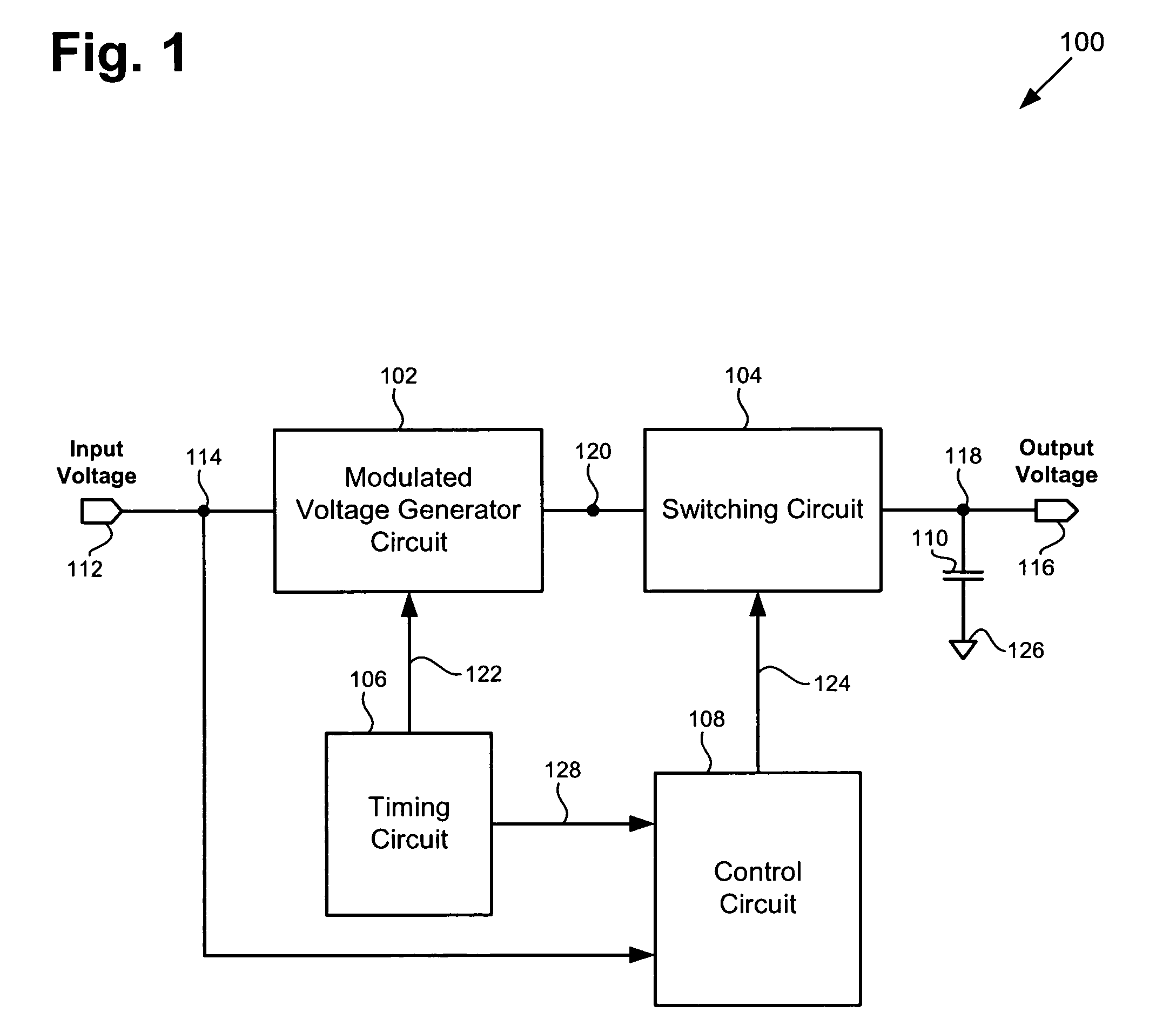
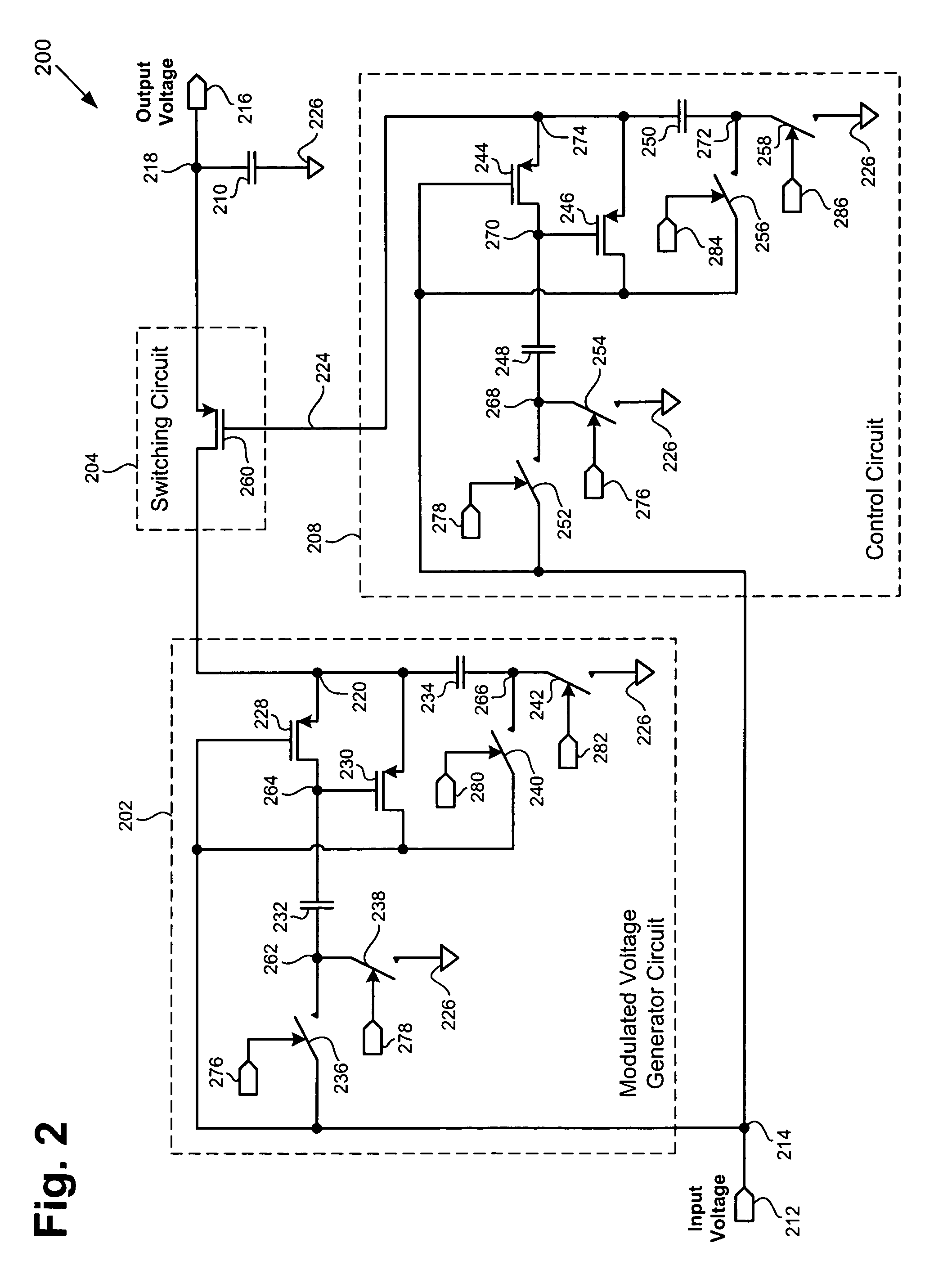
According to one exemplary embodiment, a voltage up-conversion circuit includes a modulated voltage generator circuit, where the modulated voltage generator circuit is configured to receive an input voltage and generate a modulated voltage, and where the modulated voltage generator circuit includes at least one transistor. The voltage up-conversion circuit further includes a switching circuit coupled to the modulated voltage generator circuit, where the switching circuit is configured to couple the modulated voltage to a load capacitor when the modulated voltage is at a high level and decouple the modulated voltage to the load capacitor when the modulated voltage is at a low level. In the voltage up-conversion circuit, the load capacitor reaches a voltage greater a breakdown voltage of the at least one transistor in the modulated voltage generator circuit. The breakdown voltage can be a reliability breakdown voltage.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
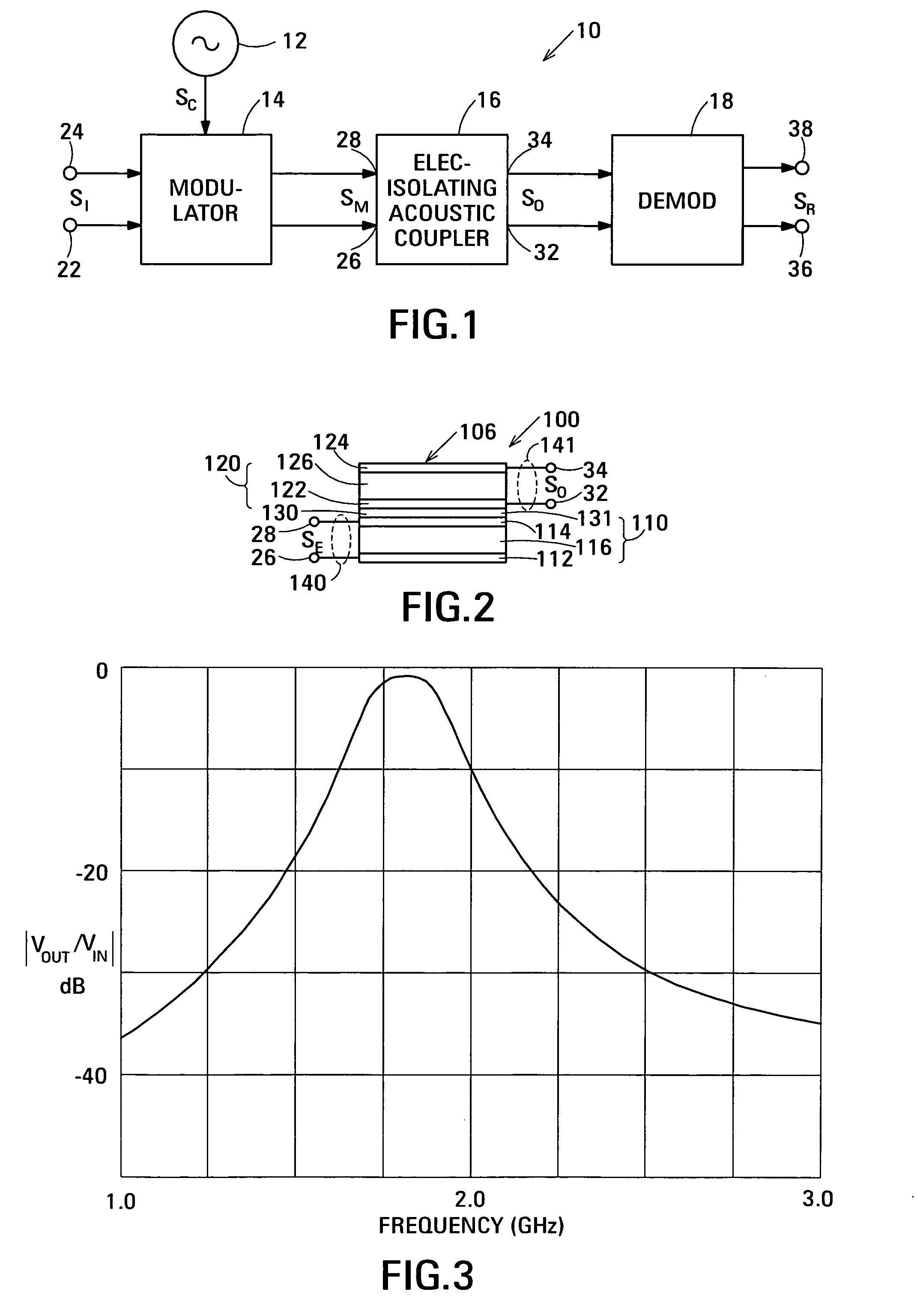
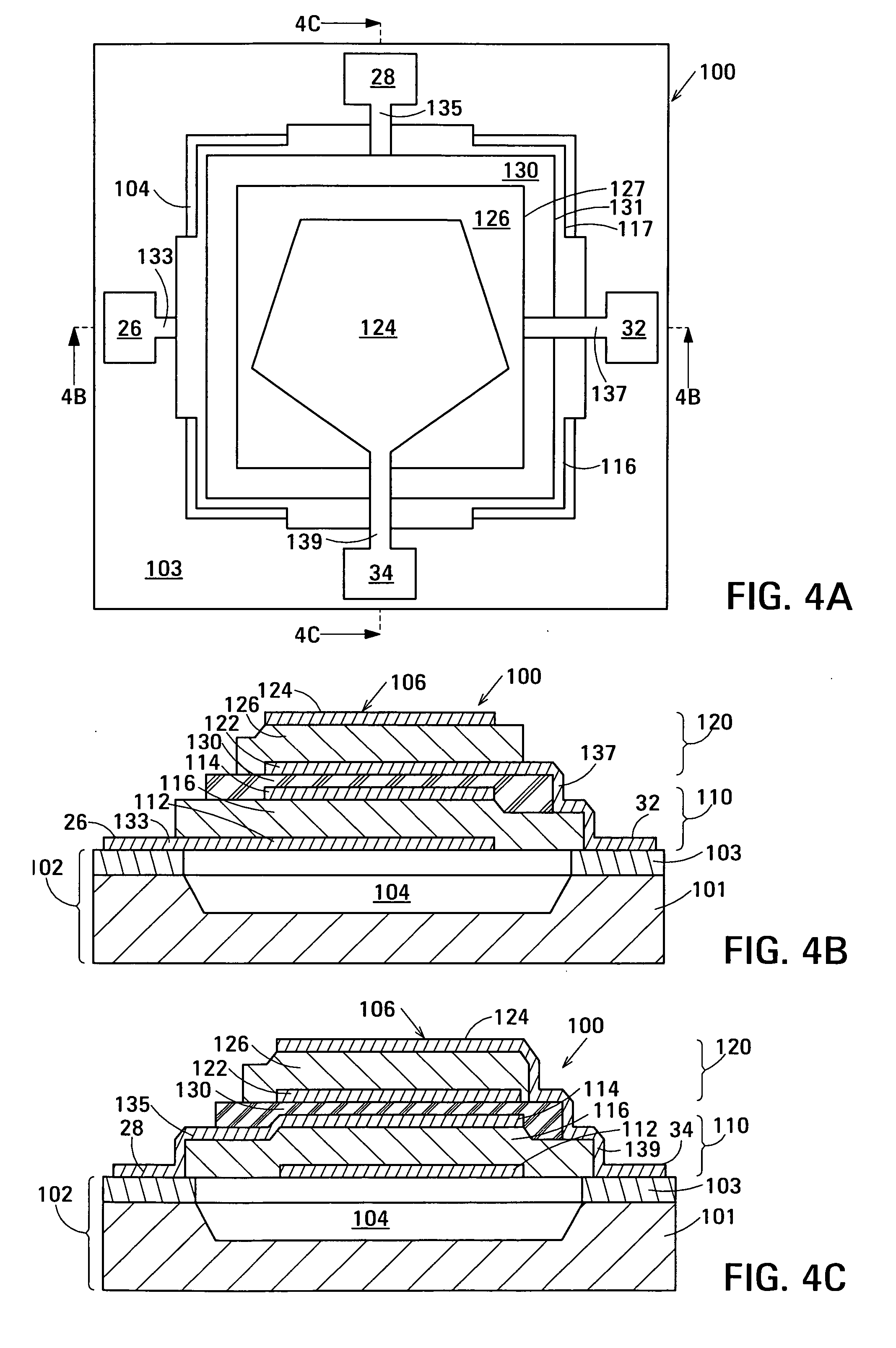
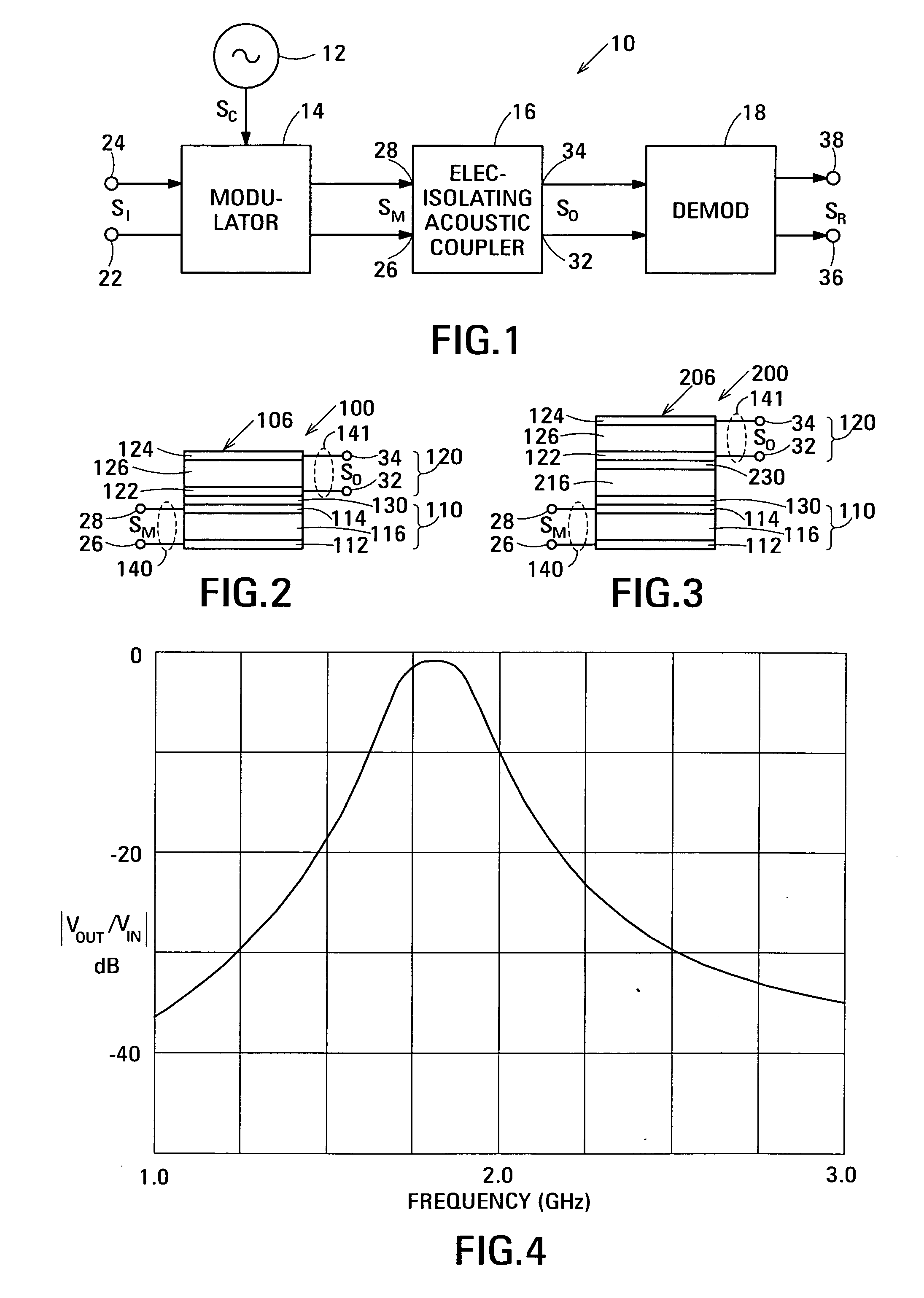
Acoustic galvanic isolator
Embodiments of the acoustic galvanic isolator comprise a carrier signal source, a modulator connected to receive an information signal and the carrier signal, a demodulator, and an electrically-isolating acoustic coupler connected between the modulator and the demodulator. In an exemplary embodiment, the electrically-isolating acoustic coupler comprises film bulk acoustic resonators (FBARs). An electrically-isolating acoustic coupler is physically small and is inexpensive to fabricate yet is capable of passing information signals having data rates in excess of 100 Mbit / s and has a substantial breakdown voltage between its inputs and its outputs.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Acoustic galvanic isolator incorporating single insulated decoupled stacked bulk acoustic resonator with acoustically-resonant electrical insulator
ActiveUS20070085447A1Inexpensive to fabricateCapable of couplingPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksData rateCarrier signal
Embodiments of the acoustic galvanic isolator comprise a carrier signal source, a modulator connected to receive an information signal and the carrier signal, a demodulator, and an electrically-isolating acoustic coupler connected between the modulator and the demodulator. The acoustic coupler comprises no more than one decoupled stacked bulk acoustic resonator (IDSBAR). An electrically-isolating acoustic coupler based on a single IDSBAR is physically small and is inexpensive to fabricate yet is capable of passing information signals having data rates in excess of 100 Mbit / s and has a substantial breakdown voltage between its inputs and its outputs.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
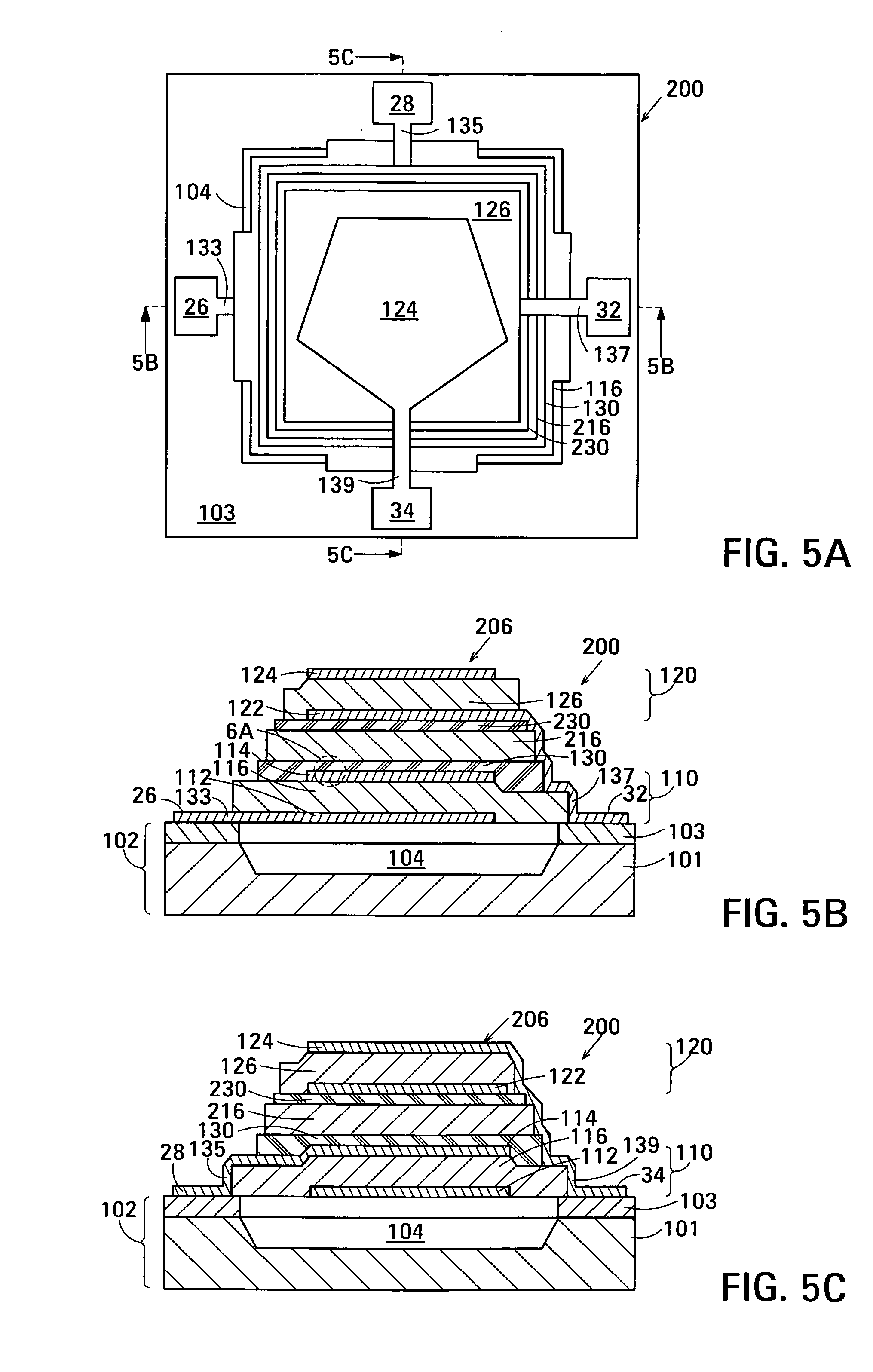
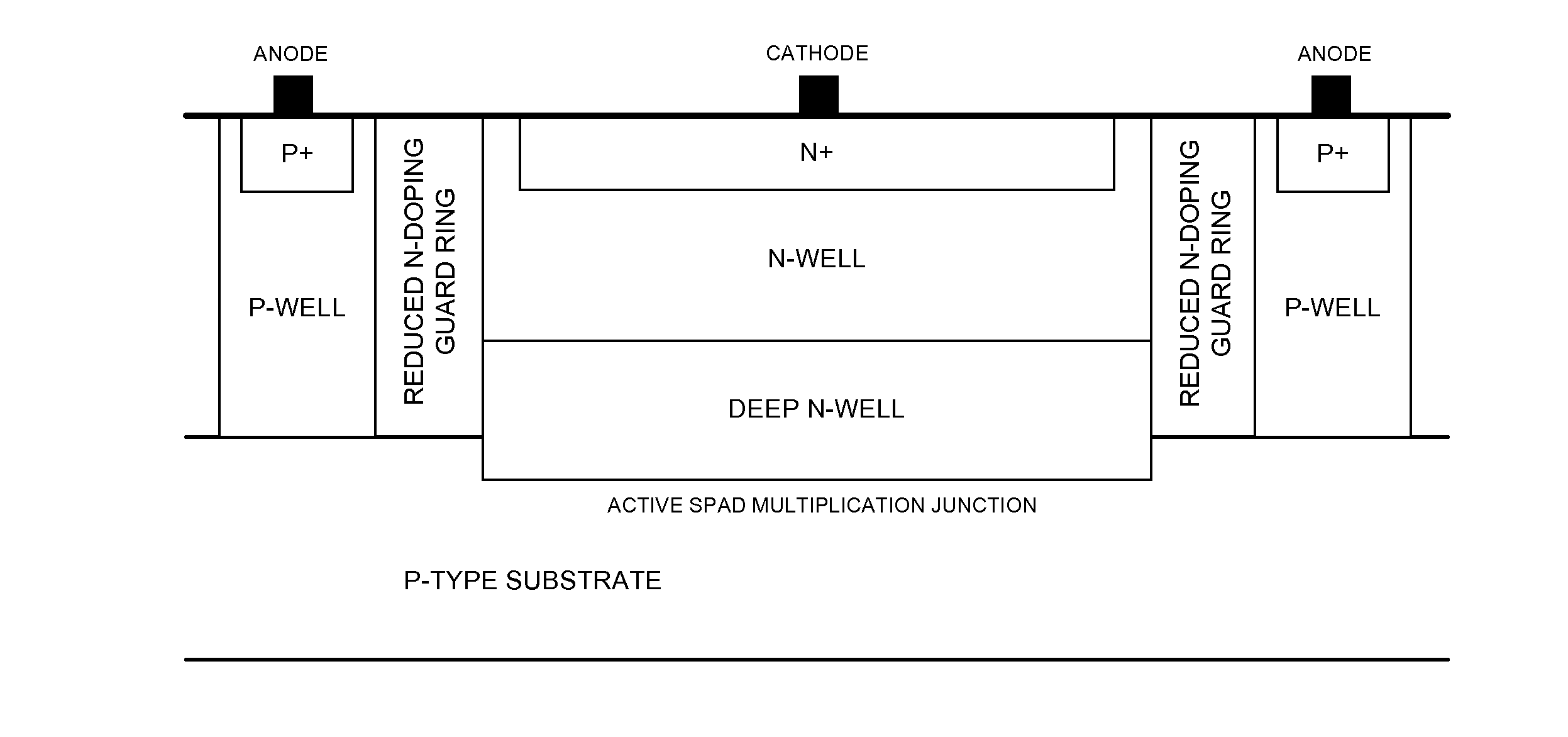
Single photon avalanche diode for CMOS circuits
ActiveUS20130193546A1Improves blue responseImproved broad spectrum sensitivityFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesCMOSSingle-photon avalanche diode
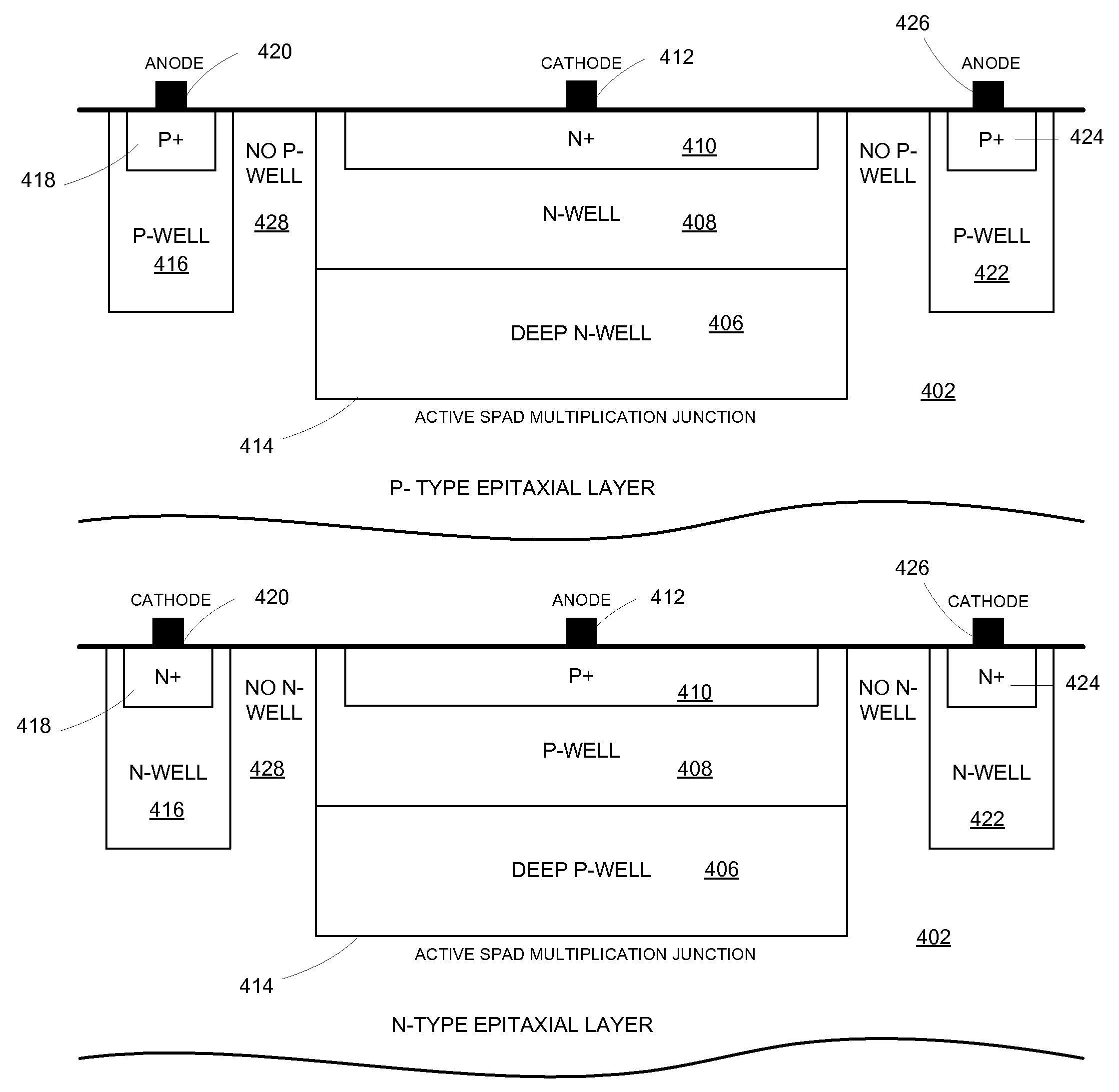
A single photon avalanche diode for use in a CMOS integrated circuit includes a deep n-well region formed above a p-type substrate and an n-well region formed above and in contact with the deep n-well region. A cathode contact is connected to the n-well region via a heavily doped n-type implant. A lightly doped region forms a guard ring around the n-well and deep n-well regions. A p-well region is adjacent to the lightly doped region. An anode contact is connected to the p-well region via a heavily doped p-type implant. The junction between the bottom of the deep n-well region and the substrate forms a multiplication region when an appropriate bias voltage is applied between the anode and cathode and the guard ring breakdown voltage is controlled with appropriate control of the lateral doping concentration gradient such that the breakdown voltage is higher than that of the multiplication region.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS RES & DEV +1
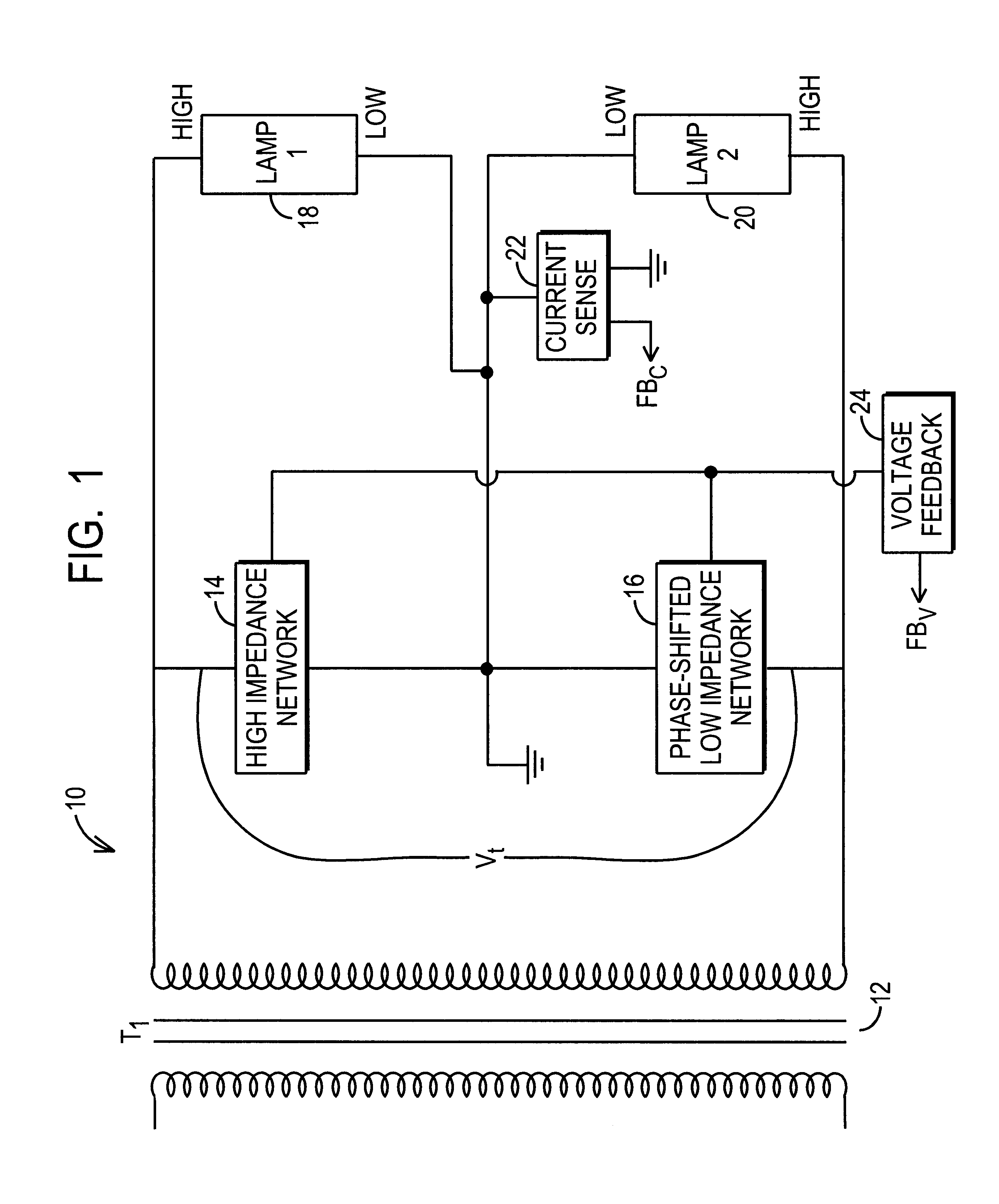
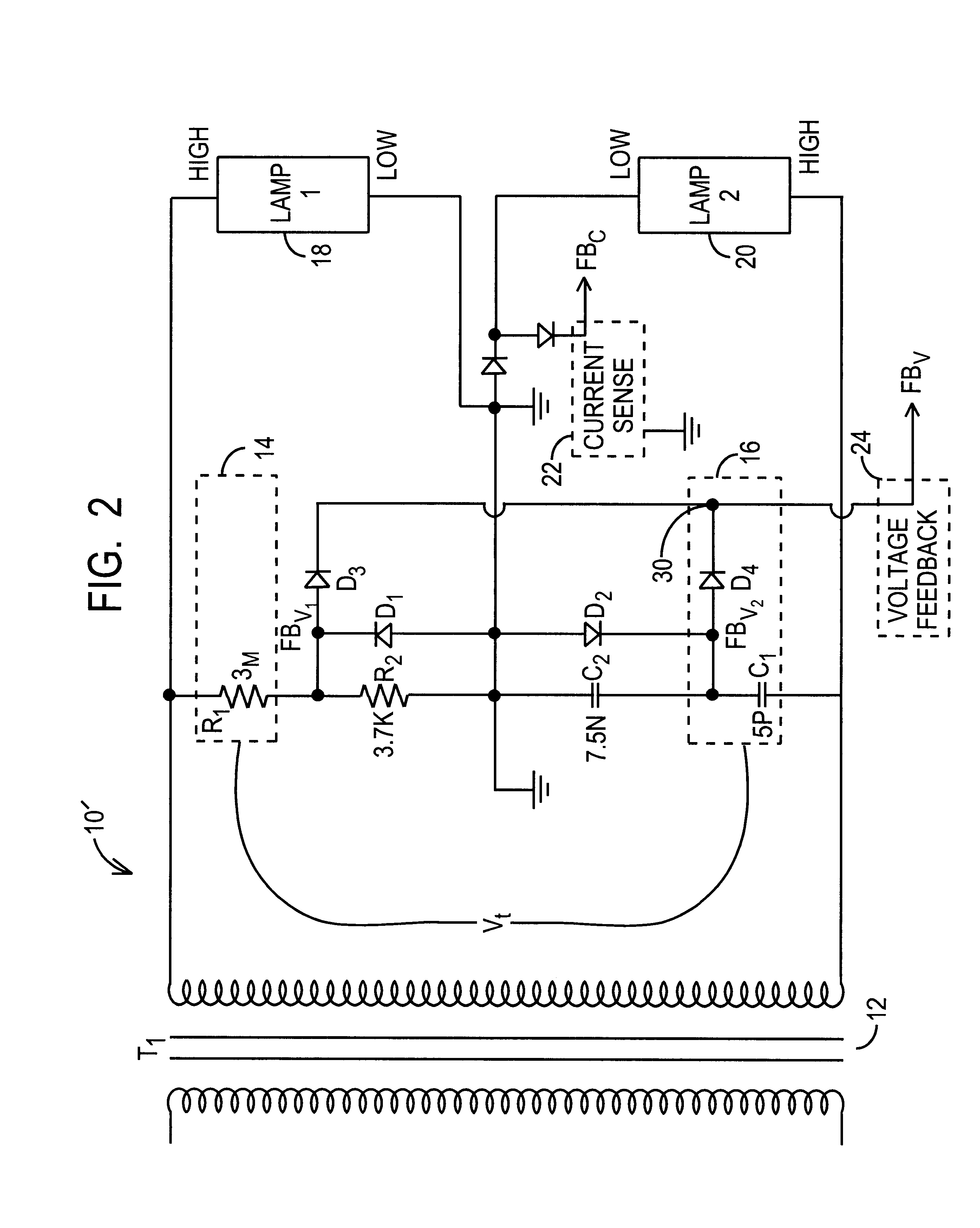
Lamp driving topology
InactiveUS6559606B1Low voltage requirementLess developmentElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementPhase shiftedEngineering
A lamp driving system that includes a first impedance and a second impedance coupled to the secondary side of a transformer, where the second impedance has a phase shifted value compared to the first impedance. Two lamp loads are connected in series together, and in parallel to the first and second impedances and to the transformer. The phase shift between the impedances ensures that the transformer need not supply double the striking voltage to strike the series-connected lamps. A difference in the resistance between the first and second impedances ensures that the lamps ignite in a specified sequence.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
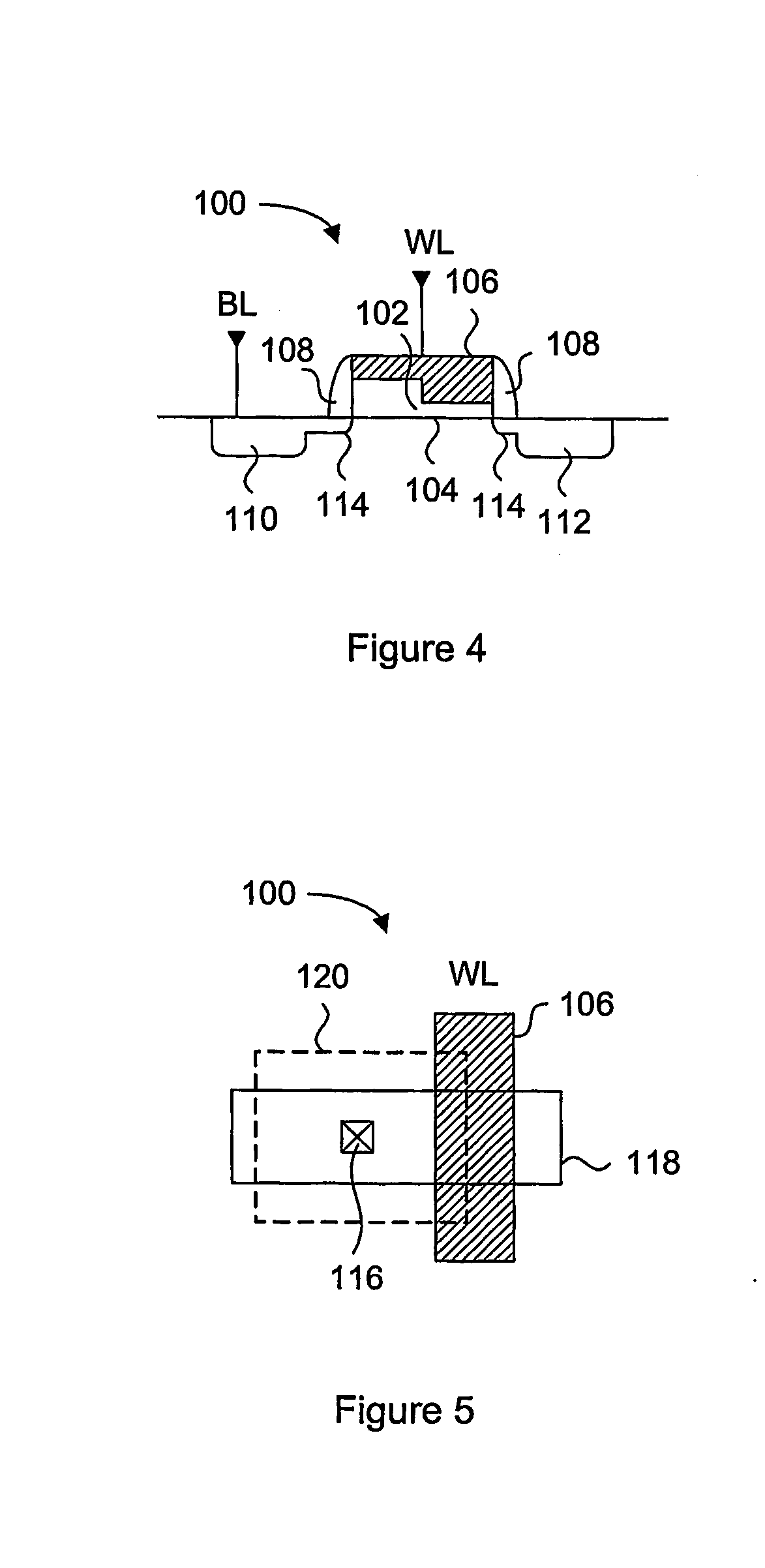
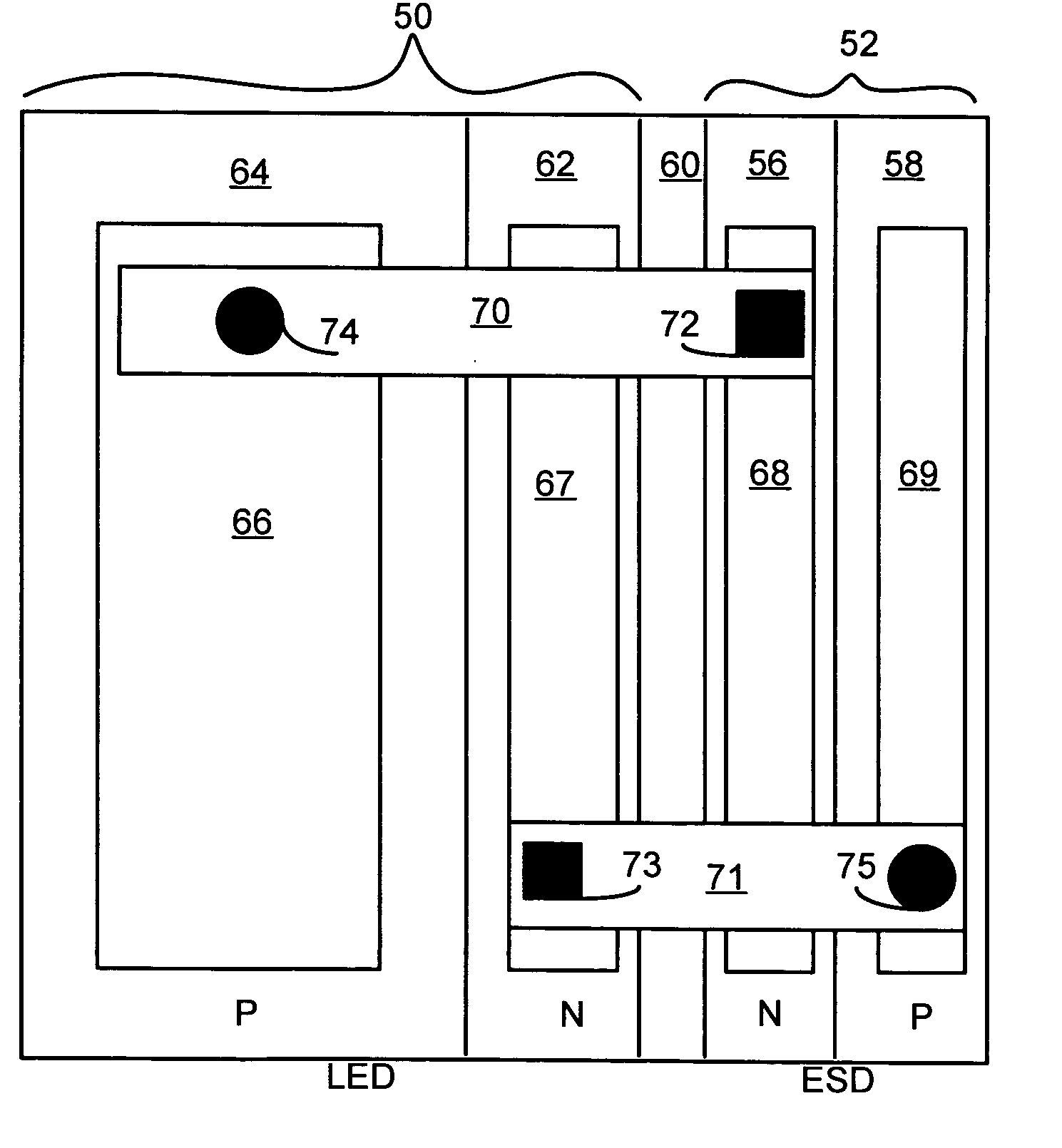
LED chip with integrated fast switching diode for ESD protection
ActiveUS20050274956A1Reduced series resistanceImprove breakdown voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsLight-emitting diode
A relatively small ESD protection diode is formed on the same chip as a light emitting diode. In one embodiment, the ESD diode is a mesa-type diode isolated from the light emitting diode by a trench. To reduce the series resistance of the ESD diode, the PN junction and metal contact to the semiconductor material is made long and expands virtually the width of the chip. Various configurations of the PN junction and the N and P metal contacts for the ESD diode are described for increasing the breakdown voltage and for improved testing.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV +1
LDMOS transistors and methods for making the same
InactiveUS6900101B2Reduce or inhibit current flow constrictionLower on-state resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantDielectric
LDMOS transistor devices and fabrication methods are provided, in which additional dopants are provided to region of a substrate near a thick dielectric between the channel and the drain to reduce device resistance without significantly impacting breakdown voltage. The extra dopants are added by implantation prior to formation of the thick dielectric, such as before oxidizing silicon in a LOCOS process or following trench formation and before filling the trench in an STI process.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Single photon avalanche diode for CMOS circuits
ActiveUS9178100B2Reduce cost and complexityLong wavelength detection propertyFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesCMOSSingle-photon avalanche diode
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (RES & DEV) LTD +1
Self-aligned structures and methods for asymmetric GAN transistors & enhancement mode operation
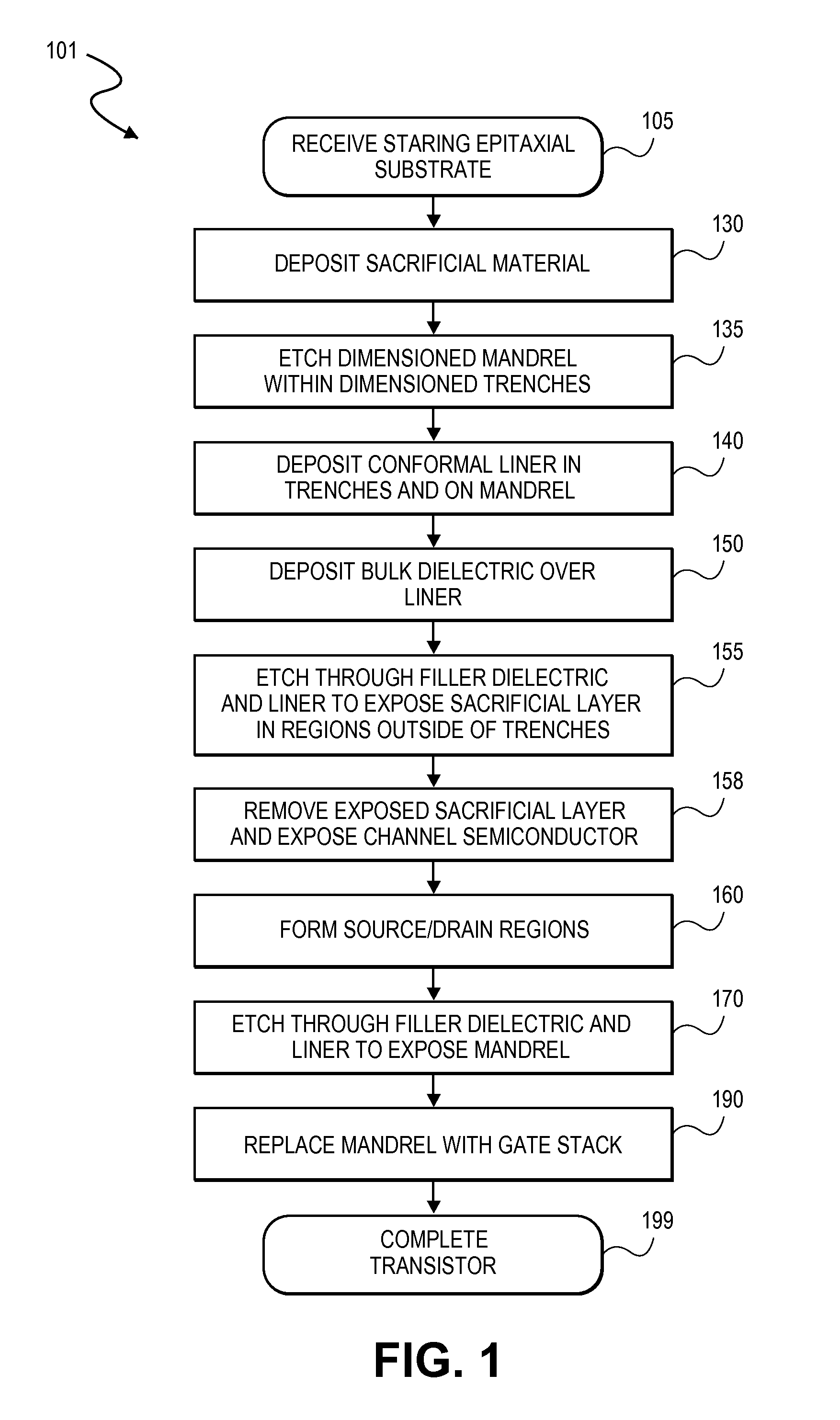
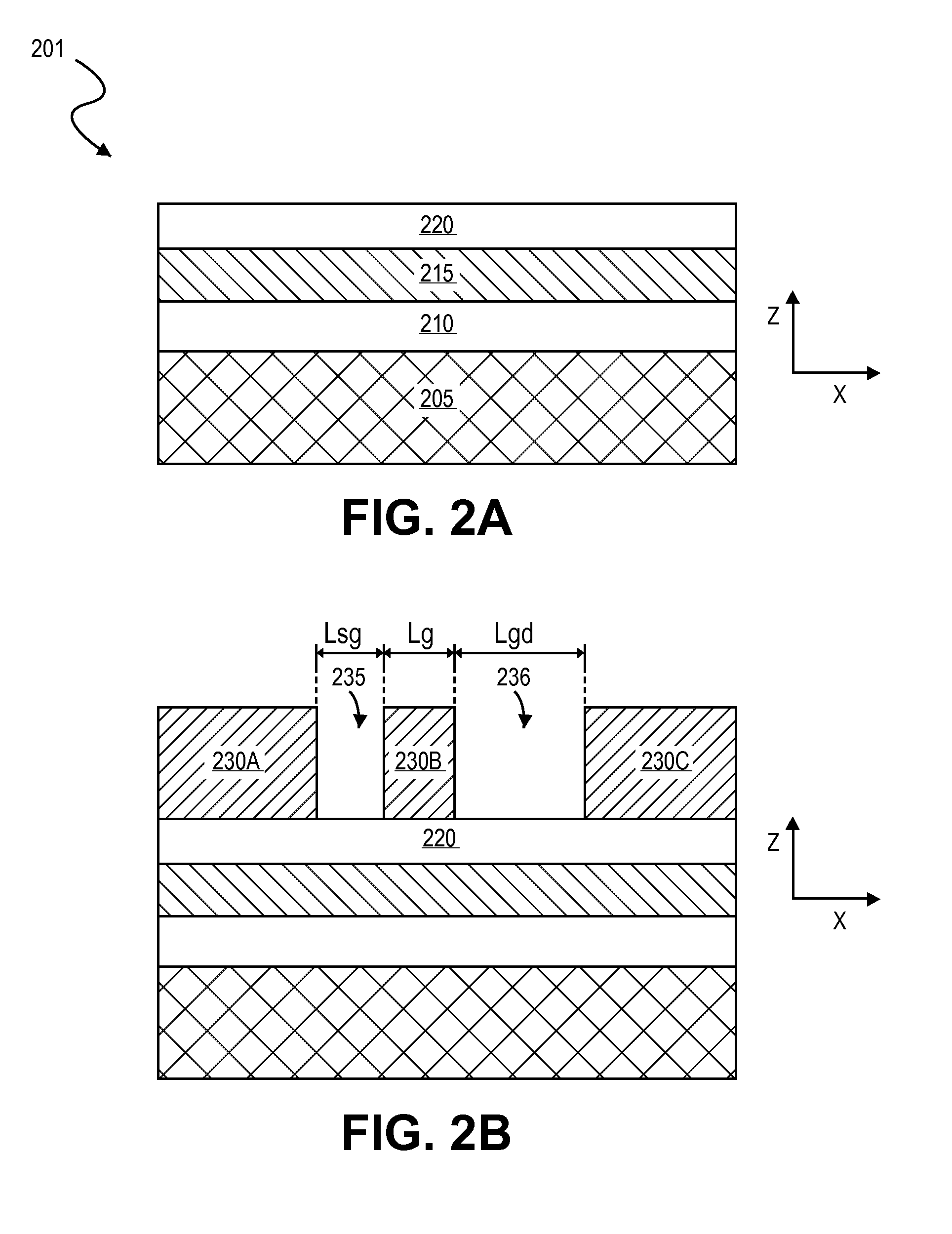
ActiveUS20140091308A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesNon symmetricEngineering
Embodiments include high electron mobility transistors (HEMT). In embodiments, a gate electrode is spaced apart by different distances from a source and drain semiconductor region to provide high breakdown voltage and low on-state resistance. In embodiments, self-alignment techniques are applied to form a dielectric liner in trenches and over an intervening mandrel to independently define a gate length, gate-source length, and gate-drain length with a single masking operation. In embodiments, III-N HEMTs include fluorine doped semiconductor barrier layers for threshold voltage tuning and / or enhancement mode operation.
Owner:INTEL CORP
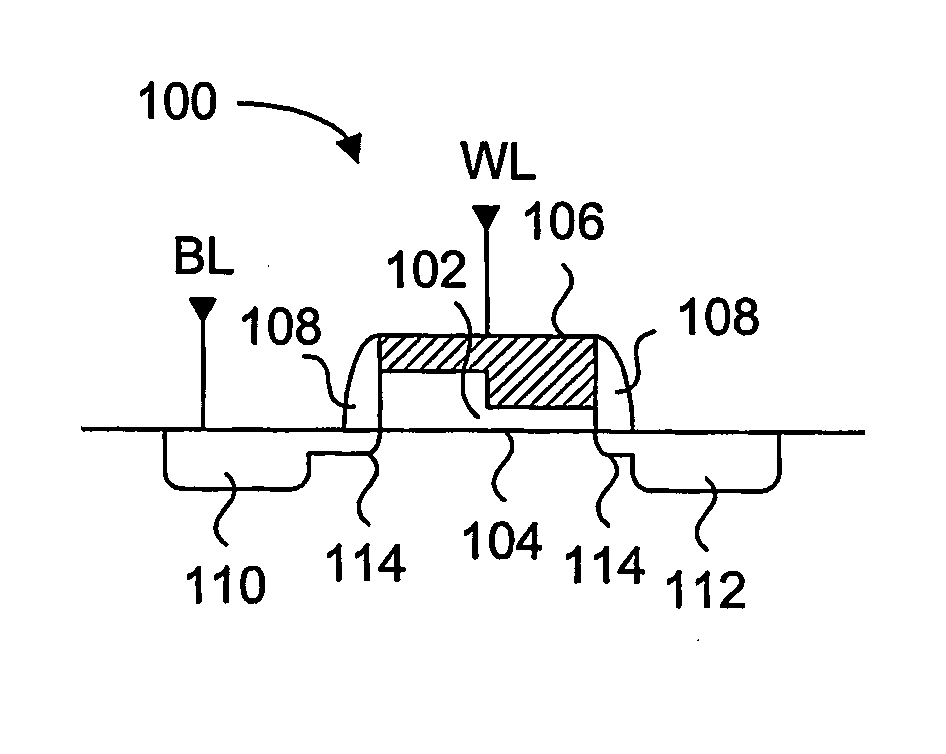
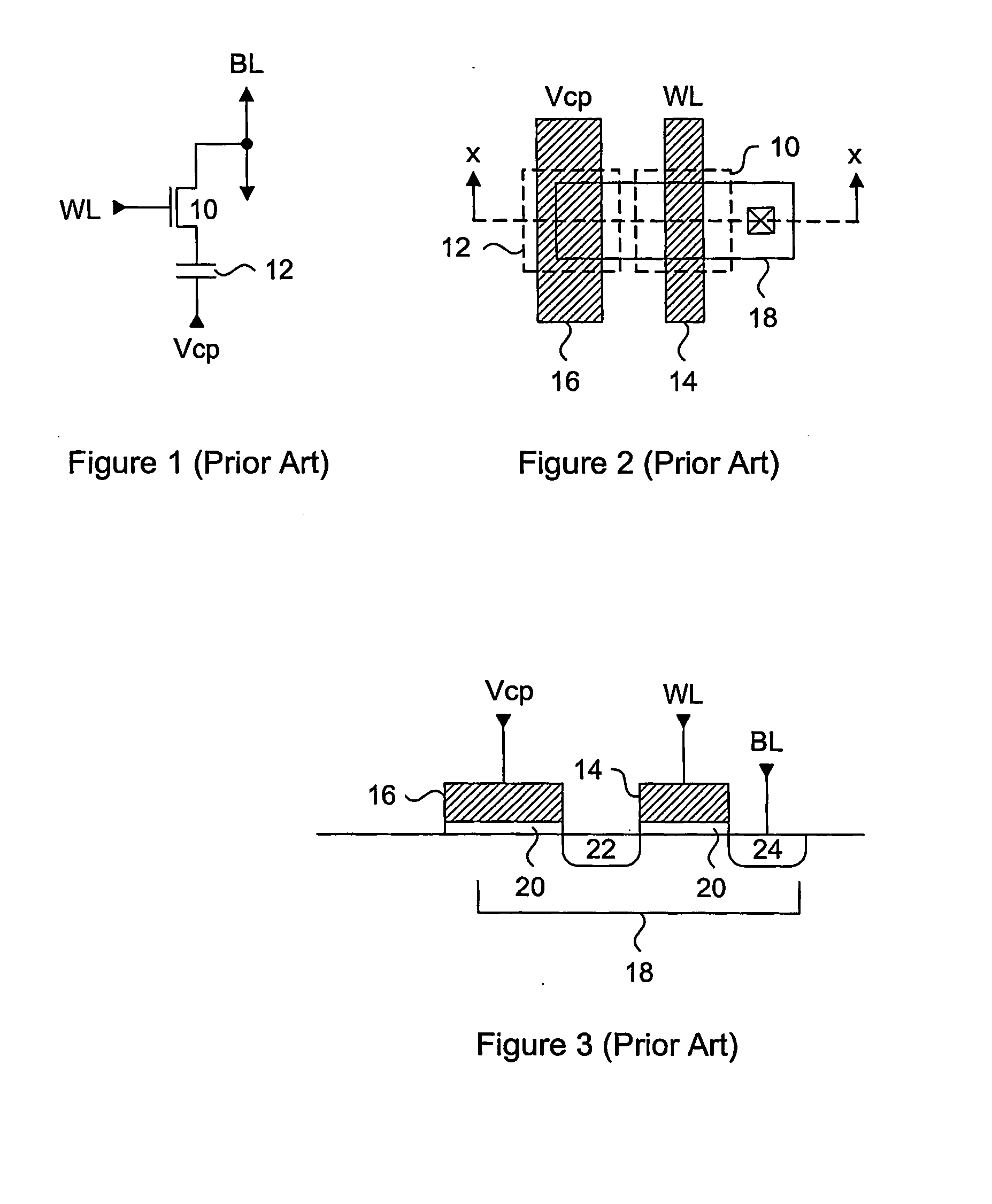
High density semiconductor memory cell and memory array using a single transistor and having variable gate oxide breakdown
A programmable memory cell comprised of a transistor located at the crosspoint of a column bitline and a row wordline is disclosed. The transistor has its gate formed from the column bitline and its source connected to the row wordline. The memory cell is programmed by applying a voltage potential between the column bitline and the row wordline to produce a programmed n+ region in the substrate underlying the gate of the transistor. Further, a gate dielectric of the transistor has a higher breakdown voltage near the source connected to the row wordline than its drain.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
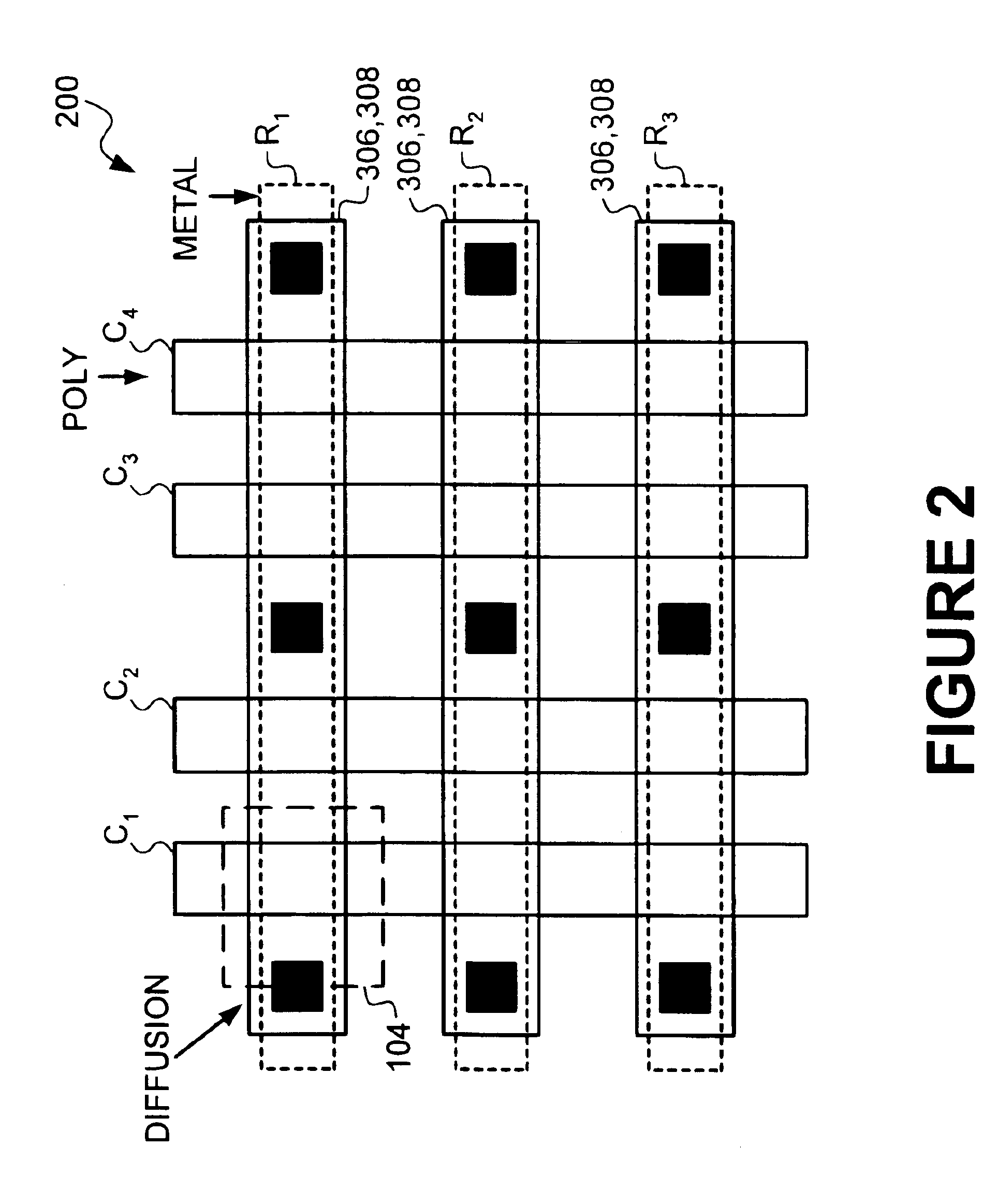
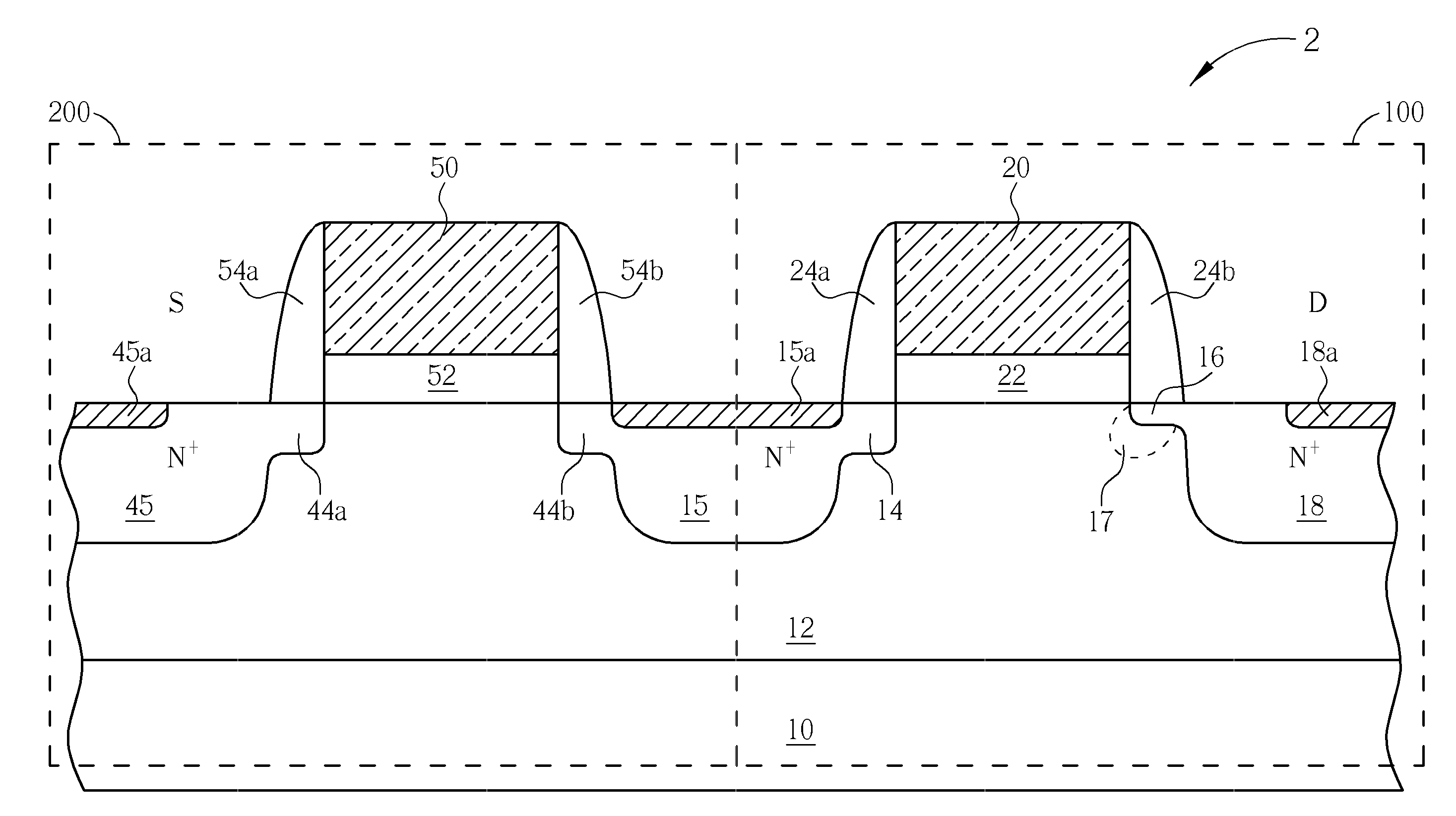
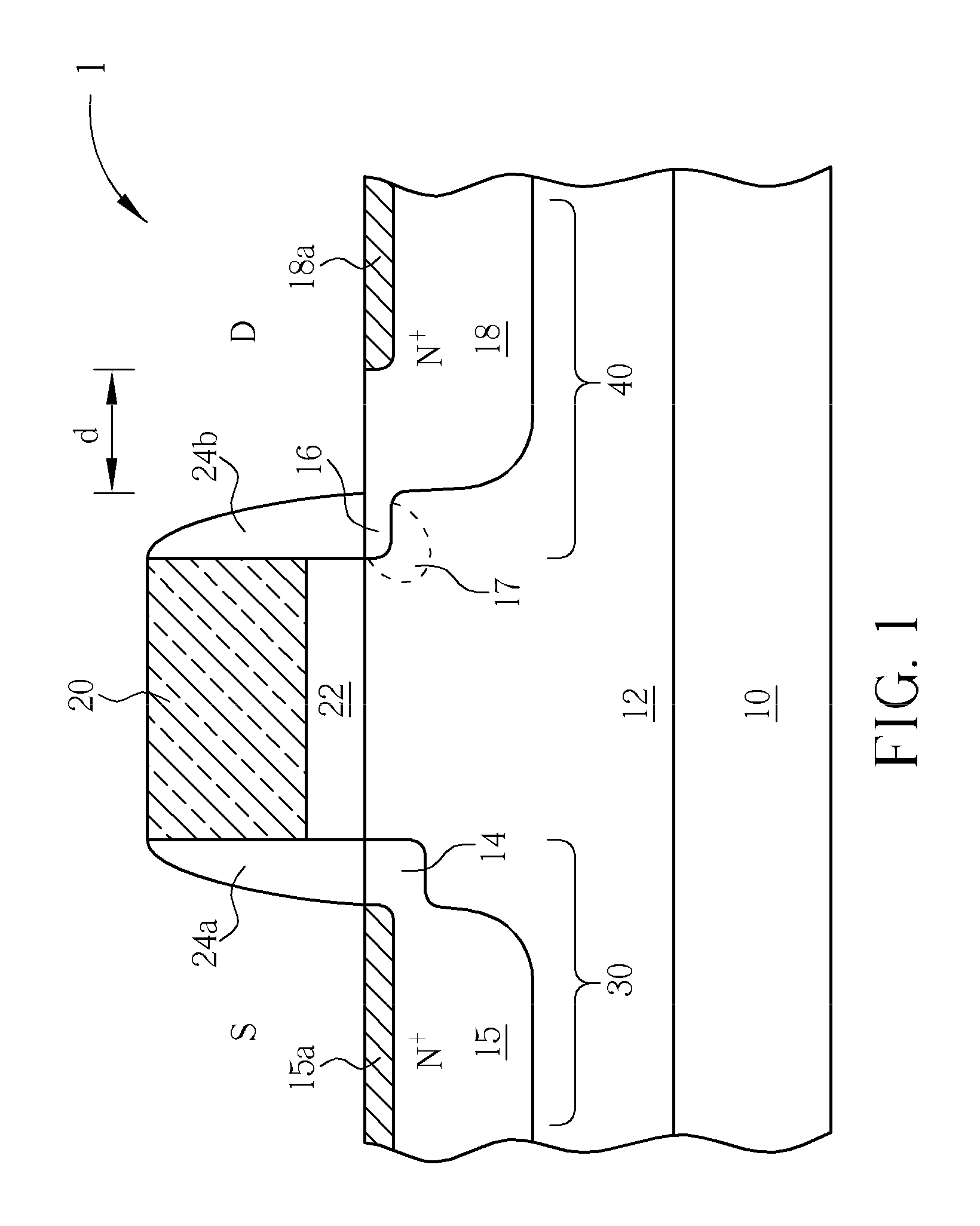
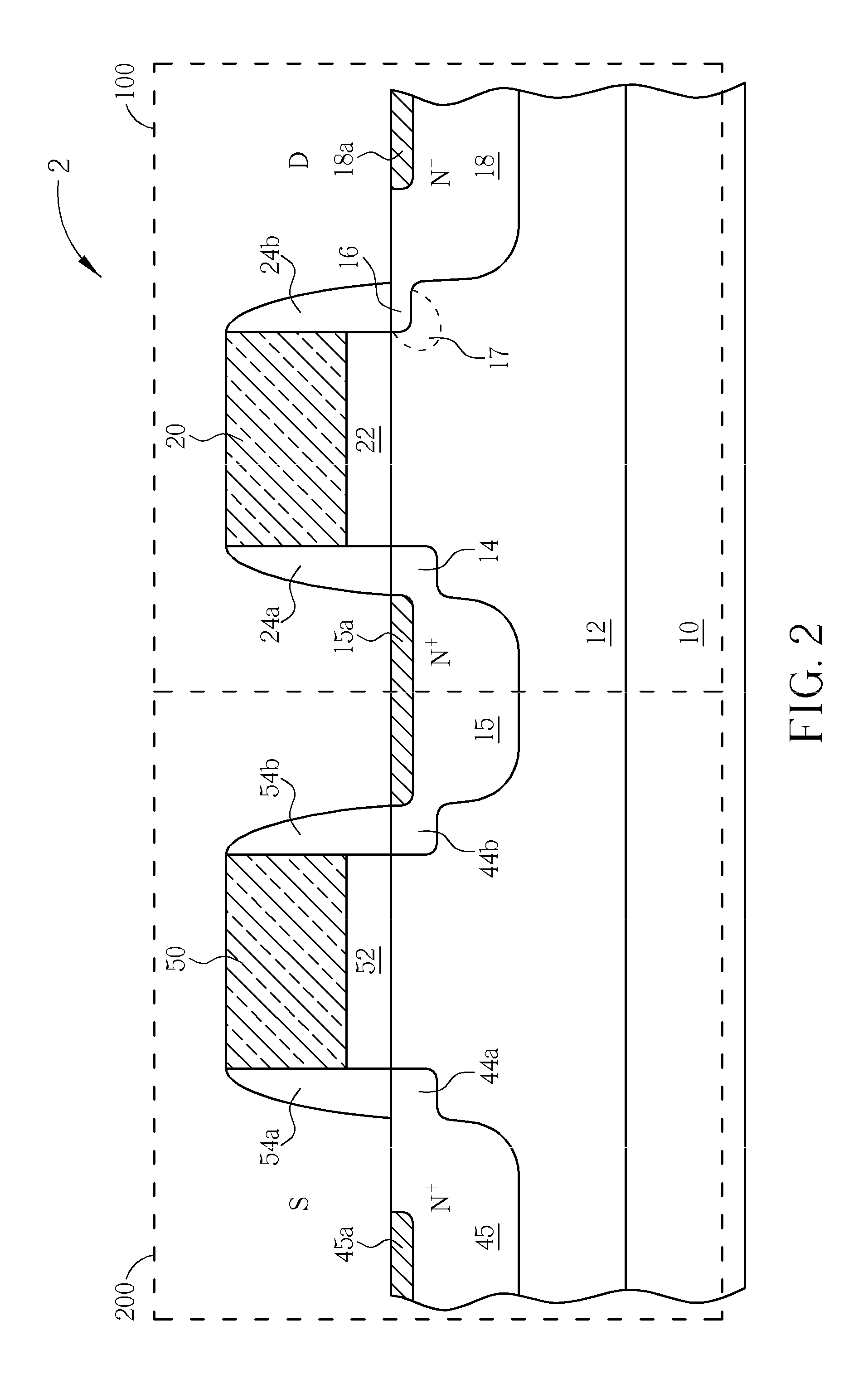
Input/output electrostatic discharge device with reduced junction breakdown voltage
InactiveUS20110037121A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricEngineering
An I / O electrostatic discharge (ESD) device having a gate electrode over a substrate, a gate dielectric layer between the gate electrode and the substrate, a pair of sidewall spacers respectively disposed on two opposite sidewalls of the gate electrode, a first lightly doped drain (LDD) region disposed under one of the sidewall spacers, a source region disposed next to the first LDD region, a second LDD region disposed under the other sidewall spacer, and a drain region disposed next to the second LDD region, wherein a doping concentration of the second LDD region is larger than a doping concentration of the first LDD region.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
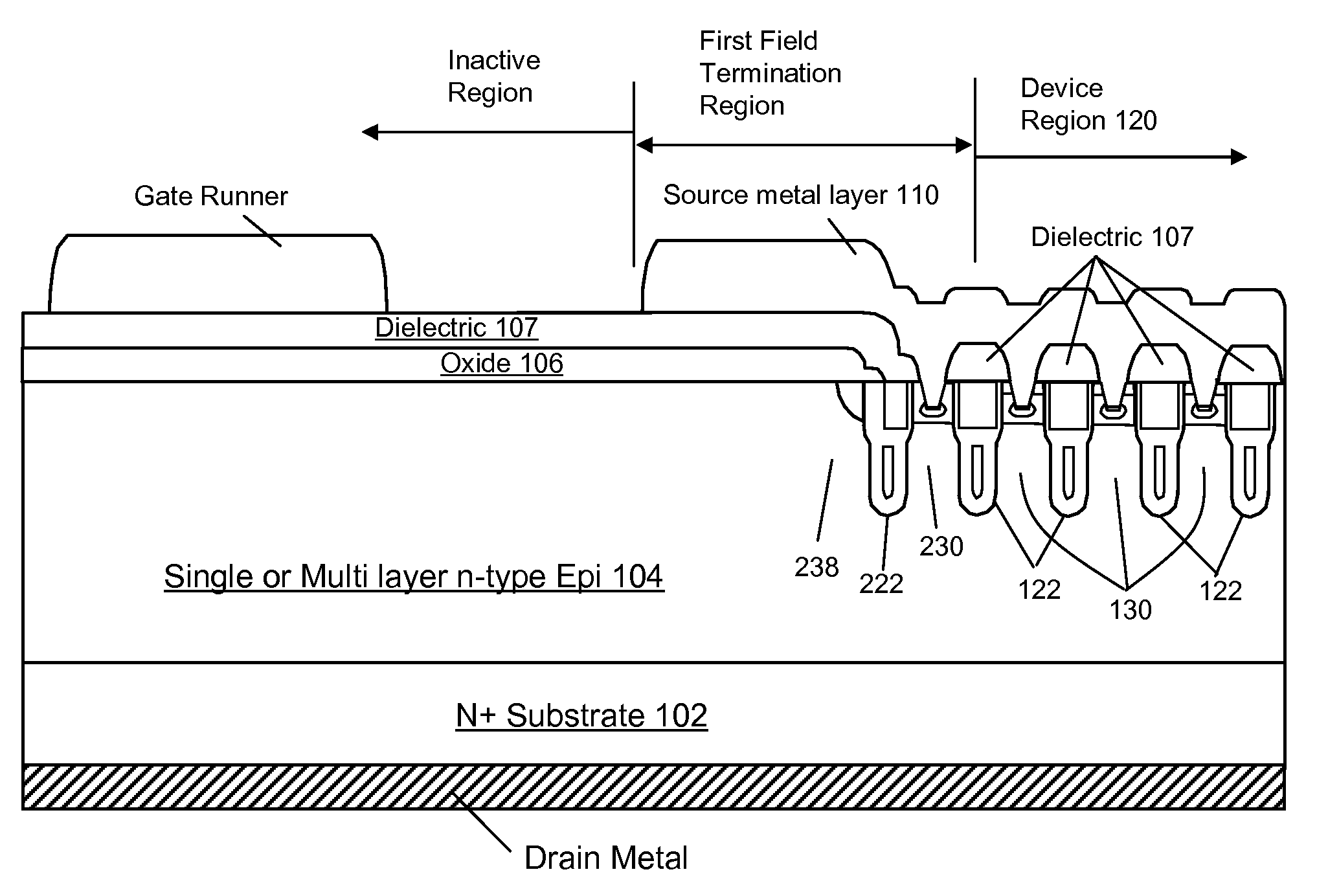
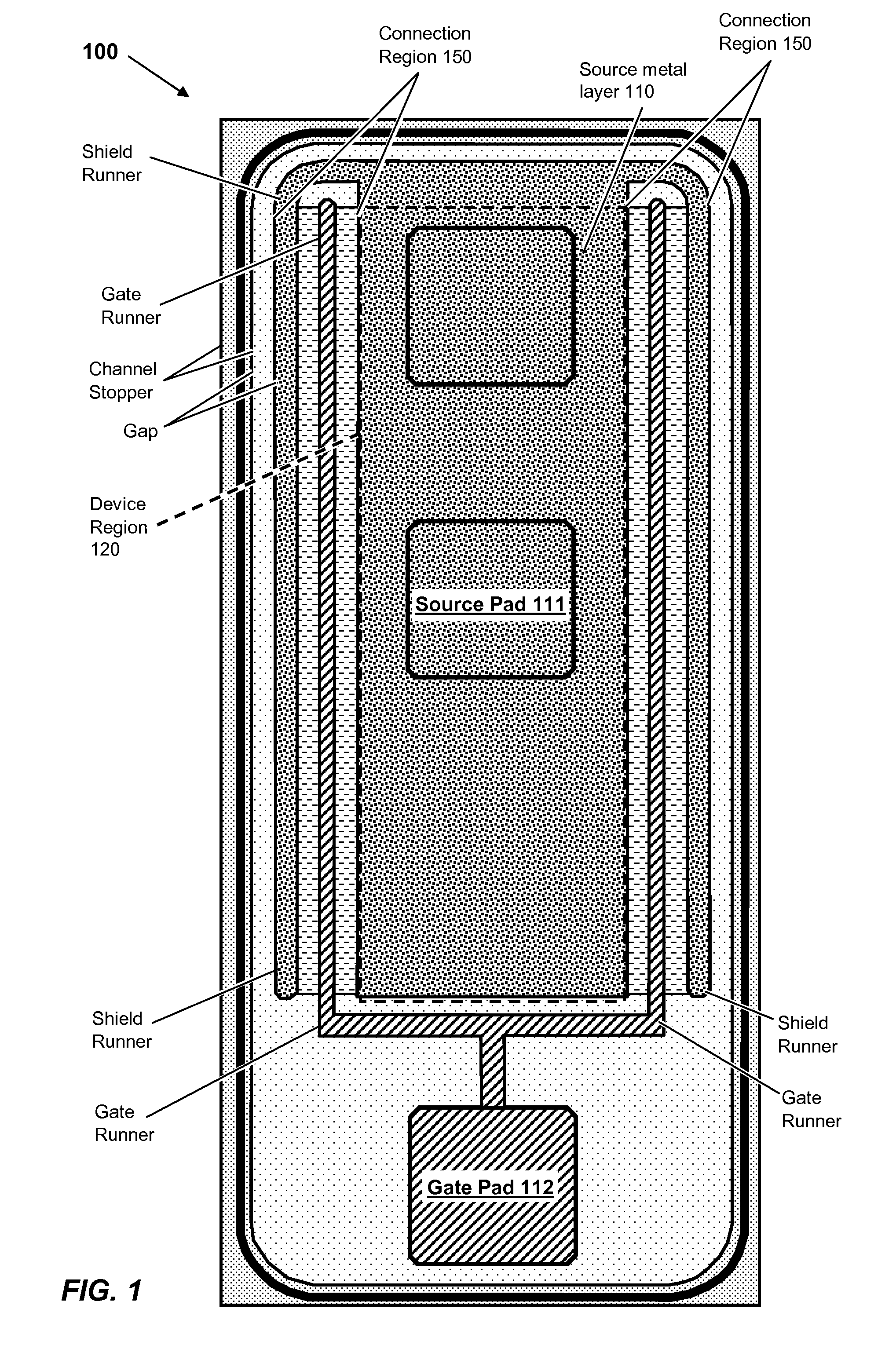
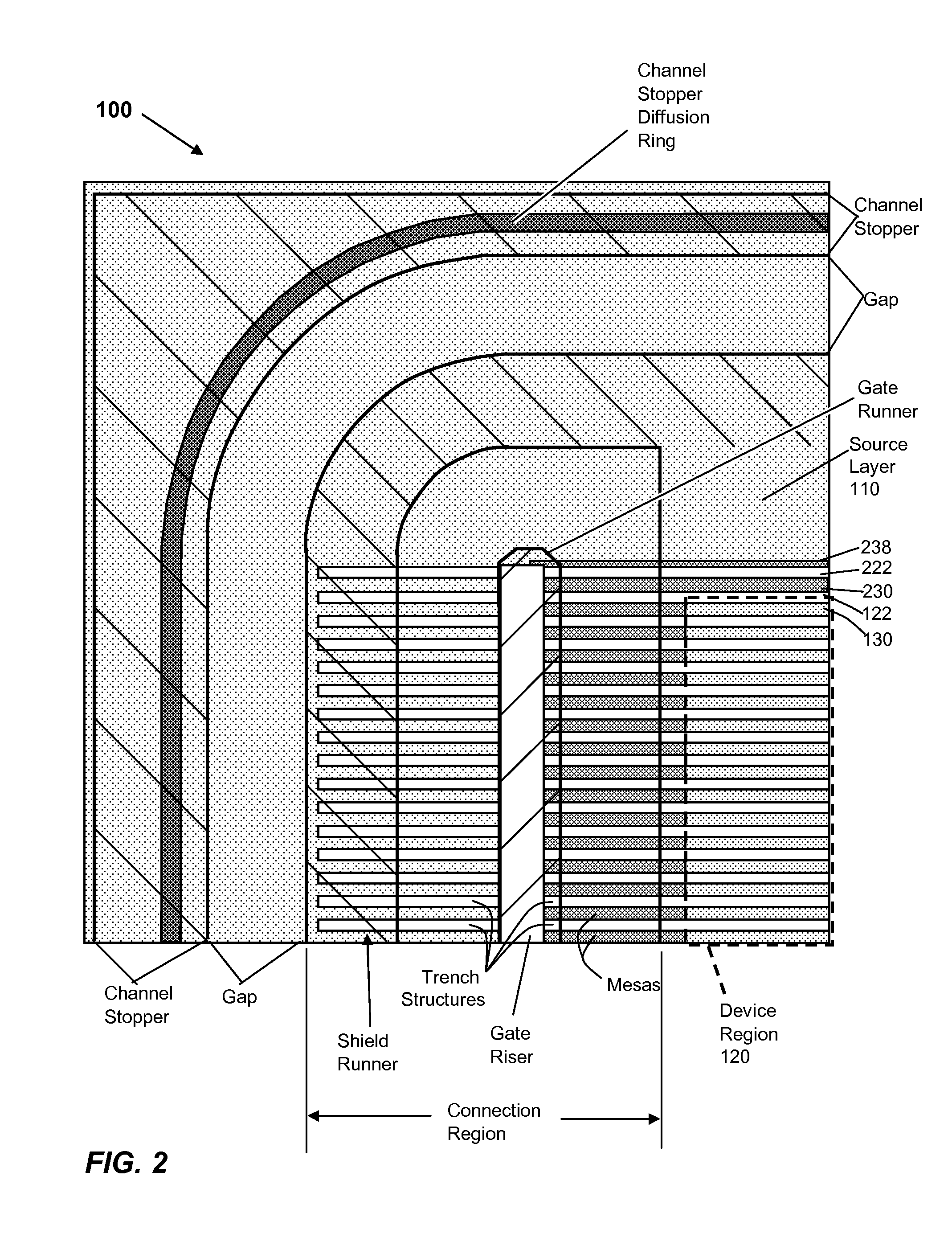
Trench-Based Power Semiconductor Devices with Increased Breakdown Voltage Characteristics
ActiveUS20100140689A1Improve breakdown voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor
Exemplary power semiconductor devices with features providing increased breakdown voltage and other benefits are disclosed.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com