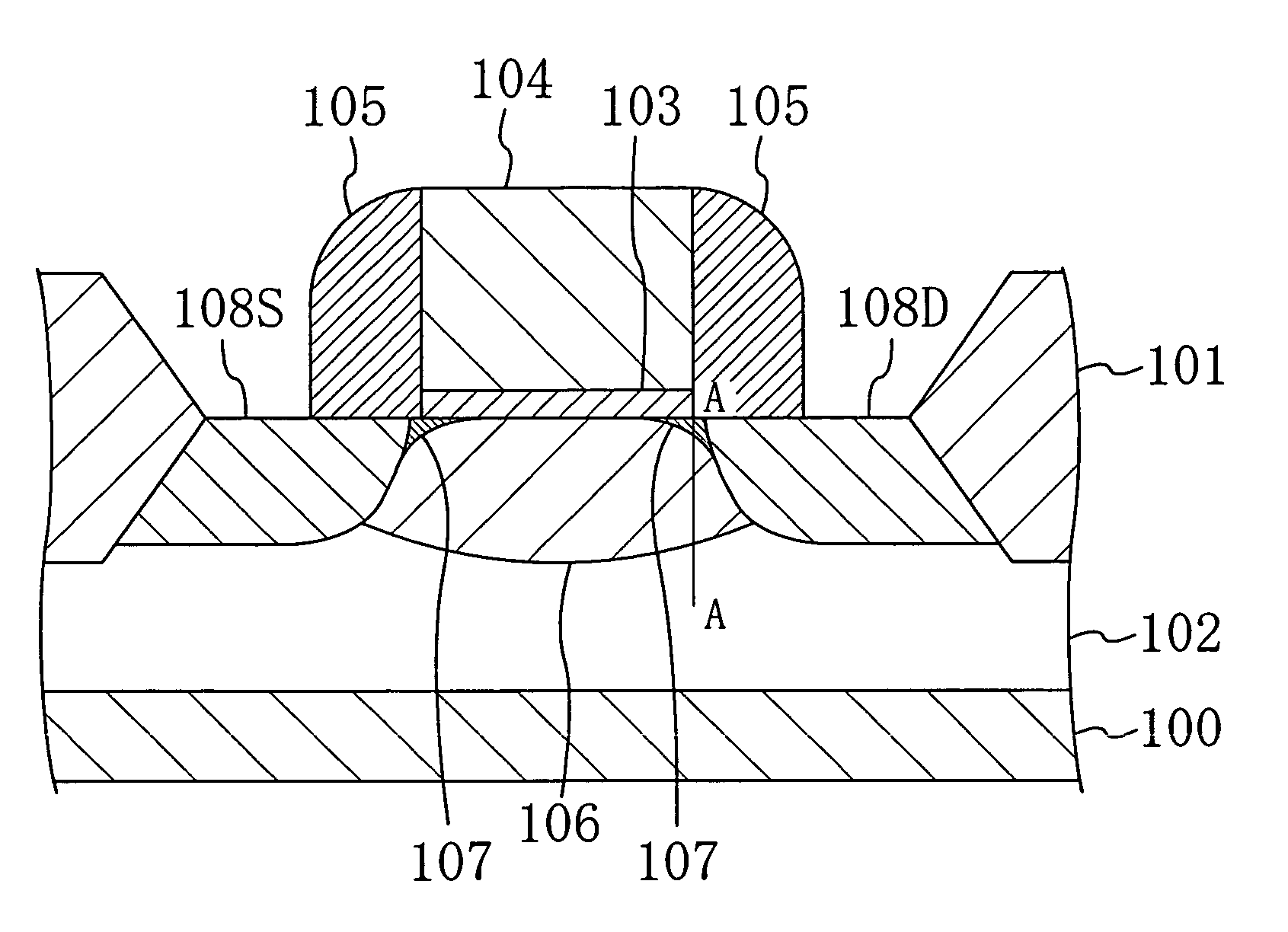
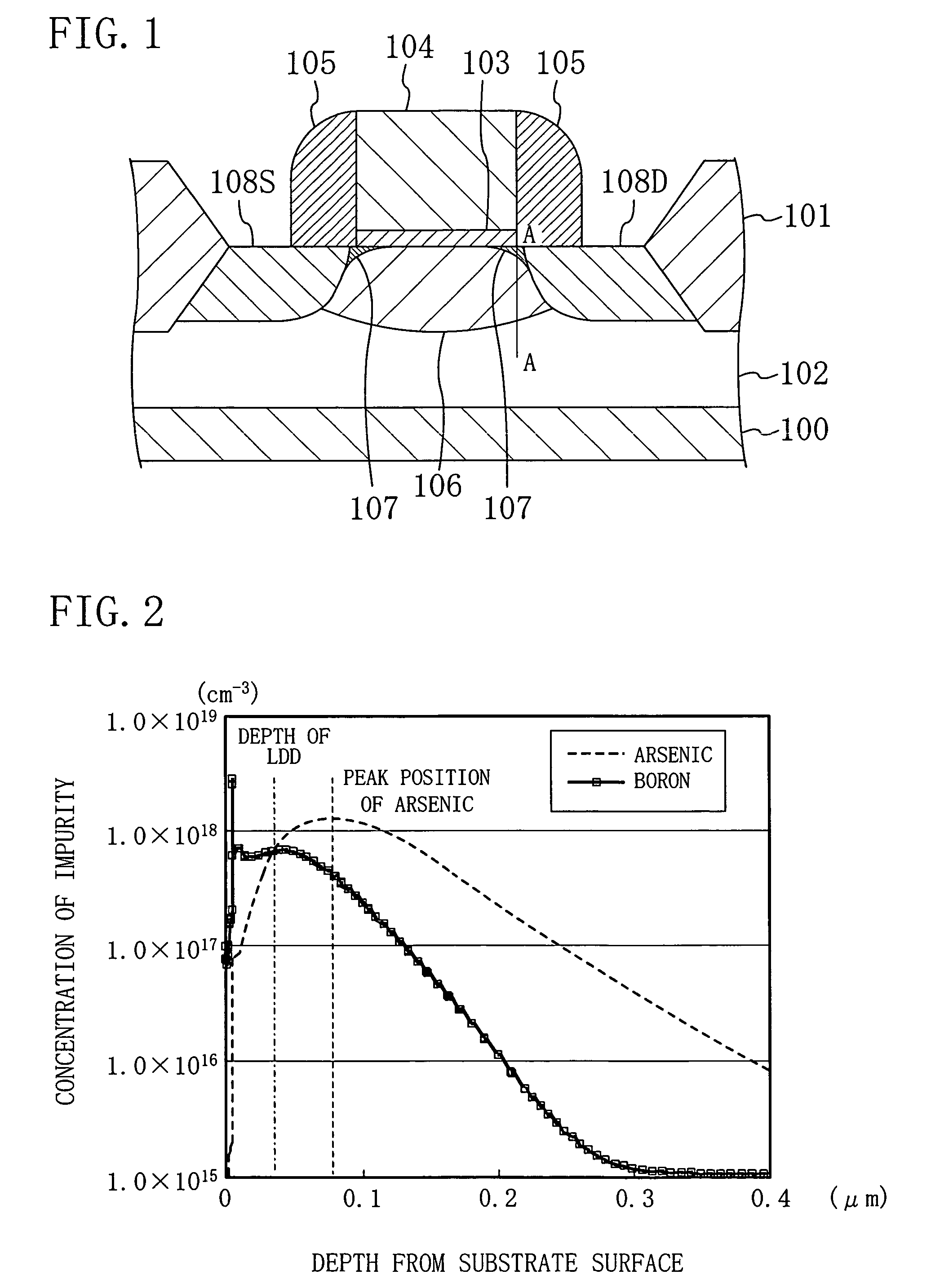
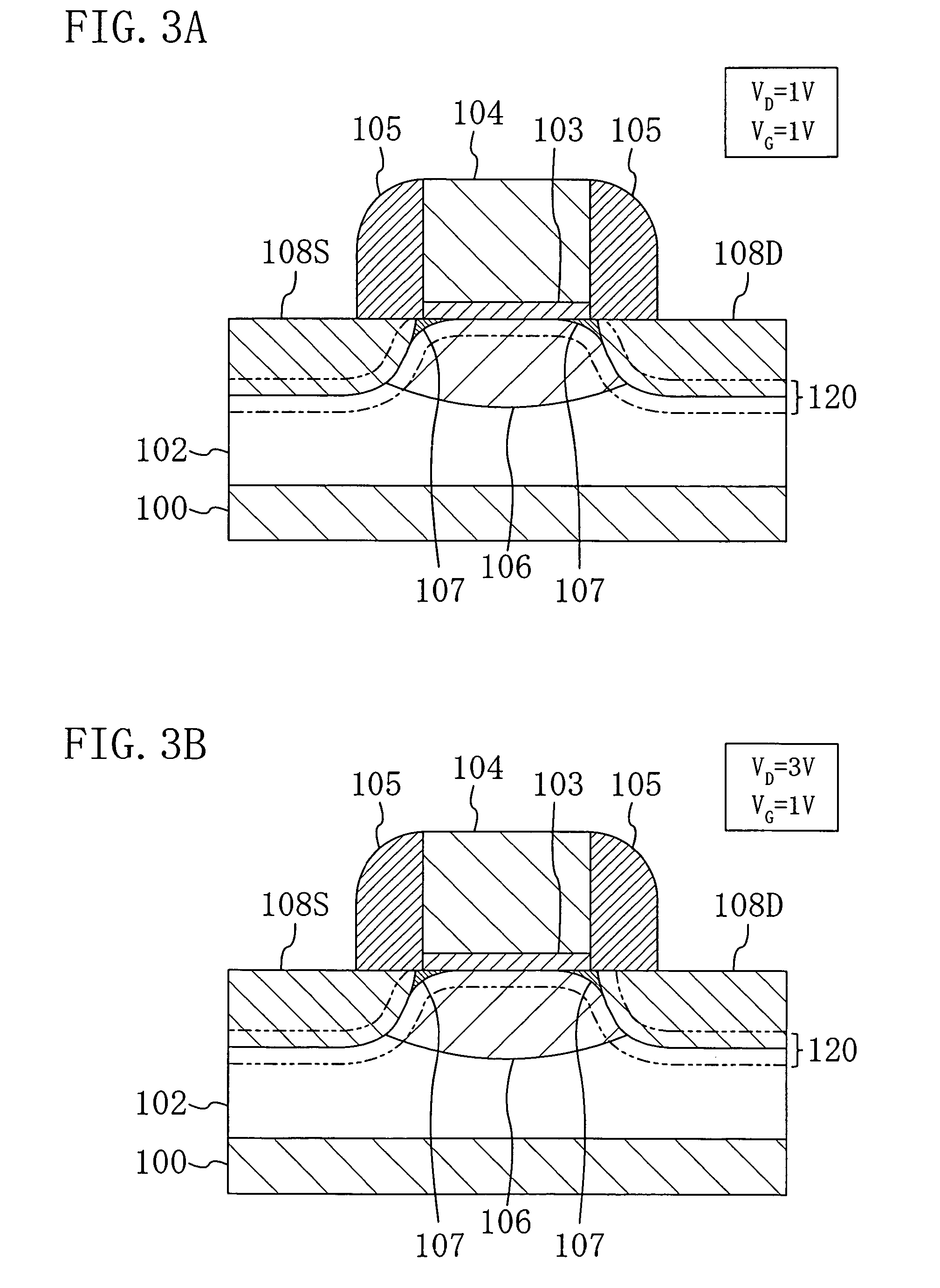
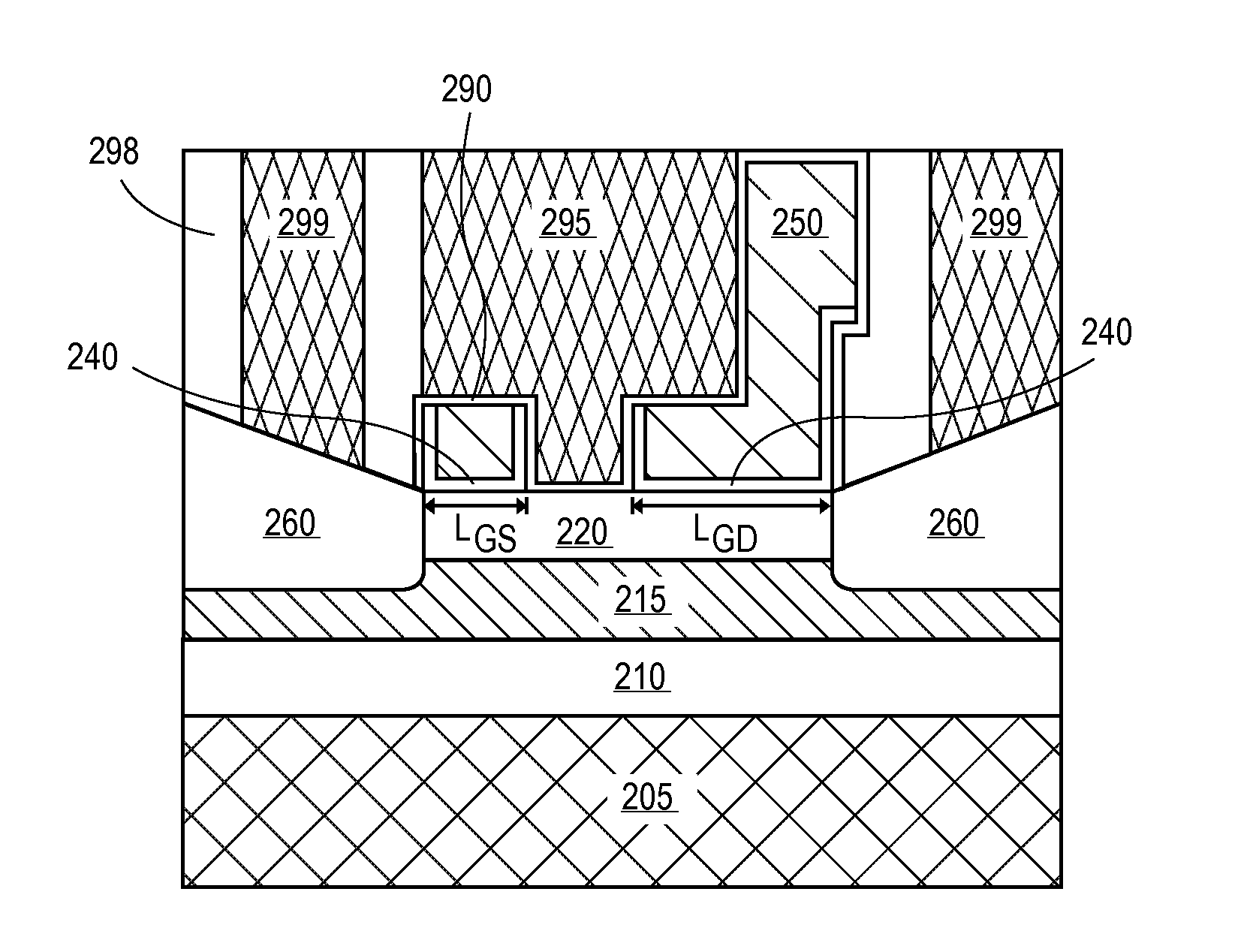
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
817 results about "Gate length" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
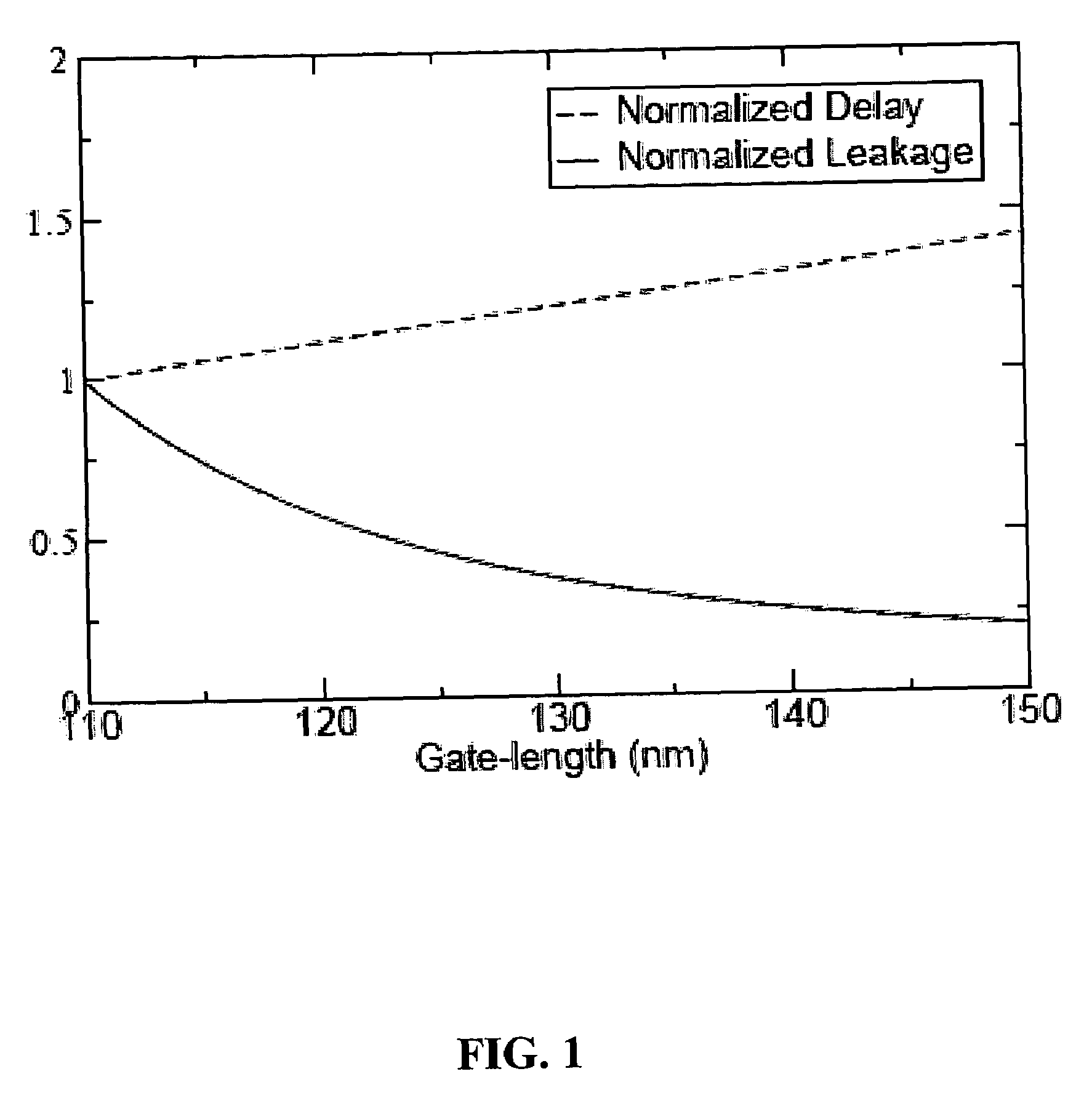
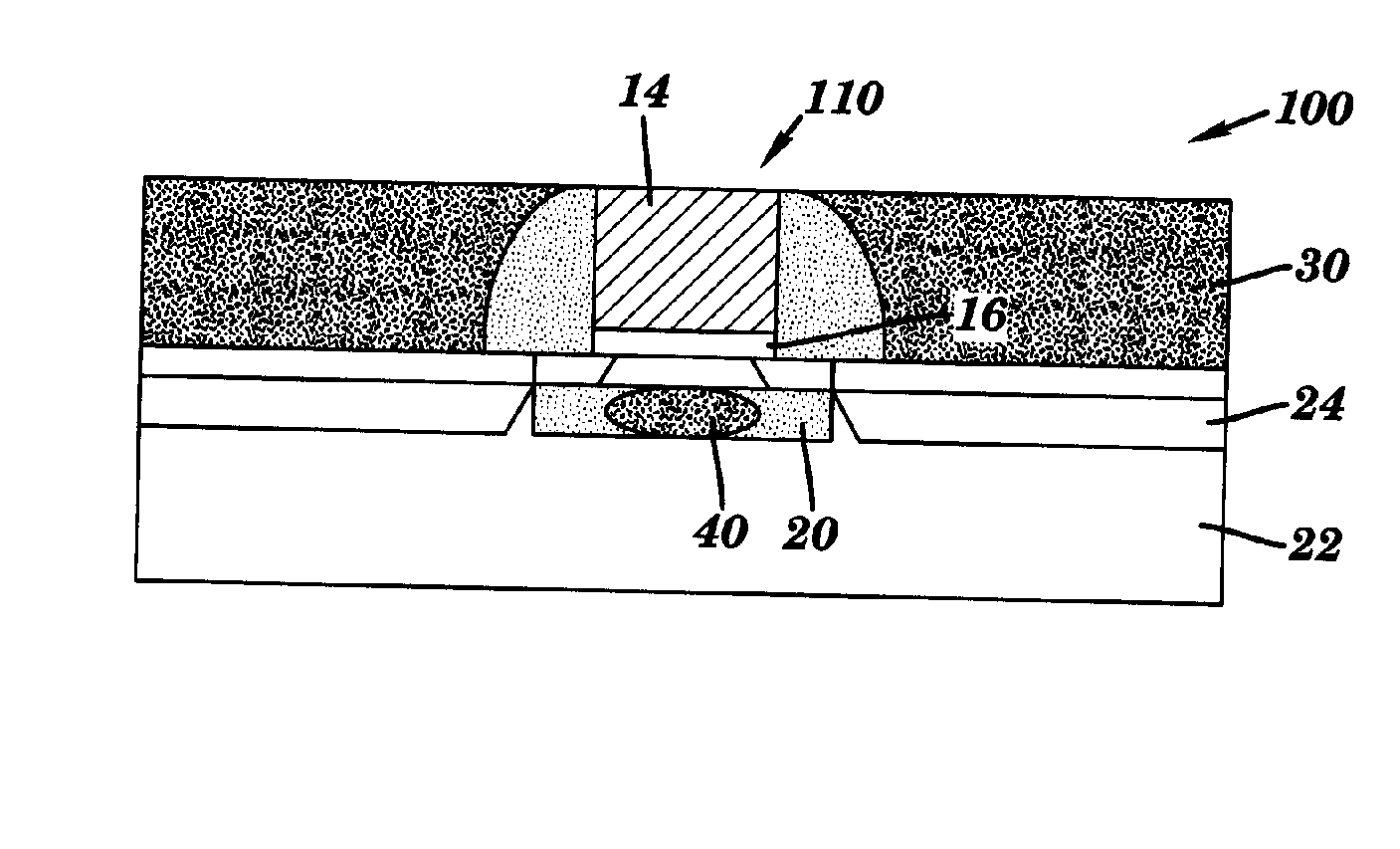
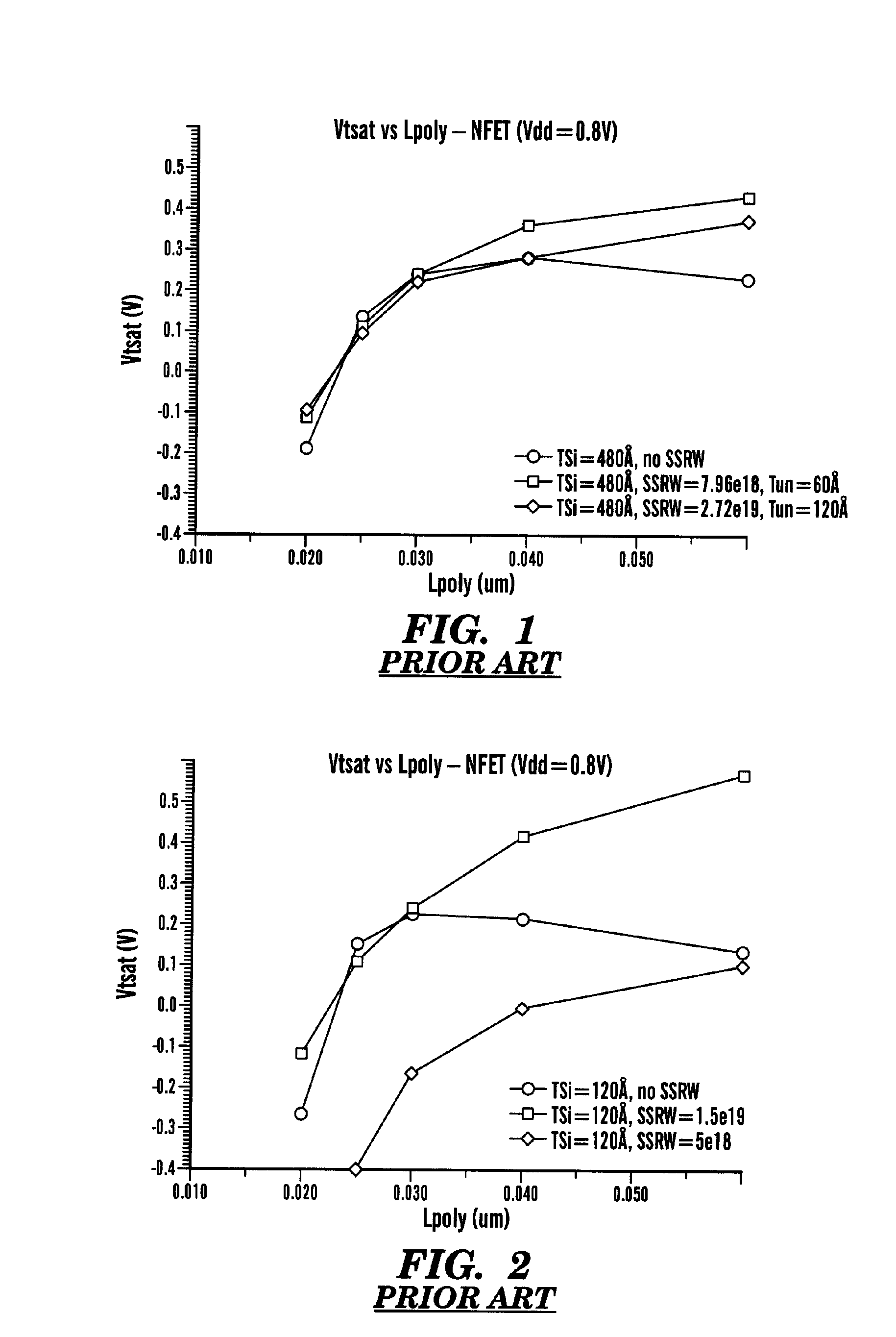
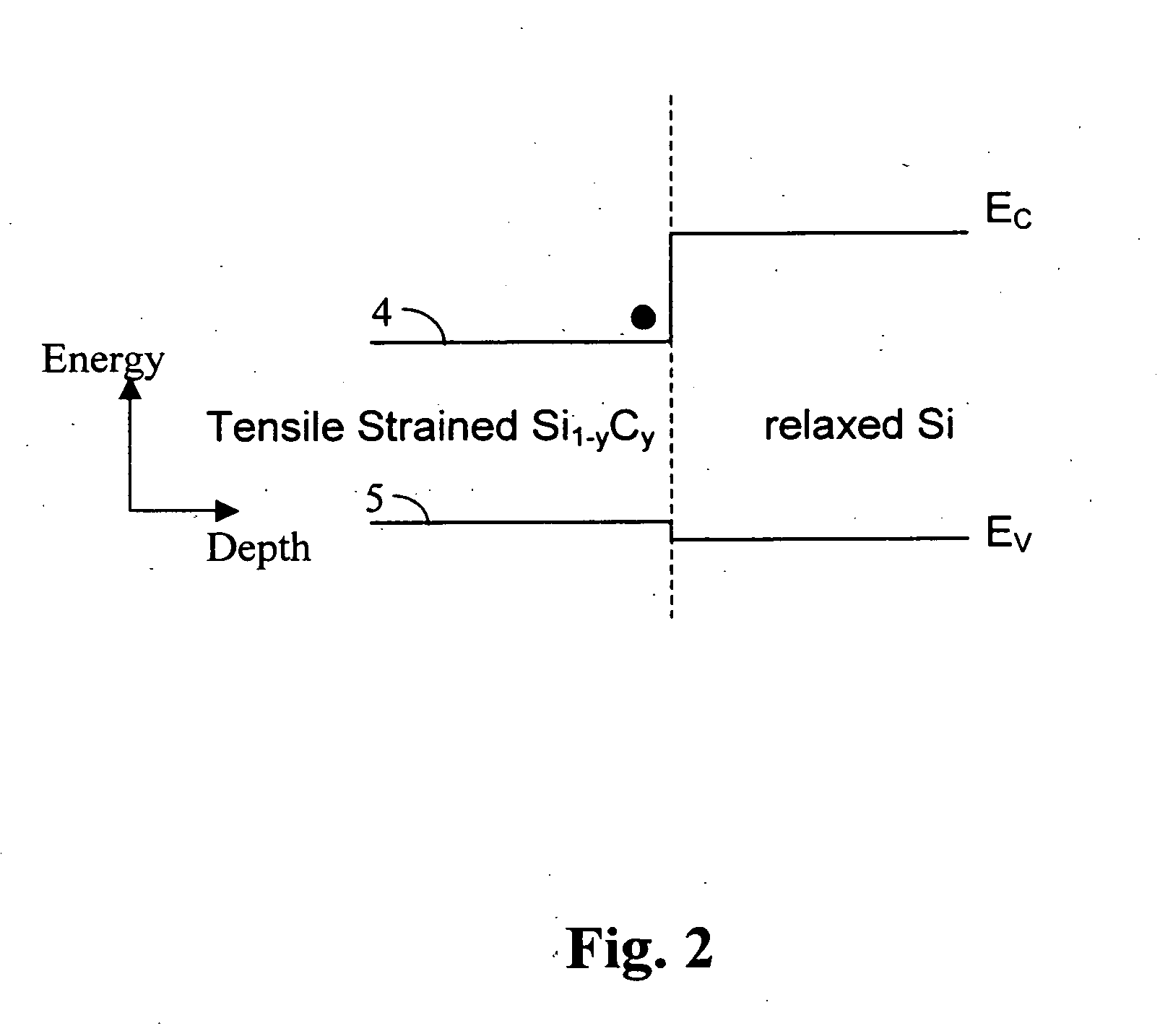
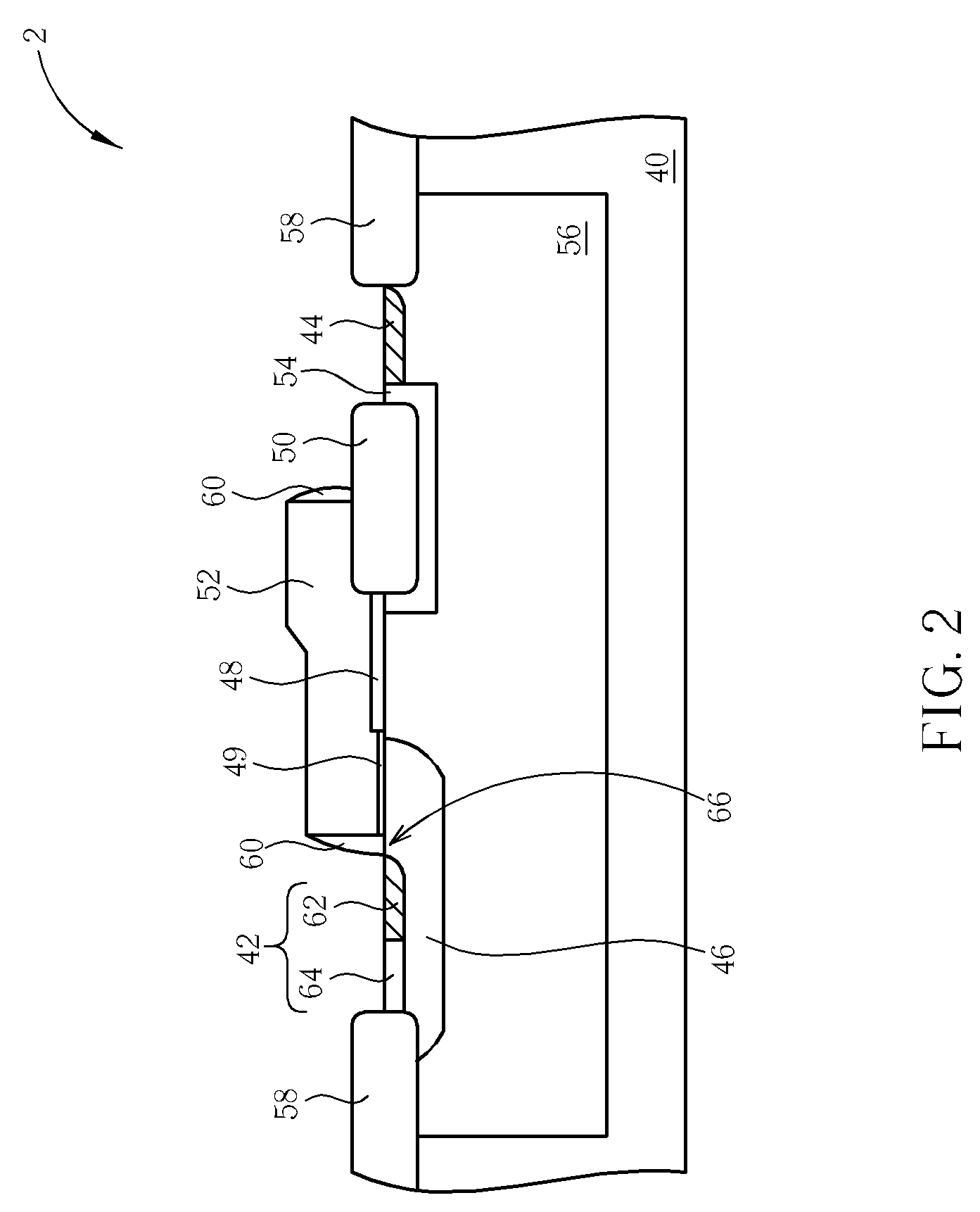
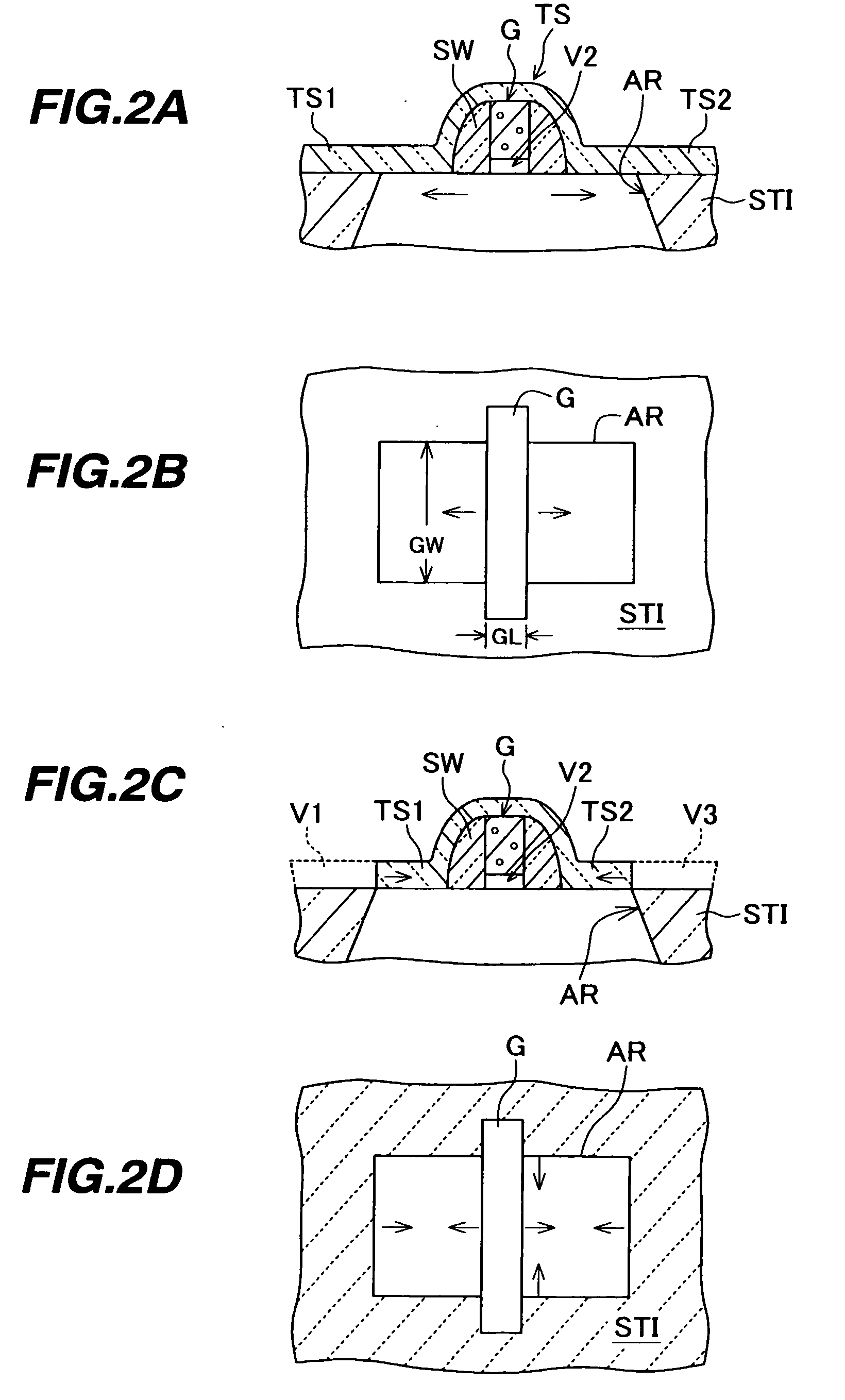
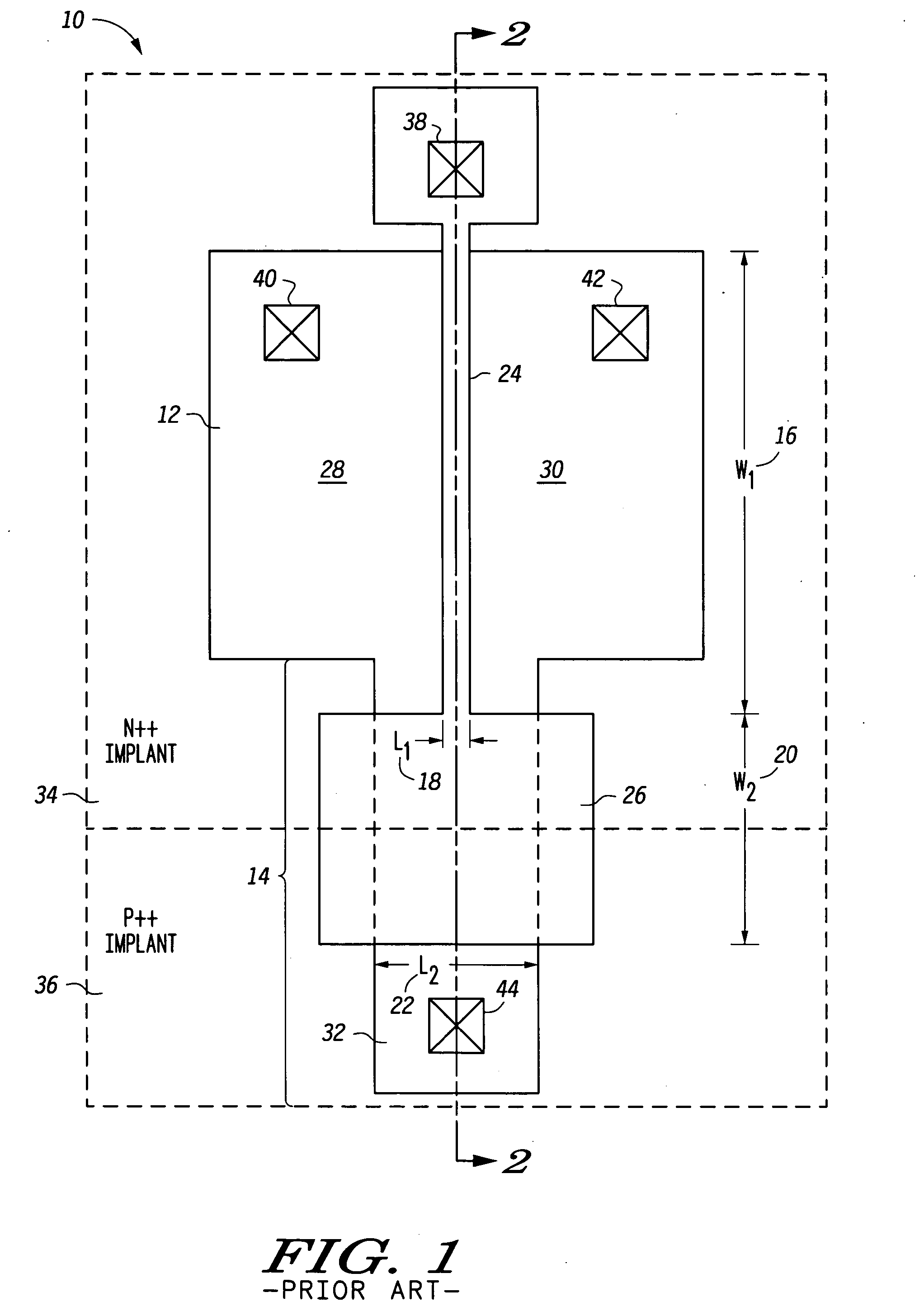
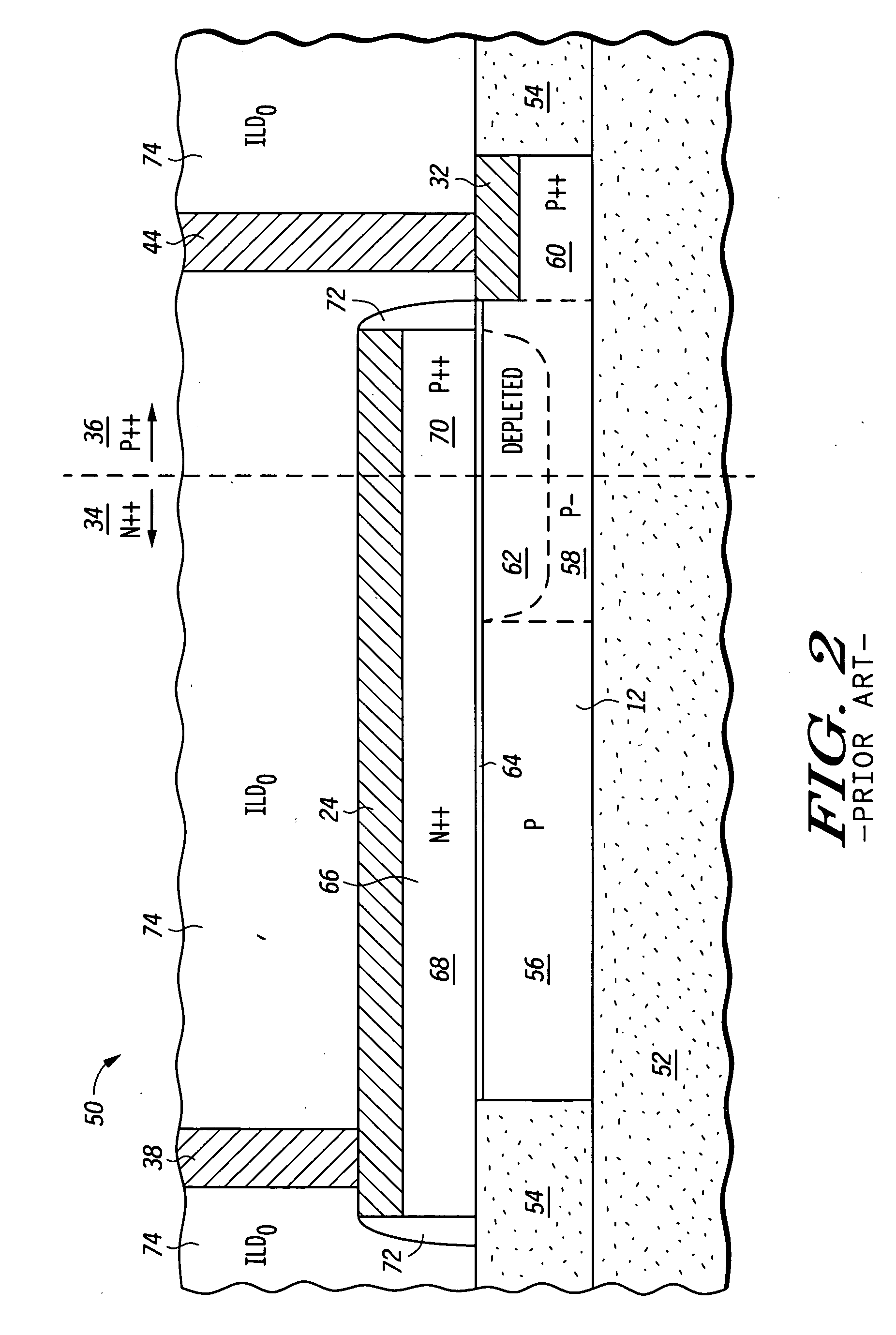
This fourth terminal serves to bias the transistor into operation; it is rare to make non-trivial use of the body terminal in circuit designs, but its presence is important when setting up the physical layout of an integrated circuit. The size of the gate, length L in the diagram, is the
Low leakage heterojunction vertical transistors and high performance devices thereof
InactiveUS6943407B2Superb performanceSuperb scalabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesReverse short-channel effectHeterojunction
A method for forming and the structure of a vertical channel of a field effect transistor, a field effect transistor and CMOS circuitry are described incorporating a drain, body and source region on a sidewall of a vertical single crystal semiconductor structure wherein a hetero-junction is formed between the source and body of the transistor, wherein the source region and channel are independently lattice strained with respect the body region and wherein the drain region contains a carbon doped region to prevent the diffusion of dopants (i.e., B and P) into the body. The invention reduces the problem of short channel effects such as drain induced barrier lowering and the leakage current from the source to drain regions via the hetero-junction and while independently permitting lattice strain in the channel region for increased mobility via choice of the semiconductor materials. The problem of scalability of the gate length below 100 nm is overcome by the heterojunction between the source and body regions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
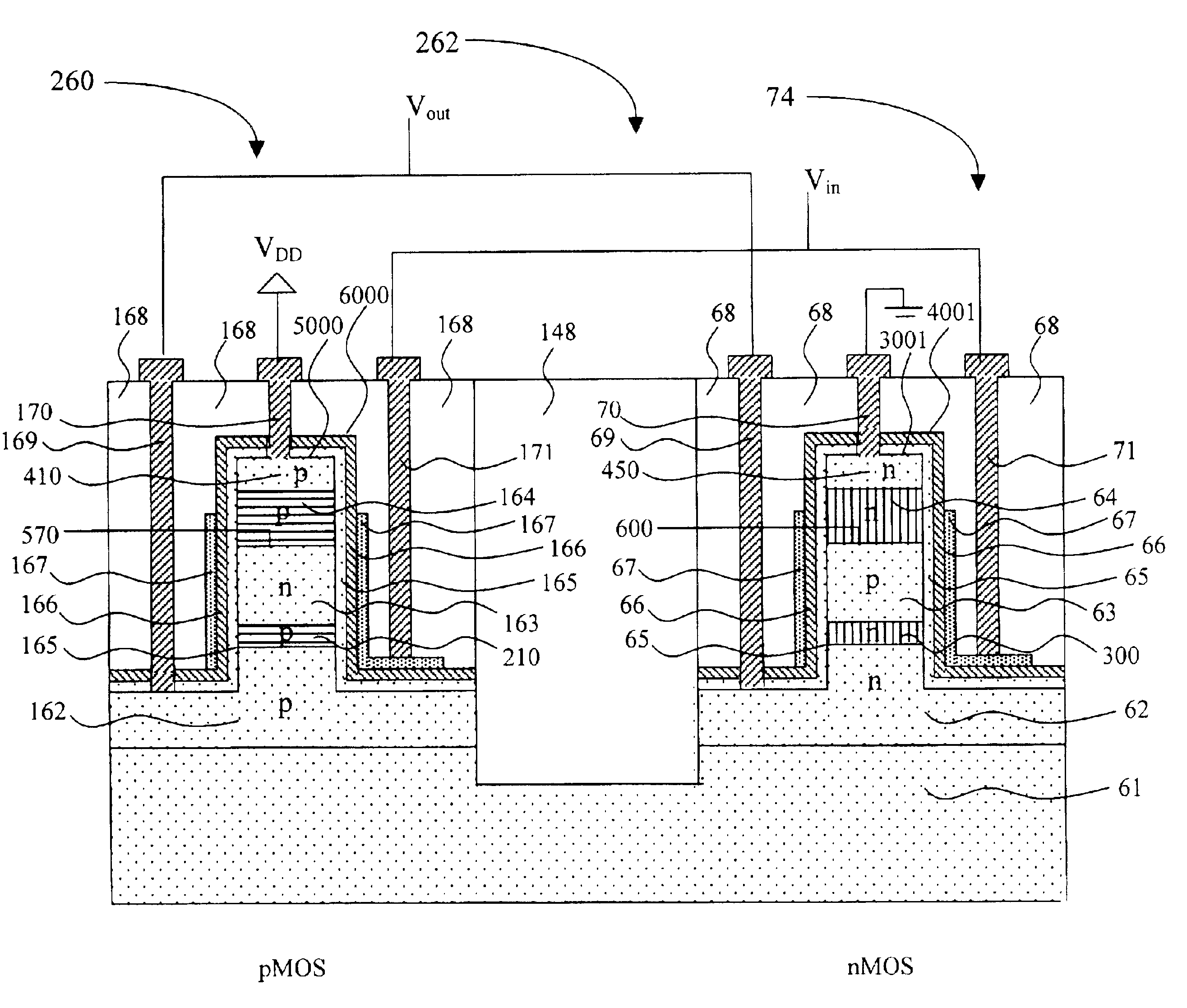
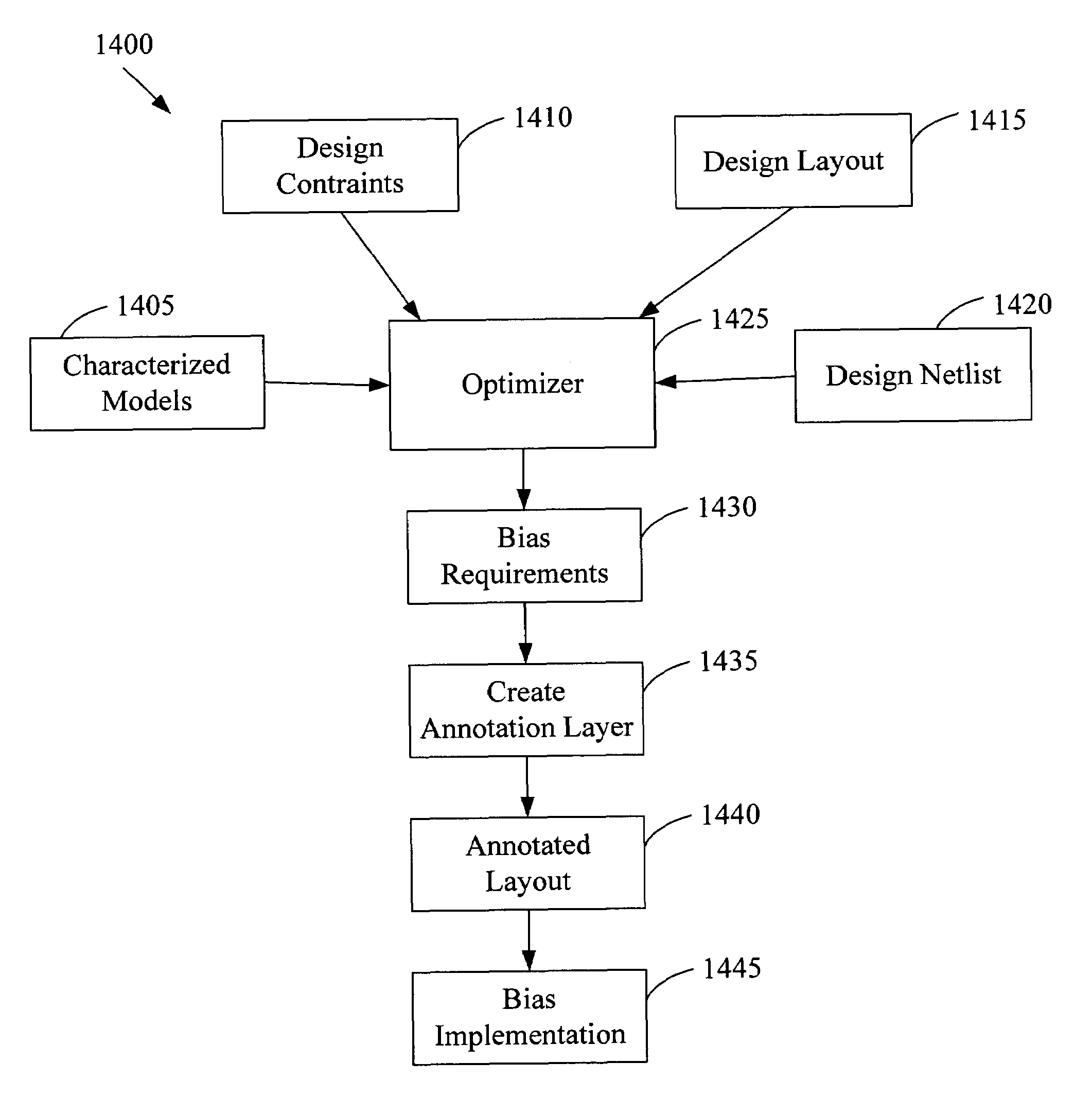
Gate-length biasing for digital circuit optimization
InactiveUS7441211B1Reduce impactImpairing time delay performance only linearlySolid-state devicesCAD circuit designEngineeringDigital electronics
Methods and apparatus for a gate-length biasing methodology for optimizing integrated digital circuits are described. The gate-length biasing methodology replaces a nominal gate-length of a transistor with a biased gate-length, where the biased gate-length includes a bias length that is small compared to the nominal gate-length. In an exemplary embodiment, the bias length is less than 10% of the nominal gate-length.
Owner:RPX CORP
Semiconductor device and a method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060125024A1Improve reliabilityGood effectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMask ROMDevice material
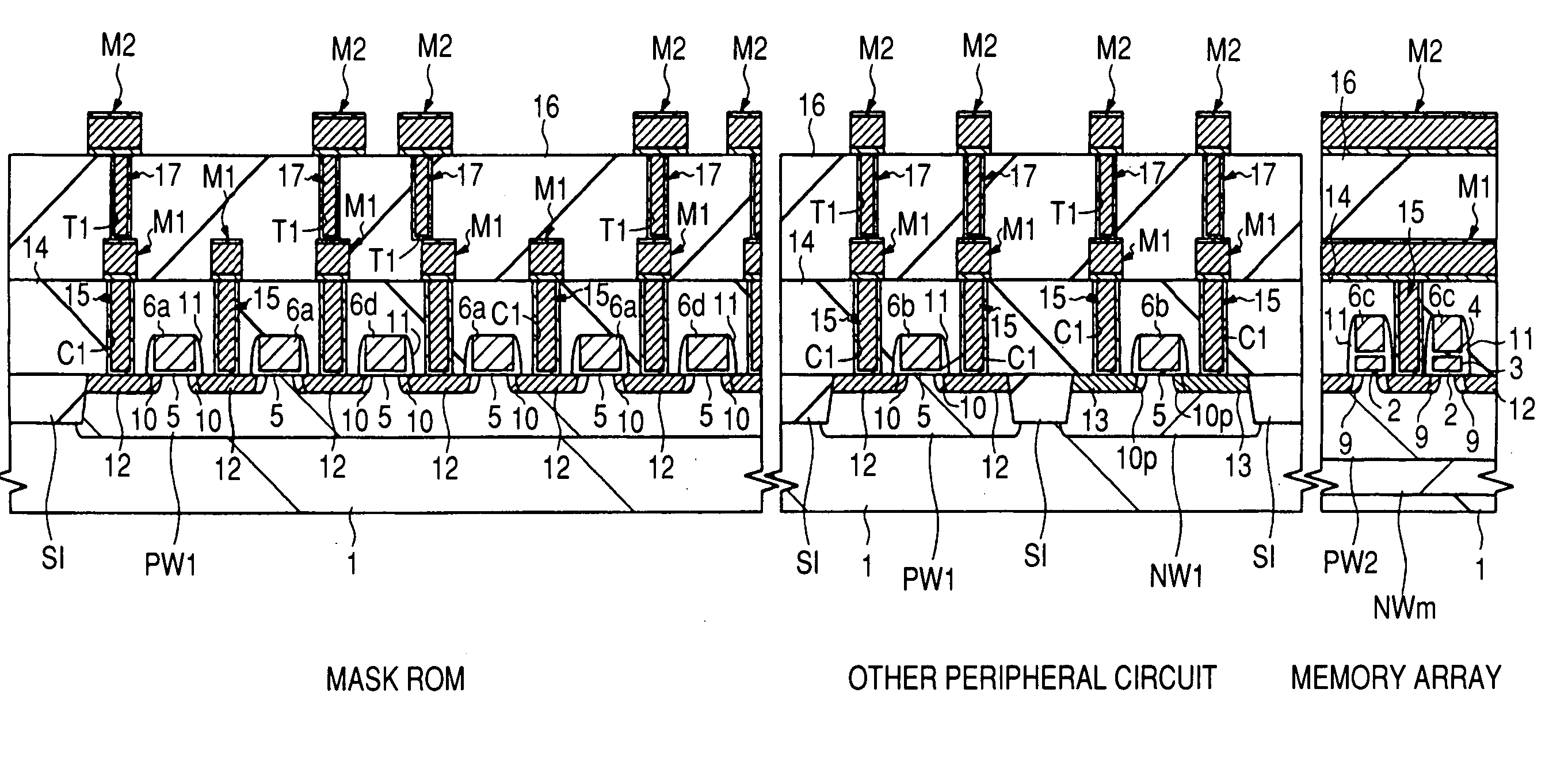
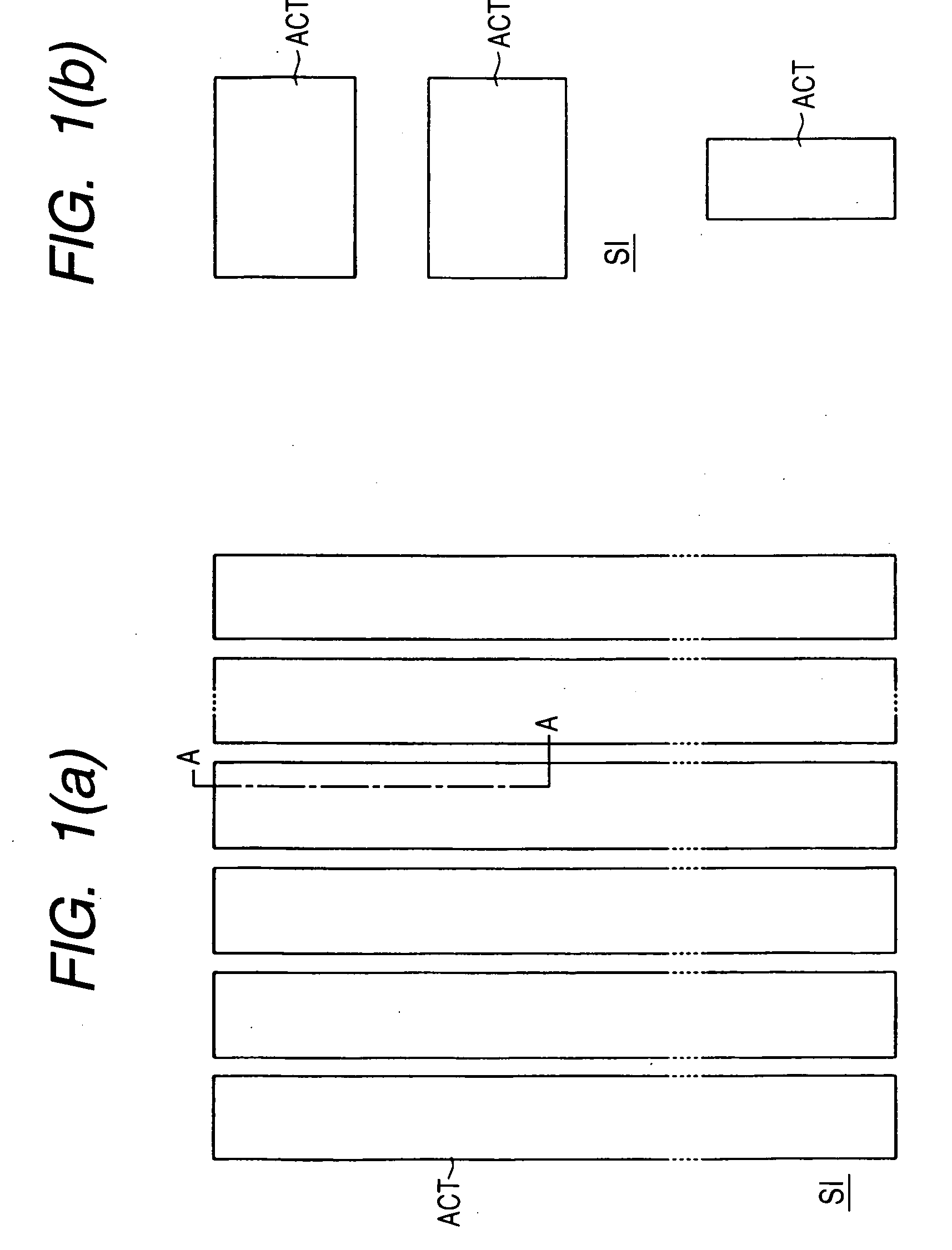
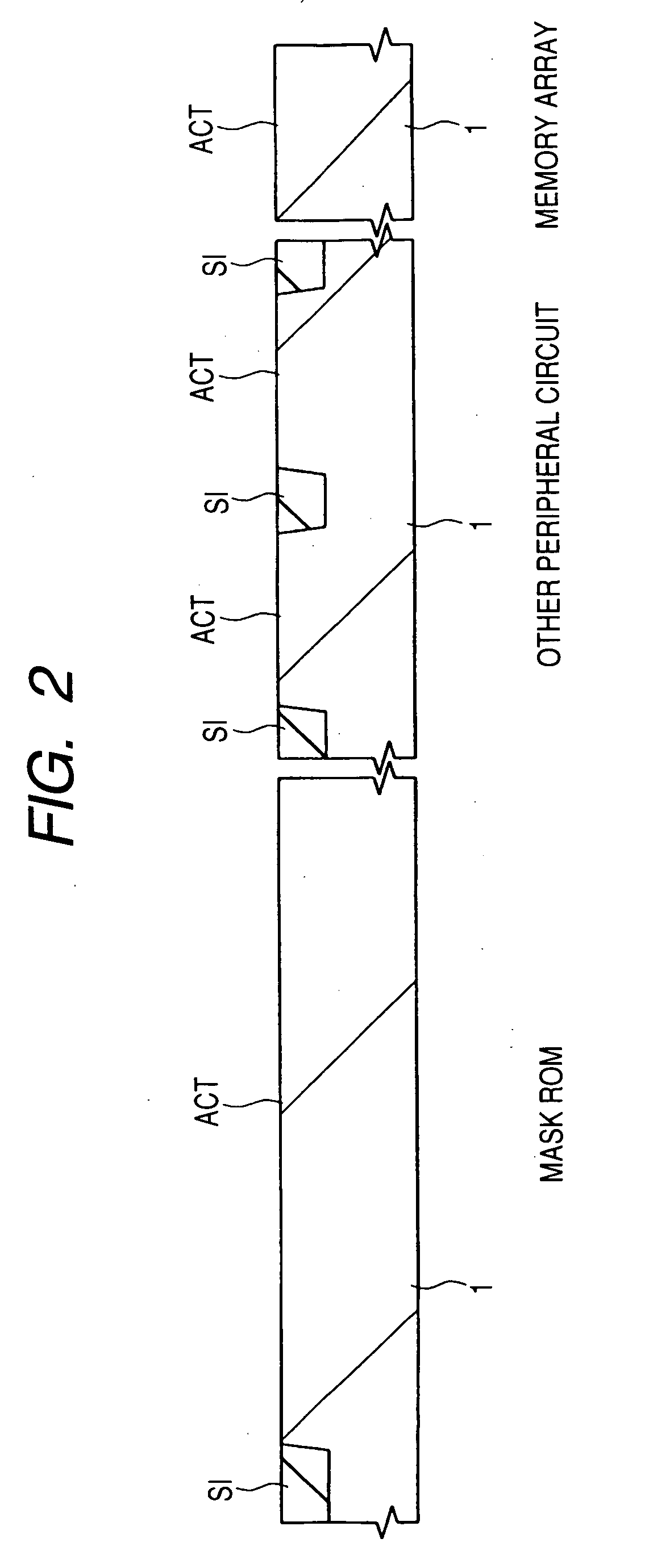
To improve reliability of FETs having element isolation regions for electrically isolating field effect transistors adjacent to each other in the gate length direction in a mask ROM region, the isolation regions are each constructed by field plate isolation formed simultaneously with gate electrodes of the field effect transistors. This relatively lessens a stress generated in an active region ACT sandwiched by the element isolation regions even if the isolation width of each element isolation region is made relatively small, specifically, less than 0.3 μm. It is therefore possible to relax or prevent the generation of crystal defects resulting from the stress, thereby reducing occurrence of an undesired leak current between the source and drain of each field effect transistor.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
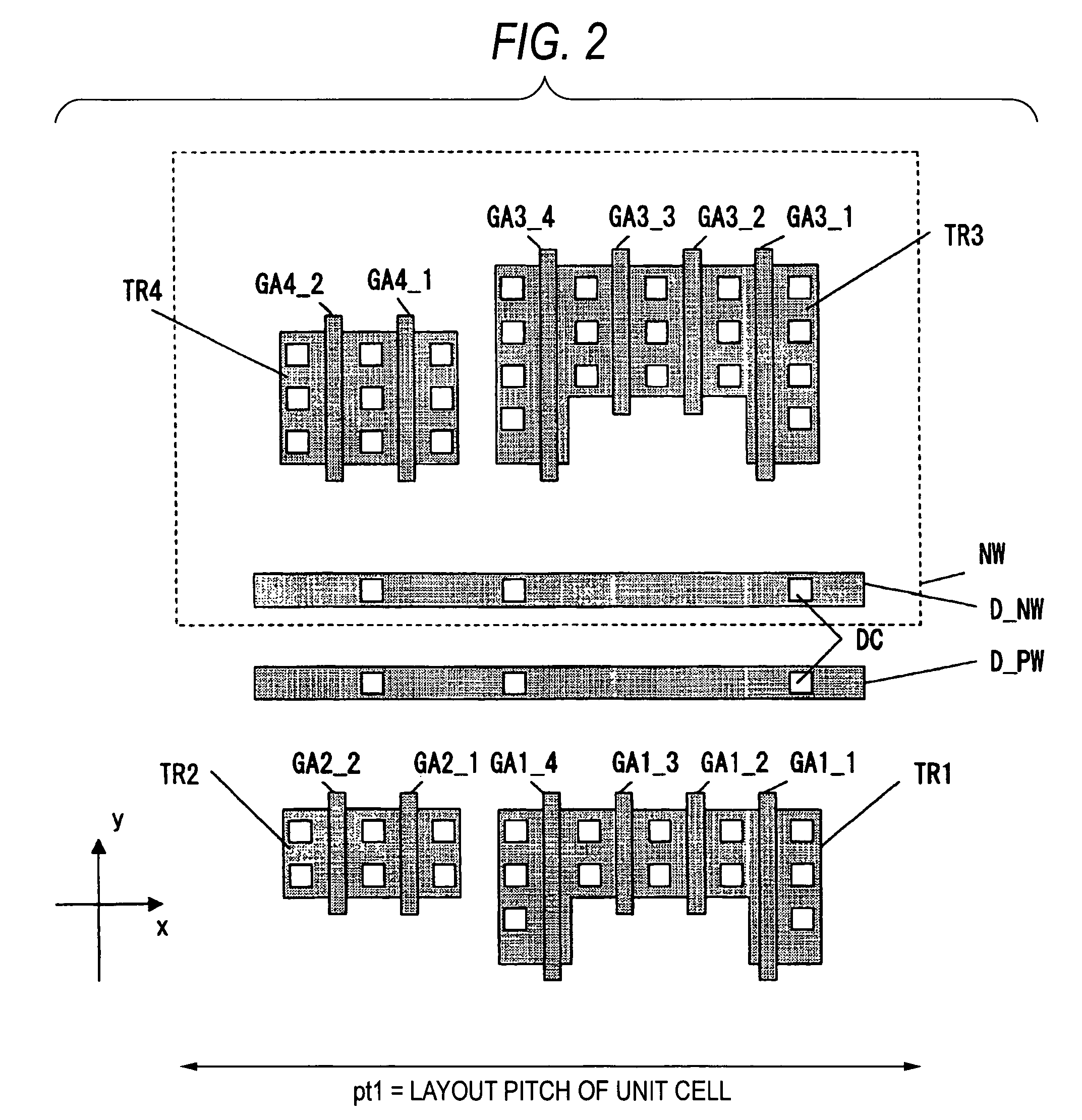
Integrated circuit cells
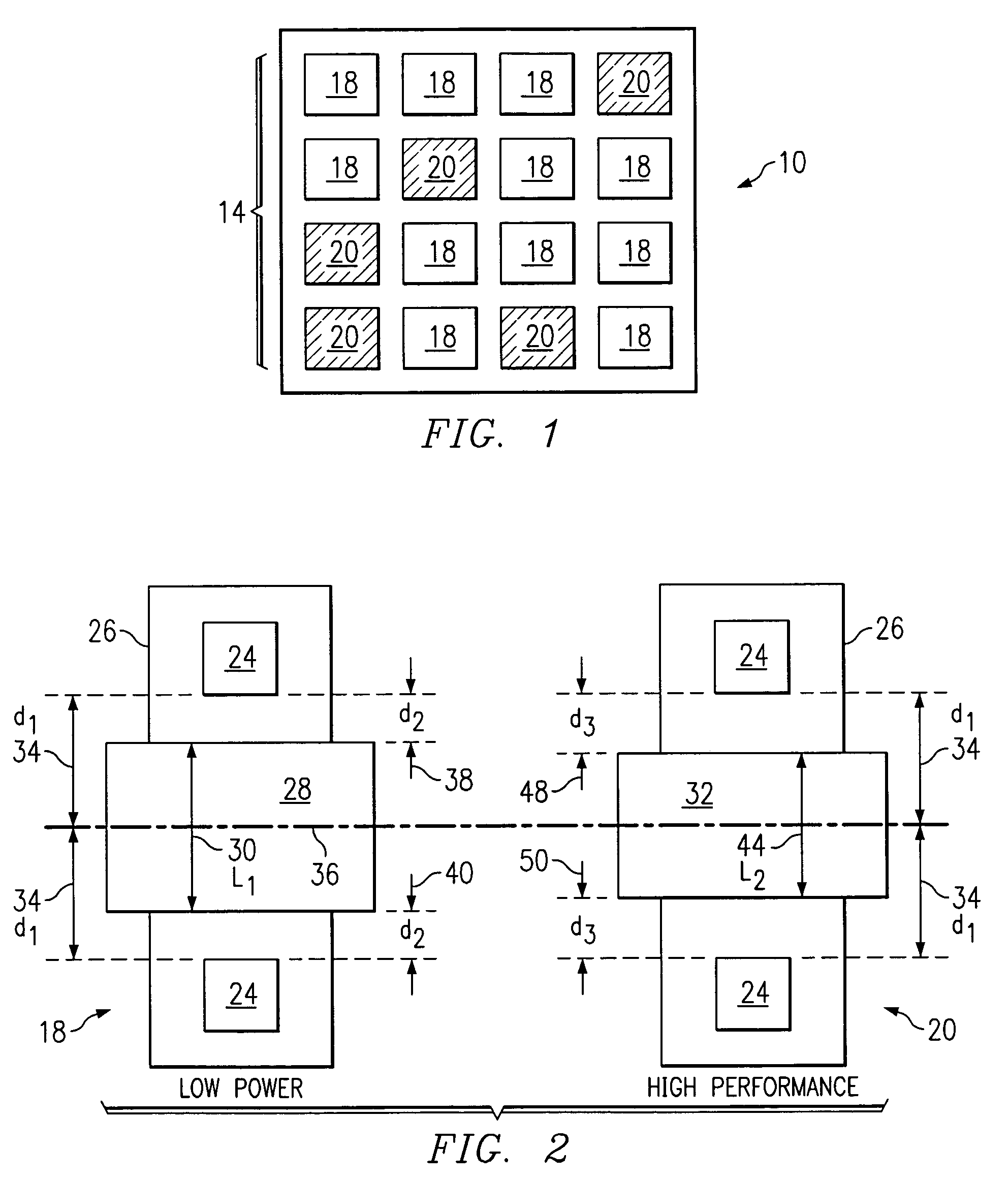
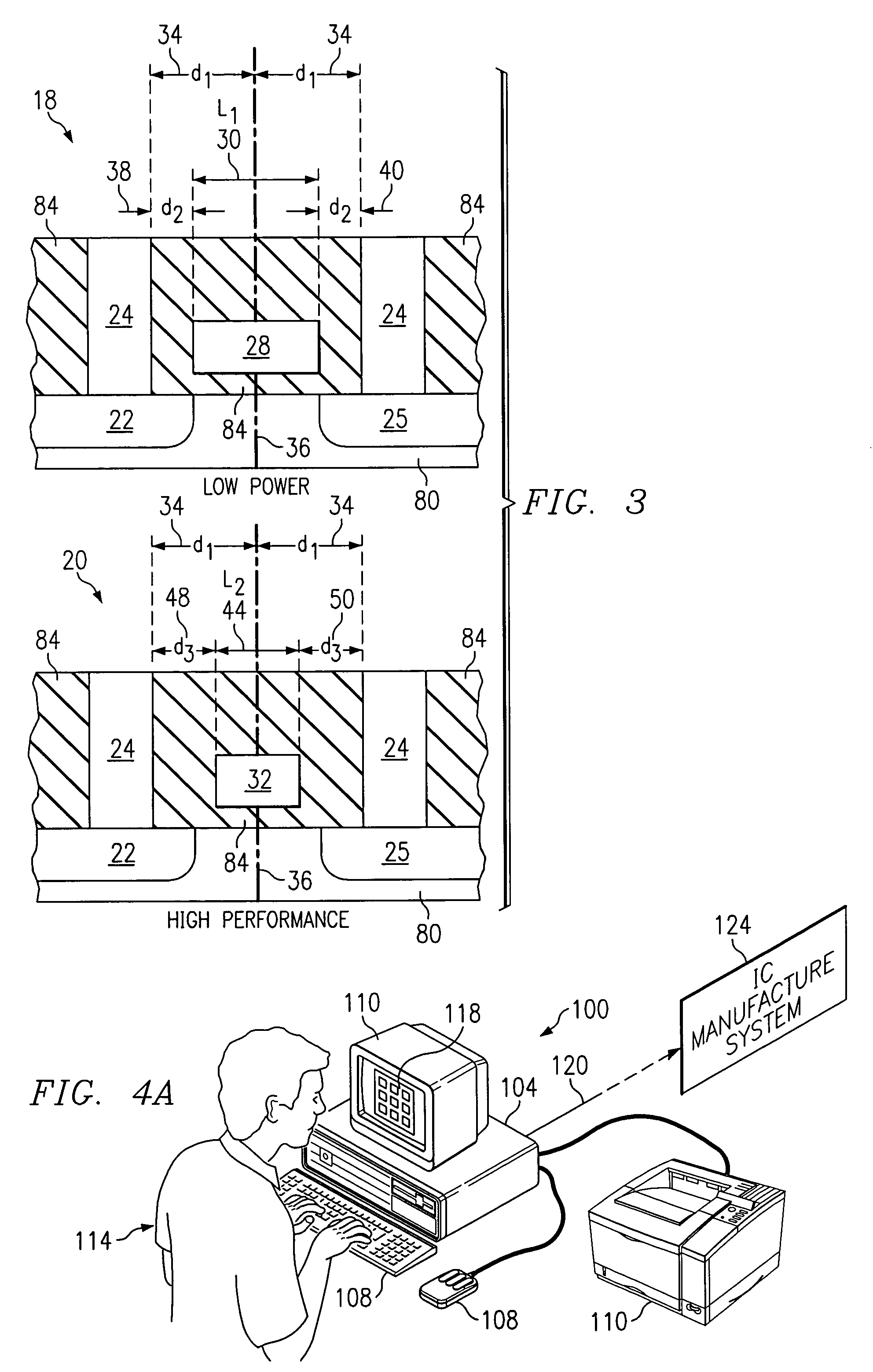
InactiveUS6954918B2Simple designSimple manufacturing processSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIntegrated circuitGate length
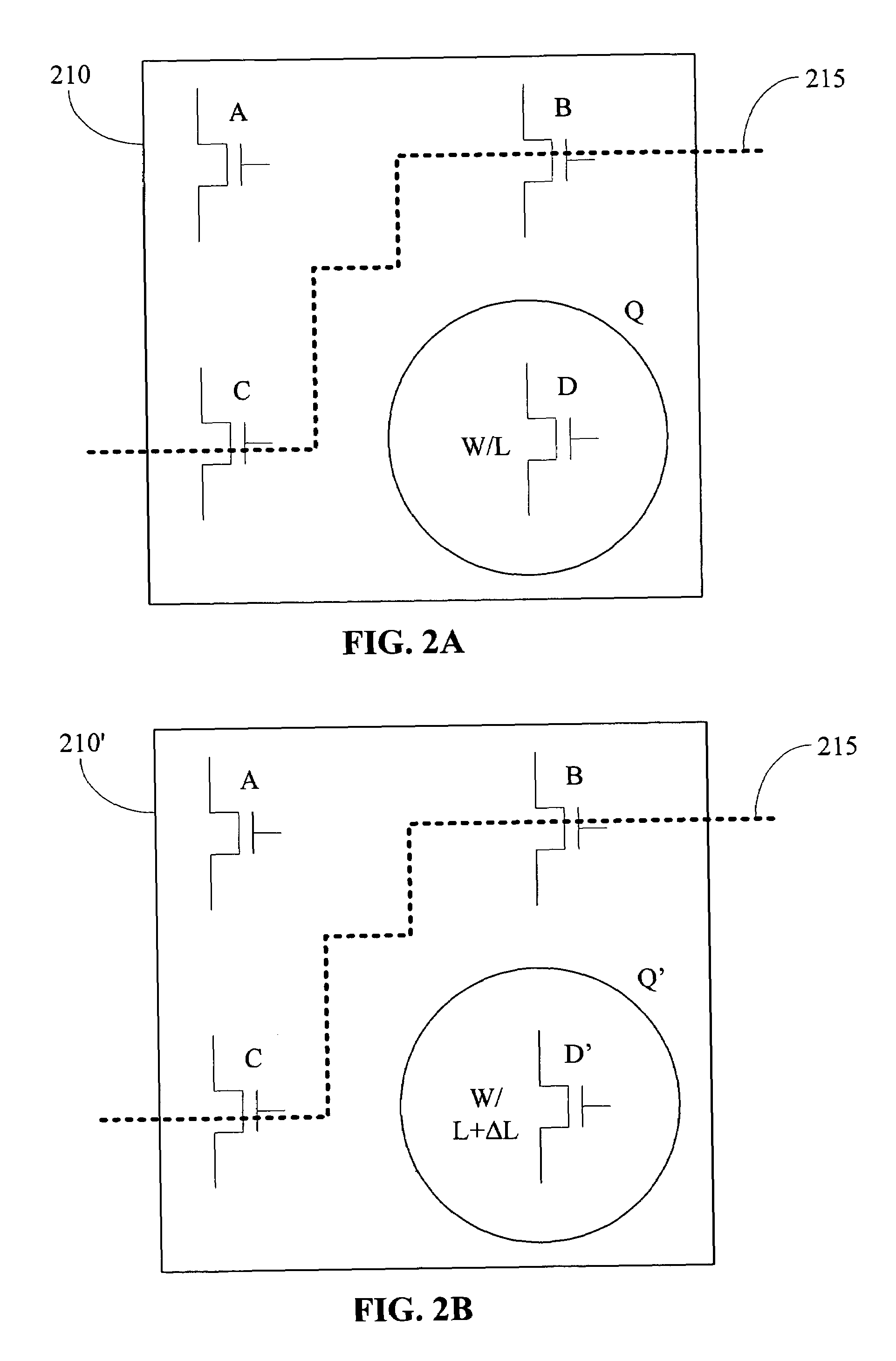
According to one embodiment of the invention, a method for designing an integrated circuit is provided. The method includes providing a first transistor in a first logic path. The first transistor has a first contact, a first gate length and a first contact to gate centerline spacing. The method also includes providing a second transistor in a second logic path. The second transistor has a second contact, a second gate length and a second contact to gate centerline spacing. The first contact to gate centerline spacing is substantially equal to the second contact to gate centerline spacing. The method also includes selecting a different gate length for the first gate length using a predetermined design criterion.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
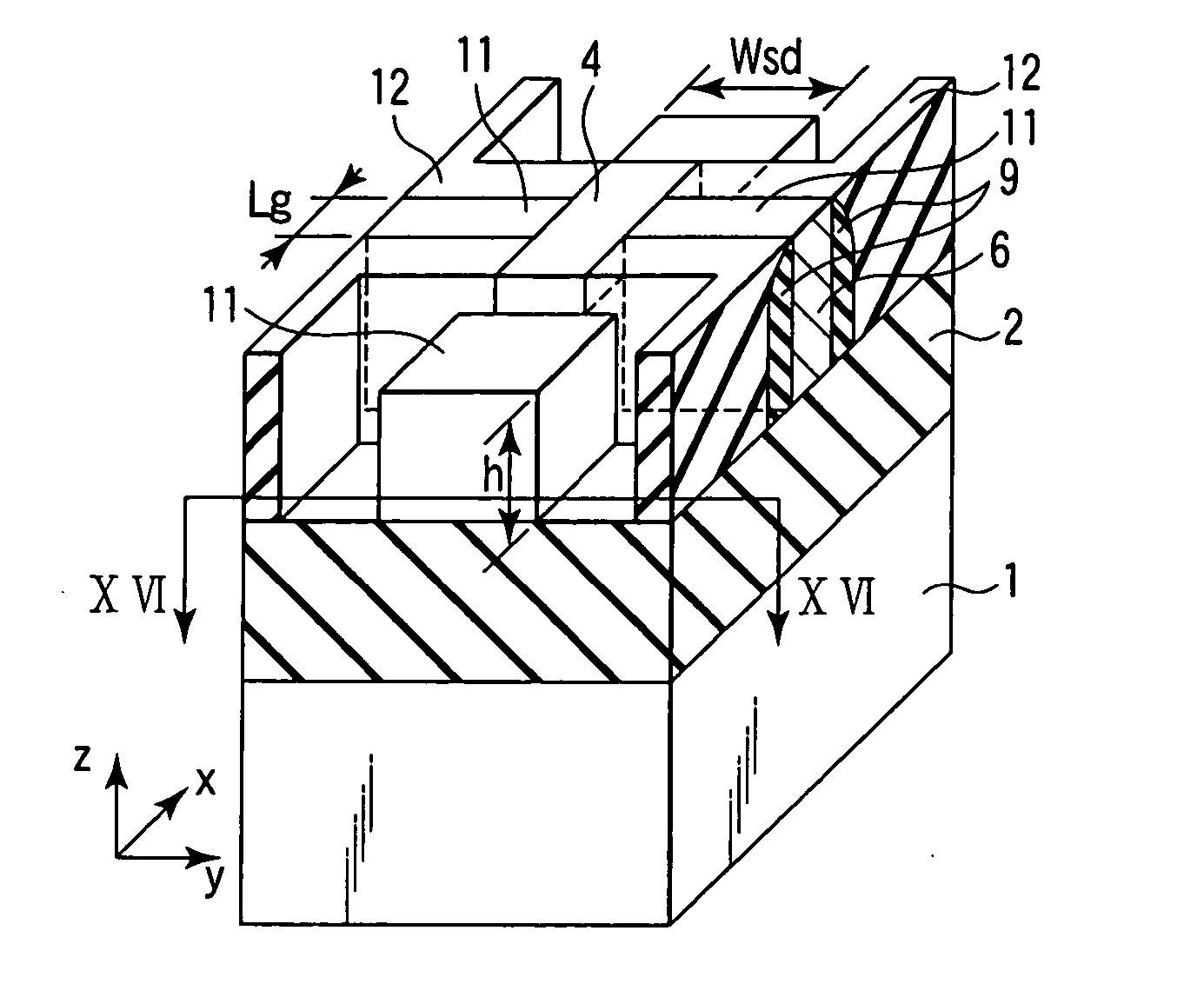
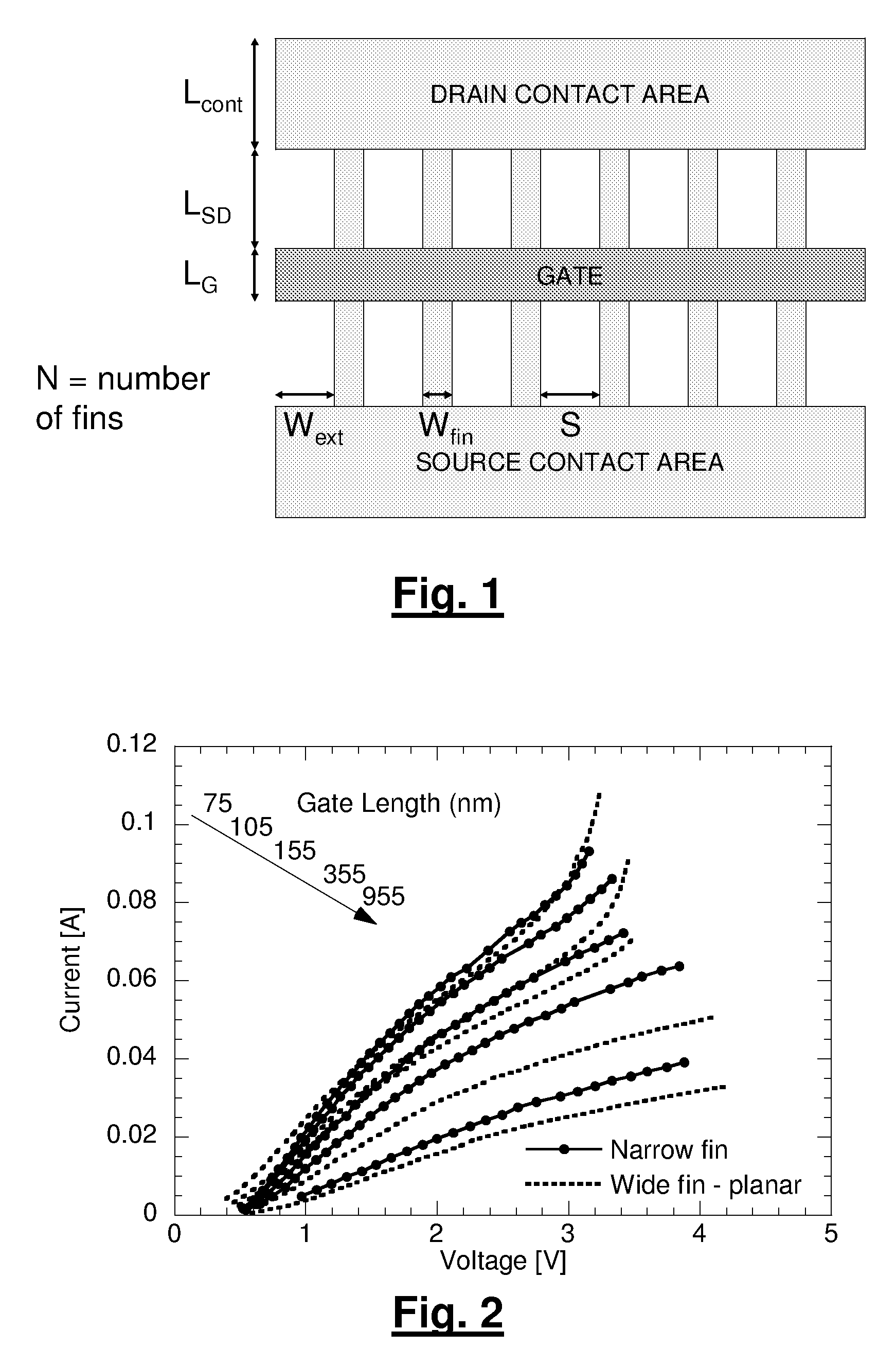
A semiconductor layer in which a primary part of a FinFET is formed, i.e., a fin has a shape which is long in a direction x and short in a direction y. A width of the fin in the direction y changes on three stages. First, in a channel area between gate electrodes each having a gate length Lg, the width of the fin in the direction y is Wch. Further, the width of the fin in the direction y in a source / drain extension area adjacent to the channel area in the direction x is Wext (>Wch). Furthermore, the width of the fin in the direction y in a source / drain area adjacent to the source / drain extension area in the direction x is Wsd (>Wext).
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Standard cell, standard cell library, and semiconductor integrated circuit
ActiveUS20050280031A1Variation in characteristicTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
In a standard cell, at least one of transistors on either side of a transistor having gate length different from that of the other transistors are set to be always in the OFF state. This prevents influence to the operation of the standard cell even with variation in final gate dimension, suppressing variation in characteristics of the standard cell.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Design Methodology for MuGFET ESD Protection Devices
InactiveUS20090280582A1Easy to optimizePromote resultsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesManufacturing technologyEngineering
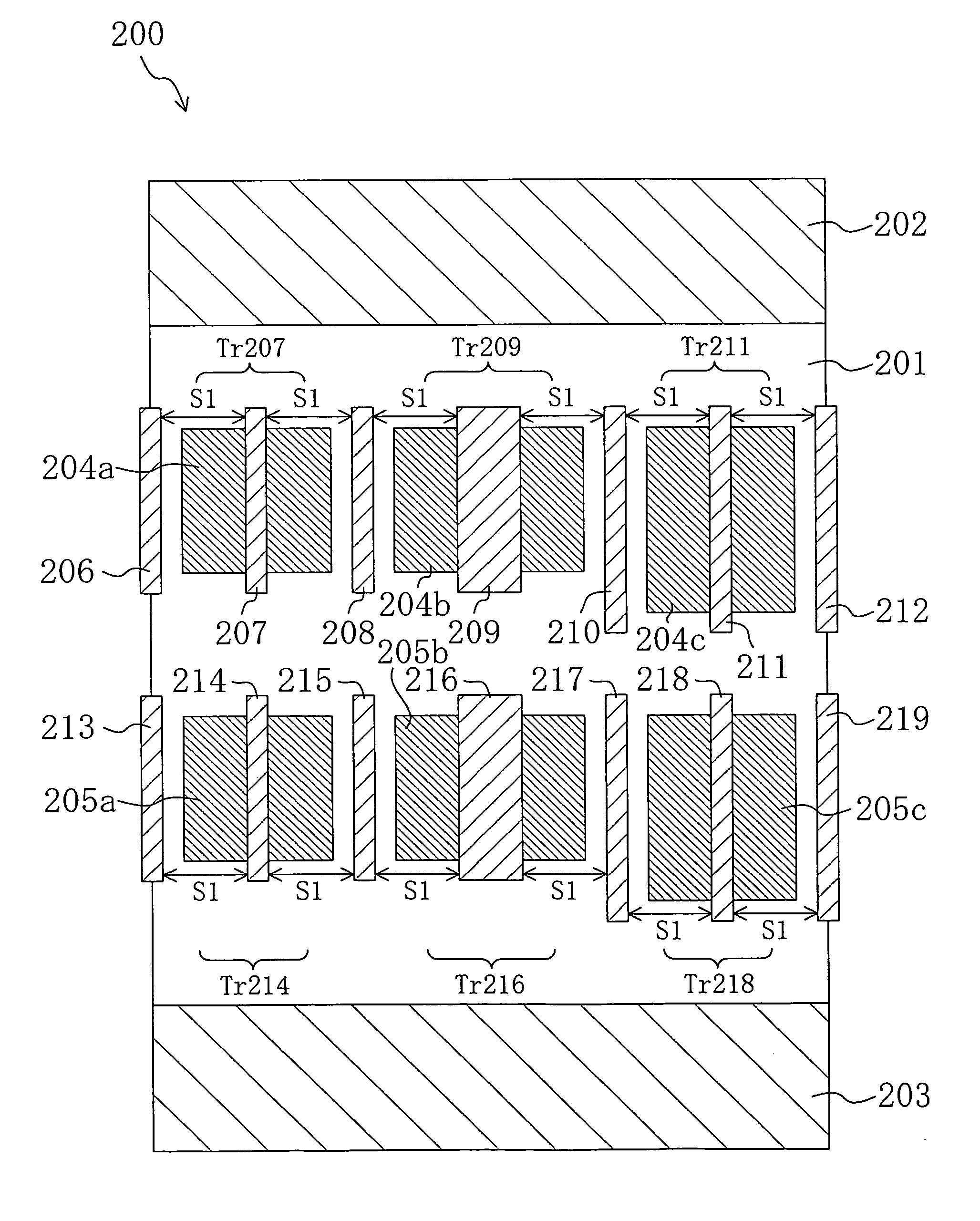
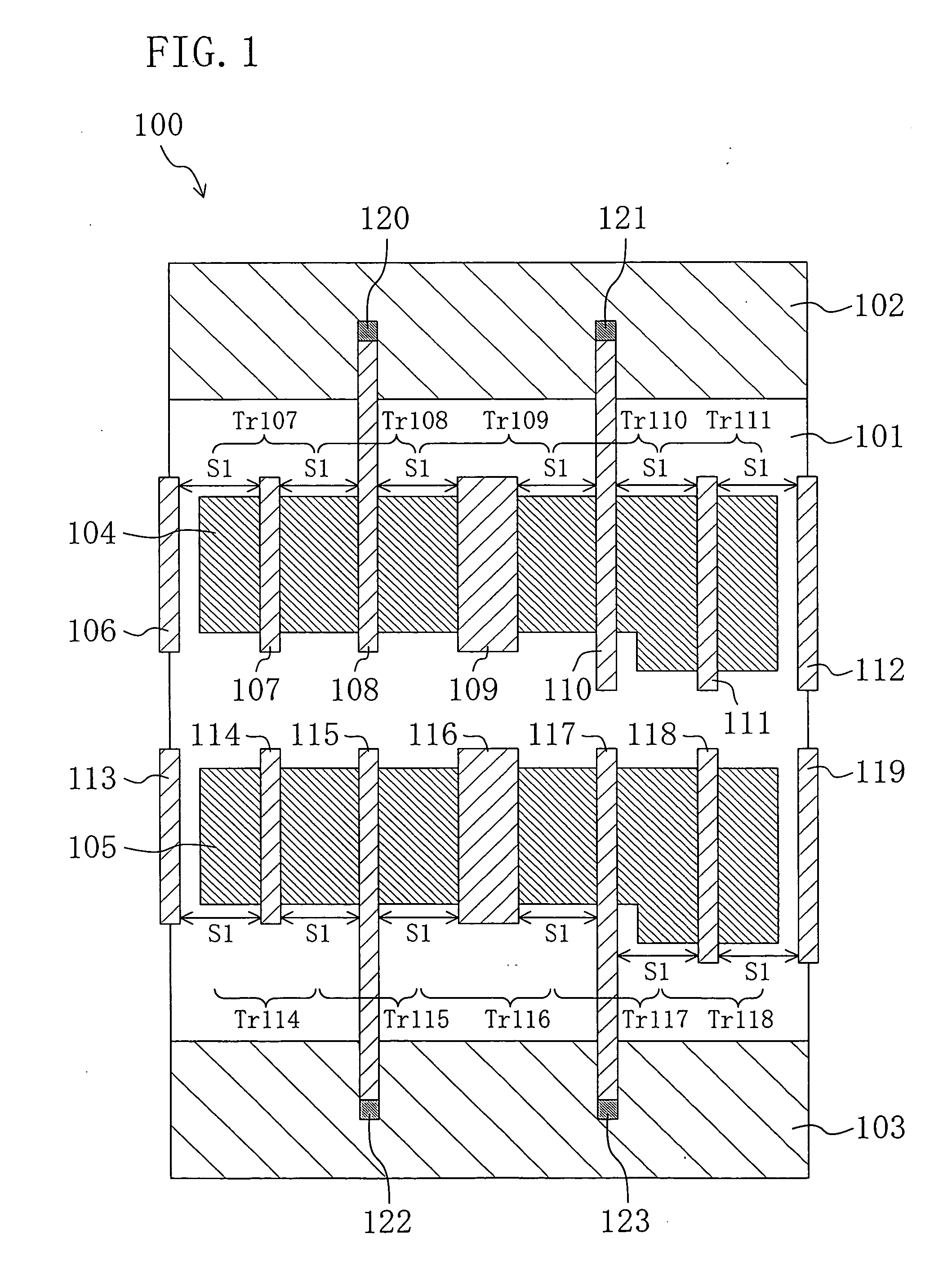
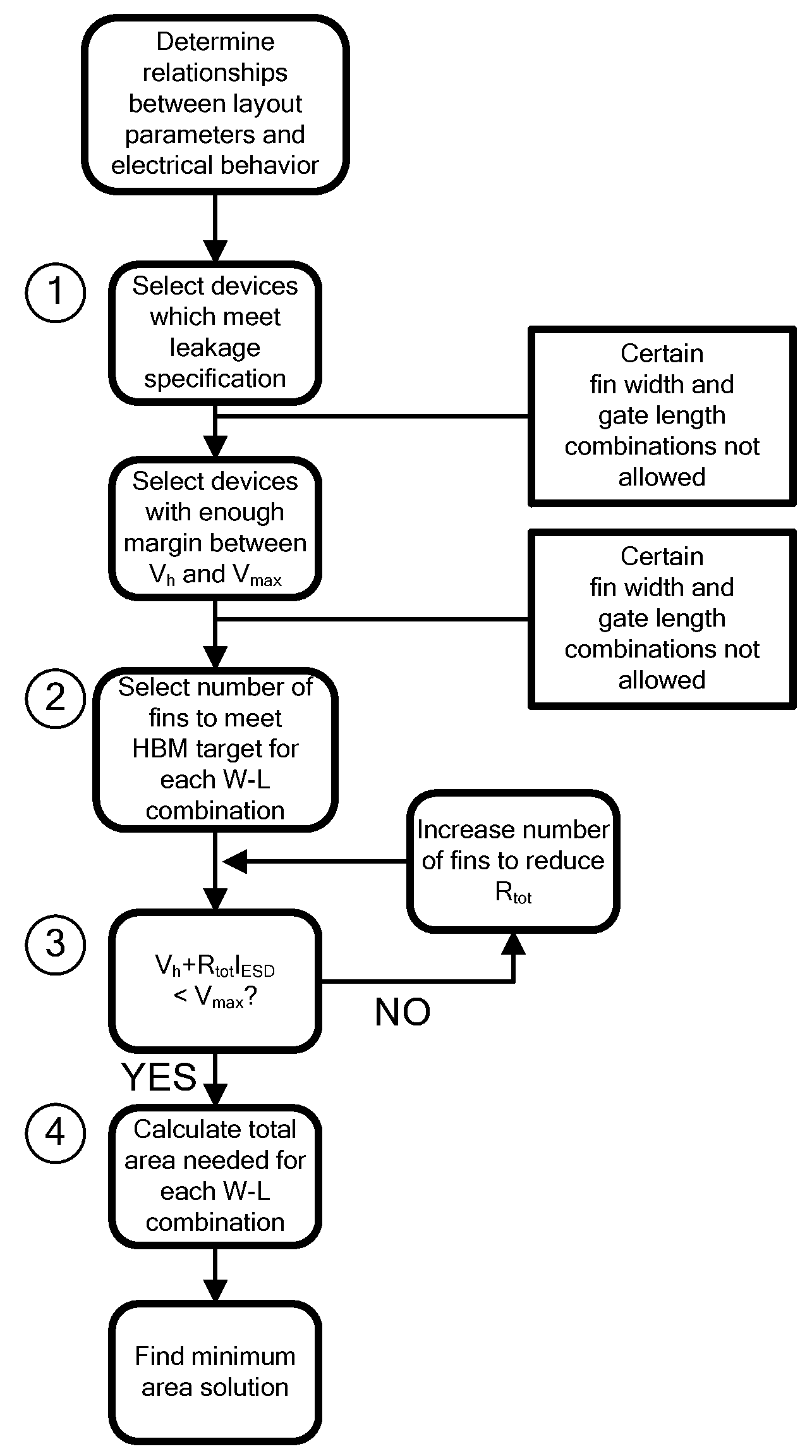
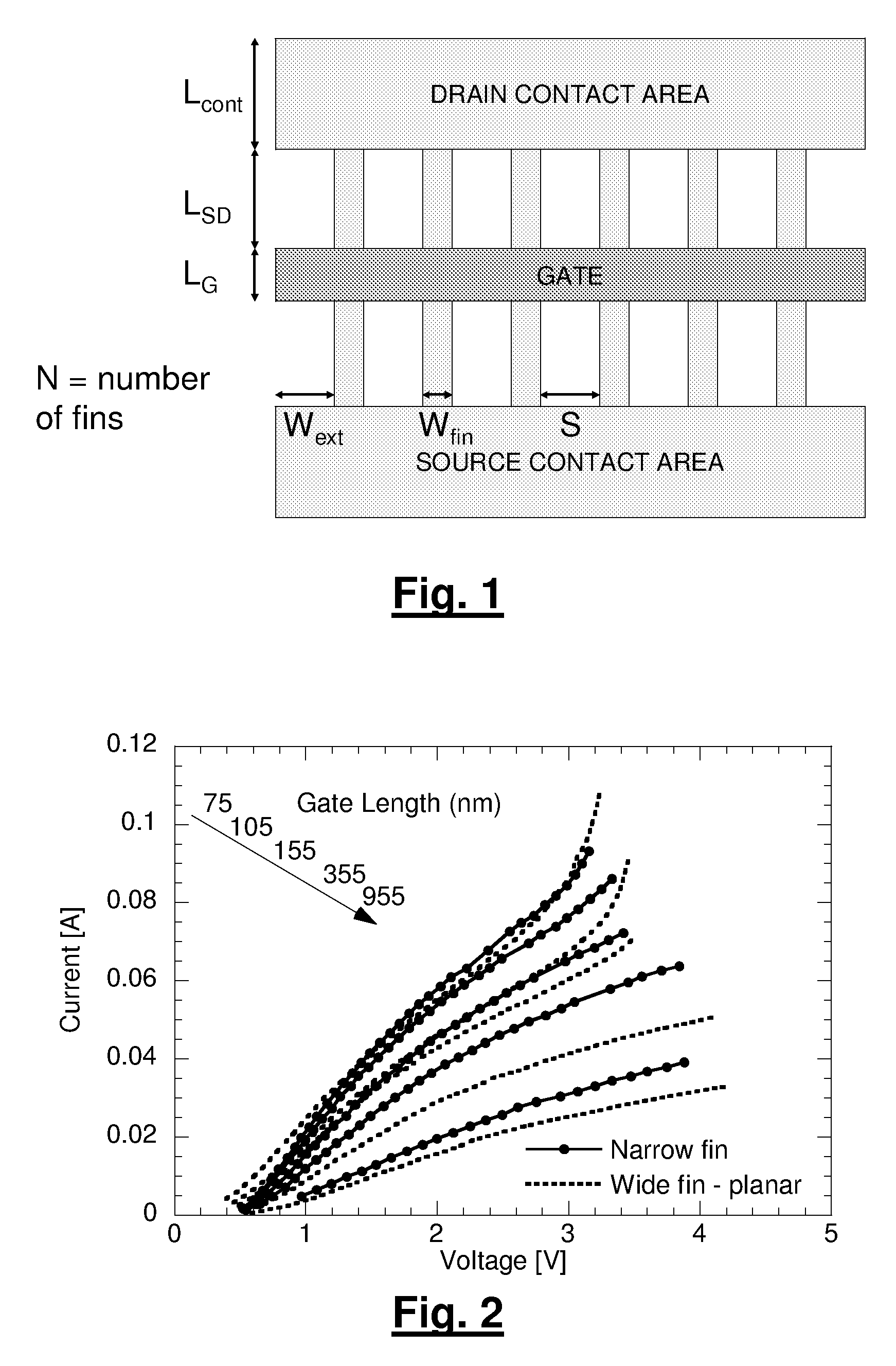
A method for manufacturing a MuGFET ESD protection device having a given layout by means of a given manufacturing process, the method comprising selecting multiple interdependent layout and process parameters of which a first set are fixed by said manufacturing process and a second set are variable, selecting multiple combinations of possible layout and process parameter values which meet predetermined ESD constraints; determining an optimum value for at least one other parameter in view of a predetermined design target apart from the predetermined ESD constraints; determining values for fin width (Wfin), gate length (LG) and number of fins (N) on the basis of the optimum value; and manufacturing said MuGFET ESD protection device using the given manufacturing and process values.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Design methodology for MuGFET ESD protection devices
InactiveUS7923266B2Promote resultsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesManufacturing technologyEngineering
A method for manufacturing a MuGFET ESD protection device having a given layout by means of a given manufacturing process, the method comprising selecting multiple interdependent layout and process parameters of which a first set are fixed by said manufacturing process and a second set are variable, selecting multiple combinations of possible layout and process parameter values which meet predetermined ESD constraints; determining an optimum value for at least one other parameter in view of a predetermined design target apart from the predetermined ESD constraints; determining values for fin width (Wfin), gate length (LG) and number of fins (N) on the basis of the optimum value; and manufacturing said MuGFET ESD protection device using the given manufacturing and process values.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Gate length proximity corrected device
InactiveUS20050009312A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical conductorSemiconductor
An electronic device including: a semiconductor substrate having an array of gate conductors, each having a length and a width, comprised of dummy gate conductors and functional gate conductors extending in a widthwise direction, the gate conductors positioned substantially parallel to each other in the widthwise direction and periodically spaced apart a fixed distance in a direction substantially perpendicular to the widthwise direction.
Owner:QIMONDA +1
SRAM cell
InactiveUS20070108528A1Increase effective widthImprove carrying capacityTransistorSolid-state devicesDriving currentEngineering
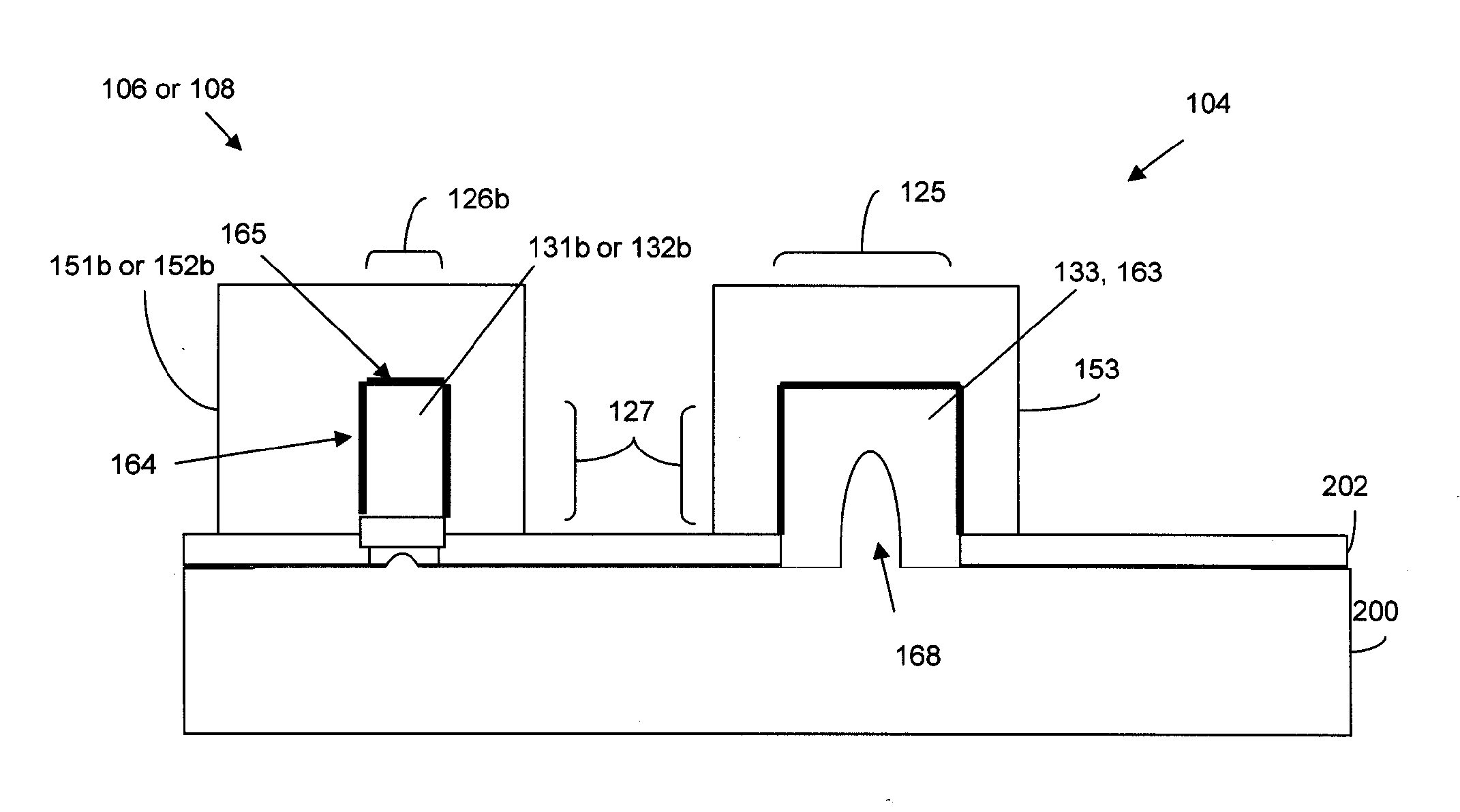
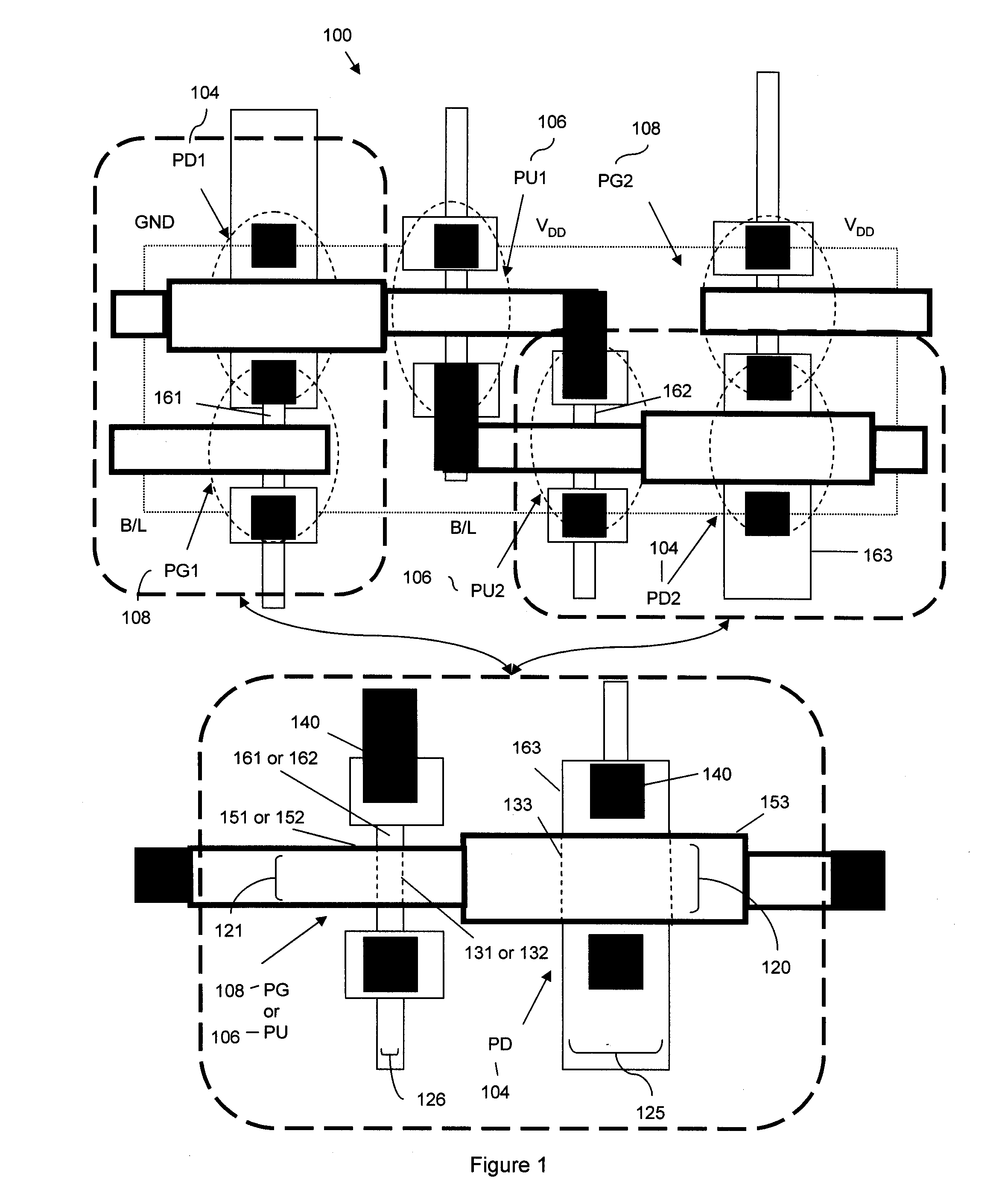
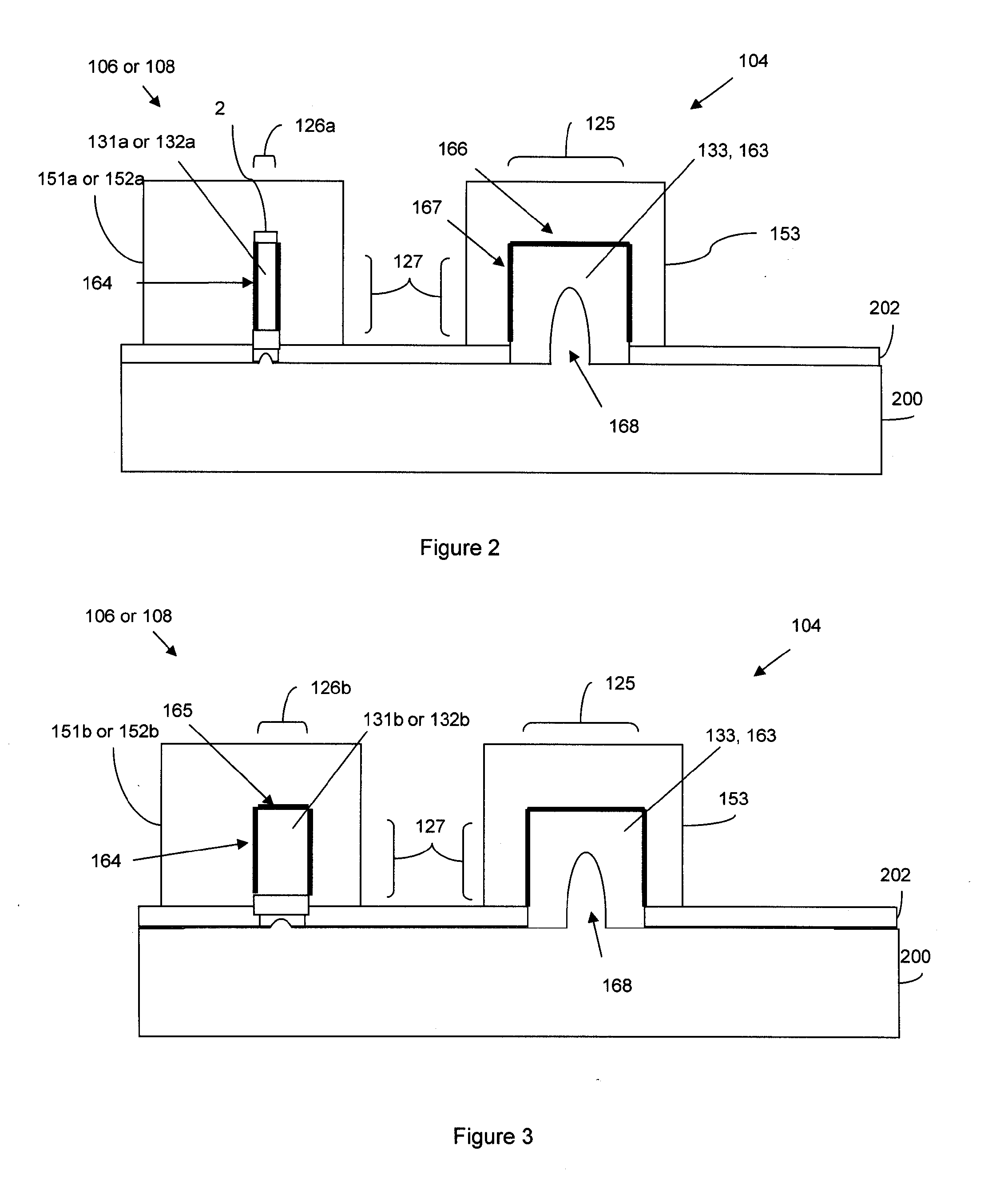
Disclosed is an SRAM cell on an SOI, bulk or HOT wafer with two pass-gate n-FETs, two pull-up p-FETs and two pull-down n-FETs and the associated methods of making the SRAM cell. The pass-gate FETs and pull-down FETs are non-planar fully depleted finFETs or trigate FETs. The pull-down FETs comprise non-planar partially depleted three-gated FETs having a greater channel width and a greater gate length and, thus, a greater drive current relative to the pass-gate and pull-up FETs. Additionally, for optimal electron mobility and hole mobility, respectively, the channels of the n-FETs and p-FETs can comprise semiconductors with different crystalline orientations.
Owner:IBM CORP
Vertical trench-formed dual-gate FET device structure and method for creation
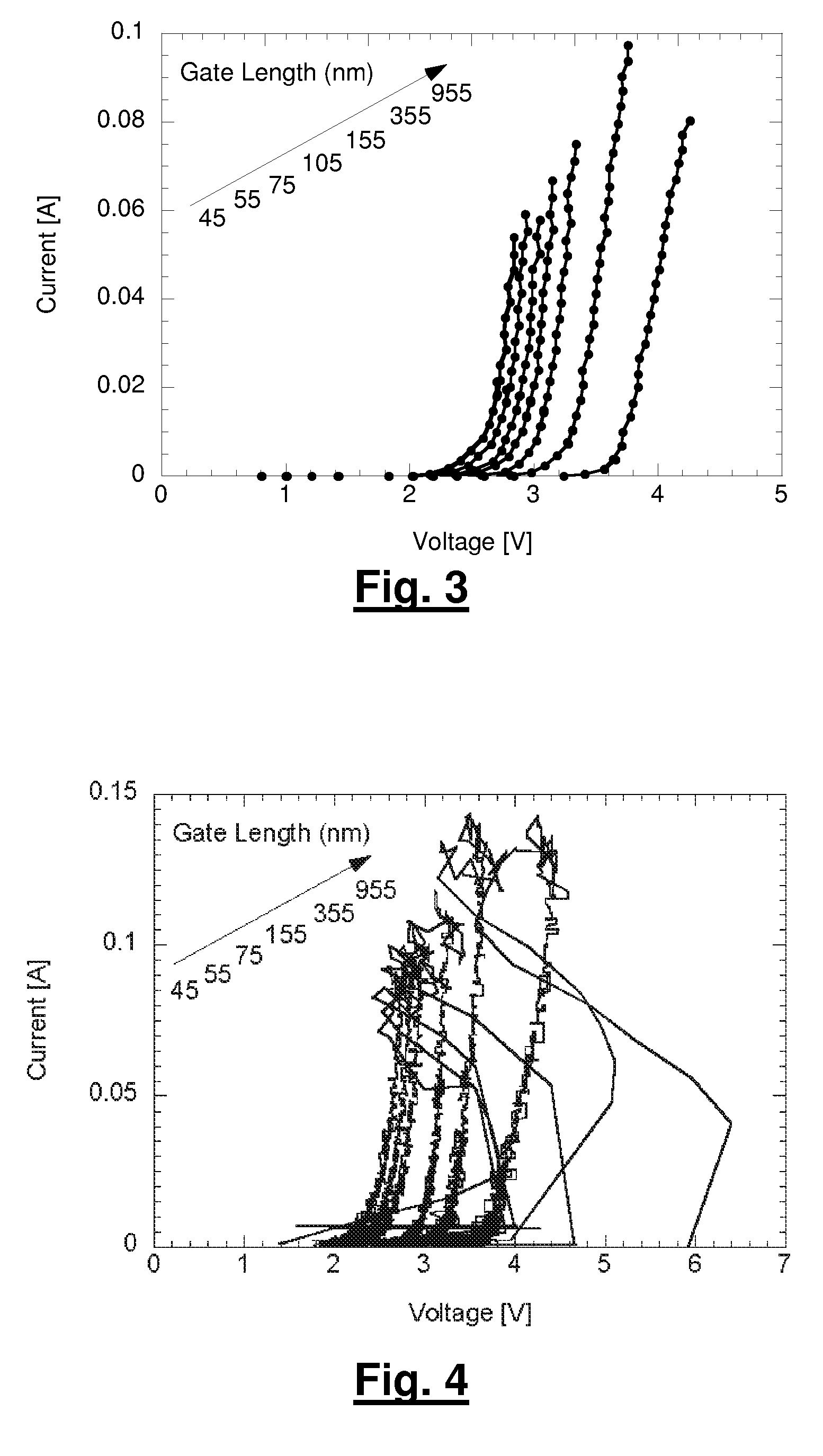
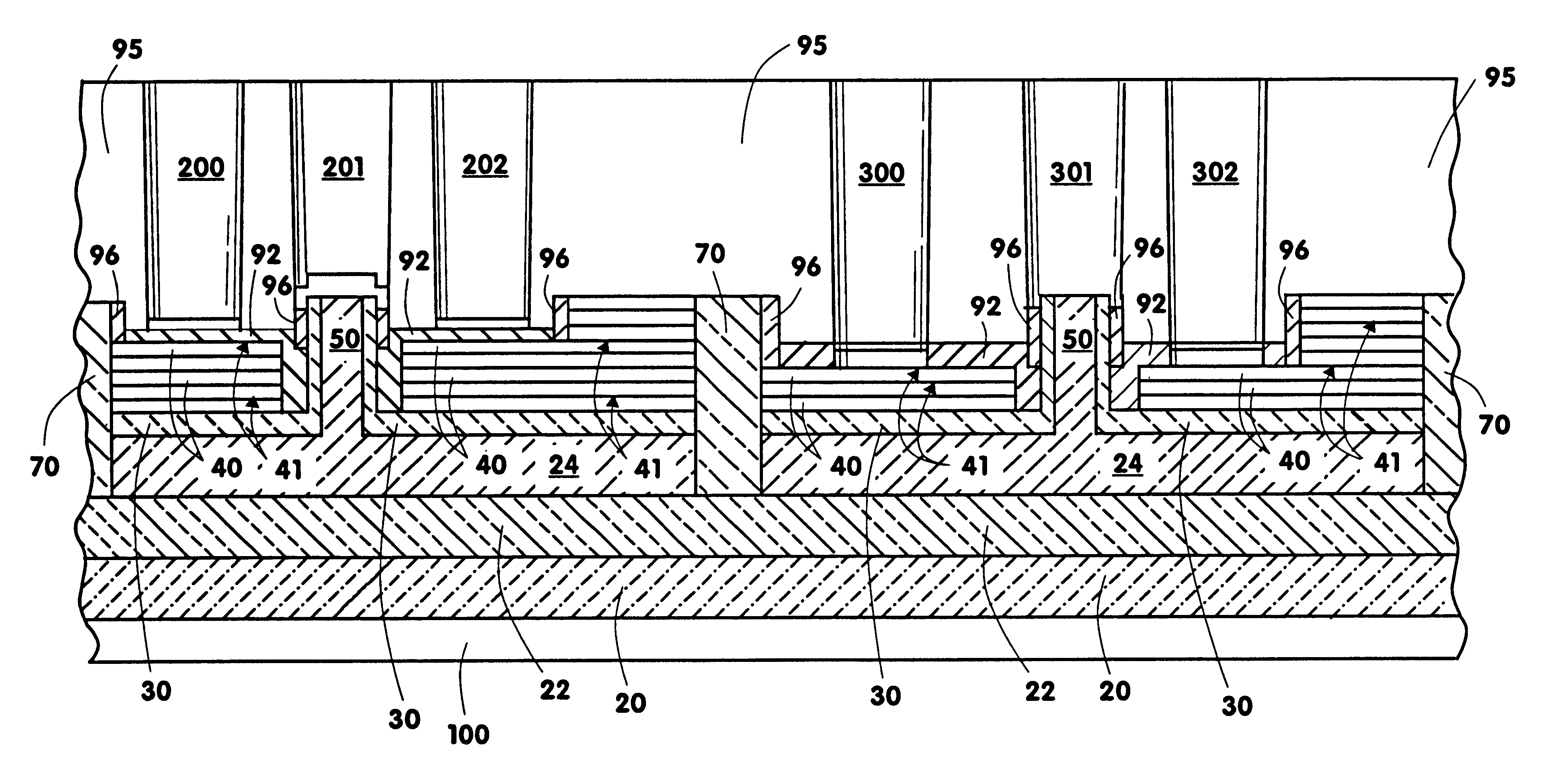
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method of forming one or more FETs having a vertical trench-formed double-gate, with a plurality of nitride layers having oxide marker etch-stop layers provided periodically there-through, thereby adapting the FETs to have a plurality of selectable gate lengths. The present invention provides for control and formation of gate lengths scaled down to about 5 nm to about 100 nm, preferably from about 5 nm to about 50 nm. The plurality of pad nitride layers with the oxide etch-stop layers provide for the present FET to be connected to a plurality of contacts having a variety of connection depths corresponding to the gate lengths used, by etching a plurality of via in the pad nitride layers whereby such vias stop at selected ones of the etch-stop layers to provide vias adapted to connect with the selected ones of such contacts. Additional gate material may be deposited over a top surface of the selected plurality of nitride layers to allow for contacts to the gate electrodes of any given FET.
Owner:IBM CORP
pMOS device having ultra shallow super-steep-retrograde epi-channel with dual channel doping and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS6881987B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantP channel
The present invention provides a p-channel metal-oxide-semiconductor (pMOS) device having an ultra shallow epi-channel satisfying a high doping concentration required for a device of which gate length is about 30 nm even without using a HALO doping layer and a method for fabricating the same. The pMOS device includes: a semiconductor substrate; a channel doping layer being formed in a surface of the semiconductor substrate and being dually doped with dopants having different diffusion rates; a silicon epi-layer being formed on the channel doping layer, whereby constructing an epi-channel along with the channel doping layer; a gate insulating layer formed on the silicon epi-layer; a gate electrode formed on the gate insulating layer; a source / drain extension region highly concentrated and formed in the semiconductor substrate of lateral sides of the epi-channel; and a source / drain region electrically connected to the source / drain extension region and deeper than the source / drain region.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
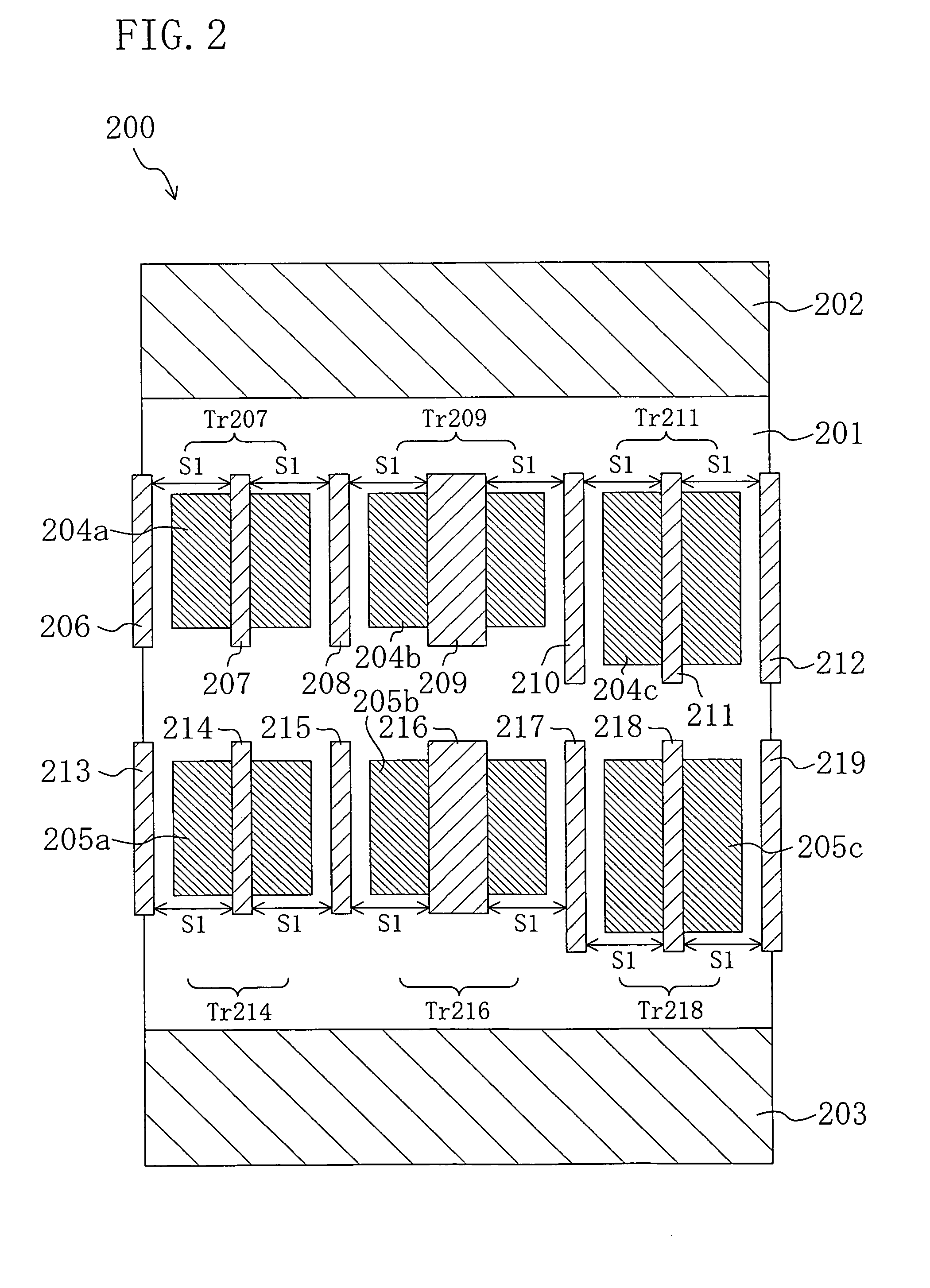
Standard cell, standard cell library, and semiconductor integrated circuit with suppressed variation in characteristics
In a standard cell, at least one of transistors on either side of a transistor having gate length different from that of the other transistors are set to be always in the OFF state. This prevents influence to the operation of the standard cell even with variation in final gate dimension, suppressing variation in characteristics of the standard cell.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Increasing doping of well compensating dopant region
InactiveUS20060154428A1More compensation dopingIncreasing gate-lengthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantEngineering
Methods and resulting structure of implementing a compensating implant that creates more compensation doping as the gate length is increased are disclosed. In particular, the invention performs an angled compensation implant through a gate opening during the damascene process such that the compensating dopant concentration increases as the gate length increases. In this fashion, the threshold voltage of a longer device is reduced much more than the threshold voltage of a shorter device, thereby reducing the threshold voltage of the longer device to acceptable levels without affecting the threshold voltage of the shorter device. The invention is especially advantageous relative to super-steep retrograde wells.
Owner:IBM CORP
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS7279727B2Suppress mutationImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorSemiconductor
A semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate; a diffusion region which is formed in the semiconductor substrate and serves as a region for the formation of a MIS transistor; an element isolation region surrounding the diffusion region; at least one gate conductor film which is formed across the diffusion region and the element isolation region, includes a gate electrode part located on the diffusion region and a gate interconnect part located on the element isolation region, and has a constant dimension in the gate length direction; and an interlayer insulating film covering the gate electrode. The semiconductor device further includes a gate contact which passes through the interlayer insulating film, is connected to the gate interconnect part, and has the dimension in the gate length direction larger than the gate interconnect part.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Semiconductor device and layout design method therefor
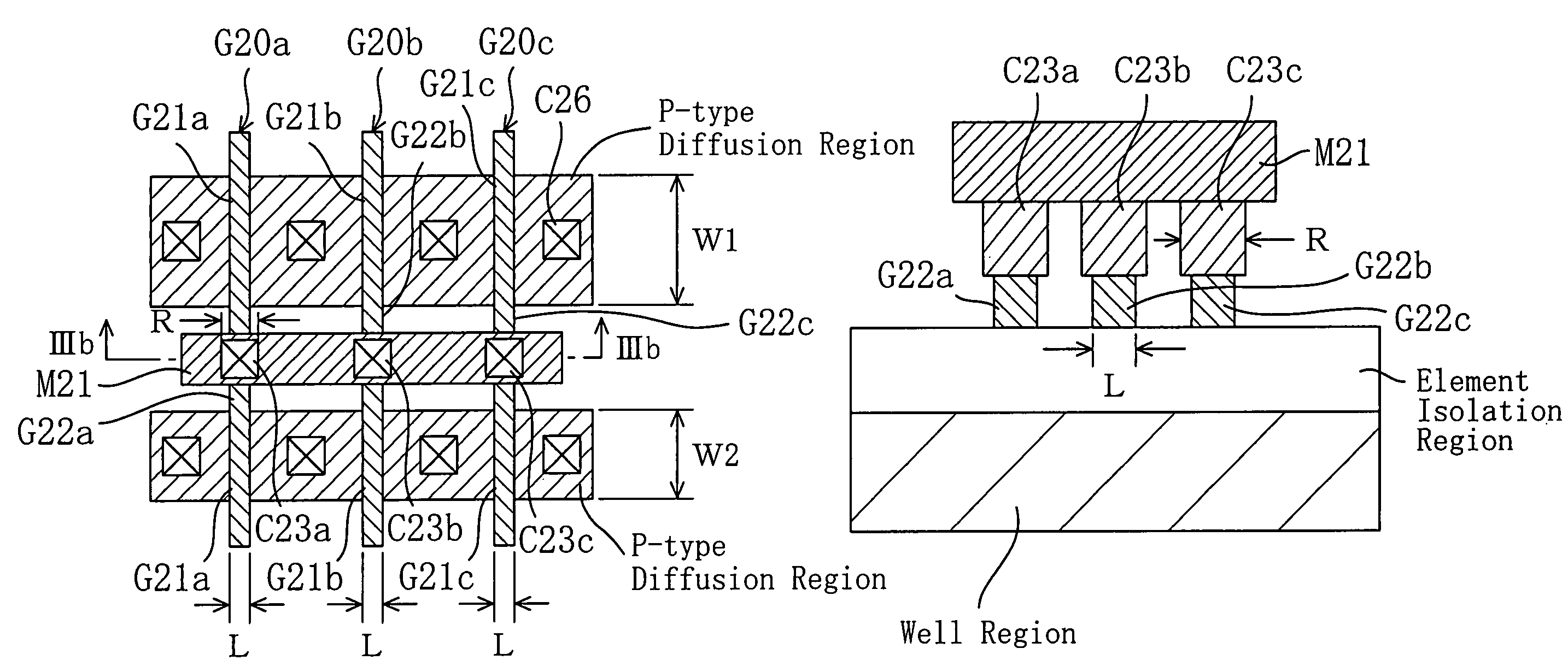
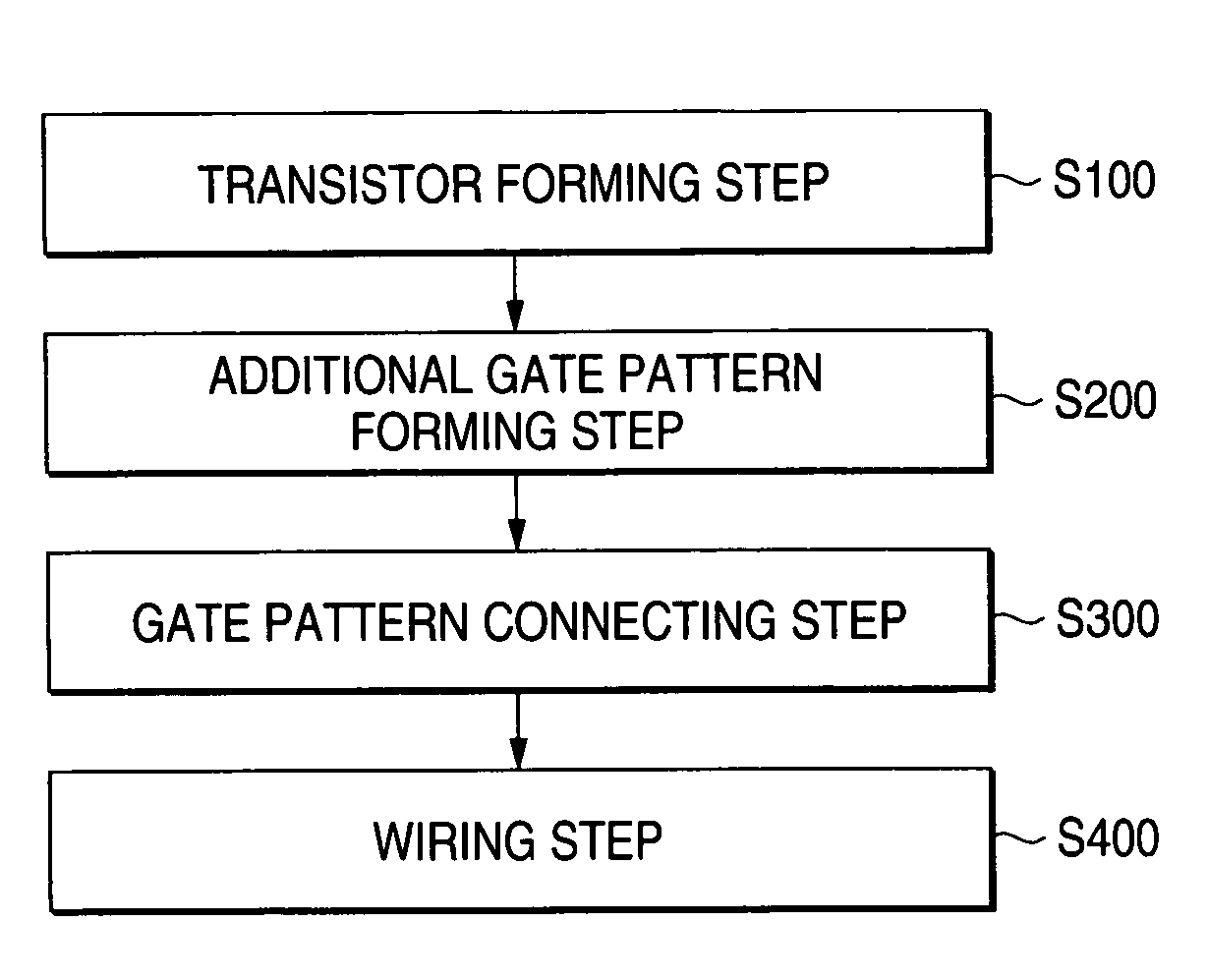
A layout design method for a semiconductor device includes a step of arranging transistors, a dummy gate forming step of forming dummy gates, which has a shape identical with a shape including gate electrodes or the gate electrodes and projected parts from active regions of the gate electrodes, in positions in parallel with and a fixed distance apart from the gate electrodes arranged at both ends in a gate length direction on active regions of the transistors and, when the transistors have plural gate electrodes with different gate widths, extending the projected parts to the outside of the active regions by a necessary length, a gate connecting step of, when gate patterns and contact regions are connected to the gate electrodes of the transistors, connecting the gate electrodes and the dummy gates according to a positional relation between the gate electrodes and the dummy gates, and a wiring step of wiring a metal layer. It is possible to design a semiconductor device having a smaller area than that in the past and with a less design man-hour.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Metal gated ultra short MOSFET devices
MOSFET devices suitable for operation at gate lengths less than about 40 nm, and methods of their fabrication is being presented. The MOSFET devices include a ground plane formed of a monocrystalline Si based material. A Si based body layer is epitaxially disposed over the ground plane. The body layer is doped with impurities of opposite type than the ground plane. The gate has a metal with a mid-gap workfunction directly contacting a gate insulator layer. The gate is patterned to a length of less than about 40 nm, and possibly less than 20 nm. The source and the drain of the MOSFET are doped with the same type of dopant as the body layer. In CMOS embodiments of the invention the metal in the gate of the NMOS and the PMOS devices may be the same metal.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Fabrication of nano-sheet transistors with different threshold voltages
ActiveUS9653289B1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringThreshold voltage
A method of forming two or more nano-sheet devices with varying electrical gate lengths, including, forming at least two cut-stacks including a plurality of sacrificial release layers and at least one alternating nano-sheet channel layer on a substrate, removing a portion of the plurality of sacrificial release layers to form indentations having an indentation depth in the plurality of sacrificial release layers, and removing a portion of the at least one alternating nano-sheet channel layer to form a recess having a recess depth in the at least one alternating nano-sheet channel layers, where the recess depth is greater than the indentation depth.
Owner:TESSERA LLC
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS6909242B2Reduce in quantityAvoid noise impactTransistorStatic indicating devicesLight emitting deviceLight emission
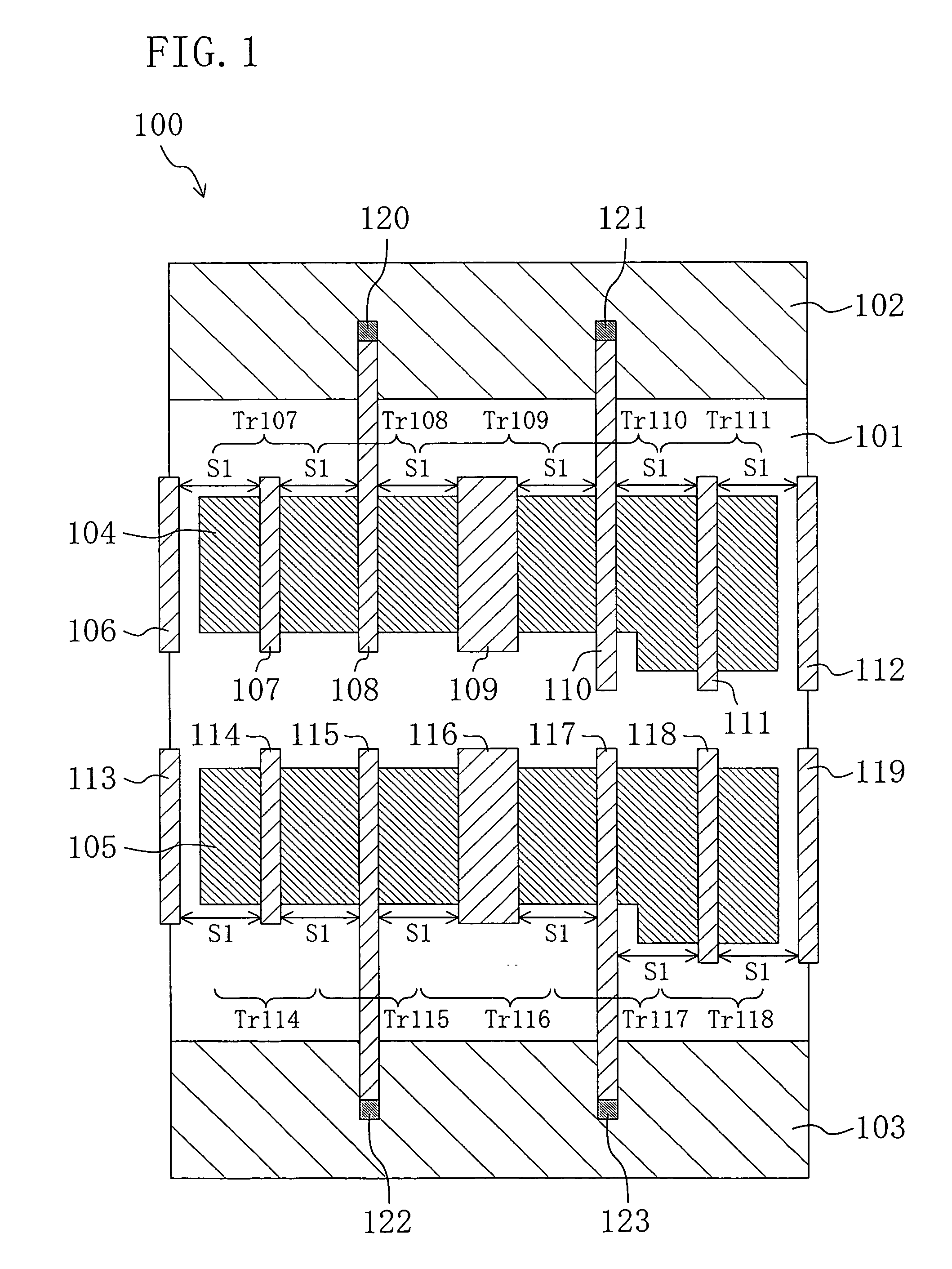
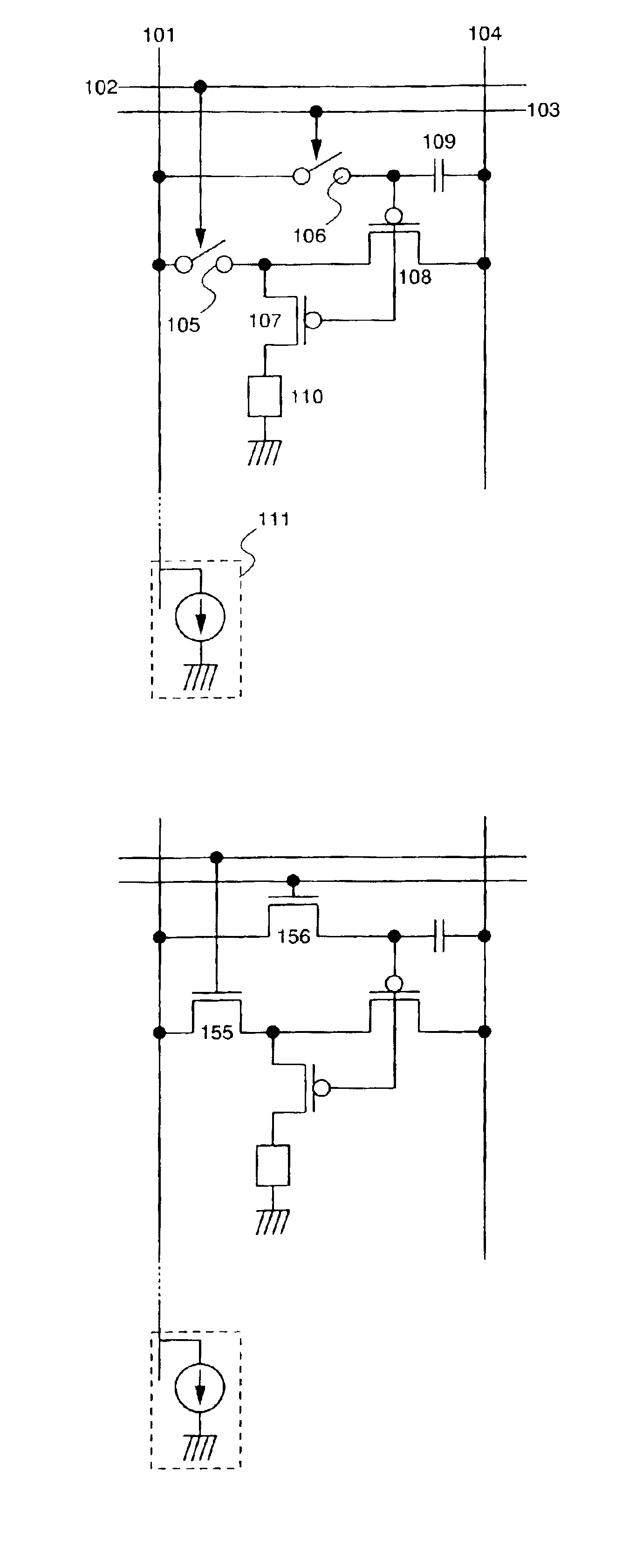
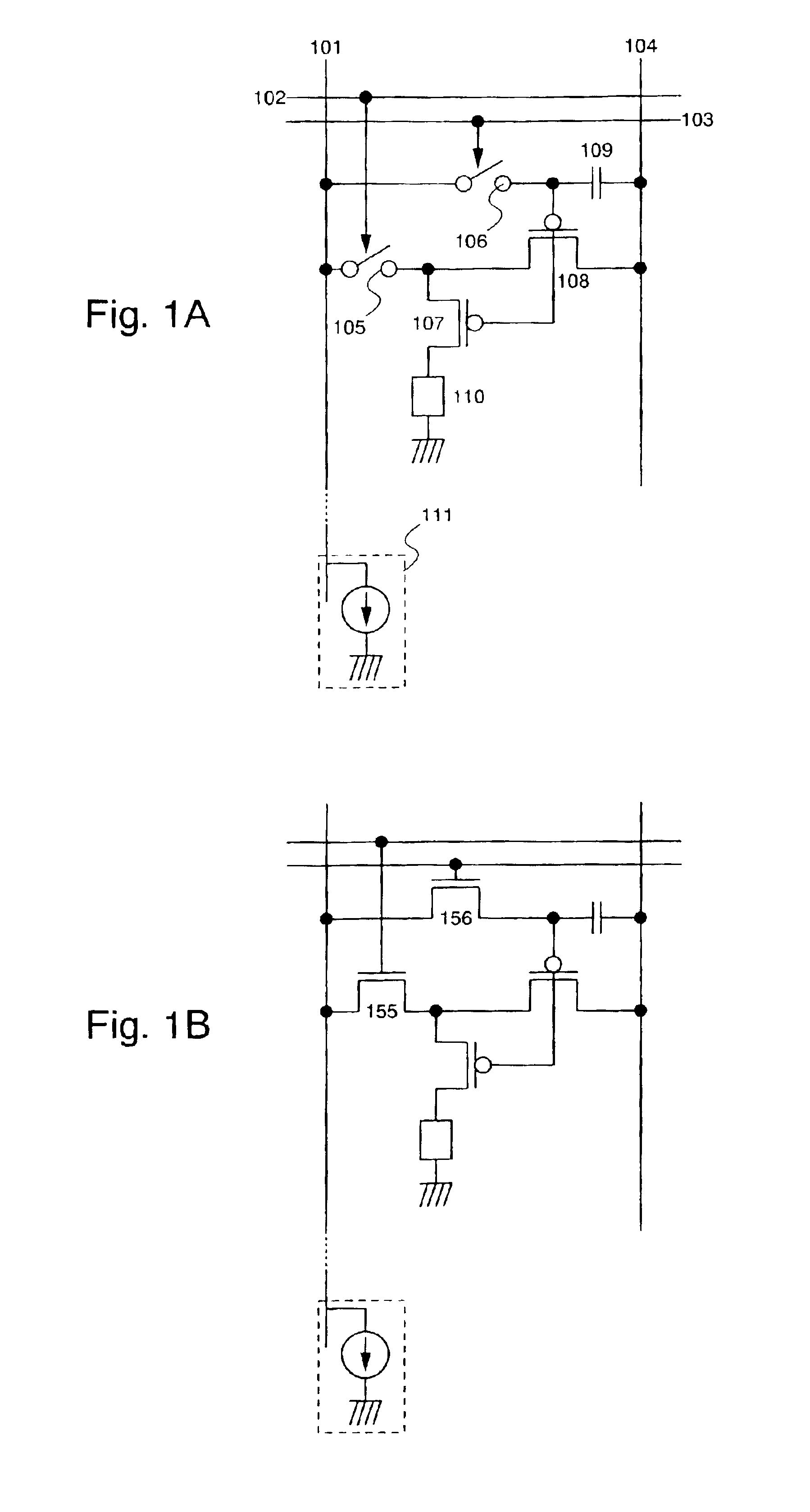
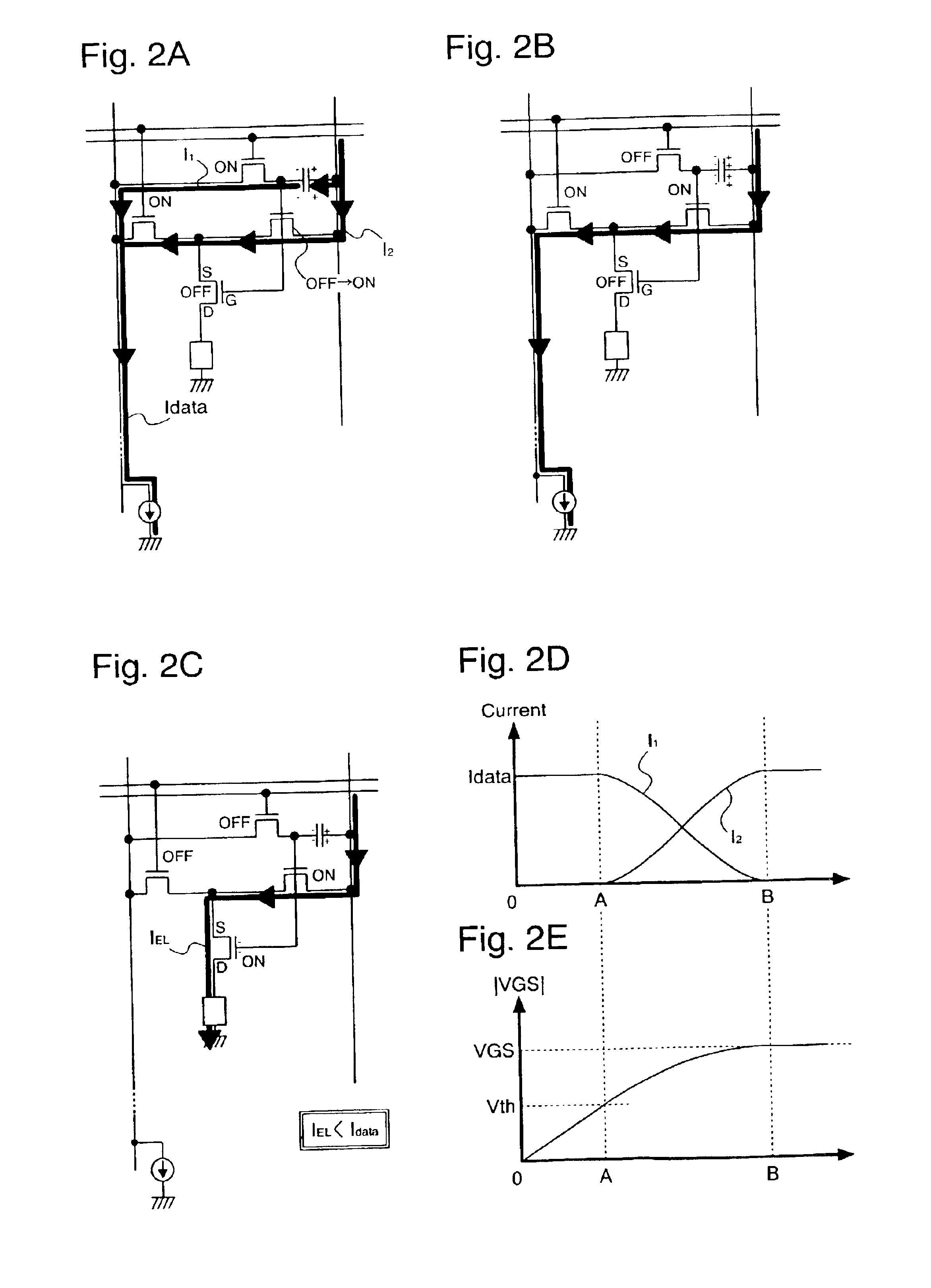
A light emitting device capable of performing signal electric current write-in operations at high speed and without dispersion in the characteristics of TFTs structuring pixels influencing the brightness of light emitting elements is provided. The gate length L of a transistor in which an electric current flows during write-in of a signal electric current is made shorter than the gate length L of a transistor in which electric current supplied to EL elements flows during light emission, and high speed write-in is thus performed by having a larger electric current flow than the electric current flowing in conventional EL elements. A converter and driver transistor (108) is used for signal write-in. By using the converter and driver transistor (108) and a driver transistor (107) when supplying electric current to a light emitting element during light emission, dispersion in the transistor characteristics can be made to have less influence on brightness than when using a structure in which write-in operations and light emission operations are performed using different transistors.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Threshold voltage control layer in a semiconductor device
ActiveUS7304350B2Extension region can be suppressedHigh currentTransistorSolid-state devicesControl layerPeak value
A semiconductor device has a well region having a first conductivity type and formed in an upper portion of a semiconductor substrate, a gate insulating film and a gate electrode formed successively on the well region of the semiconductor substrate, a threshold voltage control layer for controlling a threshold voltage formed in the portion of the well region which is located below the gate electrode and in which an impurity of the first conductivity type has a concentration peak at a position shallower than in the well region, an extension region having a second conductivity type and formed in the well region to be located between each of the respective portions of the well region which are located below the both end portions in the gate-length direction of the gate electrode and the threshold voltage control layer, and source and drain regions each having the second conductivity type and formed outside the extension layer in connected relation thereto. The junction surface between the threshold voltage control layer and the extension region has an upwardly protruding configuration.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Self-aligned structures and methods for asymmetric GAN transistors & enhancement mode operation
ActiveUS20140091308A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesNon symmetricEngineering
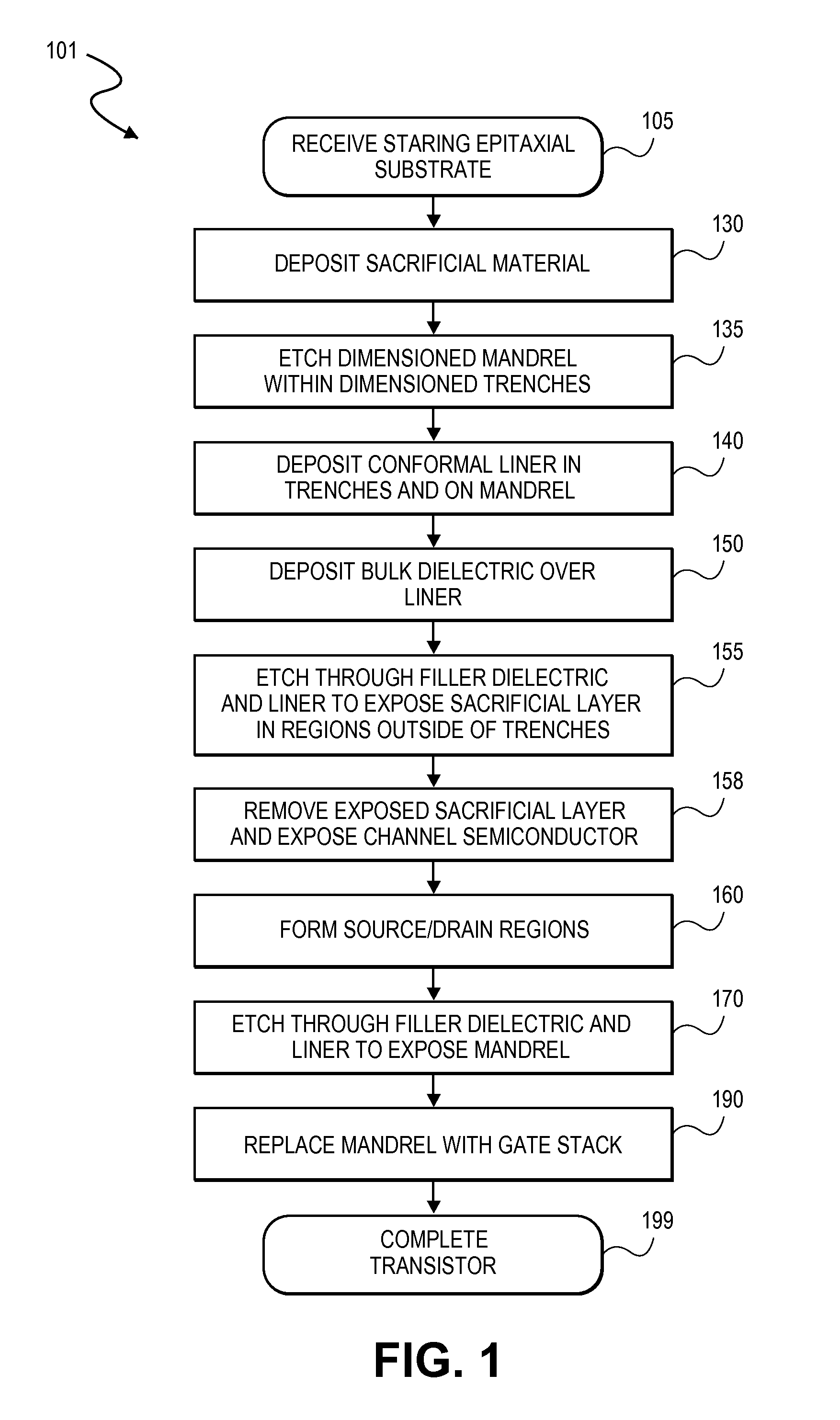
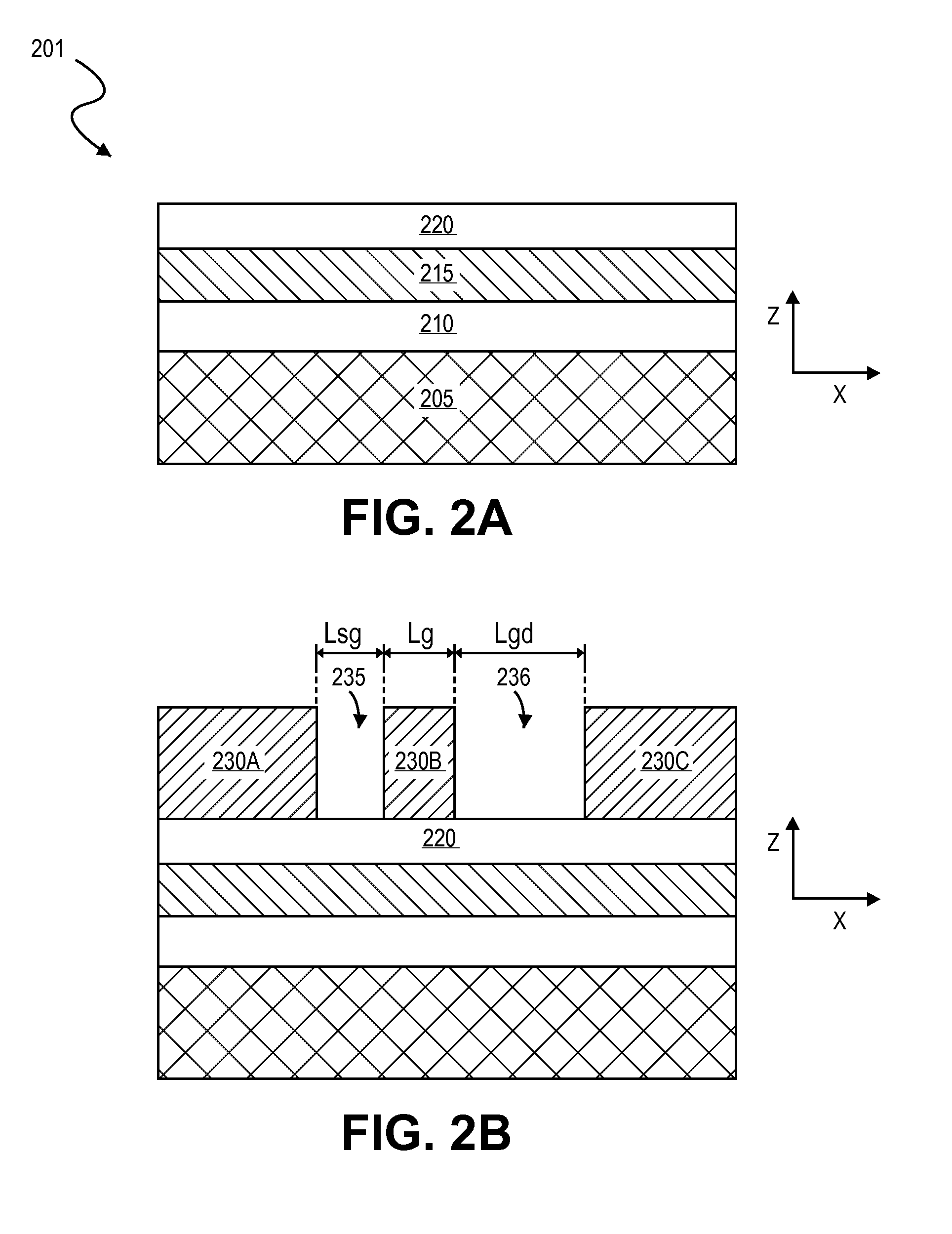
Embodiments include high electron mobility transistors (HEMT). In embodiments, a gate electrode is spaced apart by different distances from a source and drain semiconductor region to provide high breakdown voltage and low on-state resistance. In embodiments, self-alignment techniques are applied to form a dielectric liner in trenches and over an intervening mandrel to independently define a gate length, gate-source length, and gate-drain length with a single masking operation. In embodiments, III-N HEMTs include fluorine doped semiconductor barrier layers for threshold voltage tuning and / or enhancement mode operation.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Low leakage heterojunction vertical transistors and high performance devices thereof
InactiveUS20070148939A1Superb performanceSuperb scalabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionSemiconductor materials
A method for forming and the structure of a vertical channel of a field effect transistor, a field effect transistor and CMOS circuitry are described incorporating a drain, body and source region on a sidewall of a vertical single crystal semiconductor structure wherein a hetero-junction is formed between the source and body of the transistor, wherein the source region and channel are independently lattice strained with respect the body region and wherein the drain region contains a carbon doped region to prevent the diffusion of dopants (i.e., B and P) into the body. The invention reduces the problem of short channel effects such as drain induced barrier lowering and the leakage current from the source to drain regions via the hetero-junction and while independently permitting lattice strain in the channel region for increased mobility via choice of the semiconductor materials. The problem of scalability of the gate length below 100 nm is overcome by the heterojunction between the source and body regions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
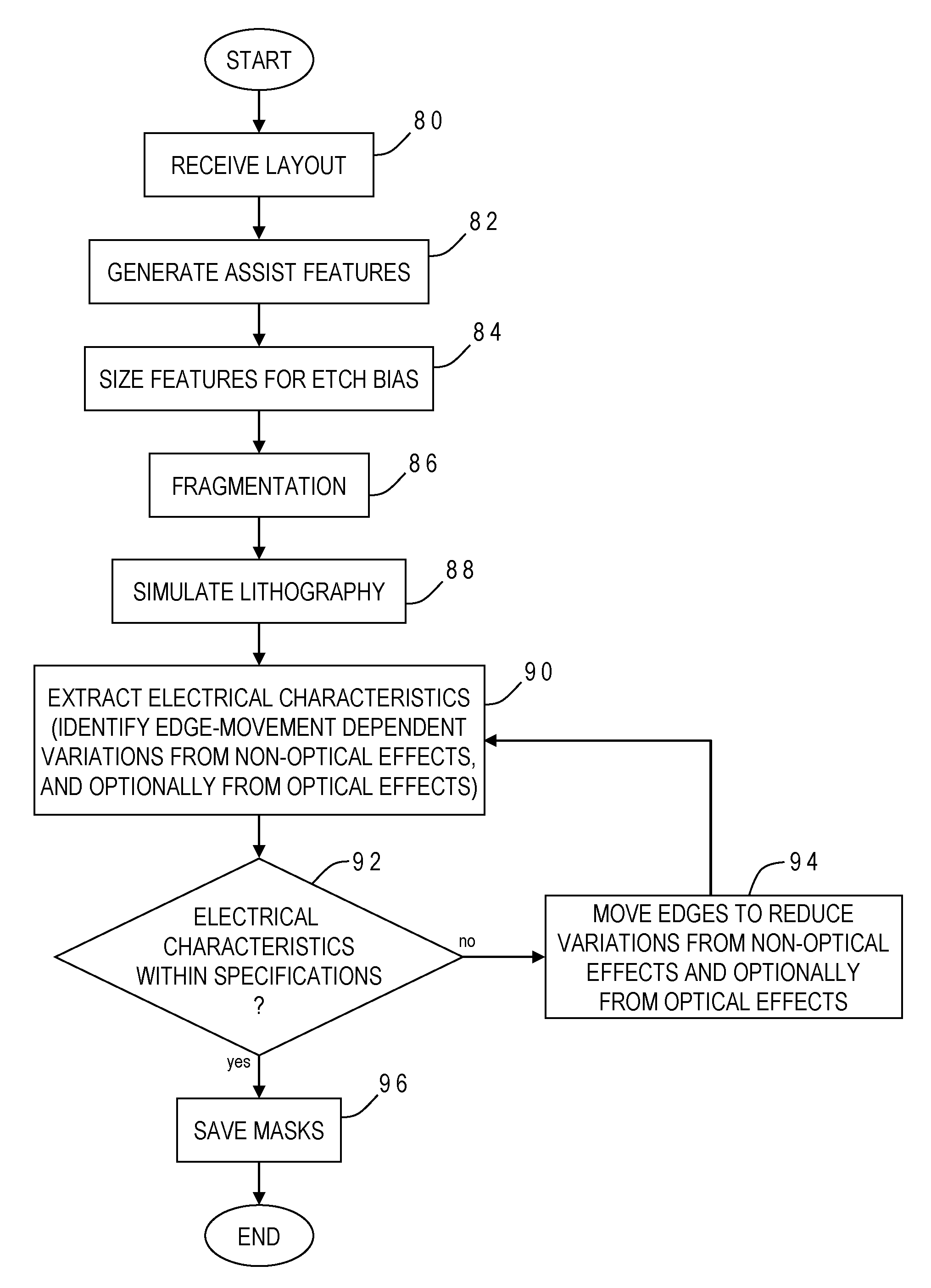
Electrically-driven optical proximity correction to compensate for non-optical effects
ActiveUS8103983B2Improve performancePhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentCapacitanceEngineering
A contour of a mask design for an integrated circuit is modified to compensate for systematic variations arising from non-optical effects such as stress, well proximity, rapid thermal anneal, or spacer thickness. Electrical characteristics of a simulated integrated circuit chip fabricated using the mask design are extracted and compared to design specifications, and one or more edges of the contour are adjusted to reduce the systematic variation until the electrical characteristic is within specification. The particular electrical characteristic preferably depends on which layer is to be fabricated from the mask: on-current for a polysilicon; resistance for contact; resistance and capacitance for metal; current for active; and resistance for vias. For systematic threshold voltage variation, the contour is adjusted to match a gate length which corresponds to an on-current value according to pre-calculated curves for contour current and gate length at a nominal threshold voltage of the chip.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Highly scalable thin film transistor
ActiveUS7888205B2Minimizing dopant diffusionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantOptoelectronics
Shrinking the dimensions of PMOS or NMOS thin film transistors is limited by dopant diffusion. In these devices an undoped or lightly doped channel region is interposed between heavily doped source and drain regions. When the device is built with very short gate length, source and drain dopants will diffuse into the channel, potentially shorting it and ruining the device. A suite of innovations is described which may be used in various combinations to minimize dopant diffusion during fabrication of a PMOS or NMOS polycrystalline thin film transistor, resulting in a highly scalable thin film transistor. This transistor is particularly suitable for use in a monolithic three dimensional array of stacked device levels.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Laterally diffused metal-oxide-semiconductor device and method of making the same
ActiveUS20090072308A1Minimize impactSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLDMOSGate dielectric
A laterally diffused metal-oxide-semiconductor (LDMOS) device as well as a method of making the same is disclosed. A gate is formed on a semiconductor substrate between a source region and a drain region with one side laterally extending onto a part of a field oxide layer and the opposite side beside the source region. A gate dielectric layer is formed between the gate and the semiconductor substrate, wherein the gate dielectric layer comprises two or more portions having different thicknesses arranged laterally in a way that the thicknesses of the portions gradually increase from one side beside the source doping region to the opposite side bordering the field oxide layer. With such structure, the hot carrier impact is minimized and the gate length can be scaled down to gain Idlin.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
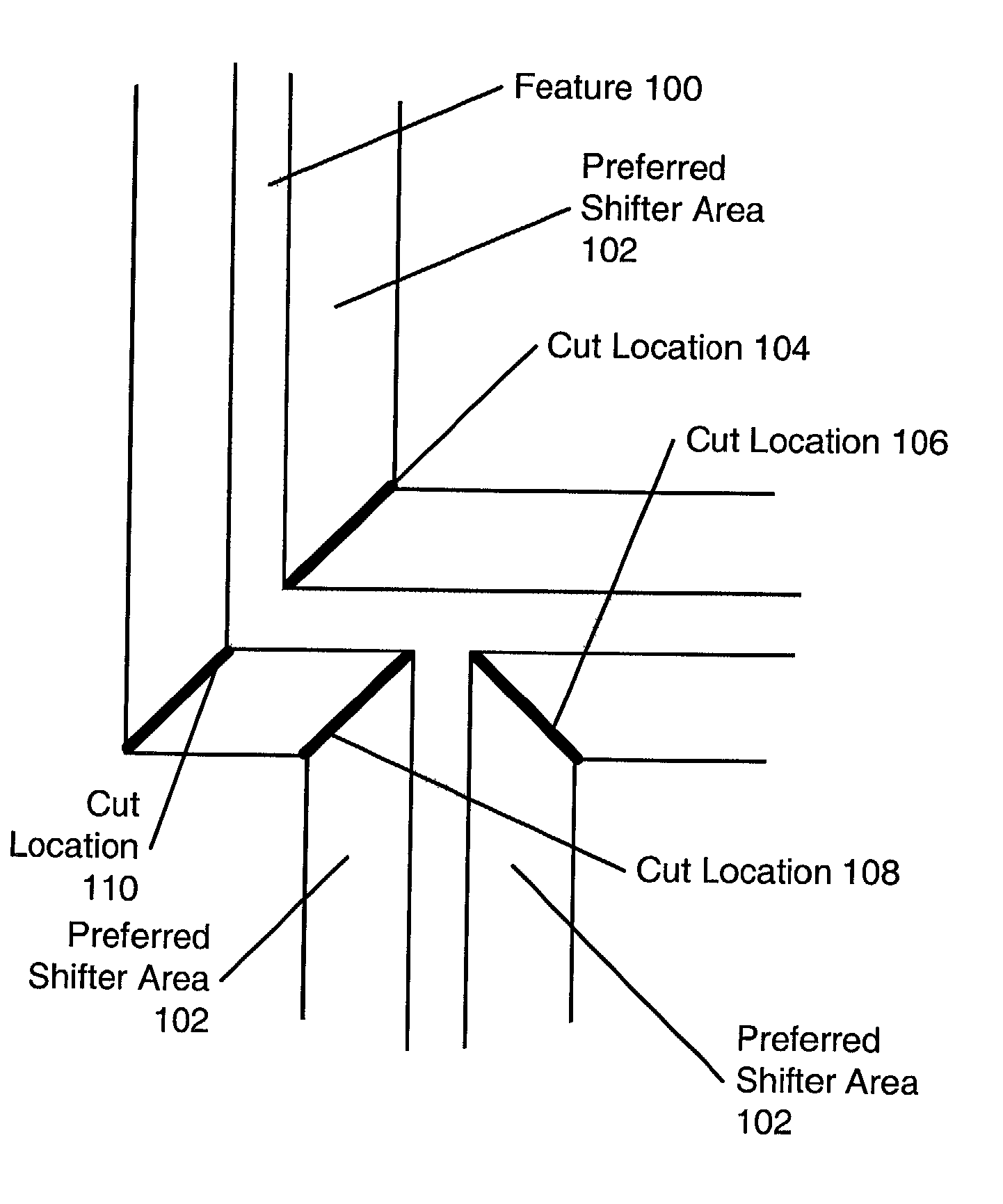
Phase shifting design and layout for static random access memory
InactiveUS20020129327A1Increase productionIncreased circuit densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
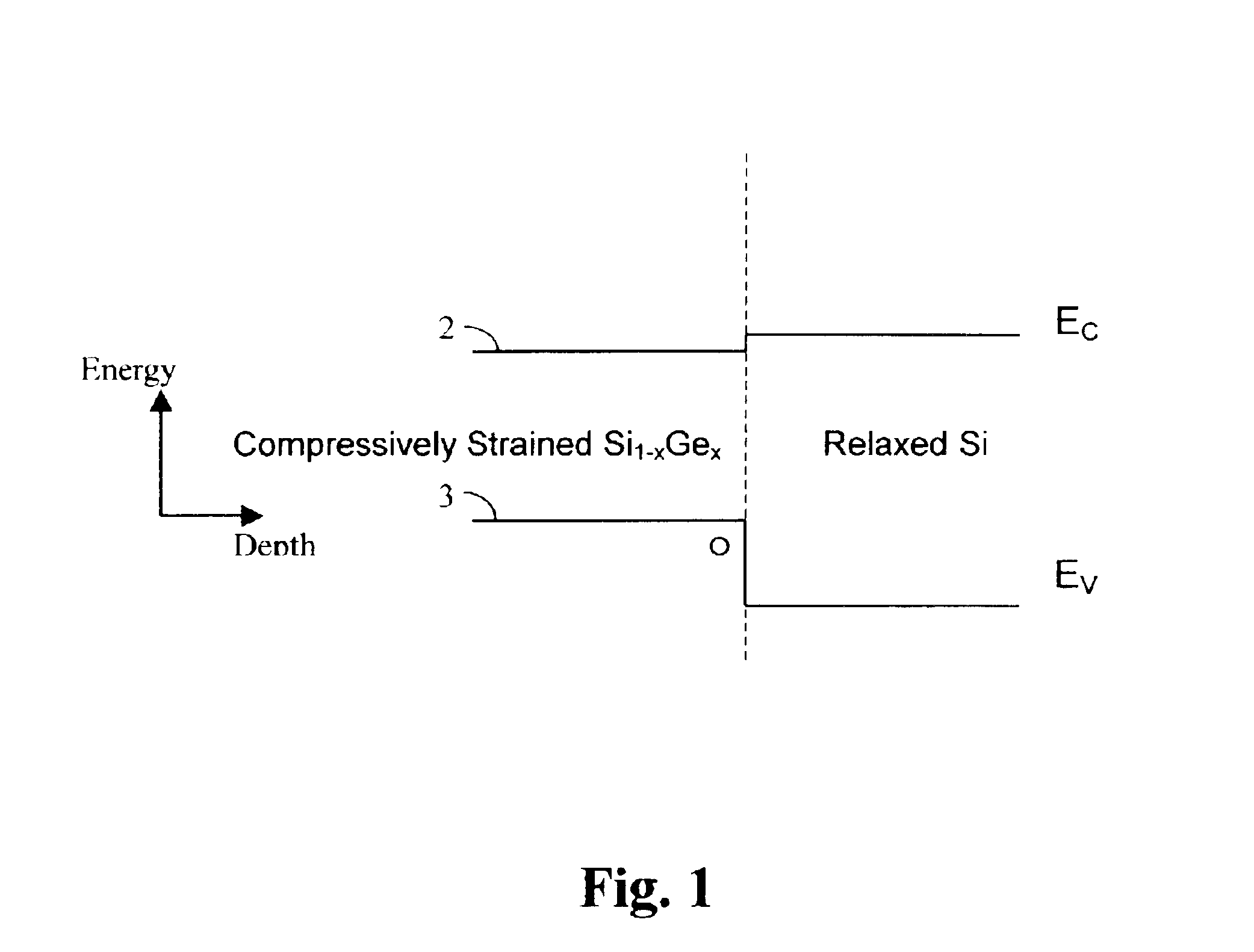
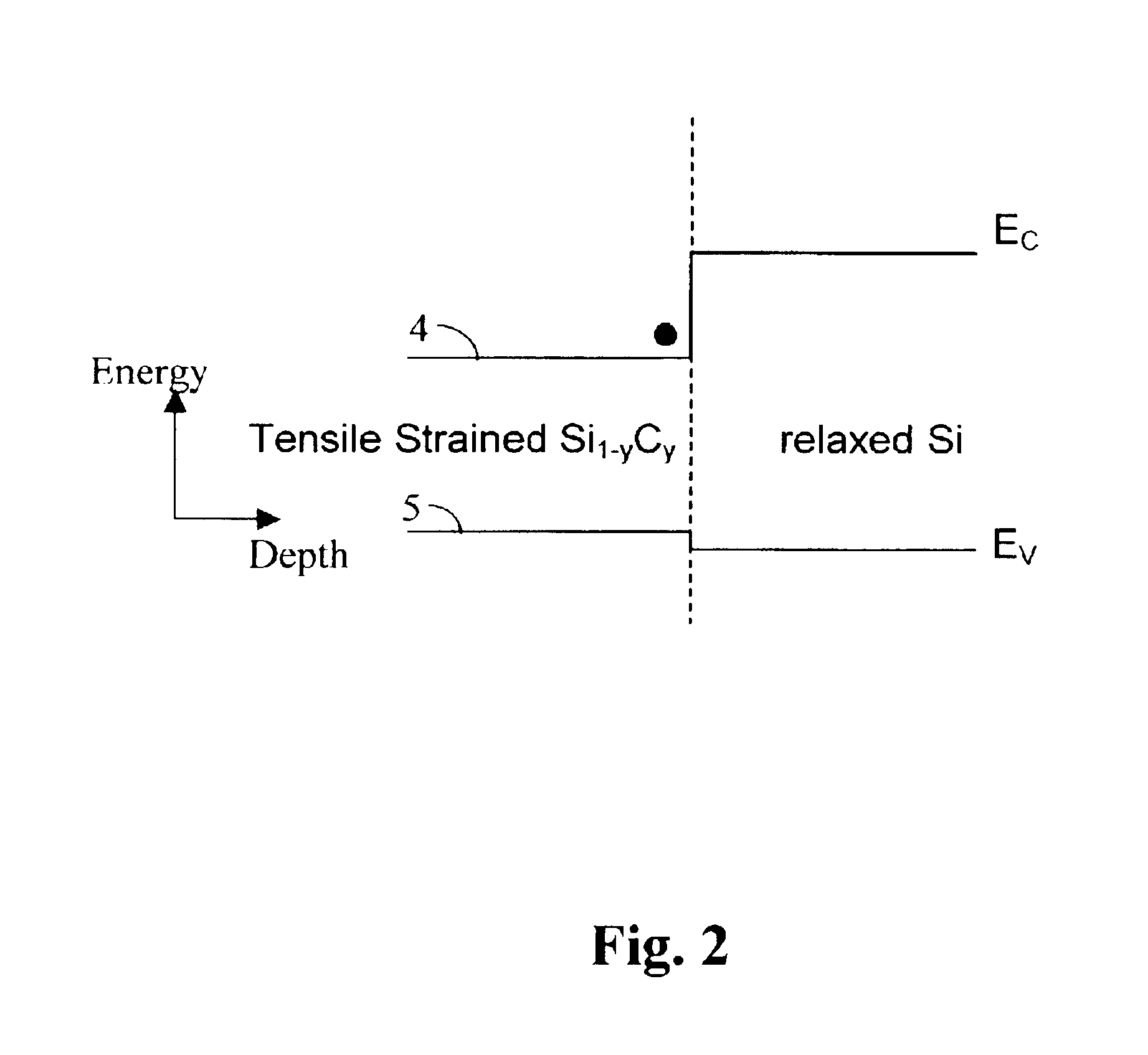
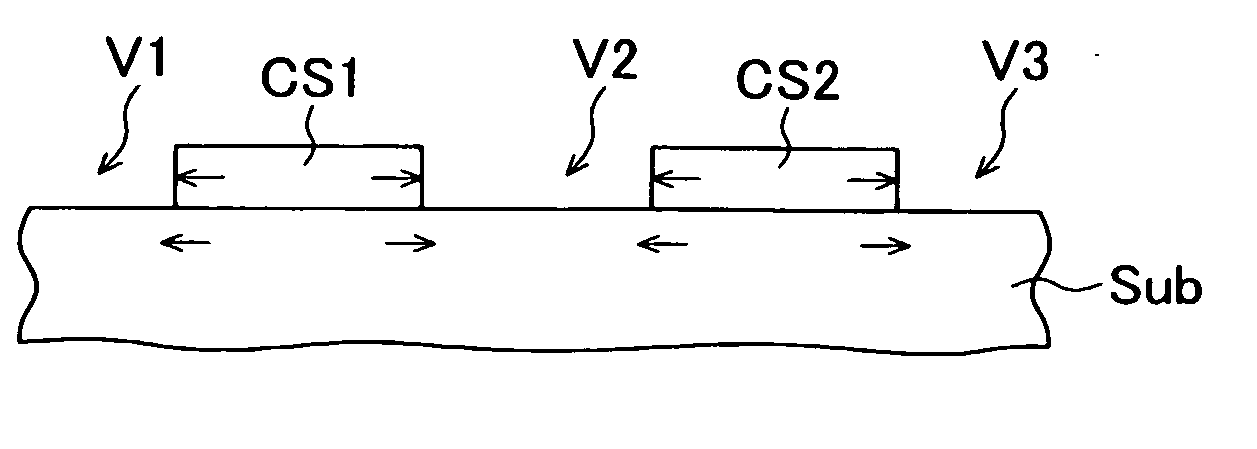
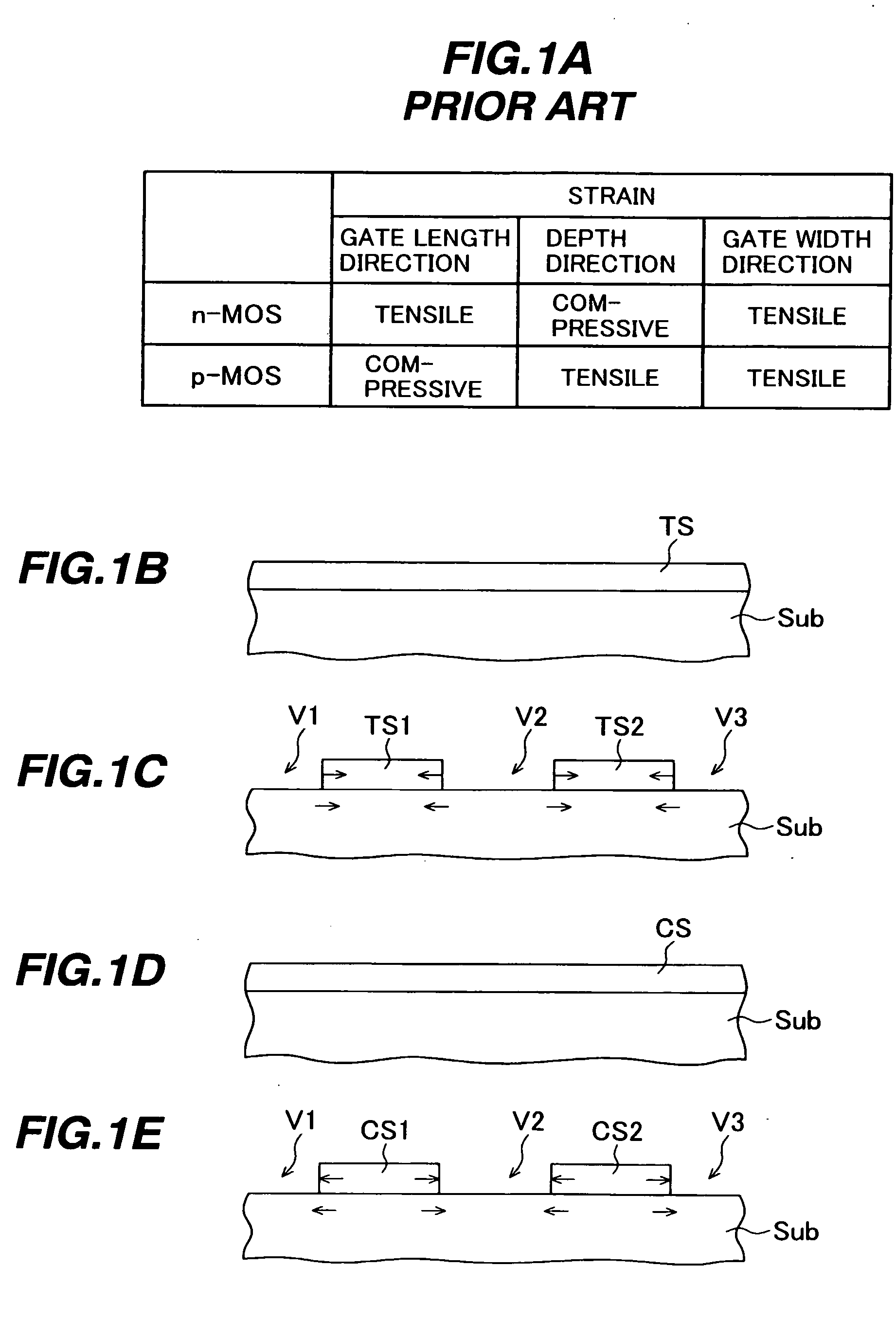
Semiconductor device with strain
ActiveUS20050285137A1Improve performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialSemiconductor
A semiconductor device includes: a semiconductor substrate having a p-MOS region; an element isolation region formed in a surface portion of the semiconductor substrate and defining p-MOS active regions in the p-MOS region; a p-MOS gate electrode structure formed above the semiconductor substrate, traversing the p-MOS active region and defining a p-MOS channel region under the p-MOS gate electrode structure; a compressive stress film selectively formed above the p-MOS active region and covering the p-MOS gate electrode structure; and a stress released region selectively formed above the element isolation region in the p-MOS region and releasing stress in the compressive stress film, wherein a compressive stress along the gate length direction and a tensile stress along the gate width direction are exerted on the p-MOS channel region. The performance of the semiconductor device can be improved by controlling the stress separately for the active region and element isolation region.
Owner:TRINITY SEMICON RES
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device and method of manufacturing the same
A non-volatile semiconductor memory device comprises a plurality of memory cells, each including a semiconductor substrate, a first insulating film formed on the semiconductor substrate, a floating gate formed on the semiconductor substrate with the inclusion of the first insulating film, a second insulating film formed on the floating gate, and a control gate formed on the floating gate with the inclusion of the second insulating film; an element isolation insulating film formed in the semiconductor substrate and extending in a gate-length direction to isolate between memory cells adjoining in a gate-width direction; and an air gap formed on the element isolation insulating film and between floating gates adjoining in the gate-width direction.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Multiple-gate MOSFET device with lithography independent silicon body thickness and methods for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20050093028A1Suppression of short channel effectsAvoidance and mitigationTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETSemiconductor materials
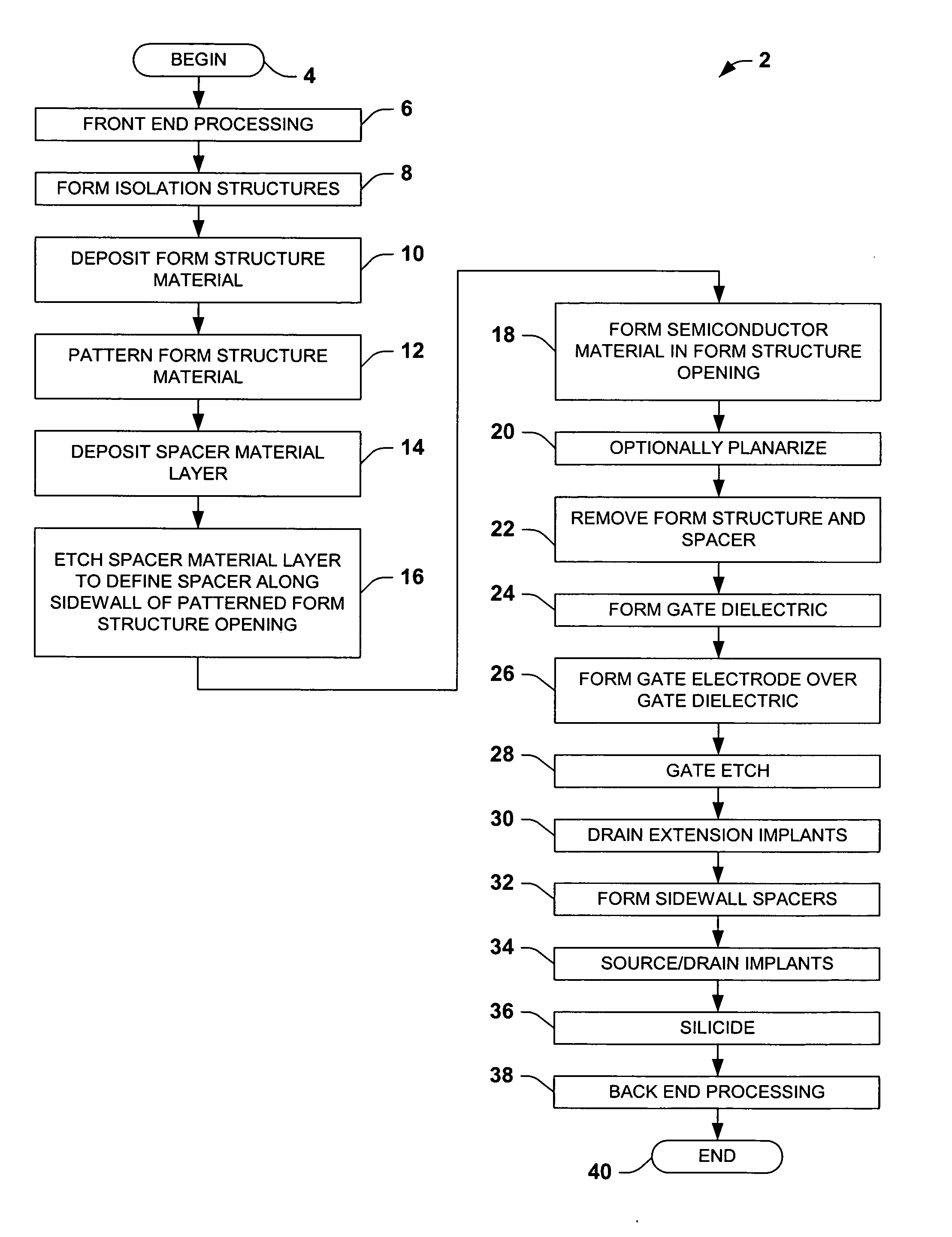
Multi-gate MOS transistors and fabrication methods are described, in which the transistor semiconductor body thickness or width is lithography independent, allowing scaled triple and quad-gate devices having semiconductor bodies smaller than a lateral gate length dimension. A form structure is provided over a semiconductor wafer starting structure, and spacers are formed along one or more sidewalls of an opening in the form structure. A semiconductor material is deposited in the opening by epitaxial growth or other deposition process, and the form structure and the spacer are removed. A gate structure is then formed along the top and sides of a central portion of the formed semiconductor body. The spacer may be L-shaped, providing an undercut or recess at the bottom of the semiconductor body sidewall, and the gate may be formed in the undercut area to allow fabrication of more than three gates.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
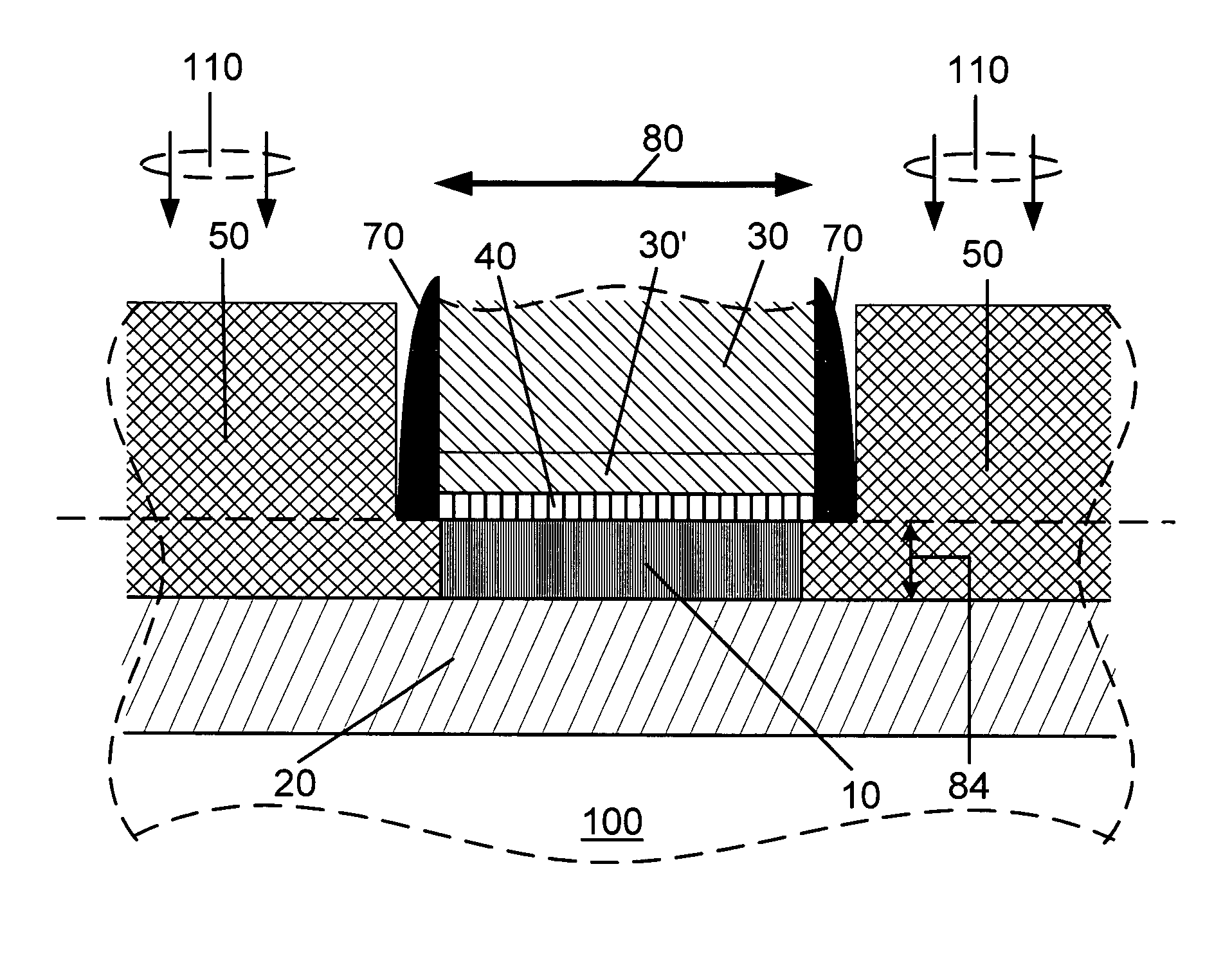
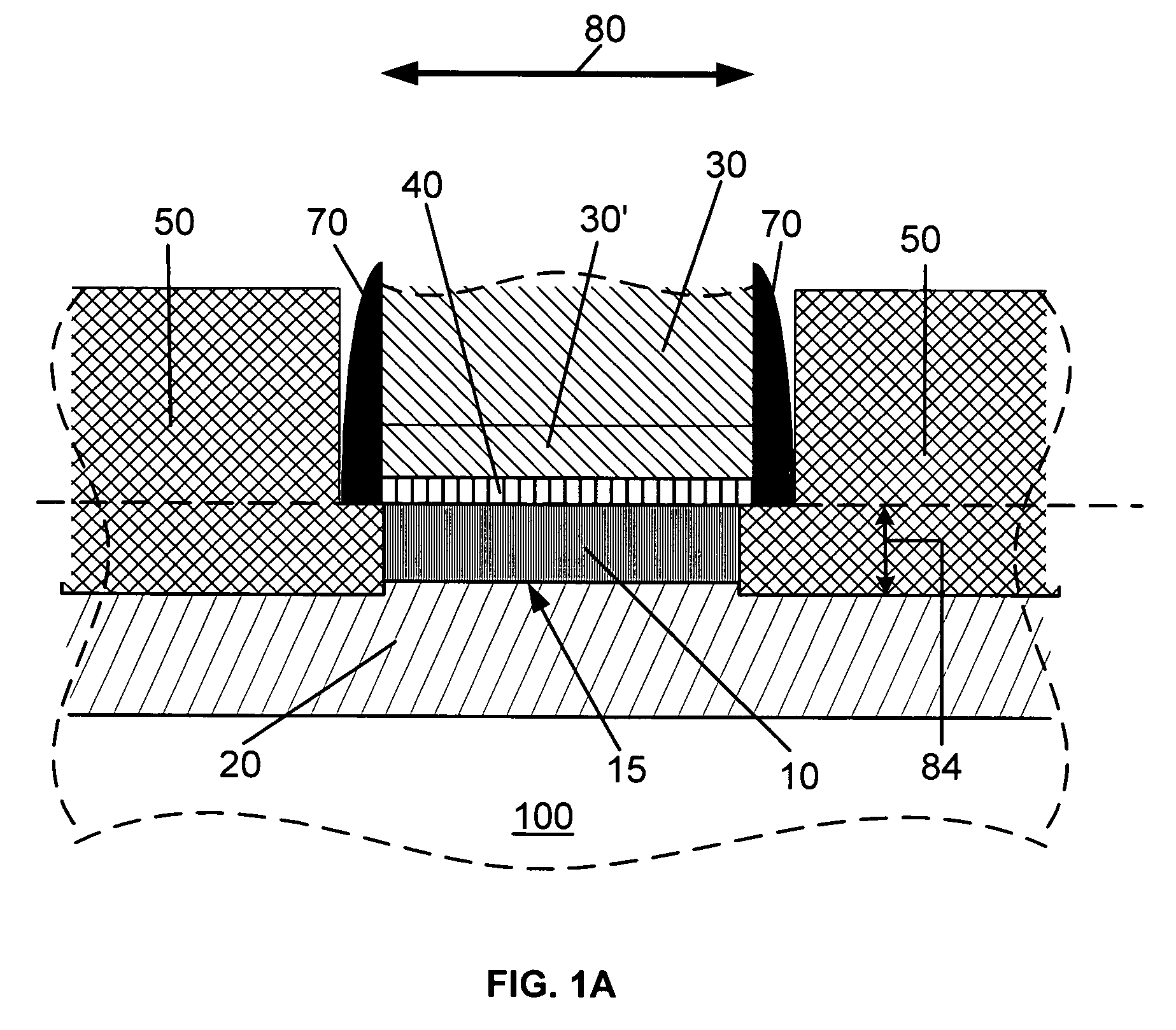
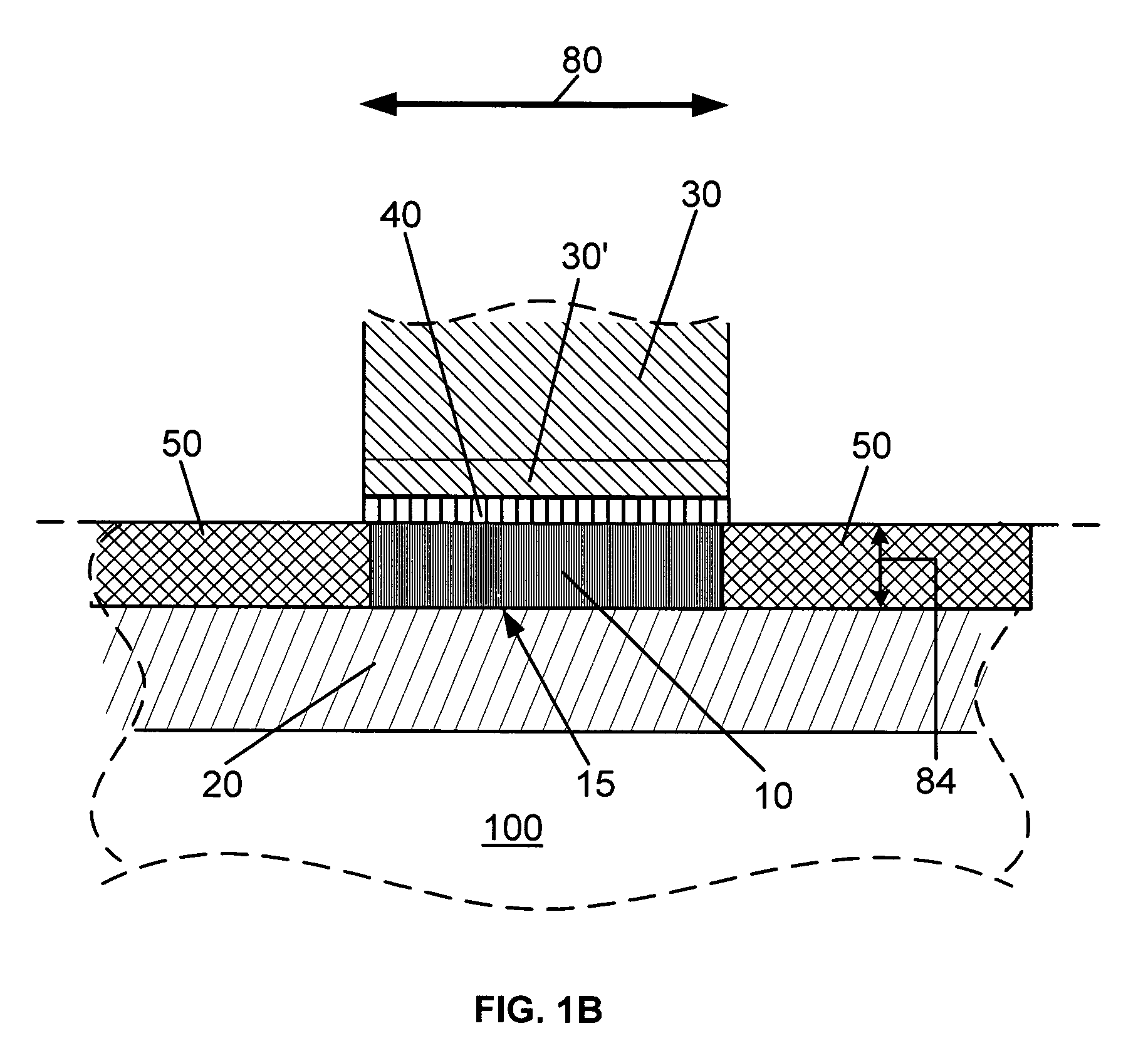
Method and apparatus for forming an SOI body-contacted transistor
ActiveUS20050127442A1Minimize parasitic capacitanceMinimize gate electrode leakageTransistorSolid-state devicesBody contactParasitic capacitance
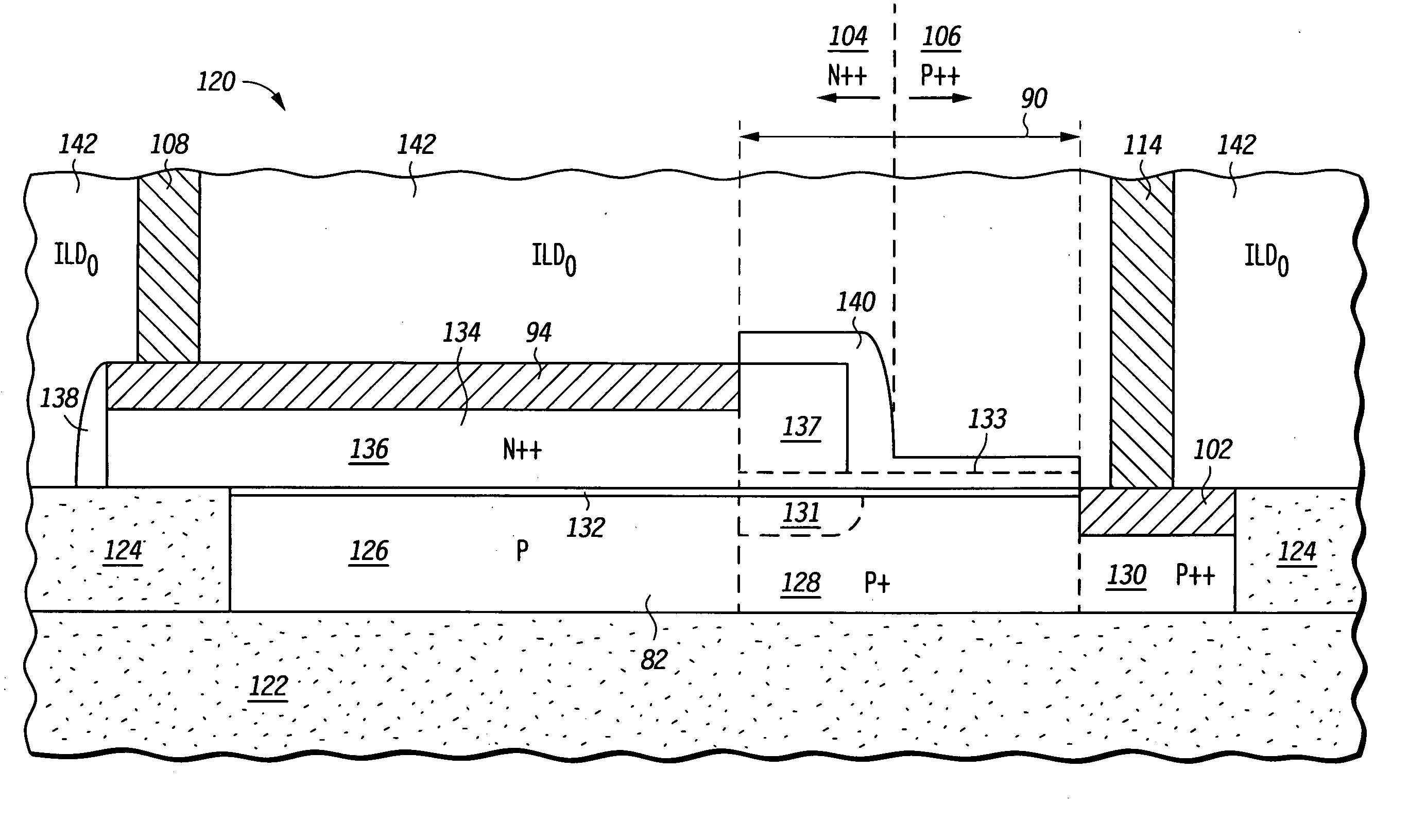
A method for forming a silicon-on-insulator transistor (80) includes forming an active region (82) overlying an insulating layer (122), wherein a portion of the active region provides an intrinsic body region (126). A body tie access region (128) is also formed within the active region, overlying the insulating layer and laterally disposed adjacent the intrinsic body region, making electrical contact to the intrinsic body region. A gate electrode (134) is formed overlying the intrinsic body region for providing electrical control of the intrinsic body region, the gate electrode extending over a portion (137) of the body tie access region. The gate electrode is formed having a substantially constant gate length (88) along its entire width overlying the intrinsic body region and the body tie access region to minimize parasitic capacitance and gate electrode leakage. First and second current electrodes (98,100) are formed adjacent opposite sides of the intrinsic body region. In addition, a body tie diffusion (130) is formed within the active region and laterally offset from the body tie access region and electrically coupled to the body tie access region.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com