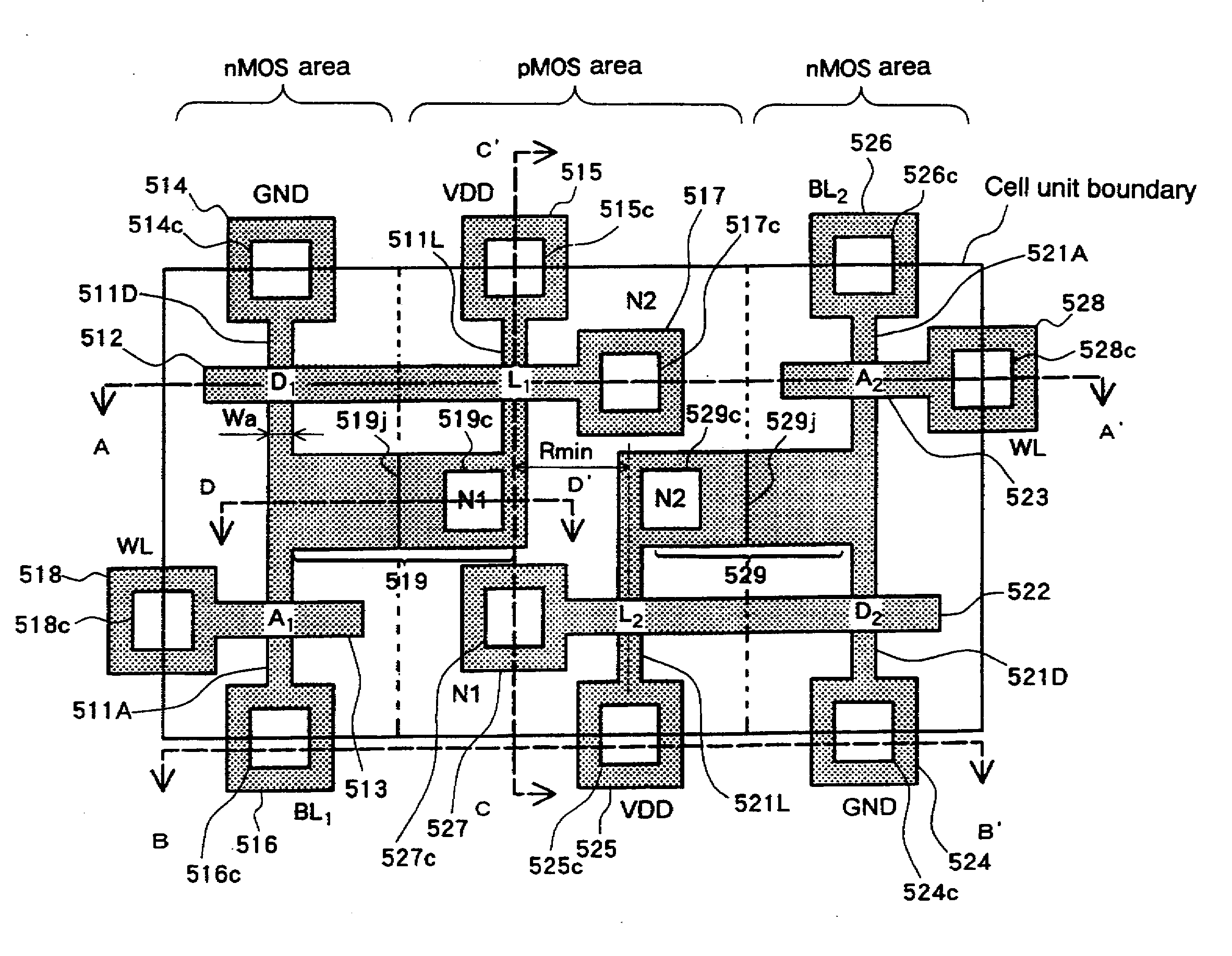
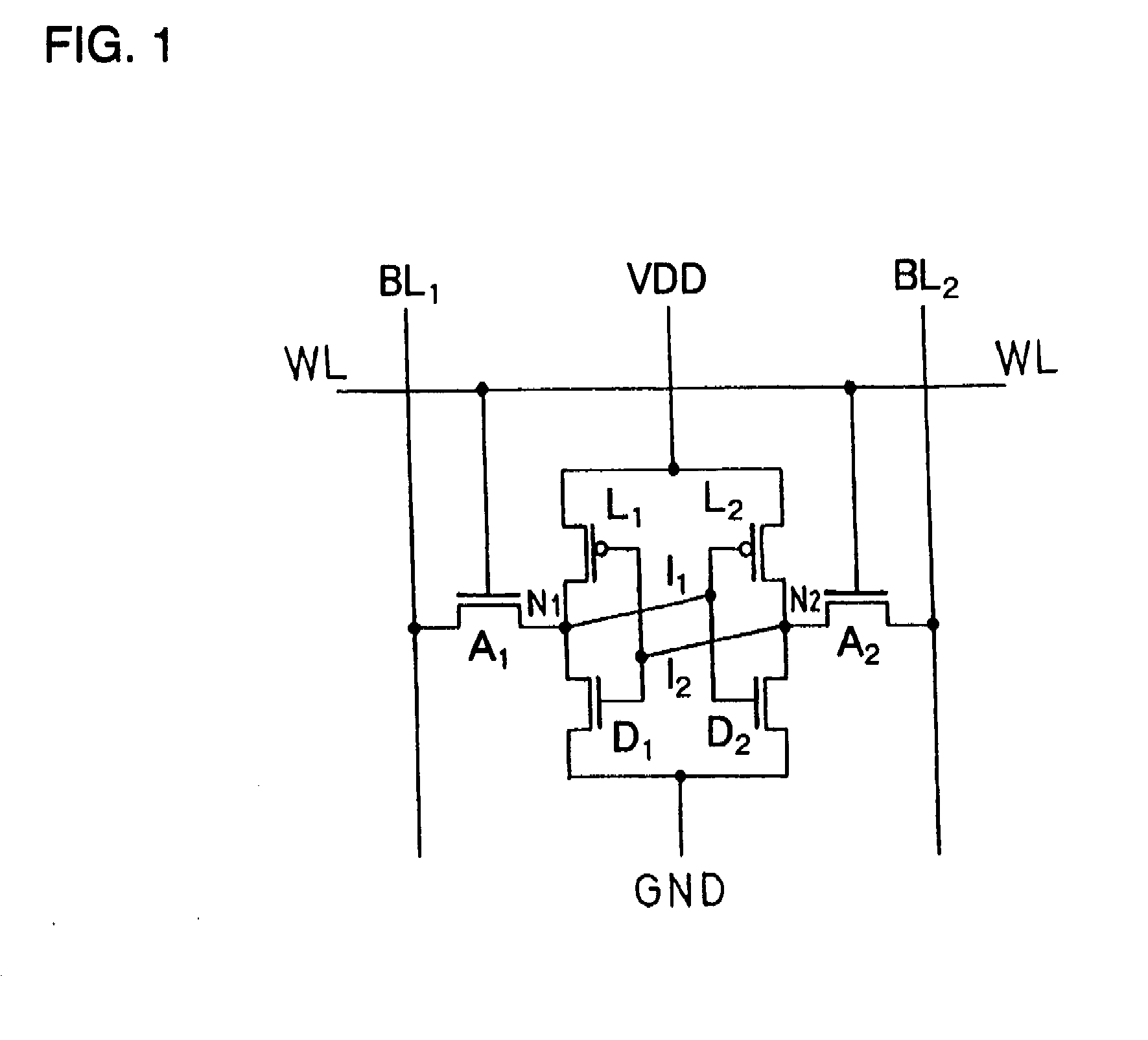
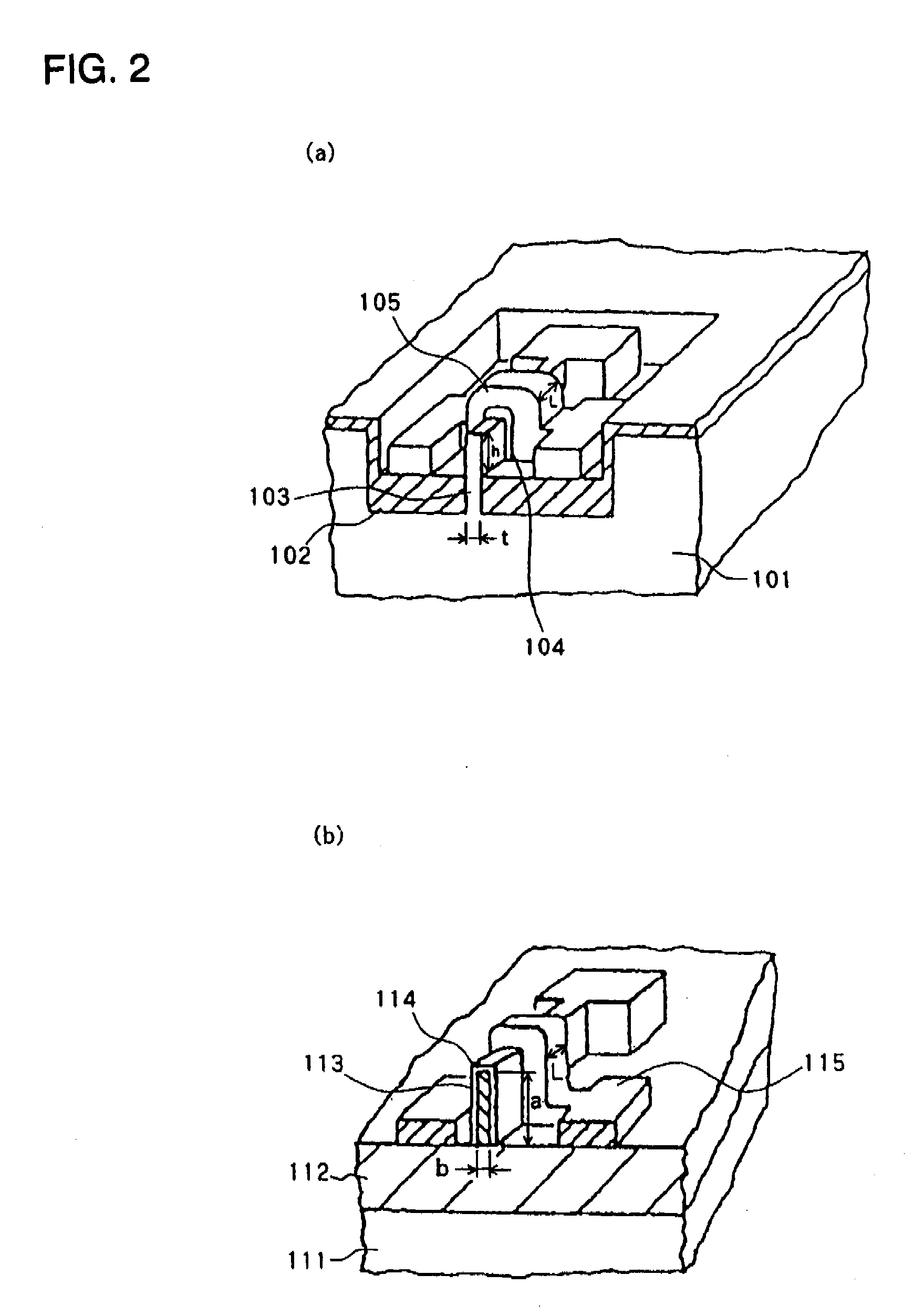
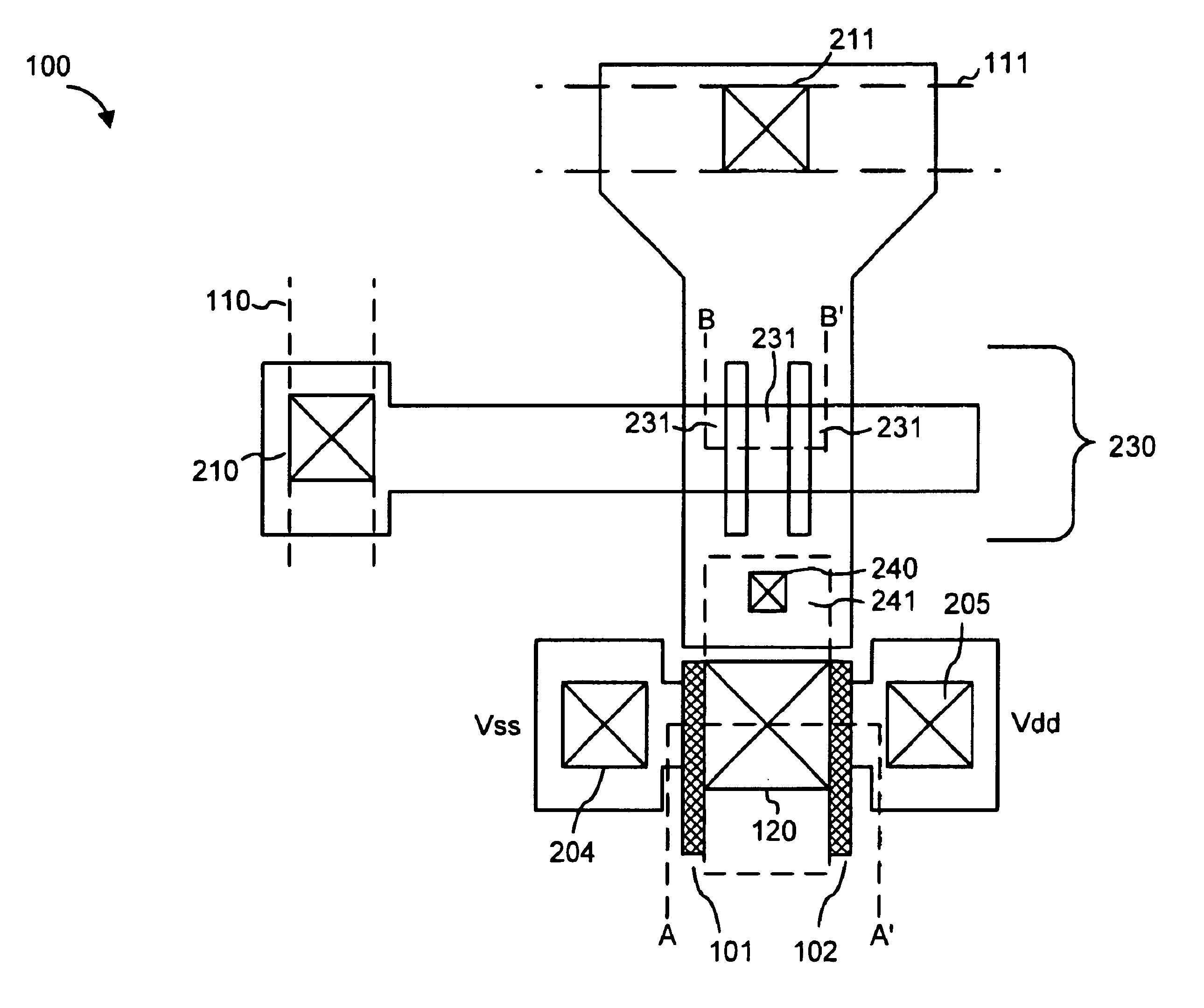
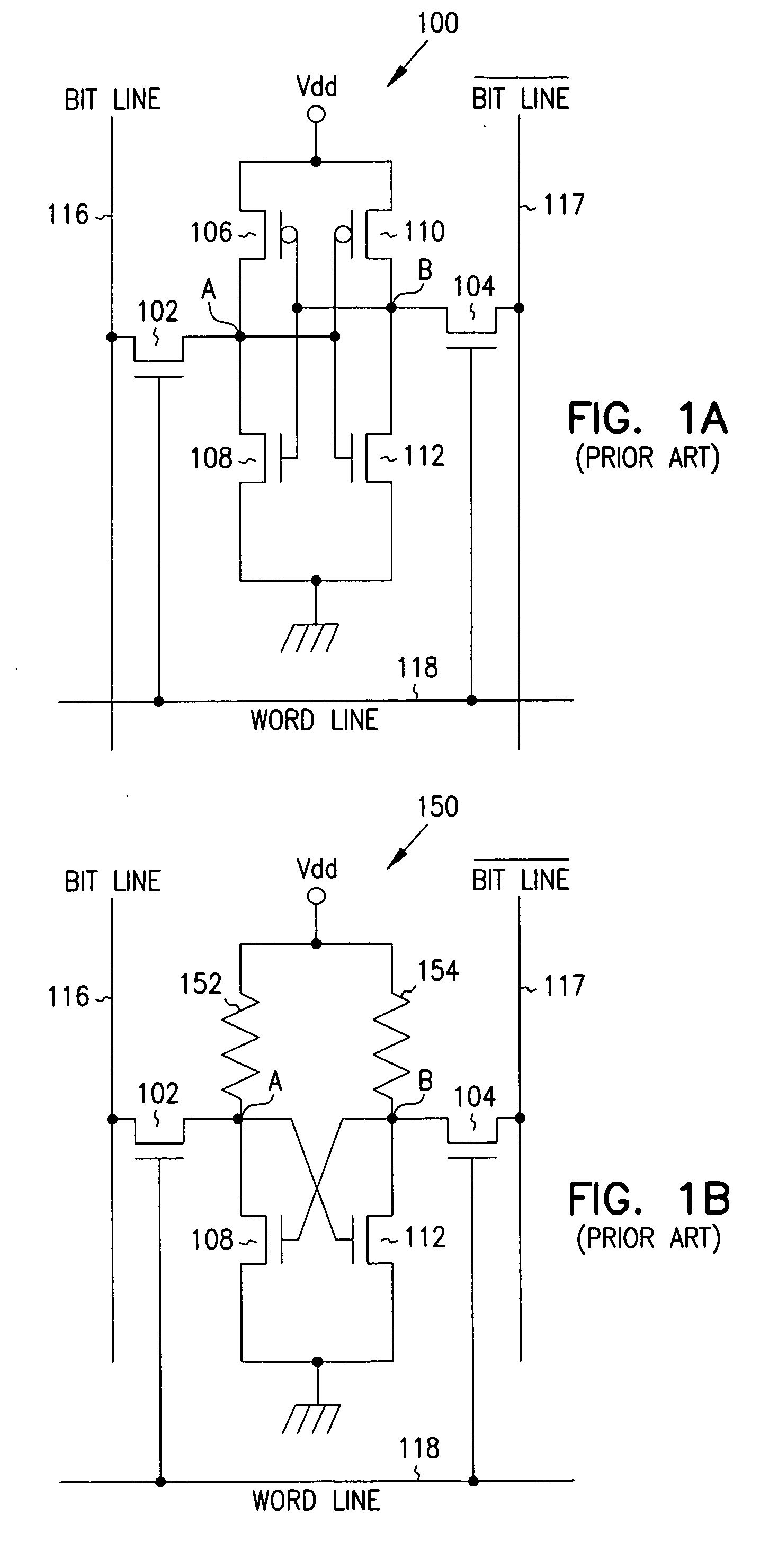
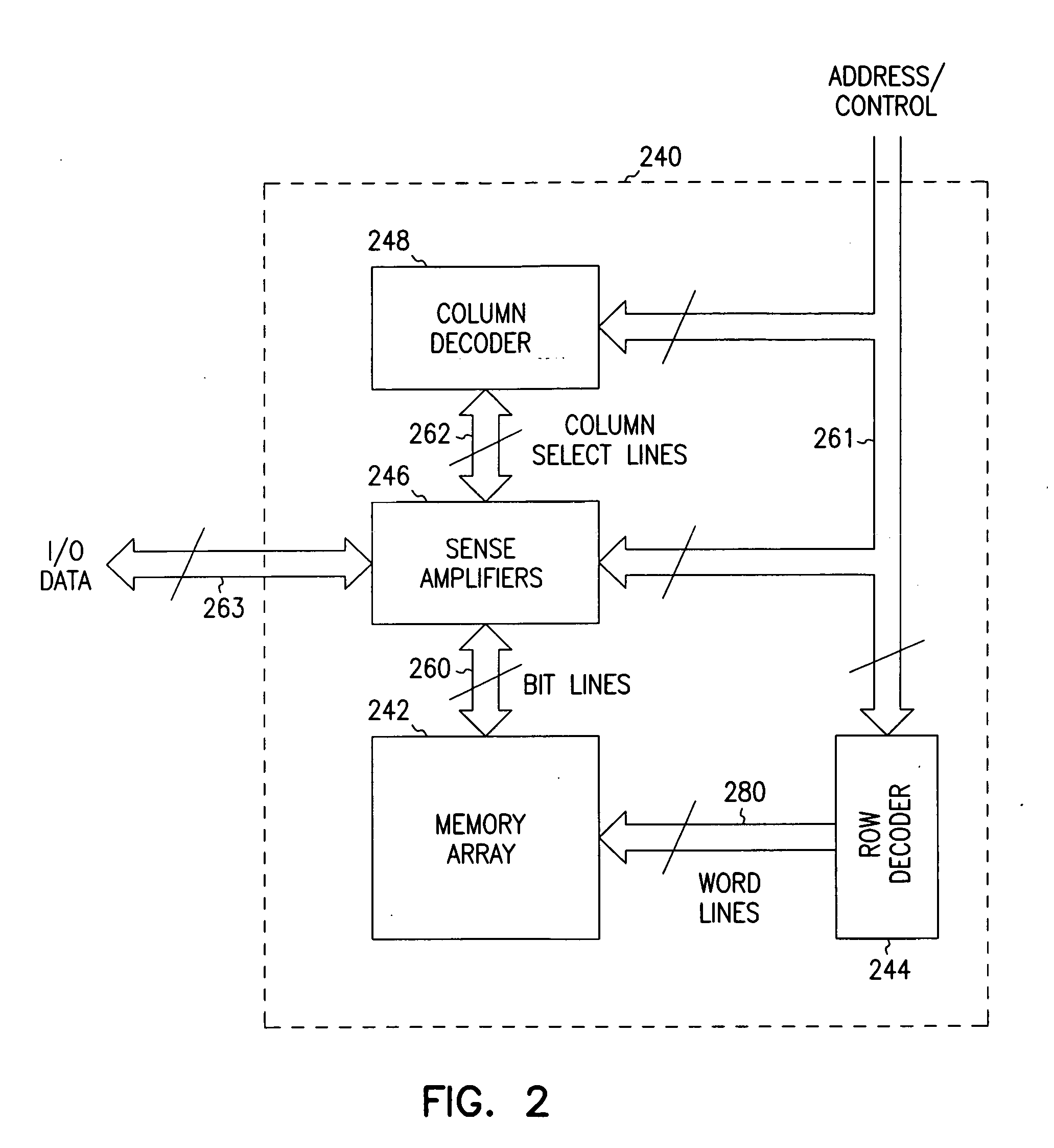
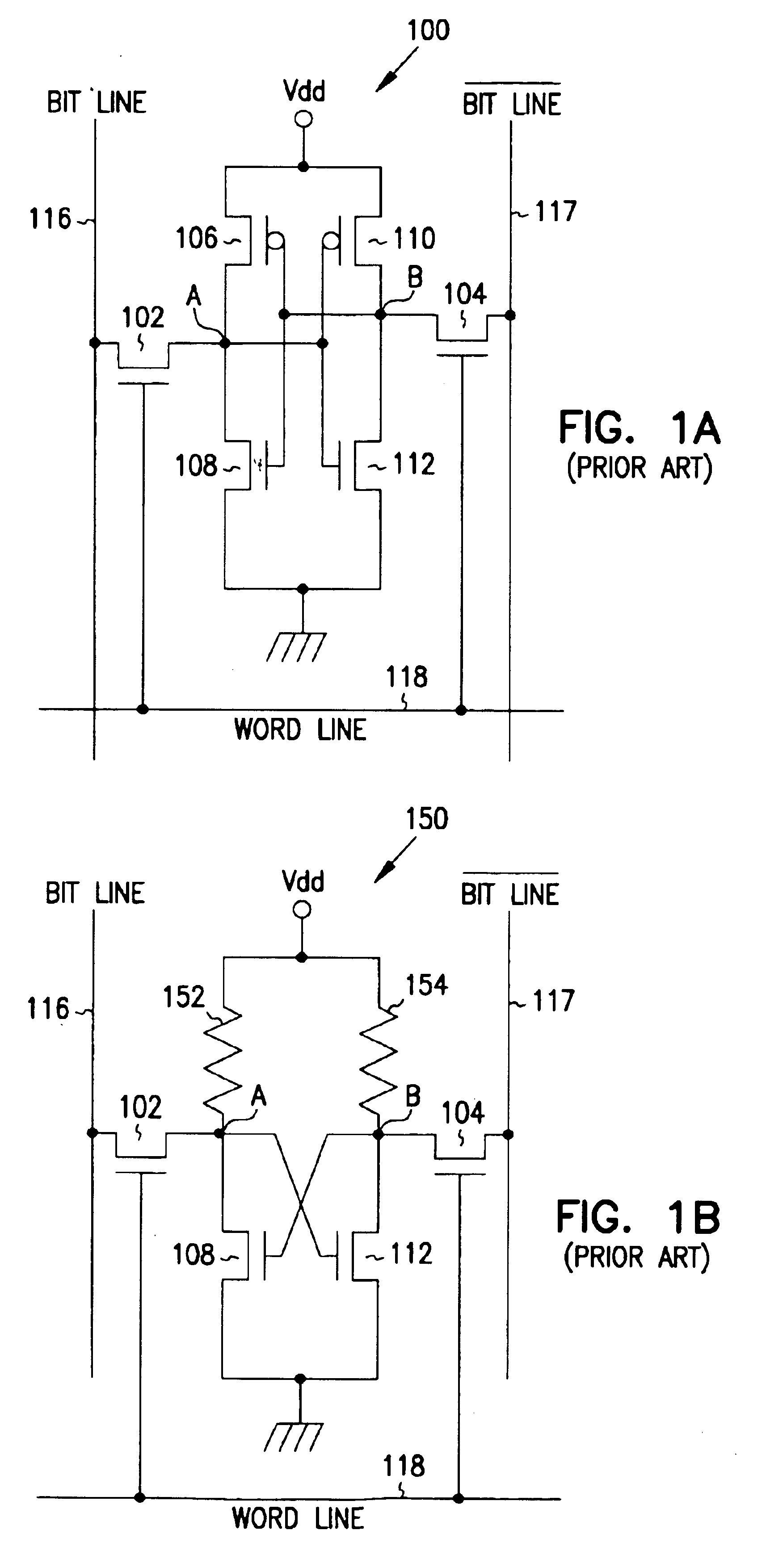
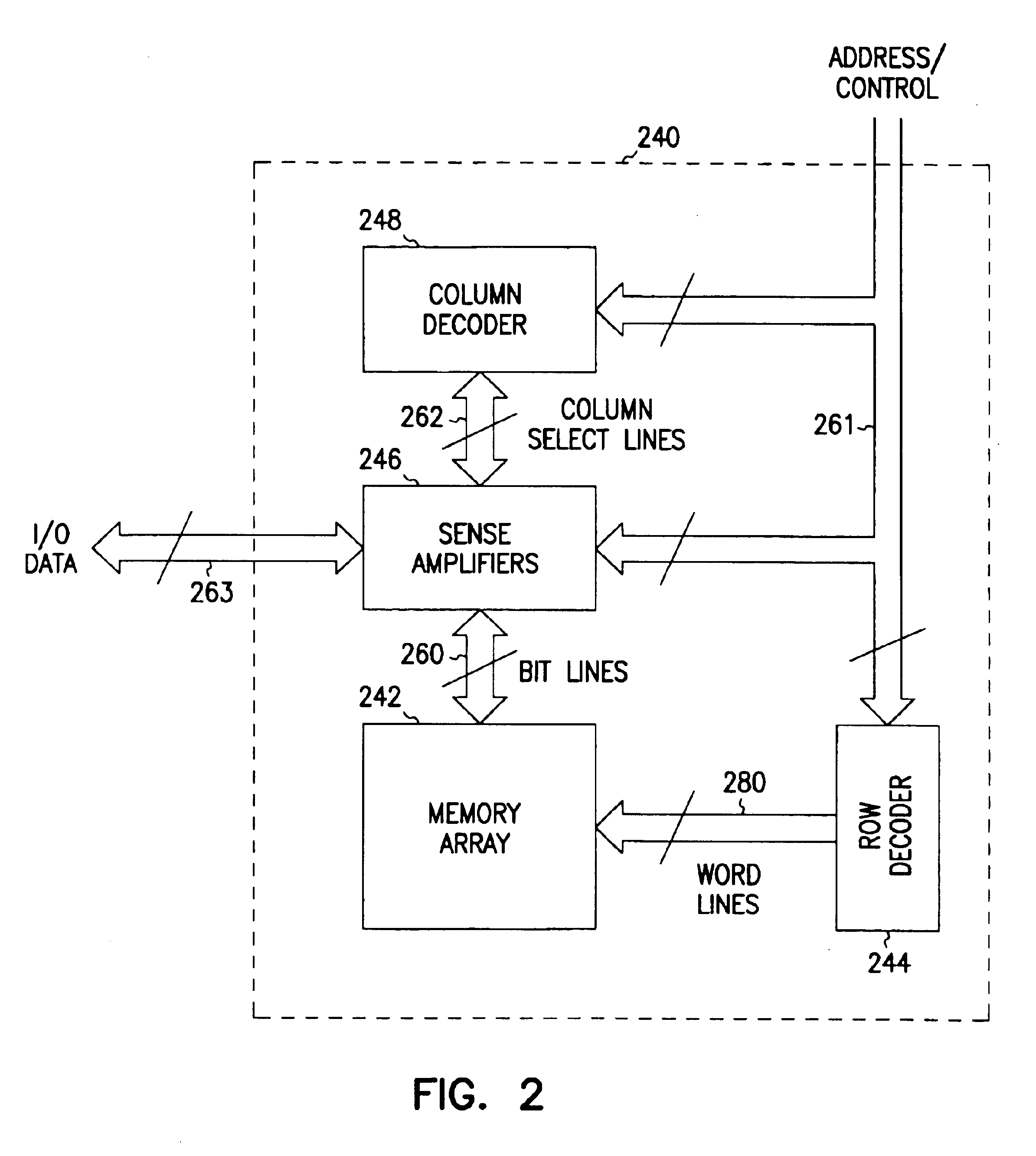
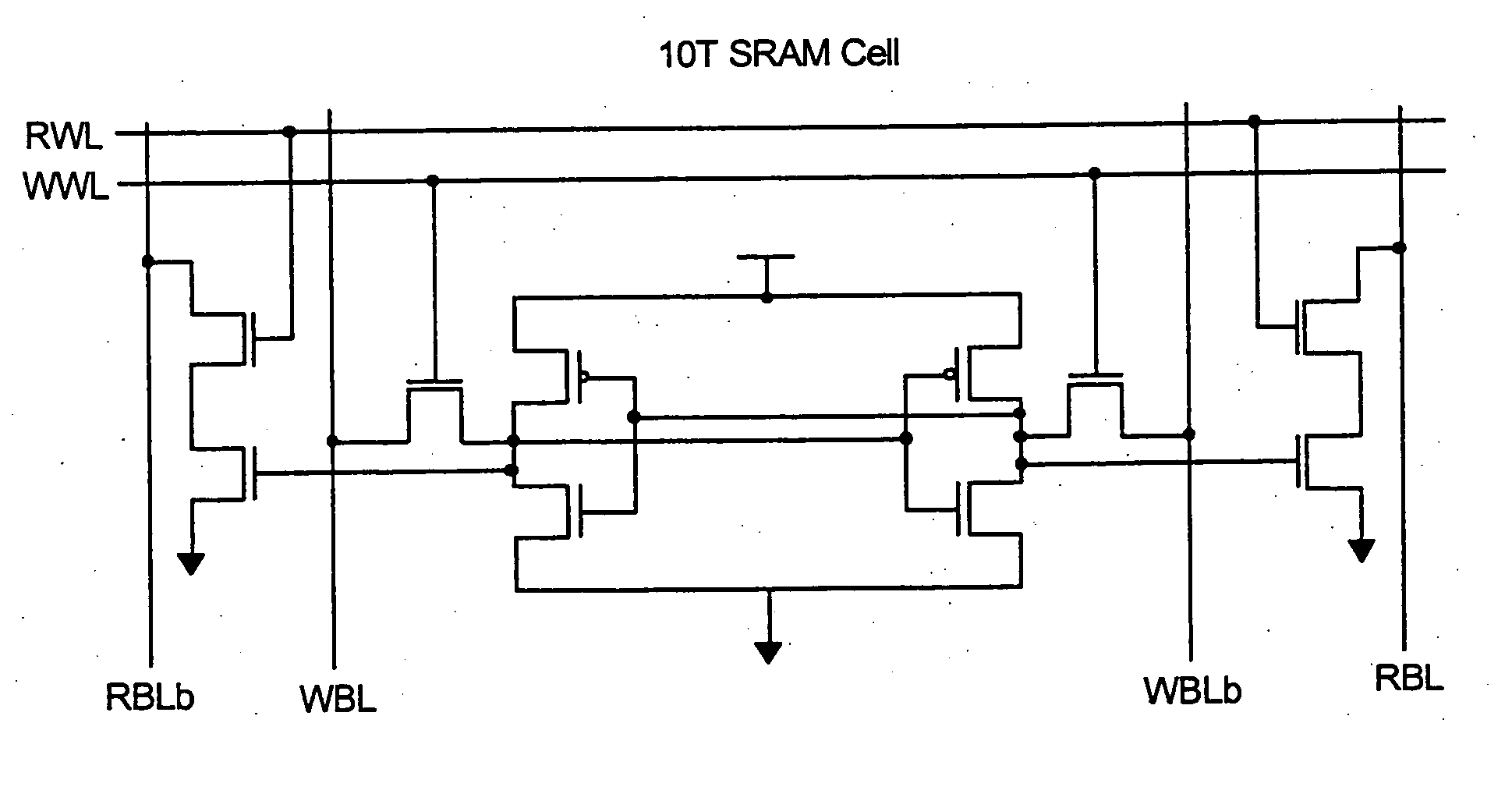
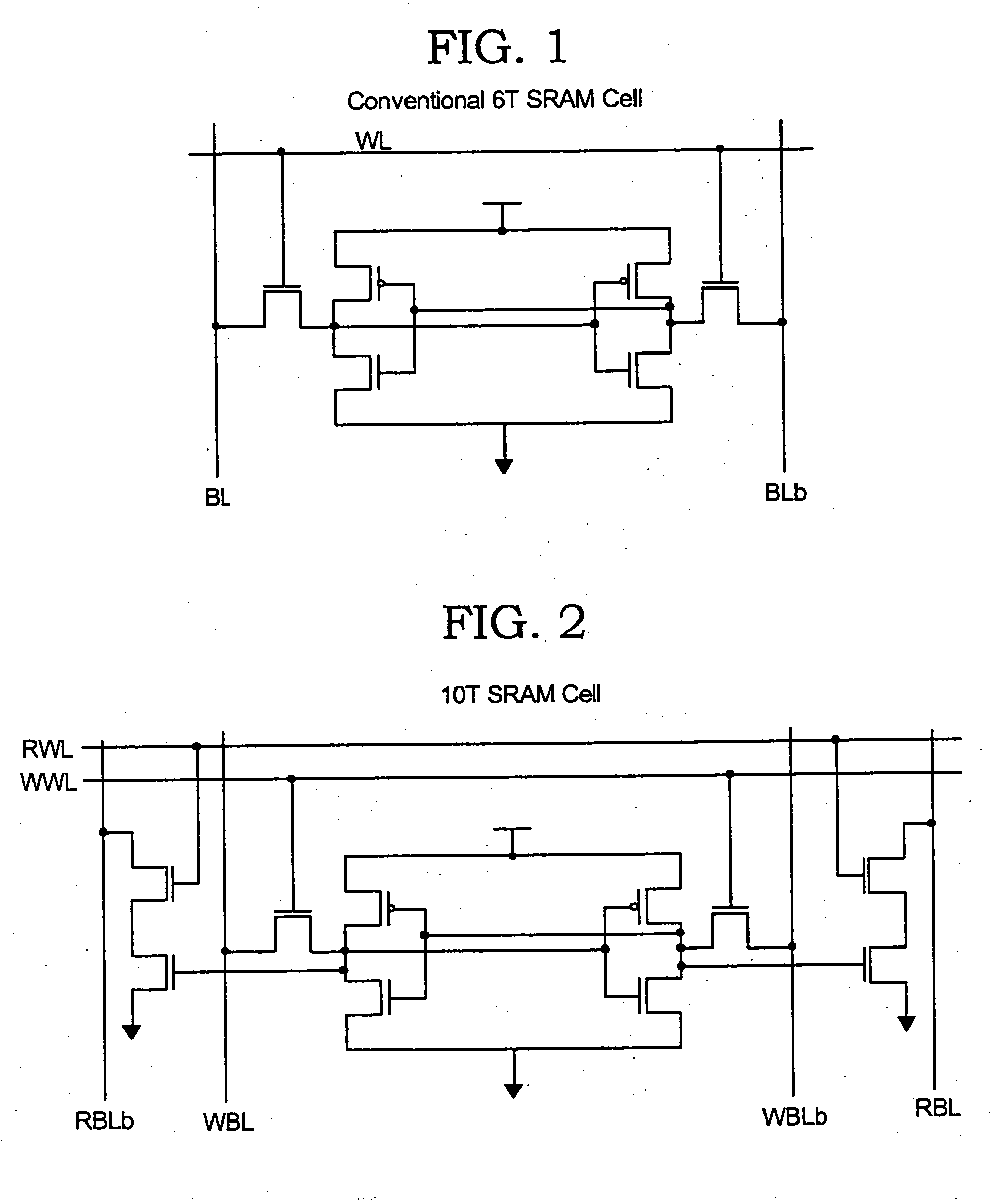
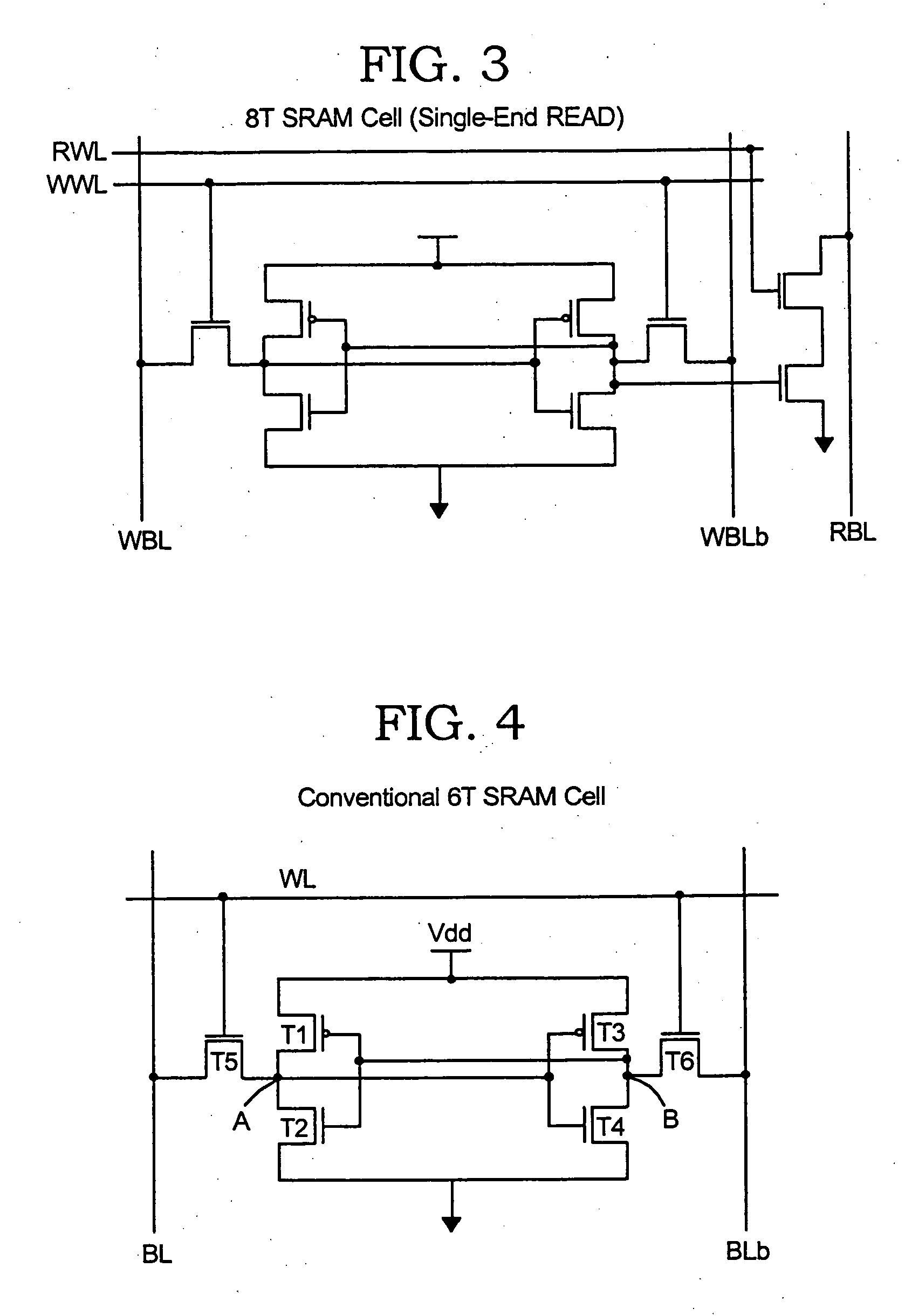
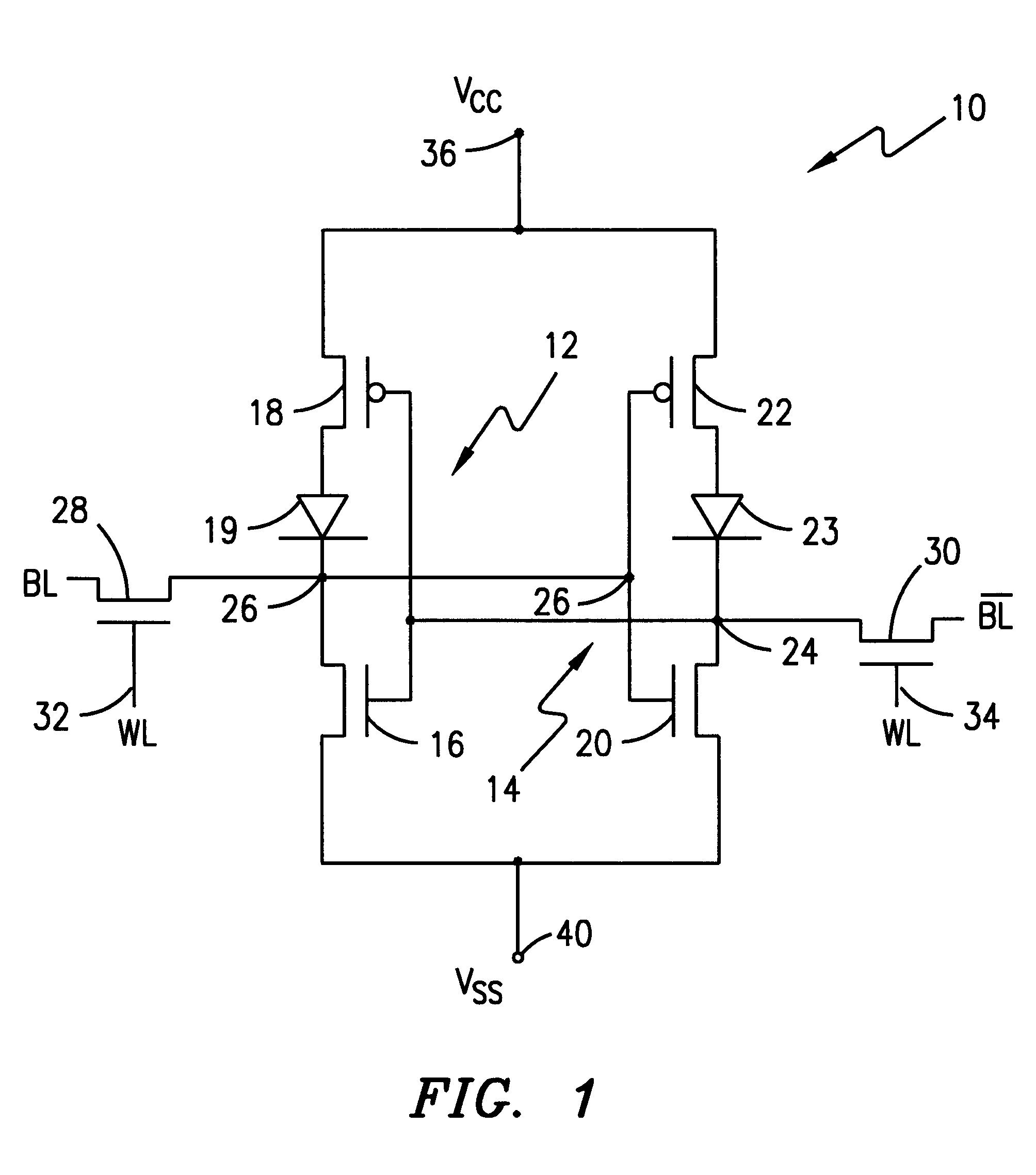
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
950 results about "Sram cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
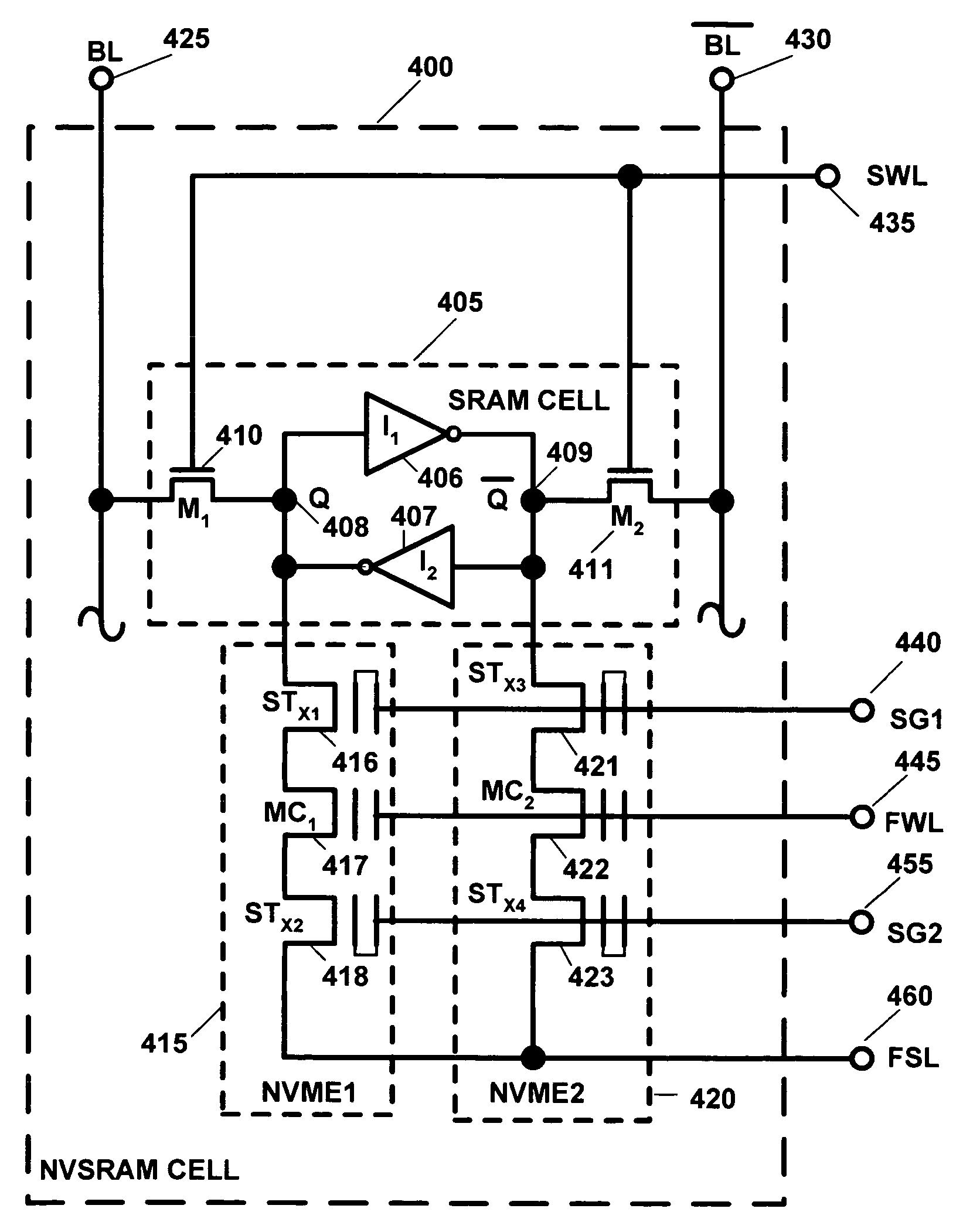
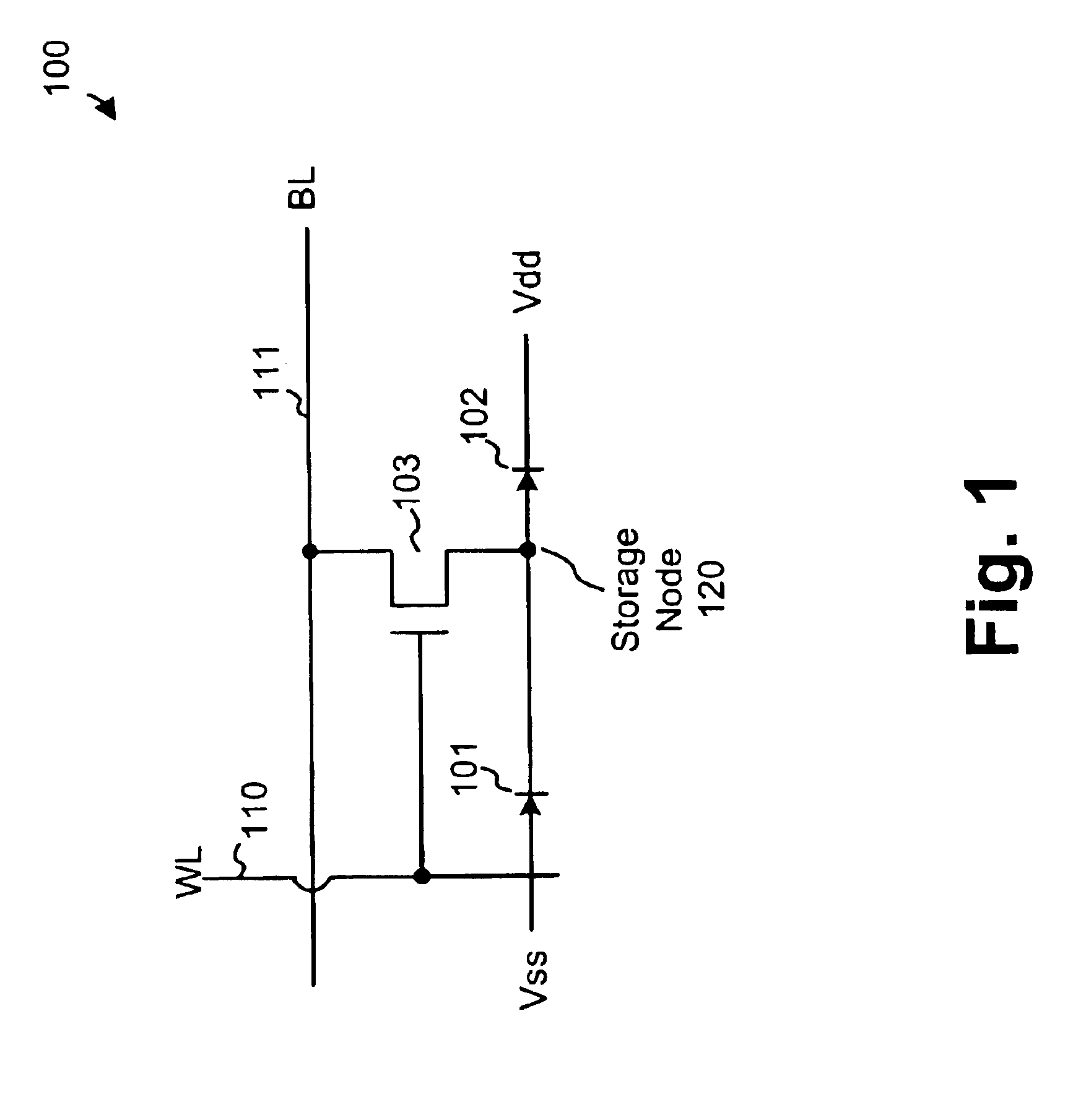
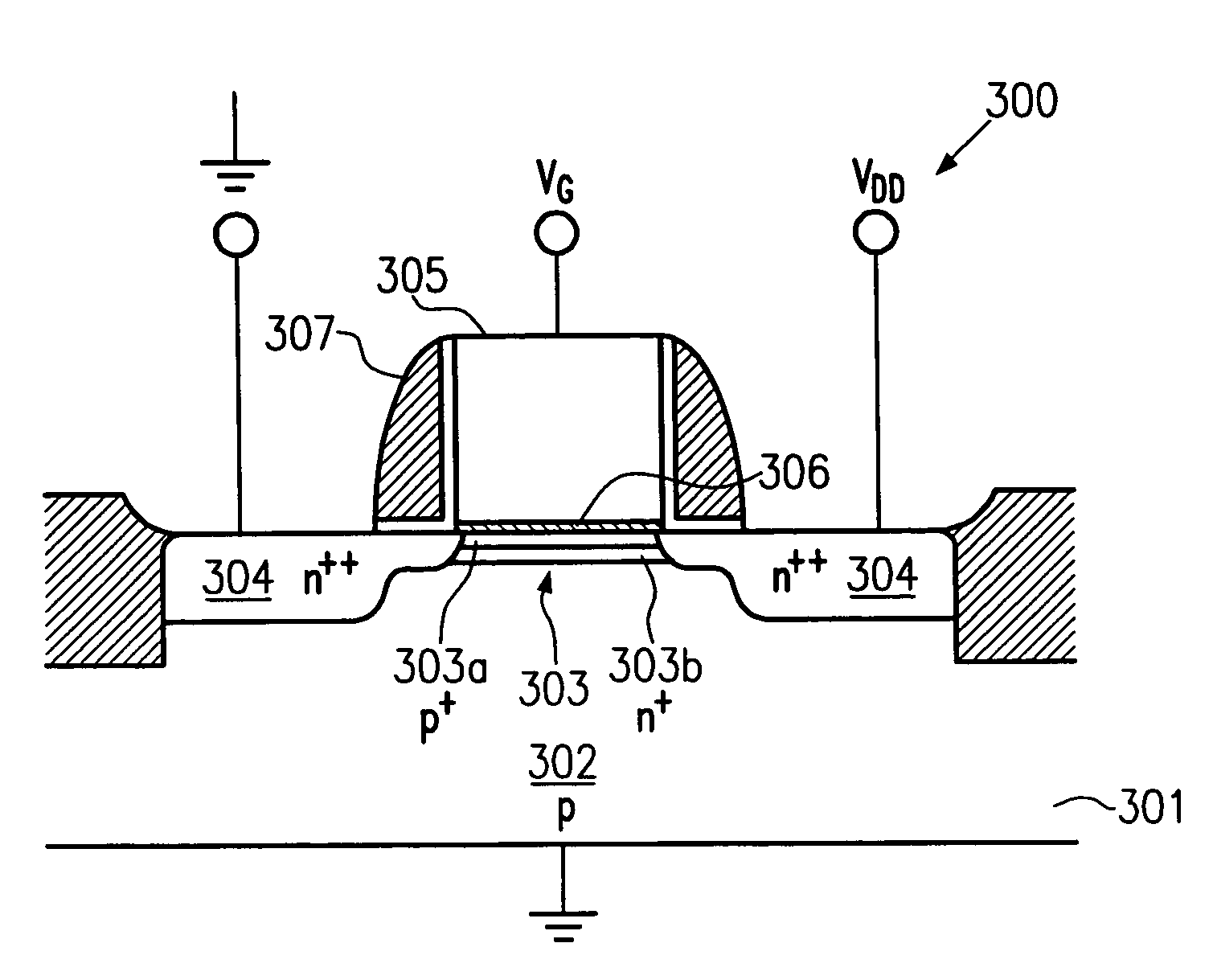
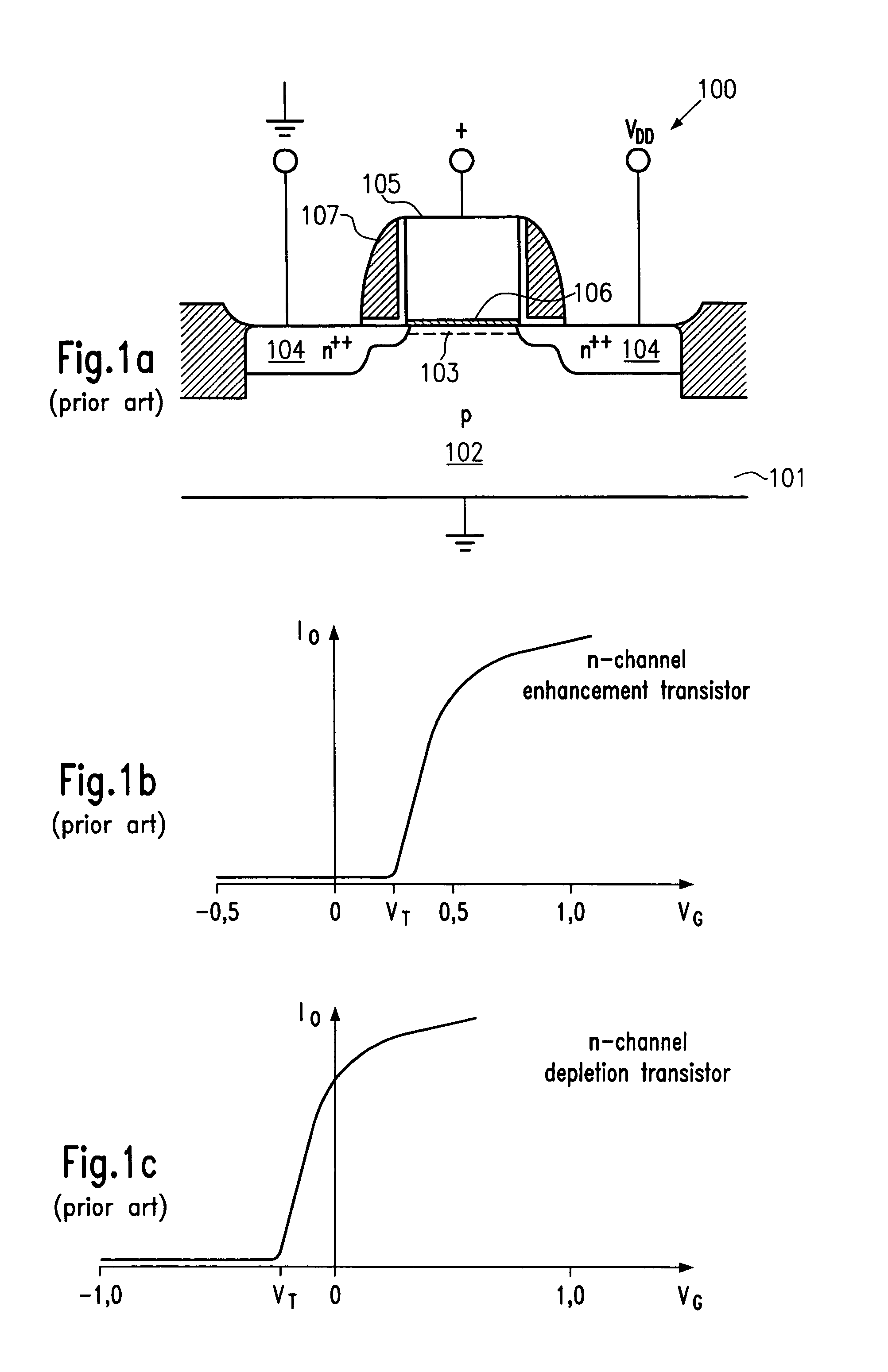
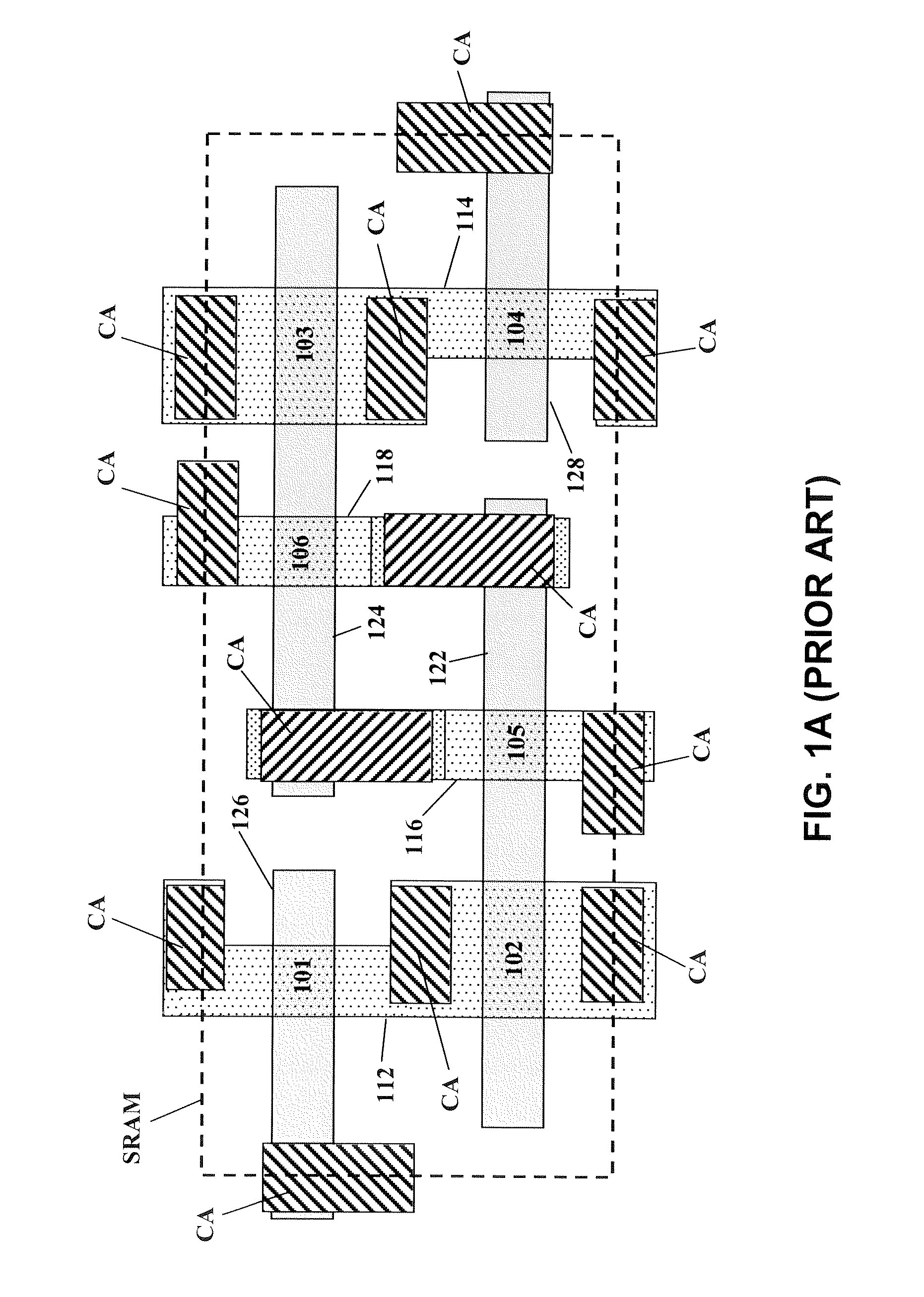
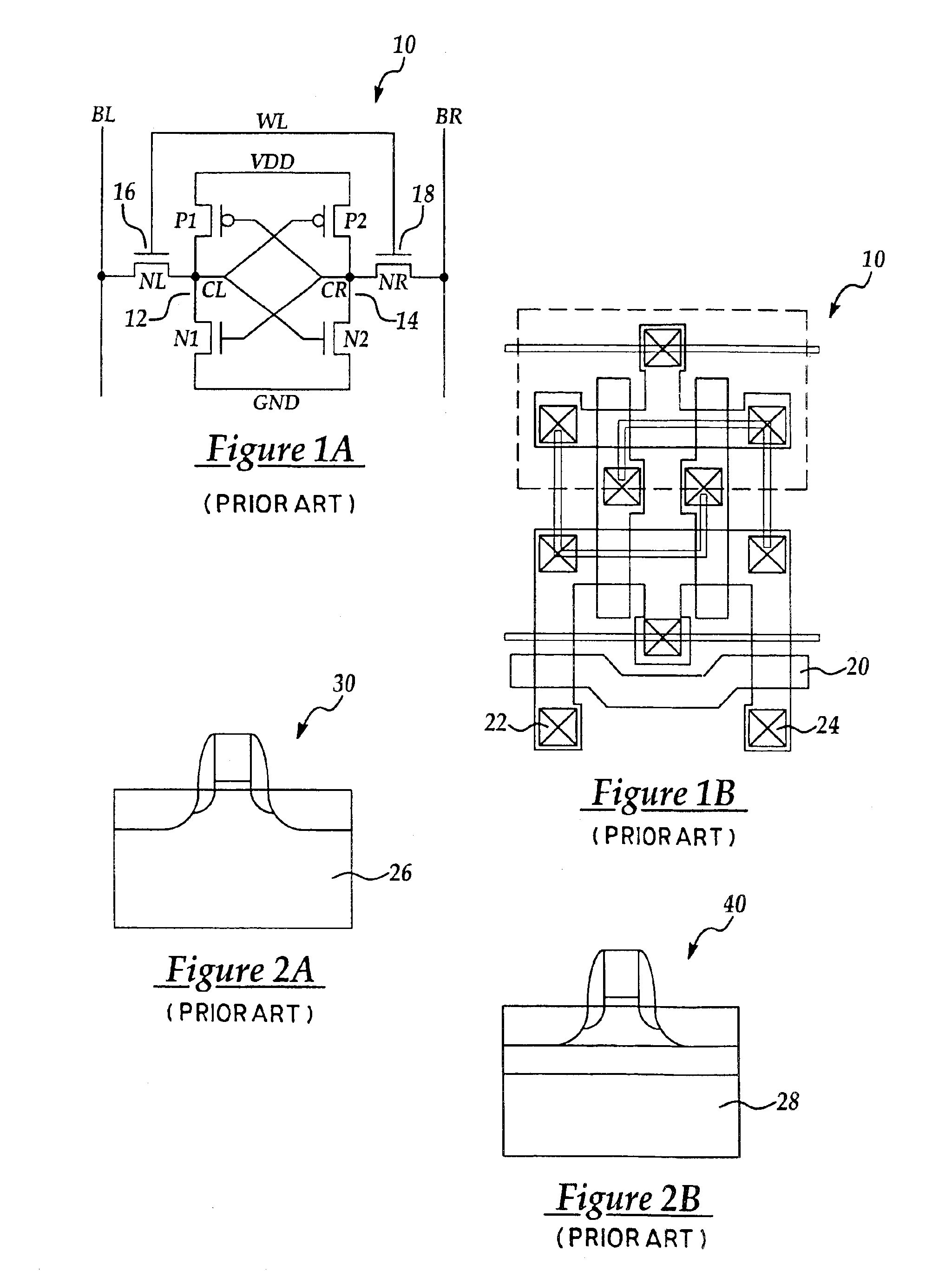
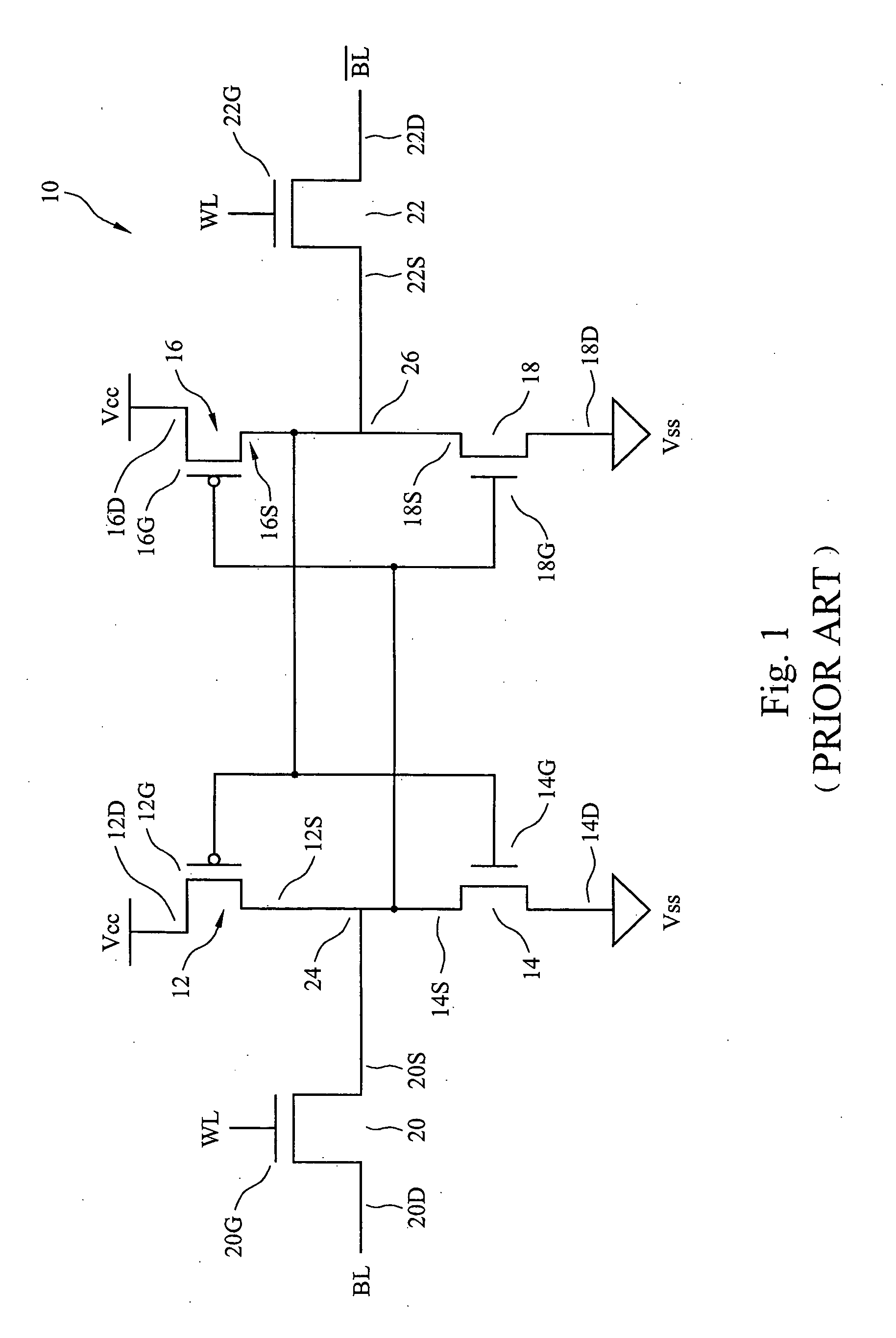
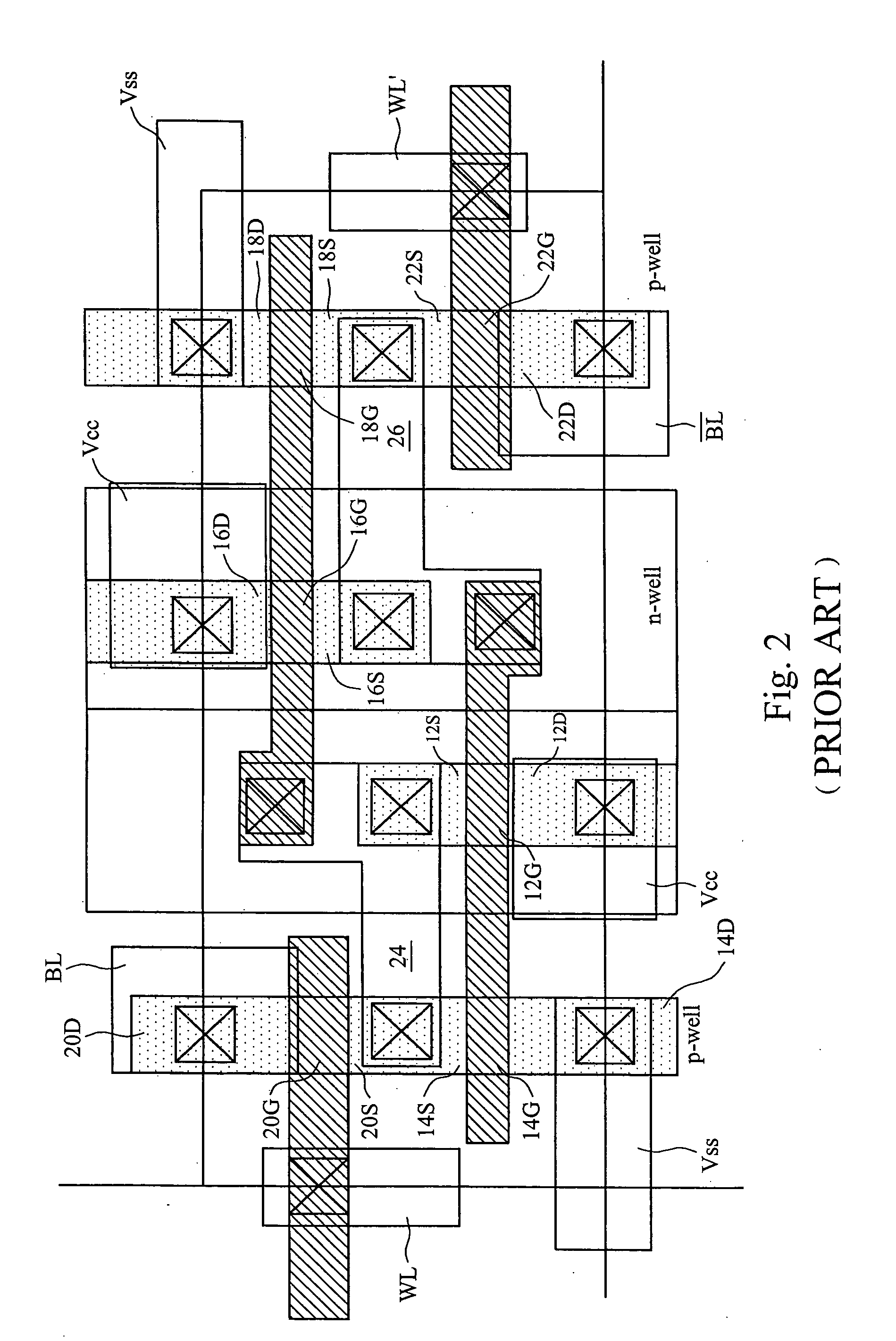
NVRAM memory cell architecture that integrates conventional SRAM and flash cells
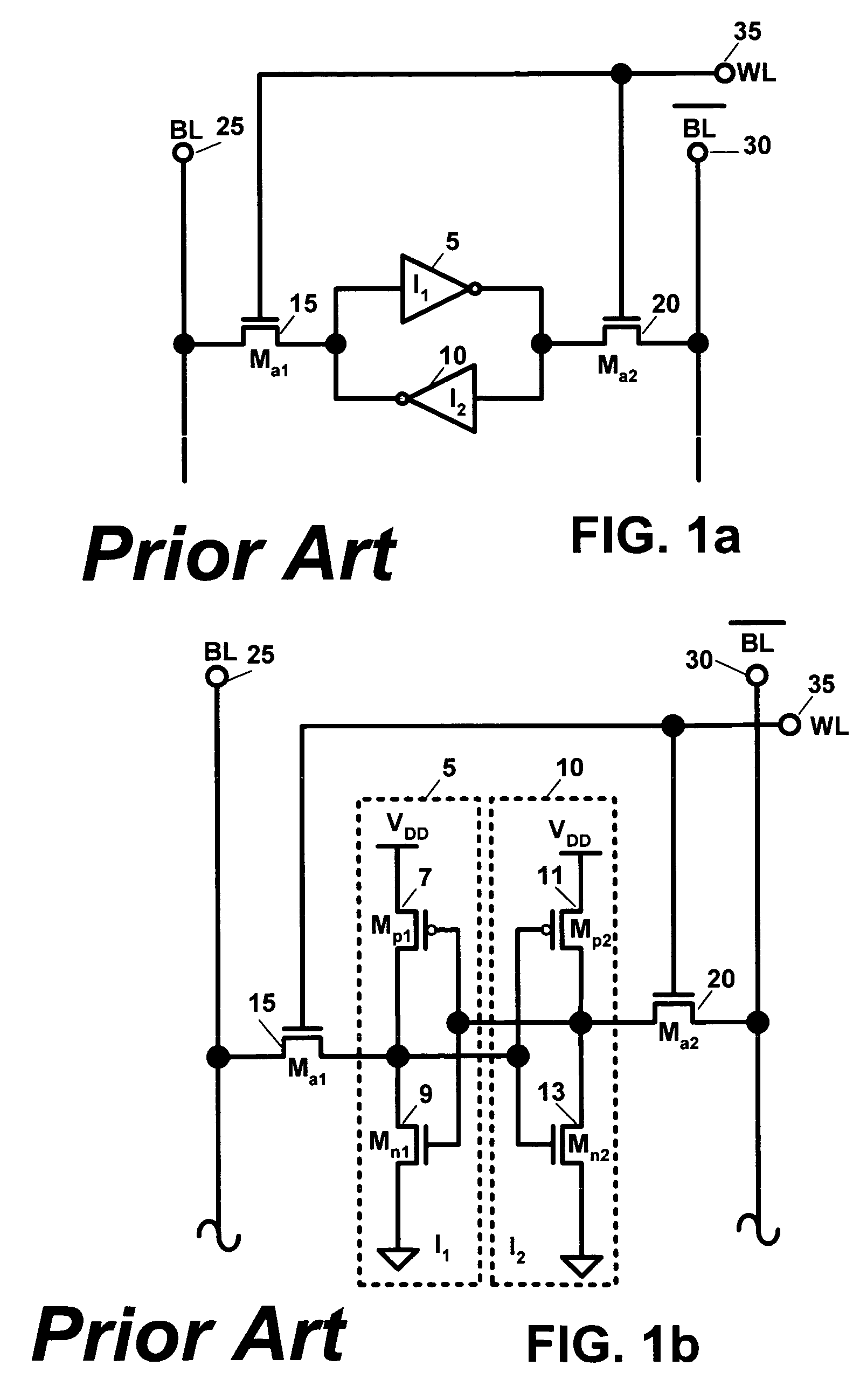
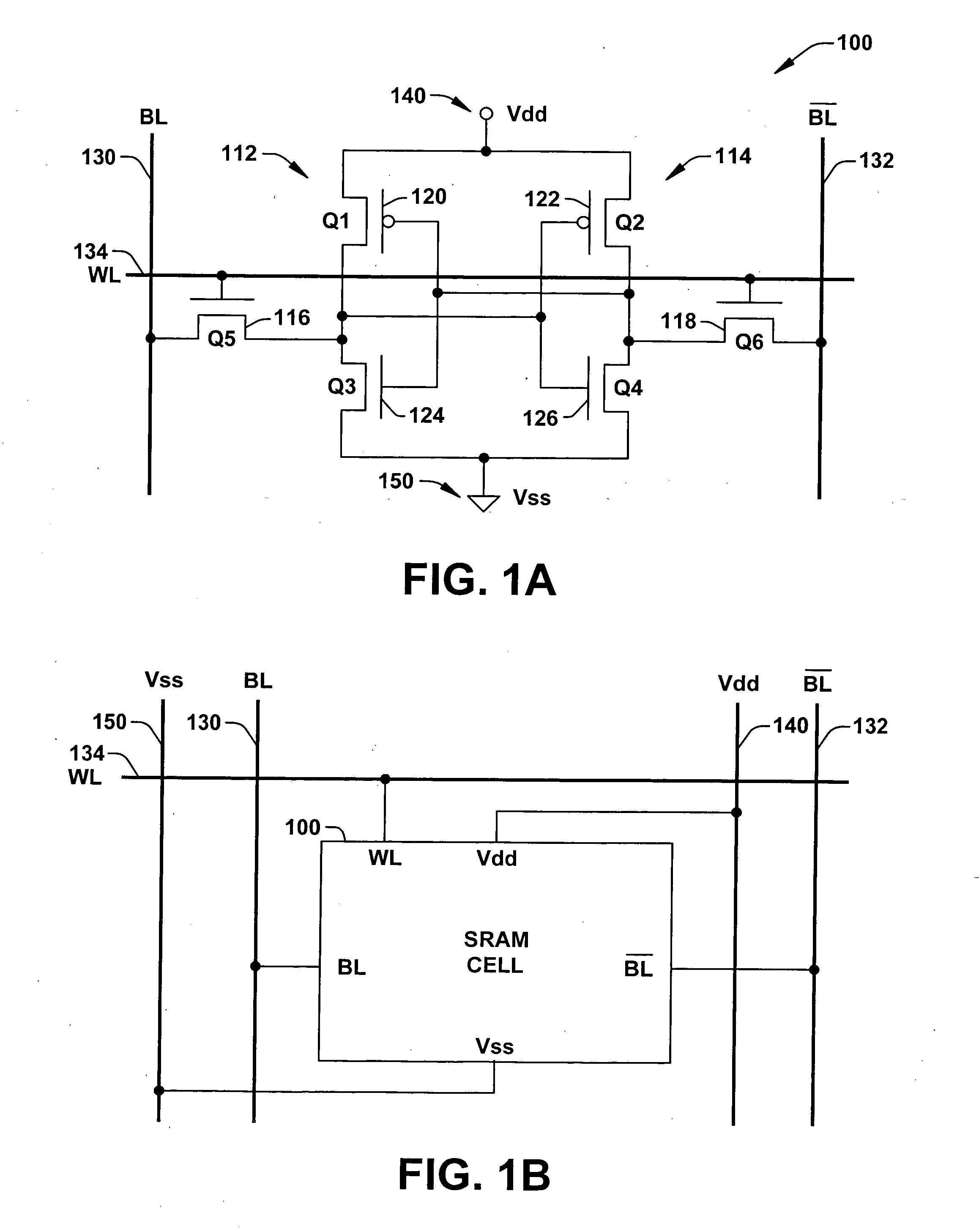
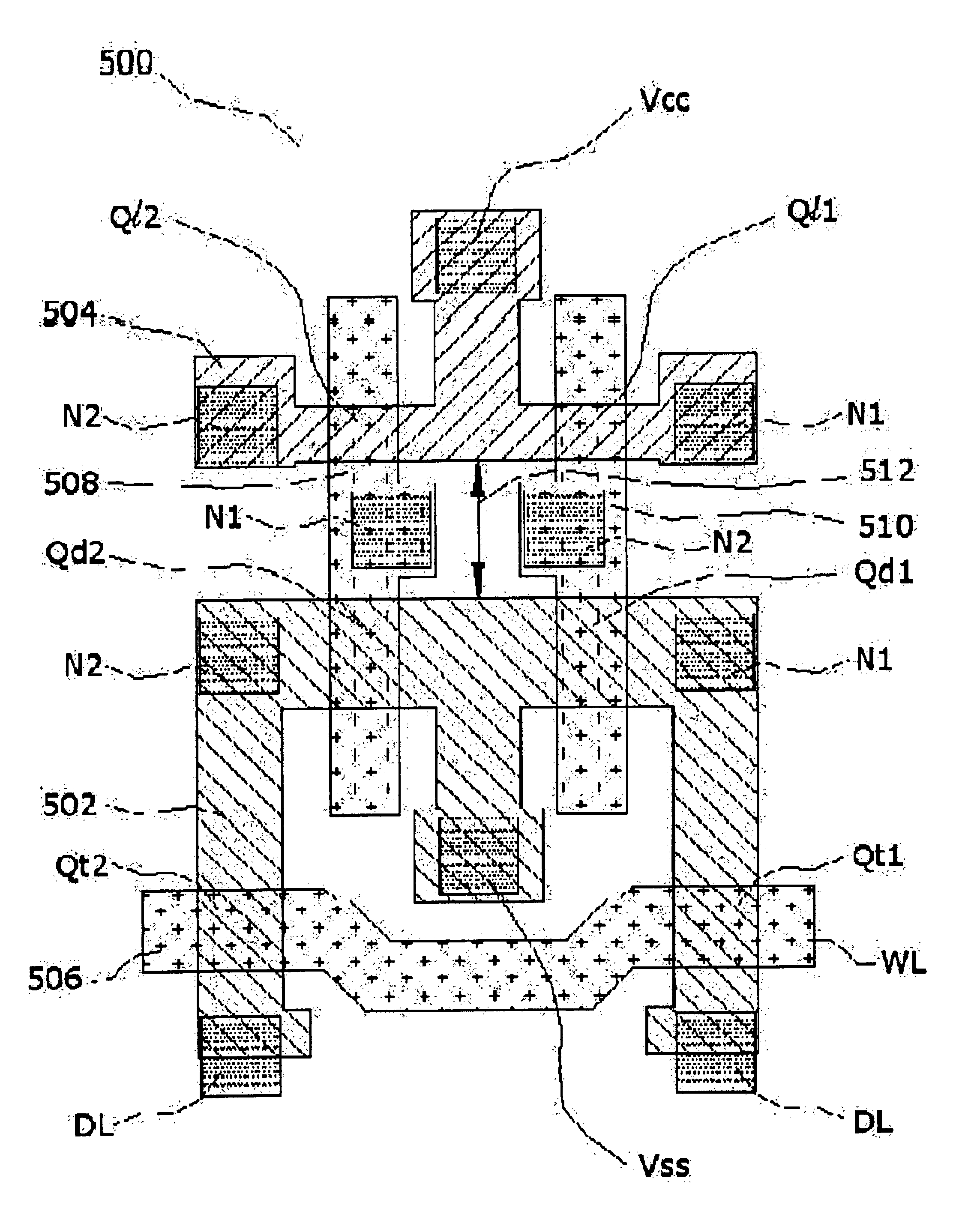
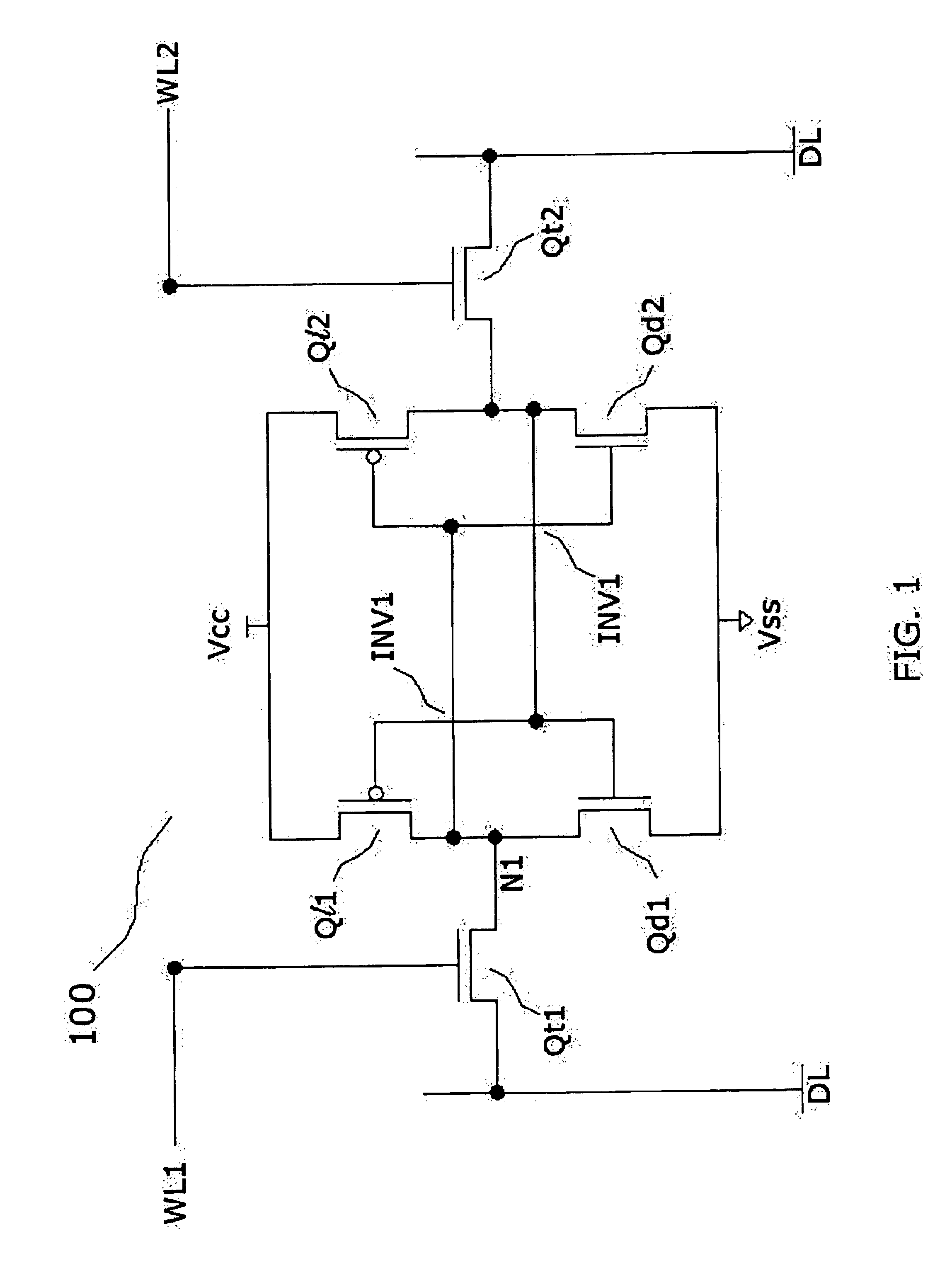
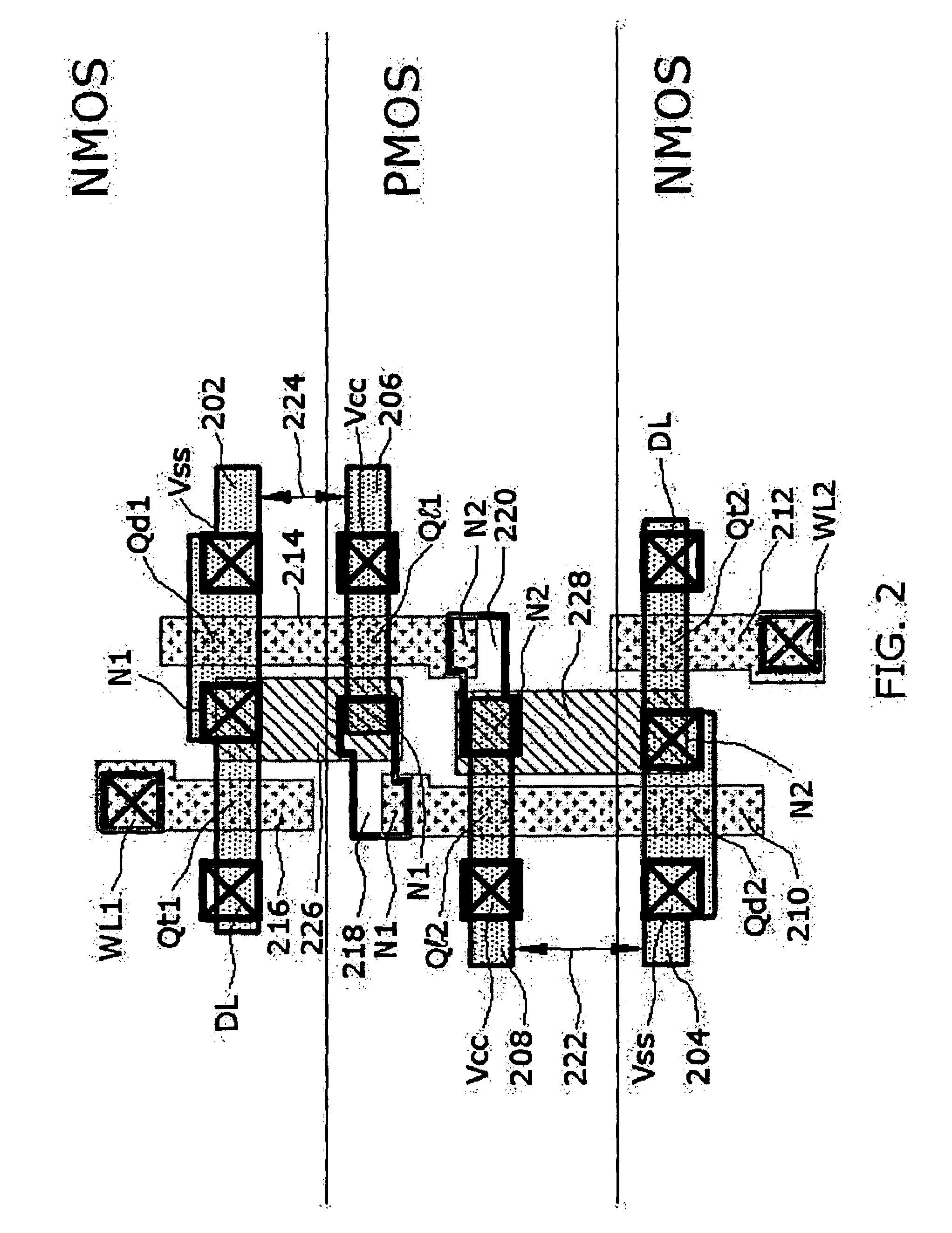
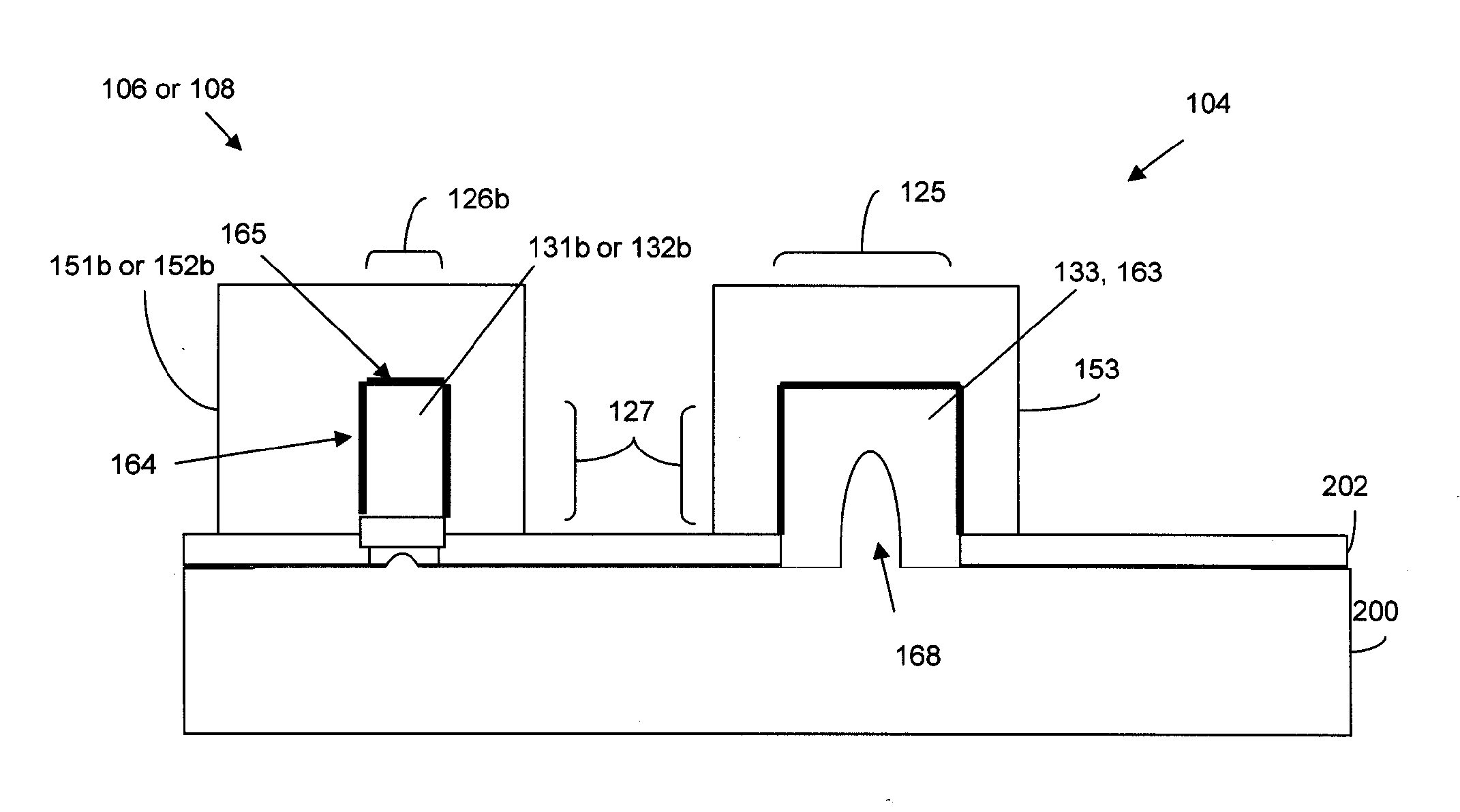
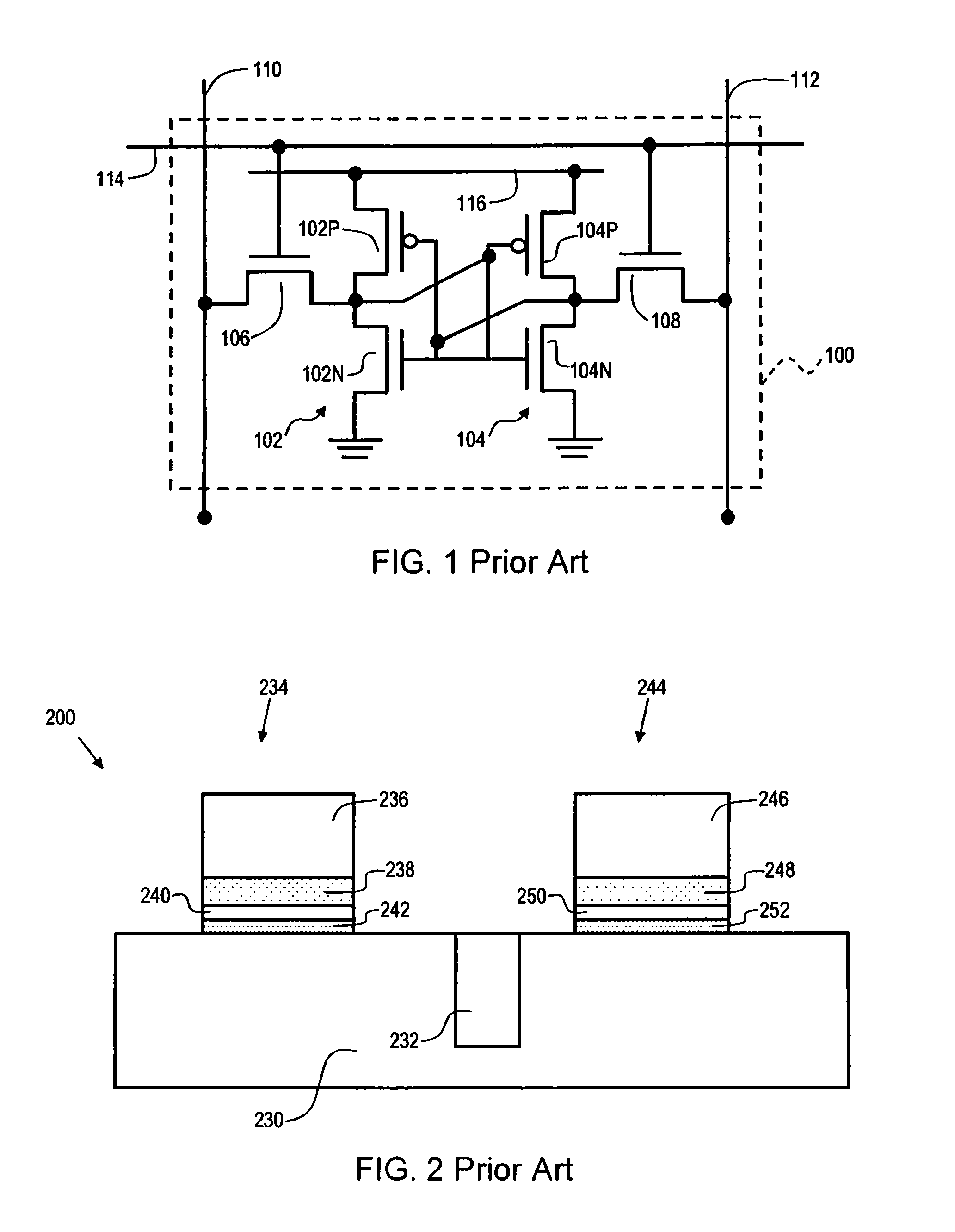
A nonvolatile SRAM array has an array of integrated nonvolatile SRAM circuits arranged in rows and columns on a substrate. Each of the integrated nonvolatile SRAM circuits includes an SRAM cell, a first and second nonvolatile memory element. The SRAM cell has a latched memory element in communication first and second nonvolatile memory elements to receive and permanently retain the digital signal from the latched memory element. A power detection circuit detects a power interruption and a power initiation and communicates the detection of the power interruption and power initiation to the plurality of integrated nonvolatile SRAM circuits. The SRAM cell, upon detection of the power interruption, transmits the digital signal to the first and second nonvolatile memory elements. The SRAM cell of each of the nonvolatile static random access memories upon detection of the power initiation, receives the digital signal from the first and second nonvolatile memory elements.
Owner:ABEDNEJA ASSETAB L L C
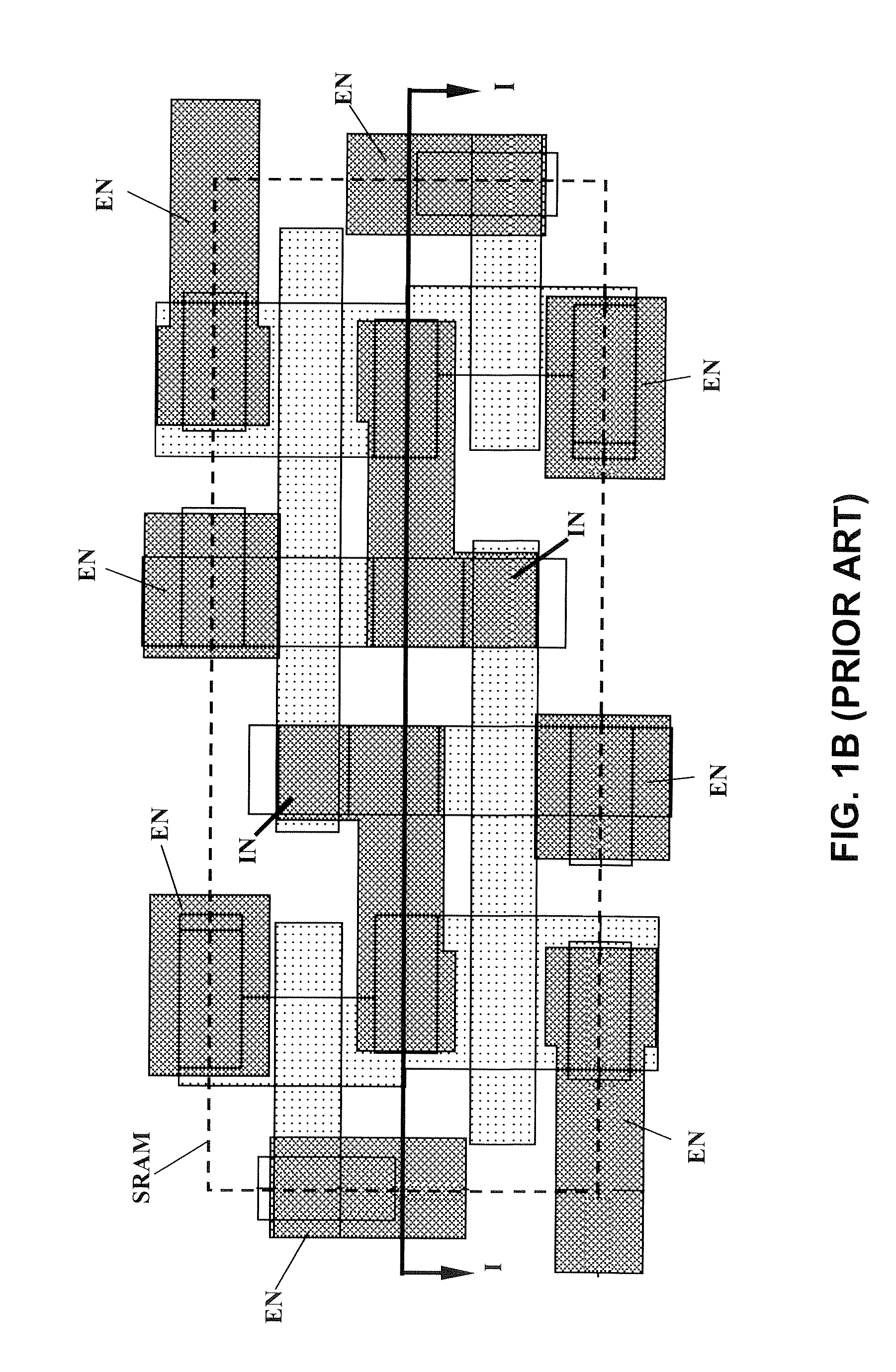
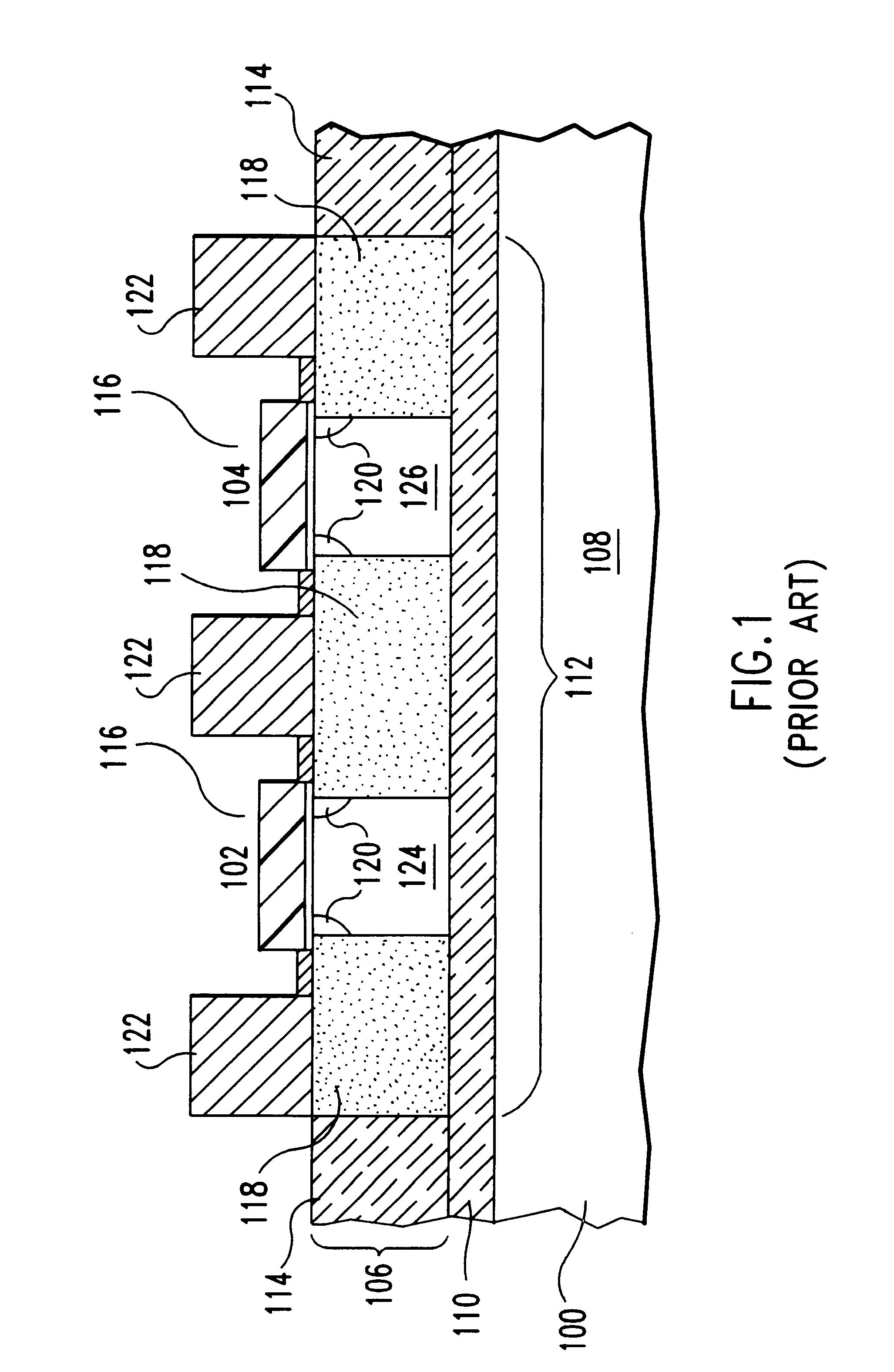
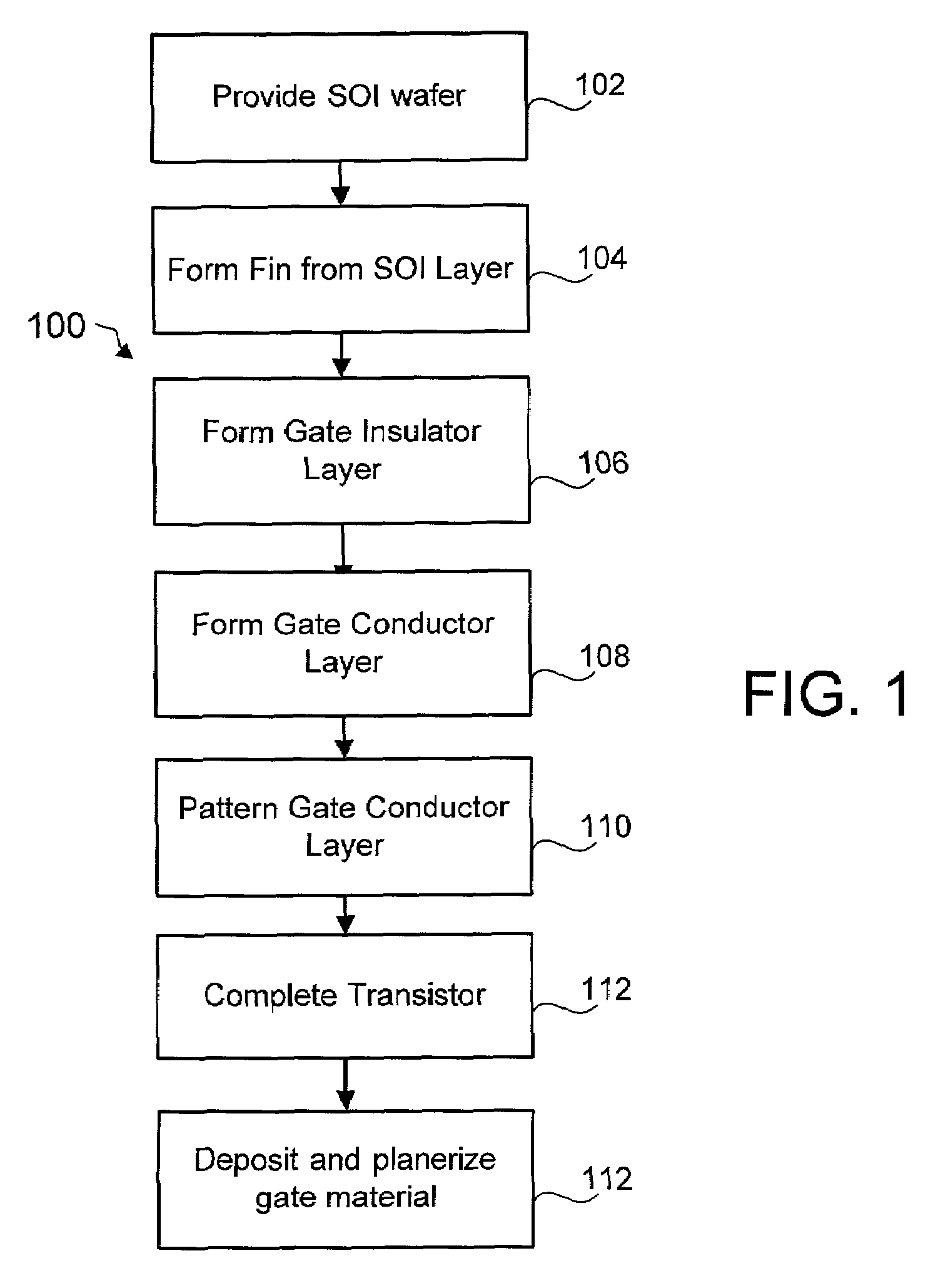
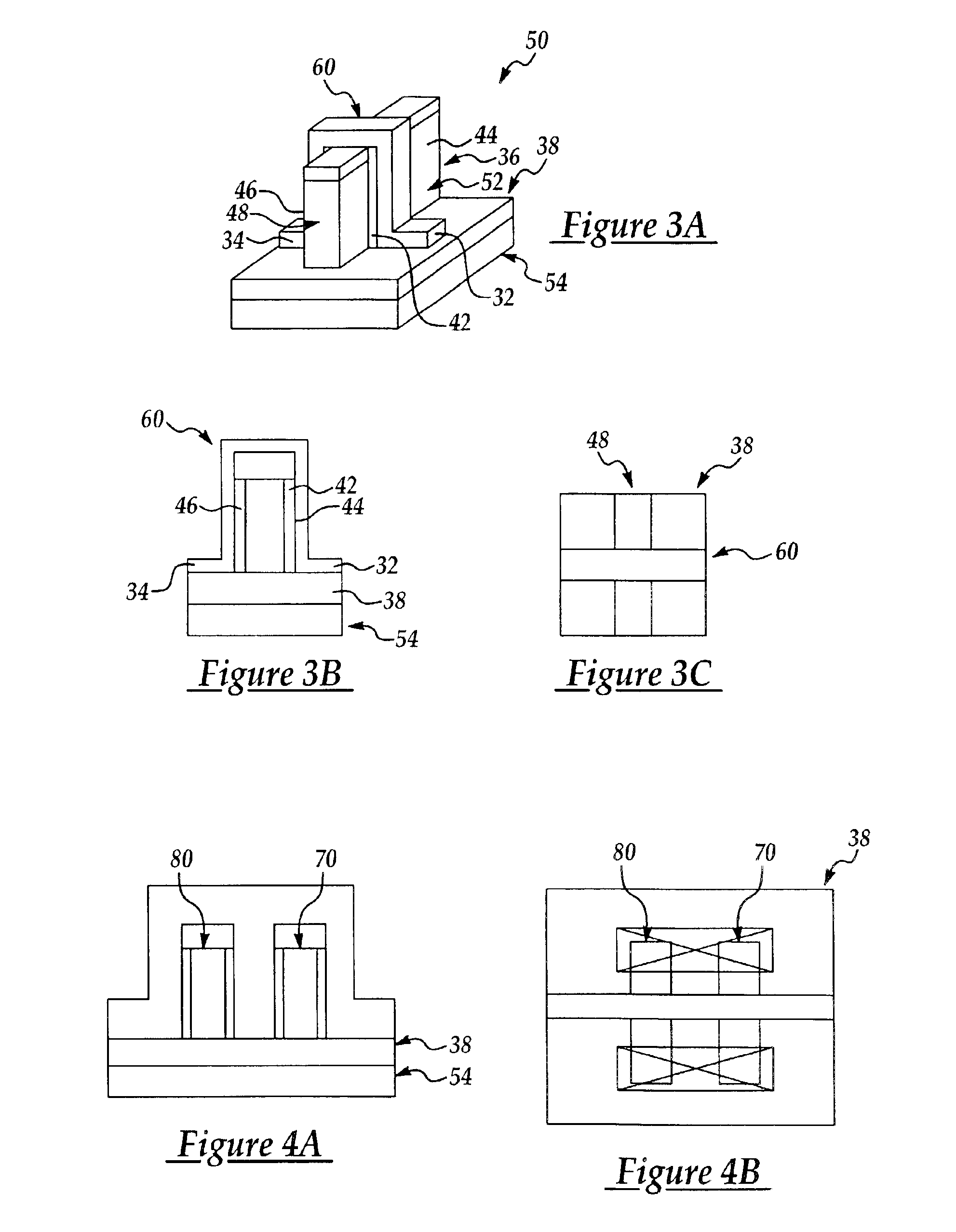
FinFET SRAM cell with chevron FinFET logic
An electronic device, and SRAM and a method of forming the electronic device and SRAM. The semiconductor device including: a pass gate transistor having a fin body having opposing sidewalls aligned in a first direction and having a first majority carrier mobility and a gate adjacent to both sidewalls of the fin body; a pull down latch transistor having a fin body having opposing sidewalls aligned in a second direction and having a second majority carrier mobility and a gate adjacent to both sidewalls of thc fin body; a pull up latch transistor having a fin body having opposing sidewalls aligned in a third direction and having a third majority carrier mobility and a gate adjacent to both sidewalls of the fin body; and CMOS chevron logic circuits, wherein crystal planes of each fin body and of CMOS transistor of the chevron logic are co-aligned.
Owner:IBM CORP
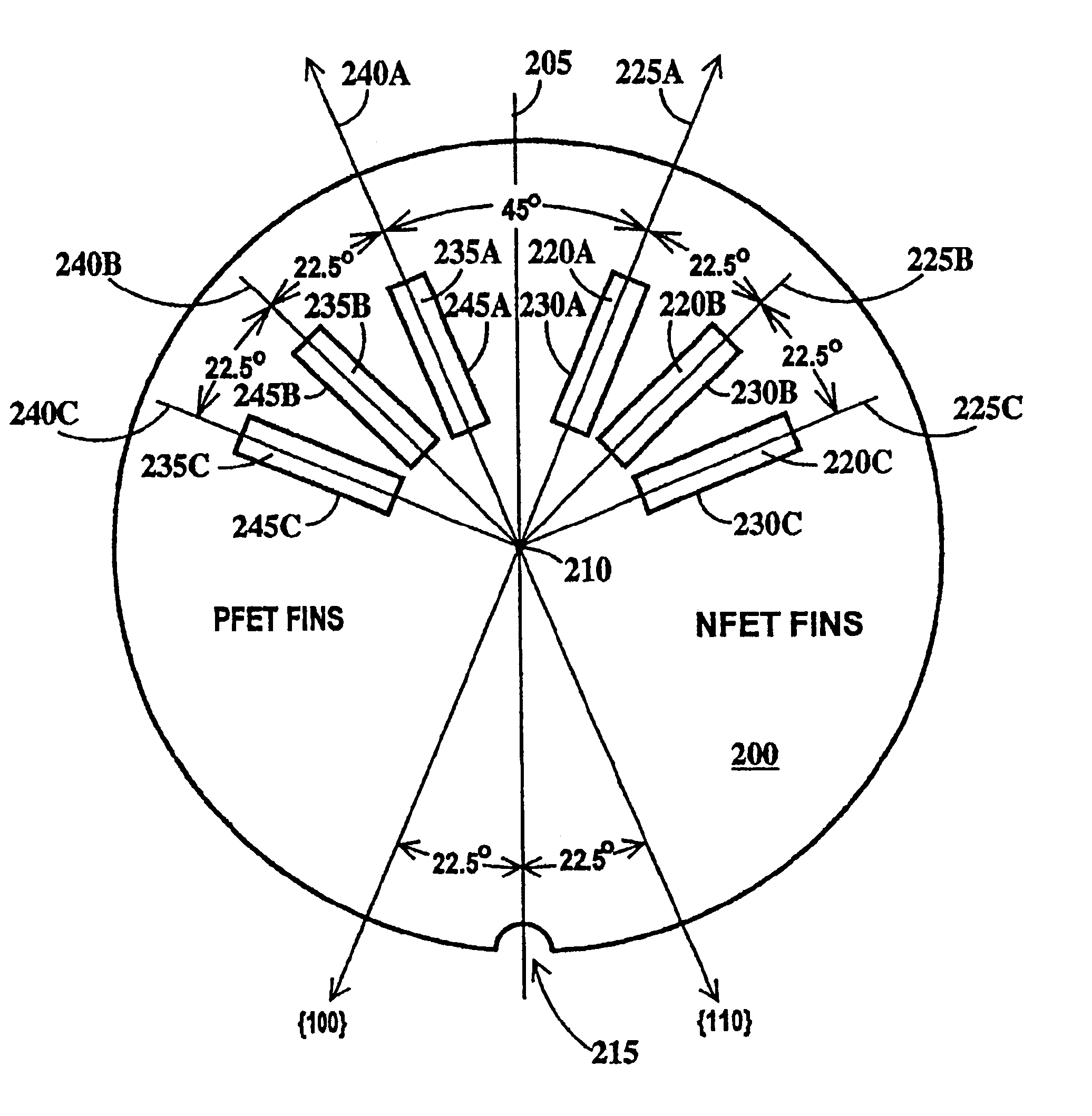
FinFET SRAM cell using low mobility plane for cell stability and method for forming
InactiveUS20050121676A1High gainAccurate operationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStatic random-access memoryLow mobility
The present invention provides a device design and method for forming the same that results in Fin Field Effect Transistors having different gains without negatively impacting device density. The present invention forms relatively low gain FinFET transistors in a low carrier mobility plane and relatively high gain FinFET transistors in a high carrier mobility plane. Thus formed, the FinFETs formed in the high mobility plane have a relatively higher gain than the FinFETs formed in the low mobility plane. The embodiments are of particular application to the design and fabrication of a Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) cell. In this application, the bodies of the n-type FinFETs used as transfer devices are formed along the {110} plane. The bodies of the n-type FinFETs and p-type FinFETs used as the storage latch are formed along the {100}. Thus formed, the transfer devices will have a gain approximately half that of the n-type storage latch devices, facilitating proper SRAM operation
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
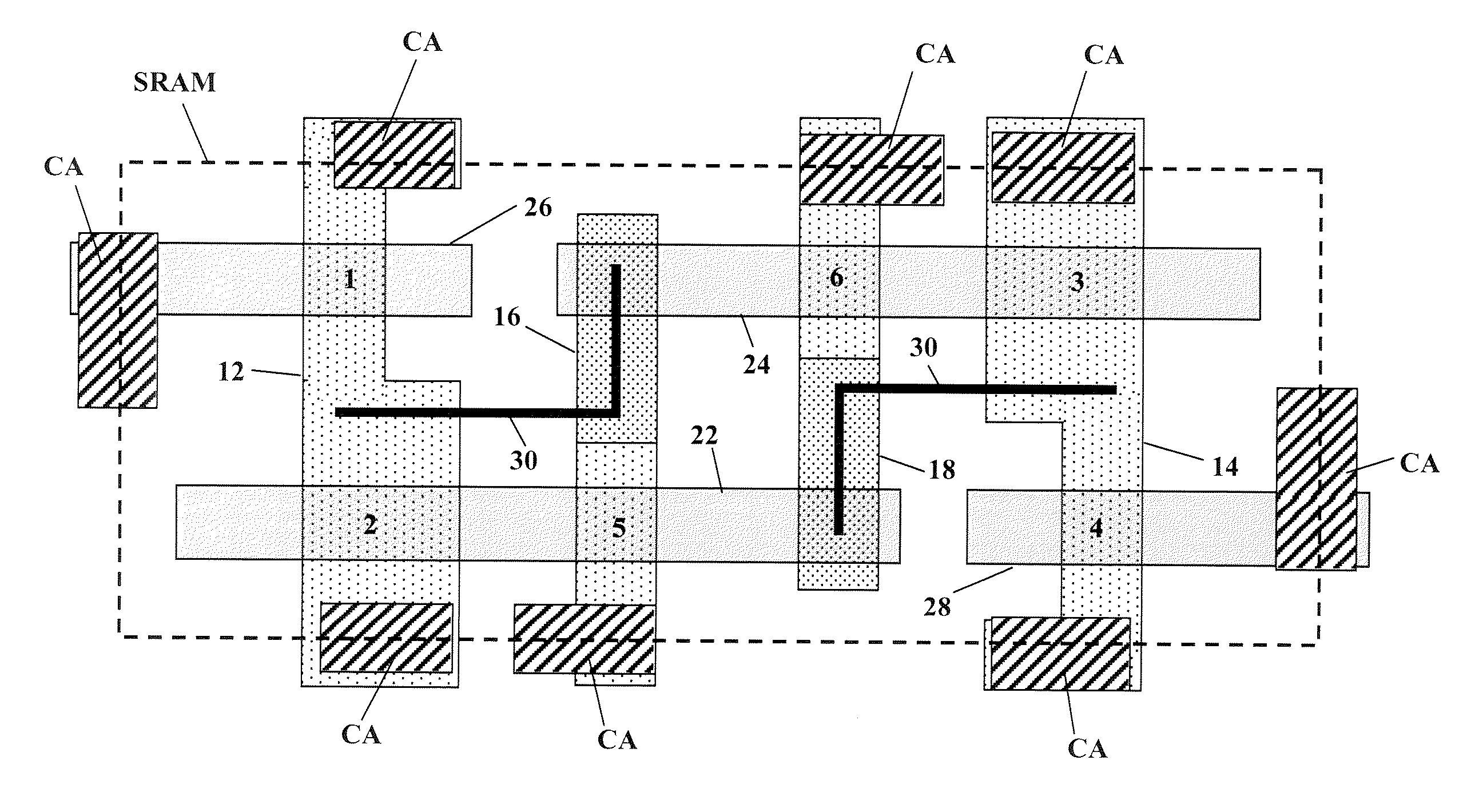
Area efficient implementation of small blocks in an SRAM array
ActiveUS20070002617A1Minimize changesImprove device performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineCell pattern
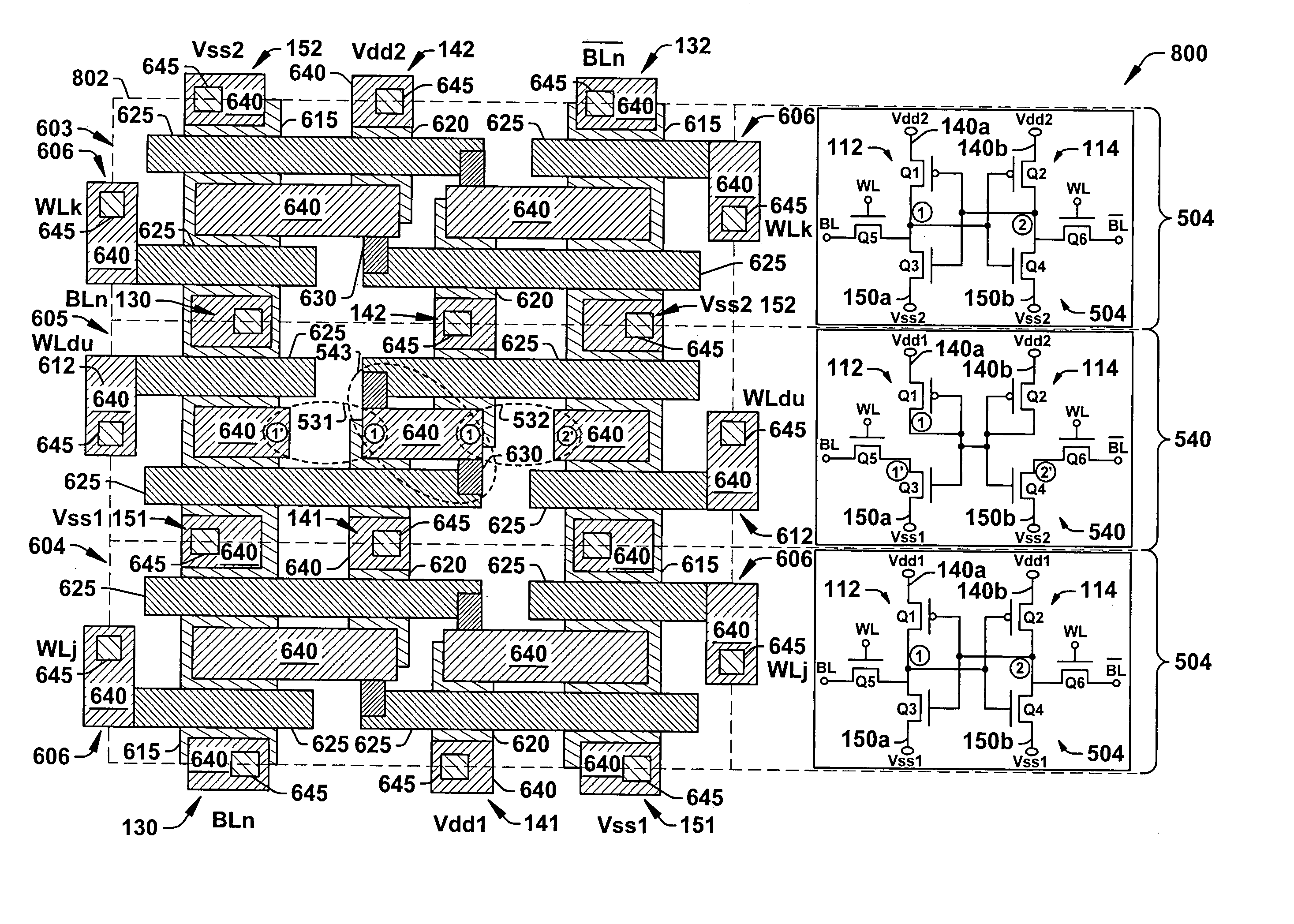
An SRAM array and a dummy cell row structure is discussed that permits an SRAM array to be divided into segments isolated by a row pattern of dummy cells. The dummy cell structure avoids the use of special OPC conditions at the power supply line and block boundaries by providing a continuous cell array at the lower cell patterning levels in an area efficient implementation. In one implementation, the SRAM array comprises a first and second array block each comprising an SRAM cell having a first layout configuration, one or more of the dummy cells having a second layout configuration arranged along the row pattern associated with a wordline of the SRAM array, a first power supply voltage line connected to the first array block, and a second different power supply voltage line connected to the second array block. The first and second power supply voltage lines of the array blocks are further connected to the one or more dummy cells. Beneficially, the bitlines of the array may be continuous across the first and second array blocks and a dummy cell associated therewith.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Compact SRAM cell with FinFET
InactiveUS6924560B2Distance minimizationTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorSemiconductor package
A method and system is disclosed for an SRAM device cell having at least one device of a first semiconductor type and at lease one device of a second semiconductor type. The cell has a first device of the first type constructed as a part of a first FinFET having one or more devices of the first type, a first device of the second type whose poly region is an extension of a poly region of the first device of the first type with no contact needed to connect therebetween, wherein the two devices are constructed using a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) technology so that they are separated by an insulator region therebetween so as to minimize the distance between the two devices.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
SRAM cell
InactiveUS20070108528A1Increase effective widthImprove carrying capacityTransistorSolid-state devicesDriving currentEngineering
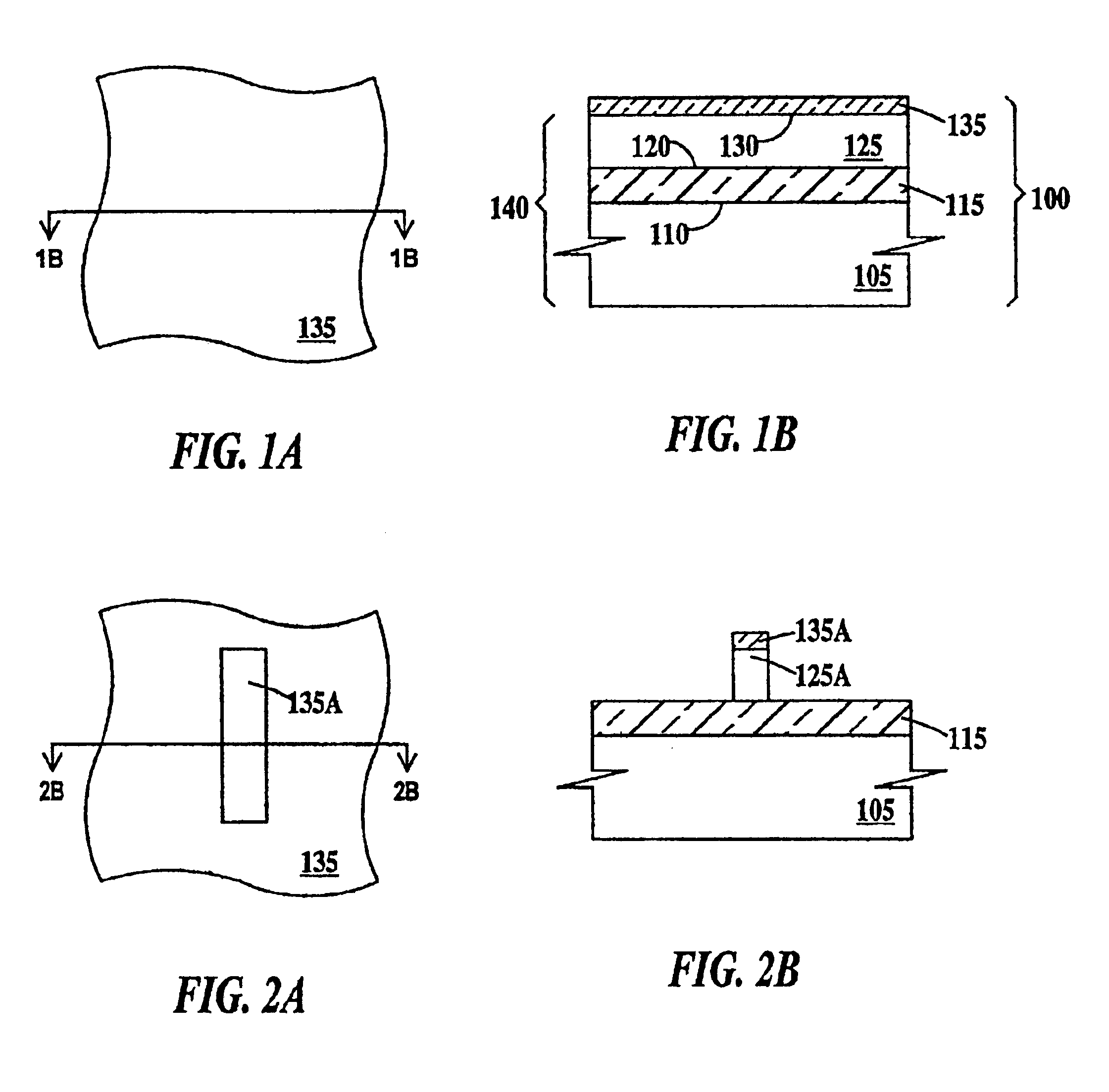
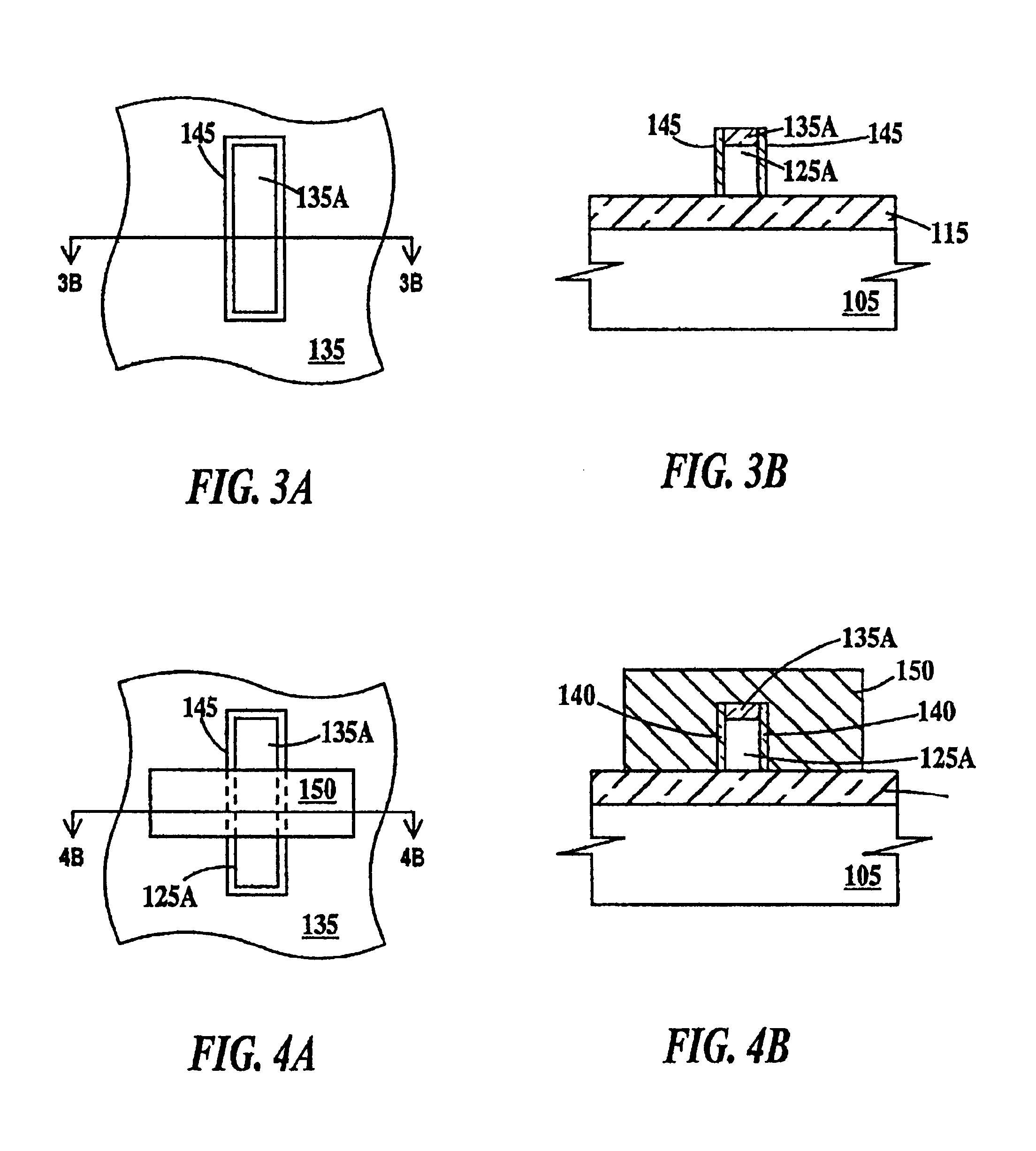
Disclosed is an SRAM cell on an SOI, bulk or HOT wafer with two pass-gate n-FETs, two pull-up p-FETs and two pull-down n-FETs and the associated methods of making the SRAM cell. The pass-gate FETs and pull-down FETs are non-planar fully depleted finFETs or trigate FETs. The pull-down FETs comprise non-planar partially depleted three-gated FETs having a greater channel width and a greater gate length and, thus, a greater drive current relative to the pass-gate and pull-up FETs. Additionally, for optimal electron mobility and hole mobility, respectively, the channels of the n-FETs and p-FETs can comprise semiconductors with different crystalline orientations.
Owner:IBM CORP
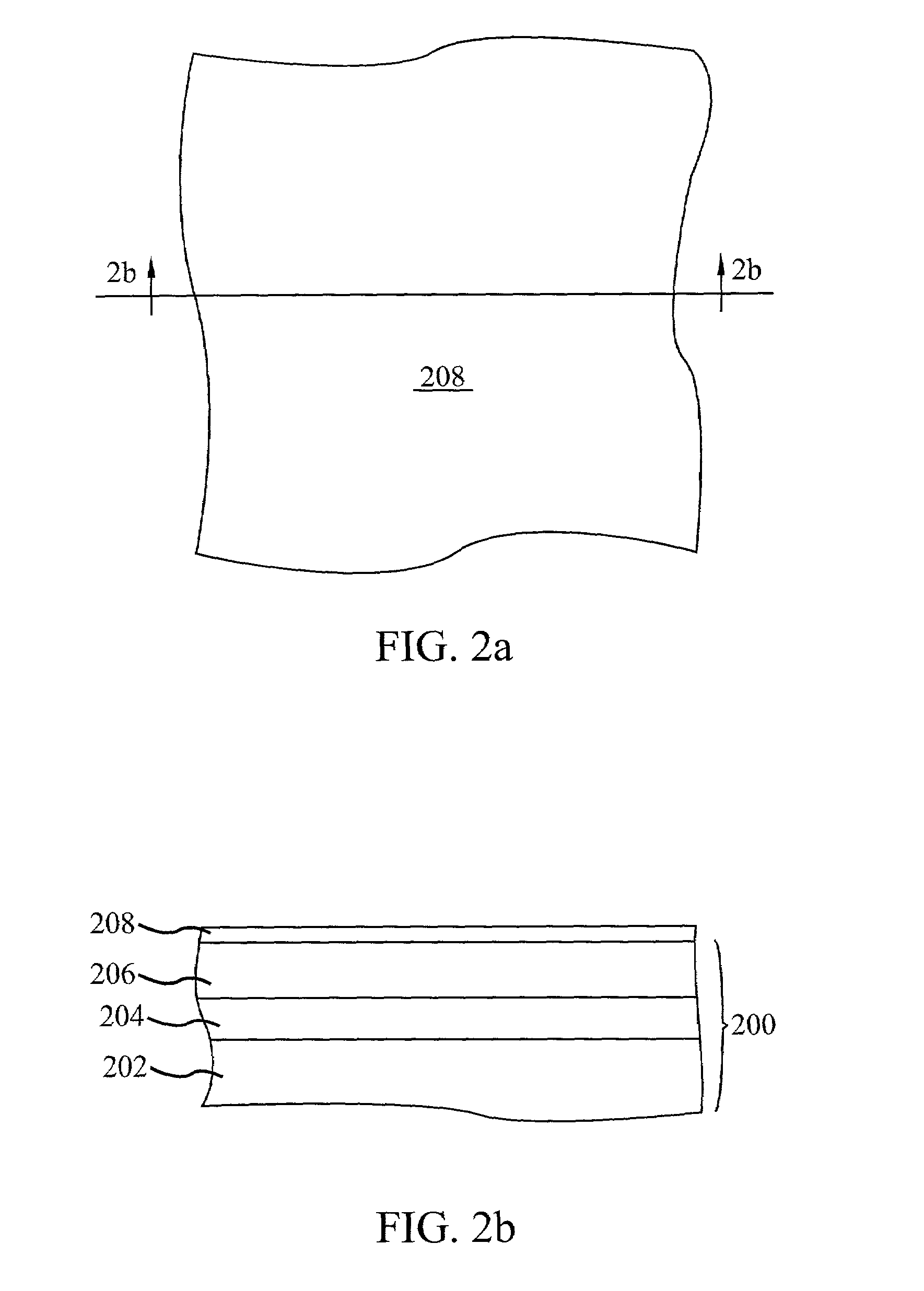
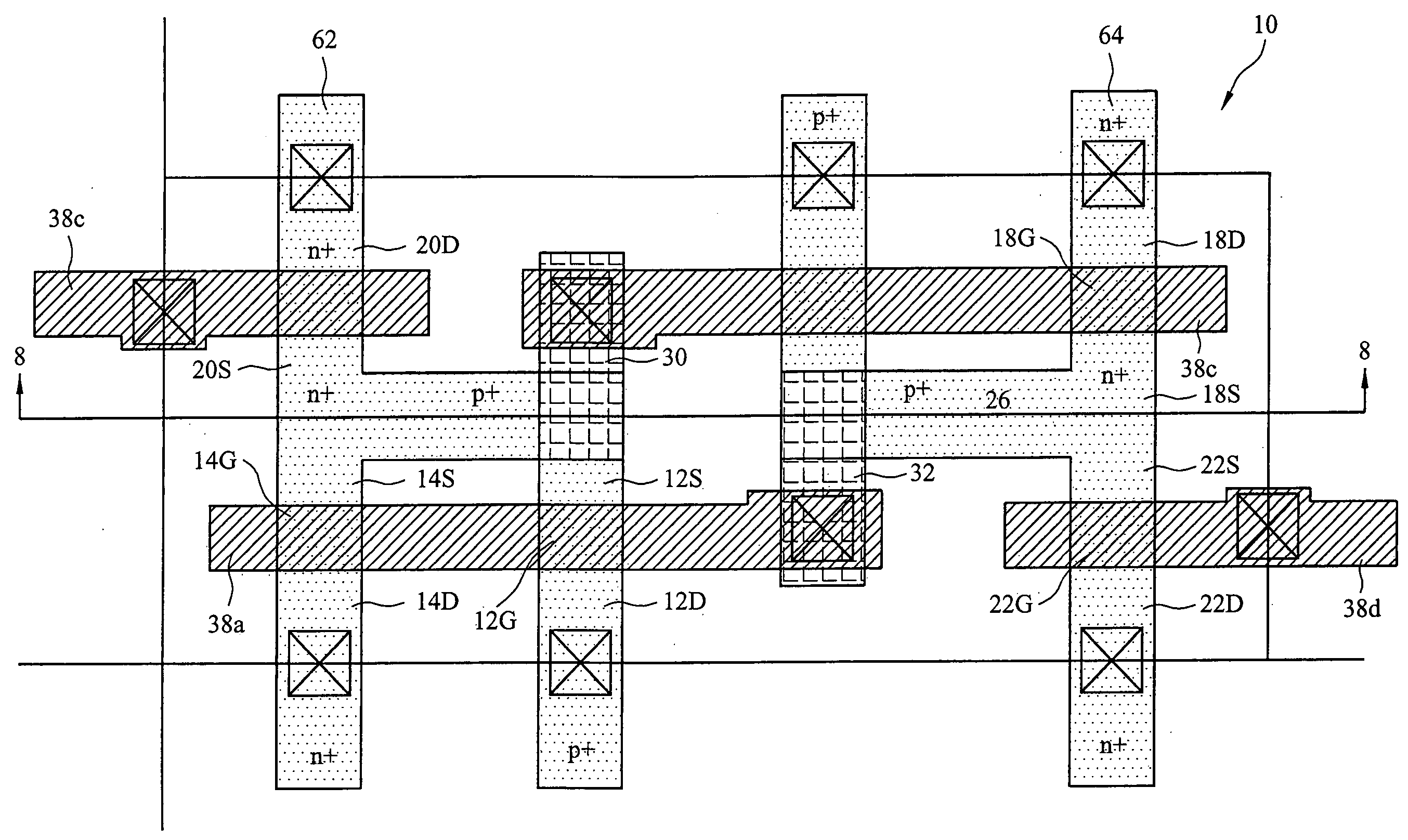
Memory cell structure
An SRAM device includes an SRAM cell in a deep NWELL region in a substrate. PWELL regions in the SRAM cell occupy less than about 65% of the cell area of the SRAM cell. A ratio of a longer side of a cell area of the SRAM cell to a shorter side of the SRAM cell is larger than about 1.8. A total area of the active regions in the plurality of NMOS transistors in the SRAM cell occupies less than about 25% of the SRAM cell area. A ratio of the channel width of a pull up transistor in the SRAM cell to the channel width of a pull down transistor in the SRAM cell is greater than about 0.8. The SRAM cell further includes a boron free inter-layer-dielectric layer, an inter-metal-dielectric layer with dielectric constant less than about 3, and a polyimide layer with a thickness of less than about 20 microns.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Nanomesh SRAM Cell
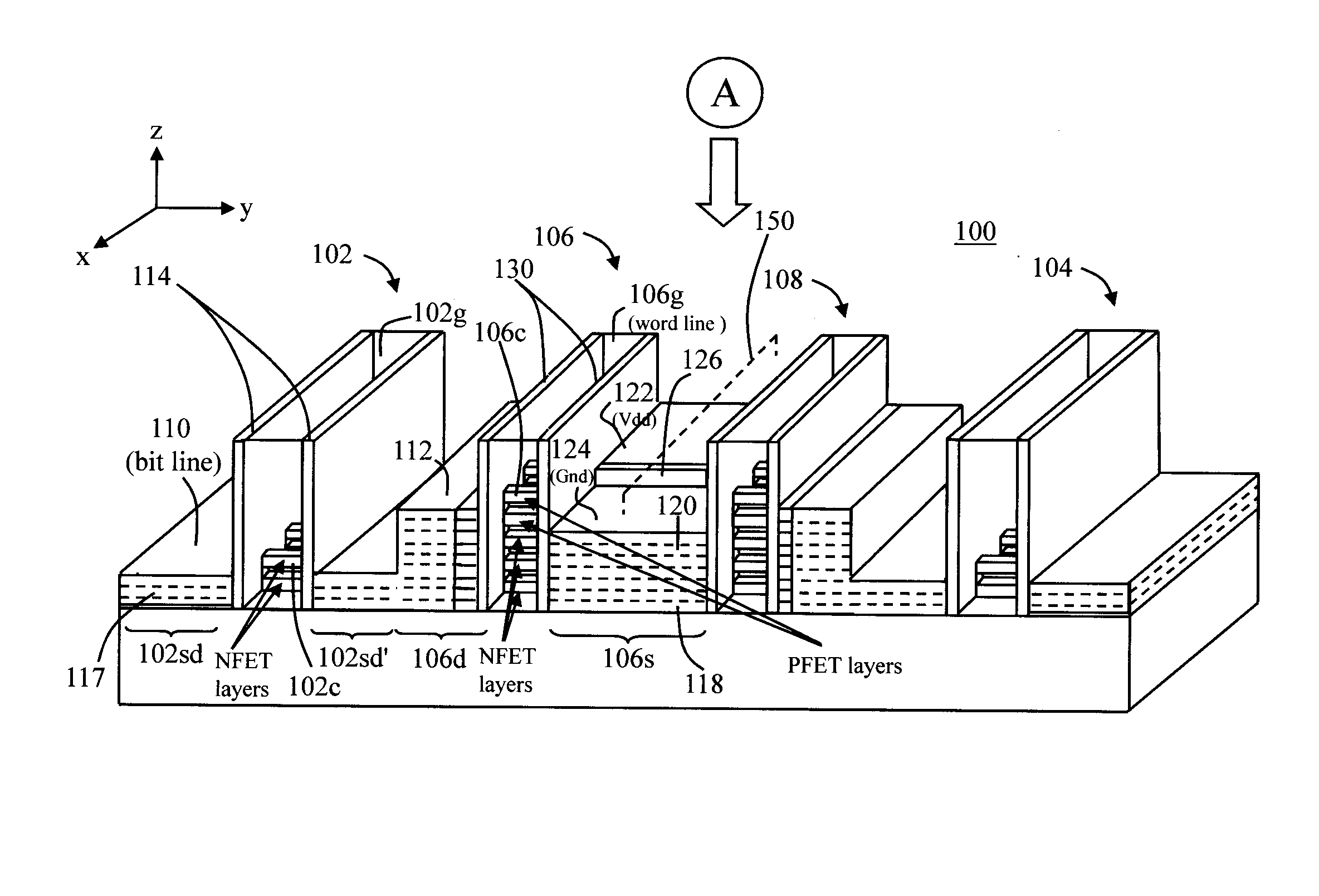
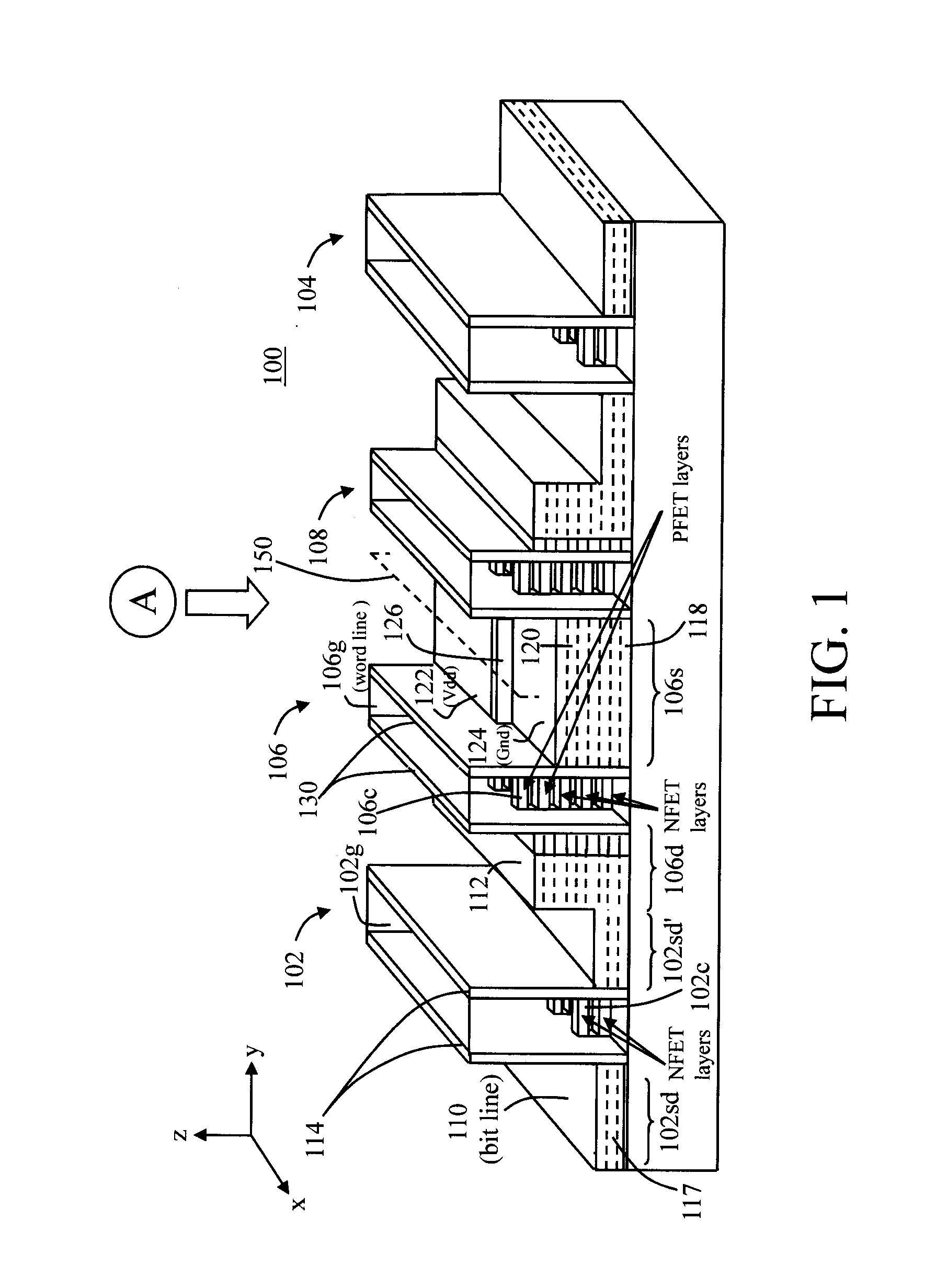
Nanowire-based devices are provided. In one aspect, a SRAM cell includes at least one pair of pass gates and at least one pair of inverters formed adjacent to one another on a wafer. Each pass gate includes one or more device layers each having a source region, a drain region and a plurality of nanowire channels connecting the source region and the drain region and a gate common to each of the pass gate device layers surrounding the nanowire channels. Each inverter includes a plurality of device layers each having a source region, a drain region and a plurality of nanowire channels connecting the source region and the drain region and a gate common to each of the inverter device layers surrounding the nanowire channels.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Semiconductor Device and Method for Manufacturing the Same
InactiveUS20070257277A1Easy to manufactureCompact structureTransistorSolid-state devicesSram cellSemiconductor
A semiconductor device having SRAM cell units each comprising a pair of driving transistors, a pair of load transistors and a pair of access transistors, in which each of the transistors has a semiconductor layer projecting upward from a substrate plane, a gate electrode extending on opposite sides of the semiconductor layer so as to stride over a top of the semiconductor layer, a gate insulting film interposed between the gate electrode and the semiconductor layer, and a pair of source / drain areas formed in the semiconductor layer; a longitudinal direction of each semiconductor layer extends along a first direction; and between the adjacent SRAM cell units in the first direction, the semiconductor layer in one of the corresponding transistors is located on a center line of the semiconductor layer in the other transistor which center line extends along the first direction.
Owner:NEC CORP
FinFET-based SRAM cell
A SRAM cell includes a single FinFET and two resonant tunnel diodes. The FinFet has multiple channel regions formed from separate fins. The resonant tunnel diodes may be formed from FinFET type fins. In particular, the resonant diodes may includes a thin, undoped silicon region surrounded by a dielectric. The SRAM cell is small and provides fast read / write access times.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
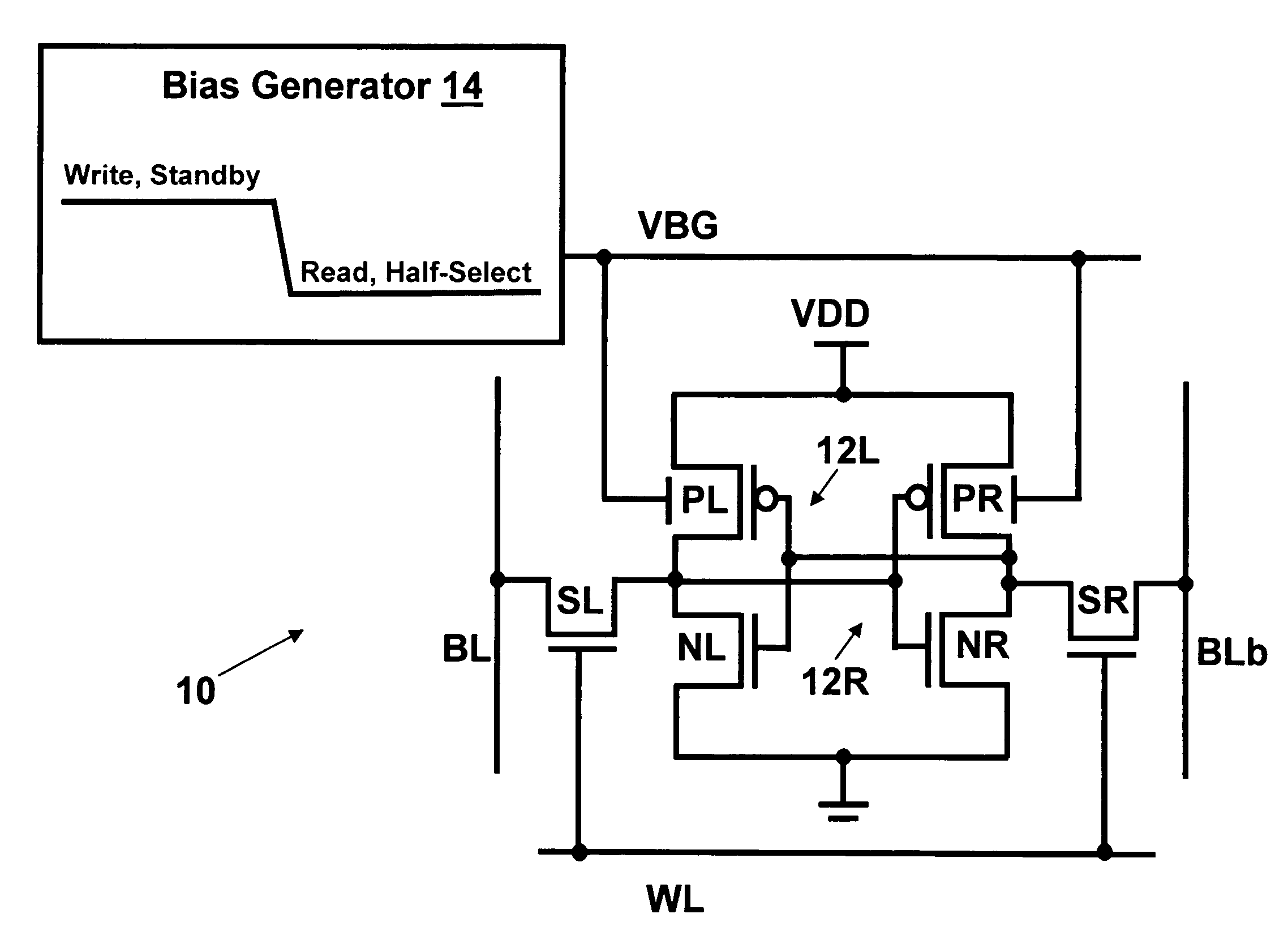
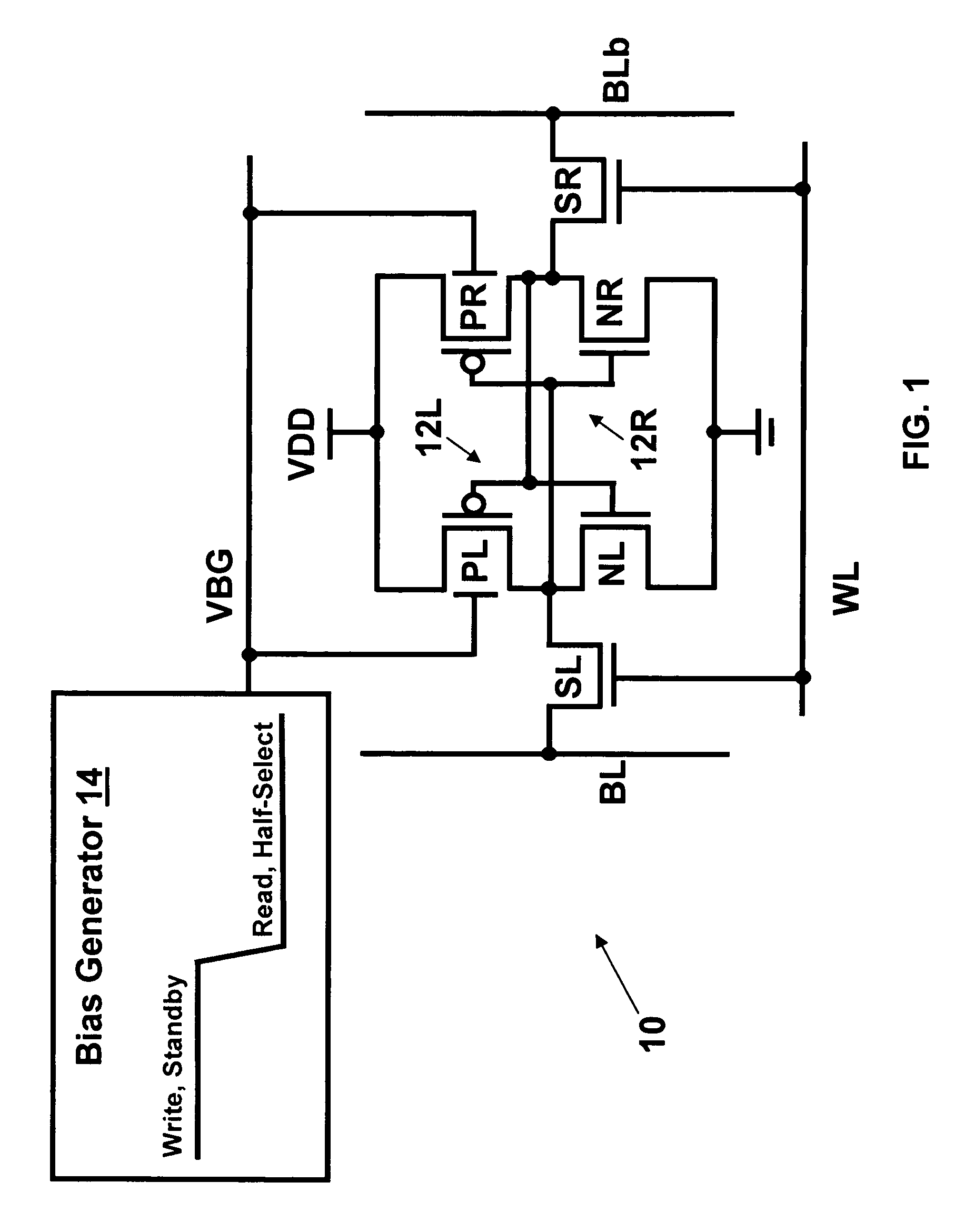
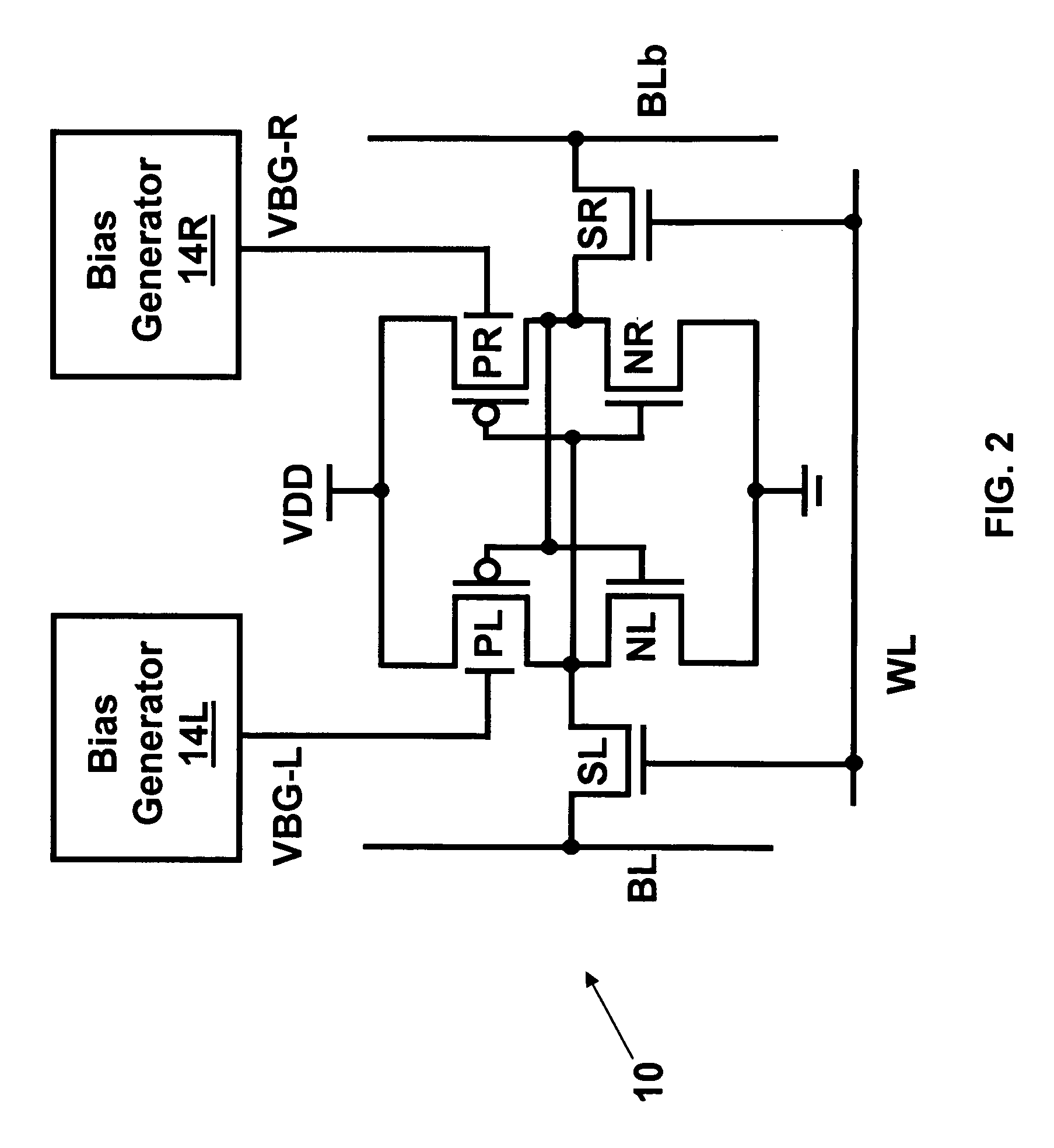
Dynamic control of back gate bias in a FinFET SRAM cell
The present invention provides dynamic control of back gate bias on pull-up pFETs in a FinFET SRAM cell. A method according to the present invention includes providing a bias voltage to a back gate of at least one transistor in the SRAM cell, and dynamically controlling the bias voltage based on an operational mode (e.g., Read, Half-Select, Write, Standby) of the SRAM cell.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Self-biasing transistor structure and an SRAM cell having less than six transistors
ActiveUS7442971B2Function increaseSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingActive componentEngineering
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Structure and method for making low leakage and low mismatch nmosfet
An improved SRAM and fabrication method are disclosed. The method comprises use of a nitride layer to encapsulate PFETs and logic NFETs, protecting the gates of those devices from oxygen exposure. NFETs that are used in the SRAM cells are exposed to oxygen during the anneal process, which alters the effective work function of the gate metal, such that the threshold voltage is increased, without the need for increasing the dopant concentration, which can adversely affect issues such as mismatch due to random dopant fluctuation, GIDL and junction leakage.
Owner:IBM CORP
FinFET SRAM cell using low mobility plane for cell stability and method for forming
InactiveUS7087477B2Accurate operationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStatic random-access memoryLow mobility
The present invention provides a device design and method for forming the same that results in Fin Field Effect Transistors having different gains without negatively impacting device density. The present invention forms relatively low gain FinFET transistors in a low carrier mobility plane and relatively high gain FinFET transistors in a high carrier mobility plane. Thus formed, the FinFETs formed in the high mobility plane have a relatively higher gain than the FinFETs formed in the low mobility plane. The embodiments are of particular application to the design and fabrication of a Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) cell. In this application, the bodies of the n-type FinFETs used as transfer devices are formed along the {110} plane. The bodies of the n-type FinFETs and p-type FinFETs used as the storage latch are formed along the {100}. Thus formed, the transfer devices will have a gain approximately half that of the n-type storage latch devices, facilitating proper SRAM operation.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
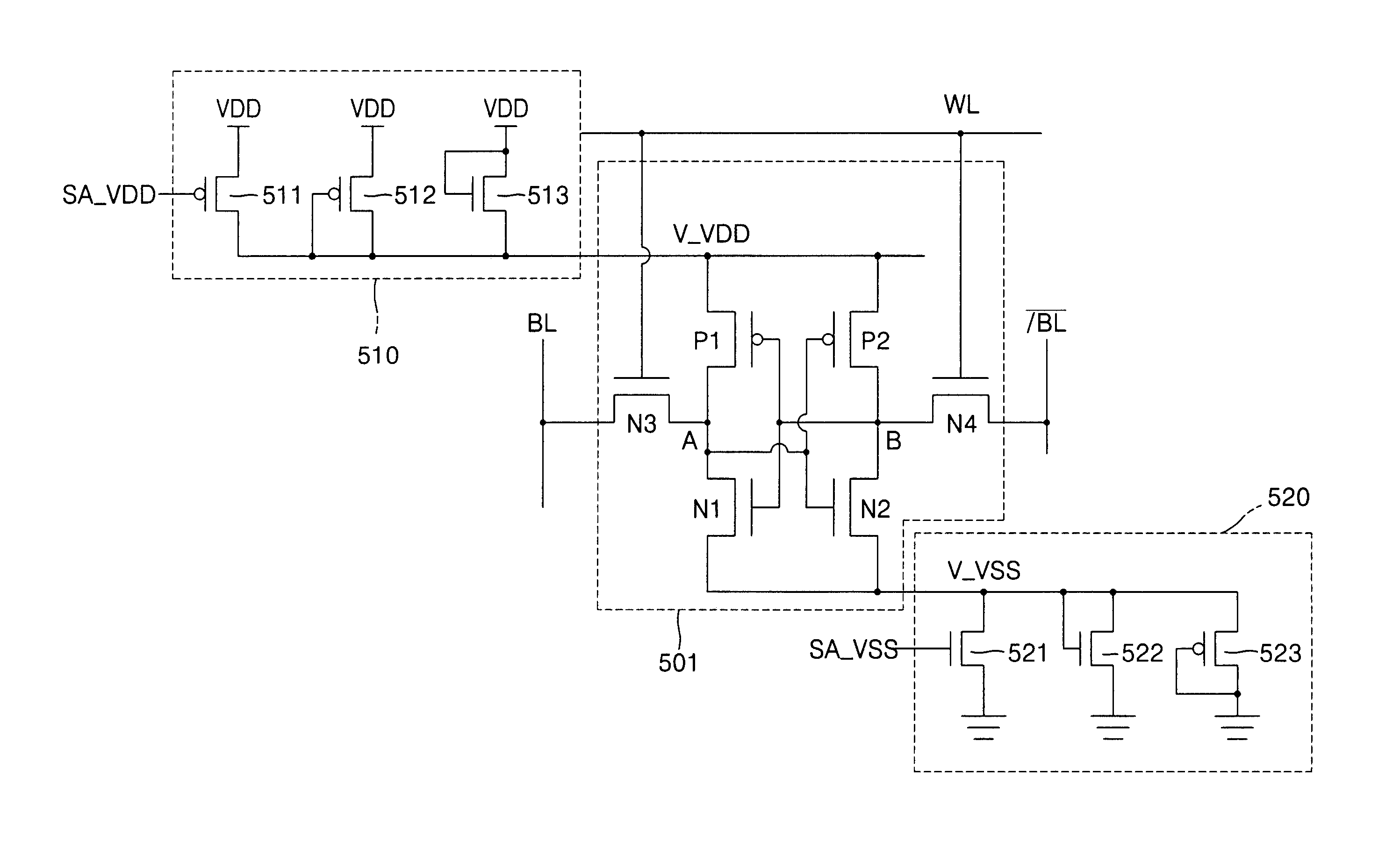
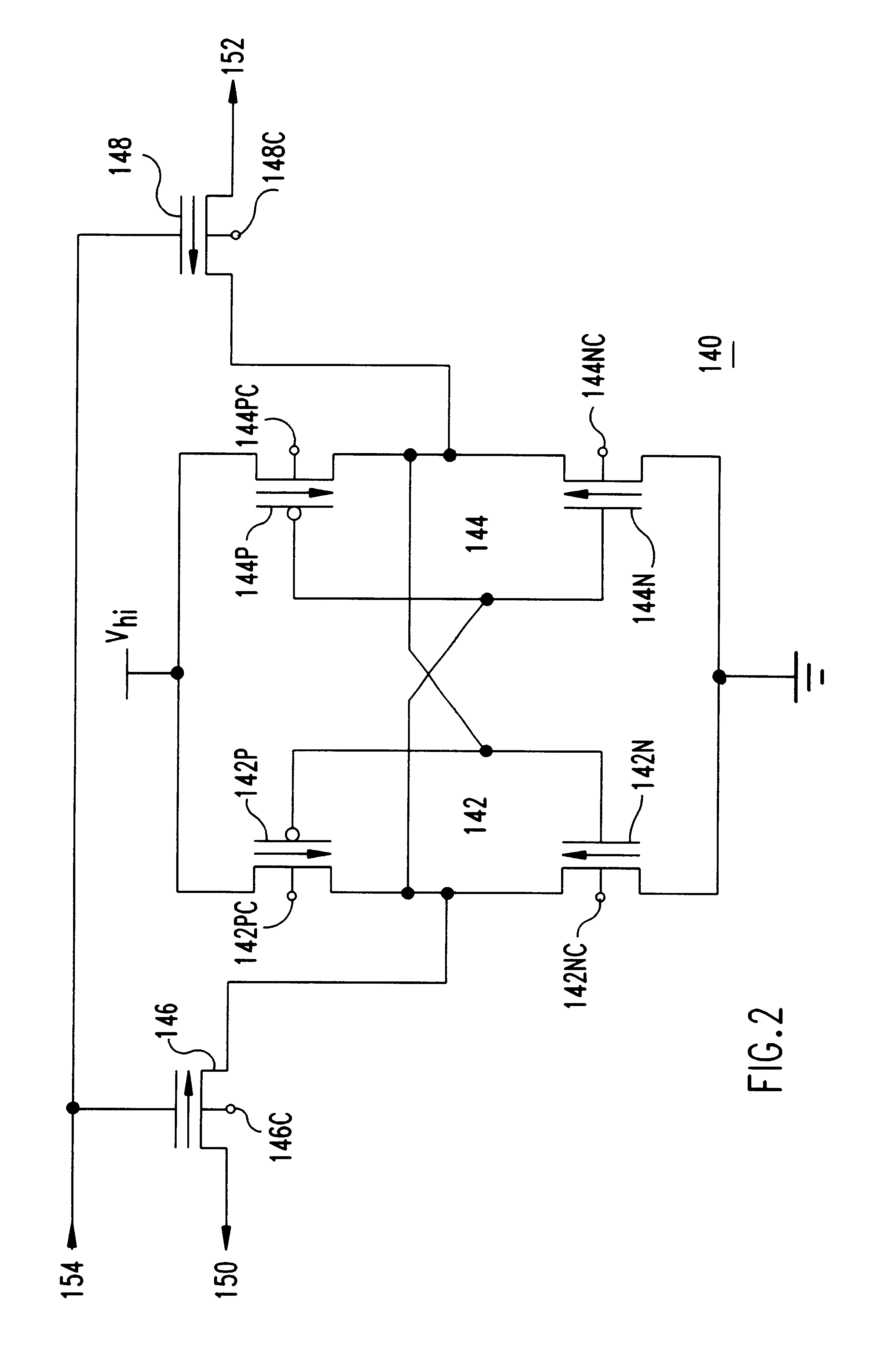
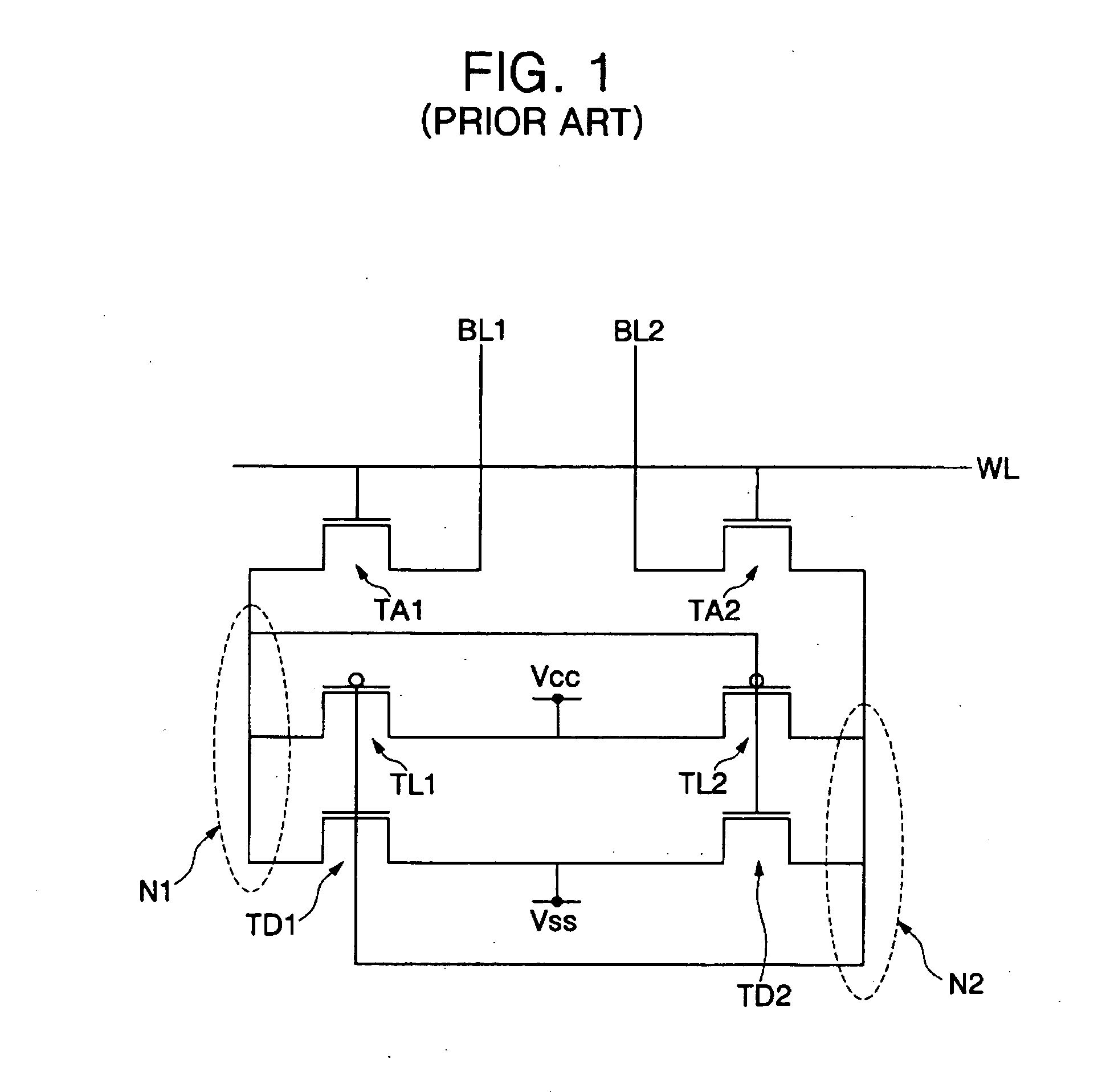
SRAM employing virtual rail scheme stable against various process-voltage-temperature variations
An SRAM employs a virtual rail configuration that is stable against process-voltage-temperature (PVT) variation. The SRAM provides a virtual power supply voltage to an SRAM cell that is obtained by lowering a power supply voltage by a threshold voltage of a transistor and a virtual ground voltage obtained by raising a ground voltage by a threshold voltage of a transistor. Due to the use of PMOS and NMOS transistors of diode types connected between the power supply voltage and the virtual power supply voltage and the use of NMOS and PMOS transistors of diode types connected between the ground voltage and the virtual ground voltage, a virtual power supply voltage level and a virtual ground voltage level that are stable even against various PVT variations are provided, so that low-leakage current characteristics are stable.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
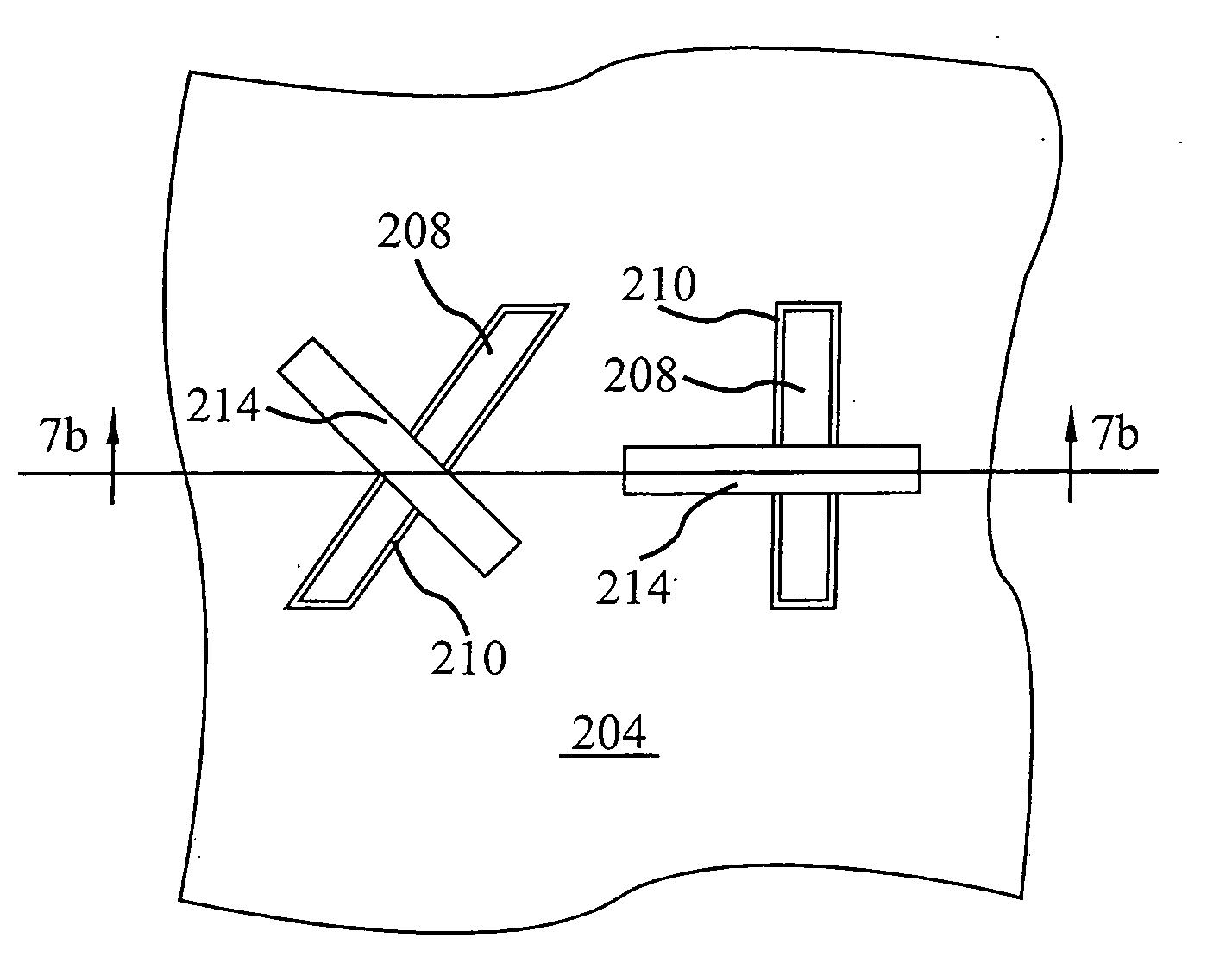
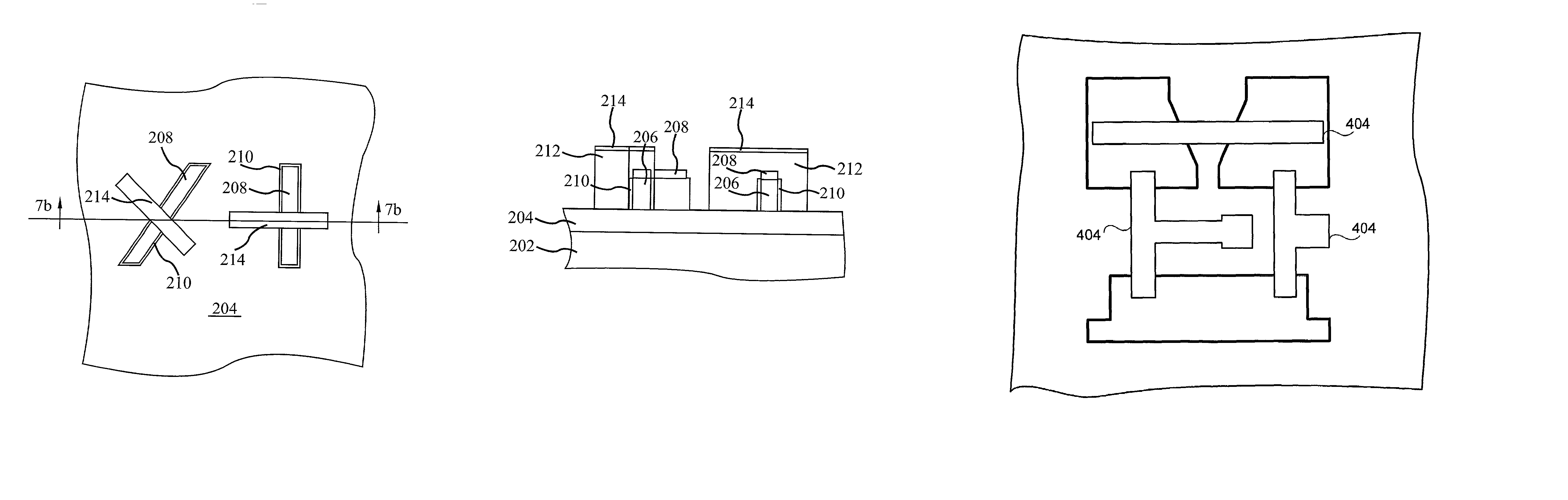
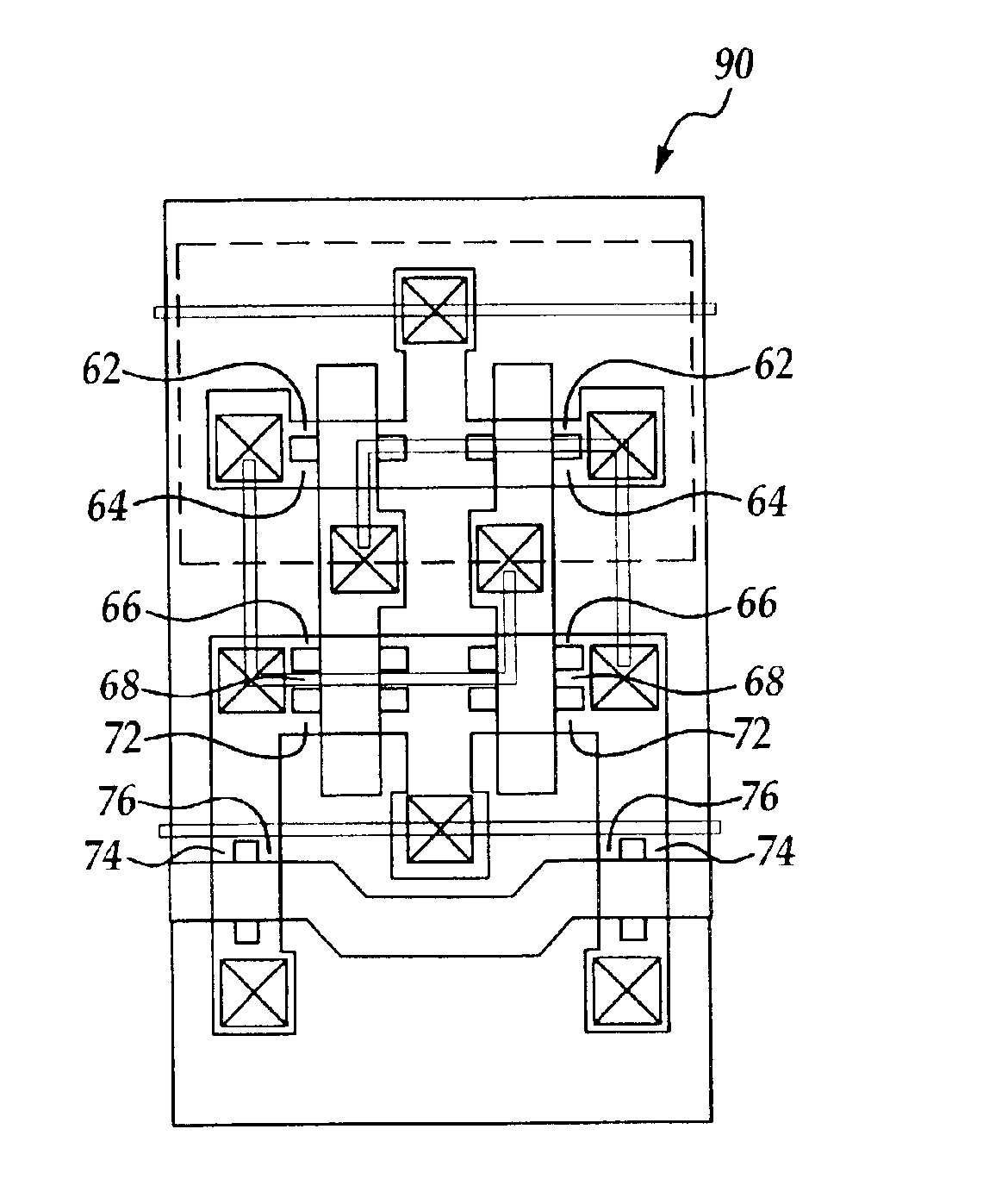
Sub-lithographic local interconnects, and methods for forming same
InactiveUS20080083991A1Achieve scaleReduce in quantityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsStatic random-access memorySram cell
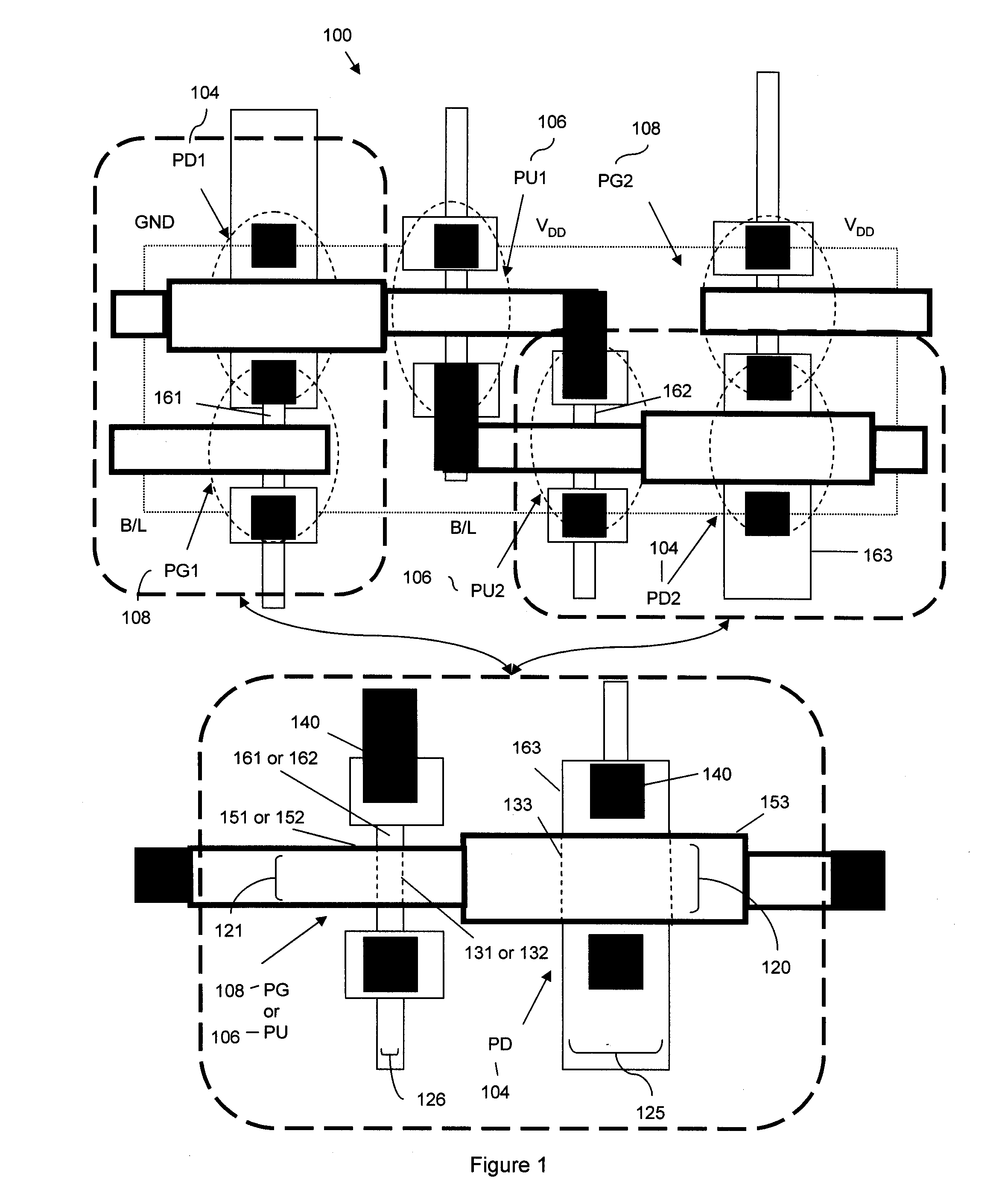
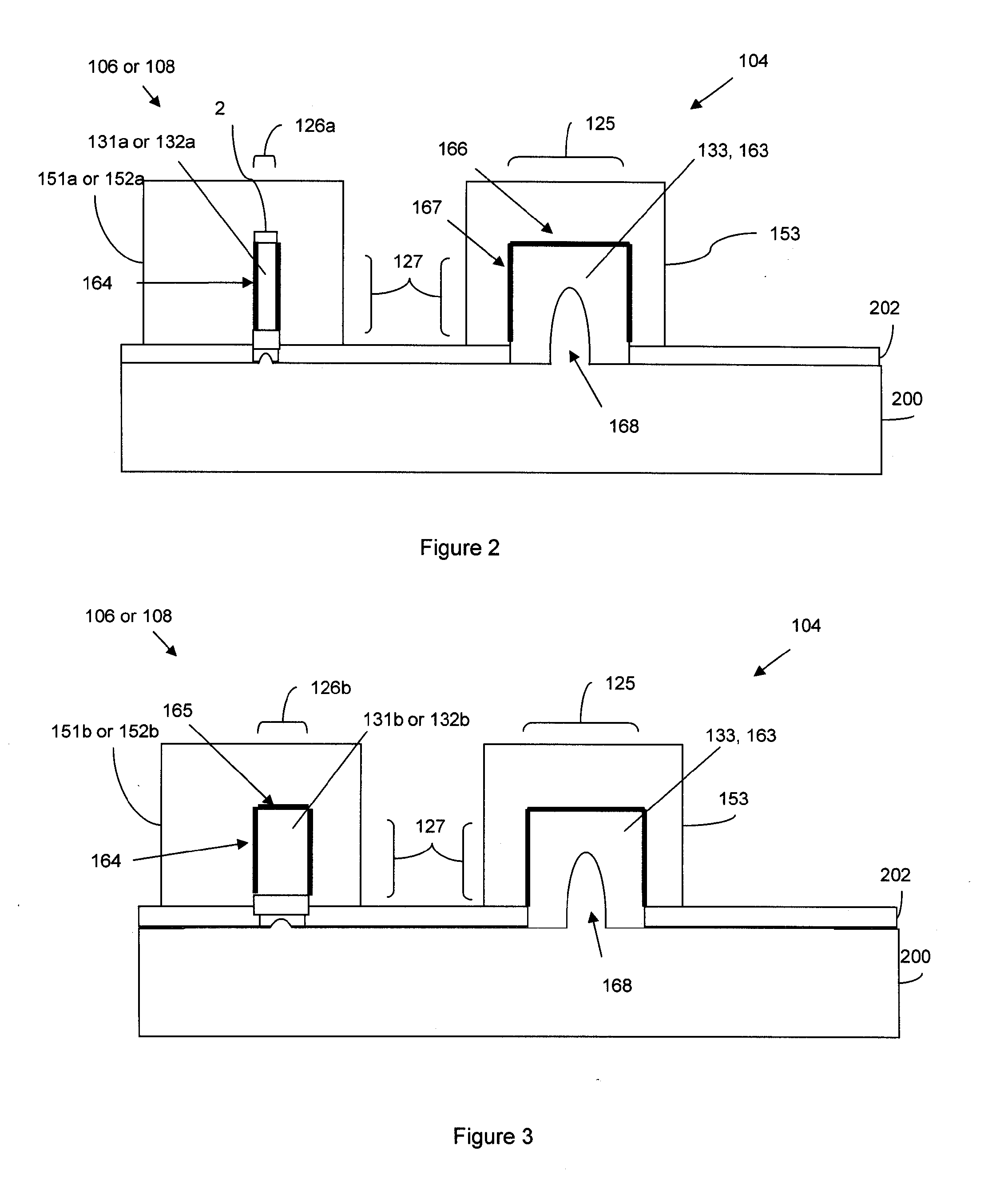
The present invention relates to a semiconductor device having first and second active device regions that are located in a semiconductor substrate and are isolated from each other by an isolation region therebetween, while the semiconductor device contains a first sub-lithographic interconnect structure having a width ranging from about 20 nm to about 40 nm for connecting the first active device region with the second active device region. The semiconductor device preferably contains at least one static random access memory (SRAM) cell located in the semiconductor substrate, and the first sub-lithographic interconnect structure directly cross-connects a pull-down transistor of the SRAM cell with a pull-up transistor thereof without any metal contact therebetween. The first sub-lithographic interconnect structure can be readily formed by lithographic patterning of a mask layer, followed by formation of sub-lithographic features using either self-assembling block copolymers or dielectric sidewall spacers.
Owner:IBM CORP
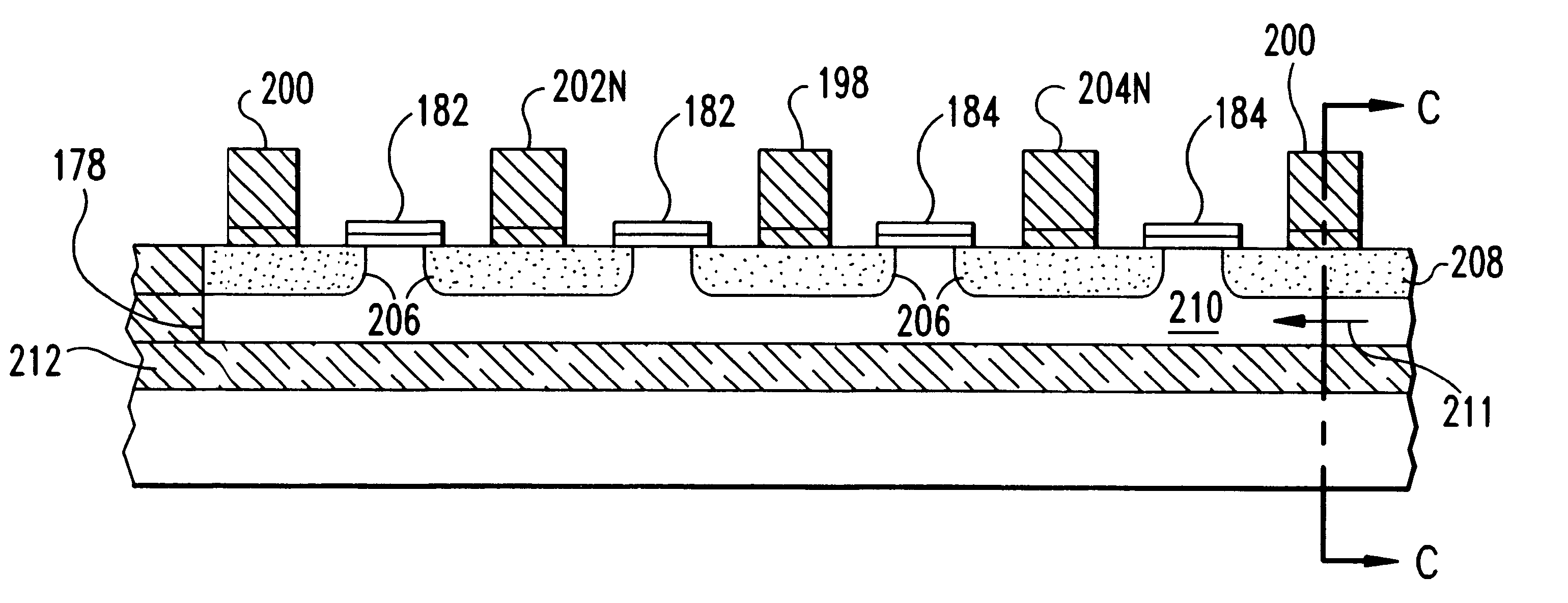
Silicon on insulator field effect transistors having shared body contact
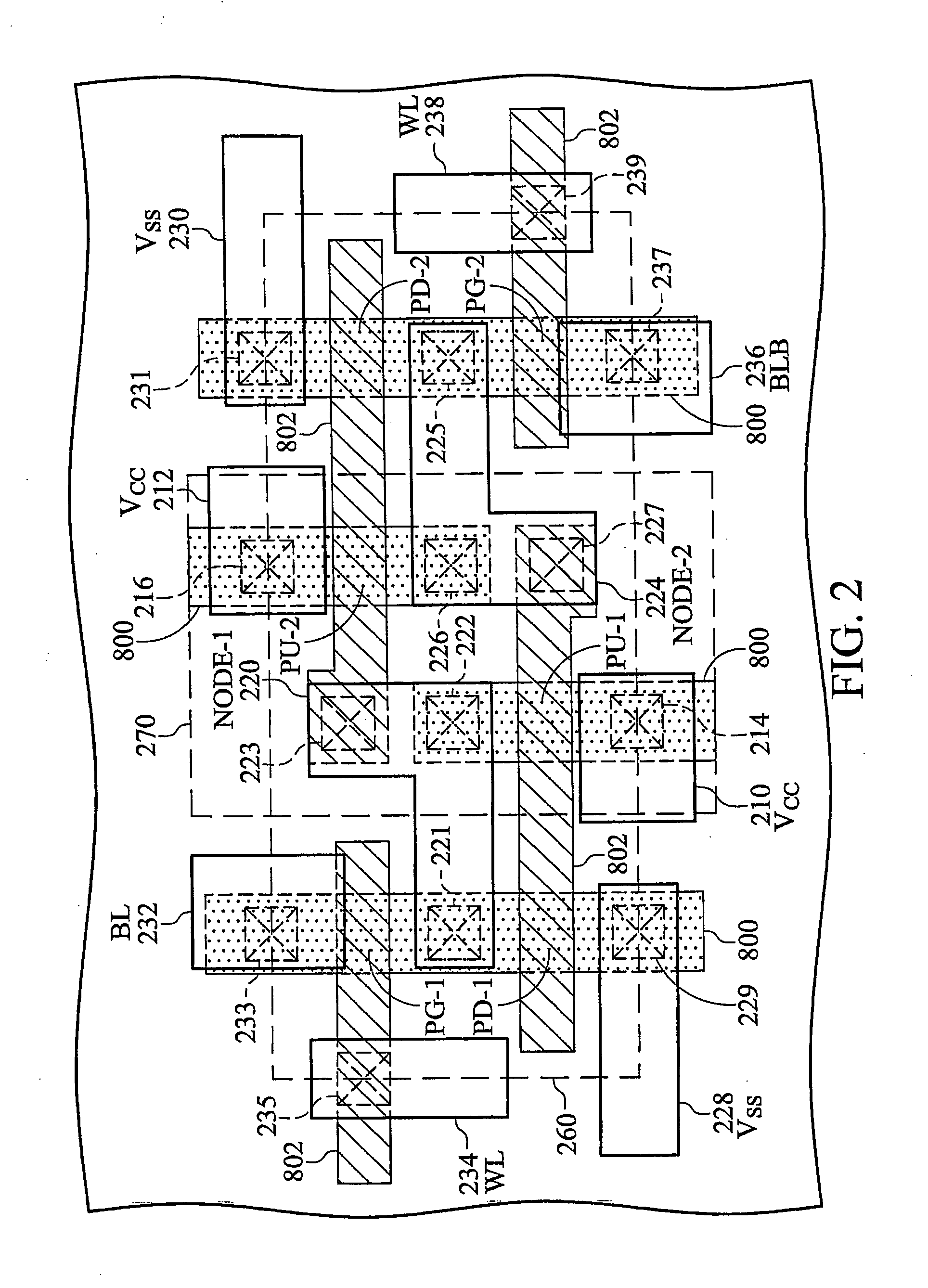
InactiveUS6624459B1Improve memory cell stabilityImprove stabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineBody contact
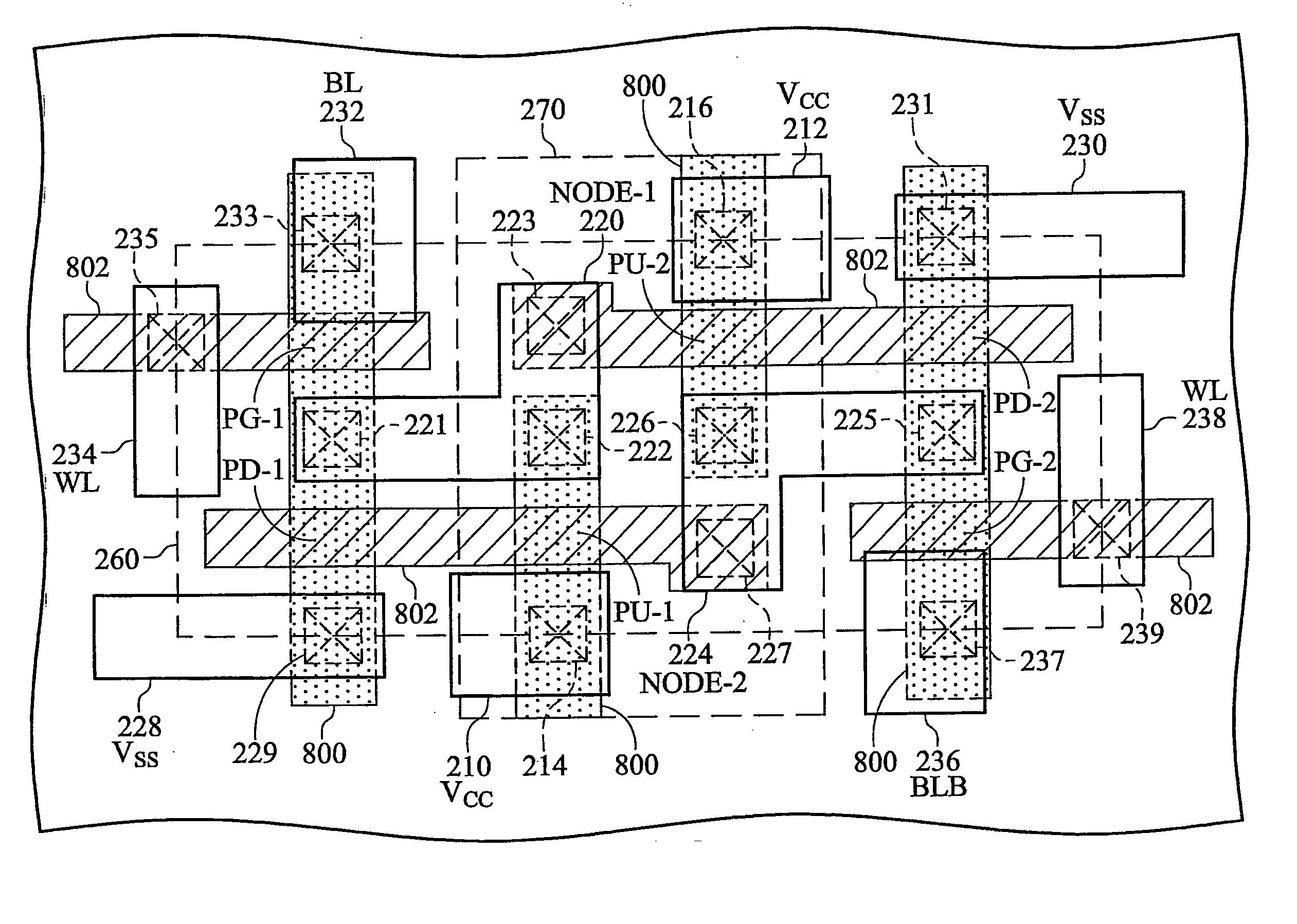
Silicon on insulator (SOI) field effect transistors (FET) with a shared body contact, a SRAM cell and array including the SOI FETs and the method of forming the SOI FETs. The SRAM cell has a hybrid SOI / bulk structure wherein the source / drain diffusions do not penetrate to the underlying insulator layer, resulting in a FET in the surface of an SOI layer with a body or substrate contact formed at a shared contact. FETs are formed on SOI silicon islands located on a BOX layer and isolated by shallow trench isolation (STI). NFET islands in the SRAM cells include a body contact to a P-type diffusion in the NFET island. Each NFET in the SRAM cells include at least one shallow source / drain diffusion that is shallower than the island thickness. A path remains under the shallow diffusions between NFET channels and the body contact. The P-type body contact diffusion is a deep diffusion, the full thickness of the island. Bit line diffusions shared by SRAM cells on adjacent wordlines may be deep diffusions.
Owner:INT BUSIENSS MACHINES IBM +1
Finfet SRAM cell using low mobility plane for cell stability and method for forming
InactiveUS6967351B2Accurate operationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStatic random-access memoryLow mobility
The present invention provides a device design and method for forming the same that results in Fin Field Effect Transistors having different gains without negatively impacting device density. The present invention forms relatively low gain FinFET transistors in a low carrier mobility plane and relatively high gain FinFET transistors in a high carrier mobility plane. Thus formed, the FinFETs formed in the high mobility plane have a relatively higher gain than the FinFETs formed in the low mobility plane. The embodiments are of particular application to the design and fabrication of a Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) cell. In this application, the bodies of the n-type FinFETs used as transfer devices are formed along the {110} plane. The bodies of the n-type FinFETs and p-type FinFETs used as the storage latch are formed along the {100}. Thus formed, the transfer devices will have a gain approximately half that of the n-type storage latch devices, facilitating proper SRAM operation.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
CMOS SRAM cell configured using multiple-gate transistors
InactiveUS6864519B2High dielectric constantSave layout area andTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCMOSBit line
A complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor static random access memory cell that is formed by a pair of P-channel multiple-gate field-effect transistors (P-MGFETs), a pair of N-channel multiple-gate field-effect transistors (N-MGFETs), a second pair of N-MGFETs that has a drain respectively connected to a connection linking the respective drain of the N-MGFET of the first pair of N-MGFET to the drain of the P-MGFET of the pair of P-MGFETs; a pair of complementary bit lines, each respectively connected to the source of the N-MGFET of the second pair of N-MGFETS; and a word line connected to the gates of the N-MGFETs of the second pair of N-MGFETs.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method of forming a static random access memory with a buried local interconnect
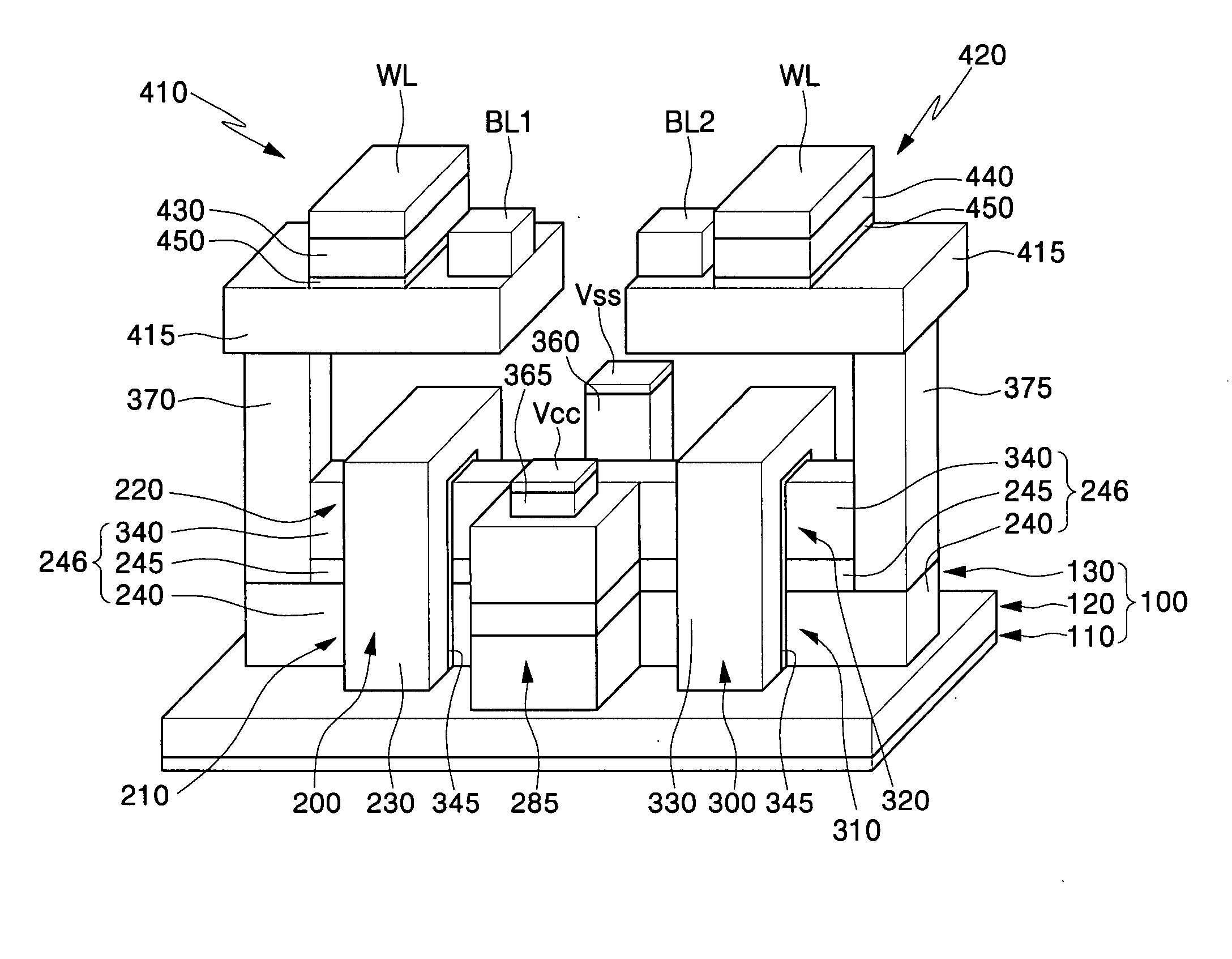
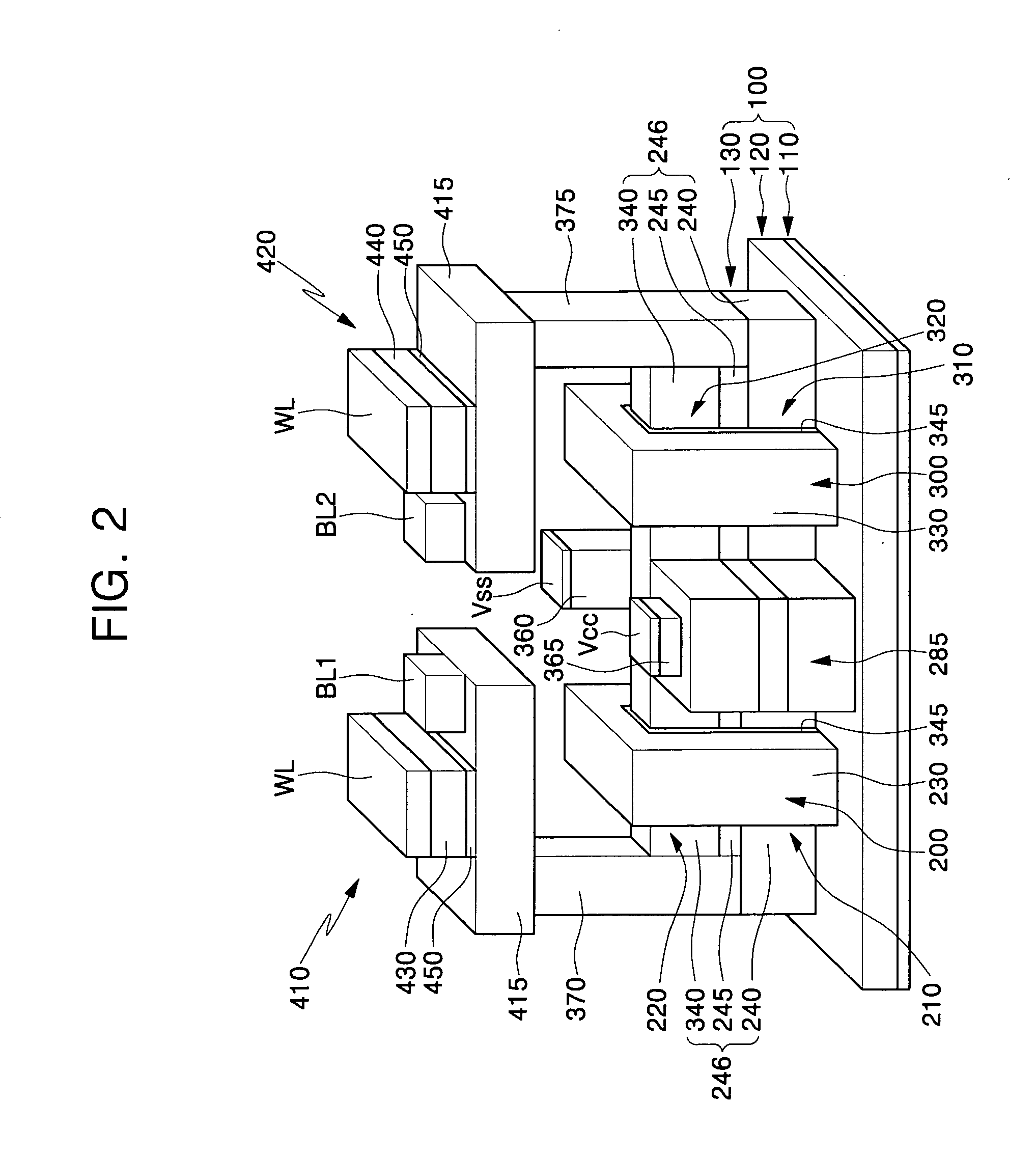
ActiveUS20060019488A1Reduce the numberReduce spacingTransistorSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryEngineering
An SRAM cell includes six transistors. The storage nodes are implemented using local interconnects. A first level of metal overlies the interconnects but is electrically isolated therefrom. Contact plugs are formed to couple the cell to the first level of metal. The contact plugs are preferably formed in a different process step than the interconnects.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
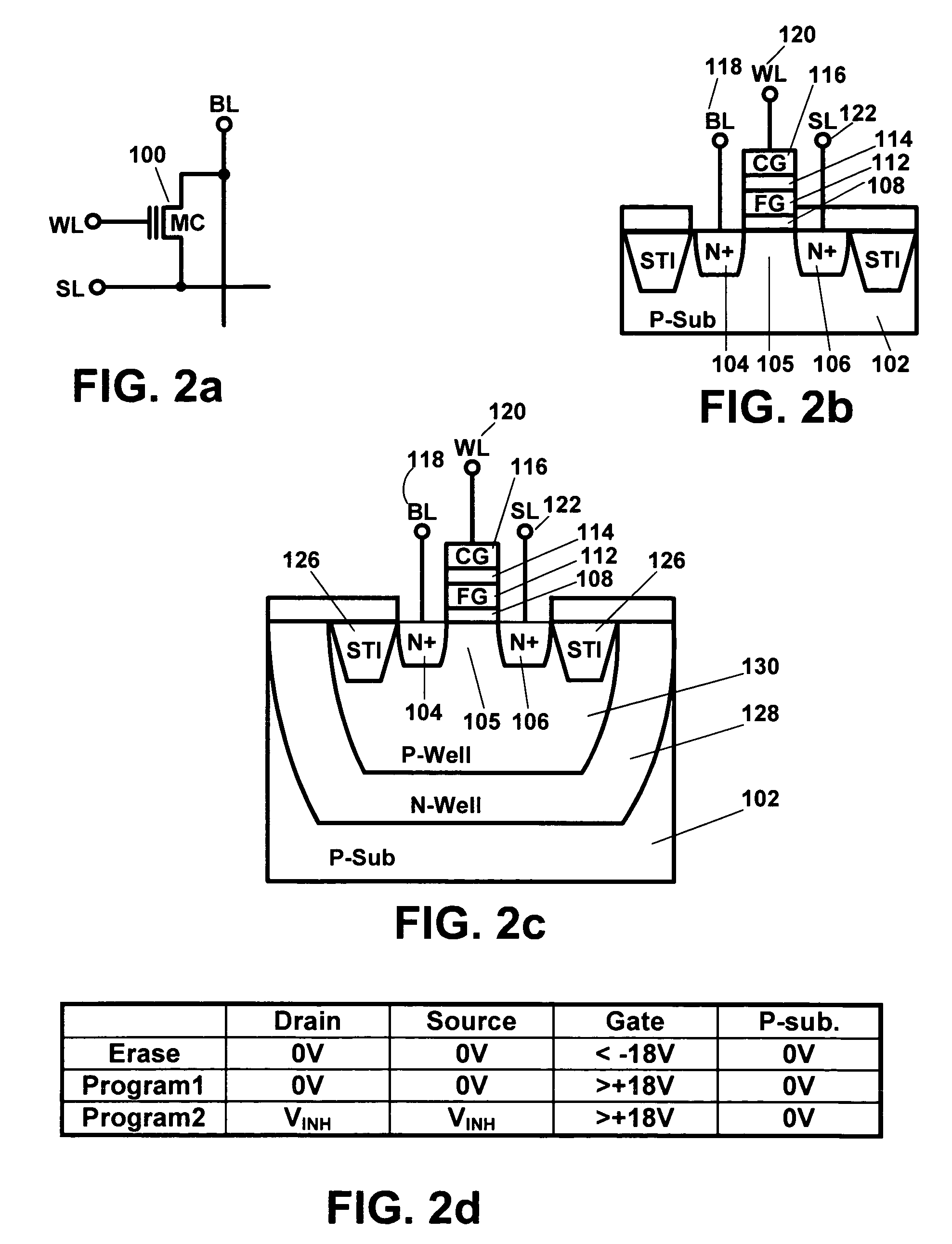
SRAM cells with repressed floating gate memory, low tunnel barrier interpoly insulators
InactiveUS20050169054A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate oxideSram cell
Structures and methods are provided for SRAM cells having a novel, non-volatile floating gate transistor, e.g. a non-volatile memory component, within the cell which can be programmed to provide the SRAM cell with a definitive asymmetry so that the cell always starts in a particular state. The SRAM cells include a pair of cross coupled transistors. At least one of the cross coupled transistors includes a first source / drain region and a second source / drain region separated by a channel region in a substrate. A floating gate opposes the channel region and separated therefrom by a gate oxide. A control gate opposes the floating gate. The control gate is separated from the floating gate by a low tunnel barrier intergate insulator.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
SRAM cells with repressed floating gate memory, low tunnel barrier interpoly insulators
Structures and methods are provided for SRAM cells having a novel, non-volatile floating gate transistor, e.g. a non-volatile memory component, within the cell which can be programmed to provide the SRAM cell with a definitive asymmetry so that the cell always starts in a particular state. The SRAM cells include a pair of cross coupled transistors. At least one of the cross coupled transistors includes a first source / drain region and a second source / drain region separated by a channel region in a substrate. A floating gate opposes the channel region and separated therefrom by a gate oxide. A control gate opposes the floating gate. The control gate is separated from the floating gate by a low tunnel barrier intergate insulator.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Back-gate controlled read SRAM cell
InactiveUS20060227595A1Reduced area overheadImprove SRAM stabilityRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineStatic random-access memory
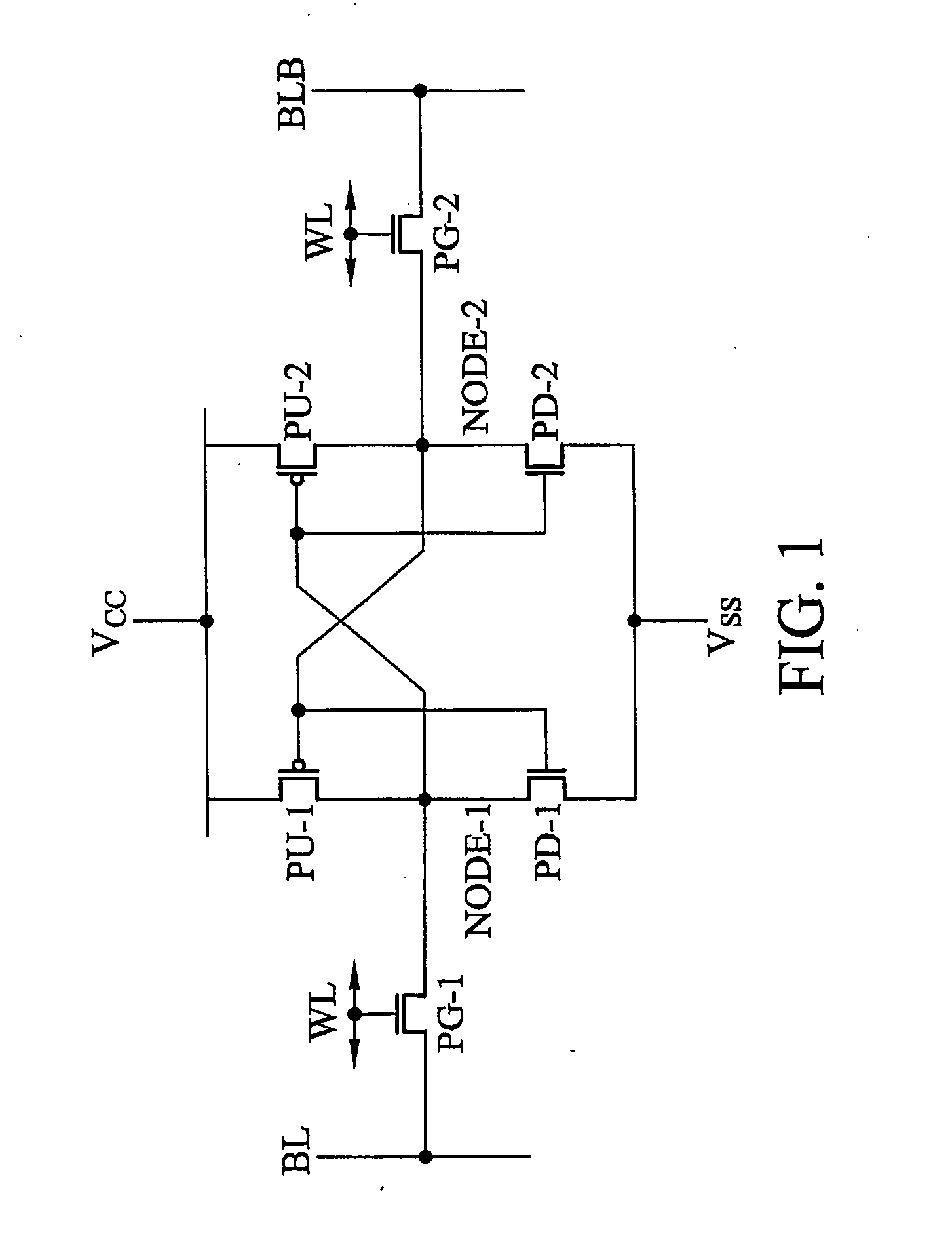
Disclosed is an eight transistor static random access memory (SRAM) device, comprising first and second inverters, a first bit line, a first complement bit line, a pair of write access transistors, and a pair of read access transistors. Each of the first and second inverters includes a respective pair of transistors, and has a respective data node. Each of a first and a second of the access transistors has a source, a drain, a front gate, and a back gate. The first access transistor is coupled to the first bit line, and the second access transistor is coupled to the first complement bit line. The back gate of the first access transistor is coupled to the data node of the first inverter; and the back gate of the second access transistor is coupled to the data node of the second inverter. This increases the difference between the threshold voltages of the first and second access transistors.
Owner:IBM CORP
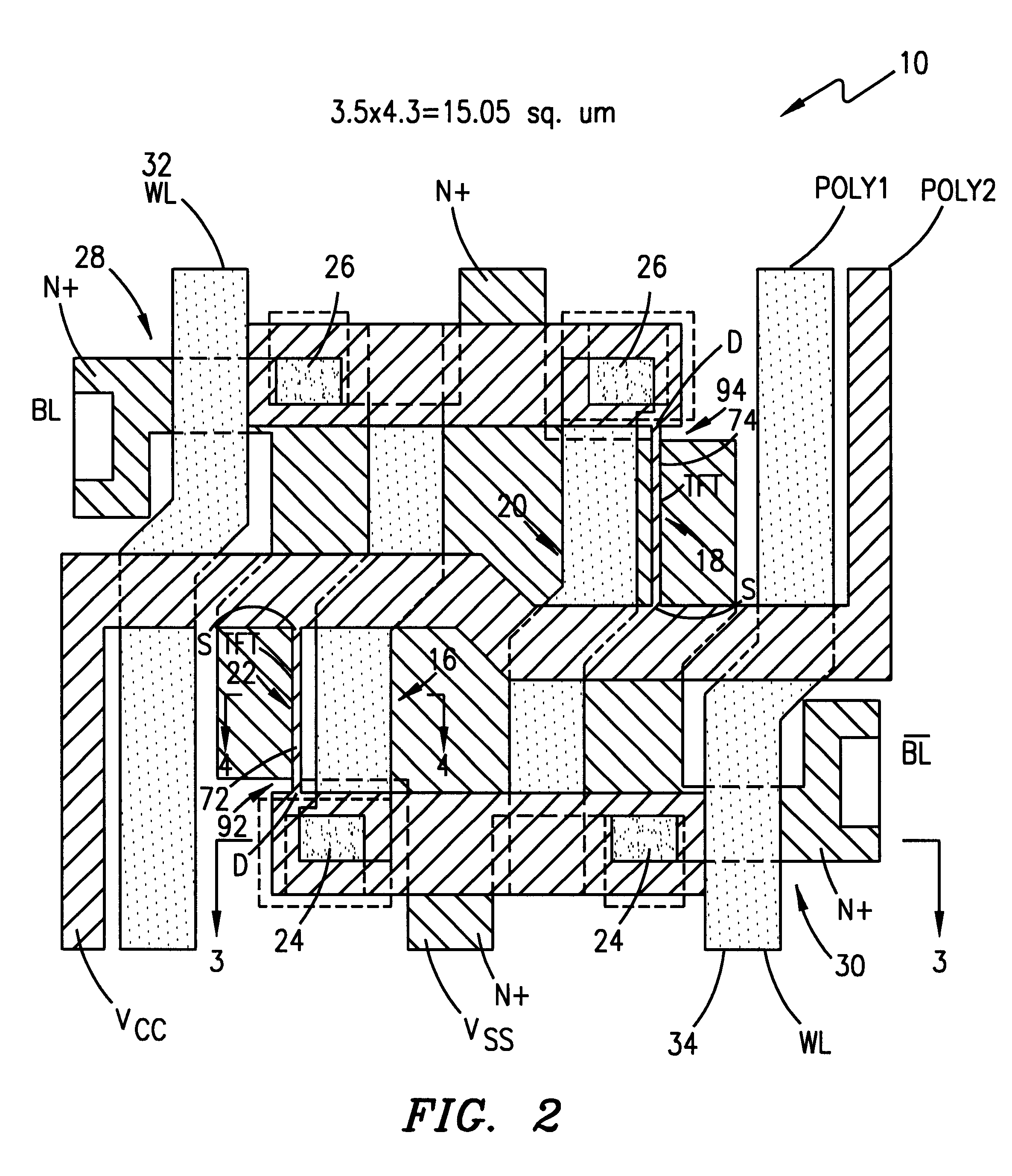
Method of making an SRAM cell and structure
A six transistor static random access memory (SRAM) cell with thin-film pull-up transistors and method of making the same includes providing two bulk silicon pull-down transistors of a first conductivity type, two active gated pull-up thin-film transistors (TFTs) of a second conductivity type, two pass gates, a common word line, and two bit line contacts. The bulk silicon pull-down transistors, two active gated pull-up TFTs, and two pass gates are connected at four shared contacts. In addition, the two bulk silicon pull-down transistors and the two active gated pull-up TFTs are formed with two polysilicon layers, a first of the polysilicon layers (poly1) is salicided and includes poly1 gate electrodes for the two bulk silicon pull-down transistors. A second of the polysilicon layers (poly2) includes desired poly2 stringers disposed along side edges of the poly1 gate electrodes, the desired poly2 stringers forming respective channel regions of the pull-up TFTs.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
CMOS SRAM cells employing multiple-gate transistors and methods fabricating the same
Complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) static random access memory (SRAM) cells include at least a first inverter formed in a fin-shaped pattern of stacked semiconductor regions of opposite conductivity type. In some of these embodiments, the first inverter includes a first conductivity type (e.g., P-type or N-type) MOS load transistor electrically coupled in series with a second conductivity type (e.g., N-type of P-type) MOS driver transistor. The first inverter is arranged so that active regions of the first conductivity type MOS load transistor and the second conductivity type driver transistor are vertically stacked relative to each other within a first portion of a vertical dual-conductivity semiconductor fin structure. This fin structure is surrounded on at least three sides by a wraparound gate electrode, which is configured to modulate conductivity of both the active regions in response to a gate signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
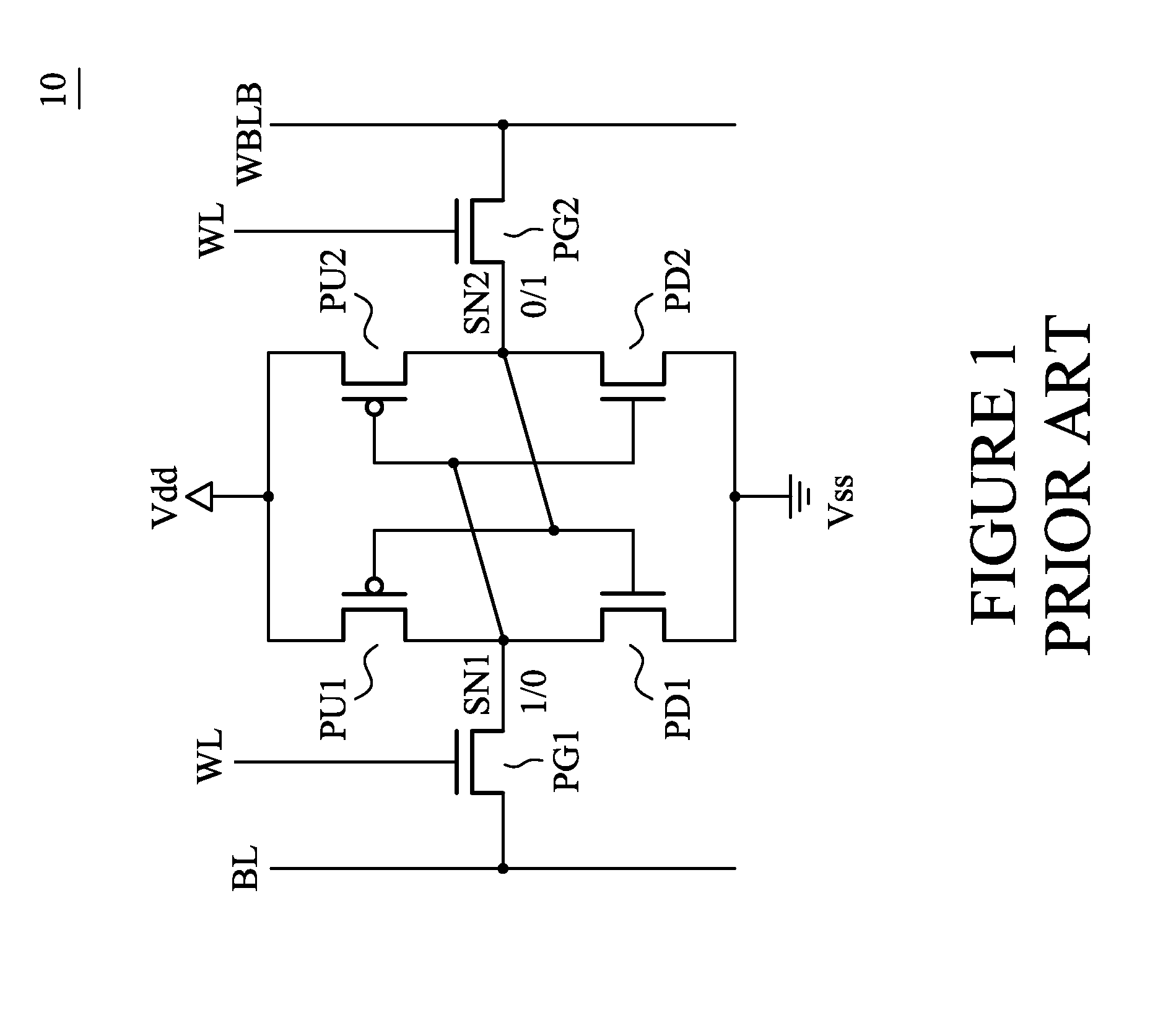
Method and apparatus for improving stability of a 6T CMOS SRAM cell
The present invention is a CMOS SRAM cell comprising two access devices, each access device comprised of a tri-gate transistor having a single fin; two pull-up devices, each pull-up device comprised of a tri-gate transistor having a single fin; and two pull-down devices, each pull-down device comprised of a tri-gate transistor having multiple fins. A method for manufacturing the CMOS SRAM cell, including the dual fin tri-gate transistor is also provided.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
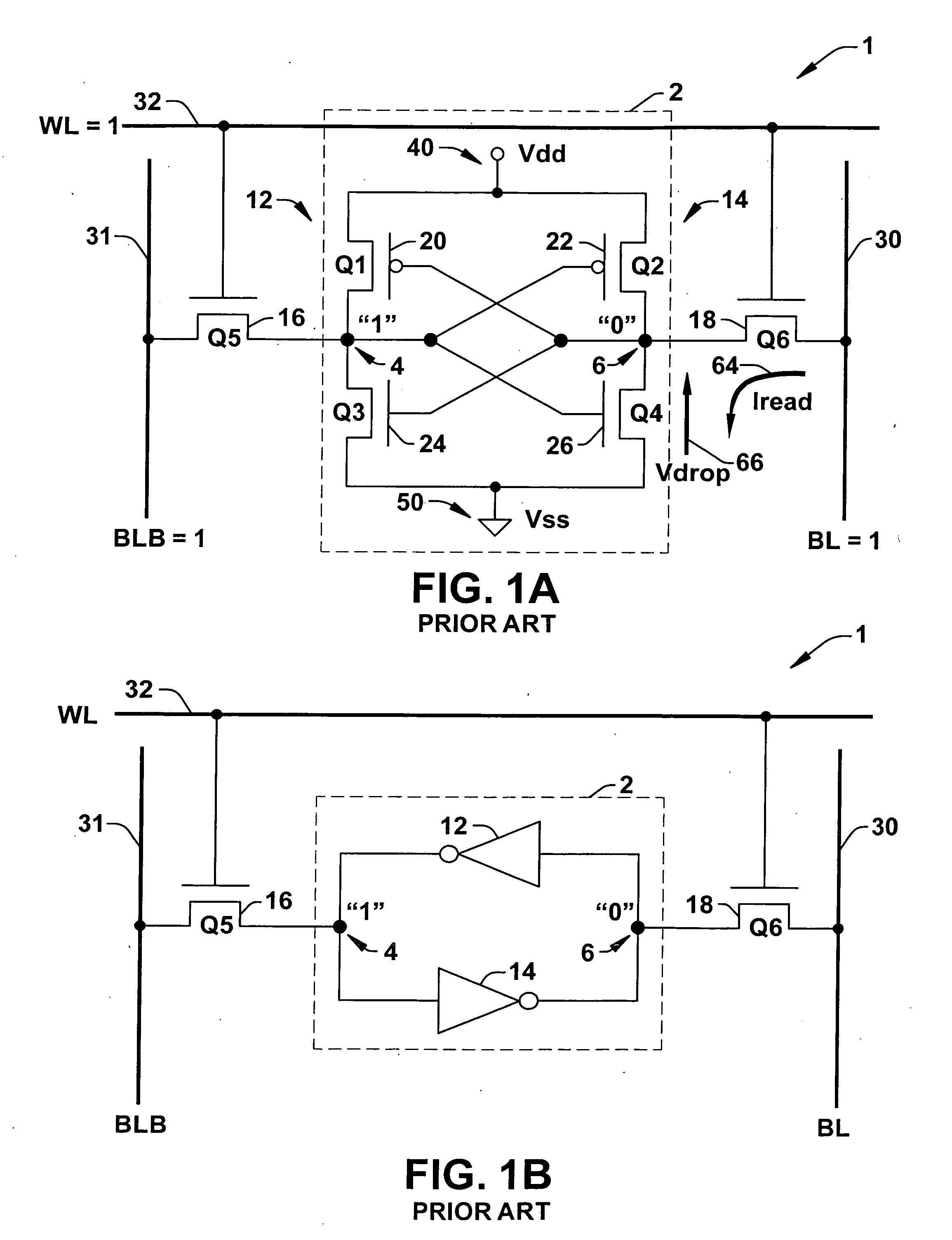
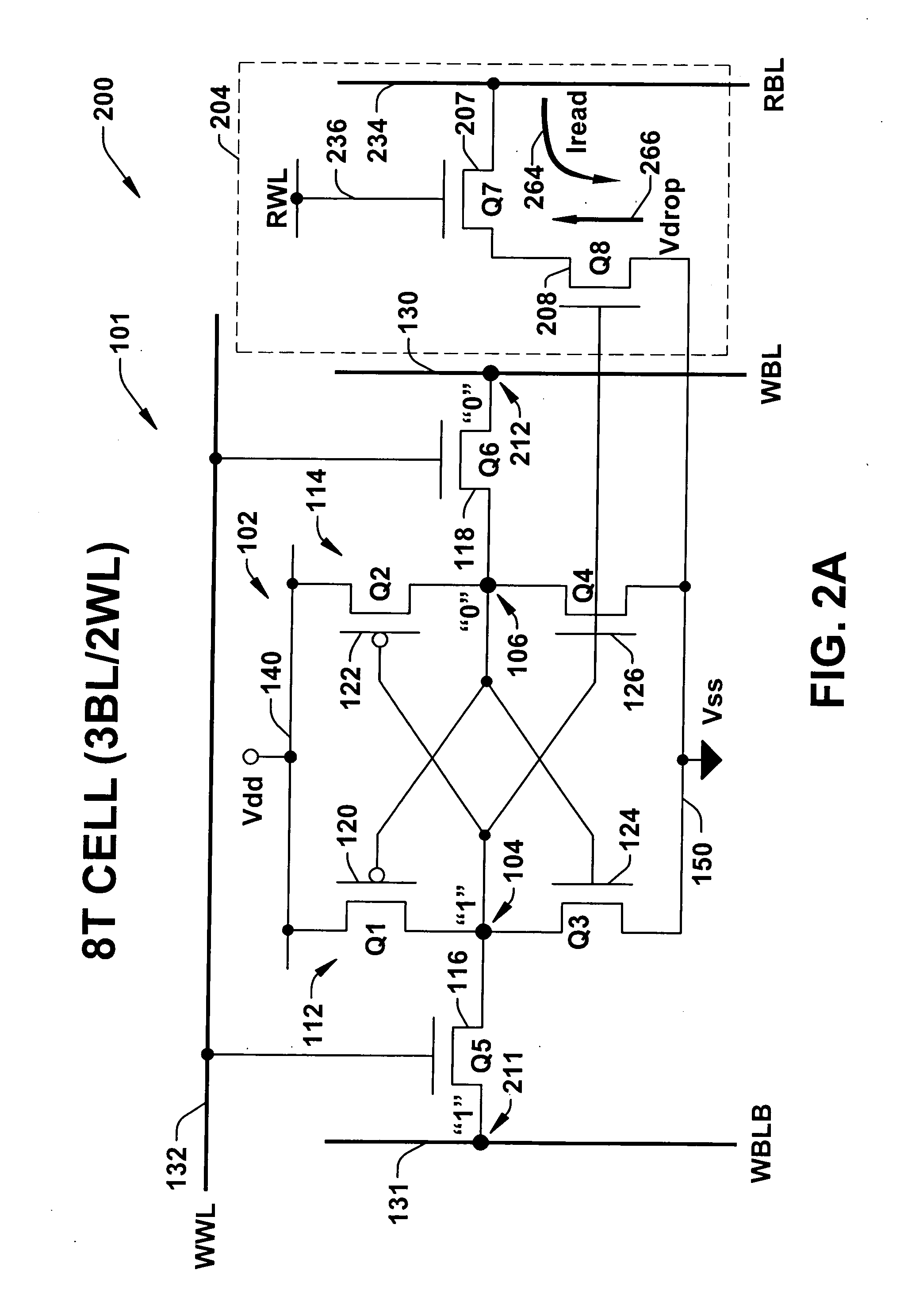
8T SRAM cell with higher voltage on the read WL
ActiveUS20070279966A1Avoid dataHigh voltageDigital storageSemiconductor devicesHemt circuitsVoltage source
The present invention provides circuitry for writing to and reading from an SRAM cell core, an SRAM cell, and an SRAM device. In one aspect, the circuitry includes a write circuit coupled to the SRAM cell core that includes a write transistor gated by a write word line. The circuitry also includes a read buffer circuit coupled to the SRAM cell core to read the cell without disturbing the state of the cell. The read buffer circuit includes a read transistor gated by a read word line, the read transistor coupled between a read bit-line and a read driver transistor that is further coupled to a voltage source Vss. The read driver transistor and a first driver transistor of the cell core are both gated by one output of the cell core. The read transistor has an electrical characteristic that differs from that of the core cell first driver transistor.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
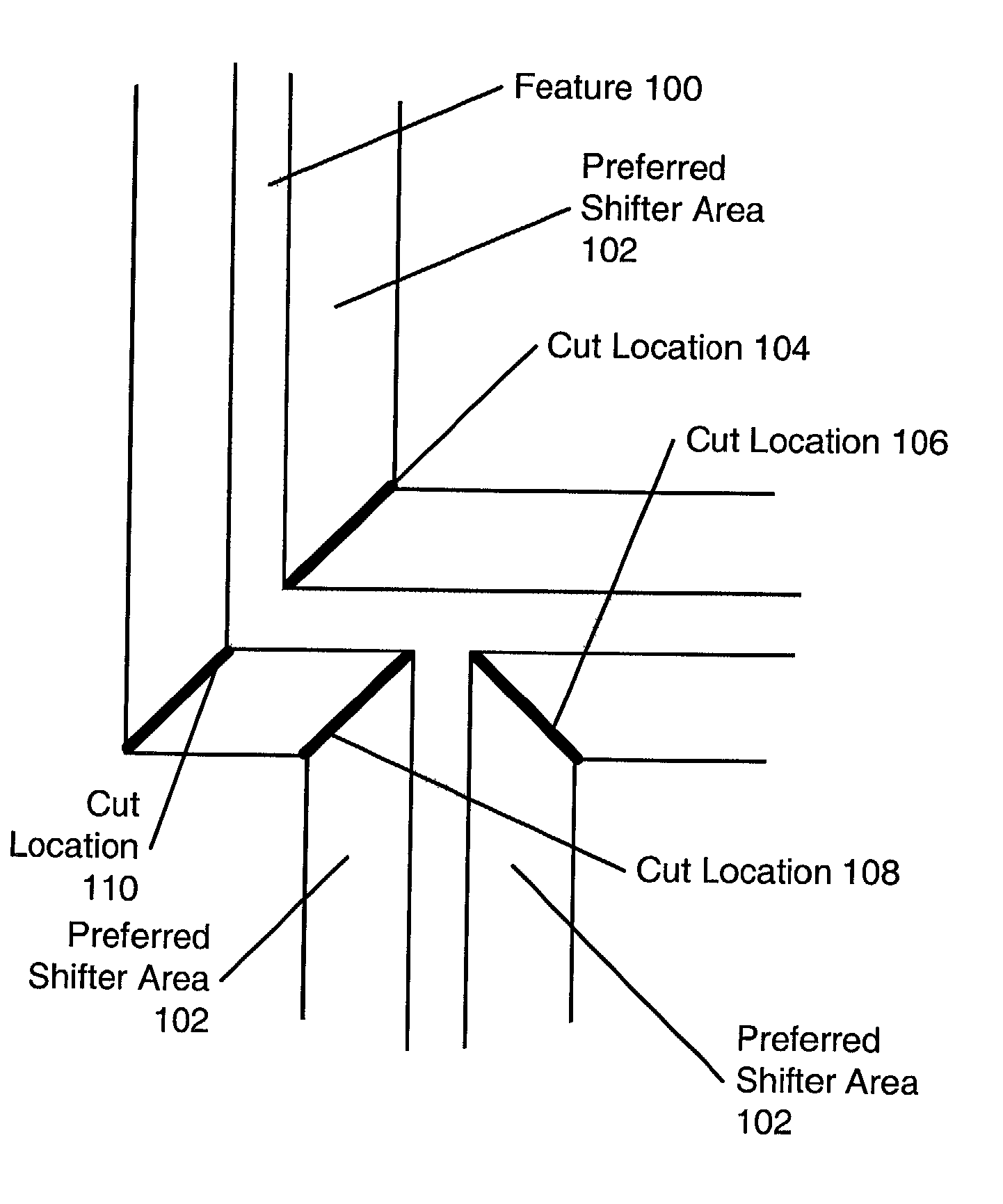
Phase shifting design and layout for static random access memory
InactiveUS20020129327A1Increase productionIncreased circuit densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
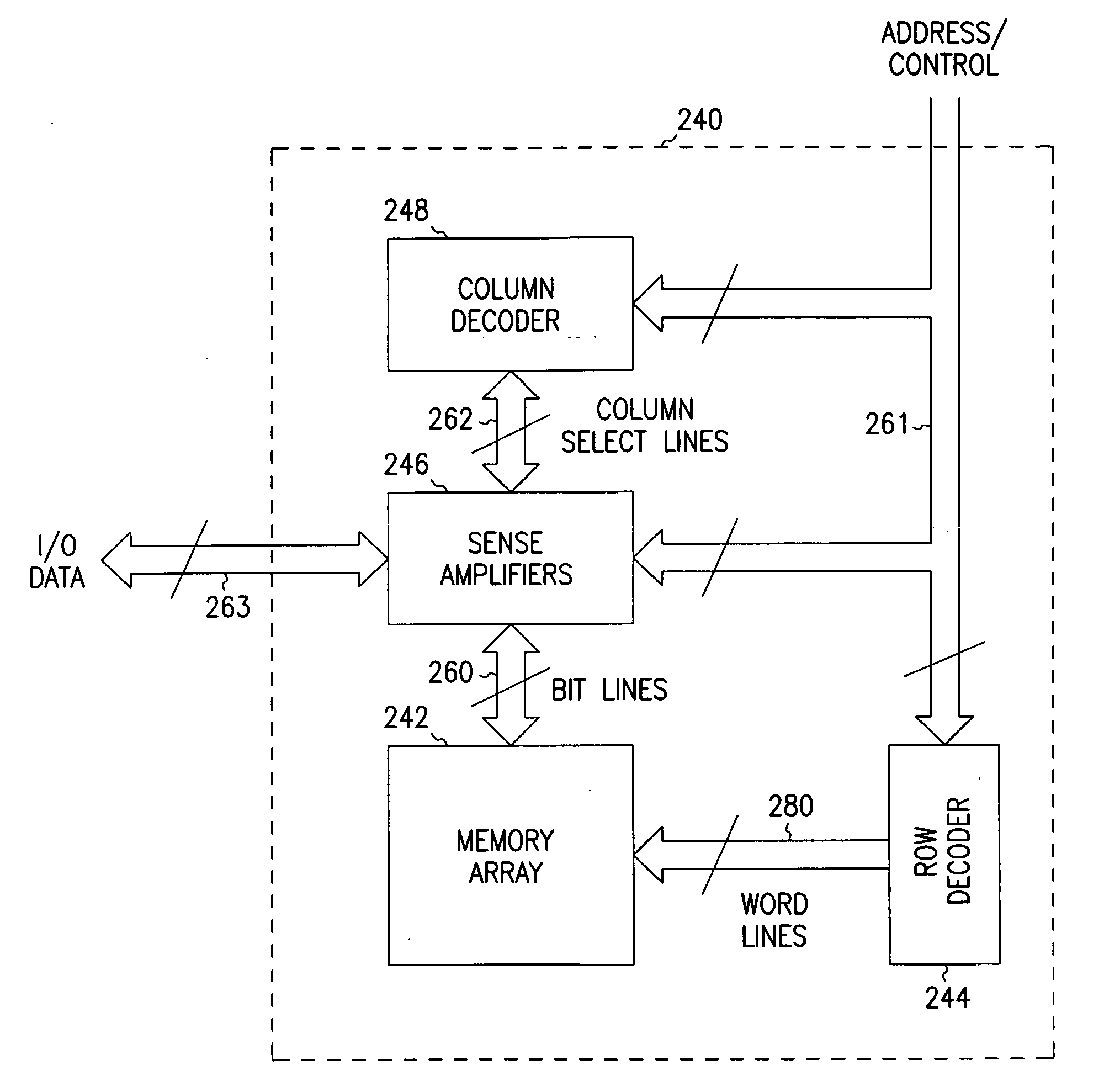
Methods and apparatus for SRAM bit cell with low standby current, low supply voltage and high speed
ActiveUS8294212B2Data stabilityLower average currentTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricGate dielectric
Circuits and methods for providing an SRAM or CAM bit cell. In one embodiment, a bit cell portion with thicker gate oxides in the storage cell transistors, and thinner gate oxides in a read port section having transistors are disclosed. The use of the thick gate oxides in the storage cell transistors provides a stable storage of data and lower standby leakage current. The use of the thinner gate oxides in the read port transistors provides fast read accesses and allows a lower Vcc,min in the read port. The methods used to form the dual gate oxide thickness SRAM cells have process steps compatible with the existing semiconductor manufacturing processes. Embodiments using high k gate dielectrics, dual gate dielectric materials in a single bit cell, and using finFET and planar devices in a bit cell are described. Methods for forming the structures are disclosed.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Write and read assist circuit for SRAM with power recycling
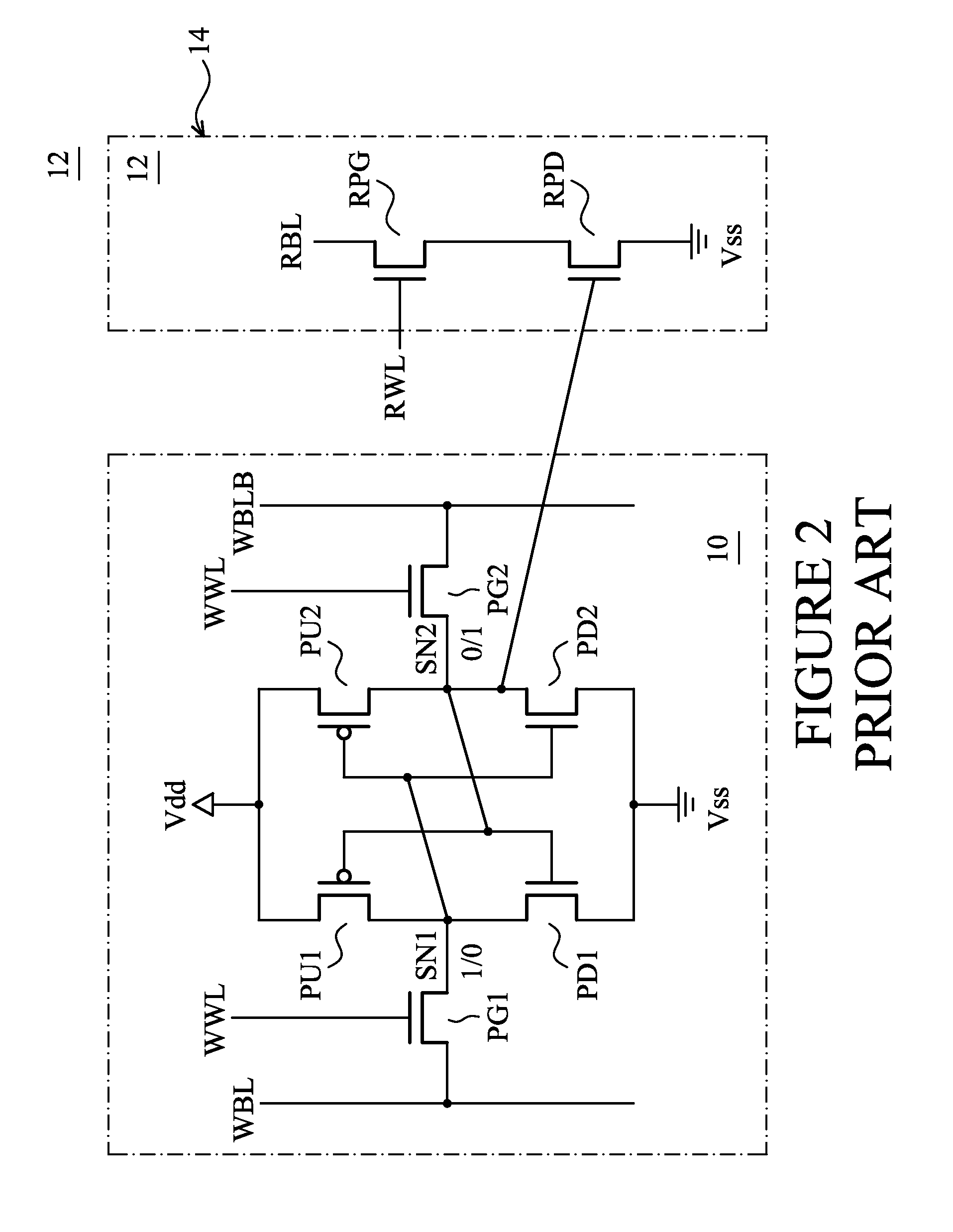
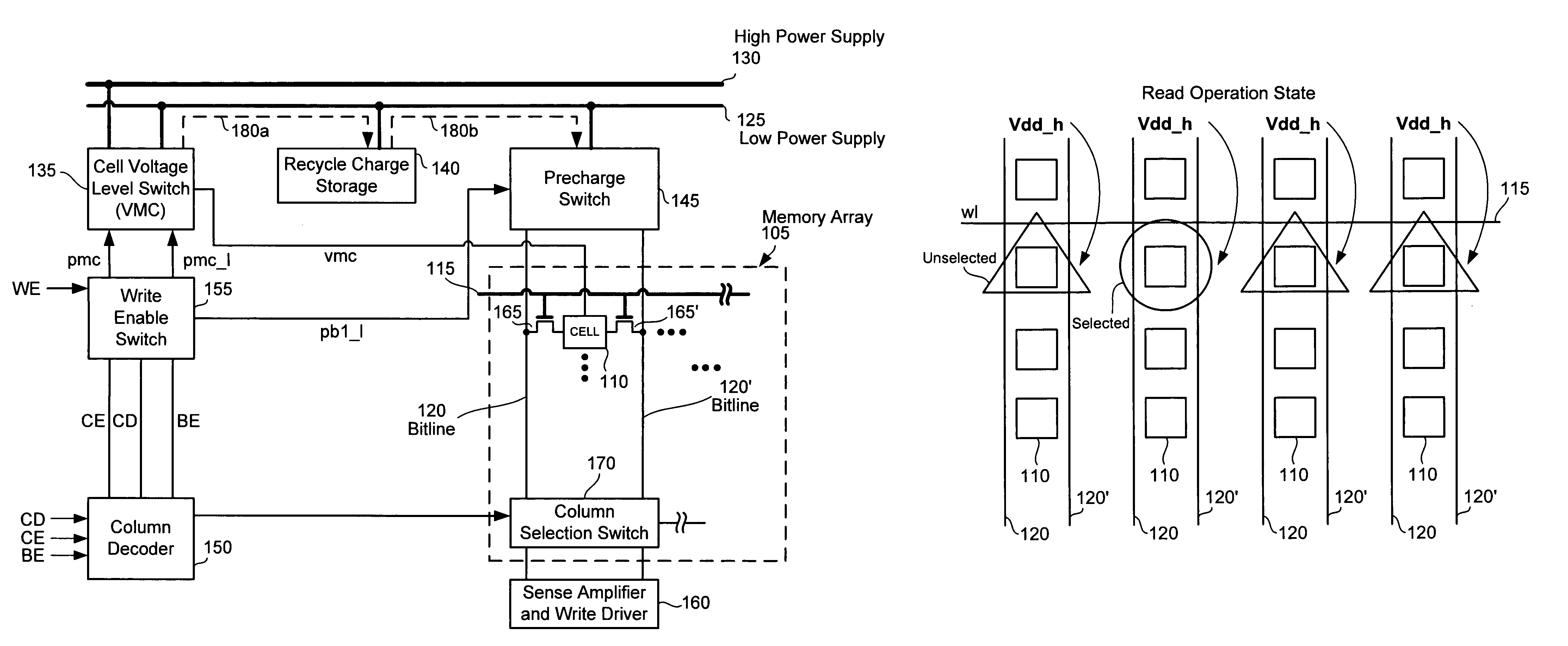
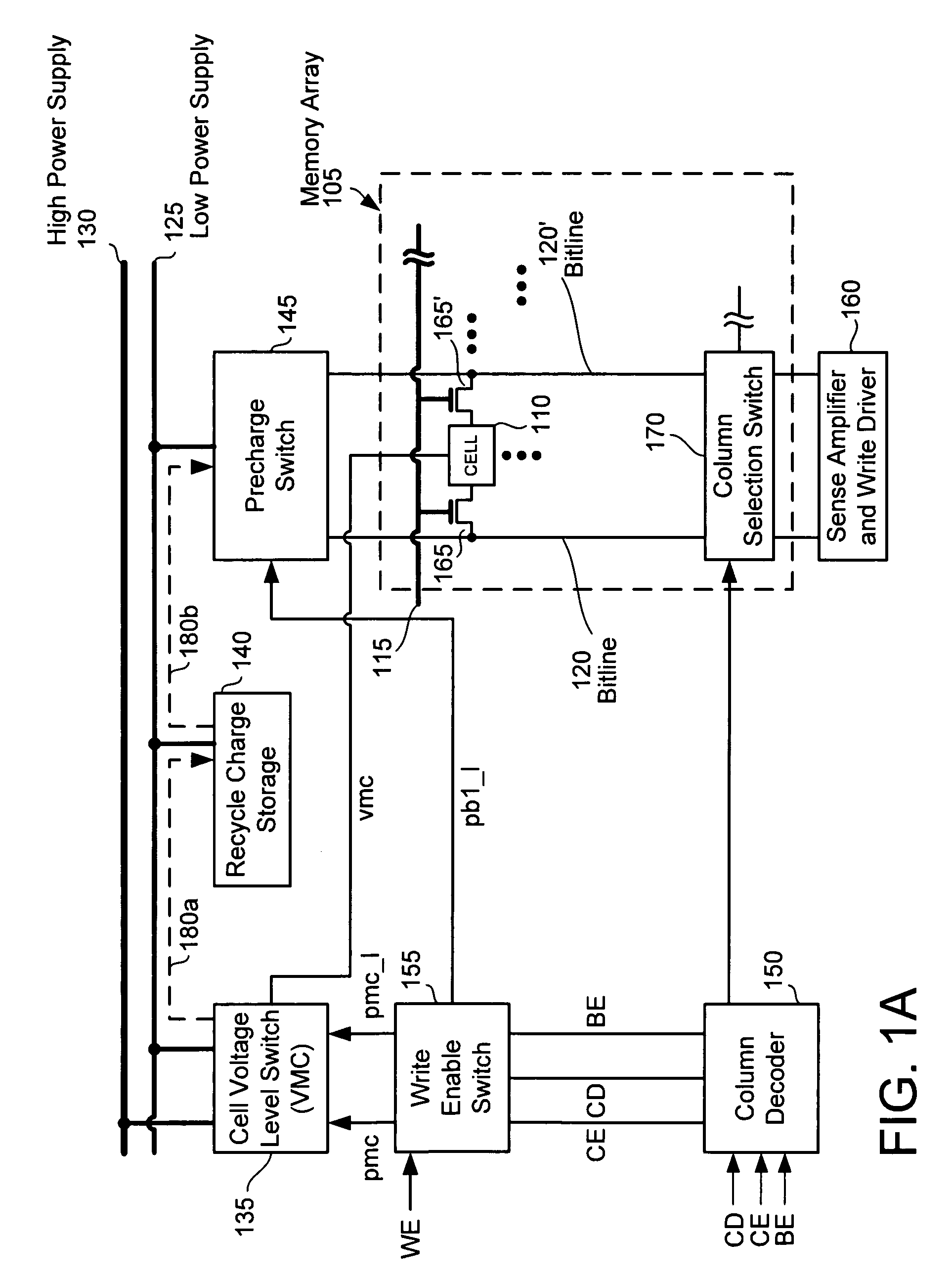
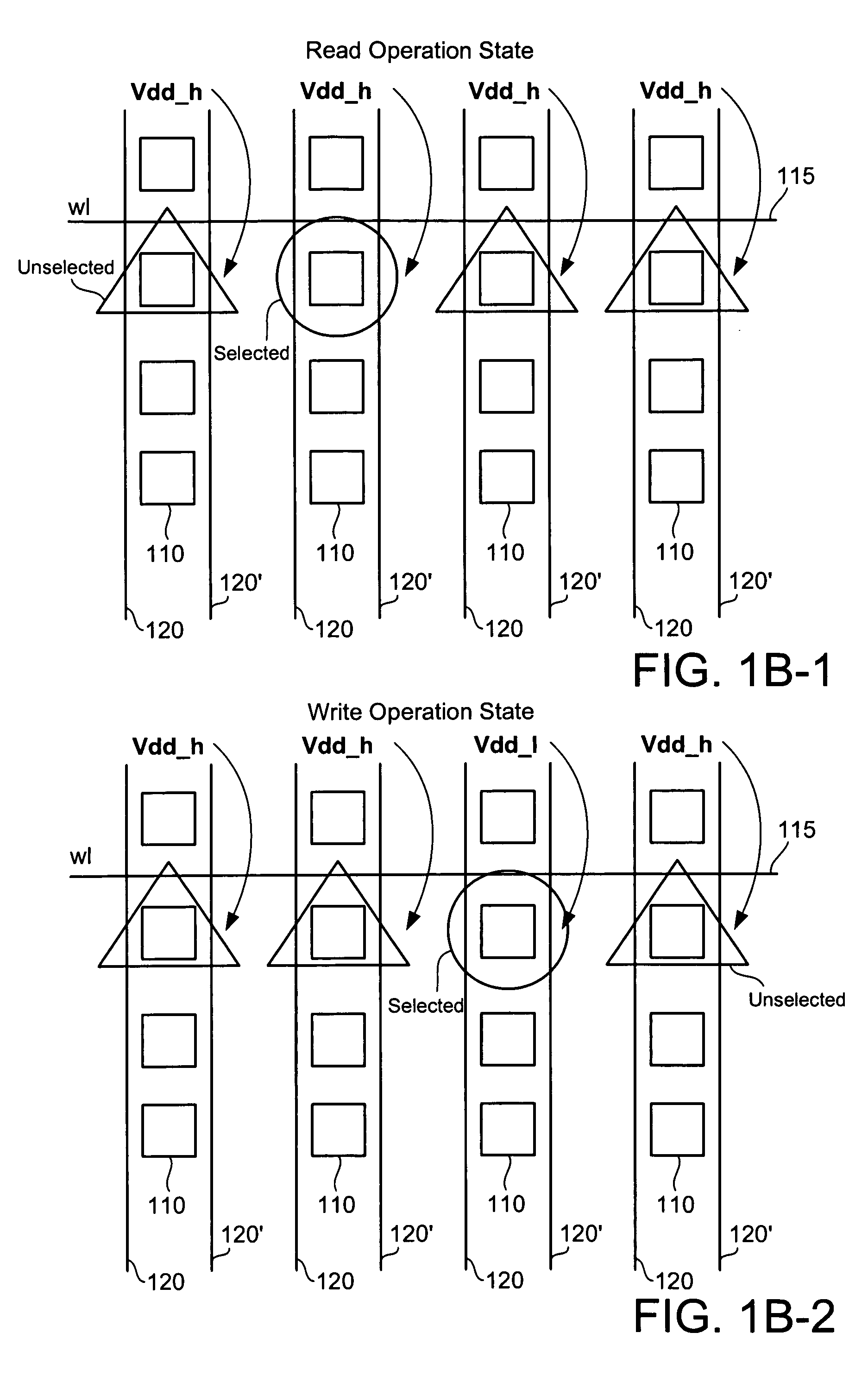
A memory circuit for reading and writing data into a SRAM memory array using charge recycling is presented. The write and read circuit includes a cell voltage level switch, a recycle charge storage, a precharge switch, a write enable switch, and column decoder. The cell voltage level switch is connected to a low power supply and a high power supply and has two states of operation: a write operation state and a read operation state. For each state of operation, the voltage level switch selectively provides a power supply if a column has been selected or if the operation is a read or write. The recycle charge storage stores excess charge from SRAM cells after a read operation or after a write operation in unselected columns. After the read or write operation, the recycle charge storage discharges excess charge to the bitlines during bitline precharging.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com