Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
134 results about "Tunnel diode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
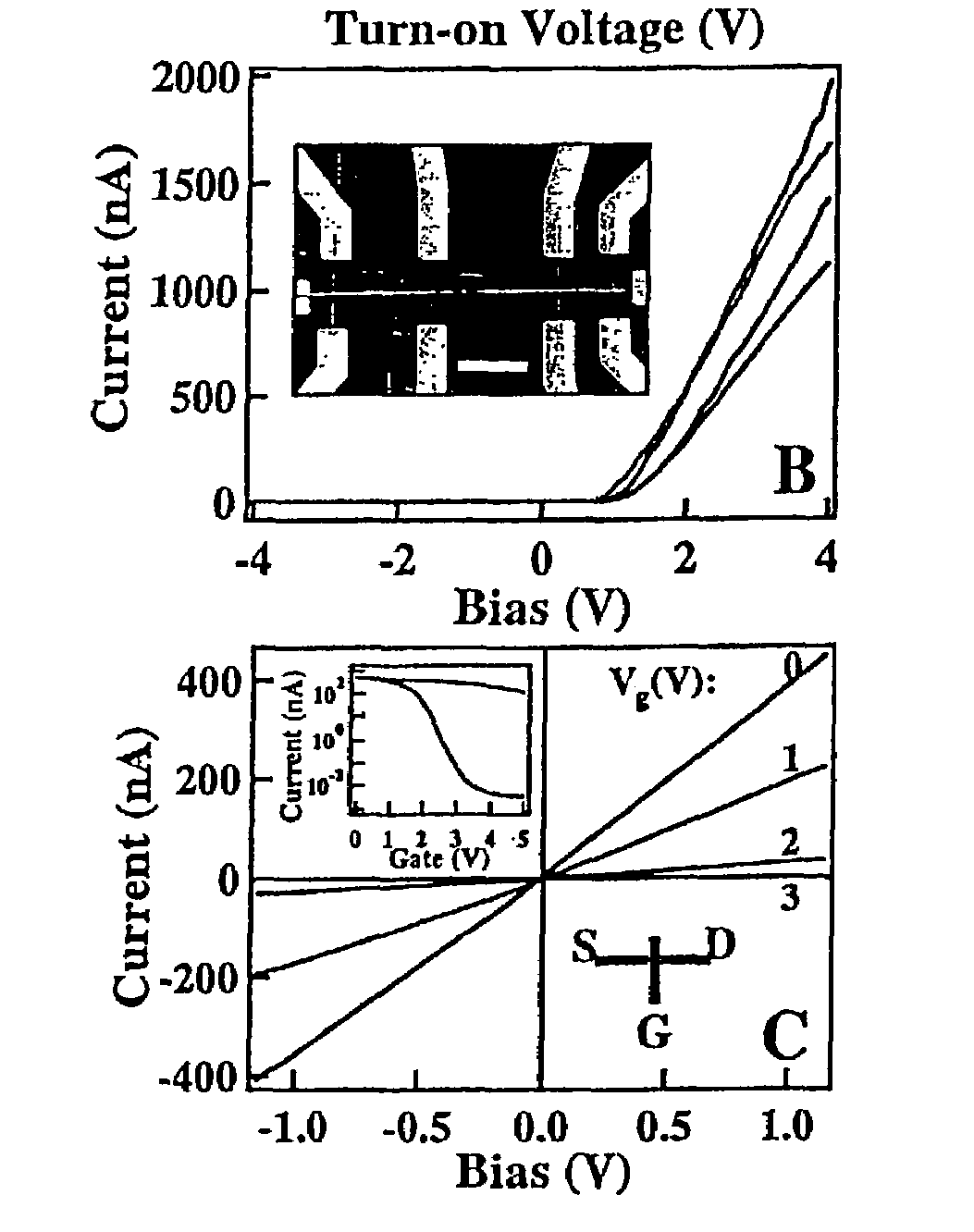
A tunnel diode or Esaki diode is a type of semiconductor diode that has negative resistance due to the quantum mechanical effect called tunneling. It was invented in August 1957 by Leo Esaki, Yuriko Kurose, and Takashi Suzuki when they were working at Tokyo Tsushin Kogyo, now known as Sony. In 1973, Esaki received the Nobel Prize in Physics, jointly with Brian Josephson, for discovering the electron tunneling effect used in these diodes. Robert Noyce independently devised the idea of a tunnel diode while working for William Shockley, but was discouraged from pursuing it. Tunnel diodes were first manufactured by Sony in 1957, followed by General Electric and other companies from about 1960, and are still made in low volume today.
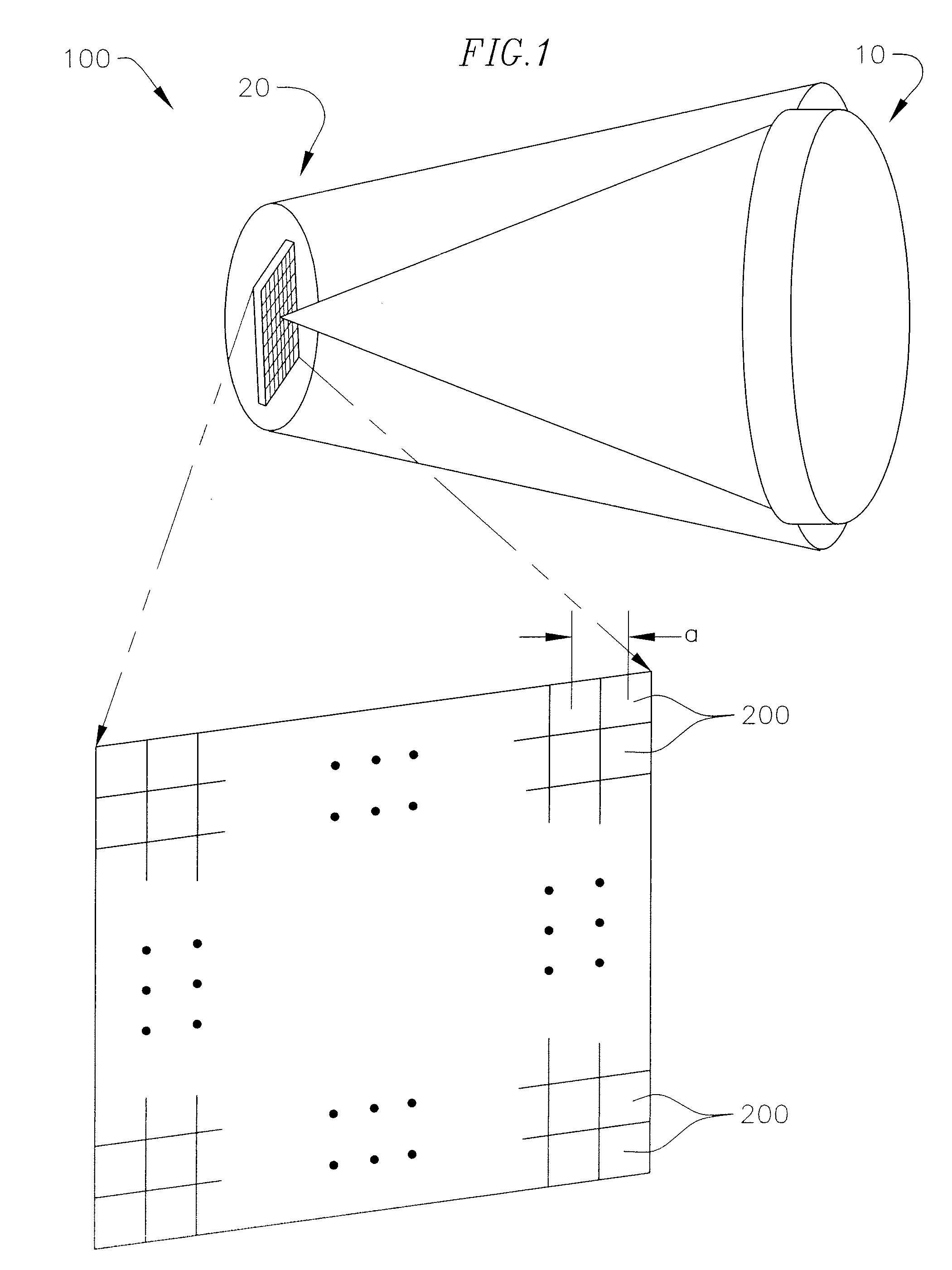
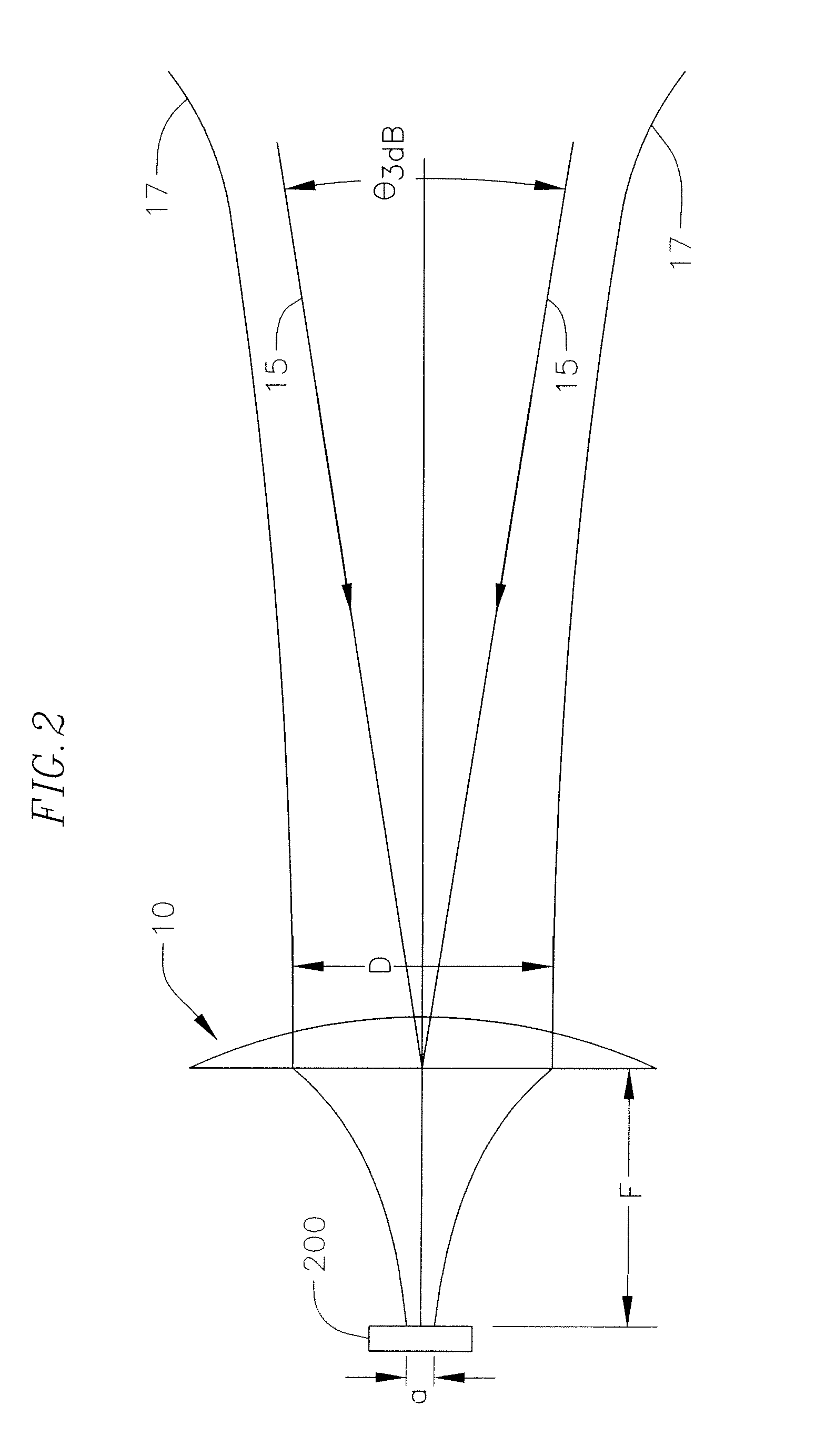
Low cost millimeter wave imager
InactiveUS7583074B1Low costUseful sensitivity levelMeasurement using dc-ac conversionMeasurement using ac-dc conversionLow noiseTunnel diode
Low cost millimeter wave imagers using two-dimensional focal plane arrays based on backward tunneling diode (BTD) detectors. Two-dimensional focal arrays of BTD detectors are used as focal plane arrays in imagers. High responsivity of BTD detectors near zero bias results in low noise detectors that alleviate the need for expensive and heat generating low noise amplifiers or Dicke switches in the imager. BTD detectors are installed on a printed circuit board using flip chip packaging technology and horn antennas direct the waves toward the flip chip including the BTD detectors. The assembly of the horn antennas, flip chips, printed circuit board substrate, and interconnects together work as an imaging sensor. Corrugated surfaces of the components prevent re-radiation of the incident waves.
Owner:HRL LAB
Nanoscale wires and related devices
The present invention relates generally to sub-microelectronic circuitry, and more particularly to nanometer-scale articles, including nanoscale wires which can be selectively doped at various locations and at various levels. In some cases, the articles may be single crystals. The nanoscale wires can be doped, for example, differentially along their length, or radially, and either in terms of identity of dopant, concentration of dopant, or both. This may be used to provide both n-type and p-type conductivity in a single item, or in different items in close proximity to each other, such as in a crossbar array. The fabrication and growth of such articles is described, and the arrangement of such articles to fabricate electronic, optoelectronic, or spintronic devices and components. For example, semiconductor materials can be doped to form n-type and p-type semiconductor regions for making a variety of devices such as field effect transistors, bipolar transistors, complementary inverters, tunnel diodes, light emitting diodes, sensors, and the like.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Nanoscale wires and related devices
InactiveUS7301199B2Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDopantTunnel diode
The present invention relates generally to sub-microelectronic circuitry, and more particularly to nanometer-scale articles, including nanoscale wires which can be selectively doped at various locations and at various levels. In some cases, the articles may be single crystals. The nanoscale wires can be doped, for example, differentially along their length, or radially, and either in terms of identity of dopant, concentration of dopant, or both. This may be used to provide both n-type and p-type conductivity in a single item, or in different items in close proximity to each other, such as in a crossbar array. The fabrication and growth of such articles is described, and the arrangement of such articles to fabricate electronic, optoelectronic, or spintronic devices and components. For example, semiconductor materials can be doped to form n-type and p-type semiconductor regions for making a variety of devices such as field effect transistors, bipolar transistors, complementary inverters, tunnel diodes, light emitting diodes, sensors, and the like.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Nanoscale wires and related devices
The present invention relates generally to sub-microelectronic circuitry, and more particularly to nanometer-scale articles, including nanoscale wires which can be selectively doped at various locations and at various levels. In some cases, the articles may be single crystals. The nanoscale wires can be doped, for example, differentially along their length, or radially, and either in terms of identity of dopant, concentration of dopant, or both. This may be used to provide both n-type and p-type conductivity in a single item, or in different items in close proximity to each other, such as in a crossbar array. The fabrication and growth of such articles is described, and the arrangement of such articles to fabricate electronic, optoelectronic, or spintronic devices and components. For example, semiconductor materials can be doped to form n-type and p-type semiconductor regions for making a variety of devices such as field effect transistors, bipolar transistors, complementary inverters, tunnel diodes, light emitting diodes, sensors, and the like.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
FinFET-based SRAM cell
A SRAM cell includes a single FinFET and two resonant tunnel diodes. The FinFet has multiple channel regions formed from separate fins. The resonant tunnel diodes may be formed from FinFET type fins. In particular, the resonant diodes may includes a thin, undoped silicon region surrounded by a dielectric. The SRAM cell is small and provides fast read / write access times.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
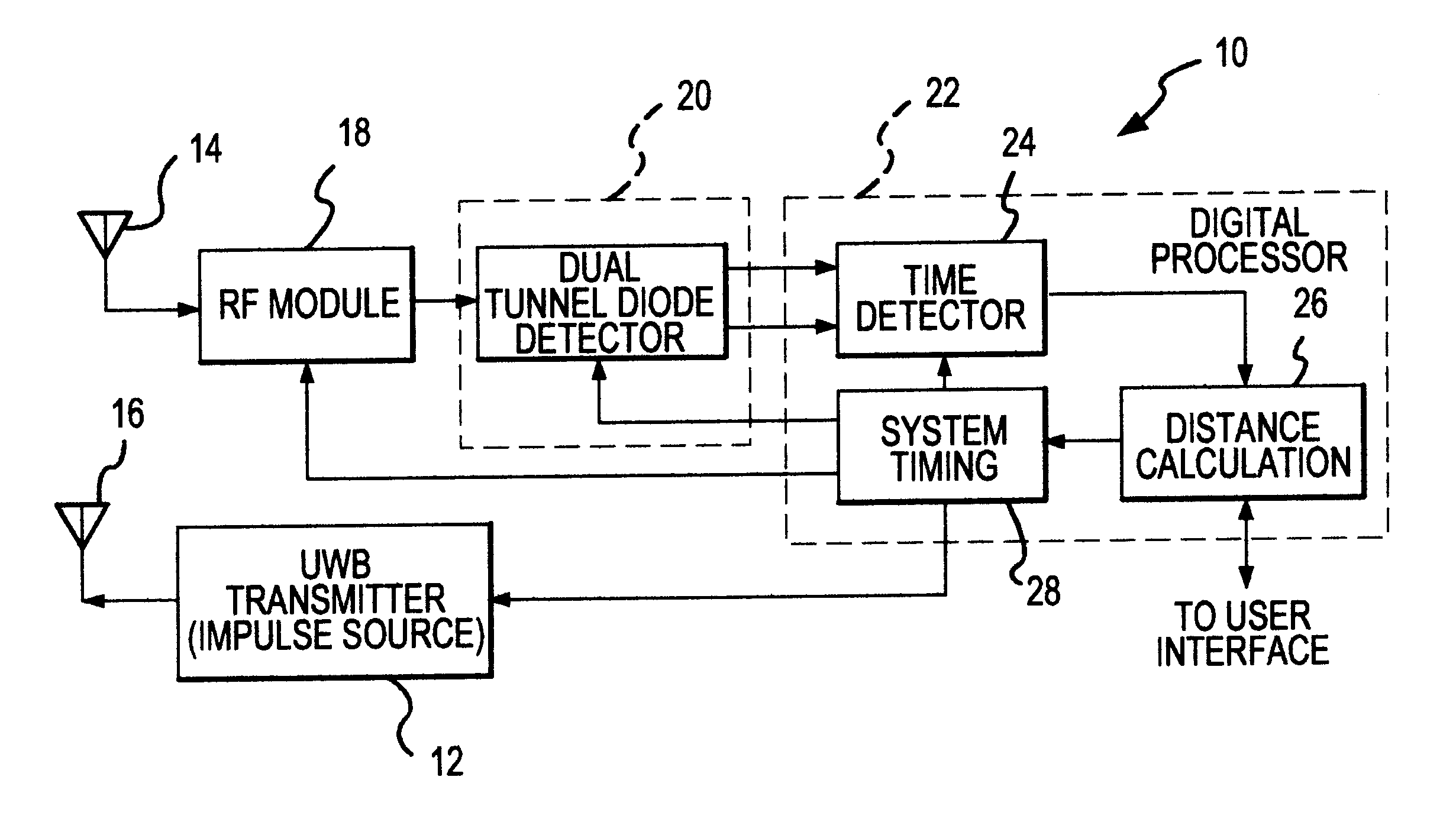
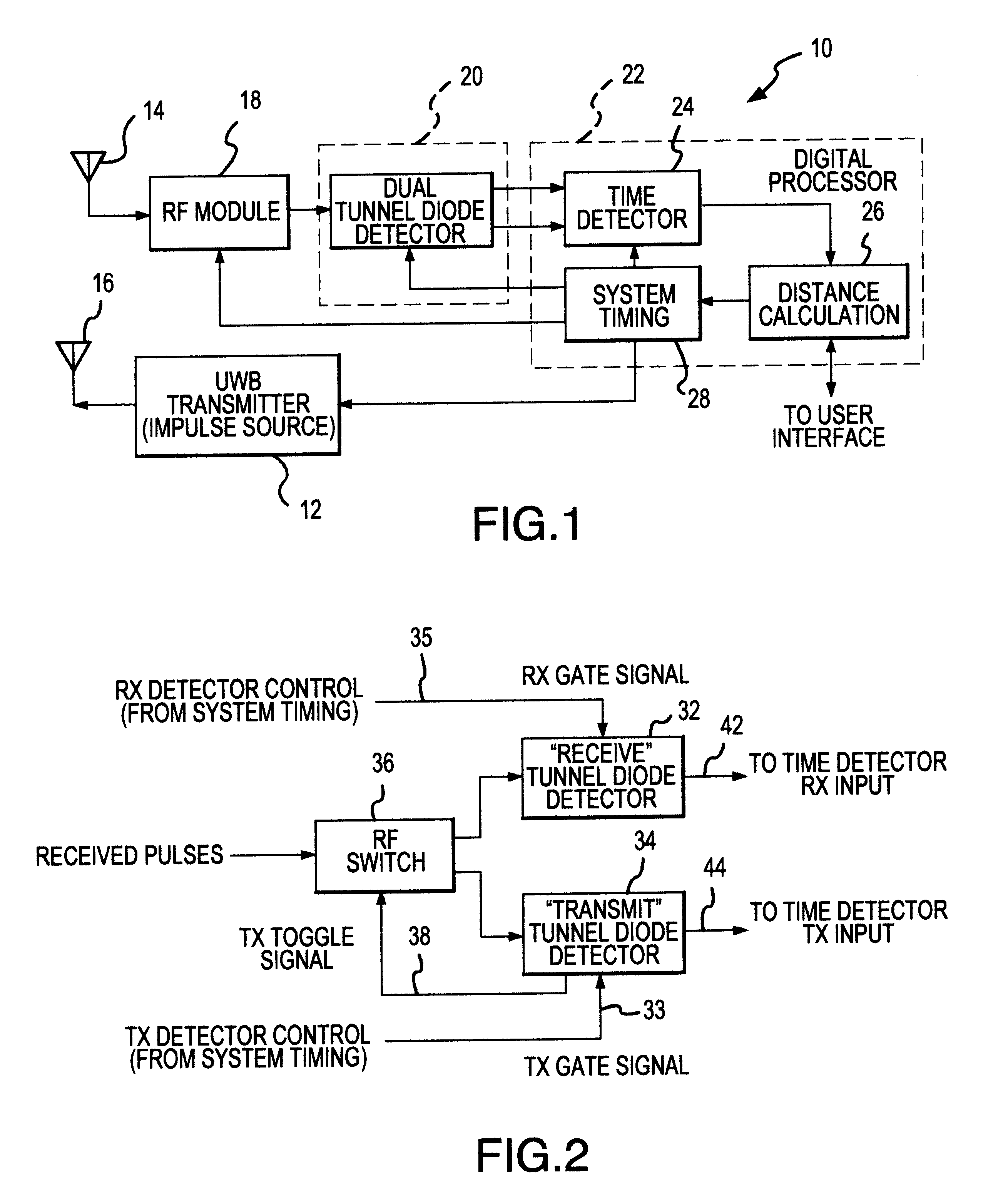
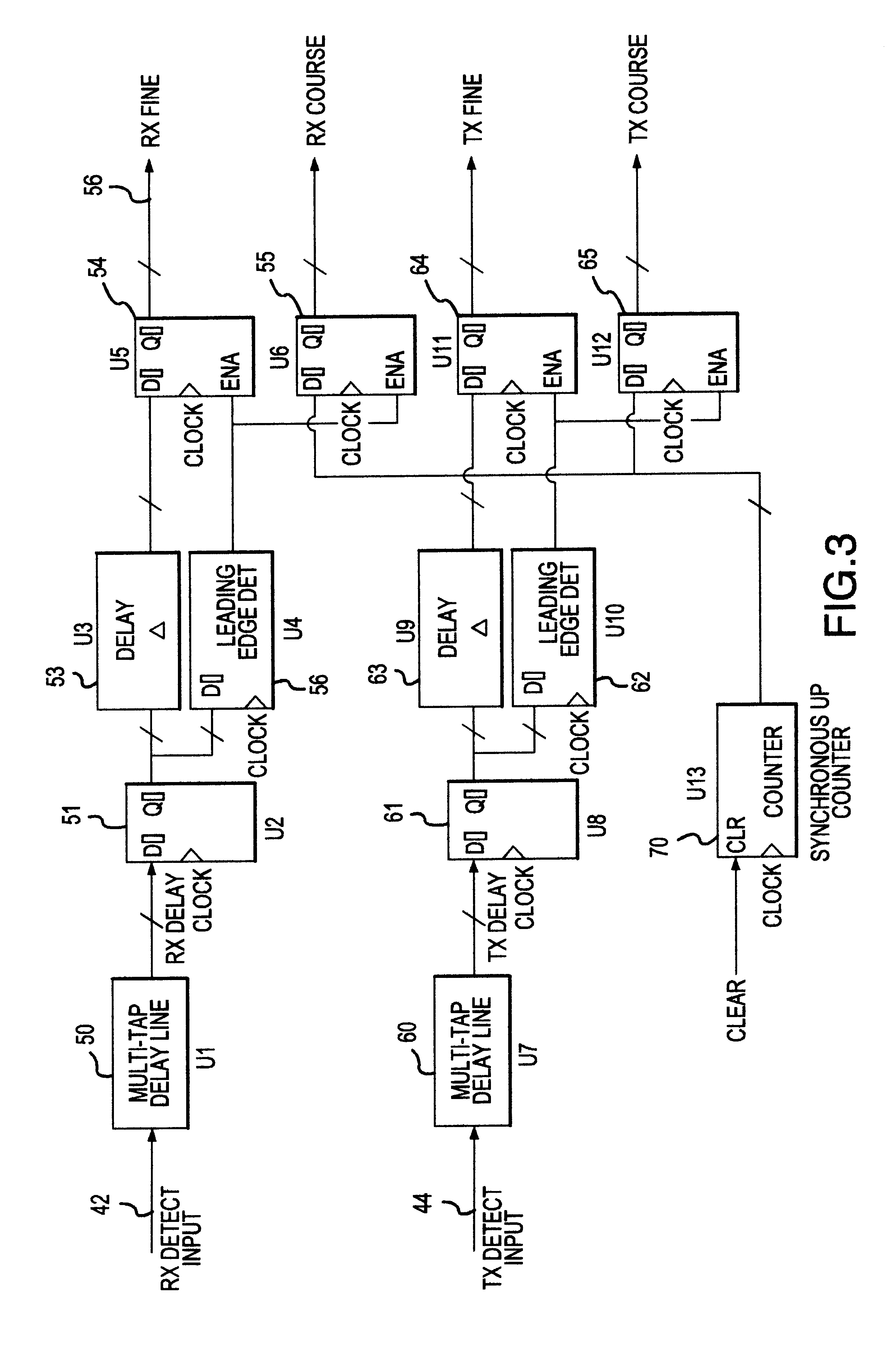
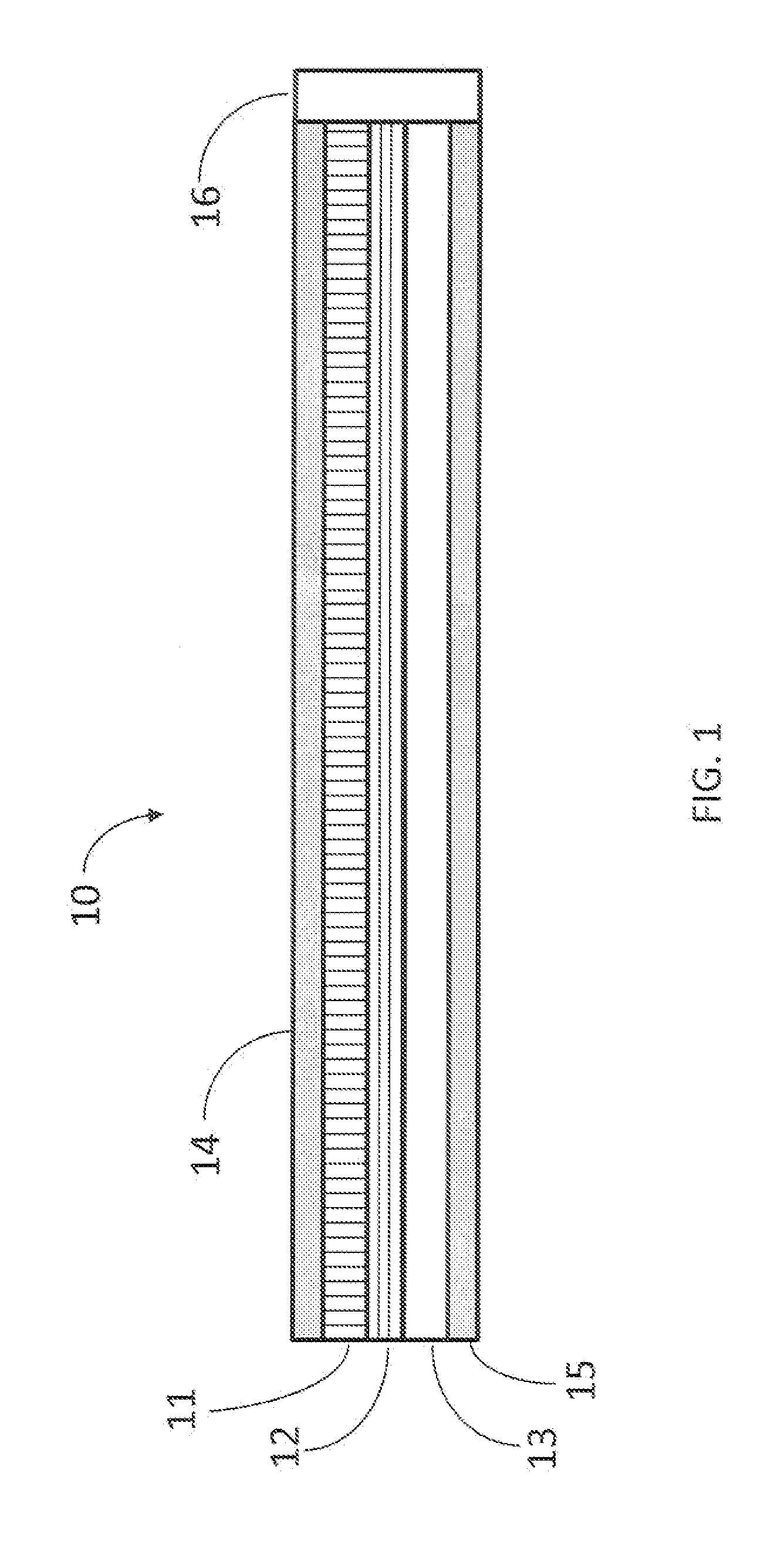
UWB dual tunnel diode detector for object detection, measurement, or avoidance
InactiveUS6239741B1Baseband system detailsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsUltra-widebandTunnel diode
A highly sensitive, high-speed dual tunnel diode detector is described for use in Ultra Wideband (UWB) object detection systems, such as a radar. The extended capability of the detector to both extremely short (sub-foot) and long distance (tens of thousands of feet) ranges is unique and permits the application of low power UWB radar to a wide variety of applications including high resolution radar altimetry at altitudes exceeding 10,000 feet and for autonomous on-deck landing operations (e.g., one-foot altitudes), the detection of extremely low radar cross section (RCS) targets for such applications as suspended wire detection for helicopters and other manned and unmanned craft, etc. High noise and interference immunity of the detector permits co-location of a UWB radar sensor with other active systems. The invention has immediate and significant application to all areas, both military and commercial, of precision distance measurement, intrusion detection, targeting, etc. over a wide range of distances.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
CMOS compatible low band offset double barrier resonant tunneling diode
InactiveUS20050056827A1Good I-V characteristicRaise the ratioTransistorNanoinformaticsCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
Three configurations of double barrier resonant tunneling diodes (RTD) are provided along with methods of their fabrication. The tunneling barrier layers of the diode are formed of low band offset dielectric materials and produce a diode with good I-V characteristics including negative differential resistance (NDR) with good peak-to-valley ratios (PVR). Fabrication methods of the RTD start with silicon-on-insulator substrates (SOI), producing silicon quantum wells, and are, therefore, compatible with main stream CMOS technologies such as those applied to SOI double gate transistor fabrication. Alternatively, Ge-on-insulator or SiGe-on-insulator substrates can be used if the quantum well is to be formed of Ge or SiGe. The fabrication methods include the formation of both vertical and horizontal silicon quantum well layers. The vertically formed layer may be oriented so that its vertical sides are in any preferred crystallographic plane, such as the 100 or 110 planes.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
Non-magnetic semiconductor spin transistor
InactiveUS20050263751A1High sensitivityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesTunnel diodeDevice material
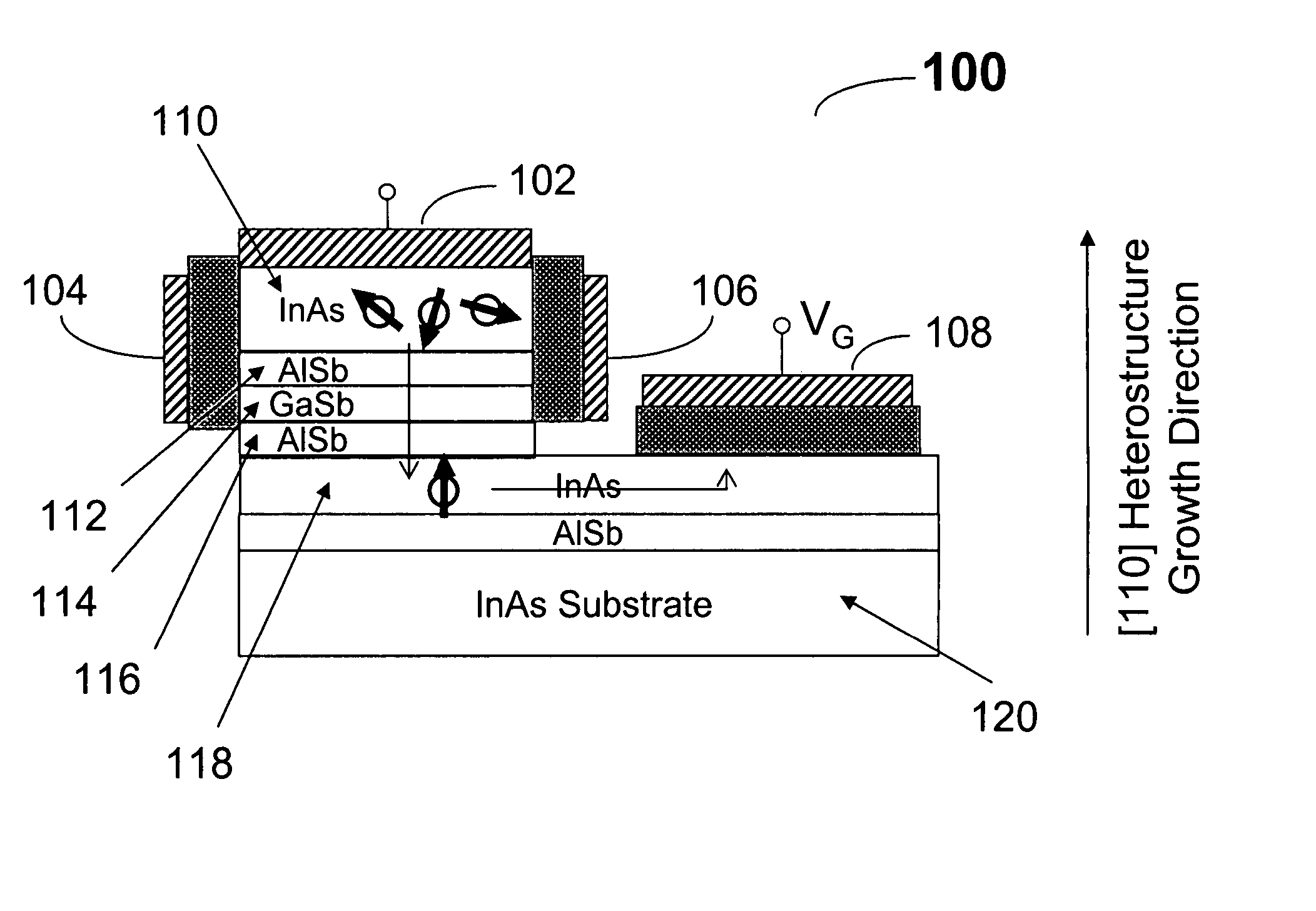
A nonmagnetic semiconductor device which may be utilized as a spin resonant tunnel diode (spin RTD) and spin transistor, in which low applied voltages and / or magnetic fields are used to control the characteristics of spin-polarized current flow. The nonmagnetic semiconductor device exploits the properties of bulk inversion asymmetry (BIA) in (110)-oriented quantum wells. The nonmagnetic semiconductor device may also be used as a nonmagnetic semiconductor spin valve and a magnetic field sensor. The spin transistor and spin valve may be applied to low-power and / or high-density and / or high-speed logic technologies. The magnetic field sensor may be applied to high-speed hard disk read heads. The spin RTD of the present invention would be useful for a plurality of semiconductor spintronic devices for spin injection and / or spin detection.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Nanoscale wires and related devices
The present invention relates generally to sub-microelectronic circuitry, and more particularly to nanometer-scale articles, including nanoscale wires which can be selectively doped at various locations and at various levels. In some cases, the articles may be single crystals. The nanoscale wires can be doped, for example, differentially along their length, or radially, and either in terms of identity of dopant, concentration of dopant, or both. This may be used to provide both n-type and p-type conductivity in a single item, or in different items in close proximity to each other, such as in a crossbar array. The fabrication and growth of such articles is described, and the arrangement of such articles to fabricate electronic, optoelectronic, or spintronic devices and components. For example, semiconductor materials can be doped to form n-type and p-type semiconductor regions for making a variety of devices such as field effect transistors, bipolar transistors, complementary inverters, tunnel diodes, light emitting diodes, sensors, and the like.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
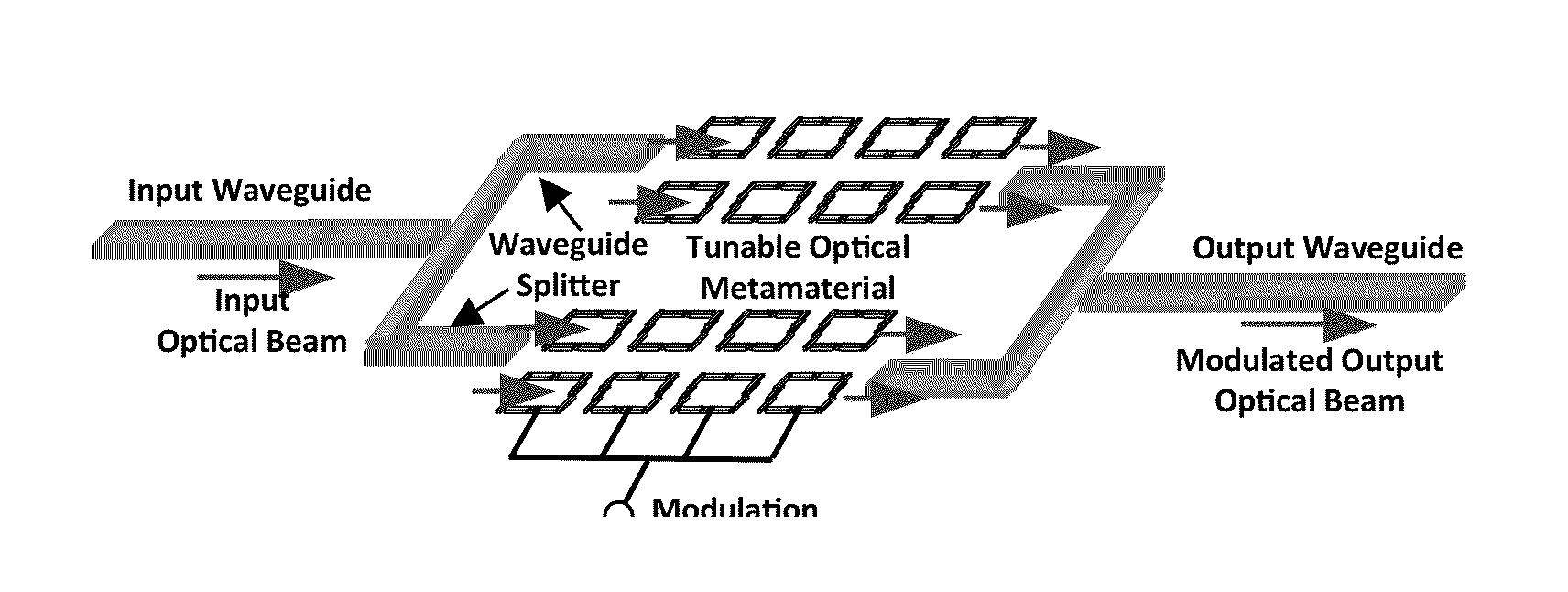
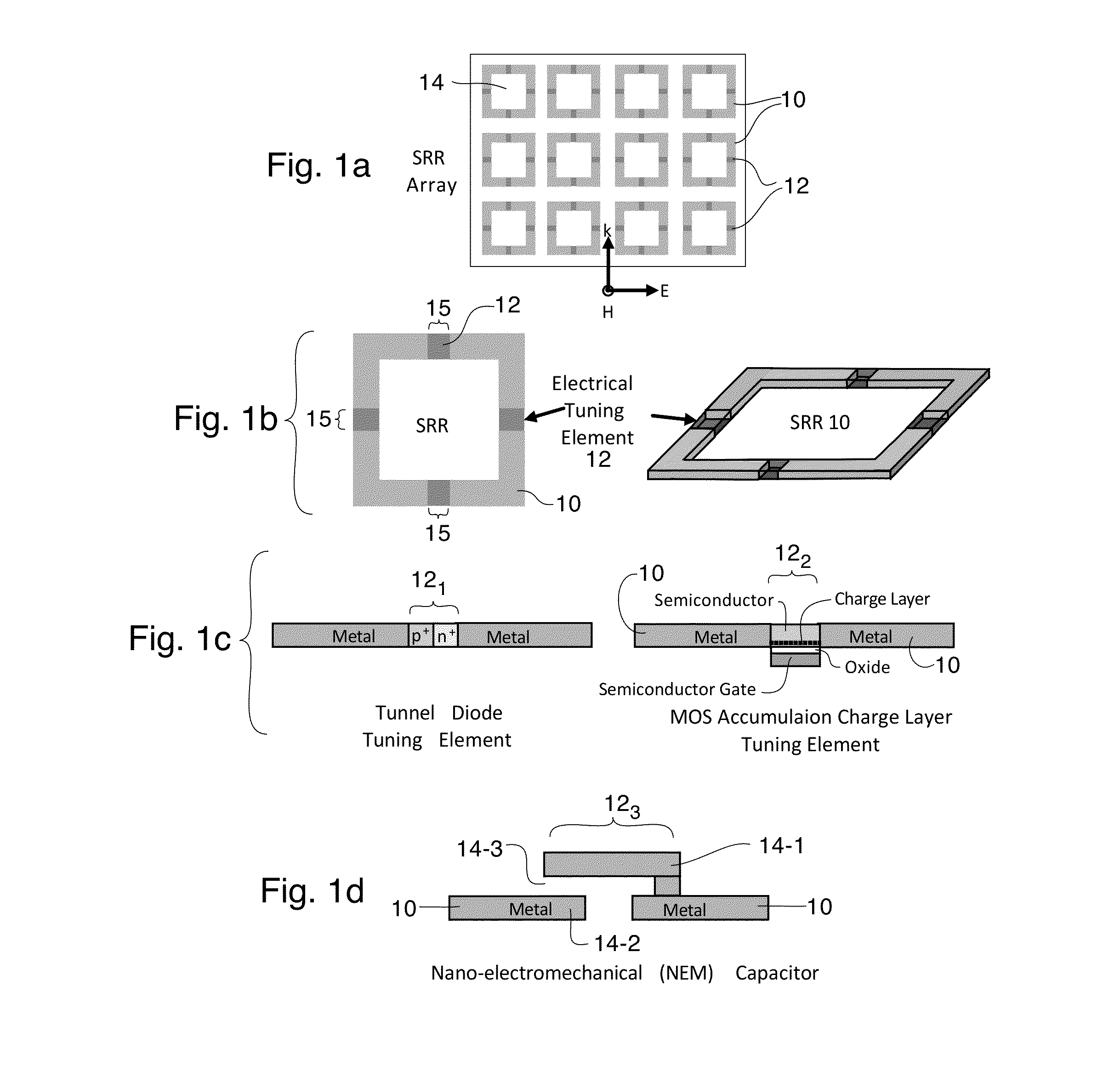
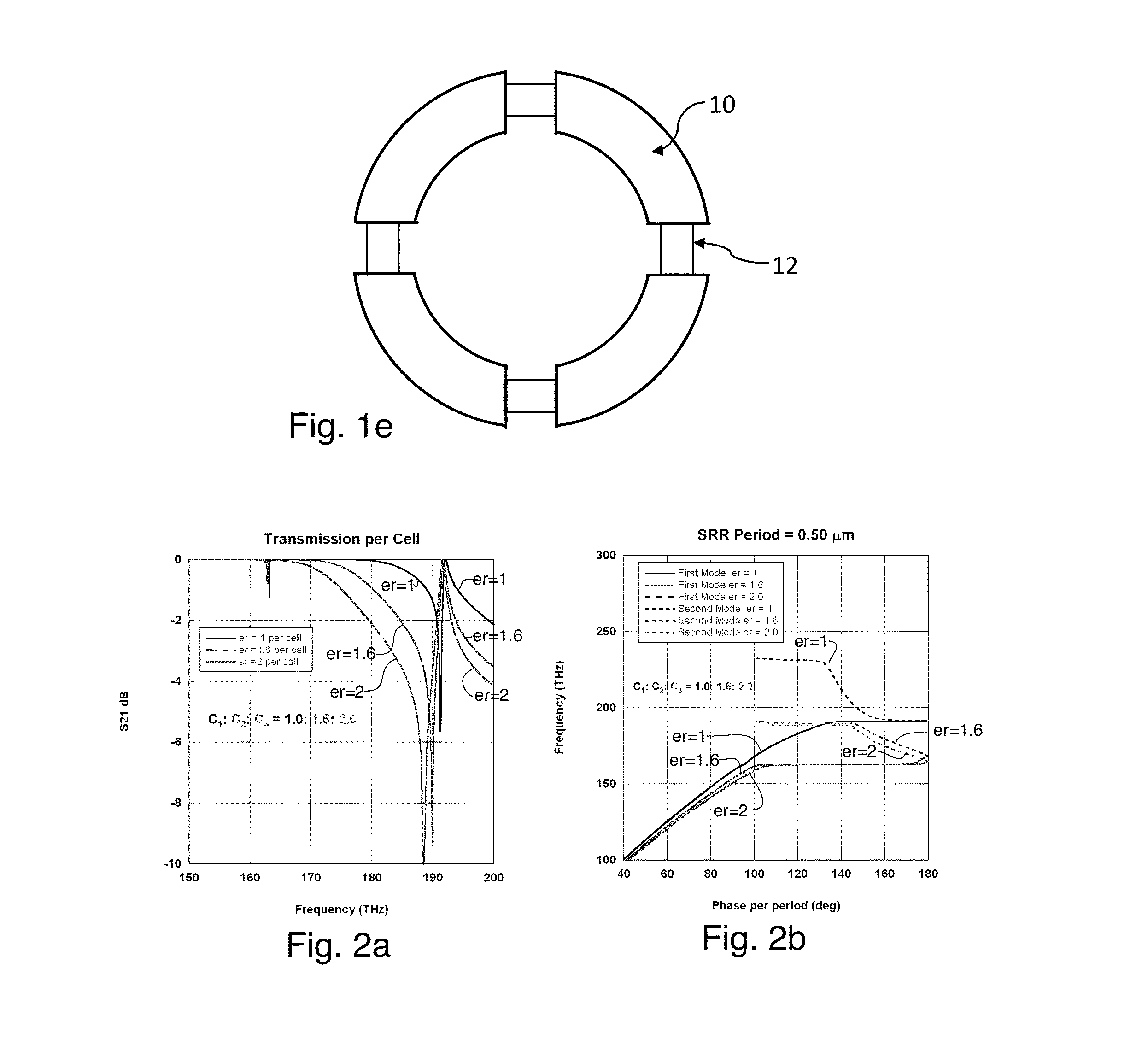
Tunable optical metamaterial
ActiveUS20140211298A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsTunnel diodeSemiconductor structure
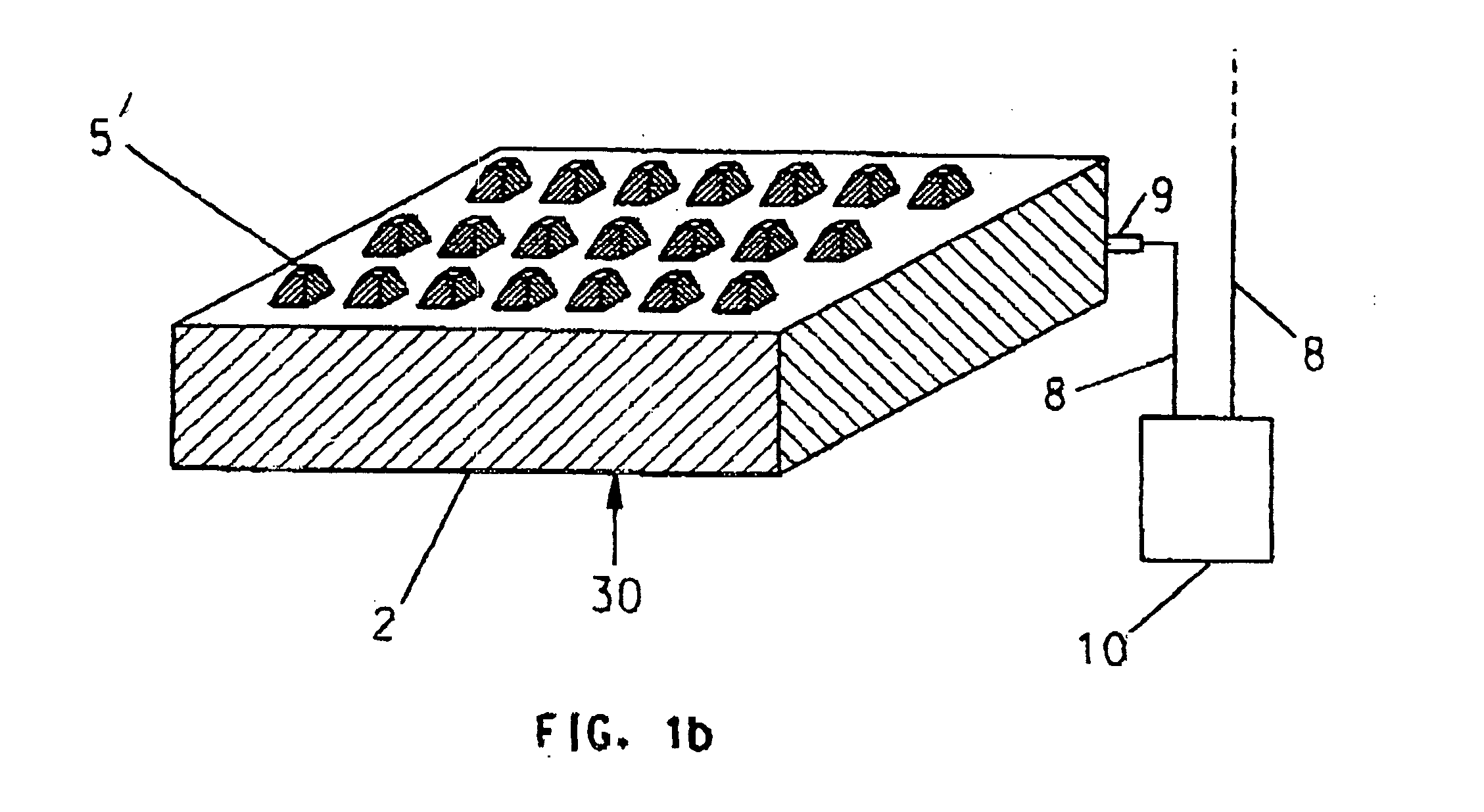
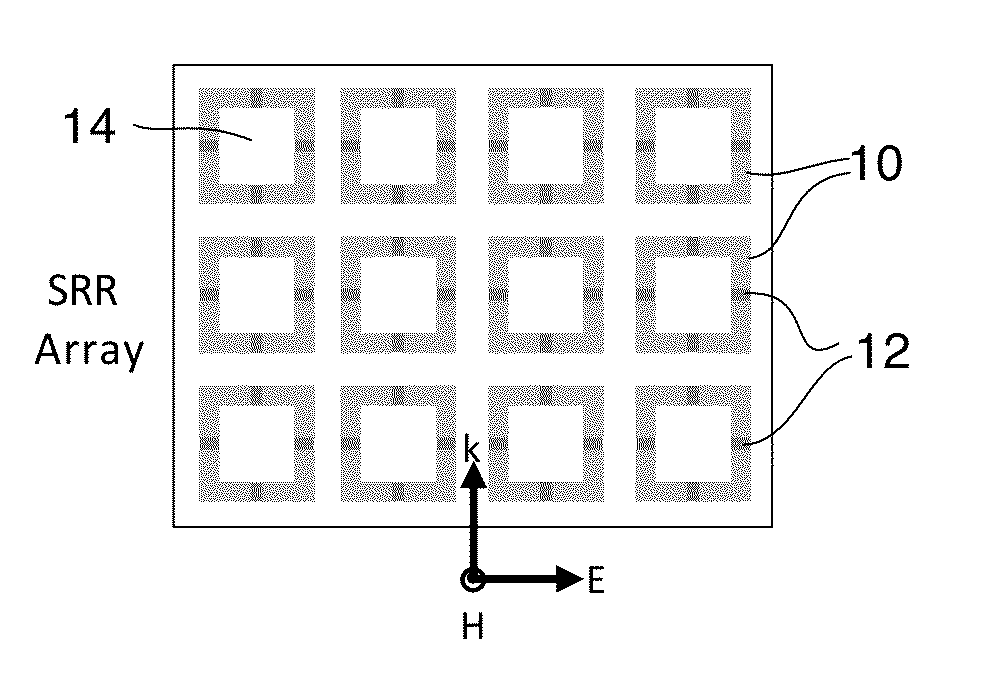
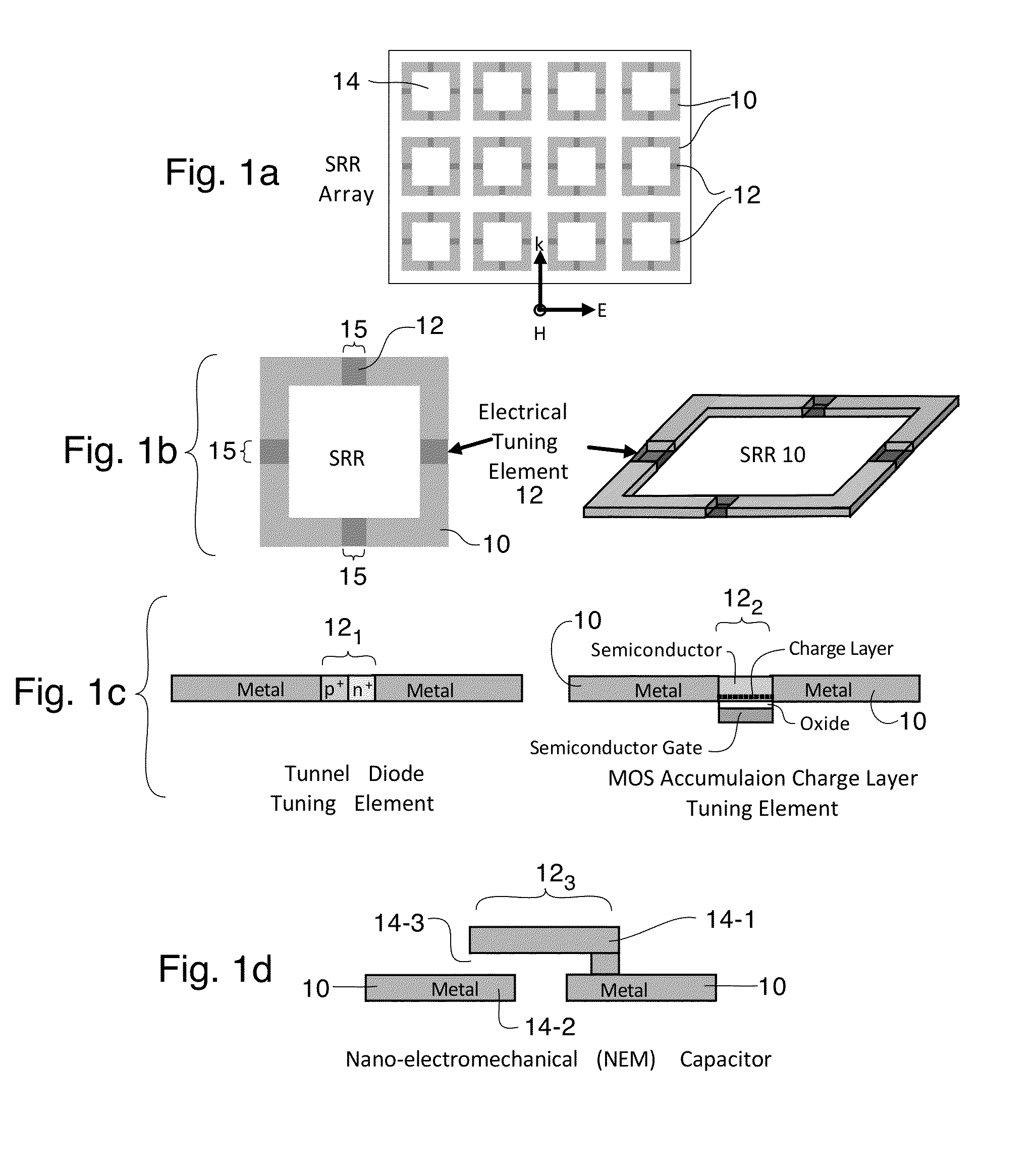
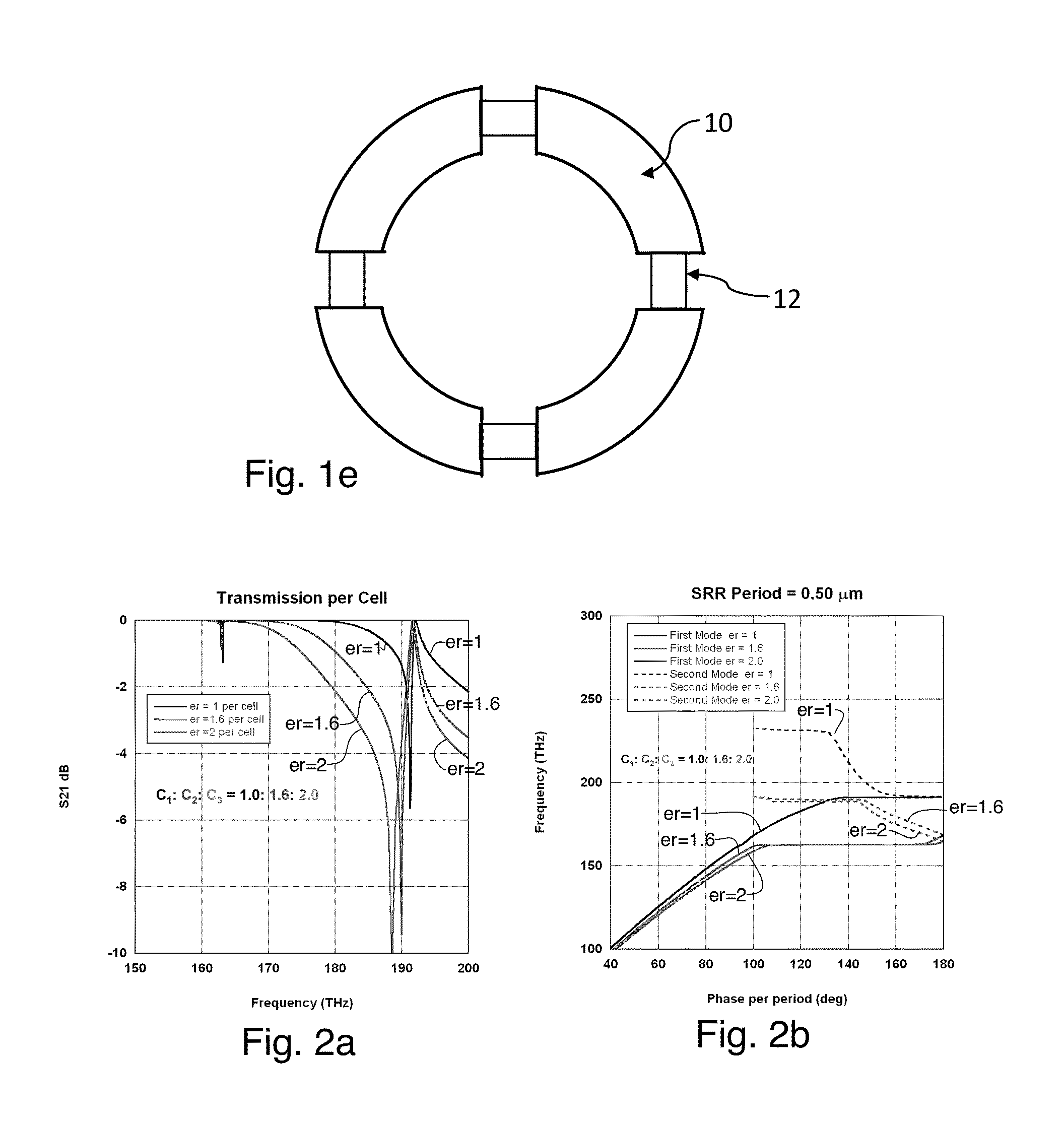
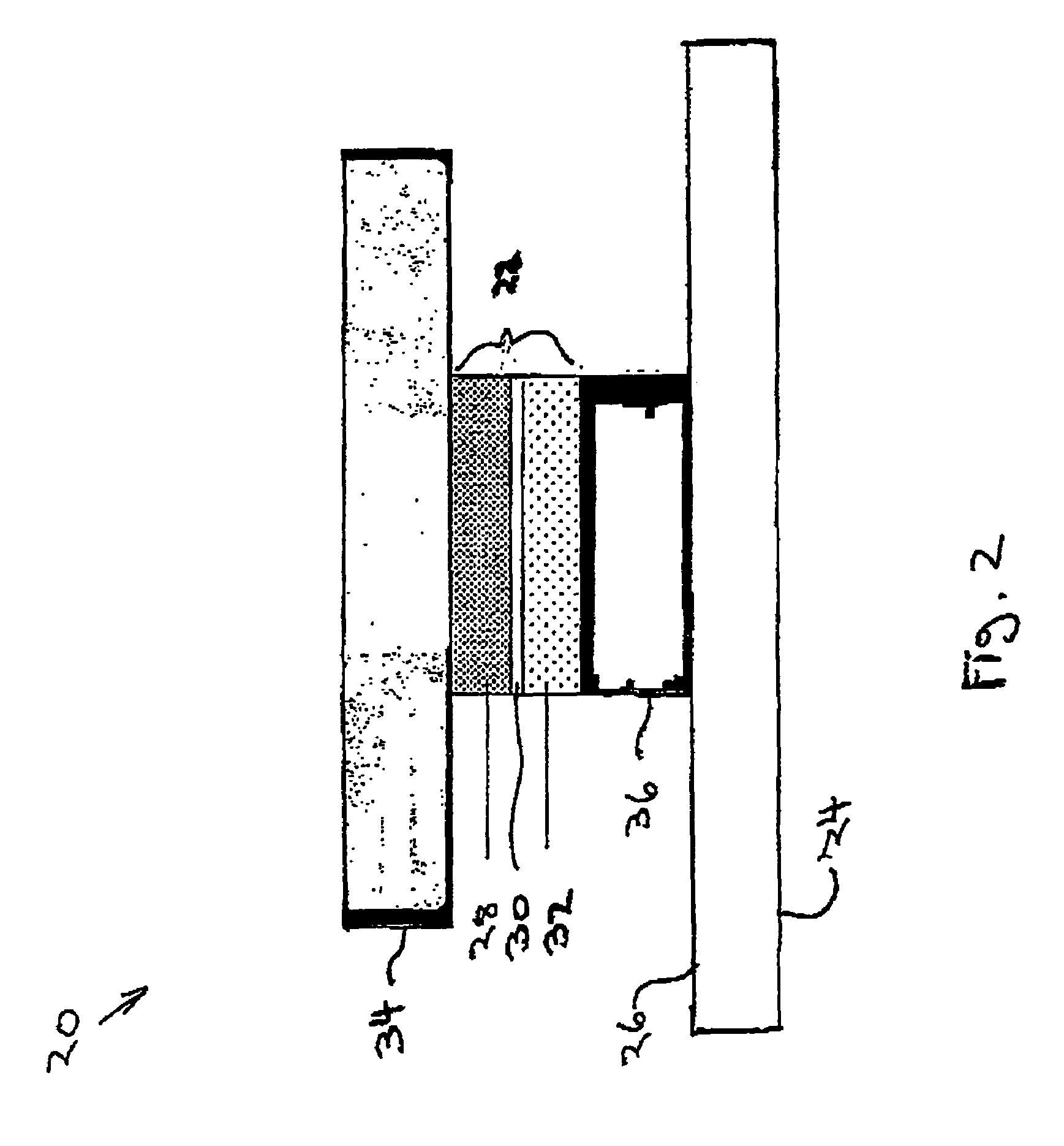
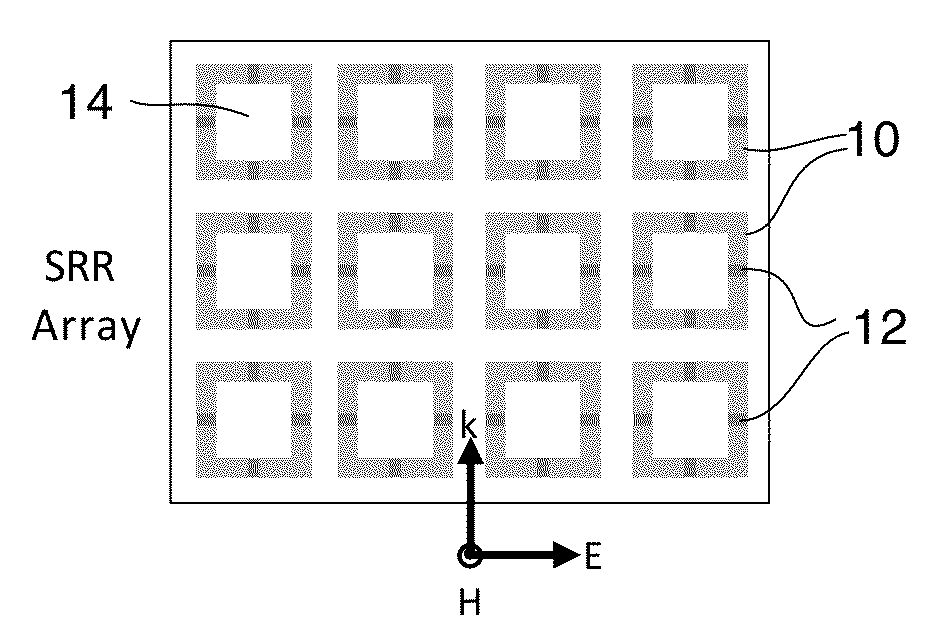
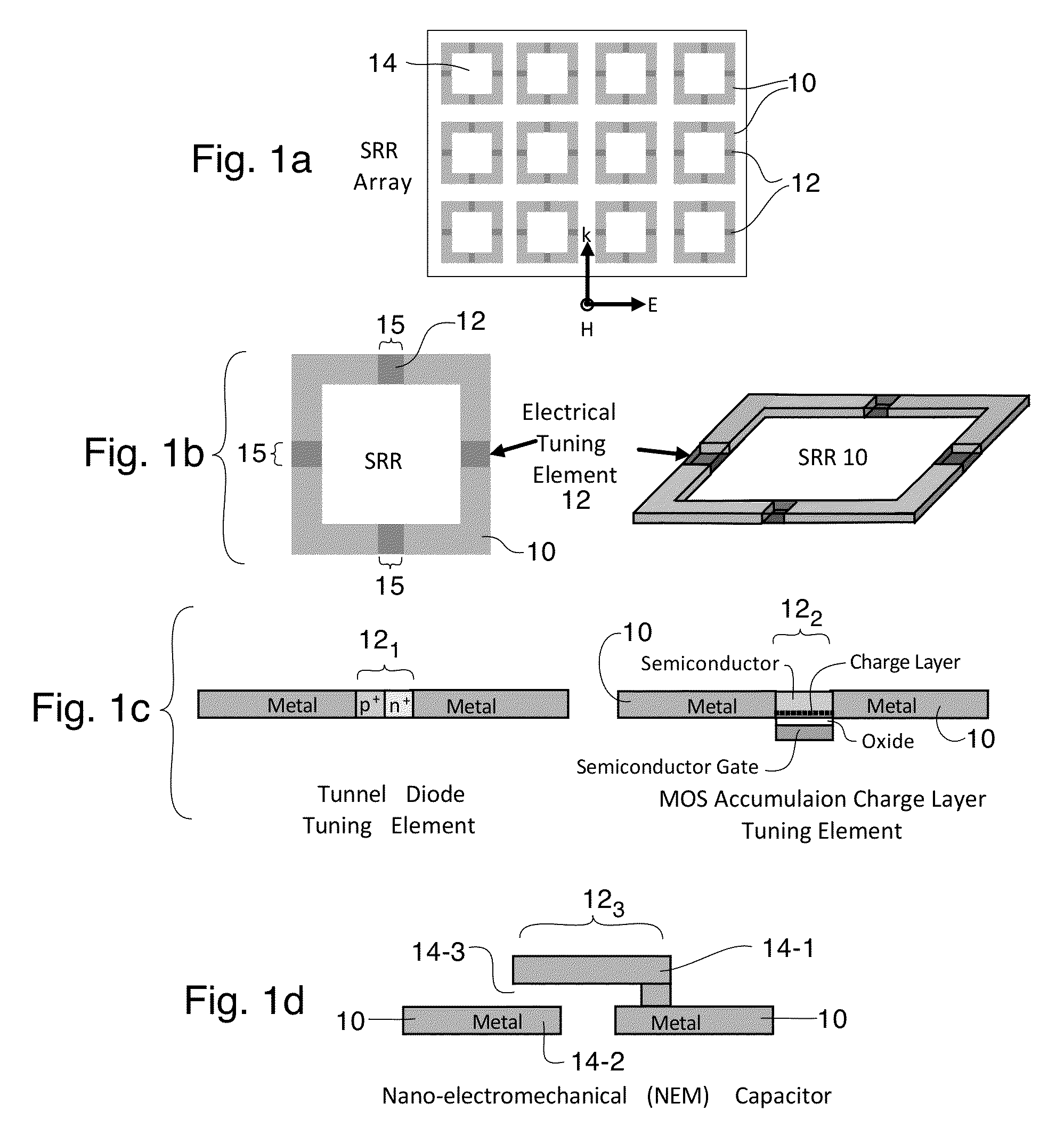
A tunable metamaterial has a two dimensional array of resonant annular ring elements; and a plurality of voltage controllable electrical tuning elements disposed in or adjacent openings in each of said ring elements, each of said voltage controllable electrical tuning element ohmically contacting portions of only one of said ring elements. The voltage controllable electrical tuning elements may comprise highly doped semiconductor tunnel diodes, or the charge accumulation layer at the semiconductor / insulator interface of a metal-insulator-semiconductor structure, or nanoelectromechanical (NEMs) capacitors. The tunable metamaterial may be used, for example, in an optical beam steering device using the aforementioned tunable optical metamaterial in which a free-space optical beam is coupled into a receiving portion of a plane of the optical metamaterial and is steered out of a transmitter portion of the plane of the optical metamaterial in controllable azimuthal and elevational directions. The tunable metamaterial additionally has other applications.
Owner:HRL LAB
Integrated resonant tunneling diode based antenna
An antenna comprising a plurality of negative resistance devices and a method for making same comprising employing a removable standoff layer to form the gap between the microstrip antenna metal and the bottom contact layer.
Owner:SANDIA
Polarization field enhanced tunnel structures
InactiveUS6878975B2Moderate and light levelEnhances a dopant-induced drift fieldDiodeSemiconductor lasersTunnel diodeElectrical conductor
A novel tunnel structure is described that enables tunnel diode behavior to be exhibited even in material systems in which extremely heavy doping is impossible and only moderate or light doping levels may be achieved. In one aspect, the tunnel heterostructure includes a first semiconductor layer, a second semiconductor layer, and an intermediate semiconductor layer that is sandwiched between the first and second semiconductor layers and forms first and second heterointerfaces respectively therewith. The first and second heterointerfaces are characterized by respective polarization charge regions that produce a polarization field across the intermediate semiconductor layer that promotes charge carrier tunneling through the intermediate semiconductor layer. In another aspect, the invention features a semiconductor structure having a p-type region, and the above-described heterostructure disposed as a tunnel contact between the p-type region of the semiconductor structure and an adjacent n-type region.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
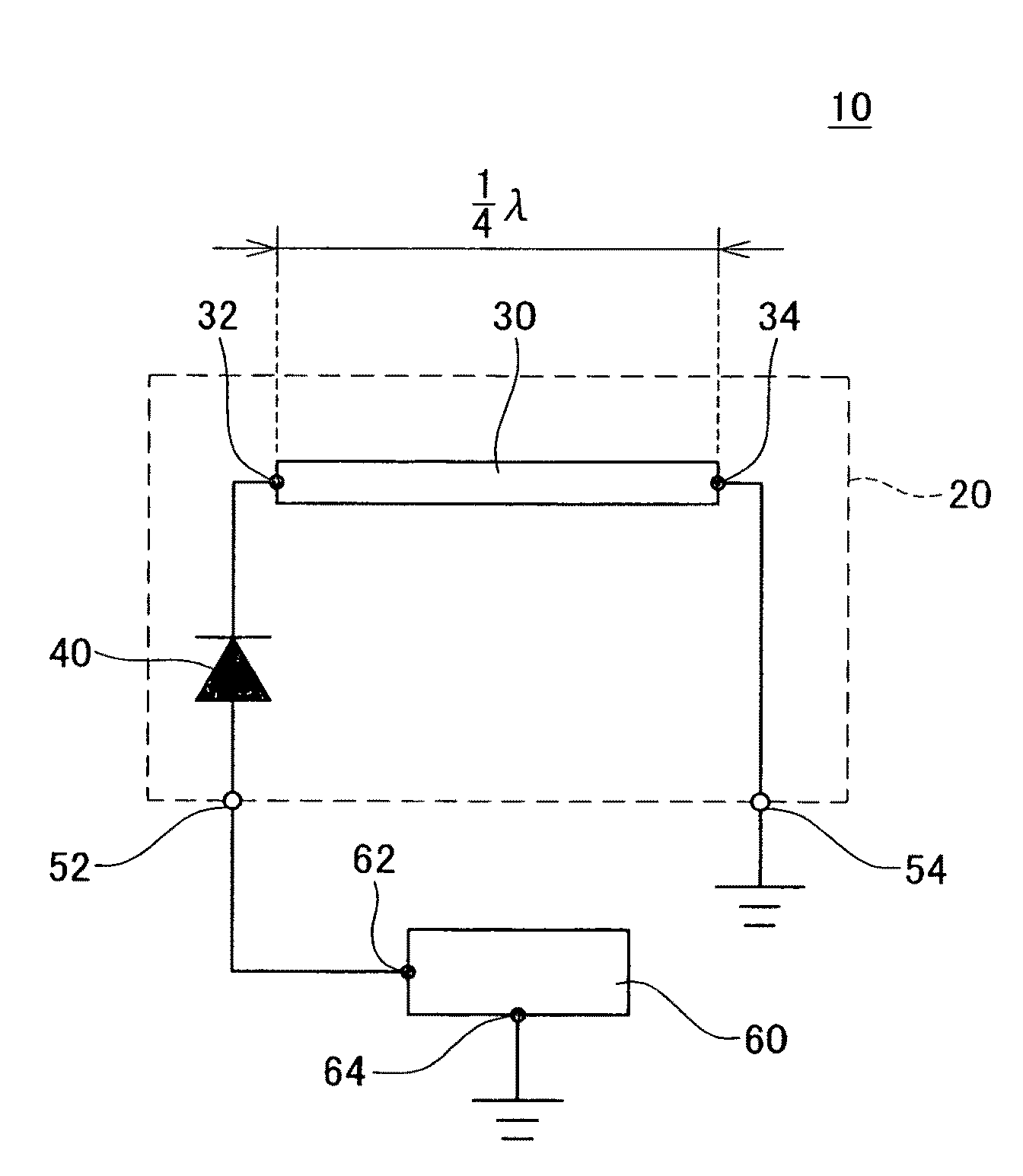
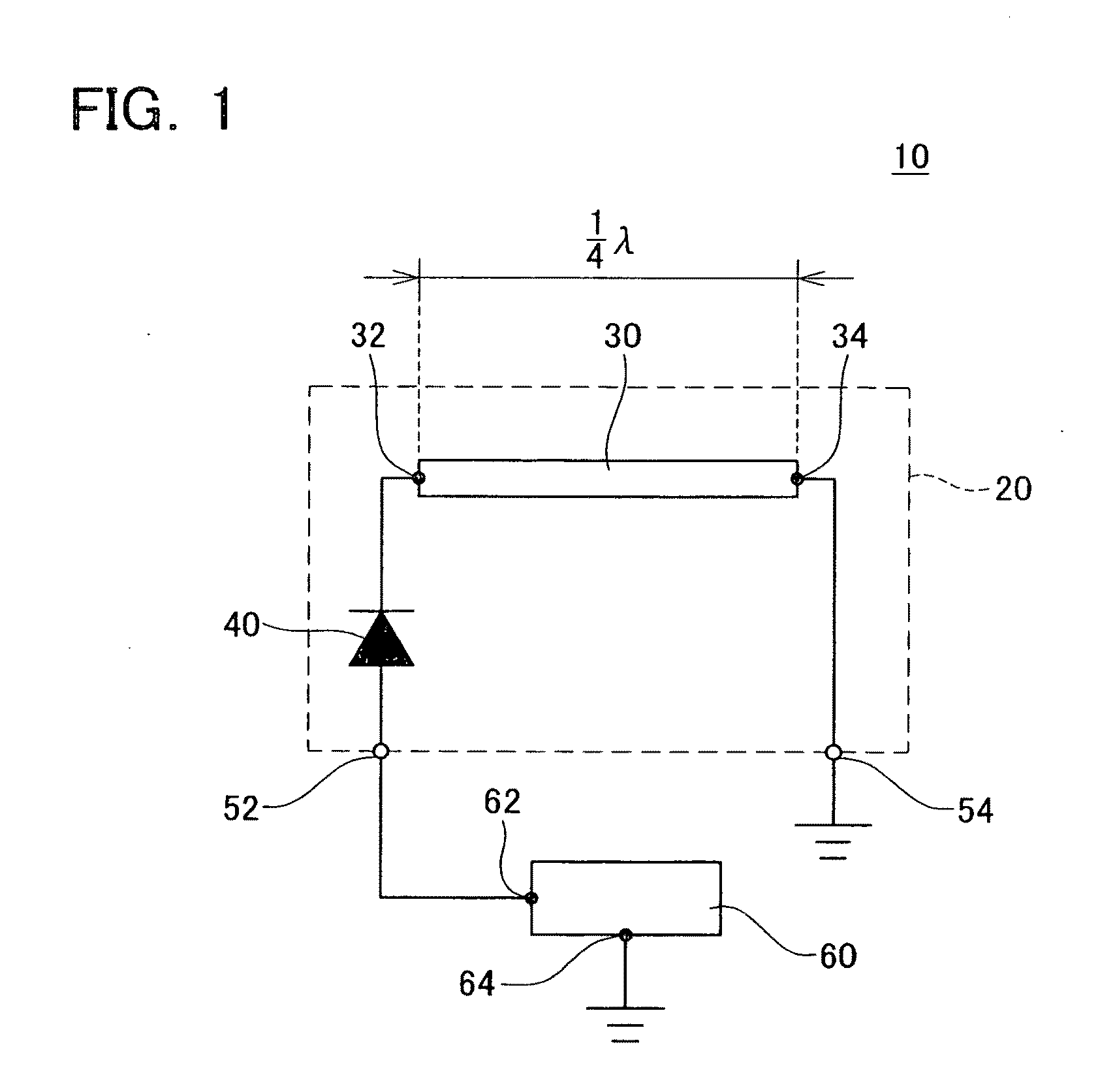
Antenna devices
InactiveUS20100244656A1Simple structureElectrically long antennasRadiating elements structural formsTunnel diodePhysics
An antenna device is provided with a first connecting electrode, a first tunnel diode, a first antenna member and a fixed electrode. The first connecting electrode is configured to be connected to a fixed potential via a load. The first tunnel diode has a pair of electrodes. One of the electrodes of the first tunnel diode is connected to the first connecting electrode, and the other electrode of the first tunnel diode is connected to the first antenna member. The first antenna member has a conductive property and includes a first portion and a second portion. The first portion of the first antenna member is connected to the other electrode of the first tunnel diode. The fixed electrode is connected to the second portion of the first antenna member. The fixed electrode is configured to be connected to the fixed potential.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC +1
Light emitting device with an integrated monitor photodiode
InactiveUS20050286593A1Increased susceptibilityLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserTunnel diode
A monolithically formed laser and photodiode. The monolithically formed laser and photodiode includes a Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser (VCSEL) that includes a first PN junction. The first PN junction includes a first p layer and a first n layer. A tunnel diode is connected to the VCSEL both physically and electronically through a wafer fabrication process. A photodiode is connected to the tunnel diode. The photodiode is connected to the tunnel diode by physical and electronic connections. The tunnel diode and photodiode may share some common layers. The tunnel diode includes a second PN junction. The monolithically formed laser and photodiode allow for an integrated structure with diode biasing flexibility including the use of a single supply to bias both the laser and photodiodes.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
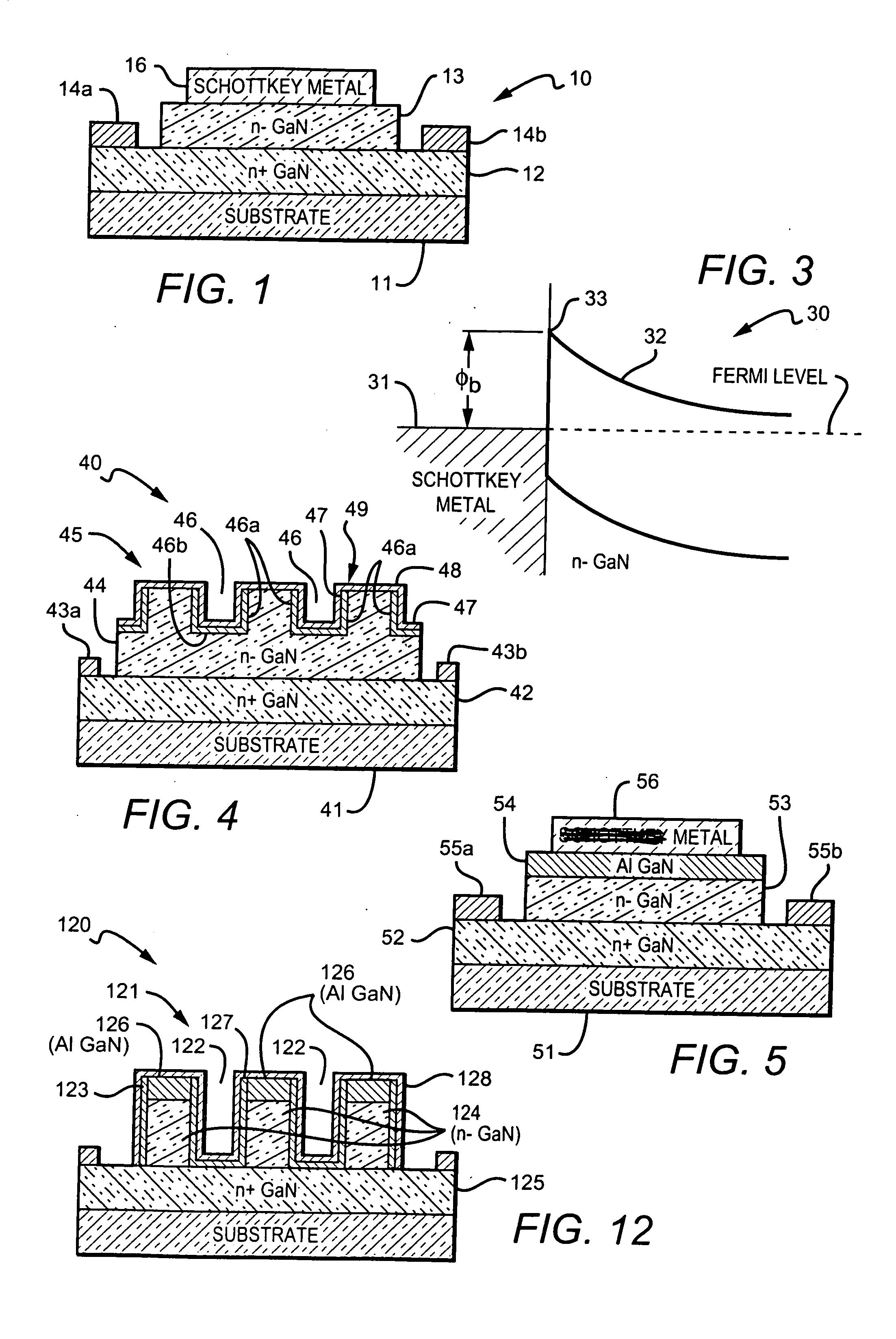
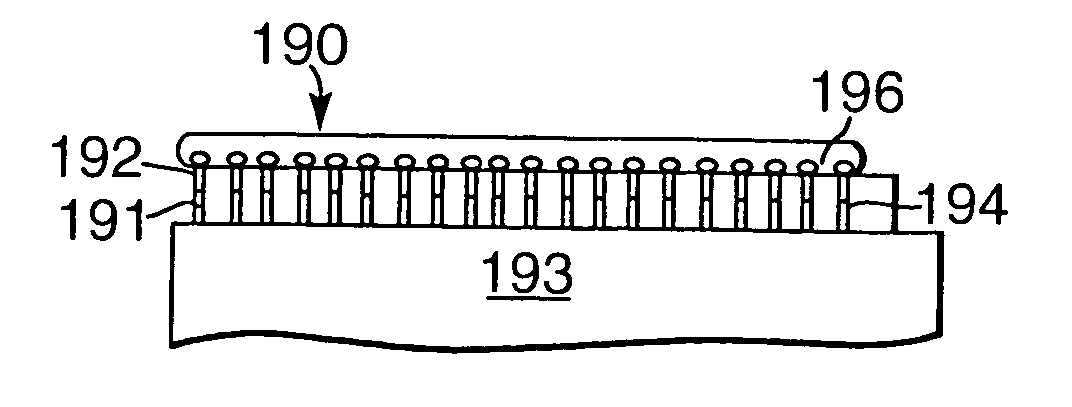
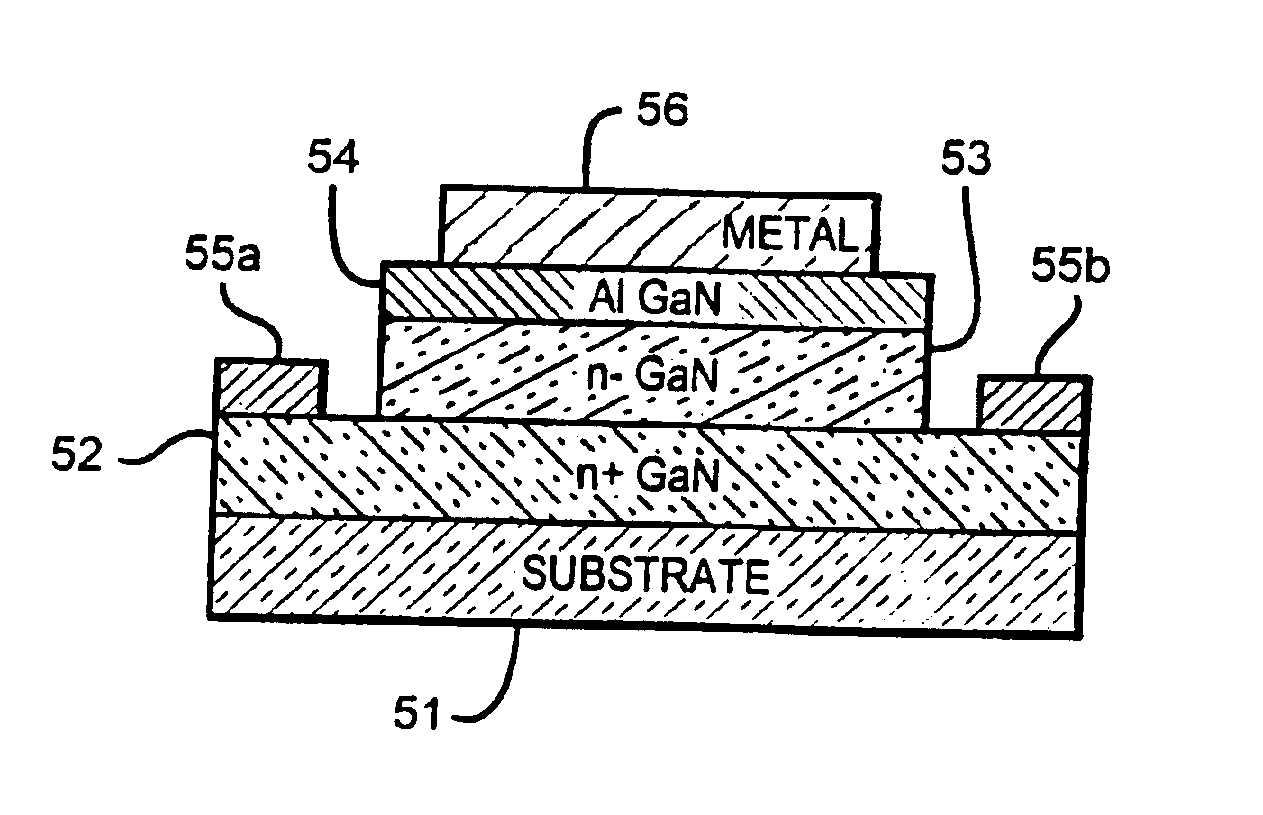
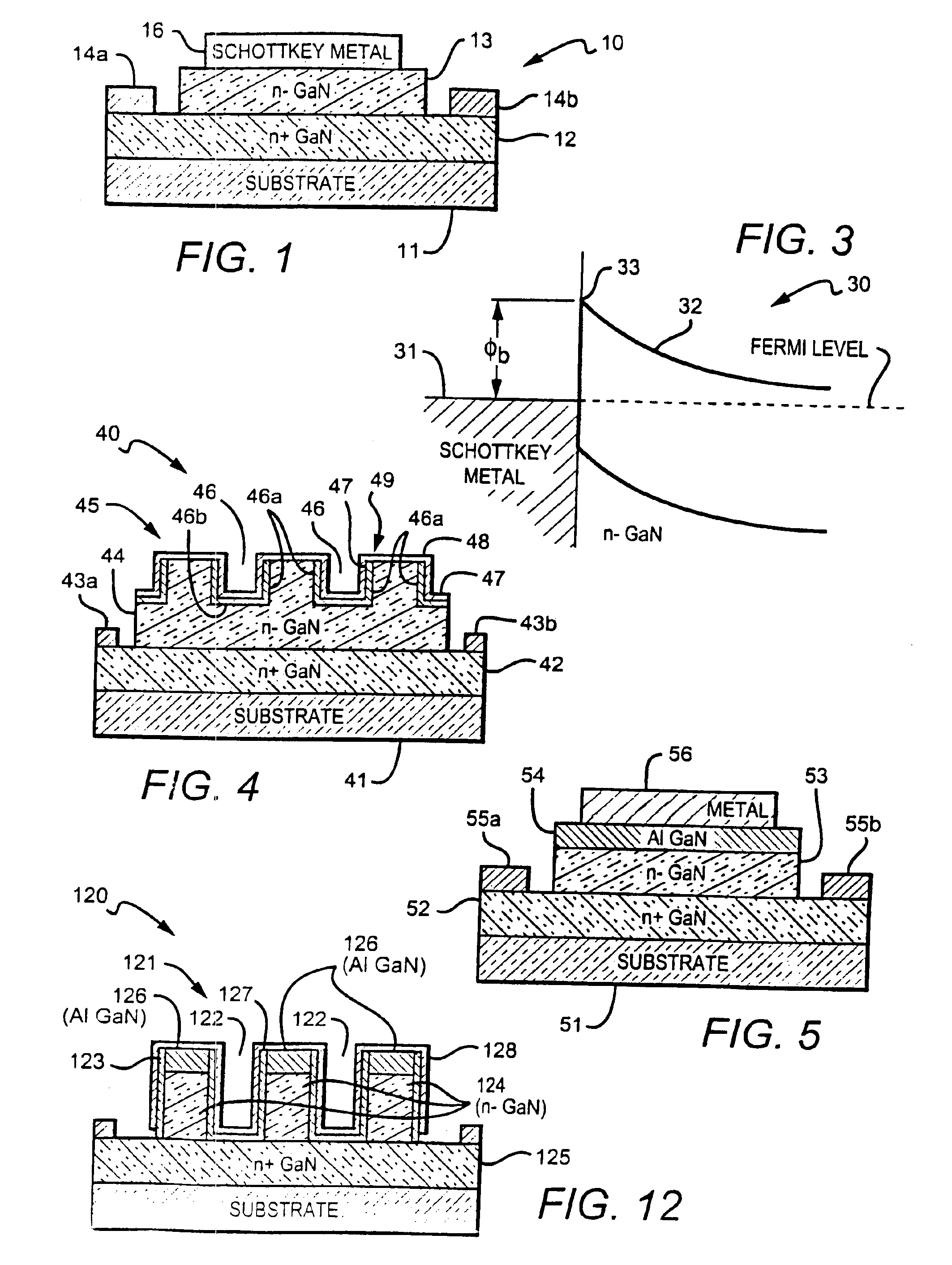
Gallium nitride based diodes with low forward voltage and low reverse current operation
InactiveUS20050242366A1Prevents an increase in the electric fieldSchottky barrier potential is loweredDiodeSemiconductor materialsTunnel diode
New Group III based diodes are disclosed having a low on state voltage (Vf) and structures to keep reverse current (Irev) relatively low. One embodiment of the invention is Schottky barrier diode made from the GaN material system in which the Fermi level (or surface potential) of is not pinned. The barrier potential at the metal-to-semiconductor junction varies depending on the type of metal used and using particular metals lowers the diode's Schottky barrier potential and results in a Vf in the range of 0.1-0.3V. In another embodiment a trench structure is formed on the Schottky diodes semiconductor material to reduce reverse leakage current. and comprises a number of parallel, equally spaced trenches with mesa regions between adjacent trenches. A third embodiment of the invention provides a GaN tunnel diode with a low Vf resulting from the tunneling of electrons through the barrier potential, instead of over it. This embodiment can also have a trench structure to reduce reverse leakage current.
Owner:CREE INC
Multispectral multipolarization antenna-coupled infrared focal plane array
InactiveUS7095027B1Reduce manufacturing costSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansTunnel diodeOptical polarization
Adjacent pixels of an infrared focal plane array (IR FPA) can be configured to have different spectral or polarization responses by adjustment of the lengths or orientations of the antenna arms which couple radiation into the sensors. The manufacturing costs of such an antenna-coupled IR FPA would be much less than integration of spectral or polarization filters onto each pixel, or fabrication of adjacent pixels with materials of different bandgaps. The antenna-coupled pixels can be made smaller than usual pixels, allowing this diversity of spectral or polarization information on the FPA without losing spatial resolution. The infrared (IR) sensors can be tunnel diodes, schottky diodes, photovoltaics, photoconductors, bolometers, and pyroelectrics. Application areas can include military and civilian remote sensing, automotive driving aids, industrial sensing, medical imaging, and general surveillance.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
Closely spaced electrodes with a uniform gap
InactiveUS20060138896A1Simple inexpensiveLow costFrom solar energyMachines/enginesTunnel diodeEngineering
An improved design for maintaining separation between electrodes in tunneling, diode, thermionic, and other devices is disclosed. At least one electrode is made from flexible material. A magnetic field is present to combine with the current flowing in the flexible electrode and generate a force that counterbalances the electrostatic force between the electrodes. The balancing of forces allows the separation and parallelism between the electrodes to be maintained at a very small spacing without requiring the use of multiple control systems, actuators, or other manipulating means, or spacers. The shape of one or both electrodes is designed to maintain a constant separation over the entire overlapping area of the electrodes. The end result is an electronic device that maintains two closely spaced parallel electrodes in stable equilibrium with a uniform gap therebetween over a large area in a simple configuration for simplified manufacturability and use to convert heat to electricity or electricity to cooling.
Owner:TEMPRONICS INC
Tunable optical metamaterial
InactiveUS20150062691A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsElectricityTunnel diode
A tunable metamaterial has a two dimensional array of resonant annular ring elements; and a plurality of voltage controllable electrical tuning elements disposed in or adjacent openings in each of said ring elements, each of said voltage controllable electrical tuning element ohmically contacting portions of only one of said ring elements. The voltage controllable electrical tuning elements may comprise highly doped semiconductor tunnel diodes, or the charge accumulation layer at the semiconductor / insulator interface of a metal-insulator-semiconductor structure, or nanoelectromechanical (NEMs) capacitors. The tunable metamaterial may be used, for example, in an optical beam steering device using the aforementioned tunable optical metamaterial in which a free-space optical beam is coupled into a receiving portion of a plane of the optical metamaterial and is steered out of a transmitter portion of the plane of the optical metamaterial in controllable azimuthal and elevational directions. The tunable metamaterial additionally has other applications.
Owner:HRL LAB
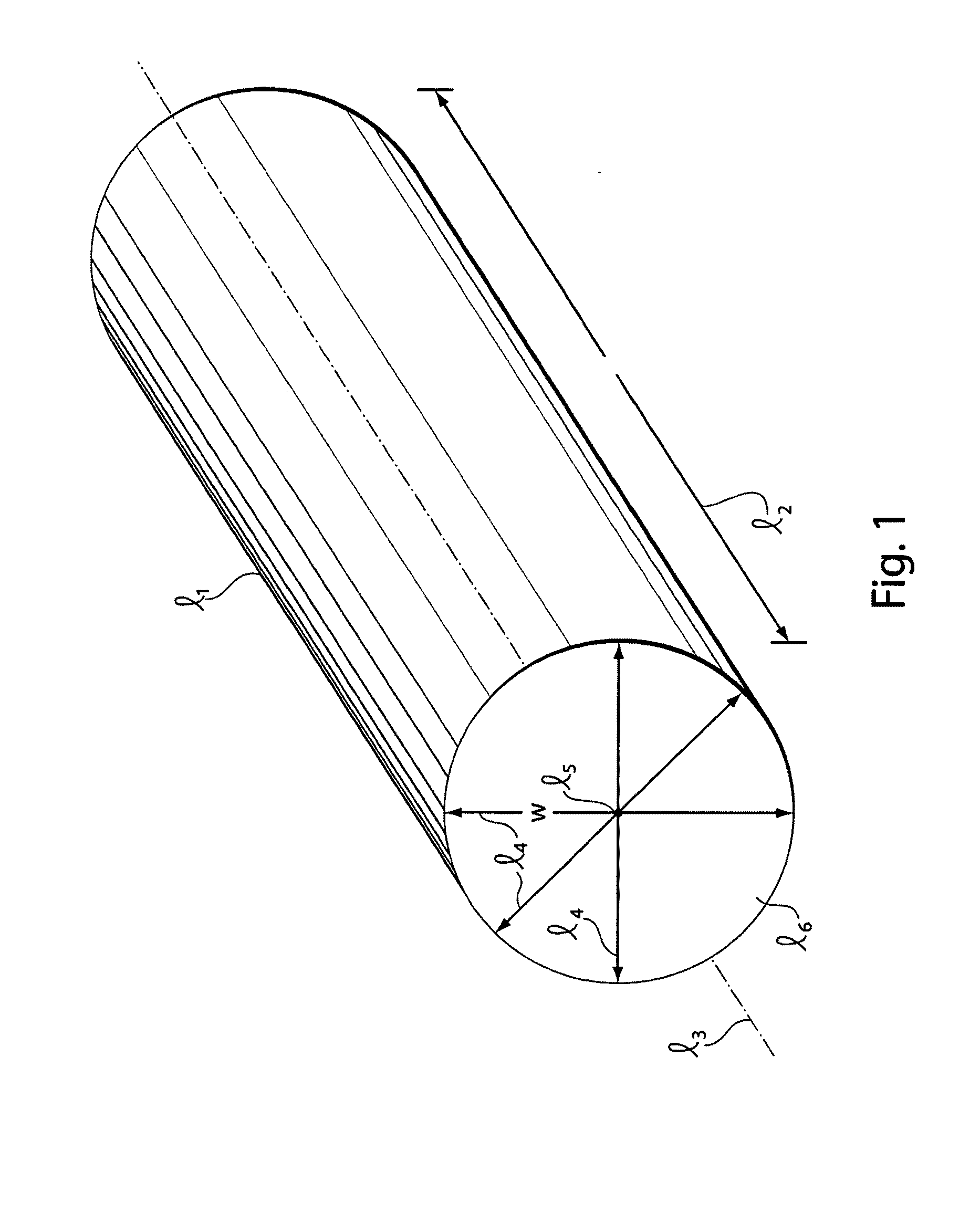
Nanostructures and methods for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080105296A1Enhances width controlAccurate diameterPolycrystalline material growthIndividual molecule manipulationTunnel diodePhotonics
Owner:QUNANO
Gallium nitride based diodes with low forward voltage and low reverse current operation
InactiveUS6949774B2Maximizes forward tunneling probabilityLow VfDiodeTunnel diodeSemiconductor materials
New Group III based diodes are disclosed having a low on state voltage (Vf), and structures to keep reverse current (Irev) relatively low. One embodiment of the invention is Schottky barrier diode made from the GaN material system in which the Fermi level (or surface potential) of is not pinned. The barrier potential at the metal-to-semiconductor junction varies depending on the type of metal used and using particular metals lowers the diode's Schottky barrier potential and results in a Vf in the range of 0.1-0.3V. In another embodiment a trench structure is formed on the Schottky diodes semiconductor material to reduce reverse leakage current. and comprises a number of parallel, equally spaced trenches with mesa regions between adjacent trenches. A third embodiment of the invention provides a GaN tunnel diode with a low Vf resulting from the tunneling of electrons through the barrier potential, instead of over it. This embodiment can also have a trench structure to reduce reverse leakage current.
Owner:CREE INC
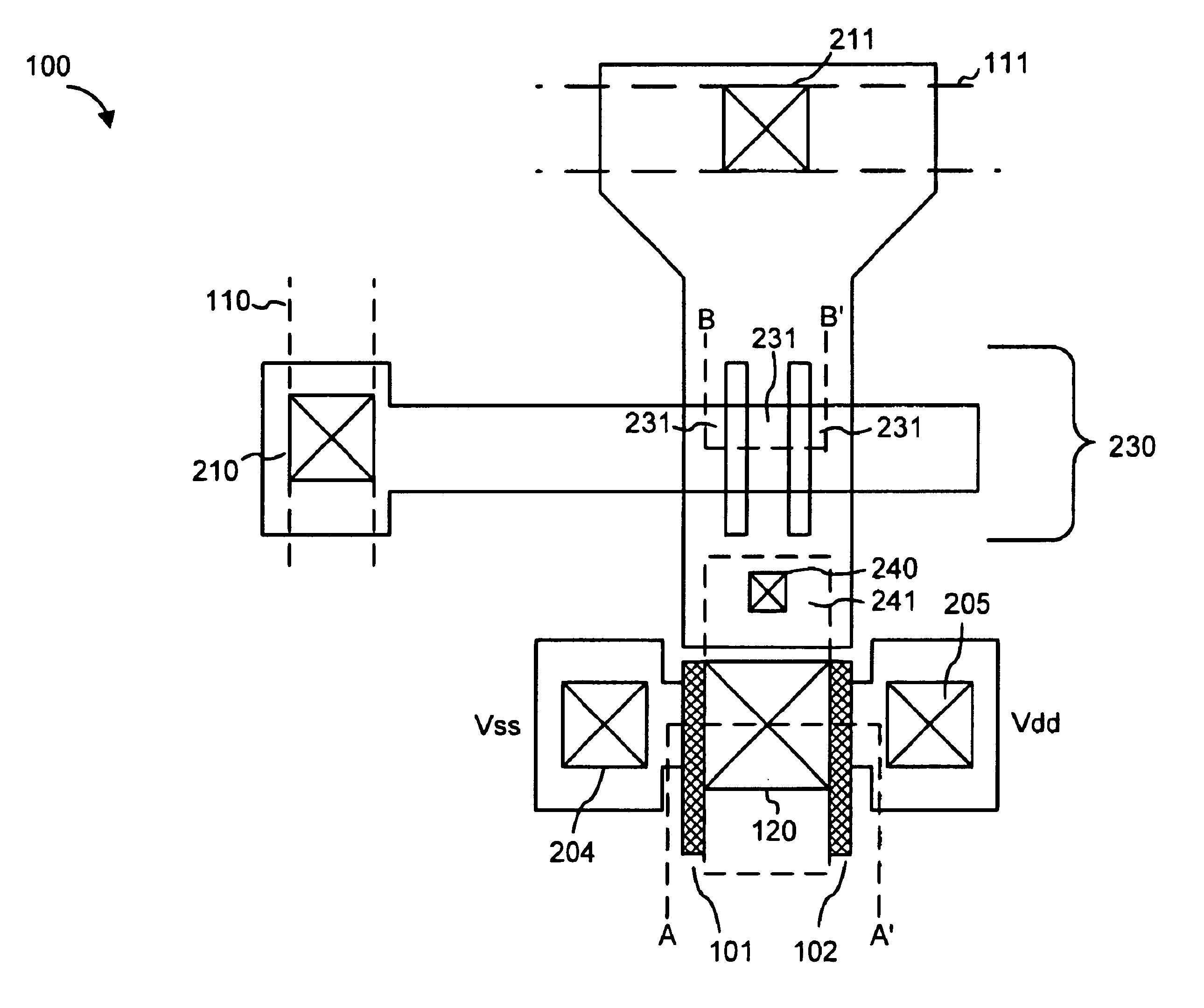
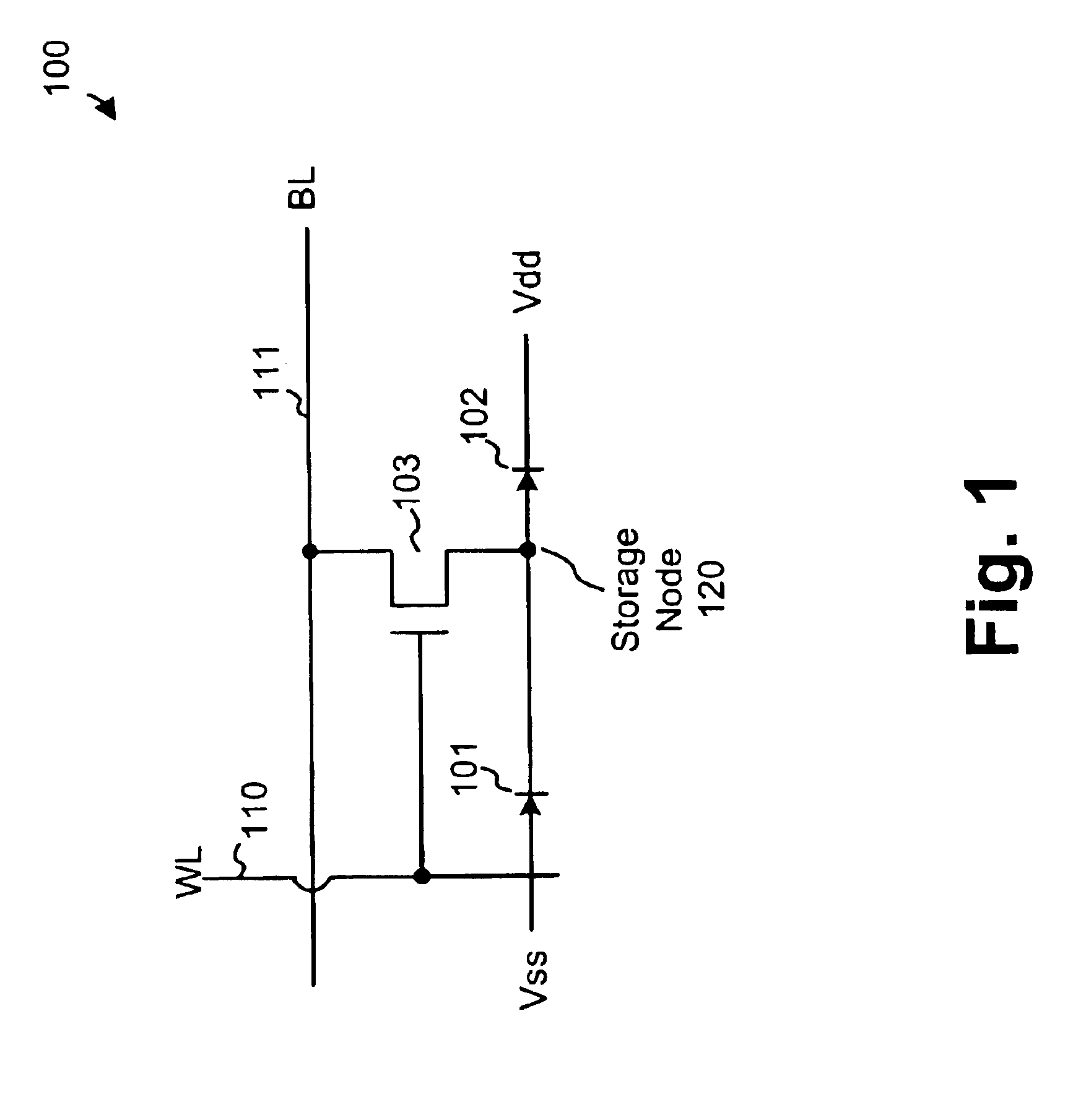
Tunneling diode magnetic junction memory
ActiveUS6965522B2Extended shelf lifeEliminate needMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsRead-only memoriesTunnel diodeSemiconductor
A tunneling diode magnetic junction memory that eliminates the need for a separate semiconductor diode is disclosed. The diode is formed by an insulating layer that is located between a free magnetic layer and a pinned magnetic layer. The present invention further discloses a method of reading the contents of a memory cell in a bi-directional manner in order to extend a storage life of the memory cell.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Tunable optical metamaterial
ActiveUS8908251B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsTunnel diodeSemiconductor structure
A tunable metamaterial has a two dimensional array of resonant annular ring elements; and a plurality of voltage controllable electrical tuning elements disposed in or adjacent openings in each of said ring elements, each of said voltage controllable electrical tuning element ohmically contacting portions of only one of said ring elements. The voltage controllable electrical tuning elements may comprise highly doped semiconductor tunnel diodes, or the charge accumulation layer at the semiconductor / insulator interface of a metal-insulator-semiconductor structure, or nanoelectromechanical (NEMs) capacitors. The tunable metamaterial may be used, for example, in an optical beam steering device using the aforementioned tunable optical metamaterial in which a free-space optical beam is coupled into a receiving portion of a plane of the optical metamaterial and is steered out of a transmitter portion of the plane of the optical metamaterial in controllable azimuthal and elevational directions. The tunable metamaterial additionally has other applications.
Owner:HRL LAB
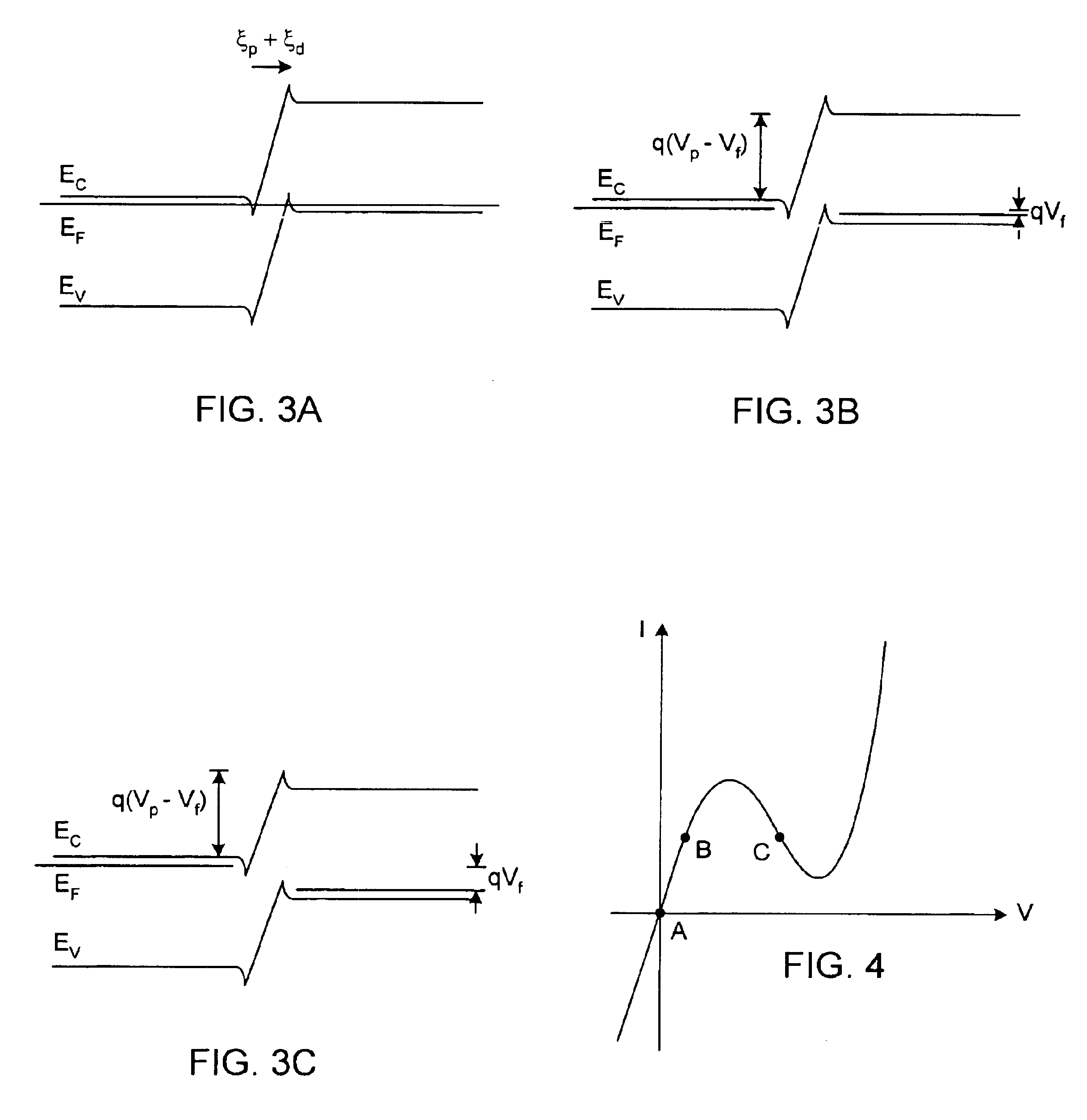
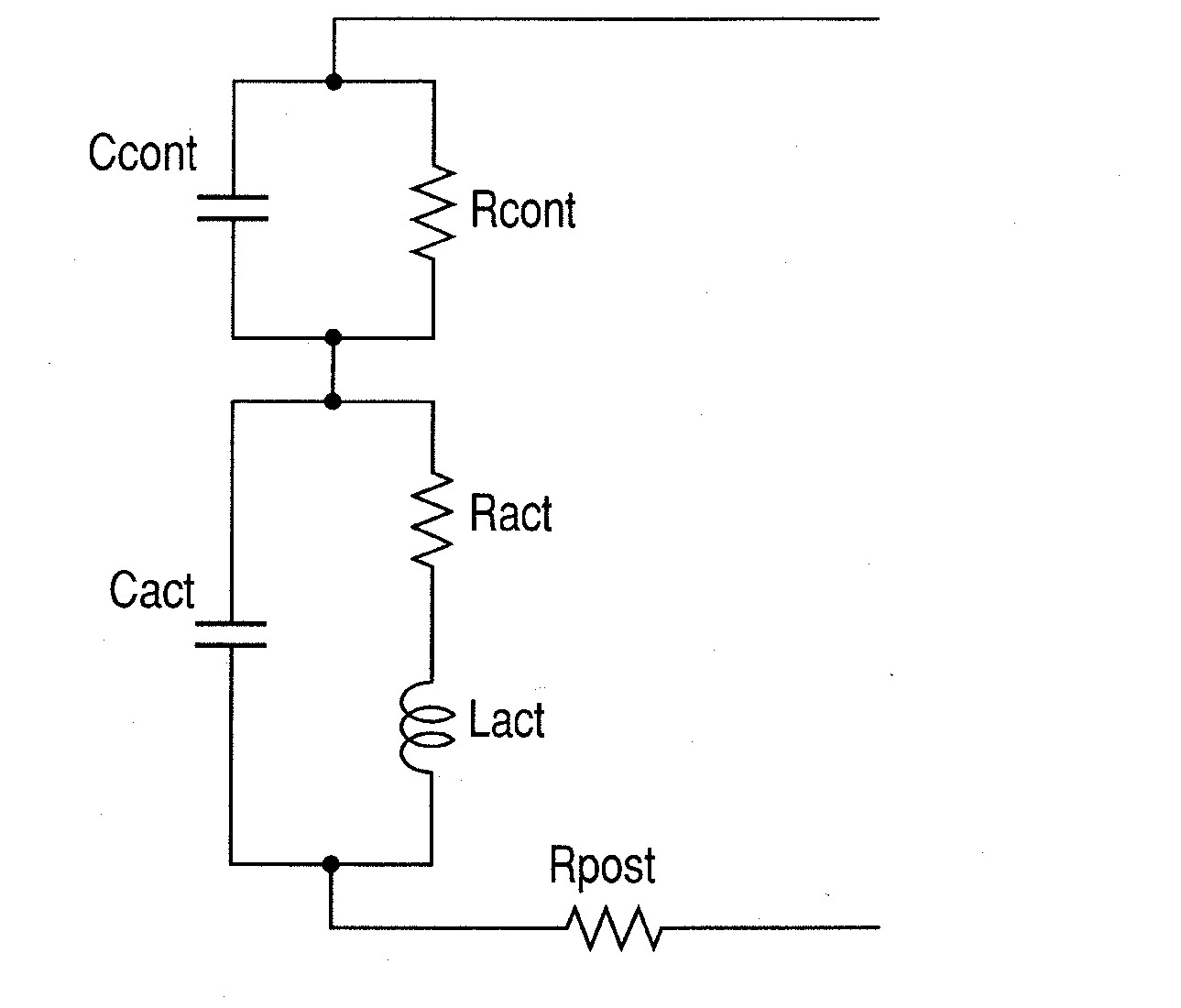
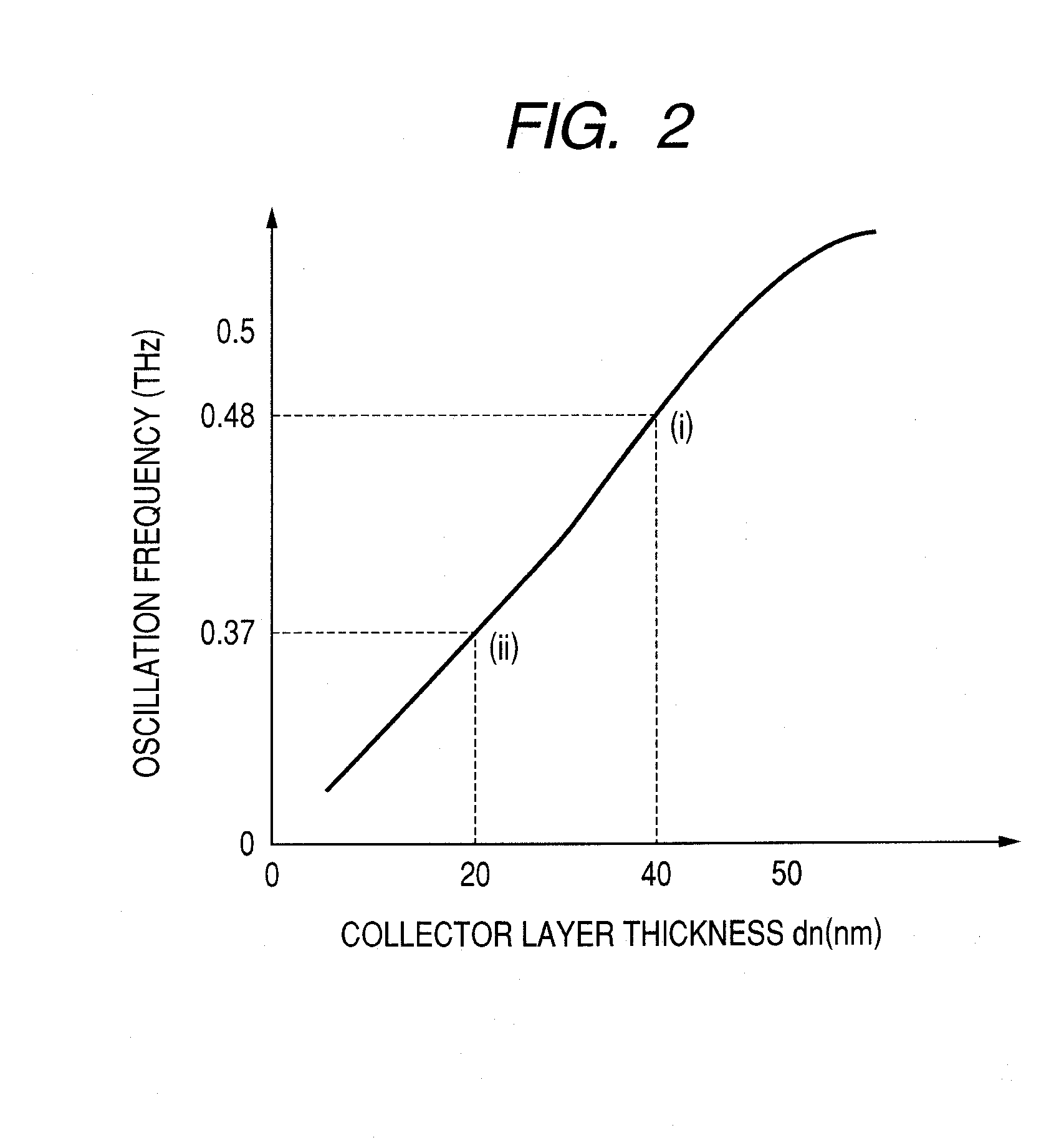
Microstrip stablized quantum well resonance-tunneling generator for millimeter and submillimeter wavelength range
ActiveUS20060055476A1Increase the oscillation frequencyIncrease speedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsSemiconductor quantum wellsTunnel diode
A microstrip stabilized quantum well resonance-tunneling generator which generates electromagnetic waves for millimeter and submillimeter wavelength range is provided The generator includes a resonant tunneling semiconductor quantum well diode, and a microstrip resonator. The resonant tunneling diode, the microstrip resonator and interconnecting lines and junctions are fabricated as a monolithic integrated device on a common substrate. As a result, the monolithic integrated device provides the expansion of the operation frequency range toward the terahertz region as a result of reduction of the parasitic inductance as well as of minimizing the other parasitic parameters of the electric circuitry connecting the resonant tunneling diode and resonator.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Low cost millimeter wave imager
InactiveUS7795859B1Low costUseful sensitivity levelMeasurement using dc-ac conversionMeasurement using ac-dc conversionLow noiseTunnel diode
Owner:HRL LAB
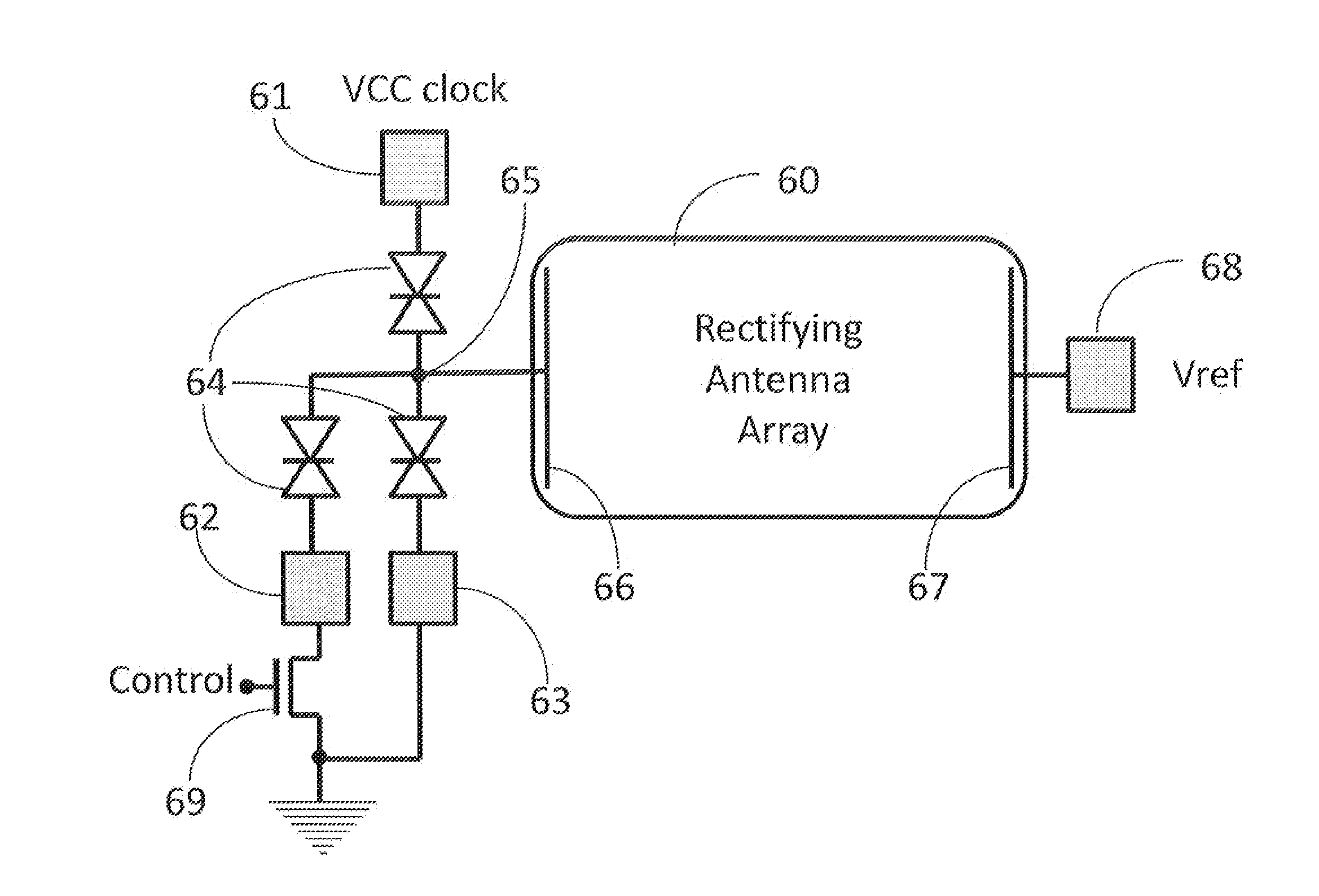
Low power semi-reflective display
A semi-reflective display and a method for fabricating and assembling a semi-reflective display are presented, where the display may be comprised of visible light rectifying antenna arrays tuned to four different colors, which when forward biased may use electric power to amplify reflected colored light, and when reversed biased may generate electric power by absorbing light. TFT-tunnel diode logic may be used to control each sub-pixel.
Owner:NOVASOLIX
Tunneling gap diodes
InactiveUS20060180829A1Good energyImprove power generation efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeTunnel diodeSemiconductor
The present invention discloses a tunneling diode having a band gap material as the collector. This increases the tunneling of electrons having greater energy than the Fermi level from emitter to collector, leading to an increase in the efficiency of heat pumping or power generation by the diode. In a further embodiment the collector comprises a semiconductor on which a layer of band gap material is deposited. This approach also reduces back tunneling of electrons from collector to emitter.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
Nanotunneling junction-based hyperspectral polarimetric photodetector and detection method
InactiveUS7501636B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioSmall currentTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesNanowireSpectral bands
A photodetector, detector array, and method of operation thereof in which nanojunctions are formed by crossing layers of nanowires. The crossing nanowires are separated by a few nm thick electrical barrier layer which allows tunneling. Each nanojunction is coupled to a slot antenna for efficient and frequency-selective coupling to photo signals. The nanojunctions formed at the intersection of the crossing wires defines a vertical tunneling diode that rectifies the AC signal from a coupled antenna and generates a DC signal suitable for reforming a video image. The nanojunction sensor allows multi / hyper spectral imaging of radiation within a spectral band ranging from terahertz to visible light, and including infrared (IR) radiation. This new detection approach also offers unprecedented speed, sensitivity and fidelity at room temperature.
Owner:NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTATION U S GOVERNMENT AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTATOR OF THE
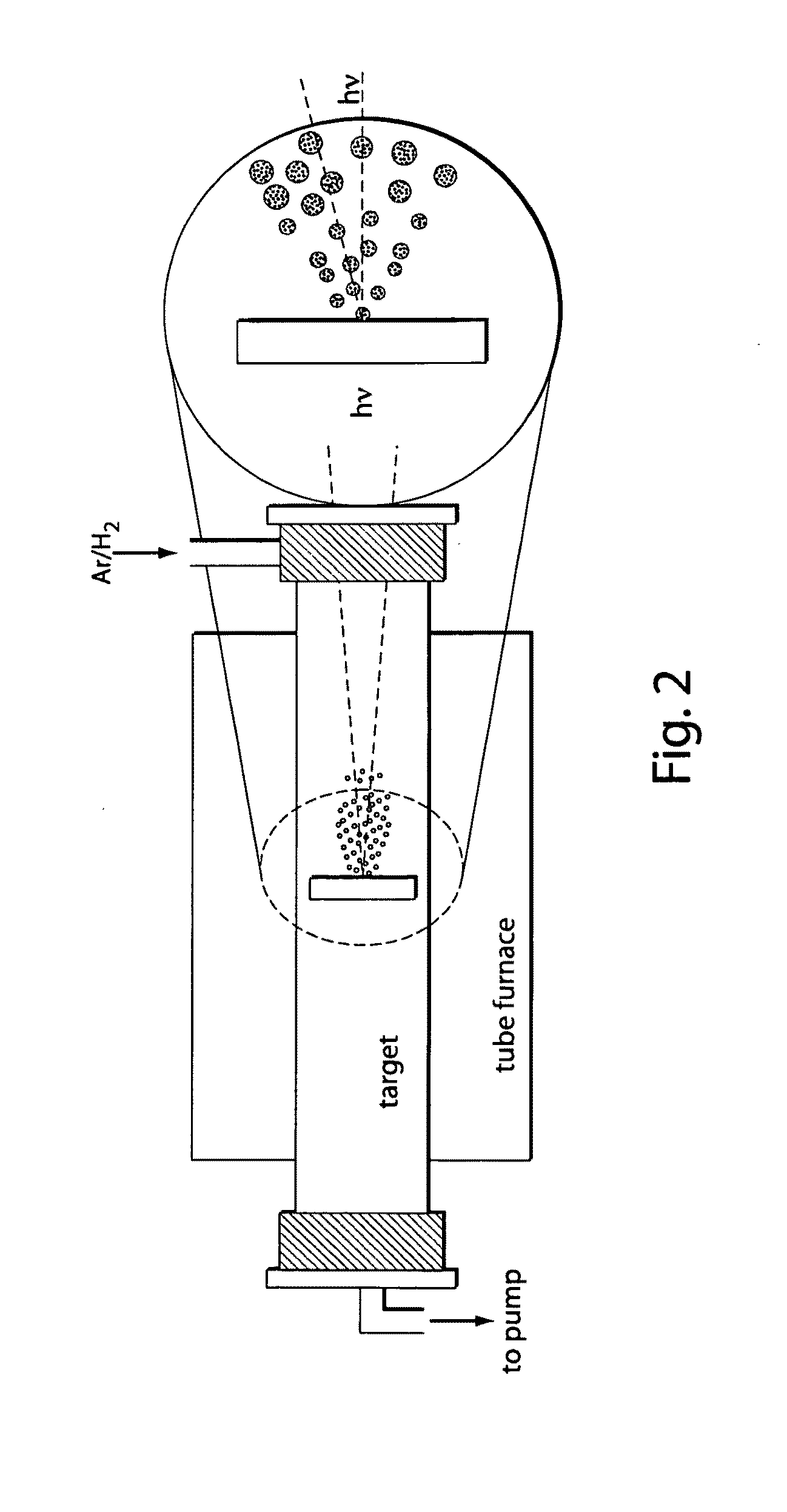
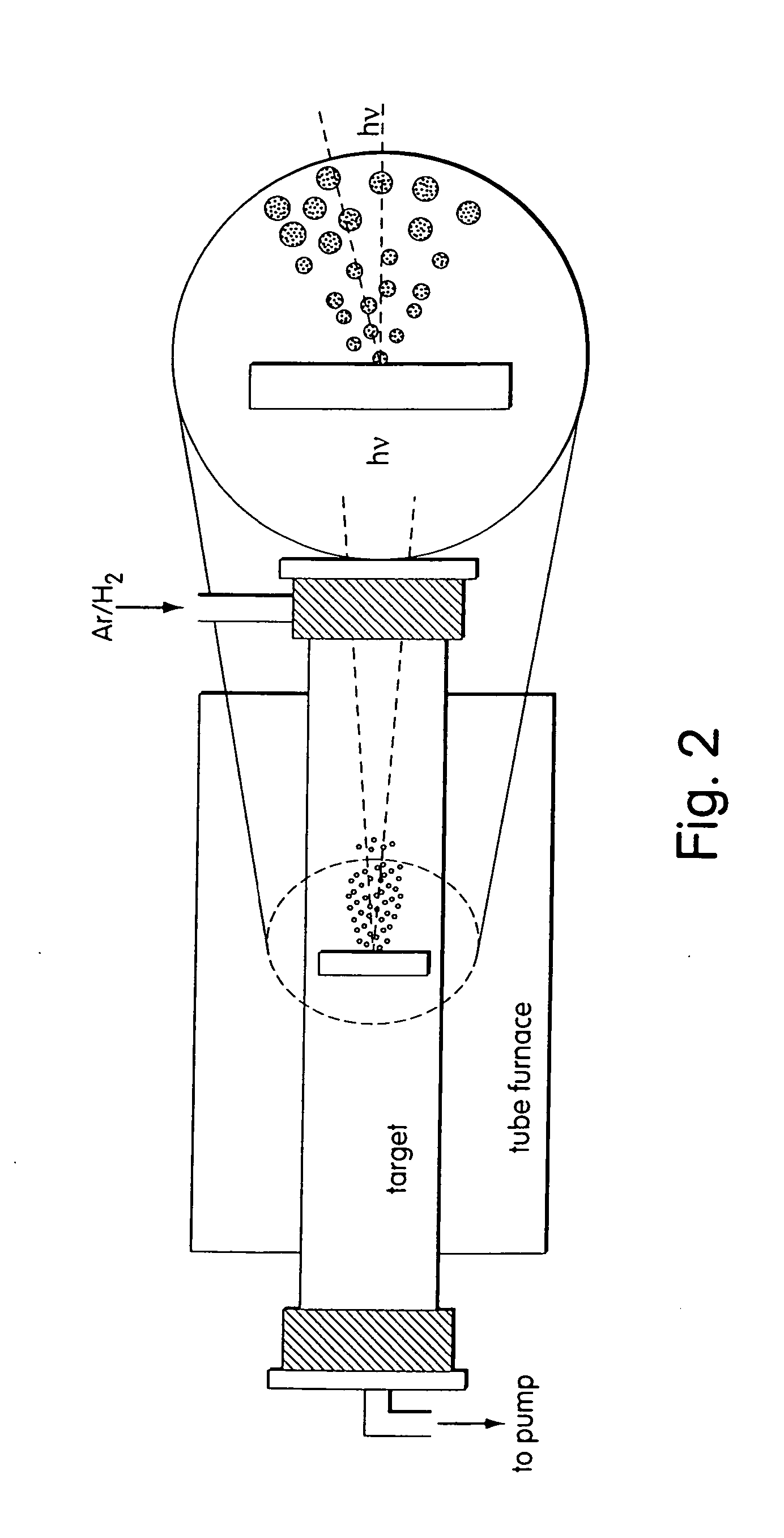
Sn-Ge-As alloy as well as preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN101423907AHigh in arsenicUniform compositionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingTunnel diodeHigh pressure
The invention provides a tin-germanium-arsenic alloy material, a method for preparing the same and application thereof. The alloy material consists of the following components in weight percentage: 0.05 to 5 percent of Ge, 1 to 10 percent of As, and the balance being Sn. The preparation method comprises the following steps: in the range of the weight percentage, the high-purity tin, germanium and arsenic materials are weighed up; according to the order of arsenic, germanium and tin, the materials are placed in a quartz crucible, and the quartz crucible is placed in a high pressure reaction kettle; the reaction kettle is pumped vacuum and filled with argon, and the temperature and pressure of the reaction kettle are controlled to melt the tin and the germanium and make arsenic vapor enter the inner part of the tin-germanium melt mass to form an intermediate alloy; the intermediate alloy is cooled down to obtain tin-germanium-arsenic intermediate alloy ingot; and according to the weight percentage, the obtained intermediate alloy ingot and the remained tin and germanium are melted together and cast to obtain the tin-germanium-arsenic alloy material. The tin-germanium-arsenic alloy material is the basic alloy material for preparing high-quality tunnel diode, in which the tin-germanium-arsenic alloy material plays a role of an electrode electrodes, transforms P<+> to N<+> to form N<+>P<+> and a narrow space charge area and can be used to prepare vaporization plating materials as well as sputtering target materials.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF NONFERROUS METALS & RARE EARTH
Oscillation device and inspection apparatus
ActiveUS20090051452A1Efficient transferReduce power consumptionElectric pulse generatorOscillations generatorsMolecular physicsVoltage
An oscillation device has a resonant tunneling diode formed by interposing a gain medium including a first barrier layer, a quantum well layer and a second barrier layer between a first thickness adjusting layer and a second thickness adjusting layer. The oscillation device also has a switch for switching the polarity of a bias voltage being applied to the resonant tunneling diode. The first thickness adjusting layer and the second thickness adjusting layer have different thicknesses. Thus, a single oscillation device is driven to oscillate with different oscillation frequencies.
Owner:CANON KK
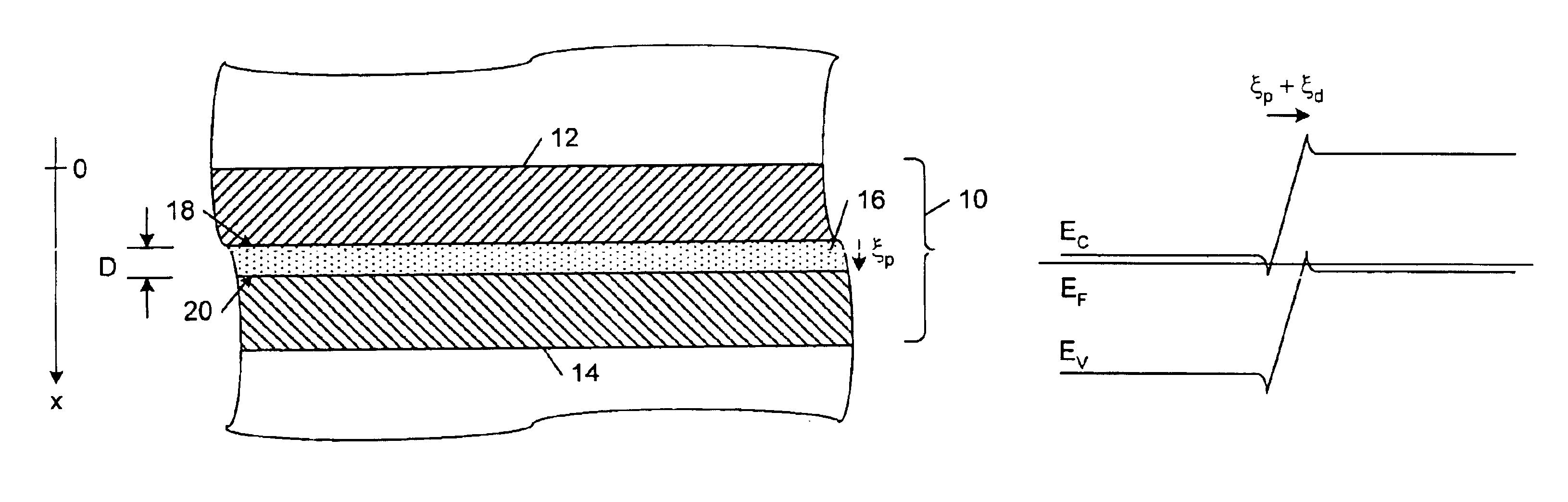
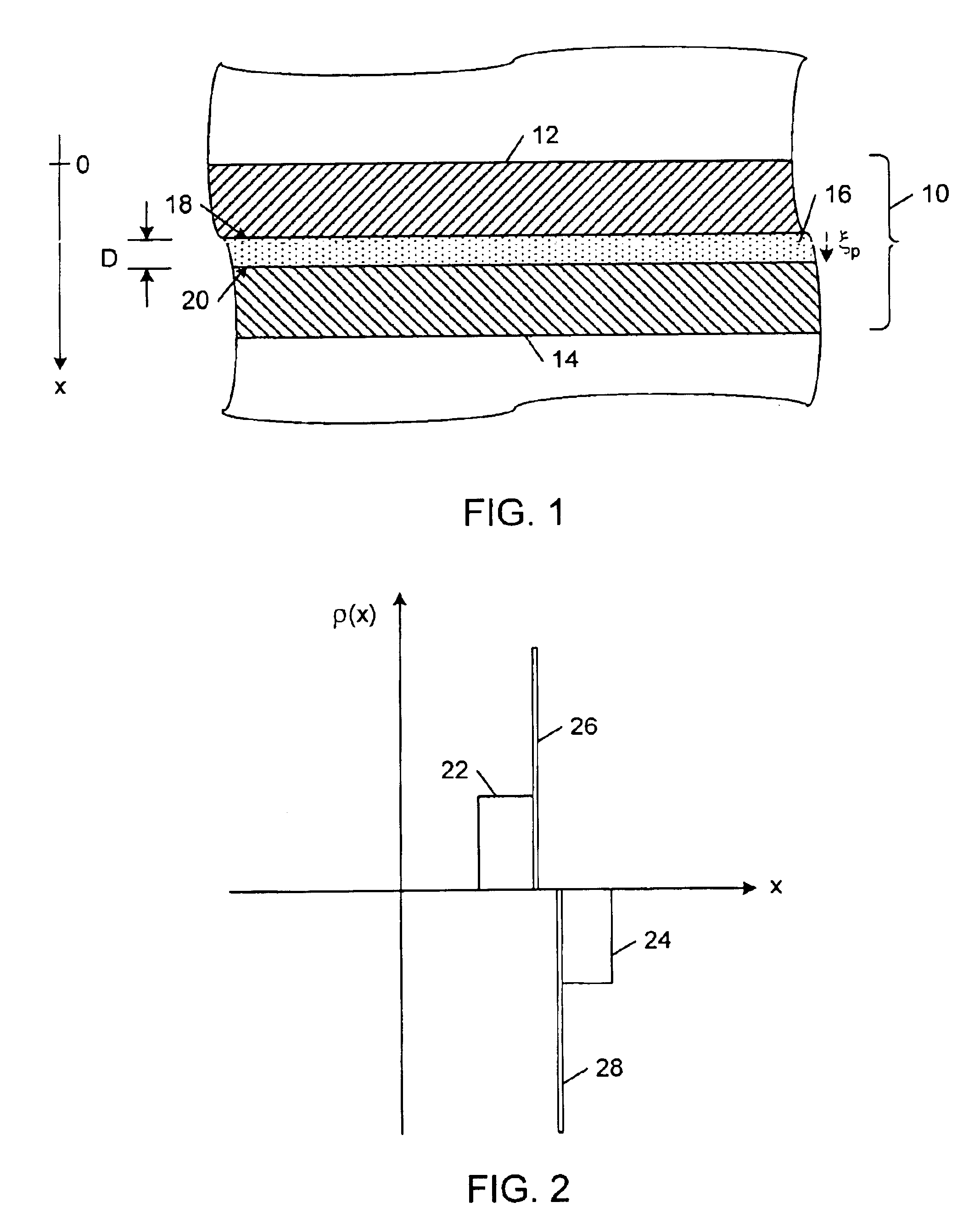
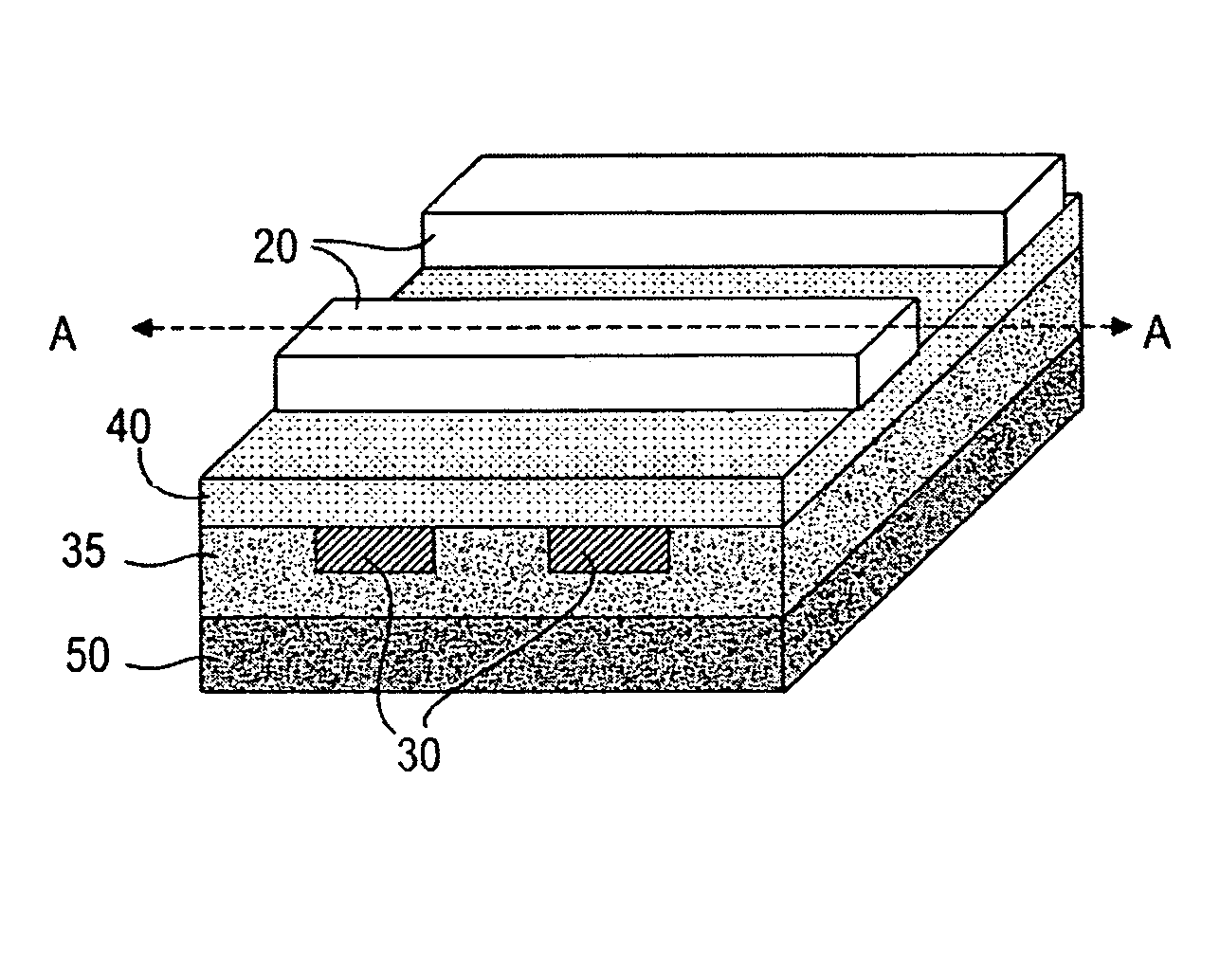
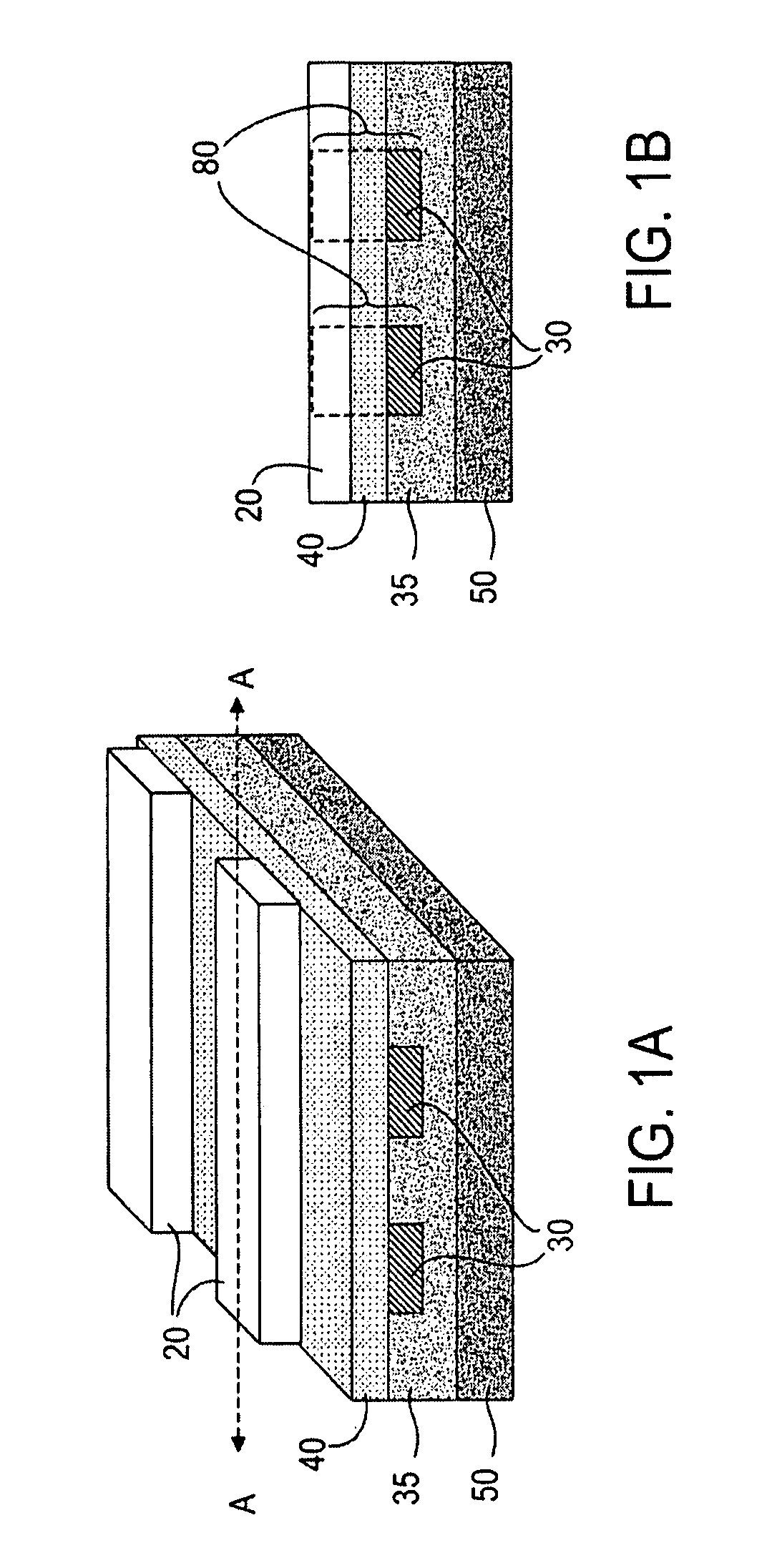
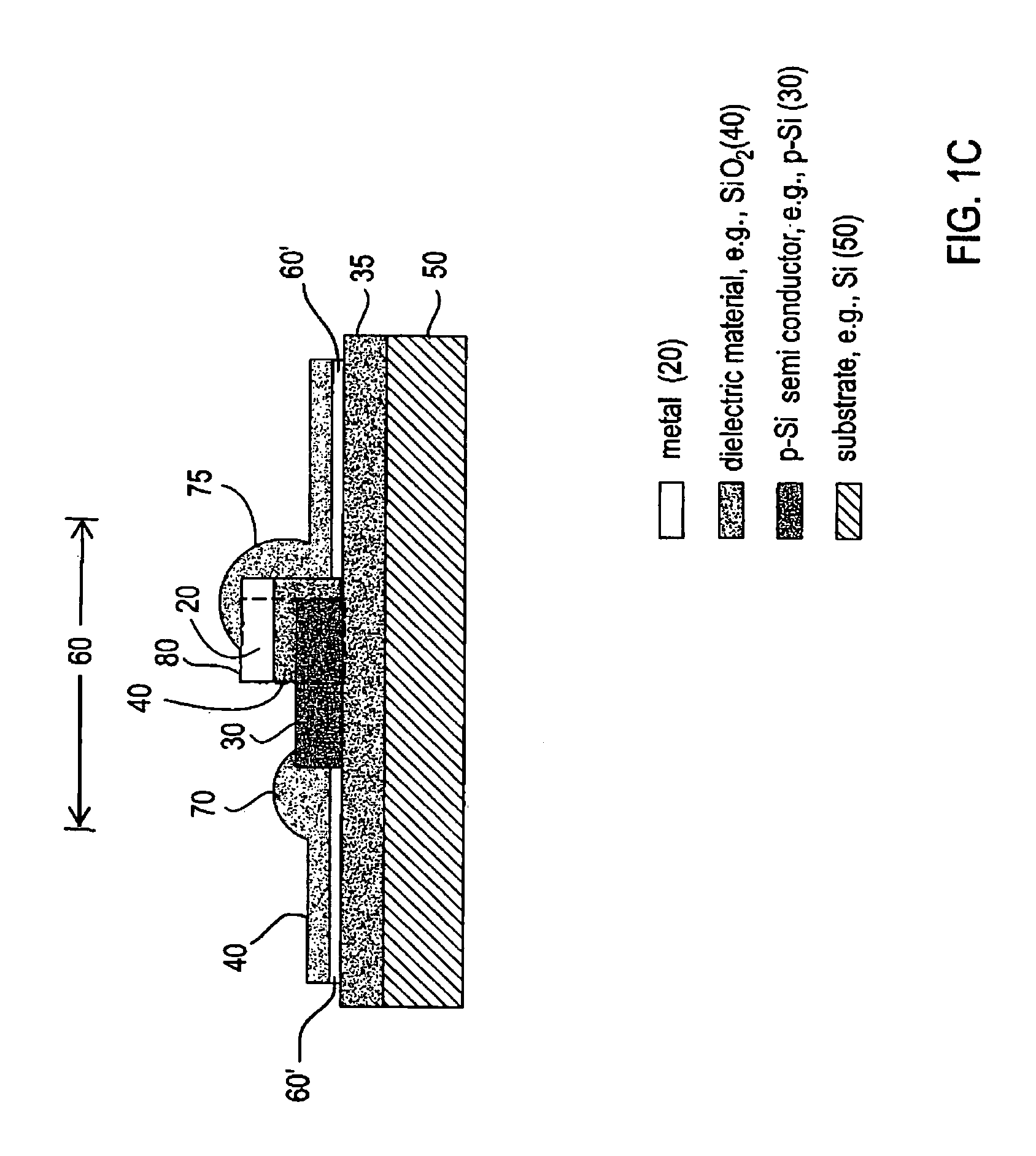
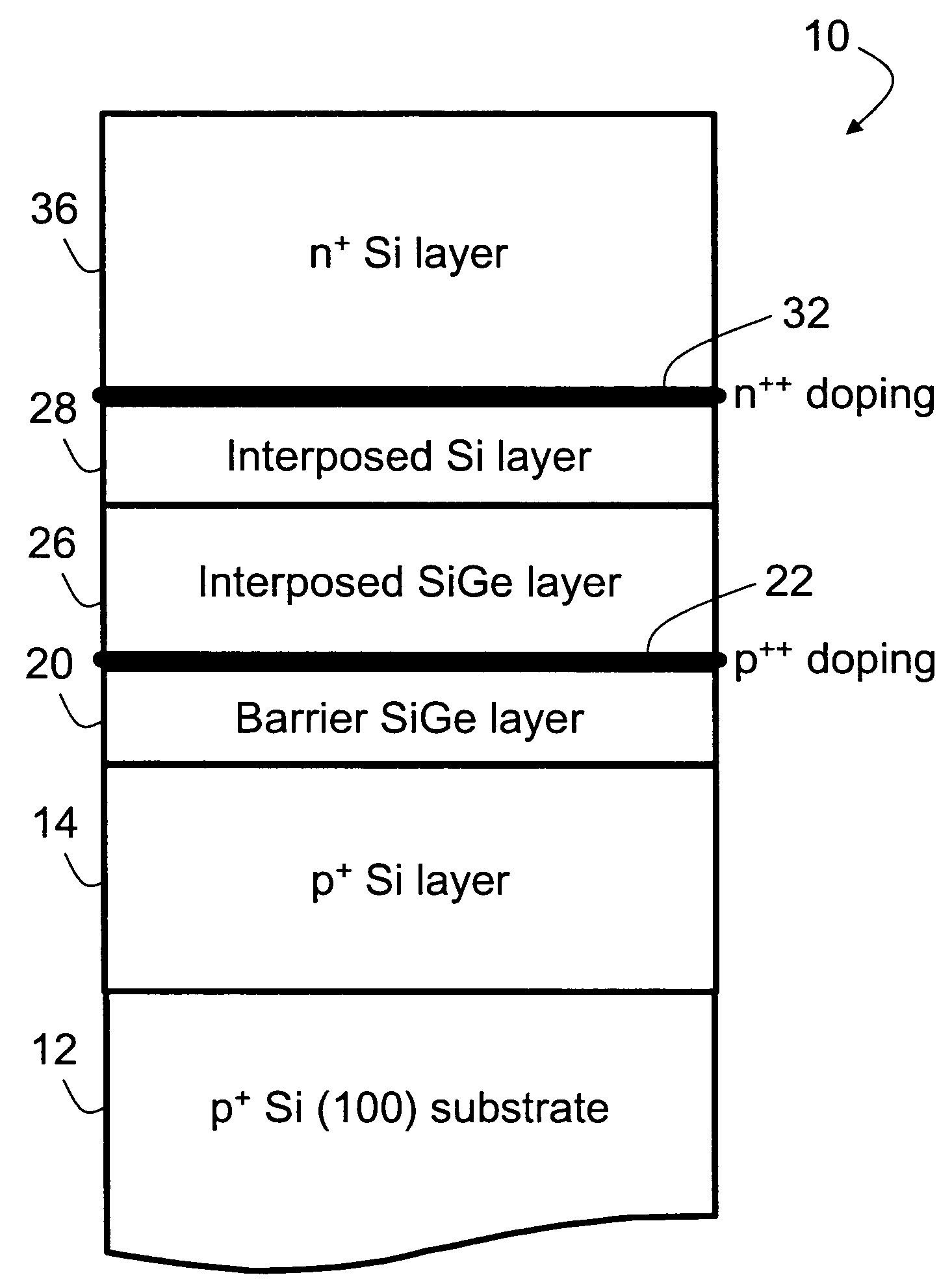
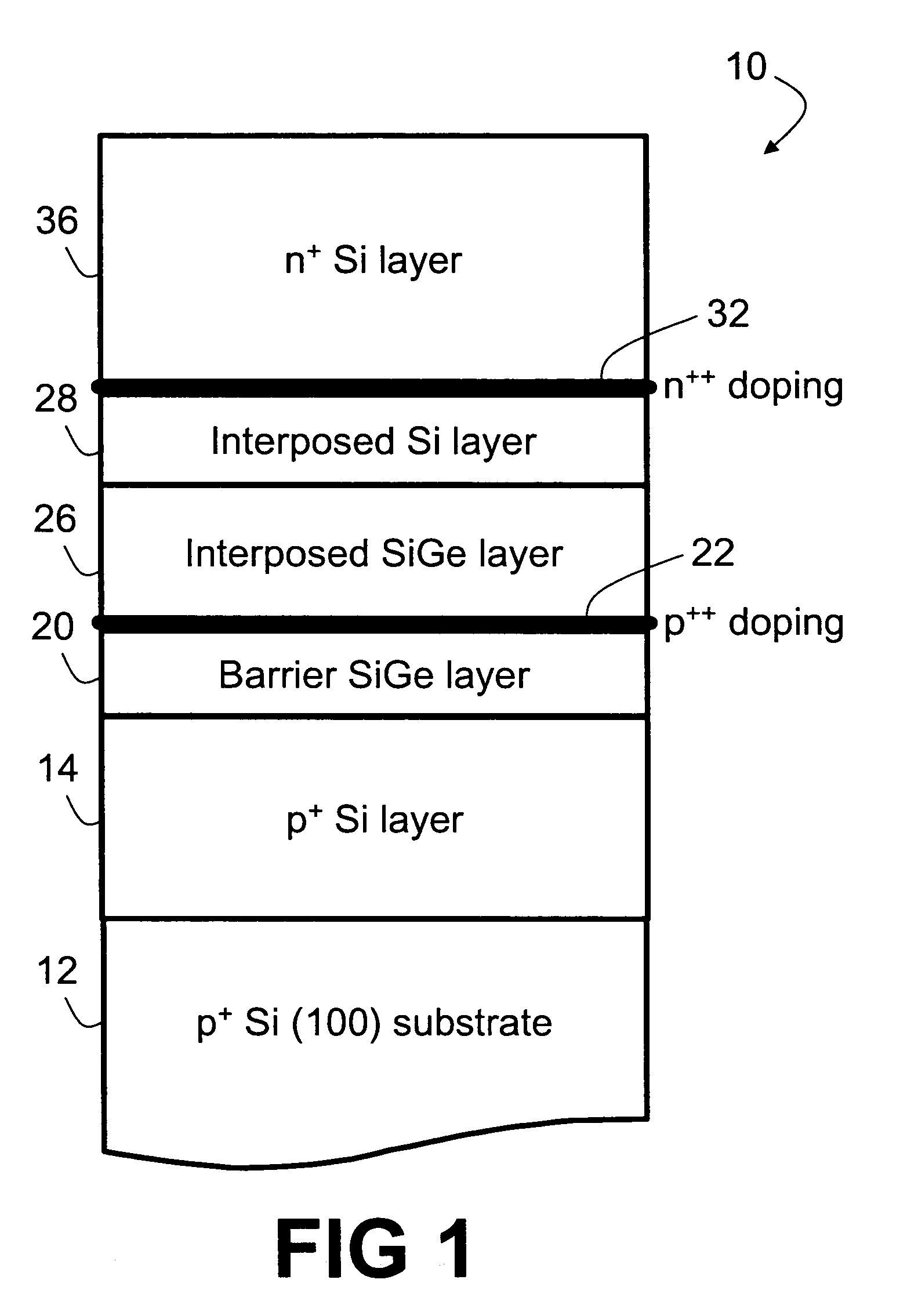
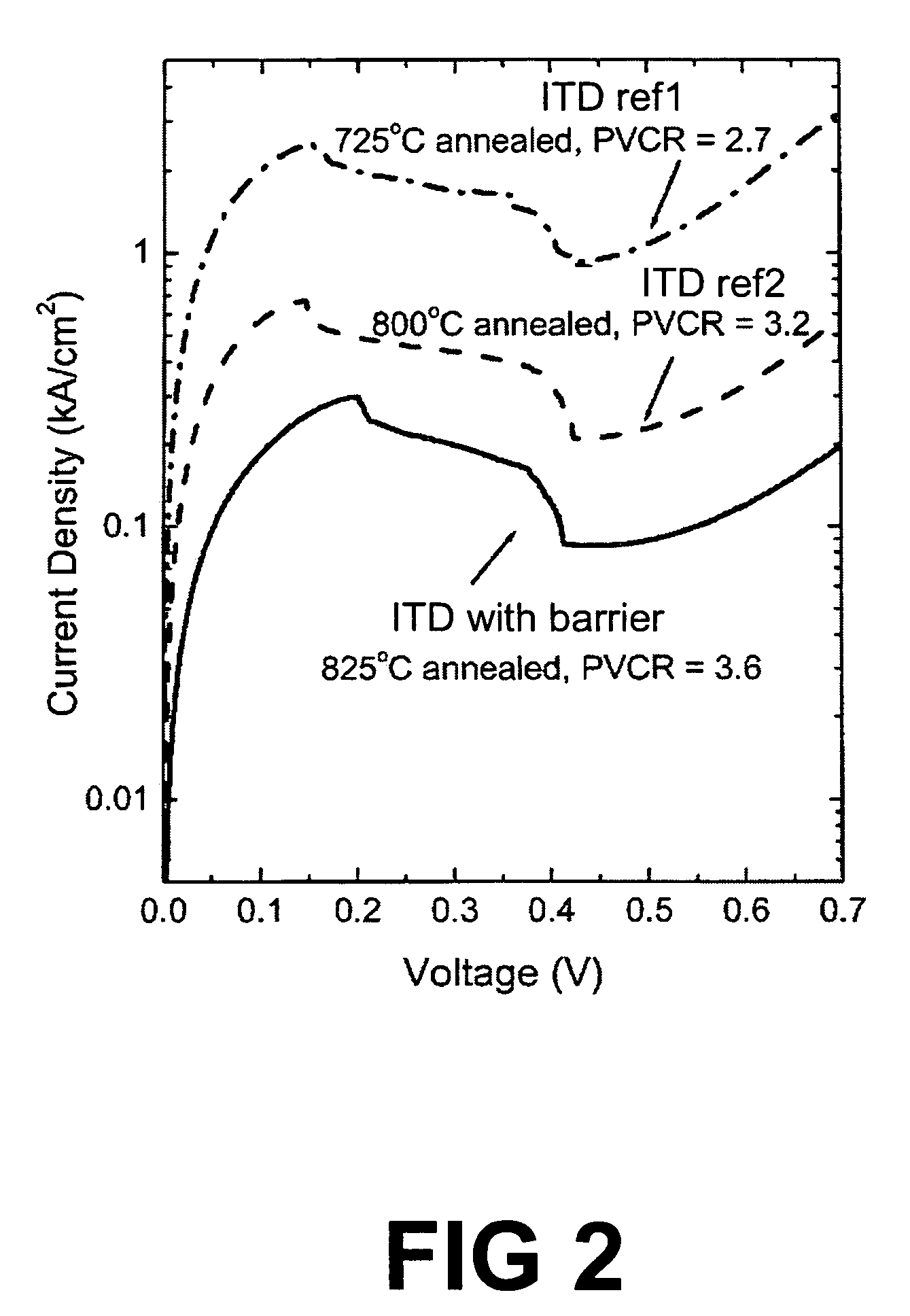
Si/SiGe interband tunneling diode structures including SiGe diffusion barriers
A silicon-based interband tunneling diode (10, 110) includes a degenerate p-type doping (22, 130) of acceptors, a degenerate n-type doping (32, 118) of donors disposed on a first side of the degenerate p-type doping (22, 130), and a barrier silicon-germanium layer (20, 136) disposed on a second side of the degenerate p-type doping (22, 130) opposite the first side. The barrier silicon-germanium layer (20, 136) suppresses diffusion of acceptors away from a p / n junction defined by the degenerate p-type and n-type dopings (22, 32, 118, 130).
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com