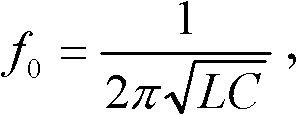Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
660 results about "Negative resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
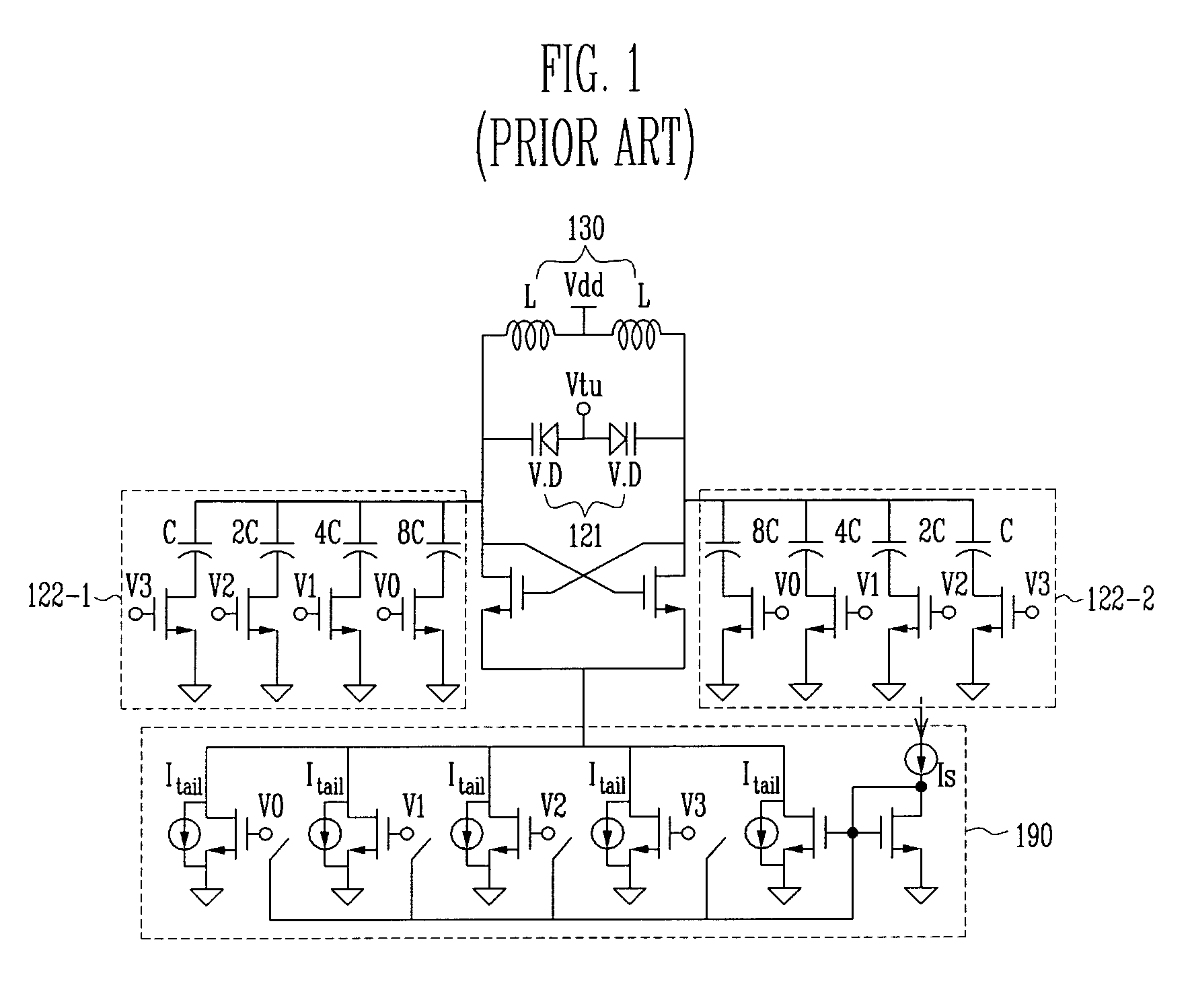
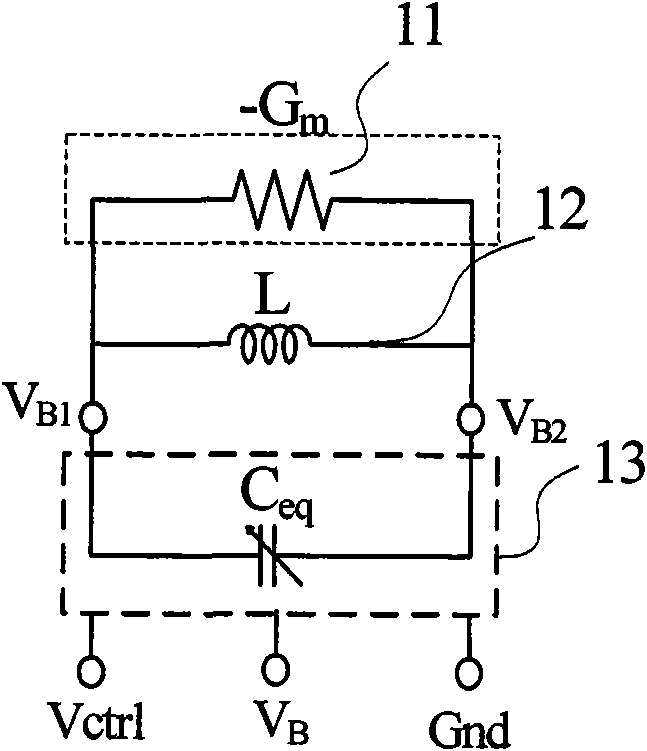
In electronics, negative resistance (NR) is a property of some electrical circuits and devices in which an increase in voltage across the device's terminals results in a decrease in electric current through it. This is in contrast to an ordinary resistor in which an increase of applied voltage causes a proportional increase in current due to Ohm's law, resulting in a positive resistance. While a positive resistance consumes power from current passing through it, a negative resistance produces power.
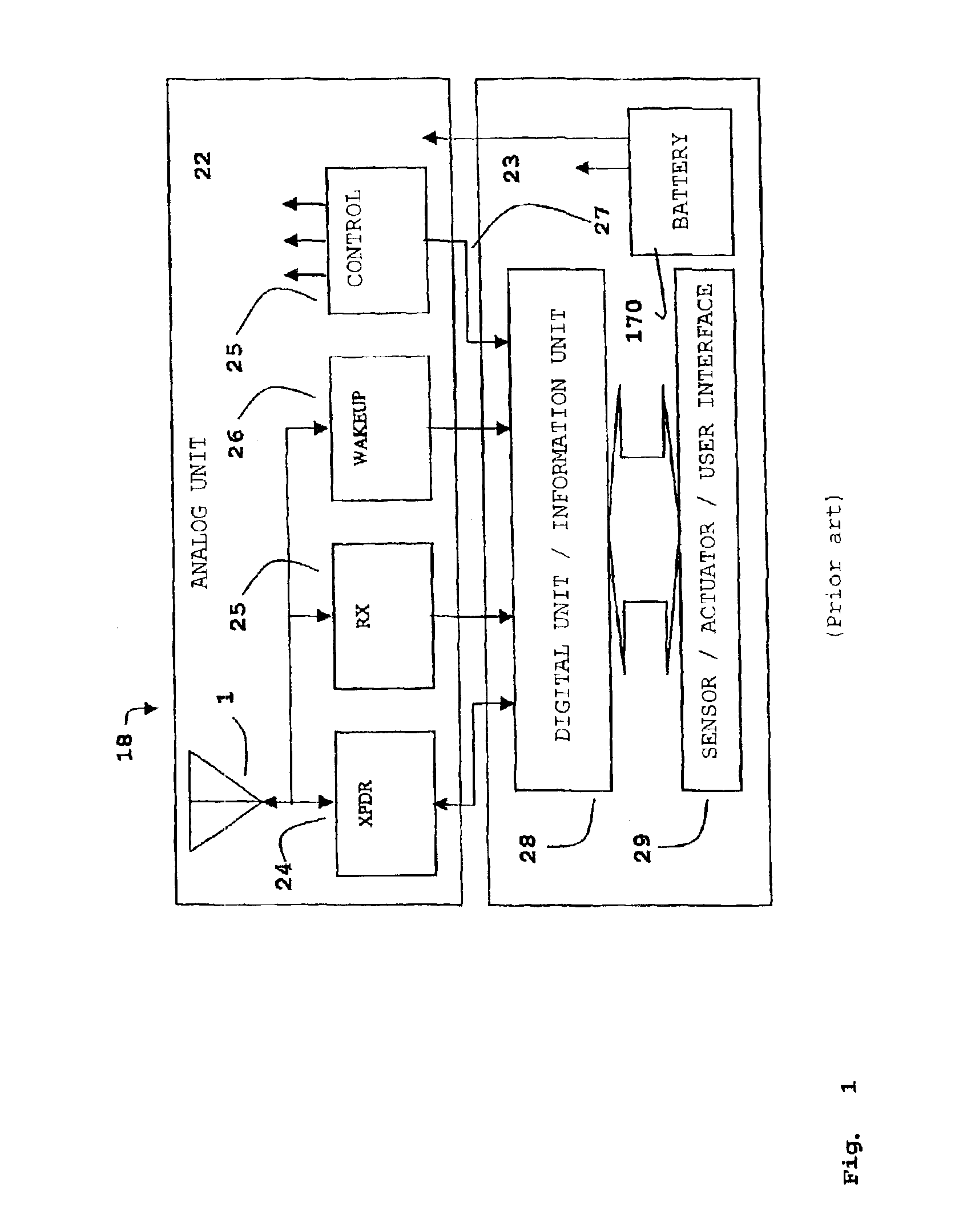
Analogue regenerative transponders including regenerative transponder systems
InactiveUS20050068223A1Expand coverageExtend radio coverageRadio relay systemsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEngineeringPositioning system
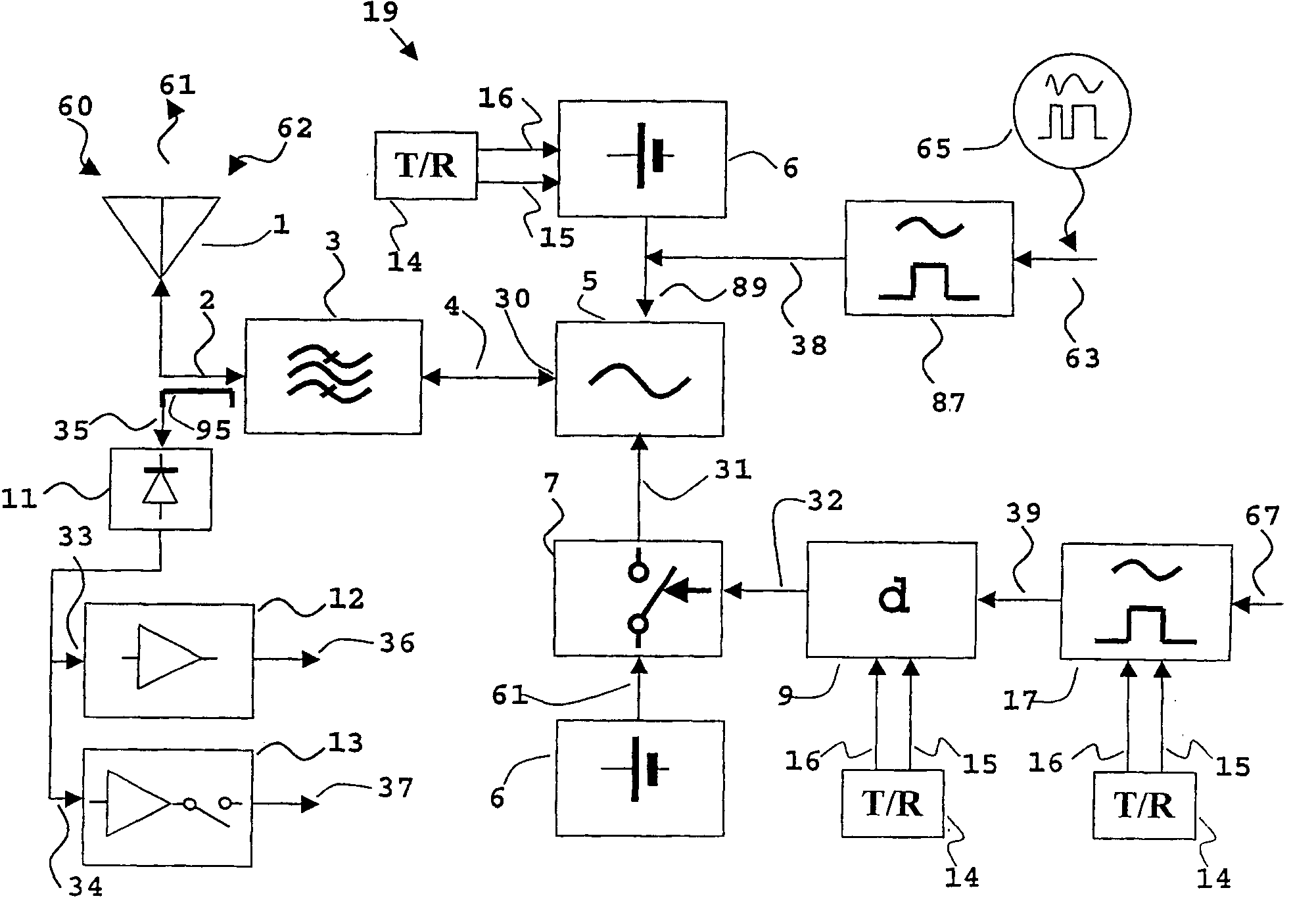
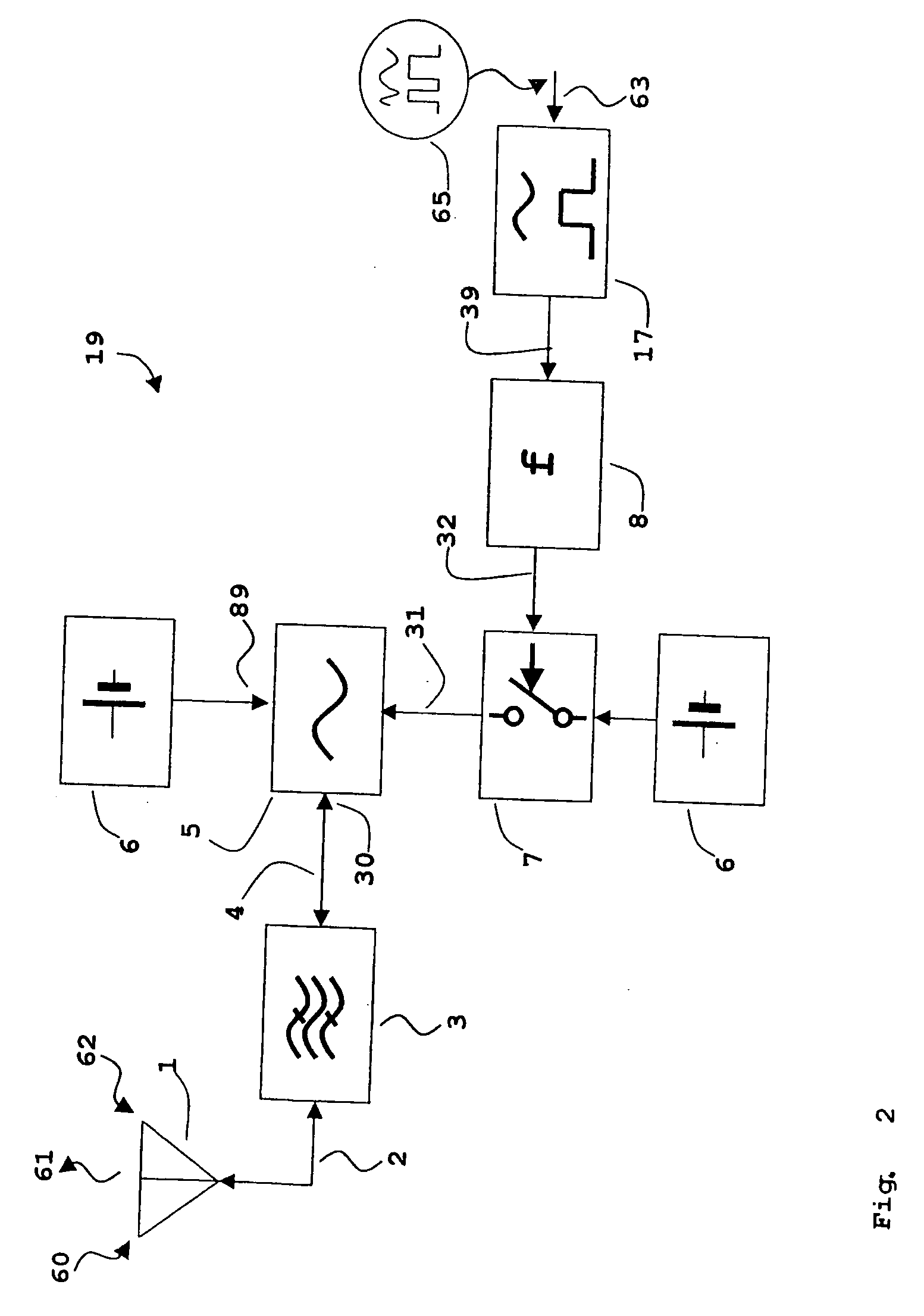
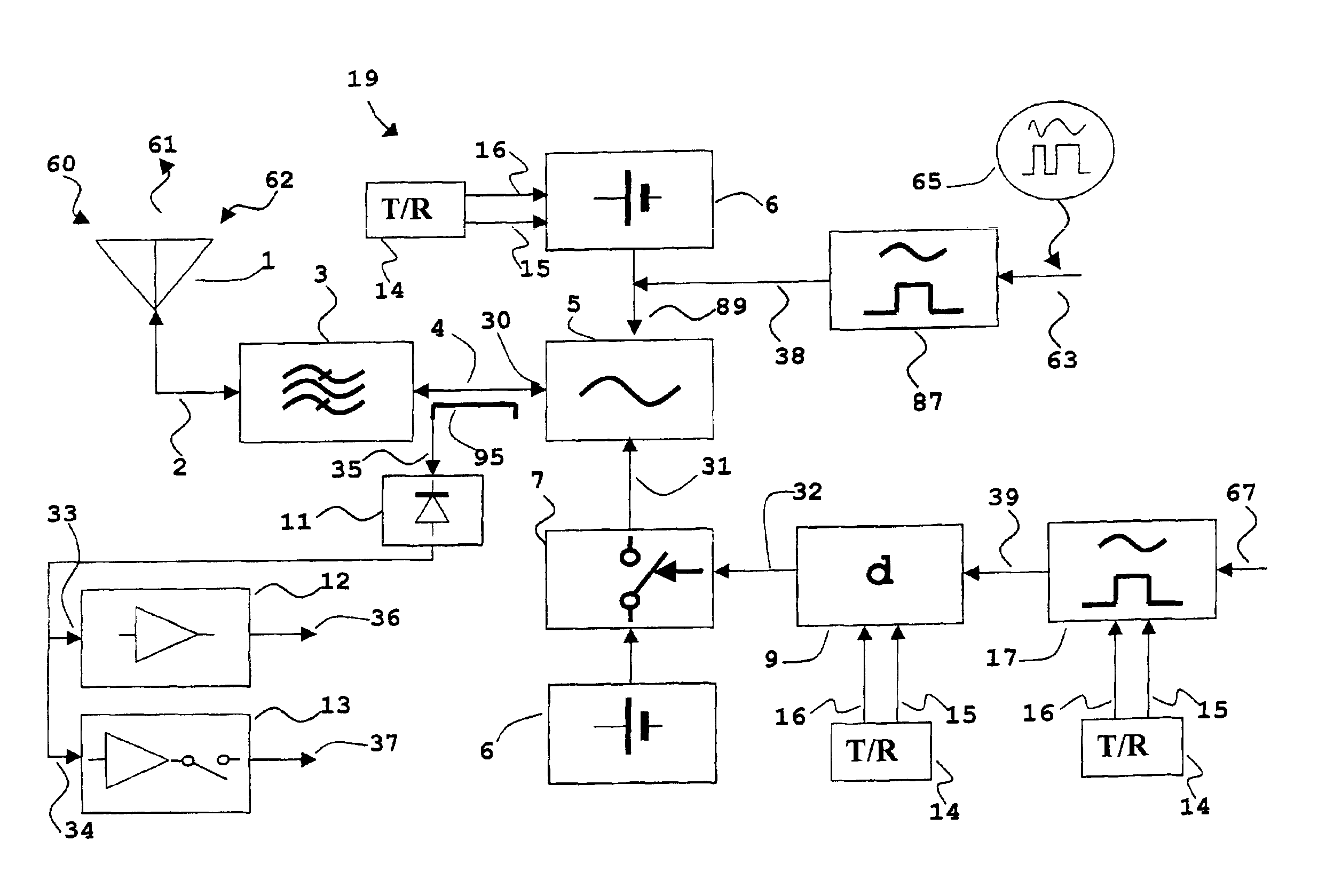
In a transponder (19) for amplification of a received signal (60) into an antenna (1), to a signal (61) for retransmission, and where the retransmitted signal (61) possibly may have information superimposed, a quenched oscillator (5) is incorporated as amplifying element. The oscillator (5) is preferably of superregenerative type and exhibits negative resistance (30) for the received signal (60). Transponders according to the present invention may be introduced as system elements in a wireless or wire based network to work as intelligent or unintelligent connections in the network. The transponders can also be used in positioning systems.
Owner:VAVIK GEIR MONSEN
Transponder, including transponder system
InactiveUS6946989B2The implementation process is simpleLarge and small propertyNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationEngineeringSystem element
Owner:VAVIK GEIR MONSEN
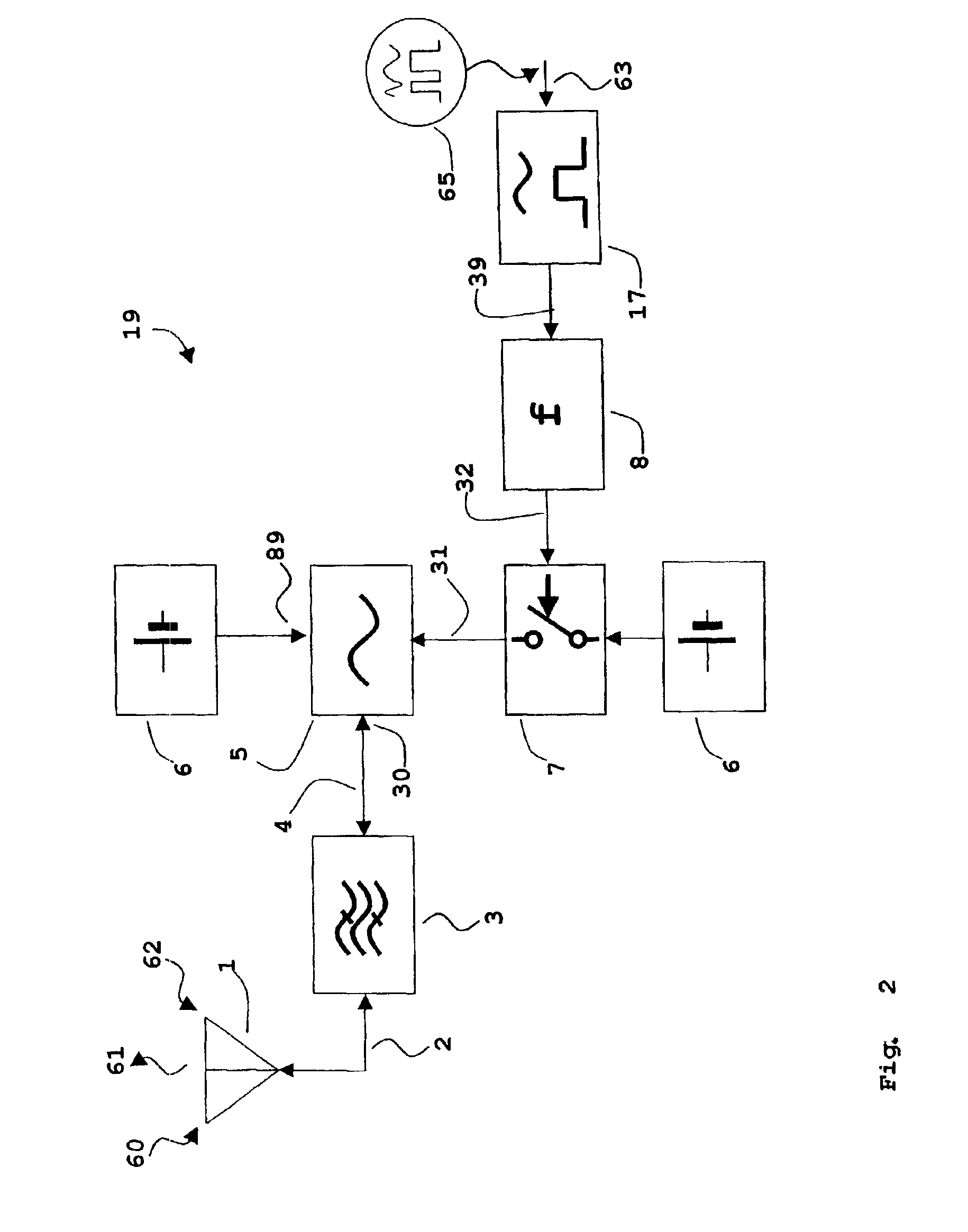
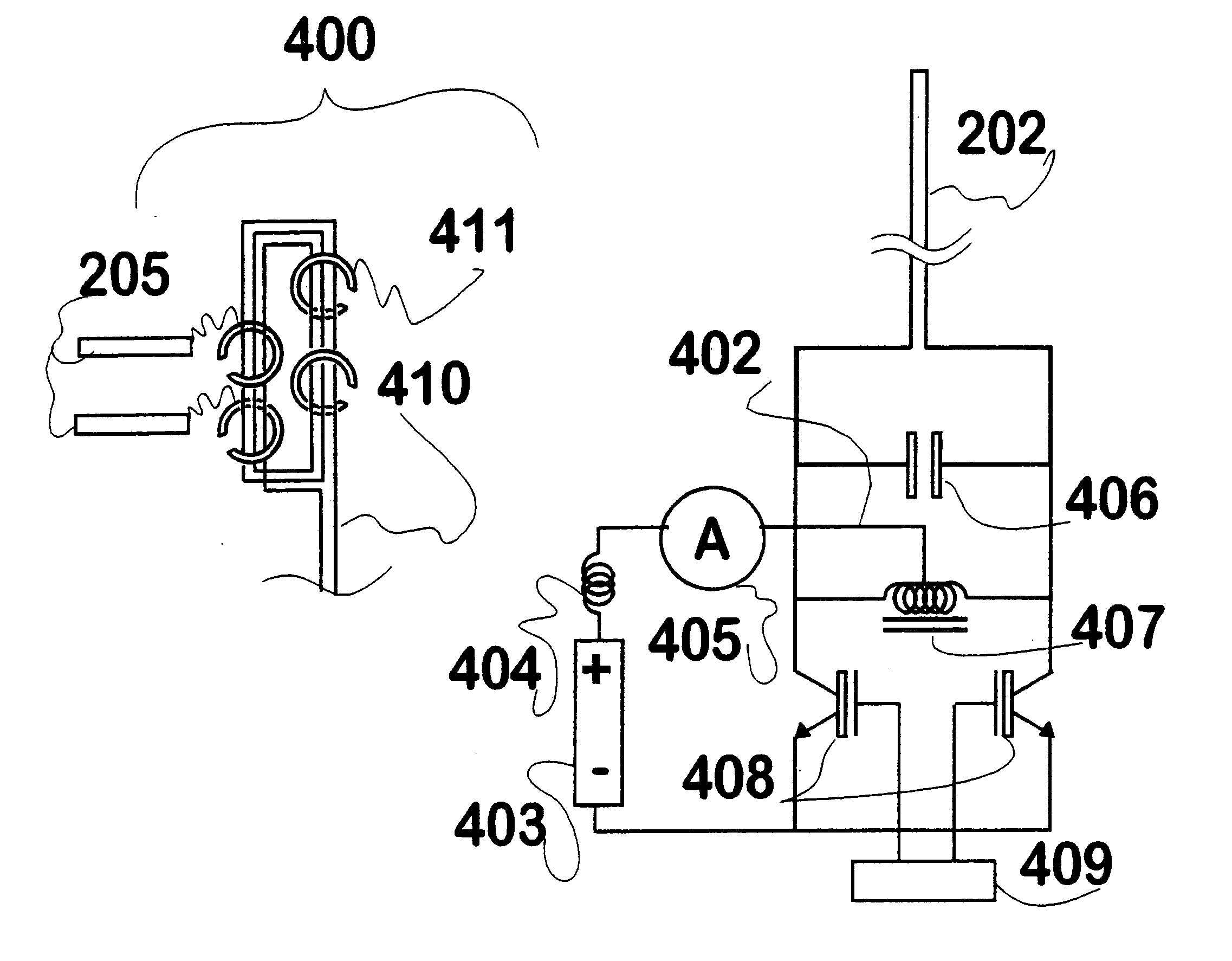
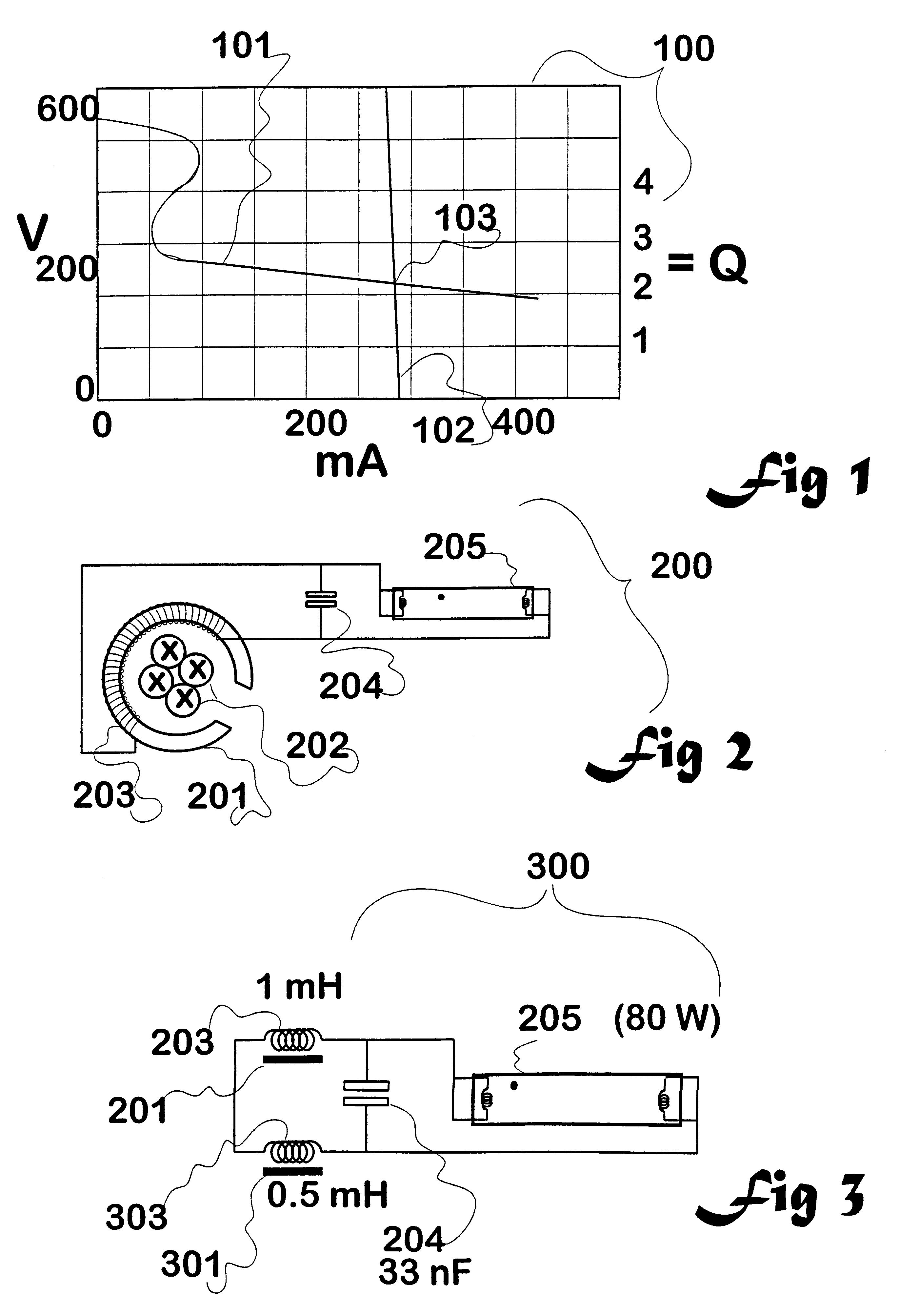
Induction circuits for lighting
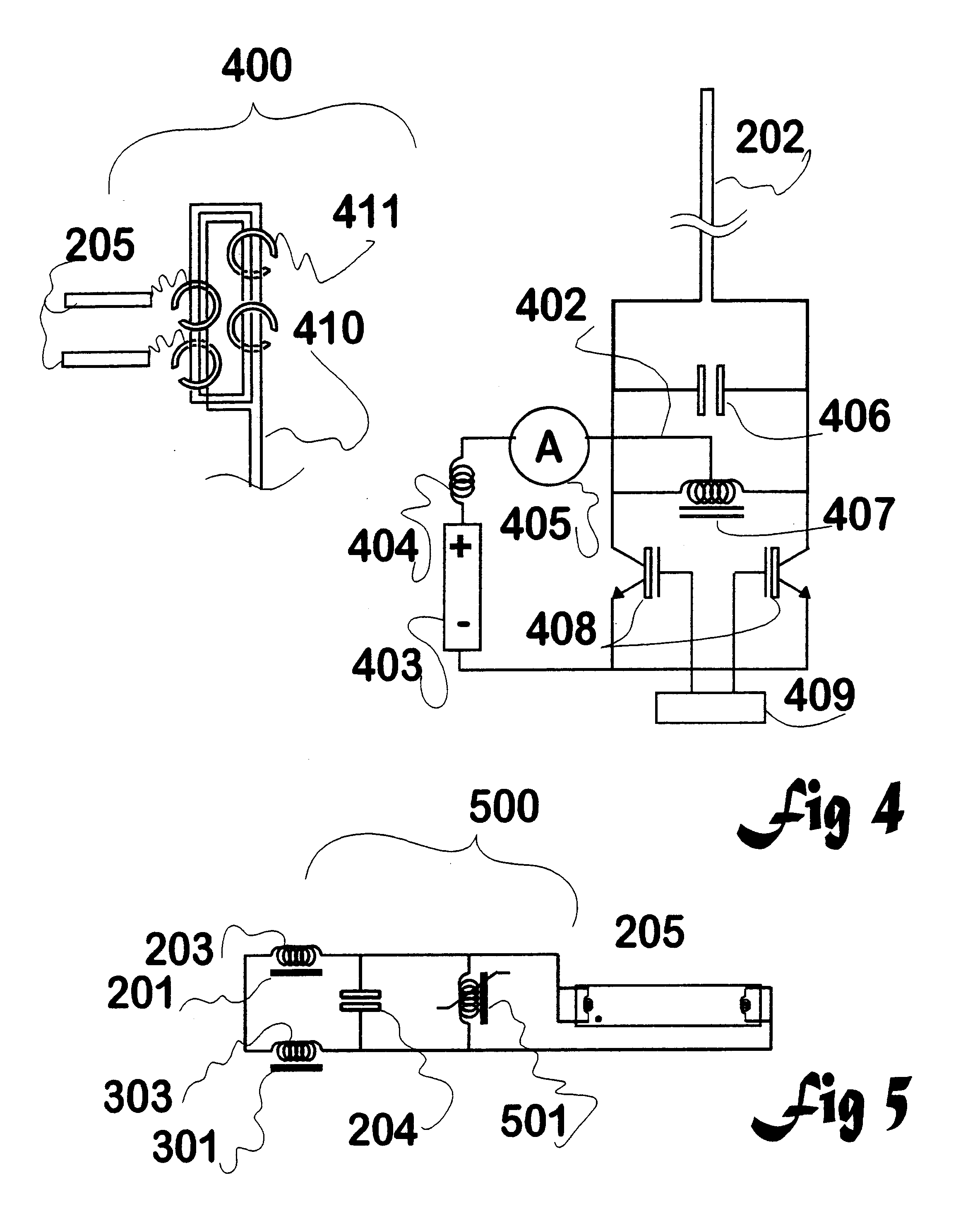
Disclosed is inductive coupling of power to devices having negative resistances, such as gas-filled discharge lamps (fluorescent tubes, neon signs, and the like) from a primary inductive loop, using resonant conditioning of the power provided to the device. A "C" shaped inductor (202) around the loop and a resonating capacitor (406) in parallel with the inductor provide a current source to the lamp (403) from across the capacitor. The circuit is capable of first igniting a lamp using a higher voltage available when the Q of the unloaded circuit is high, then running the lamp or other device at a controlled current. The lamp current is substantially proportional to the primary inductive loop flux, and substantially independent of the lamp resistance. A second inductor (404) in series with the first though not itself a collector of flux acts as a current limit. Applications include lighting, displays (optionally isolated and dimmable), and production of ultraviolet radiation.
Owner:AUCKLAND UNISERVICES LTD
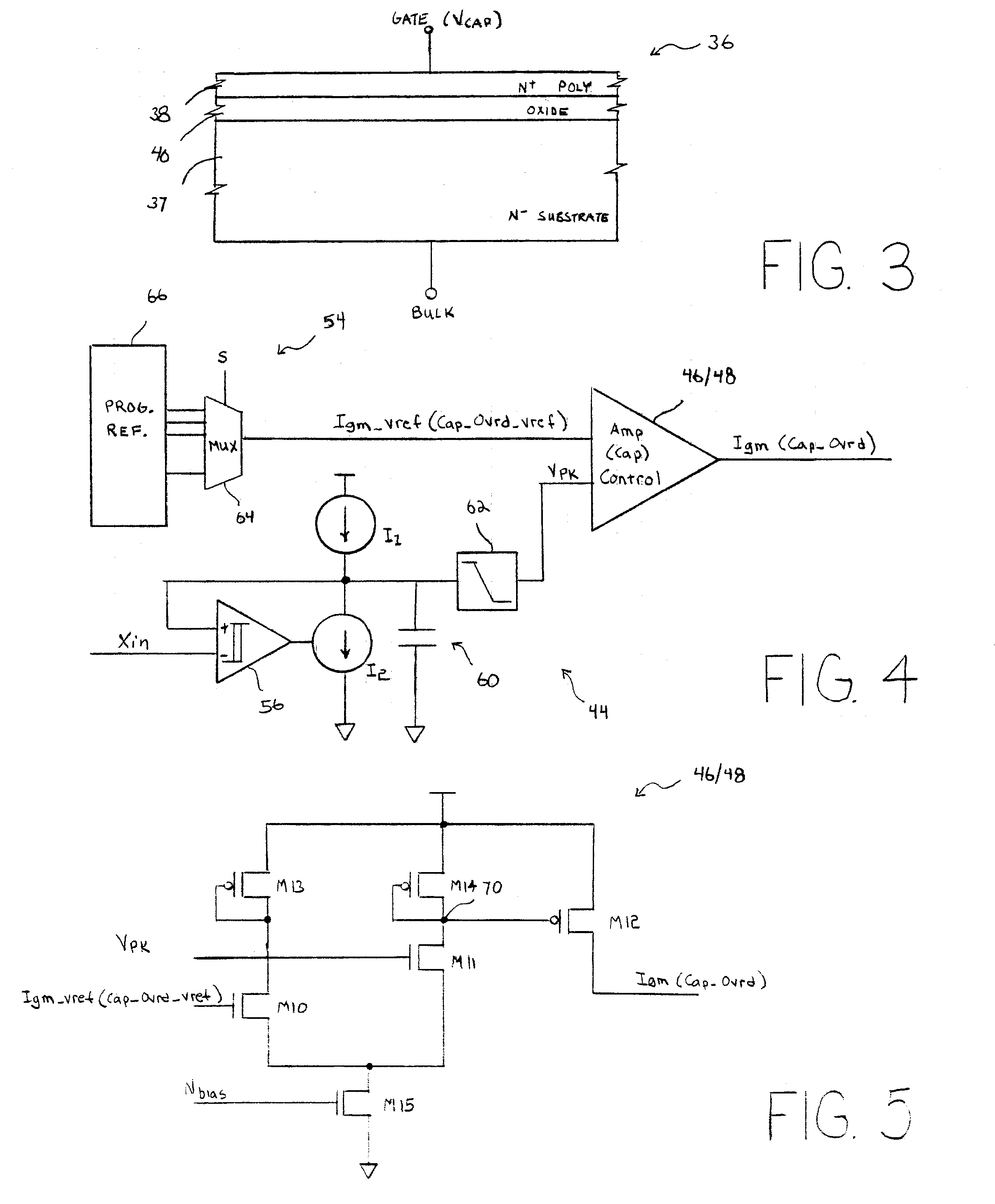
Negative resistance device
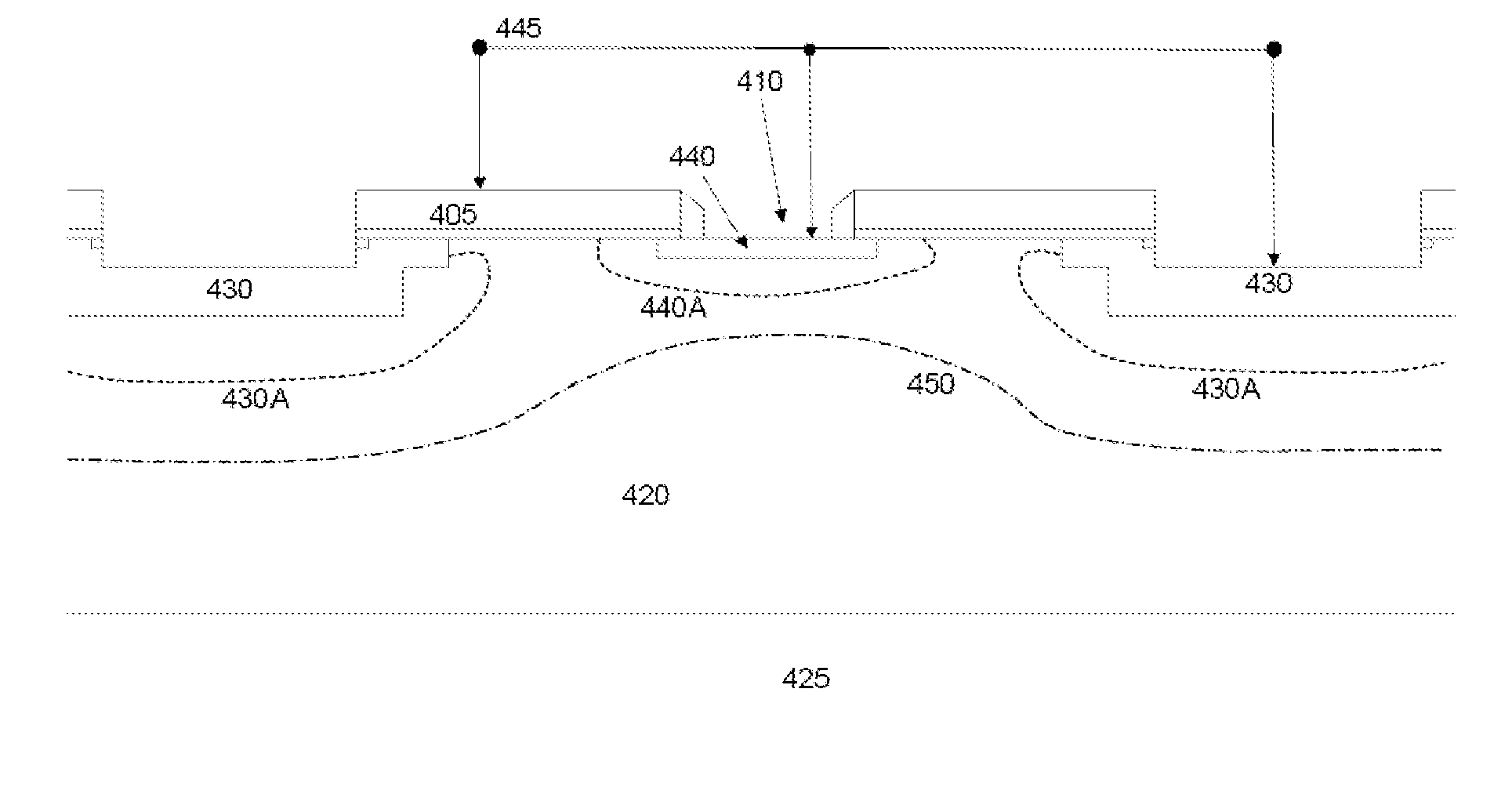
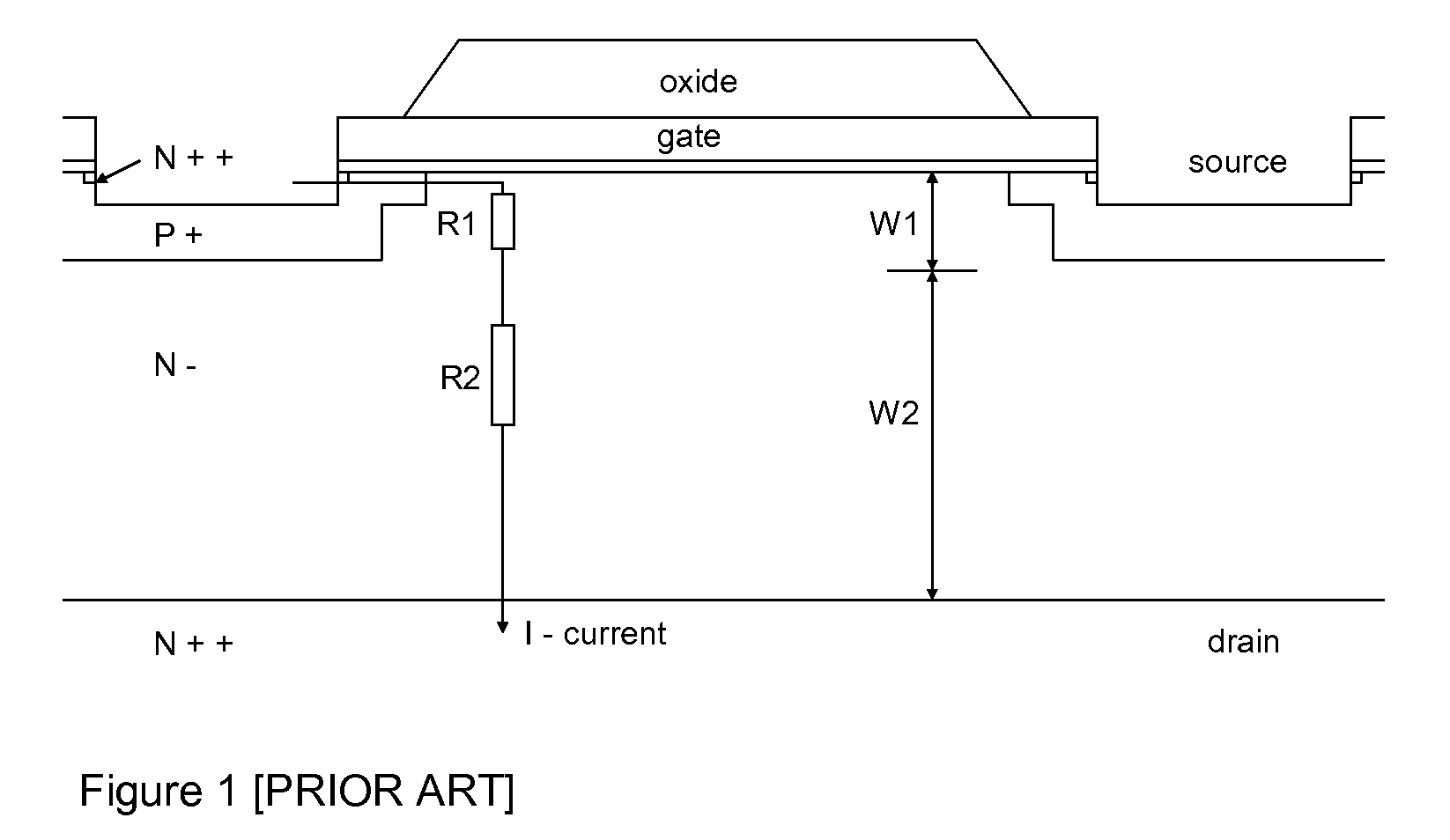
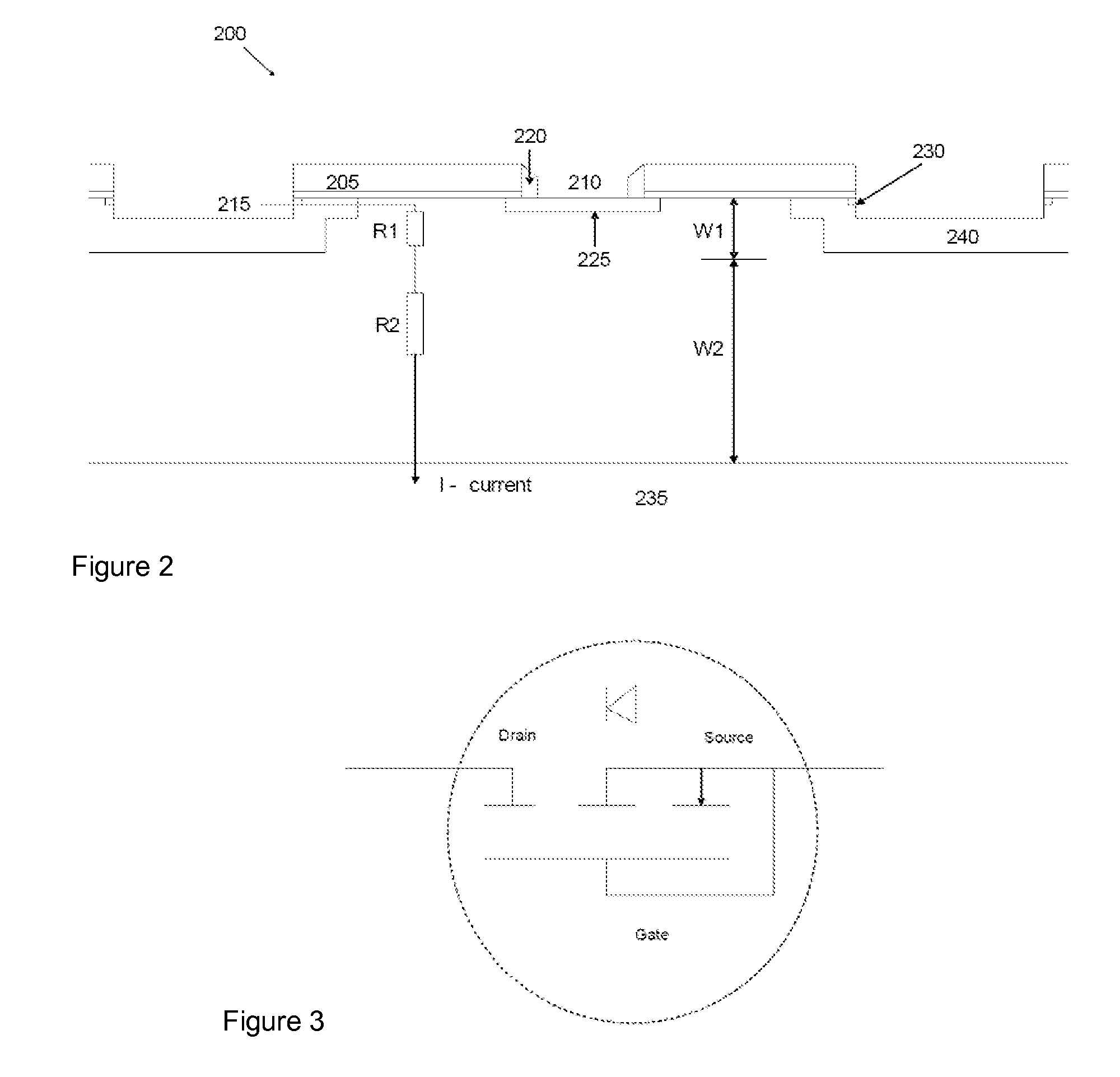
InactiveUS20010005327A1Solid-state devicesDigital storageElectrical resistance and conductanceMOSFET
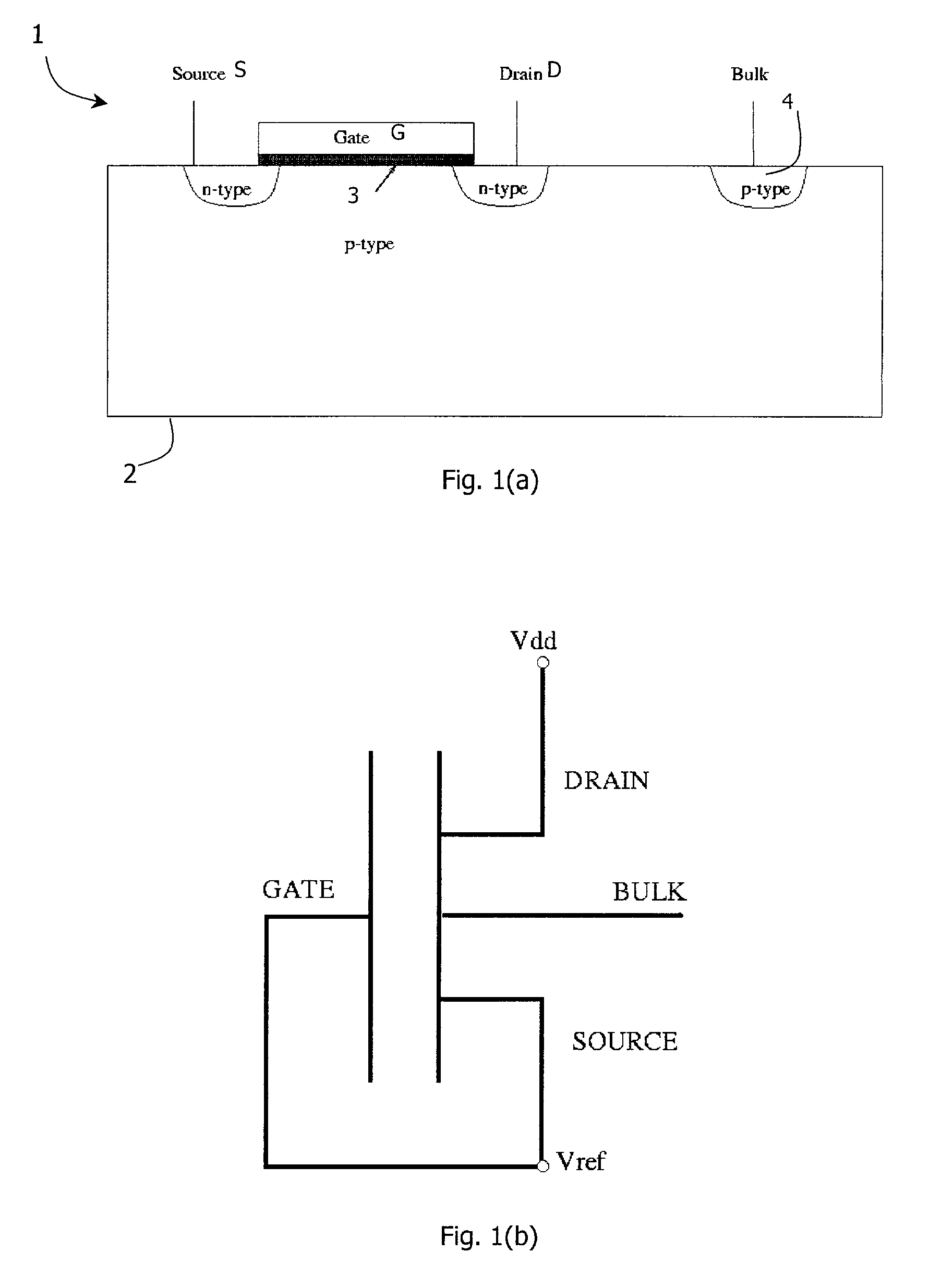
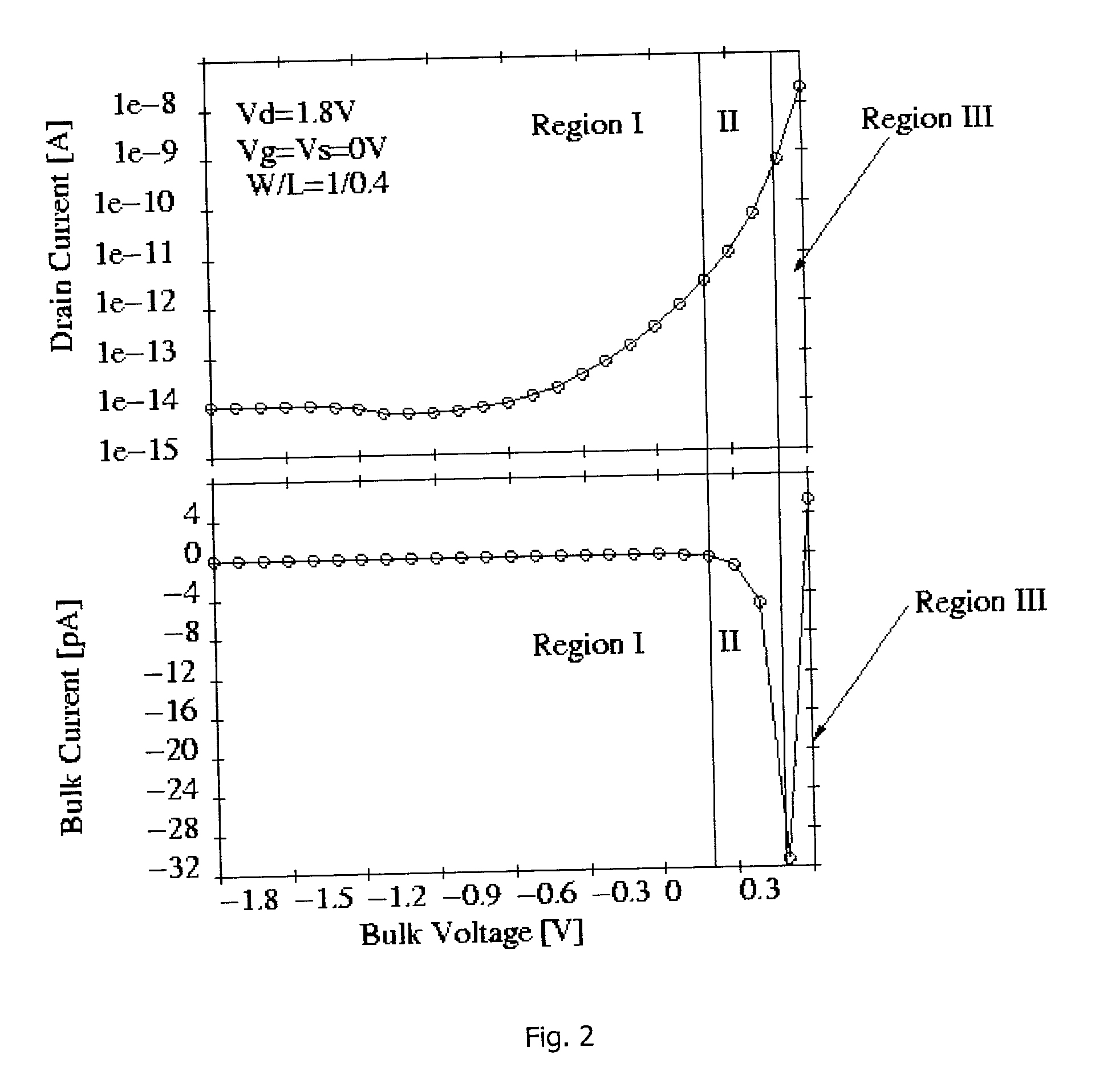
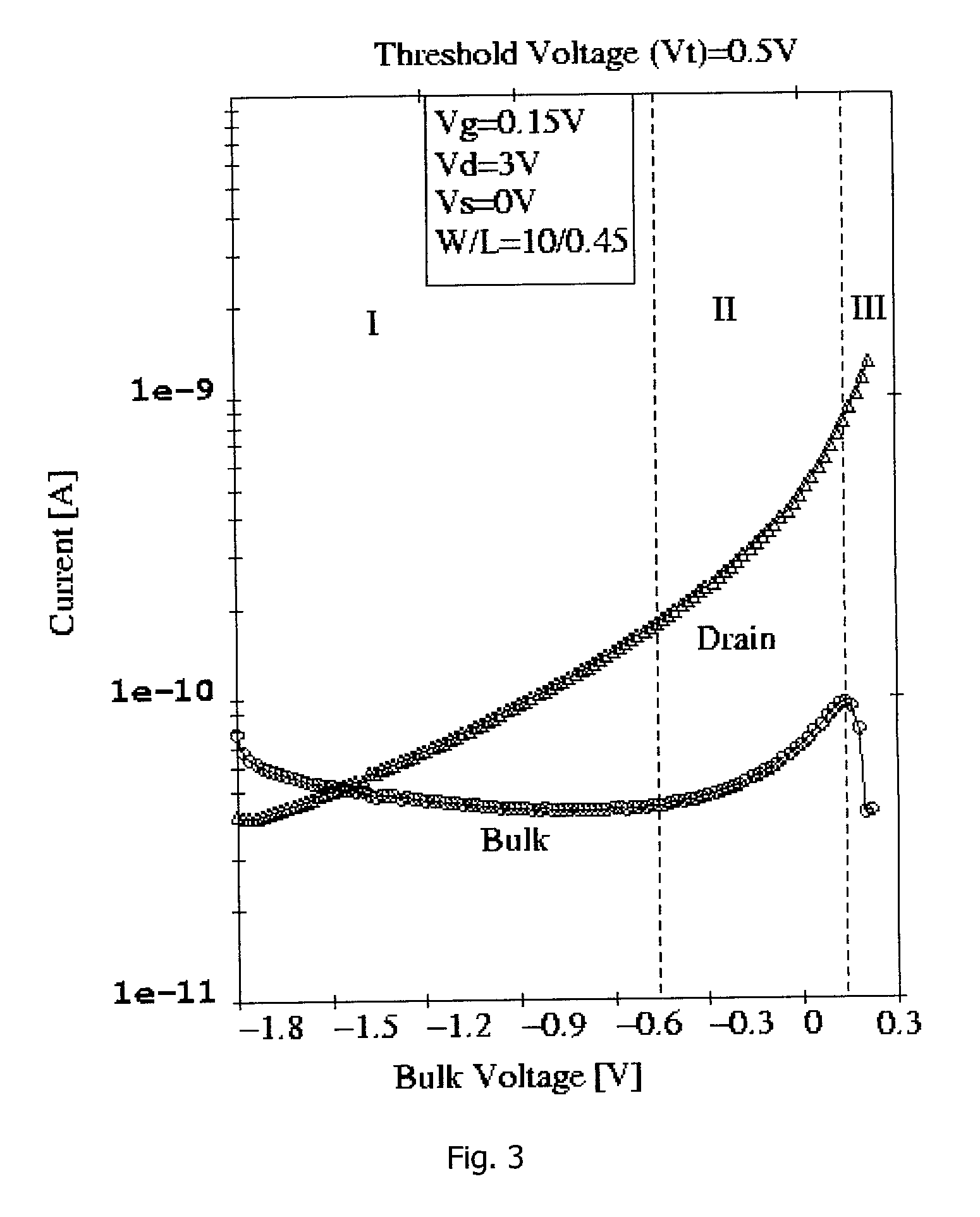
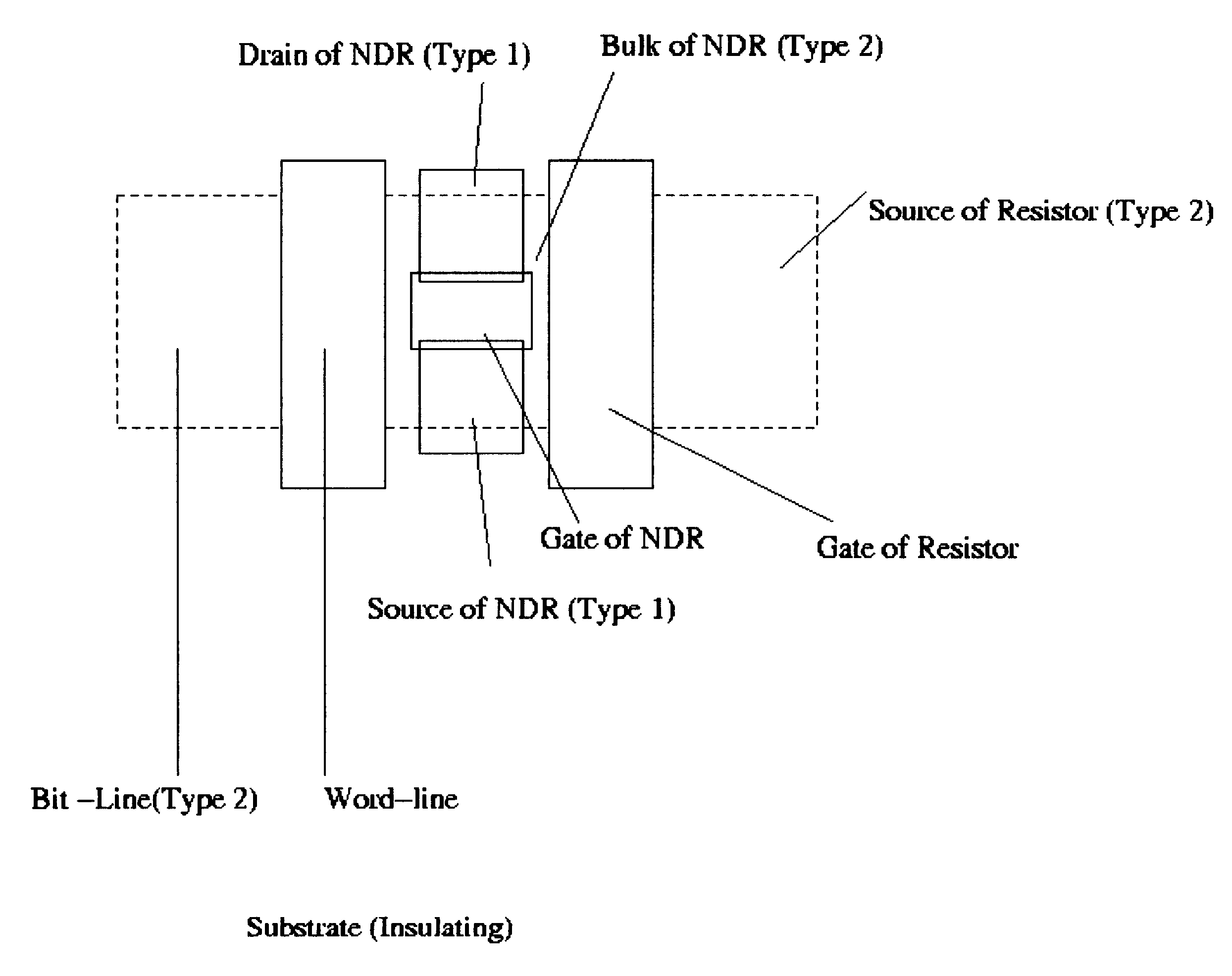
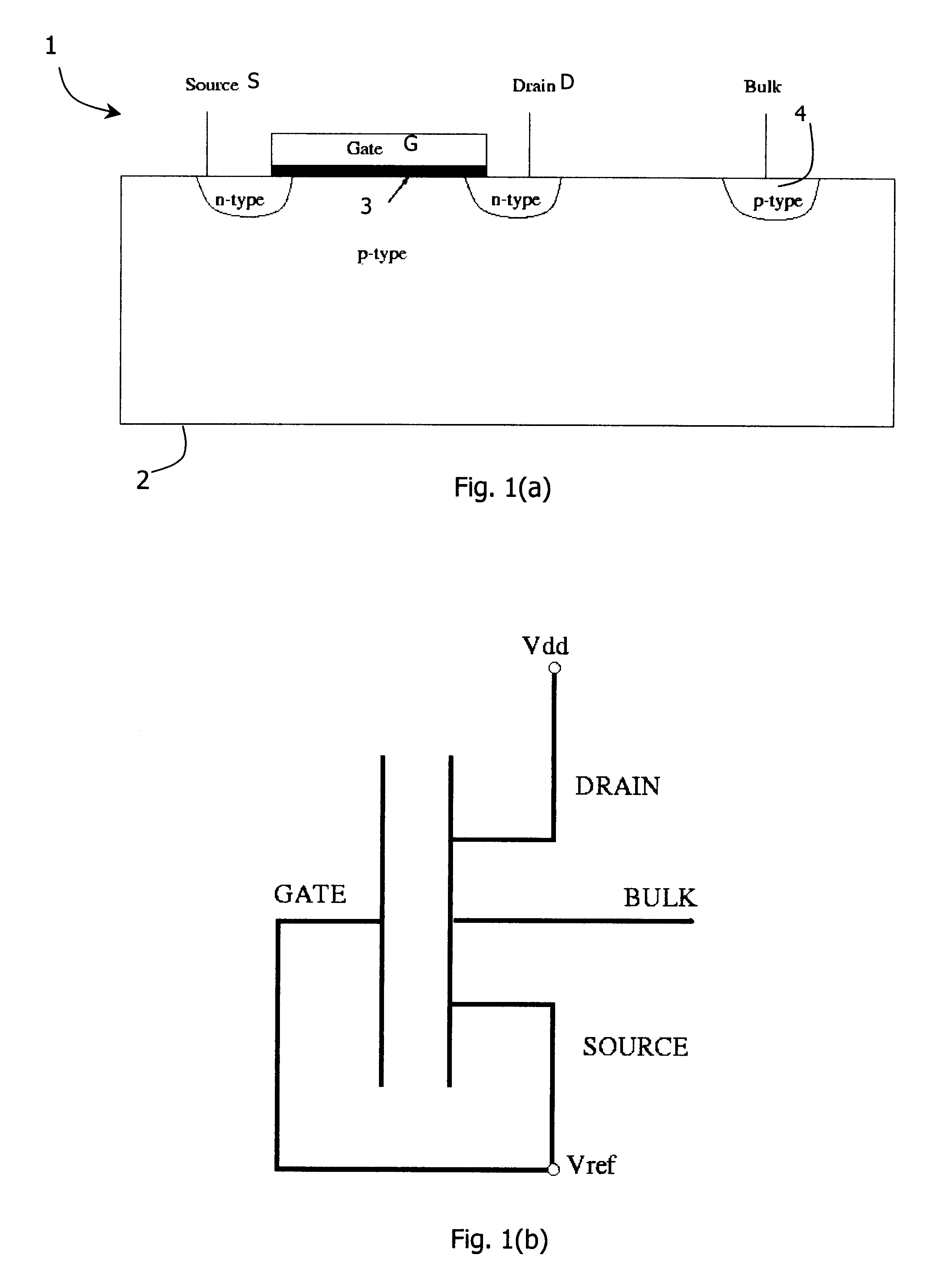
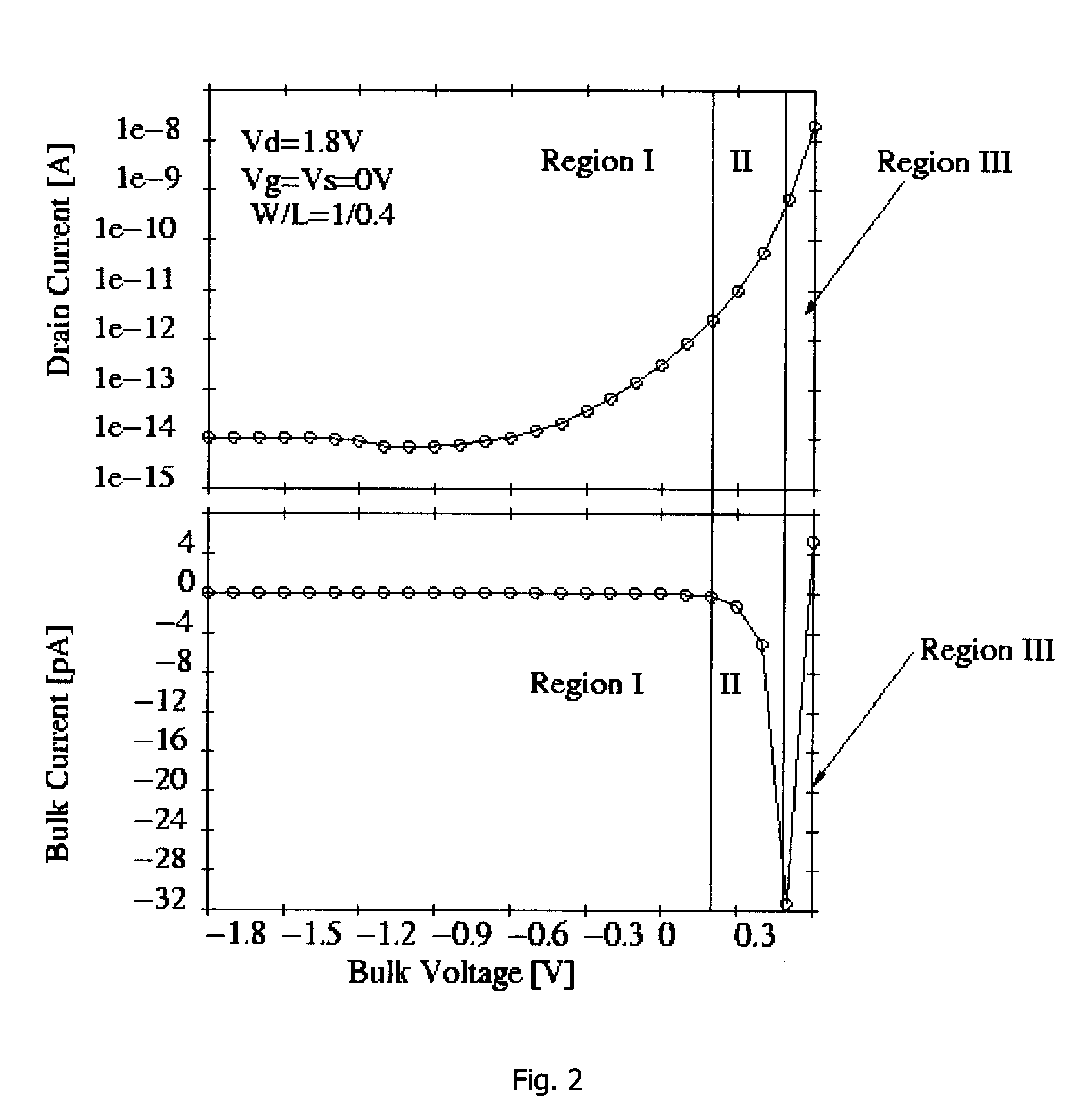
A negative resistance device (NRD) has a MOSFET-like structure, and is biased by: shorting the gate and source together at a fixed applied potential and applying a different fixed potential to the drain, and sweeping the bulk potential towards the drain potential, causing the bulk current to exhibit a negative resistance characteristic. The NRD may be used in a memory circuit (10) in which a resistor (R) is connected between the bulk (2) and a fixed potential. Two States of the circuit at which the current through the resistor matches that through the bulk of the NRD are stable, providing for bistable memory operation.
Owner:NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND
Negative resistance device
A negative resistance device (NRD) has a MOSFET-like structure, and is biased by shorting the gate and source together at a fixed applied potential and applying a different fixed potential to the drain, and sweeping the bulk potential towards the drain potential, causing the bulk current to exhibit a negative resistance characteristic. The NRD may be used in a memory circuit (10) in which a resistor (R) is connected between the bulk (2) and a fixed potential. Two States of the circuit at which the current through the resistor matches that through the bulk of the NRD are stable, providing for bistable memory operation.
Owner:NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND
Integrated resonant tunneling diode based antenna
An antenna comprising a plurality of negative resistance devices and a method for making same comprising employing a removable standoff layer to form the gap between the microstrip antenna metal and the bottom contact layer.
Owner:SANDIA
Semiconductor ceramic with negative resistance temperature coefficient and negative temperature coefficient thermistor
InactiveCN1348192ALittle change in characteristicsInhibit swellingCeramicsNegative temperature coefficient thermistorsElectrical resistance and conductanceNegative temperature
A semiconductor ceramic having a negative temperature coefficient of resistance, the element comprising about 0.1 to 20 mol % of AMnO3 (A represents at least one of Ca, Sr, Ba, La, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Th, Dy and Ho) and to a spinel composite oxide made of a solid solution of Mn and at least one element in Ti, V, Cr, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Mg and Al. As a perovskite Mn composite oxide, one or more of CaMnO3, SrMnO3, BaMnO3, LaMnO3, PrMnO3, NdMnO3, SmMnO3, EuMnO3, GdMnO3, TbMnO3, DyMnO3 and HoMnO3 may be used.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
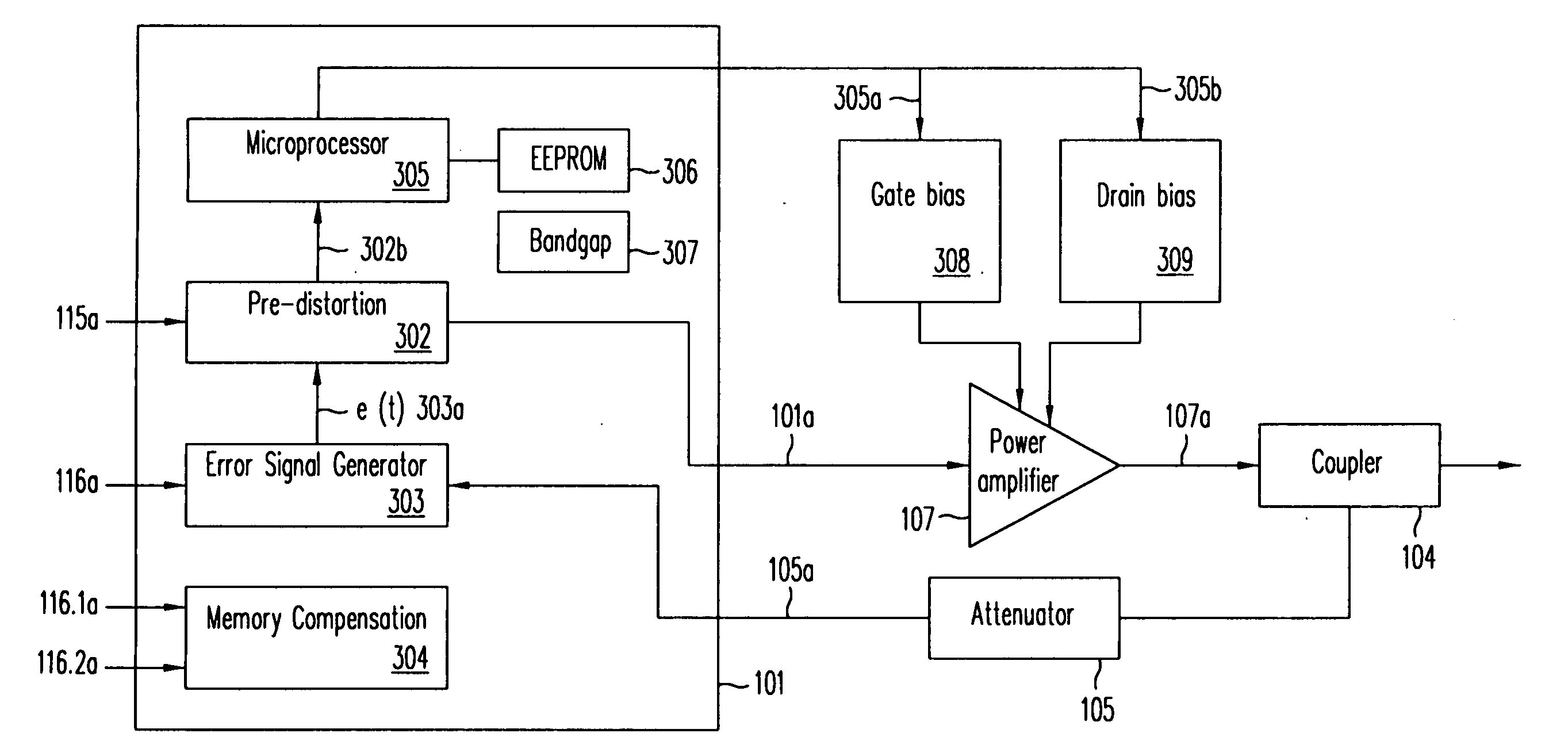
Pre-distortion apparatus
InactiveUS20080008263A1Modulated-carrier systemsAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesCorrelation coefficientLinear component
Pre-distortion apparatuses and methods for a non-linear component are provided. The apparatus comprises an adaptive block for generating a plurality of correlation coefficients, which are used to weight a plurality of synthesis work functions to pre-distort a given signal. The adaptive block can be driven by an error signal generated from a feedback signal from the non-linear component output signal and a delayed version of the input signal. The apparatus is capable of being operated directly at radio frequency. Also provided are apparatuses and methods for generation of quadrature signals, transconductance amplification employing negative resistance, variable-gain amplification, and envelope detection.
Owner:SCINTERA NETWORKS
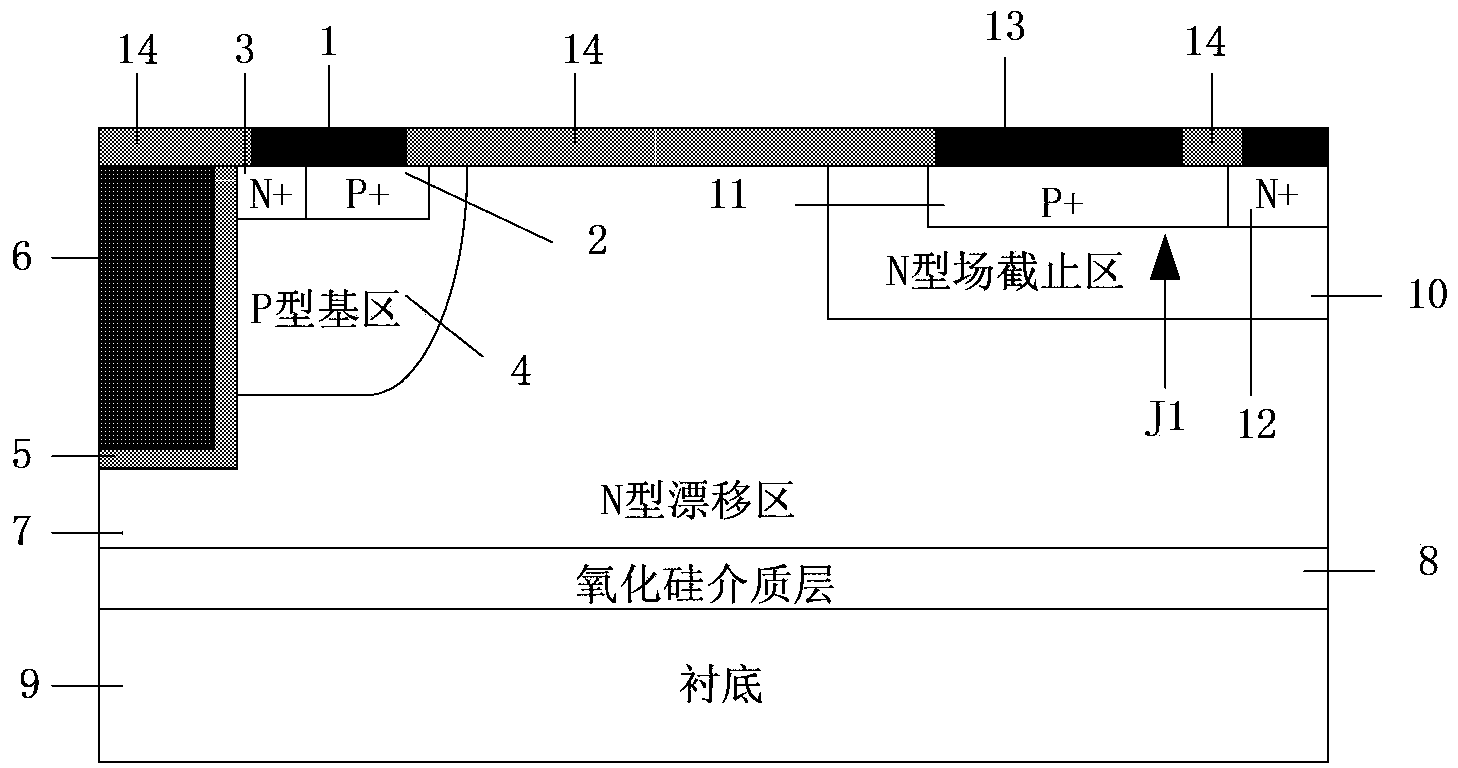
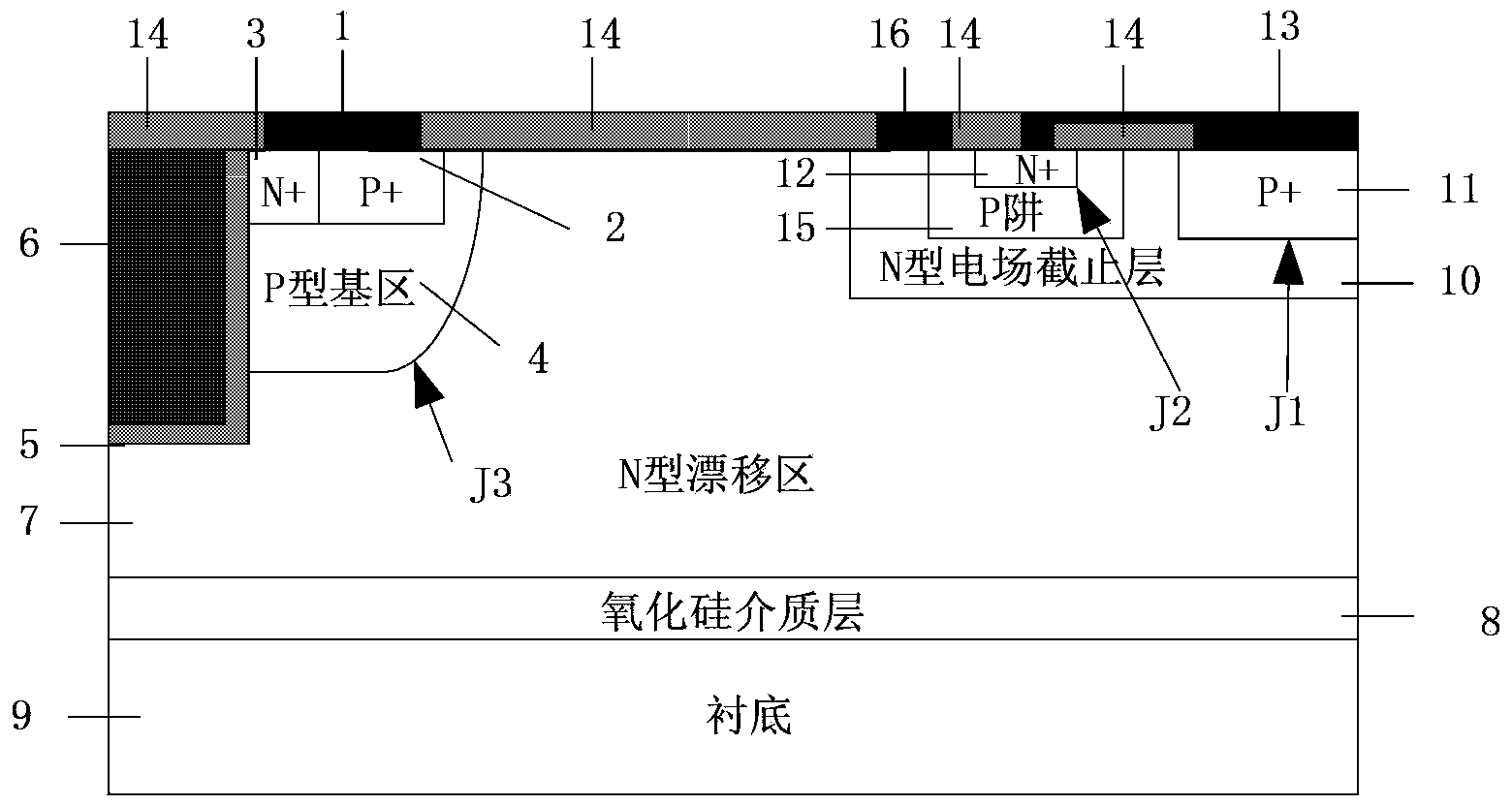
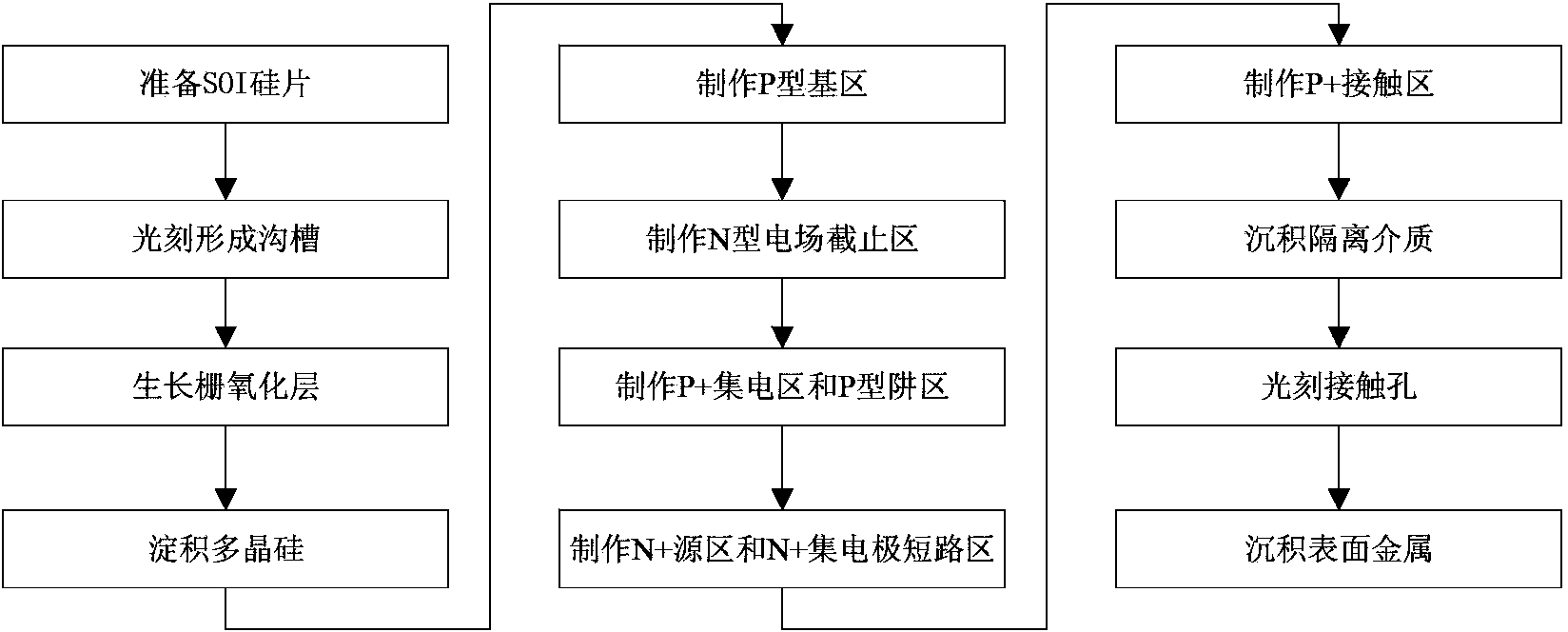
RC-LIGBT device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103413824AImprove stabilityImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor
The invention discloses an RC-LIGBT device and a manufacturing method thereof, and belongs to the field of power semiconductor devices and integrated circuits. According to the RC-LIGBT device, on the basis of a traditional RC-LIGBT structure, a P-type well region is arranged in a collector structure of the device, surrounds an N+ collector short circuit region in the collector structure and is connected with an N-type field stopping area in a short-circuited mode through connection metal. In the forward conduction process of the RC-LIGBT device, the influence on the starting process by a back N-type region can be shielded, and therefore the inherent negative resistance phenomenon of a traditional RC-LIGBT can be eliminated completely, and the stability and reliability of the device are improved. The RC-LIGBT device is suitable for the power semiconductor integrated circuits.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
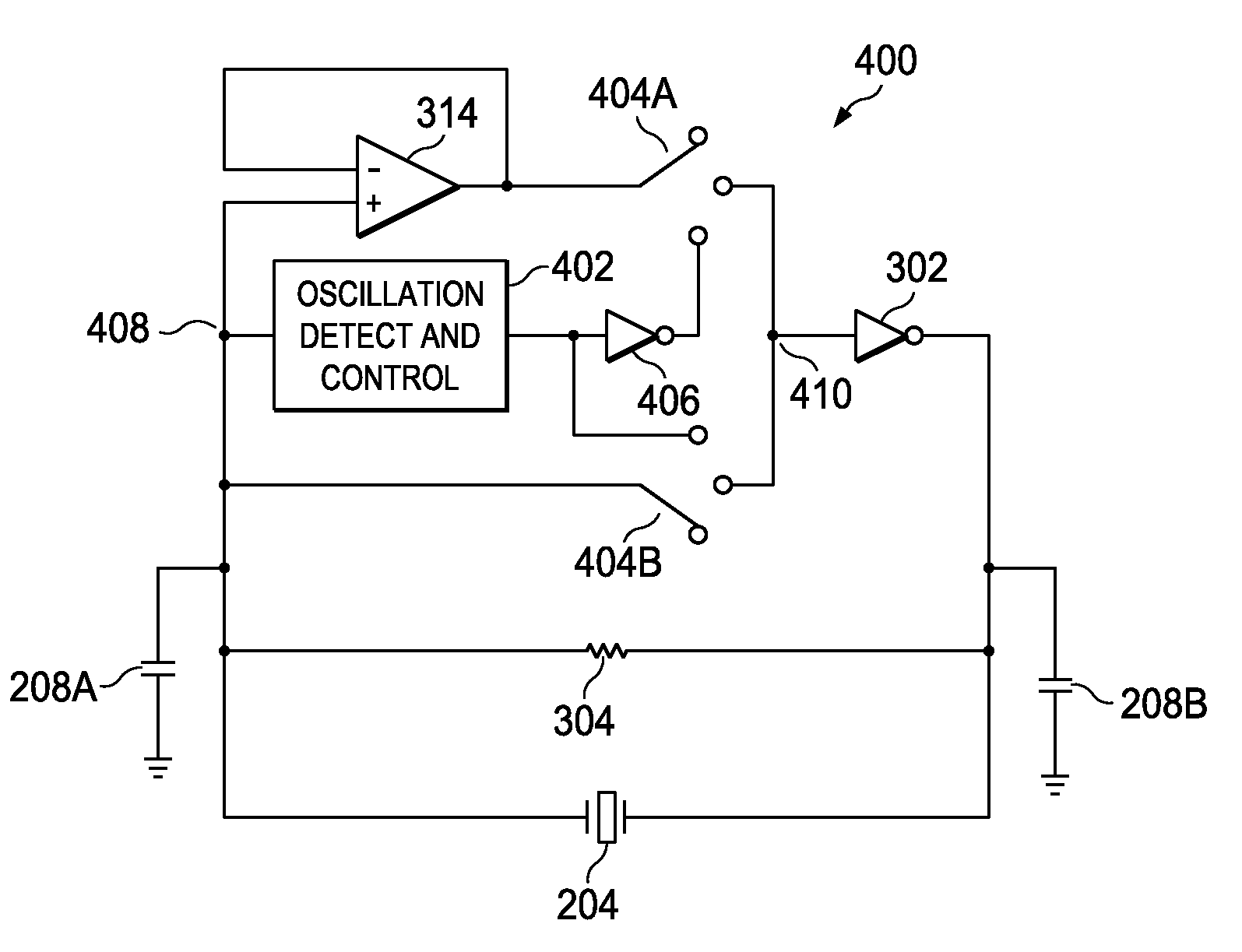
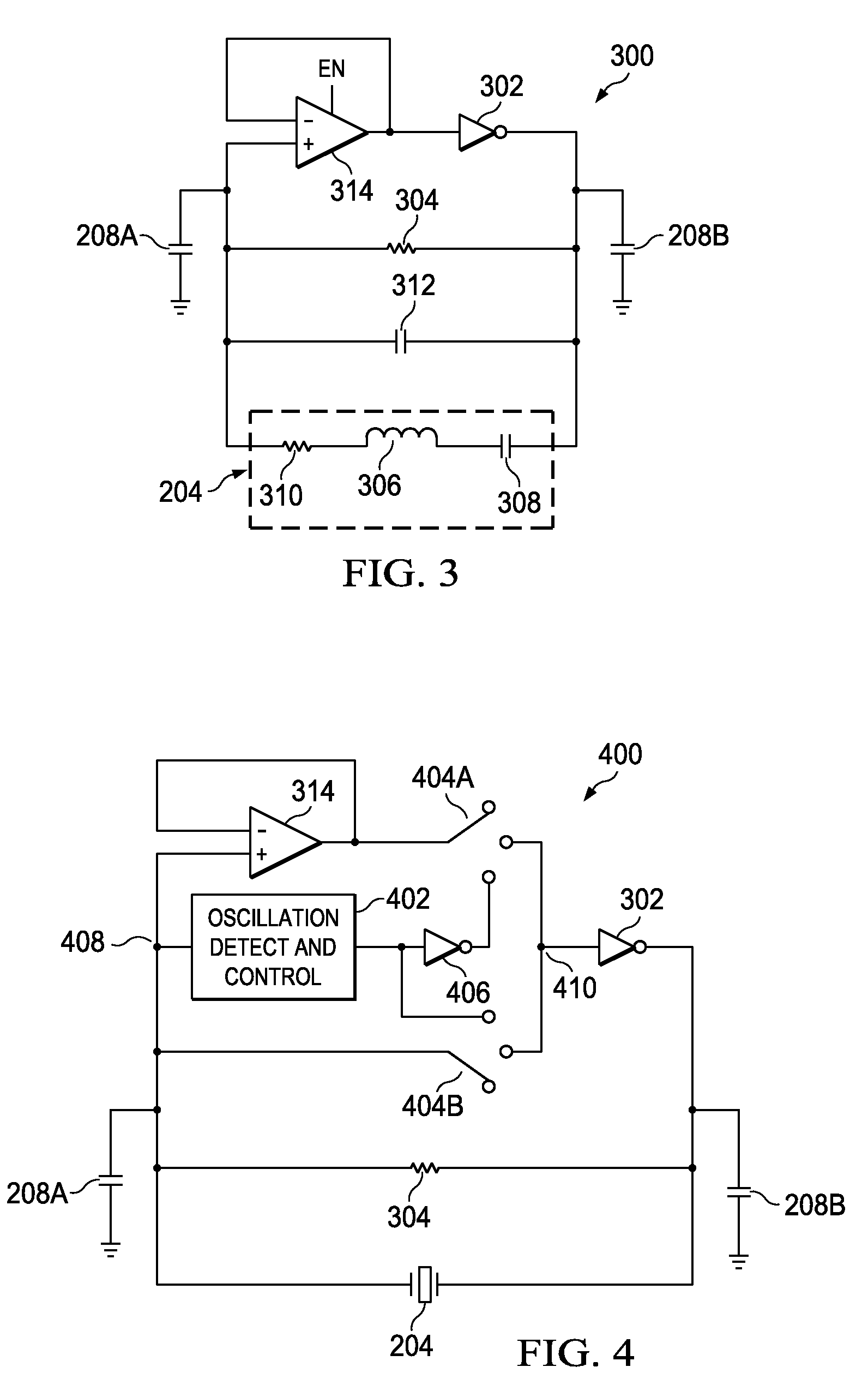
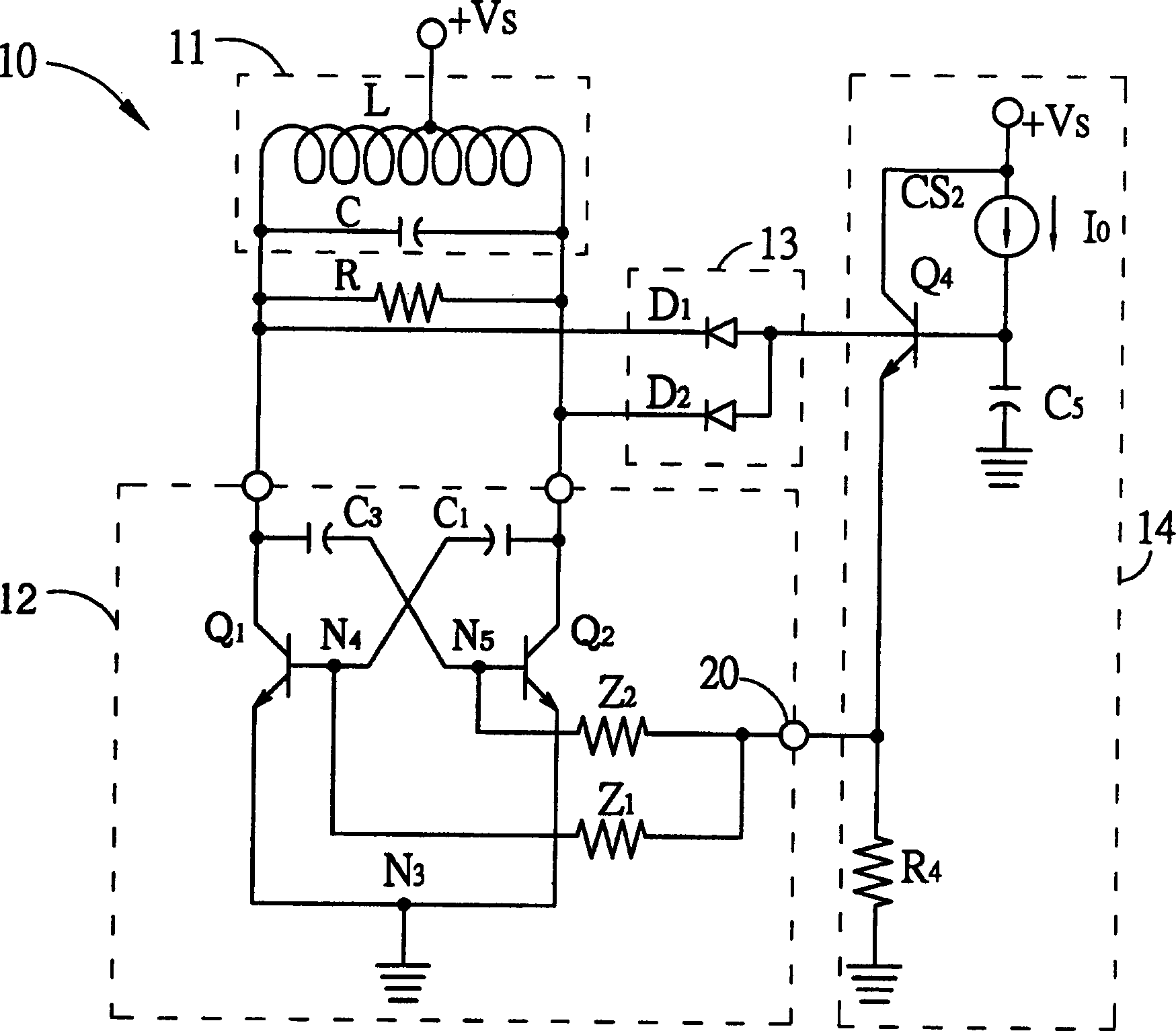
Fast start-up crystal oscillator
ActiveUS20110037527A1Reduce startup timeImprove the immunityPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsStart up timeSnubber
An exemplary fast start-up crystal oscillator with reduced start-up time. The exemplary oscillator reduces the start-up time (i.e., the time taken to attain sustained stable oscillations after the power is turned on) by increasing the negative resistance of a circuit. Increasing the negative resistance increases the rate of growth of the oscillations, thereby reducing start-up time. The exemplary crystal oscillator includes a gain stage with negative resistance. A crystal with shunt capacitance is placed in the feedback loop of the gain stage. A buffer is coupled to the gain stage such that it blocks the crystal shunt capacitance from loading the gain stage, effectively increasing the negative resistance of the gain stage. Further, an oscillation detection and control circuit is coupled between the crystal and the gain stage. The oscillation detection and control circuit connects the buffer during start-up, and disconnects the buffer once an oscillation signal attains sustained stable oscillations.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
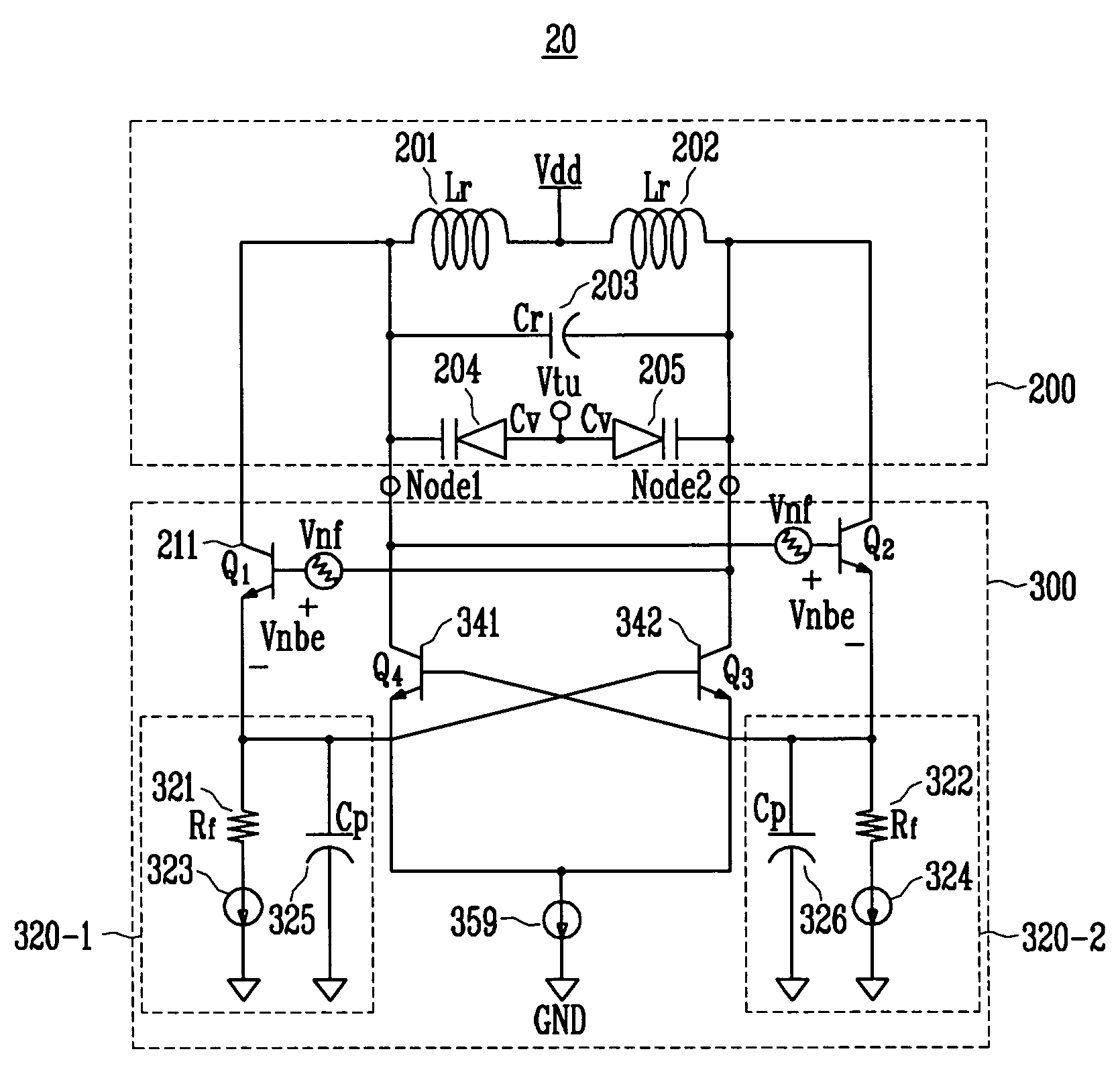
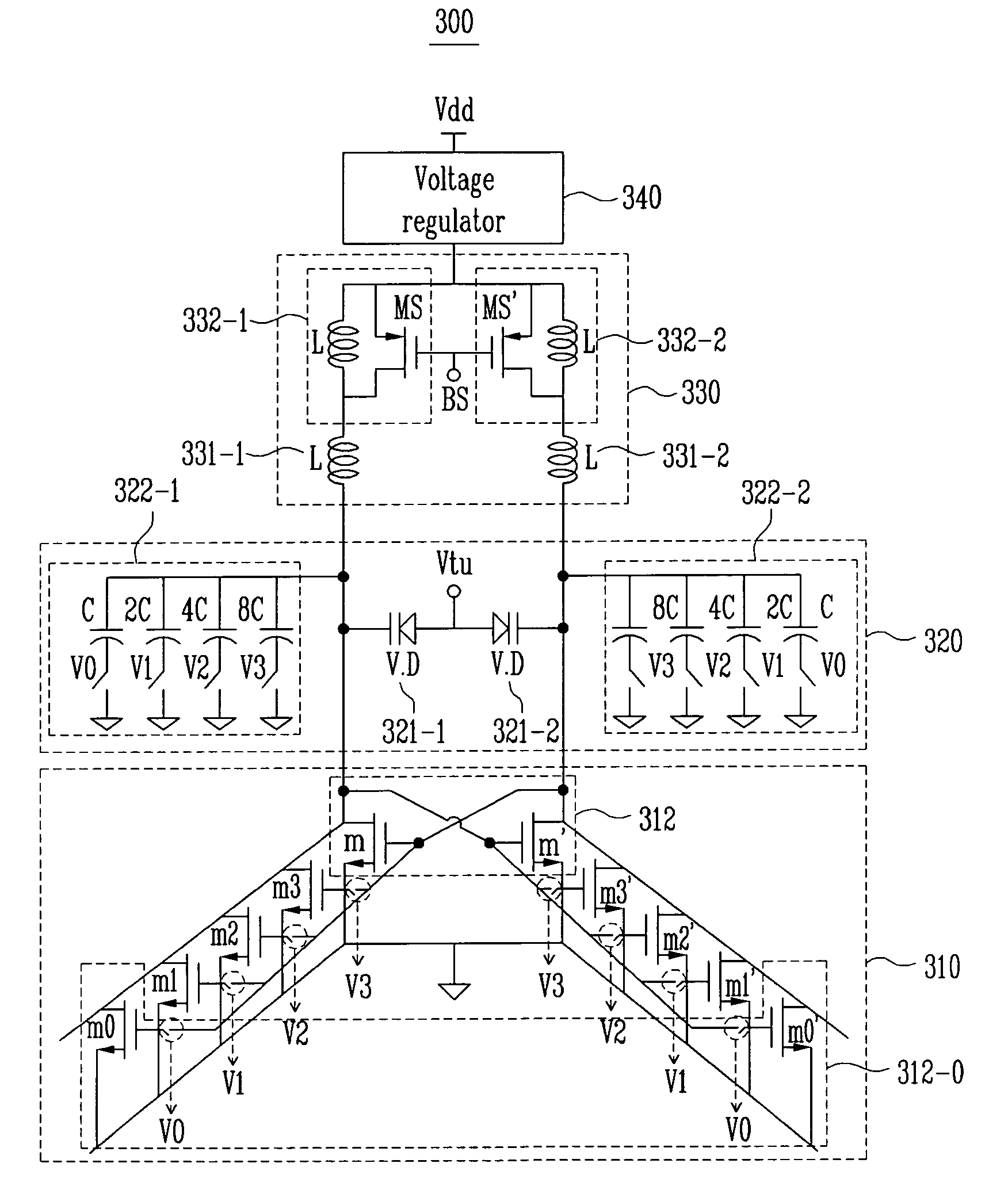
Low phase noise differential LC tank VCO with current negative feedback
ActiveUS20070132521A1Good phase noise characteristicsEliminate Phase NoiseOscillations generatorsCapacitancePhase noise
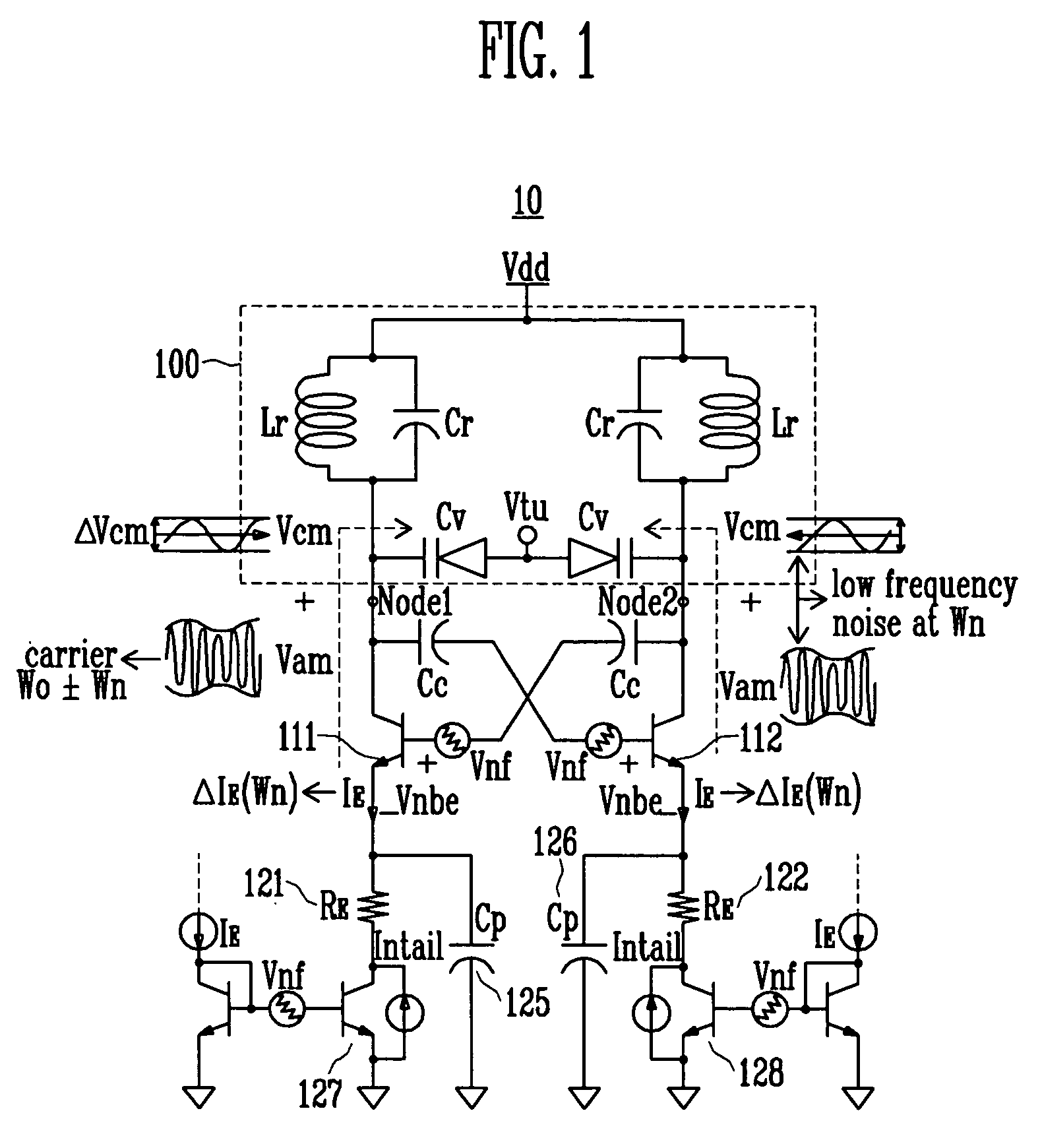
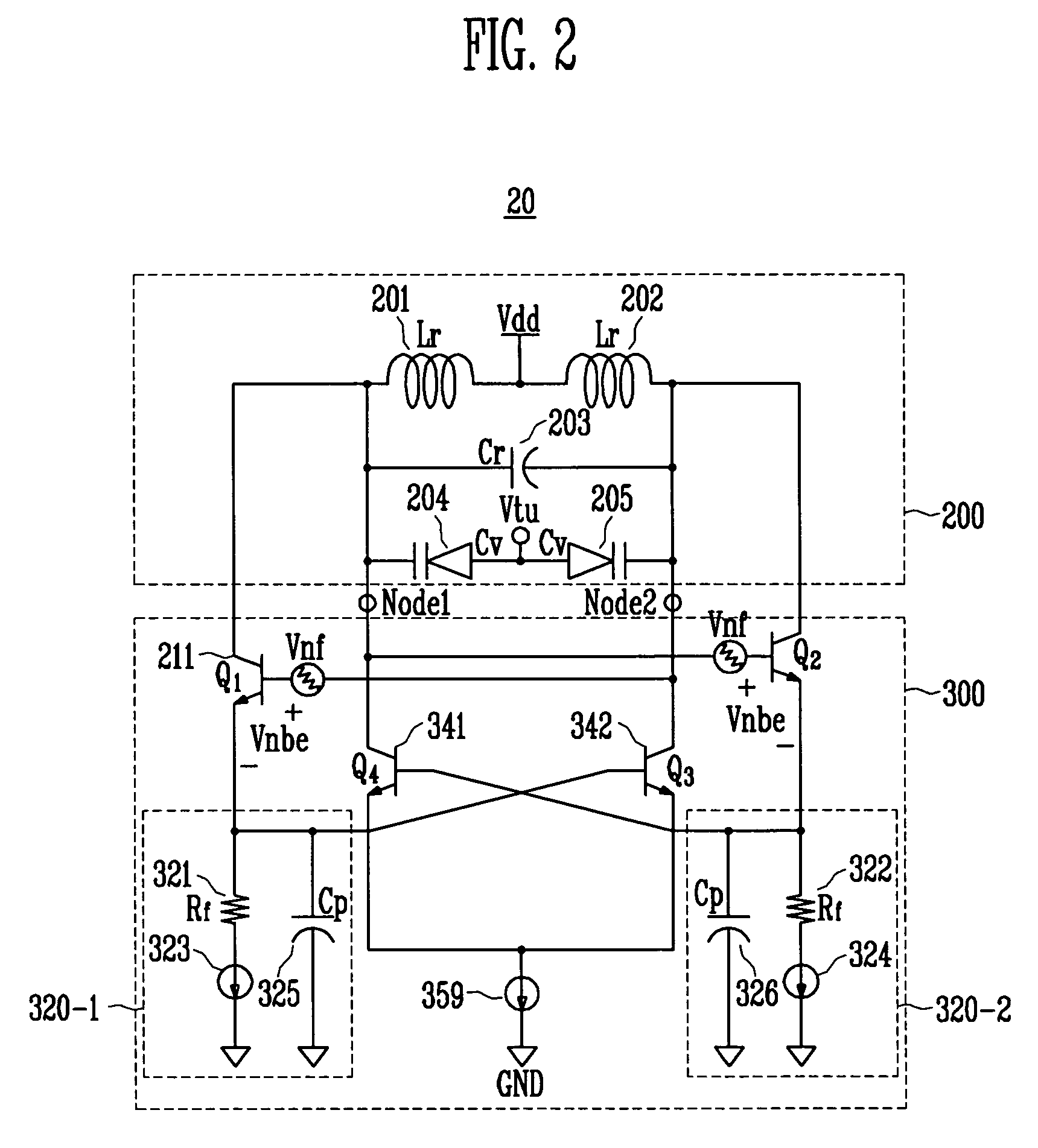
A differential voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) employed in a frequency synthesizer used as a local oscillator of a wireless communication on-chip transmitter / receiver is provided. More particularly, a differential current negative feedback VCO equipped with a current-current negative feedback circuit that suppresses low- and high-frequency noise is provided. A differential current negative feedback VCO includes a resonator determining oscillation frequency, and an oscillator generating negative resistance. In the oscillator of the differential current negative feedback VCO, transistors Q1 and Q2 form a cross-coupled pair, and negative resistance is generated by positive feedback of the cross-coupled pair. And, transistors Q1 and Q3 together with an emitter resistor and a capacitor form a current negative feedback part, and transistors Q2 and Q4 together with an emitter resistor and a capacitor form another current negative feedback part which is disposed opposite to a resonator. Thus, the VCO operates differentially. In the oscillator of the differential current negative feedback VCO, emitter noise currents generated by base noise voltages of Q1 and Q2 induced by low- and high-frequency noise sources in the bases of Q1 and Q2 are sampled by emitter resistors, amplified through bases of Q3 and Q4, and thus return to the bases of the Q1 and Q2 and suppress the base noise voltages. Measurement of the phase noise of the differential current negative feedback VCO reveals a phase noise reduction of approximately 25 dB compared to a conventional differential VCO.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
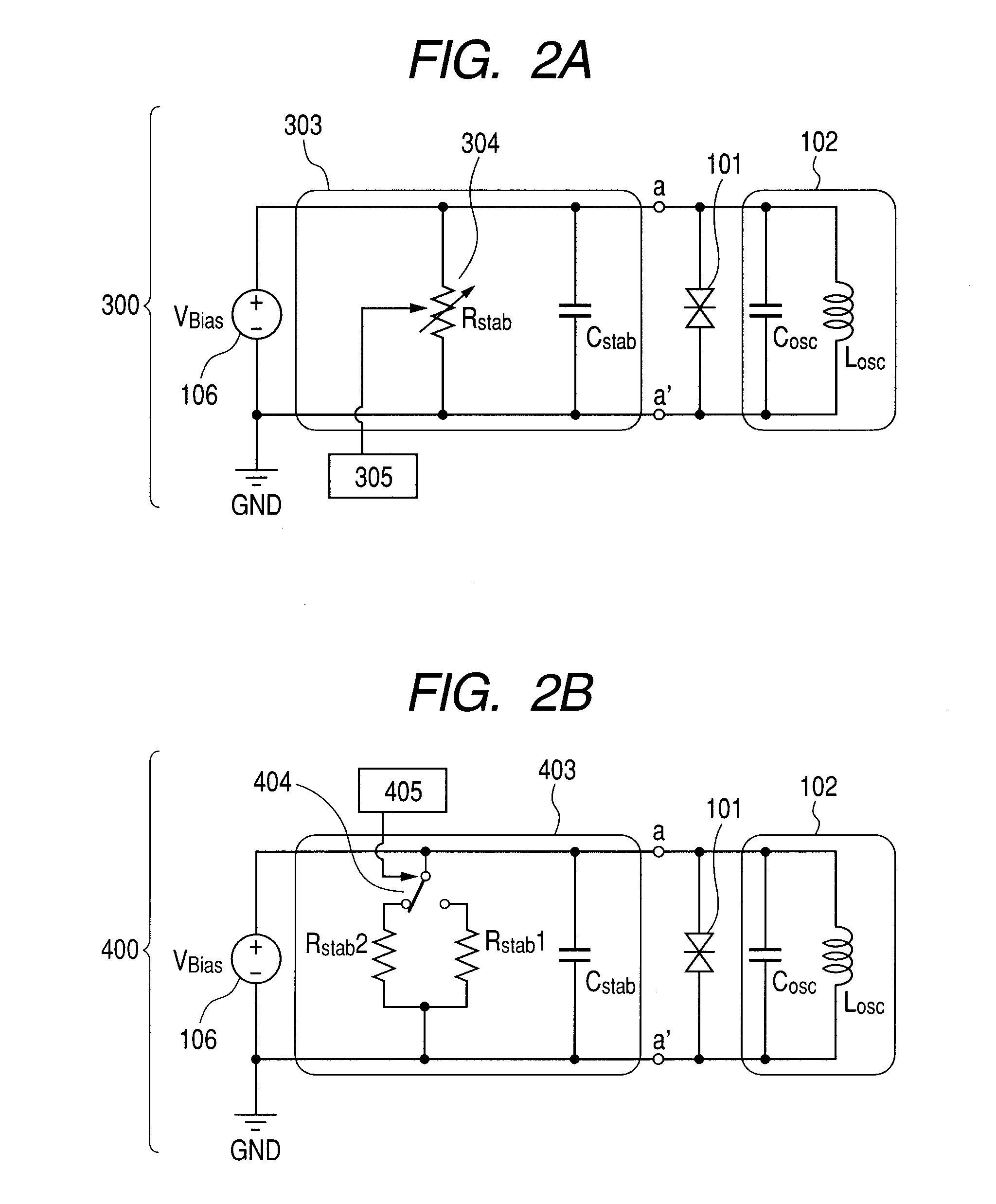
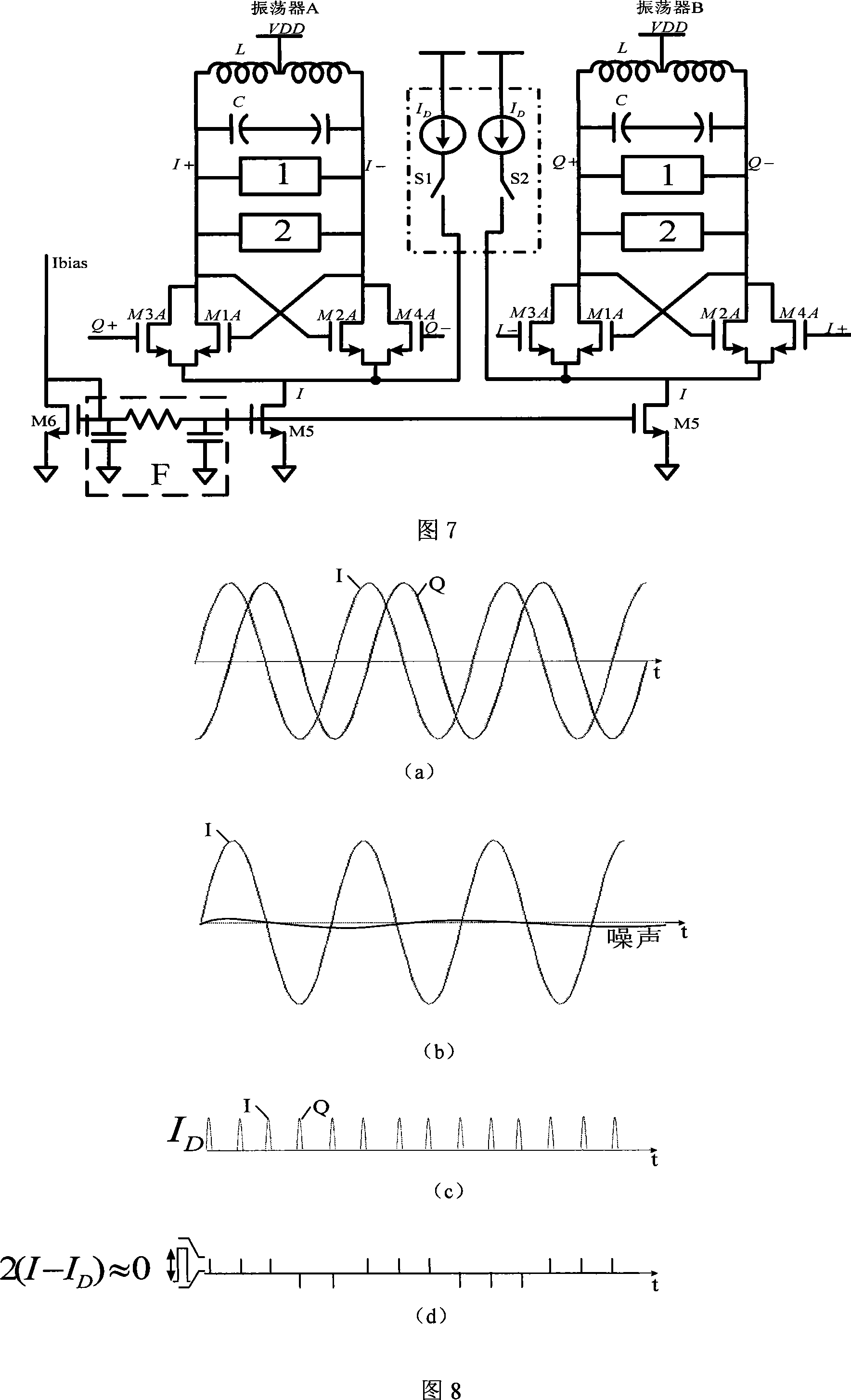
Oscillation circuit having negative resistance element and oscillator using the oscillation circuit
InactiveUS20120119838A1SpeedOperation is necessaryElectric pulse generatorOscillations generatorsElectrical resistance and conductanceResonance
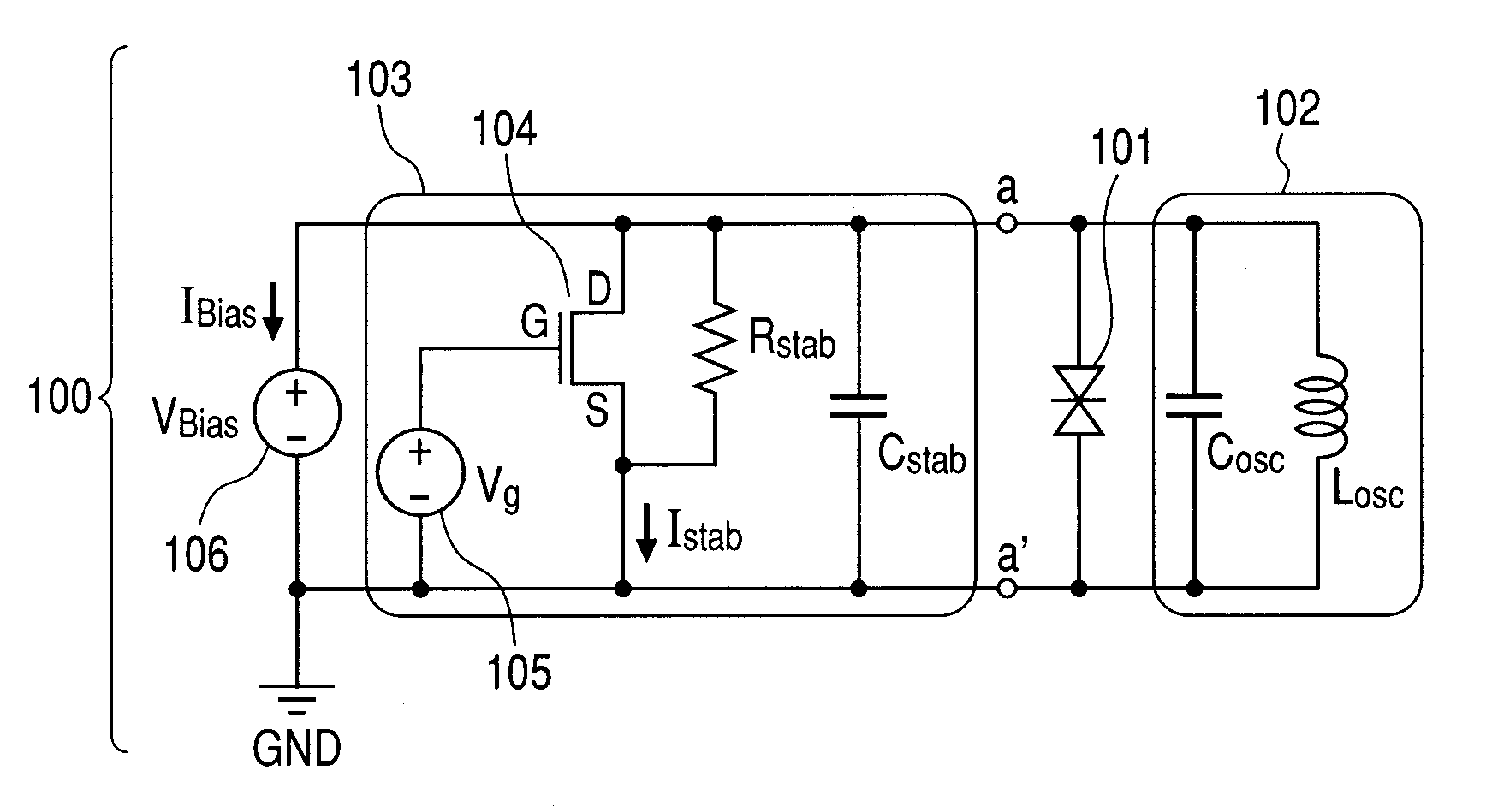
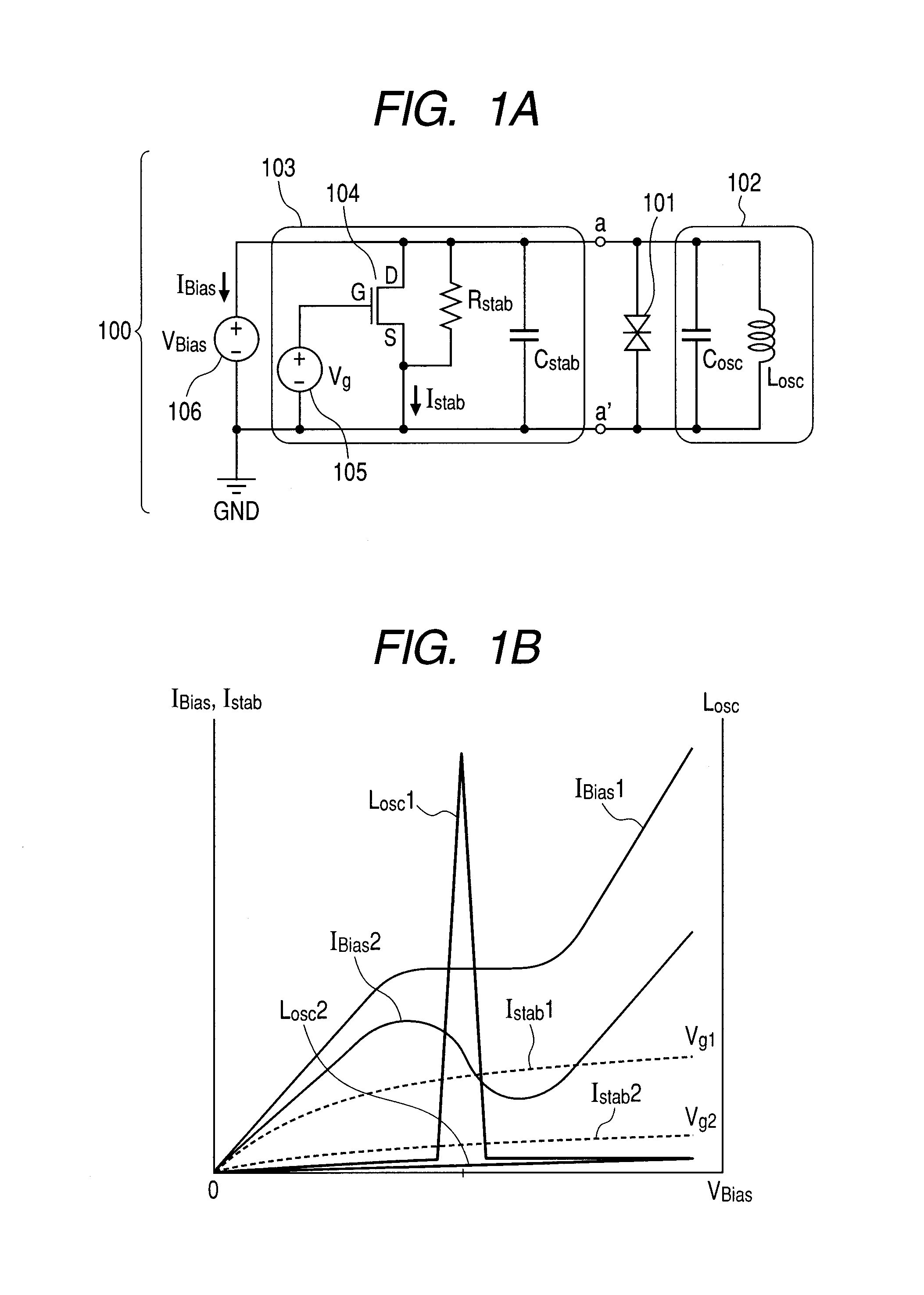
An oscillation circuit including: a negative resistance element; a resonance circuit connected to the negative resistance element; and a stabilization circuit connected in parallel with the negative resistance element to suppress parasitic oscillation, wherein the stabilization circuit includes a variable shunt resistor and a adjusting device for adjusting the shunt resistor.
Owner:CANON KK
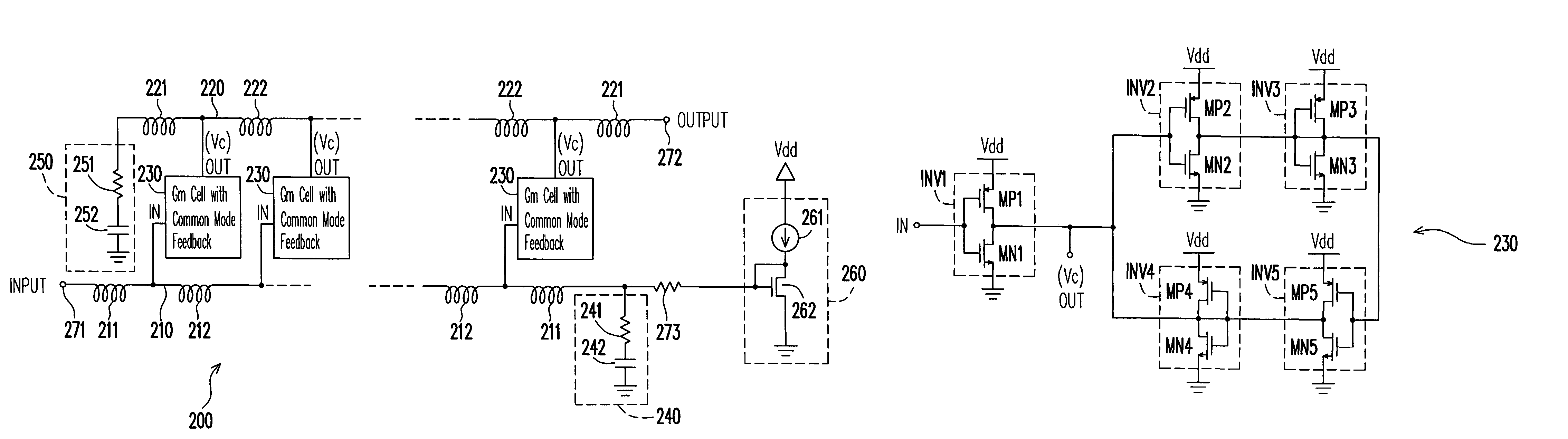
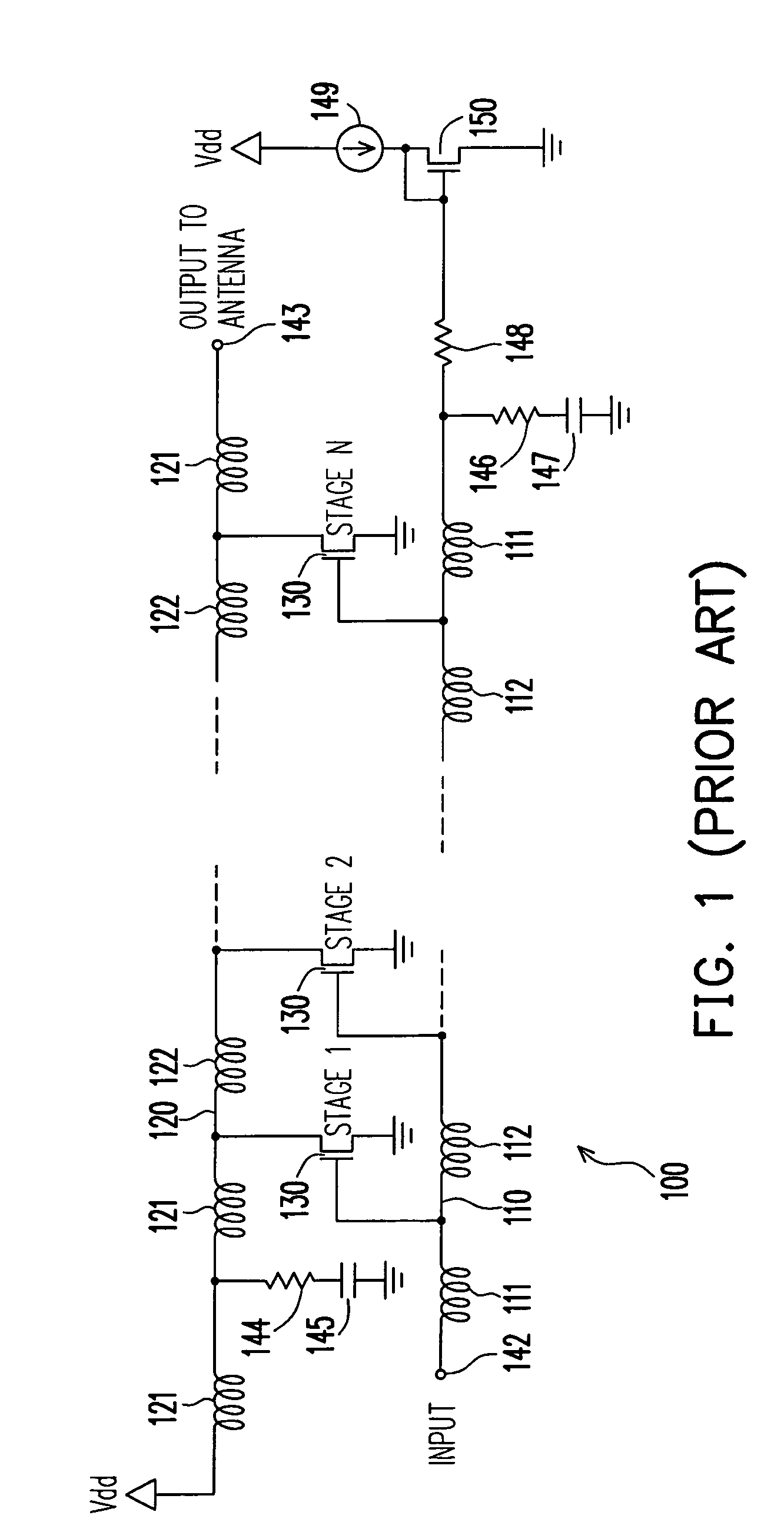
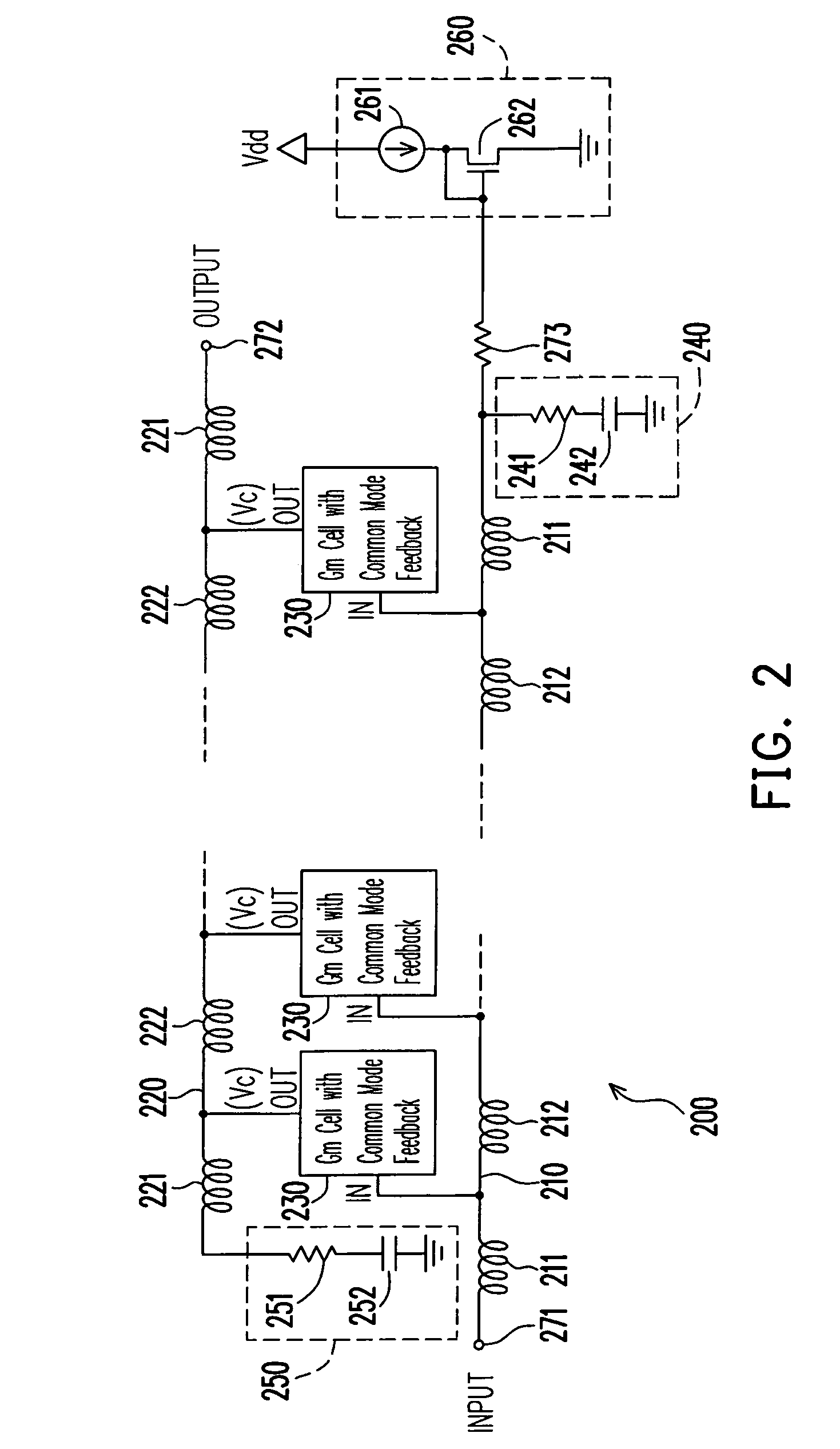
Low power comsumption, low noise and high power gain distributed amplifiers for communication systems
ActiveUS7579913B1Reduce power consumptionIncrease power gainAmplifier combinationsAmplifiers wit coupling networksLow noiseDistributed amplifier
Provided is a distributed amplifier in communication systems, including: an input transmission line; an output transmission line; an input impedance match and an output impedance match, for providing termination of the input transmission line and the output transmission line, respectively and for preventing signal reflection in the input transmission line and the output transmission line, respectively; multi-stage Gm cells with common mode feedback, the input transmission line being coupled to the output transmission line by the transconductance of the Gm cells; and an input gate bias circuit, for providing bias for the multi-stage Gm cells. In at least one of the Gm cells, one inverter performs V / I conversion while other inverters provide negative resistance to control common mode of output voltage and to enhance DC gain of the Gm cell. Due to common mode feedback, no output gate bias is needed.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
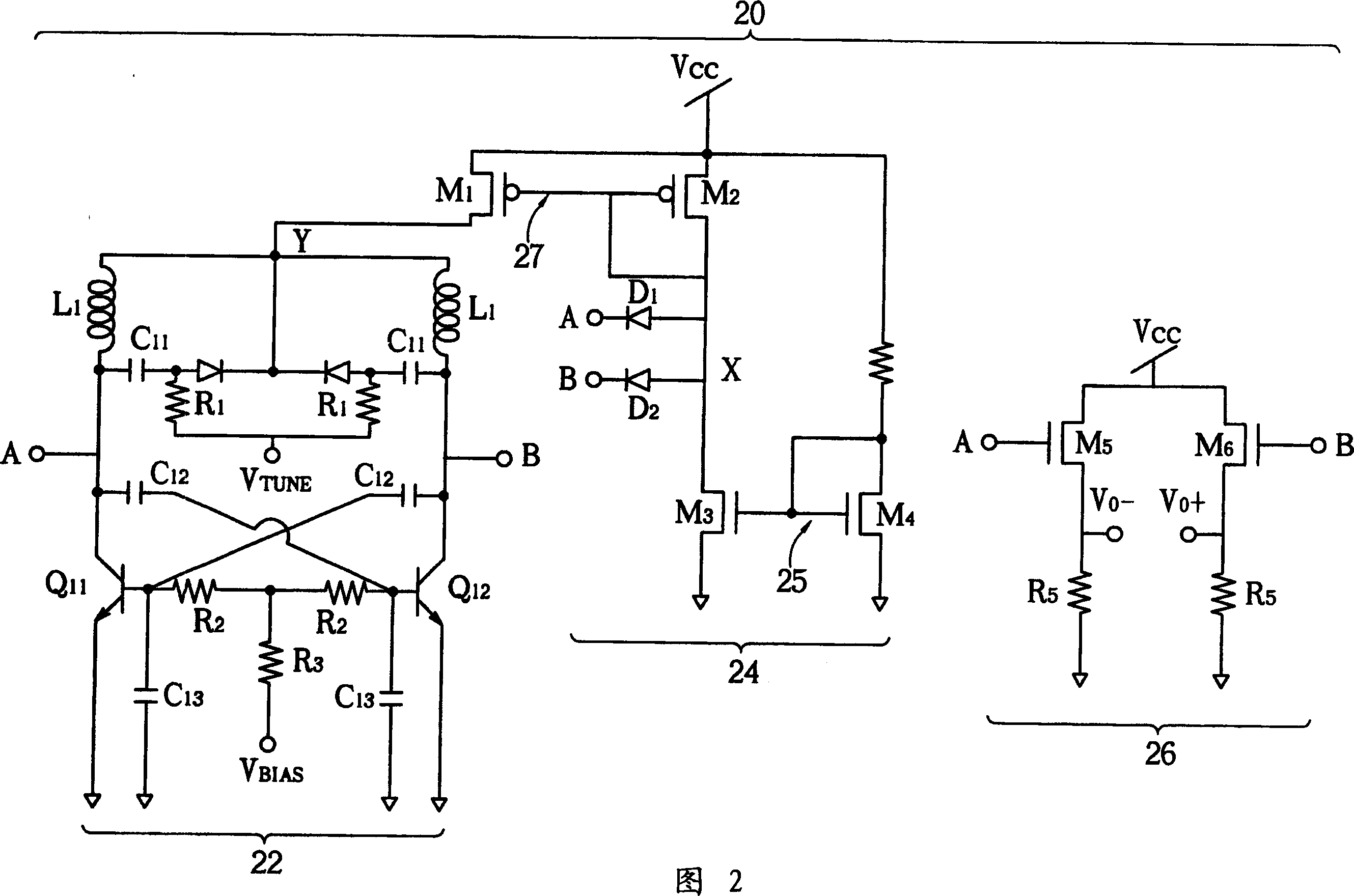
Multi-band LC resonance voltage-controlled oscillator with adjustable negative resistance cell
InactiveUS20070132522A1Suppress phase noiseSuppress noiseResonant circuit tuningPulse automatic controlCapacitanceMulti band
Provided is an LC resonance voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) used for a multi-band multi-mode wireless transceiver. In order to generate a multi-band frequency, a capacitor bank and a switchable inductor are included in the LC resonance voltage-controlled oscillator. The LC resonance voltage-controlled oscillator employs an adjustable emitter-degeneration negative resistance cell in place of tail current sources in order to compensate for non-uniform oscillation amplitude caused by the capacitor bank and prevent the degradation of a phase noise due to the tail current sources. The LC resonance voltage-controlled oscillator includes an inductor providing an inductance element partially determining the frequency of an oscillation wave; a discrete capacitor bank providing a capacitance element partially determining the frequency of the oscillation wave and being discretely determined by a control bit signal; and a discrete negative resistance cell providing a negative resistance element that is discretely determined by the control bit signal, to keep the amplitude of the oscillation wave constant.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
LC orthogonal voltage controlled oscillator capable of reducing flicker noise
InactiveCN101183851AReduce 1/f noiseOscillations generatorsFrequency-changer modificationsPhase noiseQuadrature oscillator
The invention relates to an LC quadrature VCO (voltage controlled oscillator) which can reduce the intermittent noise, belonging to the technical field of integrated circuit, . The invention is characterized in that two negative resistance oscillators are connected together with a quadrature coupler to output quadrature signals; the reduced phase noise is implemented by using a more linear narrow-band turning variable capacitor structure, multiband switching digital array with a lower parasitic capacitance and an intermittent noise eliminating circuit reducing the intermittent noise getting into the LC oscillator when inputting voltage crossing the zero point.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
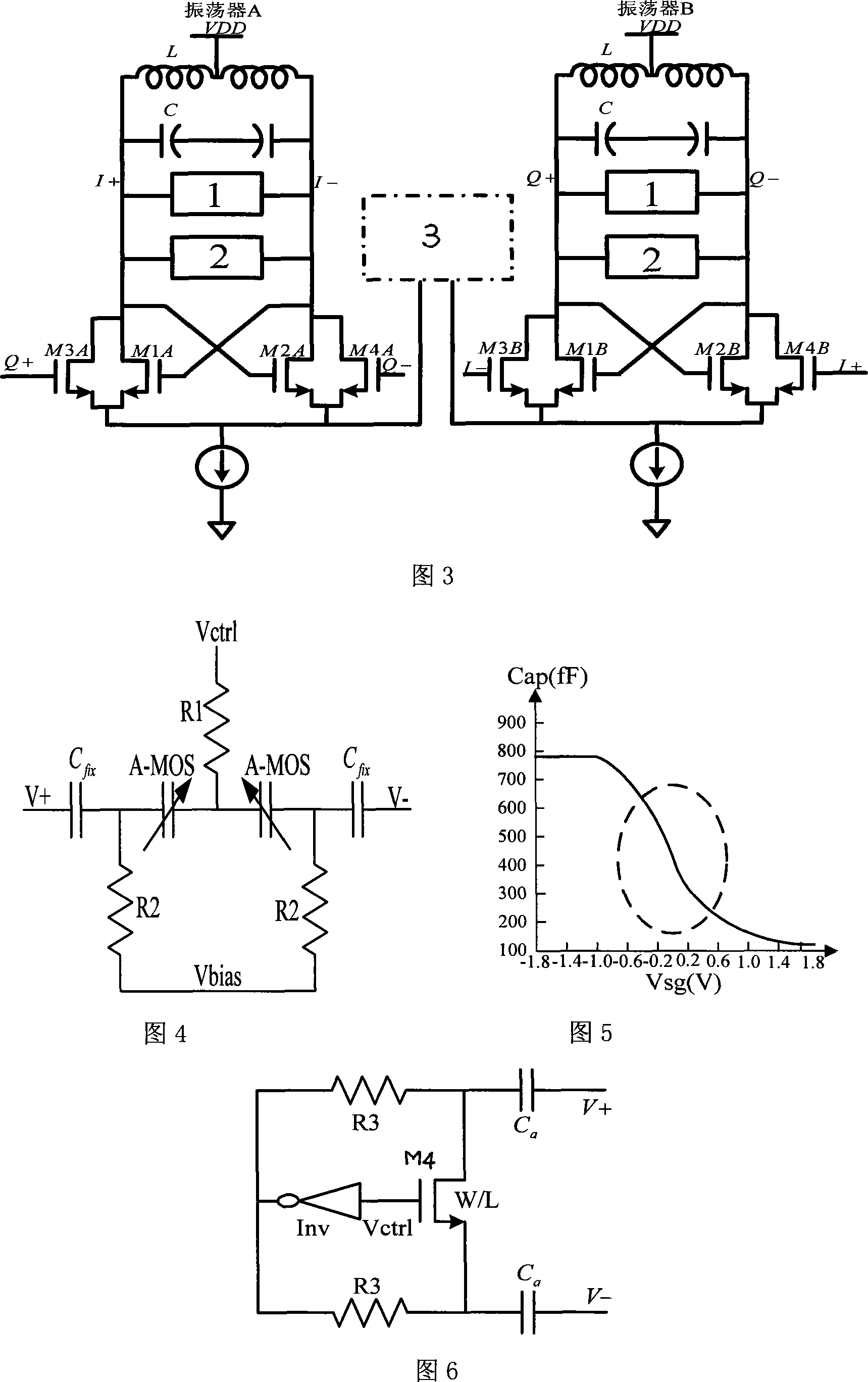
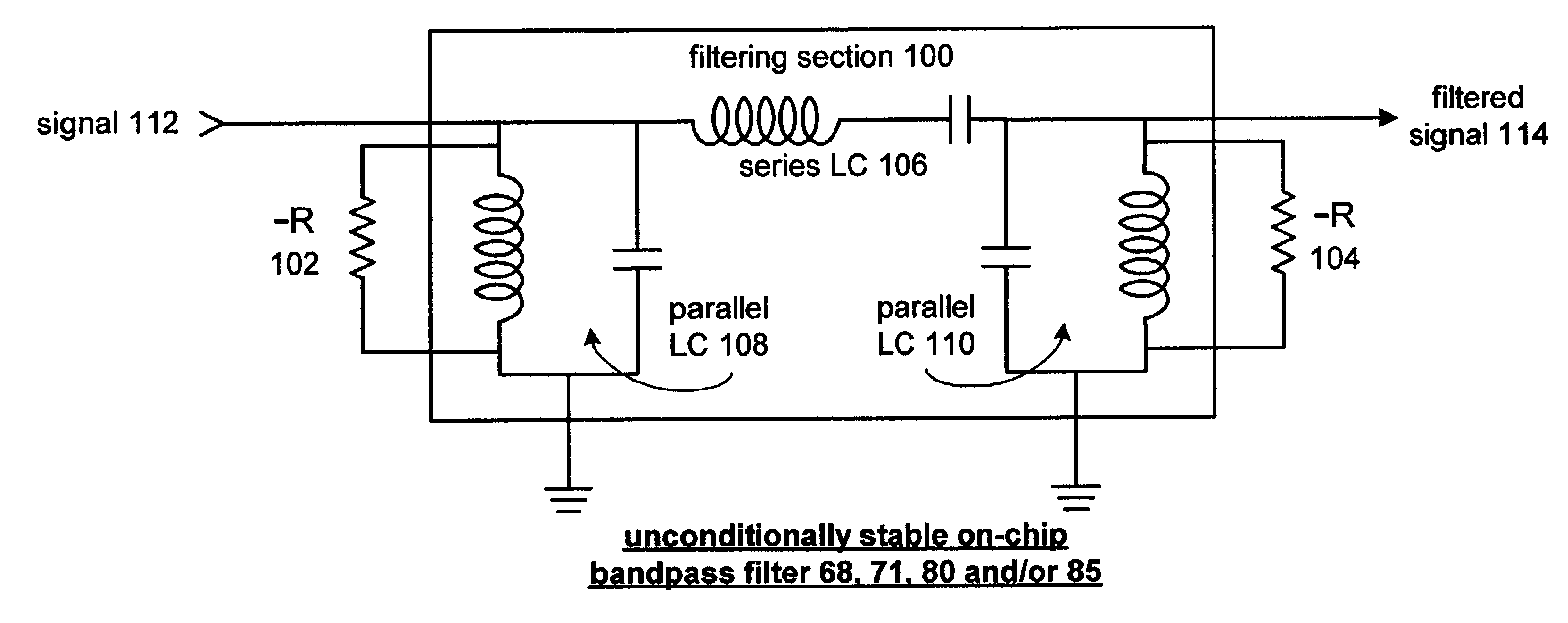
Unconditionally stable on-chip filter and applications thereof
InactiveUS6944435B2Reduced passive lossesEasy to useMultiple-port networksBalance-unbalance networksElectrical resistance and conductanceCMOS
An unconditionally stable on-chip filter includes a filtering section and at least one negative resistance module. The filtering section is operably coupled to filter a signal and includes realizable integrated circuit passive components. The at least one negative resistance module is operably coupled to compensate for integrated circuit losses of the filtering section. The realizable integrated circuit passive components have values that are robust, in comparison to parasitic values, have minimal integrated circuit real estate, and provide realizable values for various integrated circuit manufacturing processes including CMOS technology.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Negative resistance field effect element and high-frequency oscillation element
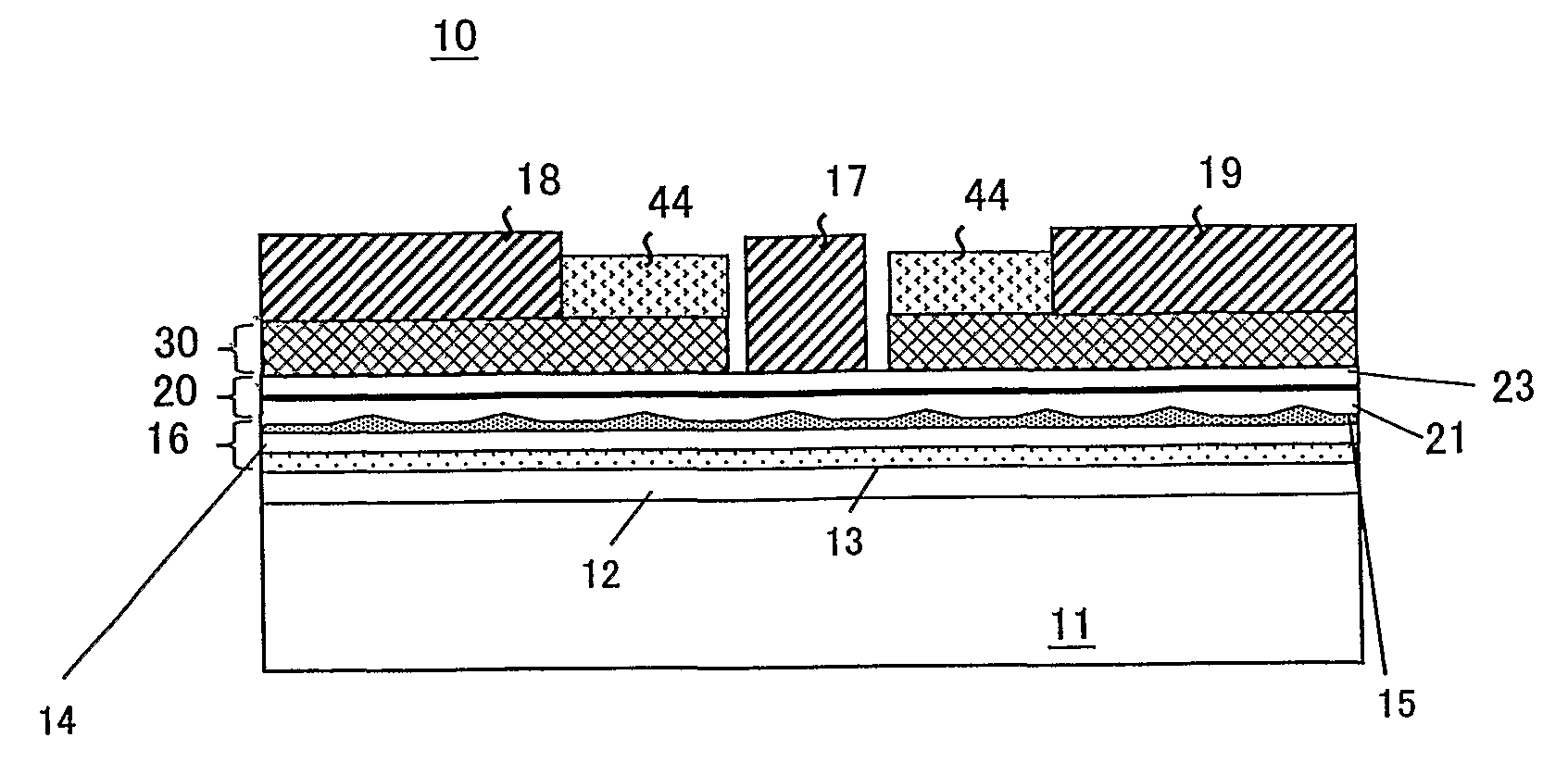
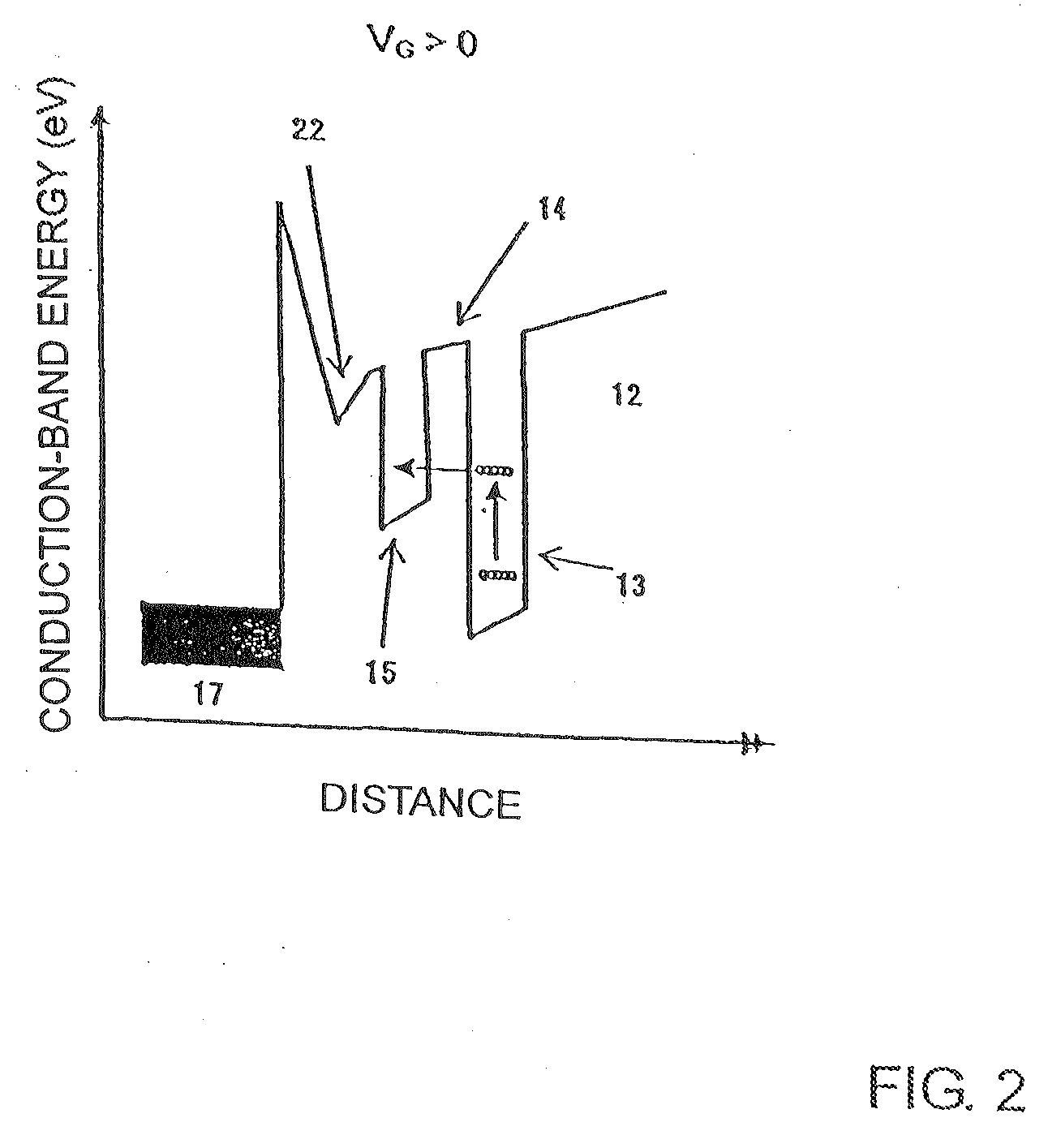
InactiveUS20090127542A1Increase resistanceNegative resistanceTransistorNanoinformaticsGate voltageElectric field
There is provided a 3-terminal negative differential resistance field effect element having a high output and high frequency characteristic, requiring low power consumption, and preferably having a high PVCR. The field effect element uses a compound hetero structure and forms a dual channel layer by connecting a high-transfer degree quantum well layer (13) to a low-transfer degree quantum dot layer (15) via a barrier layer (14) on a substrate (11). Under existence of an electric field obtained by voltage application to a gate electrode (17), the negative resistance field effect element (10) changes a carrier accelerated by a drain voltage applied to a drain electrode (19) from a high-transfer degree channel to a low-transfer degree channel by the tunnel effect or over the barrier layer, thereby exhibiting negative differential resistance for the drain current and changing the negative resistance inclination by the gate voltage.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
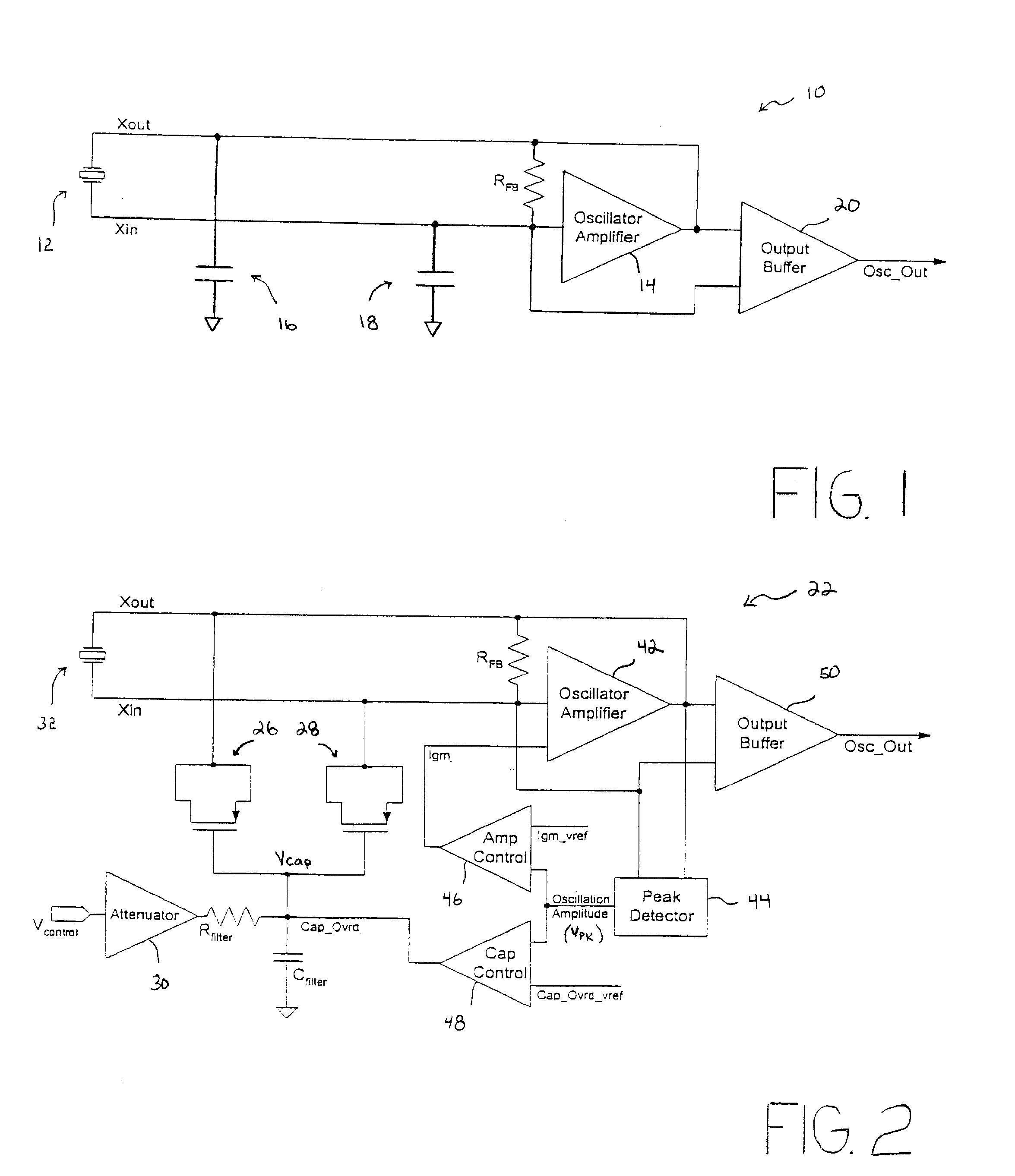
Regulated Capacitive Loading and Gain Control of a Crystal Oscillator During Startup and Steady State Operation
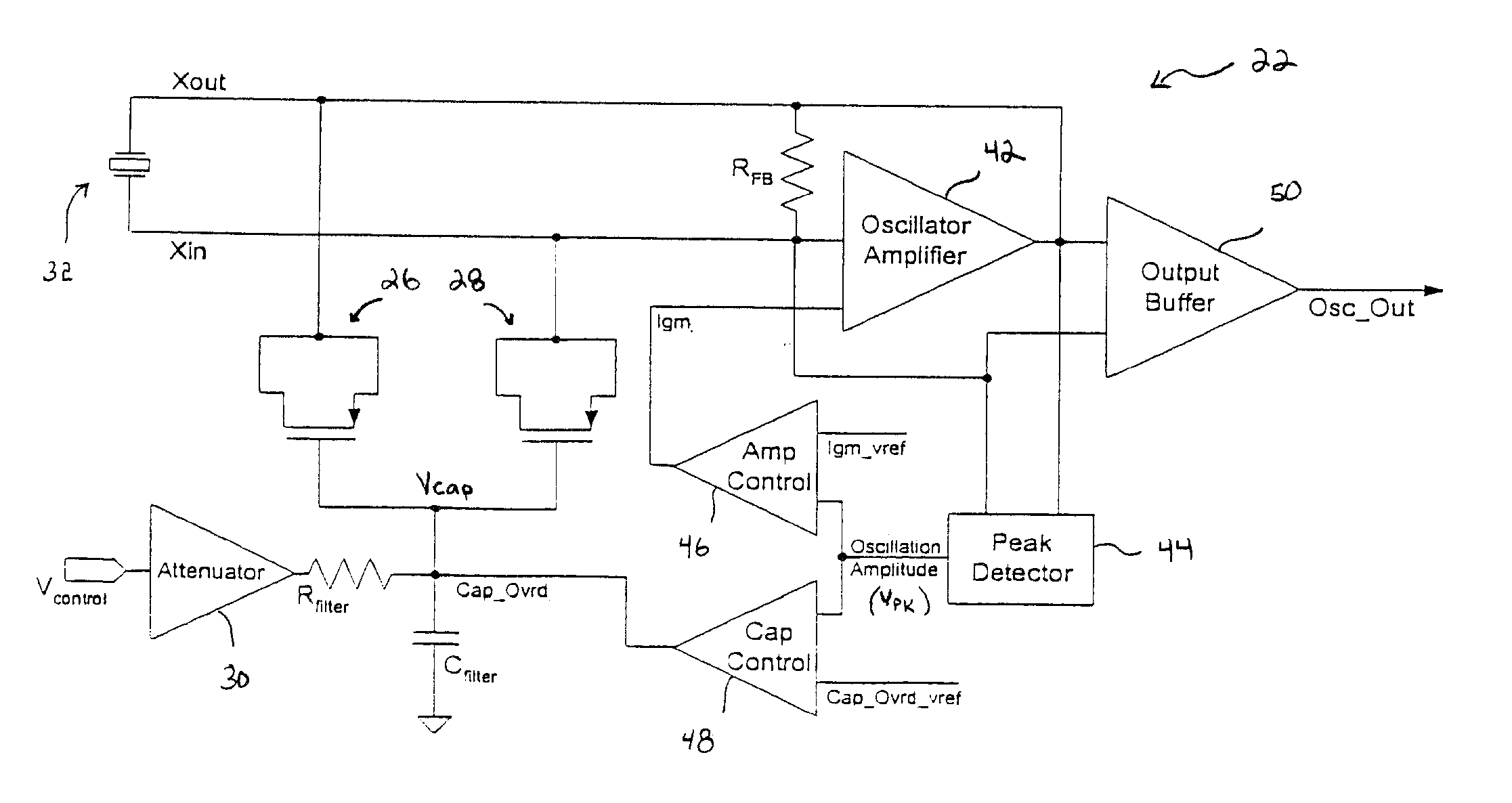
InactiveUS20070030085A1Reduce capacitive loadIncrease volumeAngle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
An oscillator circuit and system are provided having a peak detector that can determine a peak voltage value from the oscillator. The peak voltage value can then be compared against a predetermined voltage value by a controller coupled to the peak detector. The comparison value is then used to change a bias signal if the peak voltage value is dissimilar from the predetermined voltage value. A variable capacitor or varactor can be formed from a transistor and is coupled to the oscillator for receiving the bias signal upon a varactor bias node. The bias signal is used to regulate the capacitance within the varactor as applied to the oscillator nodes. Another controller can also be coupled to the peak detector to produce a second bias signal if the peak voltage is dissimilar from a second predetermined voltage value. The second bias signal can then be forwarded into an amplifier having a variable gain to regulate the gain applied to the oscillator. The combination of a varactor and variable gain amplifier regulate the negative resistance applied to the resonating circuit during startup and steady state operations to ensure a relatively fast startup, and to maintain optimal loading and accurate steady state amplitude after startup has completed.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Voltage control oscillator with low phase noise
InactiveCN1450717AImprove signal-to-noise ratioReduce phase noiseOscillations generatorsResistive circuitsPhase noise
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
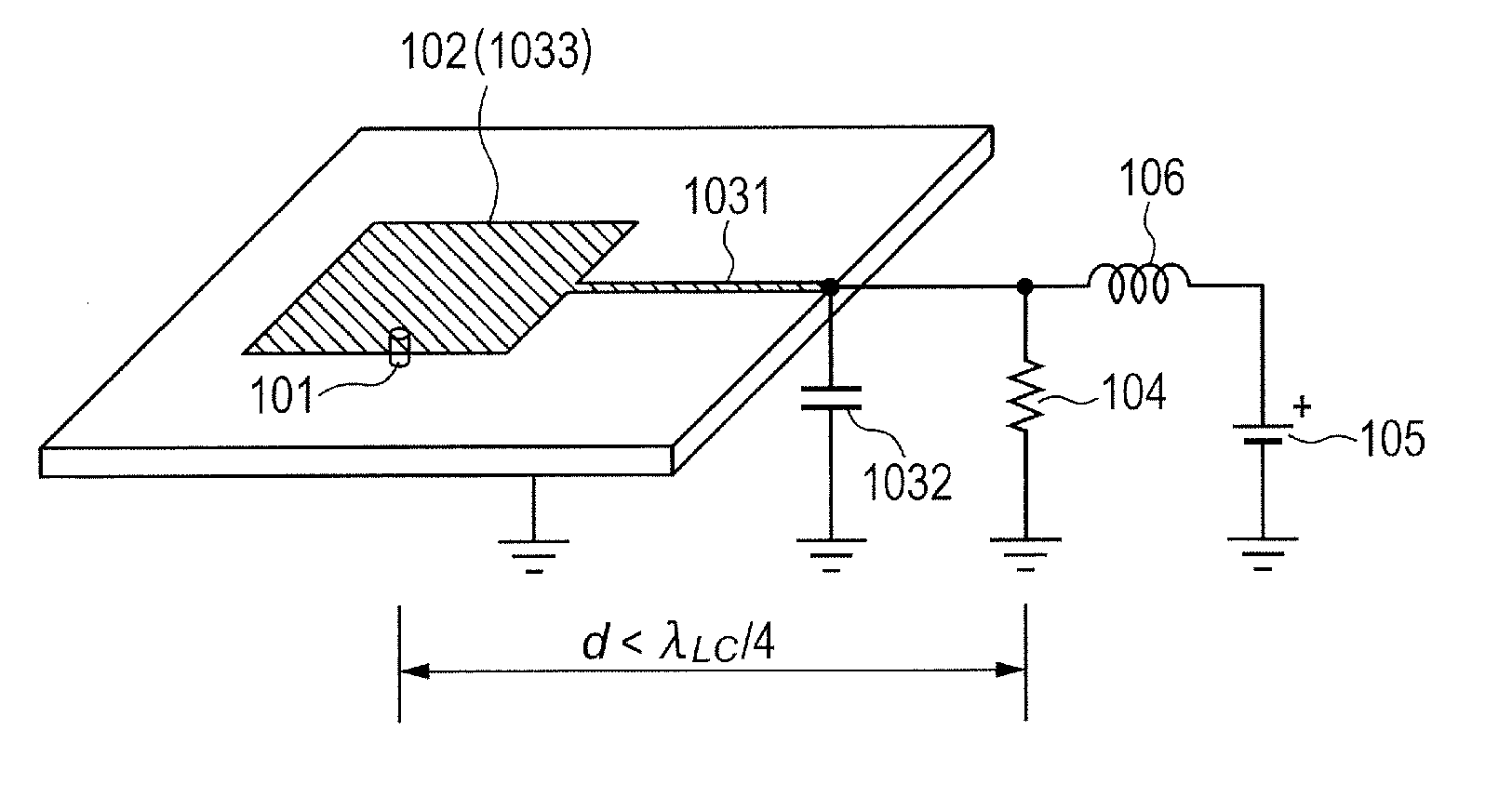
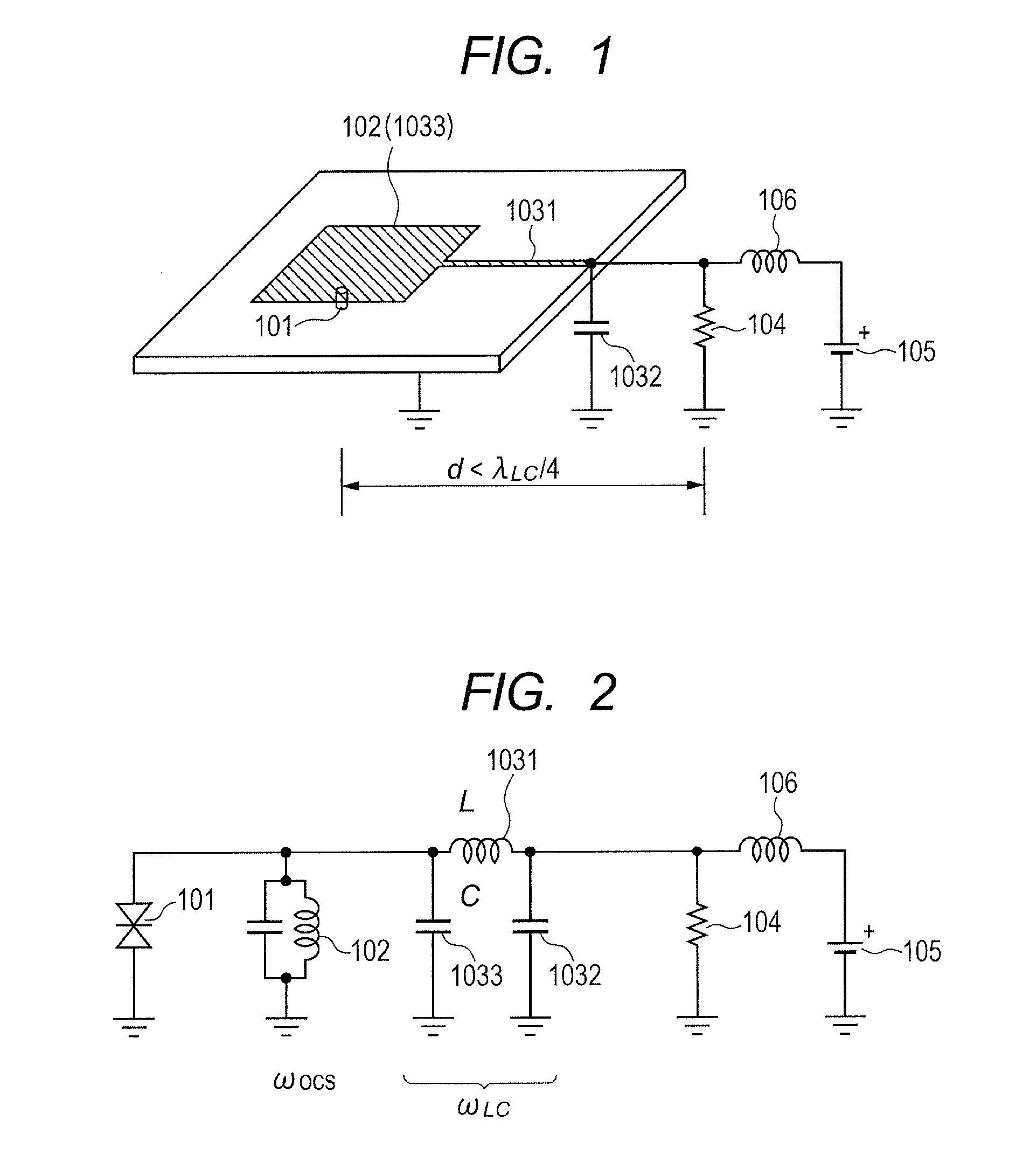
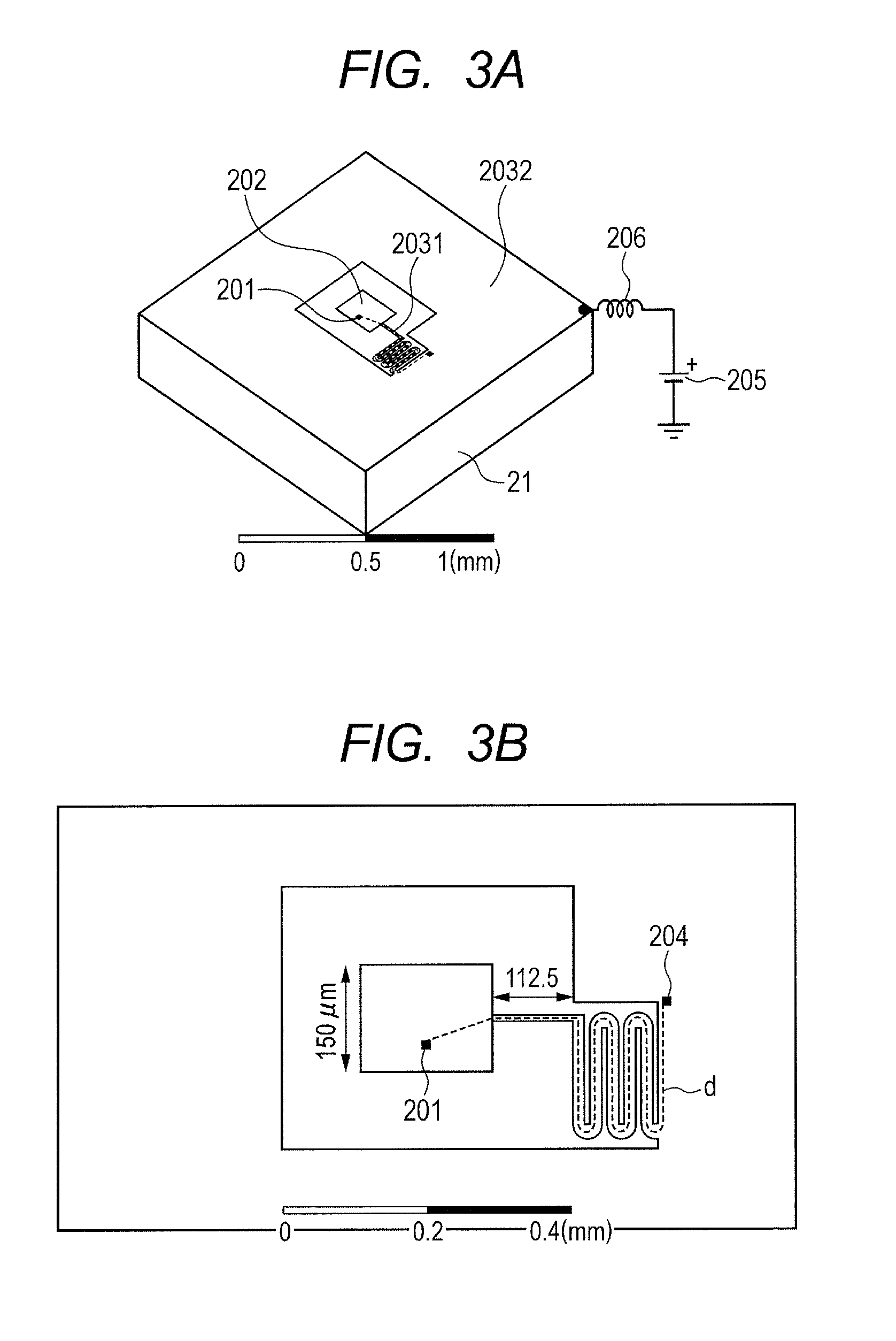
Oscillator
ActiveUS20130328635A1Suppress parasitic oscillationOscillations generatorsCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
An oscillator configured to oscillate an electromagnetic wave, including: a negative resistance device; a microstrip resonator configured to determine an oscillation frequency of an electromagnetic wave excited by the negative resistance device; a resistance device and a capacitance device, which form a low-impedance circuit configured to suppress parasitic oscillation; and a strip conductor configured to connect the capacitance device of the low-impedance circuit and the microstrip resonator to each other, in which an inductance L of the strip conductor and a capacitance C of the microstrip resonator produce a resonance frequency of ½π√LC, and ¼ of an equivalent wavelength of the resonance frequency is larger than a distance between the negative resistance device and the resistance device of the low-impedance circuit via the strip conductor, is provided.
Owner:CANON KK
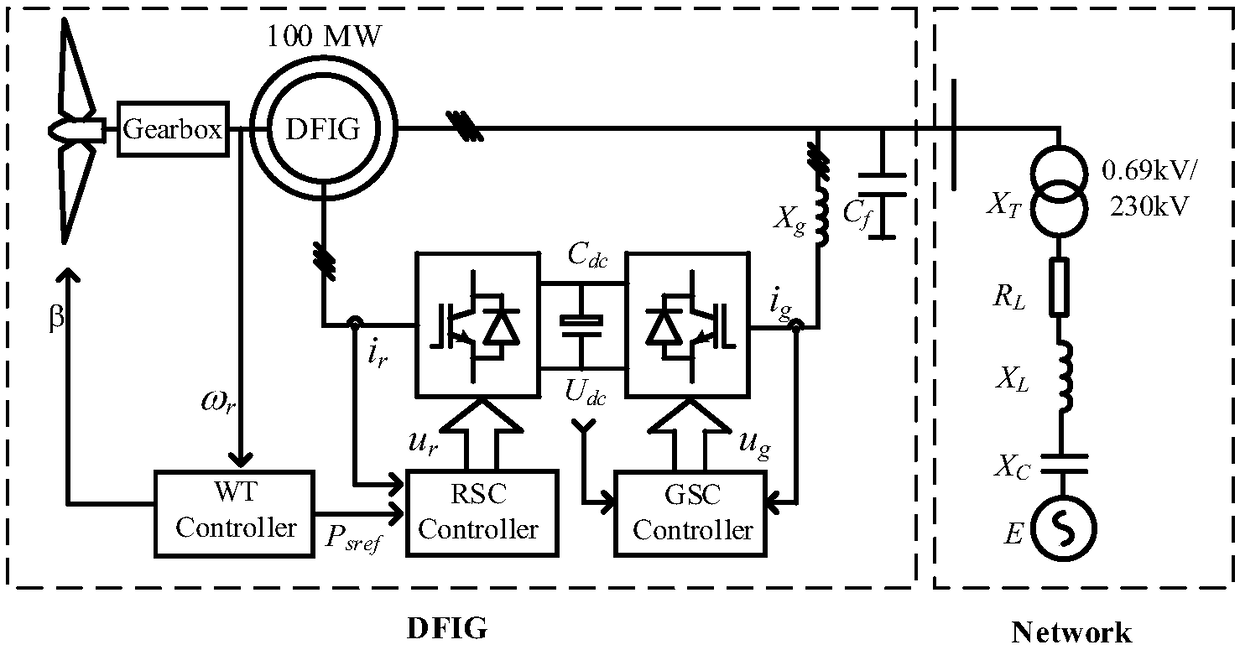
Subsynchronous oscillation suppression method for grid-connected system of double-feed wind power plant based on virtual resistance
ActiveCN109120001AReduce the magnitude of the equivalent negative resistanceSuppression of subsynchronous oscillationsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionElectrical resistance and conductanceRotor side converter
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Inverter circuit for discharge lamps for multi-lamp lighting and surface light source system
InactiveUS7282868B2Uniform lightReduce shapingElongate light sourcesStatic indicating devicesGas-discharge lampElectrical resistance and conductance
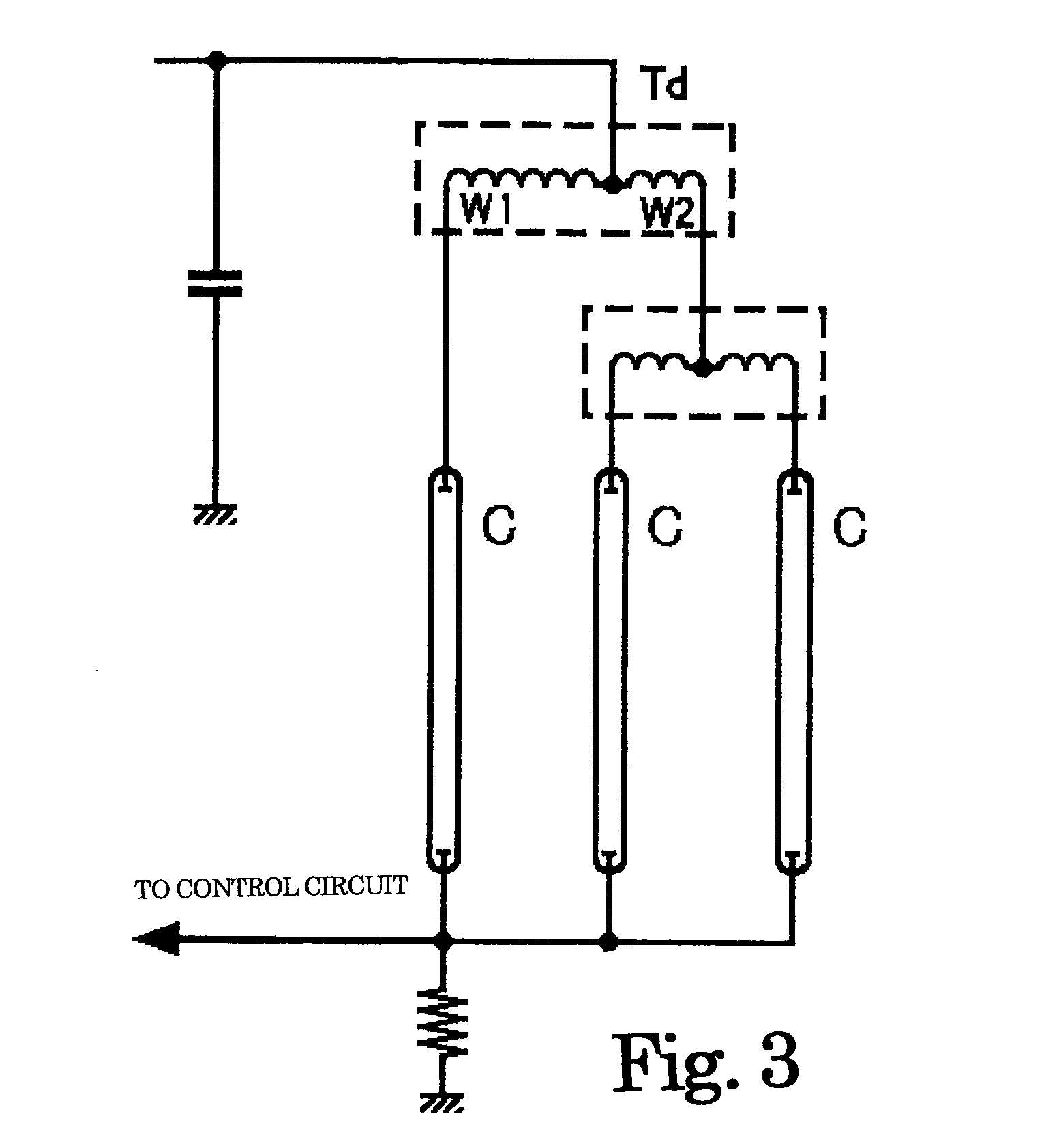
An inverter circuit for discharge lamps for multi-lamp lighting in which the value of a negative resistance characteristic of a fluorescent lamp is controlled, and an excessively set reactance is eliminated by causing a shunt transformer to have a reactance exceeding the negative resistance characteristic. Two coils connected to a secondary winding of a step-up transformer of the inverter circuit are arranged and magnetically coupled to each other to form a shunt transformer for shunting current such that magnetic fluxes generated thereby cancel each other out. Discharge lamps are connected to the coils, respectively, with currents flowing therethrough being balanced. Each discharge lamp is lighted because a reactance of an inductance related to the balancing operation which is in an operating frequency of the inverter circuit, exceeds a negative resistance of discharge lamps.
Owner:MASAKAZU USHIJIMA +1
Single stage power factor corrected power converter with reduced AC inrush
InactiveUS20070217235A1Reduced AC inrushImprove output rippleDc network circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversion without reversalConstant powerTotal harmonic distortion
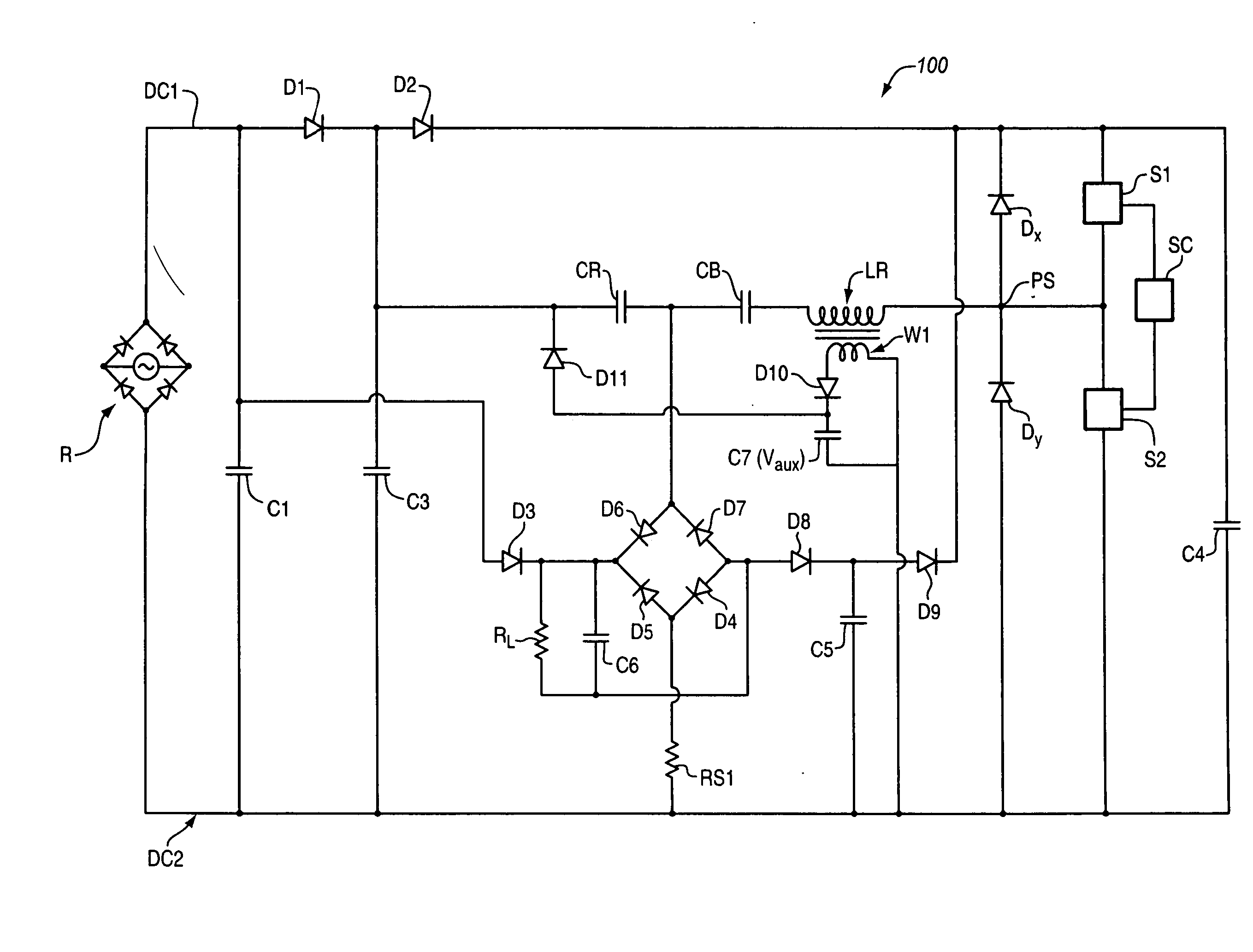
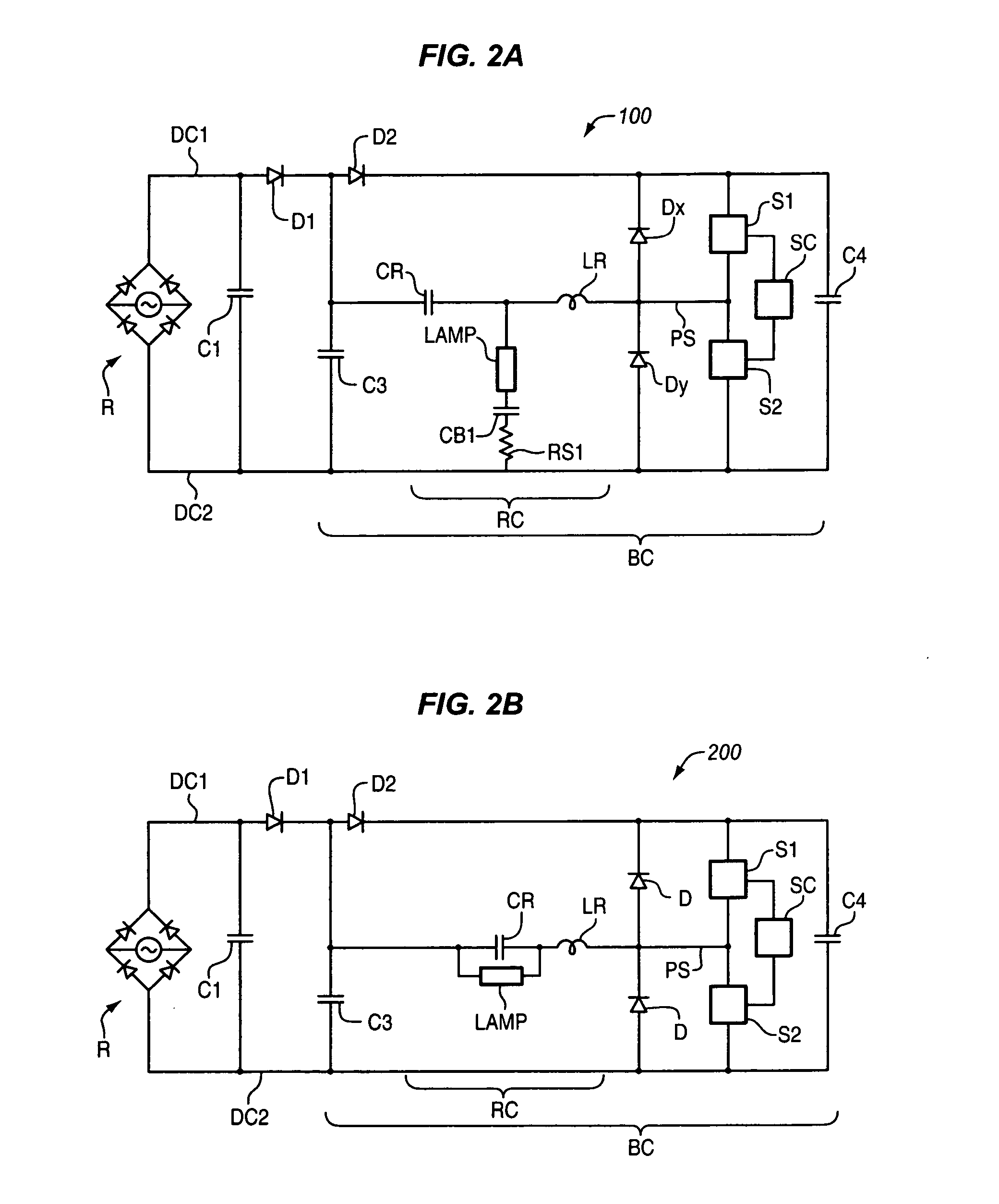
The improved single stage power converter circuit topology substantially reduces EMI that is conducted to the AC line, reduces input AC current inrush, improves output ripples by the use of an auxiliary supply near zero crossings of the line AC voltage, provides Power Factors greater than 0.95, provides Total Harmonic Distortions less than 15%, and maintains constant power, including constant power in a non-linear output load. Further, this circuit topology provides output open and short circuit protections by reducing current stress in power components. This topology can also make the power source to appear as a fast-acting variable impedance source, an ideal source for powering an output load that has negative resistance characteristics such as gas discharge lamps.
Owner:ENERGY CONSERVATION TECH
Electronic oscillators having a plurality of phased outputs and such oscillators with phase-setting and phase-reversal capability
InactiveUS7307483B2Improve noise characteristicsReduce power consumptionPulse generation by logic circuitsTime-delay networksLow voltageOpto-electronic oscillator
Disclosed are multiphase oscillators comprising a plurality of delay stages serially coupled in a loop by a plurality of nodes, with the loop being folded to provide two concentric rings of delay stages with equal numbers of allocated nodes. A second plurality of negative-resistance elements are provided, each element having a first output coupled to a node on the first concentric ring and a second output coupled to a node on the second concentric ring. Each such output switches between first and second voltage levels, and provides a negative resistance to a signal coupled to it during at least a portion of the transition between voltage levels. The outputs of an element switch to opposite voltage levels. With this construction, a high-voltage pulse propagates around the loop of delay stages, with a low-voltage pulse propagating behind it. Also disclosed are circuits to control the direction of pulse propagation.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Radio-frequency integrated band-pass filter with impedance match
The invention relates to a radio-frequency integrated band-pass filter with impedance match, belonging to the technical field of design of integrated circuits. Based on a CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Transistor) process, by utilizing an active negative resistance compensation technology, the radio-frequency integrated band-pass filter with the impedance match is composed of two LC (Inductance-Capacitance) resonance circuits, two input impedance match circuits, two output impedance match circuits, an active negative resistance compensation circuit and two NMOS (N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tail current transistors, wherein the two LC resonance circuits, the two input impedance match circuits and the two output impedance match circuits have the same connection way and symmetrical structures. The adjustment on the central frequency, the band-pass gain and the bandwidth of the band-pass filter can be realized through adjusting a bias voltage of a varactor and adjusting bias voltages of two NMOS tail current transistor grids. The radio-frequency integrated band-pass filter provided by the invention not only can carry out integration on a chip by adopting the CMOS process, but also is provided with an input-output impedance match circuit on the chip, and discrete devices out of the chip are not needed, so that the integration level is greatly improved and a feasible scheme for realizing single chip integration is supplied to a radio-frequency front end of a wireless receiver.
Owner:锐立平芯微电子(广州)有限责任公司
Self-excitation push-pull converter
ActiveCN102594193AImprove conversion efficiencyReduce no-load power consumptionAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionEffective powerHemt circuits
The invention discloses a self-excitation push-pull converter. A negative resistance characteristic constant current source is arranged between a direct-current circuit of a base electrode of a push-pull switch triode and an effective power supply end; when the work voltage of the negative resistance characteristic constant current flow is lower than a rated work voltage, higher constant current is provided; when the work voltage of the negative resistance characteristic constant current source is higher than the rated work voltage, the lower constant current is provided; when the work voltage of the negative resistance characteristic constant current source is same as the rated work voltage, the rated constant current is provided; and when the work voltage of the negative resistance characteristic source is constant, and the load changes, the output current of the negative resistance characteristic constant current source is constant. According to the self-excitation push-pull converter, when the work voltage rises, the no-load work current does not rise or descend, when the surges exist in the input voltage of the self-excitation push-pull converter, the switch triode can not be damaged, and when long-time surge voltage exists in the input voltage, the self-excitation push-pull converter of a circuit has certain surge resisting capacity.
Owner:MORNSUN GUANGZHOU SCI & TECH
Adjustable field effect rectifier
ActiveUS8148748B2Improve performanceImproving reverse recovery characteristicThyristorMOSFETHigh voltage igbt
An Adjustable Field Effect Rectifier uses aspects of MOSFET structure together with an adjustment pocket or region to result in a device that functions reliably and efficiently at high voltages without significant negative resistance, while also permitting fast recovery and operation at high frequency without large electromagnetic interference.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Multi-band LC resonance voltage-controlled oscillator with adjustable negative resistance cell
InactiveUS7554416B2Suppress noiseAngle modulation by variable impedenceResonant circuit tuningMulti bandCapacitance
Provided is an LC resonance voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) used for a multi-band multi-mode wireless transceiver. In order to generate a multi-band frequency, a capacitor bank and a switchable inductor are included in the LC resonance voltage-controlled oscillator. The LC resonance voltage-controlled oscillator employs an adjustable emitter-degeneration negative resistance cell in place of tail current sources in order to compensate for non-uniform oscillation amplitude caused by the capacitor bank and prevent the degradation of a phase noise due to the tail current sources. The LC resonance voltage-controlled oscillator includes an inductor providing an inductance element partially determining the frequency of an oscillation wave; a discrete capacitor bank providing a capacitance element partially determining the frequency of the oscillation wave and being discretely determined by a control bit signal; and a discrete negative resistance cell providing a negative resistance element that is discretely determined by the control bit signal, to keep the amplitude of the oscillation wave constant.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
VCO tuning curve compensation method and module thereof
ActiveCN101944880ALarge tuning rangeImprove stabilityMultiple-port active networksOscillations generatorsCapacitanceLow-pass filter
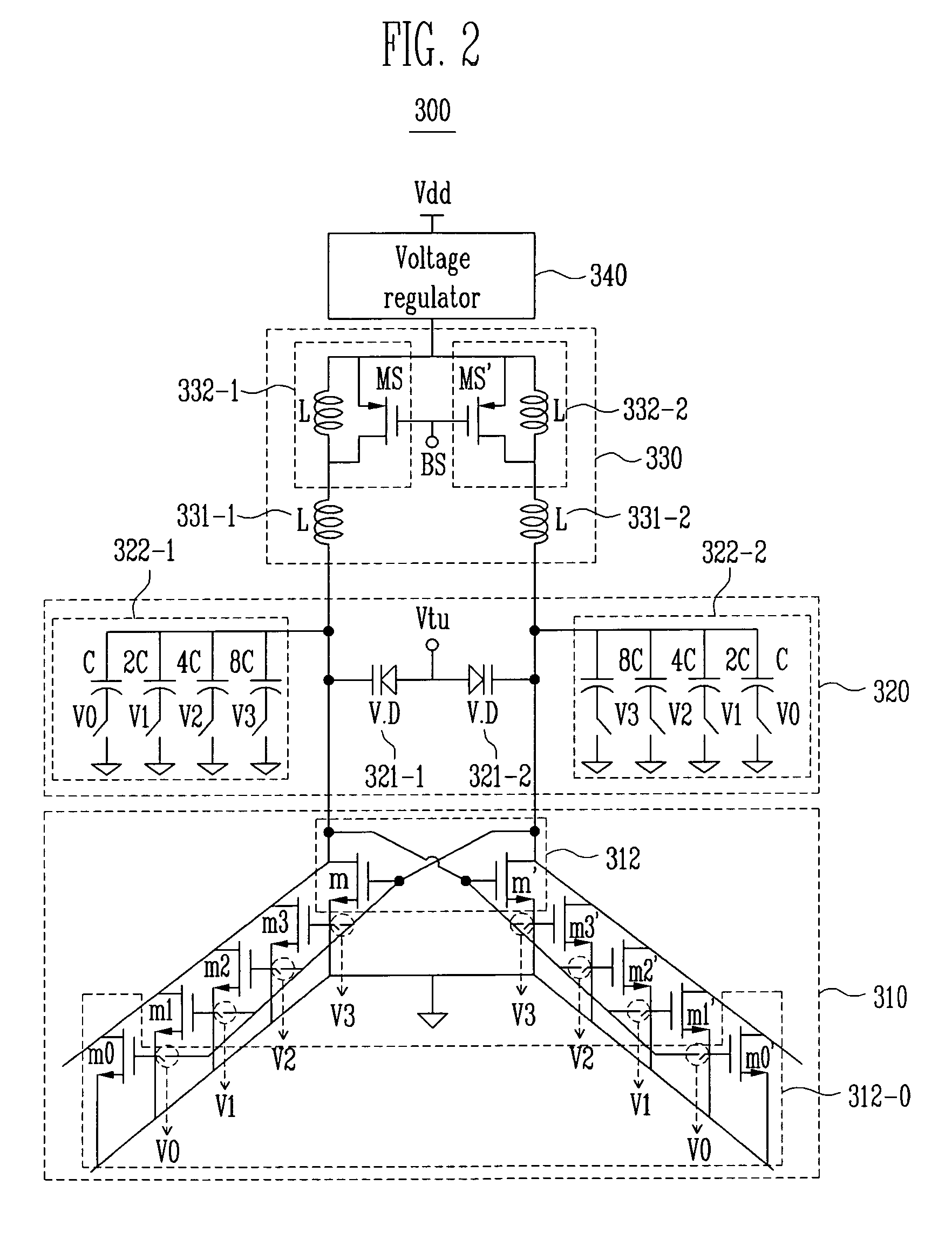
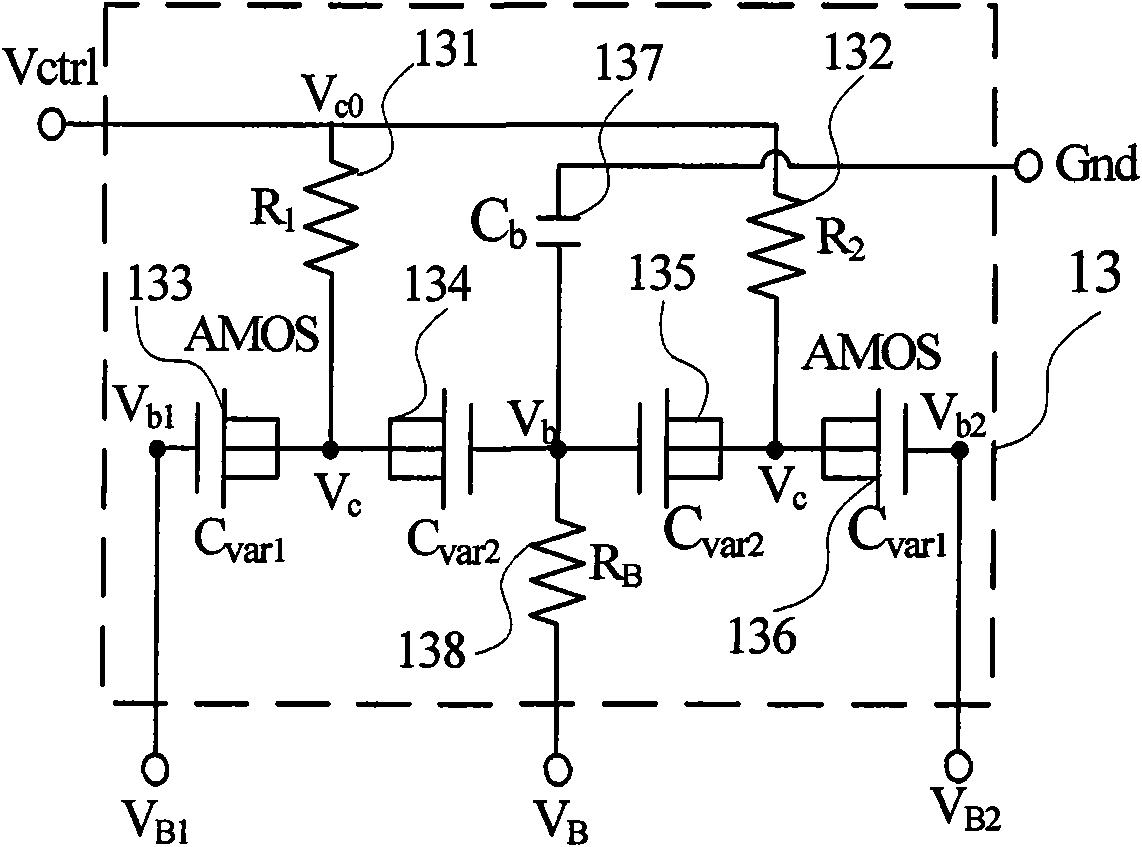
The invention provides a VCO tuning curve compensation method. In the method, a negative resistance amplifier and an inductor are connected with both ends of a variable capacitor to form a parallel-connection structure, wherein the variable capacitor structure is a five-end AMOS capacitance network, and one end is a tuning curve compensation control end of the AMOS capacitance network, which changes the equivalent capacitance of the AMOS capacitance network by adjusting the DC voltage of a control end to obtain an approximate linearized change curve with respect to VCO output frequency and VCO control voltage, thereby realizing the VCO tuning curve compensation, improving the VCO stability and enabling a VCO circuit module to work in the area having a higher Q value. The invention also provides a VCO circuit module of a differential circuit structure formed by the method. The AMOS capacitance network comprises four AMOS varactors and one RC low-pass filter, wherein the four AMOS varactors are connected in series two by two and are symmetrically arranged, and the specific arrangement mode includes grid electrode series connection and substrate series connection. The VCO module performs voltage control on the AMOS varactors to change the oscillator frequency, and realizes the tuning curve compensation to enable the frequency tuning curve to be approximately linearized by changing the DC voltage of the compensation control end of the tuning curve, thereby realizing a larger frequency tuning range.
Owner:杭州中科微电子有限公司
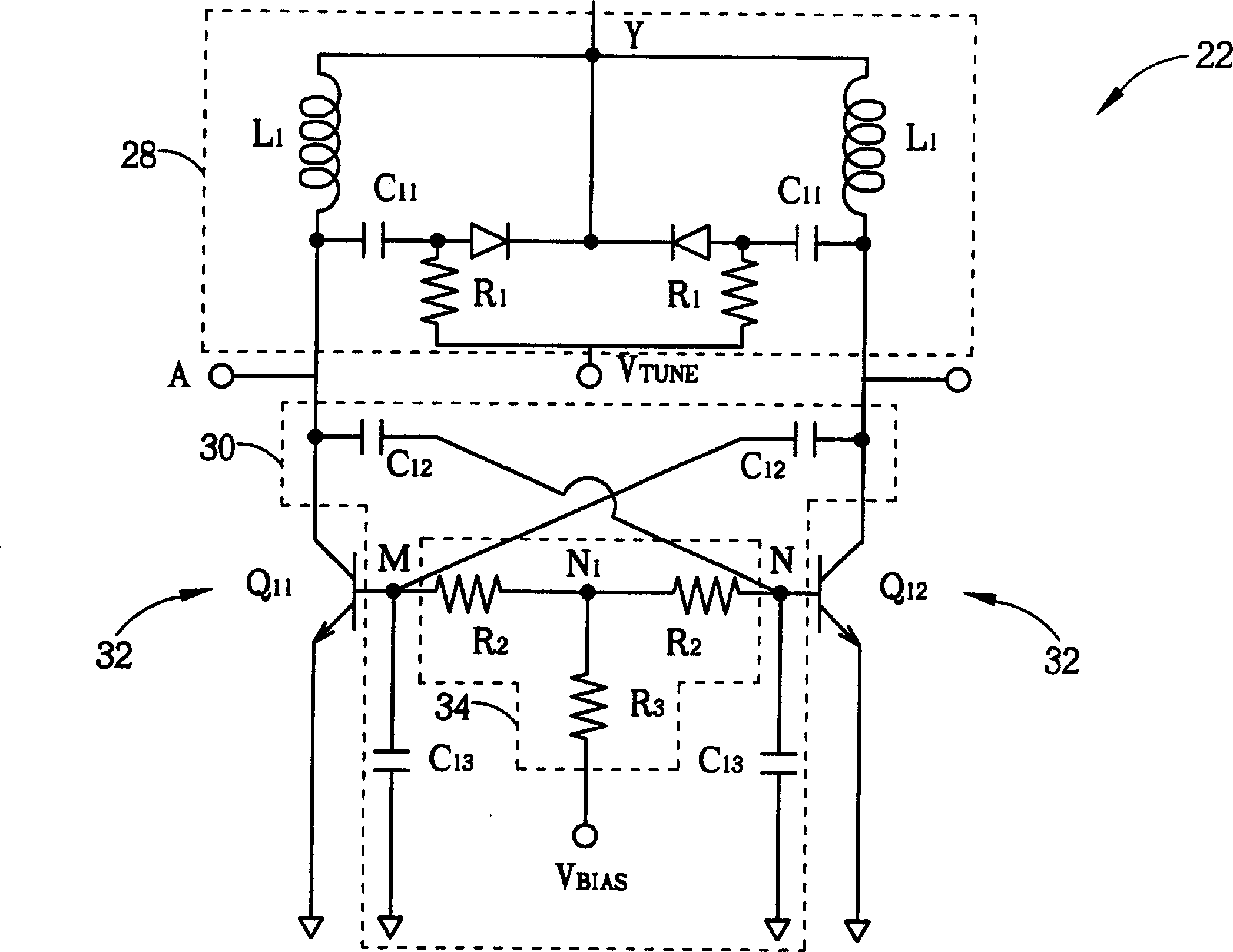
Voltage controlled oscillator
InactiveCN101212198ALarge tuning rangeLow Phase Noise PerformancePulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsCapacitancePhase noise
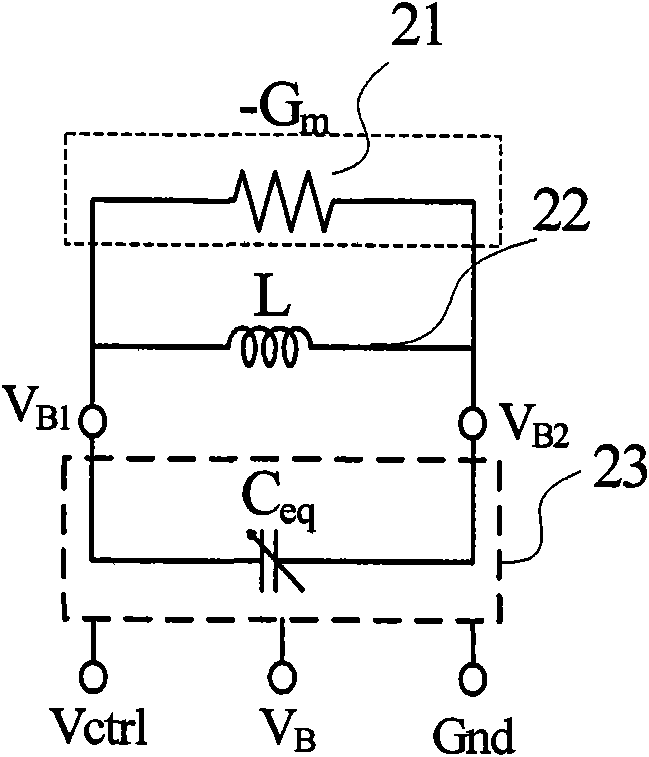
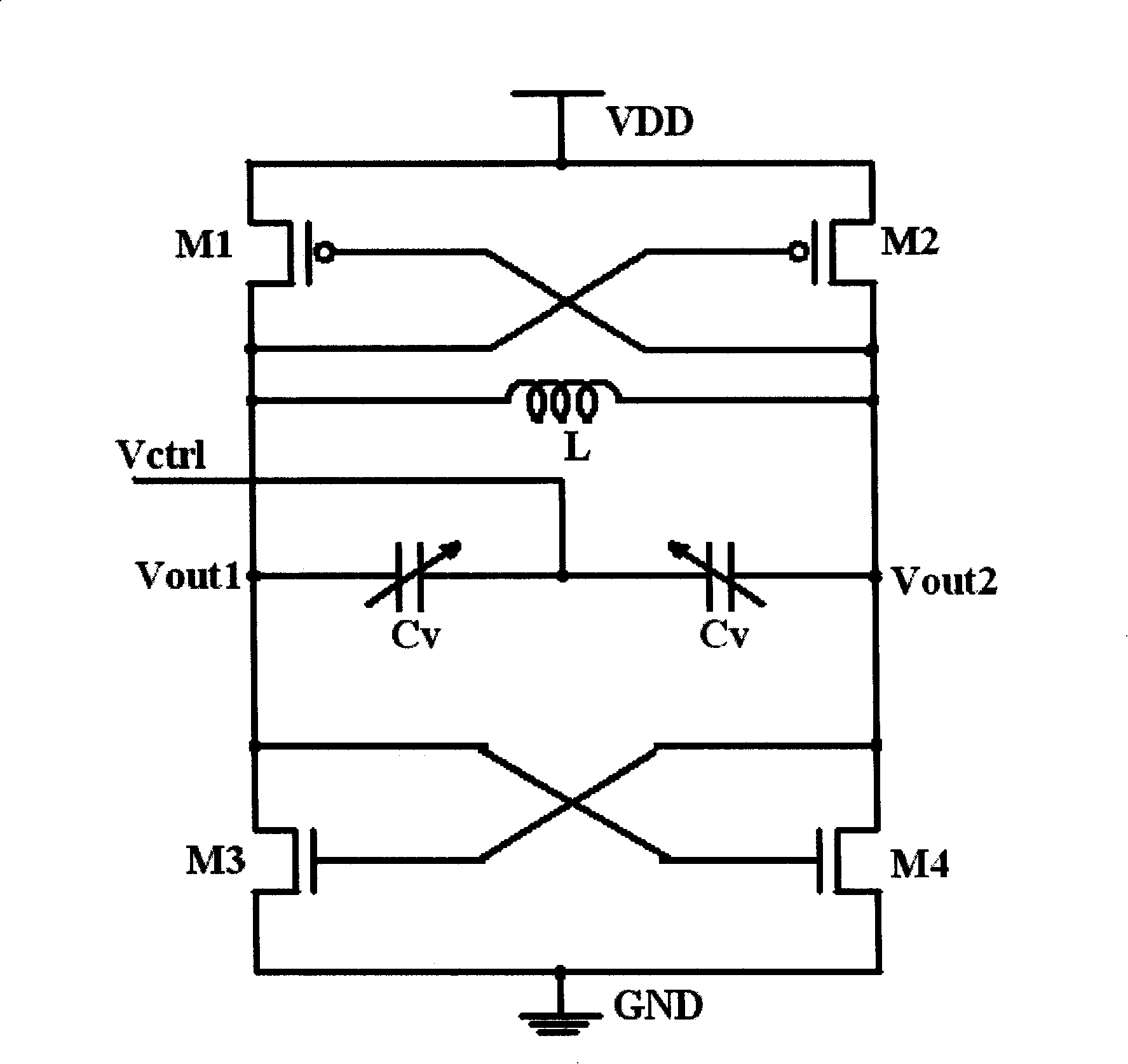
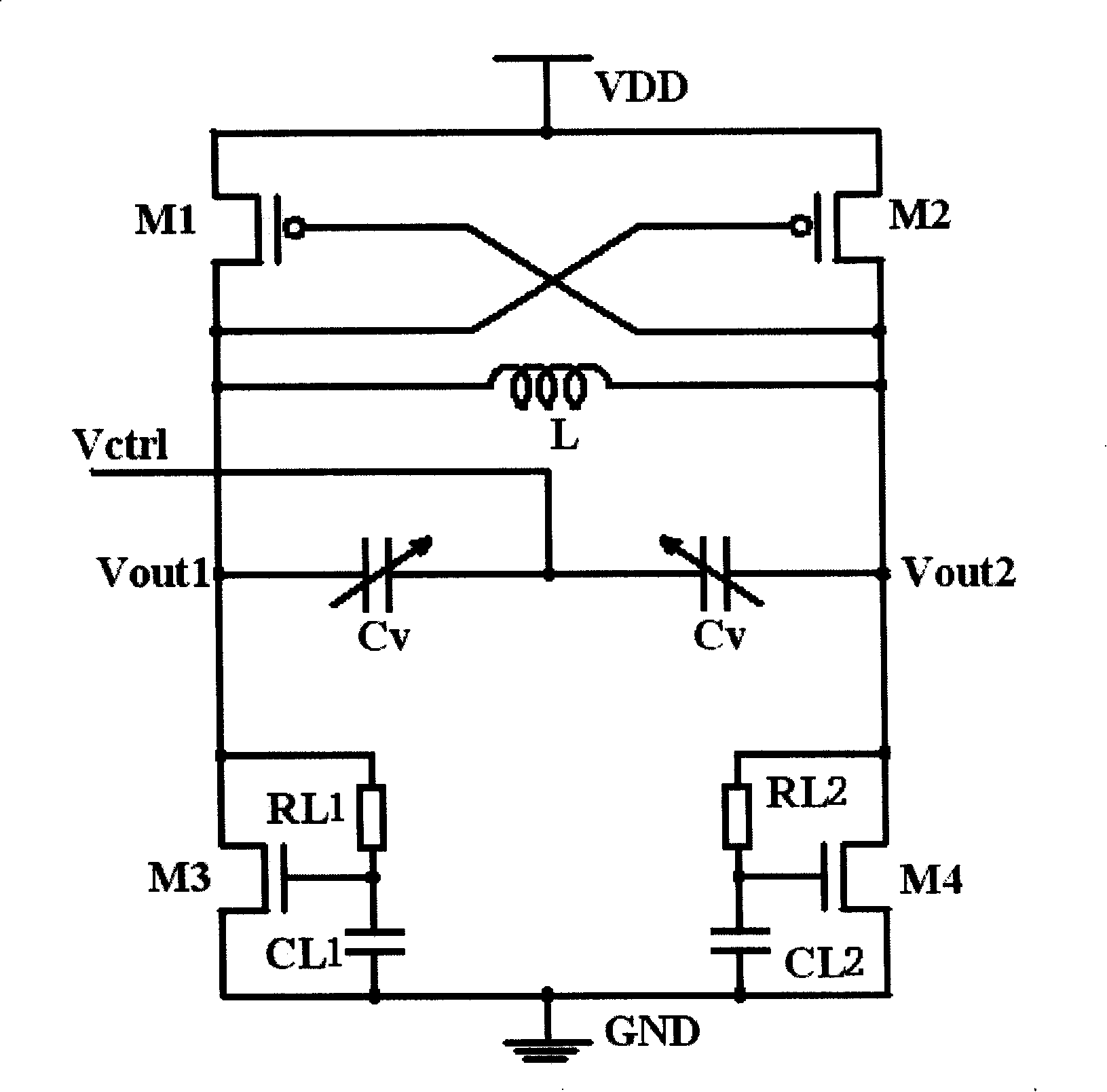
The invention relates to a voltage controlled oscillator, which comprises four transistors, an integrated on-chip inductor and two symmetric variable capacitors, wherein, two transistors realize negative resistance through cross coupling, thereby providing energy to oscillate an LC circuit comprising the inductor and the variable capacitors; by changing the capacitance of the variable capacitors, different output frequencies of the oscillator are obtained. The invention also comprises two resistors with the same value and two capacitors with the same value; a grid terminal of one of the rest transistors is connected with a terminal of a resistor and a terminal of a capacitor at the same time, which jointly form an active inductor; a grid terminal of the last transistor is connected with a terminal of a resistor and a terminal of a capacitor at the same time, thus jointly forming another active inductor; the two active inductors provide bias current for the voltage controlled oscillator. The invention enlarges the tuning range of the voltage controlled oscillator and reduces the phase noise.
Owner:BEIJING LHWT MICROELECTRONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com