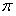Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
54 results about "Quadrature oscillator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
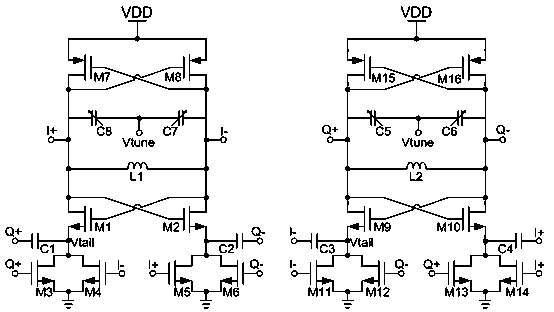
Quadrature Oscillator (Part 1) A quadrature oscillator produces two sinewaves with 90° phase difference between them. These are useful to pan signals (particularly in a quadraphonic environment), or to make a frequency-shifter when combined with a pair of ring- modulators.
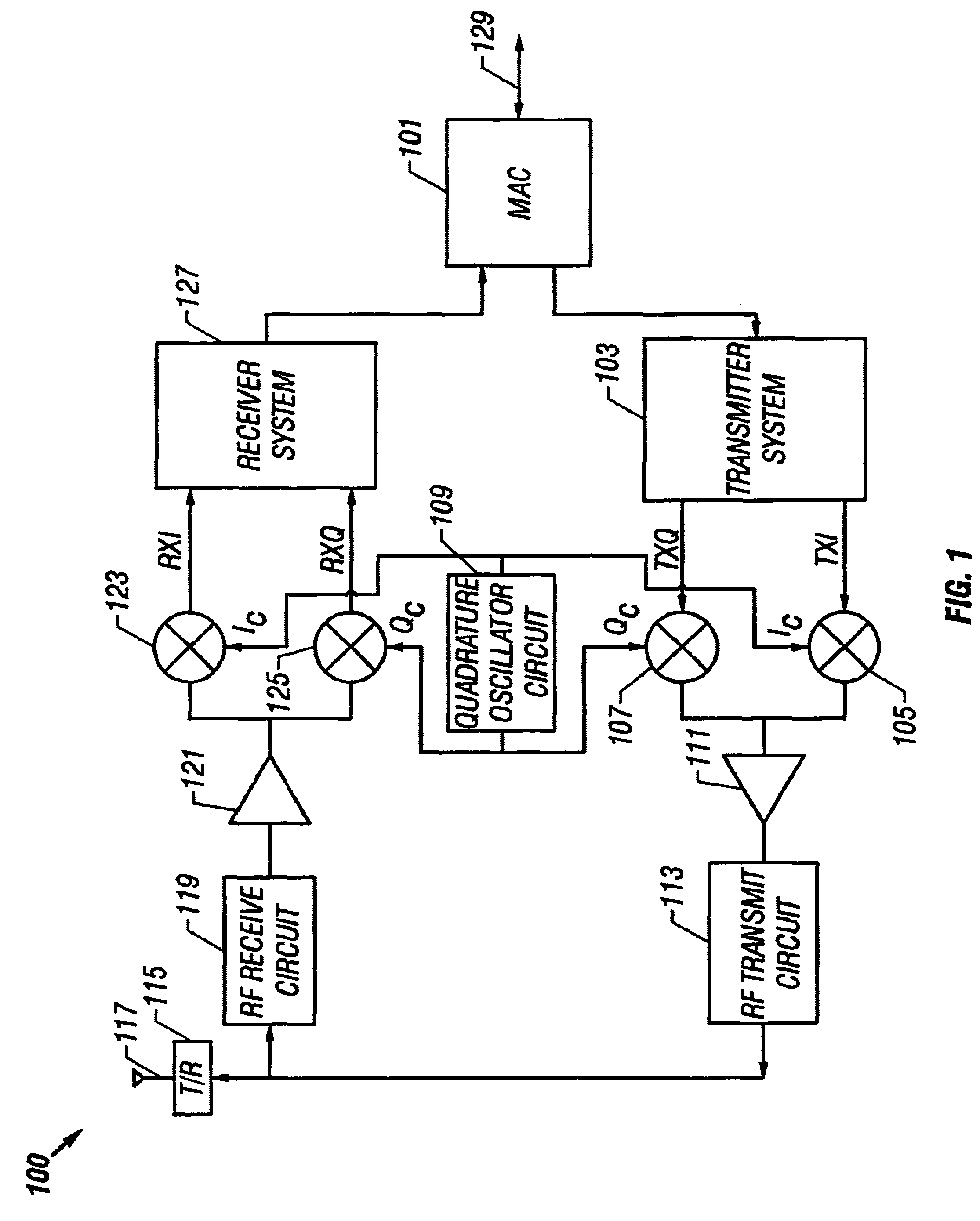
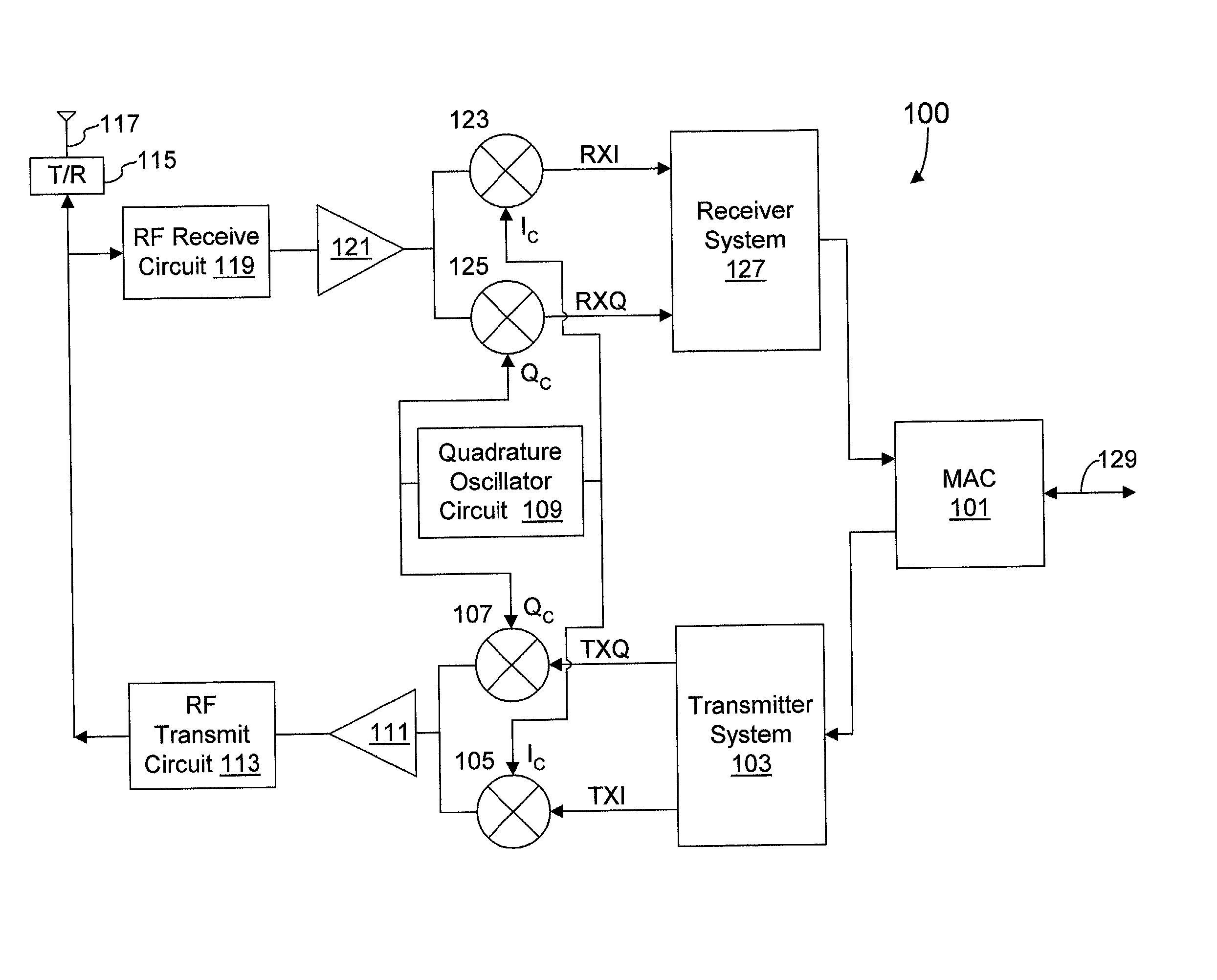
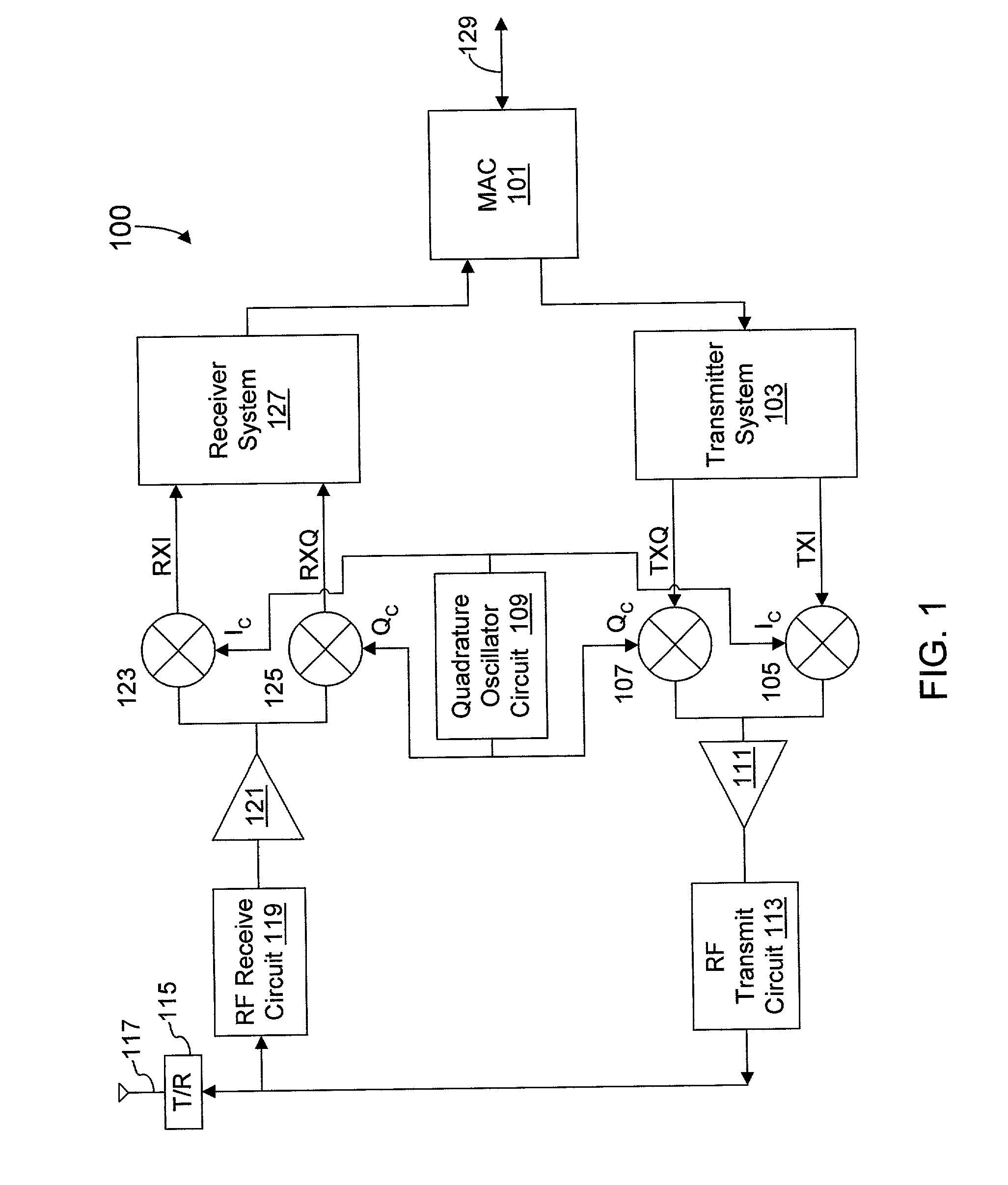
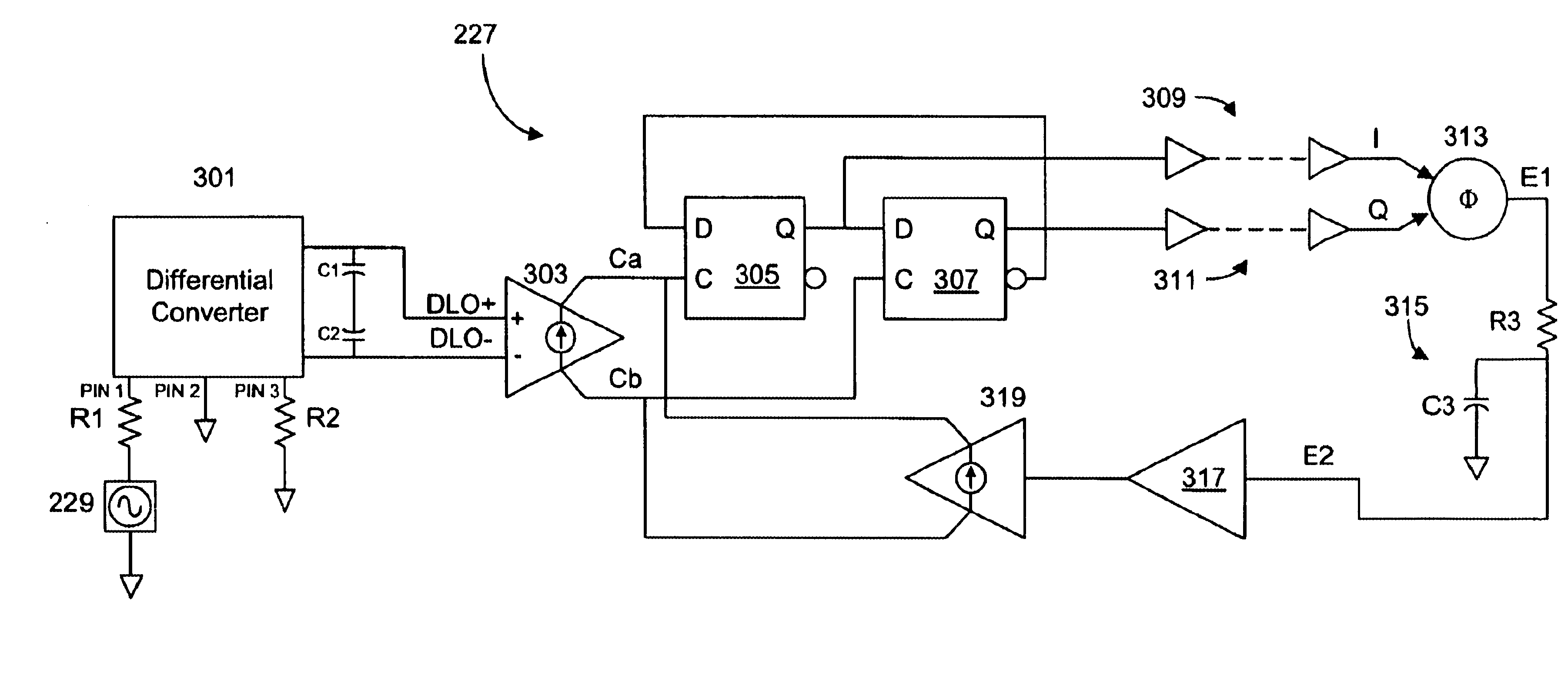
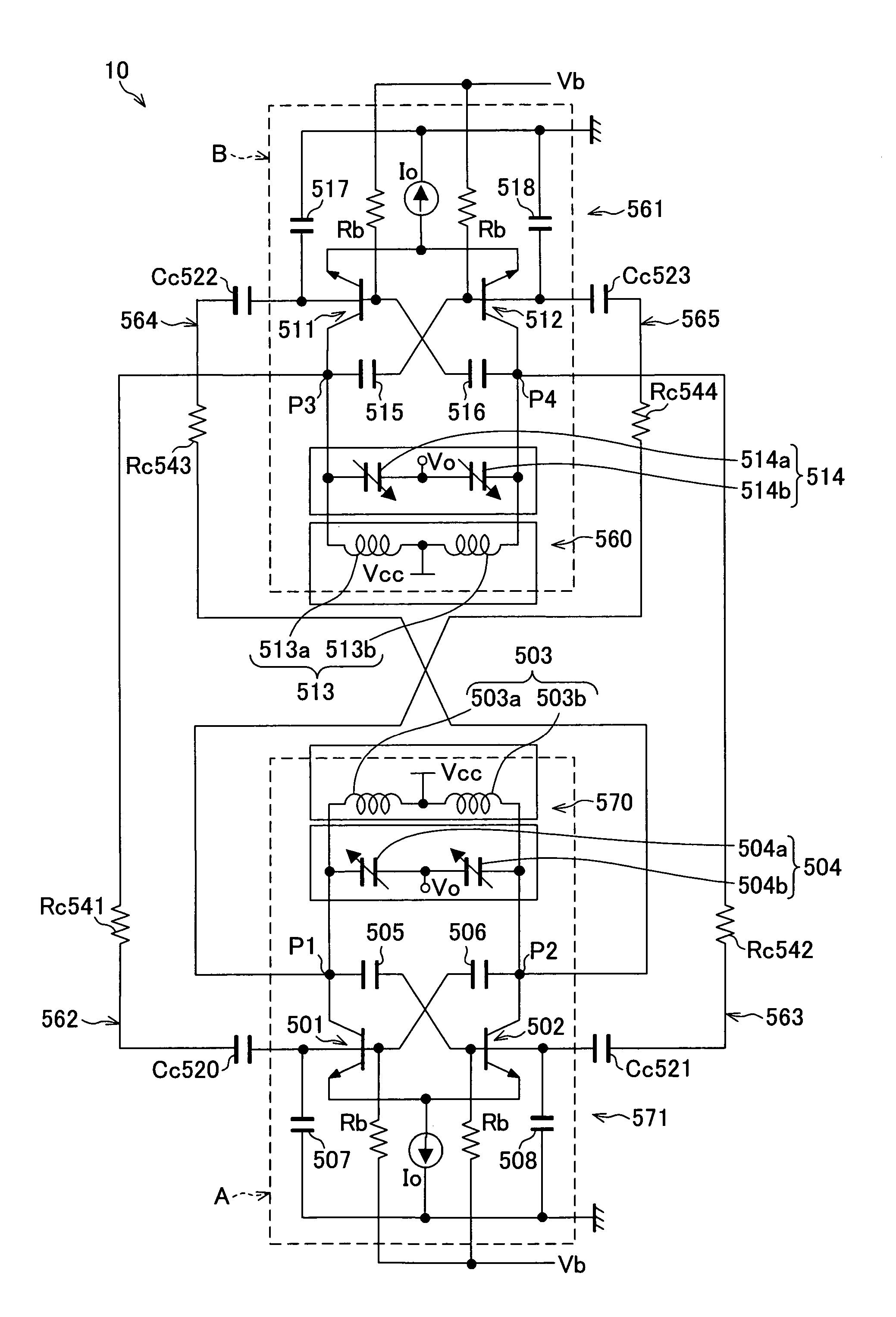
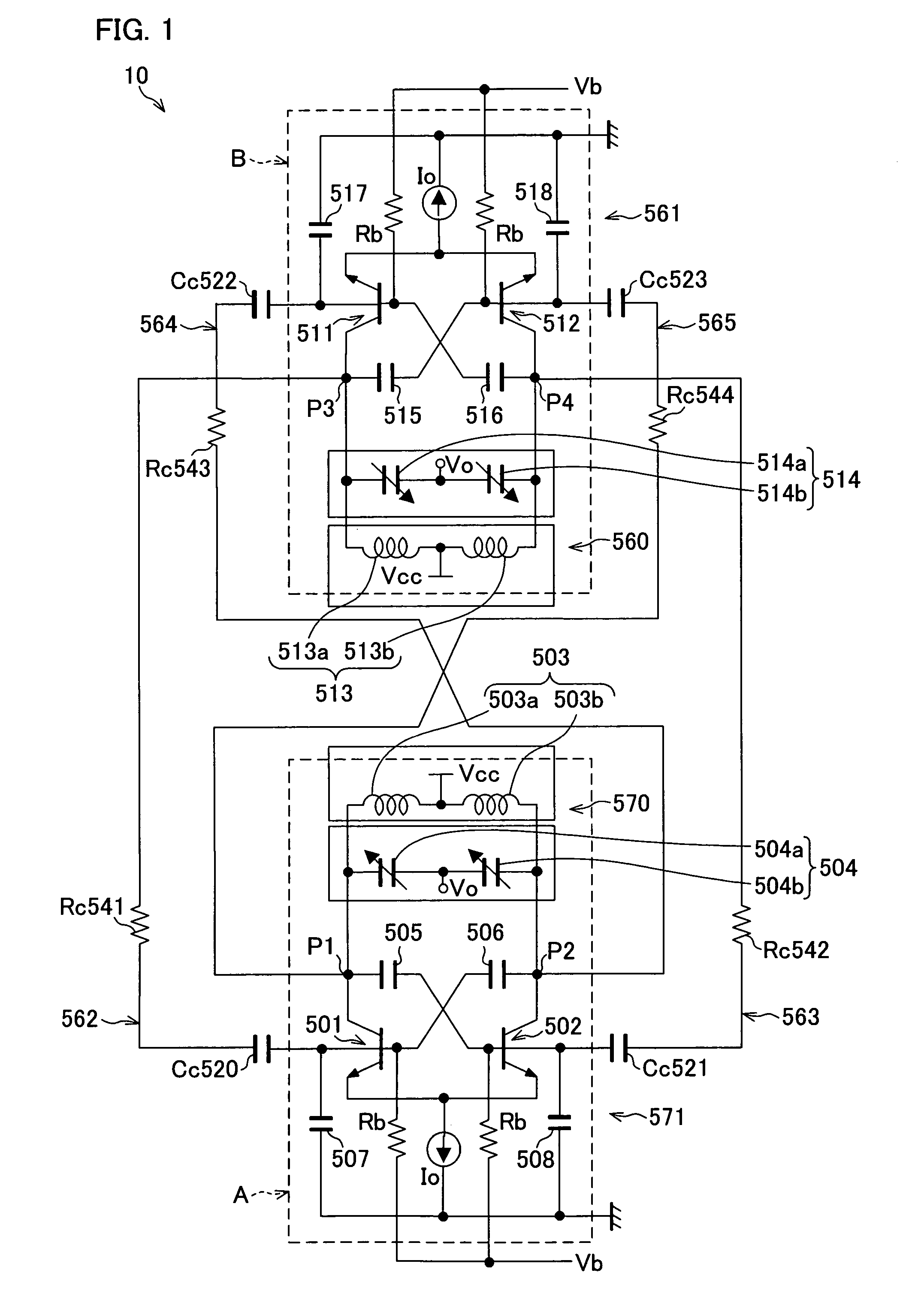
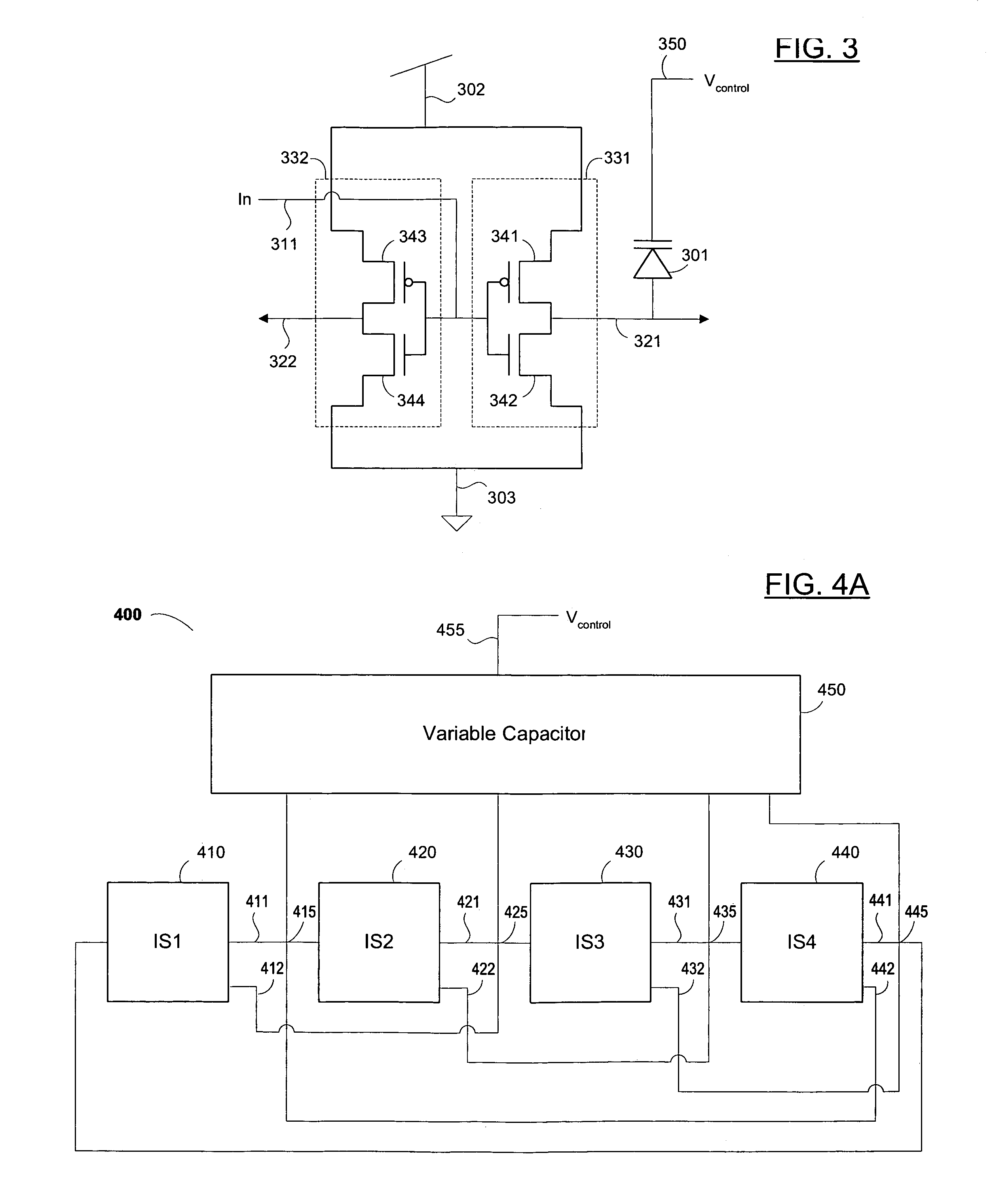
Quadrature oscillator with phase error correction
InactiveUS20020039052A1Increase volumePulse automatic controlGain controlPhase detectorAudio power amplifier
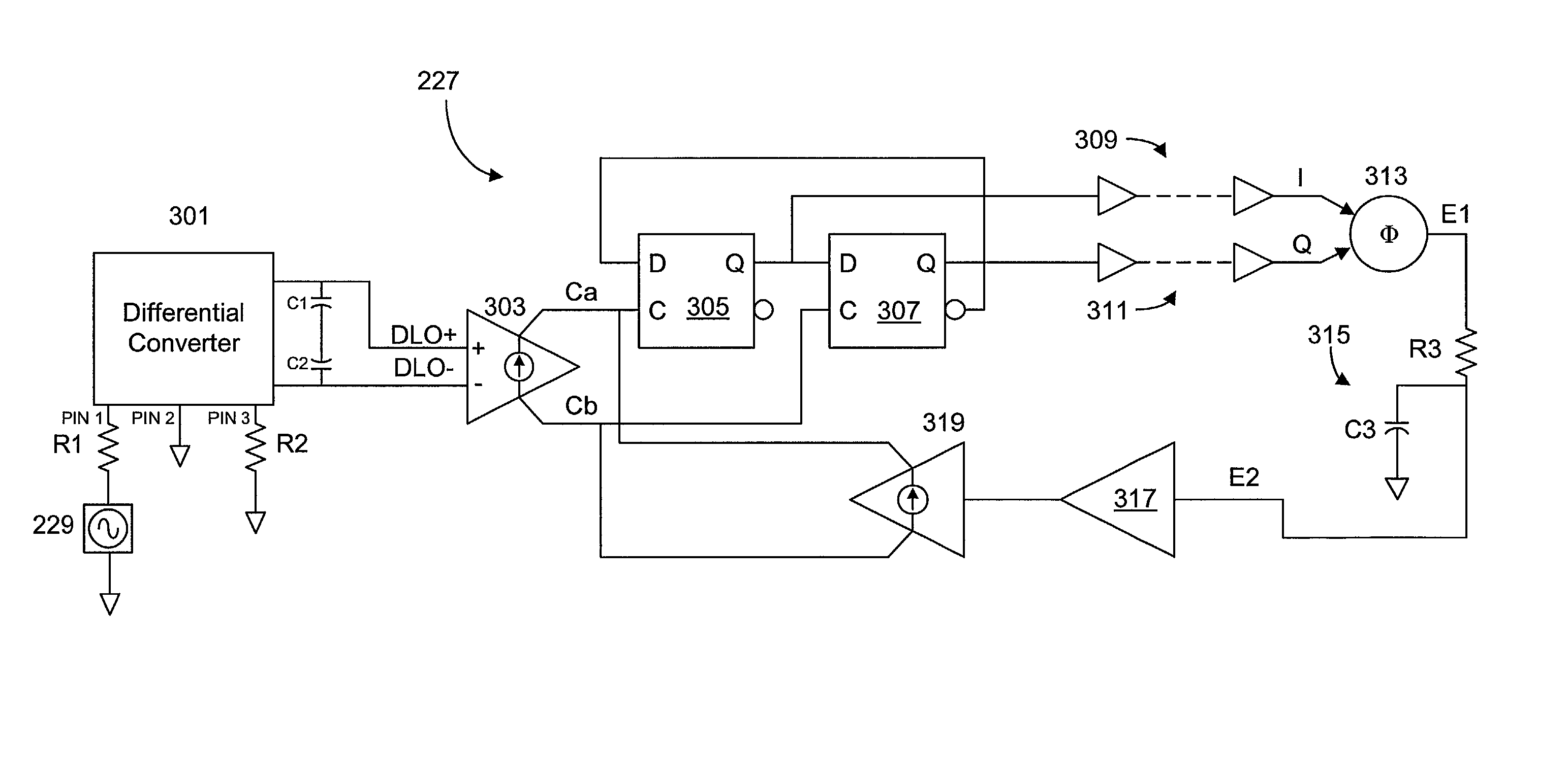
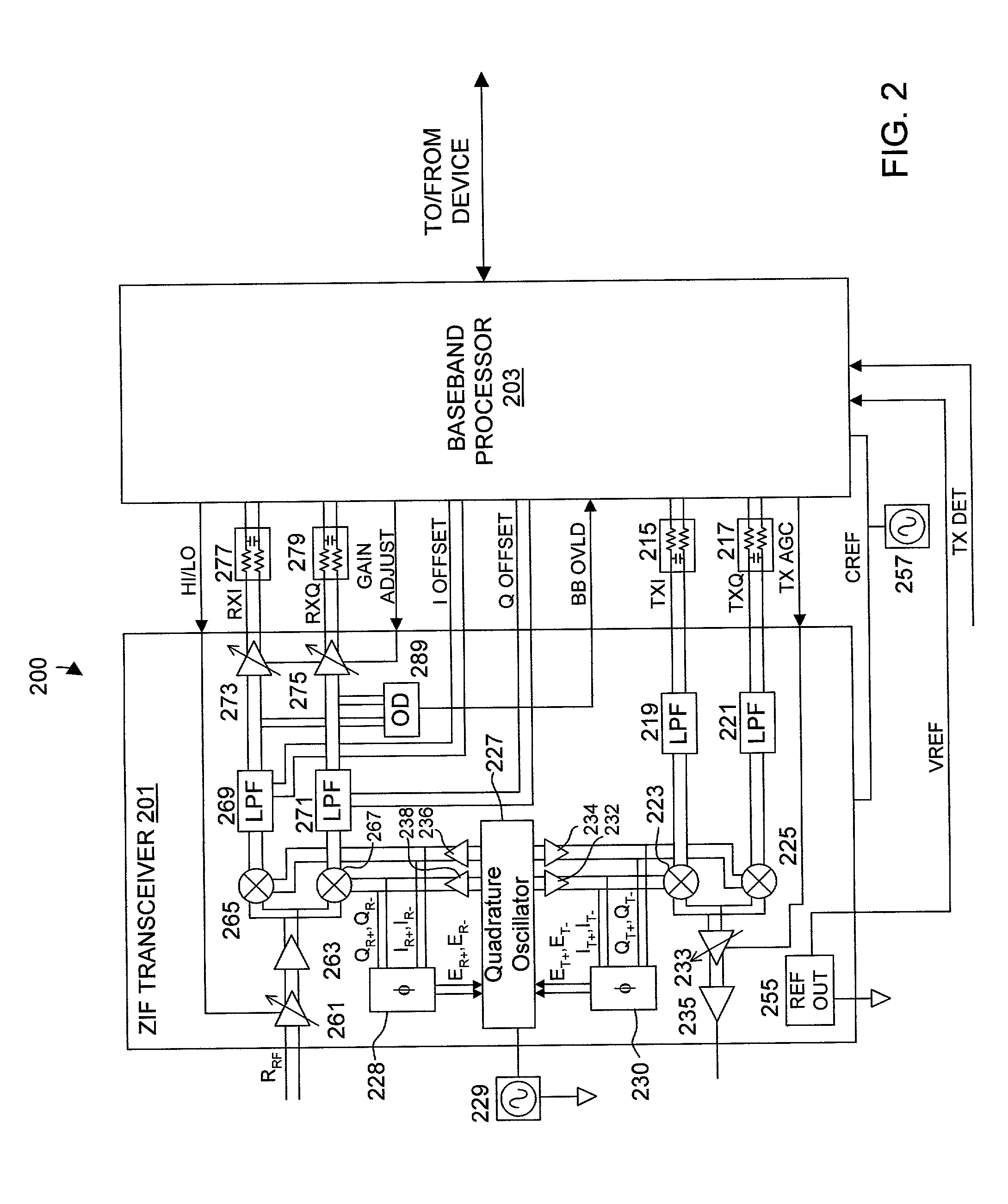
A quadrature oscillator with phase error correction including a local oscillator that generates a single-ended clock signal, a single-ended to differential converter that converts the clock signal to a differential clock signal, a quadrature generator that converts the differential clock signal into I and Q carrier signals, a phase error detector that measures a phase error between the I and Q carrier signals, and a feedback amplifier that modifies the differential clock signal based on measured phase error. The feedback amplifier applies the measured phase error as a DC offset to an AC differential clock signal. A transconductor converts the differential clock voltage signal into two pairs of differential current clock signals, where the quadrature generator generates I and Q current signal outputs from the two pairs of differential current clock signals. The phase error detector generates a phase error voltage, and the feedback amplifier includes a transconductance stage that converts phase error voltage into a DC correction current and that adds the correction current to each of the two pairs of AC differential current clock signals.
Owner:M RED INC
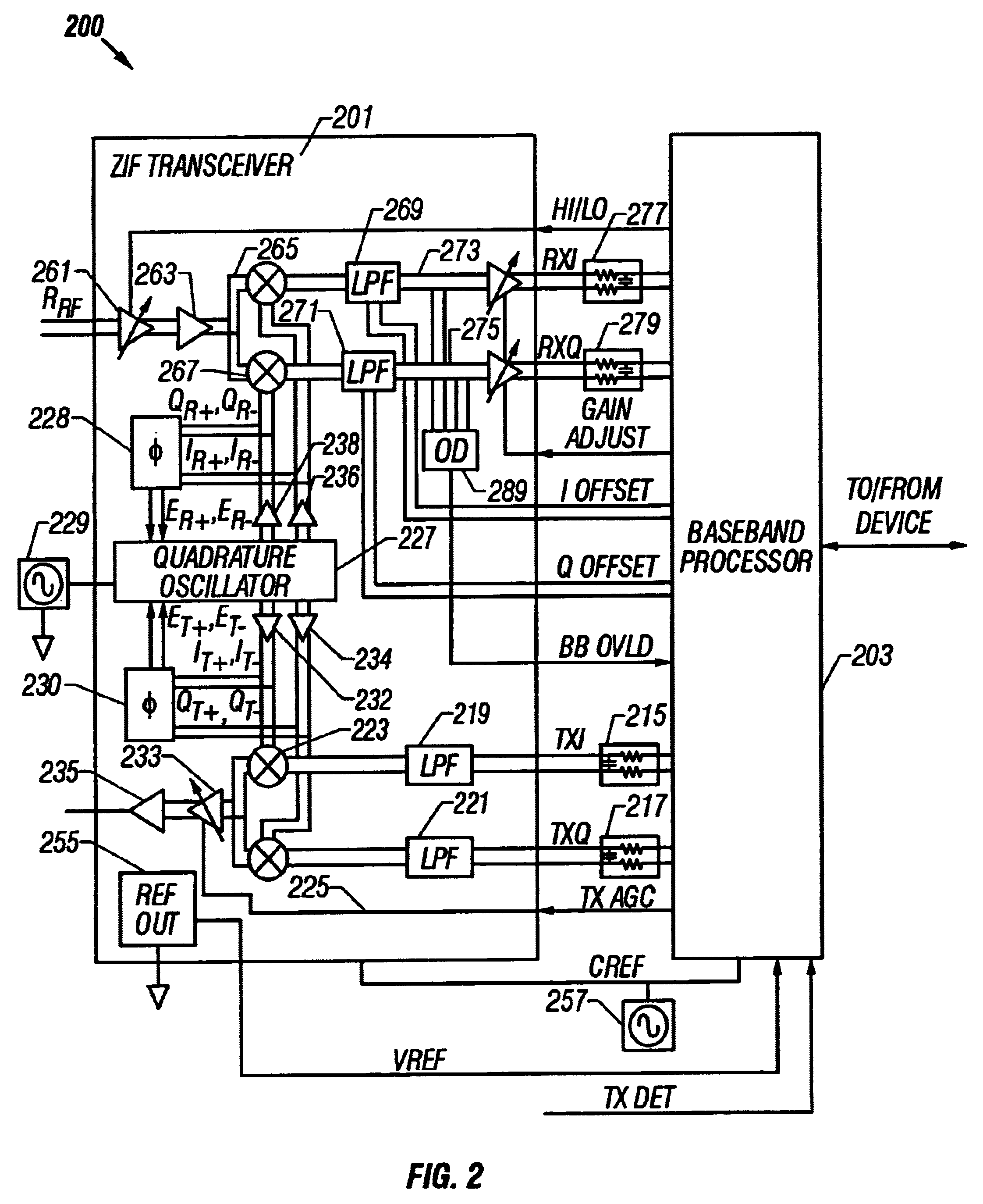
System and method for detecting and correcting phase error between differential signals
InactiveUS6674998B2Detect and reduce and otherwise eliminate phase errorIncrease the amount of dataPulse automatic controlGain controlDifferential signalingQuadrature oscillator
A phase error detector that detects phase error between differential signals. A quadrature oscillator provides in-phase (I) and quadrature phase (Q) differential carrier signals and receives a phase error signal from the phase error detector. The oscillator maintains a quarter cycle phase delay between the I and Q carrier signals based on the phase error signal. The phase error detector includes a summing network and first and second bipolar transistor mixer circuits. The summing network develops four sum signals by summing respective pairs of the differential components of the I and Q carrier signals. A bias circuit biases the transistors to turn on at positive base voltages. The mixer circuits may include filter capacitors so that the transistors are responsive to positive base voltages. The mixer circuits develop polarity signals based on the sum signals, and the resulting phase error signal is the differential of the polarity signals.
Owner:M RED INC
System and method for detecting and correcting phase error between differential signals
InactiveUS20020042255A1Improve accuracyDetect and reduce and otherwise eliminate phase errorPulse automatic controlGain controlDifferential signalingQuadrature oscillator
A phase error detector that detects phase error between differential signals. A quadrature oscillator provides in-phase (I) and quadrature phase (Q) differential carrier signals and receives a phase error signal from the phase error detector. The oscillator maintains a quarter cycle phase delay between the I and Q carrier signals based on the phase error signal. The phase error detector includes a summing network and first and second bipolar transistor mixer circuits. The summing network develops four sum signals by summing respective pairs of the differential components of the I and Q carrier signals. A bias circuit biases the transistors to turn on at positive base voltages. The mixer circuits may include filter capacitors so that the transistors are responsive to positive base voltages. The mixer circuits develop polarity signals based on the sum signals, and the resulting phase error signal is the differential of the polarity signals.
Owner:M RED INC
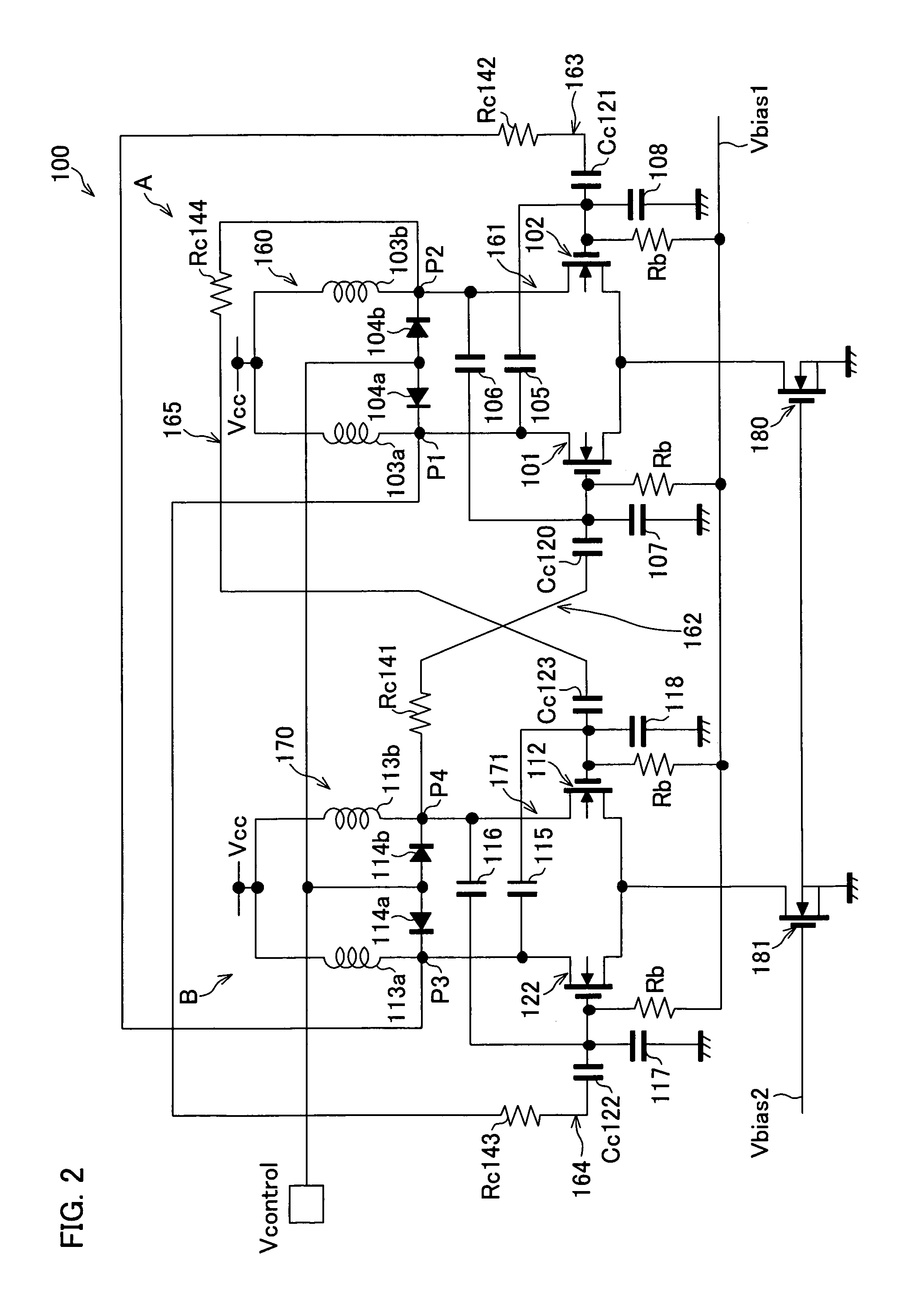
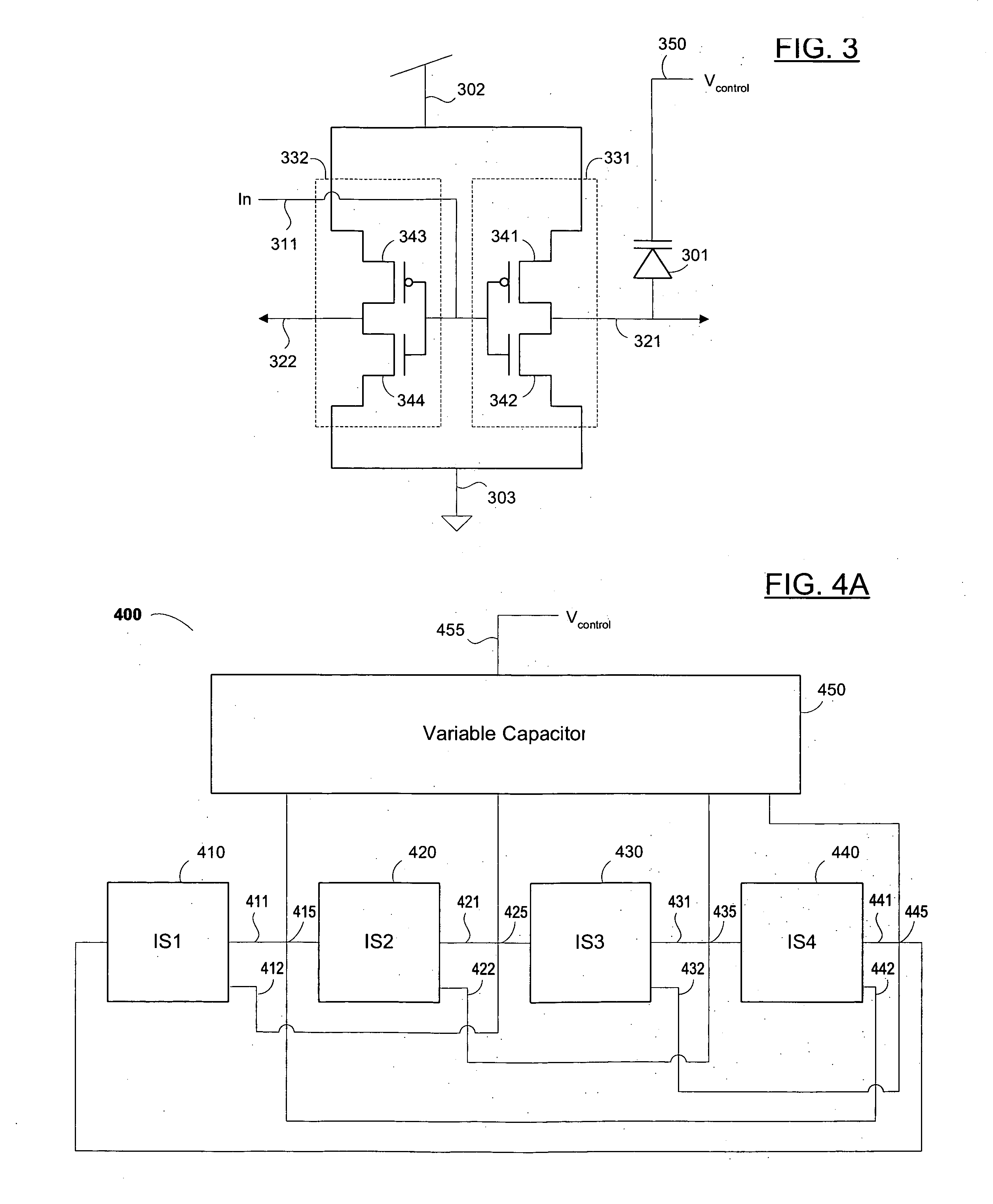
Quadrature voltage controlled oscillators with phase shift detector
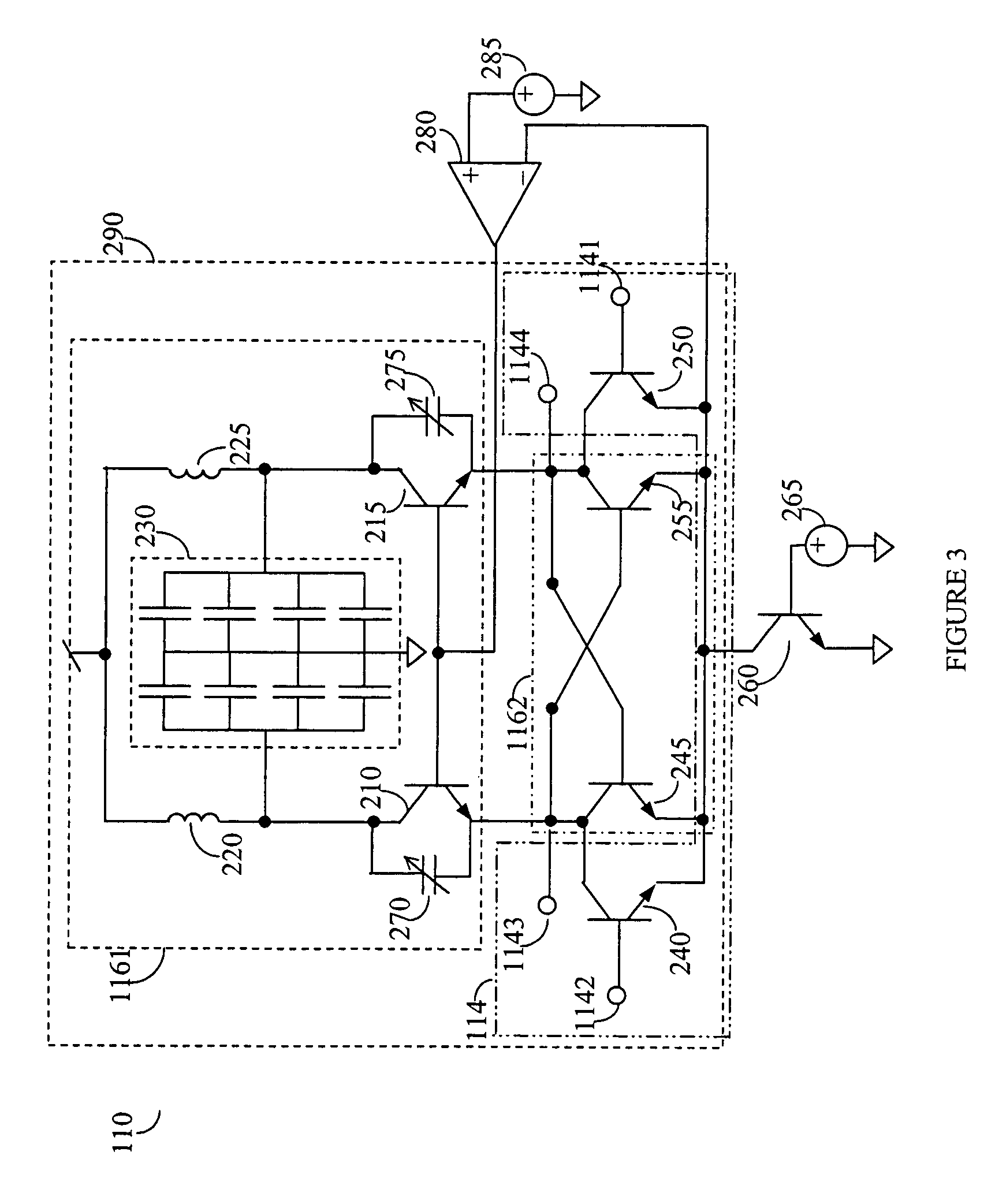
In wireless application there is made use of a quadrature oscillators that generate signals that are capable of oscillating at quadrature of each other. The quadrature oscillator is comprised of two differential modified Colpitts oscillators. A capacitor bank allows for the selection of a desired frequency from a plurality of discrete possible frequencies. The quadrature oscillator is further coupled with a phase-error detector connected at the point-of-use of the generated ‘I’ and ‘Q’ channels and through the control of current sources provides corrections means to ensure that the phase shift at the point-of-use remains at the desired ninety degrees.
Owner:THETA IP
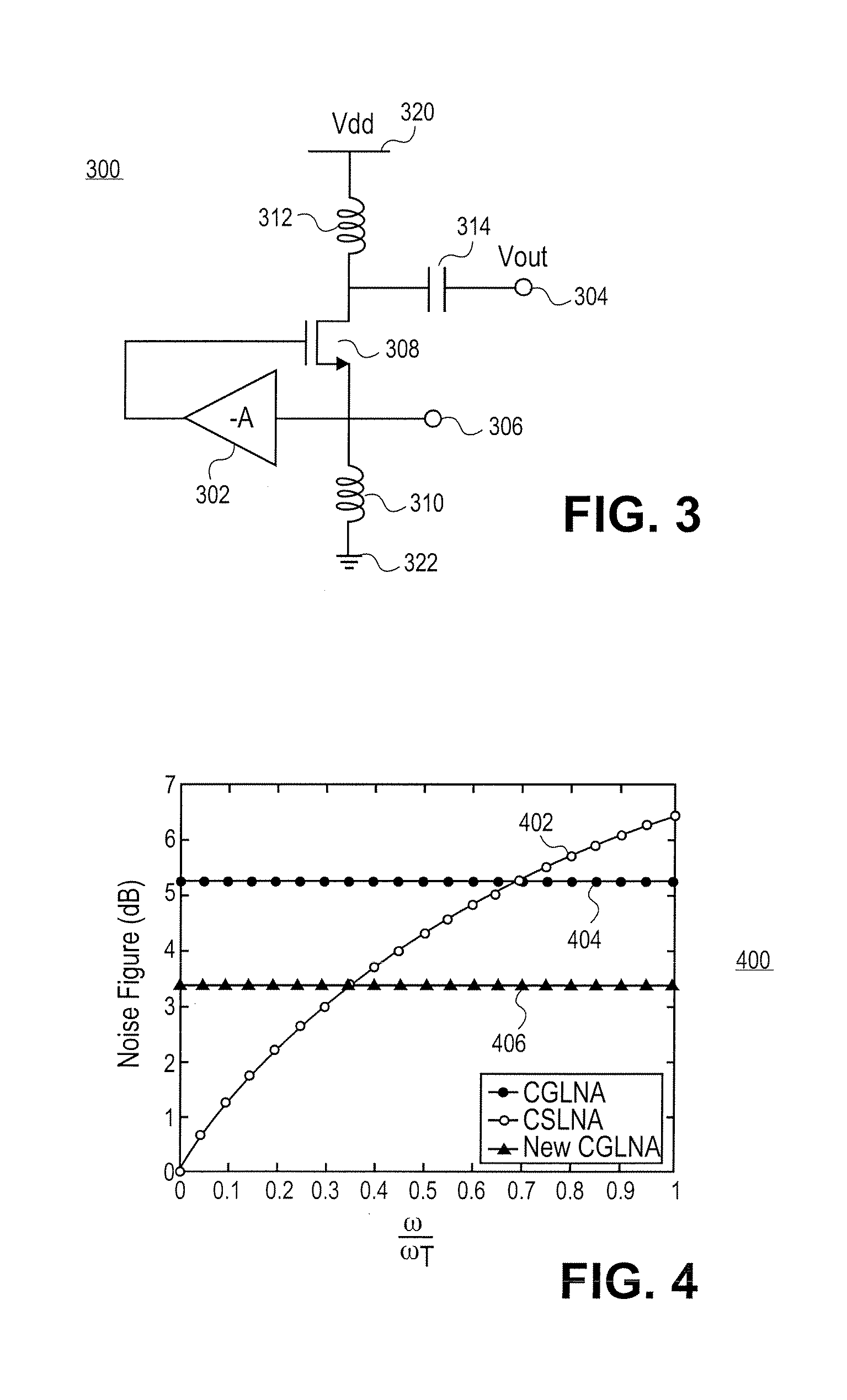
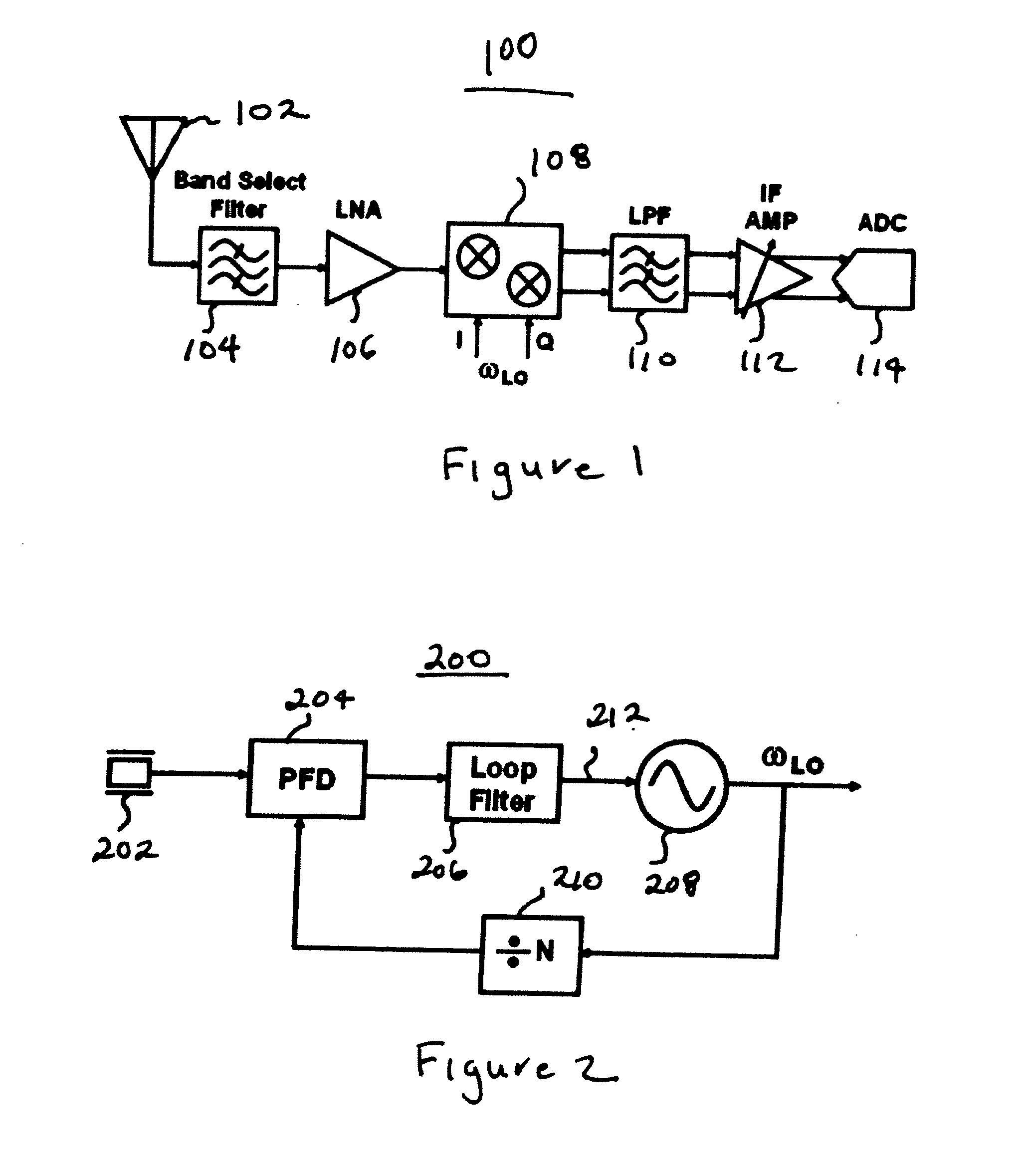
Receiver with colpitts differential oscillator, colpitts quadrature oscillator, and common-gate low noise amplifier
InactiveUS7414481B2Amplifier combinationsAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceCapacitanceSignal on
Embodiments of the present invention include a common-gate amplifier having an input terminal and an output terminal, a transistor having a source, a drain, and a gate, four inductors, and two capacitors, and a negative amplification circuitry. The negative amplification circuitry has an input terminal to receive an RF signal. The negative amplification circuitry applies negative or zero amplification to the RF signal and outputs the negative or zero amplified signal on an output terminal. Alternative embodiments include a Colpitts differential oscillator, which includes two Colpitts single-ended oscillators. Each Colpitts single-ended oscillator includes a transistor. The source of the transistor in one Colpitts single-ended oscillator may be capacitively coupled to the gate of the transistor in the other Colpitts single-ended oscillator.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Quadrature oscillator with phase error correction
A quadrature oscillator with phase error correction including a local oscillator that generates a single-ended clock signal, a single-ended to differential converter that converts the clock signal to a differential clock signal, a quadrature generator that converts the differential clock signal into I and Q carrier signals, a phase error detector that measures a phase error between the I and Q carrier signals, and a feedback amplifier that modifies the differential clock signal based on measured phase error. The feedback amplifier applies the measured phase error as a DC offset to an AC differential clock signal. A transconductor converts the differential clock voltage signal into two pairs of differential current clock signals, where the quadrature generator generates I and Q current signal outputs from the two pairs of differential current clock signals. The phase error detector generates a phase error voltage, and the feedback amplifier includes a transconductance stage that converts phase error voltage into a DC correction current and that adds the correction current to each of the two pairs of AC differential current clock signals.
Owner:M RED INC
Serially RC coupled quadrature oscillator
InactiveUS7239209B2Reduce noiseReduce power consumptionPulse generation by logic circuitsOscillations generatorsCross connectionCoupling
The oscillator includes: a first oscillator circuit in which first and second transistors cross-connected to each other are connected to a resonant circuit; and a second oscillator circuit in which third and fourth transistors cross-connected to each other are connected to a resonant circuit, wherein a coupling capacitor and coupling resistor are serially provided between a collector terminal of the first transistor and a base terminal of the fourth transistor, and a coupling capacitor and coupling resistor are serially provided between a collector terminal of the second transistor and a base terminal of the third transistor, and a coupling capacitor and coupling resistor are serially provided between a collector terminal of the third transistor and a base terminal of the first transistor, and a coupling capacitor and coupling resistor are serially provided between a collector terminal of the fourth transistor and a base terminal of the second transistor. On this account, it is possible to suppress noises and reduce power consumption.
Owner:SHARP KK
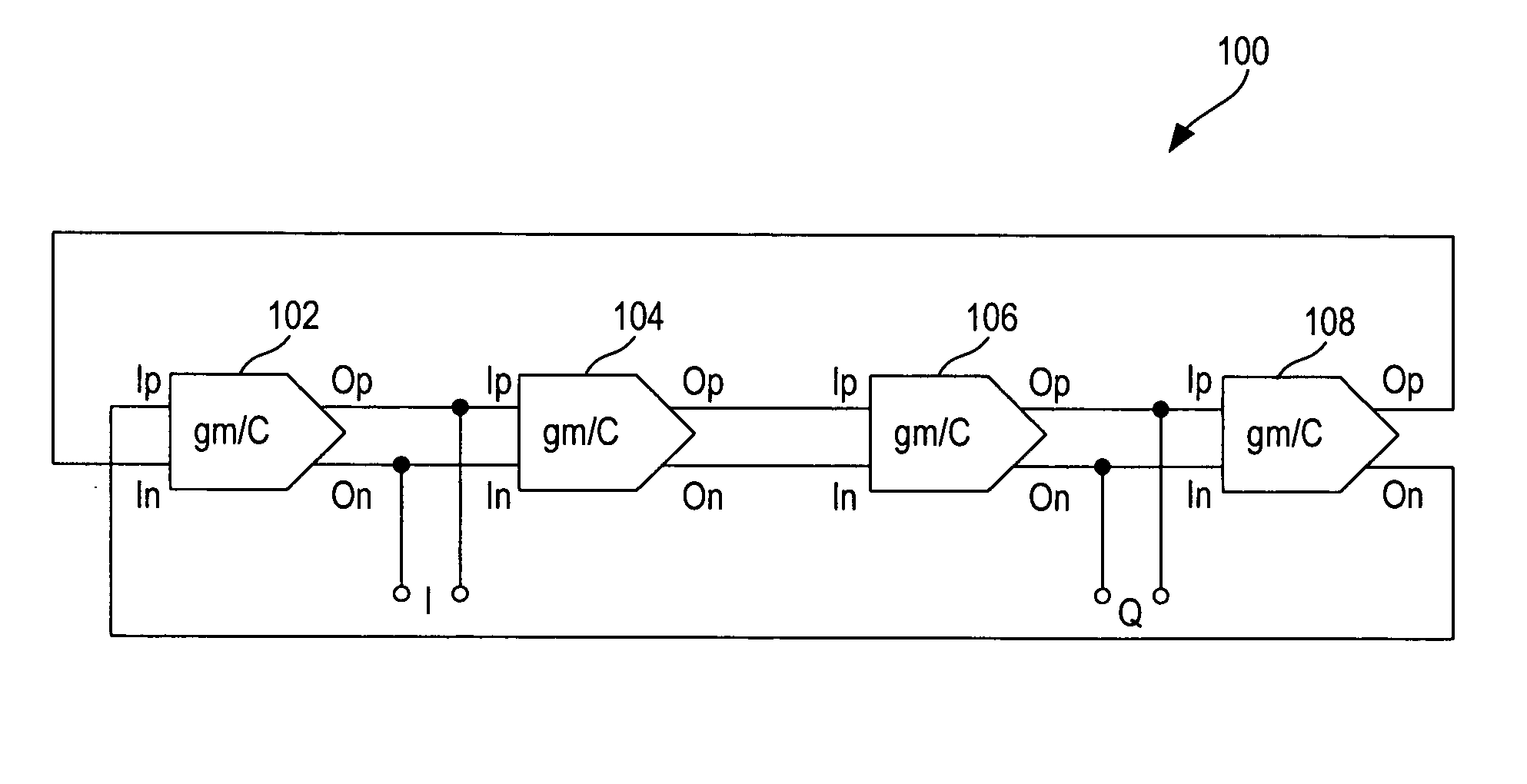
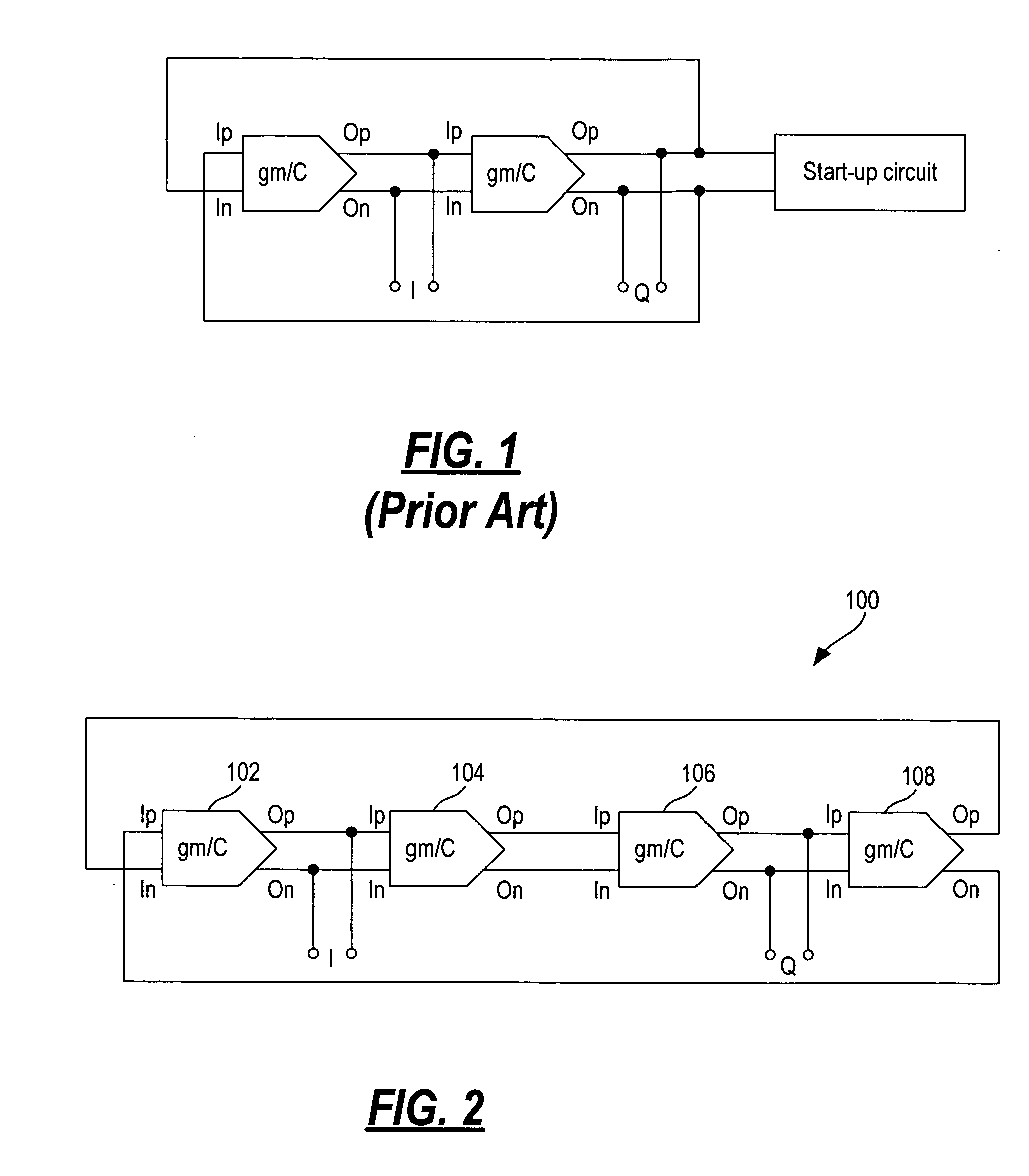
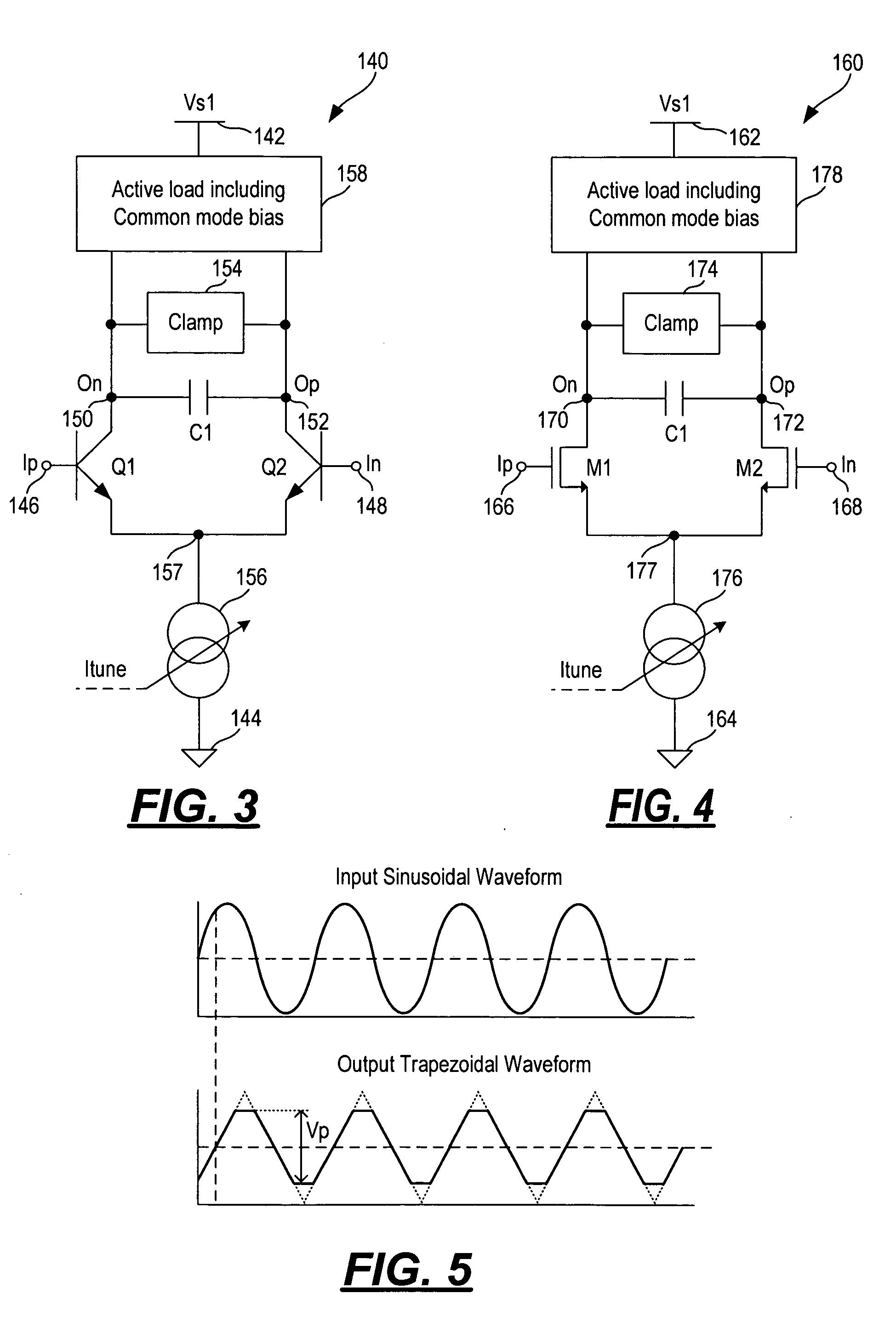
Current-controlled quadrature oscillator using differential gm/C cells incorporating amplitude limiters
InactiveUS20050253659A1Pulse generation by logic circuitsOscillations generatorsVoltage amplitudeQuadrature oscillator
An oscillator includes a series of N number of gm / C stages where each gm / C stage has a pair of input terminals and a pair of output terminals. The pair of output terminals of each gm / C stage is coupled to the pair of input terminals of the next gm / C stage except the pair of output terminals of the last gm / C stage is cross-coupled to the pair of input terminals of the first gm / C stage whereby the oscillator oscillates in quadrature. Each gm / C stage includes a differential pair of transistors, a tunable current source, a capacitor, an amplitude limiter circuit and an active load and common mode bias circuit. The capacitor and the amplitude limiter circuit are coupled between the pair of output terminals of the gm / C stage. The amplitude limiter circuit operates to limit the voltage magnitude of the output signal at the pair of output terminals of the gm / C stage.
Owner:XCEIVE CORP
LC orthogonal voltage controlled oscillator capable of reducing flicker noise
InactiveCN101183851AReduce 1/f noiseOscillations generatorsFrequency-changer modificationsPhase noiseQuadrature oscillator
The invention relates to an LC quadrature VCO (voltage controlled oscillator) which can reduce the intermittent noise, belonging to the technical field of integrated circuit, . The invention is characterized in that two negative resistance oscillators are connected together with a quadrature coupler to output quadrature signals; the reduced phase noise is implemented by using a more linear narrow-band turning variable capacitor structure, multiband switching digital array with a lower parasitic capacitance and an intermittent noise eliminating circuit reducing the intermittent noise getting into the LC oscillator when inputting voltage crossing the zero point.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
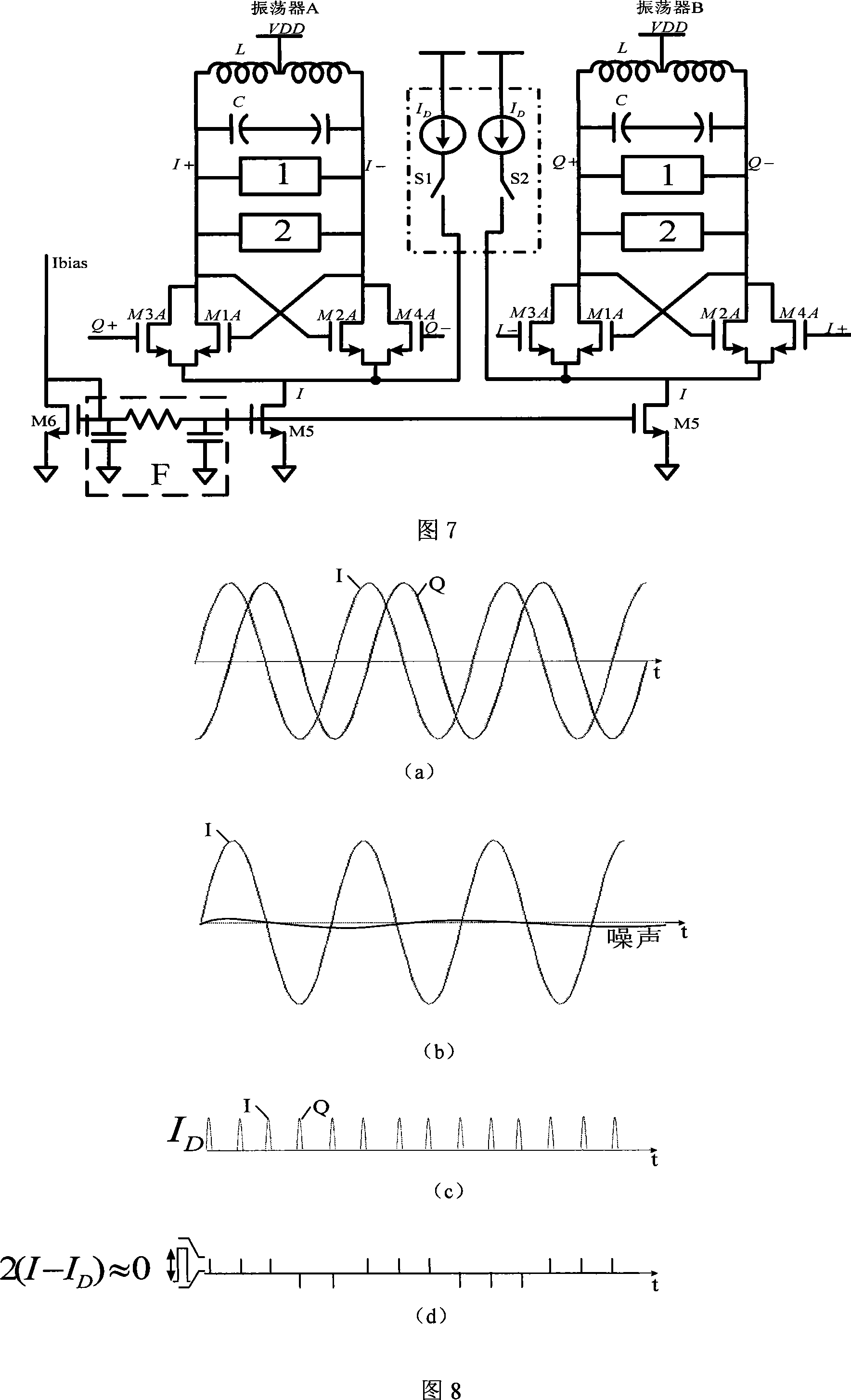
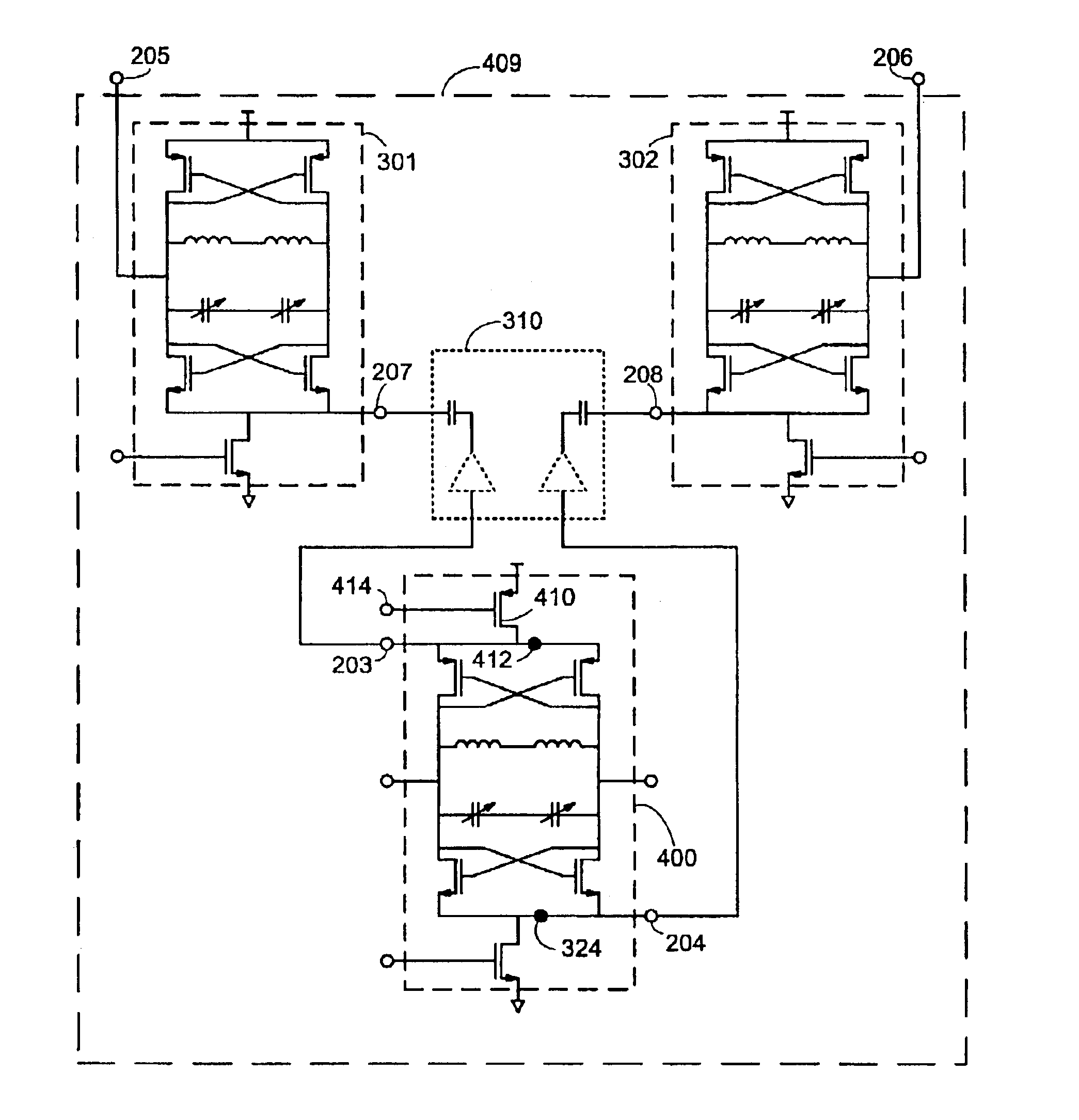
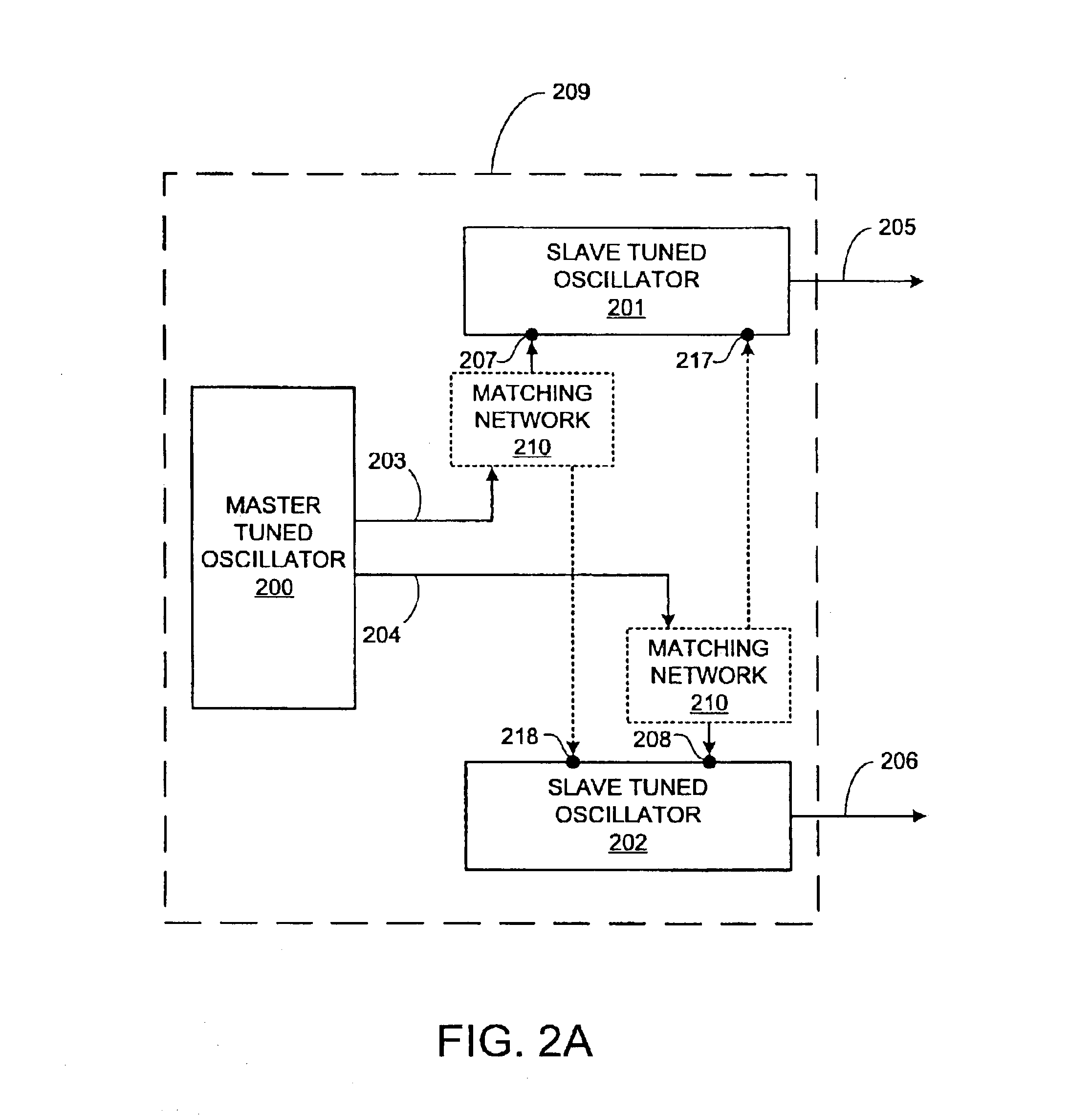
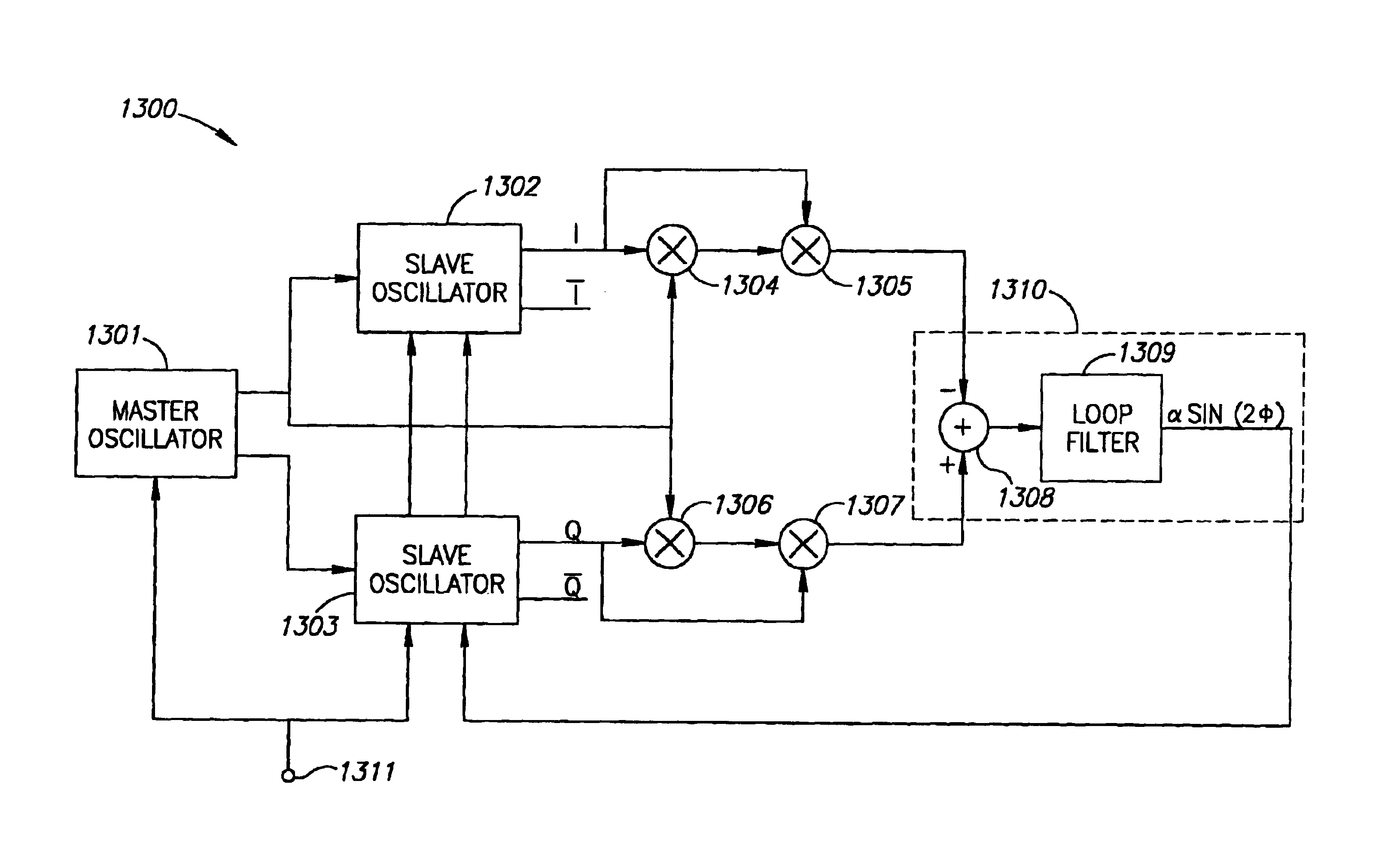
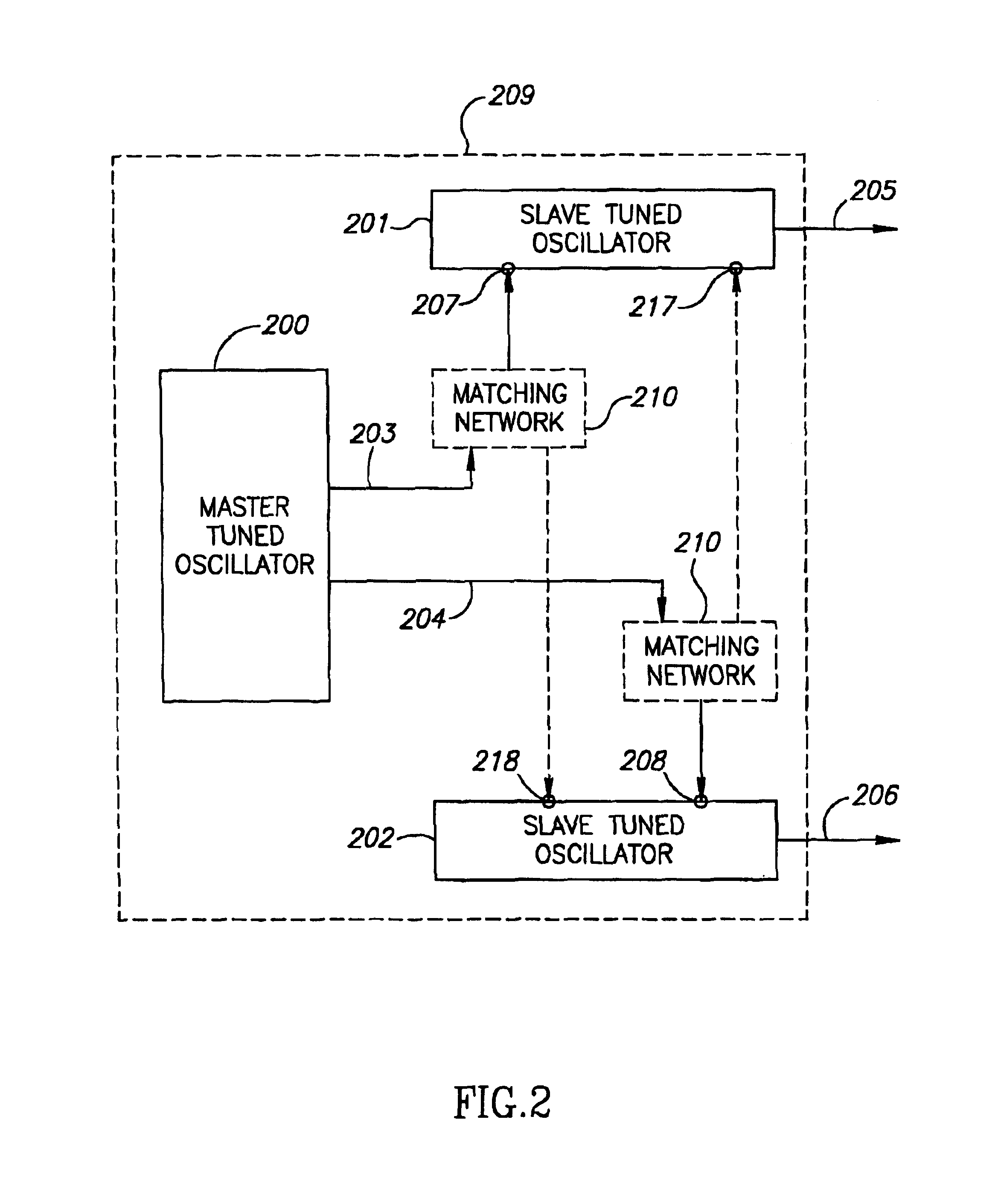
Quadrature oscillator and methods thereof
InactiveUS6850122B2Pulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsQuadrature oscillatorInjection locking
A quadrature oscillator includes a master tuned oscillator and two injection-locked slave tuned oscillators.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Device and method of quadrature oscillation
InactiveUS6937107B2Pulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsCMOSQuadrature oscillator
Briefly, devices and methods for tuning of quadrature oscillators which may be used, for example, in a Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) process. Devices and methods in accordance with some exemplary embodiments of the invention may allow, for example, improved locking, tuning and performance of slave oscillators and a master oscillator within a quadrature oscillator utilizing injection-locking.
Owner:INTEL CORP
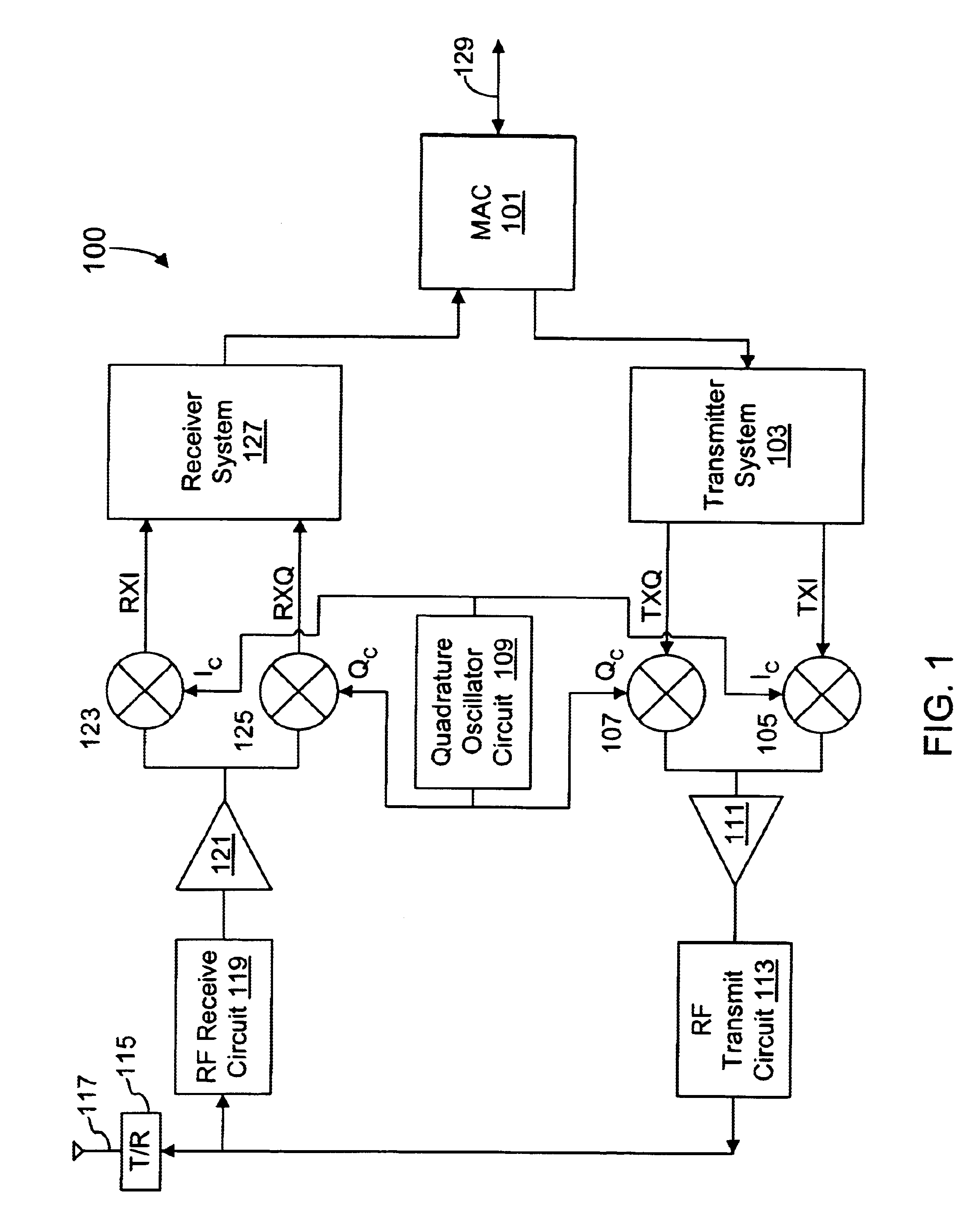
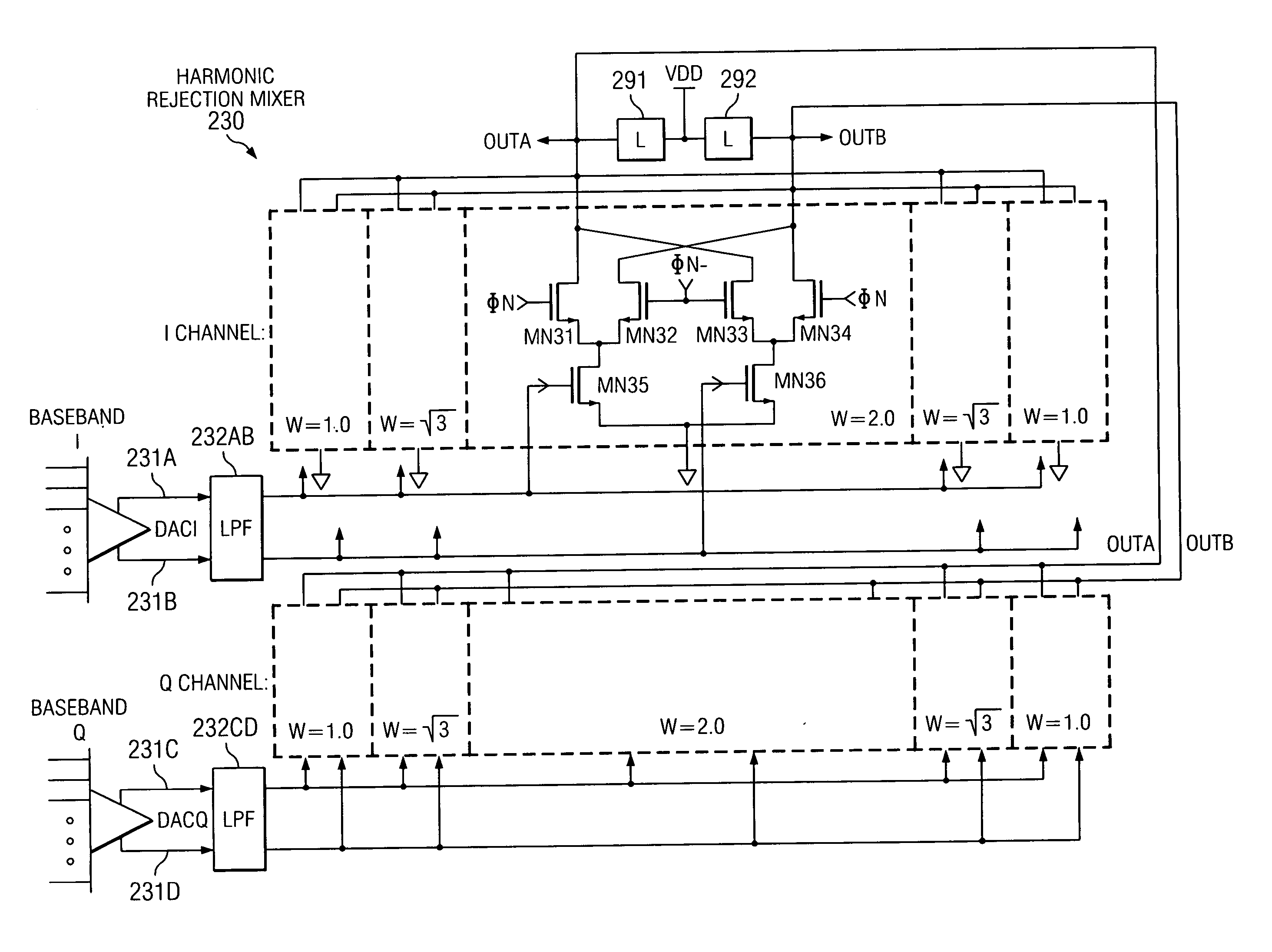
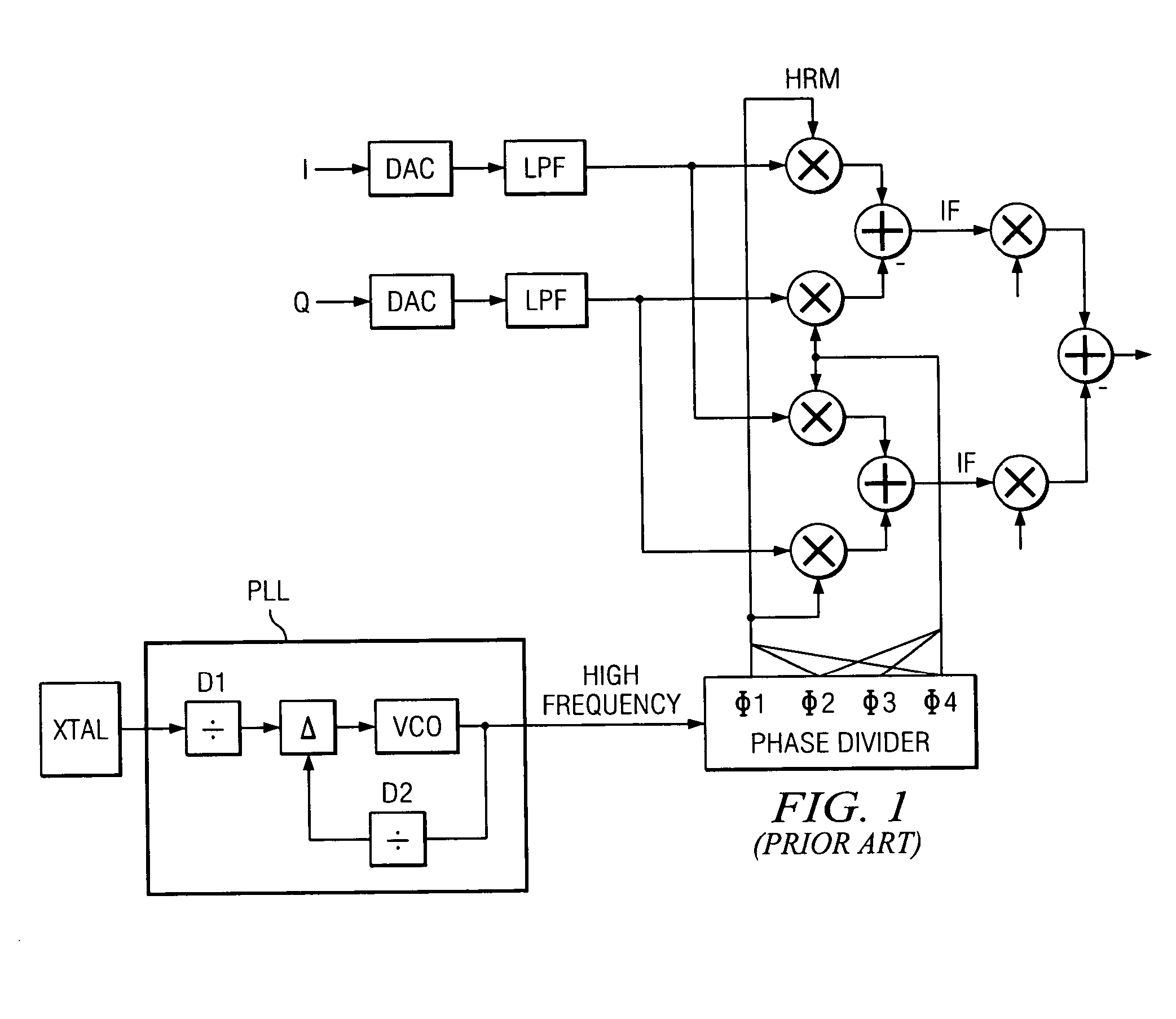
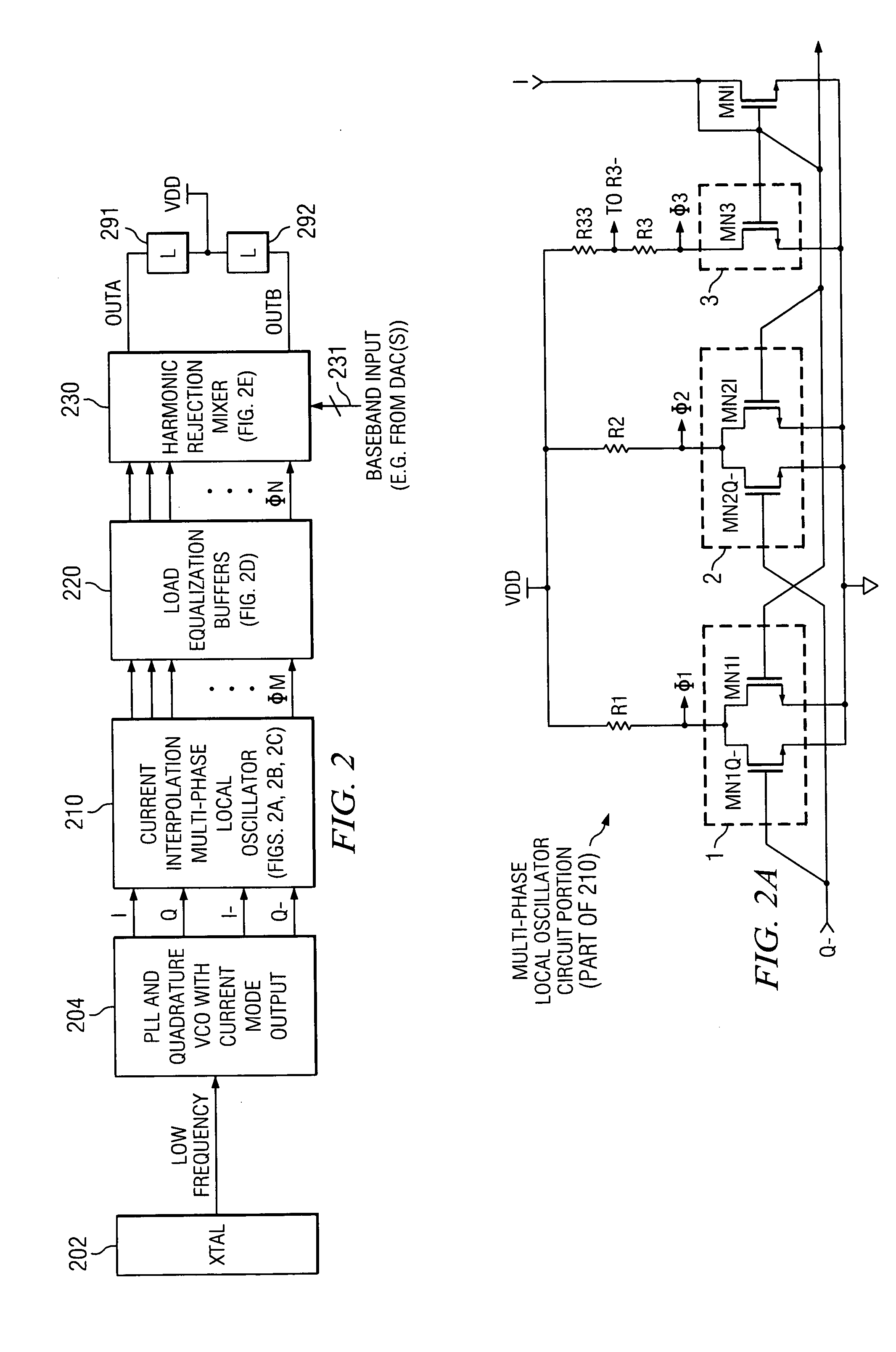
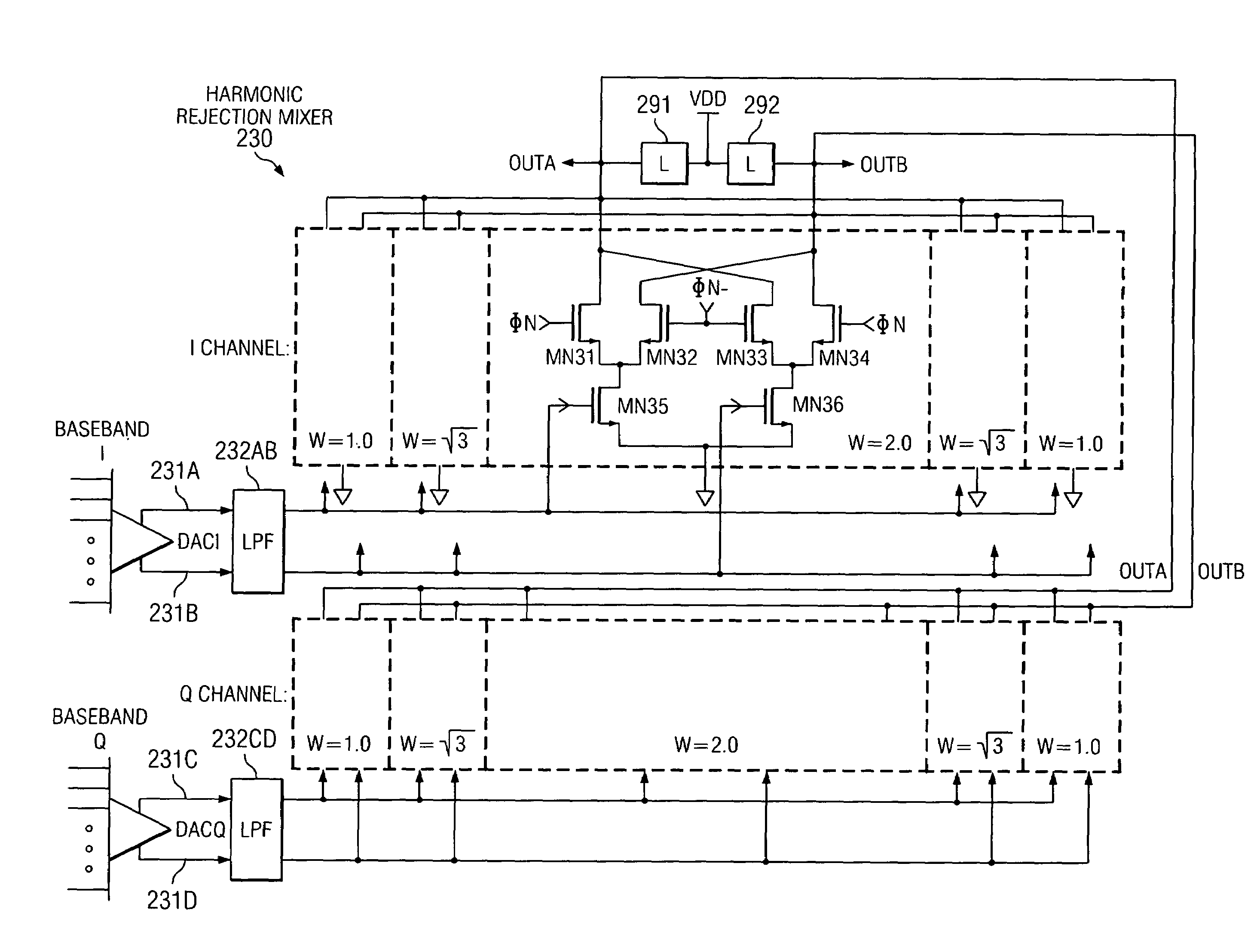
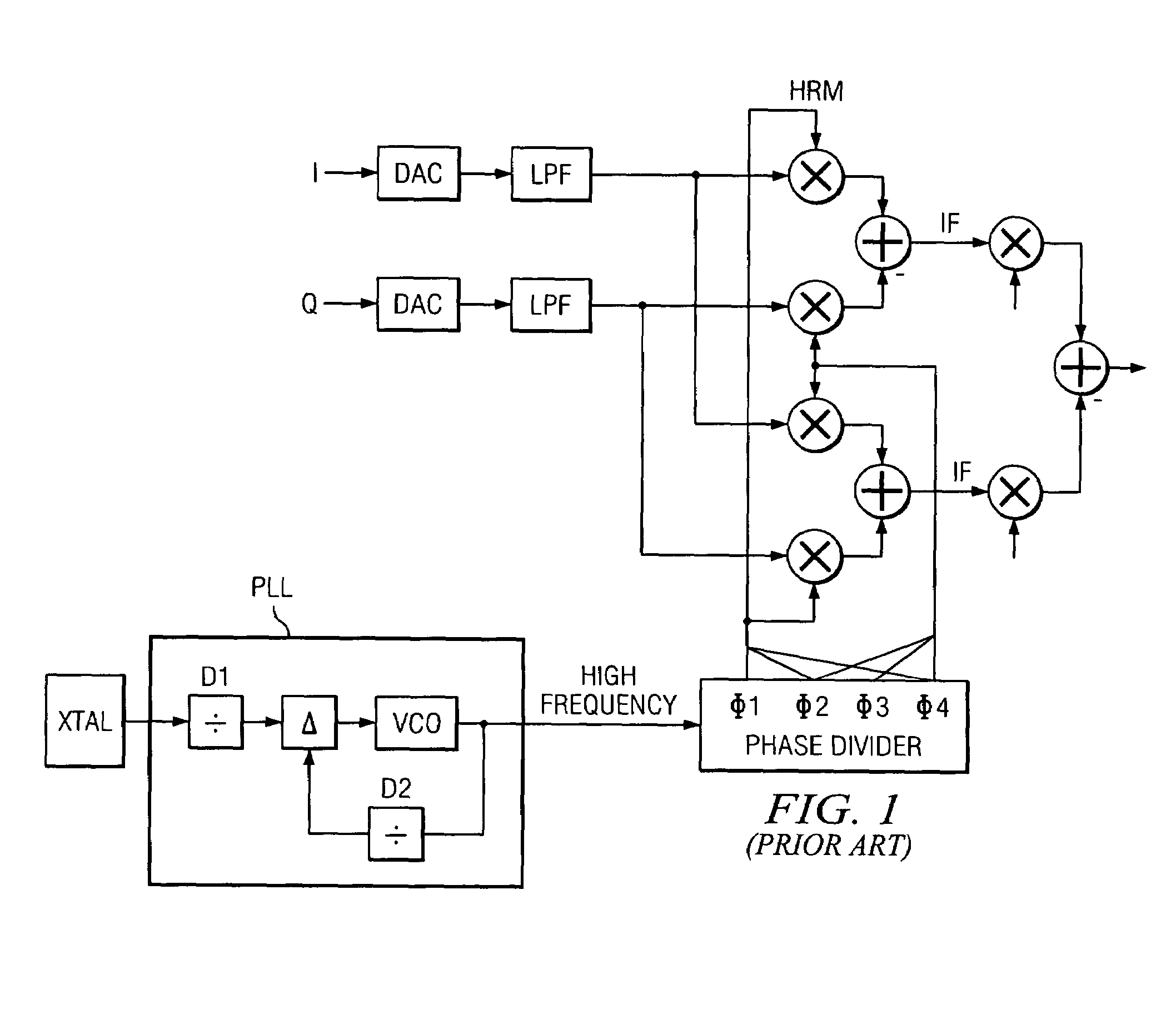
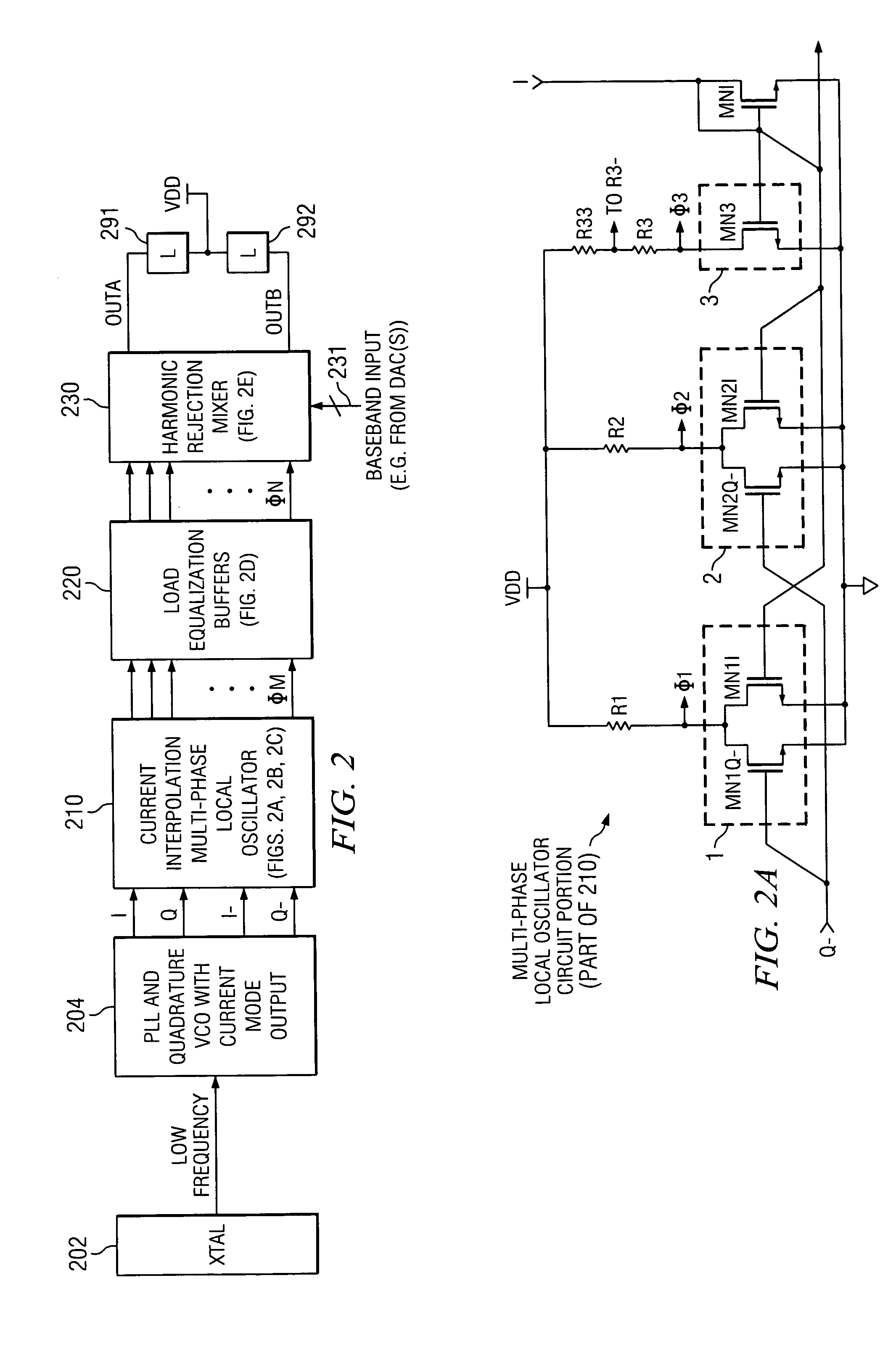
Current interpolation in multi-phase local oscillator for use with harmonic rejection mixer
ActiveUS20050215223A1Modulation transference balanced arrangementsSinusoidal oscillation interference reductionFrequency mixerHarmonic
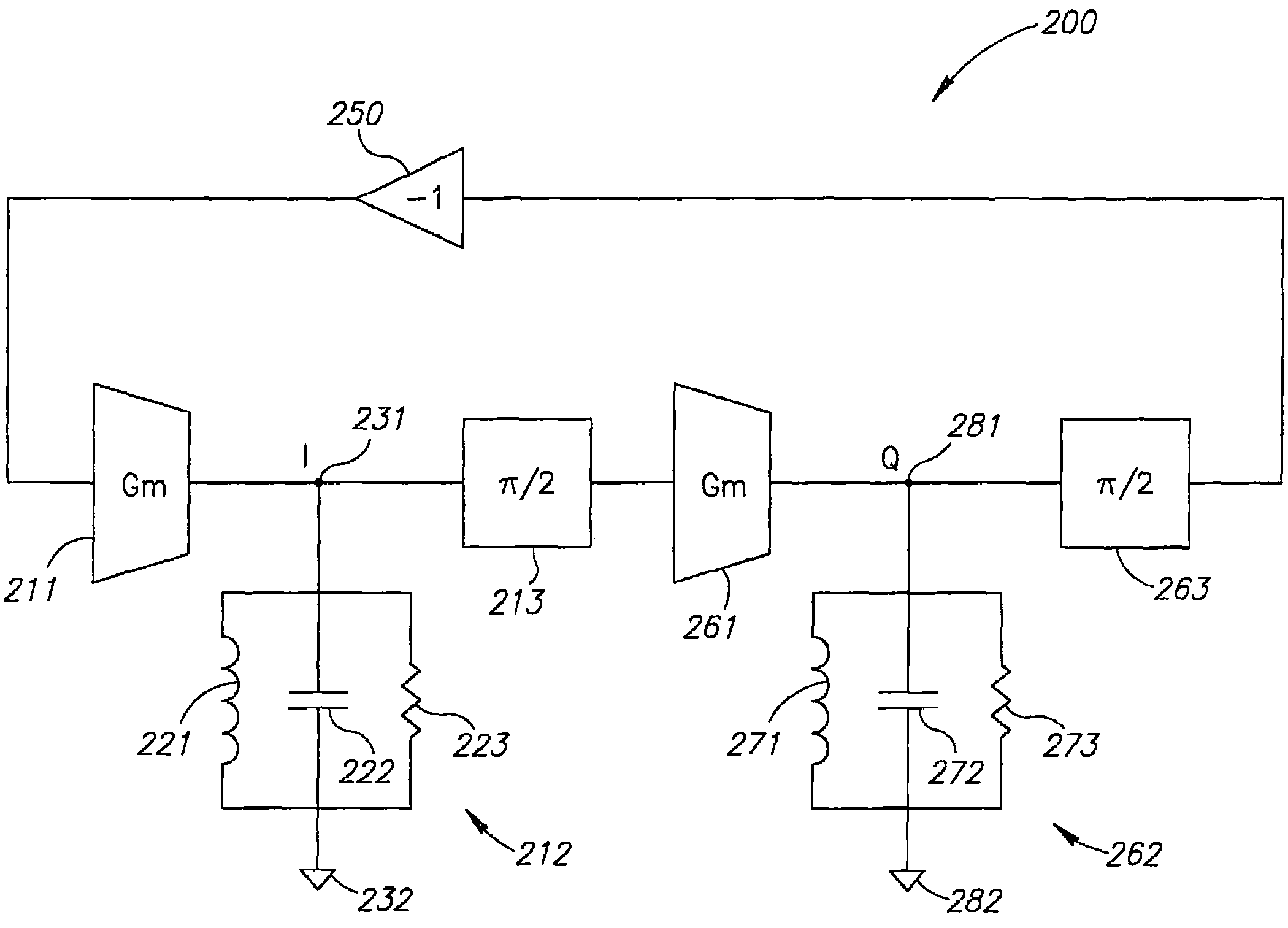
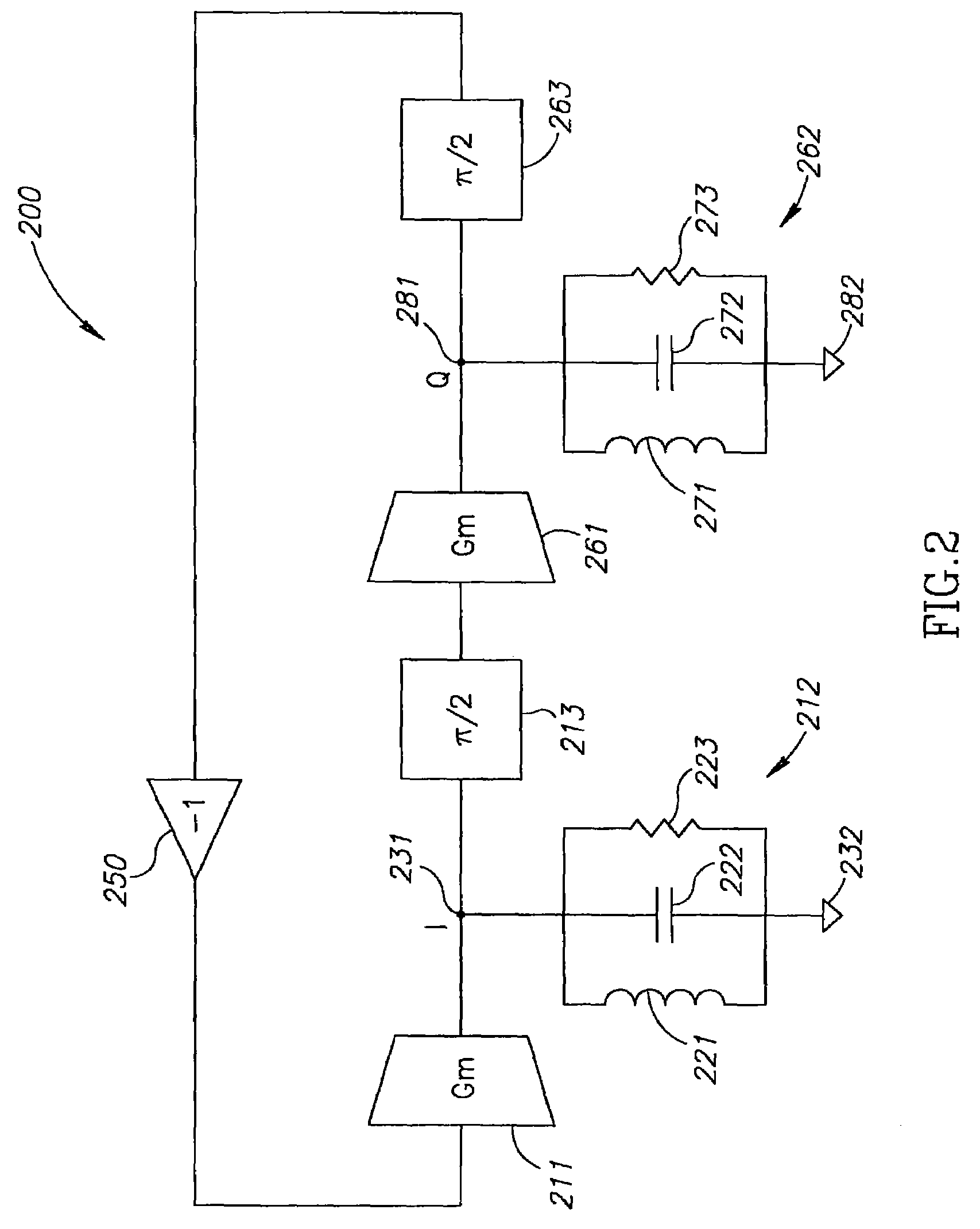
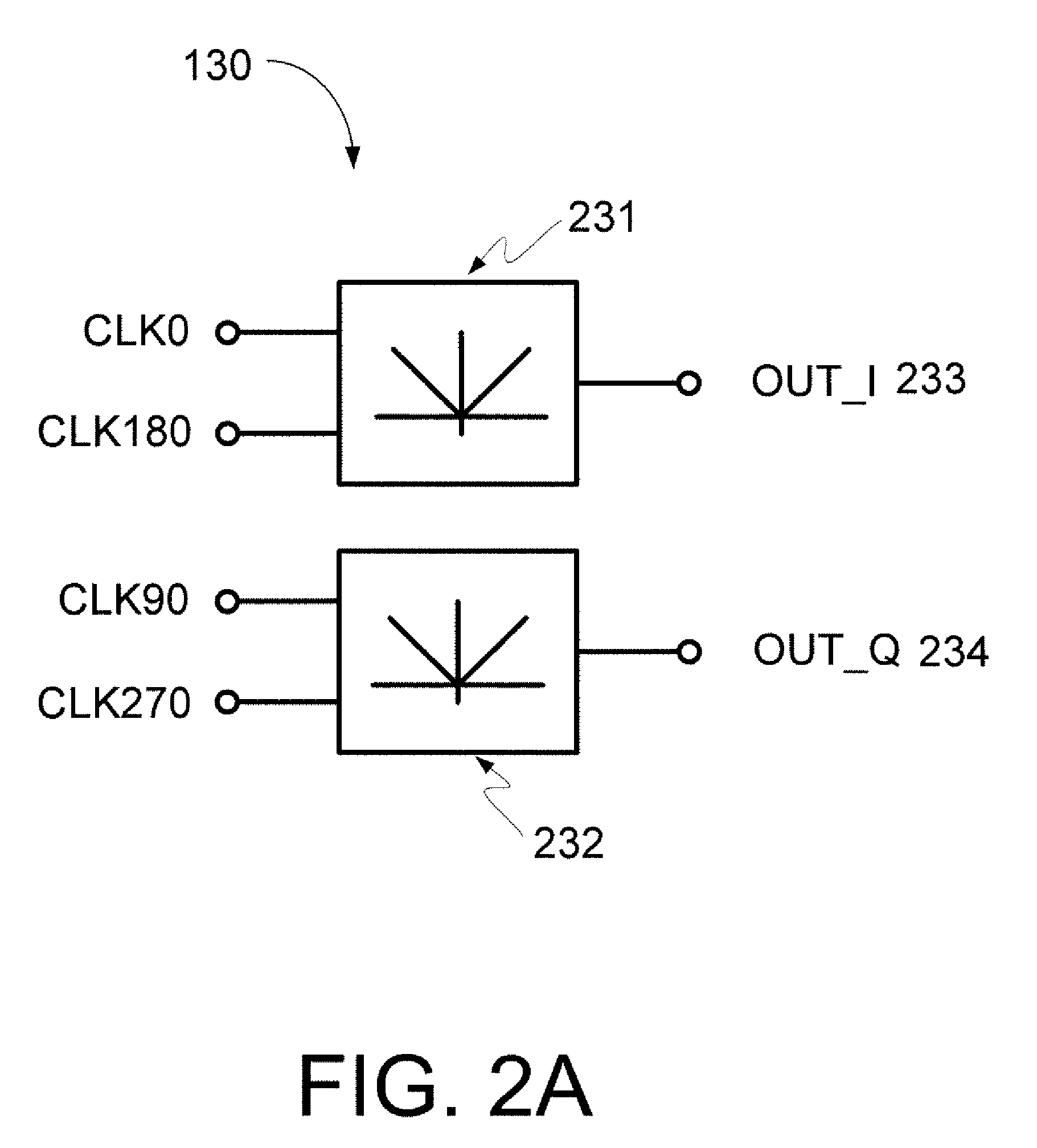
A circuit provides a reduced harmonic content output signal OUTA and / or OUTB that is modulated according to an input signal 231. The circuit has an oscillator circuit 210 and a harmonic rejection mixer (HRM) 230. The oscillator circuit 210 includes at least one “circuit portion” (FIG. 2A) configured to receive first and second orthogonal oscillator input signals (two of I, I-, Q, Q-) having respective first and second phases, and to provide an arbitrarily large number of oscillator output signals (φM) having respective mutually distinct phases that are interpolated between the first and second phases. Harmonic rejection mixer 230 is configured to use the input signal to modulate a combination of the oscillator output signals, the oscillator output signals being respectively weighted so as to provide an emulated sinusoidal signal constituting the reduced harmonic content output signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Current interpolation in multi-phase local oscillator for use with harmonic rejection mixer
A circuit provides a reduced harmonic content output signal OUTA and / or OUTB that is modulated according to an input signal 231. The circuit has an oscillator circuit 210 and a harmonic rejection mixer (HRM) 230. The oscillator circuit 210 includes at least one “circuit portion” (FIG. 2A) configured to receive first and second orthogonal oscillator input signals (two of I, I−, Q, Q−) having respective first and second phases, and to provide an arbitrarily large number of oscillator output signals (φM) having respective mutually distinct phases that are interpolated between the first and second phases. Harmonic rejection mixer 230 is configured to use the input signal to modulate a combination of the oscillator output signals, the oscillator output signals being respectively weighted so as to provide an emulated sinusoidal signal constituting the reduced harmonic content output signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
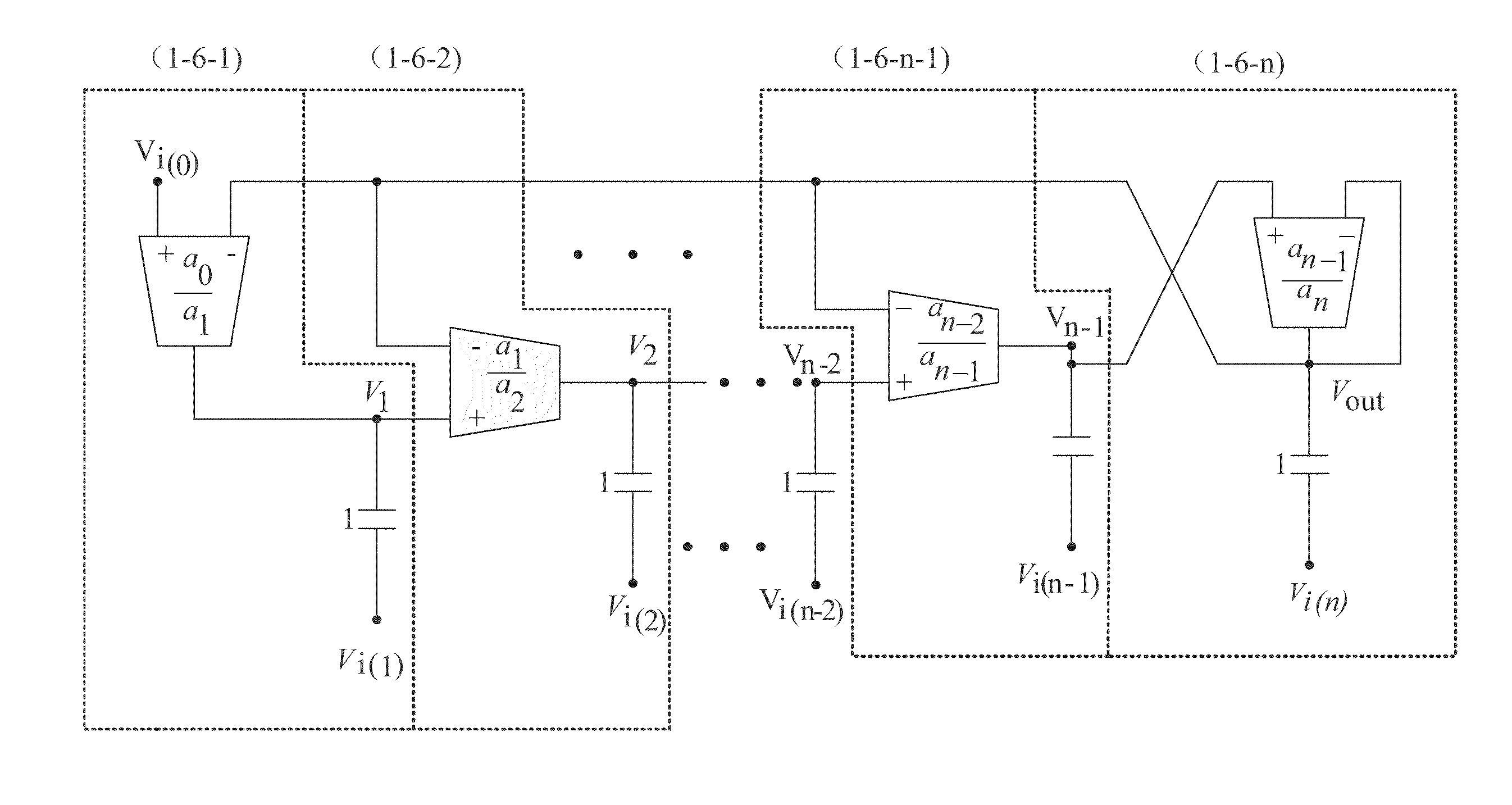
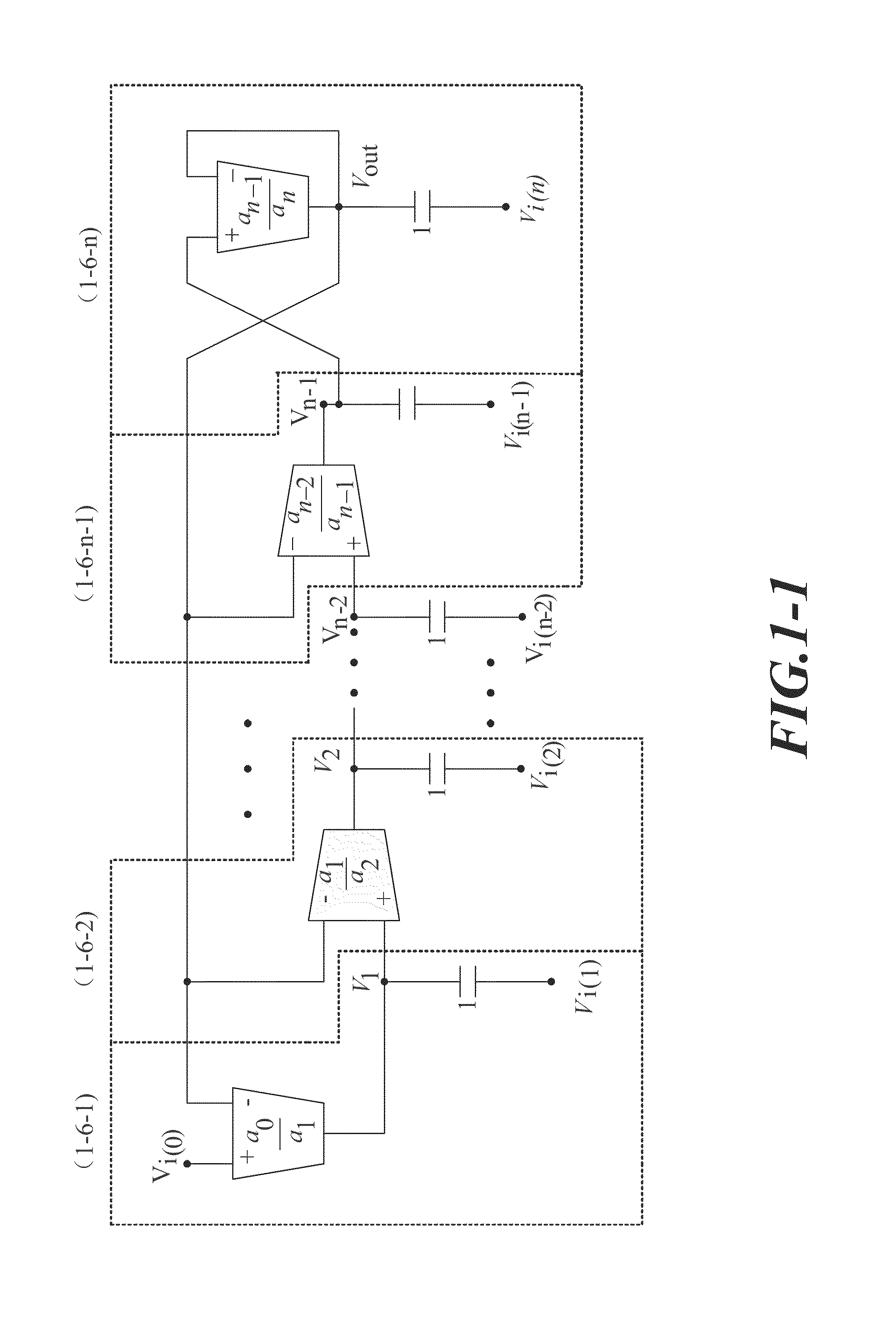
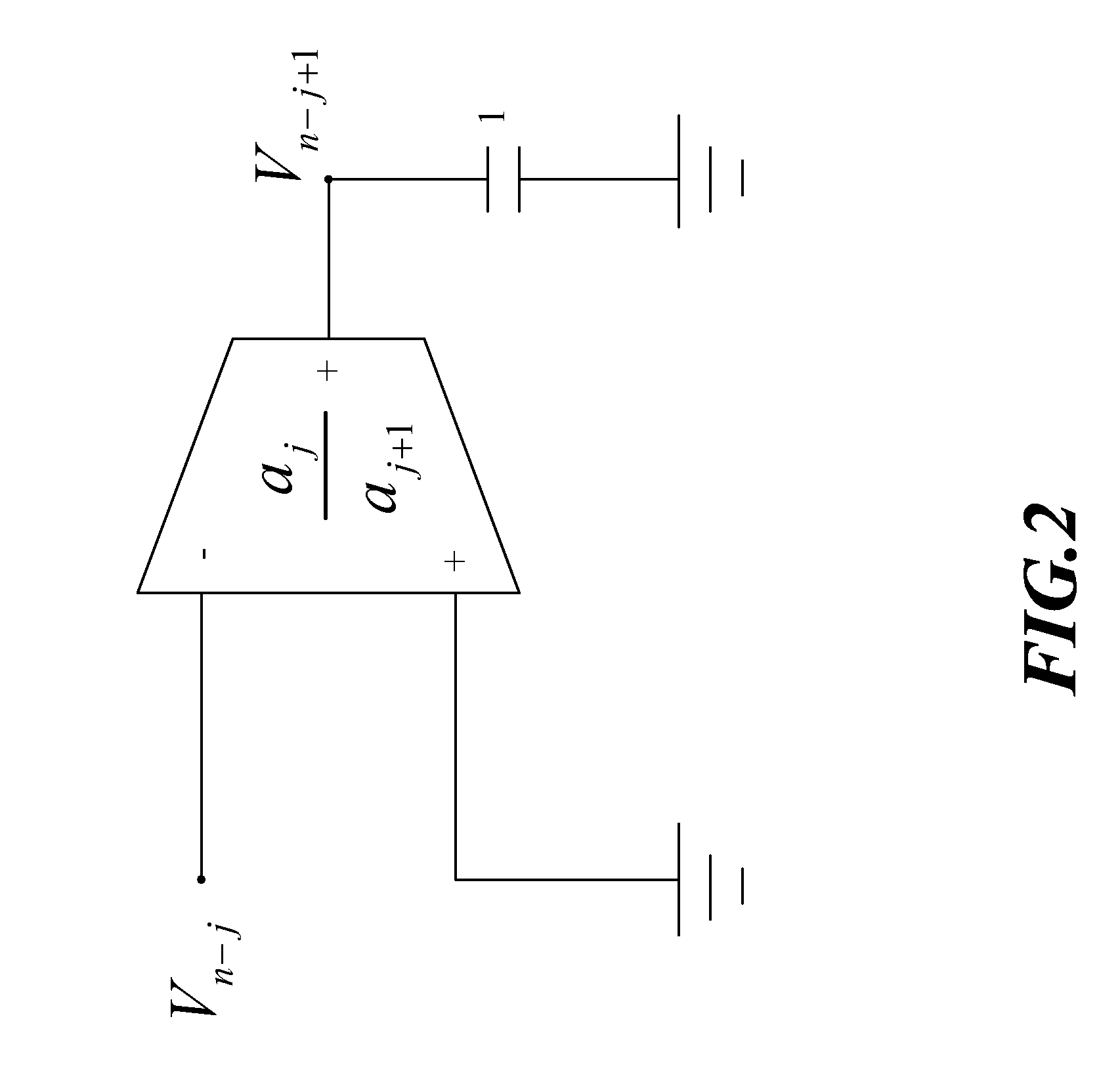
Nth-order arbitrary-phase-shift sinusoidal oscillator structure and analytical synthesis method of making the same
Nth-order voltage- and current-mode arbitrary phase shift oscillator structures are synthesized using n operational trans-conductance amplifiers (OTAs) or second-generation current controlled conveyors (CCCIIs) and n grounded capacitors. Linking up the I / O characteristics of the OTA and the CCCII and the reactance of grounded capacitor, the step of synthesis is first based on the algebraic analysis to oscillatory characteristic equations, resulting in a quadrature oscillator structure. Secondly, instead of the quadrature characteristic, to control each output signal with one another by a desired phase difference > or <90°, selectively superposing any of two fundamental OTA / CCCII-C sub-circuitries benefits the transformation of quadrature to arbitrary-phase-shift characteristic for the sinusoidal oscillator structure. Furthermore, several compensation schemes are presented for reducing the output parameter deviation due to the non-ideal effects.
Owner:CHUNG YUAN CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
Quadrature voltage controlled oscillators with phase shift detector
In wireless application there is made use of a quadrature oscillators that generate signals that are capable of oscillating at quadrature of each other. The quadrature oscillator is comprised of two differential modified Colpitts oscillators. A capacitor bank allows for the selection of a desired frequency from a plurality of discrete possible frequencies. The quadrature oscillator is further coupled with a phase-error detector connected at the point-of-use of the generated ‘I’ and ‘Q’ channels and through the control of current sources provides corrections means to ensure that the phase shift at the point-of-use remains at the desired ninety degrees.
Owner:THETA IP
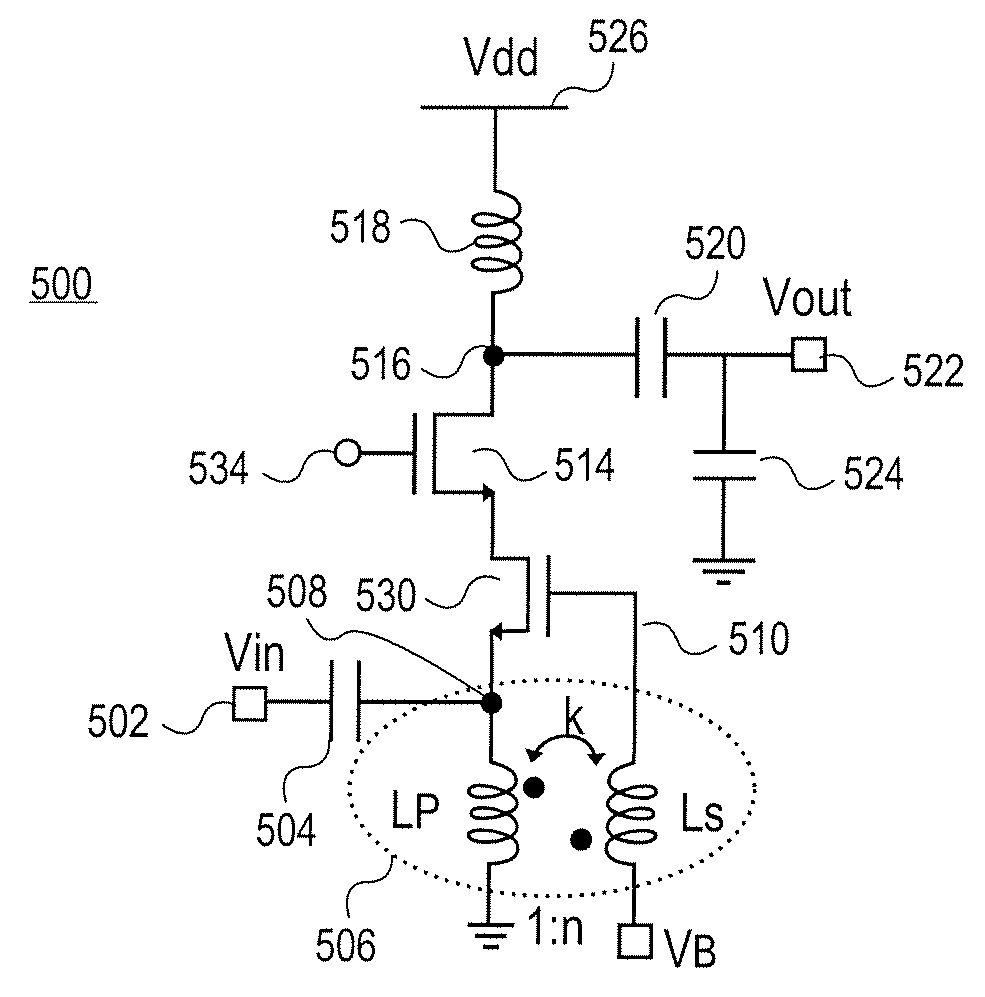
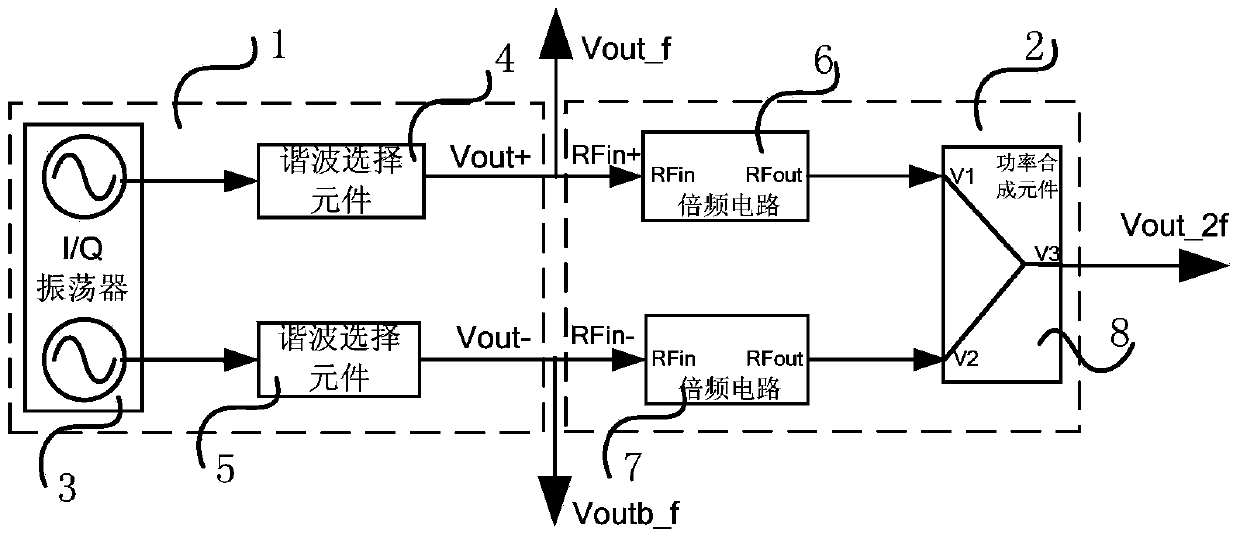
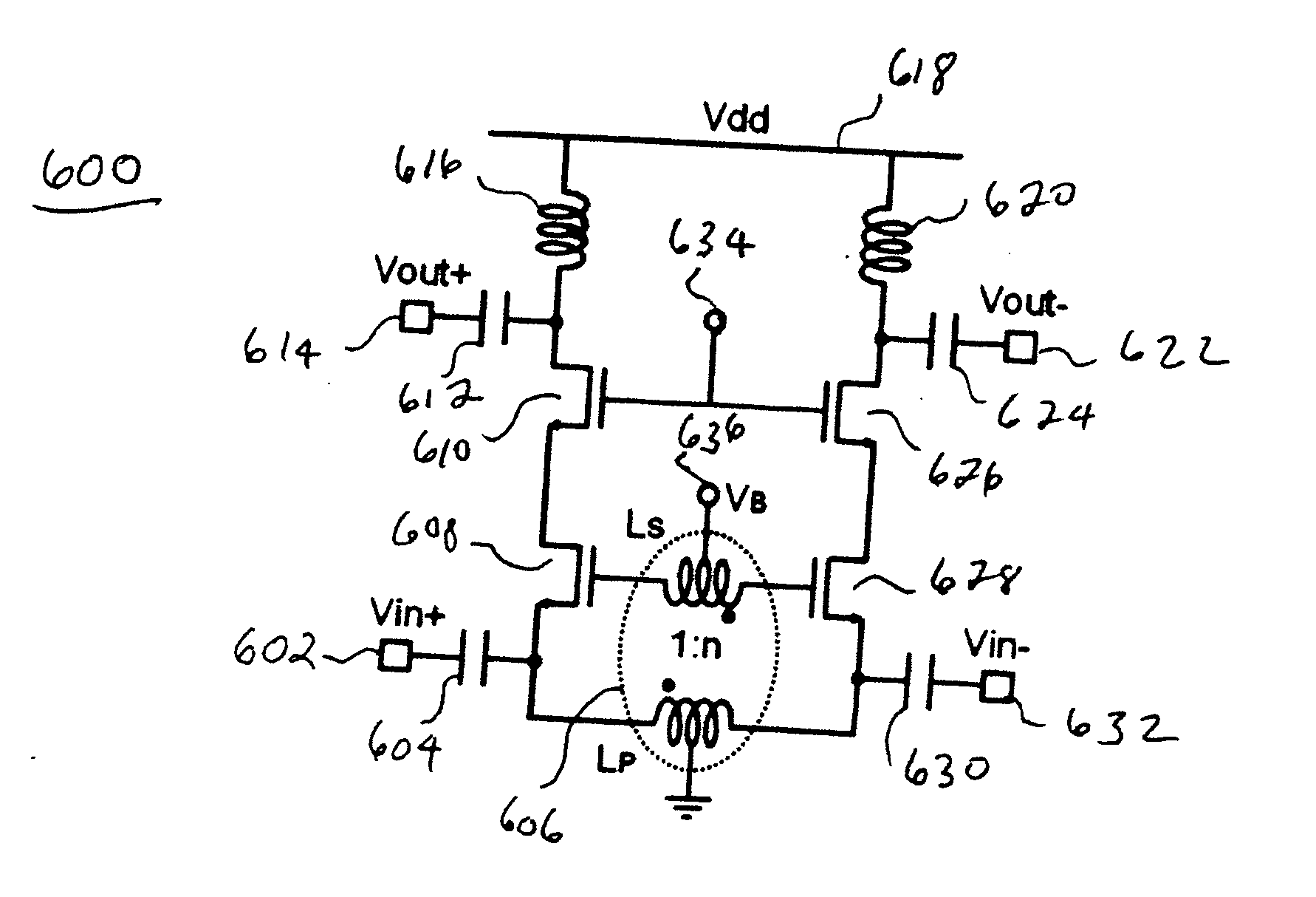
Differential push-push voltage controlled oscillator and signal generation device
The present invention discloses a differential push-push voltage controlled oscillator and signal generation device, comprising a quadrature oscillator, two harmonic selection elements, two frequency multiplier circuits and a power combination element. The quadrature oscillator generates two orthogonal signals and respective harmonic signals, two harmonic selection elements are used for extracting secondary harmonics in two output signals of the oscillator, generating the output of a differential push-push signal; two frequency multiplier circuits are used for frequency multiplication of the signal, generating two frequency multiplier signals with the same phase; the power combination element achieves the combination of power of two signals with the same phase, forming the output of a single-end signal source. The signal source achieves the output of a differential push-push voltage controlled oscillator by a harmonic extraction and frequency multiplication manner, increases the output frequency of signals and utilizes two orthogonal oscillation signals in connection with a power combination manner to increase the output power of signals.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Analytical synthesis method and ota-based circuit structure
InactiveUS20100031205A1CAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsIntegratorSynthesis methods
An analytical Synthesis Method (ASM) is clearly and effectively demonstrated in the realization of current / voltage-mode Operational Trans-conductance Amplifier and Capacitor (OTA-C) circuits, where a complicated nth-order transfer function is manipulated and decomposed by a succession of innovative algebra operations until a set of simple equations are produced, which are then realized using n integrators and a constraint circuitry. The circuits realized includes voltage-mode nth-order OTA-C universal filter structures, tunable voltage / current-mode OTA-C universal biquad filters, voltage-mode odd / even-nth-order OTA-C elliptic filter structures, voltage / current-mode odd-nth-order OTA-C elliptic high-pass filter structures, and OTA-C quadrature oscillators. Some realized OTA-C circuits can be simplified to be OTA-only (OTA-parasiic C) circuits which fit for the operation at high frequencies.
Owner:CHUNG YUAN CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
Receiver with colpitts differential oscillator, colpitts quadrature oscillator, and common-gate low noise amplifier
Embodiments of the present invention include a common-gate amplifier having an input terminal and an output terminal, a transistor having a source, a drain, and a gate, four inductors, and two capacitors, and a negative amplification circuitry. The negative amplification circuitry has an input terminal to receive an RF signal. The negative amplification circuitry applies negative or zero amplification to the RF signal and outputs the negative or zero amplified signal on an output terminal. Alternative embodiments include a Colpitts differential oscillator, which includes two Colpitts single-ended oscillators. Each Colpitts single-ended oscillator includes a transistor. The source of the transistor in one Colpitts single-ended oscillator may be capacitively coupled to the gate of the transistor in the other Colpitts single-ended oscillator.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
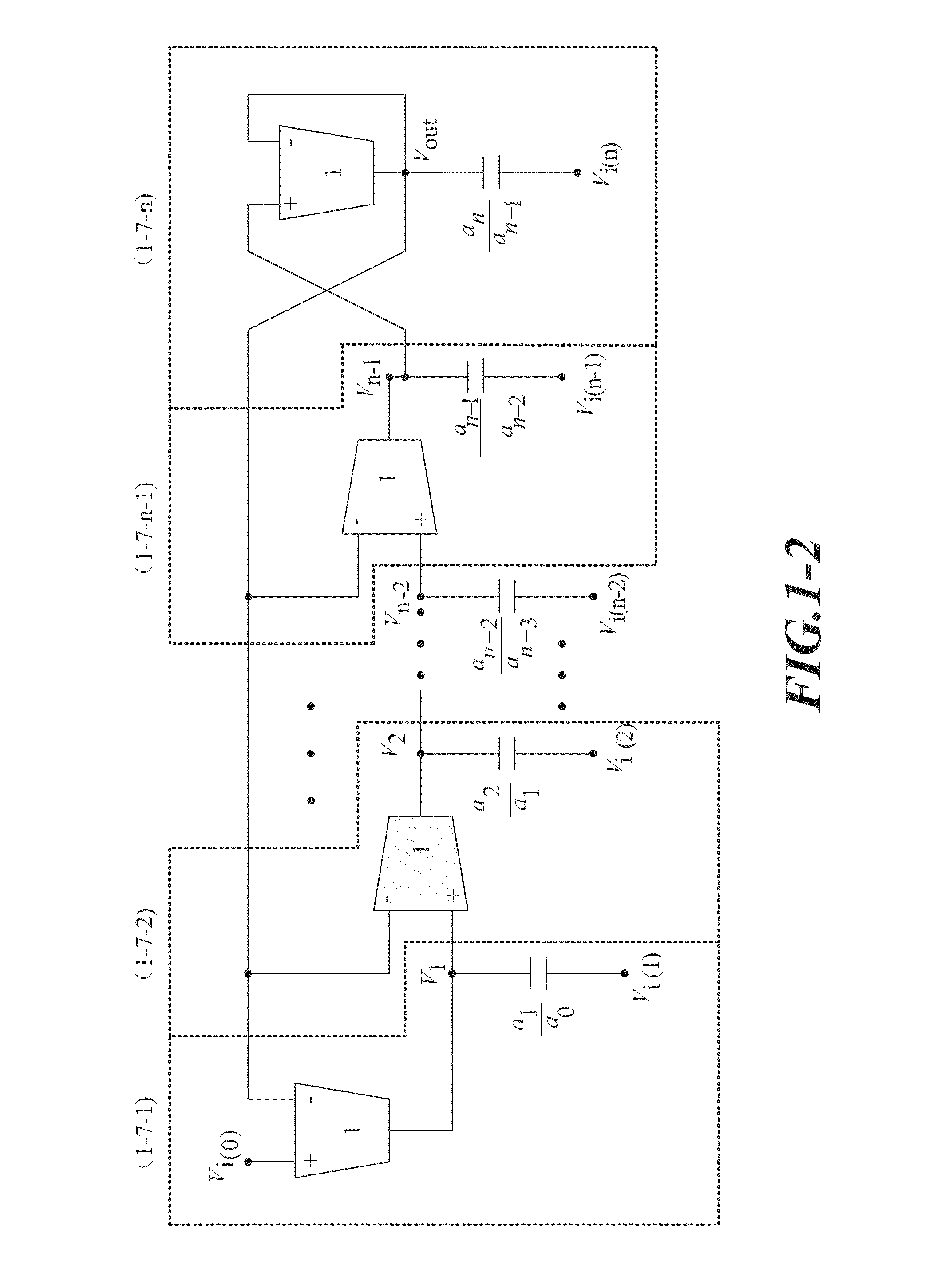
Nth-Order Arbitrary-Phase-Shift Sinusoidal Oscillator Structure and Analytical Synthesis Method of Making the same
InactiveUS20100264996A1Reduce parasiticsReduce power consumptionOscillations generatorsCapacitancePhase shifted
Nth-order voltage- and current-mode arbitrary phase shift oscillator structures are synthesized using n operational trans-conductance amplifiers (OTAs) or second-generation current controlled conveyors (CCCIIs) and n grounded capacitors. Linking up the I / O characteristics of the OTA and the CCCII and the reactance of grounded capacitor, the step of synthesis is first based on the algebraic analysis to oscillatory characteristic equations, resulting in a quadrature oscillator structure. Secondly, instead of the quadrature characteristic, to control each output signal with one another by a desired phase difference > or <90°, selectively superposing any of two fundamental OTA / CCCII-C sub-circuitries benefits the transformation of quadrature to arbitrary-phase-shift characteristic for the sinusoidal oscillator structure. Furthermore, several compensation schemes are presented for reducing the output parameter deviation due to the non-ideal effects.
Owner:CHUNG YUAN CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
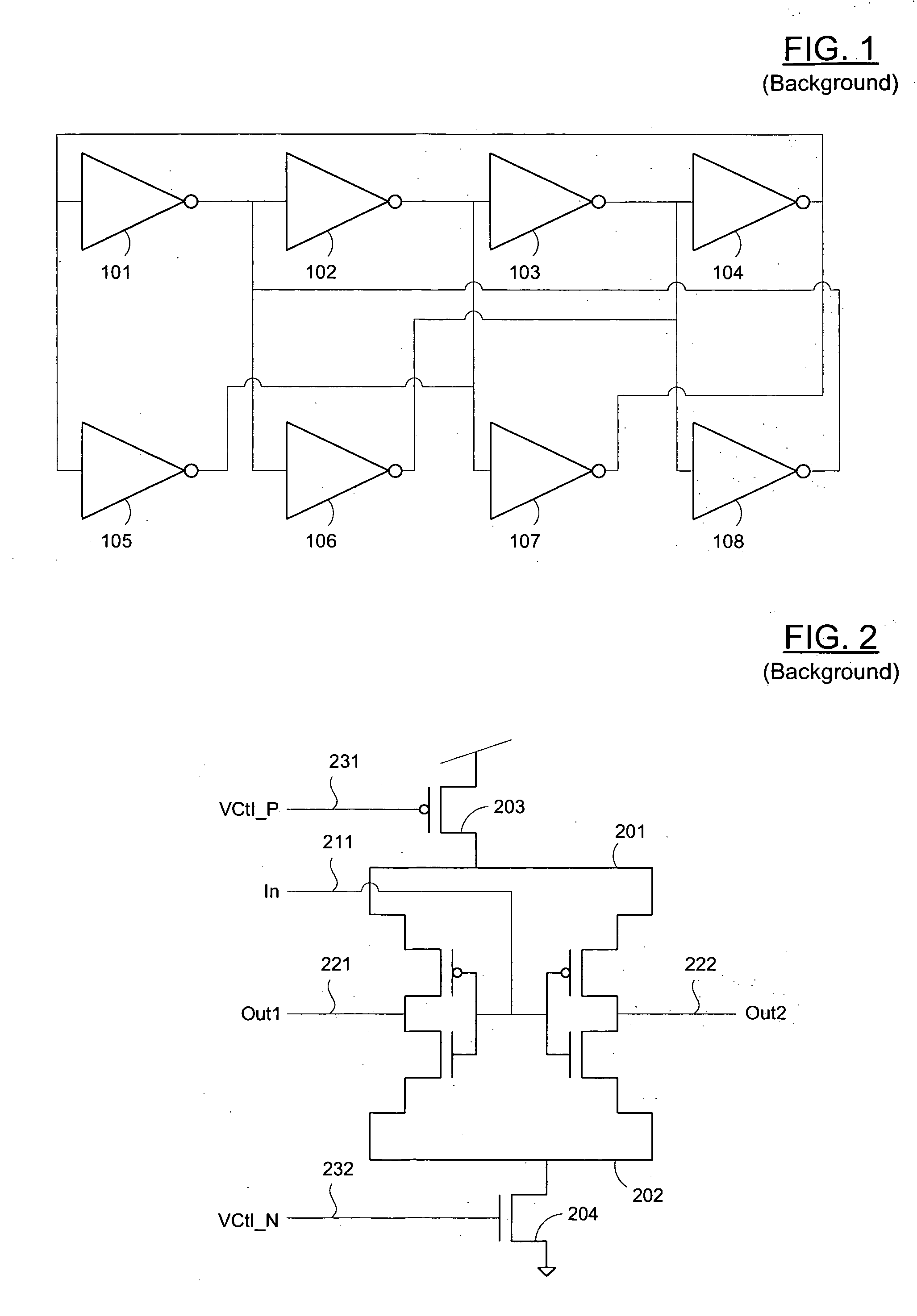
Circuits for voltage-controlled ring oscillators and method of generating a periodic signal
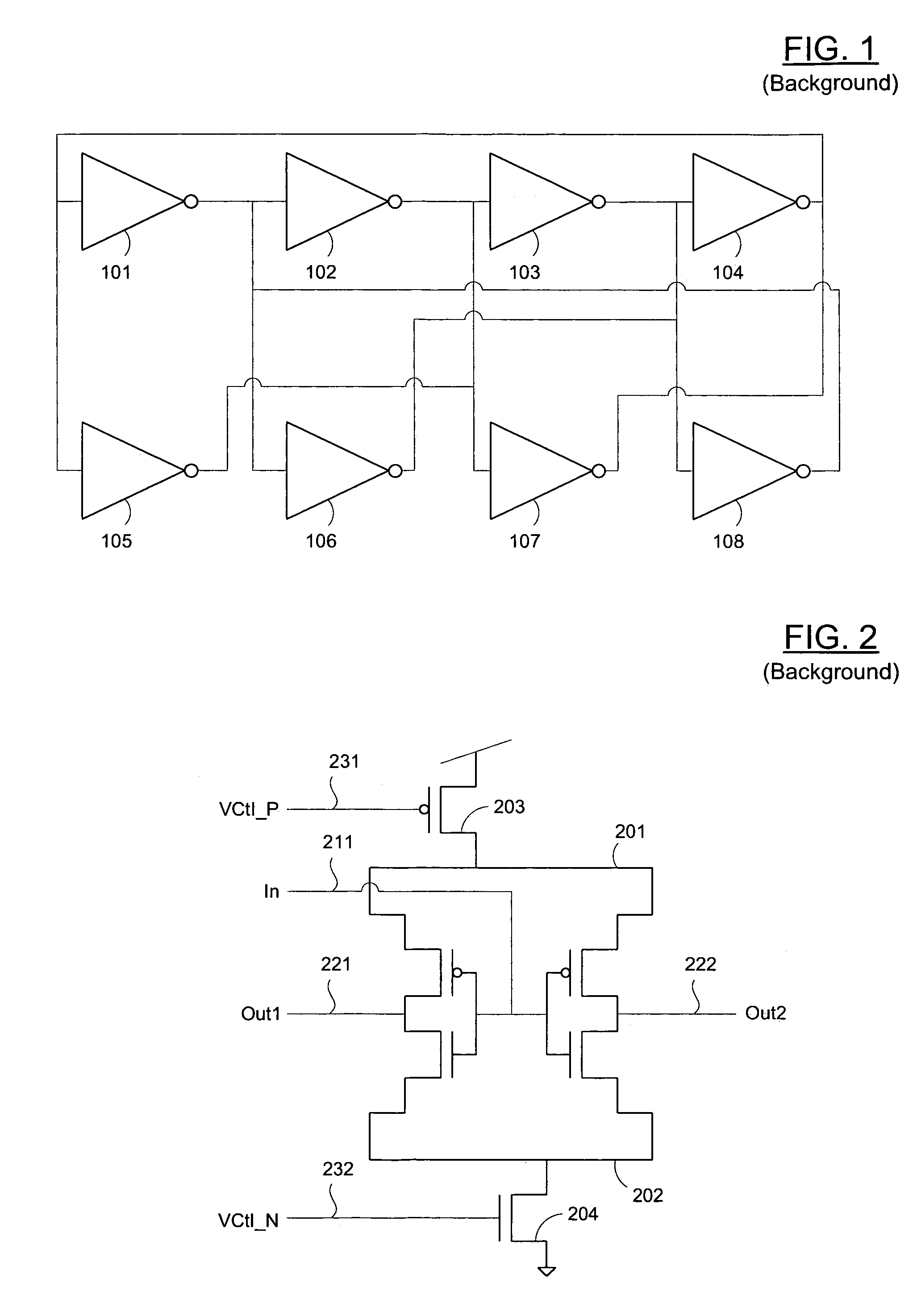
InactiveUS20060244543A1Easy to implementPulse generation by logic circuitsQuadrature oscillatorSoi cmos technology
Circuits and methods and for generating oscillator outputs using standard integrated circuit components. The basic circuit generally includes two inverters and a variable capacitor to configure a delay of the circuit input and / or output. The oscillator circuit generally includes a plurality of inverter circuits, at least one of which uses a variable capacitor to adjust a delay between stages, and thereby adjust a frequency of oscillation. Thus, the oscillator outputs may be tuned using a single control voltage. The method generally includes the steps of (1) applying an operating voltage to a ring oscillator comprising a plurality of stages; and (2) applying a control voltage to a variable capacitor coupled to a node between at least two of those stages. The circuits have particular advantage in quadrature oscillators, and may be easily implemented using widely available CMOS technology.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
System and Method for Signal Generation
InactiveUS20150288393A1Spatial transmit diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRadiation bandwidthCoupling
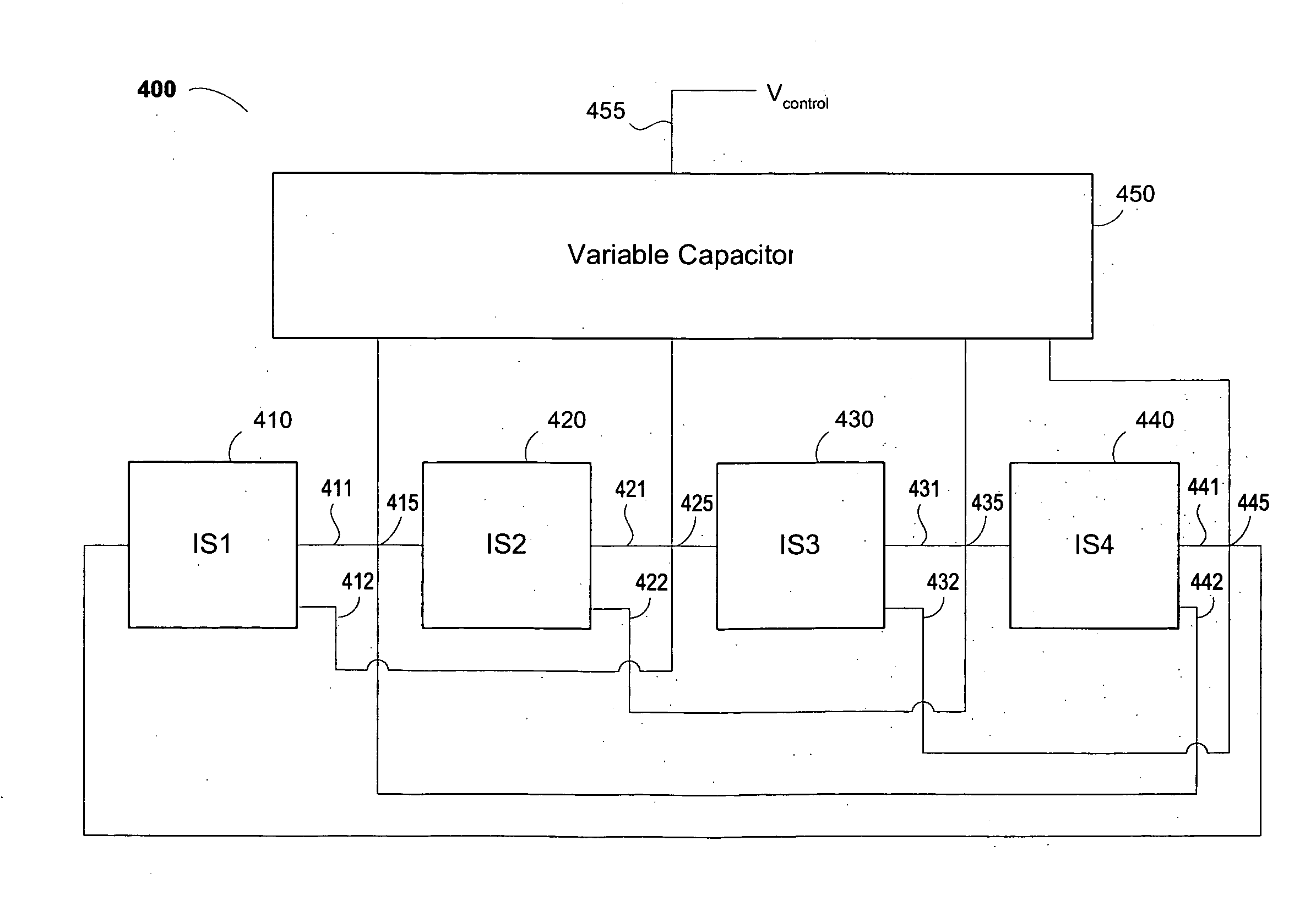
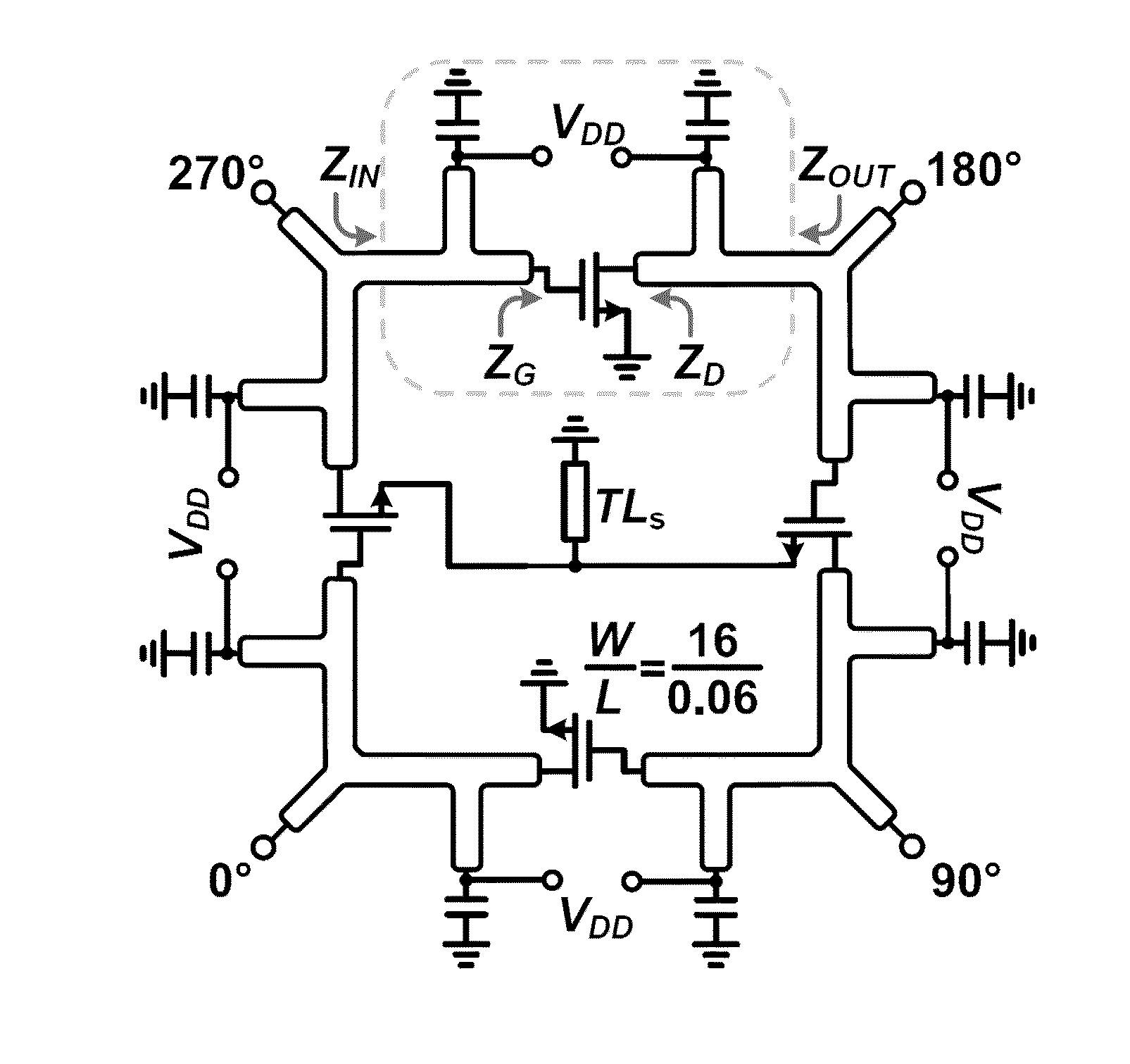
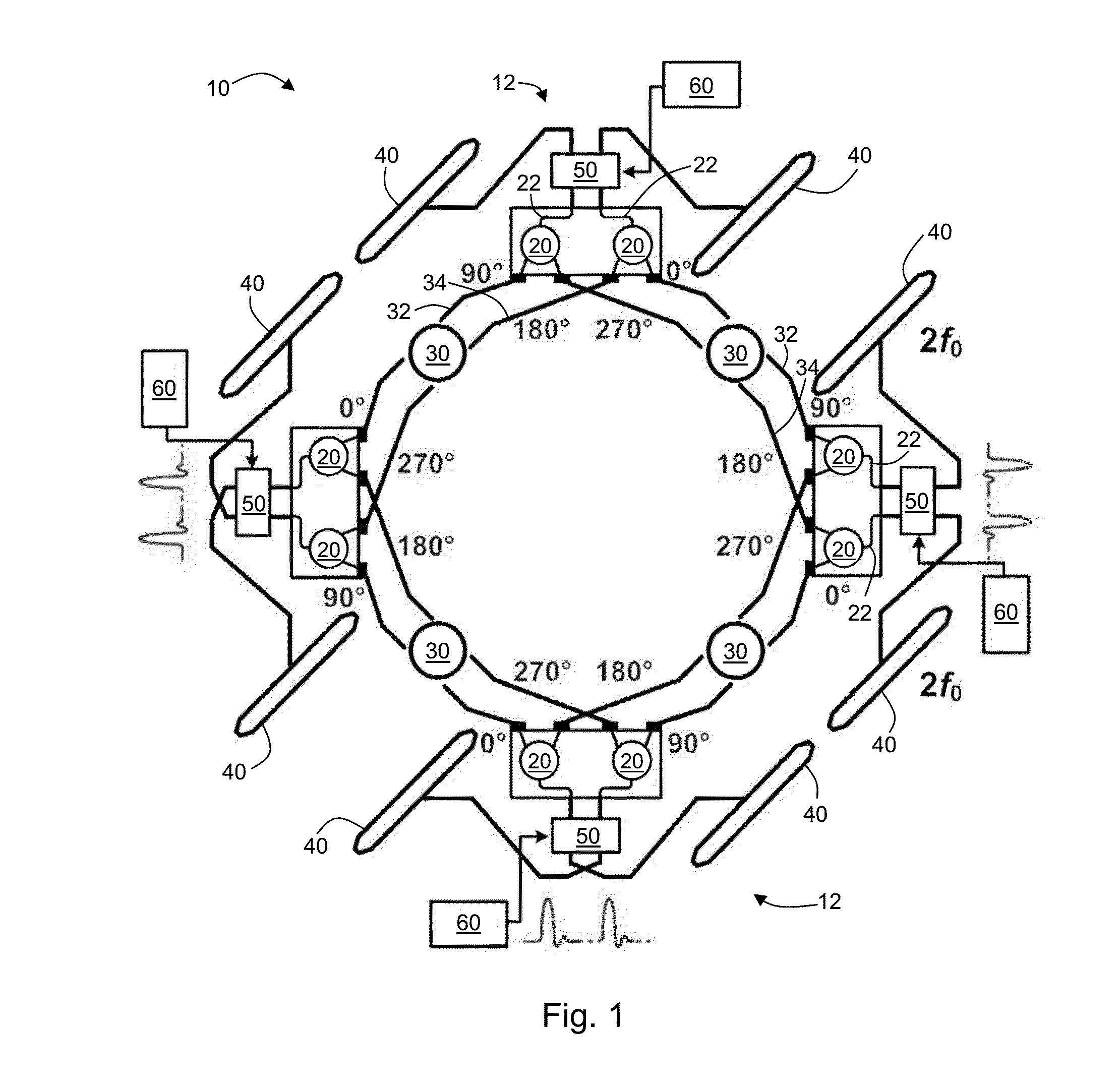
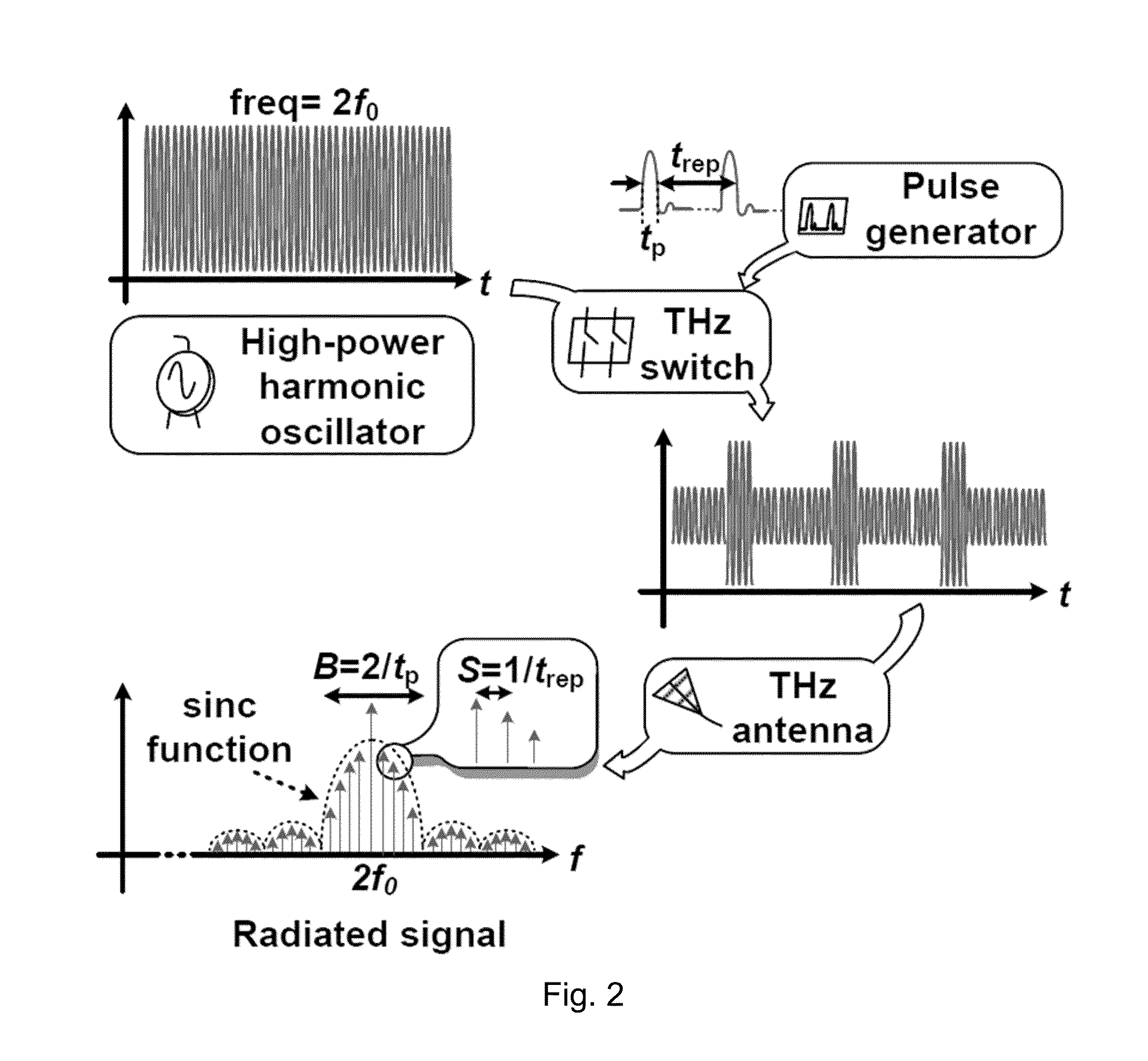
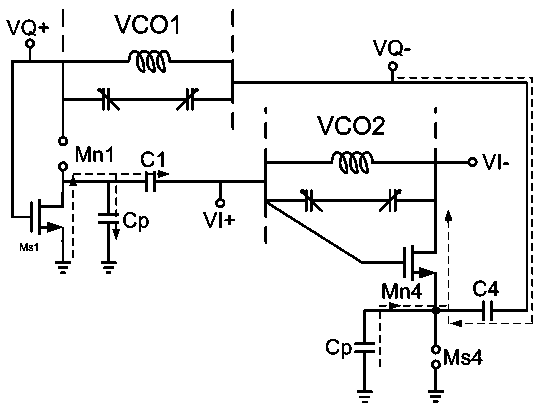
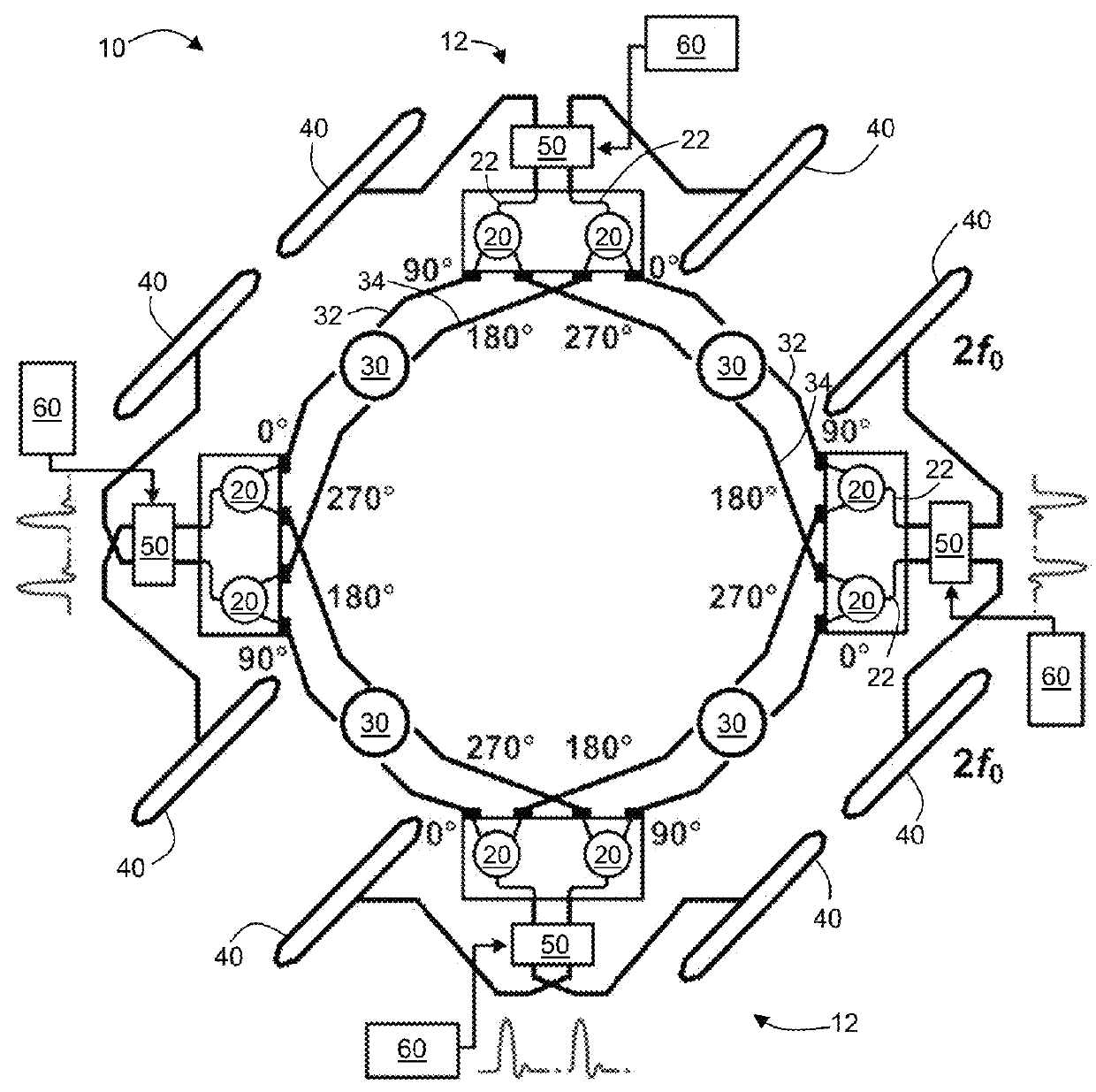
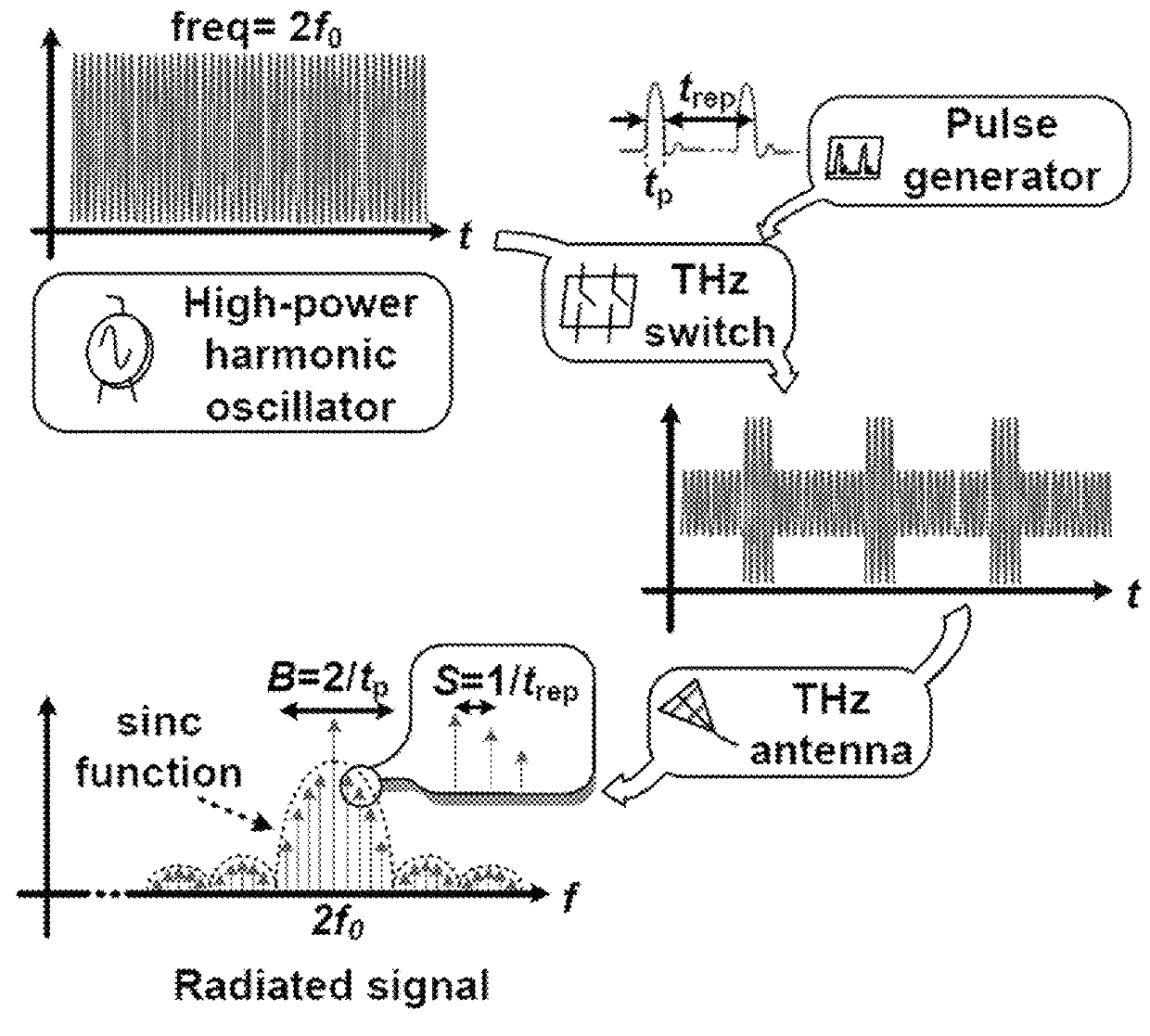
A high-power broadband radiation system and method are disclosed. The system includes an array of harmonic oscillators with mutual coupling through quadrature oscillators. Based on a self-feeding structure, the presently disclosed harmonic oscillators simultaneously achieve optimum conditions for fundamental oscillation and 2nd-harmonic generation. The signals at the second harmonic radiate through on-chip slot antennas, and are in-phase combined inside a hemispheric silicon lens attached at the backside of the chip. In some embodiments, the radiation of the system can also be modulated by narrow pulses generated on chip, thereby achieving broad radiation bandwidth.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
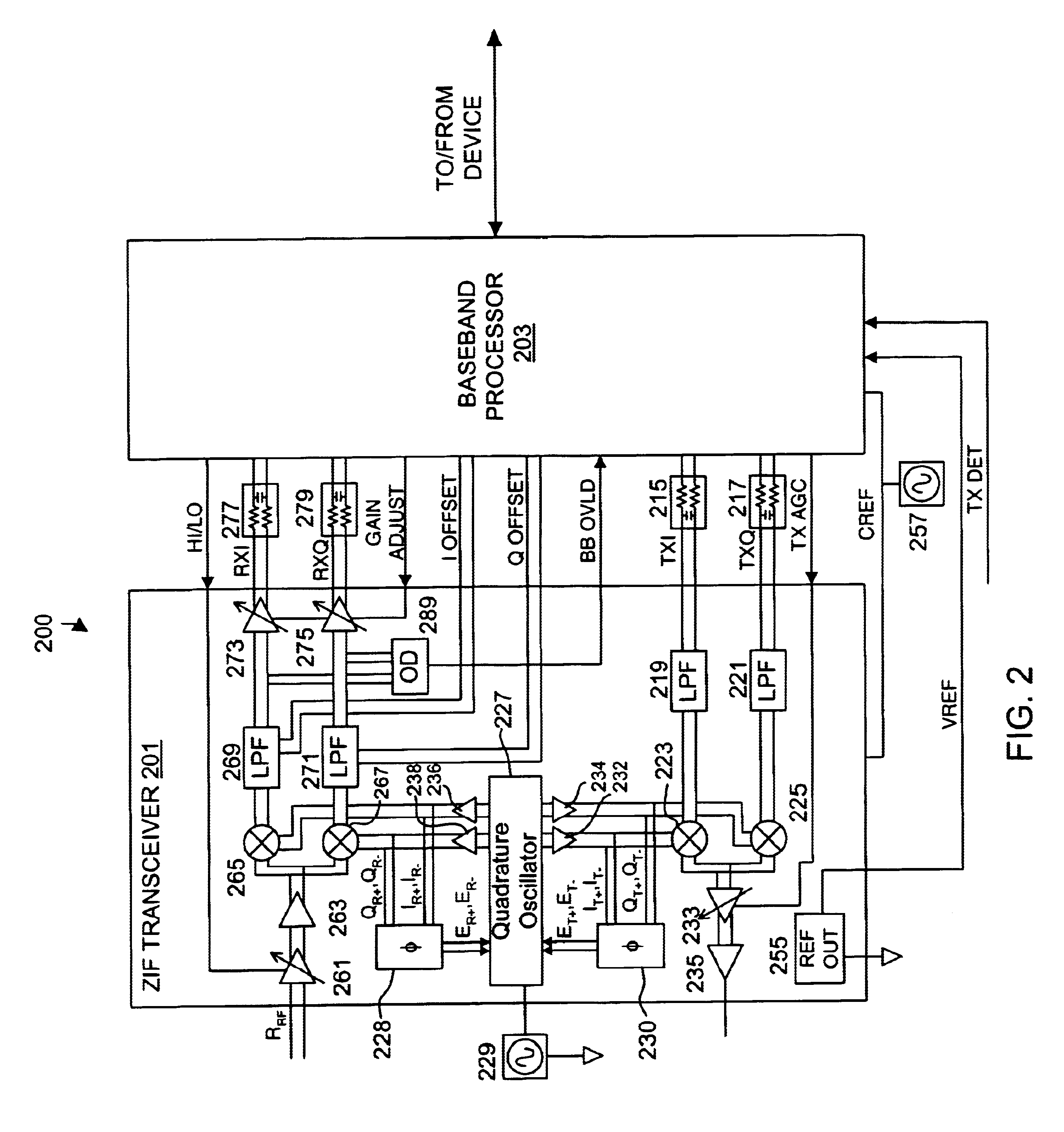
Reconfigurable multi-frequency-range transceiver radio-frequency front end
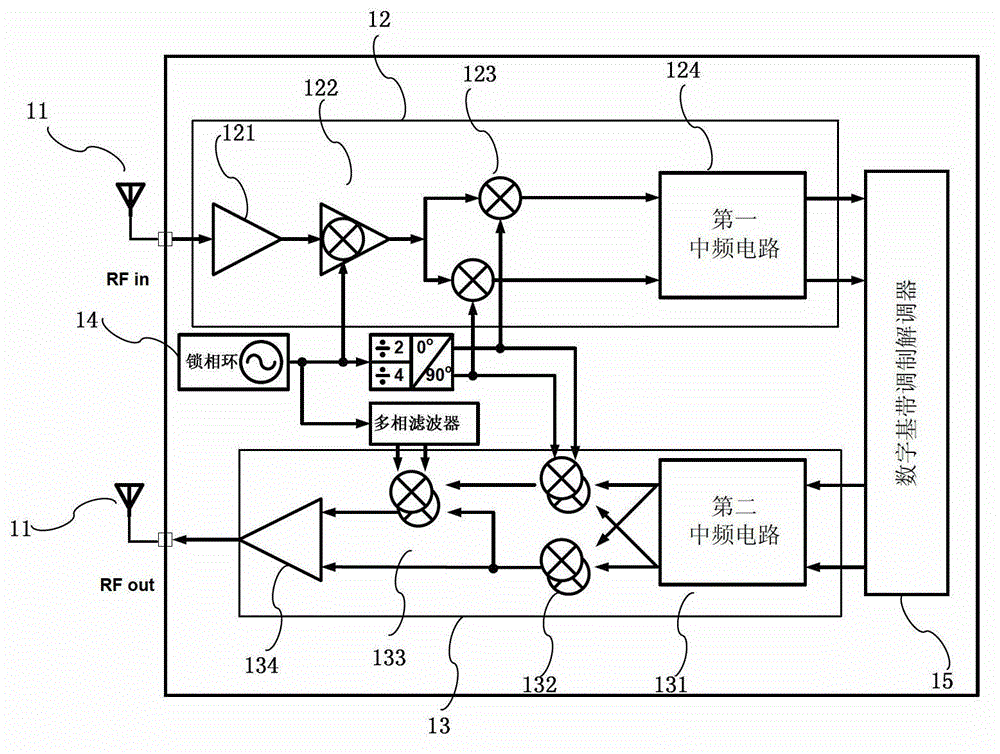
ActiveCN102916720AImprove performanceReduce power consumptionTransmissionFrequency changerTransceiver
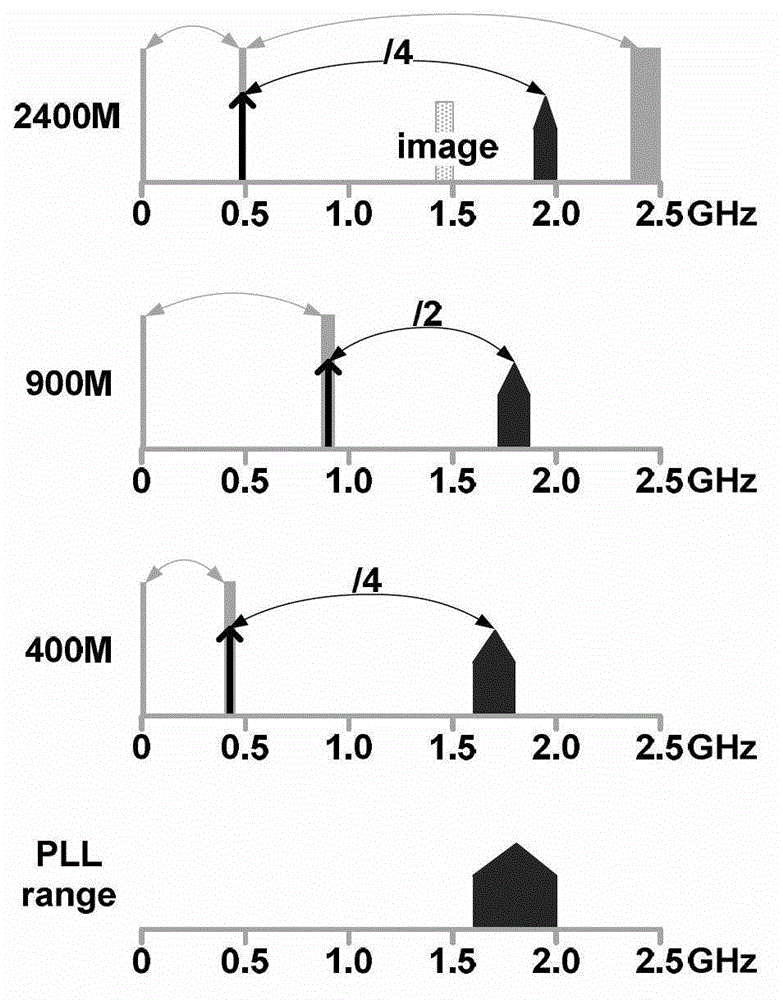
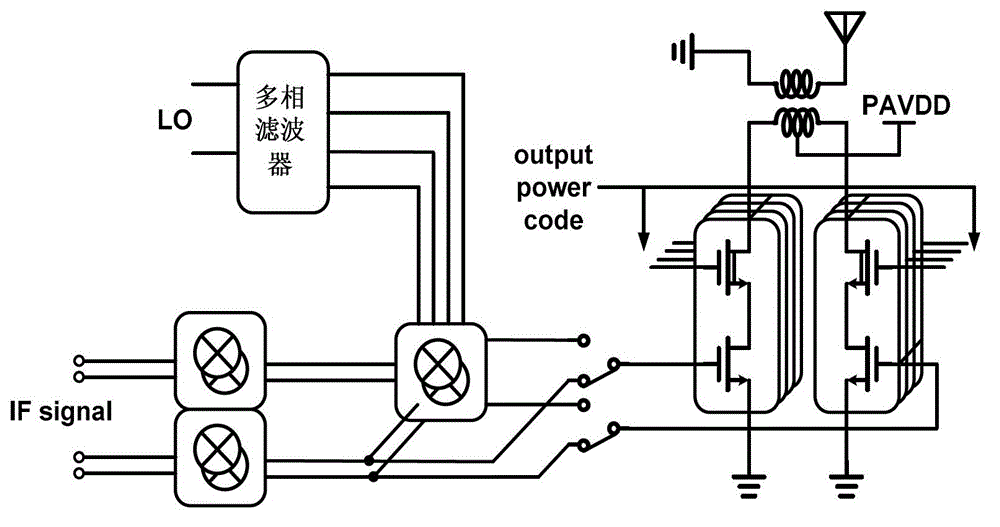
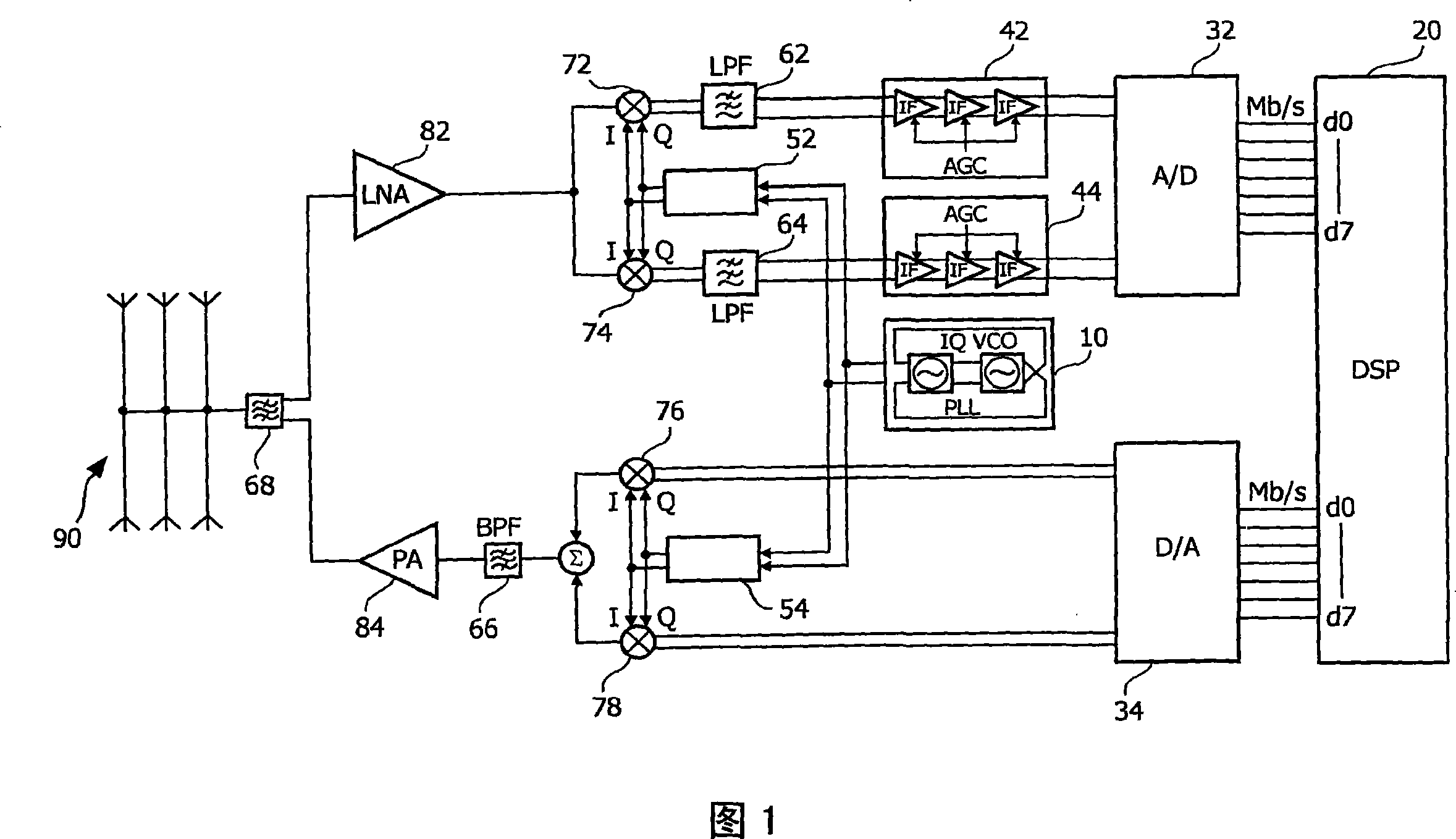
The invention discloses a reconfigurable multi-frequency-range transceiver radio-frequency front end which comprises a receiver part, a transmitter part and a frequency synthesizer, wherein the receiver part comprises a low-noise amplifier, a first-stage reconfigurable lower frequency converter, a second-stage orthogonal lower frequency converter and a first medium-frequency circuit which are sequentially connected; the first medium-frequency circuit is connected with a digital baseband modem; the transmitter part comprises a second medium-frequency circuit, a first-stage low-frequency upper frequency converter, a second-stage high-frequency upper frequency converter and a power amplifier; the second medium-frequency circuit is connected with the digital baseband modem; the frequency synthesizer comprises a phase lock ring; a frequency output of the phase lock ring is connected with the first-stage reconfigurable lower frequency converter, an orthogonal oscillator and a multi-phase filter; the orthogonal oscillator is connected with the second-stage orthogonal lower frequency converter and the first-stage low-frequency upper frequency converter; and an output of the multi-phase filter is connected with the second-stage high-frequency upper frequency converter. According to a reconfiguration method, a zero medium-frequency structure and a sliding medium-frequency structure are synthesized, so that the performance of a transceiver is improved, and the power consumption of the transceiver is reduced.
Owner:NANJING LINKWAH TECH INC
Circuits for voltage-controlled ring oscillators and method of generating a periodic signal
InactiveUS7268635B2Easy to implementAngle modulation by variable impedencePulse generation by logic circuitsSoftware engineeringQuadrature oscillator
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
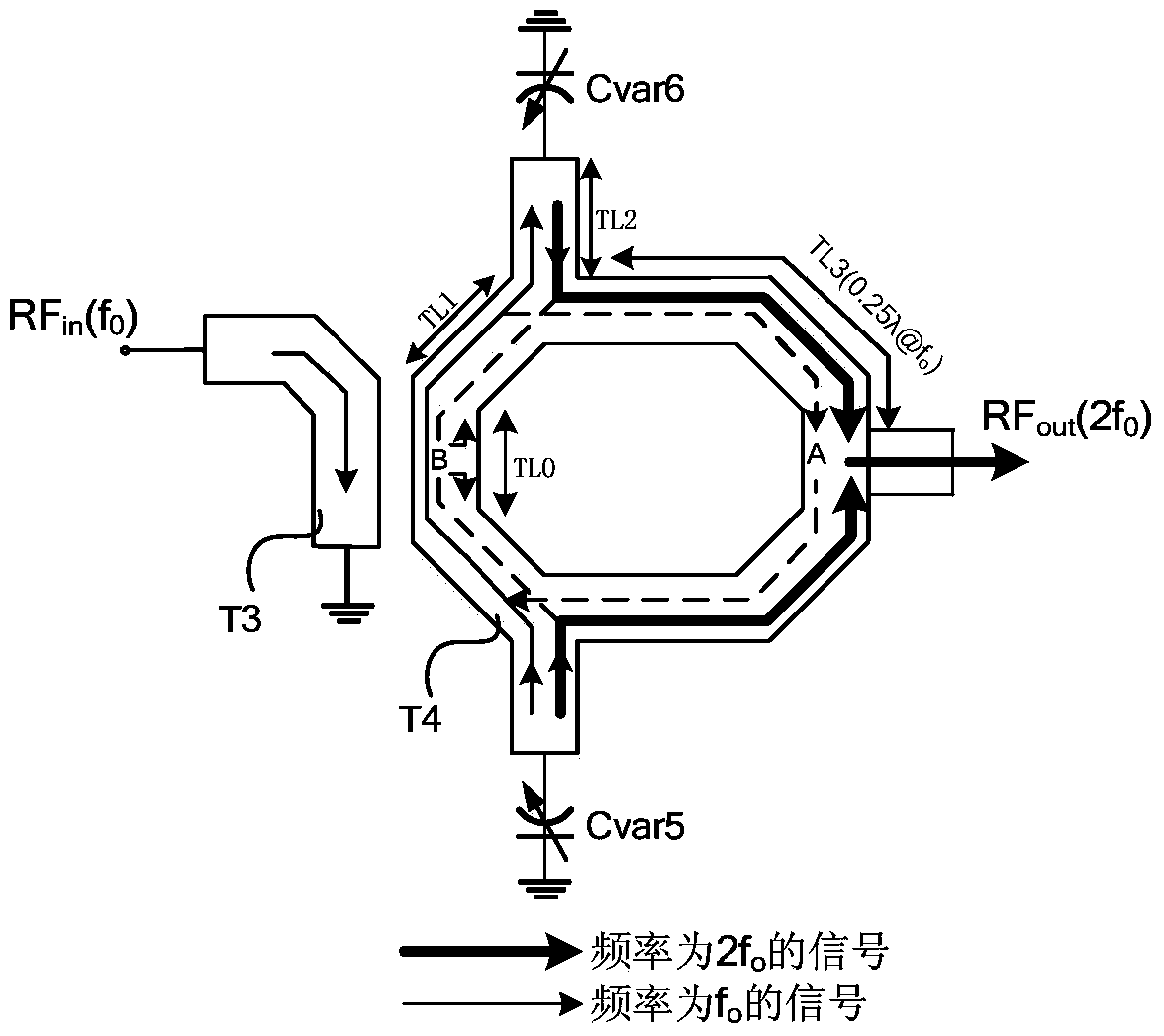
Quadrature push-push voltage-controlled oscillator based on circle structure
The invention relates to a quadrature push-push voltage-controlled oscillator based on a circle structure. The oscillator comprises a four-stage delay unit, the phase relation between output signals in a circle oscillator constructed by a four-stage inverting amplifier is combined with a harmonic wave selection element to extract secondary harmonic waves in the output signals, mutually quadrature phases of the extracted secondary harmonic waves are used as the output of the circle structure so as to form the push-push voltage-controlled oscillator in quadrature output. Under the condition that the process is limited, the structure can effectively improve the frequency of the quadrature local oscillator output signal, and the structure can be used for providing a high-quality quadrature oscillator signal for millimeter wave, submillimeter wave, in particular a terahertz frequency band transceiving front end.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Quadrature oscillator and methods thereof
InactiveUS7146140B2Automatic scanning with simultaneous frequency displayRadio transmissionPhase noisePhase shifted
Briefly, exemplary embodiments of the invention may provide devices and methods to provide precise and / or low phase-noise quadrature oscillation signals. A quadrature oscillator in accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the invention may include, for example, a phase-shift generator to provide a phase-shift of substantially π / 2 radians to an oscillation signal between a first oscillation tank, which provides substantially no phase-shift, and a second oscillation tank.
Owner:INTEL CORP
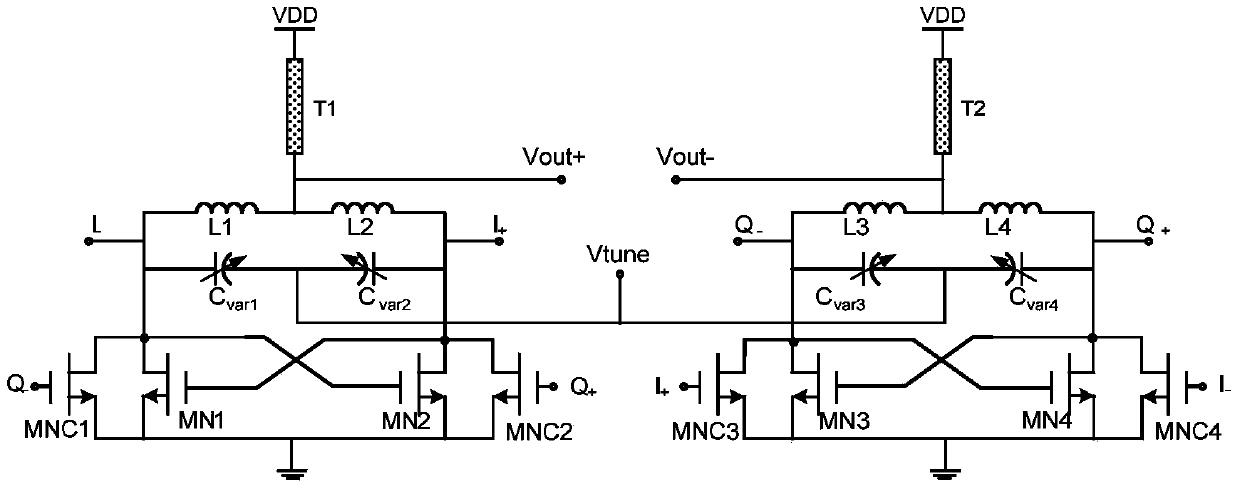
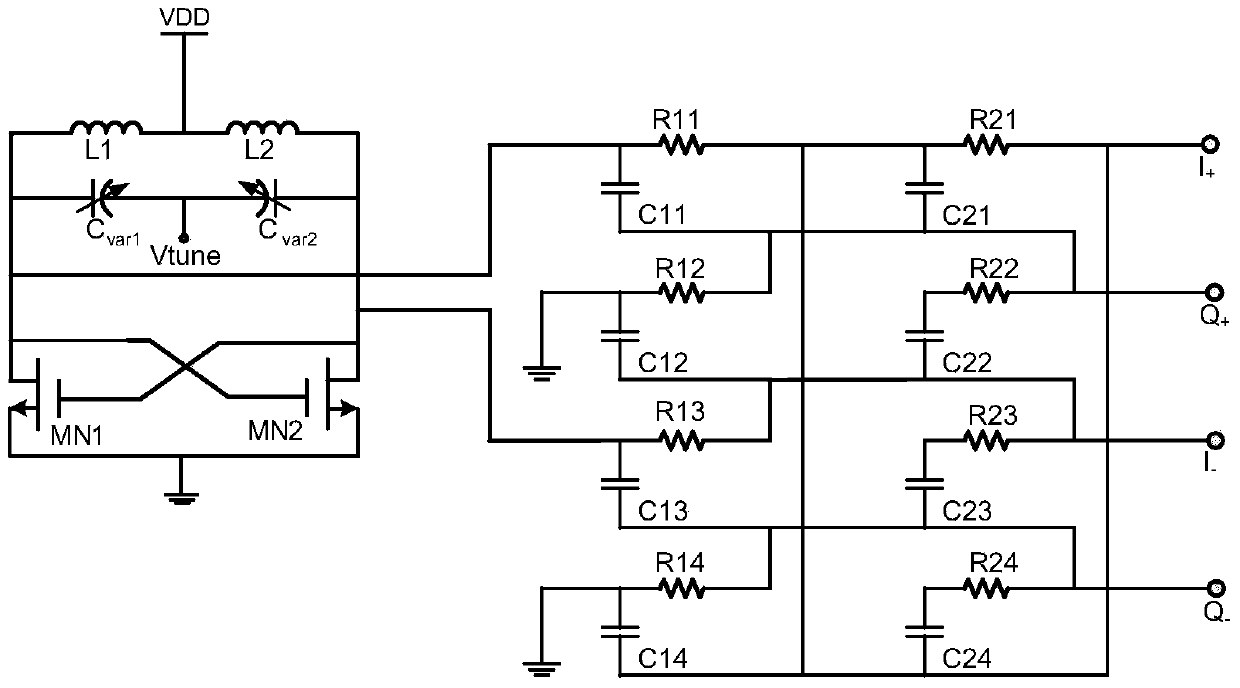
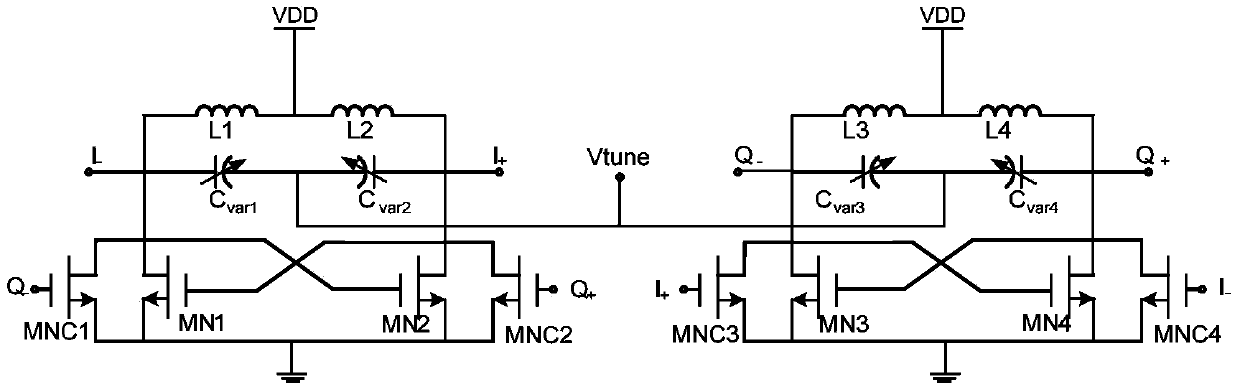
Low-phase-noise quadrature voltage-controlled oscillator
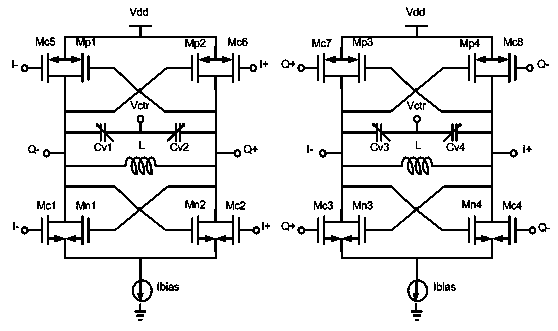
ActiveCN103414434AOscillation amplitude is largeReduce noiseOscillations generatorsCapacitanceNoise (radio)
The invention belongs to the technical field of radio frequency wireless transmitter / receiver integrated circuits, and particularly relates to a low-phase-noise quadrature voltage-controlled oscillator which can be applied to the wireless transmitter / receiver integrated circuits. The low-phase-noise quadrature voltage-controlled oscillator is composed of two LC voltage-controlled oscillators, two pairs of capacity coupling pipes and split-conversion offset pipes. Through the split-conversion-offset technology and the capacity-coupling technology, a novel quadrature voltage-controlled oscillator circuit is designed, compared with a traditional quadrature voltage-controlled oscillator, the novel circuit is added with output swings, 1 / f noise is lowered, and phase noise is lowered. The quadrature voltage-controlled oscillator has the advantages of being low in phase noise, simple in structure, small in chip area, and the like.
Owner:NANJING LOW POWER IC TECH INST CO LTD
System and method for signal generation
InactiveUS9344308B2Spatial transmit diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRadiation bandwidthCoupling
A high-power broadband radiation system and method are disclosed. The system includes an array of harmonic oscillators with mutual coupling through quadrature oscillators. Based on a self-feeding structure, the presently disclosed harmonic oscillators simultaneously achieve optimum conditions for fundamental oscillation and 2nd-harmonic generation. The signals at the second harmonic radiate through on-chip slot antennas, and are in-phase combined inside a hemispheric silicon lens attached at the backside of the chip. In some embodiments, the radiation of the system can also be modulated by narrow pulses generated on chip, thereby achieving broad radiation bandwidth.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Capacitor coupled quadrature voltage controlleed oscillator
ActiveCN102457229AImprove Phase Noise PerformanceCompact chip areaOscillations generatorsPhase noiseHarmonic
A quadrature oscillator includes a first oscillator having a first second-order harmonic node, a second oscillator having a second second-order harmonic node, and at least one capacitor coupling the first second-order harmonic node and the second second-order harmonic node. The first oscillator is configured to supply an in-phase signal and the second oscillator is configured to supply a quadrature signal.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
LC quadrature oscillator having phase and amplitude mismatch compensator
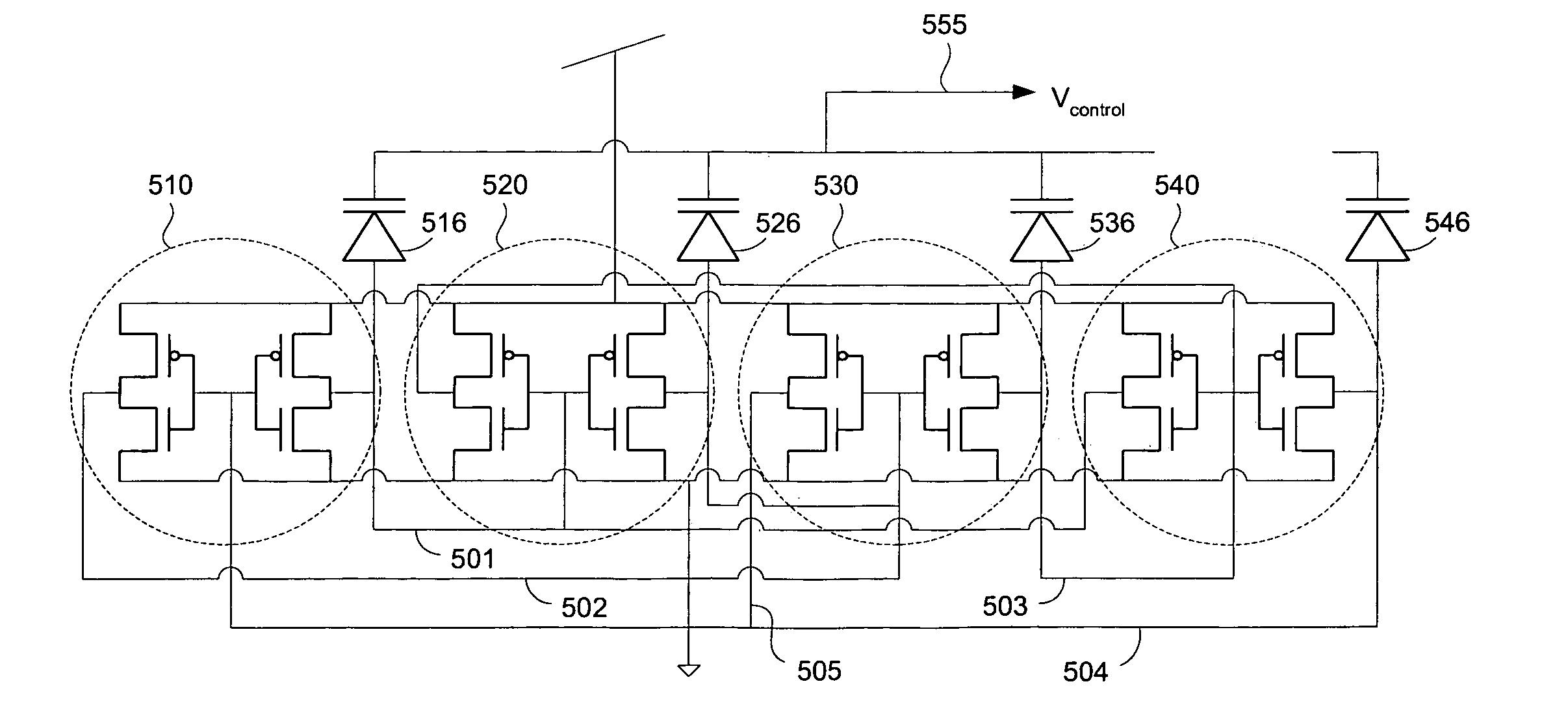
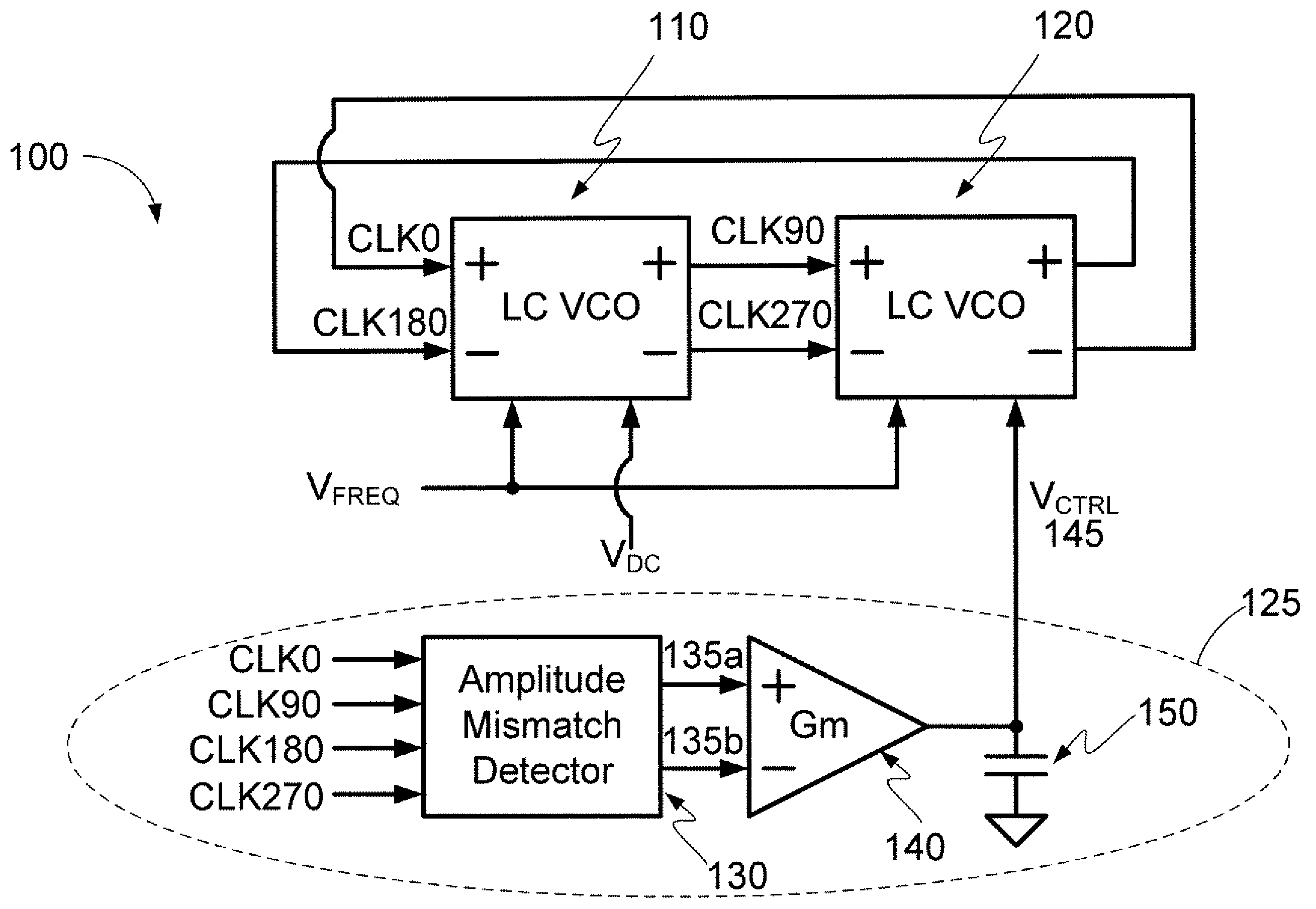
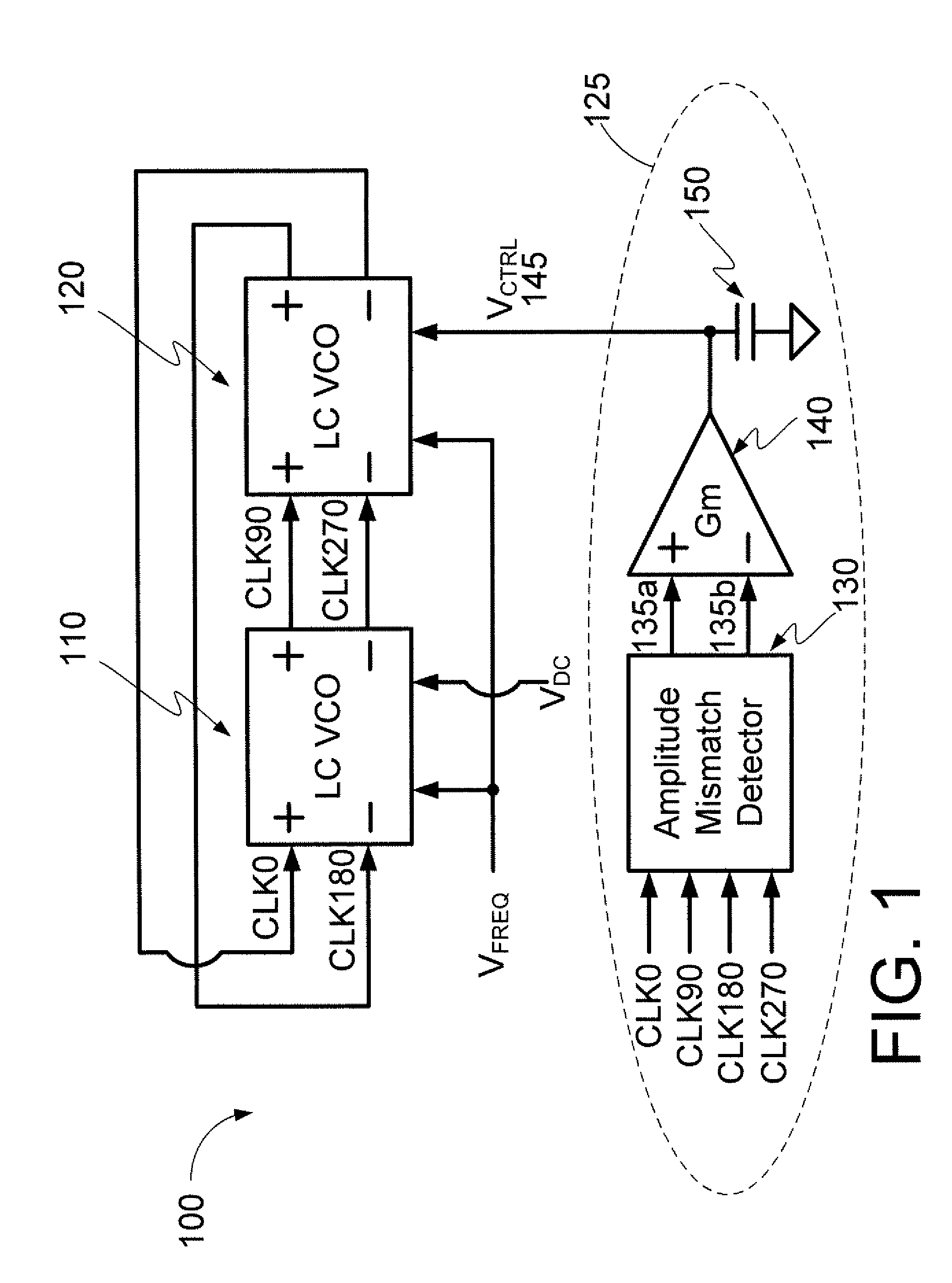
InactiveUS7595700B2Angle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlQuadrature oscillatorCross coupled
Embodiments of the invention may provide for an LC quadrature oscillator that includes two LC oscillators that are cross-coupled with each other to generate I / Q clock signals and a phase and amplitude mismatch compensator. The phase and amplitude mismatch detector may include an amplitude mismatch detector, a transconductor, and a capacitor for compensating for both phase and amplitude mismatches between I / Q clock signals generated in the LC quadrature oscillator.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD +1
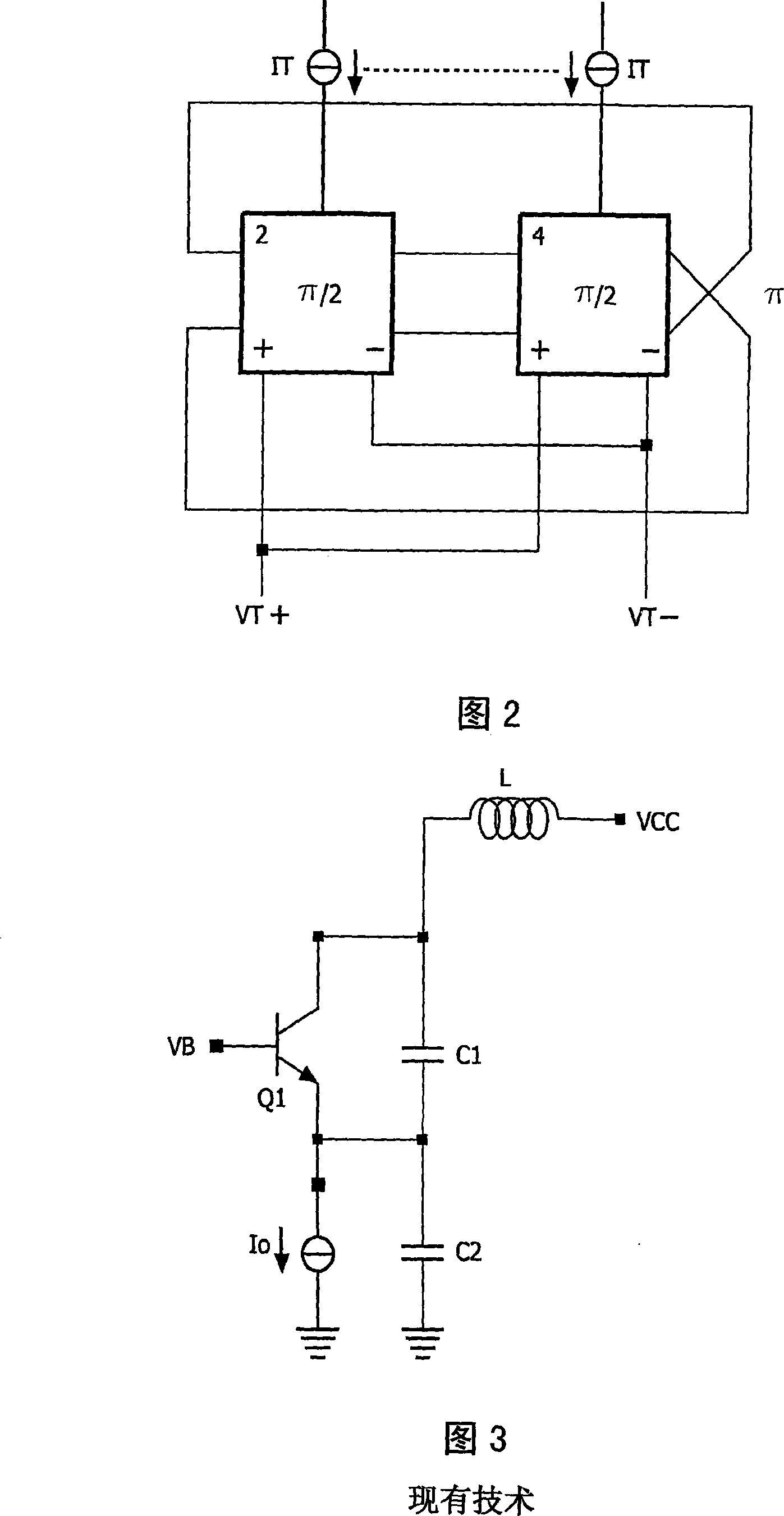
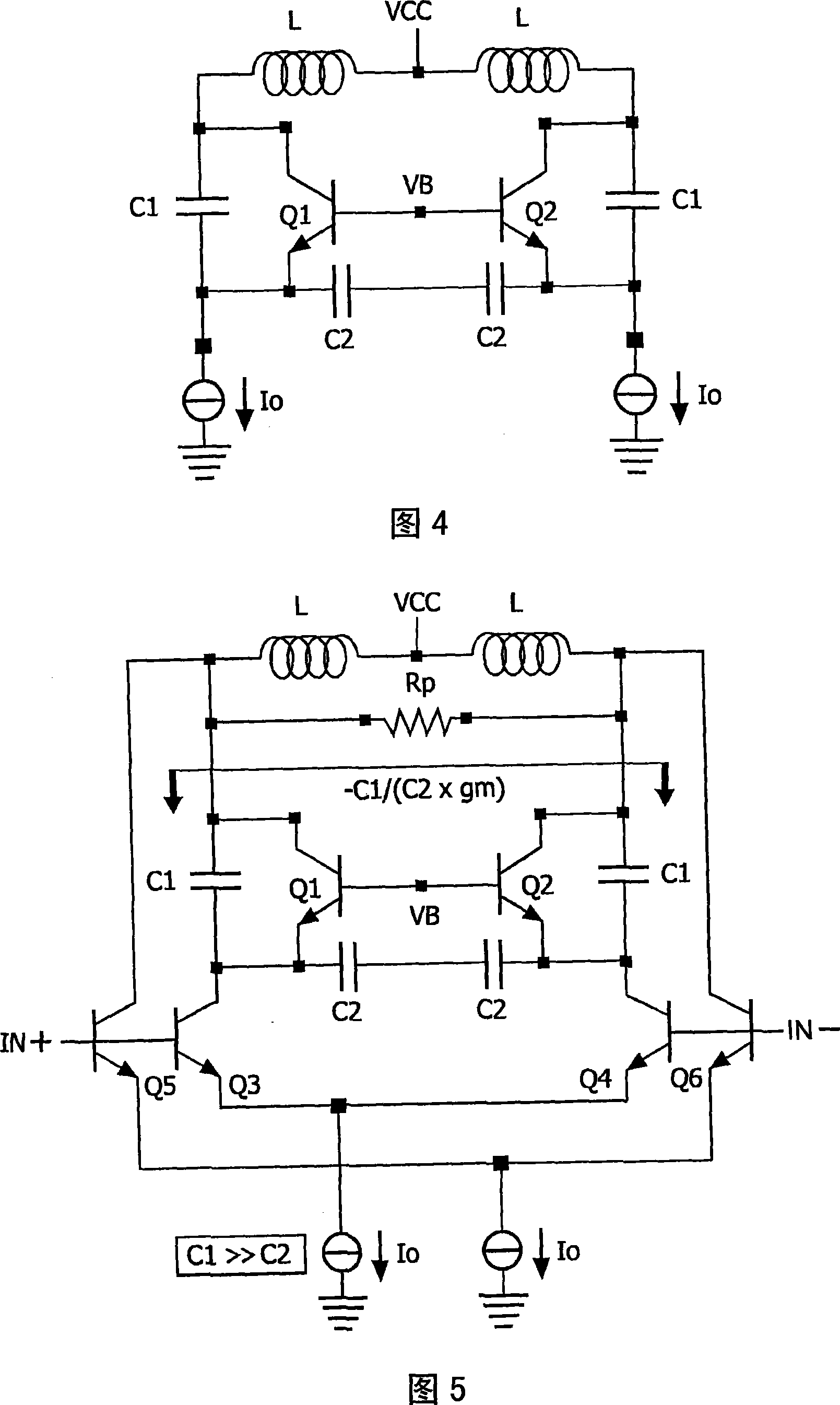
Quadrature oscillator with high linearity
The present invention relates to an oscillator circuit and a method of controlling the oscillation frequency of an in-phase signal and a quadrature signal. First oscillator means (2) with a first differential oscillator circuit and a first differential coupling circuit are provided for generating the quadrature signal. Furthermore, second oscillator means (4) with a second differential oscillator circuit and a second differential coupling circuit are provided for generating the in-phase signal. A frequency control means is provided for varying the oscillation frequency of the in-phase signal and the quadrature signal by controlling at least one of a common-mode current and a tail current of the first and second oscillator means. Thereby, a high-frequency IQ oscillator with high linearity is obtained.
Owner:NXP BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com