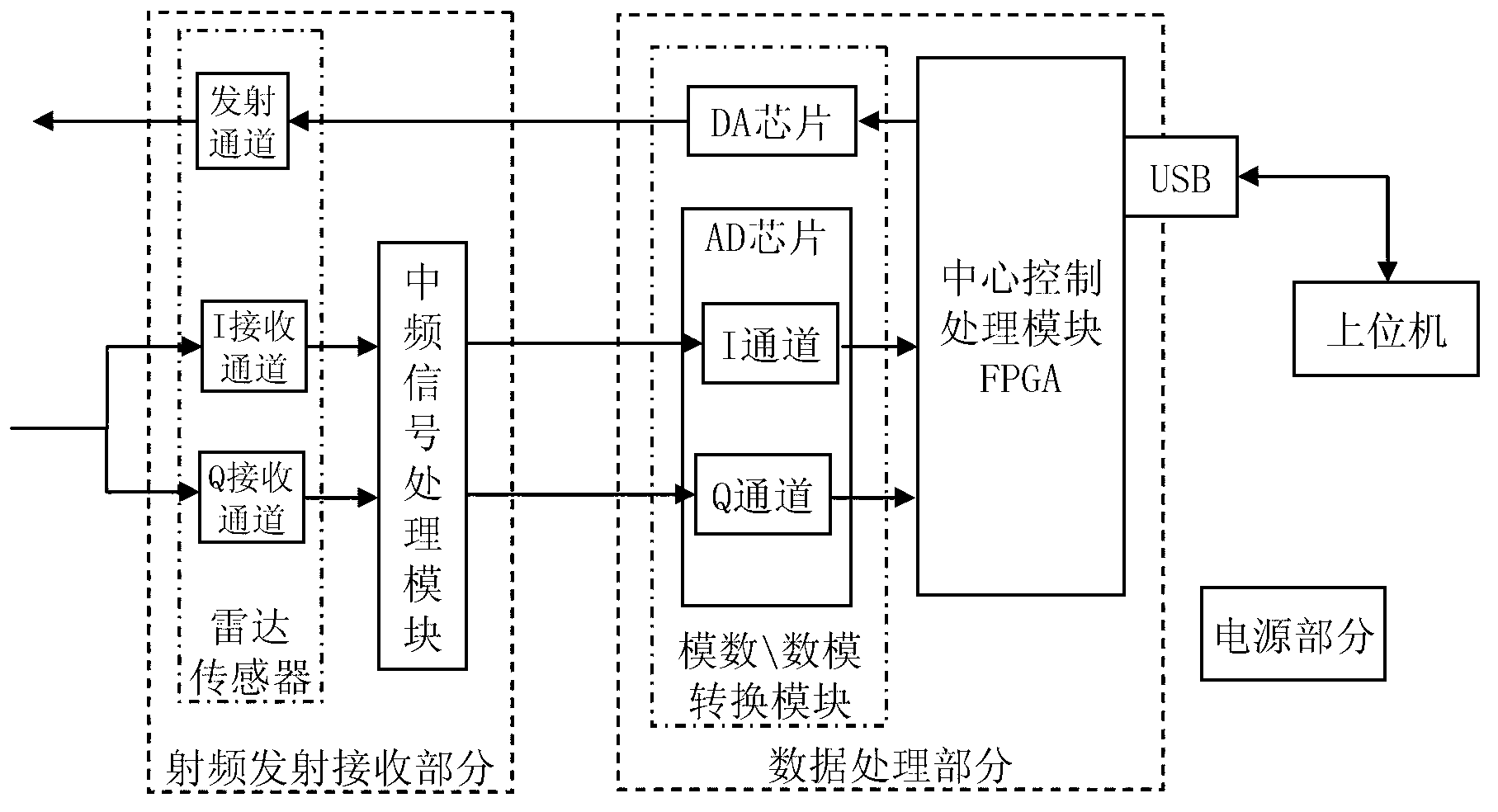
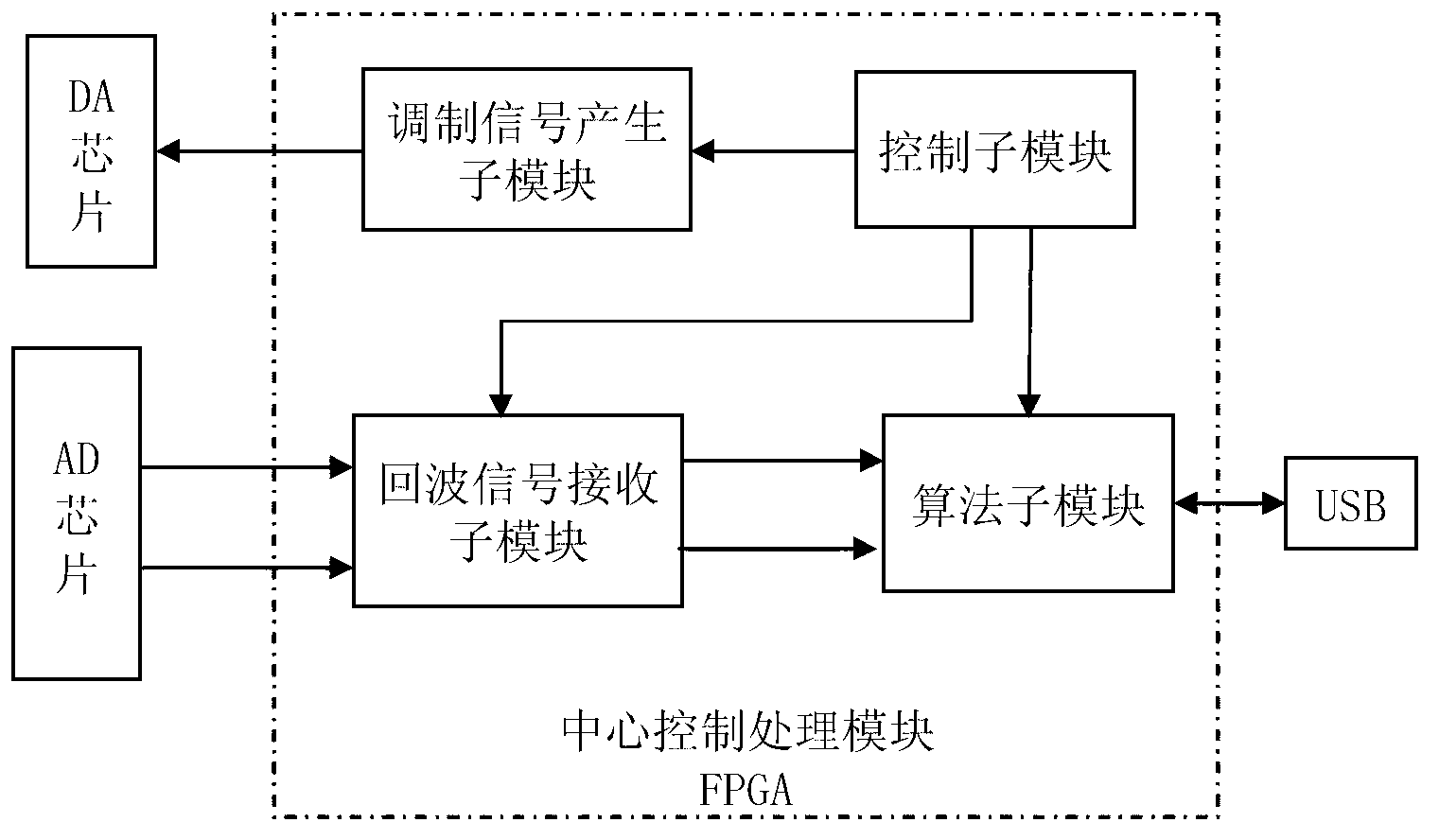
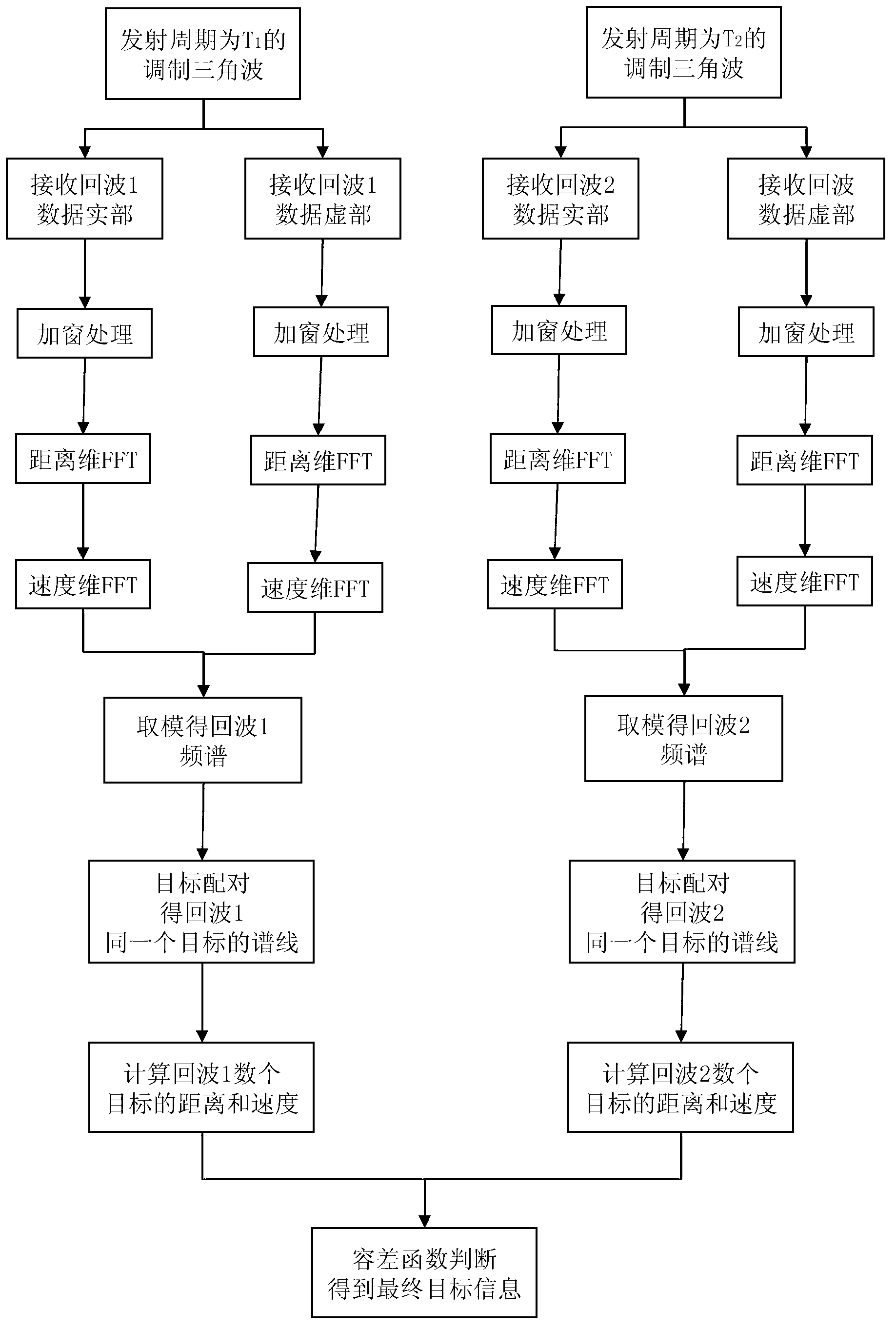
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1363 results about "Noise (radio)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In radio reception, noise is unwanted random electrical signals always present in a radio receiver in addition to the desired radio signal. Radio noise is a combination of natural electromagnetic atmospheric noise ("spherics", static) created by electrical processes in the atmosphere like lightning, manmade radio frequency interference (RFI) from other electrical devices picked up by the receiver's antenna, and thermal noise present in the receiver input circuits, caused by the random thermal motion of molecules. The level of noise determines the maximum sensitivity and reception range of a radio receiver; if no noise were picked up with radio signals, even weak transmissions could be received at virtually any distance by making a radio receiver that was sensitive enough. With noise present, if a radio source is so weak and far away that the radio signal in the receiver has a lower amplitude than the average noise, the noise will drown out the signal.
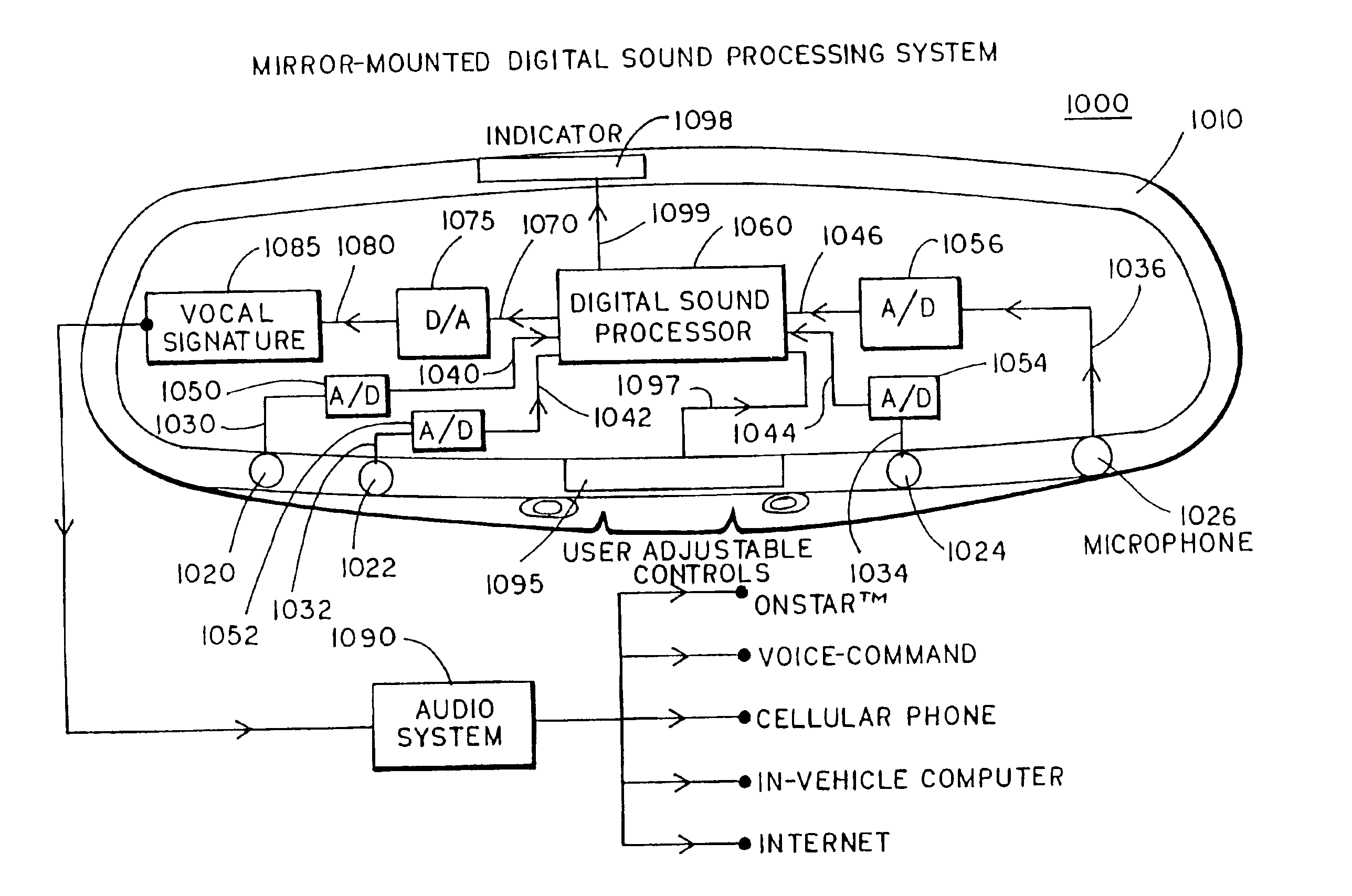
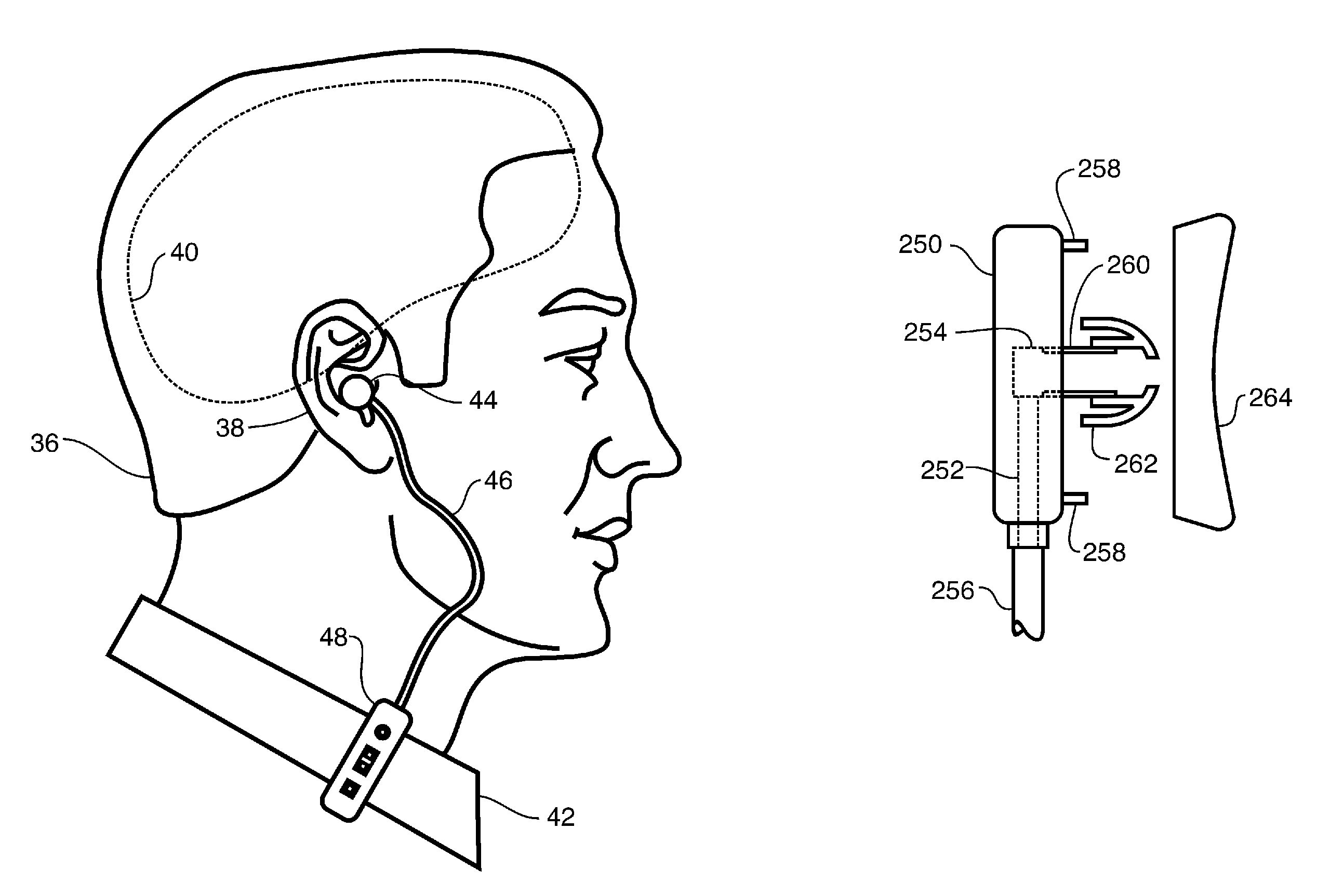
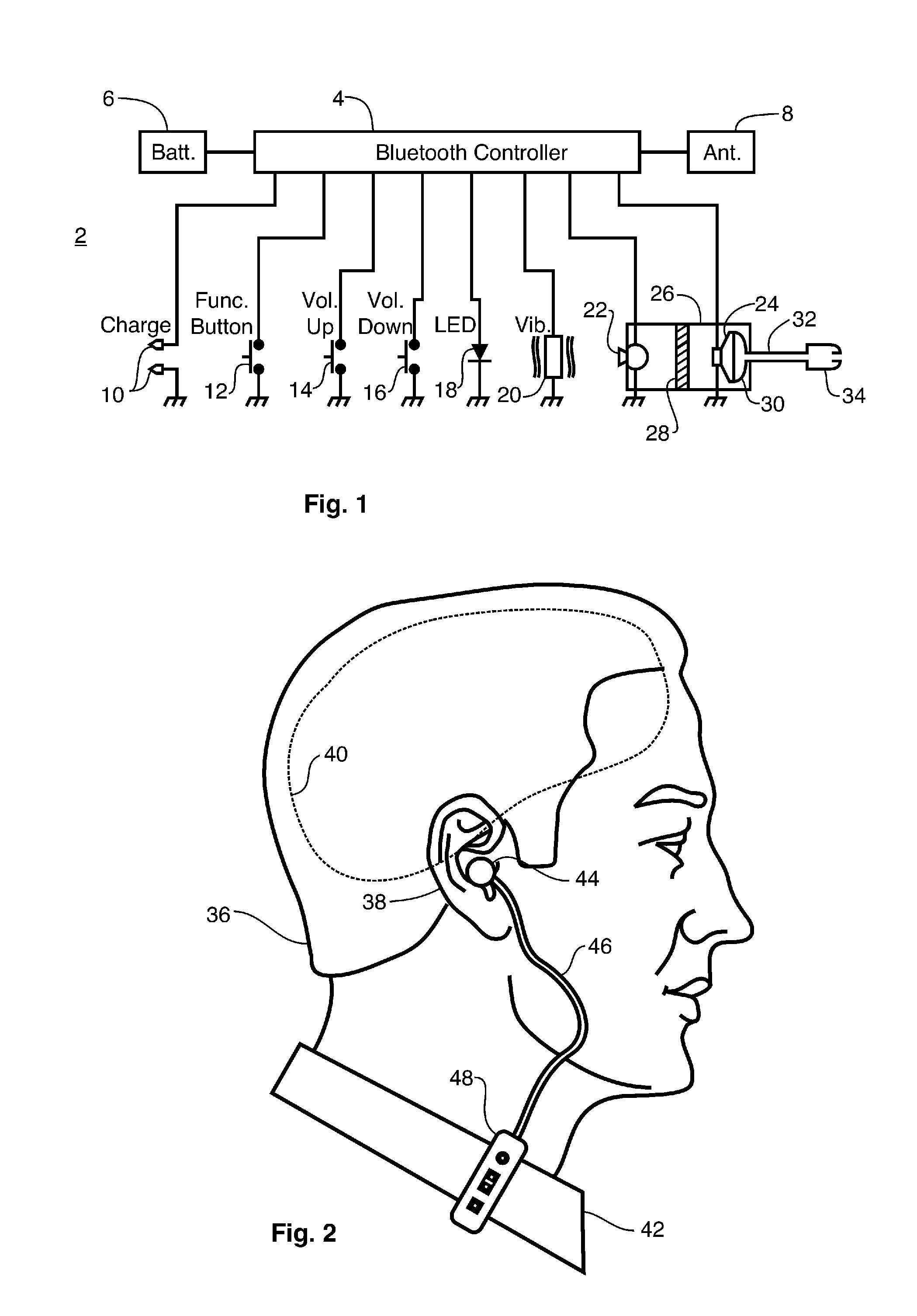
Vehicular sound-processing system incorporating an interior mirror user-interaction site for a restricted-range wireless communication system
InactiveUS6906632B2Facilitates few partEasy to installPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesOrganic chemistryCommunications systemEngineering
The interior cabin of a vehicle is provided with a vehicular sound-processing system that comprises an interior rearview mirror assembly, the mirror assembly including a mirror housing and a reflective element. An accessory is located in the interior cabin. The interior rearview mirror assembly comprises a user-interaction site for a wireless communication system, the wireless communication system communicating with the accessory. The user-interaction site comprises at least one microphone for producing an audio output in response to detection of vocal input of a human speaker in the interior cabin with the vehicle cabin noise superimposed thereon. Preferably, the user-interaction site further comprises at least one manually operated control input. The restricted-range wireless communication system preferably comprises one of a radio frequency restricted-range wireless communication system and an infrared restricted-range wireless communication system. Signals indicative of the vocal input detected at the user-interaction site of the interior mirror assembly are wirelessly broadcast to the accessory located in the interior cabin of the vehicle.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
System and method for conserving battery power in a patient monitoring system
ActiveUS20120029315A1Lifetime of devices is burdensomely limitedImprovement effortsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMonitoring systemVital signs
A vital-signs patch in a patient monitoring system is disclosed. The patch includes a housing configured to be attached to the skin of a patient, the housing containing a radio that can selectably transmit and receive on more than one frequency and a processor. The processor configures the radio to transmit and receive on a determined frequency based at least in part on the level of noise detected on the frequencies.
Owner:CAREFUSION 303 INC
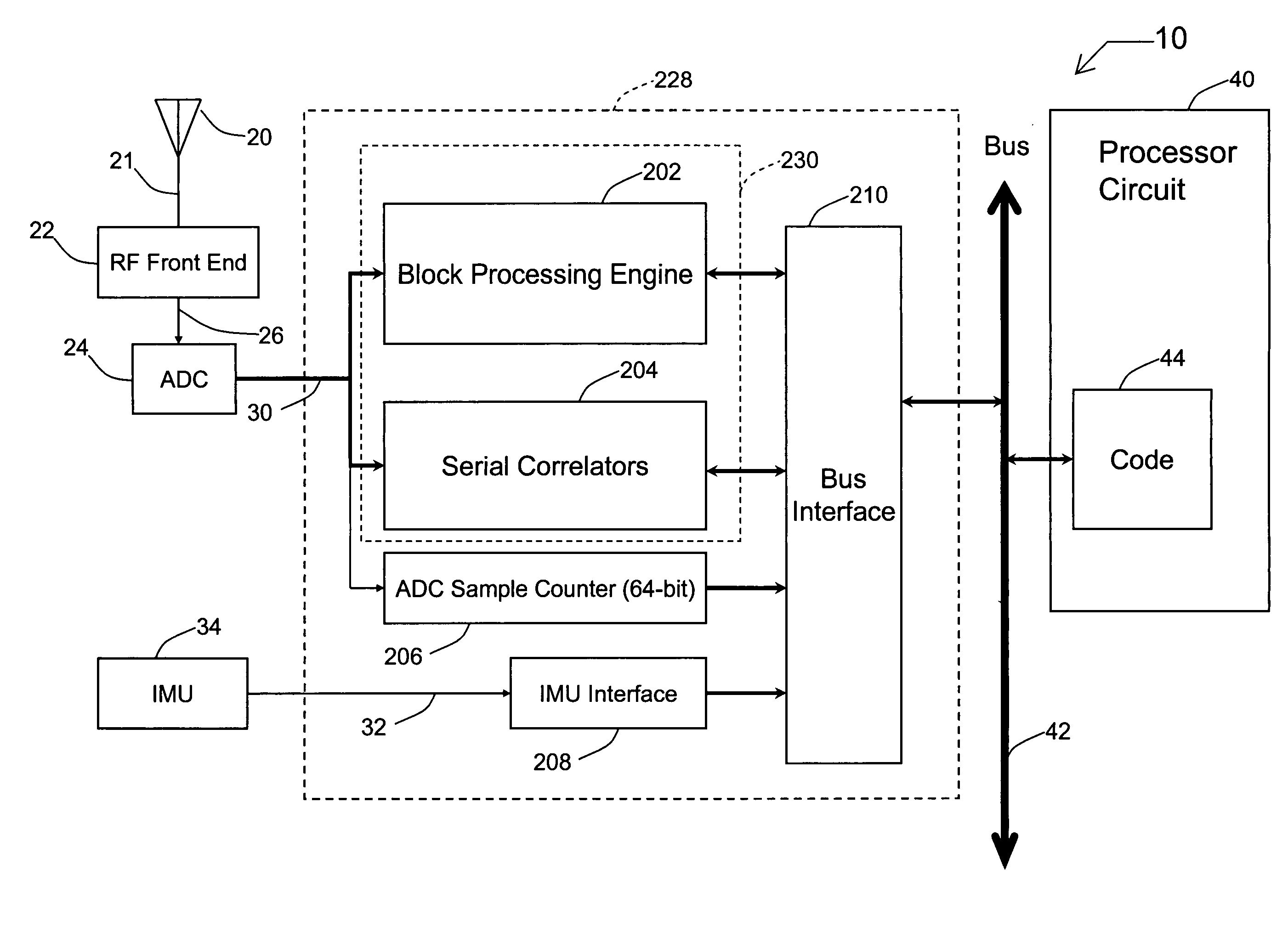
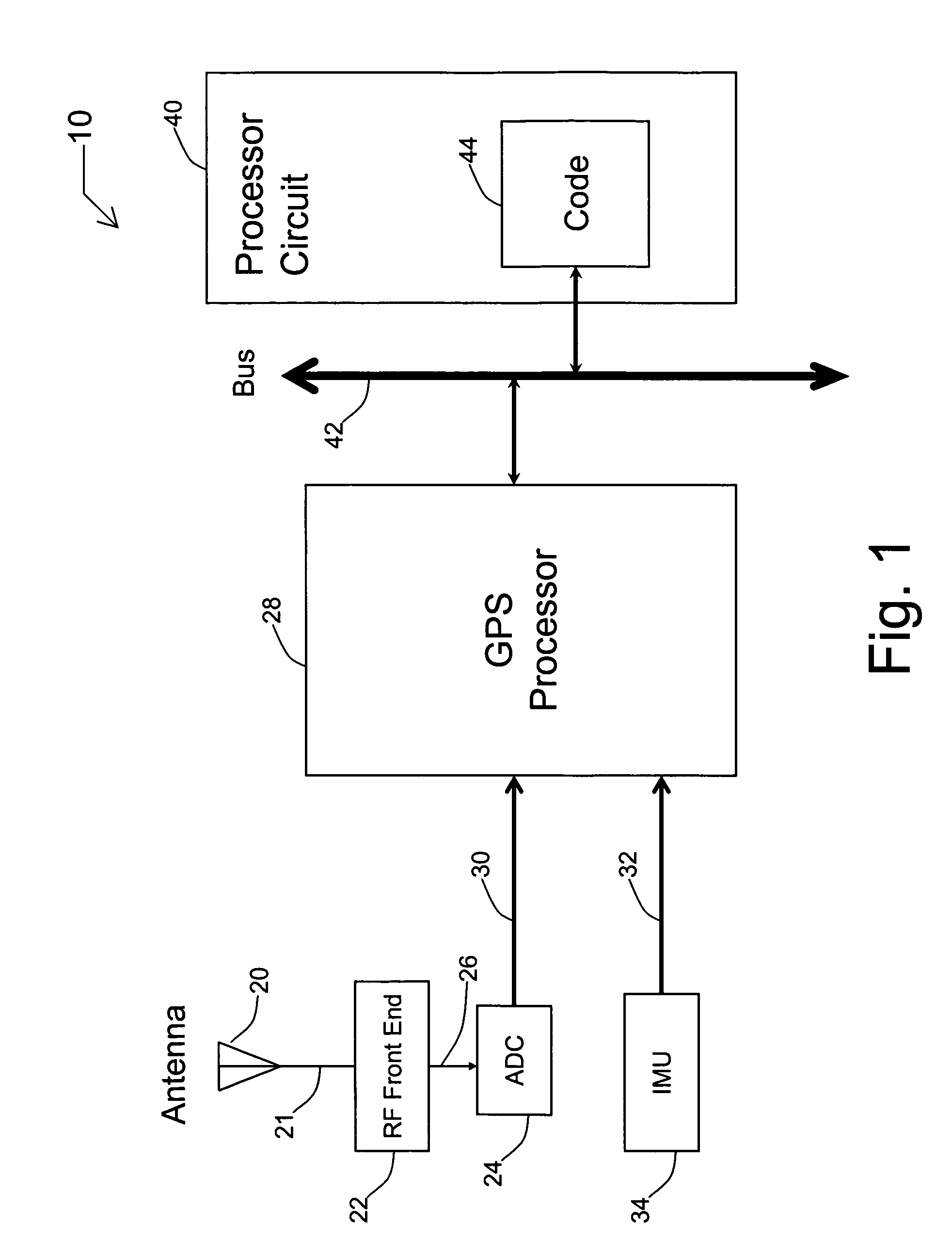
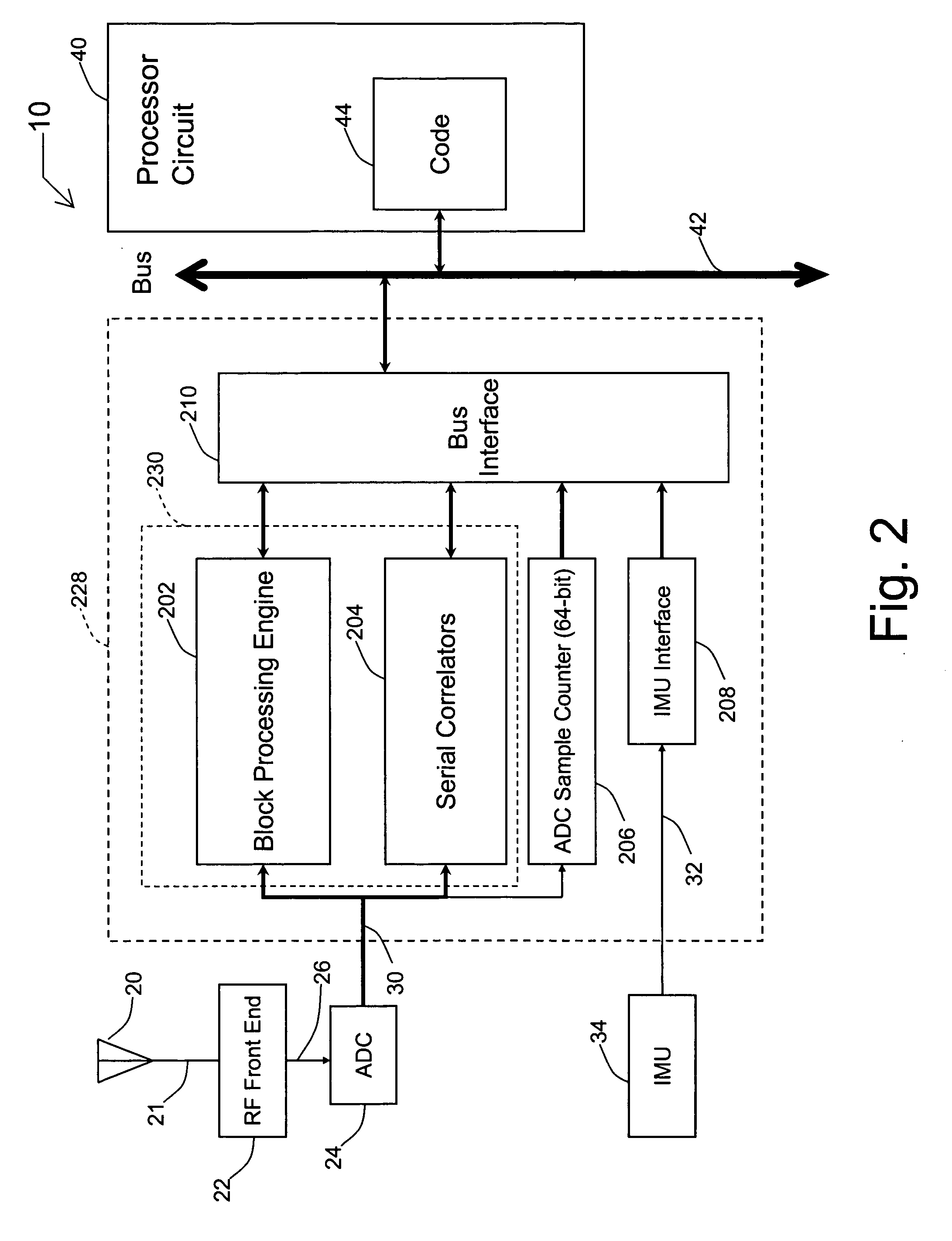
Systems and methods for acquisition and tracking of low CNR GPS signals
A receiver for continuous carrier phase tracking of low carrier-to-noise ratio (“CNR”) signals from a plurality of radio navigation satellites while the receiver is mobile. The receiver may have: a radio frequency (RF) front-end that provides satellite data corresponding to signals received from the plurality of radio navigation satellites; an inertial measurement unit (IMU) that provides inertial data; and a processor circuit in circuit communication with the RF front end and the IMU, the processor circuit being capable of using satellite data from the RF front-end and inertial data from the IMU to perform continuous carrier phase tracking of low CNR radio navigation satellite signals having a CNR of about 20 dB-Hz, while the receiver is mobile. The receiver may be a GPS receiver for continuous carrier phase tracking of low-CNR GPS signals.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
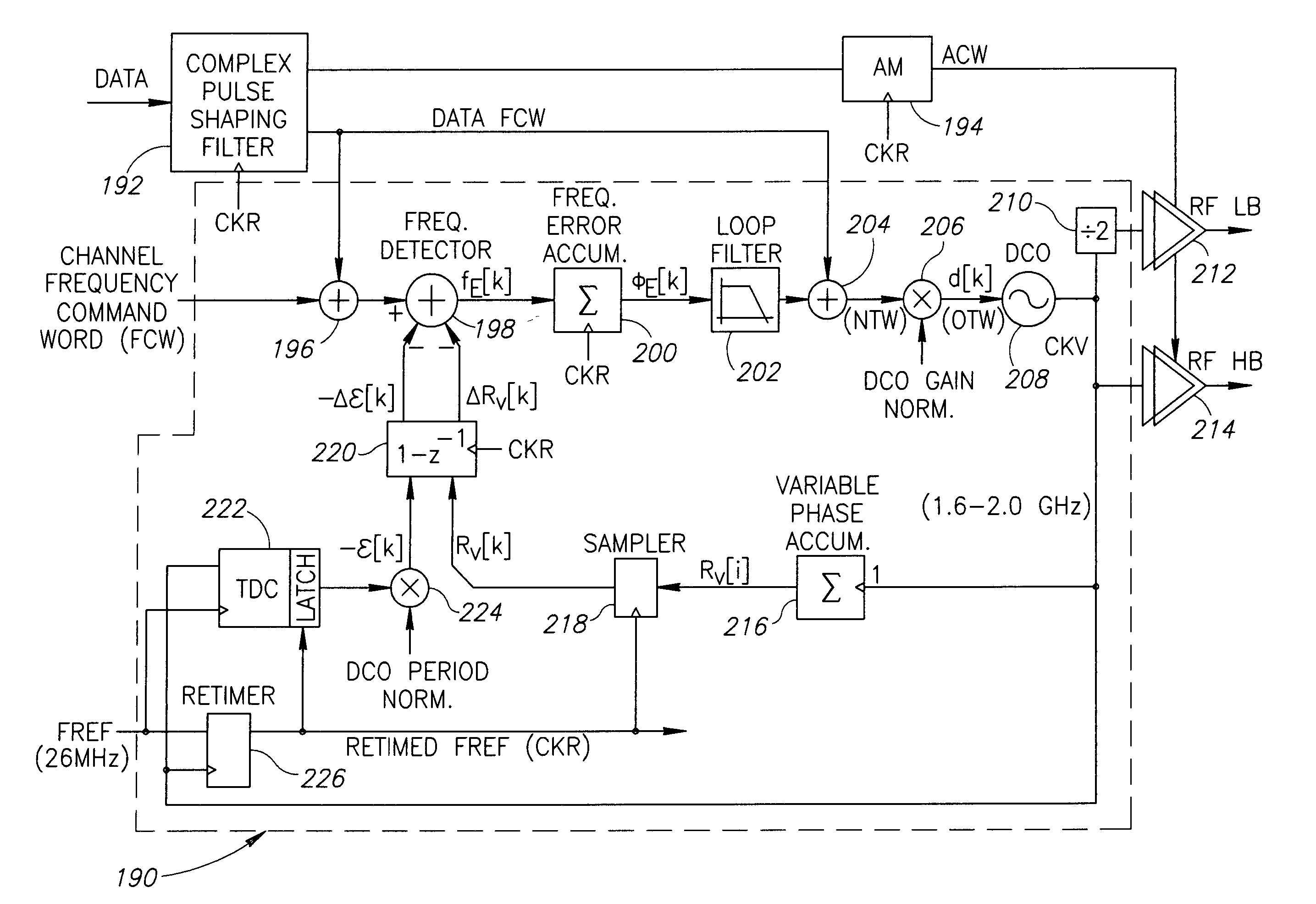
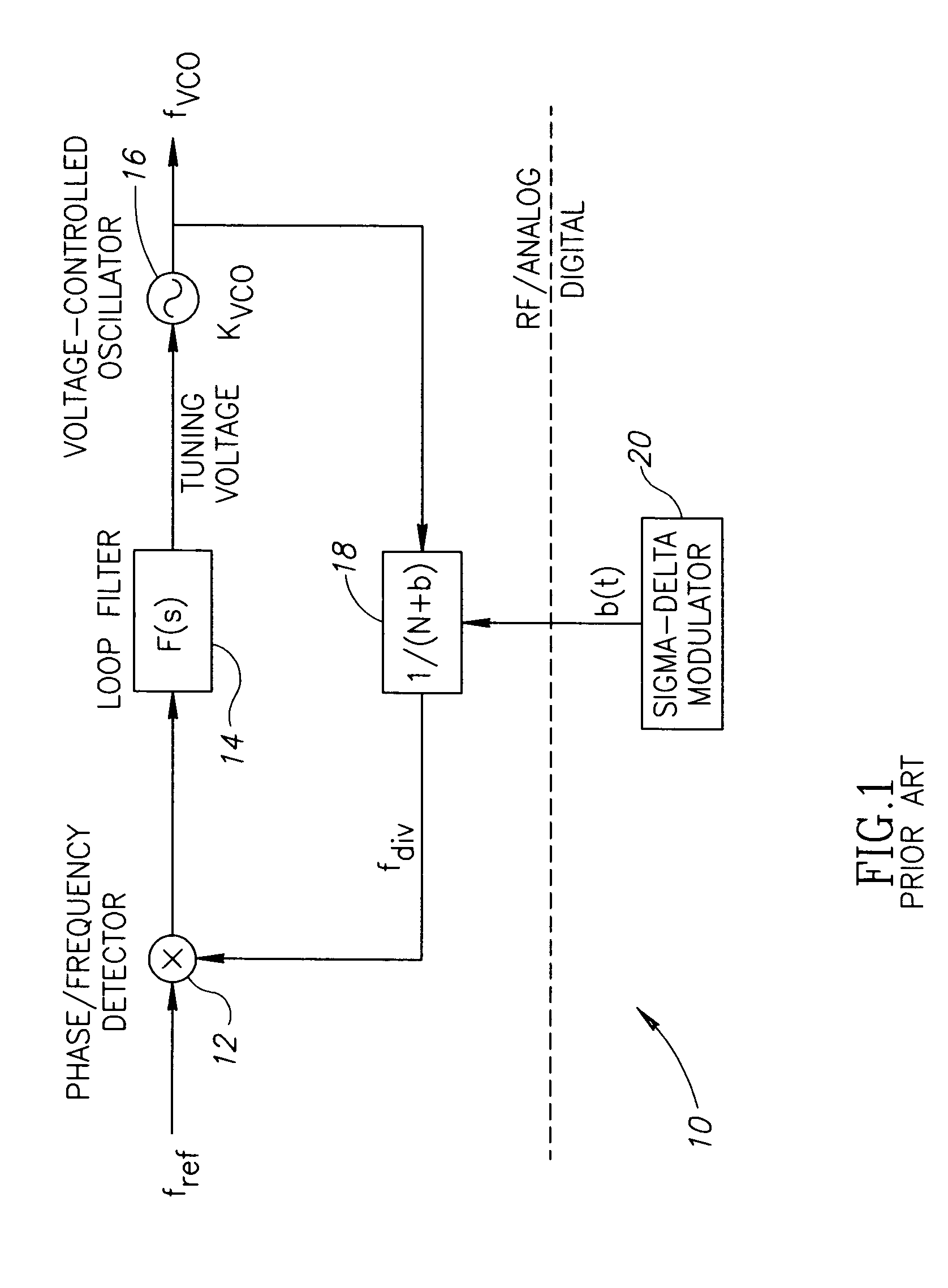
Apparatus for and method of noise suppression and dithering to improve resolution quality in a digital RF processor
InactiveUS20050186920A1Cancel noiseAvoid it happening againPulse automatic controlAngle modulationImage resolutionEngineering
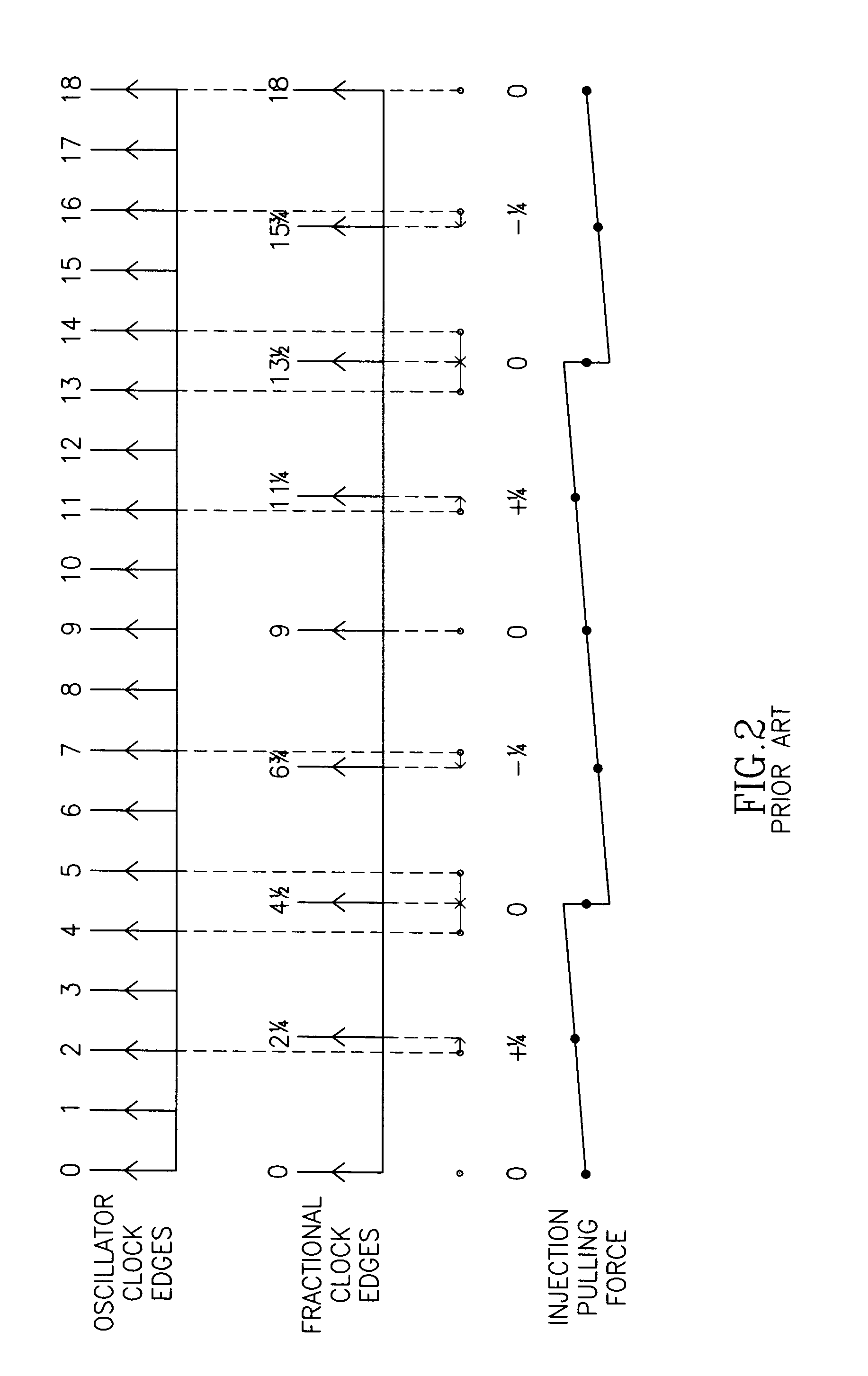
A novel apparatus for and a method of noise and spurious tones suppression in a digital RF processor (DRP). The invention is well suited for use in highly integrated system on a chip (SoC) radio solutions that incorporate a very large amount of digital logic circuitry. The noise suppression scheme eliminates the noise caused by various on chip interference sources transmitted through electromagnetic, power, ground and substrate paths. The noise suppression scheme permits an all digital PLL (ADPLL) to operate in such a way to avoid generating the spurs that would normally be generated from the injection pulling effect of interfering sources on the chip. The frequency reference clock is retimed to be synchronous to the RF oscillator clock and used to drive the entire digital logic circuitry of the DRP. This ensures that the different clock edges throughout the system will not exhibit mutual drift. A method of improving the resolution quality of a time to digital converter within the ADPLL is also taught. The method dithers the reference clock by passing it through a delay circuit that is controlled by a sigma-delta modulator. The dithered reference clock reduces the affect on the phase noise at the output of the ADPLL due to ill-behaved quantization of the TDC timing estimation.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Radio frequency modulation of variable degree and automatic power control using external photodiode sensor for low-noise lasers of various wavelengths
ActiveUS20060215716A1Increase output powerWide wavelength rangeLaser detailsSemiconductor laser optical deviceLow noiseRadio frequency
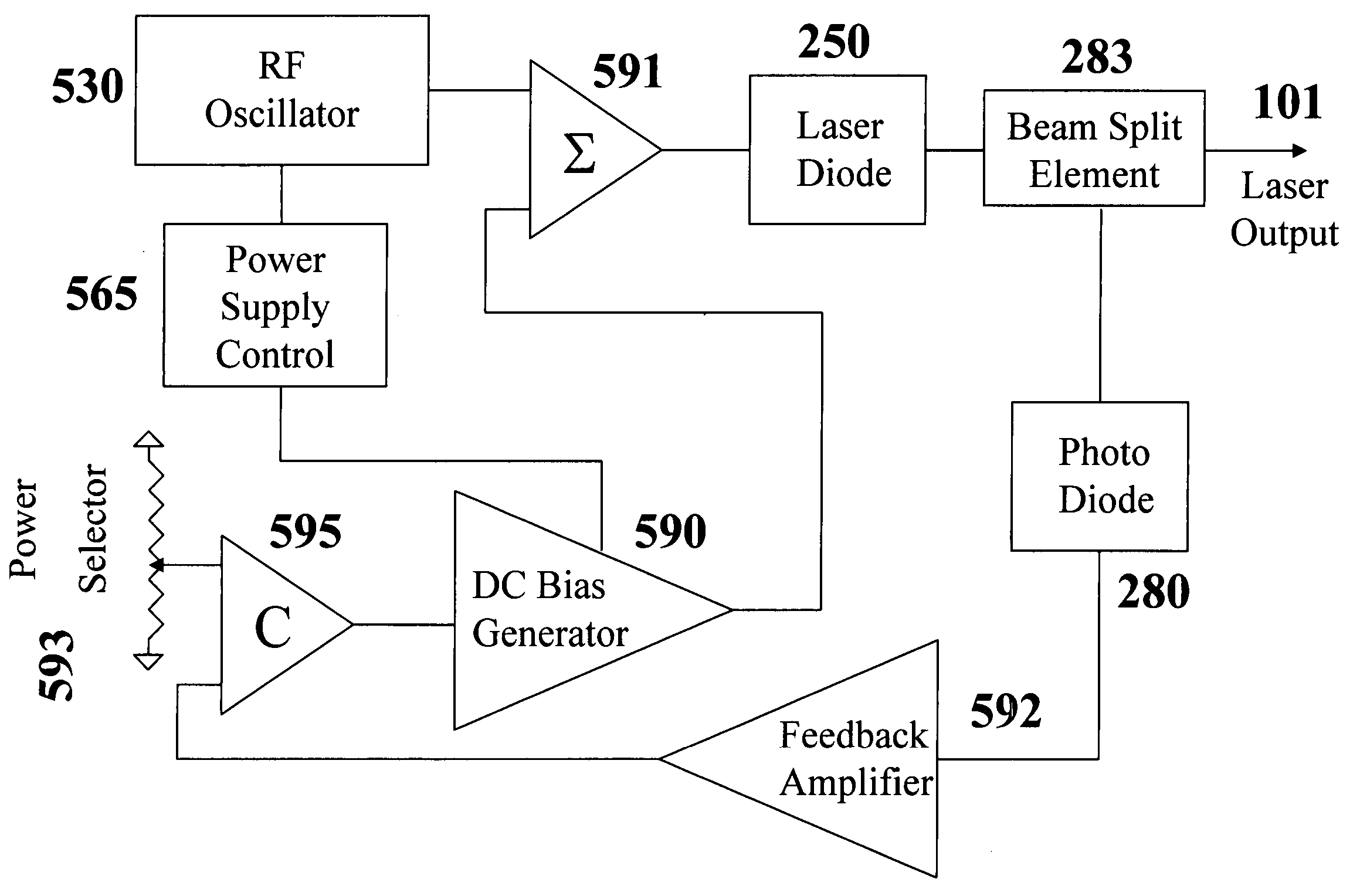
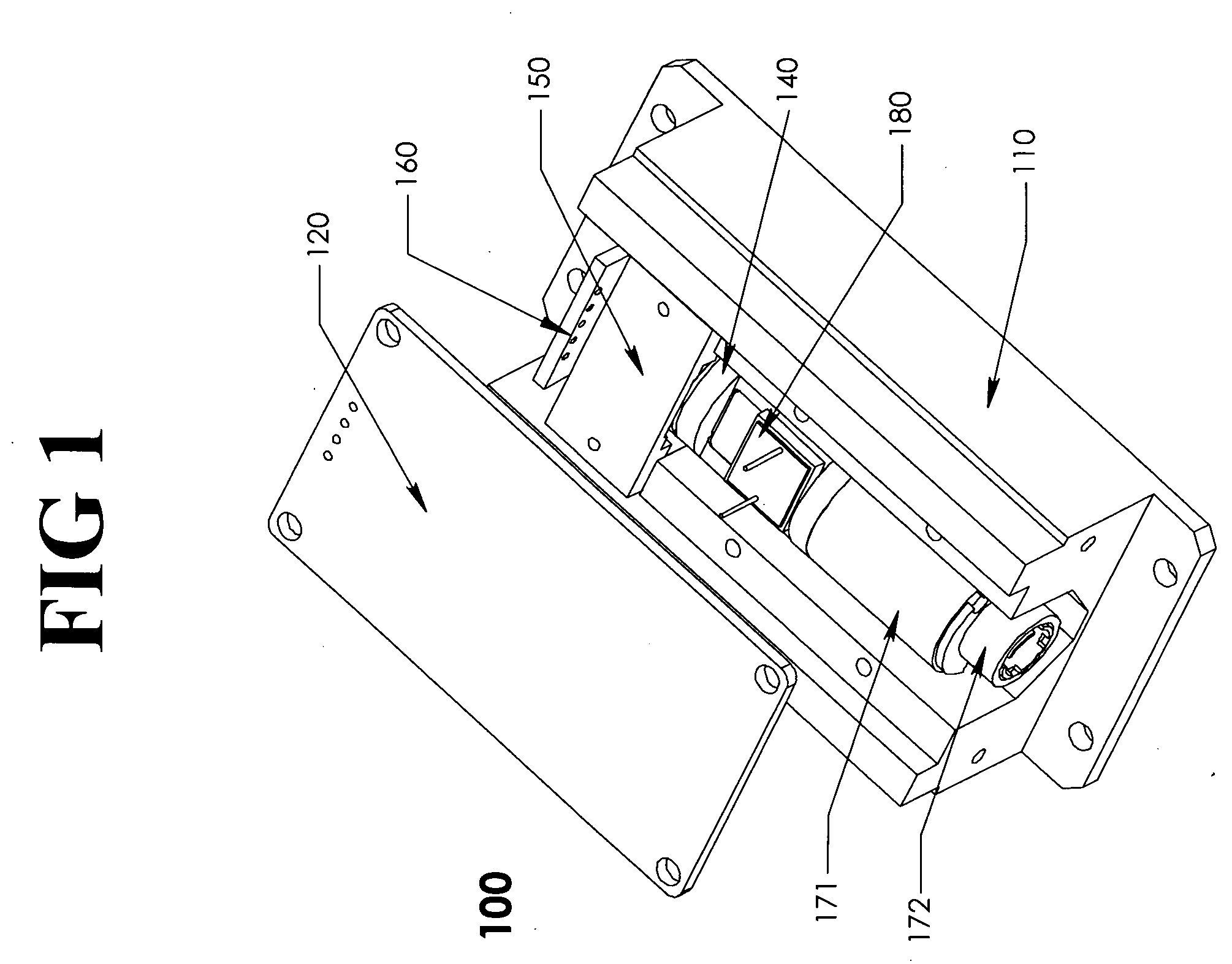
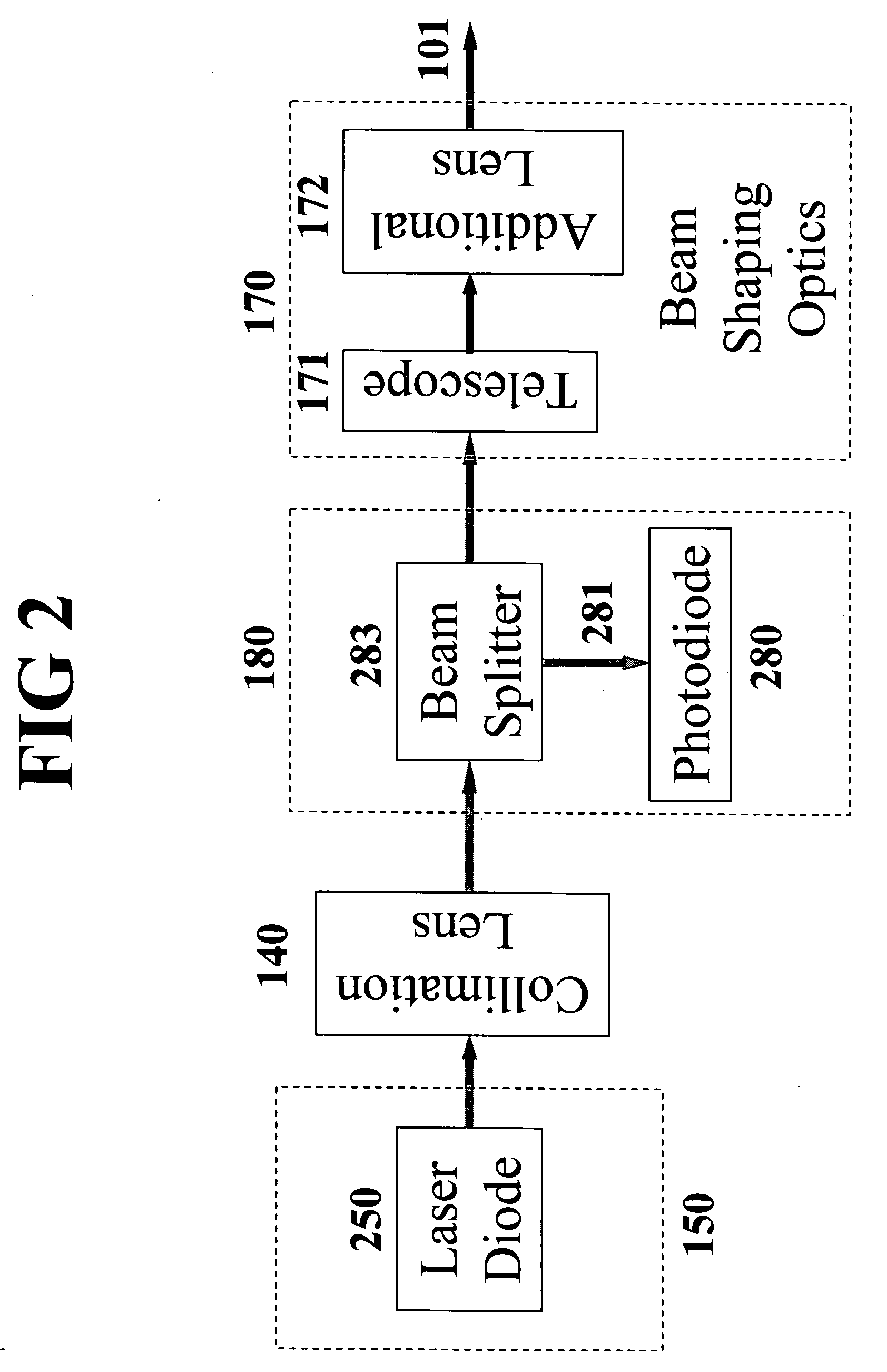
A low-noise laser diode module comprises a laser diode for emitting light with a wavelength in the range from UV to IR, a drive circuit for injecting electrical current into said diode, and an automatic power control circuit for monitoring and adjusting laser output power using front-facet photodiode external to the laser assembly and a feedback loop. Said drive circuit produces injection current modulated by an RF signal with variable degrees, depending on the wavelength to be stabilized, the desired spectral bandwidths of the laser output, and / or other applications. Said RF signal can be a sine wave, a distorted sine wave, a rectified sine wave, a non-sine wave, a series of narrow pulses, or repetitive shunt. The present invention encompasses a method for producing stable, broadband, and low-coherent laser. The present invention also encompasses a method for producing stable narrowband or single longitudinal mode laser. The present invention further encompasses a compact light source applicable to DPSS lasers, fiber lasers, optical parametric oscillators, low-speckle laser display systems, and seeders, with or without nonlinear frequency conversion processes.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION
Automotive anti-collision radar multi-target detecting method and system
InactiveCN103257346AResolve echoResolve interferenceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumIntermediate frequency
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
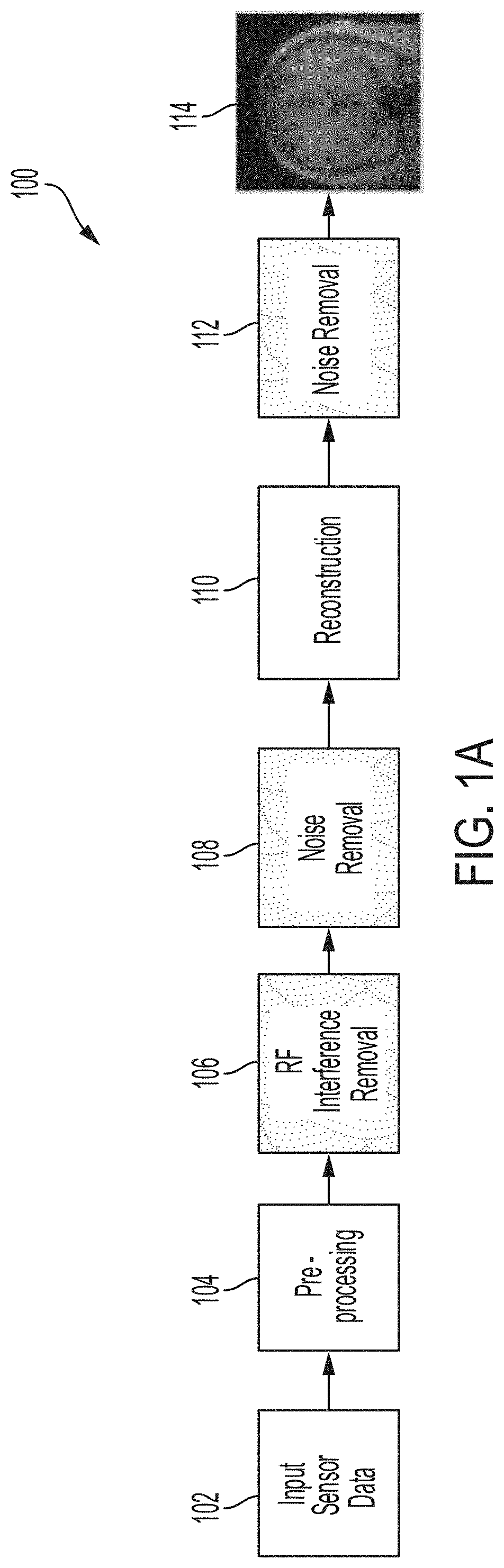
Deep learning techniques for suppressing artefacts in magnetic resonance images
Techniques for removing artefacts, such as RF interference and / or noise, from magnetic resonance data. The techniques include: obtaining input magnetic resonance (MR) data using at least one radio-frequency (RF) coil of a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system; and generating an MR image from input MR data at least in part by using a neural network model to suppress at least one artefact in the input MR data.
Owner:HYPERFINE OPERATIONS INC
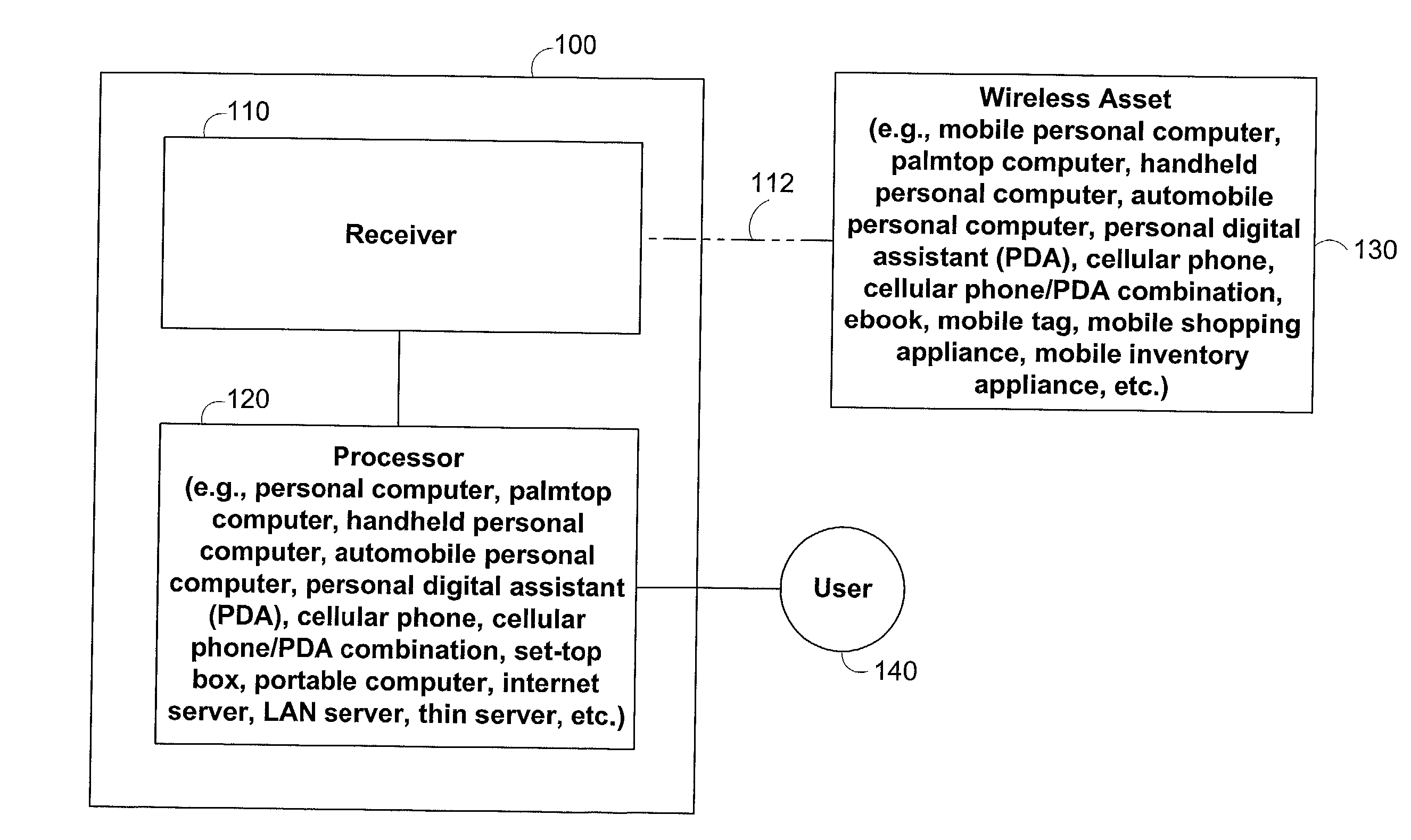
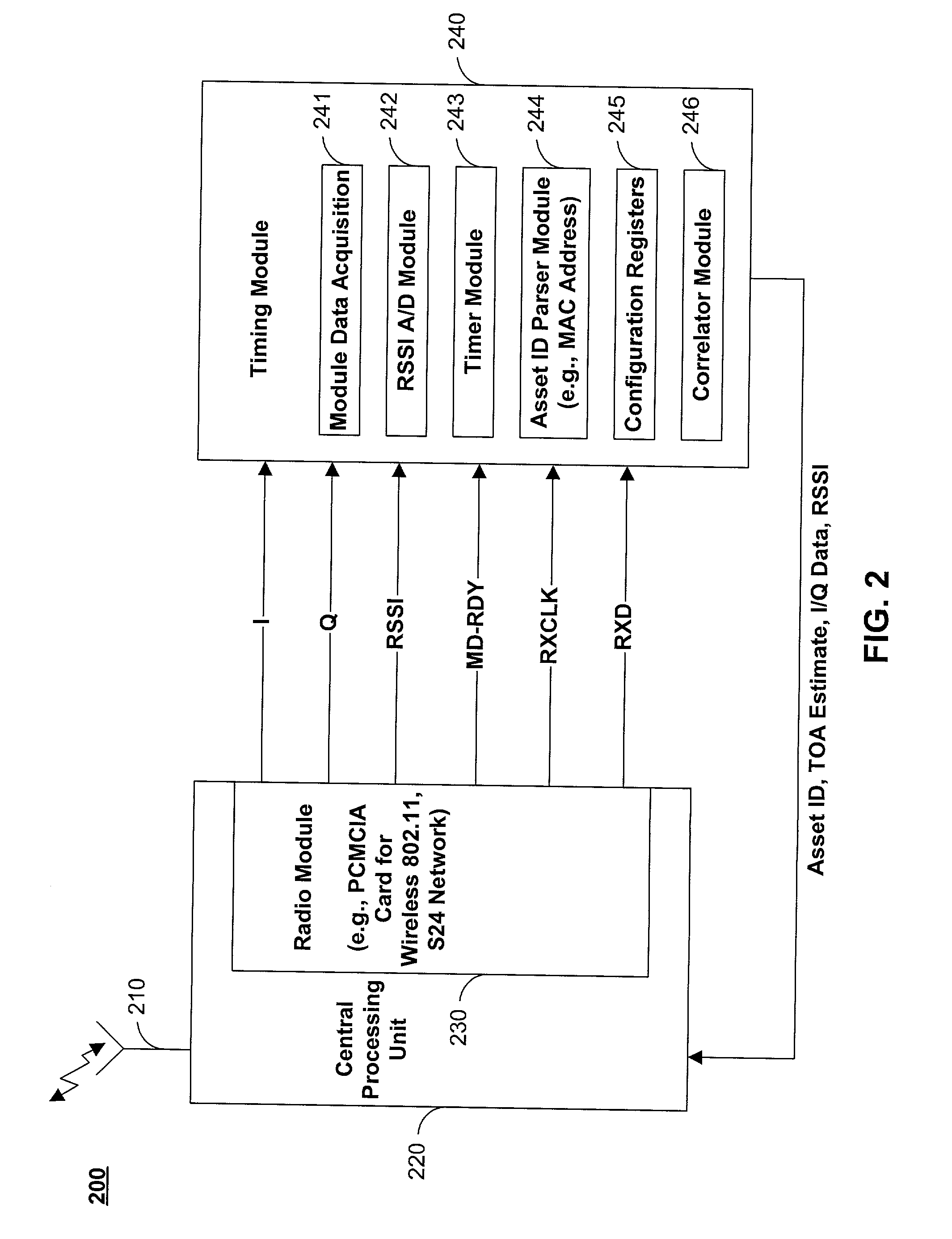
Methods and apparatus for identifying asset location in communication networks
ActiveUS20020097182A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionTelevision system scanning detailsRadio frequencyTime difference
The location of unmodified wireless assets in a wireless communication network may be identified using time differences of arrivals of a communication sequence at different network receivers. Time-stamping devices may include correlator circuits in parallel with signal decoders to time-stamp communication sequences. Cellular wireless networks may be frequency-multiplexed to increase spatial time-stamping density. Tags may be attached to passive assets to provide location identification information to network devices. Locations of assets broadcasting standard 802.11 radio frequency structures may be identified. Noise inherent in correlating a communication sequence may be reduced by using a selected correlation function.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
Gravity gradiometry
InactiveUS6837106B2Reduces linear accelerationsEfficient separationSeismologyGravitational wave measurementMobile vehicleSystems design
A gravity gradiometer is combined with a two-stage actively controlled isolation system. The gravity gradiometer and two stage isolation system may then be mounted within (or on) a mobile vehicle such as, for example, an aircraft. It has been recognized by the inventors herein that the accelerations imparted to an aircraft during normal operations can be separated through system design into two relatively distinct regimes within the frequency domain. The invention provides a first isolation mount, which forms part of the isolation system, to isolate accelerations (and resulting translations) falling within a first of the two frequency regimes. The second isolation mount, which is mounted to the first isolation mount, isolates accelerations falling within the second of the two frequency regimes. A gravity gradiometer can then be mounted to the second isolation mount. As a result of housing the gravity gradiometer within the nested isolation system (a combination of the first and second isolation mounts), the gravity gradiometer is substantially isolated from the accelerations experienced by the mobile vehicle. Consequently, gravity gradients measured by the gravity gradiometer are relatively noise free and provide heretofore-unobtainable accuracy.
Owner:GEDEX
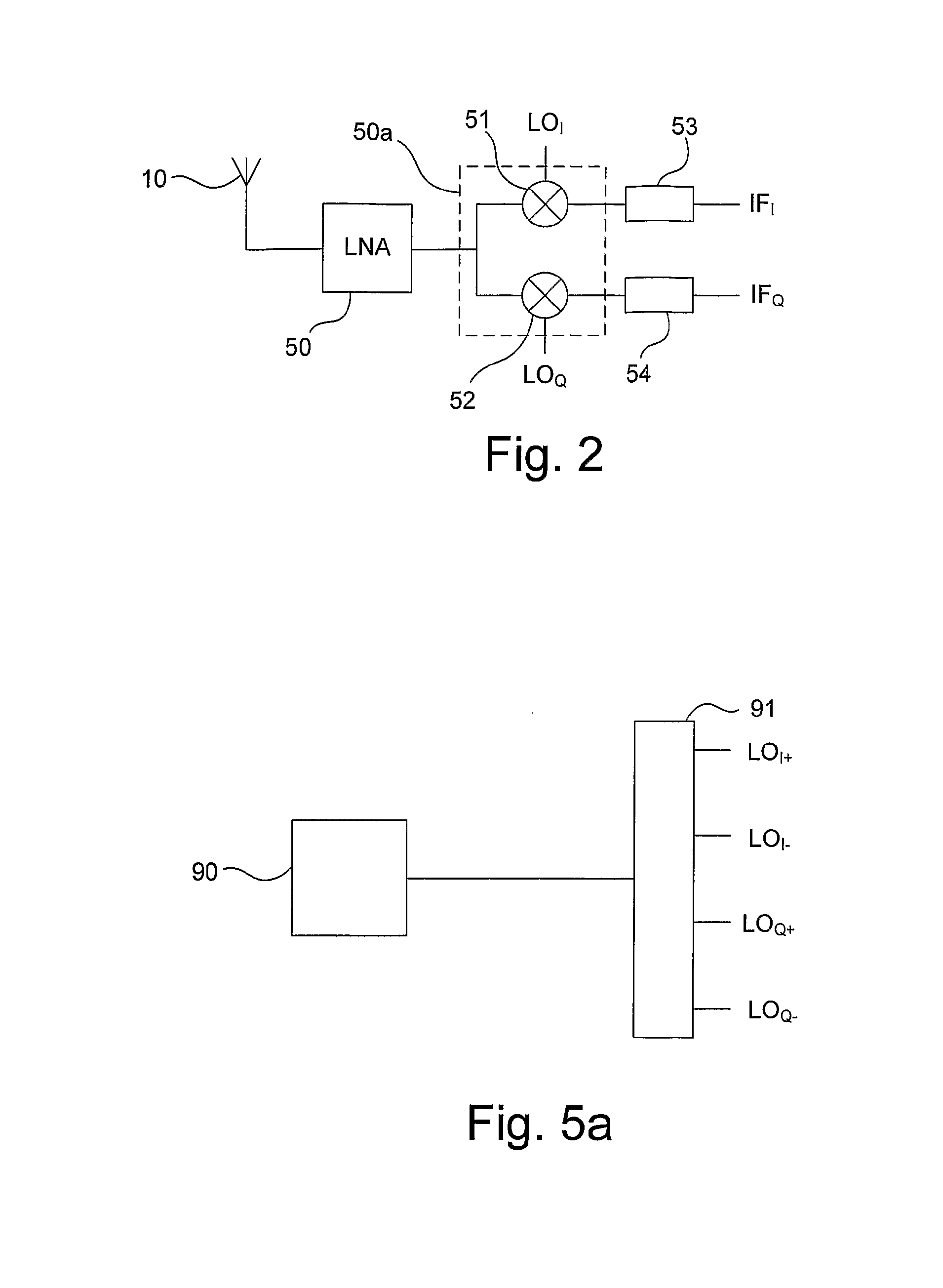
Radio-Receiver Front-End and A Method For Frequency Converting An Input Signal
InactiveUS20070287403A1Reduce complexitySmall sizeModulation transferenceTransmission noise suppressionLow noiseLocal oscillator signal
An N-phase radio receiver front-end for converting an input signal having a first frequency to output signals having a second frequency, and a method for converting an input signal in an N-phase radio receiver front-end. An input port of the N-phase radio receiver front-end is directly connected to an input port of a low noise amplifier (50). A mixer arrangement (50a) is a current mode mixer arrangement. An output port of the low-noise amplifier is directly connected to an input port of the mixer arrangement. A signal generator operatively connected to the mixer arrangement is adapted to generate N phase shifted local oscillator signals.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
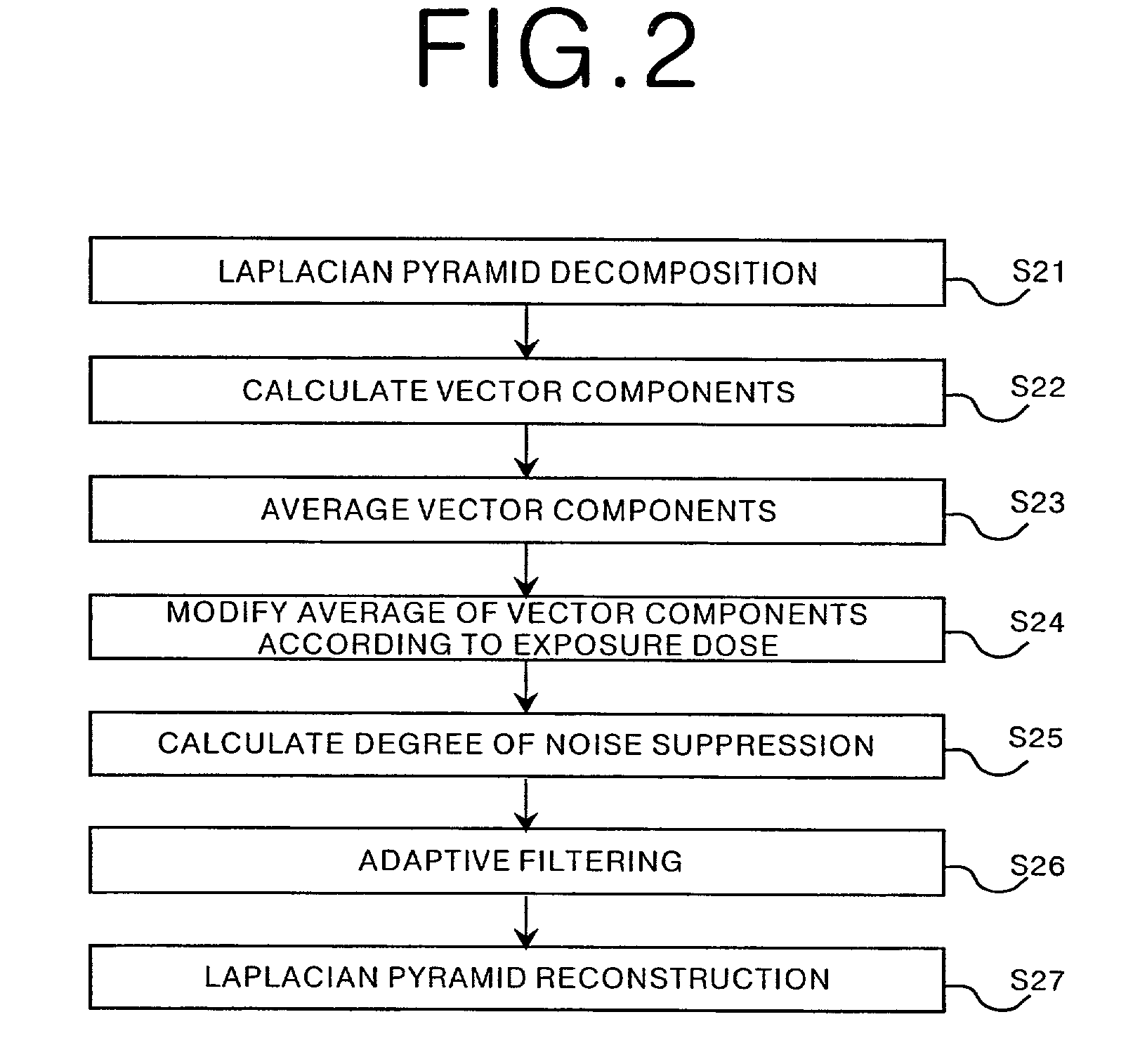
Apparatus for suppressing noise by adapting filter characteristics to input image signal based on characteristics of input image signal
InactiveUS20020071600A1Suppress noiseReduce degradationImage enhancementImage analysisNoise (radio)Radiology
In an apparatus for suppressing noise in an input image signal representing a radiographic image: at least one first characteristic of the input image signal is obtained by calculation based on information indicating an exposure dose with which the radiographic image has been produced; at least one second characteristic of a smoothing filter is adapted to the input image signal based on the at least one first characteristic; and the input image signal is processed by using the smoothing filter so as to smooth the radiographic image. In addition, a plurality of band-limited image signals respectively representing a plurality of band-limited images belonging to a plurality of different frequency bands are generated based on the input image signal, each of the plurality of band-limited image signals is processed by using the smoothing filter so as to smooth each of the plurality of band-limited images.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
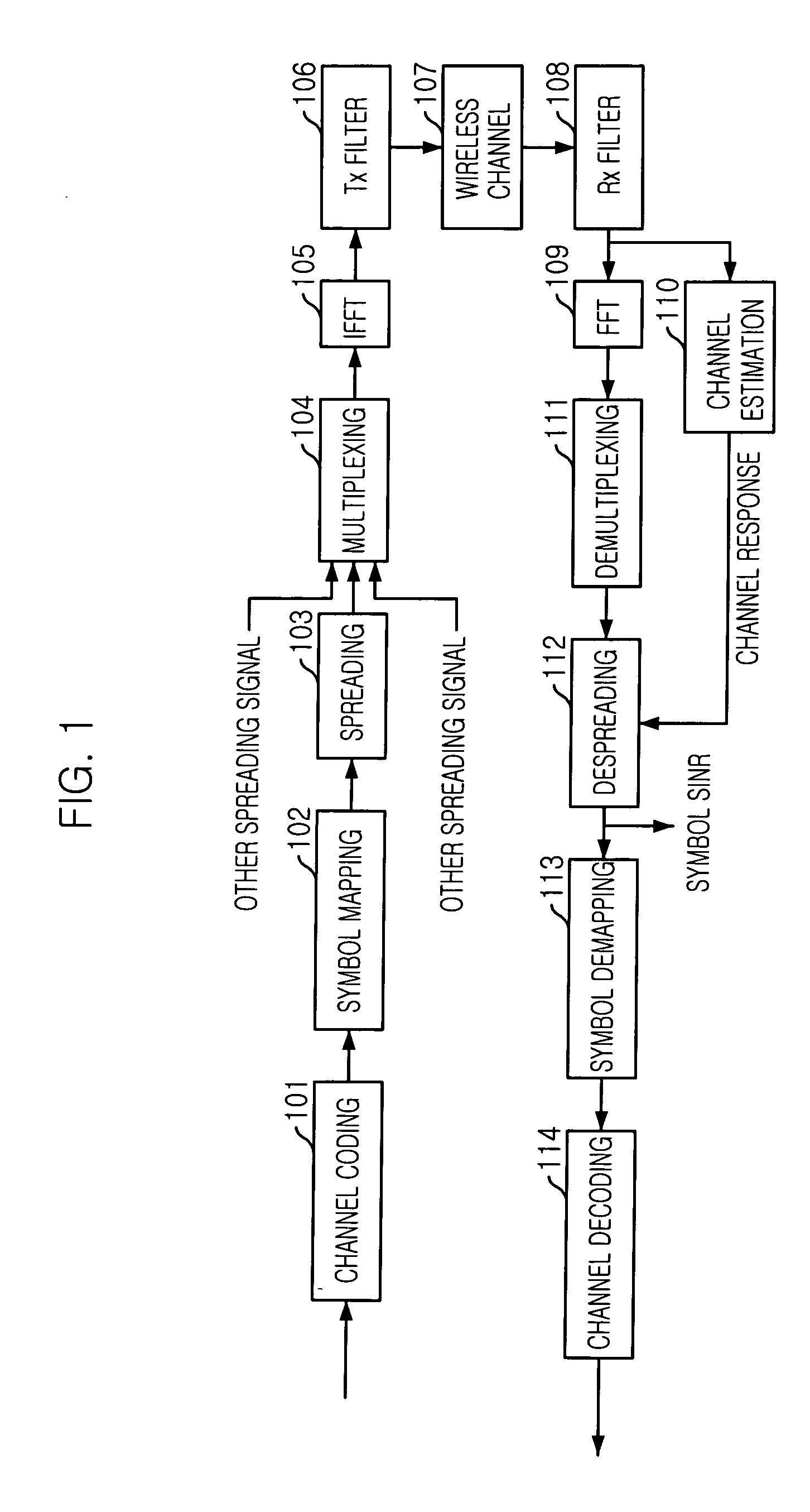
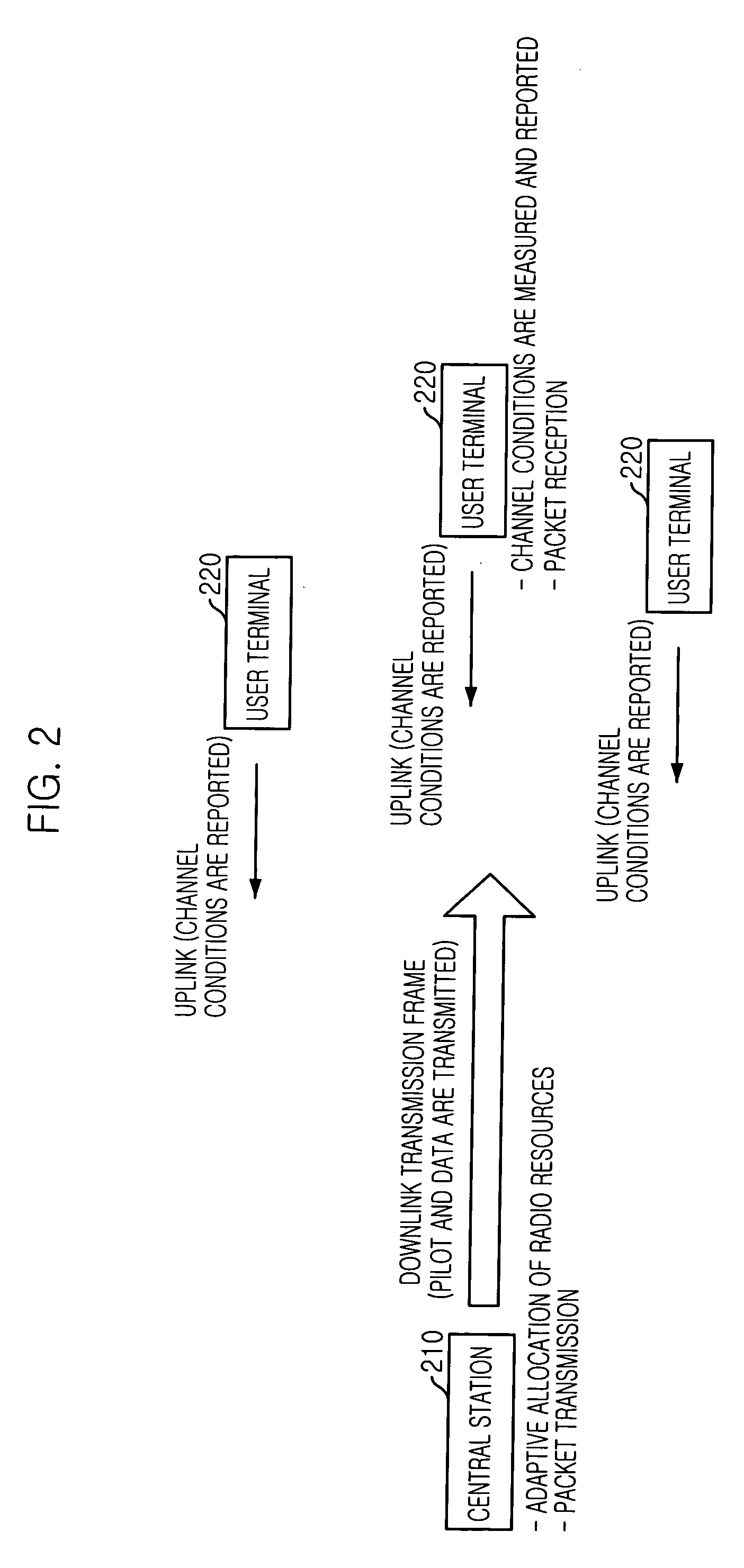
Adaptive downlink packet transmission method in multicarrier CDMA system
InactiveUS20050141473A1Minimize interferenceRadio resource efficientlyPower managementBaseband system detailsInterference factorEqualization
Disclosed is an adaptive downlink packet transmission method for a multicarrier Code Division Multiple Access (MC-CDMA) system. The method can allocate radio resources efficiently according to the variations of channel conditions for each user terminal, allocate transmission power appropriately according to the interference from the same cell, and minimize interference to adjacent cells. The adaptive downlink packet transmission method includes the steps of: a) estimating a signal-to-interference-and-noise ratio (SINR) in a user terminal after channel equalization and despreading by measuring a downlink pilot channel; b) measuring an average interference factor and an average noise power; and c) allocating radio resources adaptively in the central station by determining transmission slots in a transmission frame, the number of spreading codes to be used in each transmission slot, symbol energy for each spreading code, and a transmission method, until transmission slots and packets to be allocated are not available.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method and system for dynamically assigning channels across multiple radios in a wireless LAN
ActiveUS7327697B1Improve network performanceMinimize impactReceivers monitoringError preventionColor mappingWireless lan
In a fixed channel wireless network system with a limited number of channels, assignment of the fixed channels between remote client elements and access elements is made systematically according to a set of criteria accounting for network loading and interference, then channel assignments are dynamically updated according to a priority to maintain optimal network performance with changing conditions of load and interference. The channel utilization problem is address at a system level rather than at a local level by treating the system as a three dimensional color mapping problem. All noise is treated as having a source in virtual access elements with an appropriate performance metric. The performance metric is used to select a channel set that minimize chances of interference and maximize user performance. Specifically, there are several parameter matrices which are managed and updated by a central resource management element, namely signal strength between elements, interference, and load. These matrices are used to find the optimal channel assignments for a predetermined limited set of assignable channels.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
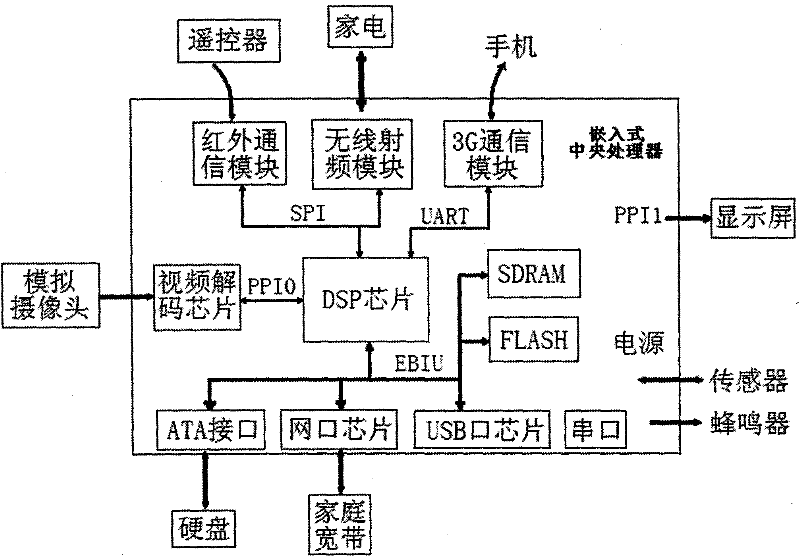
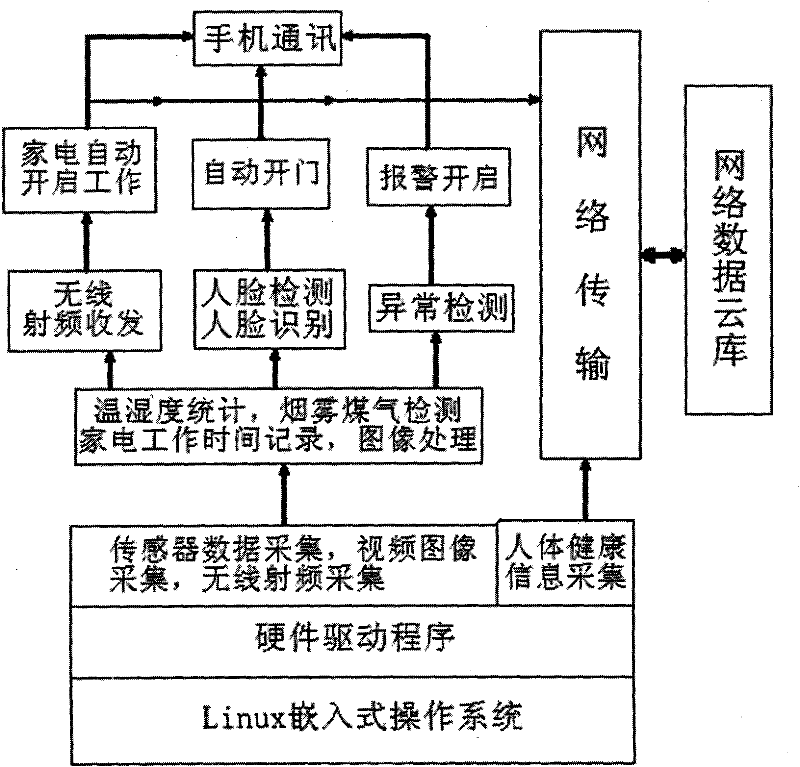
Smart home perception and control system
InactiveCN102289220AHigh degree of intelligenceImprove securityTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlInformation processingWireless control
Smart home perception and control system. The system builds an embedded platform with DSP chip as the core, connects with a large number of sensors, collects temperature and humidity, smoke concentration and noise, as well as human body temperature, heart rate, blood pressure and other health conditions. The system uses wireless radio frequency modules to wirelessly control specific home appliances in the family, connects to the network data cloud through home broadband or 3G communication, captures images through analog cameras, processes the collected information on the DSP platform, and responds accordingly according to the results. This system can intelligently control the work of home appliances according to the statistical rules of the owner's life, and can automatically control the opening and closing of the door according to the situation in front of the door; it can automatically sense the abnormal situation of the home and automatically alarm; Information, to achieve remote control, or stay at home, so that doctors can check their own health status through the network data cloud thousands of miles away.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
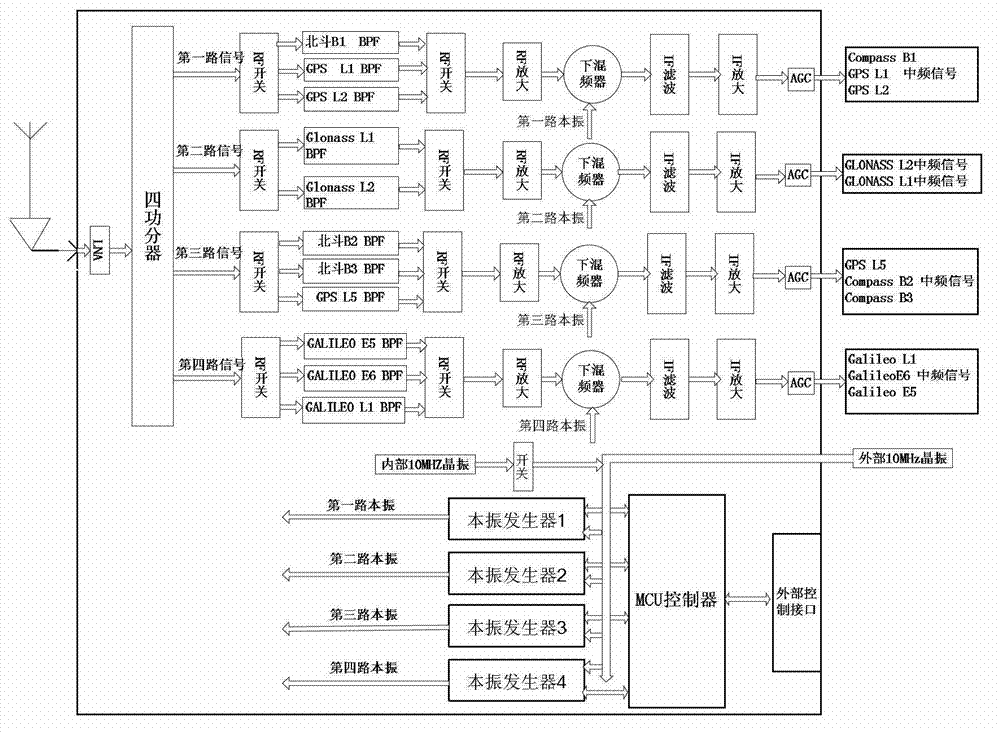
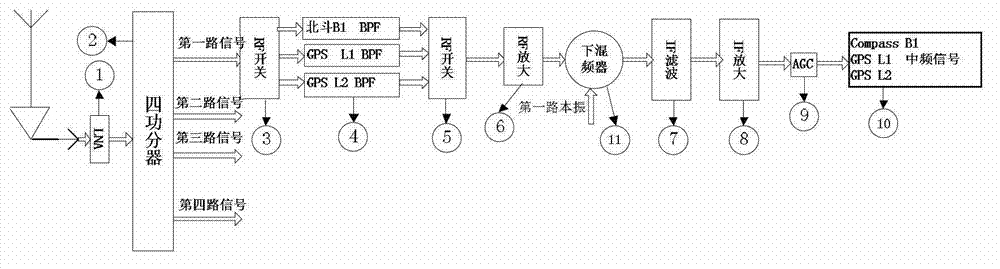
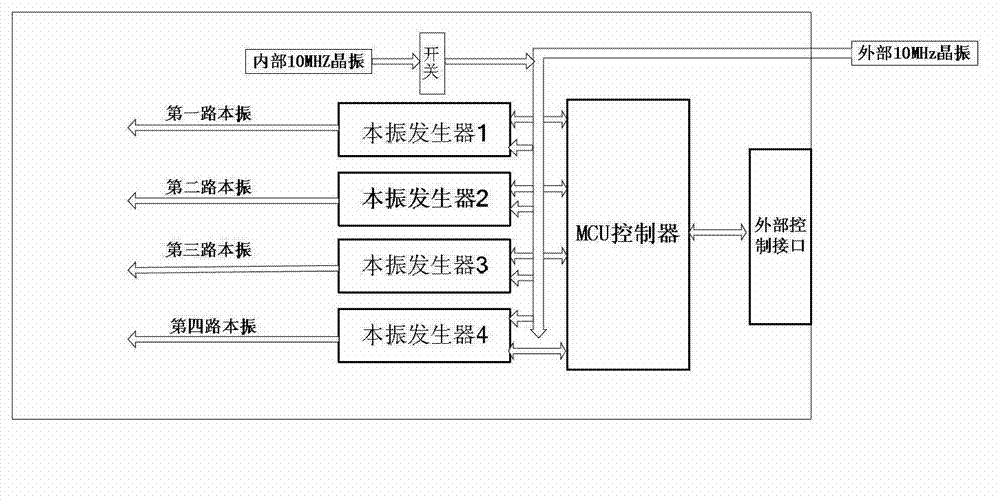
Multi-mode multi-frequency global navigational satellite system receiver radio frequency front end device
ActiveCN103117767AEasy to changeEasy to adjustSatellite radio beaconingTransmissionLow noiseSignal processing circuits
The invention discloses a multi-mode multi-frequency global navigational satellite system receiver radio frequency front end device. The device comprises a low-noise amplifier, a power divider, and multiple radio-frequency signal processing circuits, wherein the low-noise amplifier, the power divider, and the multiple radio-frequency signal processing circuits are connected in sequence. Each radio-frequency signal processing circuit comprises a first radio-frequency switch, a radio-frequency filter bank, a second radio-frequency switch, a radio-frequency amplifying module, a lower frequency mixing module, an intermediate frequency filter module, an intermediate frequency amplifying module, and an automatic gain control unit, wherein the first radio-frequency switch, the radio-frequency filter bank, the second radio-frequency switch, the radio-frequency amplifying module, the lower frequency mixing device, the intermediate frequency filter module, the intermediate frequency amplifying module, and the automatic gain control unit are connected in sequence. The lower frequency mixing module comprises a lower frequency mixing device and a local oscillating generating module which are connected with each other. A control unit is connected with the first radio-frequency switch and the second radio-frequency switch of each radio-frequency signal processing circuit and the local oscillating generating module of the lower frequency mixing module. The device can flexibly select intermediate frequency inputting from various combination frequency ranges of a quad-mode 11 frequency range, and therefore functions of collecting in the same module and processing navigation system intermediate frequency signals of four system satellites are realized, namely a global position system (GPS), Glonass, Galileo, and Big Dipper.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
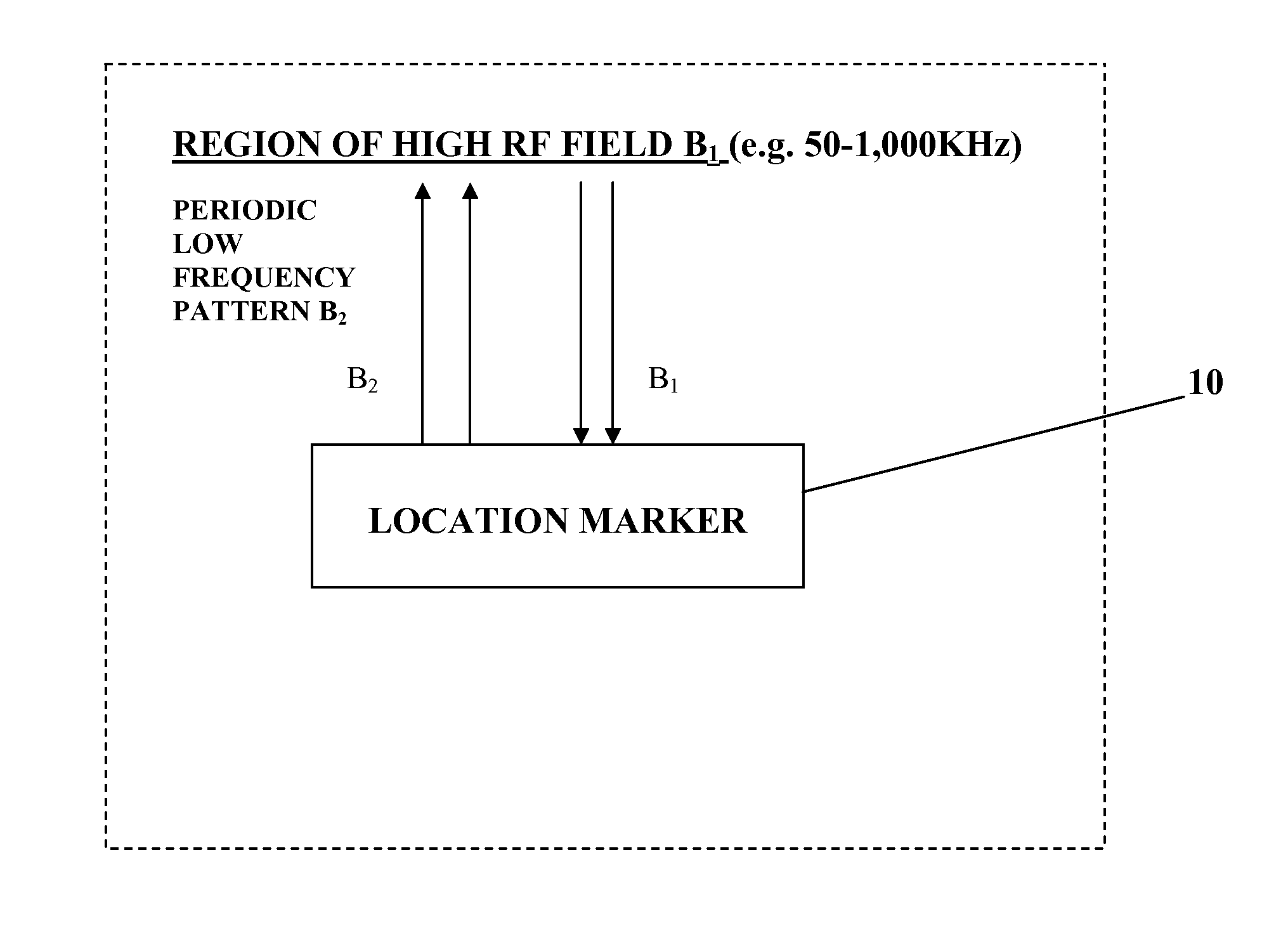
Magnetic Method and System for Locating A Target
InactiveUS20100275934A1Minimize interactionAccurate identificationSurgeryMagnetic property measurementsNoise (radio)Radio frequency
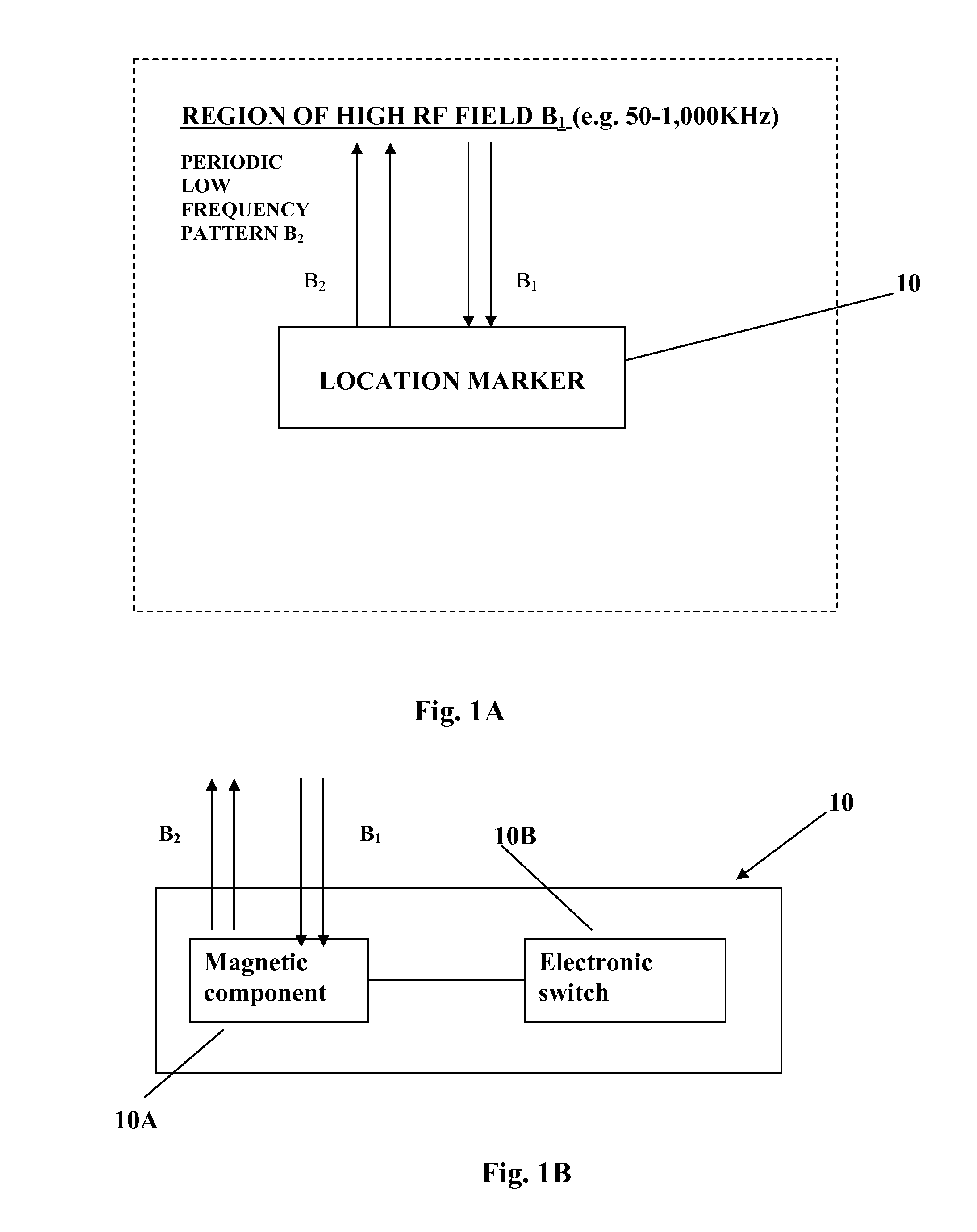
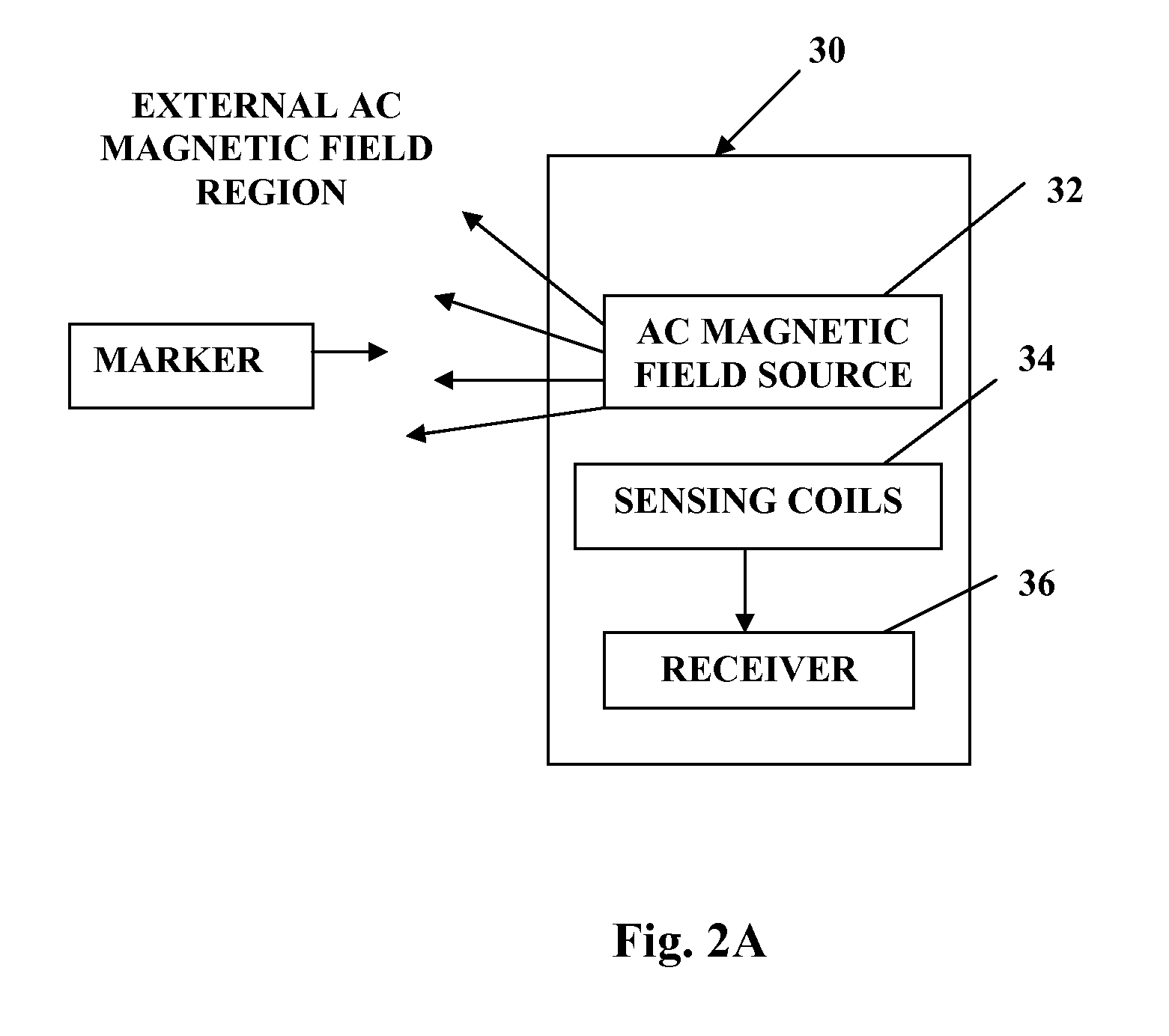
The present invention provides an accurate and real-time acquisition and monitoring of three-dimensional location information about a target, in particular a target inside a subject's body during a medical procedure. This is achieved in accordance with the invention by marking the target location by a small-size location marker, which can be detected and located with high signal-to-noise ratio of the detection by a detection system located at a distance from the target. Provided by the invention is a location marker, a target location system utilizing such marker, and also a novel antenna system suitable to be used in the target location system. The marker of the present invention is a passive electronic device, which “responds” to an external high radio frequency electromagnetic field by a periodic time pattern of a single (certain fixed value) relatively low frequency, as compared to the known devices of the kind specified emitting a frequency coded signal.
Owner:TOPSHOOTER MEDICAL IMRI
Channel correcting method of multichannel TD-RRU
InactiveCN101572576AReduce mistakesConsistent amplitude/phase characteristicsSpatial transmit diversityTime delaysIntermediate frequency
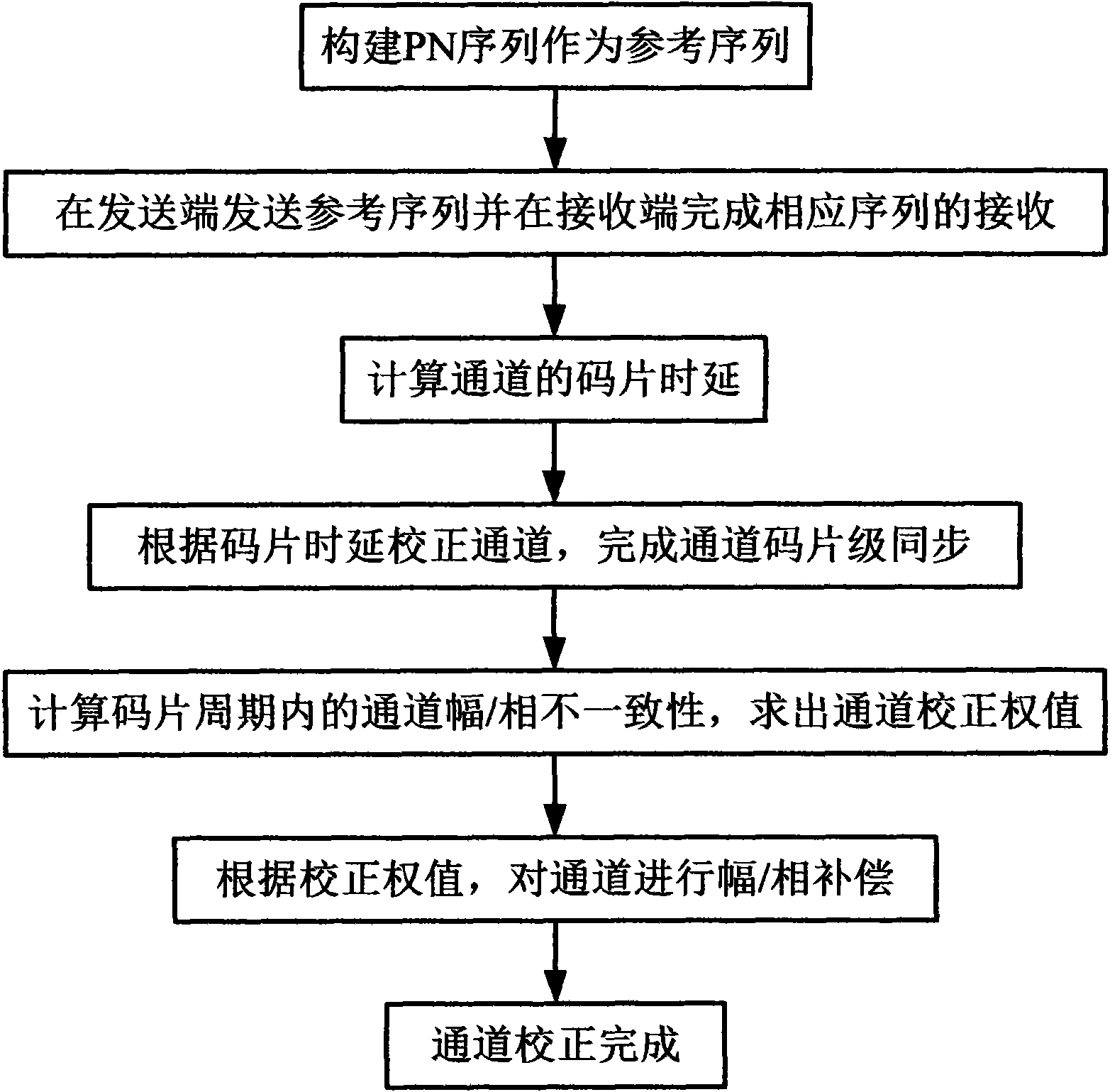
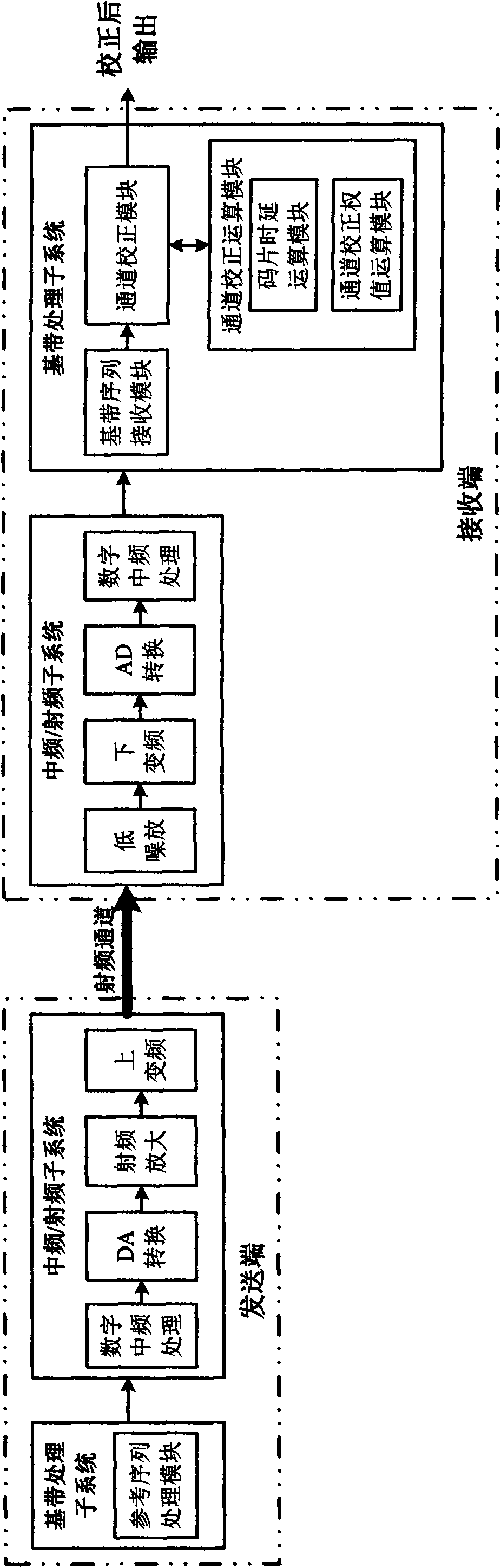
The invention provides a channel correcting method of multichannel TD-RRU, which comprises the following steps: a pseudo-noise (PN) sequence is constructed in a baseband signal as a reference sequence; after the conversion of the baseband signal and an intermediate frequency / radio frequency signal of the reference sequence at a TD-RRU sending end, the reference sequence is sent into a radio frequency channel; after the conversion of the radio frequency / intermediate frequency signal of a corresponding received signal at a TD-RUU receiving end, a processed received sequence and the reference sequence are processed by chip time delay operation to obtain the chip time delay of the radio frequency channel; the radio frequency channel is processed by time delay correction of a chip grade according to the chip time delay so as to finish chip synchronization; the received sequence and the reference sequence are processed by weight value correction operation to work out an inconsistent coefficient of amplitude / phase in the channel within a chip period so as to obtain a corrected weight value; and the channel is processed by amplitude / phase compensation according to the corrected weight value so as to eliminate the inconsistency of the channel and realize the correction of the channel. The method can reduce errors of the channel and meet the requirement on precision of a system.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM SYST CHINA LTD
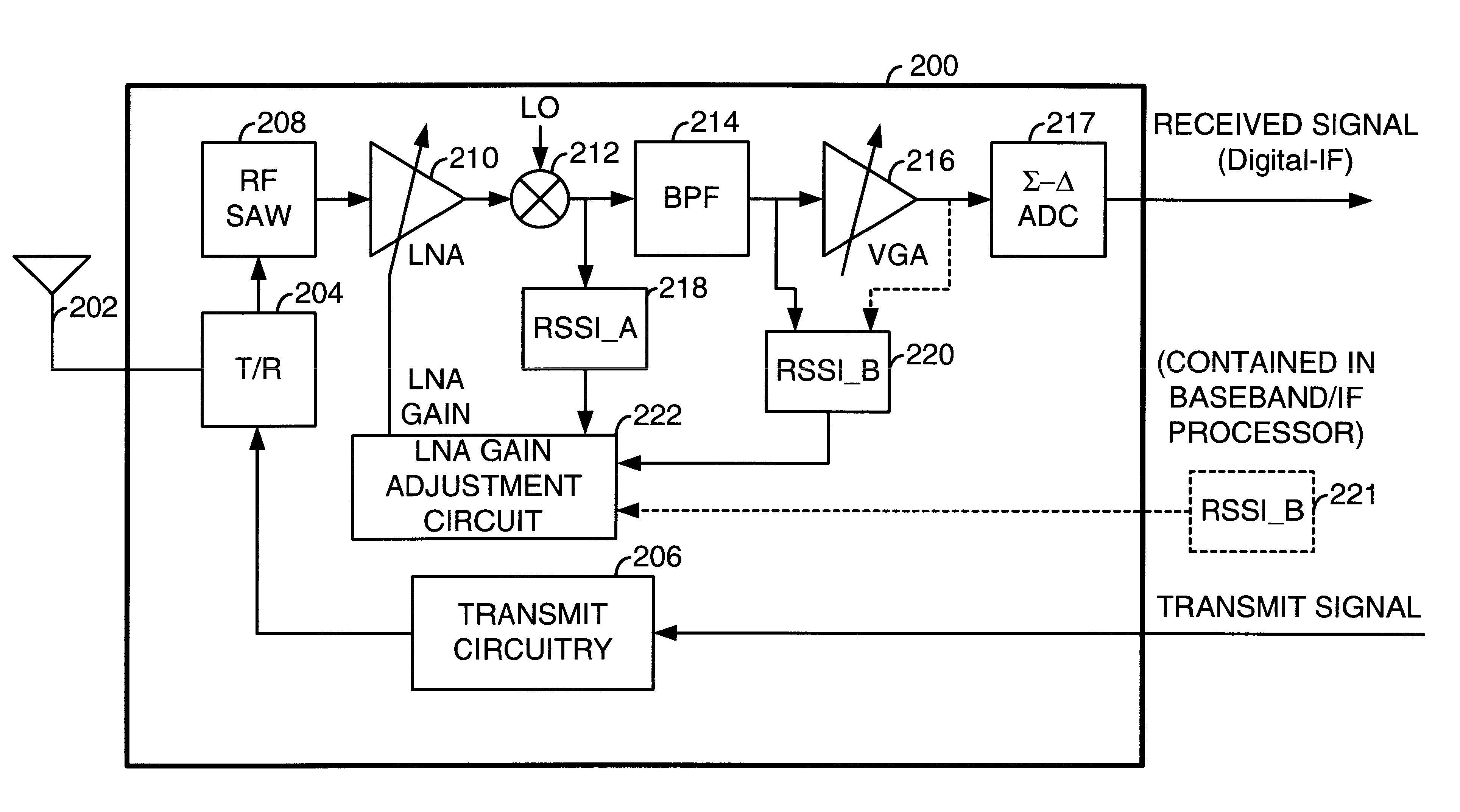
Timing based LNA gain adjustment in an RF receiver to compensate for intermodulation interference
InactiveUS6873832B2Keep linearMaximize signal to noise ratioAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlLinear regionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A Radio Frequency (RF) receiver includes a low noise amplifier (LNA) and a mixer coupled to the output of the LNA. The gain of the LNA is adjusted to maximize signal-to-noise ratio of the mixer and to force the mixer to operate well within its linear region when an intermodulation interference component is present. The RF receiver includes a first received signal strength indicator (RSSI_A) coupled to the output of the mixer that measures the strength of the wideband signal at that point. A second received signal strength indicator (RSSI_B) couples after the BPF and measures the strength of the narrowband signal. The LNA gain is set based upon these signal strengths. LNA gain is determined during a guard period preceding an intended time slot of a current frame and during a guard period following an intended time slot of a prior frame. The lesser of these two LNA gains is used for the intended time slot of the current frame.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
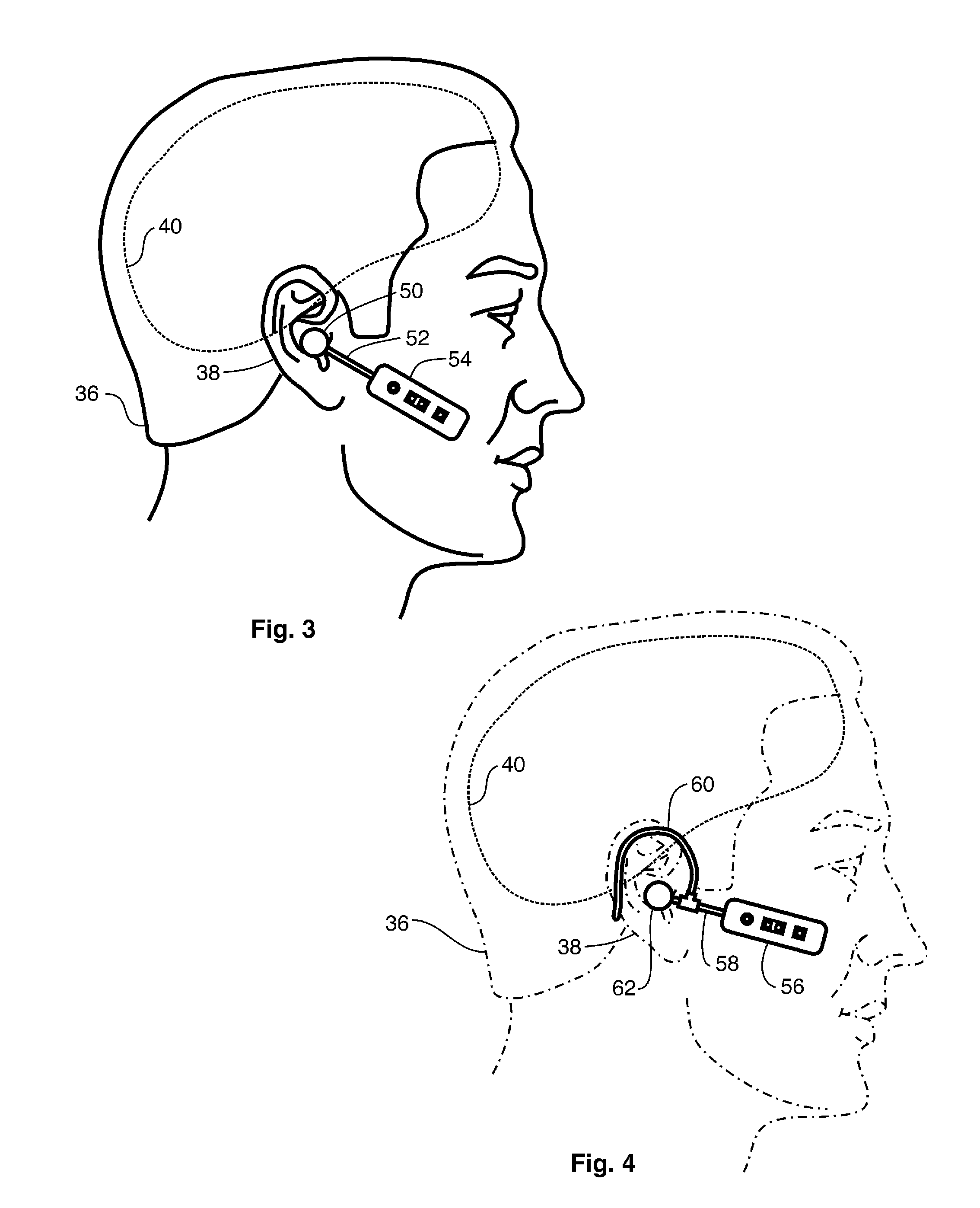
Wireless air tube headset
A wireless air tube headset that includes a wireless transceiver operating in a radio frequency band, which wireless receives audio signals. The headset includes an acoustic chamber with an acoustic port through to the exterior thereof, and an acoustic transducer that is electrically coupled to the transceiver, and that operates to generate acoustic signals. The acoustic transducer is aligned with the acoustic chamber to emit the acoustic signals through the acoustic port. There is an acoustic isolator disposed to attenuate extraneous acoustic signals emitted from the acoustic transducer and also to attenuate ambient noise entry into the acoustic chamber. An acoustic conduit is formed from an electrically non-conductive material, and has a first opening engaged with the acoustic port and a second opening engaged with an acoustic coupler, which has a first earpiece engagement means. An earpiece is engaged to the first earpiece engagement means, and thereby forms an electrically non-conductive acoustic path from the acoustic transducer to the earpiece. The acoustic path has a length to enable displacement of the transceiver and the acoustic transducer from the earpiece at a distance sufficient to yield at least a six decibel radio signal propagation power loss at the radio frequency band.
Owner:LIU FRANK KUNG FU
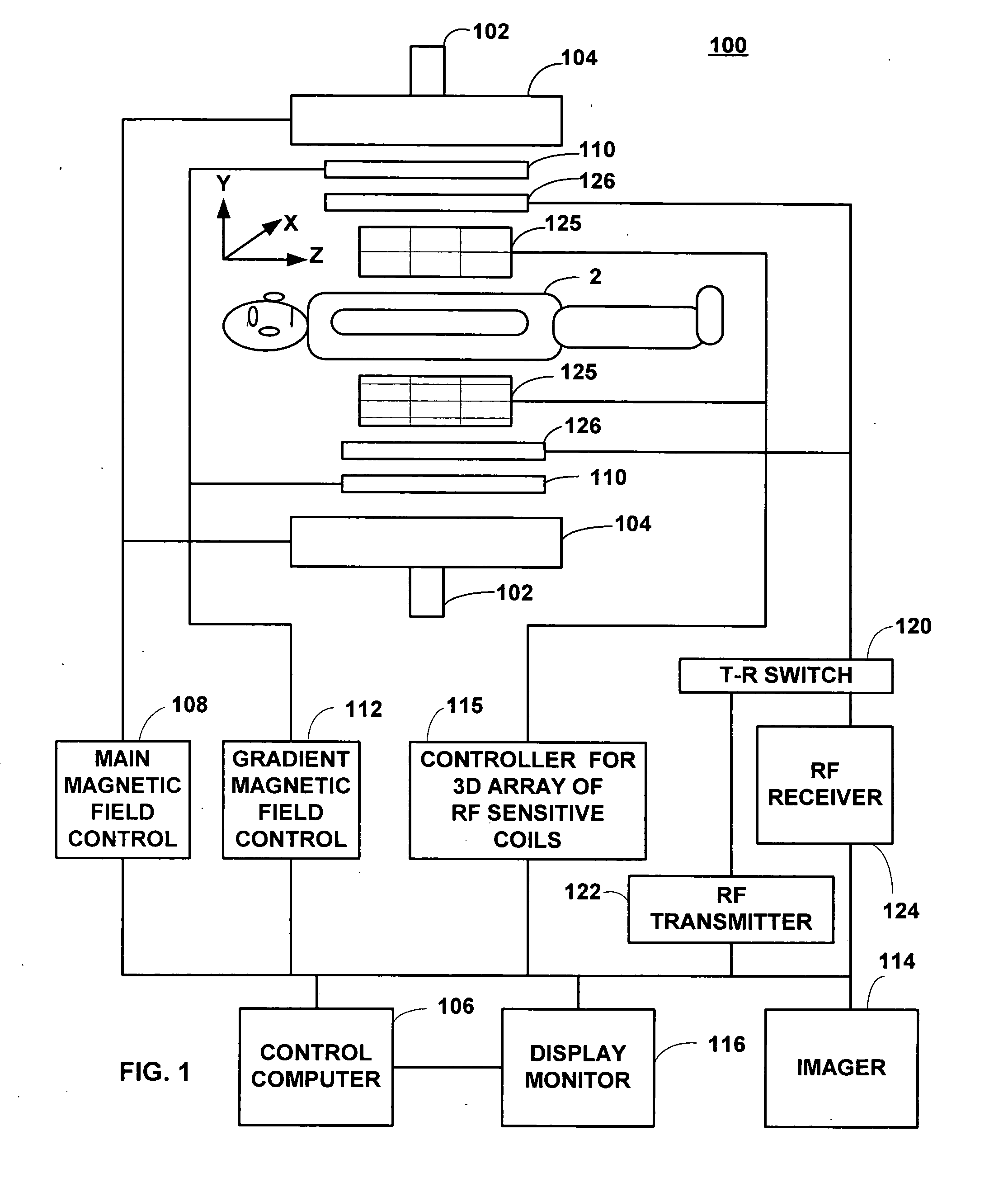
Field image tomography for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20110115485A1Shorten the length of timeReduce usageMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionObject basedSystem matrix
Field Image Tomography (FIT) is a fundamental new theory for determining the three-dimensional (3D) spatial density distribution of field emitting sources. The field can be the intensity of any type of field including (i) Radio Frequency (RF) waves in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), (ii) Gamma radiation in SPECT / PET, and (iii) gravitational field of earth, moon, etc. FIT exploits the property that field intensity decreases with increasing radial distance from the field source and the field intensity distribution measured in an extended 3D volume space can be used to determine the 3D spatial density distribution of the emitting source elements. A method and apparatus are disclosed for MRI of target objects based on FIT. Spinning atomic nuclei of a target object in a magnetic field are excited by beaming a suitable Radio Frequency (RF) pulse. These excited nuclei emit RF radiation while returning to their normal state. The intensity or amplitude distribution of the RF emission field g is measured in a 3D volume space that may extend substantially along the radial direction around the emission source. g is related to the 3D tomography f through a system matrix H that depends on the MRI apparatus, and noise n through the vector equation g=Hf+n. This equation is solved to obtain the tomographic image f of the target object by a method that reduces the effect of noise.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
Long Range Radio Frequency Identification System
ActiveUS20110032081A1Large coherent processing gainMaximizing wireless rangeMultiplex system selection arrangementsMemory record carrier reading problemsOn boardGps receiver
A method and apparatus for building a long range RFID system is disclosed. A new signaling structure called Block Pseudo Noise is described that allows for more computationally efficient decoding. A novel approach to synchronize the RFID reader local oscillator with the RFID tag oscillator using an on board GPS receiver on the RFID tags and RFID reader is also disclosed. A novel positioning technique called Asynchronous Time Difference of Arrival used to located RFID tags is also disclosed.
Owner:RING LLC
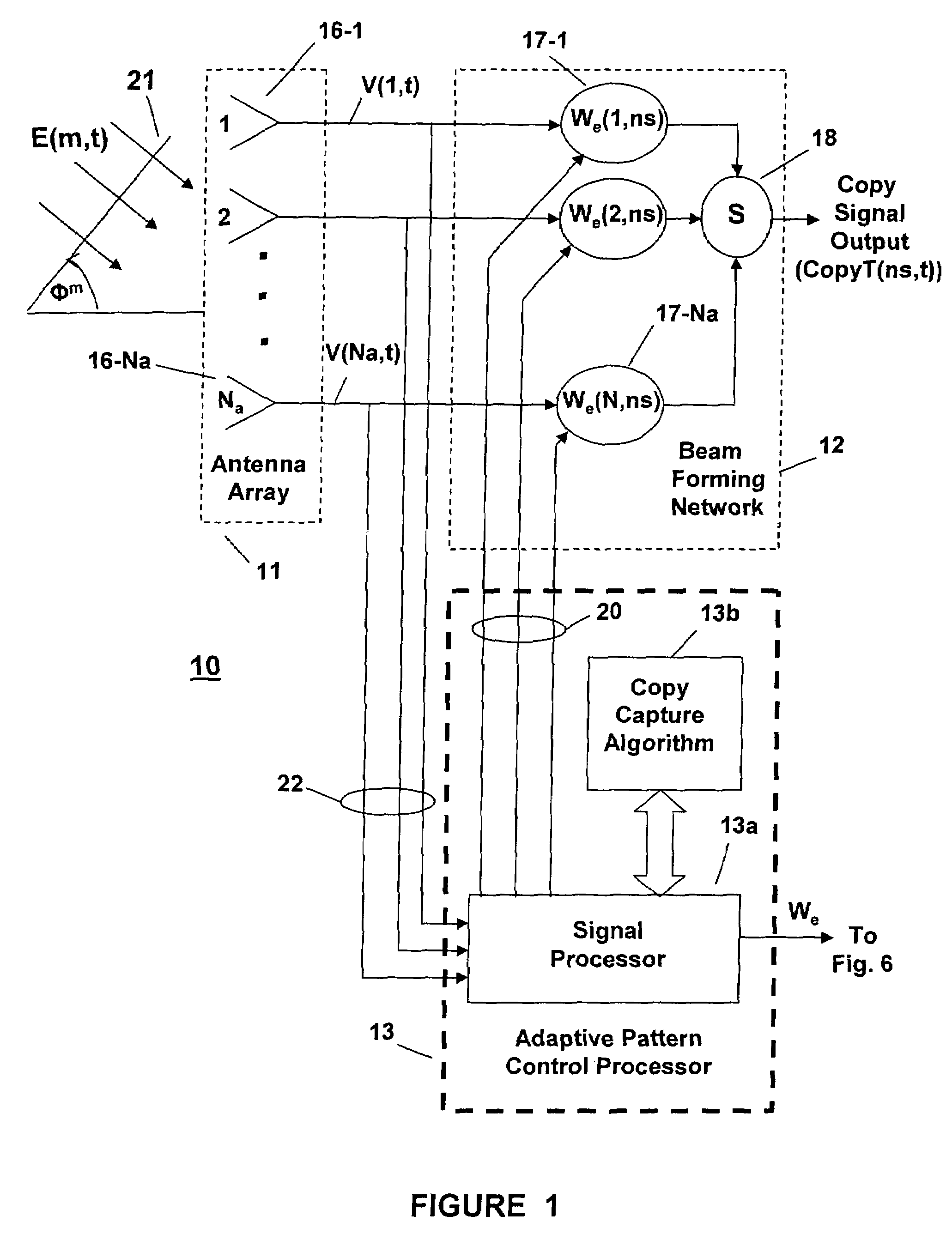
Method for separating interfering signals and computing arrival angles
ActiveUS7539273B2Computational time becomes enormousShorten the timeData representation error detection/correctionSpatial transmit diversityTime domainRadio frequency signal
A method is disclosed for processing all types of received, interfering radio frequency signals corrupted by noise to extract the individual signals without having any a priori knowledge about them. Received signals are converted for eigenspace processing and are subjected to repeated non-linear time domain and fast Fourier transform frequency domain processing that calculates eigenstream beam forming weights U. By performing calculations in eigenspace, the number of independent weights U that must be calculated is generally reduced, minimizing calculating time. Once the weights U have been calculated in eigenspace they are transformed into antenna beam forming weights W that are used to extract the individual signals and to determine the angle of arrival of each of the individual signals. Further time is saved because the weights W do not have to be updated for every time slice of the received signals.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
Measurement method and device of Bell-Bloom self-modulation three-axis magnetic field
InactiveCN104297702AGuaranteed ultra-high precisionRealize real-time vector magnetic field measurementMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesNoise (radio)Measurement device
The invention relates to a measurement method and device of a Bell-Bloom self-modulation three-axis magnetic field. A conventional Bell-Bloom magnetometer utilizes a single beam to measure a scalar magnetic field, is simple in structure, is high in measurement accuracy and is widely applied to measurement of various scalar magnetic fields. The single-beam Bell-Bloom magnetometer can only measure the scalar magnetic fields, but three-axis magnetic field information is needed in many places in scientific researches and production life, and then a vector magnetometer is needed. Based on the single-beam Bell-Bloom magnetometer, the measurement method and device of the Bell-Bloom self-modulation three-axis magnetic field realize measurement of the three-axis magnetic field by utilizing the self-modulating action on detection light of atomic procession. Compared with the common vector magnetometer, the measurement device of the Bell-Bloom self-modulation three-axis magnetic field is not provided with a radio frequency coil or a magnetic shielding barrel, thereby having a simple light path, being compact in structure and achieving miniaturization and integration easily; the measurement device is low in heating temperature and needs fewer electric elements, so that systematic power consumption is lowered and operation conditions are met more easily; the measurement device utilizes the self-modulating action on detection light of the atomic procession, is lower in noise and is high in detection accuracy.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Three-dimensional flow radiographic method and system based on optical coherence tomography of feature space
ActiveCN109907731AEliminate the effects of motion artifactsSolve the problem of unsatisfactory suppression effectSensorsAngiographyCovarianceSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention discloses a three-dimensional flow radiographic method and system based on optical coherence tomography of feature space. OCT (optical coherence tomography) scattering signals of a scattering signal sample in a three-dimensional space are collected through a collector; a two-dimensional feature space is constructed through a theoretically established classifier in combination with local signal-to-noise ratios of the OCT scattering signals and a decorrelation coefficient; dynamic flow signal and stationary tissue classification is achieved. The specific steps include calculating and analyzing the OCT scattering signals through first-order and zero-order auto-covariance to obtain the signal-to-noise ratios of the OCT scattering signals and two decorrelated features; constructing a signal-to-noise ratio reciprocal-decorrelation coefficient two-dimensional feature space; constructing a linear classifier of ID spaces based on the principle of multivariate time series, and removing background of the stationary surrounding tissues. The method and system herein can evidently inhibit the influence of system noise upon flow radiography, contrast of flow images is increased, vessel visibility of deep tissues is particularly increased, and accuracy of blood flow can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
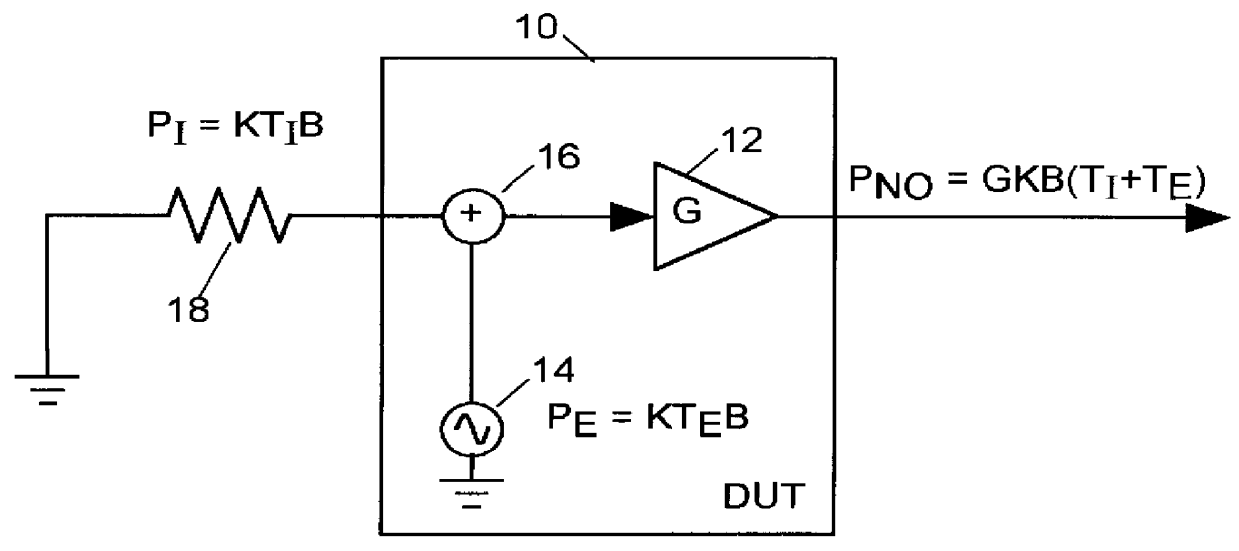
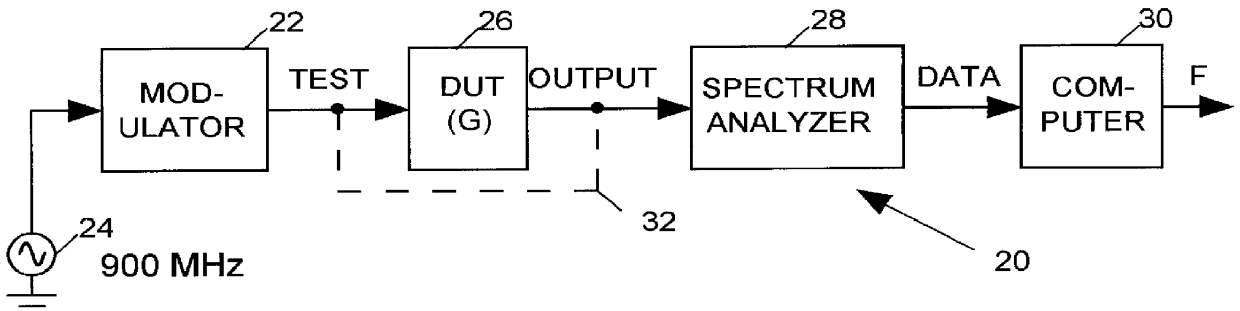
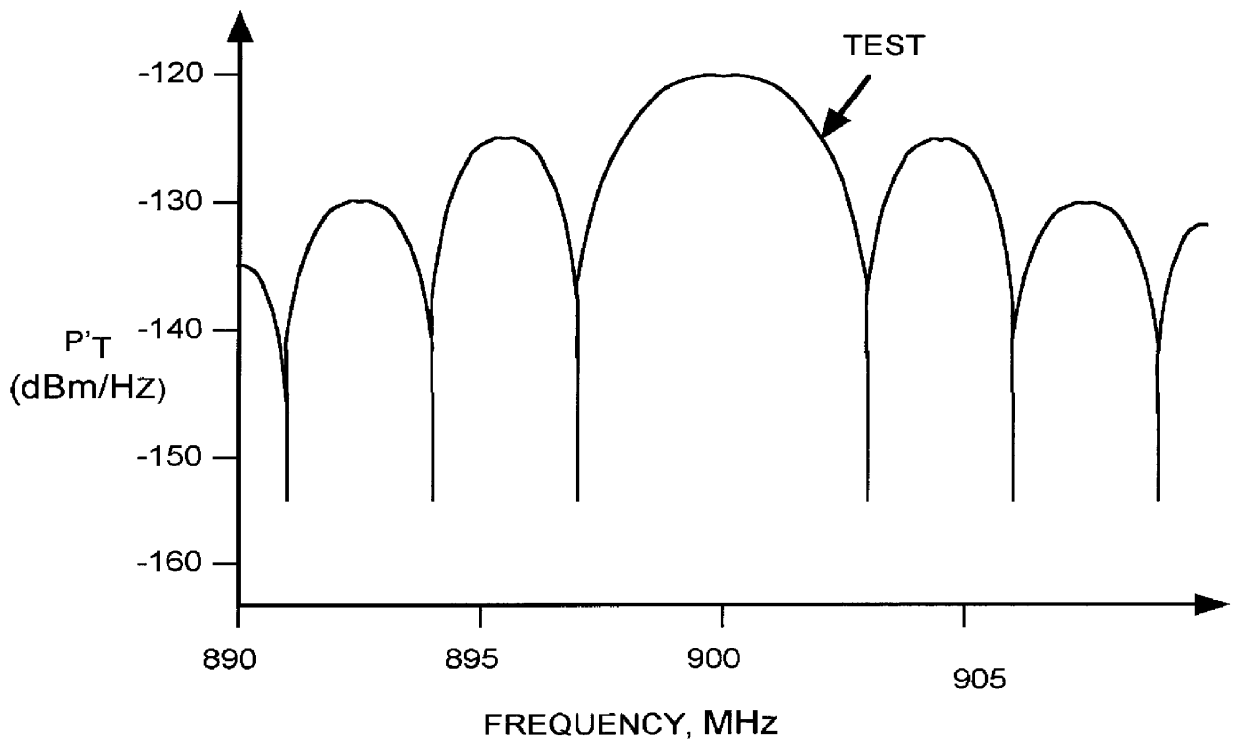
System for measuring noise figure of a radio frequency device
InactiveUS6114858AAccurate noiseWave based measurement systemsNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementRadio frequencyNoise figure
Noise factor of a radio-frequency device under test (DUT) is determined by driving the input of the DUT with a randomly modulated sine wave and measuring the power of a resulting DUT OUTPUT signal within each of a set of equally-sized frequency bands. The noise factor is computed as a combination of the power of the modulated sine wave within each of a plurality of frequency bands and the measured power of the DUT OUTPUT signal within that same plurality of frequency bands.
Owner:CREDENCE SYSTEMS
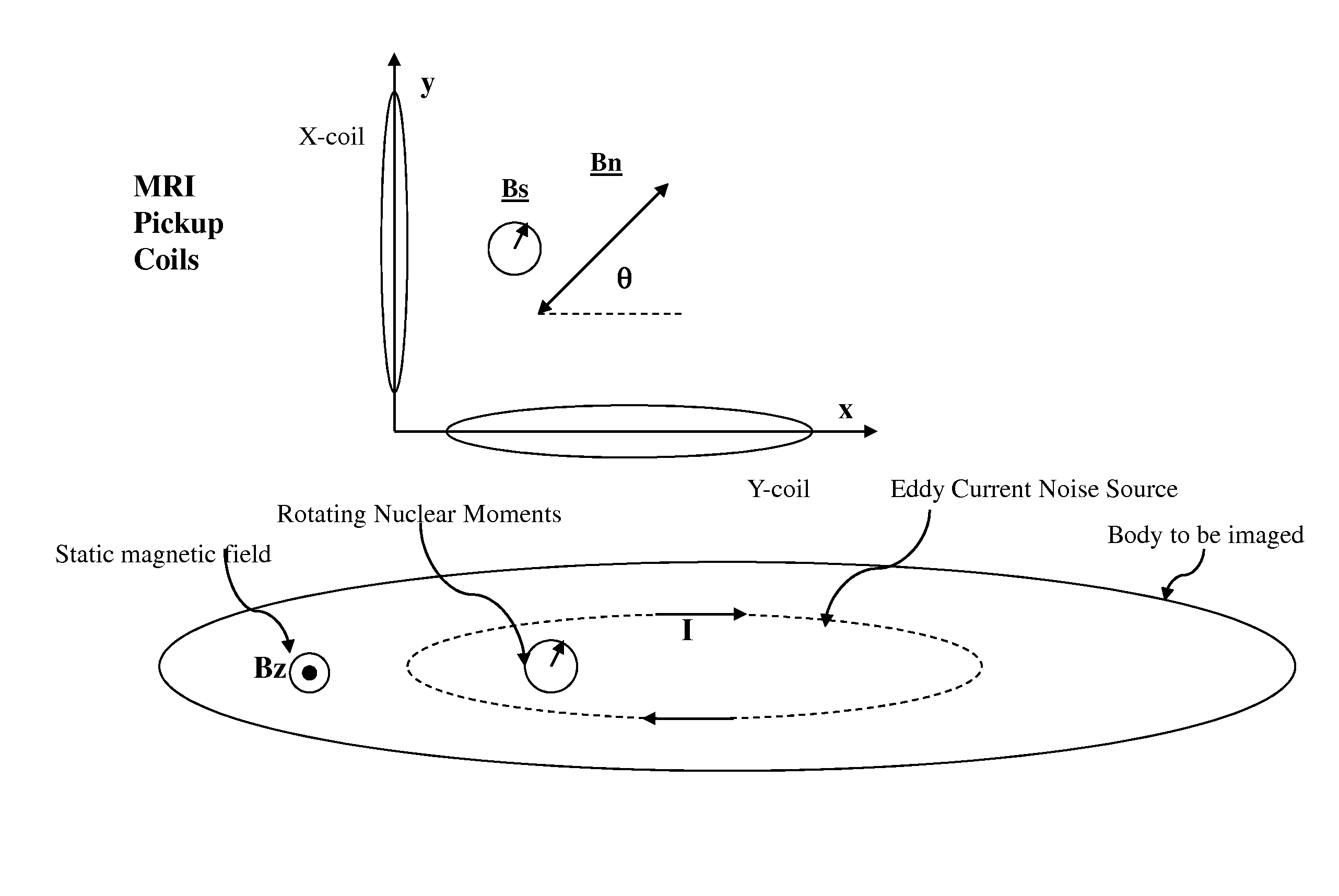
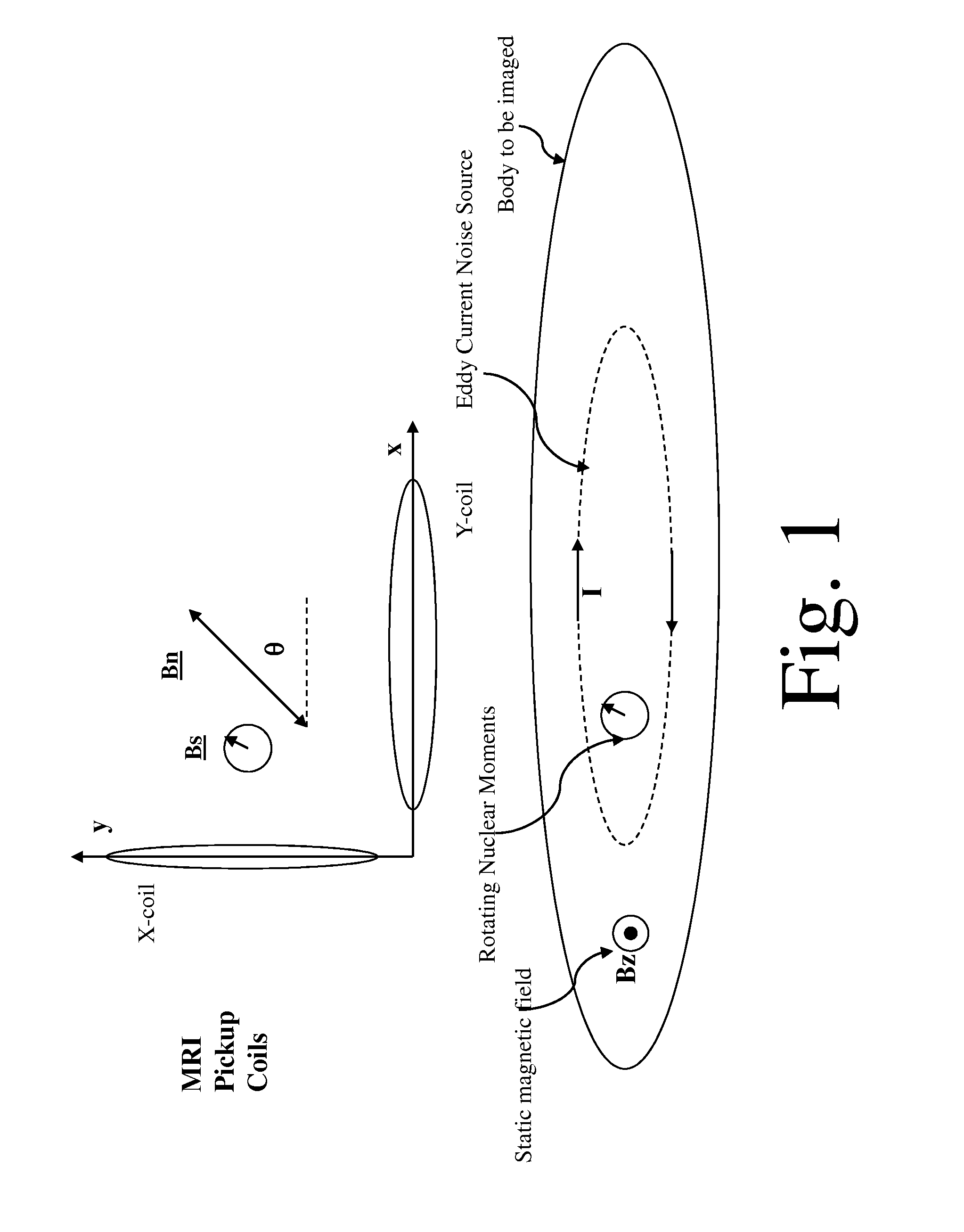
System and method for noise reduction in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS8970217B1Improve noiseSignificant signal processingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionNoise reductionSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
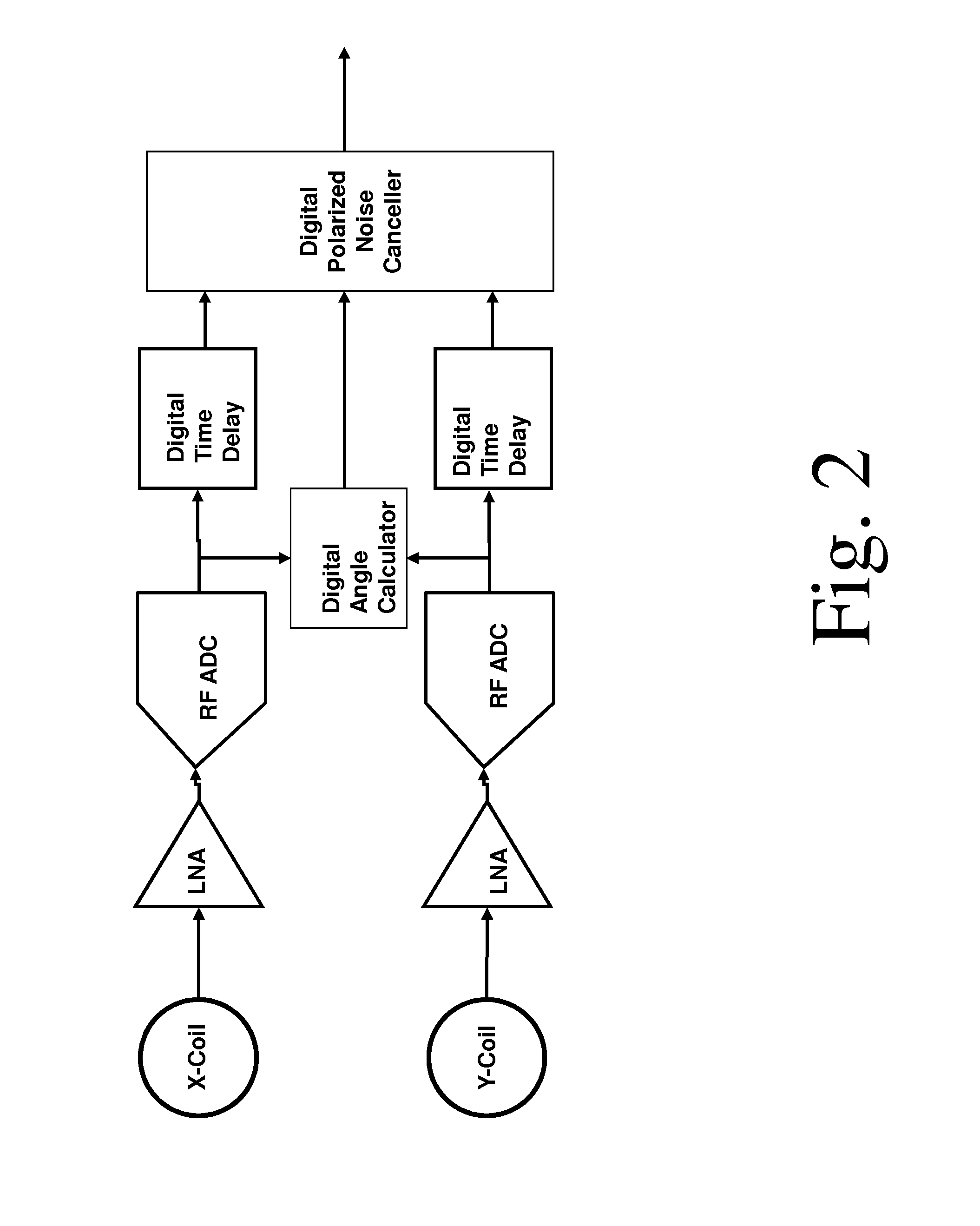
Signals of interest in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) systems comprise narrowband, circularly polarized (CP) radio-frequency magnetic fields from rotating atomic nuclei. Background “body noise” may comprise broadband, linearly polarized (LP) magnetic fields from thermally-activated eddy currents, and may exceed the signal in a band of interest, limiting the imaging resolution and requiring excessive averaging times. Noise may be selectively detected and substantially suppressed, while enhancing the signal of interest, using appropriate digital time-domain algorithms. At least two quadrature receiving antennas may be employed to distinguish and separate the LP noise from the CP signal. At least one broadband receiver may be used to identify and localize fast noise sources and to digitally filter the representation of their radio-frequency magnetic fields in the signal. Selective body noise reduction may allow enhanced signal-to-noise ratio of the system, leading to improved imaging resolution and shorter scan time.
Owner:THE JOHNSON REVOCABLE TRUST DATED 6 25 2003
Apparatus and method for selecting operation mode in MIMO communication system
InactiveUS20090097583A1Improve throughputDiversity/multi-antenna systemsTransmission monitoringInterference (communication)Noise (radio)
An apparatus and a method for selecting an operation mode to improve a throughput in a mobile communication system are provided. The apparatus includes a Carrier to Interference and Noise Ratio (CINR) predictor for predicting a probable average and dispersion for a CINR measured using a preamble of a received pilot signal or radio signal, a metric calculator for calculating a throughput for each Modulation and Coding Scheme Level (MCS_Level) by using the probable average and dispersion for the predicted CINR and for selecting an MCS_Level having a maximum throughput, and an operation mode selector for selecting an operation mode of the selected MCS_Level having the maximum throughput.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Radio frequency front-end device for dual-system and dual-frequency navigation receiver
ActiveCN101915932AReduce power consumptionReduce Power Consumption and NoiseSatellite radio beaconingProgrammable-gain amplifierPhysics
The invention discloses a radio frequency front-end device for a dual-system and dual-frequency navigation receiver. By using down-conversion structure twice, a low-noise amplifier, a first-stage frequency mixer, a second-stage frequency mixer, a frequency synthesizer, a first-stage medium frequency amplifier, a second-stage medium frequency amplifier, a variable gain amplifier, a signal power detector, a programmable gain amplifier, a five-bit analog-to-digital converter, an SPI protocol interface and a two-bit analog-to-digital converter are integrated on the same radio frequency front-end chip; and the radio frequency front-end device for the navigation receiver is formed by the chip, a first-stage filter and a second-stage filter. The device can simultaneously receive radio frequency signals of L1 and L2 wave bands of a global positioning system (GPS) and B1 and B2 wave bands of a big dipper second-generation navigation system (BD2) with high accuracy; the device reduces the power consumption and noise by using a design method of low power consumption and multi-layer isolating ring and deep N well technology; and because the device is implemented by using an up-to-date CMOS integrated circuit process, the device has the characteristics of low power consumption, low noise, small size and the like and can be widely applied to the fields of traffic, navigation, transportation and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
High performance CMOS radio frequency receiver
InactiveUS8045943B2Modulation transferenceActive element networkTuned radio frequency receiverIntermediate frequency
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
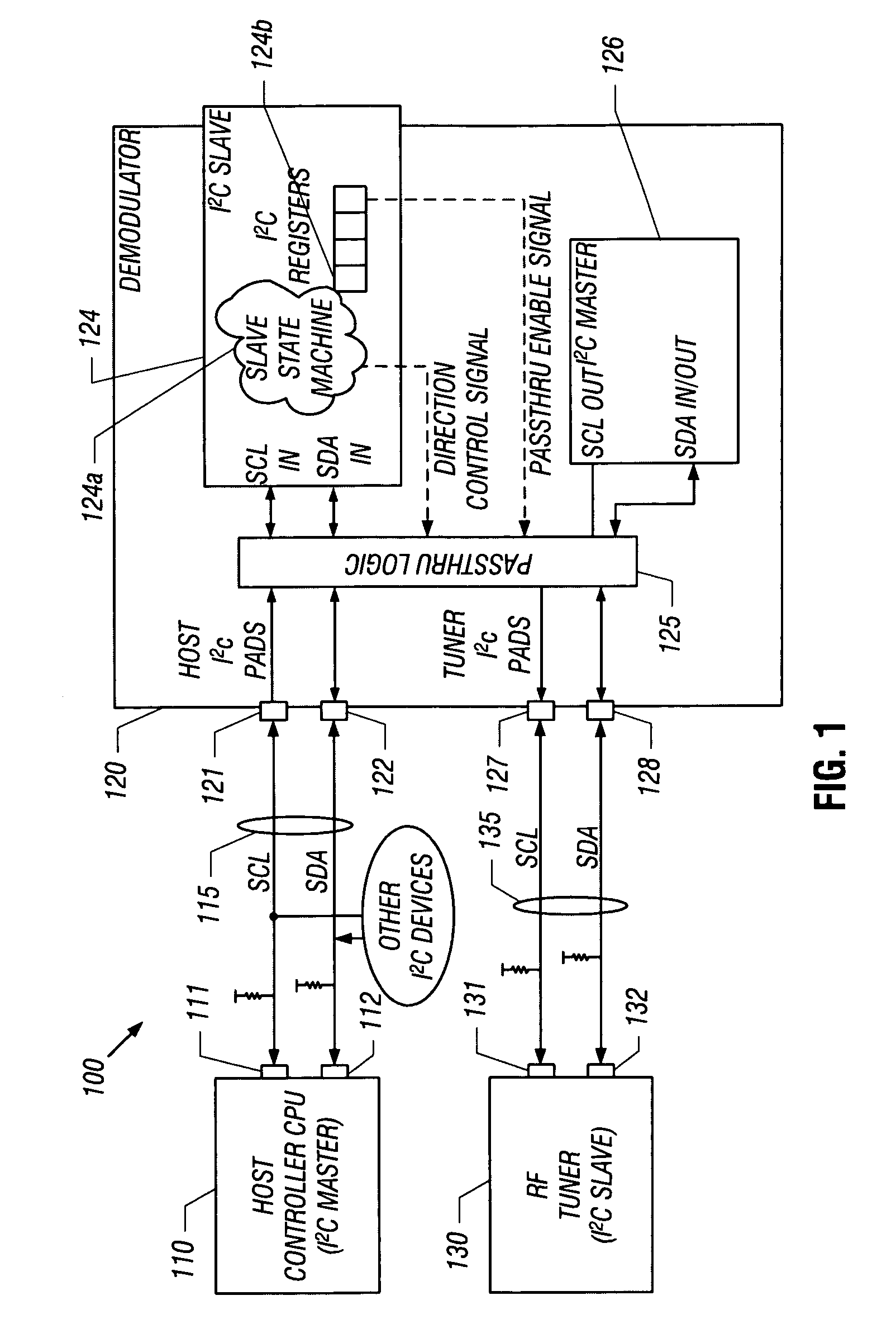
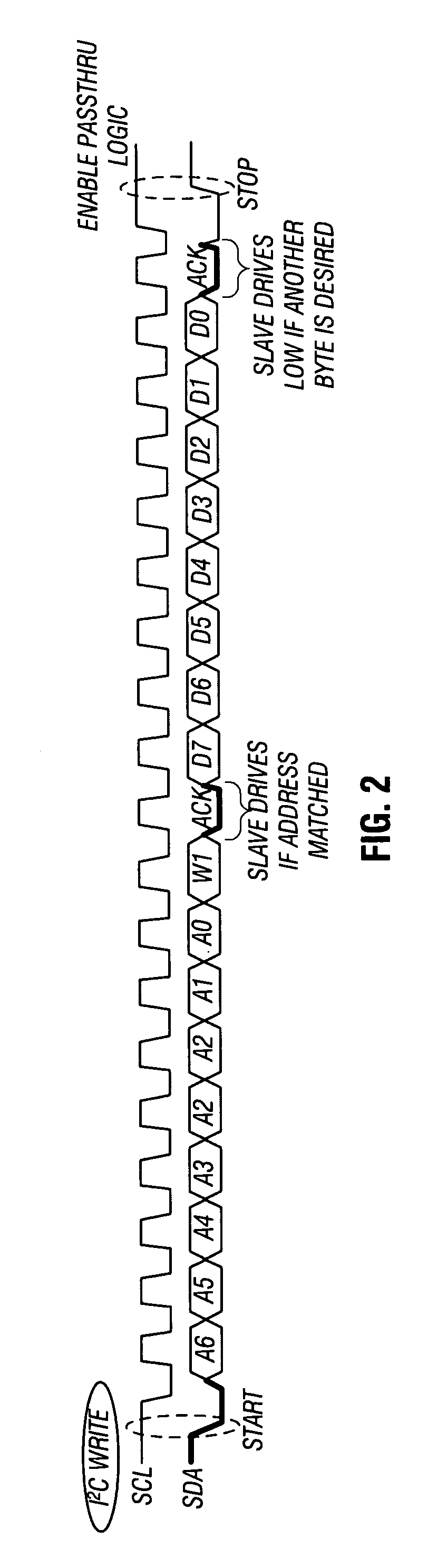
Controlling passthrough of communications between multiple buses
A demodulator can include first data and clock pads to couple the demodulator to a host device via a first bus, and second data and clock pads to couple the demodulator to a radio frequency (RF) tuner via a second bus. The device may further include passthrough logic to couple host data and a host clock from the first bus to the second bus and to couple tuner data from the second bus to the first bus during a passthrough mode. During this mode, however, the two buses may remain electrically decoupled. When the passthrough mode is disabled, the RF tuner is thus shielded from noise present on the first bus.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com