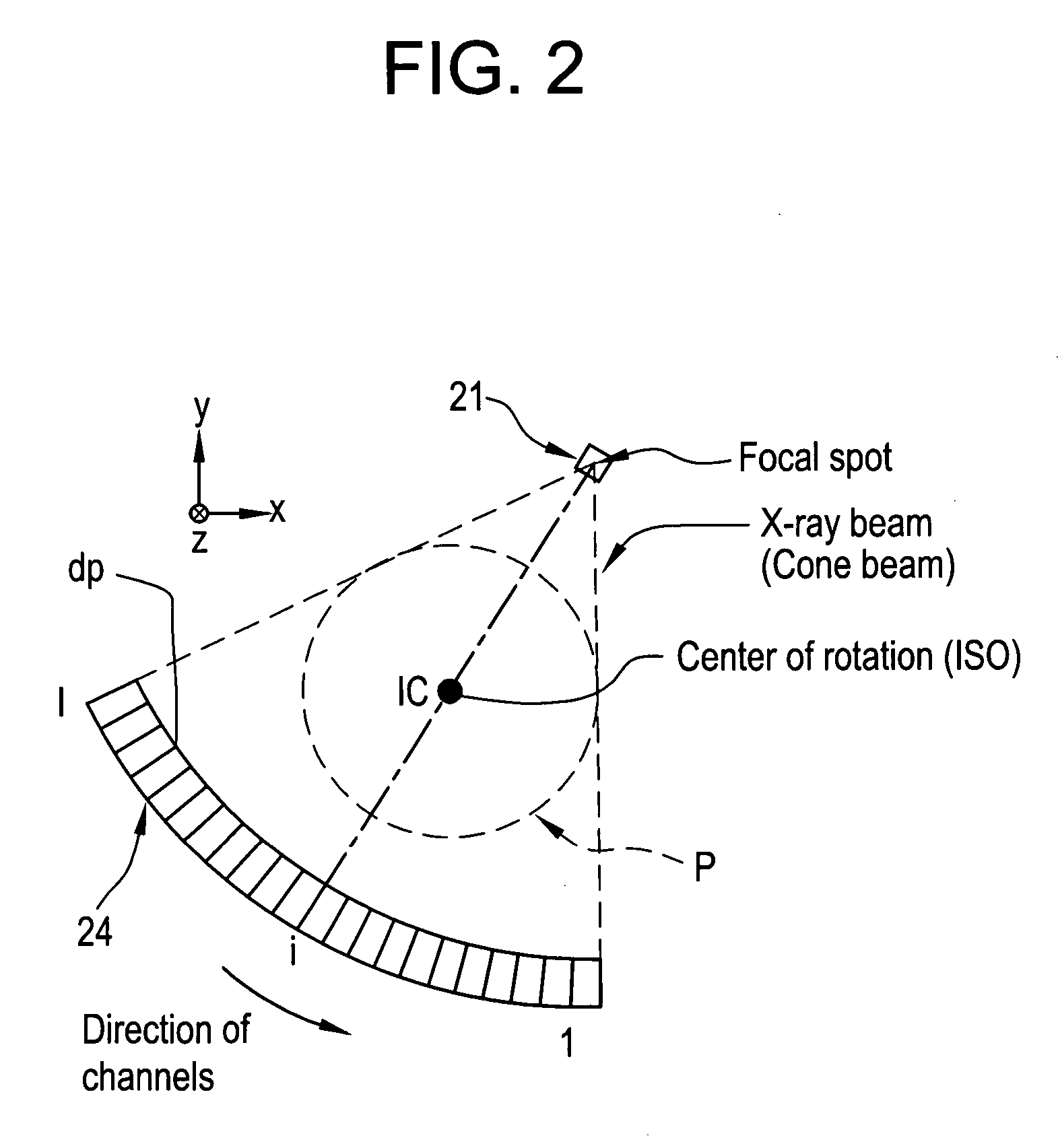
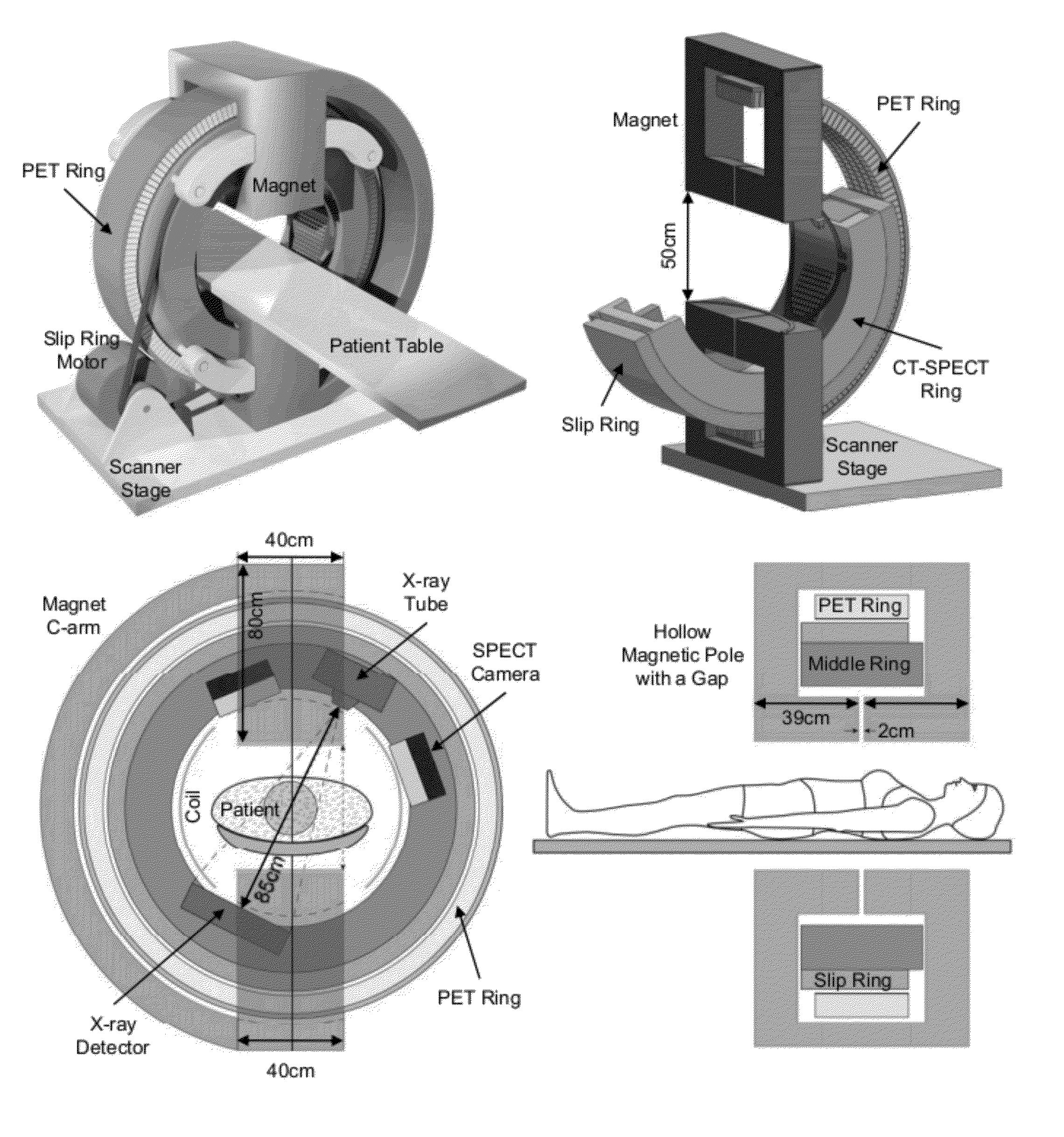
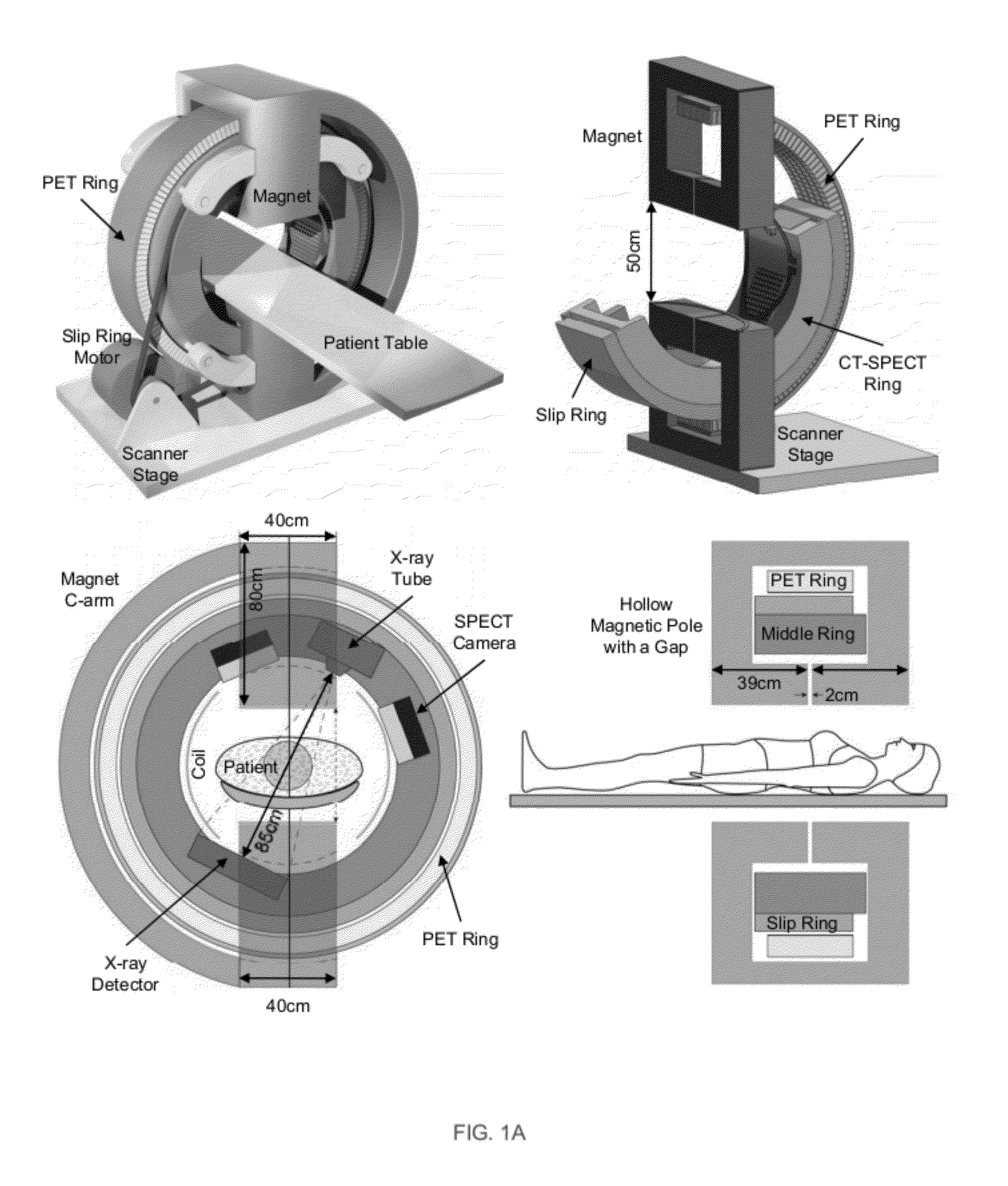
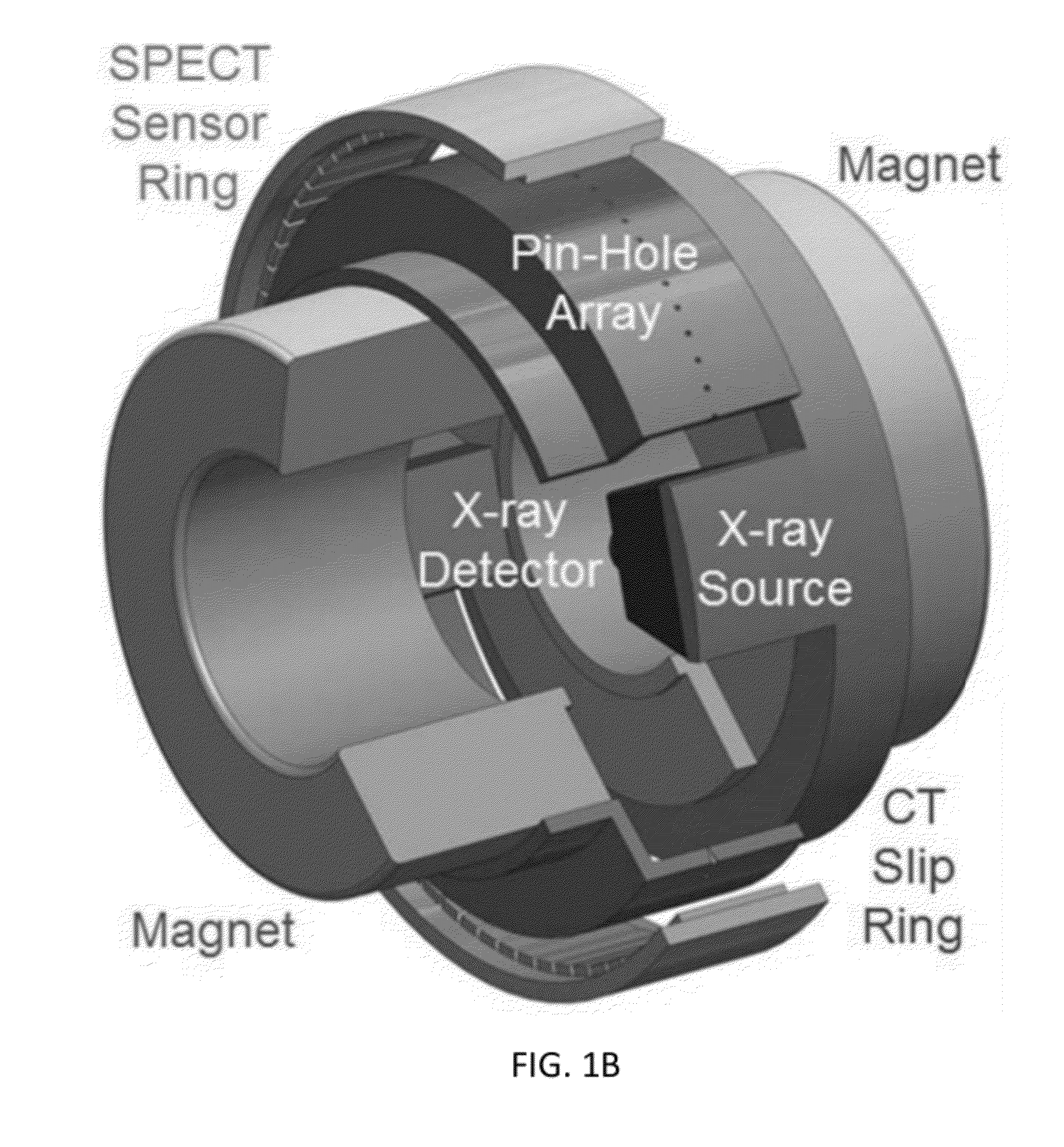
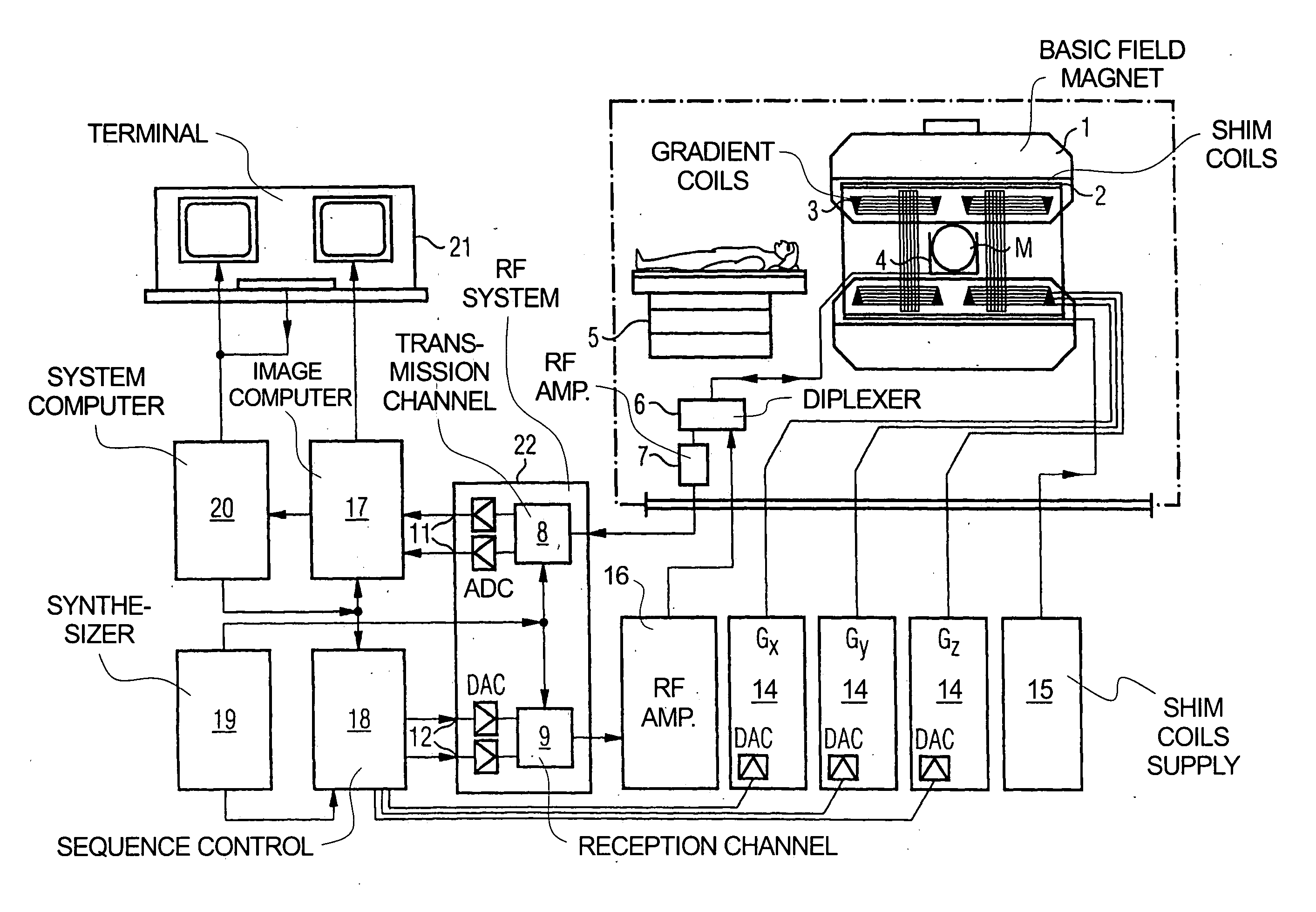
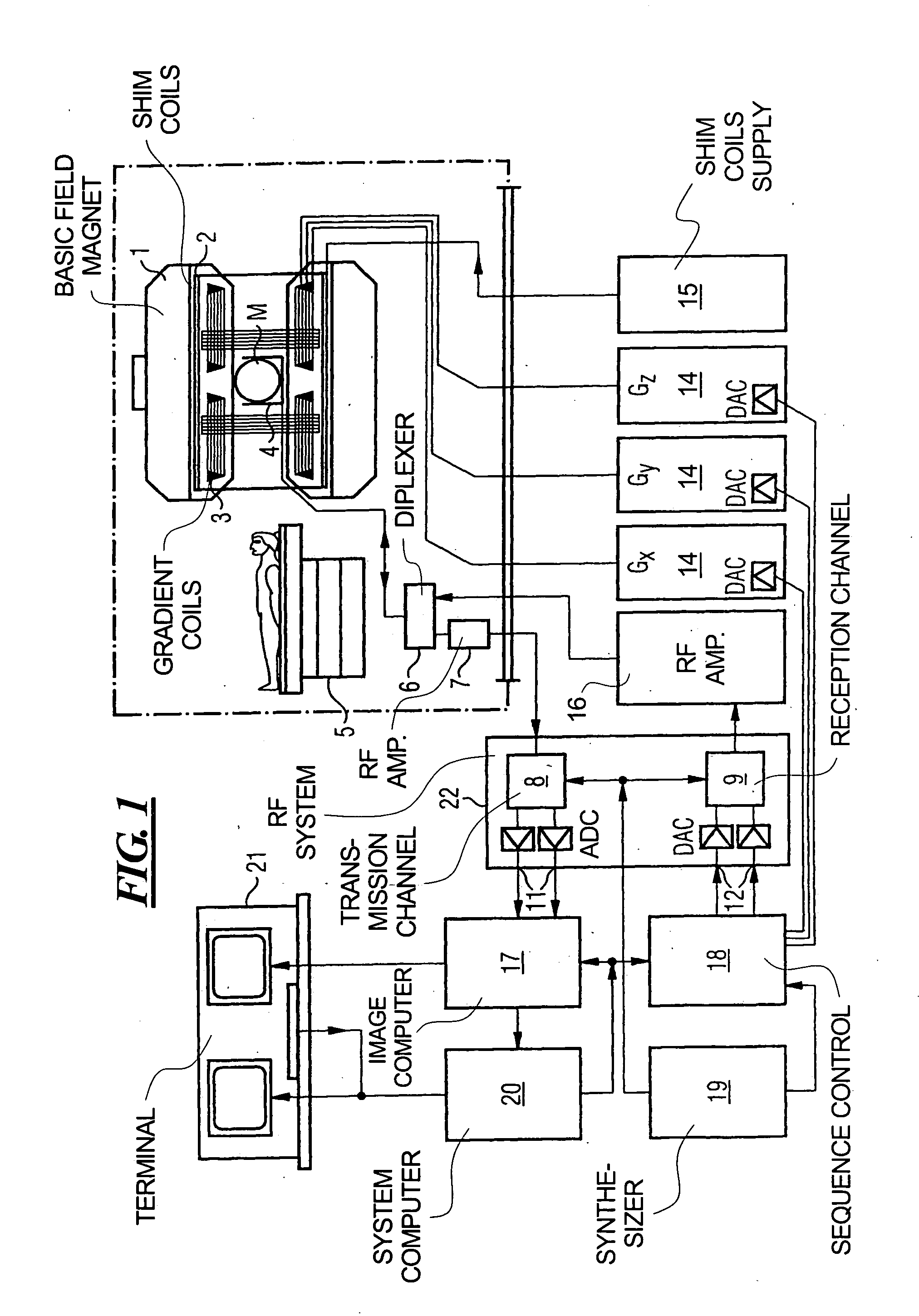
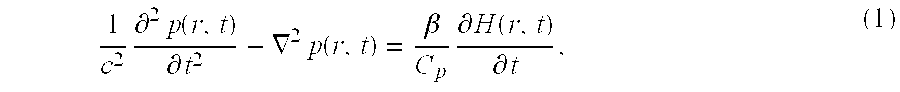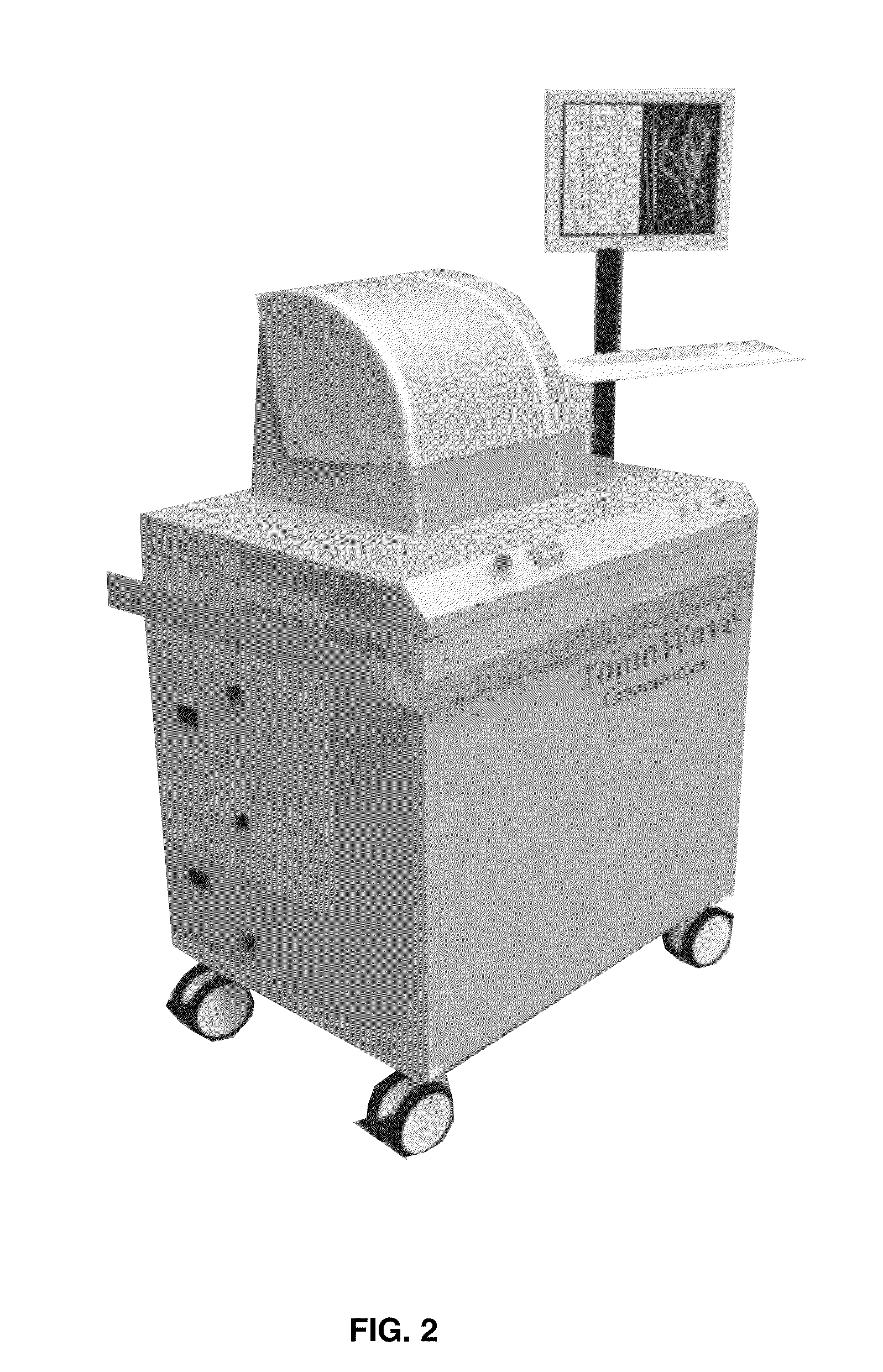Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2159 results about "Tomographic image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
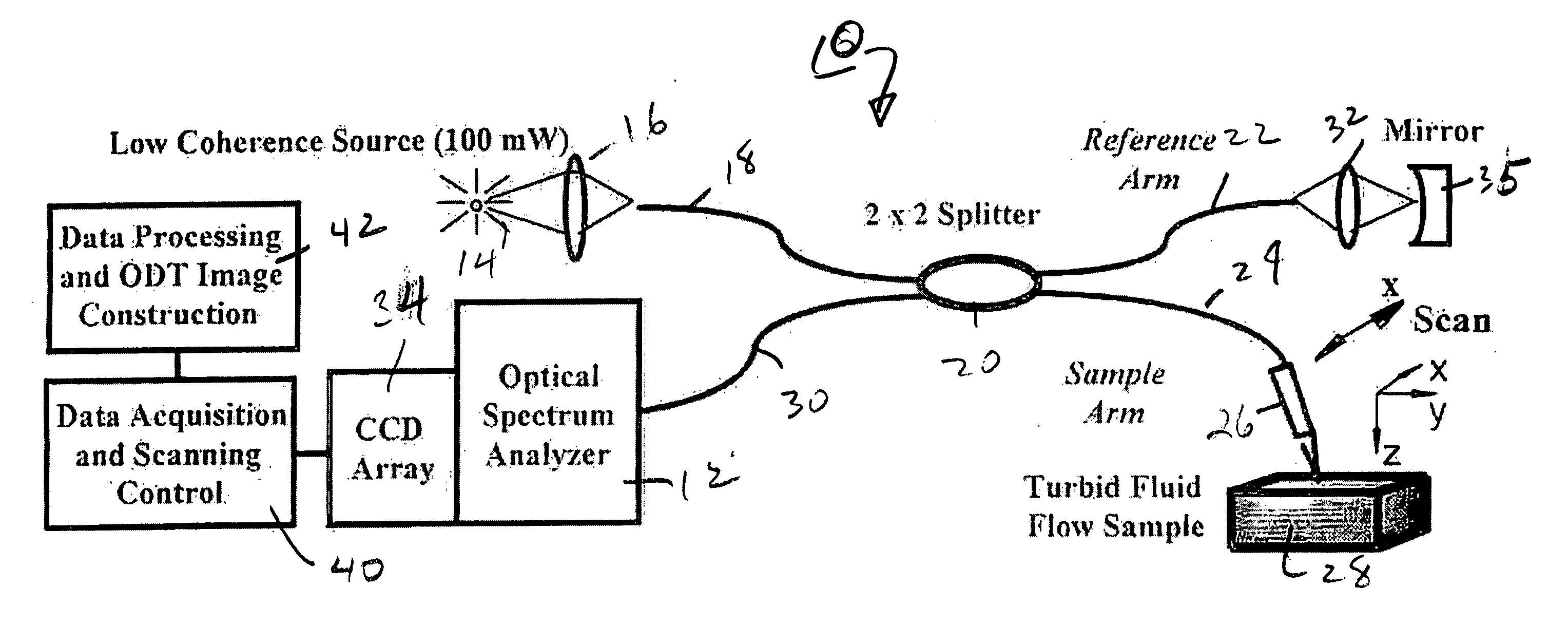
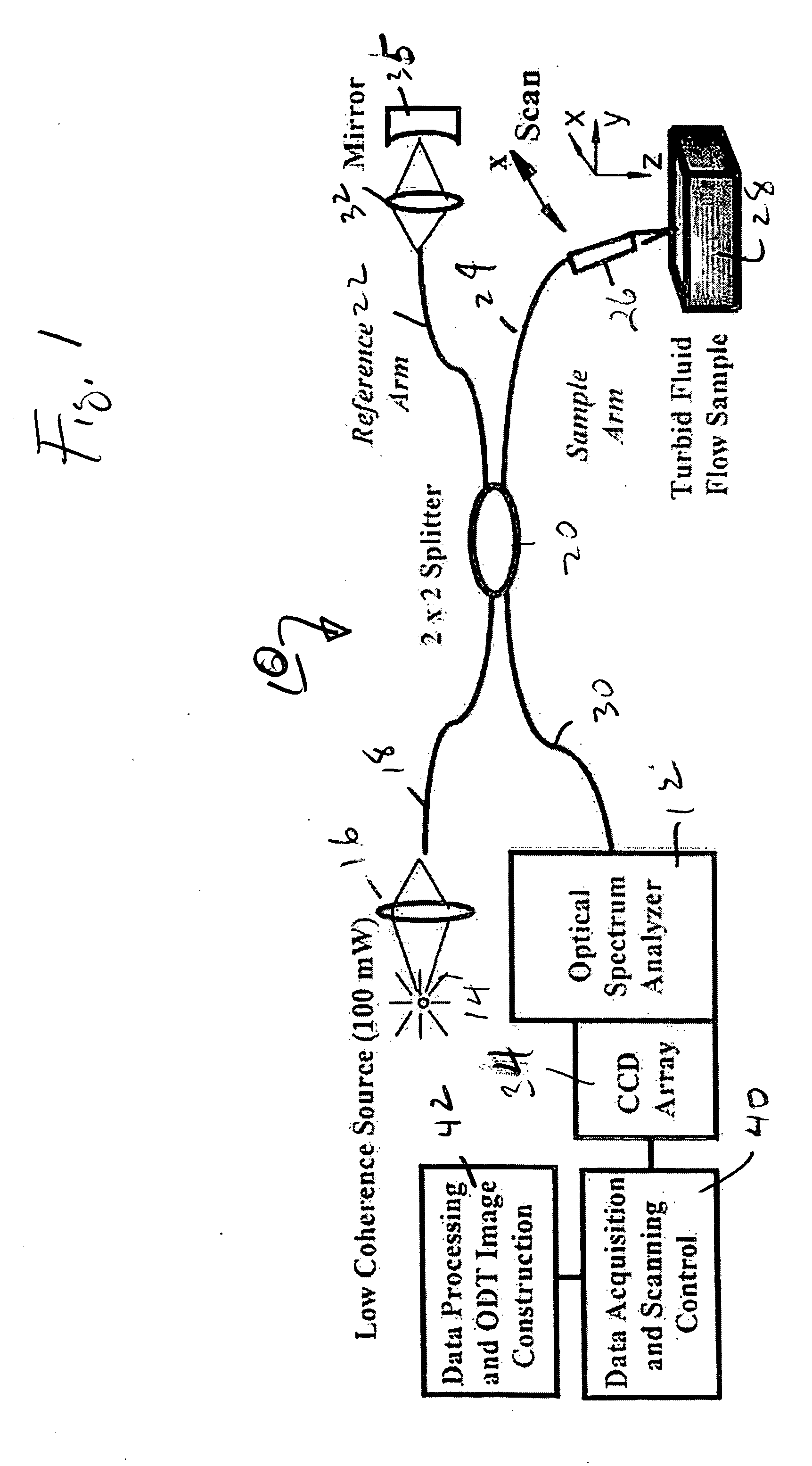
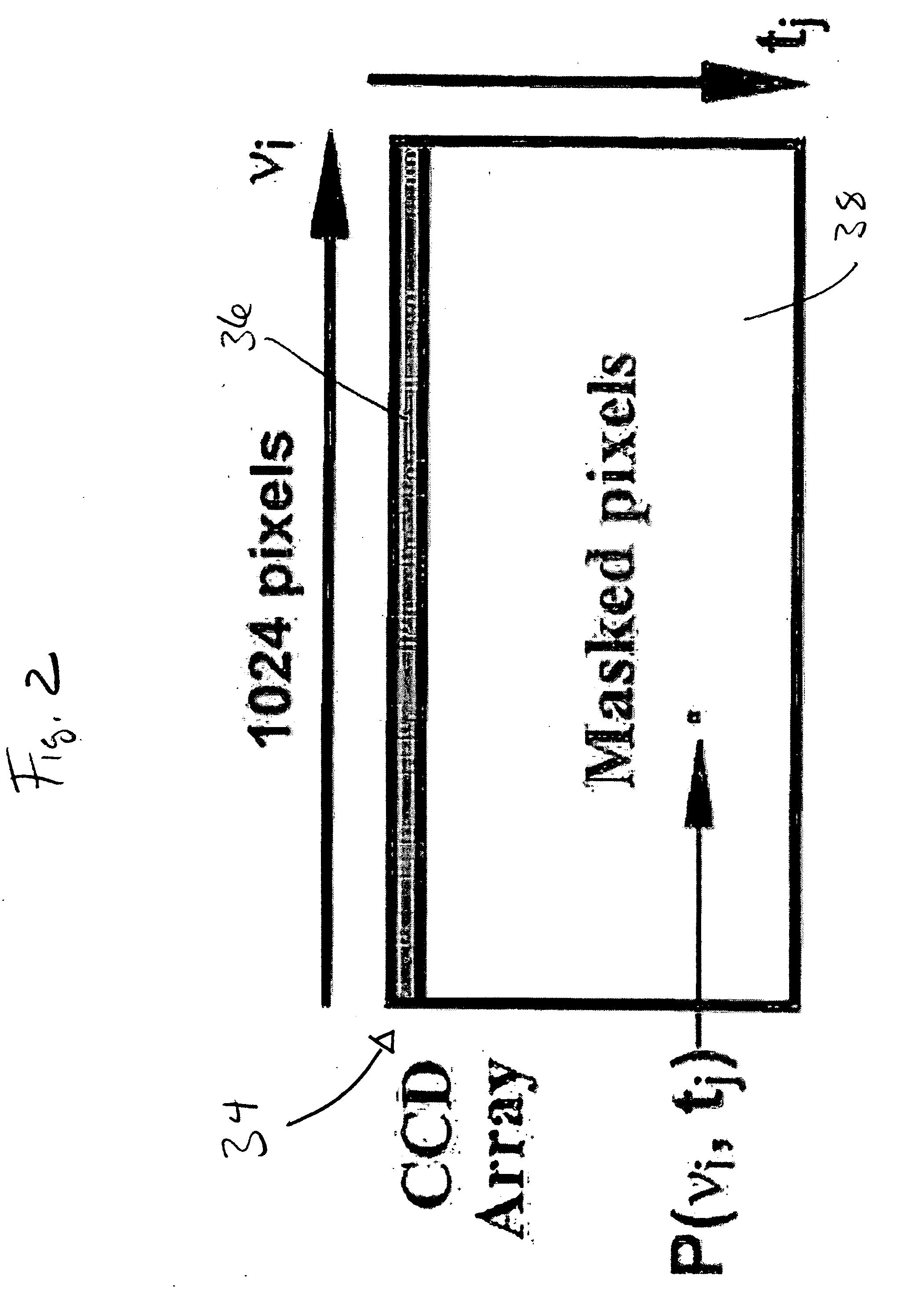
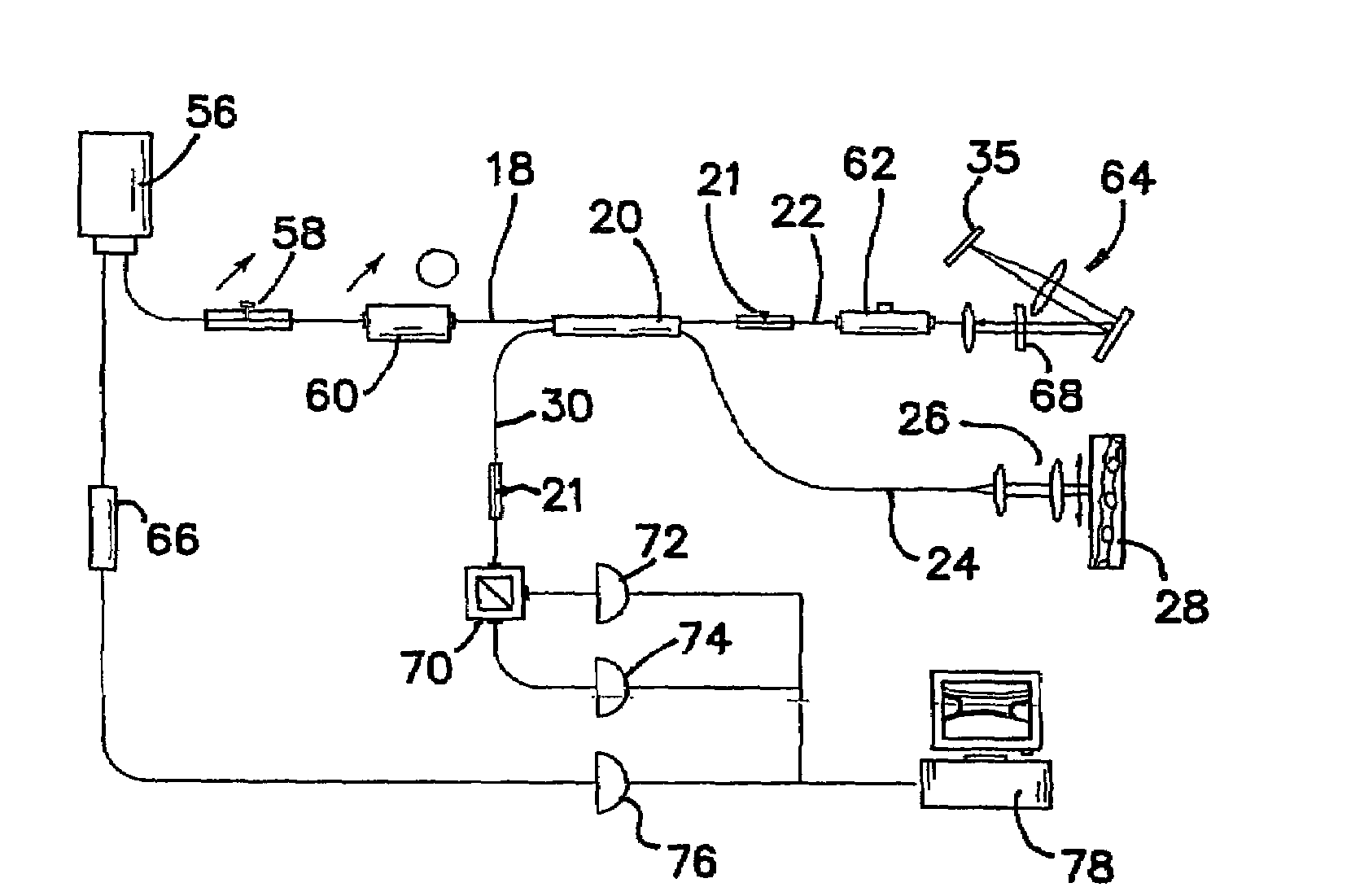
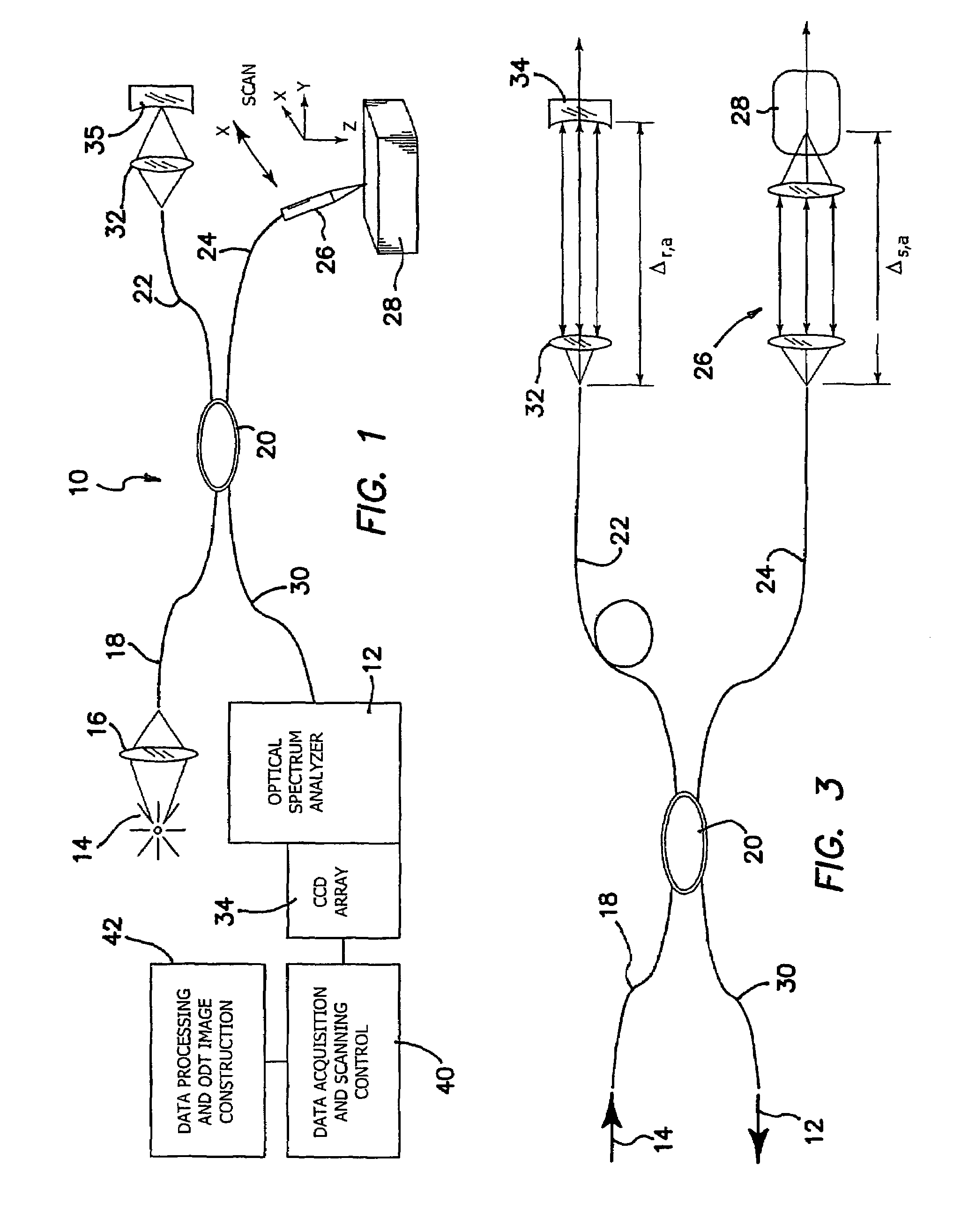
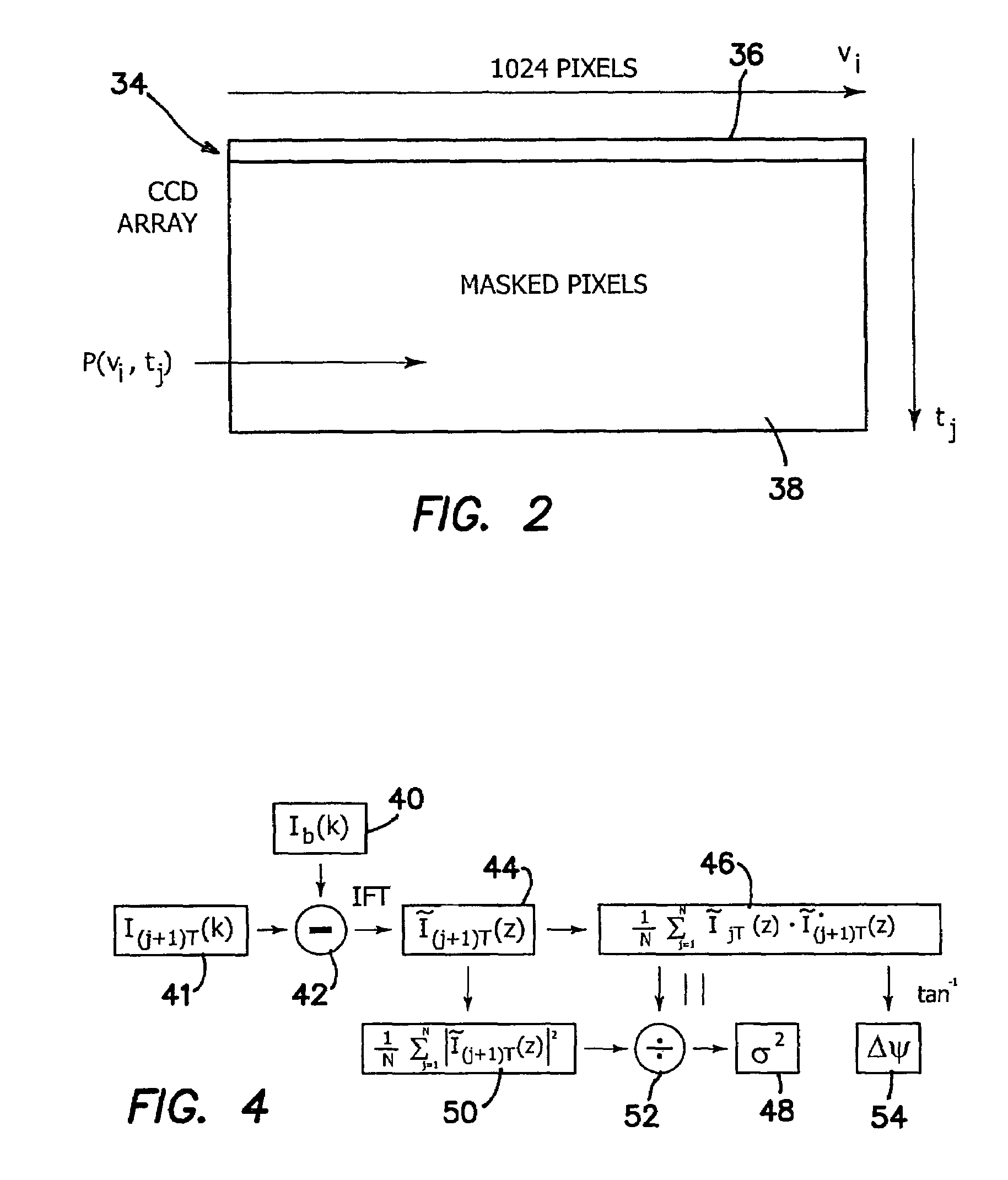
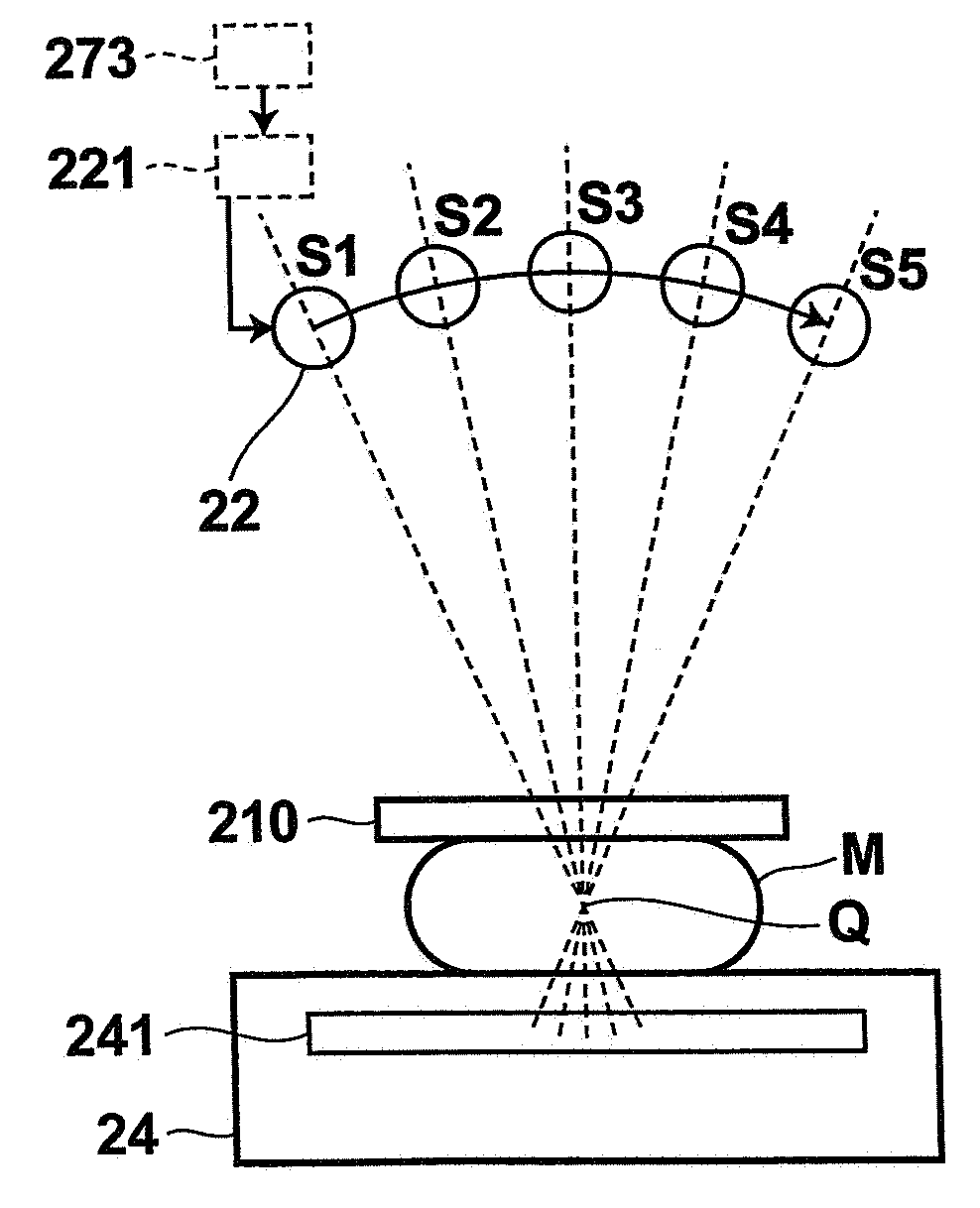
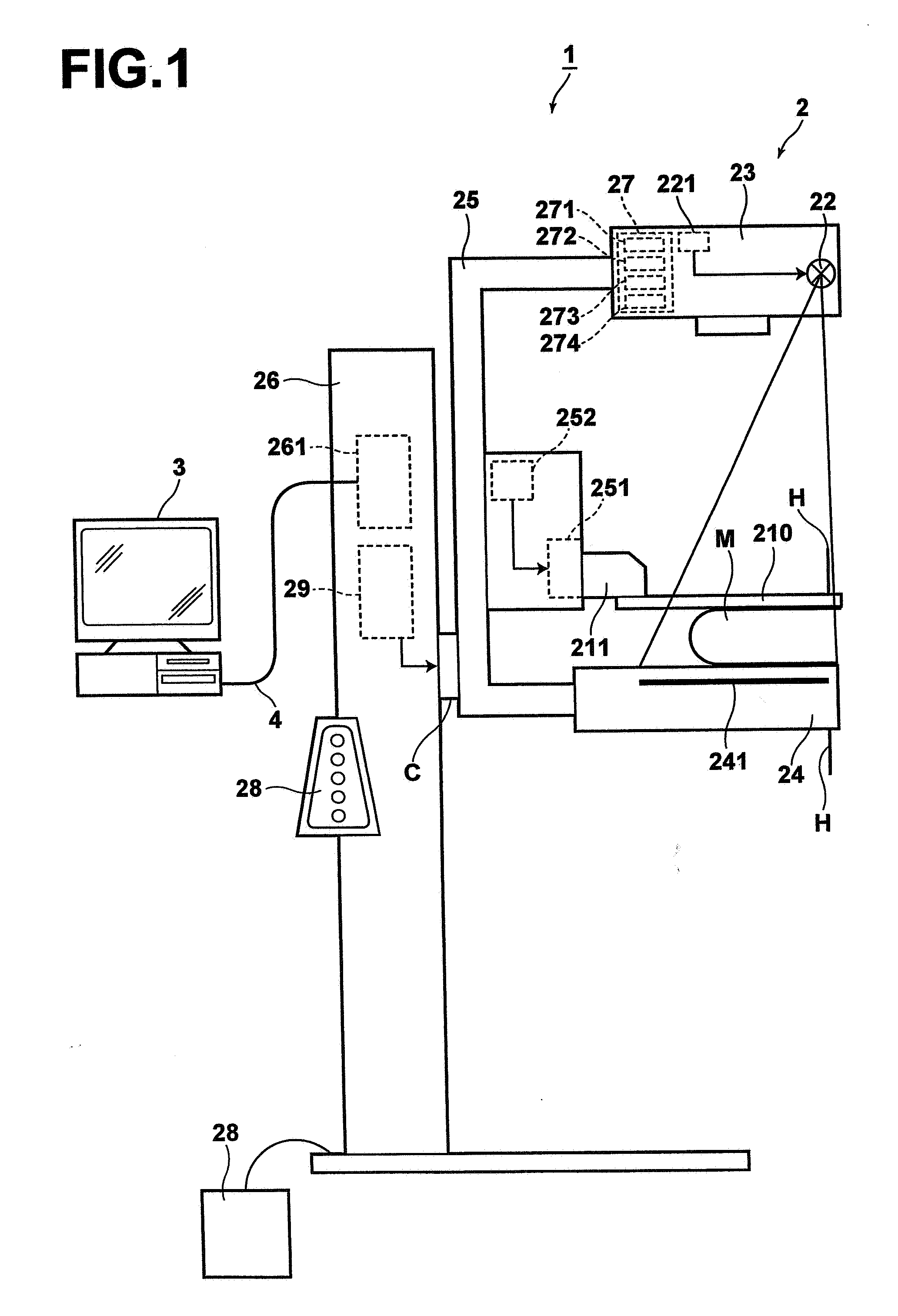
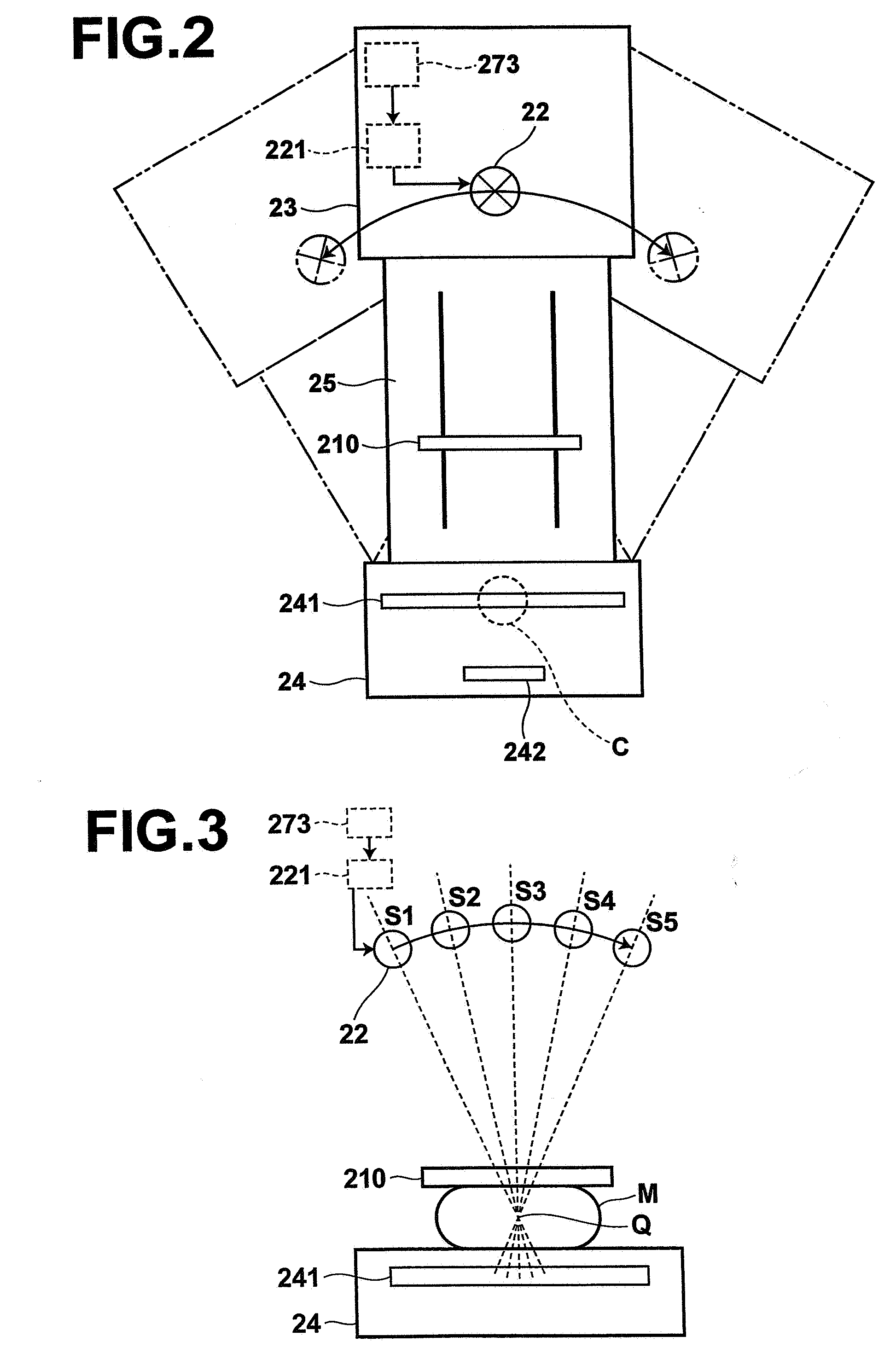
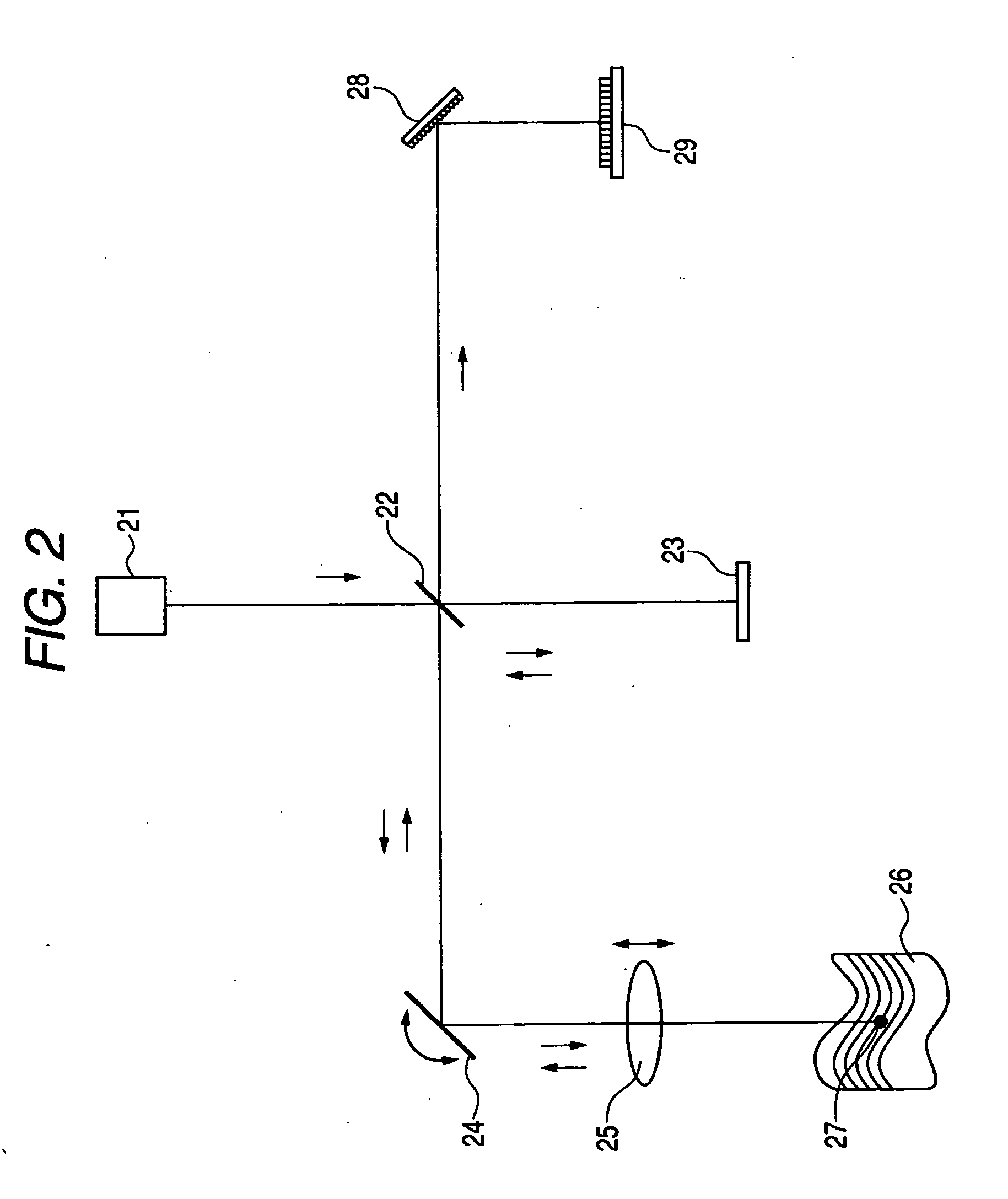
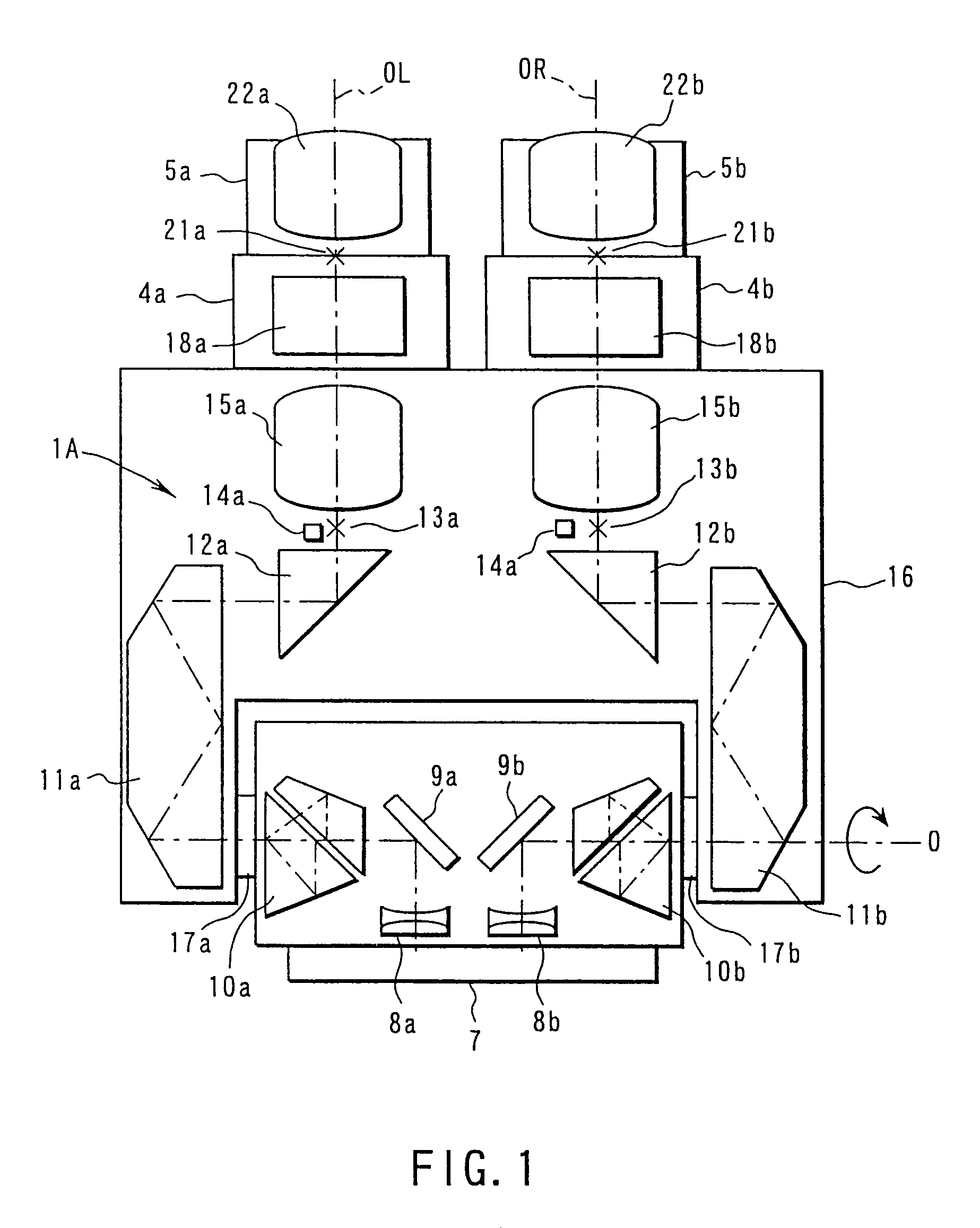
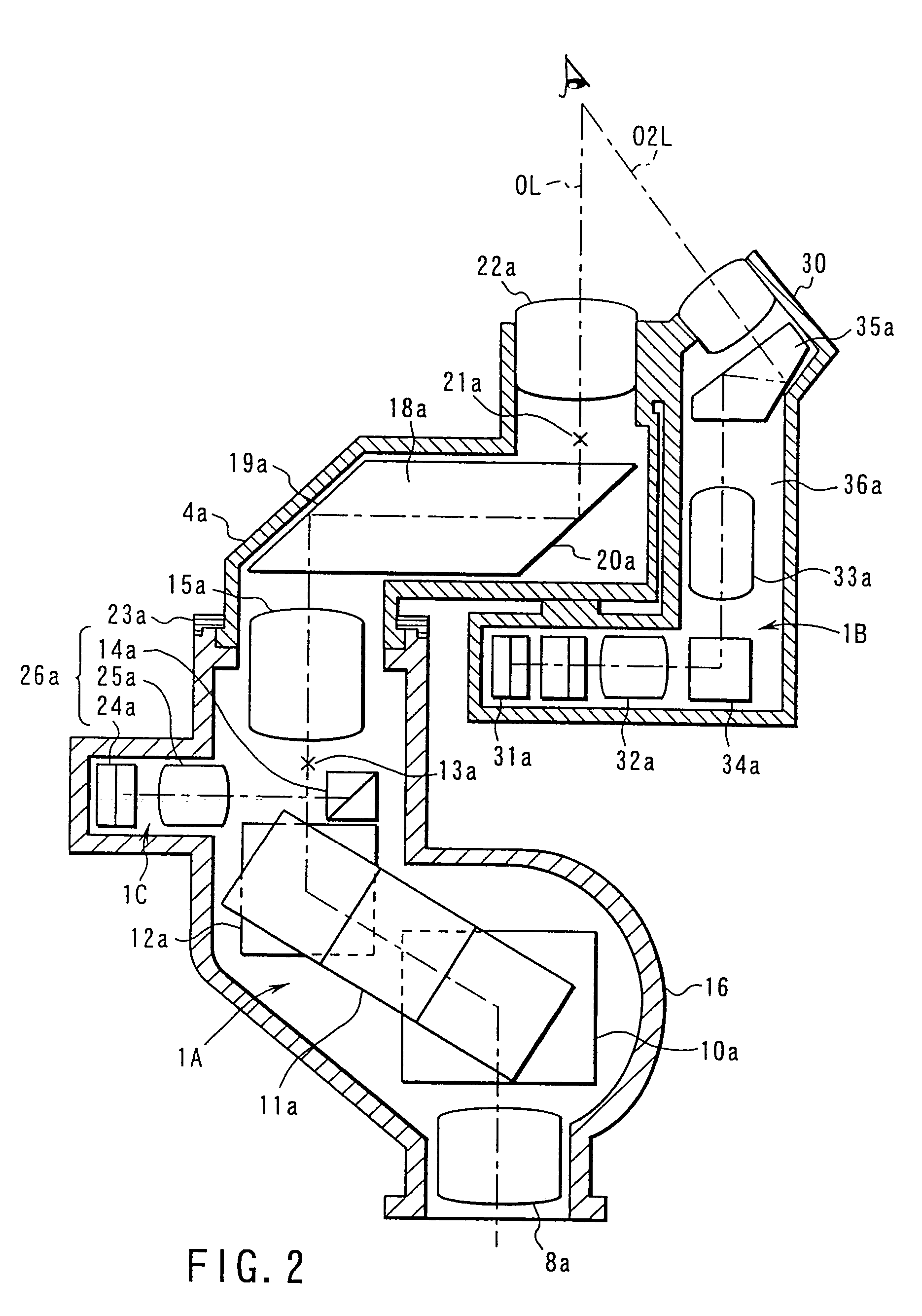
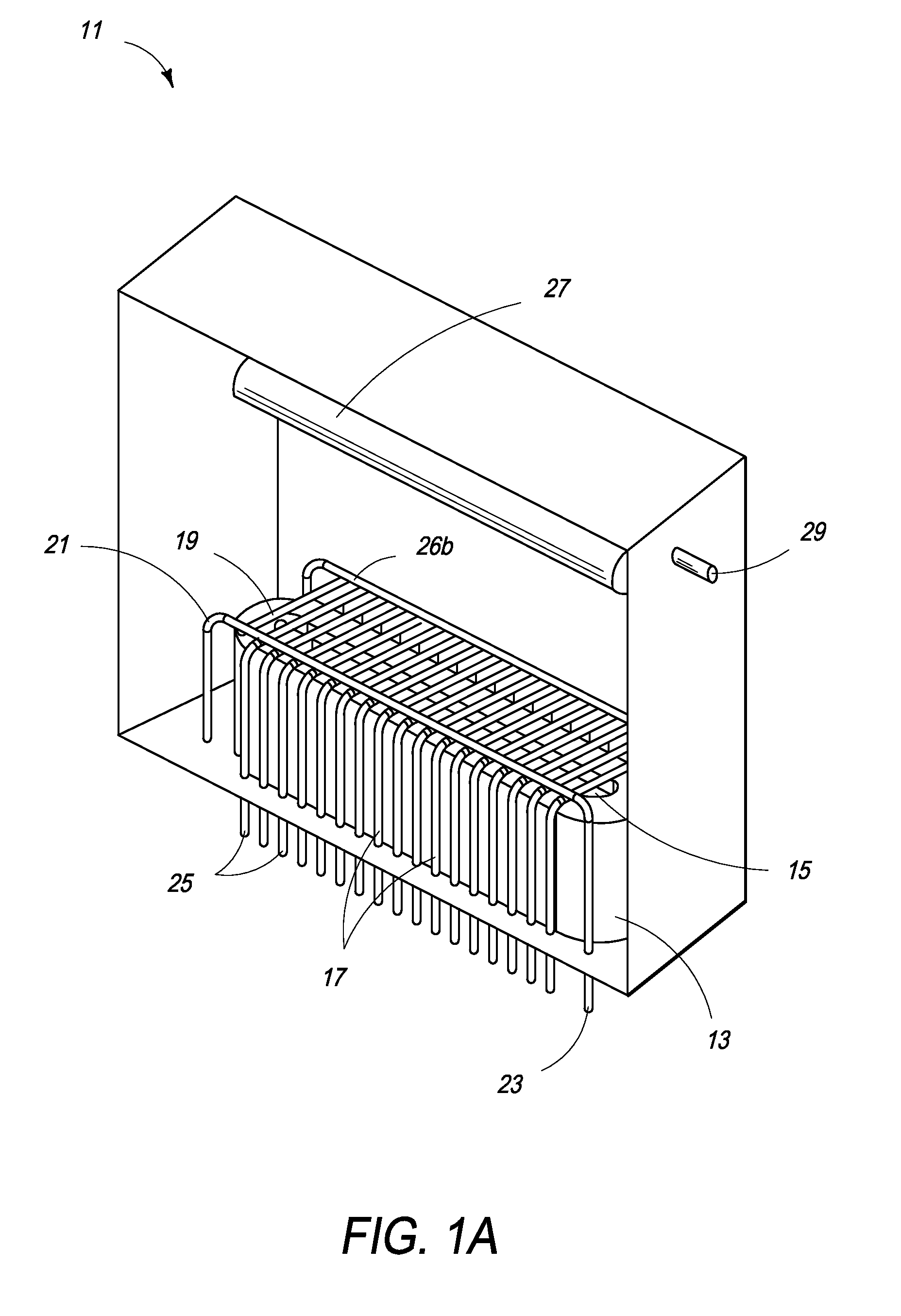
High speed spectral domain functional optical coherence tomography and optical doppler tomography for in vivo blood flow dynamics and tissue structure
ActiveUS20050171438A1Accurate settingImprove system sensitivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsBlood flowIn vivo
A method for tomographic imaging comprises the steps of providing a source of at least partially coherent radiation and a frequency-swept laser source through an interferometer; phase modulating the radiation in the interferometer at a modulation frequency for elimination of DC and autocorrelation noises as well as the mirror image; detecting interference fringes of the radiation backscattered from the sample into the interferometer to obtain a spectral signal; transforming the spectral signal of the detected backscattered interference fringes to obtain a time and location dependent signal, including the Doppler shift and variance, at each pixel location in a data window; and generating a tomographic image of the fluid flow in the data window and of the structure of the scanned fluid flow sample in the data window from the time and location dependent signal. The apparatus comprises a system for tomographic imaging operating according to the above method.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Apparatus and method for a global coordinate system for use in robotic surgery
ActiveUS20150335480A1Facilitating robotic surgeryDiagnostics using lightEye surgeryKinematicsEngineering
An apparatus and method for establishing a global coordinate system to facilitate robotic assisted surgery. The coordinate system may be established using a combination of the robotic data, i.e., kinematics, and optical coherence tomographic images generated by an overhead optical assembly and a tool-based sensor. Using these components, the system may generate a computer-registered three-dimensional model of the patient's eye. In some embodiments, the system may also generate a virtual boundary within the coordinate system to prevent inadvertent injury to the patient.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
High speed spectral domain functional optical coherence tomography and optical doppler tomography for in vivo blood flow dynamics and tissue structure
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Optical tomography apparatus
ActiveUS20070019208A1High resolutionMaintain good propertiesMaterial analysis by optical meansCatheterMultiplexingDiffusion
Low coherence light having a central wavelength λc of 1.1 μm and a full width at half maximum spectrum Δλ of 90 nm is emitted. The low coherence light has wavelength properties suited for the light absorbing properties, the diffusion properties, and the dispersion properties of living tissue. A light dividing means divides the low coherence light into a measuring light beam, which is irradiated onto a measurement target via an optical probe, and a reference light beam that propagates toward an optical path length adjusting means. A multiplexing means multiplexes a reflected light beam, which is the measuring light beam reflected at a predetermined depth of the measurement target, and the reference light beam, to form coherent light. A coherent light detecting means detects the optical intensity of the multiplexed coherent light. An image obtaining means performs image processes, and displays an optical tomographic image on a display apparatus.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
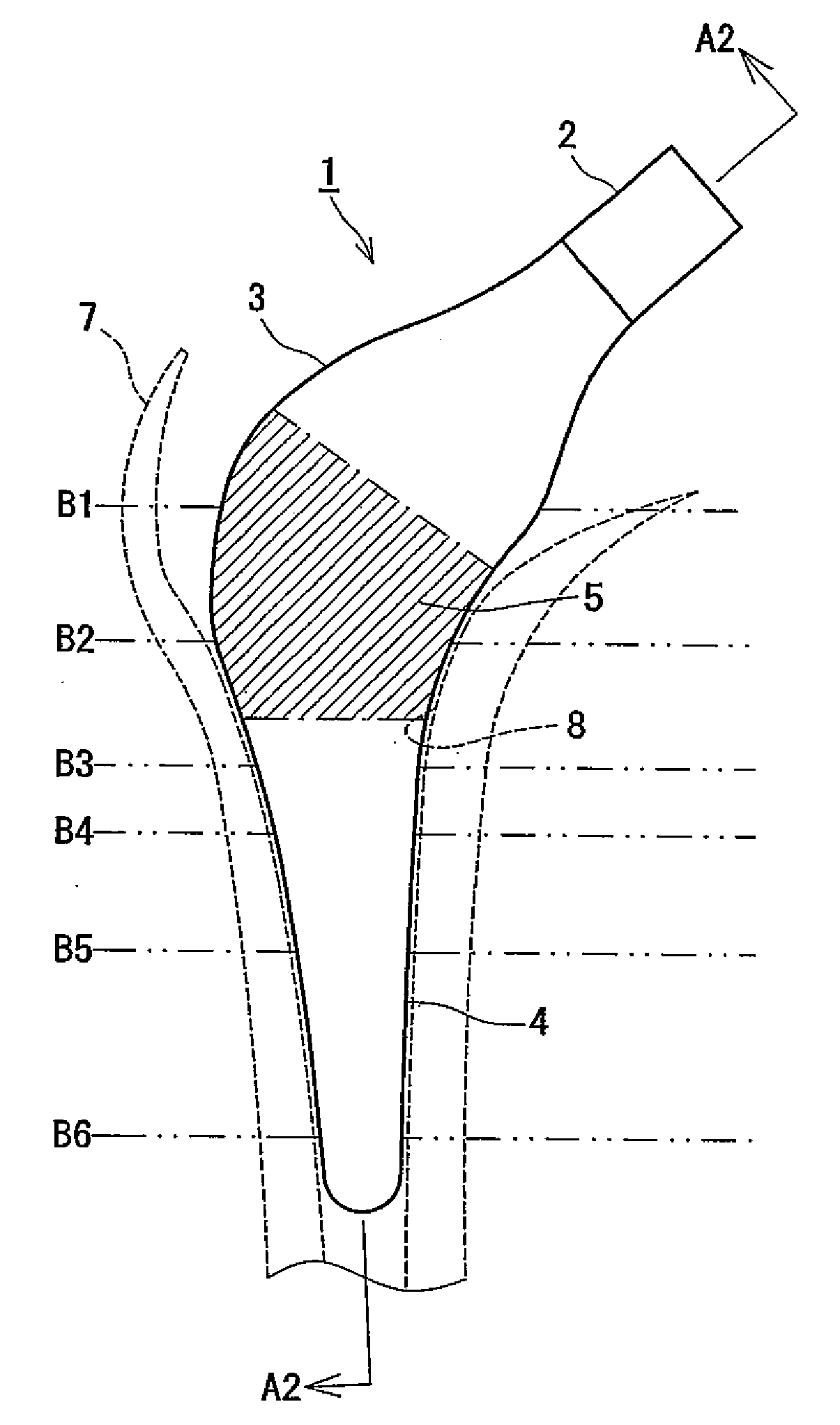
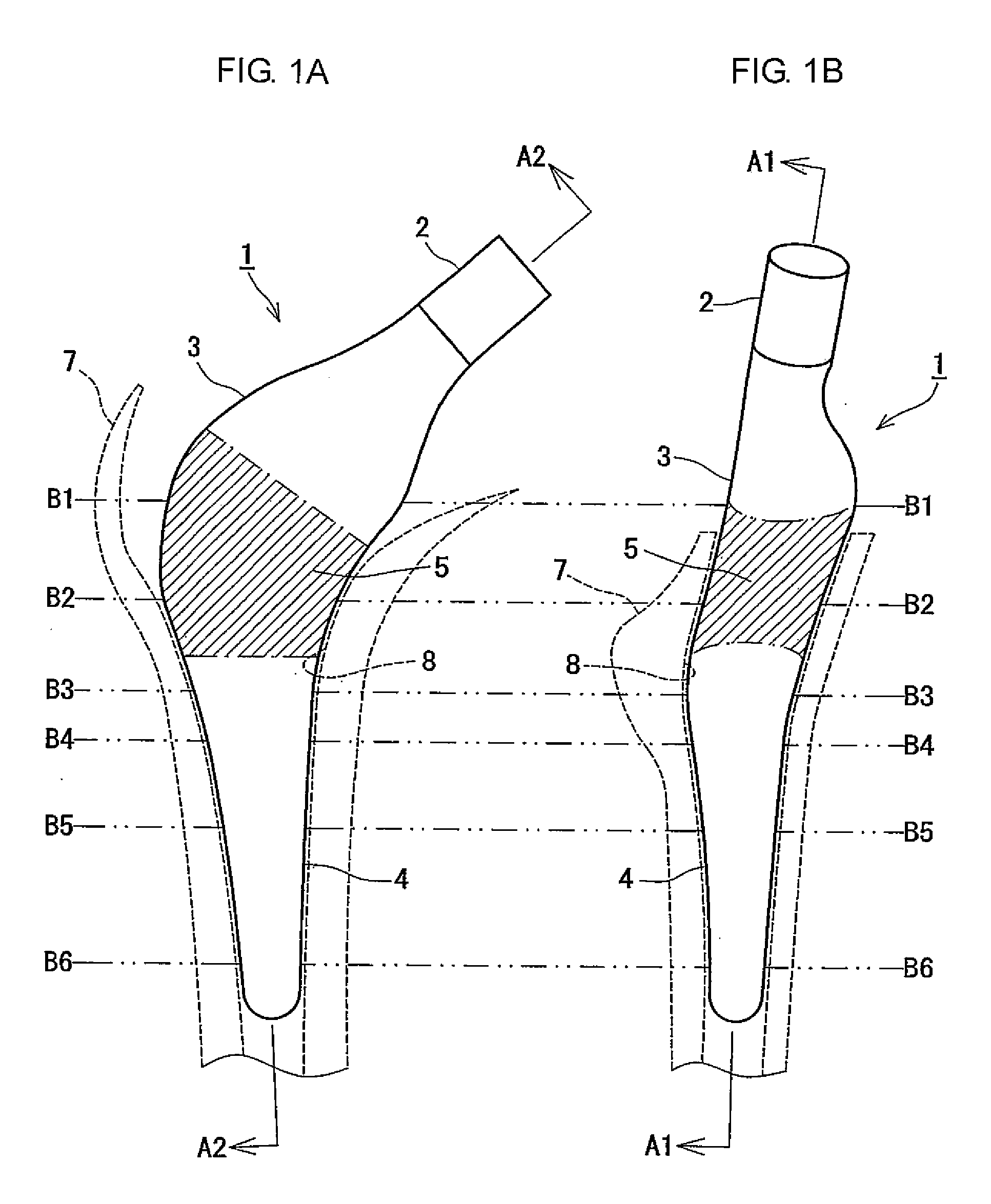
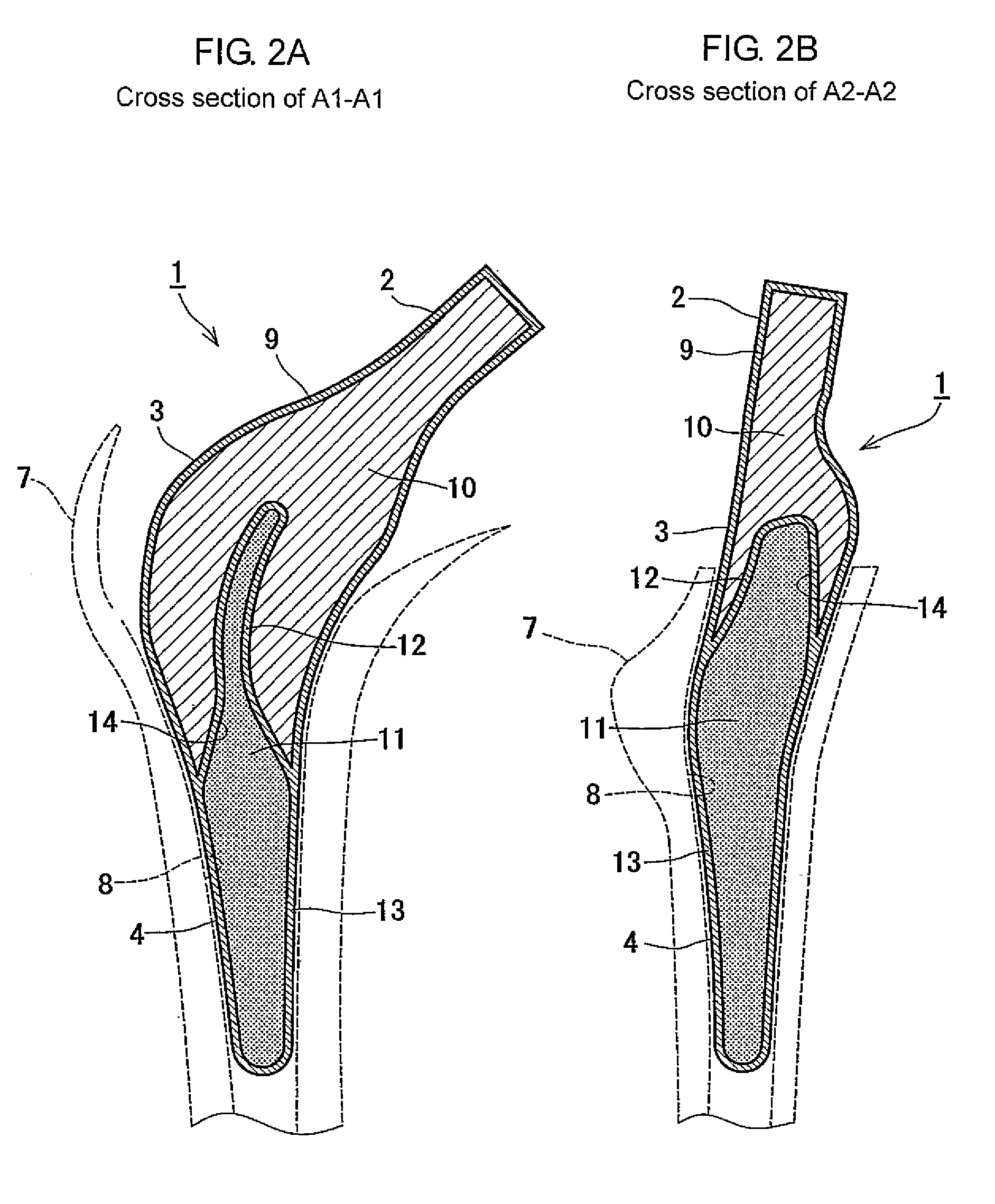
Method of Designing and Manufacturing Artificial Joint Stem with Use of Composite Material
InactiveUS20080234833A1Low costIncreased durabilityJoint implantsTomographyArtificial jointsEngineering
The method of designing and manufacturing the artificial joint stem, comprising steps of performing analysis of the internal stress of the artificial joint stem and bone and the adhesive stress of the artificial stem and bone, using the computer, based on the three dimension data indicating the structure of the bone formed by using plural tomographic images of the bone, the design condition involving the form and stiffness of the artificial joint stem configured by using at least one of the tomographic images and the three dimension data, wherein if the result of the analysis does not satisfy the design condition, the condition is changed to have the computer reanalyze and if the result of the analysis satisfies the design condition, the artificial joint stem is designed and manufactured with the stem data based on the result of analysis and the design condition.
Owner:B I TEC
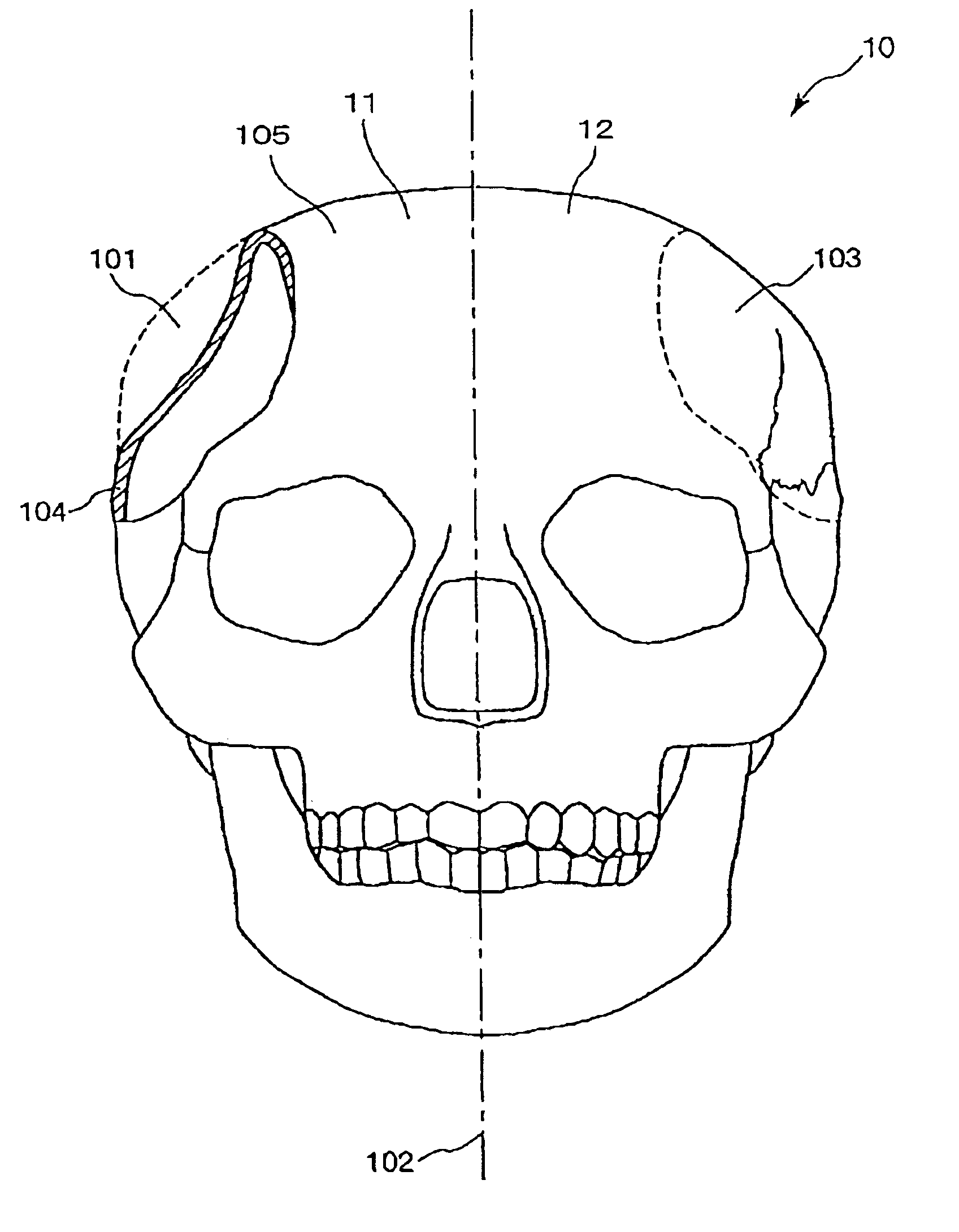
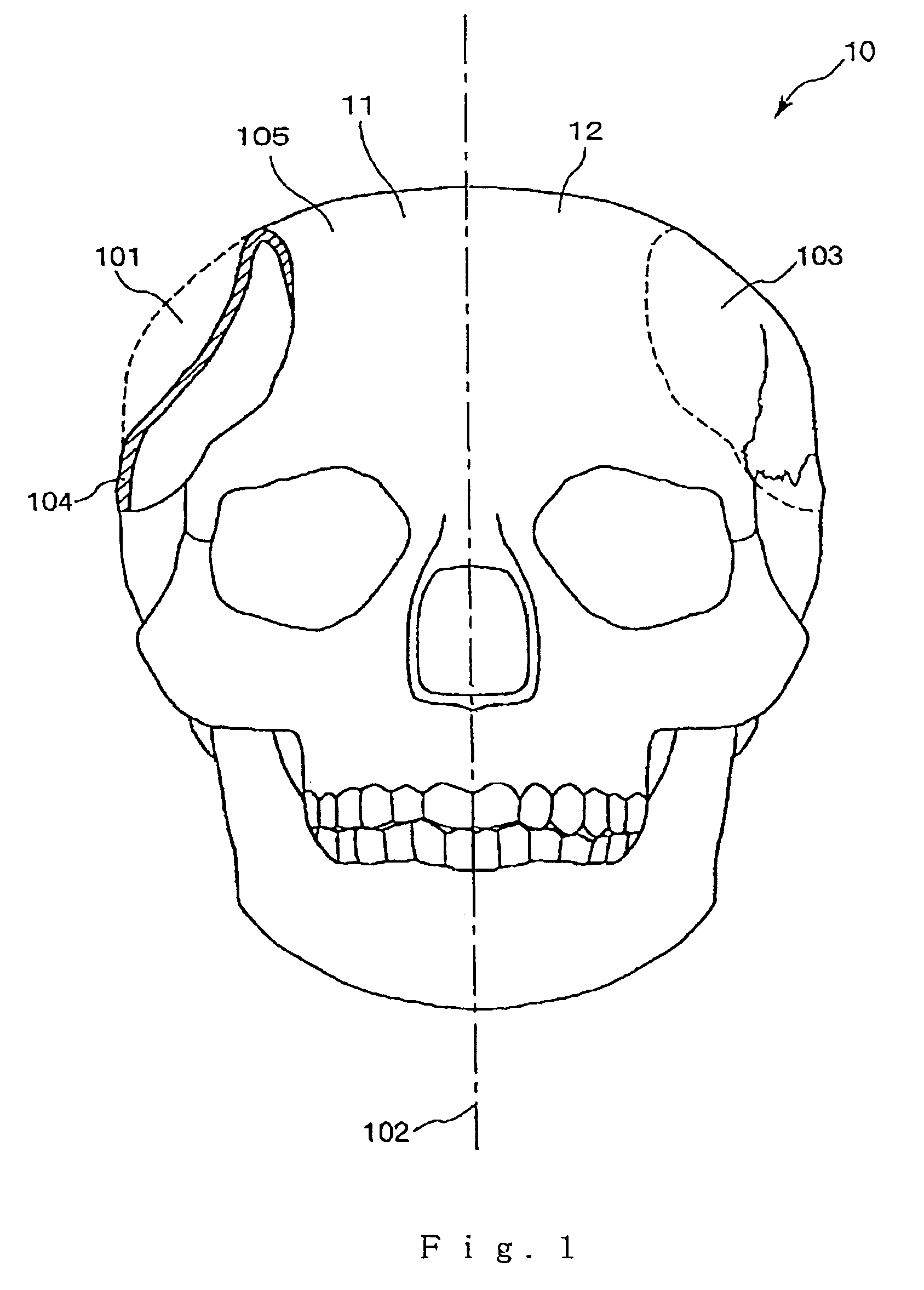
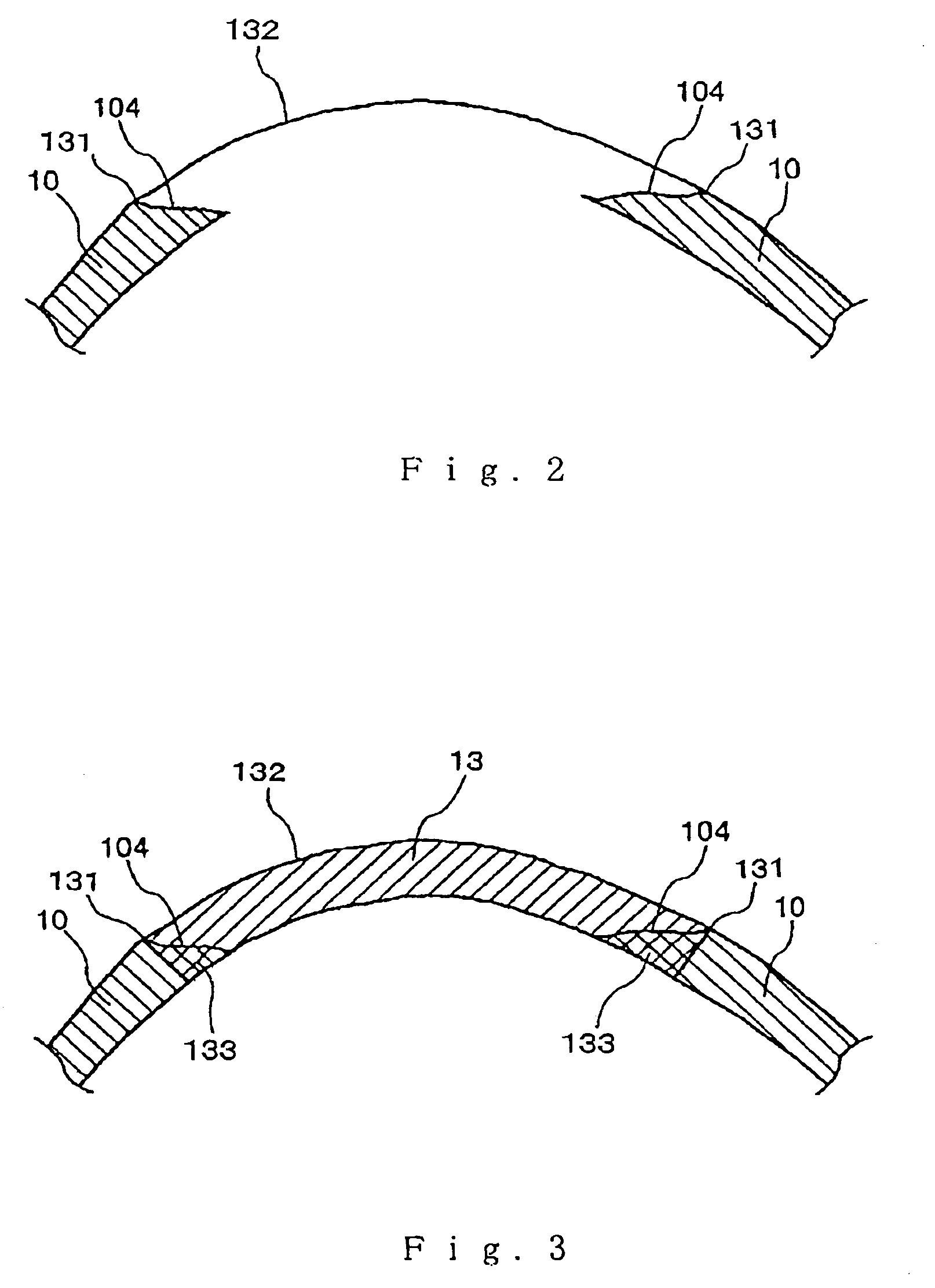
Method for modeling an implant and an implant manufactured by the method
InactiveUS7050877B2Good biocompatibilityStrong shape adaptabilitySurgeryPerson identificationTomographic imageBiomedical engineering
A method for modeling an implant to be applied to a defect of a bone comprises the steps of obtaining a plurality of tomographic image data of the bone based on measurement data by MRI, producing three-dimensional image data of the bone based on the plurality of tomographic image data, and estimating a shape of a missing born that was previously present or should have been present in the defect of the bone to obtain three-dimensional data of the implant. The estimating step comprises the steps of estimating a provisional shape of the implant which has a contour conformable with the shape of a contour of periphery of the side walls of the defect at the distal surface of the bone and has a predetermined thickness; and deleting data of portions of the provisional shape of the implant that overlap the bone from the data of the provisional shape of the implant so that the three-dimensional data of the implant has an outer peripheral shape that is conformable with the shape of the side walls of the defect.
Owner:ASAHI KOGAKU KOGYO KK +1
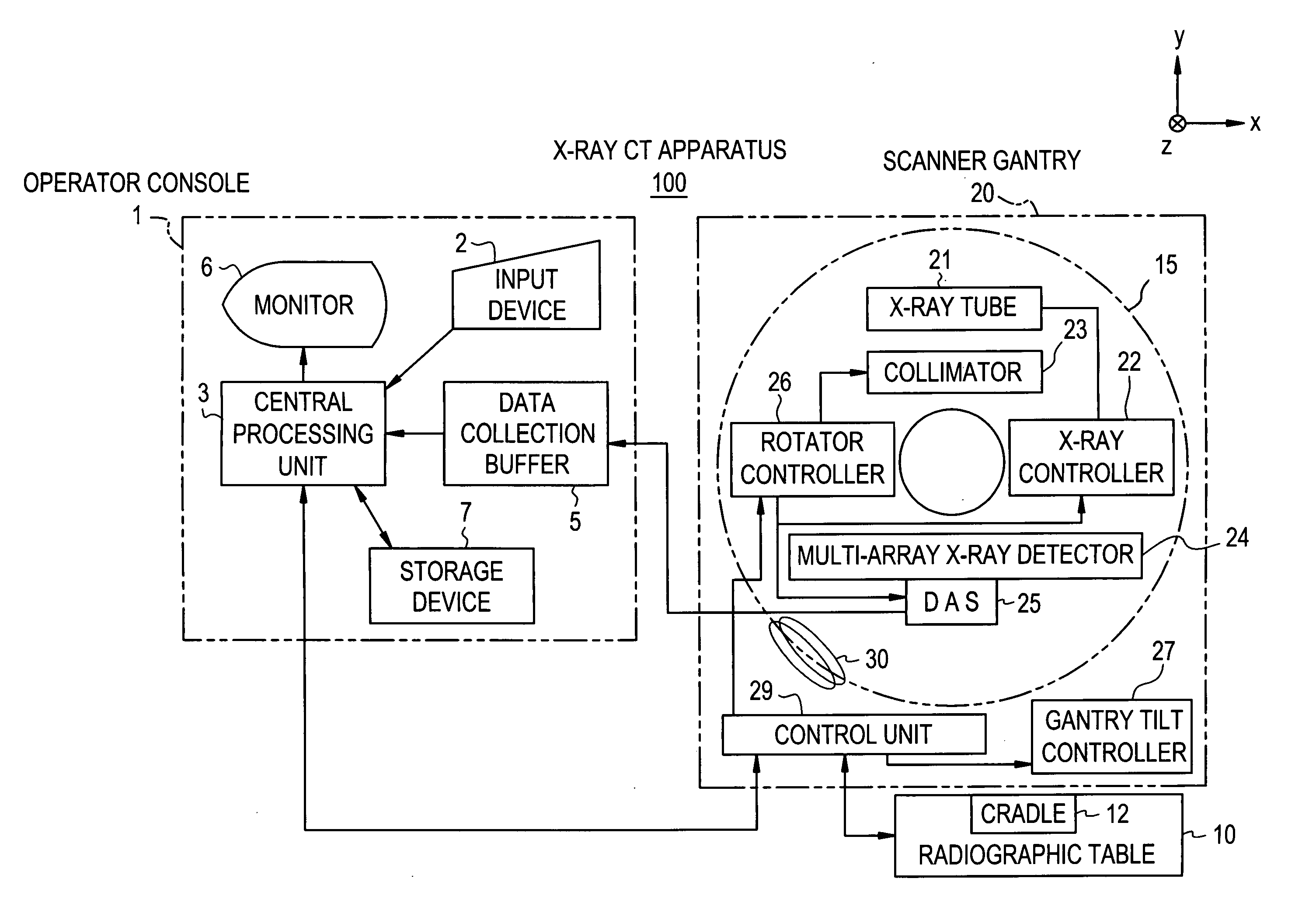
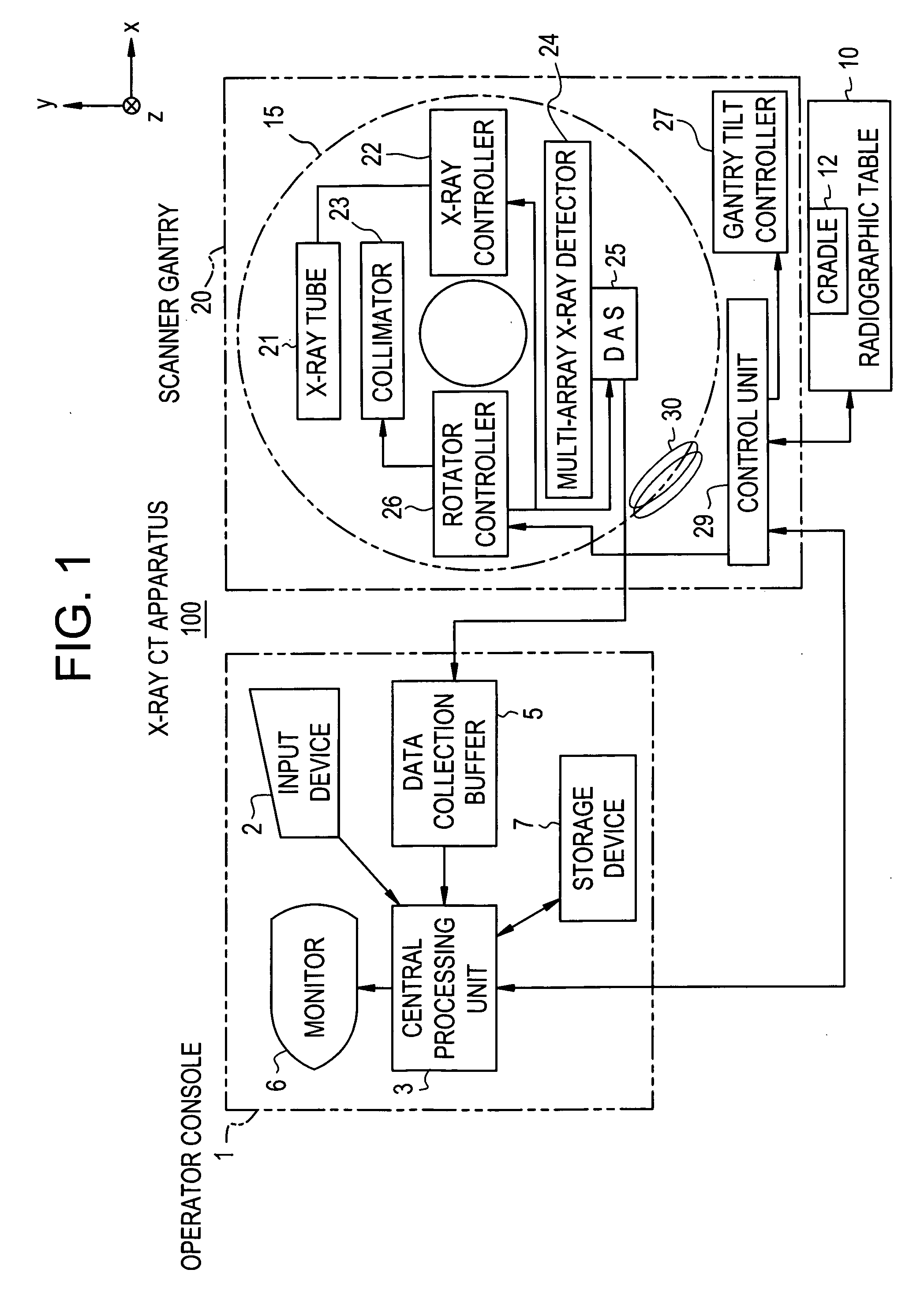
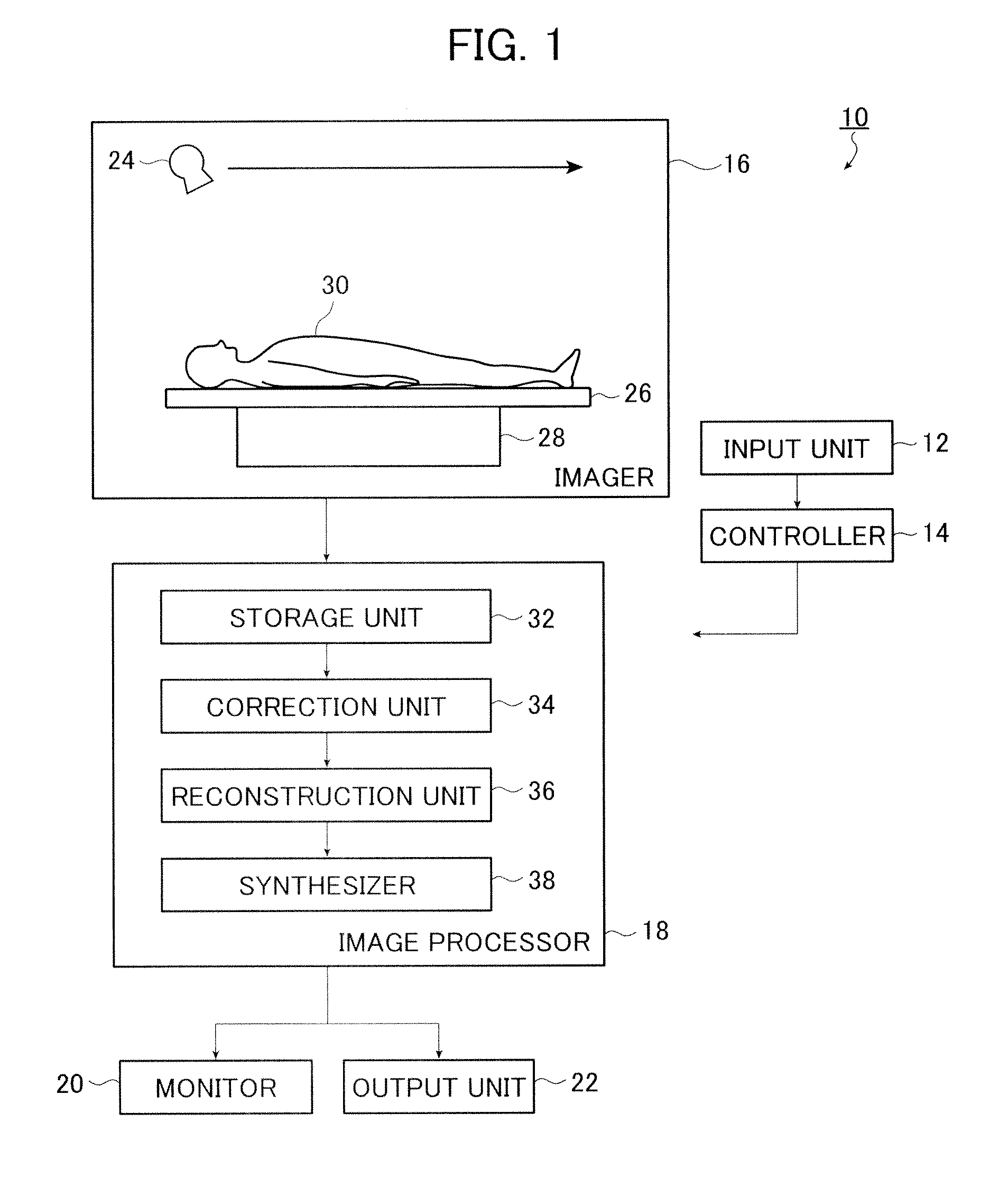
X-ray CT method and X-ray CT apparatus
InactiveUS20060291612A1Optimize radiographic conditionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-ray filterSlice thickness
In an X-ray CT apparatus, radiographic conditions (protocols) for imaging of each position represented by a z-coordinate are optimized in relation to an X-ray cone beam that spreads in a z direction. A slice thickness of a tomographic image is freely controlled in the z direction using a z filter during a conventional scan or a cine scan. For each tomographic image, a reconstruction function, an image filter, a scan field, a tomographic-image tilt angle, and a position of a tomographic image are freely adjusted or independently designated for scanning of each position in the z direction. Thus, a tomographic image is reconstructed. Moreover, the position of a beam formation X-ray filter in the z direction is shifted in order to optimize a patient dose that depends on the size of the scan field, and X-ray quality.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Omni-Tomographic Imaging for Interior Reconstruction using Simultaneous Data Acquisition from Multiple Imaging Modalities
InactiveUS20120265050A1Less importantLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityModern medicine
Embodiments of the invention relate to omni-tomographic imaging or grand fusion imaging, i.e., large scale fusion of simultaneous data acquisition from multiple imaging modalities such as CT, MRI, PET, SPECT, US, and optical imaging. A preferred omni-tomography system of the invention comprises two or more imaging modalities operably configured for concurrent signal acquisition for performing ROI-targeted reconstruction and contained in a single gantry with a first inner ring as a permanent magnet; a second middle ring containing an x-ray tube, detector array, and a pair of SPECT detectors; and a third outer ring for containing PET crystals and electronics. Omni-tomography offers great synergy in vivo for diagnosis, intervention, and drug development, and can be made versatile and cost-effective, and as such is expected to become an unprecedented imaging platform for development of systems biology and modern medicine.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Radiographic apparatus
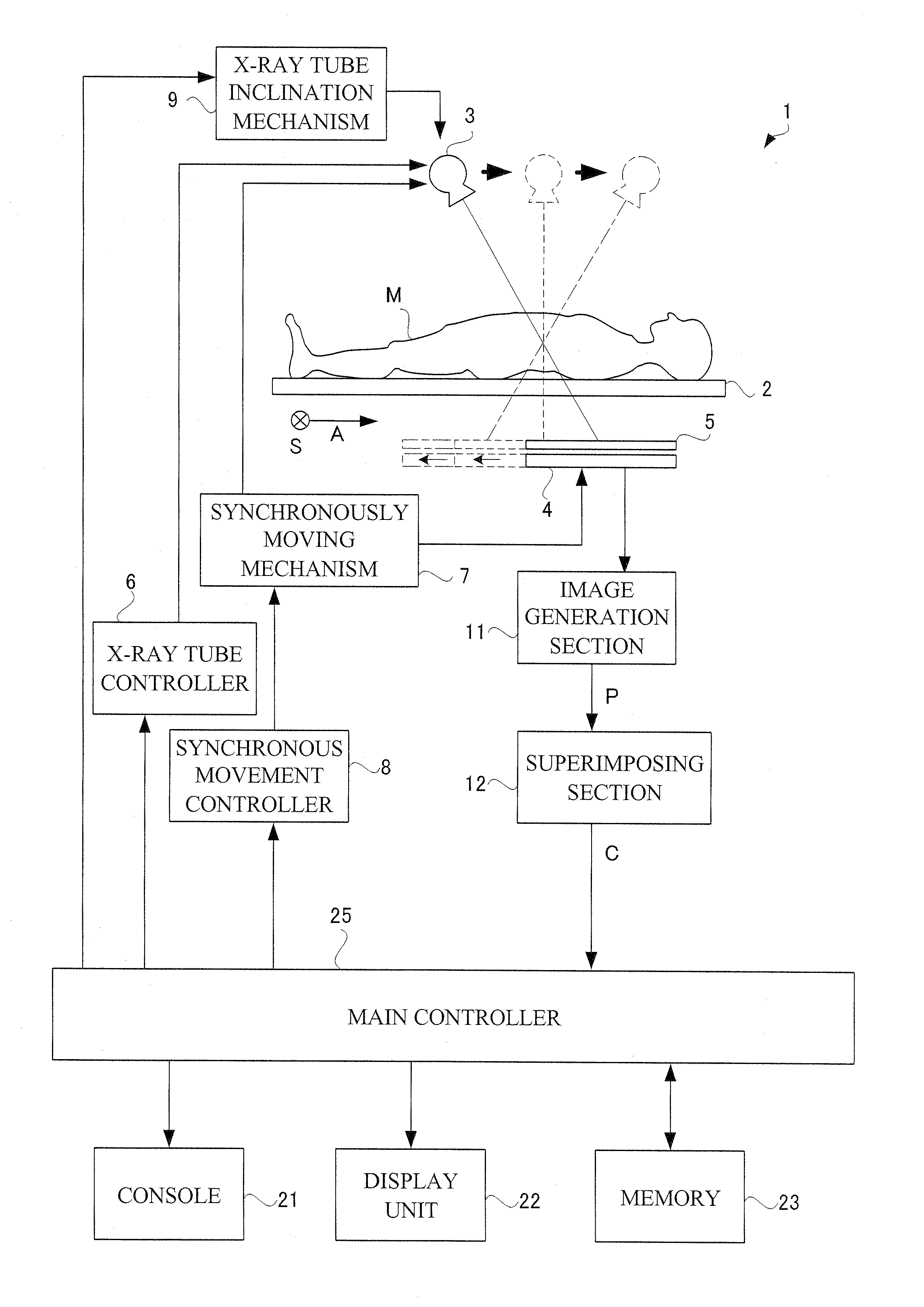
ActiveUS8798231B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingFluoroscopic imageFluorescence
One object of this invention is to provide radiography apparatus with suppressed exposure to a subject in tomography mode. An FPD provided in X-ray apparatus according to this invention converts X-rays into electric signals, and thereafter amplifies the signals to output them to an image generation section. According to this invention, an amplification factor is higher in a tomography mode than in a spot radiography mode. A tomographic image is obtained through superimposing two or more fluoroscopic image. In comparison of the fluoroscopic images, they differ from one another in appearance of the false image. Accordingly, superimposing the images may achieve cancel of the false images. In this way, the tomographic image finally obtained has no false image.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
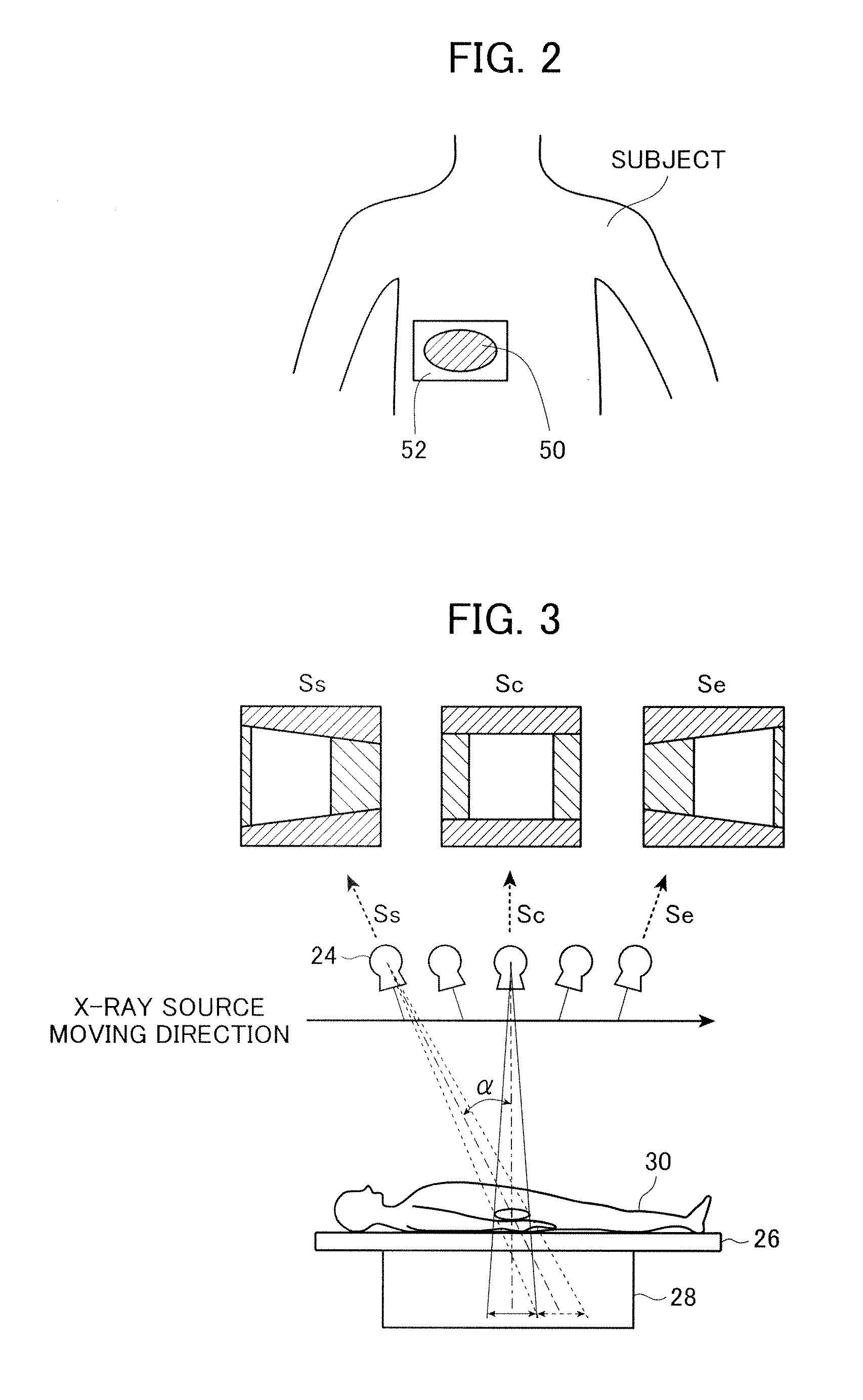
X-ray imaging system and x-ray imaging method
InactiveUS20120051498A1Reduce exposureReduced imaging timeReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayX ray image
An X-ray imaging system is for irradiating a subject with X ray from an X-ray source at a plurality of different angles to acquire X-ray images, and reconstructing an X-ray tomographic image from the X-ray images. The system comprising a region setting unit for setting a region of interest on a pre-shot image or a previously acquired X-ray tomographic image, an imaging control unit for continuously varying an aperture formed by collimator blades according to a position of the X-ray source to image the region of interest and acquiring projection data of the X-ray images in accordance with the position of the X-ray source, and an image reconstructing unit for reconstructing the X-ray tomographic image from the projection data of the X-ray images of the region of interest. The aperture formed by the collimator blades are varied so that all the X-ray images formed on the X-ray detector is rectangular regardless of the position of the X-ray source.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Optical coherence tomographic imaging apparatus and optical coherence tomographic imaging method
InactiveUS20100002241A1Increase contrastMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansLight beamImage formation
An optical coherence tomographic imaging apparatus which has a light intensity varying portion provided on a first optical path for guiding a measuring beam to an object for varying an intensity of the measuring beam; an illumination condition varying portion for varying an illumination condition of the measuring beam that has passed through the light intensity varying portion for the object between a first illumination condition in which a center part of the measuring beam is not blocked and a second illumination condition in which the center part of the measuring beam is blocked; and an image forming portion for weighting a first tomographic image acquired in the first illumination condition and a second tomographic image acquired in the second illumination condition and composing the weighted first second tomographic images to form a third tomographic image.
Owner:CANON KK
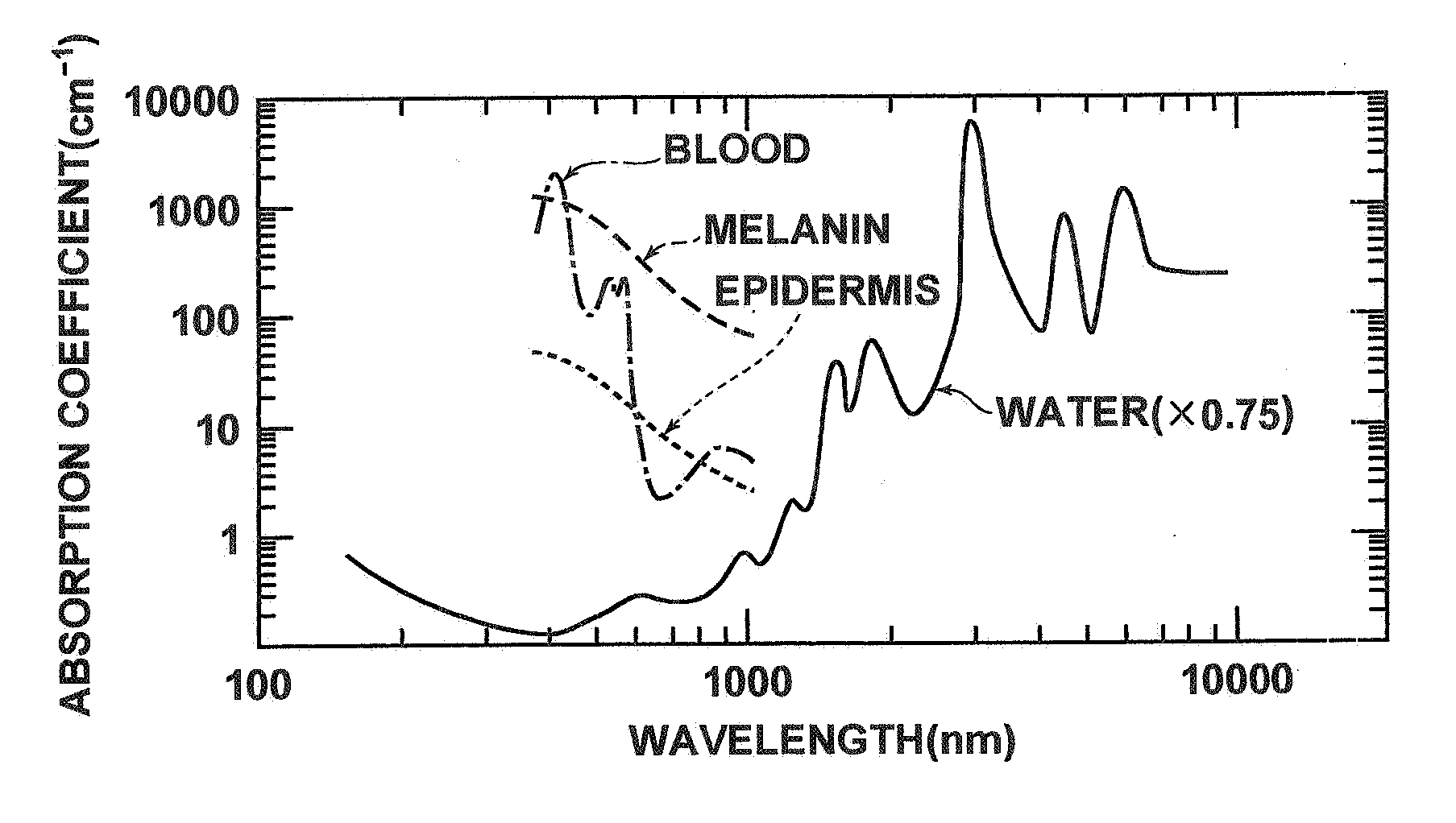
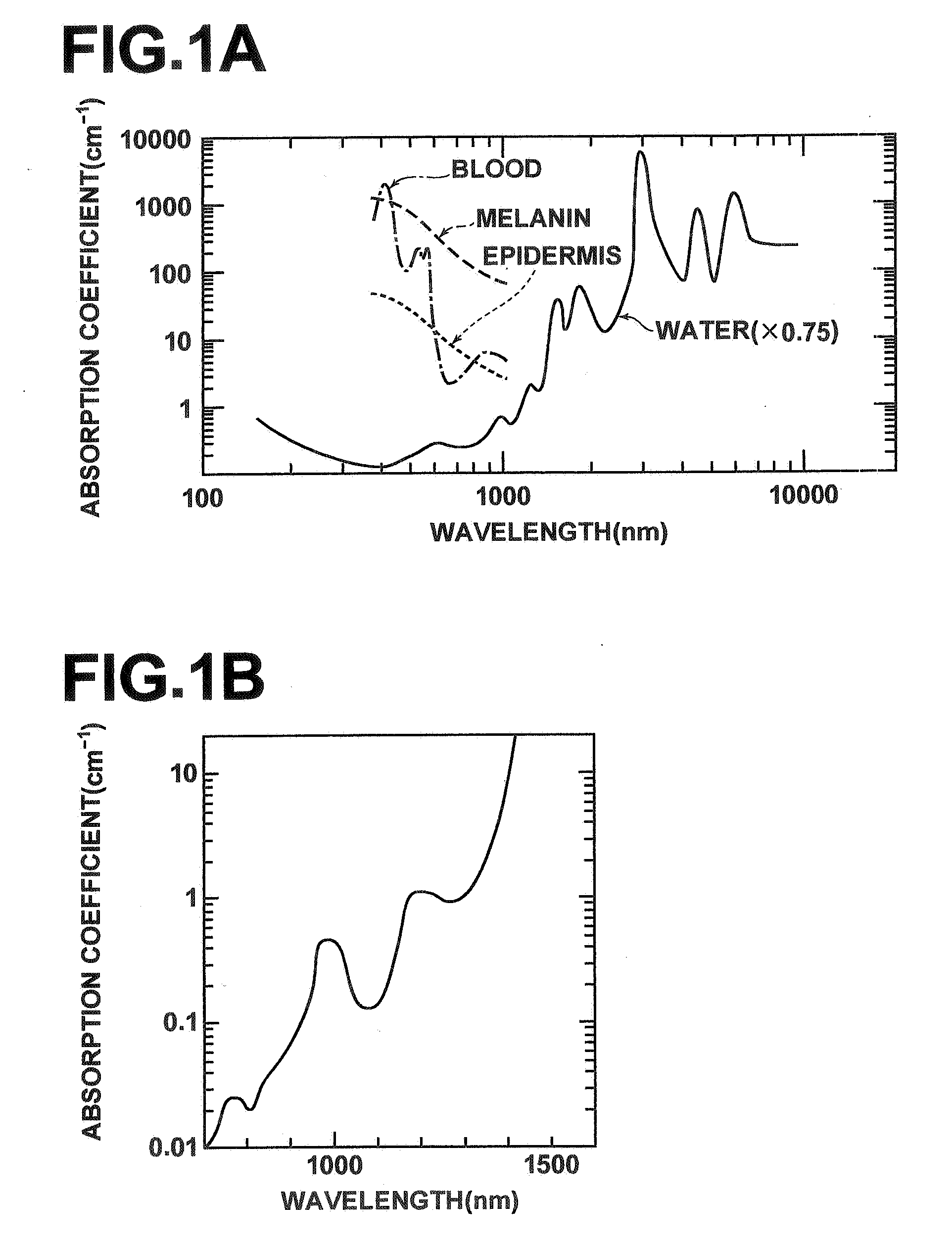
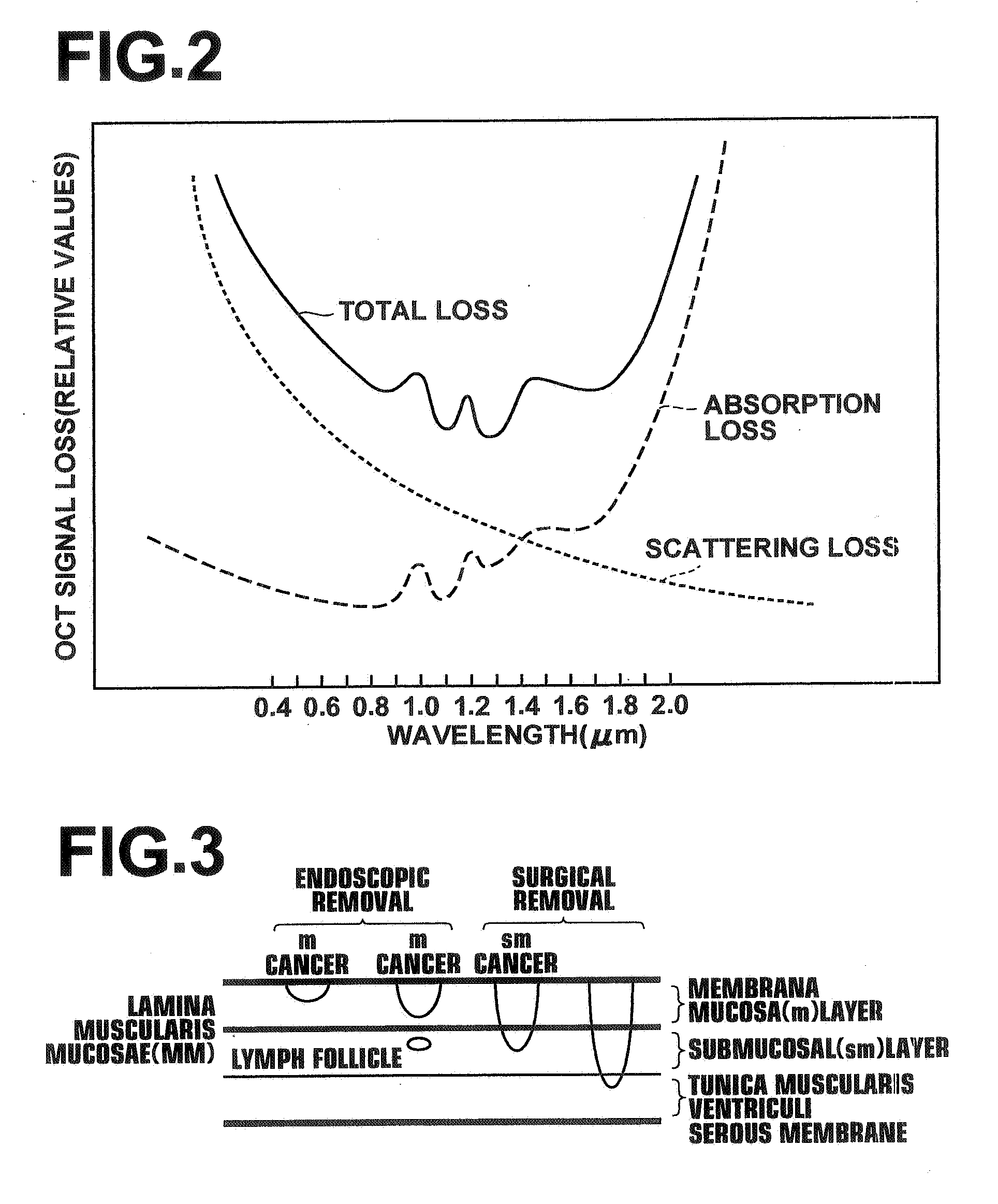
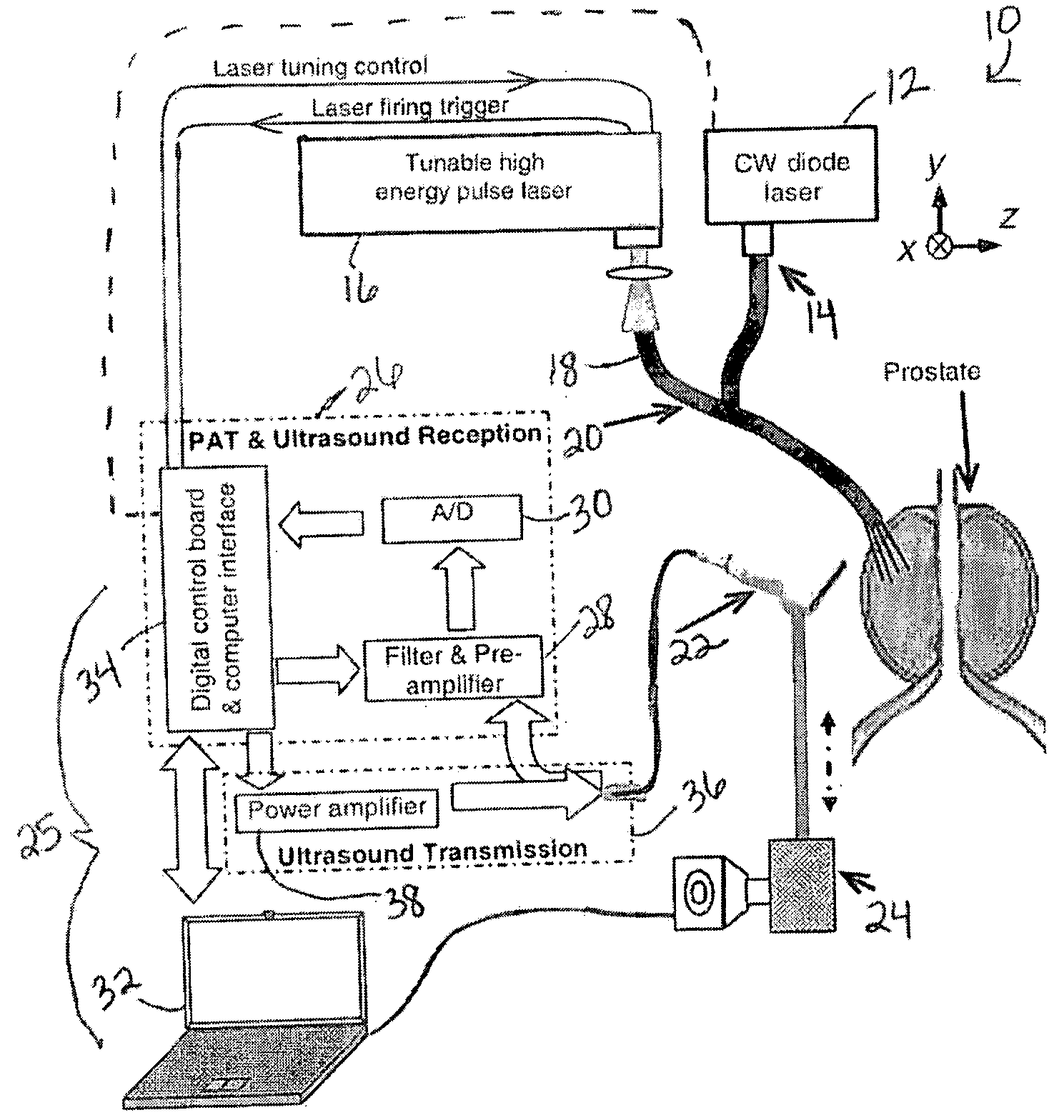
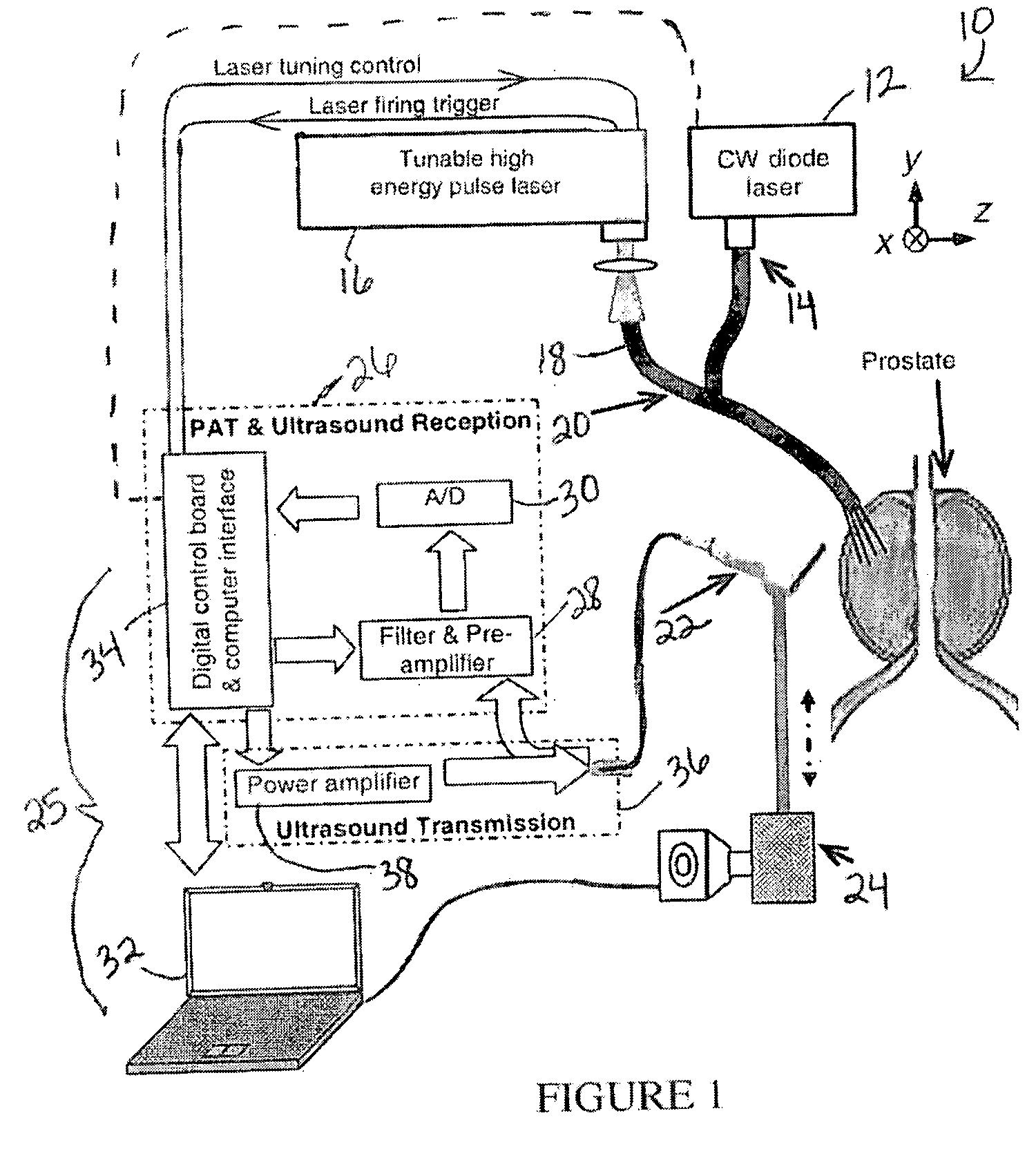
System and method for monitoring photodynamic therapy
InactiveUS20080221647A1High electromagnetic contrastHighly sensitive detection and monitoringSurgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionPhotodynamic therapyUltrasonic sensor
A system and method for monitoring photodynamic therapy of a target tissue, where the target tissue contains a photosensitizing substance, include a first light source configured to deliver light to the target tissue, the first light source having a wavelength capable of exciting the photosensitizing substance. An ultrasonic transducer receives photoacoustic signals generated due to optical absorption of light energy by the target tissue, and a control unit in communication with the ultrasonic transducer reconstructs photoacoustic tomographic images from the received photoacoustic signals to provide an indication of optical energy deposition due to the photosensitizing substance in the target tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
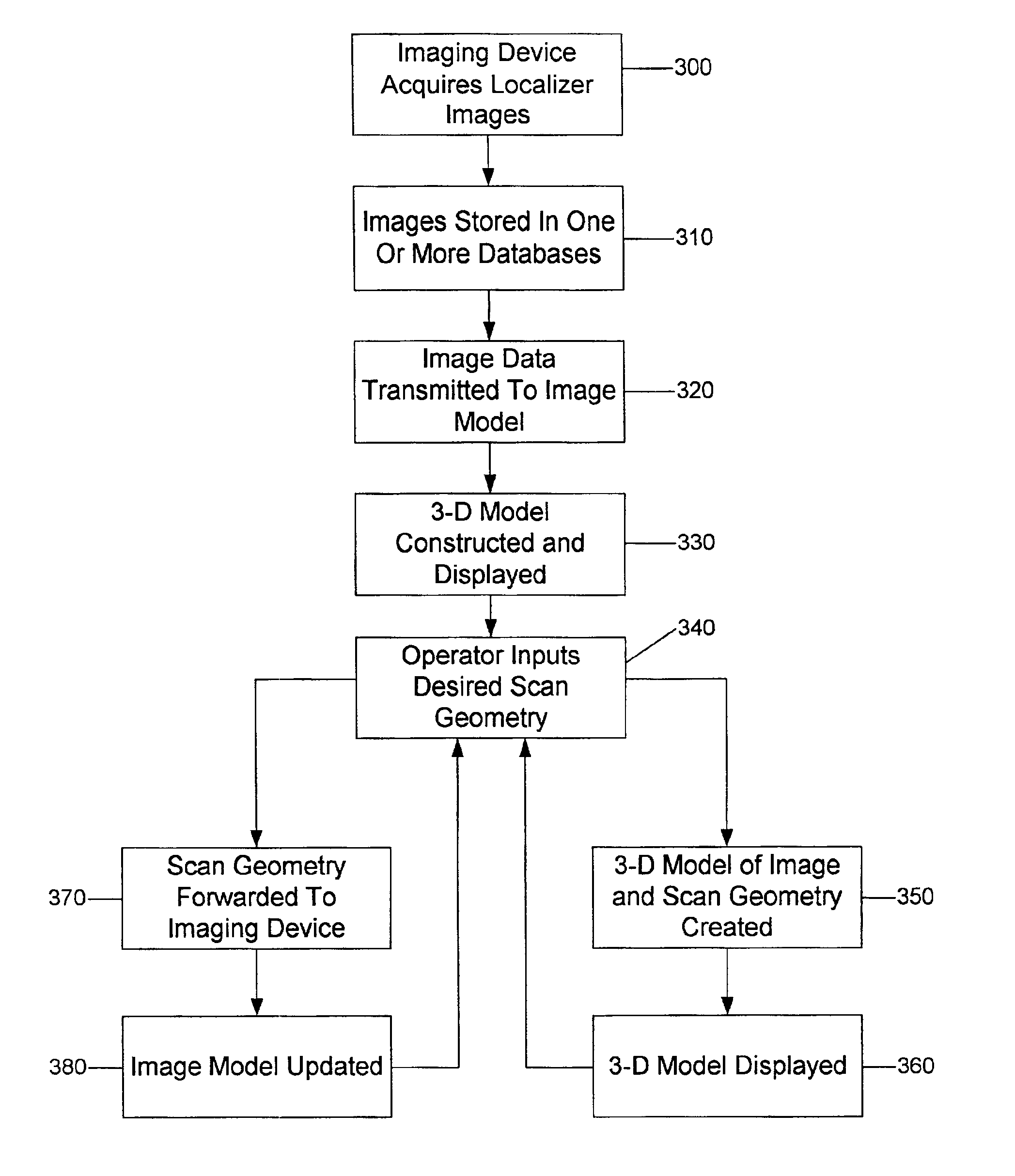
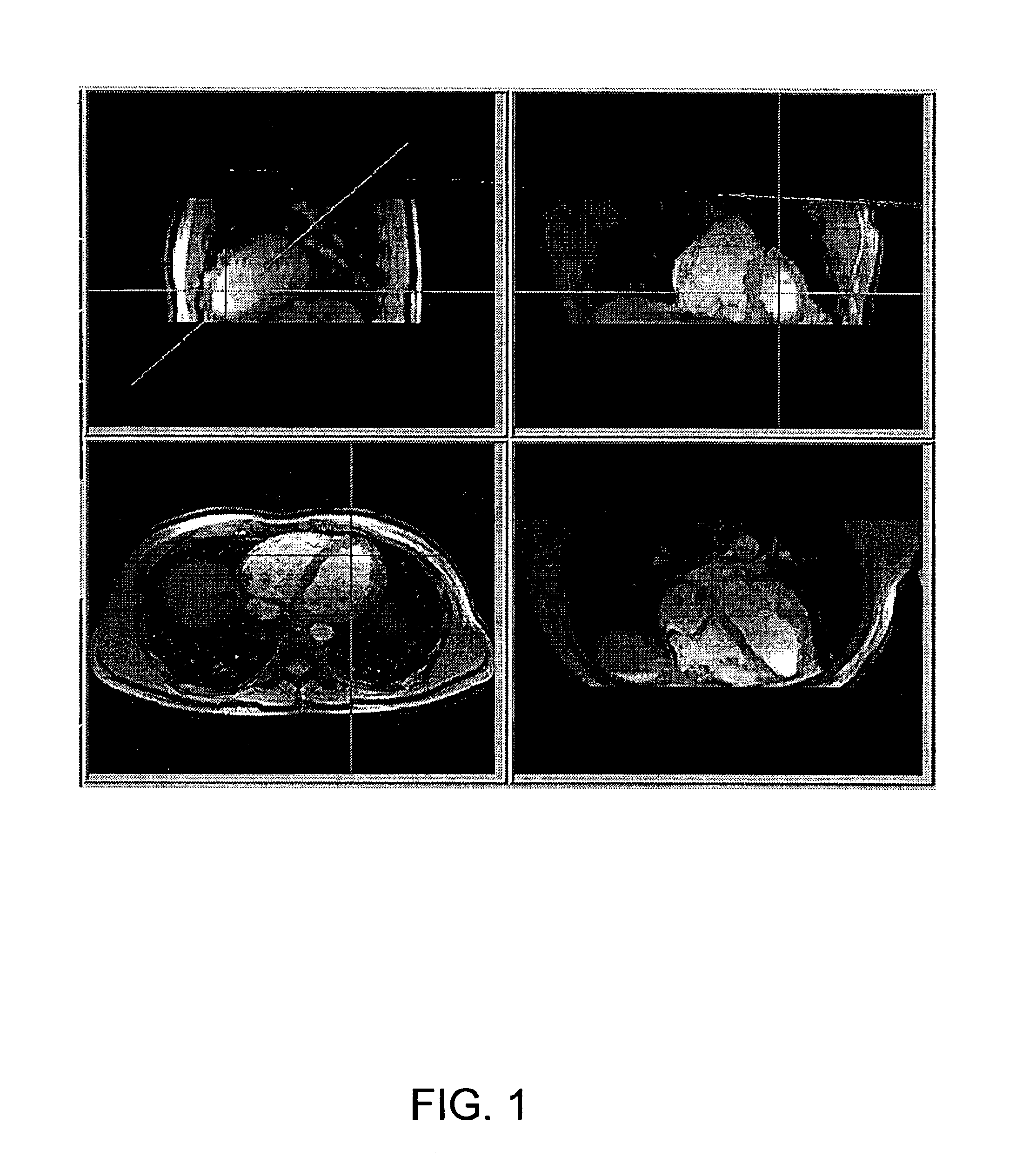
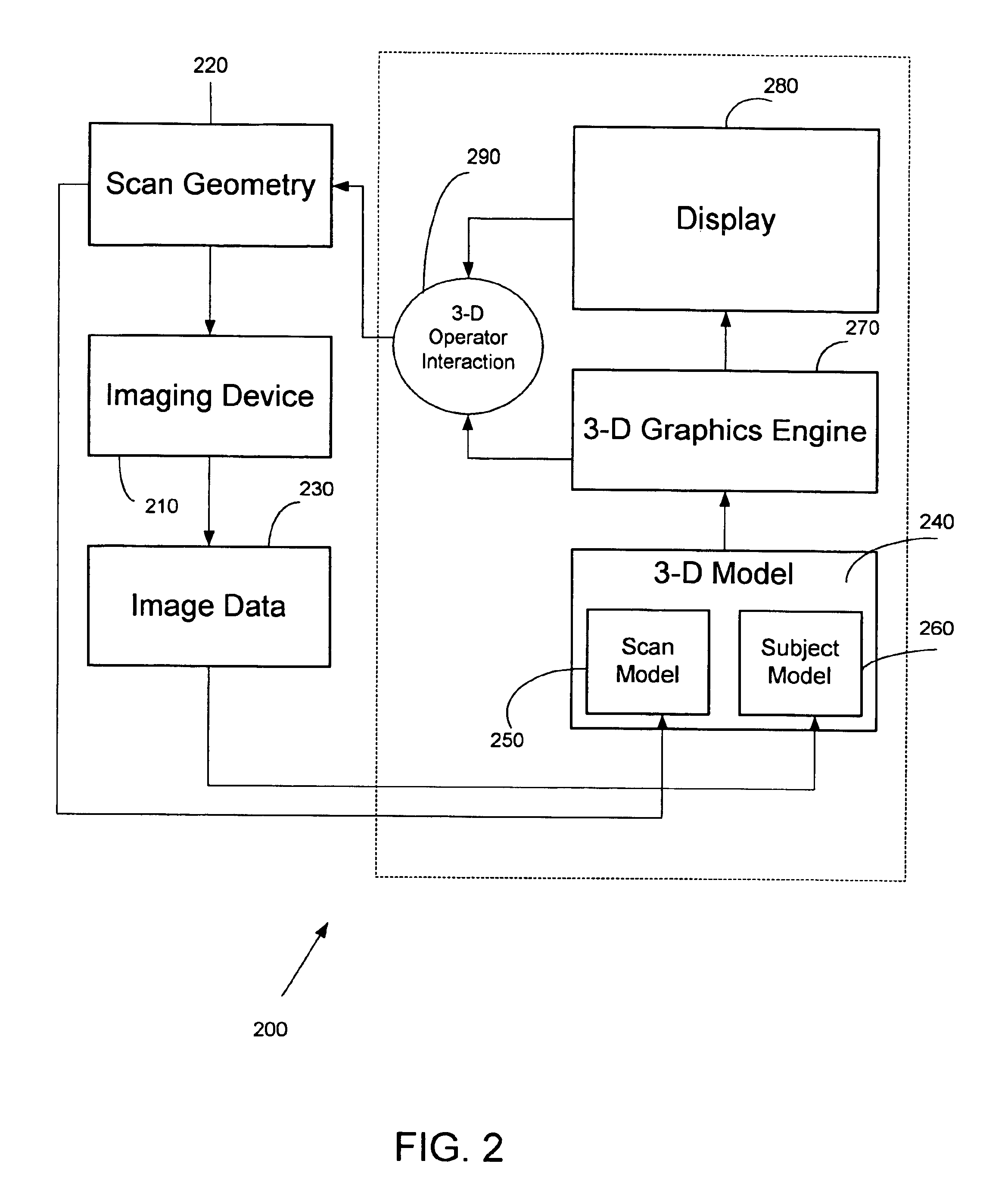
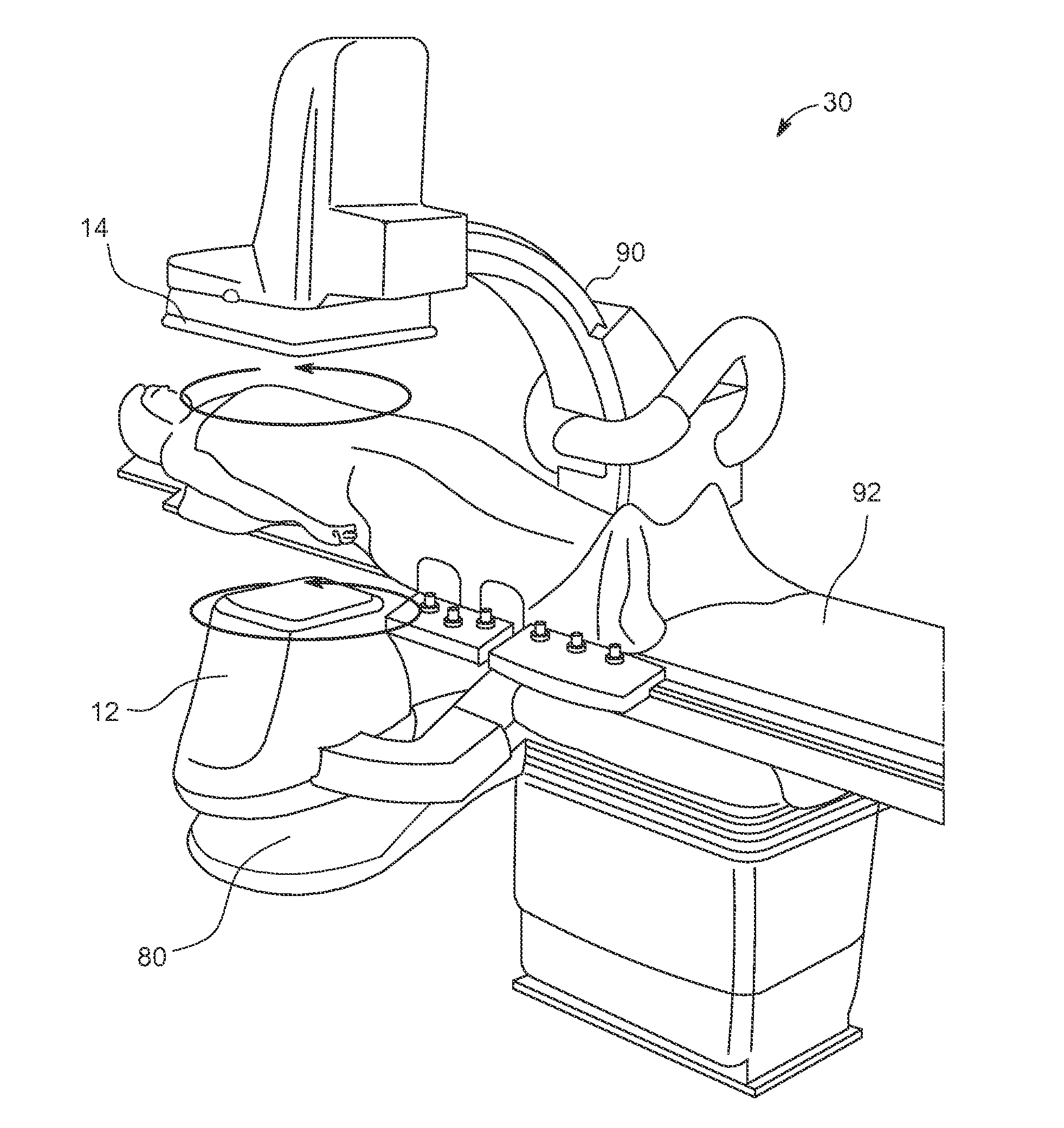
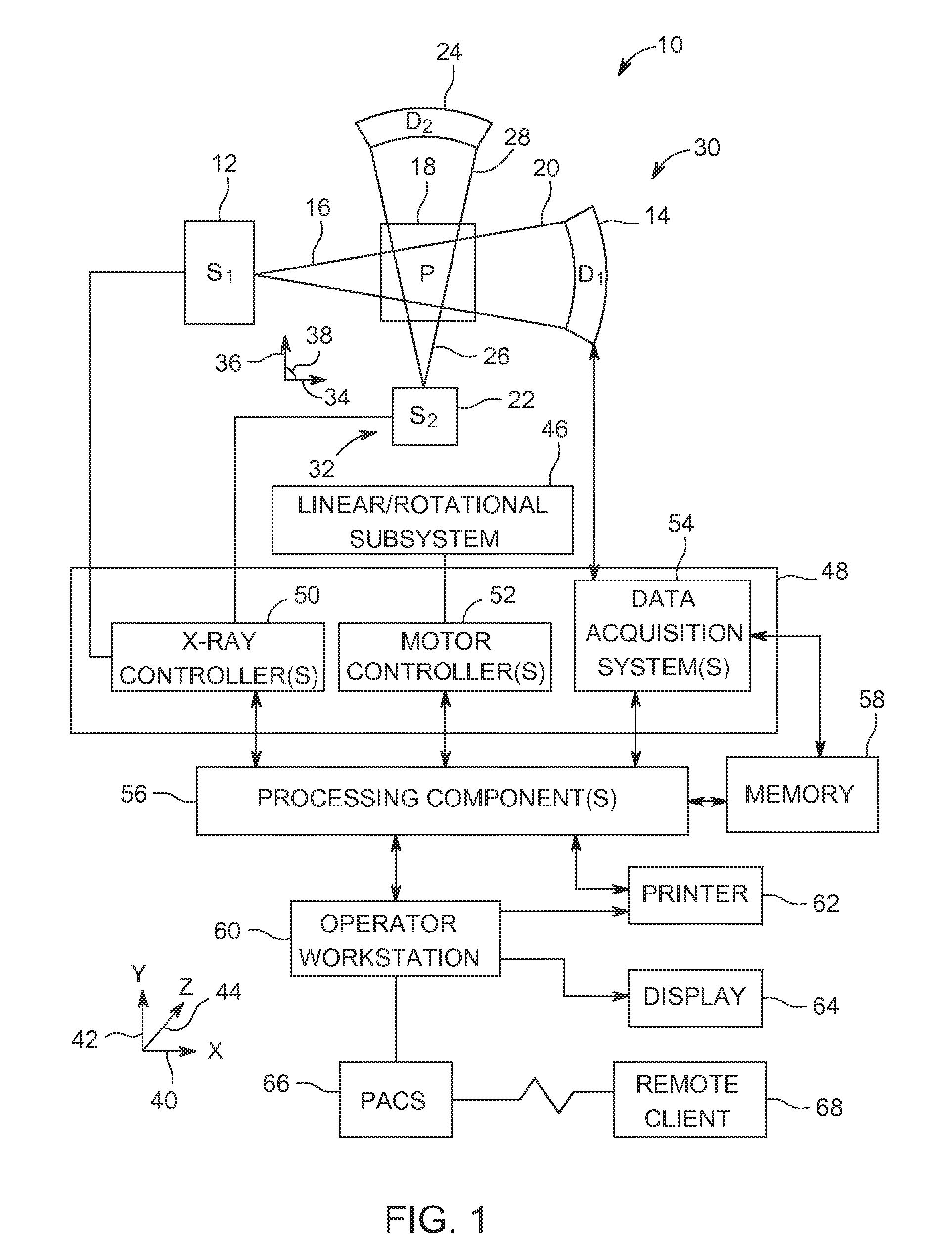
Systems, methods and computer program products for the display and visually driven definition of tomographic image planes in three-dimensional space
InactiveUS6898302B1Easy and more comprehensive understandingEasy to detectCharacter and pattern recognitionImage generationDisplay deviceData acquisition
Apparatuses, methods and computer program products for scan plane geometry definition in tomographic data acquisition via an interactive three-dimensional (3-D) graphical operator interface. The apparatuses, methods and computer program products are initially proposed for use in cardiac MRI, but have a much broader area of application. The apparatuses and methods utilize 3-D computer graphics aspect views of slice planes to show a new scan, represented as semi-transparent uniformly-colored planes. Intersections of these planes with opaque texture-mapped gray-level views of previously acquired images enable the orientation of a new scan to be viewed in a much more intuitive fashion. Advantageously, the apparatuses and methods of the present invention provide for more efficient elimination of positional ambiguity that is often associated with conventional 2-D intersection line views. In addition, any misregistration between localizer scans can be detected immediately in the integrated 3-D display by misalignment of anatomy in the previously acquires image planes.
Owner:UNIV EMORY
Tomographic imaging for interventional tool guidance
The present disclosure relates to the identification and tracking of a navigational instrument (e.g., a needle) in three-dimensions, with substantially real-time image updates of the instrument and updates of the tissue at an equal or lower rate. In certain embodiments, the images are acquired using a C-arm tomosynthesis system configured to move the X-ray source and detector in respective planes above and below the patient.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
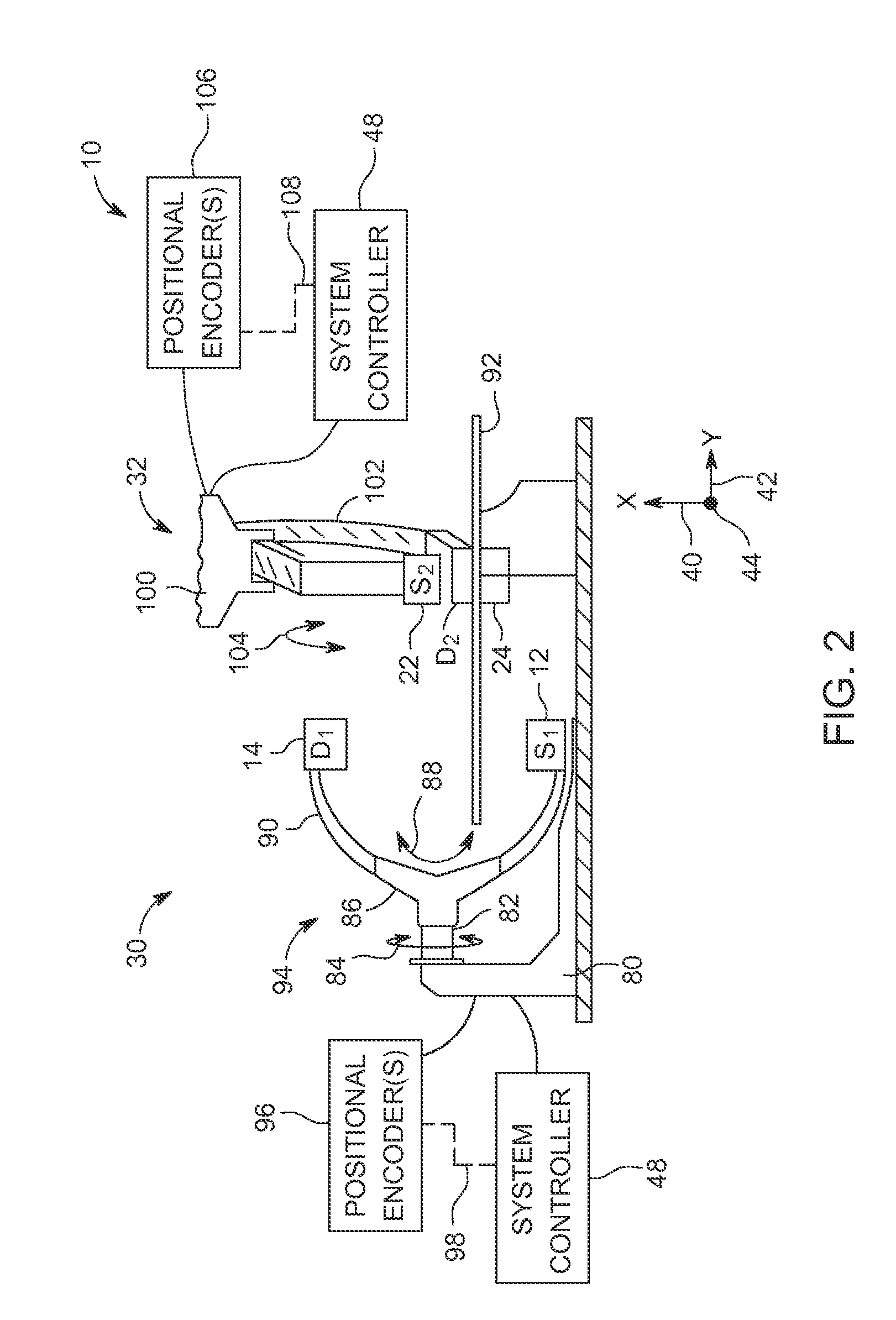
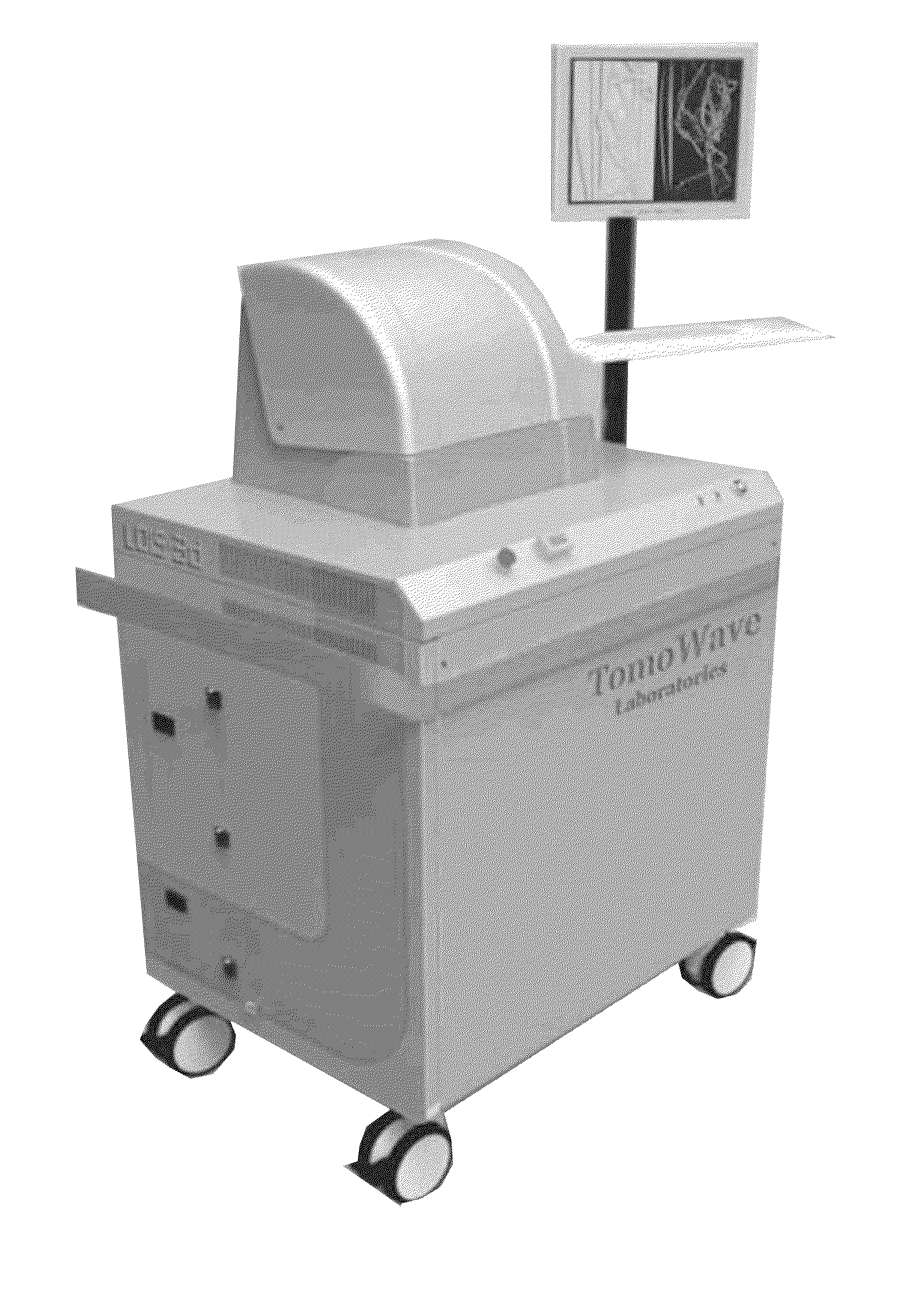
Laser Optoacoustic Ultrasonic Imaging System (LOUIS) and Methods of Use
ActiveUS20130190595A1Increase contrastImprove resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical imagingHelical computed tomographyContrast resolution
Provided herein are the systems, methods, components for a three-dimensional tomography system. The system is a dual-modality imaging system incorporates a laser ultrasonic system and a laser optoacoustic system. The dual-modality imaging system has means for generate tomographic images of a volume of interest in a subject body based on speed of sound, ultrasound attenuation and / or ultrasound backscattering and for generating optoacoustic tomographic images of distribution of the optical absorption coefficient in the subject body based on absorbed optical energy density or various quantitative parameters derivable therefrom. Also provided is a method for increasing contrast, resolution and accuracy of quantitative information obtained within a subject utilizing the dual-modality imaging system. The method comprises producing an image of an outline boundary of a volume of interest and generating spatially or temporally coregistered images based on speed of sound and / or ultrasonic attenuation and on absorbed optical energy within the outlined volume.
Owner:TOMOWAVE LAB INC
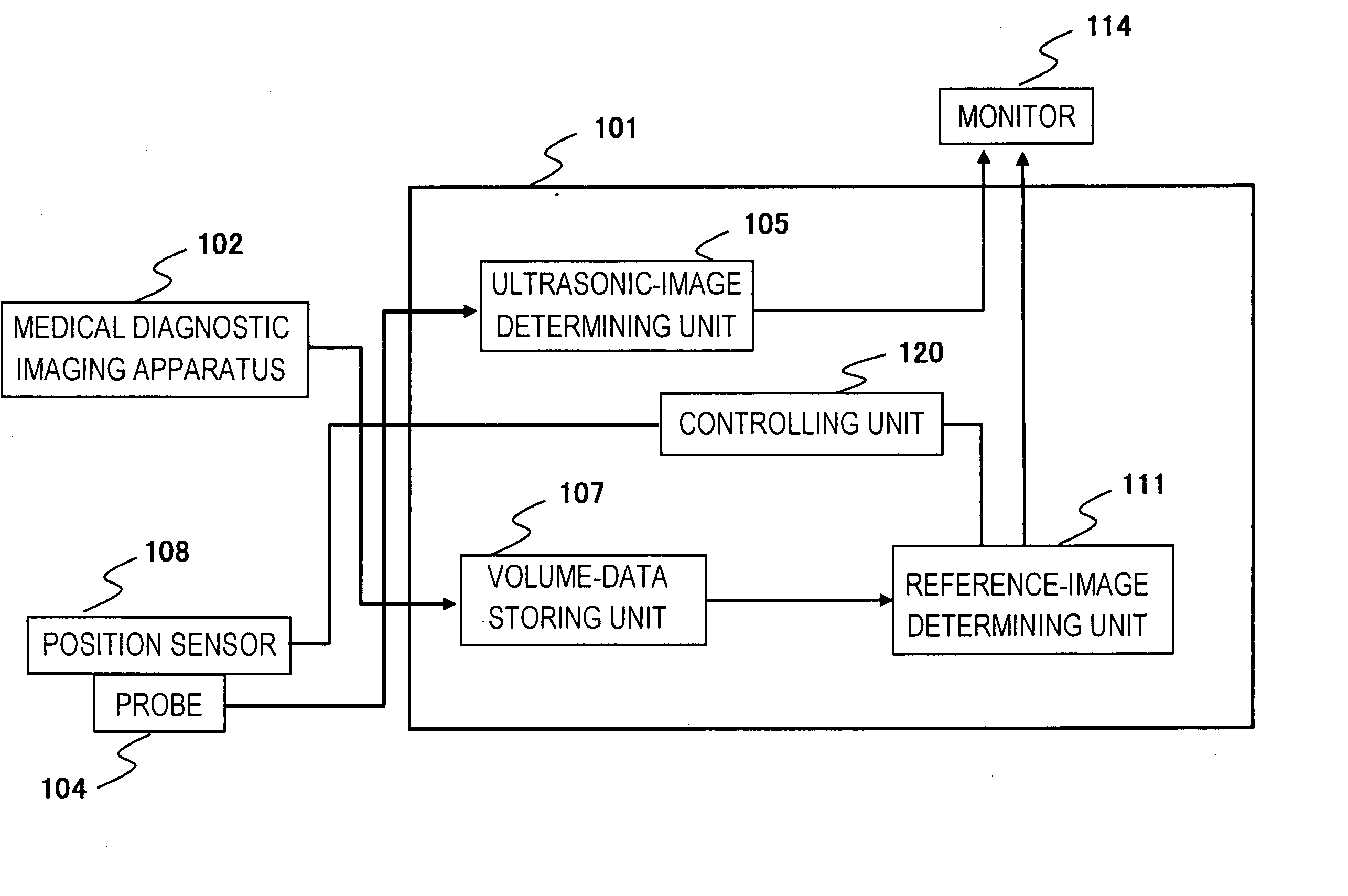
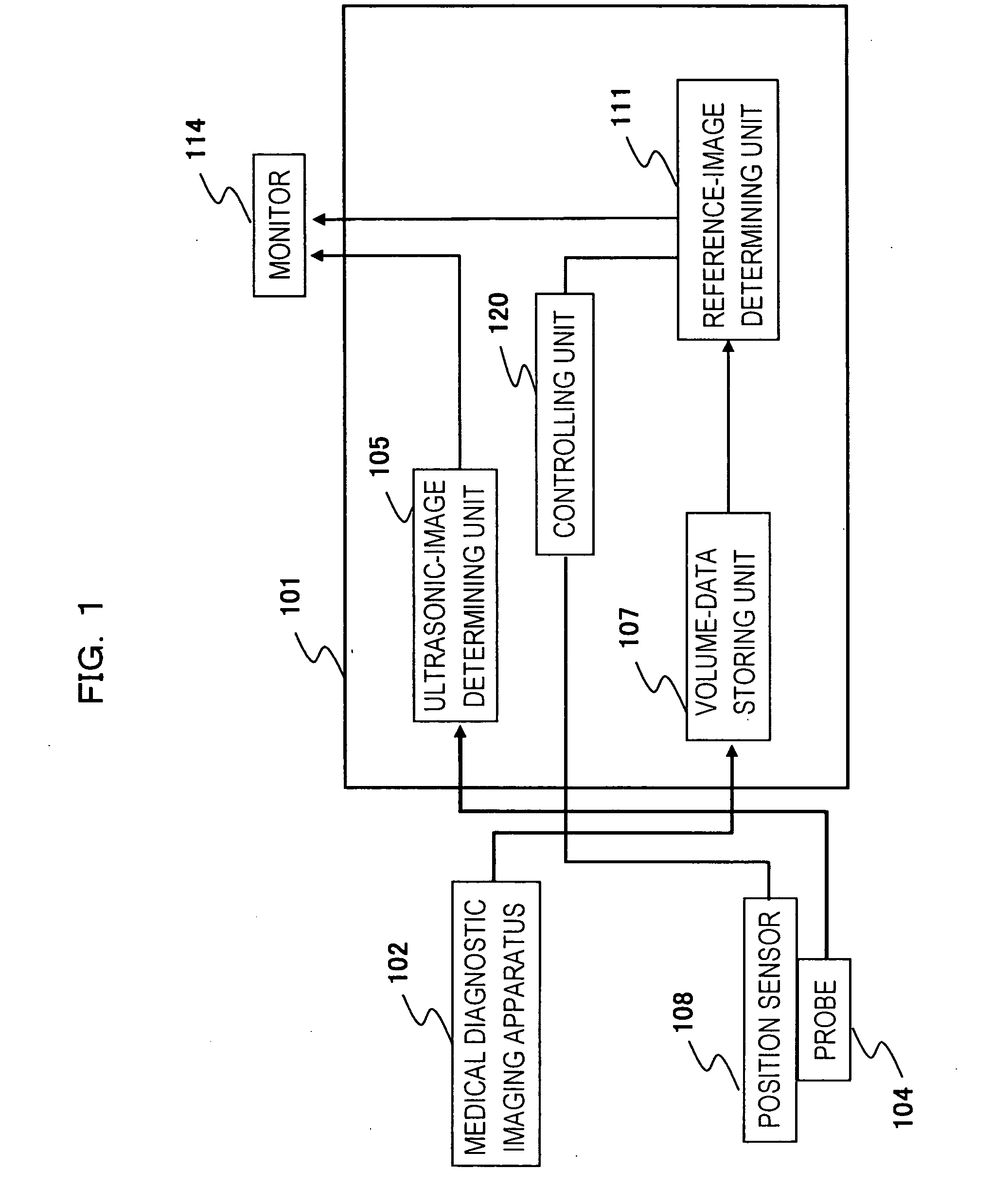
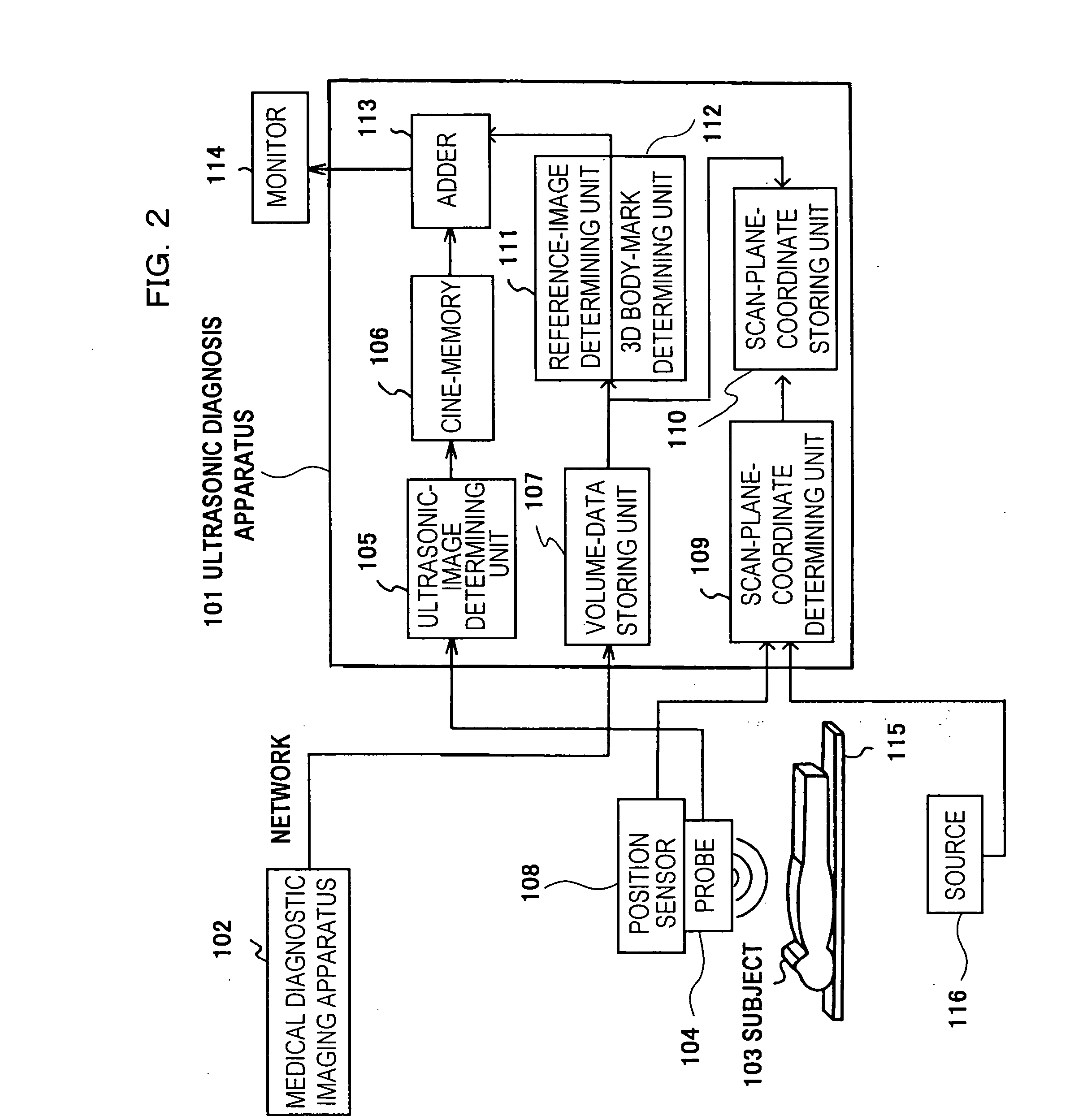
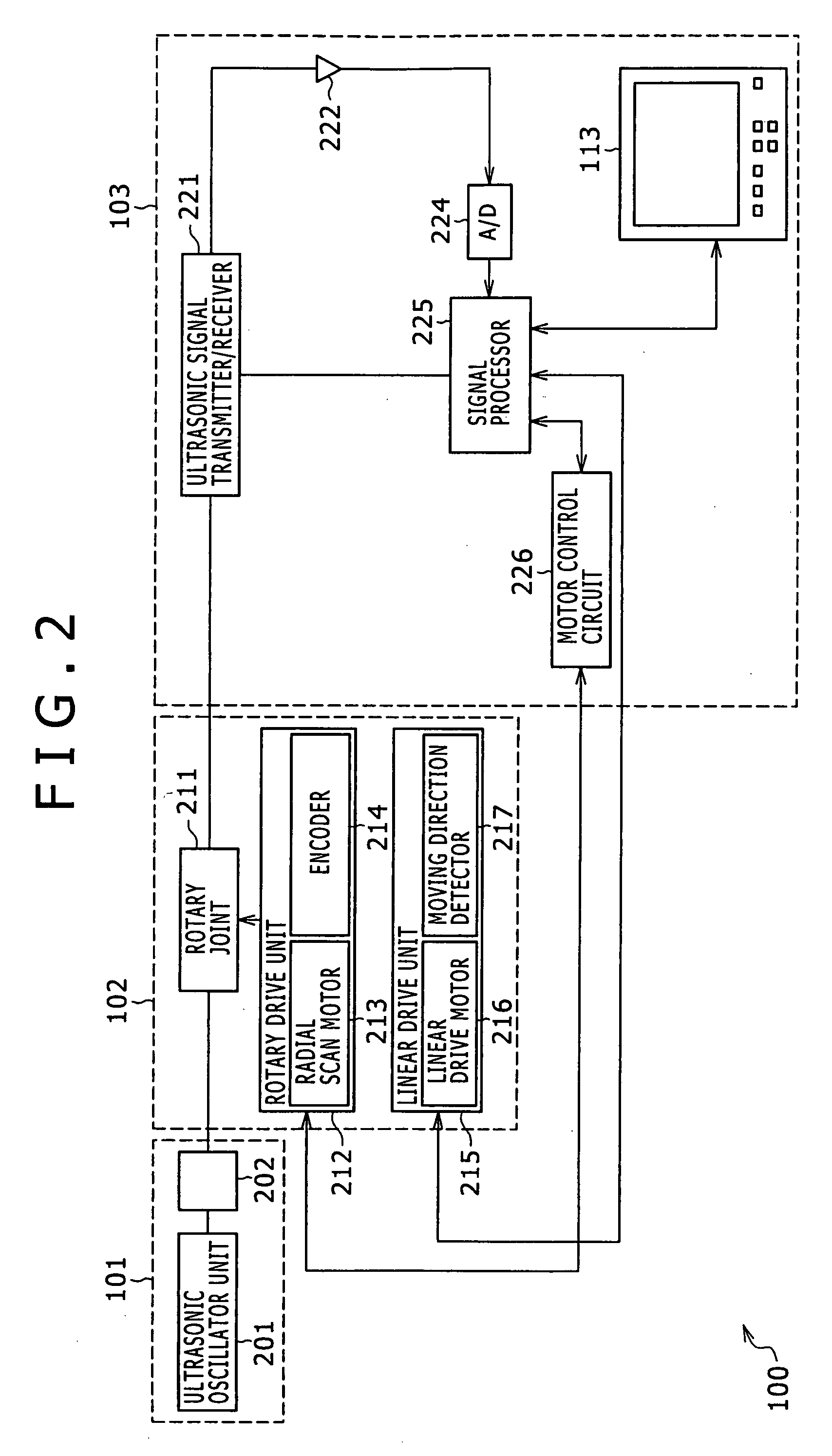
Reference image display method for ultrasonography and ultrasonograph
ActiveUS20070010743A1Increased freedom of settingImprove comparison accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementReference imageTomographic image
An ultrasonic image 105, 106 is captured by an ultrasonic probe 104. A reference image 111 is obtained by extracting a tomographic image corresponding to the scan plane of the ultrasonic image from volume image data that is pre-obtained by a diagnostic imaging apparatus 102 and that is stored in a volume-data storing unit 107. The ultrasonic image and the reference image 111 are displayed on the same screen 114. In this case, of the reference image, a portion corresponding to the view area of the ultrasonic image is extracted and the resulting reference image having the same region as the ultrasonic image is displayed as a fan-shaped image.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
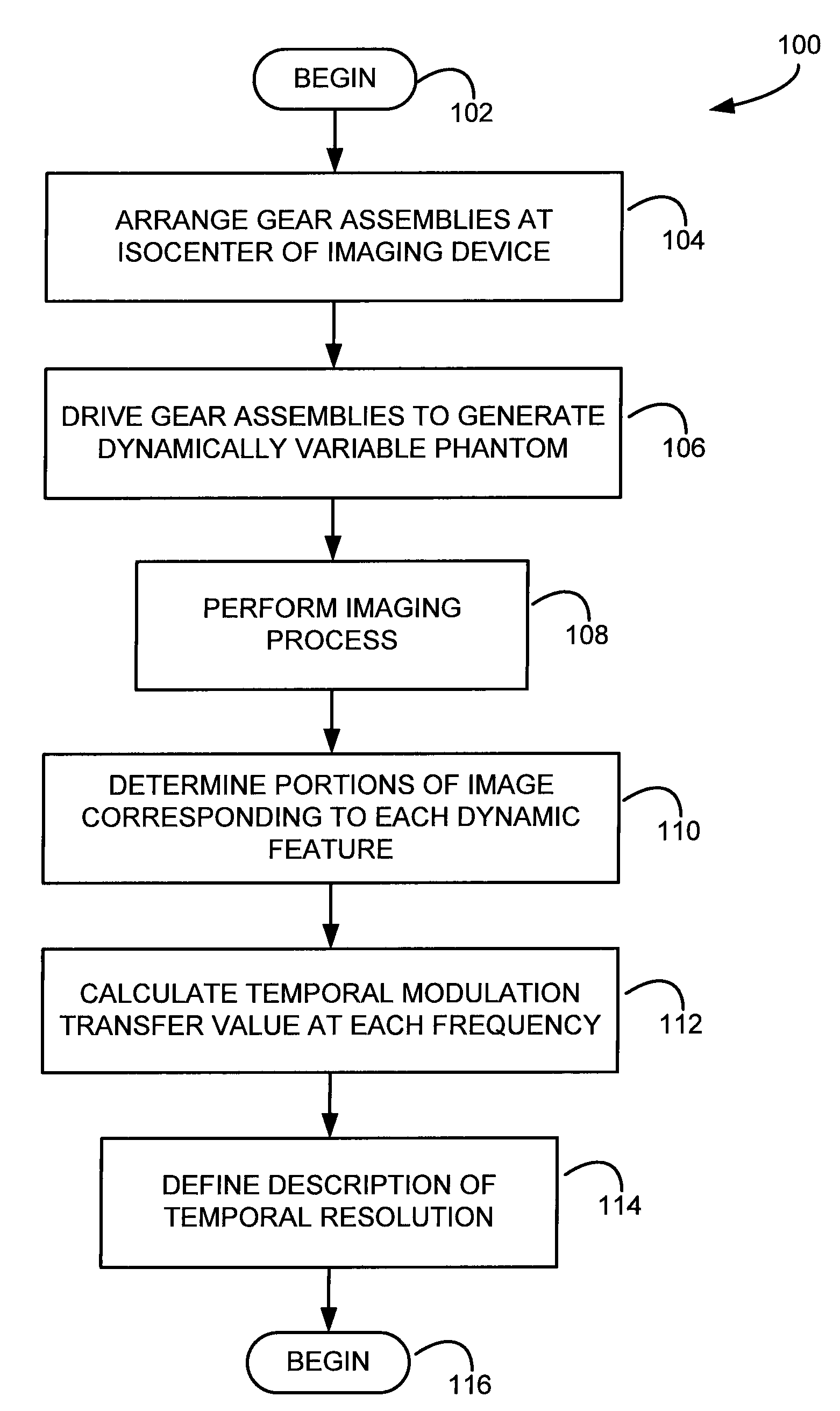
Method and apparatus for characterizing the temporal resolution of an imaging device
ActiveUS7863897B2Easy to operateFit small spaceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAdditive manufacturing apparatusMulti materialTemporal resolution
A system and method for determining the temporal resolution of a tomographic imaging device uses an apparatus to drive one or more dynamic phantoms composed of multiple materials. The apparatus is placed at or near the isocenter of the imaging device and the one or more phantoms are moved to produce a plurality of dynamic features, each having a specified frequency. The dynamic features are imaged with the device and the acquired image data corresponding to the dynamic features is analyzed to determine a temporal modulation transfer value at each of the known specified frequencies. The temporal resolution of the imaging device is determined using these temporal modulation transfer values.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
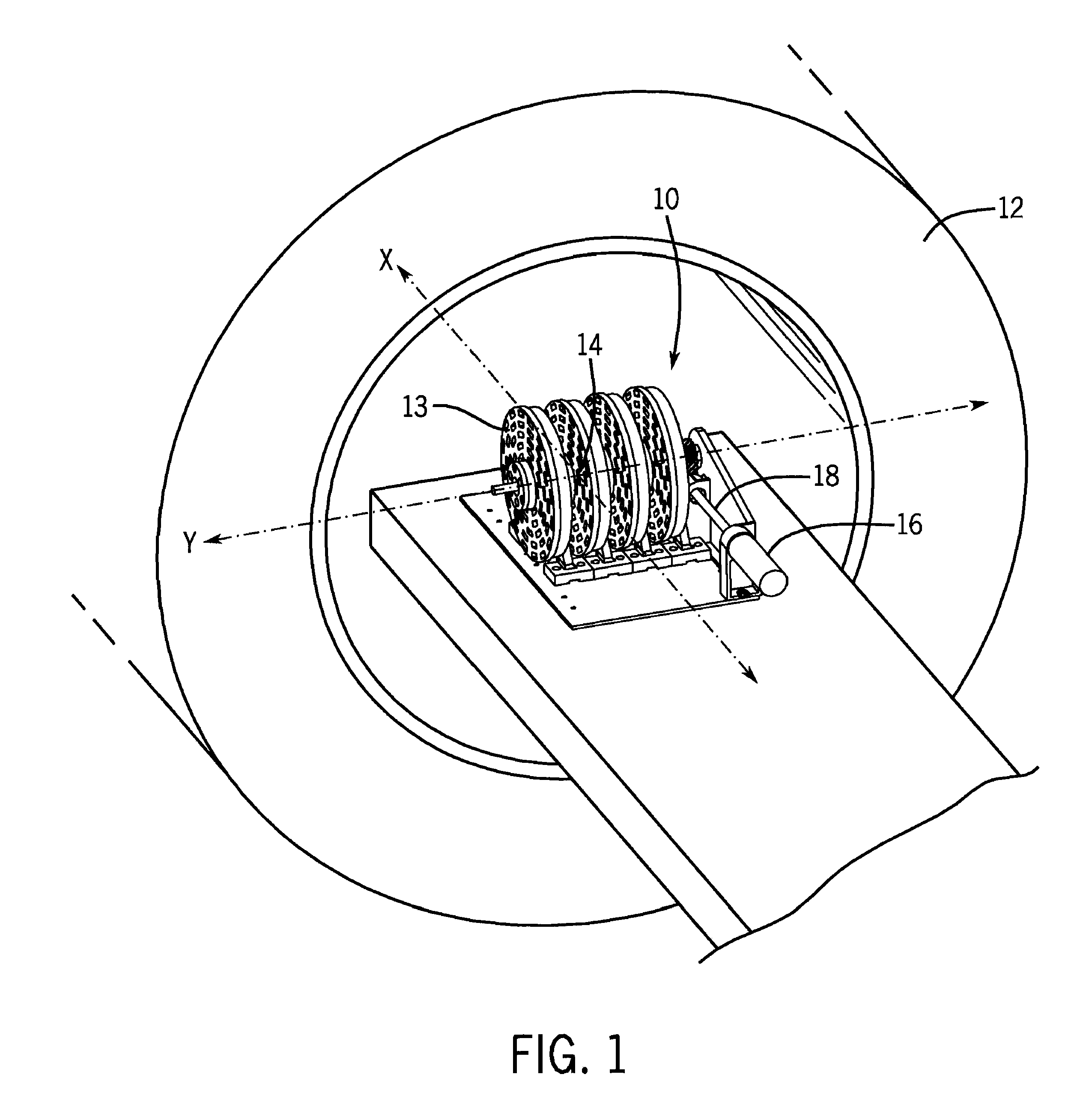
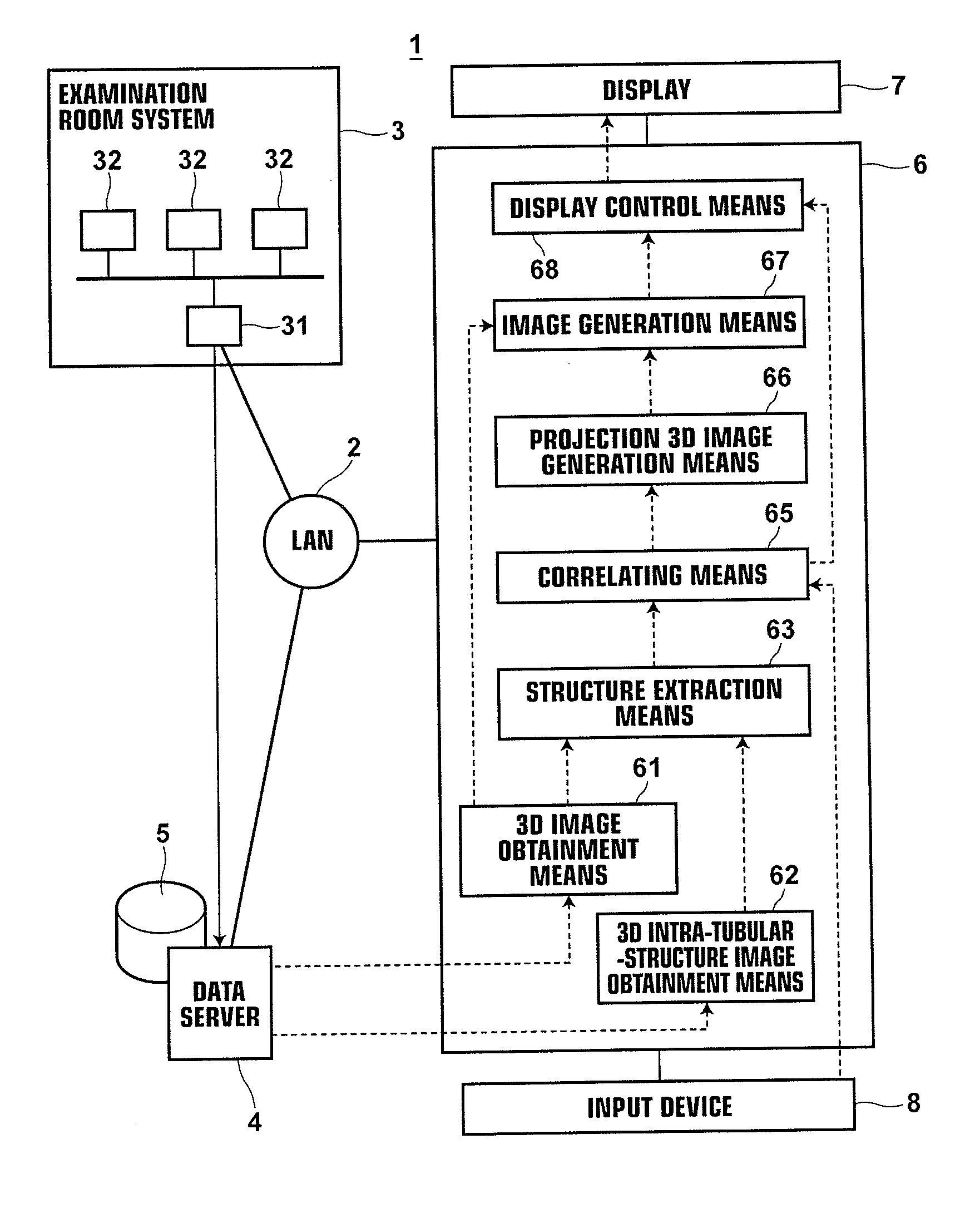
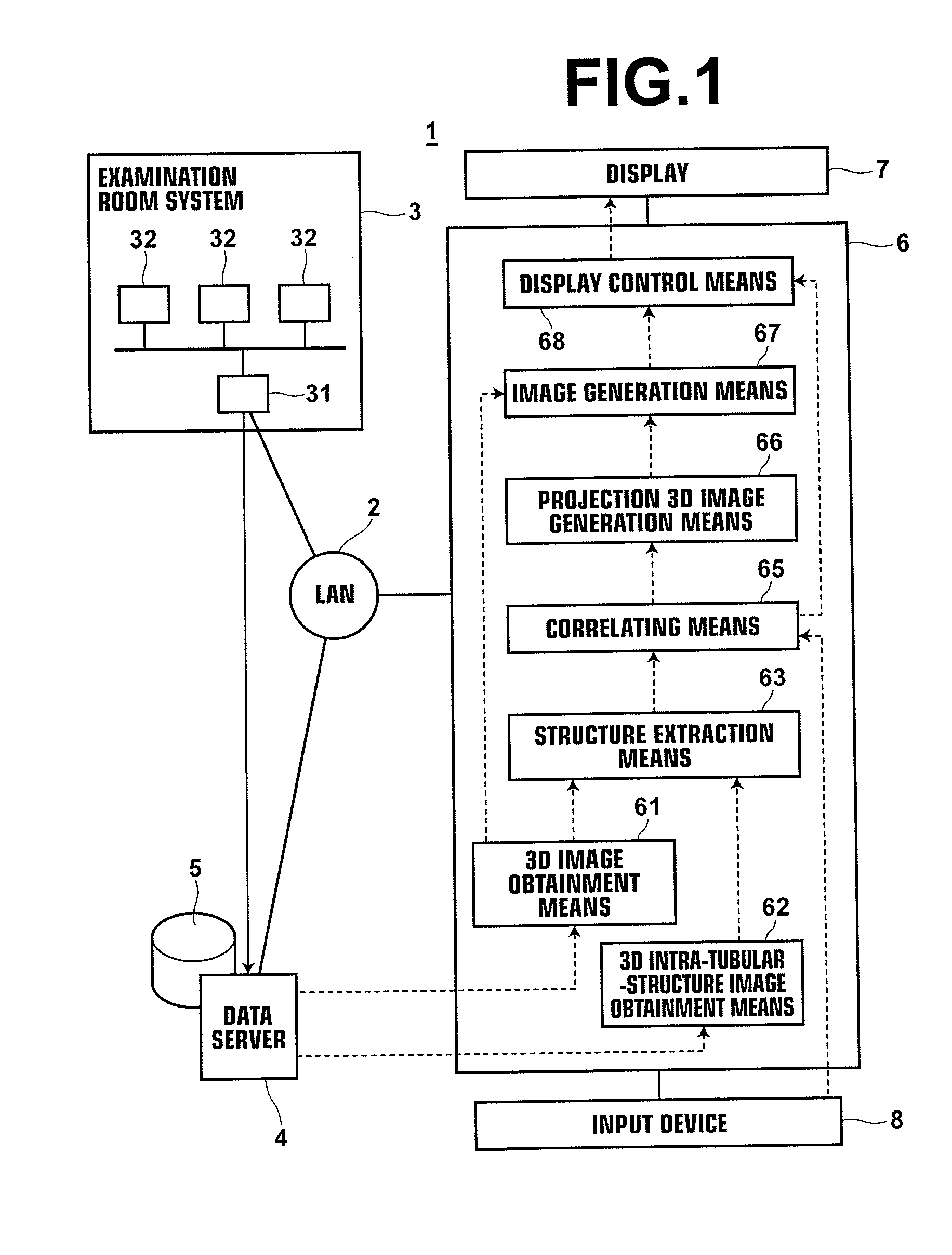
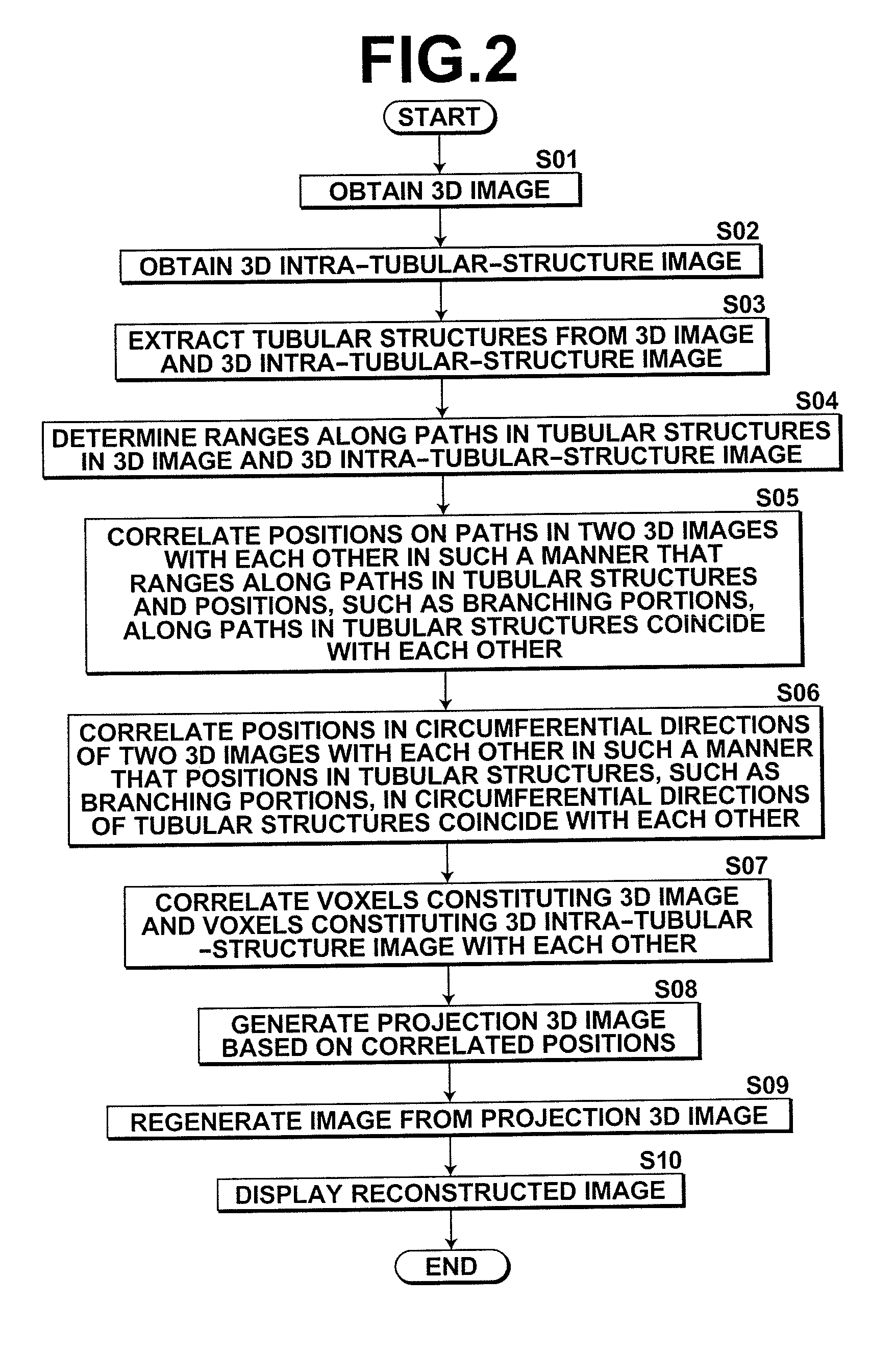
Apparatus, method and medium storing program for reconstructing intra-tubular-structure image
InactiveUS20120083696A1Easily and intuitionally recognizeEasy to identifyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementImage extractionTomography
A tubular structure, such as a blood vessel, of a subject is extracted from each of a three-dimensional image representing the tubular structure and a three-dimensional intra-tubular-structure image that has been generated from plural tomographic images of the tubular structure obtained by performing tomography on the tubular structure plural times from the inside of the tubular structure along a path in the tubular structure. Further, an arbitrary range in one of the tubular structure extracted from the three-dimensional image and the tubular structure extracted from the three-dimensional intra-tubular-structure image is correlated with a corresponding range in the other one of the tubular structures. Further, a projection three-dimensional image is generated by projecting an image of a specific structure included in the range in the three-dimensional intra-tubular-structure image into the correlated range in the three-dimensional image.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
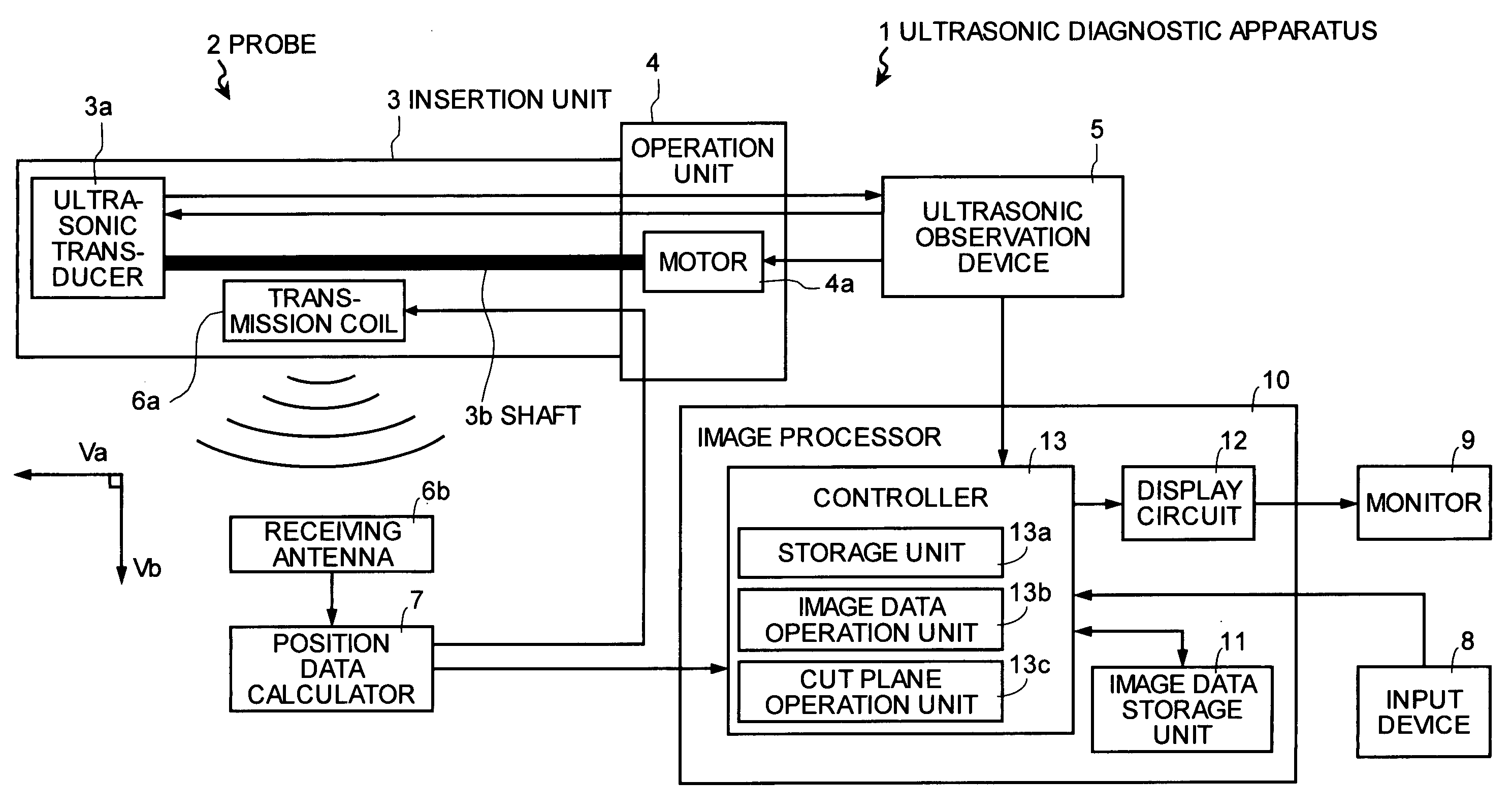
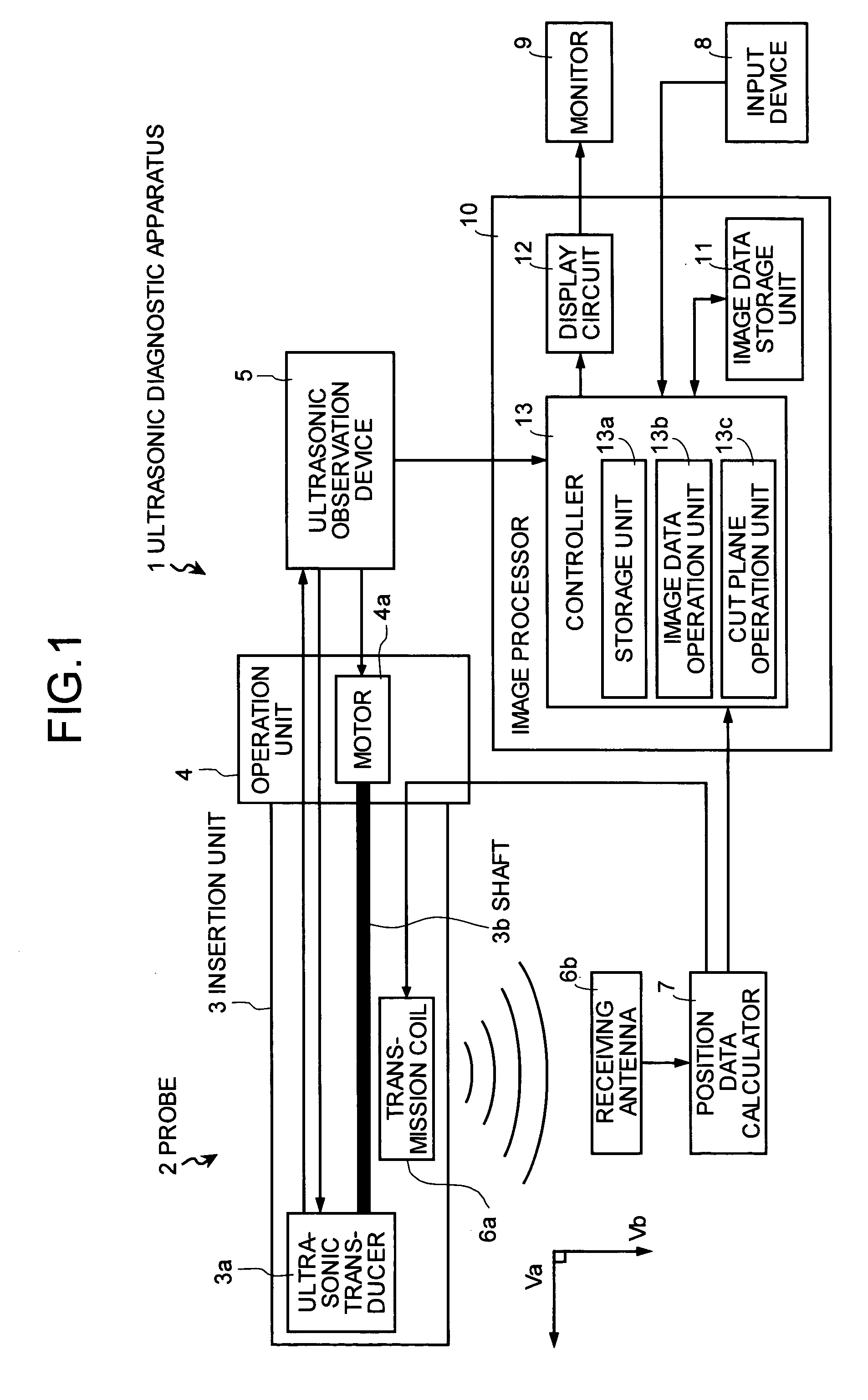
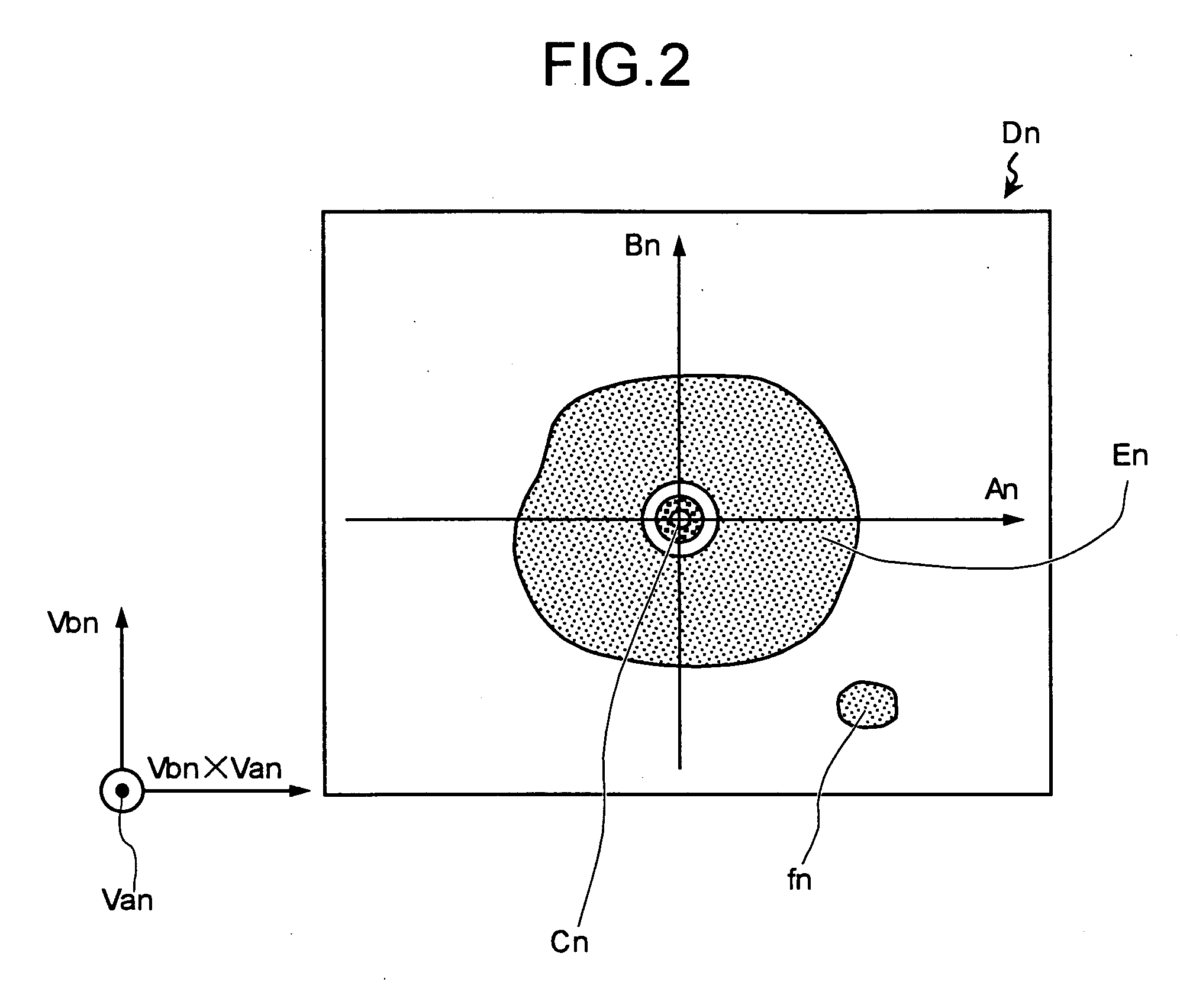
Ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus
ActiveUS20050090743A1Solve problemsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasonic sensorSonification
An ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus including: an ultrasonic observation device that transmits and receives an ultrasonic wave by an ultrasonic transducer arranged on a tip end of a probe, and that acquires a plurality of two-dimensional ultrasonic tomographic images for a subject in a living body; a position data calculator that detects information indicating a reference position of each of the two-dimensional ultrasonic tomographic images and an orientation of a tomographic plane of the each two-dimensional ultrasonic tomographic image; and an image processor is provided. The image processor generates a band-shaped longitudinal image including a curved plane along a moving path of the ultrasonic transducer.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
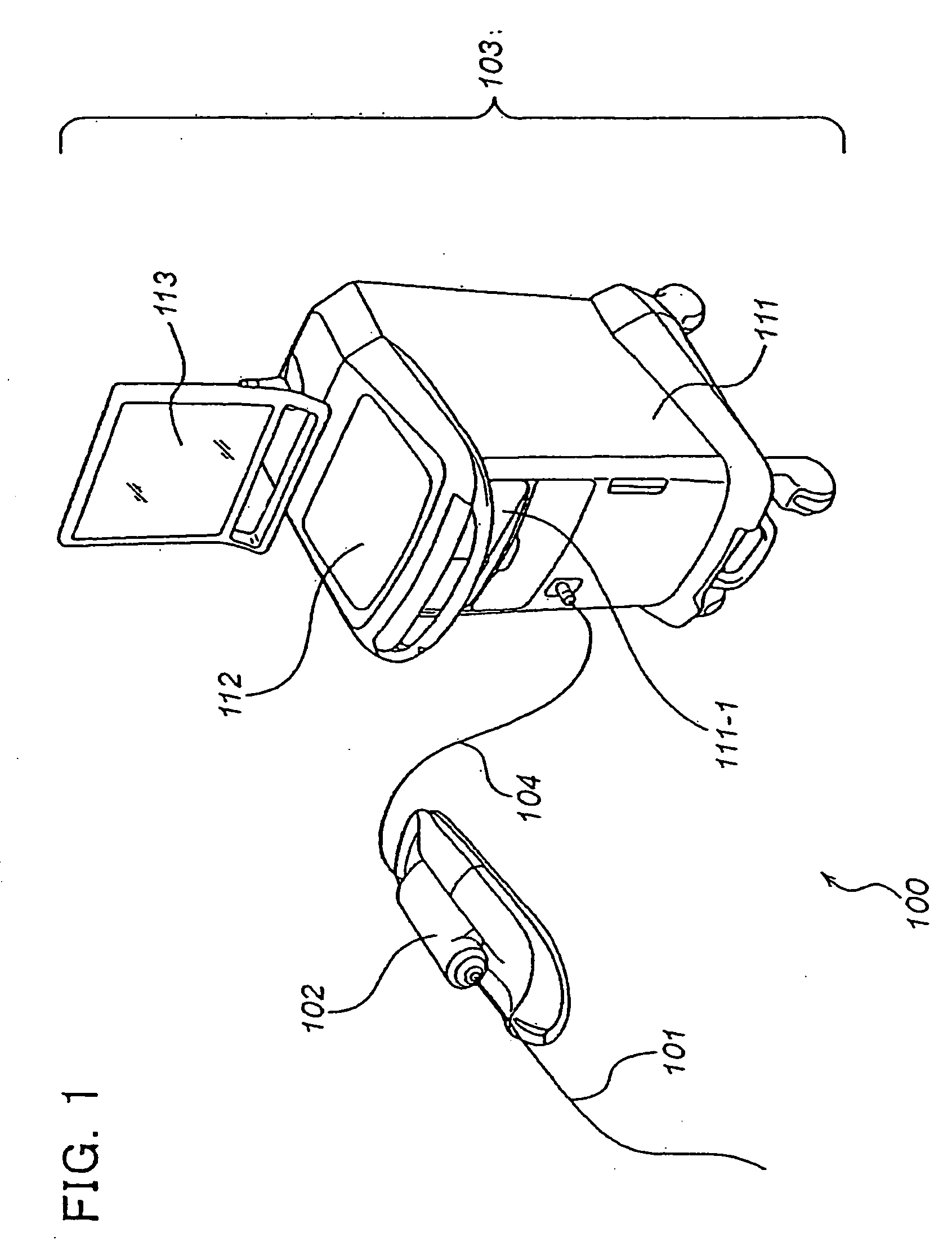
Probe, image diagnostic system and catheter
InactiveUS20070232893A1Avoid spreadingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterAcousticsTomographic image
A probe which is adapted to repeatedly transmit and receive signals during radial scanning within a body cavity to acquire reflected signals and transmit the reflected signals to an image diagnostic apparatus which, on a basis of the reflected signals, forms and outputs a tomographic image of the body cavity and biotissue surrounding the body cavity includes a hollow shaft for transmitting rotational drive force to perform the radial scanning, and a transmission line extending along the shaft to transmit the reflected signals to the image diagnostic apparatus. The shaft receives the rotational drive force via a torque limiter which possesses a thickness which is non-uniform in a circumferential direction at a part of the torque limiter along a length of the torque limiter.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Apparatus and method for a global coordinate system for use in robotic surgery
ActiveUS10383765B2Facilitating robotic surgeryDiagnostics using lightEye surgeryKinematicsEngineering
An apparatus and method for establishing a global coordinate system to facilitate robotic assisted surgery. The coordinate system may be established using a combination of the robotic data, i.e., kinematics, and optical coherence tomographic images generated by an overhead optical assembly and a tool-based sensor. Using these components, the system may generate a computer-registered three-dimensional model of the patient's eye. In some embodiments, the system may also generate a virtual boundary within the coordinate system to prevent inadvertent injury to the patient.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
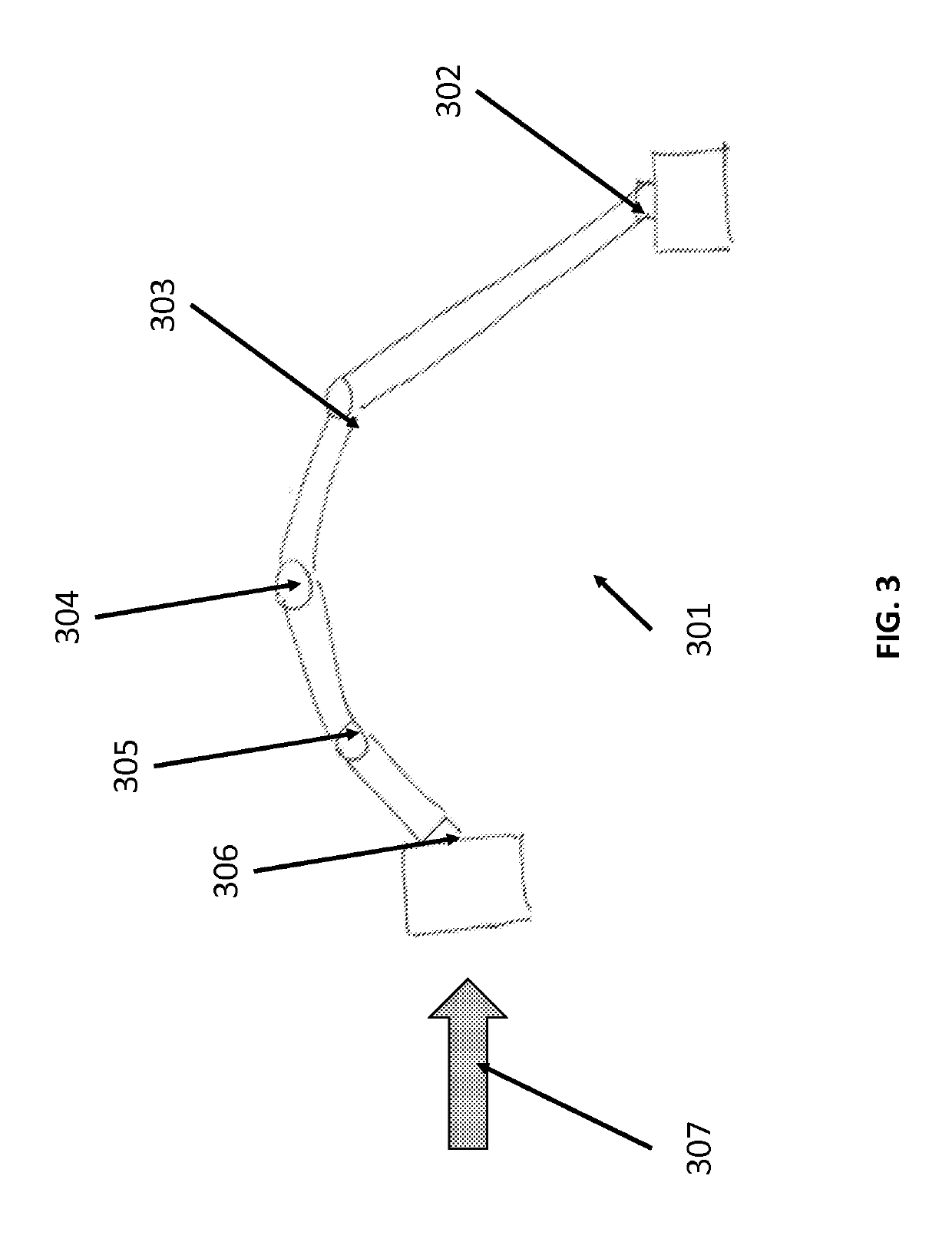
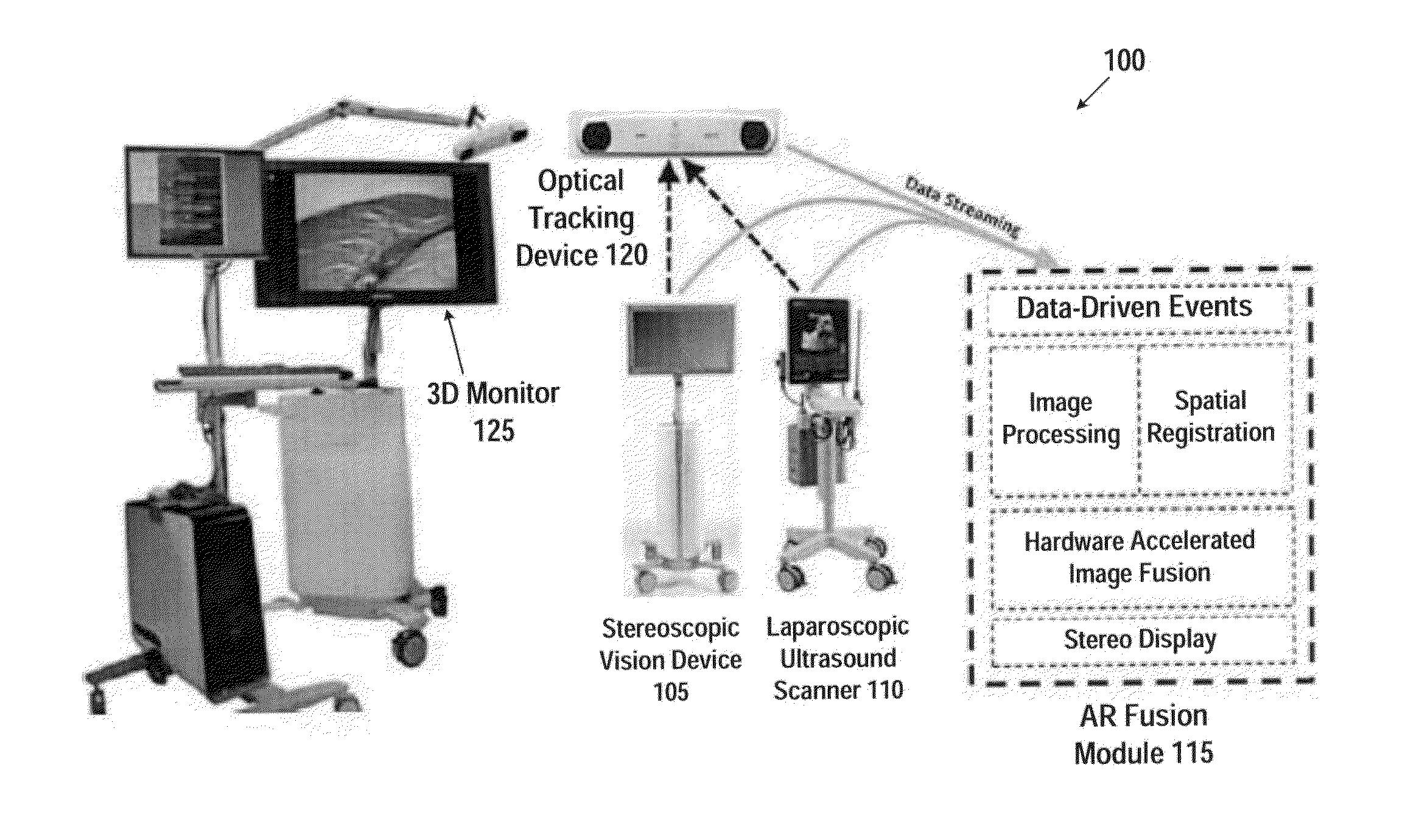
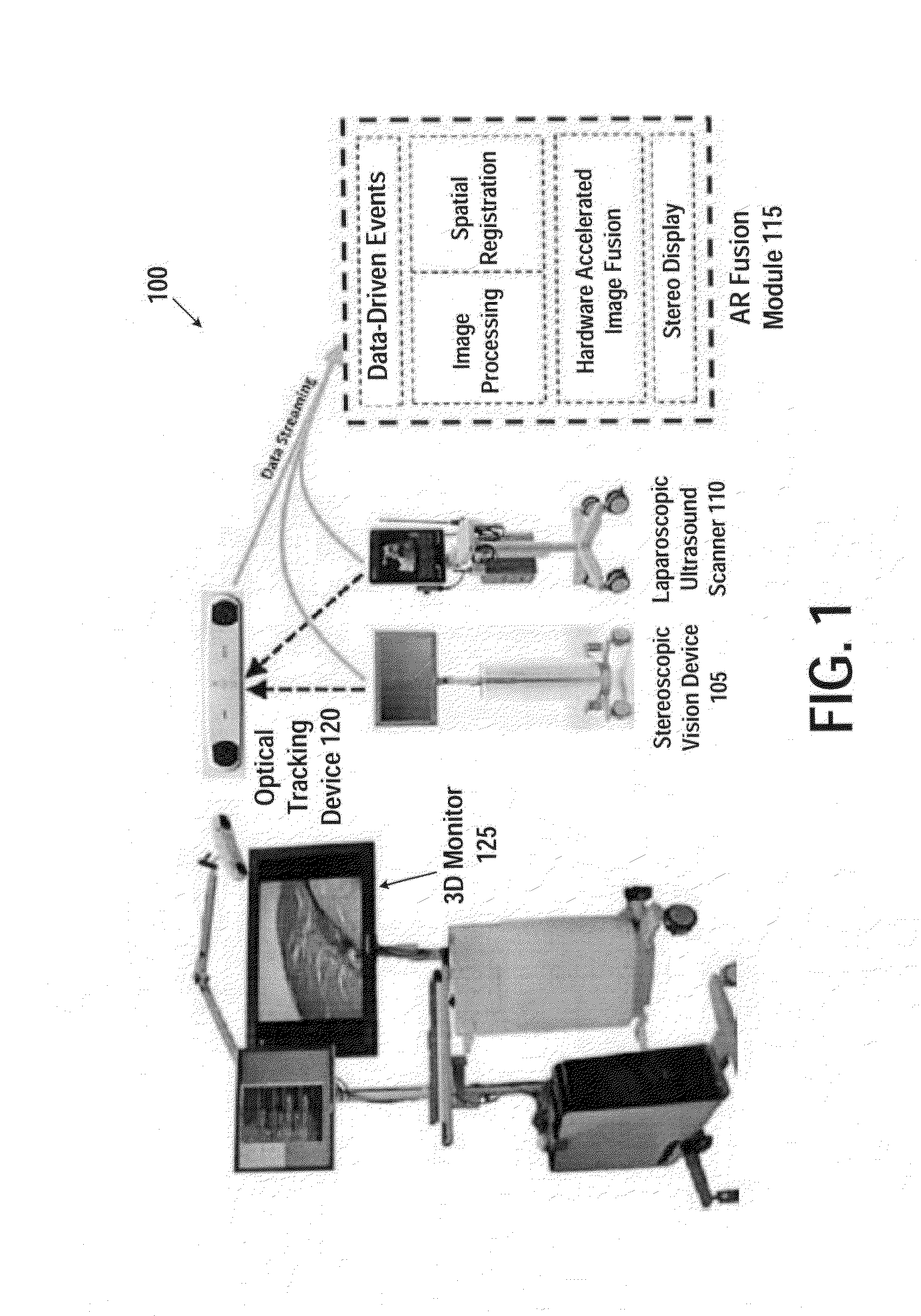
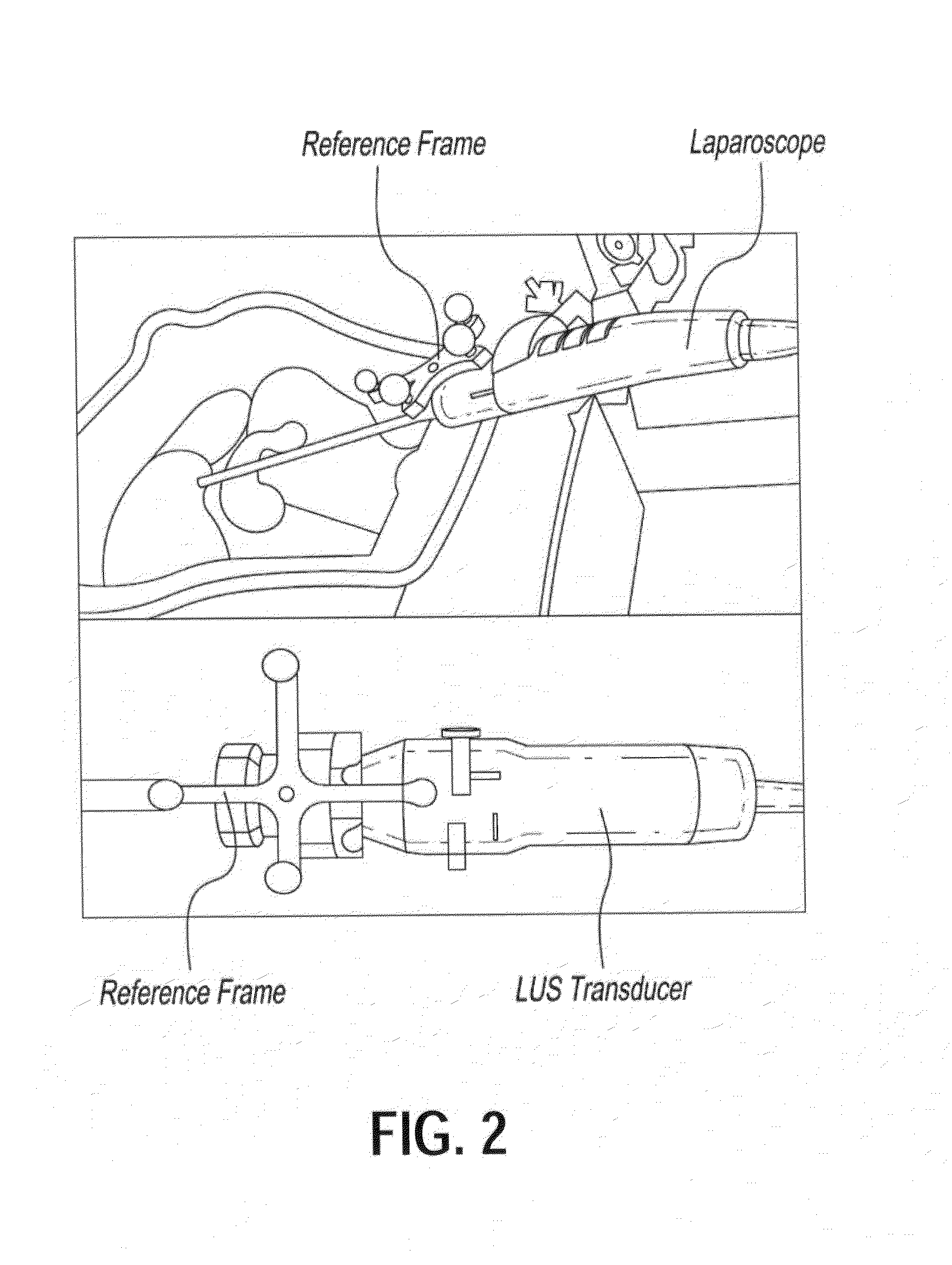
Device and method for generating composite images for endoscopic surgery of moving and deformable anatomy
ActiveUS20140303491A1Improve understandingImprove surgical efficiencyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementIntra operativeTomographic image
A device for generating composite images of dynamically changing surgical anatomy includes circuitry configured to receive, from an endoscopic imaging device, endoscopic image data. The circuitry is configured to receive, from a tomographic imaging device, intra-operative tomographic image data. The circuitry is configured to receive, from a tracking device, spatial tracking data corresponding to the endoscopic imaging device and the tomographic imaging device. The circuitry is configured to generate real-time dynamically changing composite image data by overlaying, based on the spatial tracking data, the intra-operative tomographic image data on the endoscopic image data. The circuitry is configured to output the composite image data to a display.
Owner:CHILDRENS NAT MEDICAL CENT
Tomographic image obtainment apparatus and method
ActiveUS20080101537A1Reduce intervalAccurate acquisitionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAnatomical structuresTomographic image
When radiographic images are obtained by radiography using a tomographic image obtainment apparatus, the degree of overlap of anatomical structures of a subject is obtained. Further, a condition of exposure, such as angles θ of radiography, is changed based on the degree of overlap. The angles θ of radiography are angles at which a radiation irradiation unit performs radiography at a plurality of positions to obtain a plurality of radiographic images. The tomographic image obtainment apparatus produces a tomographic image by reconstructing the tomographic image from a plurality of radiographic images obtained by irradiating the subject with radiation from various directions.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Methods for monitoring structural health conditions
InactiveUS20050075846A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalProcess moduleEngineering
Owner:ADVANCED STRUCTURE MONITORING
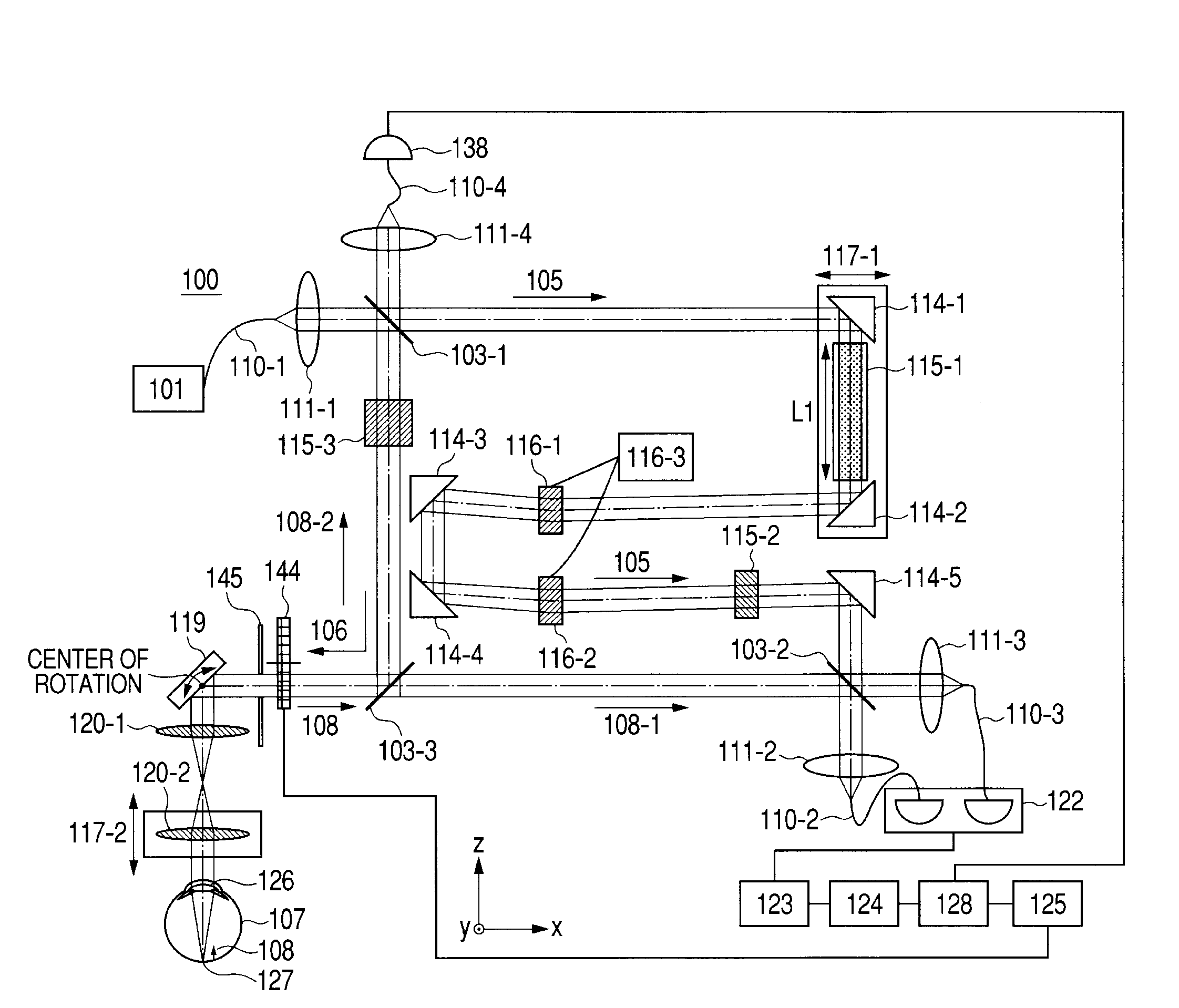
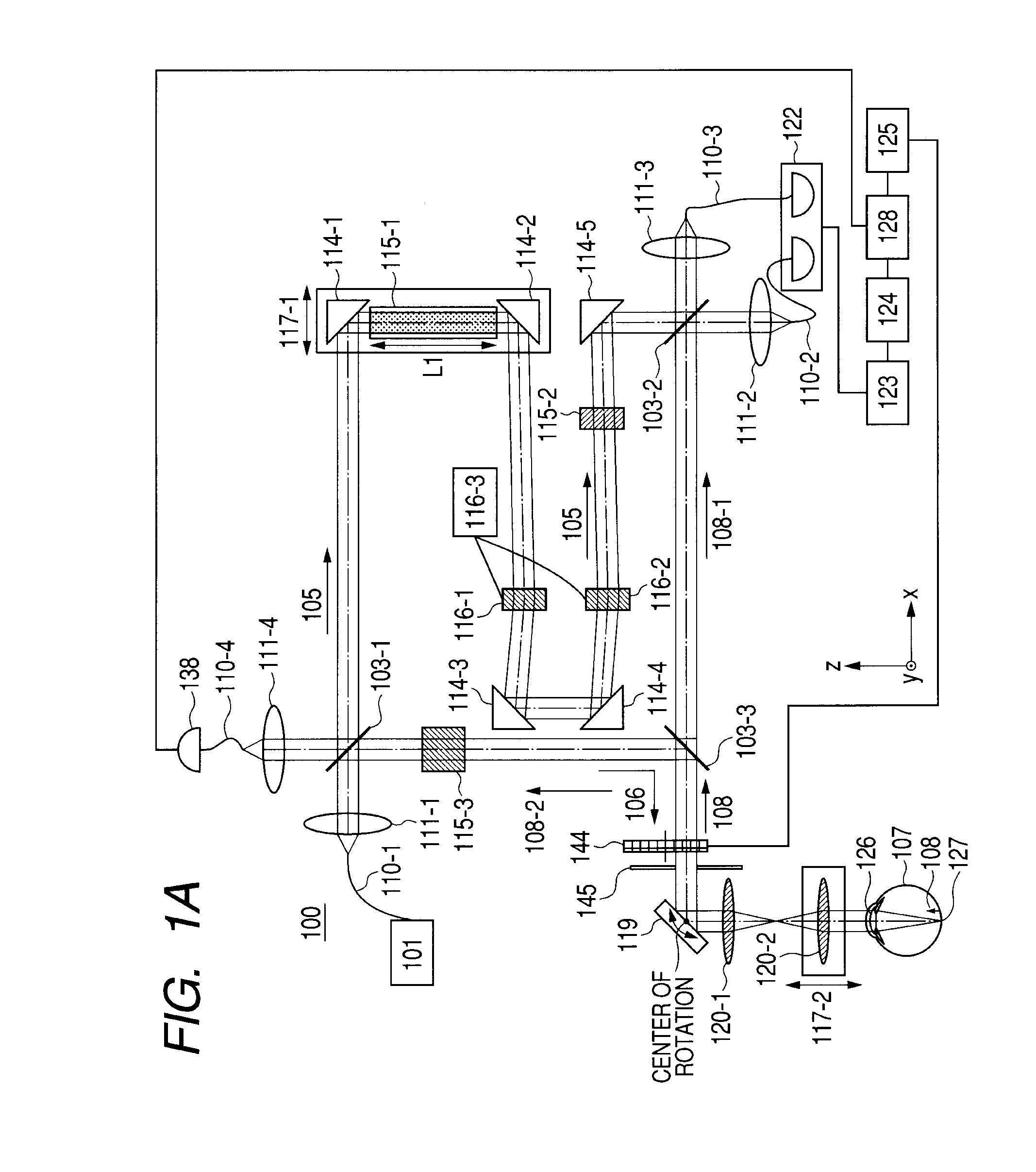
Image forming method and optical coherence tomograph apparatus using optical coherence tomography
ActiveUS20100166293A1High resolutionInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical axisImage formation
An image forming method uses an optical coherence tomography as to an optical axis direction of plural pieces of image information of an object. First image information of an object is obtained at a first focus with respect to an optical axis direction to then object. A focusing position is changed by dynamic focusing from the first focus to a second focus along the optical axis. The second image information of the object is obtained at the second focus. A third image information, tomography image information of the object and including a tomography image of the first focus or the second focus, is obtained by Fourier domain optical coherence tomography. A tomography image or a three-dimensional image of the object is formed in positional relation, in the optical axis direction, between the first image information and the second image information using the third image information.
Owner:FIFTH THIRD BANK +1
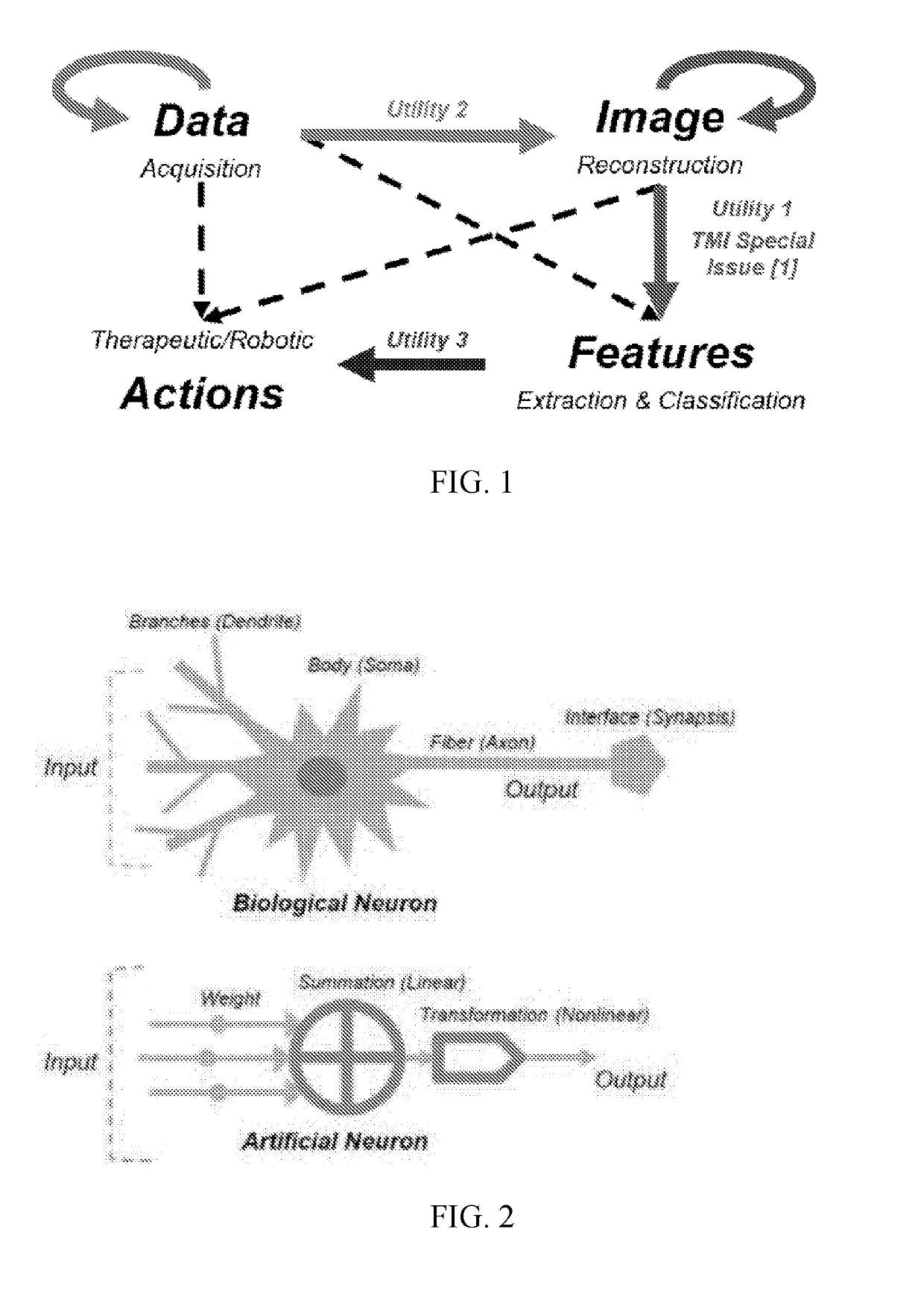
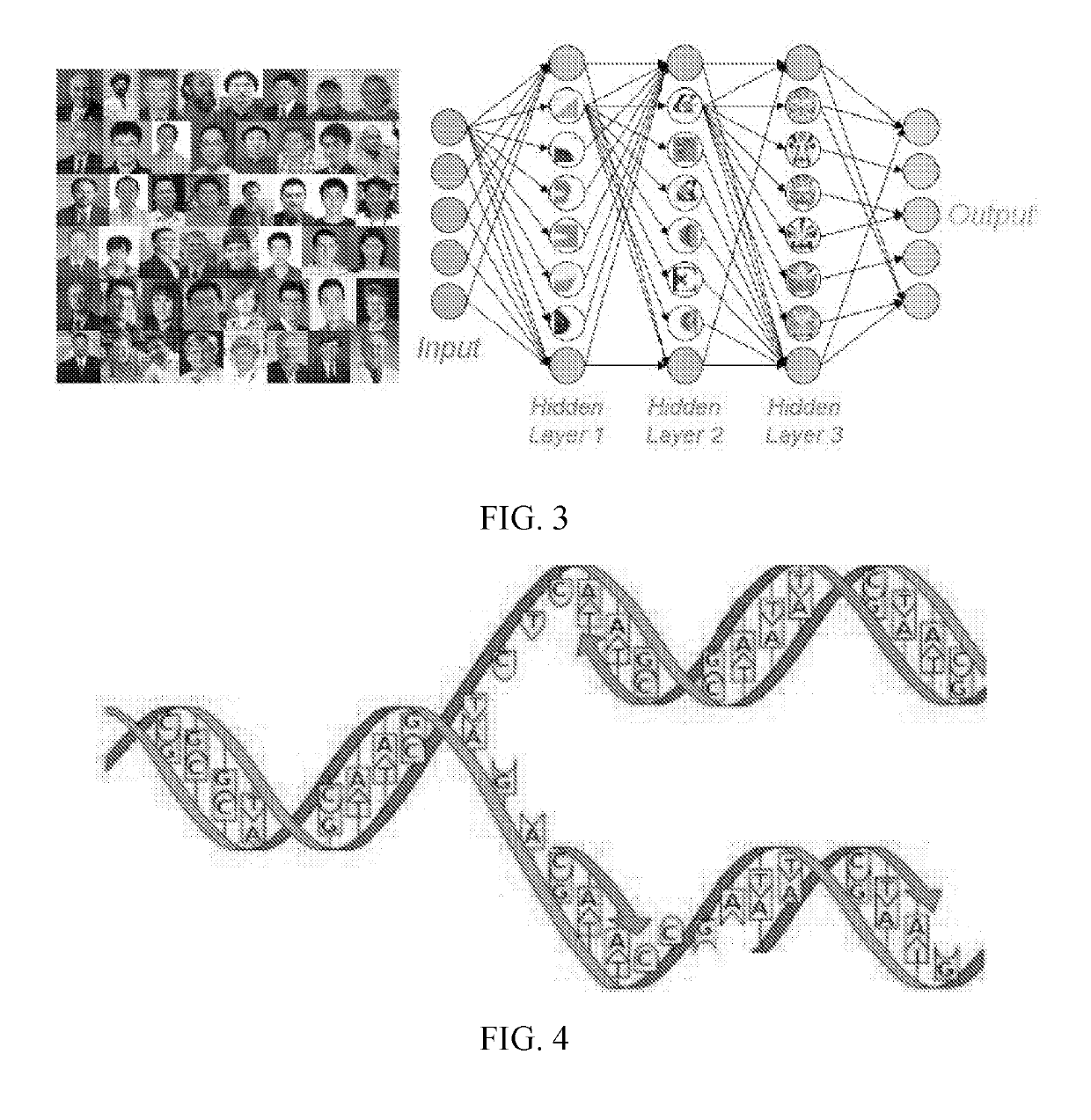
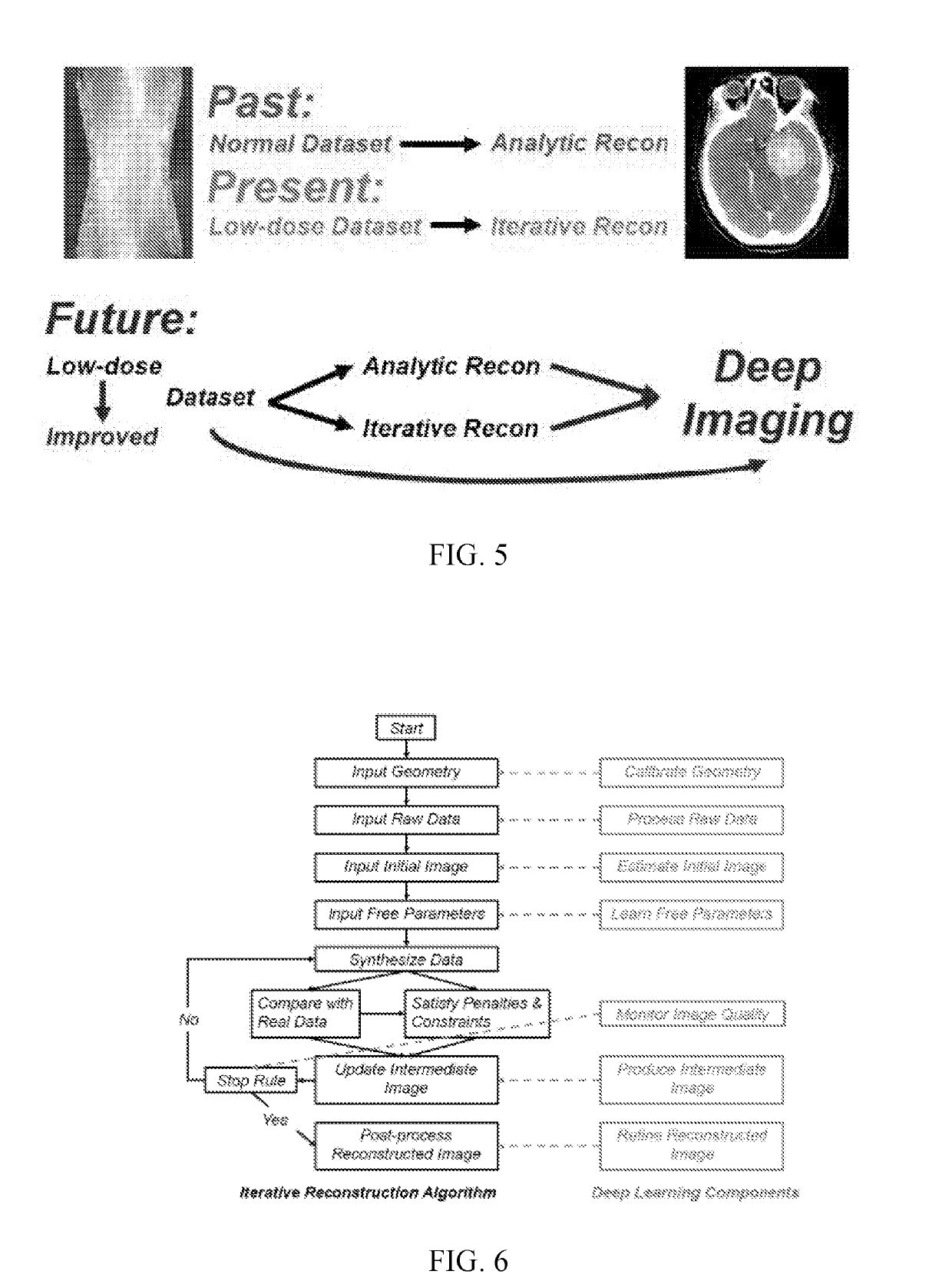
Tomographic image reconstruction via machine learning
ActiveUS20190325621A1Drawback can be addressedReconstruction from projectionDiagnostic recording/measuringPattern recognitionIntermediate image
Tomographic / tomosynthetic image reconstruction systems and methods in the framework of machine learning, such as deep learning, are provided. A machine learning algorithm can be used to obtain an improved tomographic image from raw data, processed data, or a preliminarily reconstructed intermediate image for biomedical imaging or any other imaging purpose. In certain cases, a single, conventional, non-deep-learning algorithm can be used on raw imaging data to obtain an initial image, and then a deep learning algorithm can be used on the initial image to obtain a final reconstructed image. All machine learning methods and systems for tomographic image reconstruction are covered, except for use of a single shallow network (three layers or less) for image reconstruction.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Method for slice position planning of tomographic measurements, using statistical images
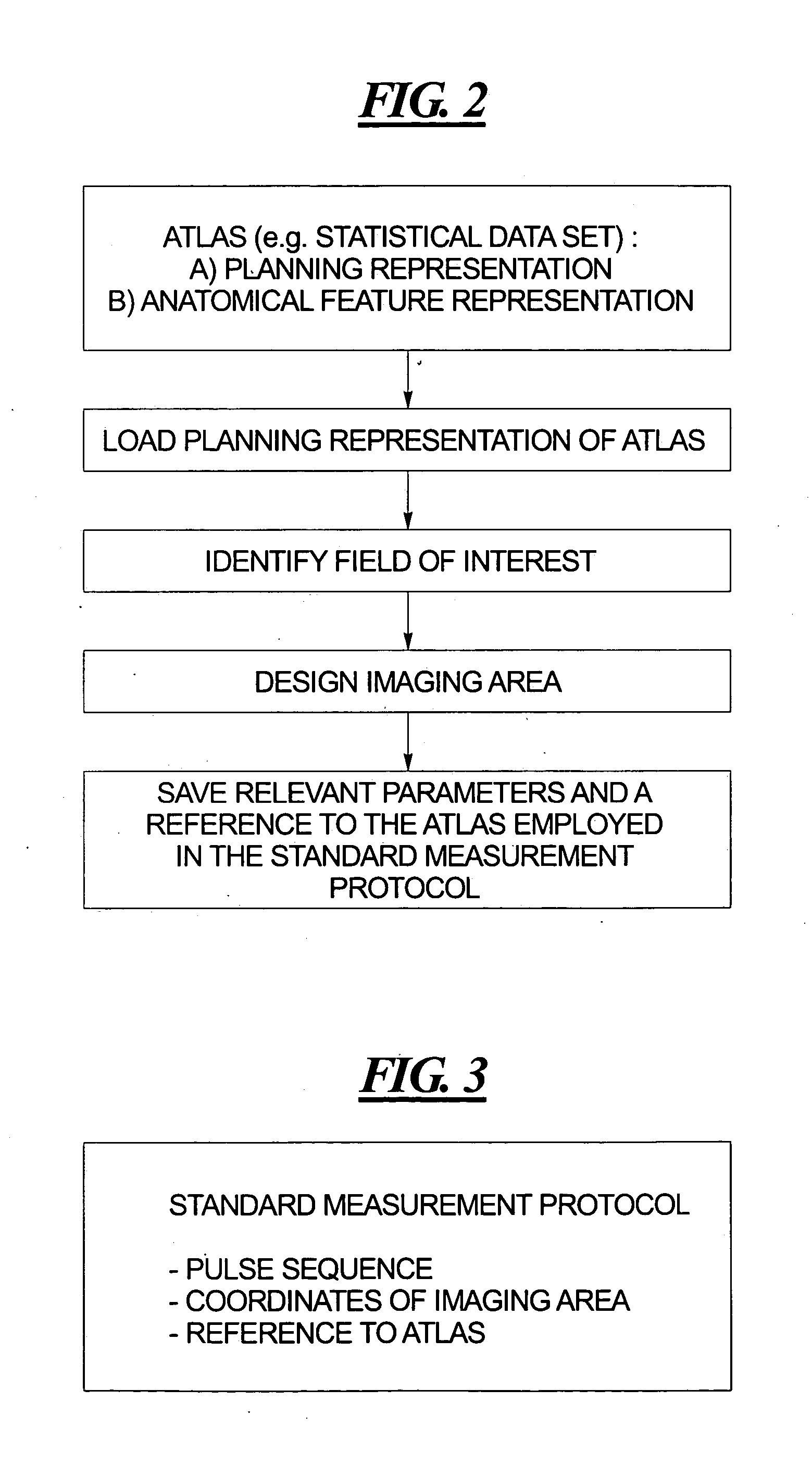
ActiveUS20050088177A1Avoid the needGood repeatabilityElectrical testingComputerised tomographsTomographyLocation planning
In a method and computer program product for operating a tomographic imaging apparatus, a standard measurement protocol is generated by displaying a planning representation of a standard object, defining a spatial position of a standard imaging area in the planning representation, and storing, as the standard measurement protocol for the standard object, a reference to the standard object and parameters of the standard imaging area. Such a standard measurement protocol can then be used in the slice position planning for an actual tomographic measurement, by obtaining data representing features of an examination object, corresponding to the standard object, determining a geometrical relation of the features of the examination object to features of the standard object, and generating an object-specific measurement protocol wherein the imaging area is positioned relative to the examination object by modification of the standard measurement protocol.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Operation microscope
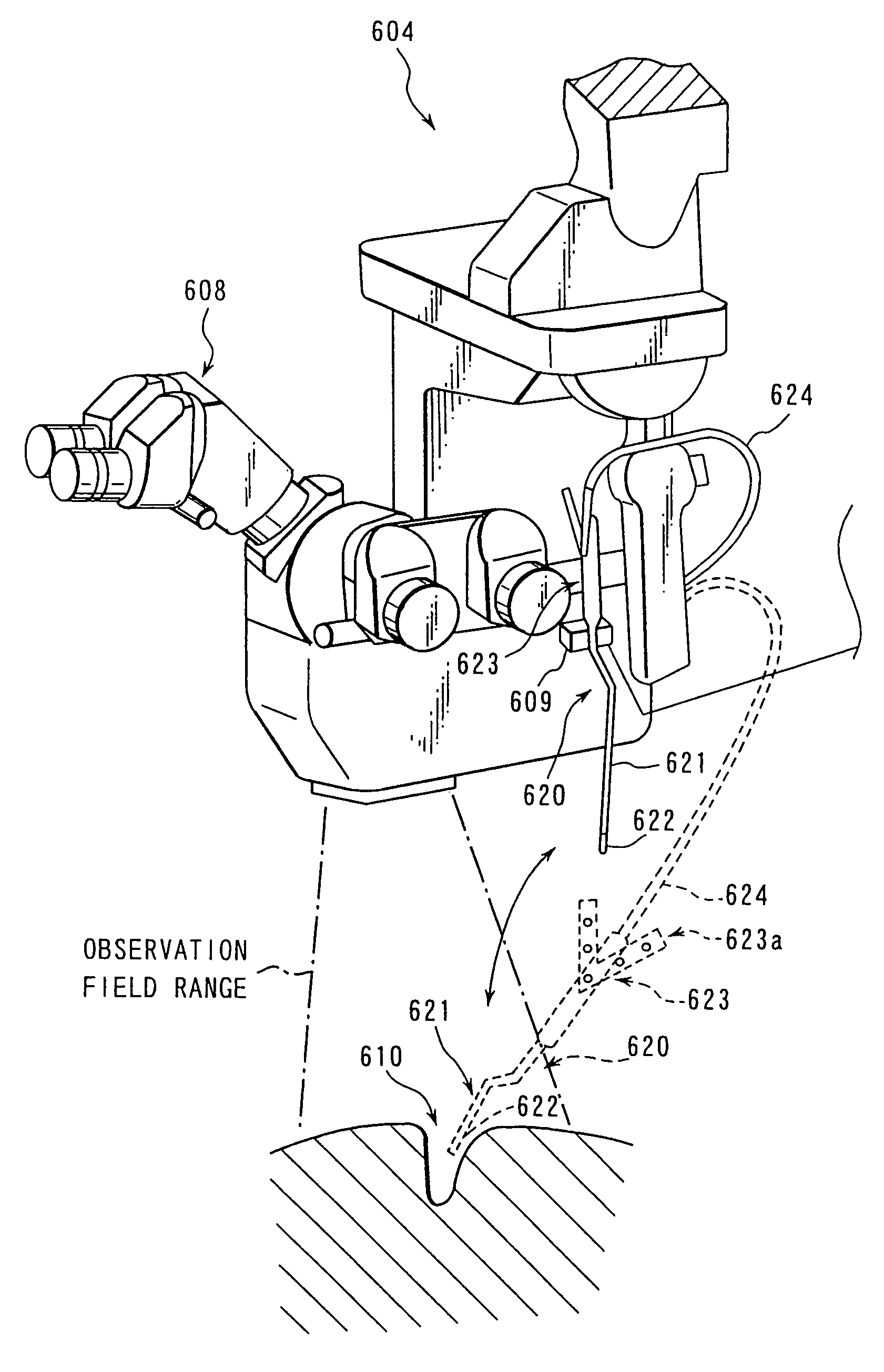
InactiveUS8221304B2Efficient executionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryOperation microscopesMicroscopic observation
There is disclosed an operation microscope in which an observing and displaying system of an operating instrument are selected, and an endoscope image for observing a dead angle of the microscope and a navigation image are selectively displayed in a microscope observation field, so that a tomographic image, three-dimensionally constructed image, and the like can be selectively displayed in a display screen in accordance with a treatment position displayed in a monitor or an observation position of the operation microscope.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
X-Ray Tomographic Inspection System for the Identification of Specific Target Items
The present invention provides for an improved scanning process with a stationary X-ray source arranged to generate X-rays from a plurality of X-ray source positions around a scanning region, a first set of detectors arranged to detect X-rays transmitted through the scanning region, and at least one processor arranged to process outputs from the first set of detectors to generate tomographic image data. The X-ray screening system is used in combination with other screening technologies, such as NQR-based screening, X-ray diffraction based screening, X-ray back-scatter based screening, or Trace Detection based screening.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
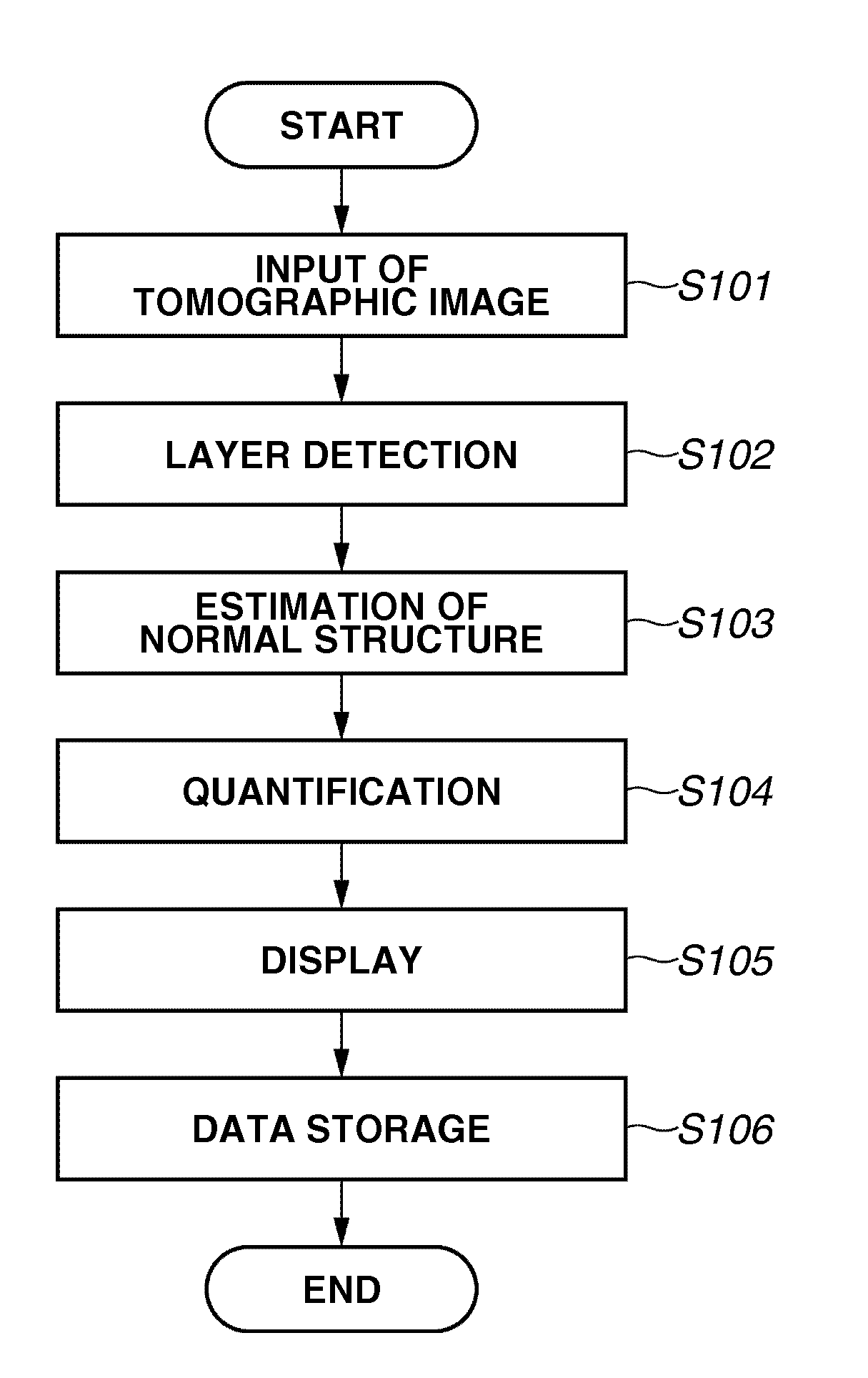
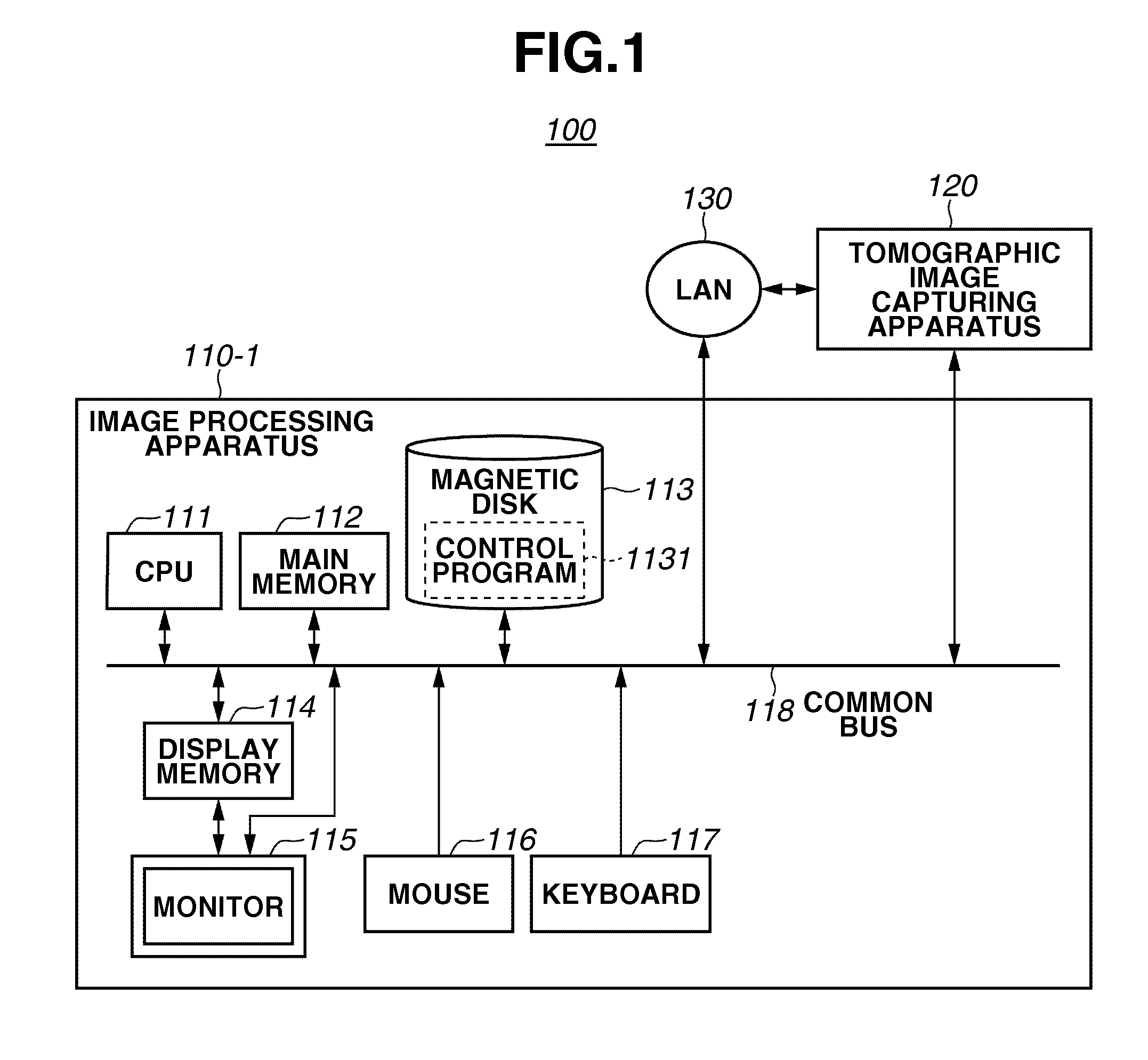
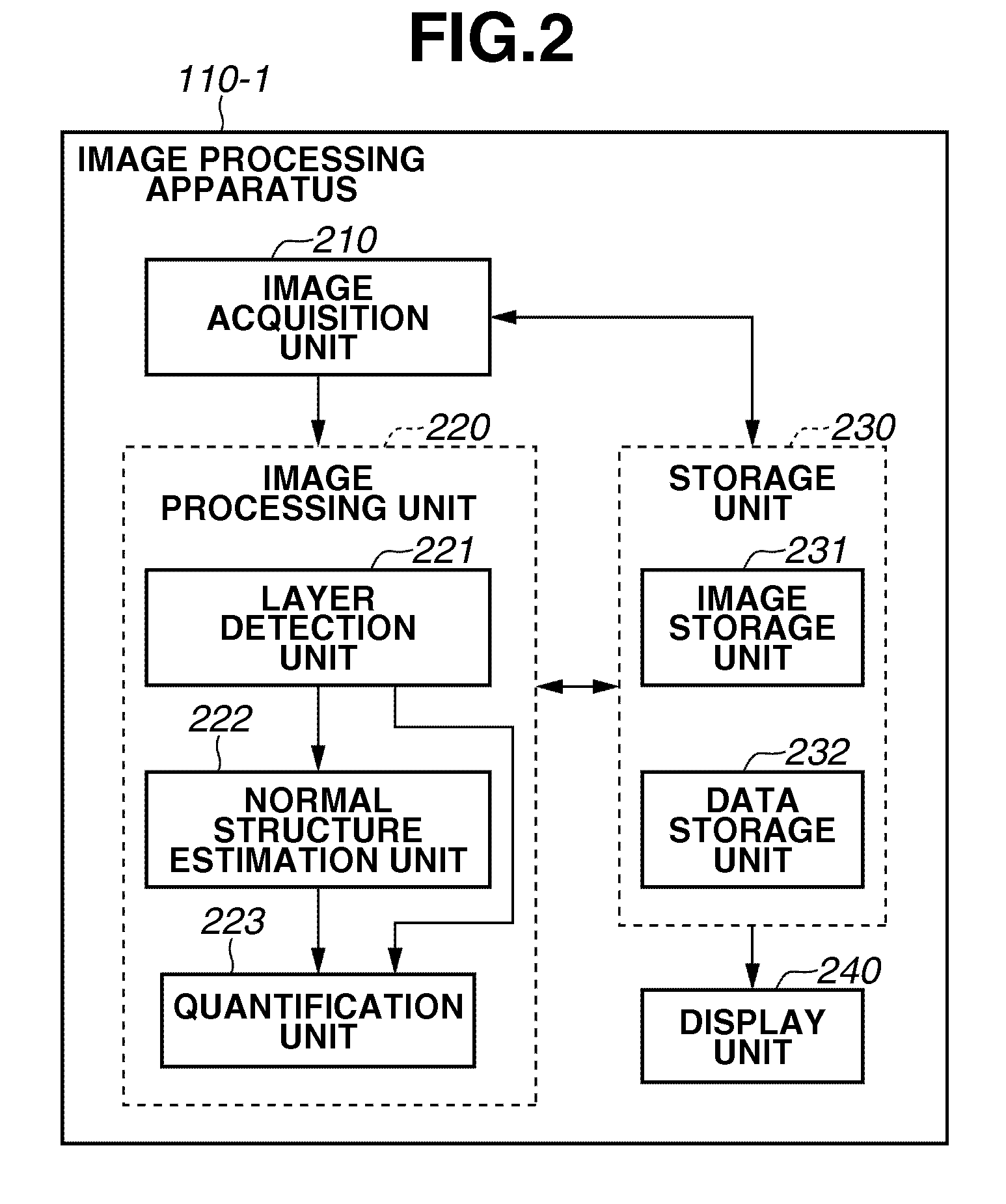
Image processing apparatus and method for controlling the same
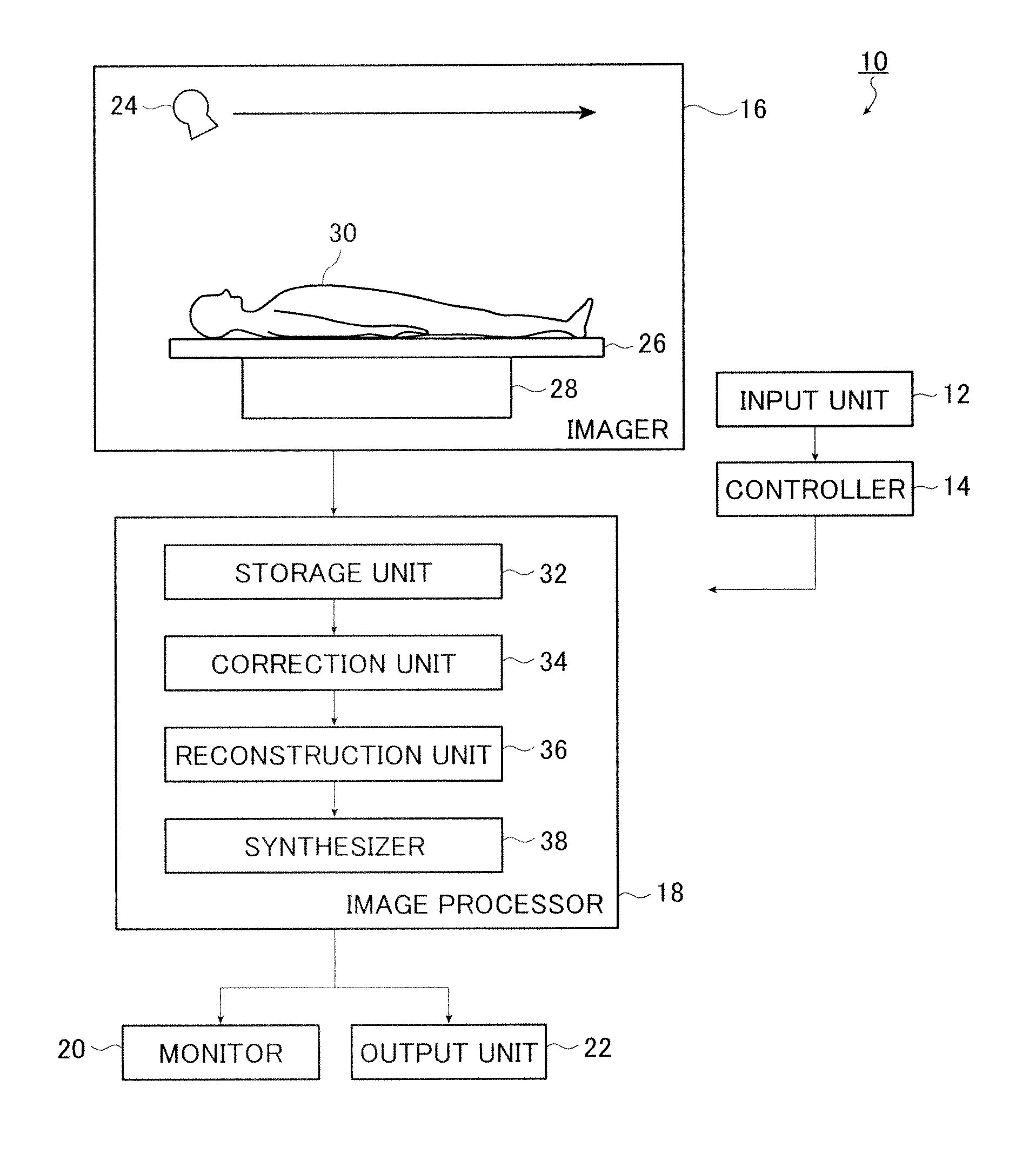
ActiveUS20100220914A1Accurate estimateImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingTomographic image
An image processing apparatus includes an image acquisition unit configured to acquire a tomographic image of an object, a layer detection unit configured to detect a layer that constitutes the object from the tomographic image acquired by the image acquisition unit, and a normal structure estimation unit configured to estimate a normal structure of the layer based on the layer detected by the layer detection unit and a feature that is modified by a lesion of the layer.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com