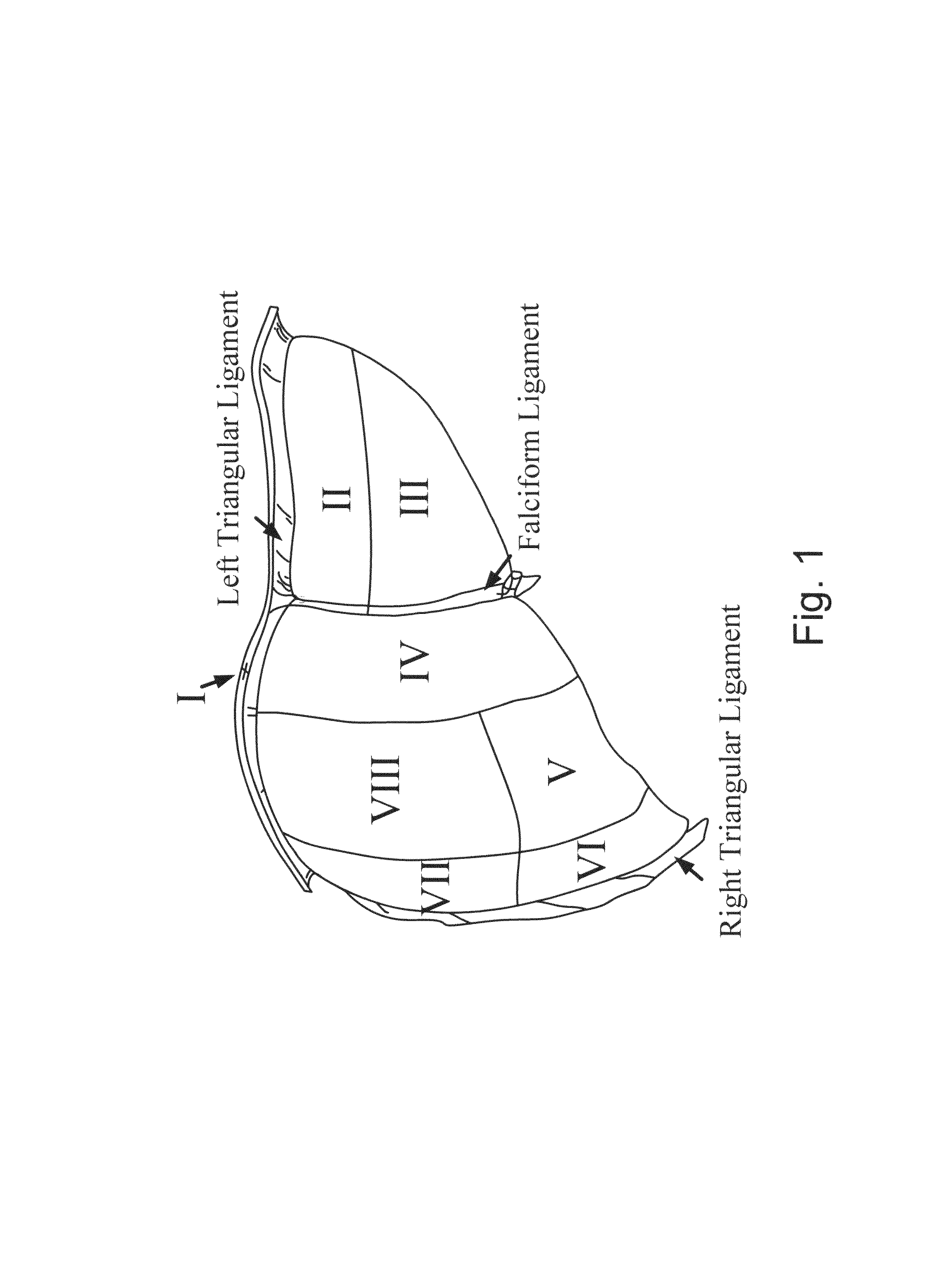
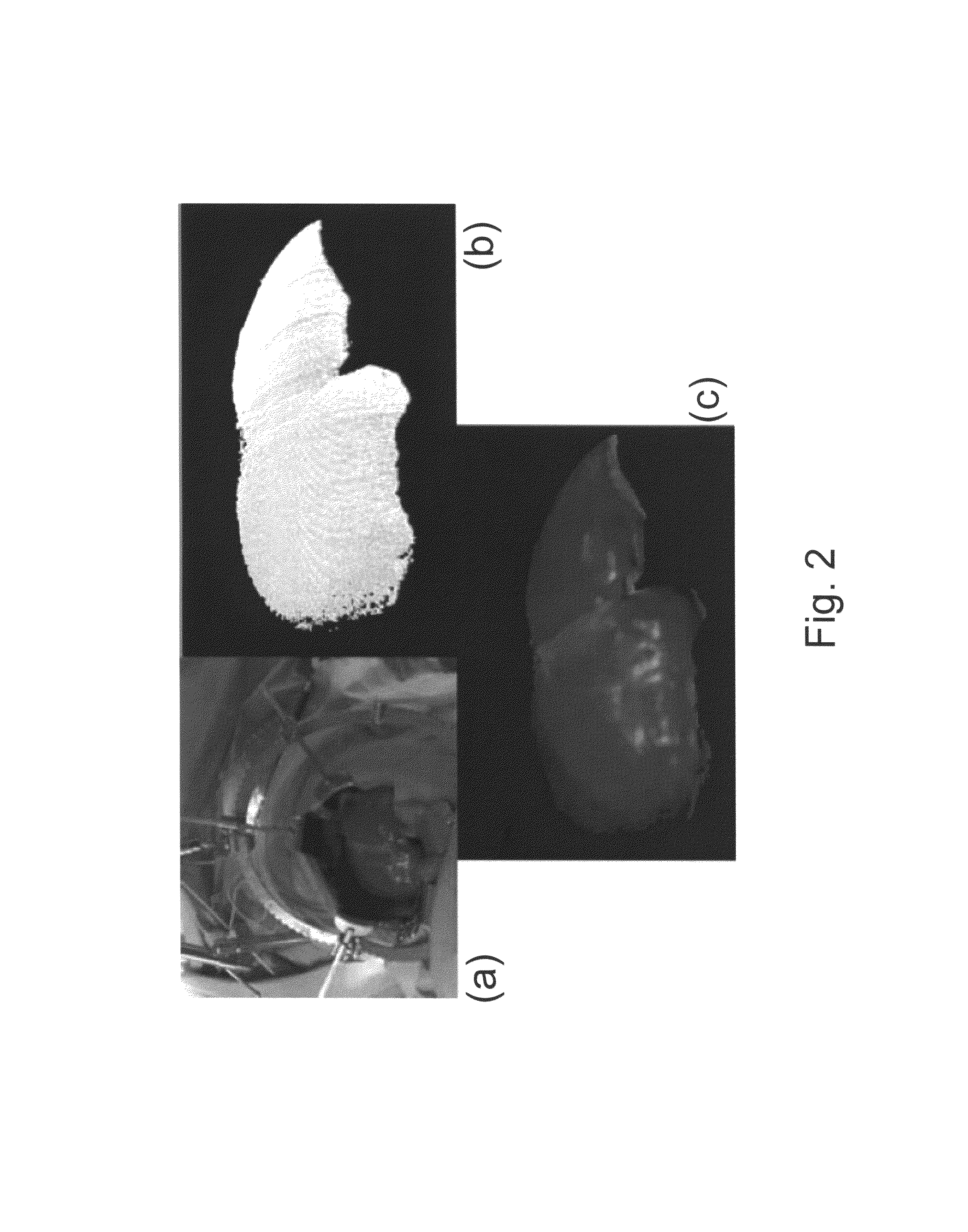
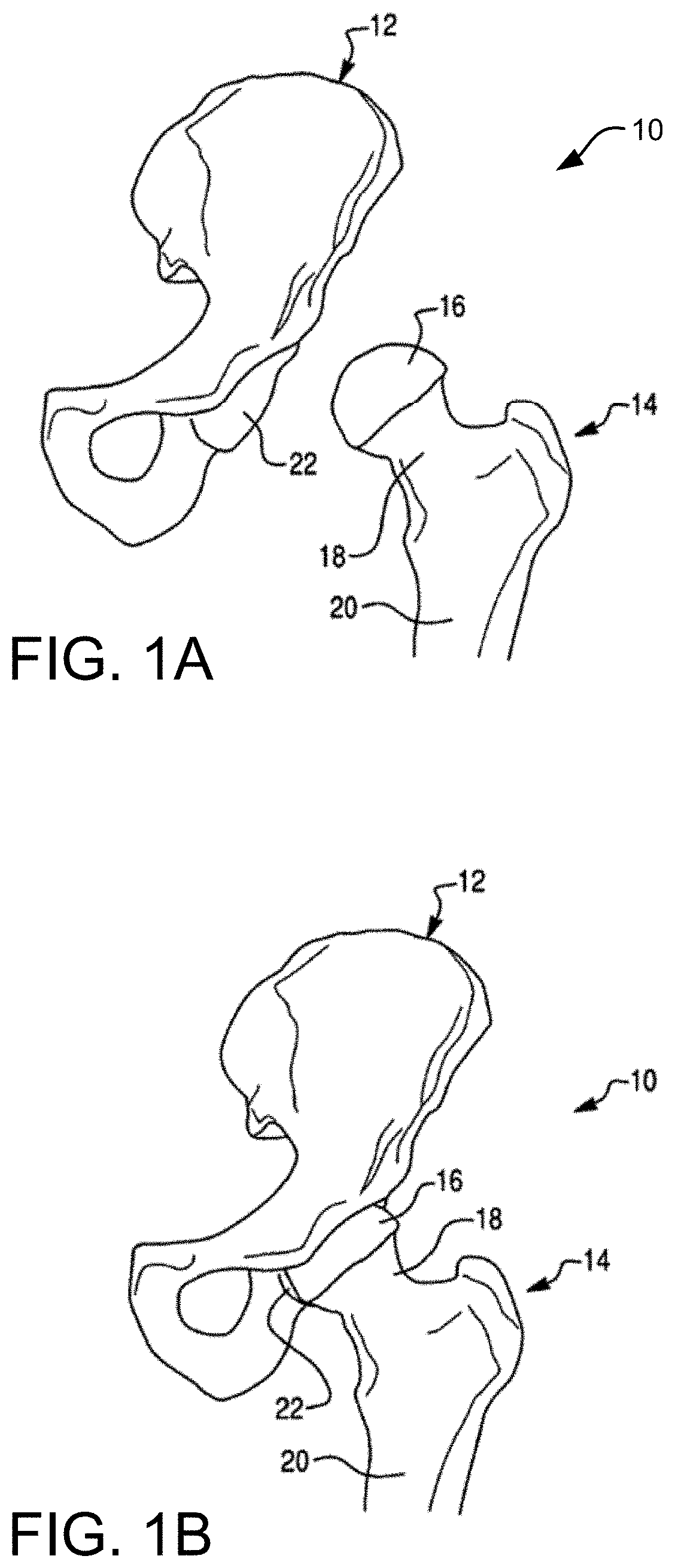
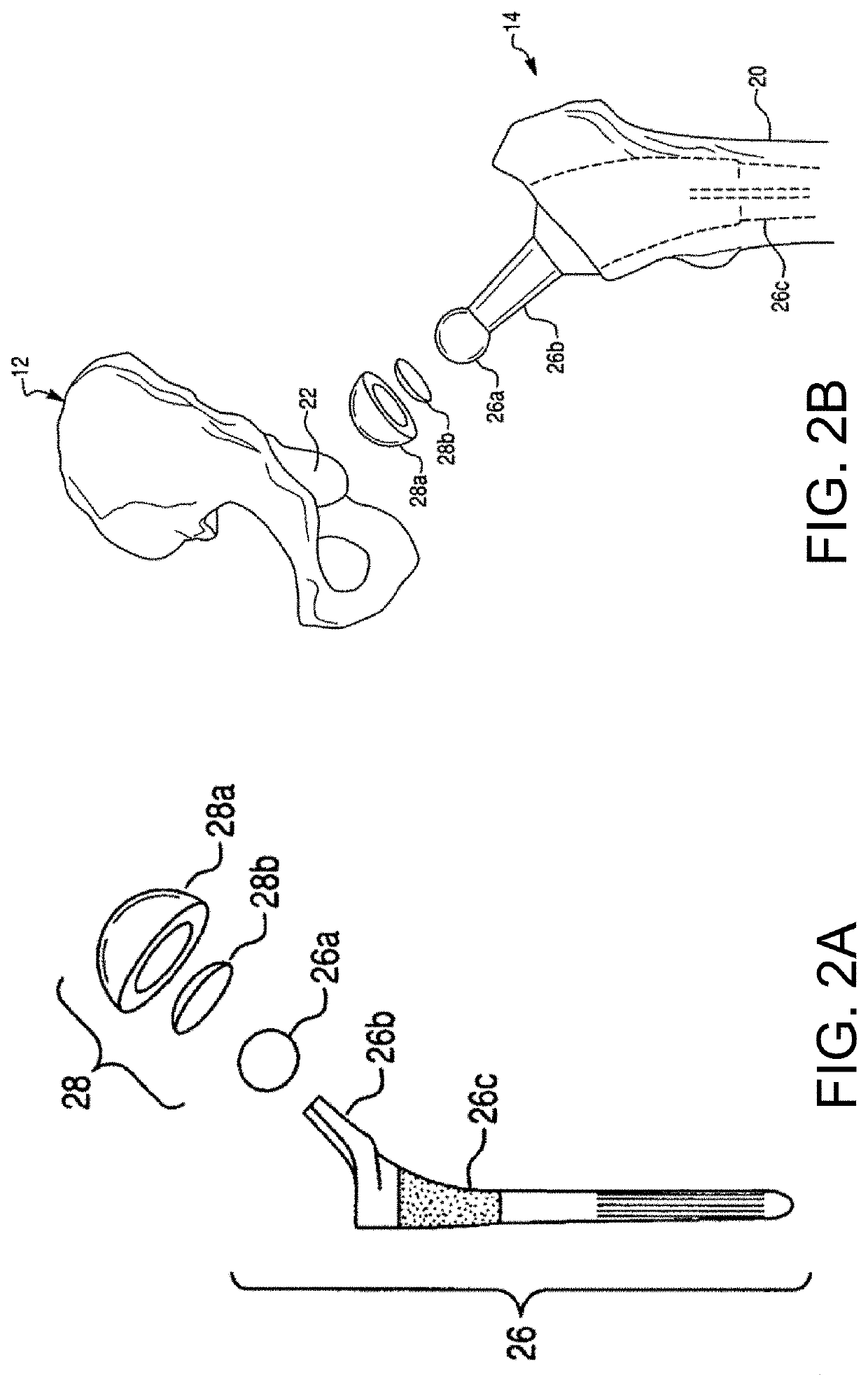
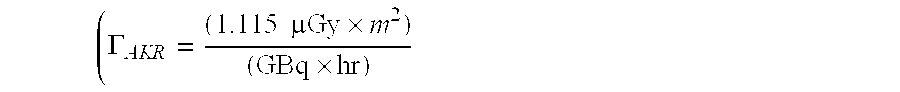Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
330 results about "Intra operative" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The term "intraoperative" refers to the time during surgery. Intraoperative care is patient care during an operation and ancillary to that operation.
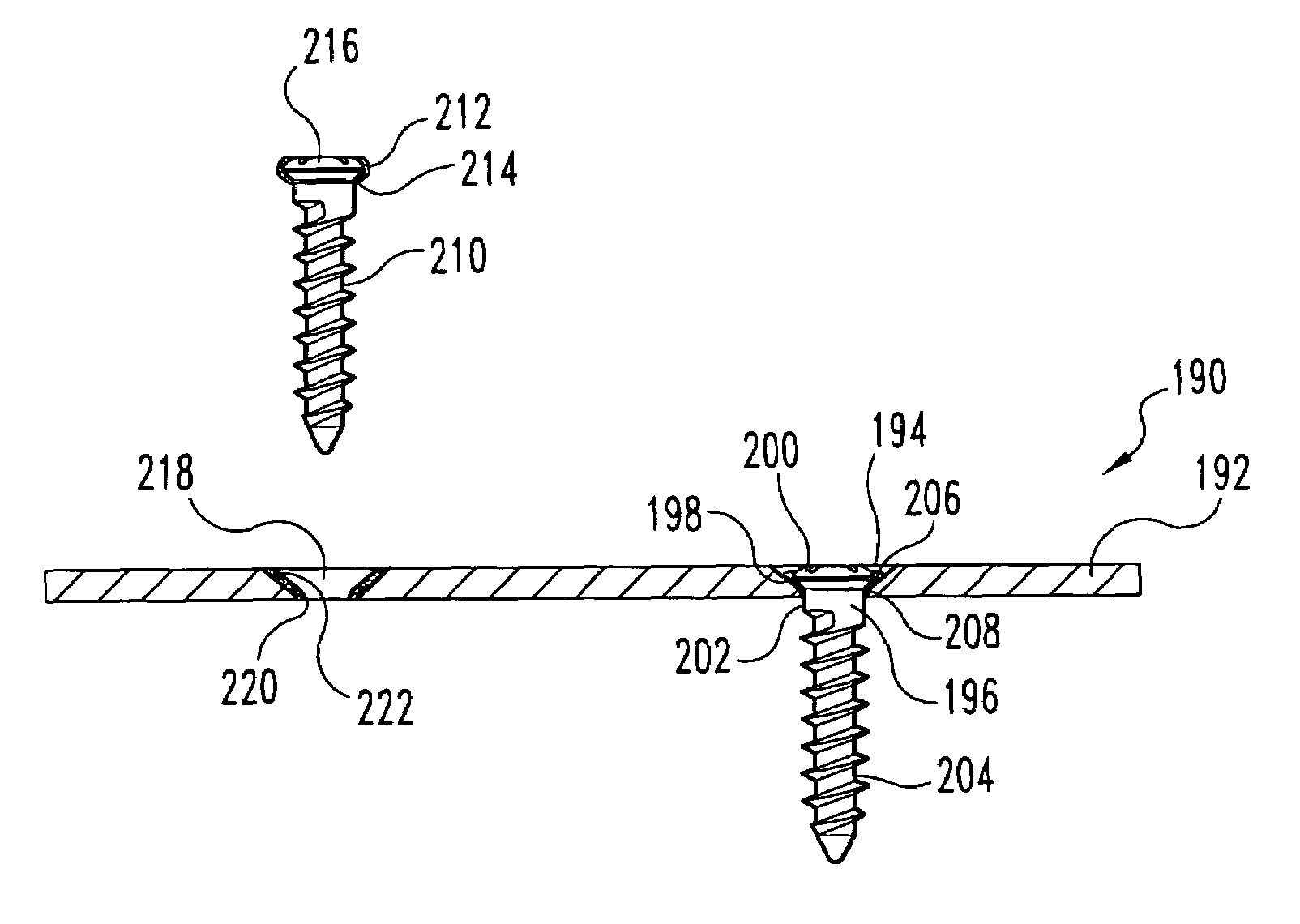
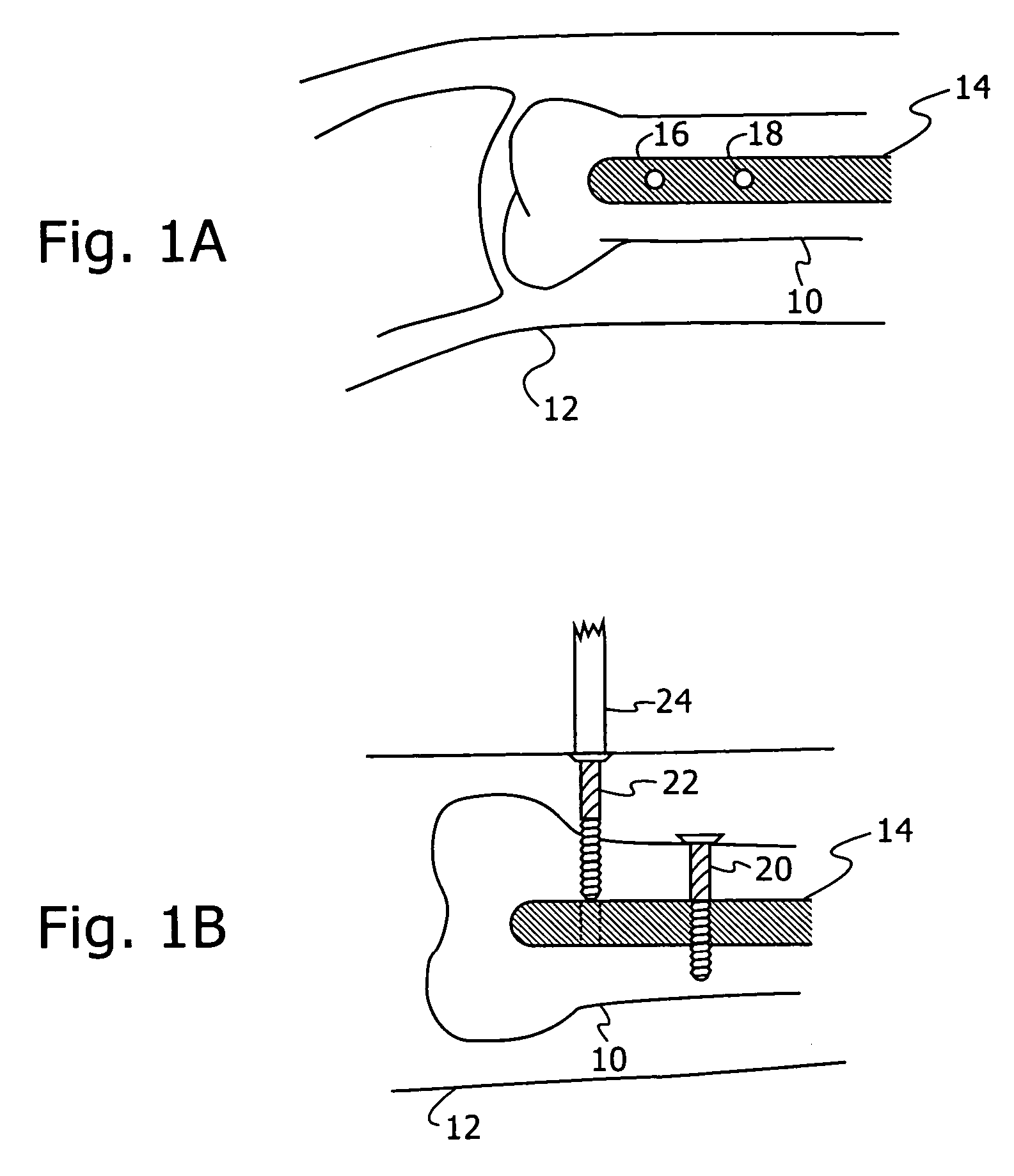
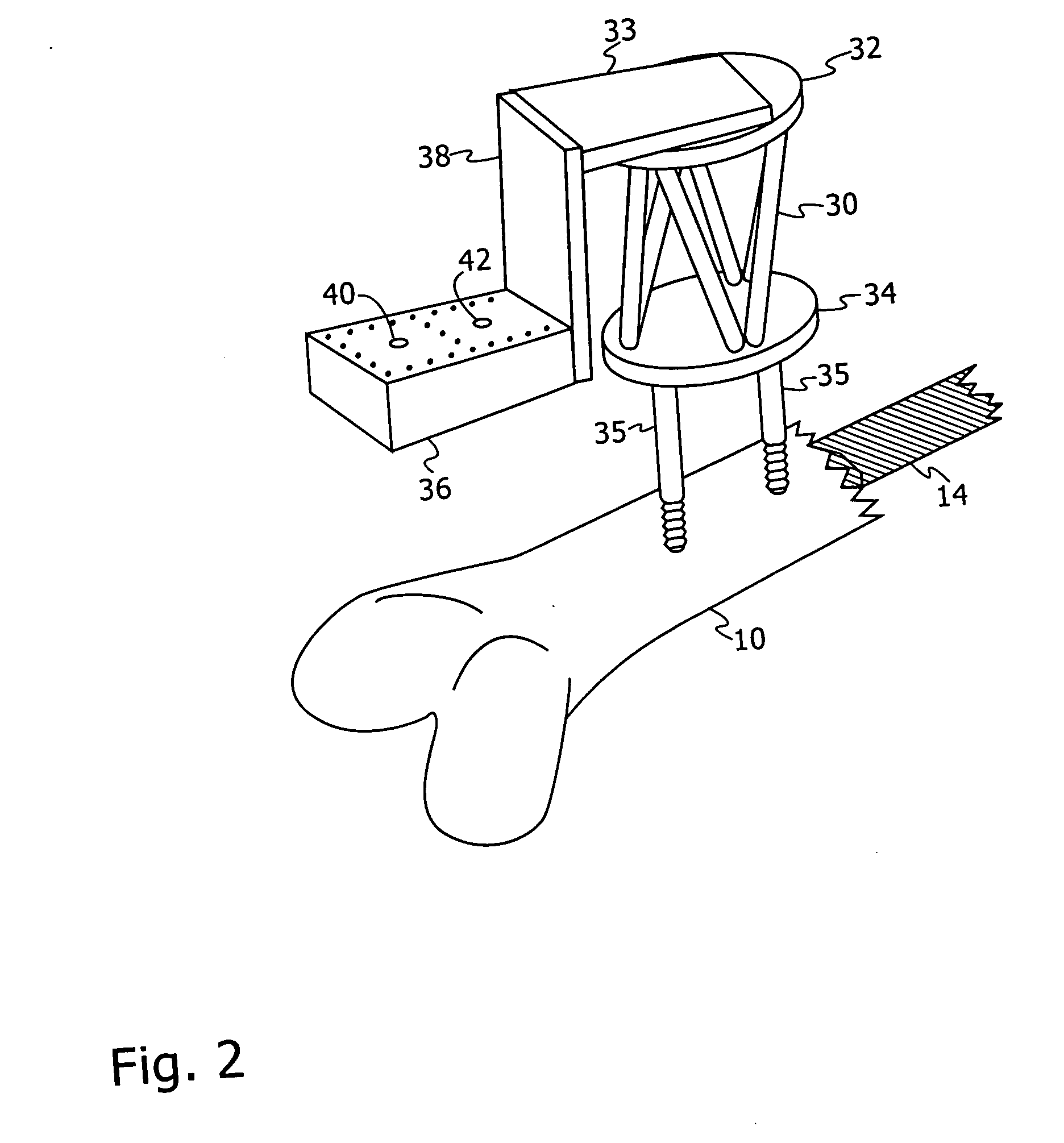
Non-metallic implant devices and intra-operative methods for assembly and fixation
This invention relates to orthopedic implants and to methods of treating bone defects. More specifically, but not exclusively, the present invention is directed to non-metallic implants and to methods for intra-operative assembly and fixation of orthopedic implants to facilitate medical treatment. The non-metallic implant assembly can be secured to underlying tissue by a fastener, such as a bone screw, that is capable of swelling on contact with fluid in the underlying tissue. Alternatively, the non-metallic implant assembly can be assembled intra-operatively using a fastener that is adhesively bonded to a bone plate or the bone plate can be deformed using heat, force, or solvents to inhibit withdrawal of the fastener. In preferred embodiments, both the fastener and the bone plate are formed of biodegradable material.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Optical sensors for intraoperative procedures
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
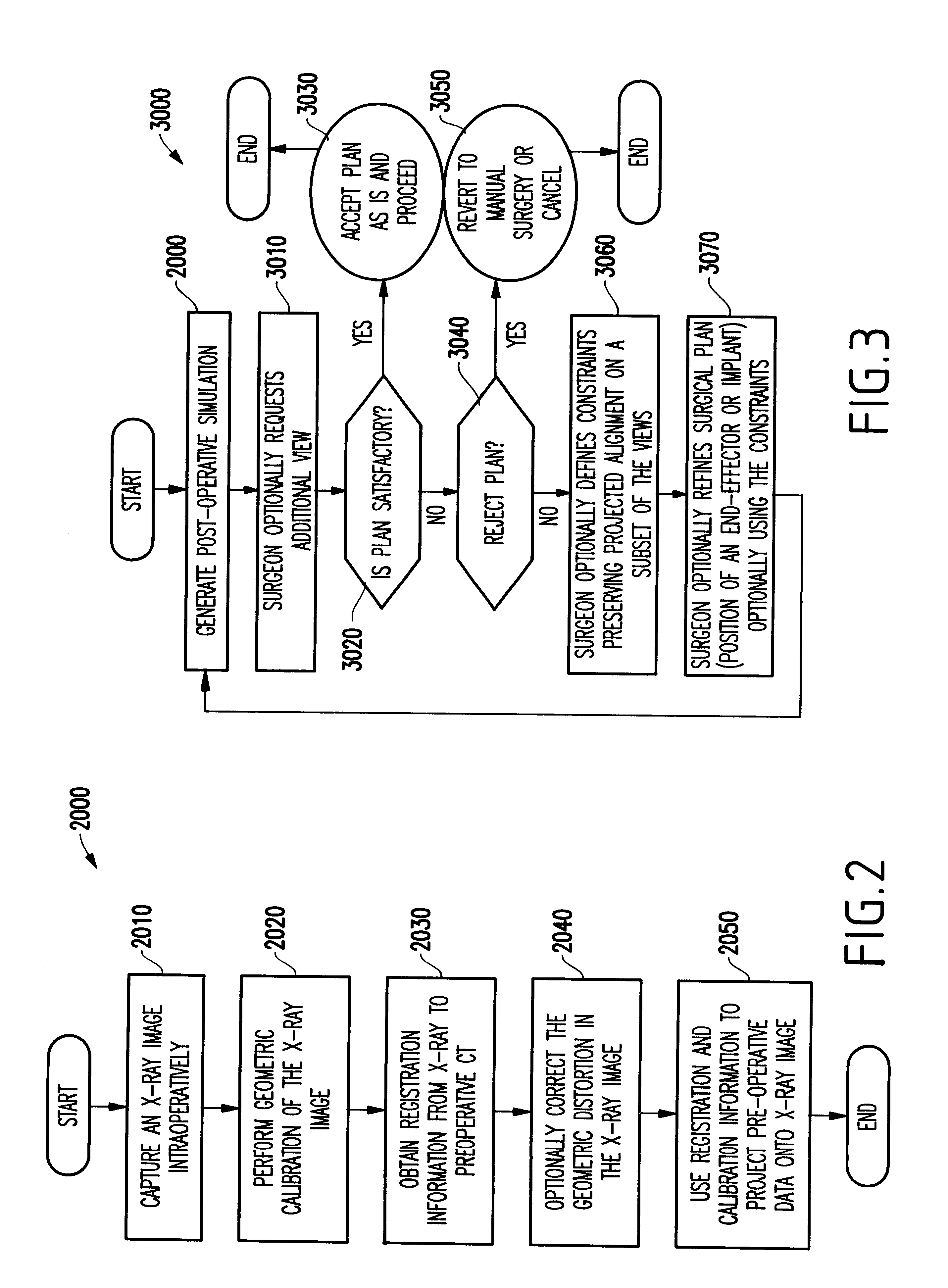
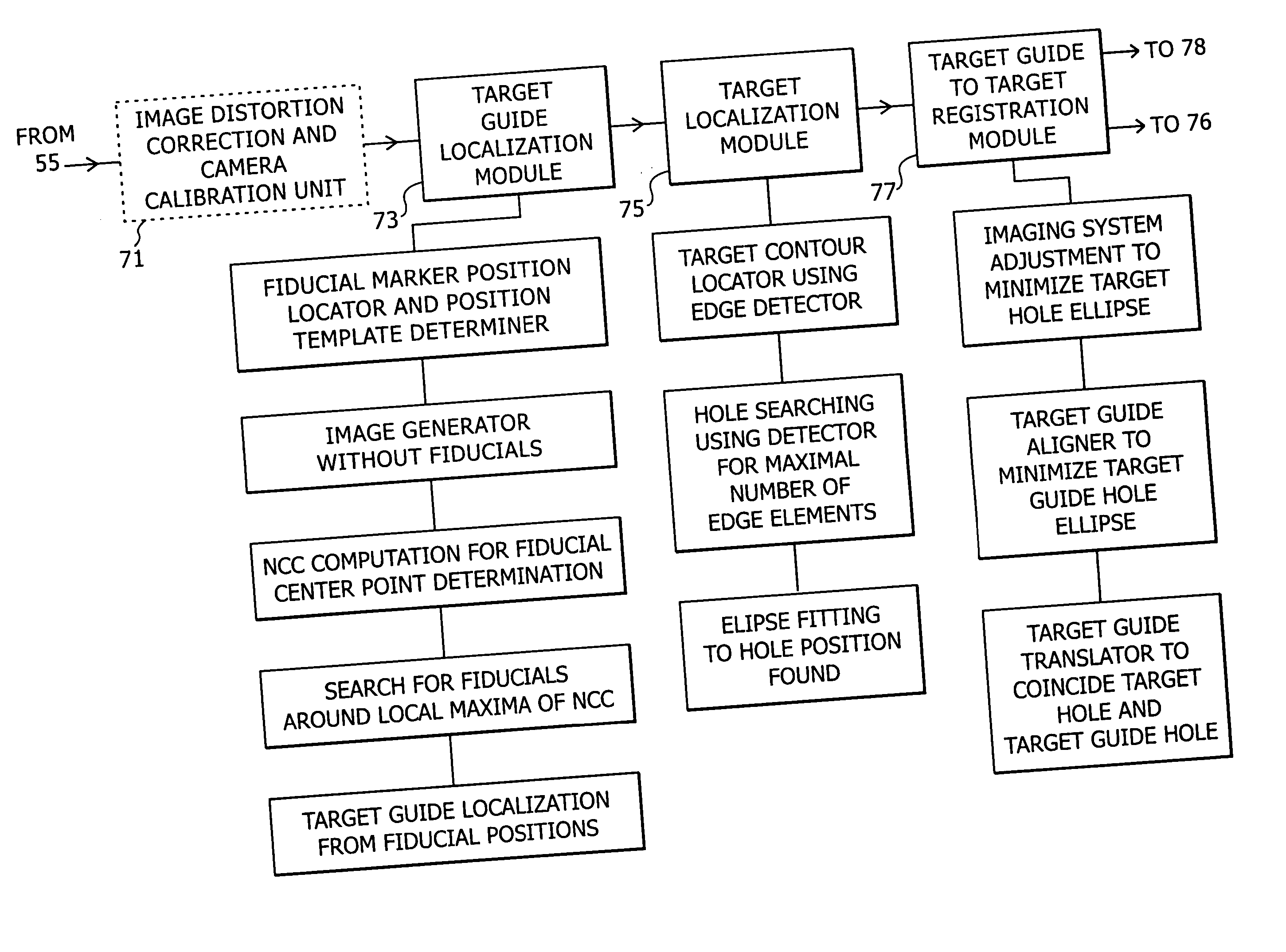
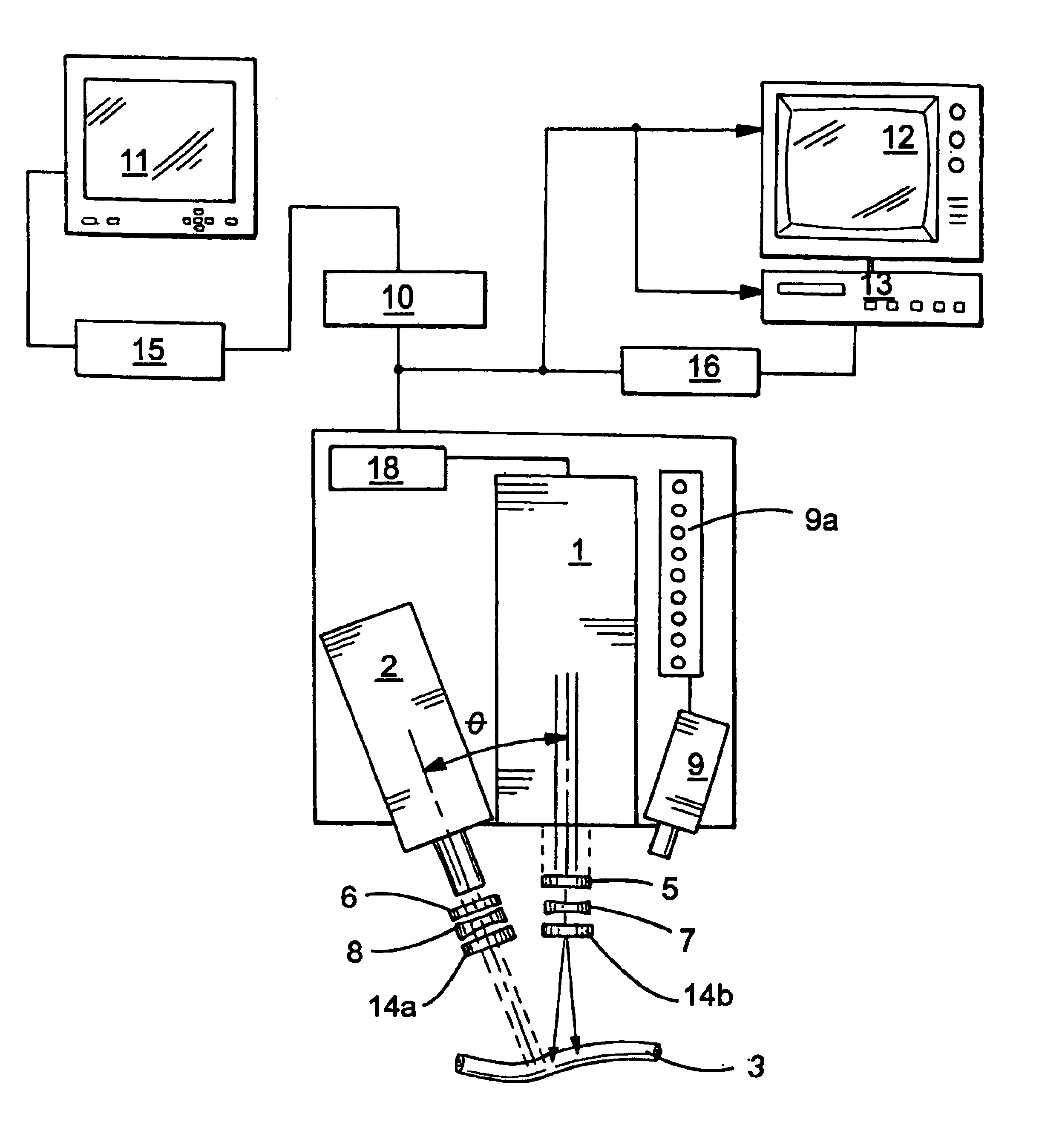
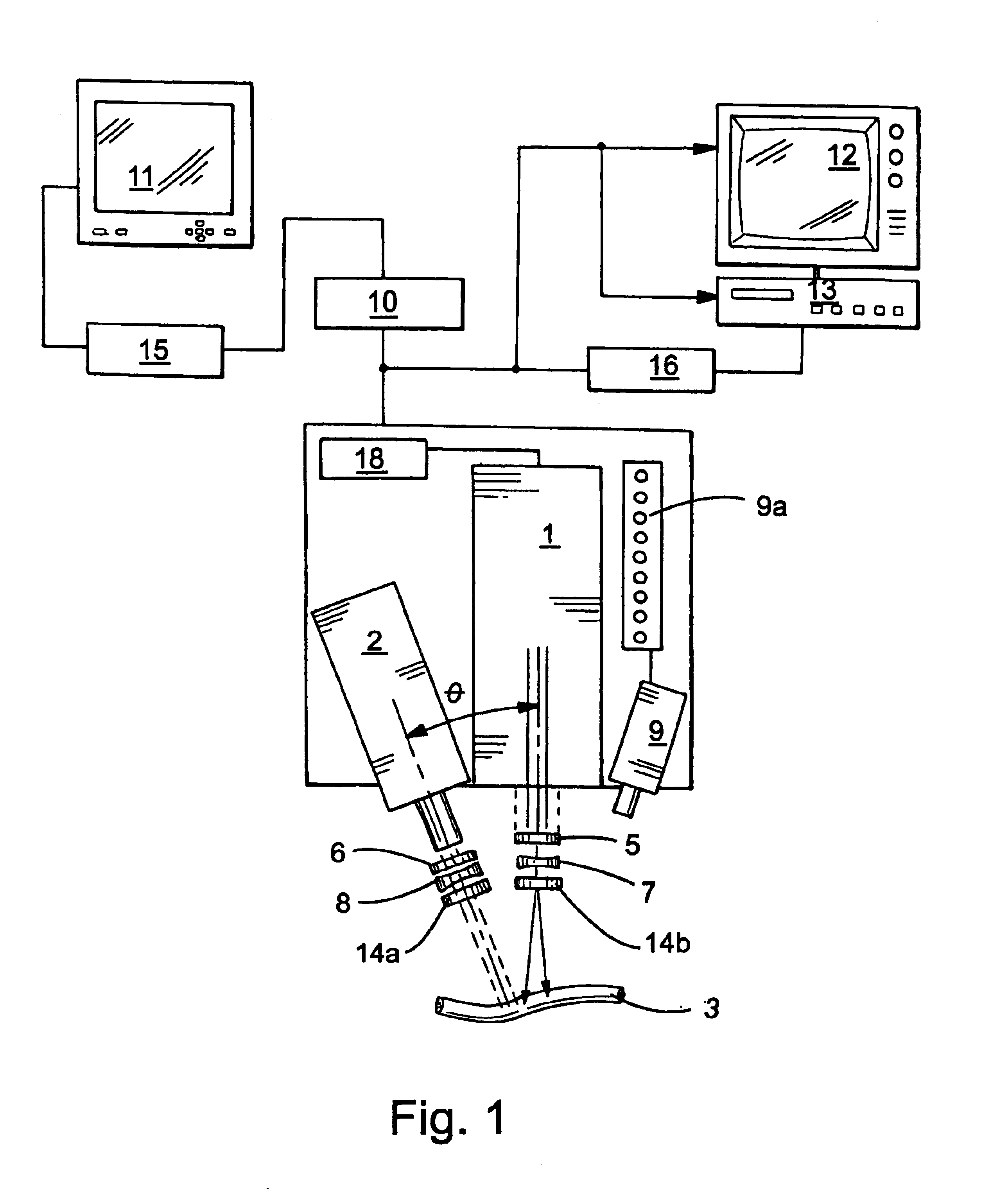
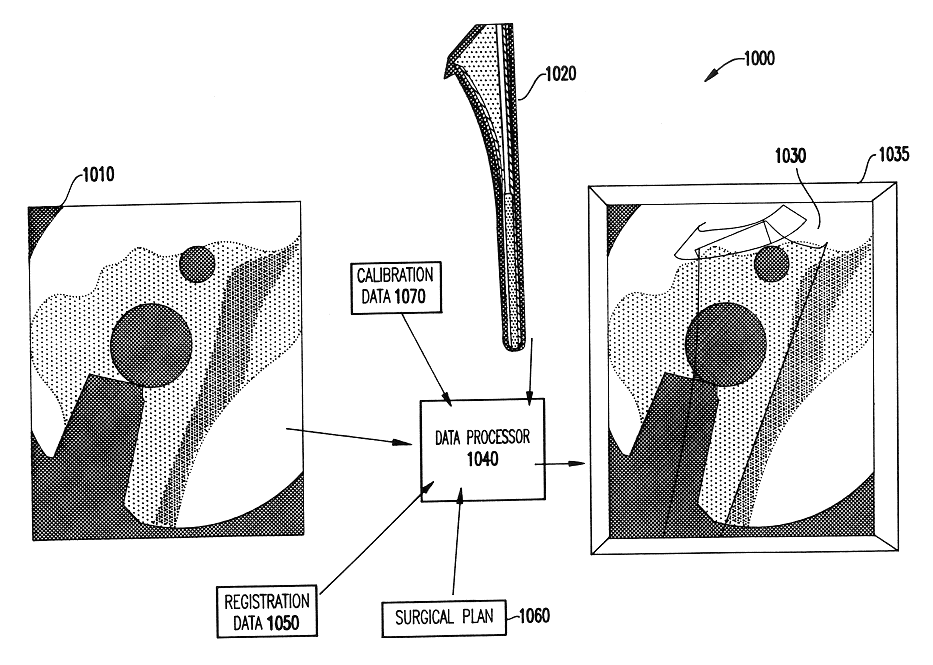
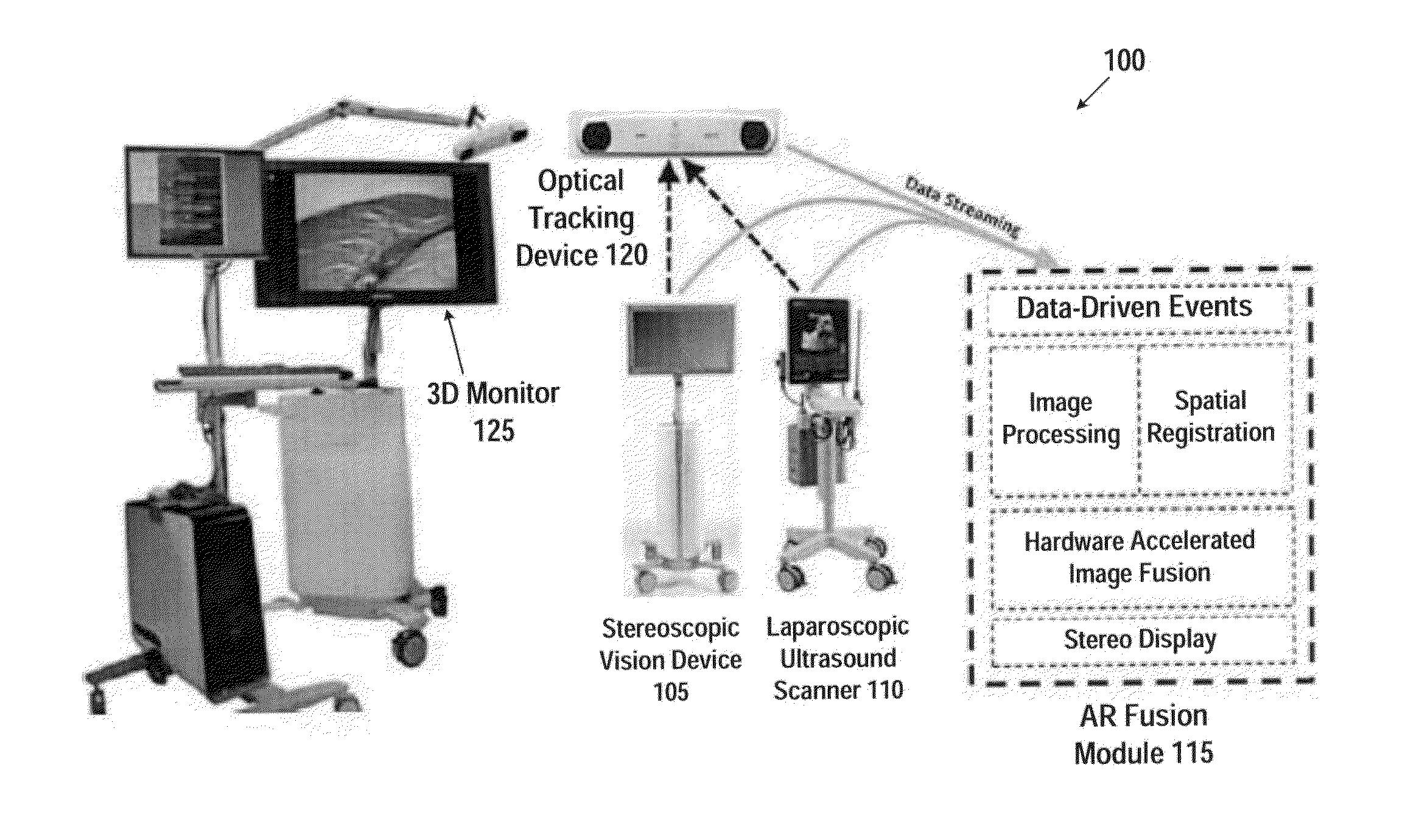
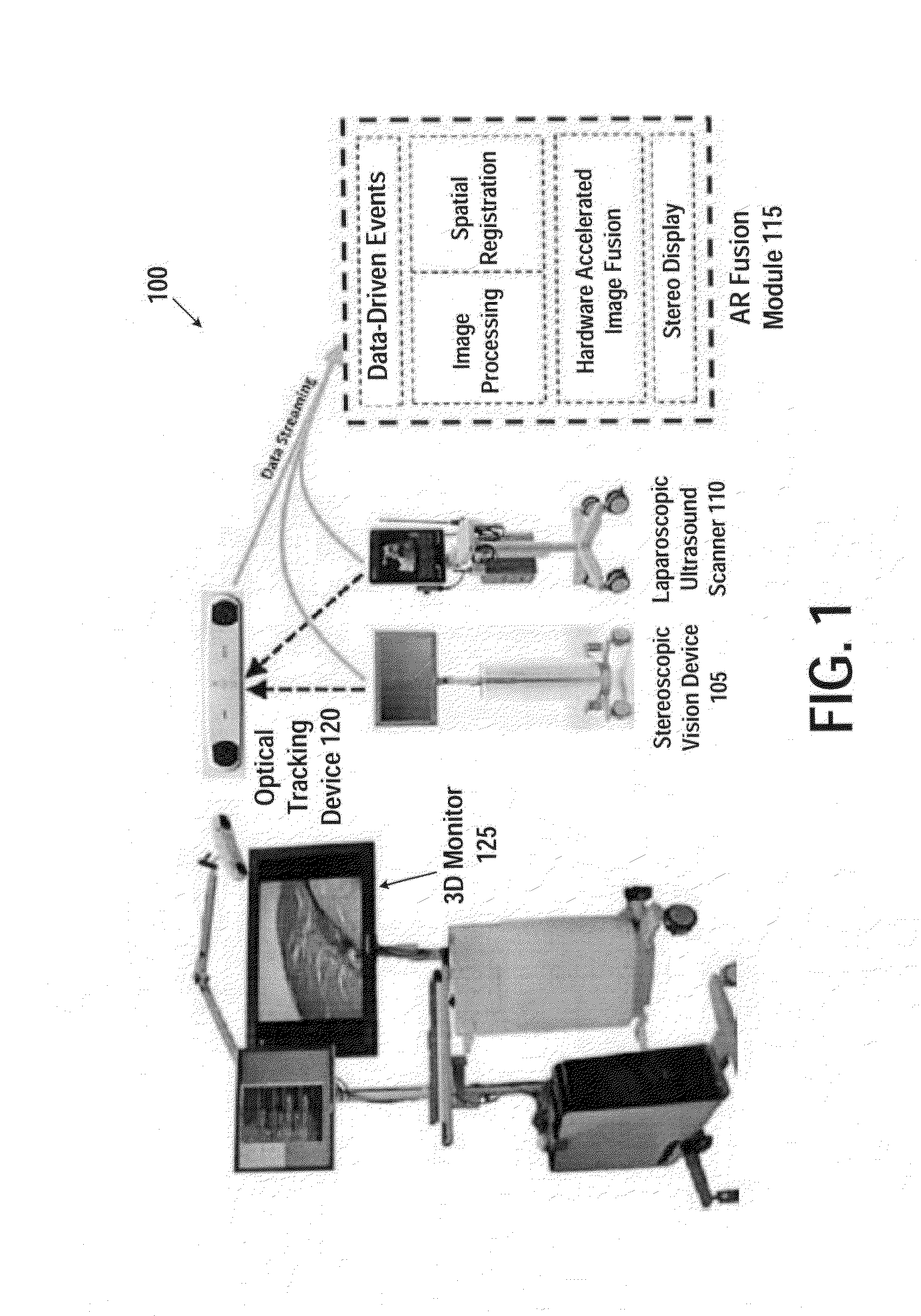
System and method for intra-operative, image-based, interactive verification of a pre-operative surgical plan
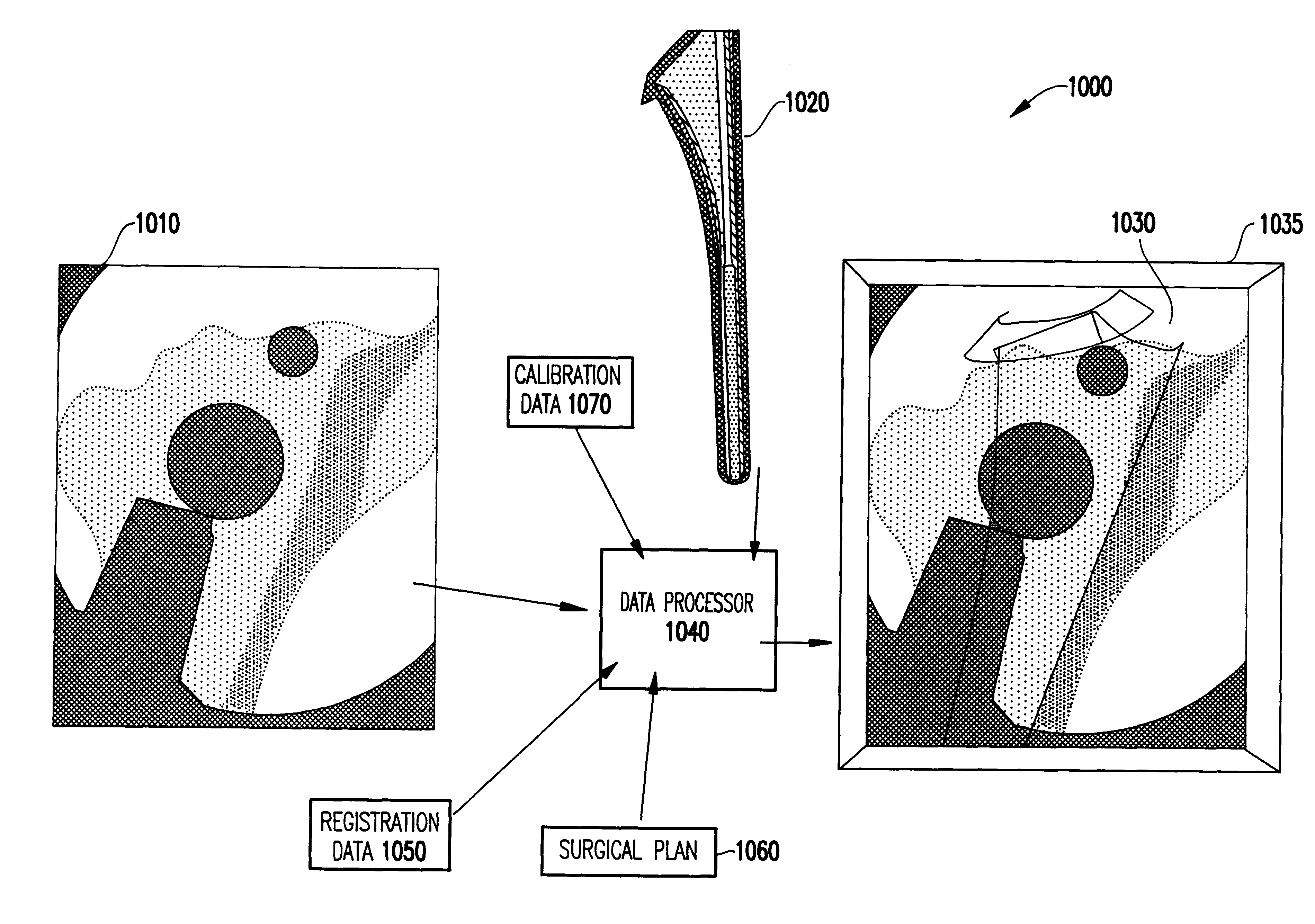
InactiveUS6301495B1Registration errorAvoid mistakesGeometric image transformationDiagnostic markersFusion mechanismPhysical space
A system and method for intra-operatively providing a surgeon with visual evaluations of possible surgical outcomes ahead of time, and generating simulated data, includes a medical imaging camera, a registration device for registering data to a physical space, and to the medical imaging camera, and a fusion mechanism for fusing the data and the images to generate simulated data. The simulated data (e.g., such as augmented X-ray images) is natural and easy for a surgeon to interpret. In an exemplary implementation, the system preferably includes a data processor which receives a three-dimensional surgical plan or three-dimensional plan of therapy delivery, one or a plurality of two-dimensional intra-operative images, a three-dimensional model of pre-operative data, registration data, and image calibration data. The data processor produces one or a plurality of simulated post-operative images, by integrating a projection of a three-dimensional model of pre-operative data onto one or a plurality of two-dimensional intra-operative images.
Owner:IBM CORP
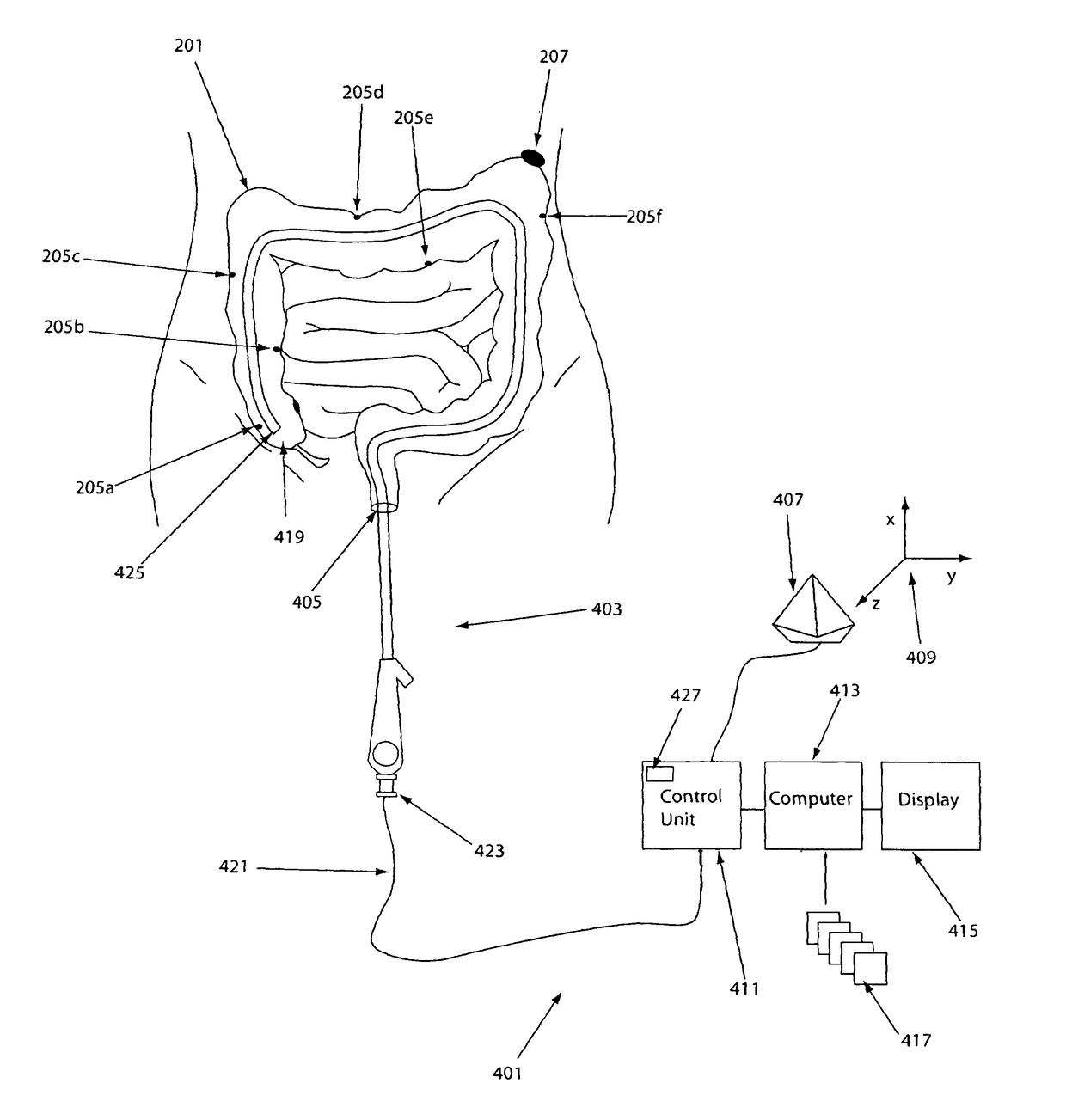
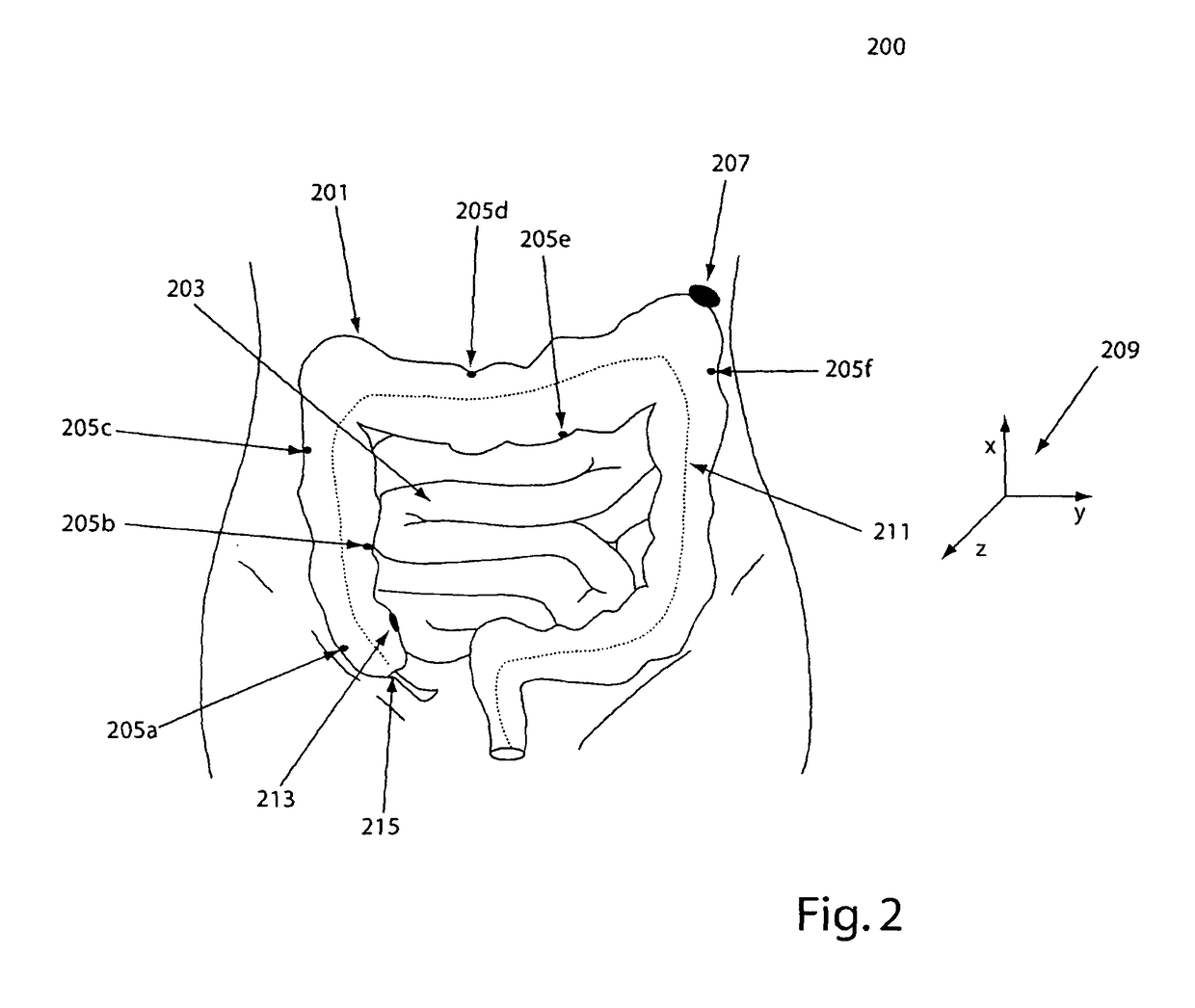
System, method and devices for navigated flexible endoscopy
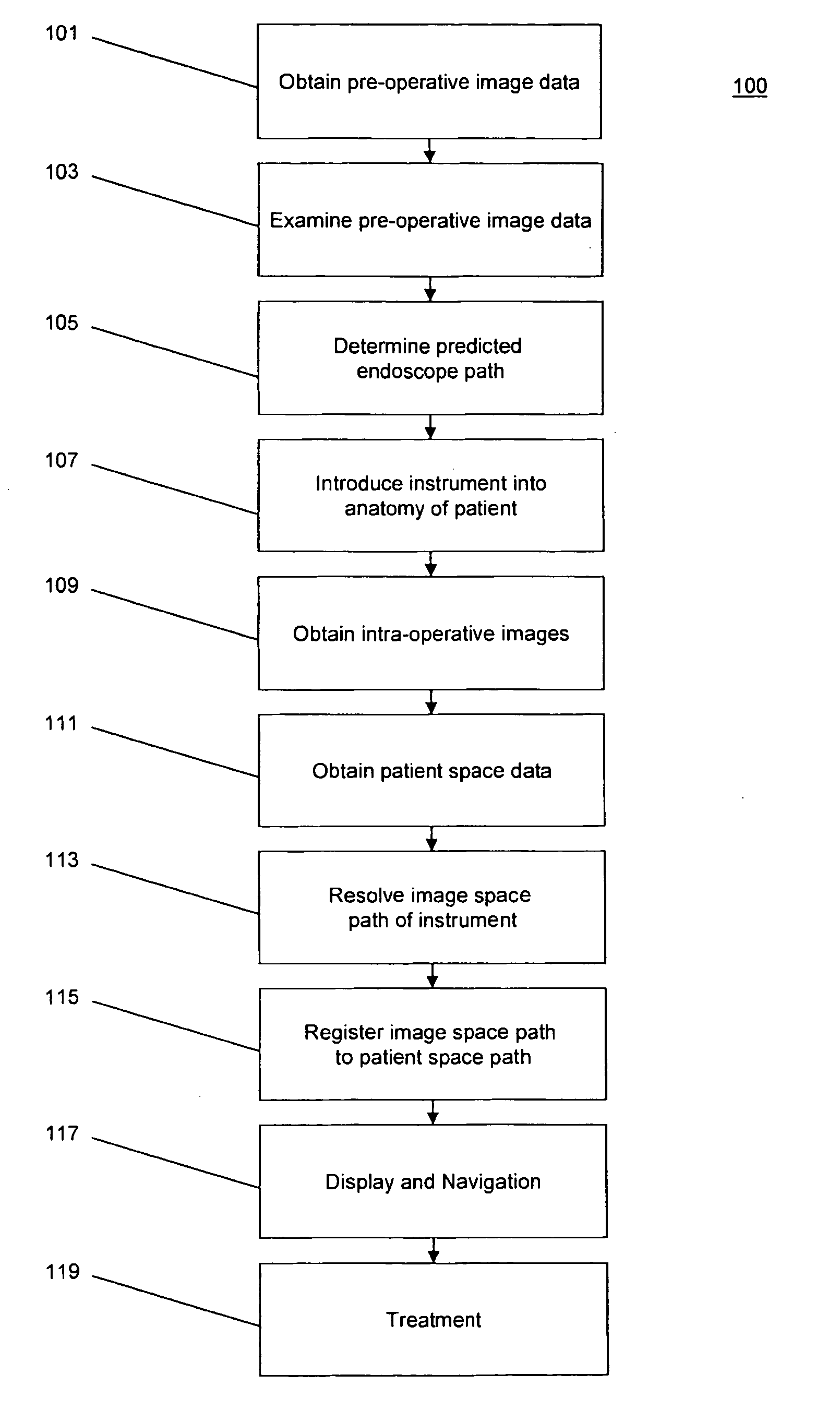
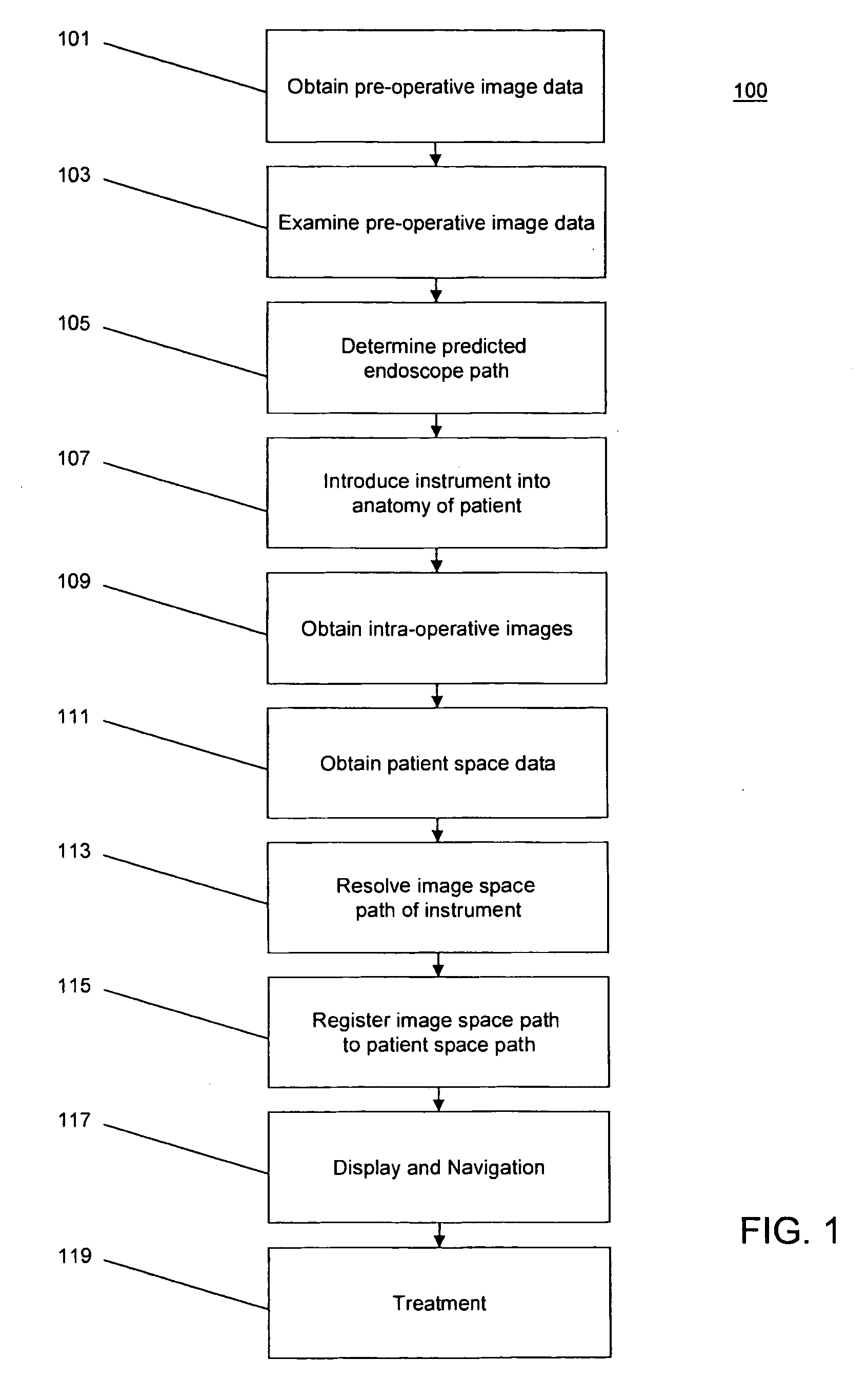
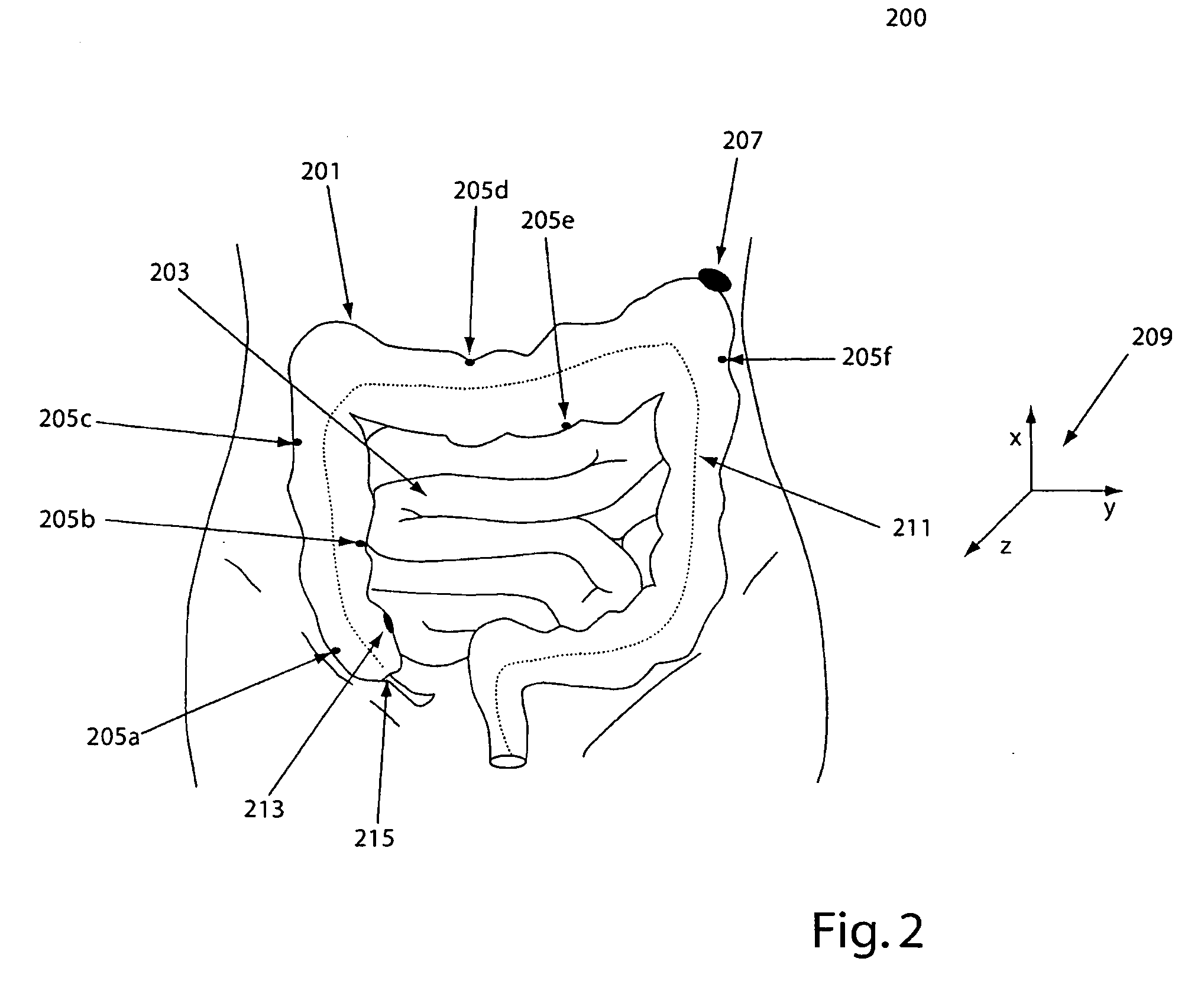
The invention provides a method and system for performing an image-guided endoscopic medical procedure. The invention may include registering image-space coordinates of a path of a medical instrument within the anatomy of a patient to patient-space coordinates of the path of the medical instrument within the anatomy of the patient. In some embodiments, the image space coordinates of the path of the medical instrument may be predicted coordinates such as, for example, a calculated centerline through a conduit-like organ, or a calculated “most likely path” of the medical instrument within the anatomy of the patient. In other embodiments, the path of the medical instrument may be an actual path determined using intra-operative images of the patient's anatomy with the medical instrument inserted therein. The registered instrument may then be navigated to one or more items of interest for performance of the endoscopic medical procedure.
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS LTD
Inertial Sensor Based Surgical Navigation System for Knee Replacement Surgery
ActiveUS20110275957A1Improve accuracyGood precisionSurgical navigation systemsPerson identificationKnee JointNavigation system
An inertial sensor based surgical navigation system for knee replacement surgery is disclosed. Inertial sensors composed of six-degree-of-freedom inertial chips, whose measurements are processed through a series of integration, quaternion, and kalman filter algorithms, are used to track the position and orientation of bones and surgical instruments. The system registers anatomically significant geometry, calculates joint centers and the mechanical axis of the knee, develops a visualization of the lower extremity that moves in real time, assists in the intra-operative planning of surgical cuts, determines the optimal cutting planes for cut guides and the optimal prosthesis position and orientation, and finally navigates the cut guides and the prosthesis to their optimal positions and orientations using a graphical user interface.
Owner:BHANDARI SACHIN
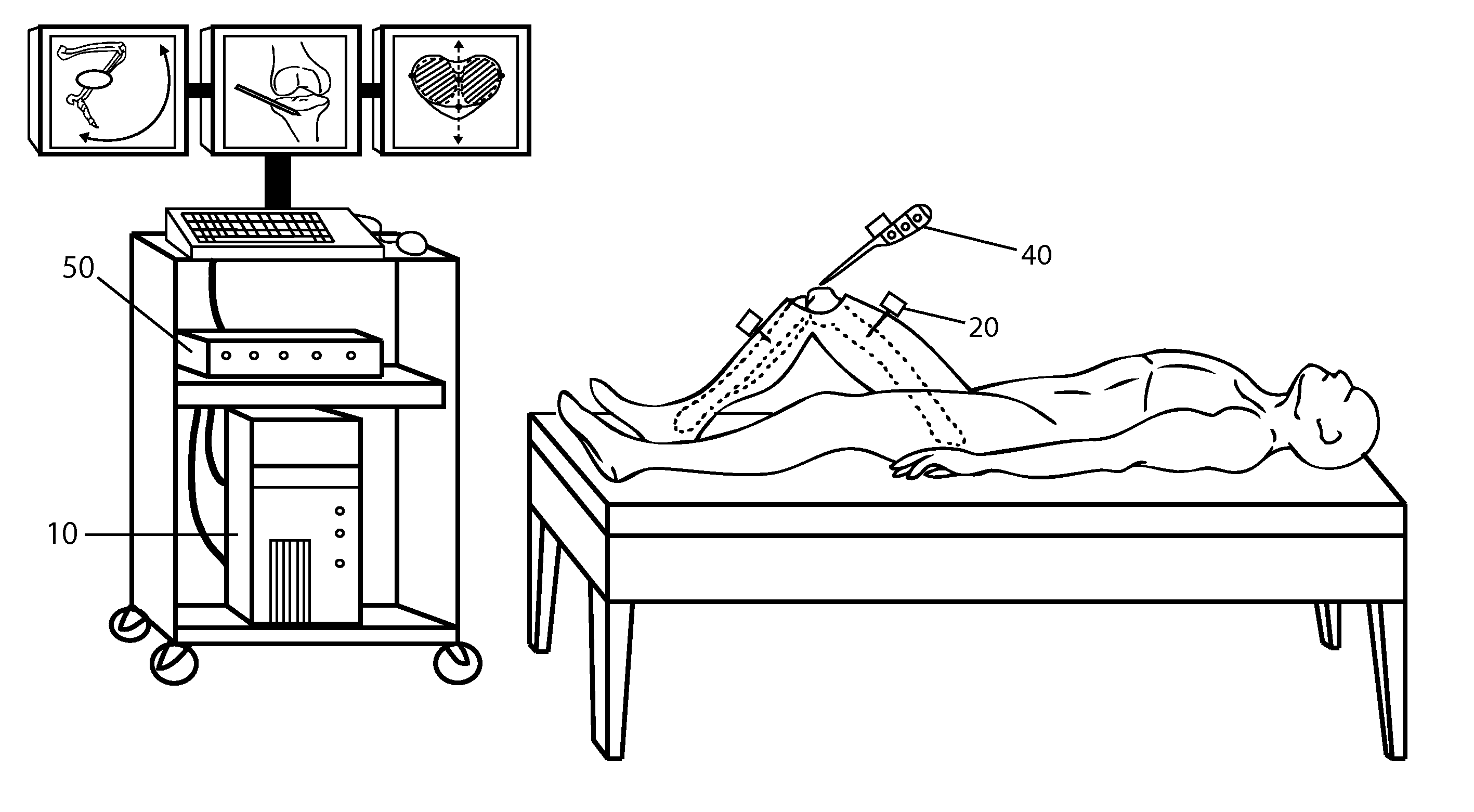
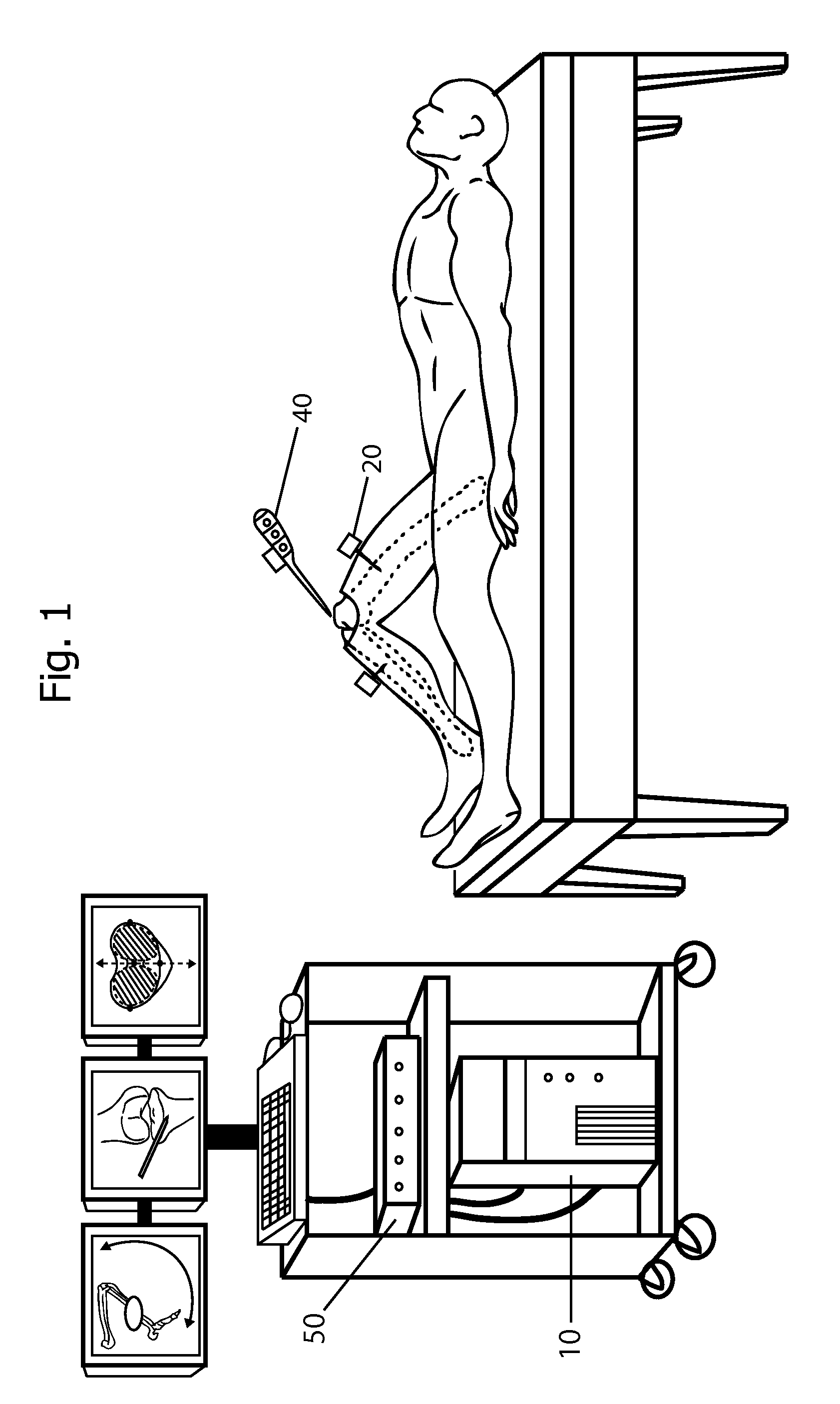
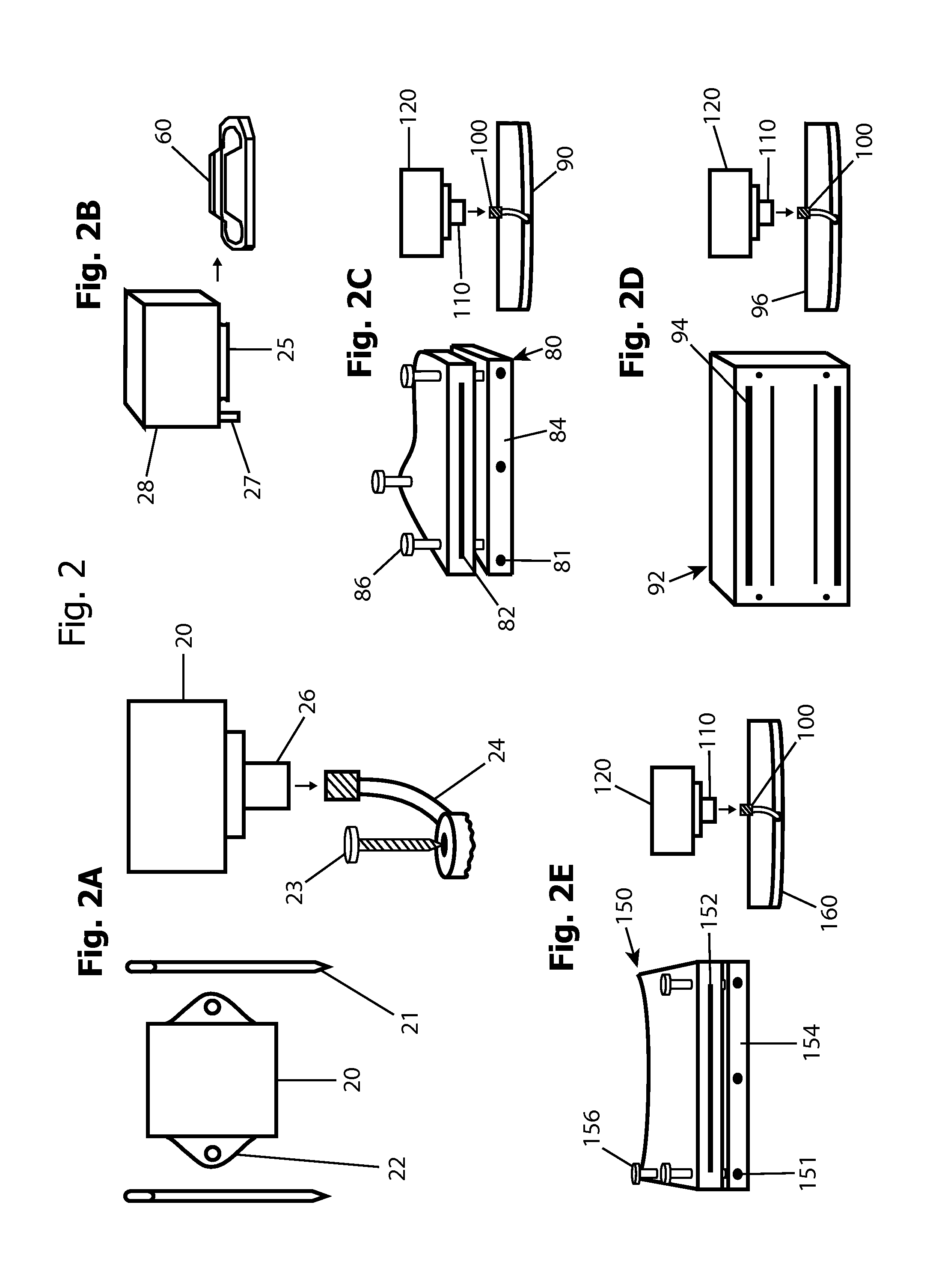
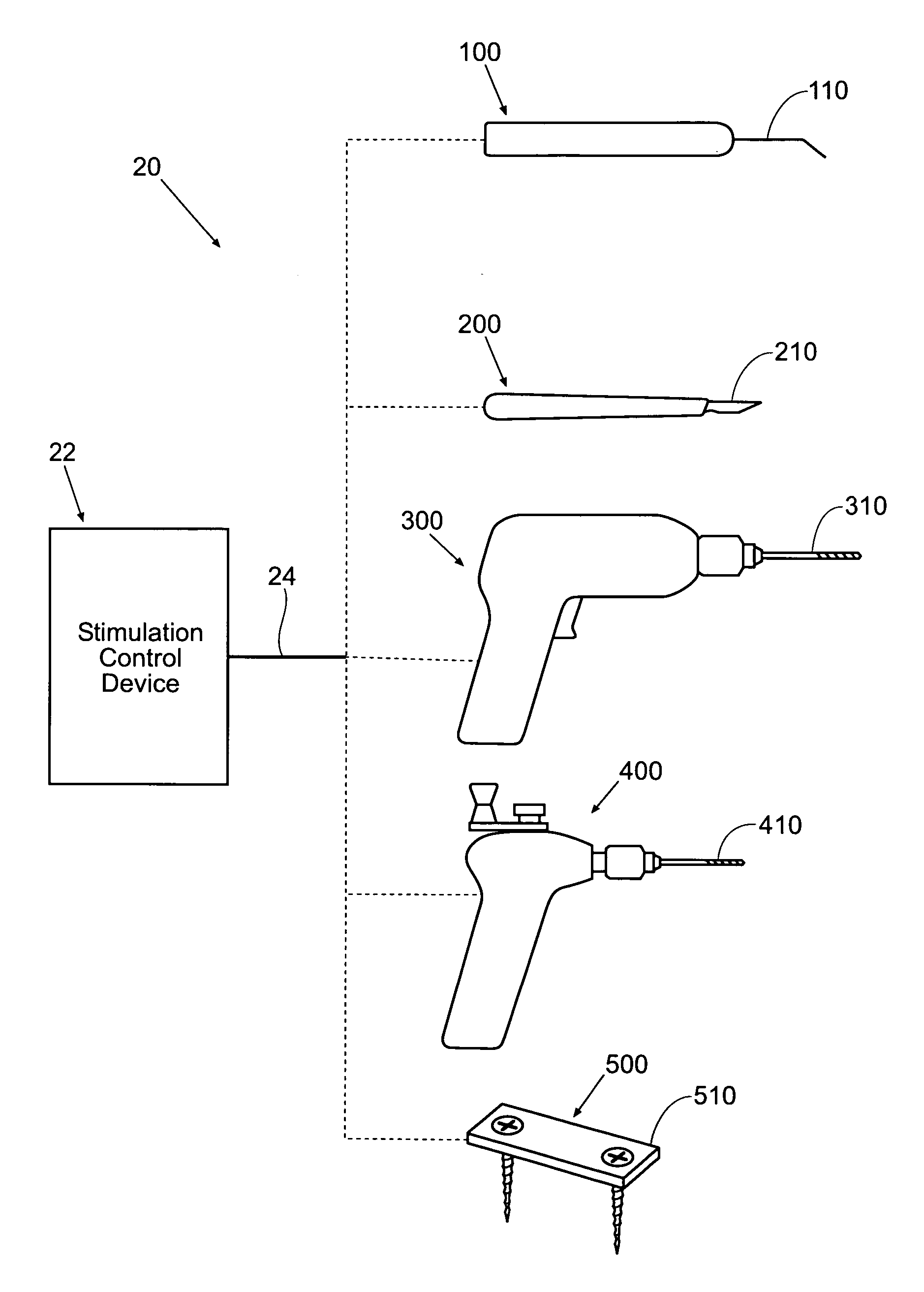
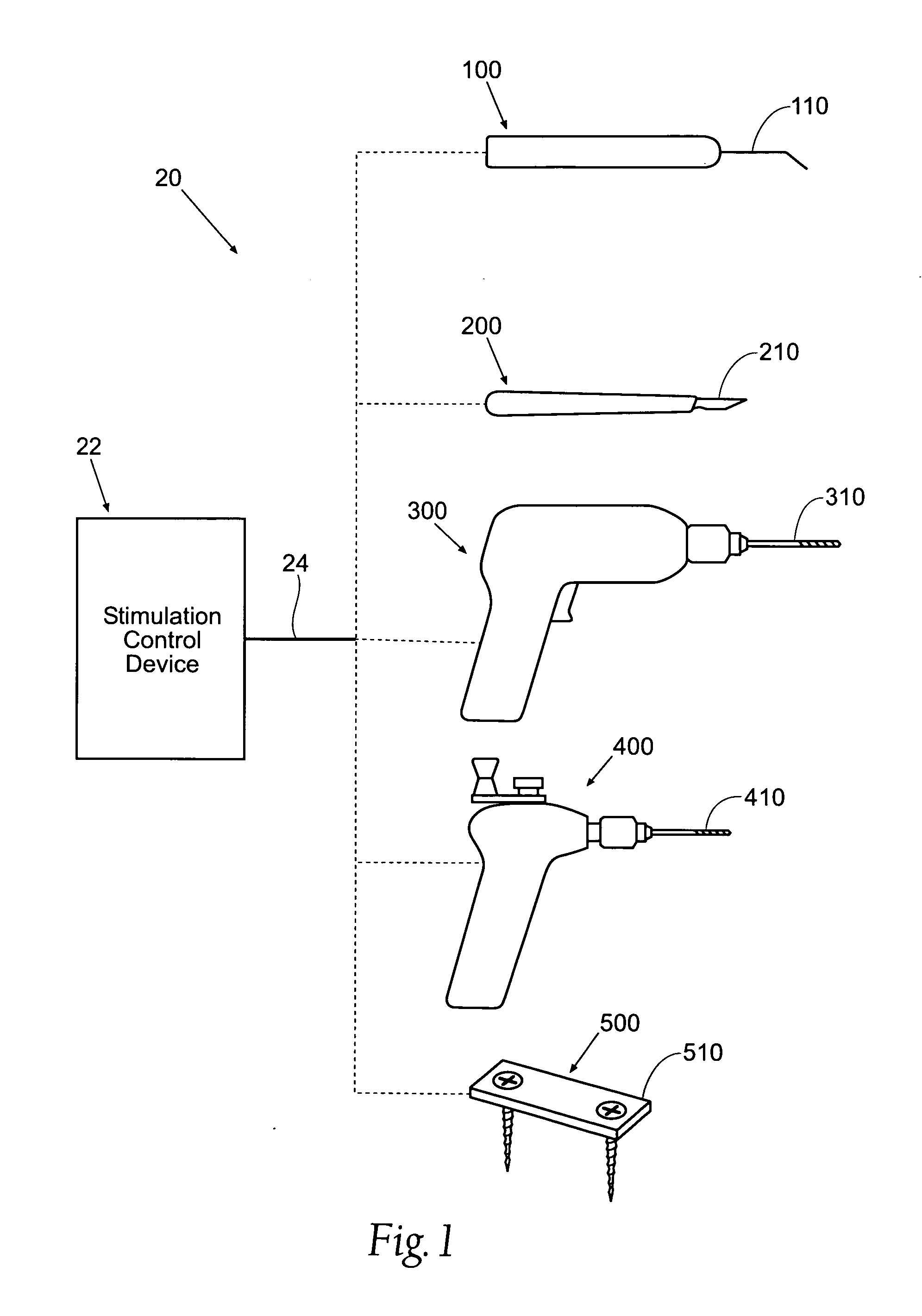
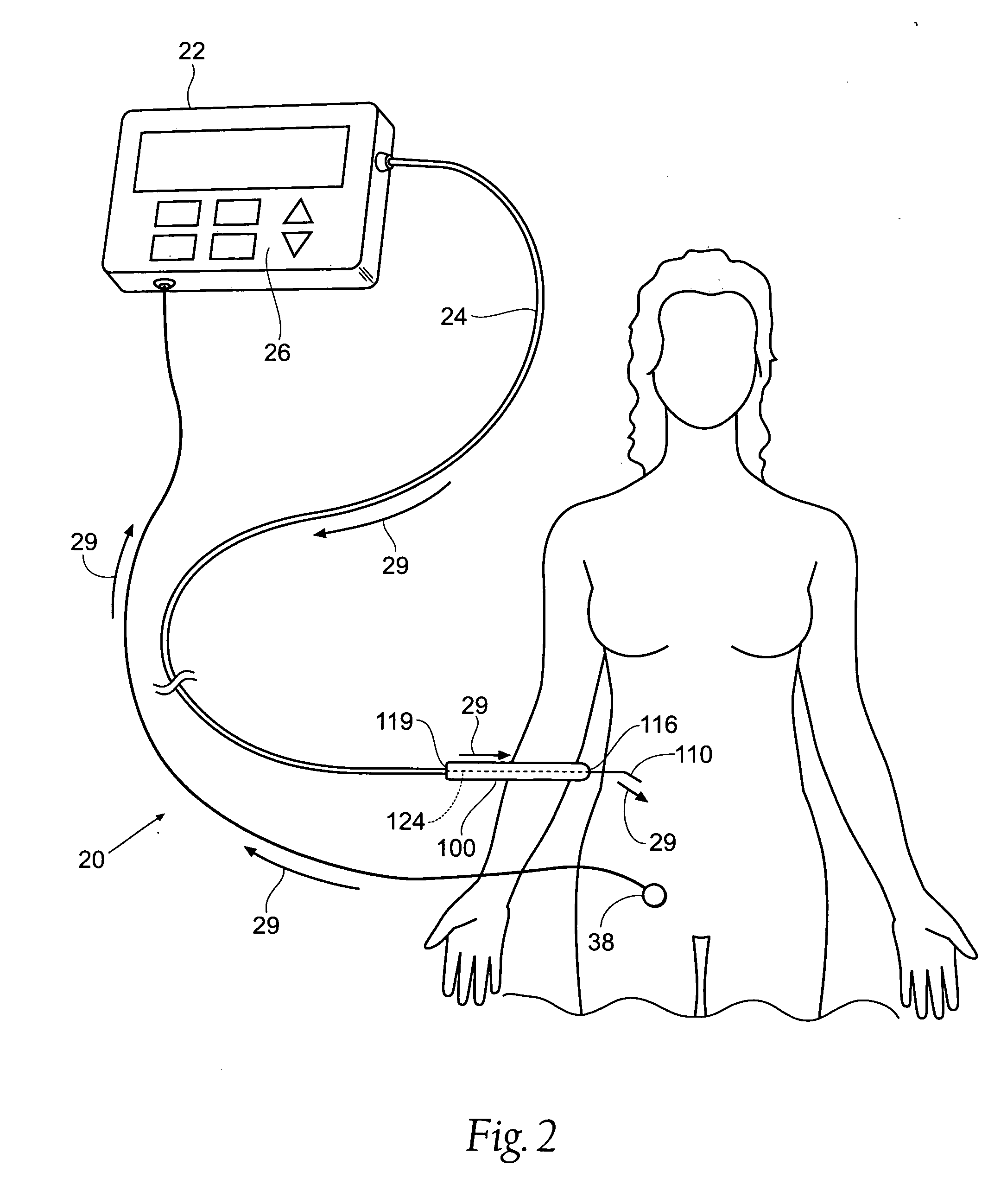
Systems and methods for intra-operative stimulation
ActiveUS20070191915A1Accurate assessmentAccurate selective stimulationElectrotherapySurgical instrument detailsMuscle contractionRange of motion
Improved assemblies, systems, and methods provide safeguarding against tissue injury during surgical procedures and / or identify nerve damage occurring prior to surgery and / or verify range of motion or attributes of muscle contraction during reconstructive surgery. A stimulation control device may incorporate a range of low and high intensity stimulation to provide a stimulation and evaluation of both nerves and muscles. A stimulation control device is removably coupled to a surgical device or is imbedded within the medical device to provide a stimulation and treatment medical device. A disposable hand held stimulation system includes an operative element extending from the housing, the housing includes an operative element adjustment portion and a visual indication to provide feedback or status to the user.
Owner:CHECKPOINT SURGICAL
Apparatus and methods of compensating for organ deformation, registration of internal structures to images, and applications of same
ActiveUS20080123927A1Cost-effectiveWeight increaseImage enhancementImage analysisBiological bodyMedicine
A method and system of compensation for intra-operative organ shift of a living subject usable in image guide surgery. In one embodiment, the method includes the steps of generating a first geometric surface of the organ of the living subject from intra-operatively acquired images of the organ of the living subject, constructing an atlas of organ deformations of the living subject from pre-operatively acquired organ images from the pre-operatively acquired organ images, generating a second geometric surface of the organ from the atlas of organ deformations, aligning the second geometric surface of the organ to the first geometric surface of the organ of the living subject to determine at least one difference between a point of the first geometric surface and a corresponding point of the second geometric surface of the organ of the living subject, which is related to organ shift, and compensating for the intra-operative organ shift.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
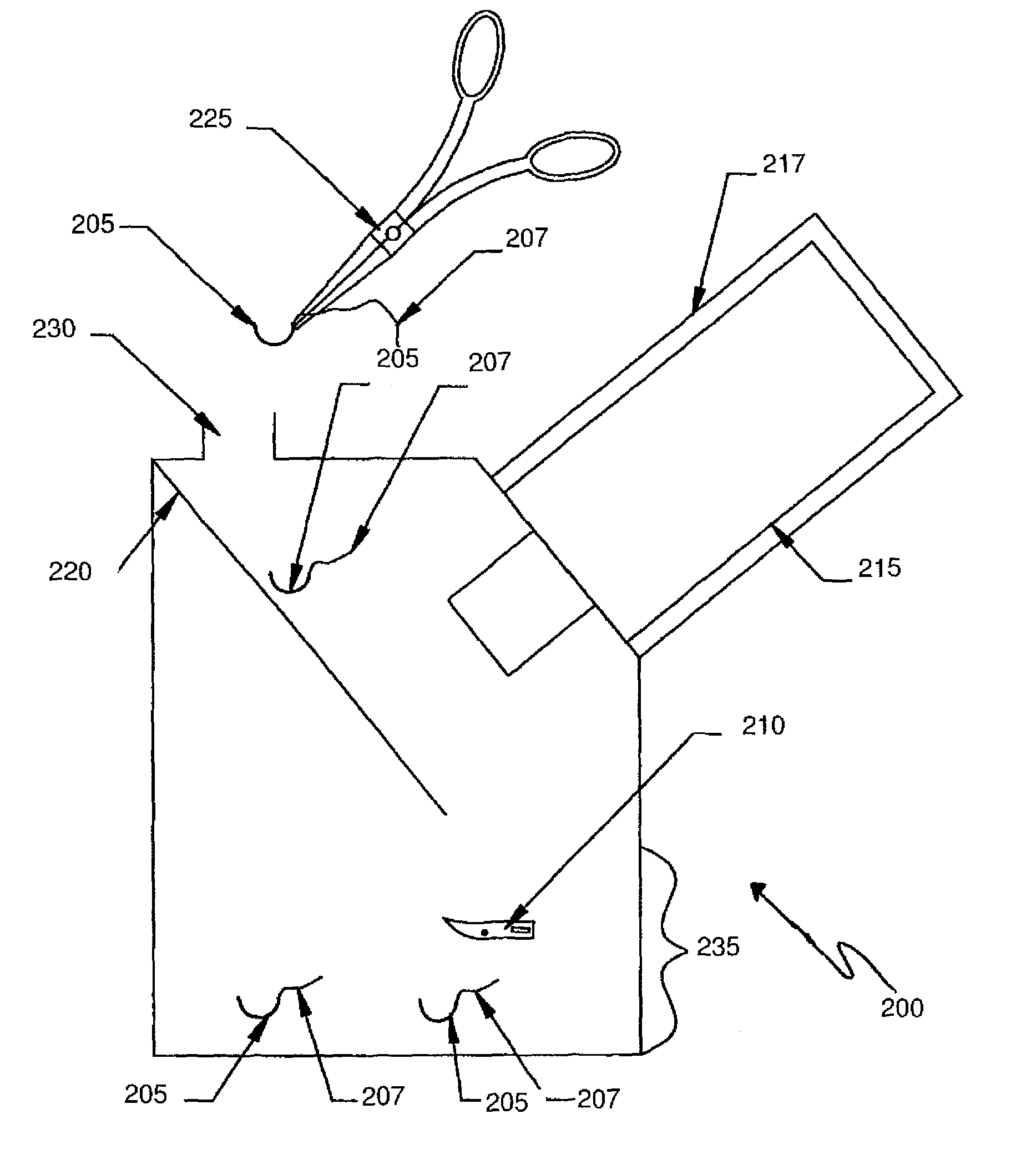
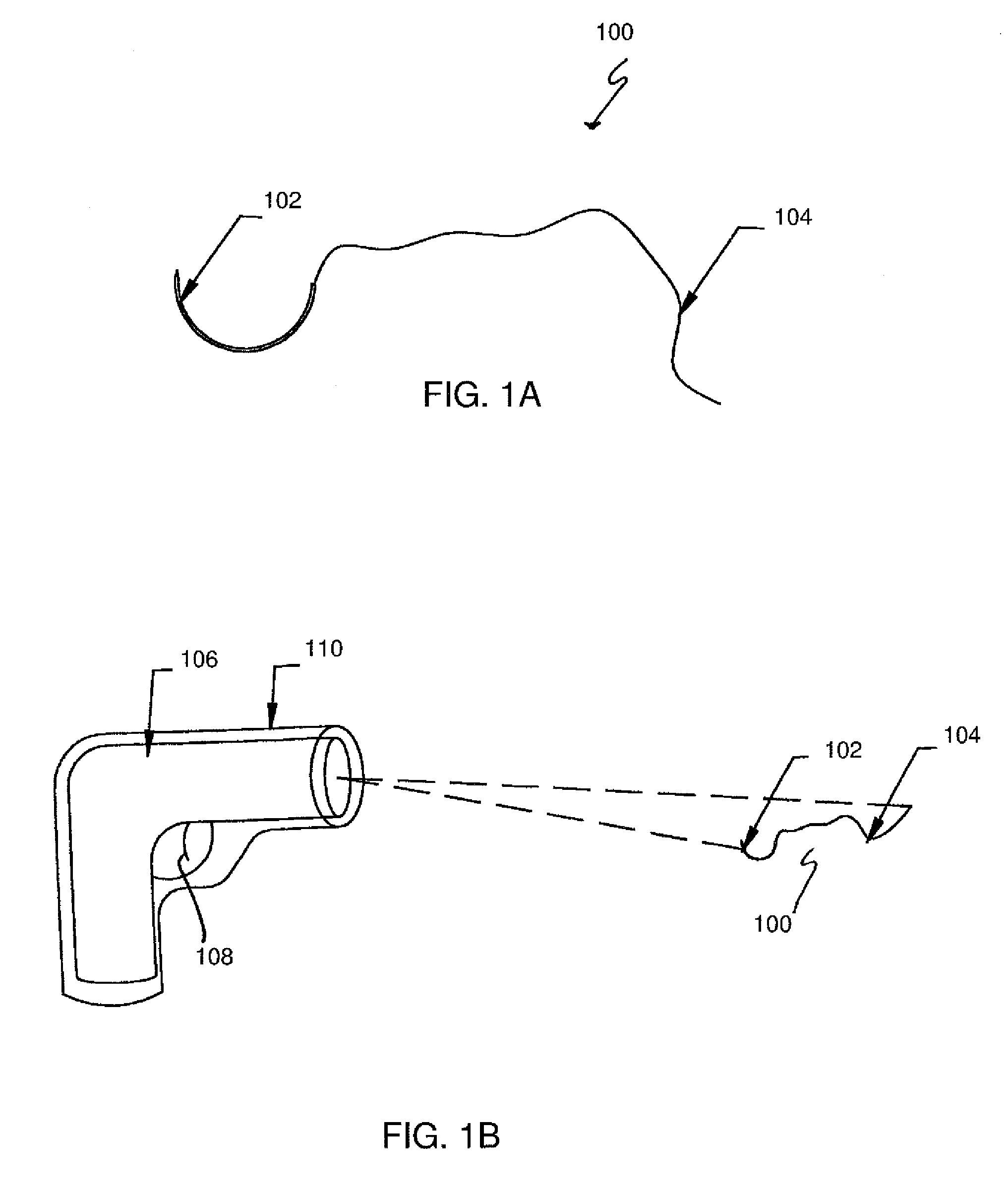
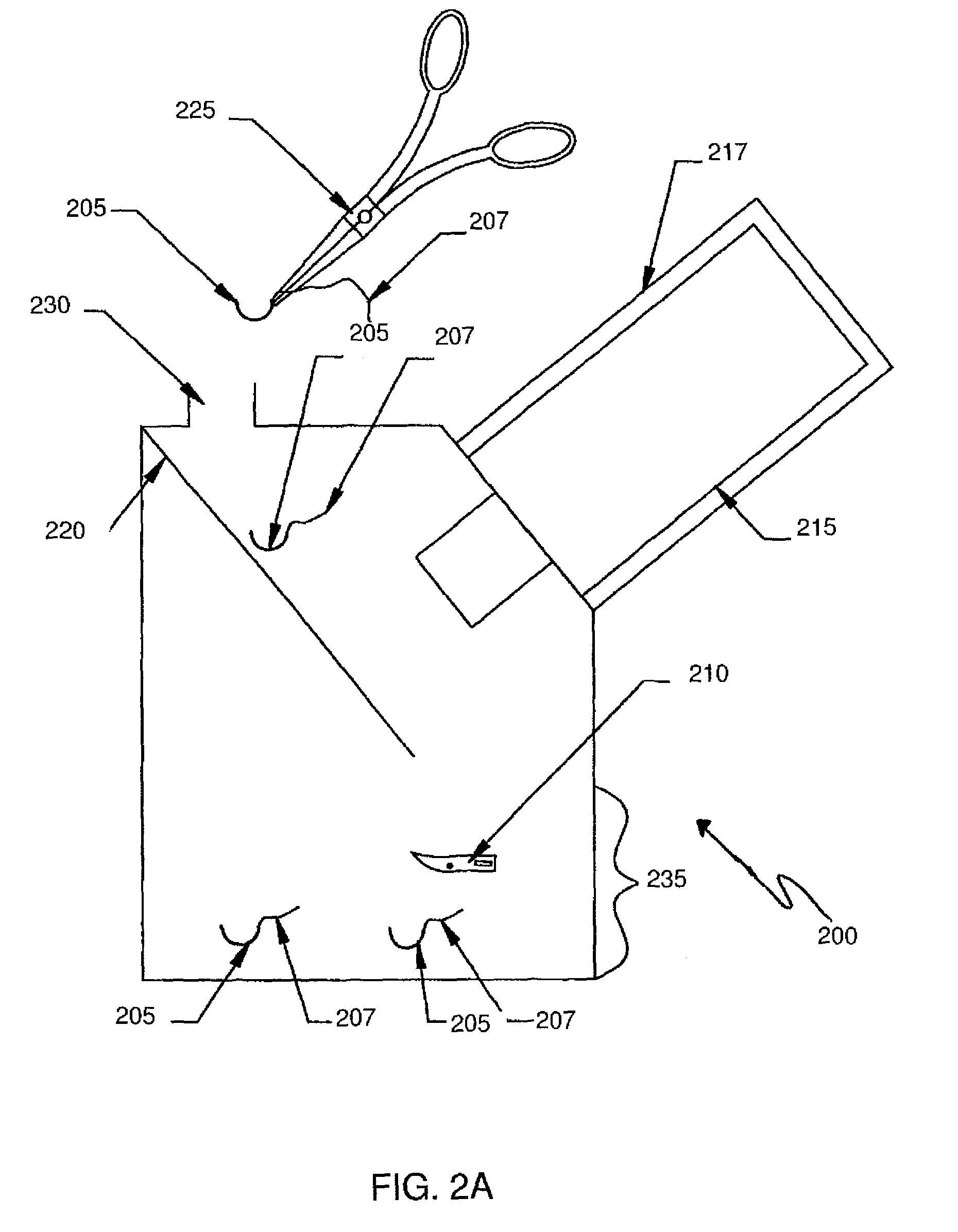
Intra-operative system for identifying and tracking surgical sharp objects, instruments, and sponges
Intra-operative systems for identifying surgical sharp objects are provided. Aspects of the systems include an intra-operative imaging device for obtaining intra-operative surgical sharp object image data; and a surgical sharp object automated shape recognition module configured to identify a surgical sharp object from intra-operative surgical sharp object image data. Systems of the invention may further include additional components, such as surgical instrument and / or sponge identification and tracking devices. Systems of the invention find use in a variety of methods and applications, including tracking of surgical items during a surgical procedure.
Owner:DEIN JOHN RICHARD
System, method and devices for navigated flexible endoscopy
The invention provides a method and system for performing an image-guided endoscopic medical procedure. The invention may include registering image-space coordinates of a path of a medical instrument within the anatomy of a patient to patient-space coordinates of the path of the medical instrument within the anatomy of the patient. In some embodiments, the image space coordinates of the path of the medical instrument may be predicted coordinates such as, for example, a calculated centerline through a conduit-like organ, or a calculated “most likely path” of the medical instrument within the anatomy of the patient. In other embodiments, the path of the medical instrument may be an actual path determined using intra-operative images of the patient's anatomy with the medical instrument inserted therein. The registered instrument may then be navigated to one or more items of interest for performance of the endoscopic medical procedure.
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS LTD
Apparatus and methods of compensating for organ deformation, registration of internal structures to images, and applications of same
A method and system of compensation for intra-operative organ shift of a living subject usable in image guide surgery. In one embodiment, the method includes the steps of generating a first geometric surface of the organ of the living subject from intra-operatively acquired images of the organ of the living subject, constructing an atlas of organ deformations of the living subject from pre-operatively acquired organ images from the pre-operatively acquired organ images, generating a second geometric surface of the organ from the atlas of organ deformations, aligning the second geometric surface of the organ to the first geometric surface of the organ of the living subject to determine at least one difference between a point of the first geometric surface and a corresponding point of the second geometric surface of the organ of the living subject, which is related to organ shift, and compensating for the intra-operative organ shift.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Systems and methods for intra-operative pelvic registration
A system for intra-operatively registering a pelvis comprising an acetabulum with a computer model of the pelvis in a coordinate system. The system may include: a) a surgical navigation system including a tracking device; and b) at least one computing device in communication with the surgical navigation system. The at least one computing device: i) receiving first data points from first intra-operatively collected points on an articular surface of the acetabulum, the first data points collected with the tracking device; ii) receiving a second data point from a second intra-operatively collected point on the pelvis, the second data point collected with the tracking device, the second data point corresponding in location to a second virtual data point on the computer model; and iii) determining an intra-operative center of rotation of the femur relative to the pelvis from the first data points.
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
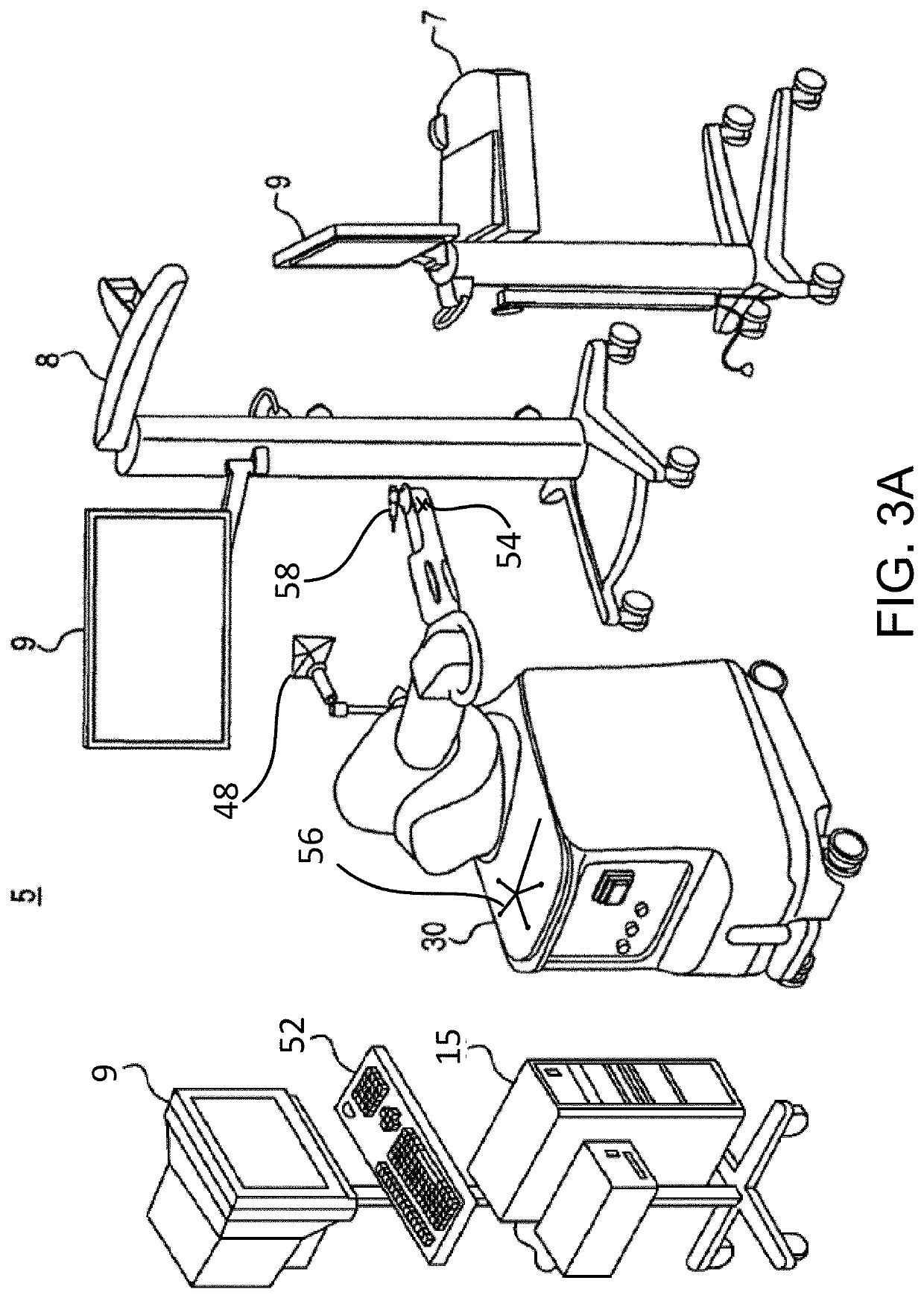
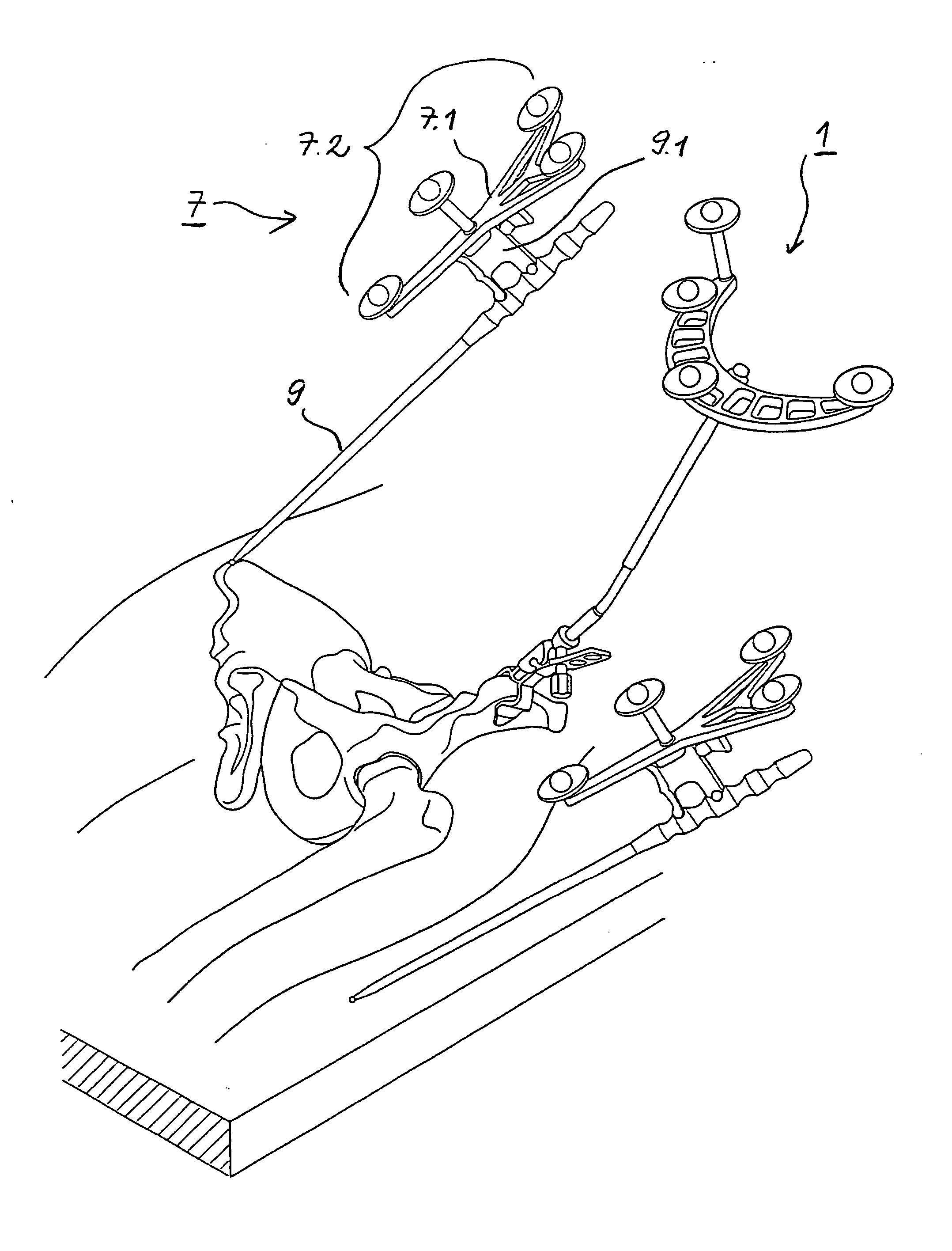
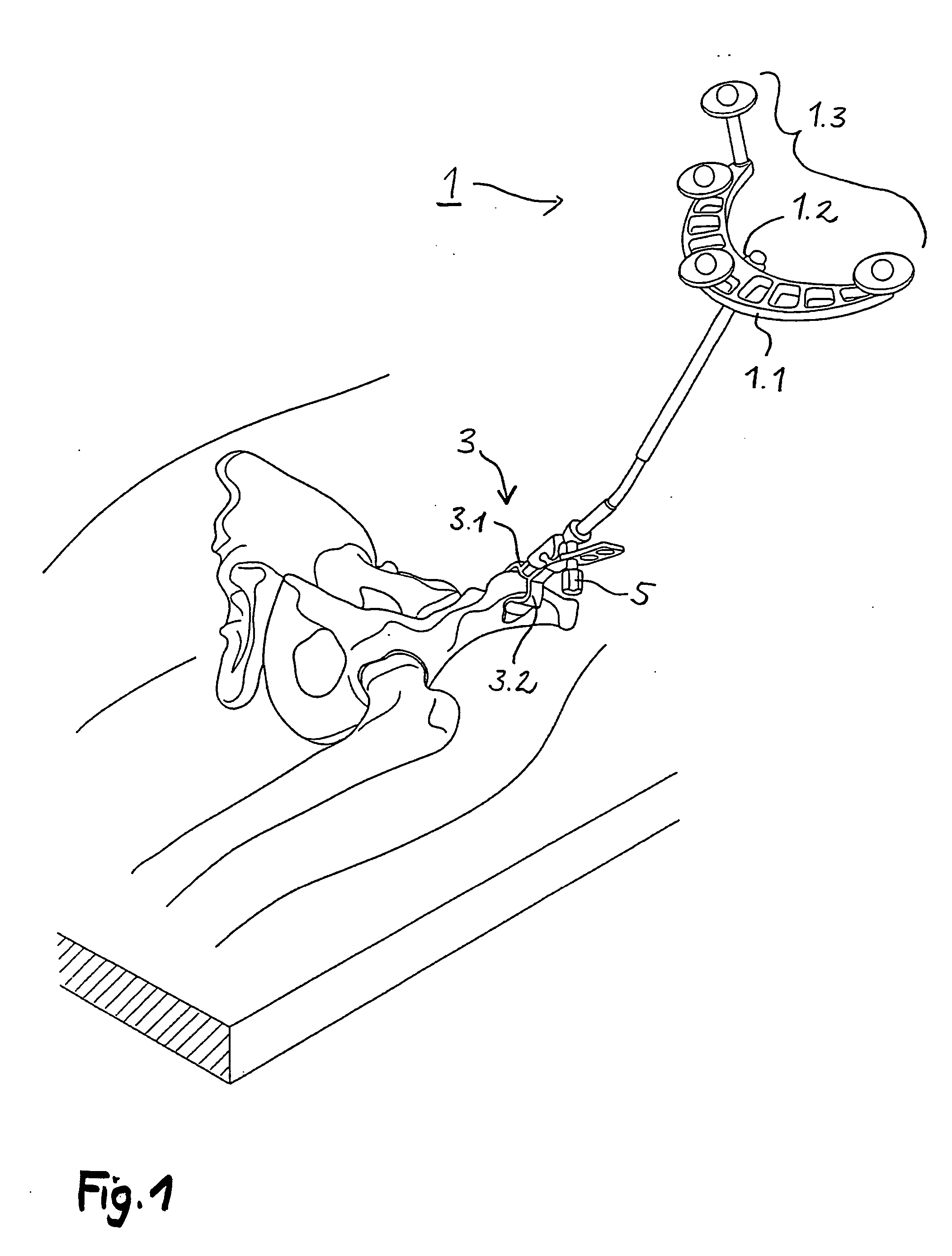
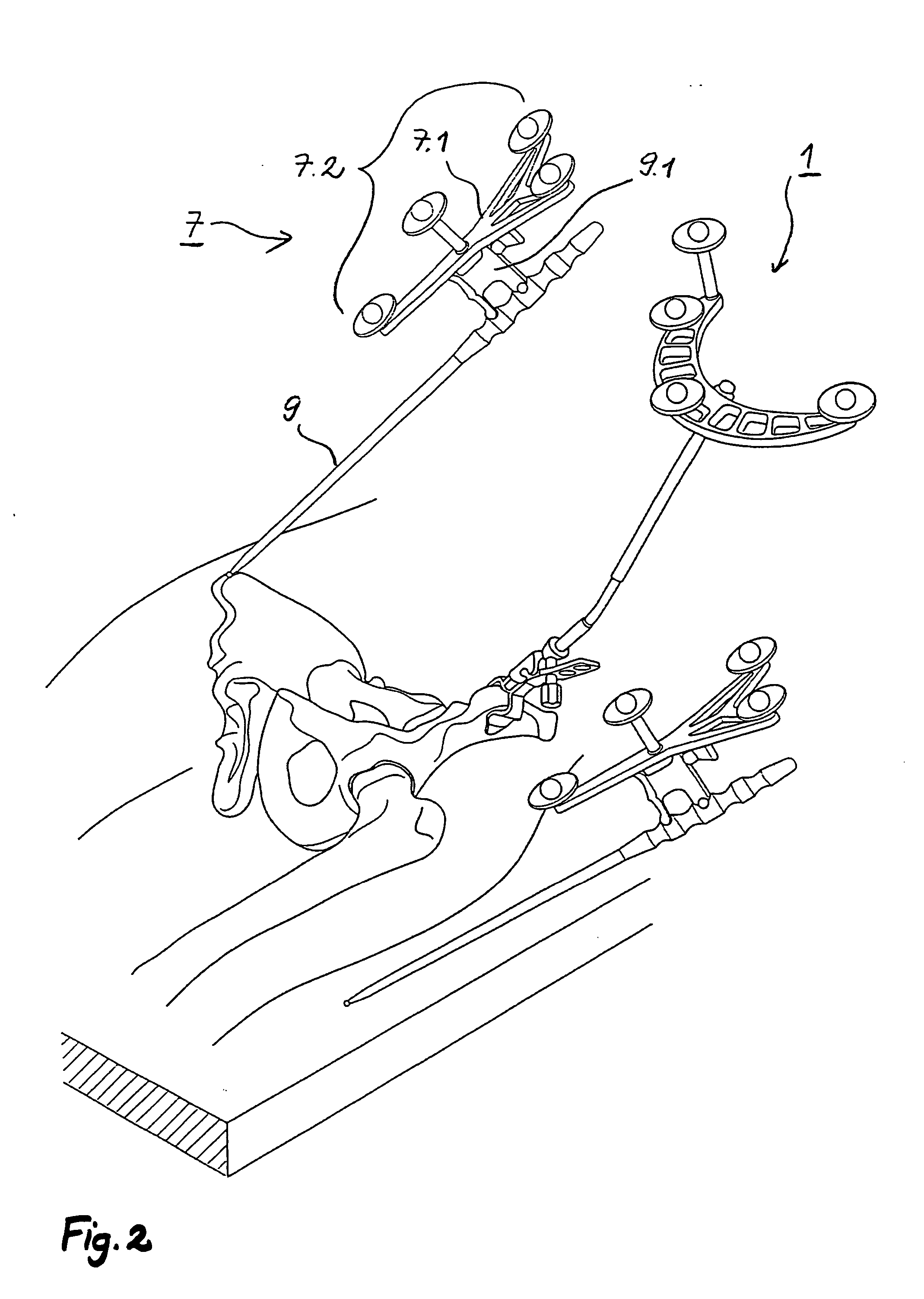
Image Guided Intra-Operative Contouring Aid
A method of contouring spinal rods, and systems therefor. The surgeon uses image guided surgery instruments to identify the locations of the screw heads through which the rod will pass. These locations allow a computer to form a best fit line that corresponds to the shape of a rod that can pass through the screw heads. This best fit line is then displayed on a projection table from both its coronal and sagittal views. The surgeon then shapes the rod using these 2-D images as a template.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Arrangement and method for the intra-operative determination of the position of a joint replacement implant
InactiveUS20050149050A1Easy to operateLow risk of errorPerson identificationJoint implantsReference vectorMeasurement point
Arrangement for the intra-operative determination of the spatial position and angular position of a joint replacement implant, especially a hip socket or shoulder socket or an associated stem implant, or a vertebral replacement implant, especially a lumbar or cervical vertebral implant, using a computer tomography method, having: a computer tomography modeling device for generating and storing a three-dimensional image of a joint region or vertebral region to be provided with the joint replacement implant, an optical coordinate-measuring arrangement for providing real position coordinates of defined real or virtual points of the joint region or vertebral region and / or position reference vectors between such points within the joint region or vertebral region or from those points to joint-function-relevant points on an extremity outside the joint region or vertebral region, the coordinate-measuring arrangement comprising a stereocamera or stereocamera arrangement for the spatial recording of transducer signals, at least one multipoint transducer, which comprises a group of measurement points rigidly connected to one another, and an evaluation unit for evaluating sets of measurement point coordinates supplied by the multipoint transducer(s) and recorded by the stereocamera, and a matching-processing unit for real position matching of the image to the actual current spatial position of the joint region or vertebral region with reference to the real position coordinates of the defined points, the matching-processing unit being configured for calculating transformation parameters with minimalization of the normal spacings.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Robot for use with orthopaedic inserts
ActiveUS20060098851A1Simple and safe processReduce the possibilityProgramme controlInternal osteosythesisX-rayTrial and error
A robot-guided system to assist orthopaedic surgeons in performing orthopaedic surgical procedures on pre-positioned inserts, including for the fixation of bone fractures, and especially for use in long bone distal intramedullary locking procedures. The system provides a mechanical guide for drilling the holes for distal screws in intramedullary nailing surgery. The drill guide is automatically positioned by the robot relative to the distal locking nail holes, using data derived from only a small number of X-ray fluoroscopic images. The system allows the performance of the locking procedure without trial and error, thus enabling the procedure to be successfully performed by less experienced surgeons, reduces exposure of patient and operating room personnel to radiation, shortens the intra-operative time, and thus reduces post-operative complications.
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
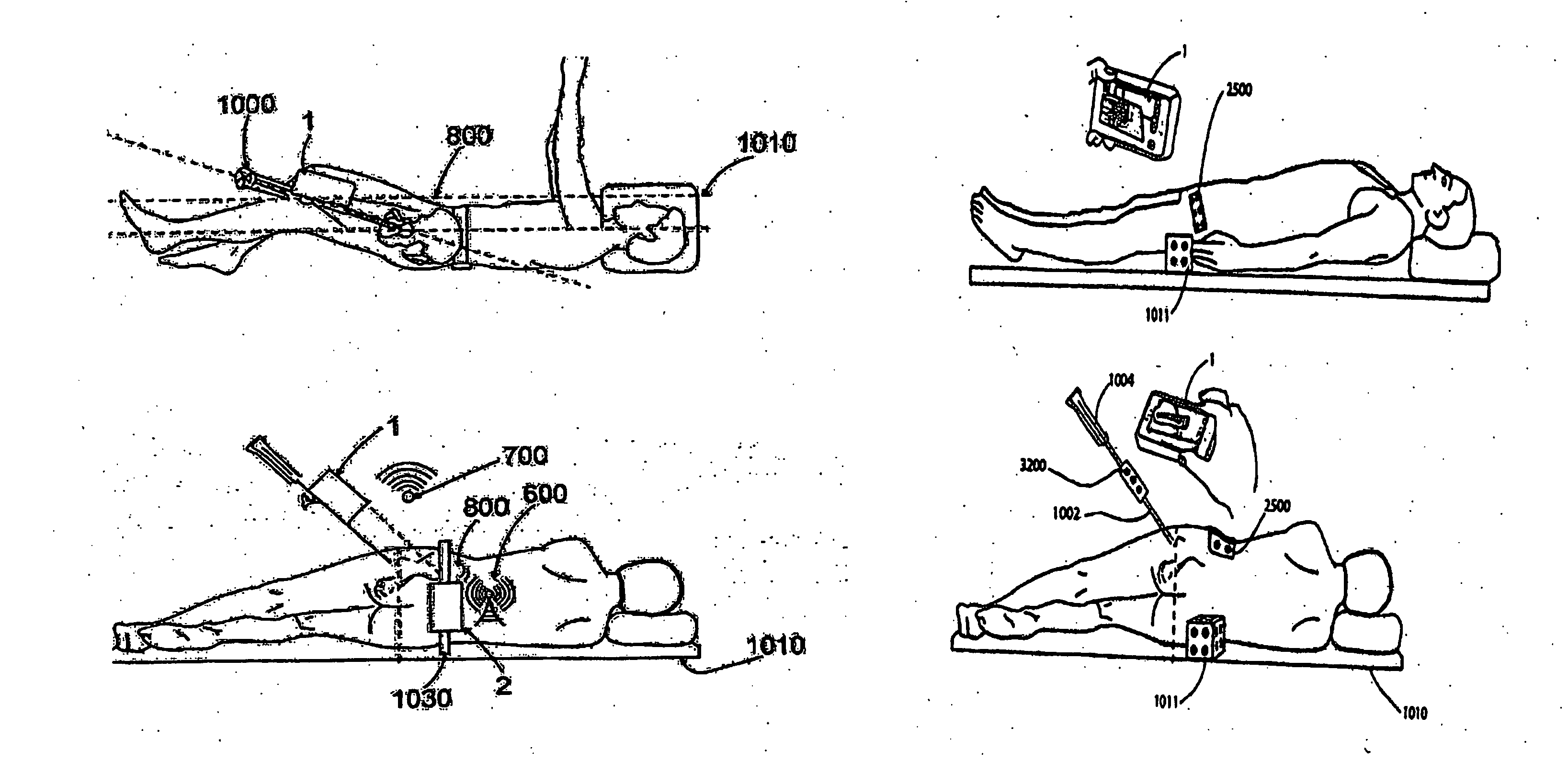
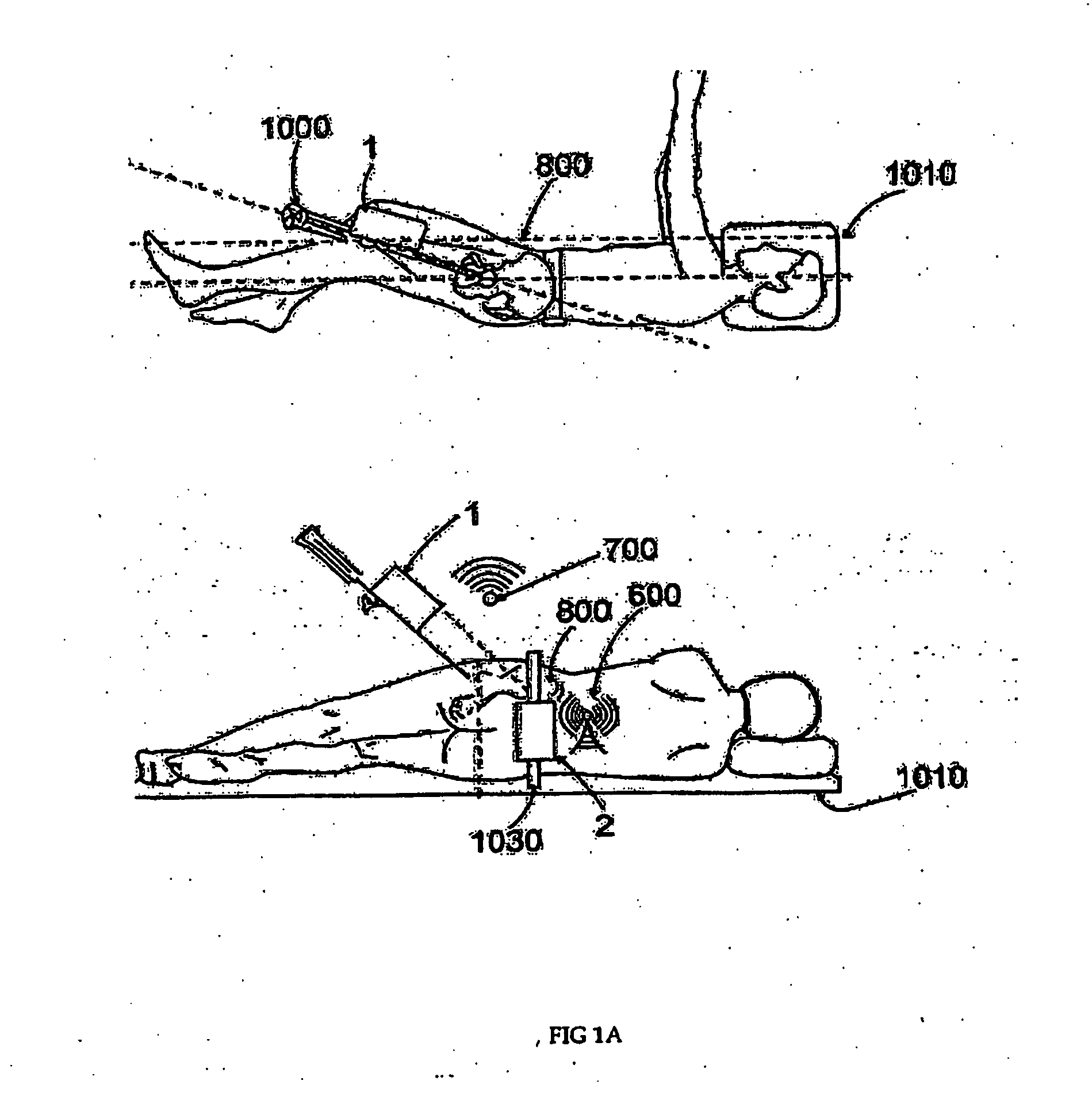
Handheld tracking system and devices for aligning implant systems during surgery
InactiveUS20150133945A1Accurate placementPrevent any length discrepancy in leg lengthSurgical navigation systemsJoint implantsSterile environmentScheie operation
The present invention discloses handheld tracking systems and devices comprising of at least one handheld tracking device for intra-operative aligning or positioning of surgical implant systems and instruments with reference to the anatomy of a patient. The handheld tracking system further comprises of at least one trackable element. The handheld device is mounted at the proposed implantation site using the holding means while trackable element(s) is / are mounted at predetermined location(s) such that data from said deployed trackable element(s) relating to the position of the patient and the surgical instruments are input continuously into the handheld devices. The handheld device then processes the data on the basis of pre-loaded preoperative scanned images in the processing means to monitor the accurate placement of said implant system onsite in sterile environment.
Owner:STRYKER GLOBAL TECH CENT
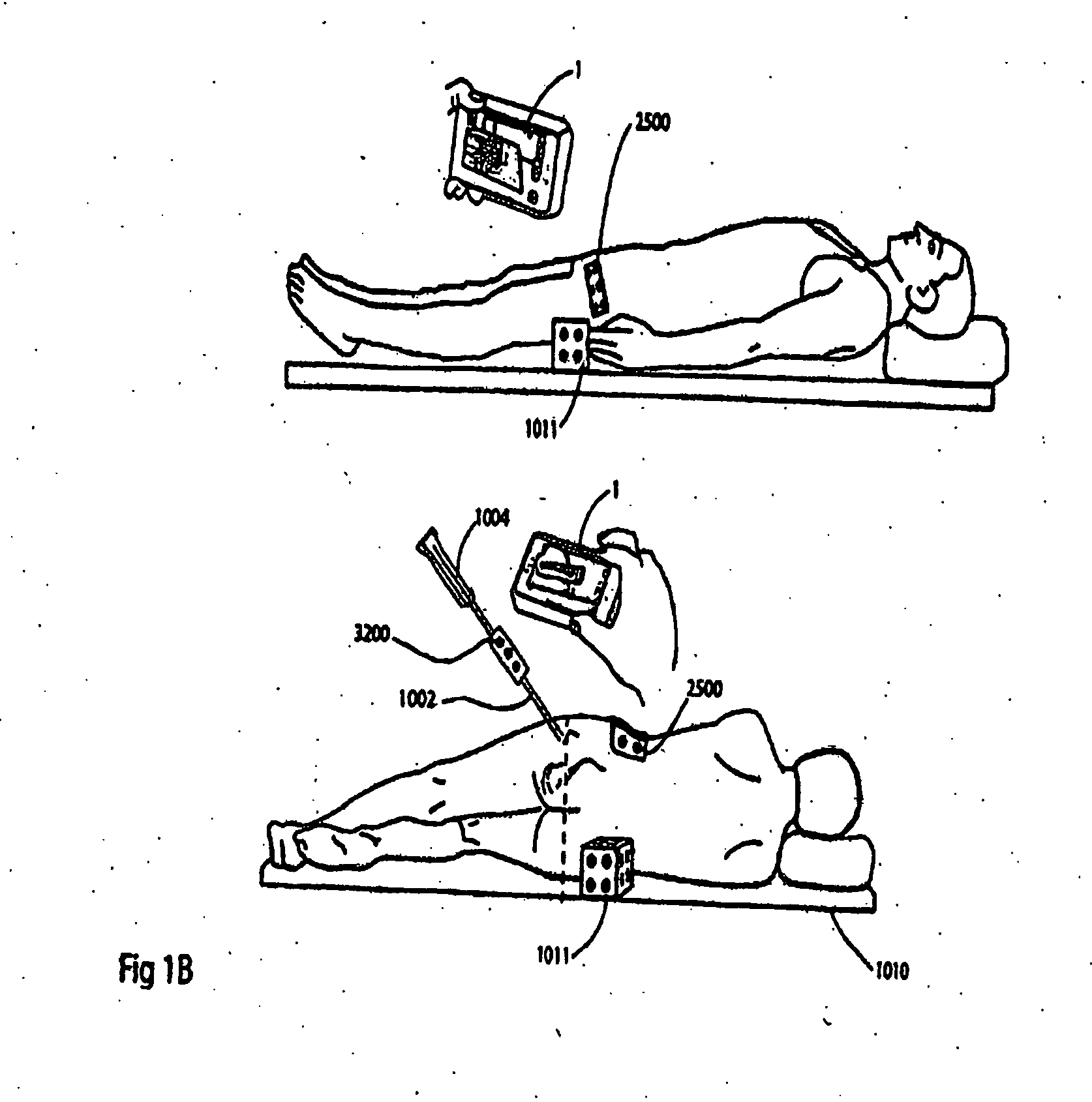
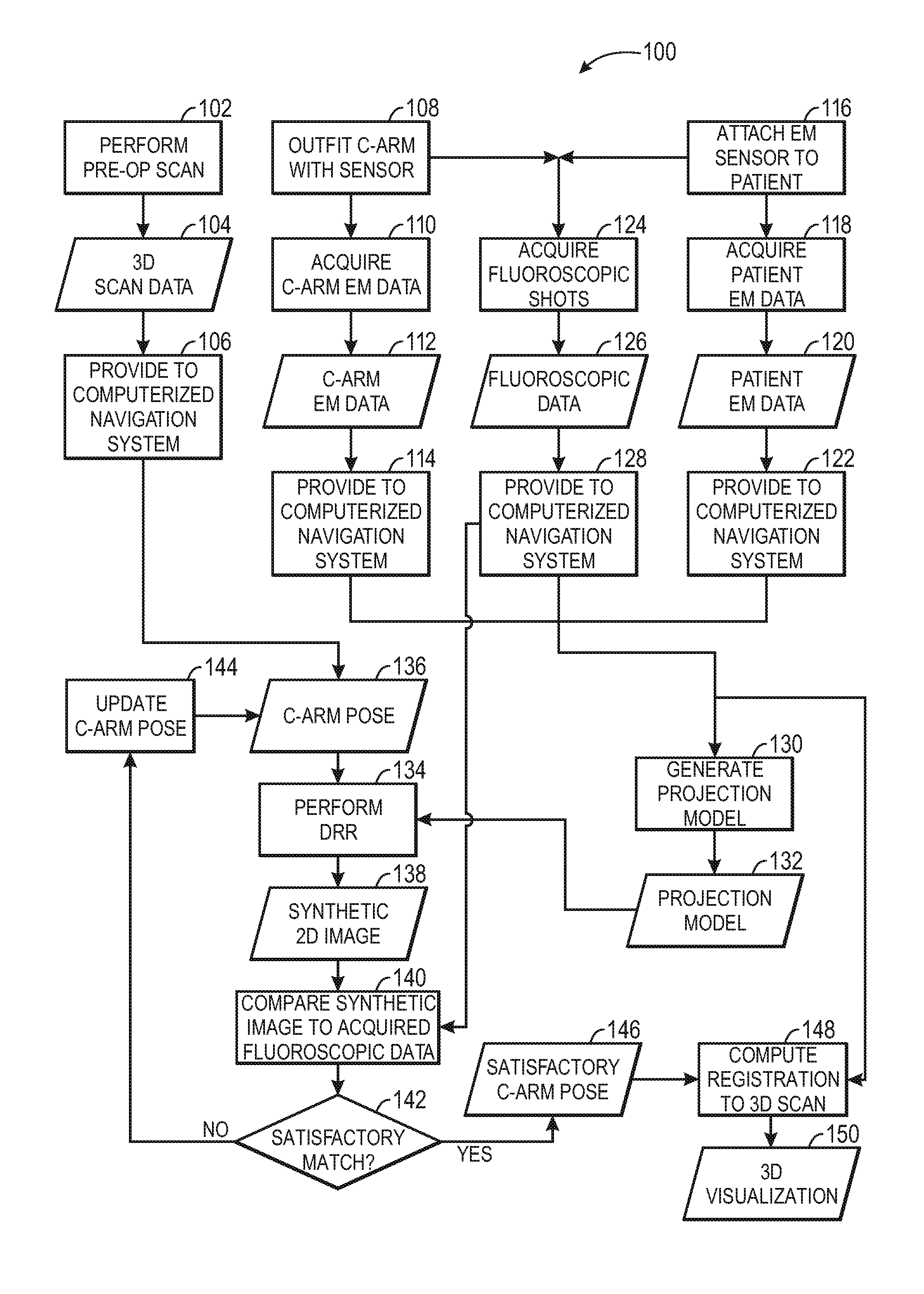
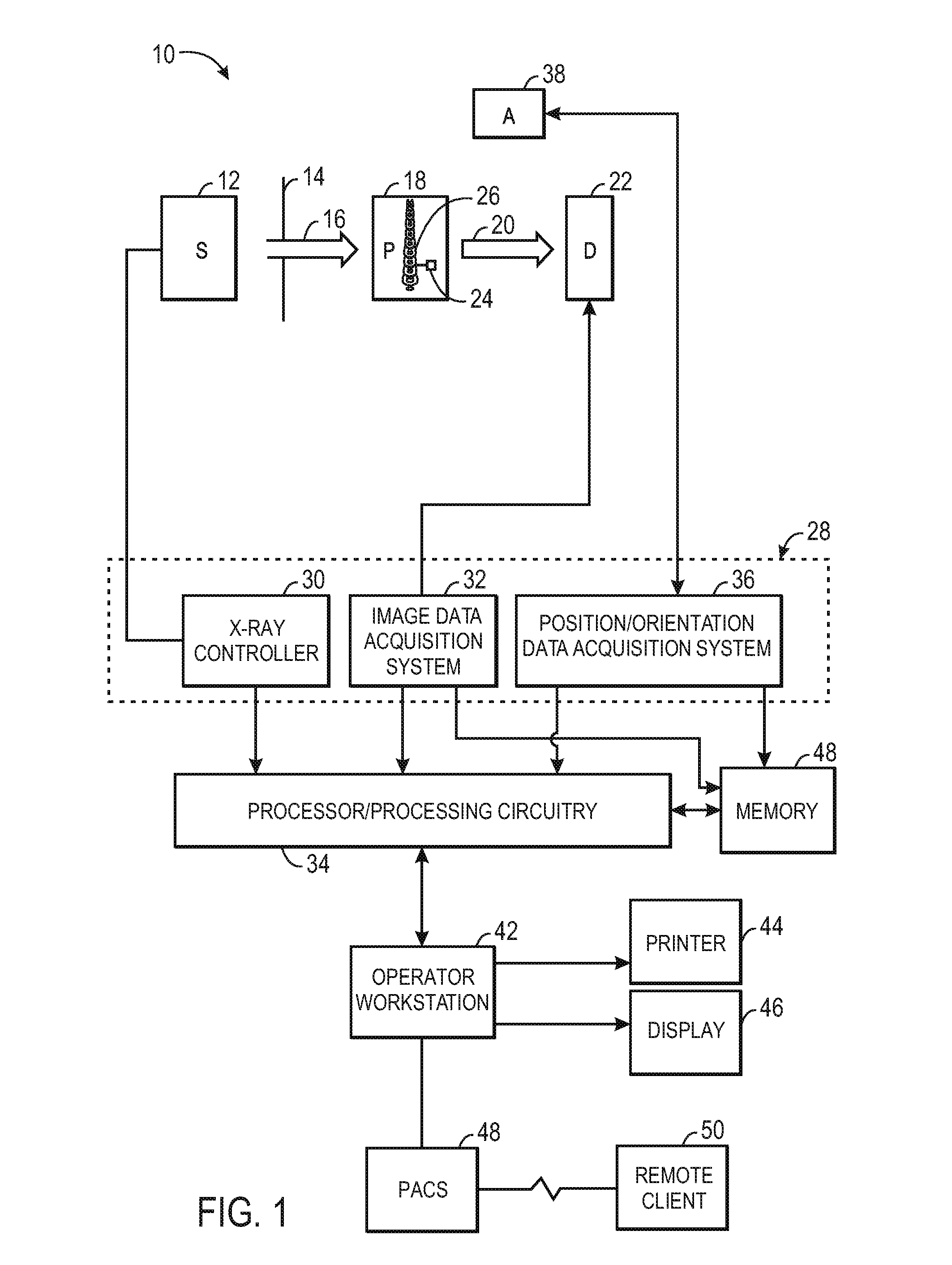
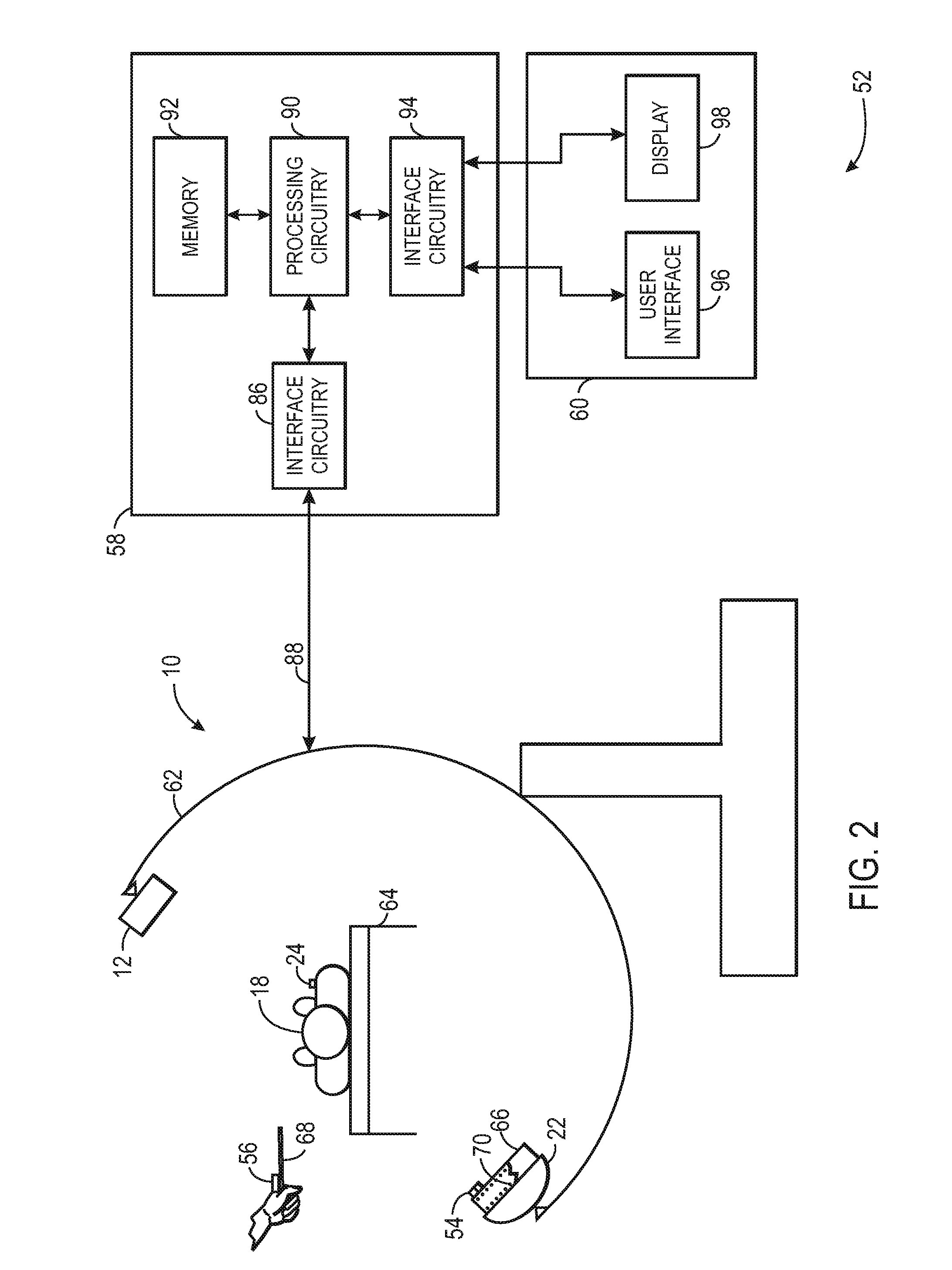
Intra-operative registration for navigated surgical procedures
ActiveUS8694075B2Surgical navigation systemsCharacter and pattern recognition3d imagePatient registration
A navigation system for use during a surgical procedure is provided. The navigation system is configured to use electromagnetic tracking data produced by electromagnetic tracking devices and 2D image data produced by a fluoroscope to intra-operatively register 2D images of a patient to a pre-operative 3D image of the patient. In some implementations, a surgeon may be able to perform an interventional or surgical procedure guided by the navigation system.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for performing intra-operative angiography
InactiveUS6915154B1Accurately determine extentSensorsBlood flow measurementAfter treatmentAv fistulas
Method for assessing the patency of a patient's blood vessel, advantageously during or after treatment of that vessel by an invasive procedure, comprising administering a fluorescent dye to the patient; obtaining at least one angiographic image of the vessel portion; and evaluating the at least one angiographic image to assess the patency of the vessel portion. Other related methods are contemplated, including methods for assessing perfusion in selected body tissue, methods for evaluating the potential of vessels for use in creation of AV fistulas, methods for determining the diameter of a vessel, and methods for locating a vessel located below the surface of a tissue.
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
Intra-operative system for identifying and tracking surgical sharp objects, instruments, and sponges
Intra-operative systems for identifying surgical sharp objects are provided. Aspects of the systems include an intra-operative imaging device for obtaining intra-operative surgical sharp object image data; and a surgical sharp object automated shape recognition module configured to identify a surgical sharp object from intra-operative surgical sharp object image data. Systems of the invention may further include additional components, such as surgical instrument and / or sponge identification and tracking devices. Systems of the invention find use in a variety of methods and applications, including tracking of surgical items during a surgical procedure.
Owner:DEIN JOHN RICHARD
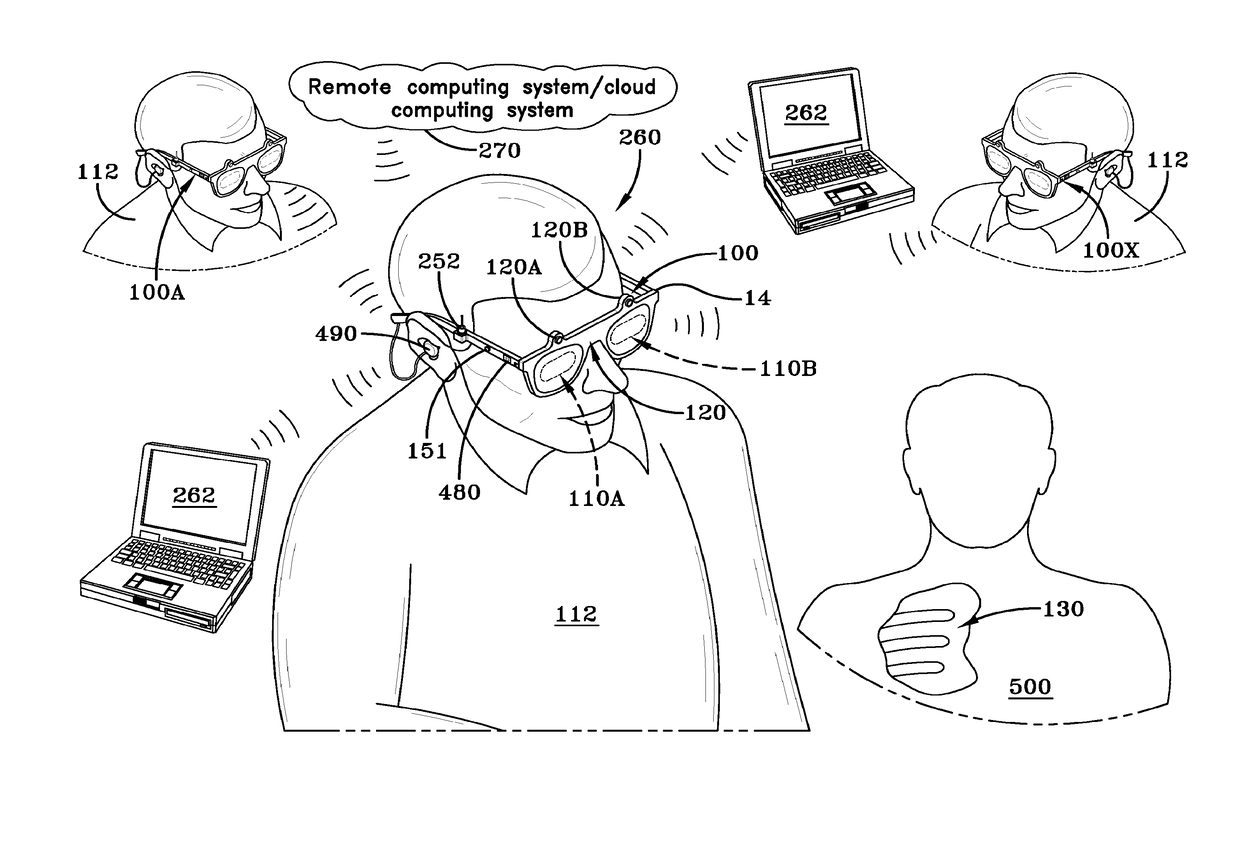
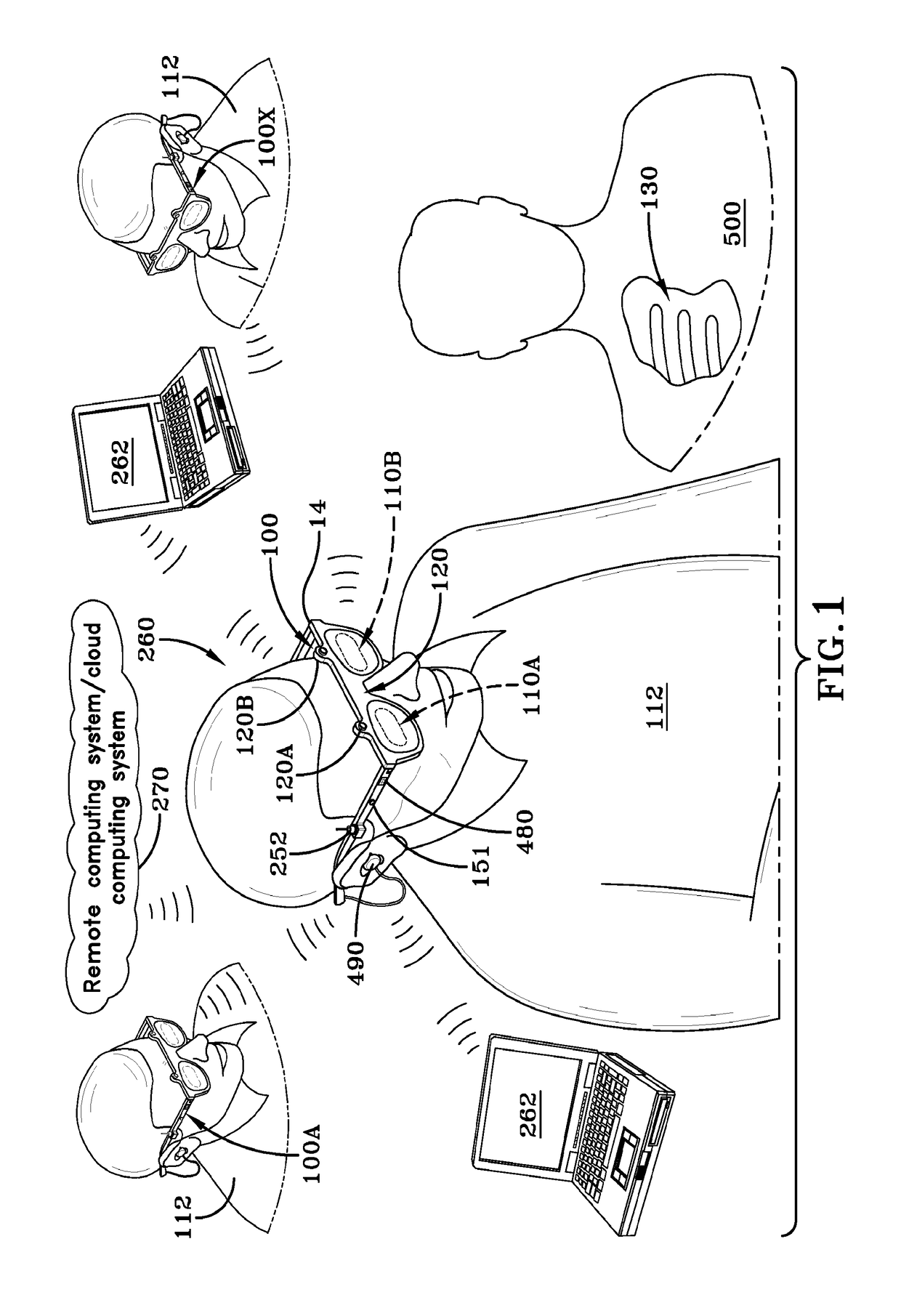
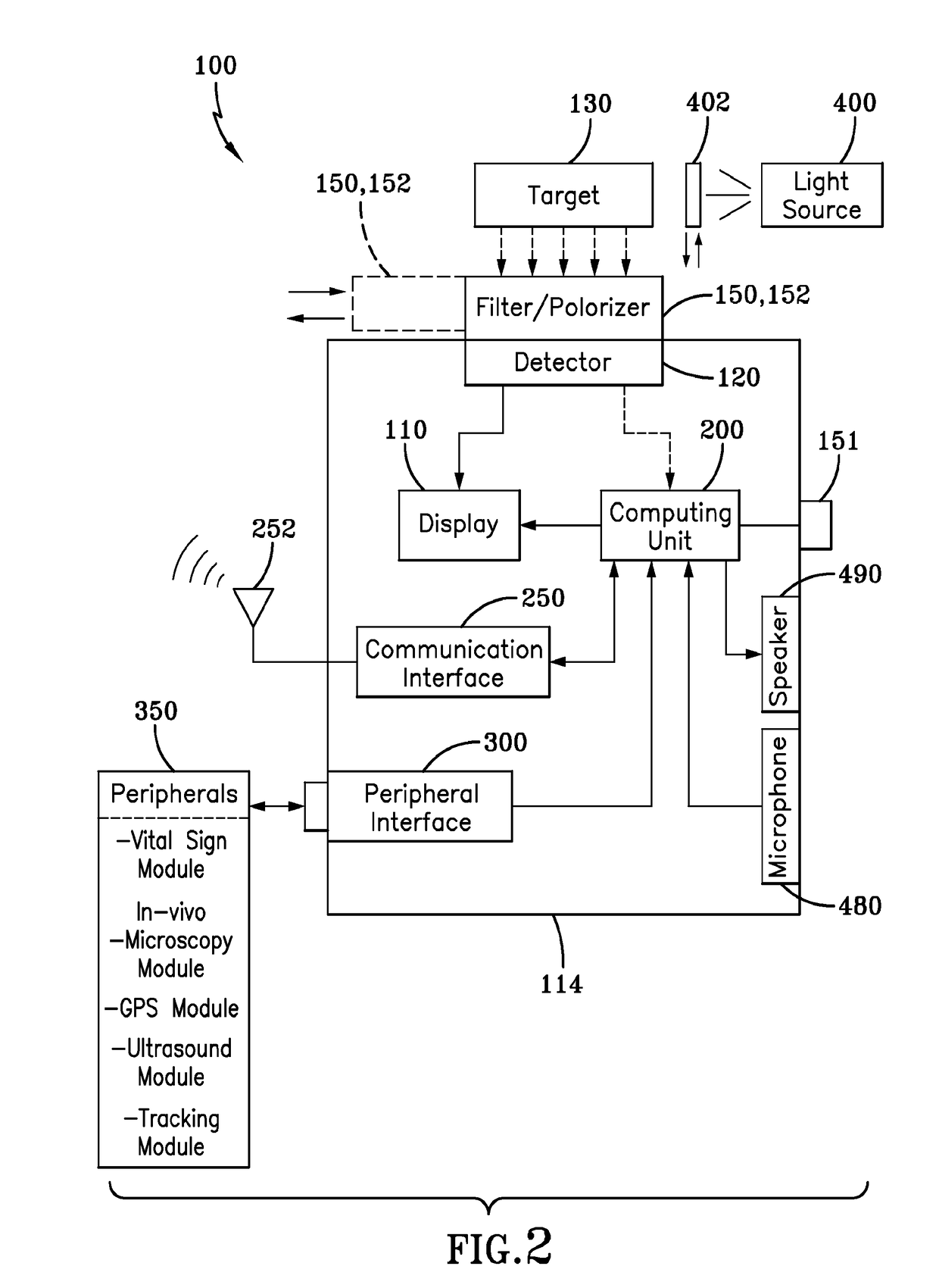
Imaging and display system for guiding medical interventions
An imaging and display system for guiding medical interventions includes a wearable display, such as a goggle display, for viewing by a user. The display presents a composite, or combined image that includes pre-operative surgical navigation images, intraoperative images, and in-vivo microscopy images or sensing data. The pre-operative images are acquired from scanners, such as MRI and CT scanners, while the intra-operative images are acquired in real-time from a camera system carried by the goggle display for imaging the patient being treated so as to acquire intraoperative images, such as fluorescence images. A probe, such as a microscopy probe or a sensing probe, is used to acquire in-vivo imaging / sensing data from the patient. Additionally, the intra-operative and in-vivo images are acquired using tracking and registration techniques to align them with the pre-operative image and the patient to form a composite image for display by the goggle display.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
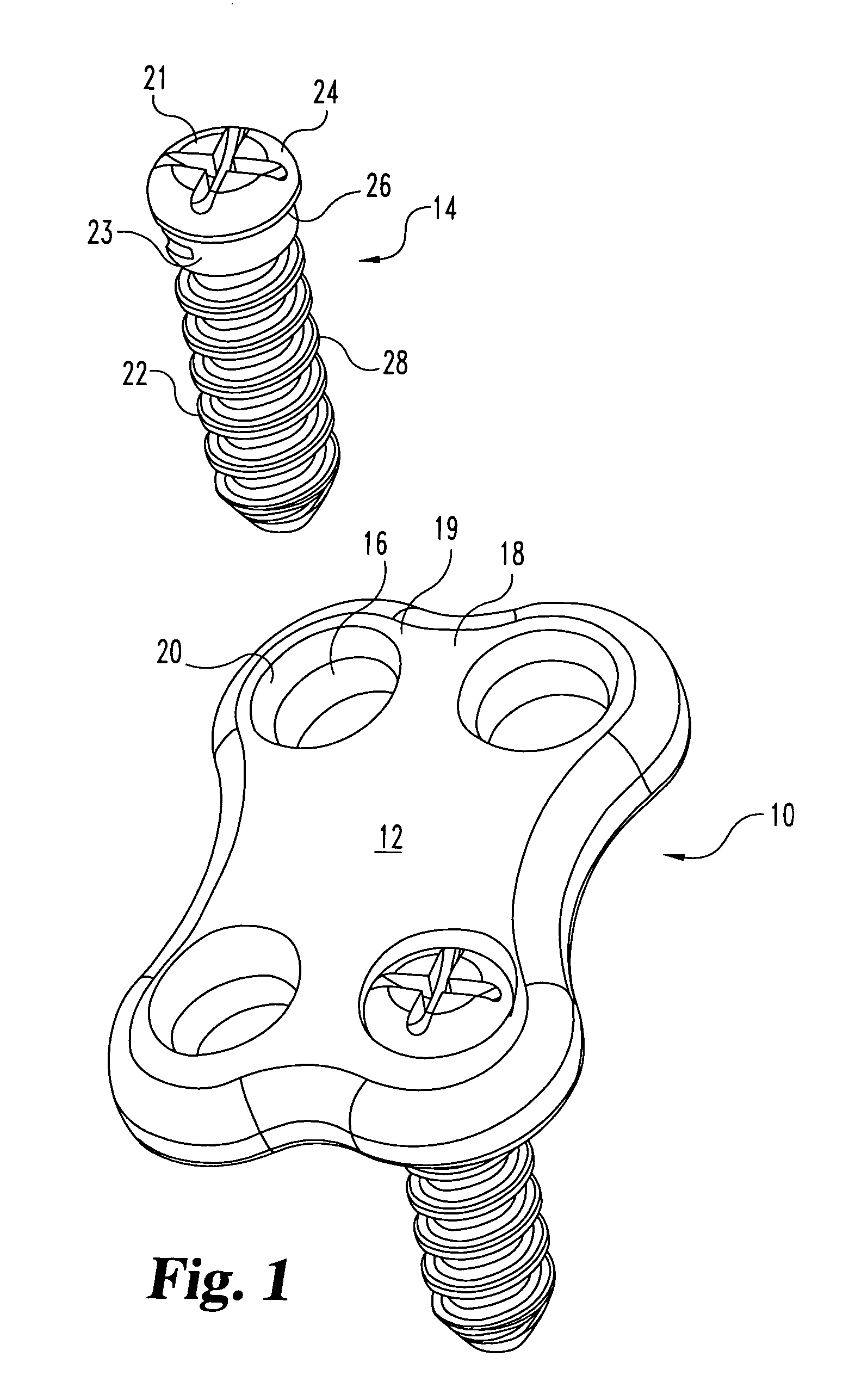
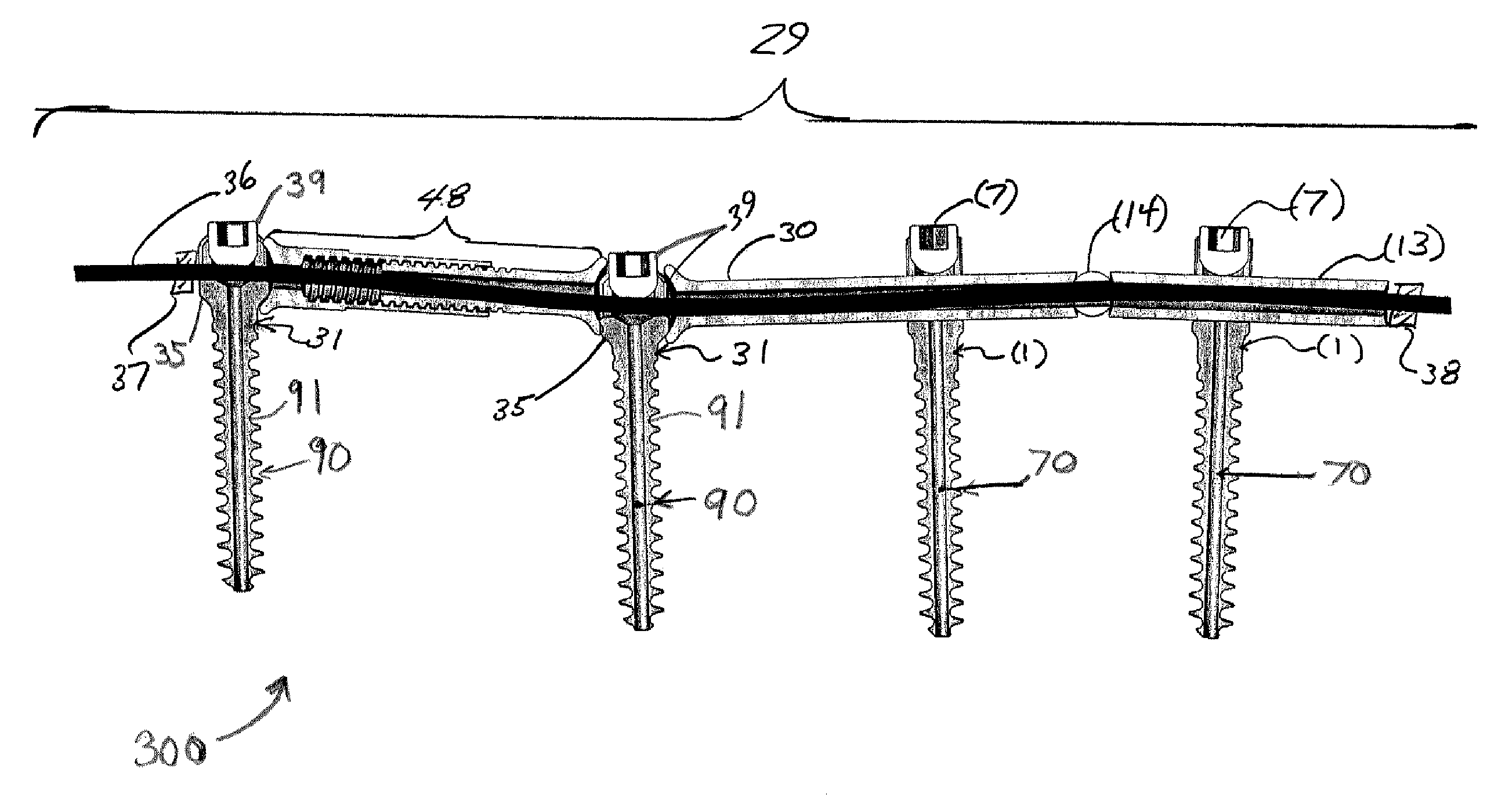
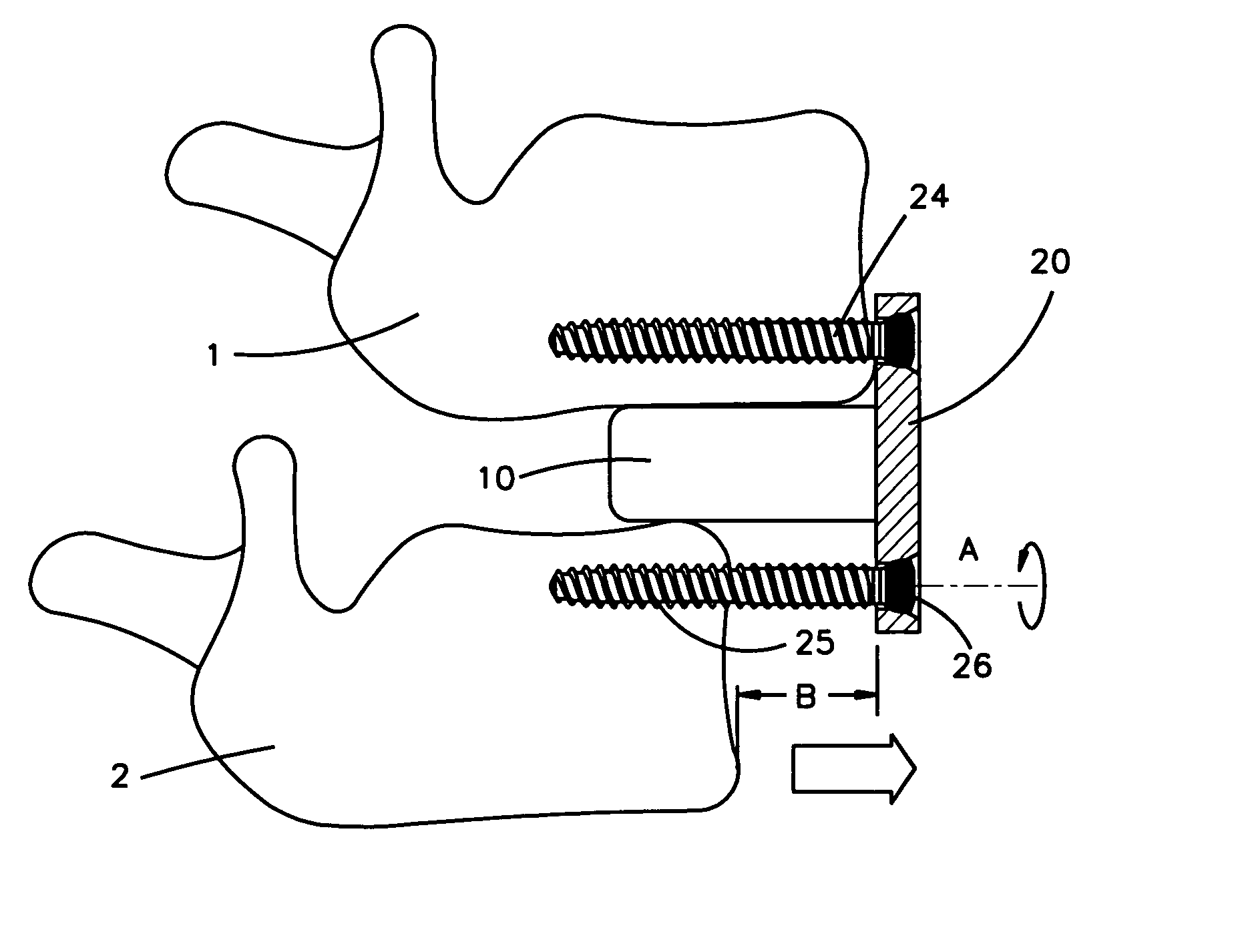
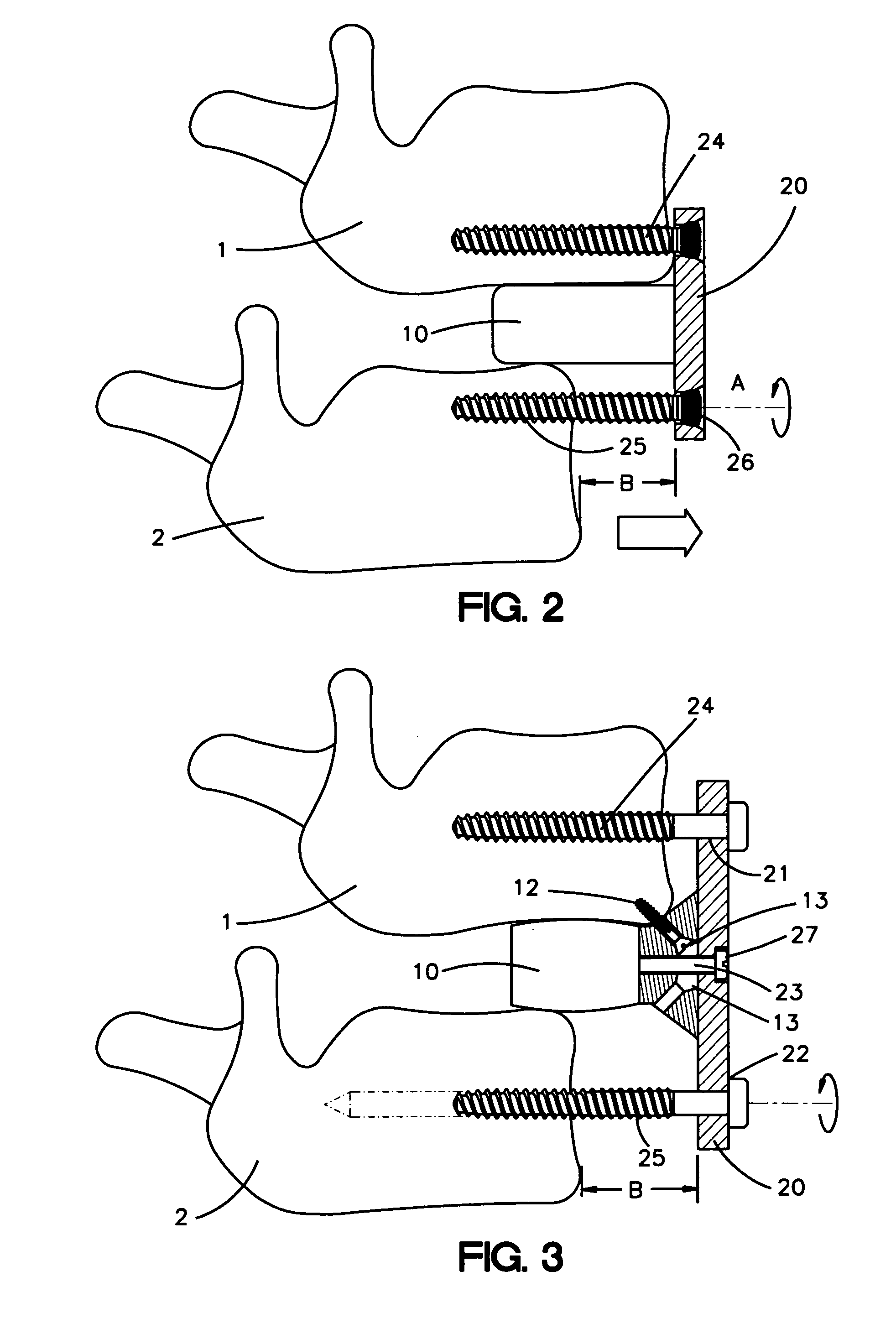
Spinal Rod System
ActiveUS20070288011A1Effective and adequate stabilizationSimple to install without the risk of applying excessive forceInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnRange of motion
A multi-axis spinal fixation device which can use a fixed head spinal or pedicle screw in combination with a multi-axial rod assembly to achieve anatomically correct fixation of vertebrae. The orthopedic fixation can be controlled by a different combination of rod elements to provide a varied range of motion between adjacent vertebrae as well as specific flexibility between the adjacent vertebrae or levels. The surgeon can make intra-operative adjustments from rigid fixation to dynamic stabilization and where desired also provide ‘soft-stabilization’ or ‘micro motion’. The unique combination of elements can provide fixed stabilization for the purpose of fusion or dynamic stabilization without fusion.
Owner:LOGAN JOSEPH NICHOLAS
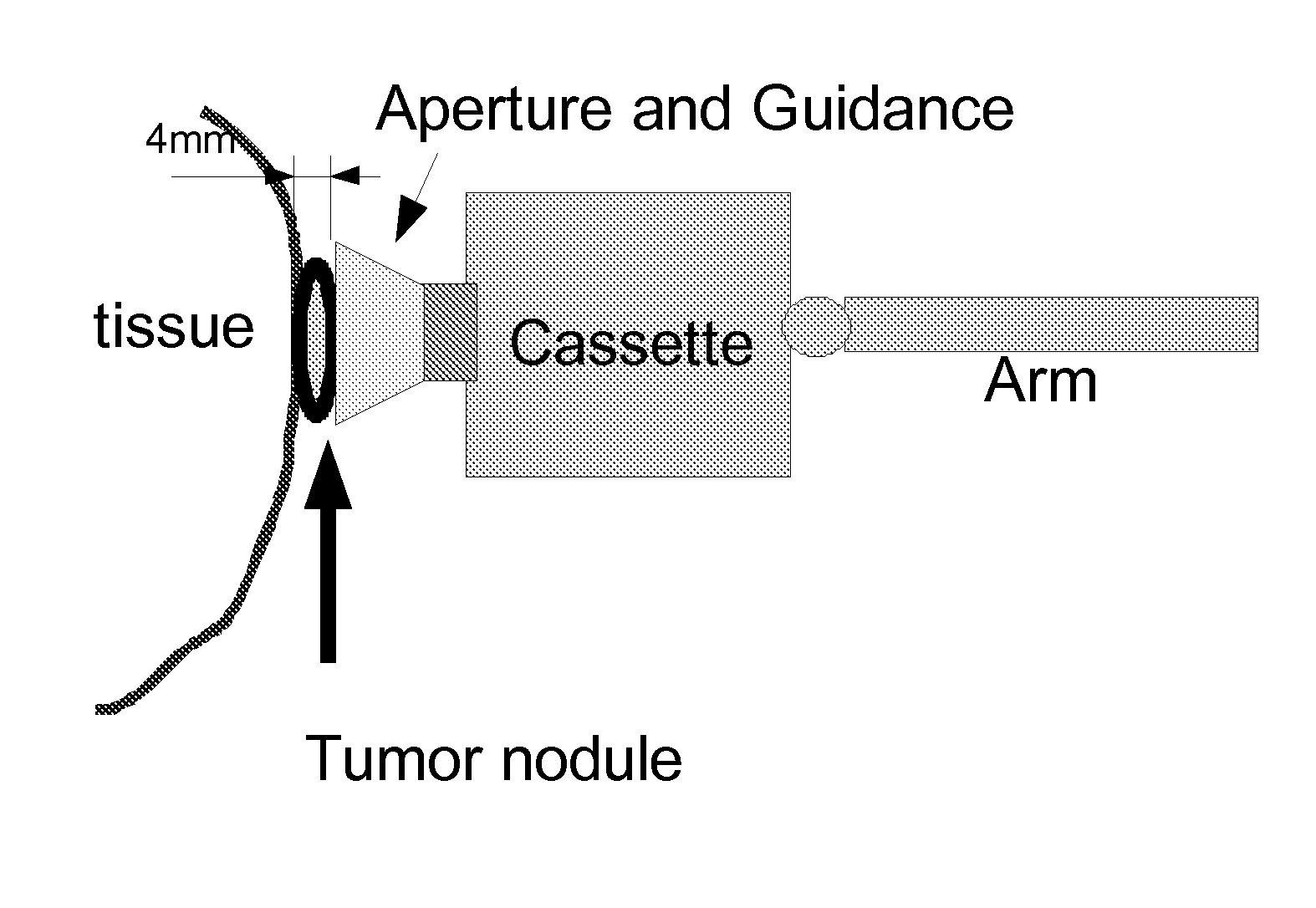
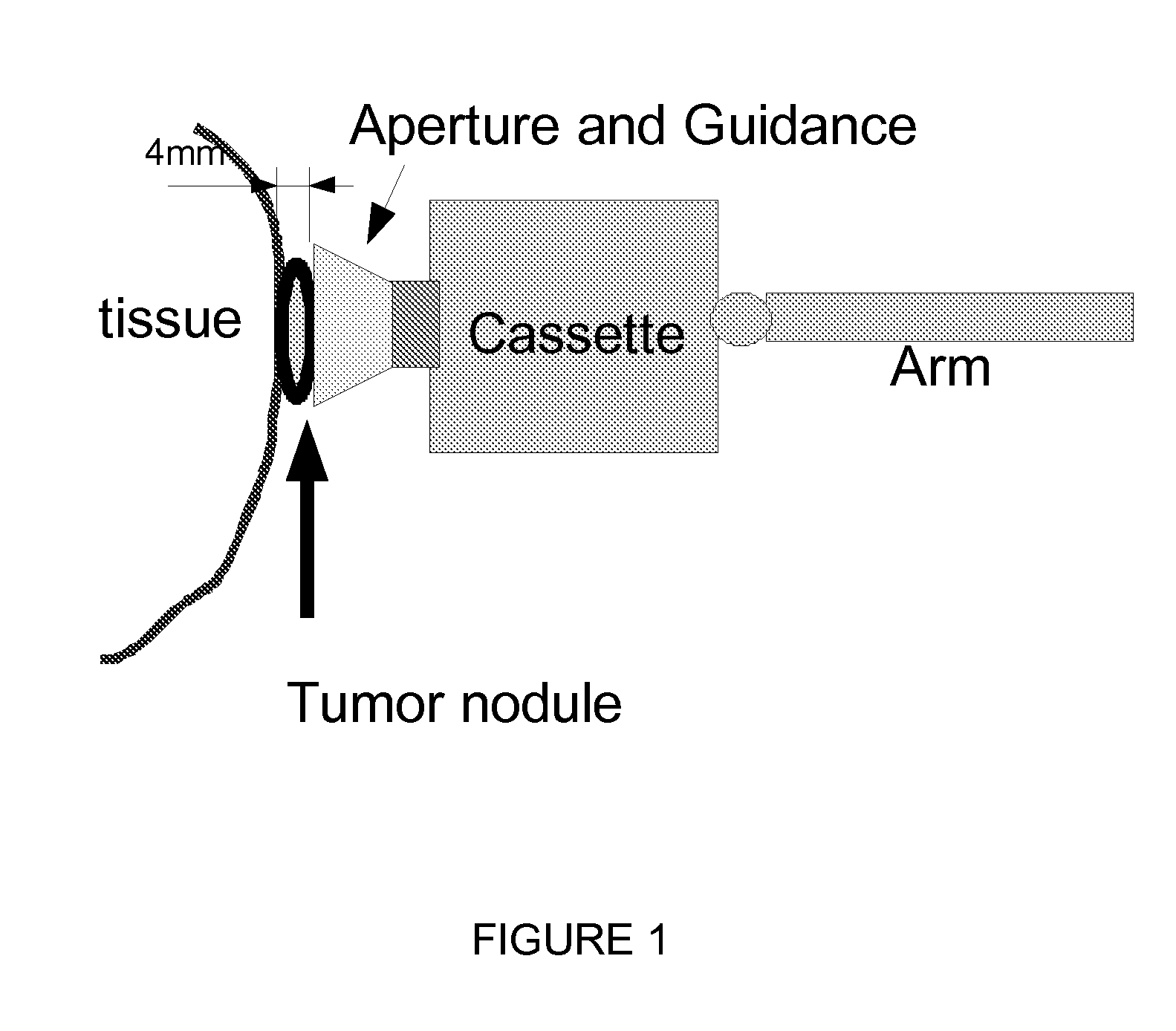
Direct visualization robotic intra-operative radiation therapy applicator device
ActiveUS8092370B2Increase probabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryX-rayTherapeutic effect
This invention proposes a robotic applicator device to be deployed internally to a patient having a capsule (also referred to as a cassette) and aperture with a means of alternately occluding and exposing a radioactive source through the aperture. The capsule and aperture will be integrated with a surgical robot to create a robotic IORT (intra-operative radiation therapy) applicator device as more fully described below. The capsule, radiation source, and IORT applicator arm would be integrated to enable a physician, physicist or technician to interactively internally view and select tissue for exposure to ionizing radiation in sufficient quantities to deliver therapeutic radiation doses to tissue. Via the robotic manipulation device, the physician and physicist would remotely apply radiation to not only the tissue to be exposed, but also control the length of time of the exposure. Control means would be added to identify and calculate margin and depth of tissue to be treated and the proper radiation source or radioactive isotope (which can be any particle emitter, including neutron, x-ray, alpha, beta or gamma emitter) to obtain the desired therapeutic effects. The invention enables stereotactical surgery and close confines radiation therapy adjacent to radiosensitive tissue.
Owner:SRIORT
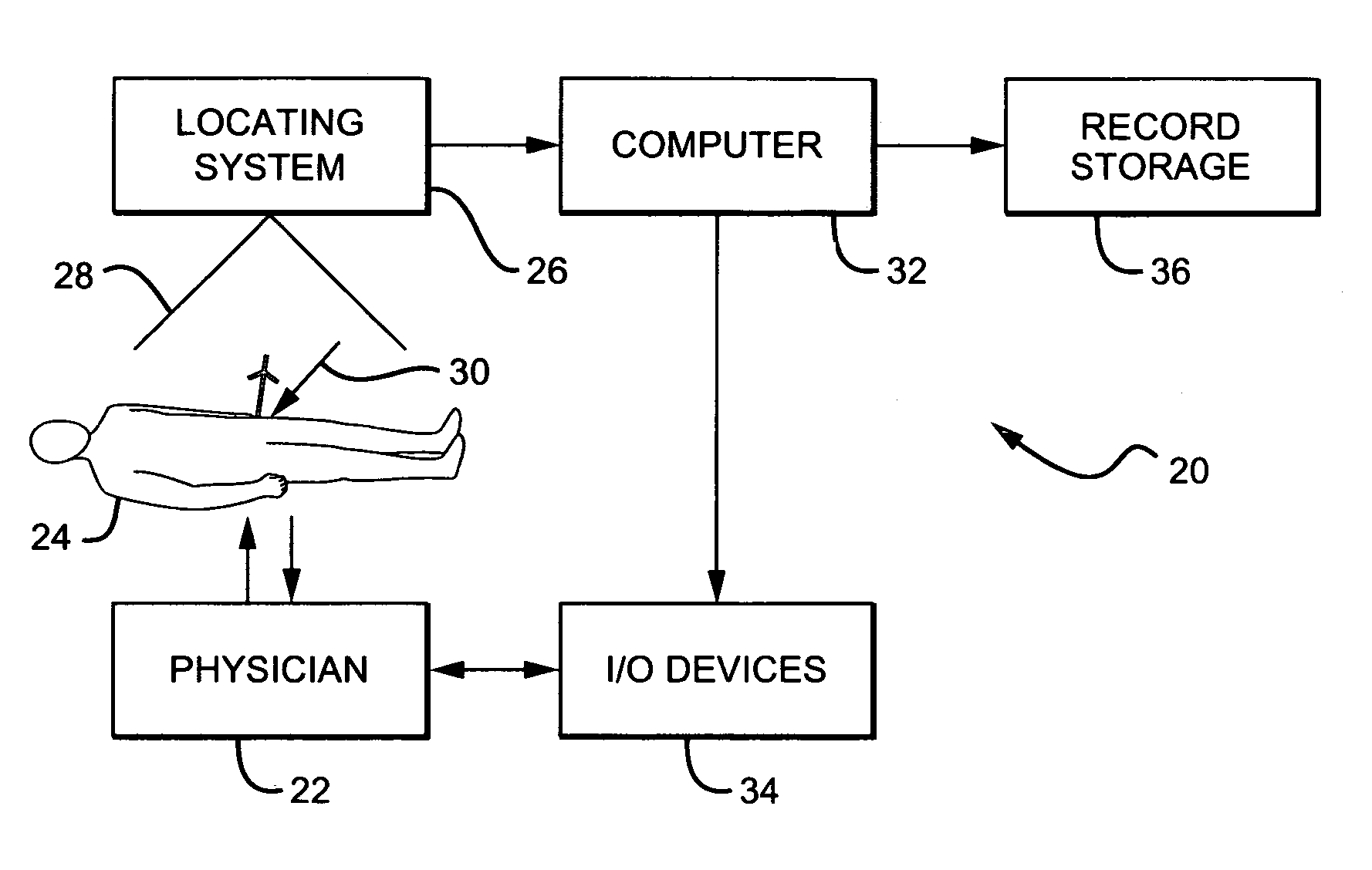
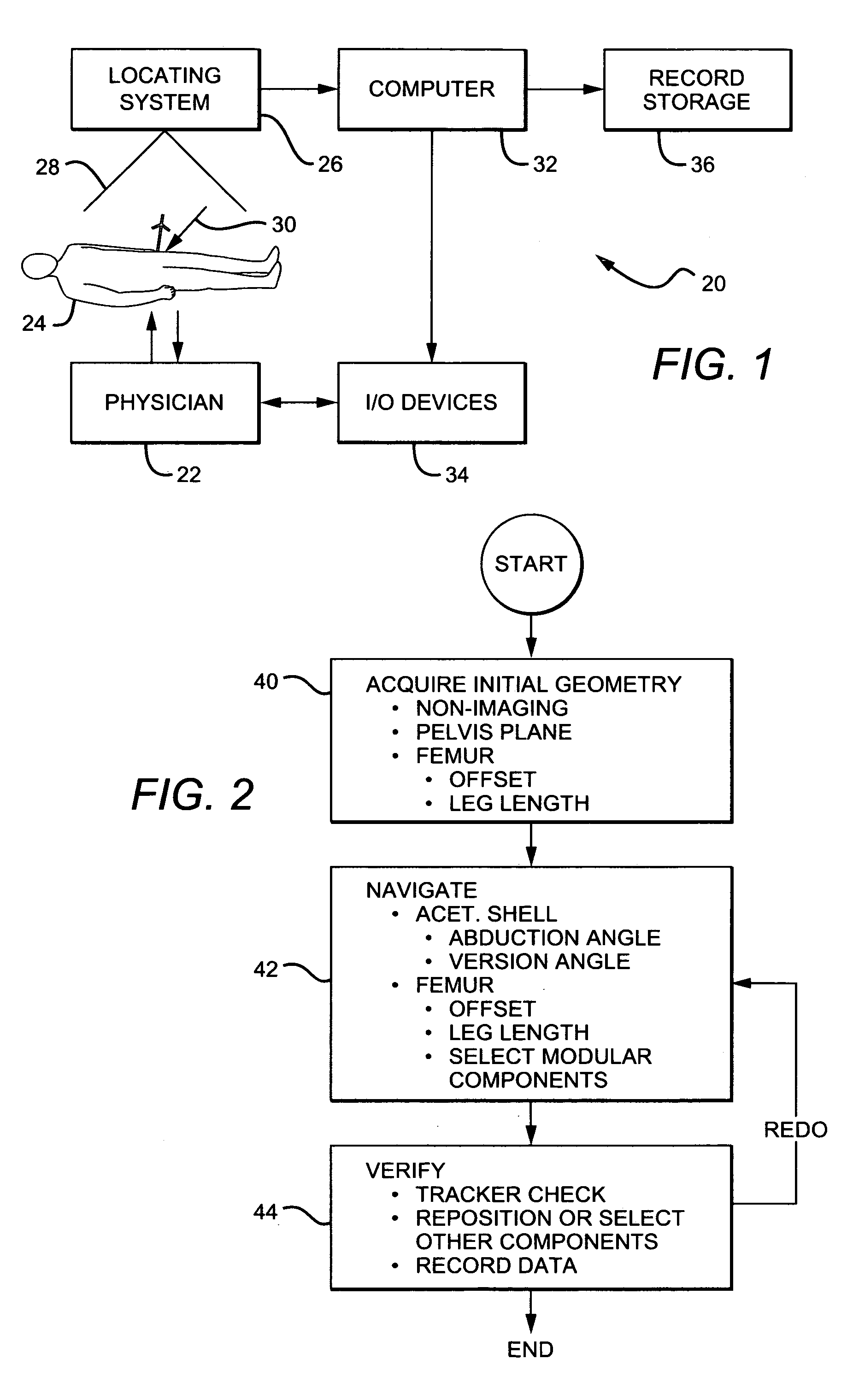
Non-image, computer assisted navigation system for joint replacement surgery with modular implant system
The invention includes a method and system for intra-operative navigation of a joint replacement operation, without recourse to pre-operative imagery of pre-operative computerized simulations. Trackable markers and a locating system are employed to track first and second bones. A computer receives positional information regarding the trackable markers and calculates (predicts) at least one suggested combination of components of a modular implant system to produce a desired post-operative skeletal relationship.
Owner:KINAMED
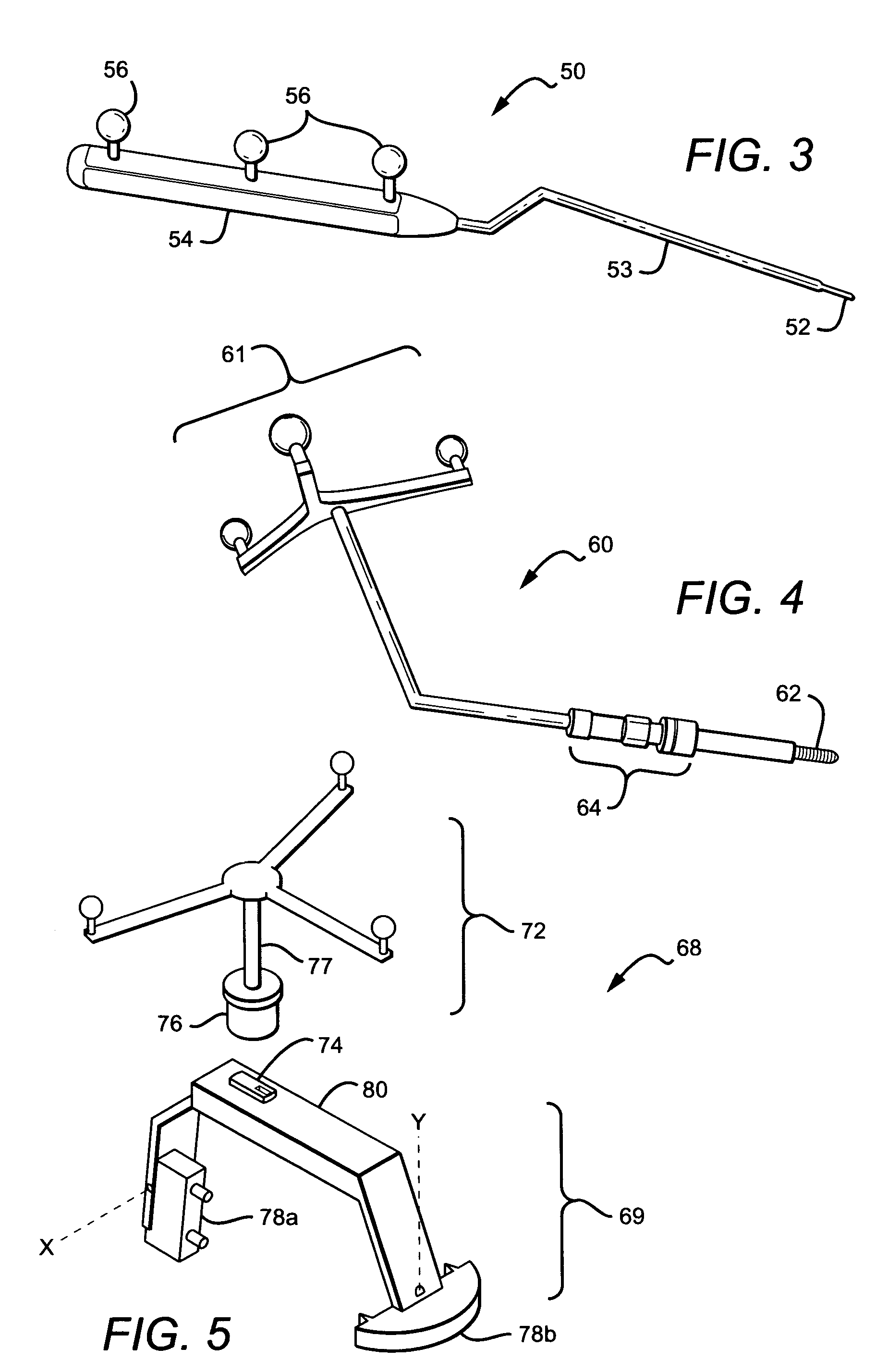
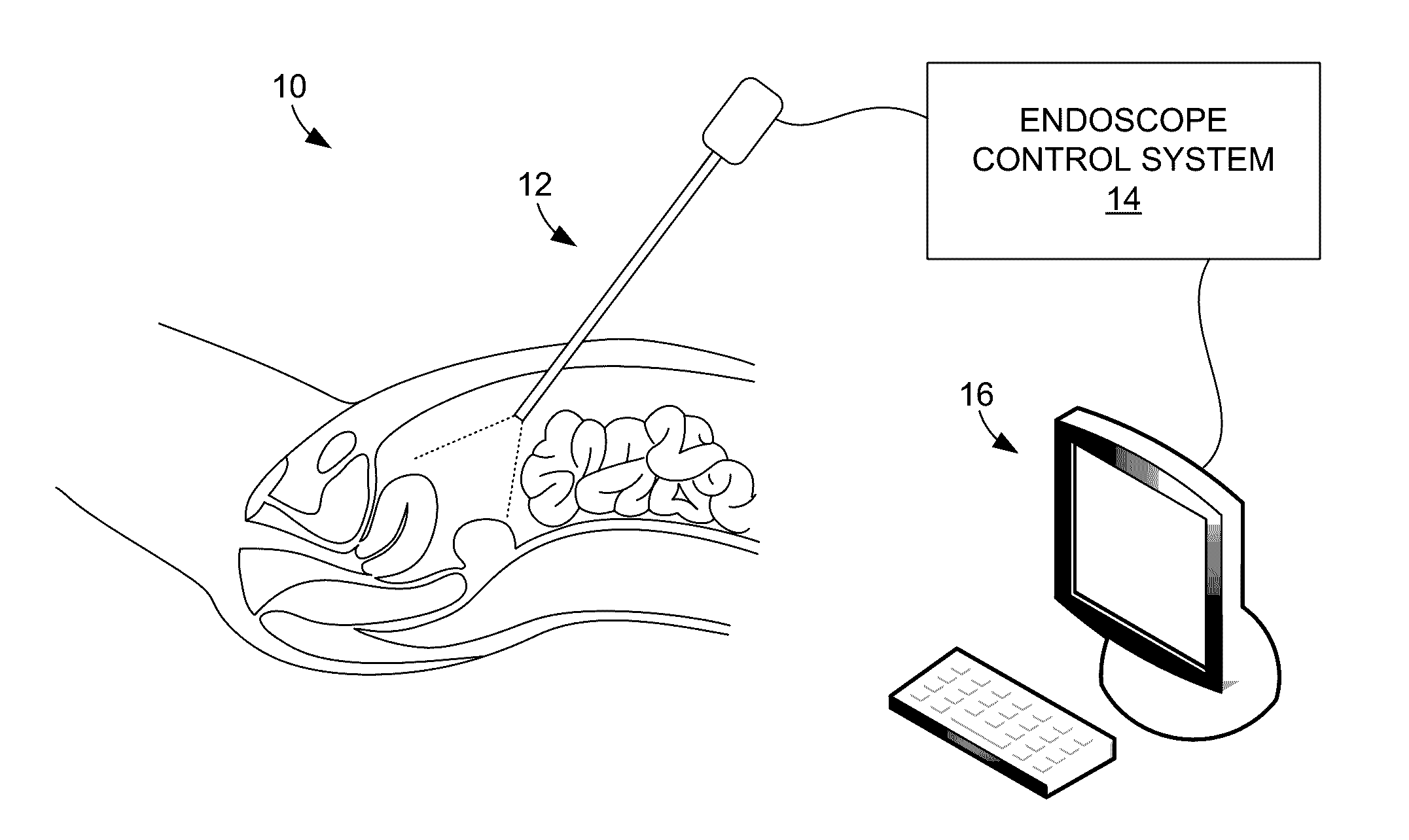
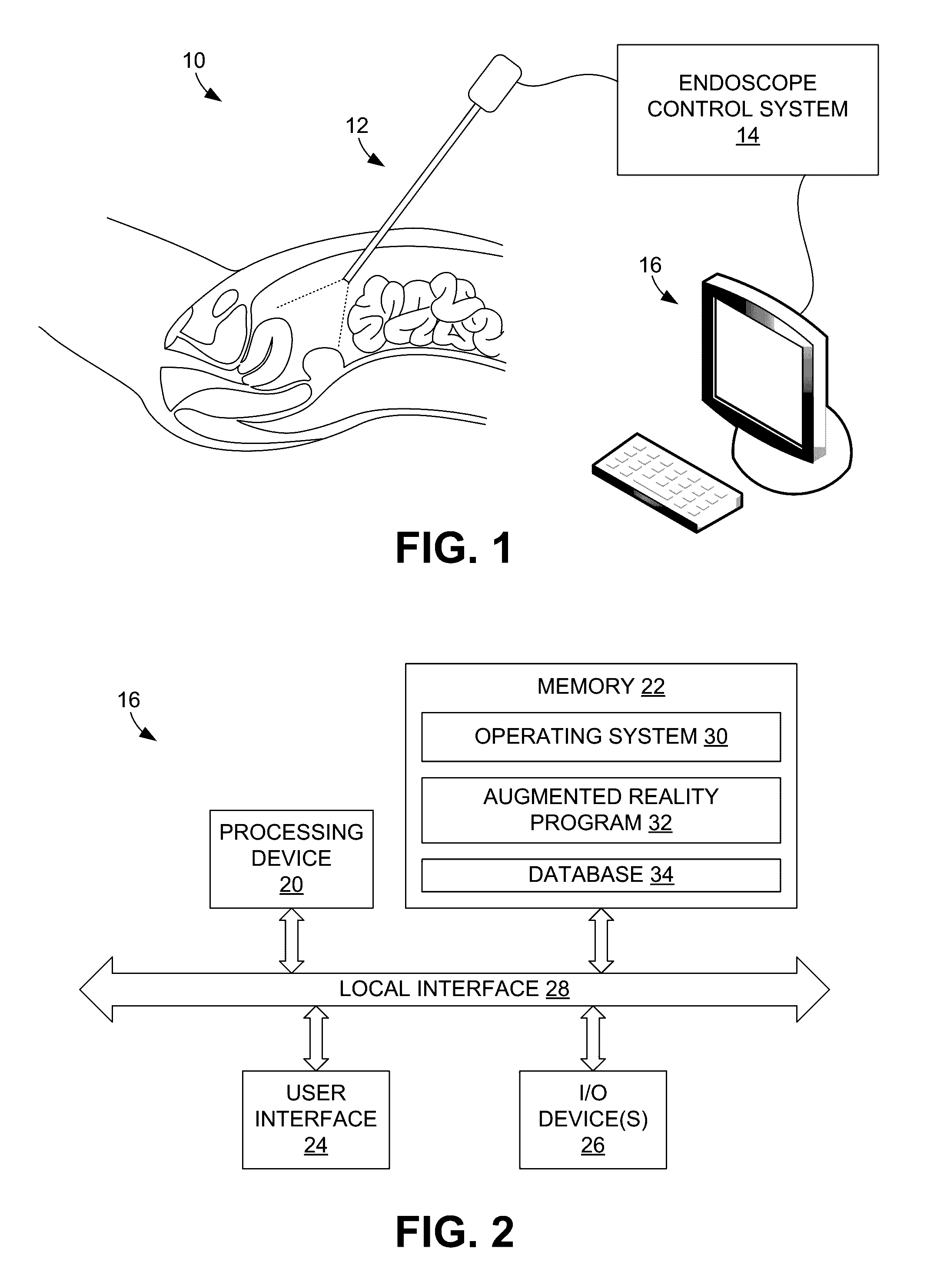
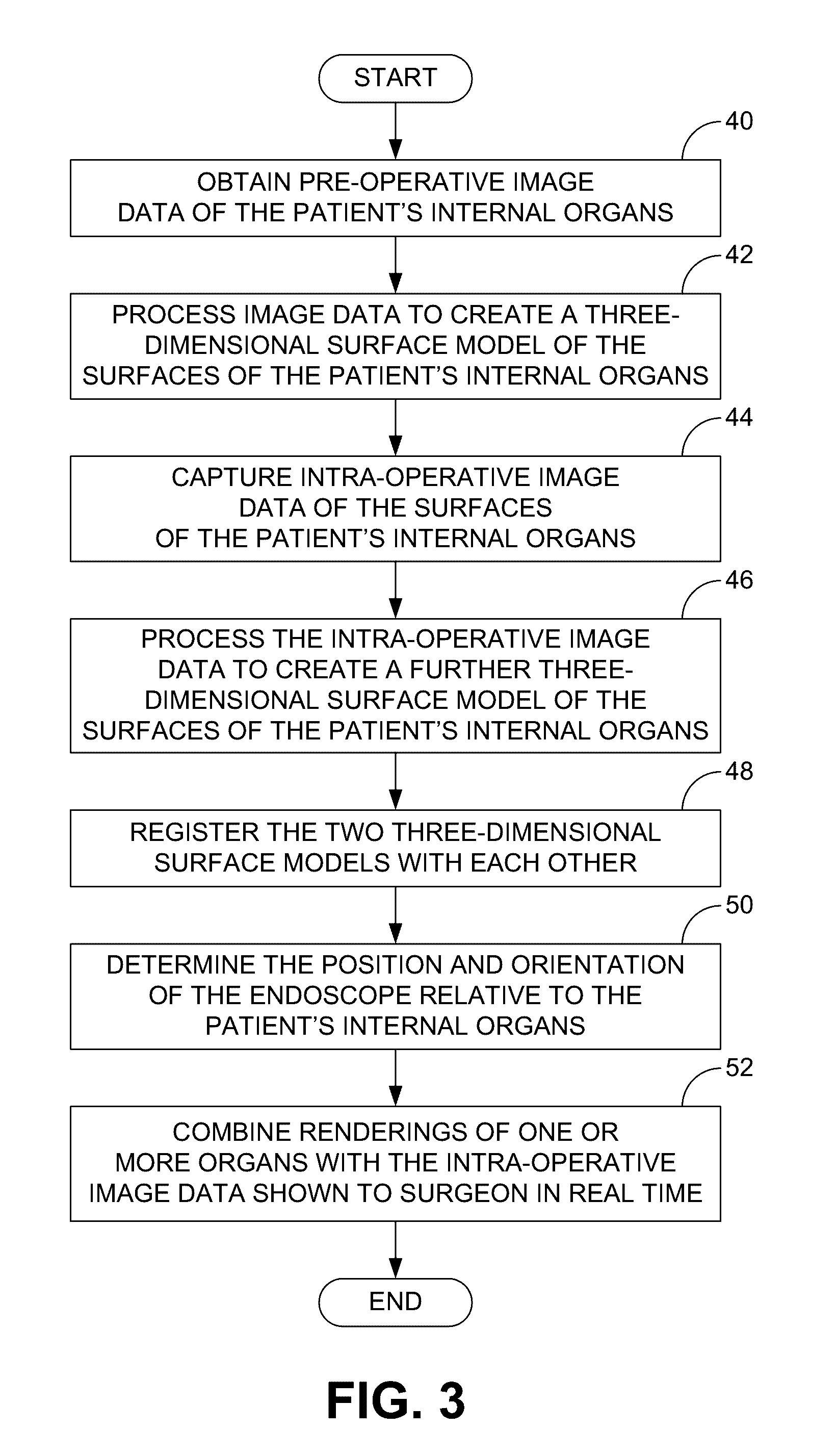
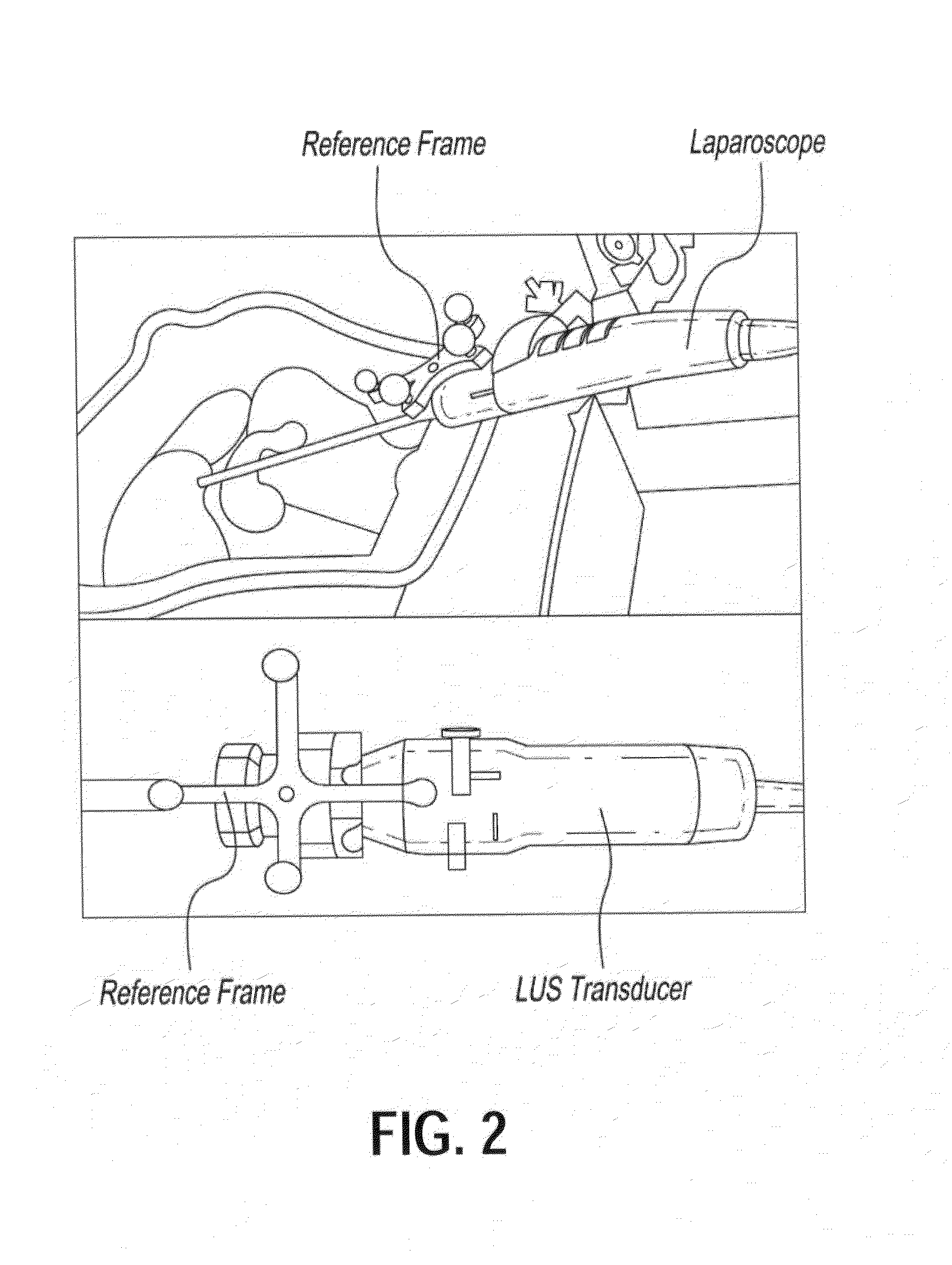
Systems and methods for providing augmented reality in minimally invasive surgery
In one embodiment, a method for providing augmented reality in minimally invasive surgery includes capturing pre-operative image data of internal organs of a patient, capturing intra-operative image data of the internal organs with an endoscope during a surgical procedure, registering the pre-operative image data and the intra-operative data in real time during the surgical procedure, tracking the position and orientation of the endoscope during the surgical procedure, and augmenting the intra-operative image data captured by the endoscope in real time with a rendering of an internal organ of the patient.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
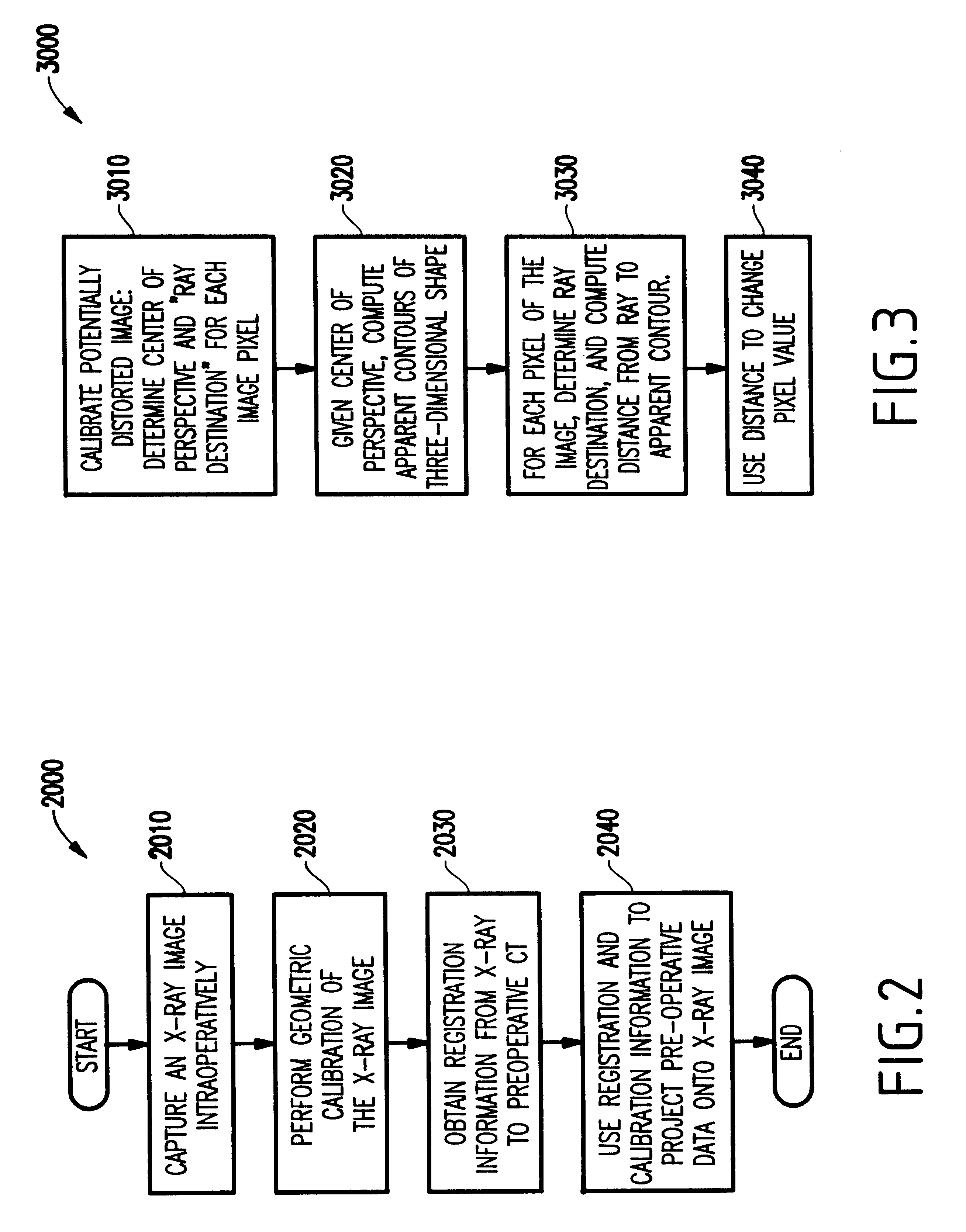
System and method for fusing three-dimensional shape data on distorted images without correcting for distortion
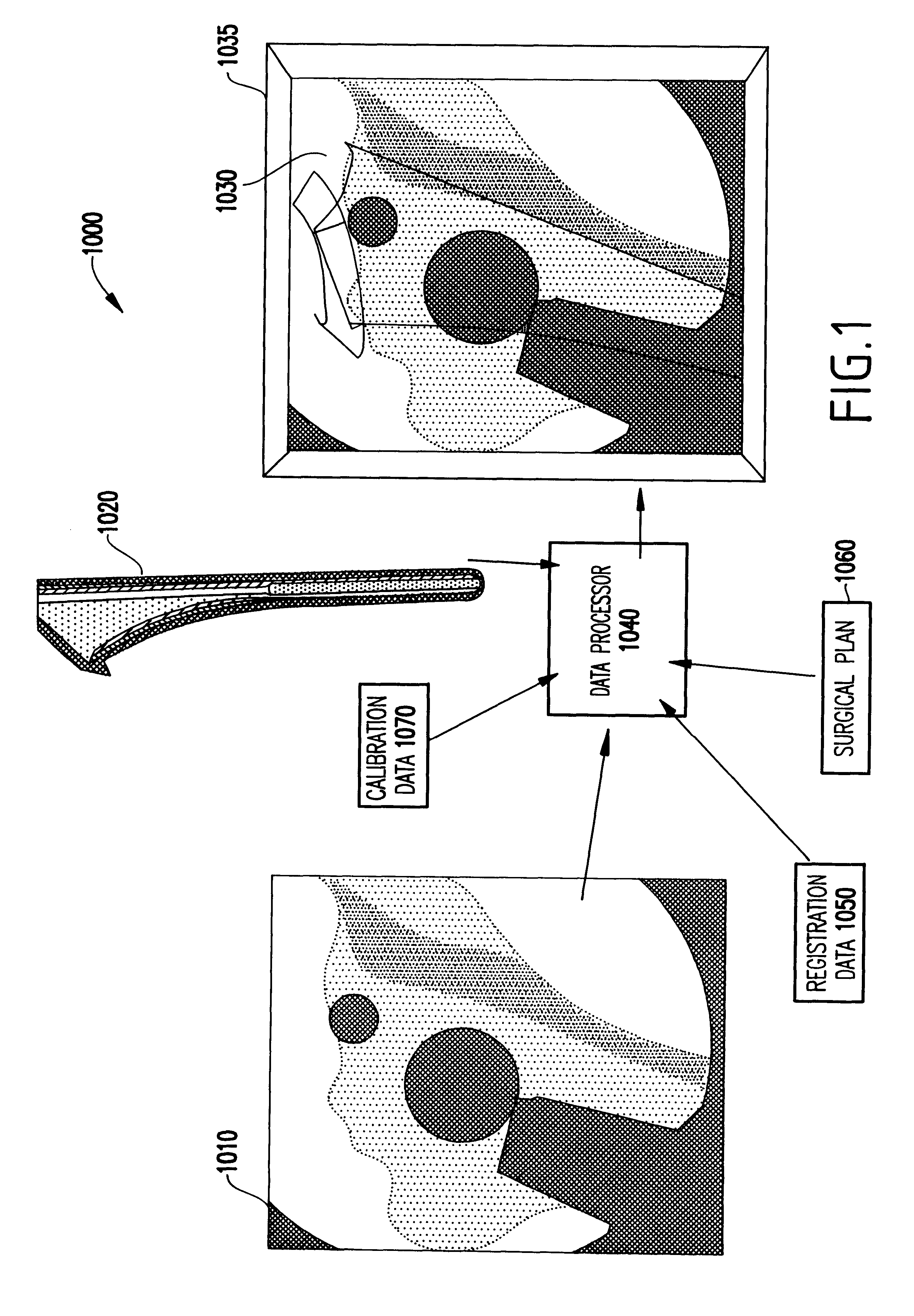
InactiveUS6747646B2Increase speedProcessing resource is not increasedCharacter and pattern recognitionComputerised tomographsPhysical spaceFusion mechanism
A system and method for intra-operatively providing a surgeon with visual evaluations of possible surgical outcomes ahead of time, and generating simulated data, includes a medical imaging camera, a registration device for registering data to a physical space, and to the medical imaging camera, and a fusion mechanism for fusing the data and the images to generate simulated data, without correcting for distortion. The simulated data (e.g., such as augmented X-ray images) is natural and easy for a surgeon to interpret. In an exemplary implementation, the system preferably includes a data processor which receives a three-dimensional surgical plan or three-dimensional plan of therapy delivery, one or a plurality of two-dimensional intra-operative images, a three-dimensional model of pre-operative data, registration data, and image calibration data. The data processor produces one or a plurality of simulated post-operative images, without correcting for distortion, by integrating a projection of a three-dimensional model of pre-operative data onto one or a plurality of two-dimensional intra-operative images.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
System and method for fusing three-dimensional shape data on distorted images without correcting for distortion
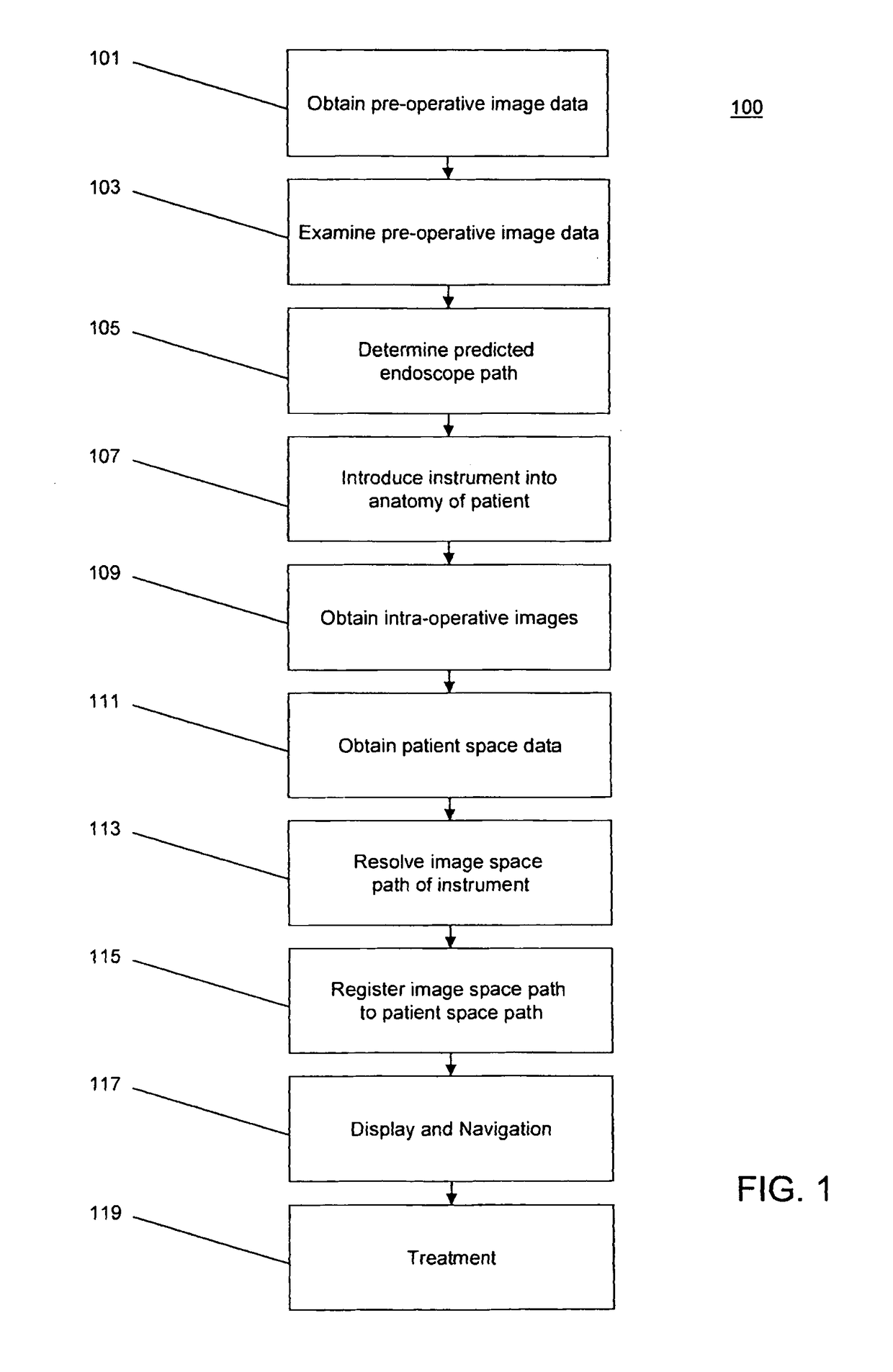
InactiveUS6415171B1Increase speedProcessing resource is not increasedComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringFusion mechanismPhysical space
A system and method for intra-operatively providing a surgeon with visual evaluations of possible surgical outcomes ahead of time, and generating simulated data, includes a medical imaging camera, a registration device for registering data to a physical space, and to the medical imaging camera, and a fusion mechanism for fusing the data and the images to generate simulated data, without correcting for distortion. The simulated data (e.g., such as augmented X-ray images) is natural and easy for a surgeon to interpret. In an exemplary implementation, the system preferably includes a data processor which receives a three-dimensional surgical plan or three-dimensional plan of therapy delivery, one or a plurality of two-dimensional intra-operative images, a three-dimensional model of pre-operative data, registration data, and image calibration data. The data processor produces one or a plurality of simulated post-operative images, without correcting for distortion, by integrating a projection of a three-dimensional model of pre-operative data onto one or a plurality of two-dimensional intra-operative images.
Owner:IBM CORP
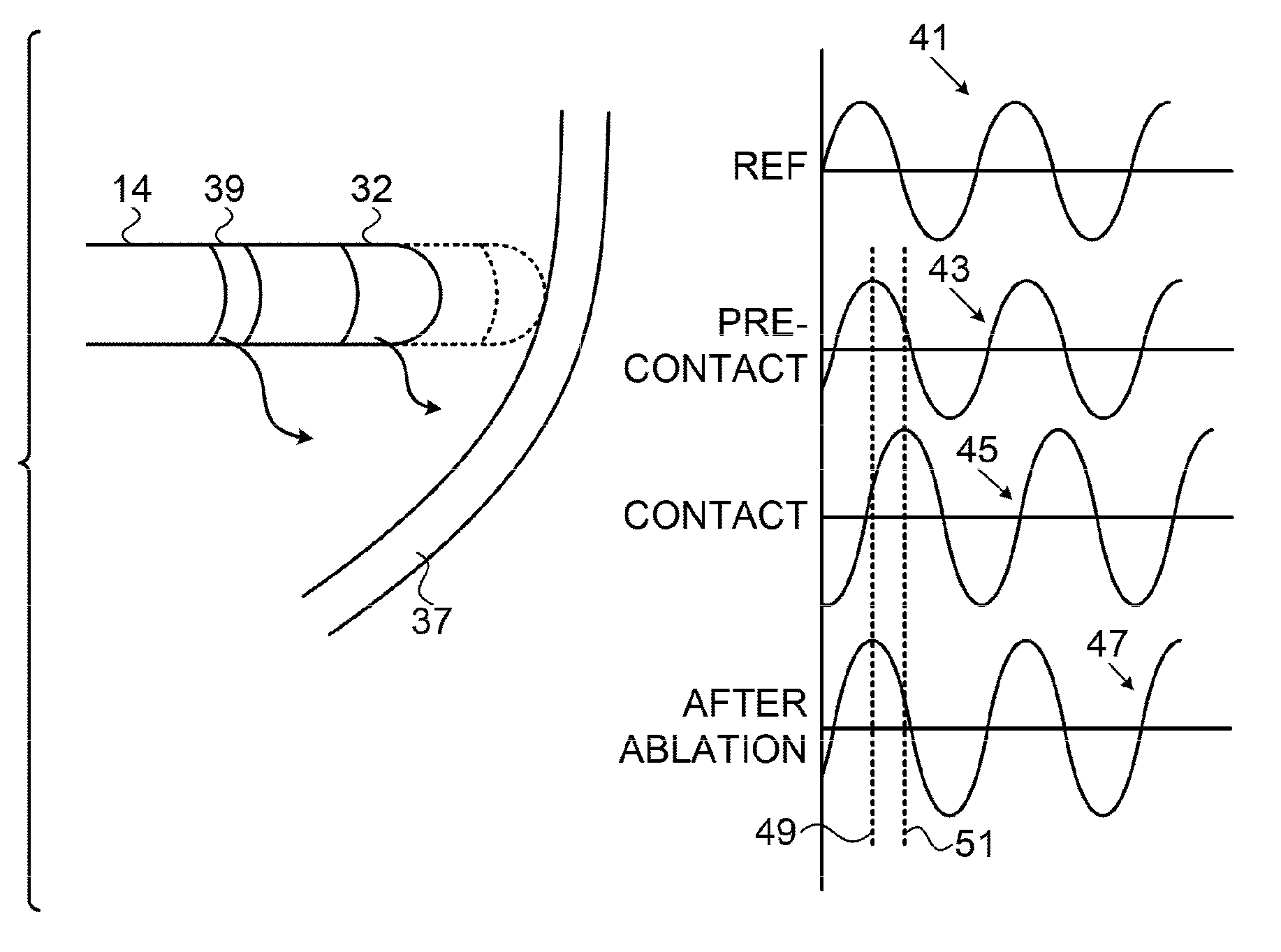
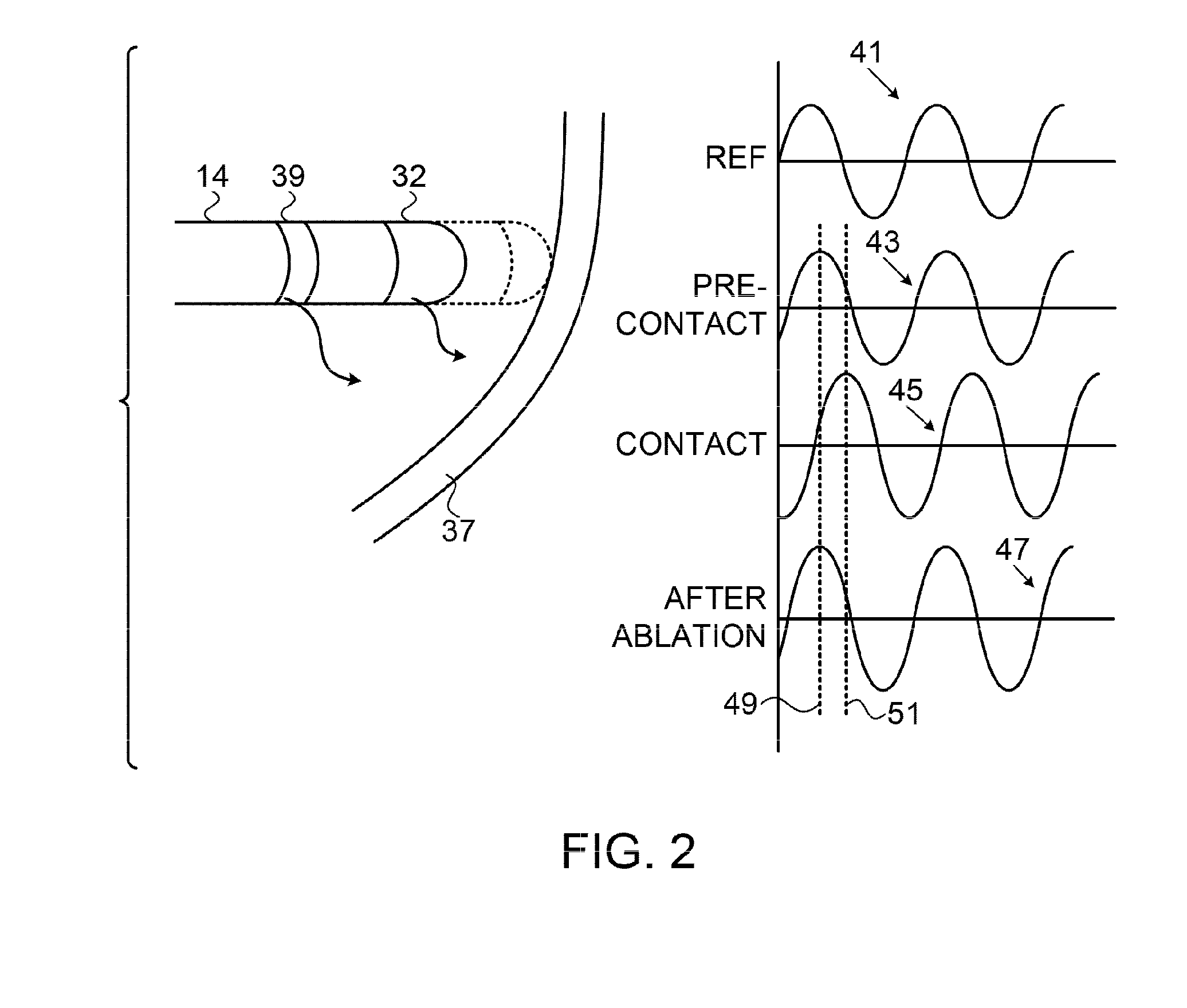
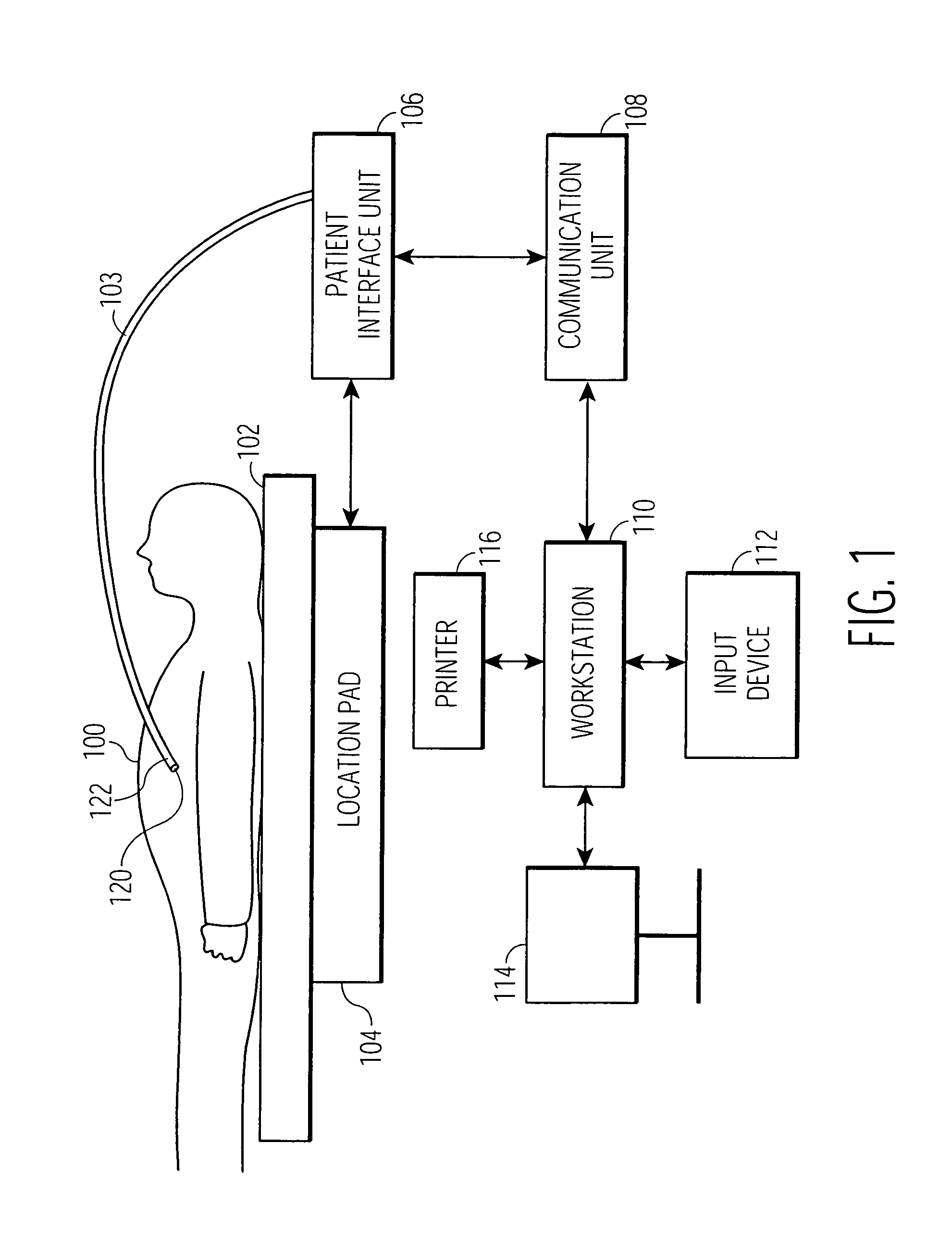
Contact assessment based on phase measurement
Methods and systems achieve tissue ablation, which is carried out by inserting a probe having an ablation electrode into a body of a living subject, and while the ablation electrode is in a non-contacting relationship to a target tissue, making a pre-contact determination of a phase of an electrical current passing between the ablation electrode and another electrode. The ablation electrode is placed in contact with the target tissue, and while the ablation electrode is in the contacting relationship, a dosage of energy is applied via the ablation electrode to the target tissue for ablation thereof. Iterative intra-operative determinations of the phase of the electrical current are made. When one of the intra-operative determinations satisfies a termination criterion, the energy application is terminated.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Noninvasive tissue assessment
InactiveUS20050113691A1Reduce measurement errorSufficient pressureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFrequency spectrumPost operative
Methods and apparatus for non-invasively assessing physiological hard of soft tissue of human and other species are described. In a preferred embodiment, tissue is vibrationally stimulated in vivo through a frequency spectrum. The tissue reacts against the stimulus and the reaction is preferably measured and recorded. Based on analytical algorithms or comparisons with previously taken measurements, changes within the tissue can be detected and used for diagnostic purposes. Further embodiments describe the usage of the device and methods for in vivo intra-operative and post-operative implant evaluations and as a therapeutic tool.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Device and method for generating composite images for endoscopic surgery of moving and deformable anatomy
ActiveUS20140303491A1Improve understandingImprove surgical efficiencyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementIntra operativeTomographic image
A device for generating composite images of dynamically changing surgical anatomy includes circuitry configured to receive, from an endoscopic imaging device, endoscopic image data. The circuitry is configured to receive, from a tomographic imaging device, intra-operative tomographic image data. The circuitry is configured to receive, from a tracking device, spatial tracking data corresponding to the endoscopic imaging device and the tomographic imaging device. The circuitry is configured to generate real-time dynamically changing composite image data by overlaying, based on the spatial tracking data, the intra-operative tomographic image data on the endoscopic image data. The circuitry is configured to output the composite image data to a display.
Owner:CHILDRENS NAT MEDICAL CENT
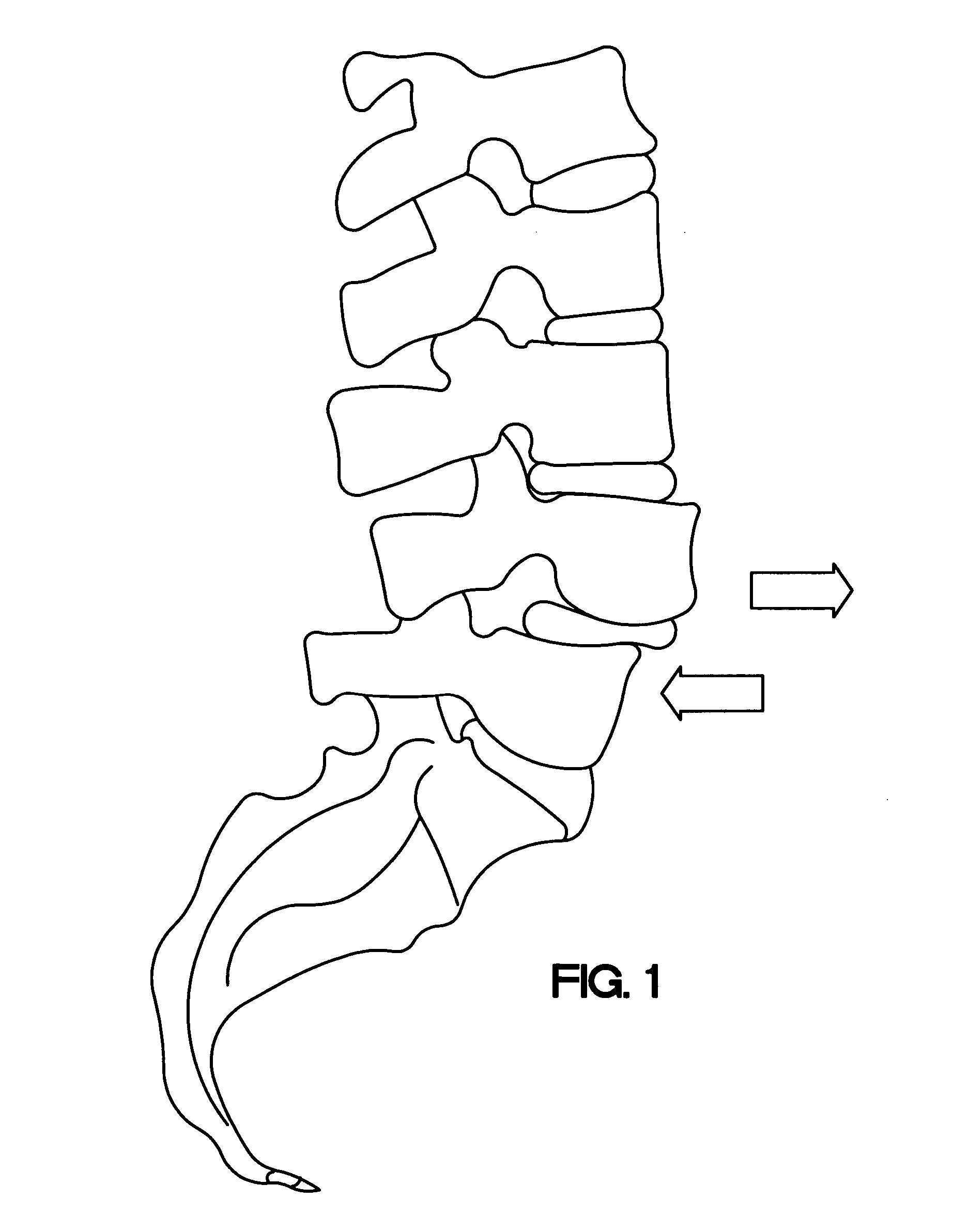
Method and instruments to treat spondylolisthesis by an anterior minimally invasive approach of the spine
InactiveUS20070123989A1Reducing surgical morbidityReduce morbidityInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsSurgical treatmentLumbar vertebrae
A method for intra-operative surgical treatment of spondylolisthesis by an anterior minimally invasive approach of the lumbar spine includes inserting an interbody spacer between two vertebrae, attaching an anatomically designed reduction plate to at least one of the two vertebrae, and attaching the interbody spacer to the reduction plate by a fastening means through a central borehole of the reduction plate and the interbody spacer. The interbody spacer may be attached to the anteriorly positioned vertebra by at least bone screw. The upper and lower parts may be attached to the upper and lower vertebra by at least one bone screw to stabilize the displaced vertebral segment of the spine.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
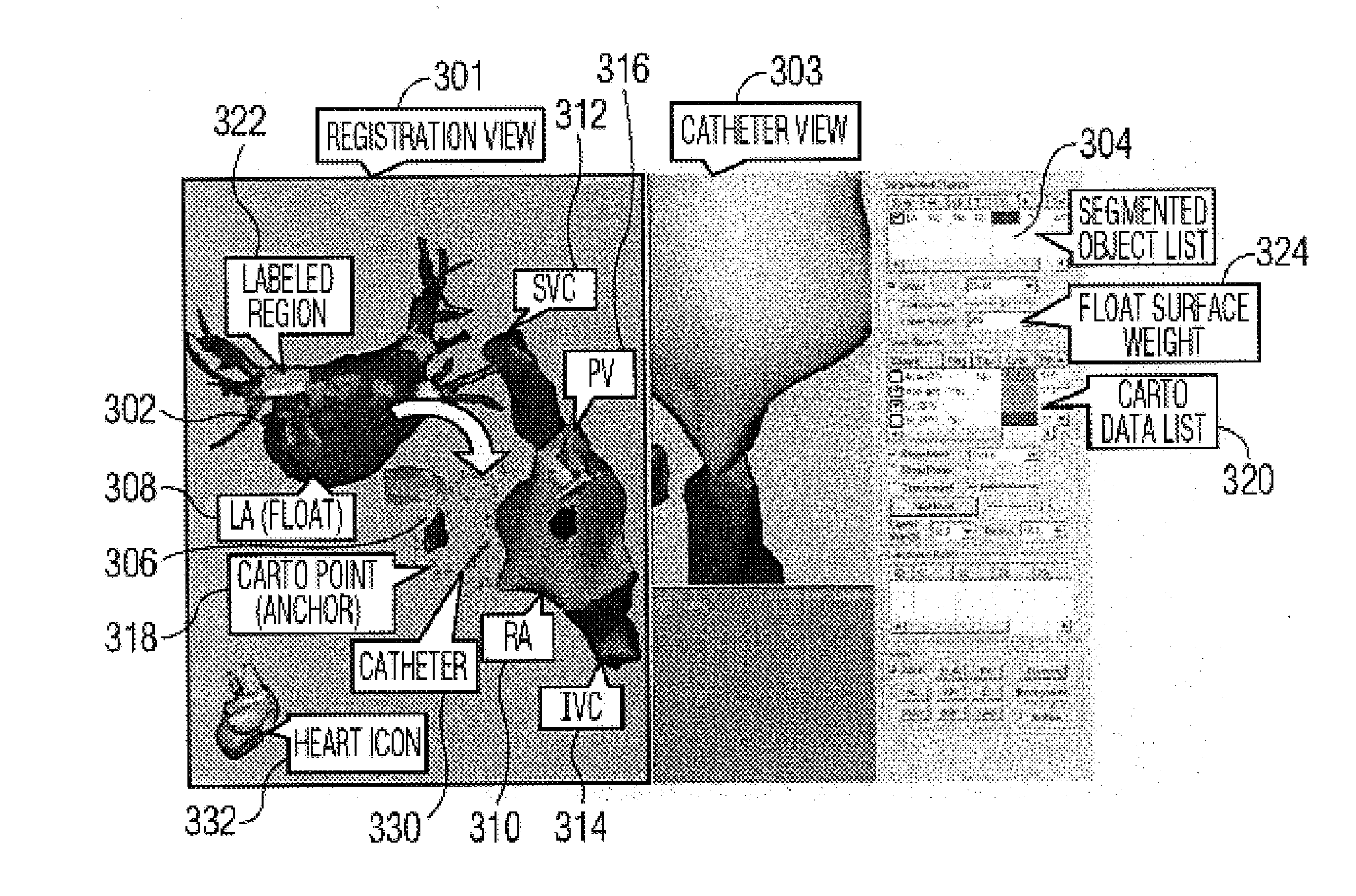
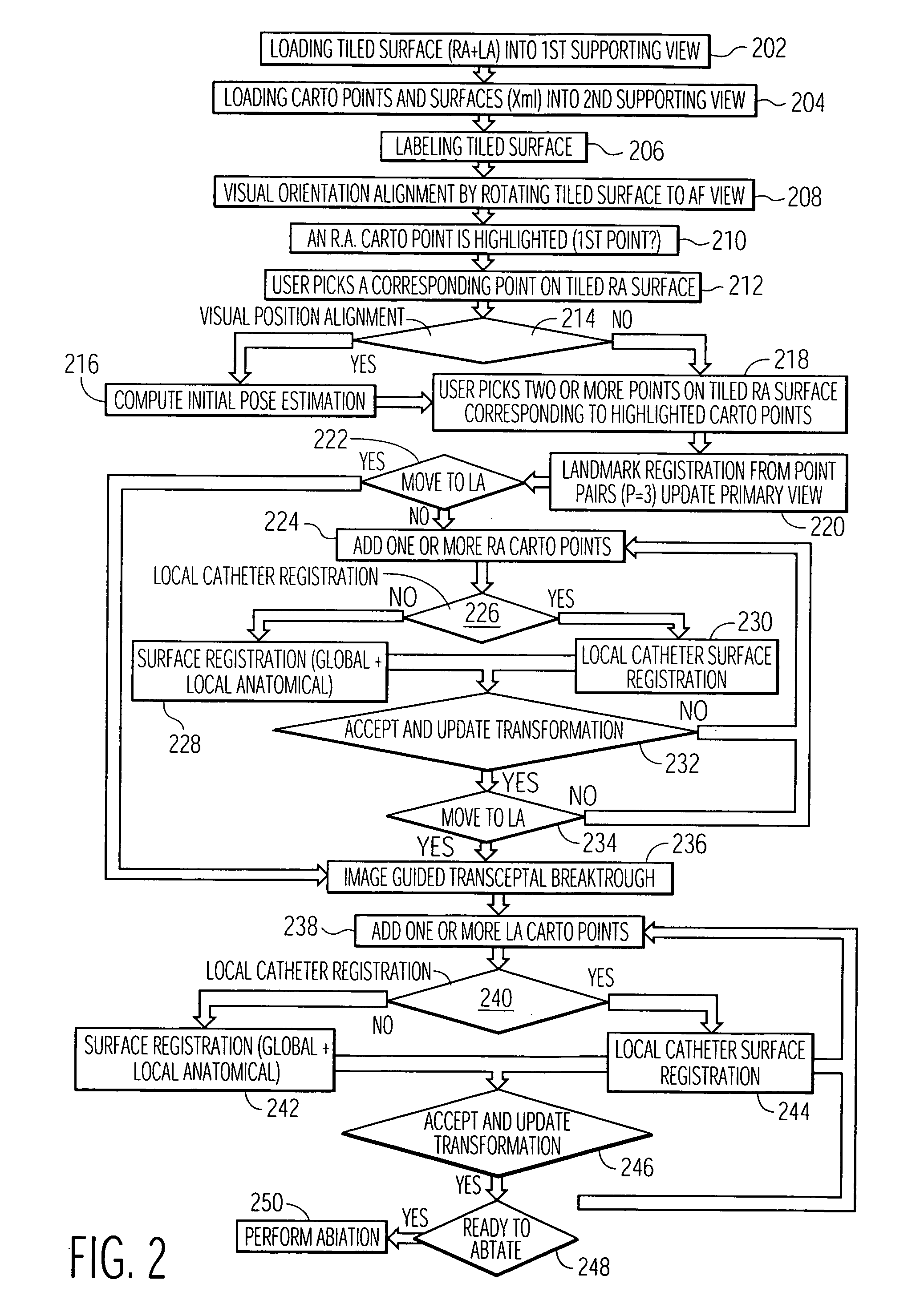
System and method for automatically registering three dimensional cardiac images with electro-anatomical cardiac mapping data
A system and method for automatically registering a three dimensional (3D) pre-operative image of an anatomical structure with intra-operative electrophysiological (EP) points of a 3D electro-anatomical (EA) image map of the anatomical structure is disclosed. The pre-operative image is displayed in a first supporting view. The intra-operative EA image map is displayed in a second supporting view. An alignment of the pre-operative image with the intra-operative map is performed by identifying at least one corresponding point on each image. The view of the pre-operative image is integrated with the EA map based on the alignment.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com