Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
238 results about "Pre operative" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Preoperative (pre-op) [prē·op′ərətiv′] Etymology: L, prae + operari, to work. pertaining to the period before a surgical procedure. Commonly the preoperative period begins with the first preparation of the patient for surgery, such as when the surgery is scheduled.
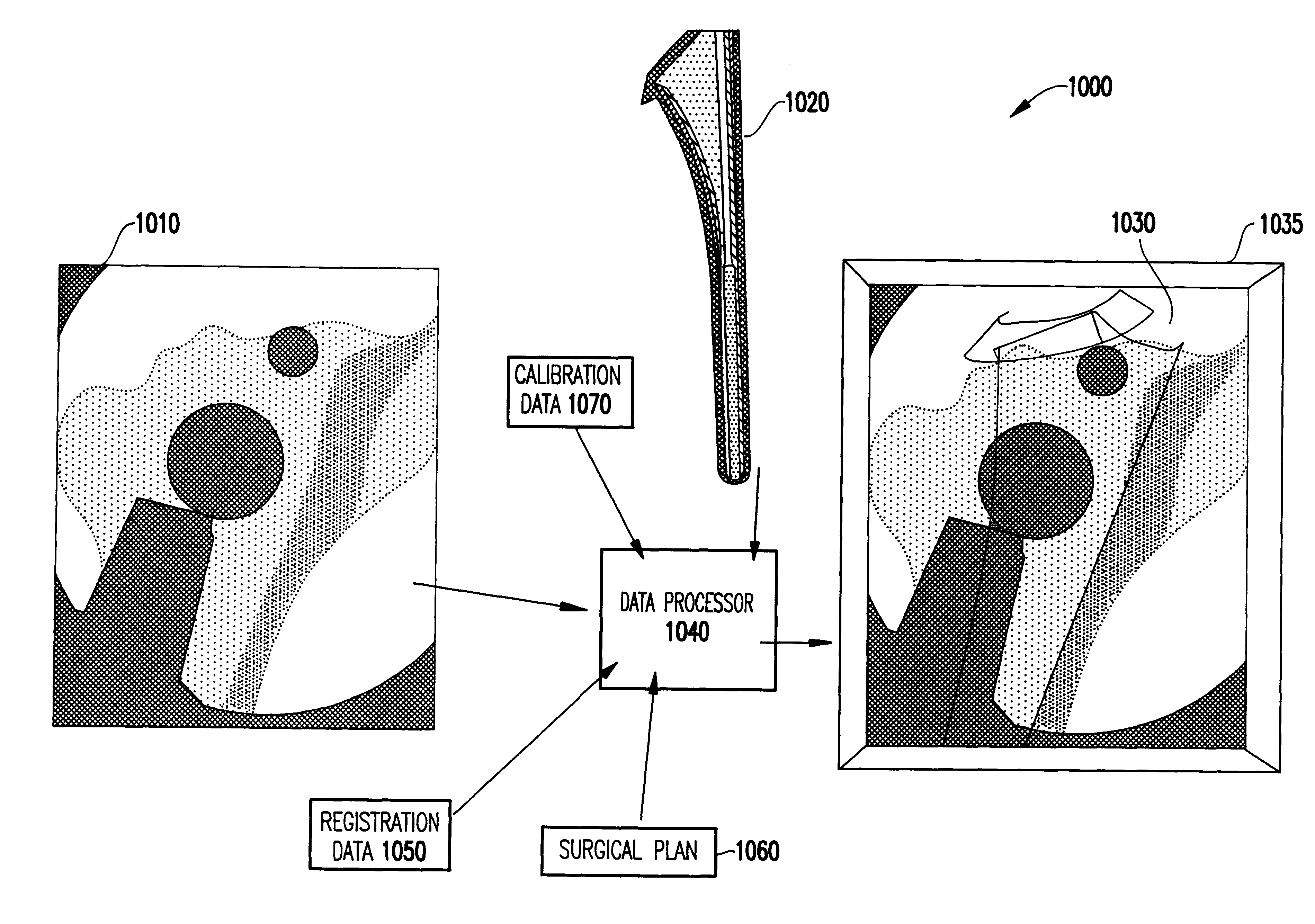
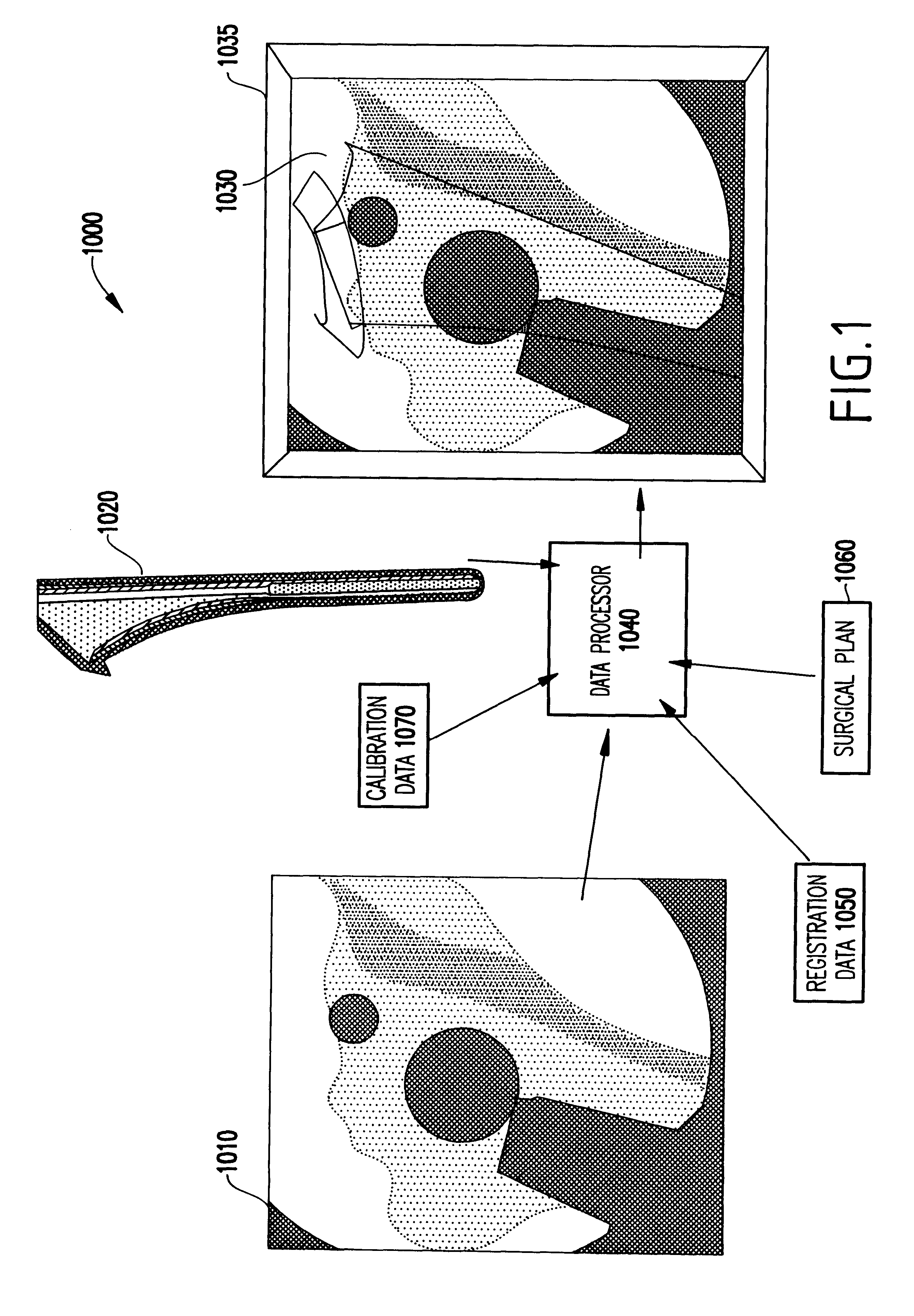
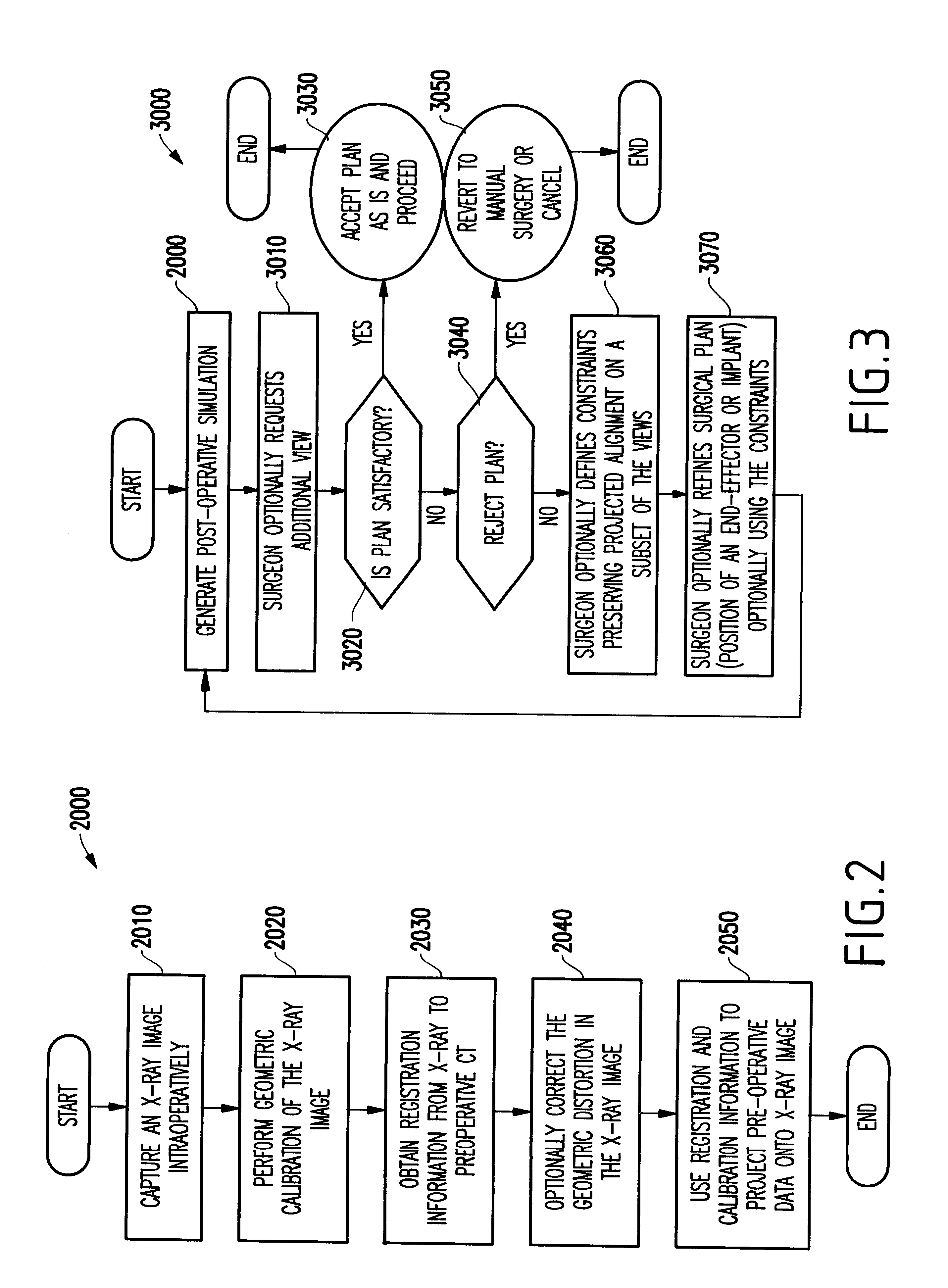
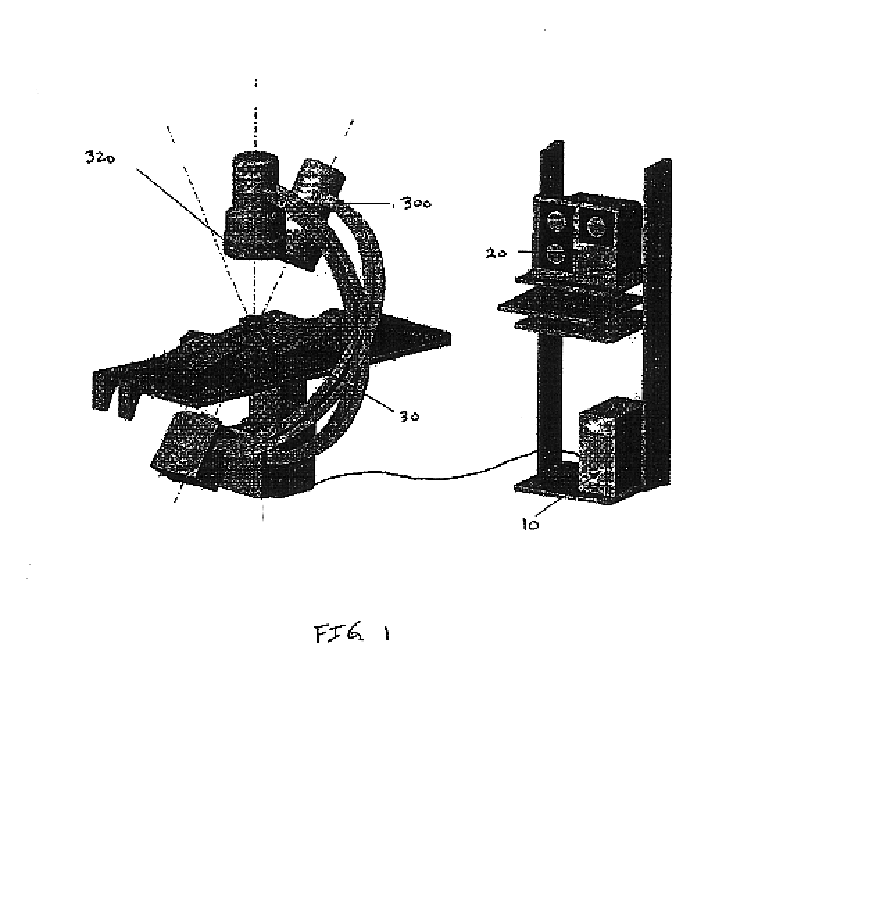
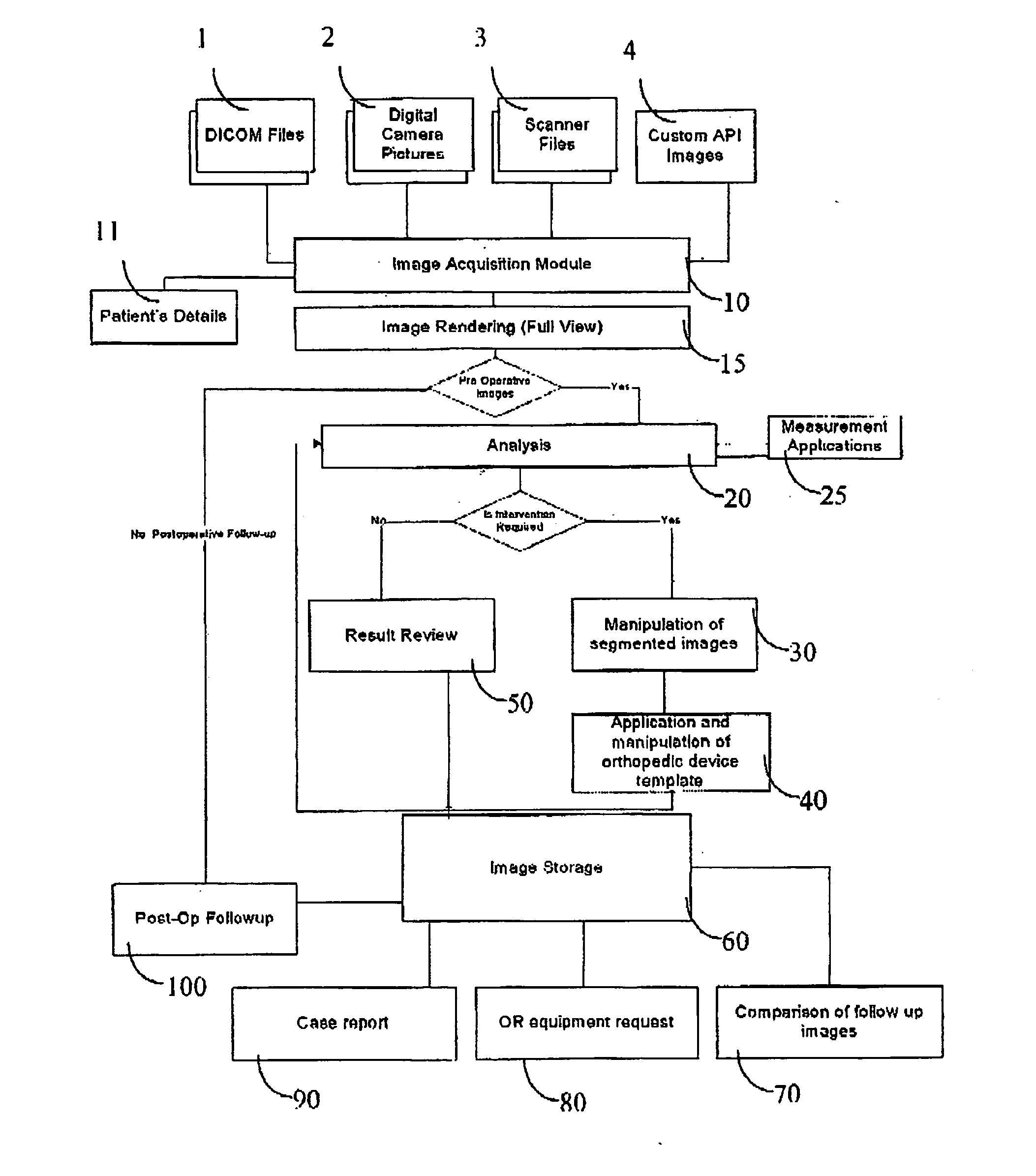
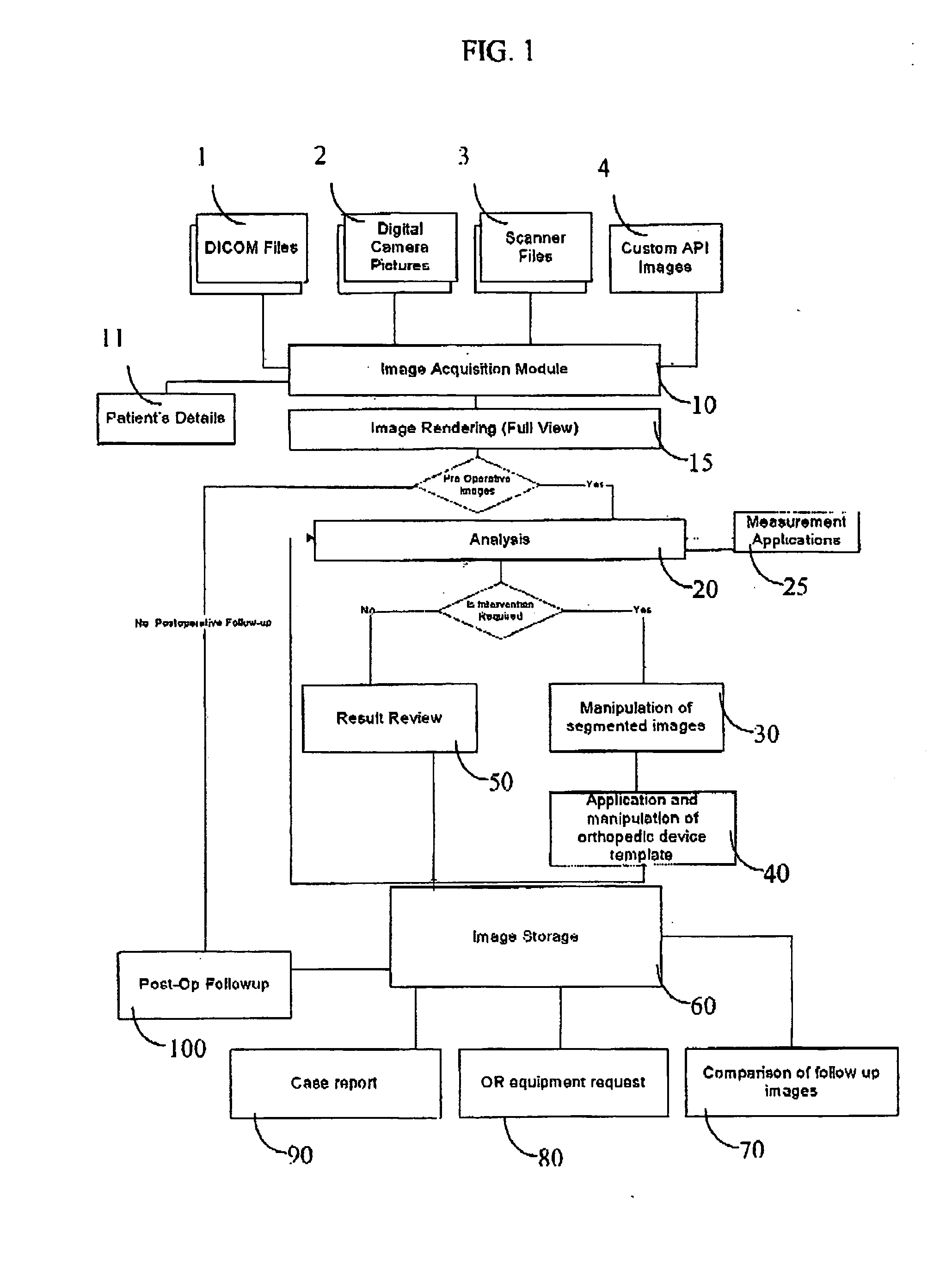
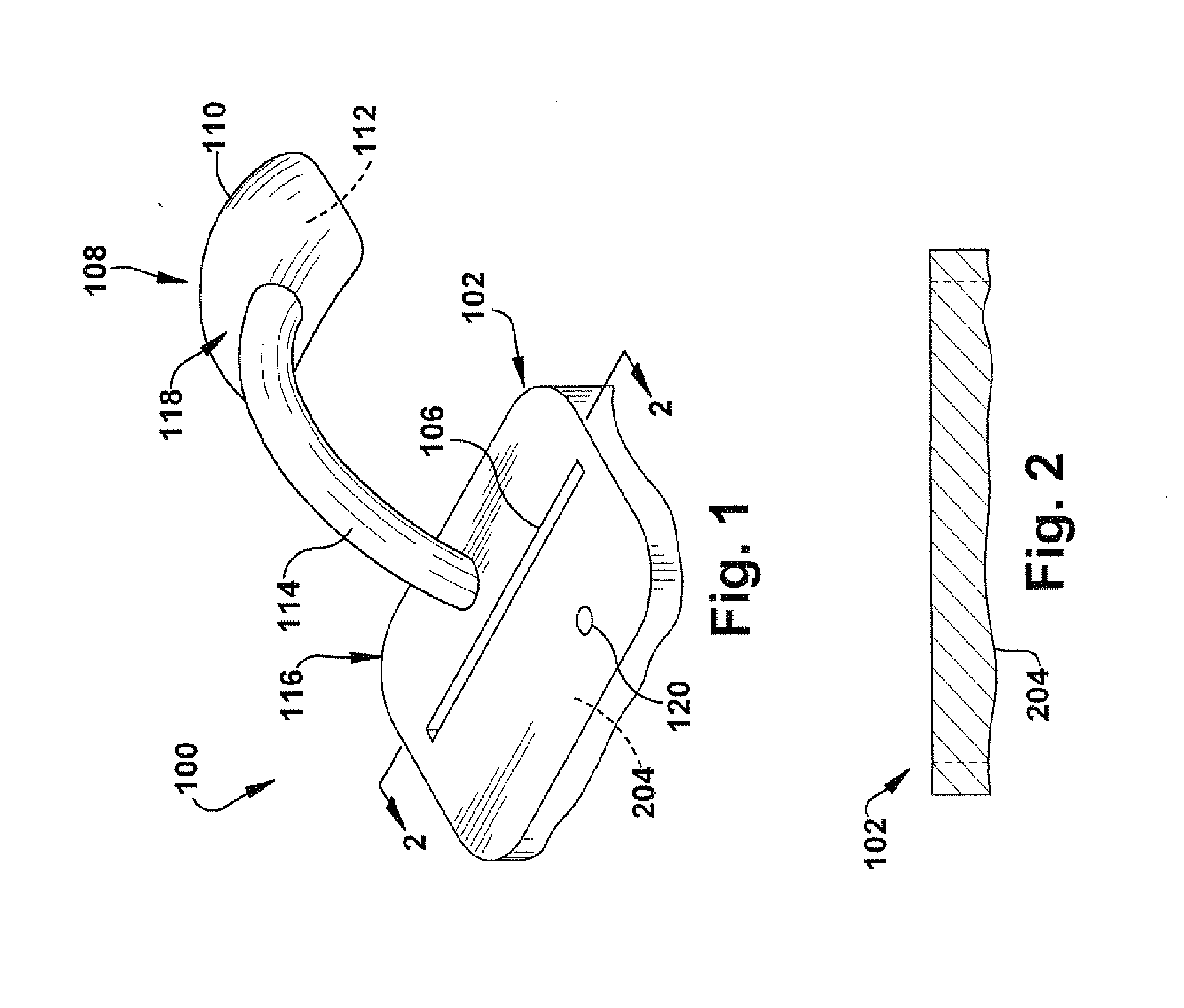
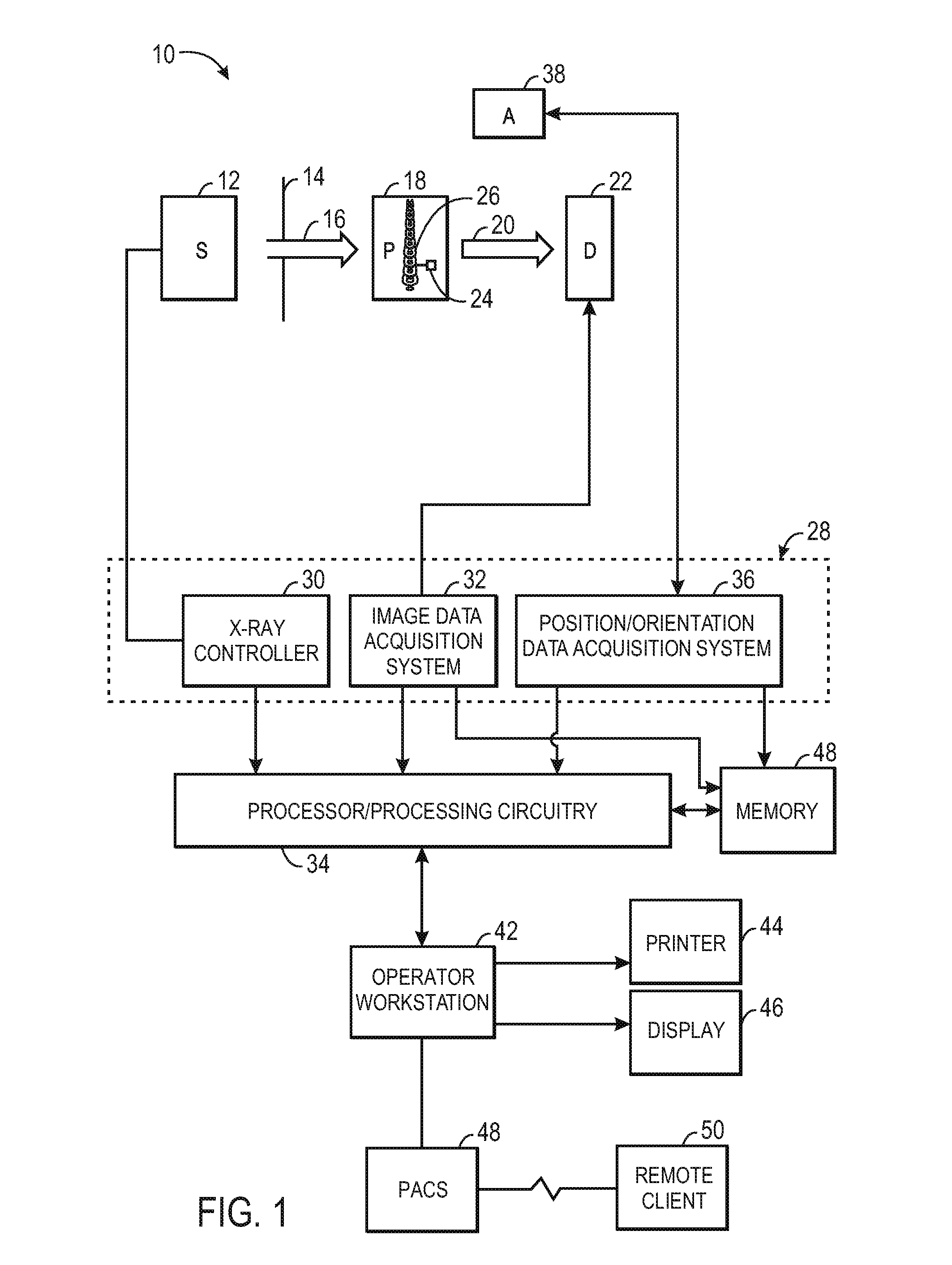
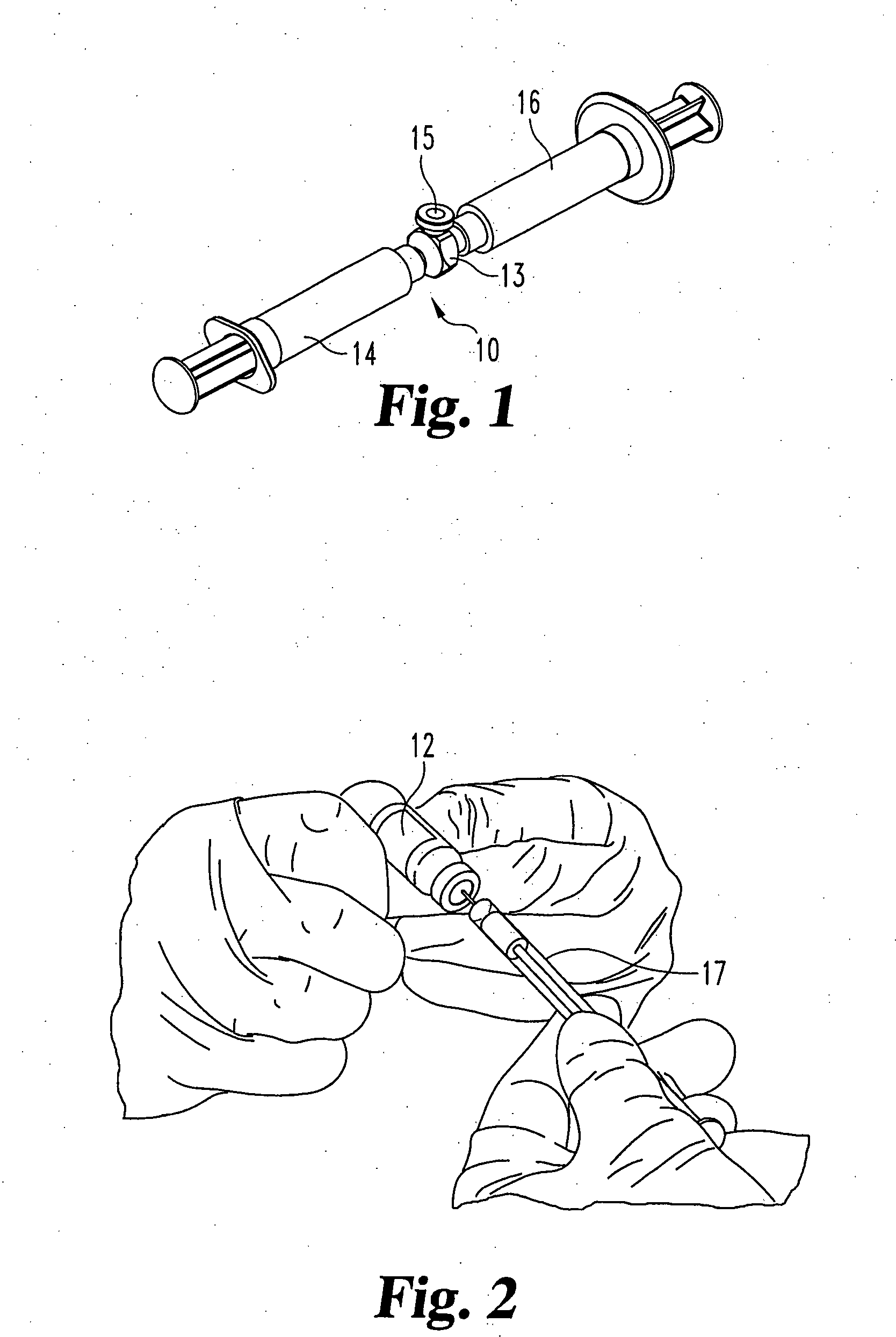
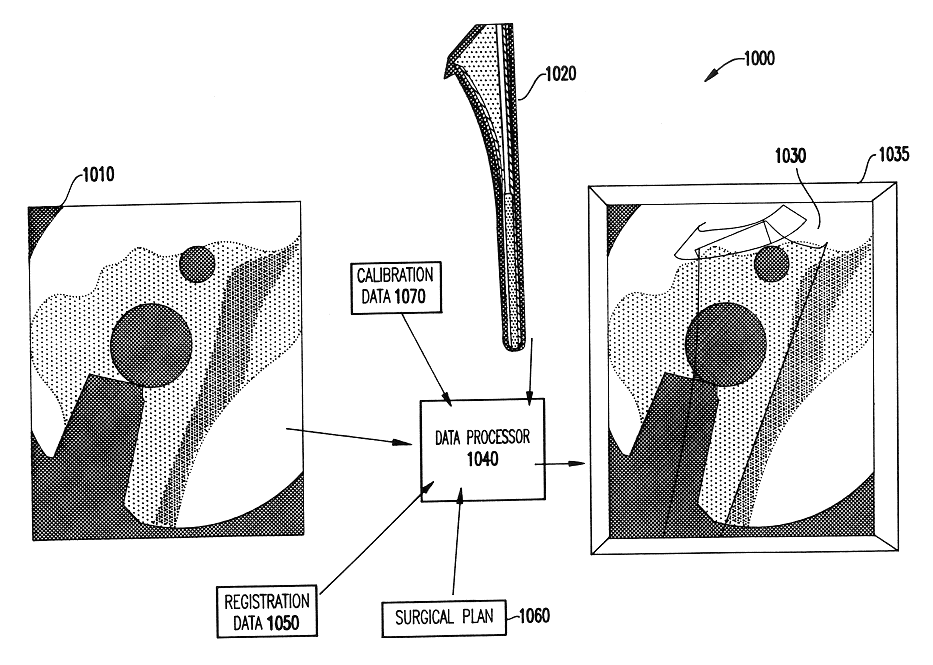
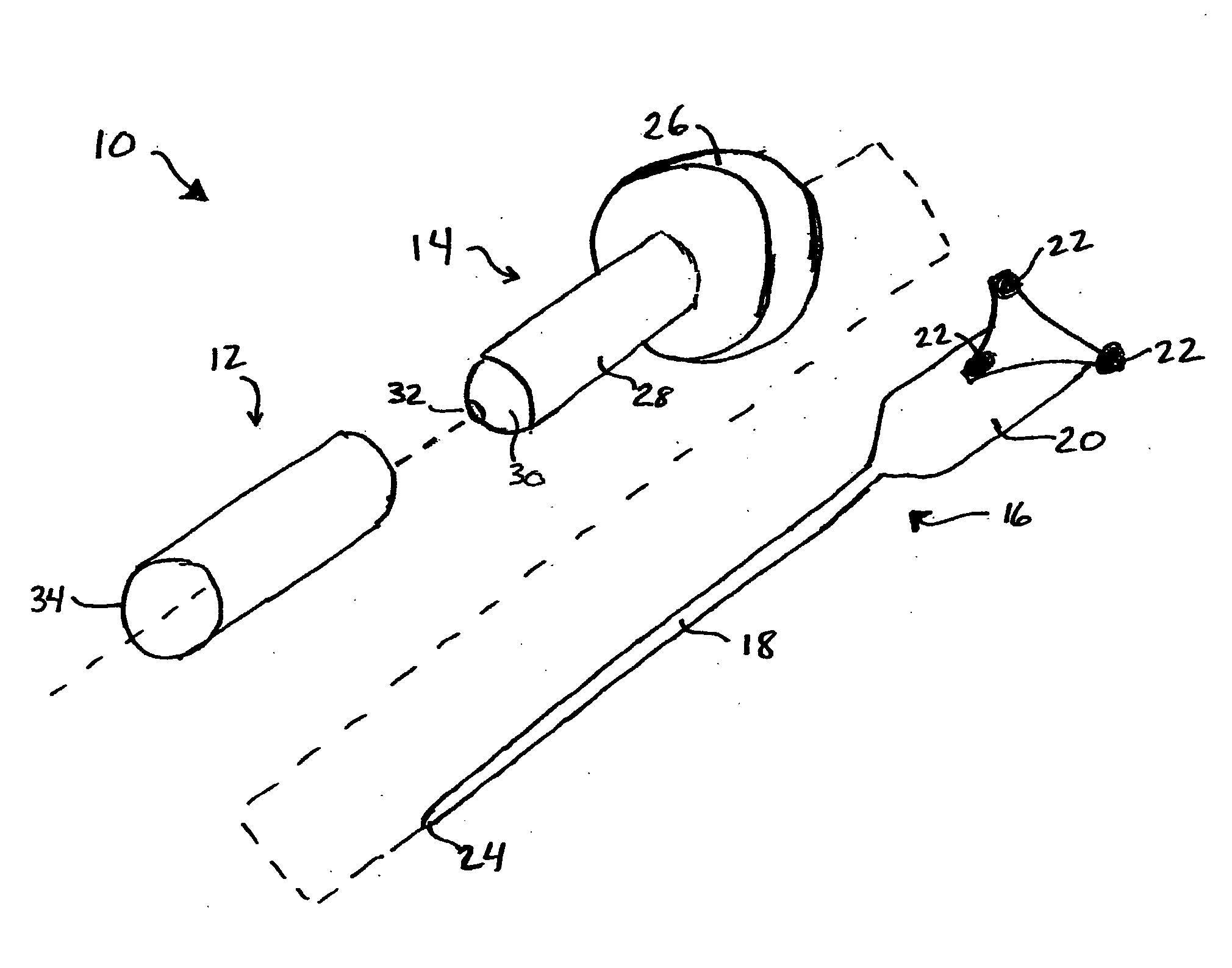
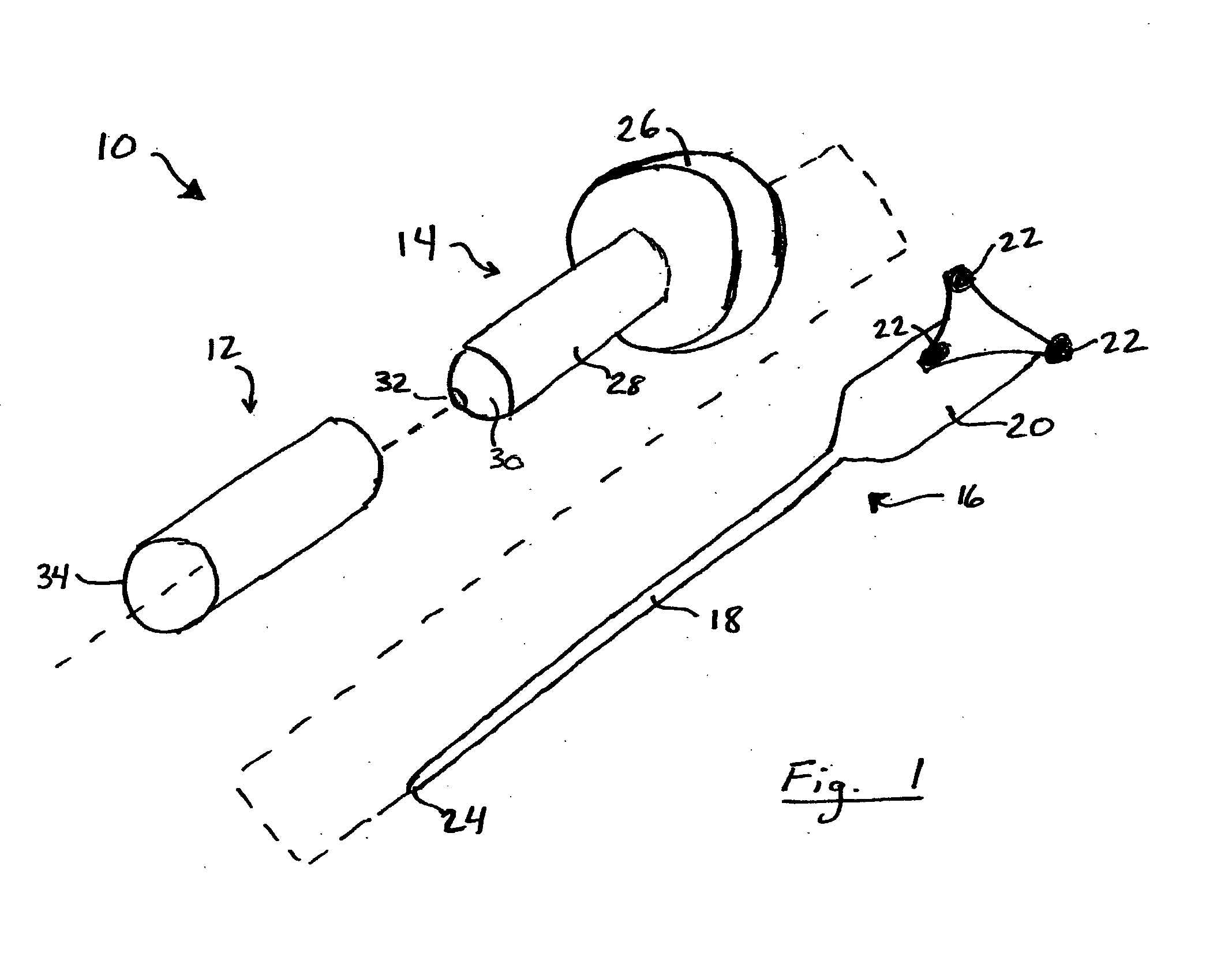
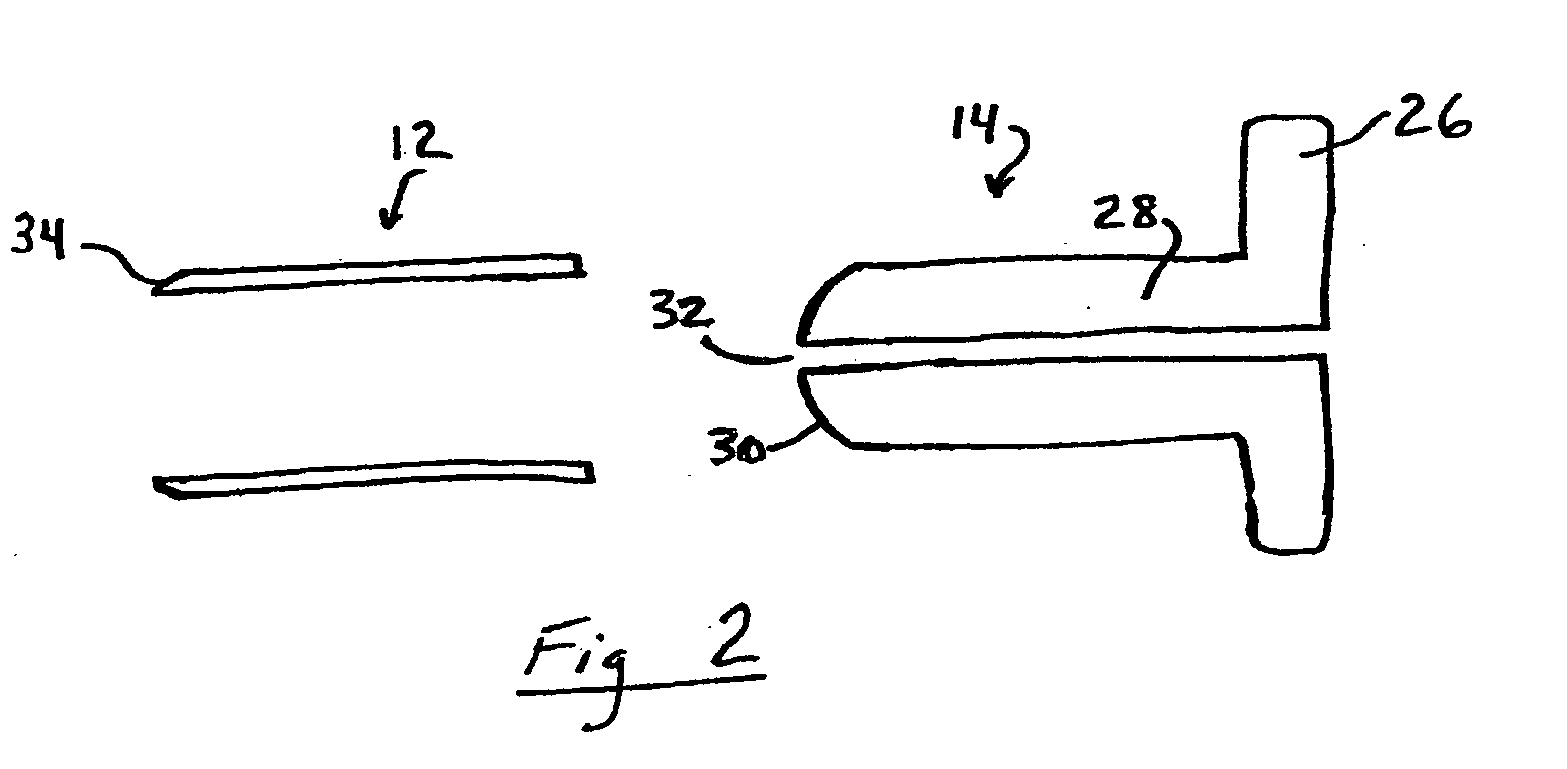
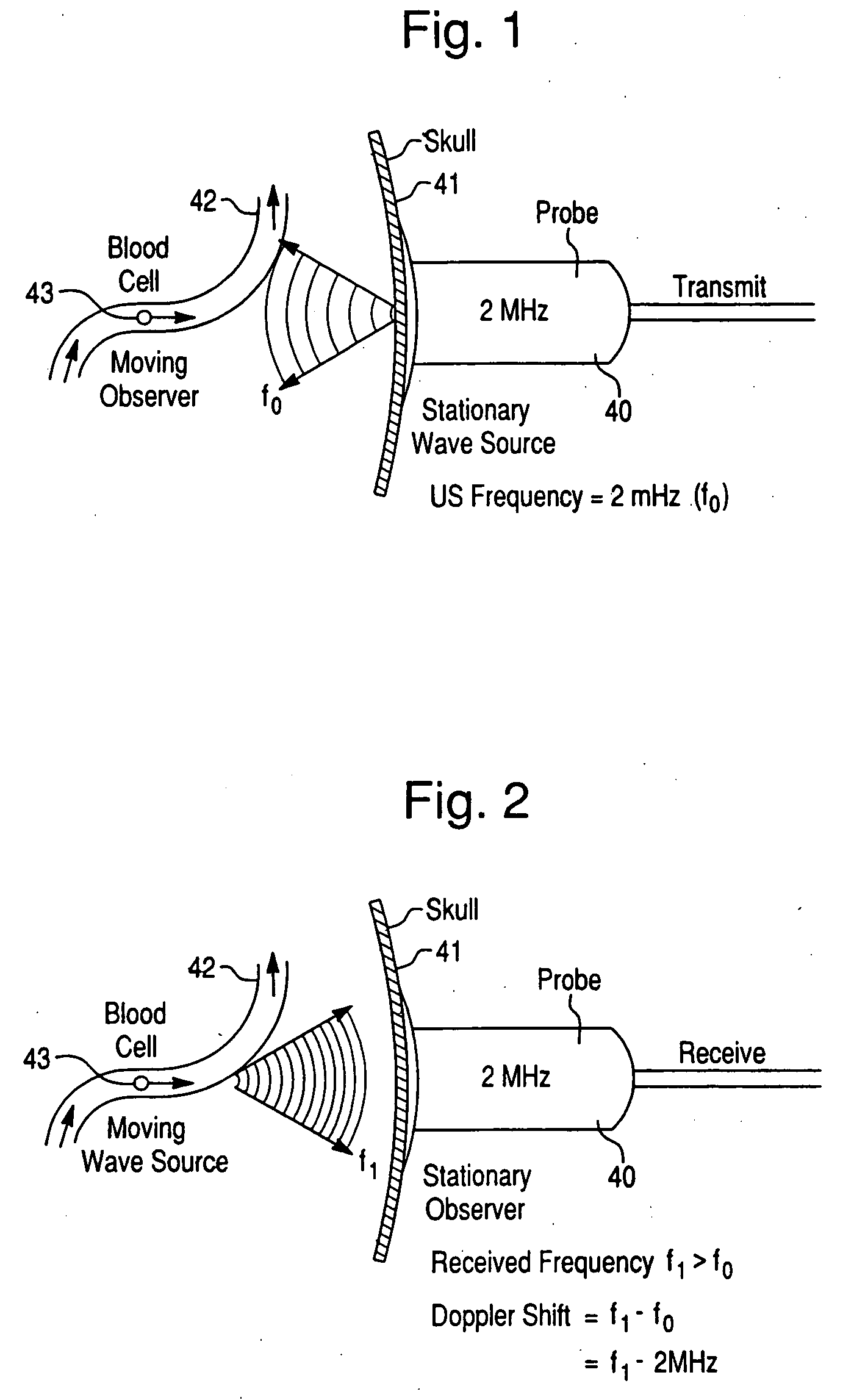
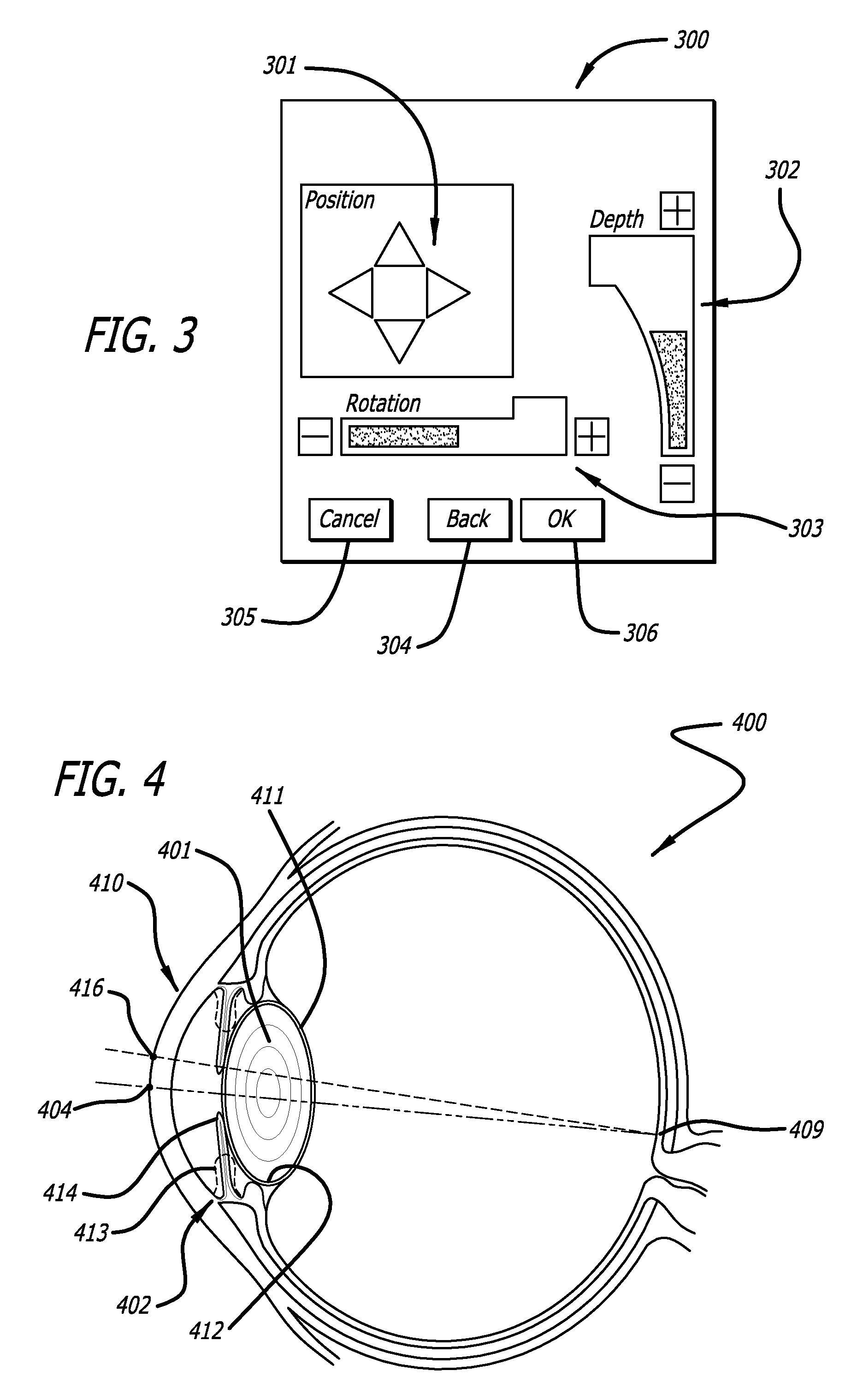
System and method for intra-operative, image-based, interactive verification of a pre-operative surgical plan
InactiveUS6301495B1Registration errorAvoid mistakesGeometric image transformationDiagnostic markersFusion mechanismPhysical space
A system and method for intra-operatively providing a surgeon with visual evaluations of possible surgical outcomes ahead of time, and generating simulated data, includes a medical imaging camera, a registration device for registering data to a physical space, and to the medical imaging camera, and a fusion mechanism for fusing the data and the images to generate simulated data. The simulated data (e.g., such as augmented X-ray images) is natural and easy for a surgeon to interpret. In an exemplary implementation, the system preferably includes a data processor which receives a three-dimensional surgical plan or three-dimensional plan of therapy delivery, one or a plurality of two-dimensional intra-operative images, a three-dimensional model of pre-operative data, registration data, and image calibration data. The data processor produces one or a plurality of simulated post-operative images, by integrating a projection of a three-dimensional model of pre-operative data onto one or a plurality of two-dimensional intra-operative images.
Owner:IBM CORP
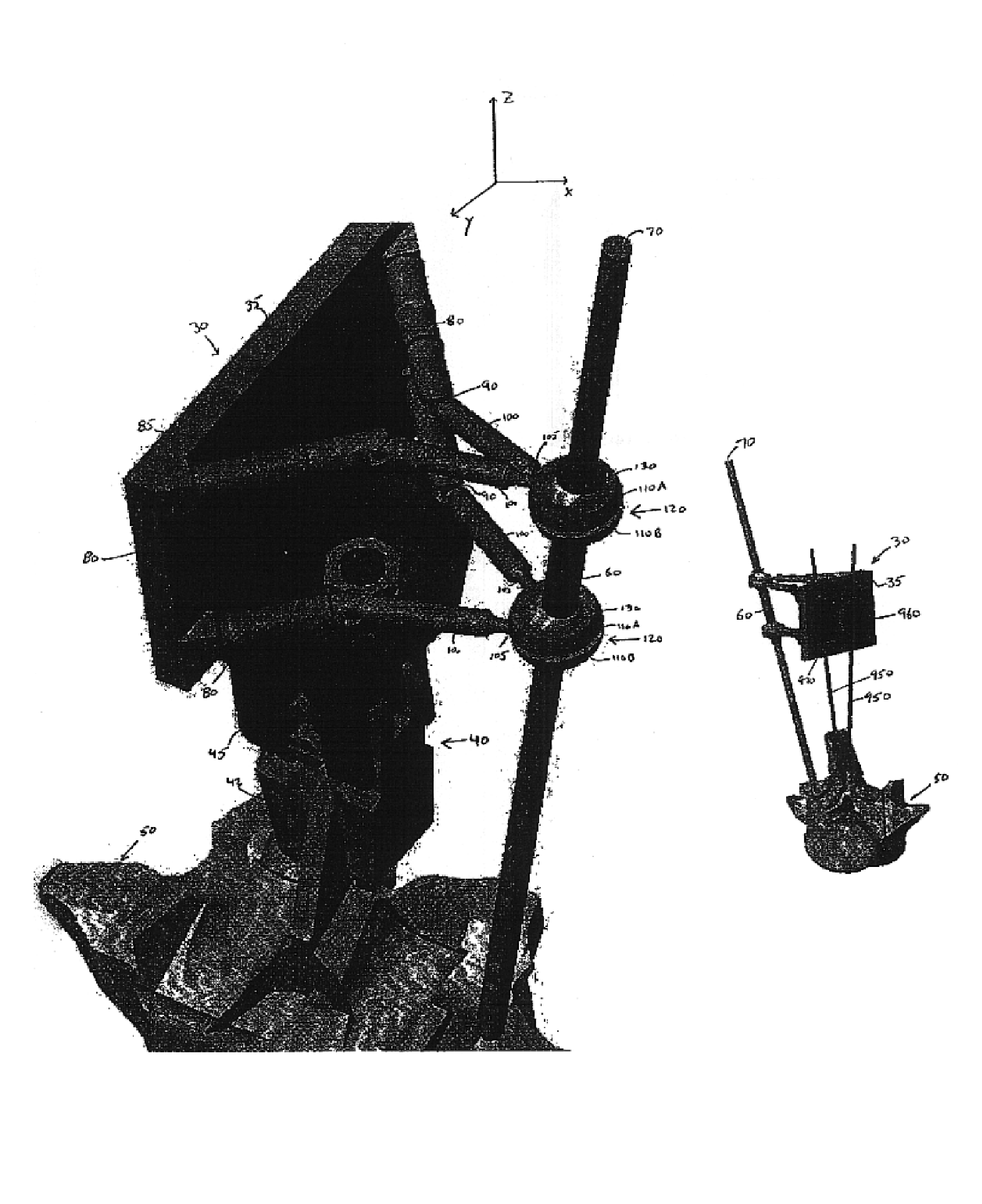
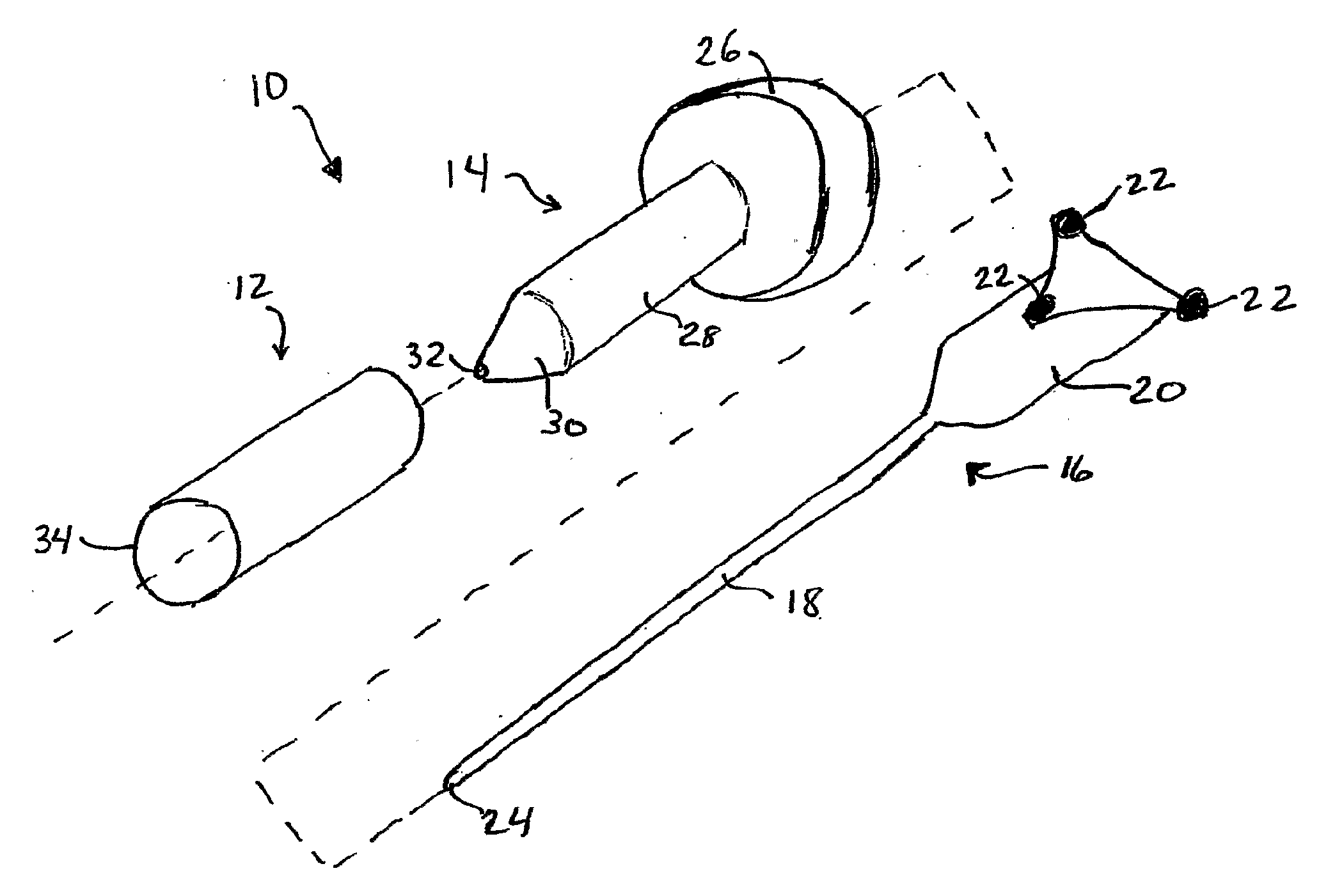
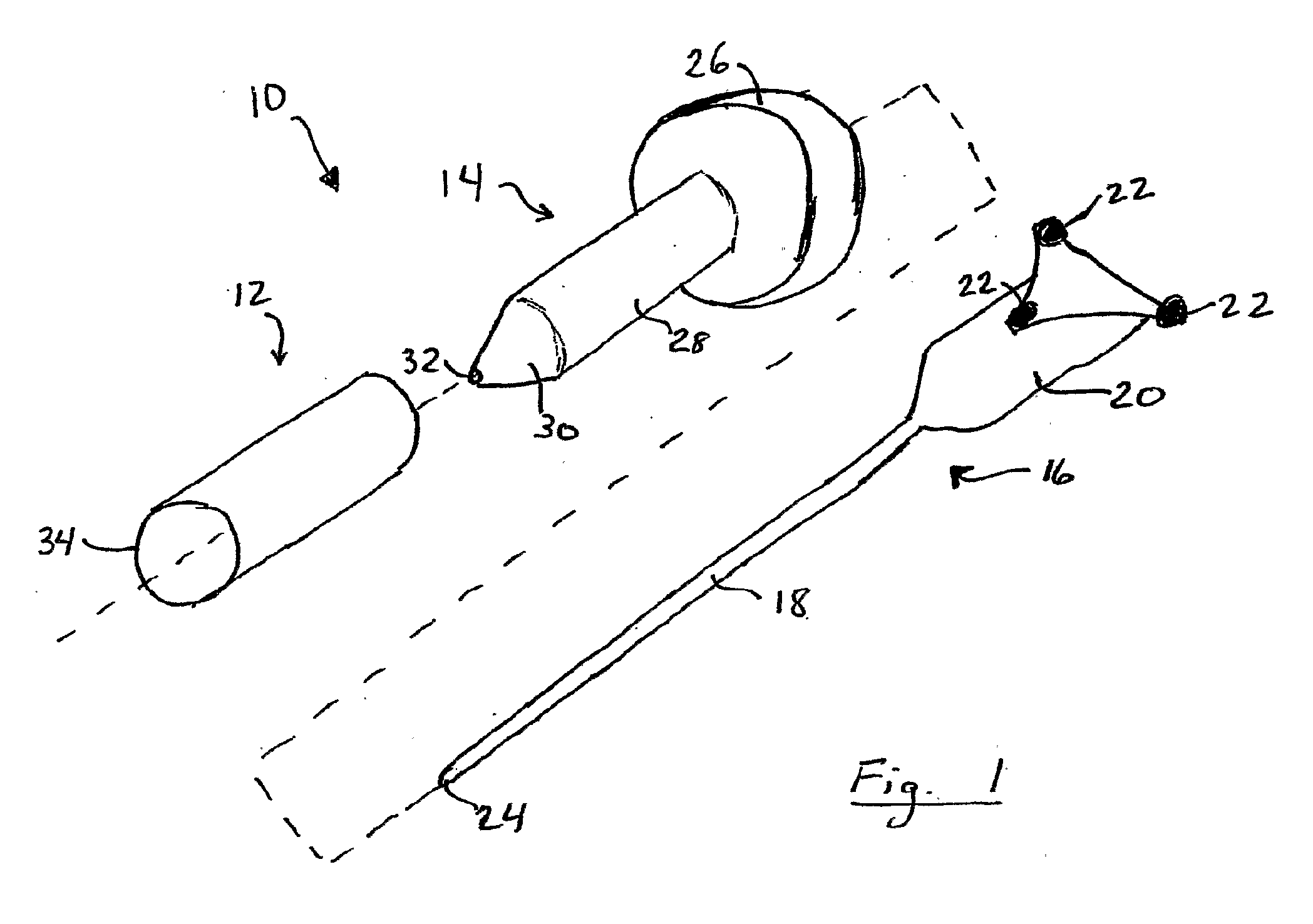
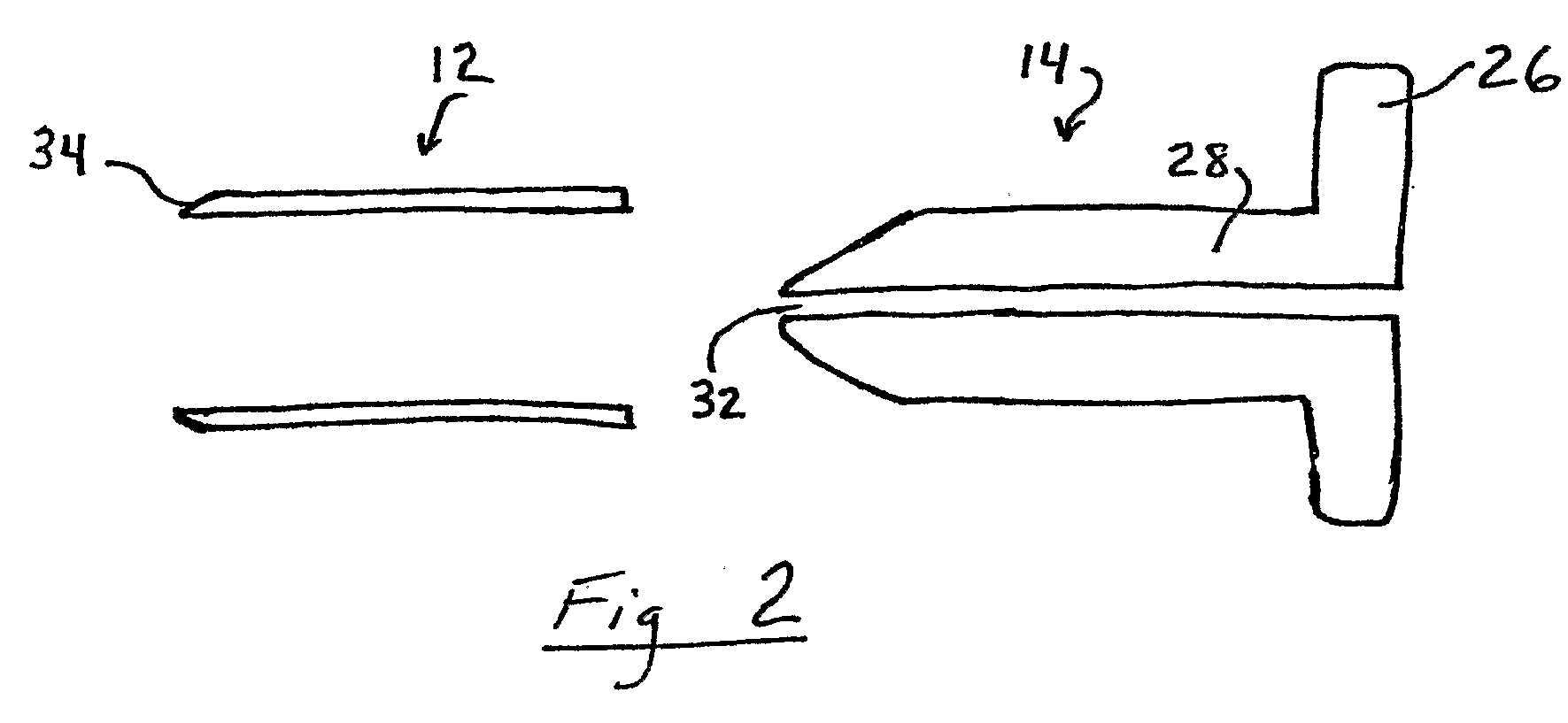
Miniature bone-mounted surgical robot
InactiveUS6837892B2Highly accurateImprove efficiencyMechanical apparatusJointsSurgical robotSurgical site
A miniature surgical robot and a method for using it are disclosed. The miniature surgical robot attaches directly with the bone of a patient. Two-dimensional X-ray images of the robot on the bone are registered with three-dimensional images of the bone. This locates the robot precisely on the bone of the patient. The robot is then directed to pre-operative determined positions based on a pre-operative plan by the surgeon. The robot then moves to the requested surgical site and aligns a sleeve through which the surgeon can insert a surgical tool.
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
Videotactic and audiotactic assisted surgical methods and procedures
InactiveUS20080243142A1Medical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesAnatomical structuresSurgical operation
The present invention provides video and audio assisted surgical techniques and methods. Novel features of the techniques and methods provided by the present invention include presenting a surgeon with a video compilation that displays an endoscopic-camera derived image, a reconstructed view of the surgical field (including fiducial markers indicative of anatomical locations on or in the patient), and / or a real-time video image of the patient. The real-time image can be obtained either with the video camera that is part of the image localized endoscope or with an image localized video camera without an endoscope, or both. In certain other embodiments, the methods of the present invention include the use of anatomical atlases related to pre-operative generated images derived from three-dimensional reconstructed CT, MRI, x-ray, or fluoroscopy. Images can furthermore be obtained from pre-operative imaging and spacial shifting of anatomical structures may be identified by intraoperative imaging and appropriate correction performed.
Owner:GILDENBERG PHILIP L
Apparatus and method for using augmented reality vision system in surgical procedures
ActiveUS9123155B2Improve eyesightAvoid enteringMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesSurgerySurgical siteX-ray
A system and method for improving a surgeon's vision by overlaying augmented reality information onto a video image of the surgical site. A high definition video camera sends a video image in real time. Prior to the surgery, a pre-operative image is created from MRI, x-ray, ultrasound, or other method of diagnosis using imaging technology. The pre-operative image is stored within the computer. The computer processes the pre-operative image to decipher organs, anatomical geometries, vessels, tissue planes, orientation, and other structures. As the surgeon performs the surgery, the AR controller augments the real time video image with the processed pre-operative image and displays the augmented image on an interface to provide further guidance to the surgeon during the surgical procedure.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Pre-operative medical planning system and method for use thereof
ActiveUS20050059873A1Reduce fracturesAvoid misplacementImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFracture reductionMedicine
Method and apparatus for pre-operative planning of orthopedic surgical procedures. The pre operative planning includes the steps of image acquisition, calibration scaling and registration, fracture reduction or matching of prosthesis, application of fixation elements and creating of planning reports.
Owner:BRAINLAB
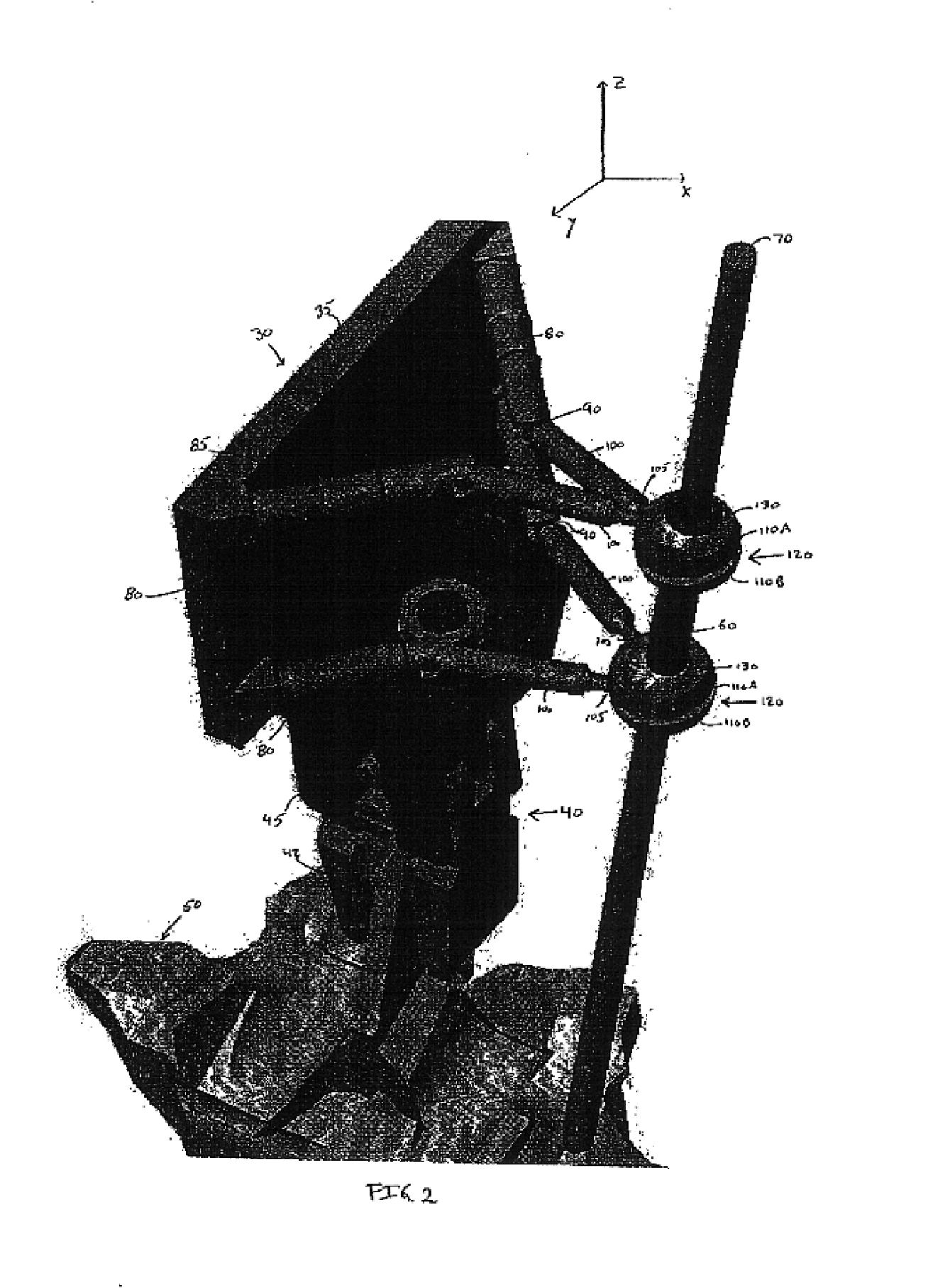
Positioning apparatus and method for a prosthetic implant
A positioning apparatus for guiding resection of a patient tissue and guiding placement of a prosthetic implant component in a desired implant position with respect to the resected patient tissue and method of use are described. A locating block includes a mating surface contoured for mating contact with the patient tissue. A cutting plane indicator provides a physical indication of a desired cutting plane for the resection. A placement indicator is spaced apart from the locating block and includes a component-contacting feature. An elongate spacing arm is operative to space the placement indicator apart from the locating block. The spacing arm is configured to place the component-contacting feature of the placement indicator at a predetermined placement position in three-dimensional space relative to the patient tissue. The placement position predetermination is at least partially based upon pre-operative imaging of the patient tissue.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
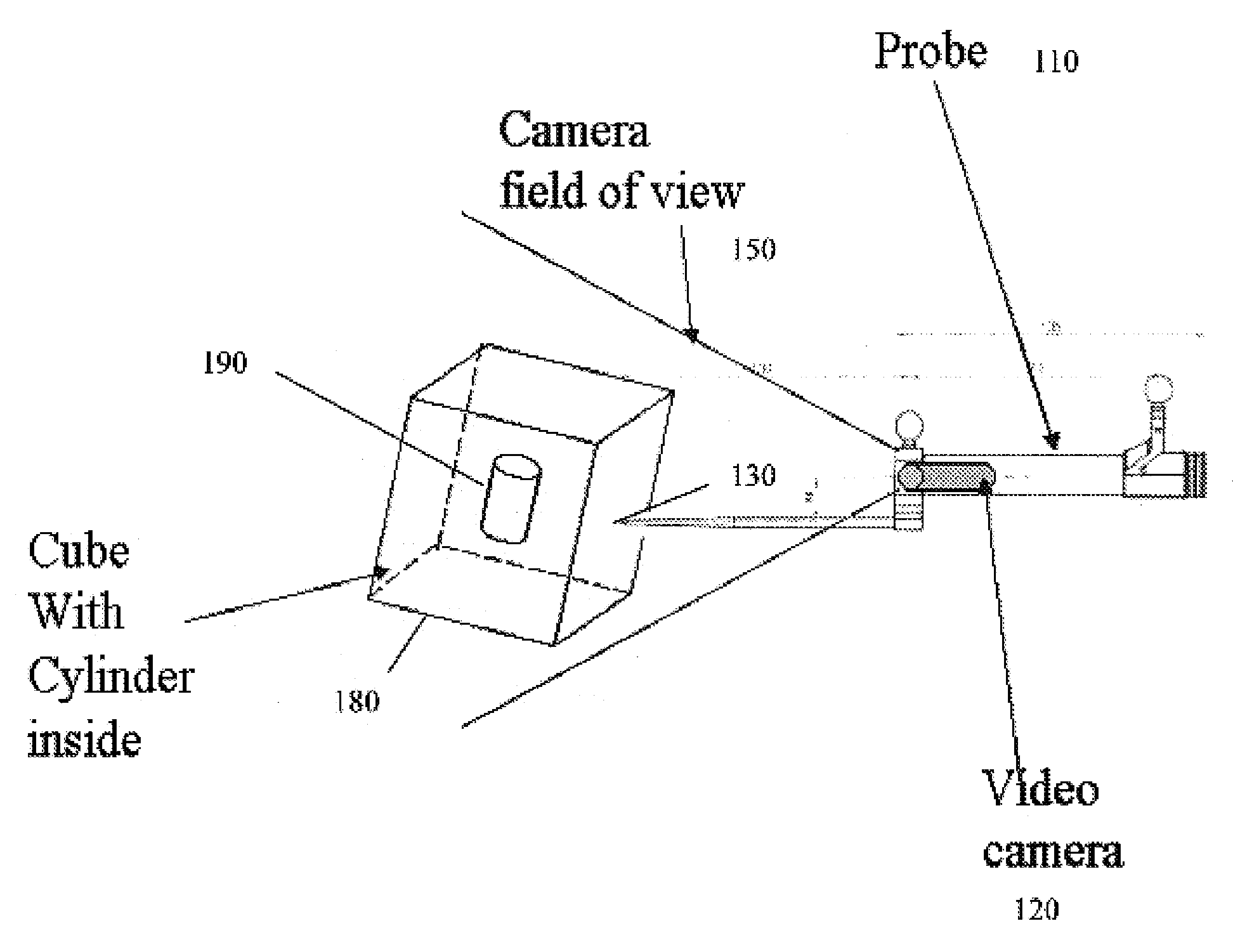
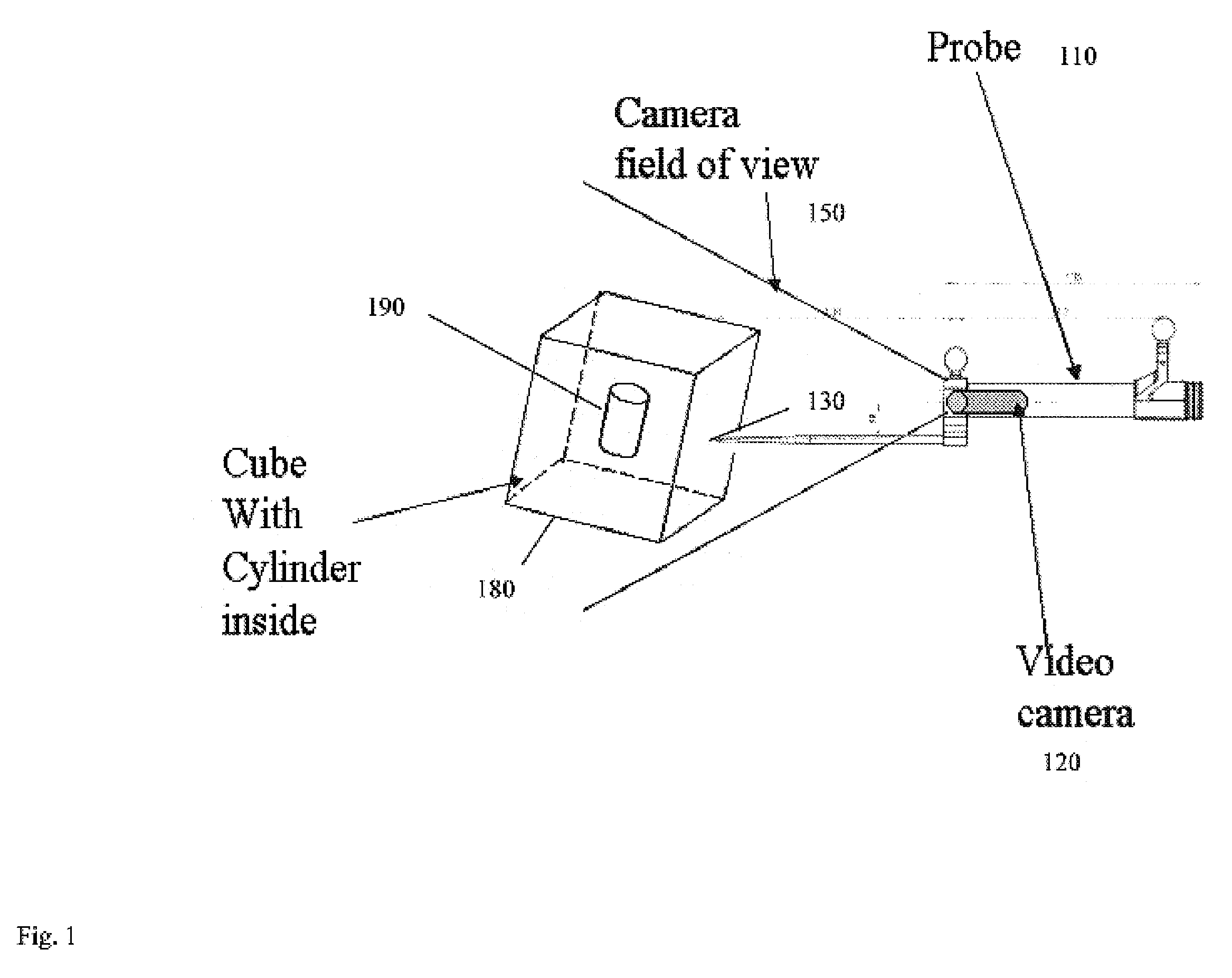
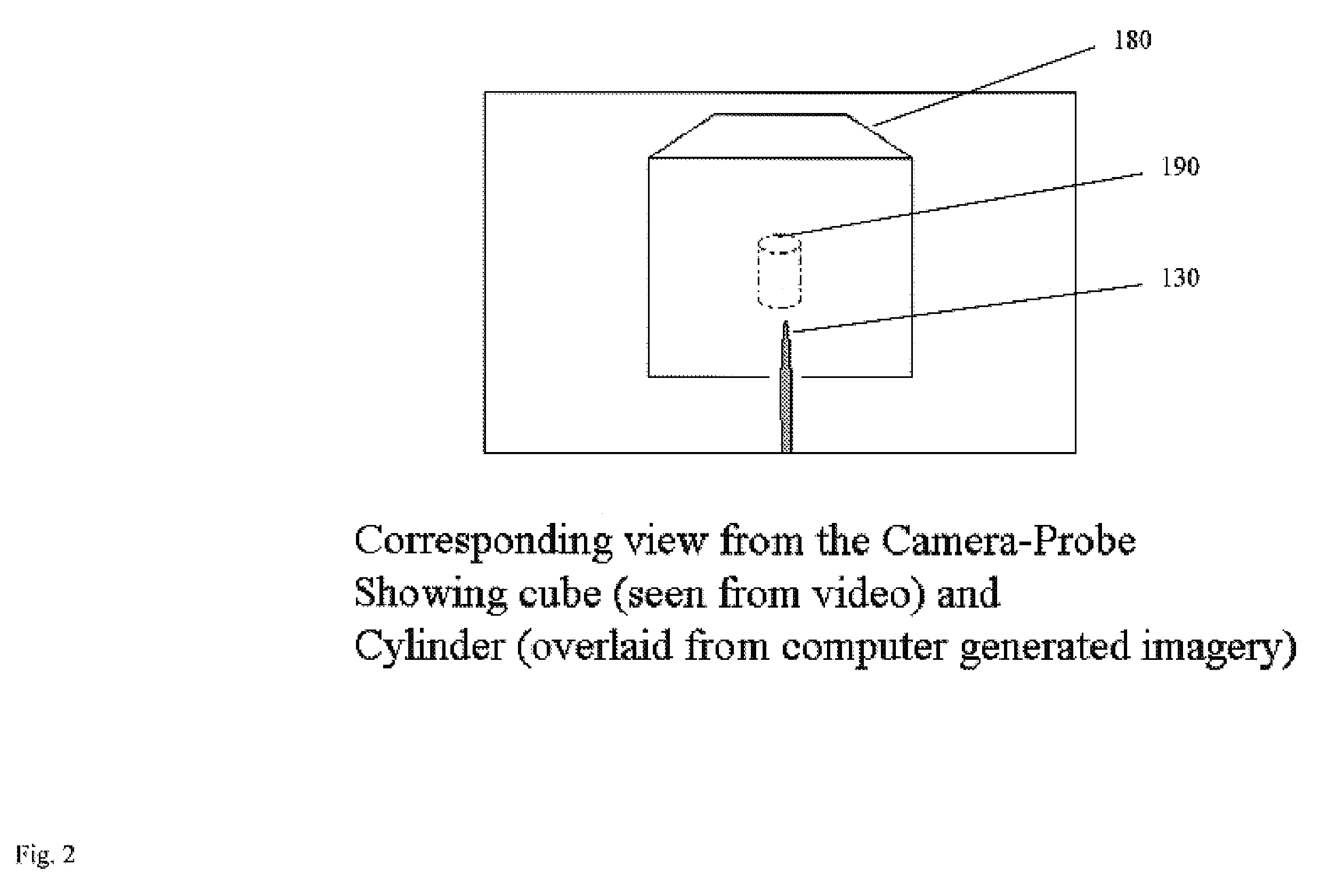
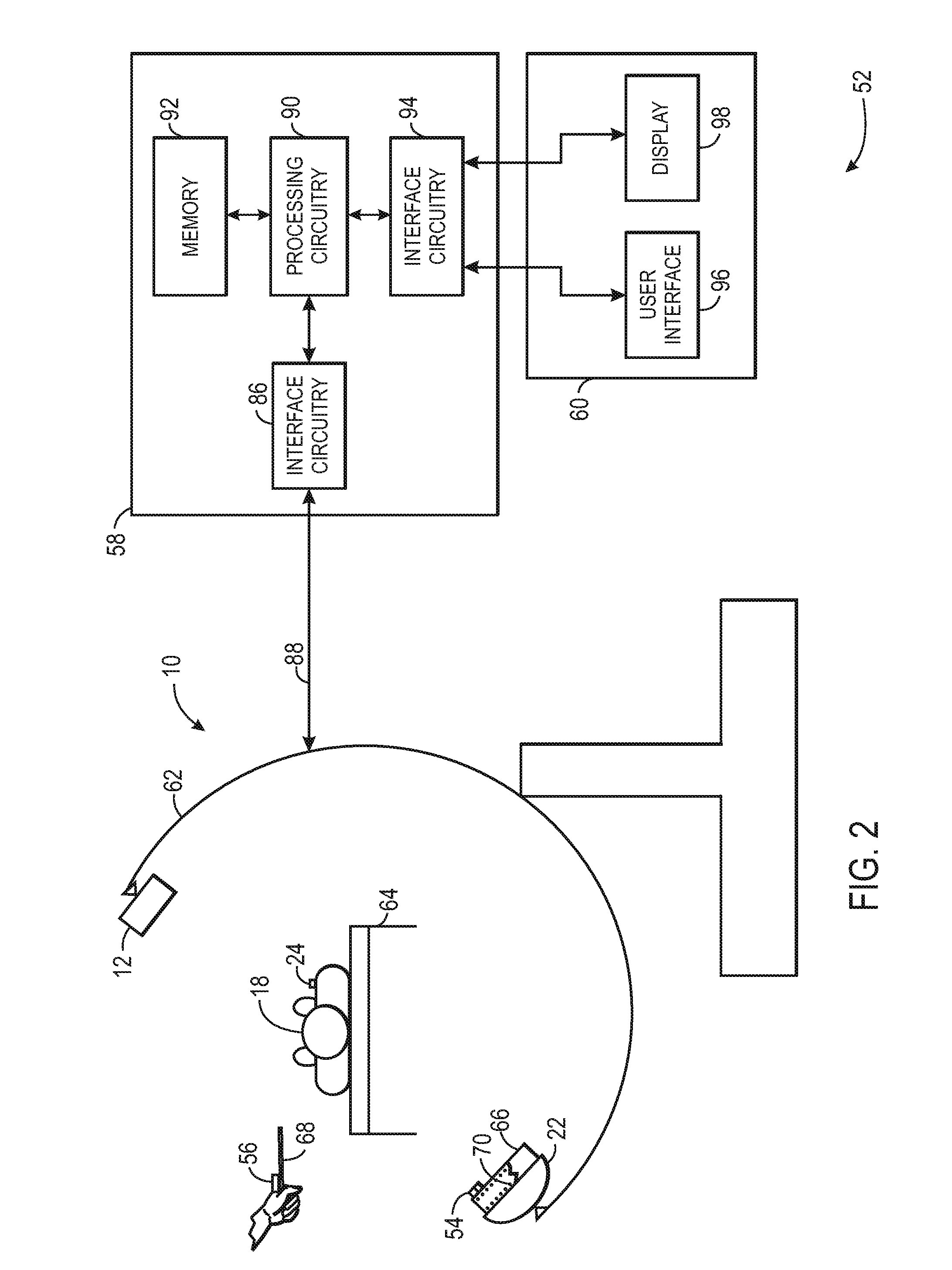
Computer enhanced surgical navigation imaging system (camera probe)
ActiveUS7491198B2Enhanced interactionEasy to navigateSurgical navigation systemsEndoscopesViewpointsSurgical approach
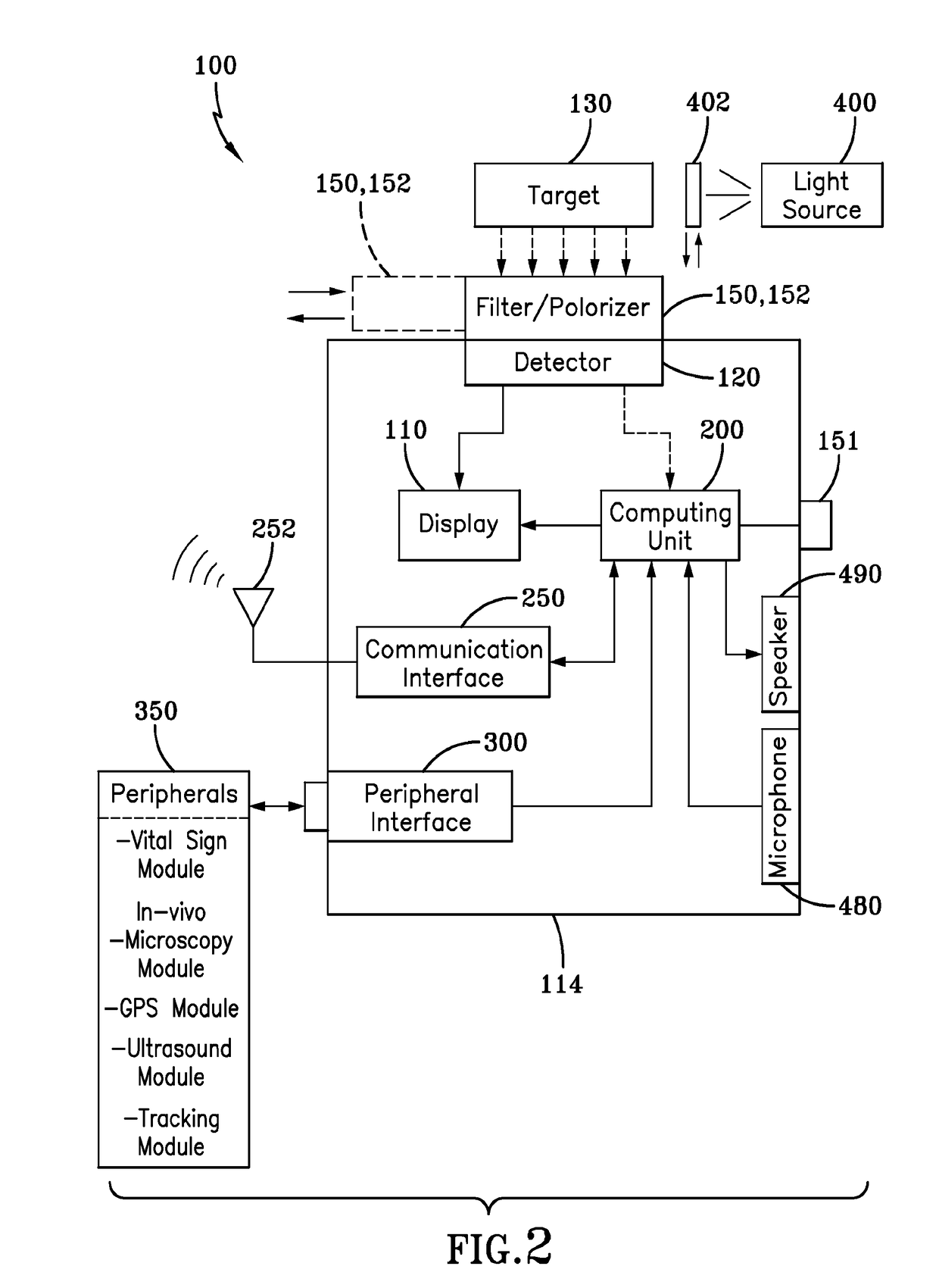
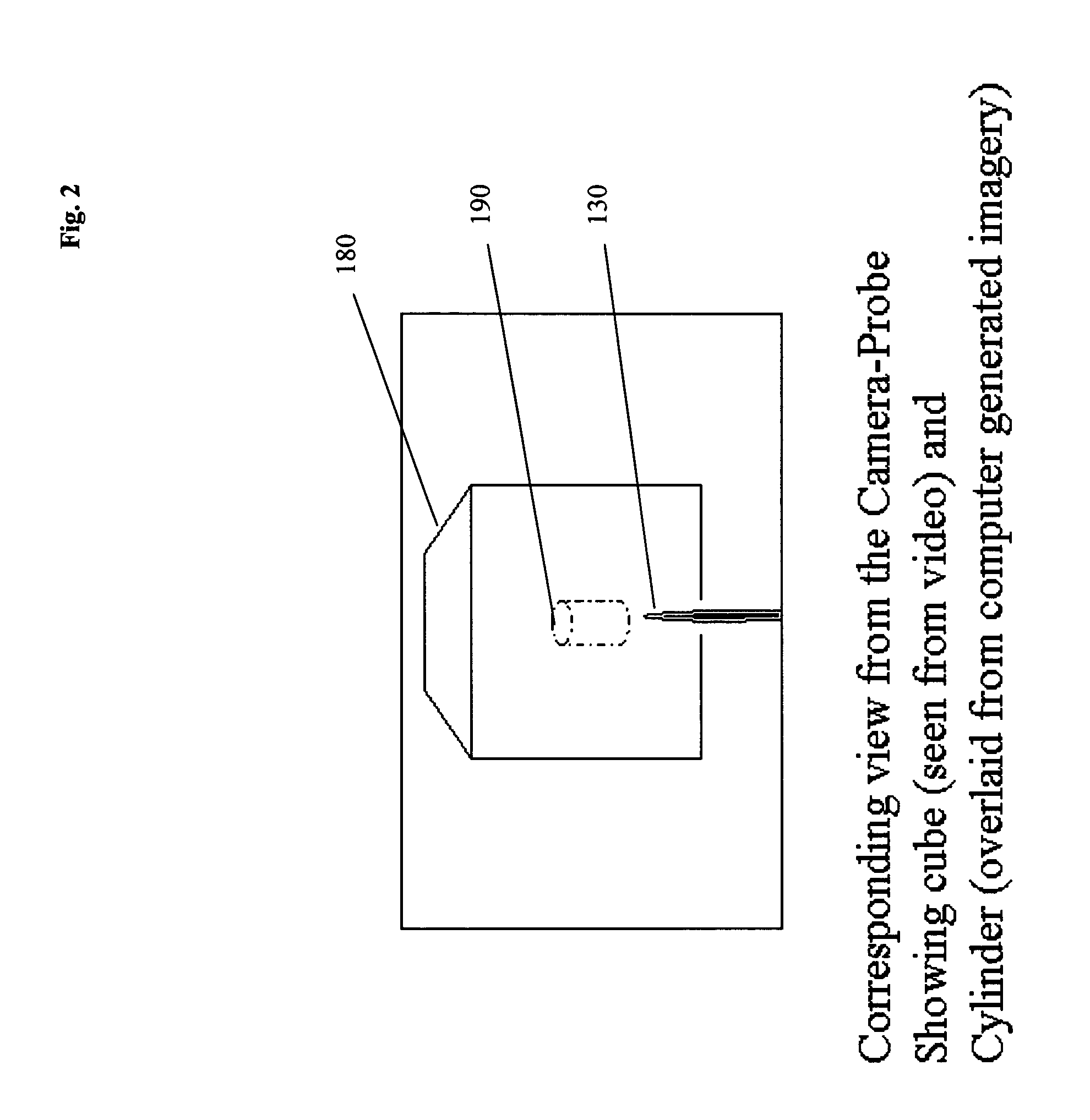
A system and method for navigation within a surgical field are presented. In exemplary embodiments according to the present invention a micro-camera can be provided in a hand-held navigation probe tracked by a tracking system. This enables navigation within an operative scene by viewing real-time images from the viewpoint of the micro-camera within the navigation probe, which are overlaid with computer generated 3D graphics depicting structures of interest generated from pre-operative scans. Various transparency settings of the camera image and the superimposed 3D graphics can enhance the depth perception, and distances between a tip of the probe and any of the superimposed 3D structures along a virtual ray extending from the probe tip can be dynamically displayed in the combined image. In exemplary embodiments of the invention a virtual interface can be displayed adjacent to the combined image on a system display, thus facilitating interaction with various navigation related functions. In exemplary embodiments according to the present invention virtual reality systems can be used to plan surgical approaches with multi-modal CT and MRI data. This allows for generating 3D structures as well as marking ideal surgical paths. The system and method presented thus enable transfer of a surgical planning scenario to a real-time view of an actual surgical field, thus enhancing navigation.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
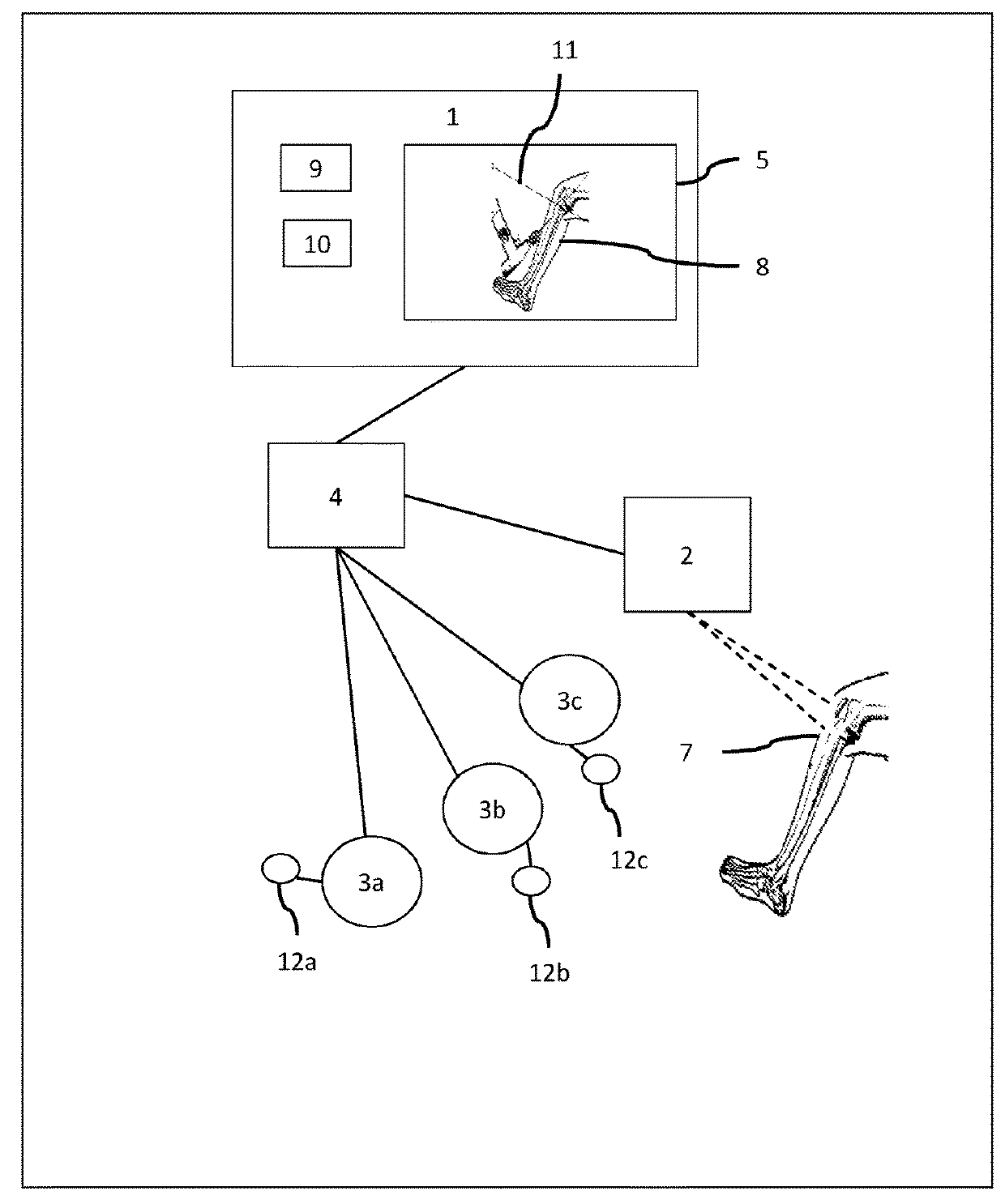
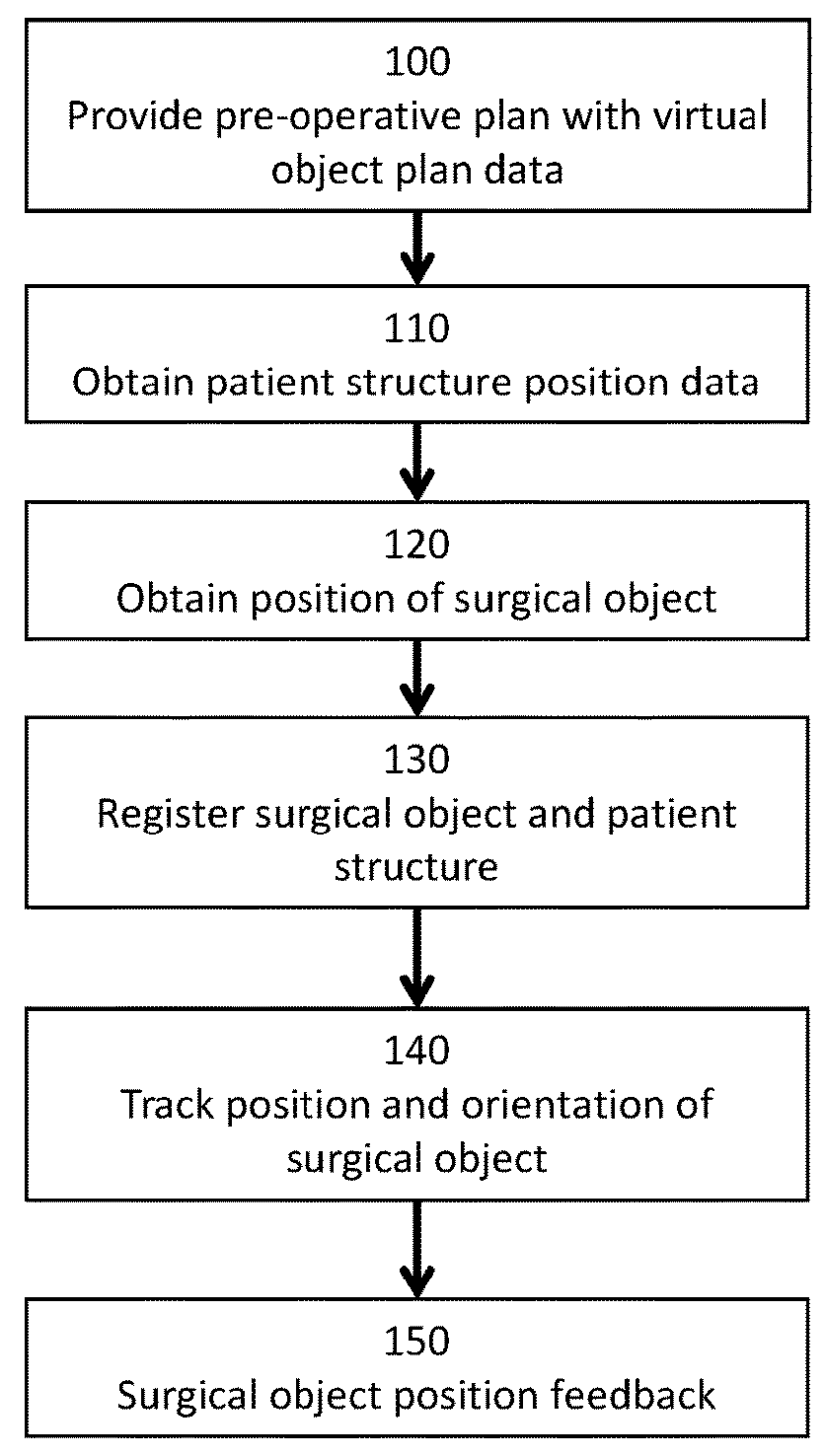
Method and system for computer assisted surgery
A method and system for computer assisted orthopedic feedback of at least one surgical object relative a pre-operative plan are disclosed. The pre-operative plan includes a virtual object, which is the virtual representation of the surgical object, and a virtual structure, which is the virtual representation of the patient structure. The method comprises providing the pre-operative plan including planned position and orientation of the virtual object relative to of the virtual structure; obtaining the position of the patient structure based on a surface of the patient structure using a surgical navigation system; obtaining the position of the surgical object using the surgical navigation system; registering the patient structure to the virtual structure and the surgical object to the virtual object; tracking a current position and orientation of the surgical object using the surgical navigation system; and providing feedback of a current position and orientation of the surgical object relative to the planned position and orientation of the virtual object based on the tracked current position and orientation of the surgical object.
Owner:ORTOMA AB
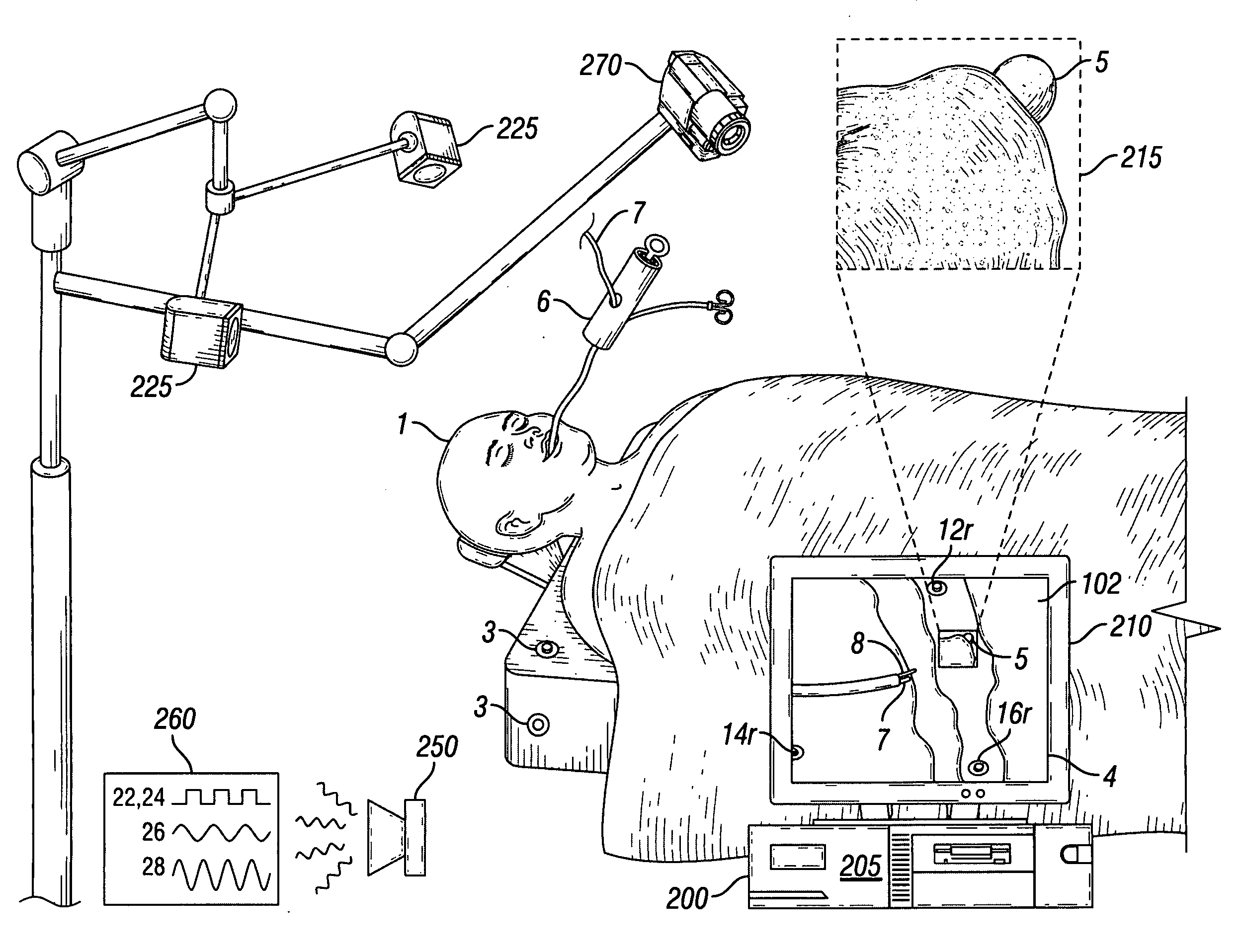
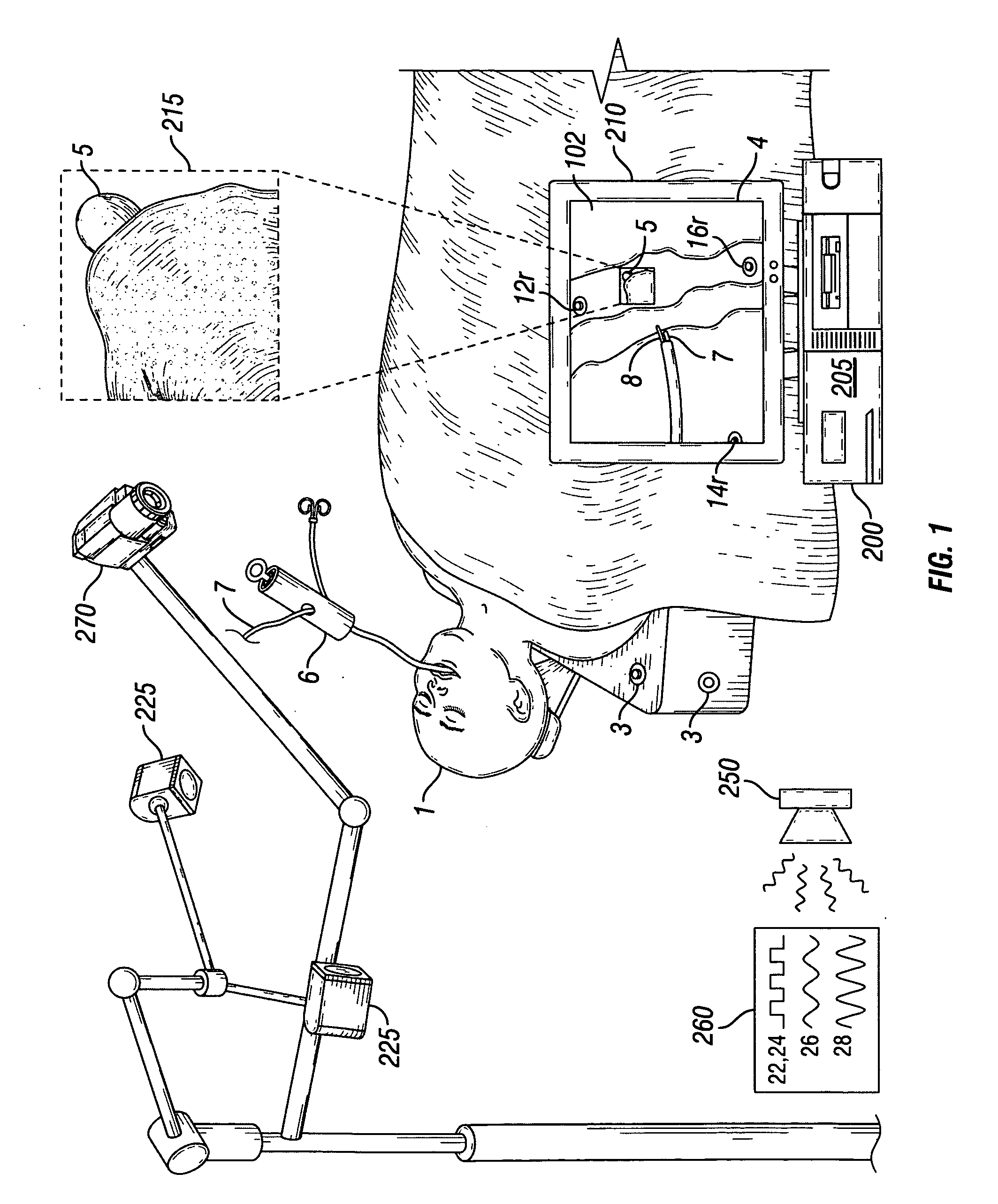
Image Registration for Image-Guided Surgery
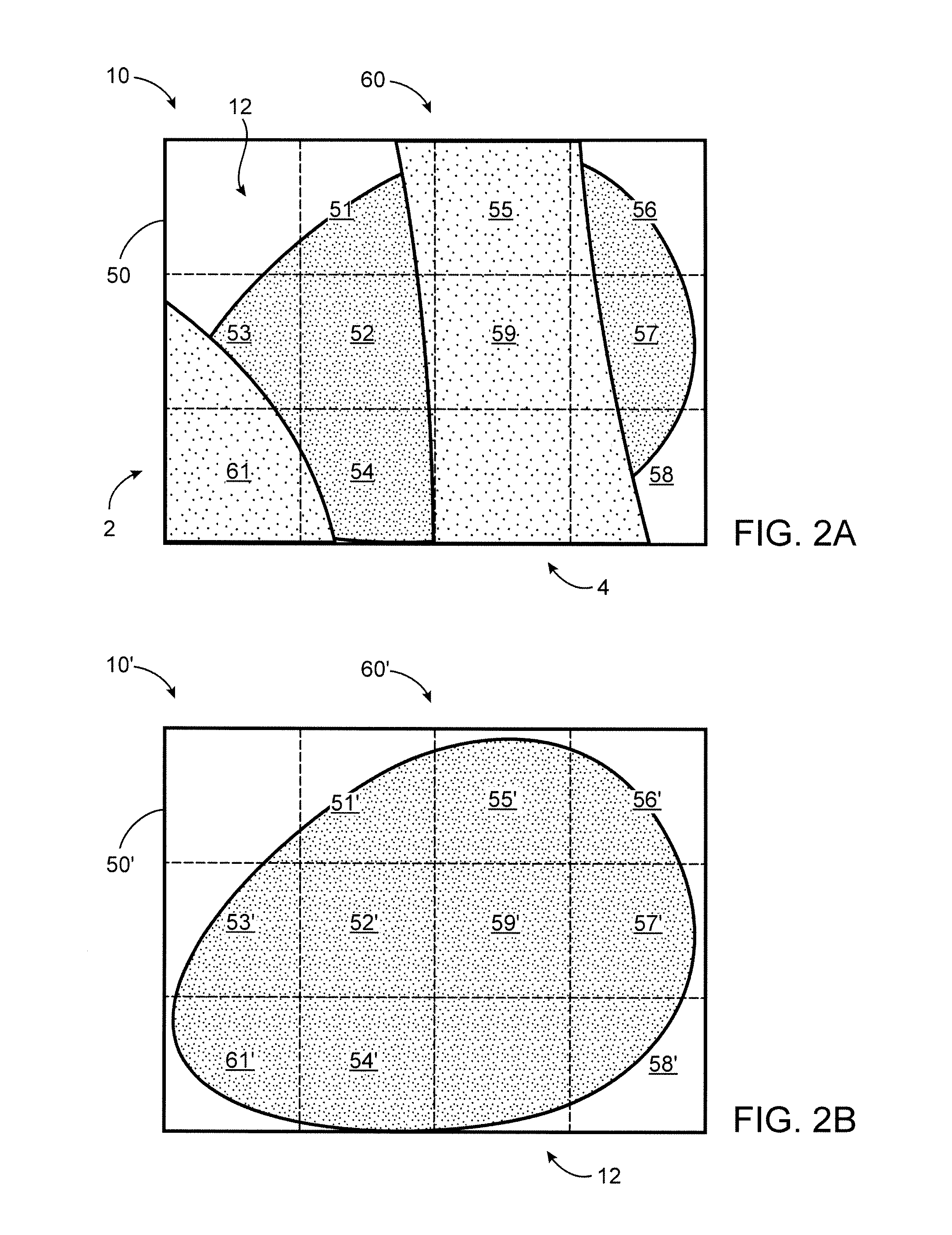
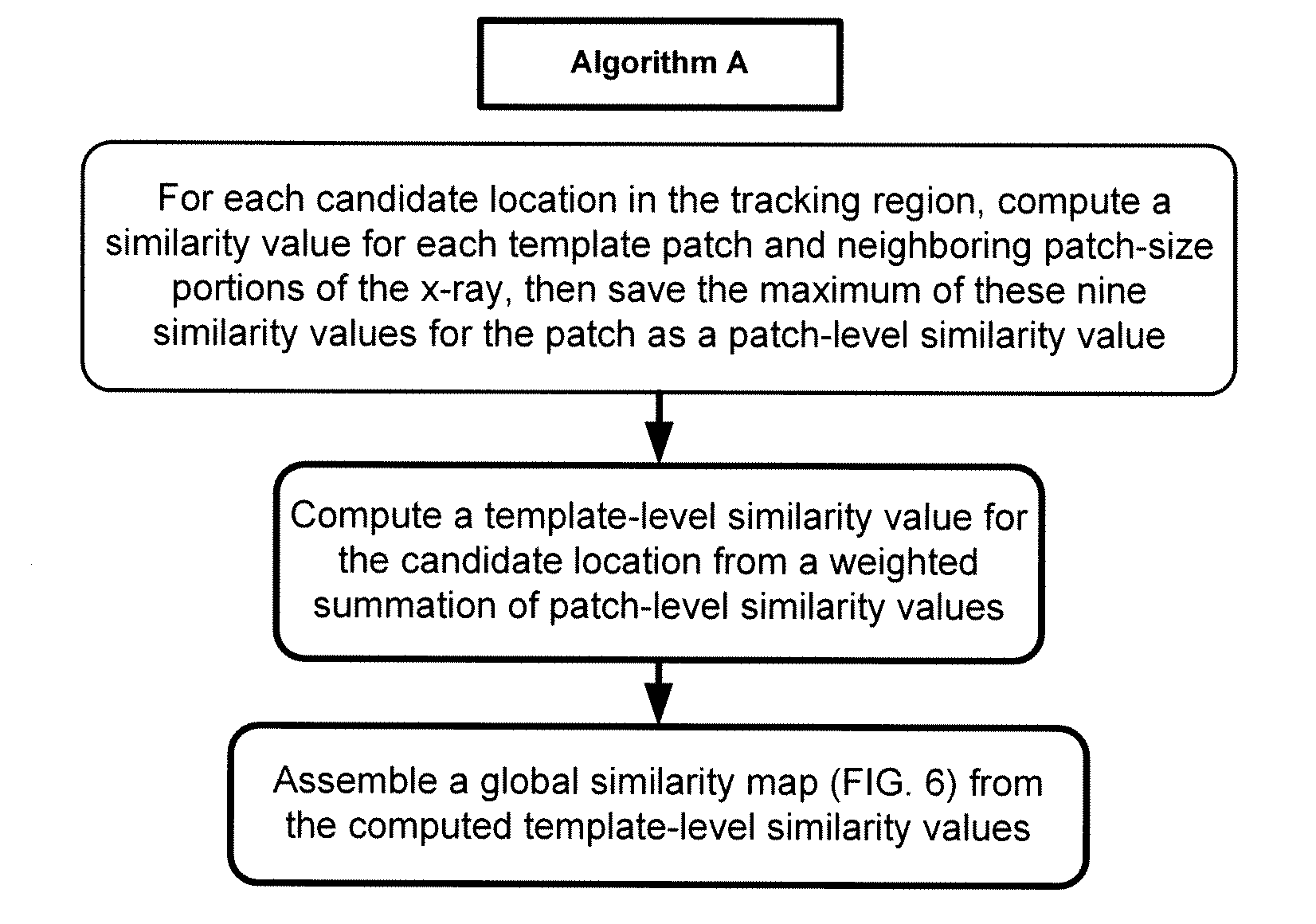
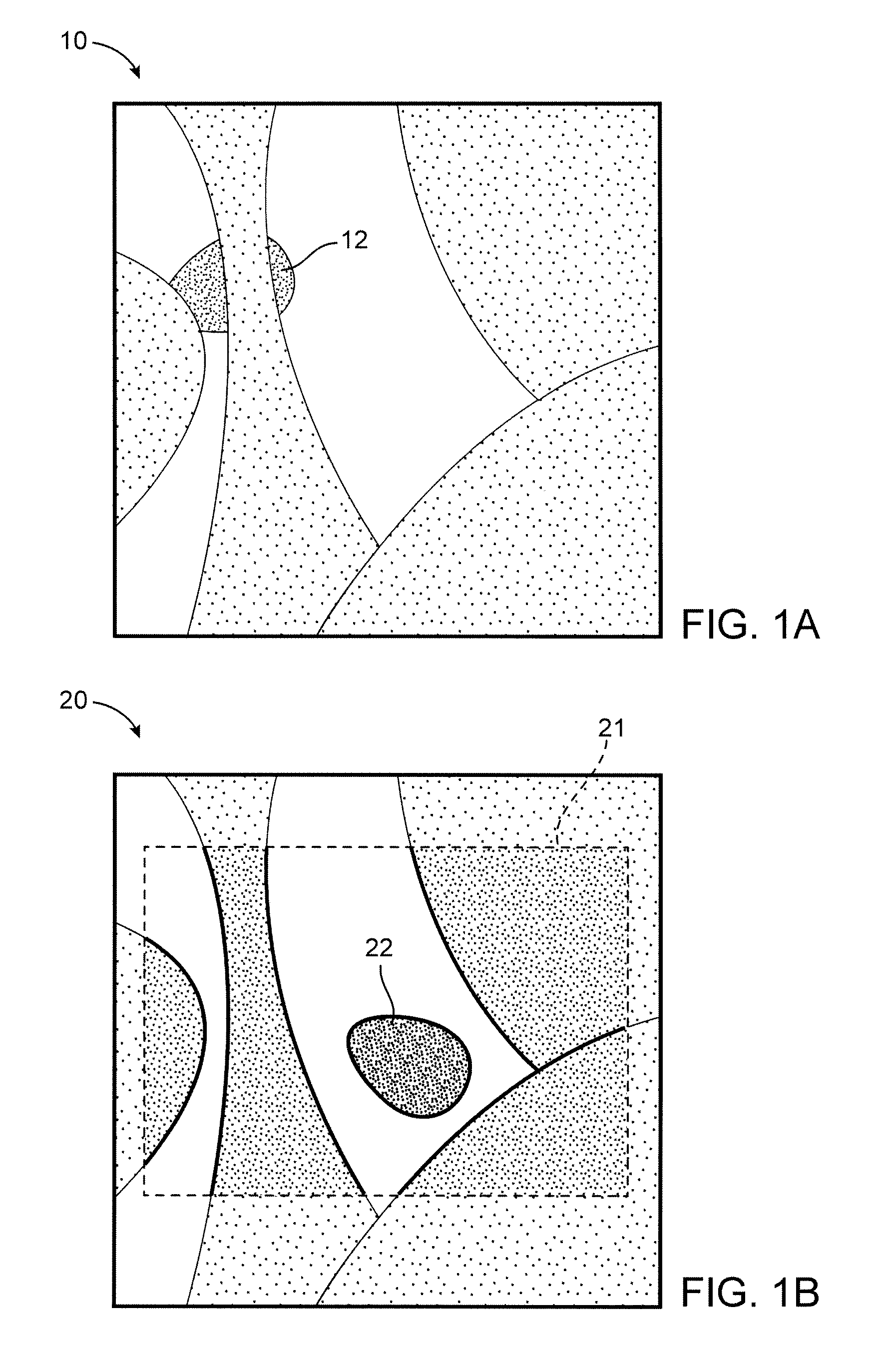
An image registration process for detecting a change in position of a surgical target, such as a tumor, within a patient is disclosed. A pre-operative model of the target and surrounding area is generated, then registered to live patient images to determine or confirm a location of the target during the course of surgery. Image registration is based on a non-iterative image processing logic that compares a similarity measure for a template of the target (generated from the pre-operative model) at one location within the live image to other locations within the live image.
Owner:ACCURAY
Image registration for image-guided surgery
An image registration process for detecting a change in position of a surgical target, such as a tumor, within a patient is disclosed. A pre-operative model of the target and surrounding area is generated, then registered to live patient images to determine or confirm a location of the target during the course of surgery. Image registration is based on a non-iterative image processing logic that compares a similarity measure for a template of the target (generated from the pre-operative model) at one location within the live image to other locations within the live image.
Owner:ACCURAY
Intra-operative registration for navigated surgical procedures
ActiveUS8694075B2Surgical navigation systemsCharacter and pattern recognition3d imagePatient registration
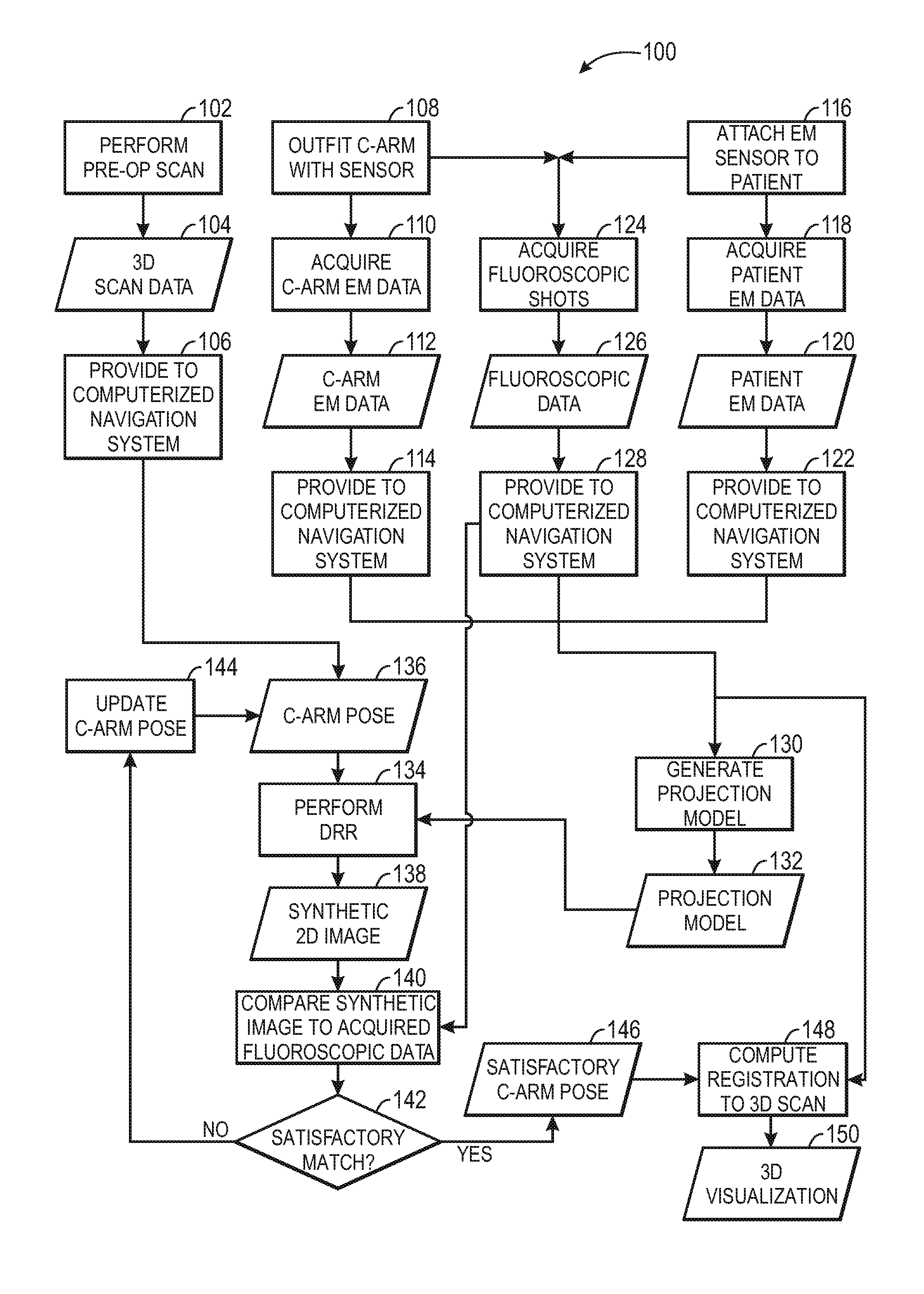
A navigation system for use during a surgical procedure is provided. The navigation system is configured to use electromagnetic tracking data produced by electromagnetic tracking devices and 2D image data produced by a fluoroscope to intra-operatively register 2D images of a patient to a pre-operative 3D image of the patient. In some implementations, a surgeon may be able to perform an interventional or surgical procedure guided by the navigation system.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
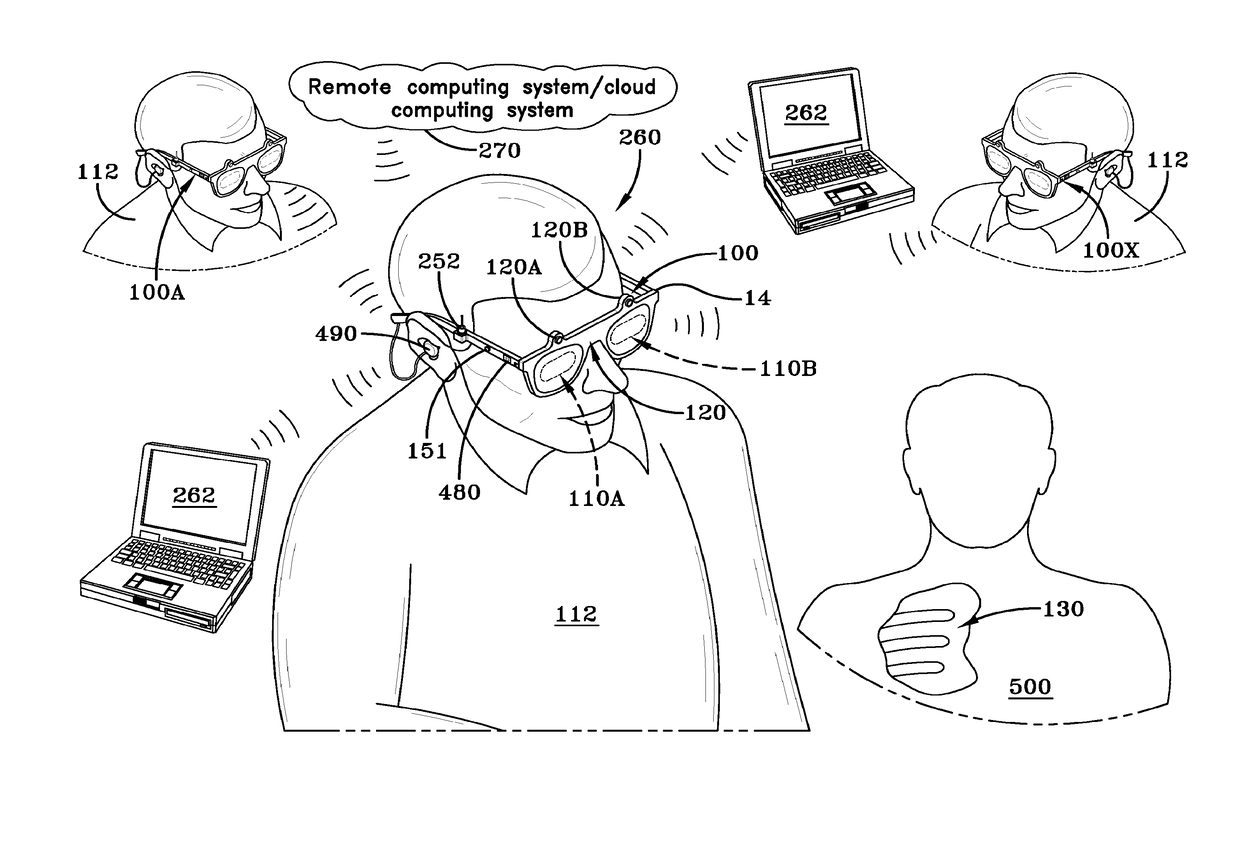
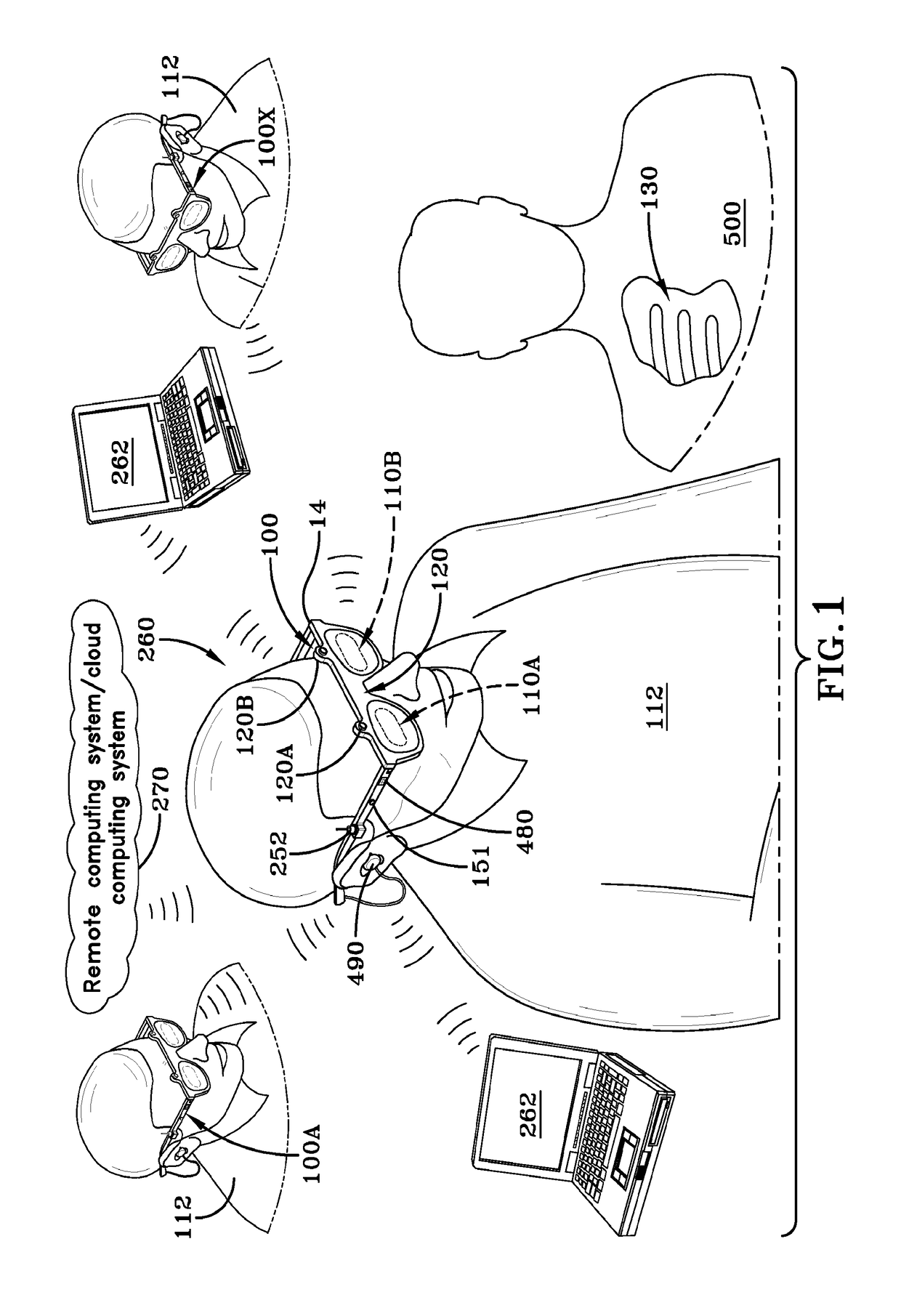
Imaging and display system for guiding medical interventions
An imaging and display system for guiding medical interventions includes a wearable display, such as a goggle display, for viewing by a user. The display presents a composite, or combined image that includes pre-operative surgical navigation images, intraoperative images, and in-vivo microscopy images or sensing data. The pre-operative images are acquired from scanners, such as MRI and CT scanners, while the intra-operative images are acquired in real-time from a camera system carried by the goggle display for imaging the patient being treated so as to acquire intraoperative images, such as fluorescence images. A probe, such as a microscopy probe or a sensing probe, is used to acquire in-vivo imaging / sensing data from the patient. Additionally, the intra-operative and in-vivo images are acquired using tracking and registration techniques to align them with the pre-operative image and the patient to form a composite image for display by the goggle display.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Computer enhanced surgical navigation imaging system (camera probe)
ActiveUS20050015005A1Enhanced interactionEasy to navigateSurgical navigation systemsEndoscopesViewpointsSurgical approach
A system and method for navigation within a surgical field are presented. In exemplary embodiments according to the present invention a micro-camera can be provided in a hand-held navigation probe tracked by a tracking system. This enables navigation within an operative scene by viewing real-time images from the viewpoint of the micro-camera within the navigation probe, which are overlaid with computer generated 3D graphics depicting structures of interest generated from pre-operative scans. Various transparency settings of the camera image and the superimposed 3D graphics can enhance the depth perception, and distances between a tip of the probe and any of the superimposed 3D structures along a virtual ray extending from the probe tip can be dynamically displayed in the combined image. In exemplary embodiments of the invention a virtual interface can be displayed adjacent to the combined image on a system display, thus facilitating interaction with various navigation related functions. In exemplary embodiments according to the present invention virtual reality systems can be used to plan surgical approaches with multi-modal CT and MRI data. This allows for generating 3D structures as well as marking ideal surgical paths. The system and method presented thus enable transfer of a surgical planning scenario to a real-time view of an actual surgical field, thus enhancing navigation.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Trajectory alignment system and methods
ActiveUS20170265943A1Easy to confirmAvoid adjustmentLocal control/monitoringDiagnosticsFiberData transformation
The navigation systems and methods facilitate aligning a tool in relation to a trajectory in real-time to receive input data from a pre-operative plan image, at least one multi-modal image, and at least one real-time multi-modal image; interactively track at least one neural fiber, whereby interactively tracked fiber data is obtainable; automatically generate output data by way of data transformation using the input data and the interactively tracked neural fiber data; and transmit the output data to at least one of: at least one display device for rendering at least one real-time interactive navigation display for facilitating neural navigation, and at least one drive device for positioning at least one tracking device in relation to the tool in real-time, whereby real-time alignment data is achievable, and whereby at least one neurological structure is preservable.
Owner:SYNAPTIVE MEDICAL INC
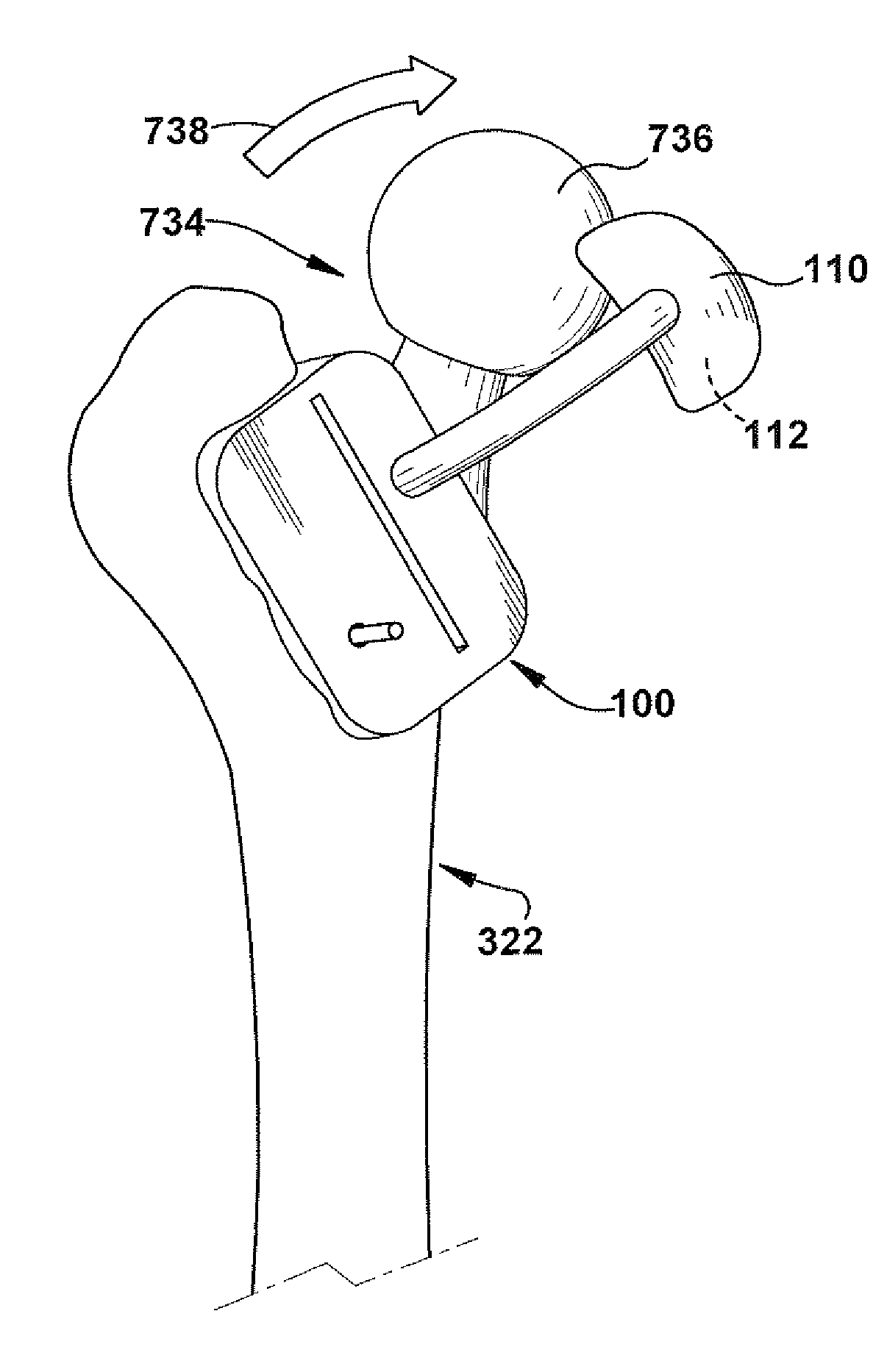
Patient-specific total hip arthroplasty
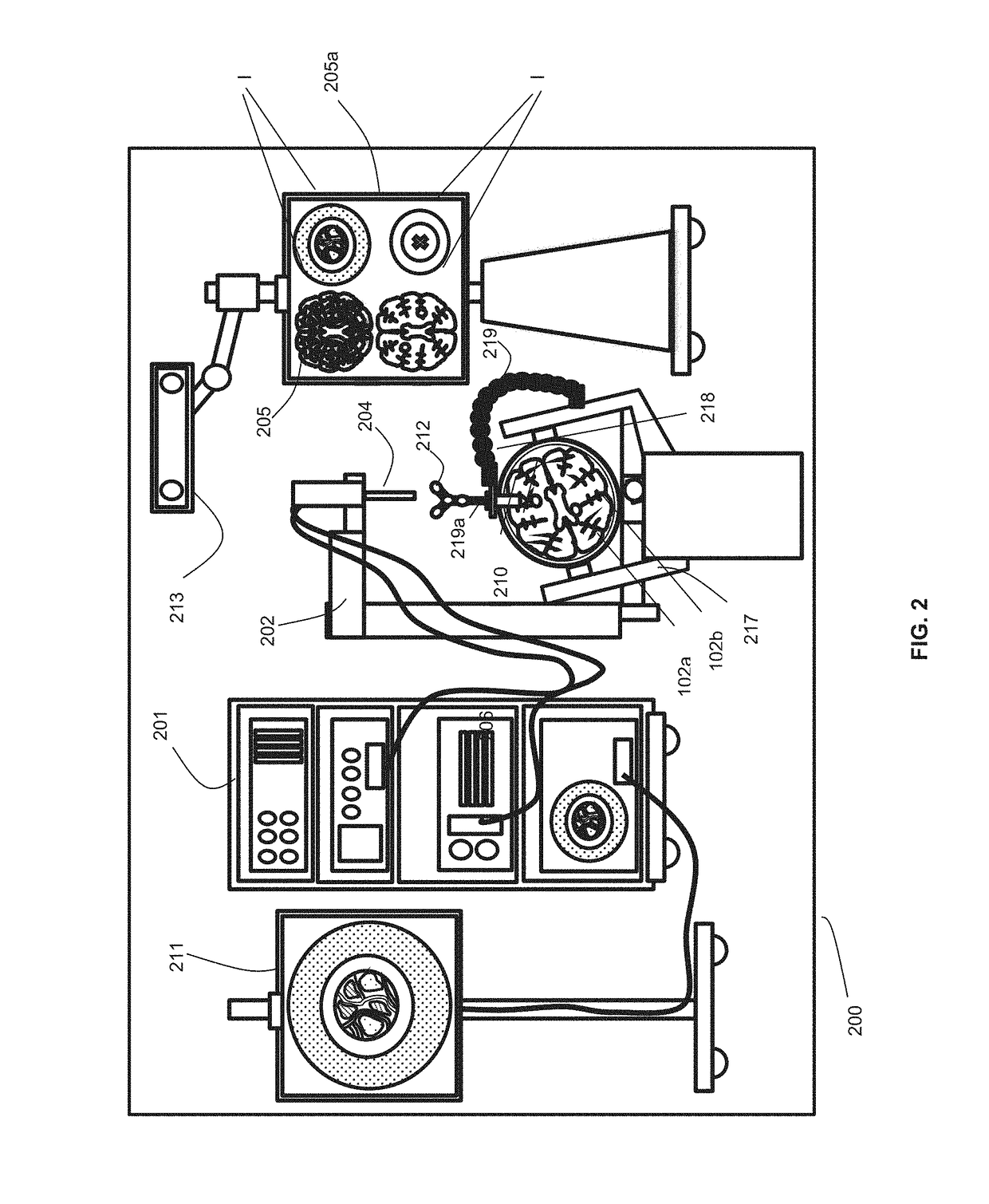
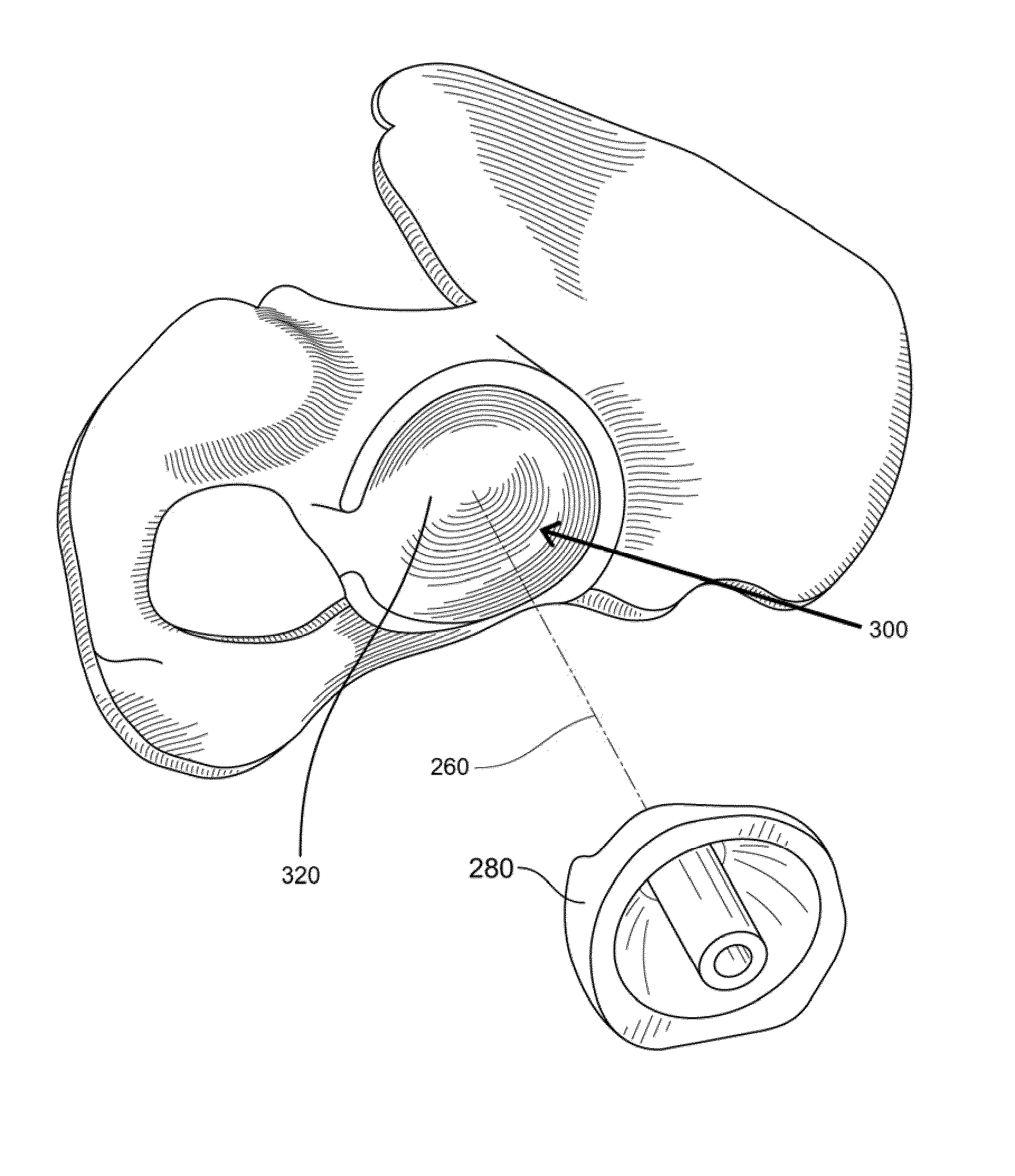
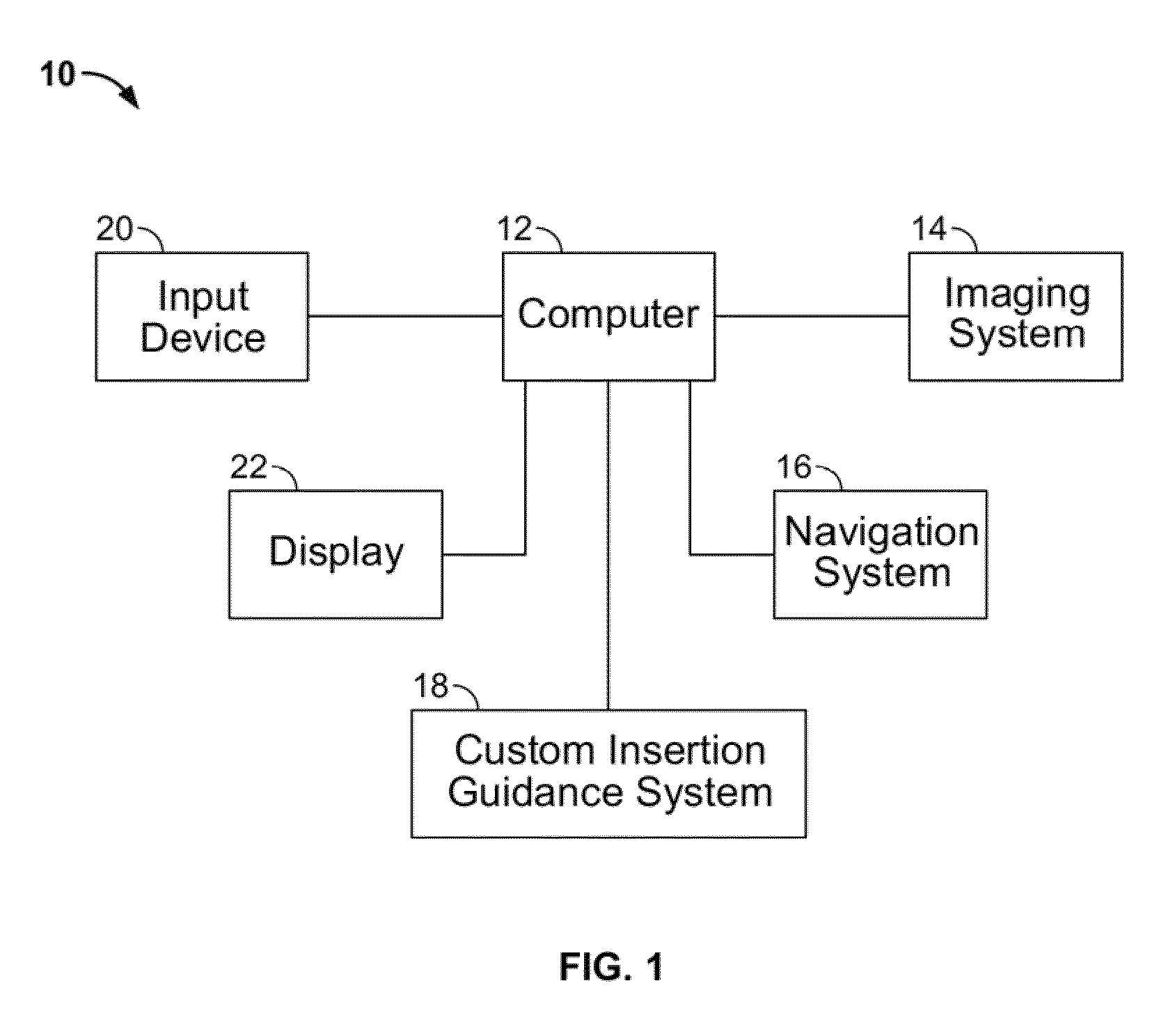
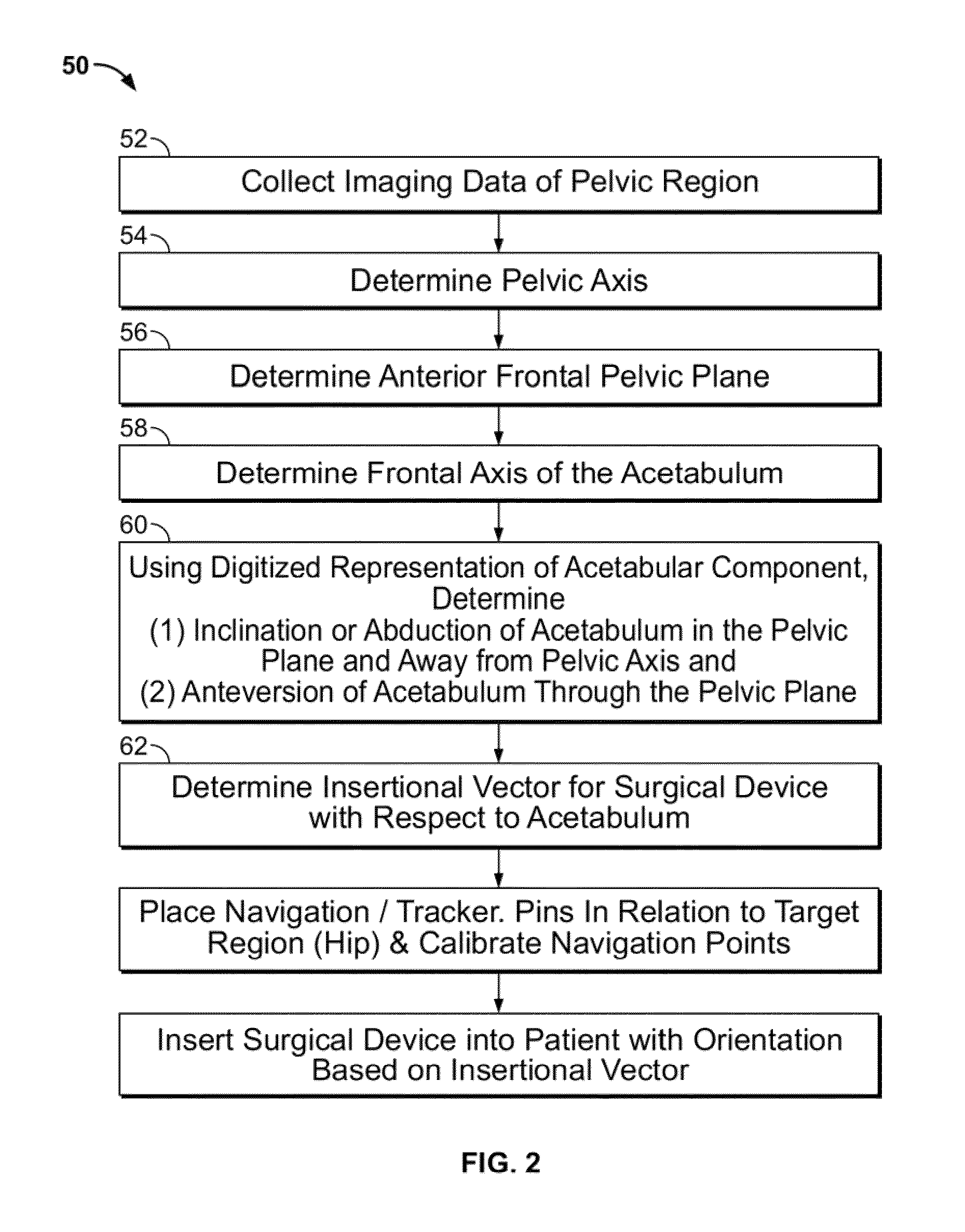
ActiveUS8932299B2Large range of motionMinimizing reaction forcePhysical therapies and activitiesMedical simulationAcetabular componentPre operative
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for performing total hip arthroplasty with patient-specific guides Pre-operative images of a pelvic region of a patient are taken in order to predefine the structure of the guides and corresponding implants. From the obtained image data an insertional vector for implanting an acetabular implant or component into an acetabulum of the patient is determined, wherein the insertional vector is coaxial with a polar axis of the acetabular component. Also from the obtained image data, a superior surface of the guides and implants can be shaped to match the acetabulum of the patient. A nub portion extending outwardly from the superior surface of the guides and implants is shaped to substantially match the shape of a fovea of the acetabulum. A guide portion of the guides forming a slot has a longitudinal axis coaxial with the determined insertional vector of a corresponding acetabular component.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
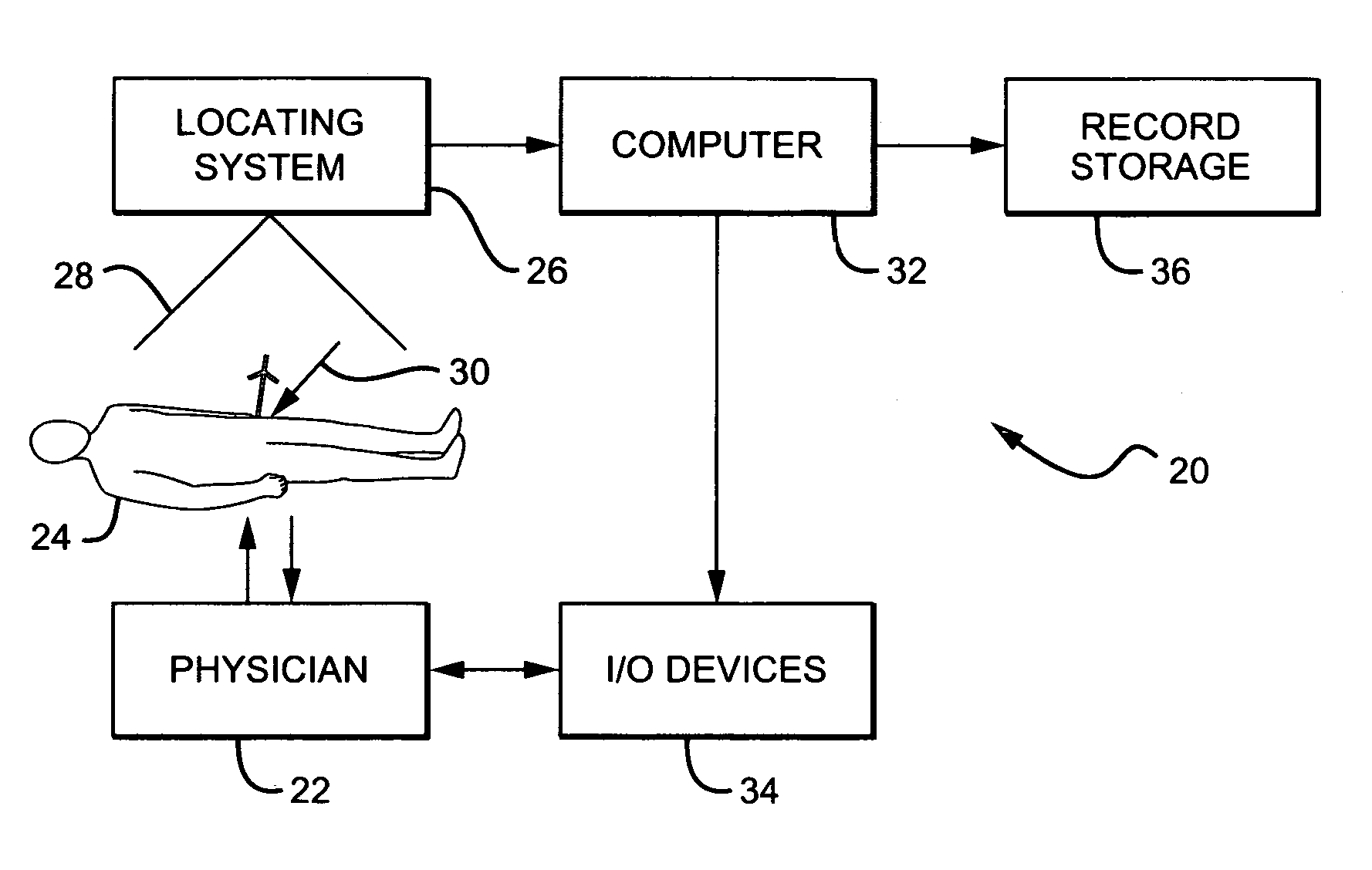
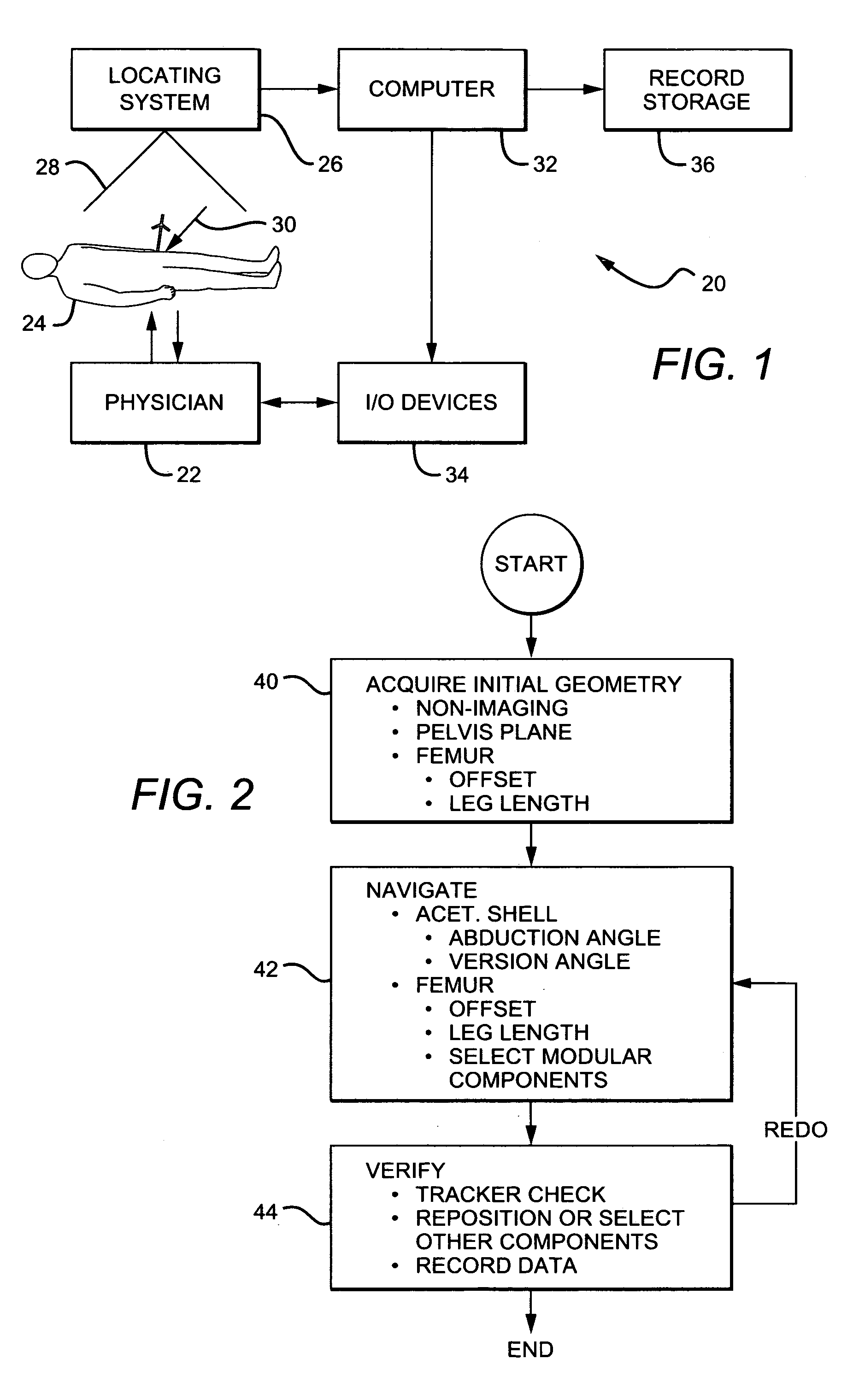
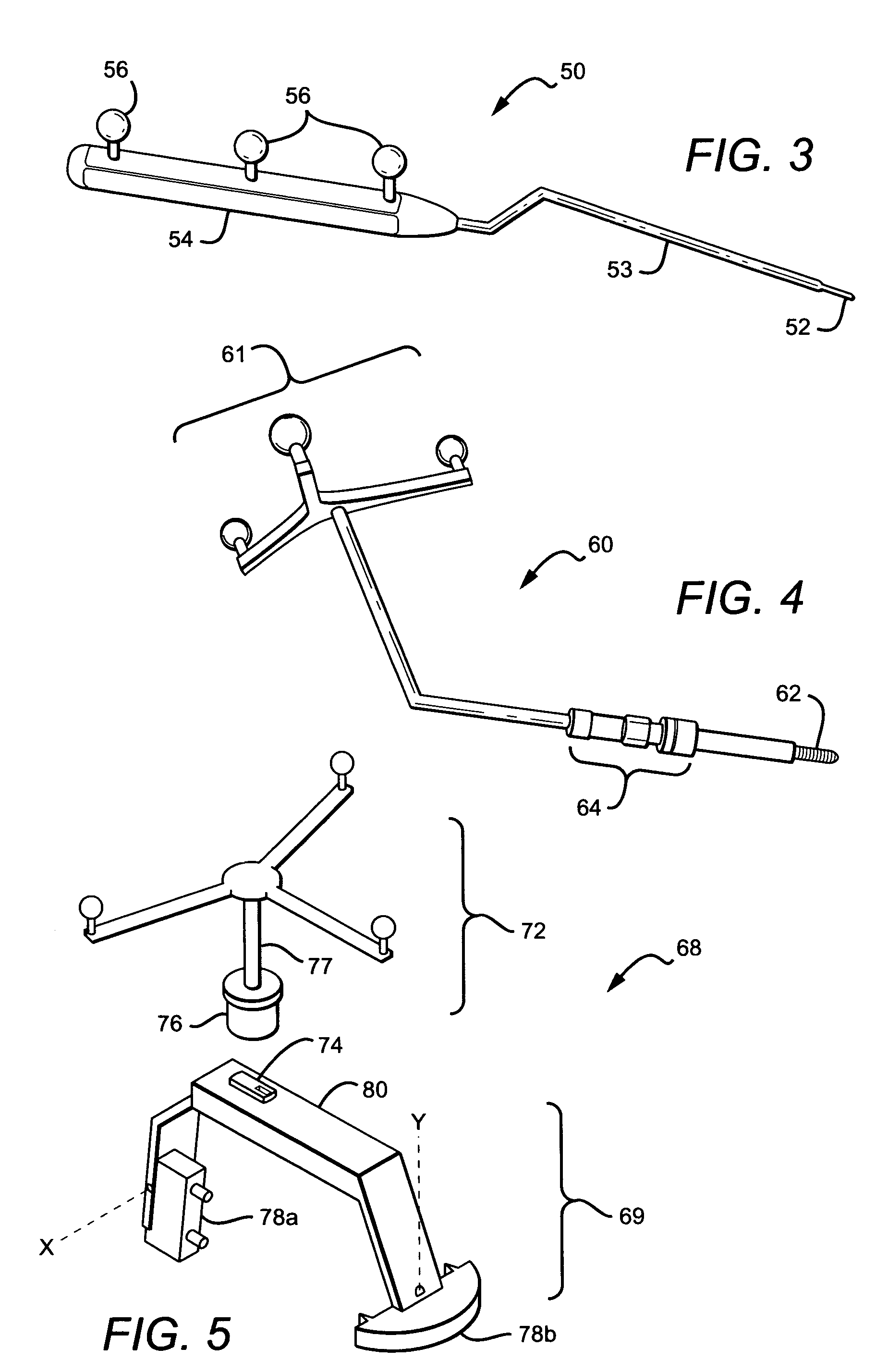
Non-image, computer assisted navigation system for joint replacement surgery with modular implant system
The invention includes a method and system for intra-operative navigation of a joint replacement operation, without recourse to pre-operative imagery of pre-operative computerized simulations. Trackable markers and a locating system are employed to track first and second bones. A computer receives positional information regarding the trackable markers and calculates (predicts) at least one suggested combination of components of a modular implant system to produce a desired post-operative skeletal relationship.
Owner:KINAMED
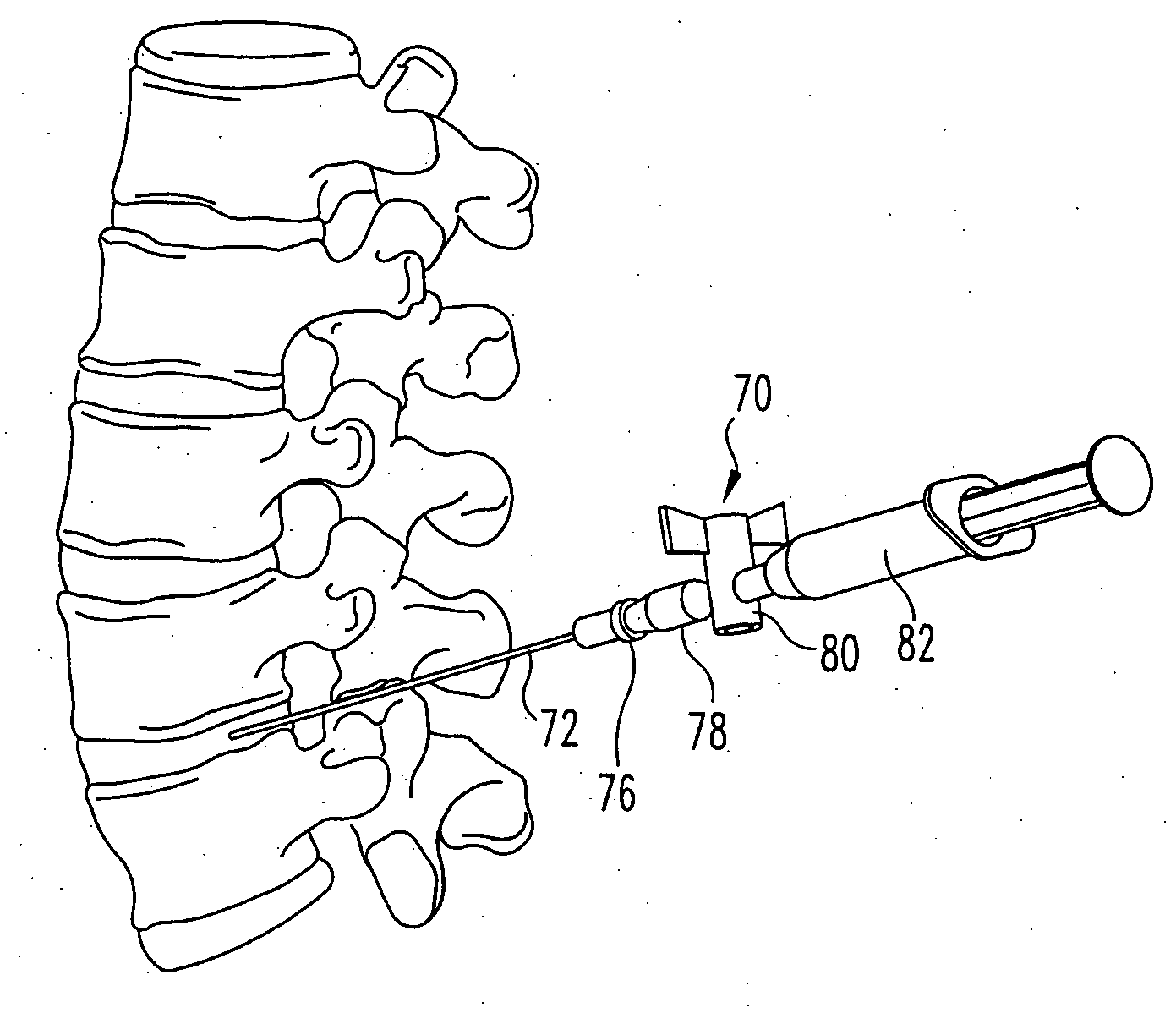
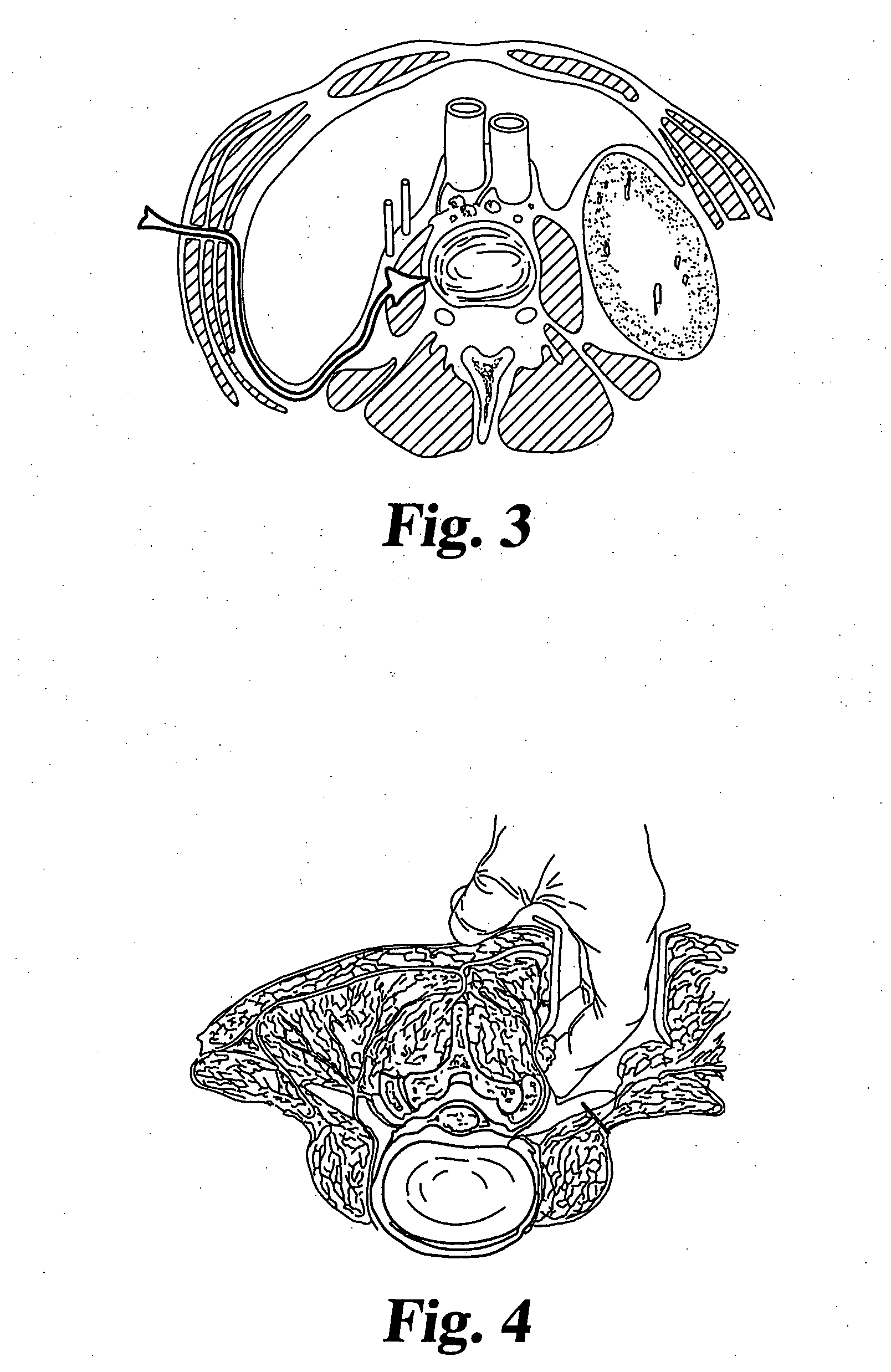
Percutaneous methods for injecting a curable biomaterial into an intervertebral space
A method for treating a spinal disc having an outer relatively intact annulus defining a disc space and an inner defective nucleus pulposus within the disc space, comprises the steps of: determining the integrity of the annulus by subjecting the annulus to a first pressure applied internally of the annulus; providing access to the nucleus pulposus through the annulus without removing any tissue from the annulus or from the nucleus pulposus; and sealably injecting curable biomaterial through the annulus access directly into the nucleus pulposus at a second pressure correlated with the first pressure. The integrity of the annulus may be determined by a pre-operative discogram using a contrast medium that has a viscosity substantially similar to the viscosity of the biomaterial to be injected. The needle is placed initially within the center of the nucleus pulposus and then withdrawn during the injection to approximately the inner border of the annulus. The second pressure is then maintained until the biomaterial is substantially cured. In steps, the curable biomaterial has strong adhesive properties and is capable of injection under pressure to fill fissures in the nucleus pulposus. The curable biomaterial may be injected under a pressure sufficient to distract opposing vertebral bodies communicating with the disc space.
Owner:SPINEWAVE
Image-overlay medical evaluation devices and techniques
InactiveUS20130172731A1Easy to makePromote lowerImpression capsAdditive manufacturing apparatusDisplay deviceComputer access
A system and methods are provided for evaluating the position of surgical implants or openings formed in anatomical tissue during medical procedures, in which an initial 3-dimensional image of the anatomical tissue is combinable with one or more subsequent 3-dimensional images of the same or correlating tissue, and without the use of ionizing radiation on a patient for at least the subsequent images. The system includes a software program, a computer with display, a radiographic image scanning device, and a non-radiographic image scanning device. The computer accesses a medical patient information database and a medical implant database for images used by the software program. A pre-operative image is combined with subsequent images to facilitate evaluation of the proposed placement of a surgical implant or opening relative to tissues of the patient anatomy. Methods of evaluating the accuracy of surgical guides and of fabricating surgical guides are also disclosed.
Owner:GOLE PHILIP D
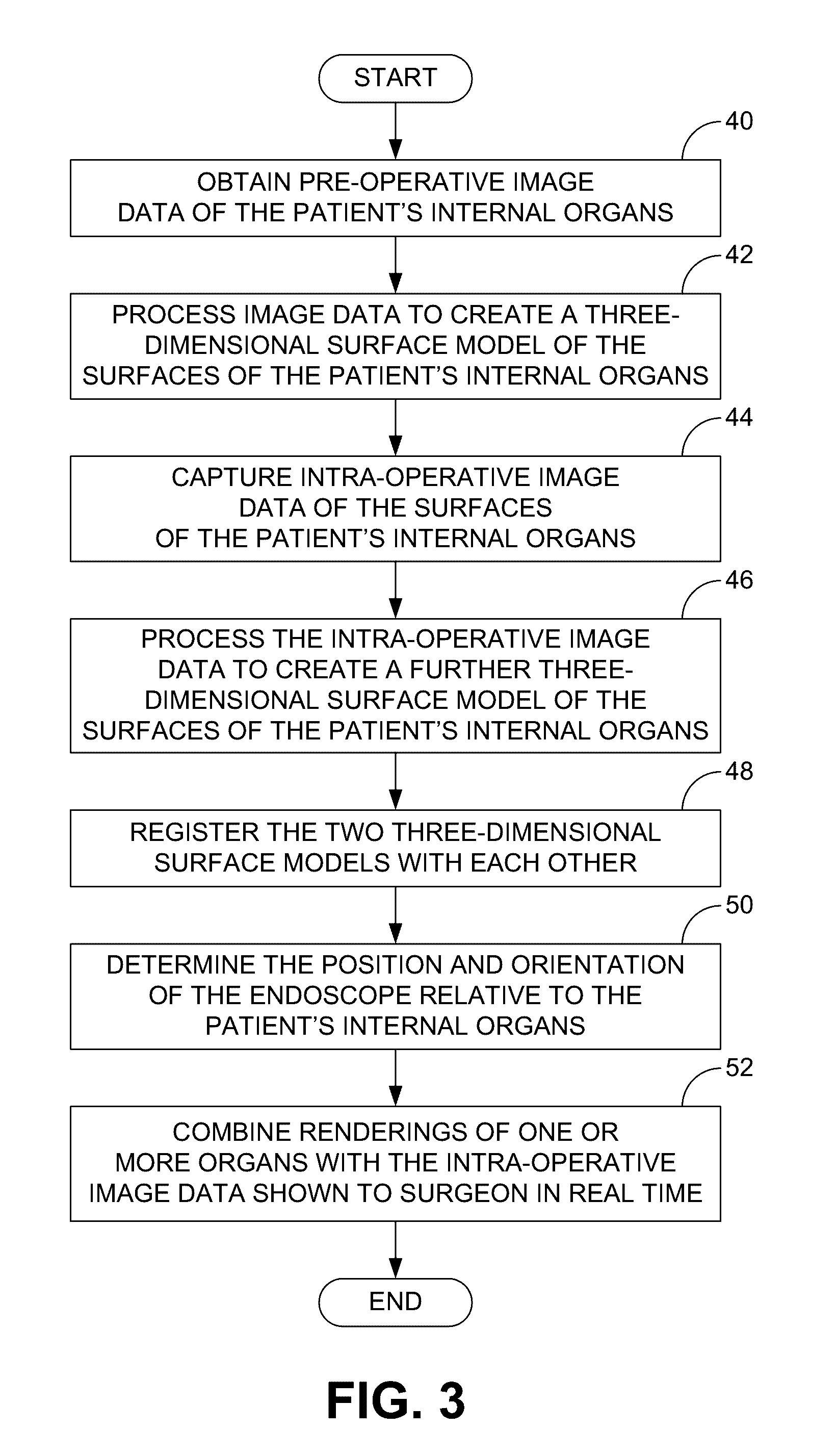
Systems and methods for providing augmented reality in minimally invasive surgery
In one embodiment, a method for providing augmented reality in minimally invasive surgery includes capturing pre-operative image data of internal organs of a patient, capturing intra-operative image data of the internal organs with an endoscope during a surgical procedure, registering the pre-operative image data and the intra-operative data in real time during the surgical procedure, tracking the position and orientation of the endoscope during the surgical procedure, and augmenting the intra-operative image data captured by the endoscope in real time with a rendering of an internal organ of the patient.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
System and method for fusing three-dimensional shape data on distorted images without correcting for distortion
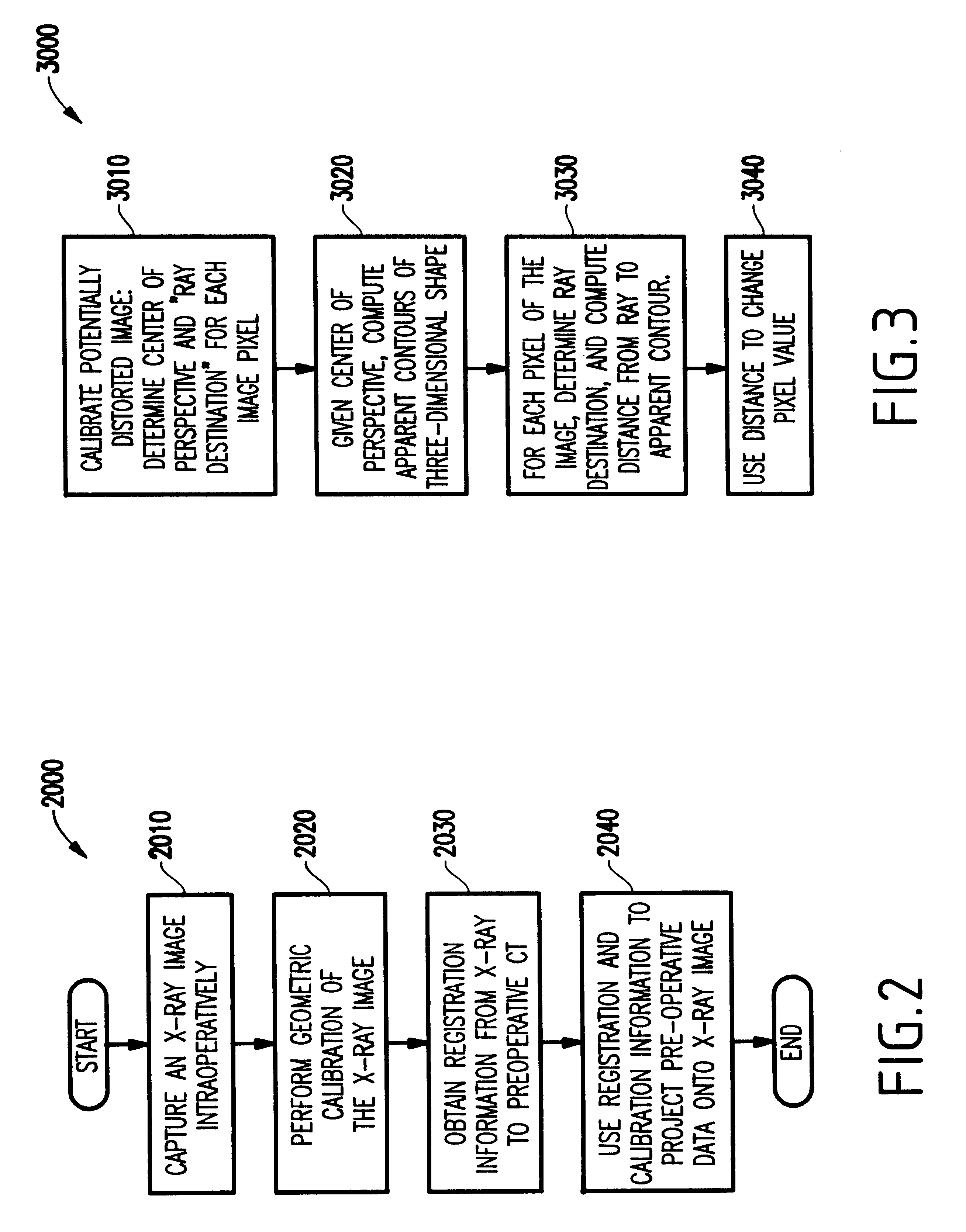
InactiveUS6747646B2Increase speedProcessing resource is not increasedCharacter and pattern recognitionComputerised tomographsPhysical spaceFusion mechanism
A system and method for intra-operatively providing a surgeon with visual evaluations of possible surgical outcomes ahead of time, and generating simulated data, includes a medical imaging camera, a registration device for registering data to a physical space, and to the medical imaging camera, and a fusion mechanism for fusing the data and the images to generate simulated data, without correcting for distortion. The simulated data (e.g., such as augmented X-ray images) is natural and easy for a surgeon to interpret. In an exemplary implementation, the system preferably includes a data processor which receives a three-dimensional surgical plan or three-dimensional plan of therapy delivery, one or a plurality of two-dimensional intra-operative images, a three-dimensional model of pre-operative data, registration data, and image calibration data. The data processor produces one or a plurality of simulated post-operative images, without correcting for distortion, by integrating a projection of a three-dimensional model of pre-operative data onto one or a plurality of two-dimensional intra-operative images.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
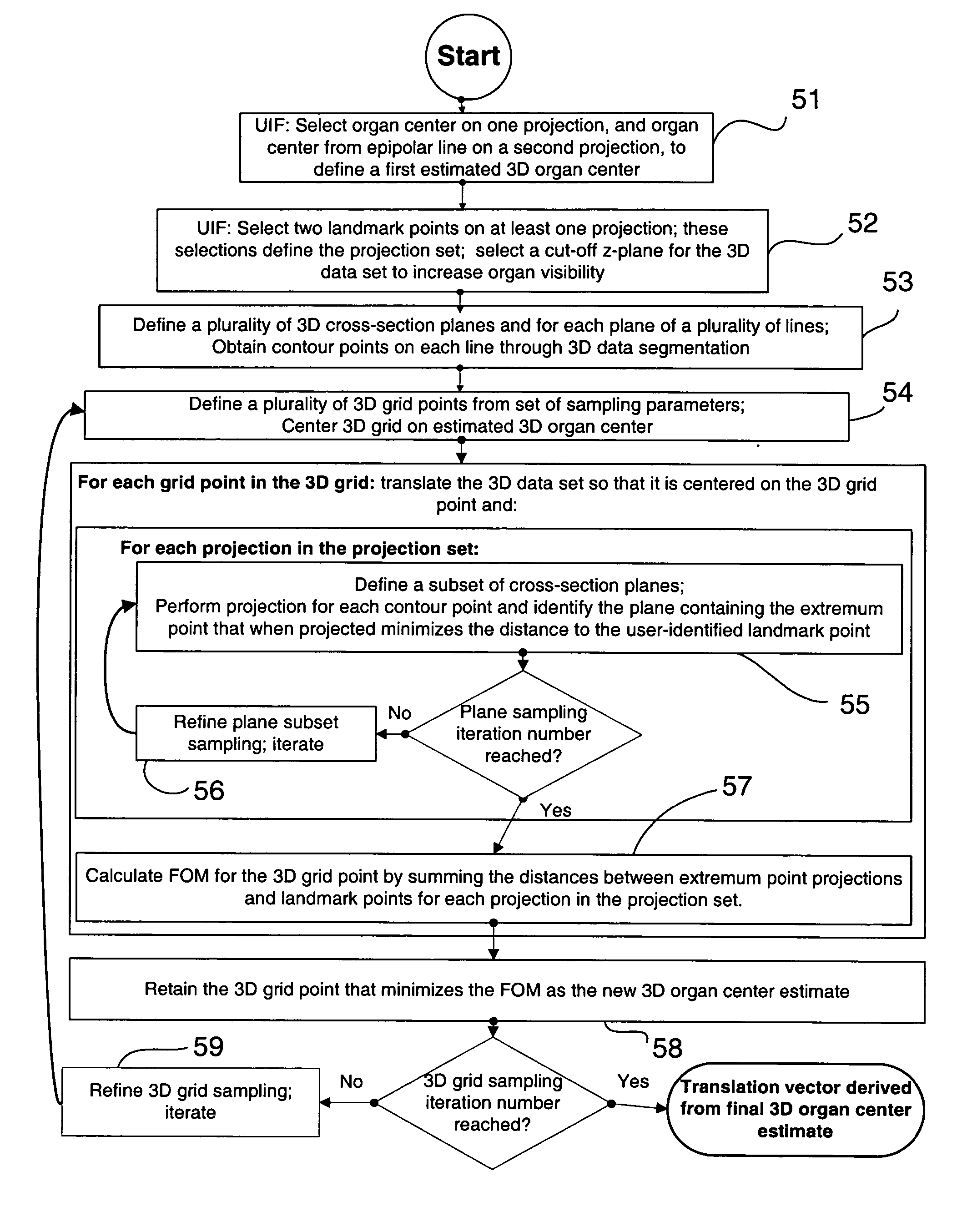
Registration of three dimensional image data with patient in a projection imaging system
A method for determining a translation of a three-dimensional pre-operative image data set to obtain a registration of the three-dimensional image data with a patient positioned in a projection imaging system. In one embodiment the user identifies an initial three-dimensional organ center from projections and extreme contour landmark points of the object on a set of projections. A set of contour points for the image object in each of a plurality of three-dimensional cross-section planes; is obtained and the points projecting nearest to the user-identified landmark points are selected. A three-dimensional grid having a predetermined number of intervals at a predetermined interval spacing centered at the user-identified organ center is defined. The three-dimensional image data contour points as centered onto each grid point are projected for evaluation and selection of the grid point leading to contour points projecting nearest to the user-identified landmark points. This selection leads to the iterative definition of a series of improved estimated three-dimensional organ centers, and associated translation vectors. Registration of a three dimensional image data to the patient positioned in a projection imaging system will allow, among other things, overlay of a visual representation of a pre-operative image object onto a projection image plane that can serve as a visual tool and a surgical navigation aid. In particular, the position and orientation of a medical device can be shown with respect to the three-dimensional image data and thus enable quicker, safer, and less invasive navigation of the medical device to and within an organ of interest.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
System and method for fusing three-dimensional shape data on distorted images without correcting for distortion
InactiveUS6415171B1Increase speedProcessing resource is not increasedComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringFusion mechanismPhysical space
A system and method for intra-operatively providing a surgeon with visual evaluations of possible surgical outcomes ahead of time, and generating simulated data, includes a medical imaging camera, a registration device for registering data to a physical space, and to the medical imaging camera, and a fusion mechanism for fusing the data and the images to generate simulated data, without correcting for distortion. The simulated data (e.g., such as augmented X-ray images) is natural and easy for a surgeon to interpret. In an exemplary implementation, the system preferably includes a data processor which receives a three-dimensional surgical plan or three-dimensional plan of therapy delivery, one or a plurality of two-dimensional intra-operative images, a three-dimensional model of pre-operative data, registration data, and image calibration data. The data processor produces one or a plurality of simulated post-operative images, without correcting for distortion, by integrating a projection of a three-dimensional model of pre-operative data onto one or a plurality of two-dimensional intra-operative images.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and Methods for Performing Brain Surgery
InactiveUS20080109026A1Easy to installAssisting understandingCannulasInfusion syringesLess invasive surgeryMedicine
Less invasive surgical techniques for performing brain surgery are disclosed in which a dilating obturator and cannula assembly is inserted into brain tissue until the obturator tip and cannula are adjacent the target tissue. The obturator is removed and surgery is performed through the cannula. In preferred embodiments the obturator and cannula are placed using image guidance techniques and systems to coordinate placement with pre-operative surgical planning. A stylet with associated image guidance may he inserted prior to insertion of the obturator and cannula assembly to guide insertion of the obturator and cannula assembly. Surgery preferable is performed using an endoscope partially inserted into the cannula with an image of the target tissue projected onto a monitor.
Owner:NICO CORP
Apparatus and methods for performing brain surgery
ActiveUS20090048622A1Many of techniqueEasy to installCannulasSurgical needlesLess invasive surgeryLess invasive
Less invasive surgical techniques for performing brain surgery are disclosed in which a dilating obturator and cannula assembly is inserted into brain tissue until the obturator tip and cannula are adjacent to the target tissue. The obturator is removed and surgery is performed through the cannula. In preferred embodiments the obturator and cannula are placed using image guidance techniques and systems to coordinate placement with pre-operative surgical planning. A stylet with associated image guidance may be inserted prior to insertion of the obturator and cannula assembly to guide insertion of the obturator and cannula assembly. Surgery preferably is performed using an endoscope partially inserted into the cannula with an image of the target tissue projected onto a monitor. Dilating obturator structures having a rounded or semi-spherical tip and / or an optical window for visualizing brain tissue during expansion are contemplated.
Owner:VYCOR MEDICAL INC
Systems and methods for using dynamic vascular assessment to improve vascular stent placement, application, design and marketing
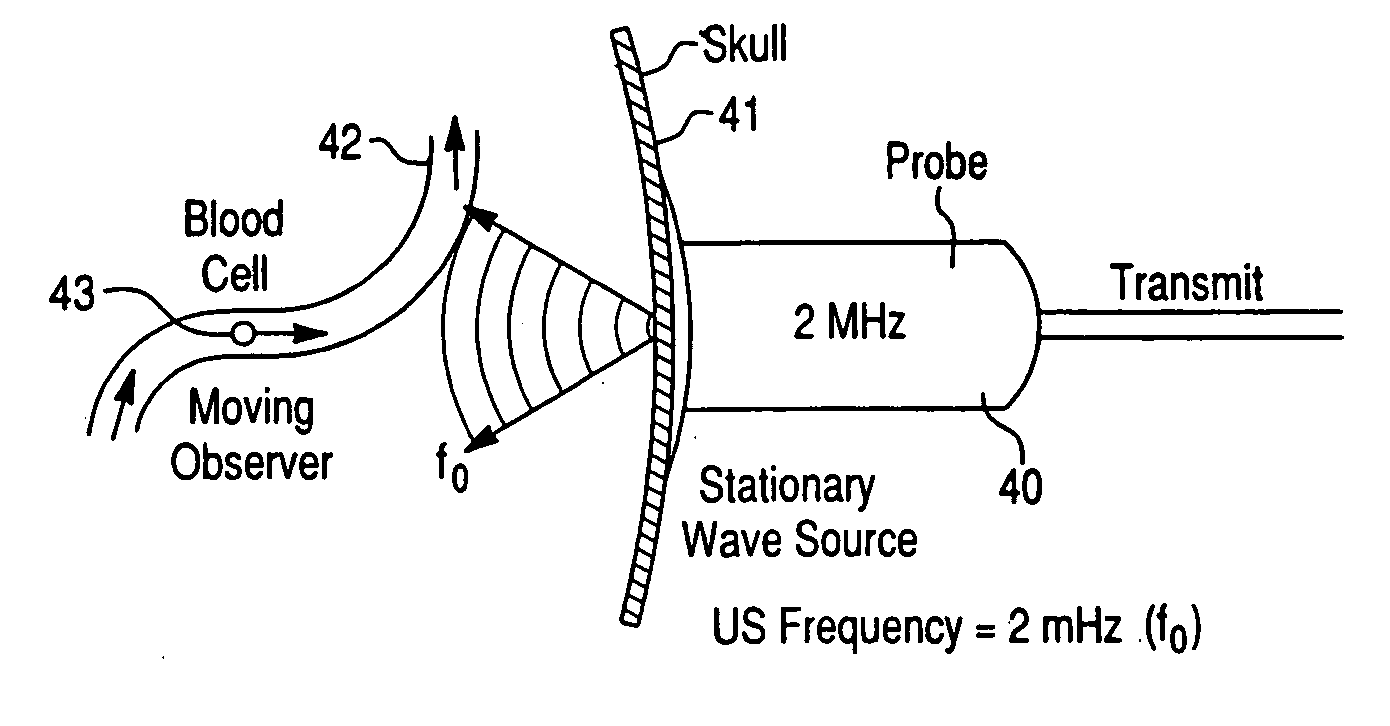
InactiveUS20050038342A1Rapid and inexpensive to performEfficient deliveryBlood flow measurement devicesMedical automated diagnosisClinical testsPre operative
The invention relates to systems and methods for assessing blood flow in single or multiple vessels and segments, for assessing vascular health, for conducting clinical trials, for screening therapeutic interventions for effect, for assessing risk factors, for evaluating intracranial pressure and for analyzing the results in a defined manner. The invention enables direct monitoring of therapies, substances and devices on blood vessels, especially those of the cerebral vasculature. Relevant blood flow parameters include mean flow velocity, systolic acceleration, and pulsatility index. Measurement and analysis of these parameters, and others, provides details regarding the vascular health of individual and multiple vessels and a global analysis of an individual's overall vascular health. The invention is applicable as both a system and method for monitoring and improving the design, performance, marketing and use of vascular stents. In particular, the invention enables DVA-assisted stenting procedures, including both pre-operative and post-operative management.
Owner:NEW HEALTH SCI
Surgical guiding tool, methods for manufacture and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110015637A1Stable and accurate guidanceShorten the timeAdditive manufacturing apparatusDiagnosticsPre operativeBiomedical engineering
Surgical guiding tools for surgery on a bone head which include a cutting component, a guiding component and a collar having a patient-specific component are disclosed. The surgical guiding tools are interconnected which ensures secure and accurate placement of the guiding tool and thus guarantees accurate implementation of the pre-operative planning of the surgical intervention.
Owner:MATERIALISE NV
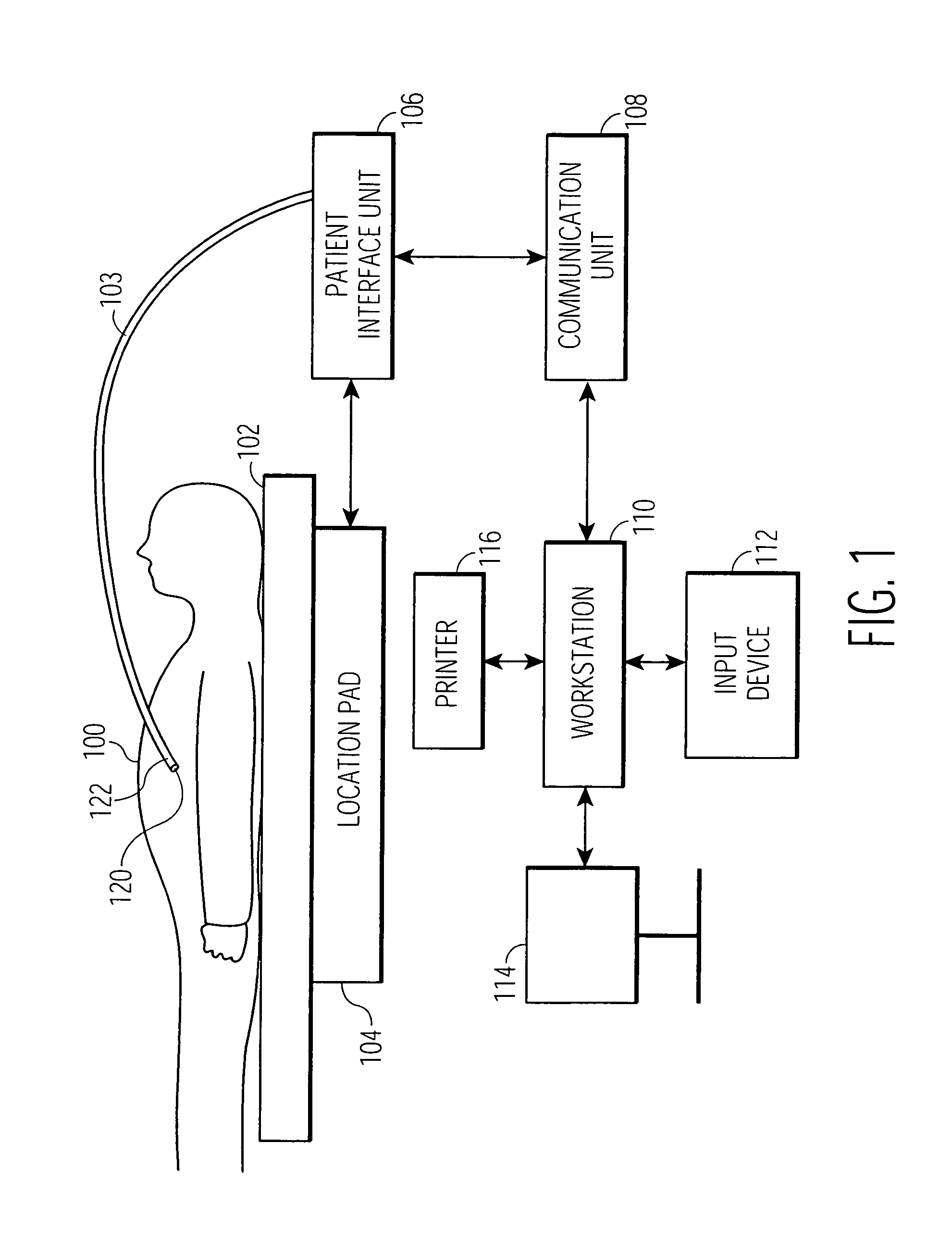
System and method for automatically registering three dimensional cardiac images with electro-anatomical cardiac mapping data
A system and method for automatically registering a three dimensional (3D) pre-operative image of an anatomical structure with intra-operative electrophysiological (EP) points of a 3D electro-anatomical (EA) image map of the anatomical structure is disclosed. The pre-operative image is displayed in a first supporting view. The intra-operative EA image map is displayed in a second supporting view. An alignment of the pre-operative image with the intra-operative map is performed by identifying at least one corresponding point on each image. The view of the pre-operative image is integrated with the EA map based on the alignment.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +1
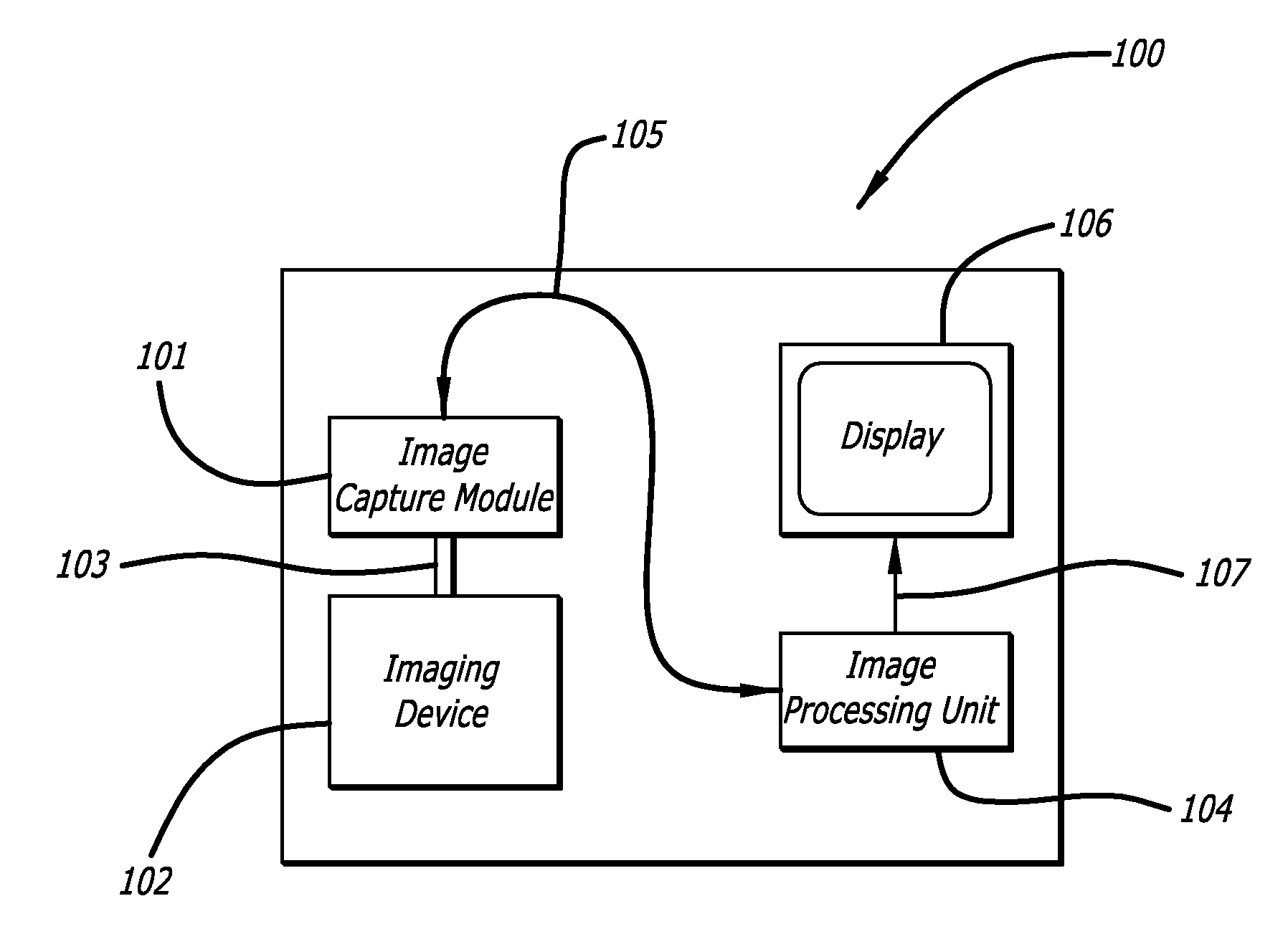
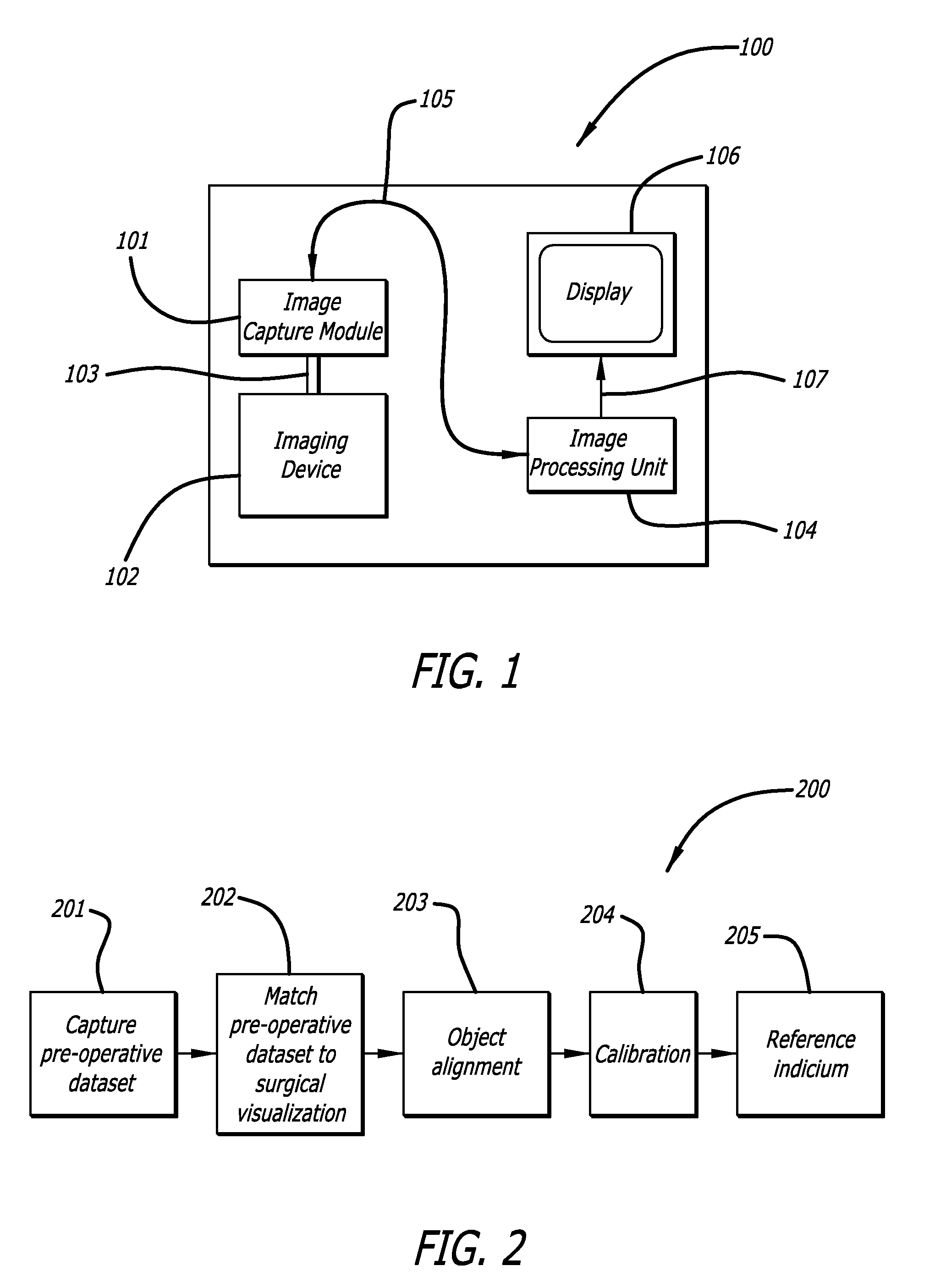
Real-time surgical reference indicium apparatus and methods for surgical applications
Described herein are apparatus and associated methods for the generation of at least one user adjustable, accurate, real-time, virtual surgical reference indicium. The apparatus includes one or more real-time, multidimensional visualization modules, one or more processors configured to produce real-time, virtual surgical reference indicia, and at least one user control input for adjusting the at least one real-time virtual surgical reference indicium. The associated methods generally involve the steps of providing one or more real-time multidimensional visualizations of a target surgical field, identifying at least one visual feature in a pre-operative dataset, aligning the visual features with the multidimensional visualization, and incorporating one or more real-time, virtual surgical reference indicium into the real-time visualization. In exemplary embodiments, the apparatus and methods are described in relation to ocular surgery, more specifically capsulorrhexis.
Owner:ALCON INC
Systems and methods for modeling spines and treating spines based on spine models
ActiveUS20190099221A1Good choicePromote resultsMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesRadiologyPre operative
Disclosed are systems and methods for rapid generation of simulations of a patient's spinal morphology that enable pre-operative viewing of a patient's condition and to assist surgeons in determining the best corrective procedure and with any of the selection, augmentation or manufacture of spinal devices based on the patient specific simulated condition. The simulation is generated by morphing a generic spine model with a three-dimensional curve representation of the patient's particular spinal morphology derived from existing images of the patient's condition.
Owner:K2M
Instrument guidance system for sinus surgery
ActiveUS20170231714A1Enhanced D perceptionImage enhancementImage analysisGuidance systemObject based
A method for generating an augmented reality image for supporting the adjustment of the position of a surgical instrument during sinus surgery comprising the steps of: selecting at least one of sinus cells, cavities and orifices of the sinus in a pre-operative image by marking them with at least one geometric primitive or tube shaped object; using real-time intra-operative imaging for displaying the operating field; determining the relative positions at least between the real-time imaging of the patient and the pre-operative image data; computing a virtual image corresponding to a real-time image comprising at least one marked geometric primitive or tube shaped object based on the determined relative positions; combining the virtual image and the real-time intraoperative image for visualization in an augmented reality image.
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com