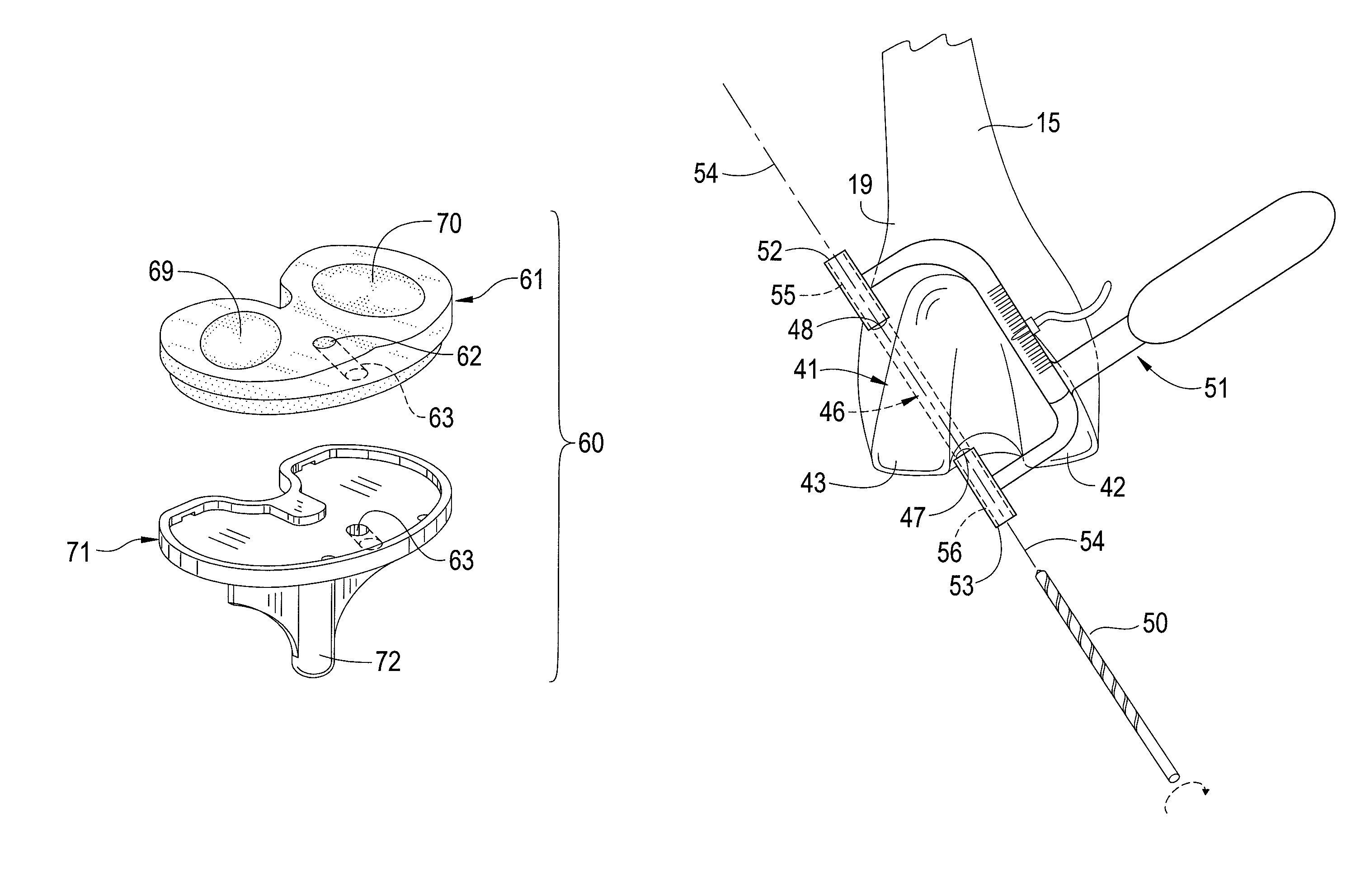
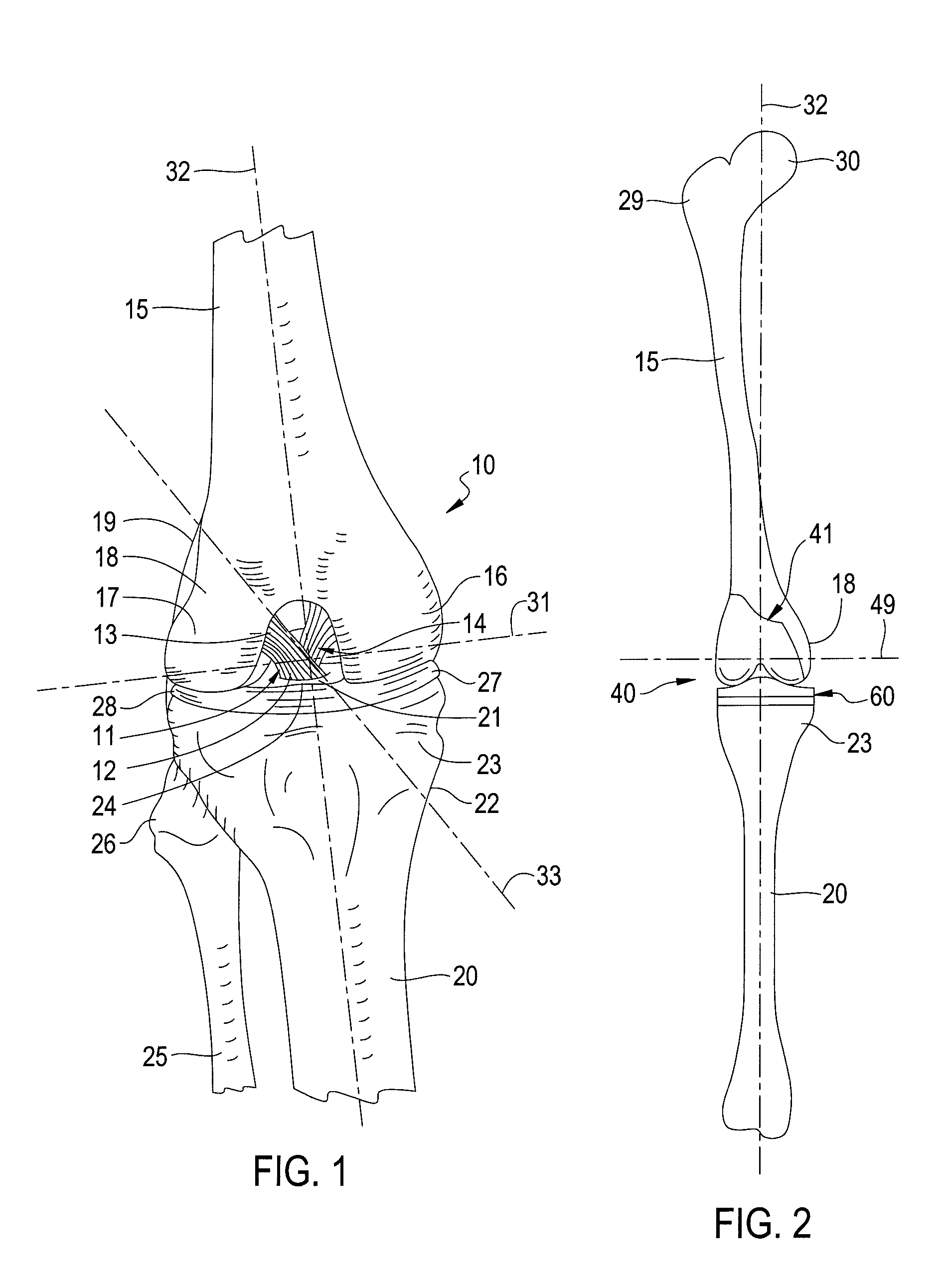
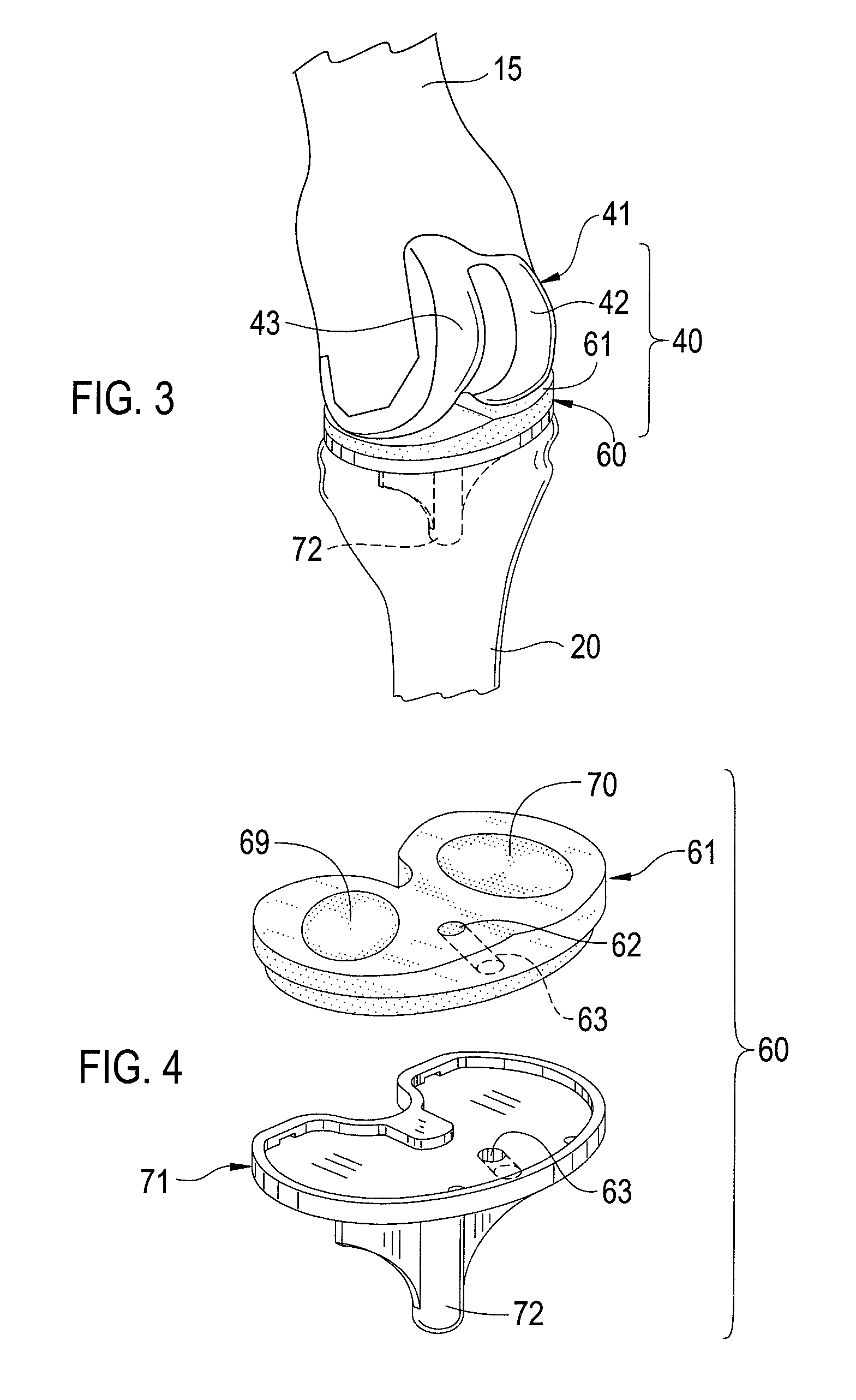
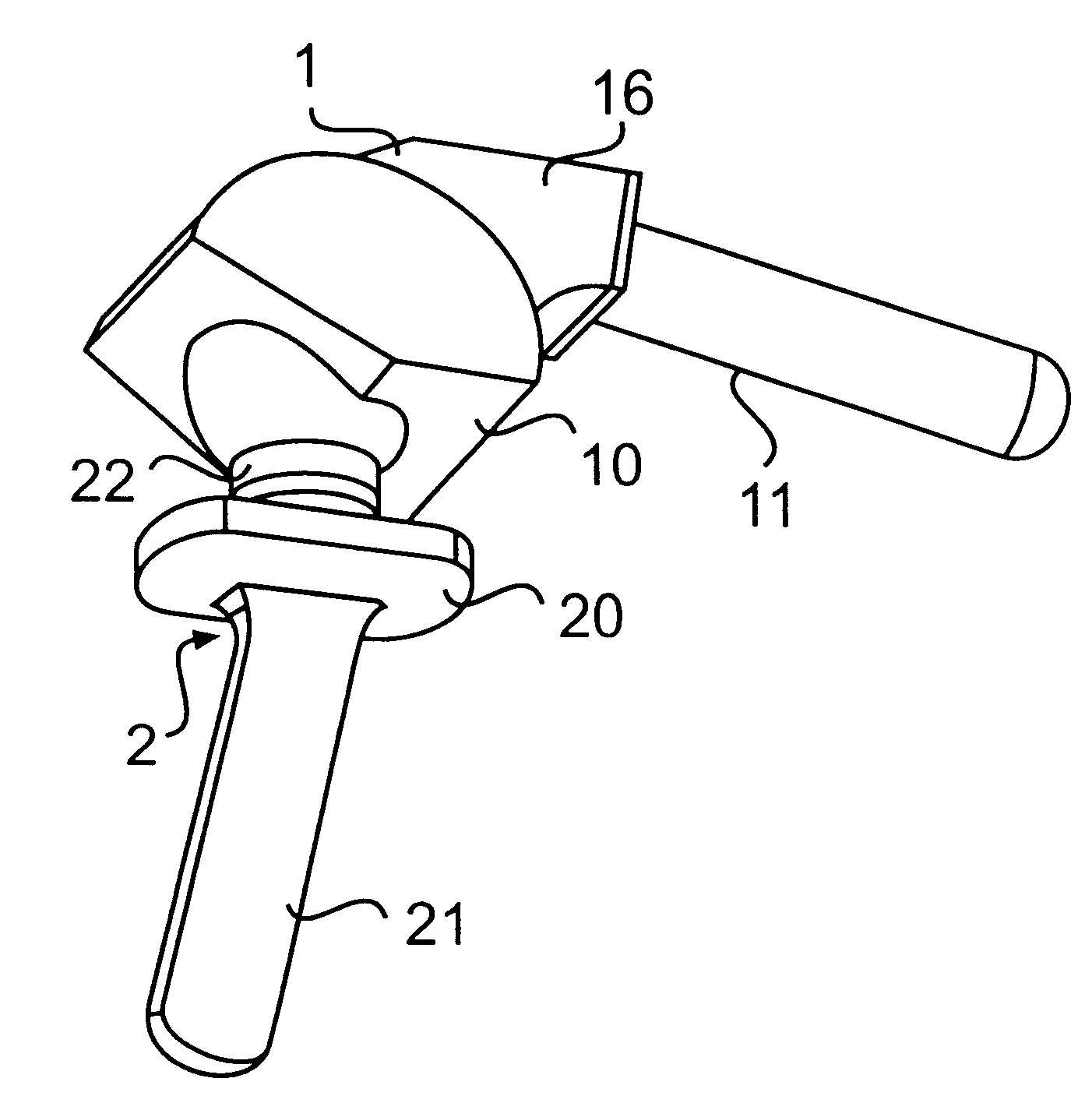
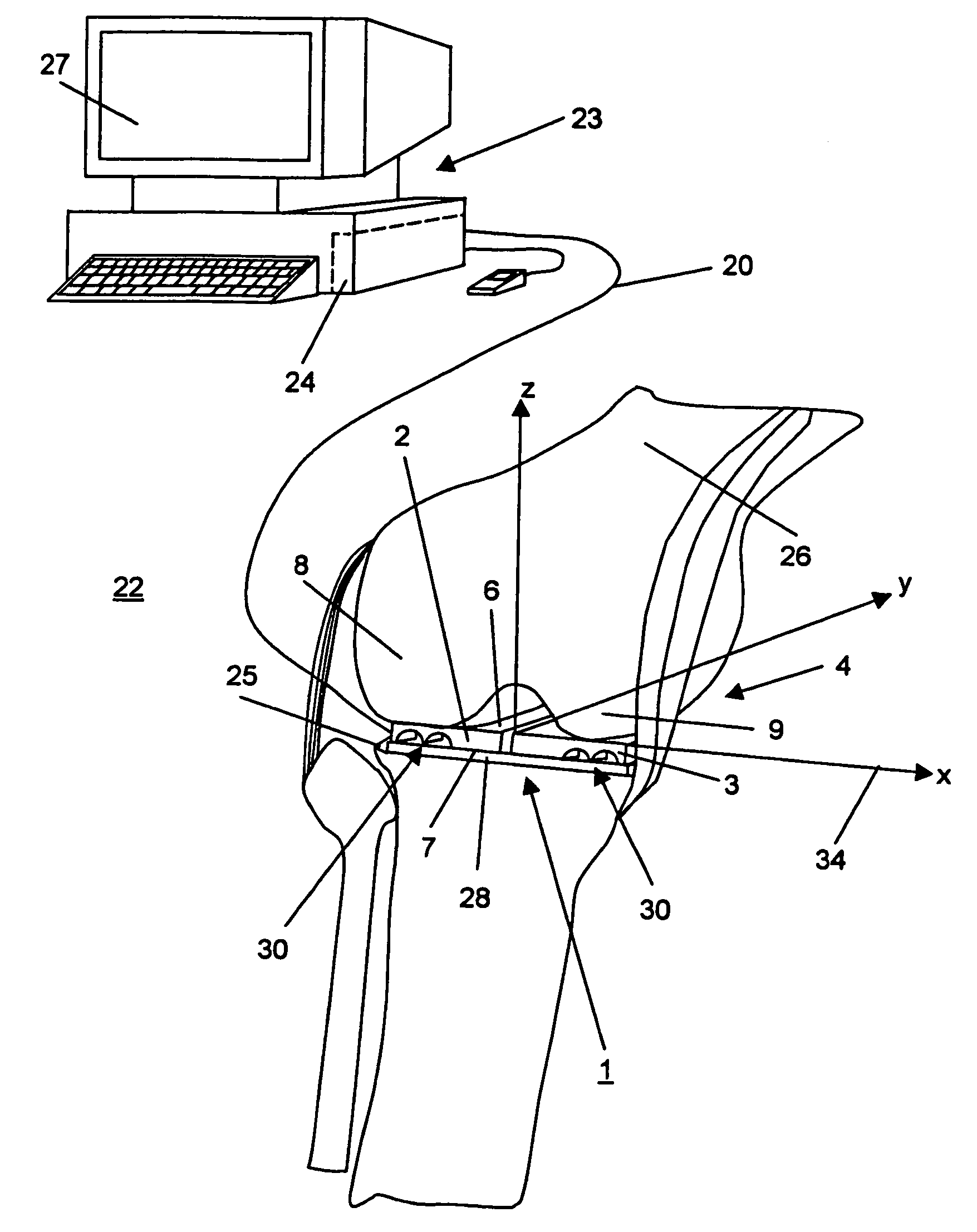
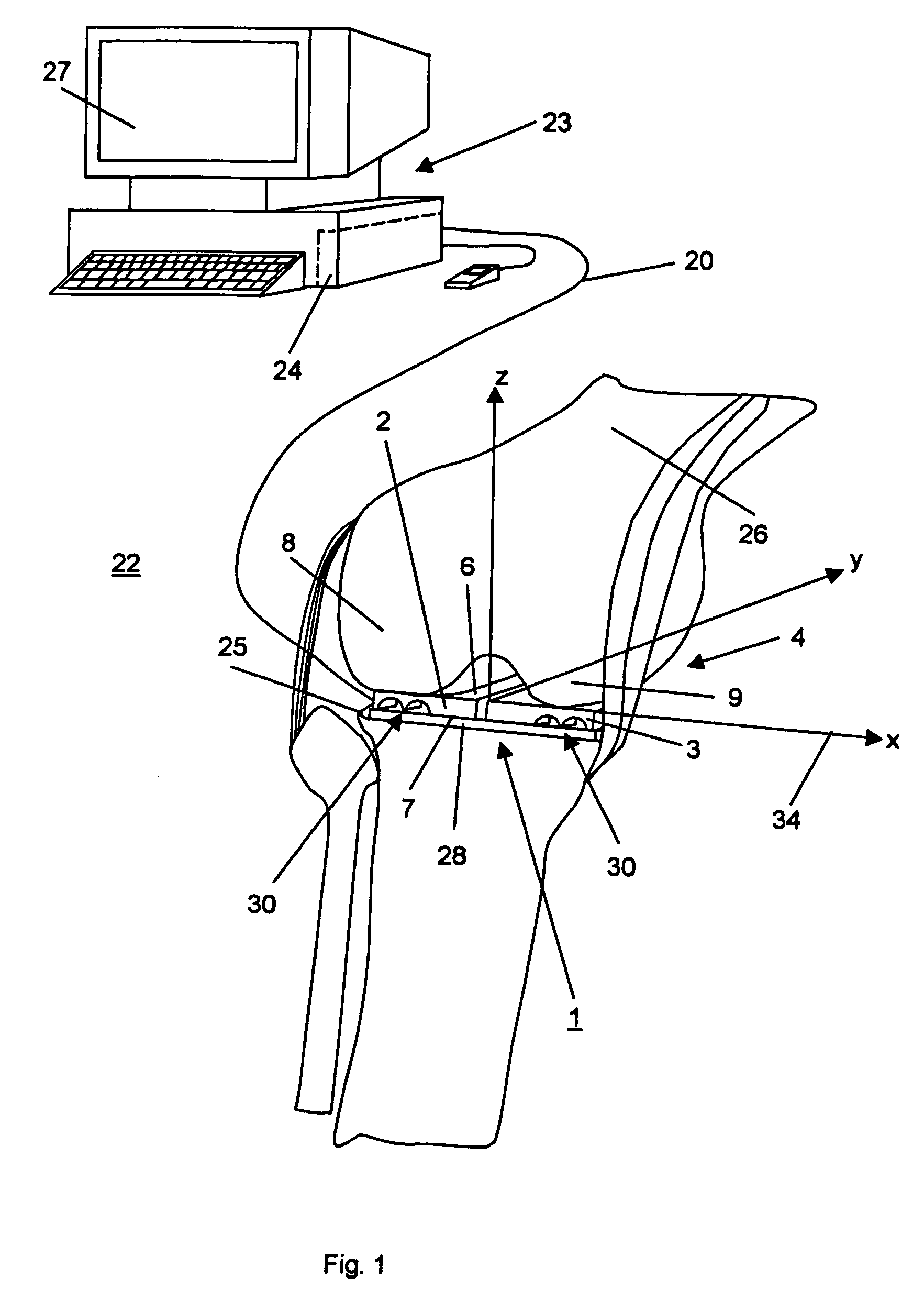
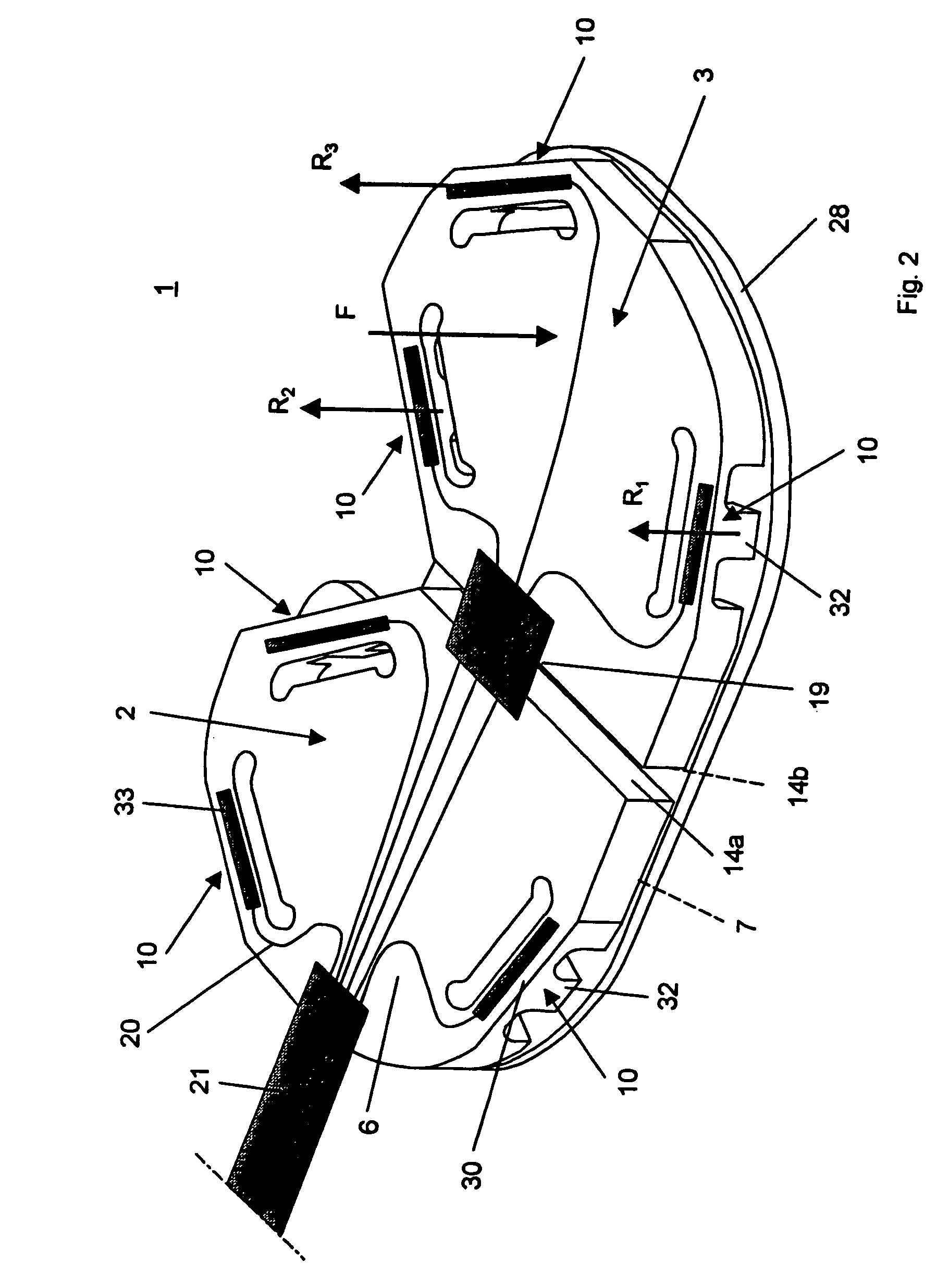
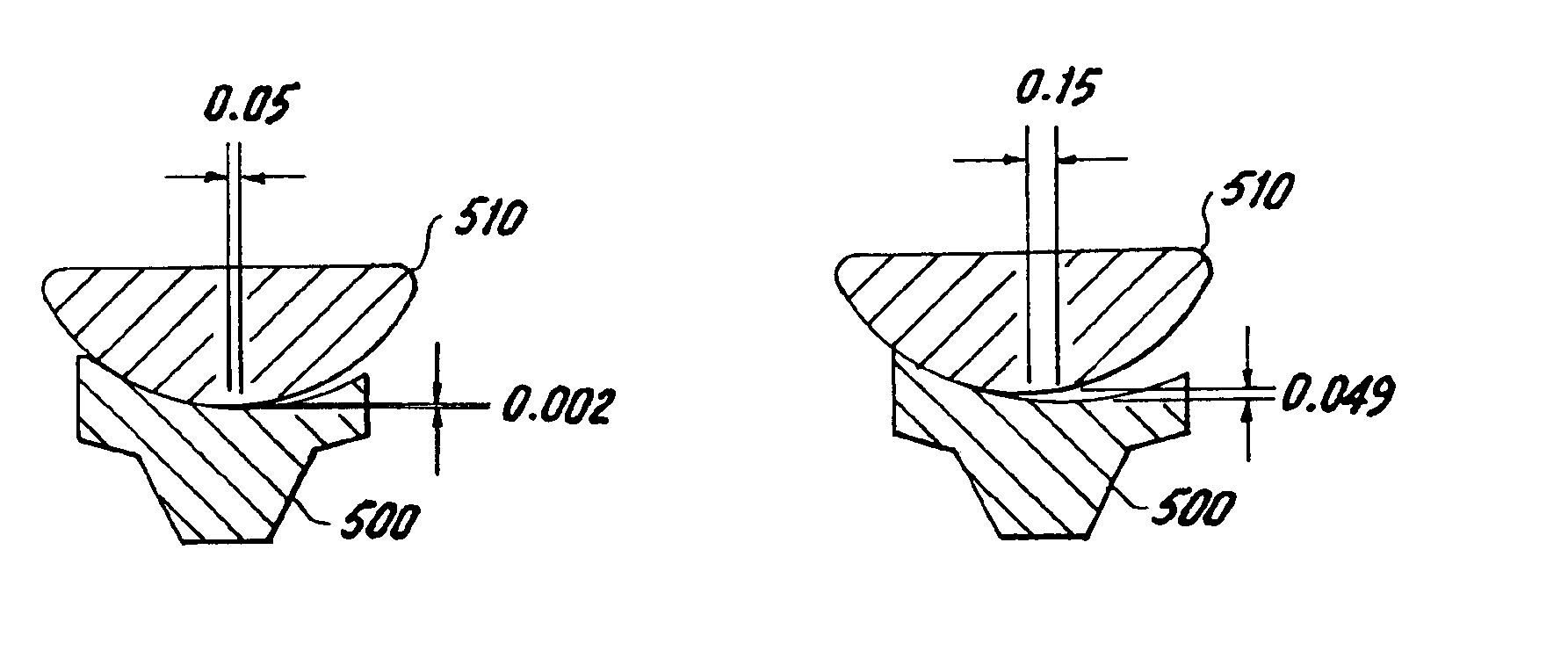
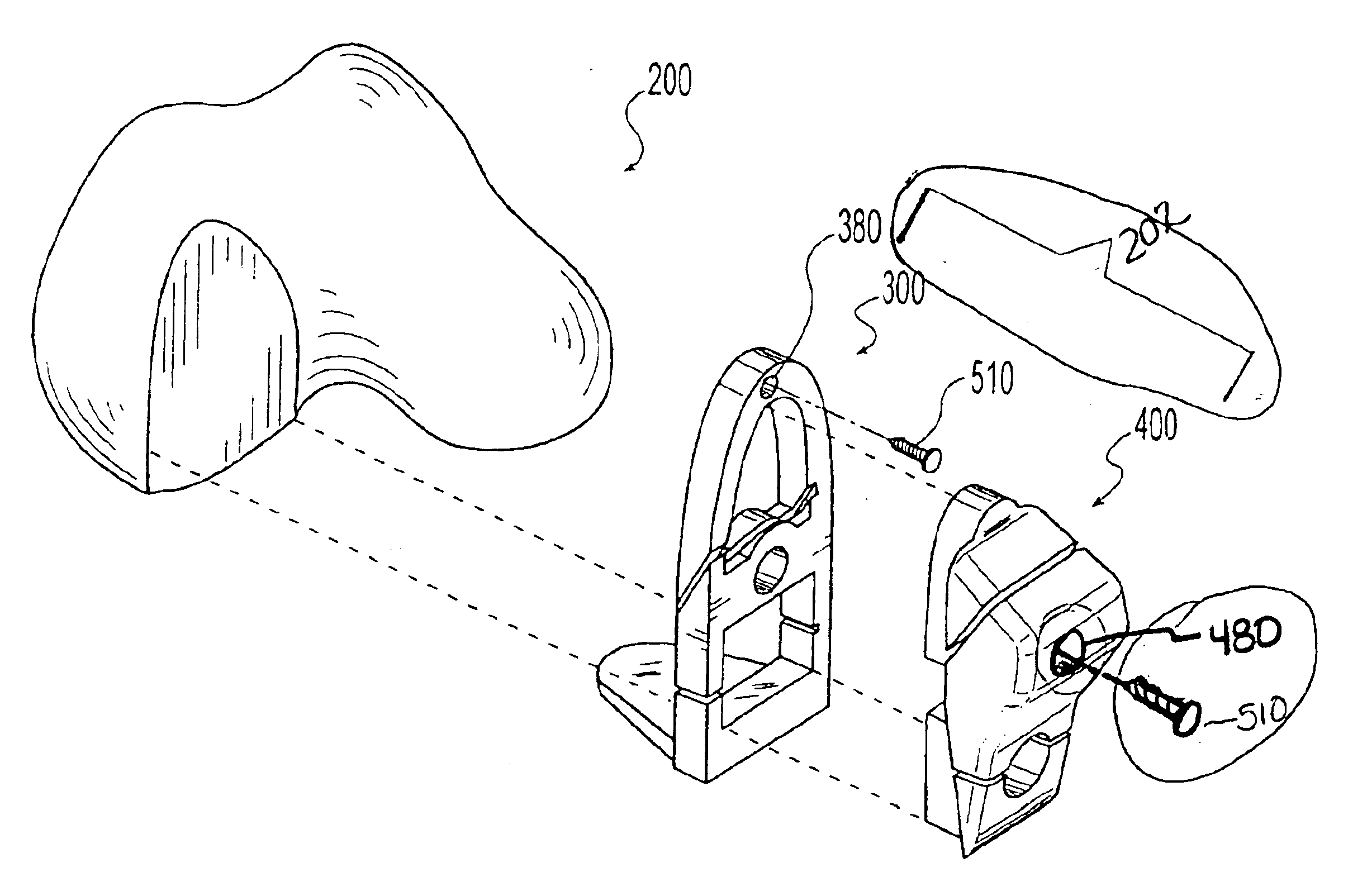
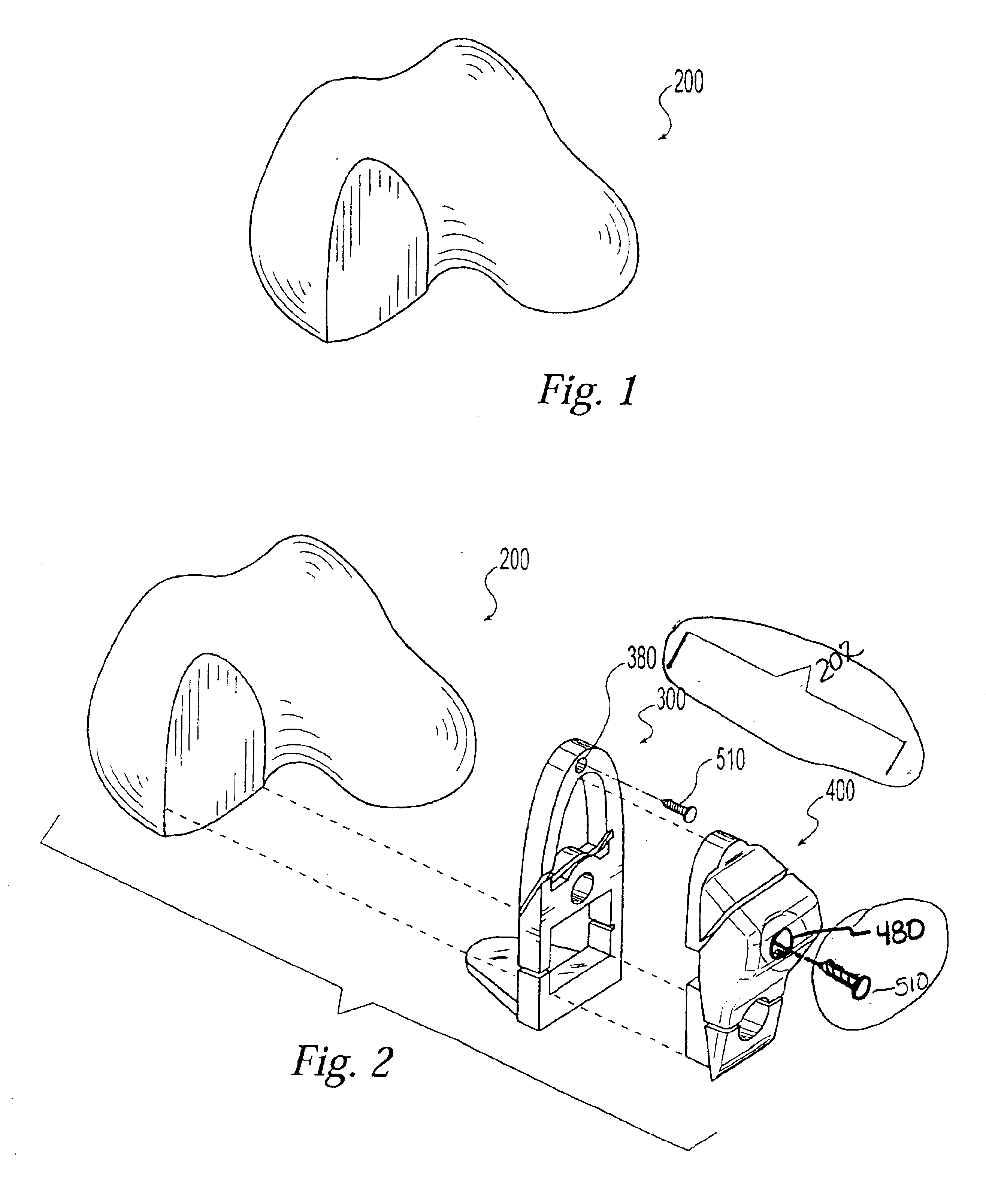
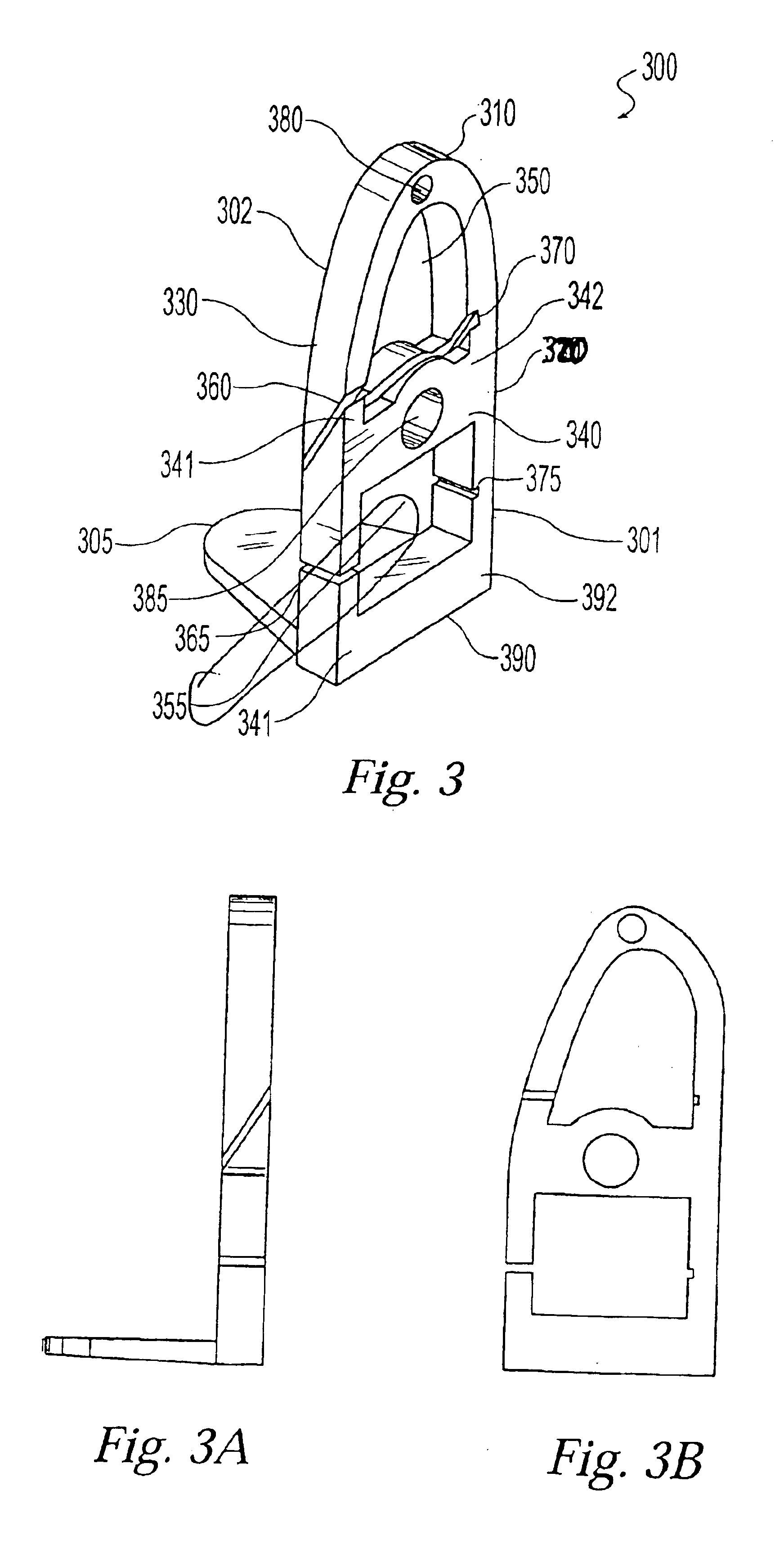
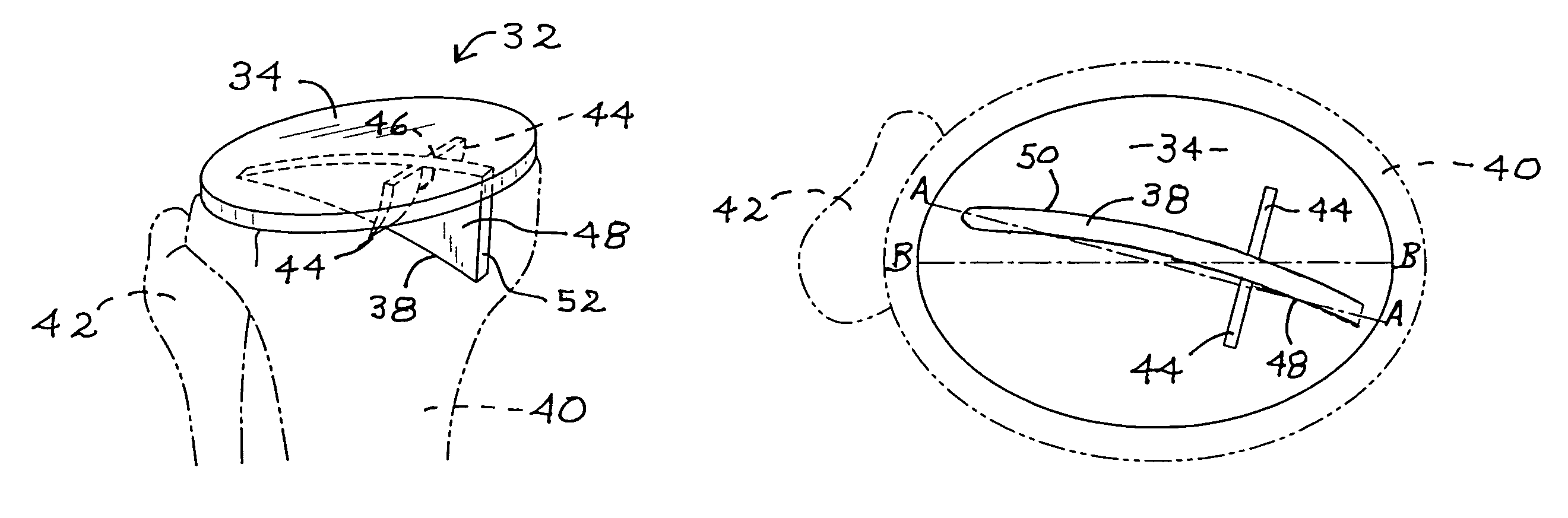
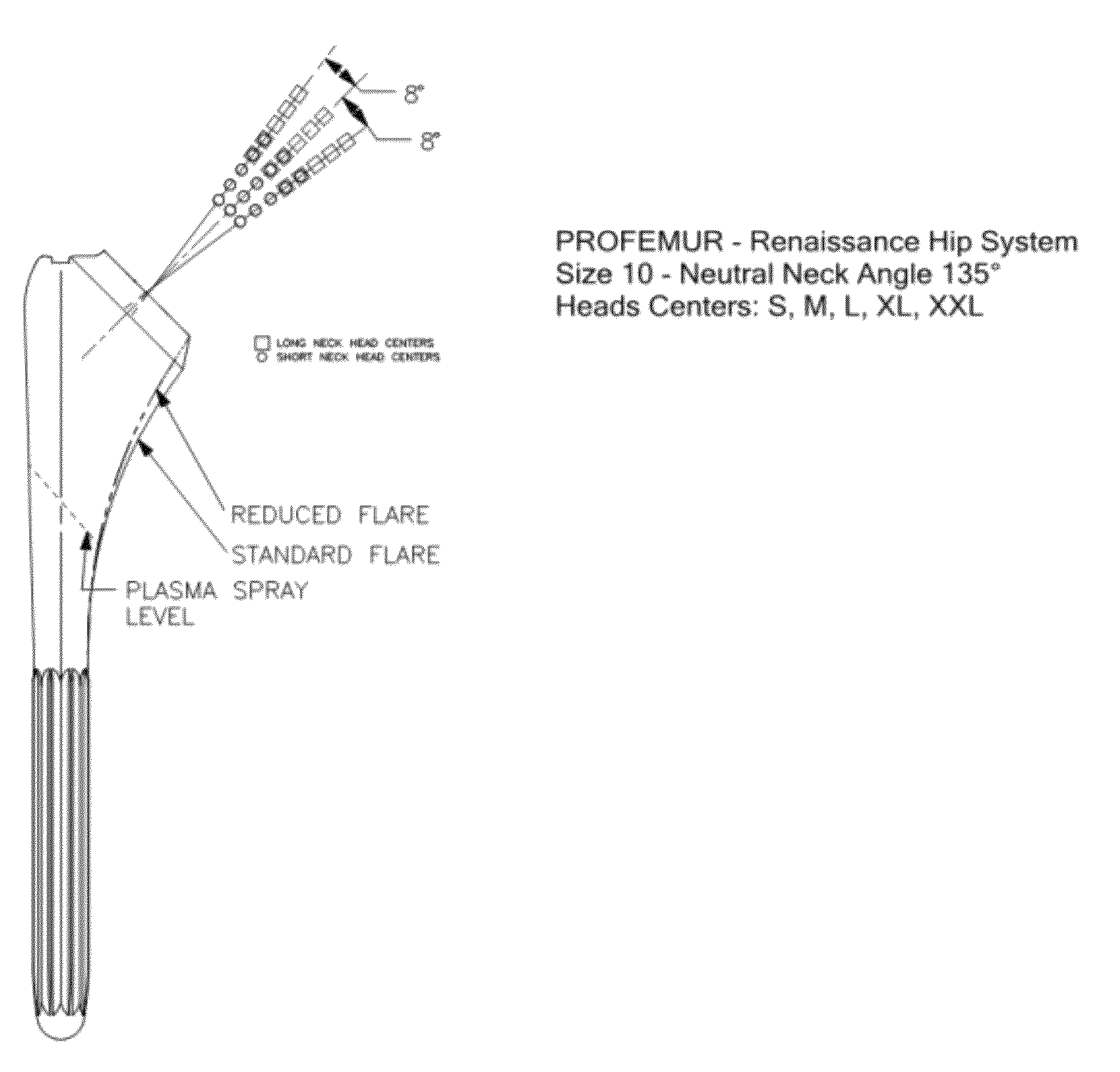
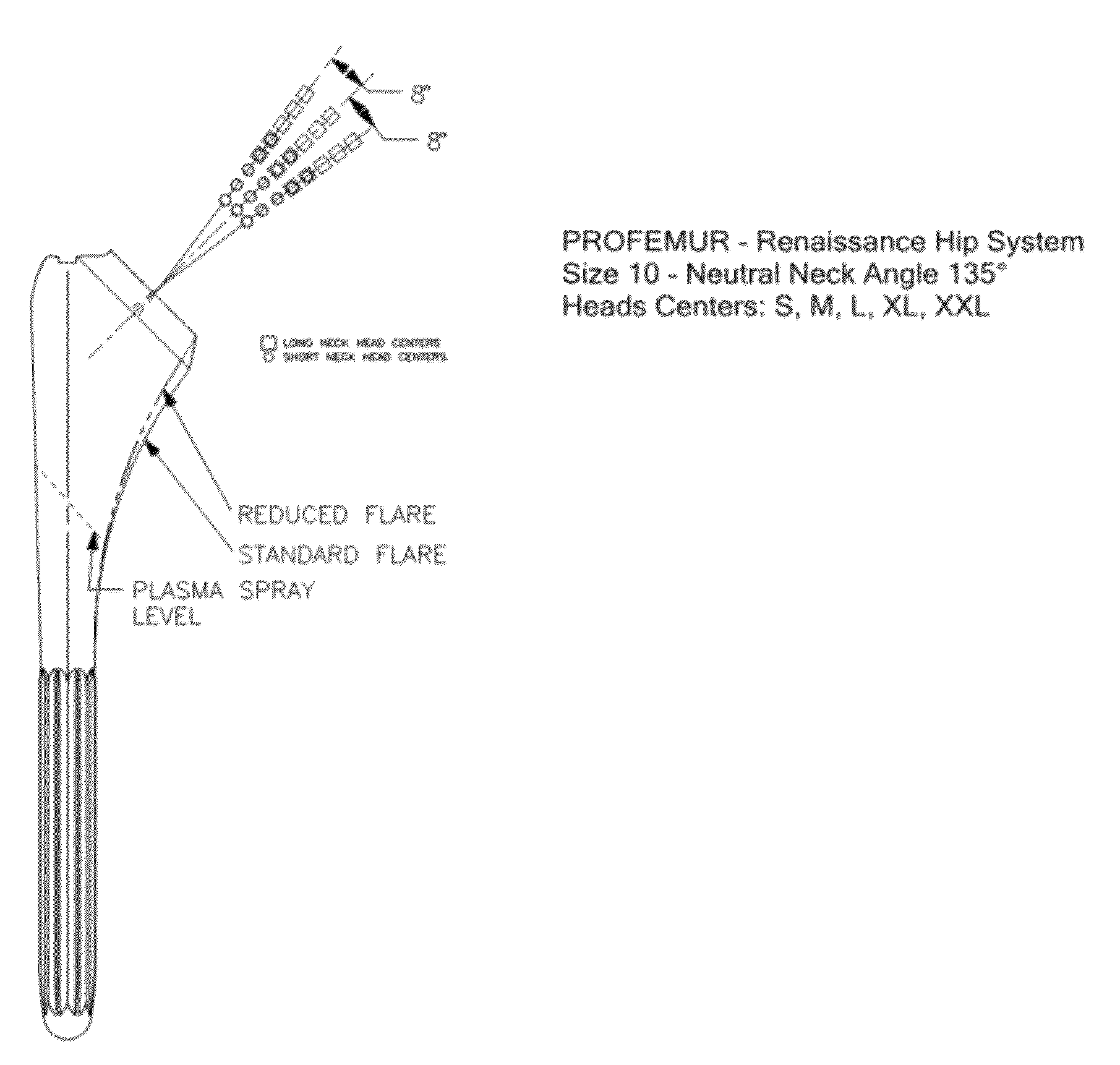
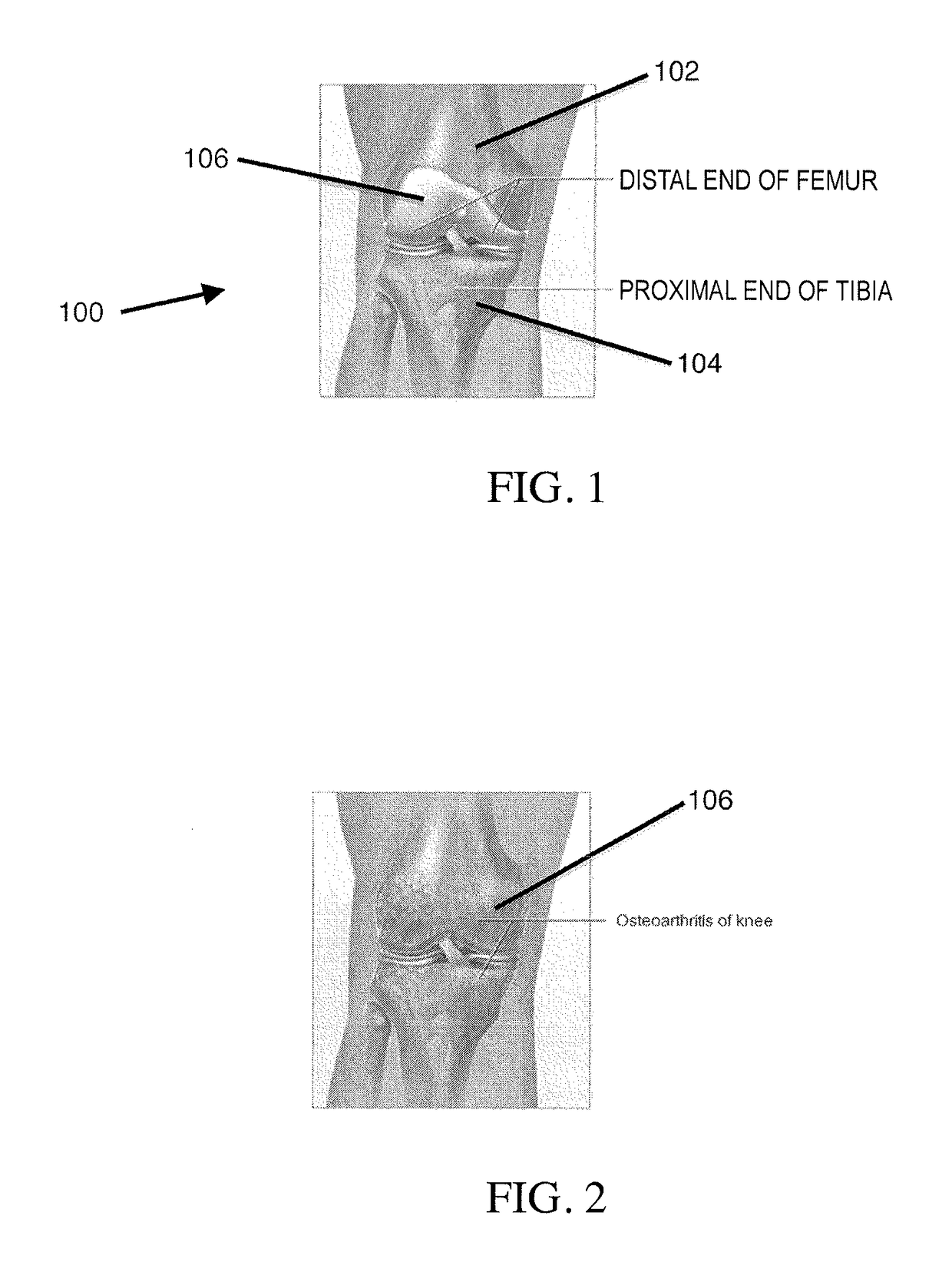
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
115 results about "Total hip arthroplasty" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
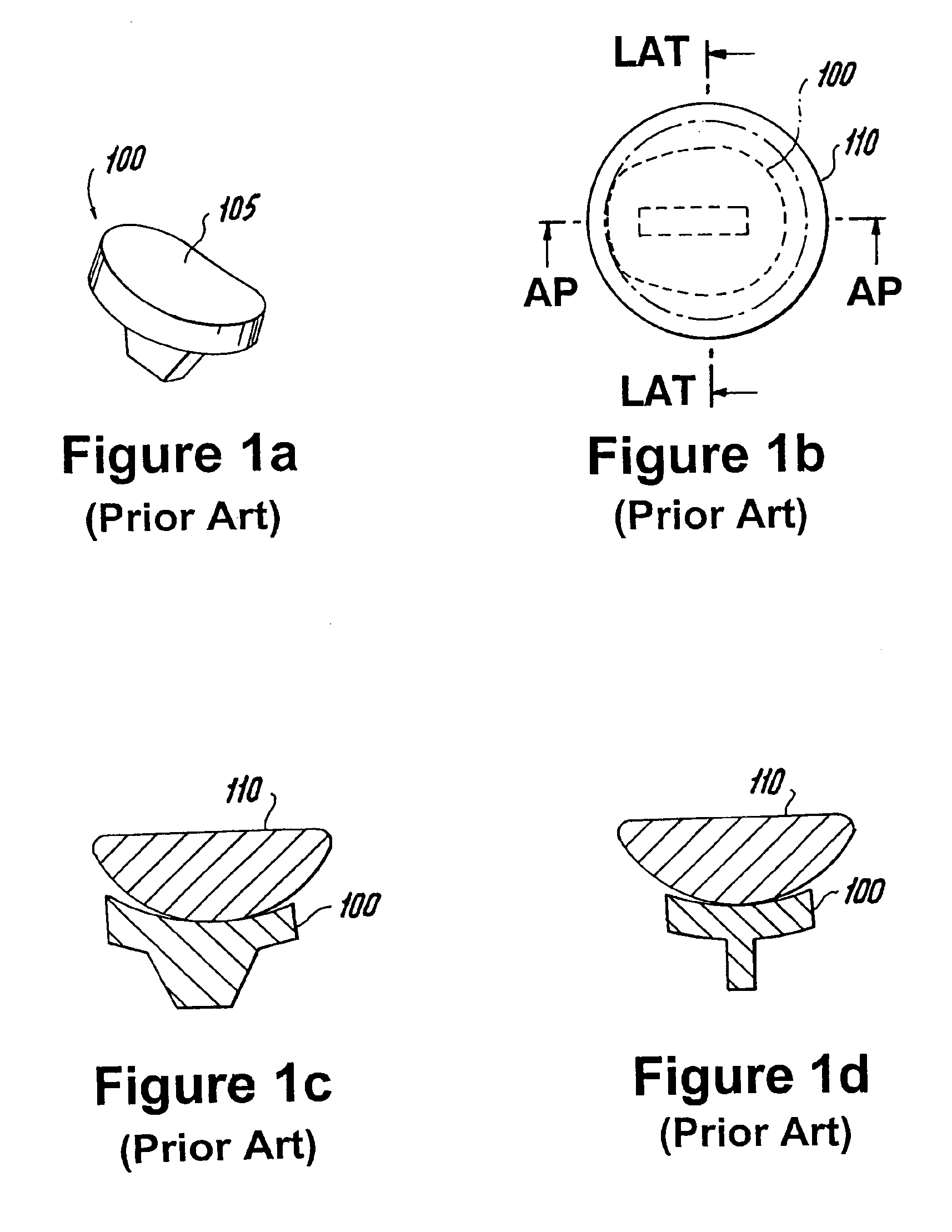
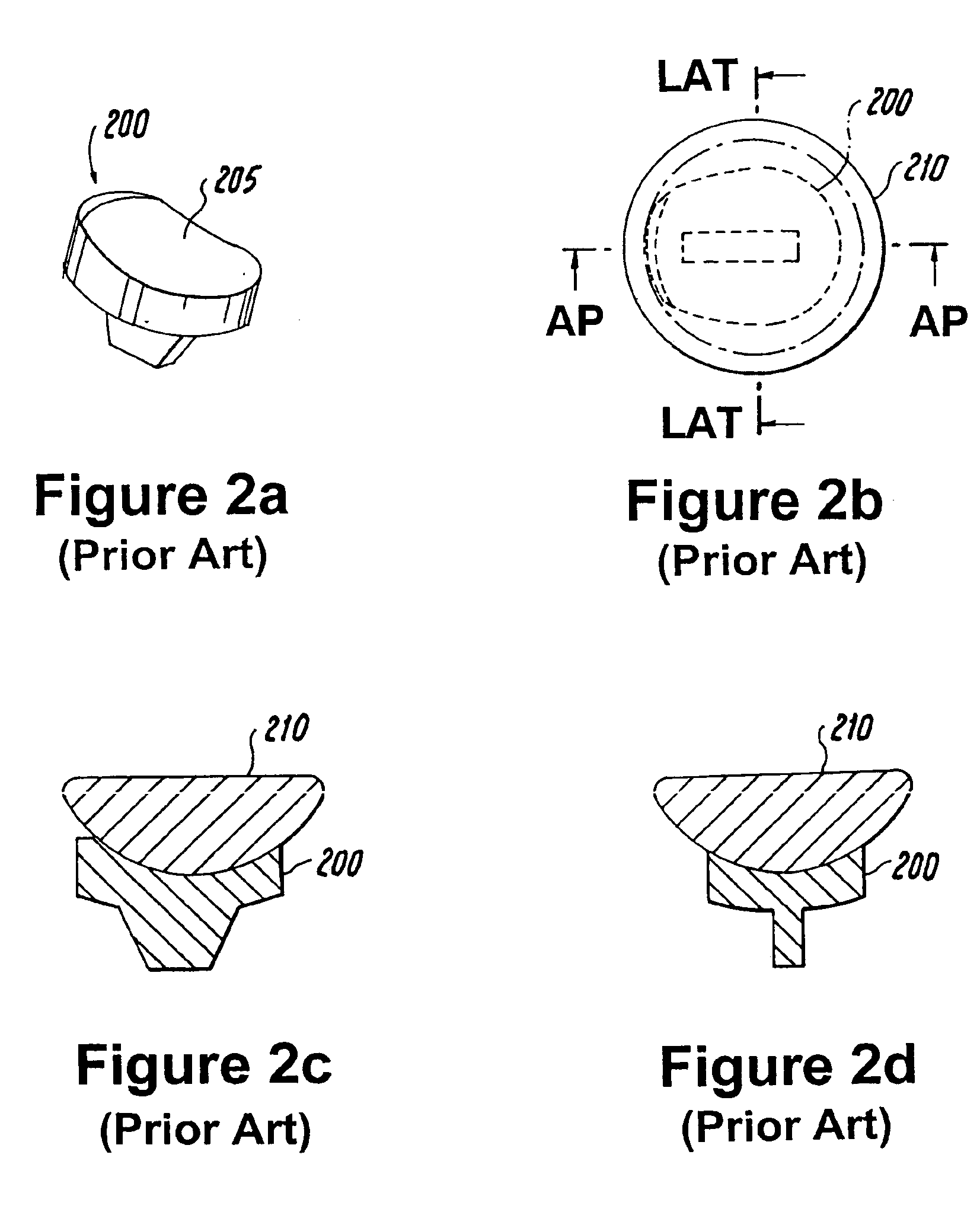
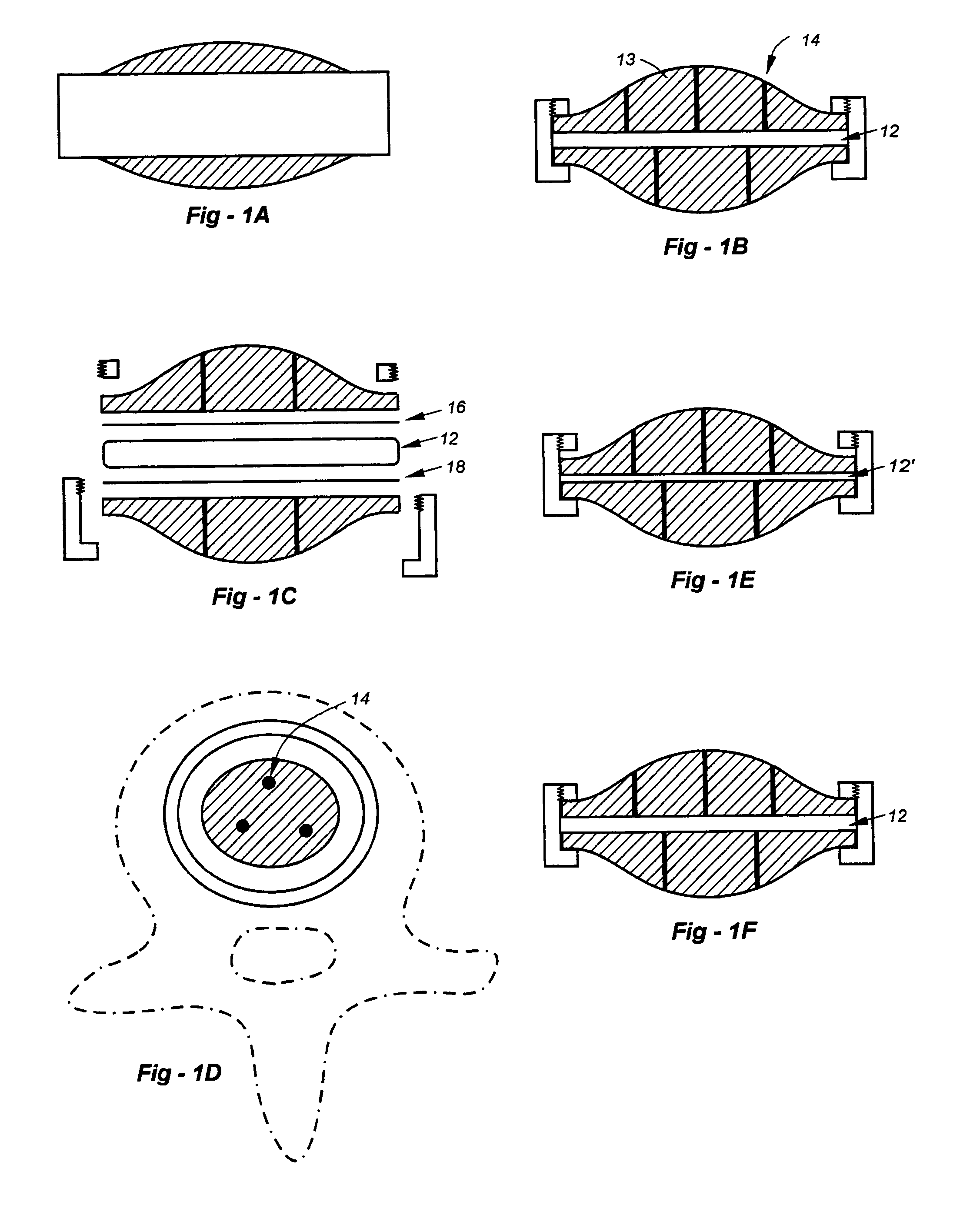
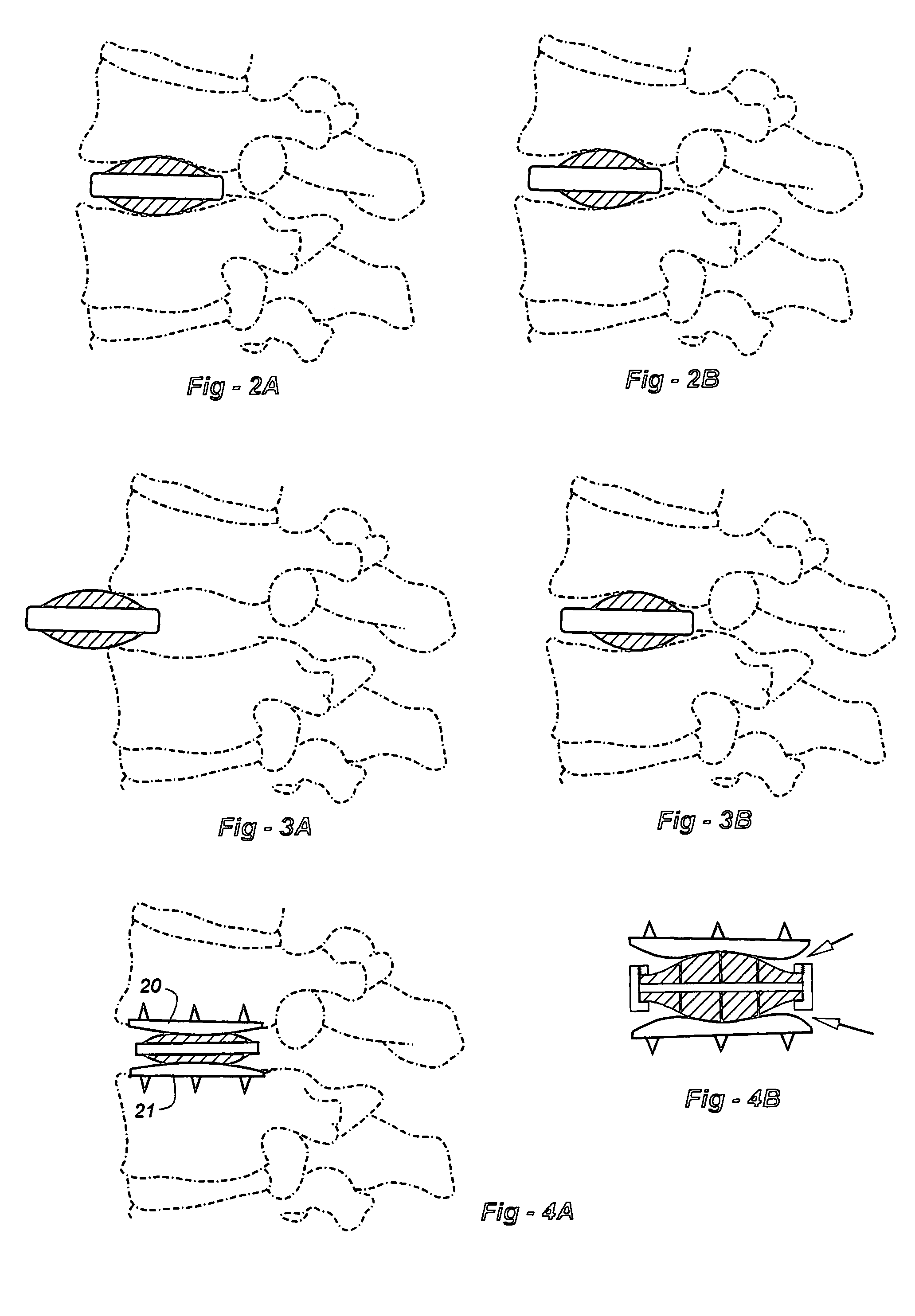
Total hip replacement, also called a total hip arthroplasty, is a procedure where worn or damaged surfaces of the hip bones are replaced with artificial parts or surfaces. During surgery, a new artificial head and socket are either cemented or pinned into the femur and pelvis. Hip replacements can last up to 10 years in 90 percent of patients.
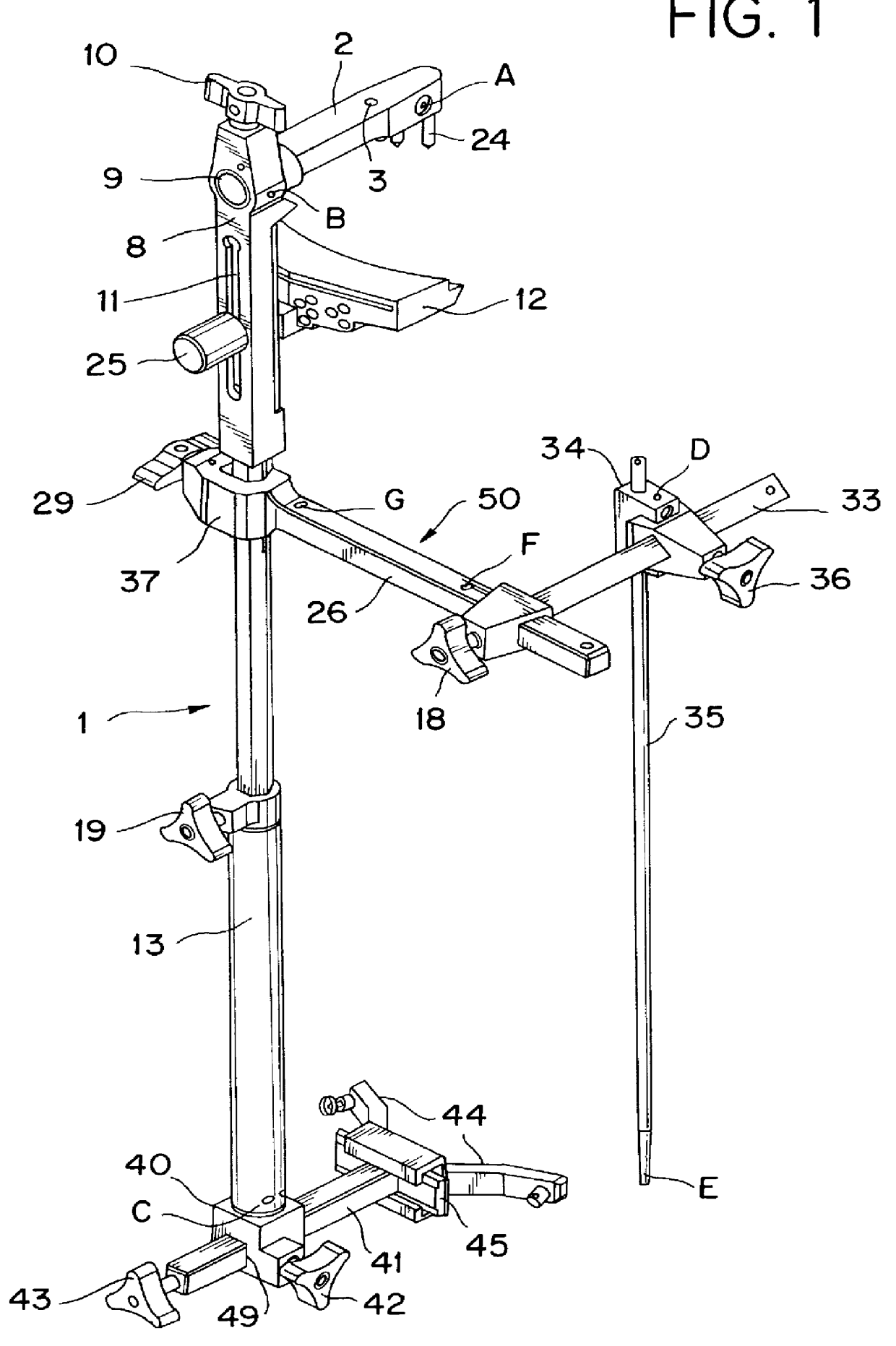
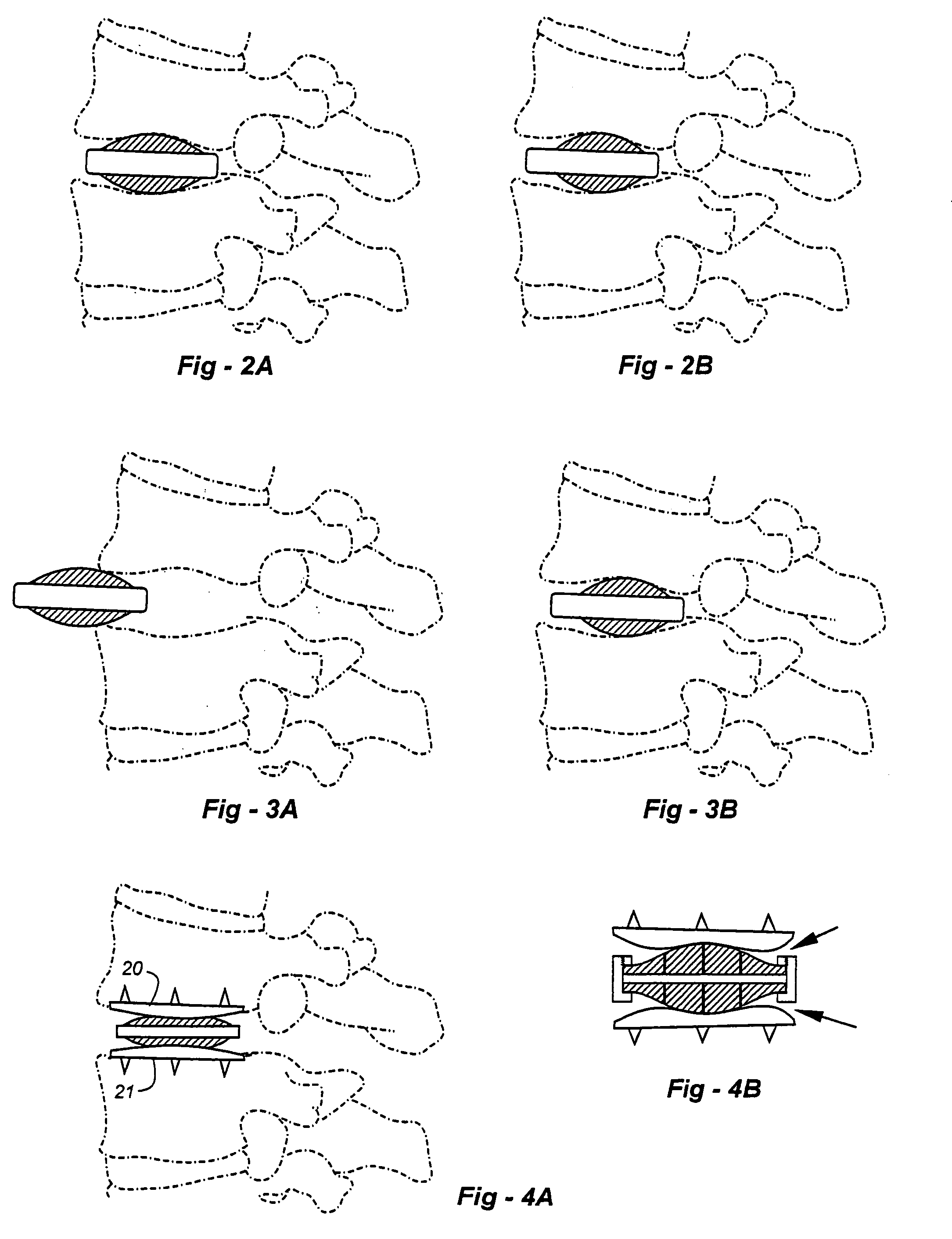
Total joint arthroplasty system
ActiveUS20090131941A1Precise alignmentImprove visualizationMedical simulationProgramme controlJoint arthroplastyTotal hip arthroplasty
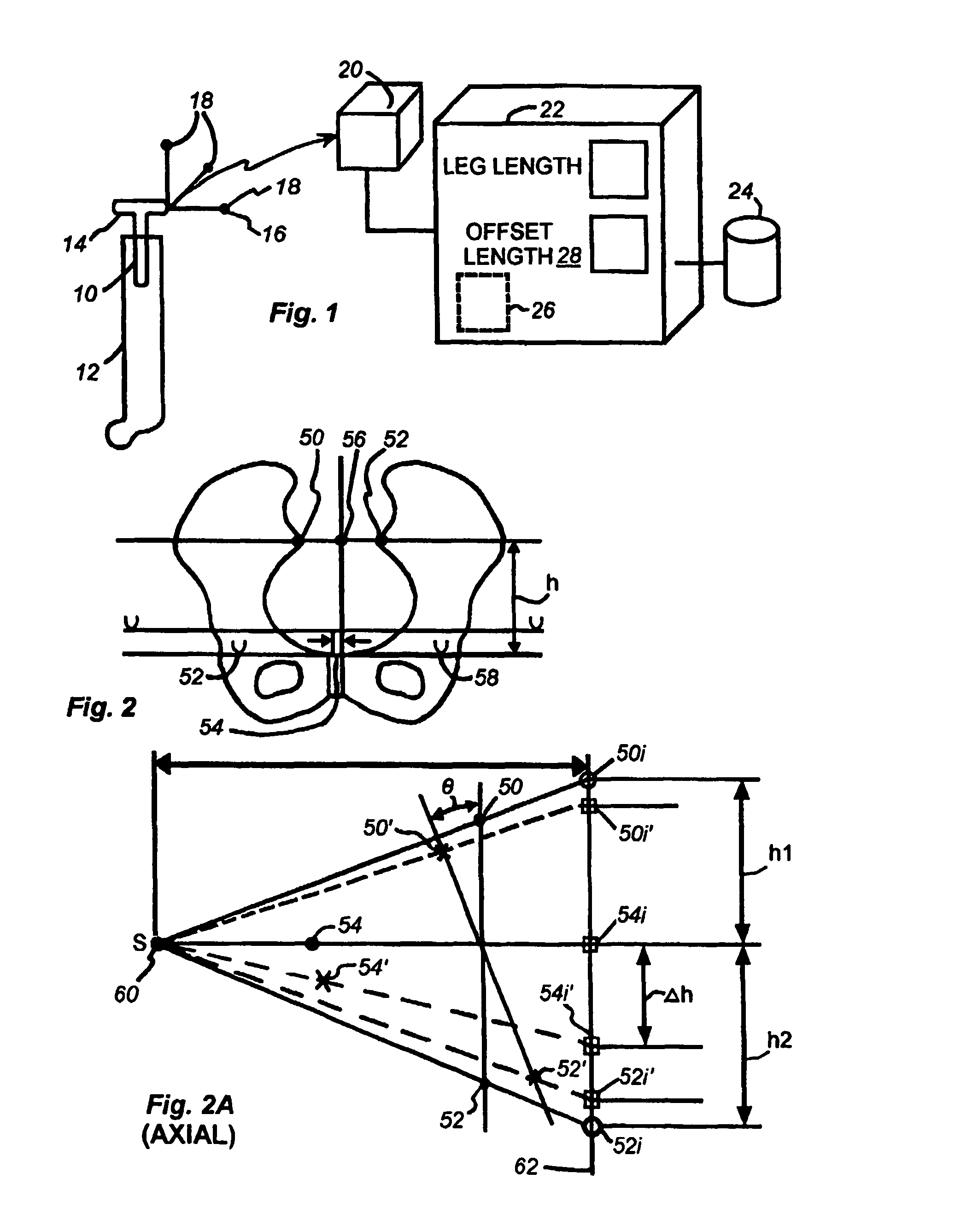
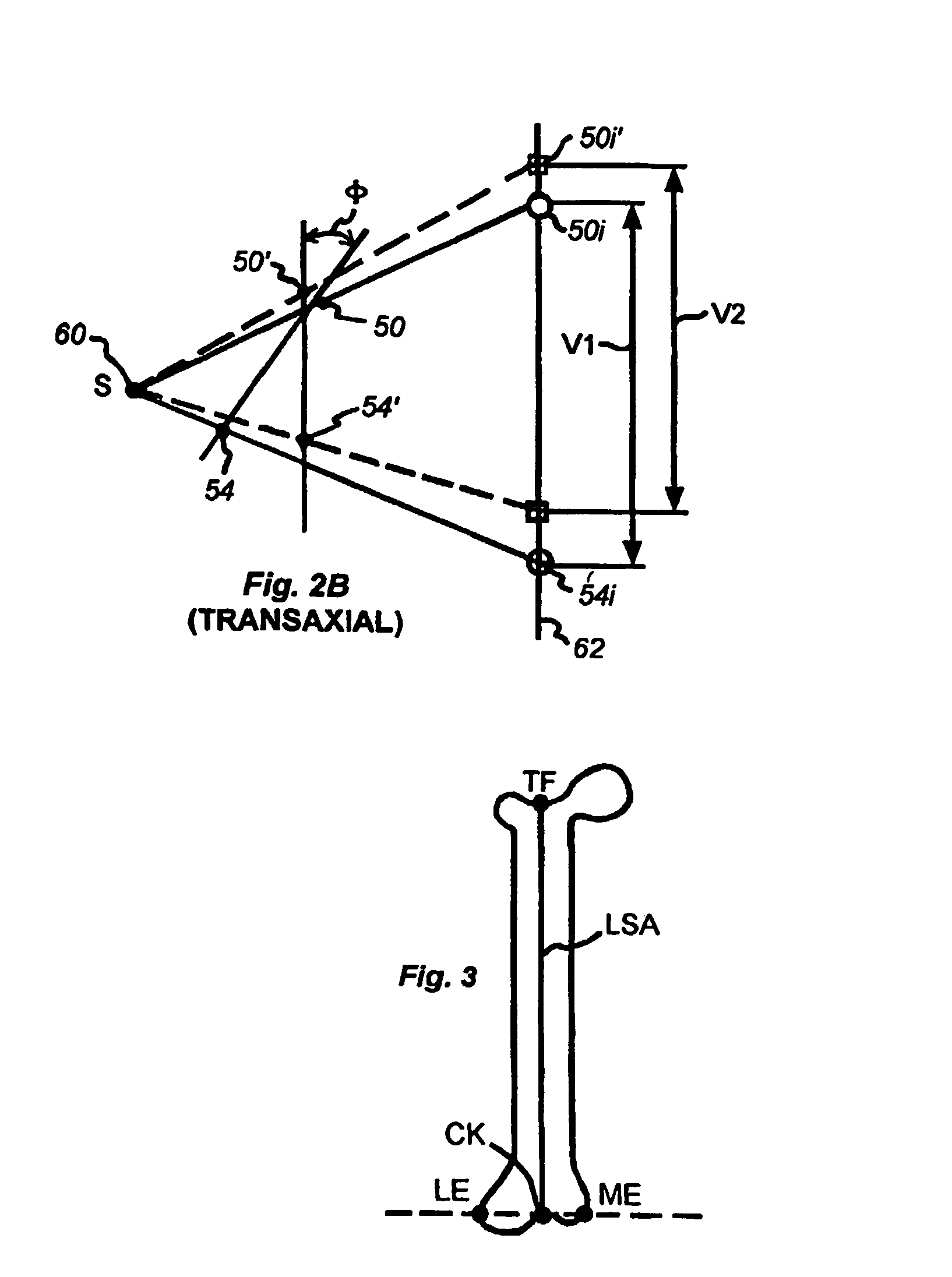
A method and system for performing a total joint arthroplasty procedure on a patient's damaged bone region. A CT image or other suitable image is formed of the damaged bone surfaces, and location coordinate values (xn,yn,zn) are determined for a selected sequence of bone surface locations using the CT image data. A mathematical model z=f(x,y) of a surface that accurately matches the bone surface coordinates at the selected bone spice locations, or matches surface normal vector components at selected bone surface locations, is determined. The model provides a production file from which a cutting jig and an implant device (optional), each patient-specific and having controllable alignment, are fabricated for the damaged bone by automated processing. At this point, the patient is cut open (once), the cutting jig and a cutting instrument are used to remove a selected portion of the bone and to provide an exposed planar surface, the implant device is optionally secured to and aligned with the remainder of the bone, and the patient's incision is promptly repaired.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
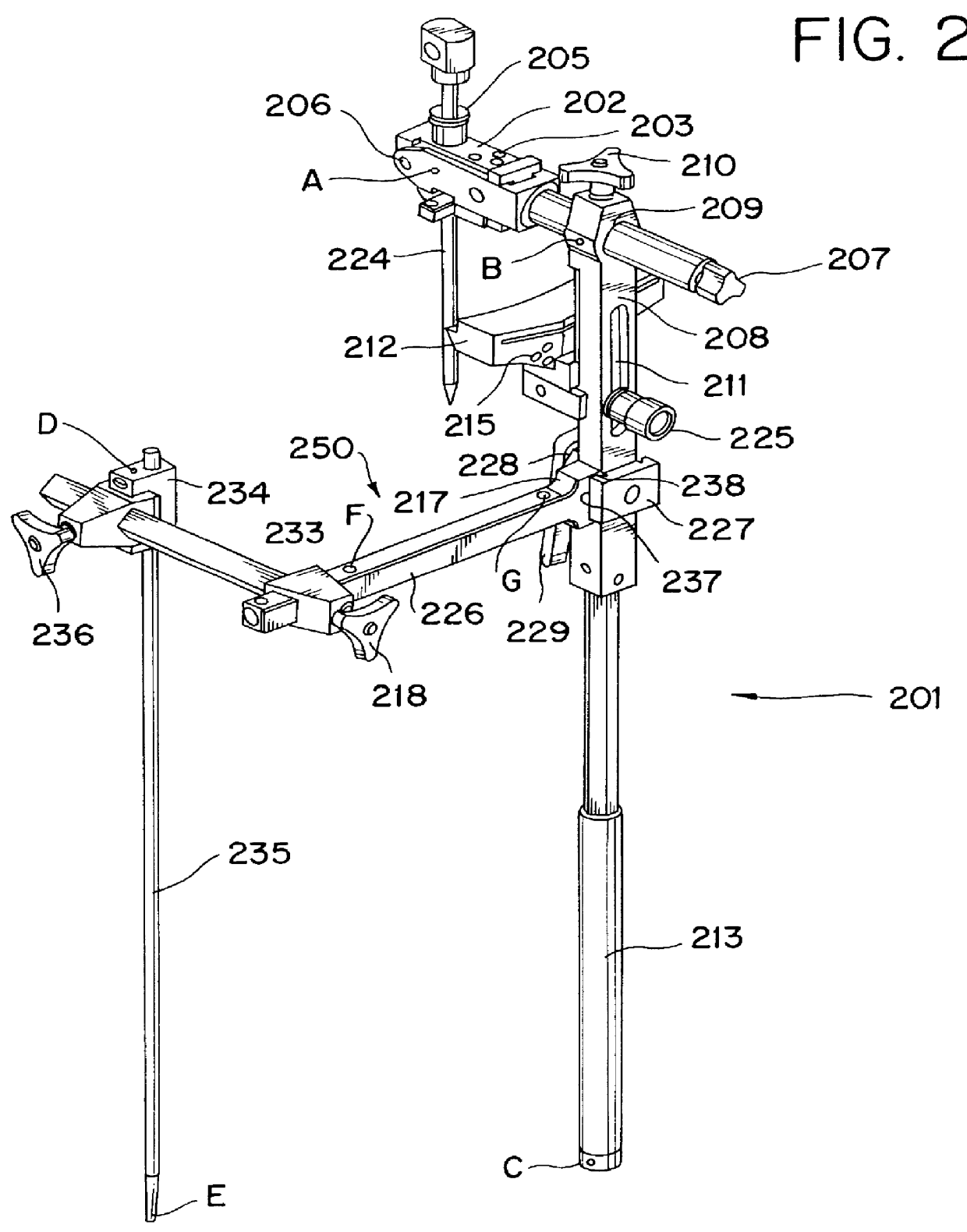
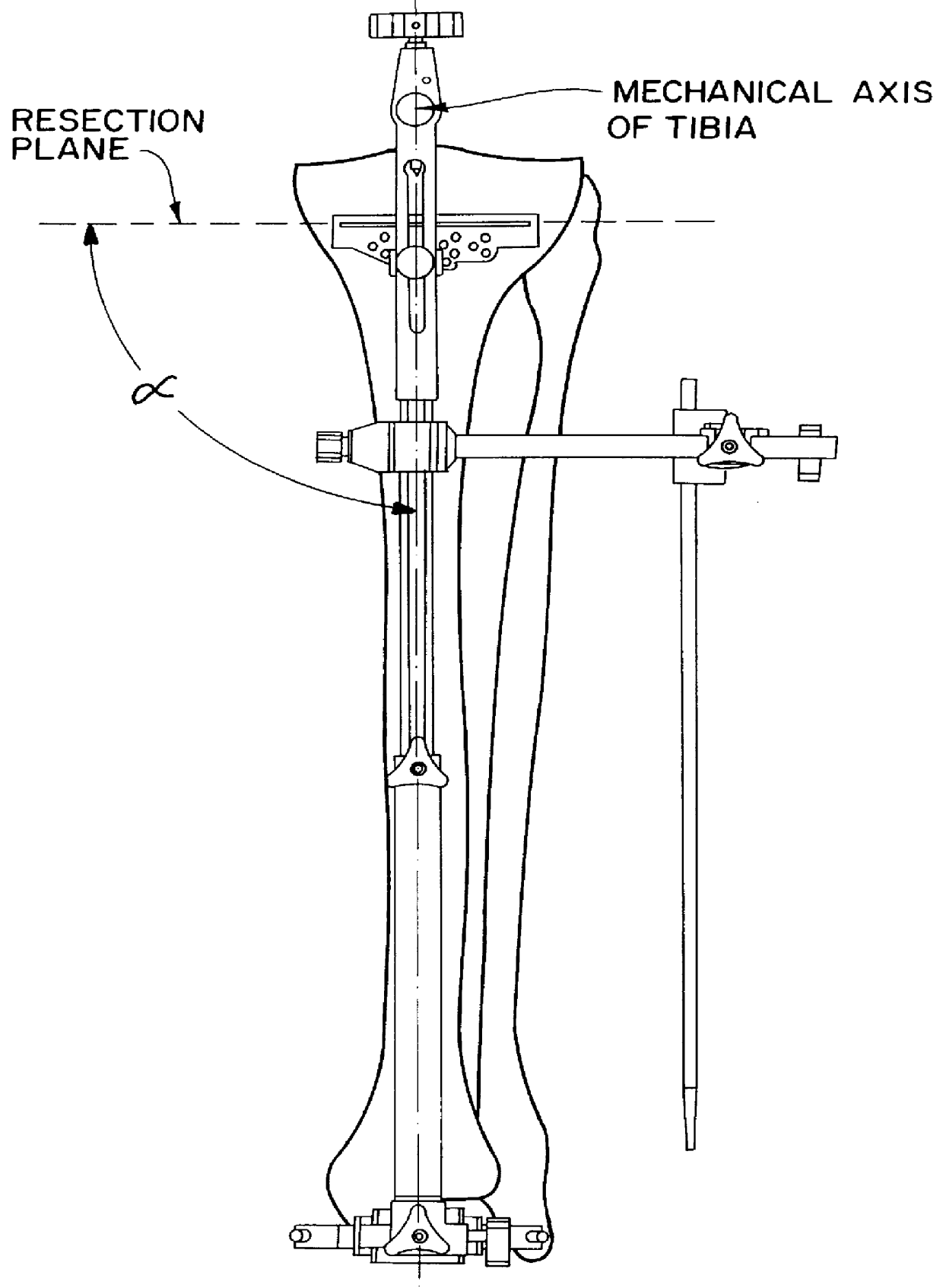
Tibial resection guide
InactiveUS6090114AEasy to identifyConstant angleJoint implantsSurgical sawsTibiaTotal hip arthroplasty
An apparatus and method for tibial alignment which allows the independent establishment of two separate geometric planes to be used as a reference for the cutting of the tibial plateau during total knee arthroplasty. Two separate frame assemblies with extending rods are coupled to the tibia with a fixed relative angle between them, thereby allowing alignment with the mechanical axis of the bone. A cutting block is mounted on one of the assembly frames and is positioned against the tibia. Stabilizing pins are then placed in the cutting block, allowing the proper tibial plateau resection plane to be created.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
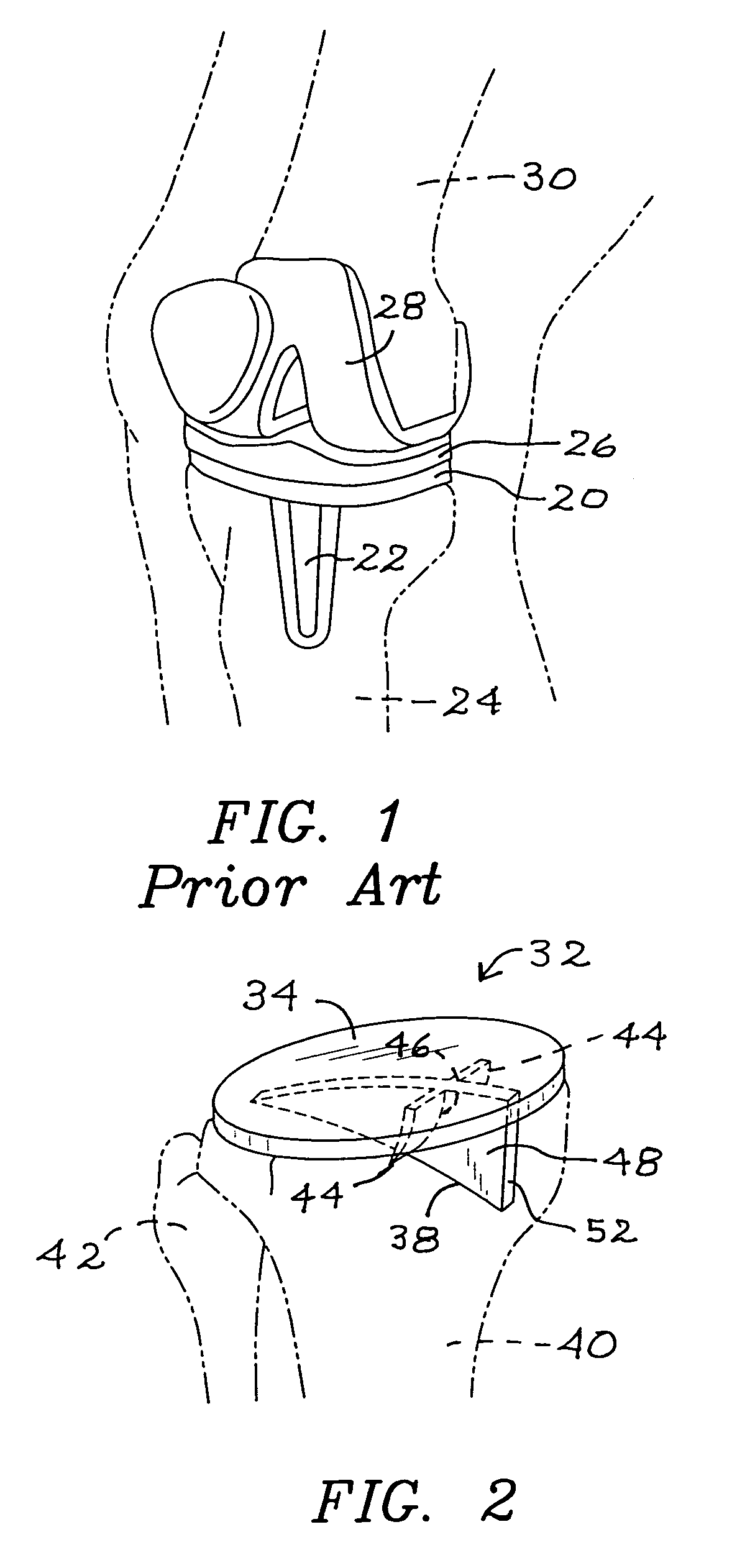
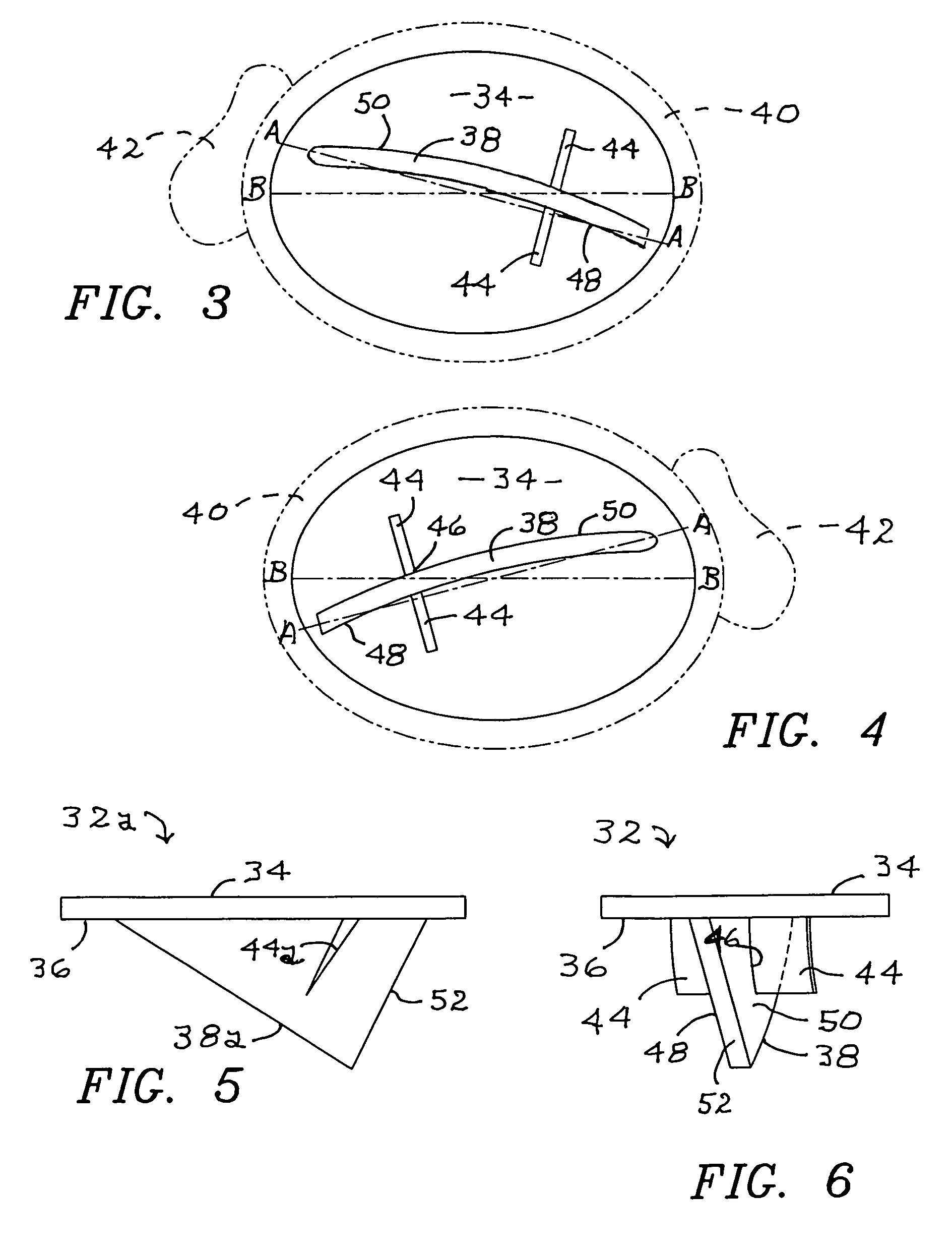
Prosthetic components with partially contained compressible resilient members
InactiveUS7066958B2Improve protectionEliminate shear stressJoint implantsSpinal implantsElastomerShape-memory alloy
One or more rigid components associated with an articulating bone are used to encase, encapsulate, contain, or otherwise protect a compressible / resilient member. The embodiments are applicable not only to artificial disc replacement (ADR) devices, but also to joint situations including total knee and hip arthroplasty. The cushion elements in the preferred embodiments include synthetic rubbers, hydrogels, elastomers, and other polymeric materials such as viscoelastic polymers and foam polyurethanes. The invention effectively combines the advantages of such materials (cushioning, shape memory, and expansion after insertion in the case of hydrogels), while providing increased protection, particularly the elimination of shear stresses. When applied to an ADR, the invention also minimizes the risk of extrusion.
Owner:FERREE BRET A
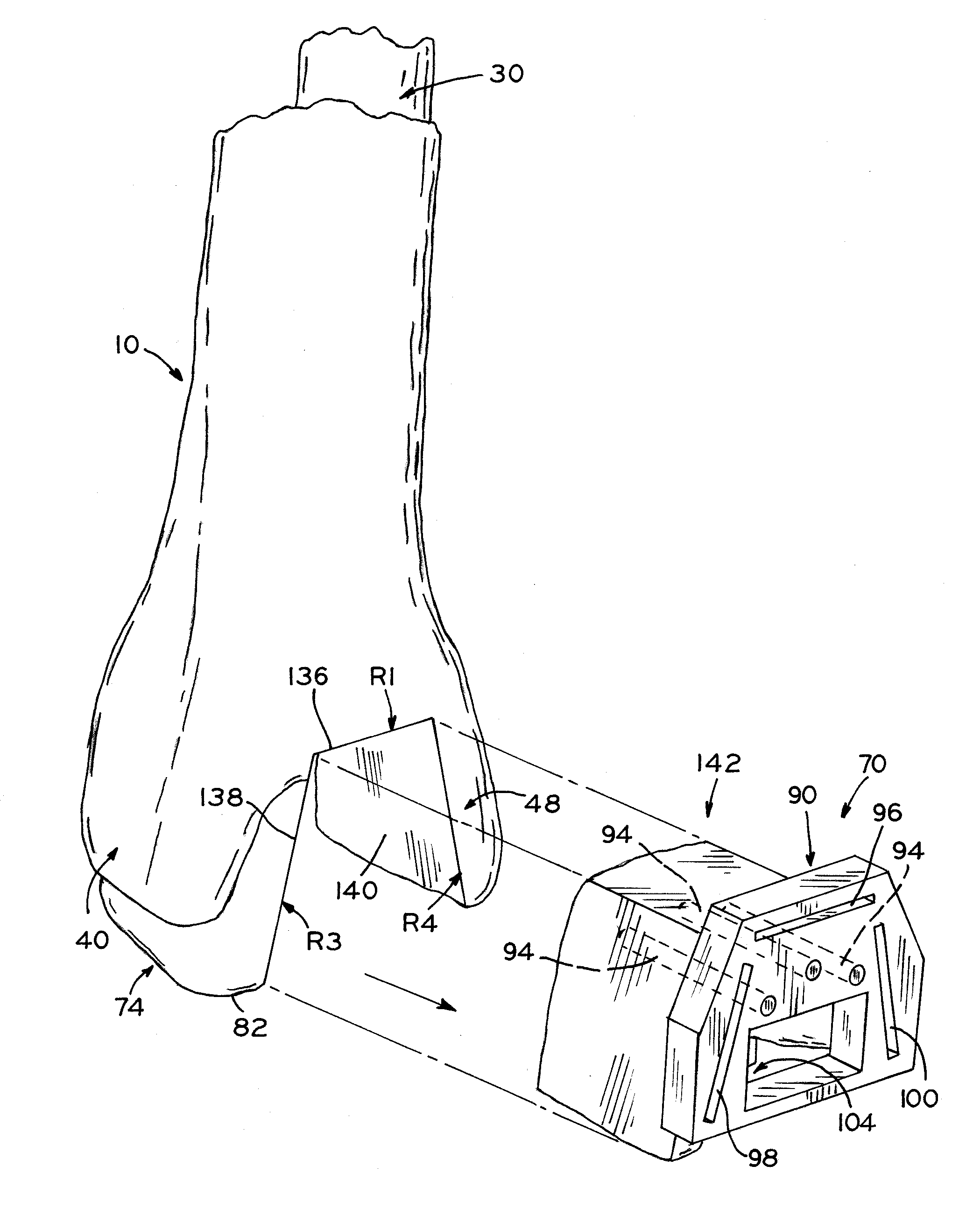
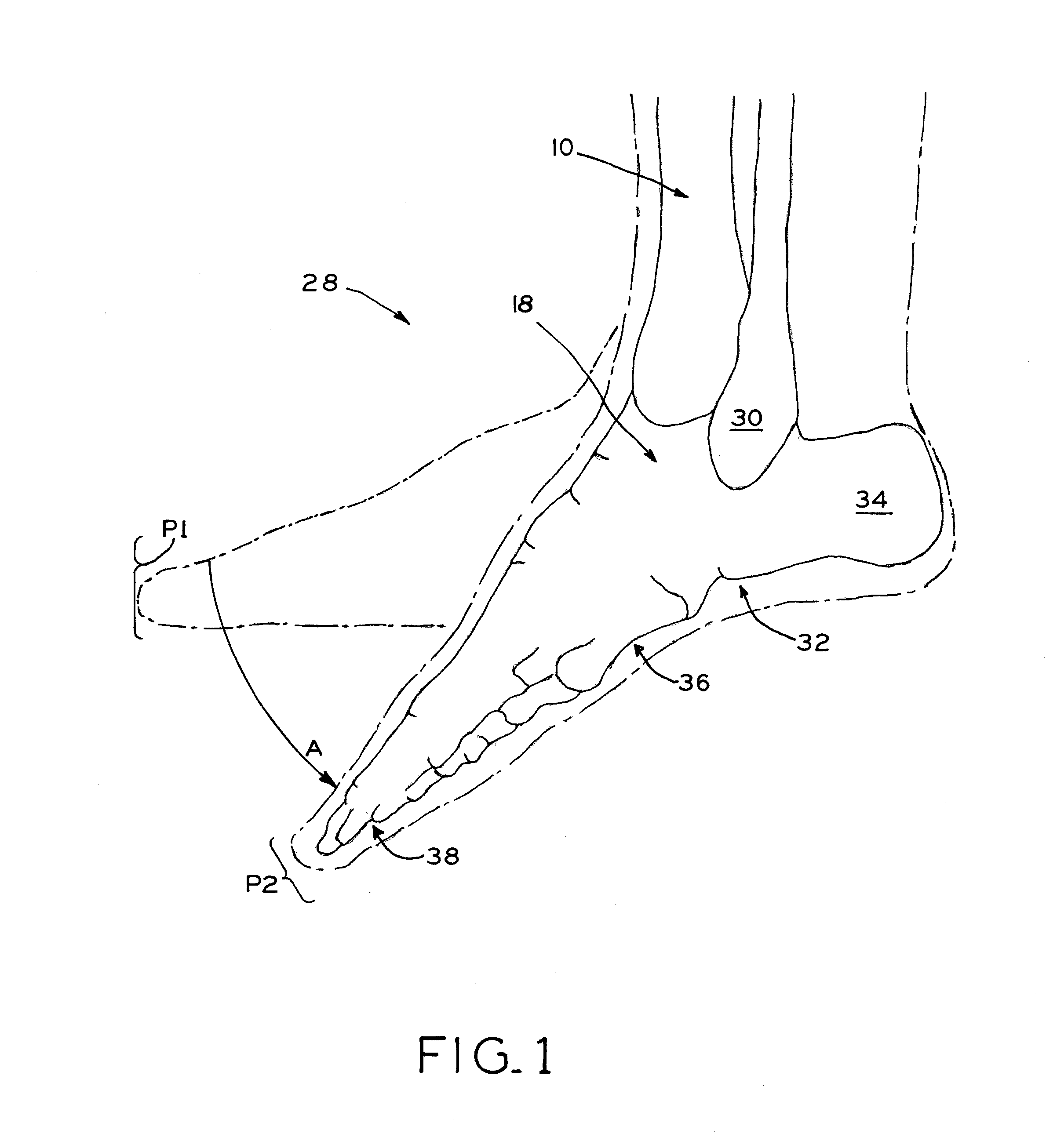
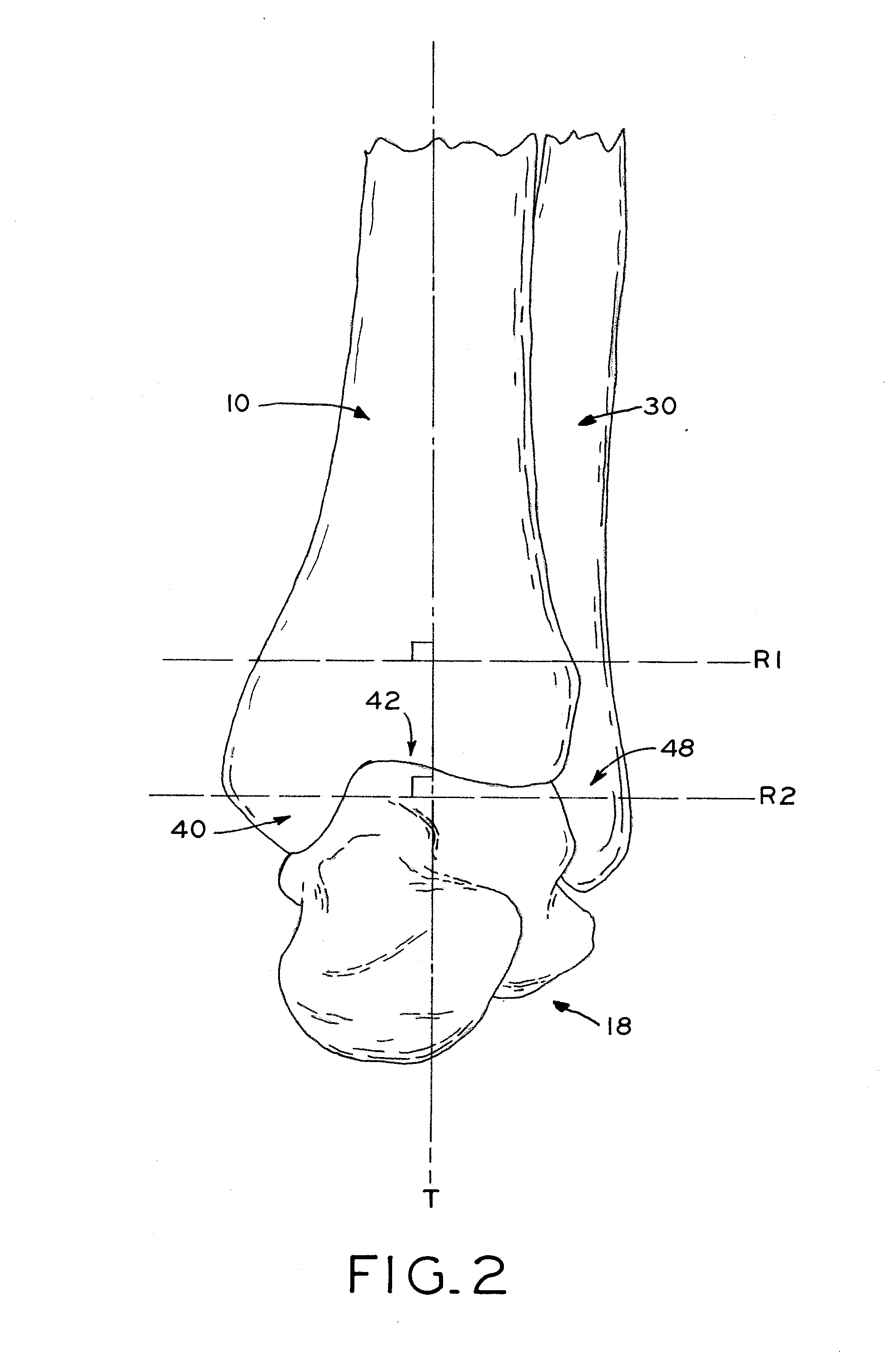
Patient-specific instruments for total ankle arthroplasty
Patient-specific instruments for preparing bones for receipt of orthopedic prostheses, such as the distal tibia and the talus in a total ankle arthroplasty (TAA) procedure. A tibial guide and a talar guide are manufactured based on patient-specific anatomical data obtained using imaging technology, and each guide includes a surface conforming to selected anatomical surfaces or regions of the tibia or talus, respectively. Each guide includes at least one cut referencing surface, such as a cut slot, to guide a resection, and may also include a guide aperture sized to guide a reaming tool for reaming the distal tibia or talus. The guides may also include pin holes positioned within a periphery defined by the cut referencing surfaces such that, when the resections are made and the resected tibial bone portion or talus bone portion is removed, the guide and its associated pins are removed along with the resected bone portion. The guides may be designed to ensure that a proximal resected surface of the distal tibia is parallel to a resected surface of the talus, with the parallel resected surfaces perpendicular to the anatomical axis of the distal tibia.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
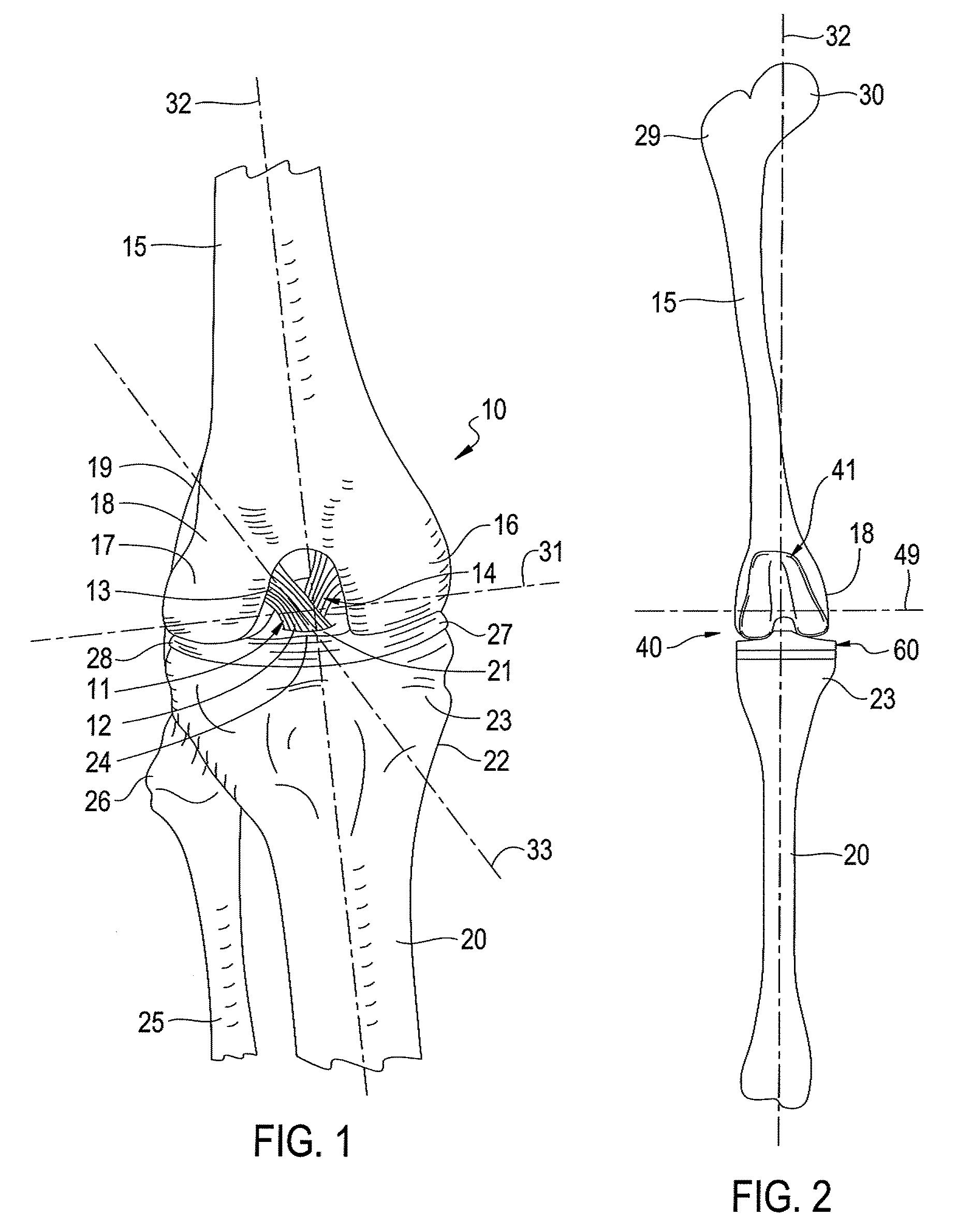
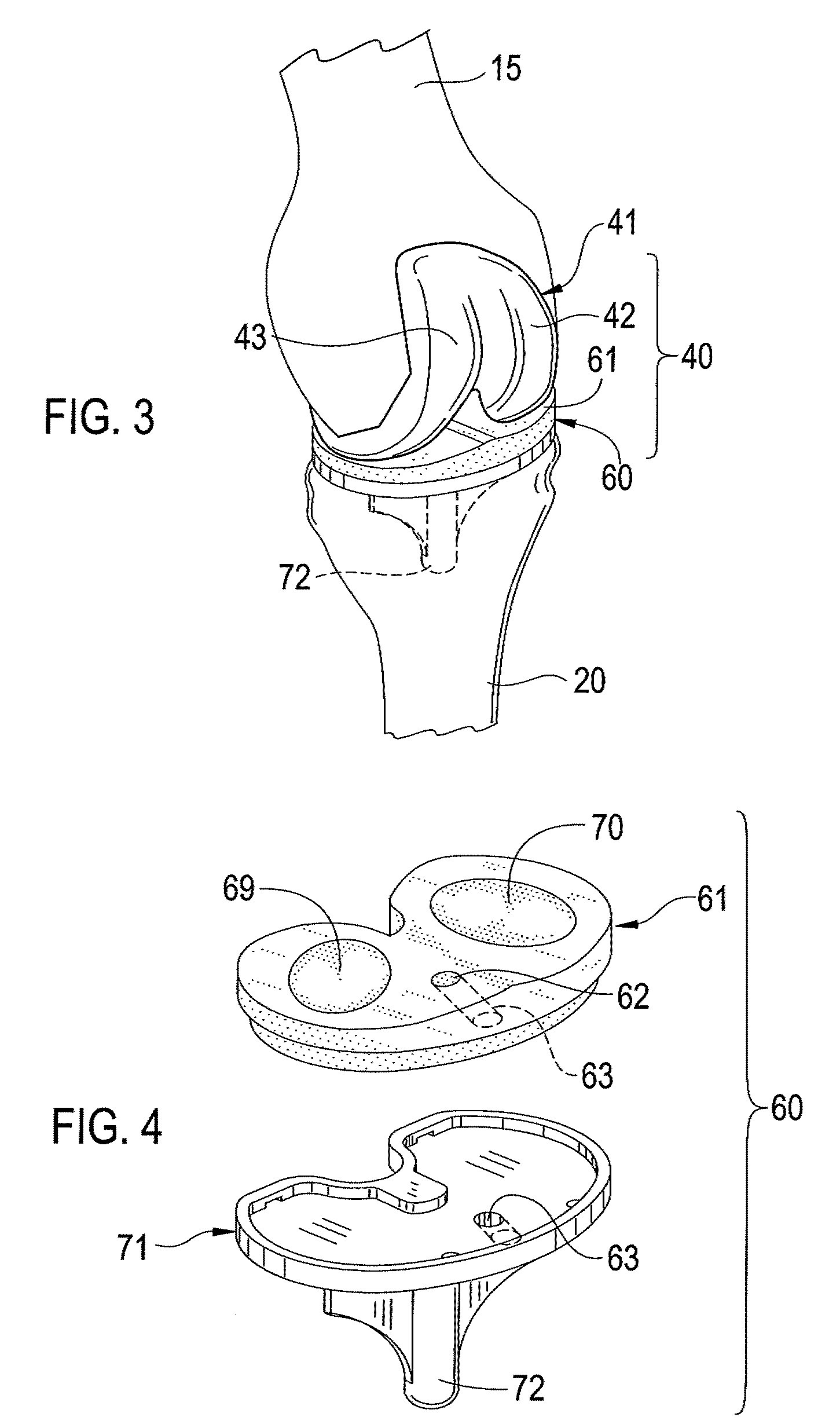
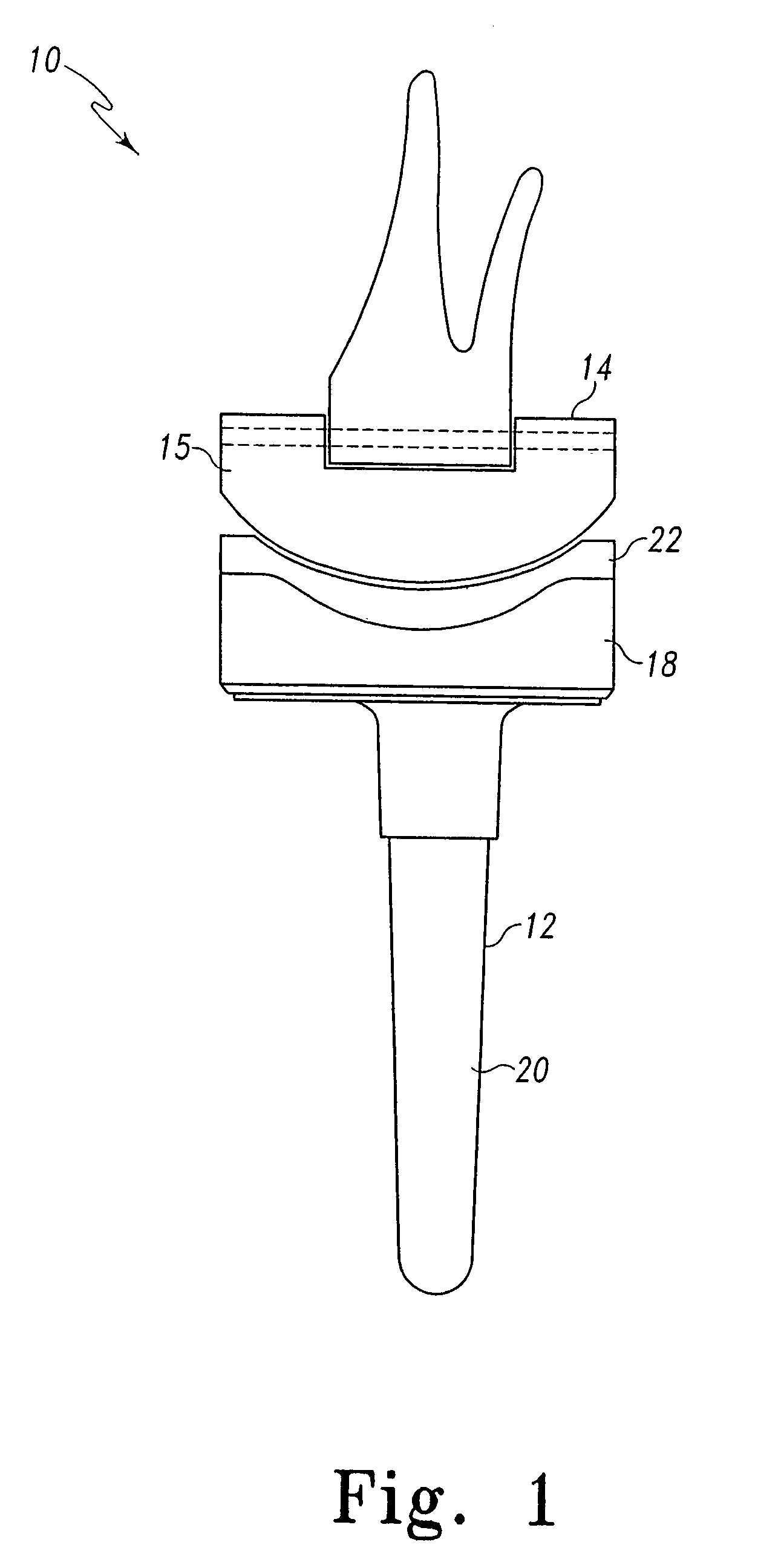
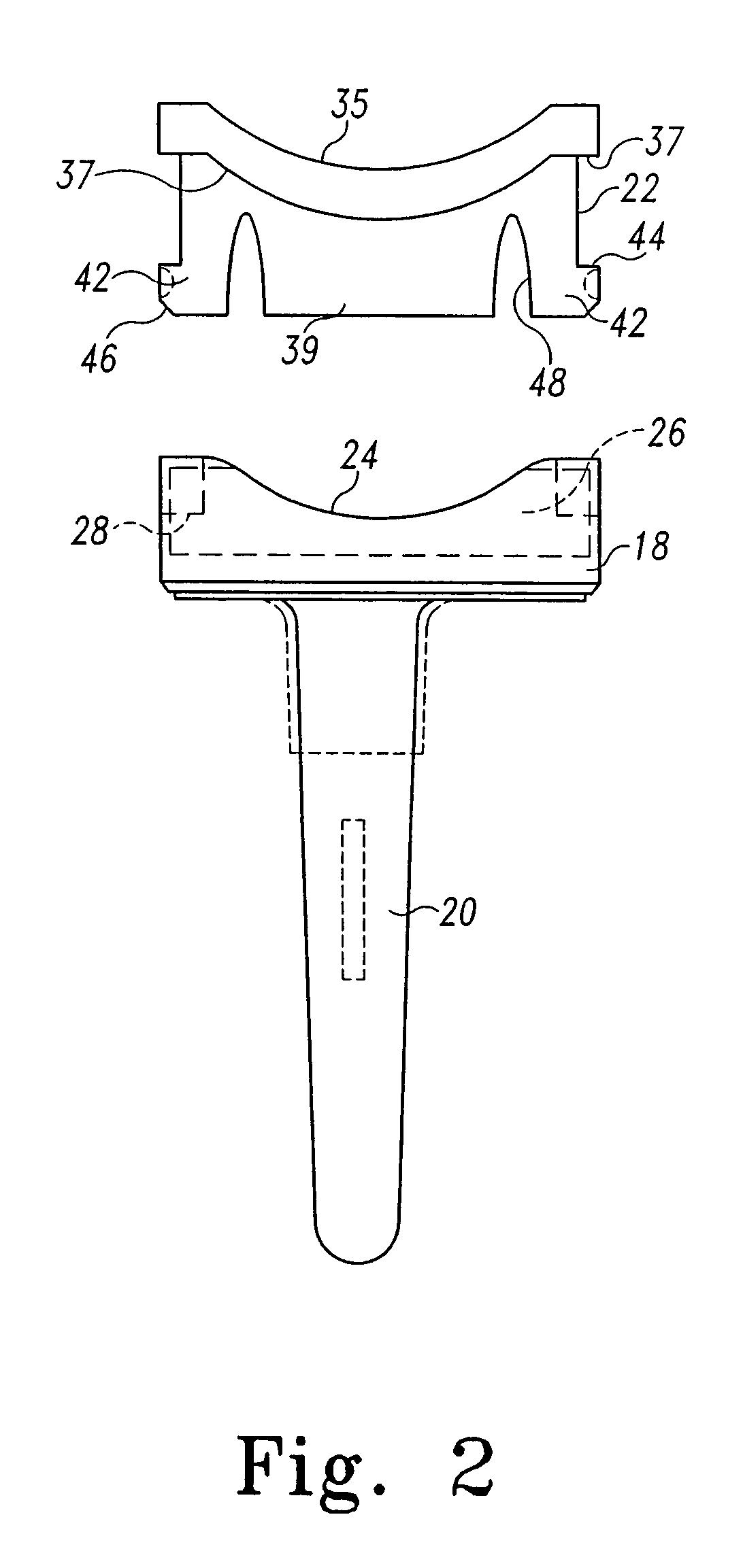
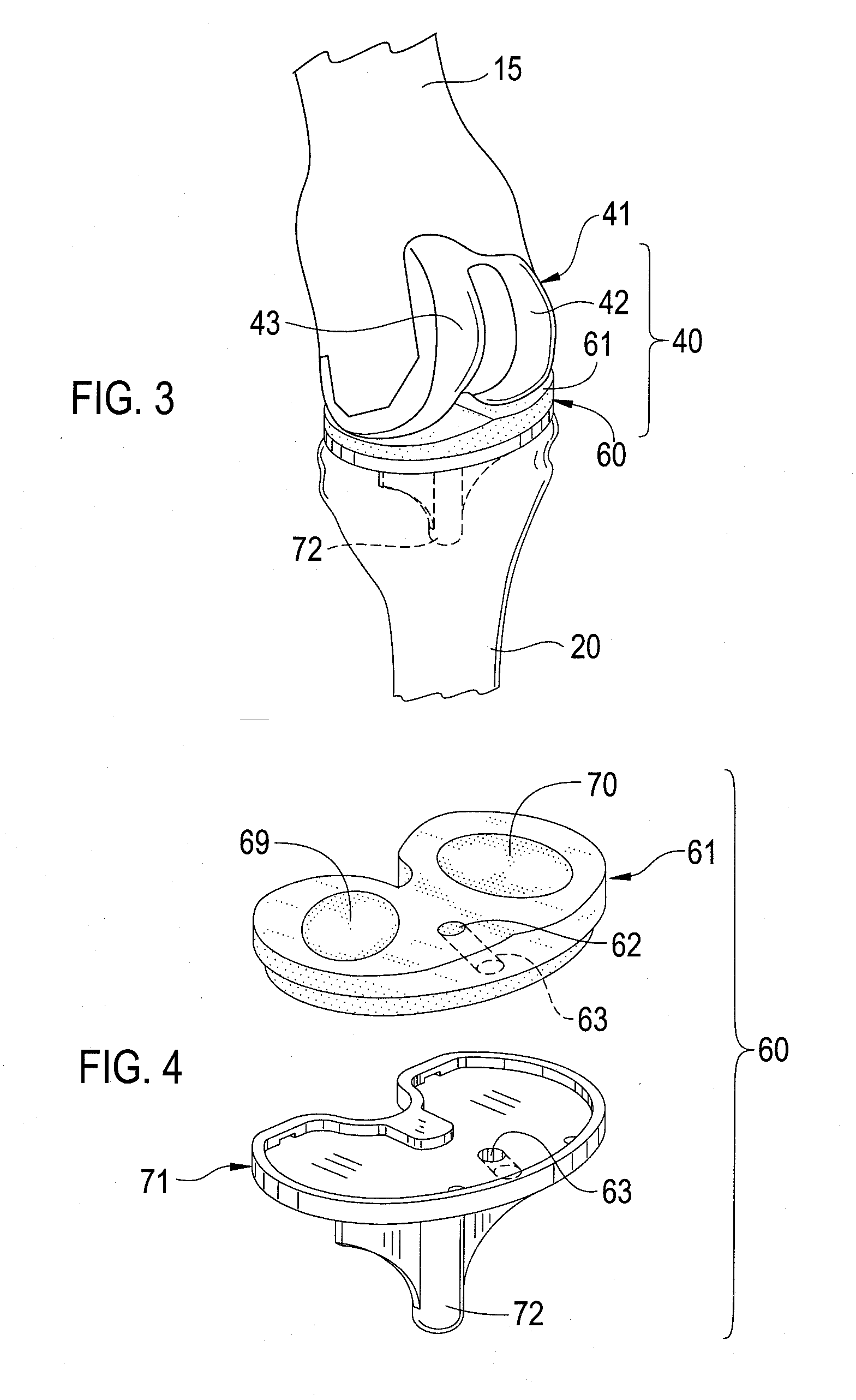
Total knee prosthesis and method for total knee arthroplasty
A prosthetic knee implant for implantation into a mammal, which accommodates an anterior cruciate ligament substitute to provide stability to the knee implant. The prosthetic knee implant includes a femoral component having a pair of condylar surfaces and a tibial component having a surface portion adapted to slidably engage the femoral component upon rotation of the same. The femoral component further includes a recess between the condyles defining an aperture through the femoral component. The tibial component further includes a center portion defining an aperture through the tibial component substantially at its center. The femoral aperture and the tibial aperture are adapted to receive an anterior cruciate ligament substitute for biasing the mammalian femur and tibia together. Also disclosed is a method used to replace the total knee joint in a mammal with the improved prosthetic knee implant of the present invention.
Owner:BLUM MICHAEL F
Total elbow arthroplasty system
A total elbow arthroplasty system, incorporating a humeral component, a radial component and a ball component, may be used as a total elbow replacement in the canine, as well as in other species. The implant of the present invention has an isometric humeral component and an isometric radial component. An isometric ball component having an isometric articular surface is mounted on the radial component. The humeral and radial components have stems for mounting in the medullary canals of the respective bones, which are angled so as to approximate the configuration of the original humerus and radius. The components work together to form a nonconstrained ball and socket joint. The invention is also directed to methods for implanting the novel endoprosthesis of the present invention in a canine elbow joint. The apparatus and methods of the present invention are useful in the treatment of elbow osteoarthritis in canines, as well as in other species, including other quadrupeds and humans.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Surgical tool assembly for total knee arthroplasty
InactiveUS20080097451A1More convenienceMinimize damageJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTotal hip arthroplastyCutting guide
A surgical tool assembly for Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) including a femoral intra-medullary (IM) rod, a femoral intra-medullary (IM) alignment guide, a distal femoral alignment guide, and a distal femoral cutting guide. After the femoral IM alignment guide is selected to fit the valgus angle and utilized with the femoral IM rod with respect to the distal femur, the distal femoral alignment guide is integrated to the complex. Then, the distal femoral cutting guide is slid to the distal femoral alignment guide in the orientation from distal to proximal through the sliding concave integrated with the sliding track.
Owner:UNITED ORTHOPEDIC CORP +1
Customized process for facilitating successful total knee arthroplasty with outcomes analysis
InactiveUS20140013565A1Address bad outcomesMedical data miningMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesBone morphologyTotal hip arthroplasty
A method for producing a custom resection jig for a current patient scheduled to receive total knee arthroplasty using outcomes analysis comprising the steps of maintaining a database on a computer system of (1) prior patient bone morphology, (2) along with anatomical and mechanical bone alignment data and (3) data defining a custom resection jig design with a generally transverse resection window operable to guide a surgeon's transverse bone cut for prior patients that have received total knee arthroplasty and a post-surgery medically recognized scoring register greater or equal to a predetermined highly successful score value for a total knee arthroplasty procedure using prior success data to guide production of a current patient custom jig resection windows.
Owner:MACDONALD M D JAMES
Device for measuring tibio-femoral force amplitudes and force locations in total knee arthroplasty
ActiveUS7412897B2Improve balanceImprove ergonomicsSurgeryForce measurementTotal hip arthroplastyPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A probe used during a total knee arthroplasty for measuring forces and locations of their points of application and thereby moments includes two load sensitive plates t to be inserted in one joint-compartment of a knee joint each and each being provided with a top surface and a bottom surface. At least two load sensors may be situated on the top surfaces and / or the bottom surface of each load sensitive plate.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Dual-radius glenoid prosthetic component for total shoulder arthroplasty
InactiveUS6875234B2Reduce loadPowerfulJoint implantsShoulder jointsArticular surfacesTotal hip arthroplasty
A dual-radius glenoid component of a shoulder joint prosthesis for use in total shoulder arthroplasty has two radii of curvature. At substantially the center of the articulating surface a first non-conforming radius of curvature is provided, while a second conforming radius of curvature, smaller than that of the first radius of curvature and more closely conforming to the curvature of the humeral component, is disposed about the periphery of the articulating surface. The central non-conforming radius of curvature provides reduced constraint of the humeral component. In contrast, the conforming peripheral radius of curvature provides maximum constraint of the humeral component. When the humeral component is substantially centered on the articulating surface reduced constraint is placed on the prosthesis and less load is transferred to the bone-implant interface. As the humeral component translates towards the periphery, constraint on the prosthesis increases to prevent dislocation.
Owner:NEW YORK SOC FOR THE RUPTURED & CRIPPLED MAINTAINING THE HOSPITAL FOR SPECIAL SURGERY
Prosthetic components with contained compressible resilient members
InactiveUS7235102B2Improve protectionEliminate shear stressJoint implantsSpinal implantsElastomerShape-memory alloy
One or more rigid components associated with an articulating bone are used to encase, encapsulate, contain, or otherwise protect a compressible / resilient member. The embodiments are applicable not only to artificial disc replacement (ADR) devices, but also to joint situations including total knee and hip arthroplasty. The cushion elements in the preferred embodiments include synthetic rubbers, hydrogels, elastomers, and other polymeric materials such as viscoelastic polymers and foam polyurethanes. The invention effectively combines the advantages of such materials (cushioning, shape memory, and expansion after insertion in the case of hydrogels), while providing increased protection, particularly the elimination of shear stresses. When applied to an ADR, the invention also minimizes the risk of extrusion.
Owner:ANOVA
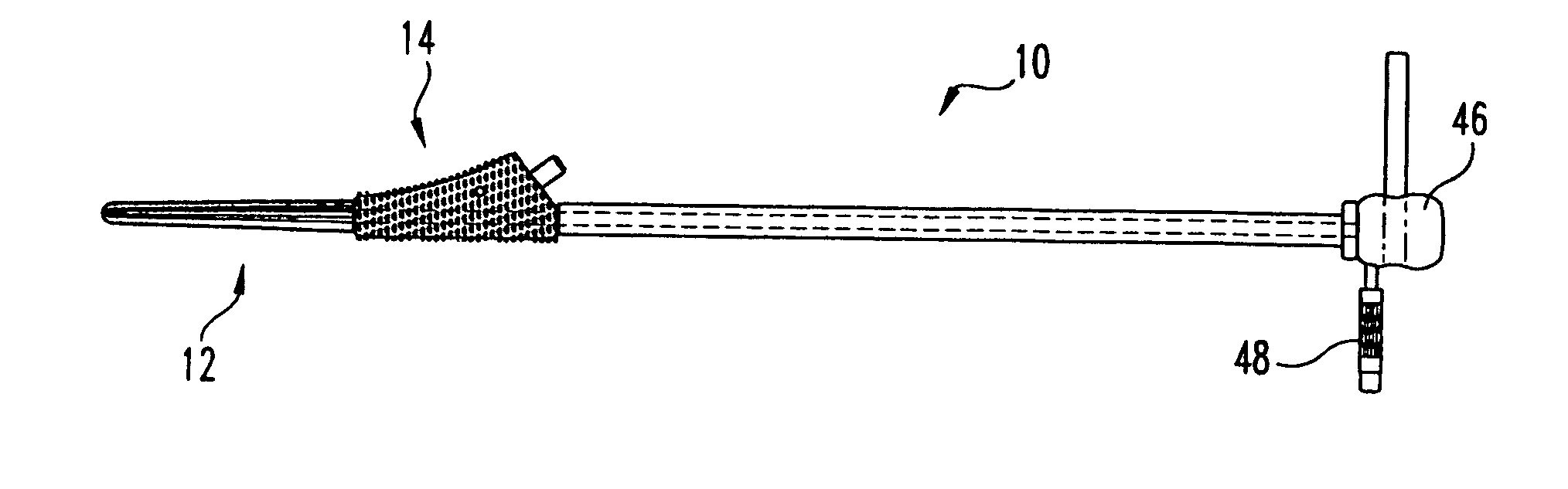
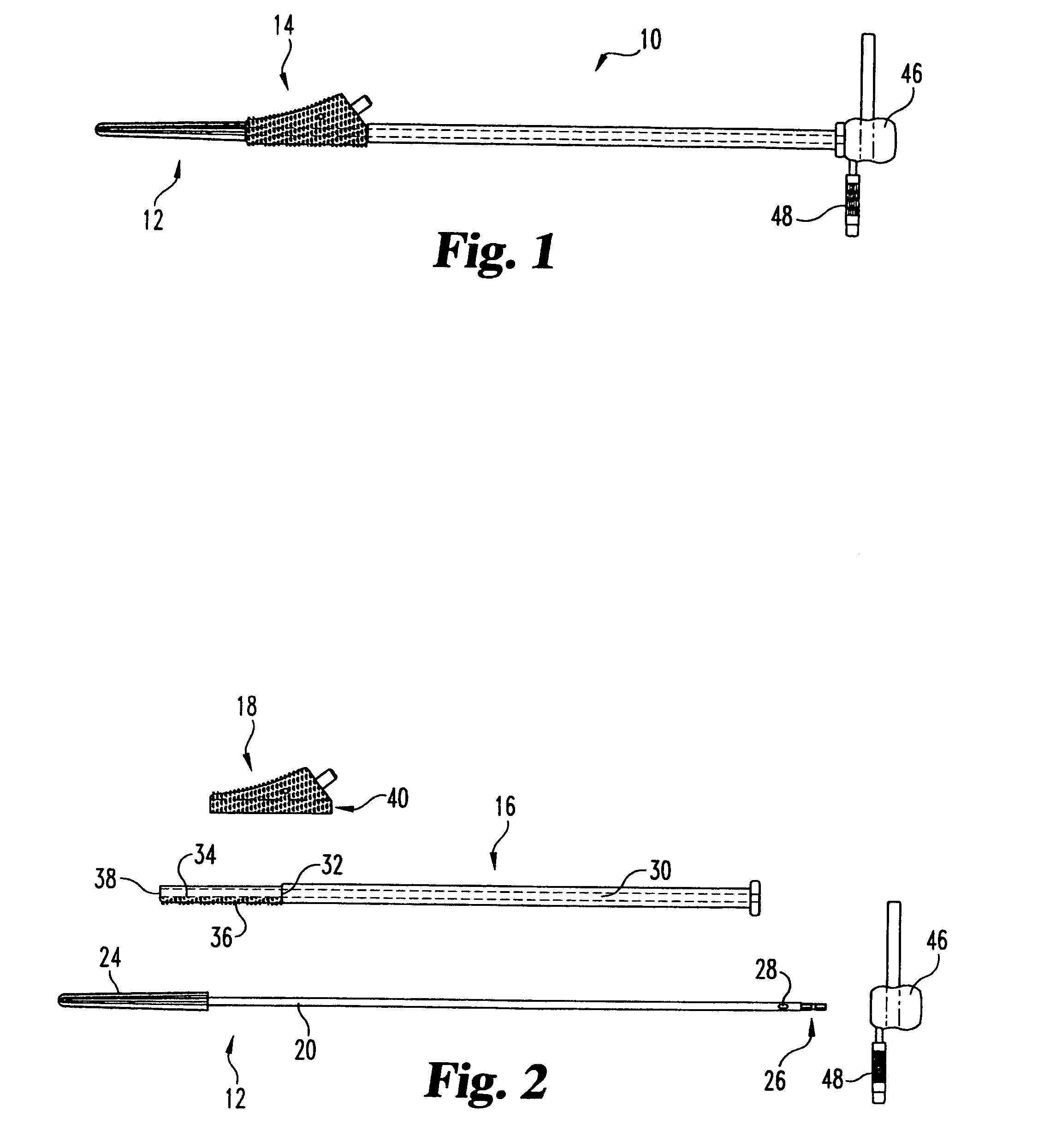
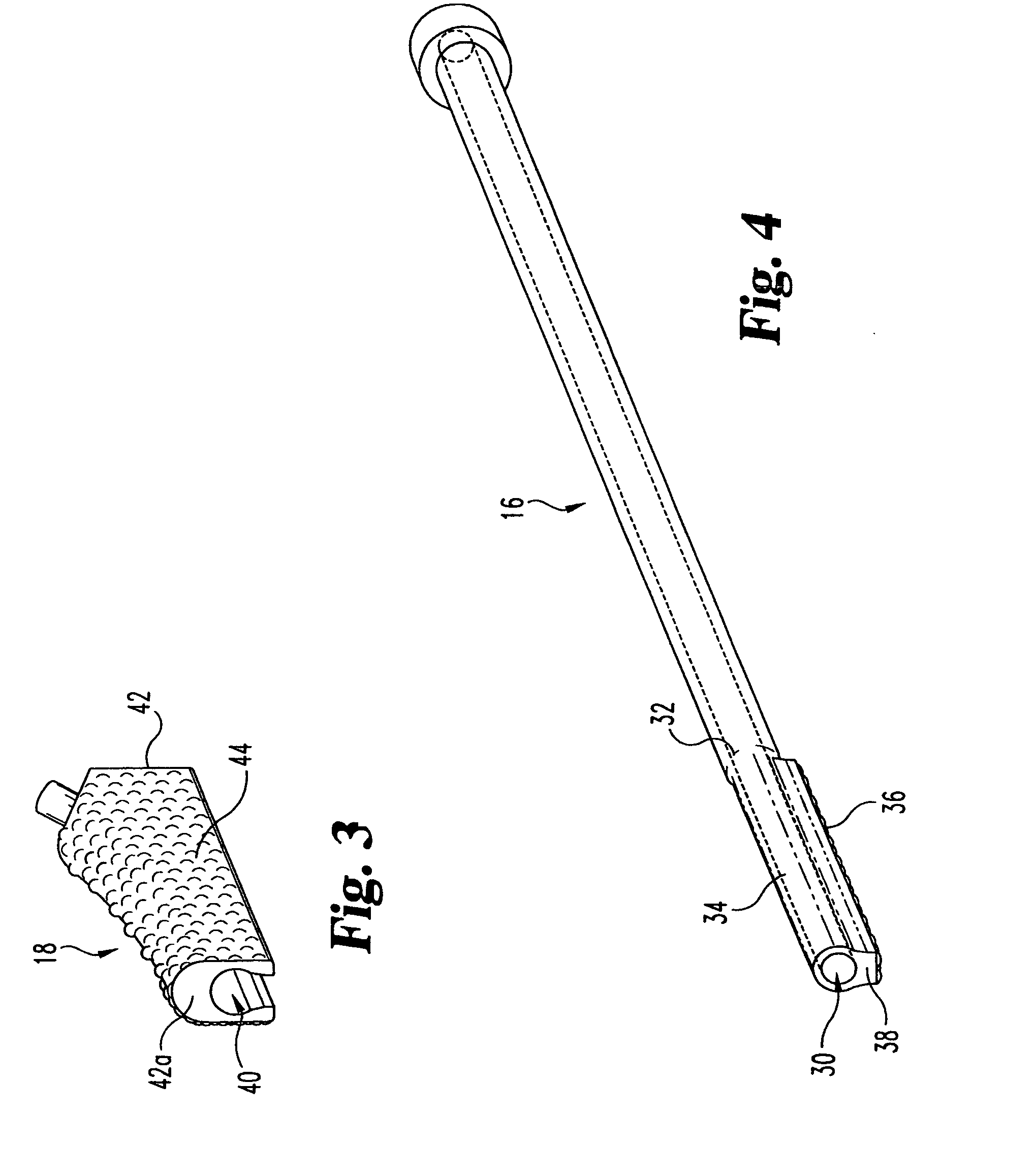
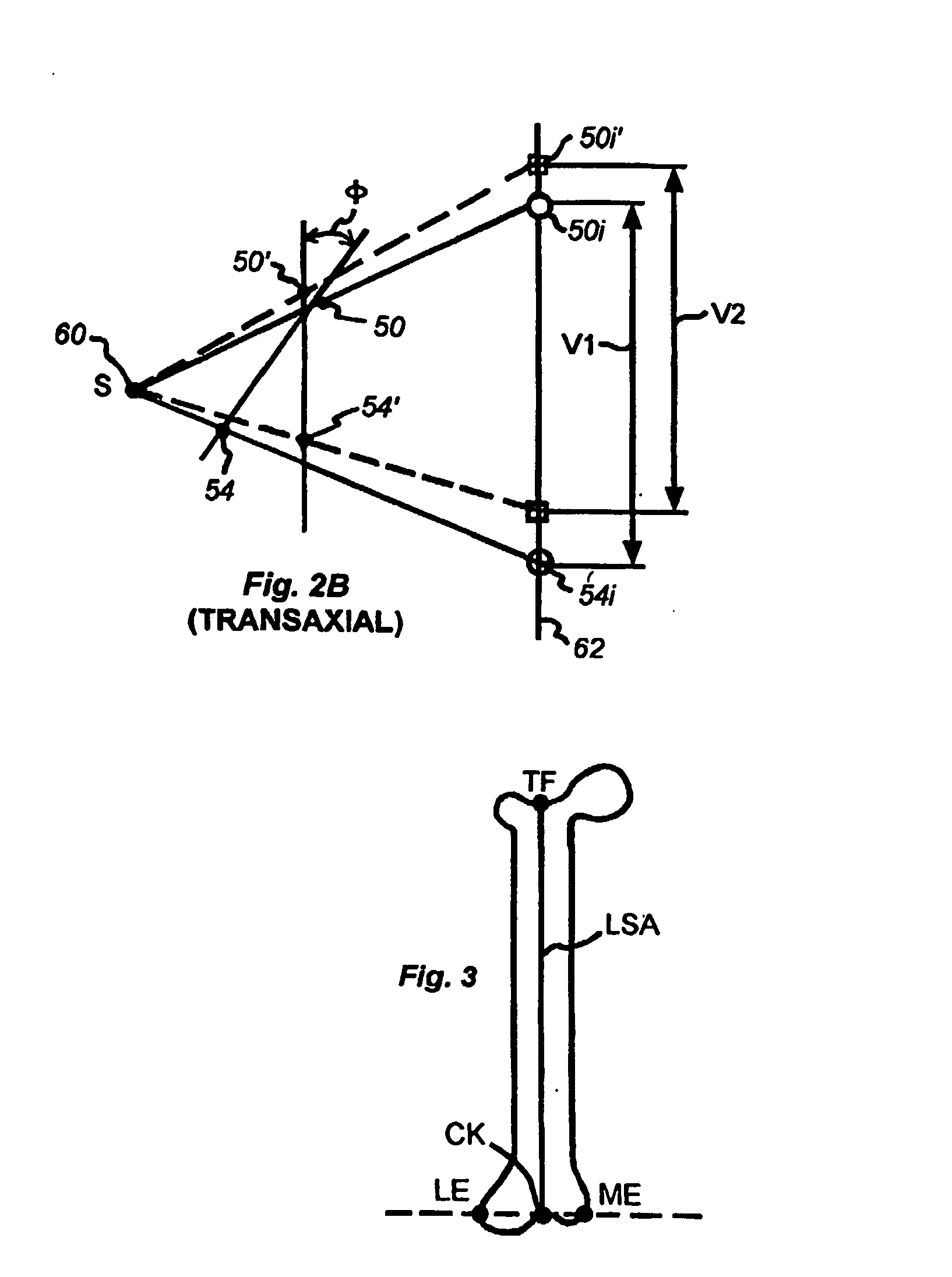
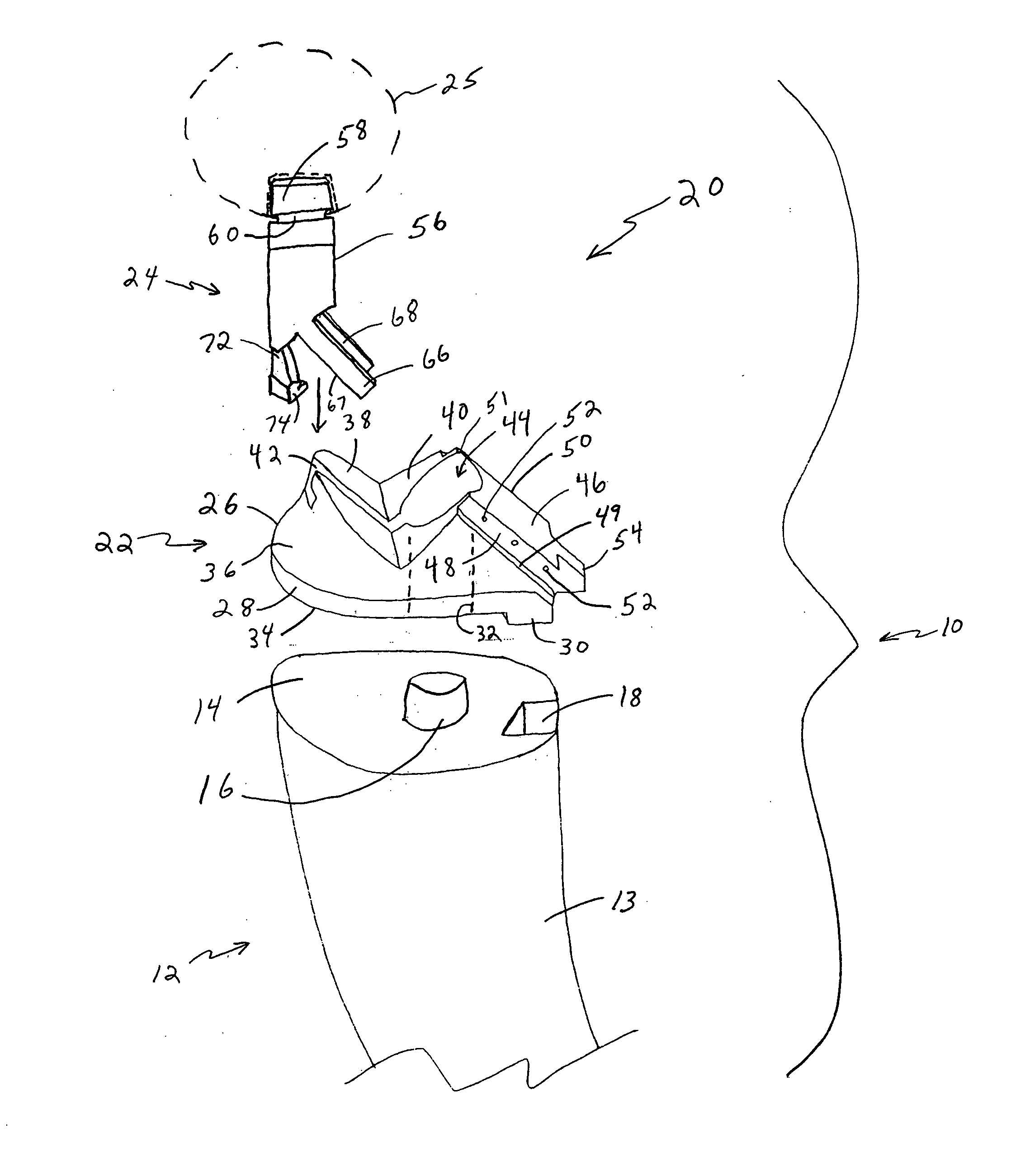
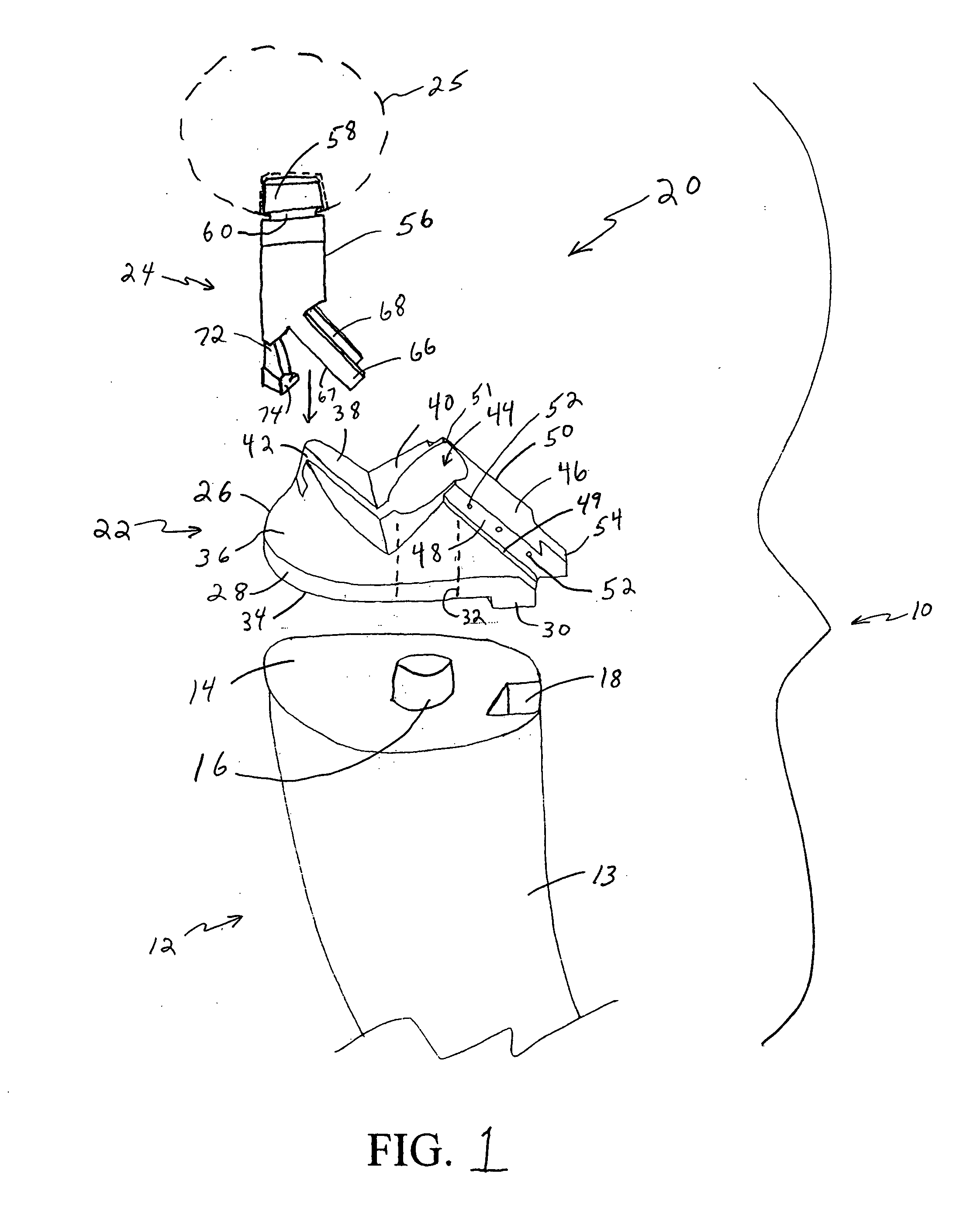
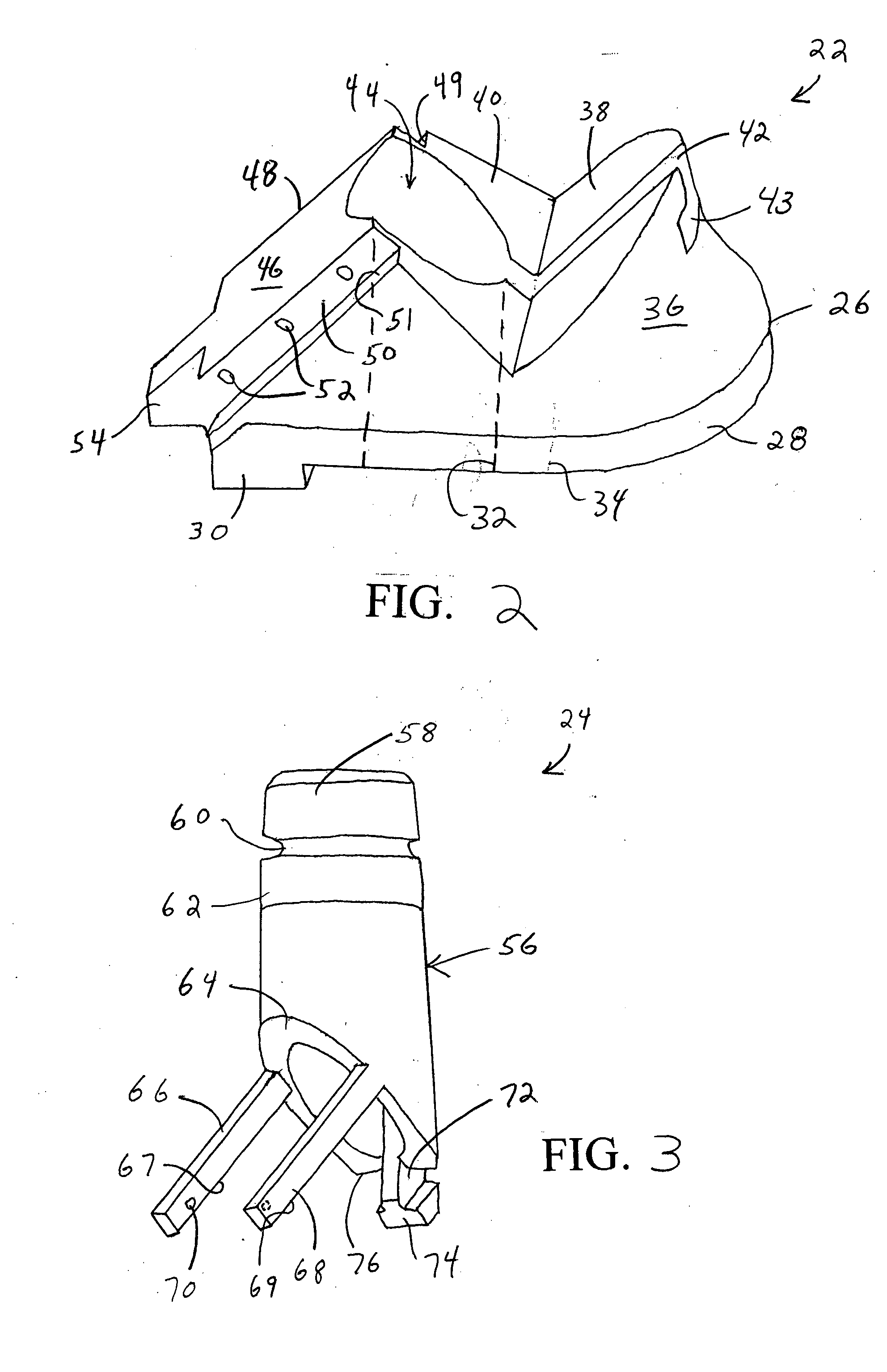
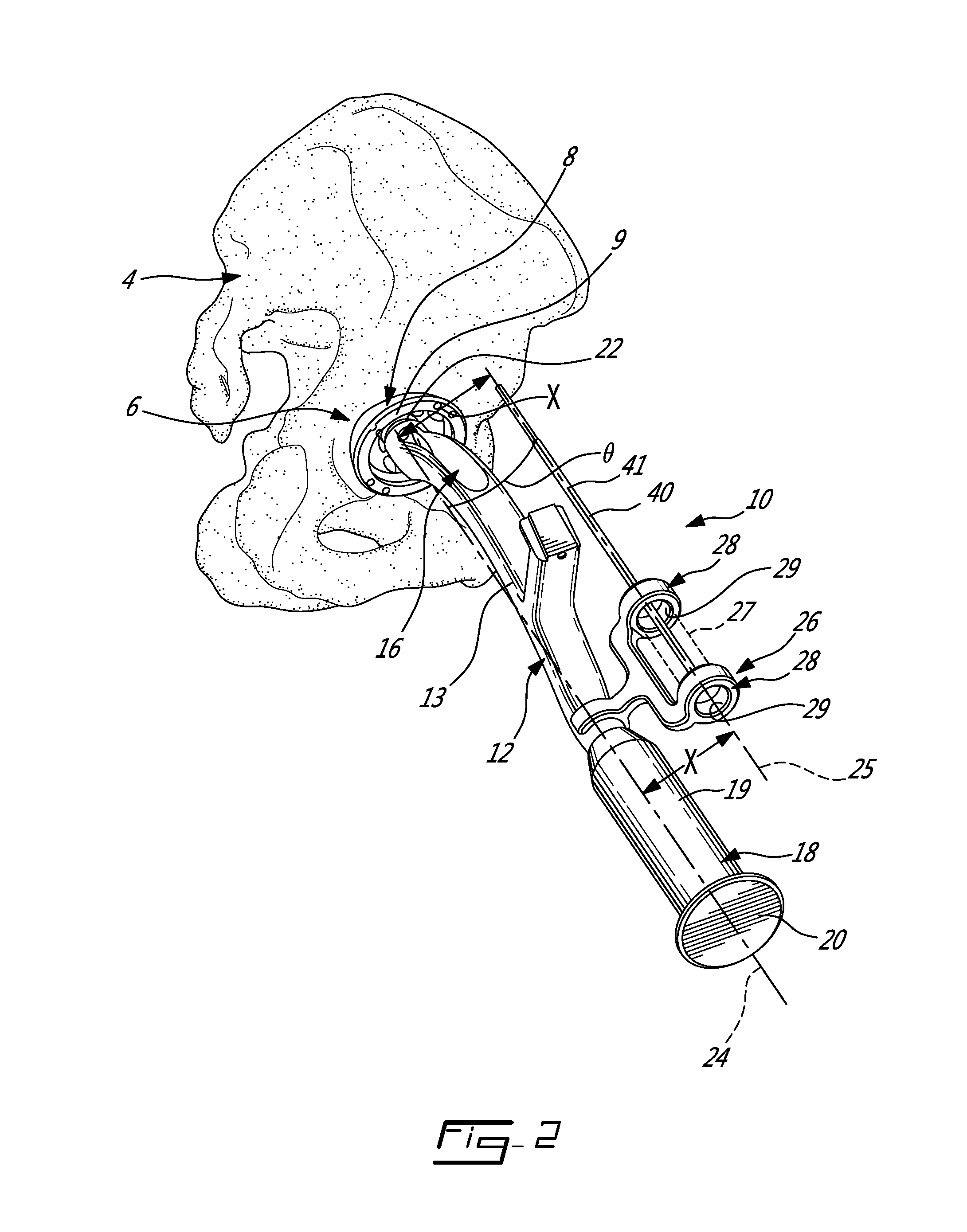
Method and instrumentation for performing minimally invasive hip arthroplasty
InactiveUS20050234463A1Reduce incision sizeSmall sizeJoint implantsFemoral headsTotal hip arthroplastyInterconnection
Broaching instruments divided into multiple parts to reduce the size of incisions necessary to perform a total hip arhroplasty, minimizing trauma to tissue surrounding the hip joint. One approach is to divide the broach head into first and second segments for insertion through posterior and anterior incisions, respectively, and interconnection within the patient. Methods of preparing the proximal medullary canal of a femur for receiving a hip stem implant utilize the multi-part broaching instruments and two-incision techniques to introduce the broaching instruments into the patient for broaching the canal in preparation for receiving the implant.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Universal double offset surgical instrument
Instruments for use in anterior approach total hip arthroplasty. Instruments according to certain embodiments of the invention connect to a shaping member such as a broach, reamer or osteotome that is used to prepare the intramedullary canal of a desired femur or other bone for total hip arthroplasty. Such an instrument according to such embodiments can be configurable to allow operation on either the left or right leg, and in doing so to provide lateral offset and anterior offset of the instrument handle relative to the shaping member so that the patient's gut, musculature or other bodily portions may be avoided while still providing desired leverage and control over the shaping member to prepare the intramedullary canal.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Total Knee Prosthesis and Method for Total Knee Arthroplasty
A prosthetic knee implant for implantation into a mammal, which accommodates an anterior cruciate ligament substitute to provide stability to the knee implant. The prosthetic knee implant includes a femoral component having a pair of condylar surfaces and a tibial component having a surface portion adapted to slidably engage the femoral component upon rotation of the same. The femoral component further includes a central femoral recess between the condyles providing access to the femur for drilling a channel through which a cruciate ligament substitute may be integrated into the femur. The tibial component further includes a center portion defining an aperture through which the ligament substitute maybe threaded through the tibia and integrated therein, or anchored upon its surface. Also disclosed is a method used to replace the total knee joint in a mammal with the improved prosthetic knee implant of the present invention.
Owner:BLUM MICHAEL F
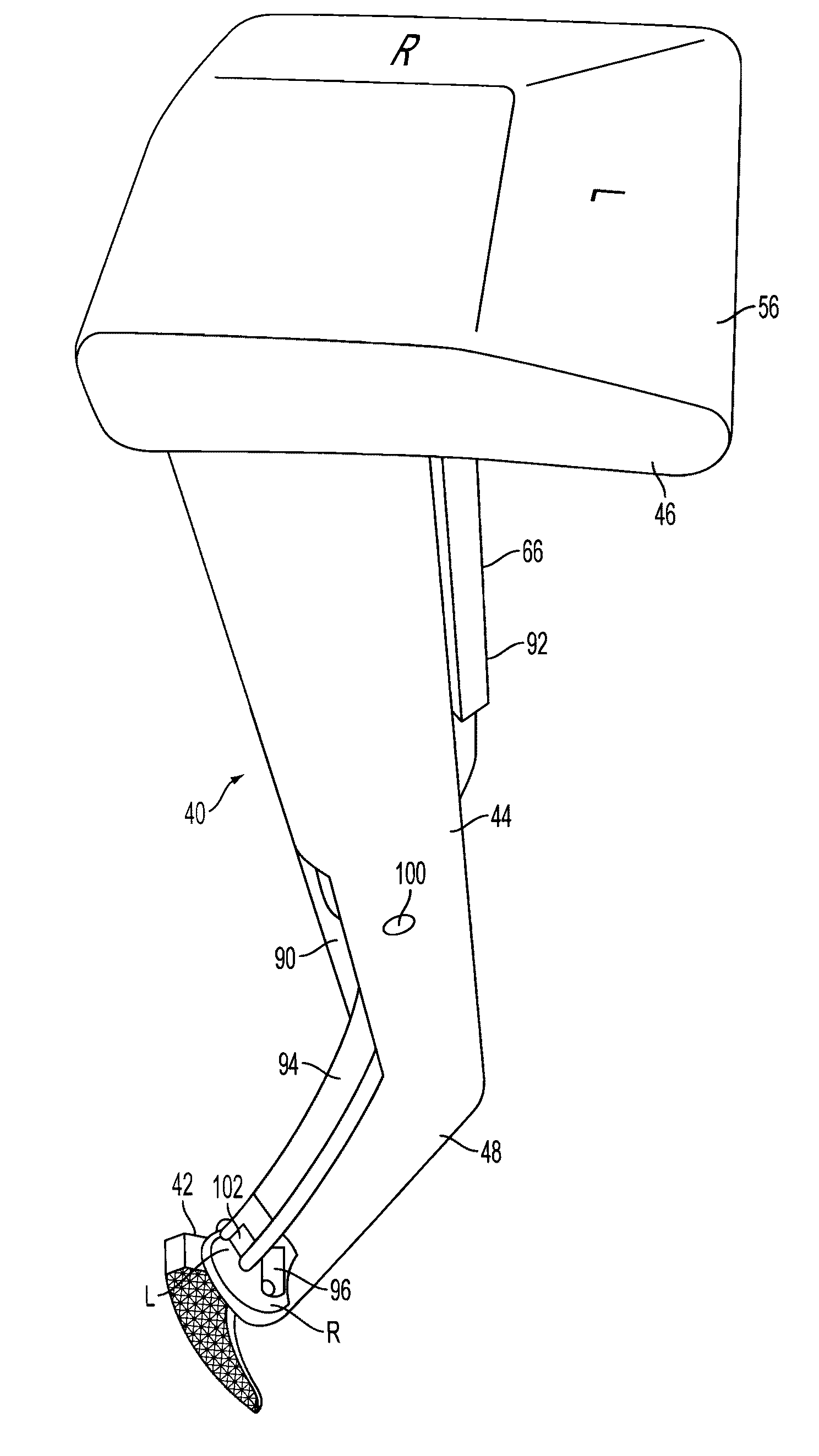
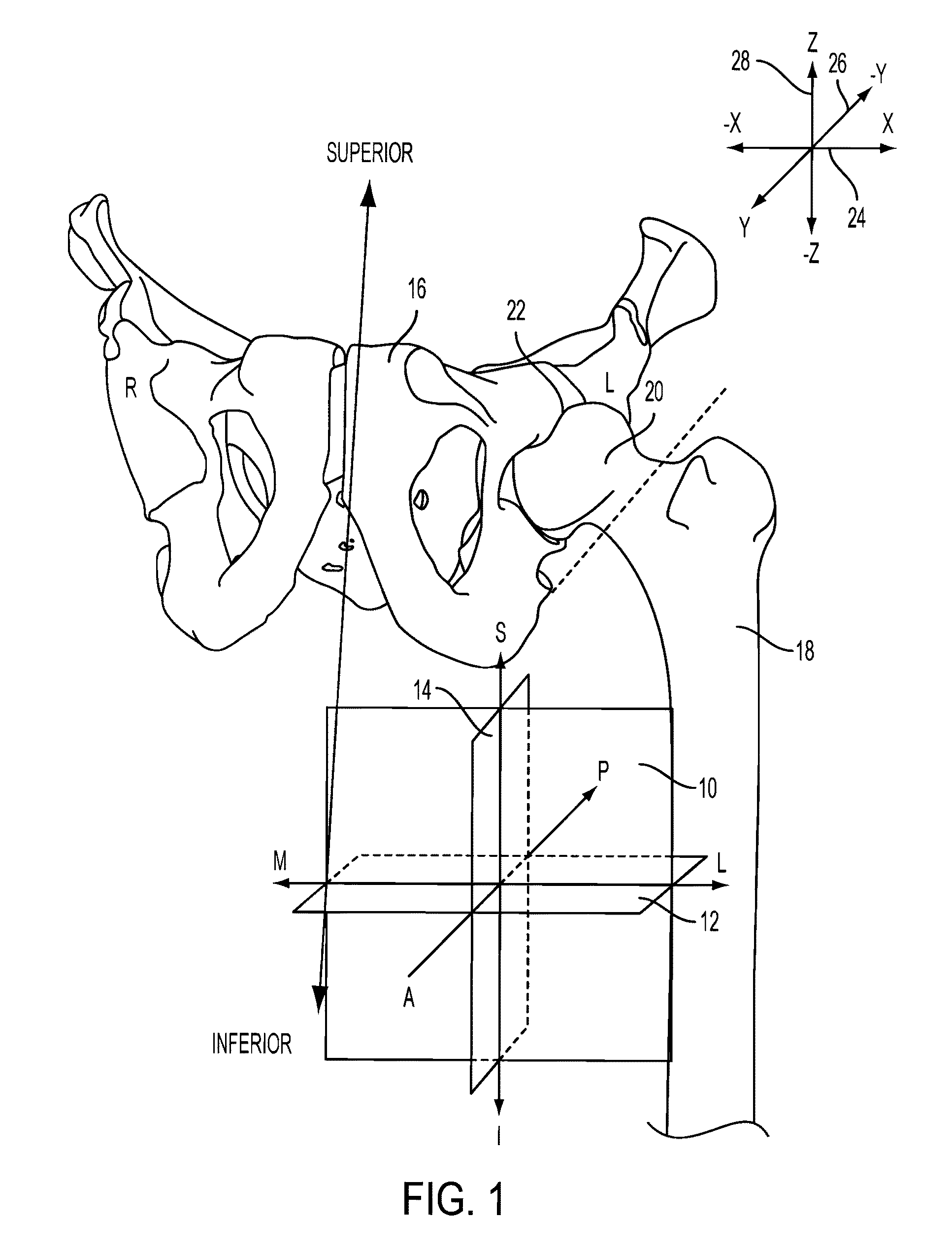
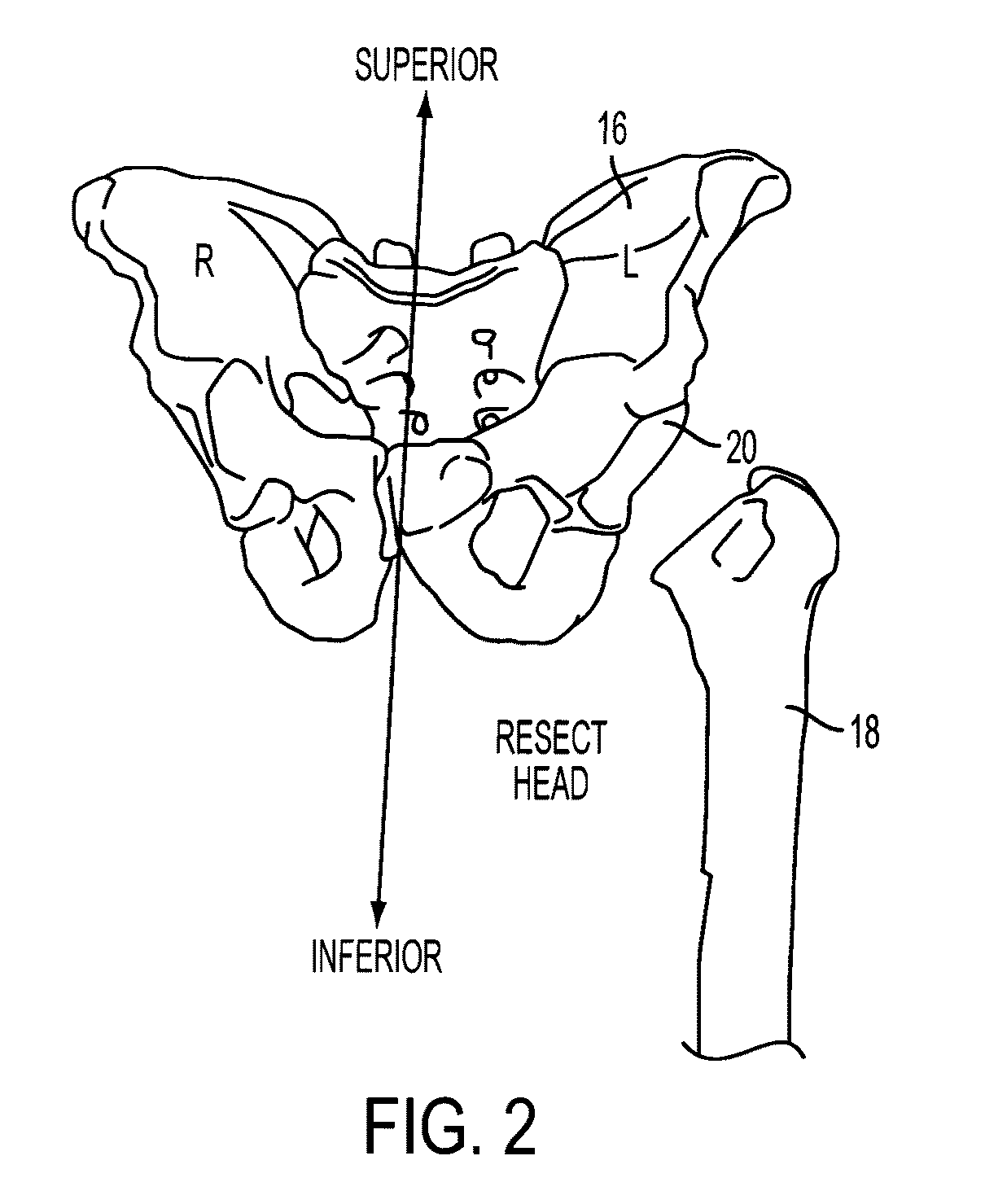
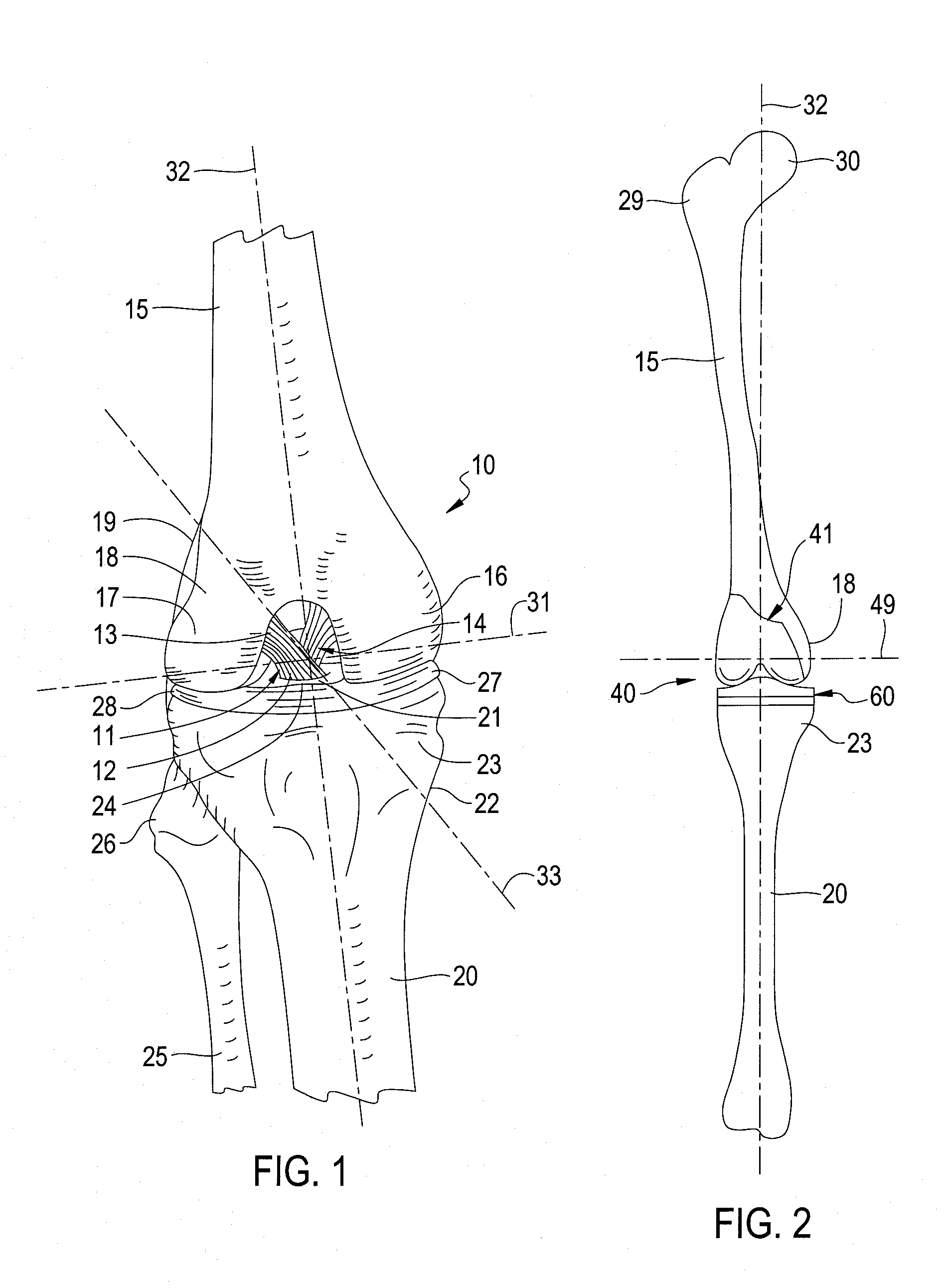
Virtual trial reduction system for hip arthroplasty and coordinate systems therefor
ActiveUS20060264731A1Accurately determineUndesirable side-effectSurgical navigation systemsPerson identificationTotal hip arthroplastyBiomedical engineering
Owner:MURPHY STEPHEN B
Modular trial neck segment
A modular trial neck segment is utilized for trialing a hip prosthesis for a total hip arthroplasty. The modular trial neck segment is preferably, but not necessarily, utilized for trialing a hip prosthesis for a total hip arthroplasty. The trial neck segment includes a mount attachable to a stem or broach, and a neck that is translatable on the mount for providing various neck offsets with respect to the mount and / or broach. Neck offset is changed via movement of the neck in a single plane of motion. This facilitates the use of the subject invention in minimally invasive arthroplasty wherein working dimensions are small. The present design replicates the biomechanics of the neck region of the implant. The mount and slidable neck provide a plurality of neck offsets and / or neck lengths for trialing a final prosthesis in a single device.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
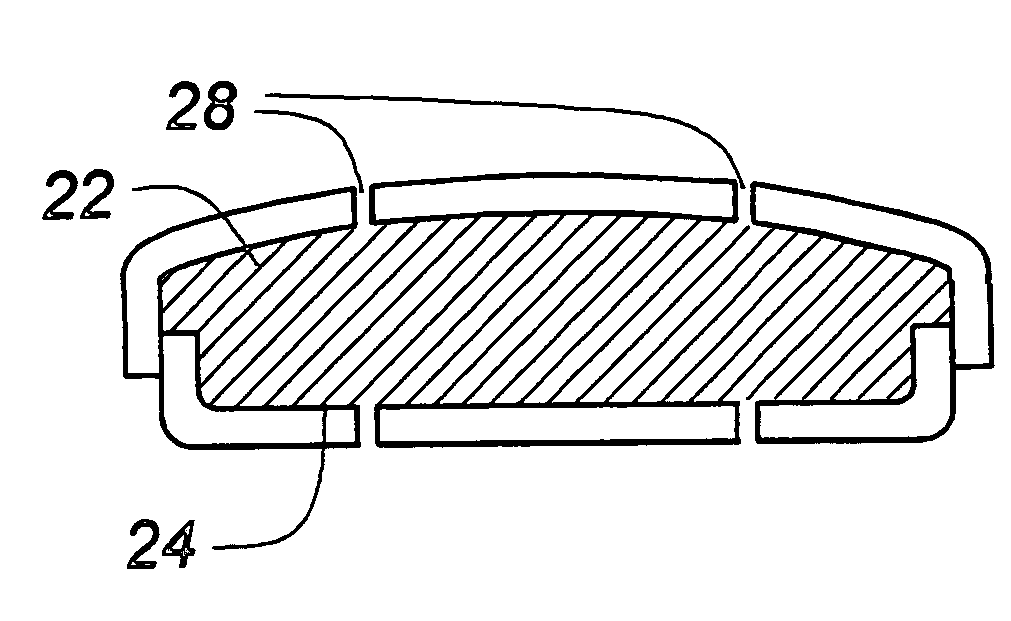
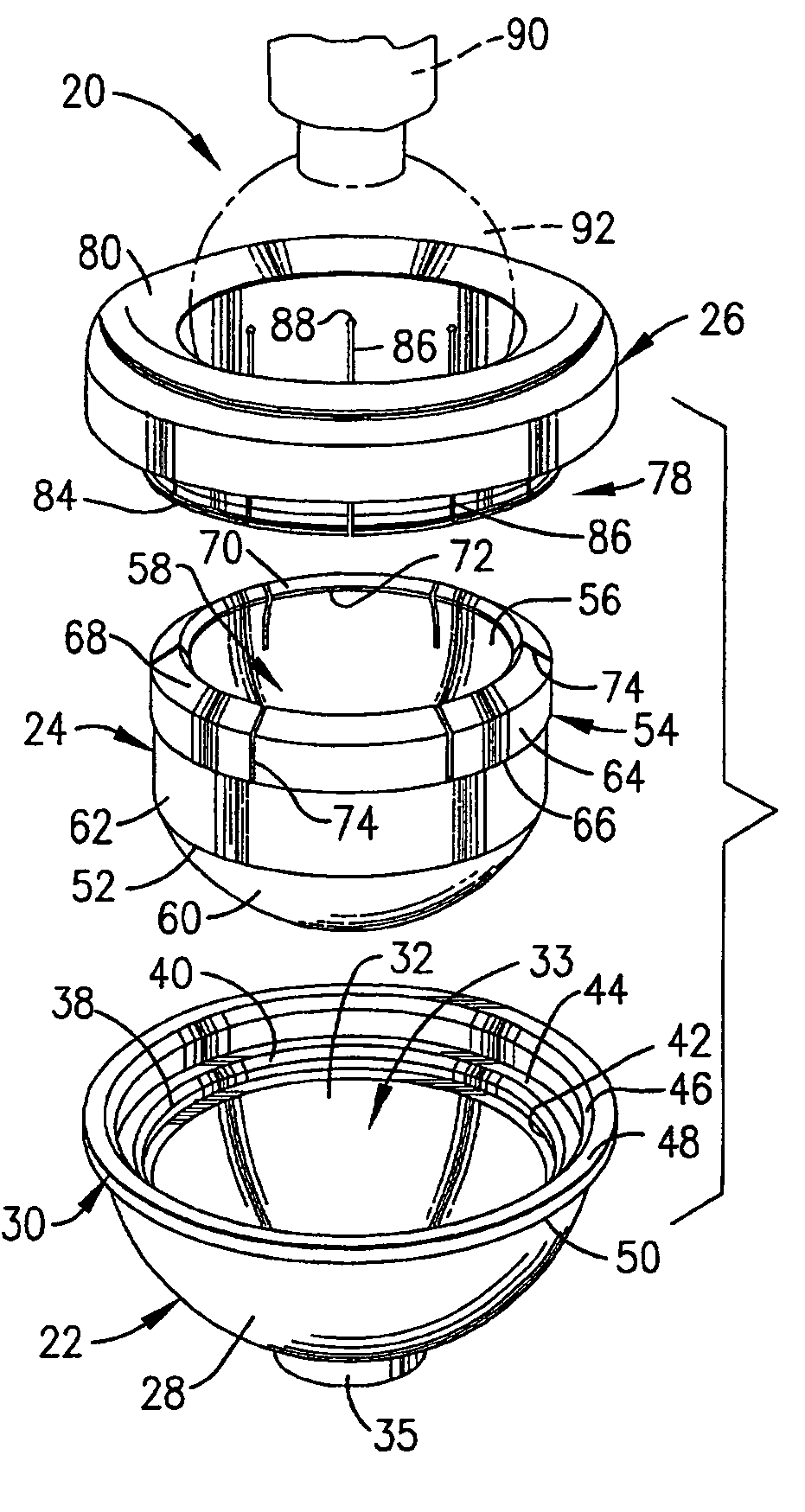
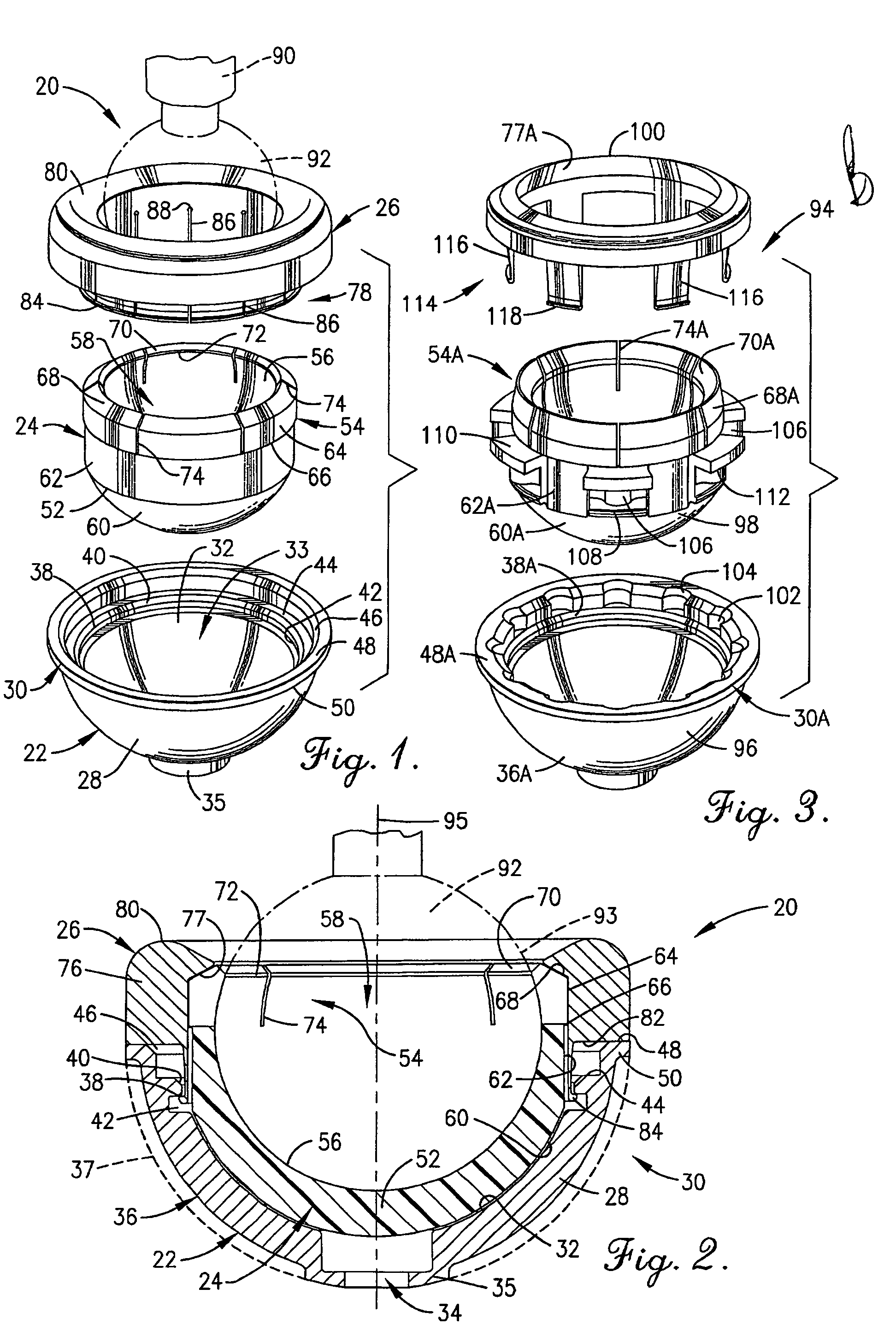
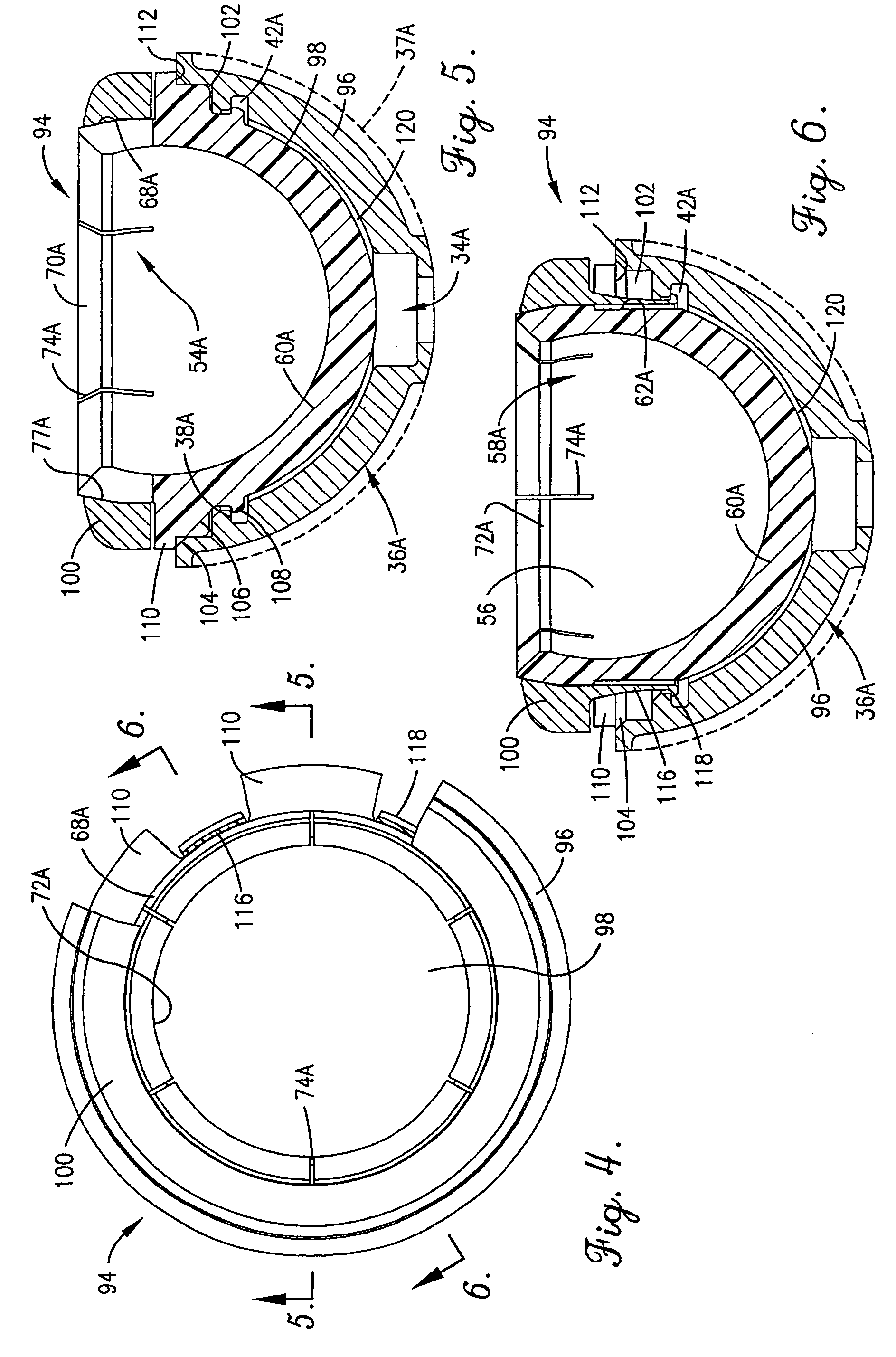
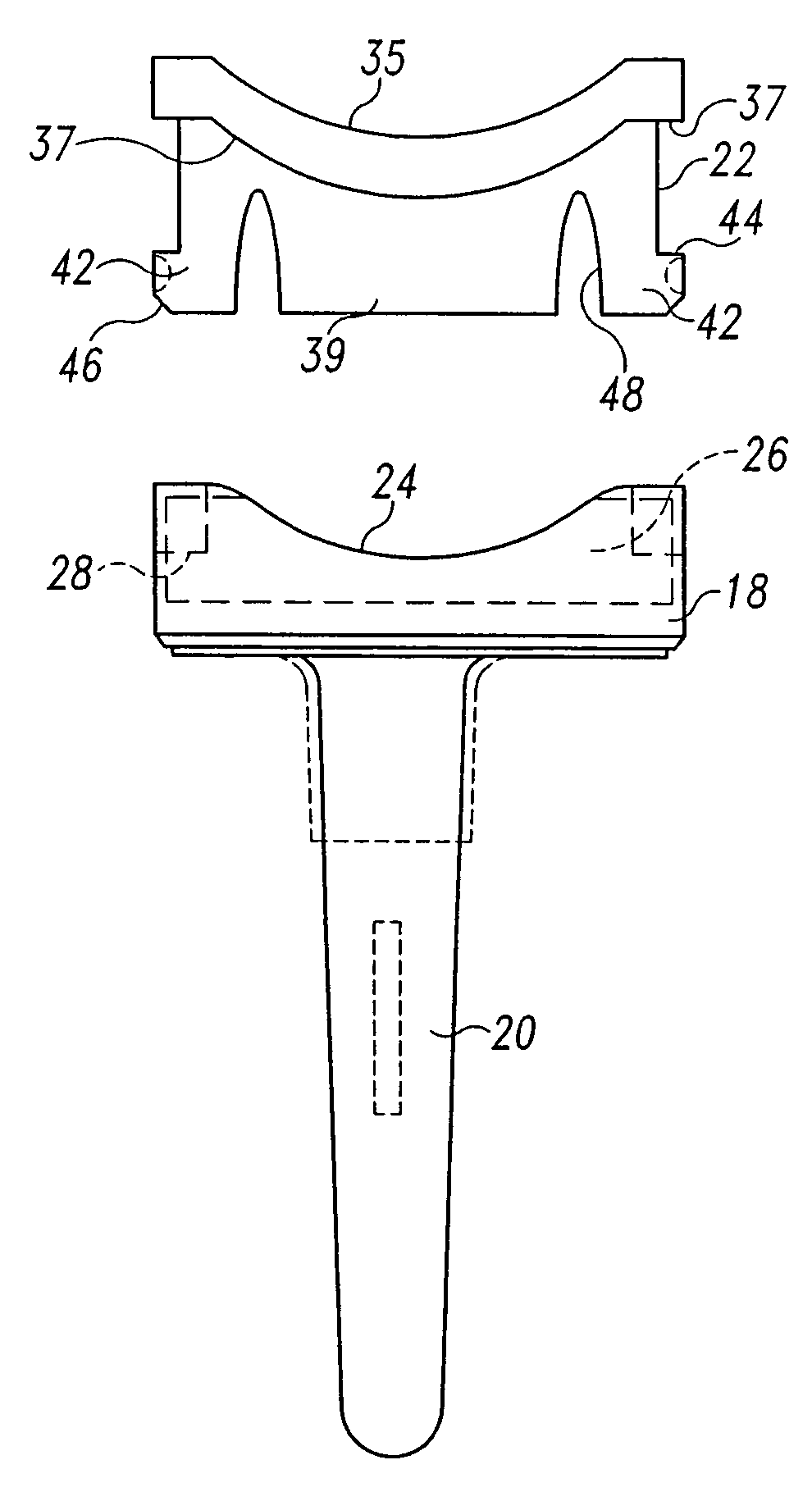
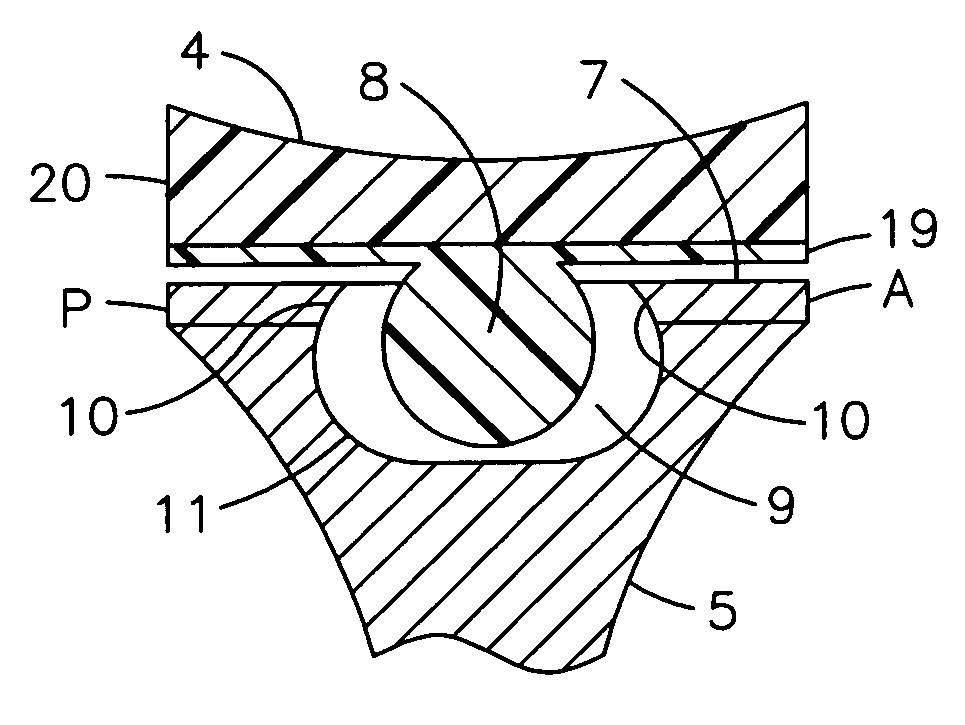
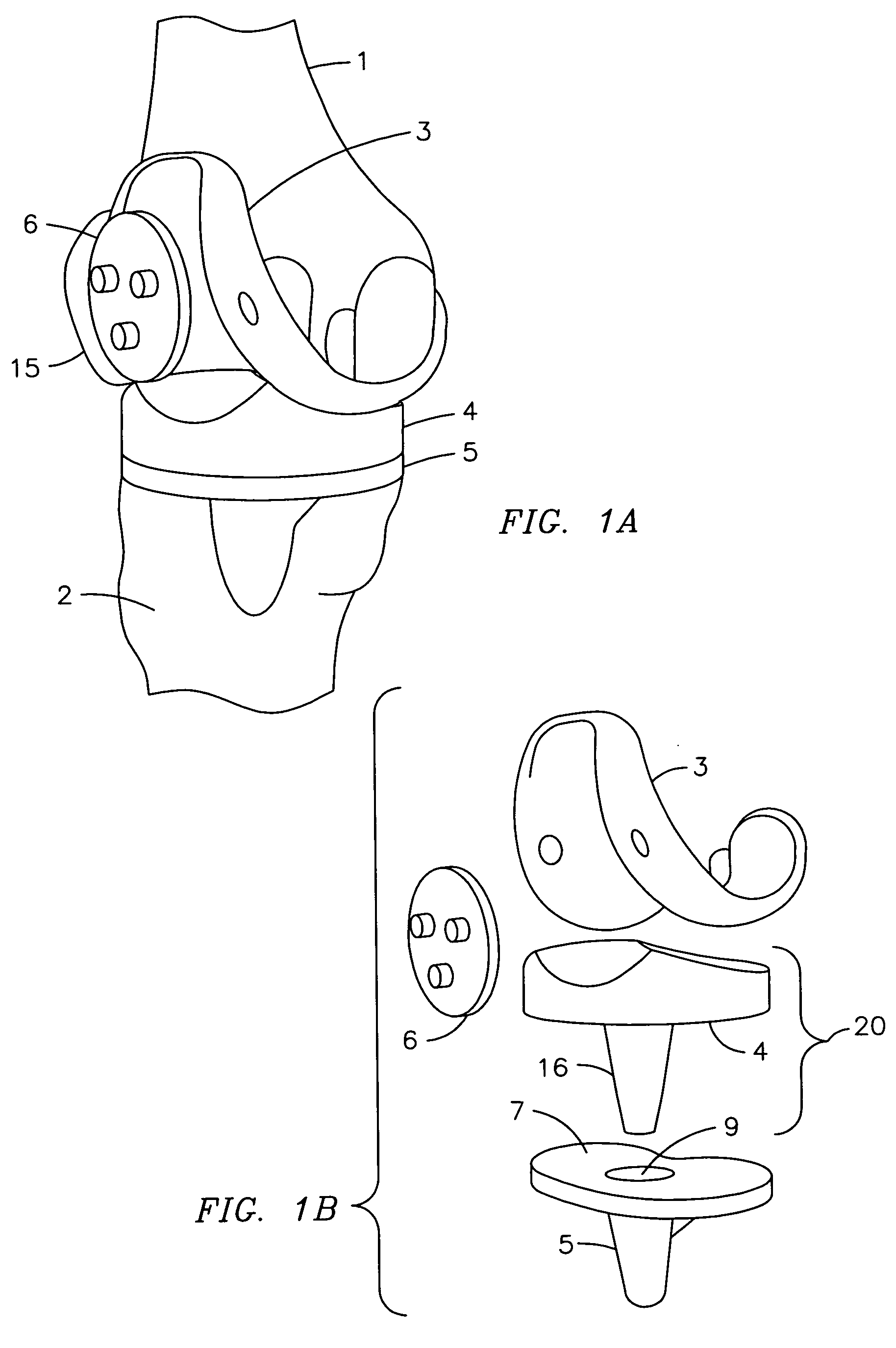
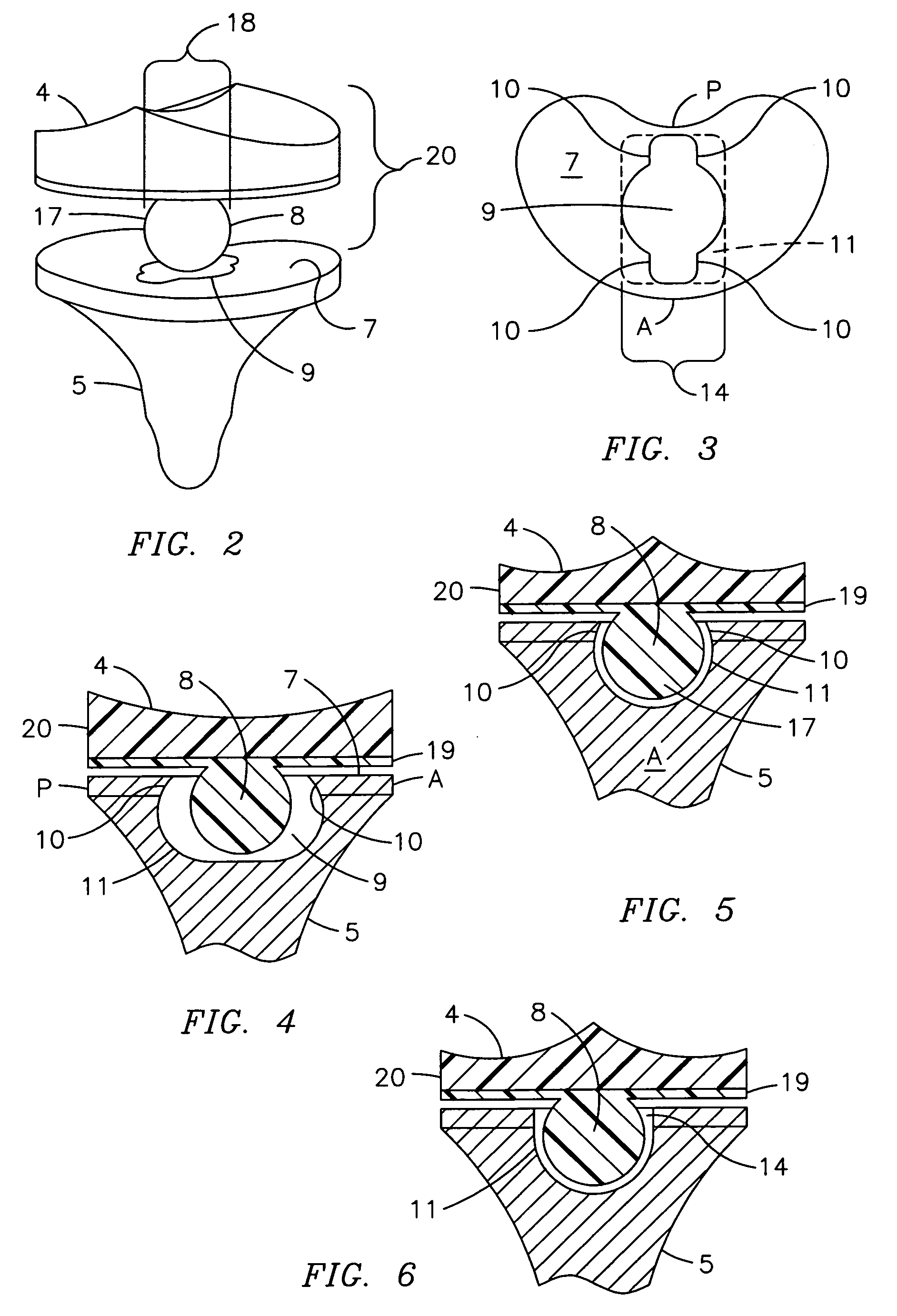
Constrained acetabular insert for total hip arthroplasty
A hip prosthesis (20) having a shell (22), liner (24), and retainer ring (26) is utilized for hip arthroplasty. The liner (24) fits inside the shell (22), which is attached to a patient's pelvis, and the retainer ring (26) engages a terminal liner margin (54) to inhibit expansion of and decrease the size of a restricted liner opening (72) defined by the liner margin (54). By inhibiting expansion of the liner opening (72), the ball (92) of a patient's femur (90) is securely held in the liner (24). In one embodiment, the liner (98) is inhibited from rotation relative to the shell (96) by a plurality of protrusions (106) which mate with recesses (102) in the shell (96). In that embodiment, the liner (98) is provided with catch lips (108) to hold the liner (98) in the shell (96) and a positioning flange (110) which operates to form a relief gap (120) between the shell (96) and the liner (98). In another embodiment, the retainer ring comprises an attachment portion (128) and a retainer portion (130) with a threaded connection (132) between the attachment portion (128) and the retainer portion (130).
Owner:ORTHOPAEDIC RES INST
Modular radial component for a total wrist arthroplasty
A radial component of a total wrist arthroplasty prosthesis includes a platform having a stem configured to be implanted within the radius bone. The platform carries an insert that provides the radial articulating component for the wrist joint. The platform and insert include mating features that allow for ready engagement or disengagement of the insert to the platform when the platform is implanted to the radius bone.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Total Knee Prosthesis and Method for Total Knee Arthroplasty
A prosthetic knee implant for implantation into a mammal, which accommodates an anterior cruciate ligament substitute to provide stability to the knee implant. The prosthetic knee implant includes a femoral component having a pair of condylar surfaces and a tibial component having a surface portion adapted to slidably engage the femoral component upon rotation of the same. The femoral component further includes a recess between the condyles defining an aperture through the femoral component. The tibial component further includes a center portion defining an aperture through the tibial component substantially at its center. The femoral aperture and the tibial aperture are adapted to receive an anterior cruciate ligament substitute for biasing the mammalian femur and tibia together. Also disclosed is a method used to replace the total knee joint in a mammal with the improved prosthetic knee implant of the present invention.
Owner:BLUM MICHAEL F
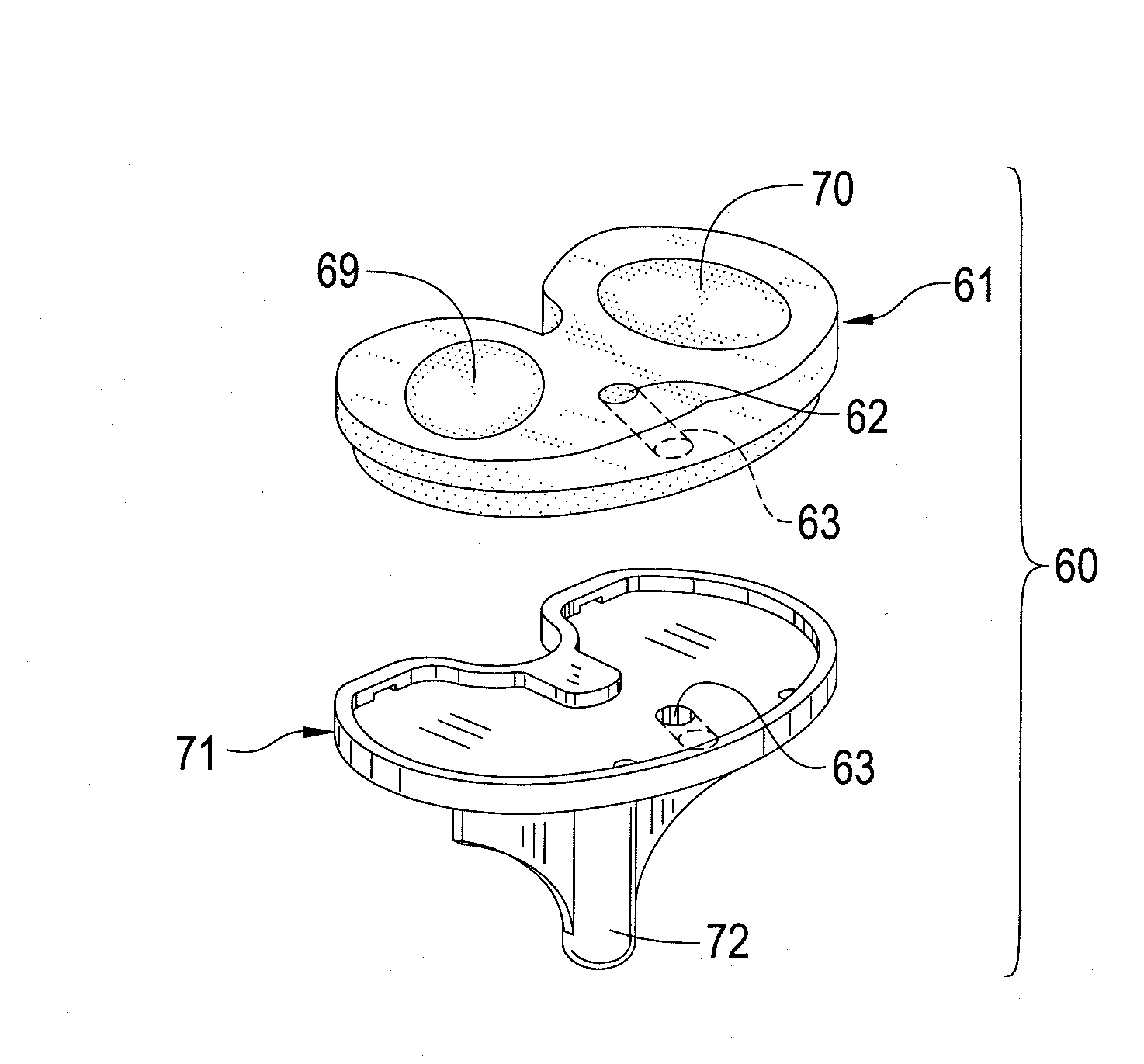
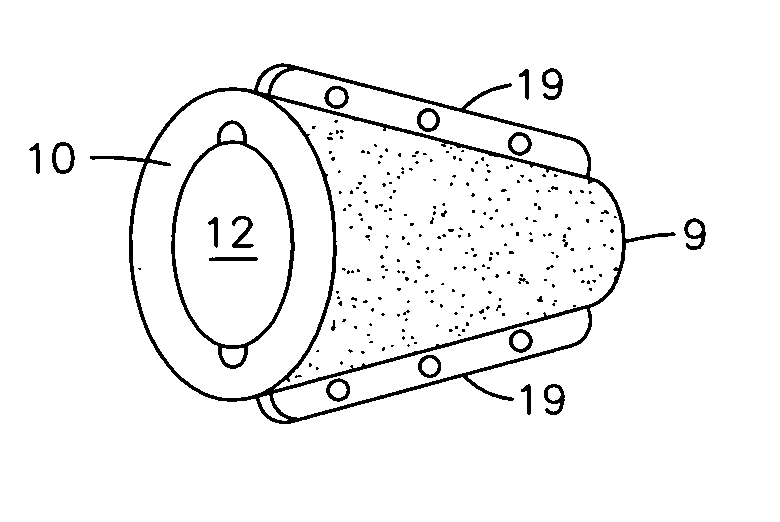
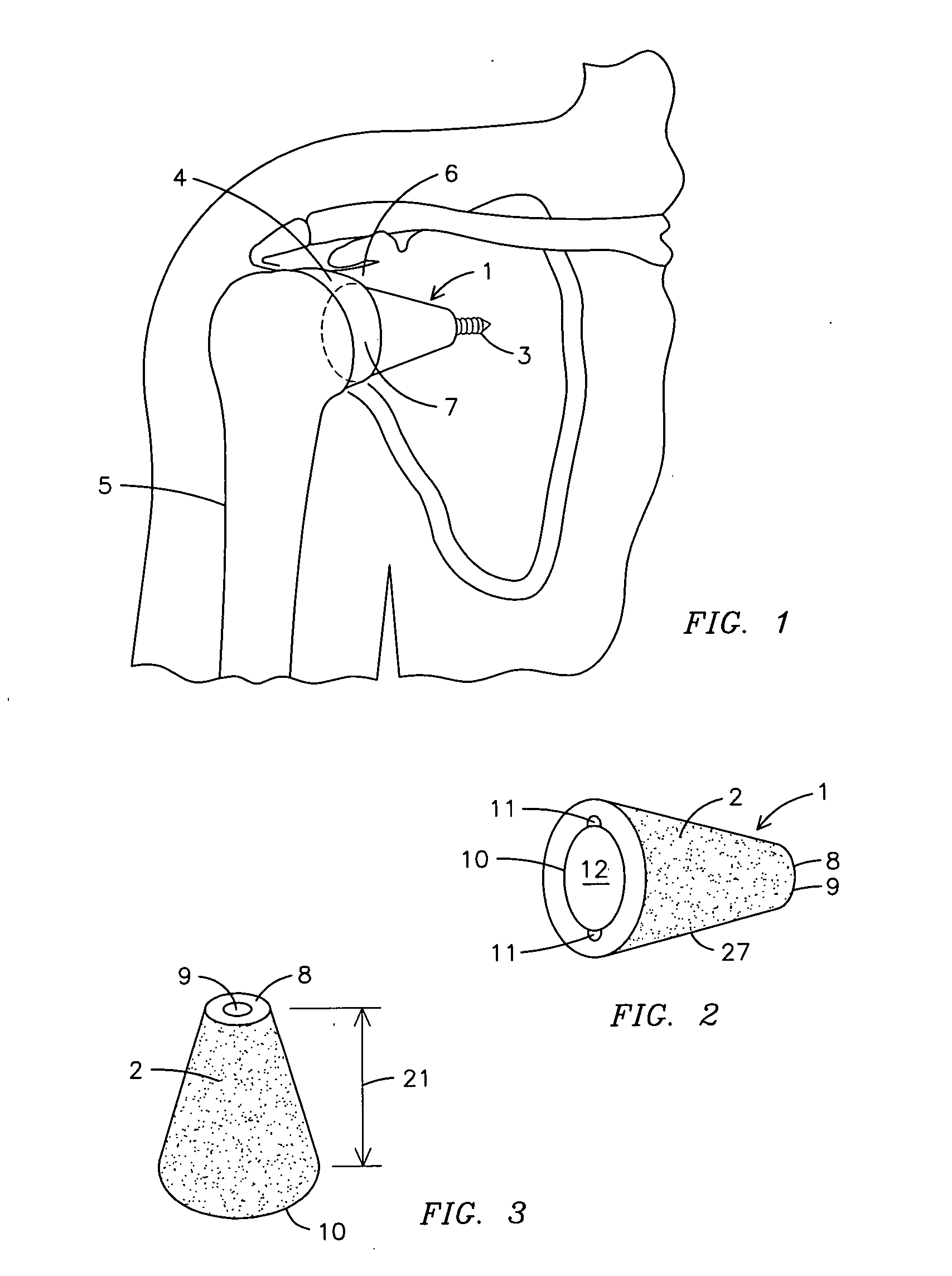
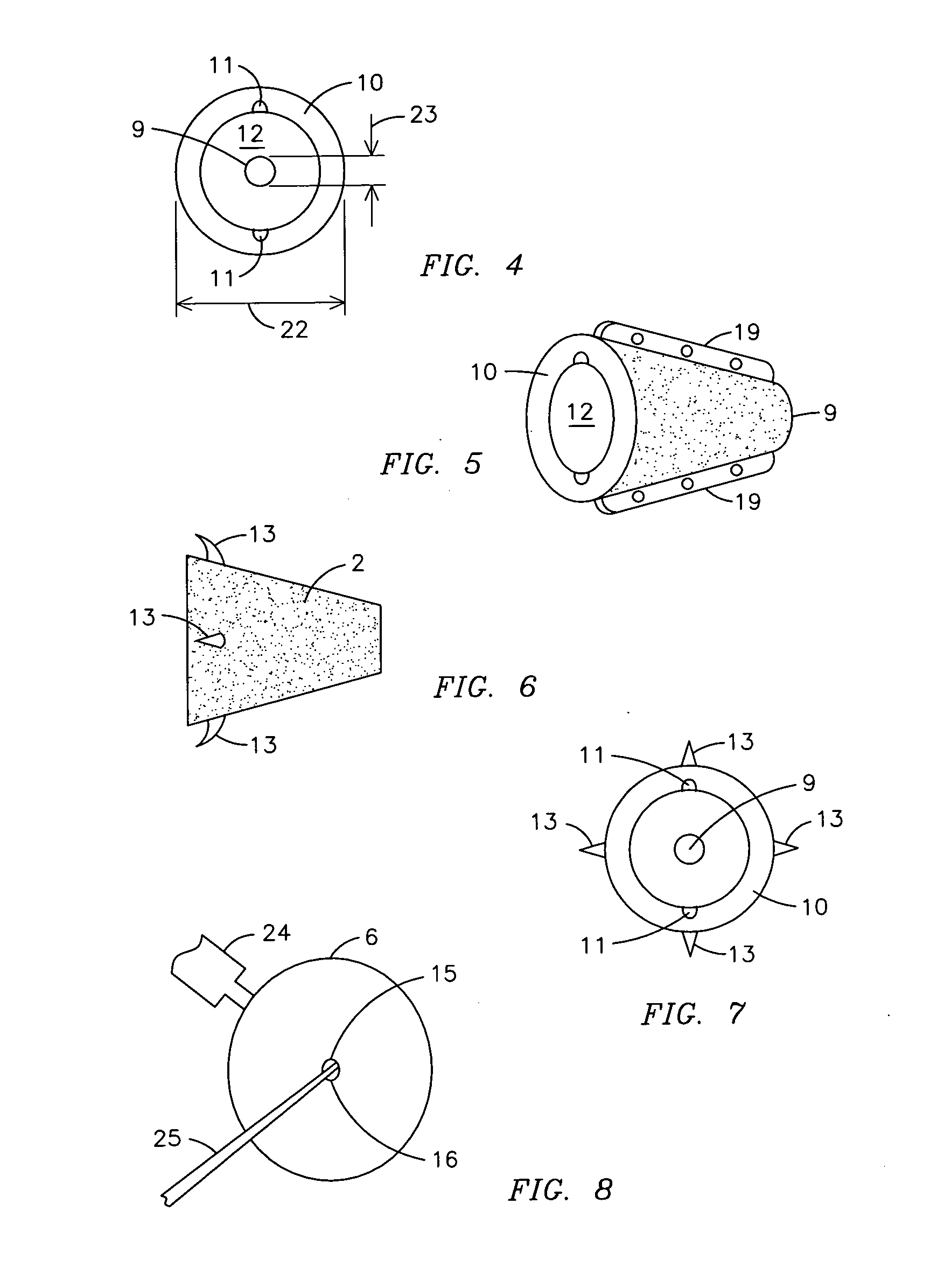
Conically-shaped glenoid implant with a prosthetic glenoid insert used in total shoulder arthroplasty and method
InactiveUS20070260321A1Promote ingrowthIncrease surface areaJoint implantsShoulder jointsTotal hip arthroplastyKeel
A conically-shaped glenoid implant (1) having a fastening means for the acceptance of a conventional prosthetic glenoid insert (7) and a hole (9) located thereon for the acceptance of a locking means. The fastening means are preferably notches (11) while the locking means is preferably reverse barbs (13). An optional screw (3) or keels (19) may be located on the exterior surface of the cone (2) for additional securement of the conically-shaped glenoid implant (1) in the glenoid (6) and to prevent rotation of the cone (27). By using the present invention, bone ingrowth is achieved because sheer forces are converted to compressive forces and surface area for ingrowth is significantly increased.
Owner:STCHUR ROBERT P
Two-piece cut block for minimally invasive surgical procedure
InactiveUS6962593B2Less initial traumaFast recovery timeJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTotal hip arthroplastyLess invasive surgery
A two-piece cut block for performing a minimally invasive partial or total knee arthroplasty. The present invention comprises a cut block that can be inserted into an incision in two parts then assembled in vivo. The two-piece design allows the relatively large surgical instrument to fit into a small, minimally invasive, surgical incision
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Tibial tray for total knee arthroplasty
InactiveUS7524334B2Improve usabilityProvide stabilitySurgeryJoint implantsTotal hip arthroplastyKeel
An improved one piece tibial tray uniquely characterized by its construction including an asymmetric keel extending from the bottom of the tibial tray base plate, whereby insertion of the tray during arthroplasty may be accomplished with a smaller than normal incision, enhancing the efficacy and safety of the surgical procedure. A fin on either or both sides of the asymmetric fin may be provided for enhanced stability of the tray.
Owner:HAIDUKEWYCH GEORGE J
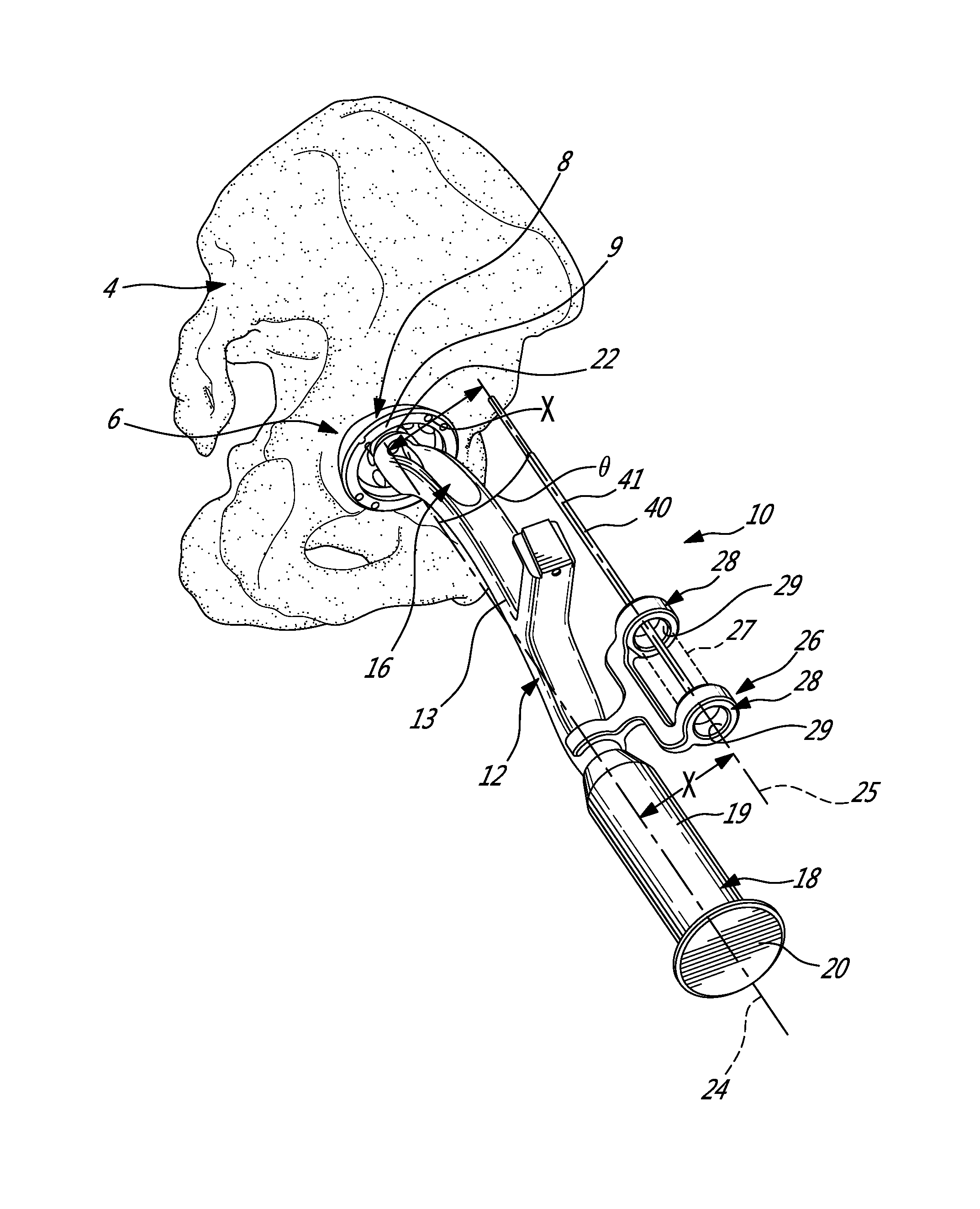
Mechanically guided impactor for hip arthroplasty
An impactor for positioning and inserting an acetabular cup into an acetabulum of a pelvis during hip arthroplasty is described. The impactor includes a guide element mounted to an elongated body and including first and second openings aligned with each other to define an axial passage. The first and second openings and the axial passage receive a guide pin therethrough that is pinned in a fixed position to the pelvis. The guide element provides a mechanical orientation guide which restricts an angular orientation of the impactor relative to the guide pin when the guide pin is pinned in the fixed position relative to the pelvis and received through the first and second openings of the guide element. Centering the openings of the guide element relative to the guide pin in the fixed position accordingly achieves a desired orientation of the impactor within a predetermined angular tolerance.
Owner:ORTHOSOFT
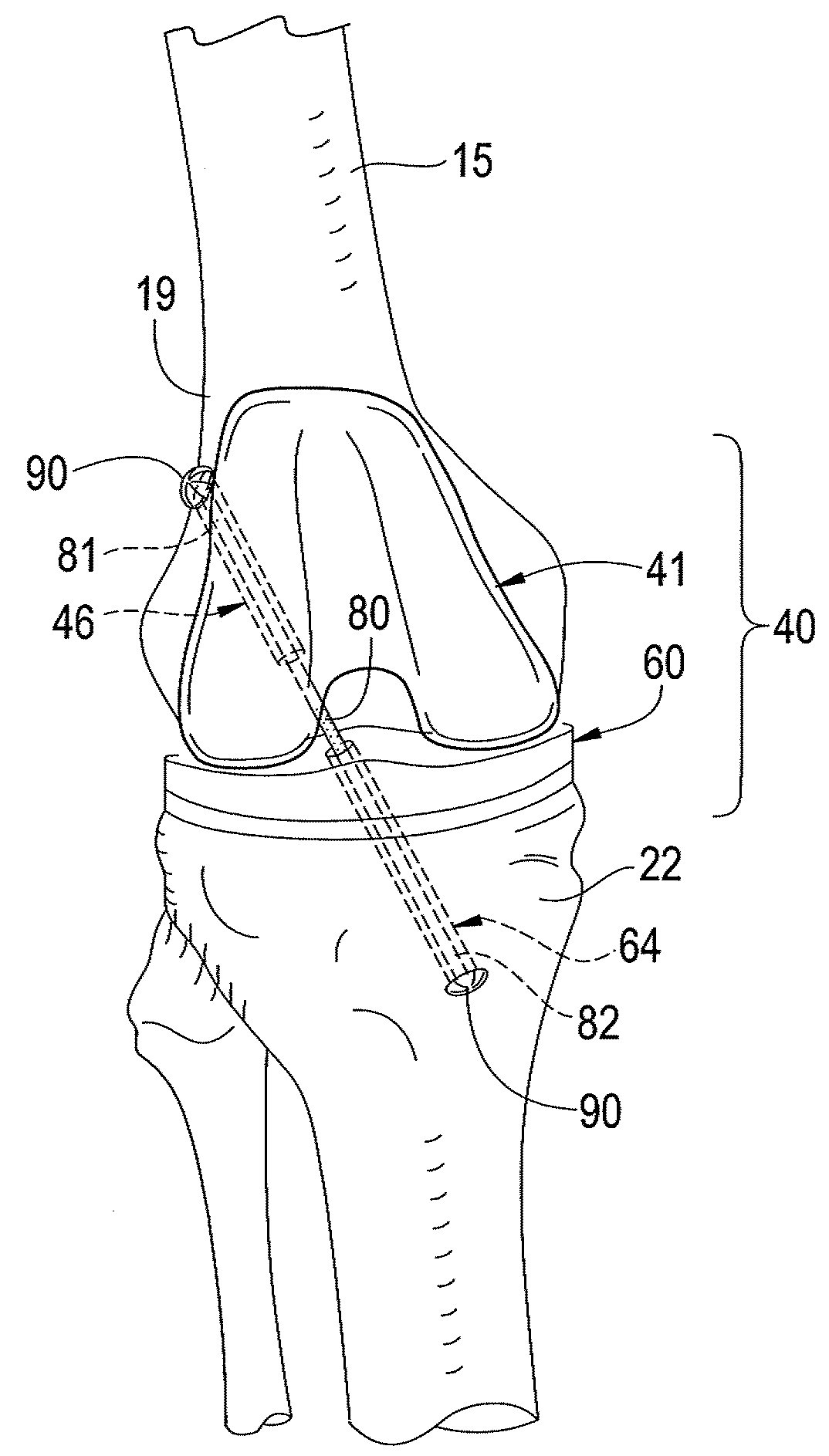
Systems and methods for providing alignment in total knee arthroplasty
ActiveUS20140276864A1Accurate and precise alignmentEfficiently and more accurately completingJoint implantsKnee jointsTotal hip arthroplastyMedicine
Systems and methods for providing alignment in total knee arthroplasty operations are provided herein. The systems and methods generally include a plurality of sensors coupled to a patient's bones or other surgical tools, the sensors detect their position and orientation in space and communicate this information to a processor. The processor can utilize the information to display data to a surgeon or other user regarding the position, angle, and alignment of a patient's bones, surgical tools, and the reconstructed knee joint.
Owner:ARTHROMEDA
Knee joint prosthesis used in total knee arthroplasty
InactiveUS20080033567A1Relieve pressureImprove survival rateJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaTotal hip arthroplasty
A knee joint prosthesis used in total knee arthroplasty having tibial components (5) and tibial bearing inserts (20) with predetermined shapes that allow for an additional degree of freedom in both an anterior-posterior direction and rotation. The tibial bearing inserts (20) include a predeterminedly-shaped extension (17), such as a sphere (8), disc (12) or trapezoid (13), that extends downwardly from the bearing (4). The tibial components (5) include a socket (9) having a corresponding predetermined shape of the extension (17) and retaining edges (10) located at a top of the socket (9) so the extension (17) may be “dropped into” the socket (9) and therein retained. In this manner, disengagement of the tibial bearing inserts (20) at extremes of anterior or posterior translation of the bearing relative to the tibial component (5) is prevented without affected the translation and rotation of the tibial component (5) and tibial bearing inserts (20).
Owner:STCHUR ROBERT P
Virtual trial reduction system for hip arthroplasty and coordinate systems therefor
ActiveUS8078254B2Accurate and efficient positioningAccurately determineSurgical navigation systemsPerson identificationTotal hip arthroplastyMedicine
A patient-specific pelvic coordinate system is produced from a single near AP intra-operative image of the patient, obviating the need for use of a patient tracker.
Owner:MURPHY STEPHEN B
Real-time visualization assistant positioning system for interior of hip joint in total hip replacement arthroplasty
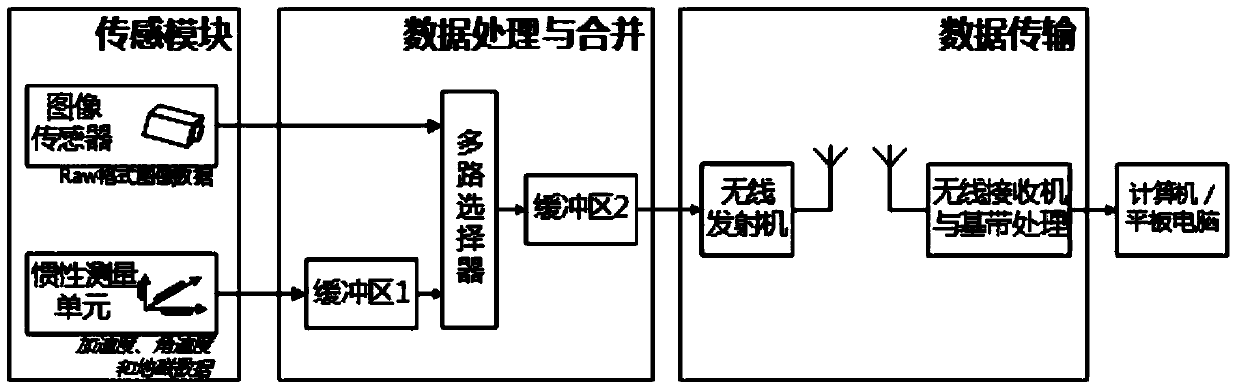
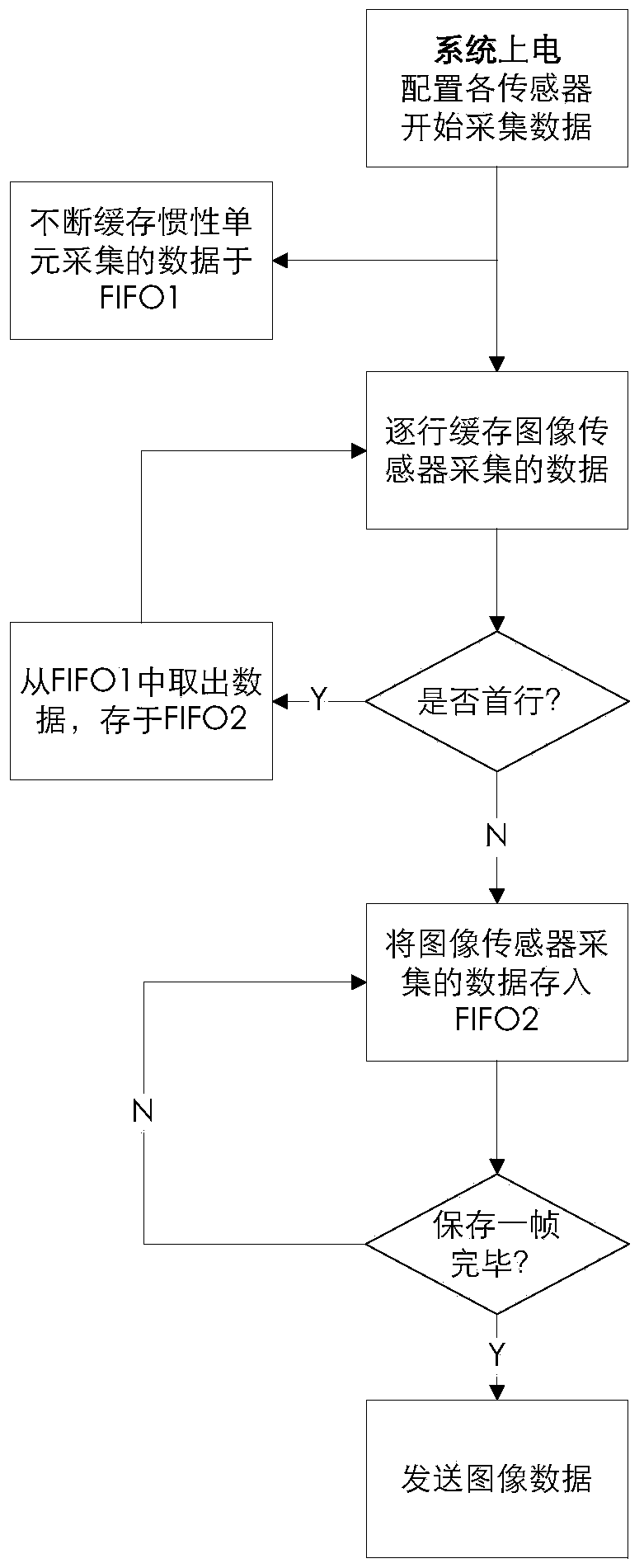
ActiveCN103735303AReduce the difficulty of surgeryImprove the success rate of surgerySurgeryFemoral headsData acquisitionPositioning system
A real-time visualization assistant positioning system for the interior of a hip joint in total hip replacement arthroplasty is divided into two portions of hardware and software, wherein the hardware can be divided into three modules of a sensing data gathering module, a data merging and processing module and a data transmission module according to functions, and takes charge of gathering information of images, accelerated speed and the like, encapsulating the information into data of an image, and transmitting the data of the image to a computer or a flat computer, and the software can be divided into four portions of a data extraction portion, a position and posture measurement and calculation module, a data fusion portion and a three dimensional (3D) display module, and takes charge of figuring out a relative position and a relative posture of an artificial thigh bone and acetabulum through various sensing data, improving precision and reliability of measurement and calculation through fusion of redundant data, and showing the relative position and the relative posture to a doctor in 3D mode. The real-time visualization assistant positioning system for the interior of the hip joint in the total hip replacement arthroplasty presents movement status of the thigh bone in the acetabulum and a relative position relation of the thigh bone and the acetabulum in real time, assists the doctor in visually observing installation status of the artificial thigh bone with the acetabulum during the operation process, and greatly improves success rate and operation curative effects of the total hip replacement arthroplasty.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Designing method and manufacturing method of knee joint femoral prosthesis used for total knee arthroplasty
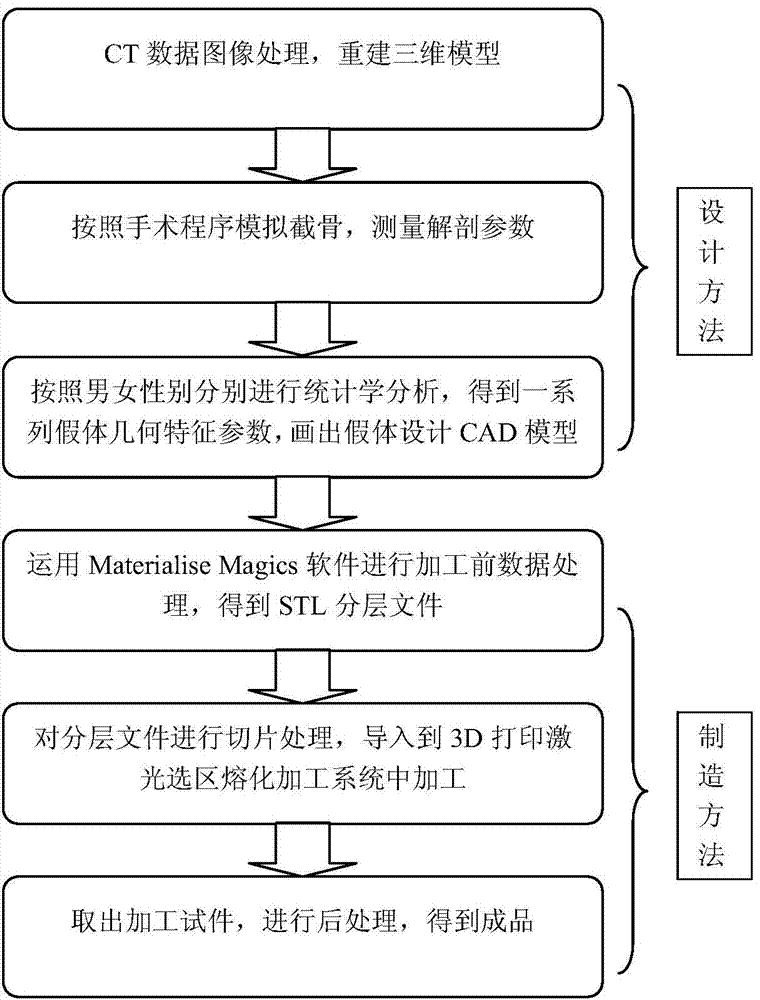
ActiveCN103584932AGood compatibilityShort processing cycleJoint implantsKnee jointsTotal hip arthroplastyDICOM
The invention discloses a designing method and a manufacturing method of a knee joint femoral prosthesis used for total knee arthroplasty. The designing method includes the following steps: S11, on the basis of CT (computed tomography) data of a normal Chinese person and in a medical image DICOM format, applying medical image software Mimics to build a three-dimensional digital model of a femur, and outputting a PLY-format file; S12, leading the digitalized femoral model PLY file in Geomagic Studio software, establishing a three-dimensional coordinate system, and utilizing a measuring tool to collect geometric parameters related to prosthesis designing; S13, performing statistical analysis on collected data by utilizing statistical software, and utilizing three-dimensional drawing software to draw a solid entity of the knee joint femoral prosthesis. The designing method and the manufacturing method have the advantages that a series of femoral prostheses different in type exist for men and women respectively, different knee joint femoral skeleton anatomical morphological features of men and women in China can be met, and matching degree of prostheses and knee joints is increased.
Owner:BEIJING NATON TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Independent digital templating software, and methods and systems using same
ActiveUS9262802B2Reduce system costImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisComputer hardwareThe Internet
Provided are a computer-aided system (medical device), a computer-aided method, and a computer program product useful in digital templating for prosthetic arthroplasty, for example, total hip arthroplasty. The invention includes digital image capture and scaling features that can be used in conjunction with any digital radiographic image stored using picture archiving and communication system (PACS), regardless of PACS provider or PACS format. Patient radiographic images are captured, imported, and scaled, e.g., to actual size, to match the scale of a digital template of any prosthesis selected by the user. The computer program product is a stand-alone product, used independently of any software interface, including software accessed through connection to a network or the internet. The software, method, and system are suitable for use with a stand-alone computer and permit improved and cost-effective selection of prostheses for any particular clinical situation.
Owner:ARTHROMEDA
Systems and methods for providing alignment in total knee arthroplasty
ActiveUS9597096B2Accurate and precise alignmentEfficiently and more accurately completingJoint implantsSurgical sawsTotal hip arthroplastyMedicine
Systems and methods for providing alignment in total knee arthroplasty operations are provided herein. The systems and methods generally include a plurality of sensors coupled to a patient's bones or other surgical tools, the sensors detect their position and orientation in space and communicate this information to a processor. The processor can utilize the information to display data to a surgeon or other user regarding the position, angle, and alignment of a patient's bones, surgical tools, and the reconstructed knee joint.
Owner:ARTHROMEDA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com